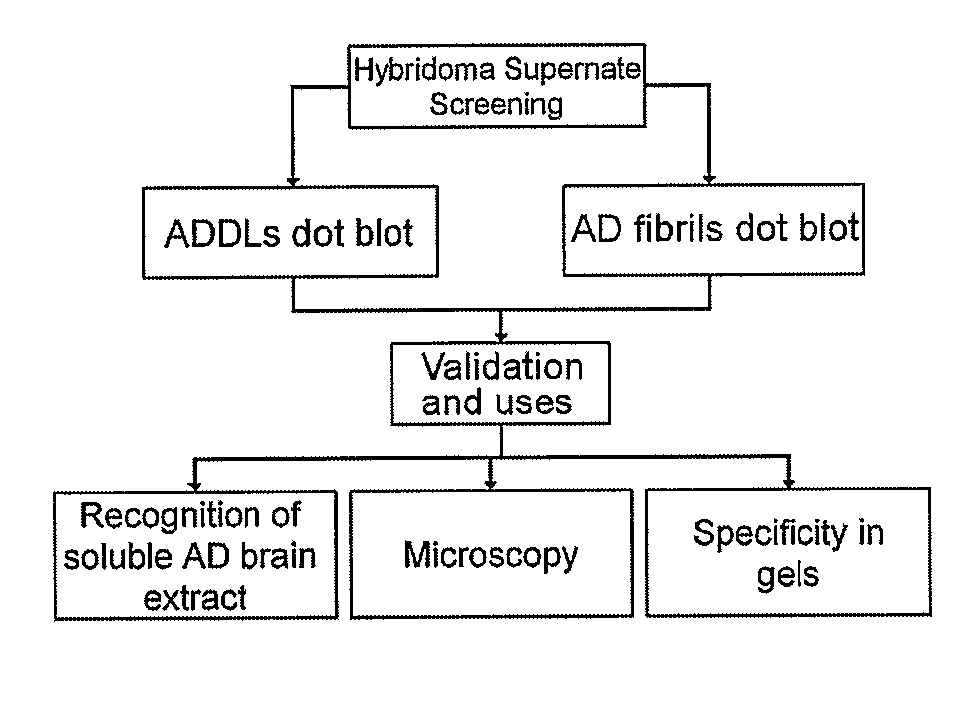
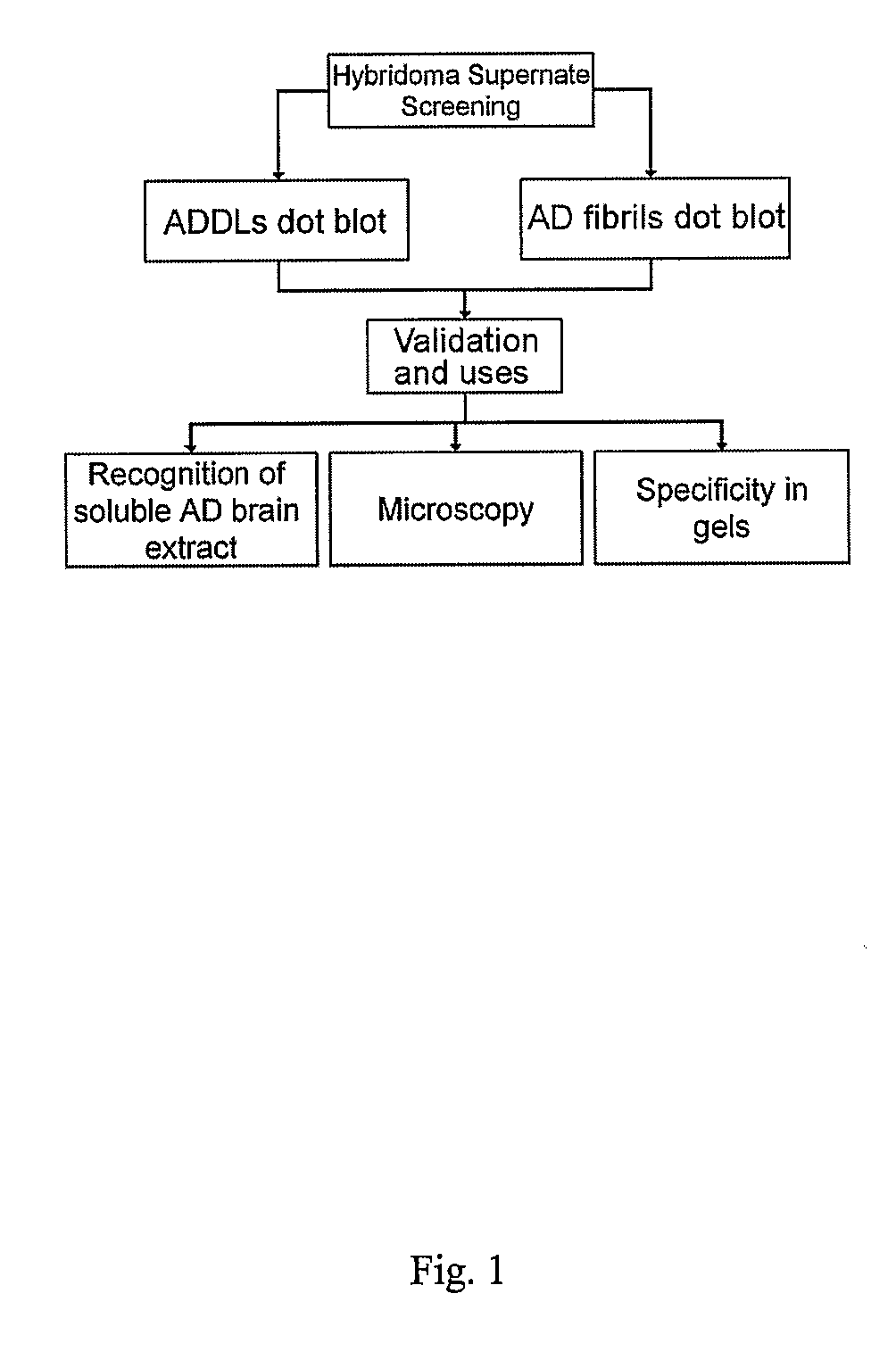
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1104 results about "Human brain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head.
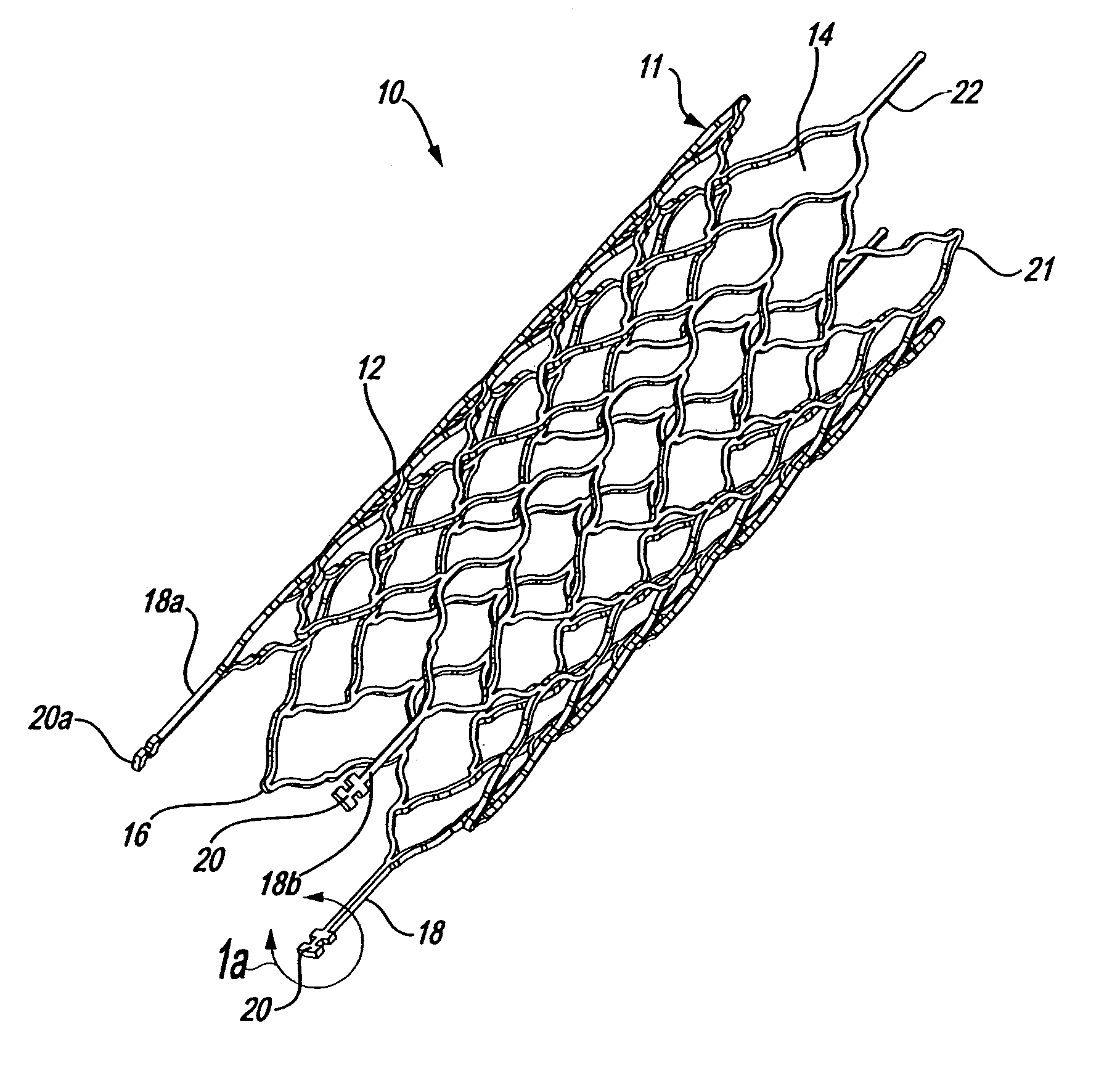
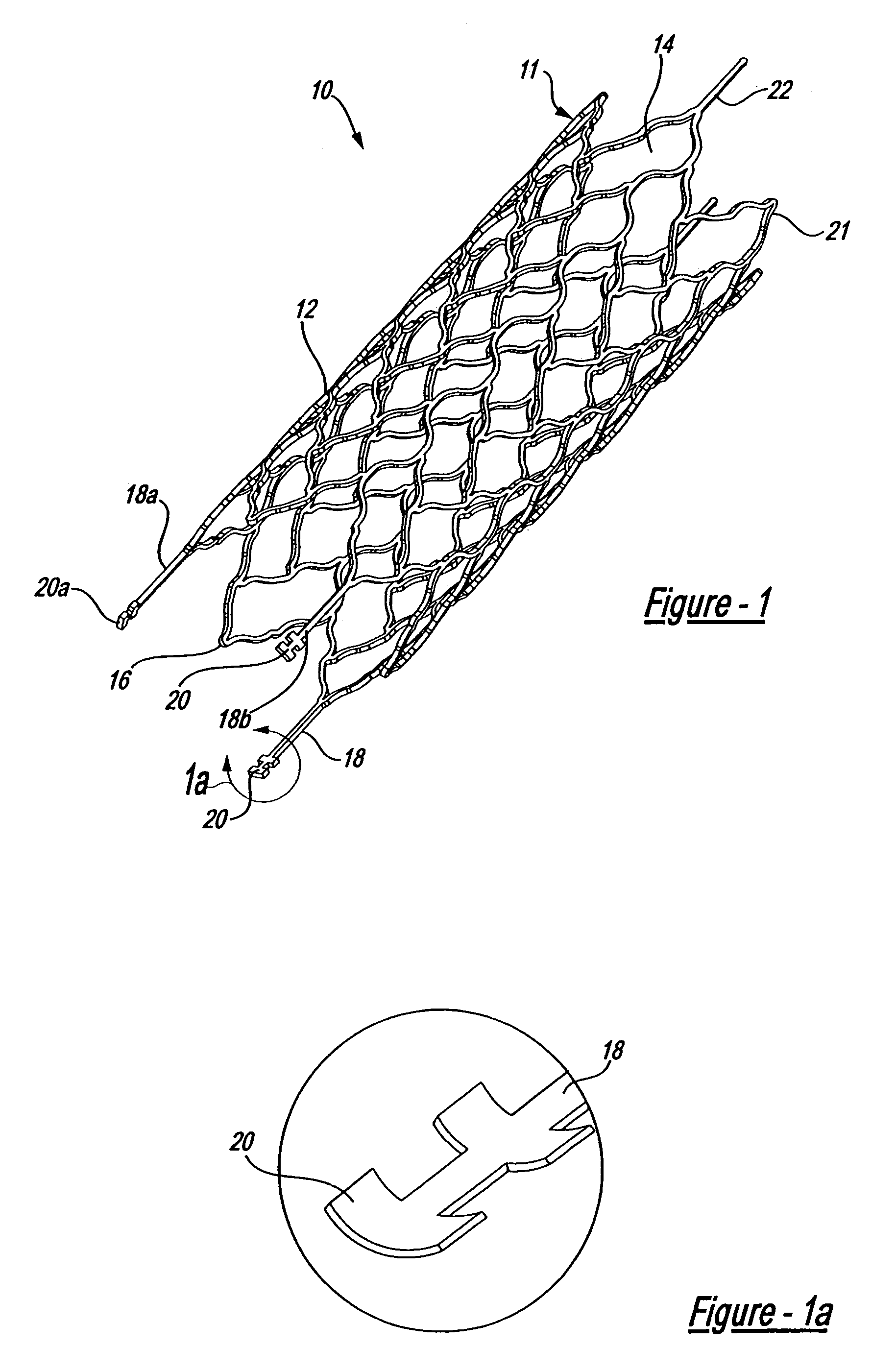
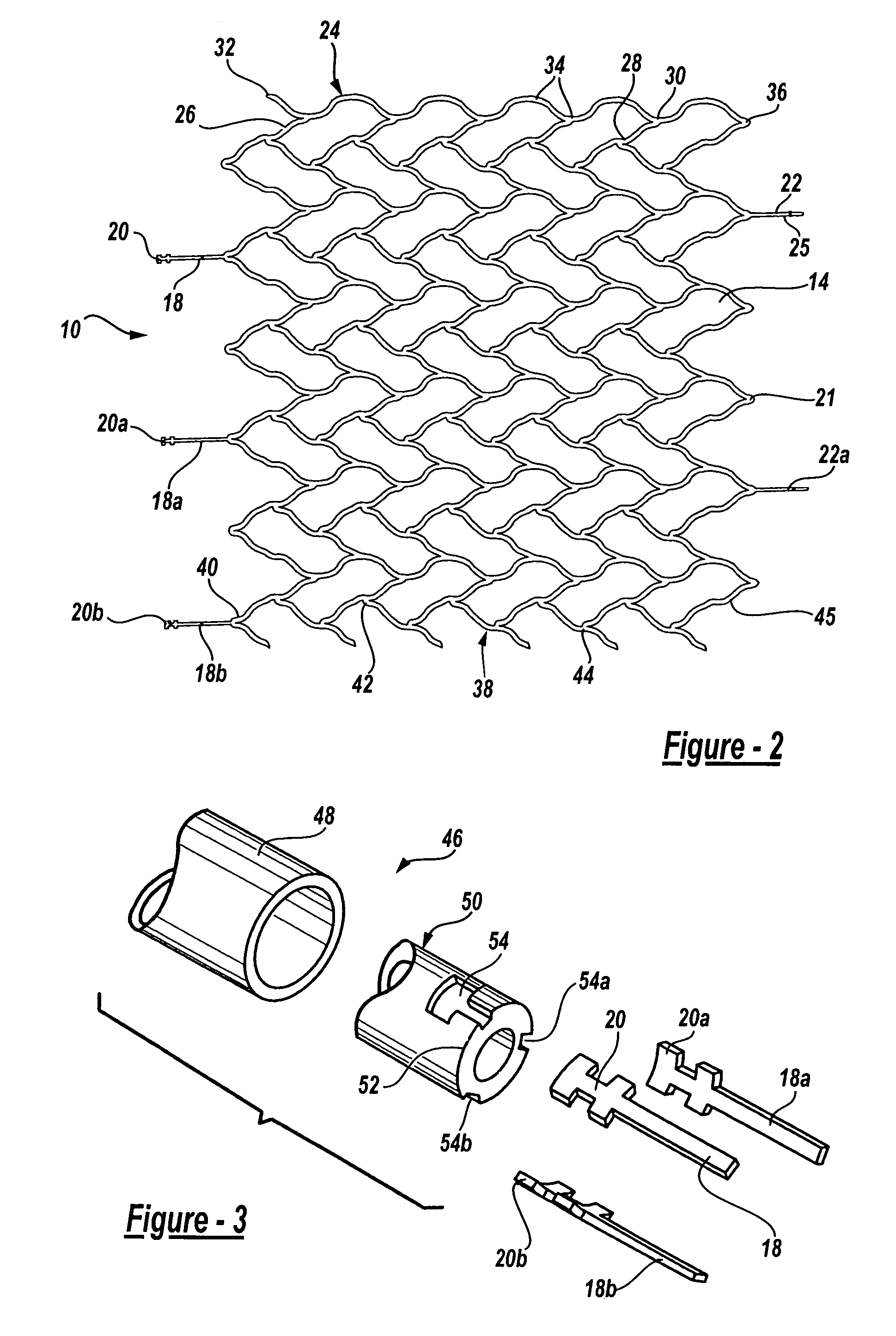
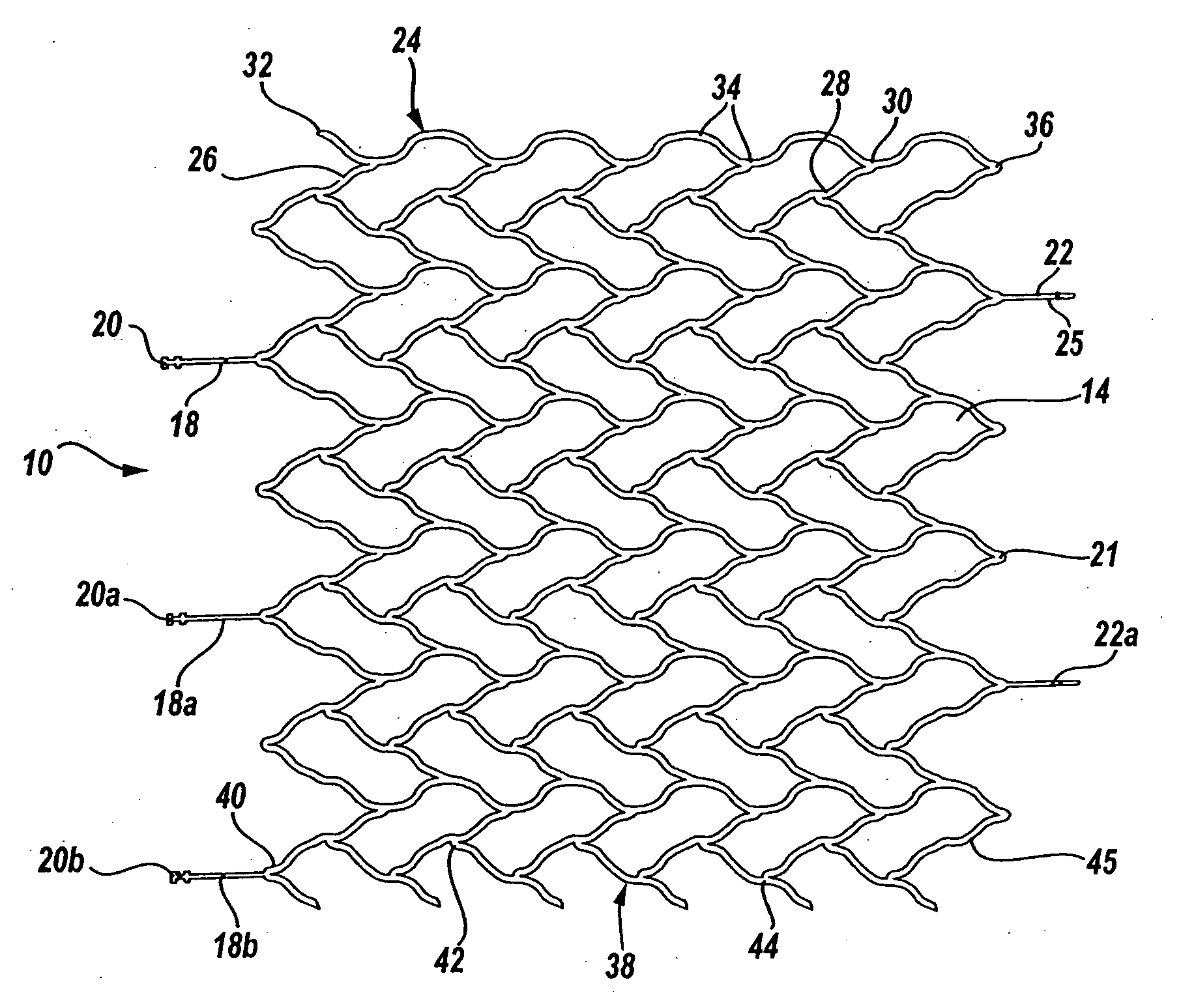
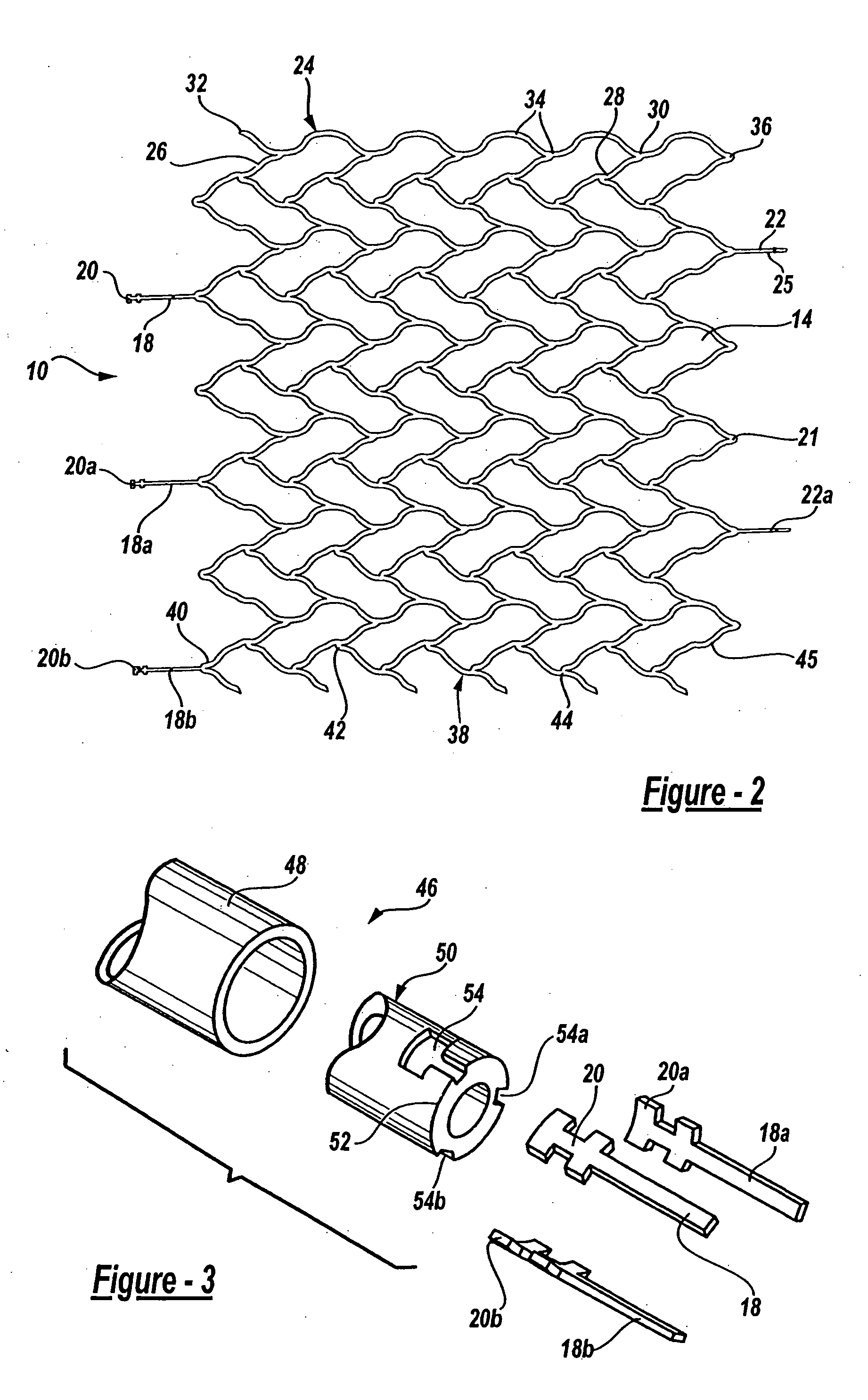
Intravascular stent device
A very small diameter intravascular stent device which may be used to occlude or partially occlude an aneurysm in the human brain which is comprised of a thin-walled skeletal cylindrical tube formed of undulating or sinusoidal elements which, when compressed, nest tightly with each other.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
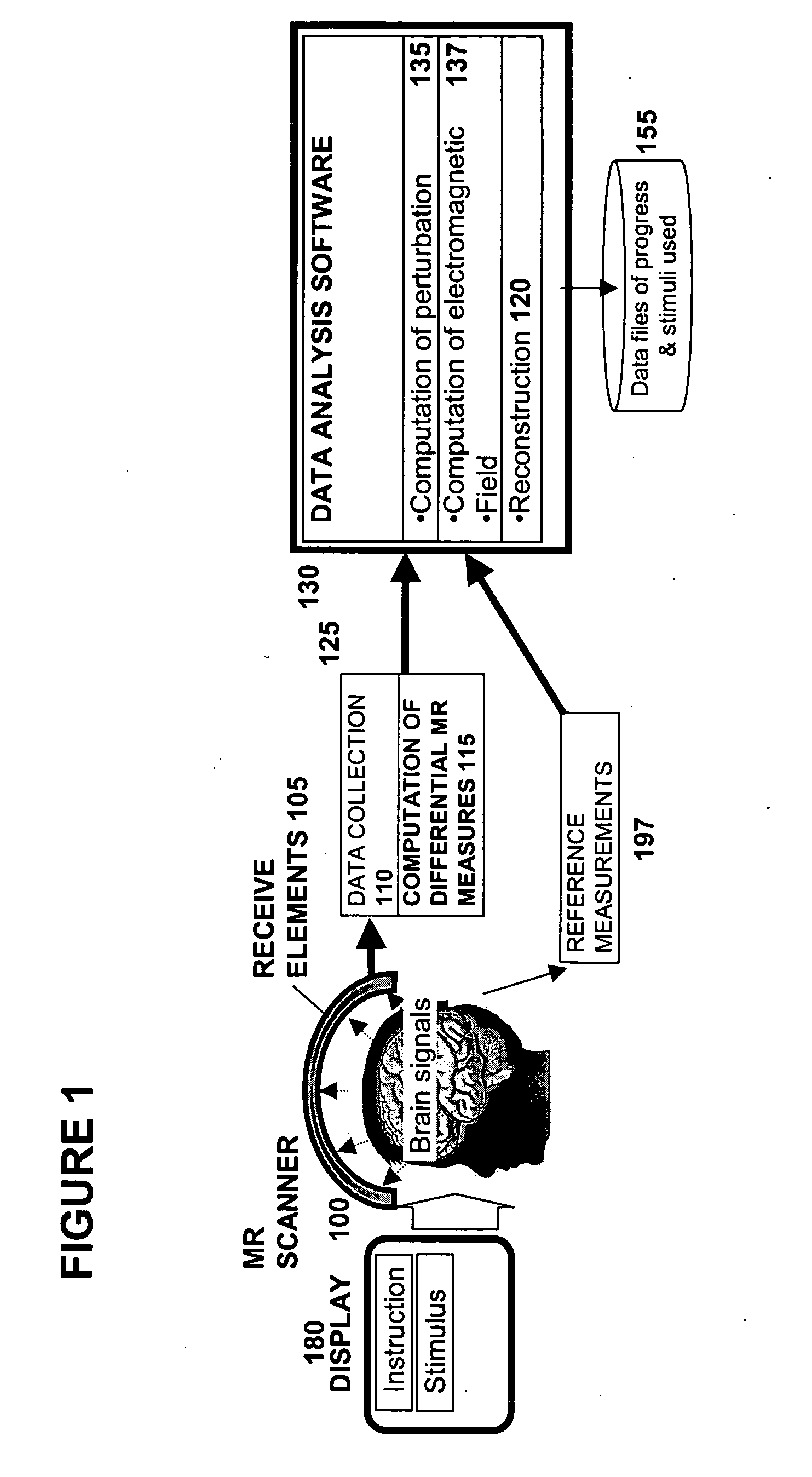
Methods for measurement of magnetic resonance signal perturbations
InactiveUS20080001600A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsNervous systemElectromagnetic field
The present invention relates to methods, software and systems for monitoring fluctuations in magnetic resonance signals. These methods may be used for measurements of the human brain and nervous system, and may be used for measuring electric currents and electromagnetic fields internal to an object. This method may include the use of a reference signal to accomplish differential recording of electromagnetic fields from two or more spatial locations.
Owner:DECHARMS RICHARD CHRISTOPHER
Methods for measurement of magnetic resonance signal perturbations
InactiveUS20050033154A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringNervous systemElectromagnetic field
The present invention relates to methods, software and systems for monitoring fluctuations in magnetic resonance signals. These methods may be used for measurements of the human brain and nervous system, and may be used for measuring electric currents and electromagnetic fields internal to an object. This method may include the use of a reference signal to accomplish differential recording of electromagnetic fields from two or more spatial locations.
Owner:DECHARMS RICHARD CHRISTOPHER
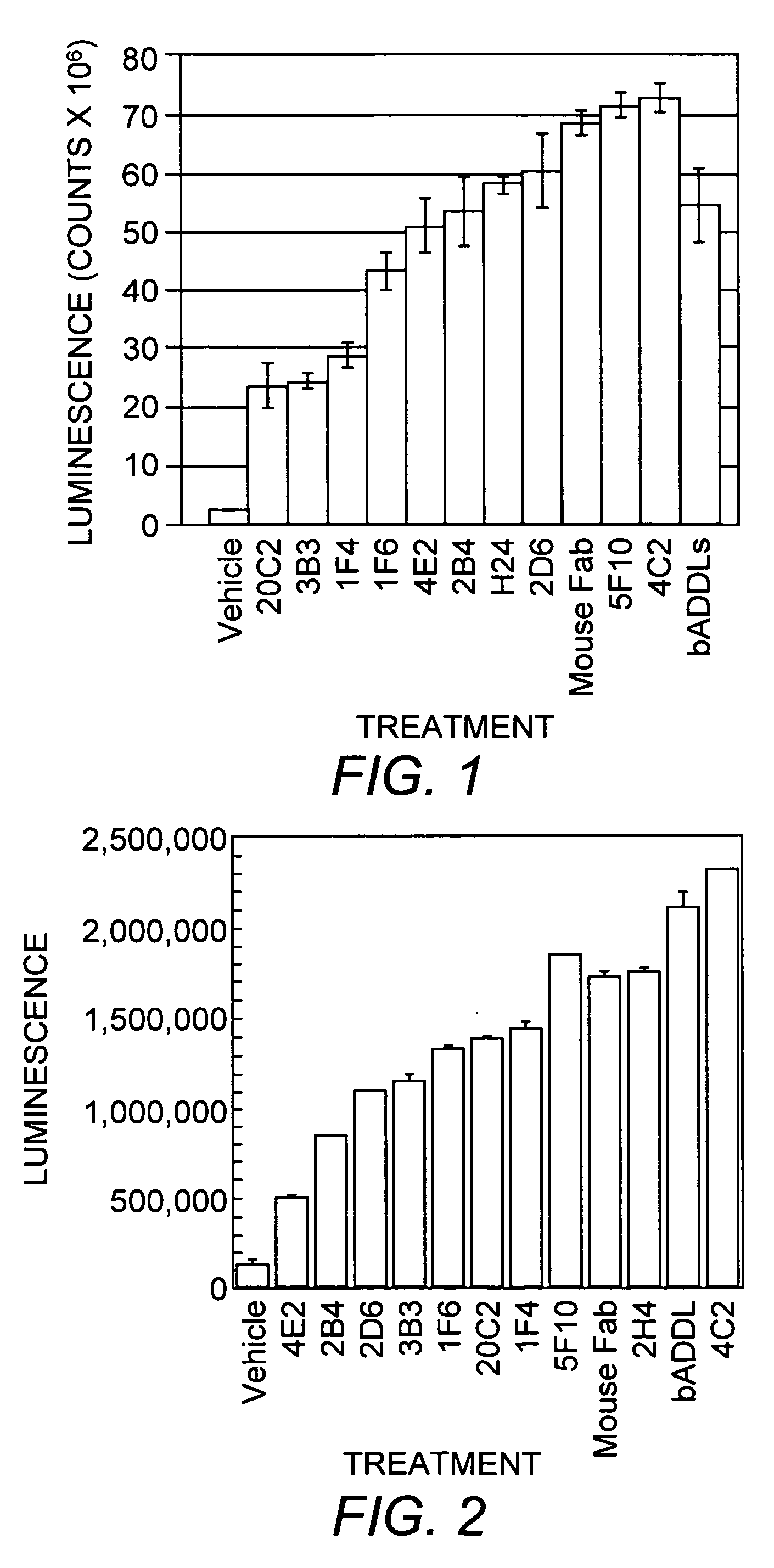
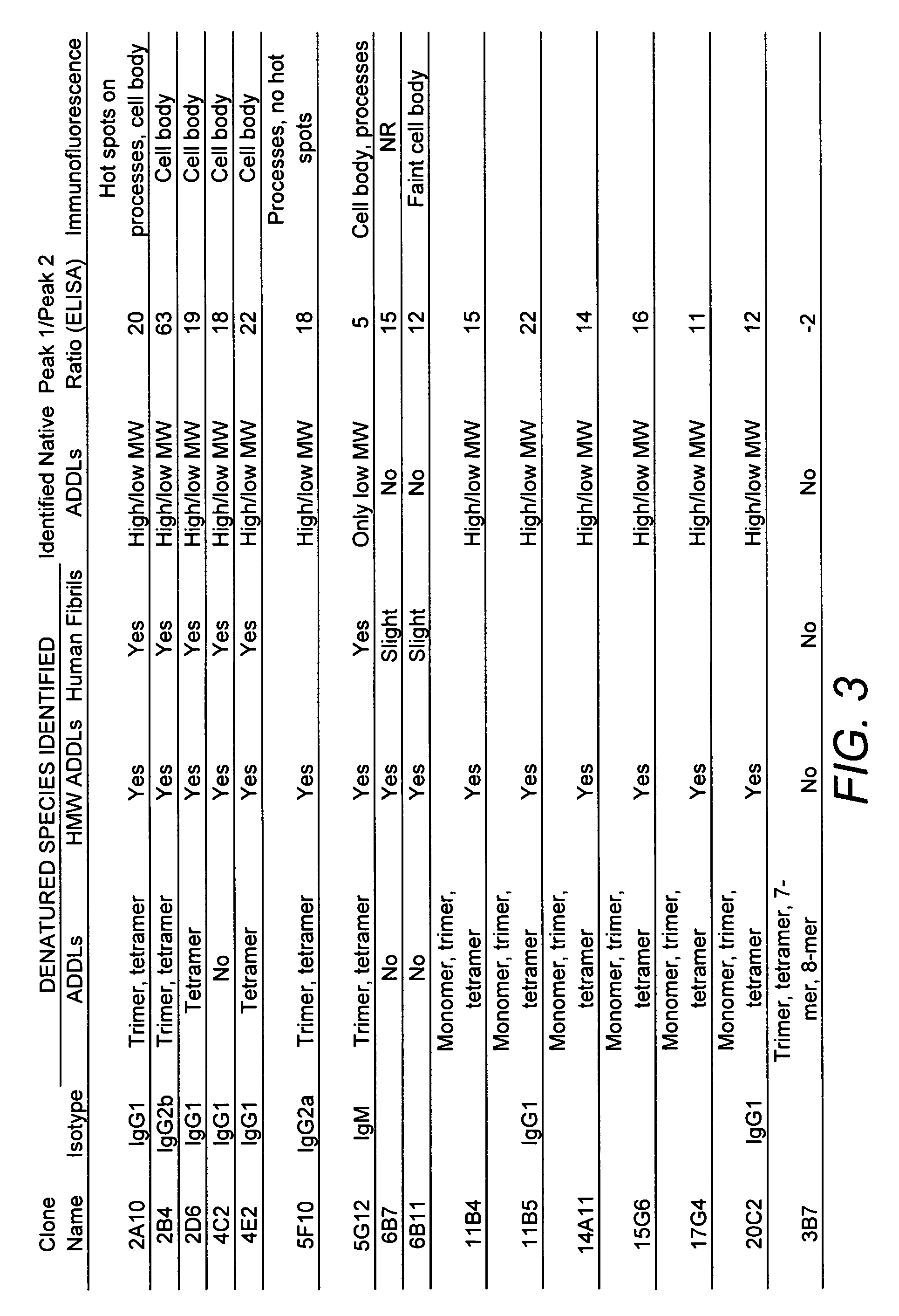
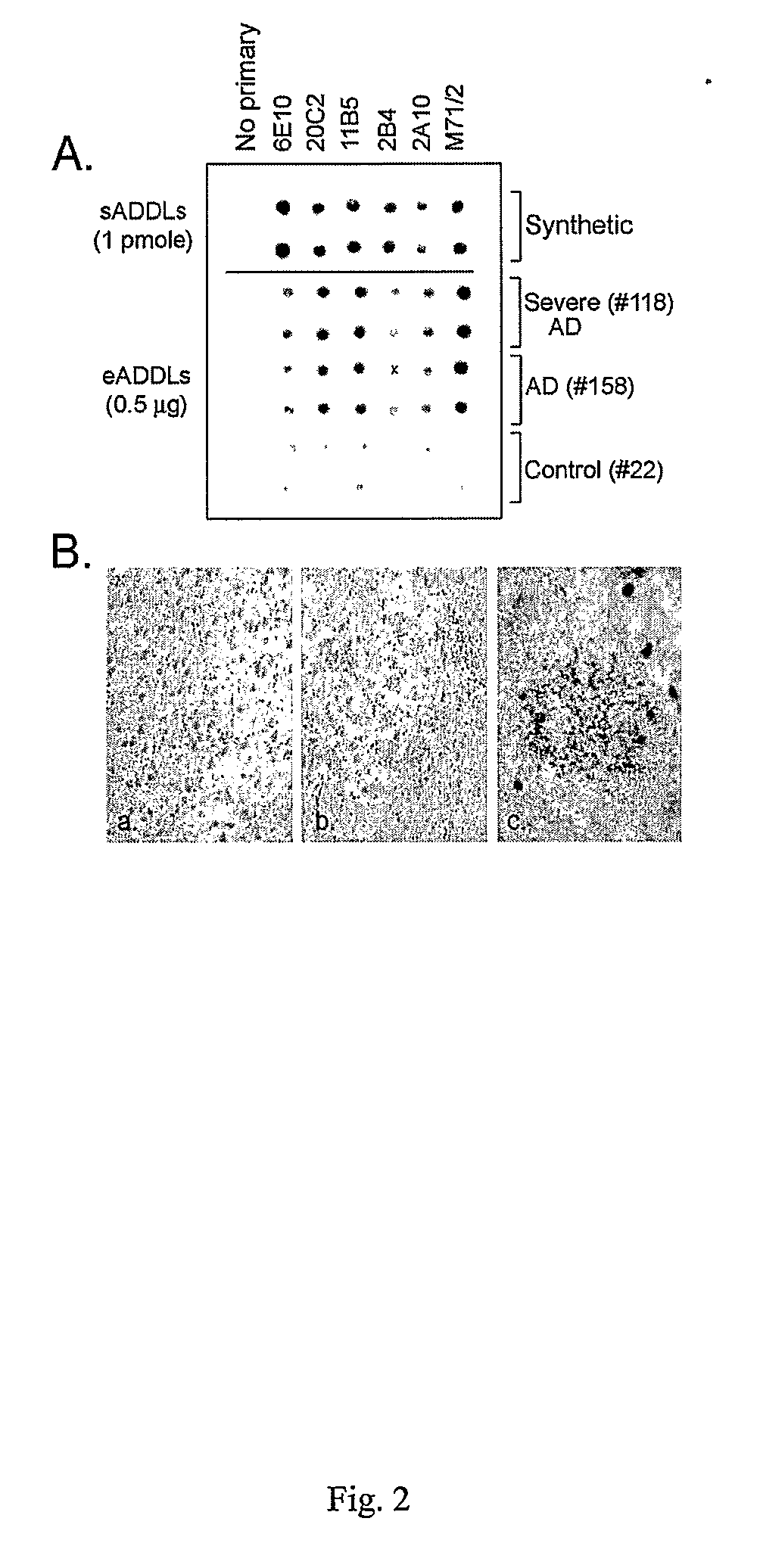
Anti-ADDL antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20060228349A1Prevent and treat diseaseInhibit phosphorylationNervous disorderMetabolism disorderOligomerAmyloid beta
The present invention relates to antibodies that differentially recognize multi-dimensional conformations of Aβ-derived diffusible ligands, also known as ADDLs. The antibodies of the invention can distinguish between Alzheimer's Disease and control human brain extracts and are useful in methods of detecting ADDLs and diagnosing Alzheimer's Disease. The present antibodies also block binding of ADDLs to neurons, assembly of ADDLS, and tau phosphorylation and are there useful in methods for the preventing and treating diseases associated with soluble oligomers of amyloid β1-42.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
System that provides early detection, alert, and response to electronic threats
InactiveUS20100031358A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsData streamProtection layer
The invention is a computer system that provides early detection alert and response to electronic threats (eThreats) in large wide area networks, e.g. the network of an Internet Services Provider or a Network Services Provider. The system of the invention accomplishes this by harnessing the processing power of dedicated hardware, software residing in specialized servers, distributed personal computers connected to the network, and the human brain to provide multi-layered early detection, alarm and response. The layers comprise: a Protection Layer, which detects and eliminates from the network data stream eThreats known to the system; a Detection Layer, which detects and creates signatures for new eThreats that are unknown to the system; an Expert Analysis Layer, which comprises a group of human experts who receive information from various components of the system and analyze the information to confirm the identity of new eThreats; and a Collaborative Detection & Protection Layer, which detects potential new eThreats by processing information received from various system agents and users. A Dynamic Sandbox Protection Layer associated with the distributed personal computers connected to the network. can optionally be part of the system of the invention.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
Apparatus and method for neural-signal capture to drive neuroprostheses or control bodily function
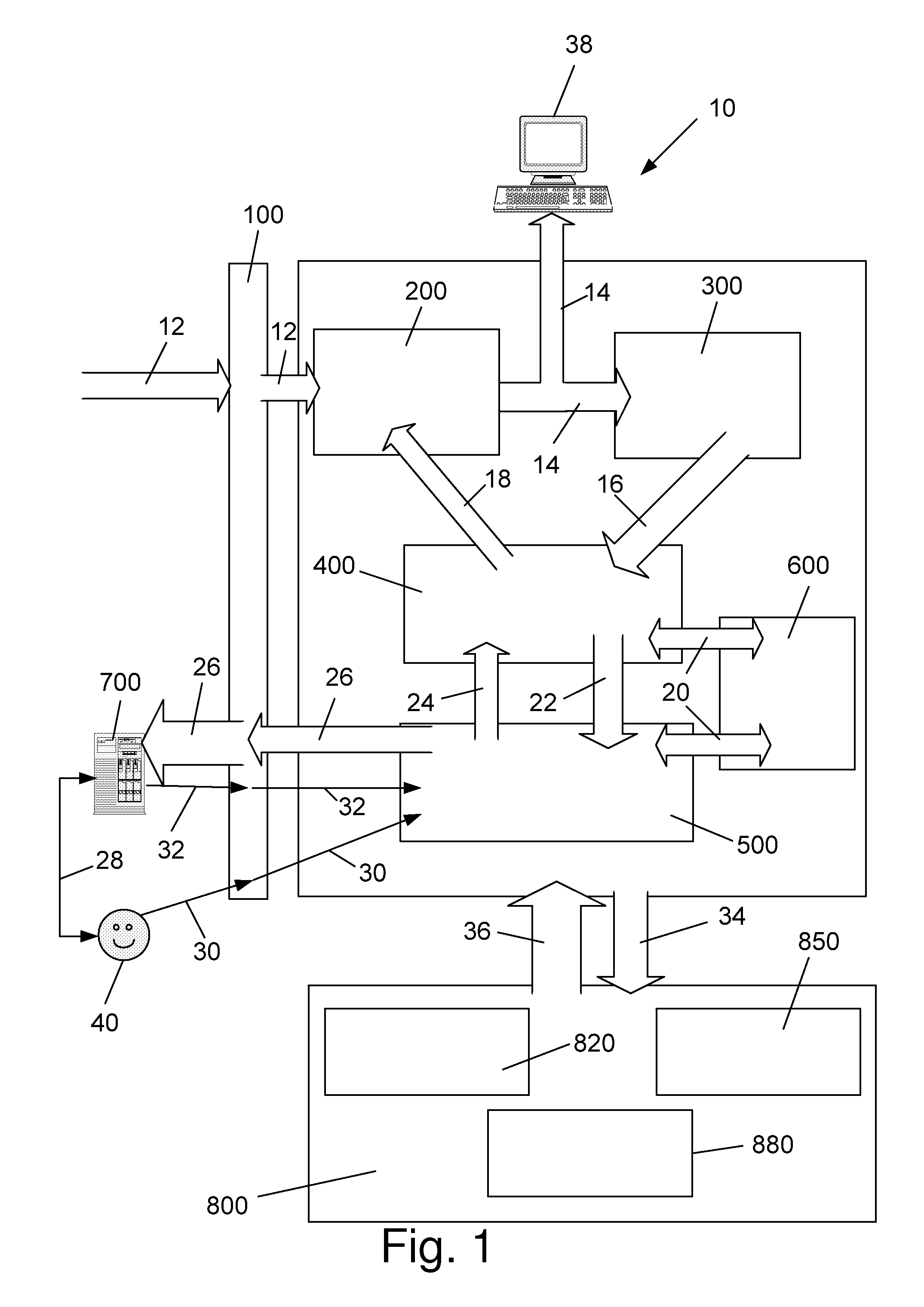
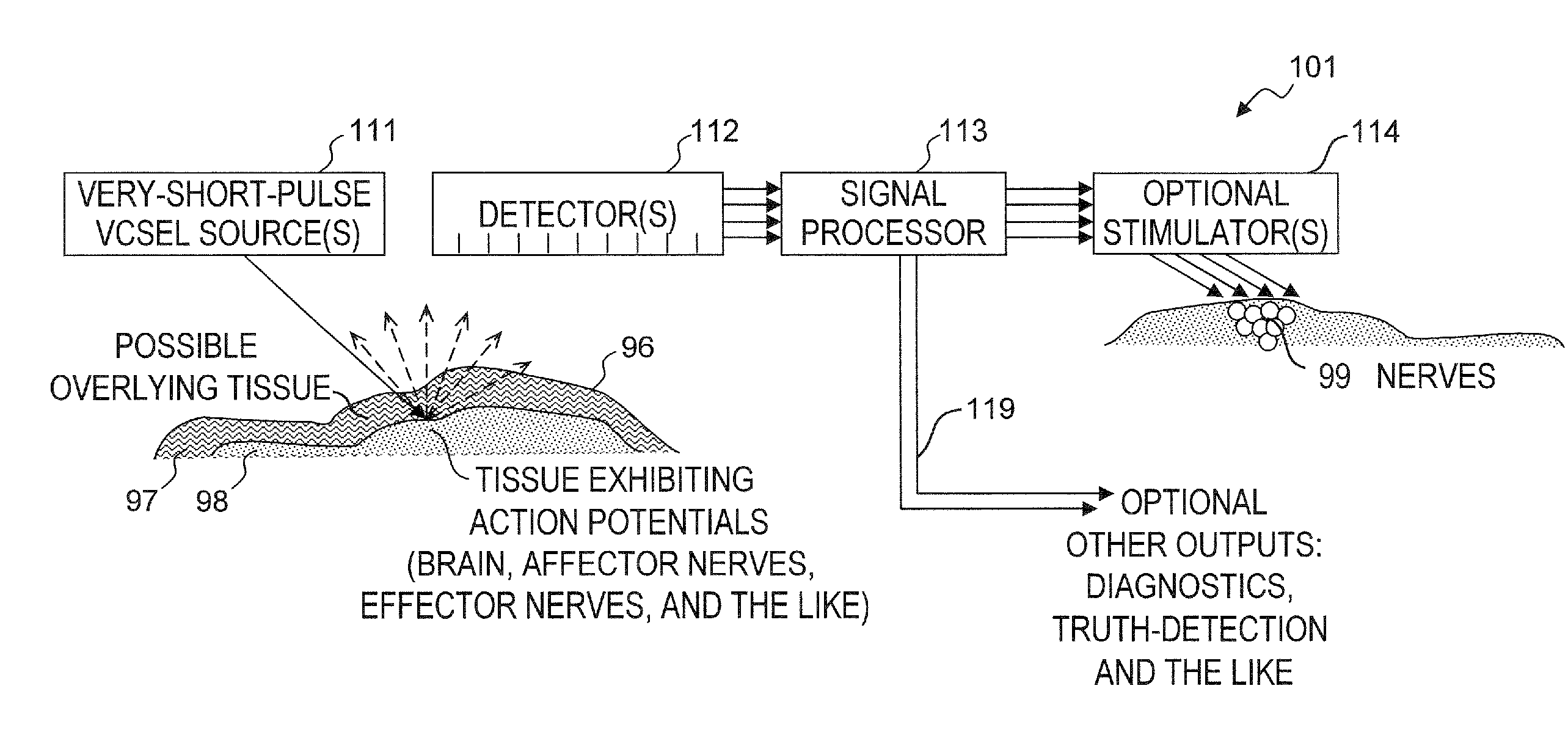
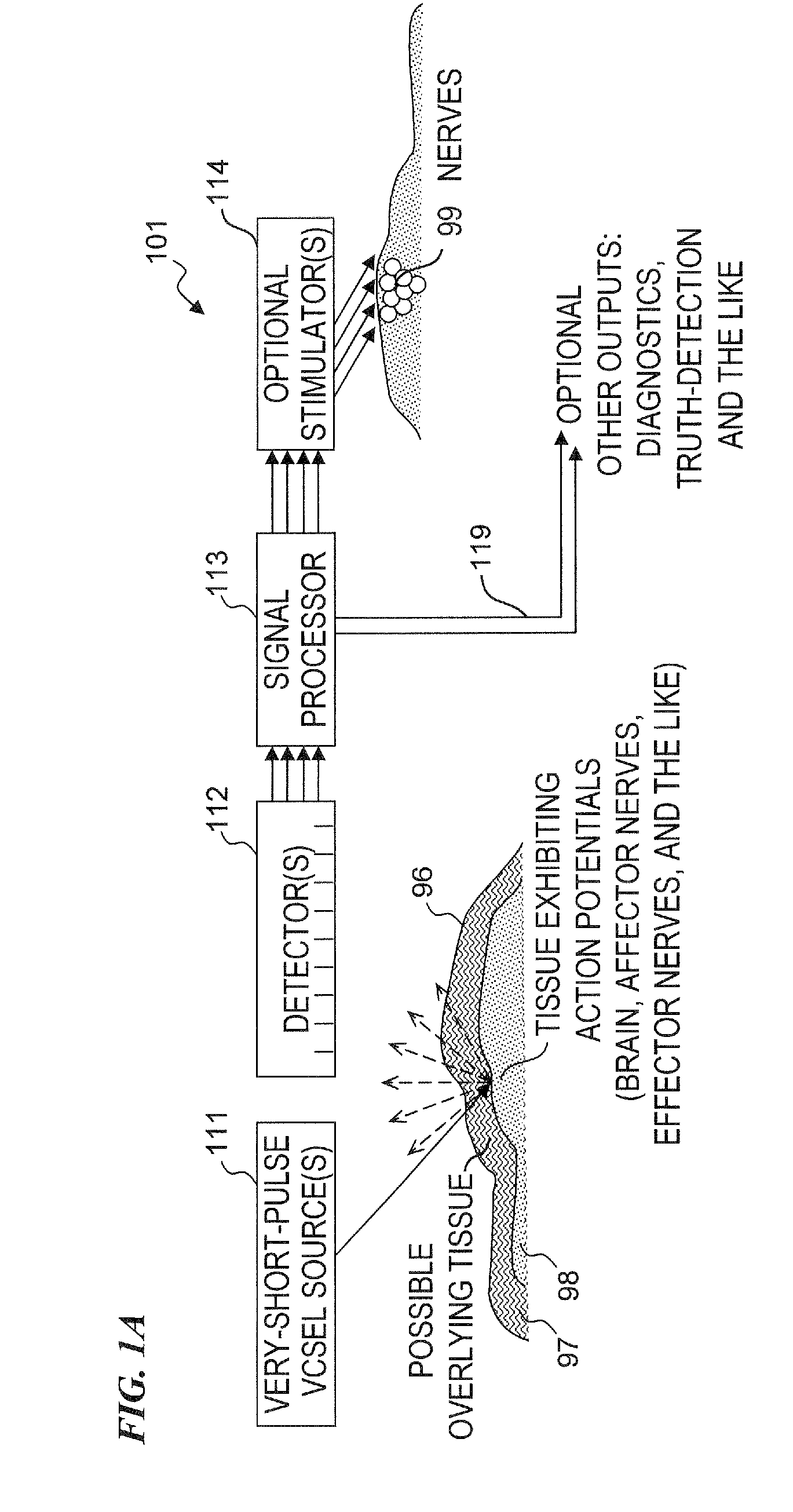
Method and apparatus for detecting nerve activity of an animal. Some embodiments include outputting a light pulse having a wavelength onto a volume of animal tissue such that the light pulse interacts with active nerves of the tissue; measuring a light signal resulting from the interaction of the light pulse with the tissue; transmitting an electrical signal based on the measured light signal; signal-processing the electrical signal; and outputting a response signal, which can optionally be used to control a prosthetic device, stimulate another nerve, or display / diagnose a condition. Some embodiments output a plurality of light wavelengths and / or pulses, which are optionally high-frequency intensity modulated. Some embodiments analyze DC, AC, and phase components of signals to spatially resolve locations of neural activity. Some embodiments output light pulse(s) and detect the resultant light from outside a human skull to detect neural activity of human brain tissue inside the skull.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
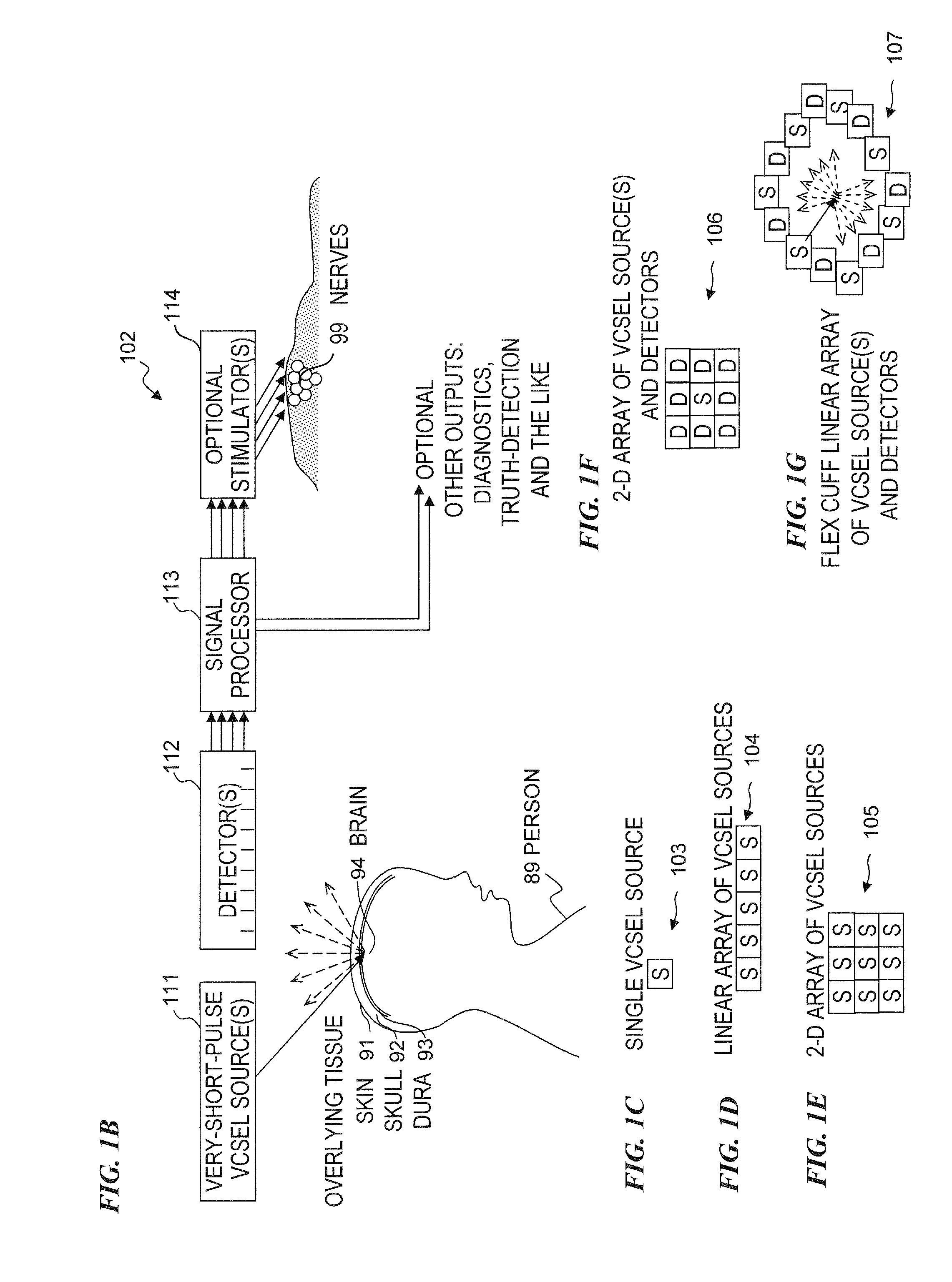
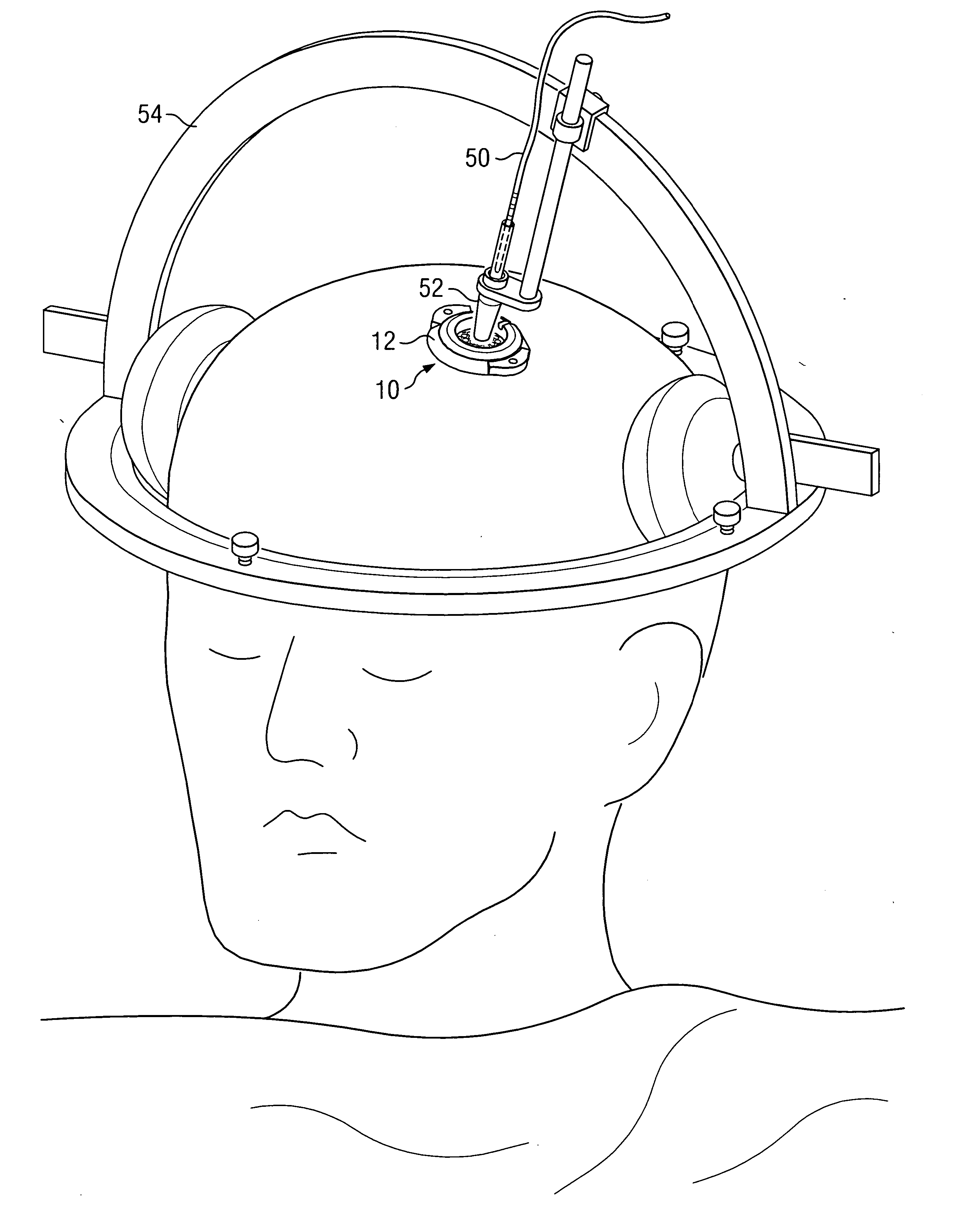
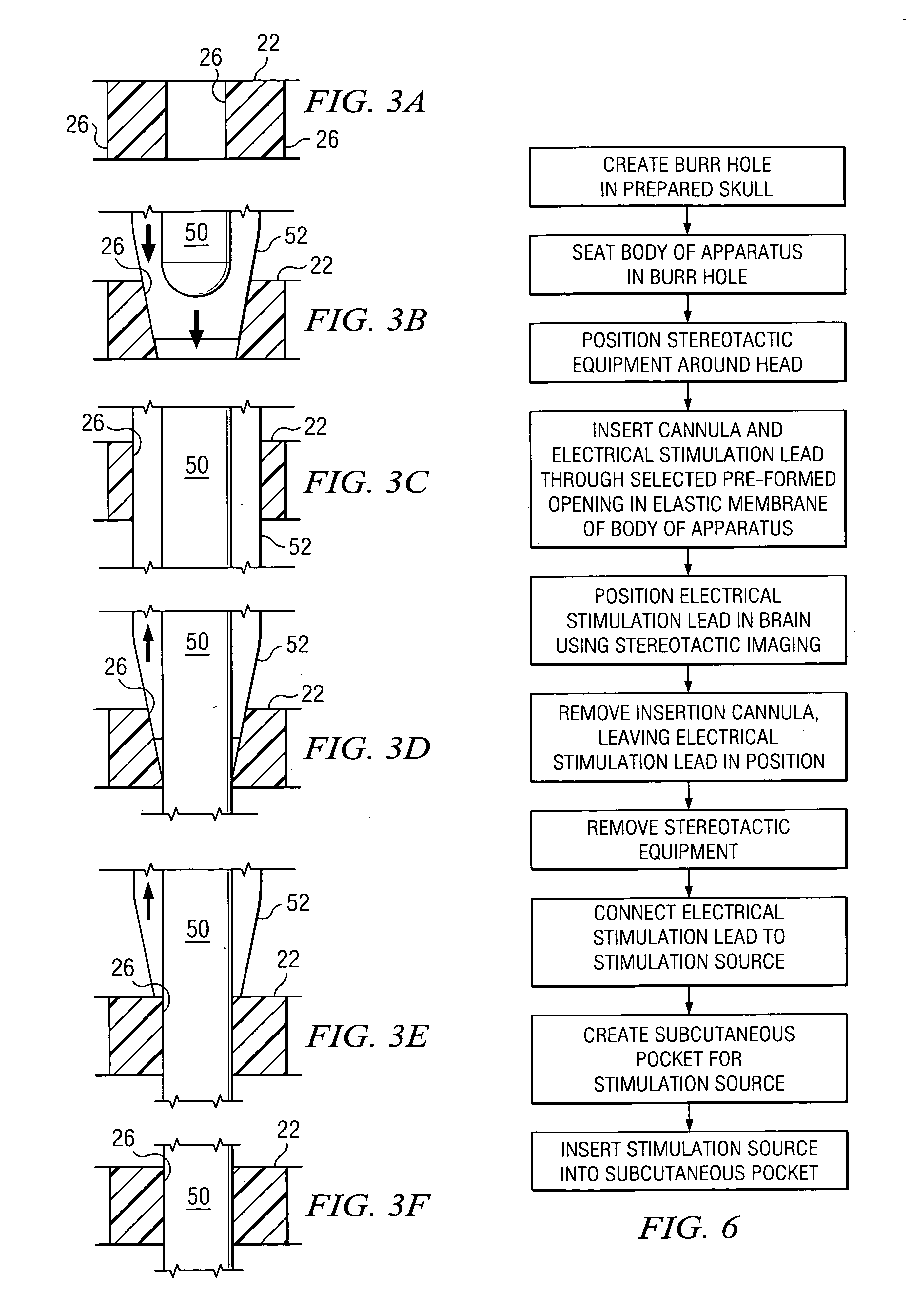
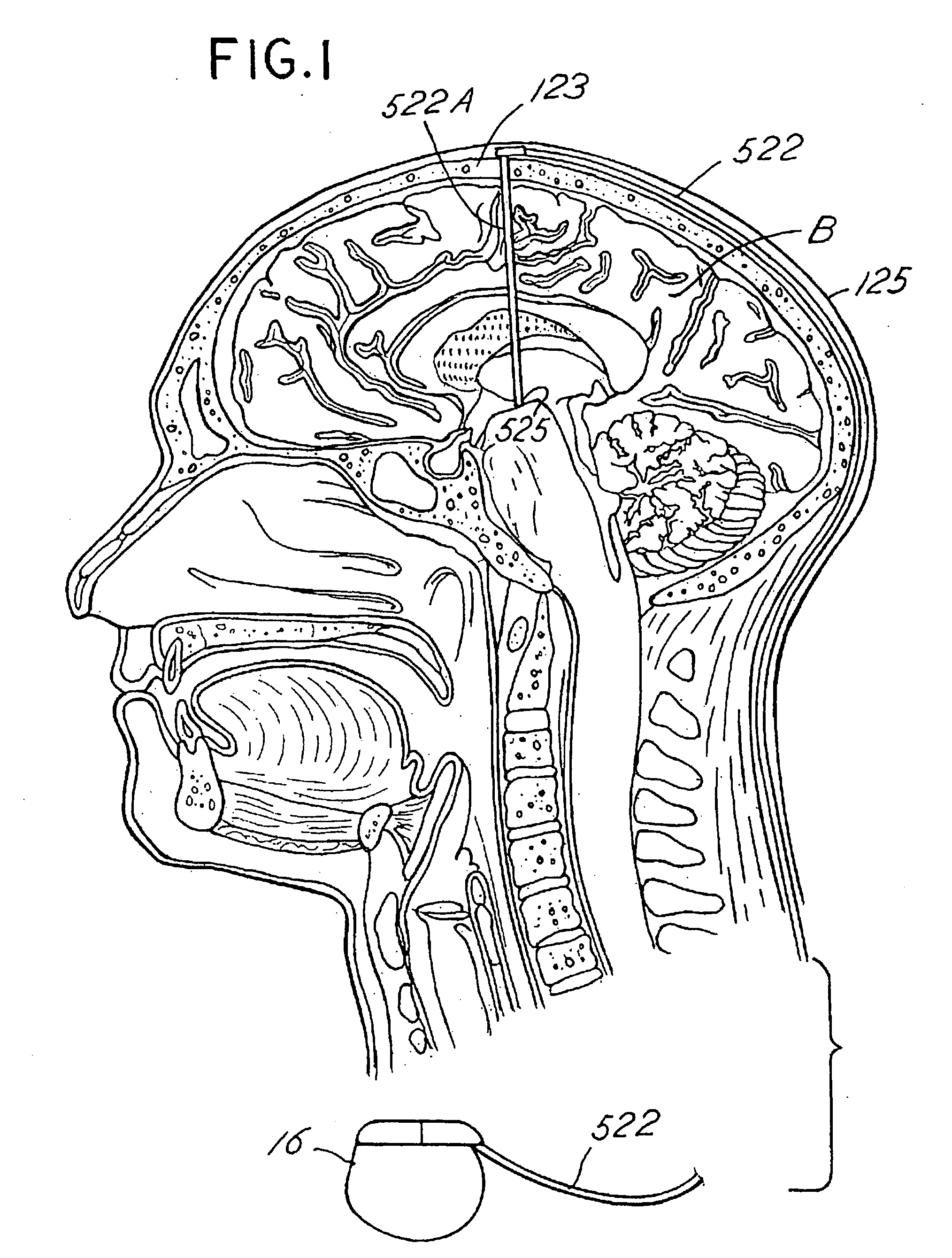
Electrical stimulation system and associated apparatus for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain
InactiveUS20050143800A1Stable positionPrevent movementHead electrodesDiagnosticsElectricityBurr holes
In one aspect, an apparatus is provided for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain. The apparatus includes a flexible disc comprising a substantially radial slot adapted to secure the lead in position within the brain after implantation. The slot is adapted to elastically expand as the lead is inserted into the slot and is also adapted to elastically contract on the lead to secure the lead in position within the brain after implantation. The apparatus further includes a ring adapted to seat within a burr hole formed in the person's skull. The ring comprises a channel adapted to receive and secure the flexible disc.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Electrical stimulation system and associated apparatus for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain
InactiveUS20050143799A1Simply and easily insertedReduce riskHead electrodesIntracranial pressure measurementElectricityBurr holes
In one aspect, an apparatus is provided for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain. The apparatus includes a body configured to seat within a burr hole formed in the person's skull. The apparatus also includes a central elastic membrane coupled to the body and extending across a central aperture of the body. The elastic membrane includes a number of pre-formed openings provided for purposes of securing the lead in position within the brain after implantation. Each pre-formed opening may penetrate through an entire thickness of the elastic membrane. Each pre-formed opening may be selected for insertion of the lead into the brain. Each pre-formed opening is adapted to elastically expand as the lead is inserted through the pre-formed opening and positioned in the brain and is adapted to elastically contract on the lead to secure the lead in position within the brain after implantation.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
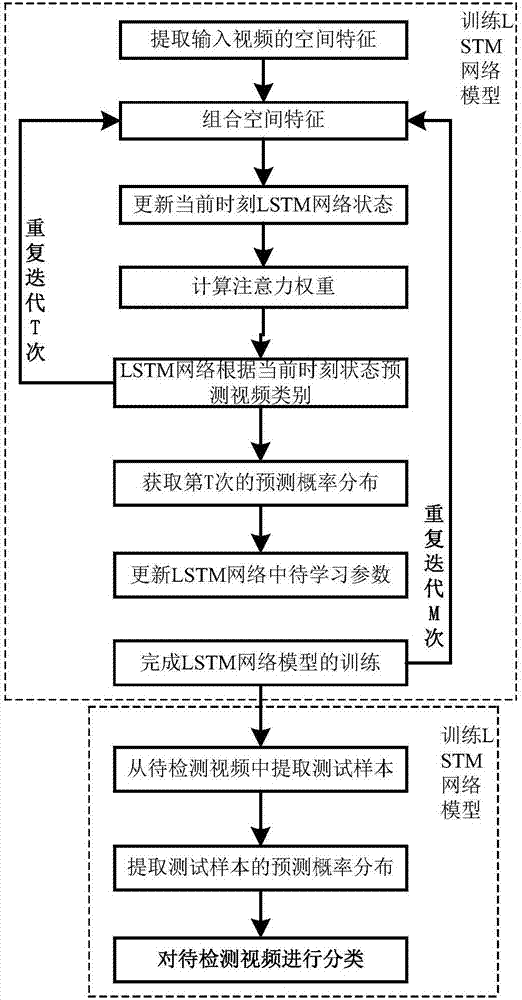
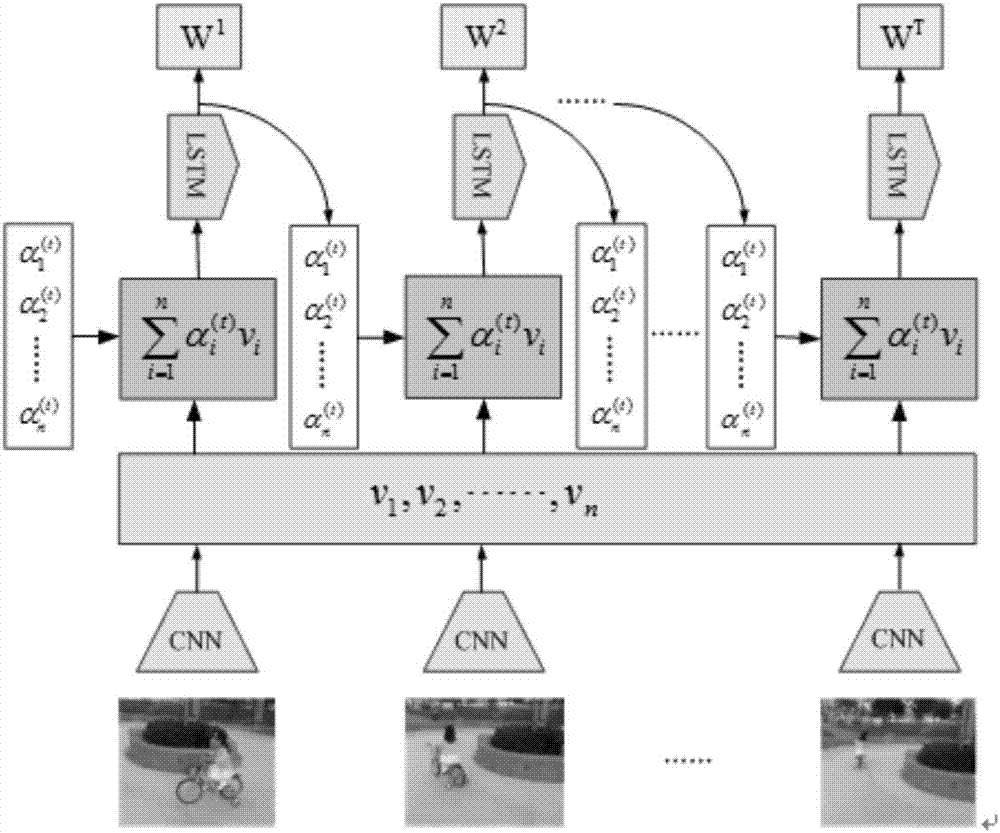
Attention mechanism-based video classification method
InactiveCN107341462AImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsClassification methodsConvolution
The invention discloses an attention mechanism-based video classification method. The attention mechanism-based video classification method comprises the steps of extracting space characteristic of a video by a convolution neural network (CNN), combining all space characteristics by attention weight, sending all space characteristics to a long- and short-time memory (LSTM) network, extracting time characteristics of the video, and finally, classifying video contents by employing a multi-classification function. An attention mechanism introduced to the LSTM network can be used for simulating an identification function of a human brain, different video contents are distinguished and handled, and the video classification accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
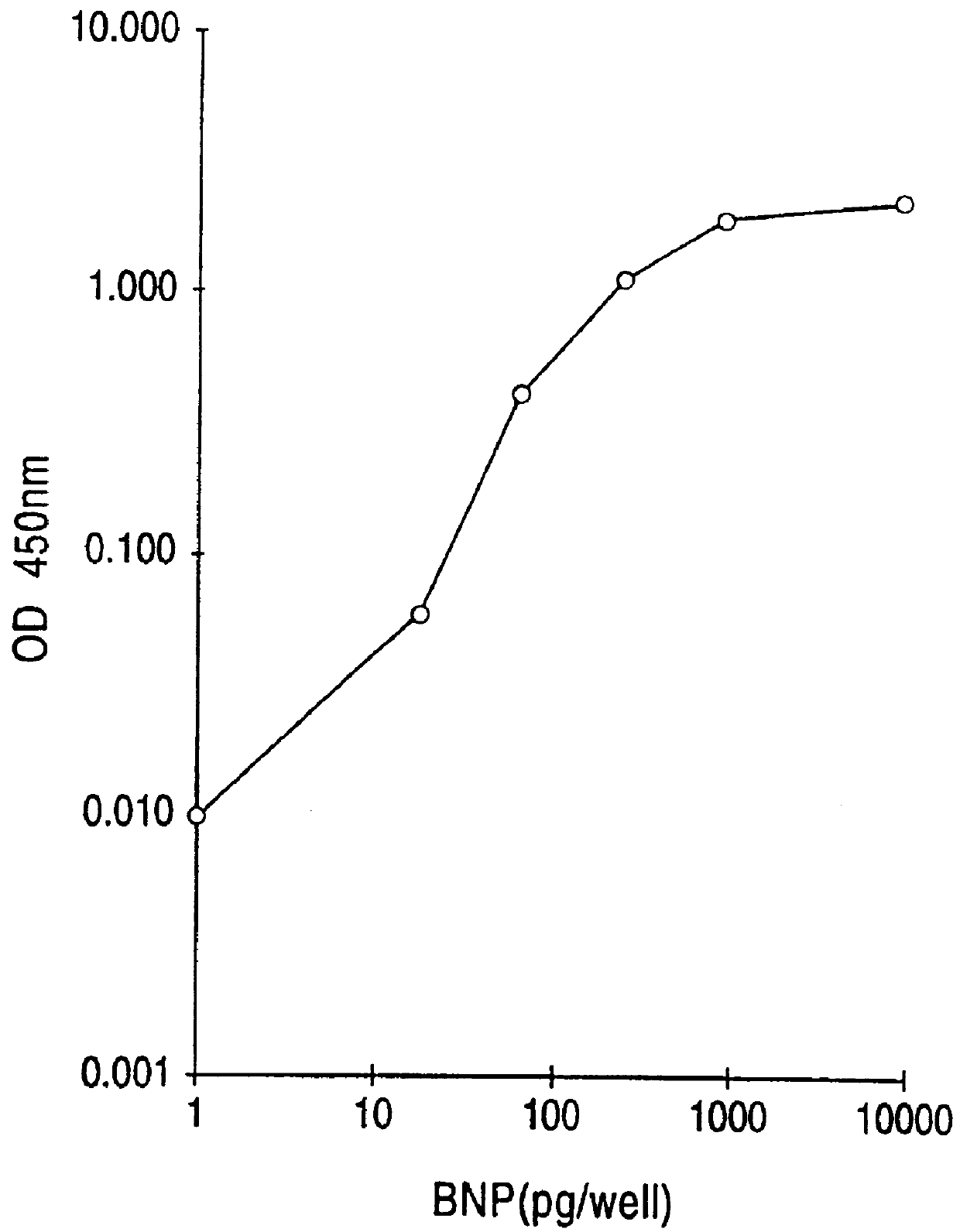
Human brain natriuretic peptides
The present invention provides reagents and assays for the quantification of hBNP in biological fluid samples such as plasma or serum. Antibodies are provided which are monospecific to epitopes comprising the amino acid sequences 5-13, 1-10 and 15-25 of hBNP. These antibodies, and peptide fragments containing these sequences, can be employed in the assays of the invention, which may be carried out in a sandwich format or a competition format.
Owner:SCIOS
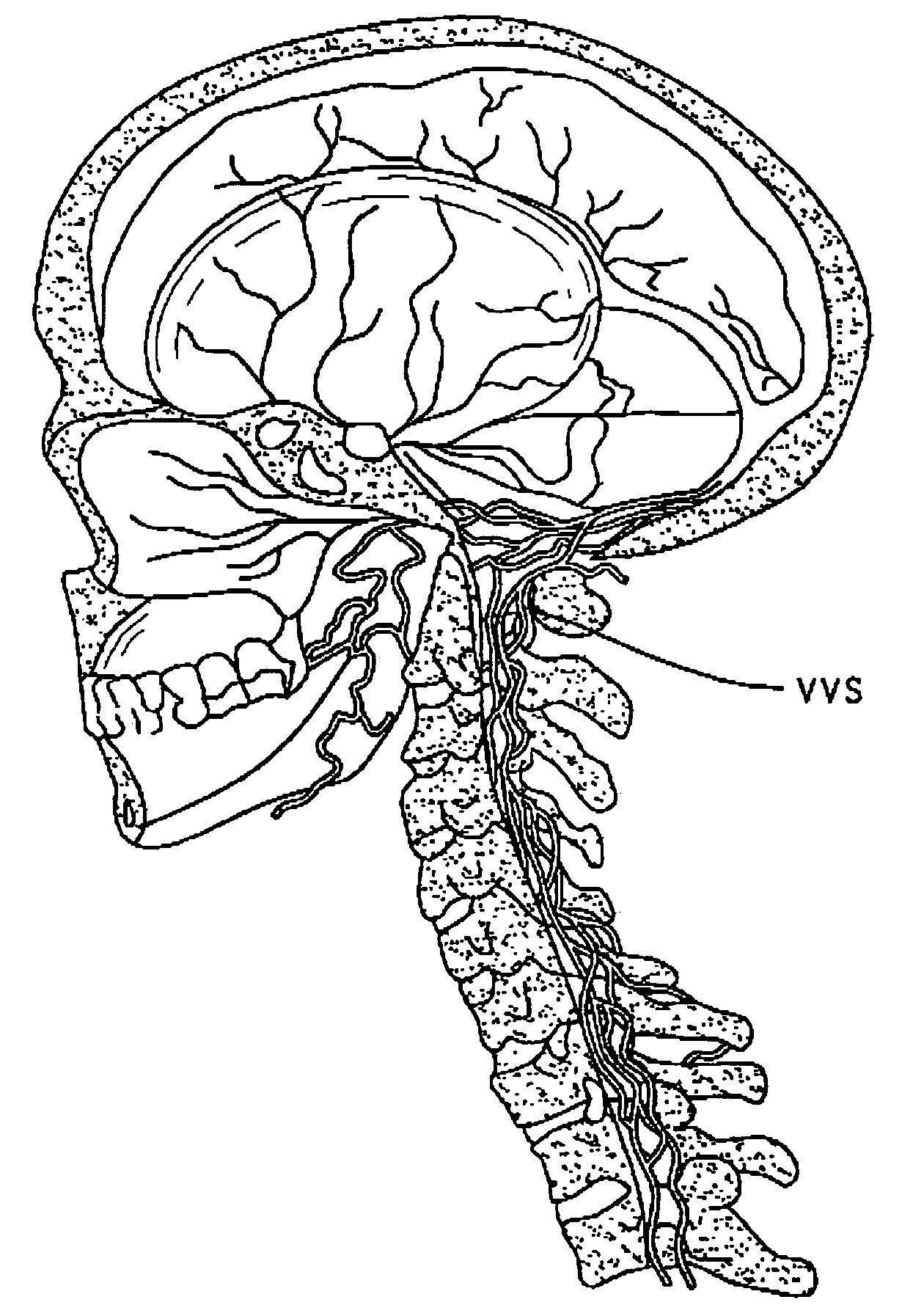
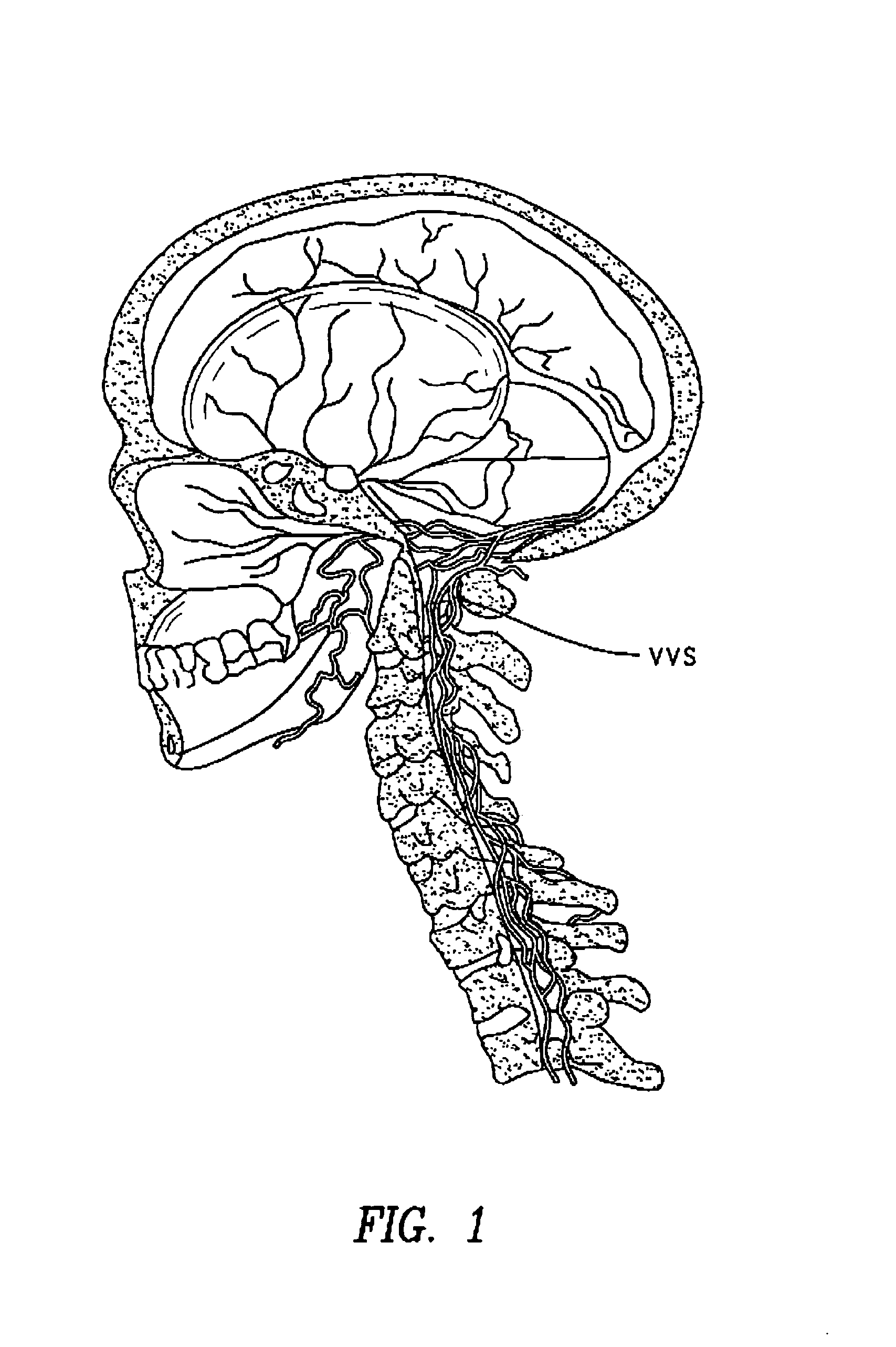
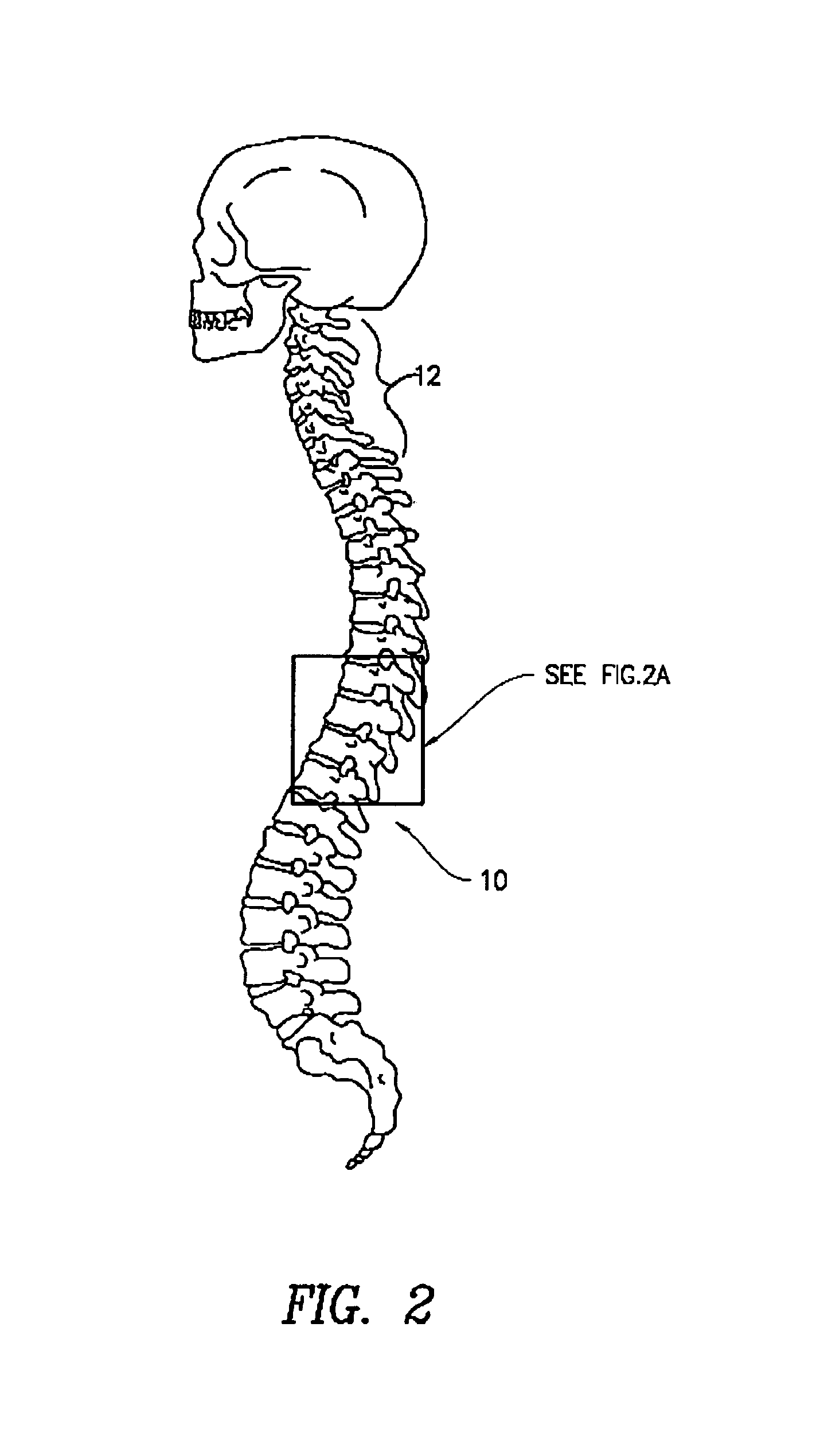
Method of delivering a TNF antagonist to the brain of a human by perispinal administration without direct intrathecal injection
InactiveUS7214658B2Improve cognitive functionReduce deliveryAnimal cellsOrganic active ingredientsEtanerceptTnf antagonists
The present invention provides specific methods of using and administering etanercept to improve cognitive function in a human, for both the treatment and prevention of cognitive impairment, or, alternatively, to enhance cognitive function including Alzheimer's Disease, Idiopathic Dementia, and Traumatic Brain Injury. The methods of the present invention include the perispinal administration of etanercept. For the purposes of this patent “perispinal” is to be considered as referring to “perispinal extrathecal;” therefore direct intrathecal administration is excluded. Perispinal administration leads to enhanced delivery of etanercept to the brain in a therapeutically effective amount, via the vertebral venous system and / or the cerebrospinal fluid. Delivery of etanercept to the brain utilizing the methods of the present invention includes the use of the vertebral venous system to deliver etanercept to the brain via retrograde venous flow. Physical maneuvers are used to enhance delivery of etanercept to the brain via this route.
Owner:TACT IP
Brain endothelial cell expression patterns
InactiveUS20060127902A1Auxiliary diagnosisCompound screeningNervous disorderAbnormal tissue growthBrain tumor
To gain a better understanding of brain tumor angiogenesis, new techniques for isolating brain endothelial cells (ECs) and evaluating gene expression patterns were developed. When transcripts from brain ECs derived from normal and malignant colorectal tissues were compared with transcripts from non-endothelial cells, genes predominantly expressed in the endothelium were identified. Comparison between normal- and tumor-derived endothelium revealed genes that were specifically elevated in tumor-associated brain endothelium. These results confirm that neoplastic and normal endothelium in human brains are distinct at the molecular level, and have significant implications for the development of anti-angiogenic therapies in the future.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
Method and apparatus for determining symmetry in 2d and 3d images
InactiveUS20040240753A1Accurate and fast determinationMaximizing modified local symmetry indexImage enhancementImage analysisSagittal plane3d image
The present invention is suitable for use in determining symmetry in images, namely 2D images or 3D images, which comprise 2D images slices. In a preferred form, a method is disclosed for extracting a midsagittal plane MSP of human brains from radiological images. The method includes the steps of: 1) determining axial slices to be processed from said radiological images; 2) analysing said axial slices to determine fissure line segments; and 3) calculating plane equation of MSP from said fissure line segments.
Owner:KENT RIDGE DIGITAL LABS
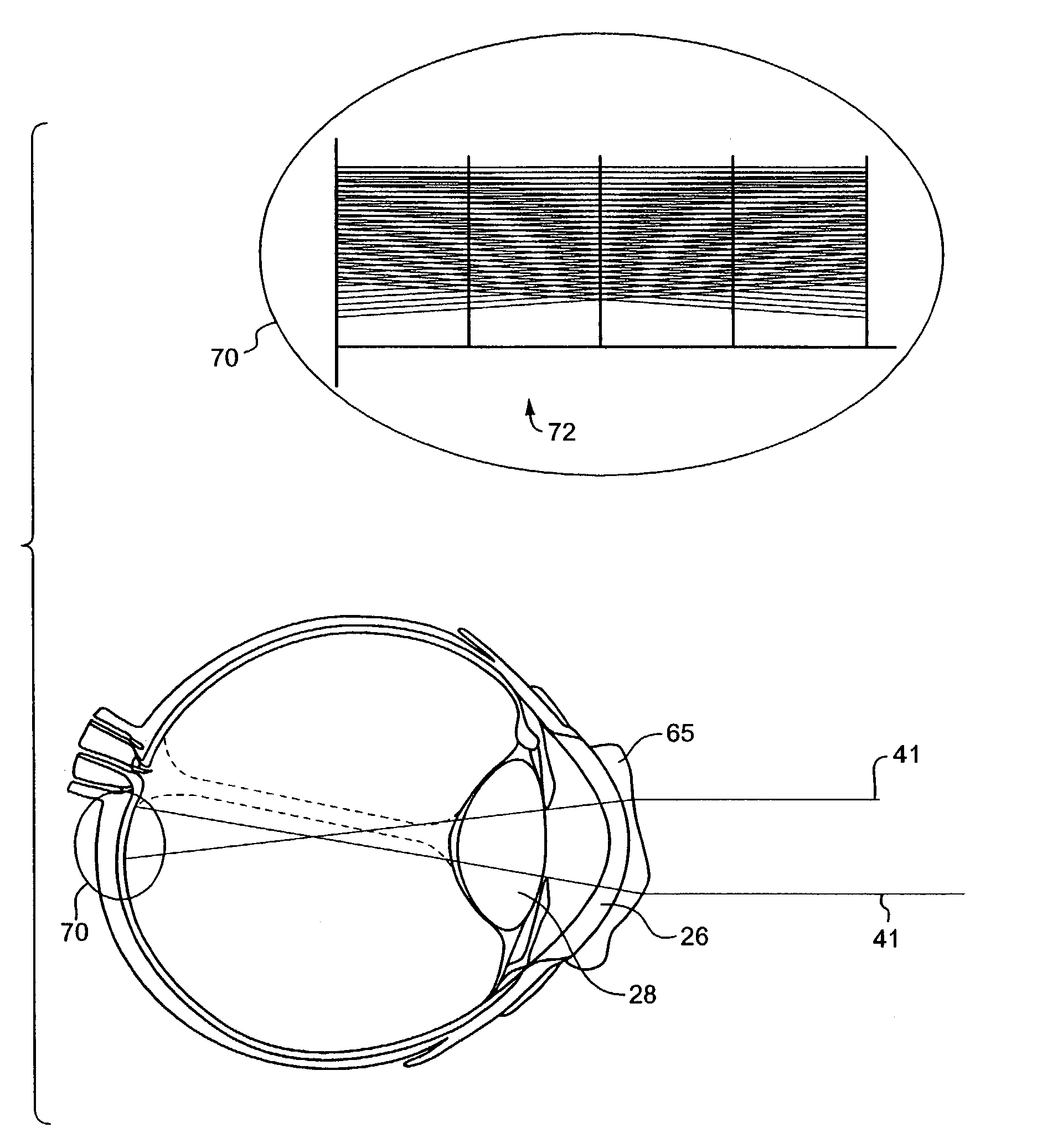
Method for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects of the eye by interaction of a patient with an examiner and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6997555B2Easy to catchGood utilization basisRefractometersSkiascopesElectronic control systemComputer science
There is now provided a method for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects of the eye. The method comprises projecting an image into the eye of the patient with an adaptive optical system having adaptive optical elements. The optical characteristics of the optical elements can be individually changed by an electrical signal. The presence of distortions of the image as perceived by the patient is determined by interaction of the patient with the examiner. By way of an electronic control system the optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements are changed through outputting of an electrical signal to obtain a modified image with minimized distortions in the eye of the patient. The optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements, as modified, are determined and vision correcting data for the eye being examined are computed from the optical characteristics of the adaptive optical elements, as modified. The method not only takes into consideration the aberrations of the optical imaging system but also the properties of reception and signal processing in the human brain. The method is further characterized in that the correction data for the aberrations of the human eye that impair the vision can be obtained by a measuring method that is actively physiologically evaluated beforehand. There is also provided an apparatus for determining vision defects and for collecting data for correcting vision defects.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
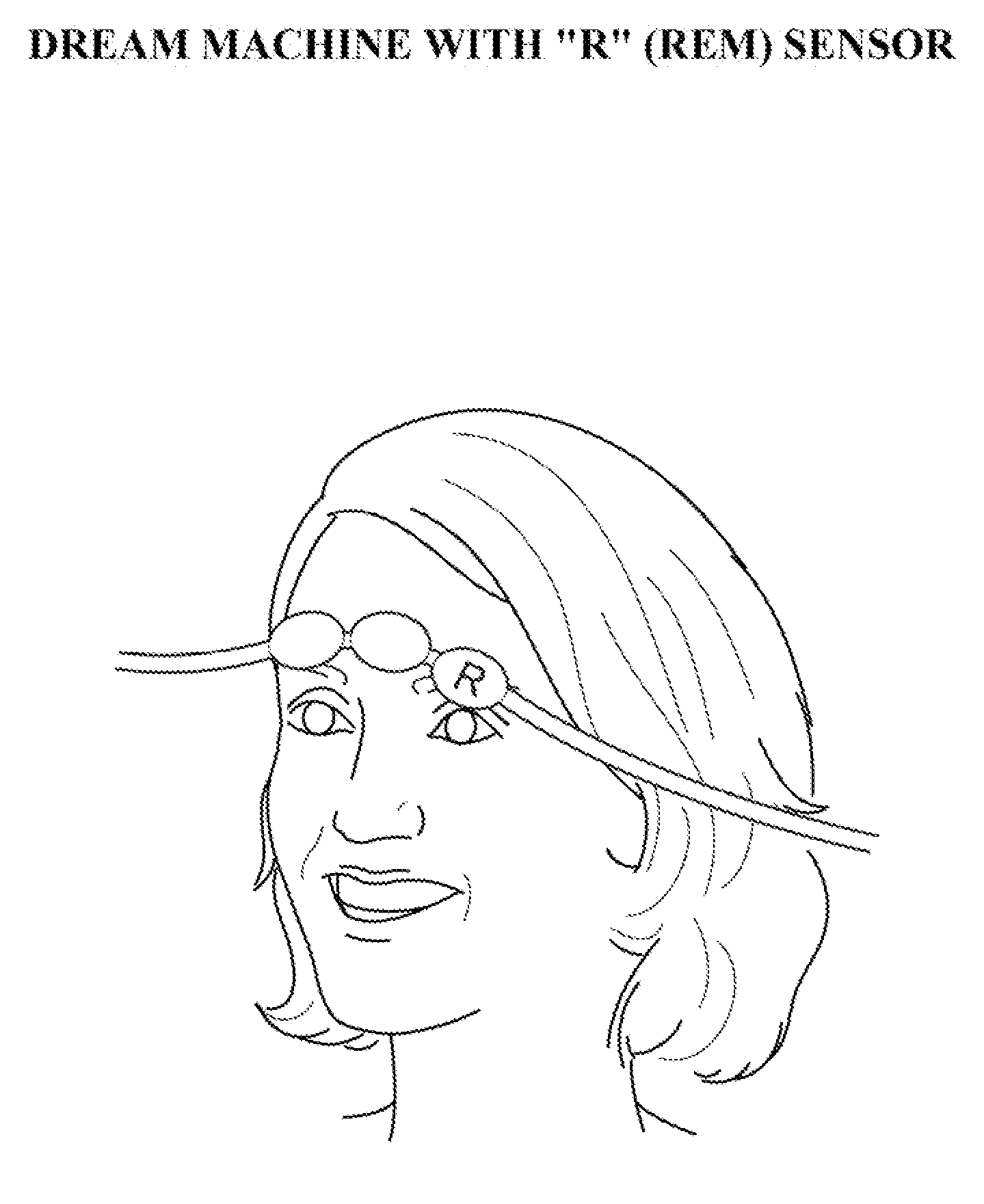
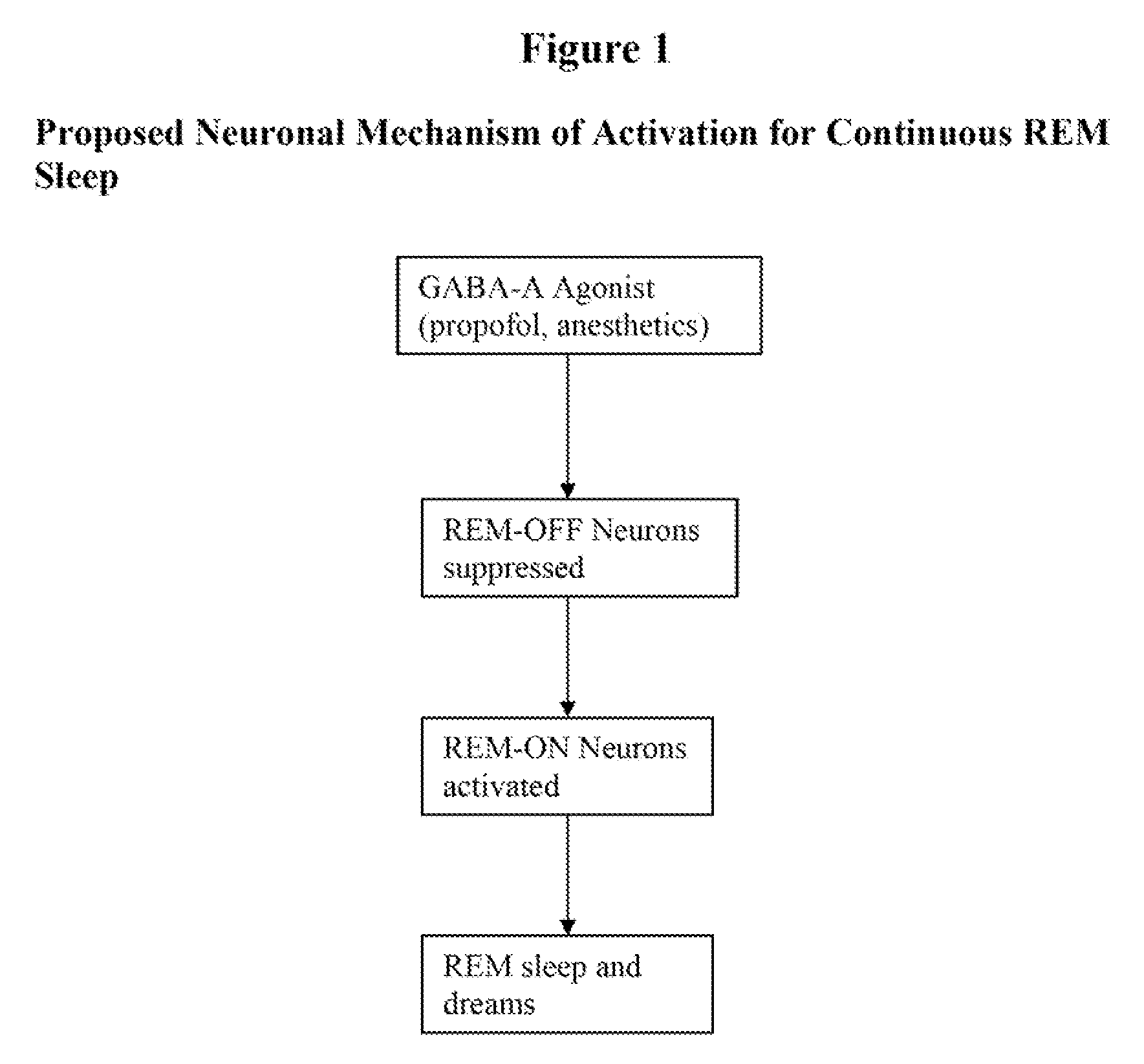
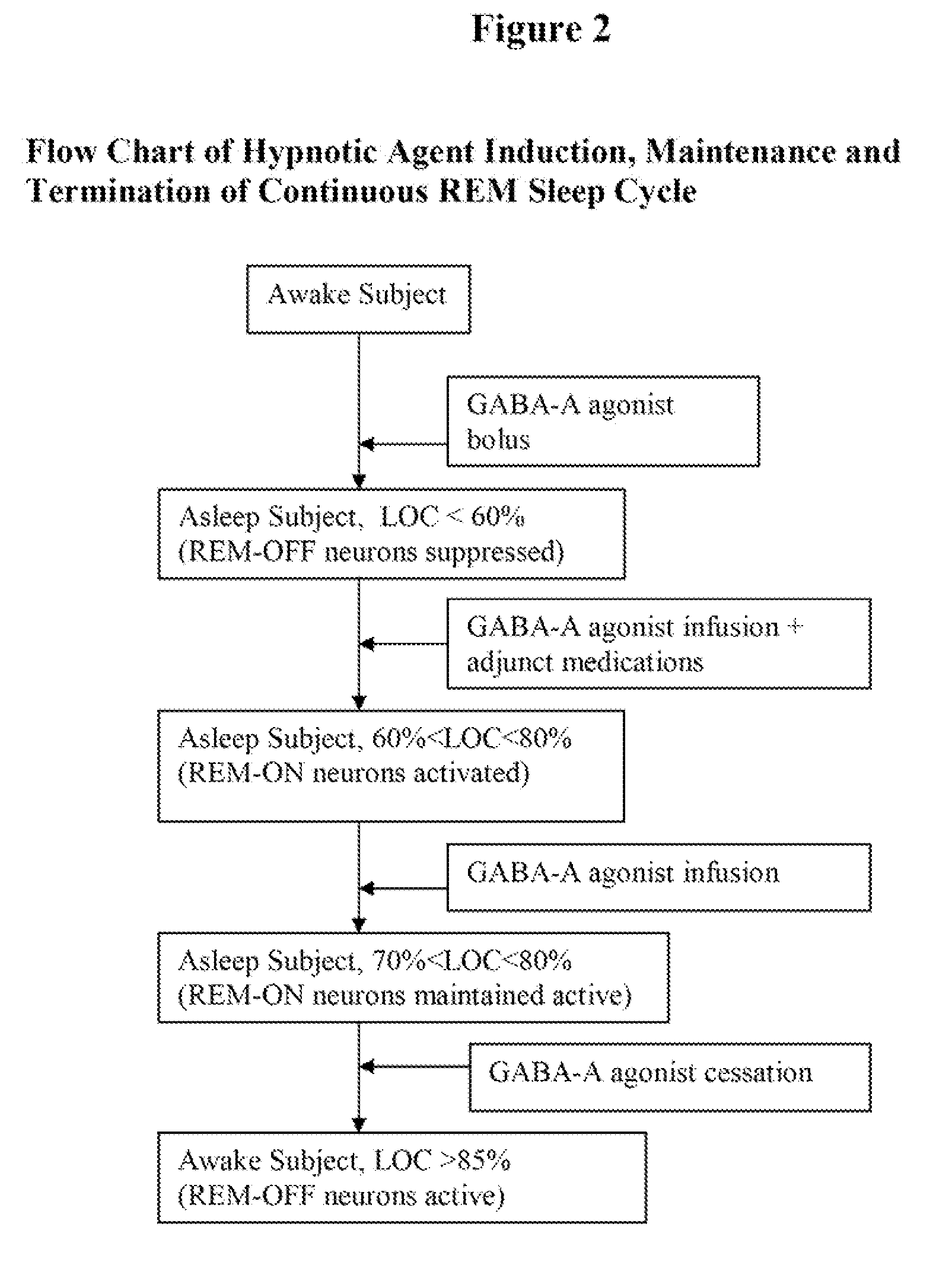
Compositions, methods, and systems for rapid induction and maintenance of continuous rem sleep
Compositions, kits, methods, and systems to induce, maintain, monitor, and interpret a continuous, un-fragmented REM sleep state in humans, generate dreams, recover sleep, create brain neuronal plasticity and activate the brain for cognition enhancement and mood stabilization are described. If potentially combined with other medications, a platform is provided to develop new research and therapies in many fields treating the human brain. The procedure reliably and quickly generates a Continuous REM Sleep cycle of pre-determined time or indefinite duration depending on therapeutic goals, allowing the patient to experience a qualitatively superior dream sleep in a shortened period of time compared to a natural sleep cycle. Profuse positive (pleasant) dreams are produced as well. REM sleep, dreams and sleep recovery can be reliably generated, and various sleep, psychological and neurological illnesses and disorders can be treated or prevented either solely by this method or in combination with additional agents.
Owner:CHOW HARRISON
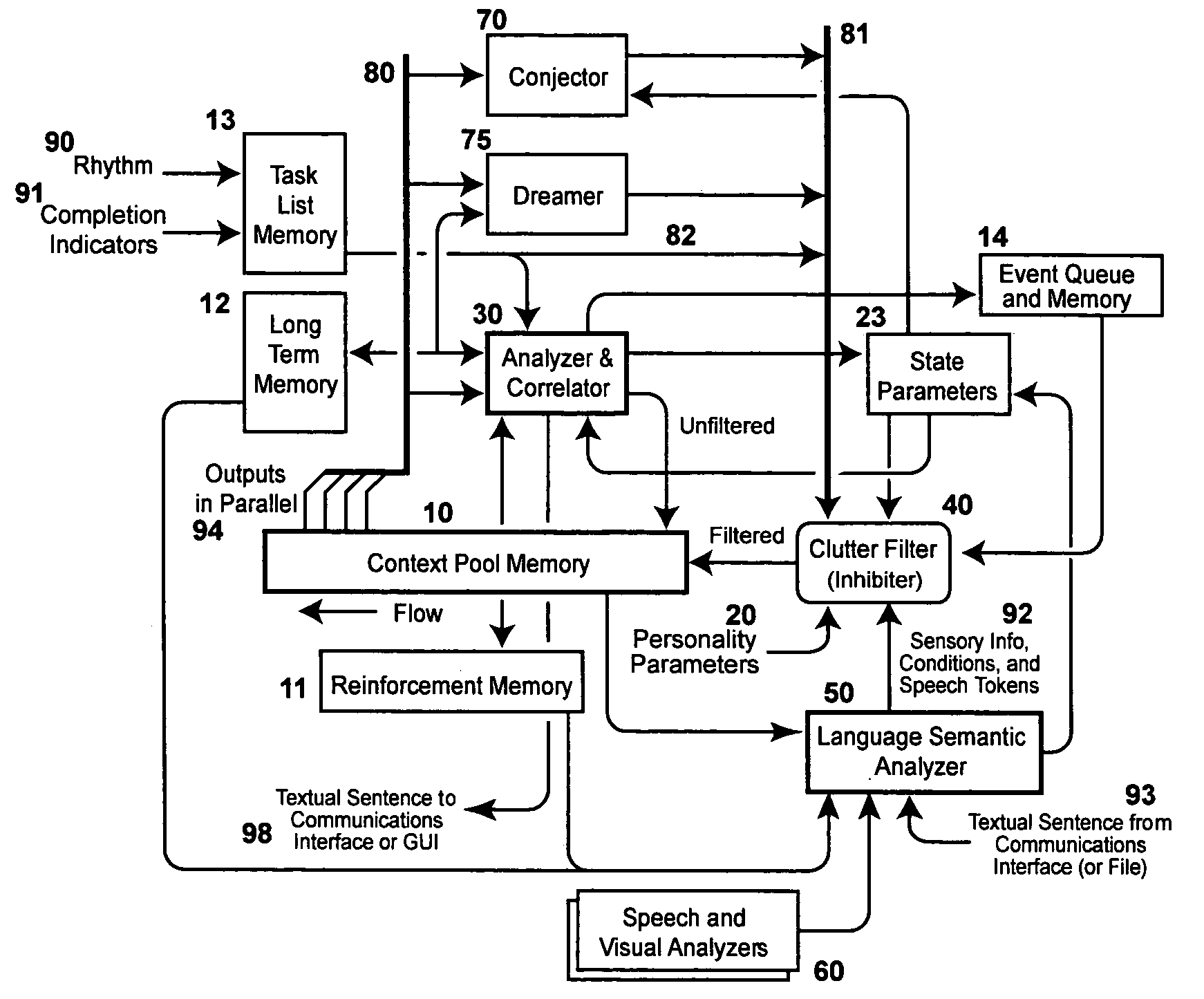
Method for inclusion of psychological temperament in an electronic emulation of the human brain
InactiveUS7089218B1Simulation is accurateAmenable to implementationSemantic analysisSpeech analysisComputer scienceHuman brain
A method of emulating the human brain with its thought and rationalization processes is presented here, as well as a method of storing human-like thought. The invention provides for inclusion of psychological profiles, experience and societal position in an electronic emulation of the human brain. This permits a realistic human-like response by that emulation to the people and the interactive environment around it.
Owner:NEURIC TECH
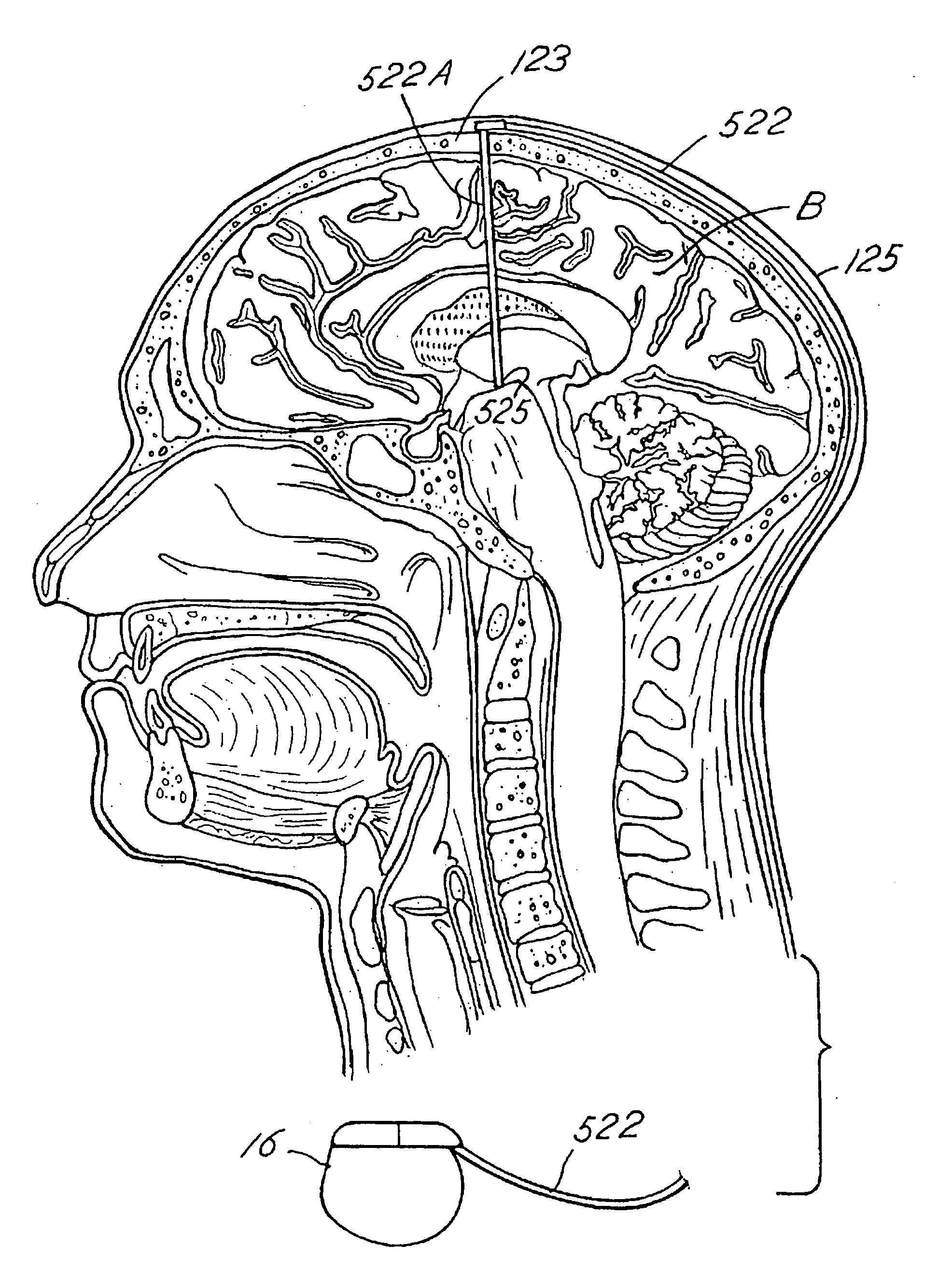
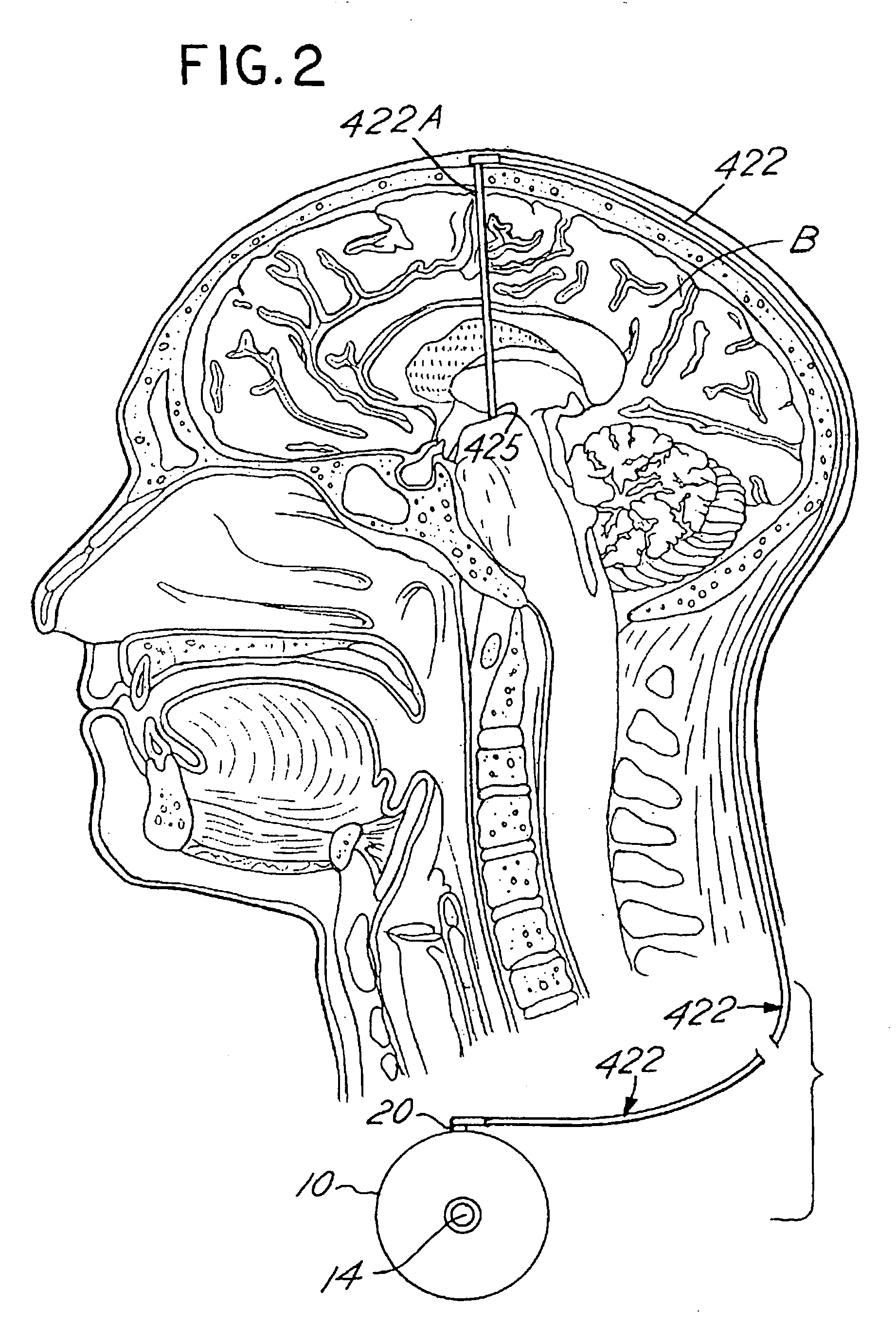
Cognitive function within a human brain
ActiveUS20070060974A1Improve cognitive functionHead electrodesWound drainsHuman givensImplanted device
Methods and apparatus for improving cognitive function within a human. The invention utilizes an implanted device, such as an implantable signal generator or an implantable pump, to affect tissue elements within a Papez circuit of the human brain as well as tissue upstream or downstream from the Papez circuit. The implanted device delivers treatment therapy to thereby improve cognitive function by the human. A sensor may be used to detect various symptoms of the cognitive disorder. A microprocessor algorithm may then analyze the output from the sensor to regulate delivery of the stimulation and / or drug therapy.
Owner:FUNCTIONAL NEUROMODULATION
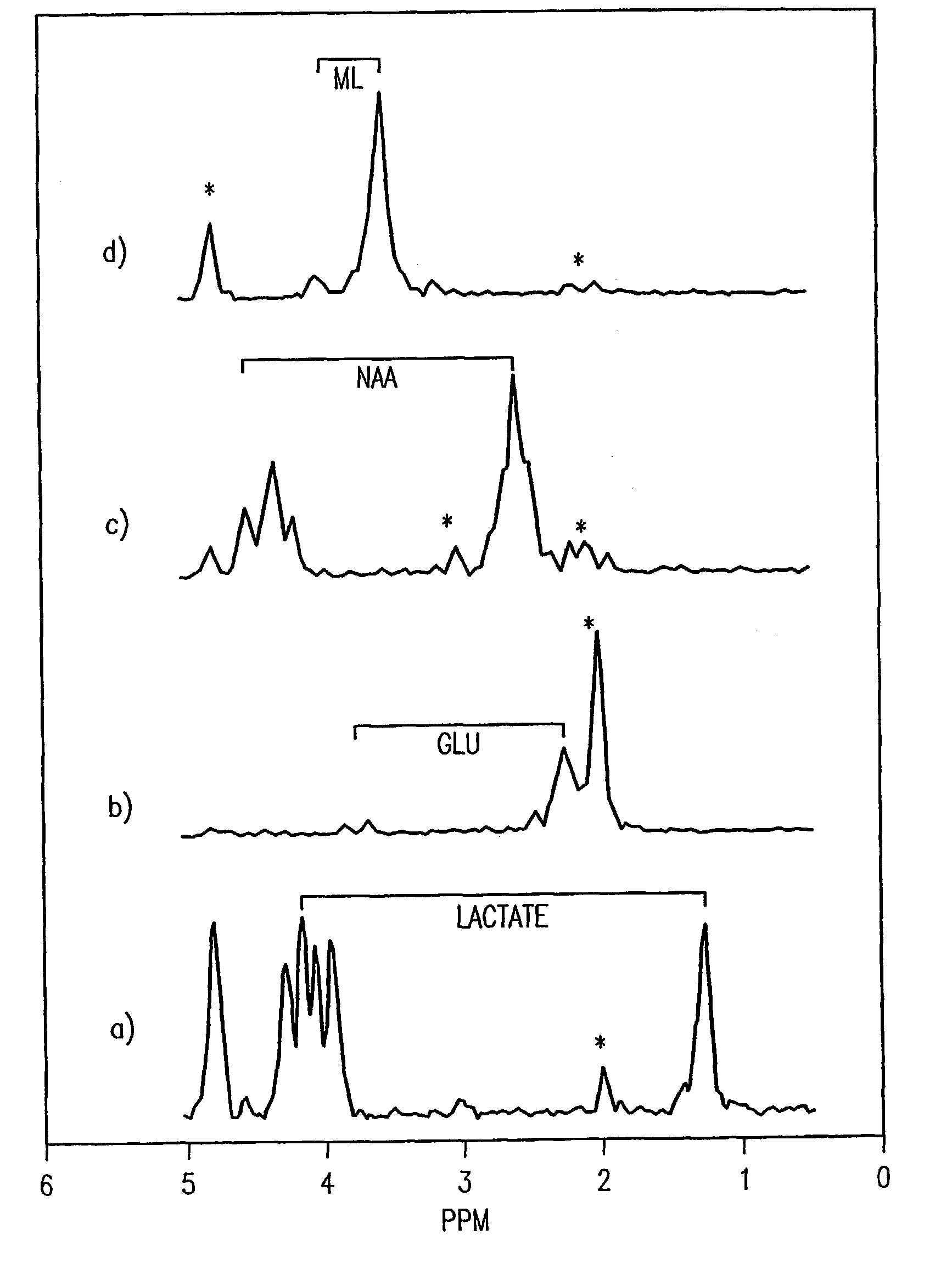
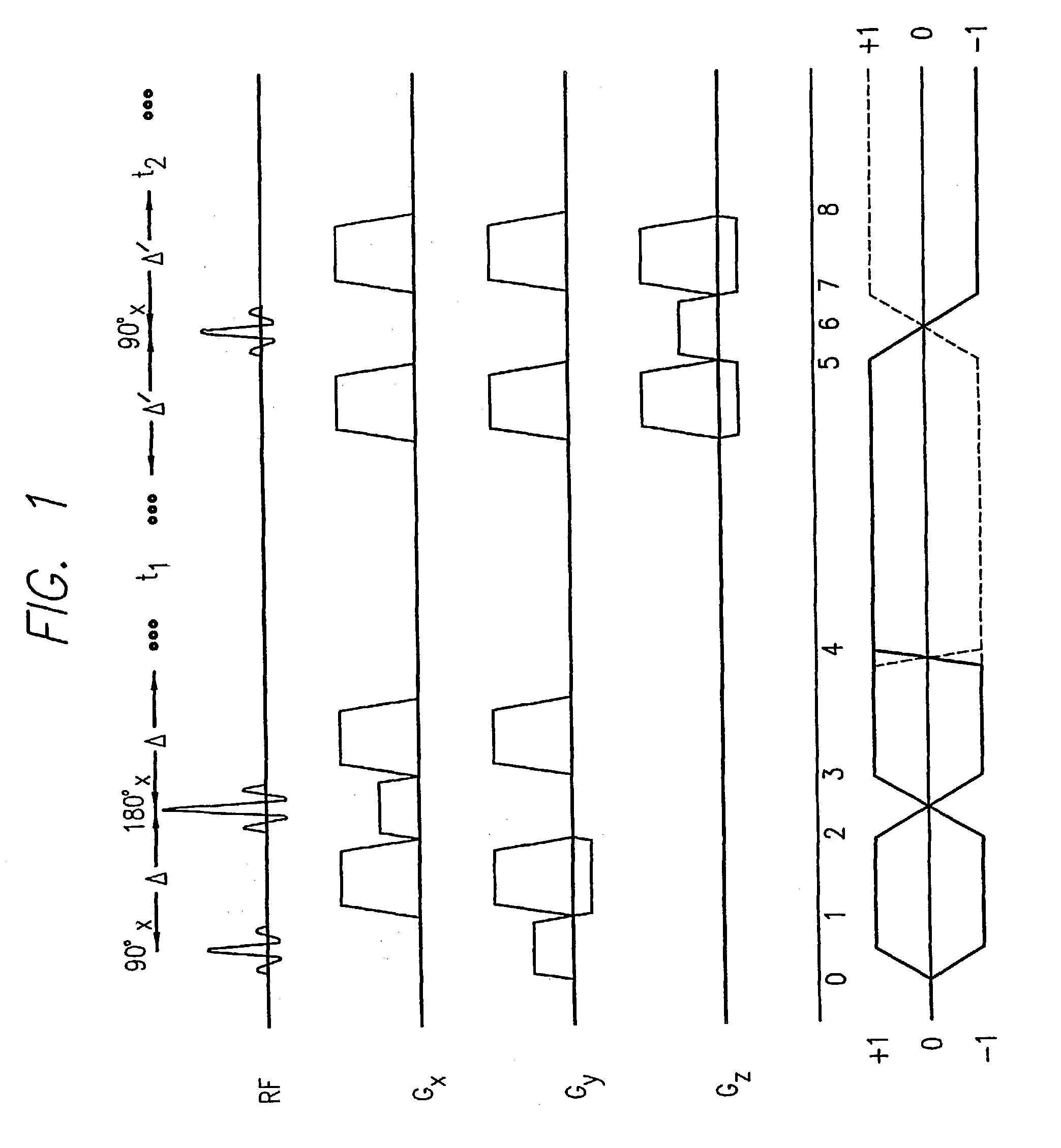
Localized two-dimensional shift correlated MR spectroscopy of human brain
InactiveUS7200430B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringWhole bodySpectroscopy
A two-dimensional (2D) chemical shift correlated MR spectroscopic (COSY) sequence integrated into a new volume localization technique (90°-180°-90°) for whole body MR Spectroscopy. Using the product operator formalism, a theoretical calculation of the volume localization as well as the coherence transfer efficiencies in 2D MRS is presented. A combination of different MRI transmit / receive rf coils is used. The cross peak intensities excited by the proposed 2D sequence are asymmetric with respect to the diagonal peaks. Localized COSY spectra of cerebral frontal and occipital gray / white matter regions in fifteen healthy controls are presented.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Behavior recognition technical method based on deep learning
PendingCN110188637AGood feature expression abilityEasy to useCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesVideo monitoringNetwork model
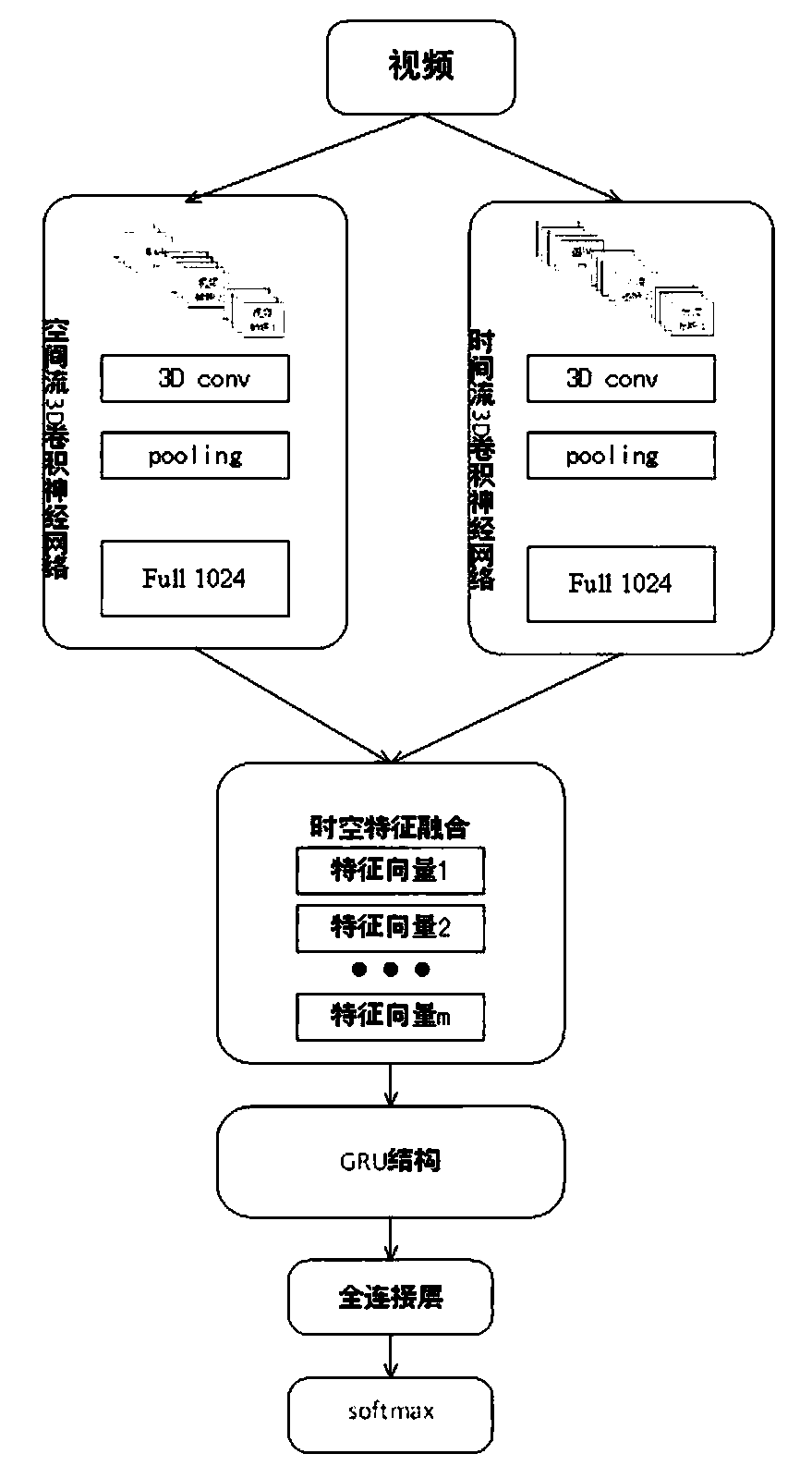
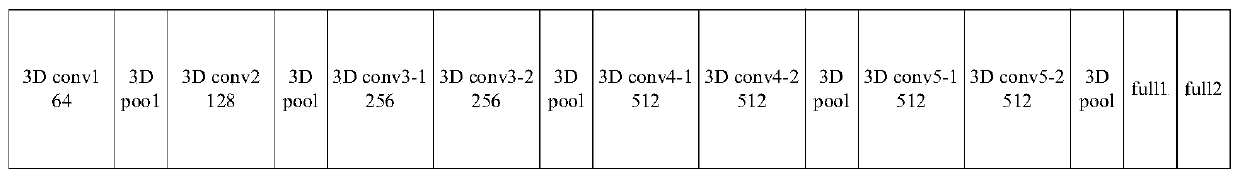
The invention discloses a behavior recognition technical method based on deep learning, which solves a problem that the intelligentization of a video monitoring system in the prior art needs to be improved. The method comprises the following steps of constructing a deeper space-time double-flow CNN-GRU neural network model by adopting a mode of combining a double-flow convolutional neural networkand a GRU network; extracting the time domain and space domain features of the video; extracting the long-time serialization characteristics of the spatial-temporal characteristic sequence according to the capability of the GRU network for memorizing information, and carrying out the behavior recognition of a video through employing a softmax classifier; proposing a new related entropy-based lossfunction; and with the help of a method for processing the mass information by referring to a human brain visual nerve attention mechanism, introducing an attention mechanism before a space-time double-flow CNN-GRU neural network model performs space-time feature fusion. The accuracy of the model provided by the technology is 61.5%, and compared with an algorithm based on a double-flow convolutional neural network, the recognition rate is improved to a certain extent.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
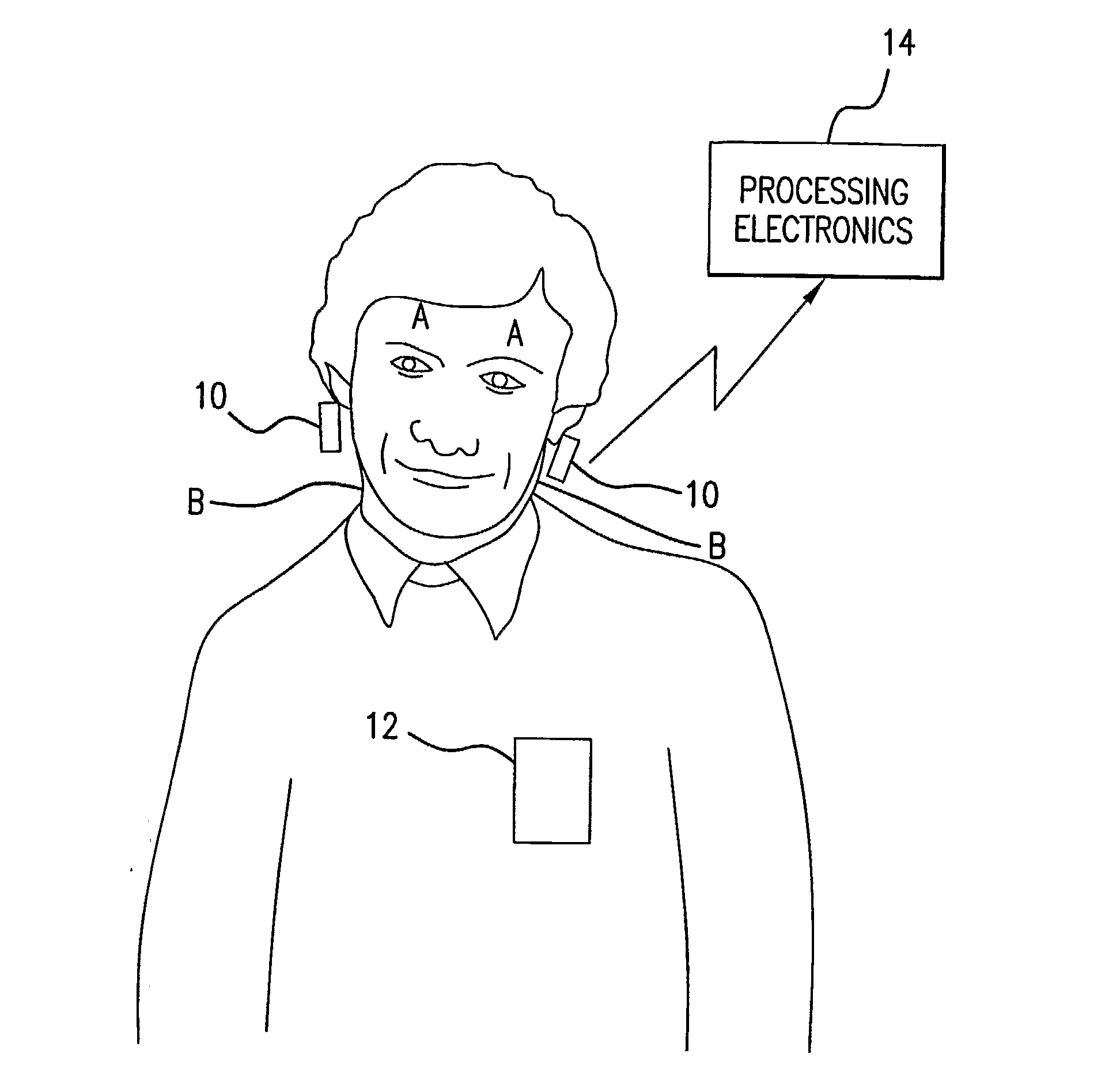
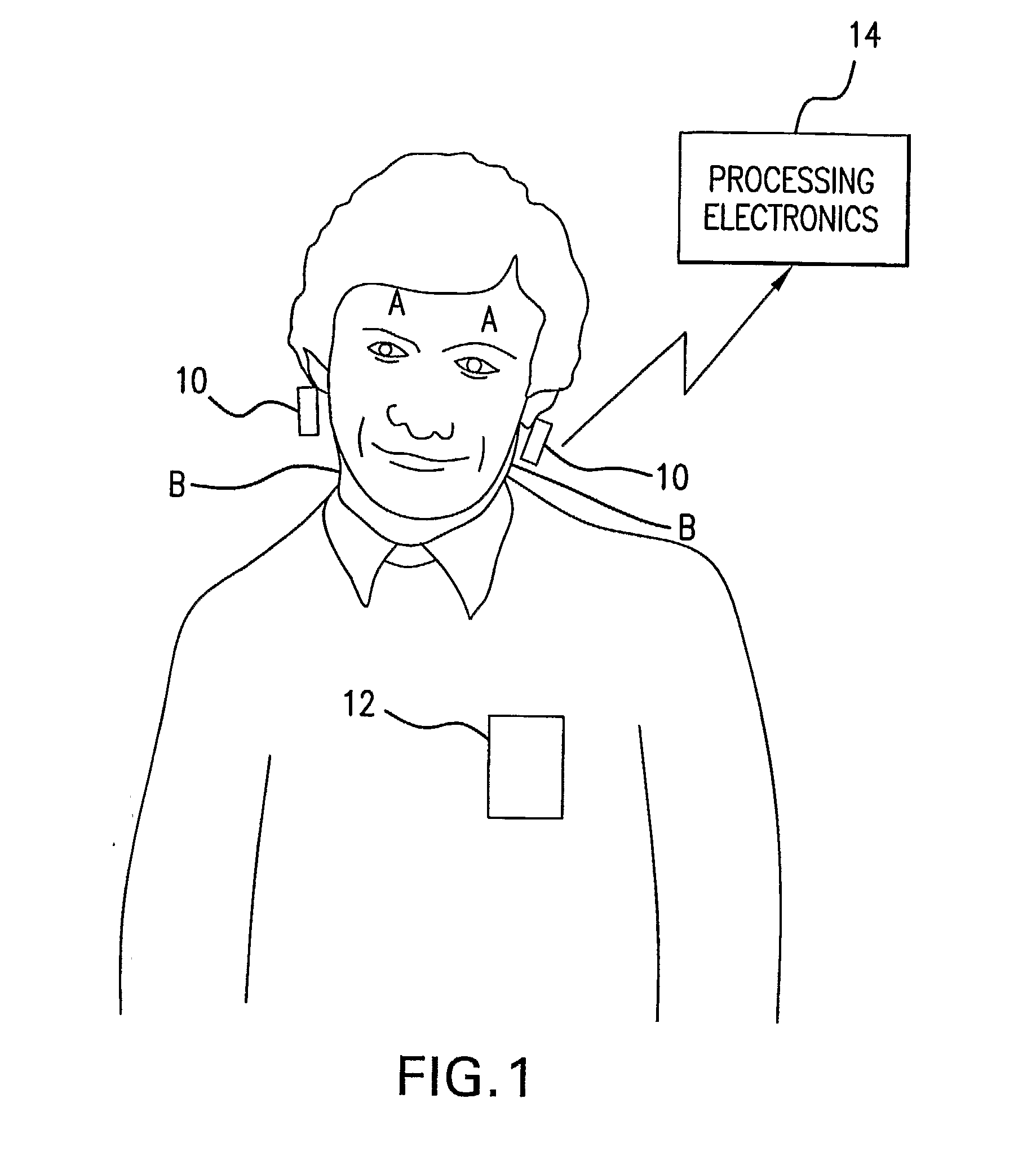
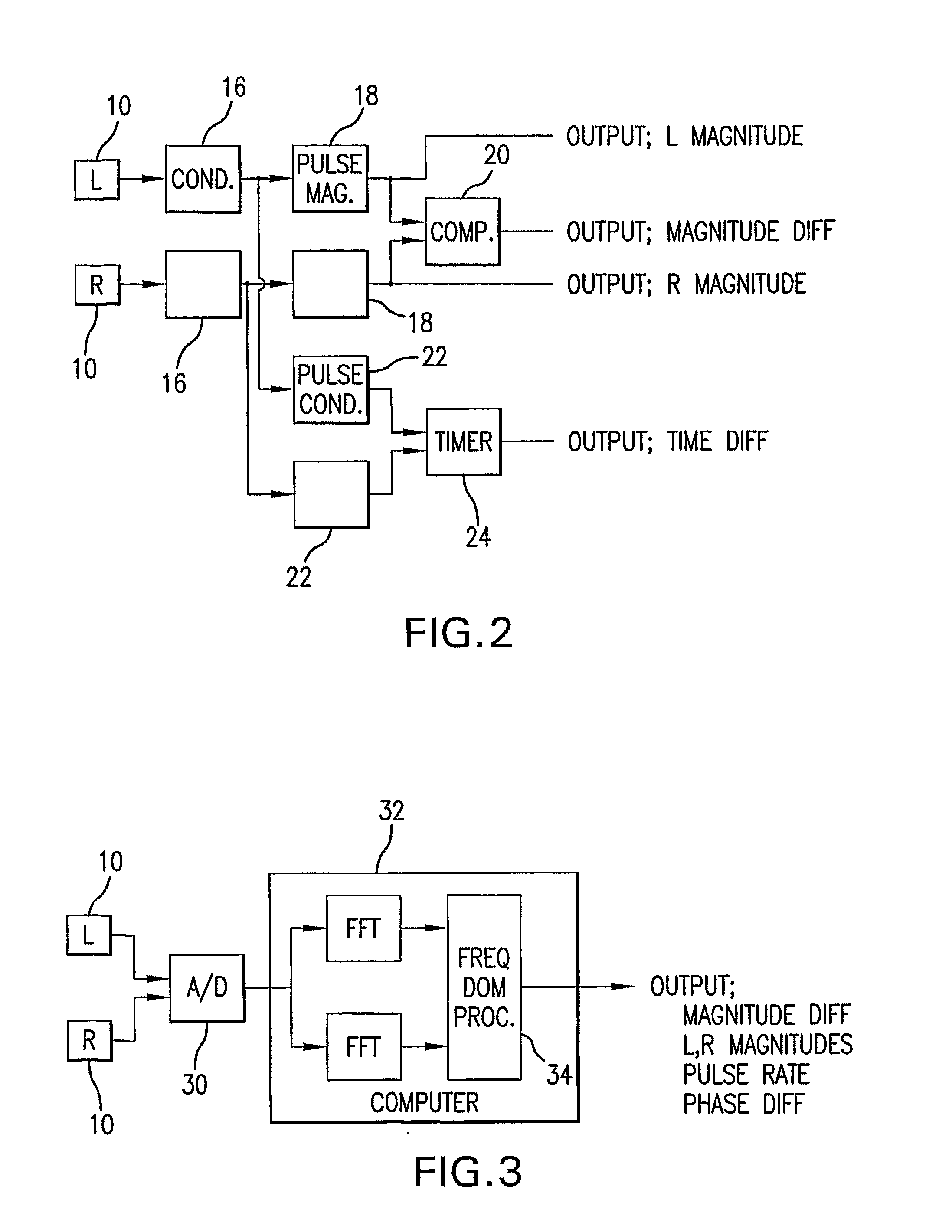
Bilateral Differential Pulse Method For Measuring Brain Activity
InactiveUS20080021332A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterPhase differencePulse characteristics
A method of measuring human brain activity includes the steps of simultaneously measuring pulses at two locations on a human subject that each receives blood from a different carotid artery that feeds a respective one of left and right hemispheres of the brain of the human subject, determining pulse characteristics from the measured pulses, and evaluating relative left and right hemisphere activity of the brain of the human subject based on the determined pulse characteristics. The method may use dual photoplethysmograhic blood pulse sensors that measure left and right hemisphere activity by determining pulse amplitude difference and time or phase differences between the earlobes while the subject carries out various mental functions. The data from the sensors are processed to provide a measure of brain function and the mental activity of the subject.
Owner:ATLANTIS PARTNERSHIP
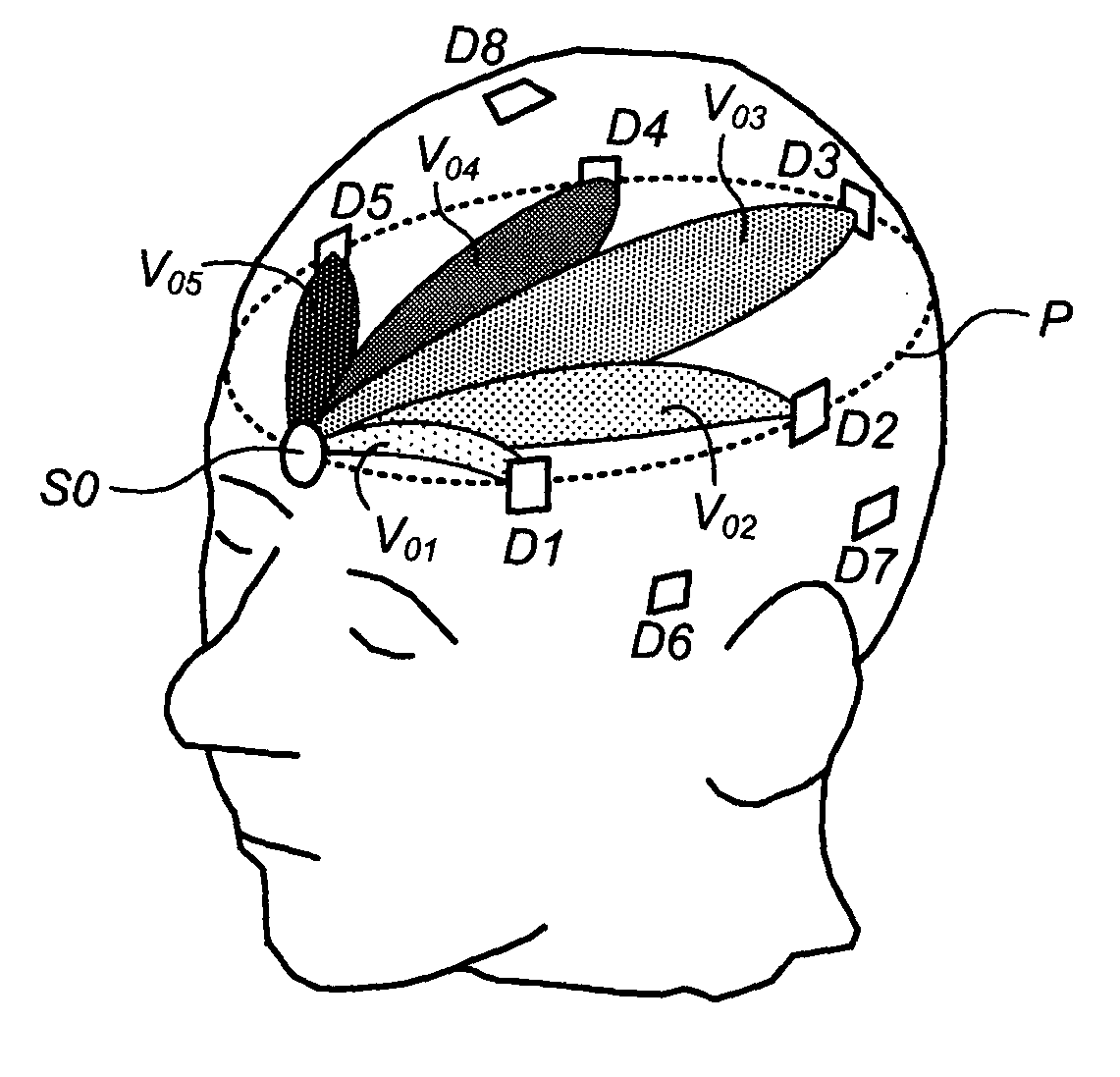
Volumetric image formation from optical scans of biological tissue with multiple applications including deep brain oxygenation level monitoring
InactiveUS20080177163A1Low costSimple cuttingCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostics using tomographyOptical radiationProperty value
Methods, systems, and related computer program products for non-invasive monitoring of a biological volume, such as a human brain, are described. In one preferred embodiment, each of a plurality of optical sources emits optical radiation into the biological volume each of a plurality of optical detectors detects optical radiation impinging thereupon from the biological volume. The optical measurements are processed to compute a requisite property value associated with each source-detector pair. For each source-detector pair, a volumetric basis region corresponding thereto is weighted by the requisite property value, the volumetric basis region being predetermined and representative of an estimated subvolume of the biological volume encountered by optical radiation emitted from that source and propagating to that detector. The weighted volumetric basis regions are accumulated into a volumetric cumulative array, and a display output is generated based at least in part on the volumetric cumulative array.
Owner:O2 MEDTECH
Intravascular stent device
A very small diameter intravascular stent device which may be used to occlude or partially occlude an aneurysm in the human brain, the stent device includes a thin-walled skeletal cylindrical tube fonned of S-shaped, or sinusoidal, elements which, when compressed, nest tightly with each other.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
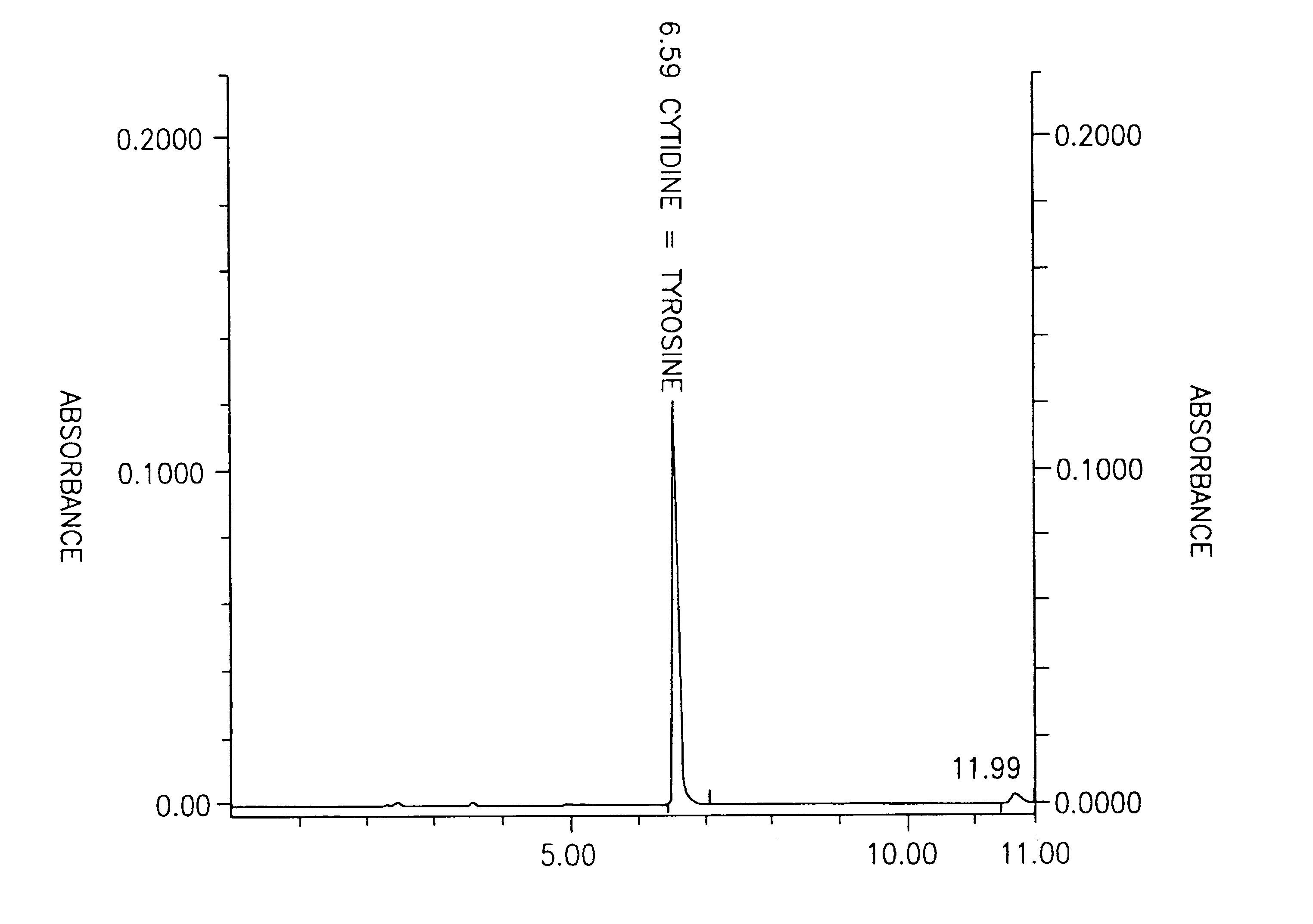
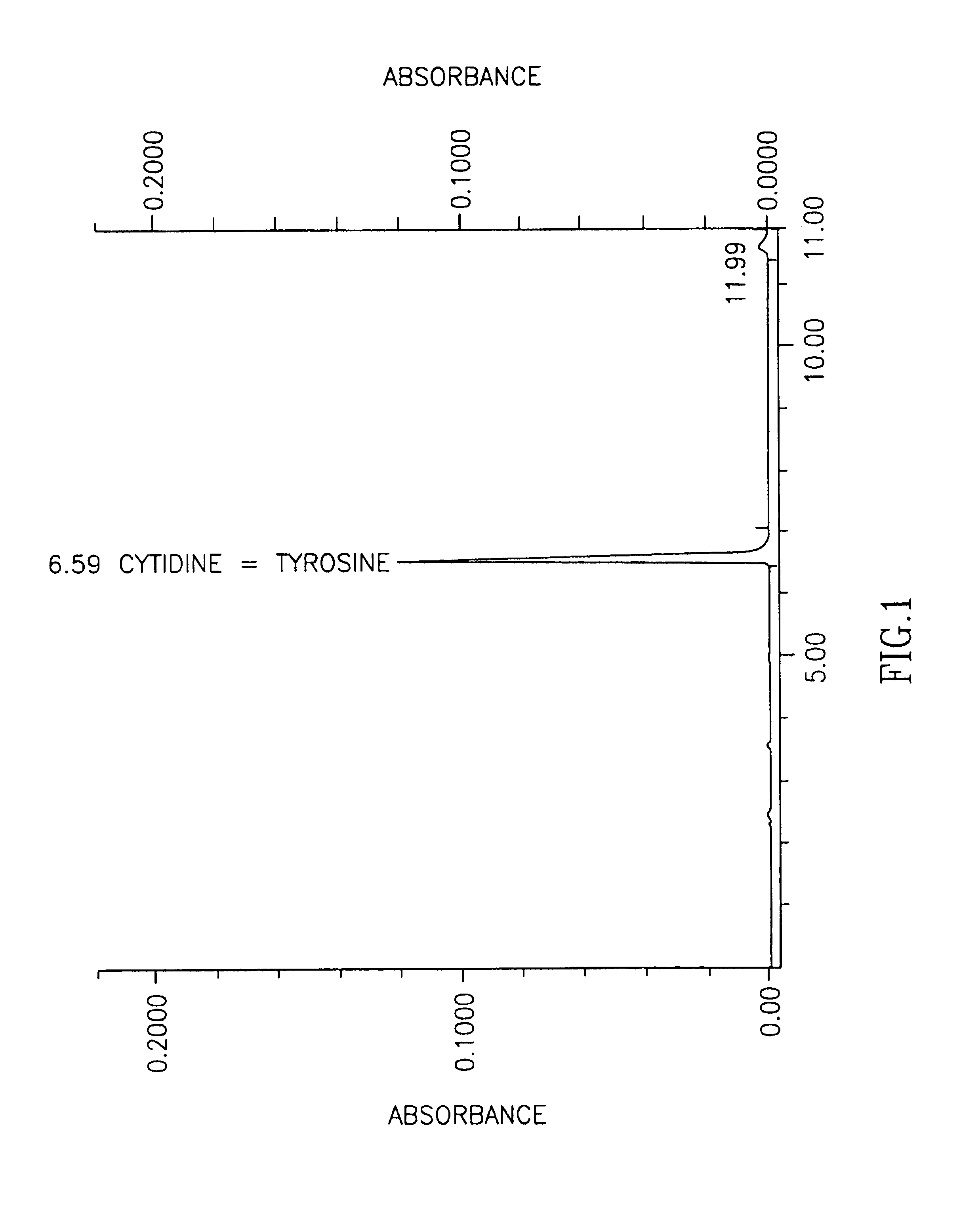
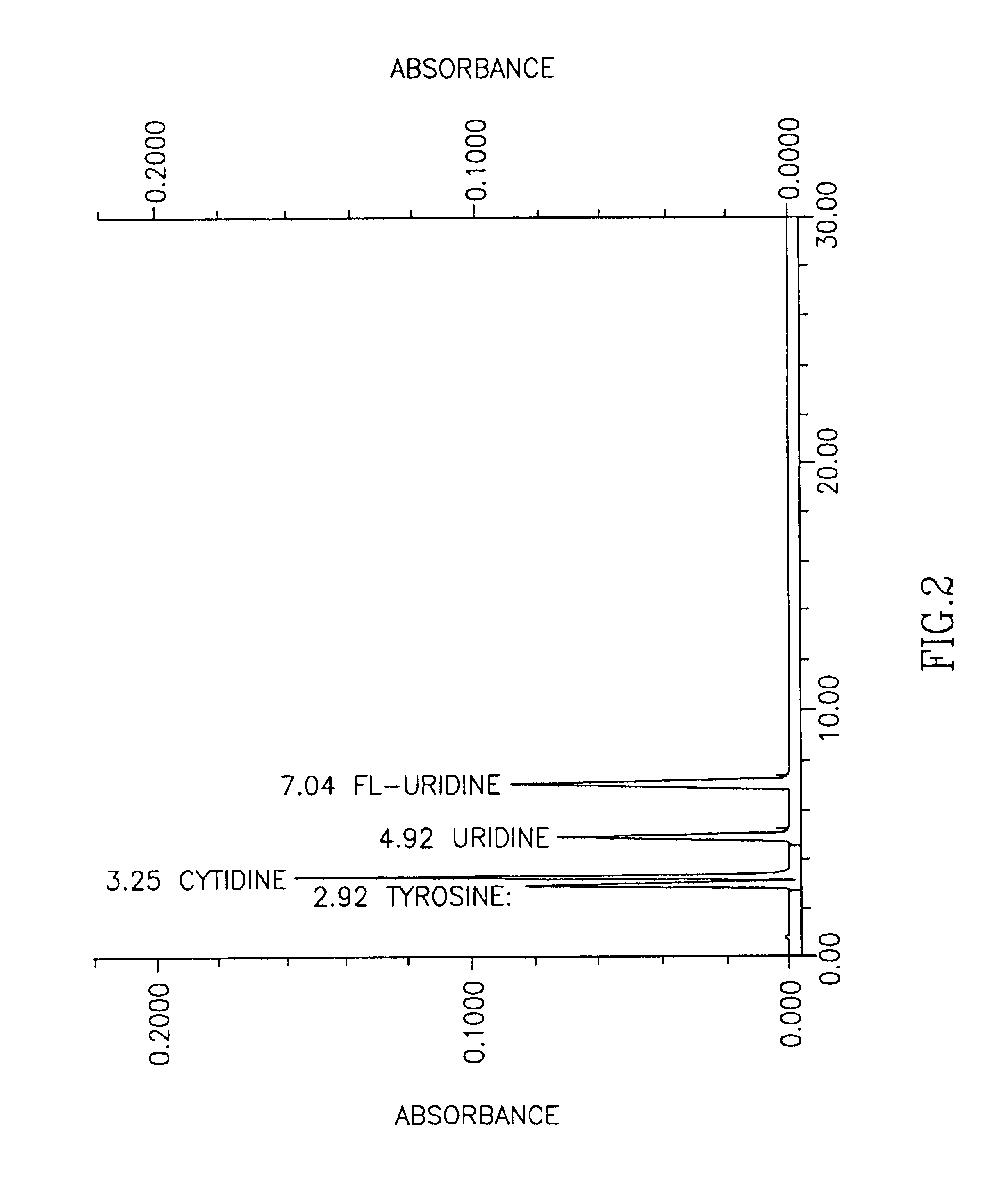
Methods for increasing blood cytidine and/or uridine levels and treating cytidine-dependent human diseases
InactiveUS6989376B2Enhancing uridine bioavailabilityBiocideNervous disorderMedicineUridine Nucleotides
Methods of treating certain neurological diseases using exogenous uridine or a uridine source alone as a precursor of endogenous cytidine, particularly in the human brain, are disclosed. Methods are also disclosed wherein exogenous uridine or a uridine source is combined either with drugs increasing uridine availability or with compounds that serve as a source of choline in phospholipid synthesis.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System that provides early detection, alert, and response to electronic threats
The invention is a computer system that provides early detection alert and response to electronic threats (eThreats) in large wide area networks, e.g. the network of an Internet Services Provider or a Network Services Provider. The system of the invention accomplishes this by harnessing the processing power of dedicated hardware, software residing in specialized servers, distributed personal computers connected to the network, and the human brain to provide multi-layered early detection, alarm and response. The layers comprise: a Protection Layer, which detects and eliminates from the network data stream eThreats known to the system; a Detection Layer, which detects and creates signatures for new eThreats that are unknown to the system; an Expert Analysis Layer, which comprises a group of human experts who receive information from various components of the system and analyze the information to confirm the identity of new eThreats; and a Collaborative Detection & Protection Layer, which detects potential new eThreats by processing information received from various system agents and users. A Dynamic Sandbox Protection Layer associated with the distributed personal computers connected to the network. can optionally be part of the system of the invention.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
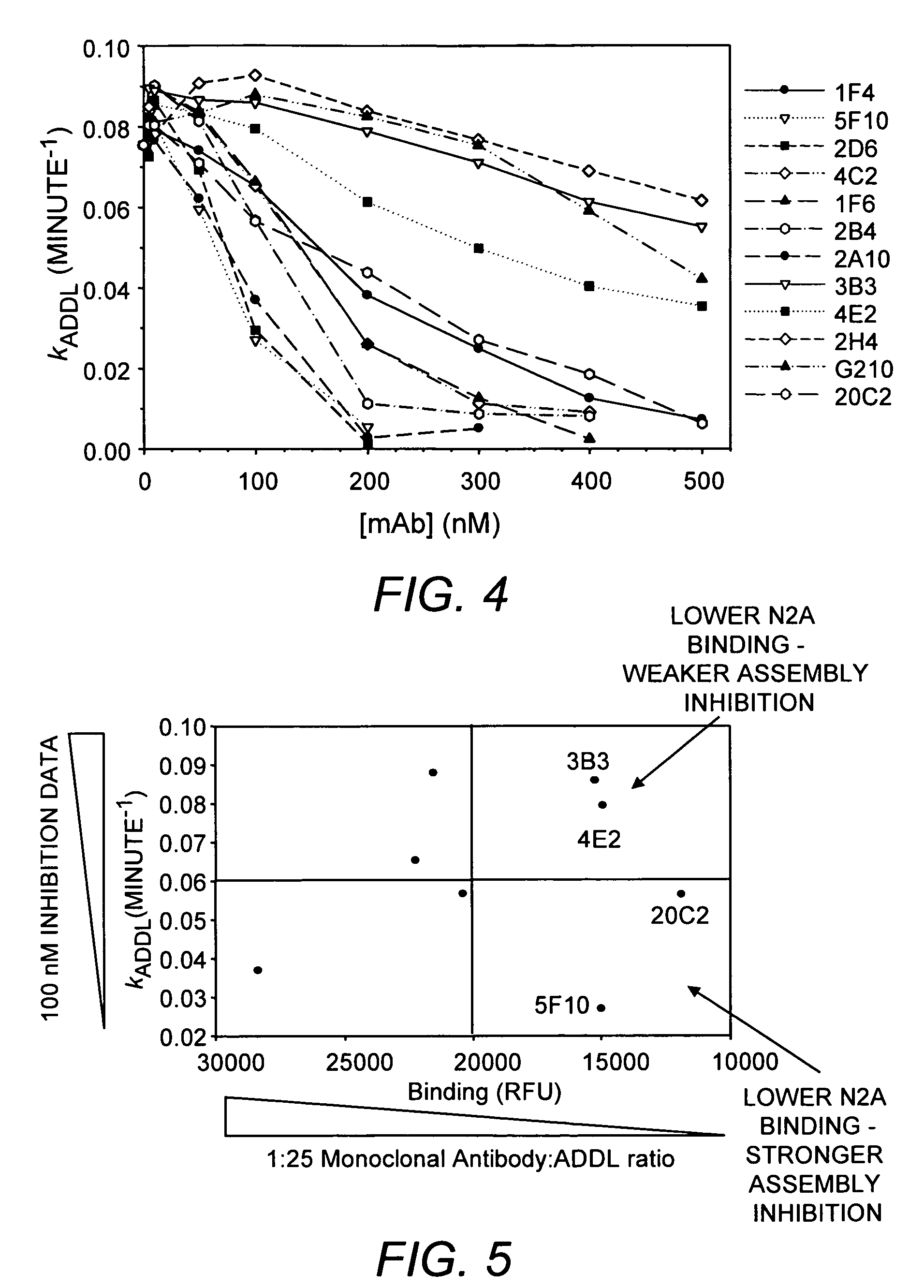
Monoclonal Antibodies That Target Pathological Assemblies Of Amyloid B (Abeta)
ActiveUS20070218499A1Nervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansOligomerMonoclonal antibody
Disclosed herein are antibodies that bind with high specificity to soluble oligomers of amyloid β (Abeta) and methods of employing those antibodies. The antibodies are able to distinguish between Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and control human brain extracts. The antibodies identify endogenous Abeta oligomers in AD brain slices and also bind to Abeta oligomers on cultured hippocampal cells. The antibodies neutralize endogenous Abeta oligomers and Abeta oligomers produced in solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Intravascular stent device
A very small diameter intravascular stent device which may be used in balloon angioplasty or in the treatment of an aneurysm in the human brain, which is comprised of a thin-walled skeletal cylindrical tube formed of undulating or sinusoidal elements which, when compressed, nest tightly with each other.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Extended depth of field optics for human vision
The present invention provides extended depth of field to human eyes by modifying contact lenses, intraocular implants, and / or the surface of the eye itself. This may be accomplished by applying selected phase variations to these optical elements (e.g., by varying surface thickness of the cornea of the eye). The phase variations EDF-code the wavefront and cause the optical transfer function to remain essentially constant within a range of distances from the in-focus position. This provides a coded image on the retina. The human brain decodes this coded image, resulting in an in-focus image over an increased depth of field.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Microfabricated neurostimulation device
Described herein are microelectrode array devices, and methods of fabrication and use of the same, to provide highly localized and efficient electrical stimulation of a neurological target. The device includes multiple microelectrode elements arranged along an elongated probe shaft. The microelectrode elements are dimensioned and shaped so as to target individual neurons, groups of neurons, and neural tissue as may be located in an animal nervous system, such as deep within a human brain. Beneficially, the neurological probe can be used to facilitate location of the neurological target and remain implanted for long-term monitoring and / or stimulation.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
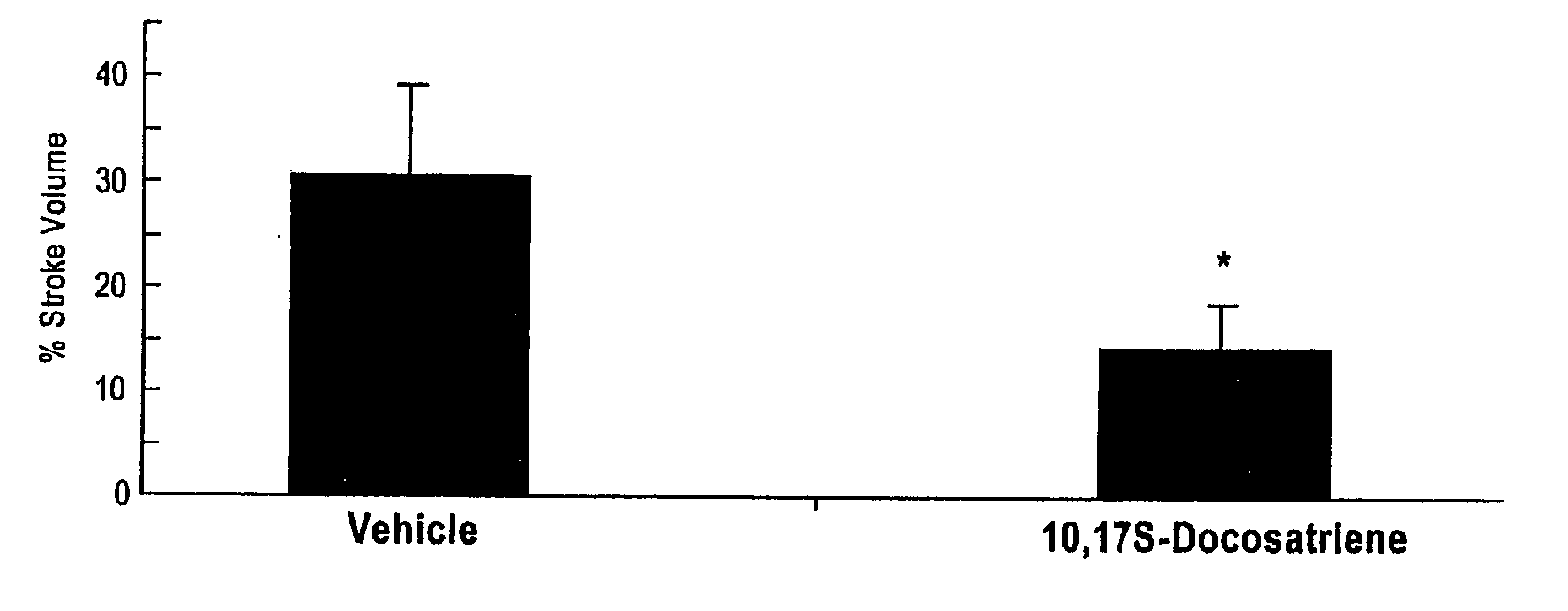
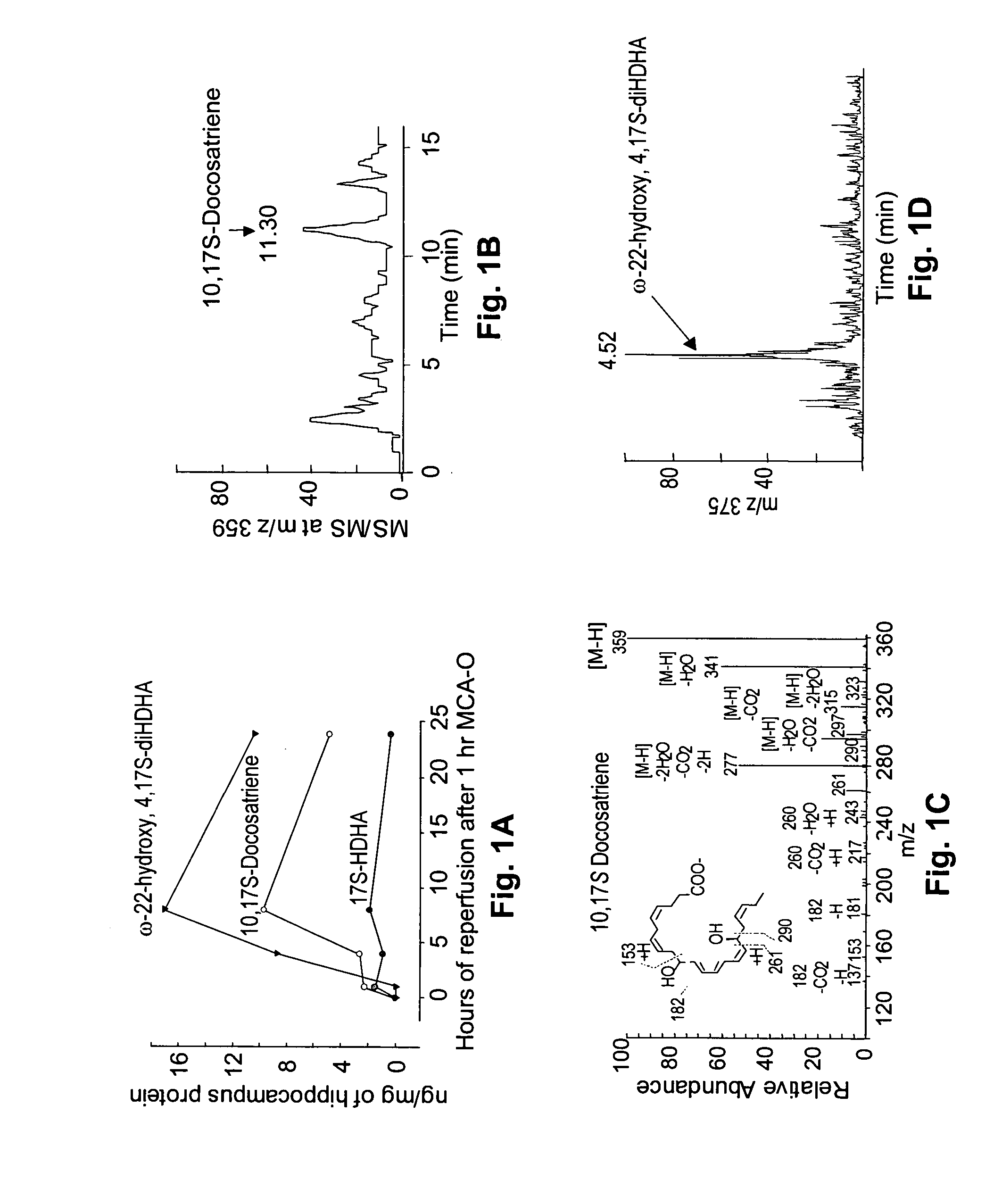
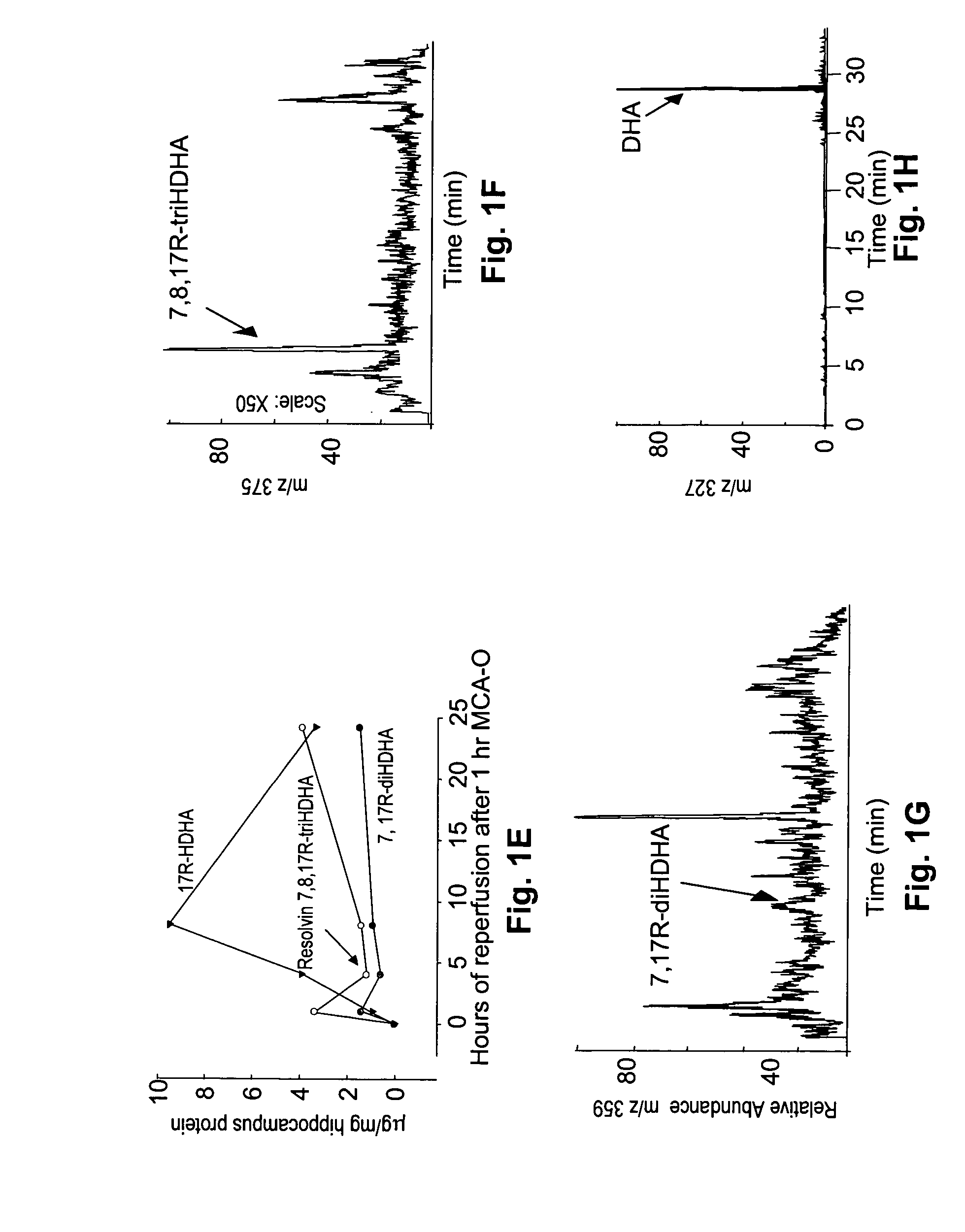
Neuroprotectin D1 protects against cellular apoptosis, stroke damage, alzheimer's disease and retinal diseases
InactiveUS20050075398A1Increase secretionReduce secretionBiocideSenses disorderRisk strokeRetinal pigment epithelial cell
A unique DHA product, 10, 17S-docosatriene (“Neuroprotectin D1” or “NPD1”), was found to provide surprisingly effective neuroprotection when administered right after an experimental stroke. Moreover, both nerve cells and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells were found to synthesize 10,17S-docosatriene (NPD1) from DHA. NPD1 also potently counteracted H2O2 / TNFα oxidative stress-mediated cell apoptotic damage. Under the same oxidative-stress conditions, NPD1 up-regulated the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, and decreased expression of the pro-apoptotic proteins, Bad and Bax. Moreover, in RPE cells NPD1 inhibited oxidative stress-induced caspase-3 activation, IL-1β-stimulated human COX-2 promoter expression, and apoptosis due to N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E). Overall, NPD1 protected both nerve and retinal pigment epithelial cells from cellular apoptosis and damage due to oxidative stress. NPD1 concentration in the brain of Alzheimer's patients was found to be significantly decreased from that of controls. In cultured human brain cells, NPD1 synthesis was up-regulated by neuroprotective soluble β amyloid, and NPD1 was found to inhibit secretion of toxic β amyloid peptides.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
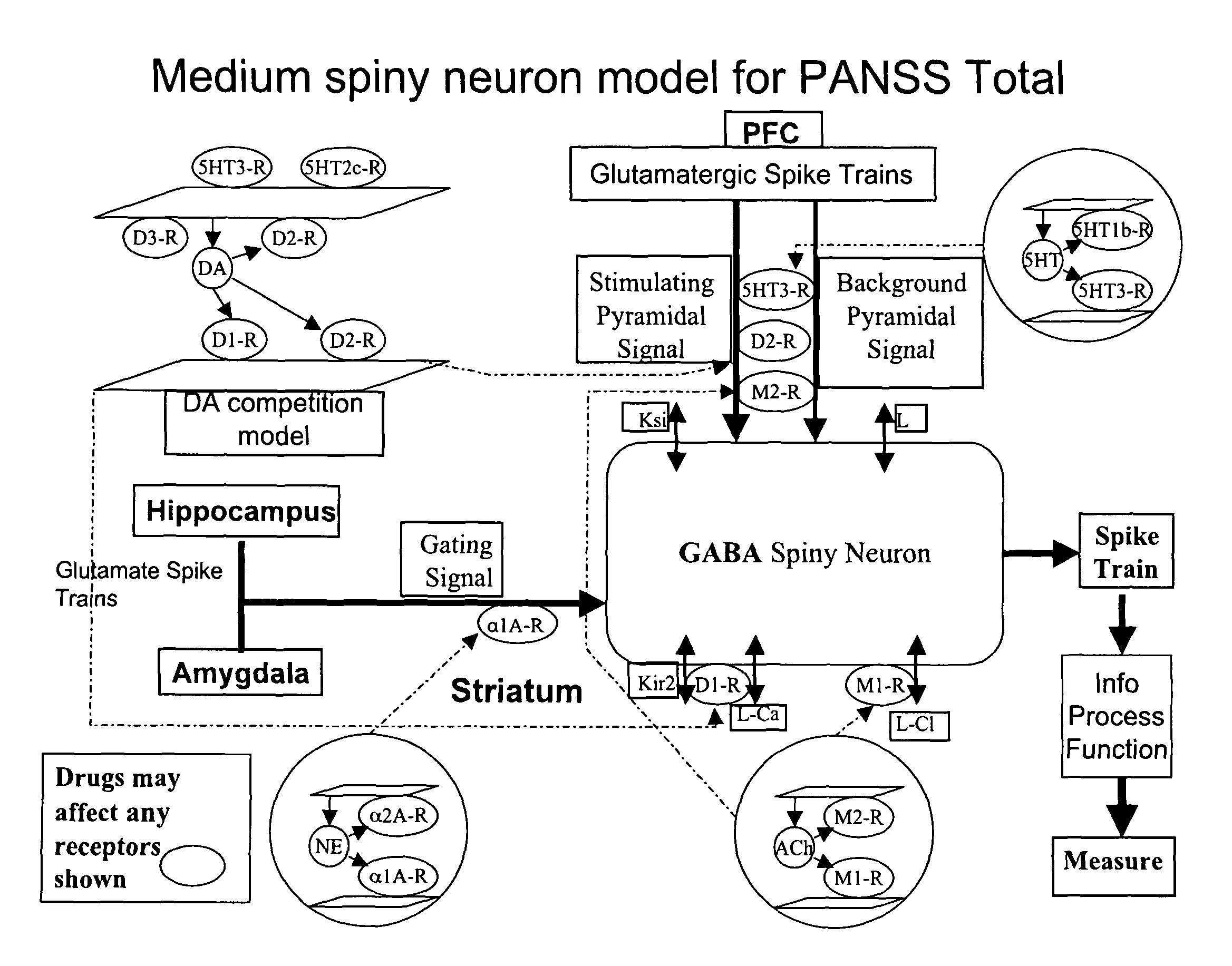
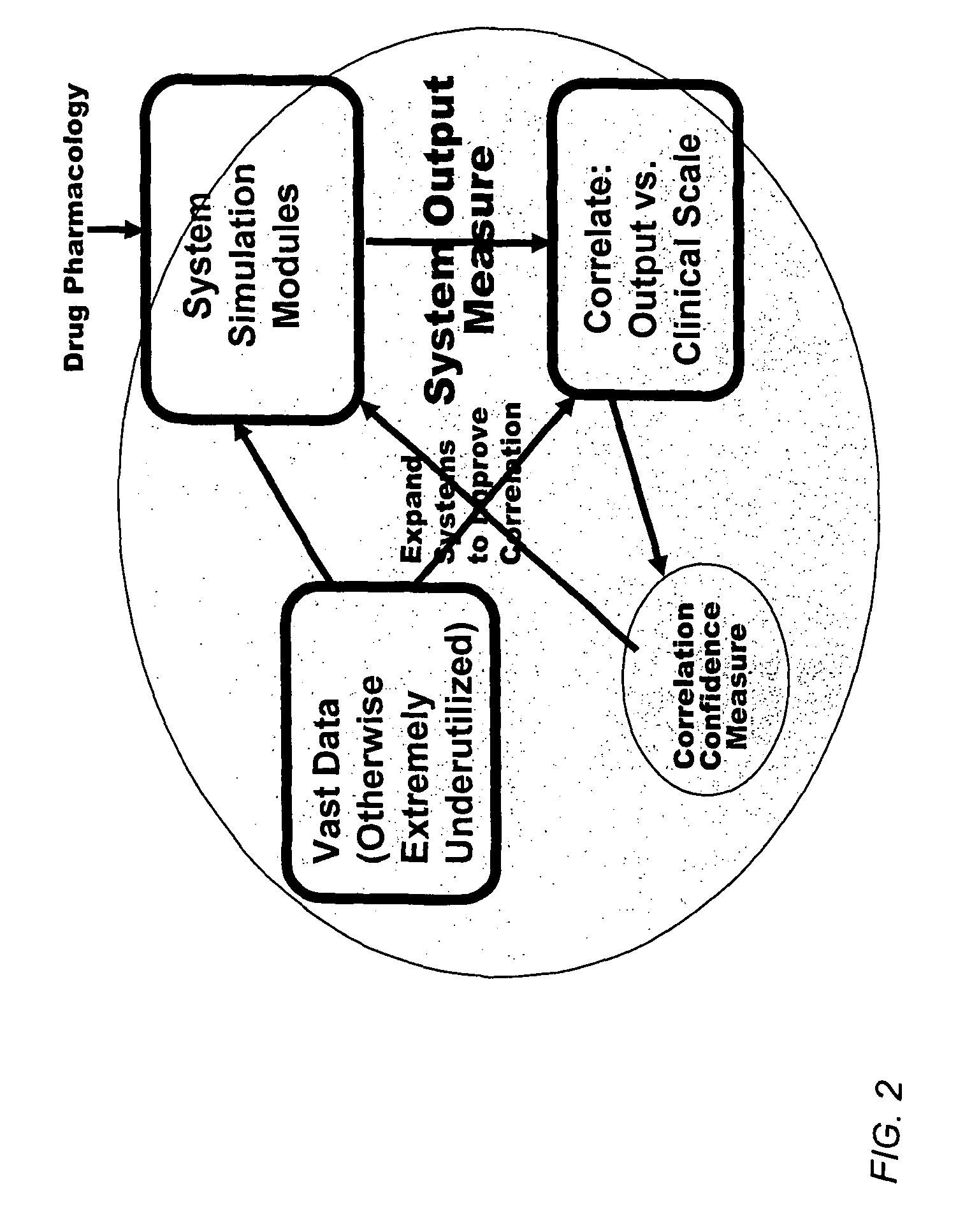
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases
ActiveUS8150629B2Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserAmygdala
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases on one or more clinical scales. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. The computer model preferably uses the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, as well as certain mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com