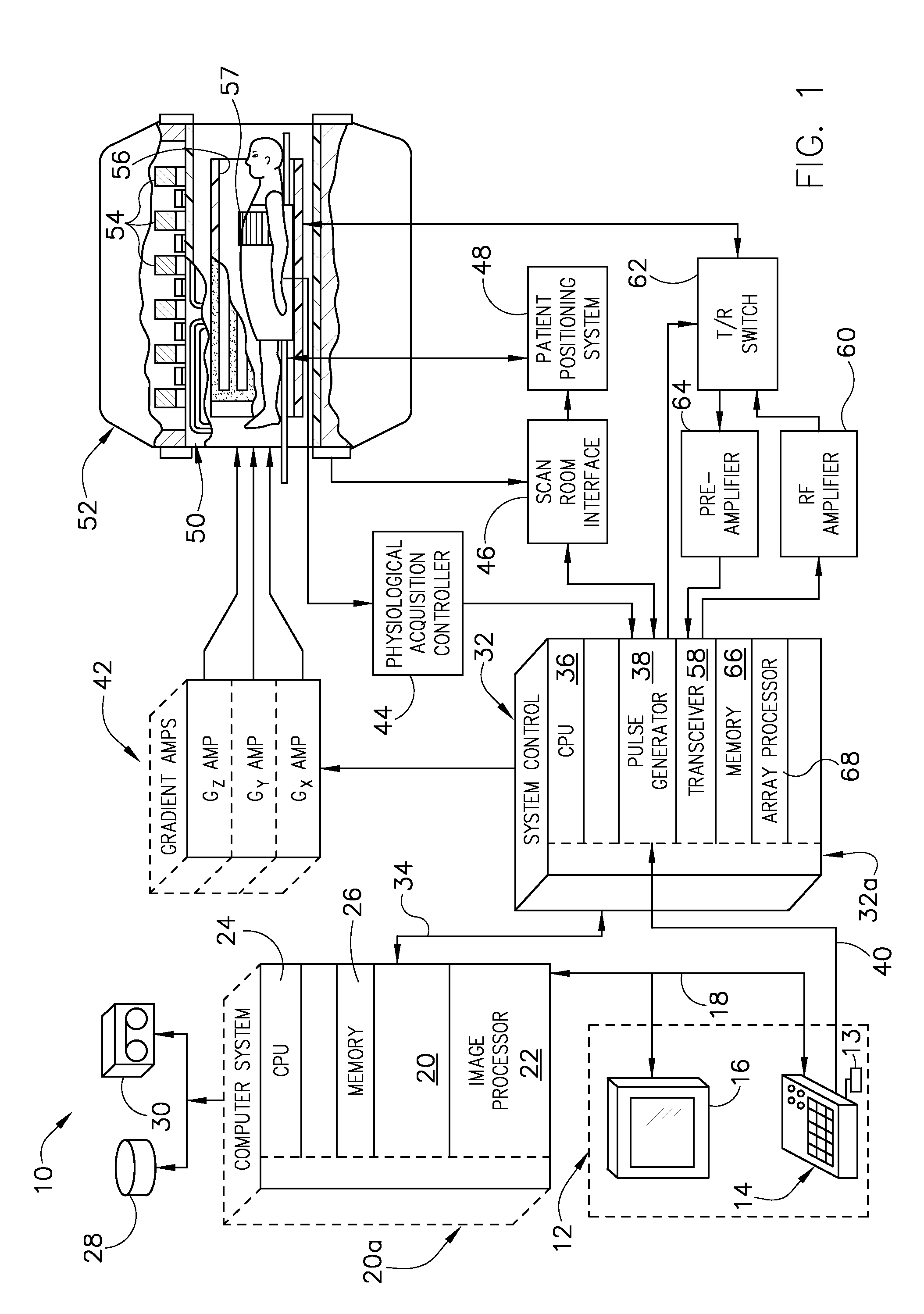
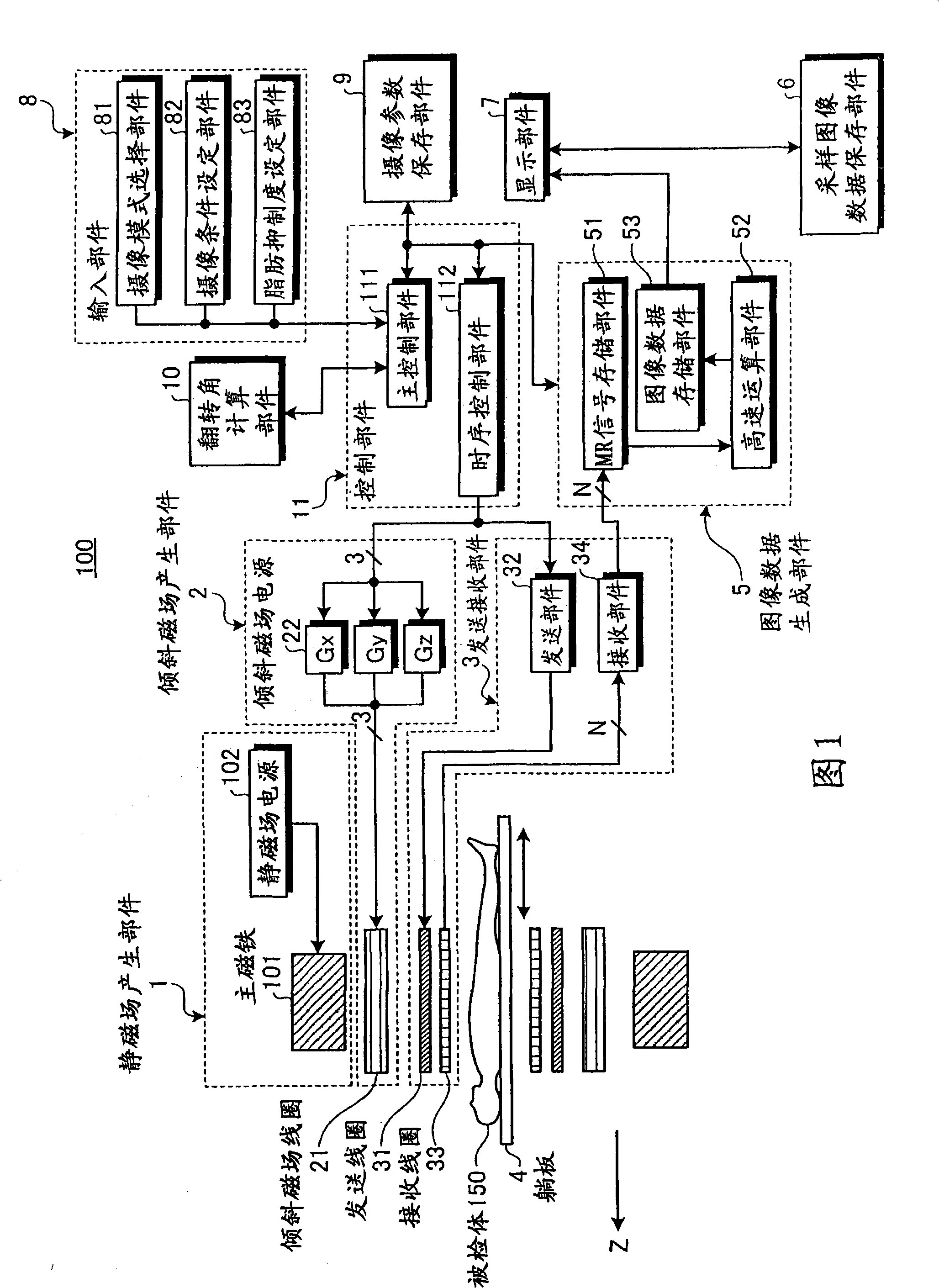
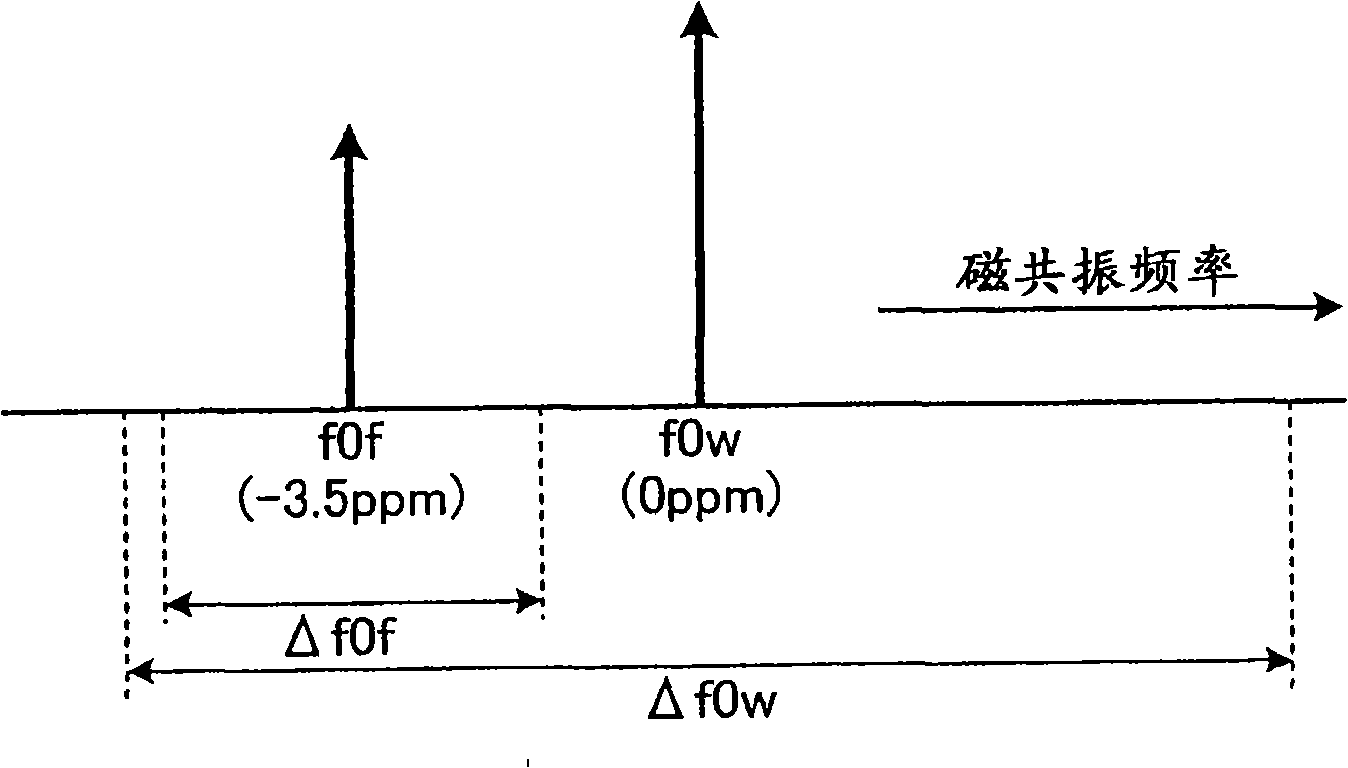
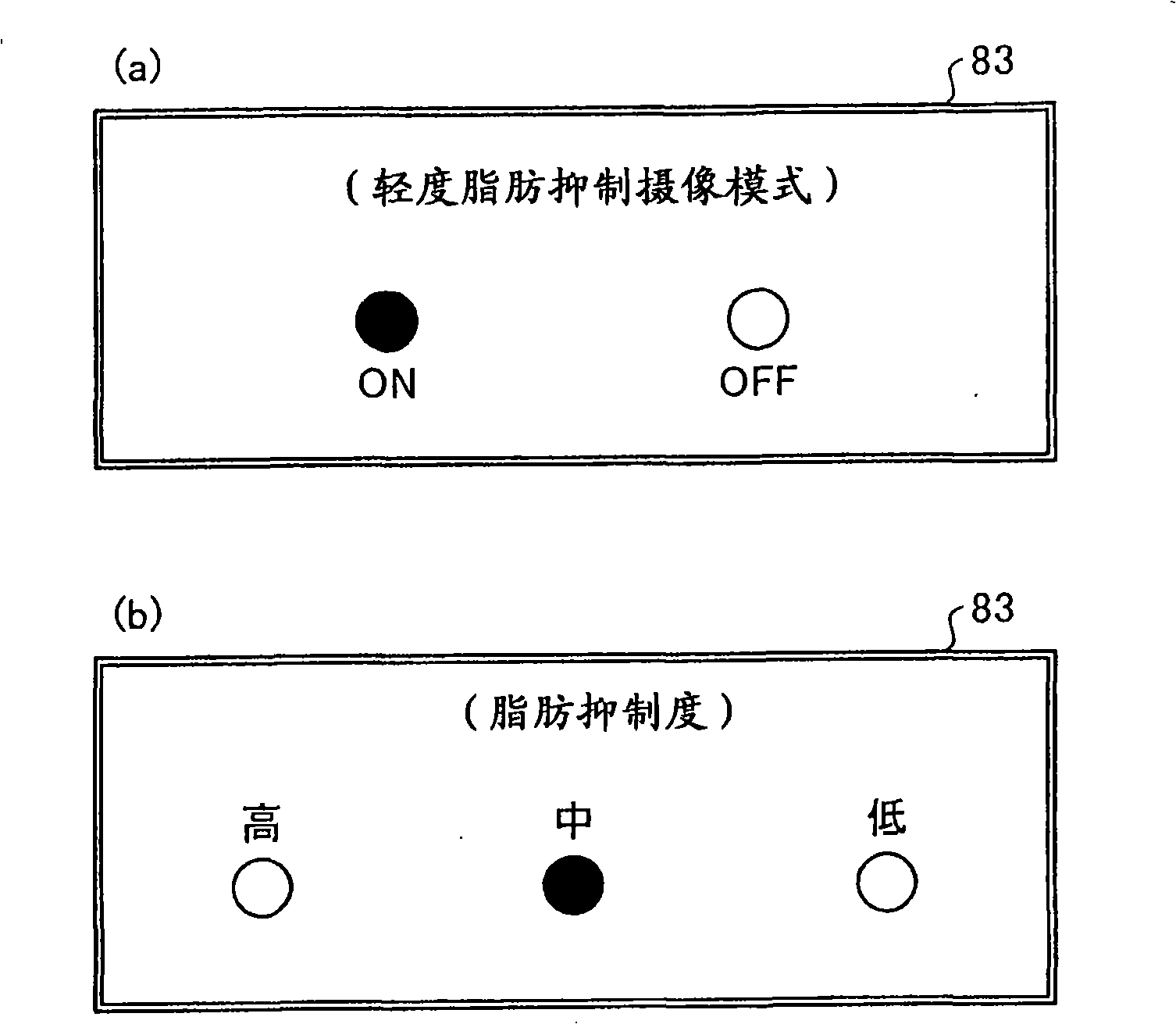
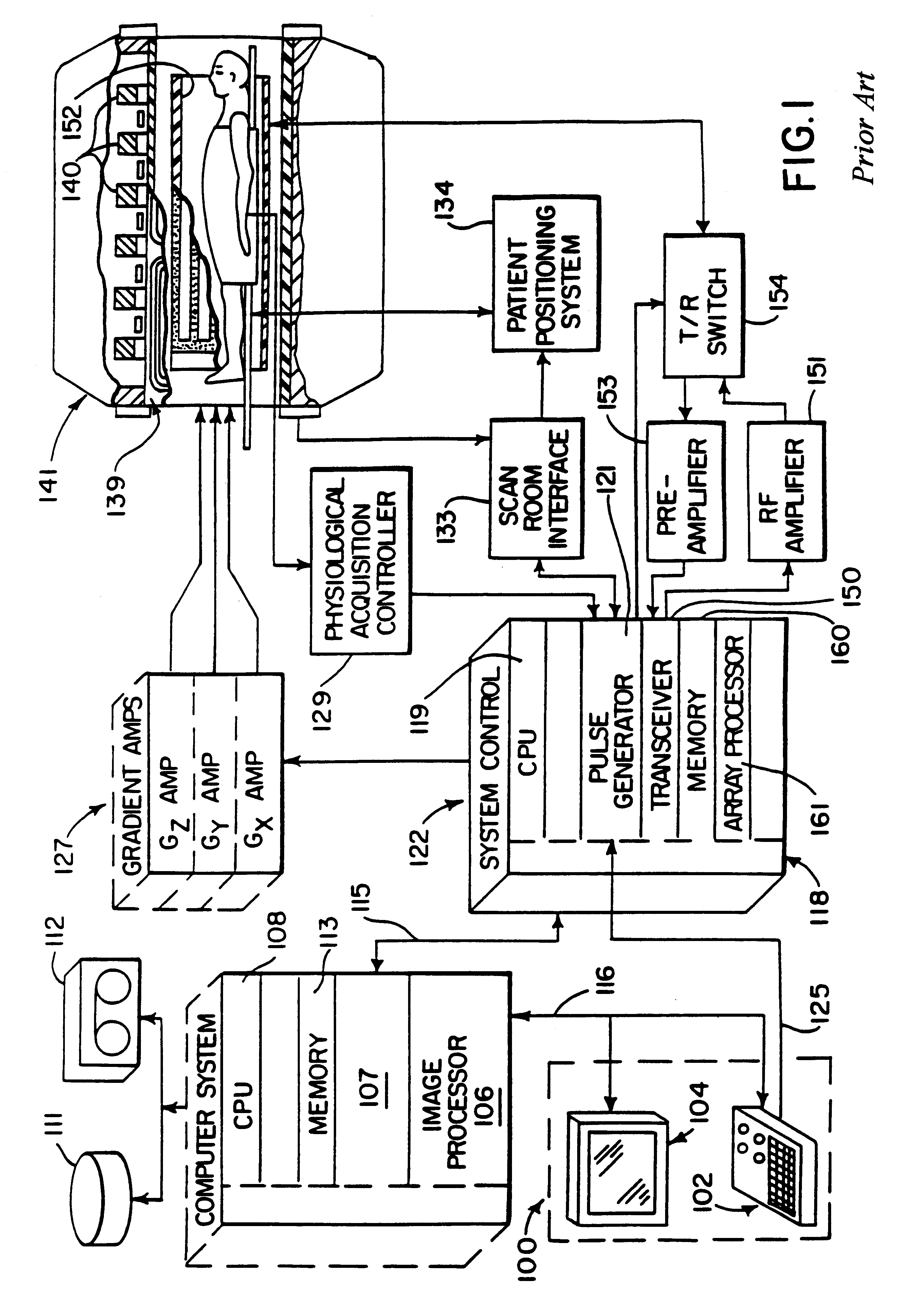
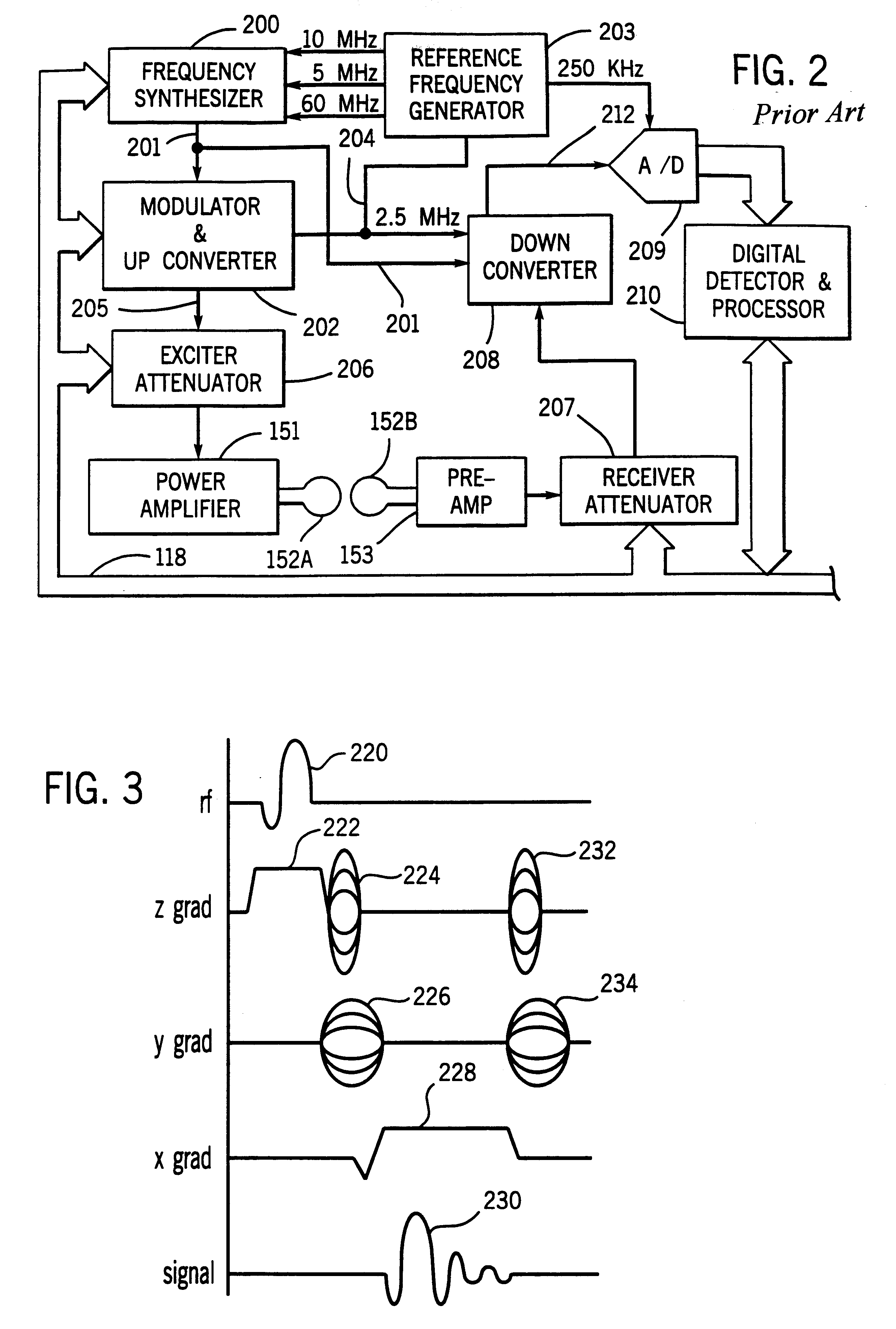
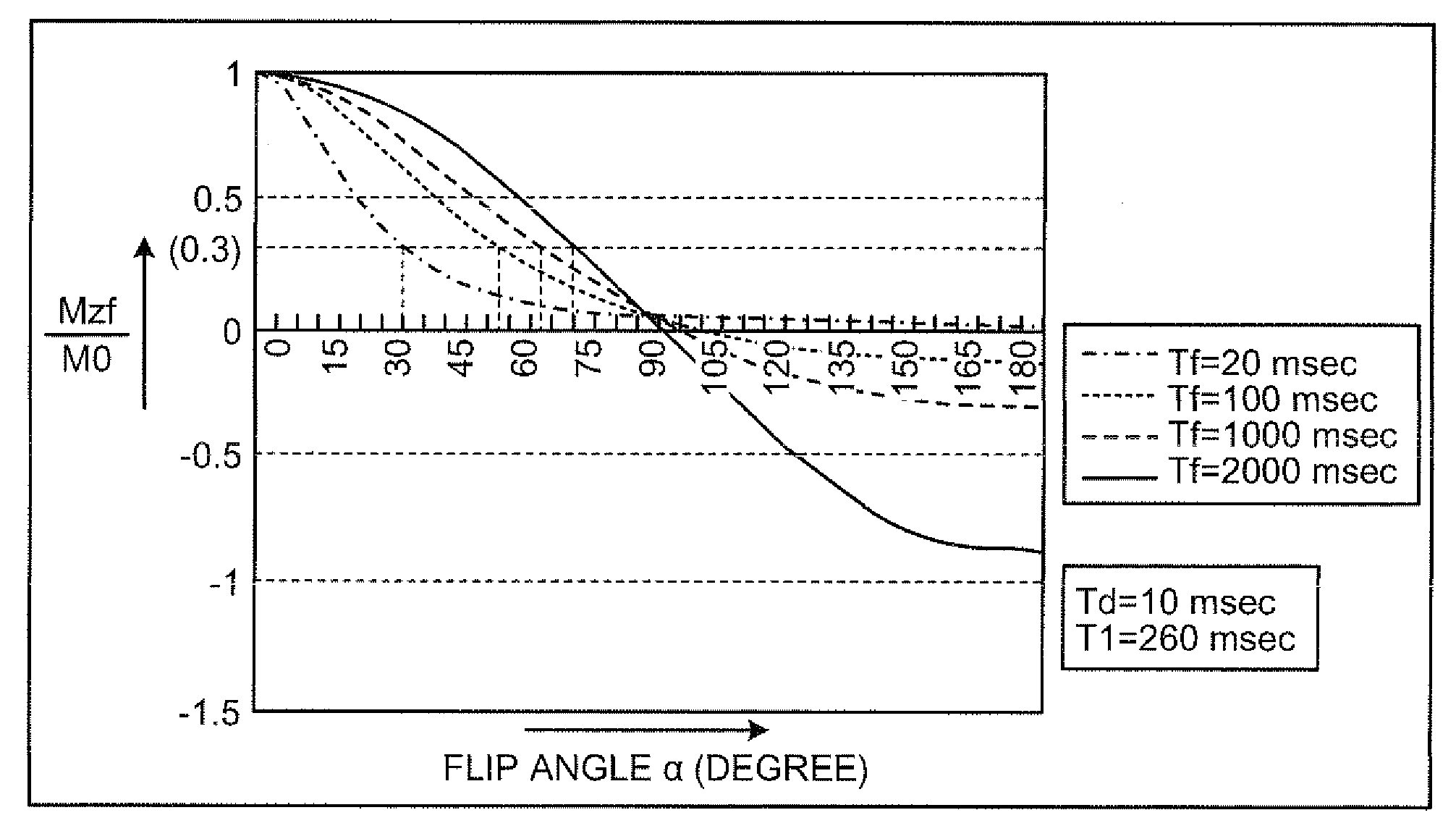
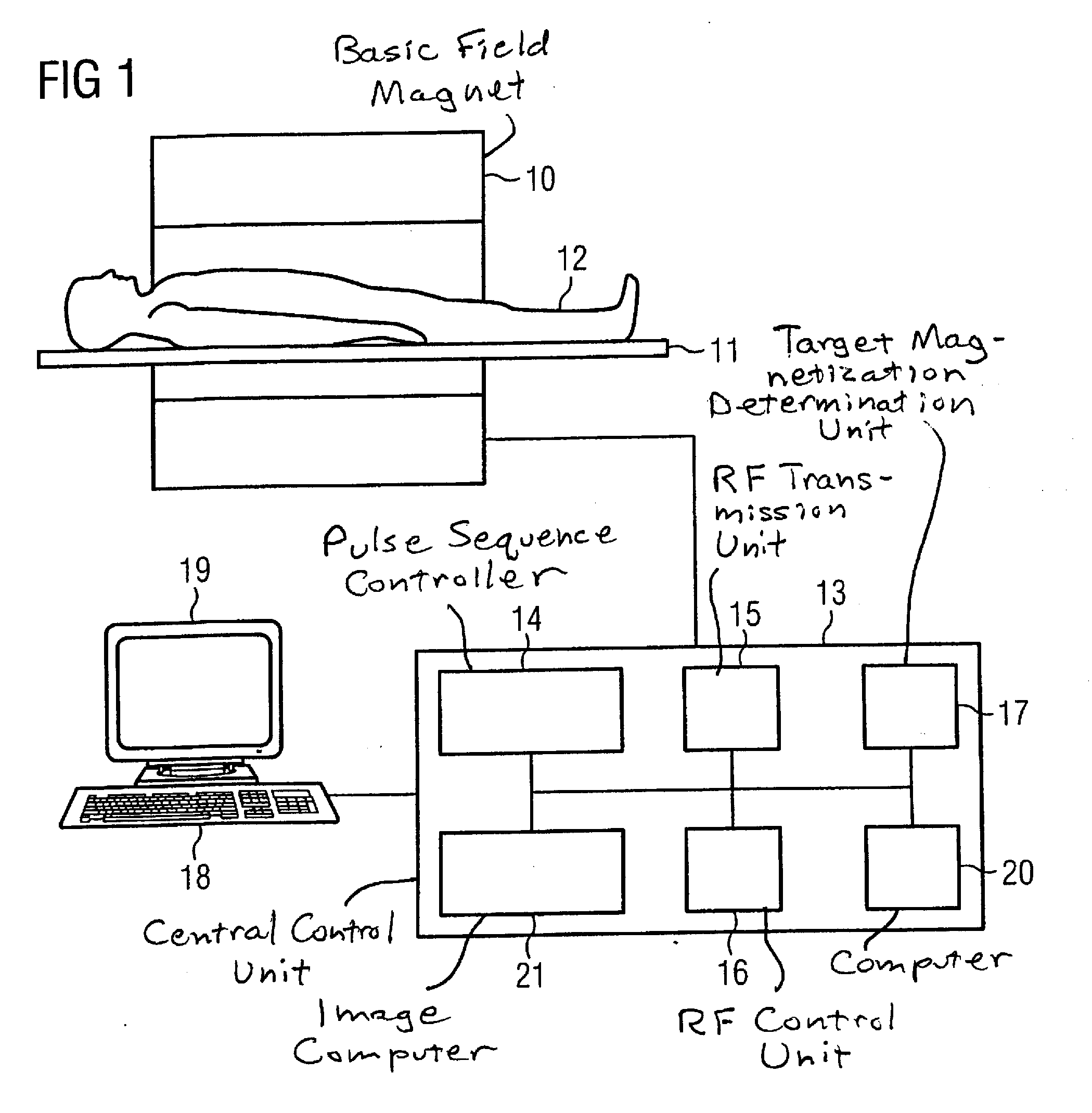
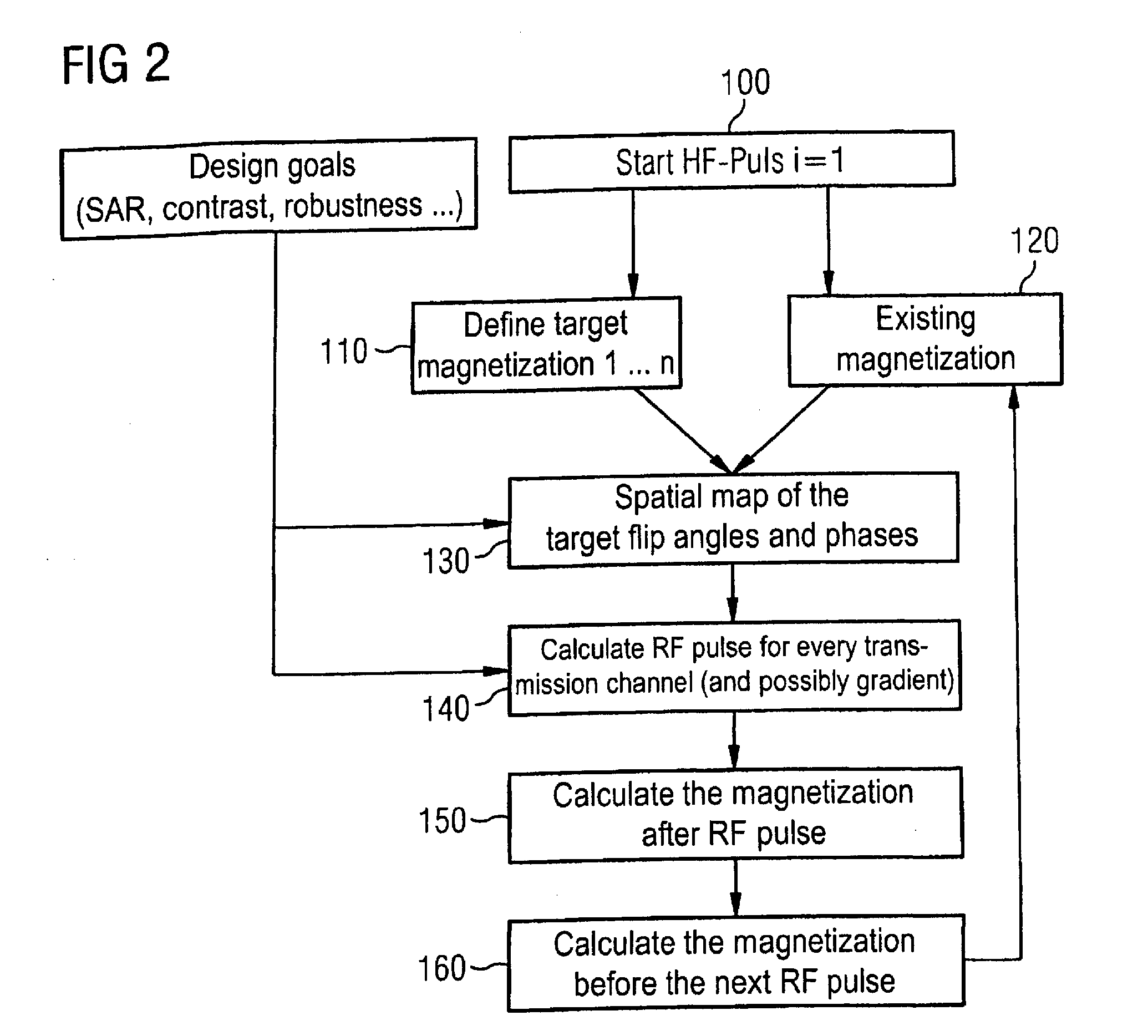
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
332 results about "Flip angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The flip angle is the rotation of the net magnetization vector by a radiofrequency pulse relative to the main magnetic field. To improve the signal when Magnetic Resonance imaging, the flip angle needs to be chosen using the Ernst angle.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) fingerprinting
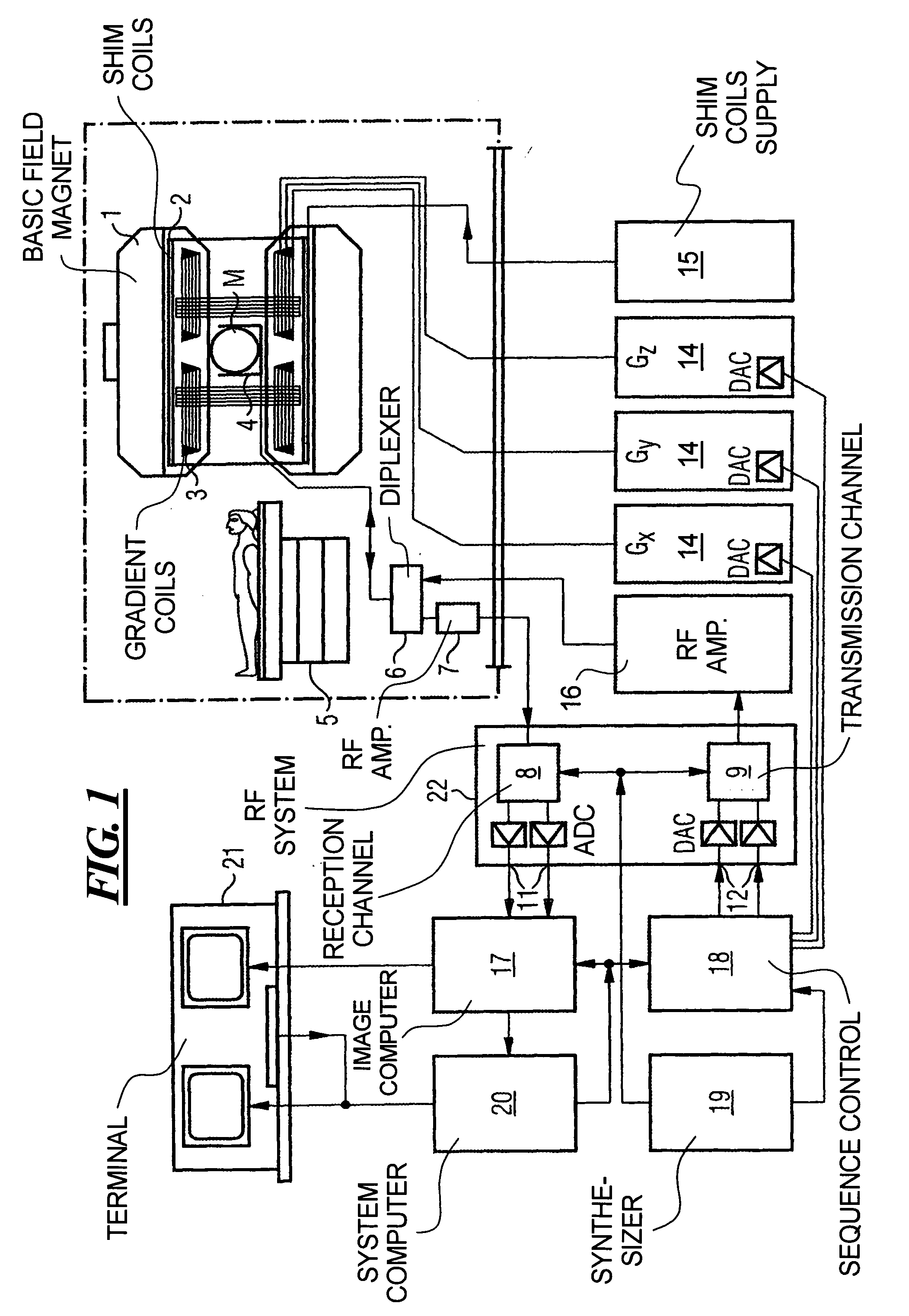
ActiveUS20120235678A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
Apparatus, methods, and other embodiments associated with NMR fingerprinting are described. One example NMR apparatus includes an NMR logic configured to repetitively and variably sample a (k, t, E) space associated with an object to acquire a set of NMR signals. Members of the set of NMR signals are associated with different points in the (k, t, E) space. Sampling is performed with t and / or E varying in a non-constant way. The varying parameters may include flip angle, echo time, RF amplitude, and other parameters. The NMR apparatus may also include a signal logic configured to produce an NMR signal evolution from the NMR signals, a matching logic configured to compare a signal evolution to a known, simulated or predicted signal evolution, and a characterization logic configured to characterize a resonant species in the object as a result of the signal evolution comparisons.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
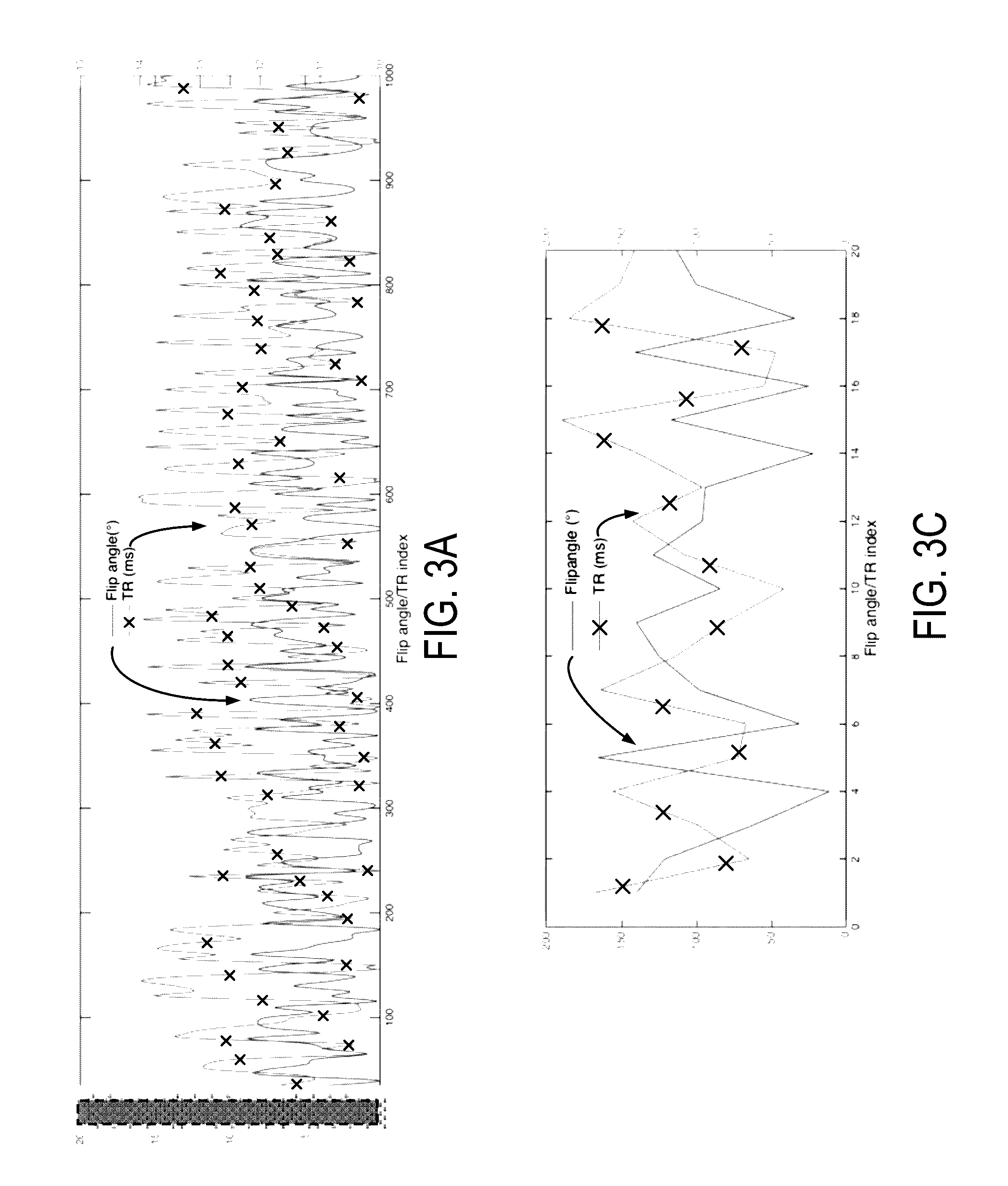
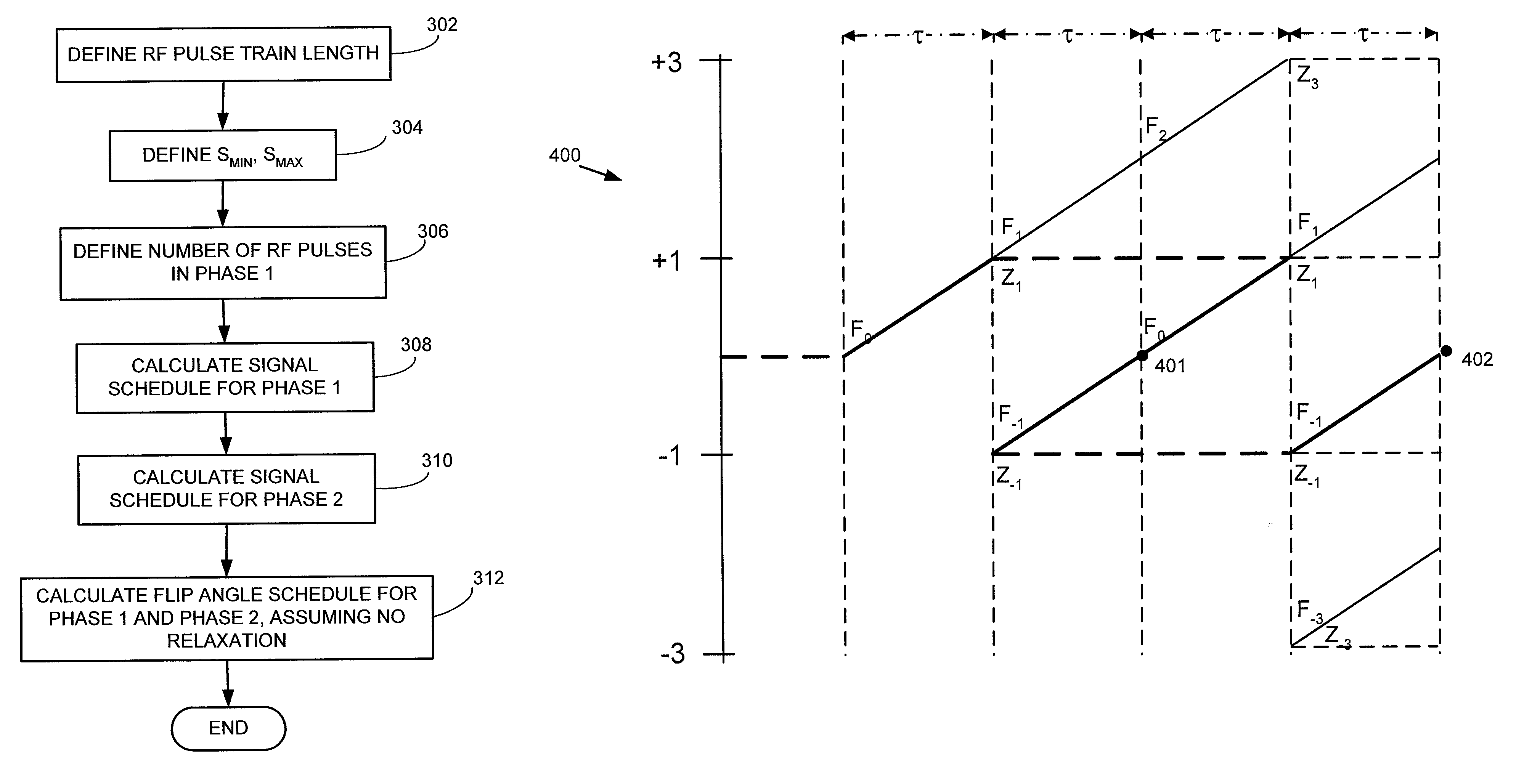
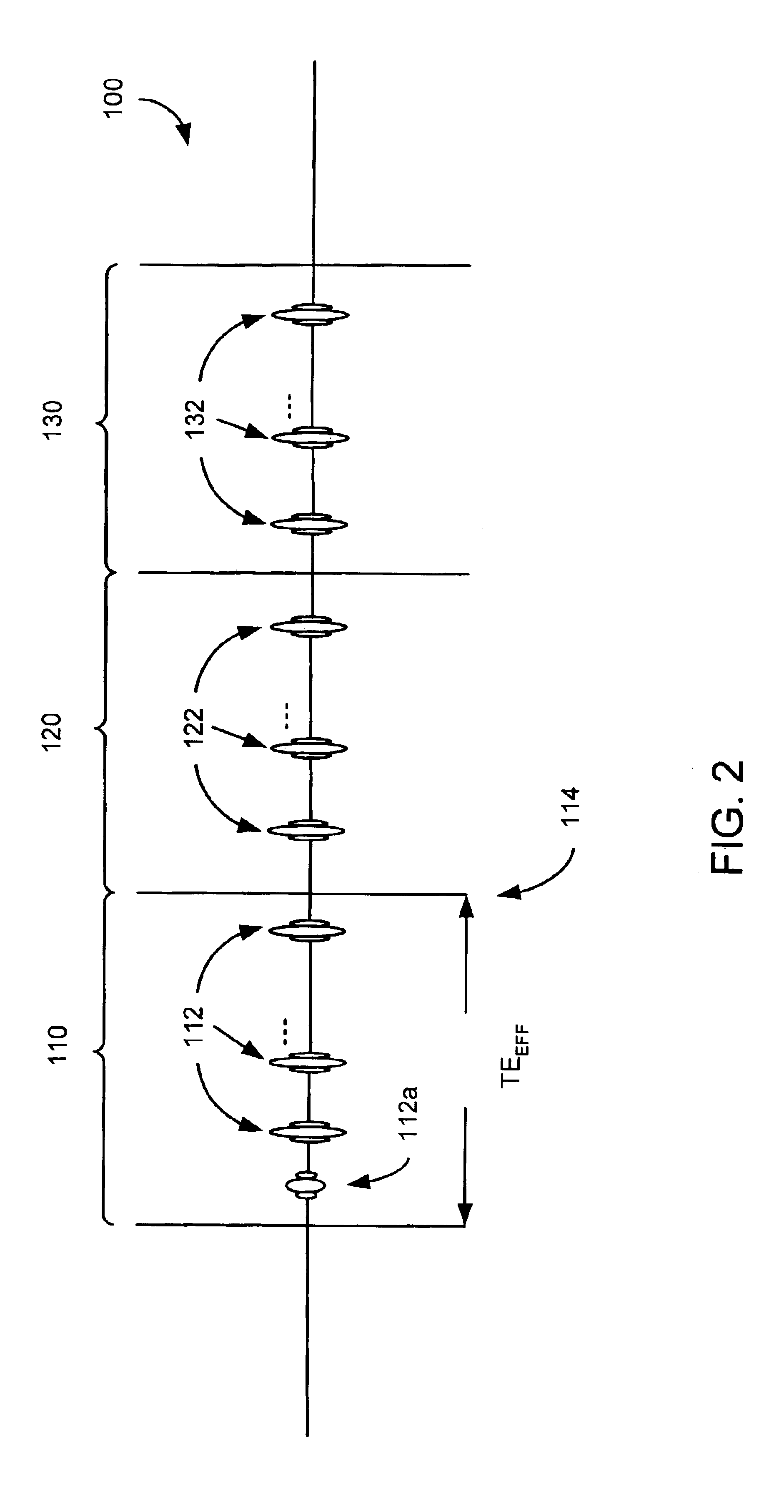
Method and apparatus for generating a flip angle schedule for a spin echo train pulse sequence
ActiveUS20080319301A1Reduced refocusing flip angleMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTarget signalPulse sequence
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System for Motion Corrected MR Diffusion Imaging
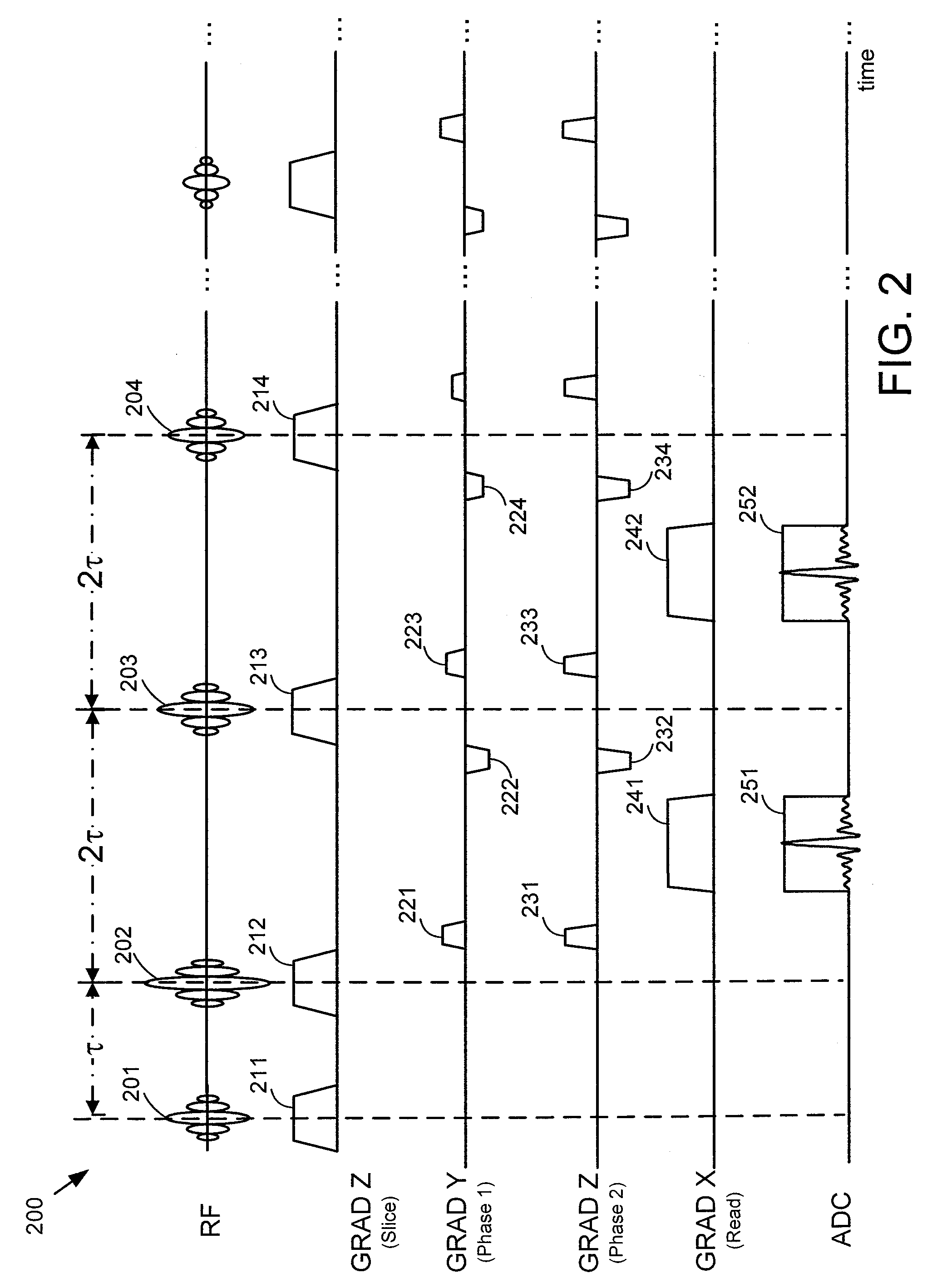
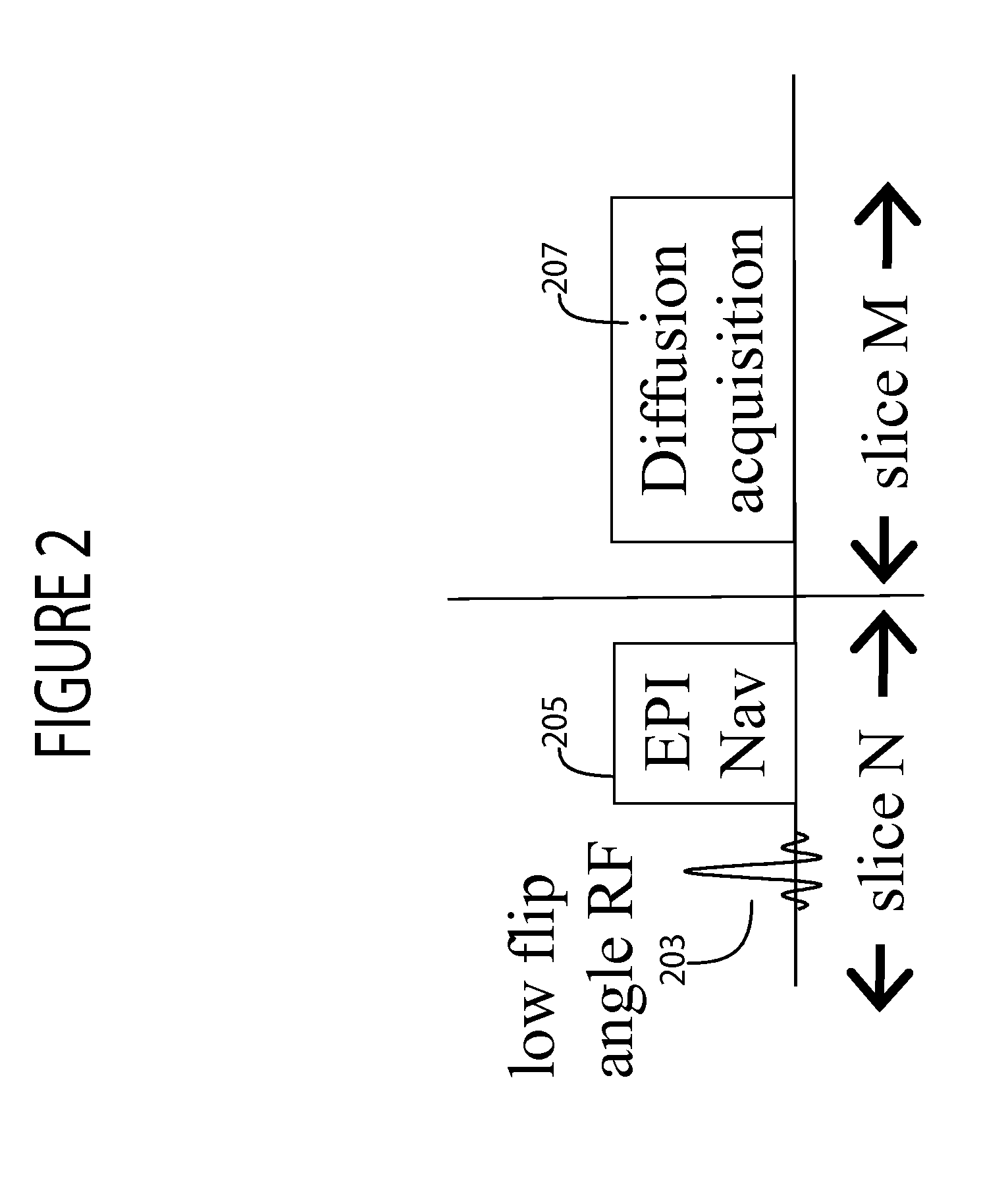
A system determines motion correction data for use in diffusion MR imaging using an RF signal generator and magnetic field gradient generator which sequentially acquire in a single first direction through a volume, first and second slice sets individually comprising multiple individual diffusion image slices. The first set of slices and the second set of slices are spatially interleaved within the volume, by providing in acquiring the second slice set, a low flip angle RF pulse successively followed by a non-diffusion image data readout magnetic field gradient for acquisition of data representing a two dimensional (2D) non-diffusion image used for motion detection of the first slice set successively followed by, a first diffusion imaging RF pulse followed by a first diffusion imaging phase encoding magnetic field gradient for preparation for acquiring data representing a diffusion image slice of the second slice set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method employing a true FISP sequence with improved off-resonant behavior of two spin ensembles
InactiveUS7020509B2Significant differenceImprove stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setPhase Code
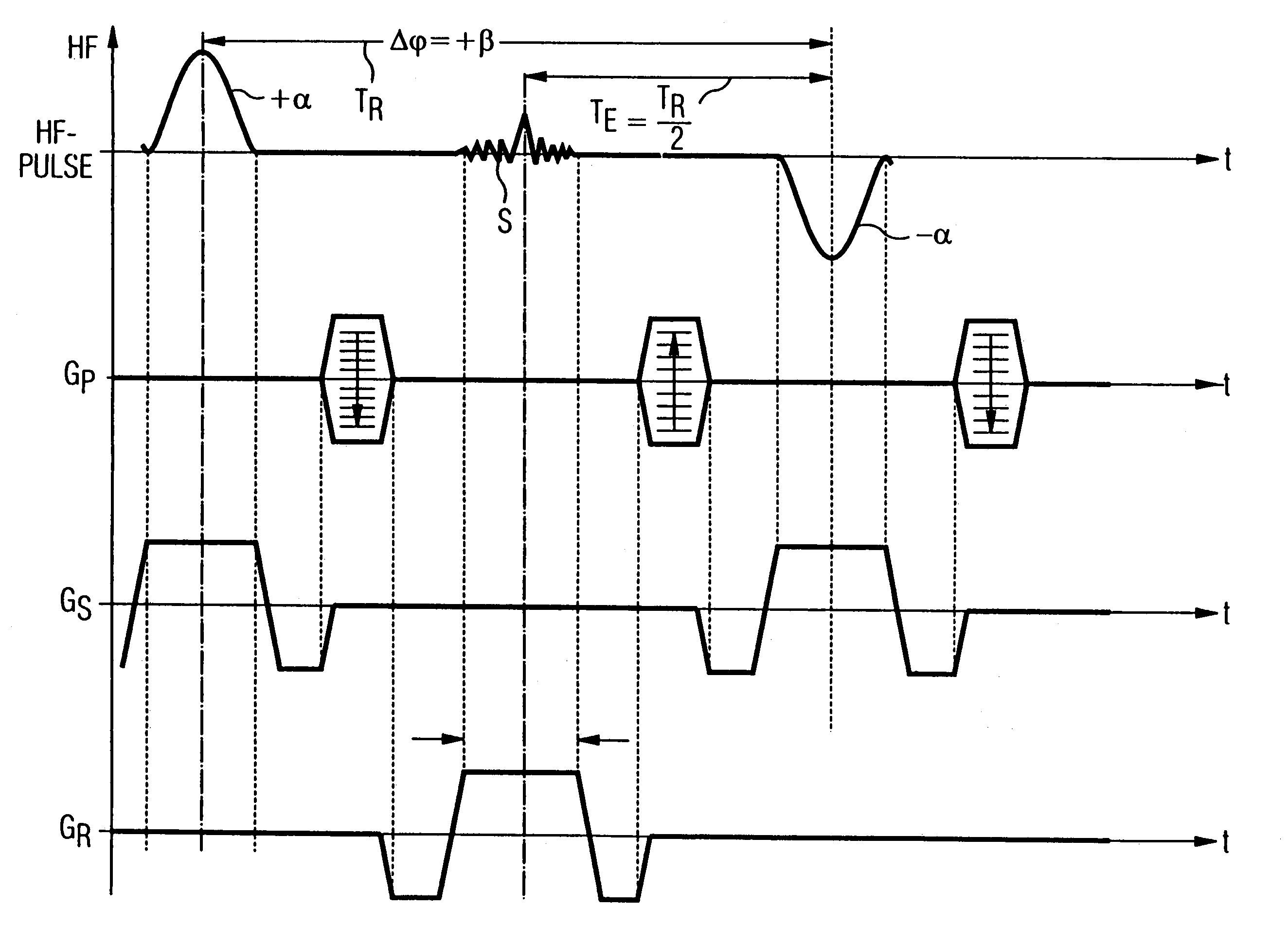
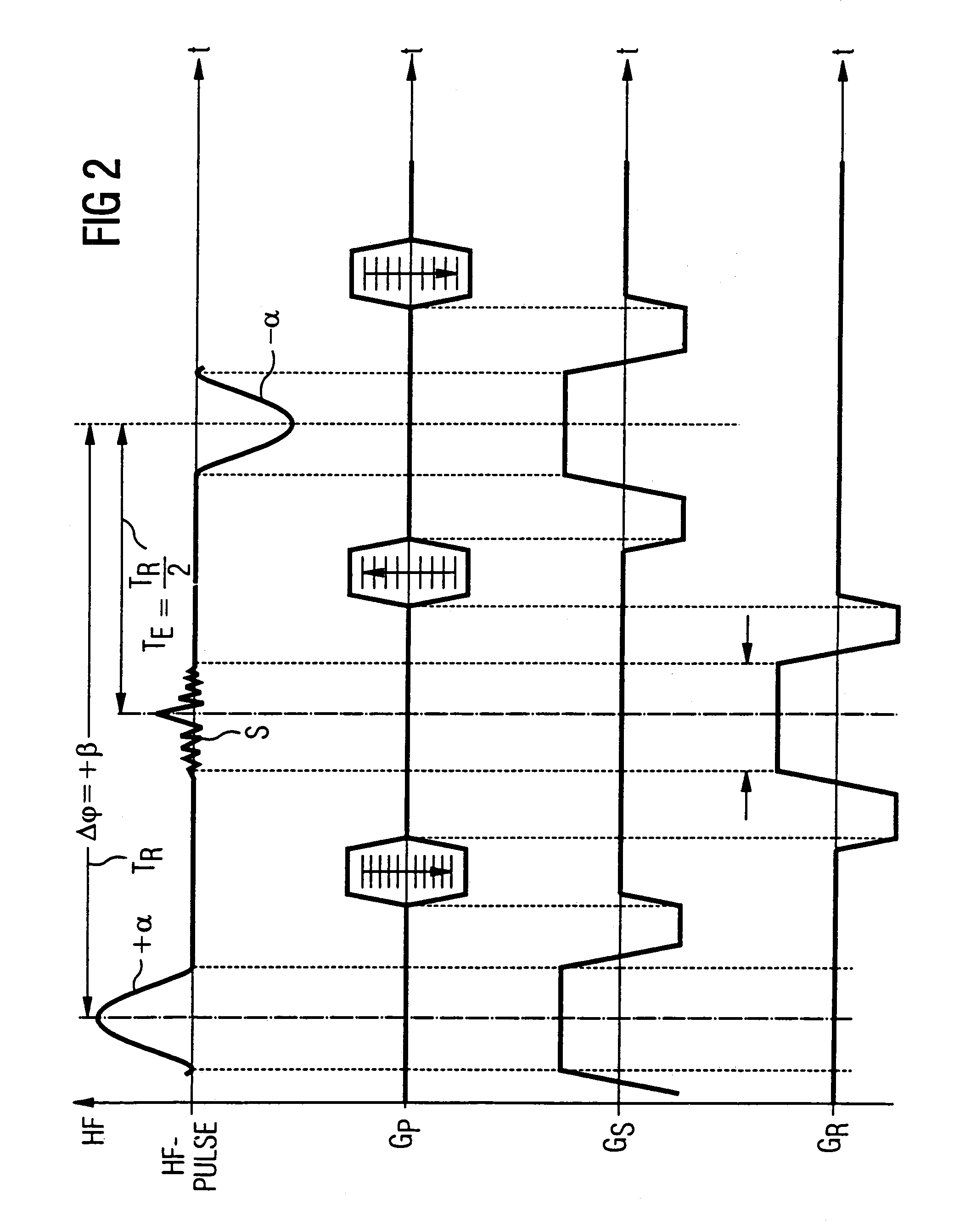
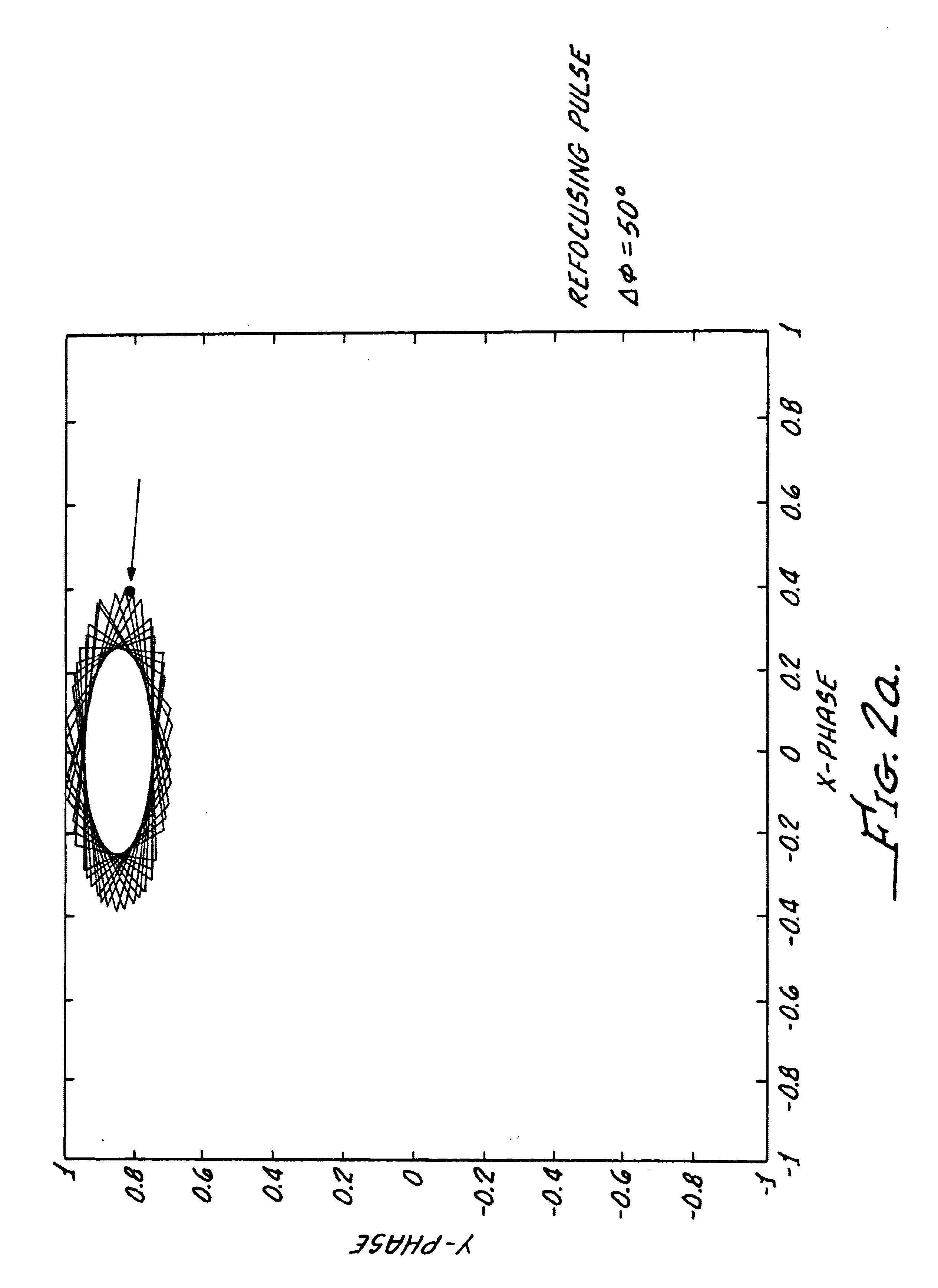
In a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus employing a FISP pulse sequence, the pulse sequence is repeated with a repetition time TR with different phase-coding gradient directions and with an alternating operational sign of the flip angle α. The gradient pulse trains are thereby completely balanced. A phase increment ΔΦ=β is generated in addition to the alternating operational sign of the flip angle α between successive excitation pulses, so that the steady state signals for a first and a second spin ensemble optionally have either identical or reversed signal polarities. A first dataset on the basis of identical signal polarities and a second dataset on the basis of reversed signal polarities are obtained by means of the free selection of the mutual signal polarities. A pure image of the first and the second spin ensembles is thus obtained by the addition and / or subtraction of the first and second datasets.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for designing multi-channel RF pulses for MR imaging
ActiveUS7466131B1Improve image qualityImprove scanning efficiencyMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationEngineering
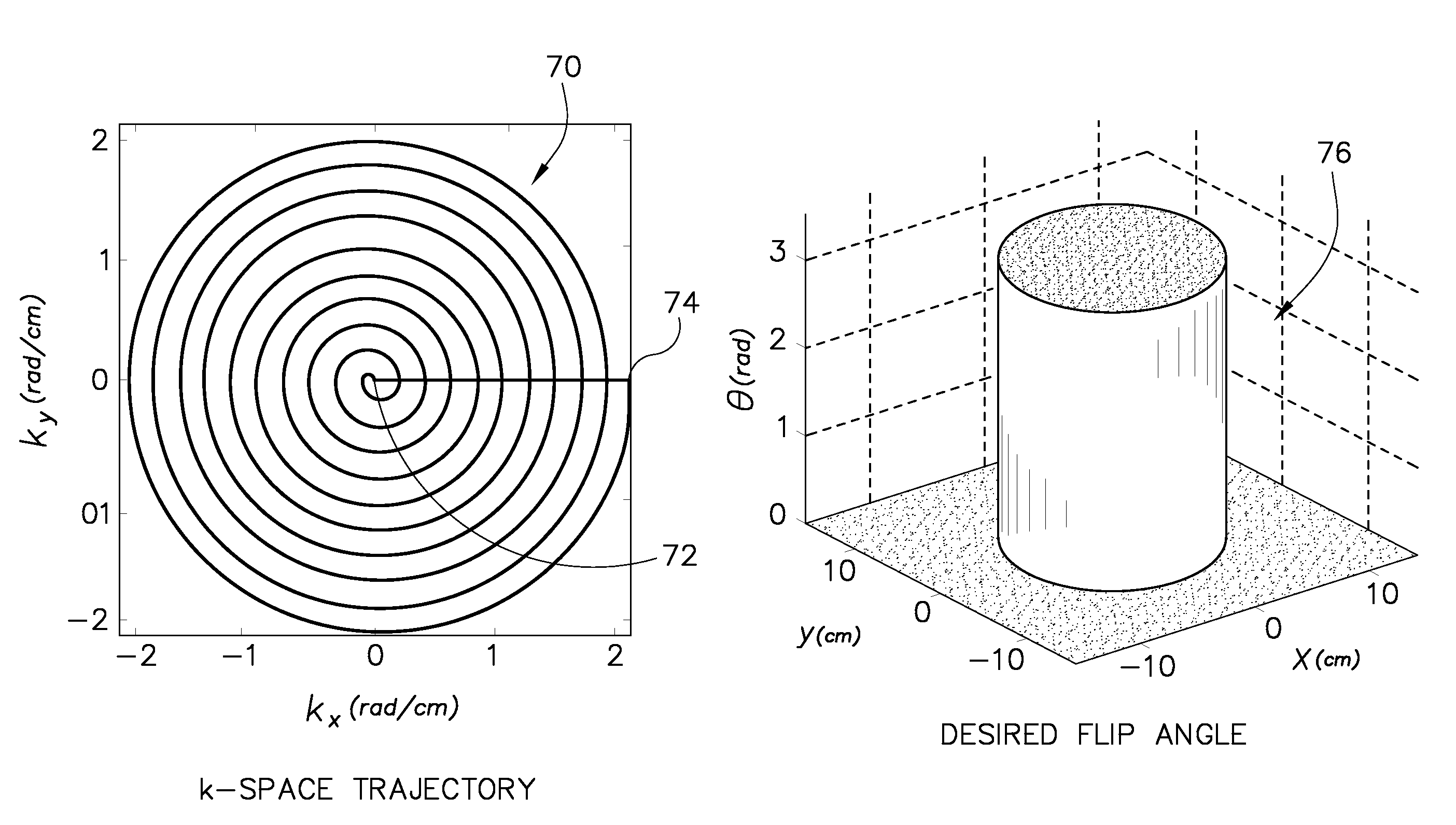
A system and method are provided for designing RF pulses for multi-channel and / or multi-dimensional spatially-selective applications using a linear approximation. Embodiments of the system and method may use a generalized linear-class large tip angle approximation to design RF pulses for multi-channel and parallel transmission. Further, some of these approximations allow for the design of arbitrarily large flip angles, irregularly-shaped flip angle profiles, or arbitrary initial magnetization values. Embodiments of the system and method may also provide for the design of k-space trajectories which aid in maintaining assumptions of the various linear class approximations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA--CHAMPAIGN +2
MRI apparatus
ActiveCN101401723ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFat suppressionPulse sequence
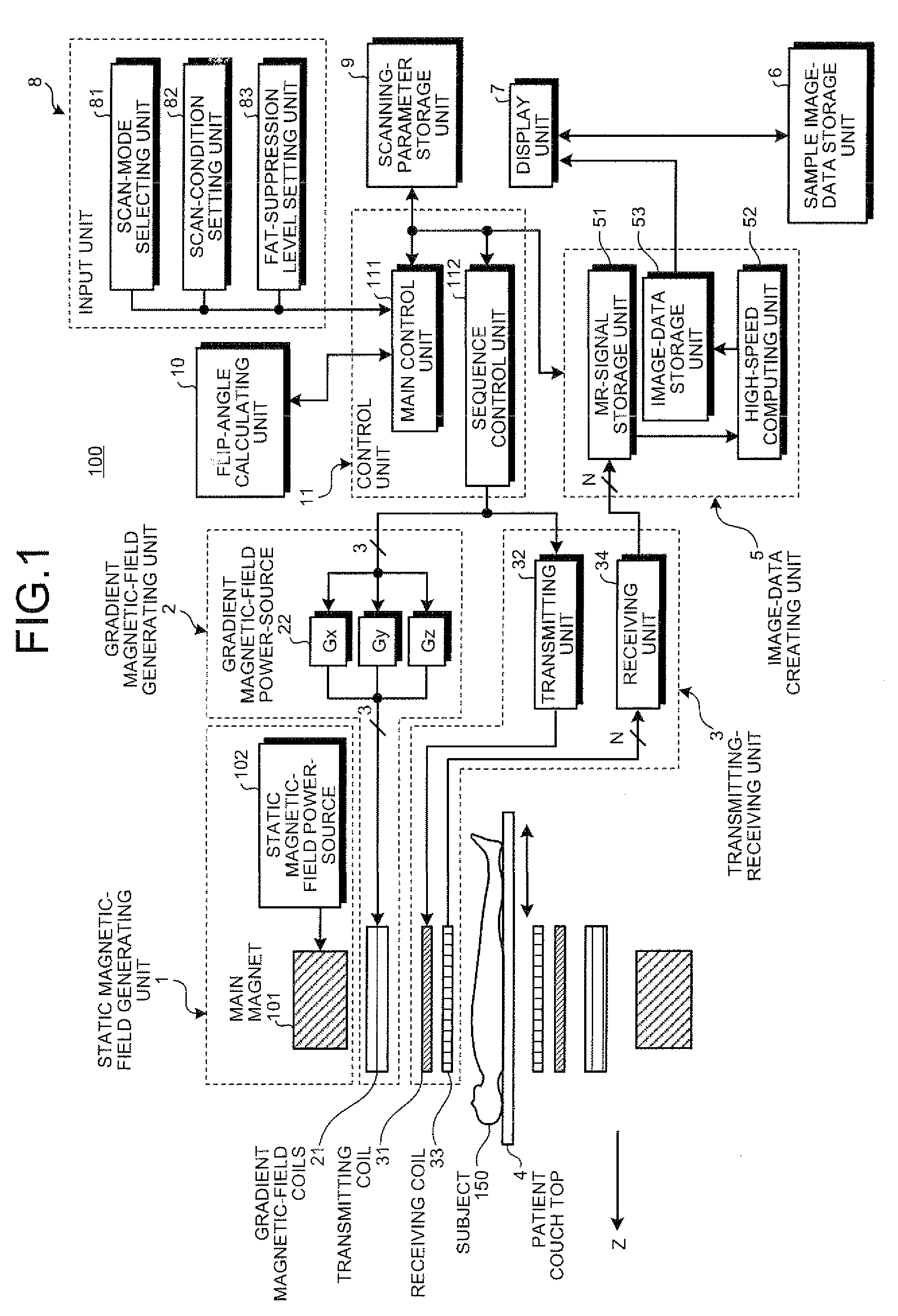
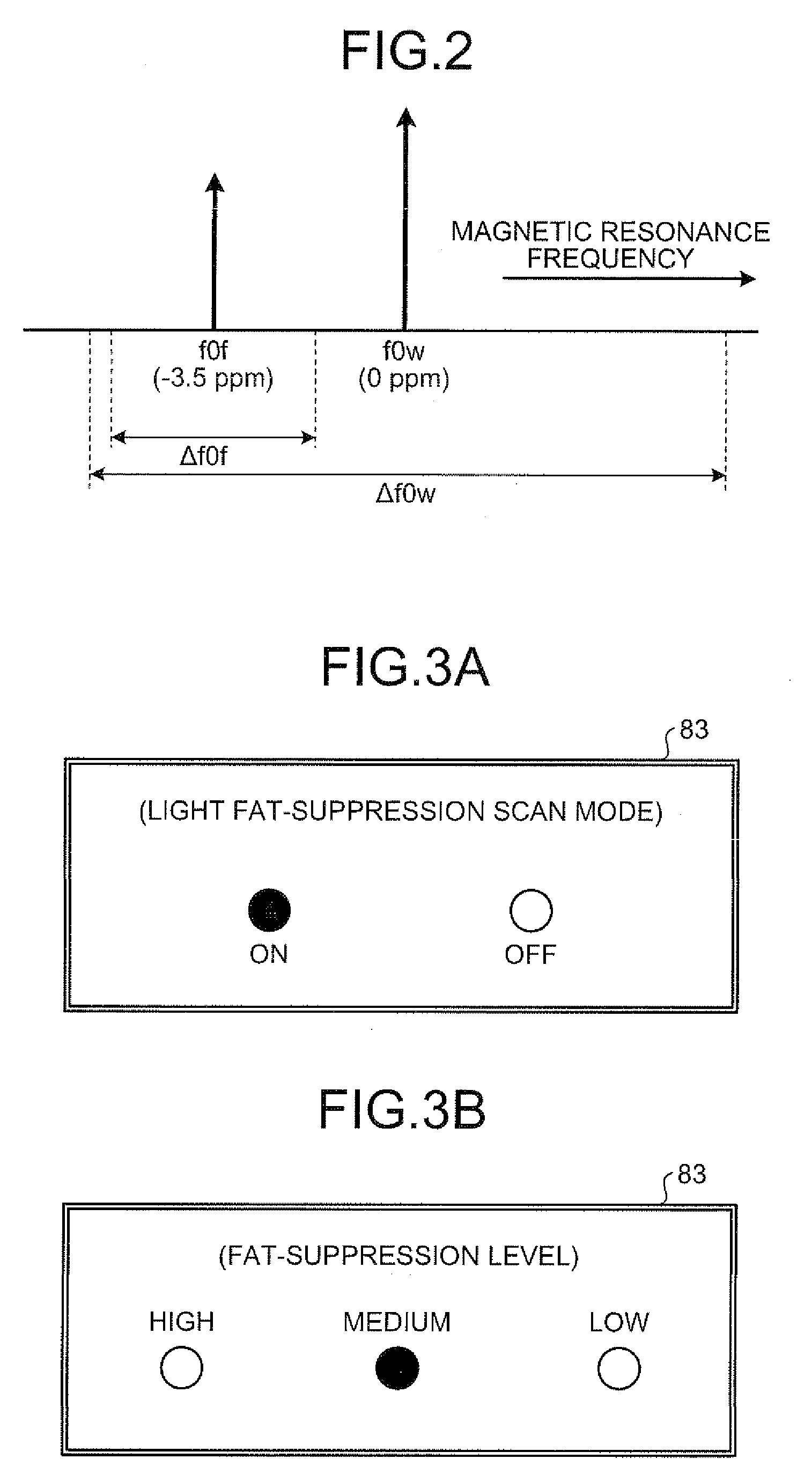
The present invention provides a MRI device, wherein, a flip-angle calculating unit calculates a flip angle of a fat-suppression pulse by inputting scanning parameters read from a scanning-parameter storage unit based on scanning conditions set by a scan-condition setting unit and a desired fat-suppression level, into a predetermined computing program. A control unit suppresses fat signals to a desired level by performing irradiation of a fat-suppression pulse having the calculated flip angle and application of a spoiler gradient magnetic field onto a scan target portion of a subject by controlling a gradient magnetic-field generating unit and a transmitting-receiving unit, and further performs irradiation of an RF pulse and application of a gradient magnetic field in accordance with a predetermined pulse sequence, thereby detecting water signals and suppressed fat signals as MR signals. An image-data creating unit creates image data by reconstructing the MR signals.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
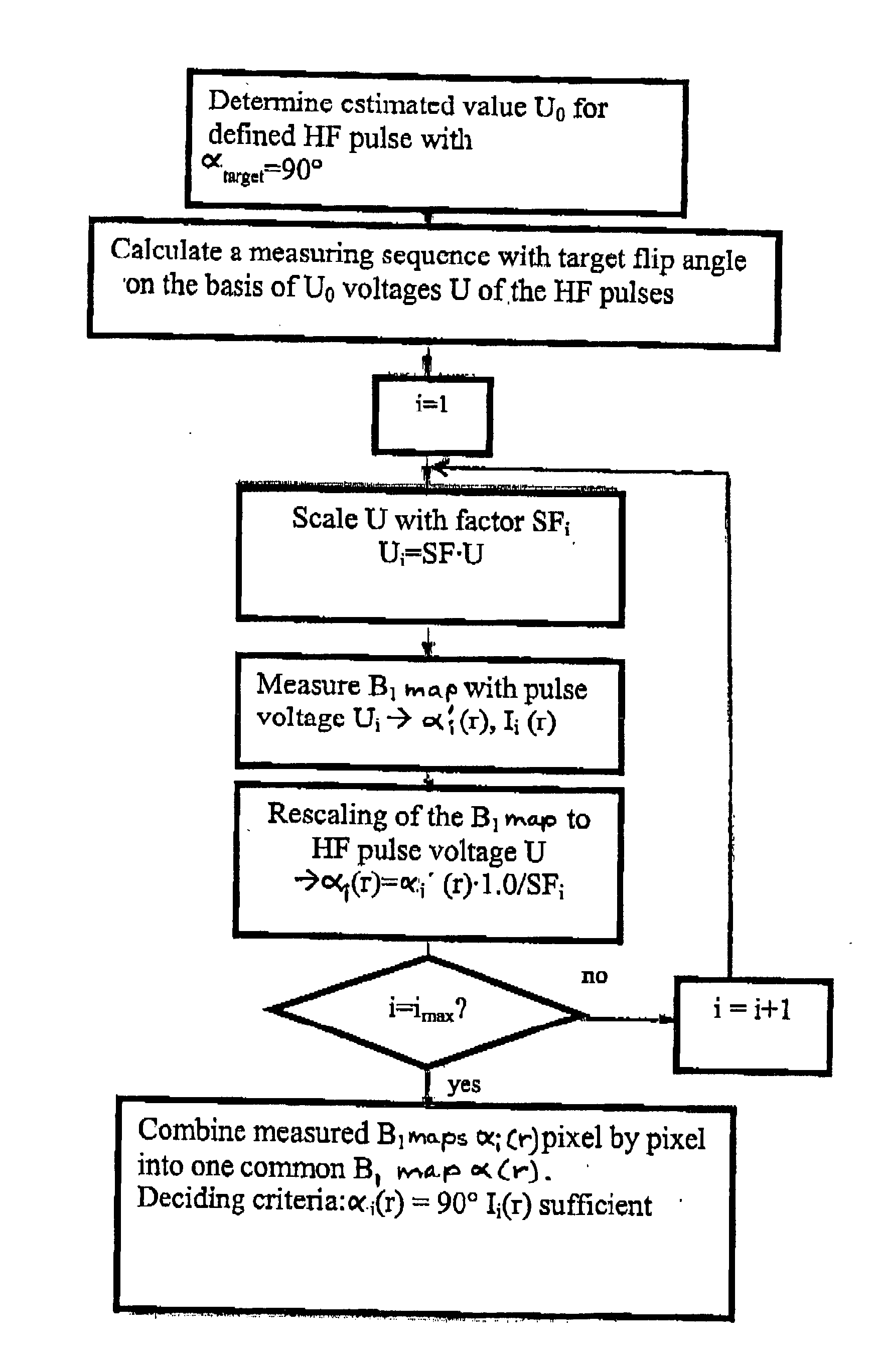
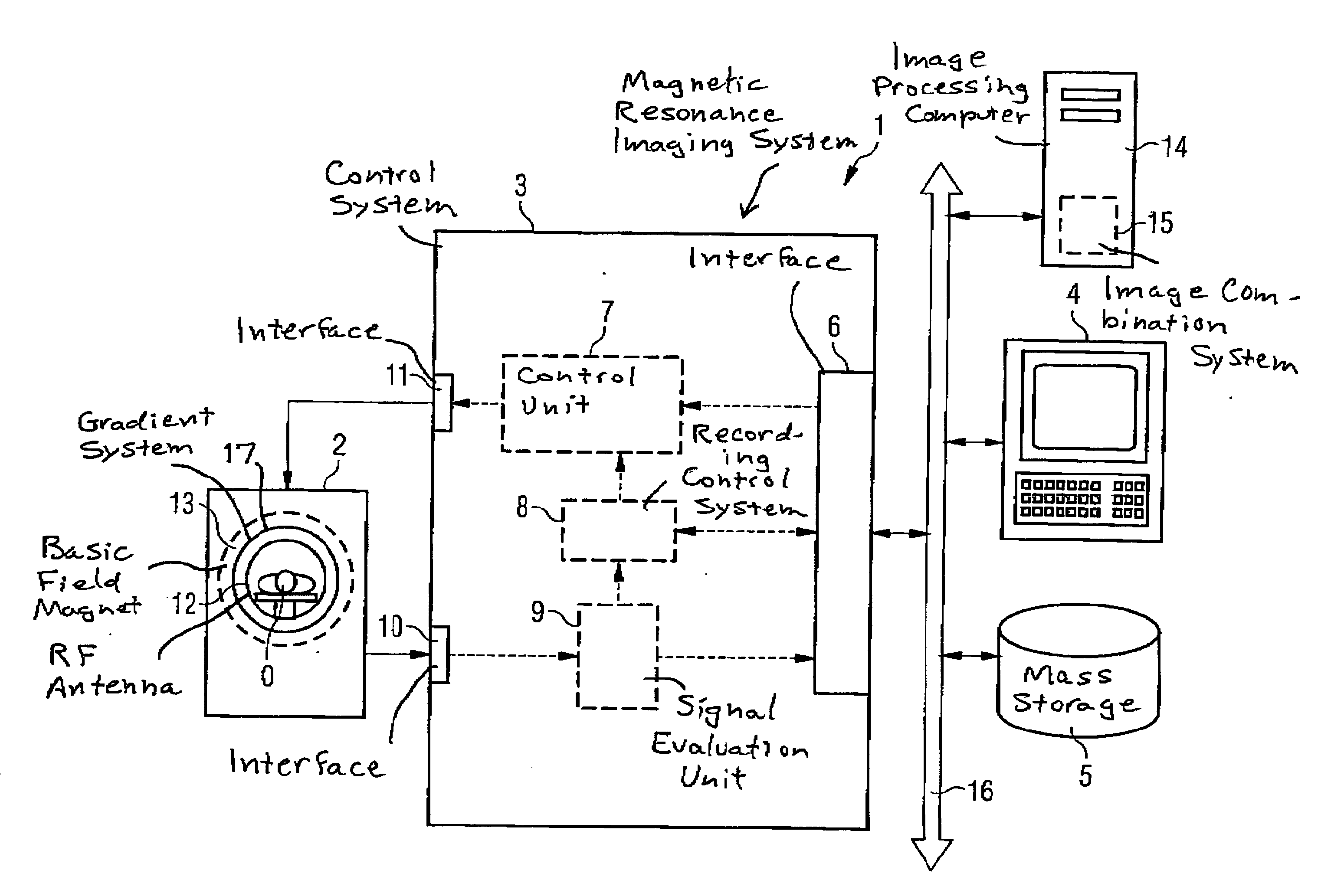
Method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the B1 field distribution
ActiveUS20050073304A1High overall measuring timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurement deviceSelective excitation
In a method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the magnetic high frequency field distribution in the apparatus, a double echo high frequency pulse sequence with a first excitation pulse following by at least two refocusing pulses are emitted for generation of a first echo and a following second echo. At least the excitation pulse is slice selective. In an excitation layer defined by the slice selective excitation pulse a first echo image and second echo image are spatially resolved by using suitable gradient pulses for phase or frequency encoding Using the relationships of the amplitudes of the first and second echo image in the various locations the flip angles representing the field strength at the relevant locations in the relevant slice are determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
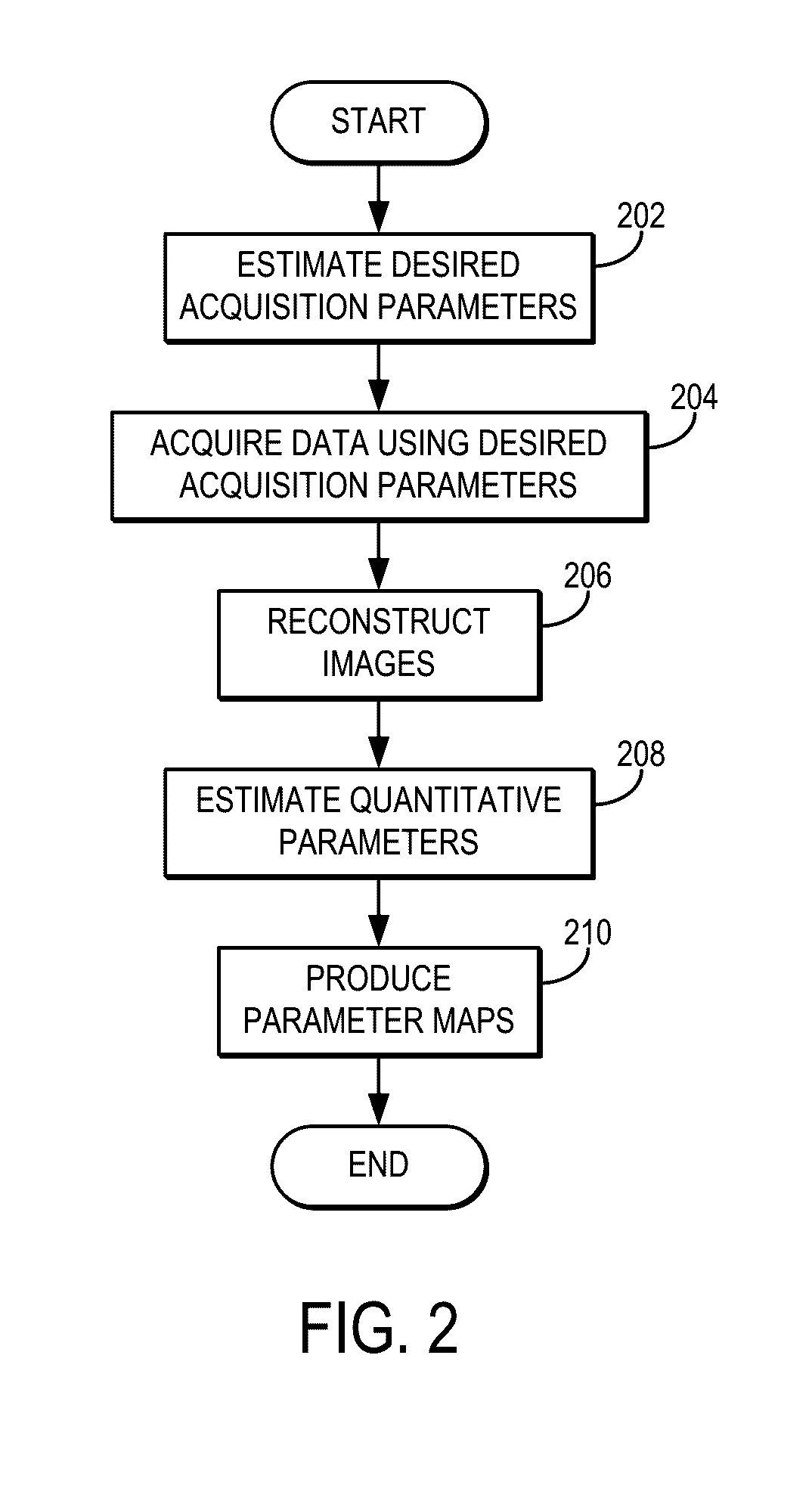
3D Balanced EPI Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting
Provided is a system and method for performing a magnetic resonance fingerprinting imaging process. The process includes determining acquisition parameters including at least one of repetition time (TR) or flip angle (FA), selected to control one of a duration and a number of repetitions of for a pulse sequence that samples k-space in a Cartesian acquisition pattern by acquiring an echo train. The process also includes controlling a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system to perform the pulse sequence a plurality of times to acquire magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) data corresponding to signals from the subject excited by the pulse sequence. The process also includes estimating quantitative tissue properties of the subject by comparing the MRF data to a database and reconstructing, from the MRF data, at least one image of the subject indicating the estimated quantitative tissue properties.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and apparatus for generating a flip angle schedule for a spin echo train pulse sequence
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus to simulate MR properties of human brain for MR applications evaluation
InactiveUS6965235B1Increase contrastImproves white matterMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionVolumetric Mass DensityT1 weighted
A system and method for mimicking a human brain for MR imaging at various magnetic field strengths is disclosed. A phantom is constructed of a structure having a number of sections. A first section contains a mixture of nickel chloride, agarose gel powder, potassium sorbate, deuterium oxide, and water such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the first section mimic white matter of the human brain. A second section contains different amounts of the same components such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the second section mimic gray matter of the human brain. As such, when the phantom is scanned in an MR imaging machine, an optimized flip angle for T1-weighted imaging to improve contrast between white matter and gray matter of the human brain that takes into account proton density differences therebetween can be determined.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus to reduce RF power in high field MR imaging incorporating multi-phase RF pulse flip angles
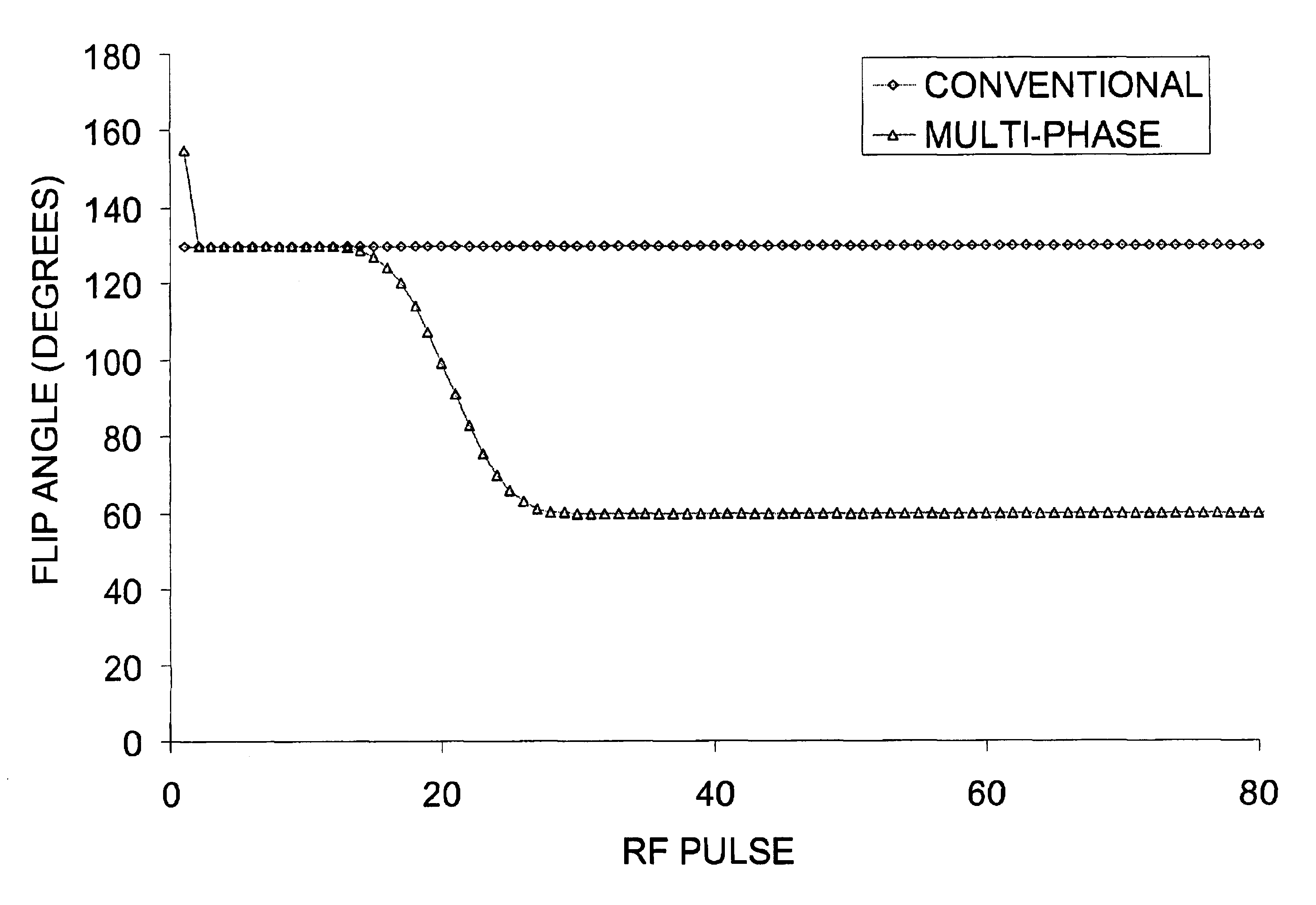
ActiveUS20050001617A1Reducing RF powerOvercomes drawbackDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImage resolutionHigh field mr
A technique is set forth that is designed to reduce RF induced power in high field MR imaging that includes application of an initial contrast preserving phase of RF pulses. These initial RF pulses are designed to have a constant, relatively high flip angle over the initial contrast preserving phase. Following an effective TE, a ramp down phase is applied that has a limited number of RF pulses with a flip angle that is less than the flip angle of those in the initial contrast preserving phase. Further, the RF pulses in the ramp down phase have a flip angle that is decreased over the ramp down phase. This technique provides improved resolution and steady contrast and SNR, while significantly reducing induced RF power.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
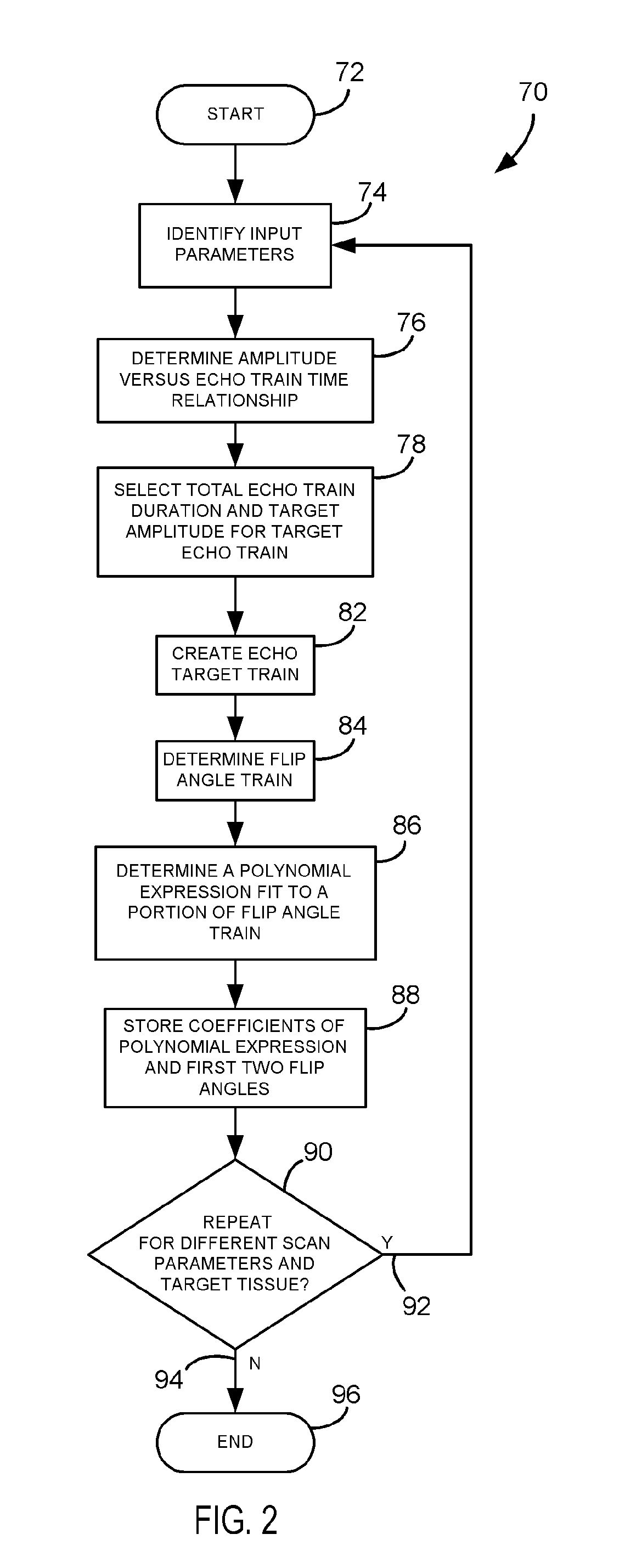
Method and apparatus of multi-echo MR data acquisition with non-discrete flip angle train
ActiveUS7227356B1Reduced ringing artifactsOvercomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImaging qualityData acquisition
An imaging technique is disclosed to reduce ringing artifacts from amplitude decay in MR multi-echo acquisition. A flip angle train is determined to match scan parameters for an MR scan to acquire MR data from a given tissue. Reducing the effects of amplitude decay in the echo signal reduces ringing artifacts and thereby improves image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
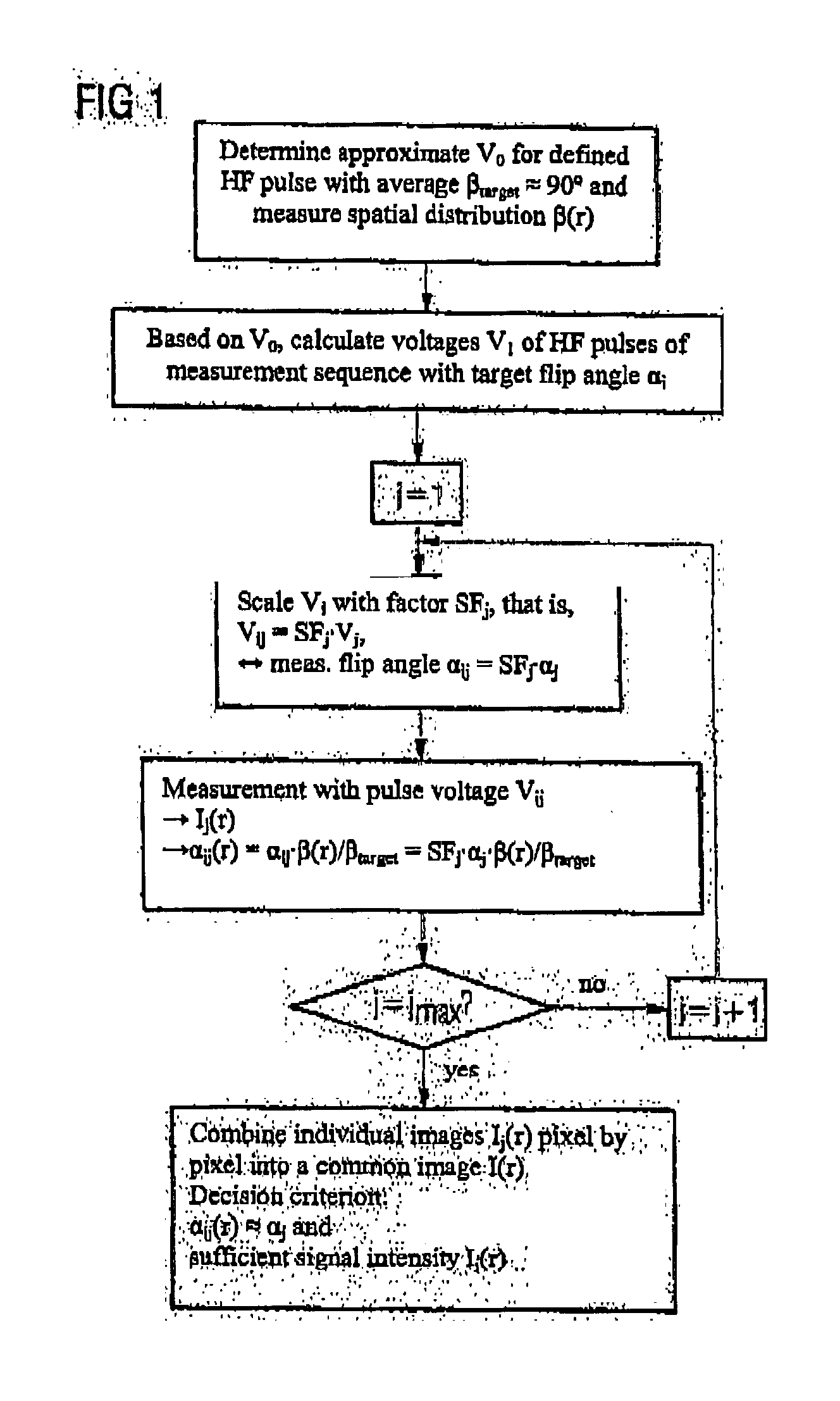
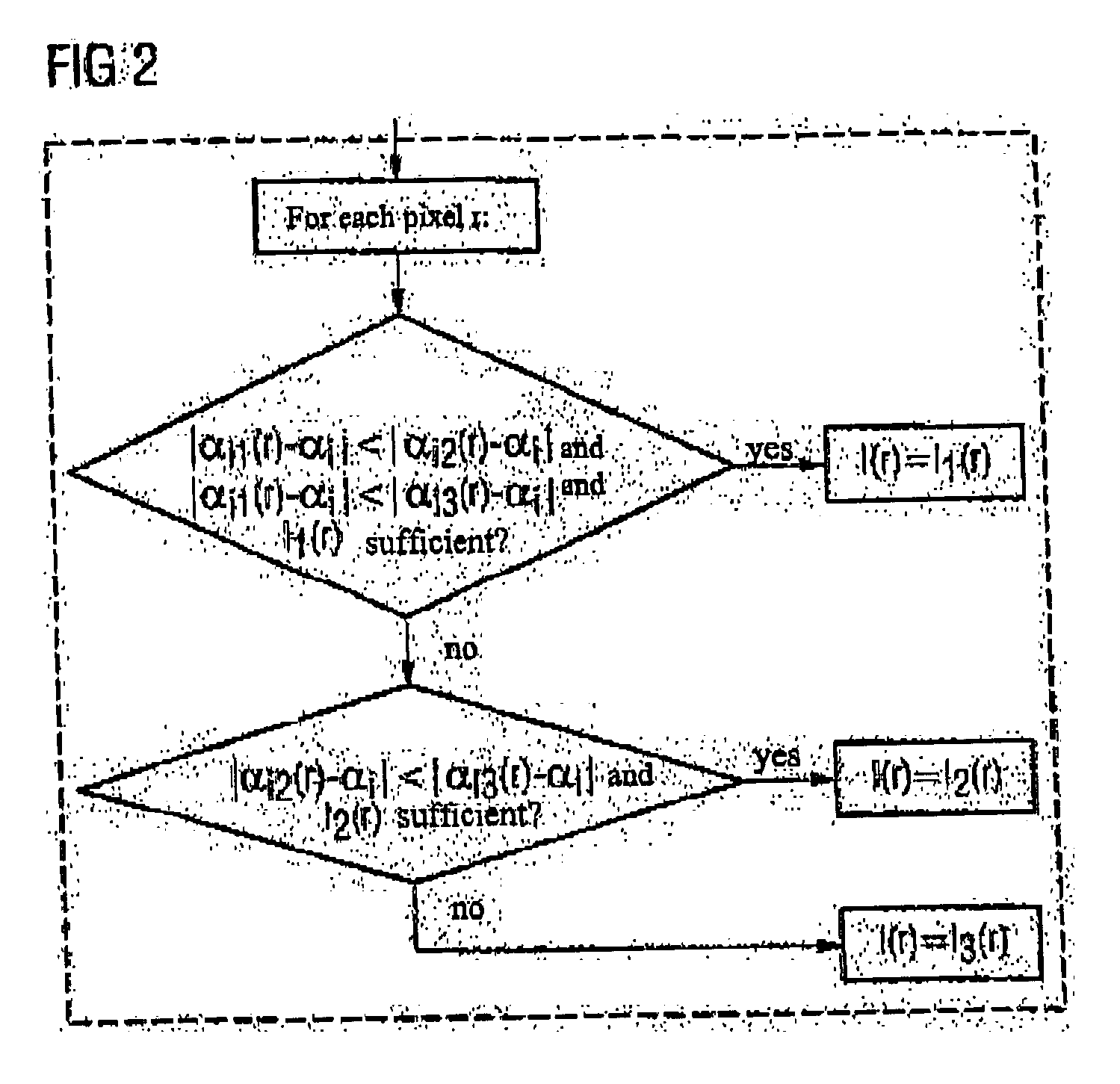
Method and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus for compensating contrast inhomogeneities in magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS20050083054A1Sharp contrastMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonancePulse sequence
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for compensation of contrast inhomogeneities in magnetic resonance images caused by spatial distributions of the radio frequency field associated with the radio frequency pulses that are emitted in order to acquire magnetic resonance (MR) data, multiple individual MR images of a particular region of a subject are recorded with different radio frequency pulse sequences leading to different flip angles. A common contrast-homogenized image for the affected region then is generated based on the different individual images, so that within the contrast-homogenized image, intensity variations due to a distribution of the flip angle are smaller than in the individual images, at least in some areas.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
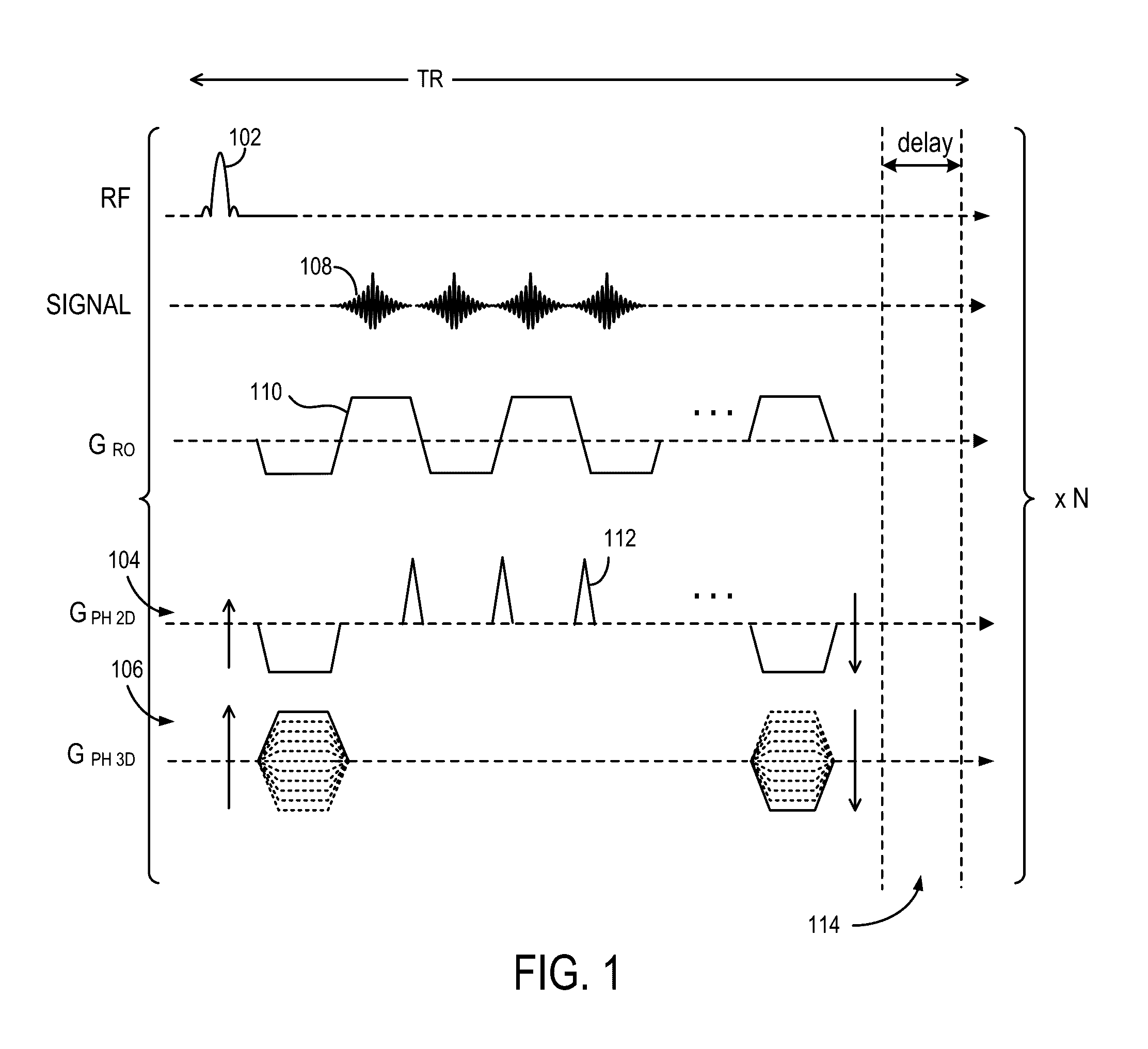
System for Accelerated Segmented MR Image Data Acquisition
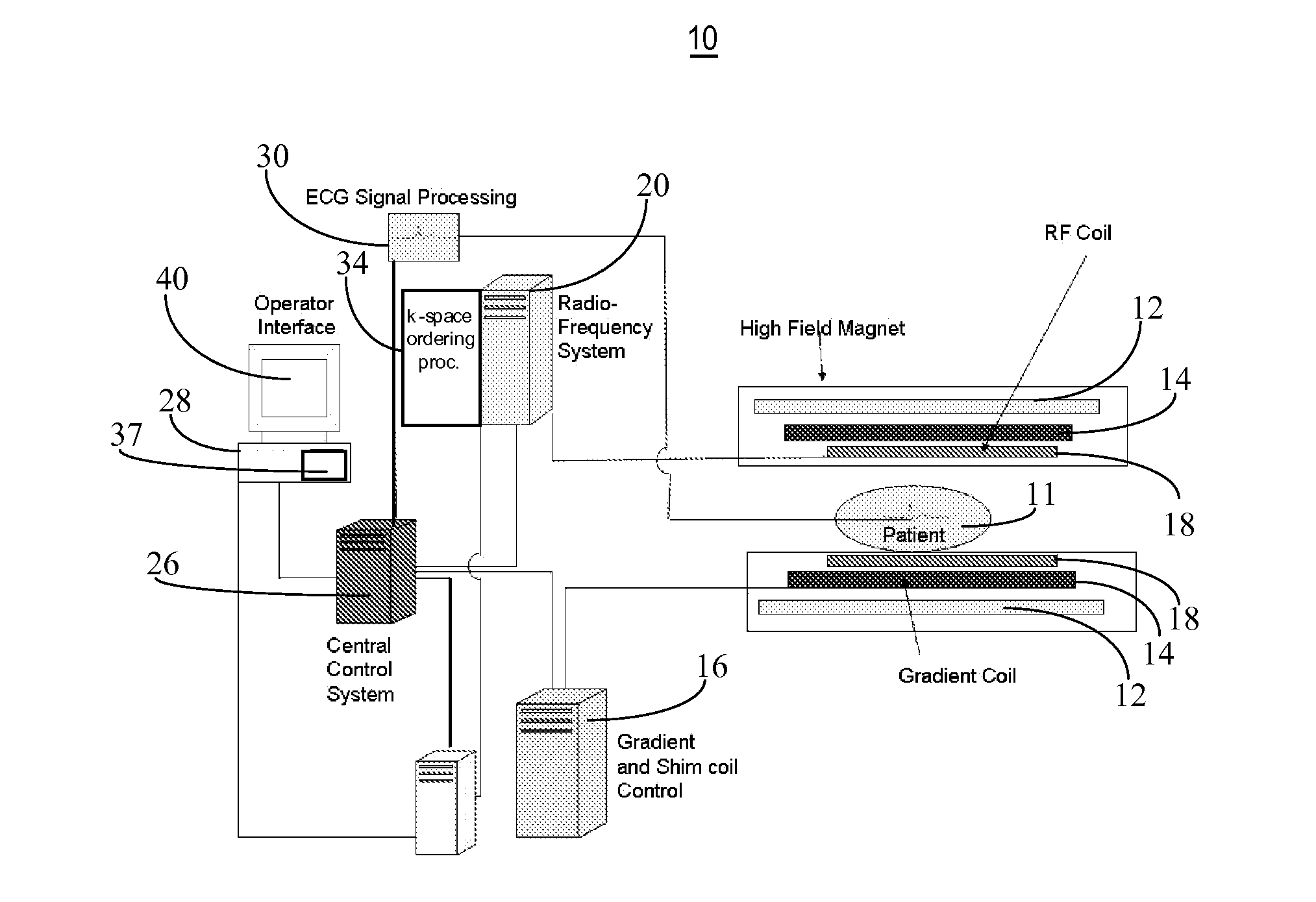
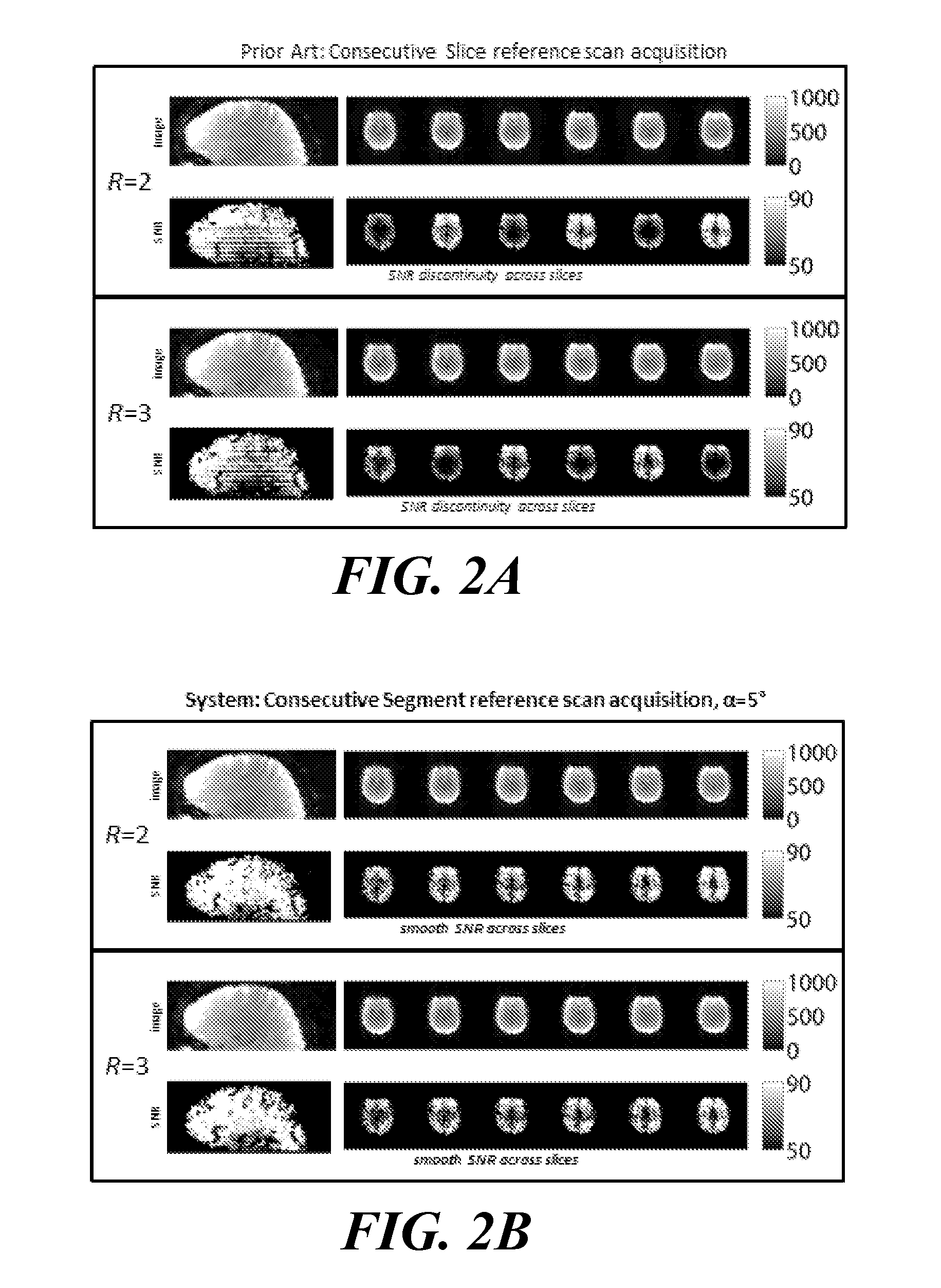
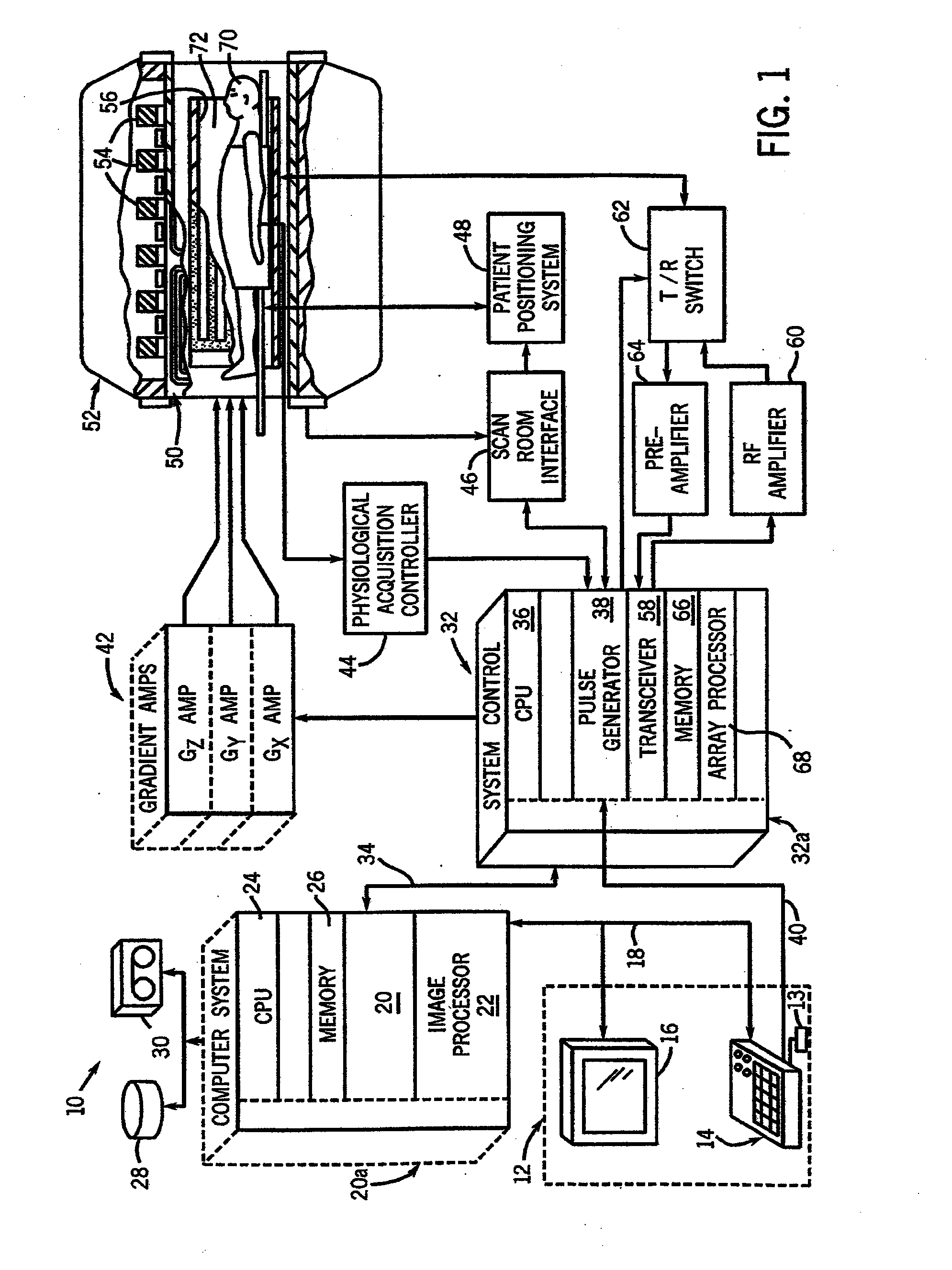
ActiveUS20140037171A1Accelerates segmented magnetic resonance (MR) image data acquisitionReconstruction from projectionMagnetic measurementsMagnetic field gradientResonance
A system for accelerated segmented magnetic resonance (MR) image data acquisition includes an RF (Radio Frequency) signal generator and a magnetic field gradient generator. The RF signal generator generates RF excitation pulses in anatomy and enabling subsequent acquisition of associated RF echo data. The magnetic field gradient generator generates magnetic field gradients for anatomical volume selection, phase encoding, and readout RF data acquisition in a three dimensional (3D) anatomical volume. The RF signal generator and the magnetic field gradient generator acquire consecutive segments of k-space line data representative of an individual image slice in a gradient echo method by adaptively varying RF excitation pulse flip angle between acquisition of the consecutive segments.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH +1
Method and apparatus for generating a magnetic resonance image
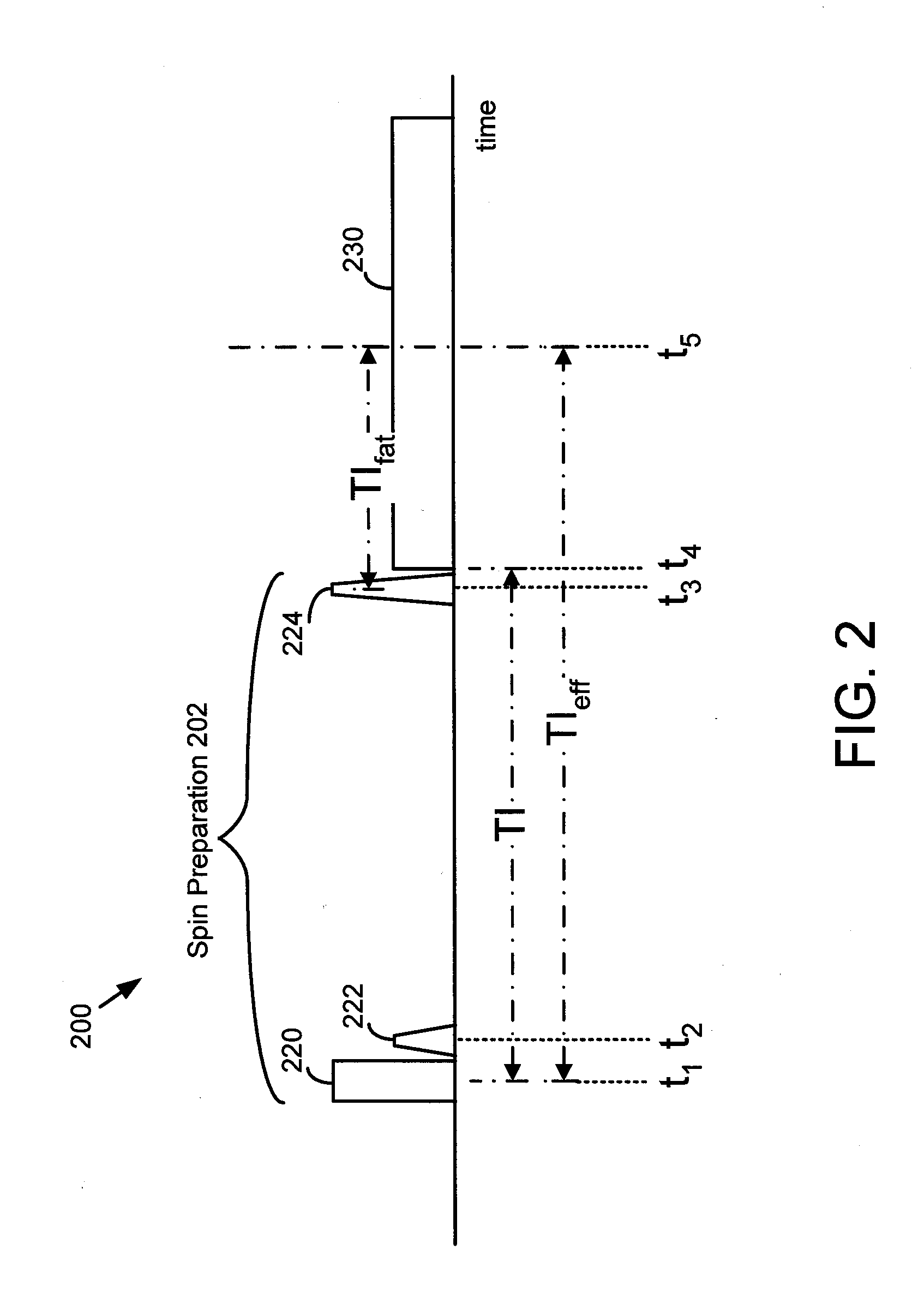
A method for generating a magnetic resonance image includes a series of inversion and saturation pulses, in which the pulses null the MRI signal from both fat and a second tissue for a single MRI acquisition. An inversion pulse is used to provide a null point for the second tissue. A pair of fat-selective saturation and inversion pulses are used to null the MRI signal from fat at approximately the same time as the second tissue reaches its null point. The saturation pulse is used to create a known state for the fat magnetization, allowing the flip angle of the fat-selective inversion pulse to be determined such that the null point of fat approximately coincides with the null point of the second tissue.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveCN102772206AMeet the requirements of dynamic imagingAchieve any positionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFat suppressionDynamic contrast
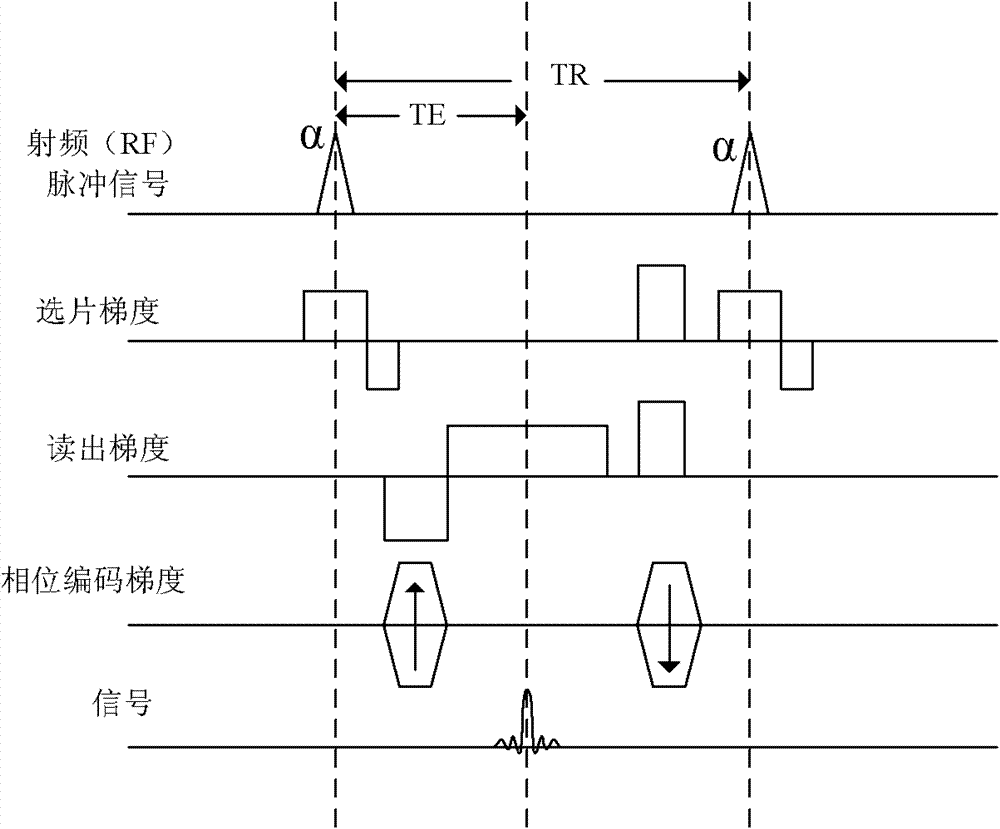
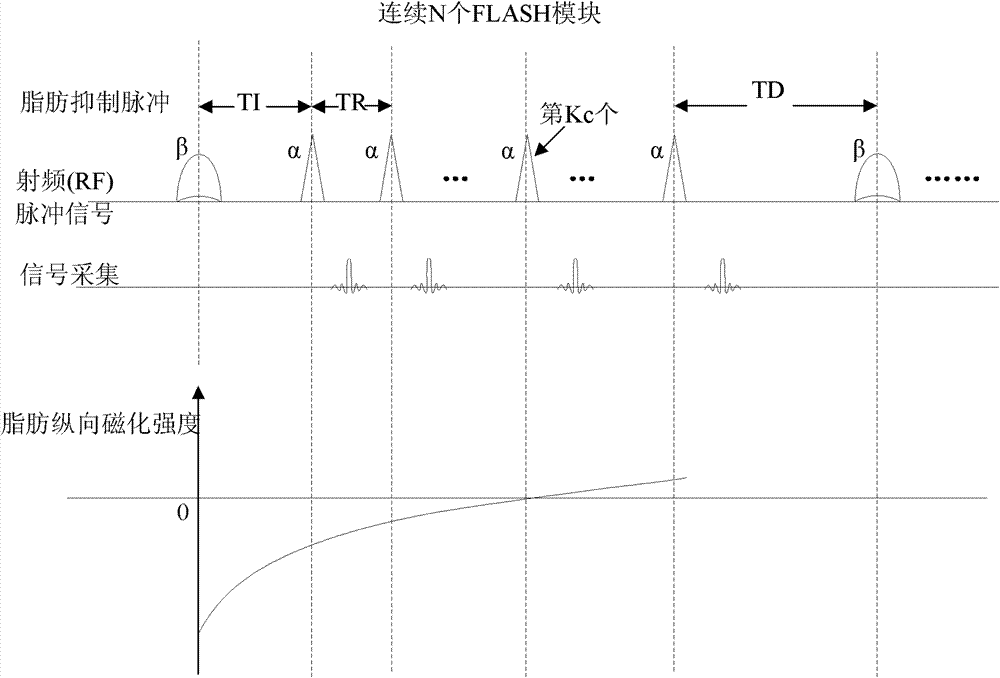
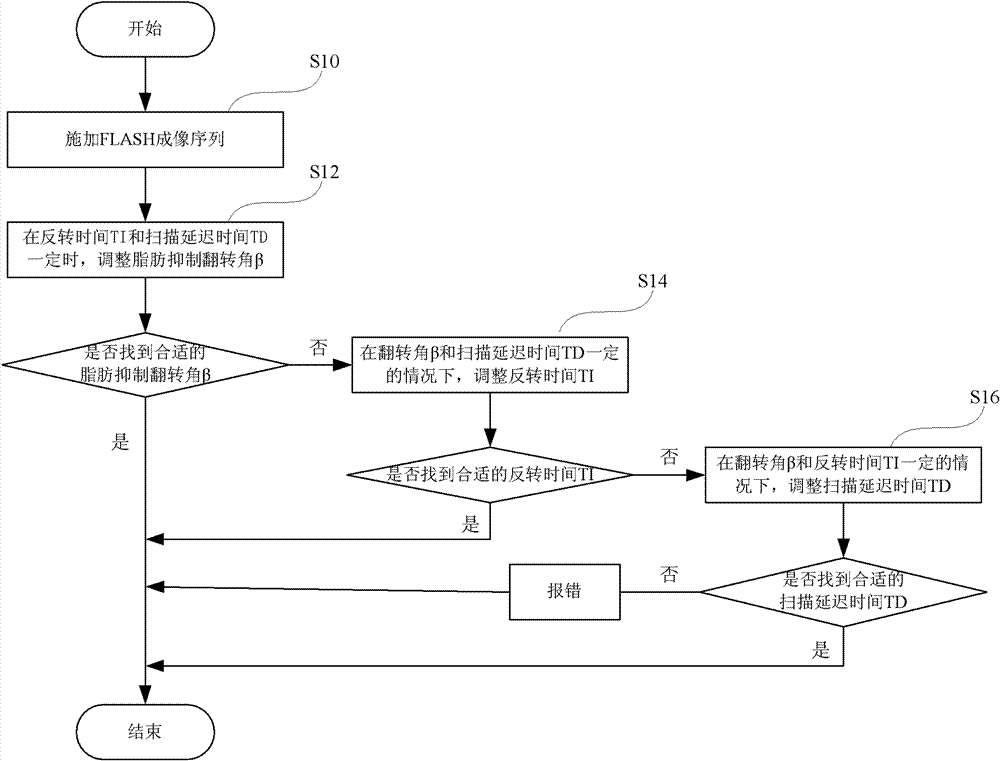
The invention provides a magnetic resonance imaging method for dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging based on a three-dimensional pulse sequence of fast low angle shot FLASH. The method comprises the steps of: applying a FLASH imaging pulse sequence to an objected to be examined in a static magnetic field, wherein the FLASH imaging pulse sequence comprises radio frequency shot pulses a and fat inhibiting pulses b, and N radio frequency shot pulses a are comprised between two adjacent fat inhibiting pulses b; adjusting a fat inhibiting flip angle b with certain time of inversion T1 and time of scan delay TD to obtain the optimal fat inhibiting effect; and adjusting the time of inversion T1 and / or the time of scan delay TD to obtain the optimal fat inhibiting effect in a condition that the optimal fat inhibiting effect cannot be obtained by adjusting the fat inhibiting flip angle b. Compared with the prior art, the magnetic resonance imaging method provided by the invention has the advantages of good fat inhibiting effect and high imaging quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Flip angle modulated magnetic resonance angiography
InactiveUS6198960B1Improvement in signal enhancementEnhanced signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPulse sequenceMR - Magnetic resonance
A dynamic MRA study of a subject is performed using a 3D fast gradient-recalled echo pulse sequence after the subject is injected with a contrast agent. The flip angle of an rf excitation pulse in the pulse sequence is modulated during the acquisition as a function of contrast agent concentration in the region of interest. In one embodiment the flip angle is updated by interleaving measurement pulse sequences which measure in real-time contrast agent concentration. In another embodiment the contrast concentration profile is determined in advance and a corresponding table of optimal flip angles are calculated and played out during the image acquisition.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
MRI apparatus
ActiveUS20090091324A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionSignal Repression
A flip-angle calculating unit calculates a flip angle of a fat-suppression pulse by inputting scanning parameters read from a scanning-parameter storage unit based on scanning conditions set by a scan-condition setting unit and a desired fat-suppression level, into a predetermined computing program. A control unit suppresses fat signals to a desired level by performing irradiation of a fat-suppression pulse having the calculated flip angle and application of a spoiler gradient magnetic field onto a scan target portion of a subject by controlling a gradient magnetic-field generating unit and a transmitting-receiving unit, and further performs irradiation of an RF pulse and application of a gradient magnetic field in accordance with a predetermined pulse sequence, thereby detecting water signals and suppressed fat signals as MR signals. An image-data creating unit creates image data by reconstructing the MR signals.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and apparatus of gradient echo imaging with on-the-fly optimization of tissue suppression
InactiveUS20050070785A1Minimize timeSuppress signalDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData acquisitionMagnetization
The present invention provides a system and method for on-the-fly optimization of the timing of suppression pulses and a k-space filling scheme for user-prescribed imaging parameters. The invention also minimizes total data acquisition time for the sequence tailored to the particular user-prescribed imaging parameters. A pulse sequence uses a 180° pulse to invert the magnetization corresponding to the suppressed tissue so that a maximum amount of time is provided to play out alpha or imaging pulses after each inversion. The pulse sequence optimizes the number of alpha pulses played out after each inversion pulse based on a specific protocol or imaging parameters selected by the user. This pulse sequence allows for a modified k-space filling scheme that places, at the center of k-space, the echo that most closely corresponds to the null point of the suppressed tissue. For the first inversion pulse, a flip angle less than 180° is used to drive the suppressed tissue magnetization into a steady-state condition immediately.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and operating method allowing multiple scans in rapid succession
InactiveUS6366090B1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonancePrecession
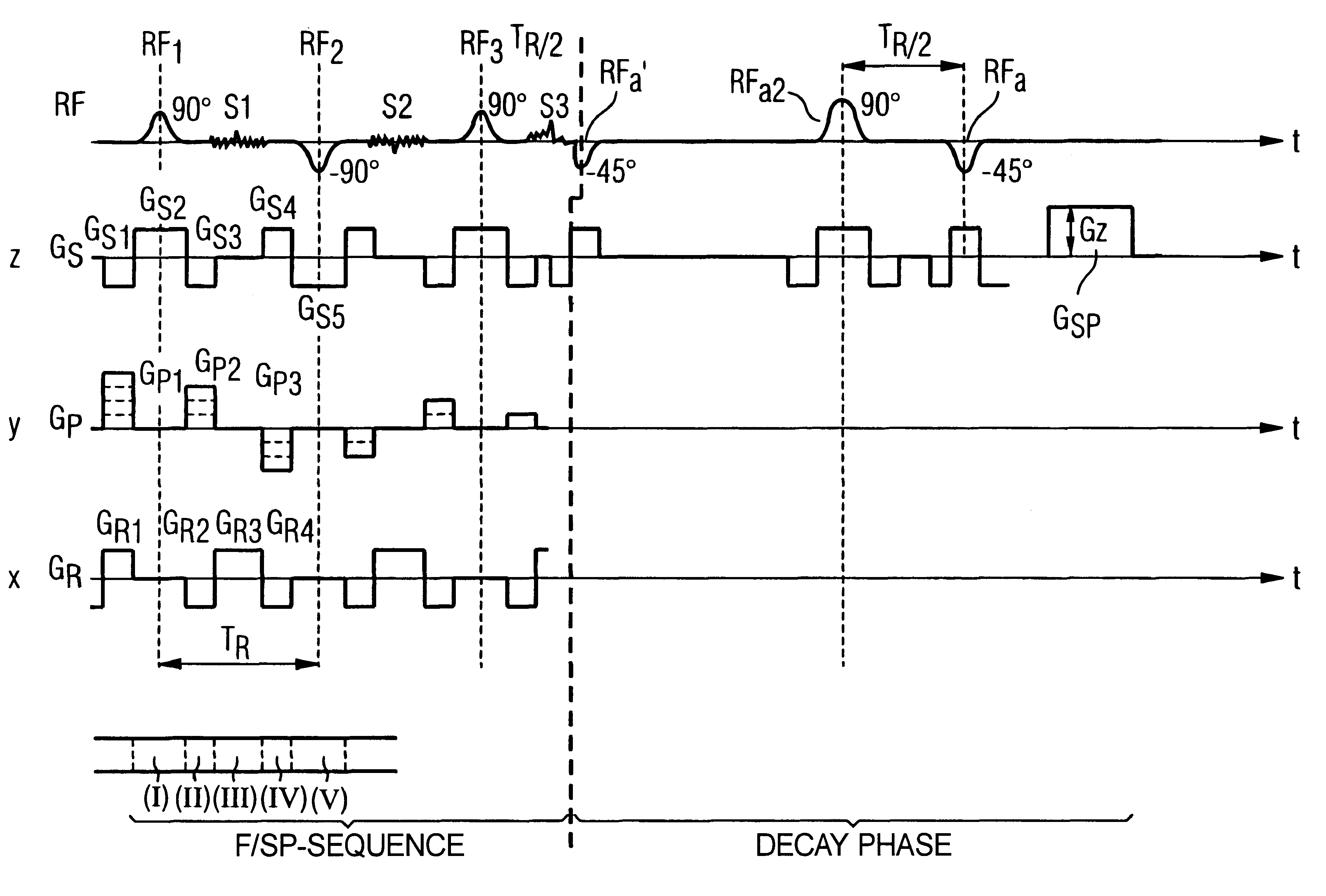
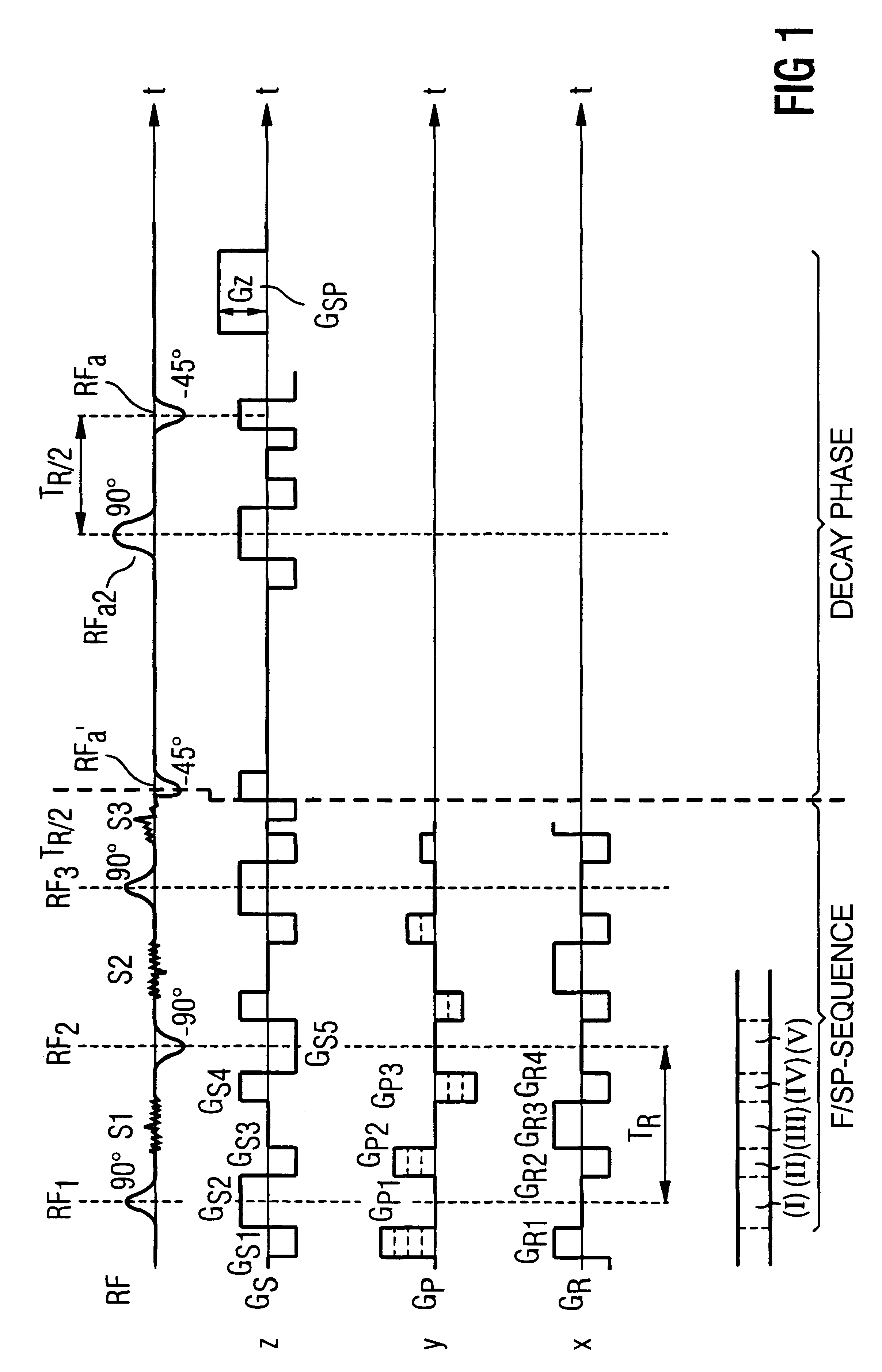
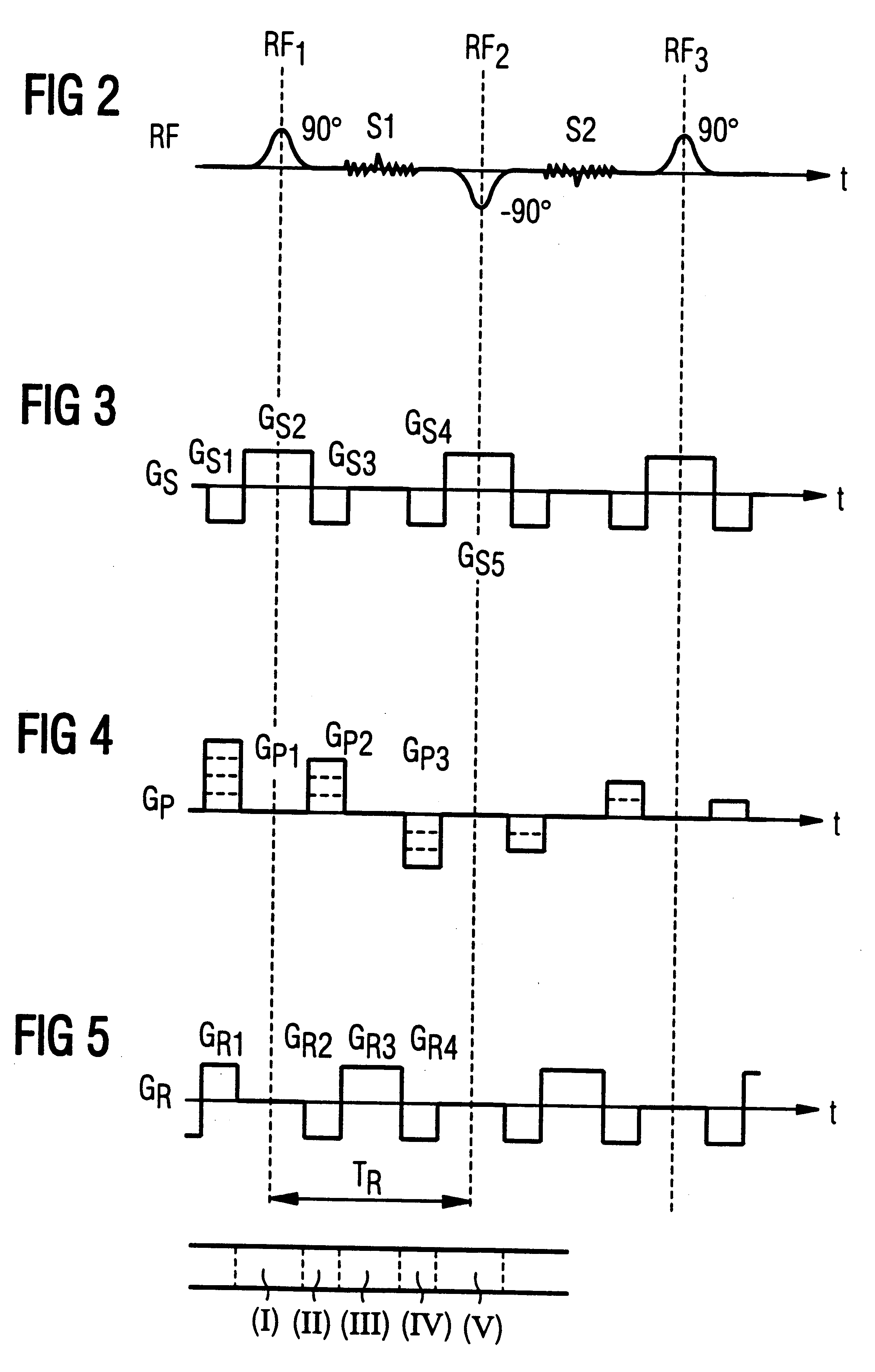
In a method in the form of a pulse sequence for operating a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus, and in a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus operated according to the method, image data are obtained according to a SSFP or FISP (Fast Image Steady Precession) pulse sequence. After the end of the imaging sequence, a decay radio-frequency pulse having a flip angle of approximately .alpha. / 2 with a phase angle inverted relative to the last excitation pulse of the imaging sequence is emitted wherein .alpha. is the flip angle of the excitation pulses of the imaging sequence. The decay radio-frequency pulse is emitted at an interval T.sub.R / 2 following the last excitation pulse, where T.sub.R is the repetition time of the imaging sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Turbospin echo imaging sequence with long echo trains and optimized t1 contrast
ActiveUS20080278159A1Minimize impactShorten the lengthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionT1 contrastResonance
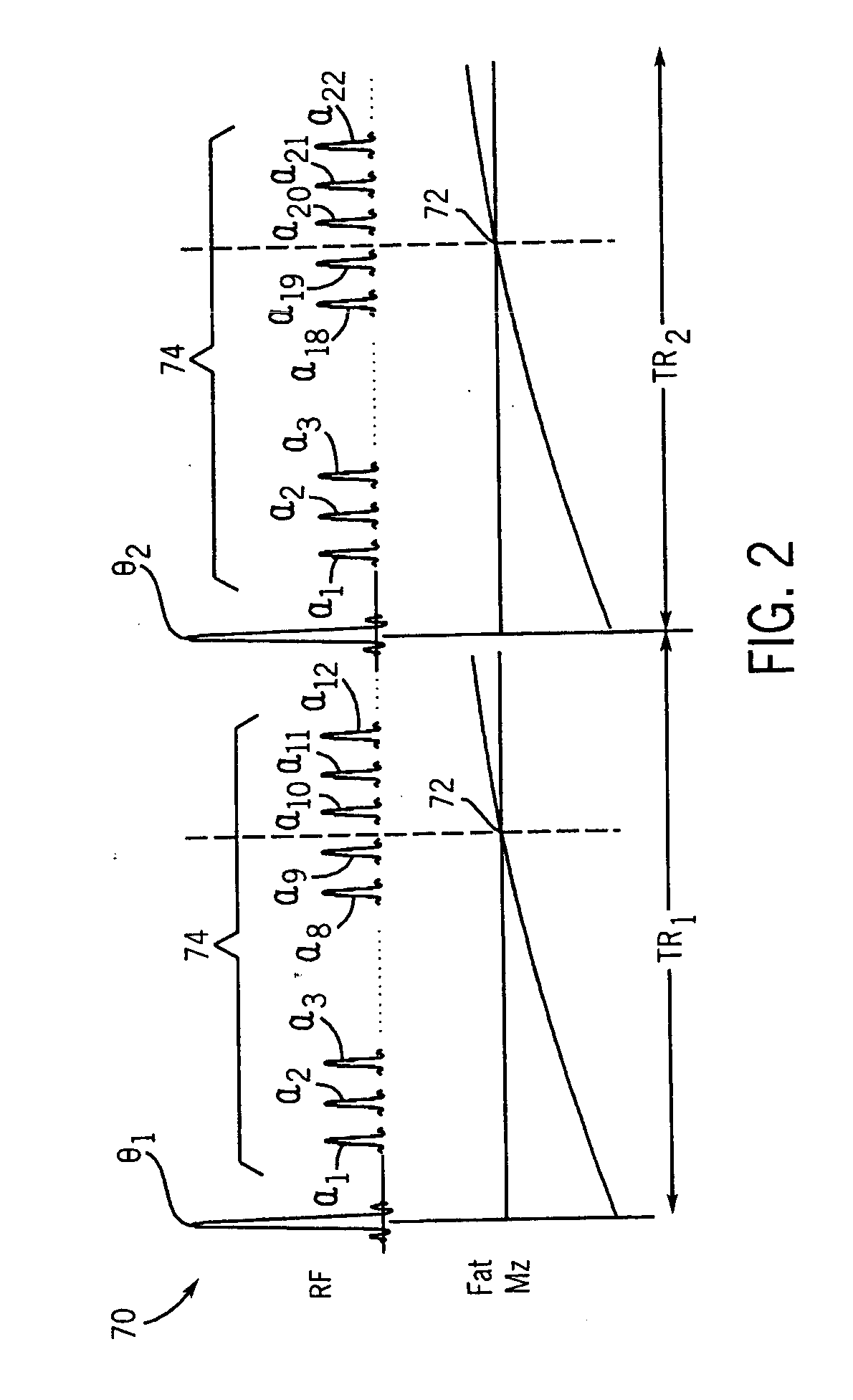
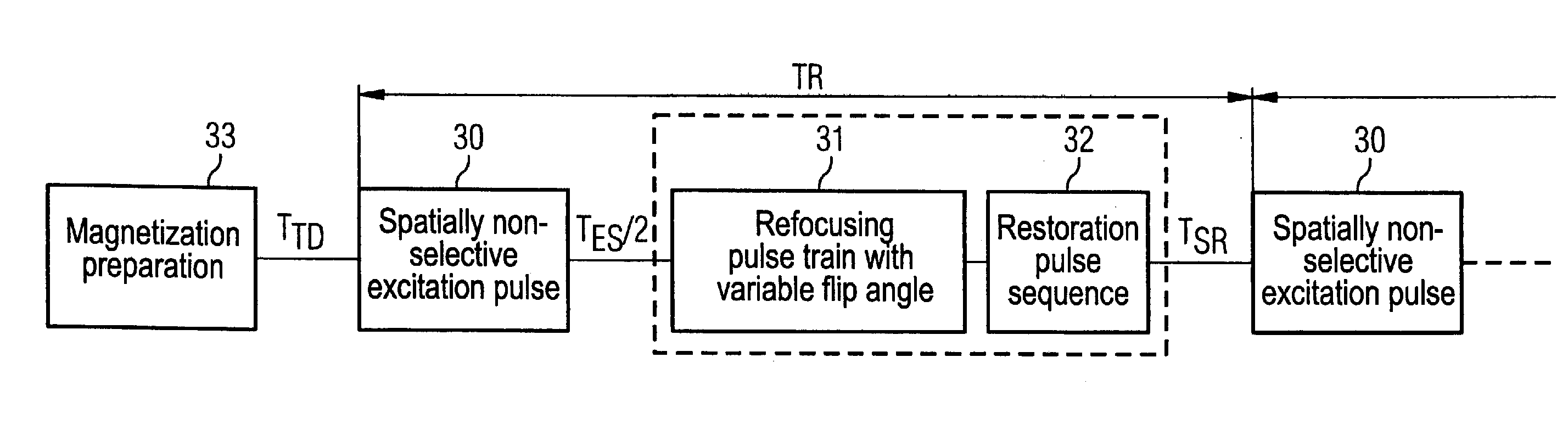
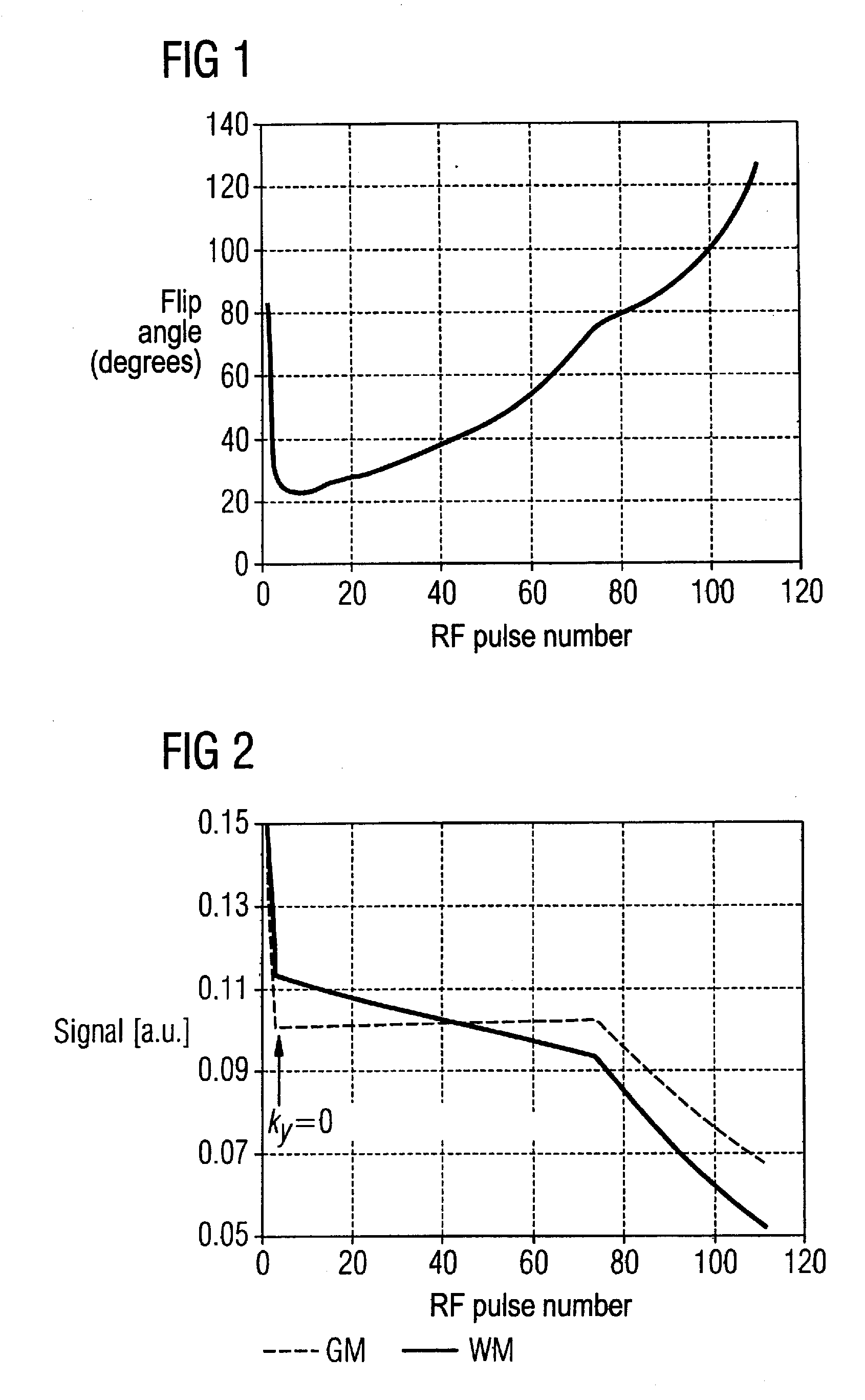
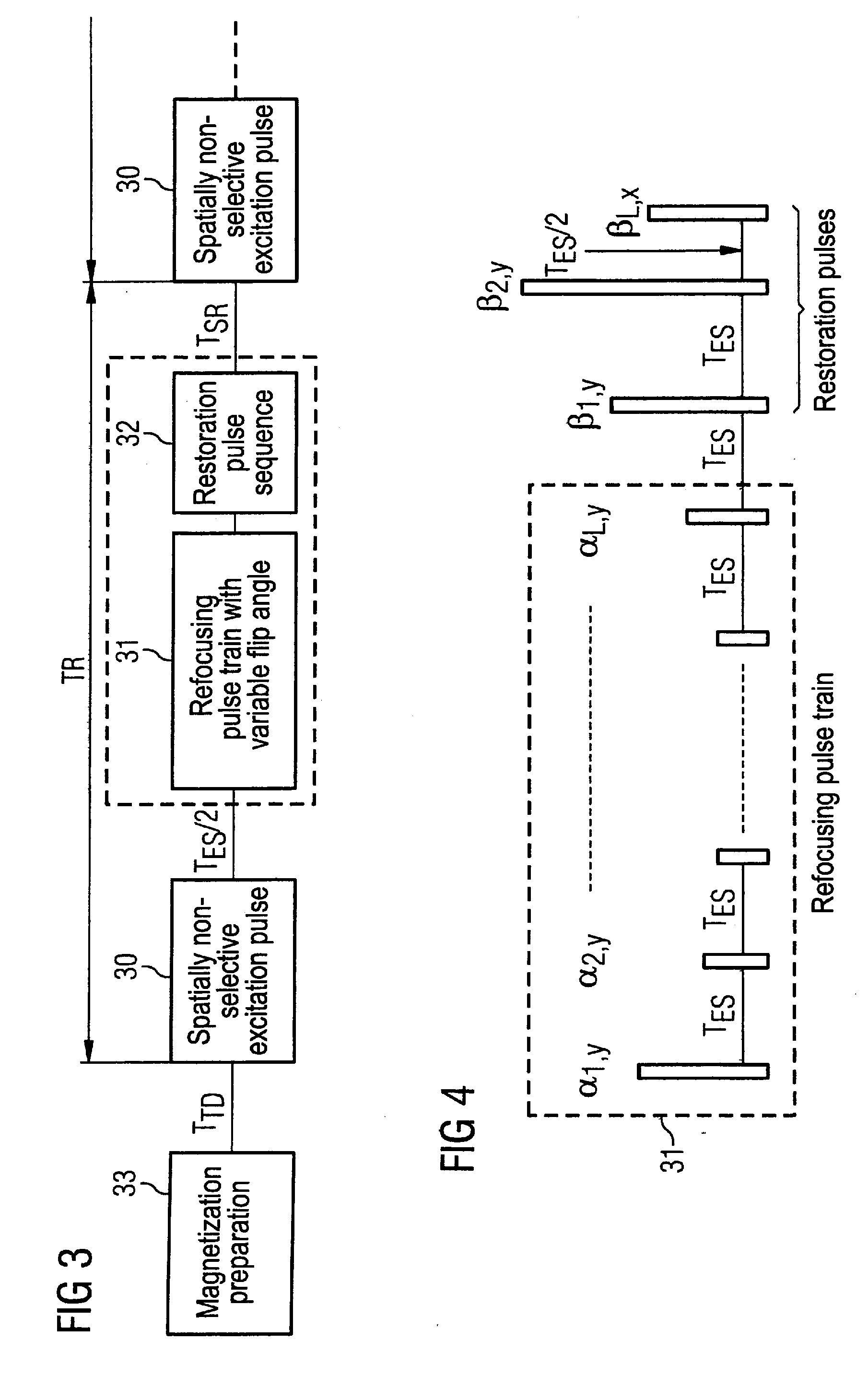
In a method in the form of a turbo spin echo imaging sequence with long echo trains and optimized T1 contrast for generation of T1-weighted images of an examination subject by magnetic resonance, magnetization in the examination subject is excited with an RF excitation pulse, a number N of RF refocusing pulses with variable flip angle are radiated to generate multiple spin echoes for an excitation pulse, a restoration pulse chain is activated after switching of the N refocusing pulses and before the next RF excitation pulse. The restoration pulse chain influences the magnetization such that the magnetization is aligned opposite to the direction of the basic magnetic field by the restoration pulse chain before the next RF excitation pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus to reduce RF power in high field MR imaging incorporating multi-phase RF pulse flip angles
InactiveUS6956374B2Reduce total powerReduce depositionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImage resolutionHigh field mr
A technique is set forth that is designed to reduce RF induced power in high field MR imaging that includes application of an initial contrast preserving phase of RF pulses. These initial RF pulses are designed to have a constant, relatively high flip angle over the initial contrast preserving phase. Following an effective TE, a ramp down phase is applied that has a limited number of RF pulses with a flip angle that is less than the flip angle of those in the initial contrast preserving phase. Further, the RF pulses in the ramp down phase have a flip angle that is decreased over the ramp down phase. This technique provides improved resolution and steady contrast and SNR, while significantly reducing induced RF power.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for measuring the magnetic resonance (NMR) by means of spin echoes
InactiveUS6850063B2Reduce trainingReducing RF energyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationSpectroscopy
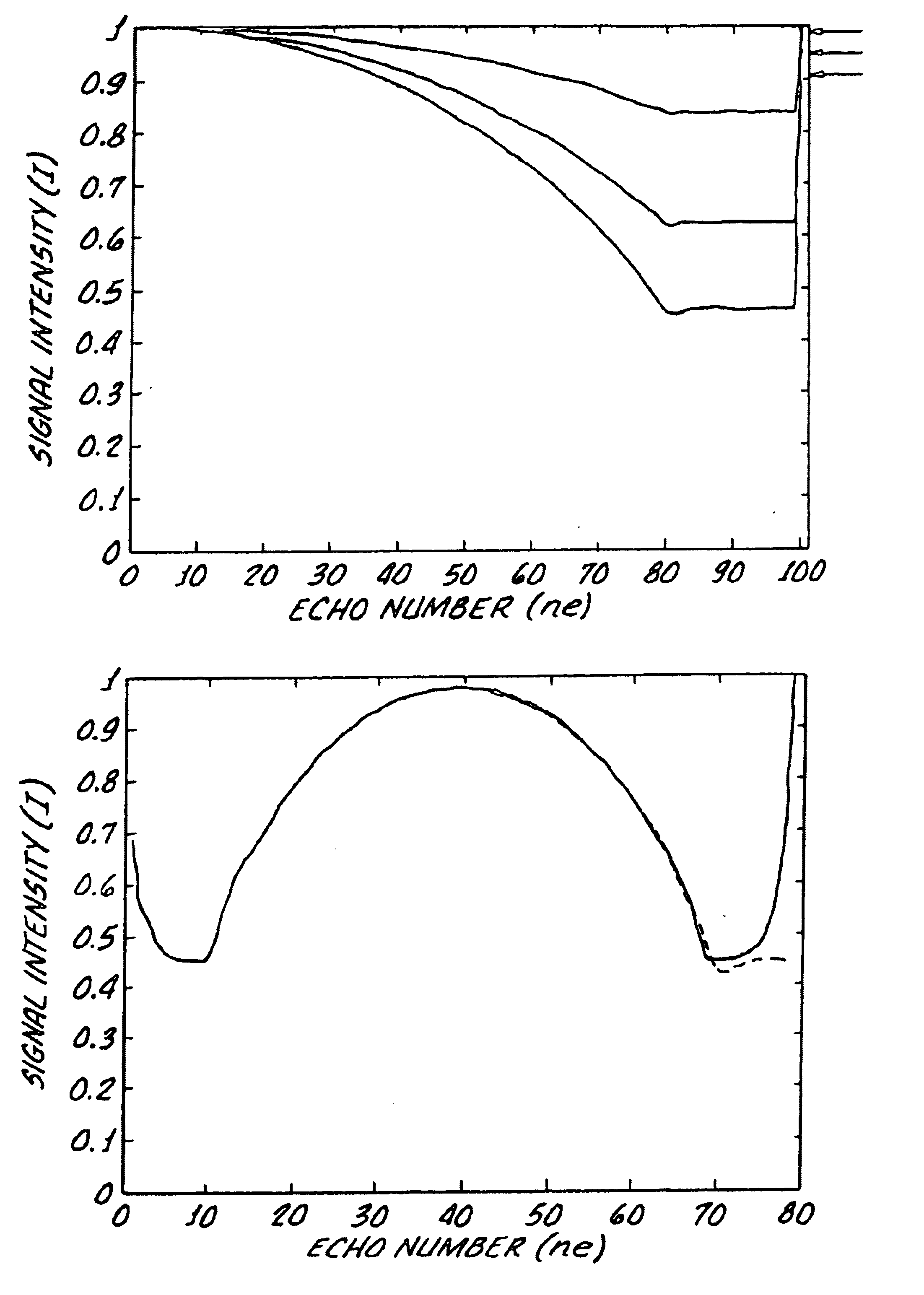
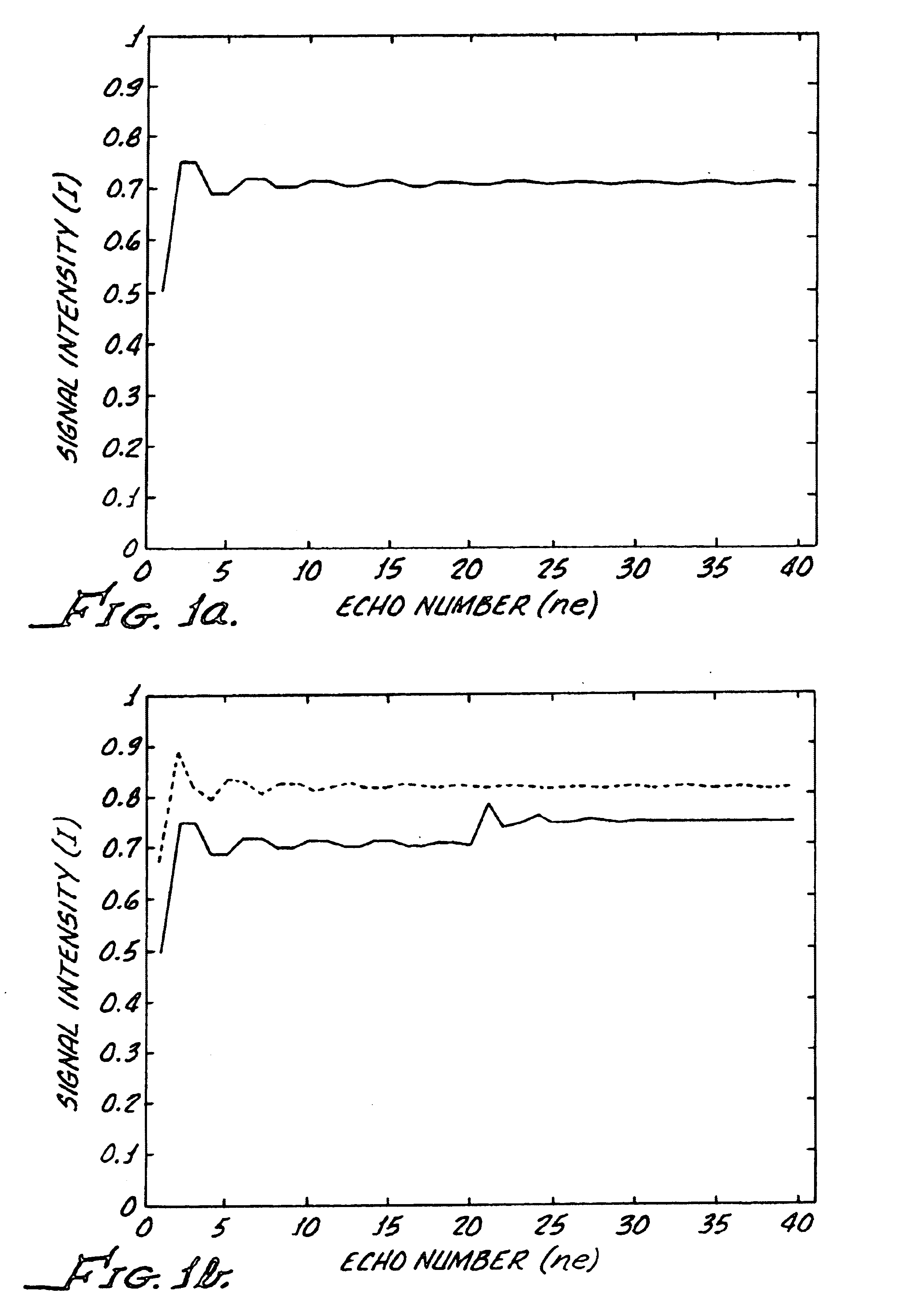
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy or tomography method wherein a sequence of temporally mutually offset radio frequency (RF) pulses is applied onto a spin ensemble like a CPMG multi echo experiment, and wherein the magnetization produced after an initial excitation pulse is transferred to or close to the static pseudo steady state of the initially applied refocussing flip angle α1 is characterized in that magnetization is transferred through gradual change of the refocussing flip angle in subsequent refocussing intervals to or close to the static pseudo steady state of the respectively used refocussing pulse with refocussing flip angle αn such that the echo amplitude of the nth echo generated in this fashion approaches the maximum possible value corresponding to the respective refocussing pulse with refocussing flip angle αn. The RF energy required for excitation of the nuclear spins can thereby be considerably reduced without having to accept signal intensity losses.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20090134871A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImaging conditionResonance
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes a data acquisition unit and an image generating unit. The data acquisition unit acquires MR data according to an imaging condition for obtaining a SSFP in flowing matter by applying excitation pulses having a same flip angle with a constant TR and gradient magnetic fields to an object. The image generating unit generates an image of the flowing matter based on the MR data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method to determine a predetermined signal amplitude in mr measurements
In a method and apparatus to determine a predetermined signal amplitude of an examination subject in an MR measurement in which multiple RF pulses are radiated into the examination subject in a pulse sequence in a pulse series with a repetition time TR that is smaller than the T2 times of the examination subject, a target magnetization is established for a predetermined point in time after radiation of the respective RF pulse for essentially all RF pulses from the pulse series, a target flip angle and a target phase are determined for different regions of the examination subject for essentially all RF pulses depending on the respective target magnetization, a respective amplitude and phase response is determined for essentially all RF pulses to generate the respective target magnetization after radiation of the respective RF pulse, and the RF pulses with the respective determined amplitude and phase response are radiated into the examination subject.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system of determining parameters for MR data acquisition with real-time B1 optimization
ActiveUS7078900B2High resolutionFast and simple and effectiveMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData acquisitionPulse sequence
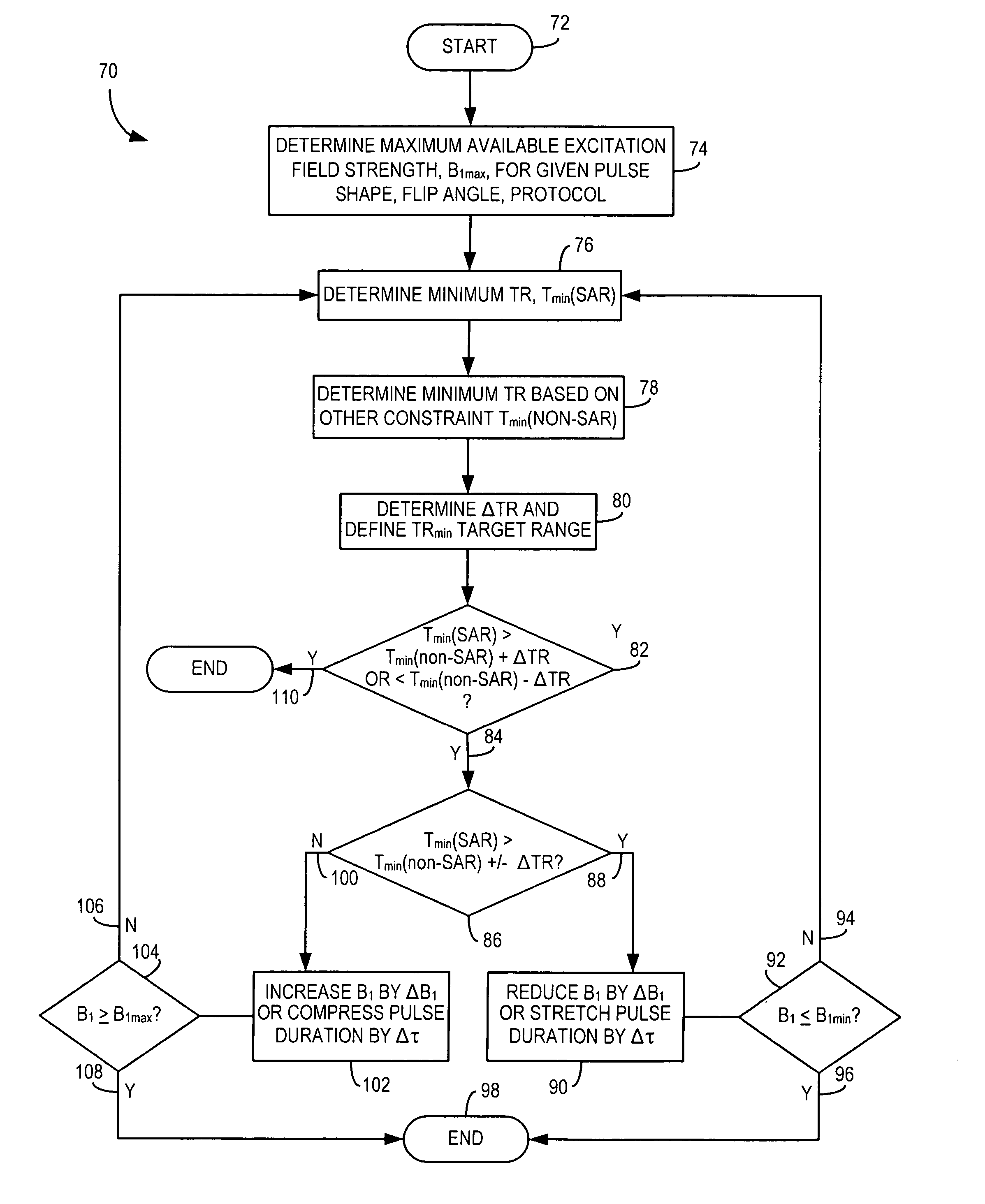
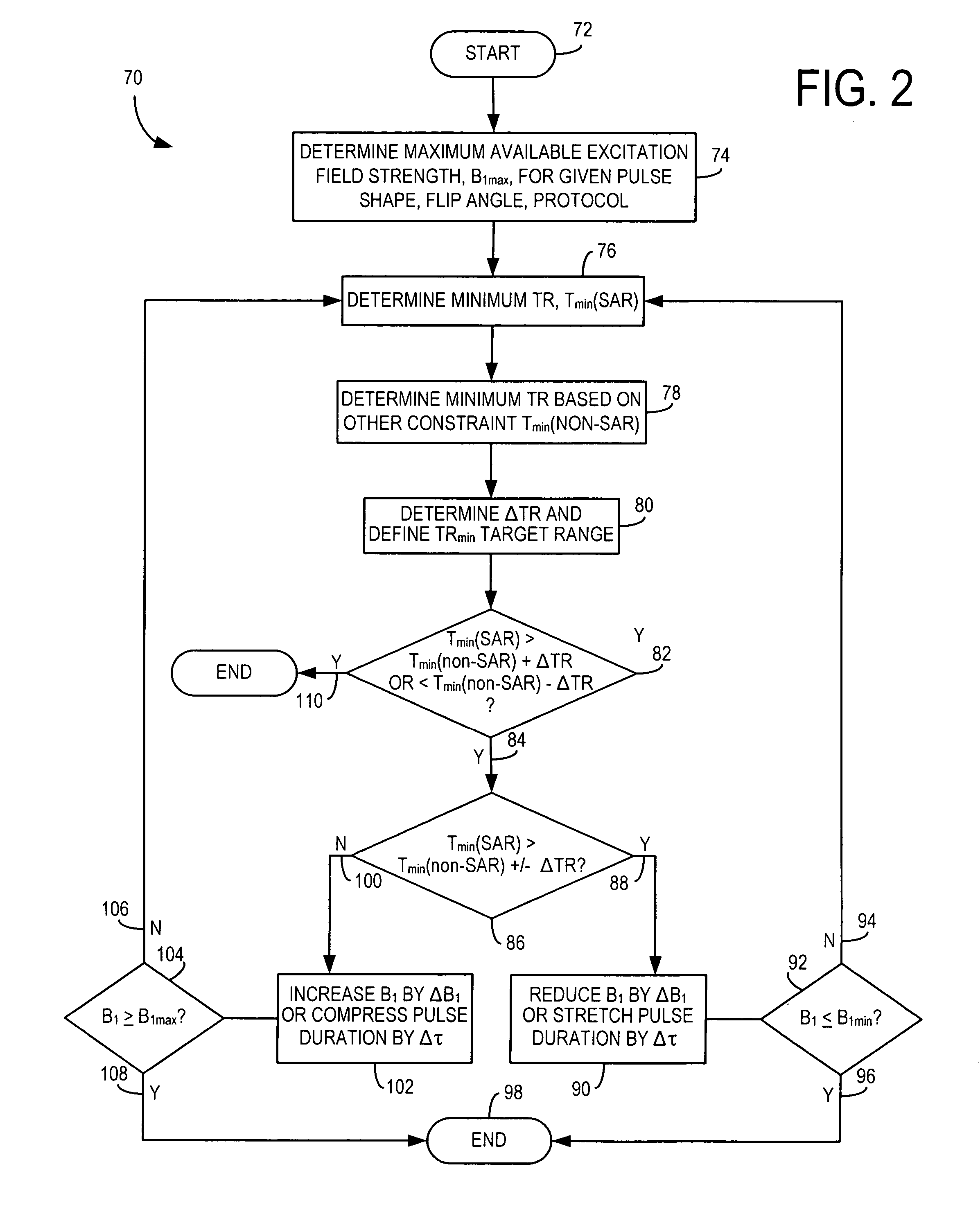
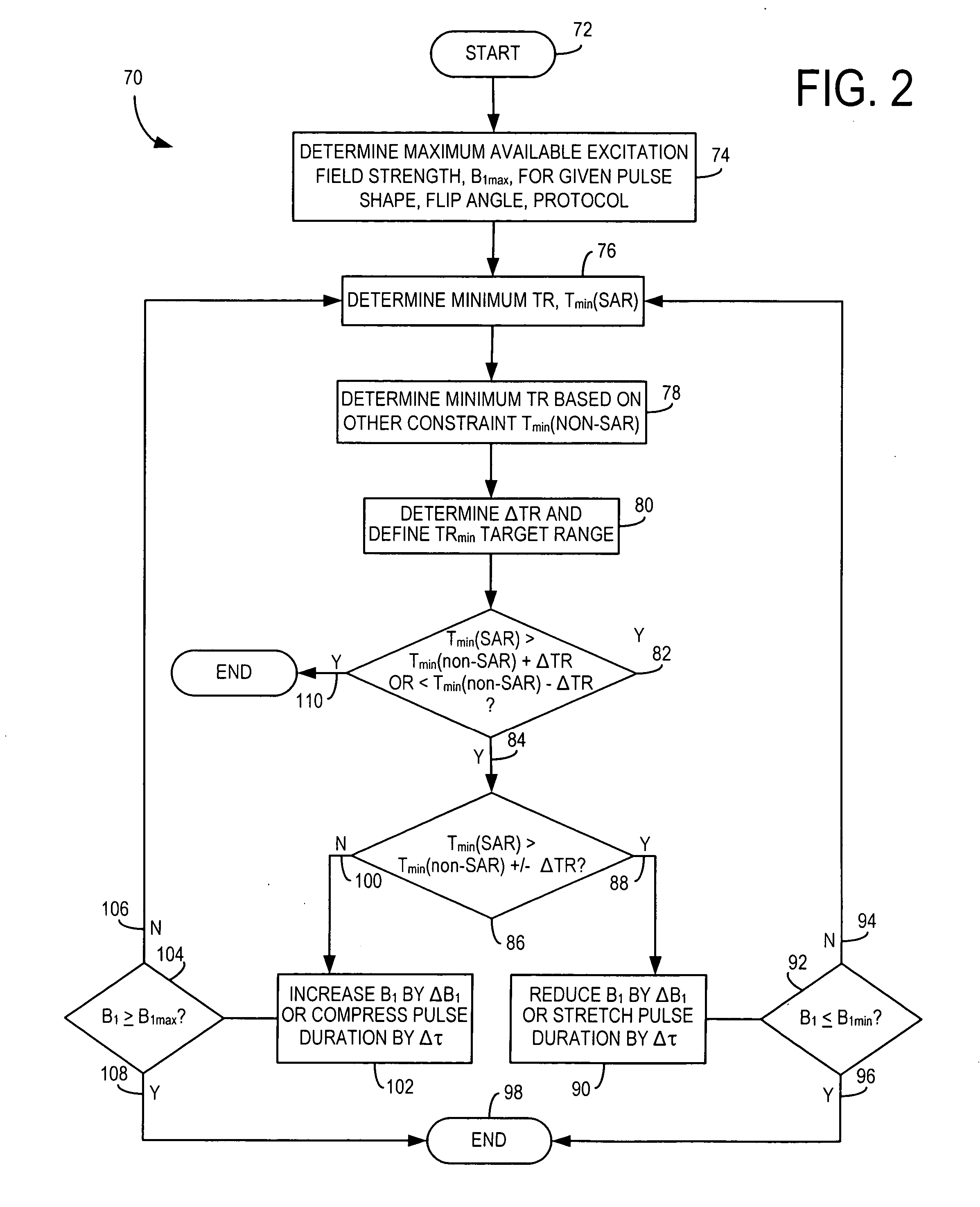
The present invention provides a system and method of MR scan prescription to achieve in a fast, simple, and effective manner the optimal peak excitation field strength for a given pulse shape and flip angle such that the minimum TR for the MR scan can be optimized and based on SAR constraints. The present invention provides a technique to obtain optimal B1 parameters for an arbitrary shape and flip angle of an excitation pulse in real-time while satisfying SAR and / or RF hardware limits to determine the minimum achievable repetition time for a pulse sequence. The present invention is particularly applicable with breath-hold and cardiac imaging techniques that are carried out at relatively high field strengths.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method
ActiveCN107153169AHigh precisionSuppresses Motion ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRadio frequencyImage sequence
The invention discloses a steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method. The steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method comprises the following steps of on the basis of a steady-state procession imaging sequence for conventional scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging system, repeatedly exciting the imaging area by a radio frequency pulse at the interval of 10ms magnitude or smaller short cycle TR; setting a pulse flip angle into +alpha / 2 in a first sequence repetition cycle, and eliminating the sampling period; alternatively setting the pulse flip angle into +alpha and -alpha in the subsequent sequence repetition cycle; using the layer selection gradient, phase encoding gradient and frequency encoding gradient to perform three-dimensional encoding, wherein the sum of integral areas of gradients in each bearing is zero, and the proton magnetizing vector procession is approximate to the steady state; enabling the magnetizing vectors to form three or two gradient echoes under the action of three or two positive and negative alternating frequency encoding gradients in each TR period, wherein the integral area of gradients in the frequency encoding direction is zero; performing direct phase encoding on the three or two echoes according to echo peak interval and water and grease chemical displacement difference value.
Owner:谱影医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
Method and system of determining parameters for MR data acquisition with real-time B1 optimization
ActiveUS20060017437A1Optimal peak excitation field strengthHigh resolutionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData acquisitionPeak value
The present invention provides a system and method of MR scan prescription to achieve in a fast, simple, and effective manner the optimal peak excitation field strength for a given pulse shape and flip angle such that the minimum TR for the MR scan can be optimized and based on SAR constraints. The present invention provides a technique to obtain optimal B1 parameters for an arbitrary shape and flip angle of an excitation pulse in real-time while satisfying SAR and / or RF hardware limits to determine the minimum achievable repetition time for a pulse sequence. The present invention is particularly applicable with breath-hold and cardiac imaging techniques that are carried out at relatively high field strengths.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance method using a phase-modulated pulse train with a constant small flip angle
InactiveUS20110241667A1Good signalReasonable ratioMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance measurementPulse sequence
A method for performing magnetic resonance measurements on a sample includes applying a first predetermined number of pulse trains for excitation, each pulse train having a constant amplitude and including a second predetermined number of pulses spaced by a predetermined time interval. The pulse trains are modulated by a bent function. After each pulse, data is sampled. Preferably a square number of pulses is generated being constant in power, and the Walsh transform of the sequence of their phases is constant in power, so that the power of the excitation in time and frequency domain is constant. The method can reduce power requirements and may permit undercutting specific absorption rate (SAR) limits due to the small excitation power necessary to create time signals with reasonable signal to noise ratio.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV +1
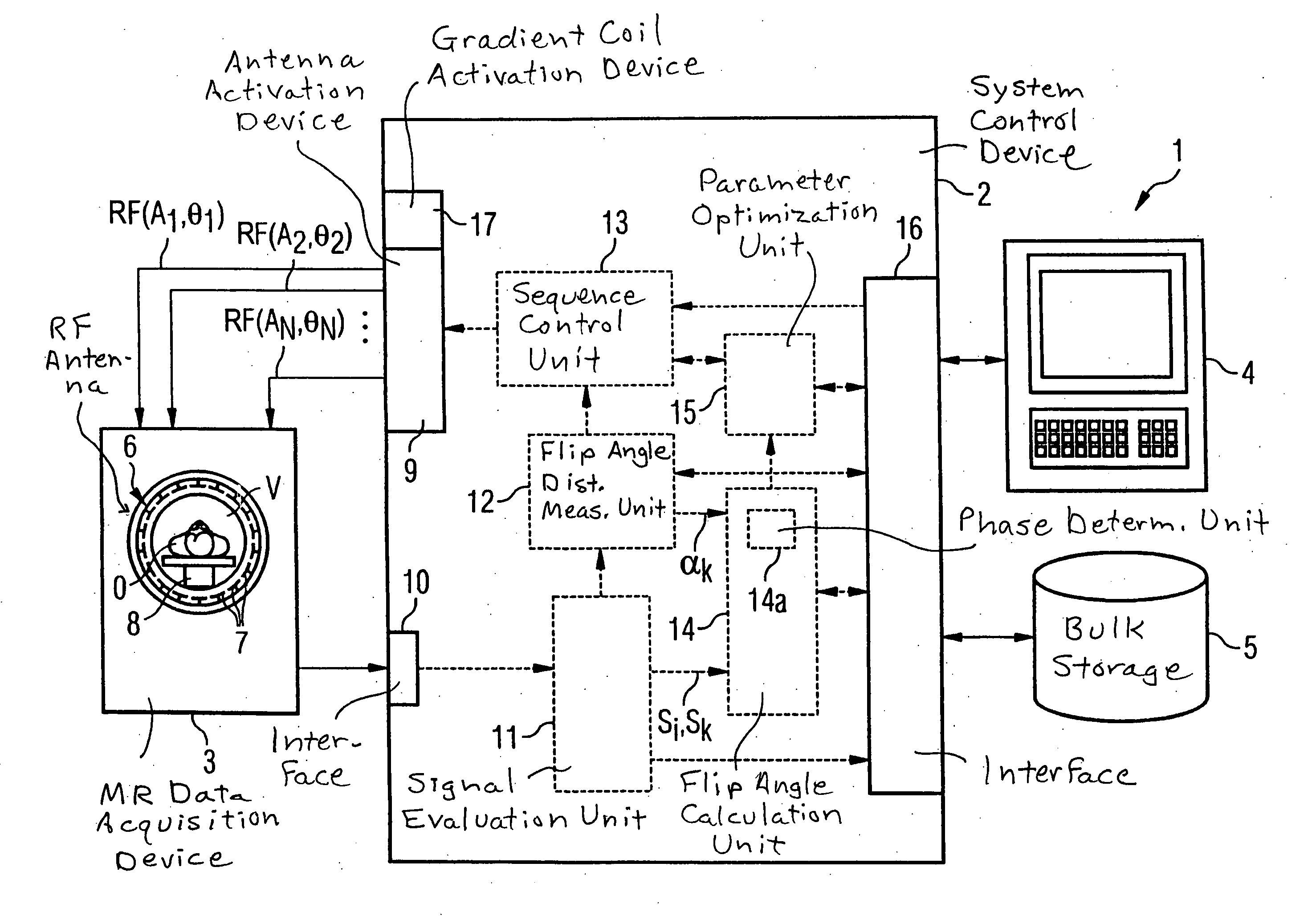
Method and magnetic resonance system for determining the flip angle distribution in a volume of an examination subject
InactiveUS20070085537A1Quick fixSimple methodMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementSpatial correlation
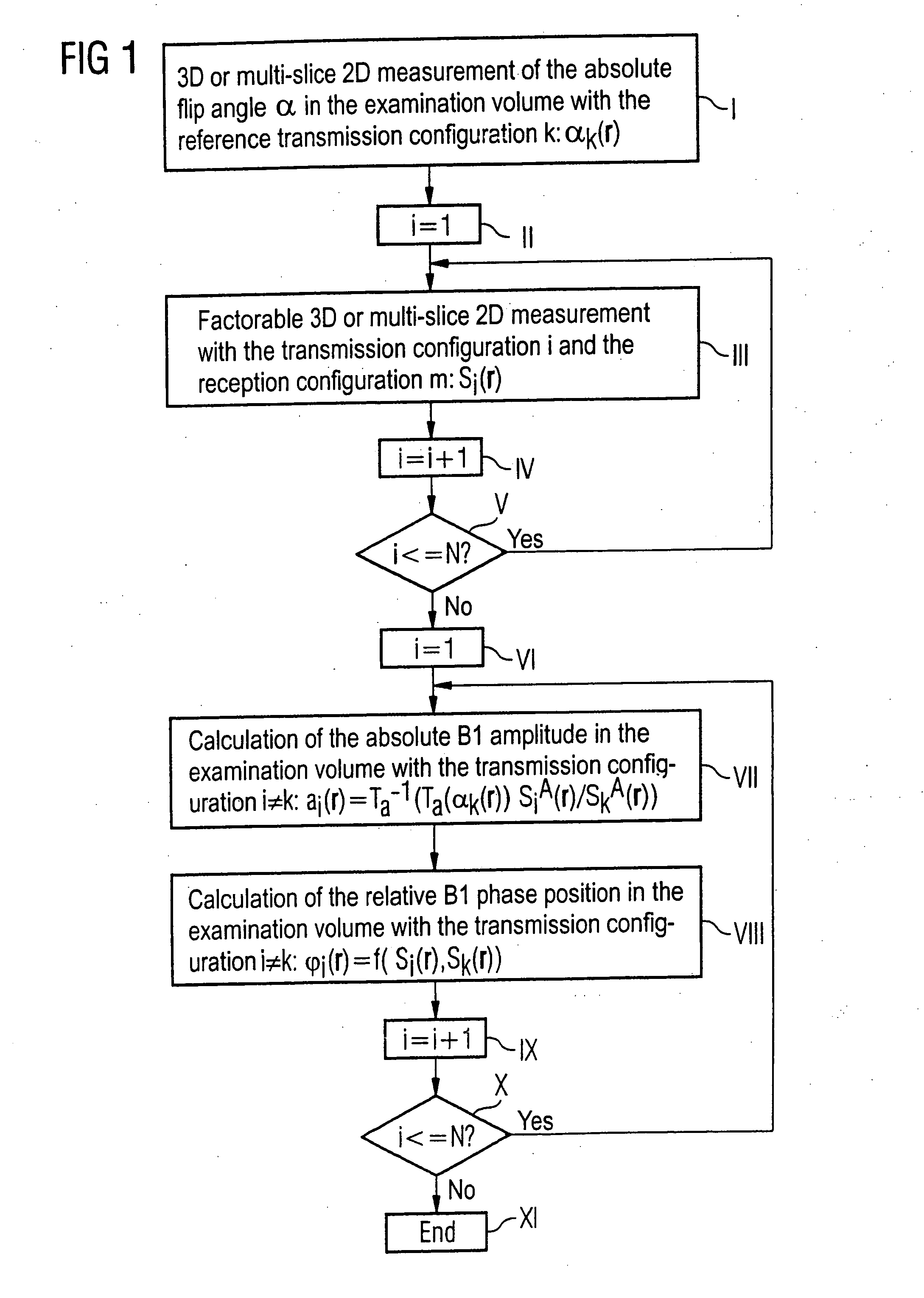
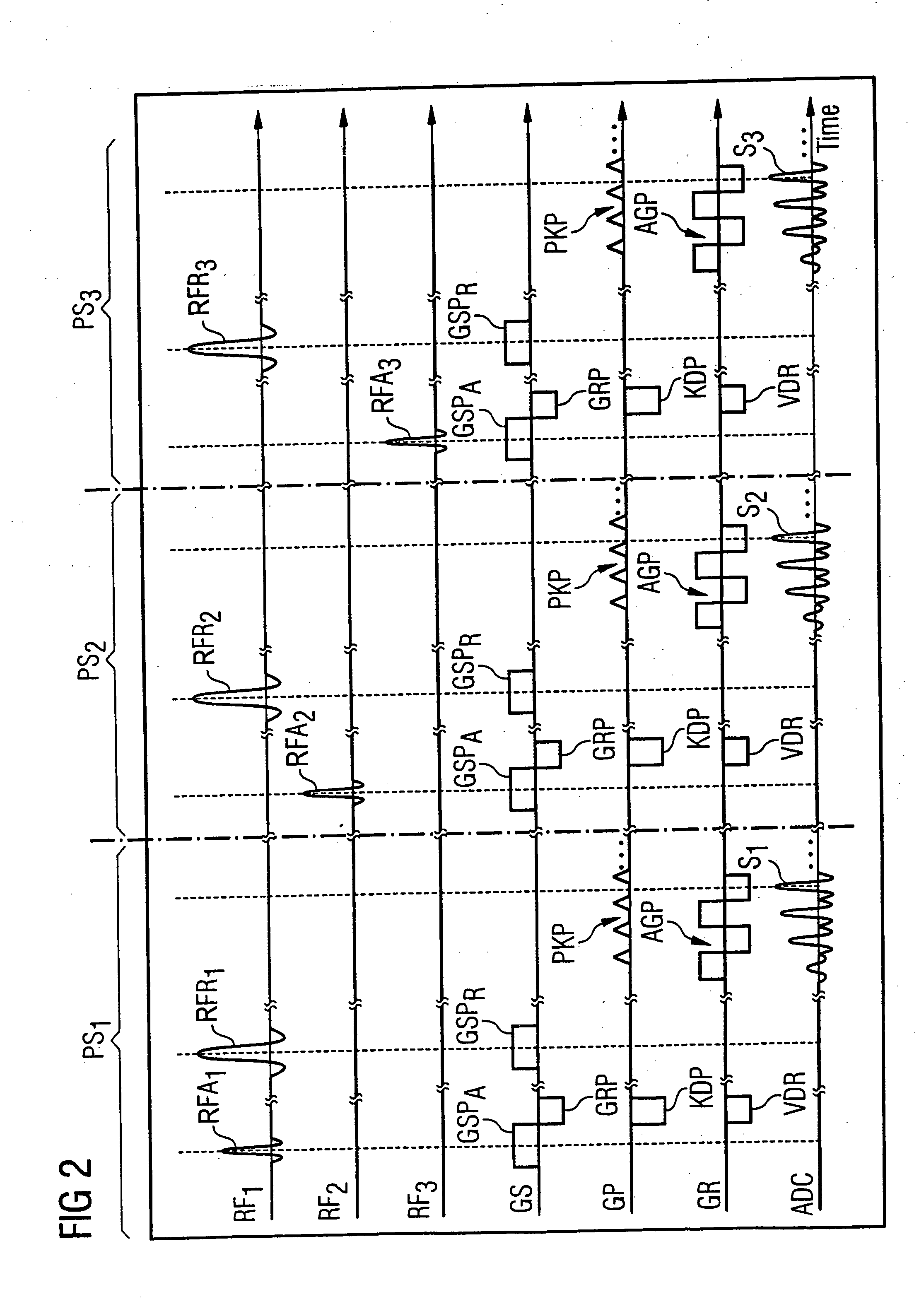
In a method for determination of flip angle distributions for various antenna transmission configurations in a magnetic resonance system, magnetic resonance measurements are implemented with the various transmission configurations, with the reception configuration being identical for all implemented magnetic resonance measurements, and all magnetic resonance measurements for the various transmission configurations are implemented with a specific pulse sequence. This pulse sequence is selected such that the total function that describes the dependency of the image signal at a specific location on the flip angle achieved at this location with the radiated radio-frequency field, as well as on further MR-relevant parameters, can be factored into a first sub-function that describes the dependency of the image signal on the achieved flip angle and a second sub-function (Tb) that describes the dependency of the image signal on the further MR-relevant parameters, and such that the functional dependency of the image signal on the achieved flip angle is known. The absolute flip angle distribution is measured for a reference transmission configuration, and the flip angle distributions of the other transmission configurations are then respectively determined on the basis of the absolute flip angle distribution of the reference transmission configuration and on the basis of the ratio of the spatially-dependent image signals of the magnetic resonance measurements of the respective transmission configuration to the corresponding spatially-dependent image signals of the magnetic resonance measurement of the reference transmission configuration.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com