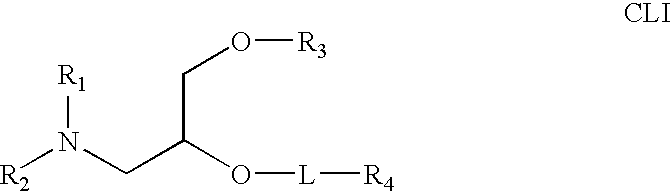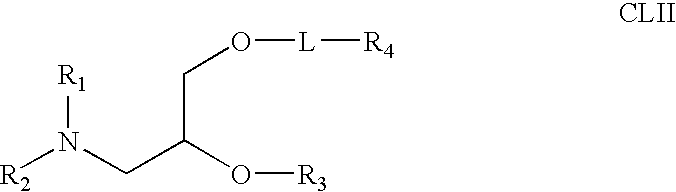Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
289 results about "Antisense nucleic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Naturally occurring complementary RNA which regulates gene expression by binding to mRNA; or, DNA of genes which code acoantisense RNA; or, synthetic complementary DNA or RNA probes based on antisense sequences.
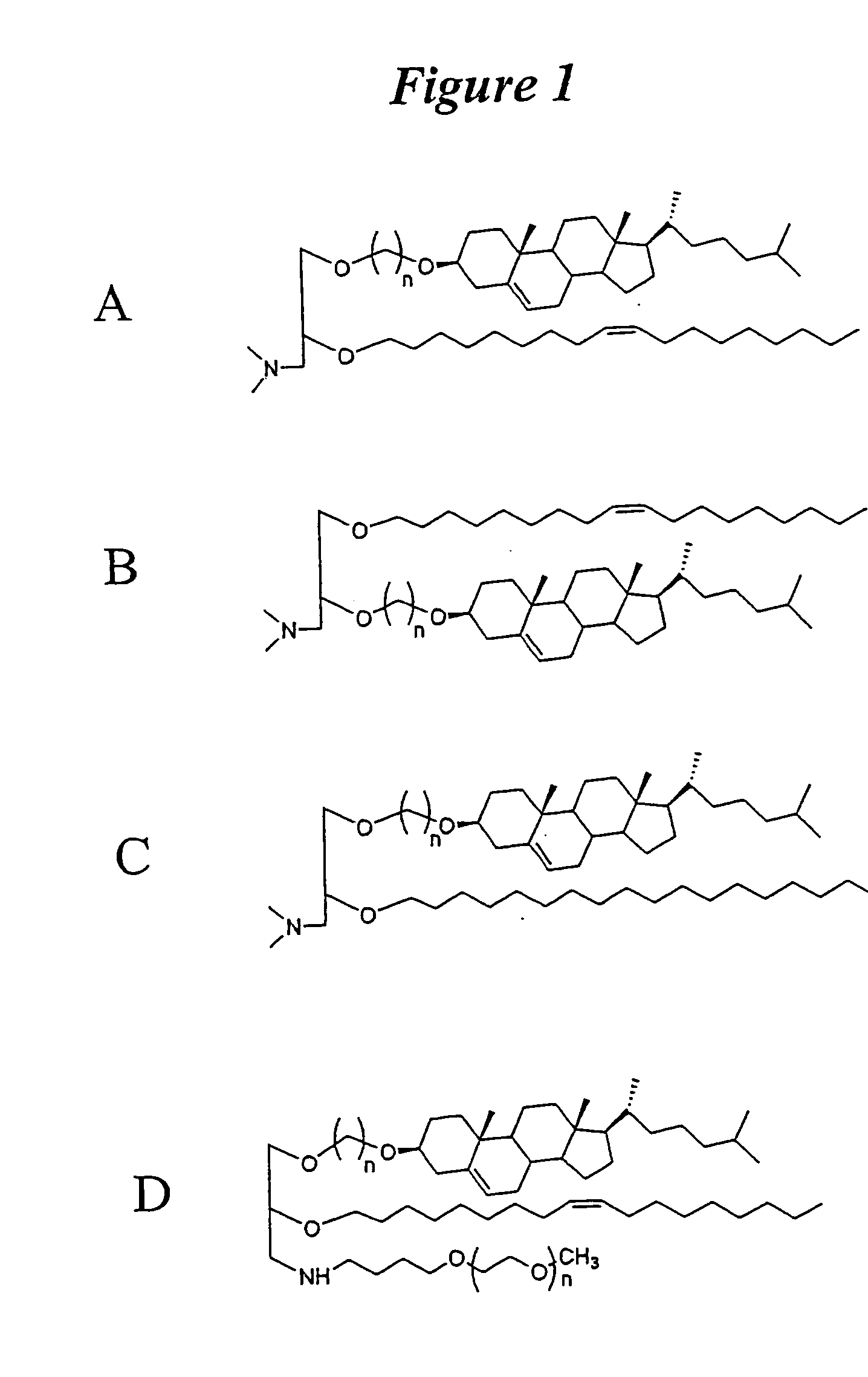
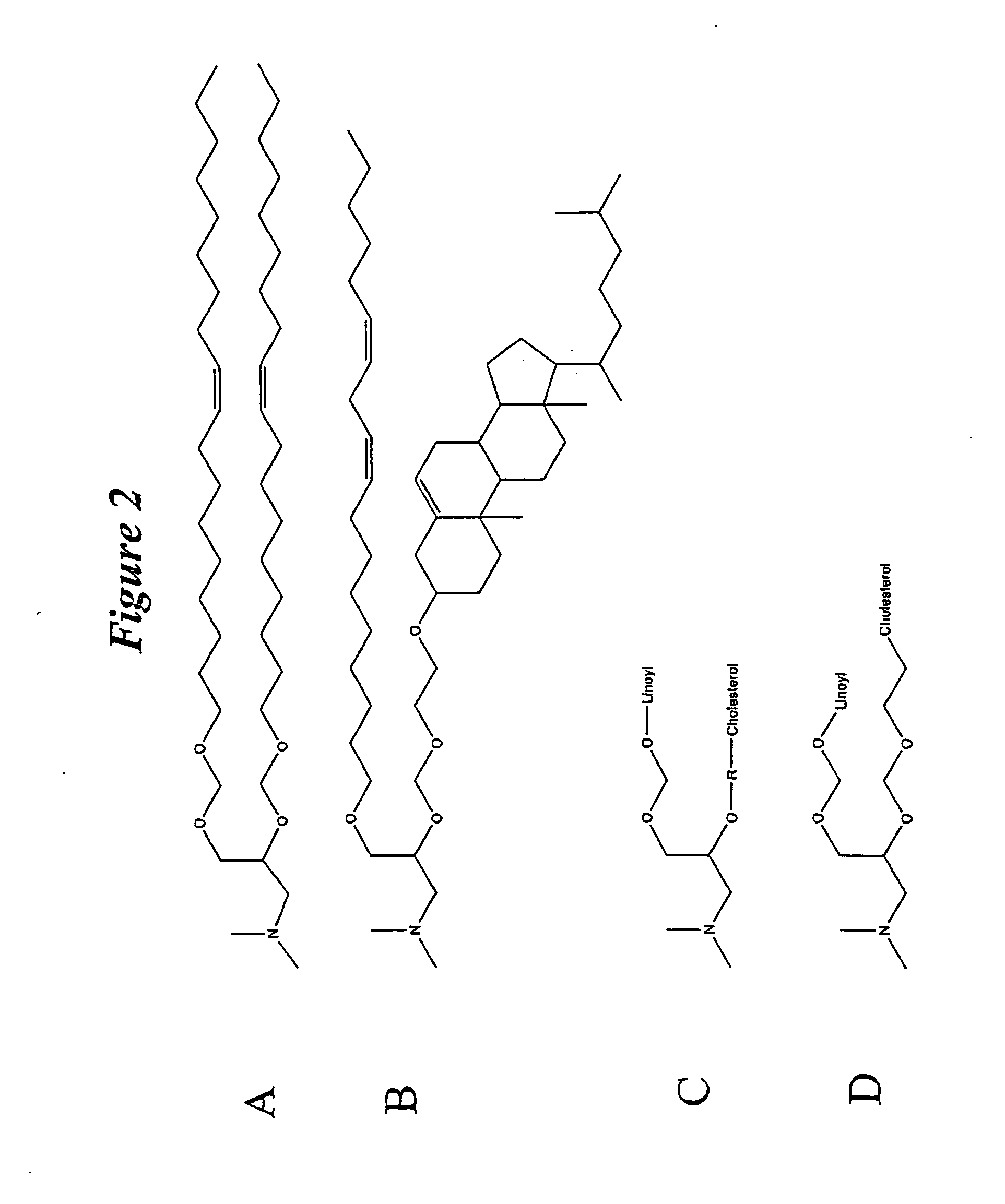
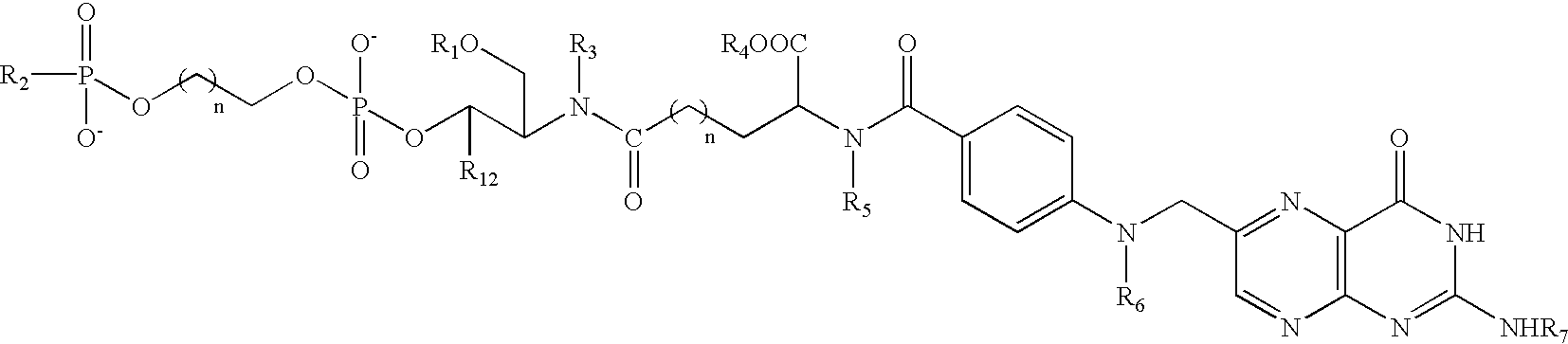
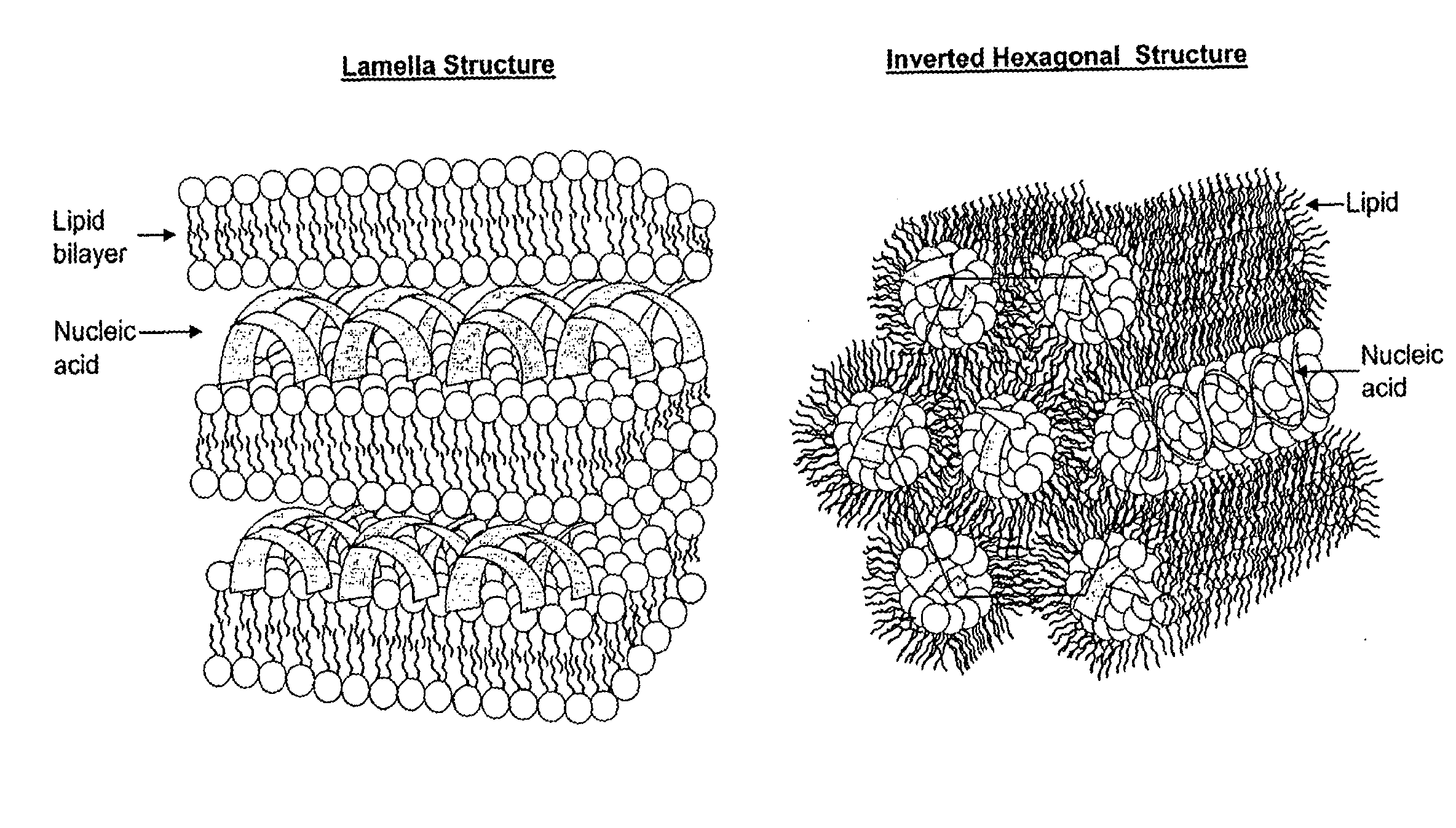
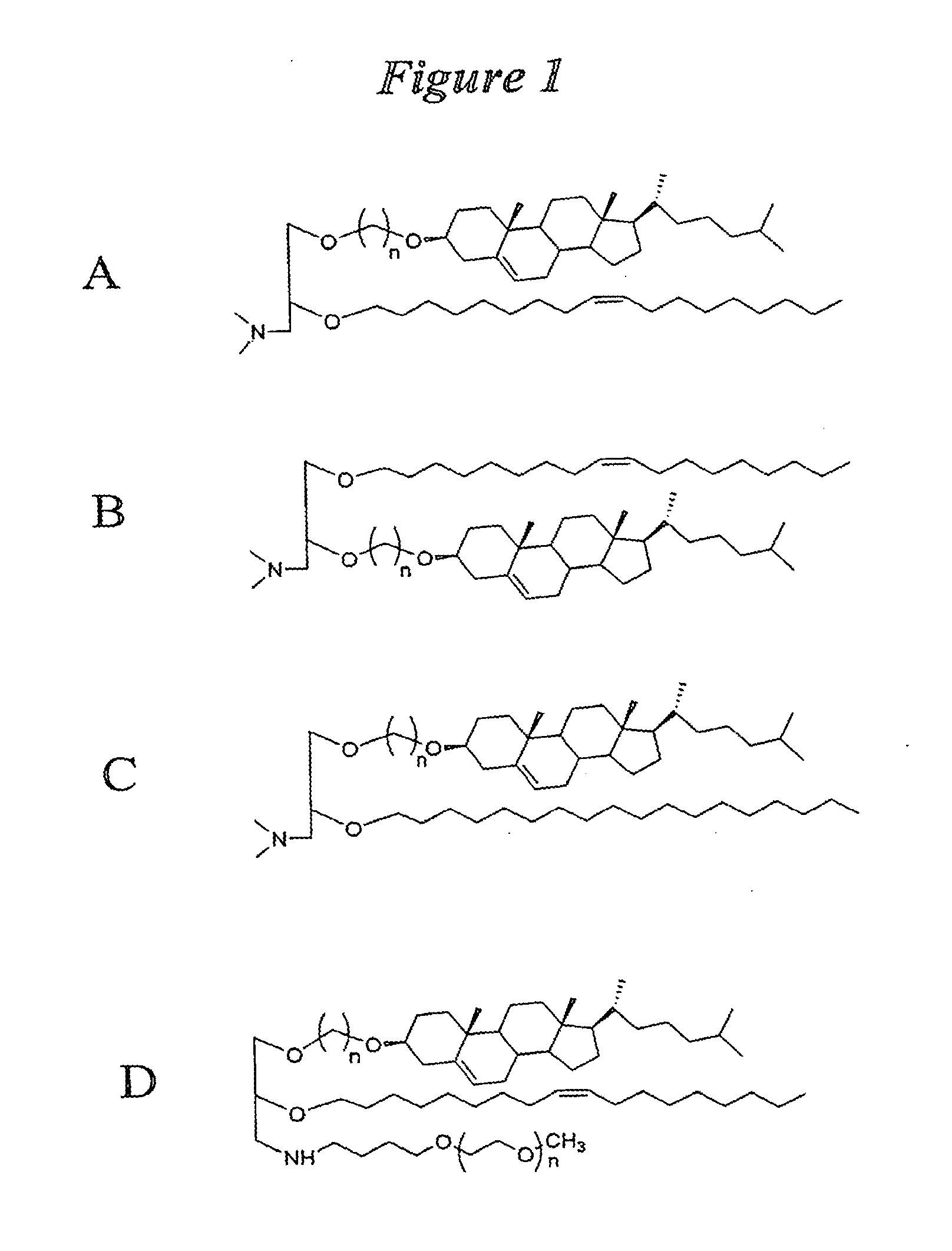
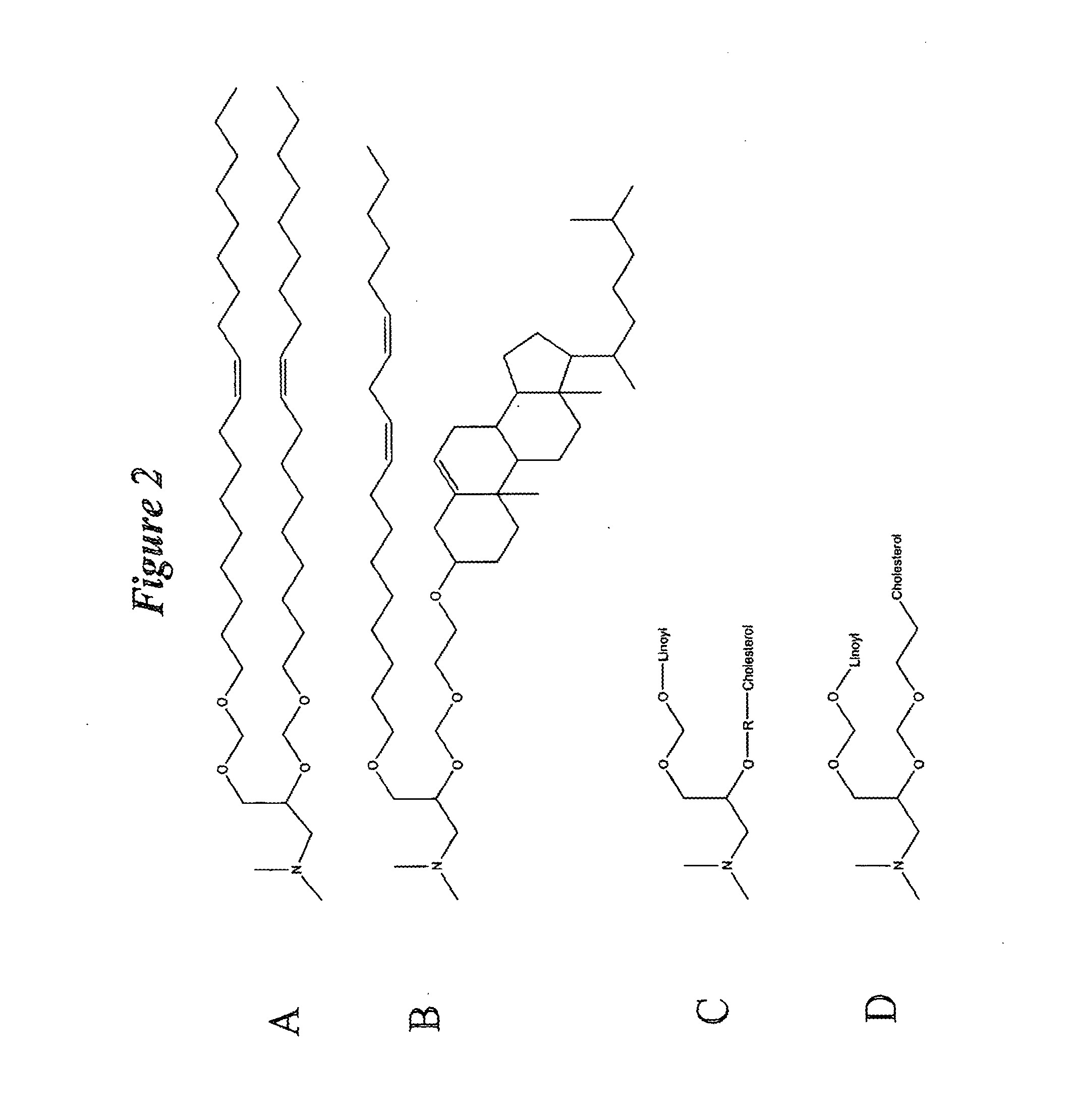
Application of lipid vehicles and use for drug delivery
InactiveUS7063860B2Reduce and prevent antibody-mediated resistanceIncrease stimulationBiocideAntipyreticAnticarcinogenCapsaicin
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the administration of lipid-based vehicles to treat various disorders, including bladder inflammation, infection, dysfunction, and cancer. In various aspects, the compositions and methods of the invention are useful for prolonged delivery of drugs, e.g., antibiotics, pain treatments, and anticancer agents, to the bladder, genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal system, pulmonary system, and other organs or body systems. In particular, the present invention relates to liposome-based delivery of vanilloid compounds, such as resiniferatoxin, capsaicin, or tinyatoxin, and toxins, such as botulinum toxin, for the treatment of bladder conditions, including pain, inflammation, incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. Further related are methods of using these vehicles alone or in conjunction with antibodies, e.g., uroplakin antibodies, to improve duration of liposome attachment, and provide a long-term intravesical drug delivery platform. The present invention specifically relates to antibody-coated liposomes that are useful for targeting specific receptors for drug, peptide, polypeptide, or nucleic acid delivery. In one particular aspect, the present invention relates to liposomes coated with antibodies against nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor and containing NGF antisense nucleic acids, which are used as a treatment for neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
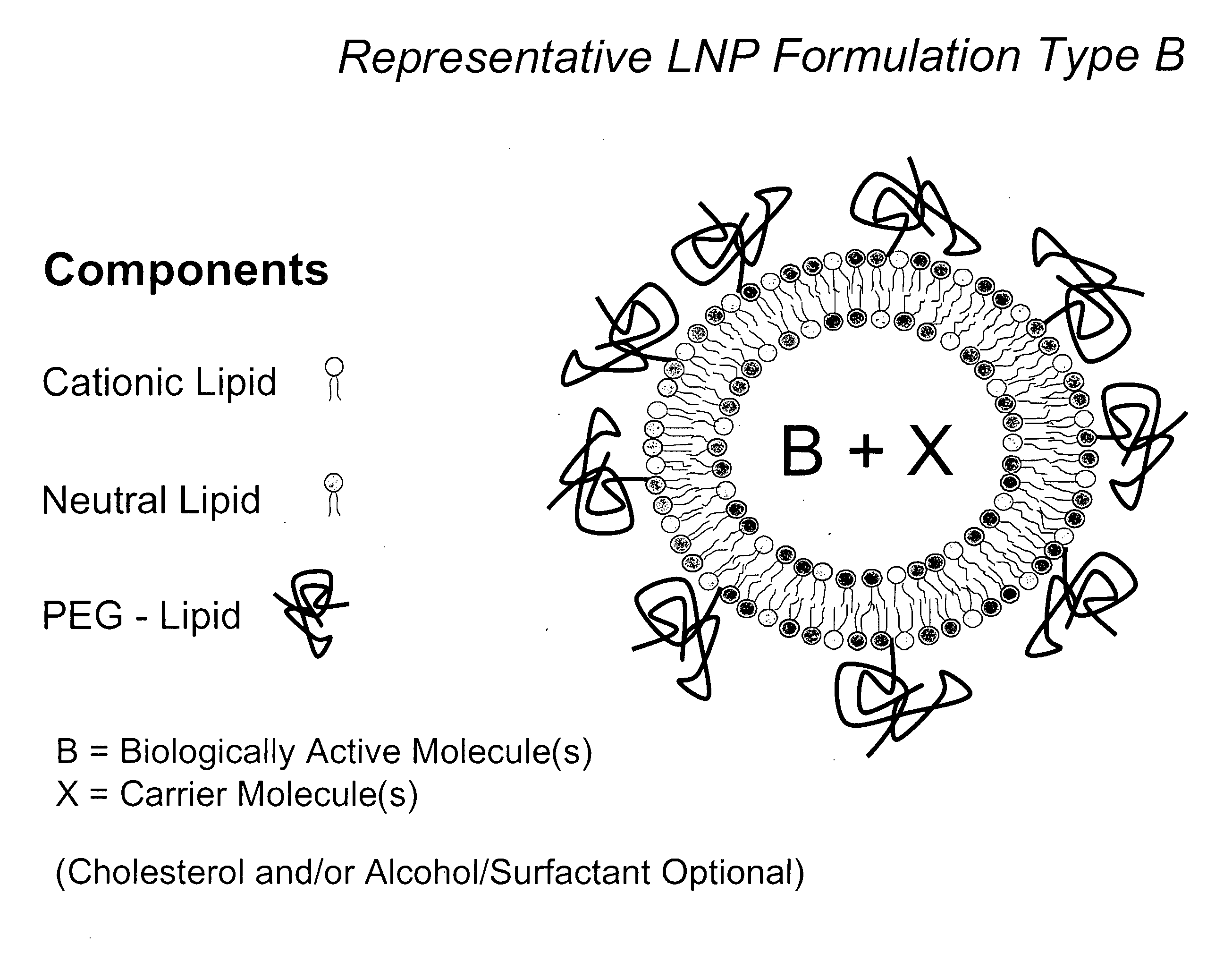
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS20080020058A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryLipid formationCholesterol
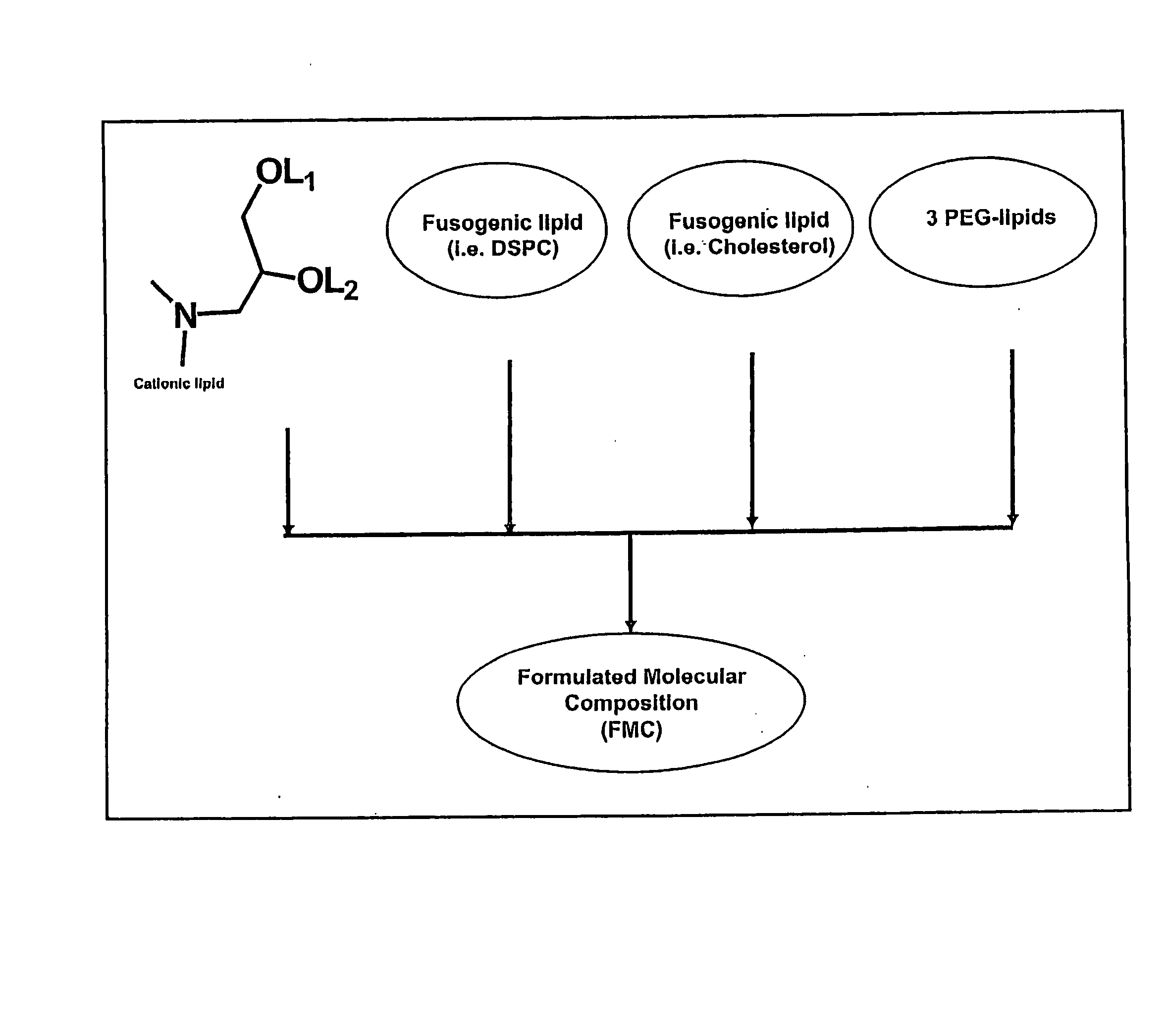
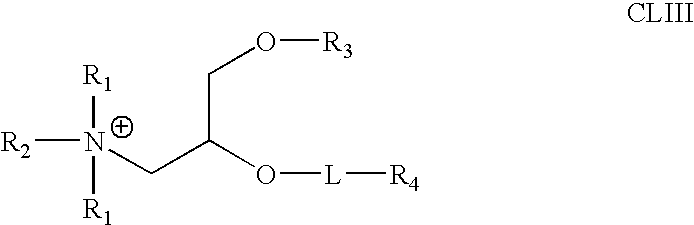
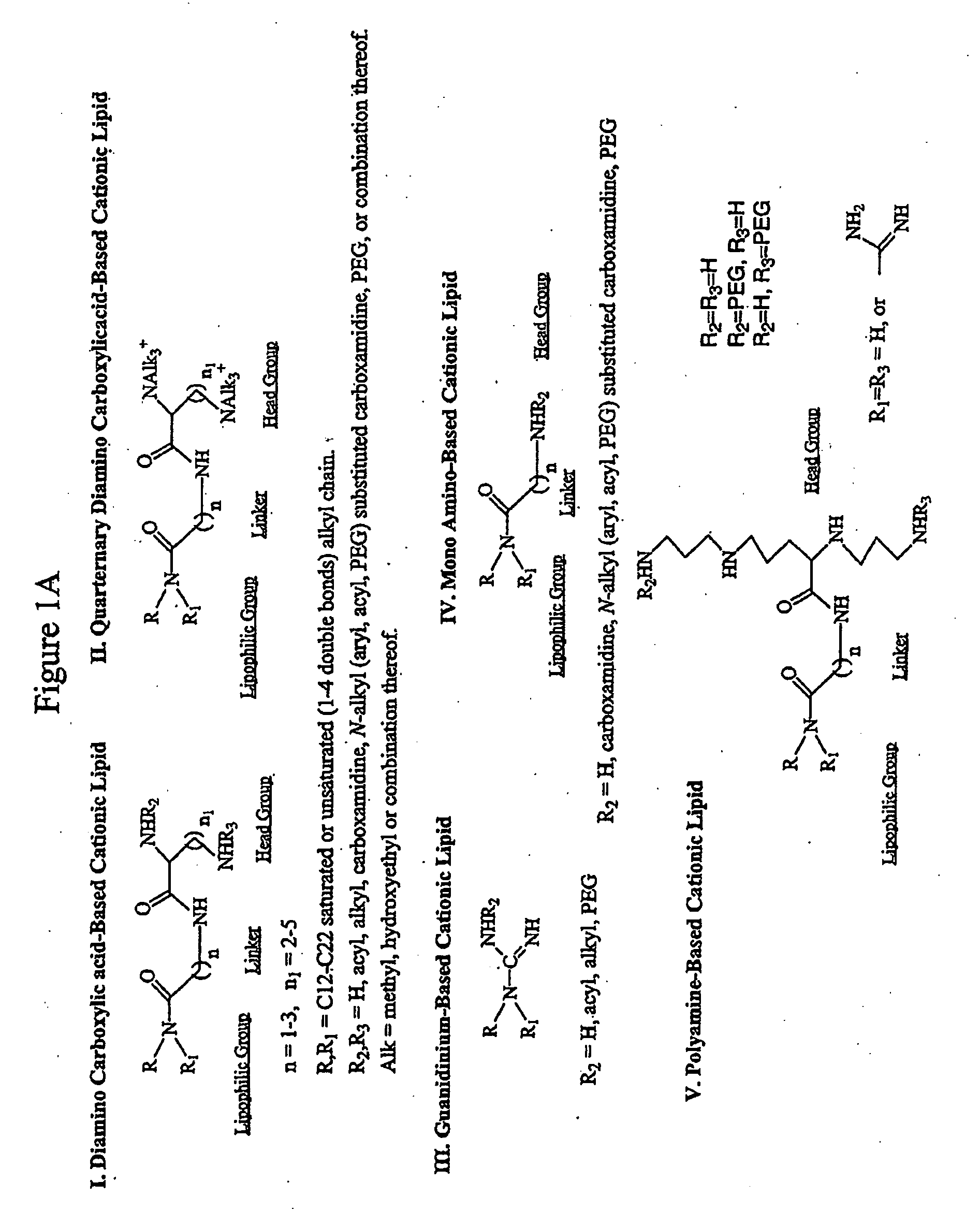
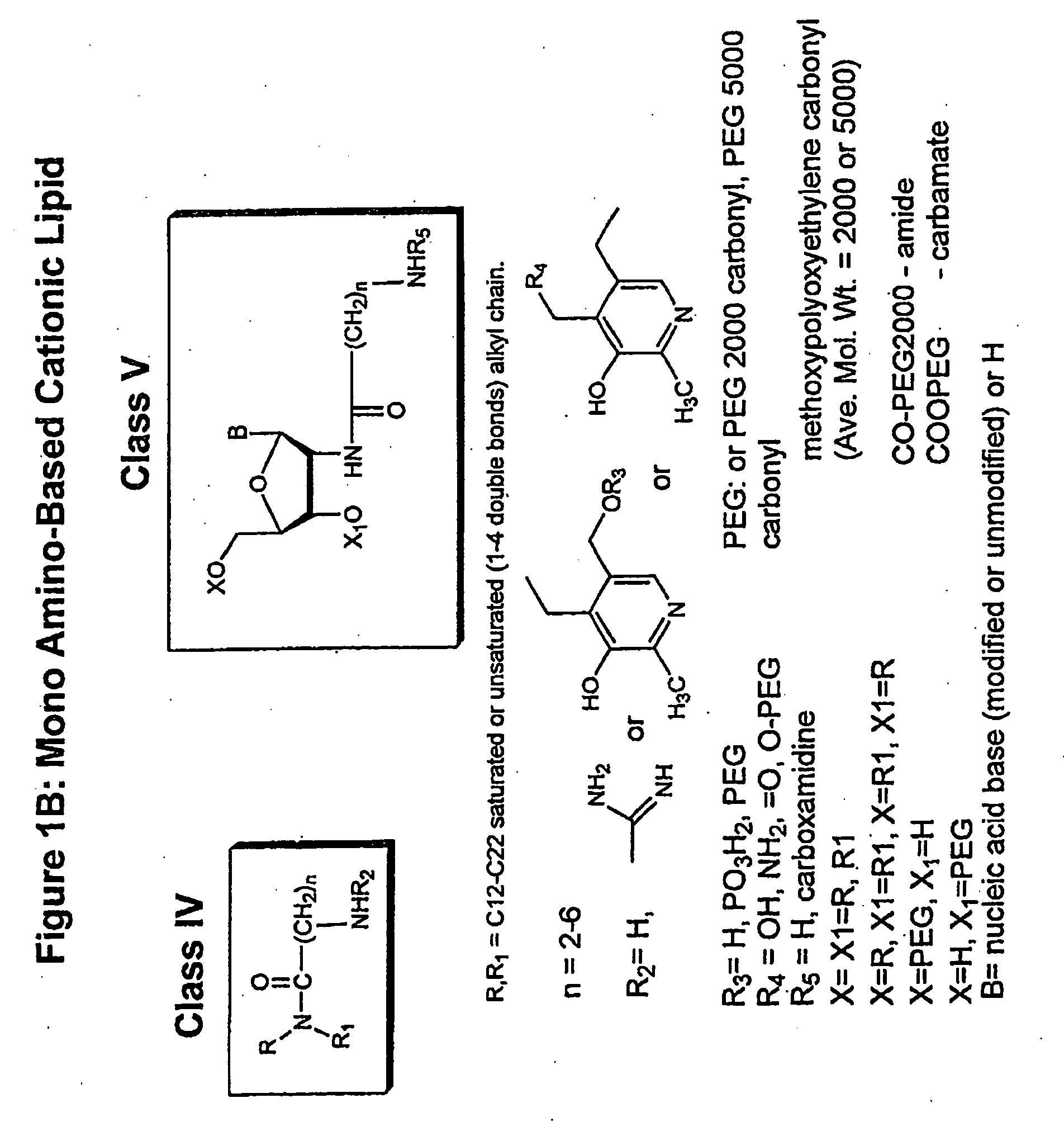
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and RNAi inhibitor molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Novel Compositions for the Delivery of Negatively Charged Molecules
InactiveUS20100036115A1Facilitated DiffusionReduce deliverySugar derivativesDipeptide ingredientsMembrane permeabilityAntisense nucleic acid
This invention features permeability enhancer molecules, and methods, to increase membrane permeability of various molecules, such as nucleic acids, polynucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acid molecules, antisense nucleic acid molecules, 2-5A antisense chimeras, triplex forming oligonucleotides, decoy RNAs, dsRNAs, siRNAs, aptamers, or antisense nucleic acids containing nucleic acid cleaving chemical groups, peptides, polypeptides, proteins, carbohydrates, steroids, metals and small molecules, thereby facilitating cellular uptake of such molecules.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Conjugates and compositions for cellular delivery
InactiveUS20050239739A1Efficient deliveryEfficient subsequent releaseBiocideSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidNucleoside X
This invention features conjugates, compositions, methods of synthesis, and applications thereof, including folate derived conjugates of nucleosides, nucleotides, non-nucleosides, and nucleic acids including enzymatic nucleic acids and antisense nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Nucleic acids encoding costimulatory molecule B7-4
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules, designated B7-4 nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel B7-4 polypeptides. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing B7-4 nucleic acid molecules, host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced, and nonhuman transgenic animals in which a B7-4 gene has been introduced or disrupted. The invention still further provides isolated B7-4 proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and anti-B7-4 antibodies. Diagnostic, screening, and therapeutic methods utilizing compositions of the invention are also provided.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Methods of identifying compounds that upmodulate T cell activation in the presence of a PD-1 mediated signal
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules, designated PD-L2 nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel B7-related molecules which are ligands for PD-1. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PD-L2 nucleic acid molecules, host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced, and nonhuman transgenic animals in which a PD-L2 gene has been introduced or disrupted. The invention further provides isolated PD-L2 polypeptides, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and anti-PD-L2 antibodies. The invention still further provides methods for promoting or inhibiting the interaction between PD-L2 and PD-1. The invention further provides methods of identifying compounds that upmodulate T cell activation in the presence of a PD-1-mediated signal. Diagnostic and treatment methods utilizing compositions of the invention are also provided.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
Conjugates and compositions for cellular delivery
ActiveUS7109165B2Reduce deliveryPromotes associationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAntisense nucleic acidNucleotide
This invention features conjugates, compositions, methods of synthesis, and applications thereof, including folate derived conjugates of nucleosides, nucleotides, non-nucleosides, and nucleic acids including enzymatic nucleic acids and antisense nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
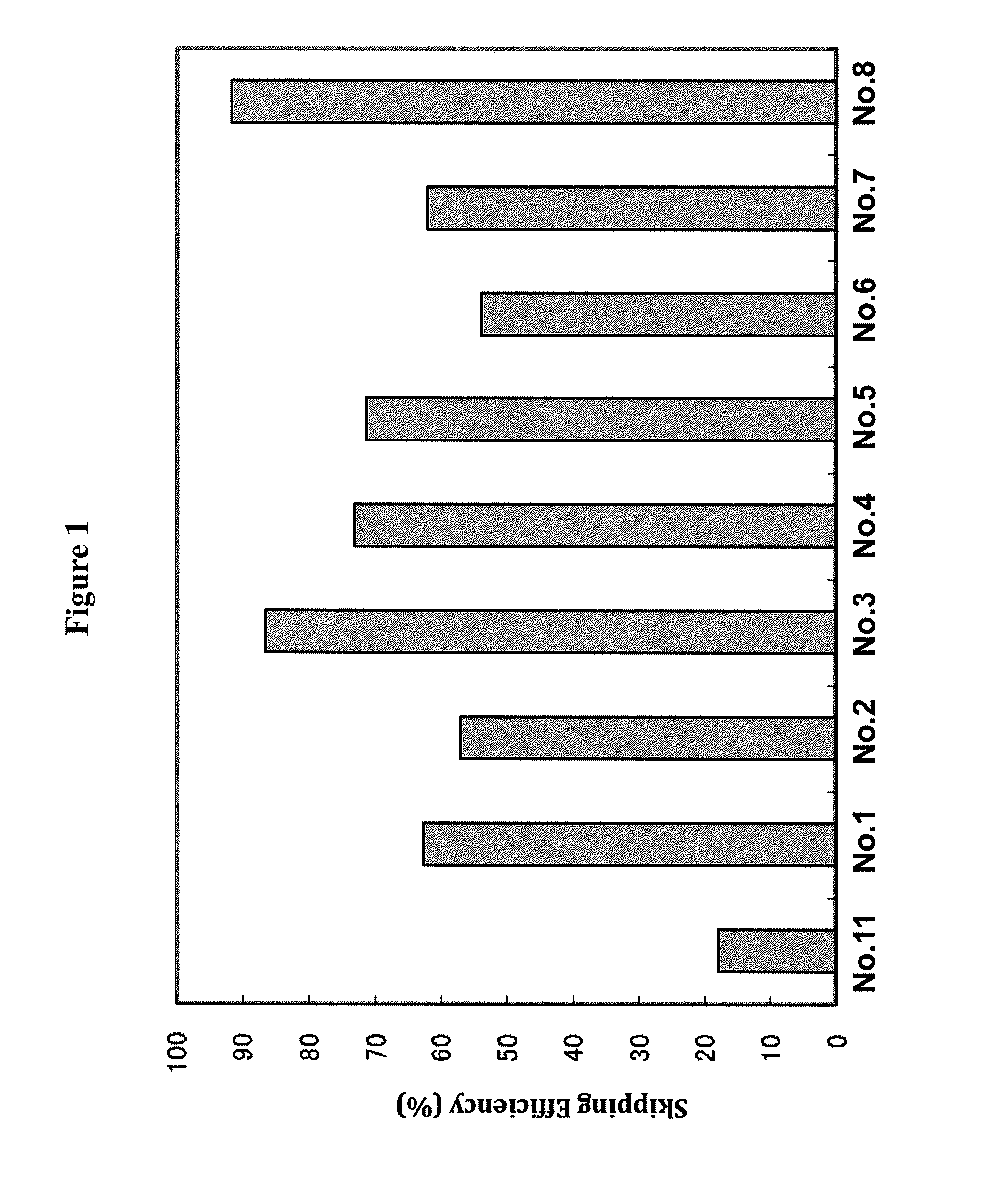
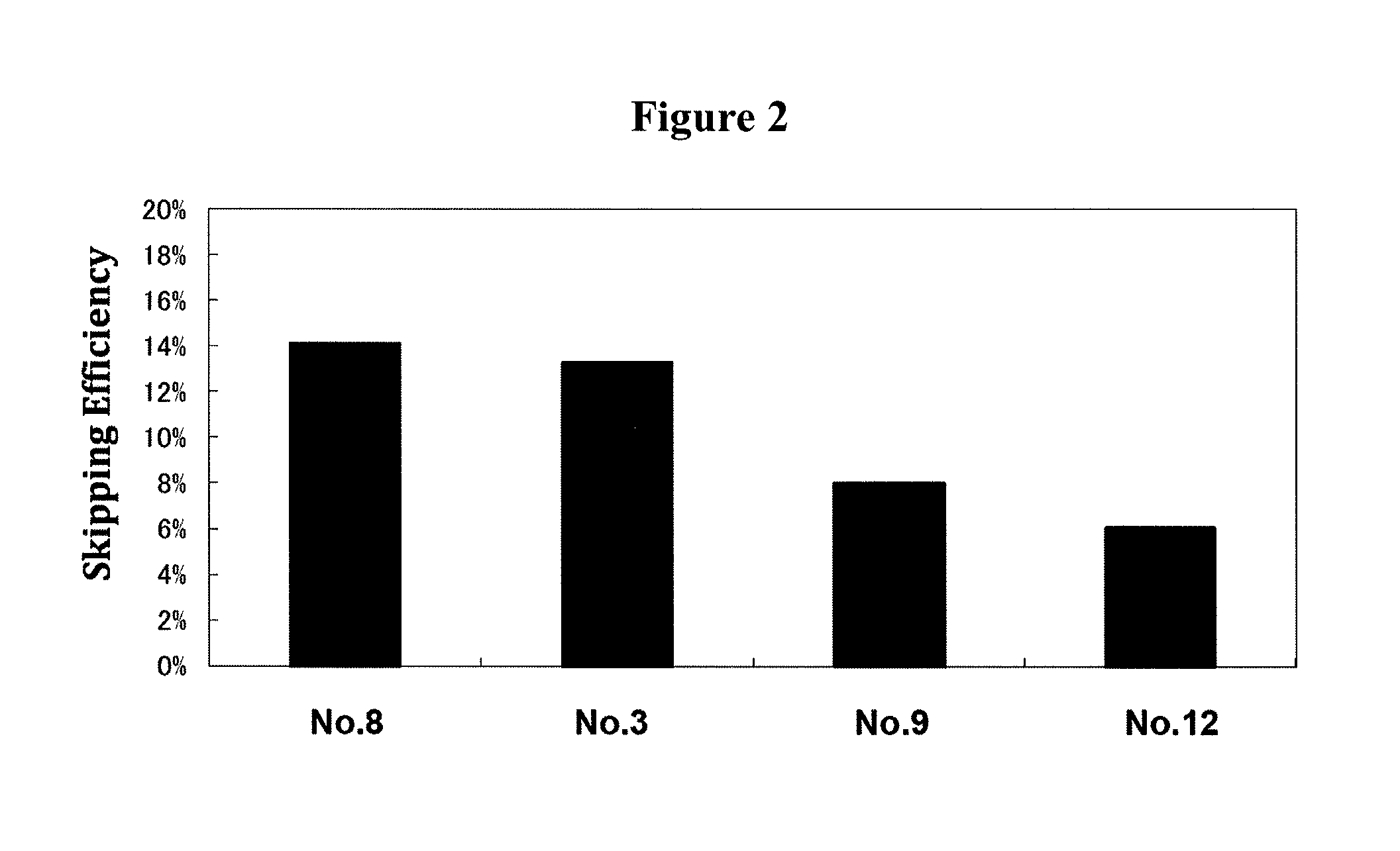
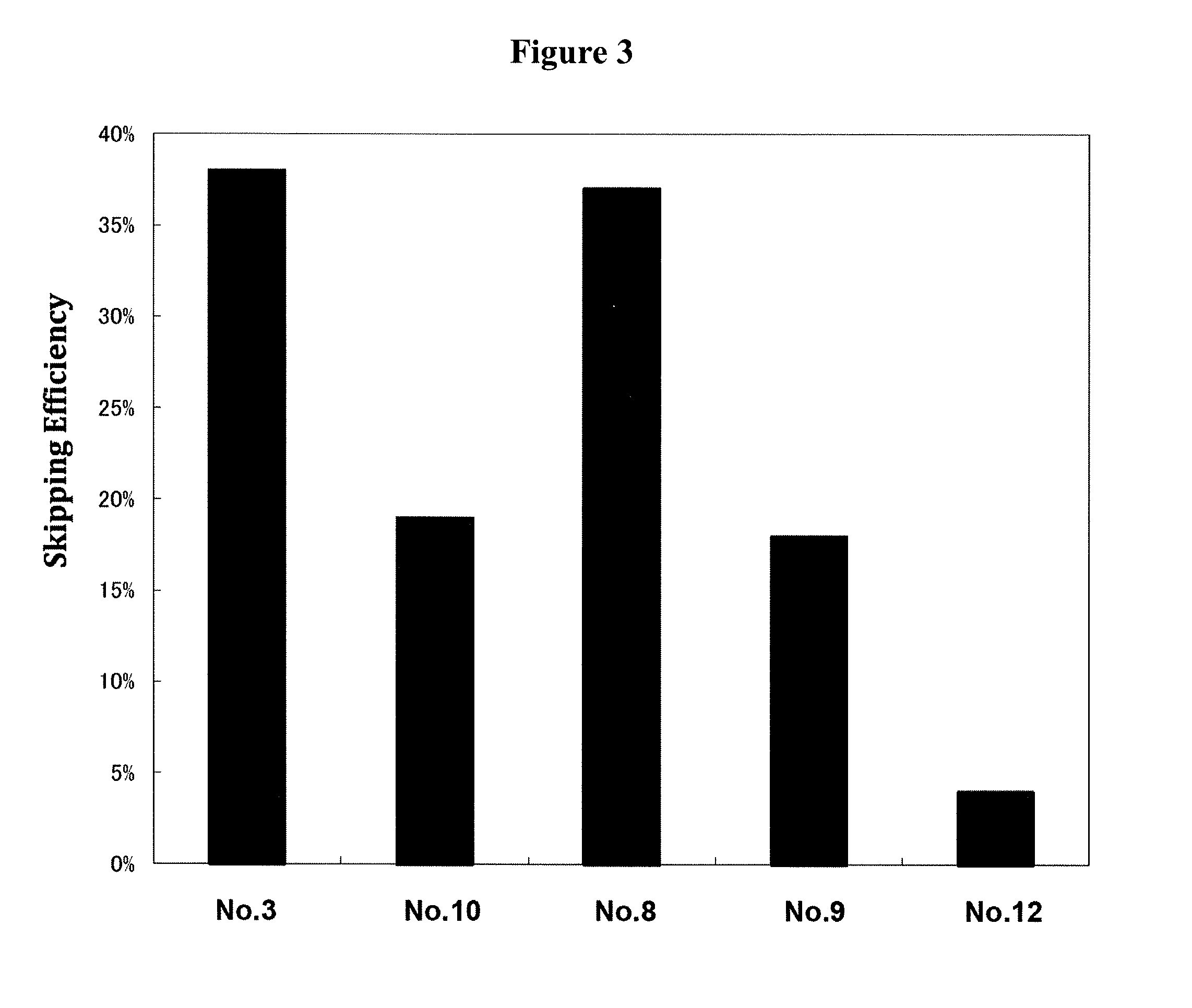
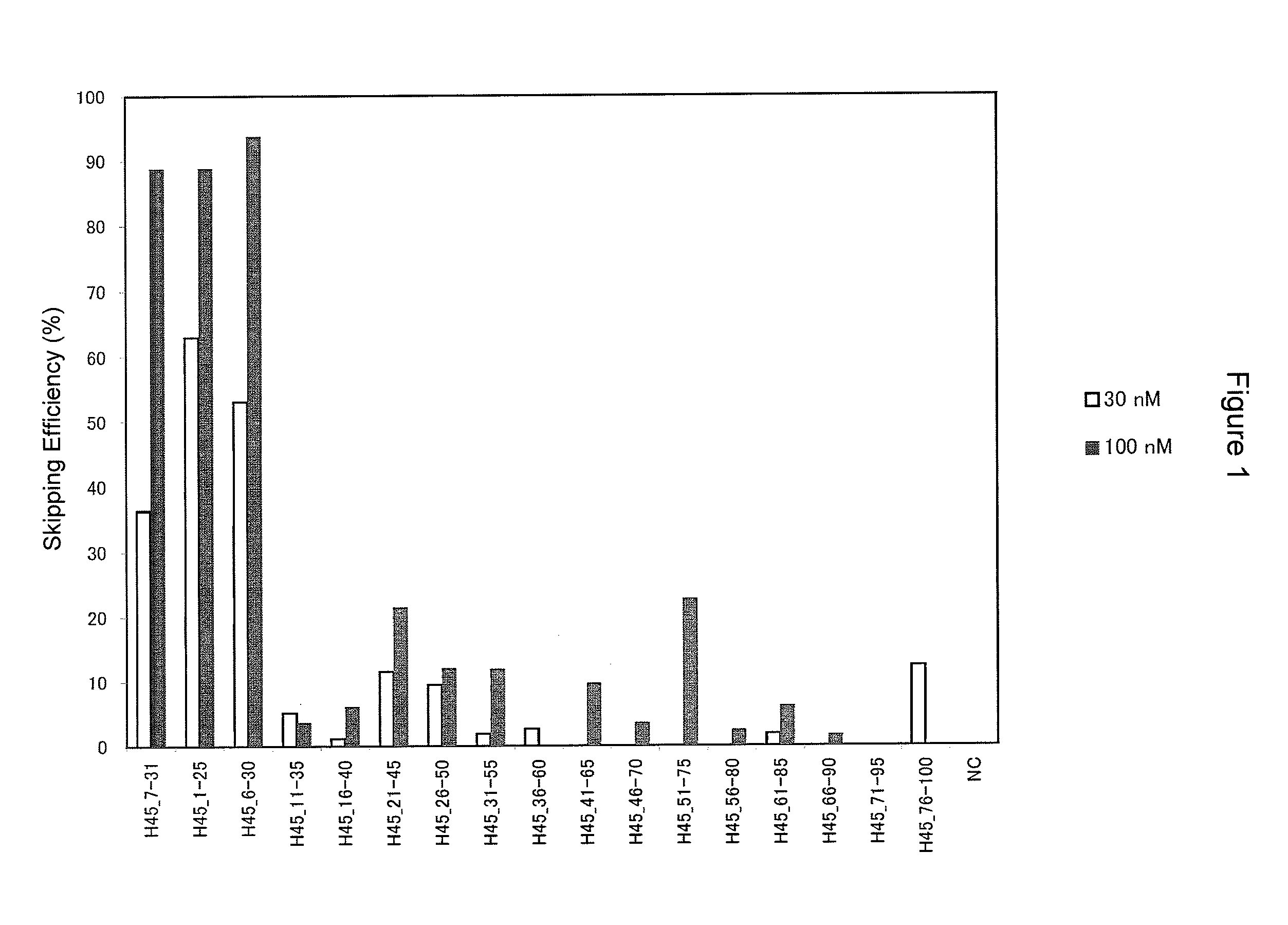
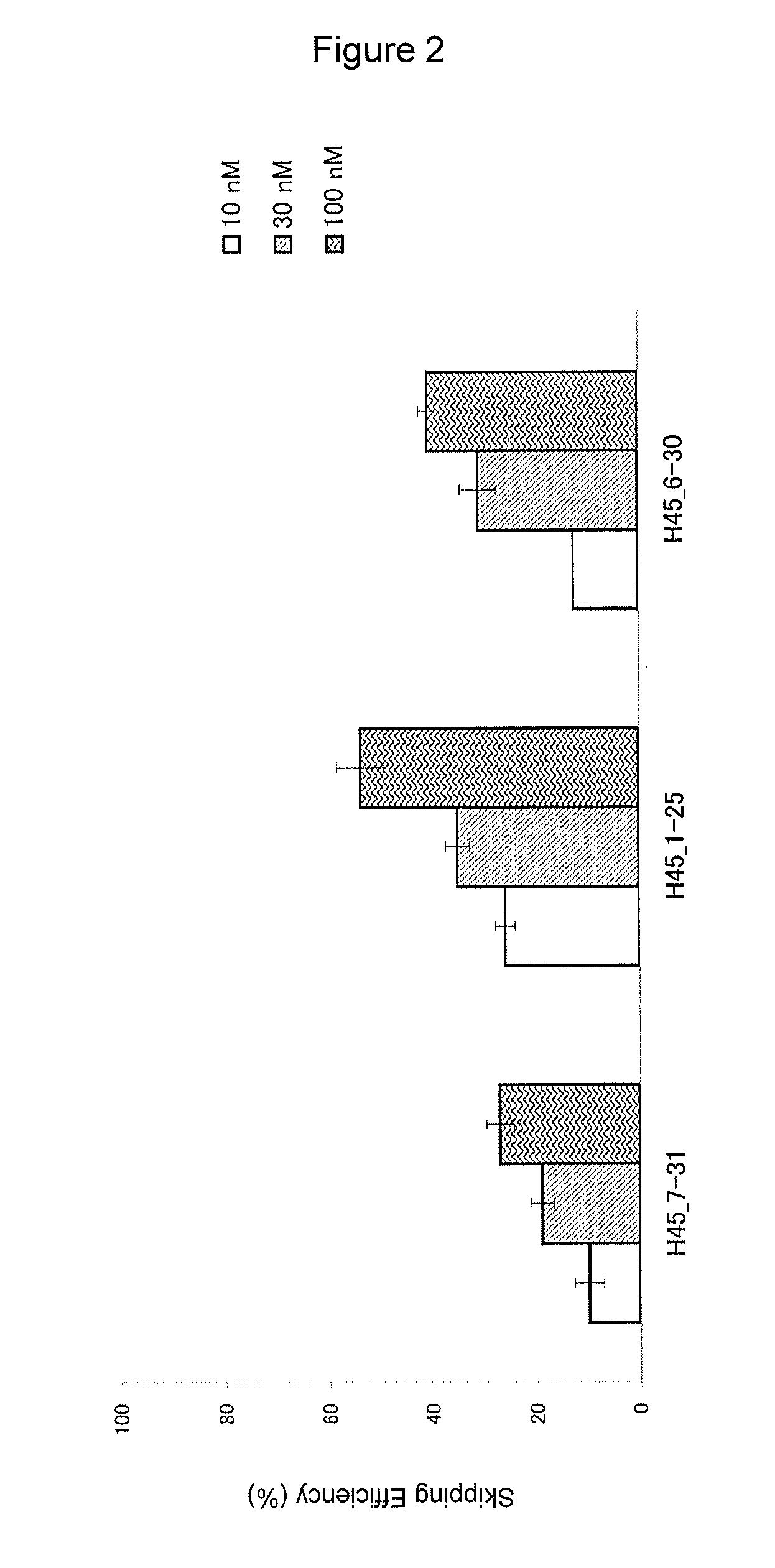
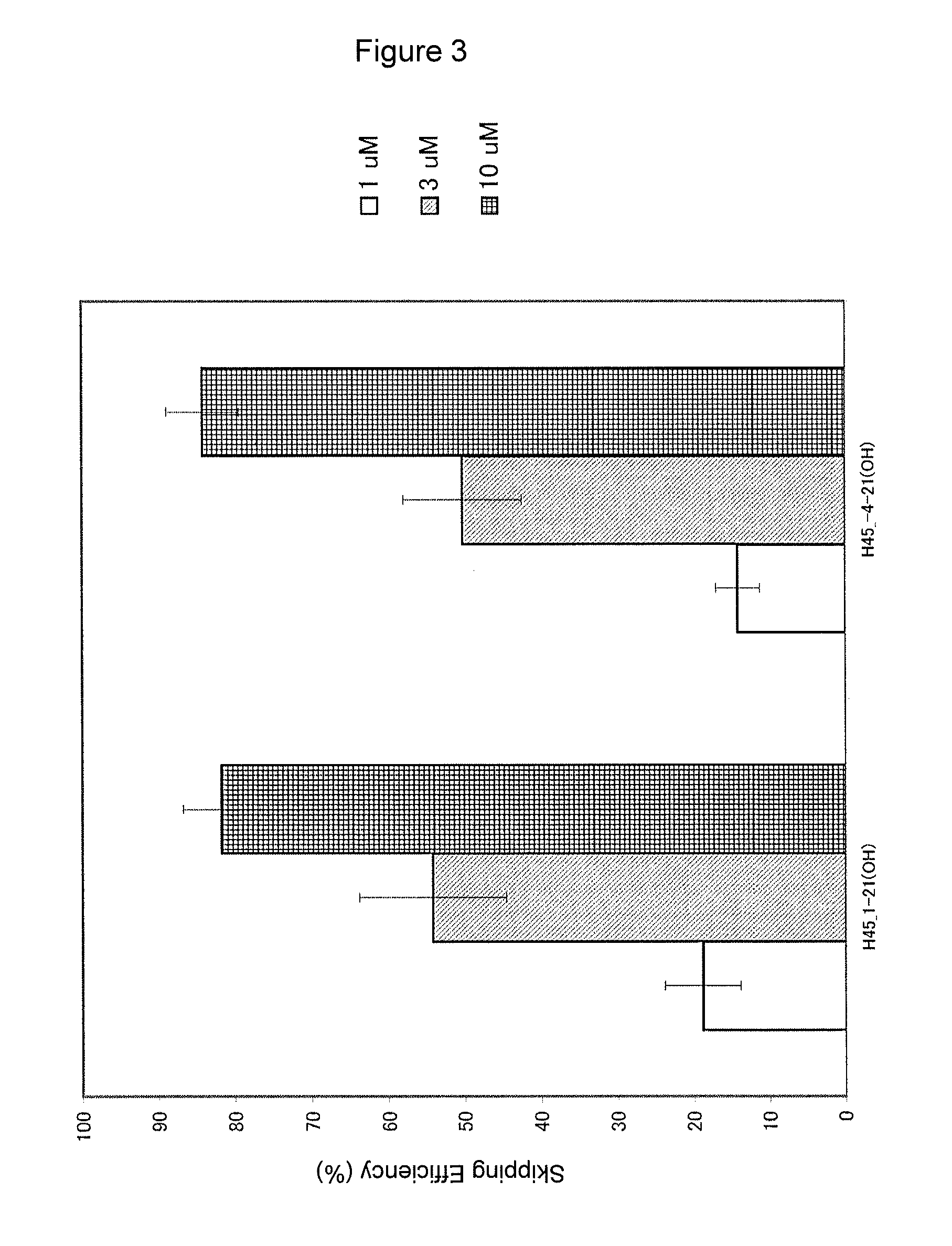
Antisense nucleic acids
ActiveUS20130211062A1Improve efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationOligomerAntisense nucleic acid
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition which causes skipping of the 53rd exon in the human dystrophin gene with a high efficiency.The present invention provides an oligomer which efficiently enables to cause skipping of the 53rd exon in the human dystrophin gene.
Owner:NIPPON SHINYAKU CO LTD +1
PD-L2 Molecules: Novel PD-1 Ligands and Uses Therefor
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules, designated PD-L2 nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel B7-related molecules which are ligands for PD-1. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PD-L2 nucleic acid molecules, host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced, and nonhuman transgenic animals in which a PD-L2 gene has been introduced or disrupted. The invention further provides isolated PD-L2 polypeptides, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and anti-PD-L2 antibodies. The invention still further provides methods for promoting or inhibiting the interaction between PD-L2 and PD-1. Diagnostic and treatment methods utilizing compositions of the invention are also provided.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Neisseria meningitidis antigens and compositions
InactiveUS20070026021A1Improve protectionImmunoglobulins against bacteriaDepsipeptidesAntisense nucleic acidImmunogenicity
This invention provides, among other things, protein, polypeptides, and fragments thereof, derived from bacteria Neisseria meningitidis B. Also provided are nucleic acids encoding for such proteins, polypeptides, and / or fragments, as well as nucleic acids complementary thereto (e.g., antisense nucleic acids). Additionally, this invention provides antibodies which bind to the proteins, polypeptides, and / or fragments. This invention further provides expression vectors useful for making the proteins, polypeptides, fragments, and / or nucleic acids, for use as vaccines, diagnostic reagents, immunogenic compositions, and the like. Methods of making the compositions and methods of treatment with the compositions are also provided. This invention also provides methods of detecting the proteins, polypeptides, fragments and / or nucleic acids.
Owner:J CRAIG VENTER INST +1
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding regulatory proteins
InactiveUS20050153402A1High yieldIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated MR nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel MR proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing MR nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated MR proteins, mutated MR proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of MR genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
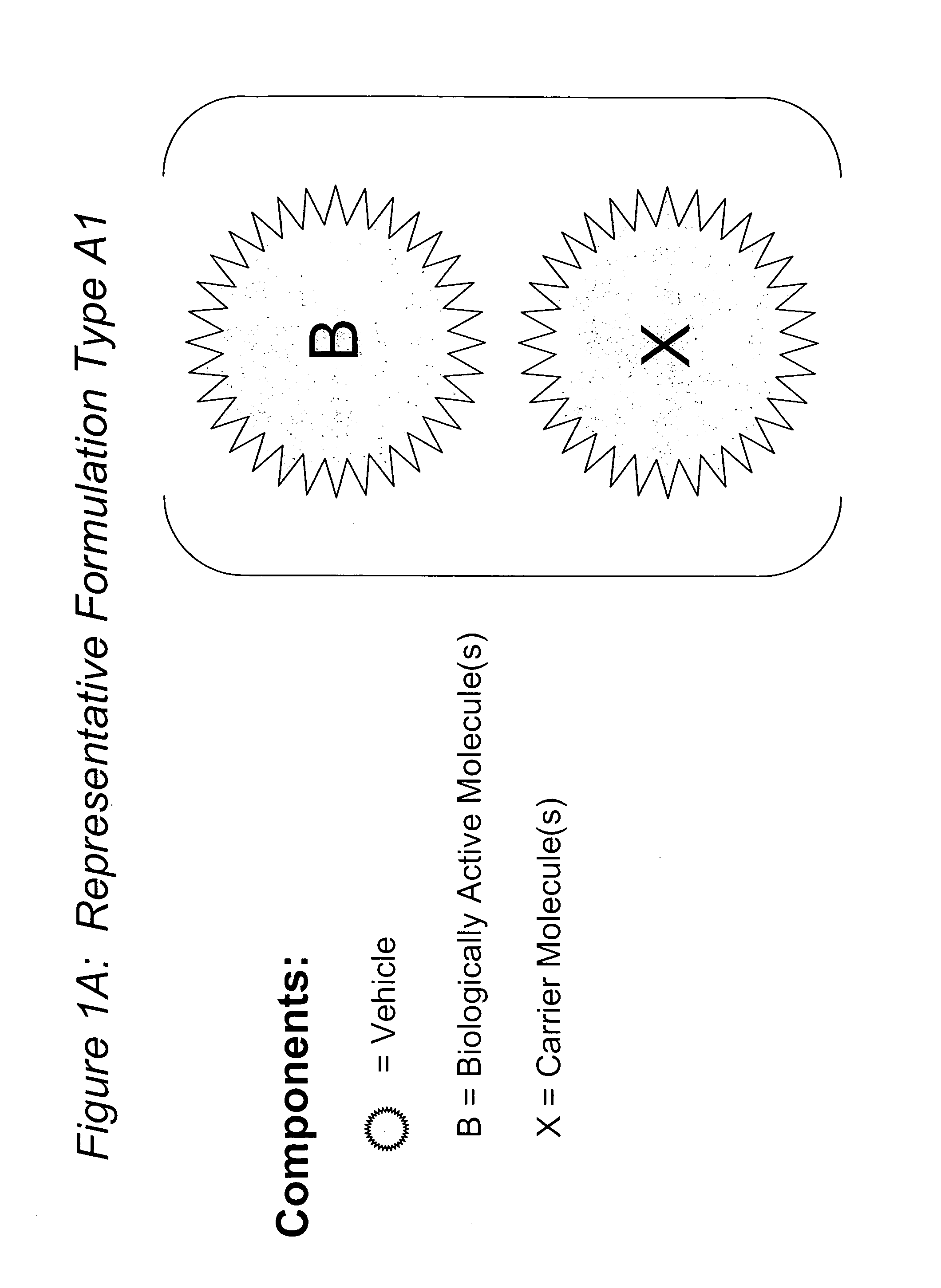
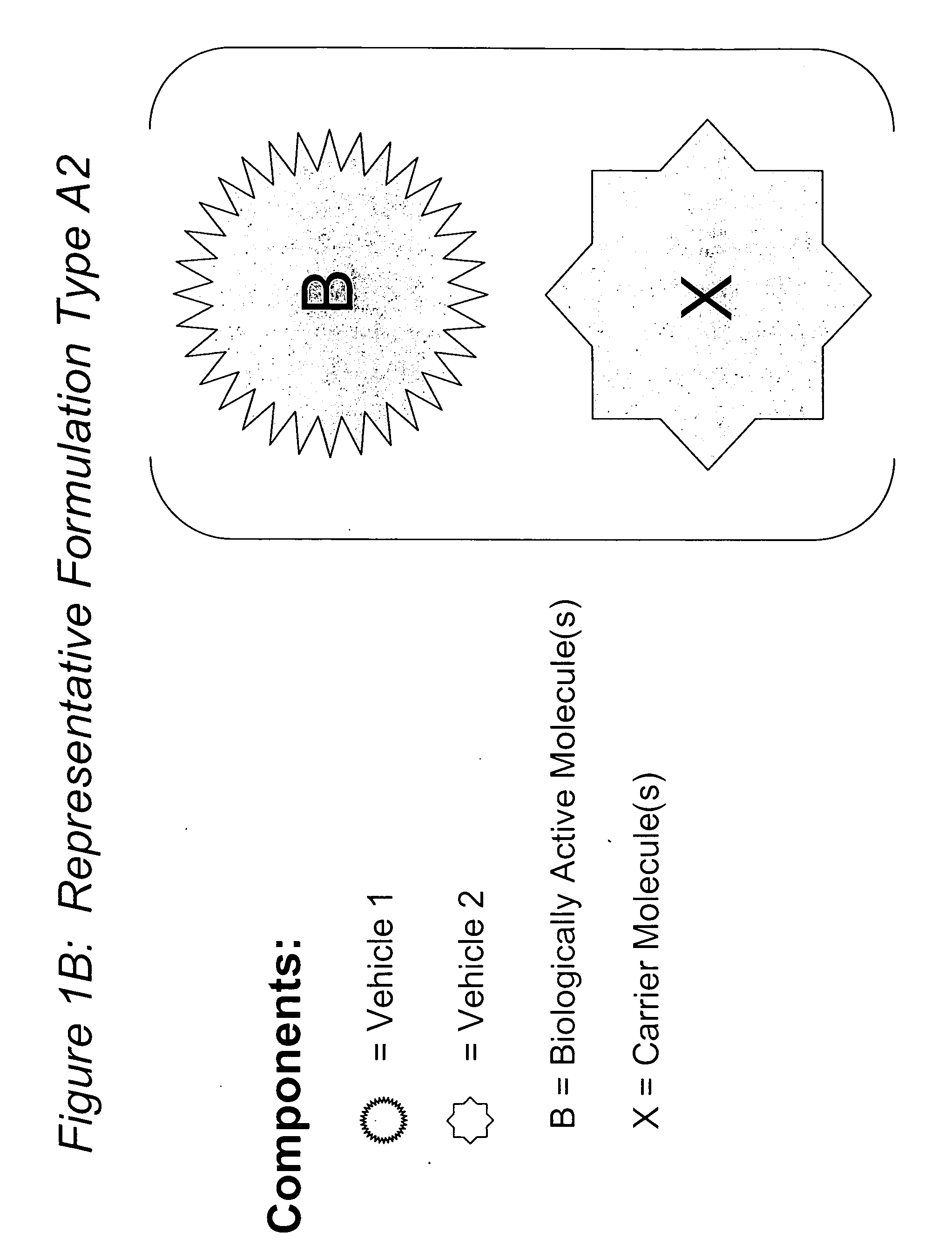
Compositions and methods for potentiated activity of biologically active molecules
InactiveUS20100015218A1Reduce deliveryLow in DOOrganic active ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedDiseaseLipid formation
The present invention relates to novel compositions and methods for potentiating the activity of biologically active molecules in conjunction with one or more delivery vehicles and one or more carrier molecules. Specifically, the invention features the use of a carrier molecule in combination with a delivery vehicle and a biologically active molecule of interest to potentiate the activity of the biologically active molecule. The carrier molecule can be biologically inert, inactive, or attenuated; or can alternately be biologically active in the same or different manner than the biologically active molecule of interest. Specifically, the invention features novel particle forming delivery agents including cationic lipids, microparticles, and nanoparticles that are useful for delivering various biologically active molecules to cells in conjunction with a carrier molecule. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism that are delivered intracellularly in conjunction with a carrier molecule. In various embodiments, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism, in conjunction with one or more carrier molecules. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that are used in conjunction with one or more carrier molecules are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Antisense nucleic acids
ActiveUS20140343266A1Improve efficiencyExcellent skipping efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationAntisense nucleic acidGene
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical agent which causes skipping of the 55th, 45th, 50th or 44th exon in the human dystrophin gene with a high efficiency.The present invention provides an oligomer which efficiently enables to cause skipping of the 55th, 45th, 50th or 44th exon in the human dystrophin gene.
Owner:NIPPON SHINYAKU CO LTD +1
Novel narc sc1, narc 10a, narc 1, narc 12, narc 13, narc17, narc 25, narc 3, narc 4, narc 7, narc 8, narc 11, narc 14a, narc 15, narc 16, narc 19, narc 20, narc 26, narc 27, narc 28, narc 30, narc 5, narc 6, narc 9, narc 10c, narc 8b, narc 9, narc2a, narc 16b, narc 1c, narc 1a, and narc 25 molecules and uses therefor
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules and proteins, designated NARC SC1, NARC 10A, NARC 1, NARC 12, NARC 13, NARC17, NARC 25, NARC 3, NARC 4, NARC 7, NARC 8, NARC 11, NARC 14A, NARC 15, NARC 16, NARC 19, NARC 20, NARC 26, NARC 27, NARC 28, NARC 30, NARC 5, NARC 6, NARC 9, NARC 10C, NARC 8B, NARC 9, NARC2A, NARC 16B, NARC 1C, NARC 1A, and NARC 25, nucleic acid molecules and proteins. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing said nucleic acid molecules, host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced, nonhuman transgenic animals in which a said genes have been introduced or disrupted, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and antibodies to said proteins. Diagnostic and therapeutic methods utilizing compositions of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
High throughput screening of gene function using libraries for functional genomics applications
InactiveUS7029848B2Altered phenotypeIncrease capacityFungiBacteriaGenomicsHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Novel means and methods for their use are provided to determine the function of the product(s) of one or more sample nucleic acids. The sample nucleic acids are synthetic oligonucleotides, DNA, or cDNA and encode polypeptides, antisense nucleic acids, or GSEs. The sample nucleic acids are expressed in a host by a vehicle to alter at least one phenotype of the host. The altered phenotype(s) is / are identified as a means to assign a biological function to the product(s) encoded by the sample nucleic acid(s).
Owner:GALAPAGOS GENOMICS
Method of preparing adenosine-resistant anti-tumor T lymphocytes for adoptive immunotherapy
In the past, adoptive immunotherapy often failed because the transferred immune cells were inactive in vivo. This disclosure provides a method of producing immune cells that are highly active in vivo. The immune cells may be expanded in vitro in the presence of an adenosine receptor agonist or an antisense nucleic acid that downregulates expression of an adenosine receptor, for example. The immune cells may be tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), natural killer (NK) cells, or lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells, for example. The methods described herein may be used to treat a number of diseases including cancer, infectious diseases, and immunodeficiencies.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Pro-protein converting enzyme
InactiveUS6380171B1Successfully silenceInhibited carotid stenosisBiocideHydrolasesRestenosisAngiotensin-converting enzyme
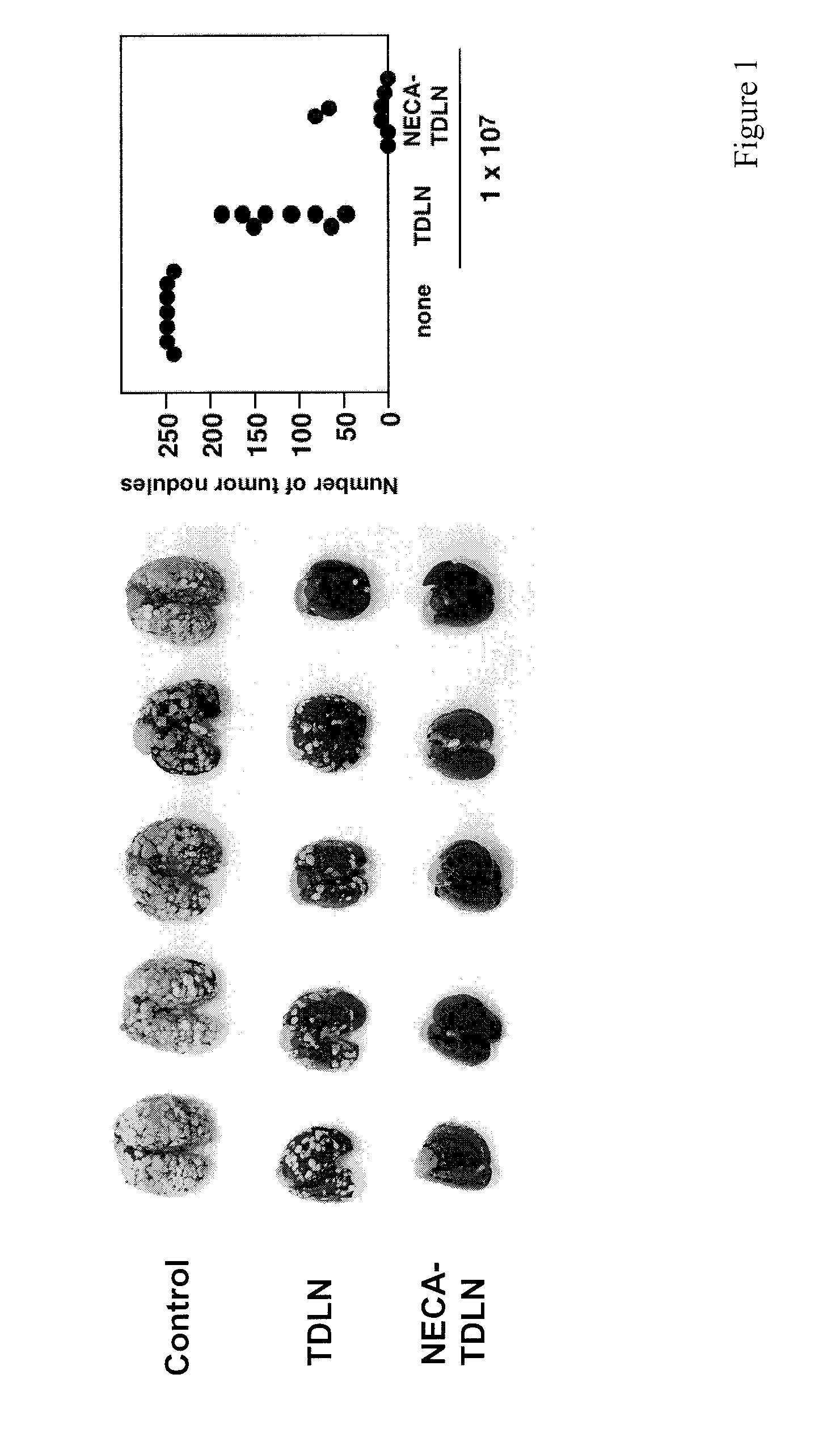
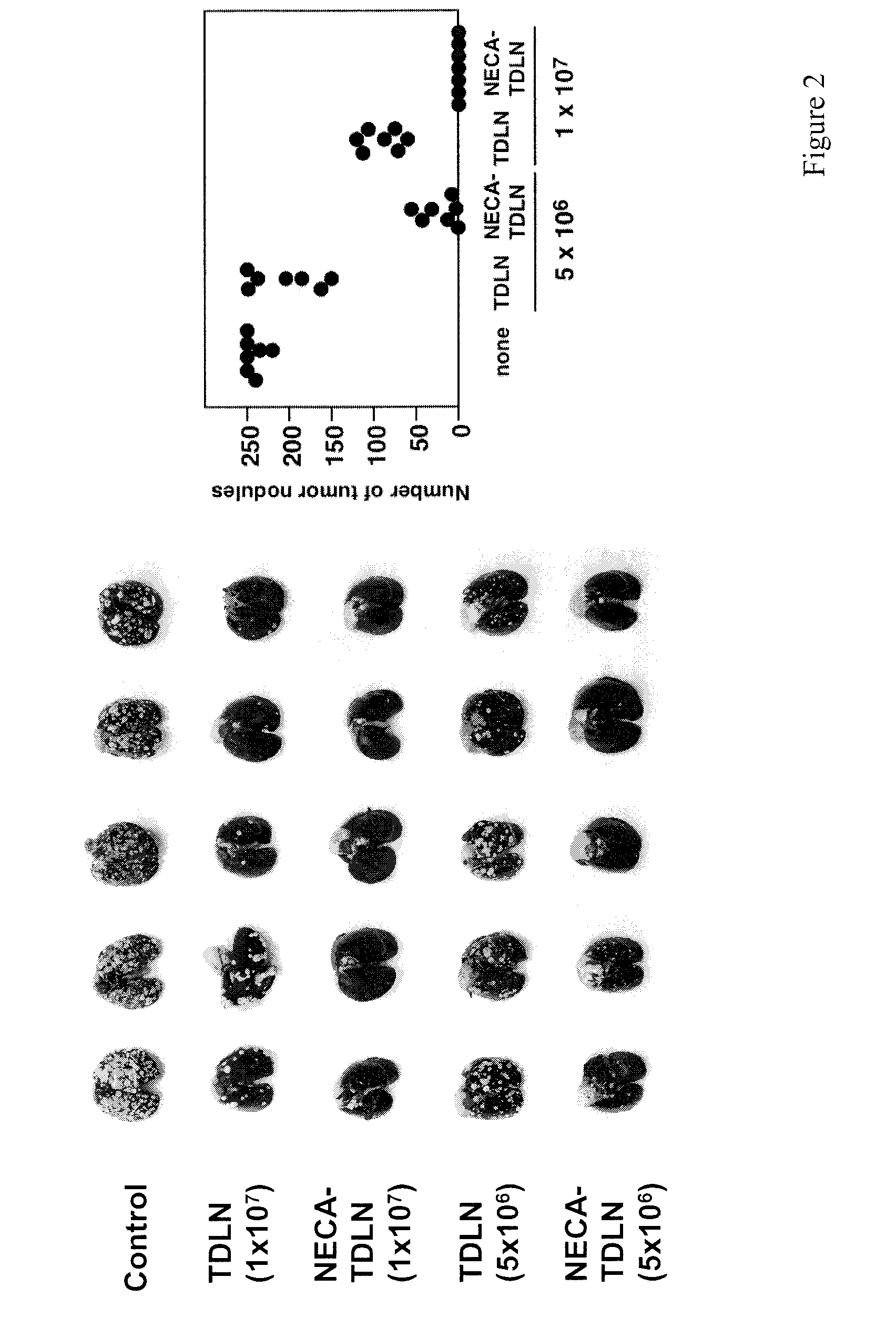
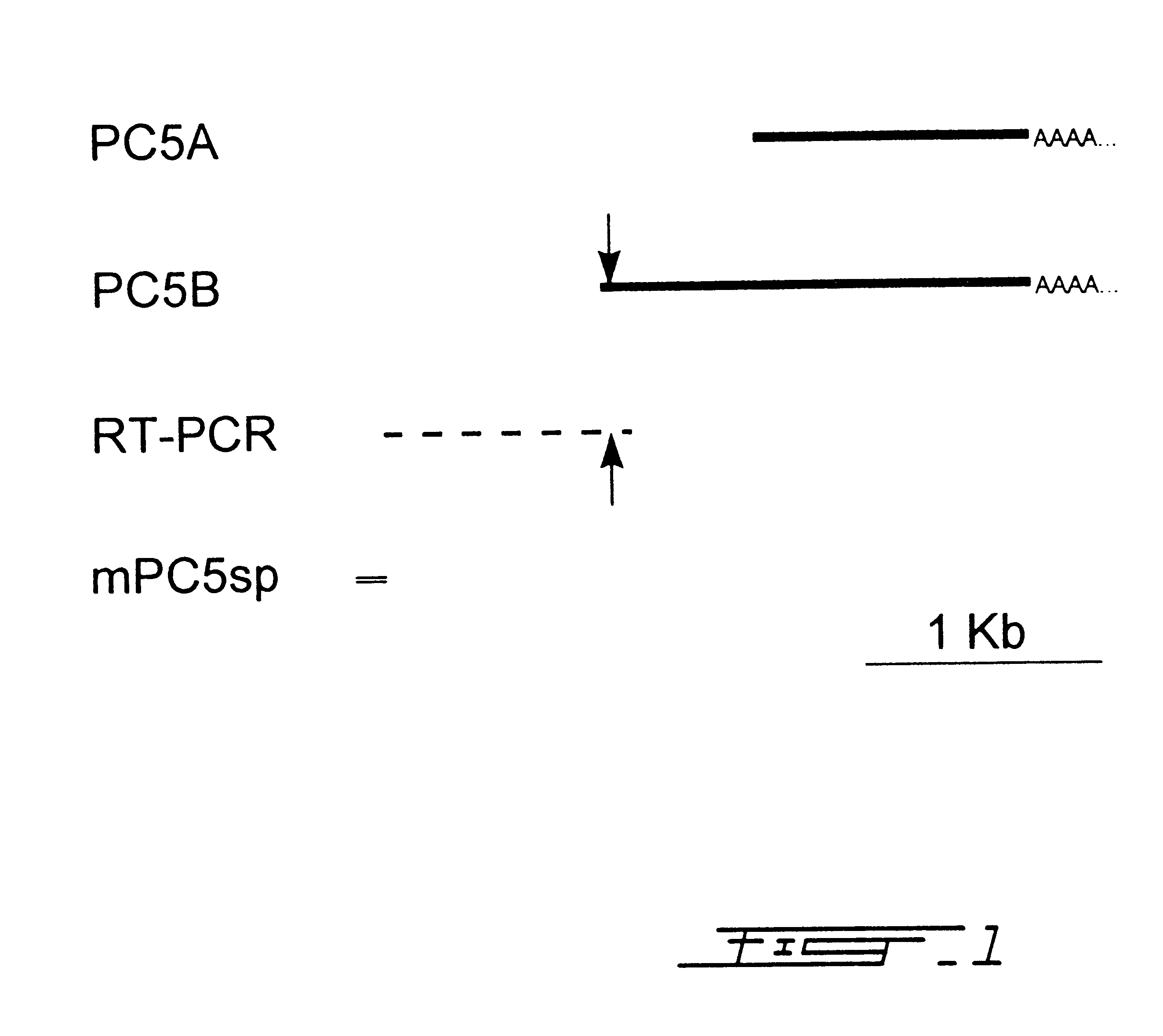
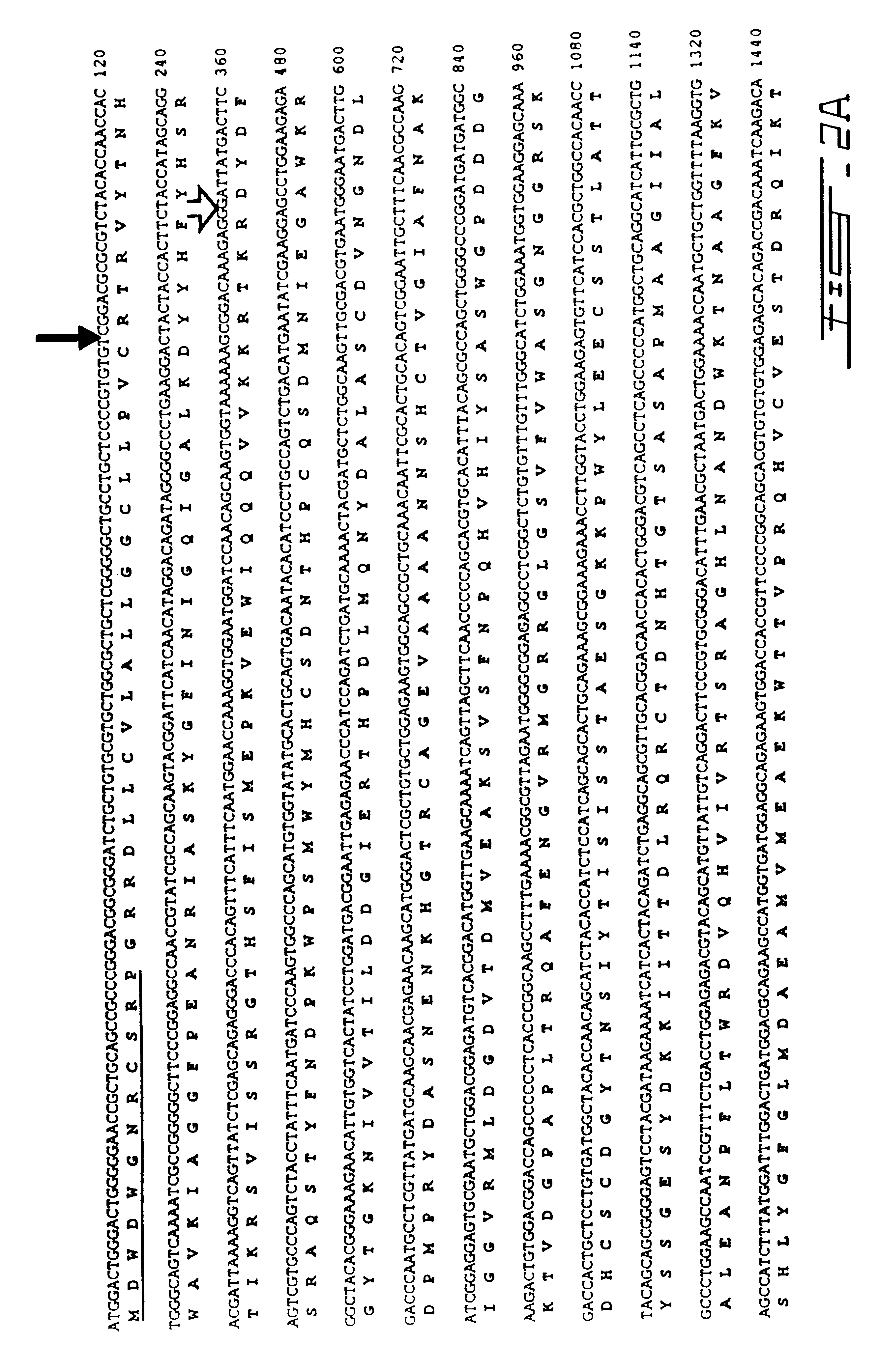
The present invention relates to the cloning of human pro-protein converting enzyme 5 (PC5) CDNA isolated from human adrenal gland messenger RNA. Additionally, this invention relates to a method for reducing restenosis occurring at an injured vascular site comprising delivering to the injured site an antisense nucleic acid to suppress the expression of human PC5.
Owner:CLINICAL RES INST OF MONTREAL +2
Compositions and methods for restoring sensitivity of tumor cells to antitumor therapy and inducing apoptosis
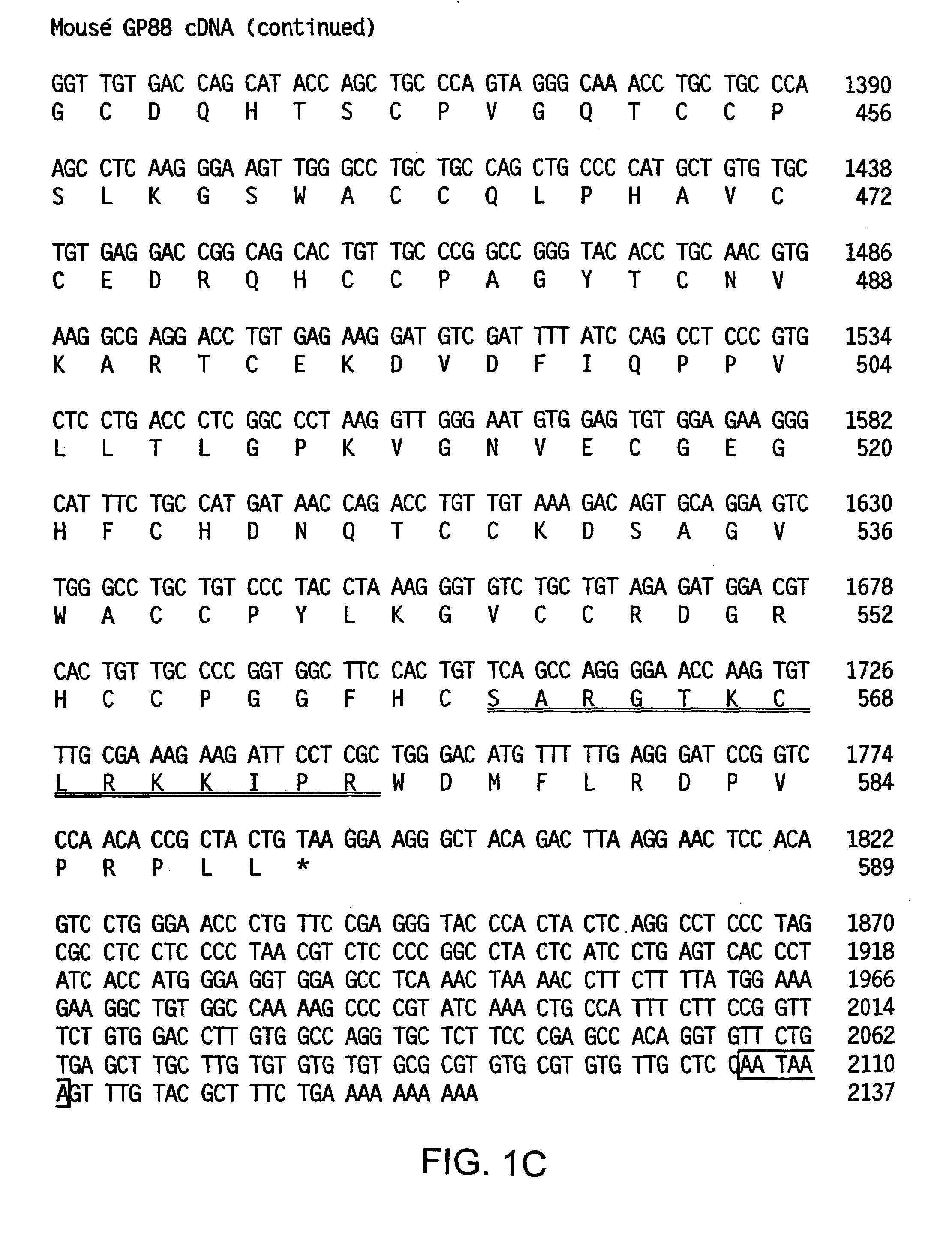
Methods and compositions for restoring sensitivity to the antitumorigenic effects of antiestrogen therapy and / or cytotoxic therapy and inducing cell apoptosis are provided. Contacting tumor cells to GP88 antagonists (e.g., anti-GP88 antibodies, anti-GP88 antisense nucleic acids, GP88 siRNA, and small molecules) induces apoptosis and restores sensitivity to the antitumorigenic effects of antiestrogen therapy and cytotoxic therapy.
Owner:A & G PHARMA
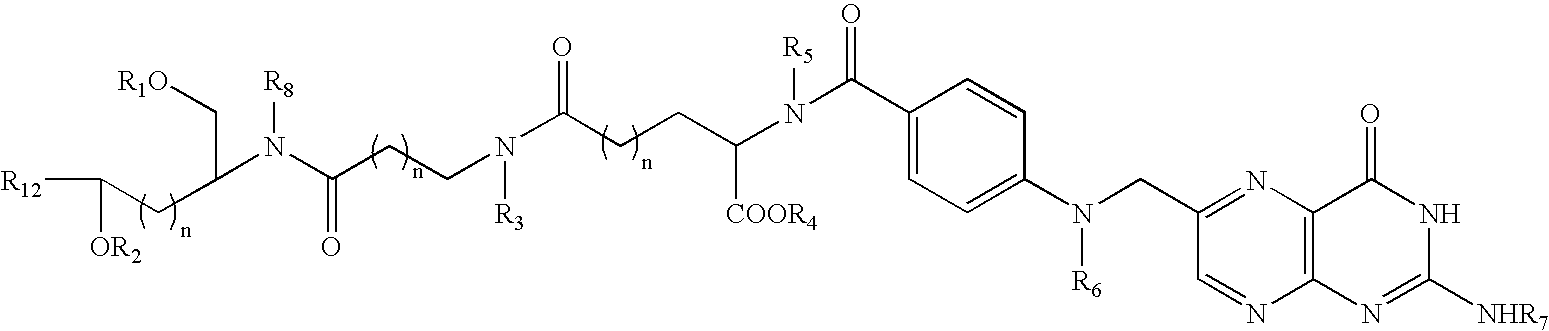
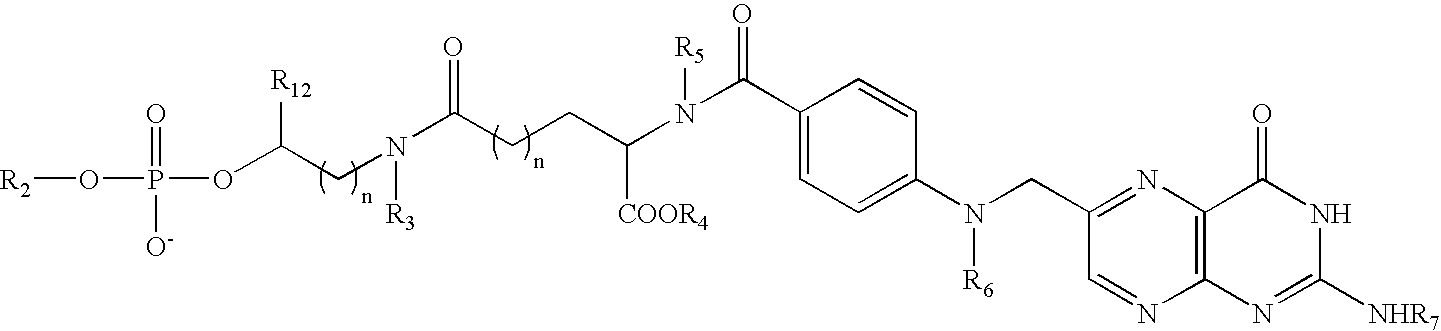
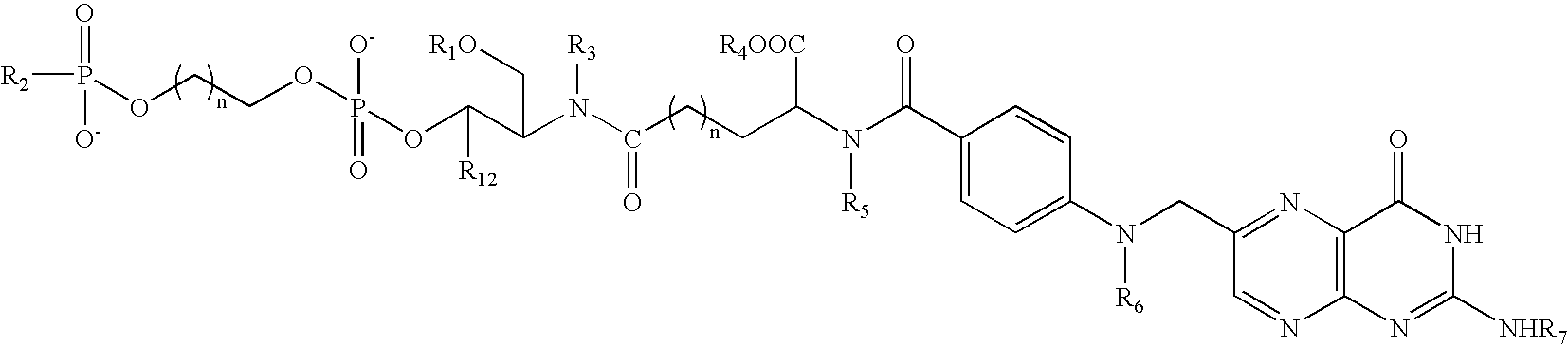
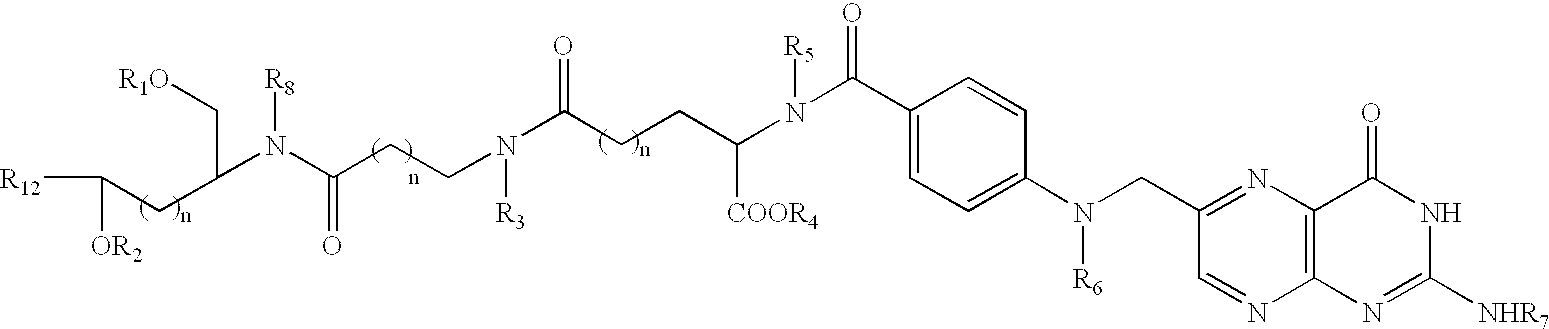
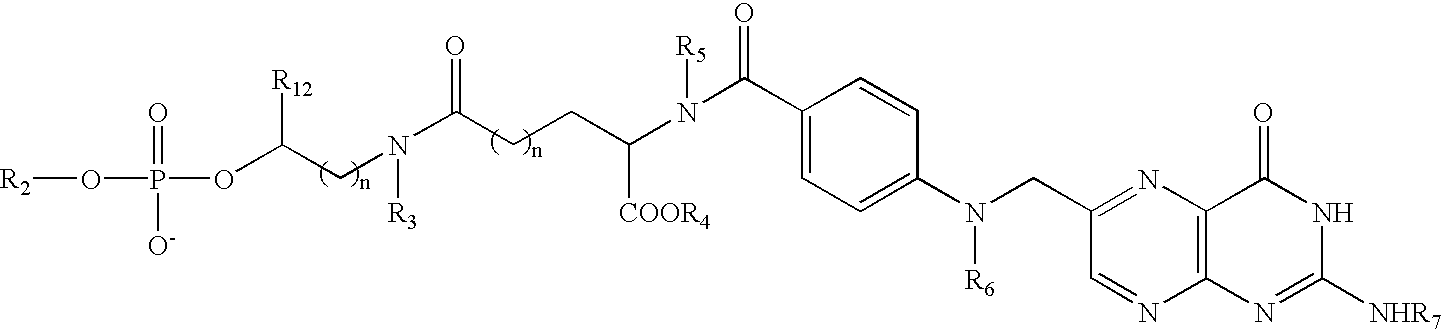
Polymalic Acid-Based Multi-Functional Drug Delivery System
ActiveUS20070259008A1Low toxicityReadily availableOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNatural sourceFluorescence
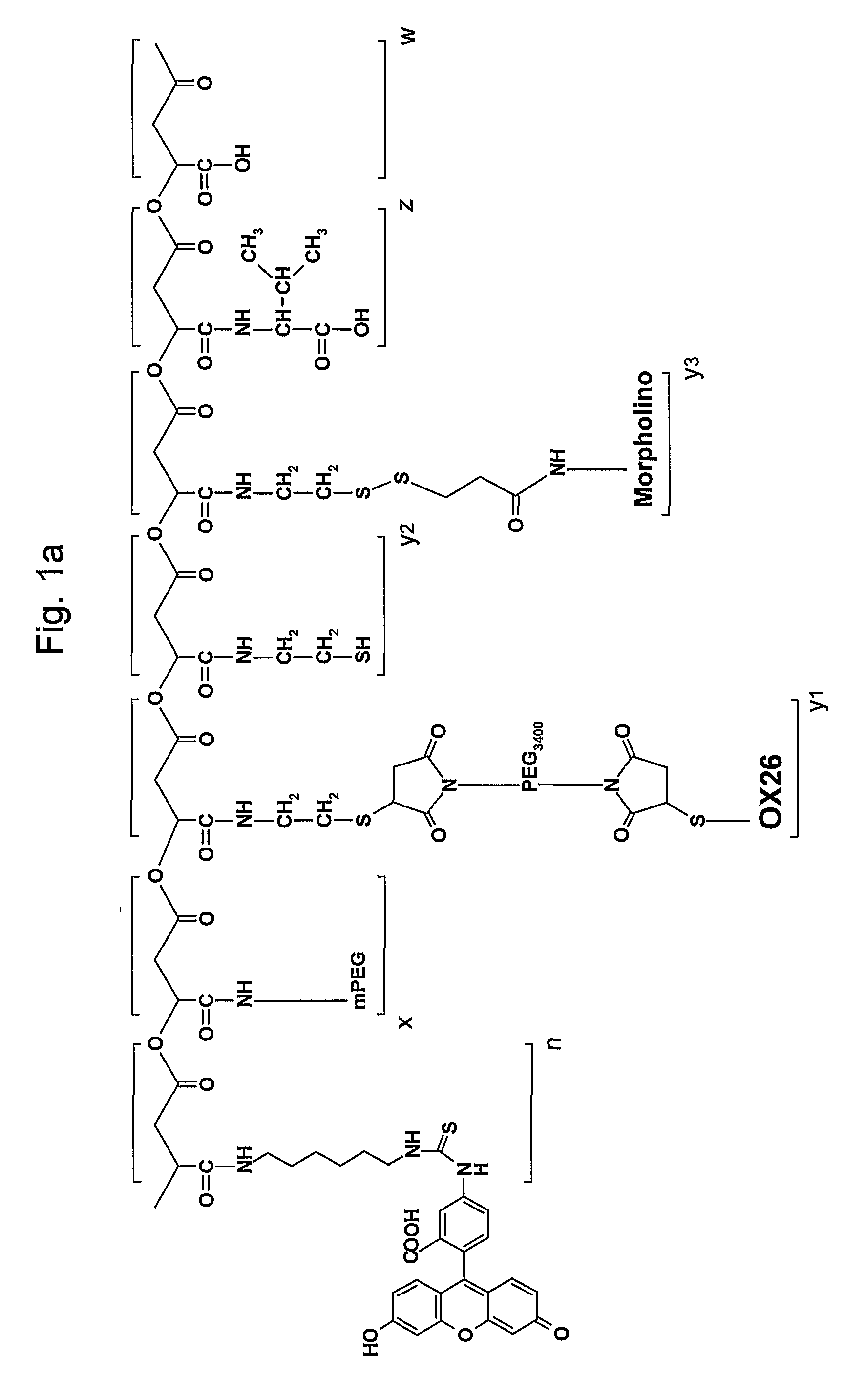
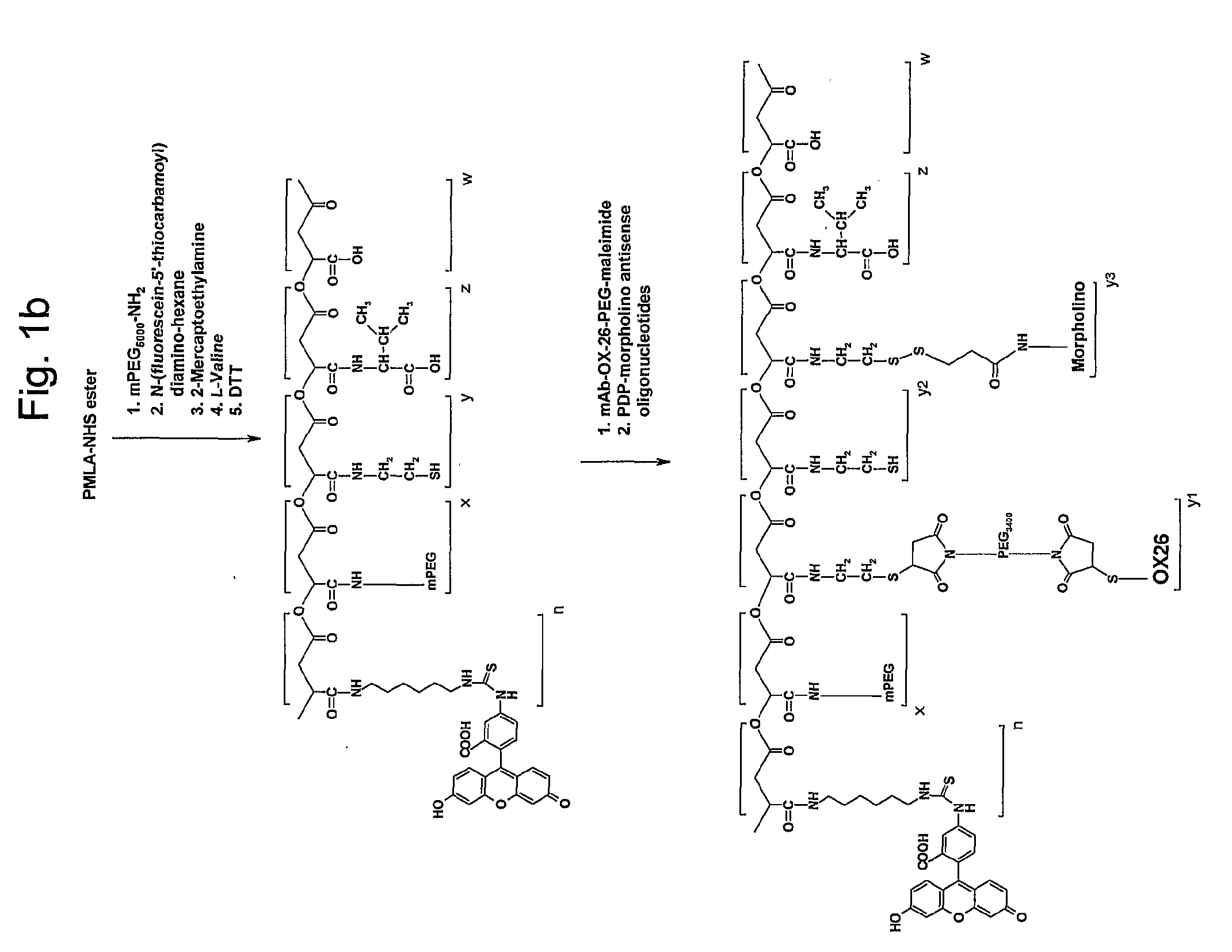
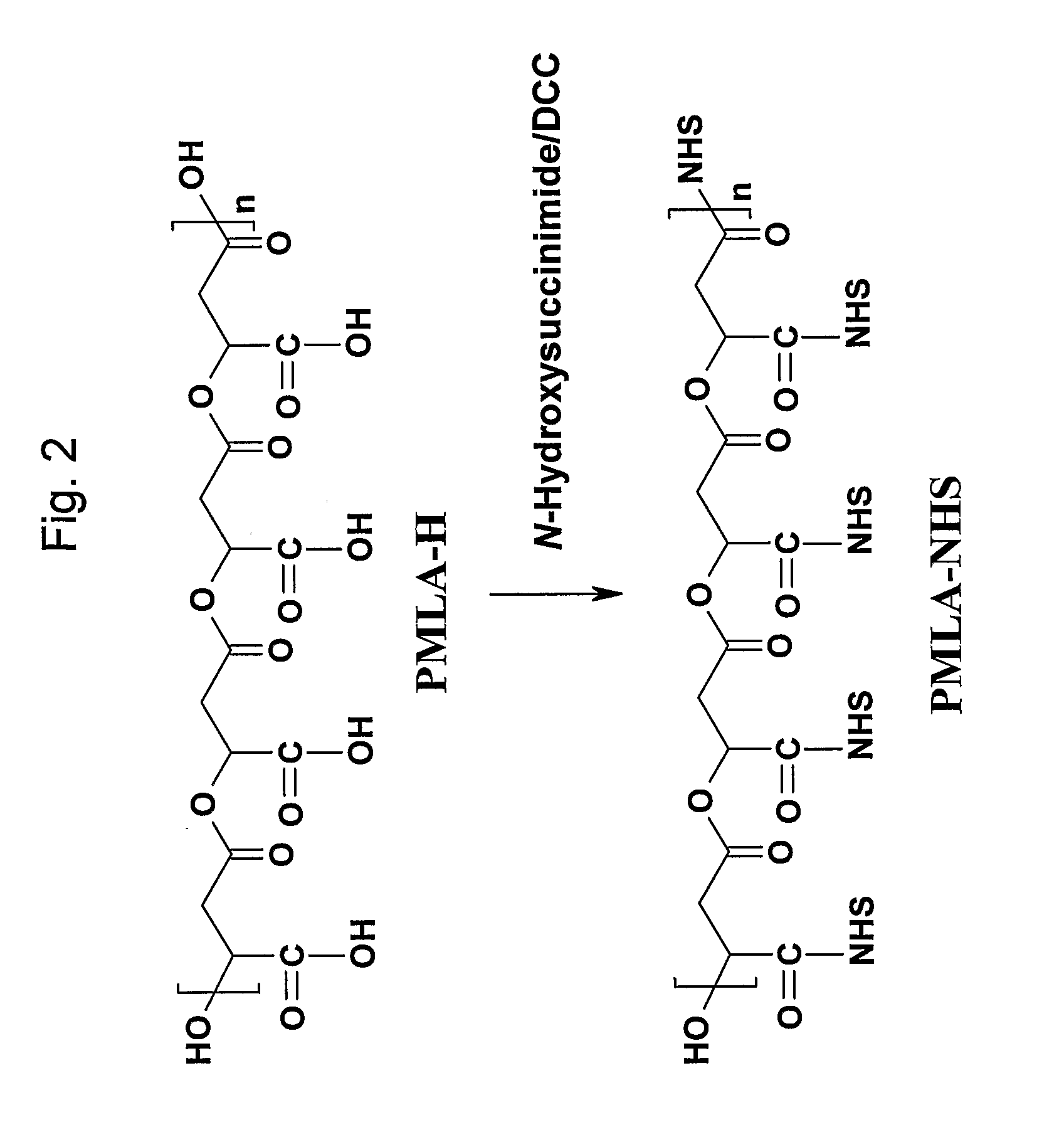
A structured drug system that is useful for delivering a drug payload to a specific tissue or cell type is disclosed. The system is based on purified polymalic acid. This polymer isolated from natural sources is biocompatible, biodegradable and of very low toxicity. The polymer is extremely water soluble and contains a large number of free carboxyl groups which can used to attach a number of different active molecules. In the examples disclosed N-hydroxysuccinimide esters of the carboxyl groups are used to attach such molecules. The active molecules include monoclonal antibodies to promote specific cellular uptake and specific pro-drugs such as antisense nucleic acids designed to modify the cellular metabolism of a target cell. The pro-drugs are advantageously linked by a somewhat labile bond so that they will be released under specific conditions. In addition, the system contains amide-linked valine to encourage membrane disruption under lysosomal conditions. Polyethylene glycol groups are attached to extend the drug system's circulation half-life. In addition, fluorescent reported groups can be readily included to aid in visualizing and confirming drug system targeting. The drug system can deliver treatments for a wide range of diseases and is specially advantageous for treatment of neoplasms.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding proteins involved in DNA replication, protein synthesis, and pathogenesis
InactiveUS20060269975A1Efficient producerImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidGenetic engineering
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated RRP nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel RRP proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing RRP nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated RRP proteins, mutated RRP proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of RRP genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
Transfection agents
The present invention provides compounds, compositions and methods that enhance the transfer of an agent into a cell. The agents can include polypeptides, polynucleotides such as genes and antisense nucleic acids, and other molecules. In some embodiments, the agents are modulating agents that can modulate a cellular activity or function when introduced into the cell. The compounds, compositions and methods are useful for introducing agents such as genes into individual cells, as well as cells that are present as a tissue or organ.
Owner:CANJI
Glycoprotein VI antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS6989144B1Stabilize and promote and inhibit and disrupt protein-protein interactionAbility to modulateCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAntisense nucleic acid
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid molecules and polypeptide molecules that encode glycoprotein V1, a platelet membrane glycoprotein that is involved platelet-collagen interactions. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, expression vectors containing the nucleic acid molecules of the invention, host cells into which the exposure vectors have been introduced, and non-human transgenic animals in which a nucleic acid molecule of the invention has been introduced or disrupted. The invention still further provides isolated polypeptides, fusion polypeptides, antigenic peptides and antibodies. Diagnostic, screening and therapeutic methods utilizing compositions of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC +1
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system proteins
InactiveUS6884614B1Increase productionHigh yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidProtein isolate
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated PTS nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel PTS proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PTS nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated PTS proteins, mutated PTS proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of PTS genes in this organism.
Owner:DAESANG
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding proteins involved in membrane synthesis and membrane transport
InactiveUS20050244935A1Efficient producerImprove production efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated MCT nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel MCT proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing MCT nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated MCT proteins, mutated MCT proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of MCT genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
GL50 polypeptides
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules, designated GL50 nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel GL50 polypeptides. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing GL50 nucleic acid molecules, host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced, and nonhuman transgenic animals in which a GL50 gene has been introduced or disrupted. The invention still further provides isolated GL50 polypeptides, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and anti-GL50 antibodies. Diagnostic, screening, and therapeutic methods utilizing compositions of the invention are also provided.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Application of lipid vehicles and use for drug delivery
InactiveUS20070003610A1Reduce and prevent antibody-mediated resistanceIncrease stimulationBiocideAntipyreticDiseaseAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the administration of lipid-based vehicles to treat various disorders, including bladder inflammation, infection, dysfunction, and cancer. In various aspects, the compositions and methods of the invention are useful for prolonged delivery of drugs, e.g., antibiotics, pain treatments, and anticancer agents, to the bladder, genitourinary tract, gastrointestinal system, pulmonary system, and other organs or body systems. In particular, the present invention relates to liposome-based delivery of vanilloid compounds, such as resiniferatoxin, capsaicin, or tinyatoxin, and toxins, such as botulinum toxin, for the treatment of bladder conditions, including pain, inflammation, incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. Further related are methods of using these vehicles alone or in conjunction with antibodies, e.g., uroplakin antibodies, to improve duration of liposome attachment, and provide a long-term intravesical drug delivery platform. The present invention specifically relates to antibody-coated liposomes that are useful for targeting specific receptors for drug, peptide, polypeptide, or nucleic acid delivery. In one particular aspect, the present invention relates to liposomes coated with antibodies against nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor and containing NGF antisense nucleic acids, which are used as a treatment for neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Conjugates and compositions for cellular delivery
InactiveUS7858625B2Reduced activityPromotes associationBiocideSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidNucleotide
This invention features conjugates, compositions, methods of synthesis, and applications thereof, including folate derived conjugates of nucleosides, nucleotides, non-nucleosides, and nucleic acids including enzymatic nucleic acids and antisense nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Functional nucleic acids and methods
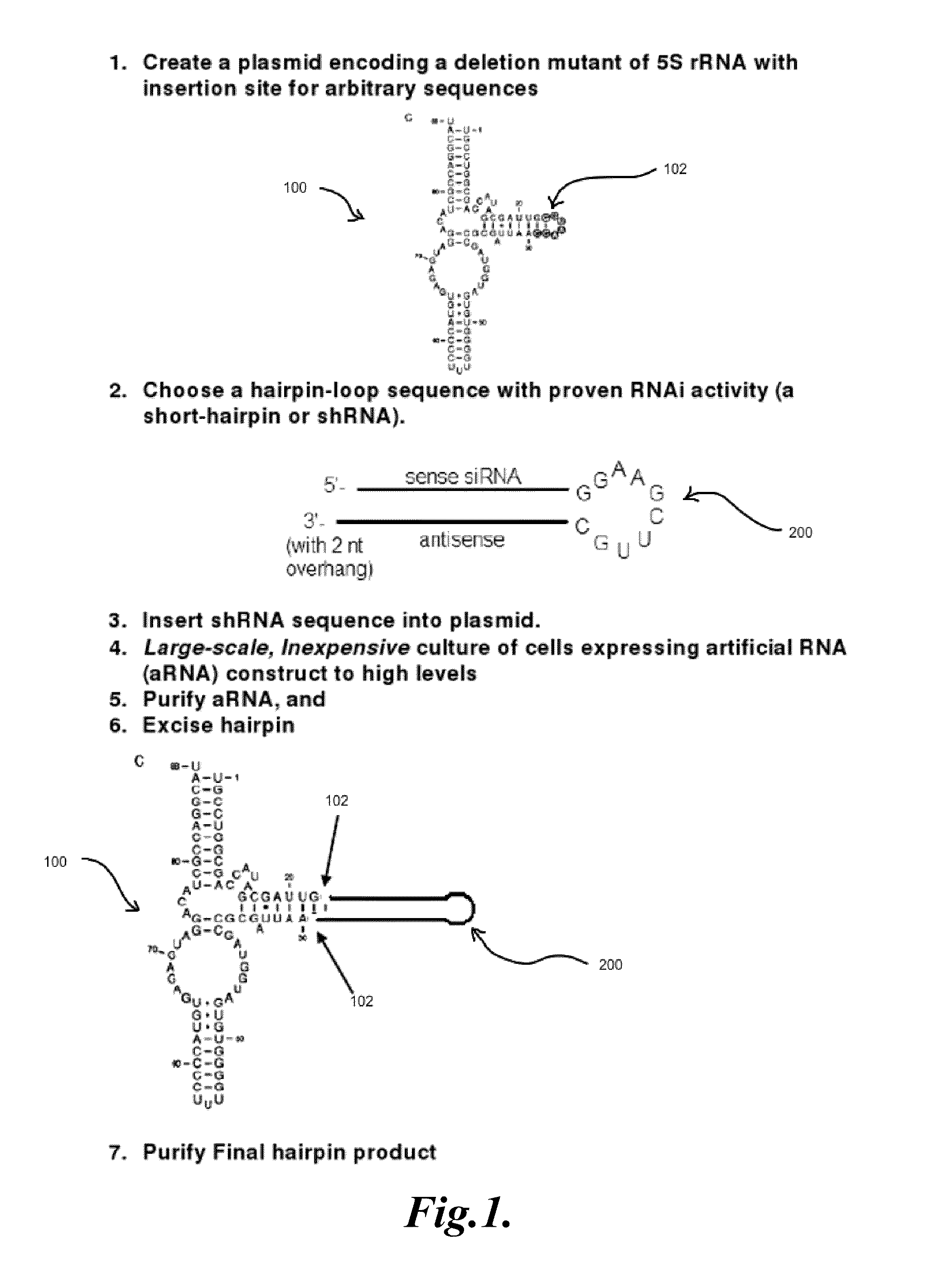
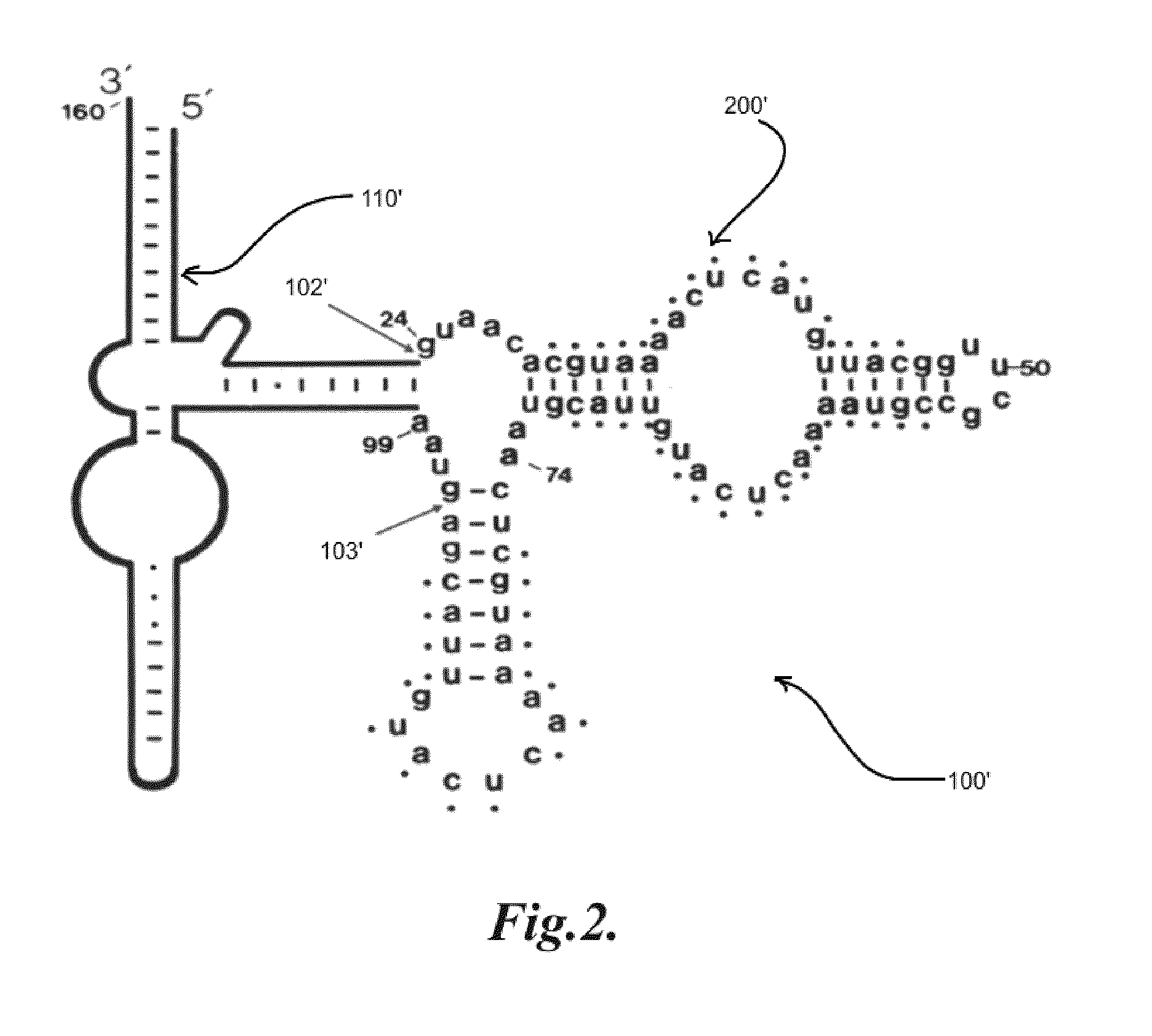
InactiveUS20100087336A1High affinityIncrease stringencyMicroorganismsTissue cultureAntisense nucleic acidNucleic Acid Probes
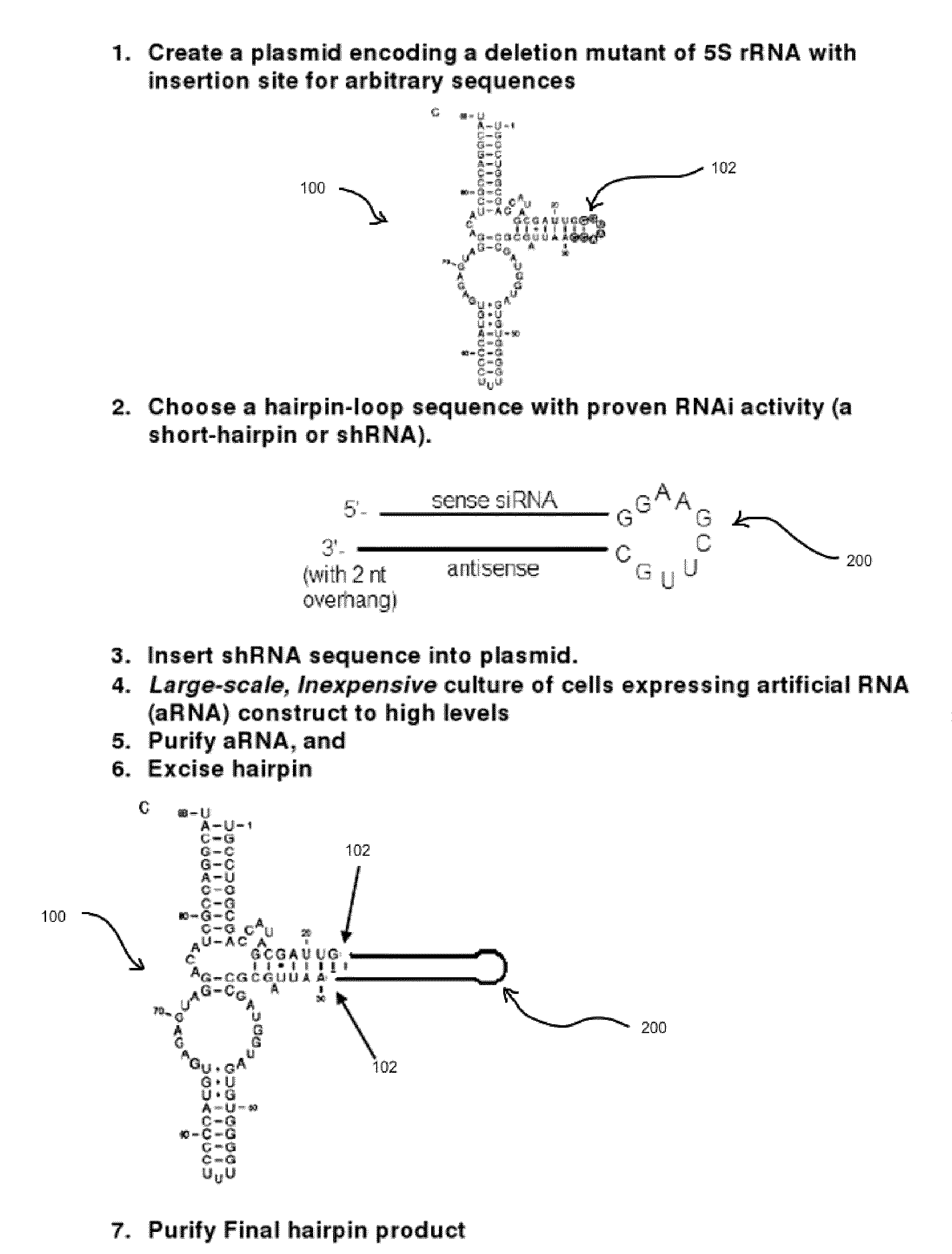
The present invention relates to methods of generating amounts of selective nucleic acids. The present invention further relates to selective nucleic acids incorporated within non-coding nucleic acids, capable of binding to or altering a target molecule. Selective nucleic acids may generally refer to, but are not limited to, deoxyribonucleic acids (DNAs), ribonucleic acids (RNAs), artificially modified nucleic acids, combinations or modifications thereof. Selective nucleic acids may also generally refer to, but are not limited to, nucleic acid aptamers, aptazymes, ribozymes, deoxyribozymes, nucleic acid probes, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), micro RNAs (miRNAs), short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), antisense nucleic acids, diagnostic probes or probe libraries, aptamer inhibitors, precursors of any of the above and / or combinations or modifications thereof. In one aspect, a method for generating amounts of selective nucleic acids includes incorporating a selective nucleic acid sequence into a carrier nucleic acid. In general, the carrier nucleic acid may be transcribed by a cell into a product nucleic acid which may carry an incorporated selective nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:BIOTEX +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com