Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
394 results about "Corynebacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Corynebacterium (/kɔːˈraɪnəbækˌtɪəriəm, -ˈrɪn-/) is a genus of bacteria that are Gram-positive and aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more particularly, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name (coryneform means "club-shaped").
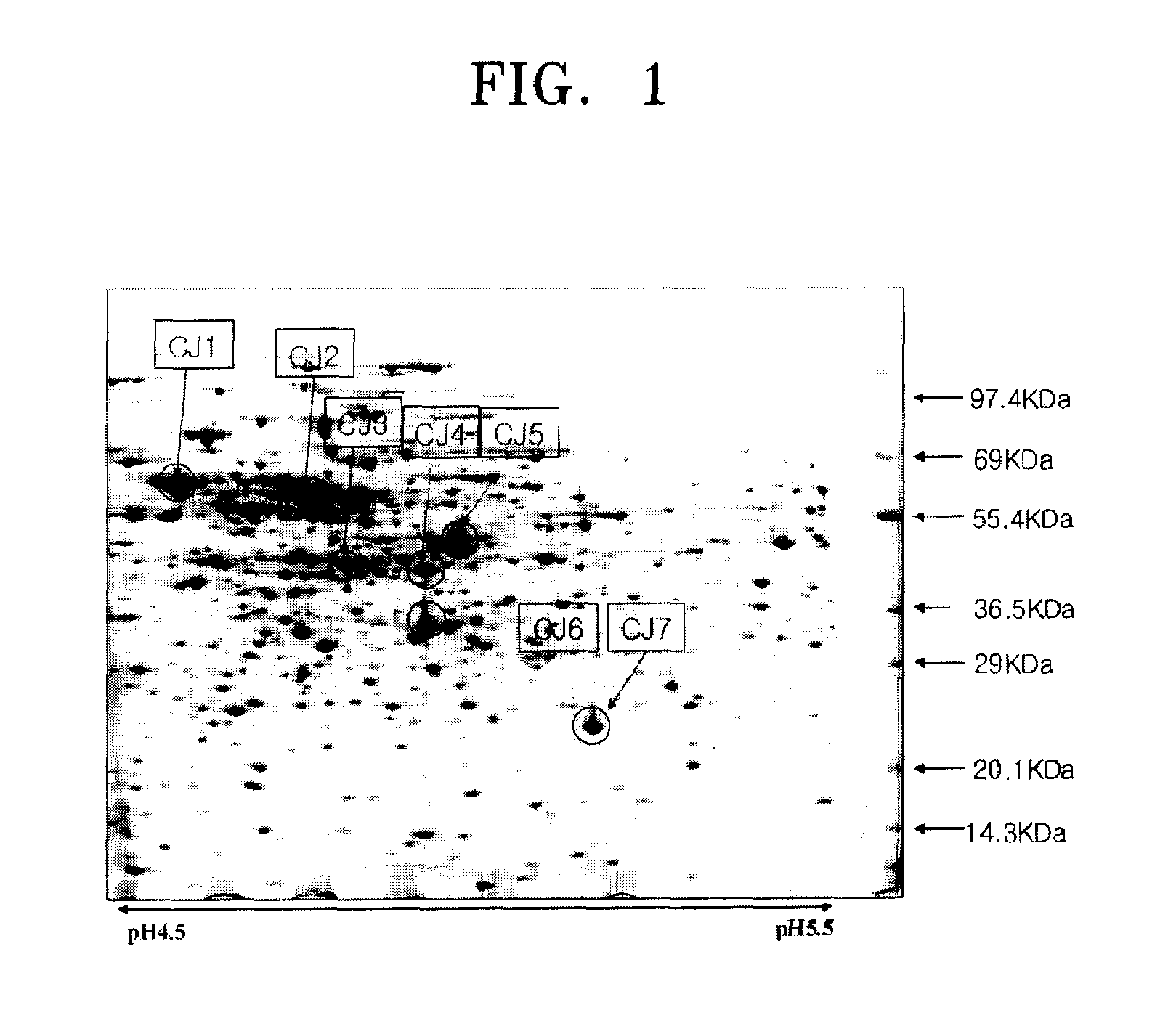
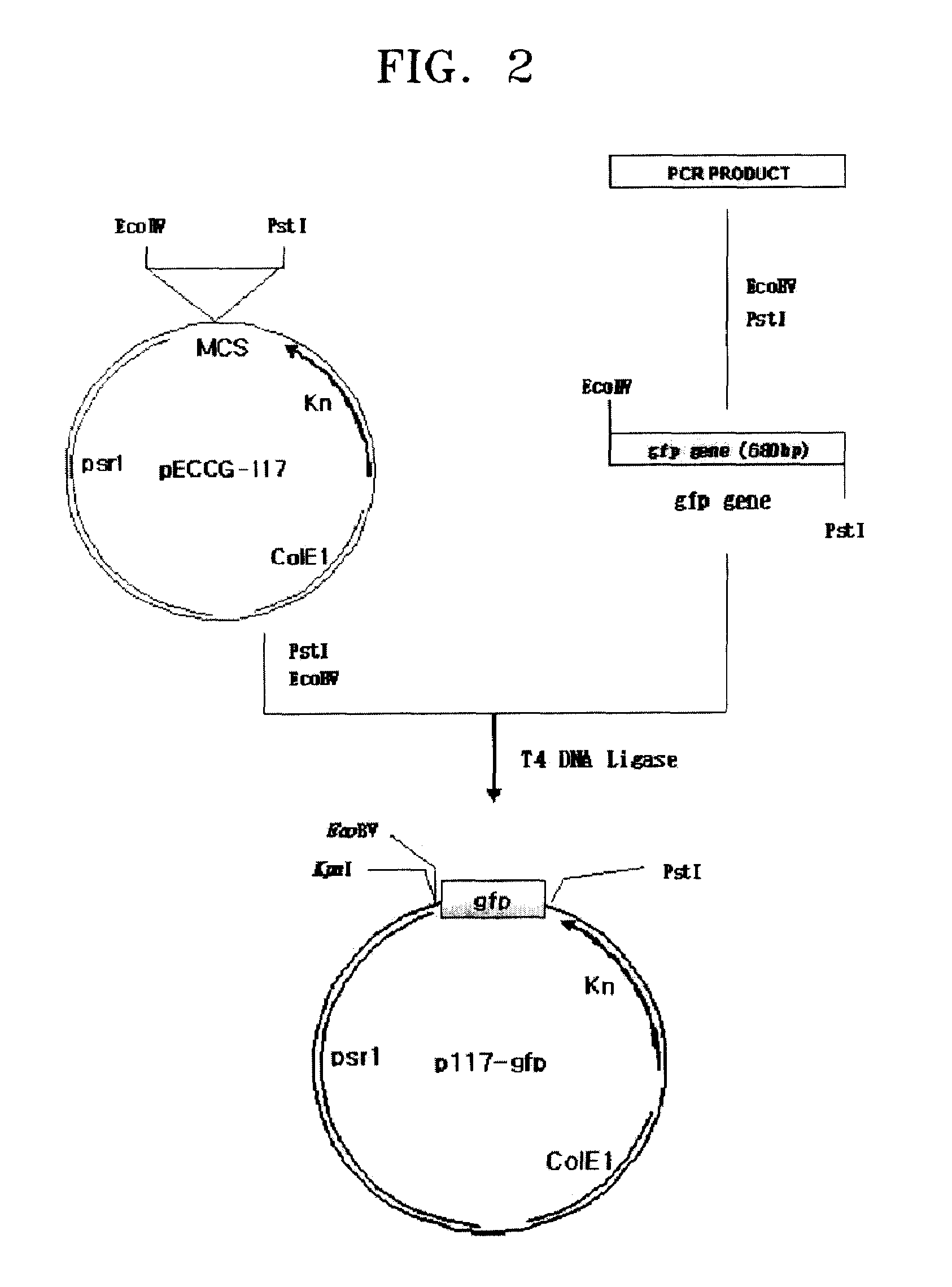
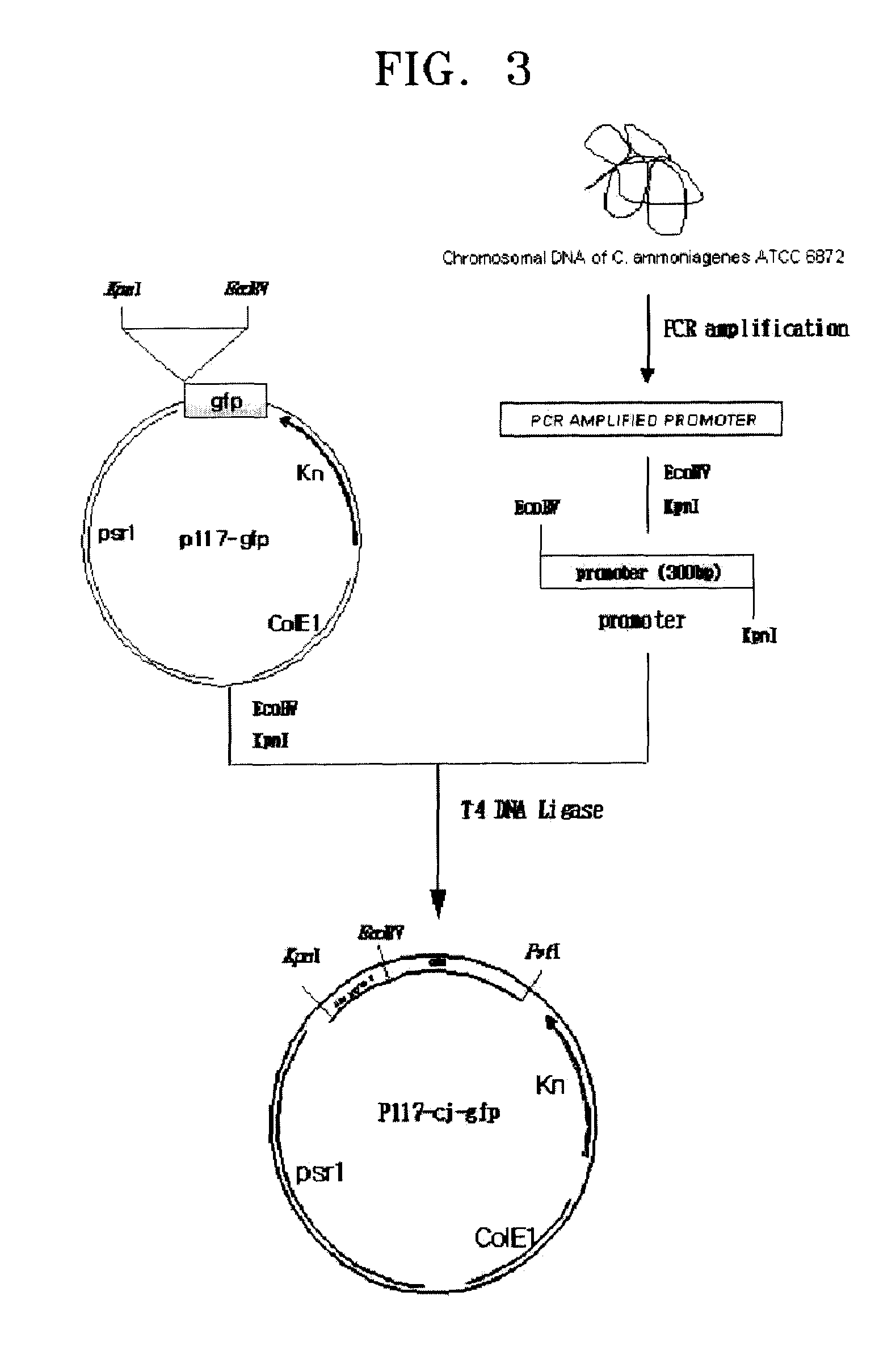
Promoter sequences from Corynebacterium ammoniagenes
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
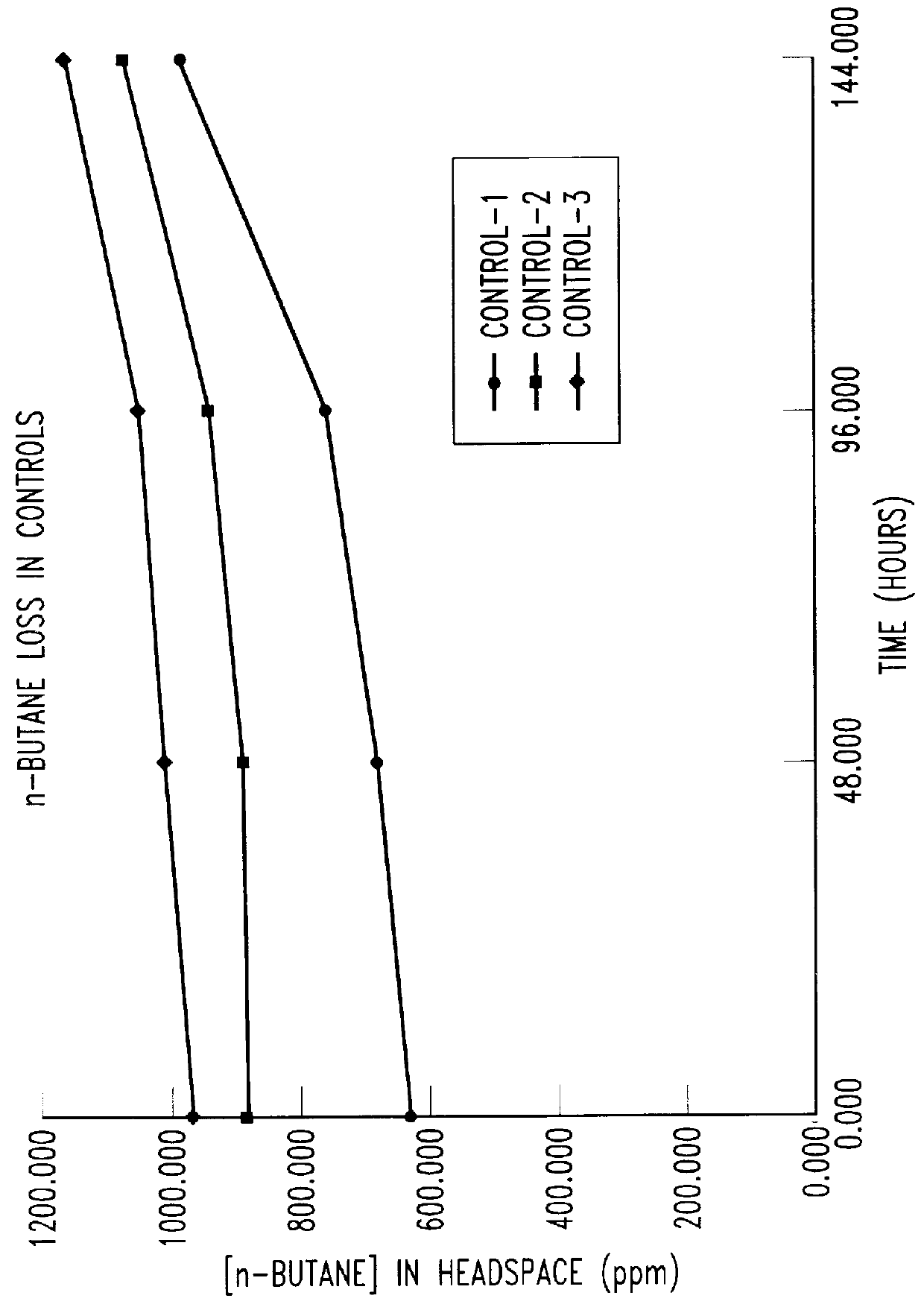
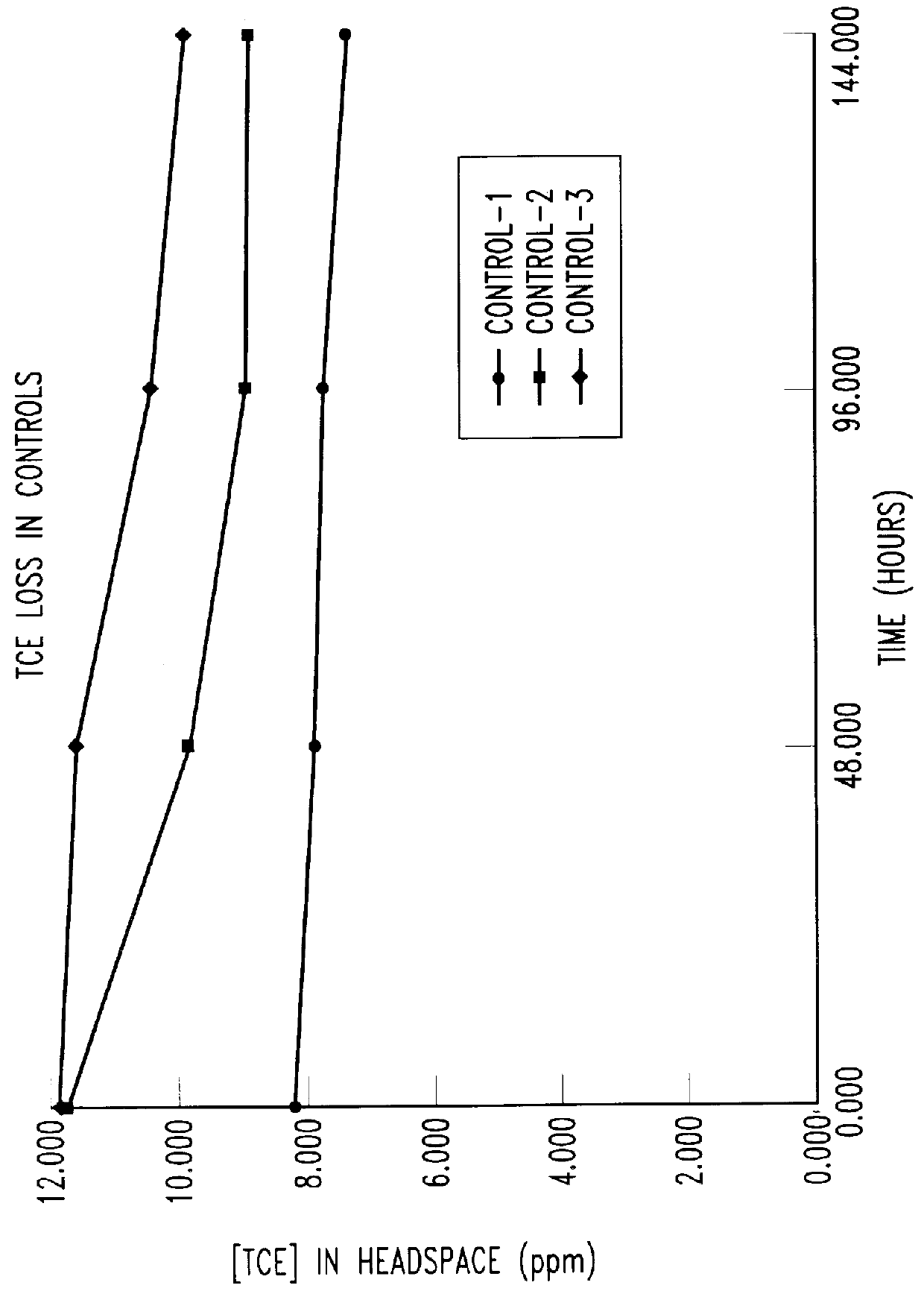
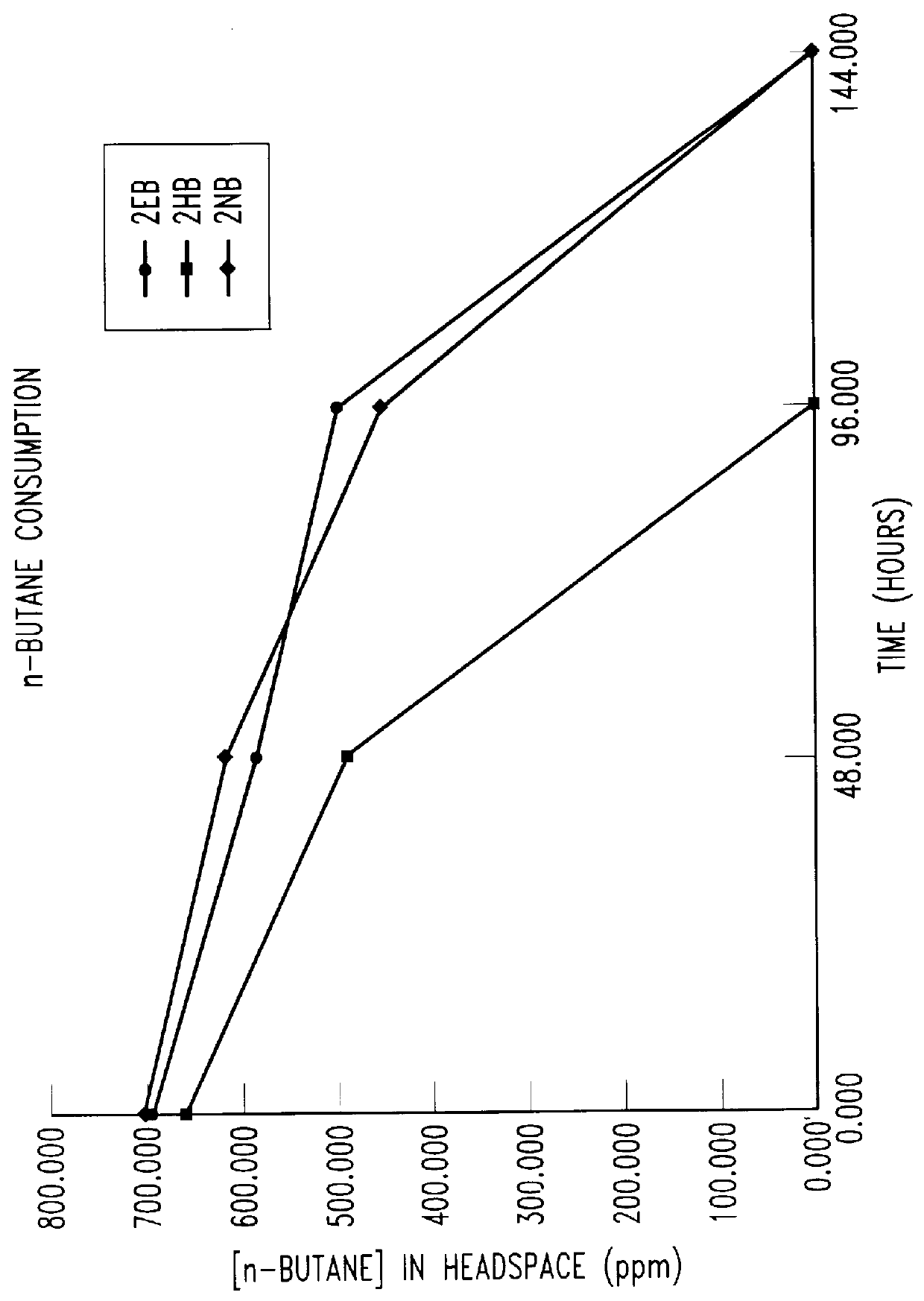
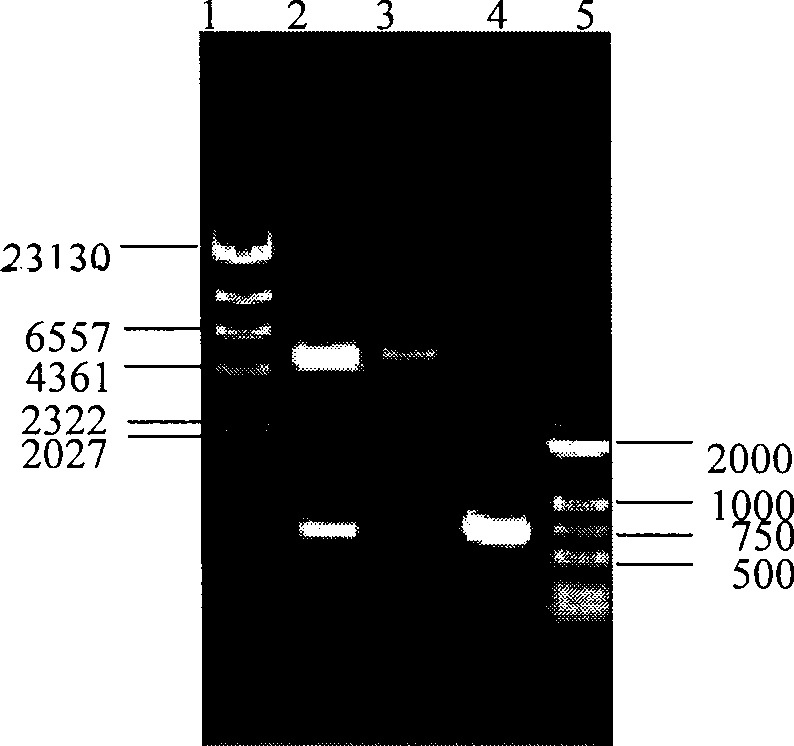
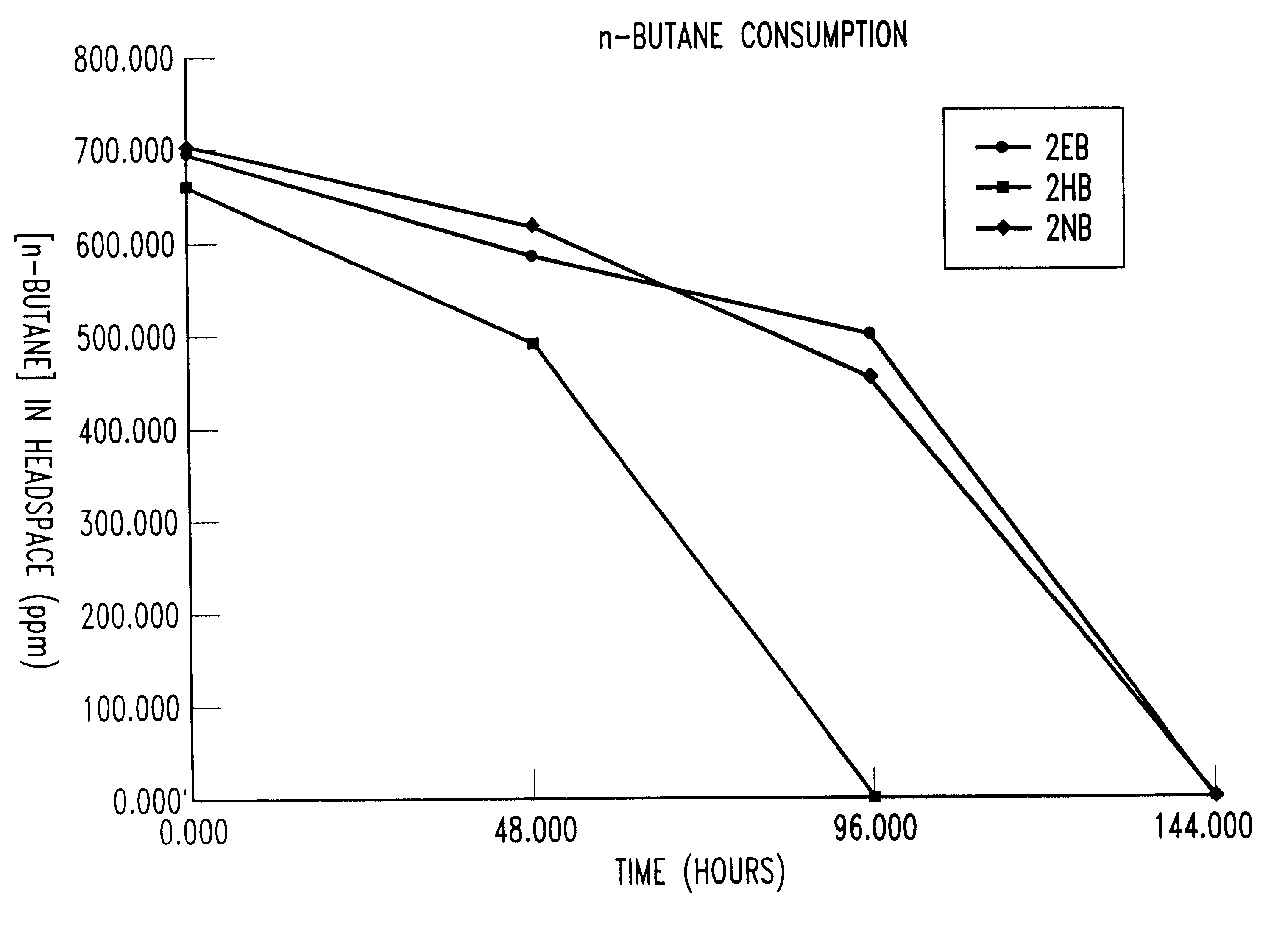
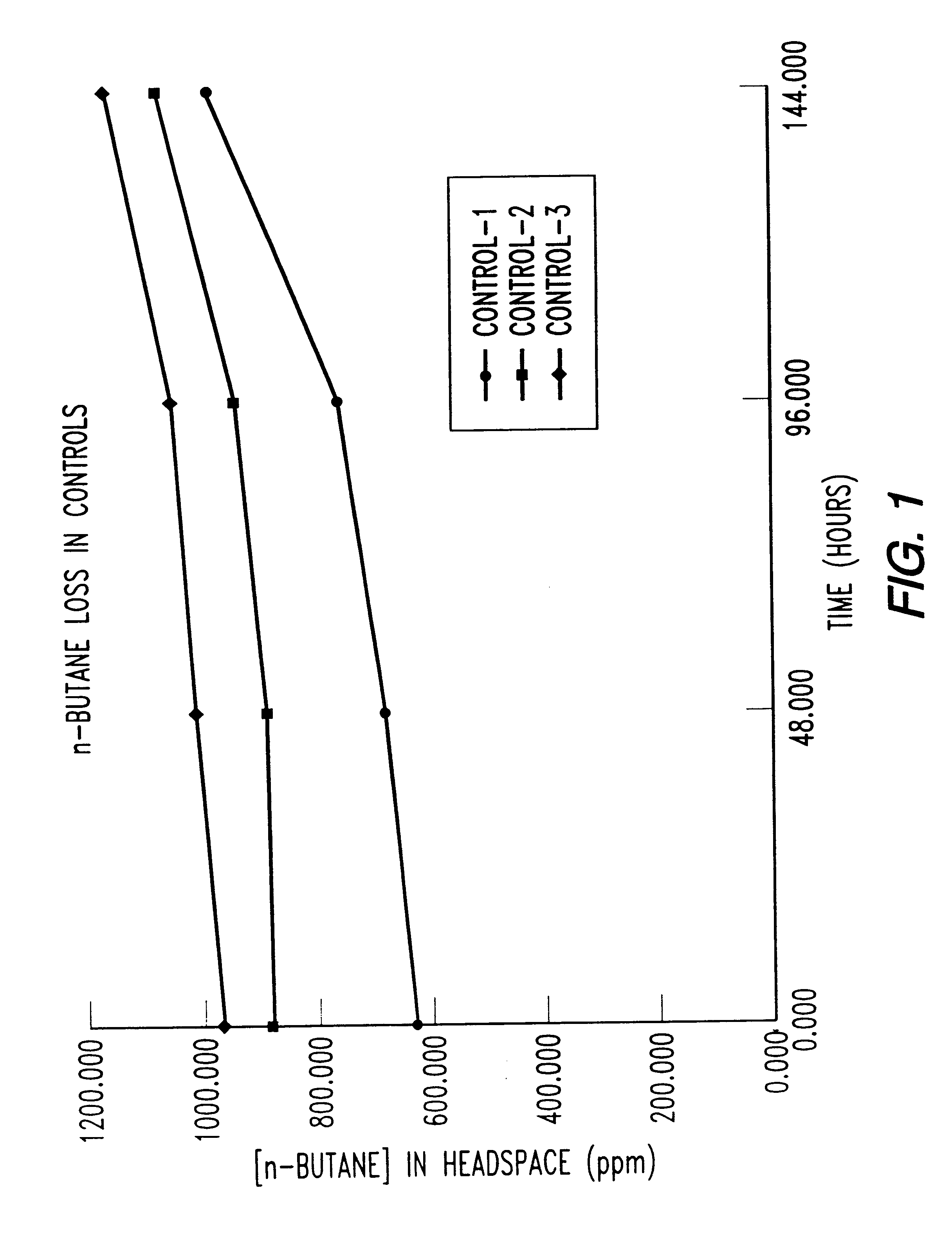
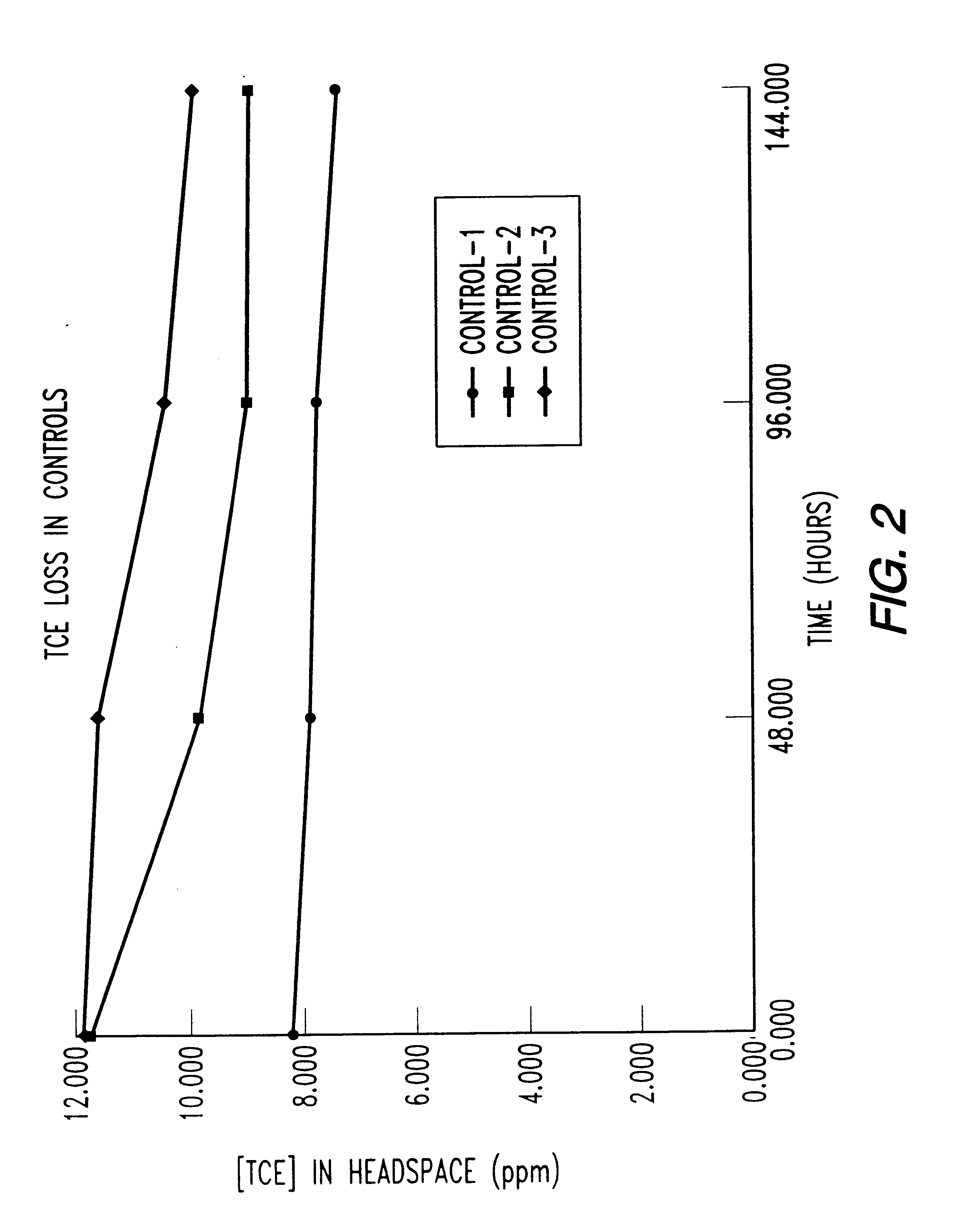
Bioreactor for remediation of pollutants with butane utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6051130AReduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesComamonas
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Lipolytic enzyme: uses thereof in the food industry
The invention encompasses the use of a lipolytic enzyme obtainable from one of the following genera: Streptomyces, Corynebacterium and Thermobifida in various methods and uses, wherein said lipolytic enzyme is capable of hydrolysing a glycolipid or a phospholipid or transferring an acyl group from a glycolipid or phospholipids to an acyl acceptor. Preferably, the lipolytic enzyme for use in these methods and uses comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 4, 5, 7, 8, 12, 14 or 16 or an amino acid sequence having at least 70% identity therewith or comprises a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 3, 6, 9, 13, 15 or 17 or a nucleotide sequence which has at least 70% identity therewith. The present invention also relates to a lipolytic enzyme capable of hydrolysing at least a galactolipid or capable of transferring an acyl group from a galactolipid to one or more acyl acceptor substrates, wherein the enzyme is obtainable from Streptomyces species and includes a lipolytic enzyme comprising an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence which has at least 60% identity thereto. The enzyme may be encoded by a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of: a) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence show in SEQ ID NO: 3; b) a nucleic acid which is related to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 by the degeneration of the genetic code; and c) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence which has at least 70% identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
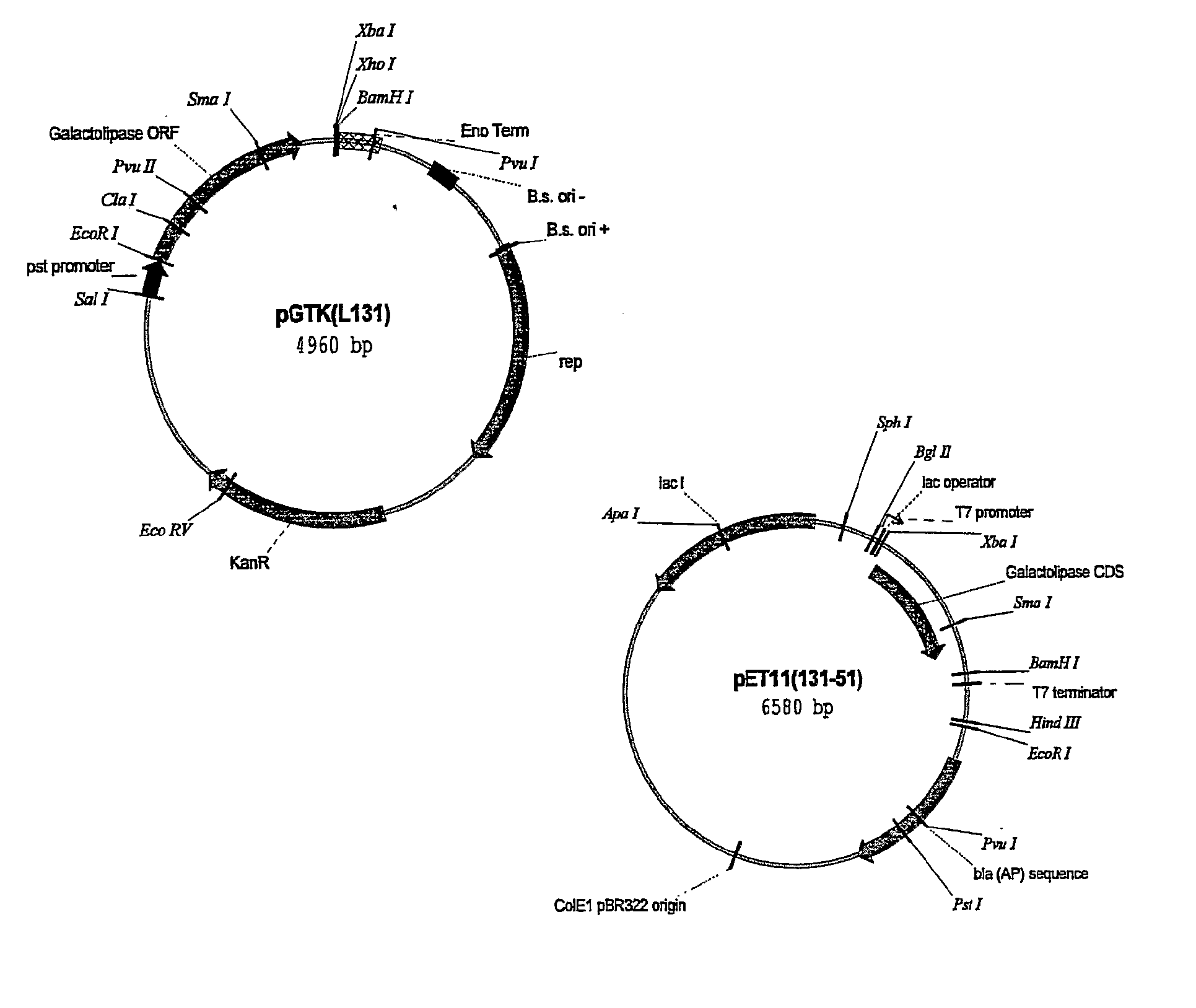
Recombinant corynebacterium crenatum for over expression of N-acetylglutamate kinase and application thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant corynebacterium crenatum to enhance the expression of N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase and the application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The classification and nomenclature of the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum to enhance the expression of N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase is corynebacterium crenatum SYPA / pJC1-tac-argB with an access number of CCTCC NO: M 208133; The application is as follows: using a key enzyme N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase from corynebacterium crenatum pathway arginine to construct a corynebacterium crenatum expression vector pJC1-tac-argB; introducing the corynebacterium crenatum expression vector pJC1-tac-argB into corynebacterium crenatum SYPA by electrotransformation to obtain the recombinant corynebacterium crenatum SYPA / pJC1-tac-argB; and excessively expressing N-acetyl glutamic acid kinase, which greatly enhances the utilization rate of a precursor glutamic acid and allows the metabolic flow to flow to the arginine synthesis pathway, weakens the synthesis of proline, achieves the purpose of improving the output of arginine and the output of arginine is increased by 23.4 percent than C. crenatum SYPA.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bioremediation of pollutants with butane-utilizing bacteria
InactiveUS6210579B1Reduce and eliminate hydrocarbon pollutantEasy to transportGas treatmentTreatment using aerobic processesBacteroidesComamonas
Butane-utilizing bacteria are used to degrade hydrocarbon pollutants such as trichloroethene (TCE). In-situ or ex-situ techniques may be used to reduce or eliminate hydrocarbon pollutants from liquid, gas and solid sources. In a preferred embodiment, TCE concentrations in various aqueous environments are reduced by contacting a contaminated water source with butane-utilizing bacteria in the presence of oxygen to degrade the TCE by cometabolism or direct metabolism. Suitable butane-utilizing bacteria include Pseudomonas, Variovorax, Nocardia, Chryseobacterium, Comamonas, Acidovorax, Rhodococcus, Aureobacterium, Micrococcus, Aeromonas, Stenotrophomonas, Sphingobacterium, Shewanella, Phyllobacterium, Clavibacter, Alcaligenes, Gordona, Corynebacterium and Cytophaga. The butane-utilizing bacteria have relatively low TCE toxicity in comparison with conventional methane-utilizing bacteria, and demonstrate an improved ability to degrade TCE.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding proteins involved in membrane synthesis and membrane transport
InactiveUS20050244935A1Efficient producerImprove production efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated MCT nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel MCT proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing MCT nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated MCT proteins, mutated MCT proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of MCT genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
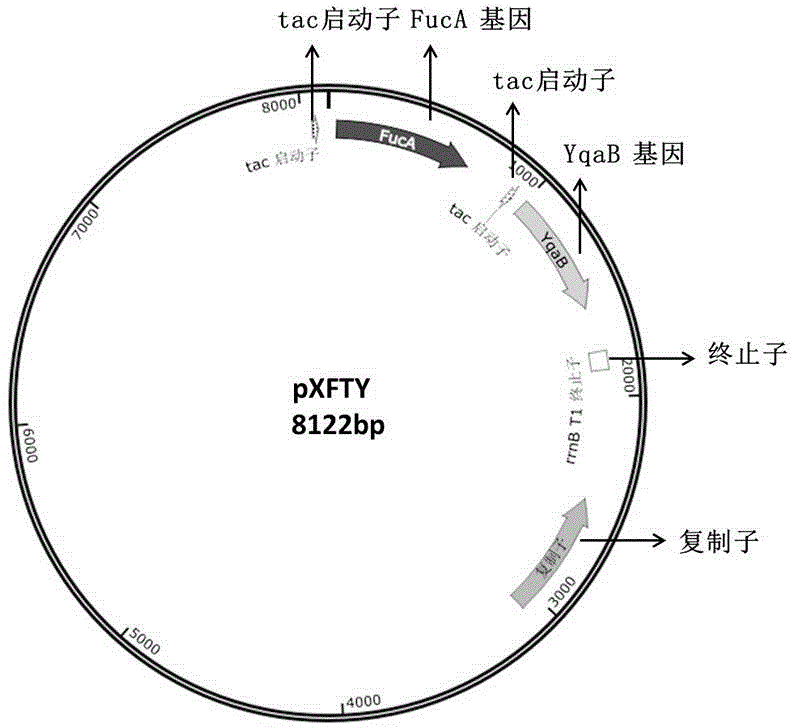
Recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and production method
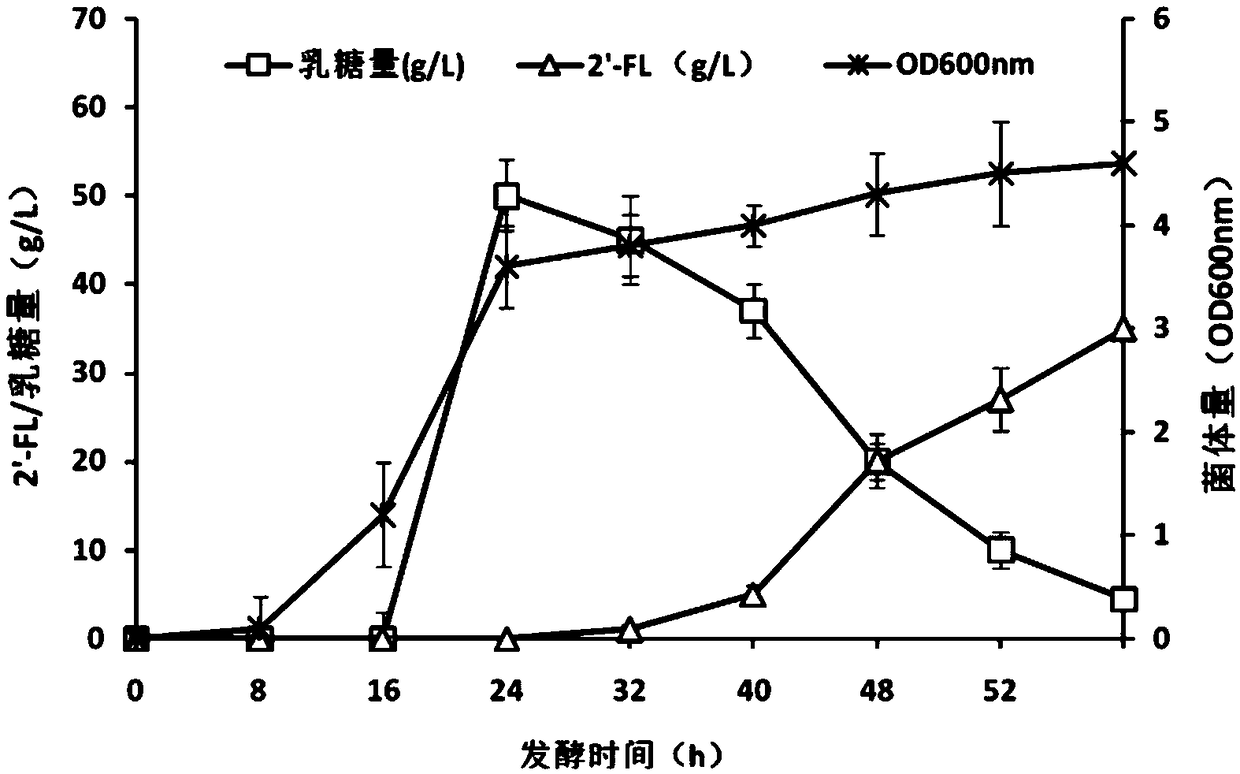
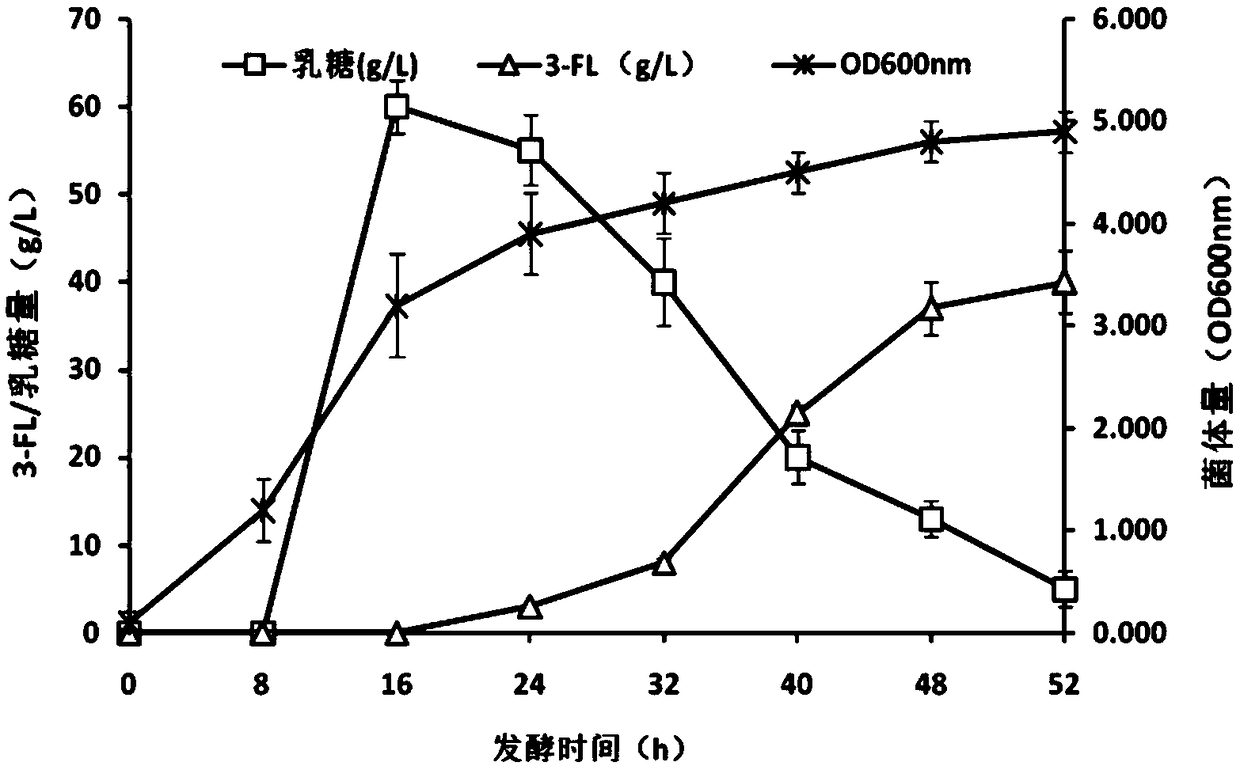
The invention relates to a recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and a production method and belongs to the fields of metabolic engineering, food fermentation and the like. In the invention, genes for encoding GDP-mannose-6-dehydrogenase, GDP-fucose synthetase, lactose permease, and alpha-1,2-fucose transferase or alpha-1,3-fucosetransferase, which are required in a de-novo synthesis route of the fucose-based lactose, are expressed in corynebacterium glutamicum, so that recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is constructed toachieve synthesis of 2'-fucose-based lactose or 3'-fucose-based lactose. In addition, by over-expression of the genes for encoding phosphomannose isomerase, phosphomannose mutase, and mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase in the corynebacterium glutamicum, high yield of the fucose-based lactose is achieved. According to the method, the engineering bacteria can synthesize the fucose-based lactose by means of glucose or glycerol, has advantages of high growth speed and good safety, and has significant industrial potential.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Comprehensive method for extracting L-tryptophan from fermentation liquor
ActiveCN101914054AReduce wasteIn line with the new concept of green environmental protectionOrganic chemistryClimate change adaptationLiquid wasteTryptophan
The invention discloses a comprehensive method for extracting L-tryptophan from fermentation liquor. The L-tryptophan is extracted from fermentation liquor which is made from corynebacterium glutmicum as a strain; meanwhile, generated waste liquor is recycled. The comprehensive method comprises the steps of: extracting the L-tryptophan and recycling the waste liquor, wherein the waste liquor generated in an extraction process is treated or recycled for application or used for preparing a compound fertilizer, a feed additive and feed protein. The method completely, effectively and comprehensively utilizes resources, recycles the generated waste liquor while extracting the L-tryptophan, reduces the resource waste, basically realizes the zero emission of waste water, effectively recycles the resources, and lightens the environment-protecting pressure.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Method of producing protein feed by liquid-solid two-step fermentation method
InactiveCN105010758APromote growthFast fermentationFood processingAnimal feeding stuff[Candida] apicolaBacilli
The invention discloses a method of producing a protein feed by a liquid-solid two-step fermentation method. The method comprises the following steps: performing liquid culture on corynebacterium glutamicum, candida utilis, bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus plantarum and aspergillus oryzae so as to obtain corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation liquor, candida utilis fermentation liquor, bacillus subtilis fermentation liquor, lactobacillus plantarum fermentation liquor and aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor; mixing the corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation liquor, the candida utilis fermentation liquor, the bacillus subtilis fermentation liquor, the lactobacillus plantarum fermentation liquor and the aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor so as to obtain mixed bacterium liquor; loading raw materials of soybean meal, cluster bean meal, cottonseed meal and the like into an explosion vat for performing steam explosion; after steam explosion, mixing materials, the mixed bacterium liquor and molasses in proportion, and adding an enzyme preparation so as to obtain mixed materials; conveying the mixed materials into a special modularized solid-state biological raw material continuous fermentation device for enzymolysis and fermentation, and drying the fermented materials so as to obtain the protein feed. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the modularized automatic fermentation device is adopted, the materials after explosion, the fermented bacterium liquor and the enzyme preparation are mixed, then the mixed materials are loaded into the automatic fermentation device for enzymolysis and biological fermentation, so that requirements for automatic temperature control, automatic dampness control and automatic ventilation control are met, the bioconversion rate is high, the fermentation period is short, the consumption is low, the cost is low, and mechanized and large-scale production requirements can be met.
Owner:河南双成生物科技有限公司
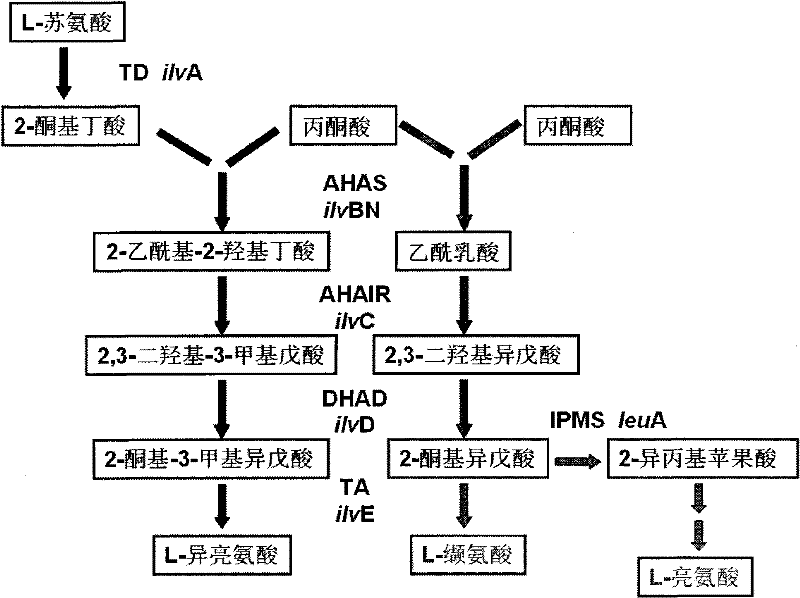
Recombinant dna, bacterial strain and method for fermentative production of l-valine
InactiveCN102286505AHigh activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcetohydroxy Acid Synthetase
The invention relates to a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), strain and method for producing L-valine by fermentation. The recombinant DNA comprises DNA sequence for coding acetohydroxy acid synthetase free of feedback inhibition of three branched-chain amino acids to acetohydroxy acid synthetase, DNA sequence for coding dihydroxy reduction isomerase, and DNA sequence for coding branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. The strain is corynebacterium or brevibacterium transformed by introducing the recombinant DNA. The method is implemented by culturing the strain to produce the L-valine. In the invention, the expression L-valine is used for producing the bacterium L-valine biosynthetic gene, so the yield of the L-valine can be greatly increased; and the fermentation model, especially the high-temperature short-time fermentation model, is constructed according to the optimum temperature of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme, so that the metabolism intensity of the strain is enhanced, the activity of the L-valine biosynthetic enzyme is enhanced, and the yield of the L-valine and the conversion rate of the sugar acid can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
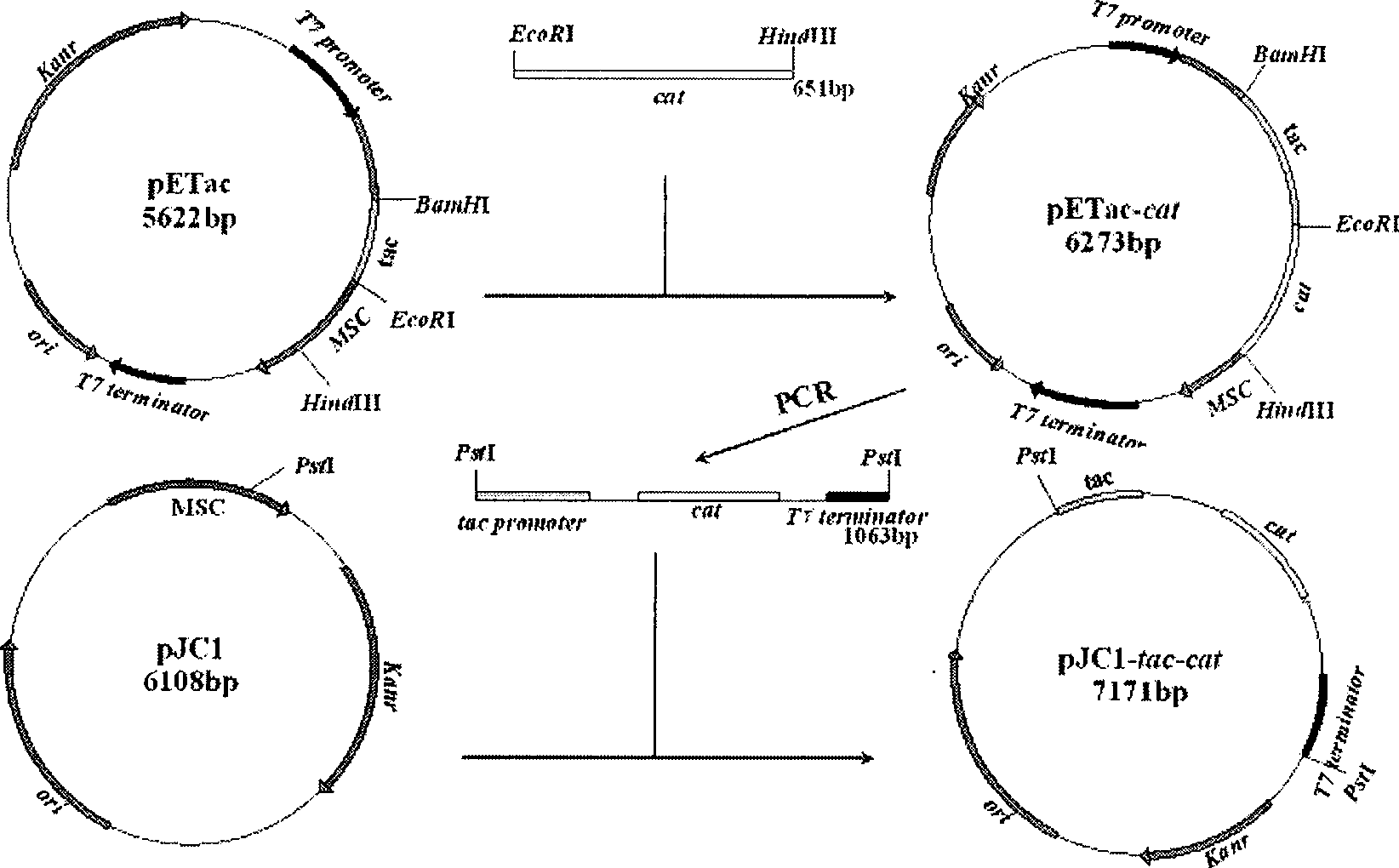
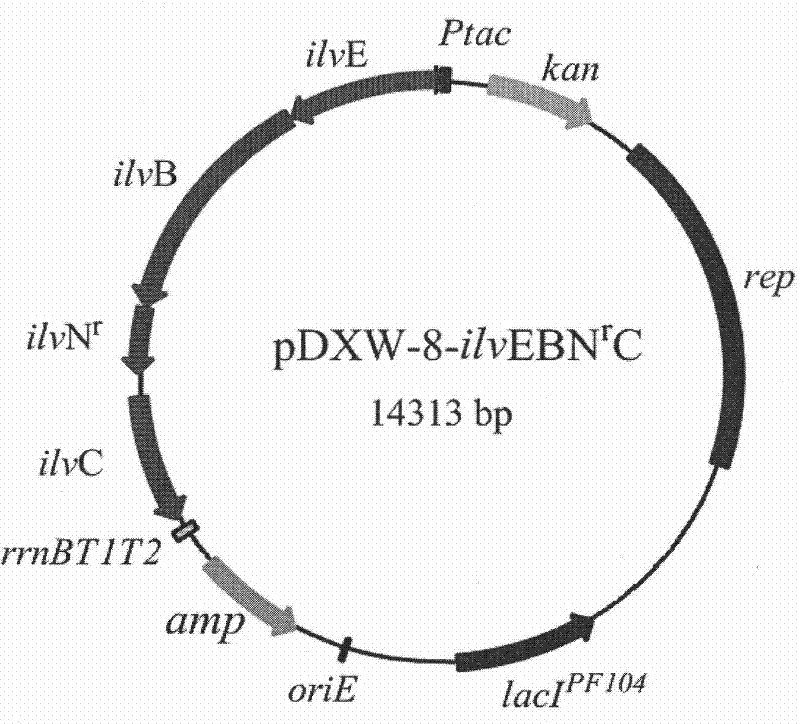
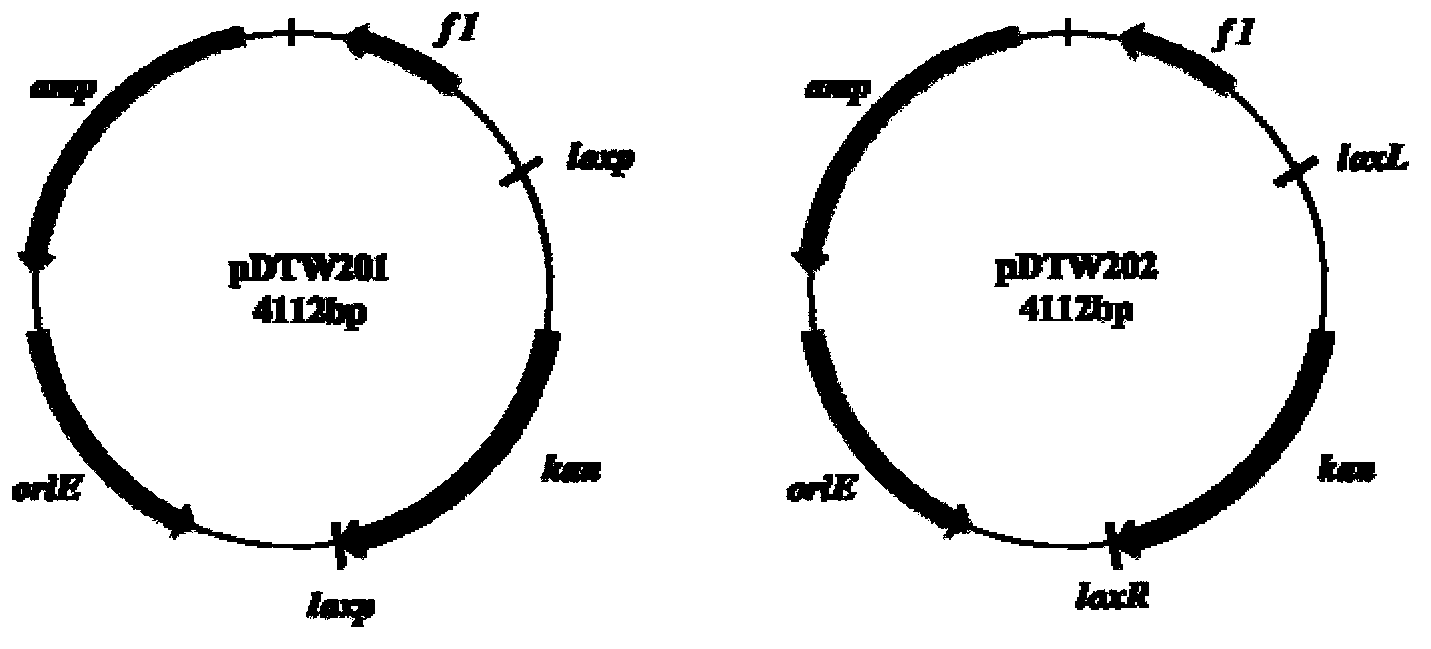
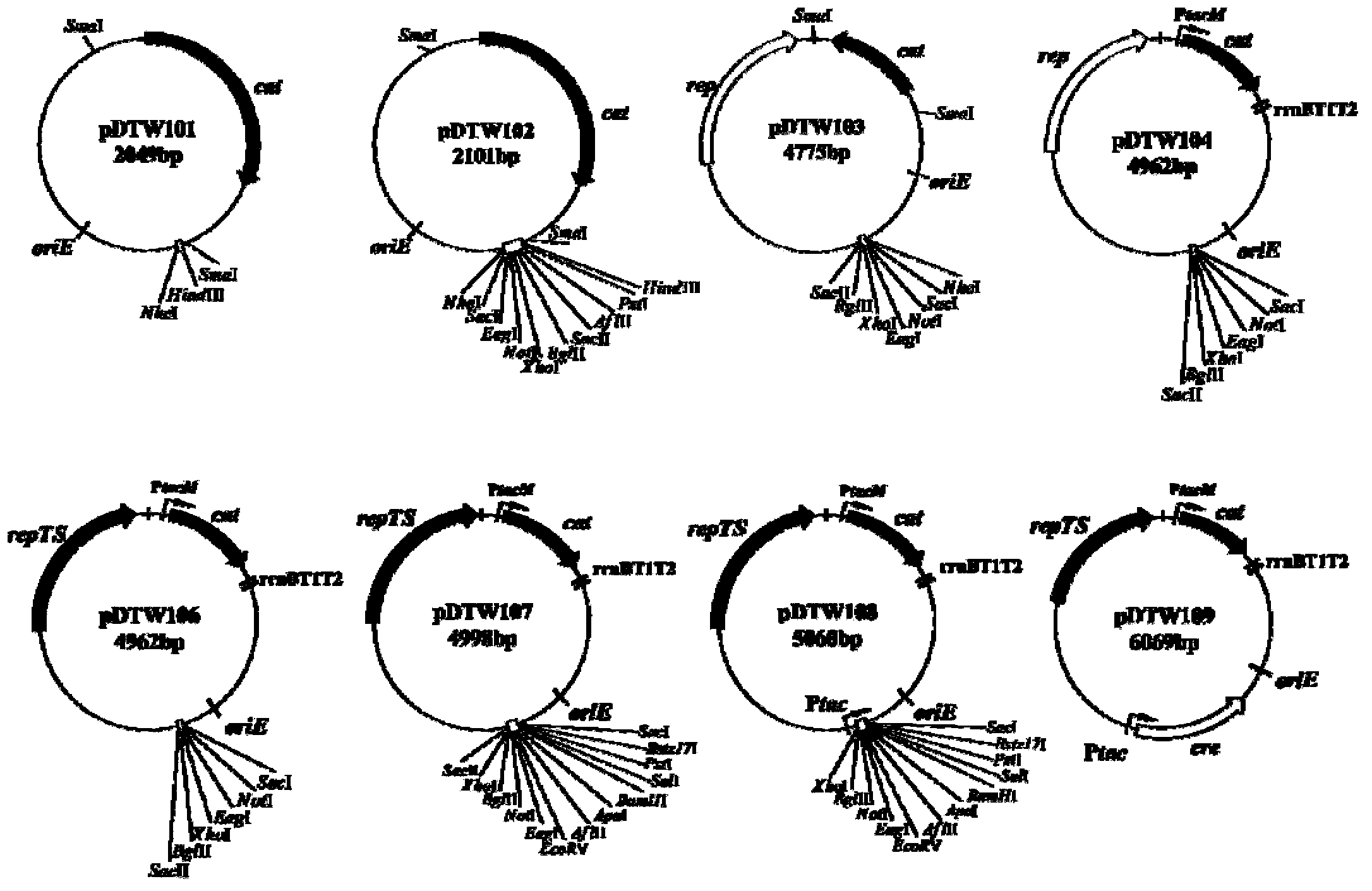
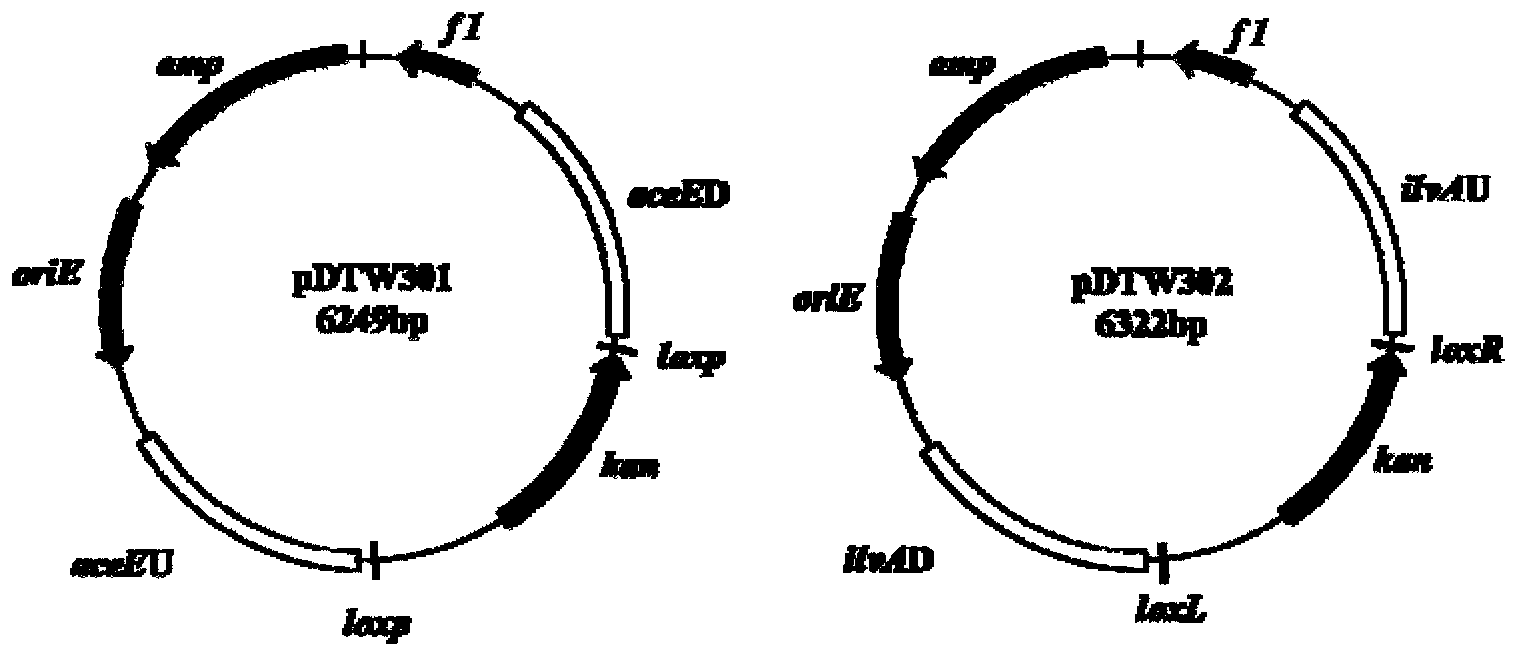
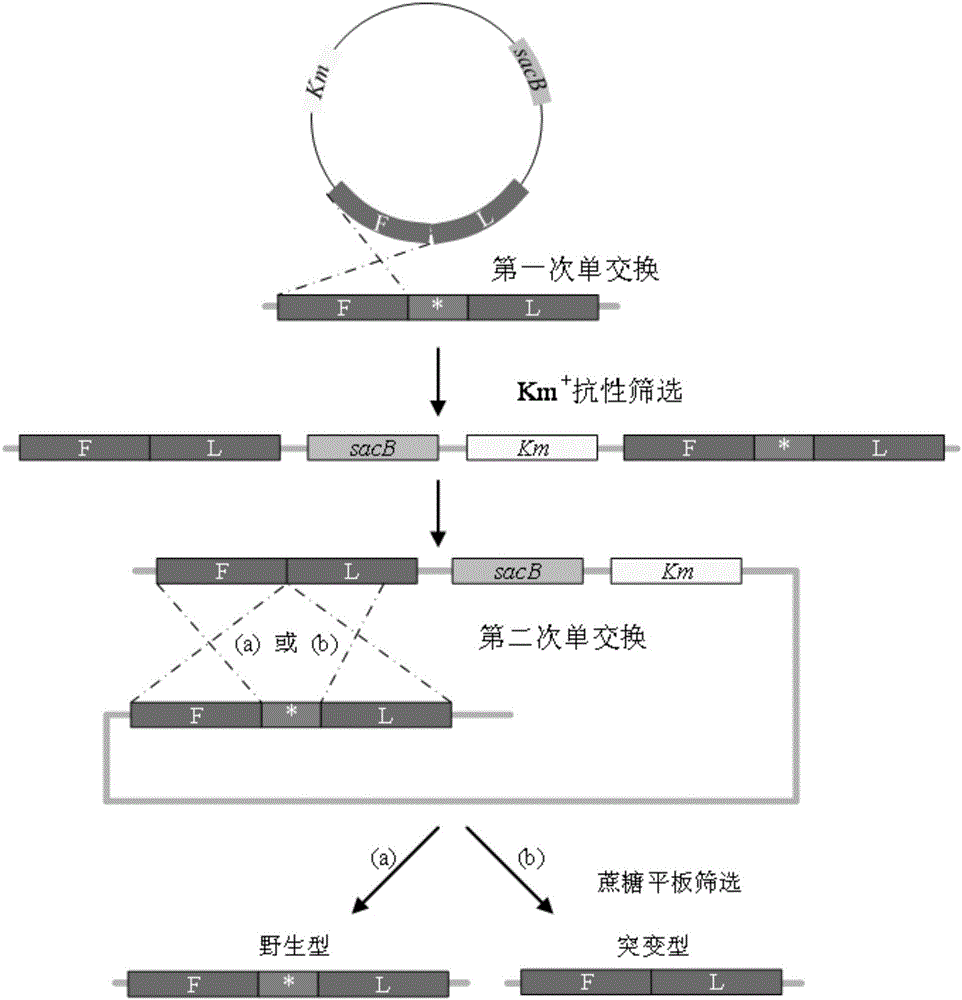
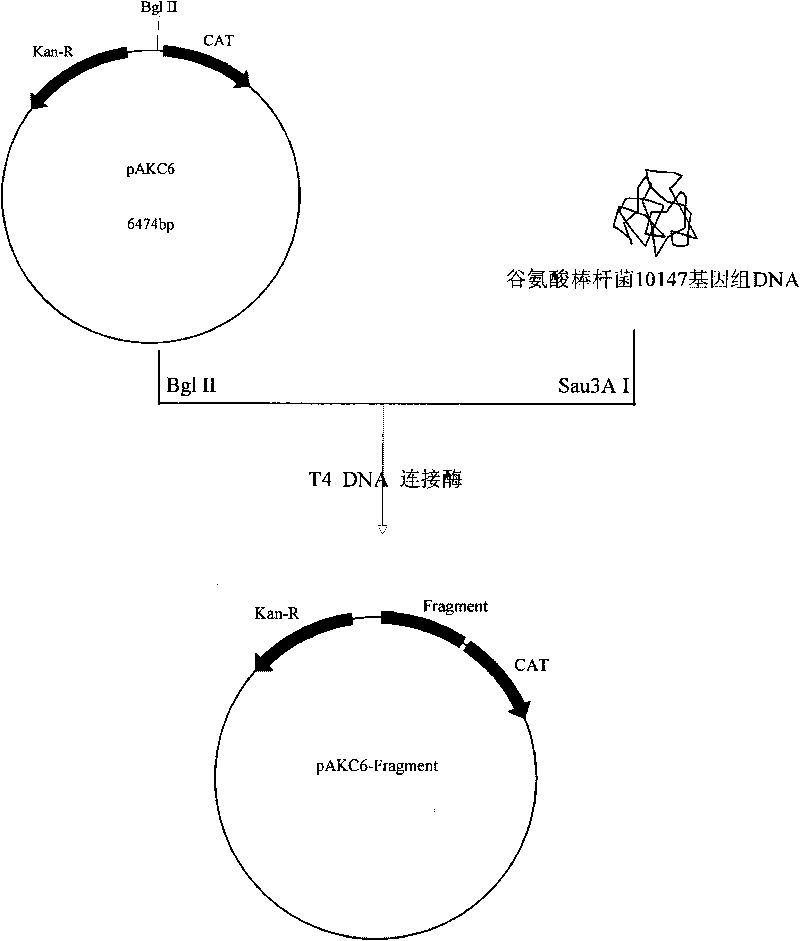
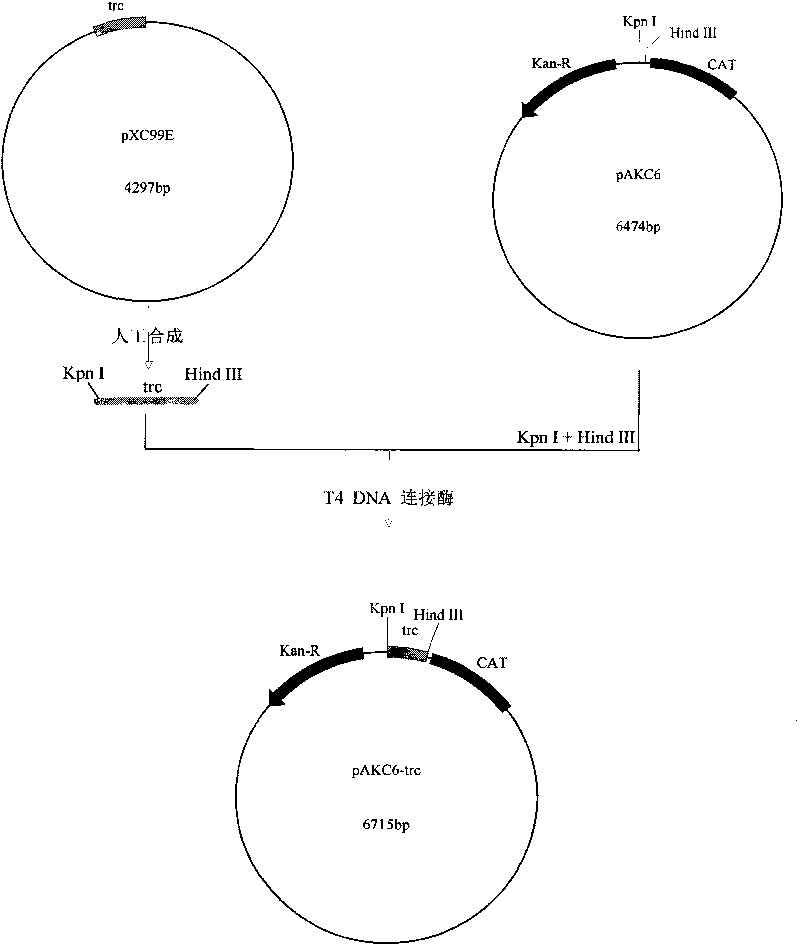
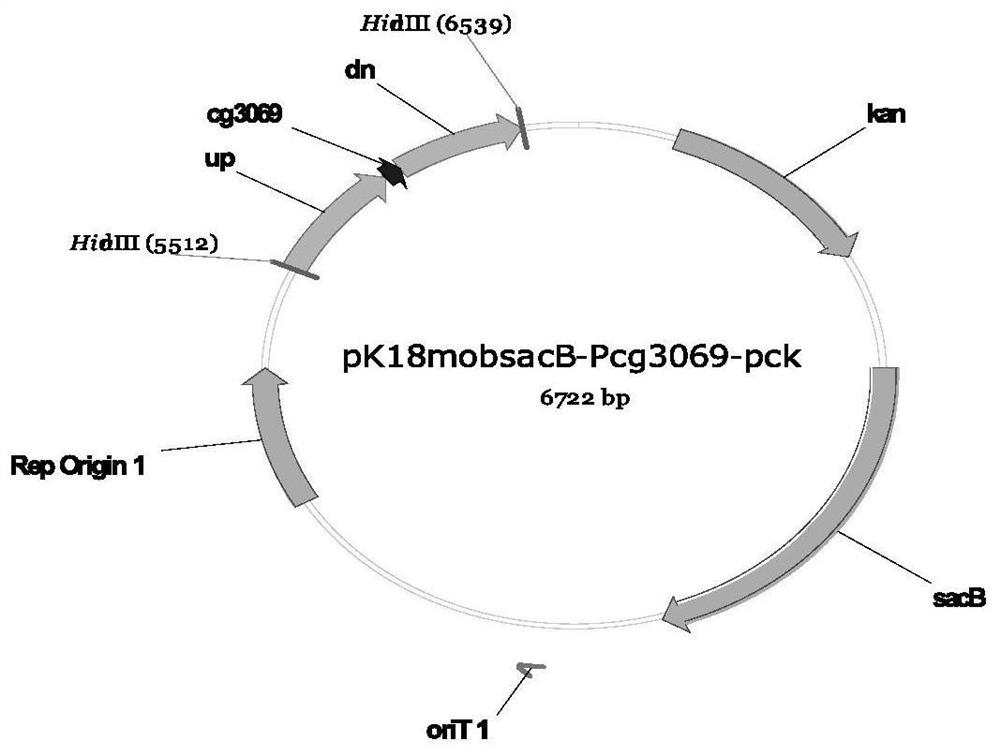
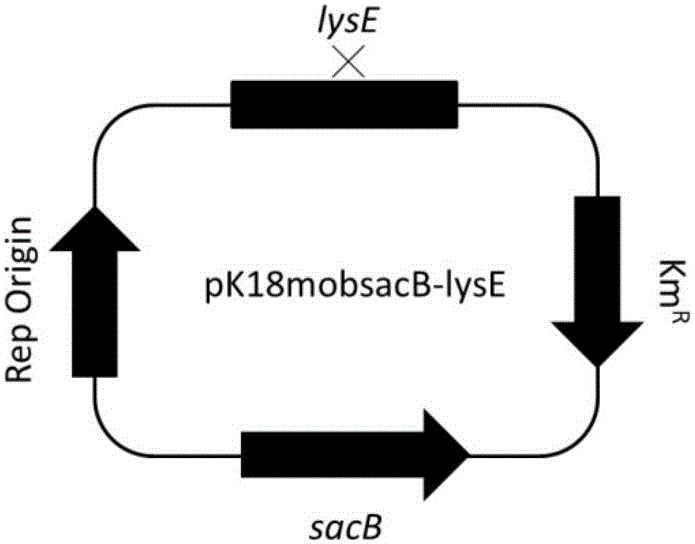
Corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system comprises a template plasmid and a temperature-sensitive expression plasmid, wherein the template plasmid provides a kan fragment (also known as a kan box) with loxp or variant loxL / R sites at two ends; and the temperature-sensitive expression plasmid carries a Cm resistance gene cat and a temperature-sensitive C. glutamicum replicon, expresses a Cre recombinant enzyme and is used for removing a Km resistance gene kan. The corynebacterium continuous knockout system disclosed by the invention can be generally used for continuous gene transformation of corynebacterium and has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation and high efficiency. By utilizing the knockout system, gene (continuous) knockout of three major typical subspecies genomes of the corynebacterium can be successfully completed, and the system is proved to be applicable to research and production of corynebacterium metabolites.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
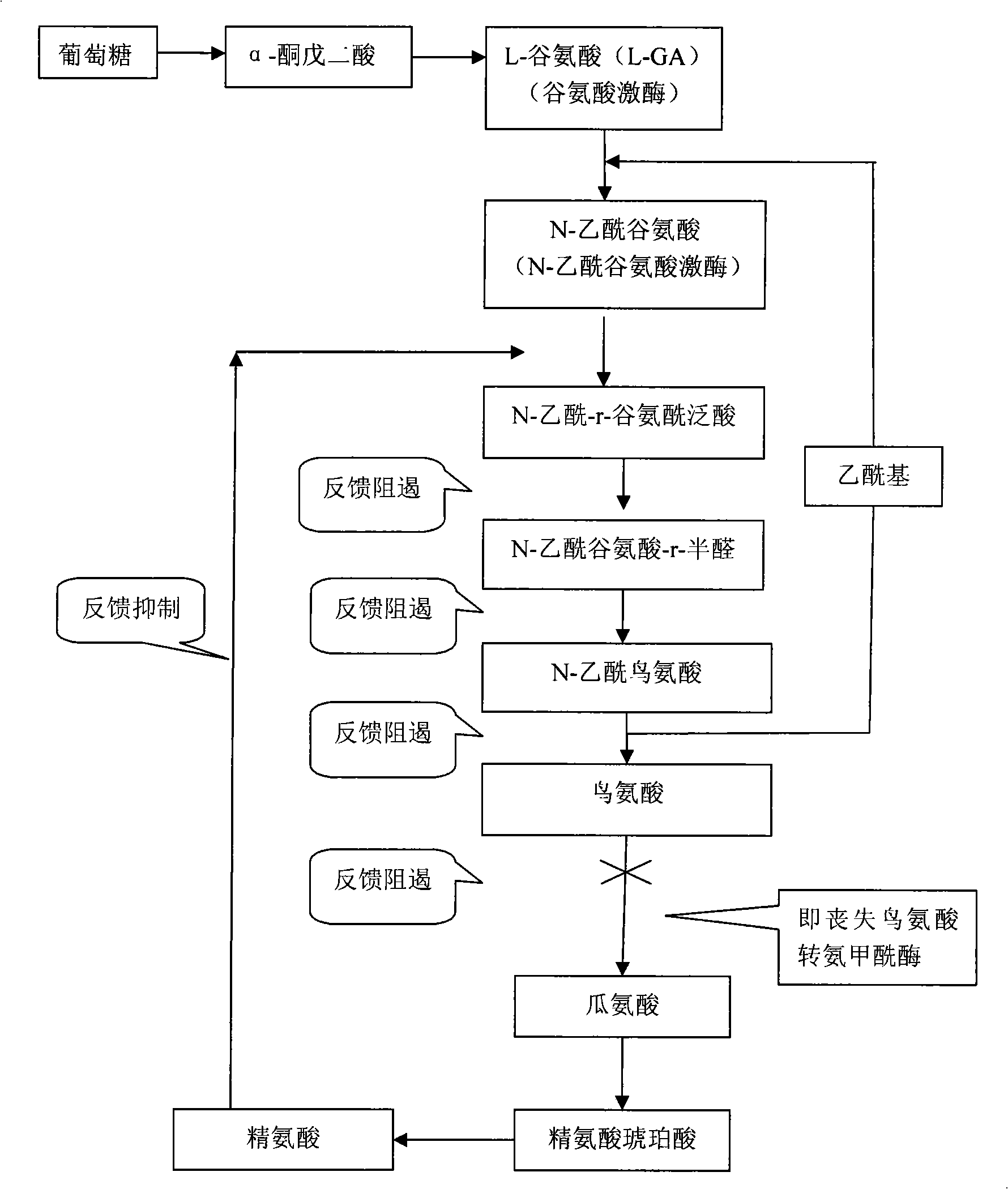
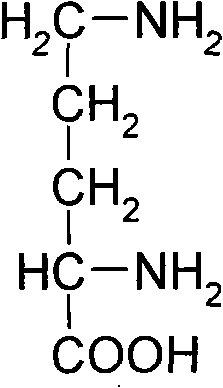
Method for producing L-ornithine by microorganism fermentation
InactiveCN101323866AFast acid productionImprove sugar conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSolubilityChemical treatment
The invention provides a method for producing L-ornithine by microbial fermentation, namely, using Corynebacterium glutamate to obtain the strains of CS-189(cit<(-)>+SG<r>) by chemical treatment, and obtain the L-ornithine hydrochloride by fermentation, culture solution micro-filtration by a ceramic membrane, ion exchange resin and extraction by a hydrothermal crystallization method with decompression concentration. The strains used in the method are auxotrophy resistant to sulfaguanidine, which significantly enhances acid yield by fermentation. Meanwhile, aiming at the problem that the solubility of the L-ornithine hydrochloride in water is extremely difficult, the hydrothermal crystallization method is adopted to obtain better extraction rate under the condition that flammable and explosive alcohol is not used. The method simplifies processes and reduces extraction cost.
Owner:上海聚瑞生物技术有限公司
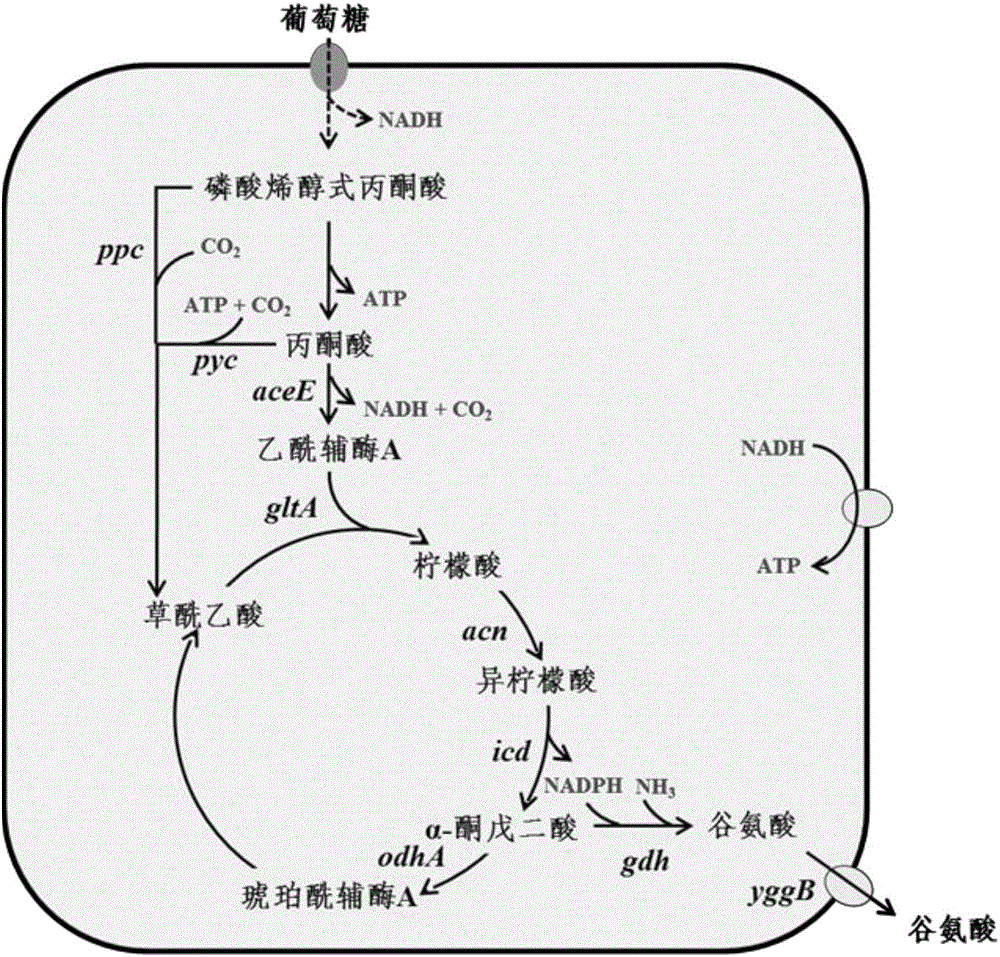
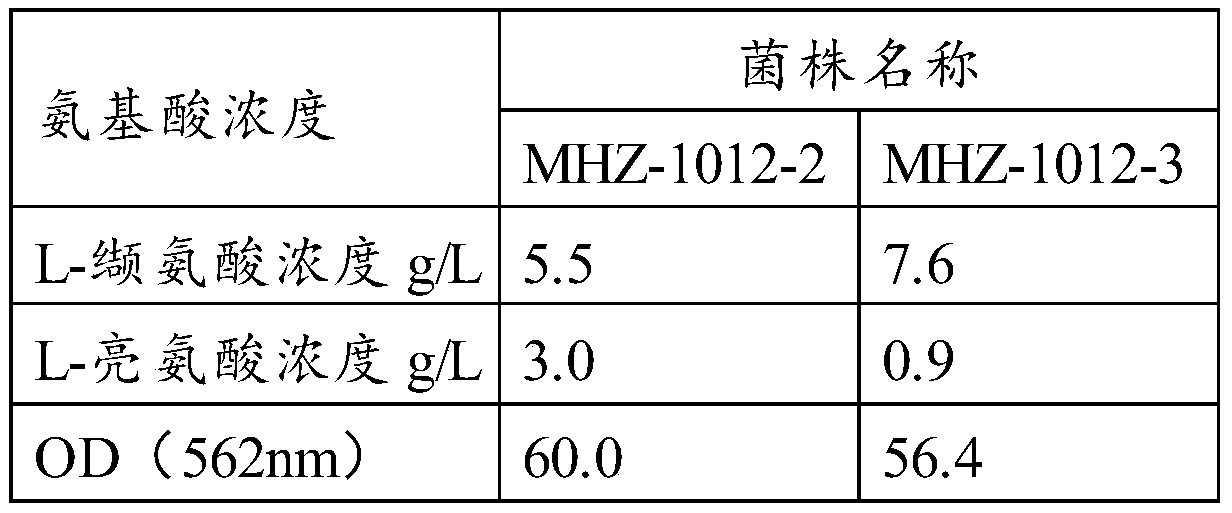
Recombinant strain and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a recombinant strain and application thereof. Experimental results show that before modification, wild corynebacterium glutanmicum ATCC 13869 almost generates no glutamic acid, and the yield of strain MHZ-0112-1 glutamic acid is 4.7 g / L; the yield of MHZ-0112-2 glutamic acid is 18.5 g / L; the yield of strain MHZ-0112-4 glutamic acid and the yield of MHZ-0112-5 glutamic acid are 23.4 g / L and 26.4 g / L respectively. When a strong promoter Psod is independently utilized for expressing a gdh gene, the yield of glutamic acid is increased about 1.8 times; when a promoter Ptuf is independently utilized for expressing a gltA gene, the enzyme activity of CS is improved 4 times, and the yield of glutamic acid is increased to 30.8 g / L; after the two genes are expressed at the same time, the yield of glutamic acid continues to be increased to 35.5 g / L, and the conversion rate reaches about 59%.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Promoter from corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof
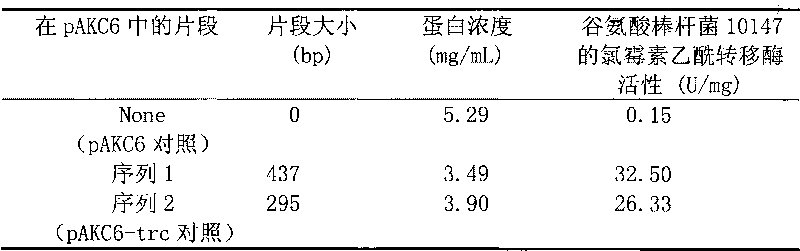
The invention discloses a promoter with a nucleotide sequence as follows: 1) a nucleotide sequence shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table; 2) a nucleotide sequence which hybridizes with the nucleotide sequence in 1) under strict conditions and has promoter activity; or 3) a nucleotide sequence which has homology of more than 70% with the nucleotide sequence in 1) and has promoter activity. The promoter provided by the invention can be applied to the biotechnology field with corynebacterium or escherichia bacteria as industrial microbes. Experiments prove a fragment with promoter activity from SEQ ID NO:1 has the activity higher than that of a trc promoter (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum high in hyaluronic acid yield and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106190939AFulfil requirementsExtraction process after simplificationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismToxin
The invention provides recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum high in hyaluronic acid yield and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum high in hyaluronic acid yield is constructed by genetic engineering technology. The invention also provides application of the recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum high in hyaluronic acid yield in the fermentative production of hyaluronic acid. The microbial Corynebacterium glutamicum of food safety grade is utilized which never secretes endotoxin, and post-extraction process is simplified; the recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum high in hyaluronic acid yield constructed by genetic engineering technology can produce hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights (3000 Da to 2000000 Da), the yield of the hyaluronic acid may reach 7 to 20 g / L according to the different molecular weights, and a product may satisfy the needs of foods, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals without complex separation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant with enhanced pH stability and application thereof
ActiveCN105296456AImprove the stability of enzyme activitySuitable for industrial production needsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGlutamate decarboxylaseRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses an acid-stable glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) mutant with pH stability migrating to neutral range, and belongs to the field of biological engineering. The encoding gene of glutamic acid decarboxylase derived from actobacillus plantarum GB01-21 glutamic acid decarboxylase is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis, and the glutamate E on the 89th site is mutated to arginine R or alanine A. The glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant has relative enzyme in pH value of 6.5 increased from the original 38% up to 72% or 84%, and the enzyme activity stability in the neutral pH range is increased significantly. For the transformation with a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant synthesized by recombinant escherichia coli, the GABA yield reaches 260 g / L, and the yield is 99.6%; and for the transformation with a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant synthesized by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum, the GABA yield reaches 116 g / L, and the yield is 99.5%. The invention reduces the fermentation equipment loss under acidic conditions, and lays foundation for the efficient synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
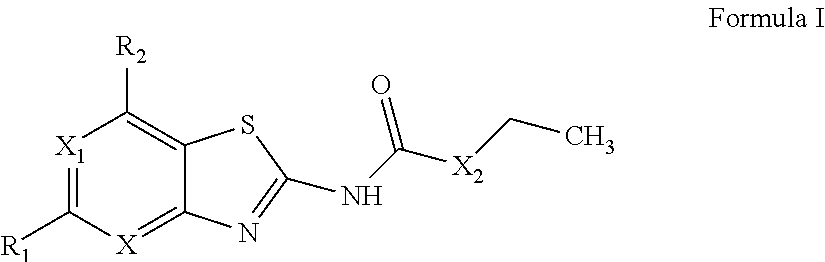
Benzothiazoles and aza-analogues thereof use as antibacterial agents
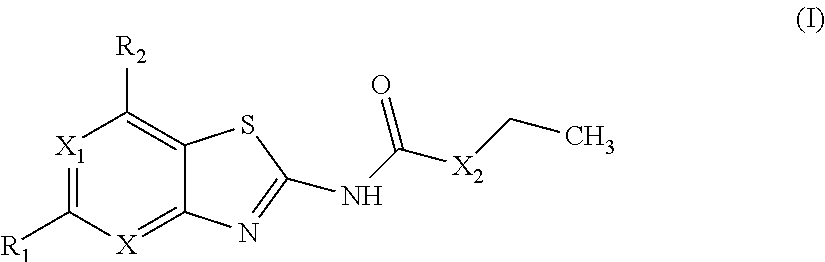
The present invention provides Gyrase B and / or Topoisomerase IV par E inhibitors, which can be used as antibacterial agents. Compounds disclosed herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed by gram positive, gram negative and anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Pseudomonas spp., Acenetobacter spp., Moraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasma spp., Legionella spp., Ktycobacterium spp., Helicobacter, Clostridium spp., Bacteroides spp., Corynebacterium, Bacillus spp., Enterobactericeae,’ (E. coli, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., etc.) or any combination thereof. Also provided, are processes for preparing compounds disclosed herein, pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds disclosed herein, and methods of treating bacterial infections. (Formula)
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Methods for the preparation of a fine chemical by fermentation
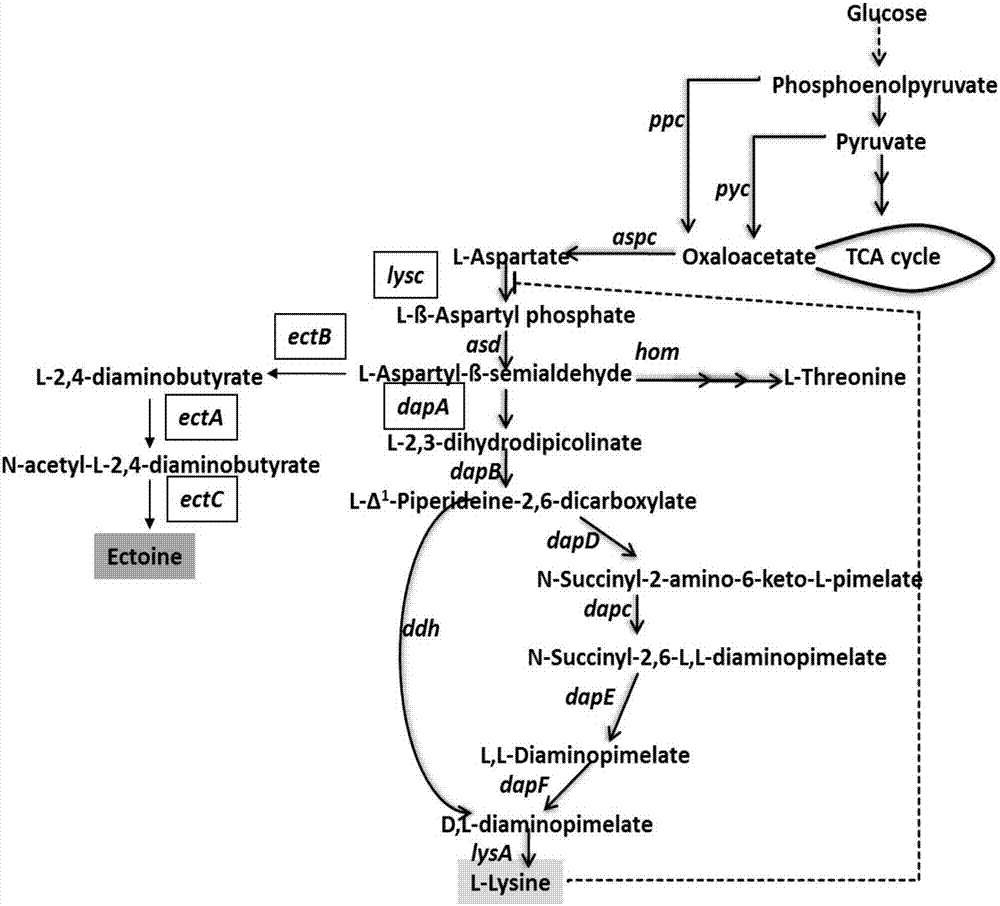
The present invention describs methods of increasing the production of a fine chemical, e.g., lysine from a microorganism, e.g., Corynebacterium by way of deregulating an enzyme encoding gene, i.e., fructose-l,6-bisphosphatase. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods of increasing the production of lysine in Corynebacterium glutamicum by way of increasing the expression of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase activity. The invention also provides a novel process for the production of lysine by way of regulating carbon flux towards oxaloacetate (OAA). In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides methods for the production of lysine by way of utilizing fructose or sucrose as a carbon source.
Owner:BASF AG
Method of producing tetrahydropyrimidine by fermenting recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum
ActiveCN107142234ALow costAddressing Biosecurity IssuesCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaBacterosiraFermentation
The invention provides a method of producing tetrahydropyrimidine by fermenting recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is obtained by the steps of performing overexpression in corynebacterium glutamicum to relieve an aspartokinase gene lysC of feedback inhibition; then replacing a promoter of a dihydropyrimidine dicarboxylic acid synthetase in the recombinant bacteria to weaken the activity of the dihydropyrimidine dicarboxylic acid synthetase; and then transferring tetrahydropyrimidine synthetic path related gene ectABC into the recombinant bacteria to obtain the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum provided by the invention can use different cheap raw materials to produce tetrahydropyrimidine by fermentation under a low salt condition, and cheap corn slurry can be also used as a nutritional component which replaces expensive yeast powder, so that the cost of the raw materials is further lowered. Meanwhile, the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum provided by the invention solves the problem of biosafety, simplifies the post-extraction process and has a good market application prospect.
Owner:北京绿色康成生物技术有限公司
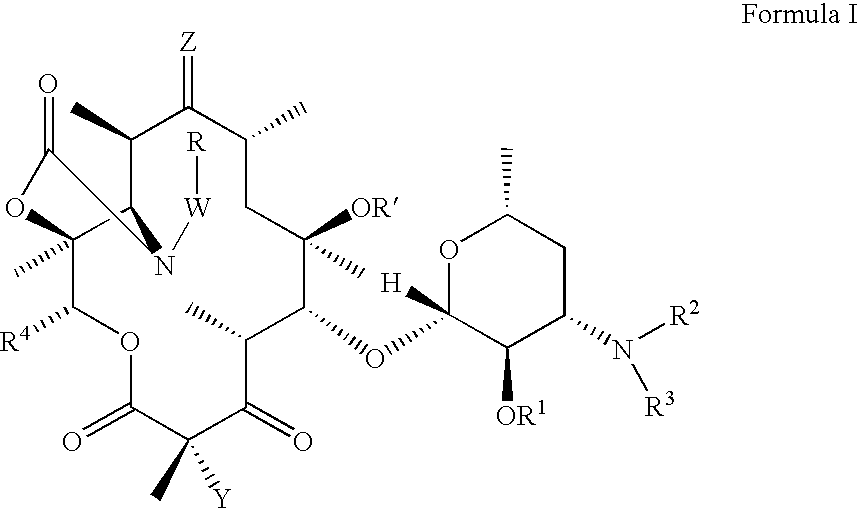
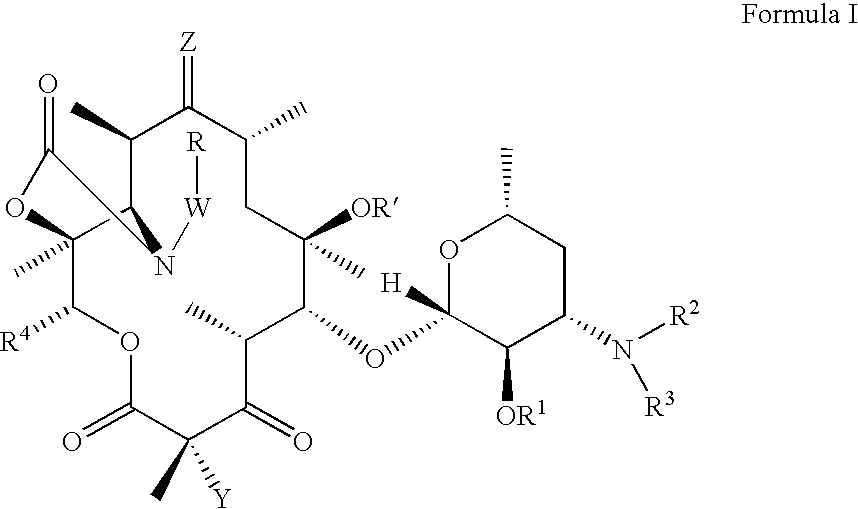
Ketolide derivatives as antibacterial agents
The present invention provides ketolide derivatives, which can be used as anti-bacterial agents. Compounds disclosed herein can be used for the treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed to by gram positive, gram negative or anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasm, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebacterium, Bacillus, Enterobactericeae or any combination thereof. Also provided are processes for preparing compounds disclosed herein, intermediates used in their synthesis, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and method for producing L-threonine
ActiveCN113322218AThe effect of acid production is remarkableBacteriaTransferasesThreonineBacterosira
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering, in particular to recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum and a method for producing L-threonine. The corynebacterium glutamicum for producing threonine is constructed by combining and transforming (or enhancing) a hom gene, a lysC gene, a thrC gene and the like which are resistant to feedback inhibition, and (or) a weakening (or knockout) pck gene and (or) a weakening (or knockout) pyk gene, and the acid production effect is very remarkable and far exceeds the highest level which is reported at present and reaches 20g / l.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum for producing gamma-polyglutamic acid as well as construction method and use of recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum
InactiveCN103146630ALow additional costSimple methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyWild type
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum for producing gamma-polyglutamic acid as well as a construction method and a use of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is characterized by being an engineering bacteria which is obtained by transferring a recombinant expression plasmid containing a gamma-PGA (Poly Glutamic Acid) synthetase composite gene pgsBCA to an original strain wild C.glutamicum ATCC13869. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum disclosed by the invention contains the gamma-PGA synthetase composite gene pgsBCA, so that much gamma-PGA can be synthesized under biotin limit or under the fermentation condition of adding Tween40, therefore, the glutamic acid adding cost in the gamma-PGA production process is reduced, and a foundation is laid for the innovation in realizing the one-step production of gamma-PGA better.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Corynebacterium capable of realizing high yield of valine as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN110982772AEfficient accumulationReduce accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlycineIsopropyl
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and discloses corynebacterium capable of realizing high yield of valine as well as a construction method and an application thereof. Theinvention provides corynebacterium capable of realizing high yield of valine as well as the construction method and the application thereof. According to the corynebacterium capable of realizing highyield of valine, alanine (A) at the first site of a 2-isopropylmalate synthetase gene leuA is mutated into glycine (G). According to the corynebacterium capable of highly producing valine, accumulation of by-product leucine is reduced by weakening a leuA gene, and the production capacity of an L-valine strain is improved. The experiments show that the corynebacterium disclosed by the invention isan L-valine high-yielding strain, can effectively accumulate L-valine and increase the yield of L-valine, lays a foundation for industrial production of L-valine, and has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
Glutamic acid corynebacterium and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN106635944AWith production capacityPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a glutamic acid corynebacterium and a construction method and application of the glutamic acid corynebacterium. The glutamic acid corynebacterium has the capability of producing L-lysine, and the activities of pyruvic carboxylase exportin and pyruvic carboxylase in a cell are both strengthened. The glutamic acid corynebacterium strengthens the activity of the pyruvic carboxylase exportin, so that the accumulation of the L-lysine is promoted, the yield of the L-lysine is increased, the activity of pyruvic carboxylase is strengthened at the same time, more precursors are provided for the synthesis of the L-lysine, the accumulation capability of the L-lysine is further improved, the amount of the L-lysine in a culture medium is increased, and the capability of production of the L-lysine through the fermentation of the strain is further improved. The experiment shows that the glutamic acid corynebacterium is a strain with high yield of L-lysine, the L-lysine is effectively accumulated, the yield of the L-lysine is improved, and a foundation is laid for the industrialized production of the L-lysine.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof
ActiveCN110699310APromote accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesBacilliBiological safety
The invention discloses tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Feedback inhibition is relieved through site-directed mutagenesis of Corynebacterium glutamicum aspartokinase gene lysC, and expression of mutational LysC is intensified through promoter replacement. Further, pentose phosphate pathway of host bacteriais further intensified through promoter replacement to meet needs on reducing power NADPH in efficient synthesis of tetrahydropyridine. Finally, tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum is obtained by transferring tetrahydropyridine synthetic gene cluster ectABC of P. stutzeri into recombinant bacteria. By recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum, tetrahydropyridine can be efficiently synthesized by utilizing cheap raw materials like glucose and maize plasm; compared with recombinant Escherichia coli produced strains, tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum hasbetter bio-safety and is of great significance to industrial production and large-scale application of tetrahydropyridine.
Owner:无锡晶扬生物科技有限公司
Fermentation type chopped chilli and processing technology thereof
InactiveCN104905195AUnique flavorClimate change adaptationFood preparationBiotechnologyMonosodium glutamate
The invention relates to fermentation type chopped chilli, which is prepared from fresh red peppers, ginger, garlic, peppers, monosodium glutamate, salt and fermentation broth. A processing technology comprises the following steps: washing the fresh red peppers with bases removed by using 0.5% saline, soaking the red peppers after washing into citric acid solution at 95-98 DEG C for 5 minutes, fishing out, rapidly placing into clear water, thus obtaining the blanched fresh red peppers; mixing saccharomycetes, bacillus aceticus, hydrocarbon corynebacterium and lactic acid bacteria, activating for 3-5min by using hot water at 30-40 DEG C, pouring the bacterium solution after activation into saline, adding rice wine into the saline, thus obtaining the fermentation broth, and regulating the pH of the fermentation broth to 4-5 by using 5% acetic acid solution for later use; and pouring the fermentation broth into the blanched fresh red peppers, adding with the ginger, the garlic, the peppers, the monosodium glutamate and salt, and performing fermentation culture for 10-15h at 20-25 DEG C, and thus obtaining the fermentation type chopped chilli. The fermentation type chopped chilli is unique in flavor and bright red and crispy, and has the shelf life longer than three years.
Owner:HUBEI YUANYEFENG FOOD
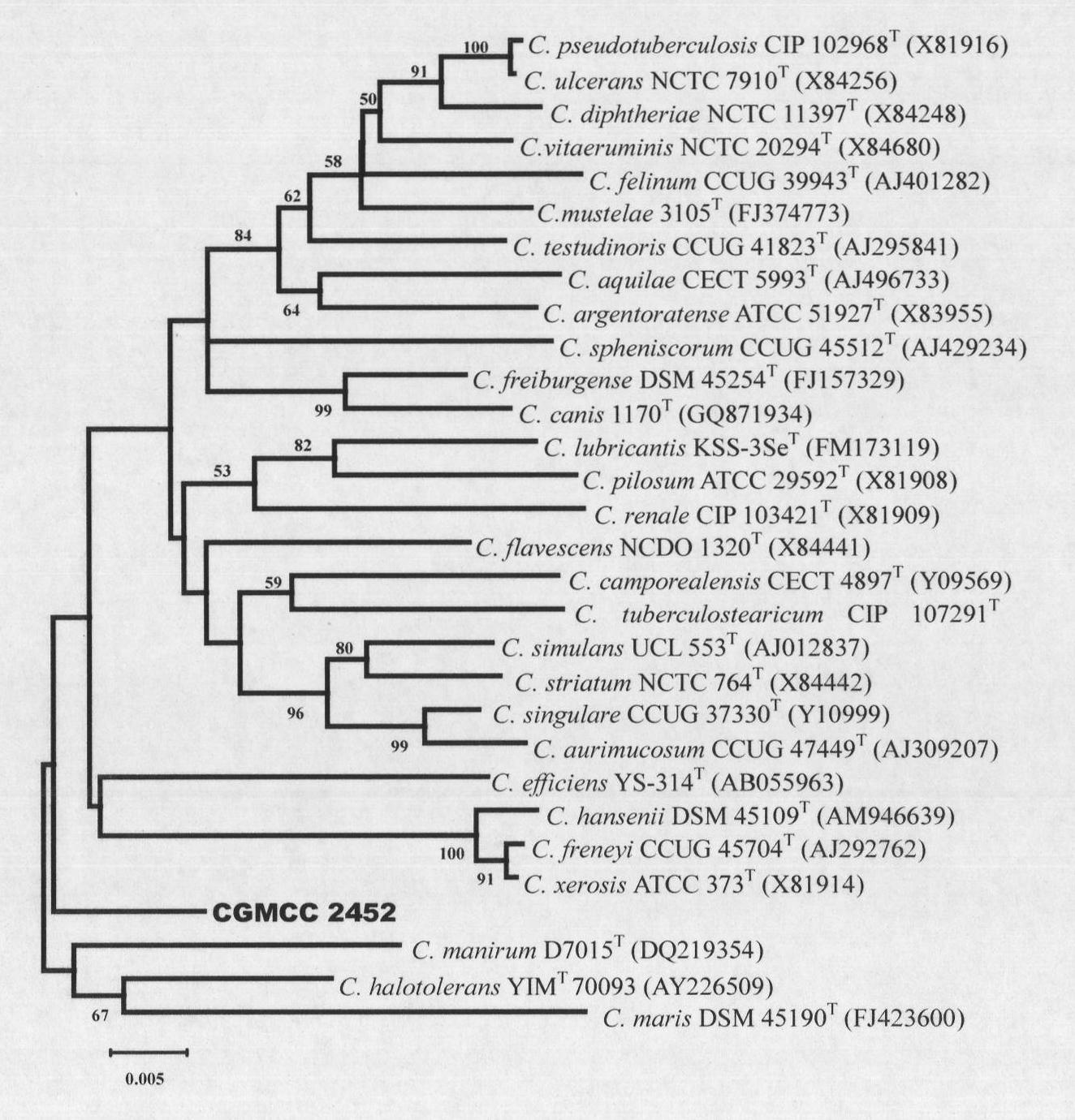
Corynebacterium humireducens and application thereof
InactiveCN101892180AUtilize a broad spectrumEfficient reduction abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationSludge
The invention discloses corynebacterium humireducens and an application thereof. The corynebacterium humireducens is obtained by separating and purifying anolyte of a sludge microbe fuel cell, and is preserved in the ordinary microbe centre of the China Microbe Culture Preservation Management Committee on April 14, 2008 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.2452. The corynebacterium humireducens has wide utilization spectrum of electron donor under the anaerobic condition, has efficient humus reduction capability and electrogenesis capability under the alkaline condition, can be widely applied to in-situ microbe restoration of organic pollutants, microbe fuel cell generating technology or recycling processing of high-concentration organic wastes.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Method for fermenting and decomposing gossypol in cottonseed meal by composite strains
InactiveCN102178035ADecreased sperm motilityReduce drug residuesFood processingAnimal feeding stuffTorula utilisCorn steep liquor
The invention discloses a method for fermenting and decomposing gossypol in cottonseed meal by composite strains. Corynebacterium, Torula utilis Henneb, Bacillus subtilis and lactic acid bacteria are used for fermenting and culturing to prepare composite strain fermentation broth; then, the composite strain fermentation broth and a cottonseed meal raw material composed of cottonseed meal, corn steep liquor, molasses, ammonium sulphate, urea and a 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution raw material are evenly mixed; and then a solid is fermented, dried, smashed and packaged by a sealed bag to finish decomposing the gossypol in the cottonseed meal. The protein solubility of the fermented cottonseed meal is improved by above 50%, the feed cost is lowered, the breeding benefit is increased, and the cottonseed meal has a wide use range.
Owner:河南宏翔生物科技有限公司
Method for synthesis of D-psicose by aldolase whole cell
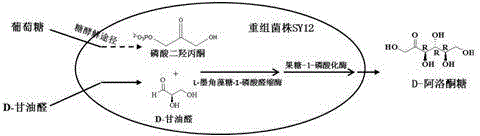
The invention discloses a method for synthesis of D-psicose by microbiological fermentation, specifically a method for synthesis of D-psicose by aldolase whole cell. The method includes: firstly constructing recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum SY12 carrying L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase gene and fructose-1-phosphorylase gene (i.e. with aldehyde condensation approach), then adding glucose and D-glyceraldehyde into a basic salt medium, synthesizing dihydroxyacetone phosphate from glucose by means of intracellular glycolysis, synthesizing a single product D-psicose from D-glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) under the action of the L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase and fructose-1-phosphorylase carried by the corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain SY12, with the conversion rate of D-glyceraldehyde being 53%. Therefore, compared with the existing method for in vitro synthesis of D-psicose by ketose3-epimerase, the biosynthesis method of D-psicose provided by the invention has the advantages of high conversion rate, single product, easy separation and the like, and lays certain foundation for mass production of D-psicose.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
Ketolide Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents
Provided herein are ketolide derivatives, which can be used as antibacterial agents. Compounds described herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed to by gram positive, gram negative or anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasm, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebacterium, Bacillus, Enterobactericeae, Propionibacterium acnes or any combination thereof. Also provided are processes for preparation of compounds described herein, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com