Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
150results about How to "Auxiliary diagnosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
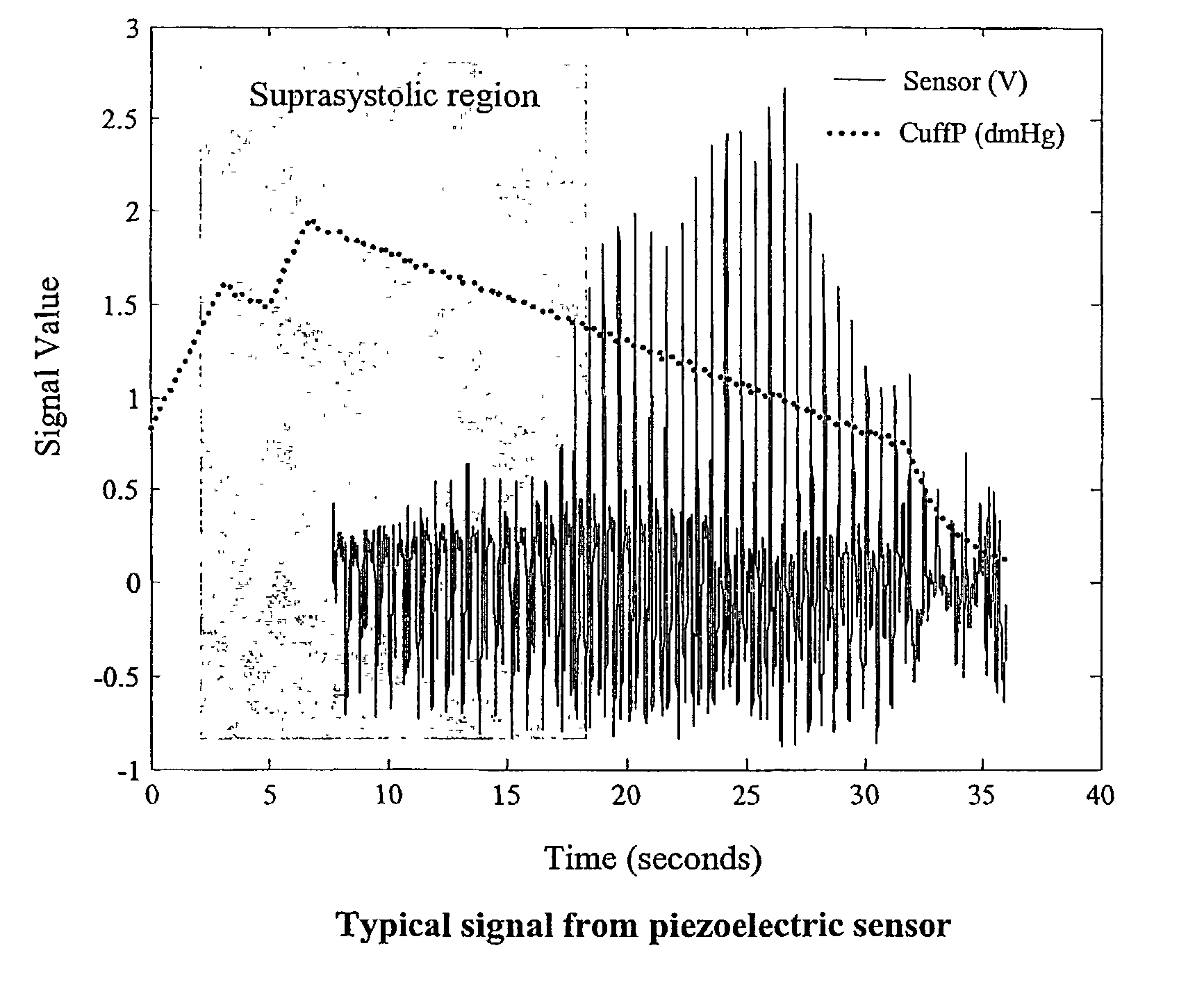
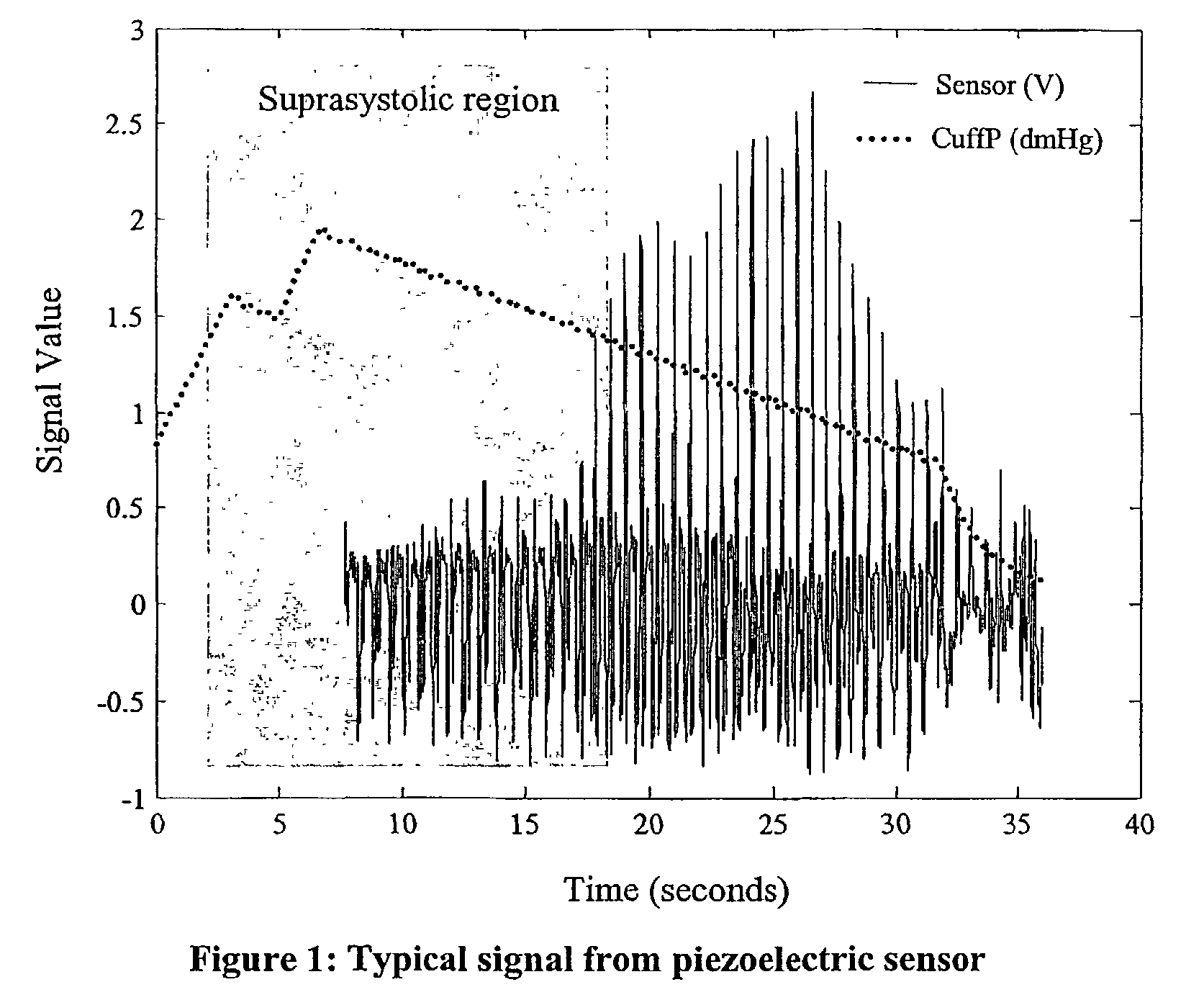
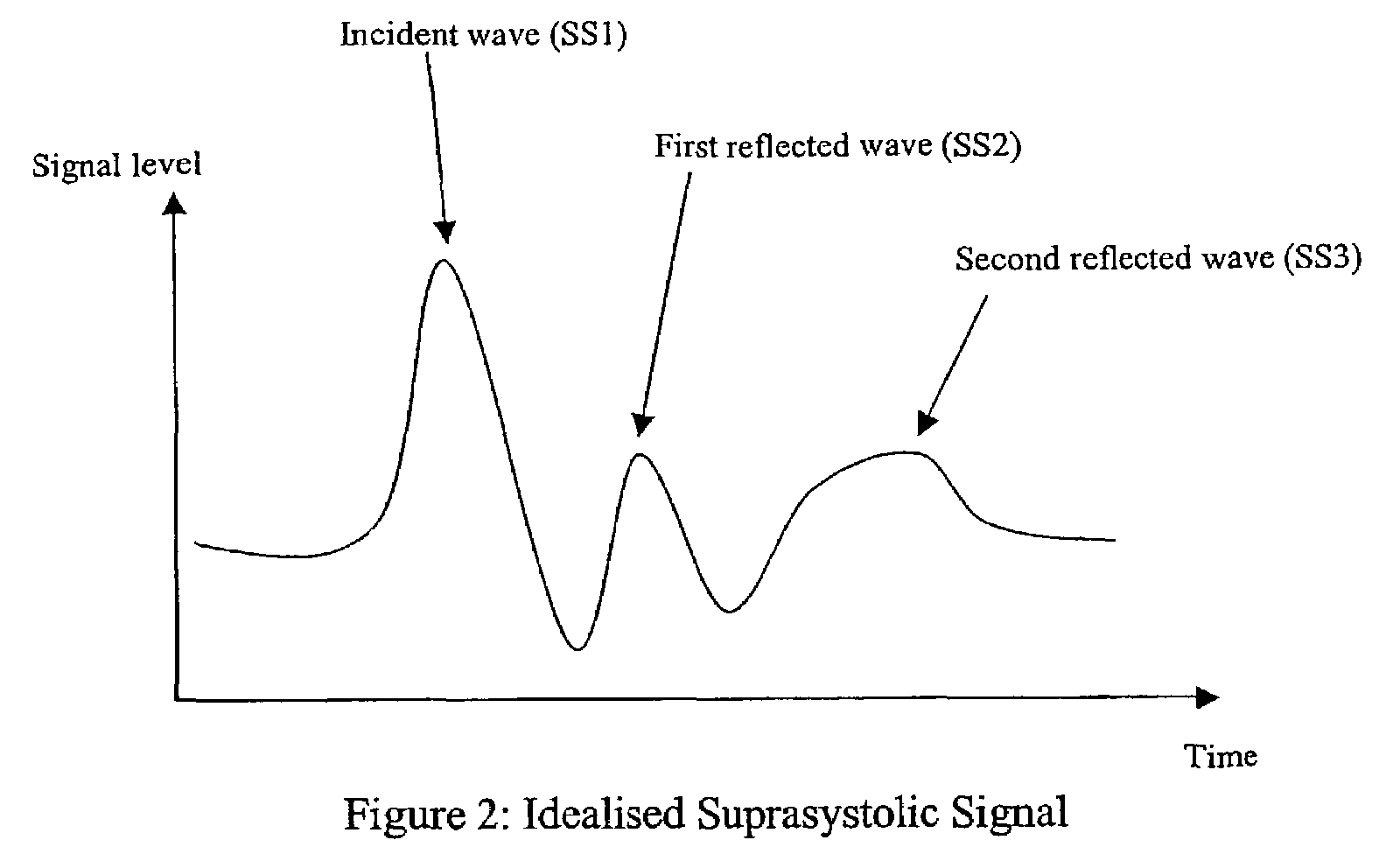
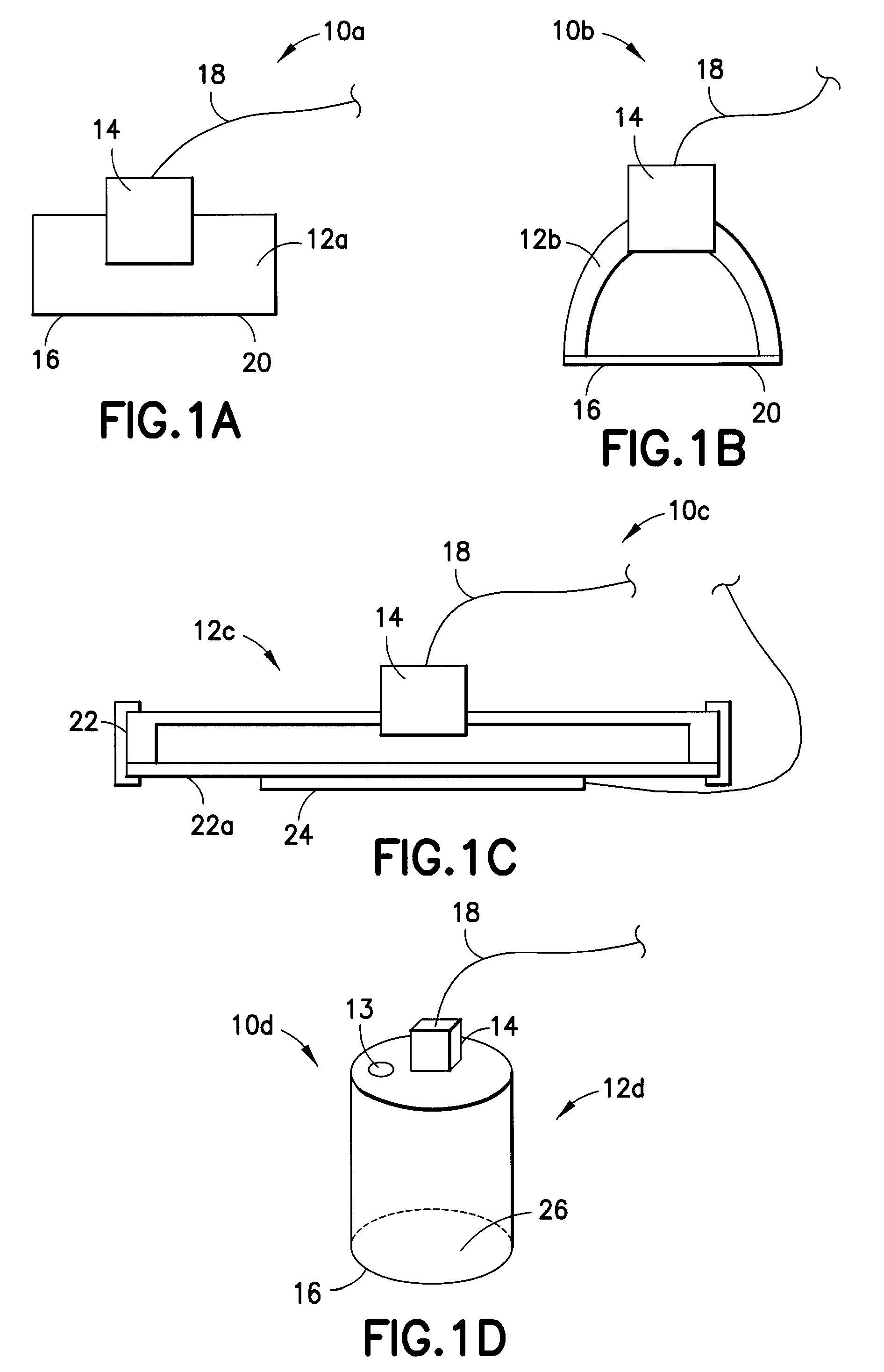
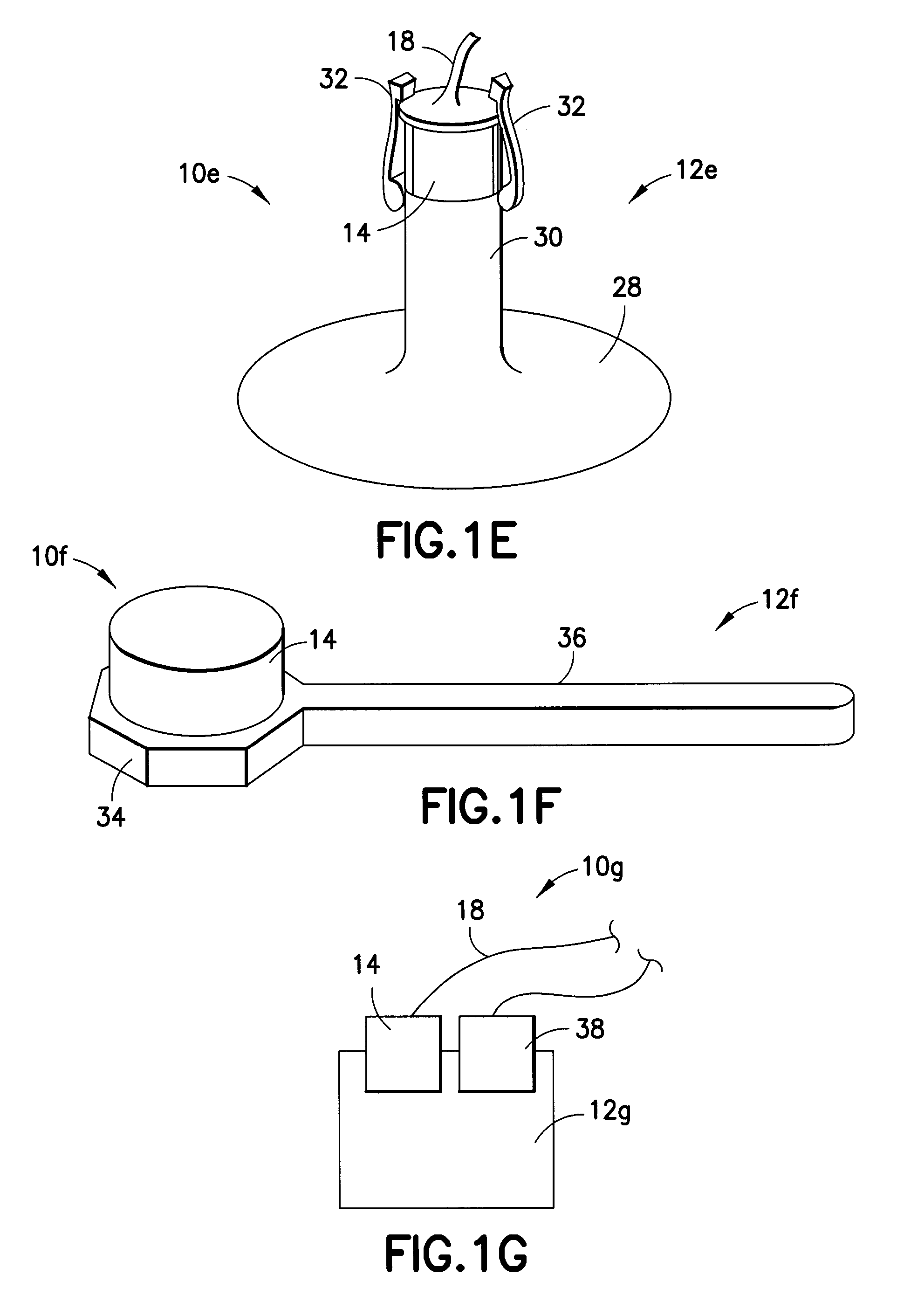
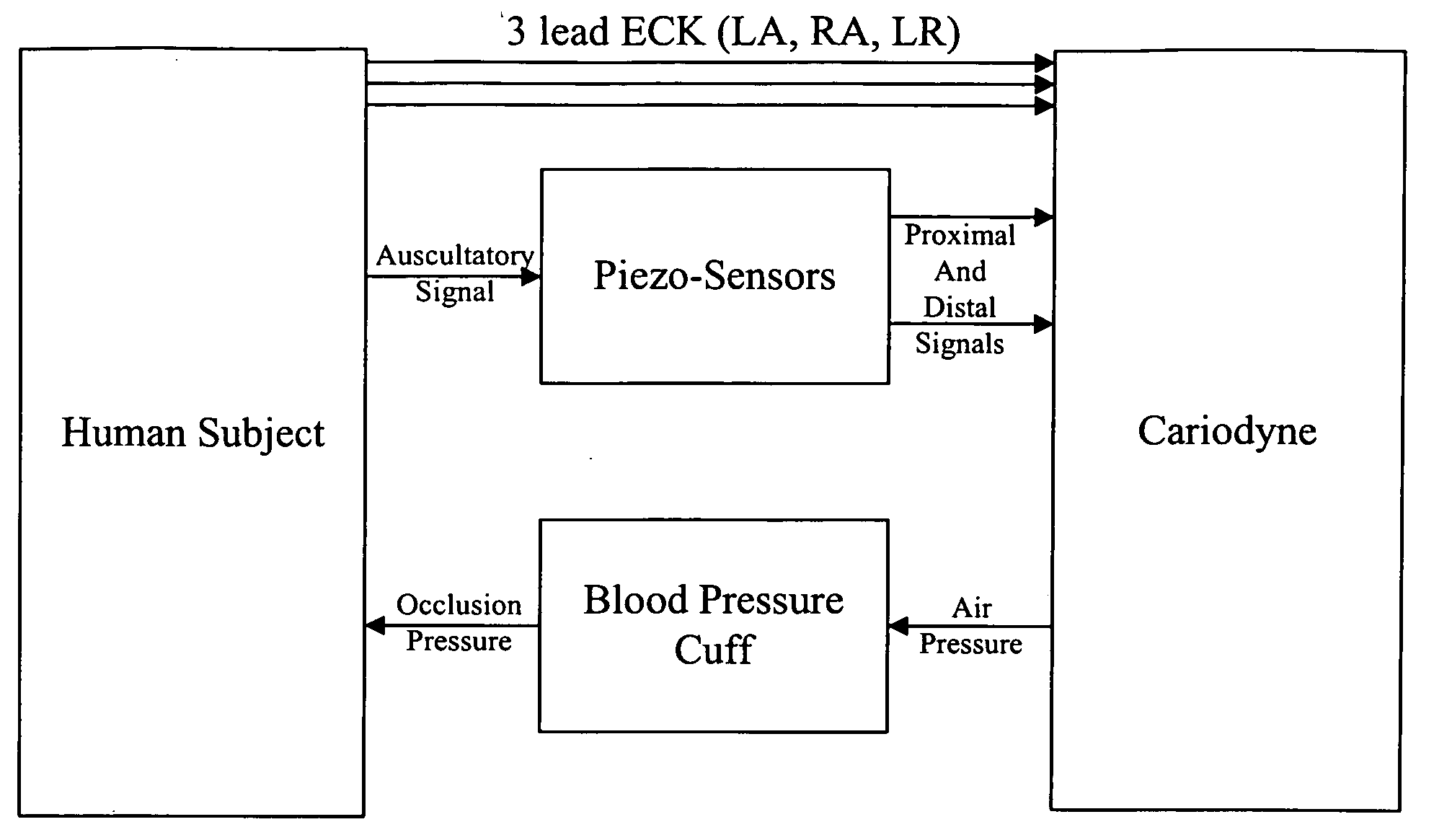
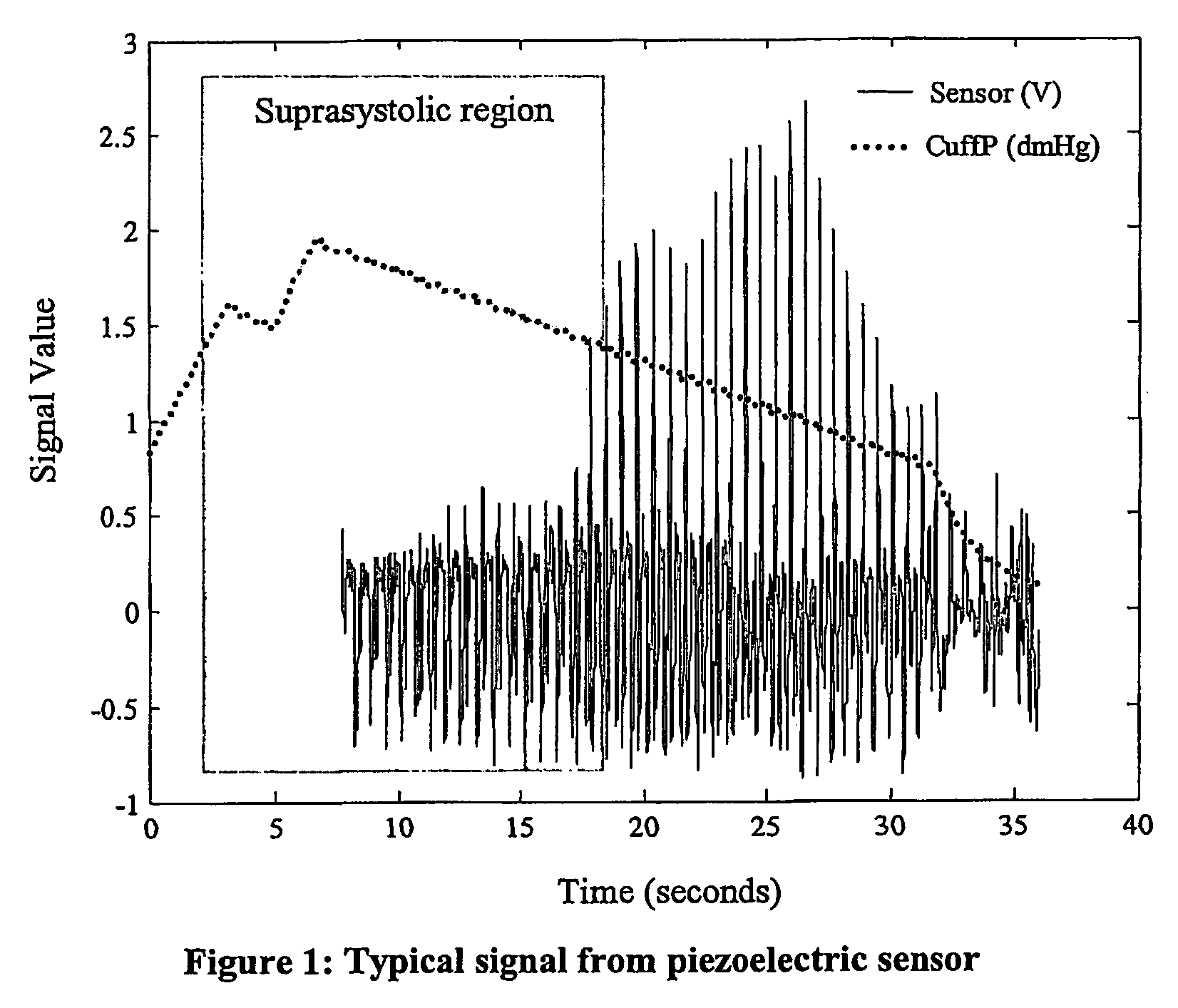
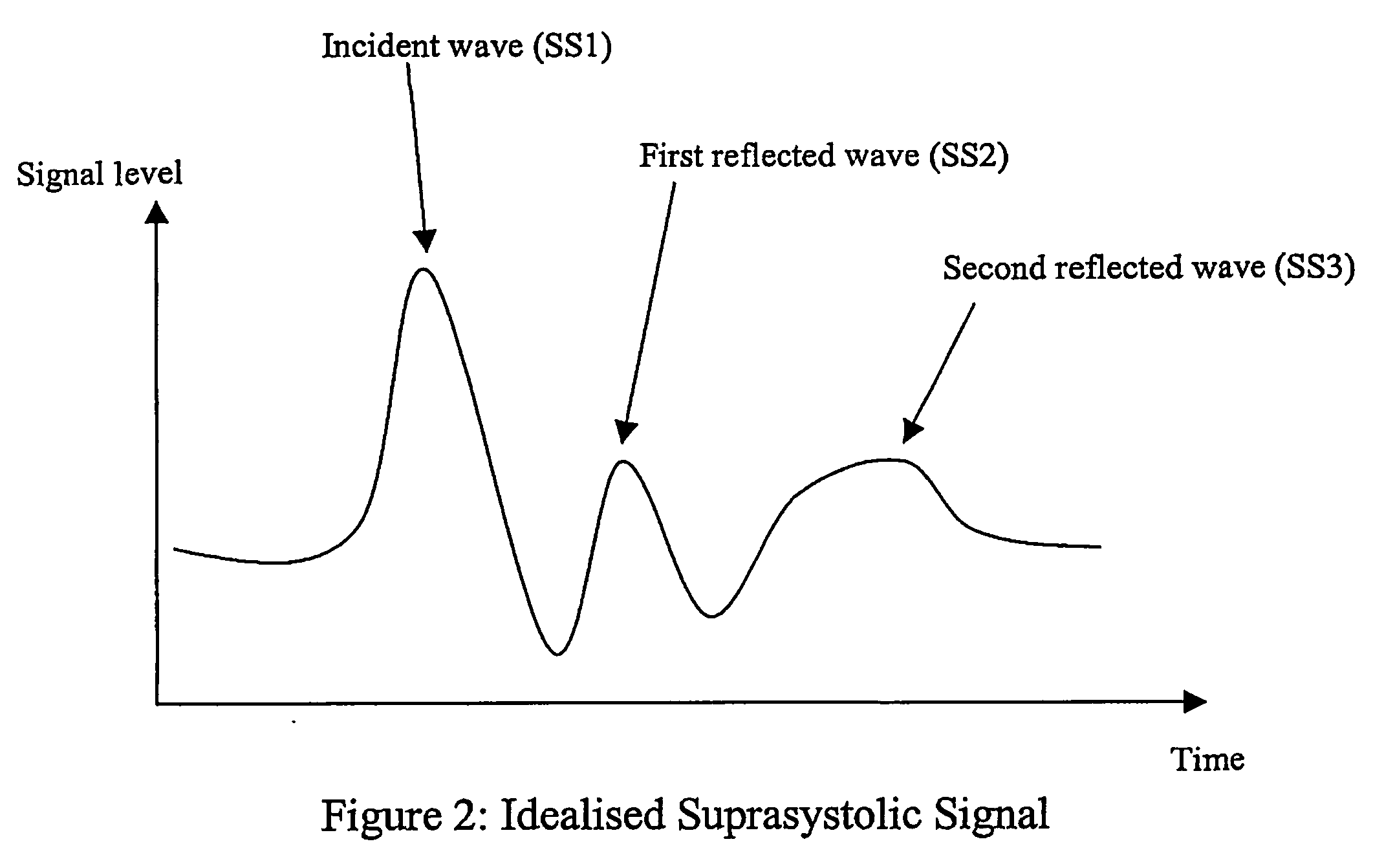
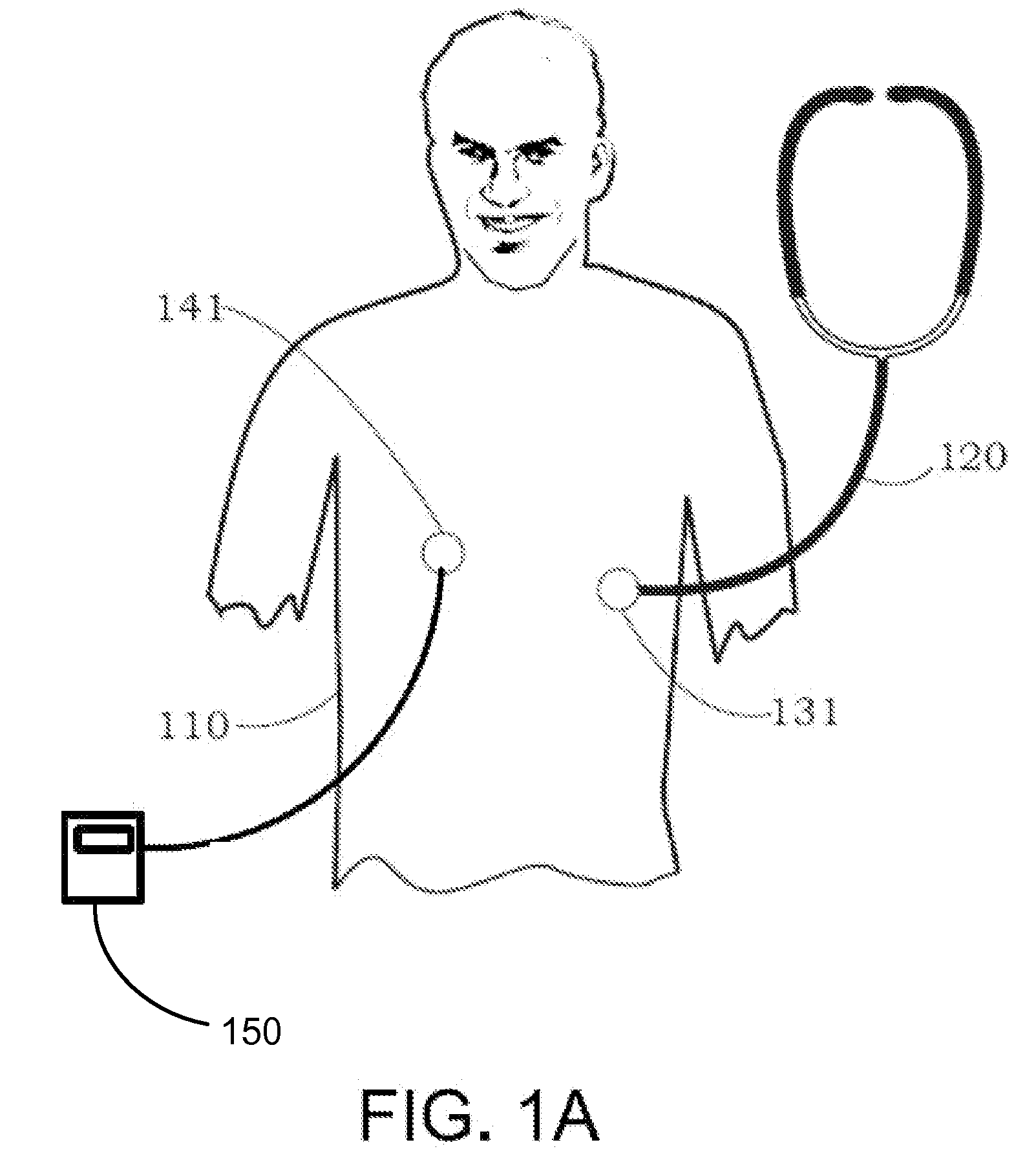
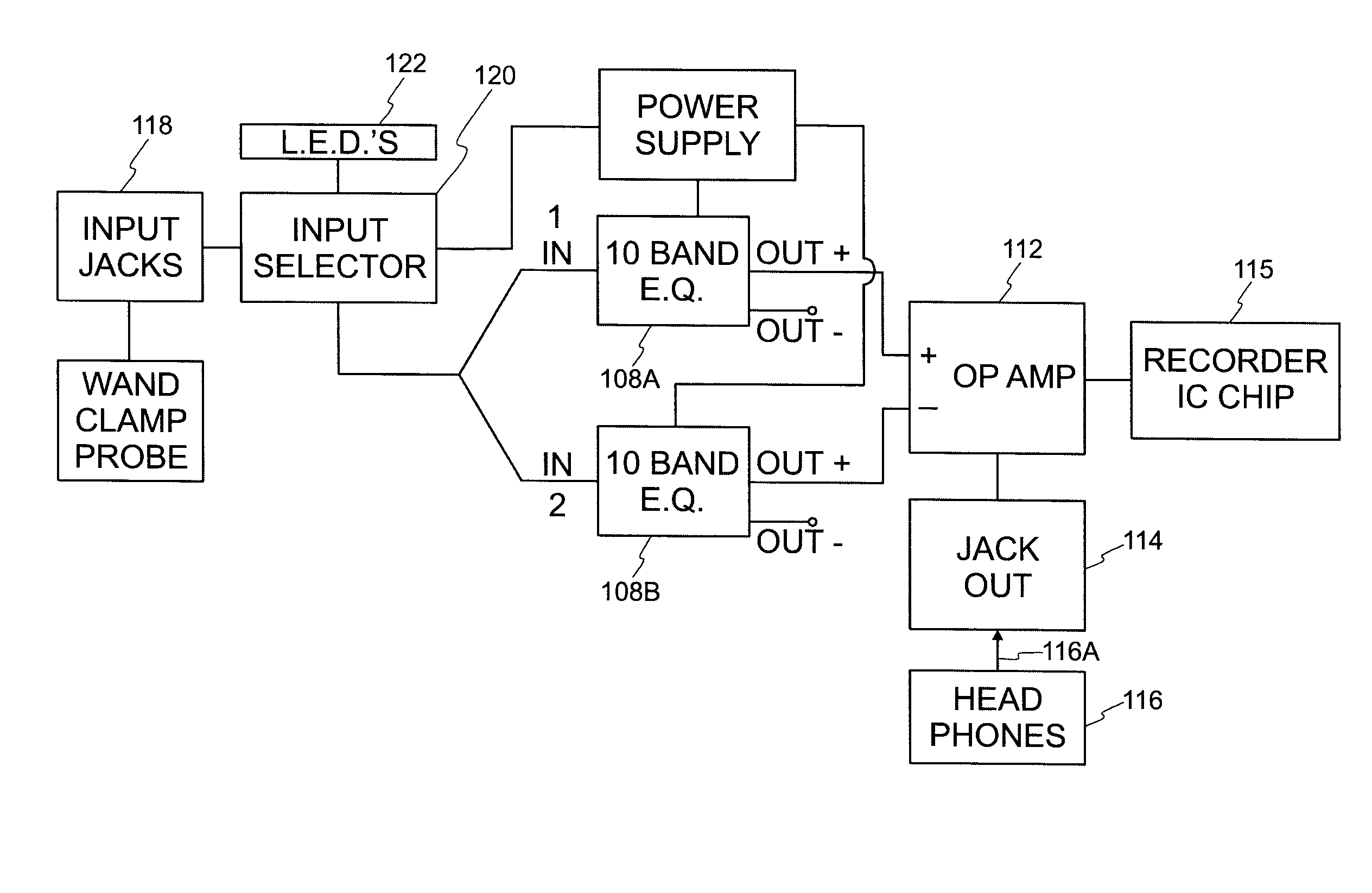
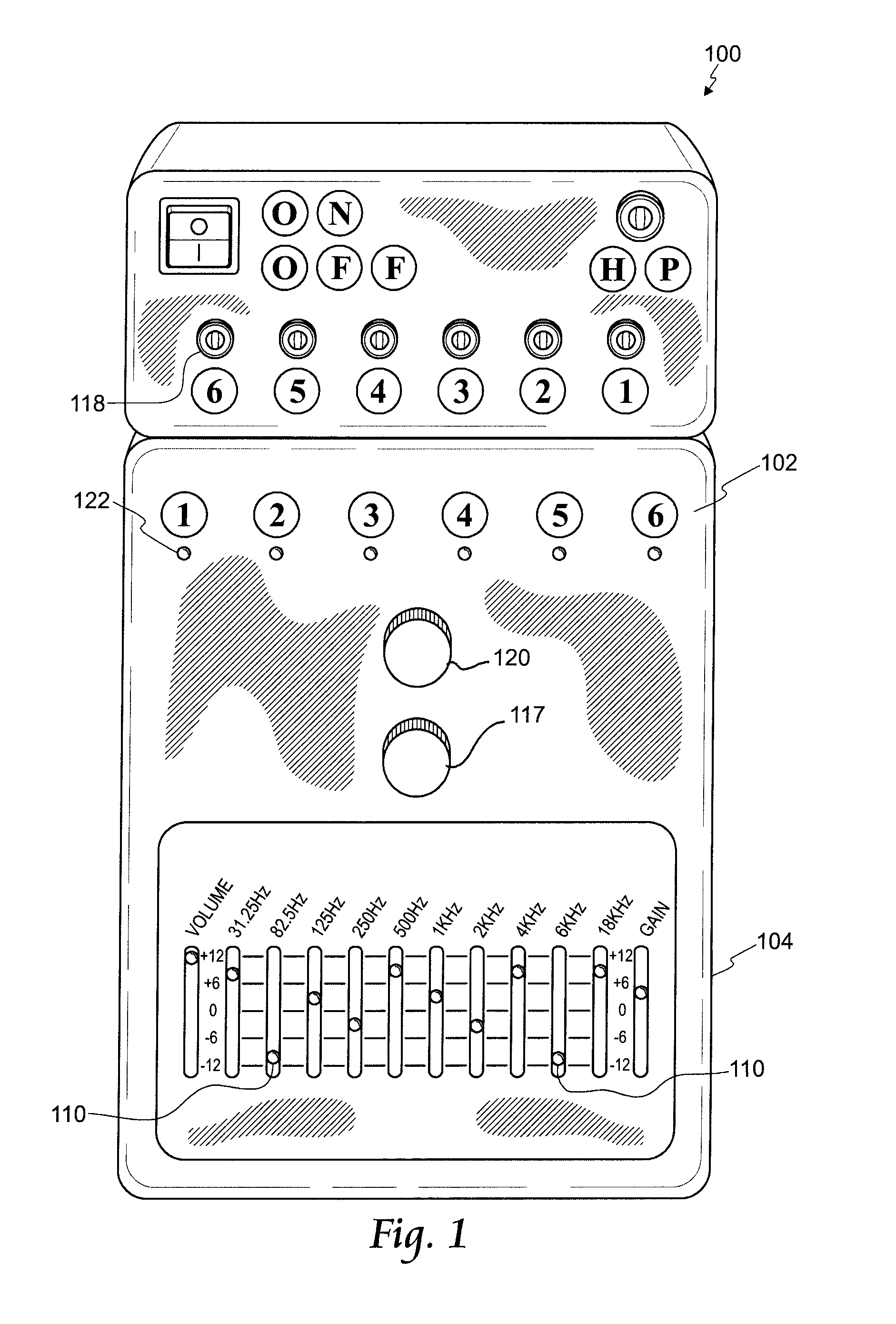
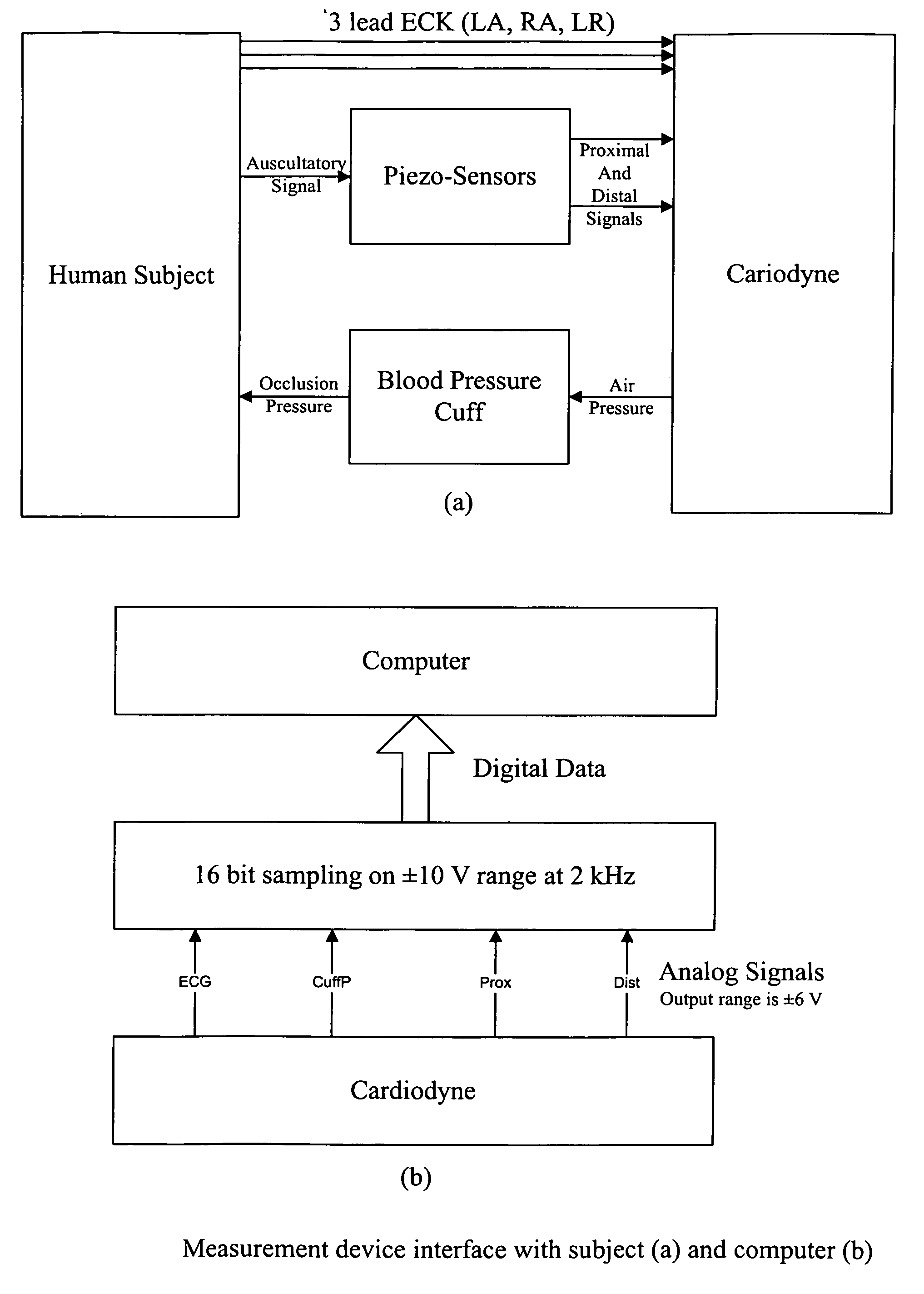
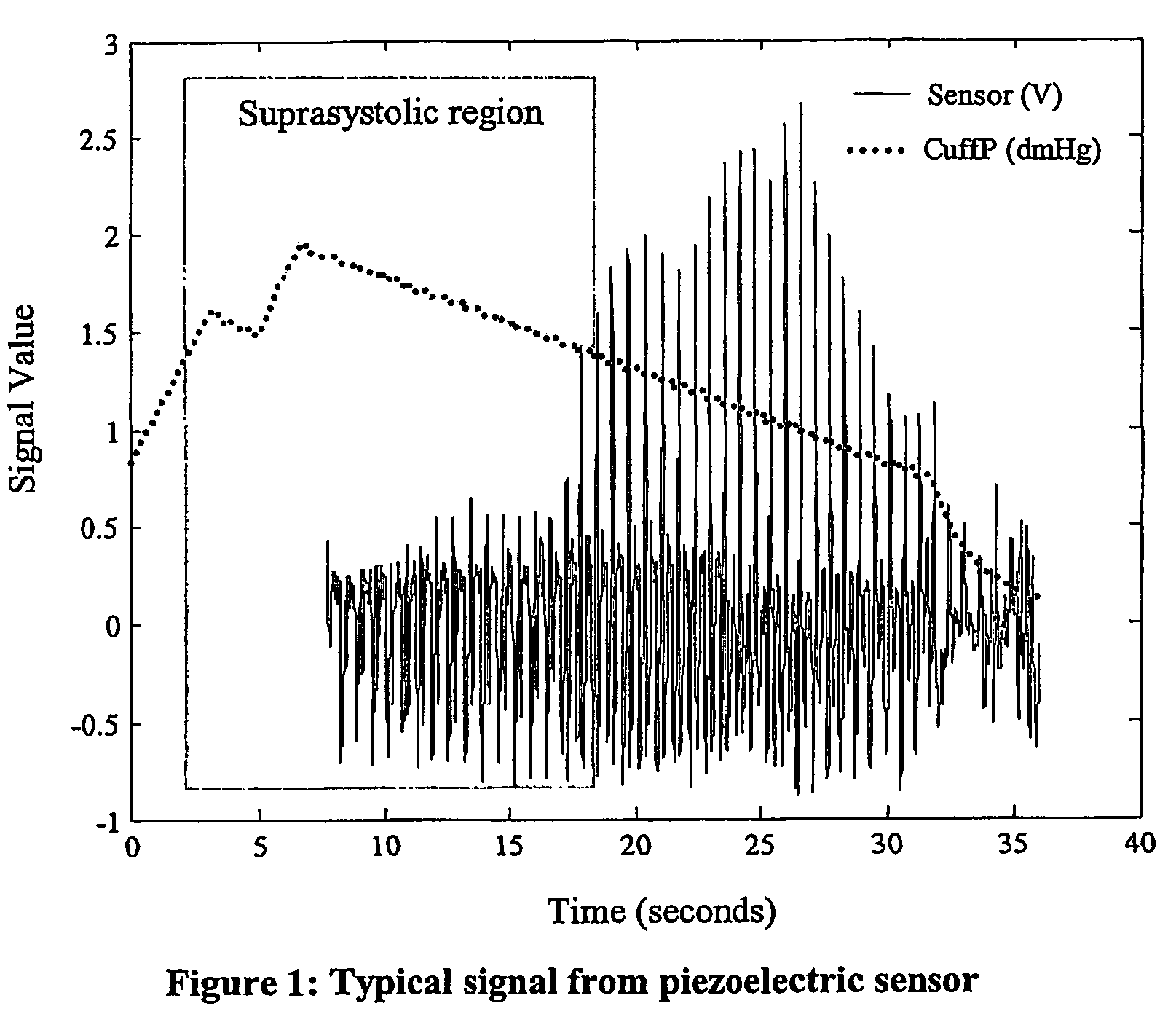
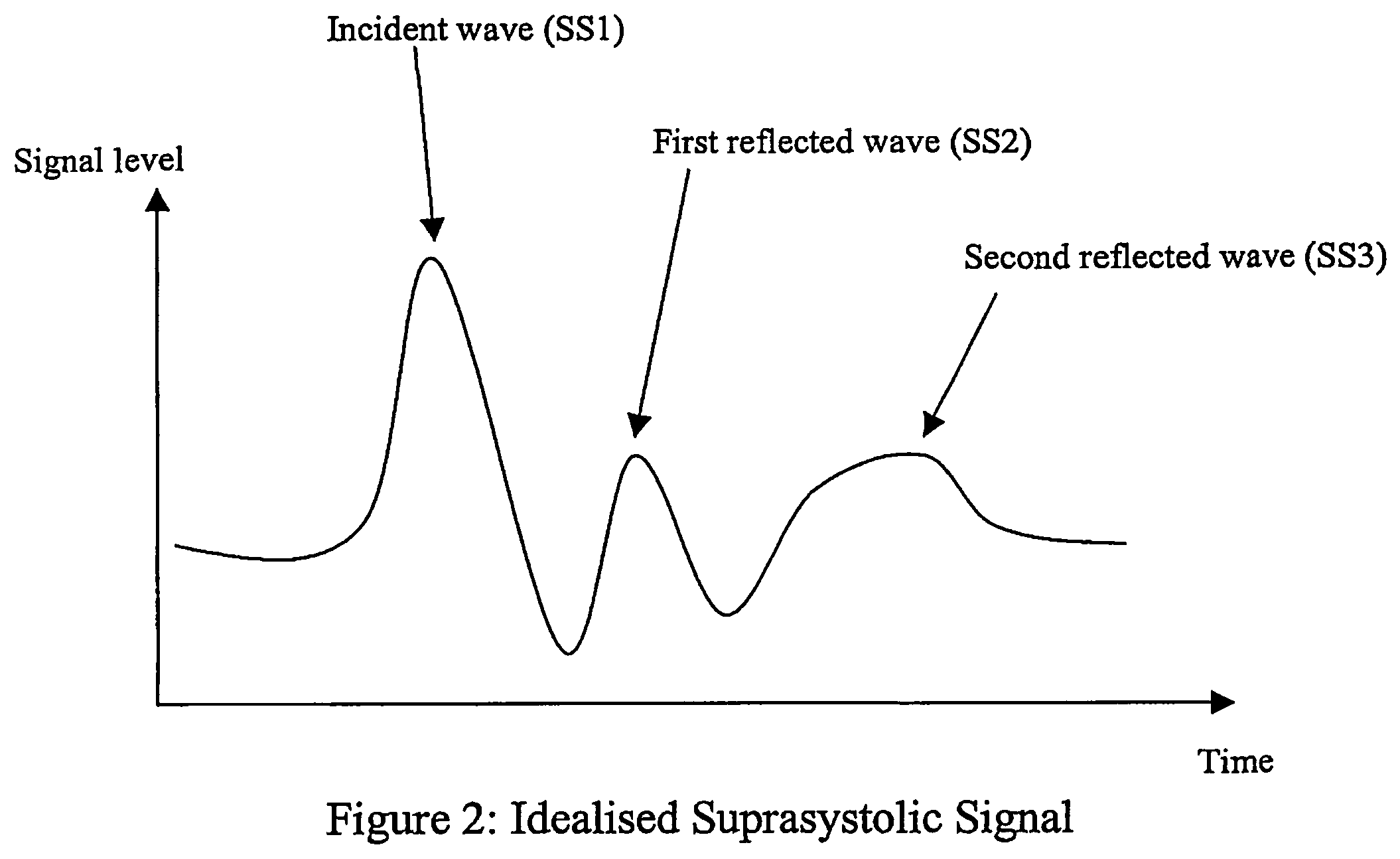
Non-invasive measurement of suprasystolic signals
InactiveUS6994675B2Reduced arterial complianceReduced endothelial dysfunctionElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsTransducerParasystole
An apparatus for assessing cardiovascular status of a mammal comprises a system for locally applying a pressure to an artery capable of restricting blood flow through said artery, a wideband external pulse transducer having an output and situated to measure suprasystolic signals proximate to said artery, and a computing device receiving said output for calculating vascular compliance values. The method described is particularly useful for determining cardiac output, assessing whether a pregnant female has preeclampsia or a patient has cardiac insufficiency, or assessing cardiac arrhythmias.
Owner:USCOM
Electronic stethoscope system
InactiveUS20090316925A1Auxiliary diagnosisStethoscopeAcoustic sensorsAbnormal bowel soundsSonification
An electronic stethoscope head includes a head member having a contact surface for contact with a patient's body, a transducer in the head member, and an adhesive on the contact surface. A processing system for an electronic stethoscope includes a conditioning circuit configured to receive a transducer signal from a transducer and to be capable of amplifying and / or filtering the transducer signal, to yield a conditioned signal. There is also a signal processor system configured to subject the conditioned signal to an audio editing process. Bodily sounds are detected by applying an electronic stethoscope head a patient's body; generating a patient sonograph of the patient's bodily sounds; and comparing the patient sonograph to a reference sonograph. An electronic stethoscope system may include an accessory device and control circuitry to control the accessory device when abnormal bowel sounds are detected or no bowel sounds are detected for a predetermined interval.
Owner:EISENFELD LEONARD
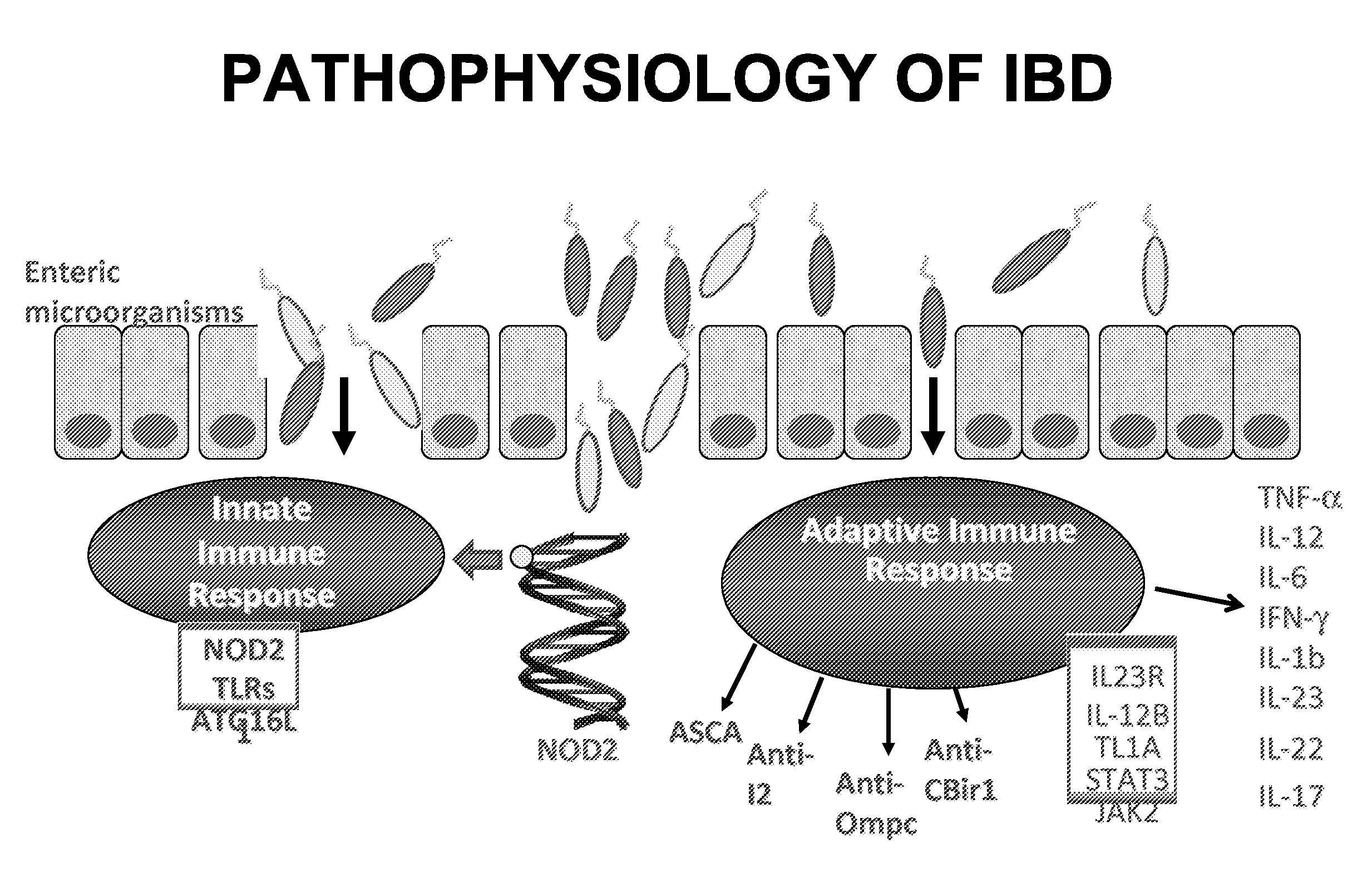
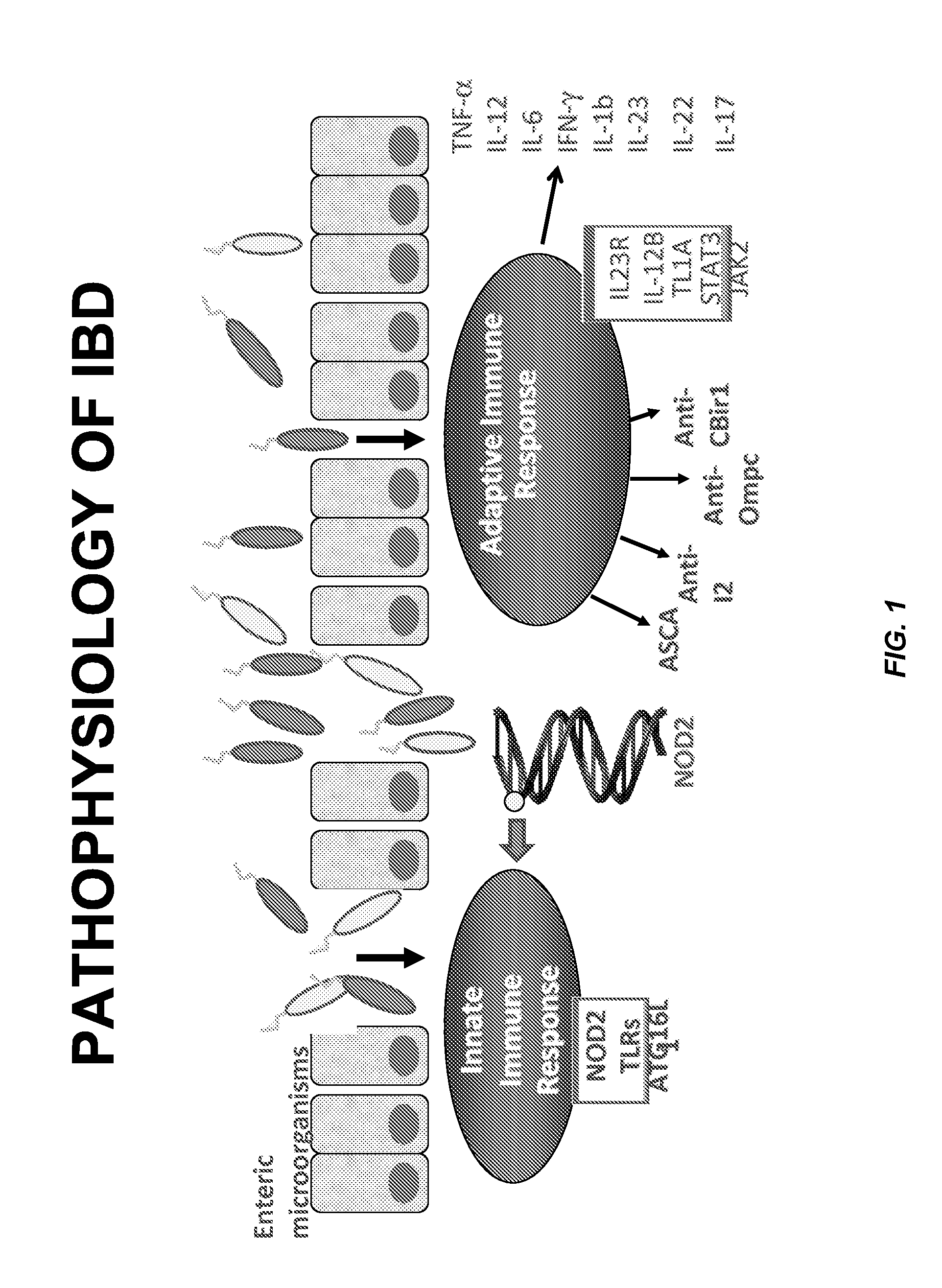
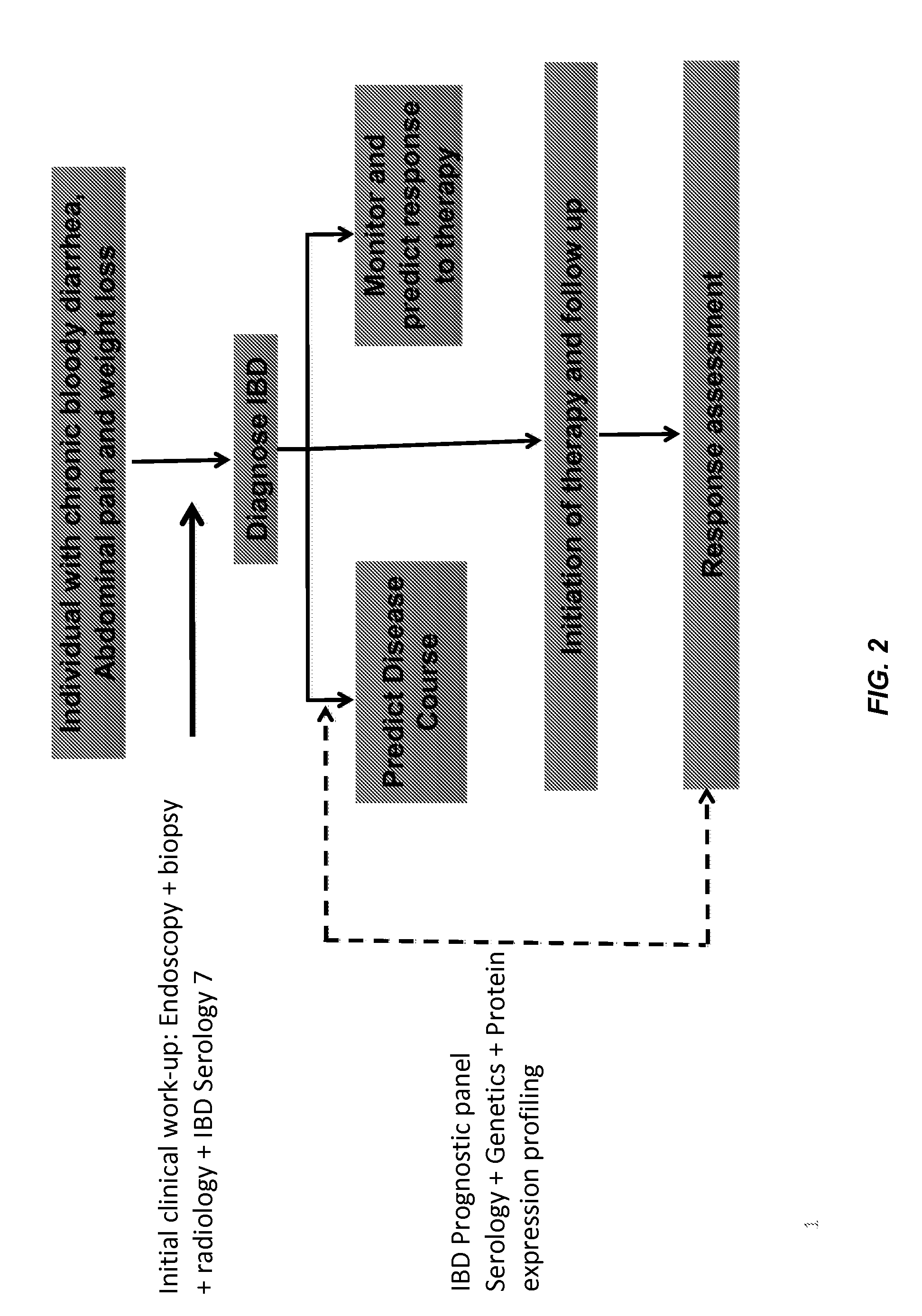
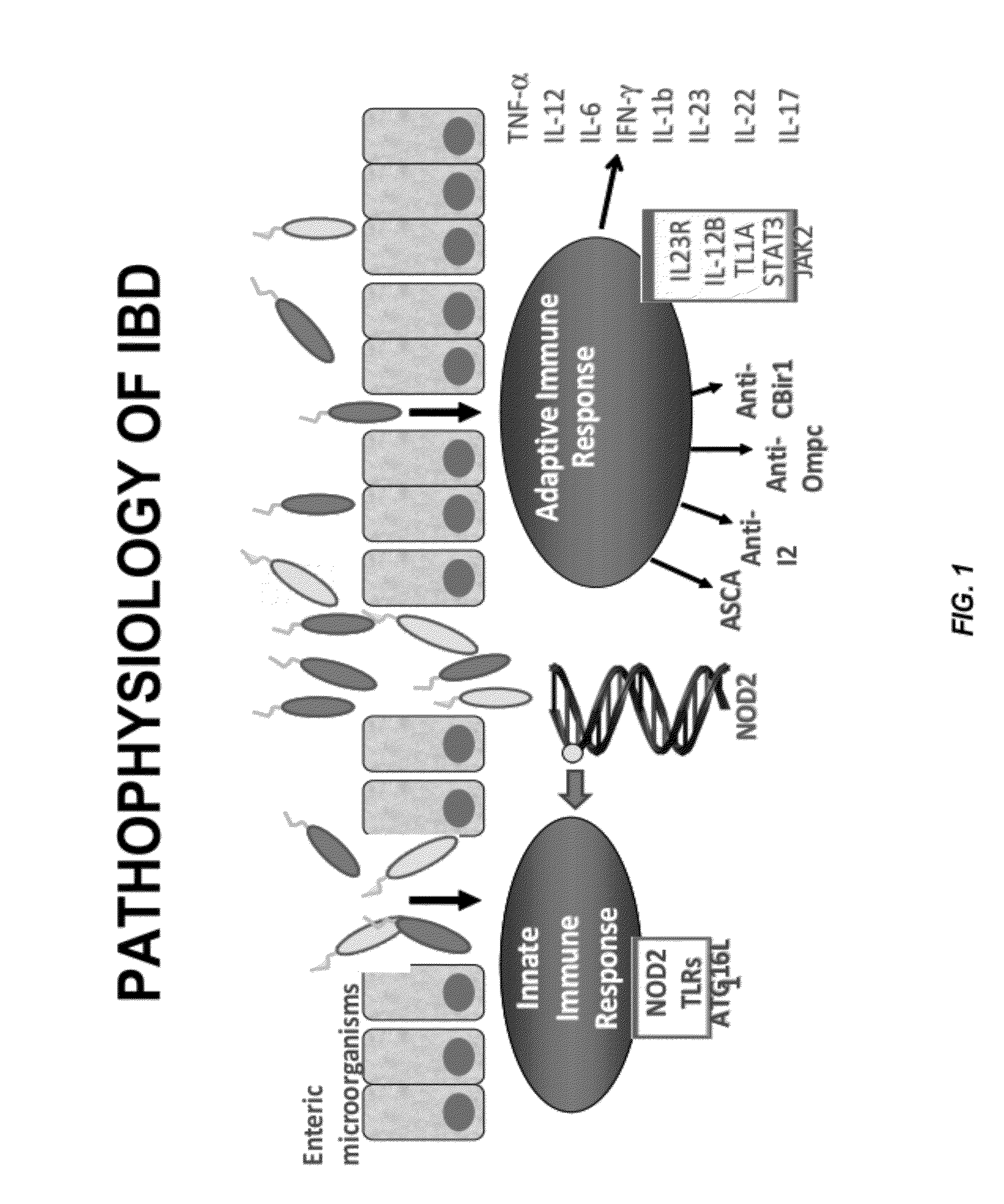
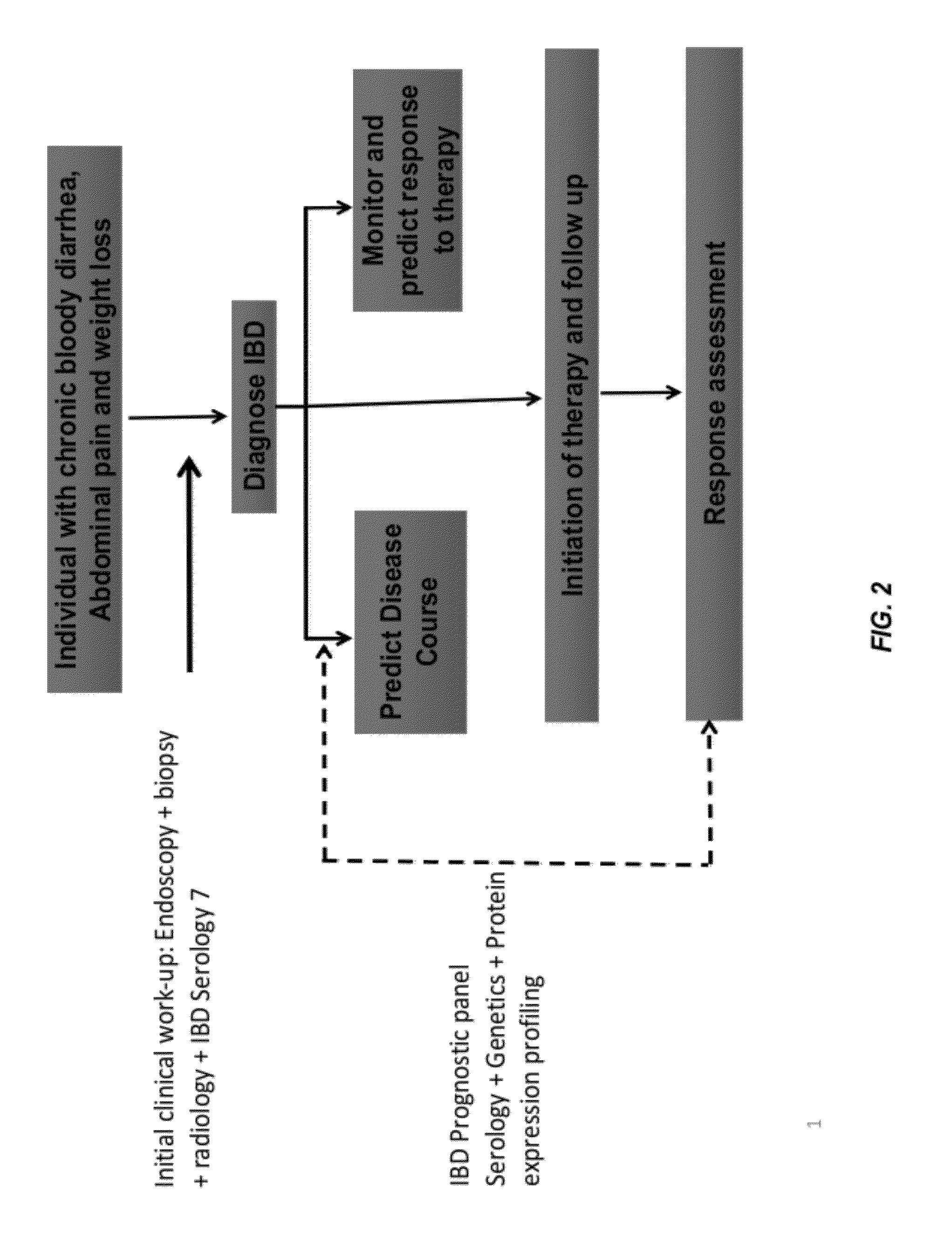
Inflammatory bowel disease prognostics
ActiveUS20110045476A1Easy diagnosisImprove complicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInflammatory bowel diseaseCvd risk
The methods and systems of the present invention are useful in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and in the prognosis of IBD progression and disease complications. With the present invention, it is possible to predict outcome of disease and patients who will have a particular risk of disease complications and / or progression to surgery.
Owner:PROMETHEUS LAB
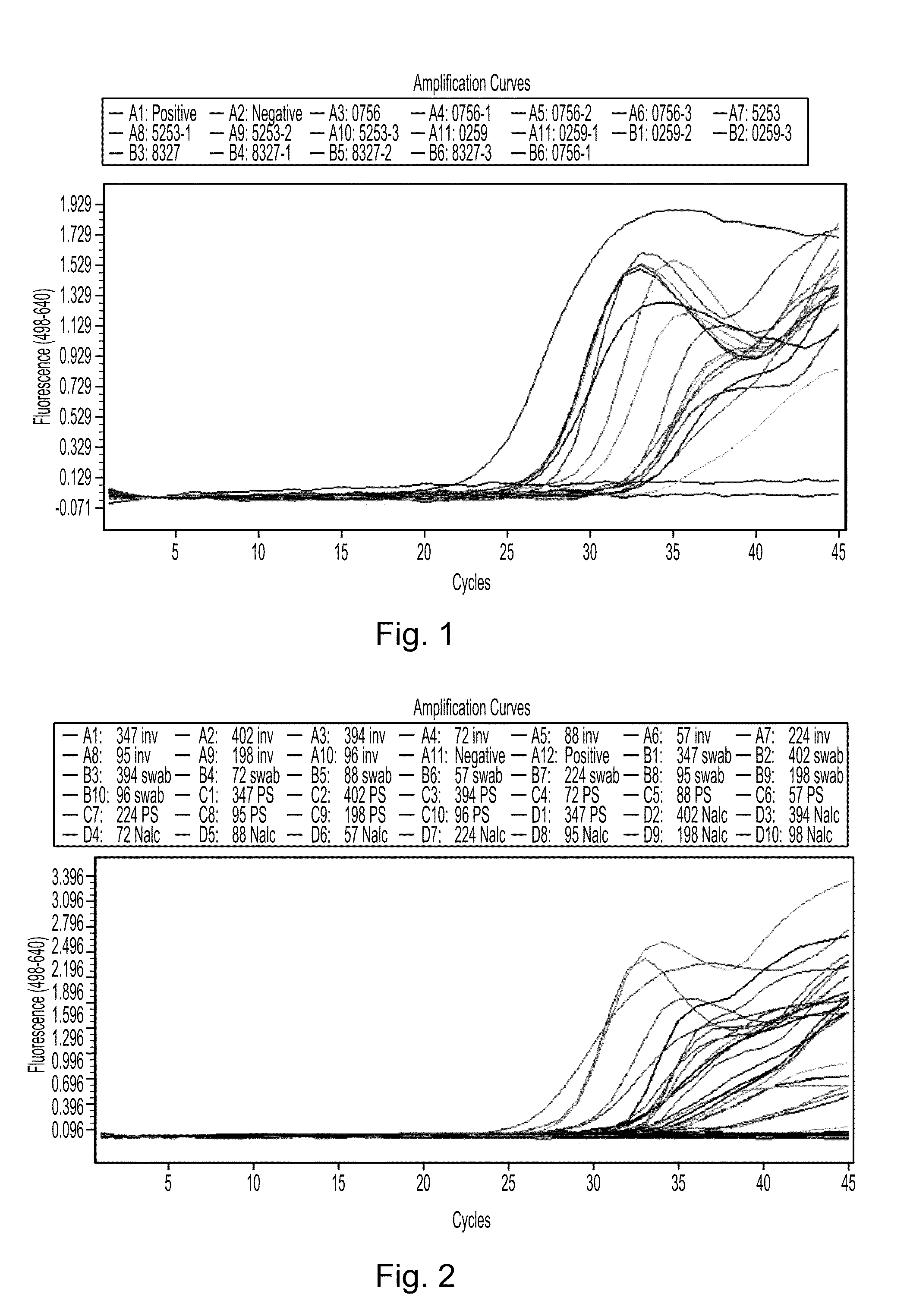
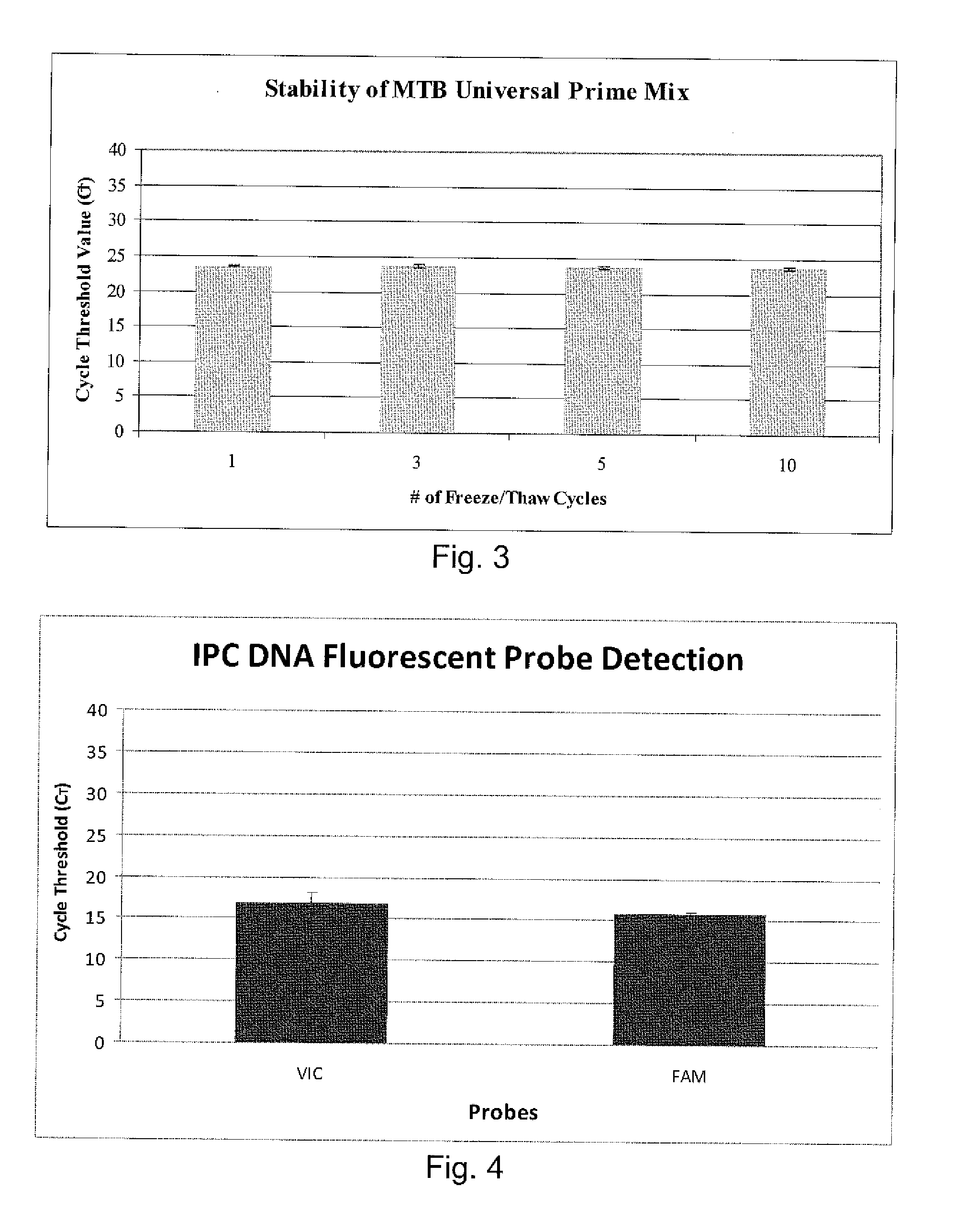
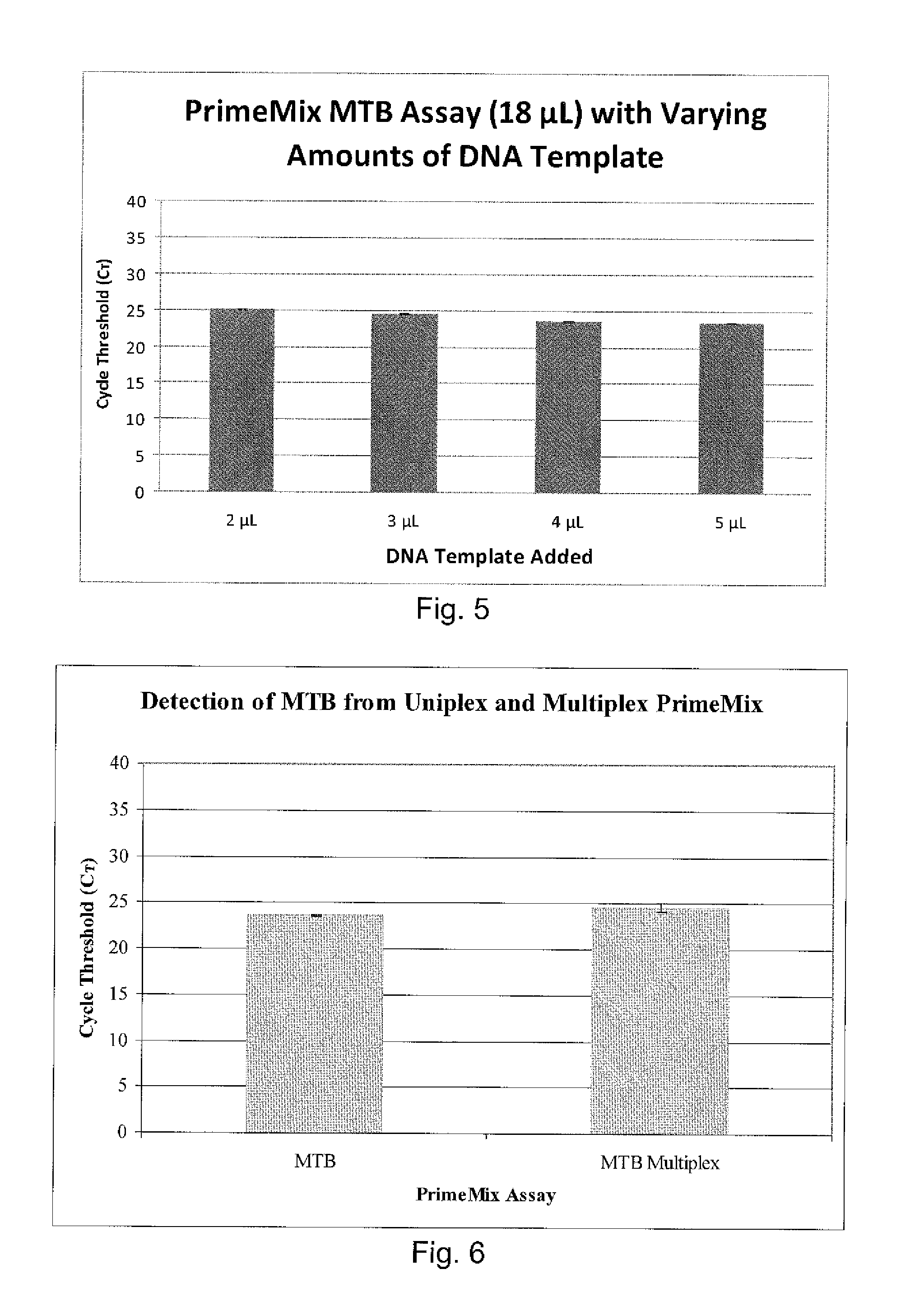
Compositions and methods for detecting, identifying and quantitating mycobacterial-specific nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110281754A1Inherent limitationAuxiliary diagnosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyTuberculosis mycobacterium
Disclosed are compositions and methods for isolating, detecting, amplifying, and quantitating Mycobacterium-specific nucleic acids in a sample. Also disclosed are compositions and diagnostic kits comprising Mycobacterium IS6110-specific oligonucleotide amplification primers and labeled oligonucleotide detection probes that specifically bind to the amplification products obtained therefrom. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for the isolation and characterization of nucleic acids that are specific to one or more tubercular pathogens, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, in particular, from a wide variety of samples including those of biological, environmental, clinical and / or veterinary origin.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Non-invasive measurement of suprasystolic signals
ActiveUS20060178585A1Reduced arterial complianceReduced endothelial dysfunctionEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterSystoleBlood flow
An apparatus for assessing cardiovascular status of a mammal comprises a system for locally applying a pressure to an artery capable of restricting blood flow through said artery, a wideband external pulse transducer having an output and situated to measure suprasystolic signals proximate to said artery, and a computing device receiving said output for calculating vascular compliance values. The method described is particularly useful for determining cardiac output, assessing whether a pregnant female has preeclampsia or a patient has cardiac insufficiency, or assessing cardiac arrhythmia.
Owner:USCOM
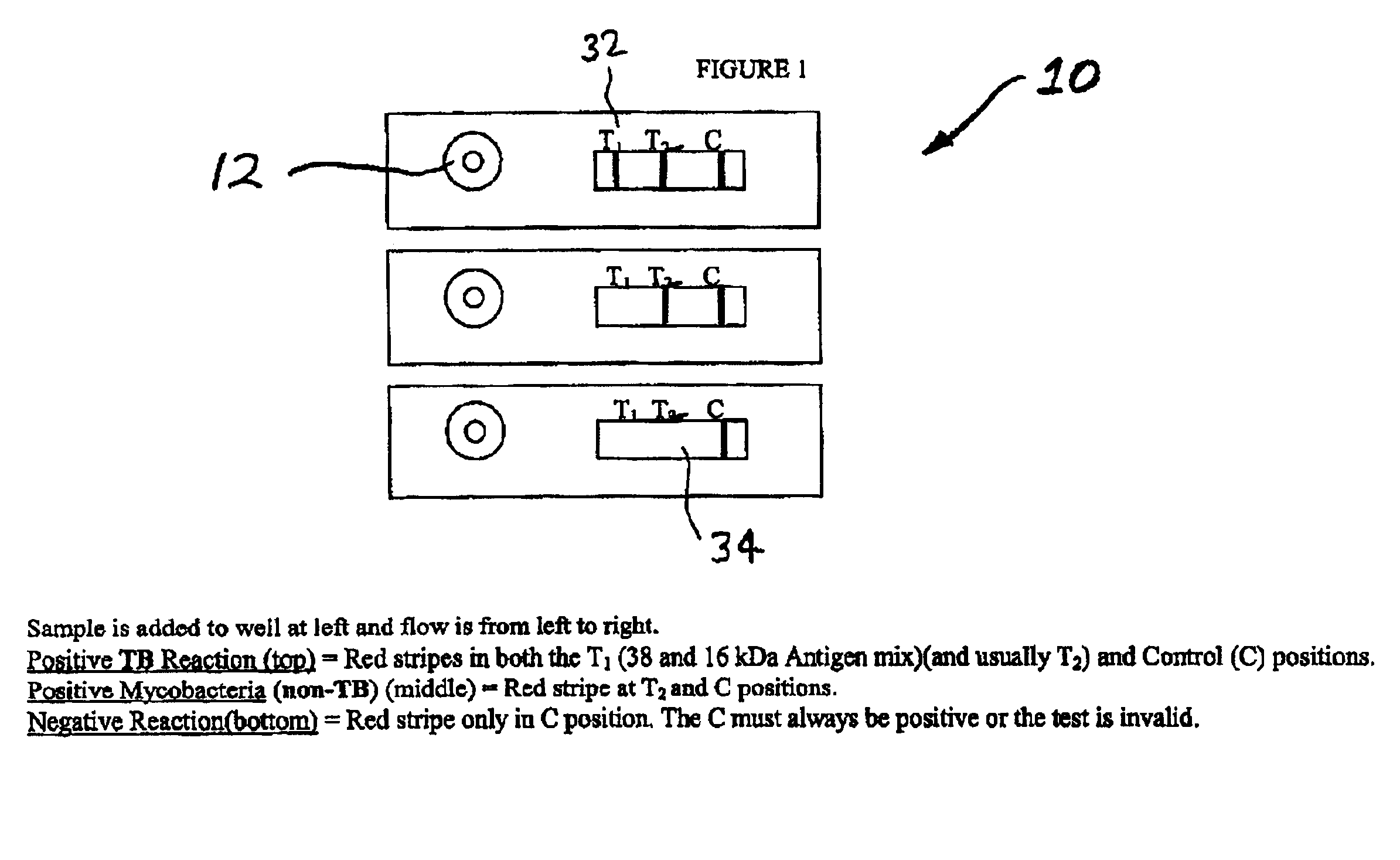
Rapid lateral flow assay for determining exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacteria
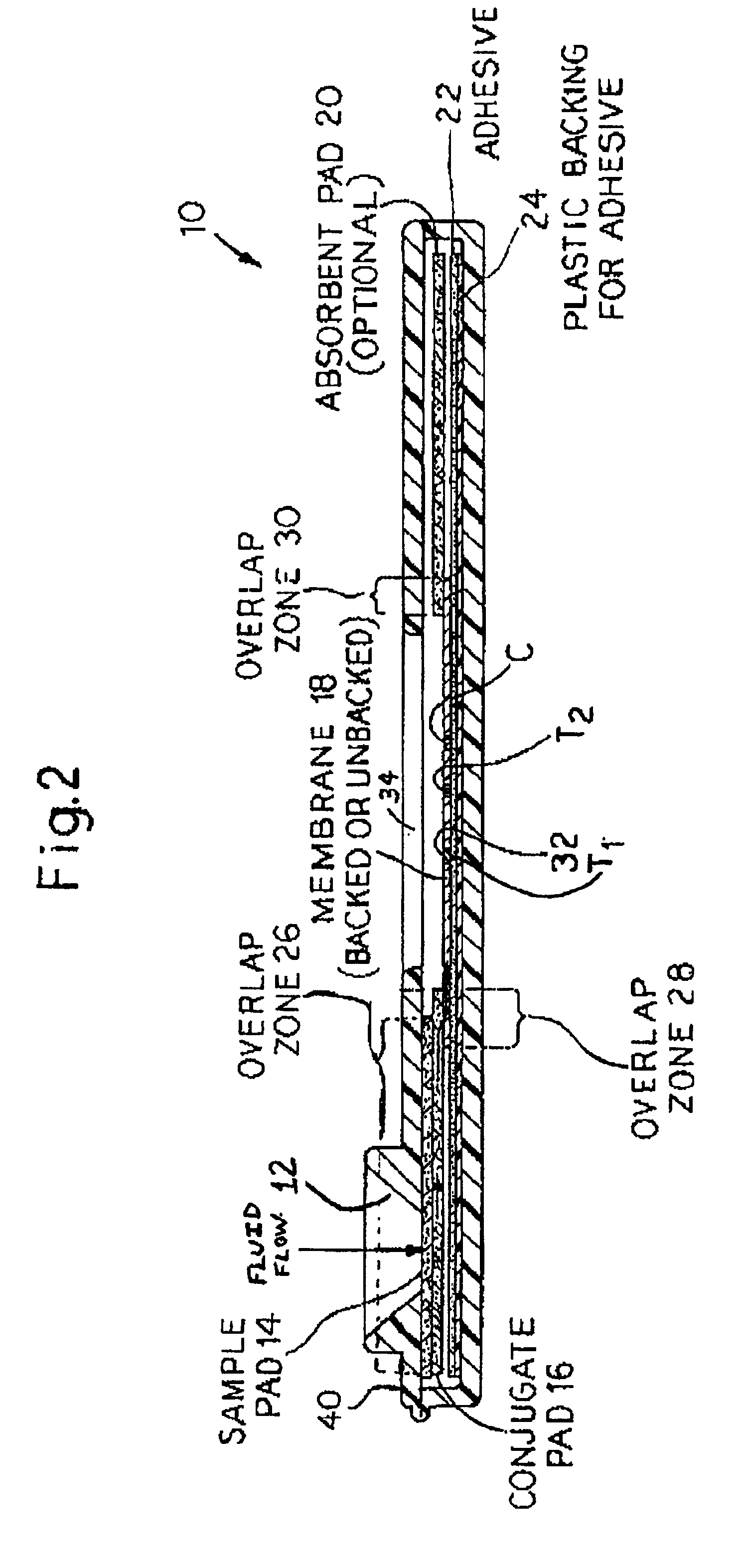
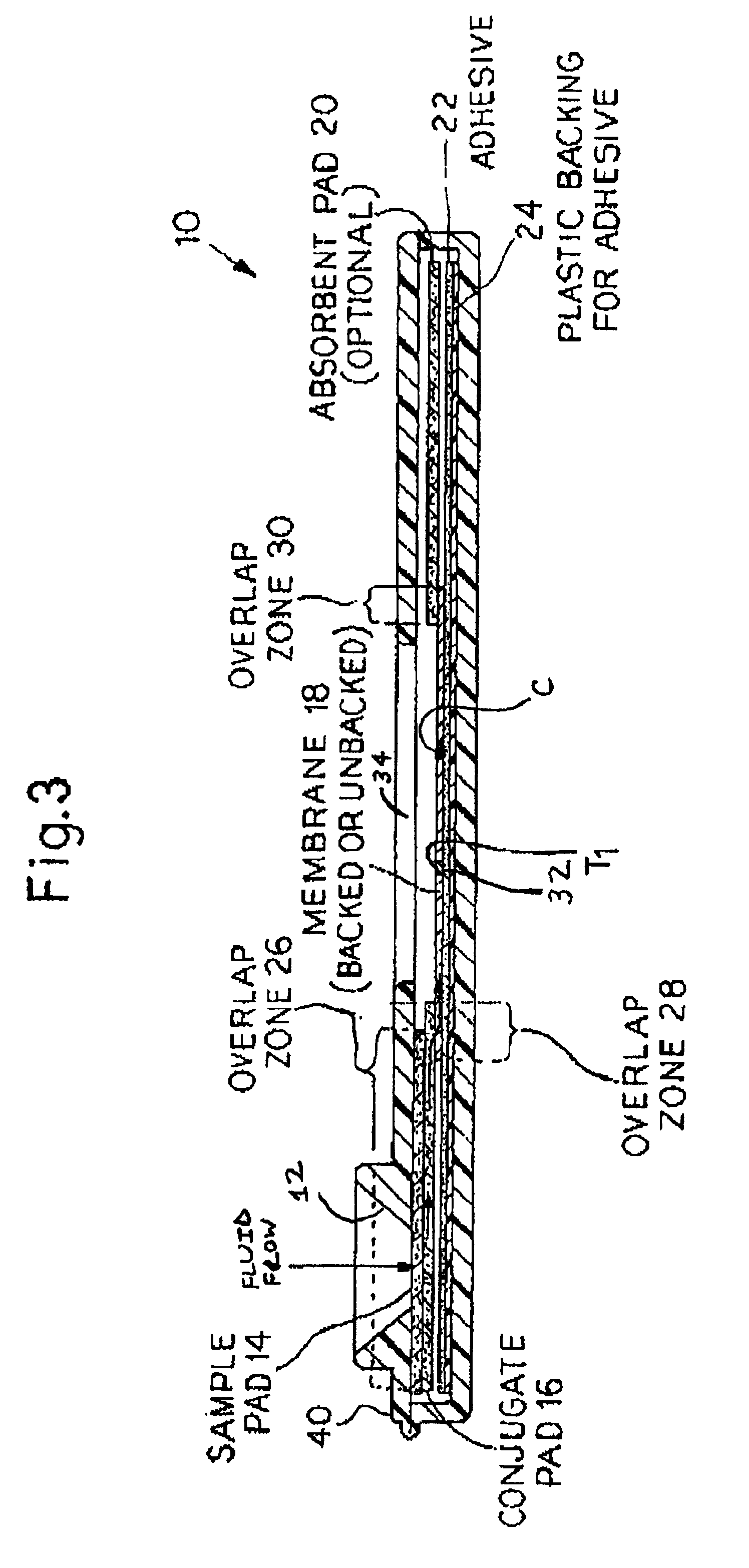
InactiveUS6841159B2Auxiliary diagnosisAuxiliary judgmentBacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMycobacterial antigenImmunization status
An assay method and kit is disclosed for detecting the presence of at least one predesignated, target antibody to a mycobacterium in a sample selected from one or more patient bodily fluids. The method comprises the following steps: (a) contacting the sample of one or more patient bodily fluids with at least one mycobacterium antigen on a lateral-flow assay membrane to bind to the target antibody in the sample; (b) previously, simultaneously or subsequently to step (a), binding the at least one mycobacterium antigen with a conjugated label producing a detectable signal; and (c) detecting the signal whereby the presence of the target antibody is determined in the sample by the intensity or presence of the signal. The method can further comprise the step of evaluating immunization status of the patient from whom the sample came by comparing the signal or lack thereof with immunizations previously received by the patient and in comparison to a known standard control. In a preferred embodiment, the mycobacterium antigen specifically binds to Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific antibodies. Preferably, the immunoassay of the present invention comprises a lateral-flow assay comprising a membrane, a conjugated label pad, and at least one mycobacterium antigen bound to the membrane. In a preferred embodiment, the at least one mycobacterium antigen is selected from the group consisting of 38 kDa and 16 kDa antigens.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Method and apparatus for pulse repetition sequence with high processing gain
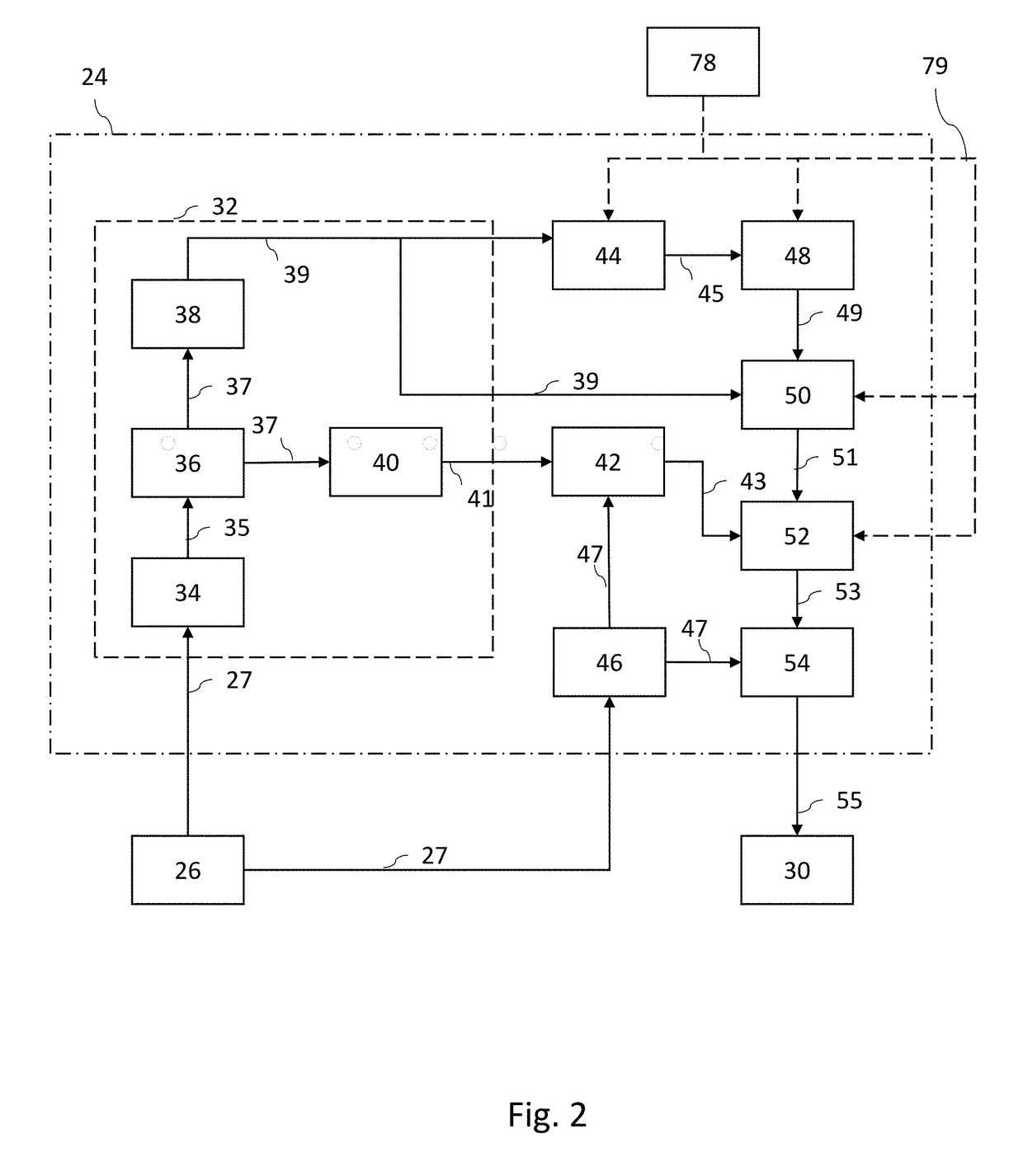
InactiveUS20180306927A1Improve customer satisfactionAuxiliary diagnosisAnti-collision systemsElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadarPulse rate
The present application generally relates communications and hazard avoidance within a monitored driving environment. More specifically, the application teaches a system and method for improved target object detection in a vehicle equipped with a laser detection and ranging LIDAR system by employing a variable LIDAR pulse rate.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
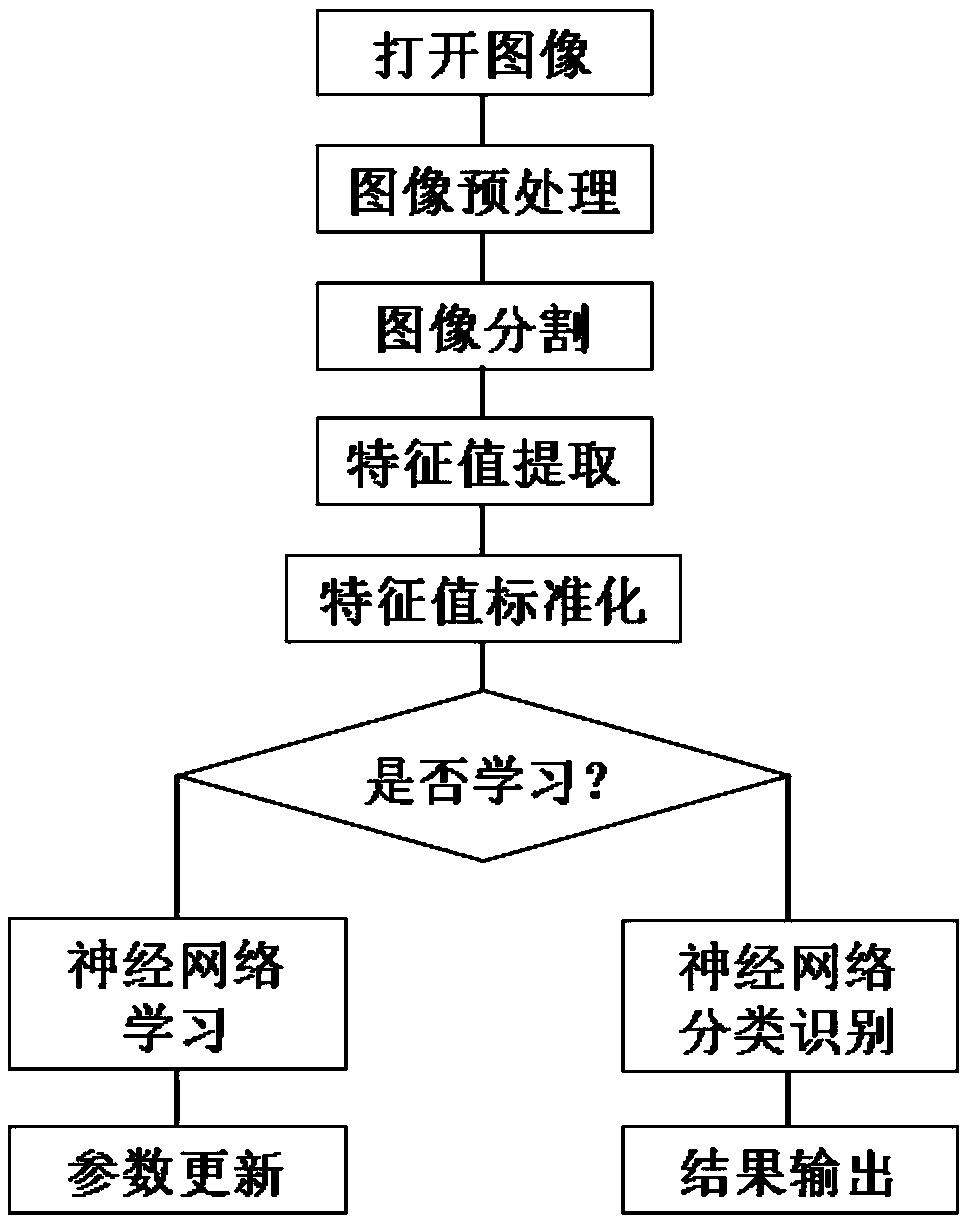
Traditional Chinese medicine face color identifying and retrieving method based on image analysis
InactiveCN102426652AMeet needsAuxiliary medical diagnosisImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFace detection
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine face color identifying and retrieving method based on image analysis, which belongs to the field of image analysis and identification. According to the invention, a retrieving and identifying platform facing traditional Chinese medicine face diagnosis is designed in view of strong subjective dependence and lack of objective quantitative basis in the traditional Chinese medicine face diagnosis. According to the invention, the method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: dividing human face through technologies like human face detection feature positioning when the user inputs a face image to be inquired; extracting the face colors of corresponding areas of internal organs; inputting characteristic vector of the face image to be inquired into a classifier so as to obtain a face color identification result in the identification module; and calculating the similarity of the characteristic vector of the face image to be inquired and the data in a face image characteristic database in the retrieving module; sequencing the characteristic vectors according to the similarity from large to small; returning the similar face image; and giving disease description of the similar face image. According to the invention, the precision rate and recall ratio are about 70% and 65%; and certain reference value is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for calibration of heart sounds
InactiveUS20080039733A1Efficiently and accurately auscultateAuxiliary diagnosisElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesTime domainAuscultation
An auscultation system includes a transducer for generating an acoustic signal at a transducing location of the subject, and a sensor for receiving an attenuated acoustic signal at a sensing location of the subject. The attenuated signal received at the sensing location is digitized, and may be analyzed in the frequency and / or time domain. The comparison of the digitized attenuated signal against the initial transduced signal allows for the computation of the degree of acoustic attenuation between the transducing and sensing locations. Acoustic attenuation may be utilized to generate an intensity ratio. The ejection fraction of the heart subject may then be computed by correlation to the intensity ratio. Pulse echo methods are also disclosed. The echo transducer is oriented on the subject and generates a series of signal pulses. The return echo on the pulse is then received and a brightness encoded image is produced. The return echo provides location data on the internal structures of the subject including location, motion and speed.
Owner:UNVER KAMIL +3
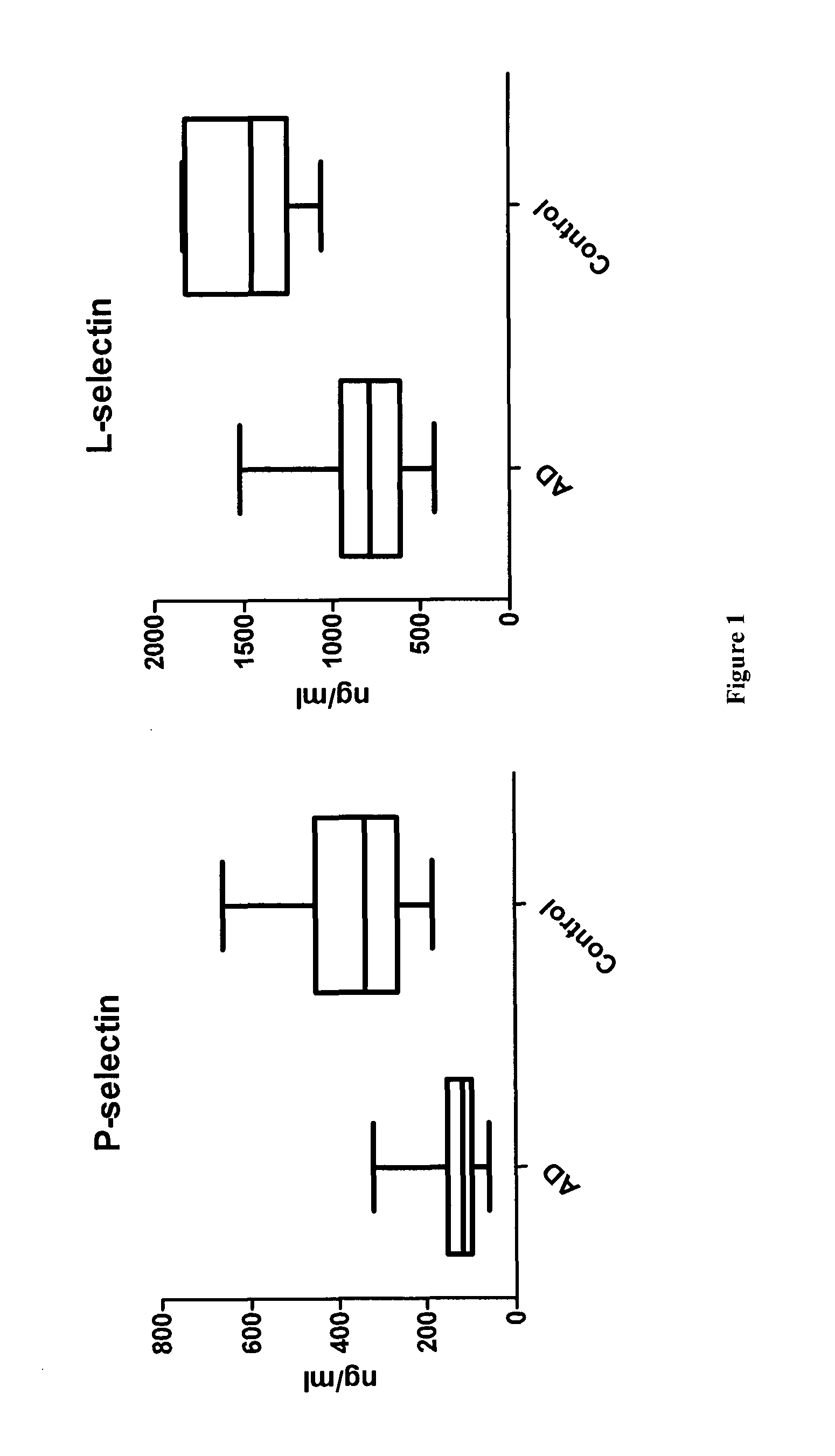
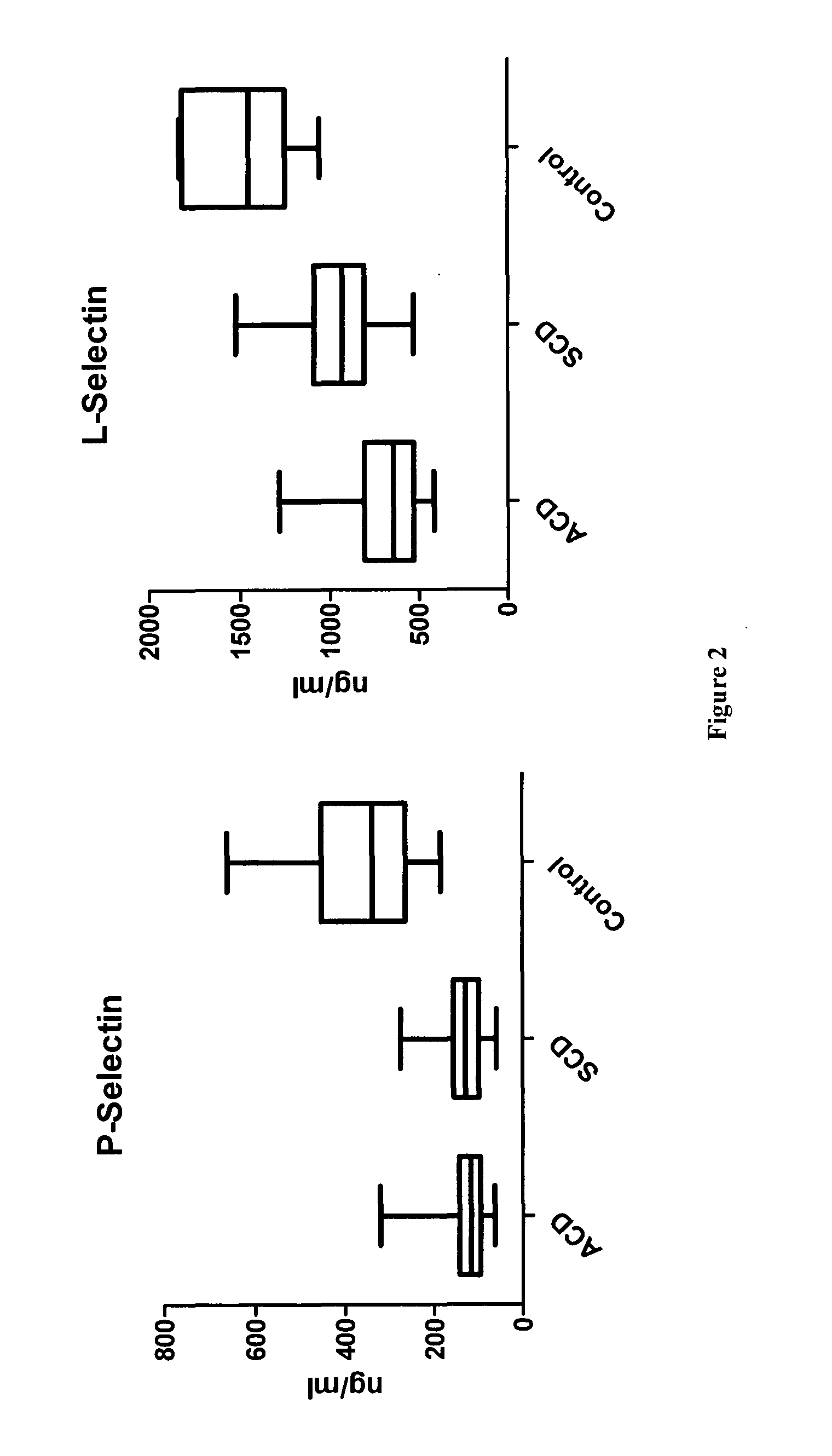
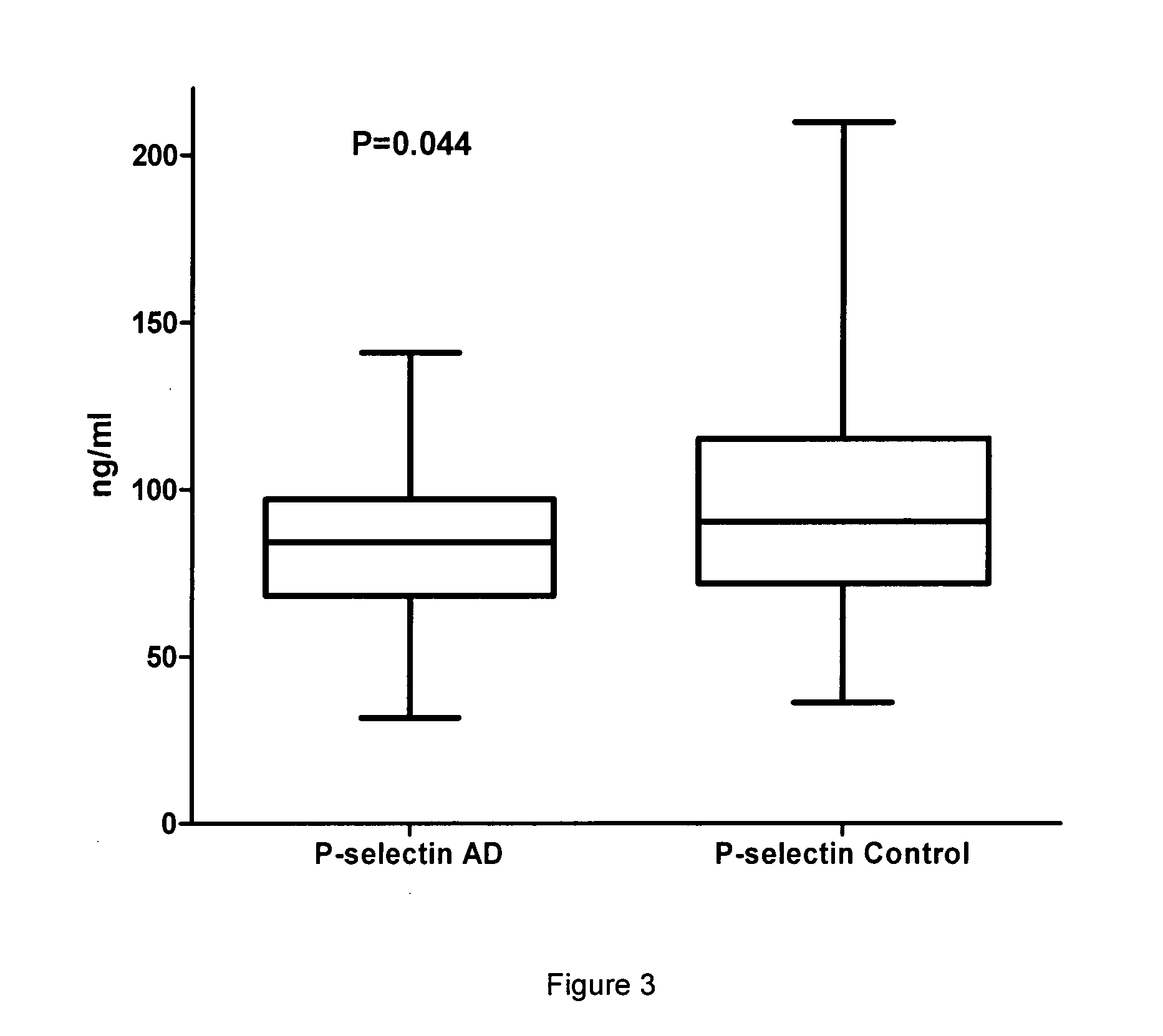
Methods and compositions for the diagnosis and prognosis of alzheimer's disease
The invention relates to methods of diagnosing Alzheimer's disease (AD) in a subject and methods of determining the prognosis in patients with AD. The adhesion molecules P-selectin and L-selectin are described for the first time for use as biomarkers to aid in the diagnosis of AD. The invention further describes the use of one or more of L-selectin, MCP-1, IL-1α, IL-8 and IFN-γ to aid in the prognosis of either accelerated cognitive decline (ACD) or slow cognitive decline (SCD) in patients with AD.
Owner:NORTHERN BANK LTD
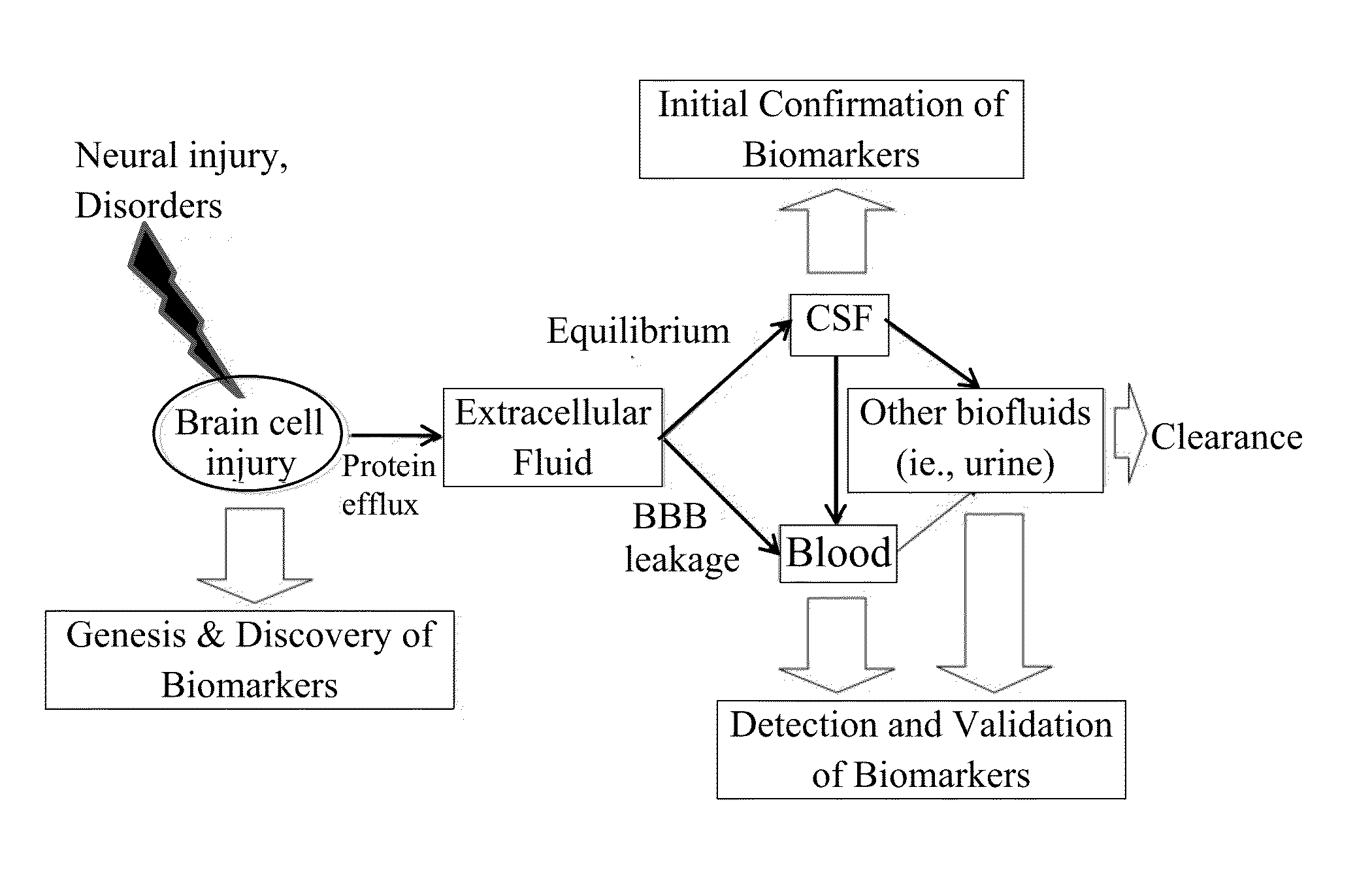
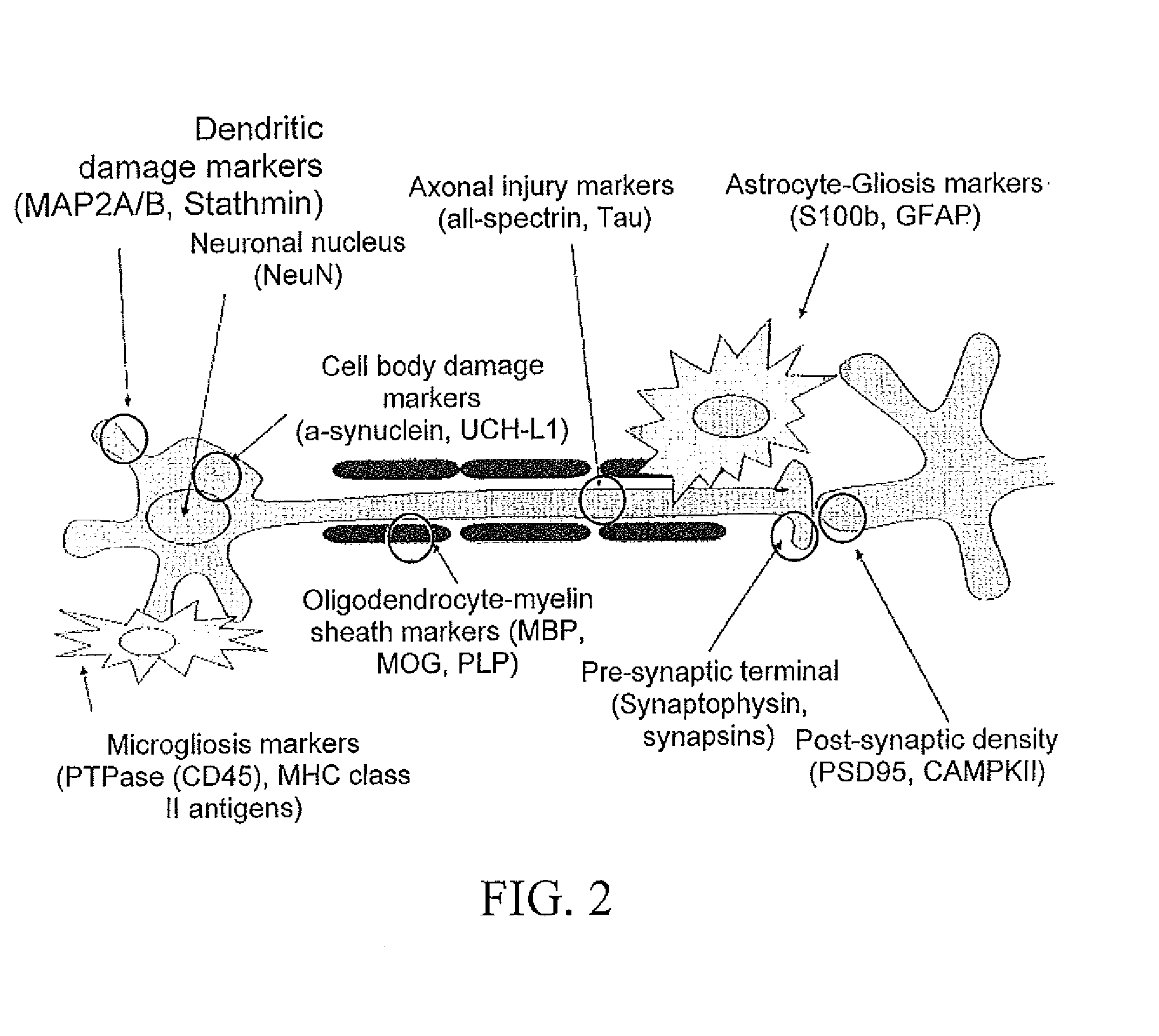
In vitro diagnostic devices for nervous system injury and other neural disorders
InactiveUS20140303041A1Auxiliary diagnosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesNervous systemDisplay device
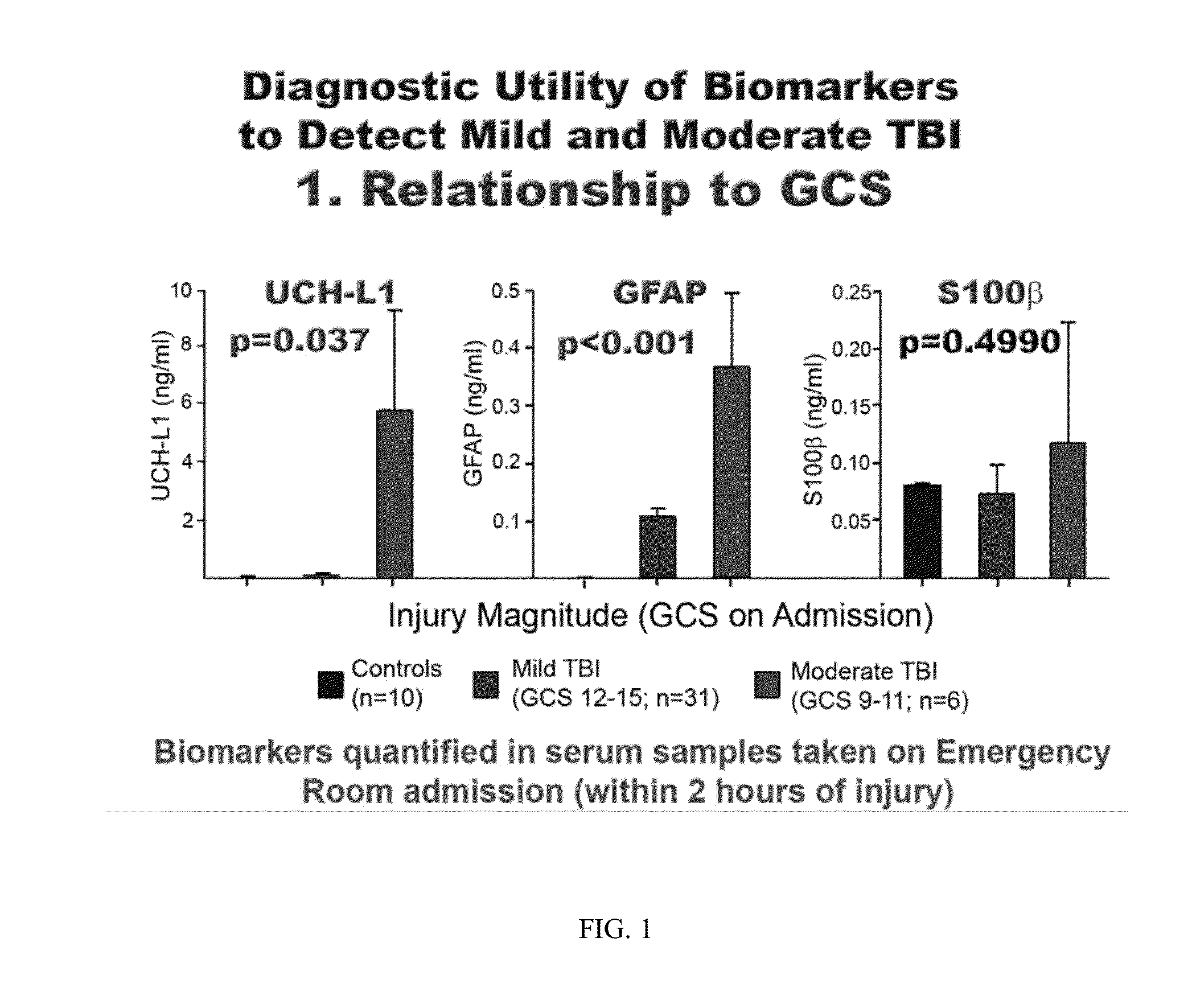
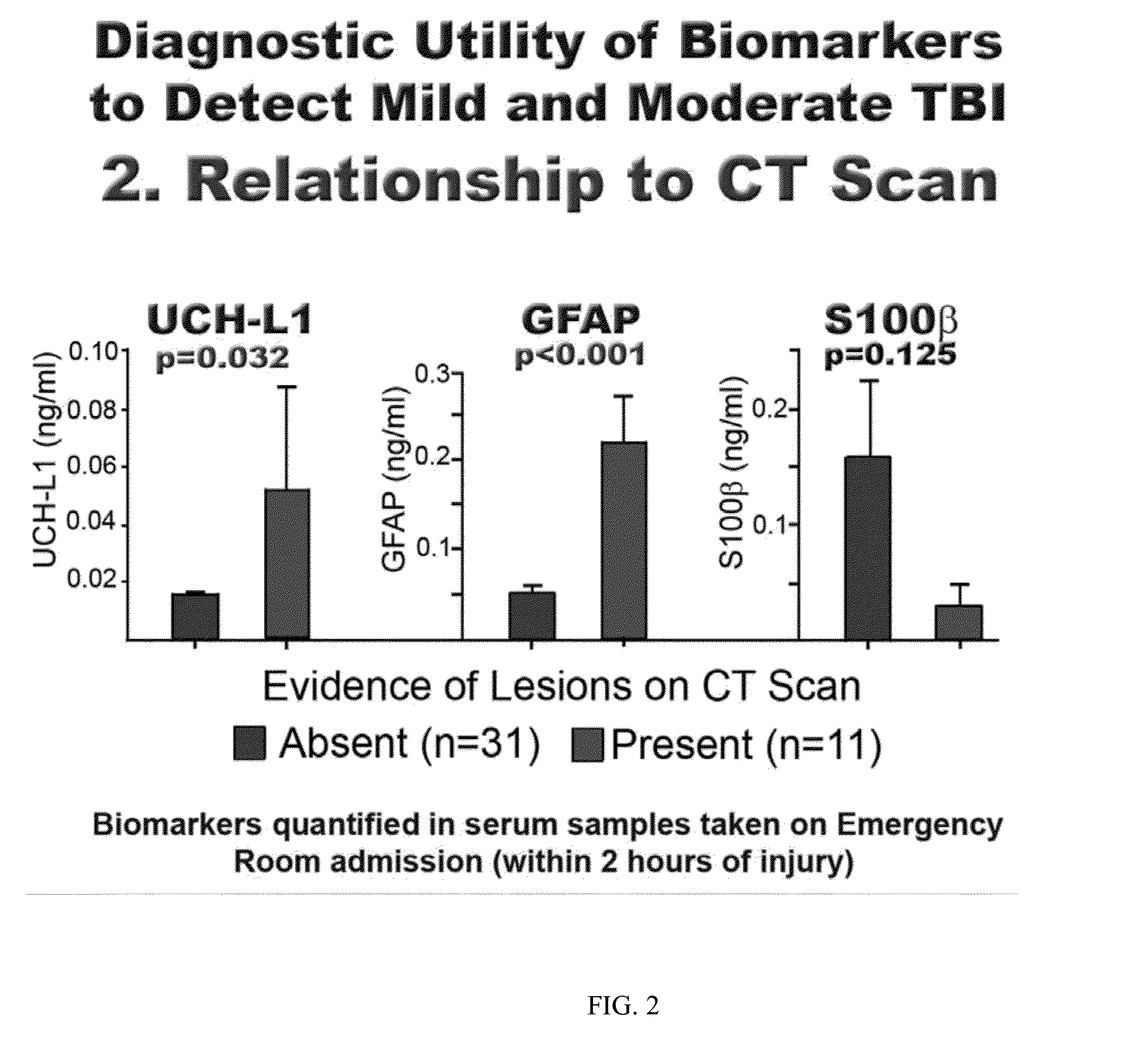
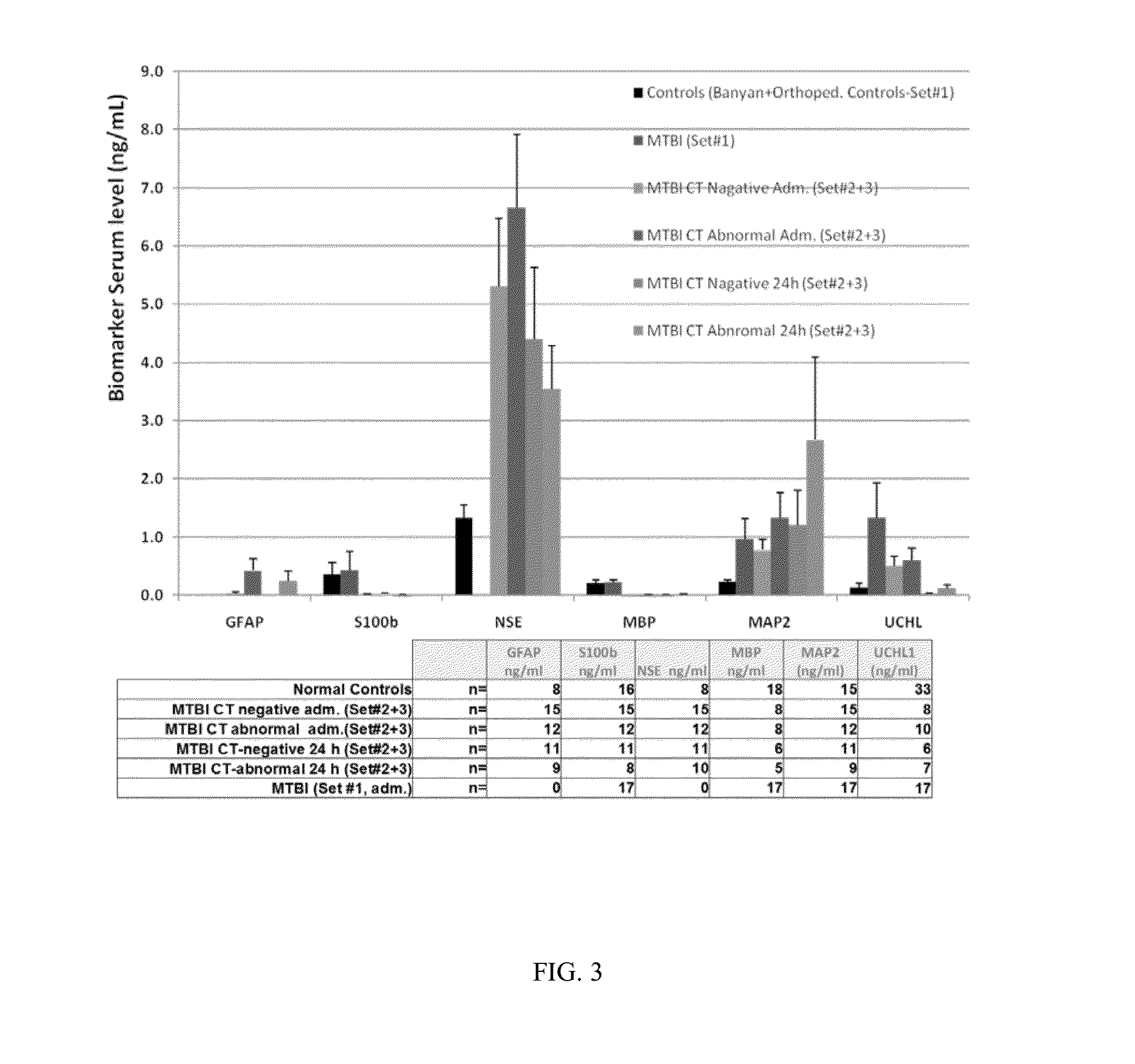
The present invention relates to an exemplary in vitro diagnostic (IVD) device used to detect the presence of and / or severity of neural injuries or neuronal disorders in a subject. The IVD device relies on an immunoassay which identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of neural injury and / or neuronal disorders in a biological sample, such as whole blood, plasma, serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The inventive IVD device may measure one or more of several neural specific markers in a biological sample and output the results to a machine readable format wither to a display device or to a storage device internal or external to the IVD.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC +1
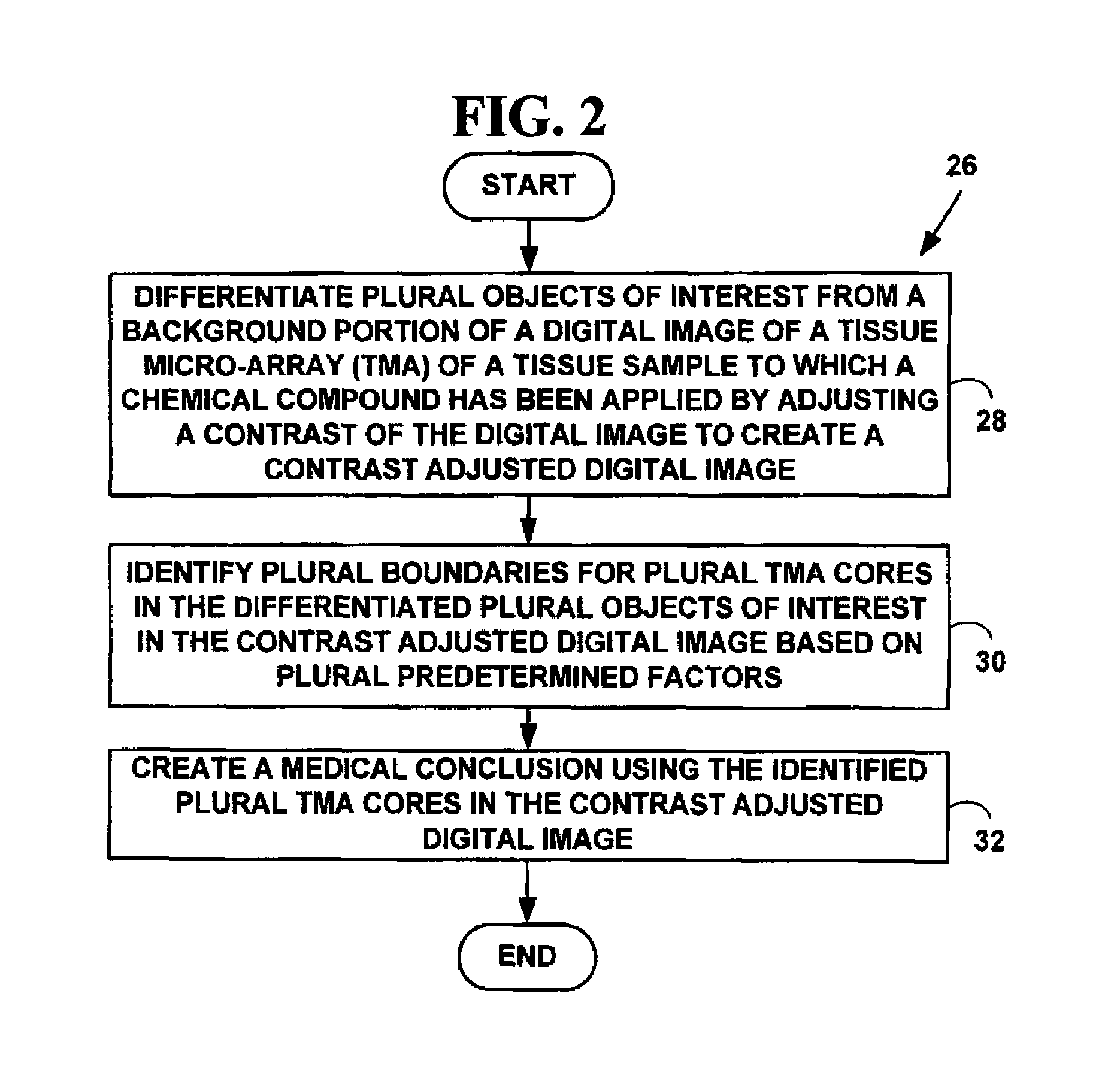
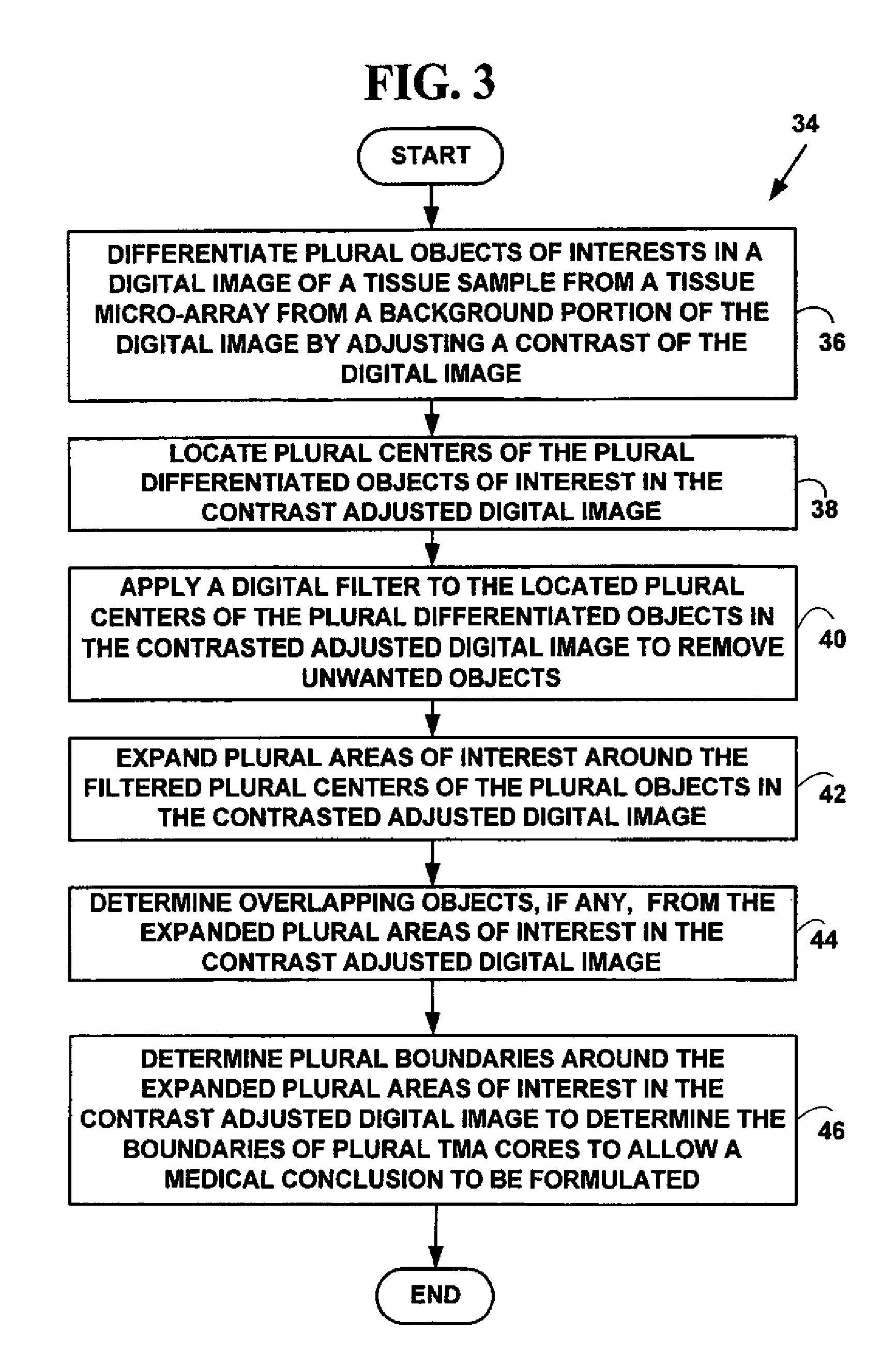
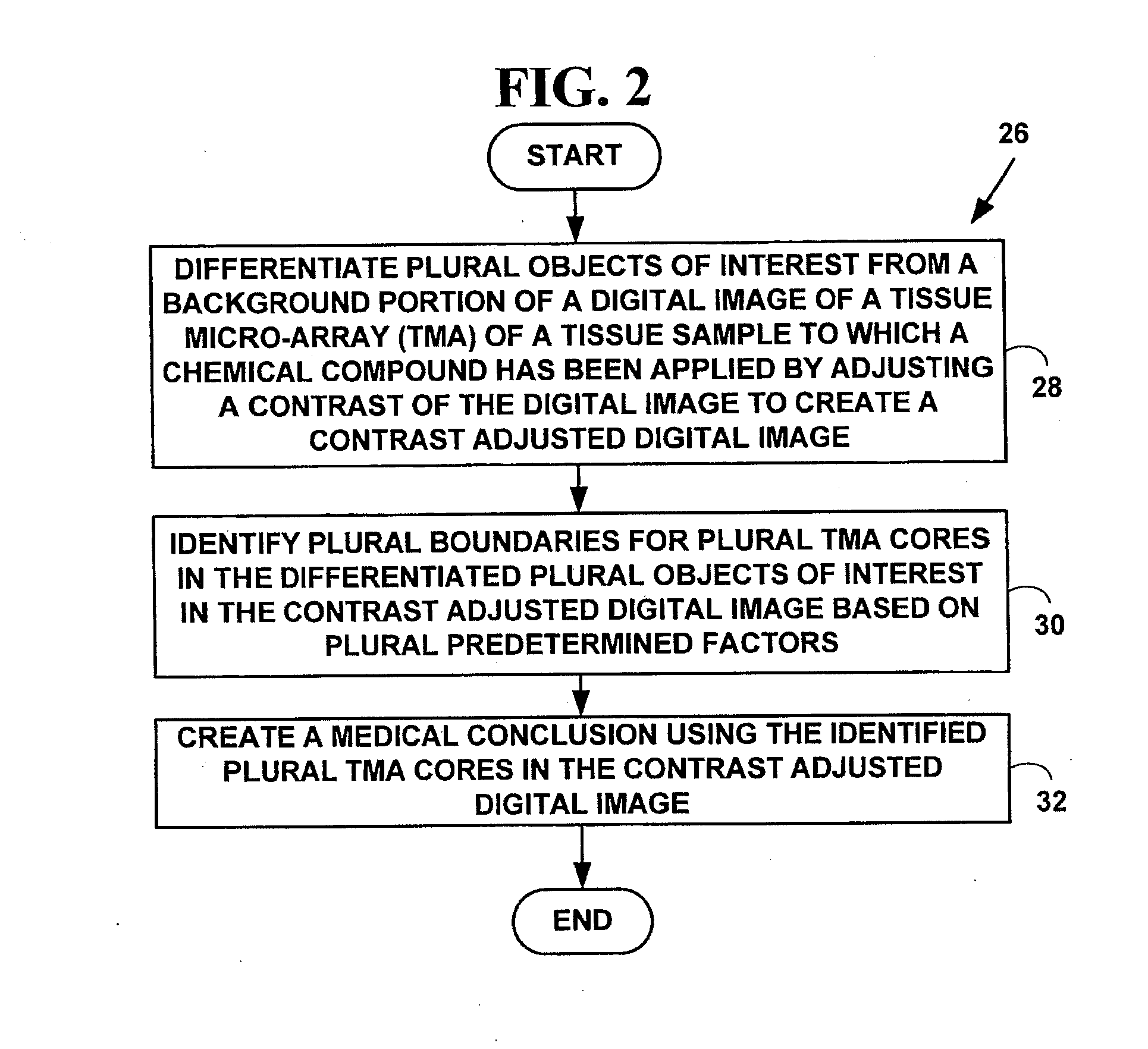
Method for automated processing of digital images of tissue micro-arrays (TMA)
ActiveUS8068988B2Facilitates automated analysisAuxiliary diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsHuman cancerTissue microarray
A method and system for automated quantitation of tissue micro-array image (TMA) digital analysis. The method and system automatically analyze a digital image of a TMA with plural TMA cores created using a needle to biopsy or other techniques to create standard histologic sections and placing the resulting needle cores into TMA. The automated analysis allows a medical conclusion such as a medical diagnosis or medical prognosis (e.g., for a human cancer) to be automatically determined. The method and system provides reliable automatic TMA core gridding and automated TMA core boundary detection including detection of overlapping or touching TMA cores on a grid.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Medical image data transmission and three-dimension visible sysem and its implementing method
InactiveCN1794246AImprove efficiencyEasy to useTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsProcess functionMedical imaging data
This invention discloses a medical image transmission and 3-D visual system and a realizing method, which develops an iconography diagnosis system operated by stand-alones and single persons to expand the image data process function of a radiation section or an image working station to computer terminals of hospitals, so that, doctors in hospitals can get the image data of patients directly from the terminals in their offices to carry out 3-D display interaction operations.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Inflammatory bowel disease prognostics
InactiveUS20120171672A1Easy diagnosisImprove complicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInflammatory bowel diseaseDisease complication
The methods and systems of the present invention are useful in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and in the prognosis of IBD progression and disease complications. With the present invention, it is possible to predict outcome of disease and patients who will have a particular risk of disease complications and / or progression to surgery.
Owner:PROMETHEUS LAB +1
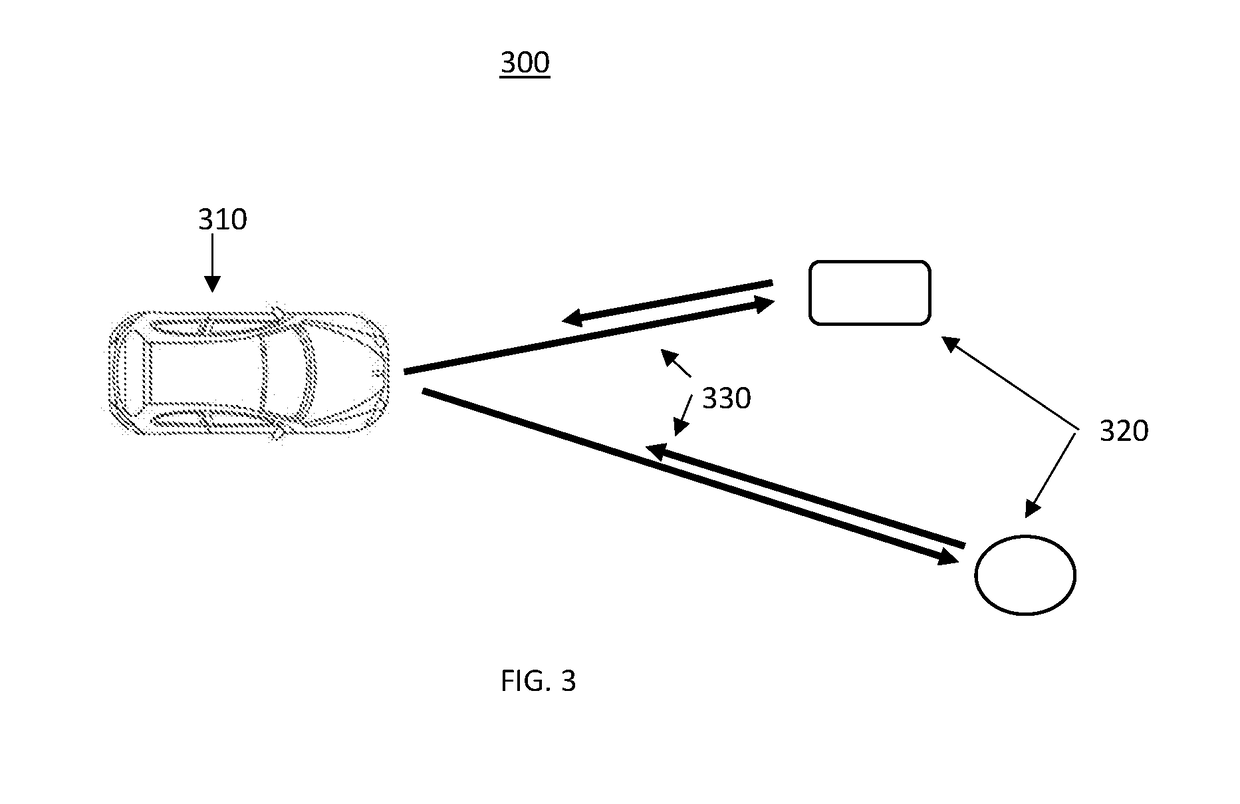
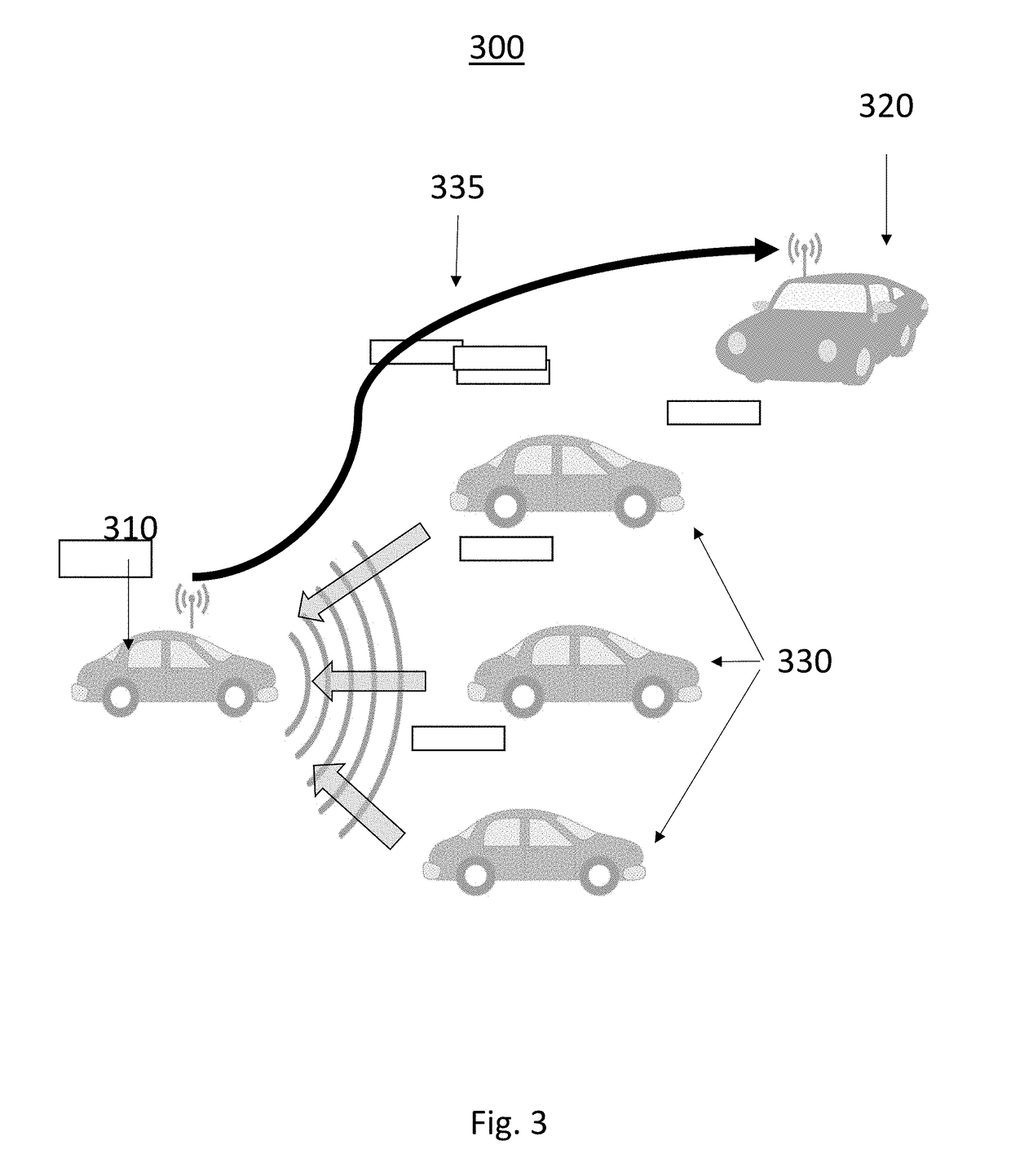
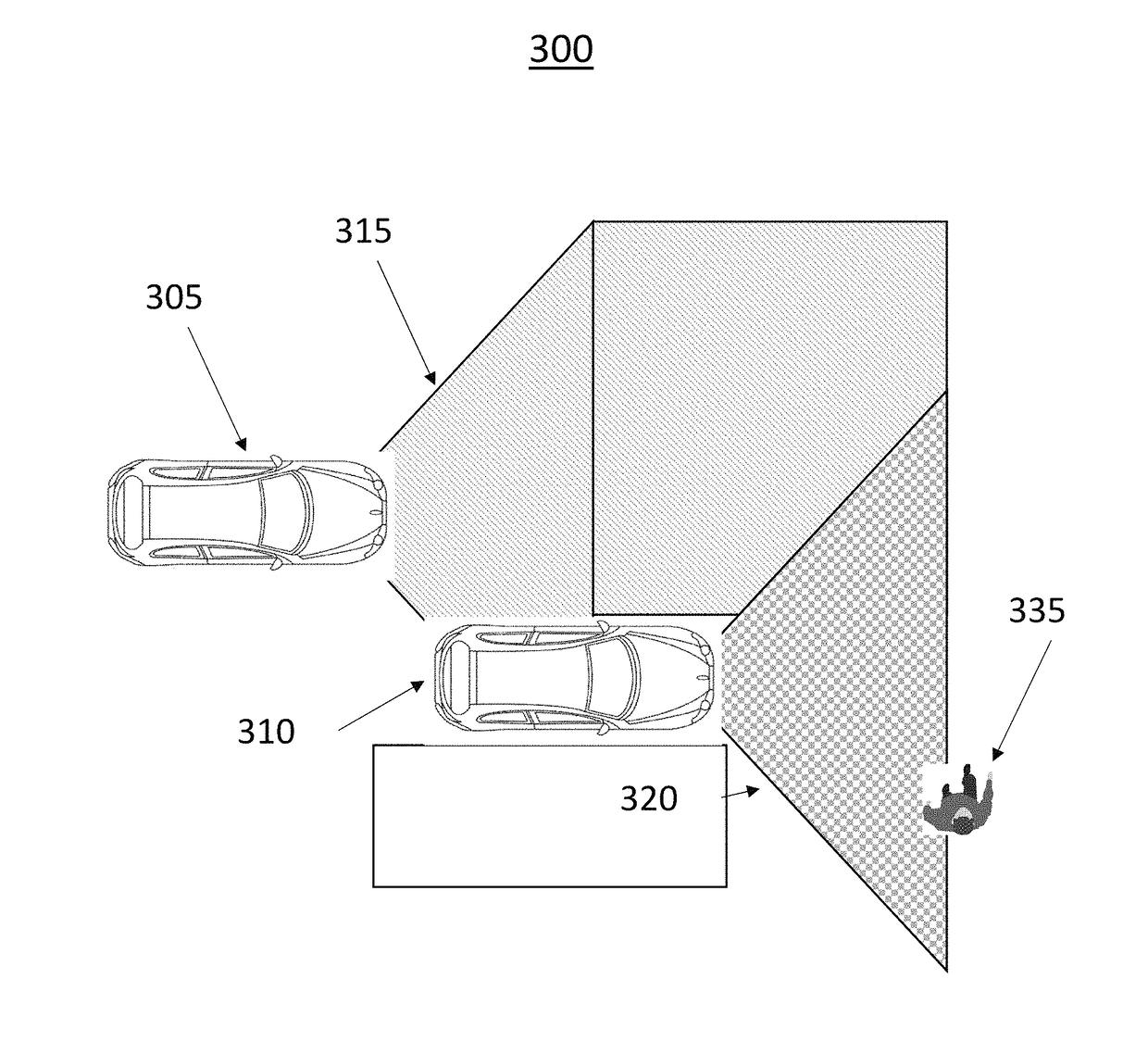
System and Method for Improved Obstable Awareness in Using a V2x Communications System
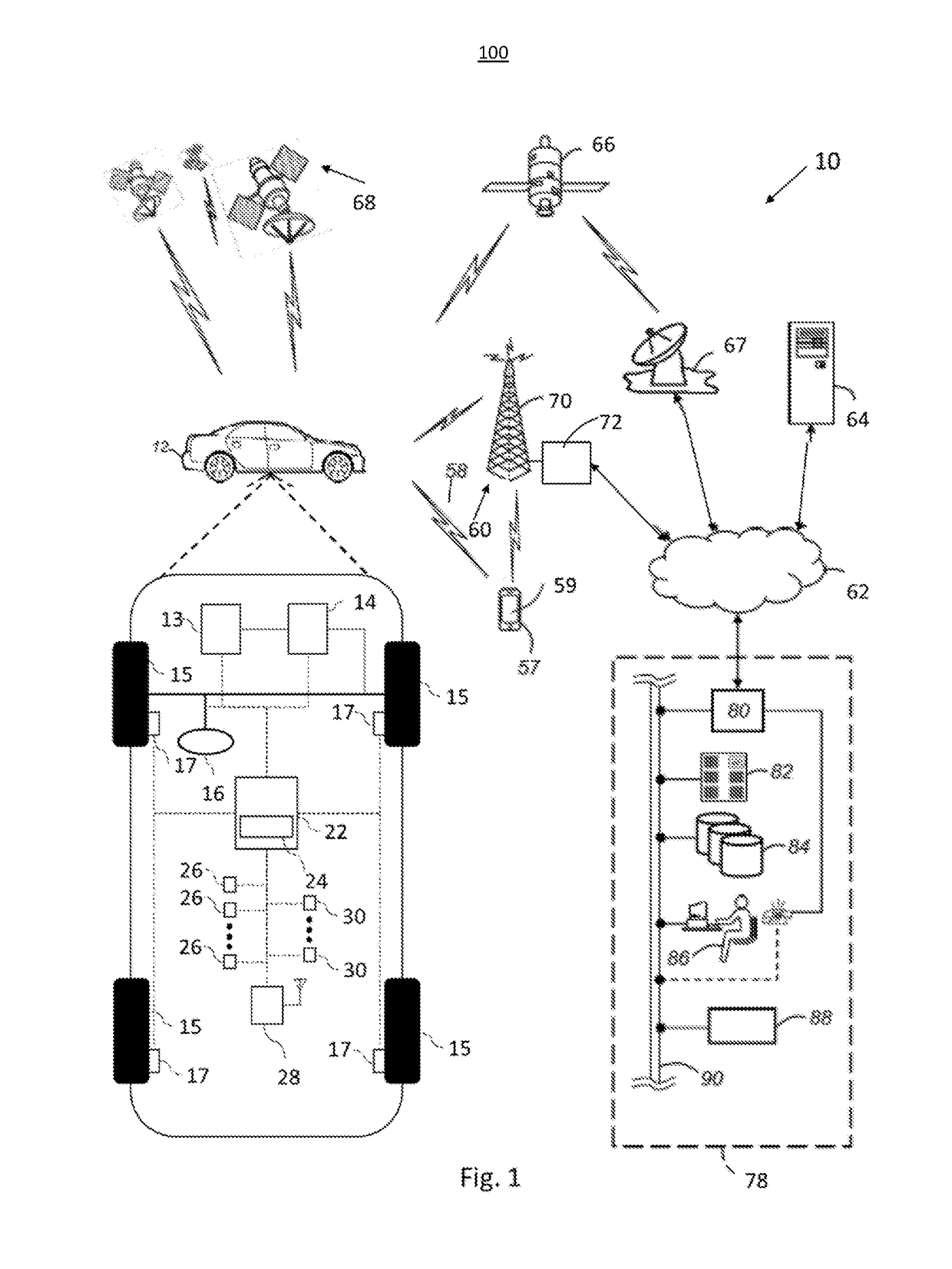
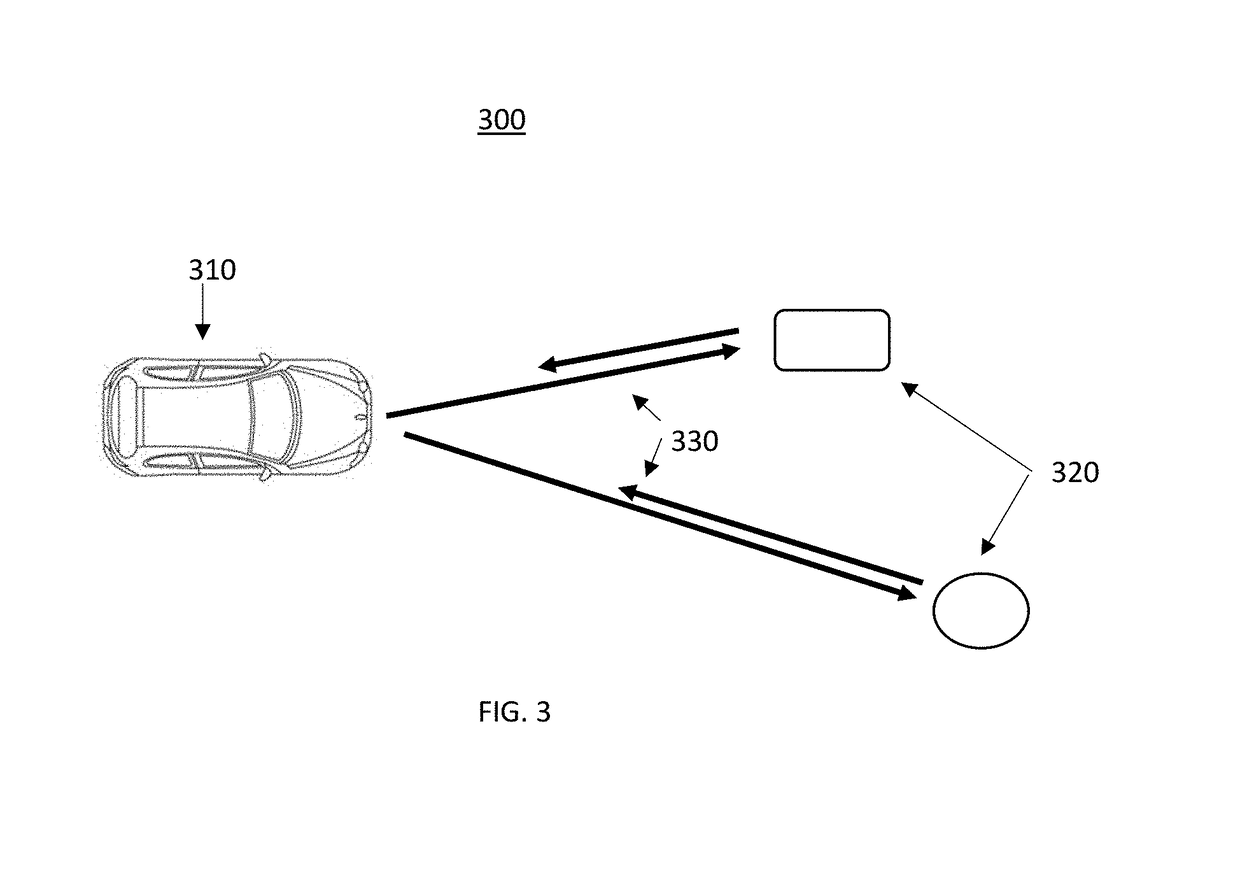
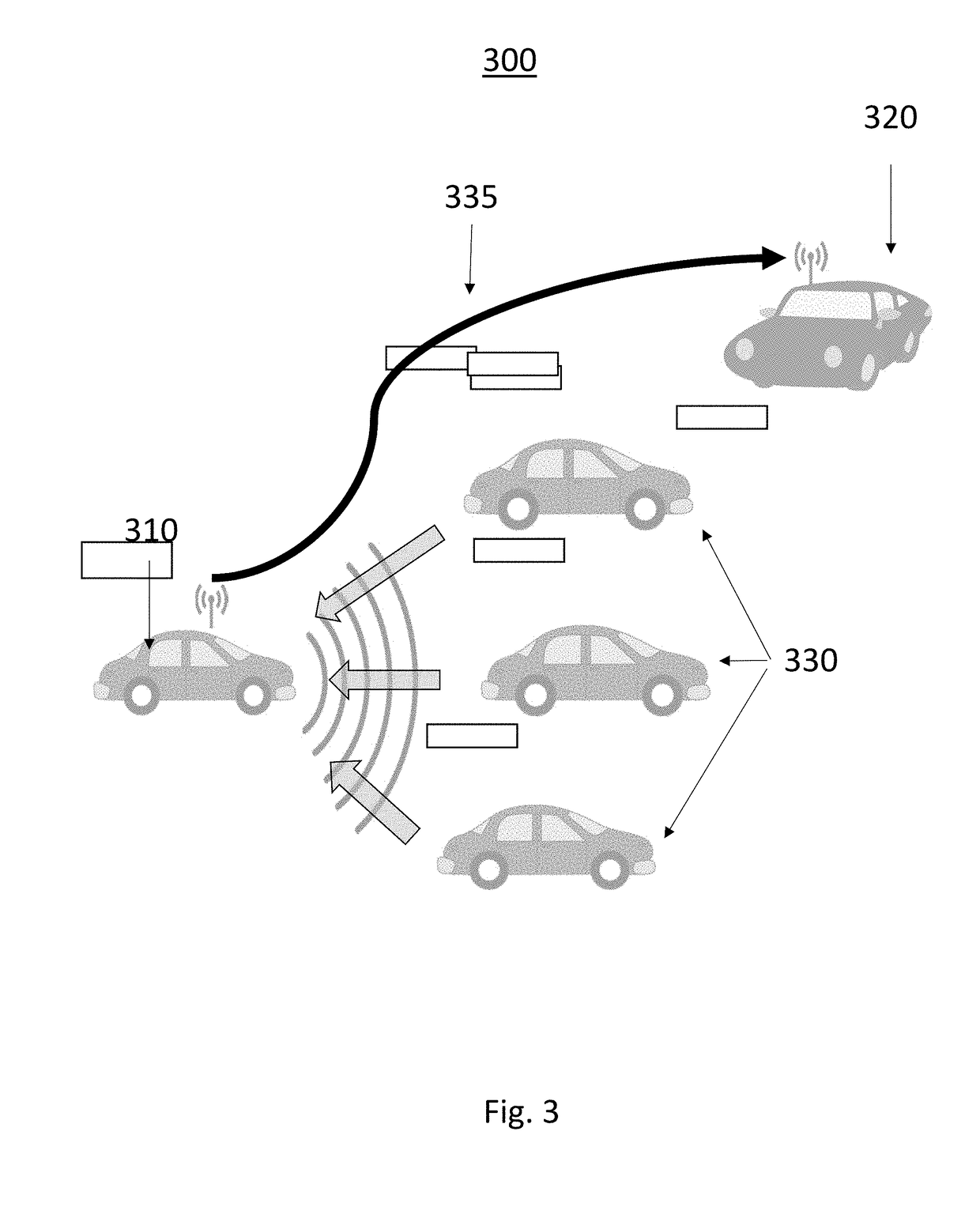
ActiveUS20190052842A1Improve customer satisfactionAuxiliary diagnosisParticular environment based servicesDetection of traffic movementComputer scienceField of view
A system and method is taught for collaborative vehicle to all (V2X) communications to improve autonomous driving vehicle performance in a heterogeneous capability environment by sharing capabilities among different vehicles. In particular, the system and method are operative to receive an image from a proximate vehicle and to augment a display within the host vehicle by providing a view of objects with an area of obstructed view.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
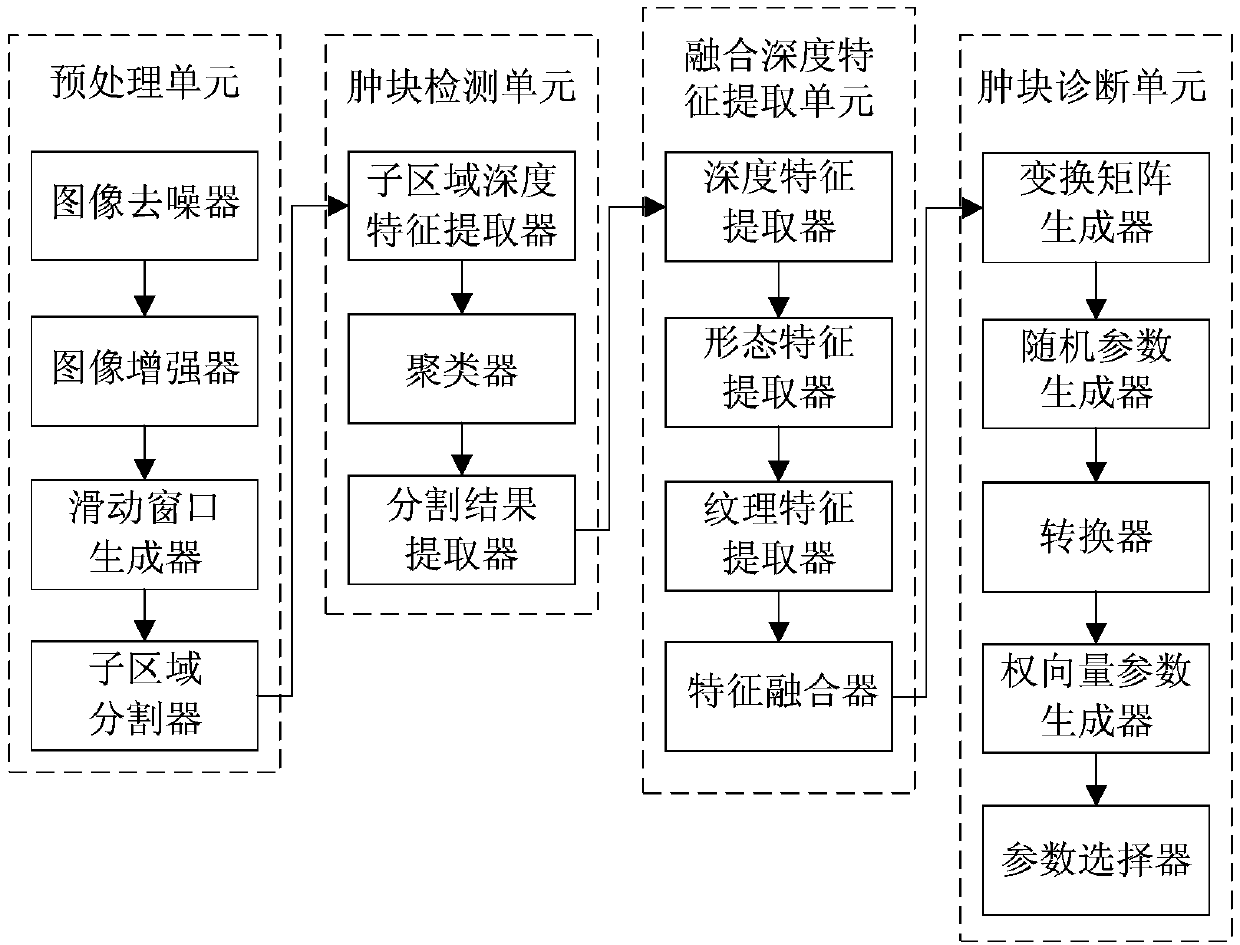
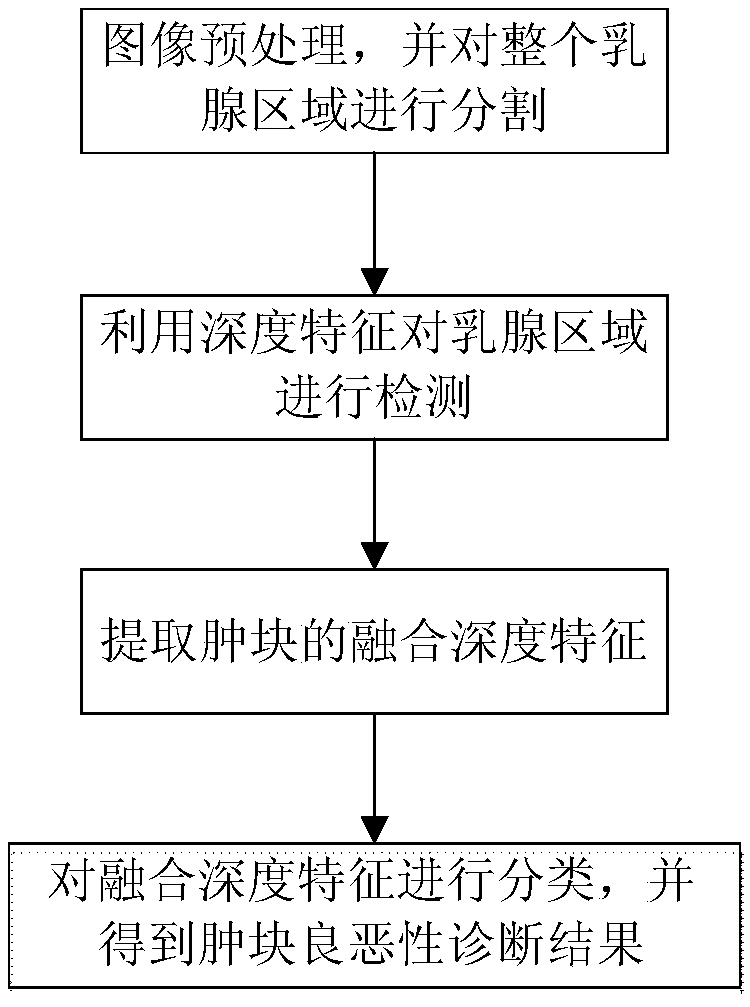
A mammary gland auxiliary diagnosis system and method based on fusion depth characteristics
ActiveCN109598709AAuxiliary diagnosisRealize detectionImage enhancementImage analysisLearning machineDisease
The invention provides a mammary gland auxiliary diagnosis system and method based on fusion depth characteristics, and relates to the technical field of medical image post-processing. The system comprises a preprocessing unit, a lump detection unit, a fusion depth feature extraction unit and a lump diagnosis unit, and is characterized in that an original mammary gland image is preprocessed, and amammary gland region is divided into a plurality of non-overlapped sub-regions; Mammary gland sub-region depth features are extracted by using a convolutional neural network CNN, and US- ELM is usedto cluster the depth characteristics of each sub-region to obtain mammary gland lumps and non-lump regions; a convolutional neural network CNN is used to extract lump depth features, lump morphology and texture features are extracted, and the lump depth, morphology and texture features are fused into a fused depth feature; And the fusion depth features are learned by using an extreme learning machine (ELM) to finally obtain benign and malignant diagnosis results of the lumps. The method is applied to breast auxiliary diagnosis, and accurate diagnosis of breast diseases can be effectively assisted.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
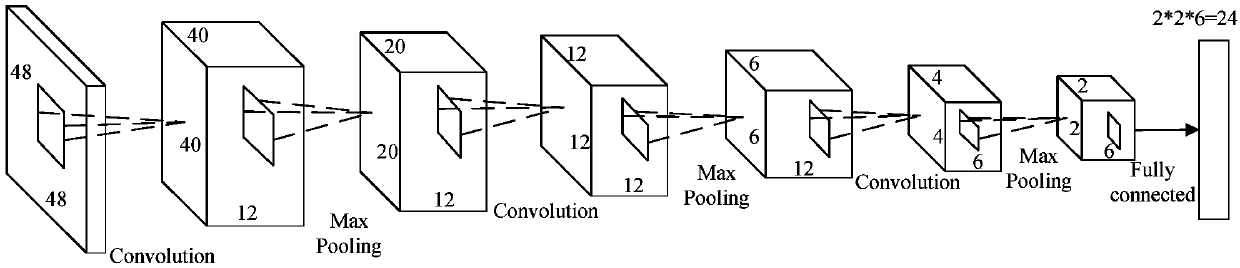
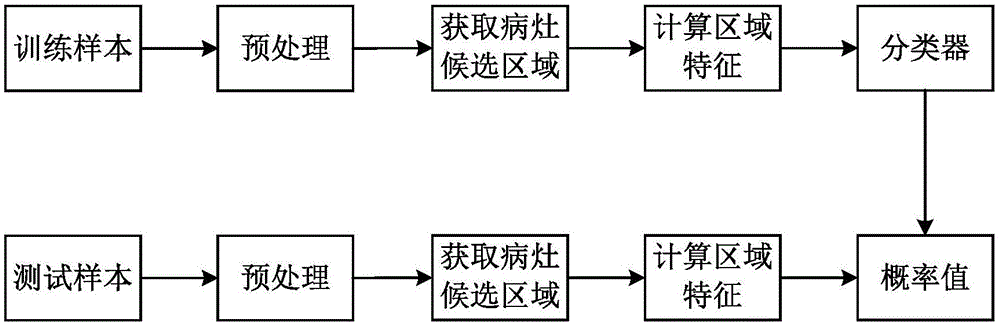
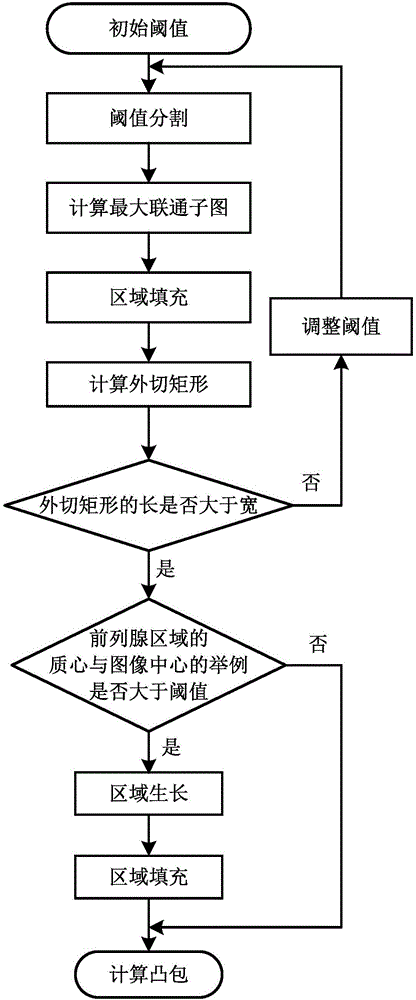
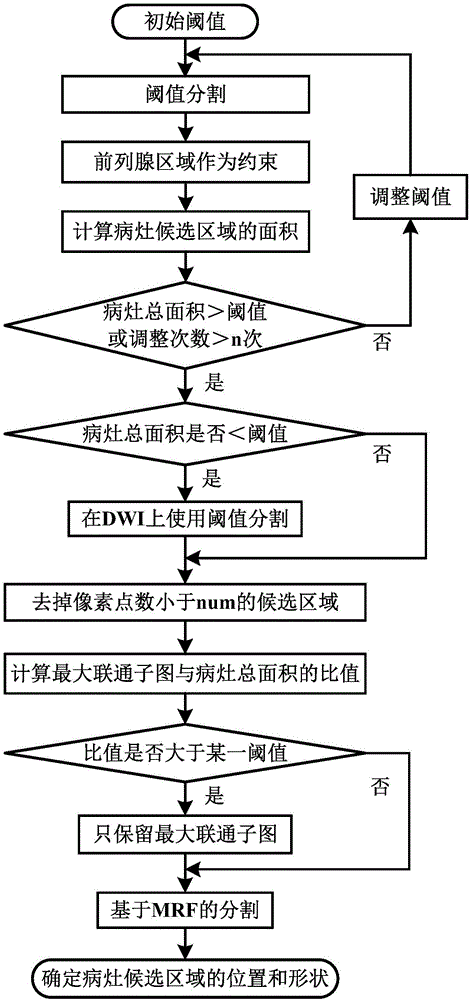
Prostatic cancer computer-assisted detection method and system based on multi-parameter MRI
ActiveCN106778005AAuxiliary diagnosisImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisMalignancyTest phase
The invention discloses a prostatic cancer computer-assisted detection method and system based on multi-parameter MRI and relates to the field of medical image processing. The method includes the following steps that at a training stage, firstly, a clinical case sample is preprocessed, then a prostate region and a focus candidate region are automatically extracted, and then features of the focus candidate region are calculated and used for training a classifier; at a testing stage, the trained classier is used for classifying the features of the focus candidate region automatically extracted from the tested clinical case sample, and a corresponding diagnosis result is obtained and serves as reference comments to be provided for doctors. A series of quantitative indexes and corresponding malignancy probability values are provided for radiologists, and the doctors can be effectively assisted in diagnosing the prostatic cancer through an MRI image.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Vehicle diagnostic listening device and method therefor
InactiveUS20090024268A1Aid in diagnosisAuxiliary diagnosisVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringInput device
A diagnostic listening device for a vehicle uses at least one input device to retrieve audible signals from the vehicle. Diagnostic circuitry is coupled to the at least one input device to allow a user to listen to the audible signals retrieved and to isolate out certain frequencies to aid in the diagnosis of the vehicle.
Owner:EAGAN CHRIS
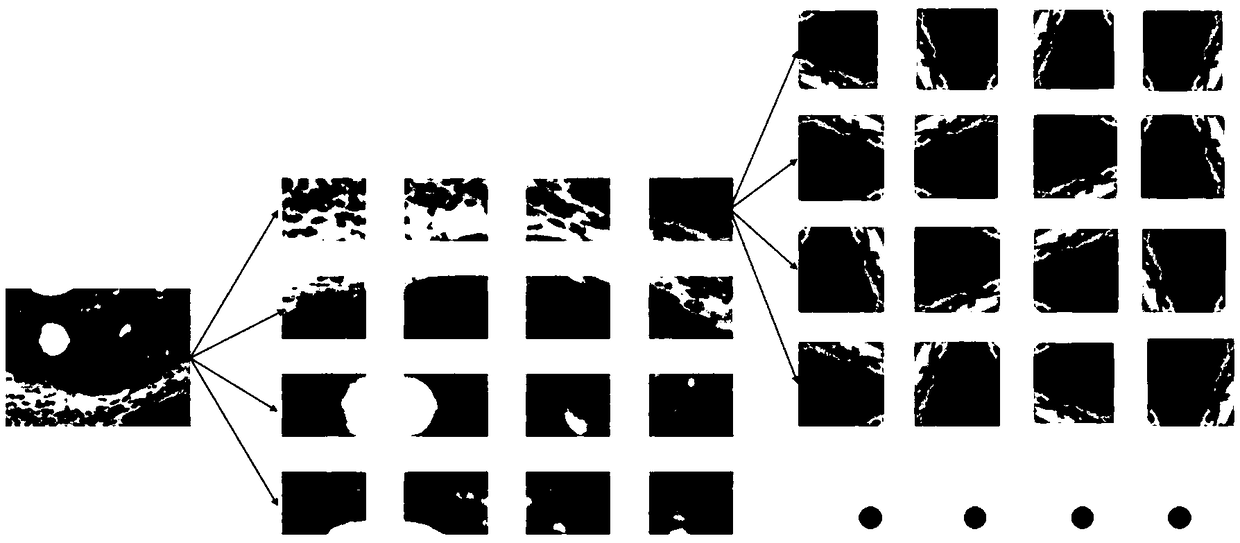
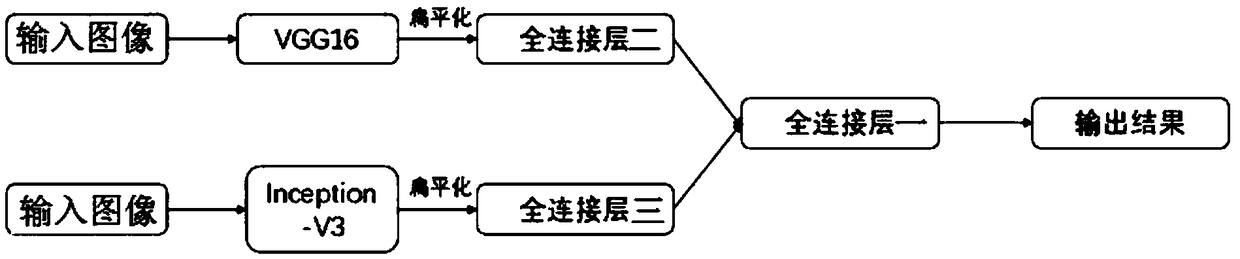
Cervical cancer histopathology image analysis method and device based on depth learning
InactiveCN109376777AHigh intelligenceAuxiliary diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorImaging analysis
The invention discloses a cervical cancer histopathology image analysis method and device based on depth learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring cervical cancer histopathology images and setting image labels for each image; training two convolution neural networks respectively based on the images used for training, and obtaining the two trained convolution neural networks; fixing parameters of the two trained convolutional neural networks, and training the all-connected layer one based on the images used for training, so that the trained all-connected layer one is obtained. The image to be tested is input into the trained classifier, and the two convolution neural networks extract feature vectors from the image respectively. The output feature vectors f1 and f2 are spliced together and input to the full connection layer 1, and the output feature vector f3. The classification result is determined by the element with the largest value in the feature vector f3 The invention can automatically classify and identify the differentiation degree of the original histopathological slice micrograph collected by the doctor and assist the doctor in diagnosis.
Owner:四川智动木牛智能科技有限公司
Self-grounding transmitting portable camera controller for use with pipe inspection system
InactiveUS20140340505A1Auxiliary diagnosisTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera controlCapacitance
A portable camera controller for use with a pipe inspection system is disclosed. The controller may include an onboard display, USB ports, wireless capability, and a built-in transmitter for energizing a pipe-inspection cable for tracing purposes. The camera controller may be configured to support auto-logging and automatic report generation of pipe inspection operations and associated locating operations. The camera controller may be self-grounding using conductive and / or capacitive grounding circuits and an associated transmitter may be used without a separate grounding stake through use of the conductive and / or capacitive grounding circuits.
Owner:SEESCAN
Apparatus and method for near-field imaging of tissue
ActiveUS7725151B2Maximize their opportunitySmall sizeElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringBroadbandTest measurement
Using pulsed or continuous-wave sources, broadband electromagnetic energy generally in the 10 MHz to 300 GHz range is applied through one or a plurality of near-field antennas such as coaxial probe tips. The electromagnetic energy reflected from the surface or transmitted through the near surface of the object (e.g. surface of skin or other tissue or cells) is detected, and the ratio of the test measurement to that from normal tissue is recorded and presented to determine the degree of dielectric contrast, hence inhomogeneity. This degree of contrast is used both on its own and in conjunction with simultaneously acquired optical images to map the boundary of an organ inhomogeneity such as a tumor. The bundle of antennas may be scanned over a surface of the object on a pixel-by-pixel basis to determine the spectra of the sample on a pixel-by-pixel basis, allowing a two dimensional display of the absorption spectra to be provided.
Owner:VAN DER WEIDE DANIEL WARREN
Non-invasive measurement of suprasystolic signals
ActiveUS7727157B2Increase strainReduce complianceEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterCardiac dysfunctionCardiac arrhythmia
An apparatus for assessing cardiovascular status of a mammal comprises a system for locally applying a pressure to an artery capable of restricting blood flow through said artery, a wideband external pulse transducer having an output and situated to measure suprasystolic signals proximate to said artery, and a computing device receiving said output for calculating vascular compliance values. The method described is particularly useful for determining cardiac output, assessing whether a pregnant female has preeclampsia or a patient has cardiac insufficiency, or assessing cardiac arrhythmia.
Owner:USCOM LTD
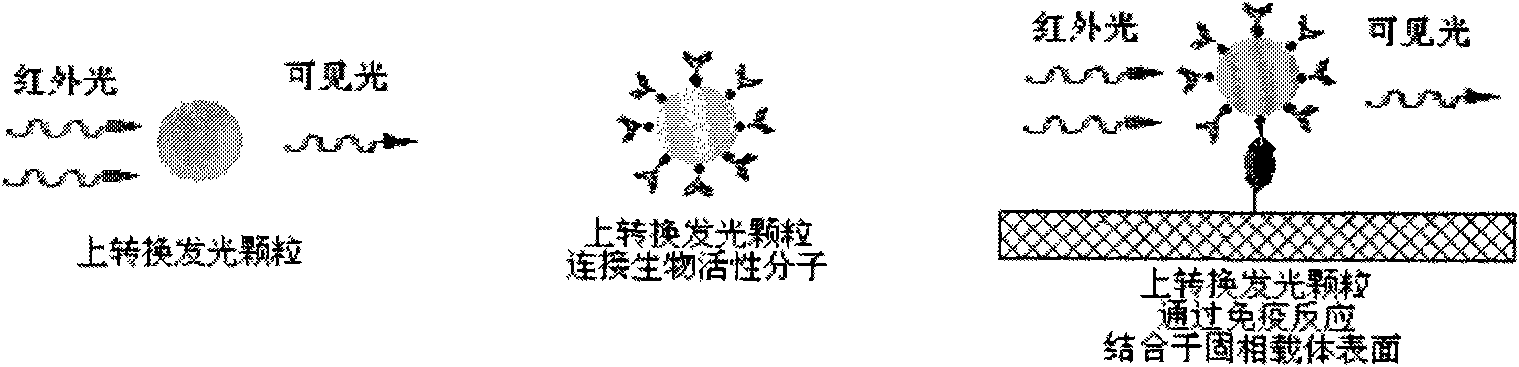
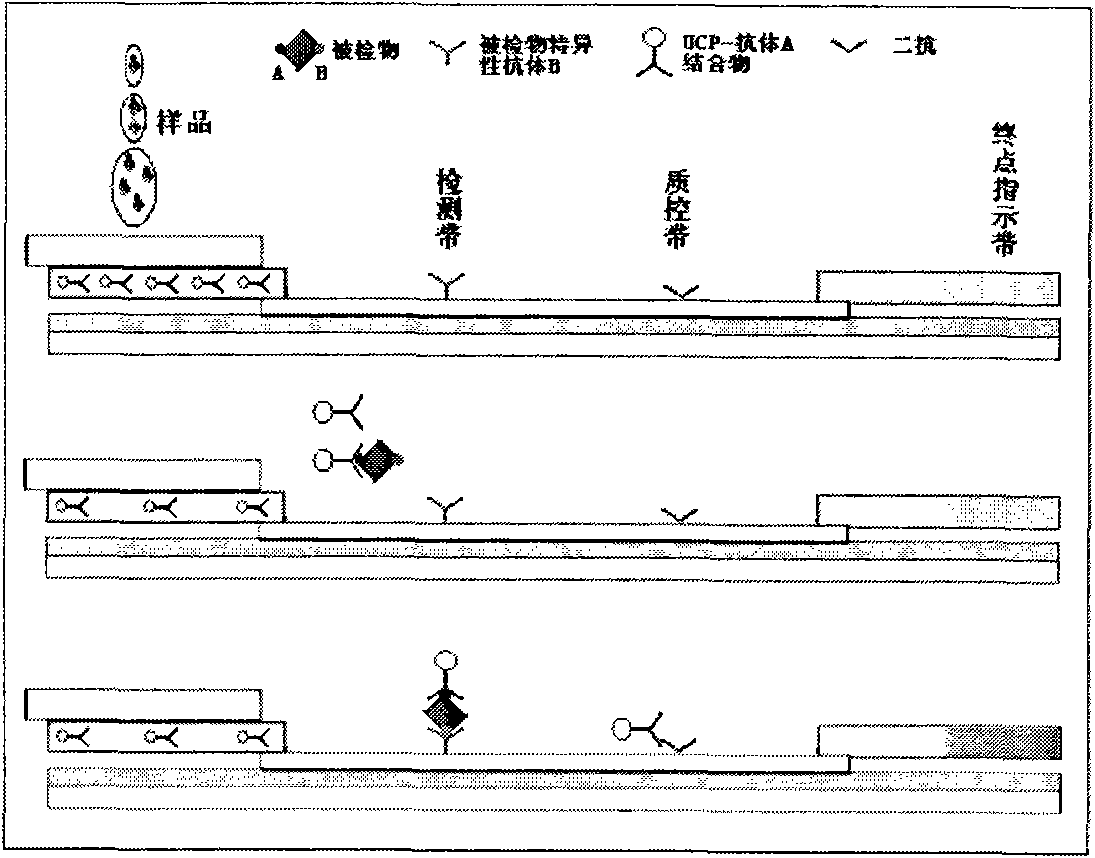
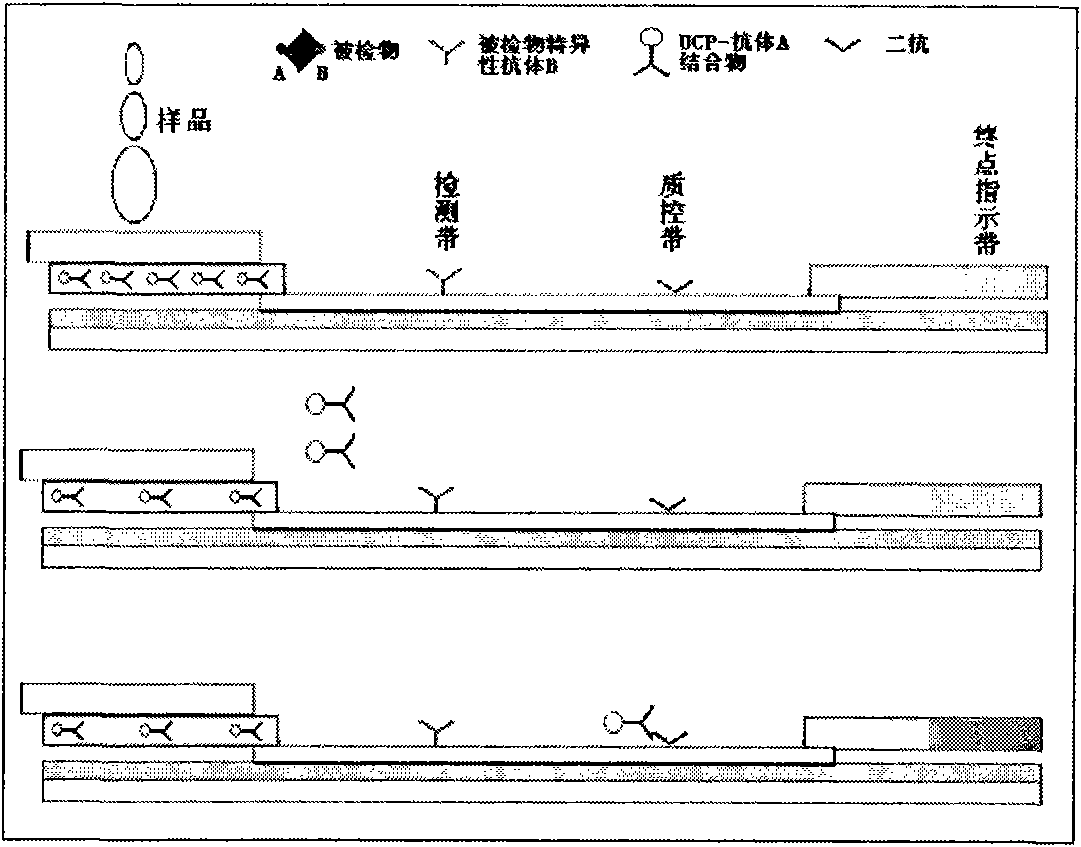
Immune chromatography test paper strip based on up-conversion luminescence technology
InactiveCN101788559AAuxiliary diagnosisImprove stabilityBiological testingUpconversion luminescenceLight signal
The invention discloses an immune chromatography test paper strip based on an up-conversion luminescence technology. The up-conversion luminescence material, i.e. UCP, is used as a biological marker, and the result can be presented in a visible light signal form under the radiation of infrared light and can be interpreted by an instrument, thereby quantitative detection on the target detected object is realized. The test paper strip mainly comprises a sample pad, a binding pad or a binder release pad, an analyzing membrane, a water absorbing pad and a plastic back plate. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the test paper strip, and application in the biological sample quantitative detection. According to different immune reaction modes of the substances to be detected, the test paper strip is classified according to a sandwich mode, a competition mode and an indirection mode, and various modes of the test paper strips can carry out quick and sensitive qualitative and quantitative detection and analysis on different substances to be detected in the sample.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for object surface estimation using reflections delay spread
ActiveUS20180373260A1Increase satisfactionImprove customer satisfactionElectromagnetic wave reradiationPosition/course control in two dimensionsObject detectionEngineering
The present application generally relates communications and hazard avoidance within a monitored driving environment. More specifically, the application teaches a system and method for improved target object detection in a vehicle equipped with a laser detection and ranging LIDAR system by transmitting a light pulse for a known duration and comparing a duration of the received pulse to the transmitted pulse in order to determine an orientation of a surface of a target.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and Method for Improved Obstable Awareness in Using a V2x Communications System
ActiveUS20190051168A1Improve customer satisfactionAuxiliary diagnosisArrangements for variable traffic instructionsParticular environment based servicesEngineeringTactical communications system
A system and method is taught for collaborative vehicle to all (V2X) communications to improve autonomous driving vehicle performance in a heterogeneous capability environment by sharing capabilities among different vehicles. In particular, the system and method are operative to facilitate path planning contention resolution among a plurality of road uses within a road segment by facilitating the election and transition of a segment leader to arbitrate conflicts.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Neural specific s100b for biomarker assays and devices for detection of a neurological condition
InactiveUS20150141528A1Auxiliary diagnosisBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDisplay deviceNeuronal disease
An in vitro diagnostic (IVD) device is used to detect the presence of and / or severity of neural injuries or neuronal disorders in a subject. The IVD device relies on an immunoassay which identifies biomarkers that are diagnostic of neural injury and / or neuronal disorders in a biological sample, such as whole blood, plasma, serum, and / or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). An IVD device may measure one or more of several neural specific markers in a biological sample and output the results to a machine readable format, either to a display device or to a storage device internal or external to the IVD.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
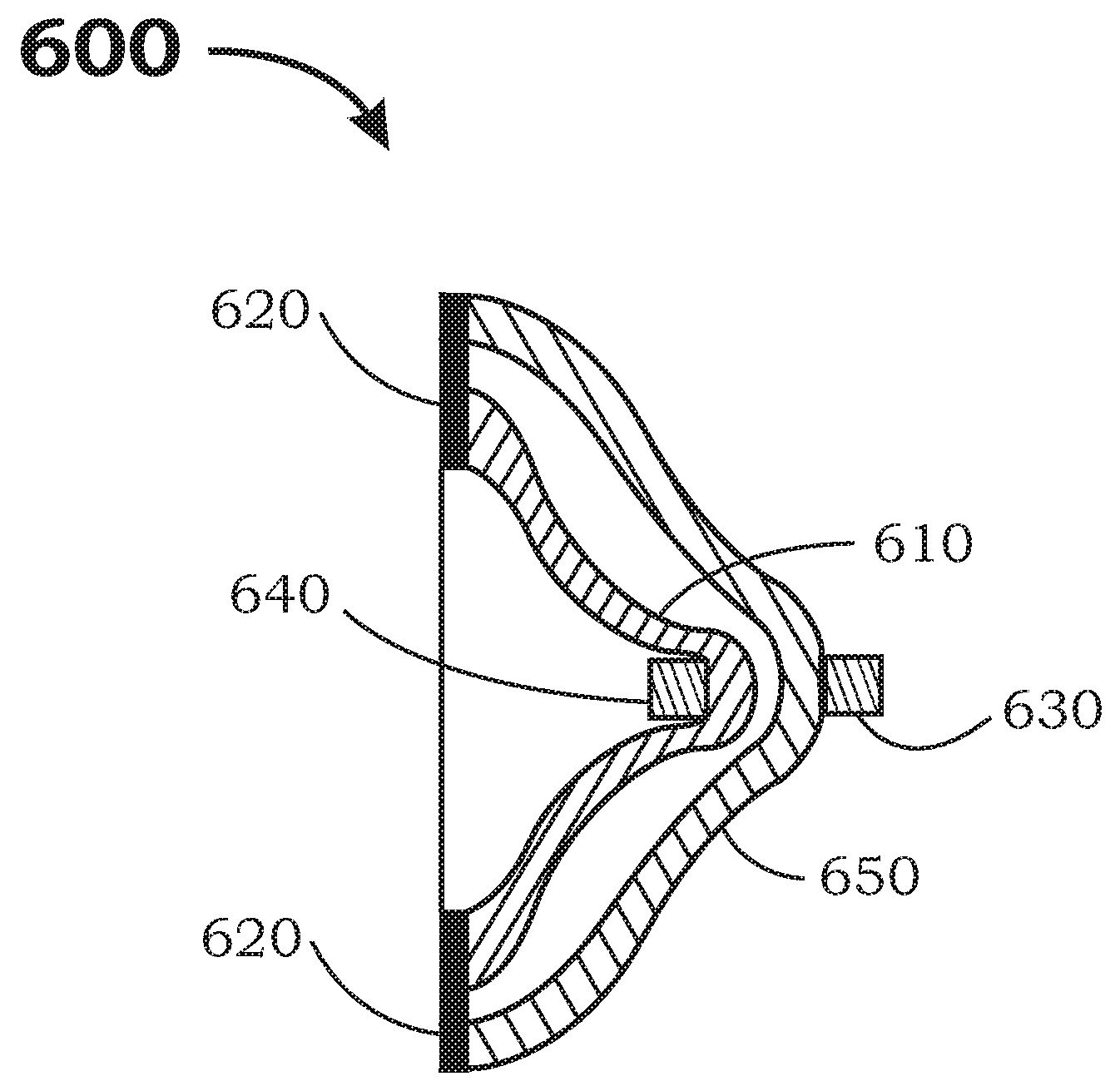
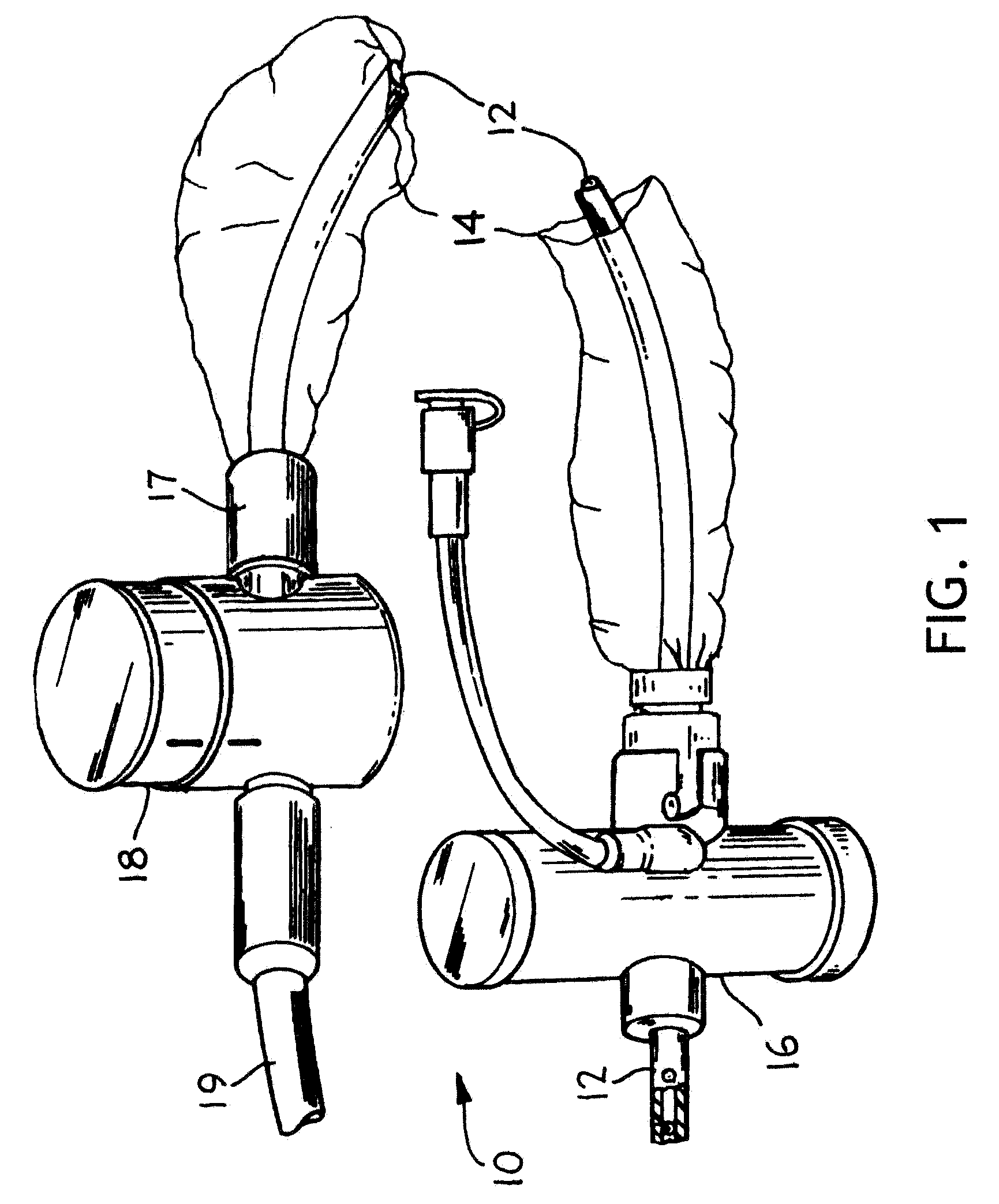
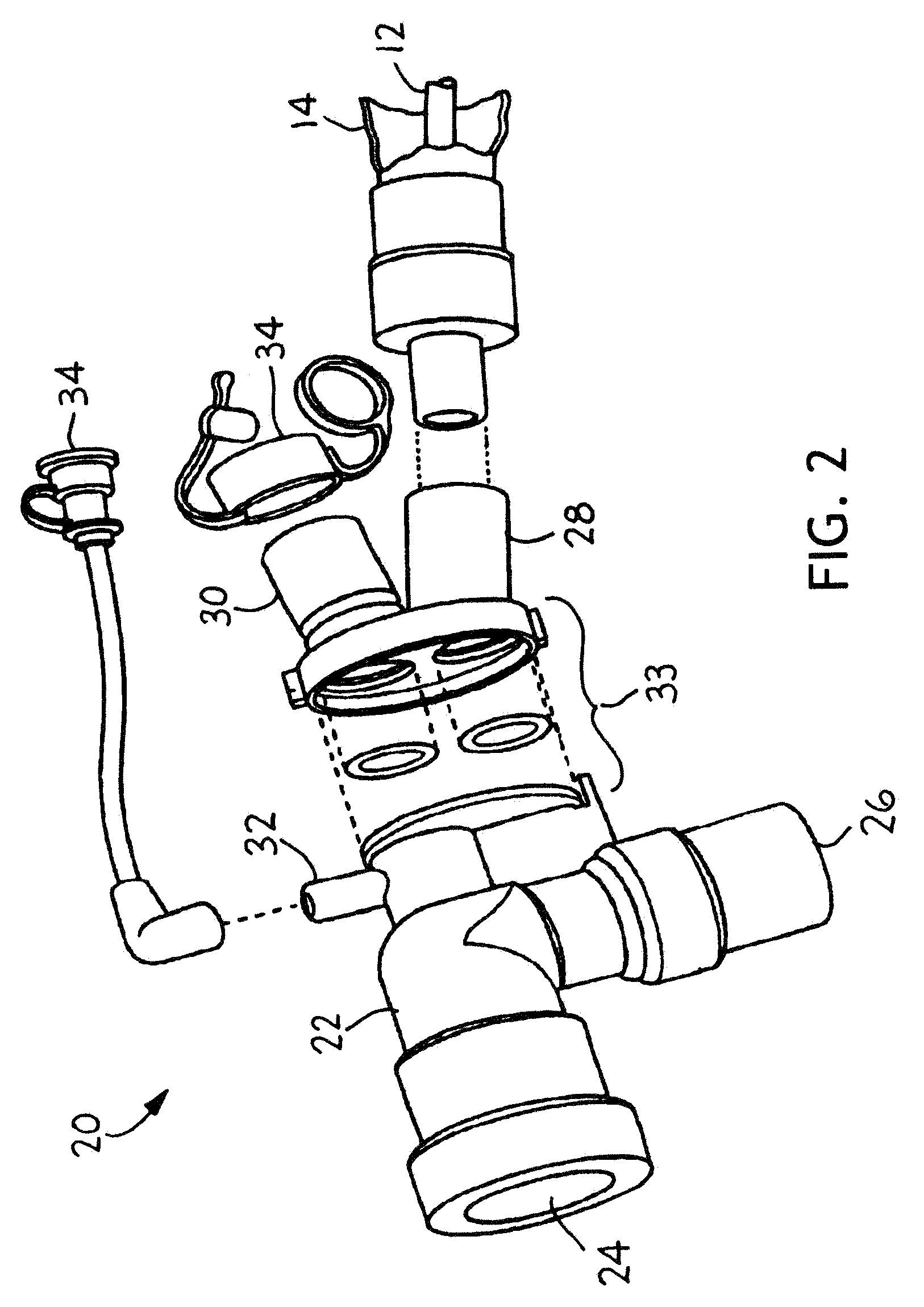
Port Sealing Cartridge for Medical Ventilating and Aspirating Devices
InactiveUS20100147296A1Easily removeMaintain cleanlinessRespiratorsRespiratory apparatusAccess portEngineering
There is provided a port sealing cartridge that allows for insertion of a catheter or other medical device into an endotracheal tube and thence the patient's lungs through an available access port. The port sealing cartridge has a primary and a secondary seal or collar that sequentially provide a pressure seal as a medical device is inserted through them and into the system. An optional tethered dust cover may also be used on the proximal end of the port seal cartridge. The port seal cartridge may desirably be fitted with a quick-connection so that it may be easily removed, disposed of and replaced. The port seal may be used for access to a patient's lungs with a bronchoalveolar catheter, bronchoscope or other medical device for treatment or sampling of the respiratory tract.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
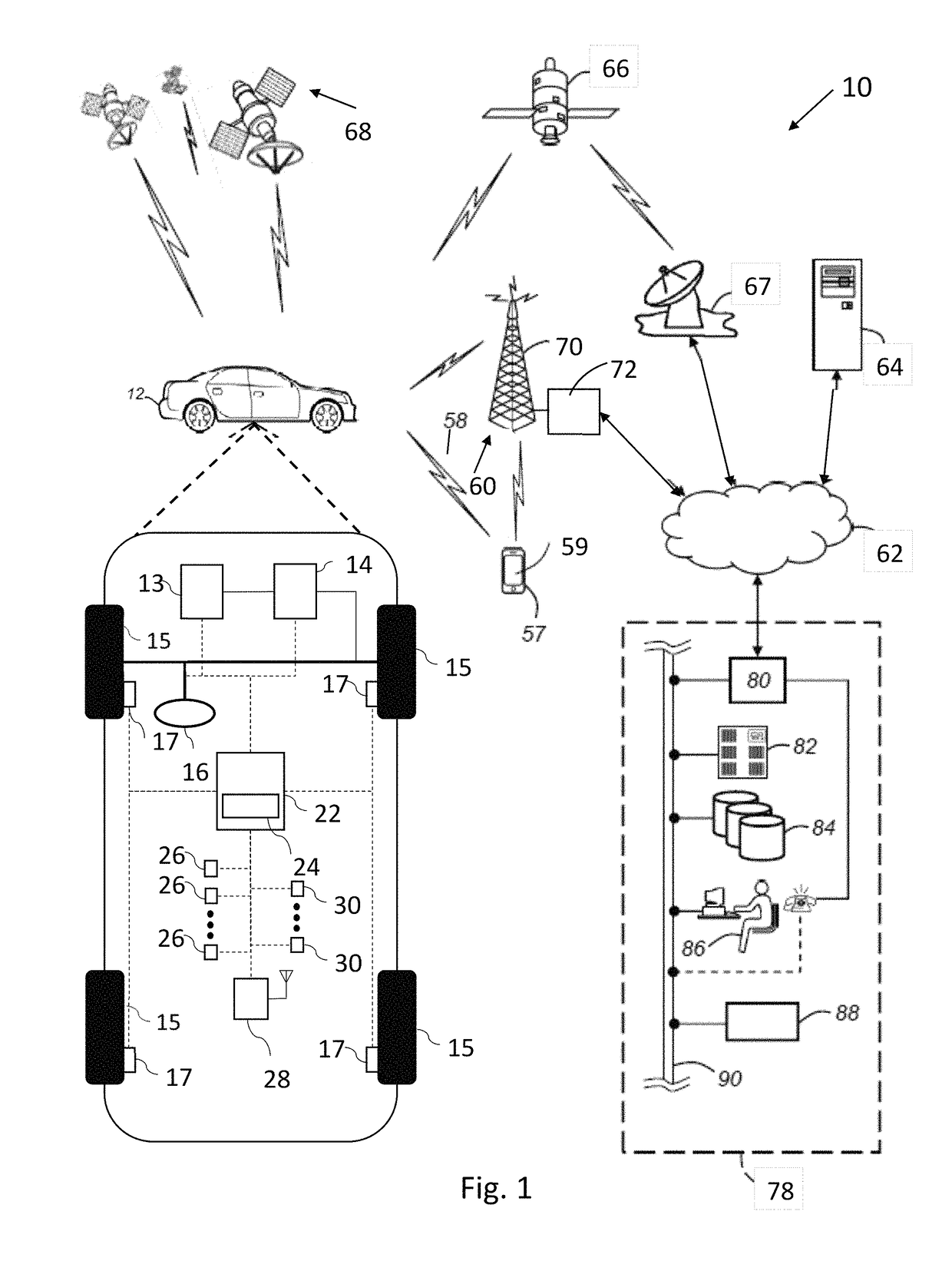
Method and apparatus of networked scene rendering and augmentation in vehicular environments in autonomous driving systems
ActiveUS10109198B2Improve customer satisfactionAuxiliary diagnosisAnti-collision systemsScene recognitionAutomatic controlAutopilot
A system and method is taught for vehicles controlled by automated driving systems, particularly those configured to automatically control vehicle steering, acceleration, and braking during a drive cycle without human intervention. In particular, the present disclosure teaches a system and method for generation situational awareness and path planning data and transmitting this information via vehicle to vehicle communications where one vehicle has an obstructed view to objects not within an obstructed view of a second vehicle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
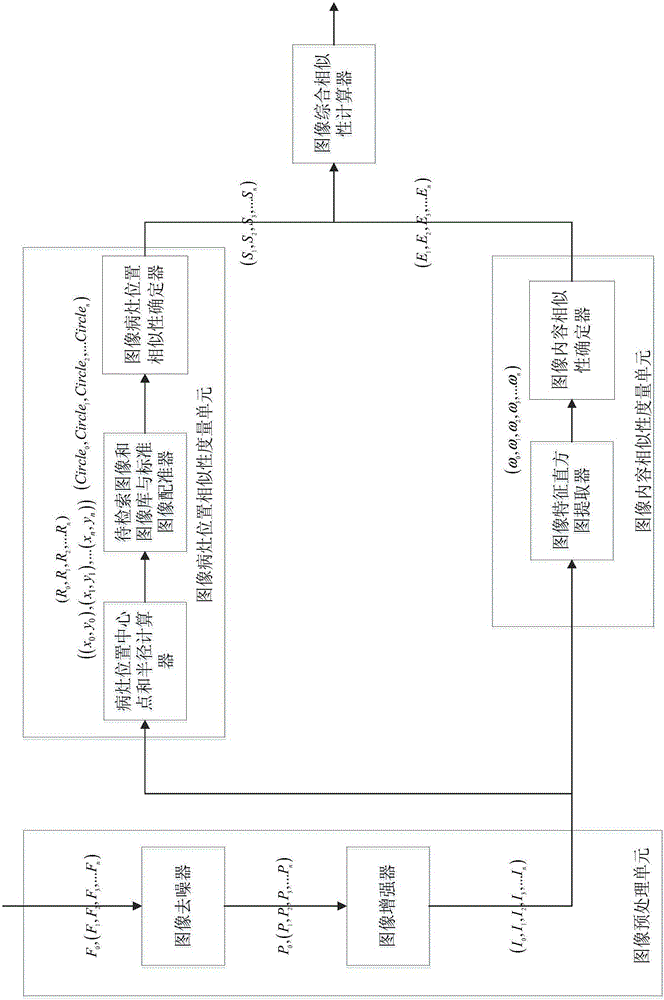
Nidus position and content-based mammary image retrieval system and method
ActiveCN105956198AImprove retrieval performanceAuxiliary diagnosisMedical image data managementSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalMammary gland disease
The invention provides a nidus position and content-based mammary image retrieval system and method. The system comprises an image preprocessing unit, an image nidus position similarity measurement unit, an image content similarity measurement unit and an image comprehensive similarity measurer. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-retrieved image of an x-ray image of a mammary molybdenum target and a historical image set; selecting a standard image; preprocessing the to-be-retrieved image and the historical image set; performing image nidus position similarity measurement on the preprocessed to-be-retrieved image and the preprocessed historical image set; and performing image content similarity measurement on the preprocessed to-be-retrieved image of the x-ray image of the mammary molybdenum target and the preprocessed historical image set to obtain an image comprehensive similarity image sequence number so as to obtain a retrieval result of the to-be-retrieved image. According to the system and method, a nidus position-based similarity measurement method is added, thereby effectively improving the retrieval performance of the x-ray image of the mammary molybdenum target and further assisting a doctor in diagnosing mammary diseases.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for automated processing of digital images of tissue micro-arrays (TMA)
ActiveUS20120093387A1Facilitates automated analysisAuxiliary diagnosisAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsBiological testingHuman cancerTissue microarray
A method and system for automated quantitation of tissue micro-array image (TMA) digital analysis. The method and system automatically analyze a digital image of a TMA with plural TMA cores created using a needle to biopsy or other techniques to create standard histologic sections and placing the resulting needle cores into TMA. The automated analysis allows a medical conclusion such as a medical diagnosis or medical prognosis (e.g., for a human cancer) to be automatically determined. The method and system provides reliable automatic TMA core gridding and automated TMA core boundary detection including detection of overlapping or touching TMA cores on a grid.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com