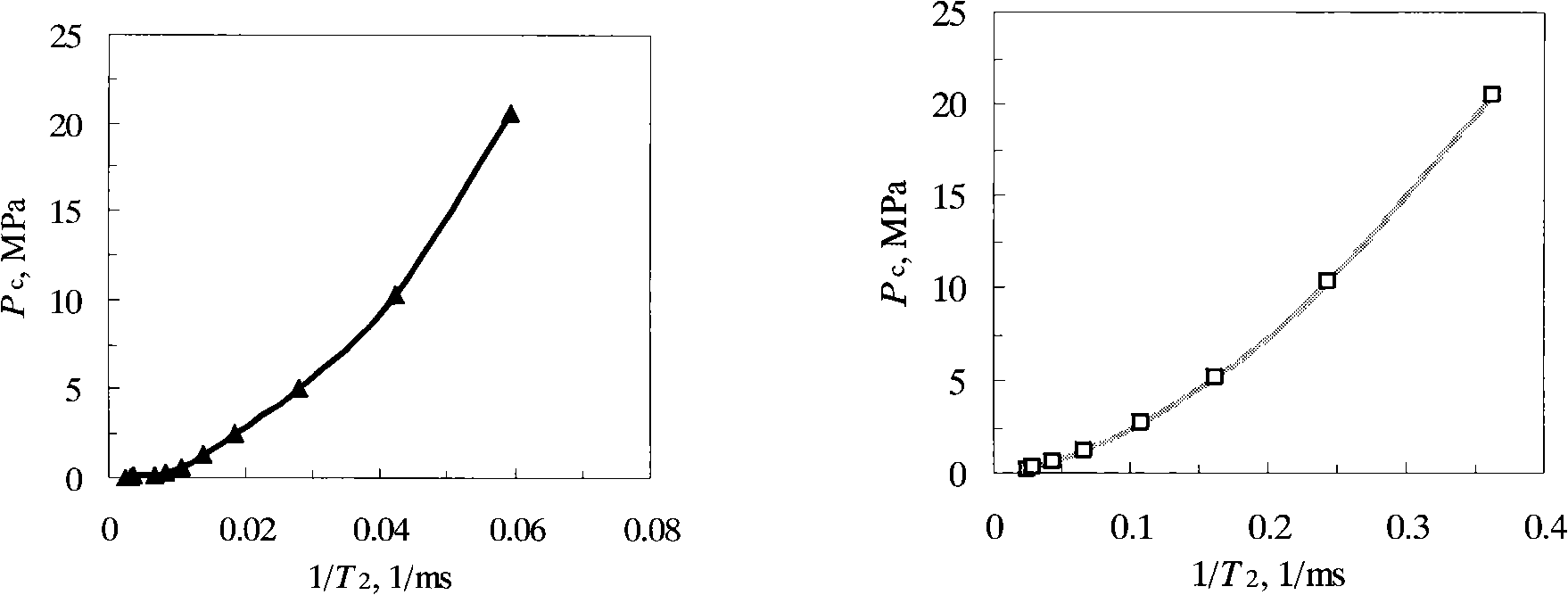Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5602 results about "NMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong static magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field and therefore not involving electromagnetic waves) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus.
Method Of Manufacture And The Use Of A Functional Proppant For Determination Of Subterranean Fracture Geometries
ActiveUS20090288820A1Accurate imagingPromote recoveryMaterial nanotechnologyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingElectricityGeophone
Proppants having added functional properties are provided, as are methods that use the proppants to track and trace the characteristics of a fracture in a geologic formation. Information obtained by the methods can be used to design a fracturing job, to increase conductivity in the fracture, and to enhance oil and gas recovery from the geologic formation. The functionalized proppants can be detected by a variety of methods utilizing, for example, an airborne magnetometer survey, ground penetrating radar, a high resolution accelerometer, a geophone, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultra-sound, impedance measurements, piezoelectric activity, radioactivity, and the like. Methods of mapping a subterranean formation are also provided and use the functionalized proppants to detect characteristics of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
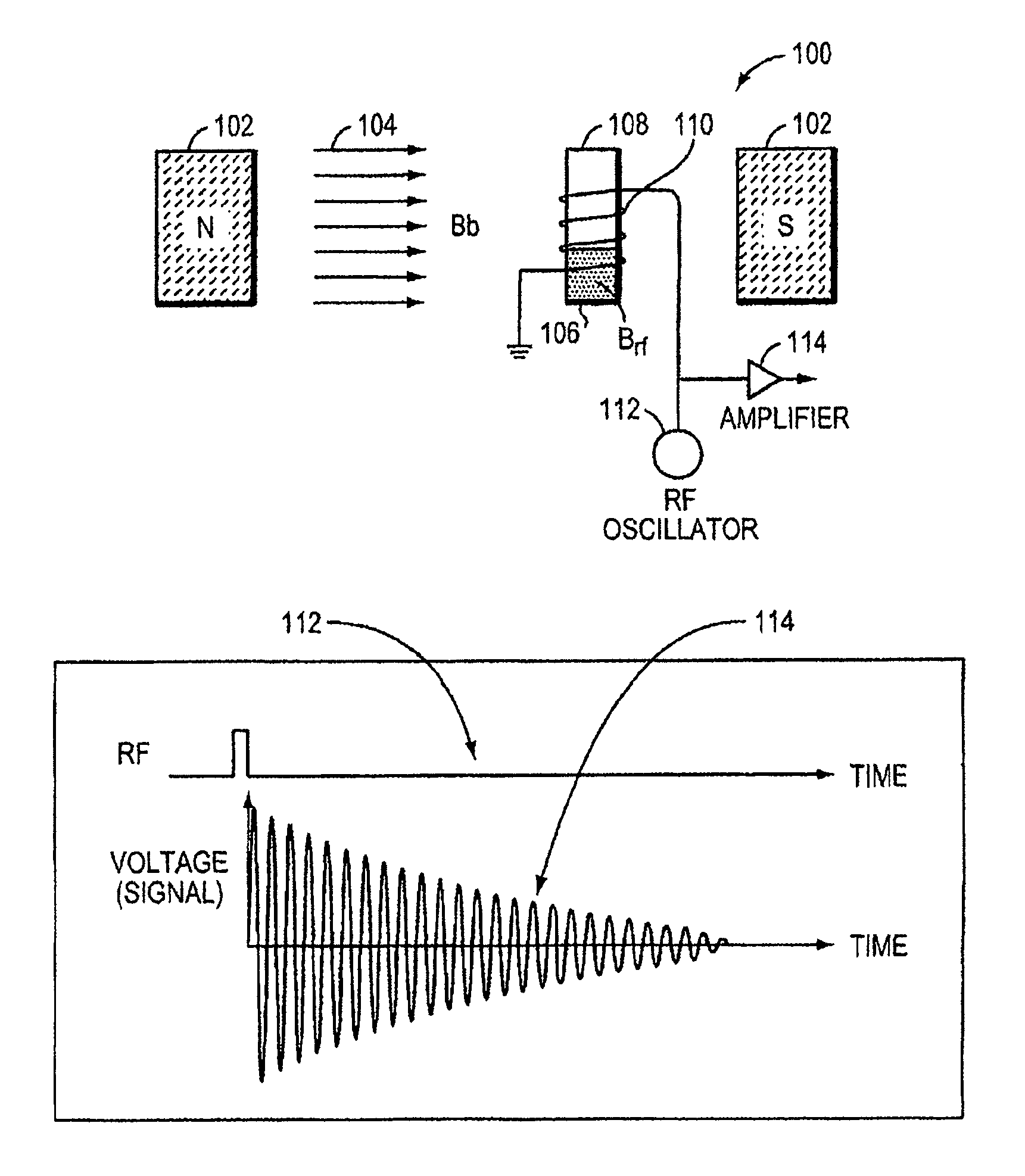
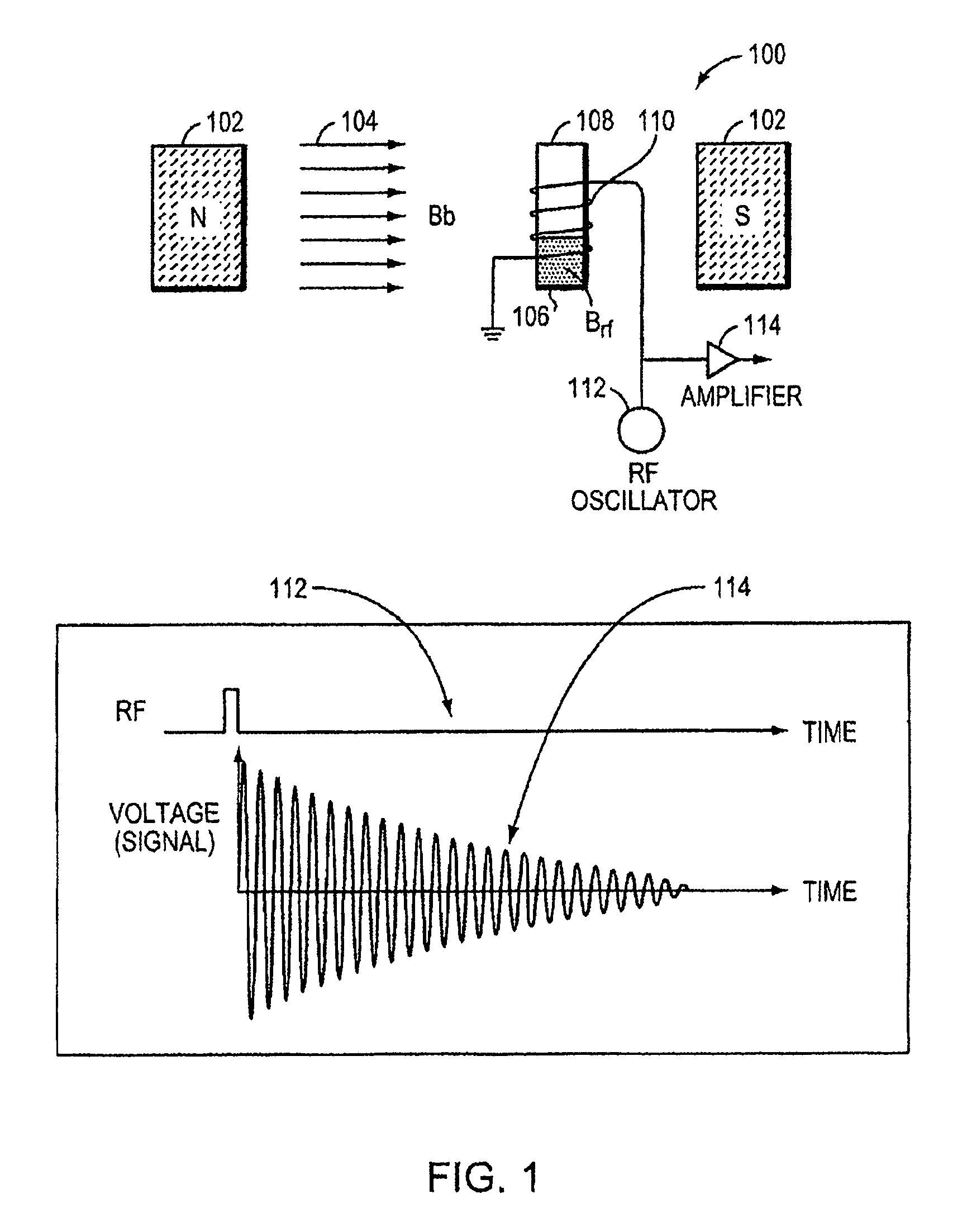
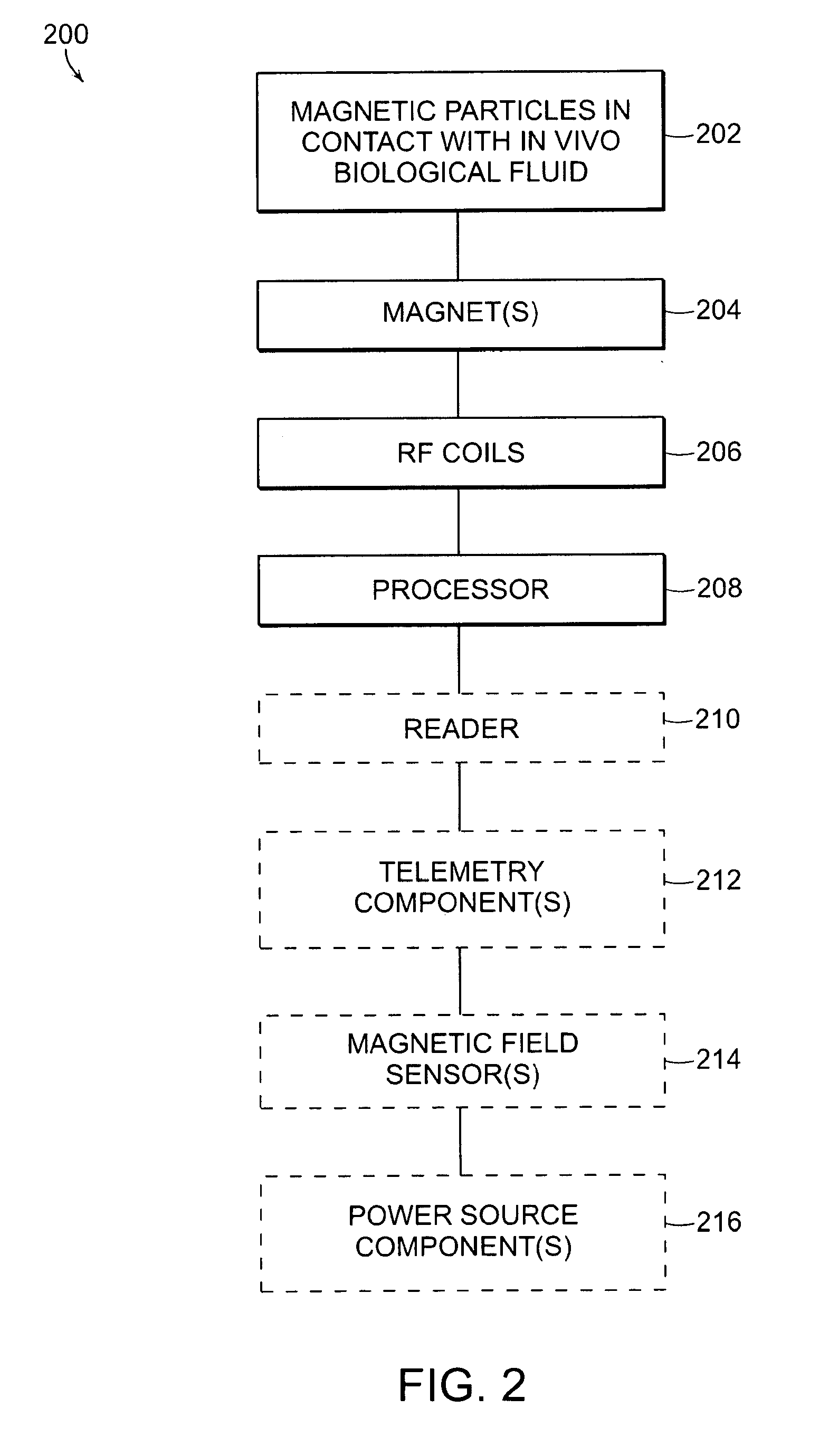
Nmr systems for in vivo detection of analytes
ActiveUS20100072994A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingAnalyteNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
This invention relates generally to NMR systems for in vivo detection of analytes. More particularly, in certain embodiments, the invention relates to systems in which superparamagnetic nanoparticles are exposed to a magnetic field and radio frequency (RF) excitation at or near the Larmor frequency, such that the aggregation and / or disaggregation of the nanoparticles caused by the presence and / or concentration of a given analyte in a biological fluid is detected in vivo from a monitored RF echo response.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
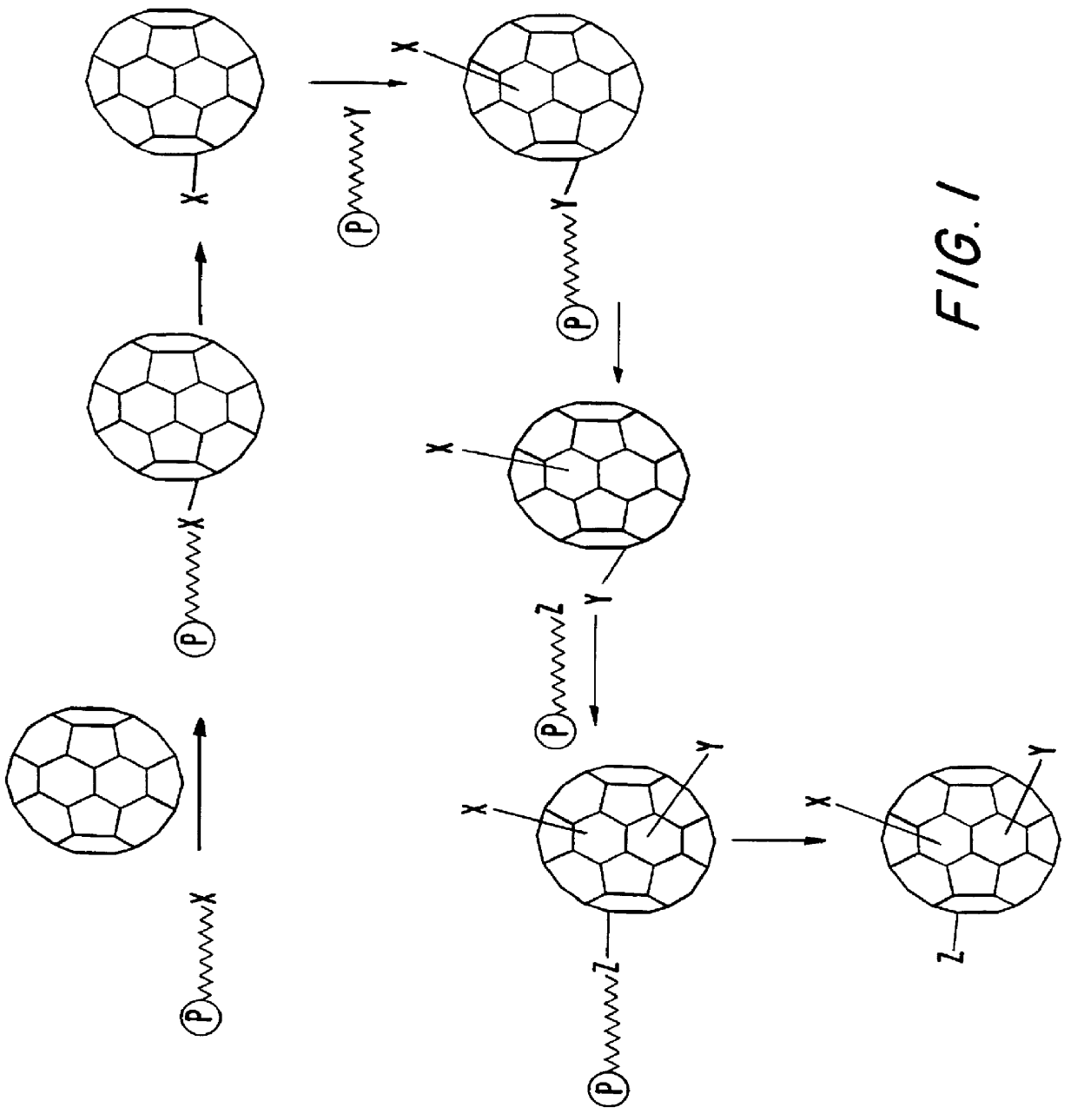
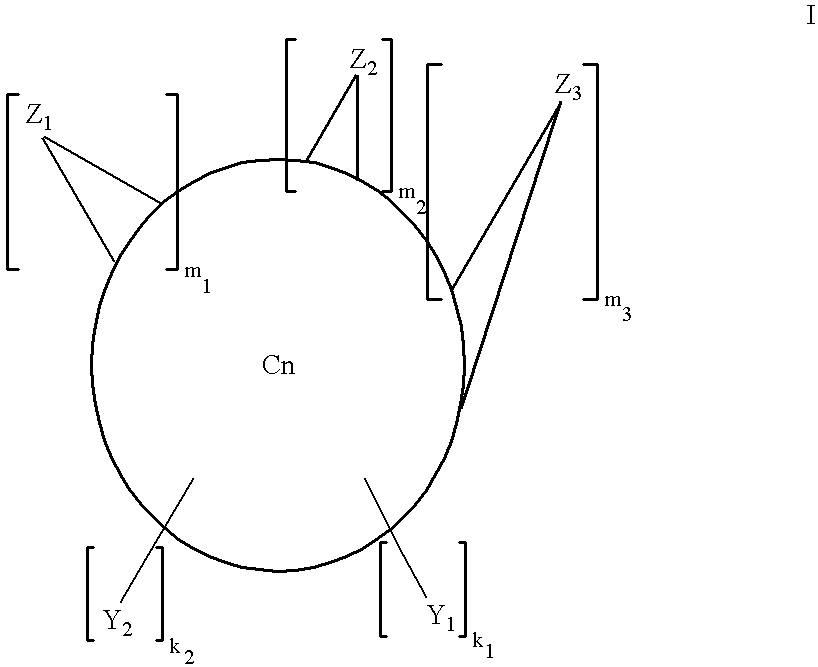
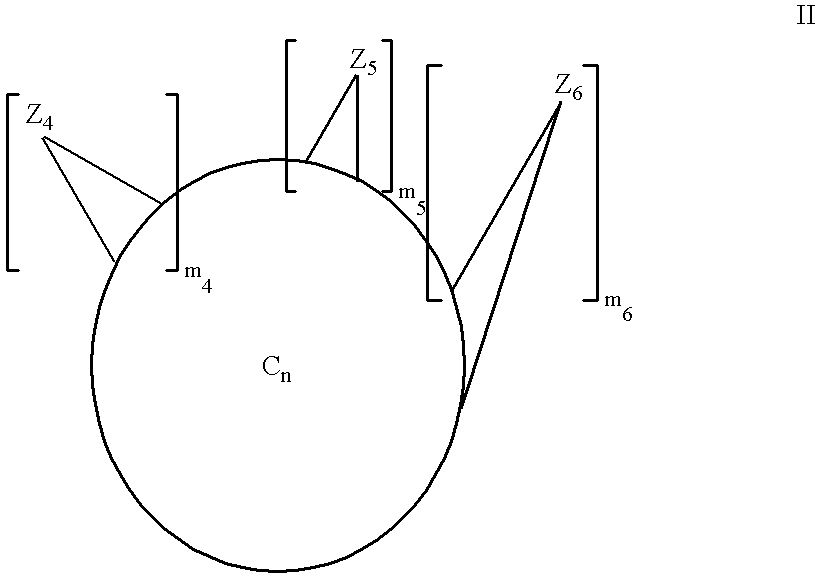
Multi-substituted fullerenes and methods for their preparation and characterization
InactiveUS6162926AGenerate efficientlyLow costSilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceCombinatorial synthesis
The invention is directed to multiply-substituted fullerene derivatives of novel configurations, and methods for their preparation and use. The methods involve the combinatorial synthesis of a library of fullerene derivatives and comprises the steps of forming a mixture of fullerene derivatives by reacting the Cn fullerene with two or more reactive precursor compounds, and removing the unreacted compounds to yield the fullerene derivatives having the desired activity. Methods for the identification and screening of a combinatorial library of fullerenes by 3He-nuclear magnetic resonance and electrospray mass spectrometry to define members with the optimal desired activity are also provided.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Methods for analysis of spectral data and their applications
InactiveUS20050130321A1Skeletal disorderMedical automated diagnosisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceCompound (substance)
This invention pertains to chemometric methods for the analysis of chemical, biochemical, and biological data, for example, spectral data, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra, and their applications, including, e.g., classification, diagnosis, prognosis.
Owner:METABOMETRIX
Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Member, Method for Manufacturing Such Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Member and Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Using Such Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Member
ActiveUS20090008673A1Improve sealingImprove heat resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceHeat resistance
A semiconductor light-emitting device member excellent in transparency, light resistance, and heat resistance and capable of sealing a semiconductor light-emitting device without causing cracks and peeling even after a long-time use is provided. Therefore, a semiconductor light-emitting device member that comprises (1) in a solid Si-nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, at least one peak selected from a group consisting of (i) peaks whose peak top position is in an area of a chemical shift of −40 ppm to 0 ppm inclusive, and whose full width at half maximum is 0.3 ppm to 3.0 ppm inclusive, and (ii) peaks whose peak top position is in an area of the chemical shift of −80 ppm or more and less than −40 ppm, and whose full width at half maximum is 0.3 ppm to 5.0 ppm inclusive, wherein (2) silicon content is 20 weight % or more and (3) silanol content is 0.1 weight % to 10 weight % inclusive is used.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
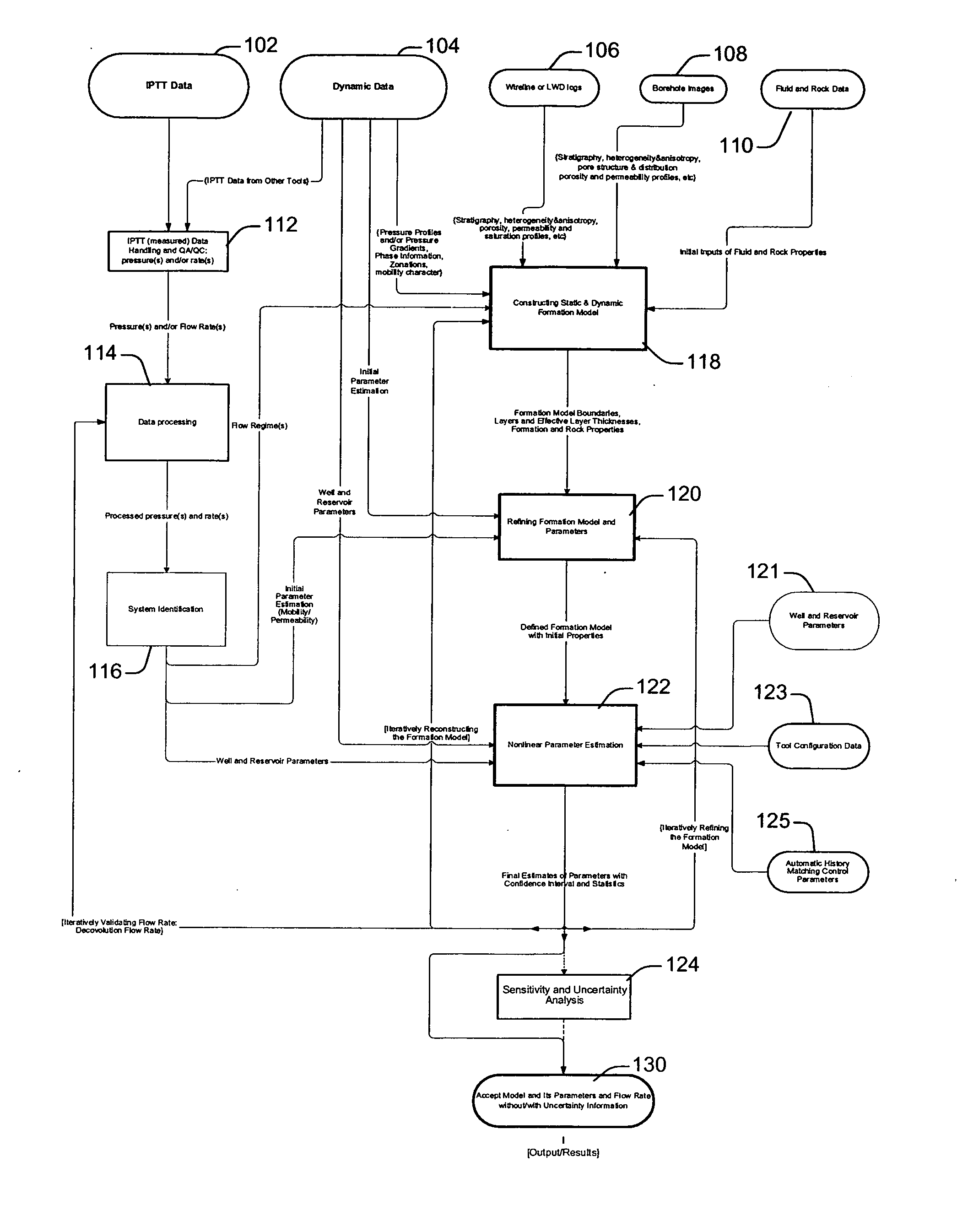
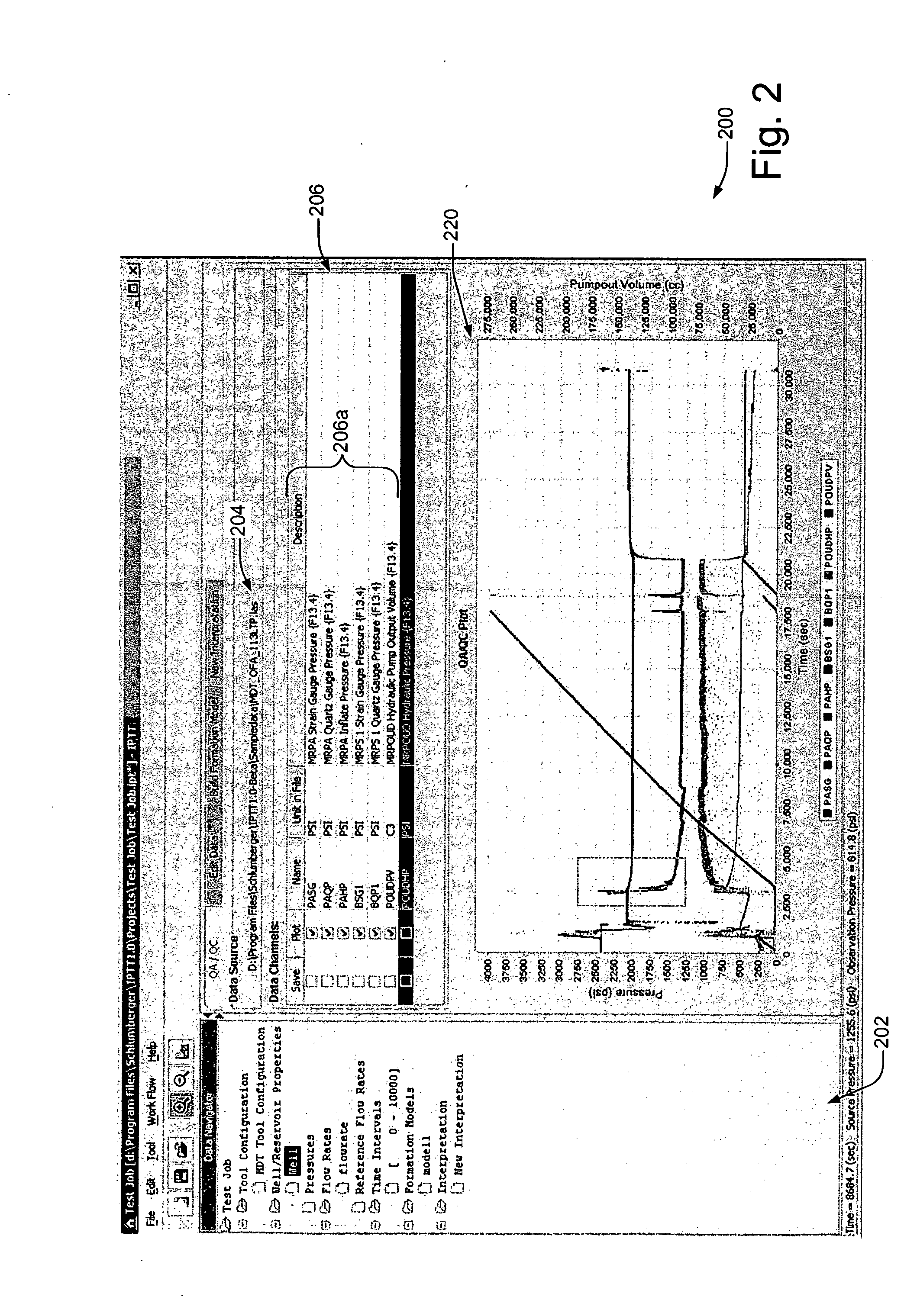
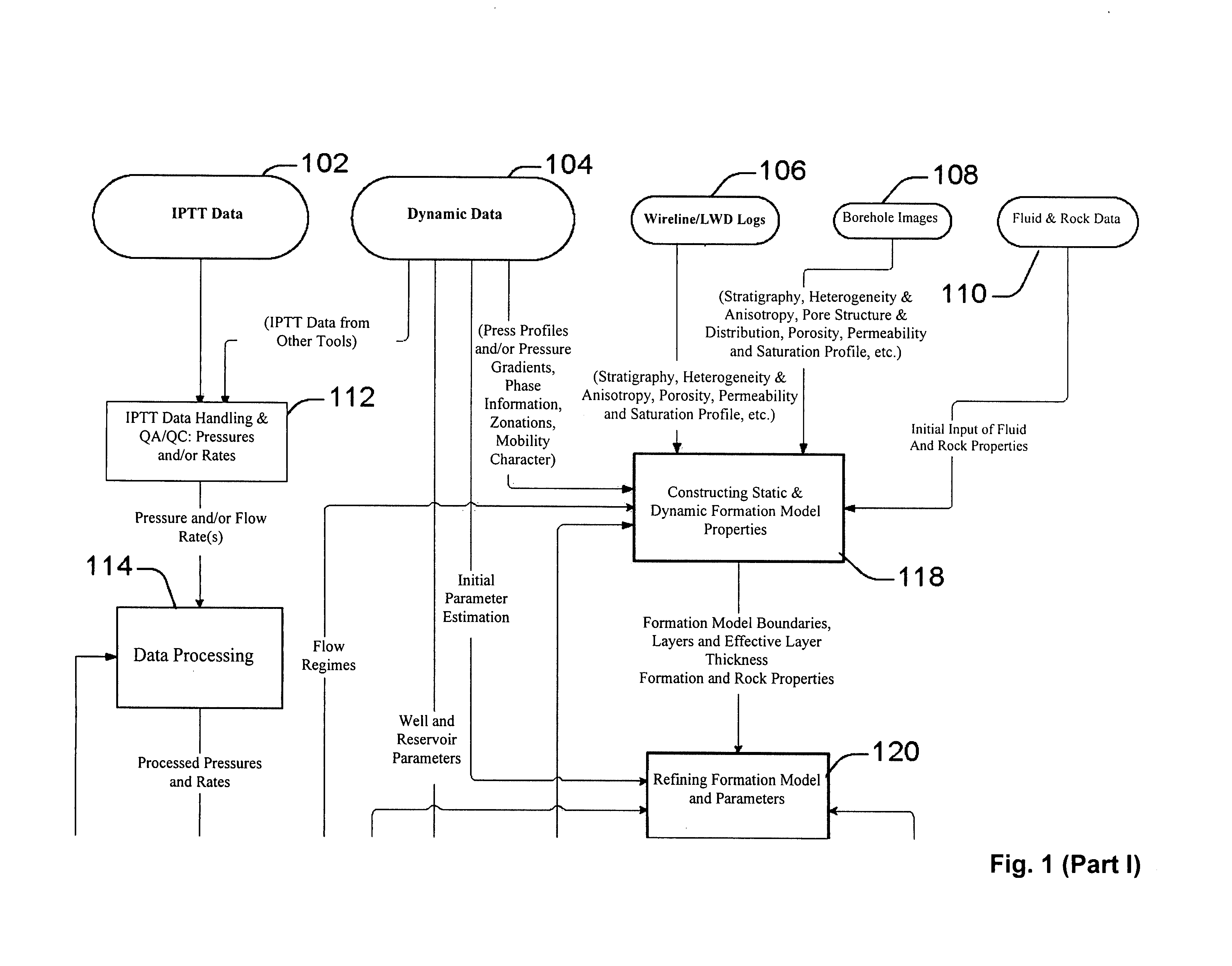
System and methods of characterizing a hydrocarbon reservoir
ActiveUS20060241867A1Facilitating in performing data processing operationEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisCompressibilityWork flow
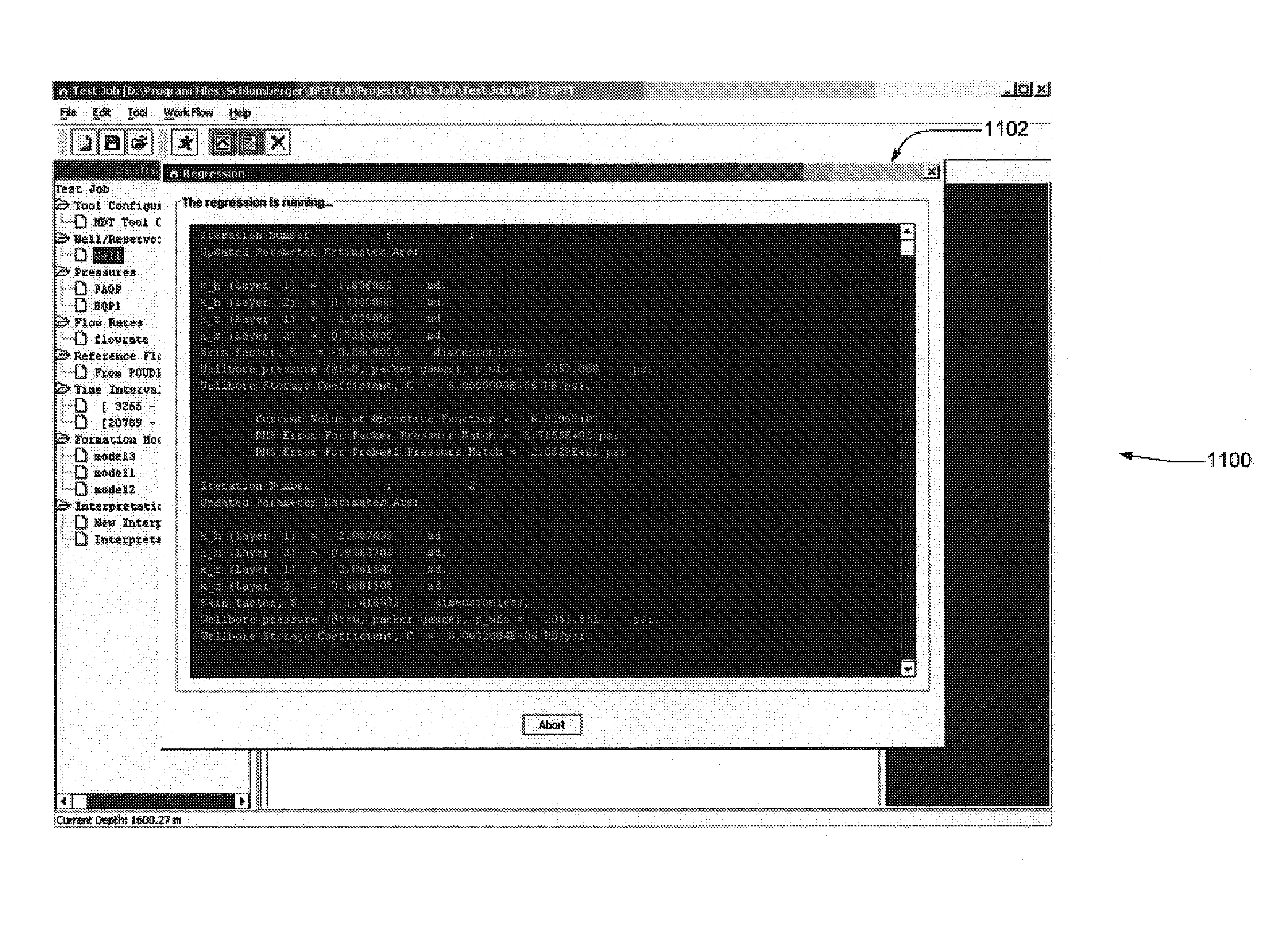
A technique is described for interpretation of IPTT tests. In one implementation, the technique may be configured or designed to standardize the complete interpretation procedure of IPTT in a heterogeneous reservoir, using if available, modern wireline logs (such as, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging), dynamic data from wireline formation testers and / or any other relevant information (such as, for example, geological description, core data and local knowledge) as constraints on the interpretation. Additionally, an iterative method may be used to define formation layering. An advanced regression technology may also be used to obtain optimized horizontal and vertical permeabilities of reservoir layers. Further a graphical user interface (GUI) based IPTT workflow technique of the present invention provides an integrated user-friendly interpretation platform for analyzing formation testing pressures and flow rate measurements in order to estimate the values and associated uncertainties of local characteristics of a hydrocarbon reservoir such as, for example, local permeability, local reservoir pressure, local compressibility, etc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
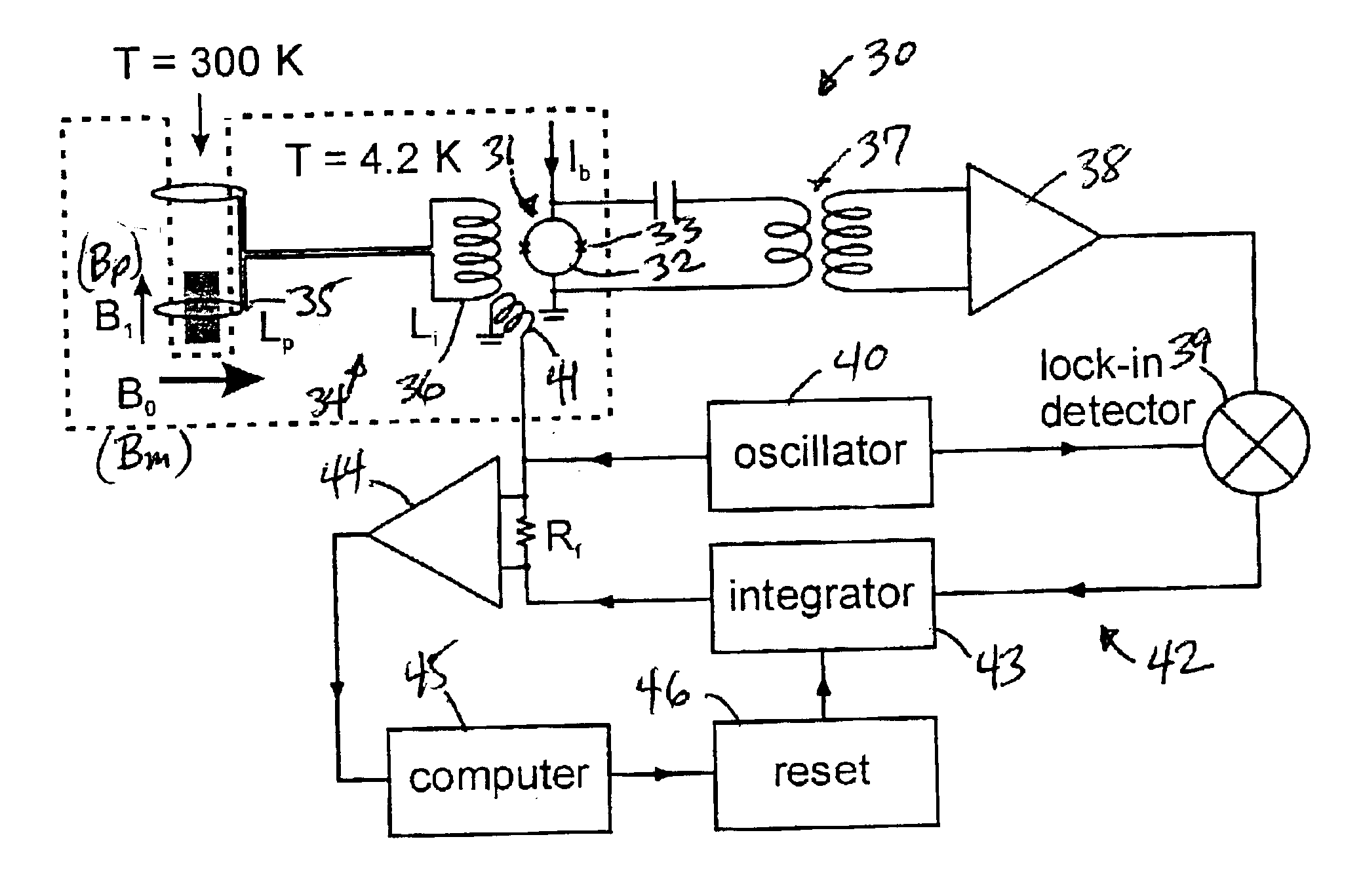
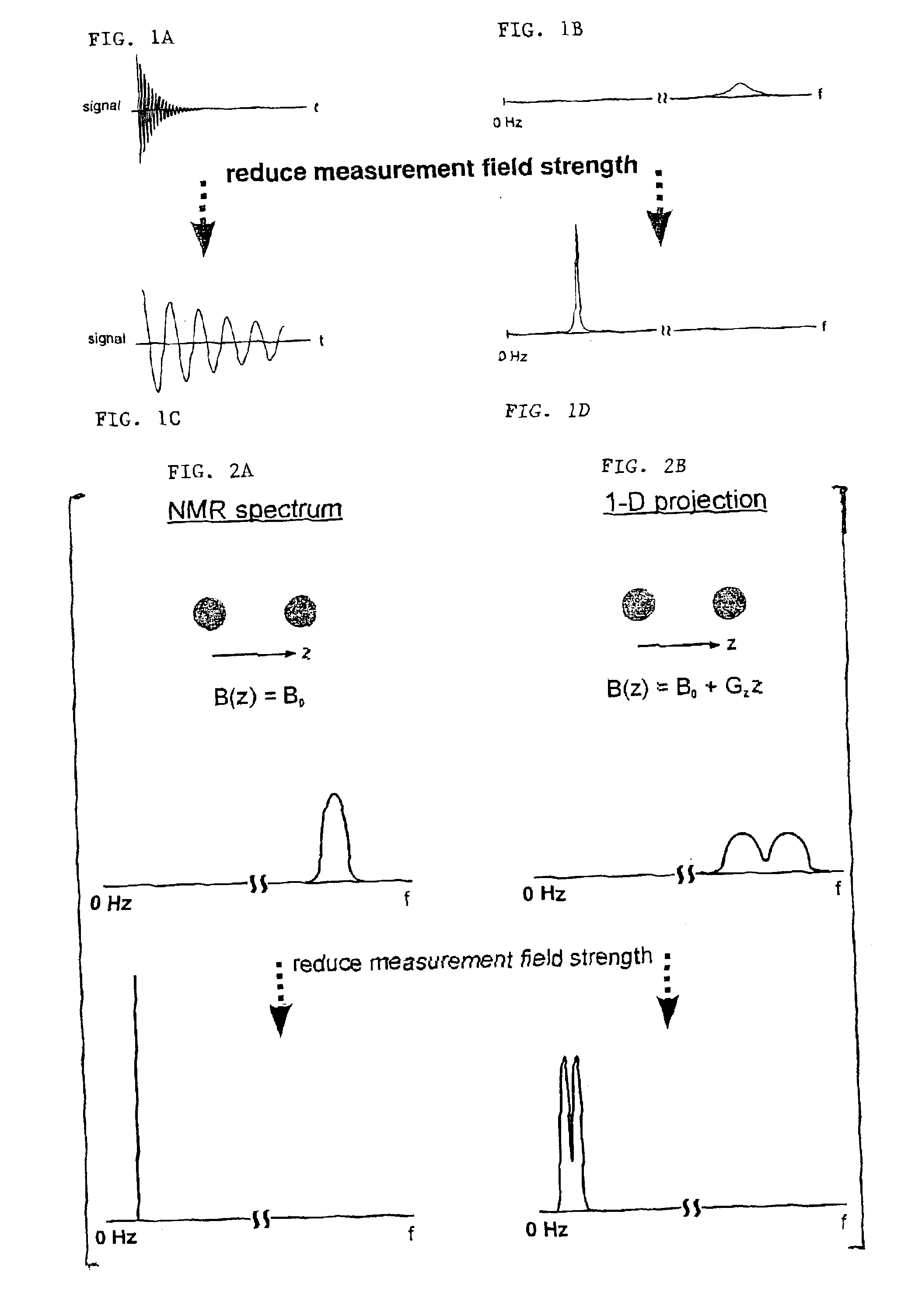
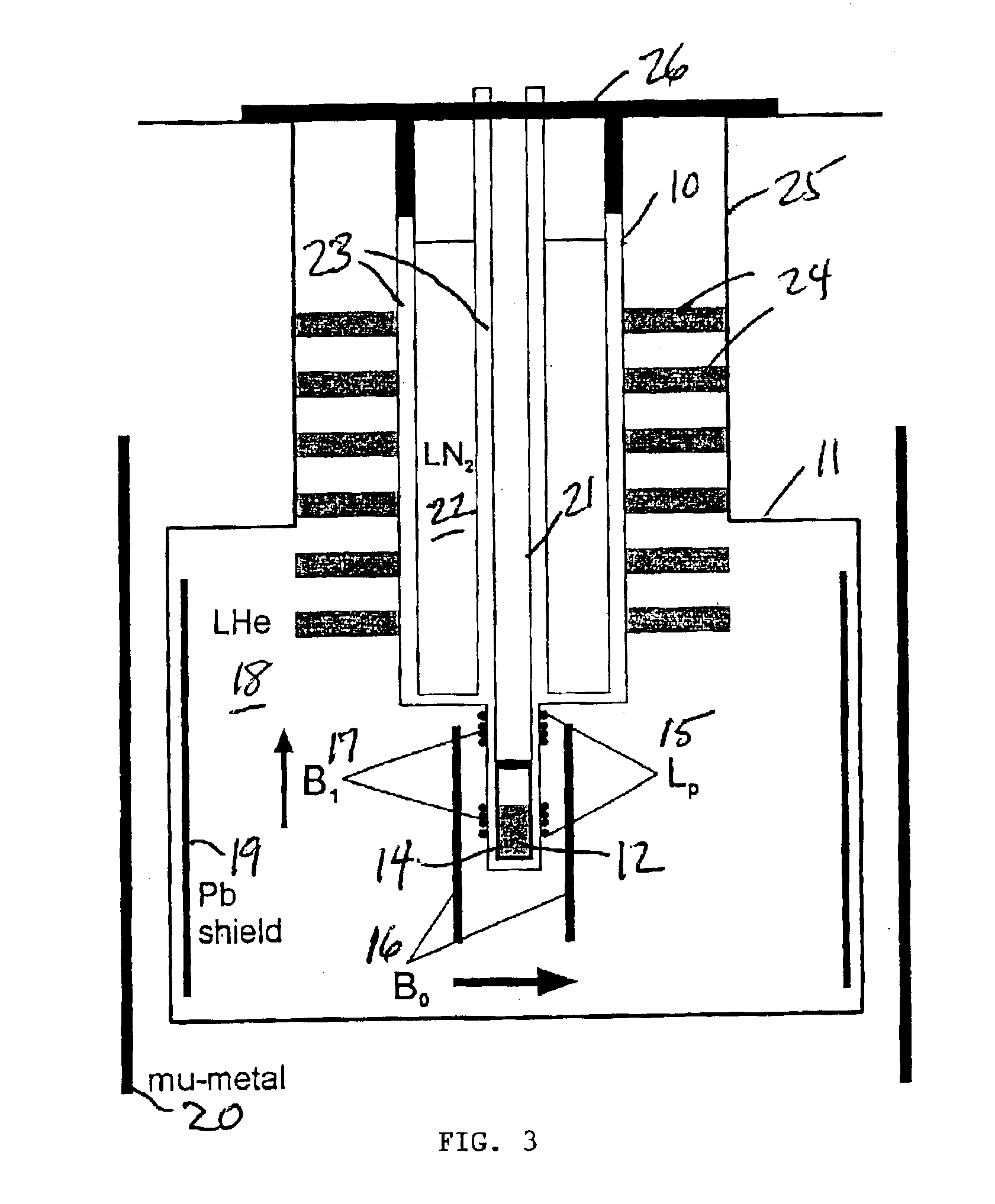
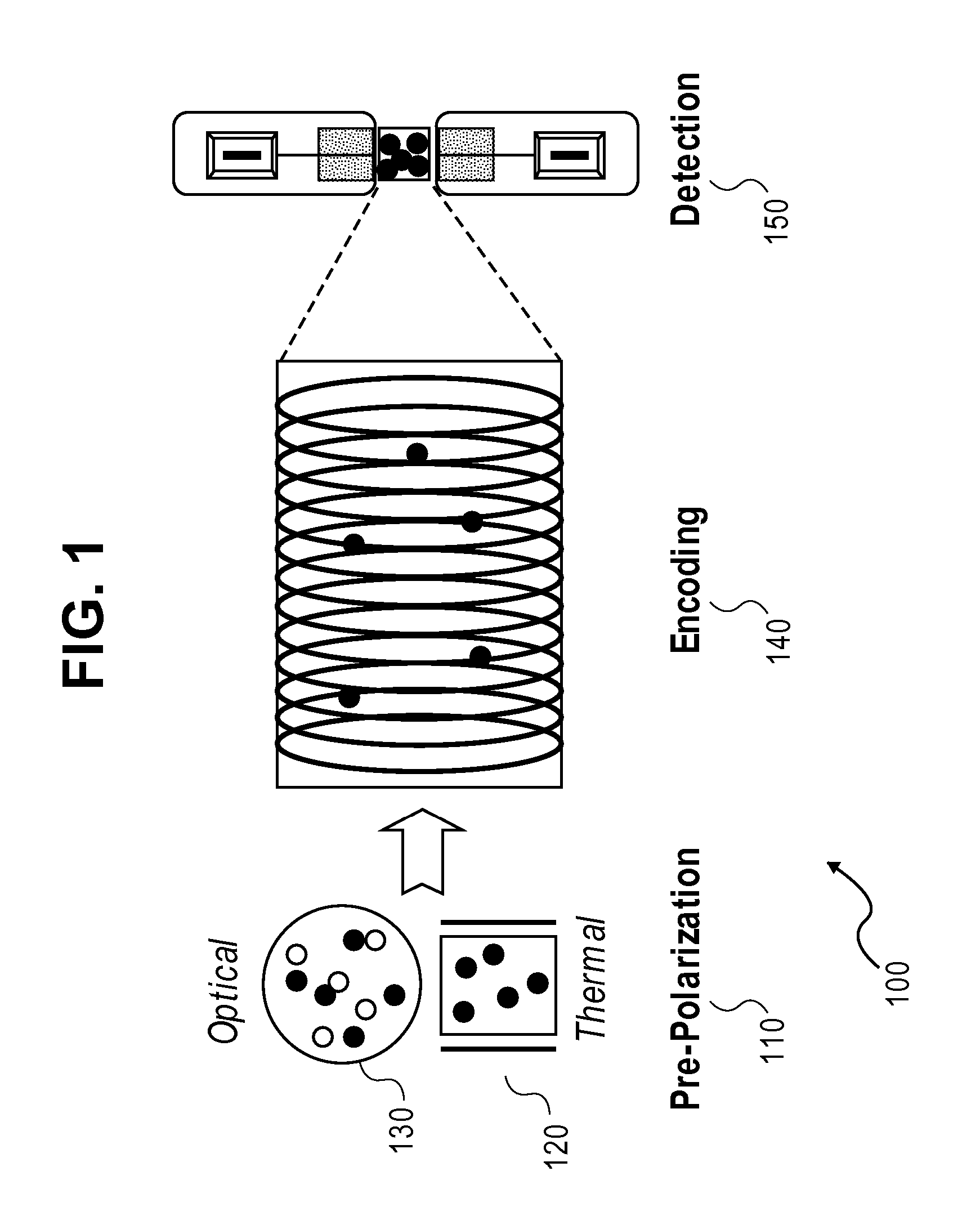
SQUID detected NMR and MRI at ultralow fields
InactiveUS6885192B2Accurate couplingReduce signal bandwidthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSignal-to-noise ratio
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signals are detected in microtesla fields. Prepolarization in millitesla fields is followed by detection with an untuned de superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer. Because the sensitivity of the SQUID is frequency independent, both signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and spectral resolution are enhanced by detecting the NMR signal in extremely low magnetic fields, where the NMR lines become very narrow even for grossly inhomogeneous measurement fields. MRI in ultralow magnetic field is based on the NMR at ultralow fields. Gradient magnetic fields are applied, and images are constructed from the detected NMR signals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of manufacture and the use of a functional proppant for determination of subterranean fracture geometries
ActiveUS8168570B2Accurate imagingPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial nanotechnologyGeophoneElectricity
Proppants having added functional properties are provided, as are methods that use the proppants to track and trace the characteristics of a fracture in a geologic formation. Information obtained by the methods can be used to design a fracturing job, to increase conductivity in the fracture, and to enhance oil and gas recovery from the geologic formation. The functionalized proppants can be detected by a variety of methods utilizing, for example, an airborne magnetometer survey, ground penetrating radar, a high resolution accelerometer, a geophone, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultra-sound, impedance measurements, piezoelectric activity, radioactivity, and the like. Methods of mapping a subterranean formation are also provided and use the functionalized proppants to detect characteristics of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Apparatus and method for noninvasive monitoring of analytes in body fluids
InactiveUS7214190B1ModificationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIntravenous devicesMedication infusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Noninvasive in vivo real time analyte measurement uses a multitude of sensors binding reversibly to the analyte whereby the response of the sensors to a noninvasive stimulus is altered by their bound versus unbound state. The stimulus and responses are electromagnetic, magnetic or any other suitable forms. The sensors are bound to a blood component providing transport through the body fluids and sensor elimination. A sensor is constructed from proteins or as a nanodevice. A noninvasive device generates the stimulus, senses the responses, determines the measurement, and controls a medication infusion pump. A non-contact device is used for population screening, and one form of such a device is a nuclear magnetic resonance imager. Measurement in fluids other than blood uses a blood component flowing out of blood and into the desired fluid.
Owner:WILSON KITCHENER CLARK
Multiply-substituted fullerenes
InactiveUS6399785B1Generate efficientlyLow costSilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceCombinatorial synthesis
The invention is directed to multiply-substituted fullerene derivatives of novel configurations, and methods for their preparation and use. The methods involve the combinatorial synthesis of a library of fullerene derivatives and comprises the steps of forming a mixture of fullerene derivatives by reacting the Cn fullerene with two or more reactive precursor compounds, and removing the unreacted compounds to yield the fullerene derivatives having the desired activity. Methods for the identification and screening of a combinatorial library of fullerenes by 3He-nuclear magnetic resonance and electrospray mass spectrometry to define members with the optimal desired activity are also provided.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS20070205767A1Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSingle polarizationGradiometer
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) fingerprinting
ActiveUS20120235678A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
Apparatus, methods, and other embodiments associated with NMR fingerprinting are described. One example NMR apparatus includes an NMR logic configured to repetitively and variably sample a (k, t, E) space associated with an object to acquire a set of NMR signals. Members of the set of NMR signals are associated with different points in the (k, t, E) space. Sampling is performed with t and / or E varying in a non-constant way. The varying parameters may include flip angle, echo time, RF amplitude, and other parameters. The NMR apparatus may also include a signal logic configured to produce an NMR signal evolution from the NMR signals, a matching logic configured to compare a signal evolution to a known, simulated or predicted signal evolution, and a characterization logic configured to characterize a resonant species in the object as a result of the signal evolution comparisons.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
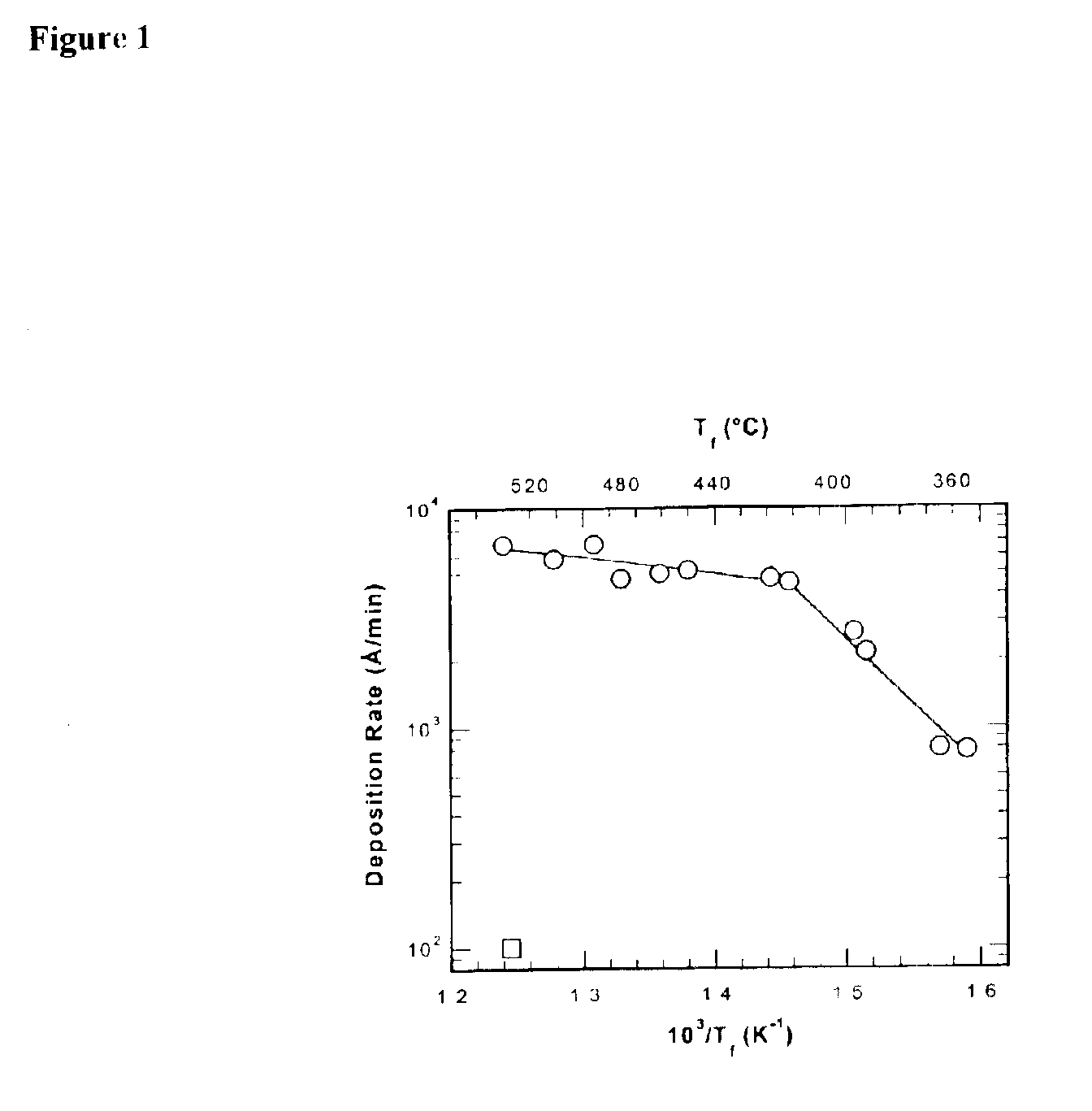
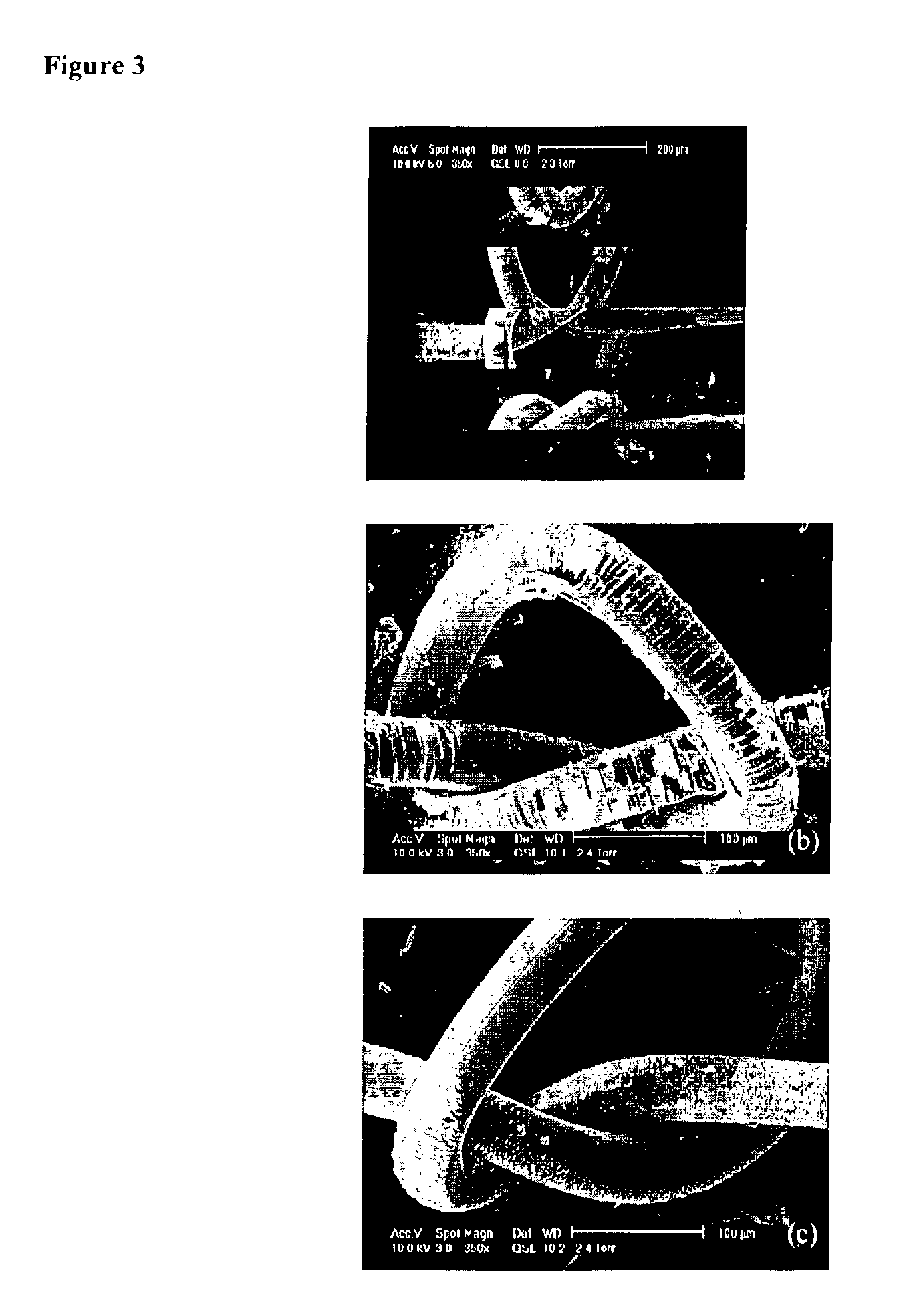
Fluorocarbon-organosilicon copolymers and coatings prepared by hot-filament chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6887578B2Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsGas phaseX-ray
Hot-filament chemical vapor deposition has been used to deposit copolymer thin films consisting of fluorocarbon and siloxane groups. The presence of covalent bonds between the fluorocarbon and organosilicon moieties in the thin film has been confirmed by Infrared, X-ray Photoelectron (XPS) and solid-state 29Si, 19F, and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The film structure consists of chains with linear and cyclic siloxane groups and CF2 groups as repeat units.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
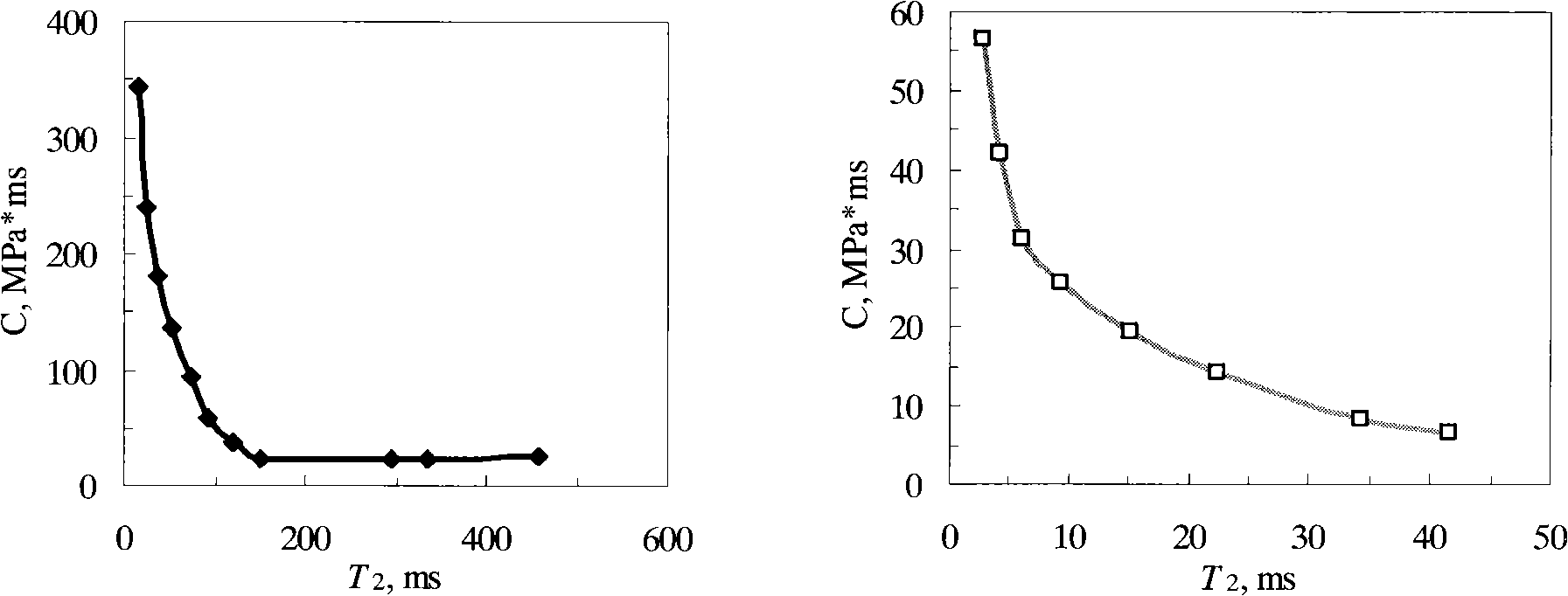
Method for continuously quantitative evaluation of pore structures of reservoir strata by utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data
ActiveCN102141637ATo achieve the purpose of classificationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingBorehole/well accessoriesThroatPressure curve
The invention relates to a method for continuously quantitative evaluation of pore structures of reservoir strata by utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data, so as to divide types of the reservoir strata. The method comprises the following steps of: classifying T2 spectrums according to parameters reflecting differences of reservoir strata, and carrying out a nonlinear calibration method on different T2 spectrums to obtain a continuously distributed capillary pressure curve of the reservoir strata; obtaining continuous reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and pore structure parameters by utilizing the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve; and evaluating the pore structure of each reservoir stratum on the basis of the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve, the features of the reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and the pore structure parameters, and dividing types of the reservoir strata. Through the adoption of the method, the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve on each depth point can be continuously obtained by utilizing the nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data, the pore structure of each reservoir stratum can be quantitatively evaluated according to the reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and the pore structure parameters of the reservoir stratum, and the types of the reservoir strata are classified, therefore, the exploitation and development efficiency of complicated oil-gas reservoir is improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
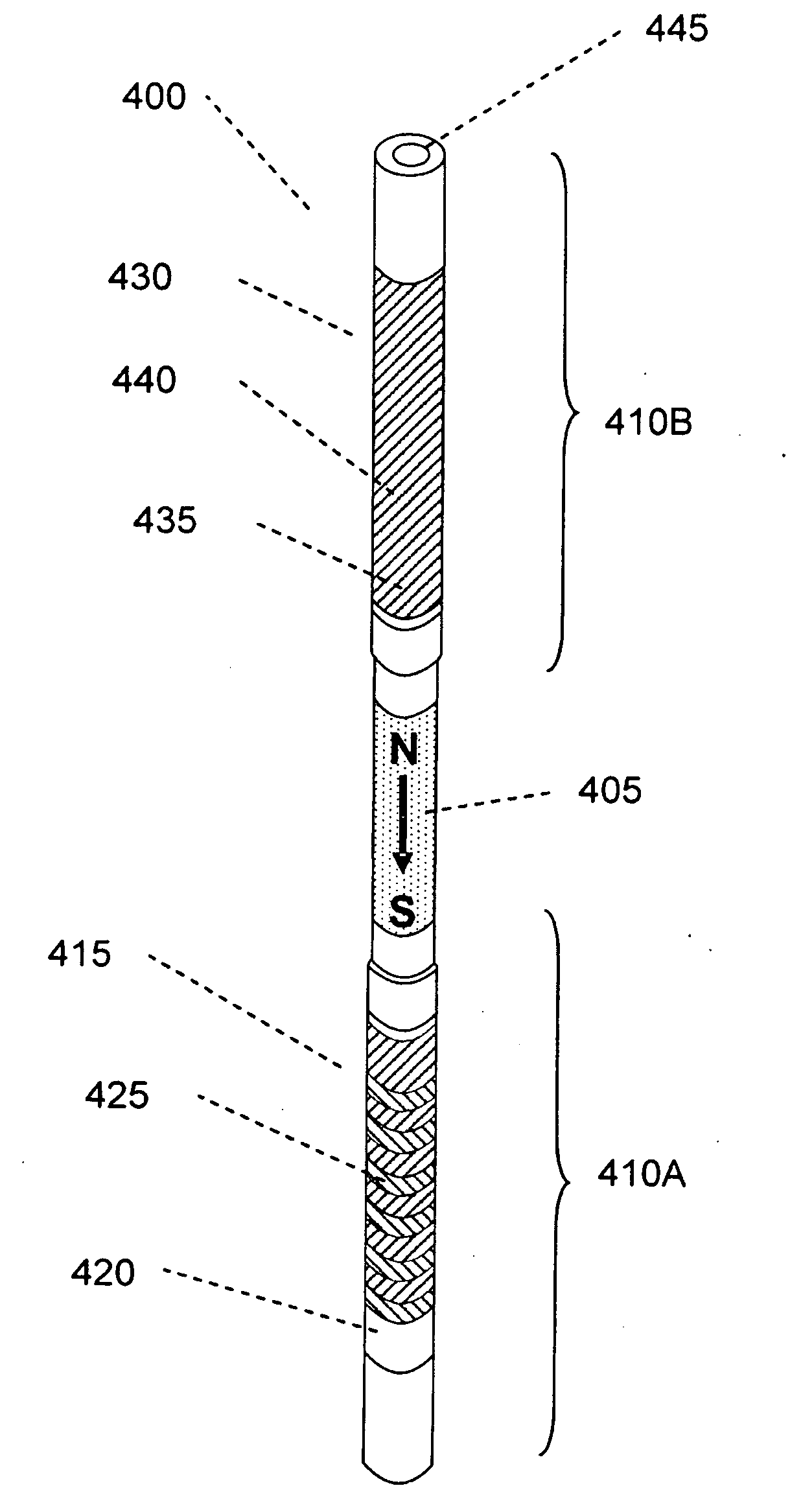
Unilateral magnet having a remote uniform field region for nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveUS6489872B1Long distanceLarge aspect ratioElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic materialsUniform fieldNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A unilateral magnet apparatus having a remote uniform field region. The apparatus' uniform remote field region is suitable for a variety of nuclear magnetic resonance applications.
Owner:NEW MEXICO RESONANCE
Method for calculating oil saturation of reservoir
ActiveCN102434152ASolve the difficulty of low accuracy in quantitative evaluation of saturationIn line with the actual lawBorehole/well accessoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
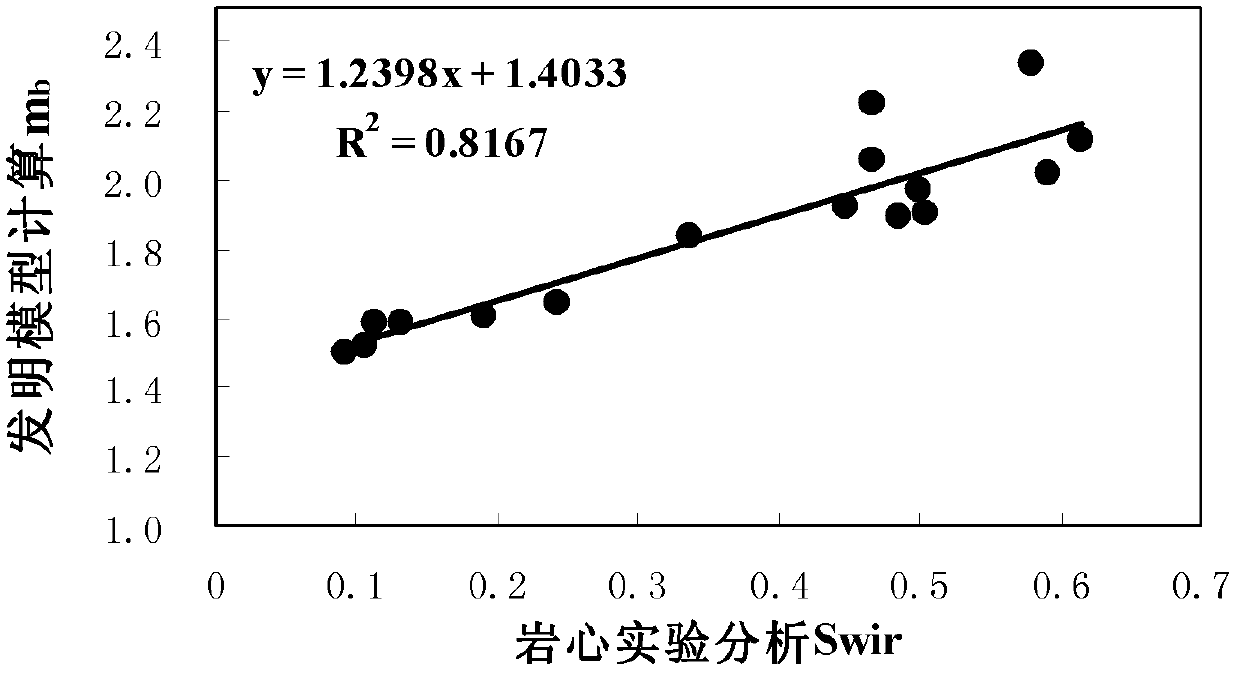
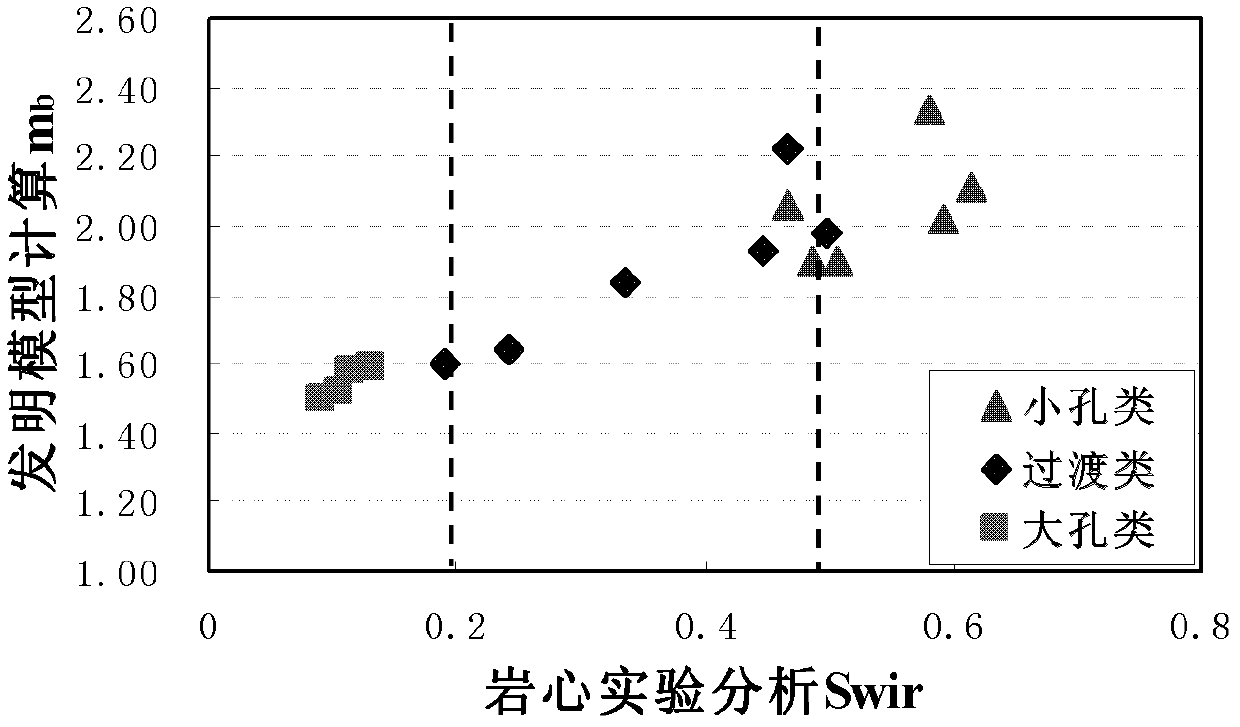
The invention discloses a method for calculating oil saturation of a reservoir. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a reservoir oil saturation model including a free fluid porosity phi f, a bound fluid porosity phi b, as well as corresponding macropore bond index mf, micropore bond index mb and micropore bond index characteristic value parameters; measuring a core porosity phi of a selected core sample; carrying out a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum experiment and an electric petrophysical experiment on the selected core sample to determine the core porosity phi and bound water saturation Swir of the selected core sample, the free fluid porosity phi f and bound fluid porosity phi b, stratum water resistivity Rw of a saturated rock sample, saturated water rock resistivity Ro of each rock sample, and resistivity Rt of each rock under different conditions of water saturation Sw; determining parameters of a reservoir oil saturation model by adopting an optimization data fitting method; establishing a relationship between the core micropore bond index mb and the bound water saturation Swir; classifying reservoir cores according to the bound water saturation; and determining a saturation index n of each type of cores by using the optimization fitting algorithm.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
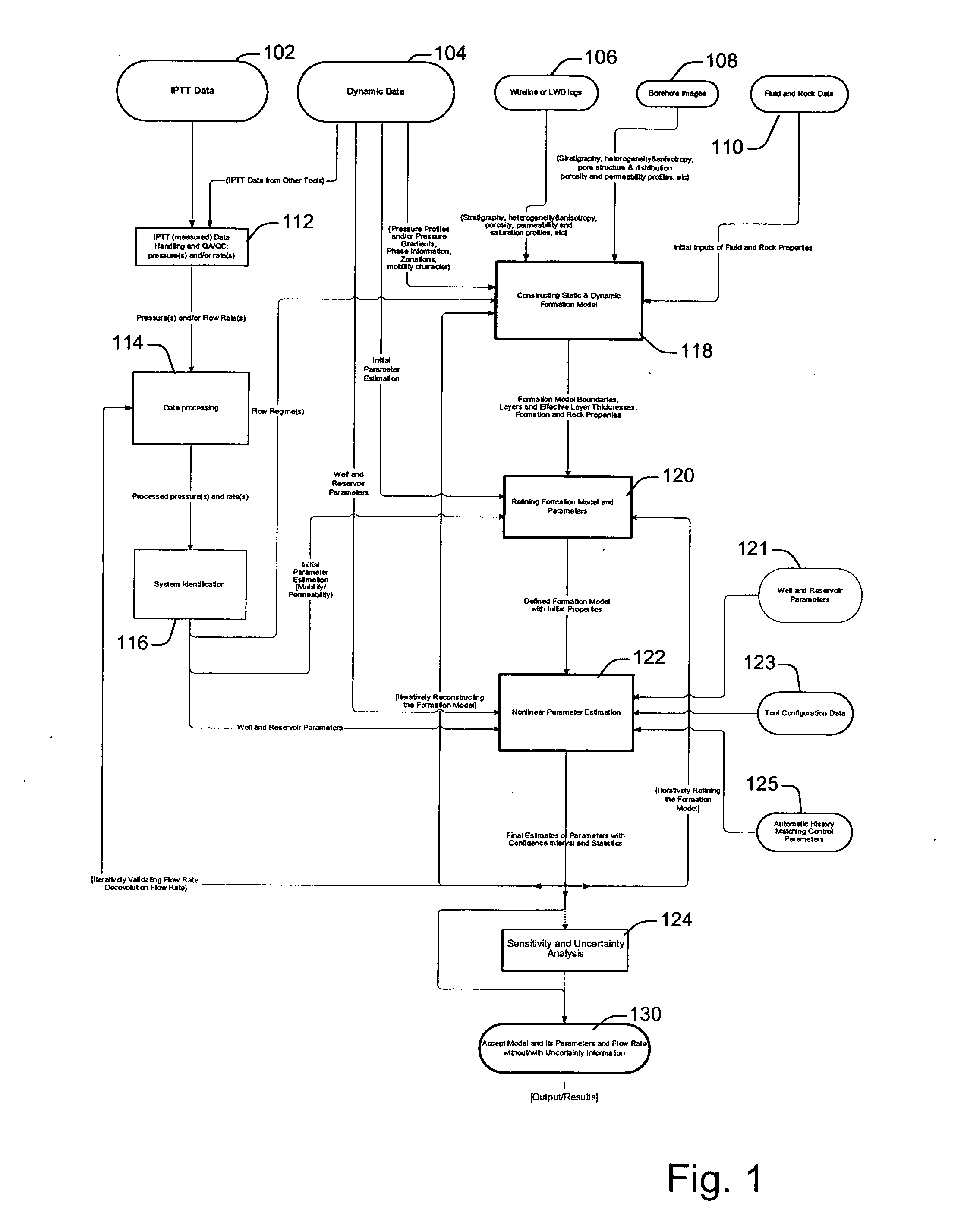
System and methods of characterizing a hydrocarbon reservoir
ActiveUS7277796B2Facilitating in performing data processing operationEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisCompressibilityIterative method
A technique is described for interpretation of IPTT tests. In one implementation, the technique may be configured or designed to standardize the complete interpretation procedure of IPTT in a heterogeneous reservoir, using if available, modern wireline logs (such as, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging), dynamic data from wireline formation testers and / or any other relevant information (such as, for example, geological description, core data and local knowledge) as constraints on the interpretation. Additionally, an iterative method may be used to define formation layering. An advanced regression technology may also be used to obtain optimized horizontal and vertical permeabilities of reservoir layers. Further a graphical user interface (GUI) based IPTT workflow technique of the present invention provides an integrated user-friendly interpretation platform for analyzing formation testing pressures and flow rate measurements in order to estimate the values and associated uncertainties of local characteristics of a hydrocarbon reservoir such as, for example, local permeability, local reservoir pressure, local compressibility, etc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
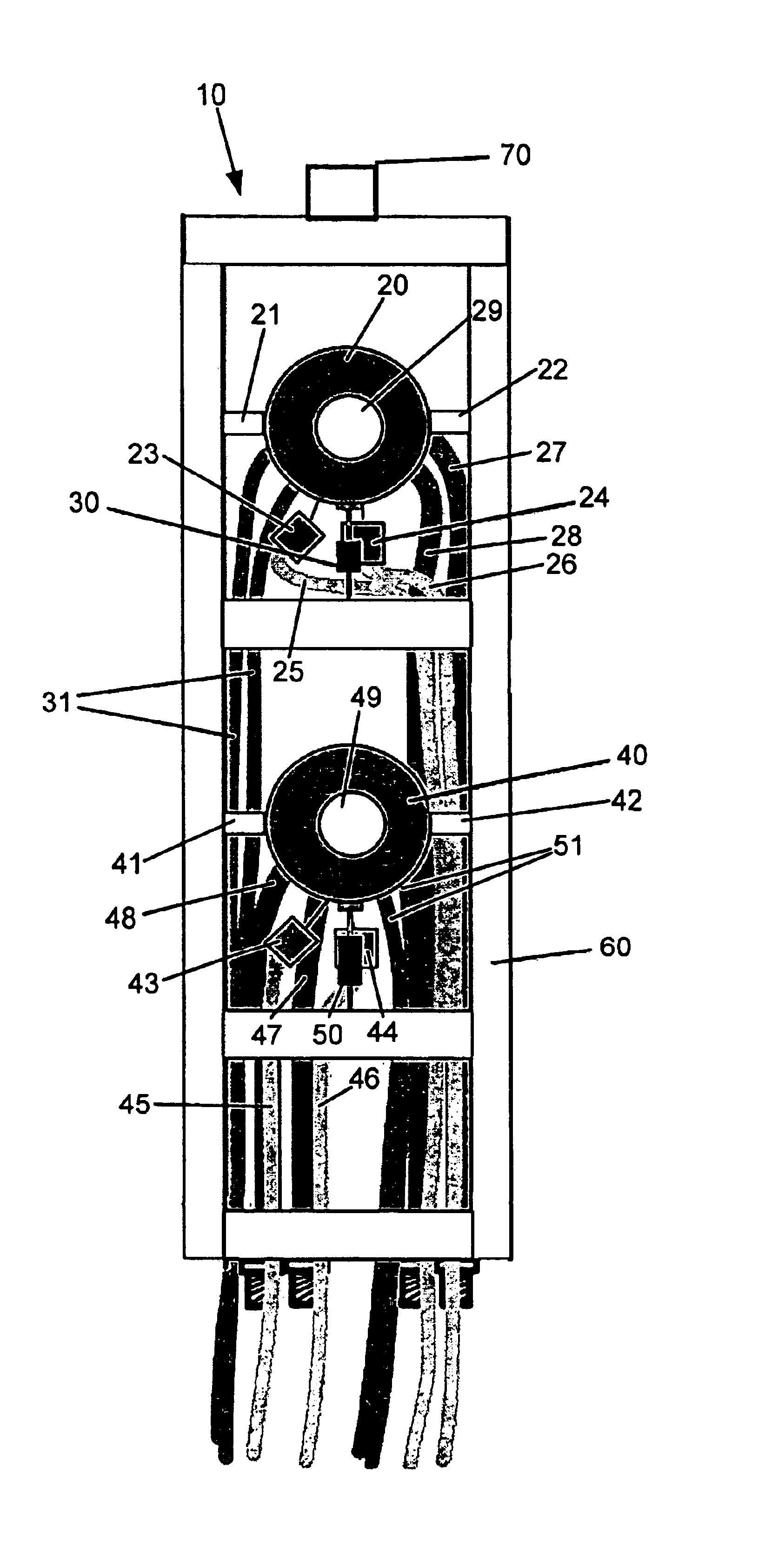
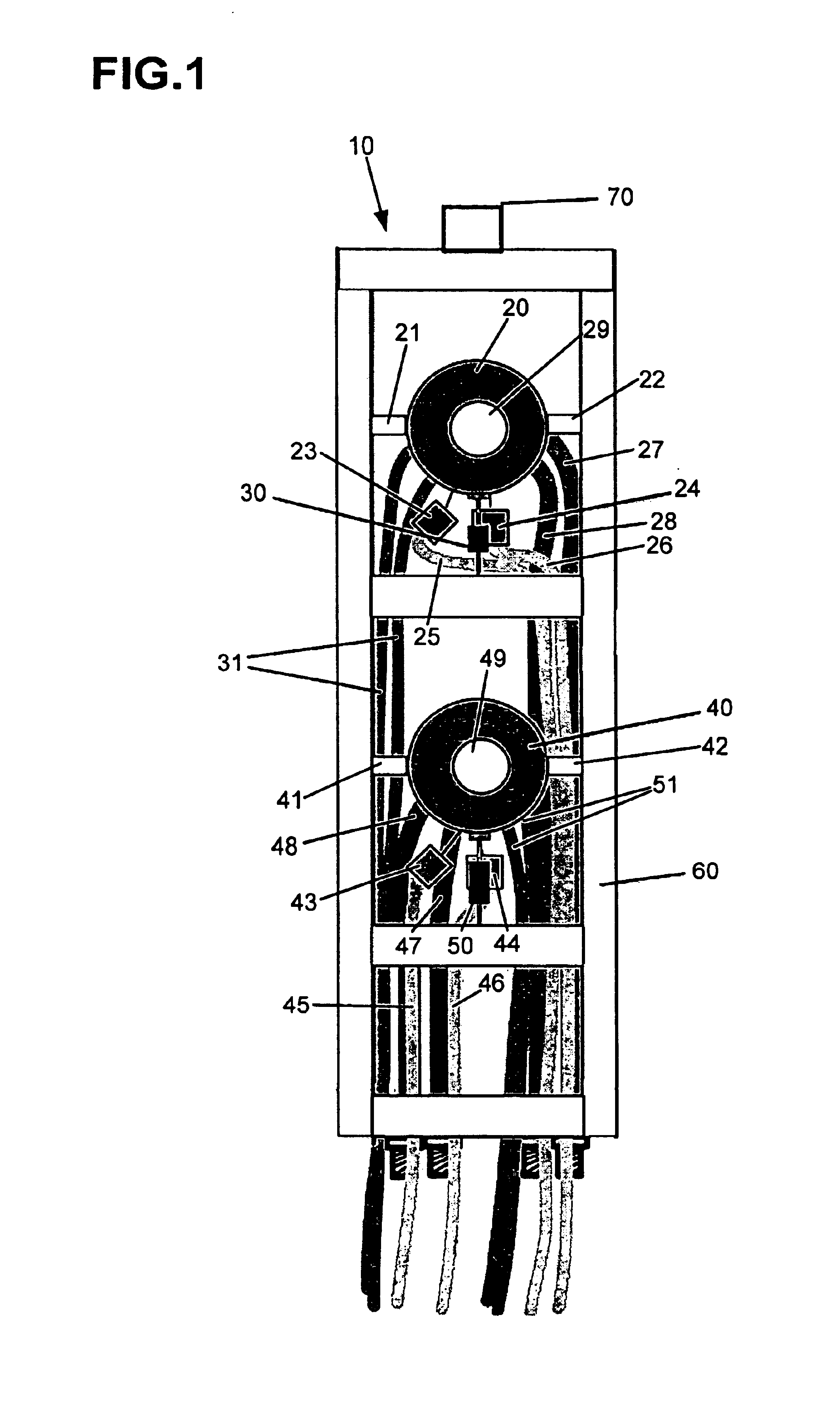
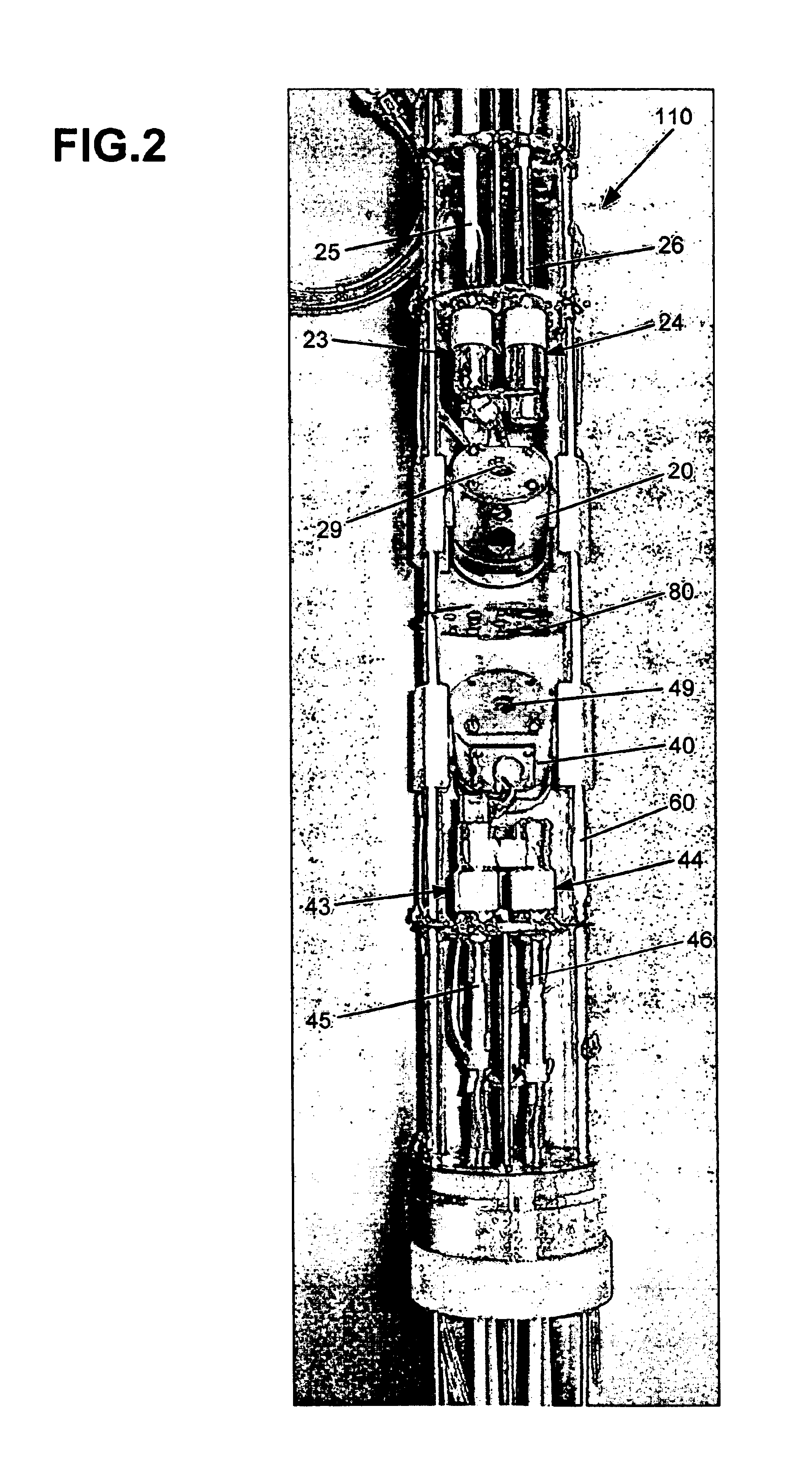
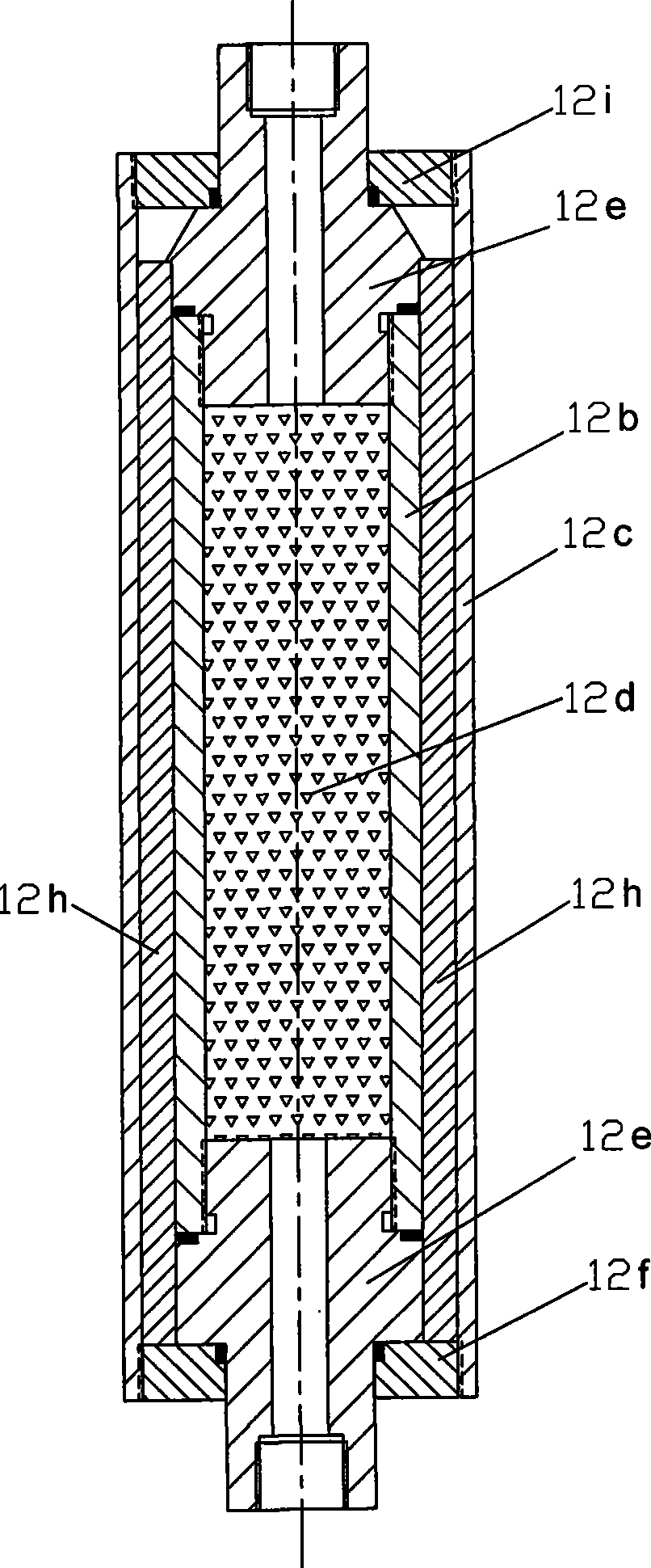
Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance probe
InactiveUS6937020B2Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetInstrumentation
A solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance probe that includes multiple sample spinning systems and detection coils is disclosed. The probe can be repositioned within the bore of the magnet to selectively maximize the throughput and sensitivity of the instrument by acquiring a spectrum from one sample at a time while at least one other sample is at or returning to an equilibrium spin state. Methods for the utilization of the probe are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Methods for analysis of spectral data and their applications osteoporosis
InactiveUS20050037515A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyBiological testingDiseaseNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
This invention pertains to chemometric methods for the analysis of chemical, biochemical, and biological data, for example, spectral data, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra, and their applications, including, e.g., classification, diagnosis, prognosis, etc., especially in the context of bone disorders, e.g., conditions associated with low bone mineral density, e.g., osteoporosis.
Owner:METABOMETRIX
Magnetic resonance apparatus and method
ActiveUS20110050223A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce and eliminate artifactMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance
An apparatus and method for performing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) on samples in metallic holders and vessels or in proximity to metallic objects is disclosed.
Owner:GREEN IMAGING TECH +1
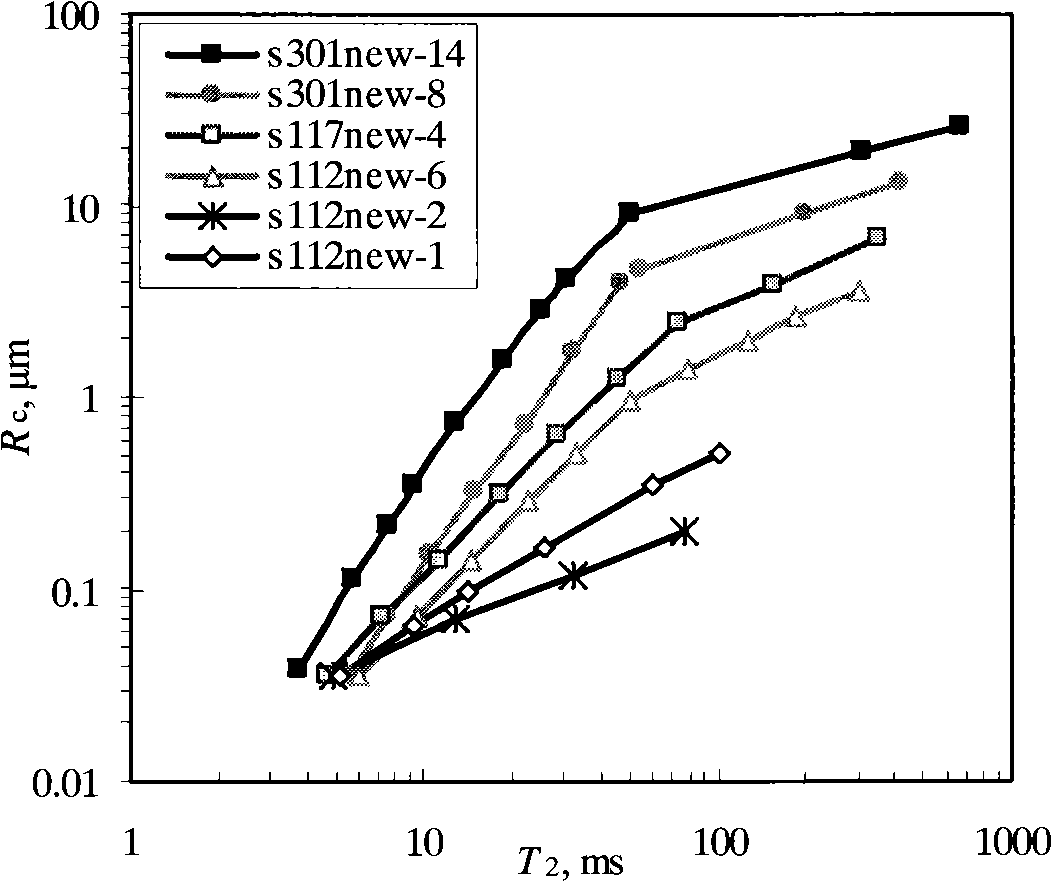
Quantitative characterization method of low penetration double-medium sandstone oil reservoir microscopic aperture structure
ActiveCN103278436AIncrease reflectionAvoid one-sidednessPermeability/surface area analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
The invention provides a quantitative characterization method of low penetration double-medium sandstone oil reservoir microscopic aperture structure, which comprises the following steps: selecting experiment samples, effectively combining various experiments, distributing samples, processing and analyzing experiment test data, combining macroscopic background and microscopic rock core, and combining static state analysis and dynamic production reality, thereby realizing quantitative characterization of ultra-low penetration double-medium sandstone oil reservoir microscopic aperture structure from qualitative analysis and semi-quantitative evaluation. The invention has the advantages that more comprehensive influence factors and micro crack, aperture throat parameter and nuclear magnetic resonance movable fluid parameter are considered, so the characterization result can better reflect change characteristics of ultra-low penetration double-medium sandstone oil reservoir microscopic aperture structure, which are consistent to the production exploitation real cases of the oil field, thereby effectively avoiding one-sidedness and limitation of single aspect evaluation result.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Carbon dioxide oil-displacing nmr imaging detection device
InactiveCN101458218AEasy to meet high pressure strength requirementsCompact designWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePorous mediumImage detection
A carbon dioxide drive nuclear magnetic resonance imaging detection device belongs to the technical field of petroleum engineering and technology. The detection device comprises: a simulation core device which is arranged in a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging device; an injection system which sequentially injects formation water, crude oil and supercritical carbon oxide into the simulation core device; a measurement and control system which is employed to control pressure and temperature of the whole system; the nuclear magnetic resonance imaging device which is employed to detect and perform quantitative analysis on an image to be tested to obtain voidage and permeability of a porous medium, and saturation seepage parameters of the supercritical carbon oxide, the formation water and the crude oil; and an output measuring system which is employed to measure volumes of the carbon dioxide gas, the formation water and the crude oil. The detection device has a design pressure of 0-40MPa and design temperature of 0-180 DEG C, and can simulate experimental studies of different displacement schemes of the supercritical CO2 under a complex petroleum reservoir condition; the simulation core device is made of a brass material, which produces no magnetism, satisfies requirements for high pressure and strength, has a compact structure, can be recycled, is conveniently operated, simple and applicable in an experimentation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Downhole high resolution NMR spectroscopy with polarization enhancement
InactiveUS7126332B2Increase amplitudeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using double resonanceSignal onProton NMR
An apparatus and method is discussed for characterizing a fluid sample downhole of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds, aromatic hydrocarbon compound, or connate mud filtrates containing carbon-13 isotopes using an enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal on a measurement-while-drilling device. To enhance the carbon-13 NMR signal these nuclei are being hyperpolarized. Either the Overhauser Effect (OE) or the Nuclear Overhauser Effect or optical pumping and the Spin Polarization Induced Nuclear Overhauser Effect (SPINOE) can serve as a mechanism for hyperpolarization of the carbon-13 nuclei.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Nuclear magnetic resonance method and logging apparatus for fluid analysis
InactiveUS6891369B2Different sensitivityReadily apparentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
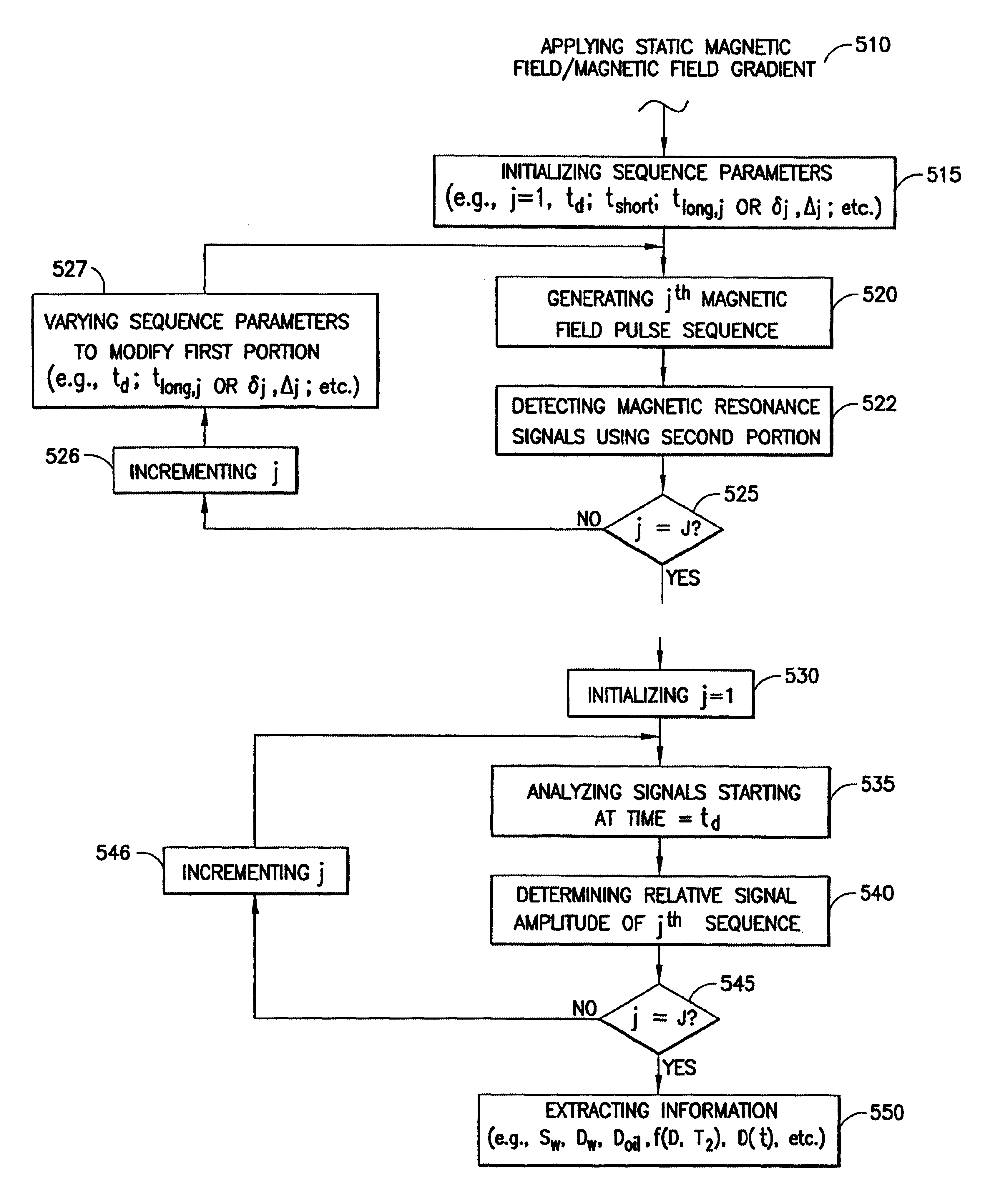
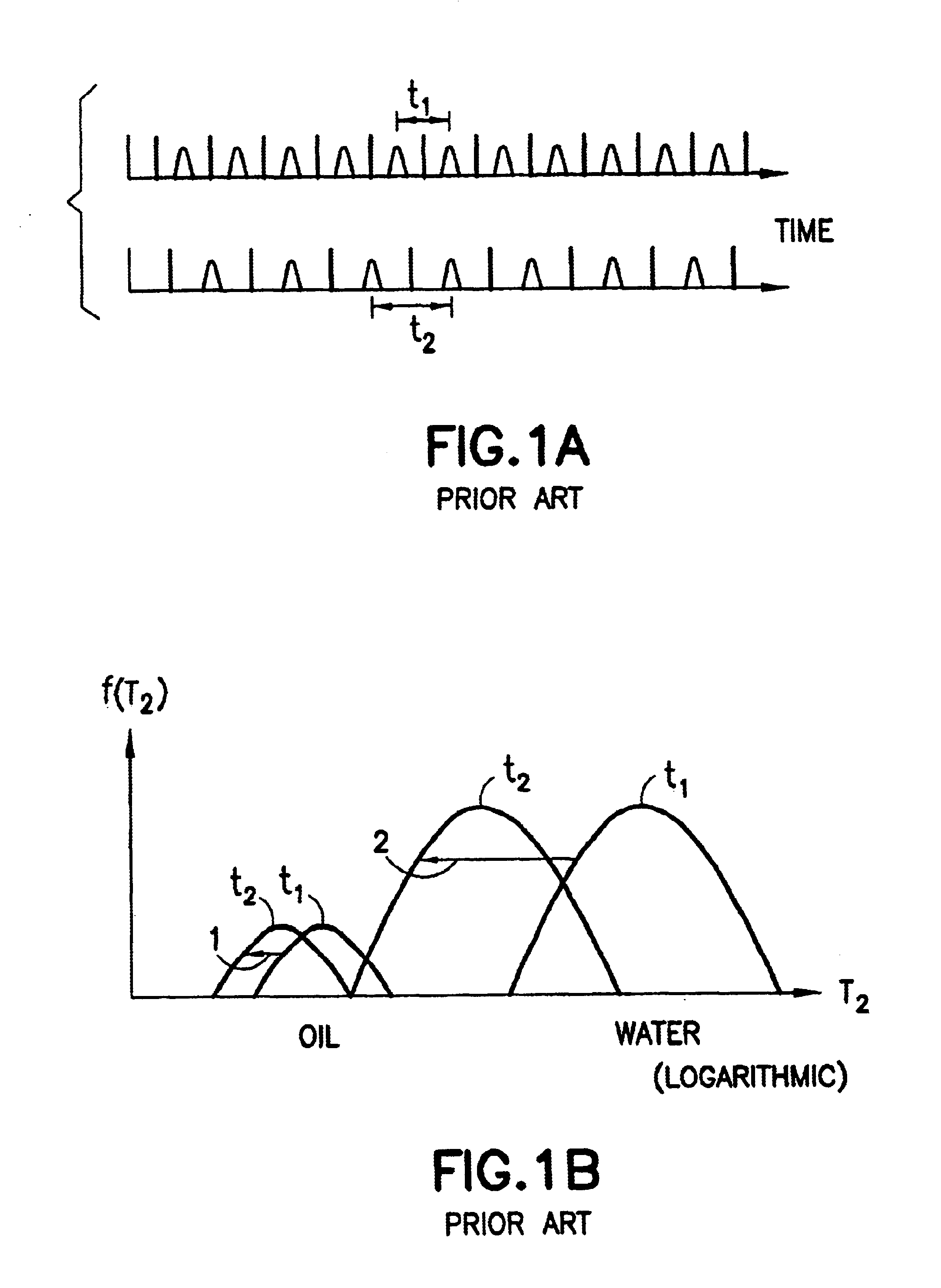
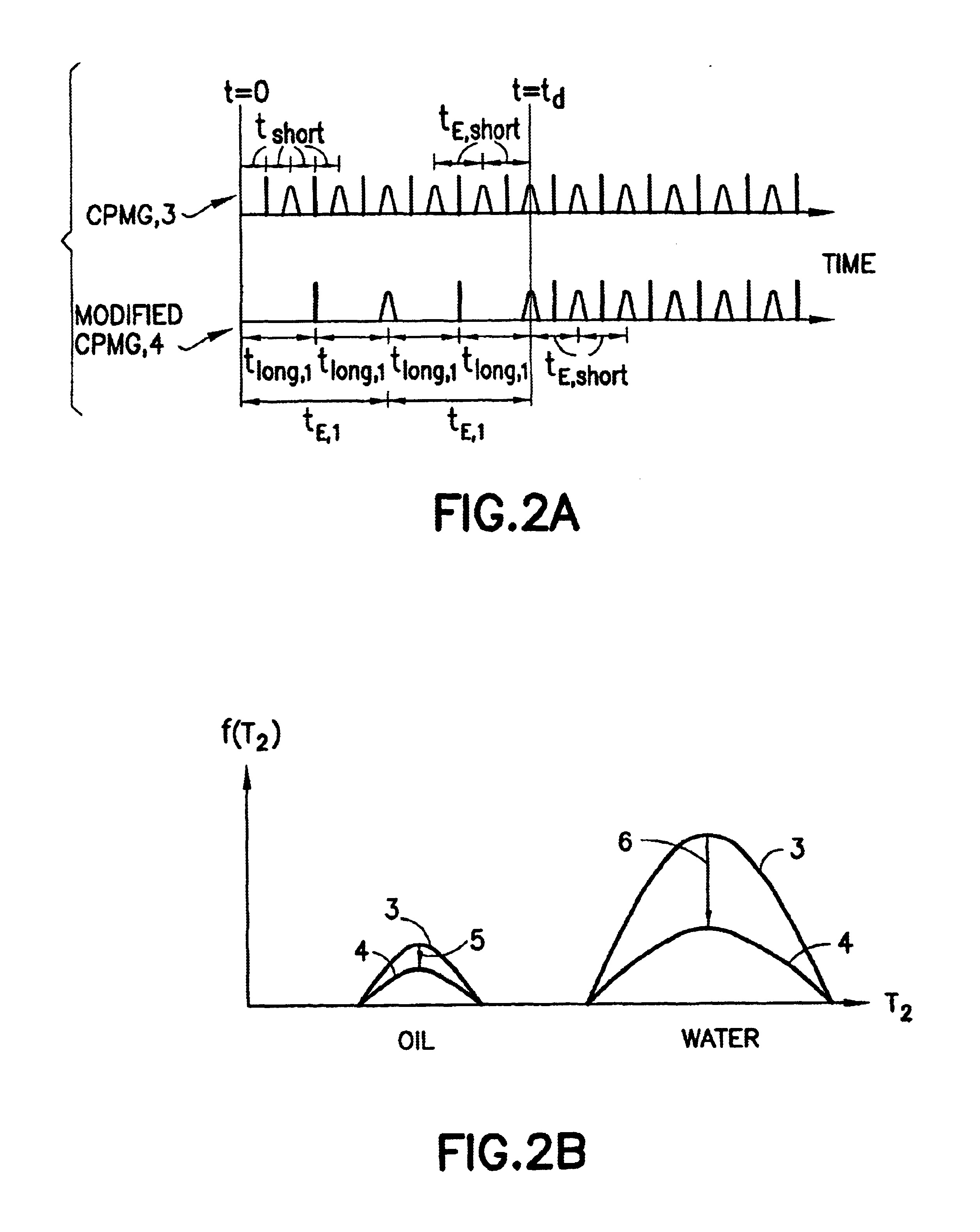
The present invention discloses a diffusion edited pulse technique that allows information about a fluid to be extracted, comprising: a) obtaining a fluid sample; b) generating a sequence of magnetic field pulses in the fluid, the sequence comprising an initial magnetic field pulse, a first portion that follows the initial magnetic field pulse, and a second portion that follows the first portion; c) detecting magnetic resonance signals using the second portion of the sequence; d) modifying the first portion of the sequence, and repeating steps (b) and (c); and e) extracting information about the fluid by determining relaxation and diffusion characteristics and their correlation based on the signals detected in steps (c) and (d). Also disclosed is a logging tool equipped with a processor to implement the diffusion edited pulse technique.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
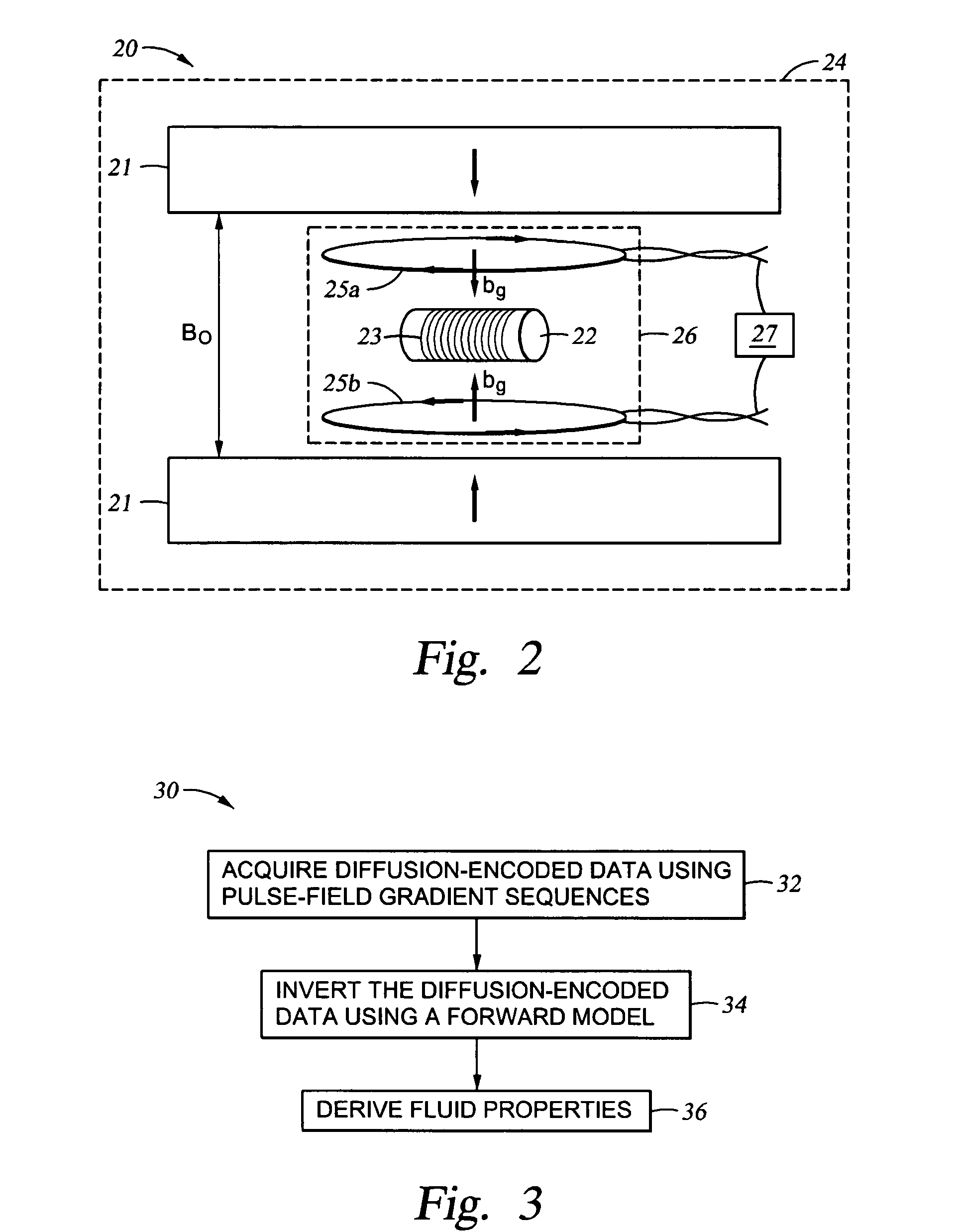
Method and apparatus for using pulsed field gradient NMR measurements to determine fluid properties in a fluid sampling well logging tool
InactiveUS20050270023A1Easy to detectRaise the ratioElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for determining a formation fluid property includes acquiring a suite of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements of a fluid sample using a pulse sequence that includes pulsed field gradient pulses for encoding diffusion information, wherein each NMR measurement in the suite is acquired with a different value in a parameter in the pulsed field gradient pulses for producing a different diffusion effect, wherein the acquiring is performed in a formation fluid sampling tool in a borehole; inverting the suite of NMR measurements to produce a distribution function that relates diffusion properties of the fluid sample with an NMR property of the fluid sample; and determining the formation fluid property from the distribution function.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
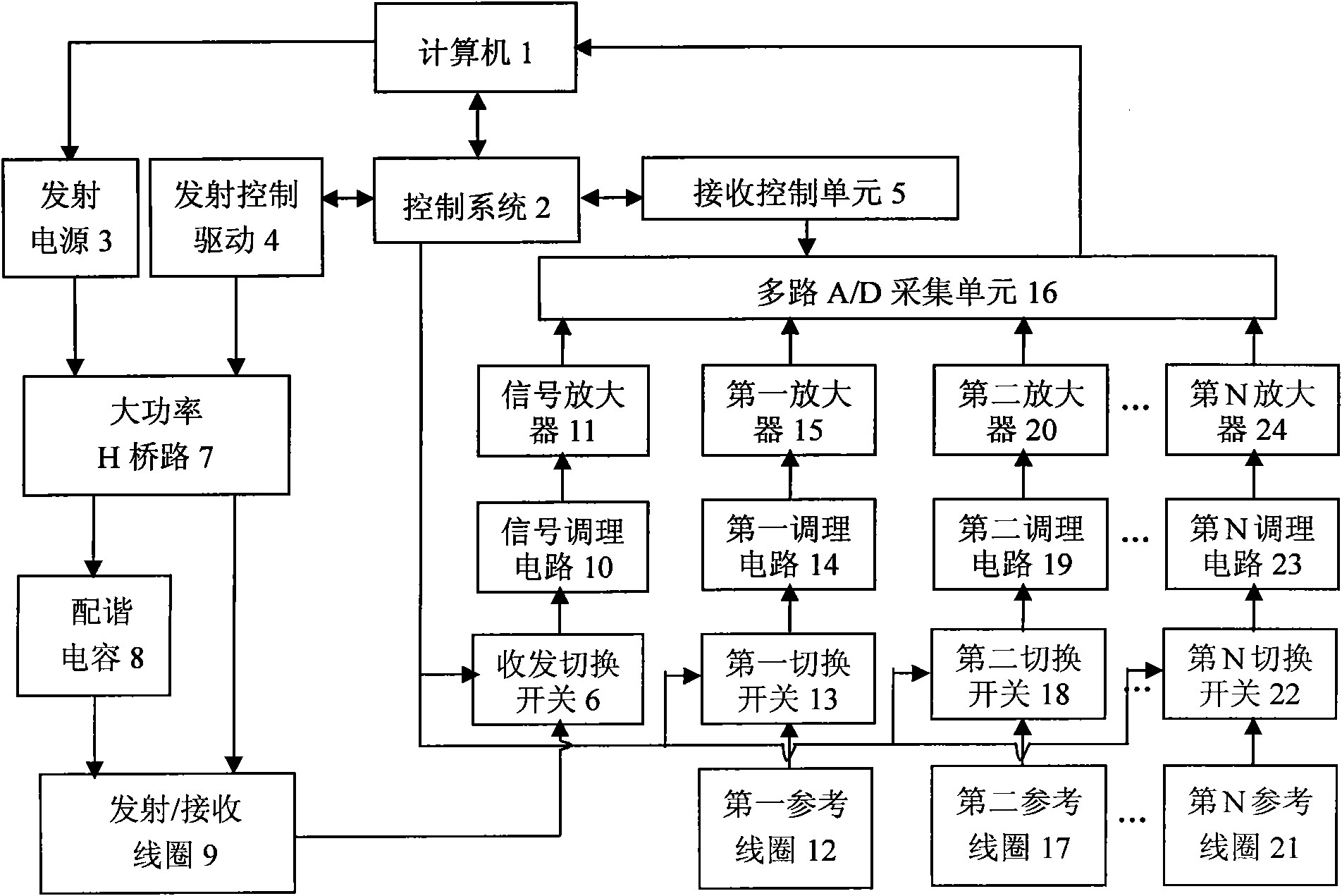
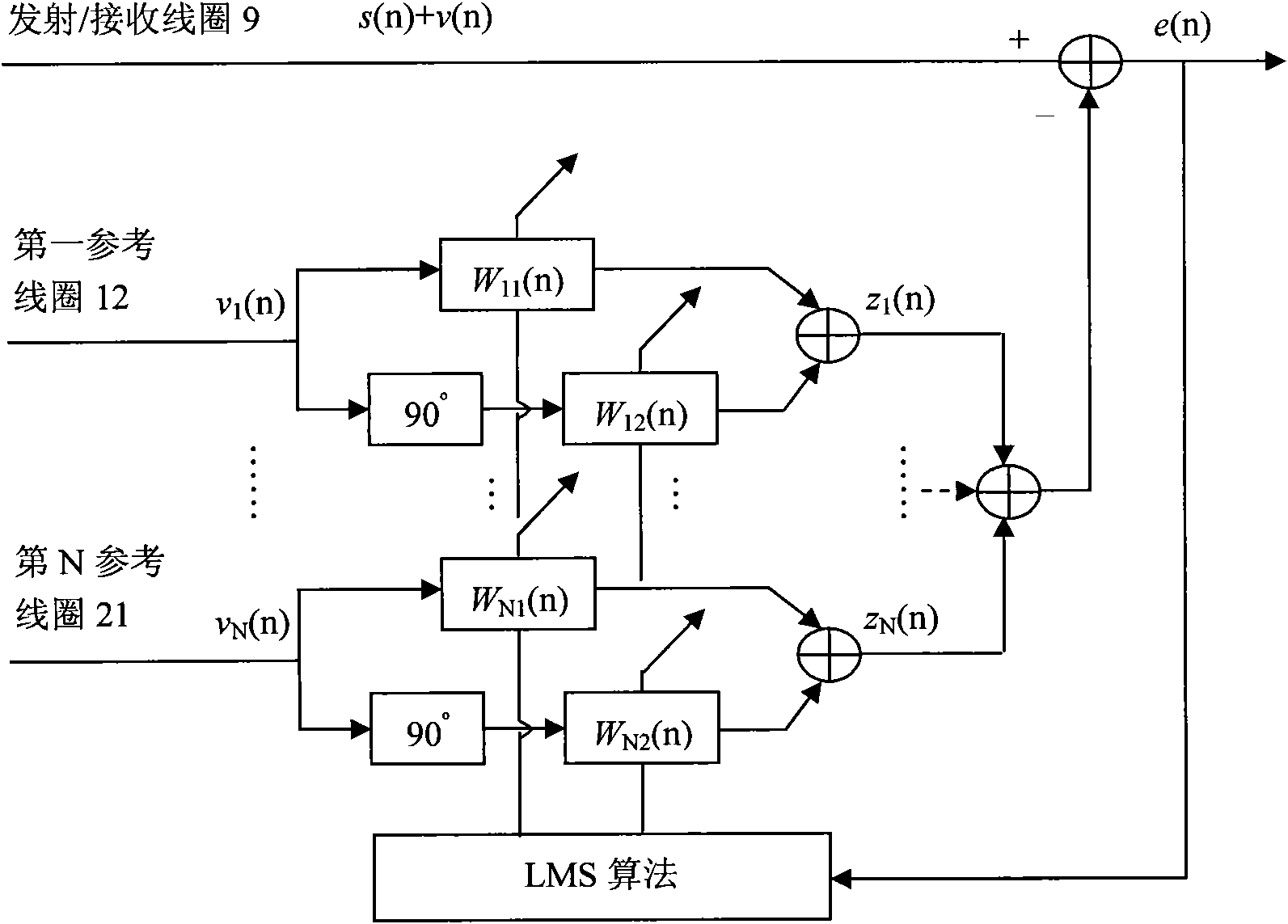
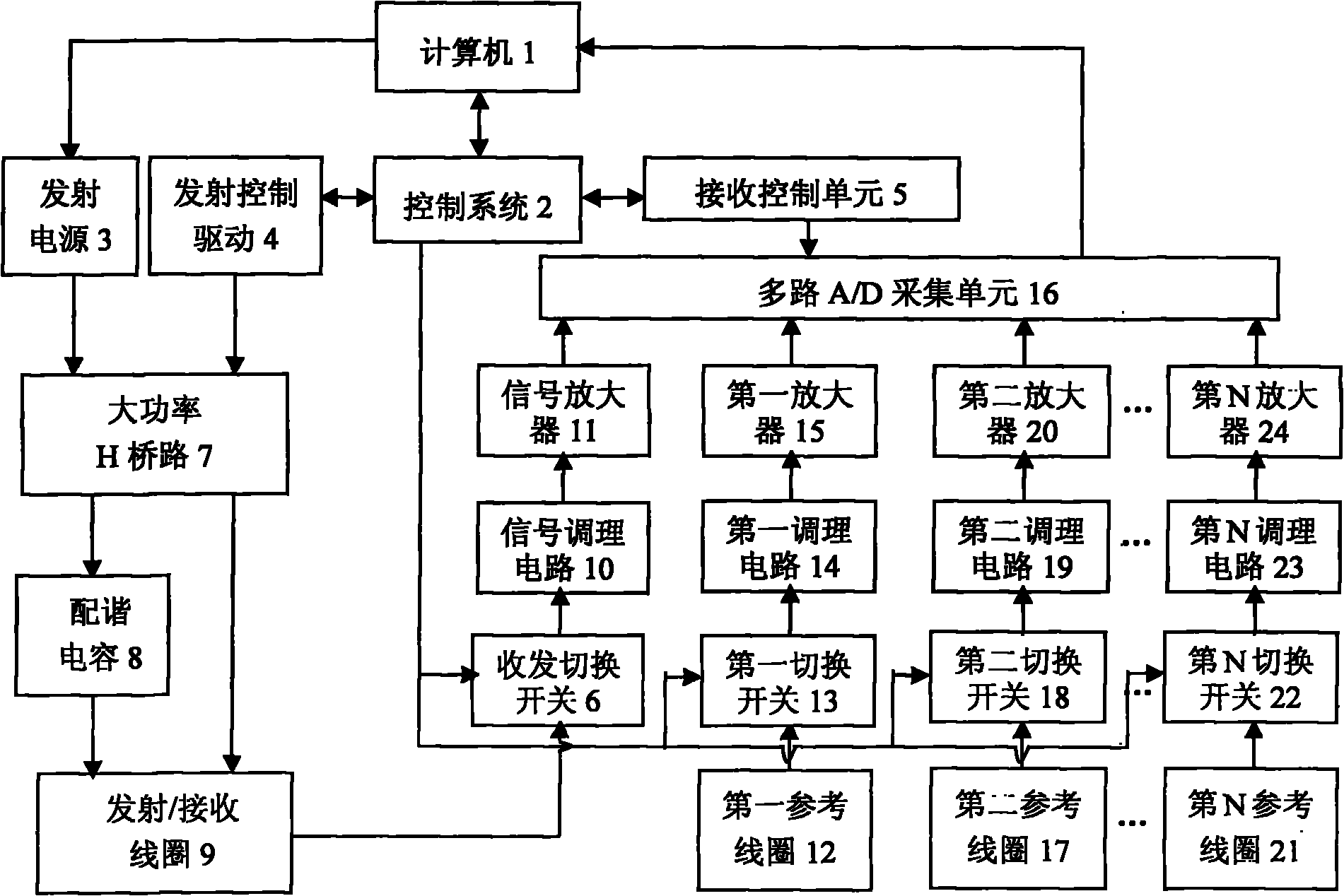
Nuclear magnetic resonance ground water detection system with reference coils and detection method
InactiveCN102053280AEfficient extractionImplement extractionWater resource assessmentDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceInterference resistance
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance ground water detection system with reference coils and a detection method. All-waveform data of nuclear magnetic resonance signals in a transmitting / receiving coil and noise signals in the reference coils are synchronously acquired through a plurality of paths of A / D acquiring units; the distribution of optimal positions and quantity of the reference coils is realized through calculating the maximum correlation of the noise signals and the nuclear magnetic resonance signals, which are acquired by the reference coils; and under the condition of unknown signal and noise statistical properties, noise in the nuclear magnetic resonance signals obtained by the transmitting / receiving coil is maximally offset by adopting a variable step adaptive algorithm, the nuclear magnetic resonance signals are extracted under the interference of multi-field source complex strong noise, thus the problems of multiple interferences of nuclear magnetic resonance detection near villages and in neighboring regions of cities and difficulty of separating multiple kinds of interference noise data are effectively solved, the interference resistance of instruments is improved, and a reliable detection device and method are provided for searching underground water near villages and in neighboring regions of cities.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
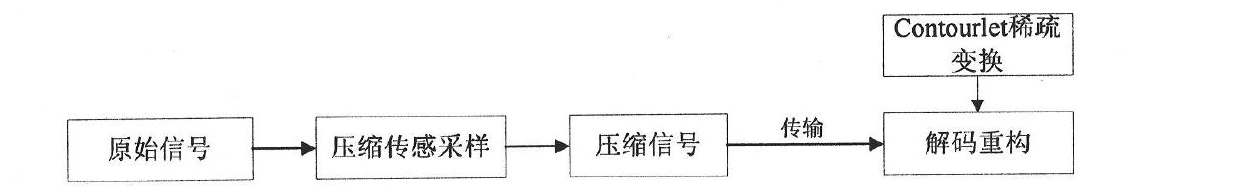
Compressed sensing theory-based reconstruction method of magnetic resonance image
InactiveCN102389309AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove visual effectsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReconstruction methodObservation matrix
The invention provides a compressed sensing theory-based reconstruction method of a magnetic resonance random sampled K space data image. The reconstruction method applies a contourlet conversion and iterative soft thresholding method to realize reconstruction of a magnetic resonance image. The method comprises the following steps: collecting K space data in a magnetic resonance image scanner according to a preset observation matrix phi to generate a measurement value, and keeping y; acquiring y from a coil of the magnetic resonance image scanner, and transmitting y to a computer; and finallyconstructing a same phi, constructing any orthogonal transformation psi, and recovering from y by adopting a compressed sensing theory-based magnetic resonance random sampled K space data image reconstruction method according to reconstruction. According to the method, scanning time is saved, quick imaging is realized, high-quality reliable image information is provided to medical nuclear magnetic resonance imaging detection, and solid theoretical and practical foundation is established for further development and large-scale popularization and application of the medical imaging detection technology.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Systems and methods for deep-looking nmr logging
ActiveUS20090072825A1Add depthAccurate estimateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic poles
An NMR logging tool for conducting NMR measurements in a plurality of sensitive volumes ranging up to a meter from the tool. The tool comprises a magnetic assembly using one or more permanent magnets and at least one pole piece for extending a magnet pole and shaping the magnetic field to simulate a magnetic monopole in a sensitive volume within the formation. Different embodiments of a segmented antenna enable directional NMR logging. The tool embodiments and methods of their use are suitable for wireline or LWD logging, and can be used for directional drilling.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Travelling-wave nuclear magnetic resonance method
InactiveUS20110115486A1Convenient verificationImprove securityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceElectromagnetic electron wave
A method for acquiring an image or spectrum of a subject or object residing within the magnetic field of a magnetic resonance apparatus, comprises the steps of:executing a predetermined pulse sequence for applying gradient magnetic fields and for coupling in electromagnetic excitation pulses to induce nuclear magnetic resonance within the subject or object;detecting an electromagnetic signal resulting from said magnetic resonance; andconstructing at least one image or magnetic resonance spectrum of said subject or object from said detected electromagnetic signal.According to the invention, said coupling in of the electromagnetic excitation pulse and / or said detecting of the electromagnetic signal are carried out substantially by means of travelling electromagnetic waves.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
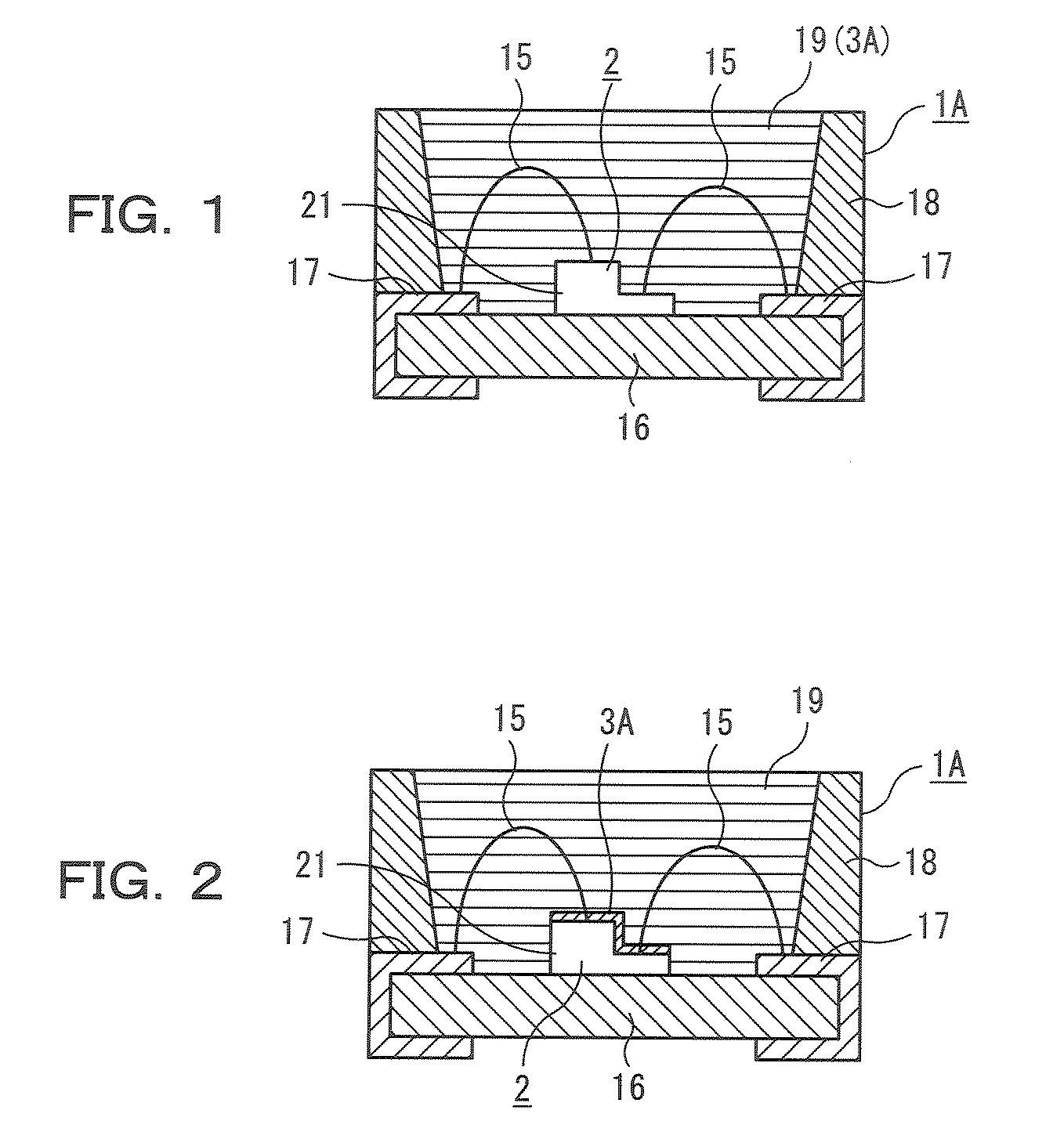
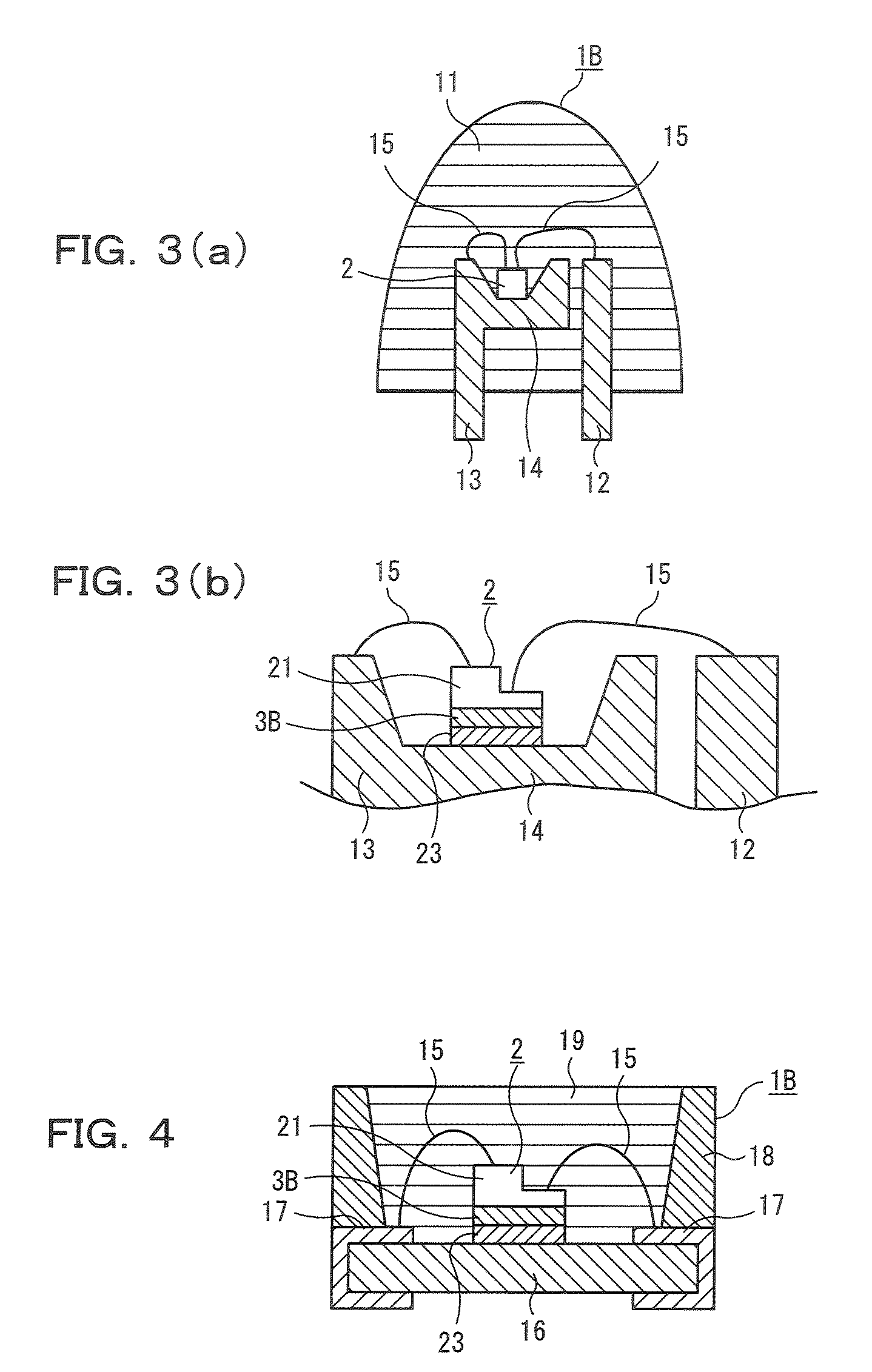
NMR probe
ActiveUS6914430B2Inhibit heat shrinkageHigh sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnet
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) probe is offered which can minimize positional shift of the detector portion caused by shrinkage of the support post due to cooling of the detector portion. The NMR probe has a vacuum-insulated container and the detector portion described above. The container has a cylindrical portion inserted in a magnet. The detector portion is made up of a detection coil and a tuning and matching circuit that are placed within the container. The detector portion is cooled by a cooling means such that NMR signals are detected with enhanced sensitivity. This probe is characterized in that the detector portion is mounted to the upper end surface or a side surface of the cylindrical portion.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com