Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
634 results about "Corynebacterium glutamicum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
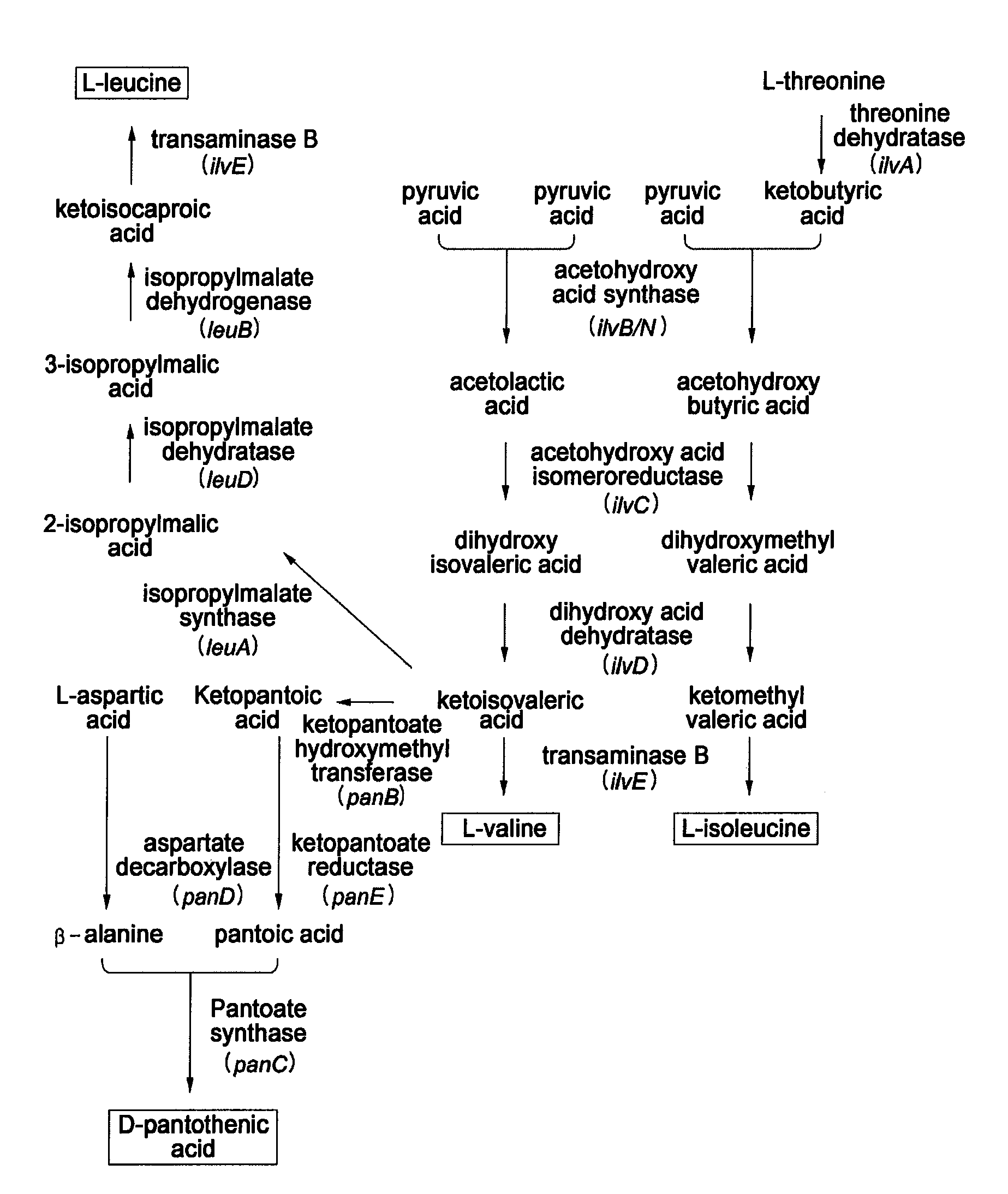
Corynebacterium glutamicum (previously known as Micrococcus glutamicus) is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium that is used industrially for large-scale production of amino acids. While originally identified in a screen for organisms secreting L-glutamate, mutants of C. glutamicum have also been identified that produce various other amino acids.
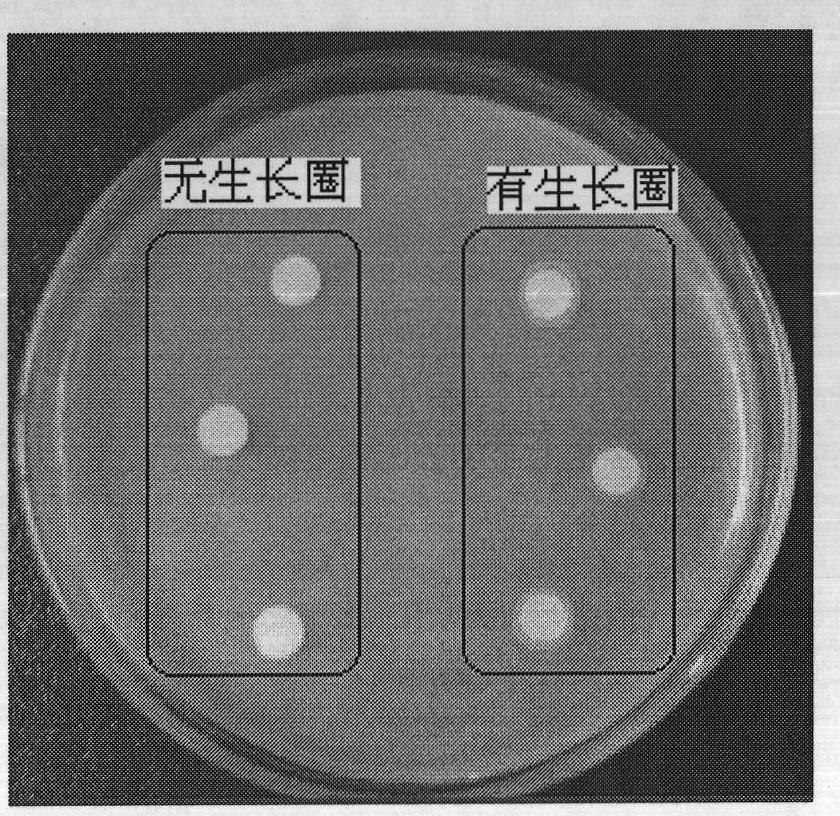
Microorganism having enhanced L-valine productivity and method for producing L-valine using the same
The present invention relates to a microorganism having an enhanced L-valine productivity and a method for producing L-valine using the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a Corynebacterium glutamicum mutant strain that has resistance to L-valine and derivatives thereof so as to have an enhanced L-valine productivity, and a method for producing L-valine using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding regulatory proteins
InactiveUS20050153402A1High yieldIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated MR nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel MR proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing MR nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated MR proteins, mutated MR proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of MR genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
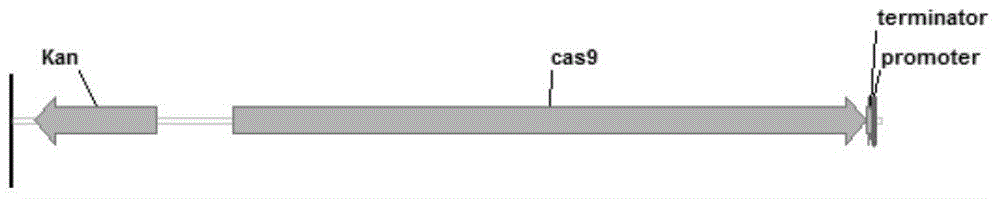
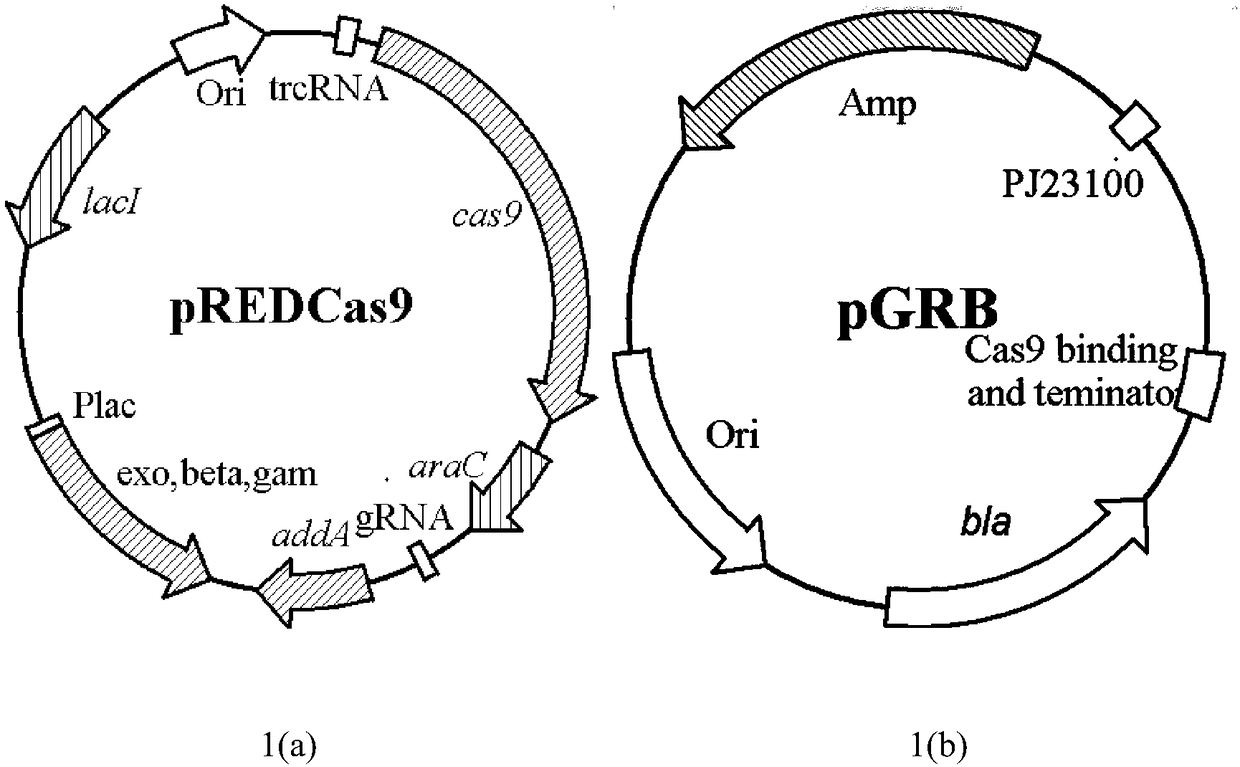
Construction and application of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing vector for microorganisms
ActiveCN105238806AQuick editShort test cycleVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses construction and application of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing vector for microorganisms. The constructed CRISPR / Cas9 gene vector consists of a replication start site, a selection marker gene, a Cas9 protein gene, gRNA coding DNA, a homologous recombinant element and an operon. The CRISPR / Cas9 gene vector constructed by the invention is capable of editing (including performing such operations as knocking out, replacing, interpolating and the like on gene or DNA sequence) escherichia coli or corynebacterium glutamicum genome; and the gene vector has the advantages of being short in test cycle, time-saving and cost-saving, high in efficiency and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing multi-vitamins and multi-enzymes high protein microorganic agent by multi-bacteria solid fermentation
InactiveCN1552233AImprove disease resistanceQuality improvementFungiFood processingBacterial strainOrganism
A process for preparing the multi-vitamine multi-enzyme high-protein microbial preparation by the solid fermentation of multiple bacterial strains includes such steps as preparing seed culture media, respectively inoculating reticularia, torula yeast, glutamic corynebacteria, Bacillus subtitis, Aspergillus niger, etc into said seed culture media, culturing at 30-35 deg.C for 15-18 hr, inoculating them into the solid culture medium, fermenting at 33+ / -0.5 deg.C for 70-80 hr, and fast drying. Its can be used as the feed containing living microbes, microbial enzymes, vitamines, etc.
Owner:哈尔滨中冠生物工程有限公司
Corynebacterium glutamicum and method for producing high-yield isoleucine with same
ActiveCN105886431ASignificant progressBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenes mutationMicroorganism
The invention relates to Corynebacterium glutamicum and a method for producing high-yield isoleucine with the same, and belongs to the field of microorganisms and genomics. The Corynebacterium glutamicum, specifically Corynebacterium glutamicum YI is preserved with a preservation number CGMCC NO. 12153. The Corynebacterium glutamicum is obtained by means of mutagenesis and is fermented in a 30L fermentation cylinder for 32-40 hours; the yield of isoleucine is up to 28g / L; accordingly, the method has the advantages of short time for fermentation and high yield and is superior to the prior art. The invention also discloses a gene mutation site of the strain relative to a standard strain, providing a new direction for correlational researches.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and structuring method and application thereof
ActiveCN105018403AIncrease productivityLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisBiotechnology
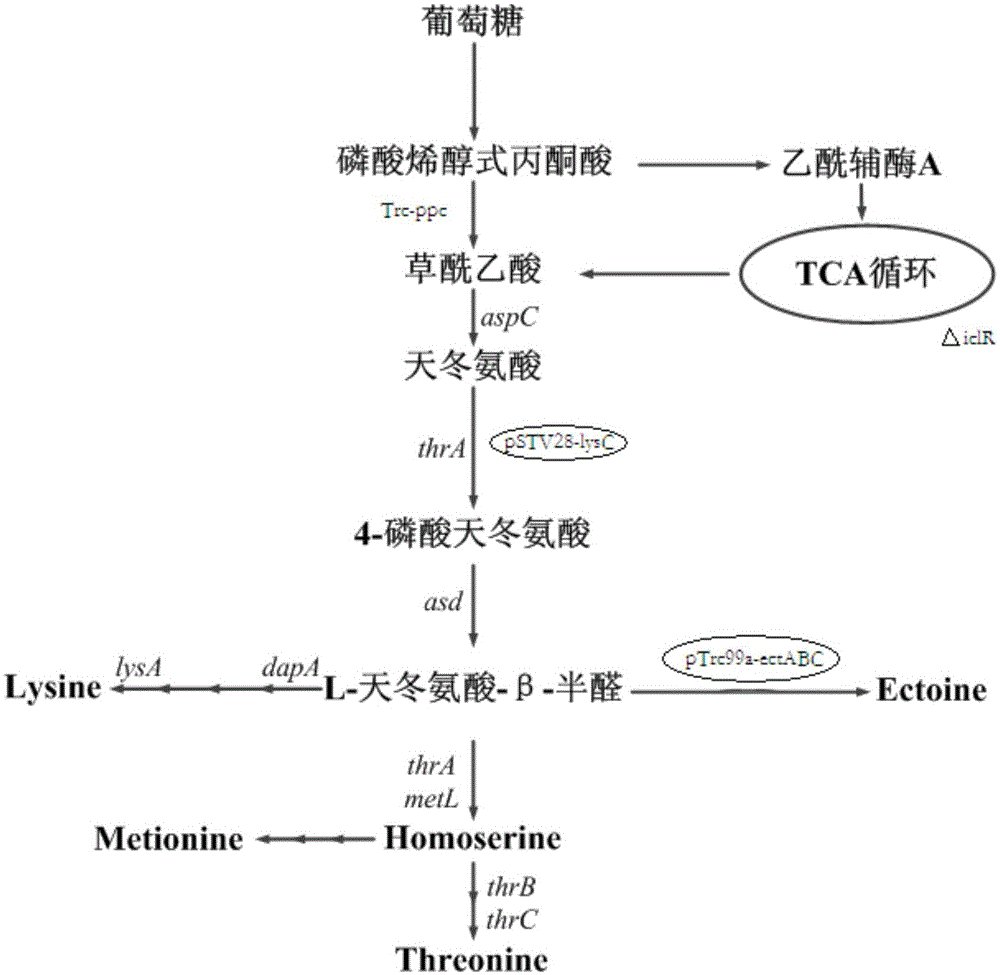
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and a structuring method and application thereof. The genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli with a specific genotype, comprises Halomonas-elogata-derived ectABC gene, has three gene deficiency variants including lysA, thrA and iclR and has corynebacterium glutamicum lysC gene controlled by a lac promoter and ppc gene controlled by a trc promoter. The defect that chemical synthesis methods have harsh reaction conditions and high energy consumption can be overcome by using the genetically engineered bacterium and utilizing glucose fermentation to produce tetrahydropyrimidine. The defect that Halomonas-elogata fermentation or enzyme-catalyzed methods are complex in process and high in production cost can be overcome. After fermentation for 20-28h, yield of tetrahydropyrimidine reaches 12-18g / L, and the genetically engineered bacterium has high industrial application value.
Owner:合肥和晨生物科技有限公司
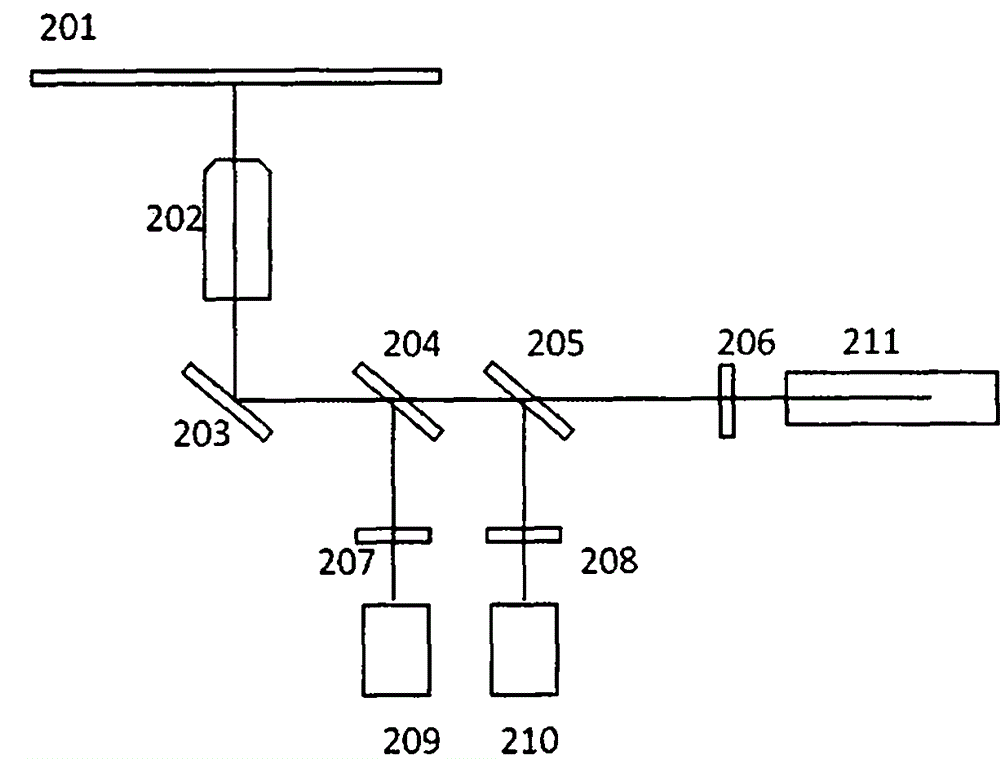
High-throughput detection system for microbe based on droplet microfluidic chip
InactiveCN104007091AImprove throughputSimple designFluorescence/phosphorescenceEscherichia coliMetabolite
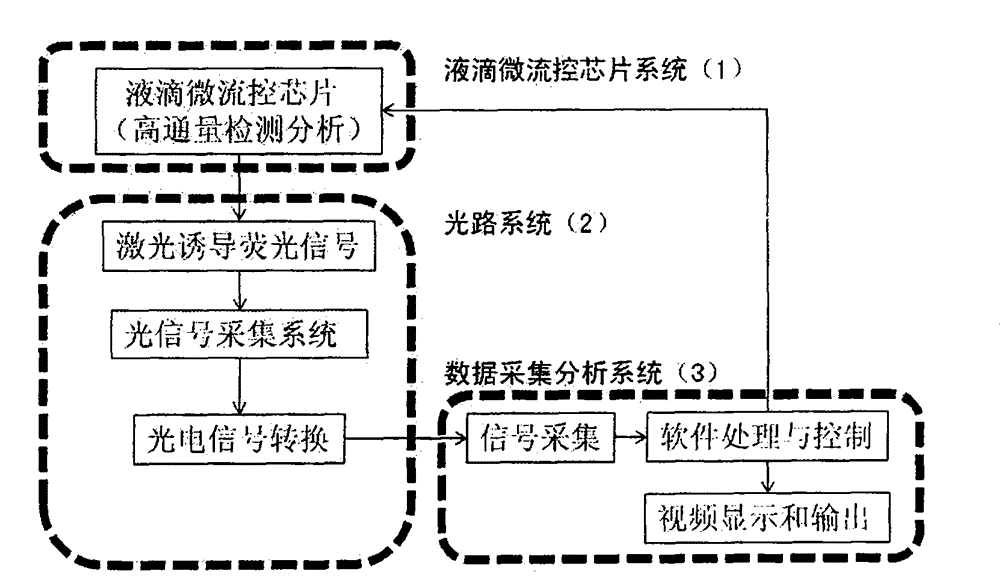
The invention relates to a high-throughput detection system for microbes based on a droplet microfluidic chip. The system mainly comprises a droplet microfluidic chip system (1), a light path system (2) and a data acquisition and analysis system (3), wherein the droplet microfluidic chip system (1) embeds to-be-detected microbe to an independent single droplet micro-reaction chamber; the light path system (2) is used for carrying out laser-induced fluorescence detection signal transmission of the microbe sample in the single droplet micro-reaction chamber; and the data acquisition and analysis system (3) carries out detection and analysis on the acquired signals through a computer software. The droplet microfluidic chip can be replaced. The system is suitable for laser-induced fluorescence detection and analysis of different types of microbes, has the advantages of simple design, low processing and manufacturing cost, low detection cost, fast speed and high throughput, and realizes efficient screening of production-related target enzymes and metabolites of different types of industrial microbes including escherichia coli, corynebacterium glutamicum and saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
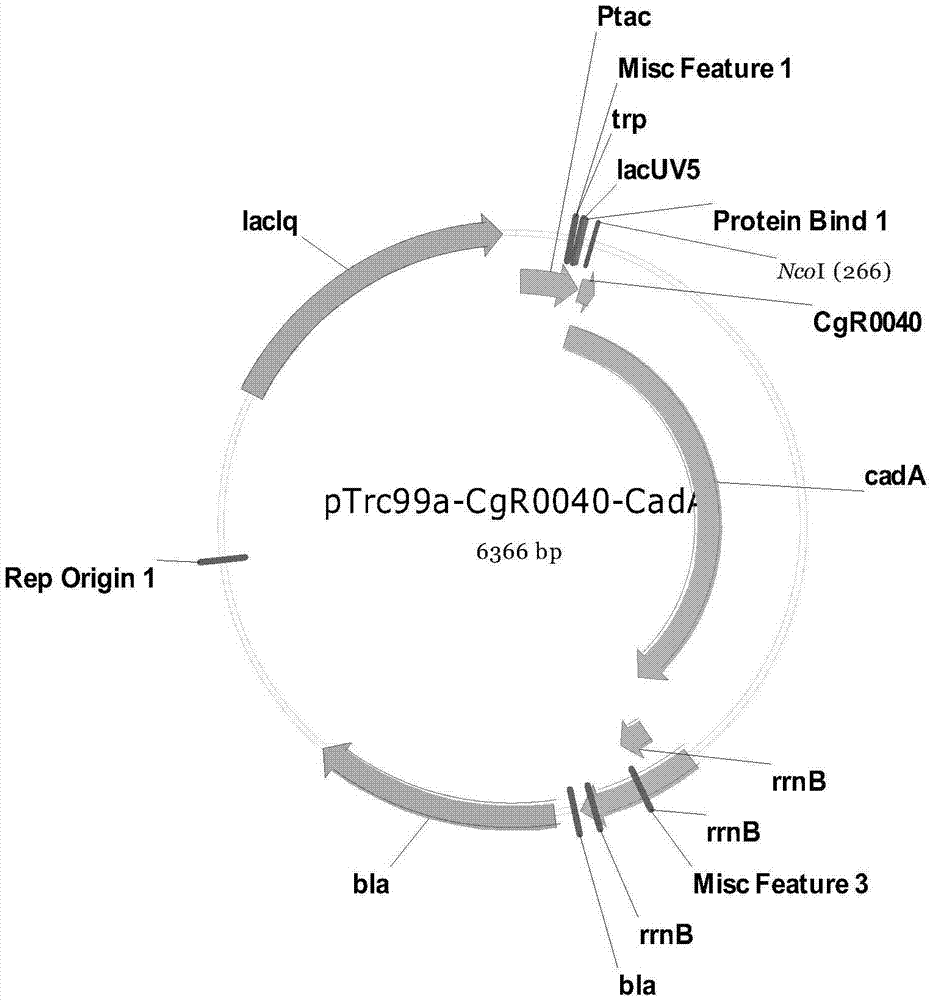
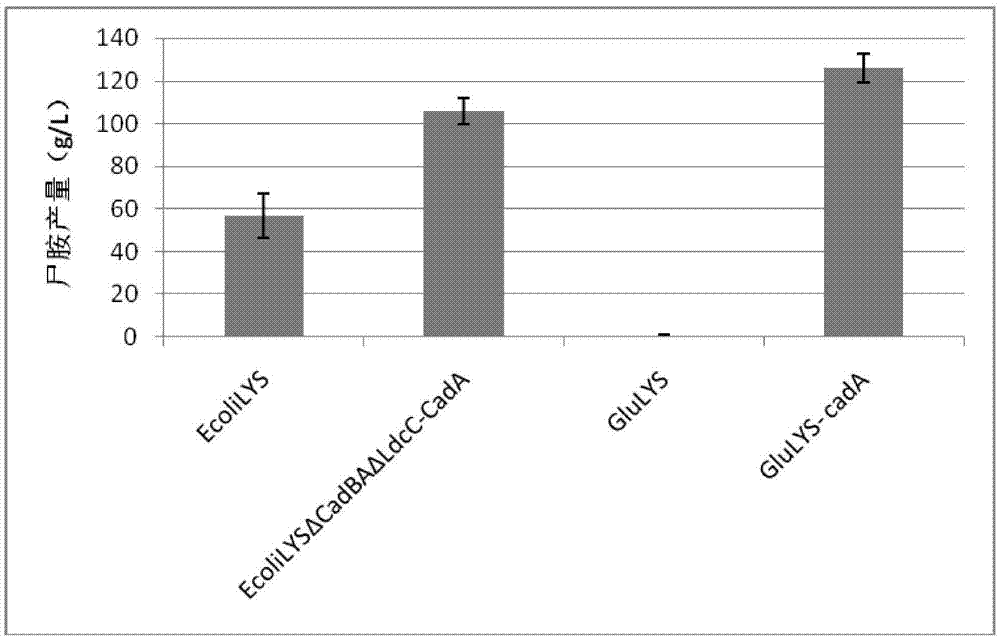
Cadaverine-producing engineering strain
InactiveCN102424811AOversynthesisCurb global warmingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynthesis methodsFermentation
The invention relates to a cadaverine-producing engineering strain, a construction method thereof and a method for producing cadaverine by using the strain. Based on a gene engineering technology, an L-lysine decarboxylase gene (cadA / LDC) and a cadaverine-lysine antiporter gene (cadB) are respectively or simultaneously cloned into Corynebacterium glutamicum and subjected to induced coexpression, the lysine is decarboxylated to generate cadaverine under the catalytic action of the CadA enzyme, and the cadaverine is transported out of cells by the CadB protein, thus constructing a high-yield cadaverine-producing engineering strain and establishing a novel one-step cadaverine synthesis method based on the fermentation of Corynebacterium glutamicum. The one-step cadaverine synthesis method based on microbial fermentation provides a new way for large-scale cadaverine production, thereby having great economic benefits and social benefits and wide market development prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding proteins involved in DNA replication, protein synthesis, and pathogenesis
InactiveUS20060269975A1Efficient producerImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidGenetic engineering
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated RRP nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel RRP proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing RRP nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated RRP proteins, mutated RRP proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of RRP genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
Methods for secretory production of proteins
The object of the present invention is to provide a method of producing a heterologous protein by making a coryneform bacterium to produce and efficiently extracellularly secrete (secreto-production) an industrially useful heterologous protein. According to the present invention, a genetic construct is used where a gene sequence encoding an intended protein which is ligated to the downstream of a sequence encoding the signal peptide derived from a coryneform bacterium, the gene construct is introduced into a mutant coryneform bacterium which has a capacity of secreting the heterologous protein at least 2-fold higher than the wild type Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13869, the mutant coryneform bacterium is cultured and the extracellularly released heterologous protein is recovered.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Corynebacterium glutamicum and application
InactiveCN106190921AIncrease productionSignificant progressCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaMicrobiologyEnzyme
The invention provides corynebacterium glutamicum and application. The corynebacterium glutamicum is compared with a genomic sequence of a corynebacterium glutamicum standard strain ATCC 13032, and multiple base mutations exist in an amino acid sequence of an enzyme related to valine synthesis. The preservation number of the corynebacterium glutamicum is CGMCC No.12152, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has an important application value in the aspect of preparing valine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deleted engineering bacterium and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102102086ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseLactic acid fermentation
The invention relates to an L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deleted engineering bacterium and a construction method and application thereof. Upstream and downstream sequences of ldh1 and ldh2 of L-lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) gene are subjected to polymerase chain reaction amplification, cloned segments are connected to a gene knock-out vector, the constructed knock-out vector is inoculated into corynebacterium glutamicum, and the gene engineering bacterium C.glutamicum Res167 delta ldh is obtained by silencing and screening L-lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) genes in the strain through a homologous recombination method. By the homologous recombination method, the L-lactate dehydrogenase genes in the corynebacterium glutamicum are silenced, so that the gene engineering bacterium for producing pureD-lactic acid is obtained. When the engineering bacterium is used for lactic acid fermentation production, the yield of the D-lactic acid is more than 20g / L, and the purity is over 99 percent. The invention has important significance for industrial production of the D-lactic acid and has wide application prospect.
Owner:FUSHUN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS SINOPEC CORP
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system proteins
InactiveUS6884614B1Increase productionHigh yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidProtein isolate
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated PTS nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel PTS proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PTS nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated PTS proteins, mutated PTS proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of PTS genes in this organism.
Owner:DAESANG
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding proteins involved in membrane synthesis and membrane transport
InactiveUS20050244935A1Efficient producerImprove production efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated MCT nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel MCT proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing MCT nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated MCT proteins, mutated MCT proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of MCT genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for coupled production of cadaverine by using microbial fermentation and microbial conversion
ActiveCN105441497AIncrease productionImprove production efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliMicrobial transformation
The invention relates to a method for coupled production of cadaverine by using microbial fermentation and microbial conversion. By use of the gene engineering technology, lysine decarboxylase genes with different sources are cloned in Escherichia coli or corynebacterium glutamicum with high yield of lysine for secretory expression, recombinant stains are fermented, the recombinant strains synthesize lysine at the first stage, lysine decarboxylase genes are induced for secretory expression at the second stage, and the lysine is converted into the cadaverine. The method for coupled production of cadaverine by using microbial fermentation and microbial conversion provides a new way for production of the cadaverine, has enormous economic benefit and social benefit and has broad market development prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Comprehensive method for extracting L-tryptophan from fermentation liquor
ActiveCN101914054AReduce wasteIn line with the new concept of green environmental protectionOrganic chemistryClimate change adaptationLiquid wasteTryptophan
The invention discloses a comprehensive method for extracting L-tryptophan from fermentation liquor. The L-tryptophan is extracted from fermentation liquor which is made from corynebacterium glutmicum as a strain; meanwhile, generated waste liquor is recycled. The comprehensive method comprises the steps of: extracting the L-tryptophan and recycling the waste liquor, wherein the waste liquor generated in an extraction process is treated or recycled for application or used for preparing a compound fertilizer, a feed additive and feed protein. The method completely, effectively and comprehensively utilizes resources, recycles the generated waste liquor while extracting the L-tryptophan, reduces the resource waste, basically realizes the zero emission of waste water, effectively recycles the resources, and lightens the environment-protecting pressure.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Method of producing protein feed by liquid-solid two-step fermentation method
InactiveCN105010758APromote growthFast fermentationFood processingAnimal feeding stuff[Candida] apicolaBacilli
The invention discloses a method of producing a protein feed by a liquid-solid two-step fermentation method. The method comprises the following steps: performing liquid culture on corynebacterium glutamicum, candida utilis, bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus plantarum and aspergillus oryzae so as to obtain corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation liquor, candida utilis fermentation liquor, bacillus subtilis fermentation liquor, lactobacillus plantarum fermentation liquor and aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor; mixing the corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation liquor, the candida utilis fermentation liquor, the bacillus subtilis fermentation liquor, the lactobacillus plantarum fermentation liquor and the aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor so as to obtain mixed bacterium liquor; loading raw materials of soybean meal, cluster bean meal, cottonseed meal and the like into an explosion vat for performing steam explosion; after steam explosion, mixing materials, the mixed bacterium liquor and molasses in proportion, and adding an enzyme preparation so as to obtain mixed materials; conveying the mixed materials into a special modularized solid-state biological raw material continuous fermentation device for enzymolysis and fermentation, and drying the fermented materials so as to obtain the protein feed. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the modularized automatic fermentation device is adopted, the materials after explosion, the fermented bacterium liquor and the enzyme preparation are mixed, then the mixed materials are loaded into the automatic fermentation device for enzymolysis and biological fermentation, so that requirements for automatic temperature control, automatic dampness control and automatic ventilation control are met, the bioconversion rate is high, the fermentation period is short, the consumption is low, the cost is low, and mechanized and large-scale production requirements can be met.
Owner:河南双成生物科技有限公司
Construction method and application of L-isoleucine producing genetically engineered bacteria
InactiveCN104480057AIncrease productionEase of industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
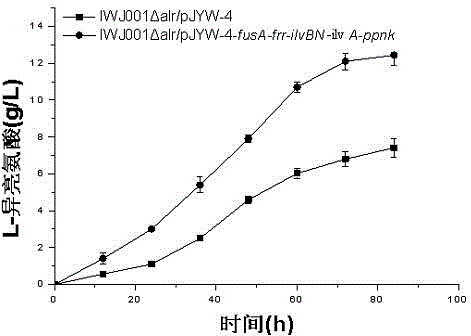
The invention discloses L-isoleucine producing genetically engineered bacteria and a construction method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation. According to the method, a knockout vector of the gene alr is constructed and electroporated into the host bacteria to obtain a deficient strain IWJ001 delta alr of the alr. The gene segments are connected to an overexpression vector by use of the PCR amplification genes fusA, frr, ilvBN, ilvA and ippnk and then electroporated into corynebacterium glutamicum IWJ001 delta alr, and the target genetically engineered bacteria, namely L-isoleucine producing genetically engineered bacteria IWJ001 delta alr / pJYW-4-fusA-frr-ilvBN-ilvA-ppnk, are obtained through antibiotic resistance screening. The L-isoleucine producing genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the method disclosed by the invention can be used for increasing the yield of L-isoleucine through fermentation in a shake flask or fermentation tank, and the method is conductive to reducing the difficulty in separation and purification and increasing the yield so as to remarkably reduce the production cost of L-isoleucine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation culture medium and corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation culture method for producing L-isoleucine
ActiveCN106701853APromotes anabolismIncrease productionBacteriaCulture processBetaineVitamin B6 synthesis
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum fermentation culture medium for producing L-isoleucine. The fermentation culture medium comprises a basic culture medium and a growth factor, wherein the growth factor is prepared from choline, betaine and vitamin B6; the content of the choline in the fermentation culture medium is 0.2-1g / L, the content of the betaine in the fermentation culture medium is 0.25-0.5mg / L, and the content of vitamin B6 in the fermentation culture medium is 0.05-0.3mg / L. The fermentation culture medium provides the growth factor for corynebacterium glutamicum, maintains osmotic pressure inside and outside the cells of the corynebacterium glutamicum to be balanced, and promotes the anabolism of amino acid, thus improving the yield and sugar-acid conversion rate of the L-isoleucine.
Owner:WUHAN GRAND HOYO
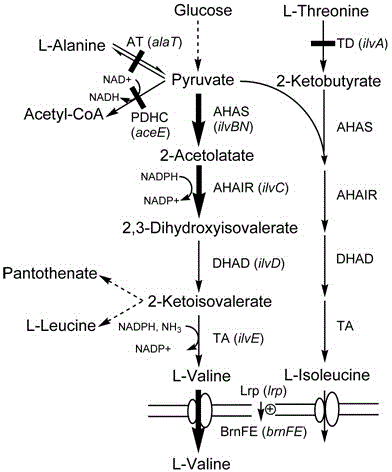
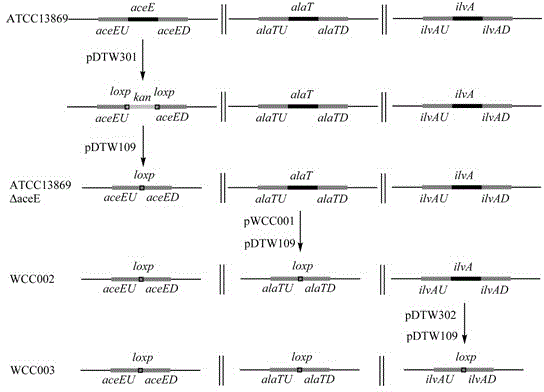
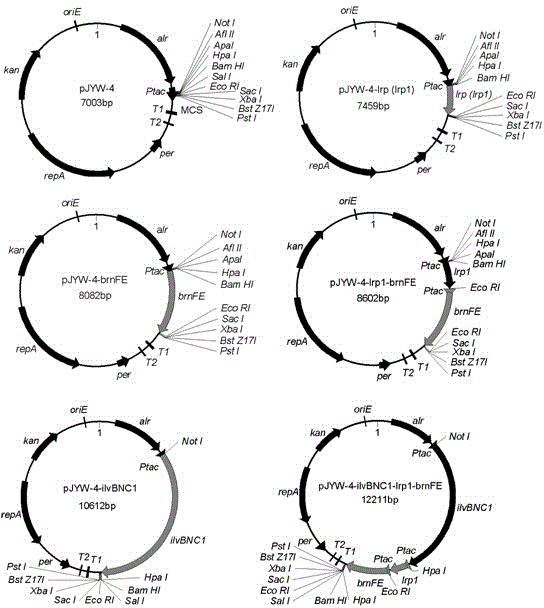
Construction of corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacteria for high-yielding production of L-valine and method for fermentation production of L-valine
The invention discloses construction of a strain of corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacteria for high-yielding production of L-valine and a method for fermentation production of L-valine, and belongs to the technical field of food biological engineering. Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13869 is used as an original bacterial strain, knockout combination of genes of aceE, alaT and ilvA is carried out, and an ATCC13869[delta]aceE[delta]alaT[delta]ilvA mutant bacterial strain is obtained and named as WCC003; expression combination of genes of lrp1, brnFE and ilvBNC1 is carried out on the WCC003, and expression-combined engineering bacteria WCC003 / pJYW-4-(ilvBNC1)-lrp1-brnFE are obtained and preserved in China center for type culture collection with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2014149; the expression-combined engineering bacteria are used for fermentation production of L-valine. The corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacteria based on the expression regulating protein Lrp, the transfer protein BrnFE and the L-valine synthetic route key gene ilvBNC1 and used for high-yielding production of L-valine are provided, advantageous mutation Arg39Trp of Lrp in corynebacterium glutamicum is clear and definite for the first time, a fact that Lrp and BrnFE are used for fermentation production of L-valine is also reported for the first time, and the study on the expression combination of the genes of lrp1, brnFE and ilvBNC1 is also created for the first time.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
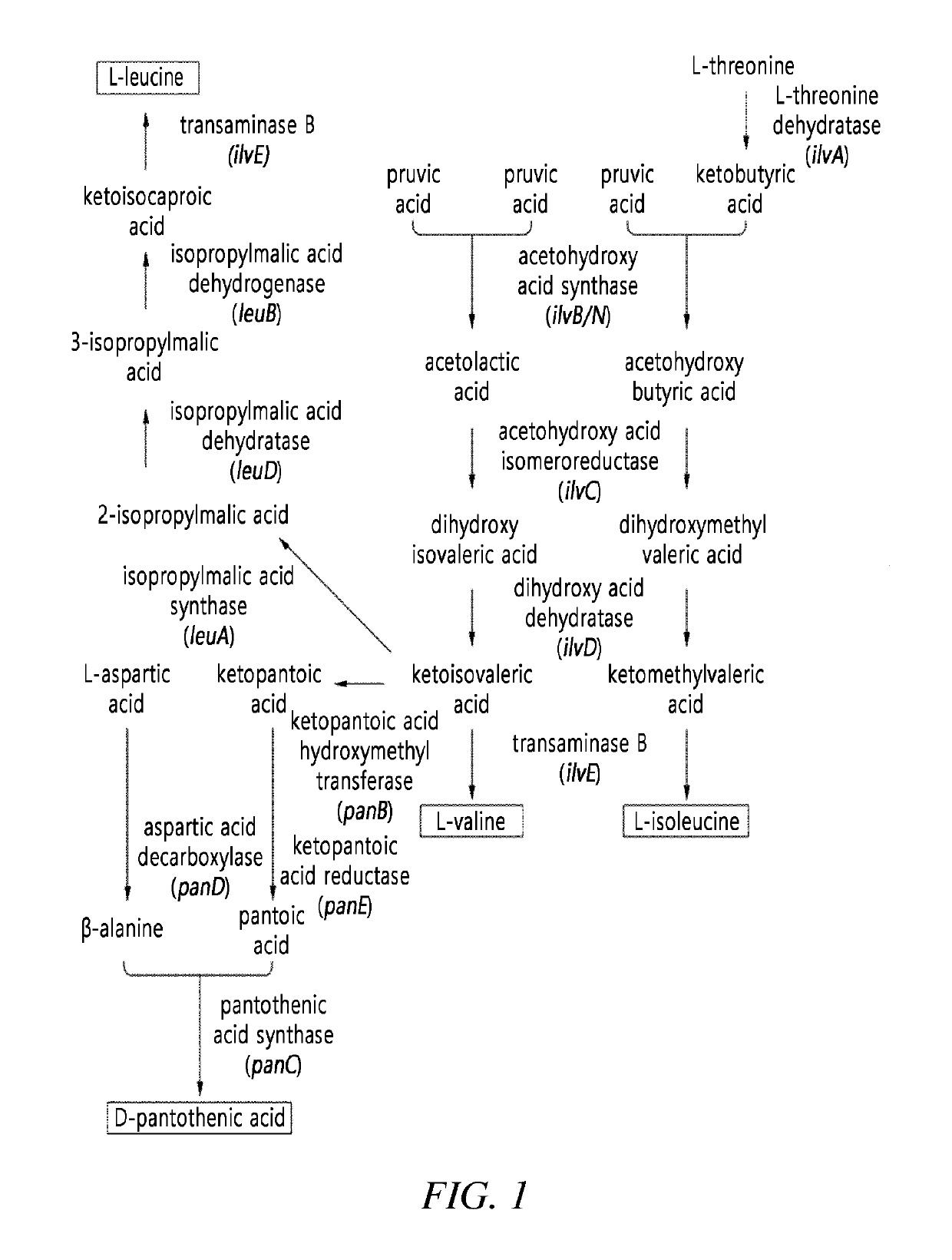
Strain for producing L-leucine and method for producing L-leucine
The invention relates to the technical field of biological engineering, in particular to a strain for producing L-leucine and a method for producing the L-leucine. According to the method, corynebacterium glutamicum is induced by using ultraviolet rays and nitrosoguanidine, then key mutants leuAG561D and ilvBG235S which are beneficial to generation of the L-leucine can be generated, research shows that under mutation conditions of leuAG561D and / or ilvBG235S, feedback inhibition of synthesis routes of the L-leucine can be released, the yield of the L-leucine can be greatly increased, a strain which can generate a great deal of the L-leucine can be obtained, the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.13408, the strain is capable of achieving efficient accumulation of the L-leucine in the fermentation process, and the L-leucine can be up to 4.7g / L.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
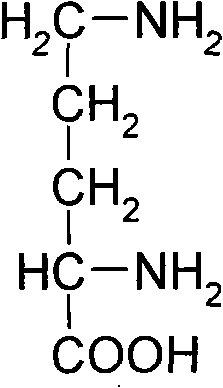
Corynebacterium glutamicum and method for preparing L-ornithine and salts thereof by using same
ActiveCN101955901AThe fermentation process is simpleEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-OrnithineCulture mediums
The invention belongs to the field of fermentation engineering and discloses corynebacterium glutamicum and a method for preparing L-ornithine and salts thereof by using the same. The corynebacterium glutamicum is corynebacterium glutamicum 1006 with the collection number of CGMCCNo.3663. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing the corynebacterium glutamicum in a culture medium containing carbon sources, nitrogen sources and inorganic salts at the temperature of between 28 and 30 DEG C to generate L-ornithine fermentation liquor; removing the thalli of the fermentation liquor by using ceramic membranes of 1 to 15 ten thousand Dalton; separating the fermentation liquor by using cation exchange resins to obtain L-ornithine solution; and decoloring and crystallizing the L-ornithine solution by a hydrochloric acid and ethanol method to obtain L-ornithine hydrochloride. The method has the advantages of simple thallus cultivation and contribution to industrialized mass production. The accumulation of the L-ornithine prepared from the corynebacterium glutamicum reaches 35 to 45g / L.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Microorganism producing L-leucine and method for producing L-leucine using the same
ActiveUS10351859B2Improved L-leucine productivityAvoid inhibitionMicroorganismsFermentationMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present disclosure relates to a microorganism producing L-leucine and a method for producing L-leucine using the same, and more specifically, to a Corynebacterium glutamicum mutant which has resistance to L-leucine and a derivative thereof and improved L-leucine producing ability, and a method for producing L-leucine using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for producing L-ornithine by microorganism fermentation
InactiveCN101323866AFast acid productionImprove sugar conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSolubilityChemical treatment
The invention provides a method for producing L-ornithine by microbial fermentation, namely, using Corynebacterium glutamate to obtain the strains of CS-189(cit<(-)>+SG<r>) by chemical treatment, and obtain the L-ornithine hydrochloride by fermentation, culture solution micro-filtration by a ceramic membrane, ion exchange resin and extraction by a hydrothermal crystallization method with decompression concentration. The strains used in the method are auxotrophy resistant to sulfaguanidine, which significantly enhances acid yield by fermentation. Meanwhile, aiming at the problem that the solubility of the L-ornithine hydrochloride in water is extremely difficult, the hydrothermal crystallization method is adopted to obtain better extraction rate under the condition that flammable and explosive alcohol is not used. The method simplifies processes and reduces extraction cost.
Owner:上海聚瑞生物技术有限公司
Mutant of trehalose synthetase from corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof
InactiveCN101629166AImprove thermal stabilityImprove conversion efficiencyMicroorganism based processesEnzymesReaction temperatureTransformation efficiency
The invention relates to a mutant of trehalose synthetase from corynebacterium glutamicum. A method for obtaining the mutant performs site-directed saturation mutation on a phenylalanine residue at the 263rd site of an amino acid sequence of trehalose synthetase from corynebacterium glutamicum by using a site-directed mutation technology, and the method for obtaining the mutant also comprises the following step: the saturation mutation is performed on at least one amino acid residue in at least 80 percent of homologous trehalose synthetase sequences of an amino acid sequence including SEQ ID NO.1, SEQID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4. The reaction kinetics of the trehalose synthetase expressed by a mutated trehalose synthetase gene changes, various enzymology characteristics such as specific activity of enzyme, optimum reaction temperature, optimum pH value, and the like also change, and the enzyme can improve the transformation efficiency of the trehalose synthetase and further reduce the production cost of the trehalose.
Owner:南宁中诺生物工程有限责任公司
Genetically engineered bacterium for high-yield production of hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN108441460AIncrease productivityImprove growth traitsBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for high-yield production of hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The strain integrates RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) polymerase which is controlled by a xylose promoter and is derived from T7 bacteriophage; a thrA gene for encoding homoserine dehydrogenase I is knocked out; a lysC gene derived from corynebacterium glutamicum, an ectABC gene cluster derived from halomonas elongate and an ectD gene for encoding tetrahydropyrimidine hydroxylase are integrated andare promoted by a strong promoter PT7; a hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine synthesis way is reconstructed; the ectD gene is integrated at a sucCD site of succinyl coenzyme A synthetase and is started by thestrong promoter PT7; the genetically engineered bacterium has the highest level of producing the hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine by a fermentation method which is reported at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Corynebacterium glutamicum and production method of alpha-ketoglutarate through fermentation thereof
ActiveCN102391977AReduce manufacturing costThe fermentation process is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMethotrexateNitrogen source
Belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, the invention relates to corynebacterium glutamicum and a production method of alpha-ketoglutarate through fermentation of corynebacterium glutamicum. The bacterial strain of the invention is corynebacterium glutamicum GKG-047, with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 5481. With a strain of glutamic acid producing strain GDK-9 as a parent, the bacterial strain of the invention is a mutant strain that is screened out through mutagenesis and sensitive to methotrexate. Under the circumstance of a limited nitrogen source supply, the bacterial strain can accumulate alpha-ketoglutarate. During fermentation, the bacterial strain is characterized by aerobic fermentation, fast bacterium growth, and rapid acid production rate. After fermentation of the bacterial strain for 32h in a fermentation tank of 10L, the maximum output of alpha-ketoglutarate can be 47.2g / L. The method provided in the invention has the advantages of simple and easily controllable fermentation process, and low production cost of alpha-ketoglutarate, thus being in favor of the popularization and application of industrial production.
Owner:江苏澳创生物科技有限公司
Glutamic acid capable of having high-yield glutamine
This invention discloses the bacillus of glutaminic acid, this fungus by name glutaminic acid bacillus (Corynebacteriumglutamicum ) G32, own to preserve in ' China model culturation preservation center ' it is CCTCC NO.M205028 of preserve number. The bacterial strain is in short bar shape when it is young, exist individually or in pairs, ' V ' shape arranged, not forming mycelium, leather blue dye is positive but easy to fade, do not move, does not give birth to the spore , does not resist the acid , facultative anaero which needs nutrition-rich medium, its colony is protruding, semitransparent, the glassy surface. The ammonia amount of Gln accumulated in this fermented liquid of fungus reaches 75-80g / L, and this fungus tolerance is up to the salt concentration of 8%- 10% of ammonium sulfate.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
High yield L-leucine engineering bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a high yield L-leucine engineering bacterium and an application of the bacterium.The invention provides a method for preparing a recombinant bacterium. The method comprises the following step of importing an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant encoding gene into a target bacterium to form the recombinant bacterium, wherein an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant is enzyme obtained by mutating 494th arginine of alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase into histidine, 497th glycine into aspartic acid and 499th leucine into valine.The high yield L- leucine engineering bacterium, particularly corynebacterium glutamicum MD0032, has higher L-leucine yield than bacterial strains produced at home at present, has a unique identification label and is a L-leucine production strain with a high production and application value.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV +1
Promoter from corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof
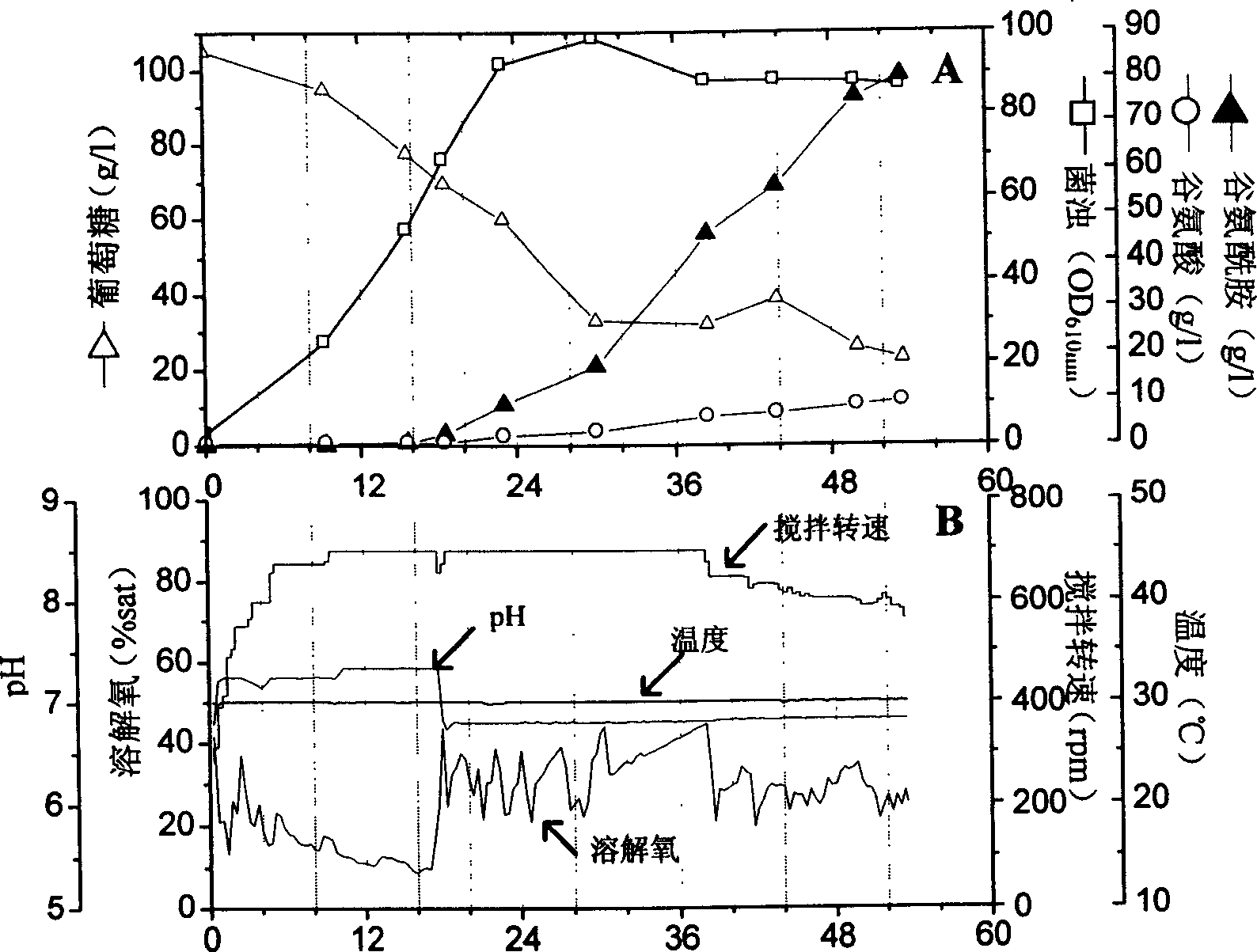
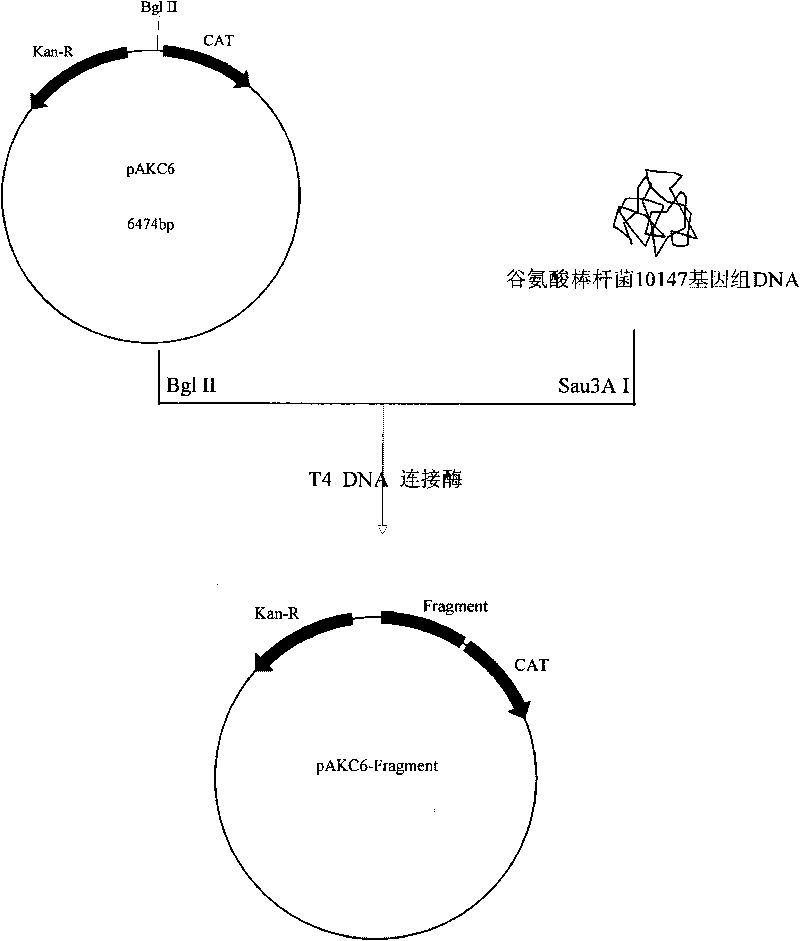
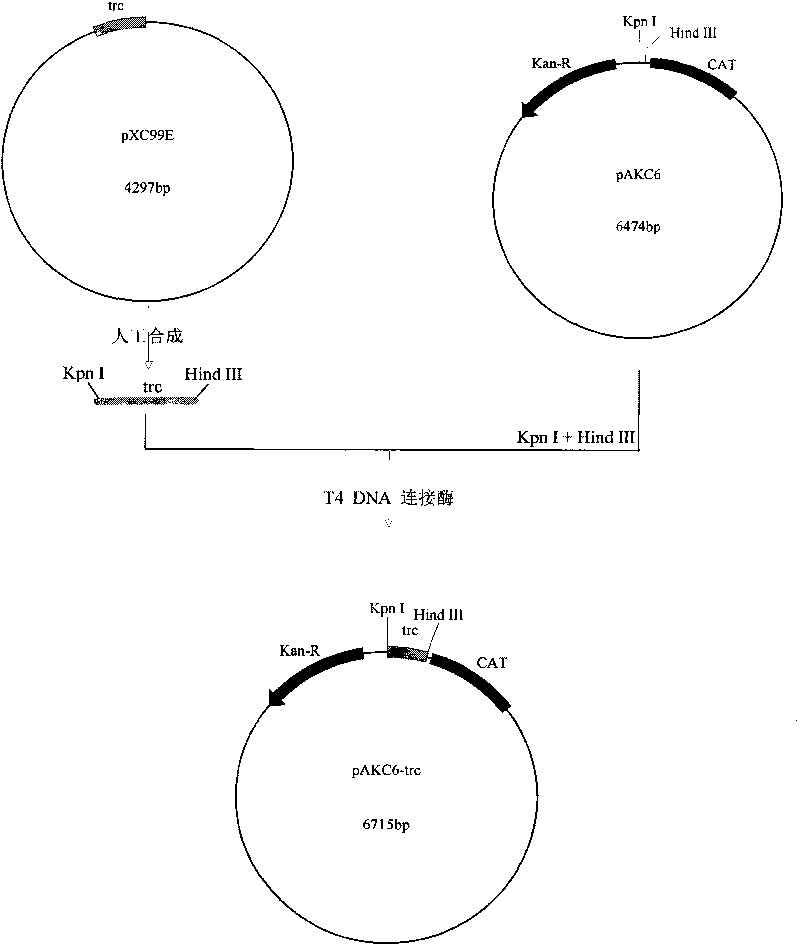
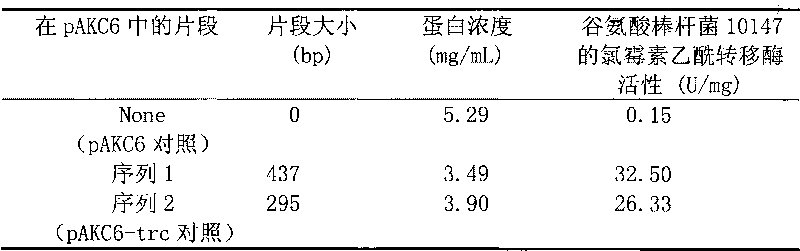
The invention discloses a promoter with a nucleotide sequence as follows: 1) a nucleotide sequence shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table; 2) a nucleotide sequence which hybridizes with the nucleotide sequence in 1) under strict conditions and has promoter activity; or 3) a nucleotide sequence which has homology of more than 70% with the nucleotide sequence in 1) and has promoter activity. The promoter provided by the invention can be applied to the biotechnology field with corynebacterium or escherichia bacteria as industrial microbes. Experiments prove a fragment with promoter activity from SEQ ID NO:1 has the activity higher than that of a trc promoter (SEQ ID NO:2).
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com