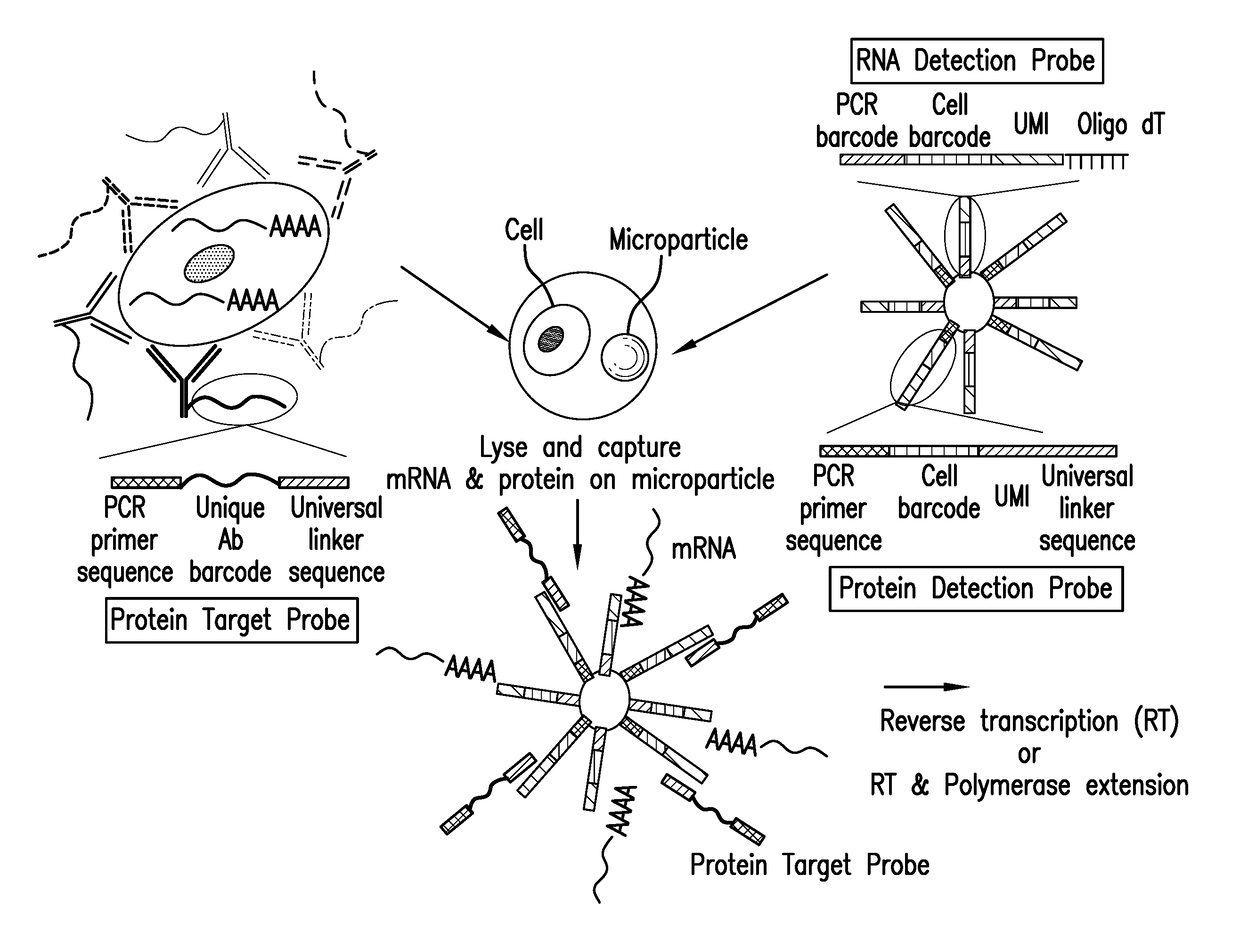
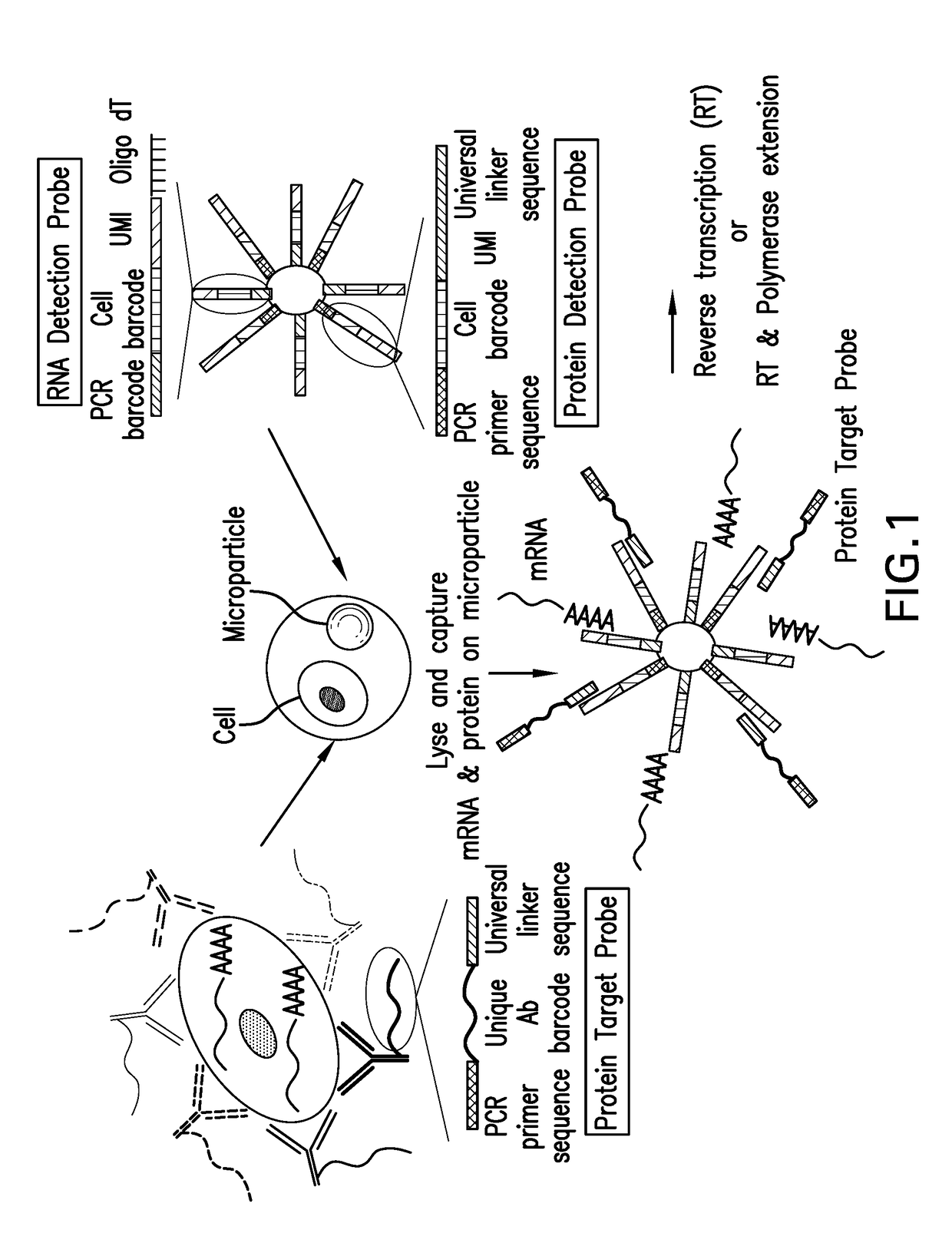
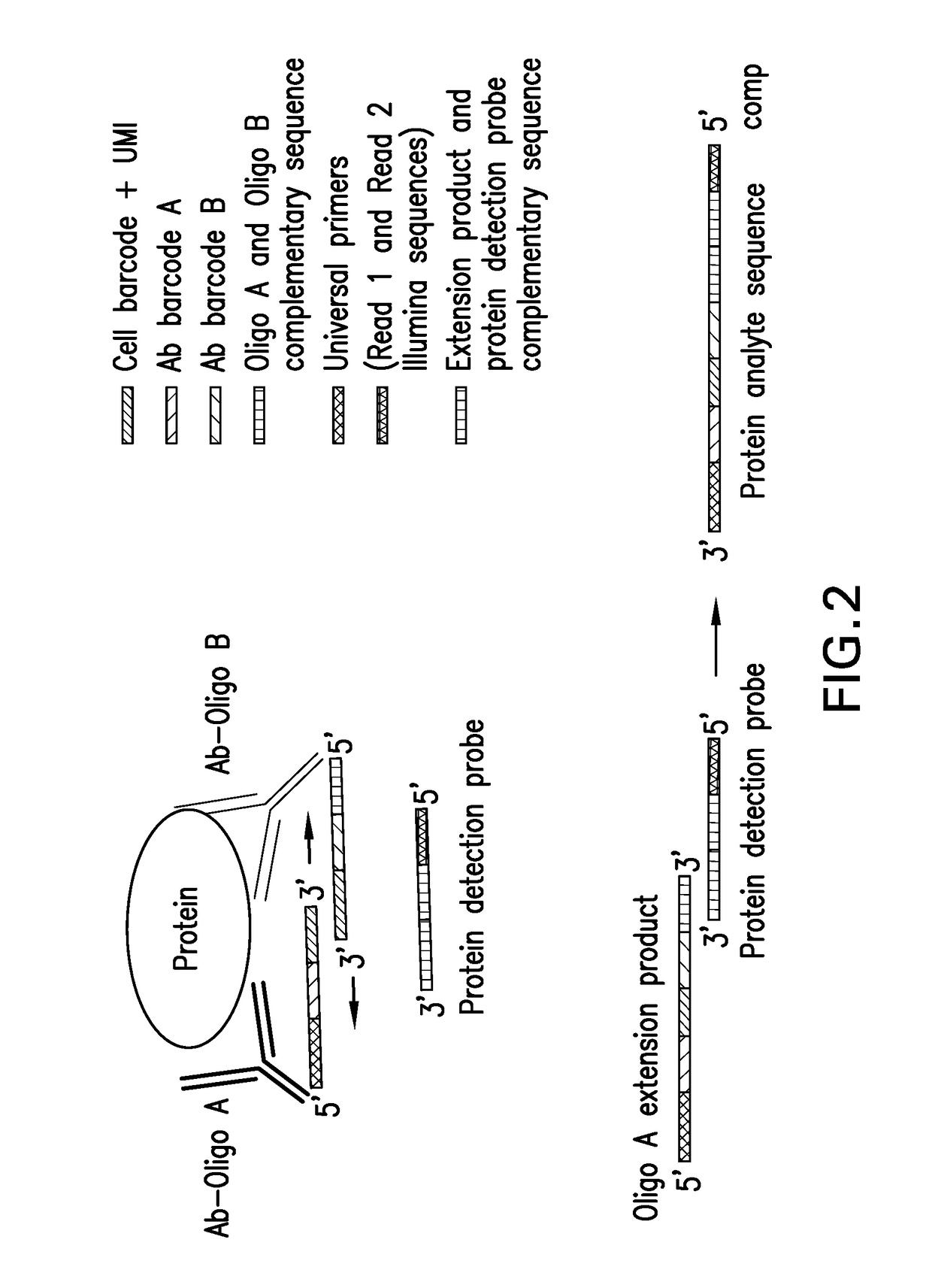
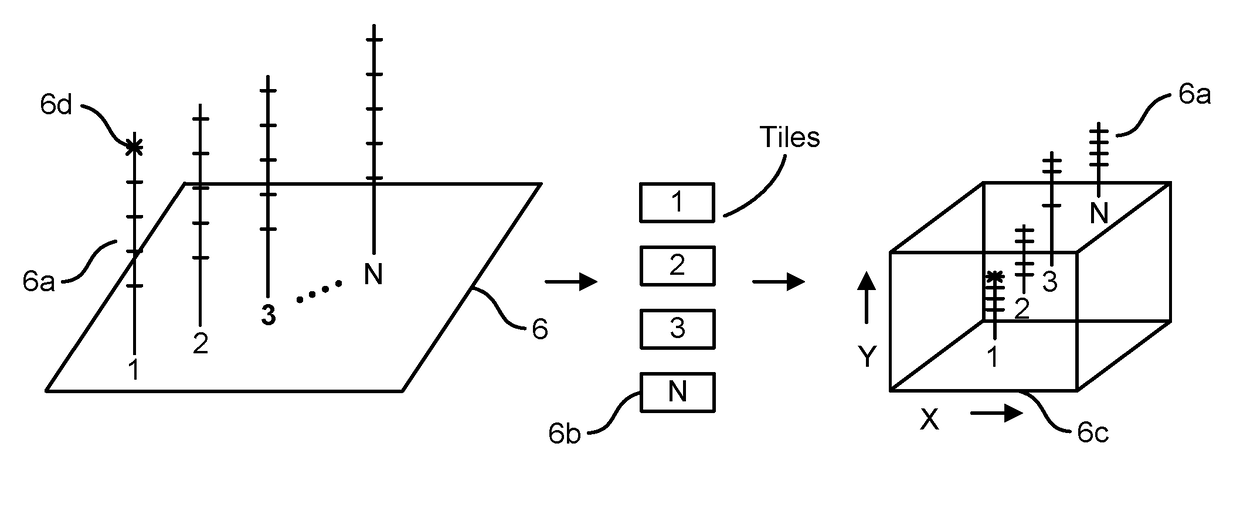
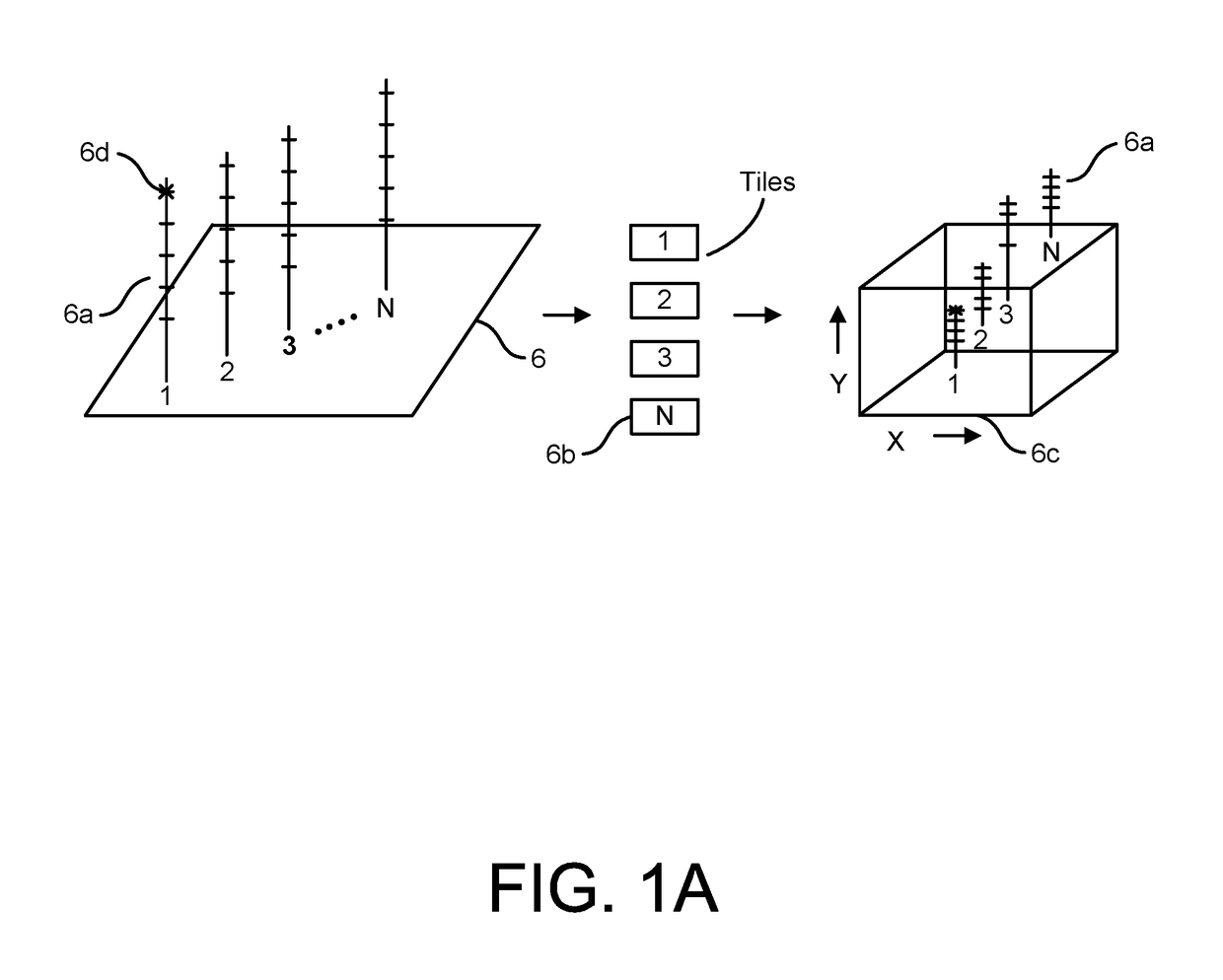
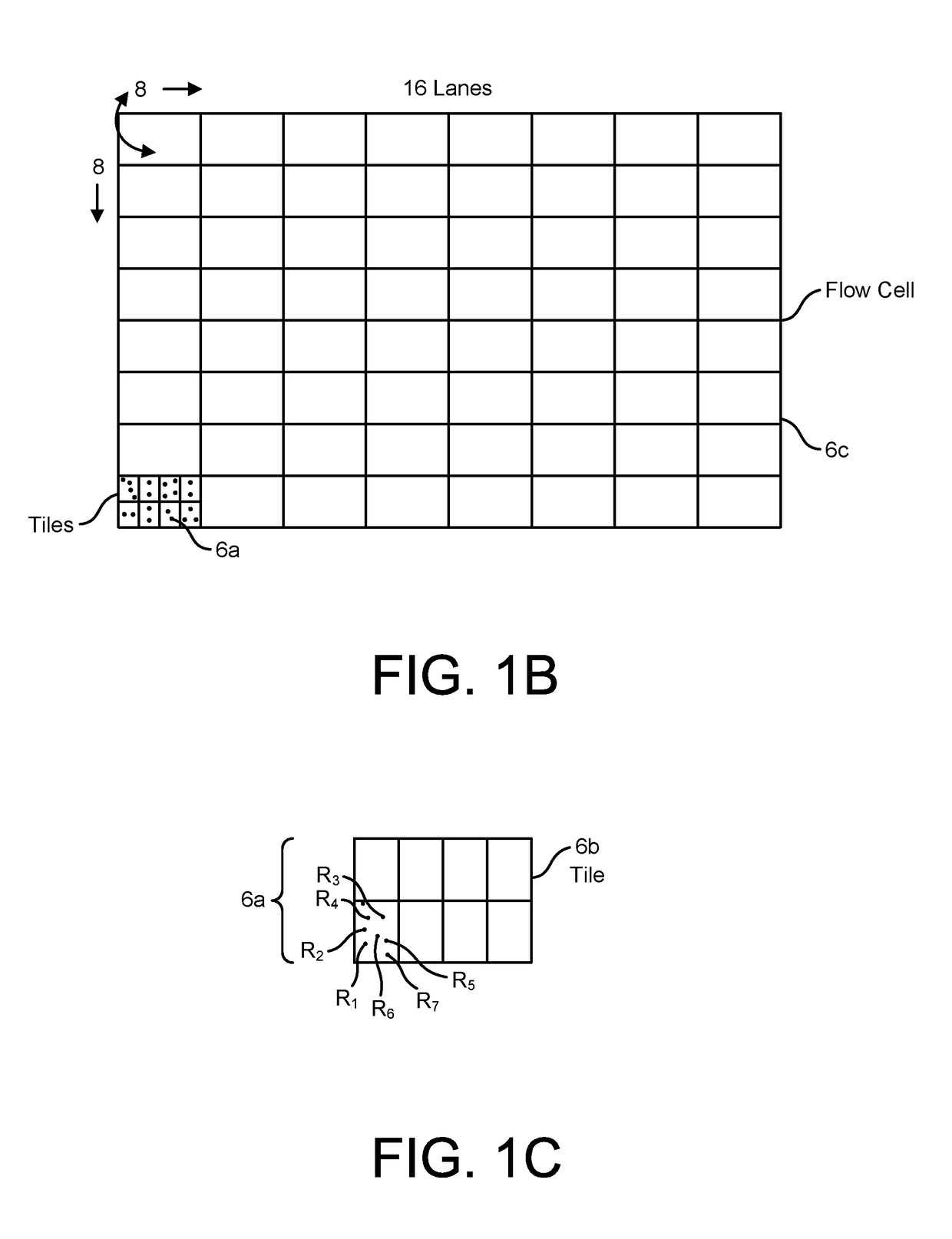
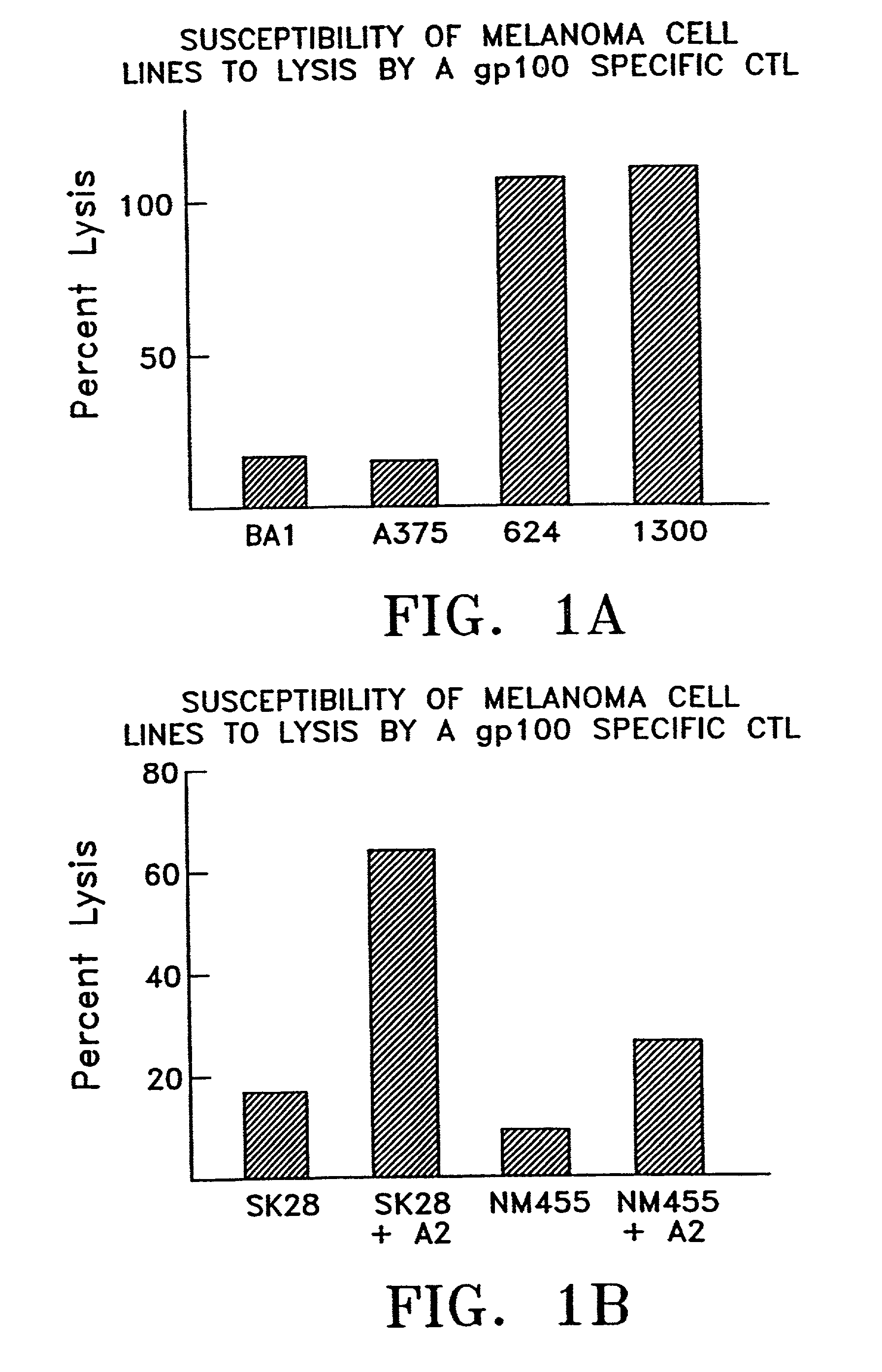
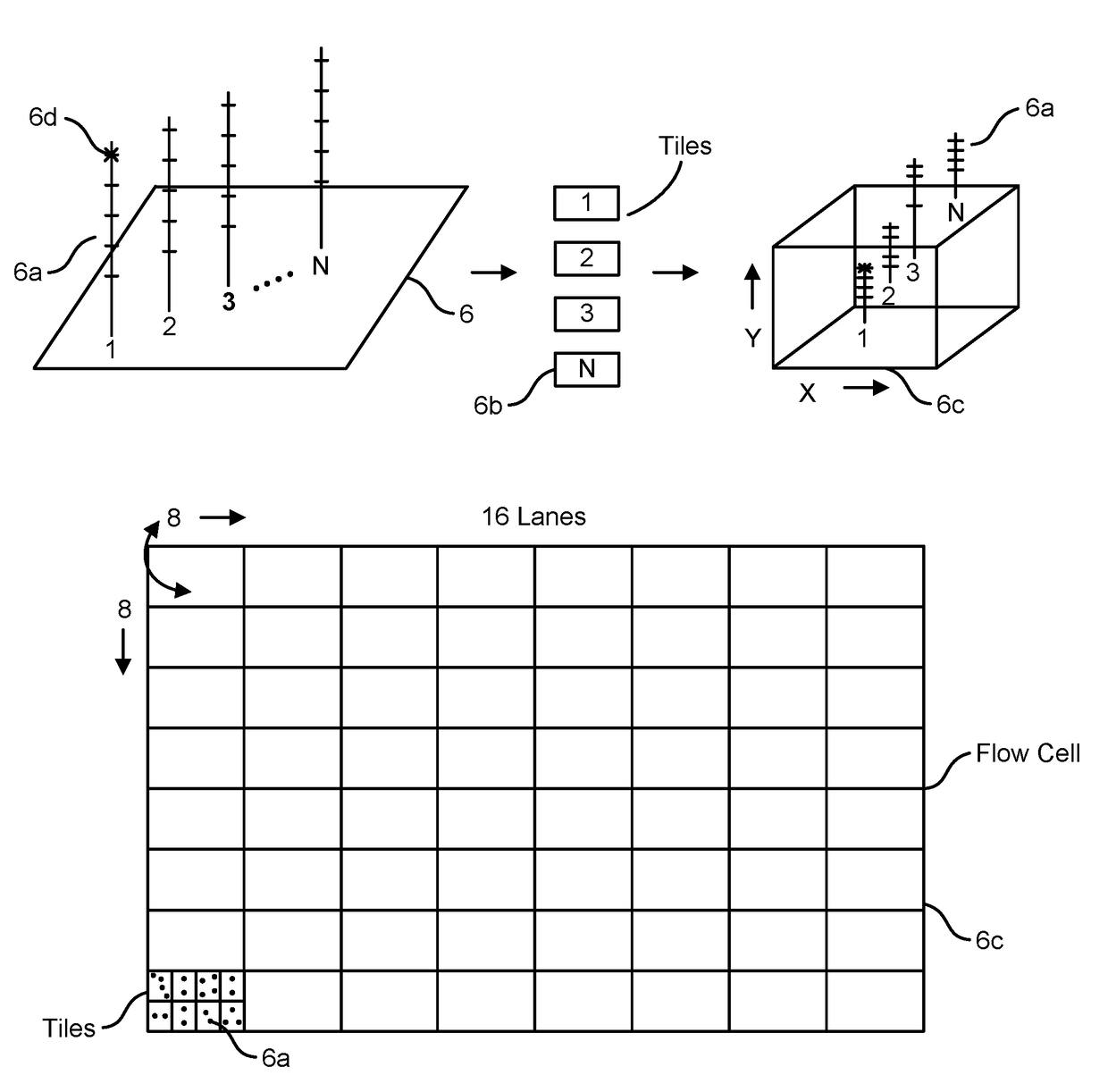
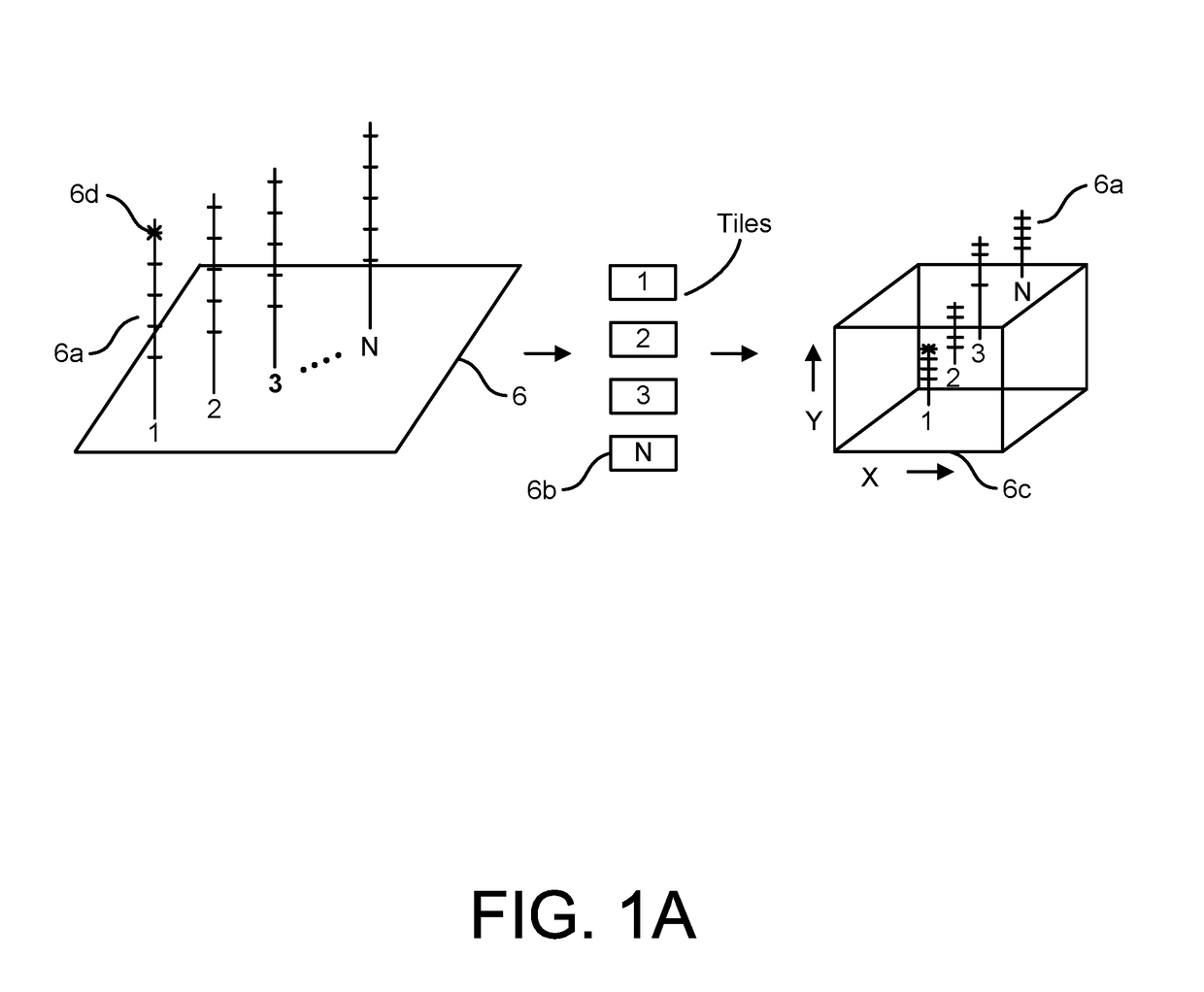
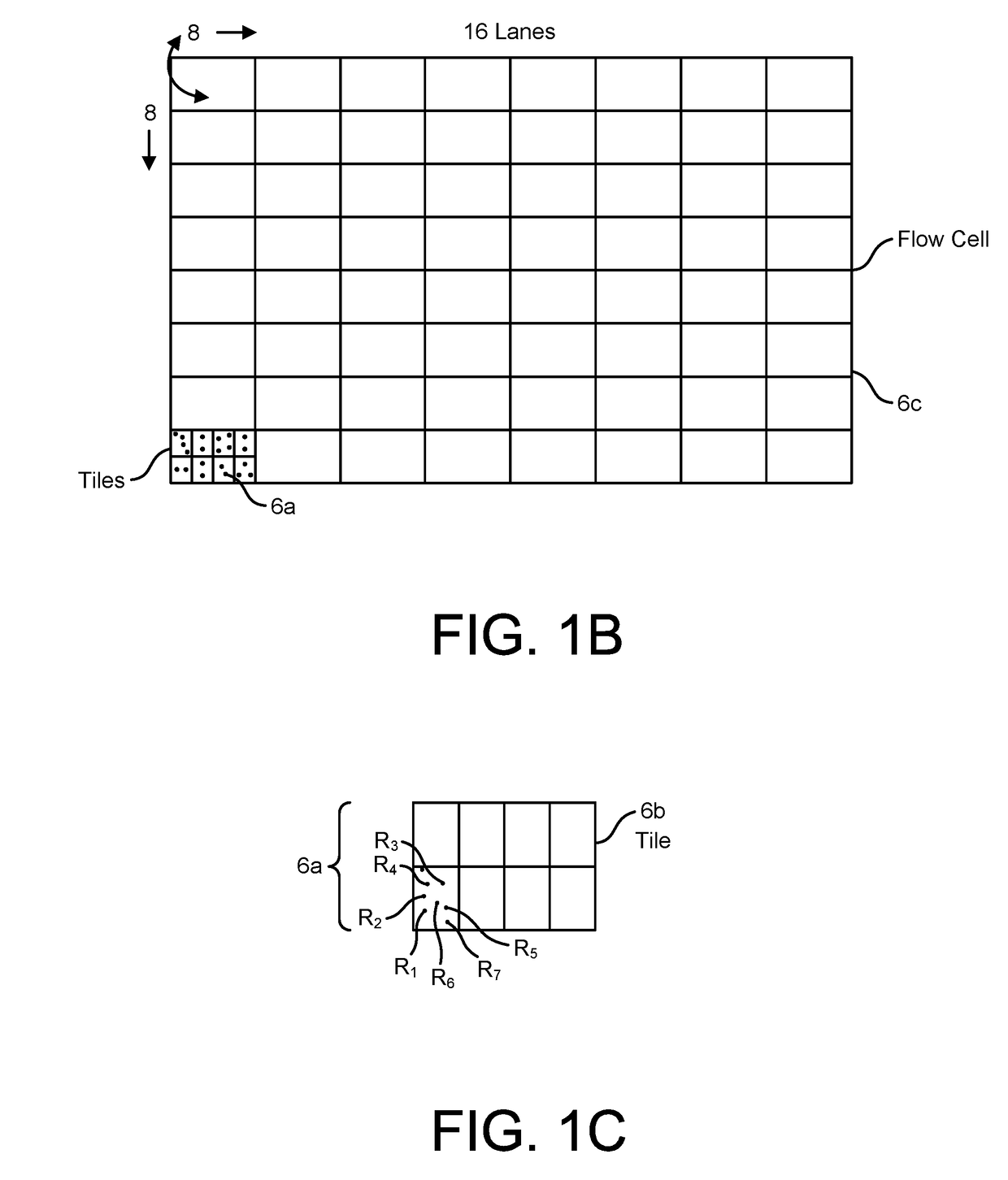
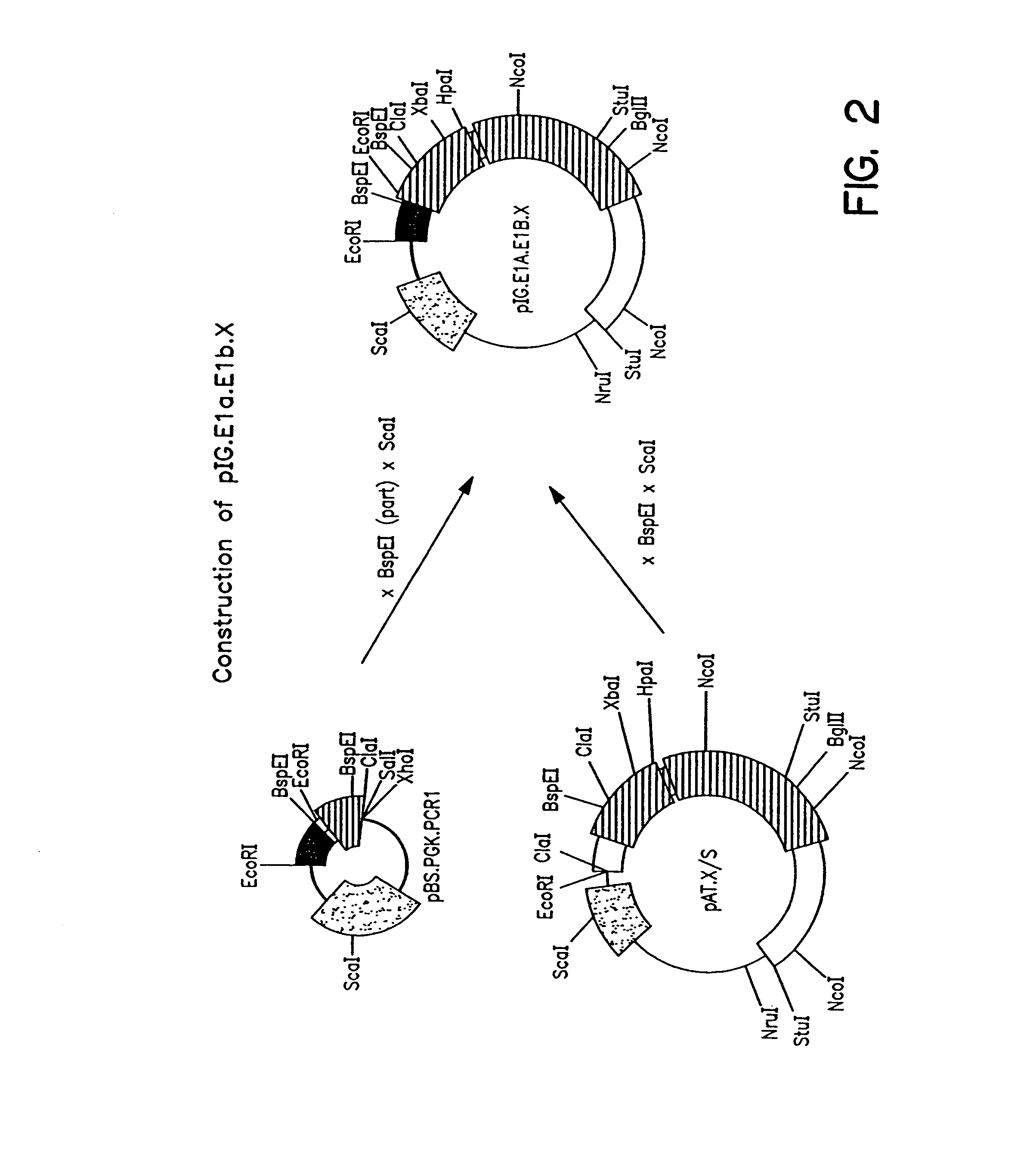
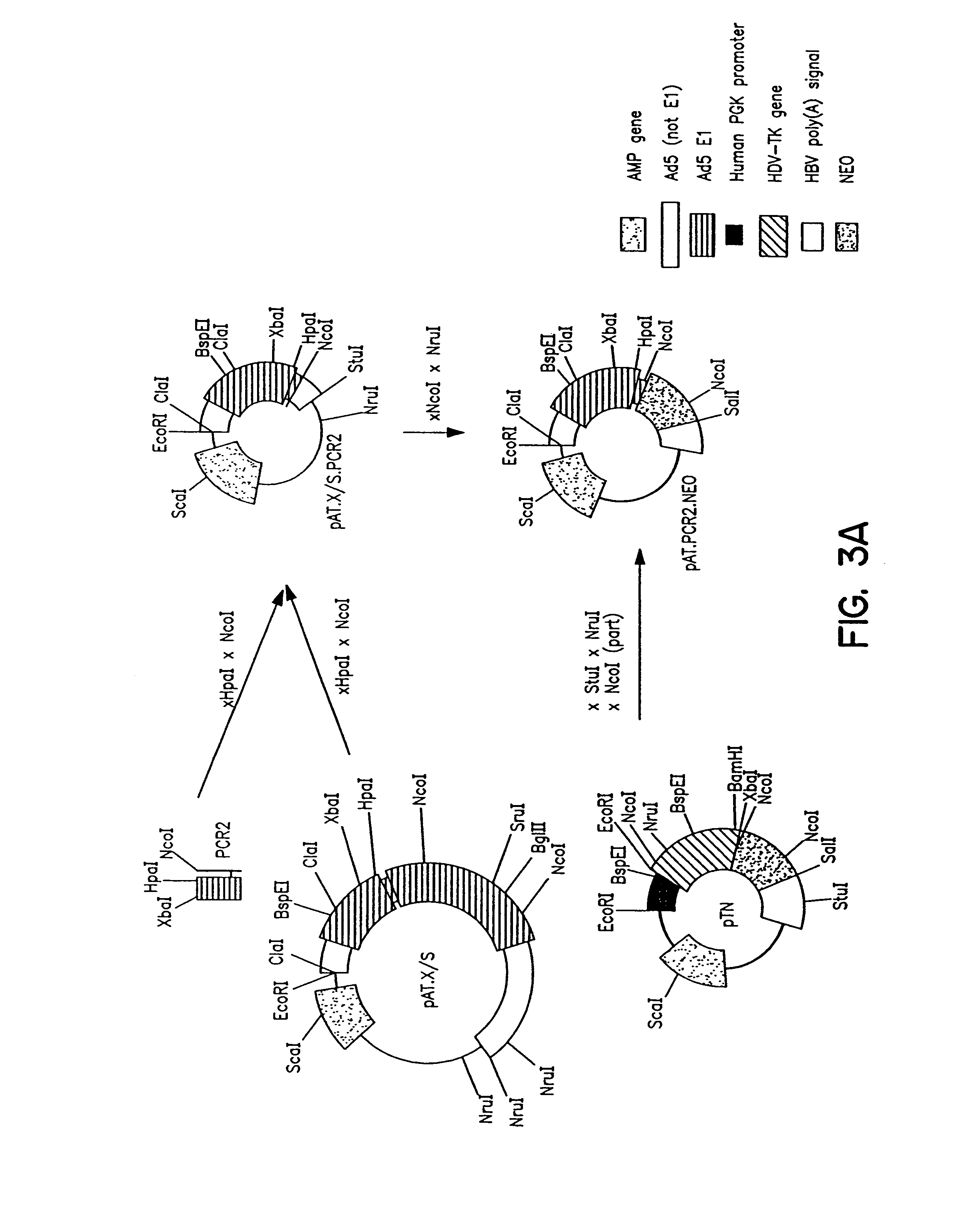
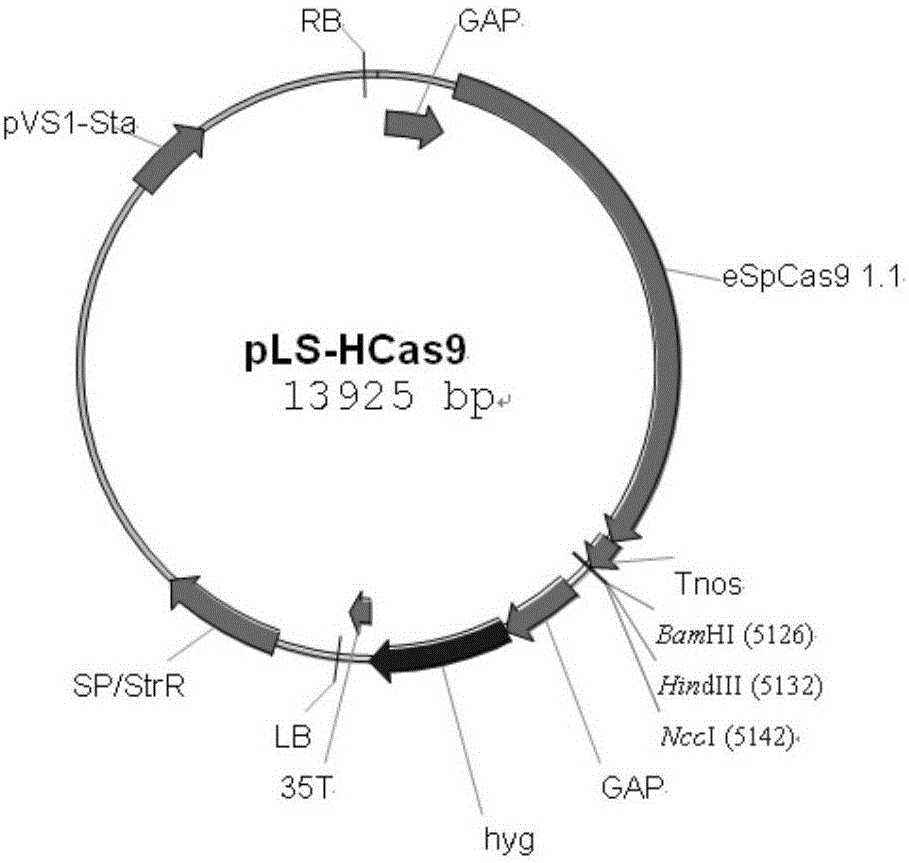
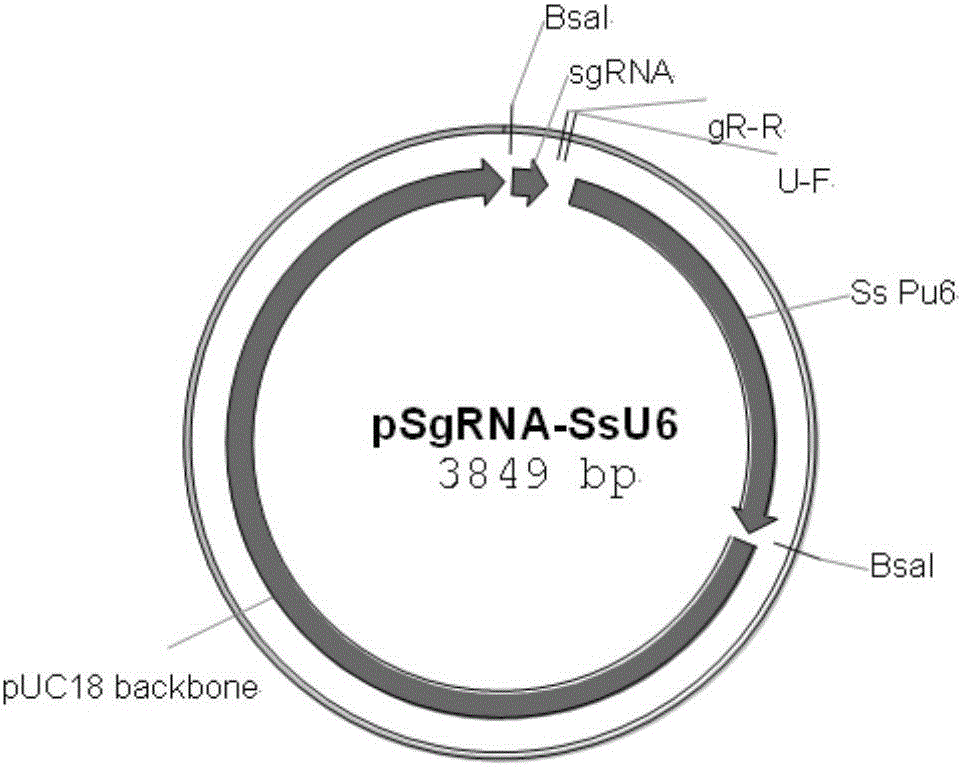
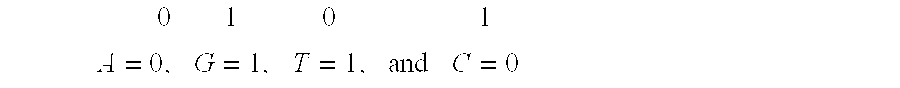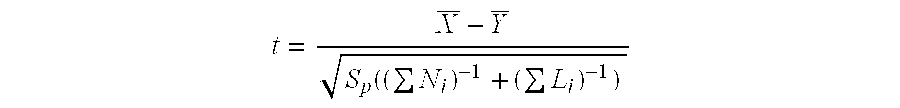Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
501 results about "Genomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
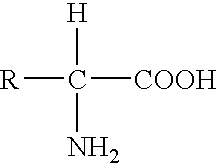
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of individual genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of all of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advances in genomics have triggered a revolution in discovery-based research and systems biology to facilitate understanding of even the most complex biological systems such as the brain.
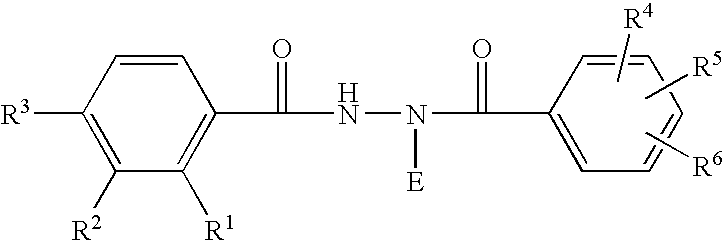
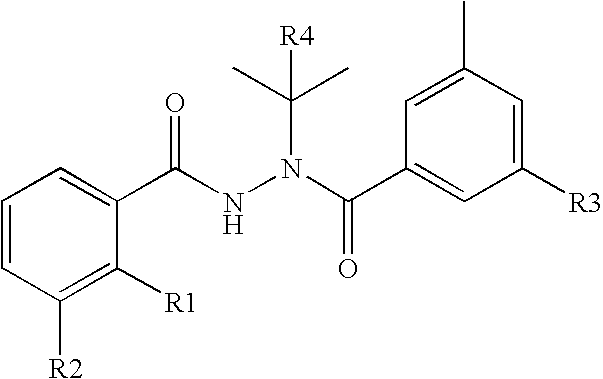
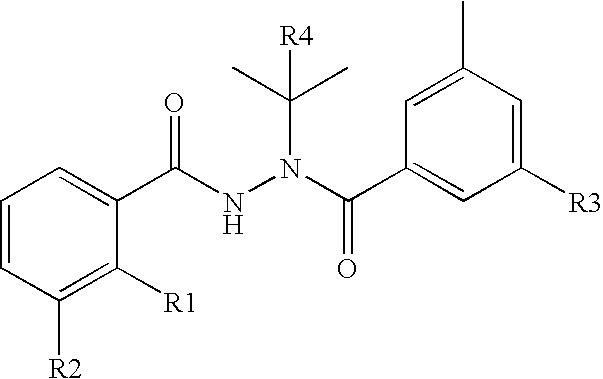
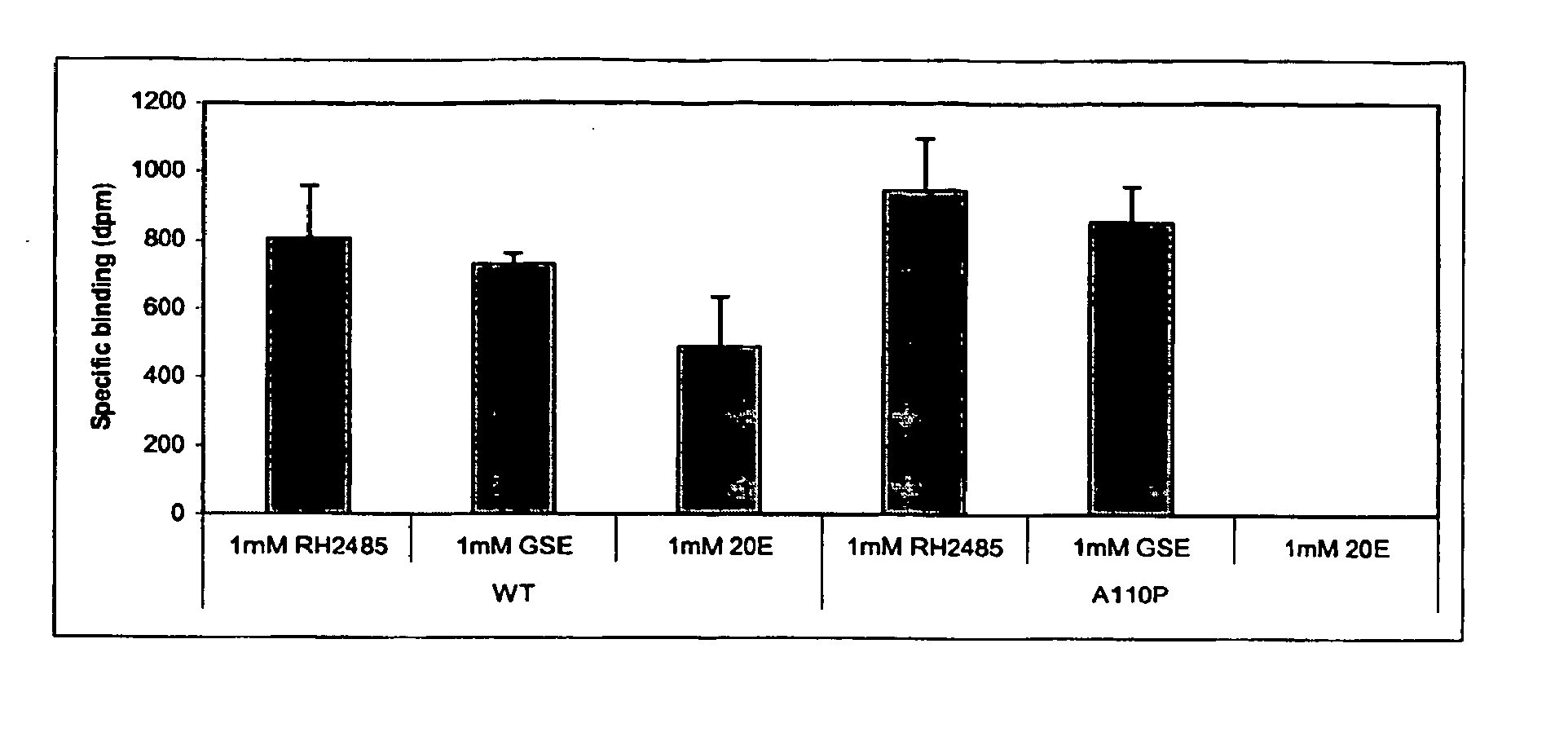
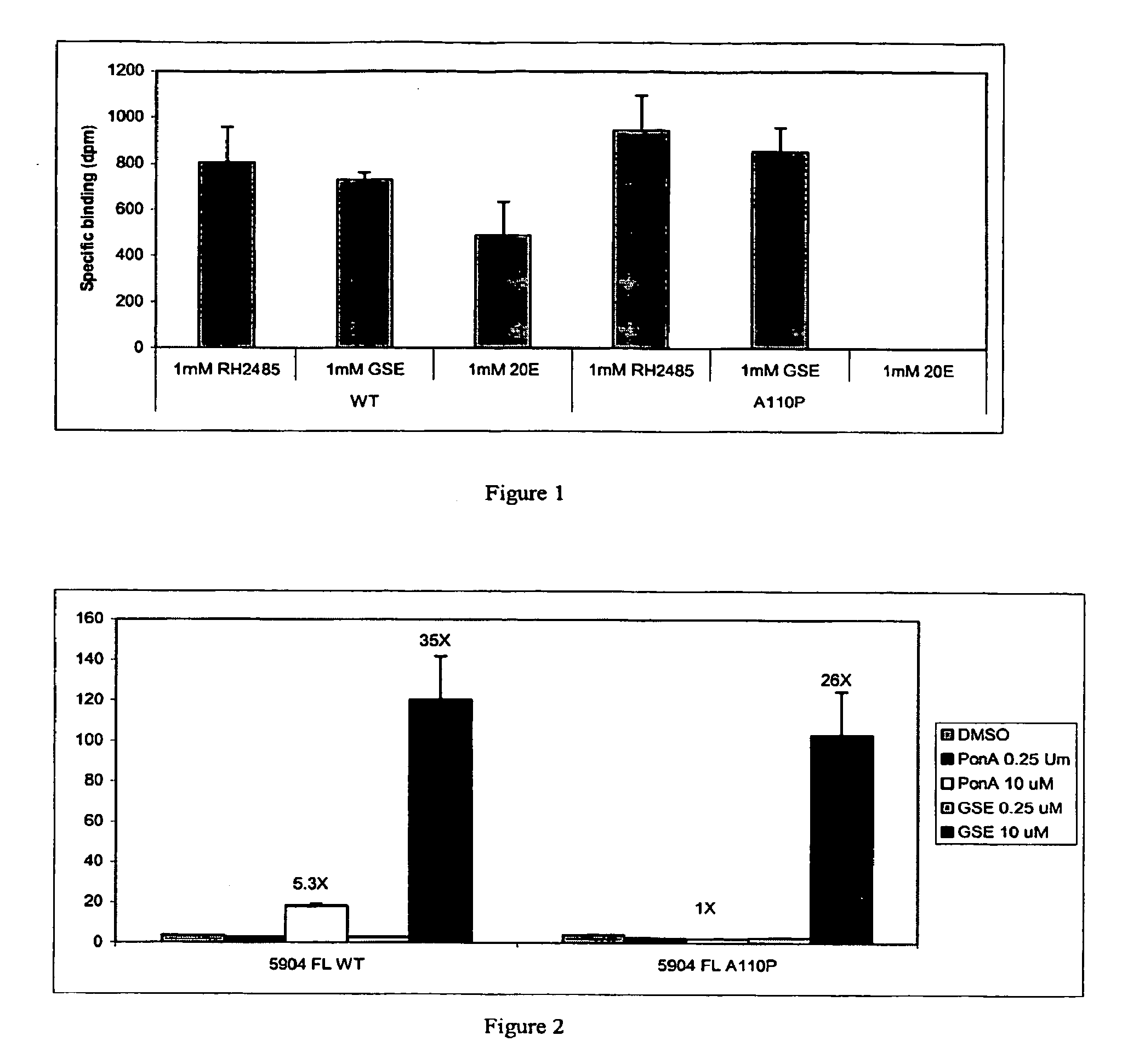
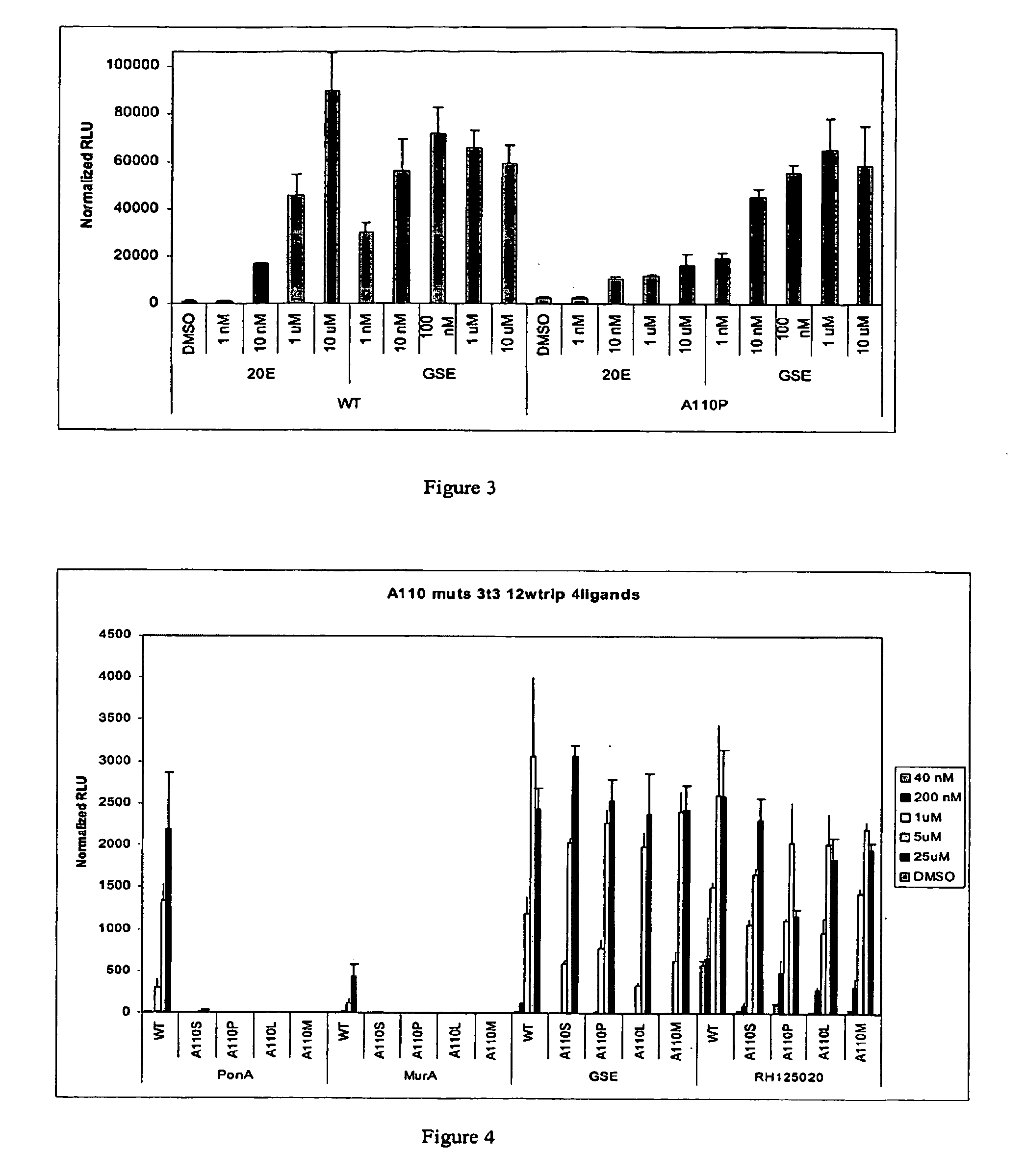
Novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in an nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a Group H nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
InactiveUS20050266457A1Improve efficiencyGreat degree of sequence similarityBiocideBacteriaHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysGenomics
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Variant annotation, analysis and selection tool
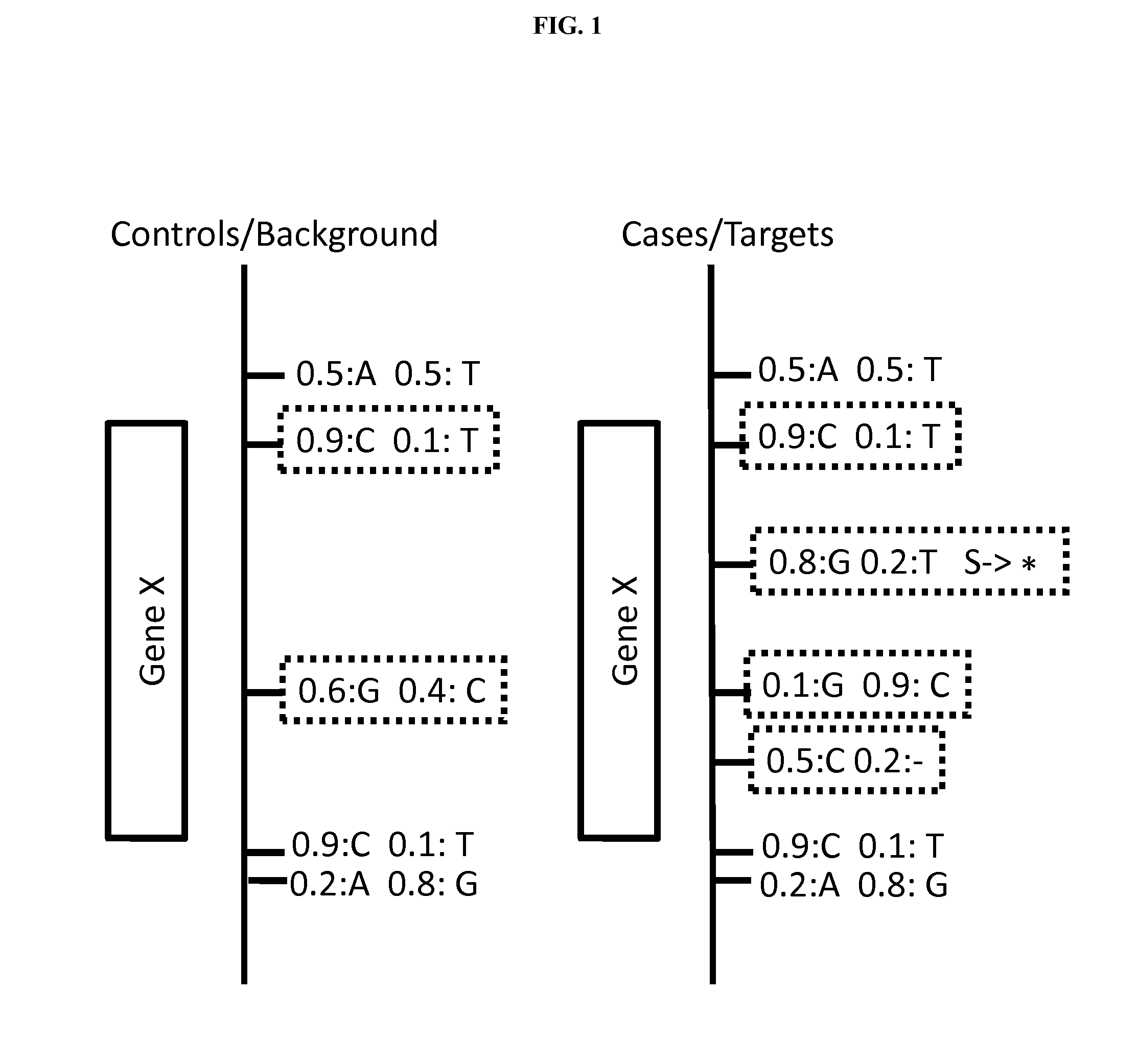
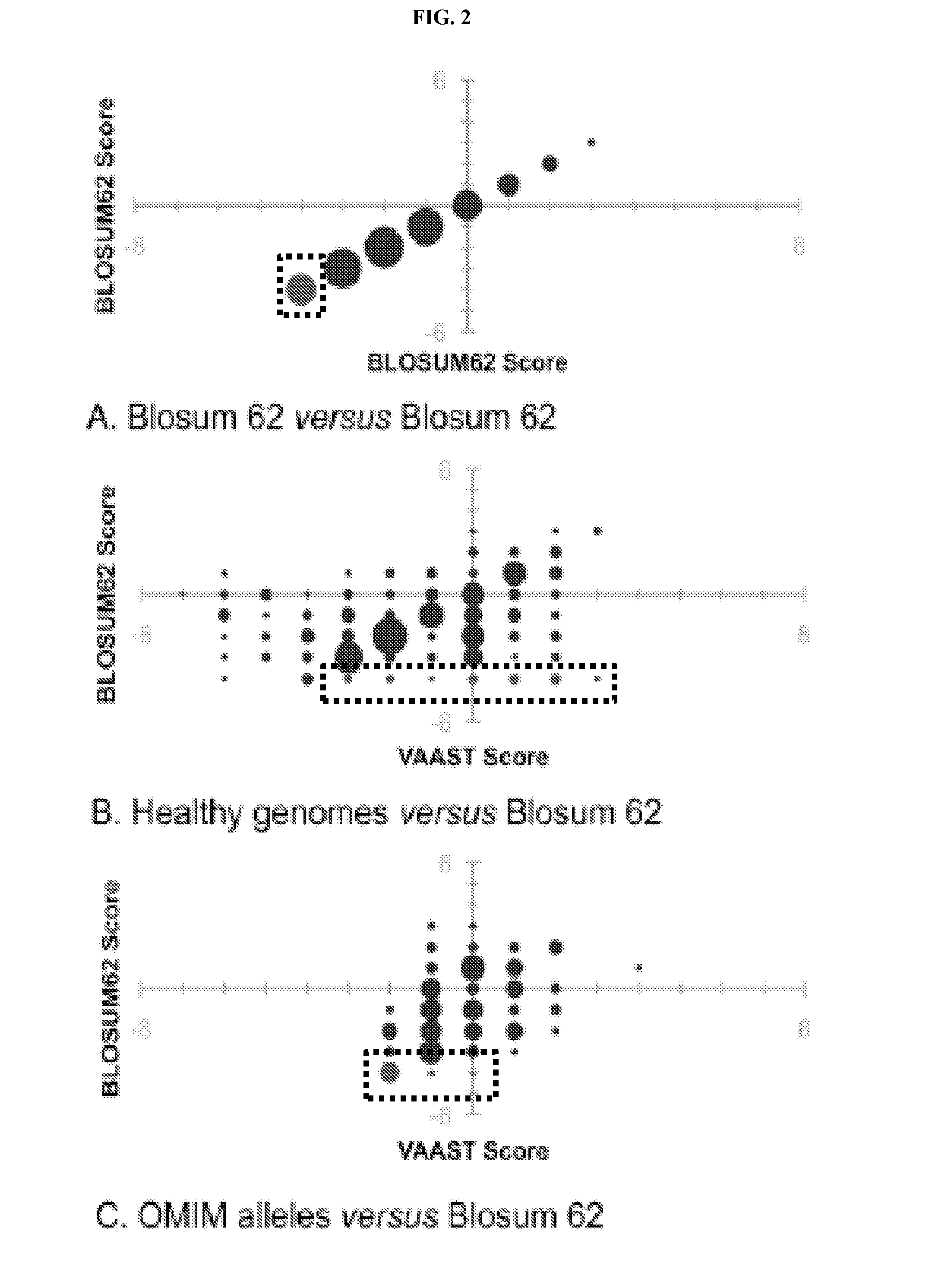
Disclosed are methods for detecting and / or prioritizing phenotype-causing genomic variants and related software tools. The methods include genomic feature based analysis and can combine variant frequency information with sequence characteristics such as amino acid substation. The methods disclosed are useful in any genomics study; for example, rare and common disease gene discovery, tumor growth mutation detection, personalized medicine, agricultural analysis, and centennial analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Functional arrays for high throughput characterization of gene expression regulatory elements
InactiveUS20070161031A1Good curative effectEliminate side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomicsHuman DNA sequencing
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment, the nucleic acid segment varying in the library and having a diversity of at least 50. The nucleic acid segments can be a large library of gene expression regulatory elements such as transcriptional promoters. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
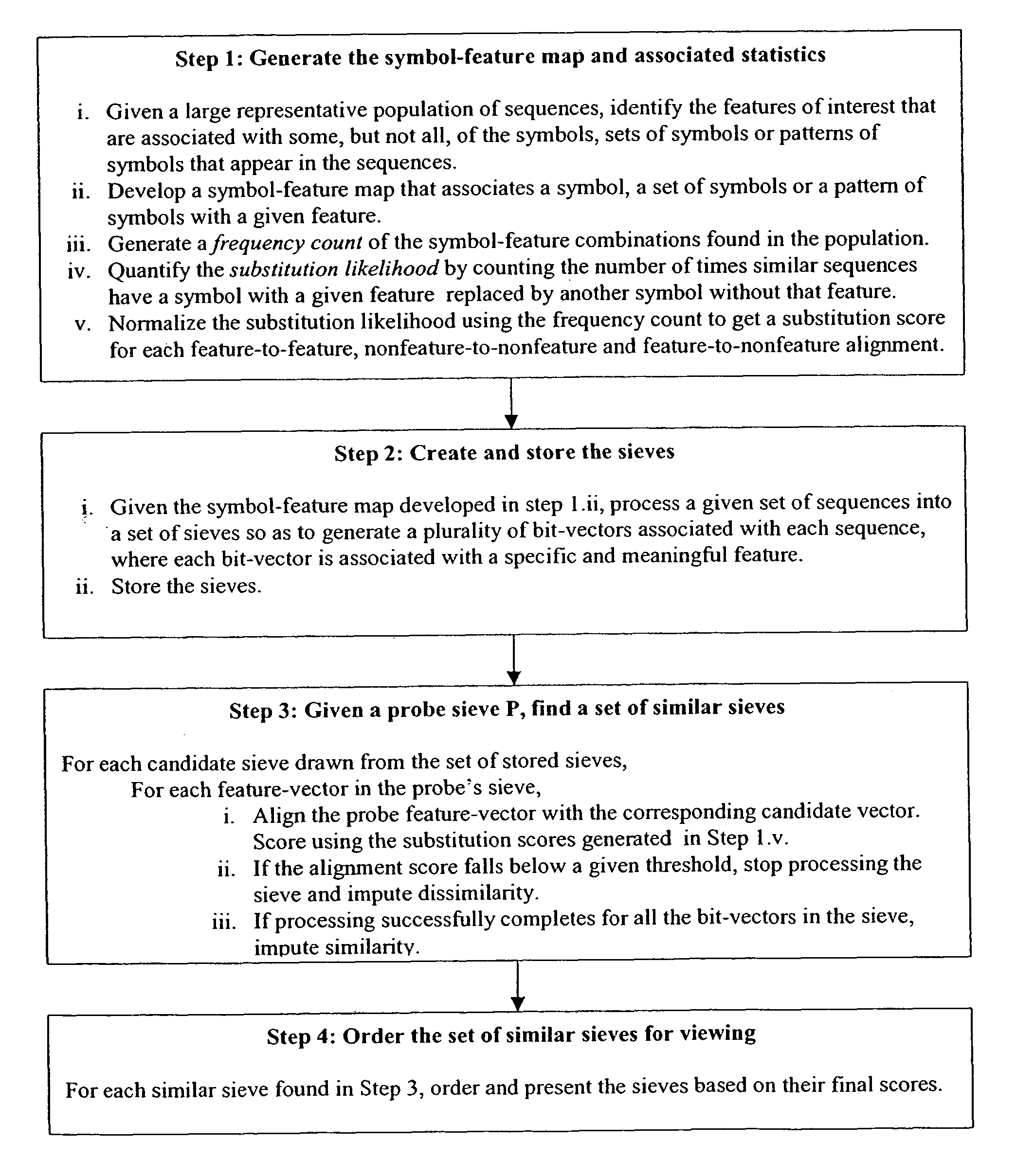
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS20050187916A1Easy to useIncrease speedSequence analysisComparison of digital valuesMedical diagnosisSequential data
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
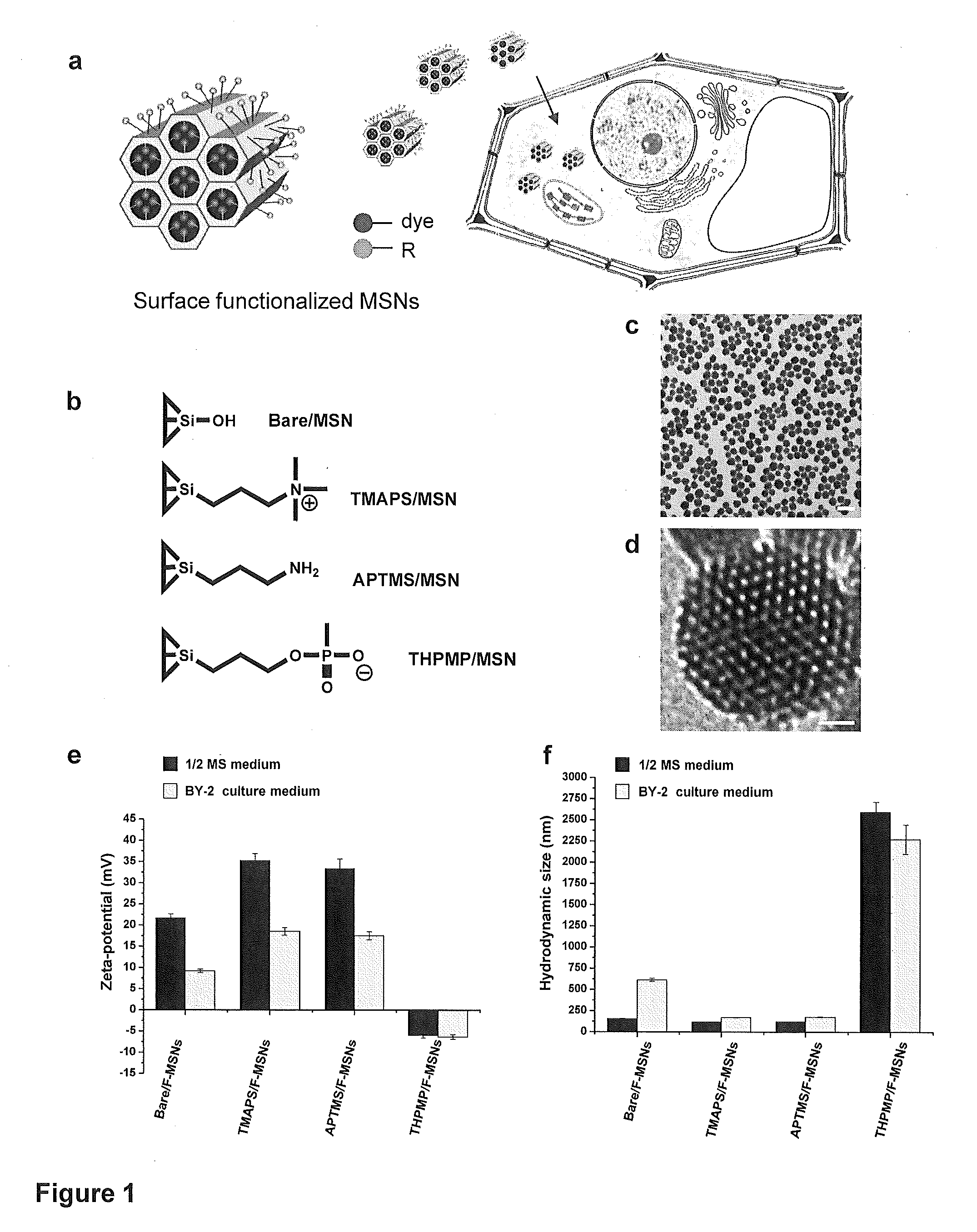
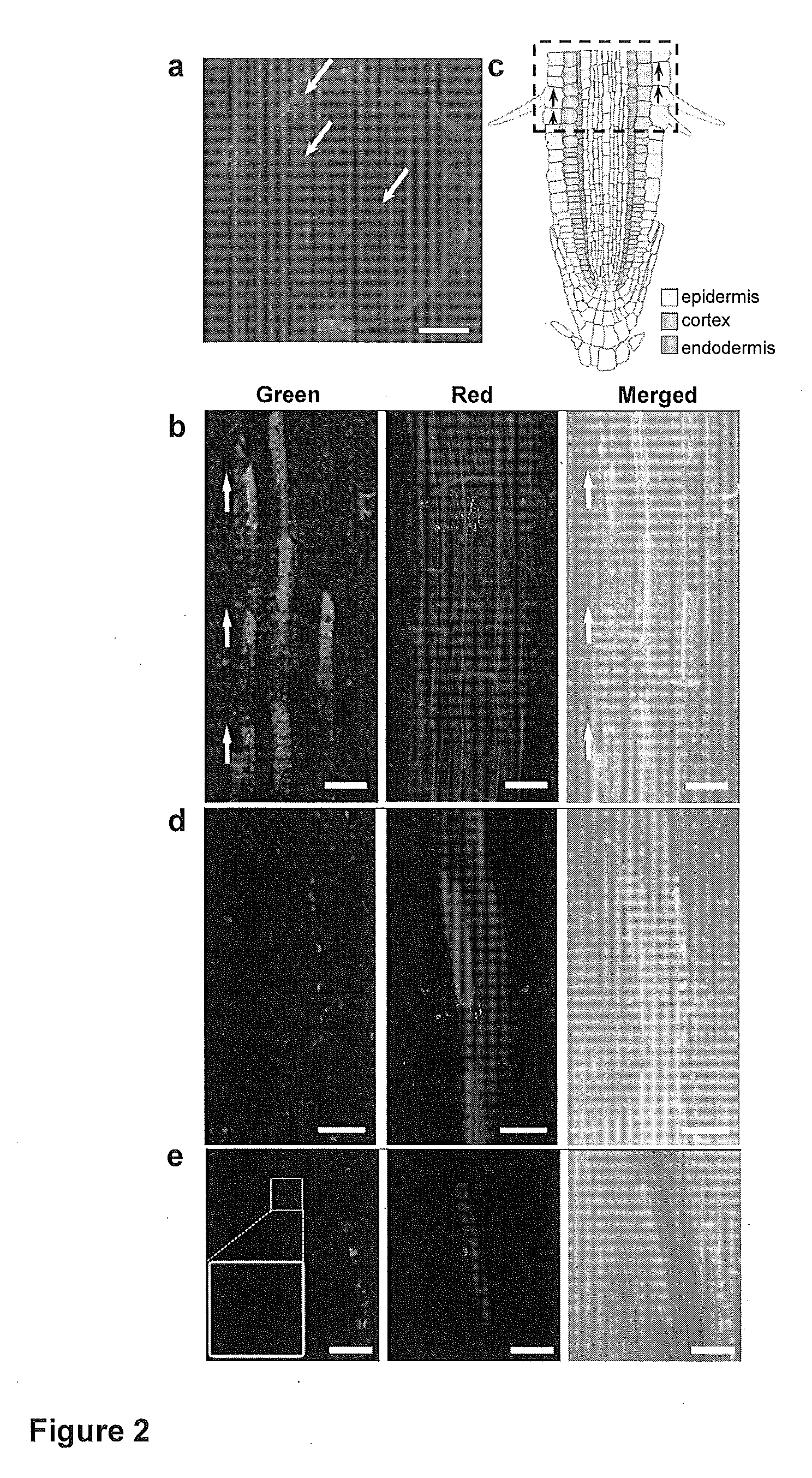
Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-mediated delivery of DNA into arabidopsis root
InactiveUS20130185823A1MicroorganismsOther foreign material introduction processesGerm layerGene delivery
Transient gene expression is a powerful tool for plant genomics studies. Recently, the use of nanomaterials has drawn great interest. Delivery with mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) has many advantages. We used surface-functionalized MSNs to deliver and express foreign DNA in Arabidopsis thaliana root cells without the aid of particle bombardment. Gene expression was detected in the epidermis layer and in the more inner cortex and endodermis root tissues. This method is superior to the conventional gene-gun method to deliver DNA, which delivers the gene to the epidermis layer only. Less DNA is needed for the MSN method. Our system is the first use of nanoparticles to deliver DNA to plants with good efficiency and without external aids. MSNs, with multifunctionality and the capability of cargo delivery to plant cells as we demonstrated, provide a versatile system for biomolecule delivery, organelle targeting, and even agriculture, such as improved nutrient uptake.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
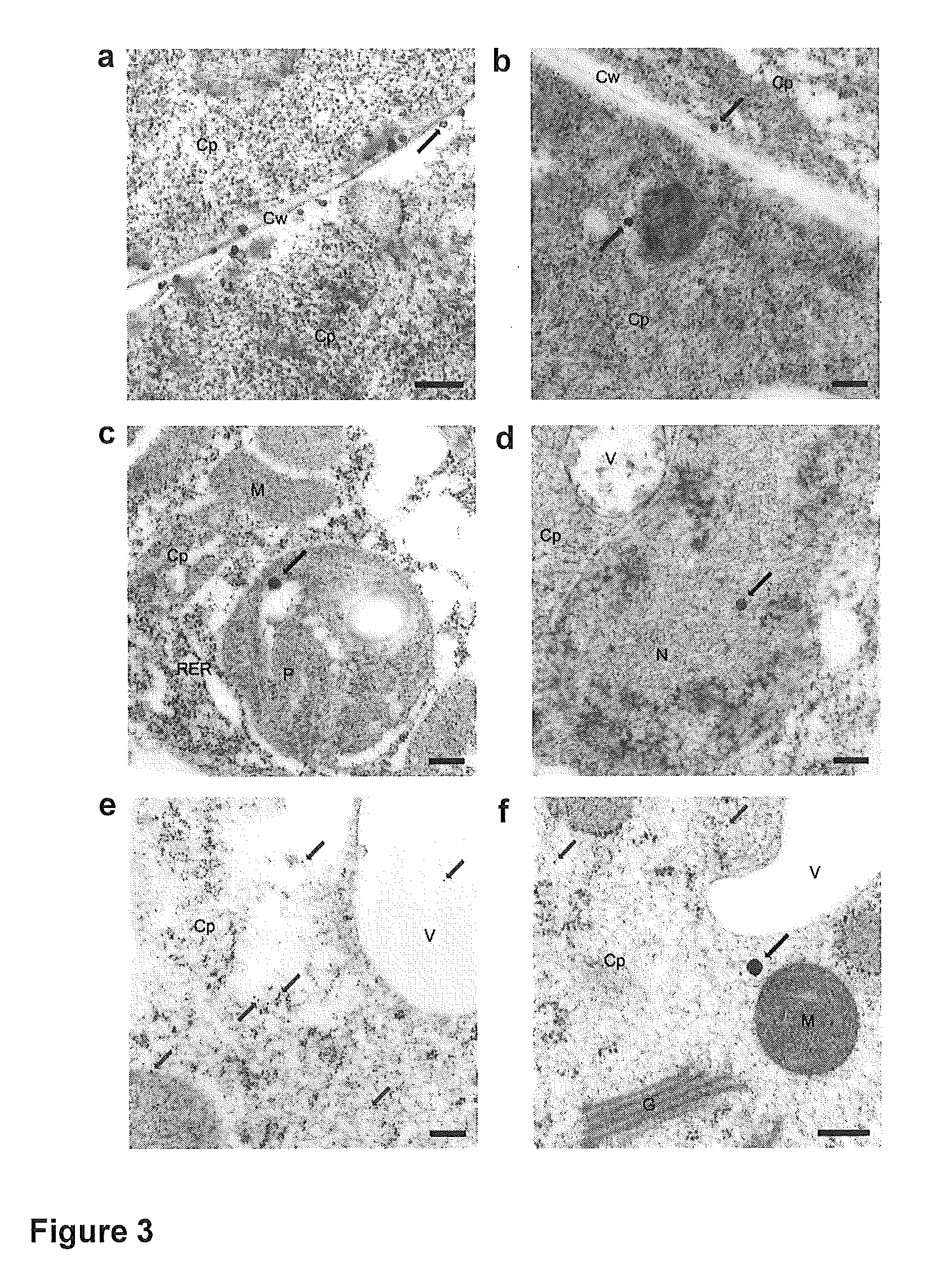
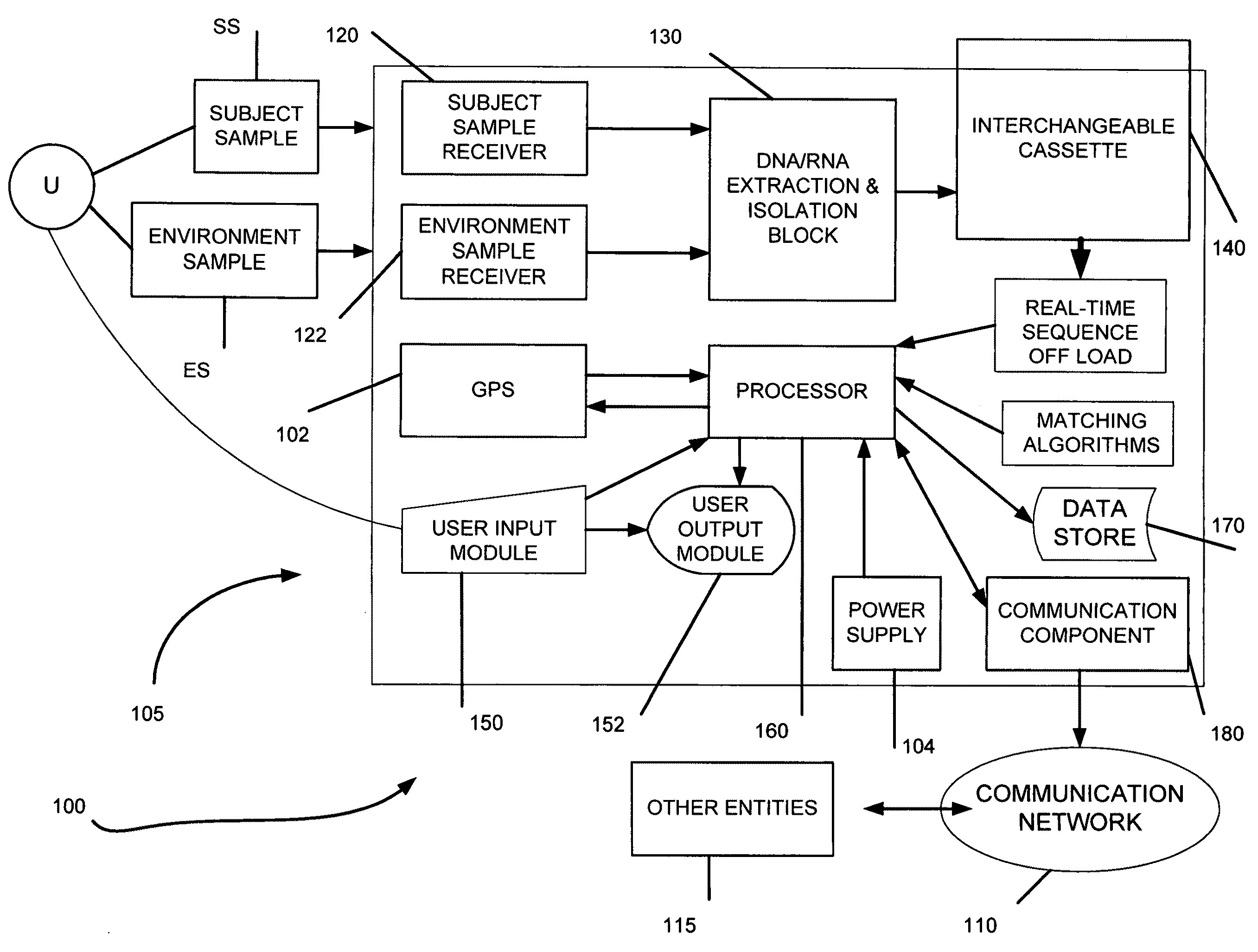
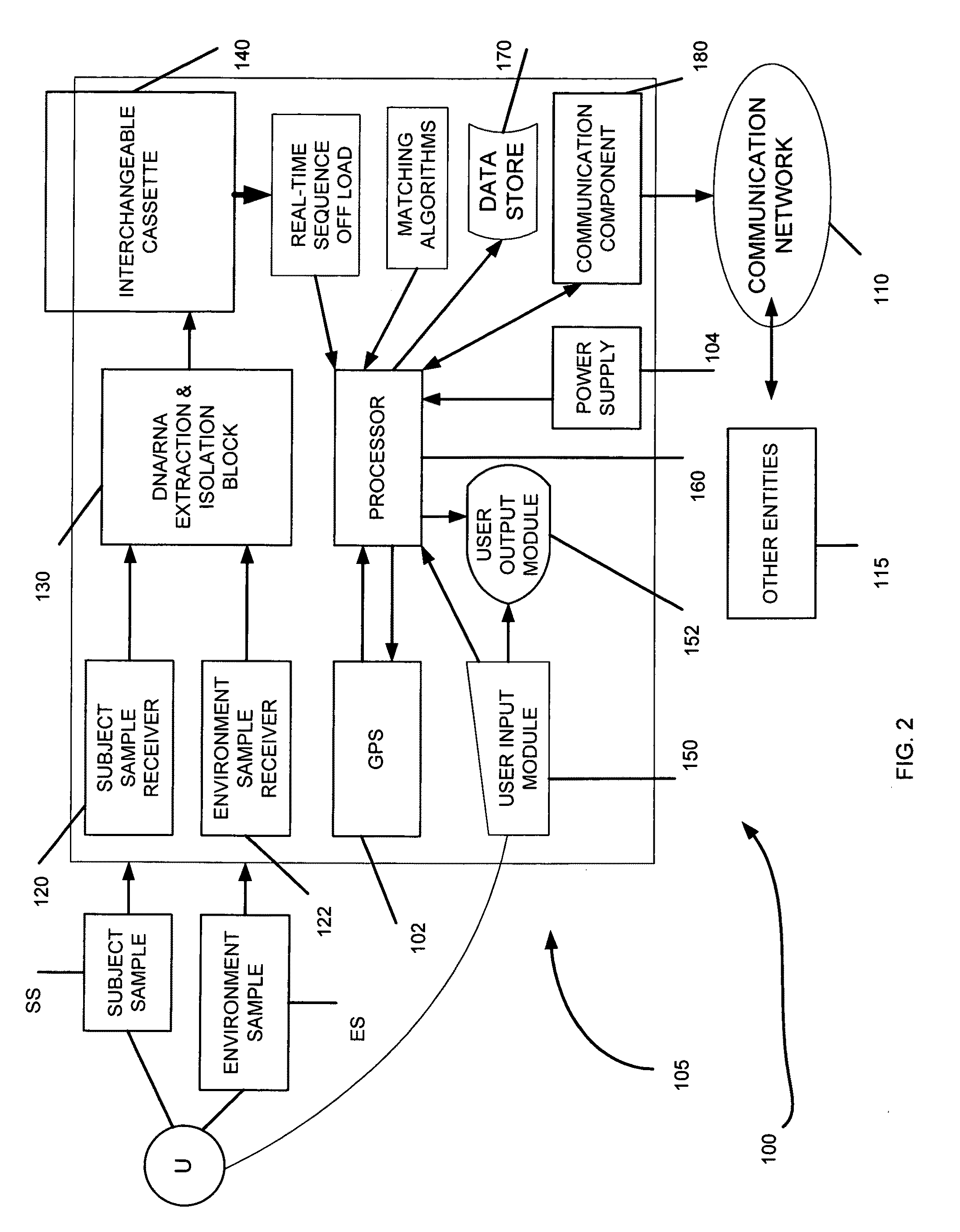
Genome identification system
The present invention belongs to the field of genomics and nucleic acid sequencing. It involves a novel method of sequencing biological material and real-time probabilistic matching of short strings of sequencing information to identify all species present in said biological material. It is related to real-time probabilistic matching of sequence information, and more particular to comparing short strings of a plurality of sequences of single molecule nucleic acids, whether amplified or unamplied, whether chemically synthesized or physically interrogated, as fast as the sequence information is generated and in parallel with continuous sequence information generation or collection.
Owner:COSMOSID INC
Assay for simultaneous genomic and proteomic analysis
InactiveUS20180208975A1High throughput screeningEfficient captureMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsAssay
The present invention is directed to a biochemical assay for simultaneous genomic and proteomic analysis.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
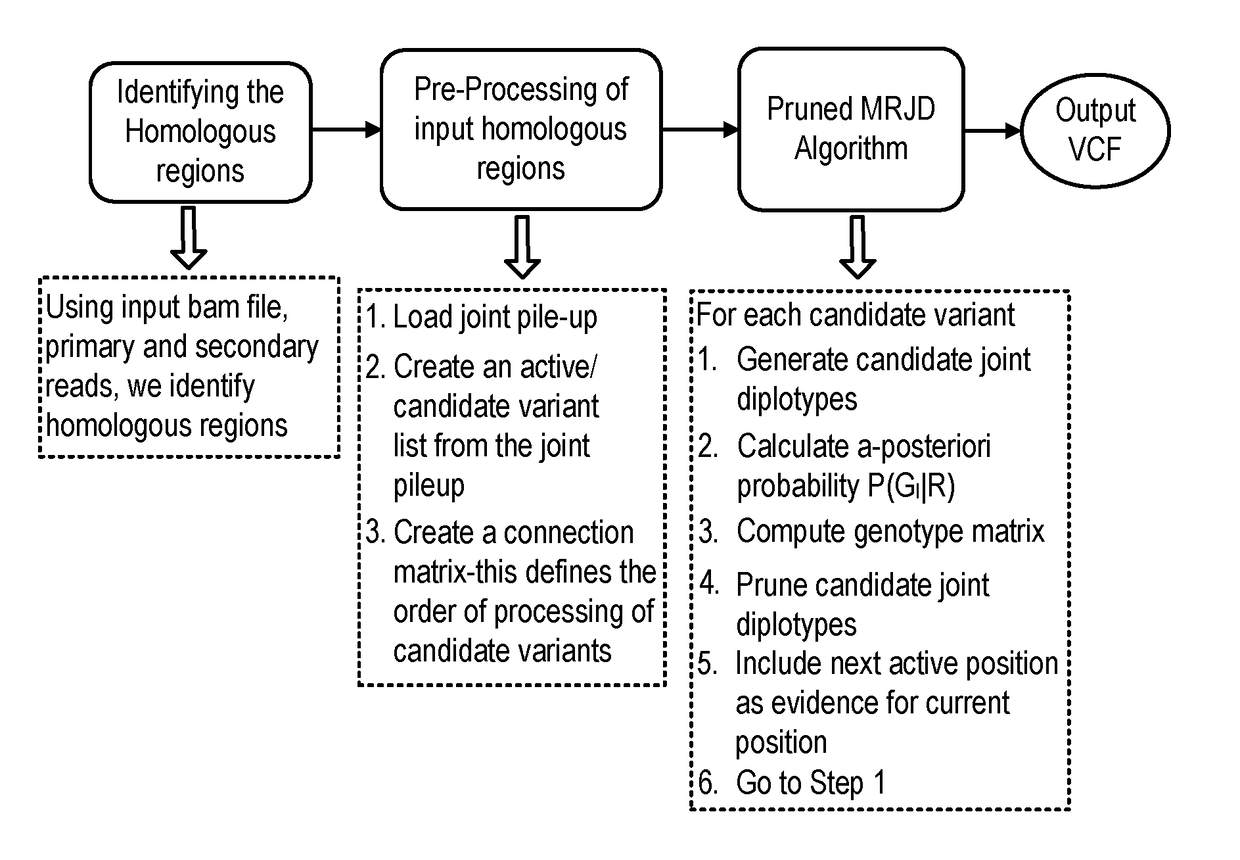
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
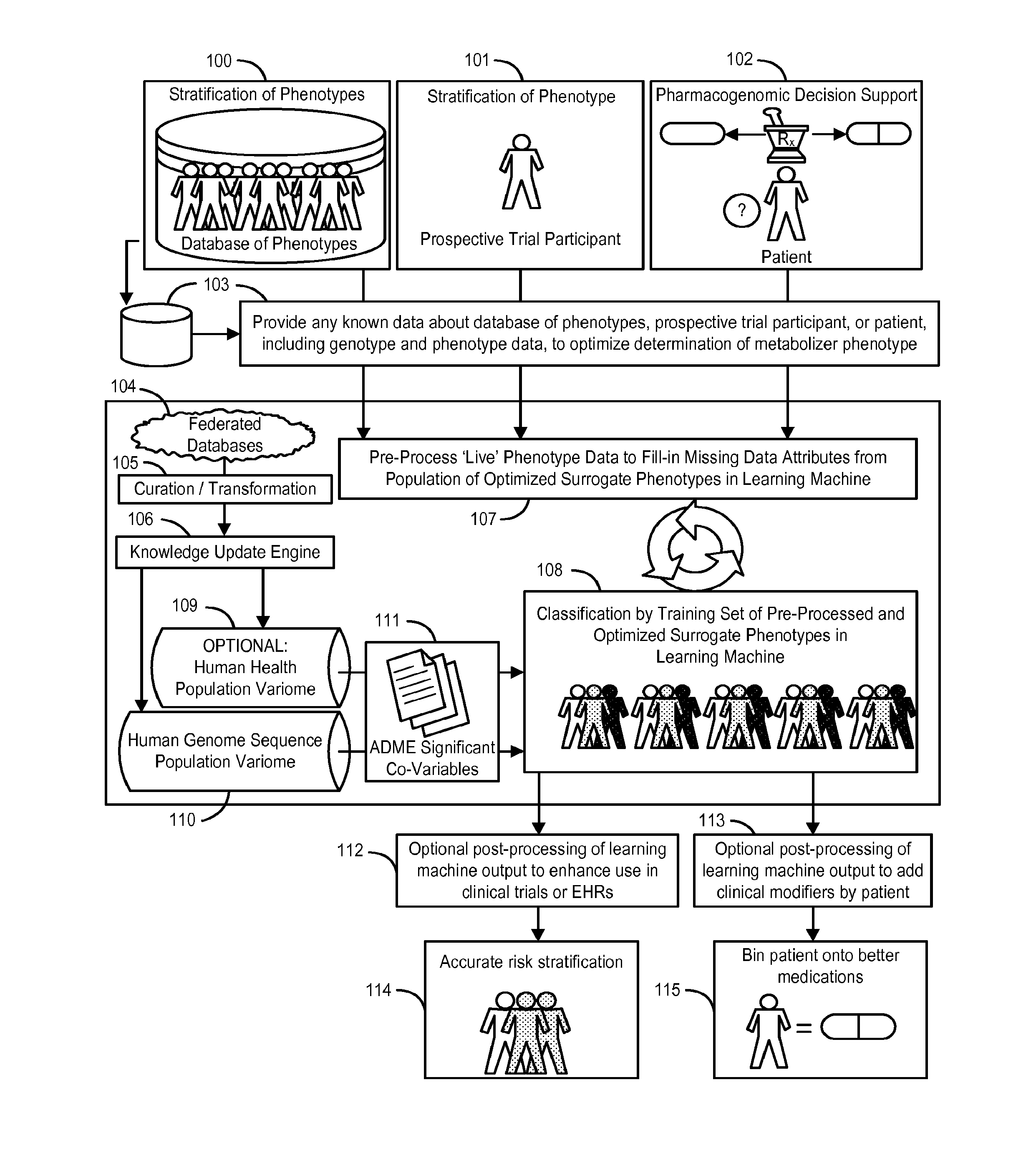
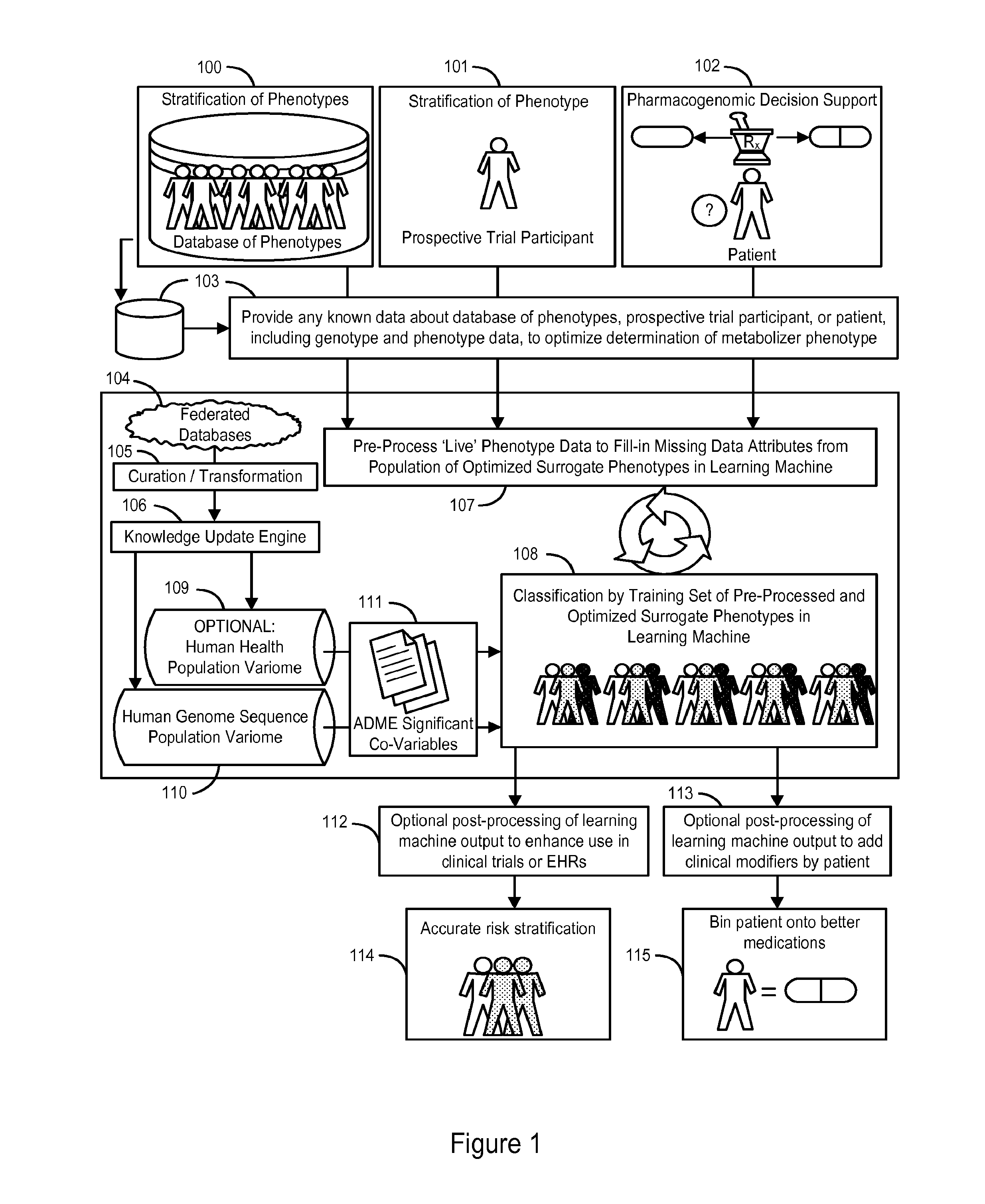
System and Methods for Pharmacogenomic Classification
InactiveUS20140222349A1Good statistical effectDataset can also become very largeBiostatisticsProteomicsGenomicsLearning machine
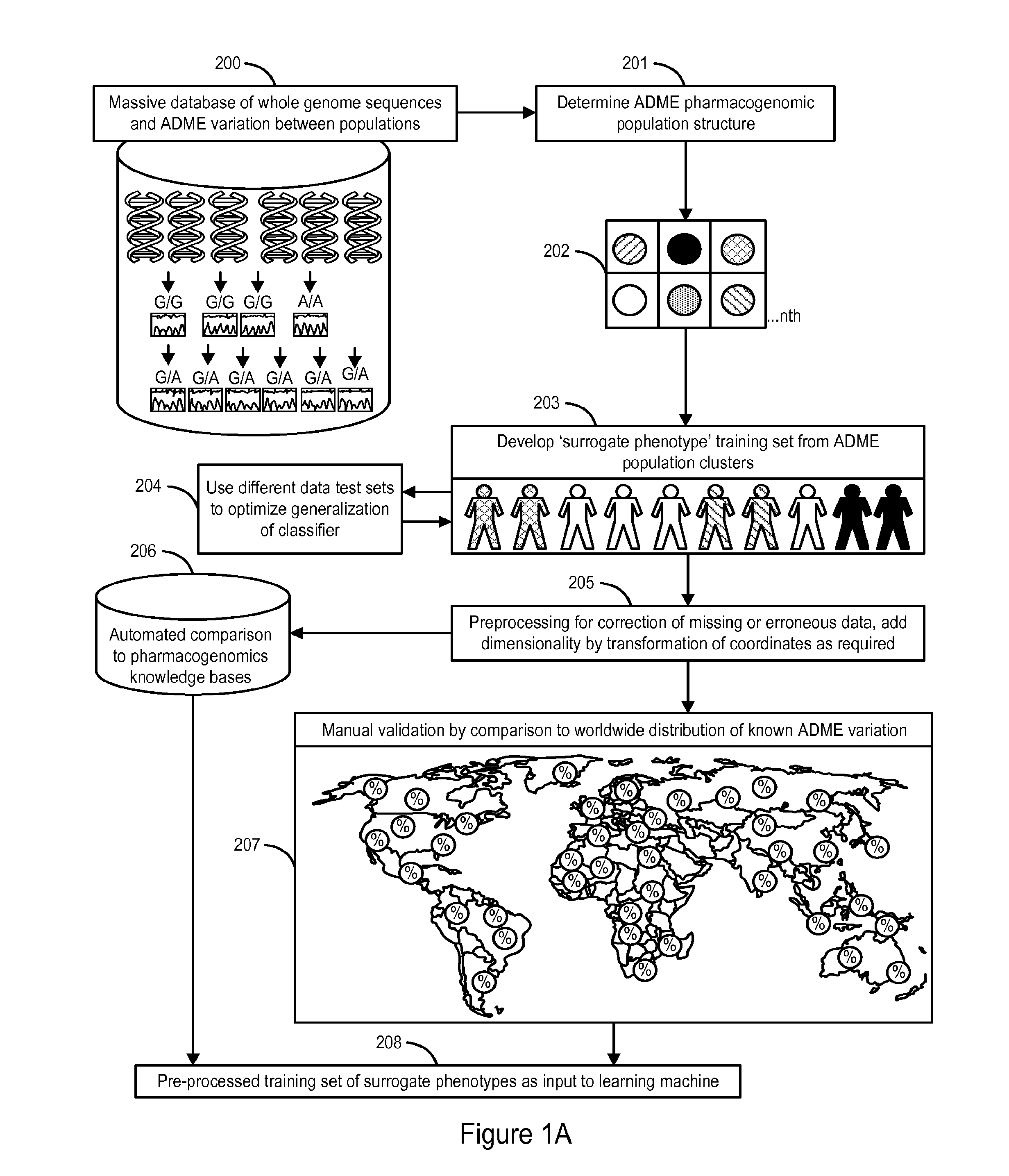
The invention provides a system and methods for the determination of the pharmacogenomic phenotype of any individual or group of individuals, ideally classified to a discrete, specific and defined pharmacogenomic population(s) using machine learning and population structure. Specifically, the invention provides a system that integrates several subsystems, including (1) a system to classify an individual as to pharmacogenomic cohort status using properties of underlying structural elements of the human population based on differences in the variations of specific genes that encode proteins and enzymes involved in the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of drugs and xenobiotics, (2) the use of a pre-trained learning machine for classification of a set of electronic health records (EHRs) as to pharmacogenomic phenotype in lieu of genotype data contained in the set of EHRs, (3) a system for prediction of pharmacological risk within an inpatient setting using the system of the invention, (4) a method of drug discovery and development using pattern-matching of previous drugs based on pharmacogenomic phenotype population clusters, and (5) a method to build an optimal pharmacogenomics knowledge base through derivatives of private databases contained in pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and academic research centers without the risk of exposing raw data contained in such databases. Embodiments include pharmacogenomic decision support for an individual patient in an inpatient setting, and optimization of clinical cohorts based on pharmacogenomic phenotype for clinical trials in drug development.
Owner:ASSUREX HEALTH INC
Method and system for genome identification
The present invention belongs to the field of genomics and nucleic acid sequencing. It involves a novel method of sequencing biological material and real-time probabilistic matching of short strings of sequencing information to identify all species present in said biological material. It is related to real-time probabilistic matching of sequence information, and more particular to comparing short strings of a plurality of sequences of single molecule nucleic acids, whether amplified or unamplied, whether chemically synthesized or physically interrogated, as fast as the sequence information is generated and in parallel with continuous sequence information generation or collection.
Owner:COSMOSID INC
Light detection device
InactiveUS6930314B2Increase flexibilityImprove reading speedSpectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsGenomicsMicroscope slide
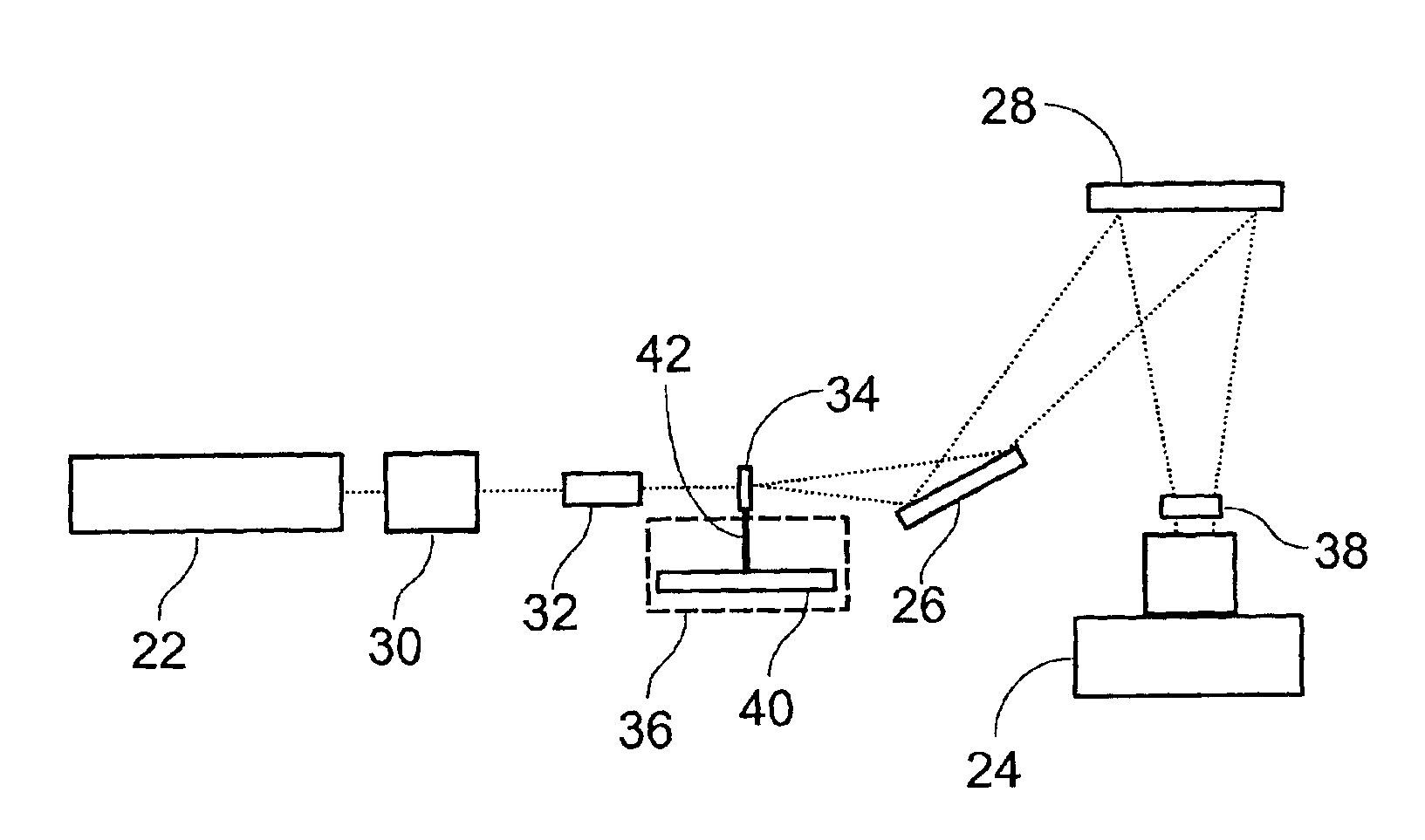
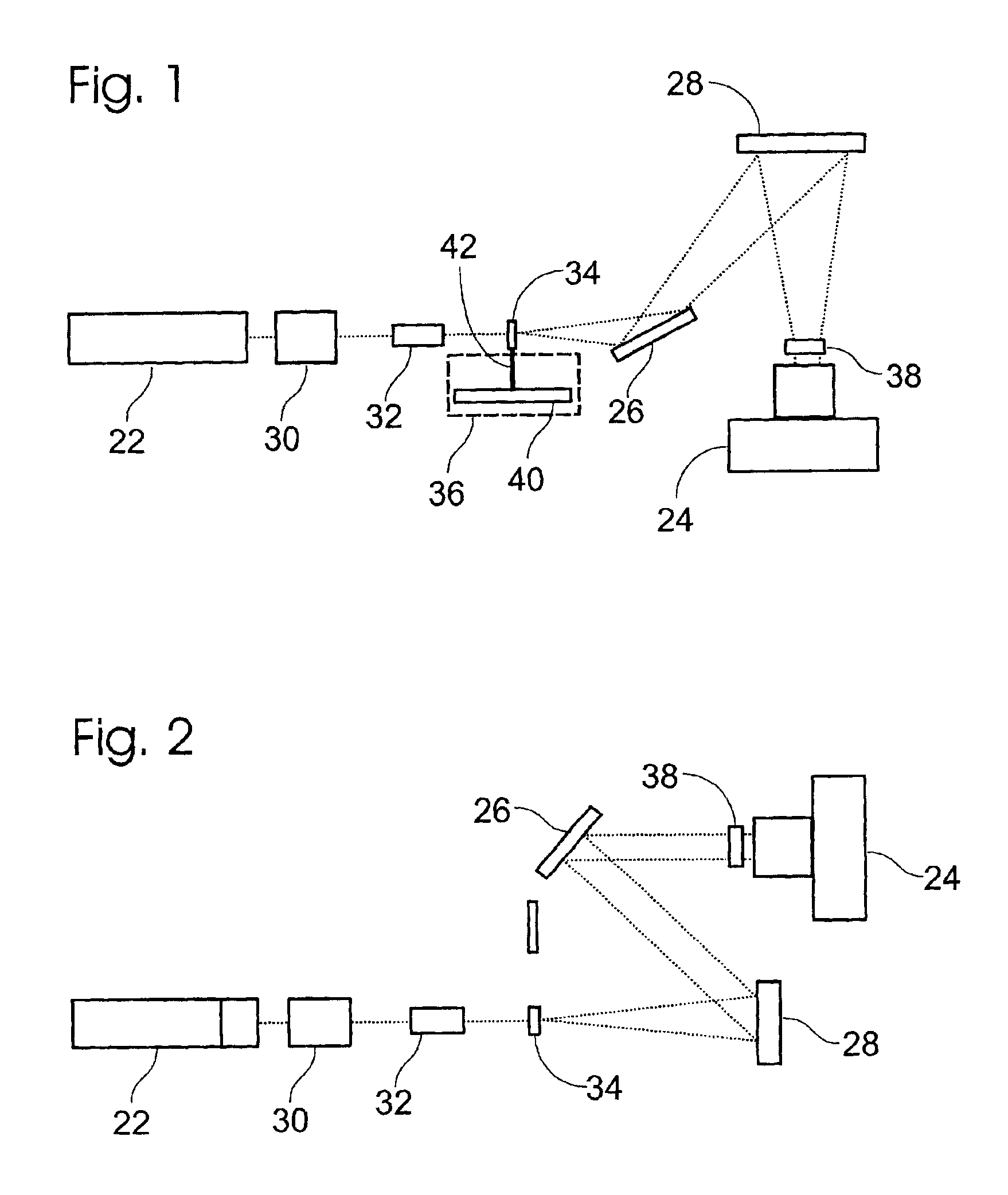
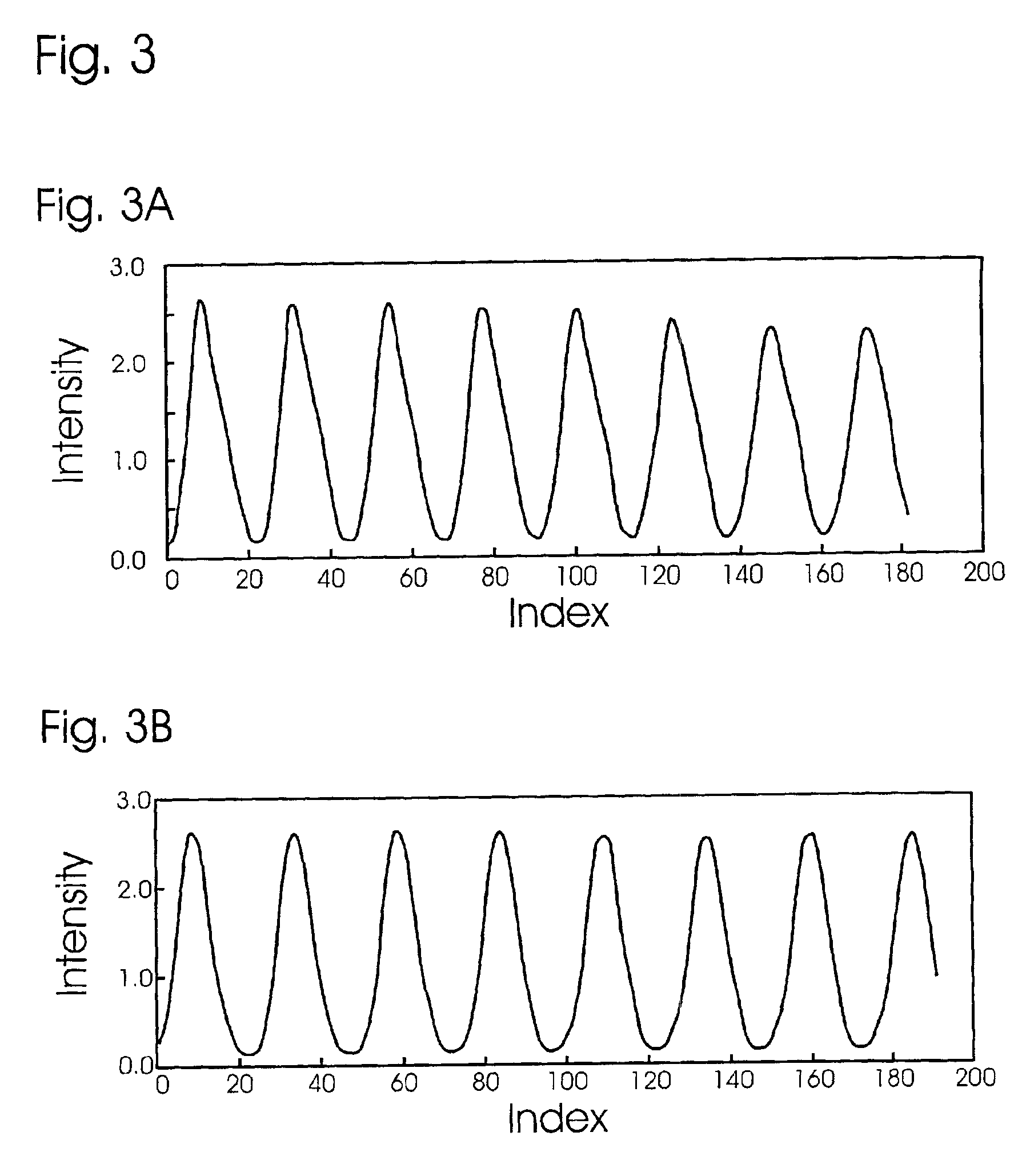
Apparatus and methods for optical illumination and / or detection with improved flexibility and / or read speed. The apparatus and methods may include mechanisms for selecting and switching between multiple excitation wavelengths and / or simultaneously reading from a plurality of sample sites. The apparatus and methods may be used with microplates, PCR plates, cell culture plates, biochips, chromatography plates, microscope slides, and other substrates for high-throughput screening, genomics, SNPs analysis, pharmaceutical research and development, life sciences research, and other applications.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
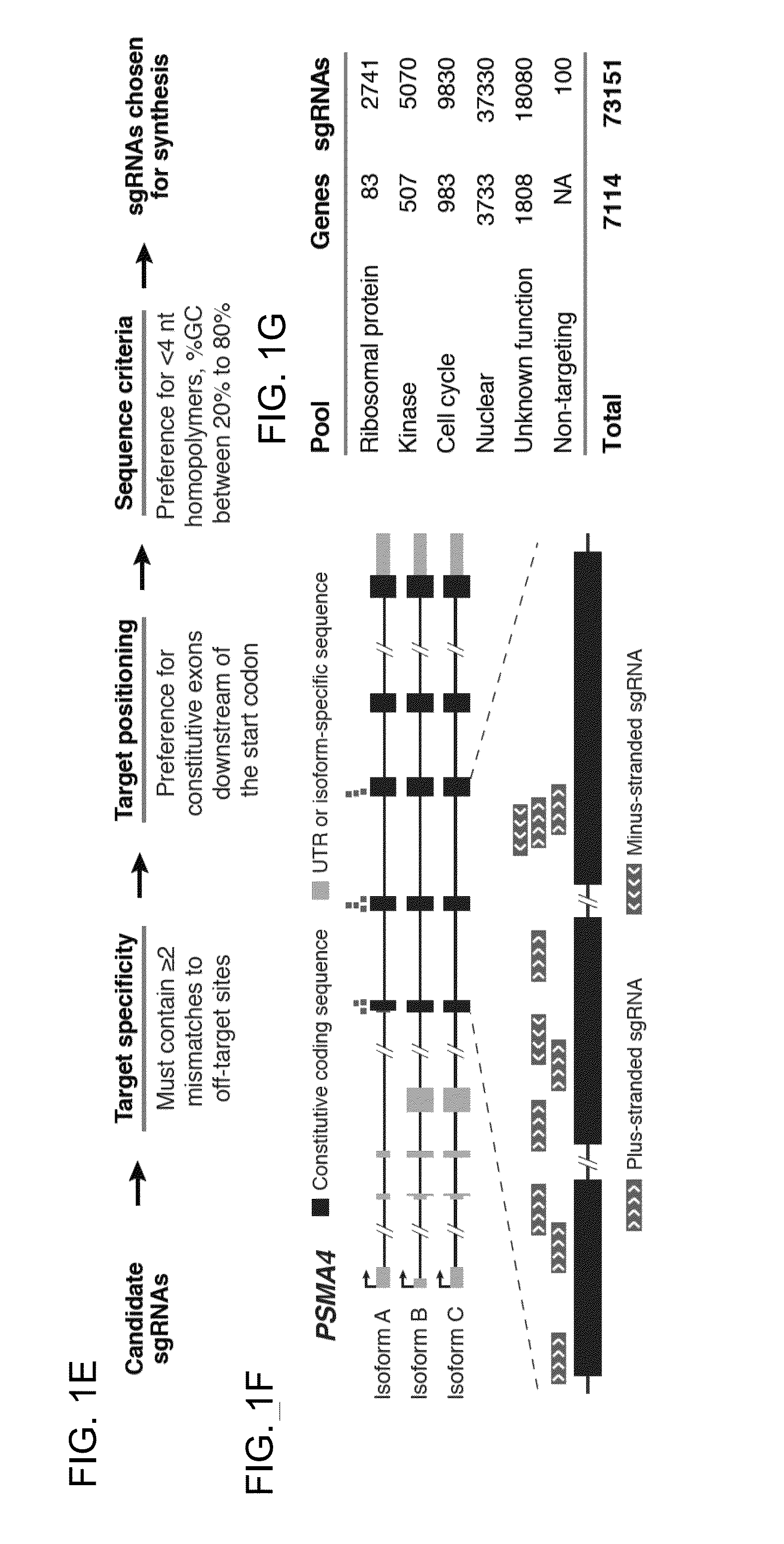
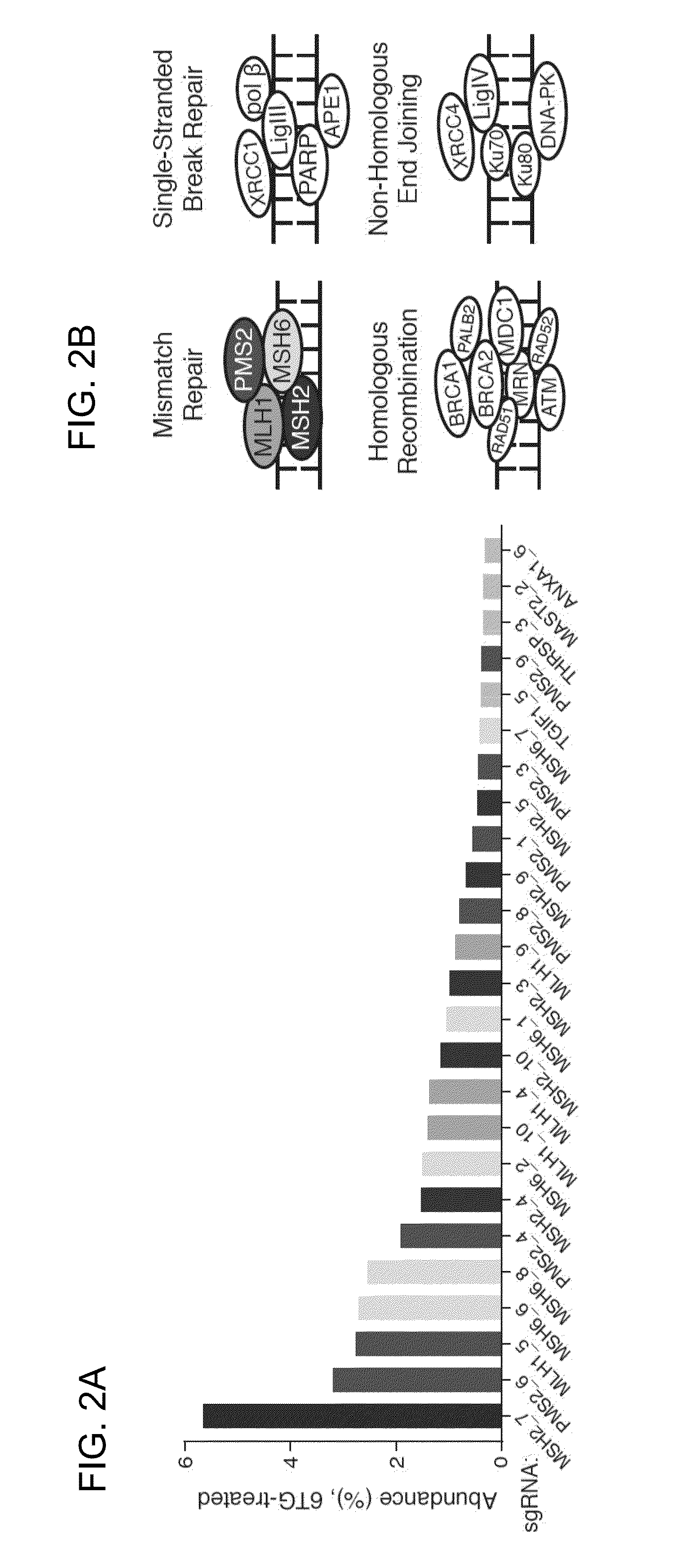
Functional genomics using crispr-cas systems, compositions, methods, screens and applications thereof
ActiveUS20160251648A1Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesStable introduction of DNAScreening processGenome scaleGenomics
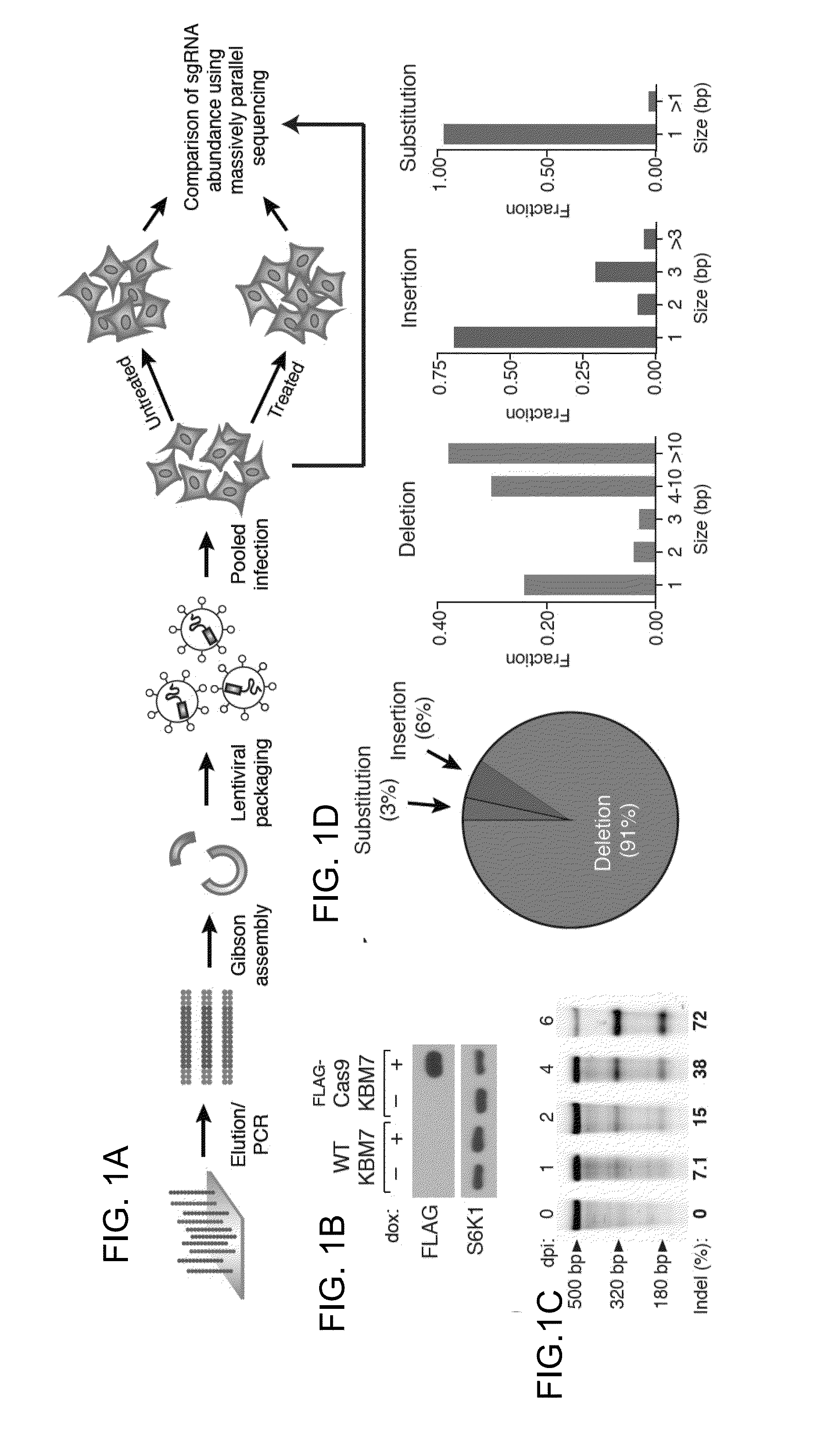
The present invention generally relates to libraries, kits, methods, applications and screens used in functional genomics that focus on gene function in a cell and that may use vector systems and other aspects related to Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems and components thereof. The present invention also relates to rules for making potent single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for use in CRISPR-Cas systems. Provided are genomic libraries and genome wide libraries, kits, methods of knocking out in parallel every gene in the genome, methods of selecting individual cell knock outs that survive under a selective pressure, methods of identifying the genetic basis of one or more medical symptoms exhibited by a patient, and methods for designing a genome-scale sgRNA library.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
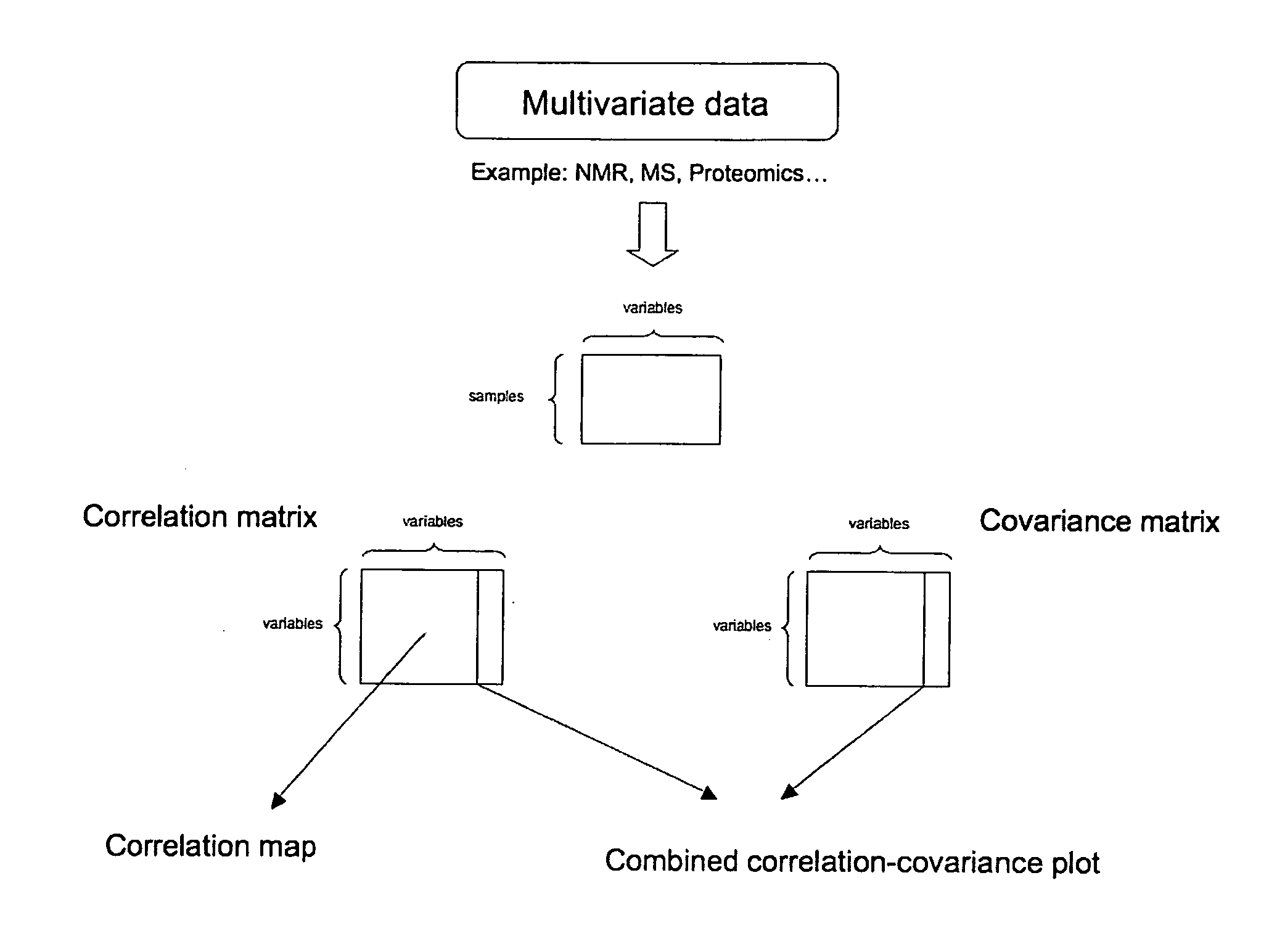
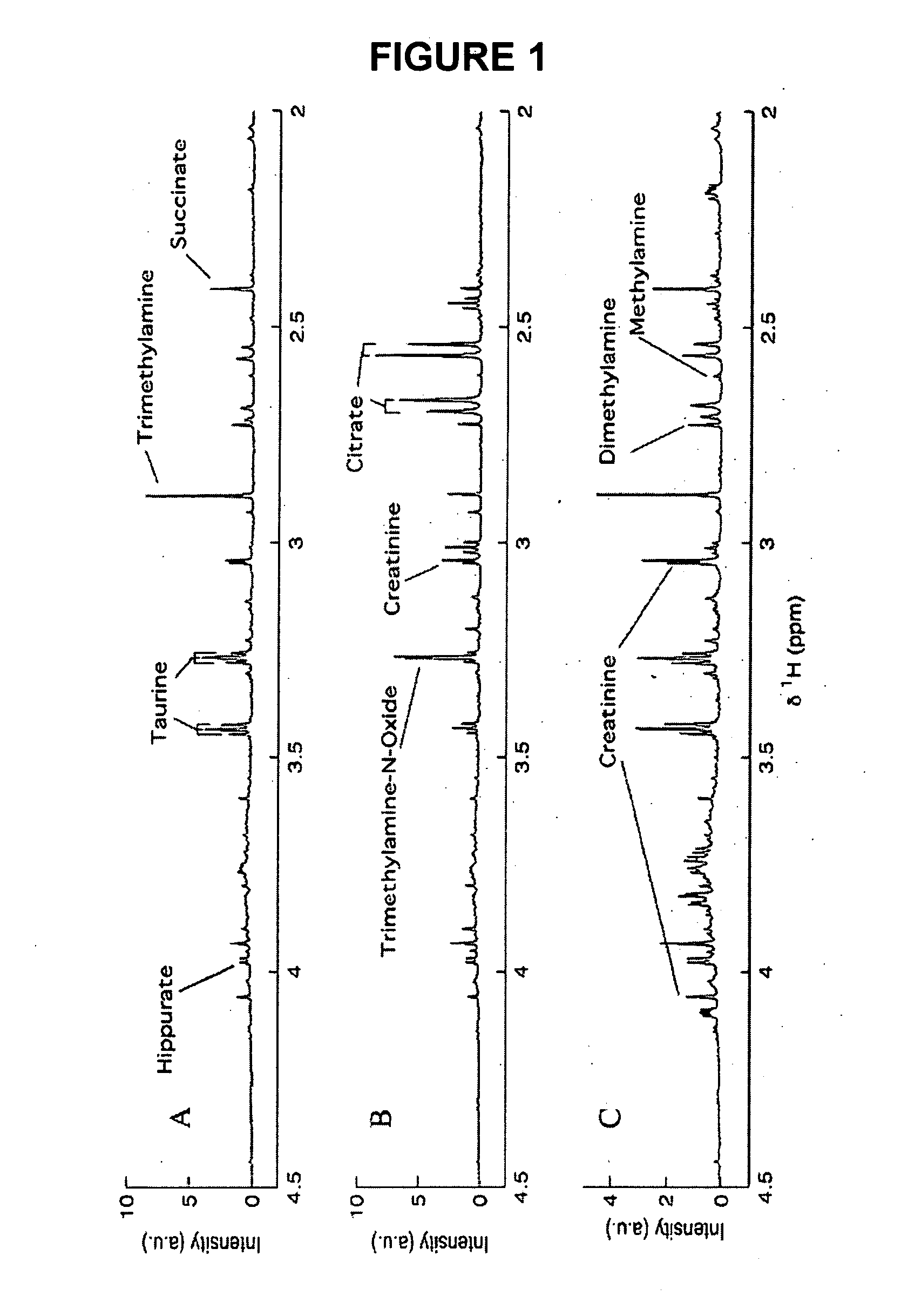
Method for the identification of molecules and biomarkers using chemical, biochemical and biological data
ActiveUS20070043518A1Molecular entity identificationProteomicsGenomicsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
This invention pertains generally to the field of multivariate statistics, and in particular to new methods for the analysis (e.g., chemometrics) of chemical, biochemical, and biological data, including, for example, spectral data, including but not limited to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral data. These methods are useful, for example, in metabonomics, proteomics, transcriptomics, genomics, etc., and form a part of other methods, for example, methods for the identification of chemical species, methods for the identification of biomarkers that are useful in methods of classification, diagnosis, prognosis, etc.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
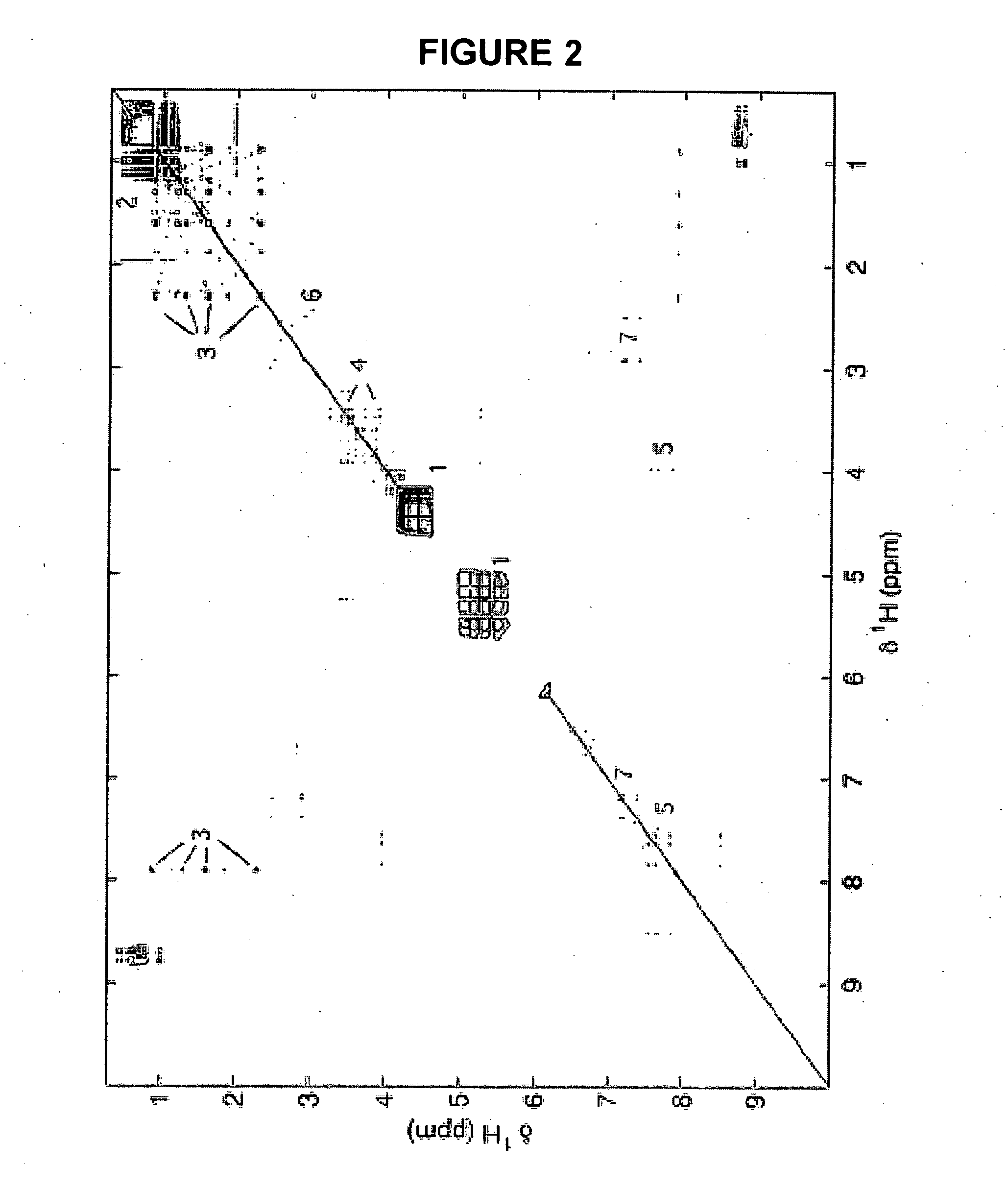
Methods for extracting information on interactions between biological entities from natural language text data
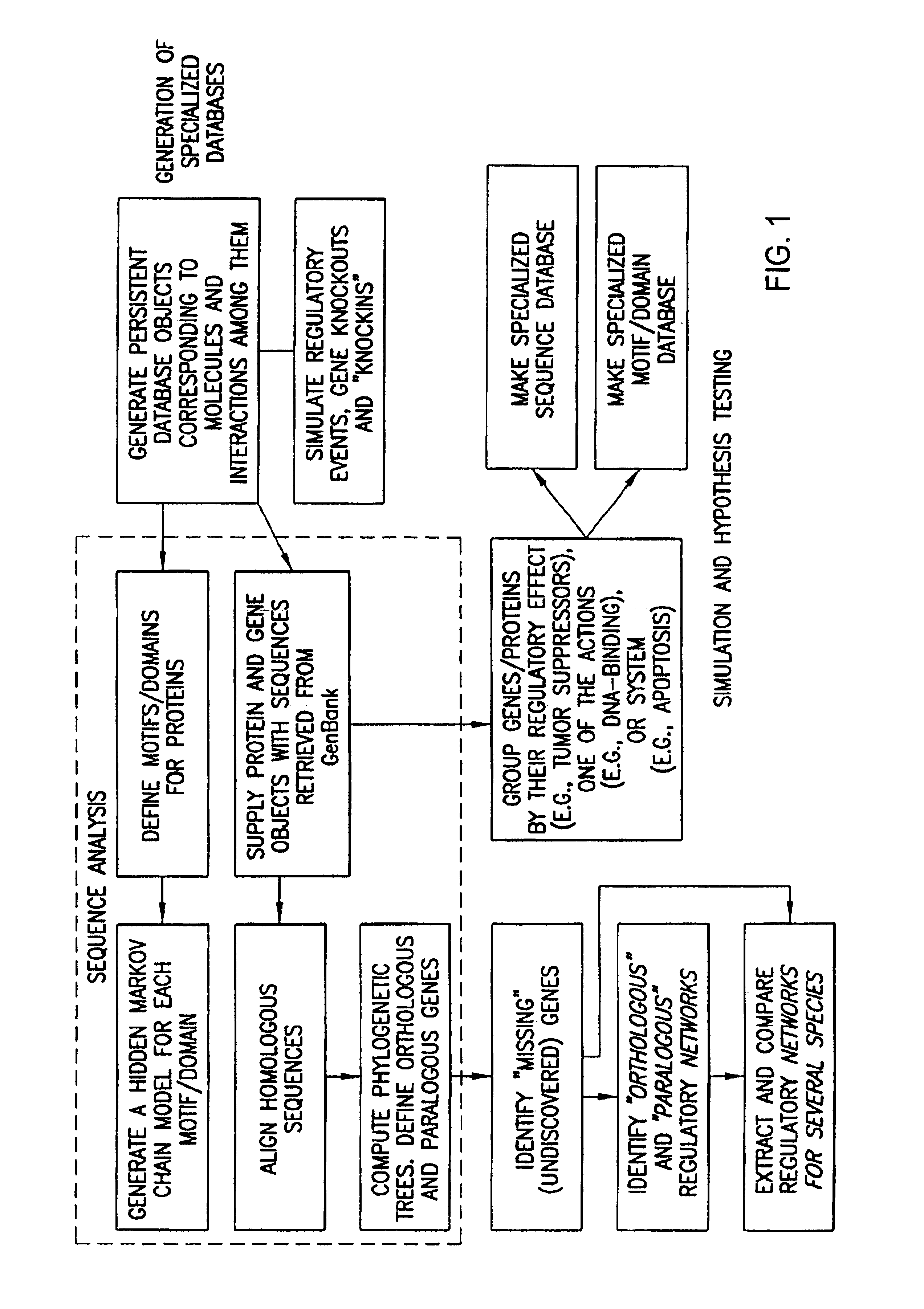
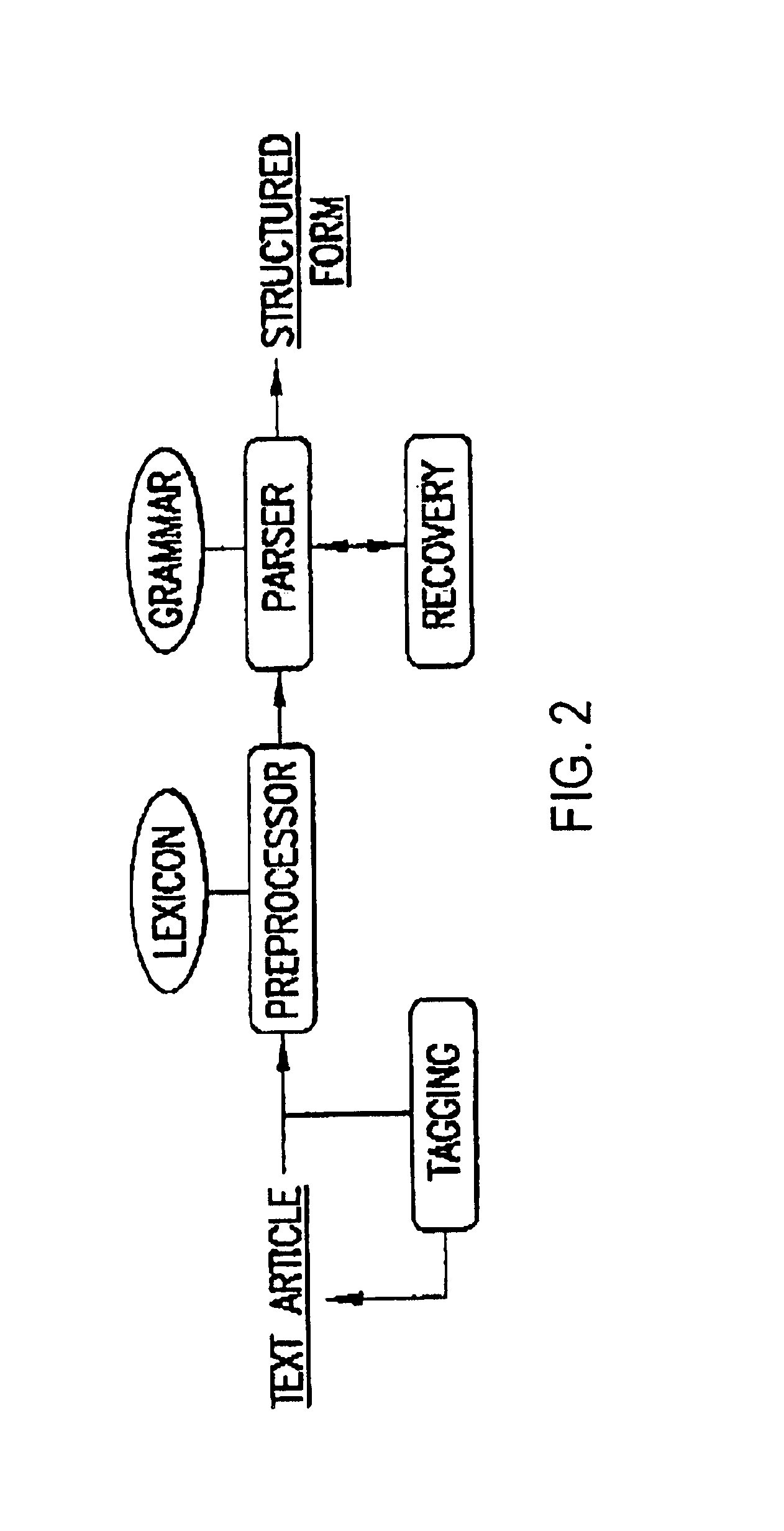
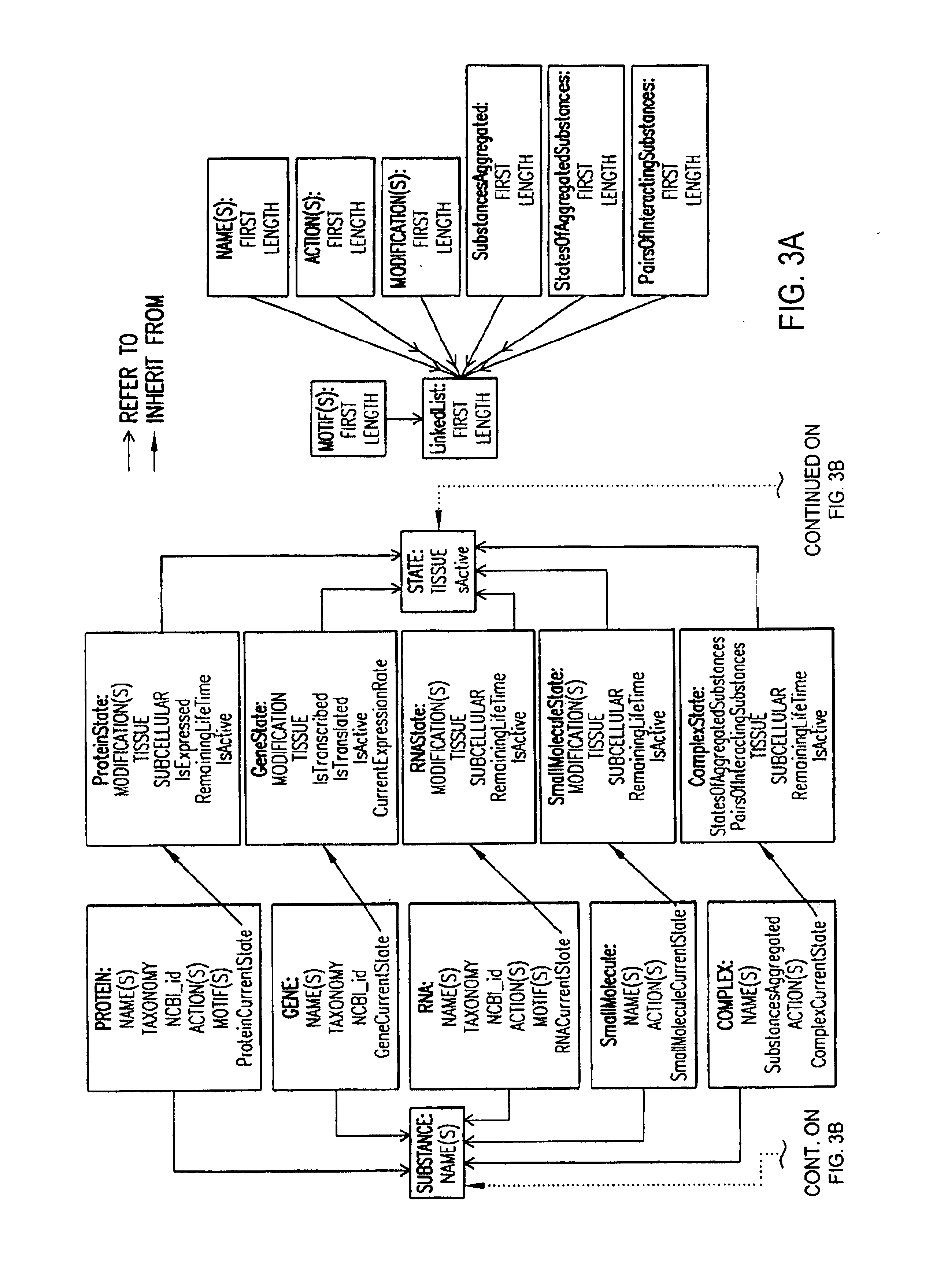
The present invention relates to methods for identifying novel genes comprising: (i) generating one and / or more specialized databases containing information on gene / protein structure, function and / or regulatory interactions; and (ii) searching the specialized databases for homology or for a particular motif and thereby identifying a putative novel gene of interest. The invention may further comprise performing simulation and hypothesis testing to identify or confirm that the putative gene is a novel gene of interest. The present invention also relates to natural language processing and extraction of relational information associated with genes and proteins that are found in genomics journal articles. To enable access to information in textual form, the natural language processing system of the present invention provides a method for extracting and structuring information found in the literature in a form appropriate for subsequent applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
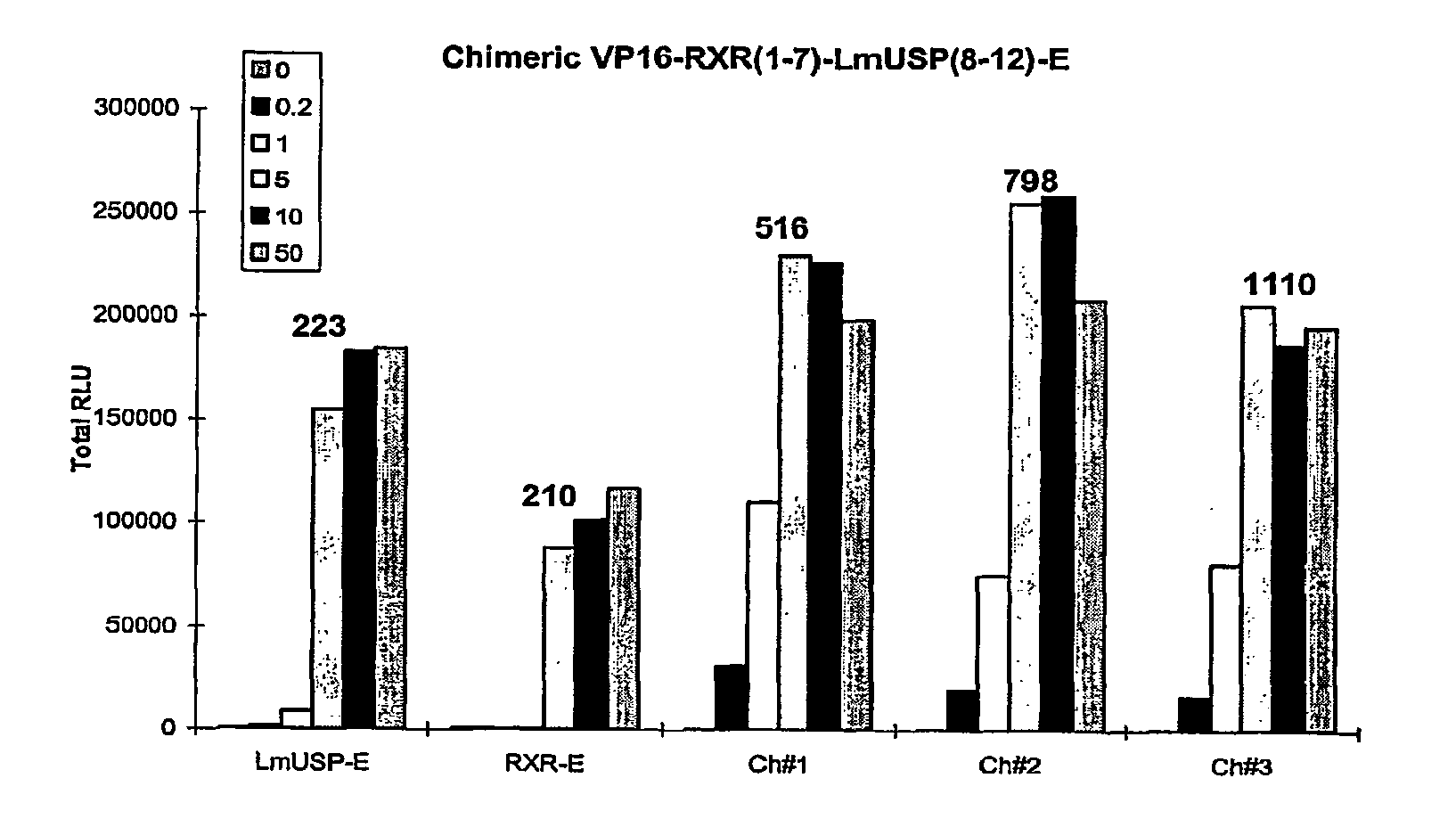
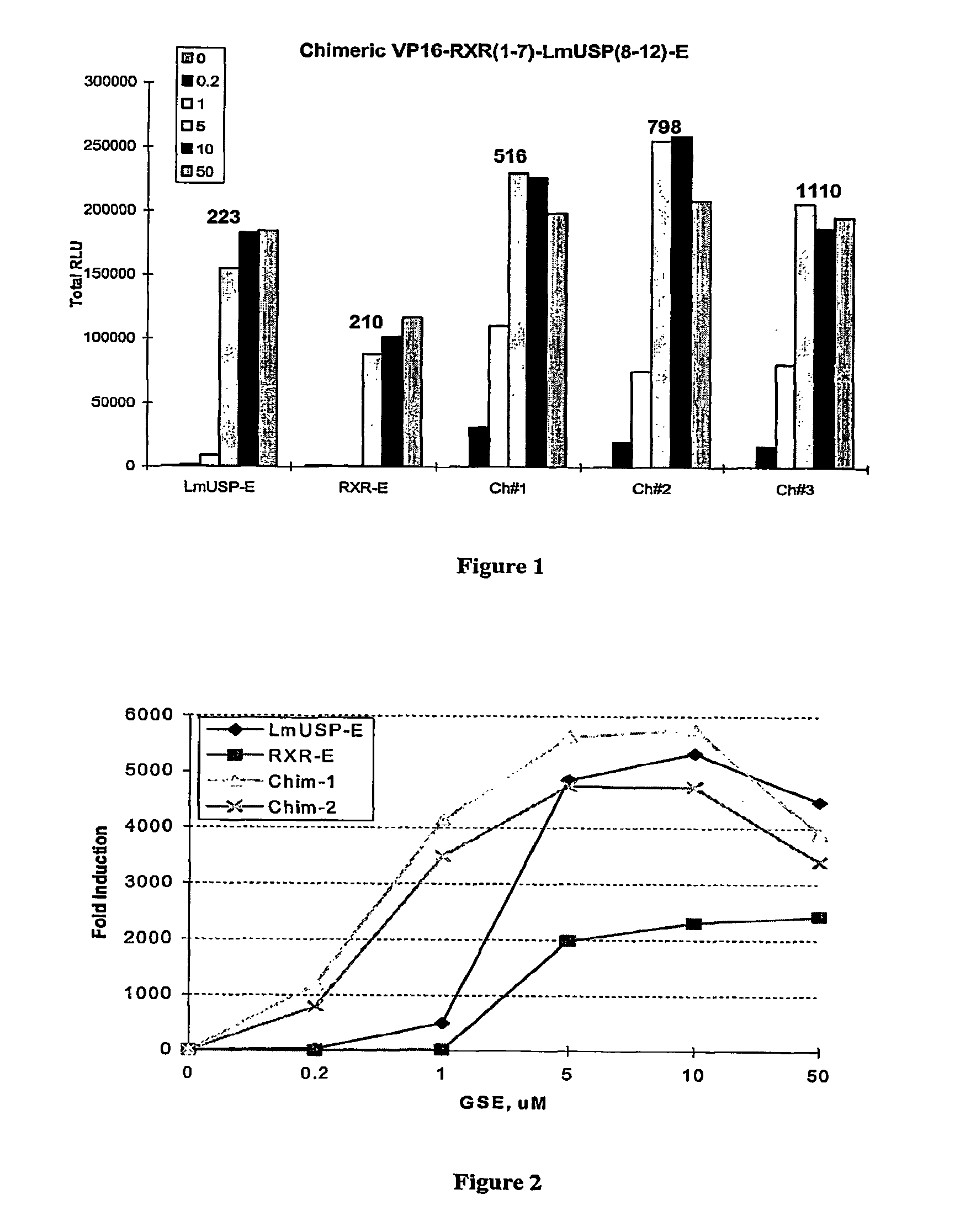
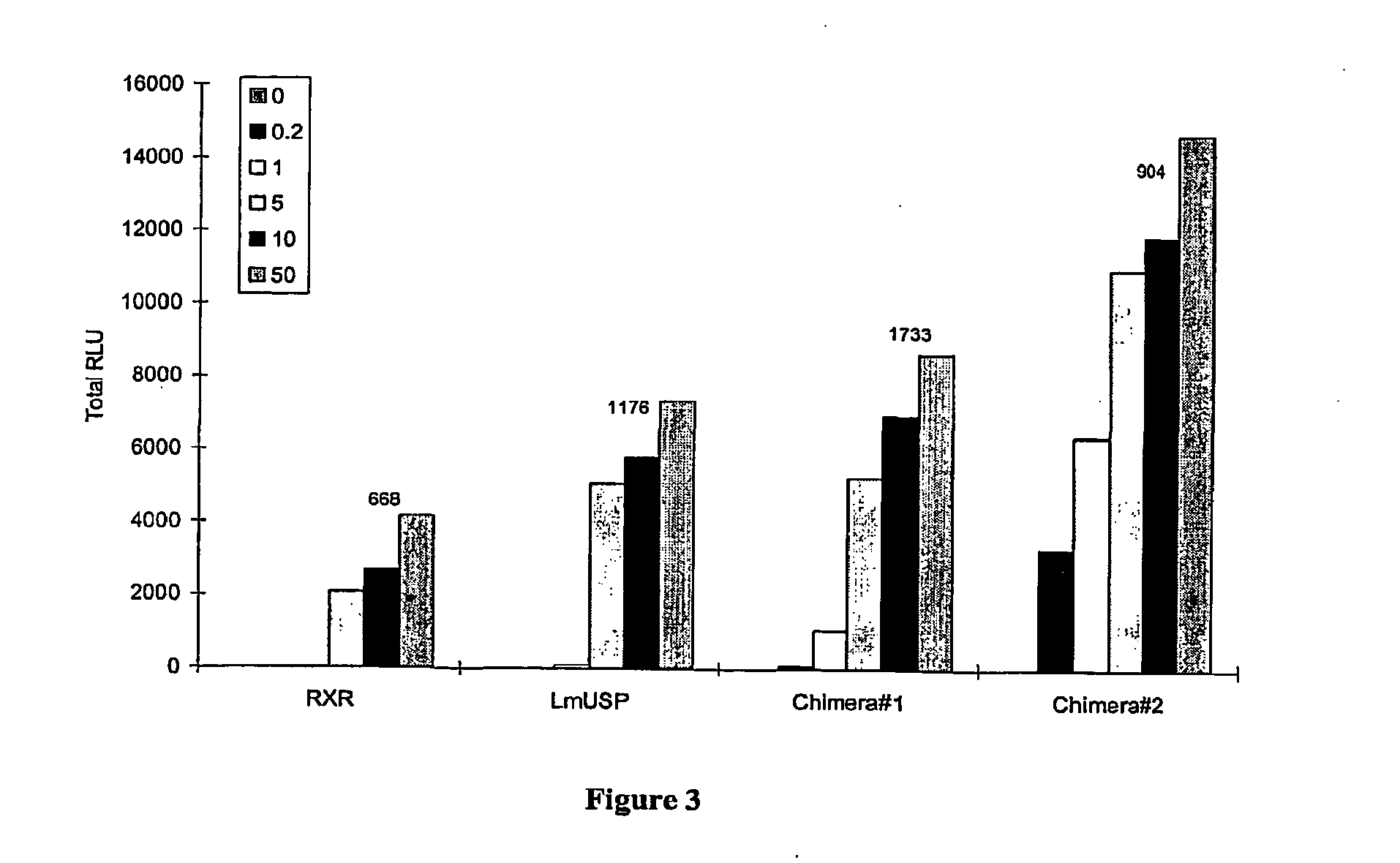
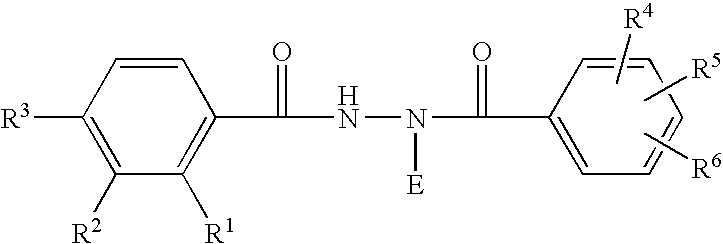
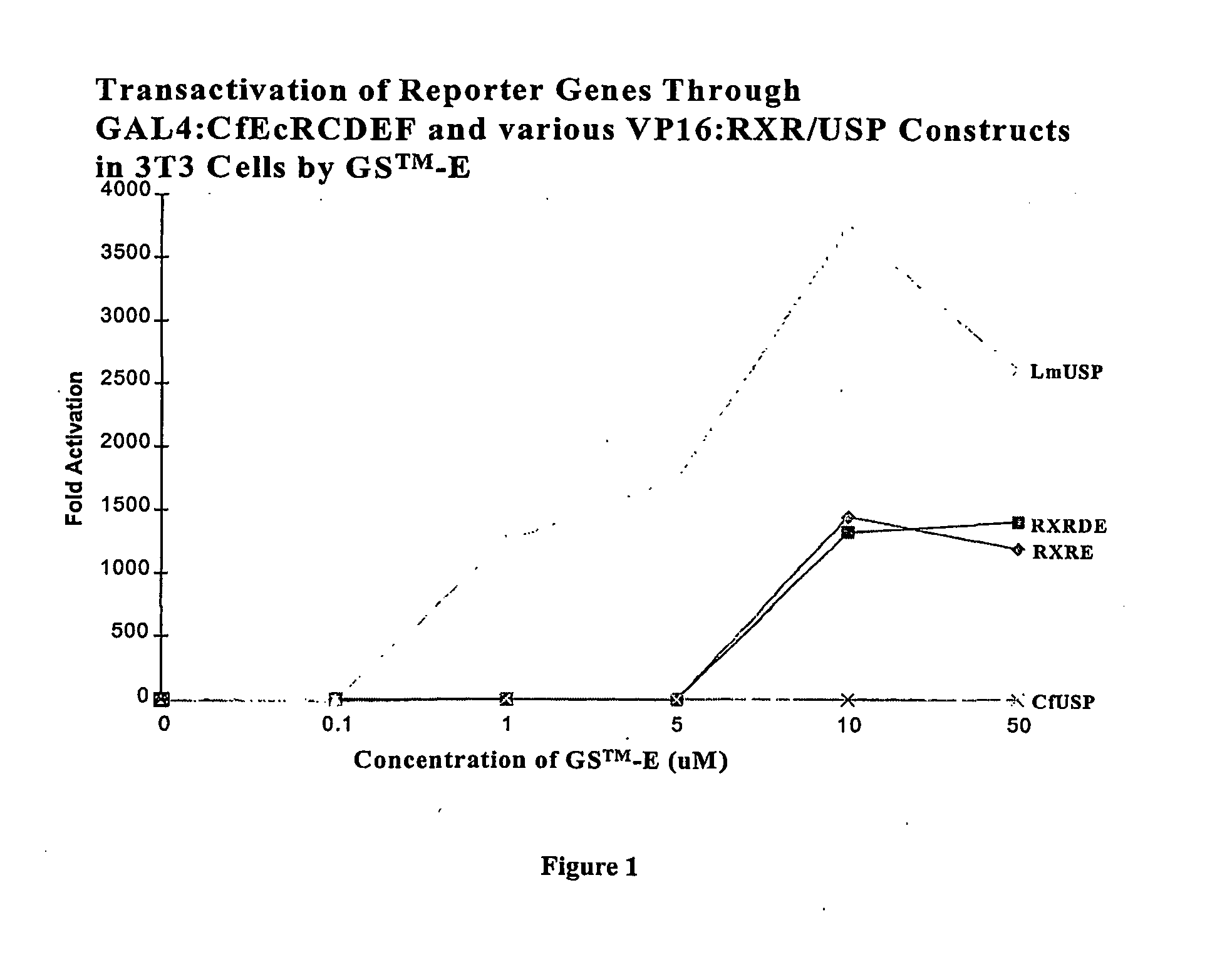
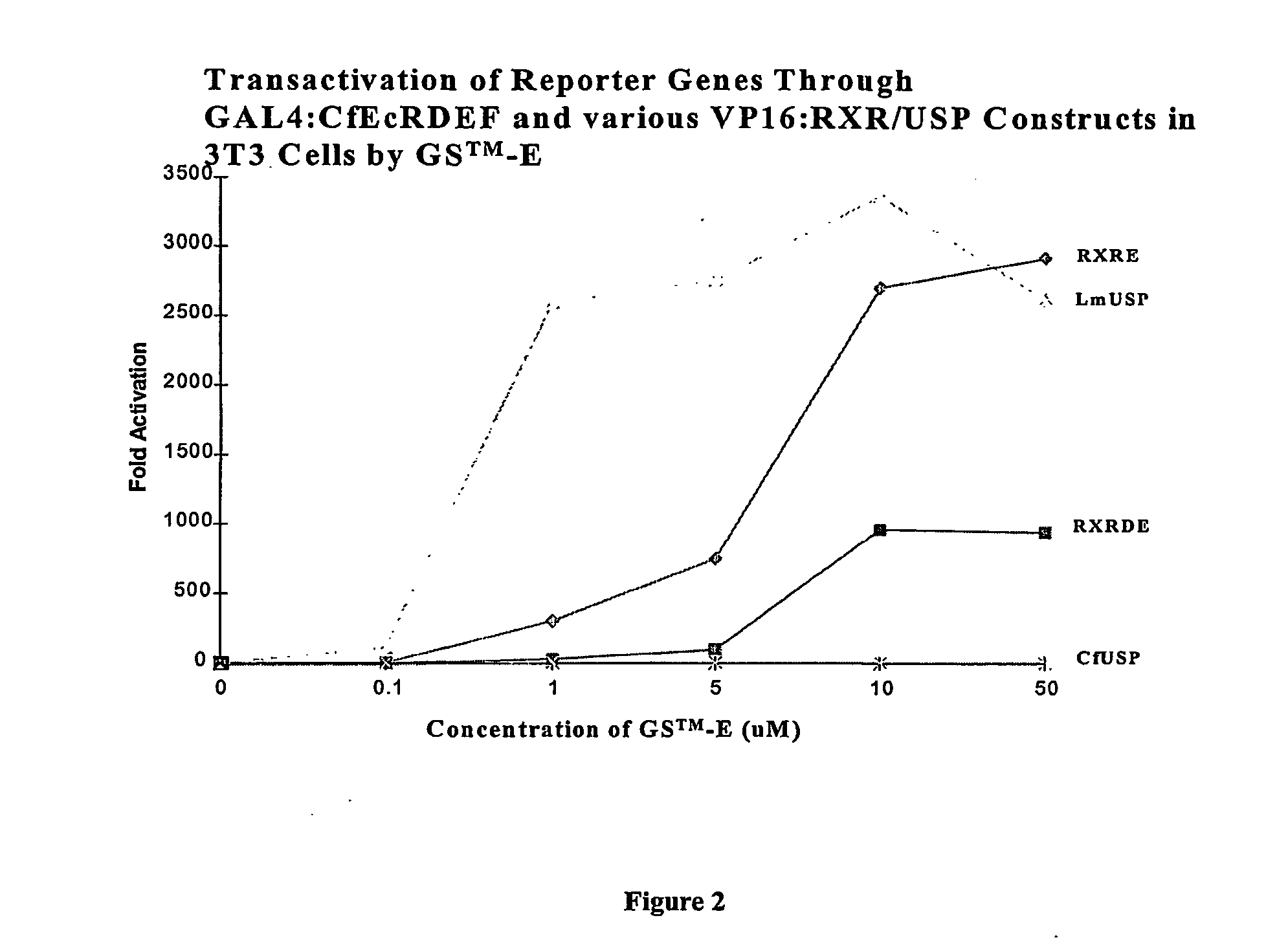
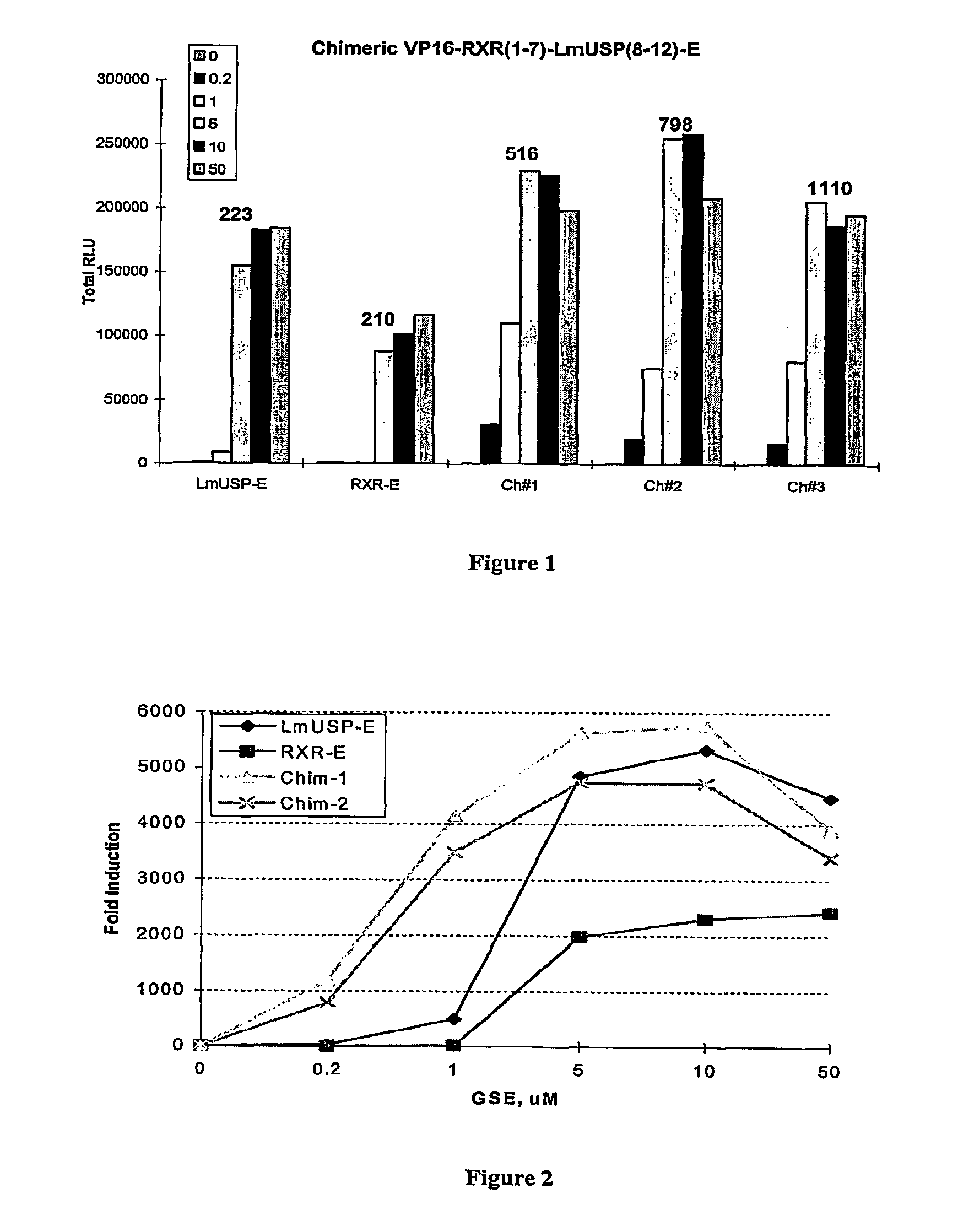
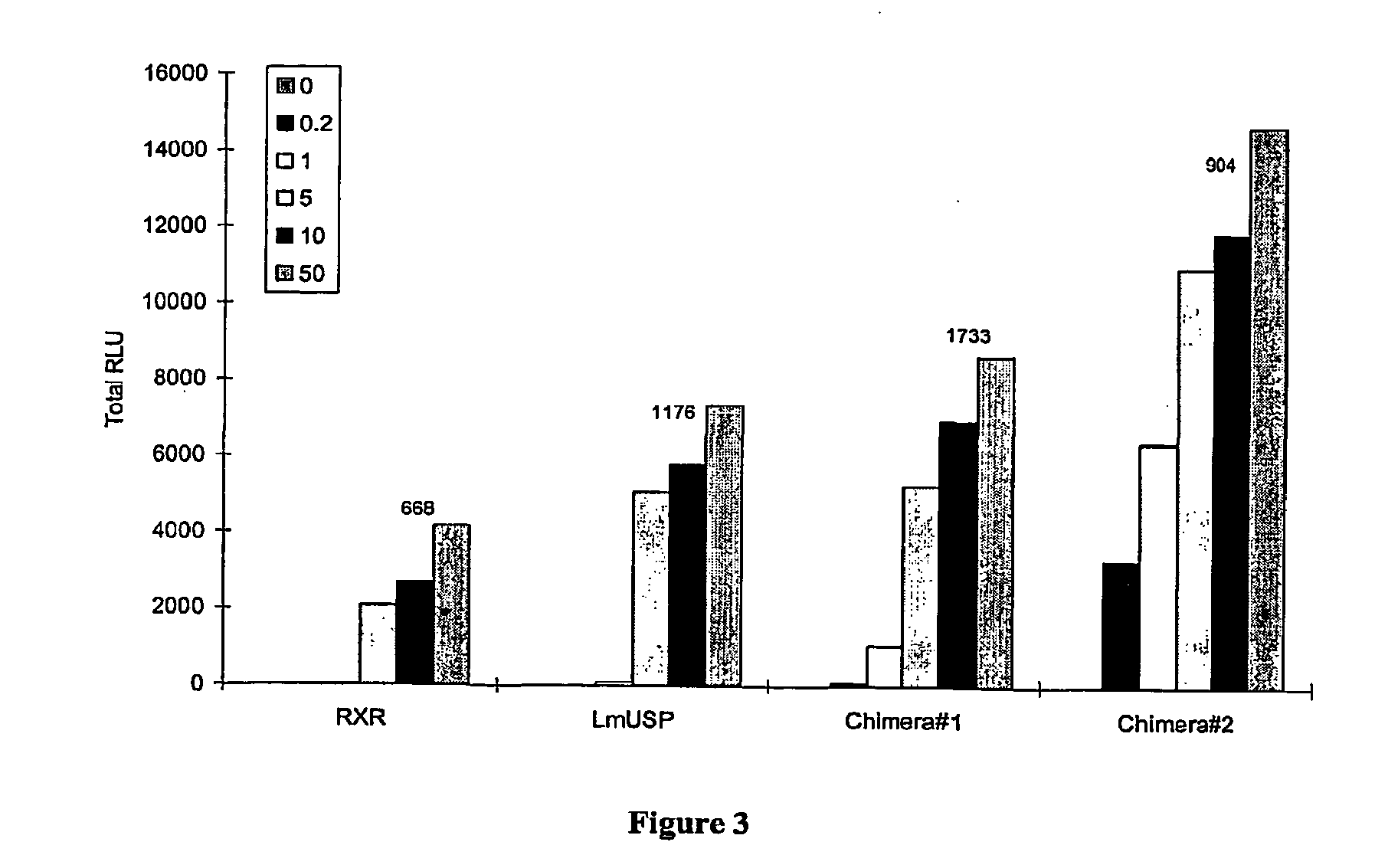
Chimeric retinoid x receptors and their use in a novel ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
InactiveUS20080263687A1FungiFusion with DNA-binding domainHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysBiotechnology
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel ecdysone receptor / chimeric retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
ActiveUS20080145935A1Improve efficiencyGreat degree of sequence similarityPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysGenomics
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Novel ecdysone receptor/invertebrate retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel ecdysone receptor / invertebrate retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS8280640B2Easy to useIncrease speedBiological testingComparison of digital valuesSequential dataMedical diagnosis
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
Chimeric retinoid x receptors and their use in a novel ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel ecdysone receptor / chimeric retinoid X receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a Group H nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating the expression of a gene in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screening assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms.
Owner:RHEOGENE INC DE
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
InactiveUS20180121601A1Improve processing speedImprove accuracyInternal/peripheral component protectionProteomicsSequence analysisGenomics
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Genes differentially expressed in cancer cells to design cancer vaccines
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Intelligent decision-making assisting system based on multi-modal ultrasomics
InactiveCN107582097AGood segmentation resultComplete individualized precision medical adviceBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseGenomics
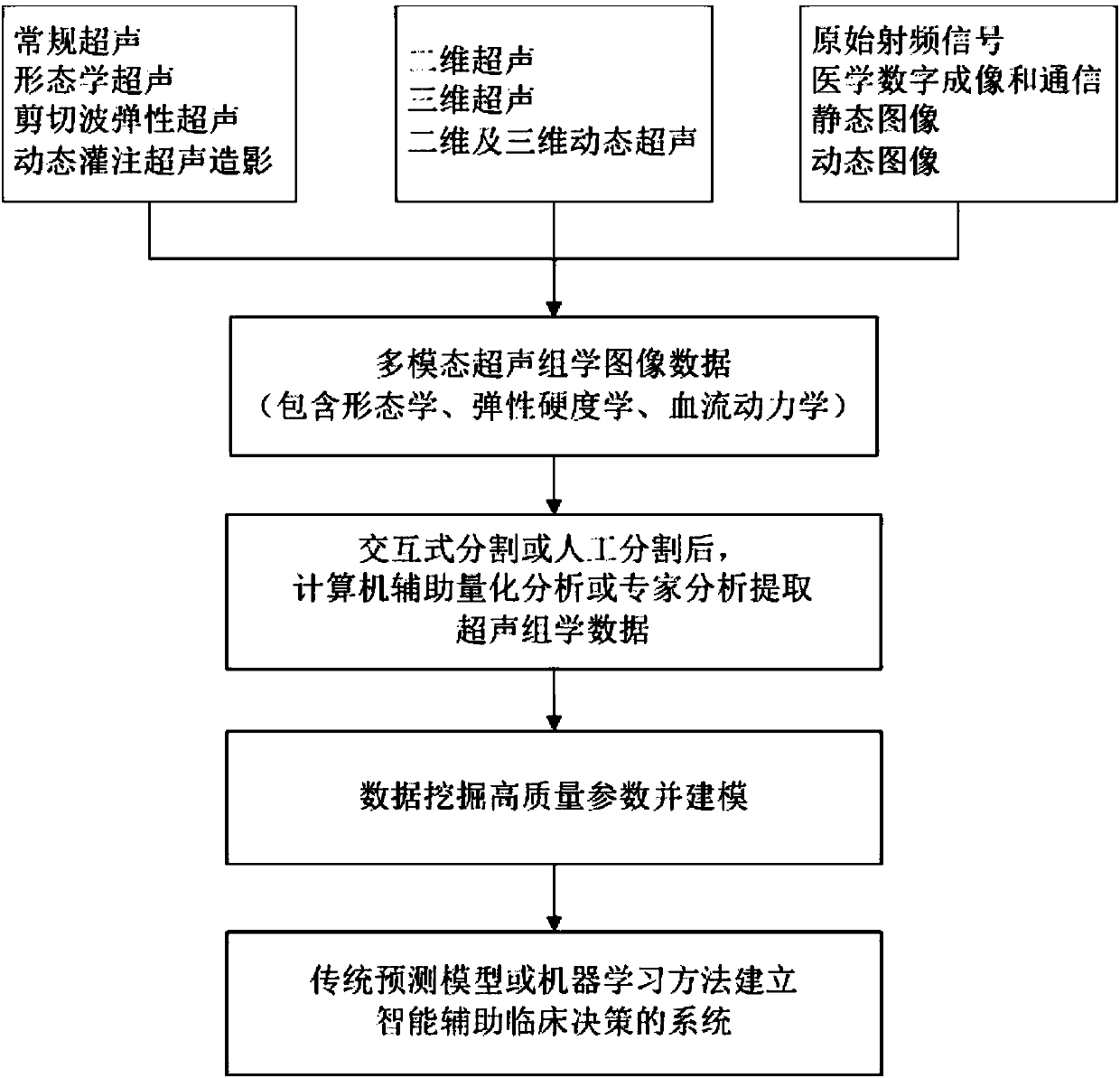
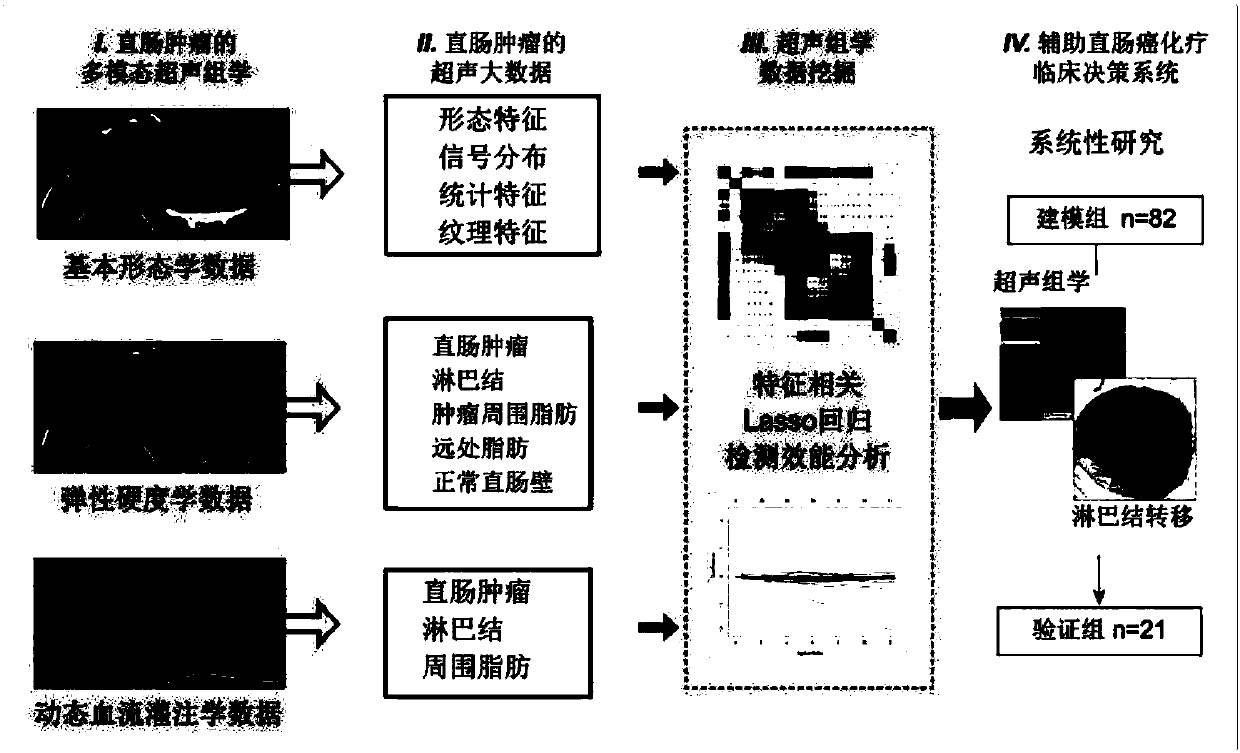
The invention discloses an intelligent decision-making assisting system based on multi-modal ULTRASOMICS. Firstly, ultrasonic data from different signal sources of an instrument is acquired, an interactive or manual dividing method is adopted to locate an interested area in an ultrasonic image, data of morphology, blood perfusion and hardness science of diseases is obtained, and a multi-modal ultrasonic characteristic database is constructed; through the combination of relevant clinical information, laboratory checking information and gene chip information, ultrasomics data is mined, a machinelearning method is utilized to construct different models, the recurrence rate and the survival rate are predicted, the curative effect and the radiotherapy and chemotherapy sensitivity are judged inthe early stage, and the correlation of ultrasomics, genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics and metabonomics is analyzed. As macroscopic ultrasomics, the intelligent decision-making assisting system provides a repeatable evaluation means for noninvasive individualized precise medicine.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Physiogenomic method for predicting response to diet
InactiveUS20070196841A1Reduce weightReduce morbiditySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsPersonalization
The present invention relates to the use of genetic variants of associated marker genes to predict an individual's response to diet. The present invention further relates to analytical assays and computational methods using the novel marker gene set. The present invention has utility for developing personalized diet regimens to optimize physiological response, including changes in body mass index (BMI) and blood lipid and triglyceride levels.
Owner:GENOMAS
High throughput screening of gene function using libraries for functional genomics applications
InactiveUS7029848B2Altered phenotypeIncrease capacityFungiBacteriaGenomicsHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Novel means and methods for their use are provided to determine the function of the product(s) of one or more sample nucleic acids. The sample nucleic acids are synthetic oligonucleotides, DNA, or cDNA and encode polypeptides, antisense nucleic acids, or GSEs. The sample nucleic acids are expressed in a host by a vehicle to alter at least one phenotype of the host. The altered phenotype(s) is / are identified as a means to assign a biological function to the product(s) encoded by the sample nucleic acid(s).
Owner:GALAPAGOS GENOMICS
Site-specific insertional inactivation method and application mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR/Cas9
ActiveCN106434651ASpecify the direction of insertionRealize fixed-point insertionPeptidesNucleic acid vectorGenomicsMobile DNA
The invention discloses a site-specific insertional inactivation method mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR / Cas9. Endogenous snRNA promoter of Ustilago scitaminea (u6 promoter of Ustilago scitaminea) is used to drive sgRNA expression cassette. CRISPR / Cas9 system integrates with Ti plasmid of agrobacterium tumefaciens to construct the Ustilago scitaminea site-specific insertional inactivation system mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens with hygromycin as a selection marker. Specific sequence of the objective gene is cloned into sgRNA expression cassette for transformation of Ustilago scitaminea basidiospores, thus the mobile DNA fragment is exactly inserted into the objective gene sequence of Ustilago scitaminea, achieving the goal of damage to gene function. The invention provides an important tool for study of Ustilago scitaminea functional genomics. The system has the advantages of high efficiency and accuracy, and is convenient to use to conduct gene function researches in Ustilago scitaminea.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
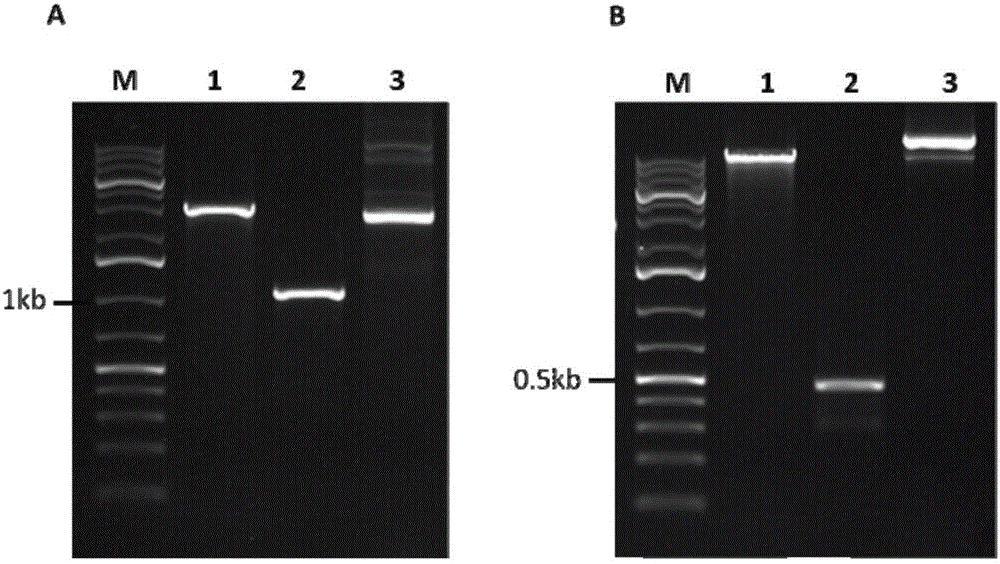
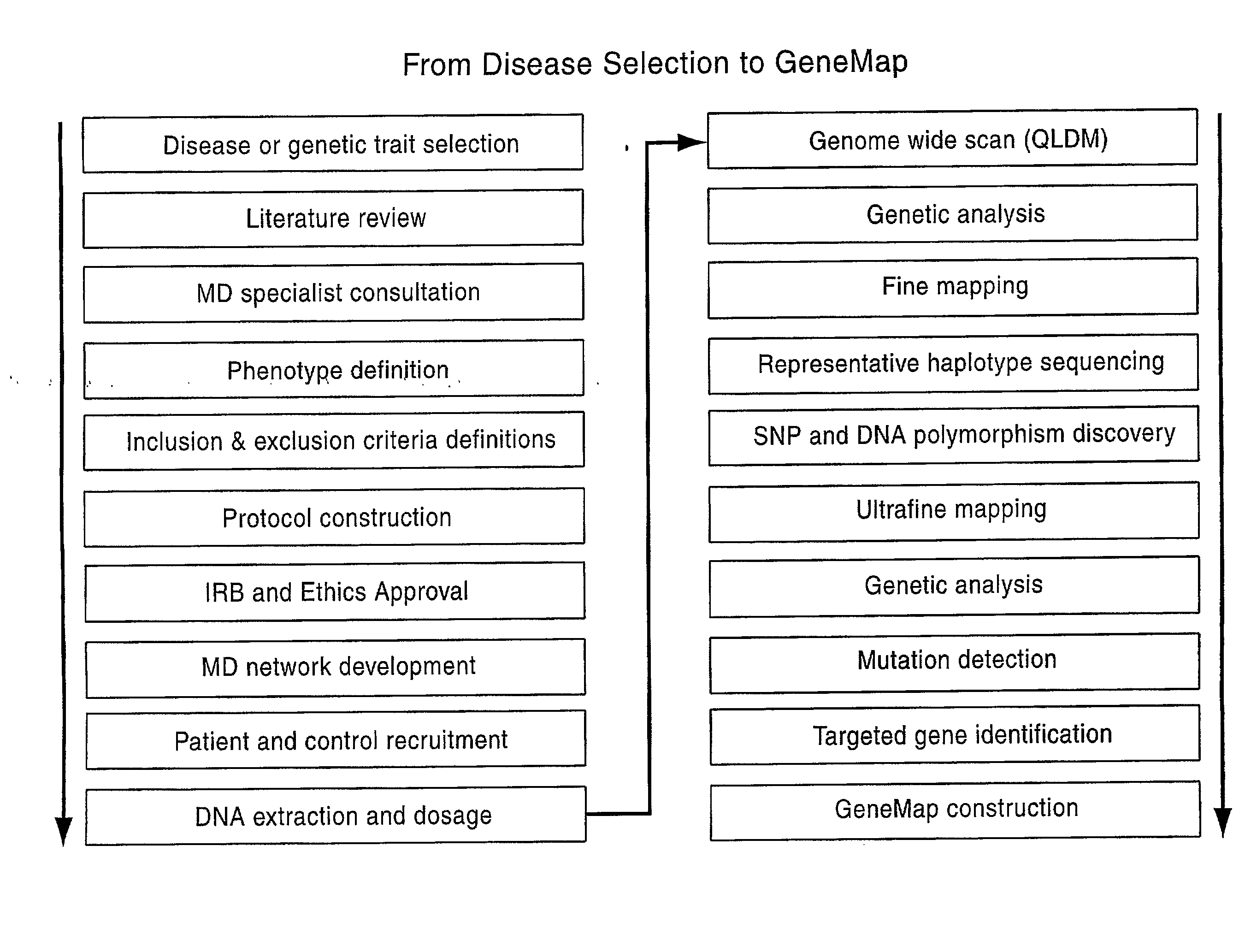
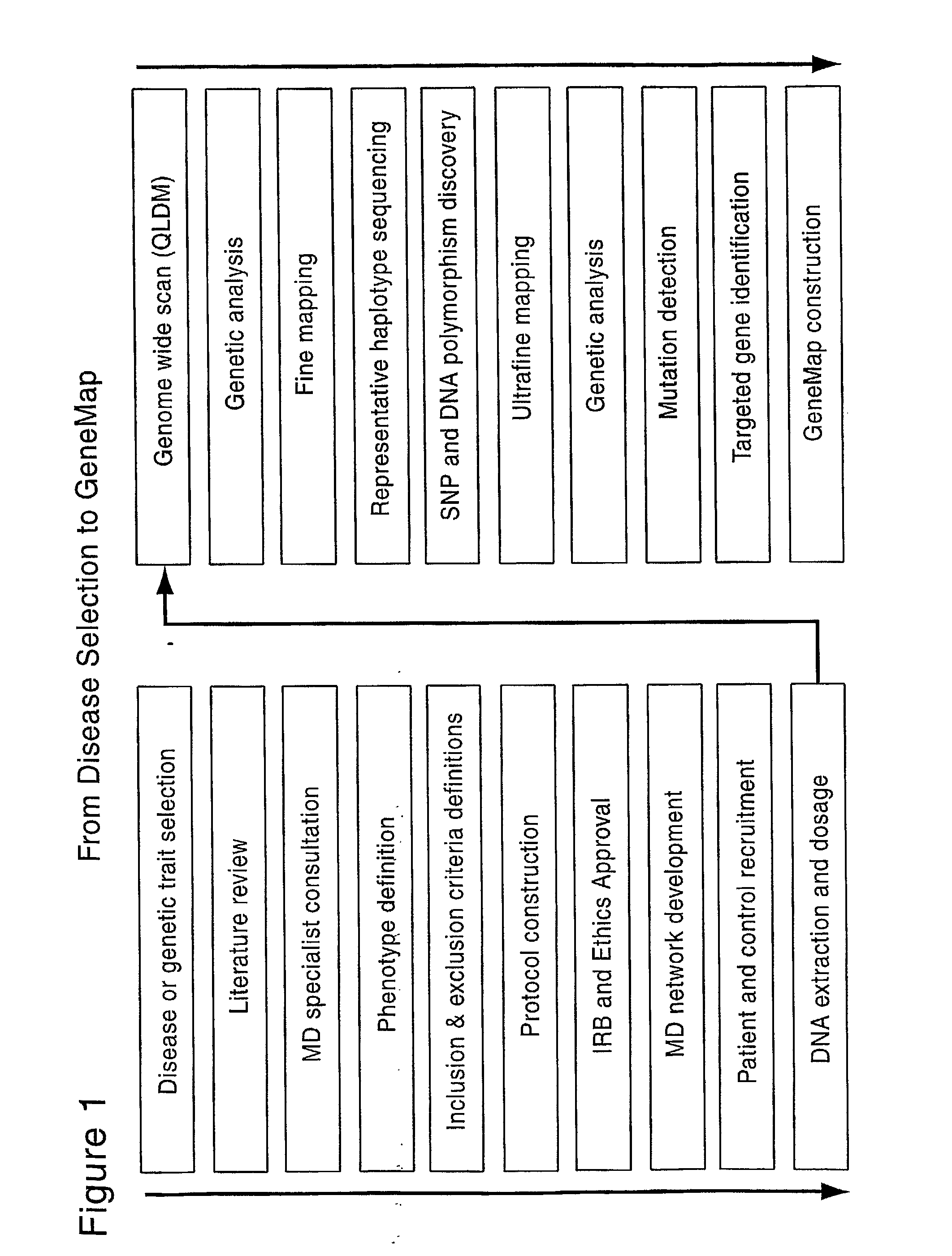
Genemap of the human genes associated with longevity
InactiveUS20090305900A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementGenomicsLinkage Disequilibrium Mapping
The present invention relates to the selection of a set of SNP markers for use in genome wide association studies based on linkage disequilibrium mapping. In particular, the invention relates to the fields of pharmacogenomics, diagnostics, patient therapy and the use of genetic haplotype information to predict an individual's longevity, their protection against age-related diseases and / or their response to a particular drug or drugs.
Owner:BELOUCHI ABDELMAJID +12
Genemap of the human genes associated with crohn's disease
InactiveUS20090081658A1Reduce frequencyTreatment safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsLinkage Disequilibrium Mapping
The present invention relates to the selection of a set of polymorphism markers for use in genome wide association studies based on linkage disequilibrium mapping. In particular, the invention relates to the fields of pharmacogenomics, diagnostics, patient therapy and the use of genetic haplotype information to predict an individual's susceptibility to Crohn's disease and / or their response to a particular drug or drugs.
Owner:GENIZON BIOSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com