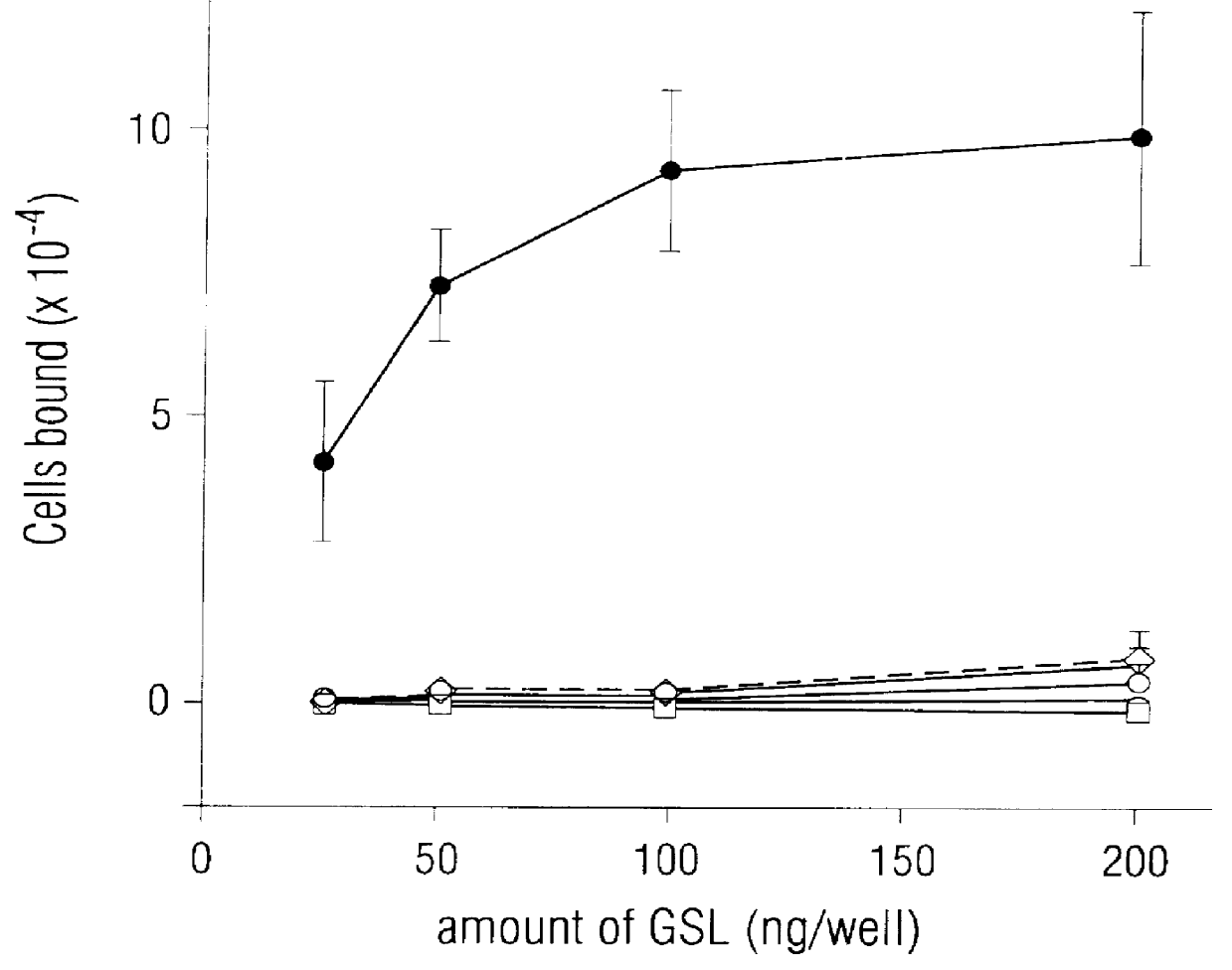
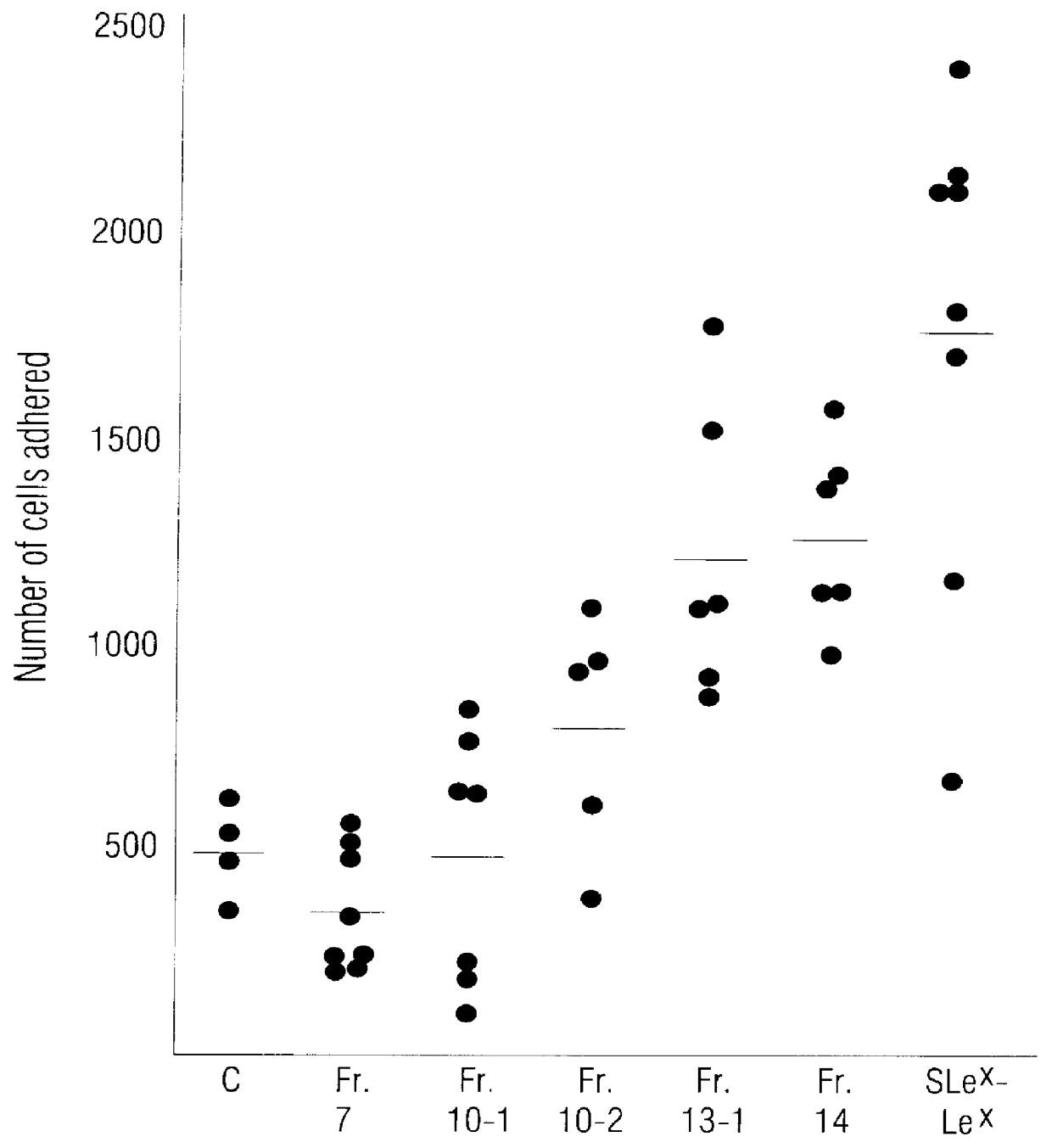
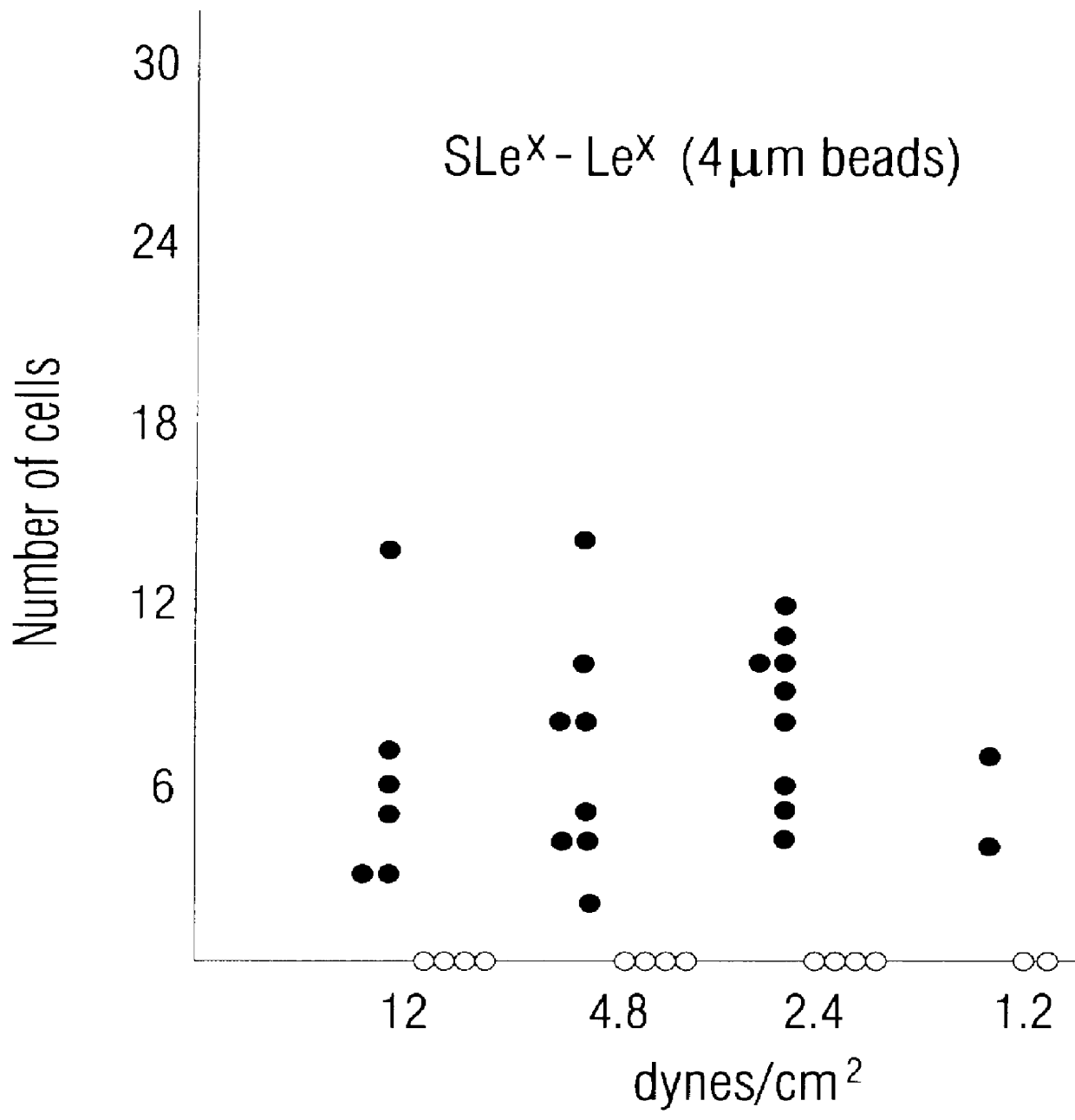
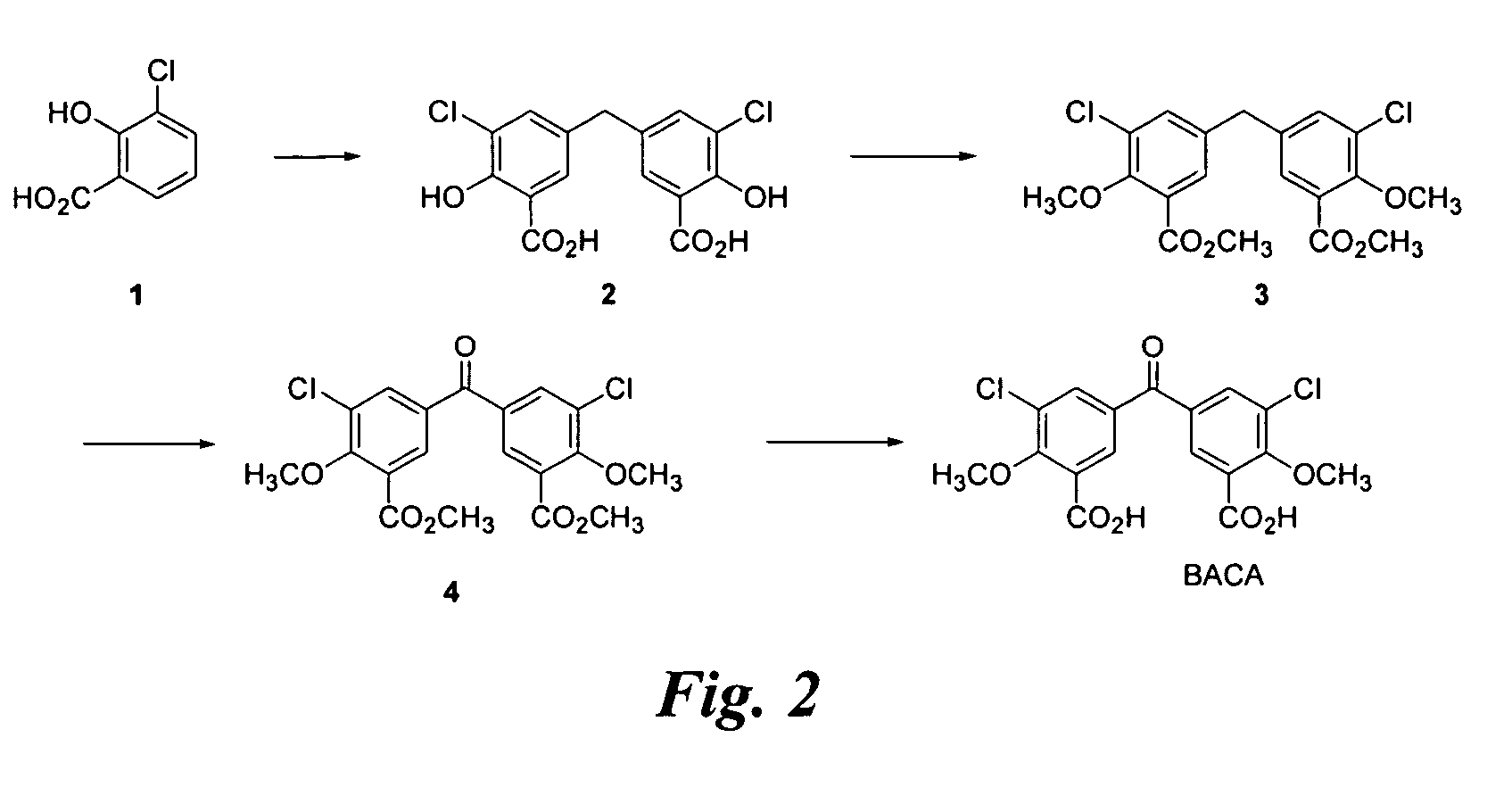
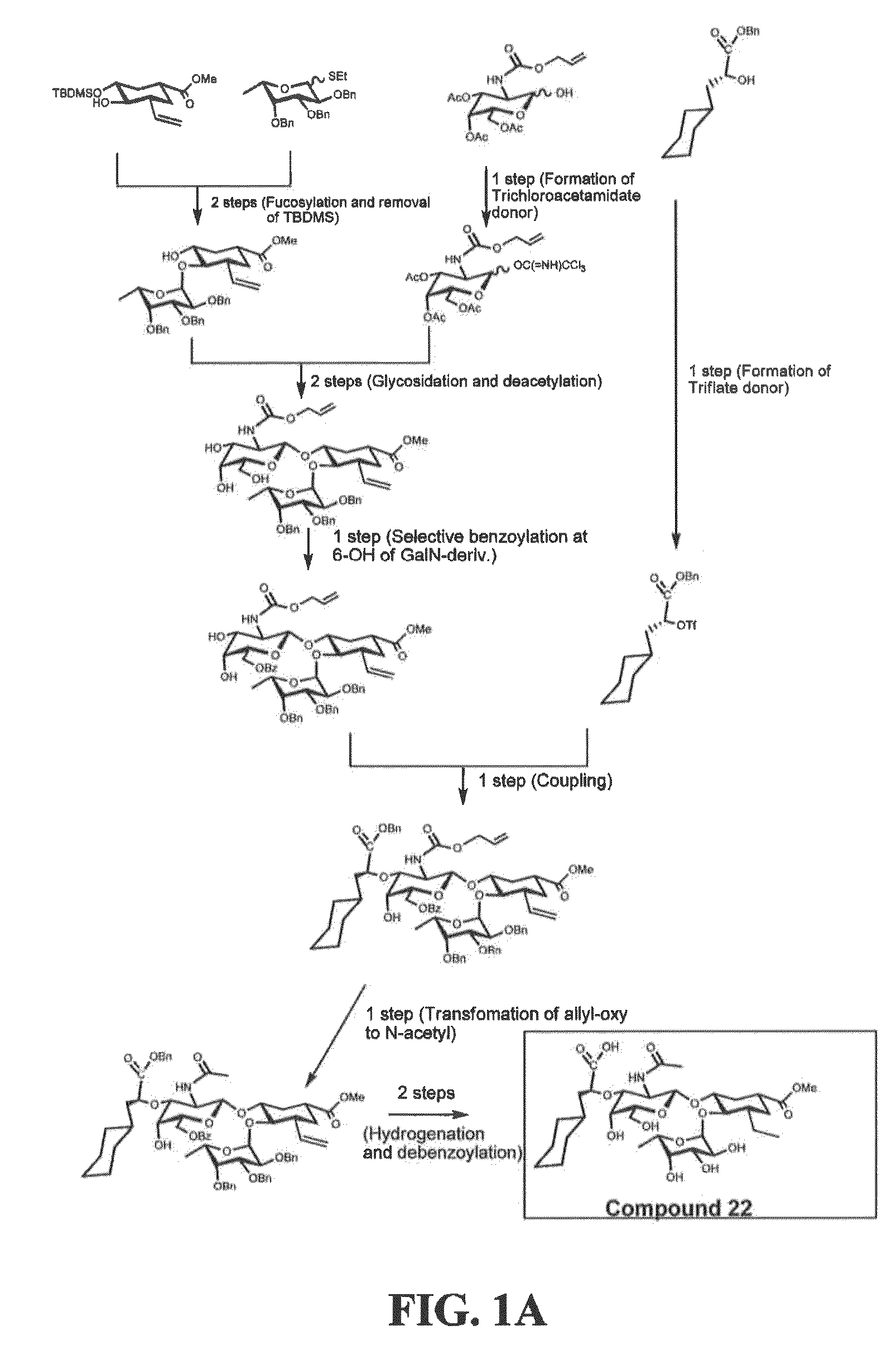
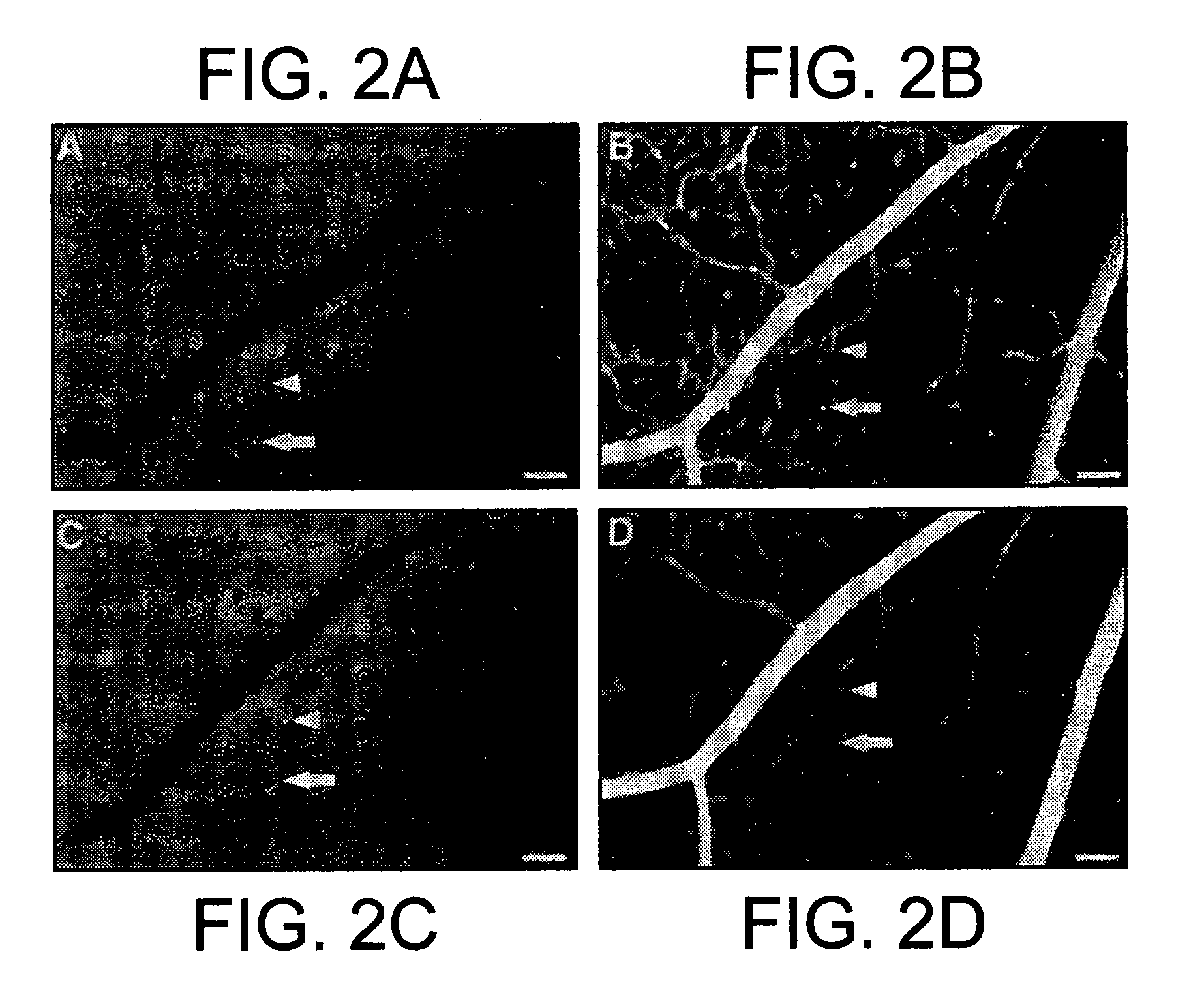
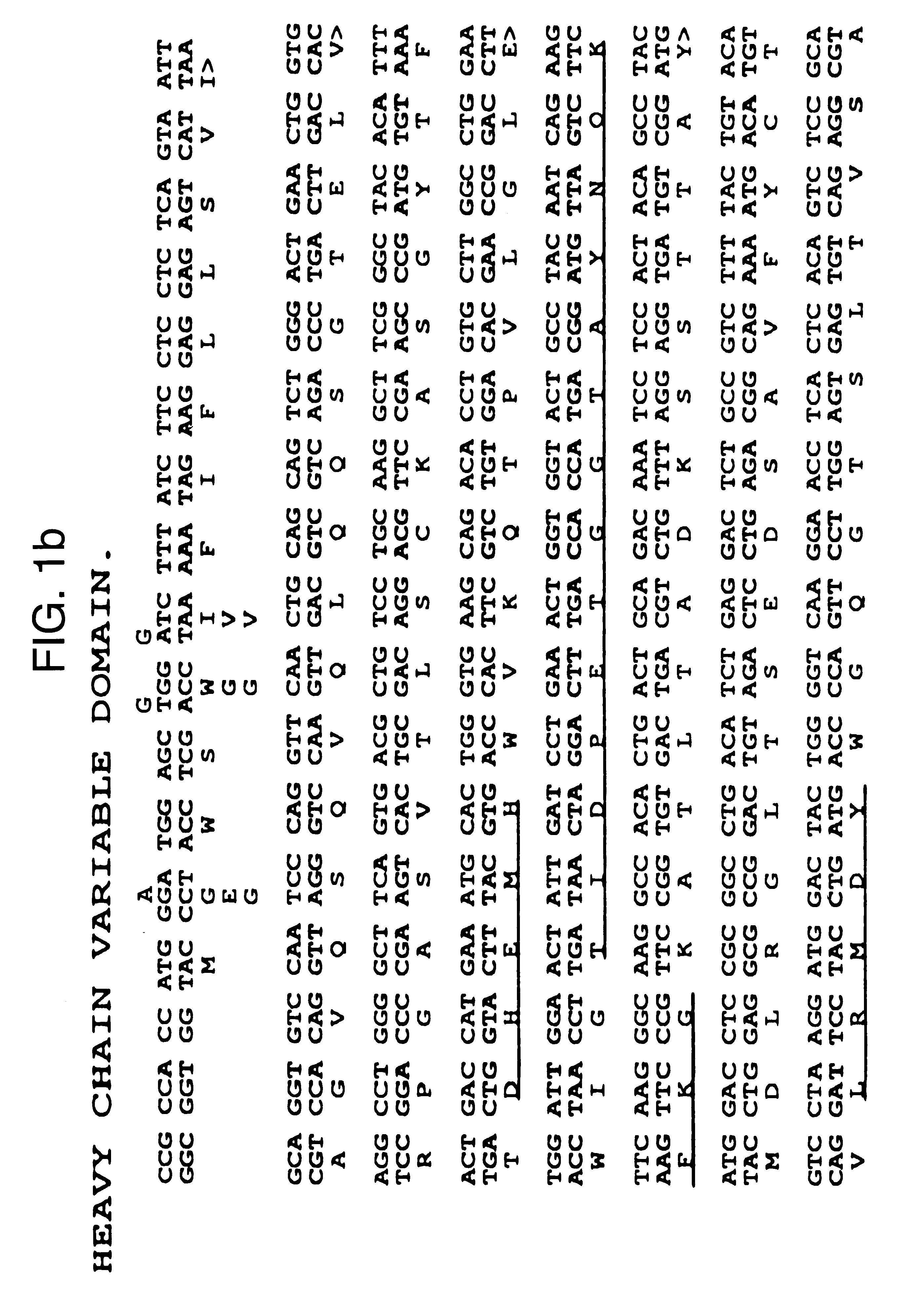
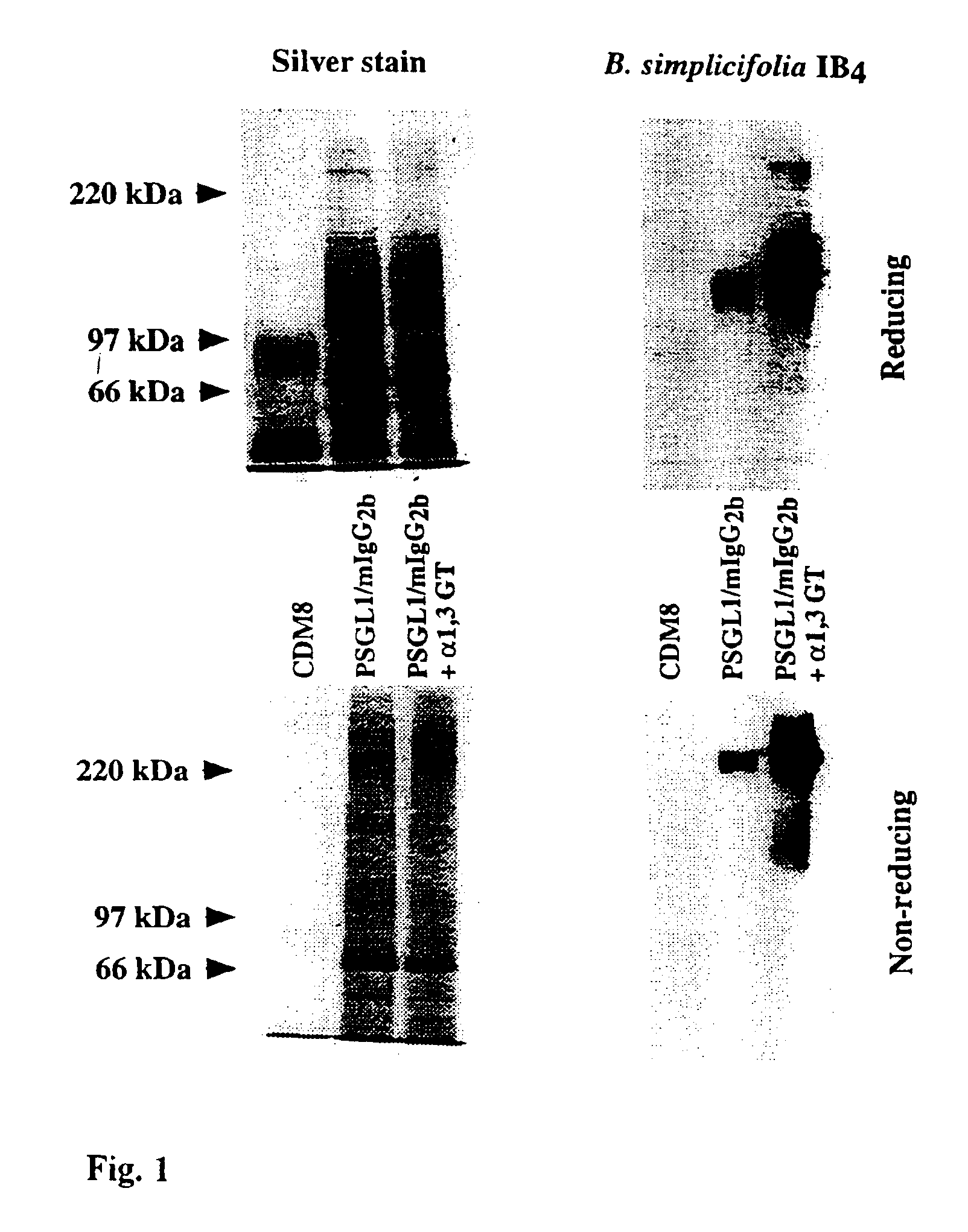
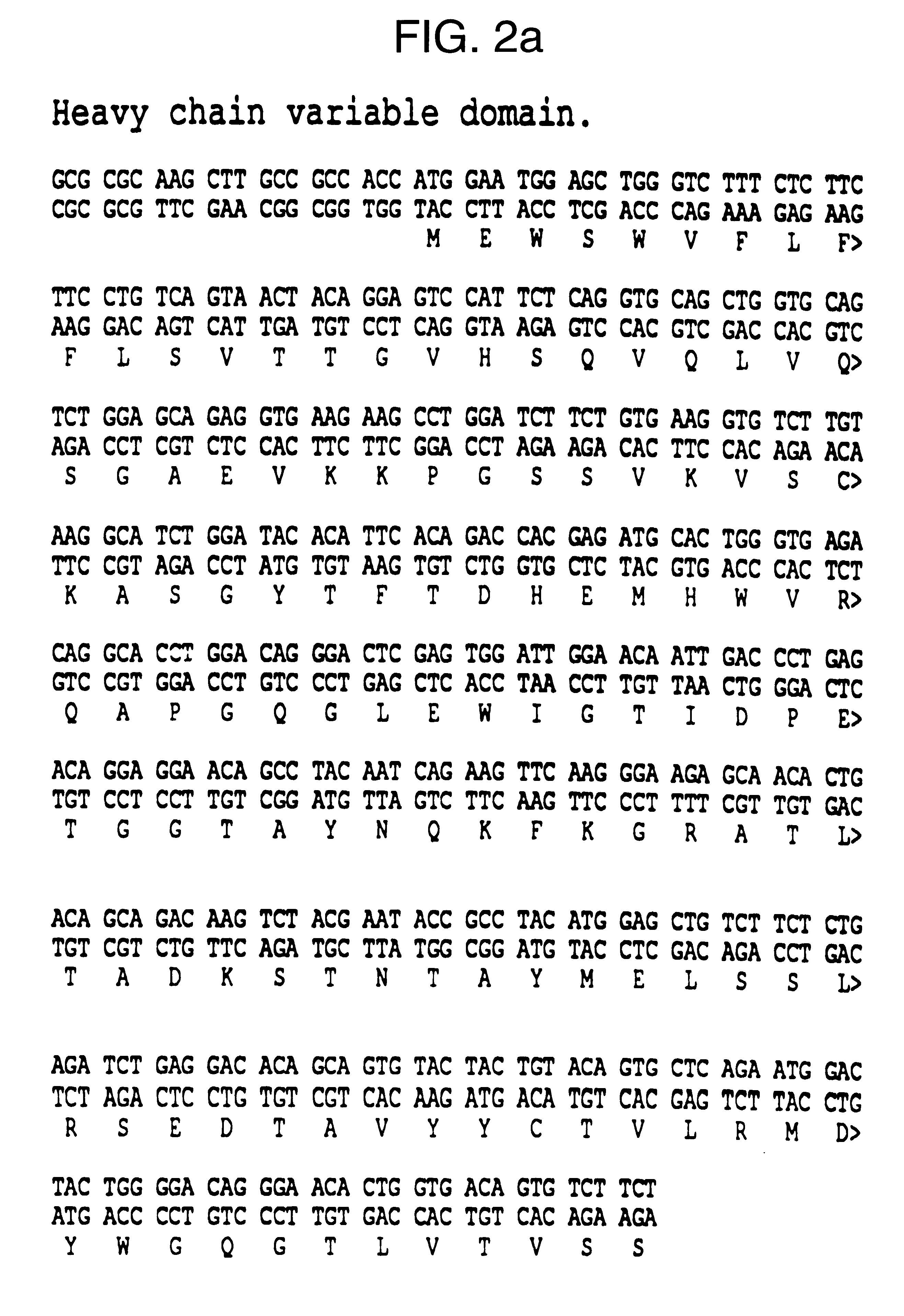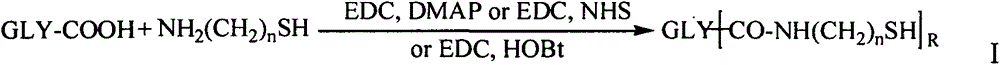Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
207 results about "Selectin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The selectins (cluster of differentiation 62 or CD62) are a family of cell adhesion molecules (or CAMs). All selectins are single-chain transmembrane glycoproteins that share similar properties to C-type lectins due to a related amino terminus and calcium-dependent binding. Selectins bind to sugar moieties and so are considered to be a type of lectin, cell adhesion proteins that bind sugar polymers.
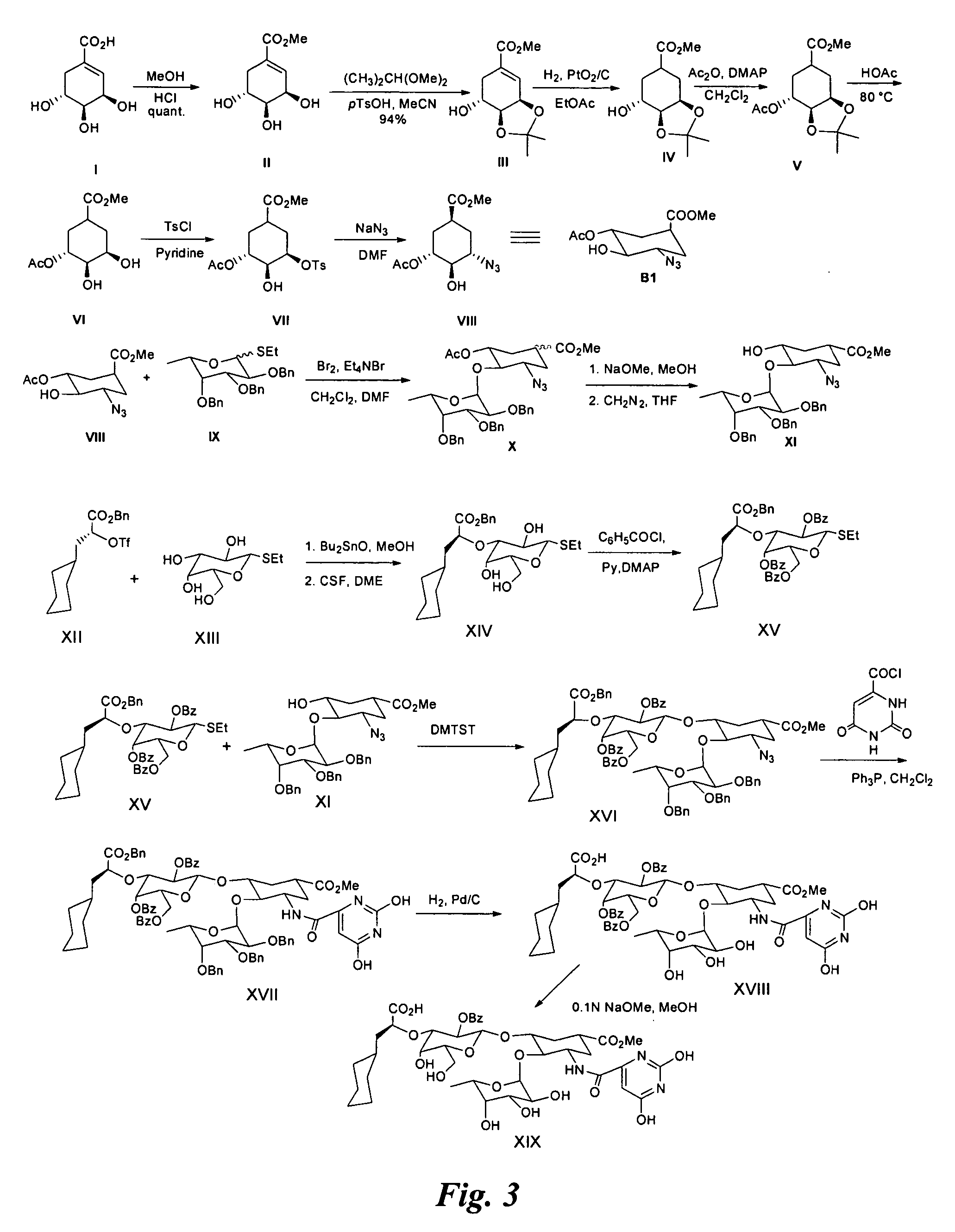
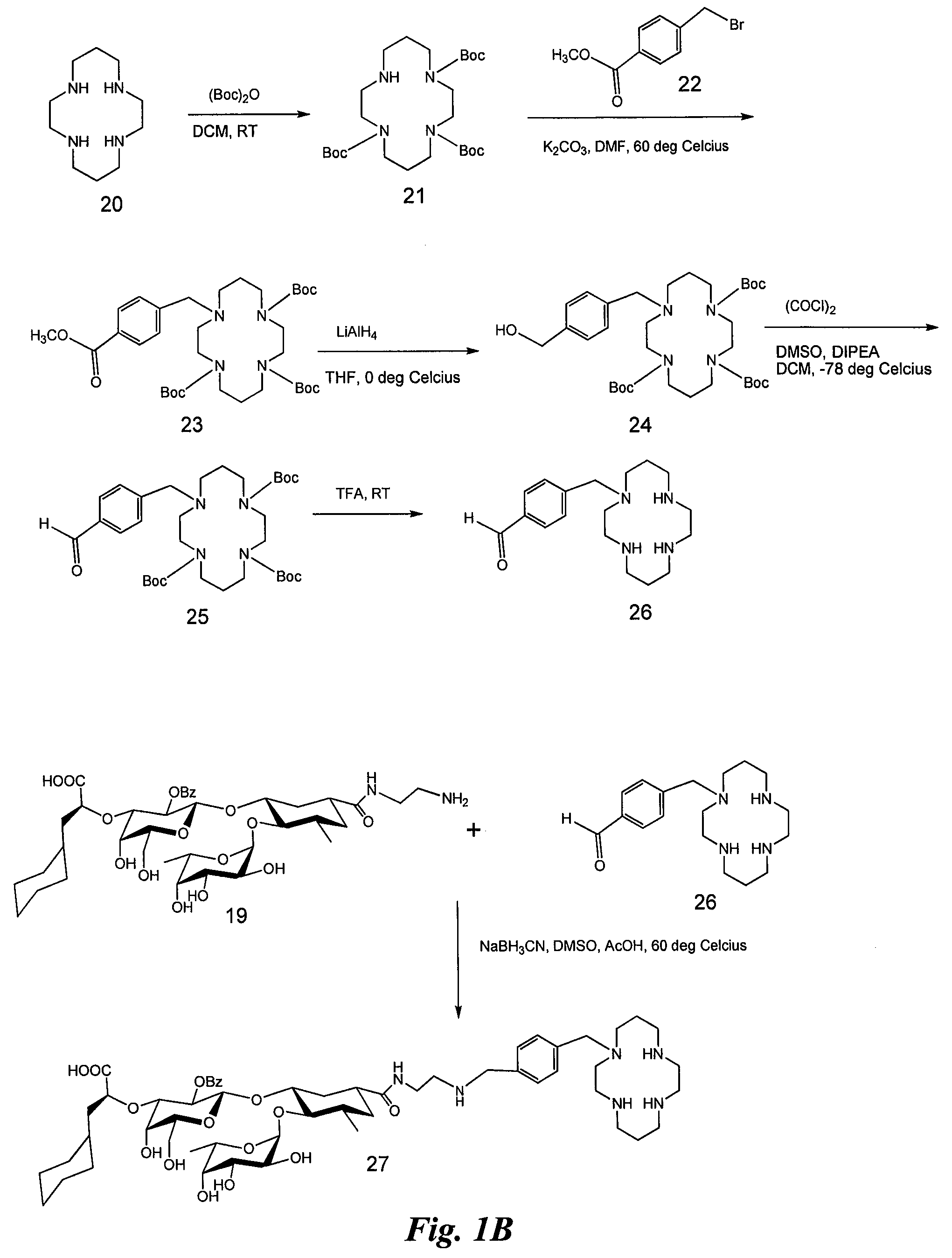
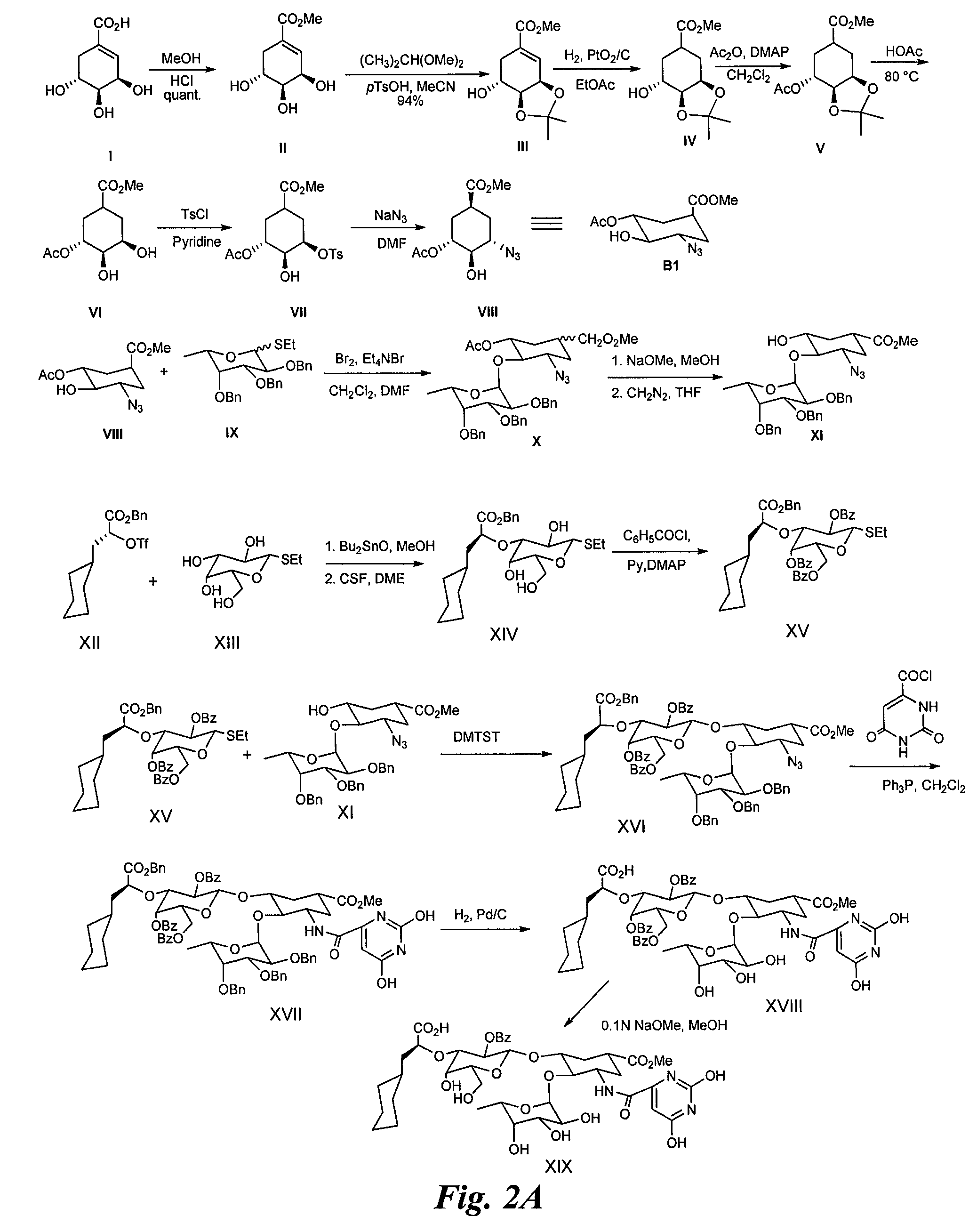
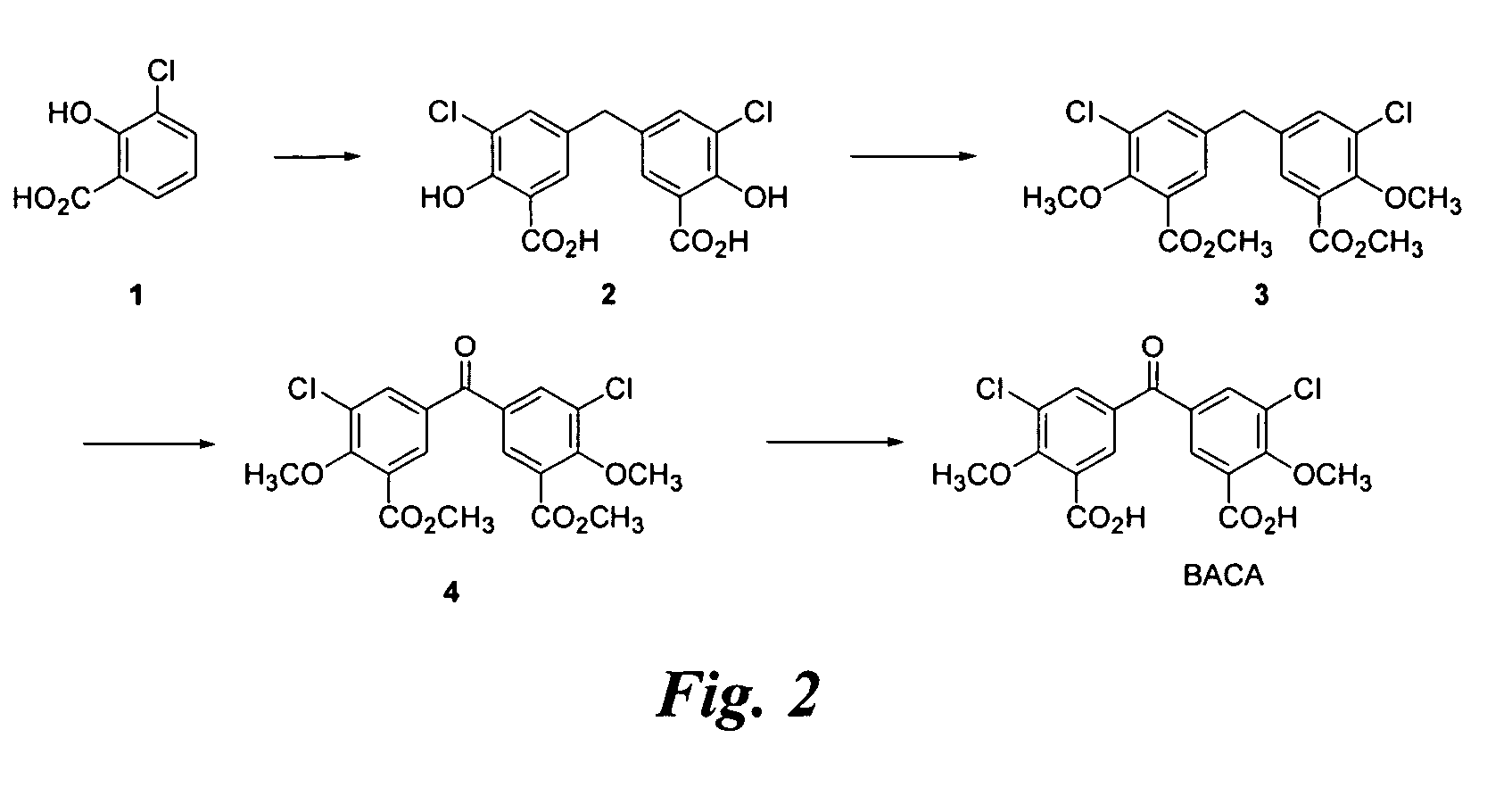
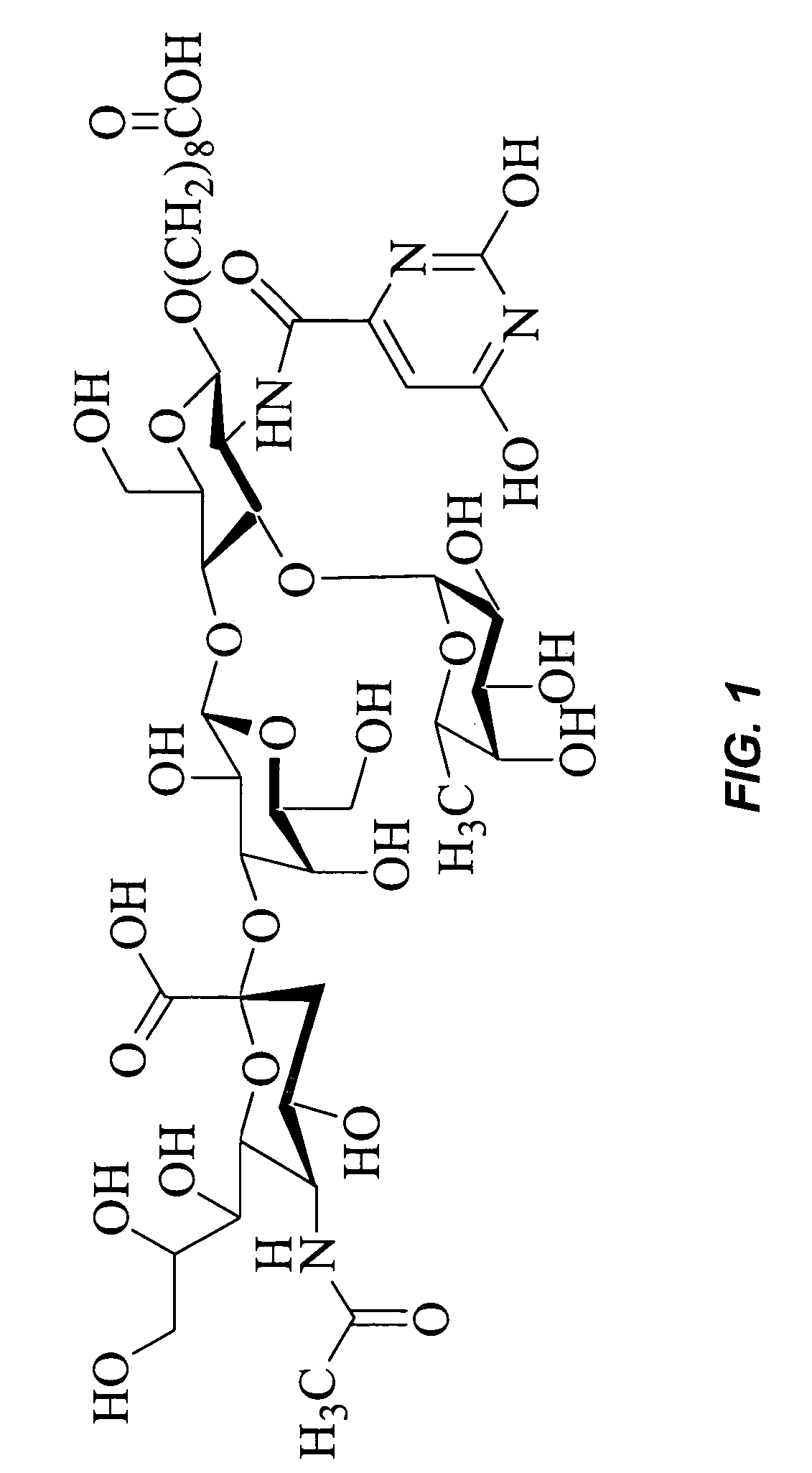
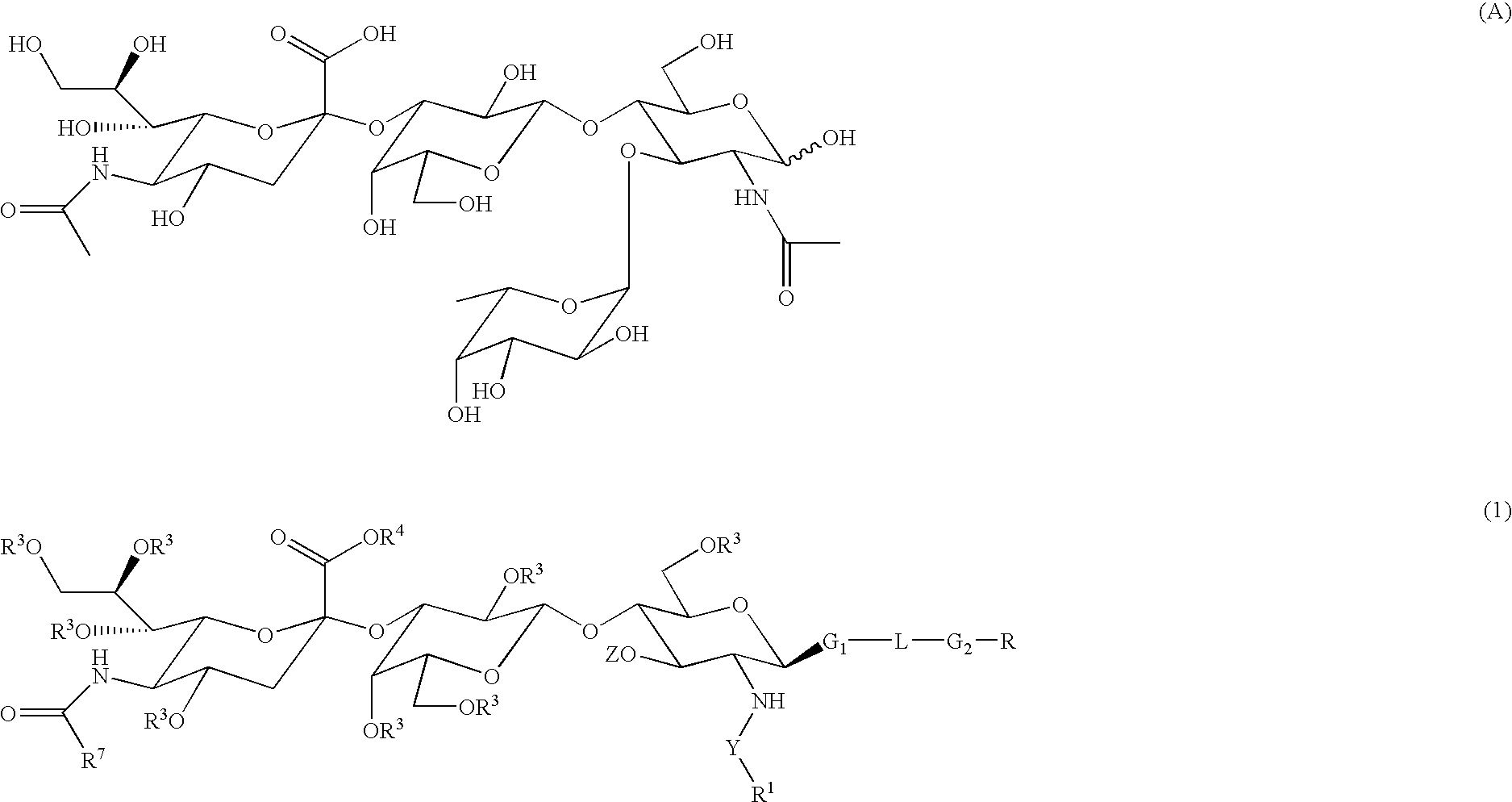
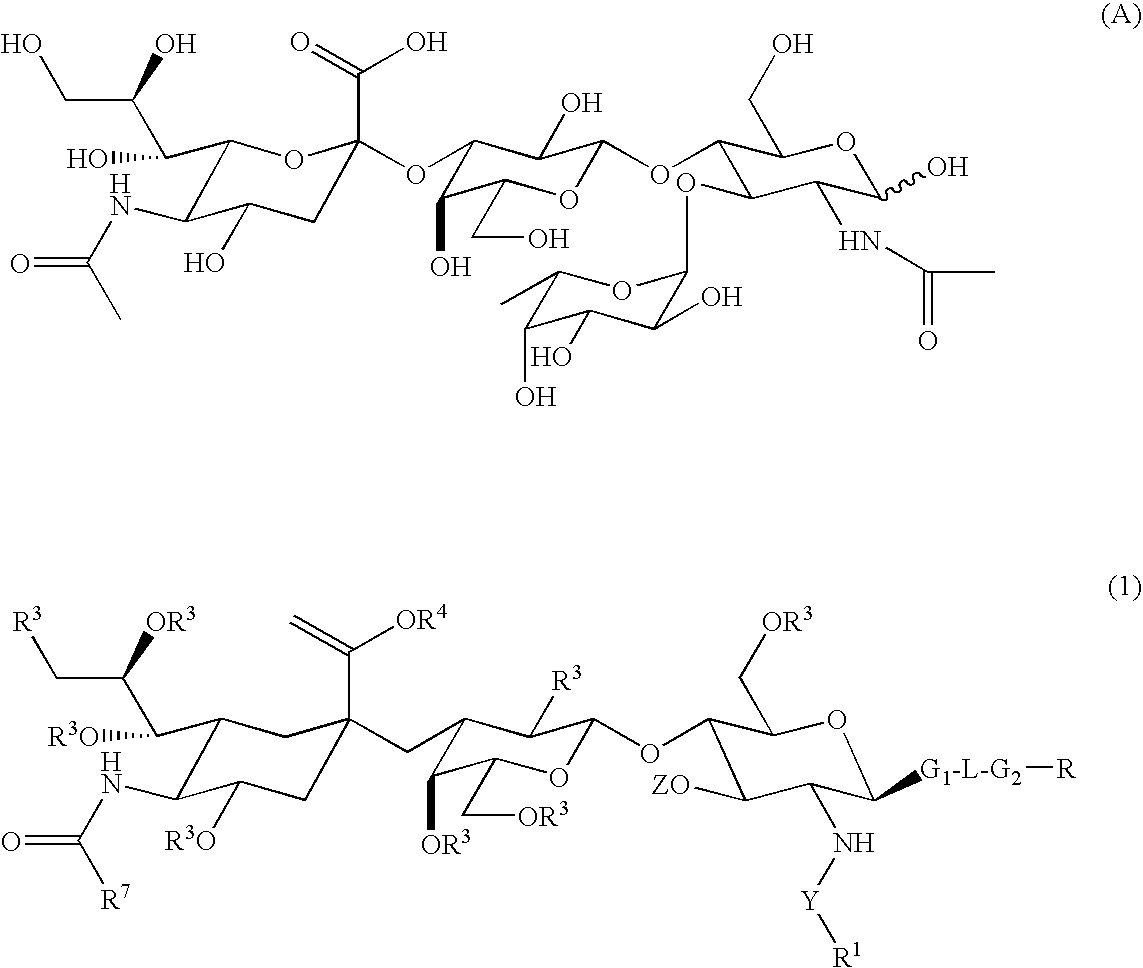
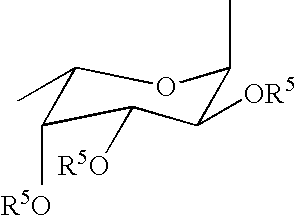
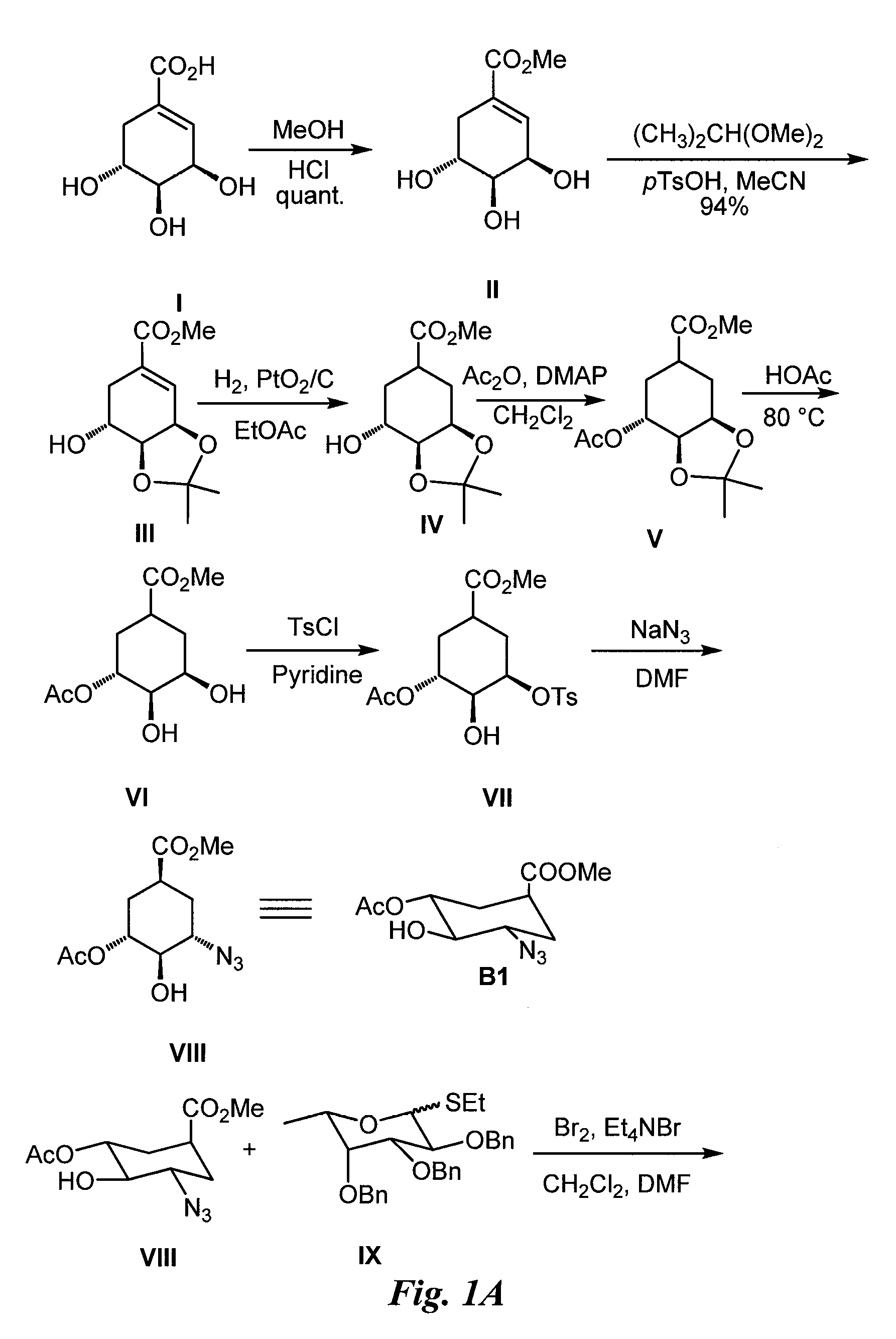
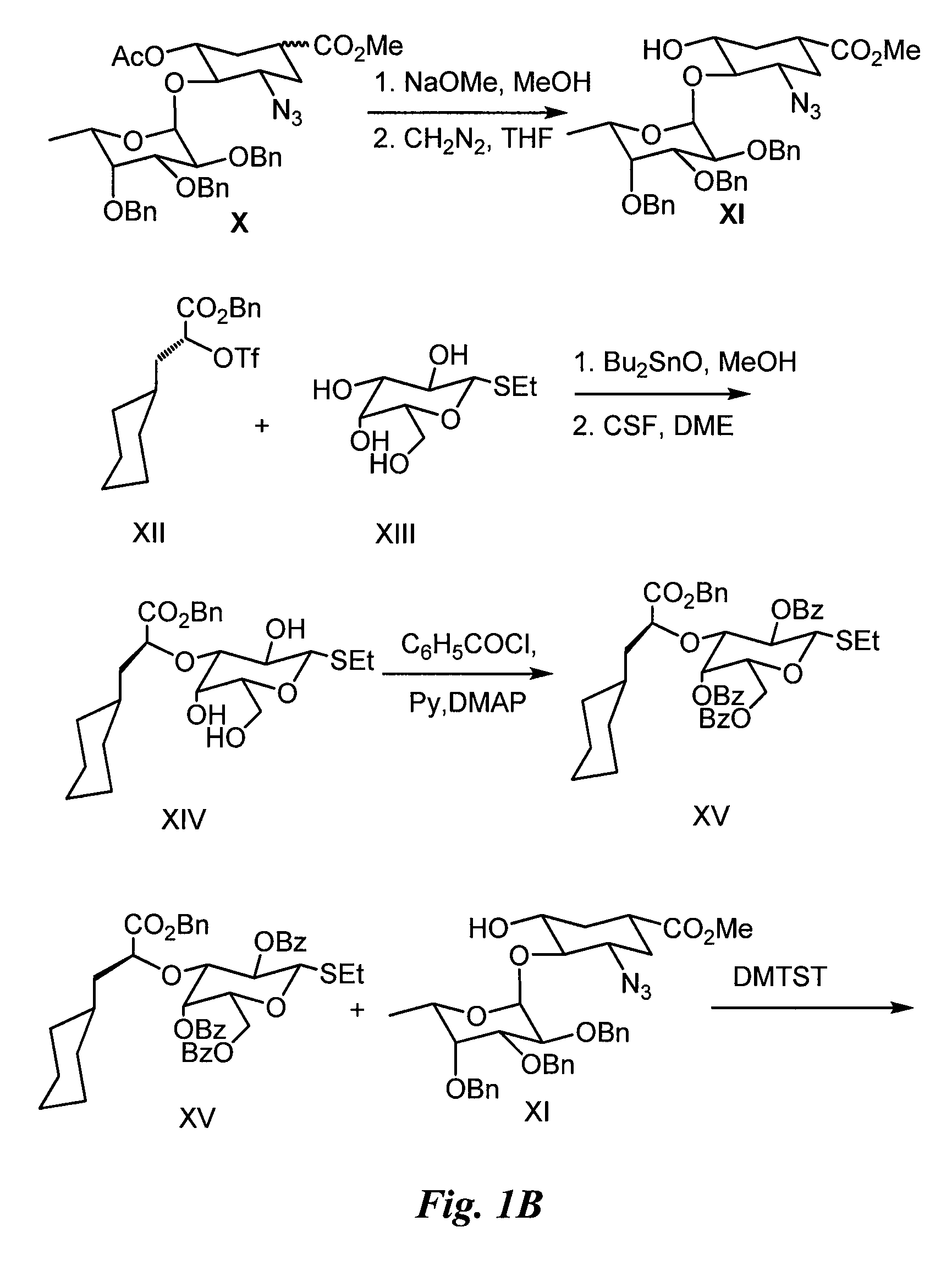
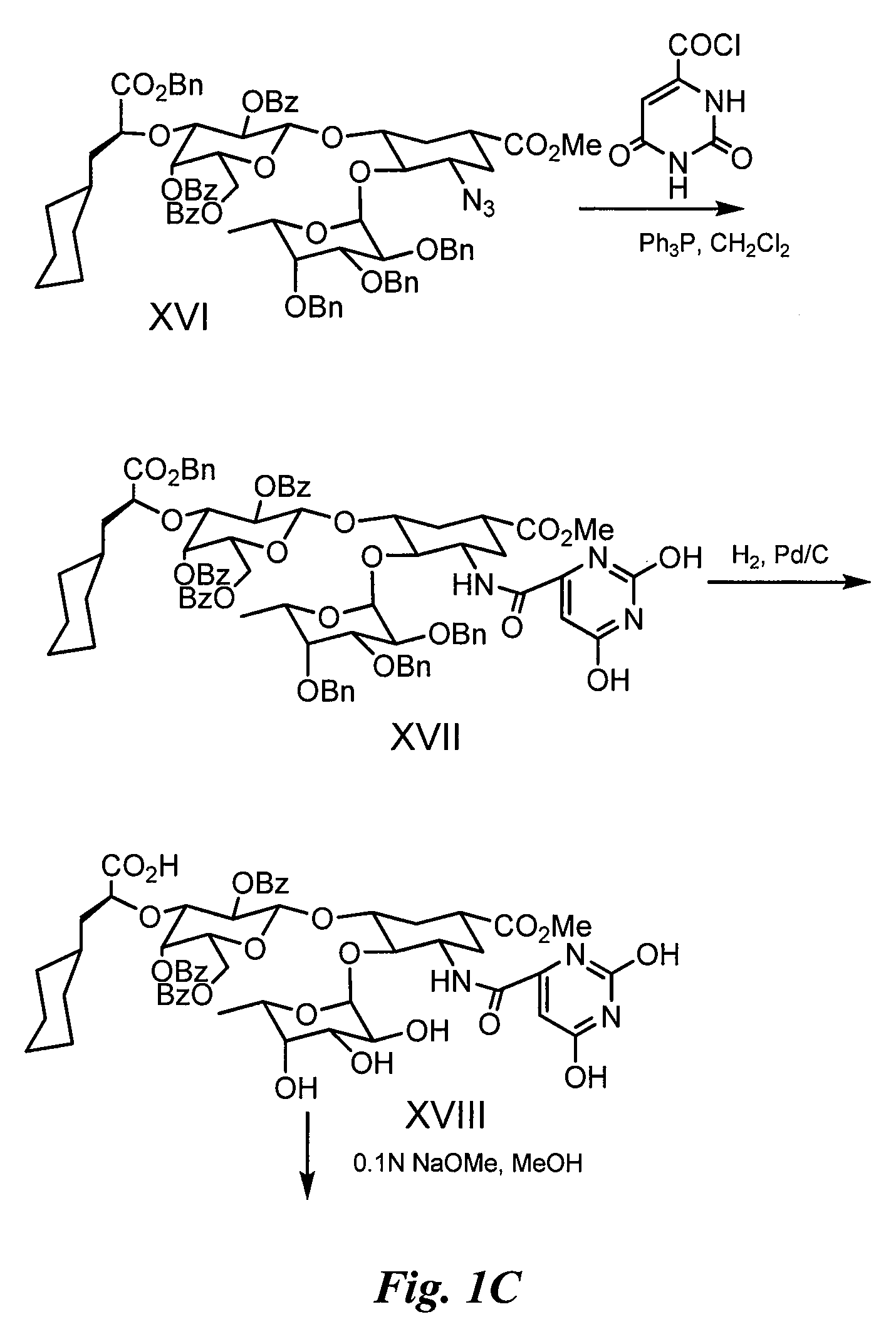
Compounds and methods for inhibiting selectin-mediated function
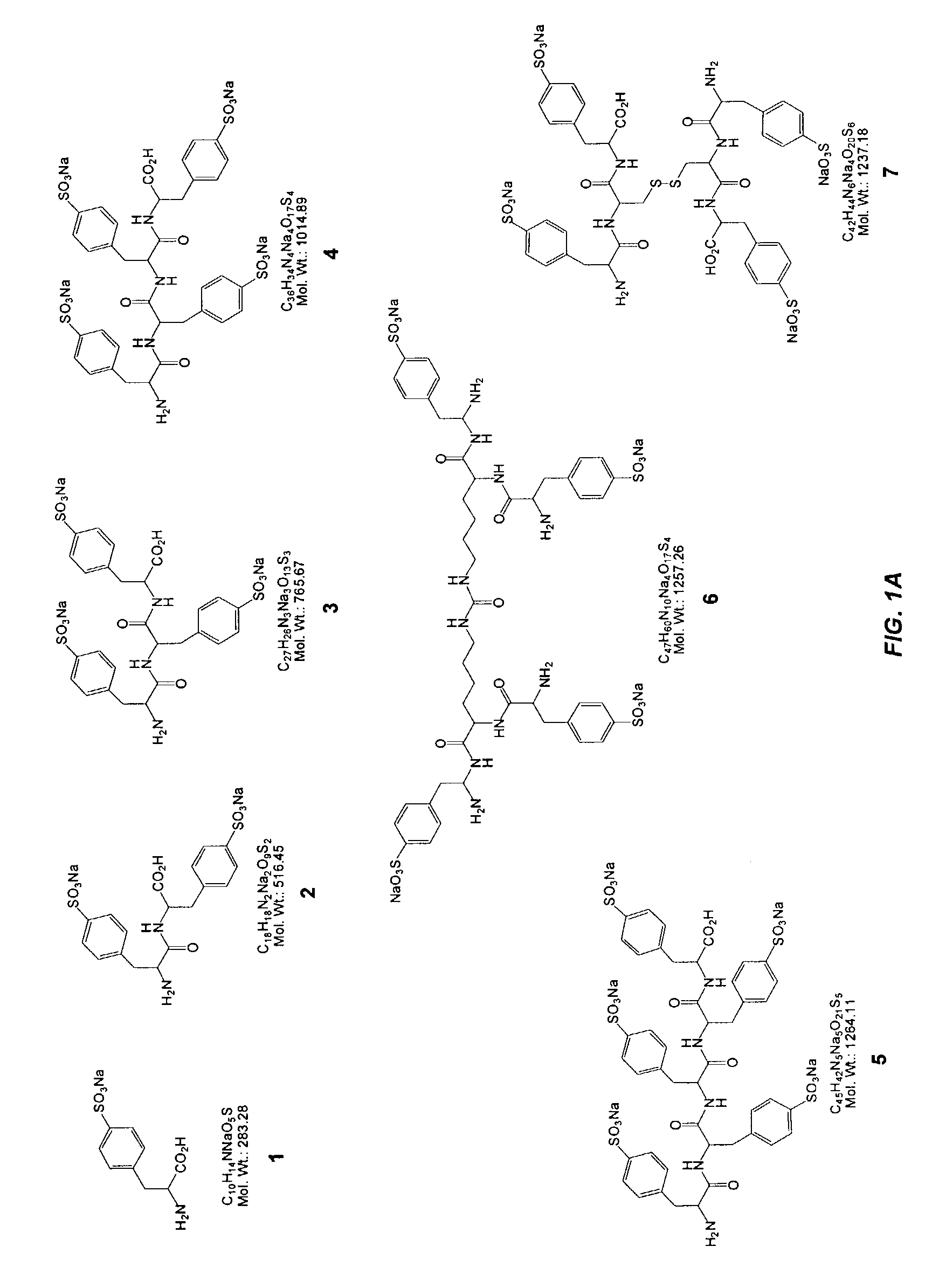
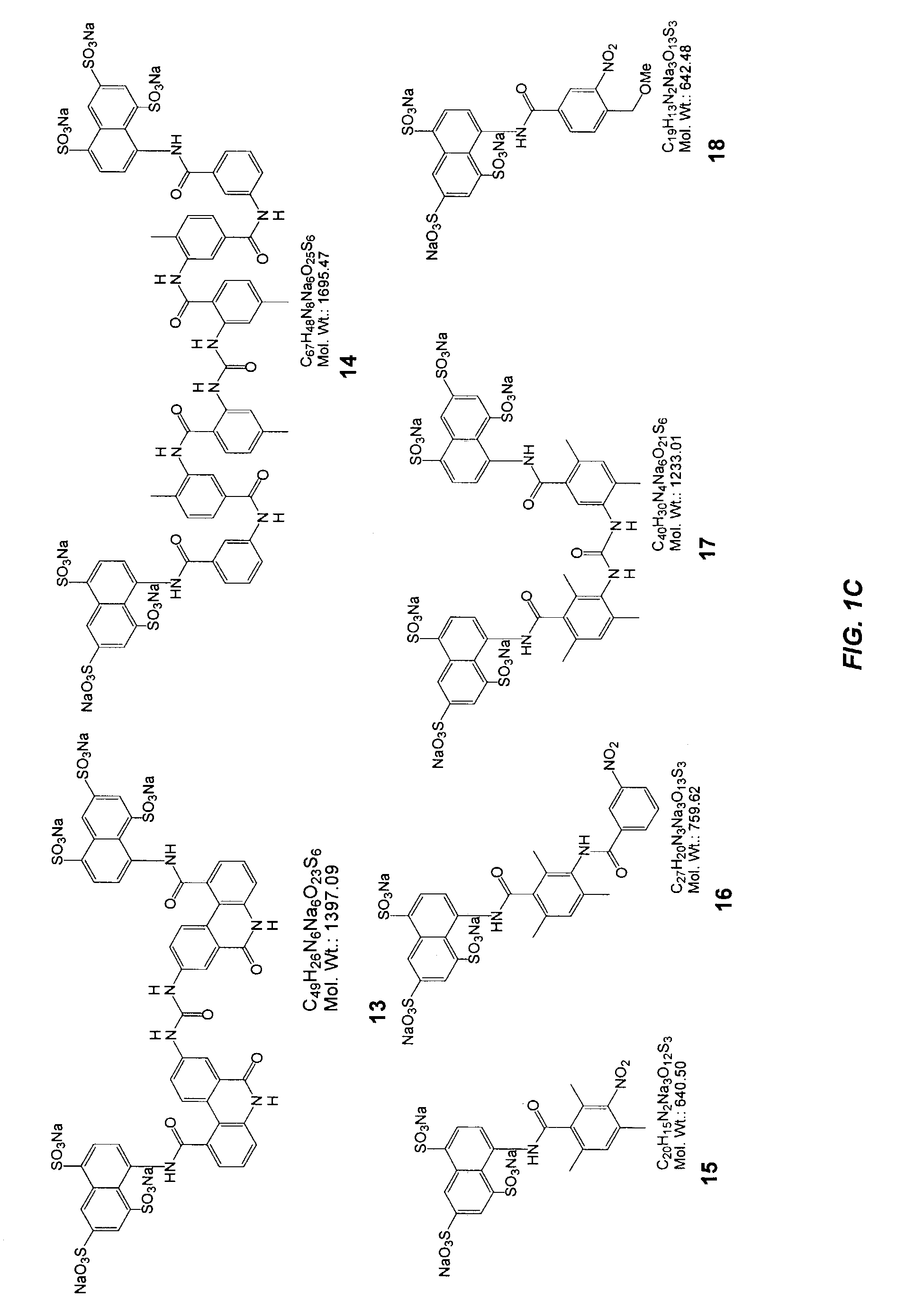
Compounds and methods are provided for modulating in vitro and in vivo processes mediated by selectin binding. More specifically, selectin modulators and their use are described, wherein the selectin modulators that modulate (e.g., inhibit or enhance) a selectin-mediated function comprise a class of compounds termed BASAs (Benzyl Amino Sulfonic Acids, which include a portion or analogue thereof) linked to a carbohydrate or glycomimetic.
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Methods for treating ischemic disorders using carbon monoxide
InactiveUS20050048133A1Avoid accumulationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGynecologySufficient time
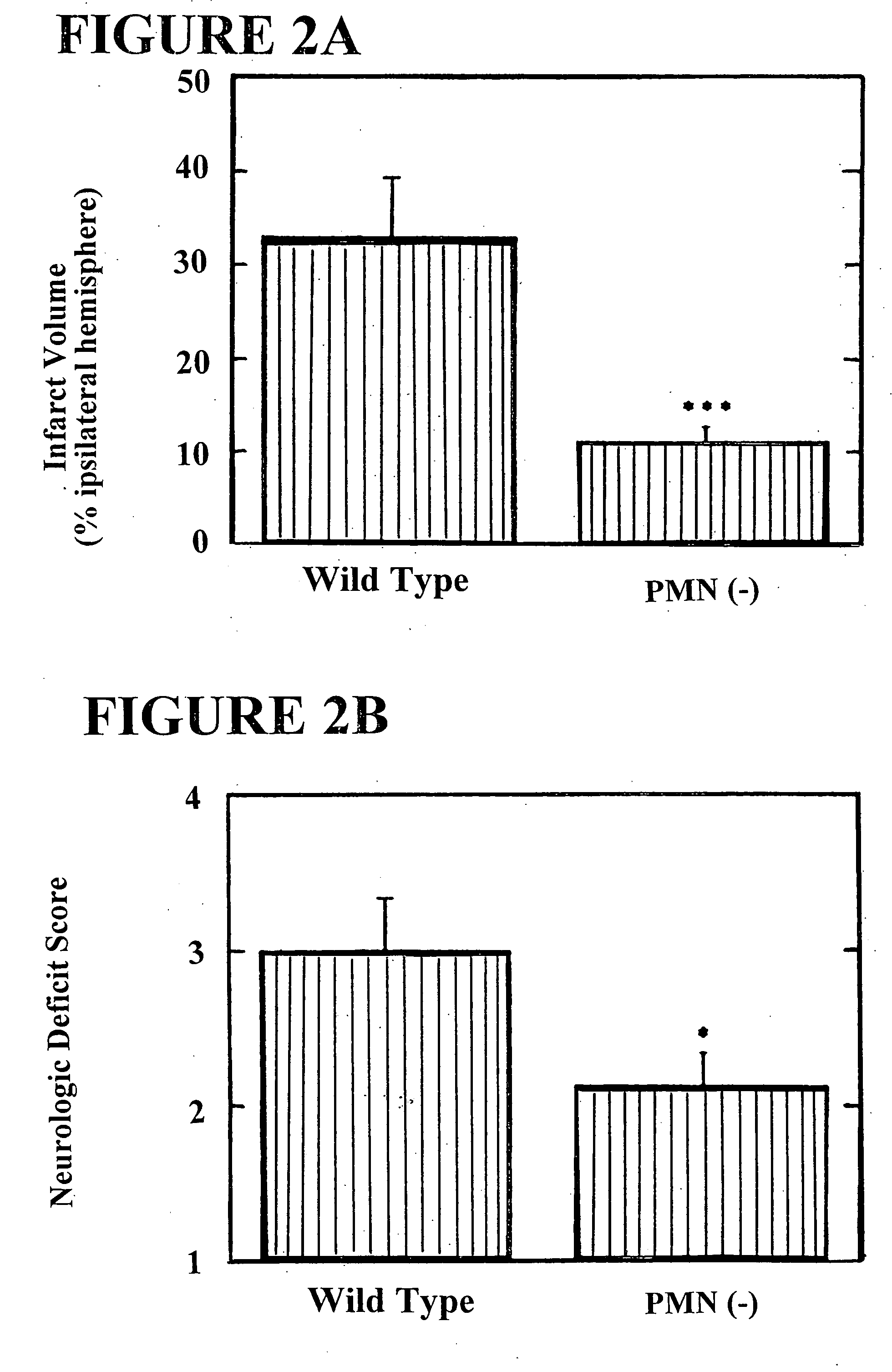
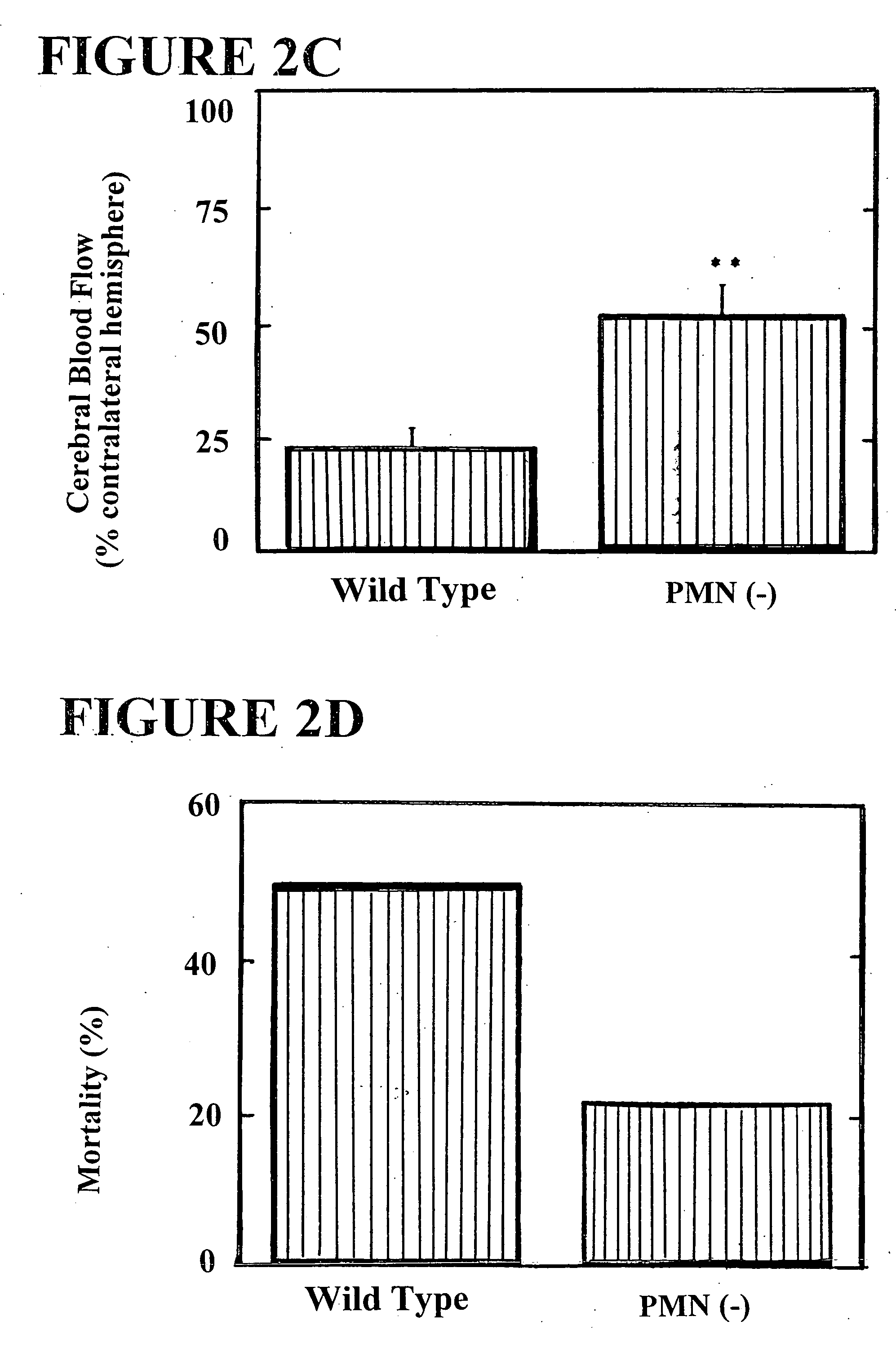
The present invention provides for a method for treating an ischemic disorder in a subject which comprises administering to the subject a pharmaceutically acceptable form of a selectin antagonist in a sufficient amount over a sufficient time period to prevent white blood cell accumulation so as to treat the ischemic disorder in the subject. The invention further provides a method for treating an ischemic disorder in a subject which comprises administering to the subject carbon monoxide gas in a sufficient amount over a sufficient period of time thereby treating the ischemic disorder in the subject. The invention further provides a method for treating an ischemic disorder in a subject which comprises administering to the subject a pharmaceutically acceptable form of inactivated Factor IX in a sufficient amount over a sufficient period of time to inhibit coagulation so as to treat the ischemic disorder in the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
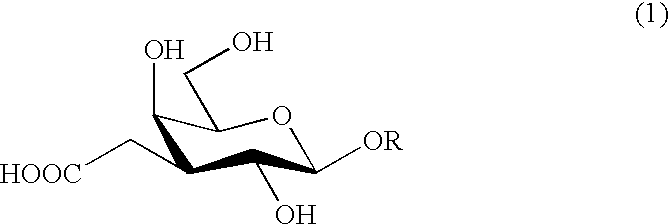
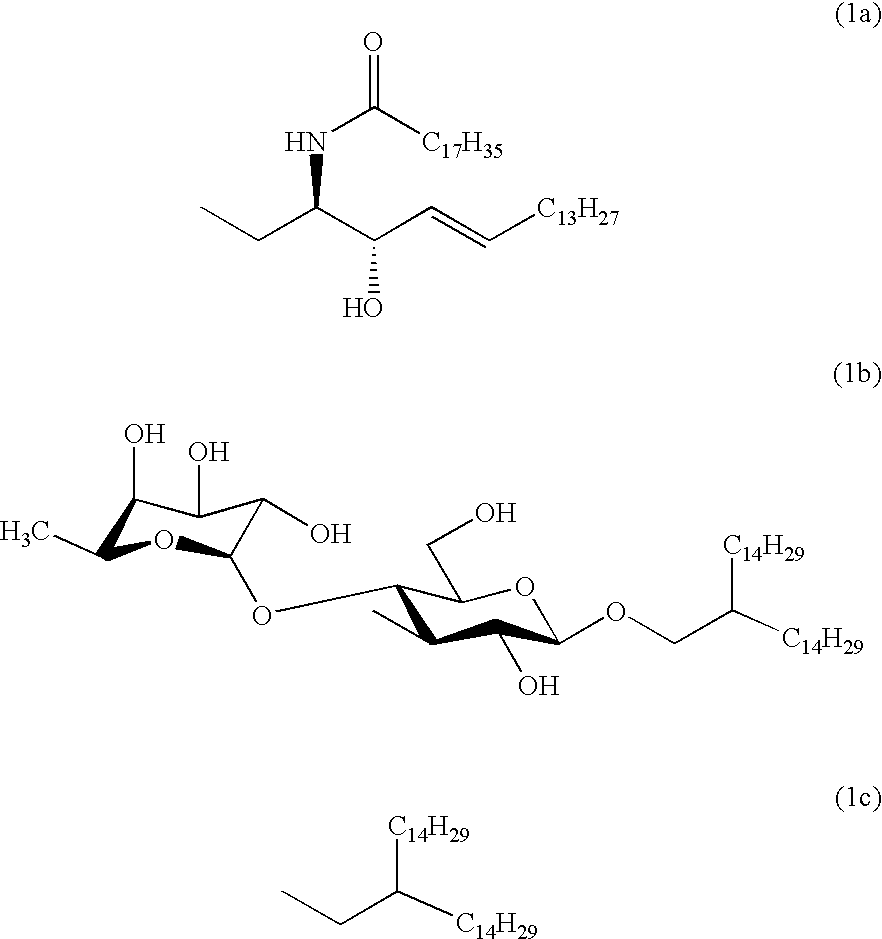
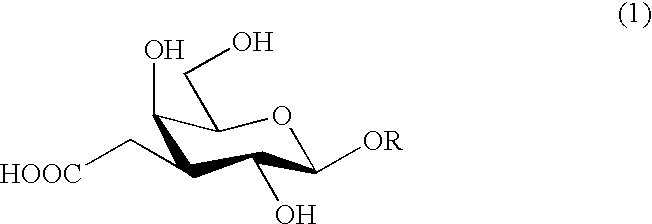
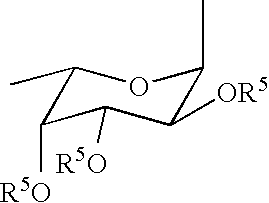
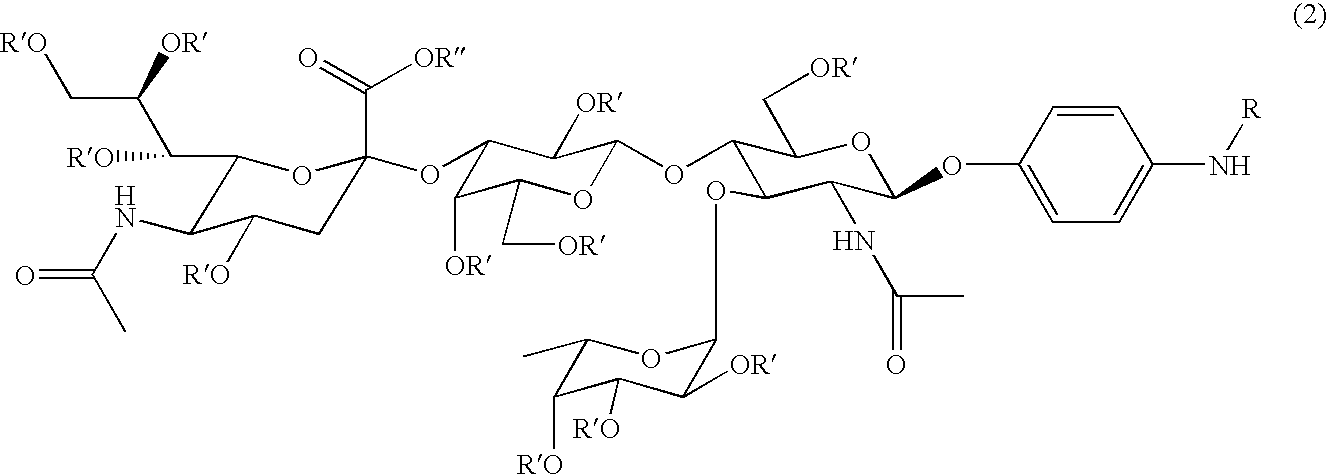
Carboxymethylgalactose derivatives
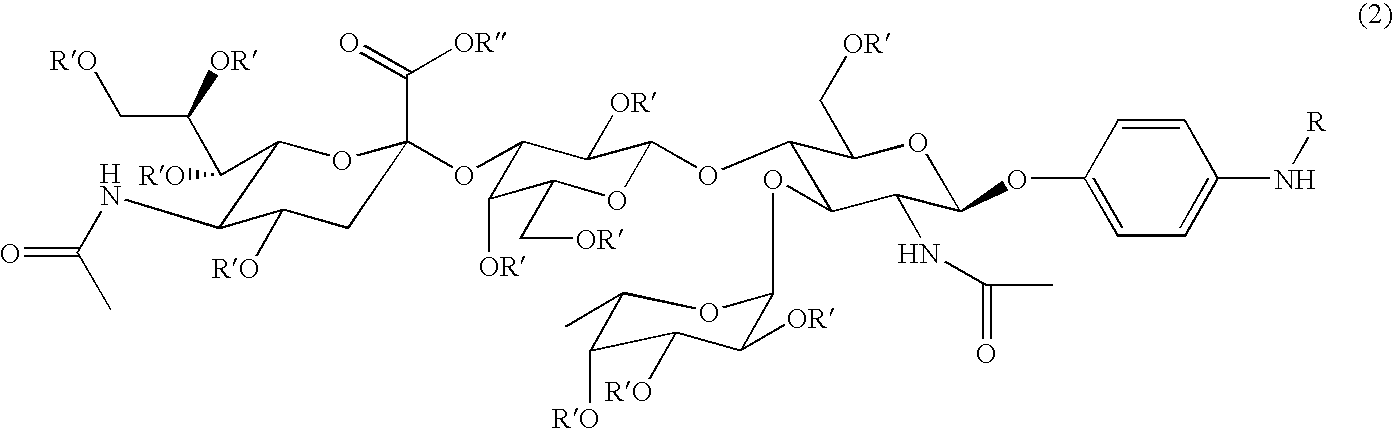
Carboxymethylgalactose derivatives represented by general formula (1);and salts thereof, which exhibit reactivity to selectins and are useful as inhibitors against selectin-related diseases such as various inflammations and cancerous metastasis; In said formula, R is a group rep resented by formula (1a), (1b) or (1c).
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Carbohydrate ligands (myelorollin) that cause E-selectin dependent cell rolling and adhesion under dynamic flow system
InactiveUS6133239AStrong rollingInhibit the inflammatory responseBiocideAntipyreticE-selectinFucosylation
An unbranched polylactosamine comprising at least 6 monosaccharides and having terminal alpha 2->3 sialylation and internal alpha 1->3 fucosylation at various N-acetylglucosamine residues except for solely at the penultimate N-acetylglucosamine residue.
Owner:BIOMEMBRANE INST +1
Heterobifunctional pan-selectin inhibitors
ActiveUS20070054870A1Avoid stickingAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsGlycomimeticSelectin
Compounds and methods are provided for modulating in vitro and in vivo processes mediated by selectin binding. More specifically, selectin modulators and their use are described, wherein the selectin modulators that modulate (e.g., inhibit or enhance) a selectin-mediated function comprise particular glycomimetics alone or linked to a member of a class of compounds termed BASAs (Benzyl Amino Sulfonic Acids) or a member of a class of compounds termed BACAs (Benzyl Amino Carboxylic Acids).
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Heterobifunctional inhibitors of E-selectins and CXCR4 chemokine receptors
Compounds, compositions and methods are provided for treating cancer and inflammatory diseases, and for releasing cells such as stem cells (e.g., bone marrow progenitor cells) into circulating blood and enhancing retention of the cells in the blood. More specifically, heterobifunctional compounds that inhibit both E-selectins and CXCR4 chemokine receptors are described.
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Lectin conjugates
InactiveUS20060251580A1Easy diagnosisLow toxic loadNanomedicineNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSelectinLanthanide
A conjugate includes at least one target-seeking unit, which specifically binds to receptors on the surface of endothelial cells, and at least one effector unit which is coupled to the unit by a linker. The effector unit exhibits at least one signal unit and optionally at least one therapeutic active substance. The target-seeking unit includes a lectin or a fragment or derivative thereof, wherein the lectin is not L-selectin and the signal unit includes a lanthanide ion.
Owner:FAUSTUS FORSCHUNGS CIE TRANSLATIONAL CANCER RES
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS20110201038A1Easy to adaptMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInterleukin 10Soluble P-Selectin
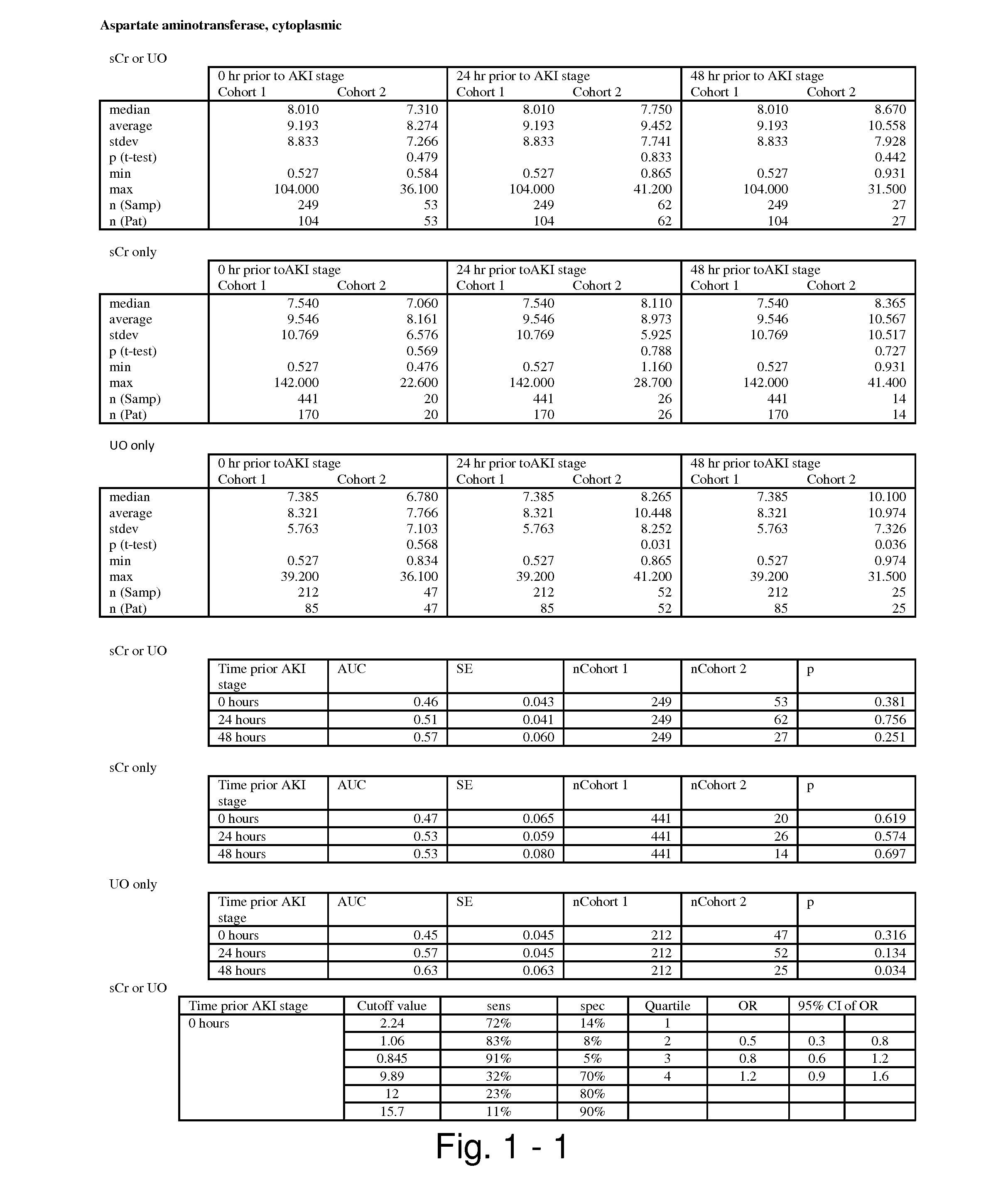
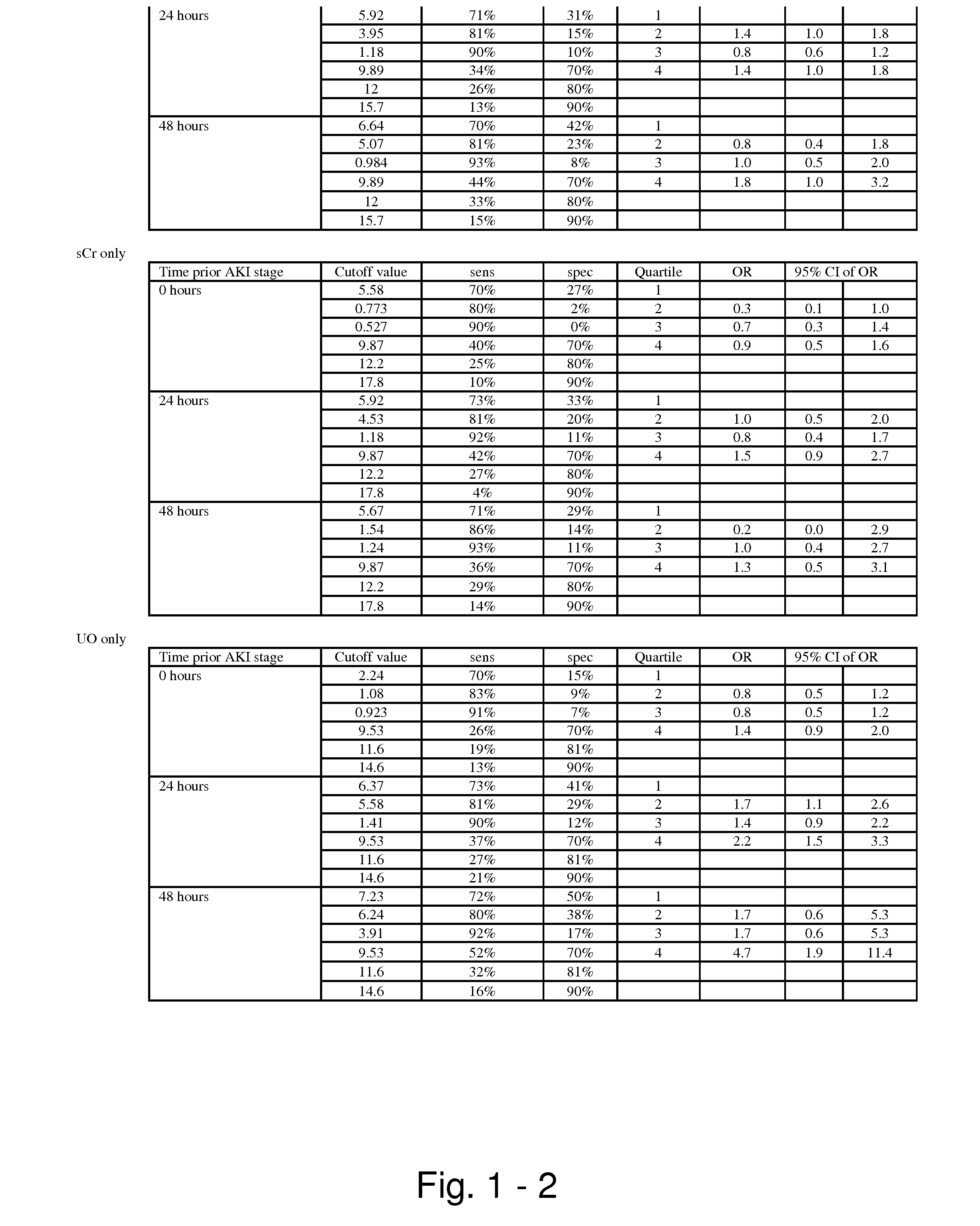
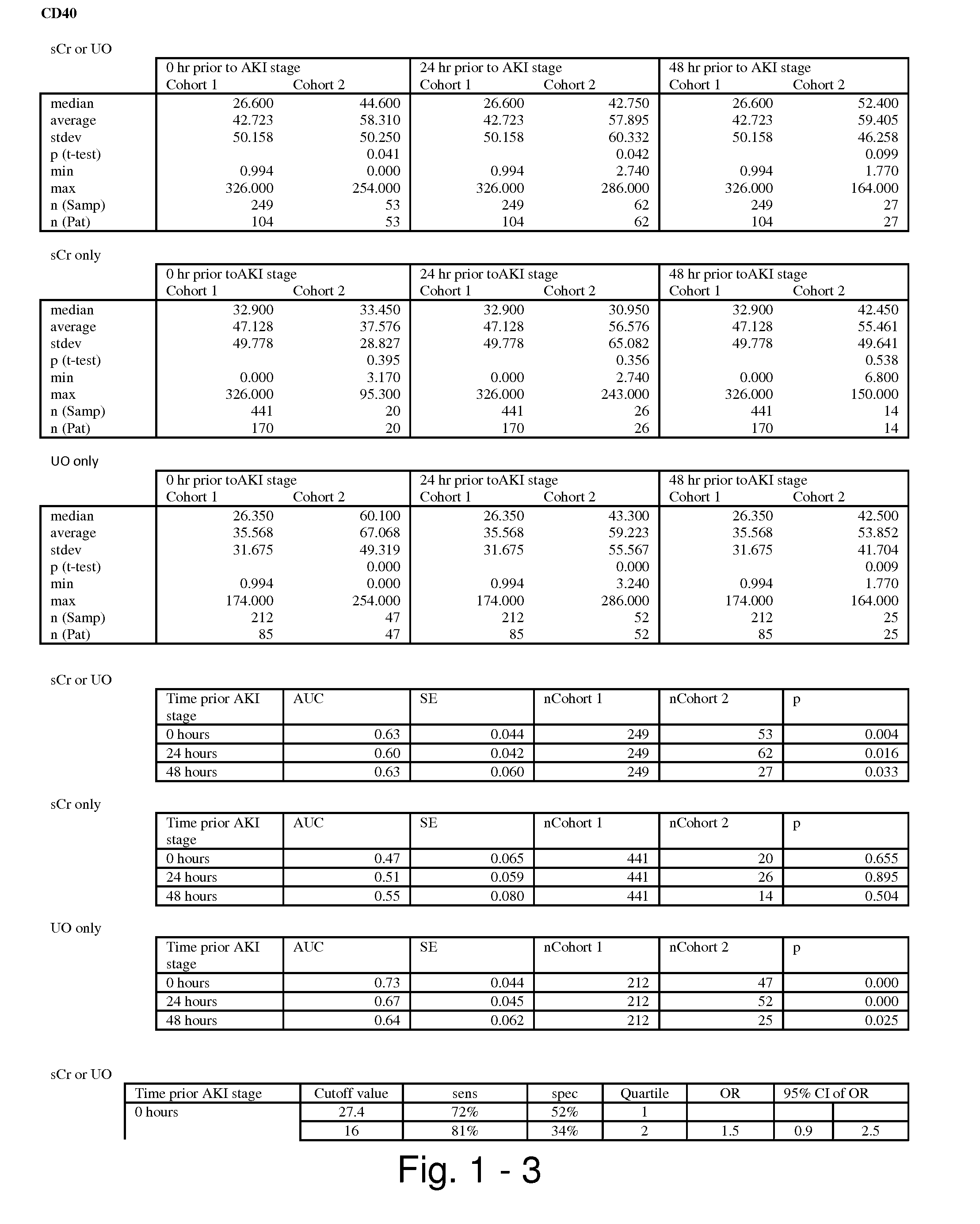
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more markers selected from the group consisting of Cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase, soluble Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5, soluble CD40 Ligand, soluble C-X-C Motif chemokine 16, S100-A12, Eotaxin, soluble E-selectin, Fibronectin, Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, Heparin-binding growth factor 2, soluble Hepatocyte growth factor receptor, Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, Interleukin-1 beta, Interleukin-10, Interleukin-15, Interleukin-3, Myeloperoxidase, Nidogen-1, soluble Oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1, Pappalysin-1, soluble P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1, Antileukoproteinase, soluble Kit ligand, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2, soluble Tumor necrosis factor, soluble Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, and Vascular endothelial growth factor A as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
E-selectin antagonist compounds, compositions, and methods of use
ActiveUS9109002B2Enhancing hematopoietic stem cell survivalReduce the likelihood of occurrenceEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsAptamerDisease
Methods and compositions using E-selectin antagonists are provided for the treatment and prevention of diseases and disorders treatable by inhibiting binding of E-selectin to an E-selectin ligand. Described herein are E-selectin antagonists including, for example, glycomimetic compounds, antibodies, aptamers and peptides that are useful in methods for treatment of cancers, and treatment and prevention of metastasis, inhibiting infiltration of the cancer cells into bone marrow, reducing or inhibiting adhesion of the cancer cells to endothelial cells including cells in bone marrow, and inhibiting thrombus formation.
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Prevention and treatment of retinal ischemia and edema
InactiveUS20080019977A1Inhibit bindingAvoid interactionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCell adhesionOphthalmology
The present invention relates to methods of treating retinopathy, retinal ischemia and / or retinal edema comprising administering an integrin or integrin subunit antagonist, leukocyte adhesion-inducing cytokine antagonist or growth factor antagonist, a selectin antagonist or adhesion molecule antagonist.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Antibodies against E-selectin
InactiveUS6204007B1Avoid consumptionAlteration of antibody side chain interactionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticNatural antibodyFc(alpha) receptor
This invention relates to whole antibodies of neutral isotype having specificity for E-selectin, process for their preparation (using vectors), pharmaceutical compositions containing them, and their use in therapy and diagnosis. Said antibodies are variants of natural antibodies altered in the Fc region, especially in the CH2 domain, so that the interactions with antibodies Fc receptors and complement are very low.
Owner:CELLTECH R & D LTD
Glycomimetic antagonists for both E-and P-selectins
Compounds and methods are provided for modulating in vitro and in vivo processes mediated by selectin binding. More specifically, selectin modulators and their use are described, wherein the selectin modulators that modulate (e.g., inhibit or enhance) a selectin-mediated function comprise particular glycomimetics linked to a member of a class of compounds termed BASAs (Benzyl Amino Sulfonic Acids).
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Antigenic fusionprotein carrying Galalpha1,3Gal epitopes
InactiveUS6943239B2Effective absorptionEasy and cheap to produceOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeImmunoglobulin IgE
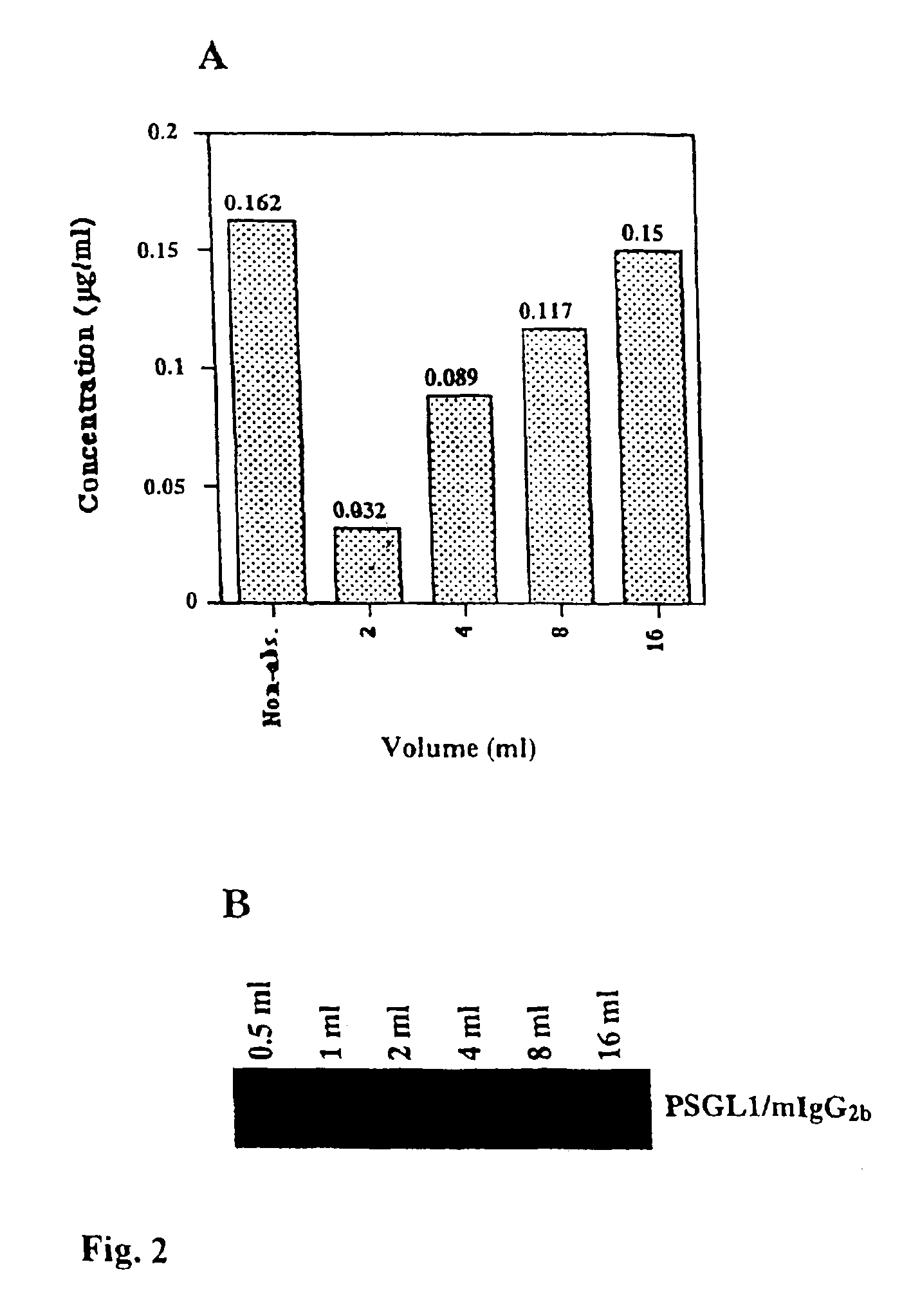
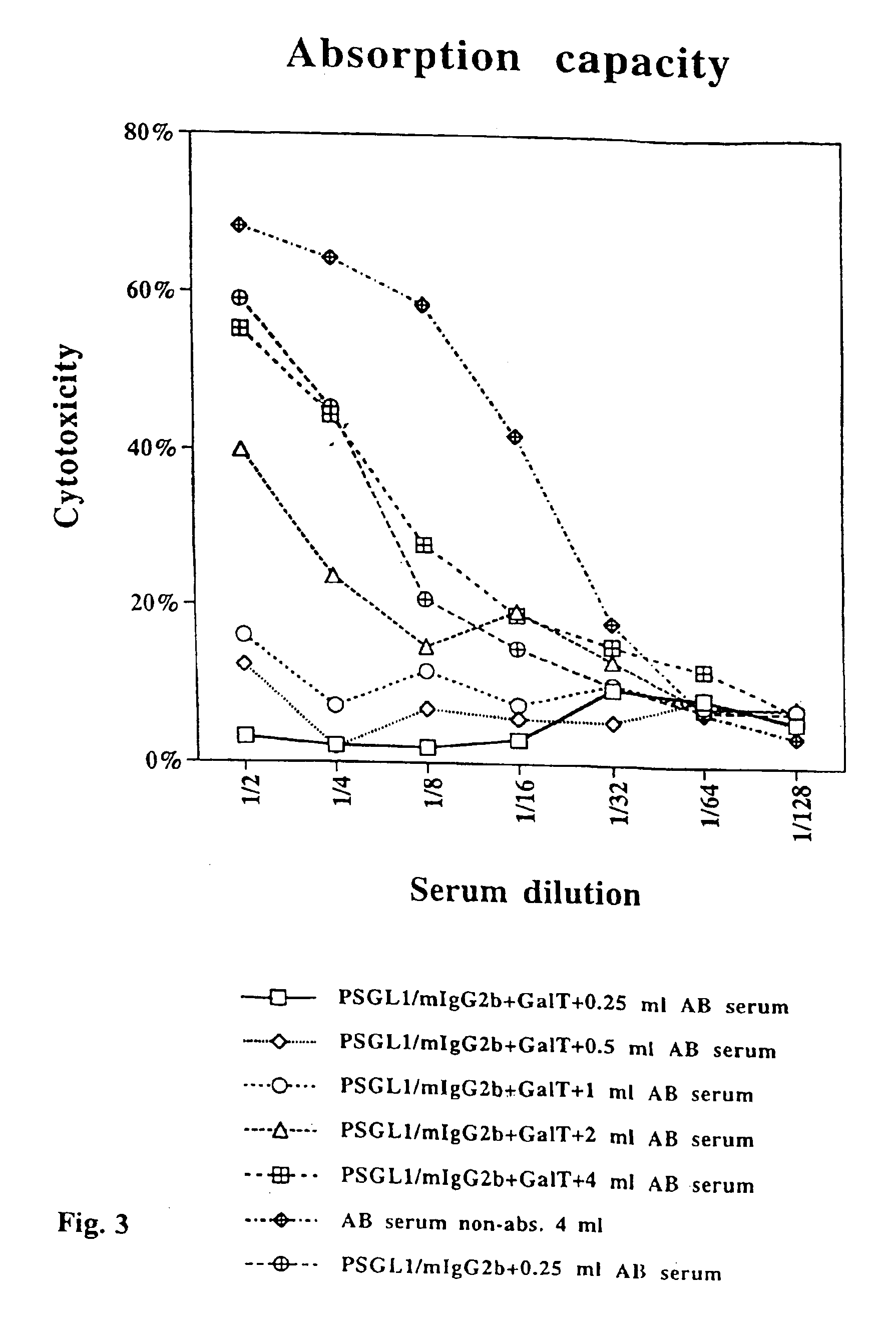
The present invention relates to an antigenic fusionprotein, which carries multiple Galα1,3Gal epitopes. The fusion protein according to the invention may also be comprised of a heavily glycosylated mucin part, which mediates binding to selectins, such as PSGL-1, and a part, which exhibits immunoglobulin properties, such as the Fc part of IgG. The fusionprotein according to the invention is preferably used as an absorber to prevent a hyperacute rejection of a xenotransplant, such as a pig tissue or organ transplanted into a human patient. In addition, the invention relates to a method for the prevention of hyperacute rejection reaction in a patient who is to receive a xenotransplant.
Owner:RECOPHARMA AB
Double T-DNA carrier and its application in cultivating of non selecting sign transgene rice
InactiveCN1597969ASmall molecular weightHigh co-transformation efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant nodule
The invention provides a simple and convenient Agrobacterium Tumefacies dual carrier containing double T-DNA structural regions, and a method of using the carrier system to cultivate transgenic rice without resistance selection label. With the help of the principle of co-conversion mediated by root nodule Agrobacterium Tumefacies, the system contains two separate T-DNA structural sections, where the first T-DNA region contains antibiotic resistance selection label gene and the second one contains a universal polyclonal site able to be arbitrarily inserted with destination gene. The double-T-DNA carrier has small molecular weight, easy to clone and after the destination gene and necessary regulation and control series are cloned in the T-DNA region containing the polyclonal site, it realizes rice co-conversion; by selfing, it selects transgenic individual with destination gene but without selectin label gene from the self-bred progeny, thus eliminating the negative effect on transgenic plant commercialized production, etc, possibly caused by selection label gene.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Heterobifunctional pan-selectin inhibitors
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Specific antagonist for both E- and P-selectins
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS INC
Compositions and methods for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20050181987A1Reduce adhesionReduce transferCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSaccharide peptide ingredientsAntigenE-selectin
Compositions containing one or more peptido-mimetics or modified peptido-mimetics of a carbohydrate ligand of an adhesion molecule in a physiologically acceptable carrier are useful for methods of reducing metastasis in a mammal and for inhibiting inflammatory response in a mammal. Particularly useful are embodiments in which the ligand is a Lewis antigen and / or the adhesion molecule is a selectin, e.g., E-selectin. Methods are disclosed for identifying peptido-mimetics of carbohydrate ligands, which may be involved in binding of tumor cells to other cells, such as endothelial cells.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY +1
Linkable sialyl Lewis X analogs
InactiveUS7422733B2Improve abilitiesHigh bonding strengthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsSialyl LexTreatment choices
Disclosed herein is a class of linkable tetrasaccharide compounds that includes the amino phenyl glycoside of sialyl Lewis X (SLeX) and related analogs. These compounds have conjugatable nucleophilic groups, making them useful in preparing multimeric SLeX compositions. In particular, the disclosed SLeX compounds can be used to prepare selectin binding ligand conjugates by linking them to a reporter moiety, such as a contrast agent, a radiodiagnostic agent, or a cytotoxic or chemotherapeutic agent. The SLeX compounds and conjugates of the invention exhibit binding to selectin that is similar to native Sialyl Lex, and are, therefore, useful for diagnosing and treating selectin-mediated disorders and related conditions.
Owner:BRACCO SUISSE SA
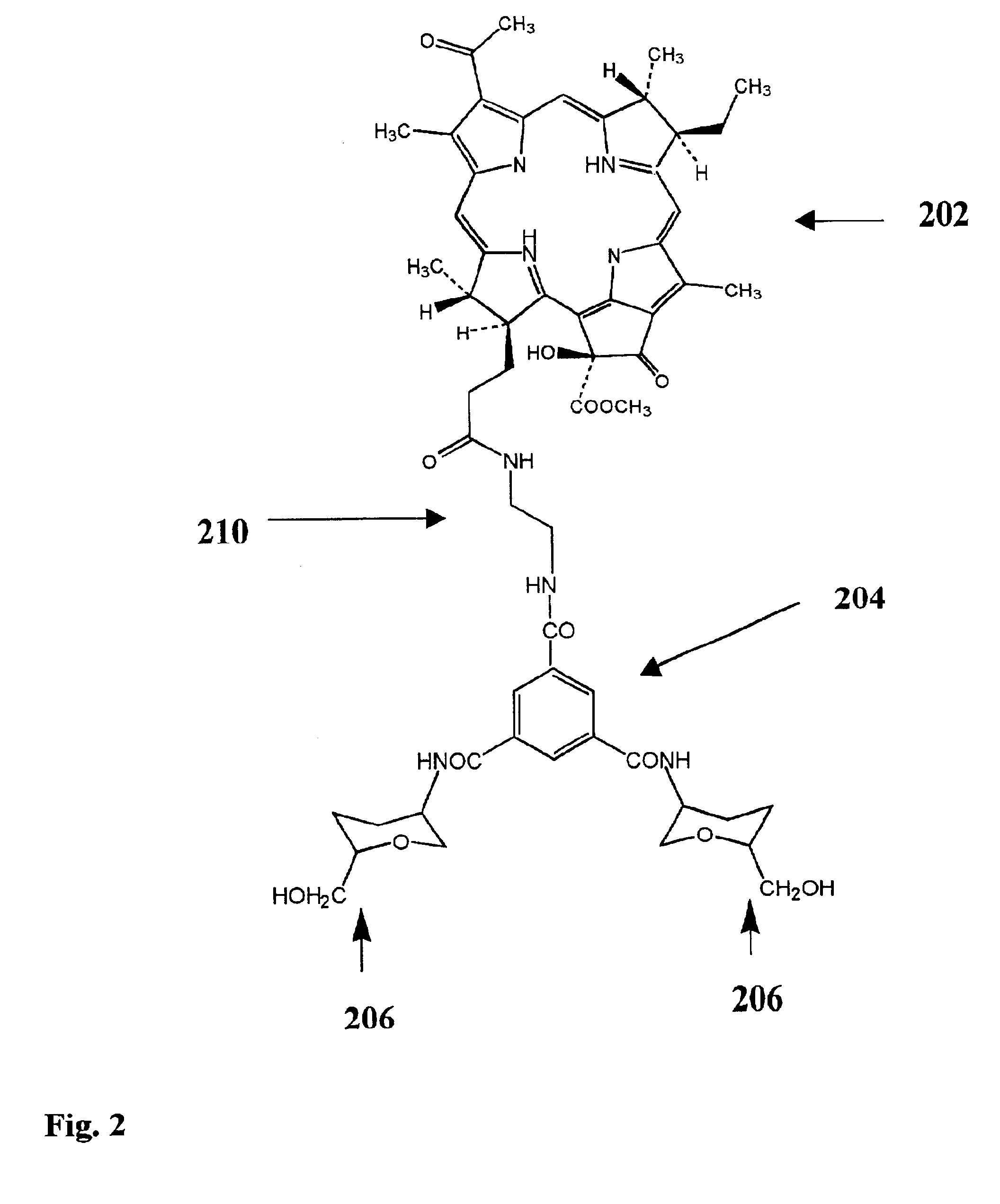
Photosensitizers with ligand targeting properties for tumor therapy
InactiveUS6806284B1Receive treatment wellEliminate side effectsBiocideDipeptide ingredientsTumor therapyTissues types
The present invention provides a drug delivery system wherein a "parachute" structure is coupled to a therapeutic compound. The "parachute" structure comprises hydrophilic branched molecules with a defined action diameter. The complex (a parachute structure coupled with a therapeutic compound) is either fixed at a cell membrane or delivered to a defined distance from the membrane within the cell. The membrane-anchoring / localizing effect of the parachute is achieved by hydrophilic structures linked with a branching unit of desired therapeutic compounds. Furthermore, the parachute structures can be connected by a spacer (e.g. beta-amino acids, gamma-amino butyric acid, or poly-amino acids) instead of directly binding to the therapeutic compound, so that the therapeutic compounds can be localized within the cells at a defined distance from the cell membrane. A spacer containing a breaking point can determine the time span, during which the drug exhibits its therapeutic activity. The hydrophilic residues can also carry signals for targeting the parachute-therapeutic complex to a defined tissue type. This can be mediated by an antibody which is specific for a tumor marker. Alternatively, a Biotin can be attached at C6 position of the sugar and then react with an Avidin-labeled tumor-specific antibody. The parachute function may also be achieved by other, more bulky hydrophilic structures such as oligosaccharides connected to the branching unit. Such sugar oligomers have specific attachment points to cell selectins, and therefore do not need additional molecular structures to target a specific tumor tissue. The use of the parachute structure gives the advantages of being able to localize a photosensitizer or chemotherapeutic drug at the site within a cell where it can destroy the tumor cell most effectively. This reduces the level of necessary systemic doses of the drugs, promotes drug excretion, and therefore considerably reduces side effects of the therapy.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG
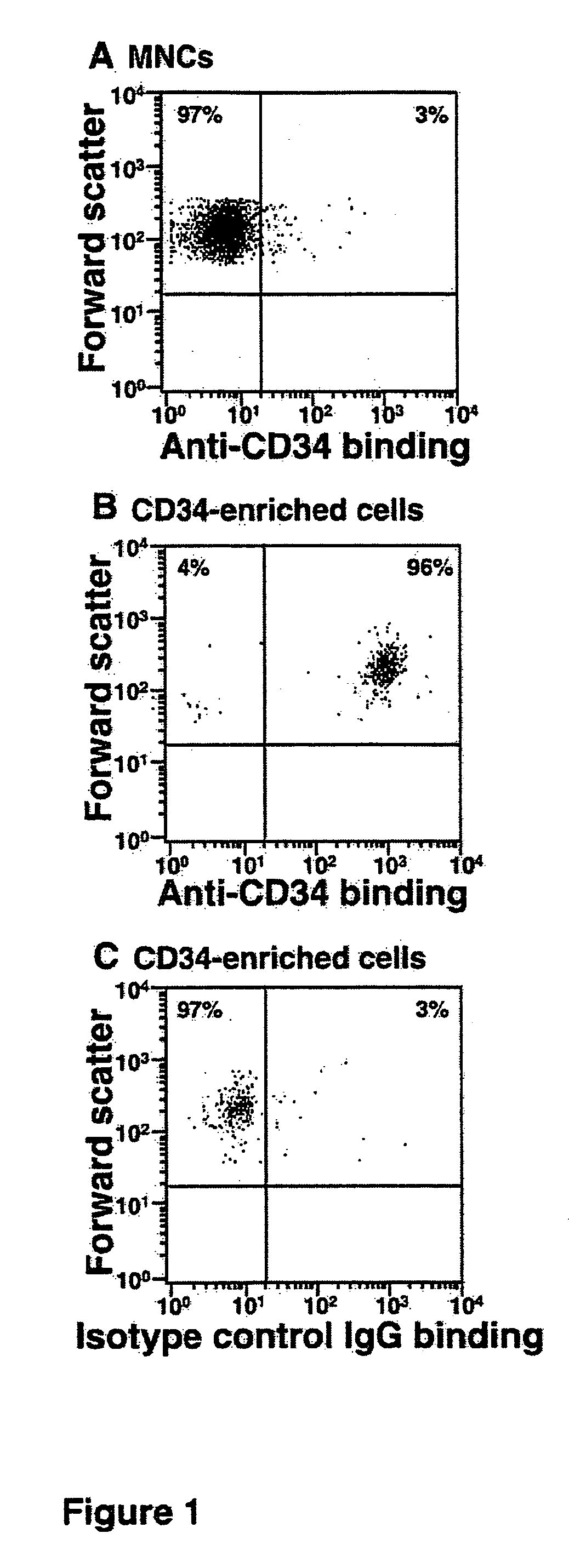
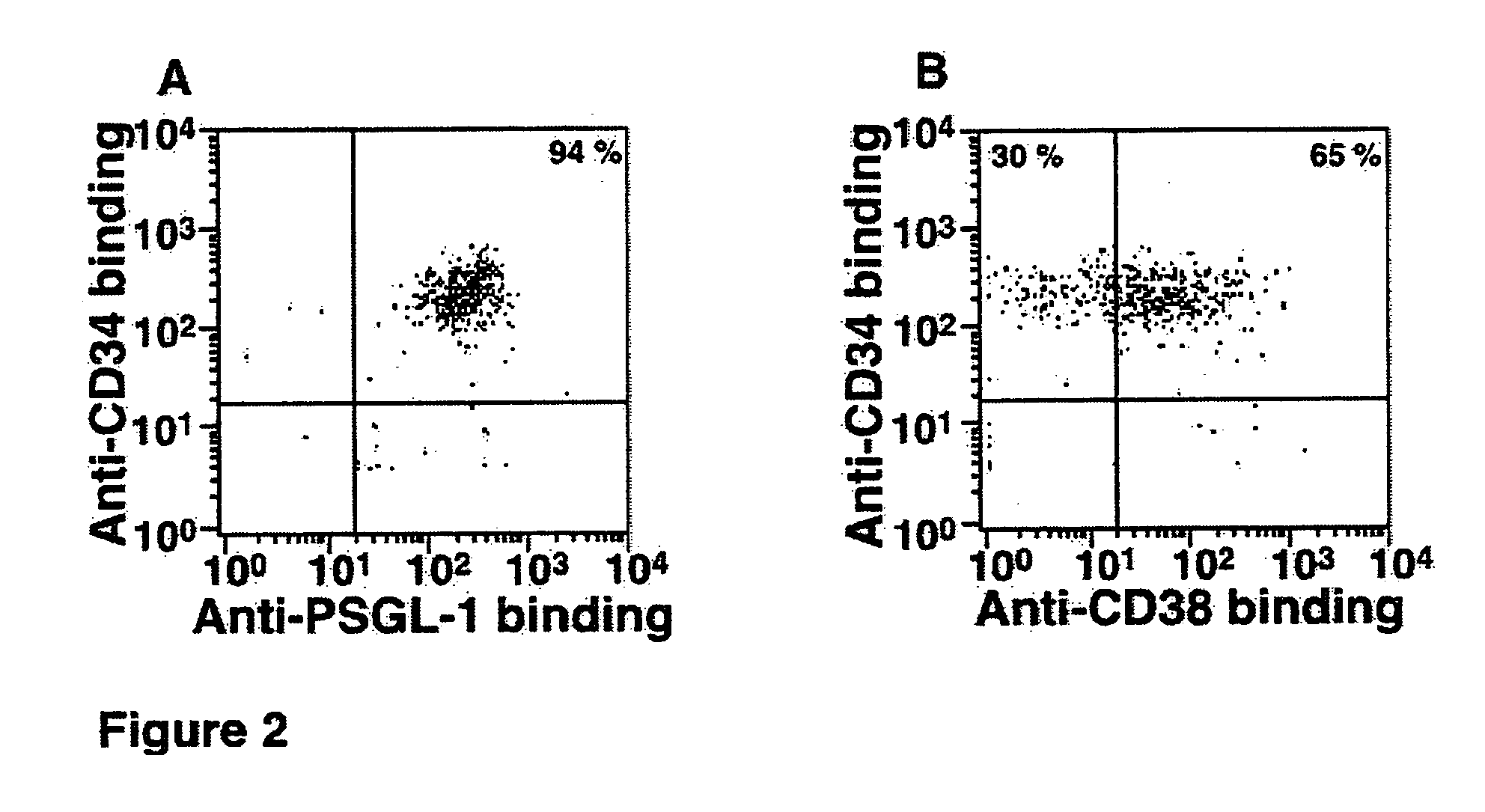
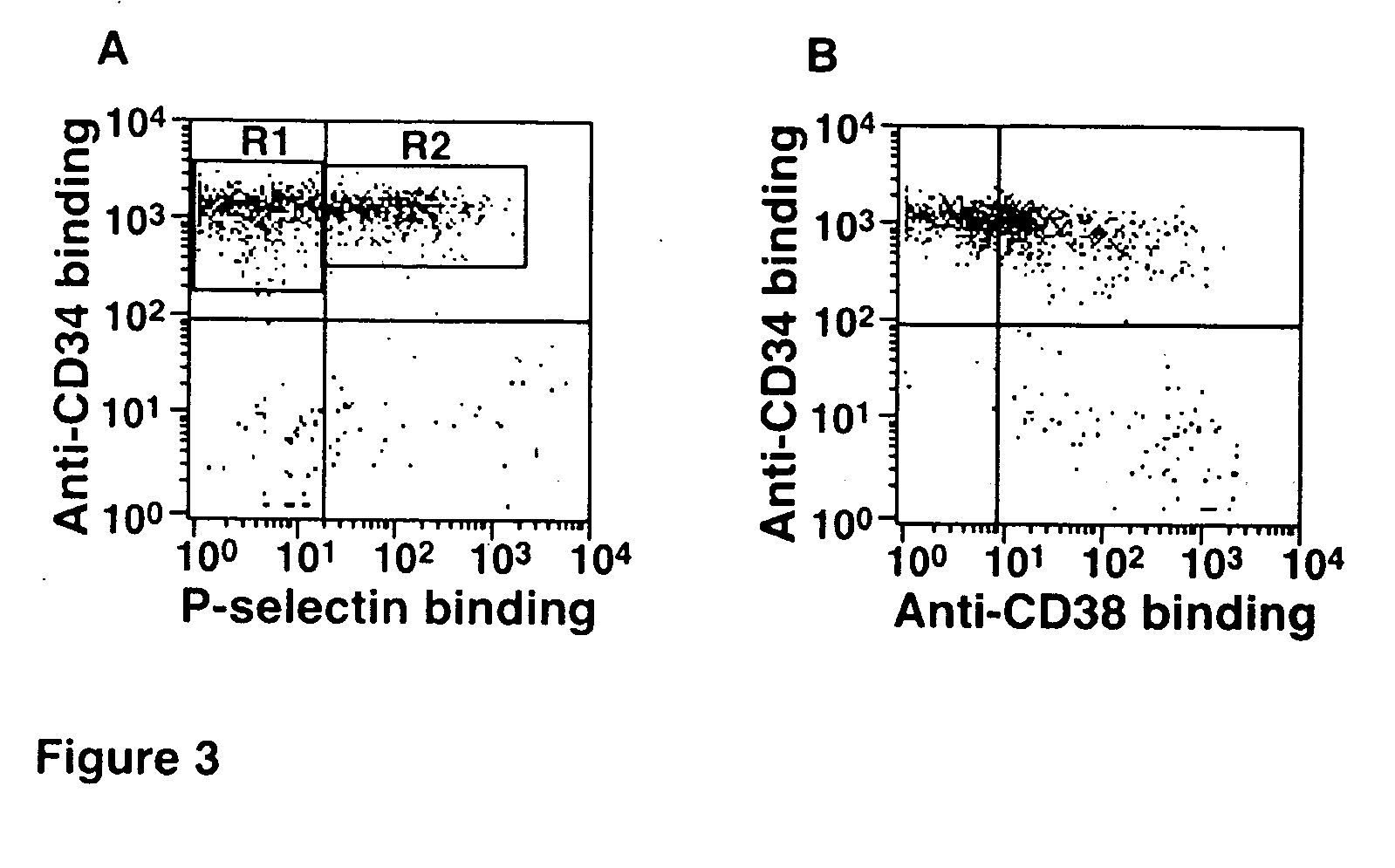
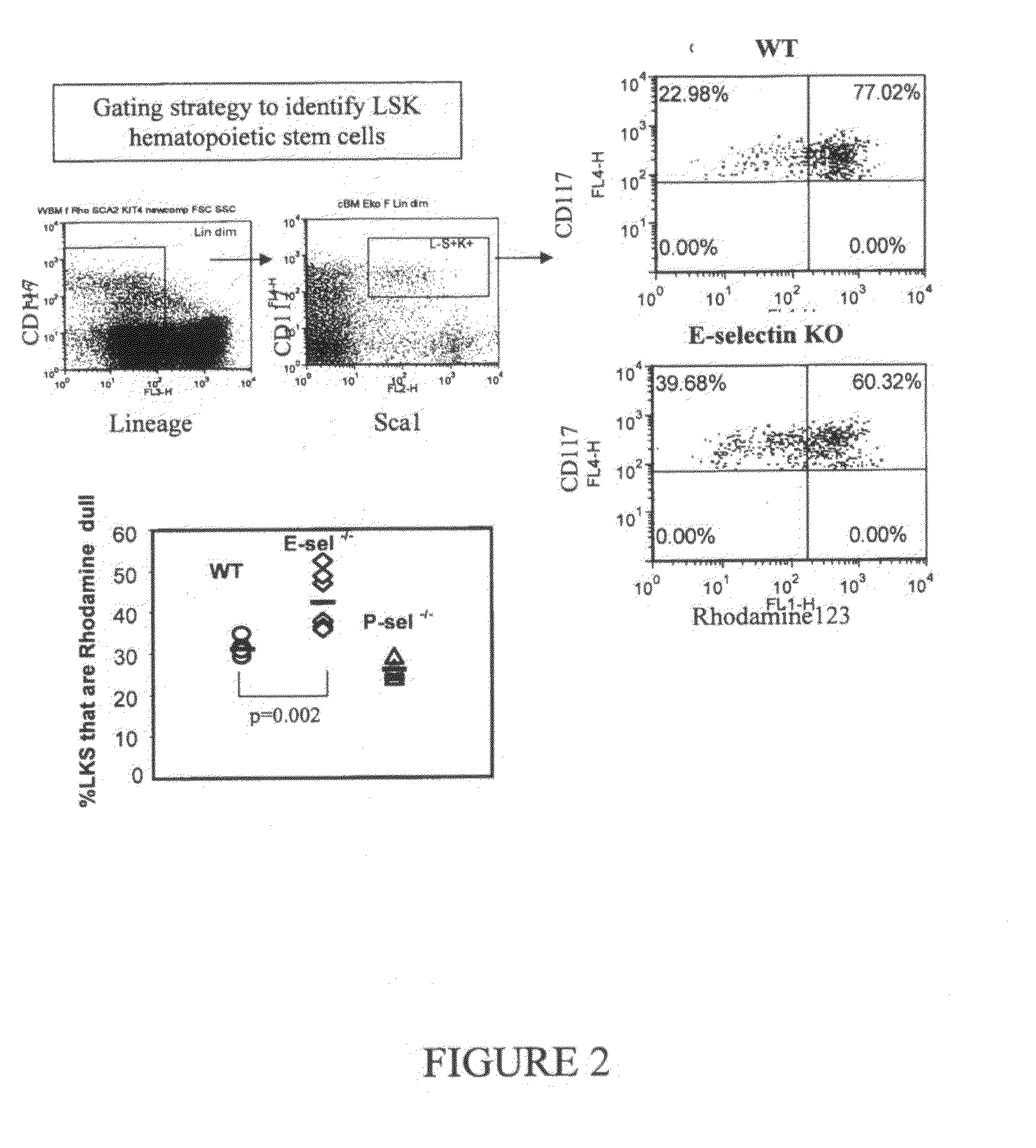
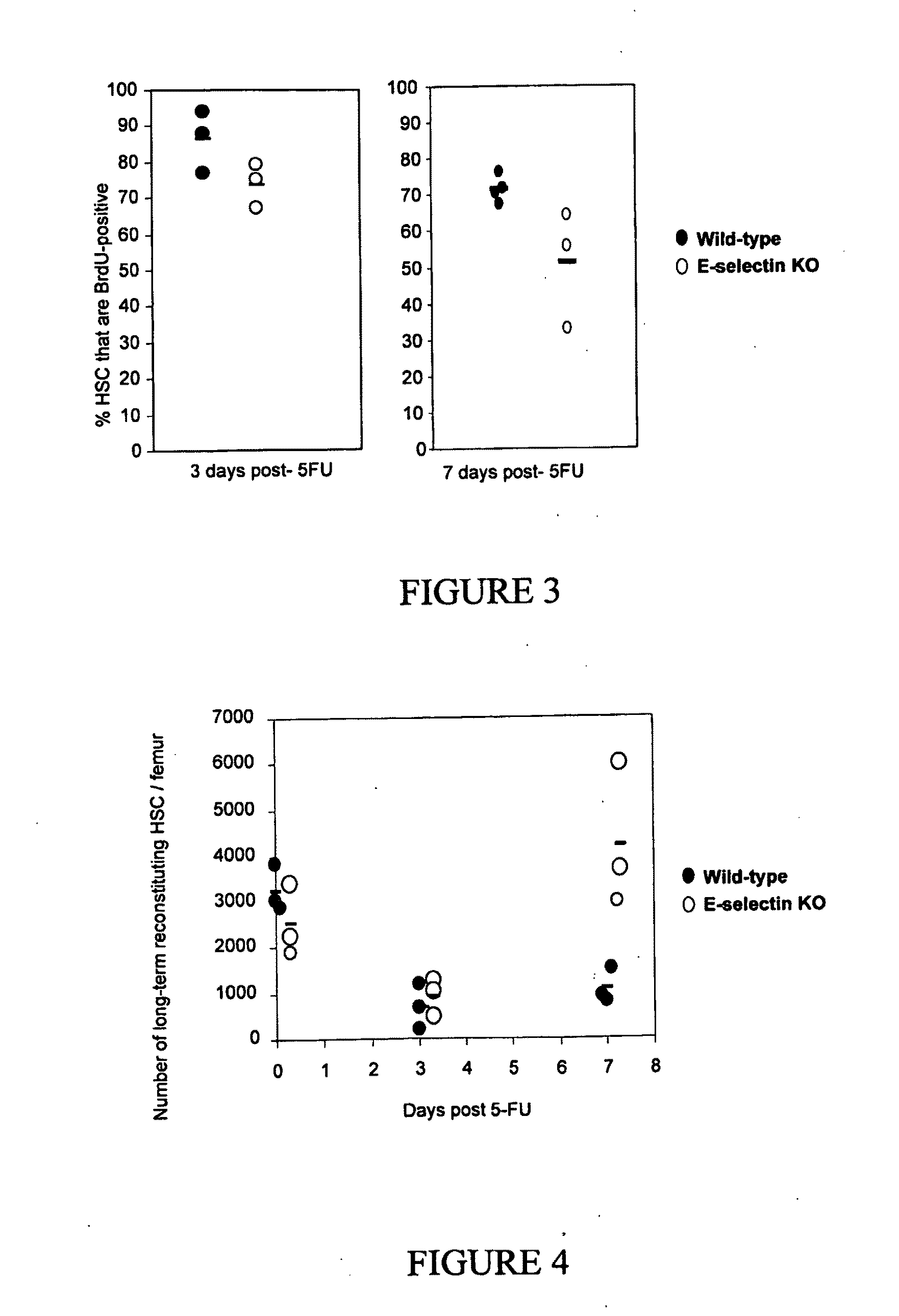
Hematopoietic stem cells treated by in vitro fucosylation and methods of use
A method of in vitro fucosylation of selectin ligands on cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem cells for bone marrow transplantation is disclosed. In this method, an effective amount of an α1,3-fucosyltransferase, e.g., α1,3-fucosyltransferase VI, is used in vitro to treat cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem cells to convert non-functional PSGL-1 or other ligands on the cell surface into functional forms that bind selectins, especially P-selectin or E-selectin. The treated cells have enhanced effectiveness in reconstituting bone marrow in patients in need of such therapy.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Hemostatic compositions, devices and methods
InactiveUS7094428B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce concentrationPowder deliveryFactor VIIFactor VIIaBiopolymer
A hemostatic composition which comprises at least one procoagulant metal ion, such as silver (I) or mercury (II), and at least one procoagulant biopolymer, such as collagen, thrombin, prothrombin, fibrin, fibrinogen, heparinase, Factor VIIa, Factor VIII, Factor IXa, Factor Xa, Factor XII, von Willebrand Factor, a selectin, a procoagulant venom, a plasminogen activator inhibitor, glycoprotein IIb-IIIa, a protease, or plasma. The composition in the form of a paste, dough, glue, liquid, lyophilized powder or foam, may be provided, for application to a wound. A hemostatic device is also described which comprises a hemostatic composition as described above. The device may be in the form of, for example, a plug, bandage, gauze, cloth, tampon, membrane or sponge. Methods are also provided for prophylaxis or treatment of bleeding at a site by application to the site of the composition or device as described.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Compounds and methods for inhibiting selectin-mediated function
Compounds and methods are provided for modulating in vitro and in vivo processes mediated by selectin binding. More specifically, selectin modulators and their use are described, wherein the selectin modulators that modulate (e.g., inhibit or enhance) a selectin-mediated function comprise a class of compounds termed BASAs (Benzyl Amino Sulfonic Acids, which include a portion or analogue thereof linked to a carbohydrate or glycomimetic.
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Enhancing the t-cells stimulatory capacity of human antigen presenting cells and their use in vaccination
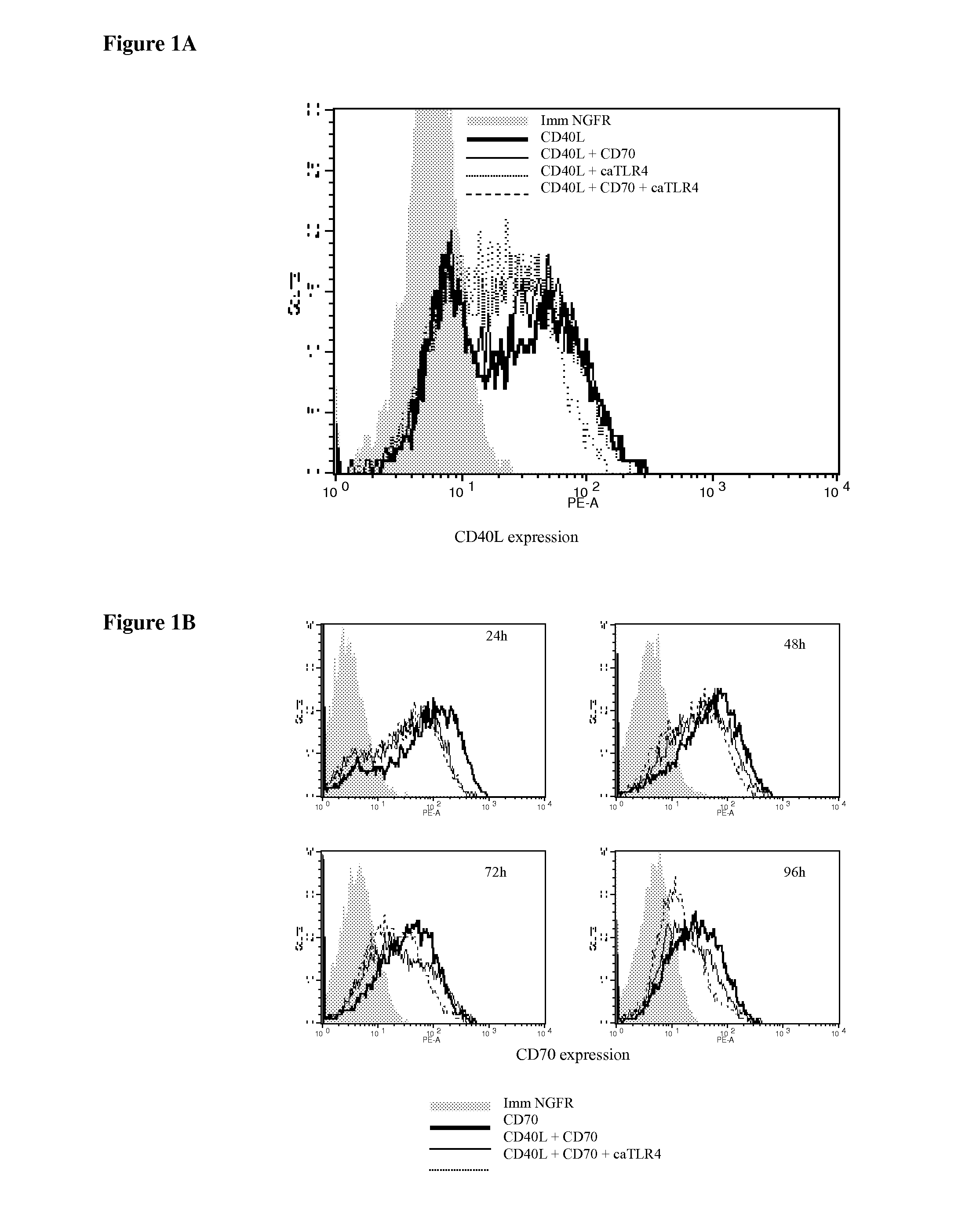
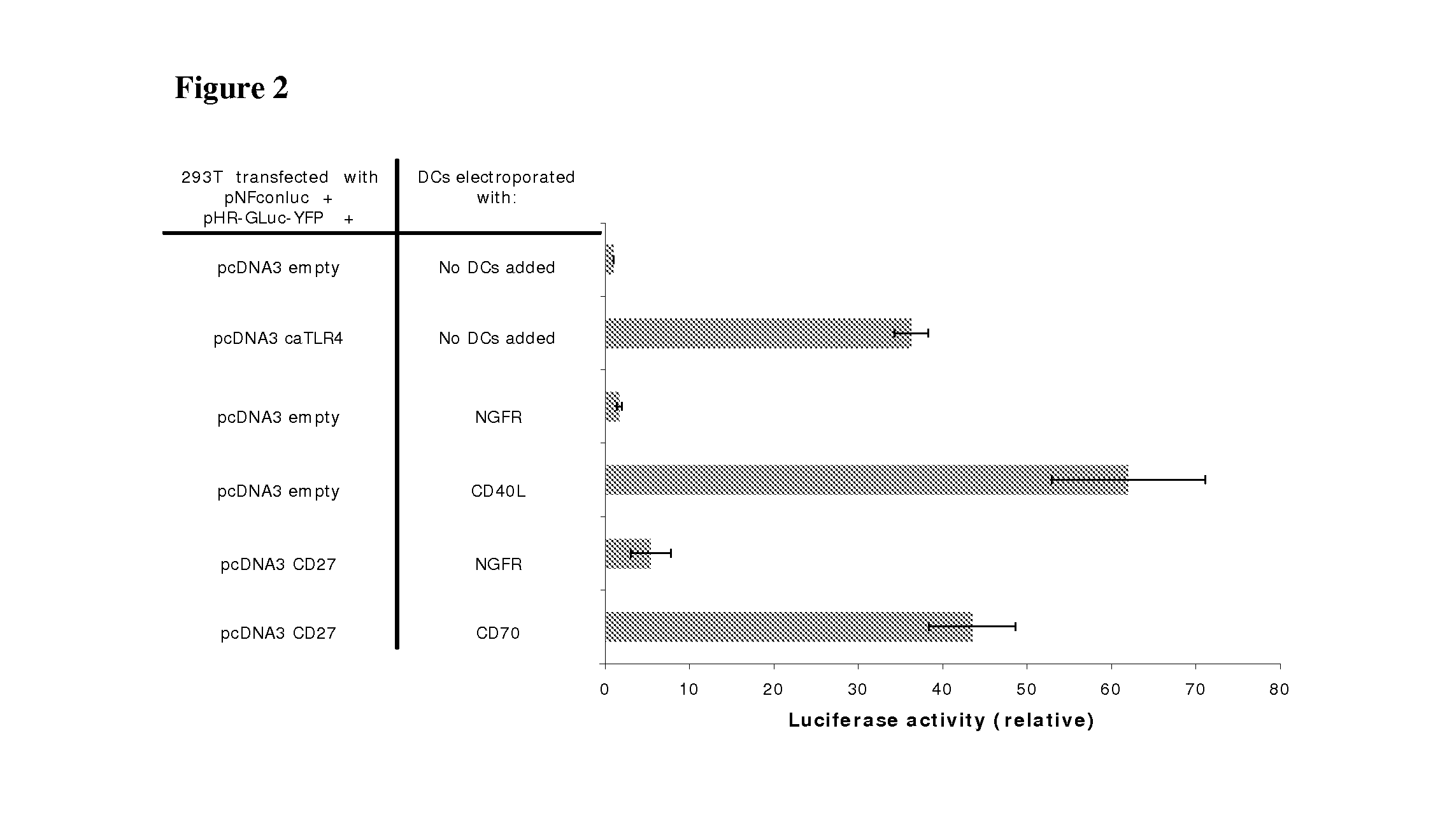
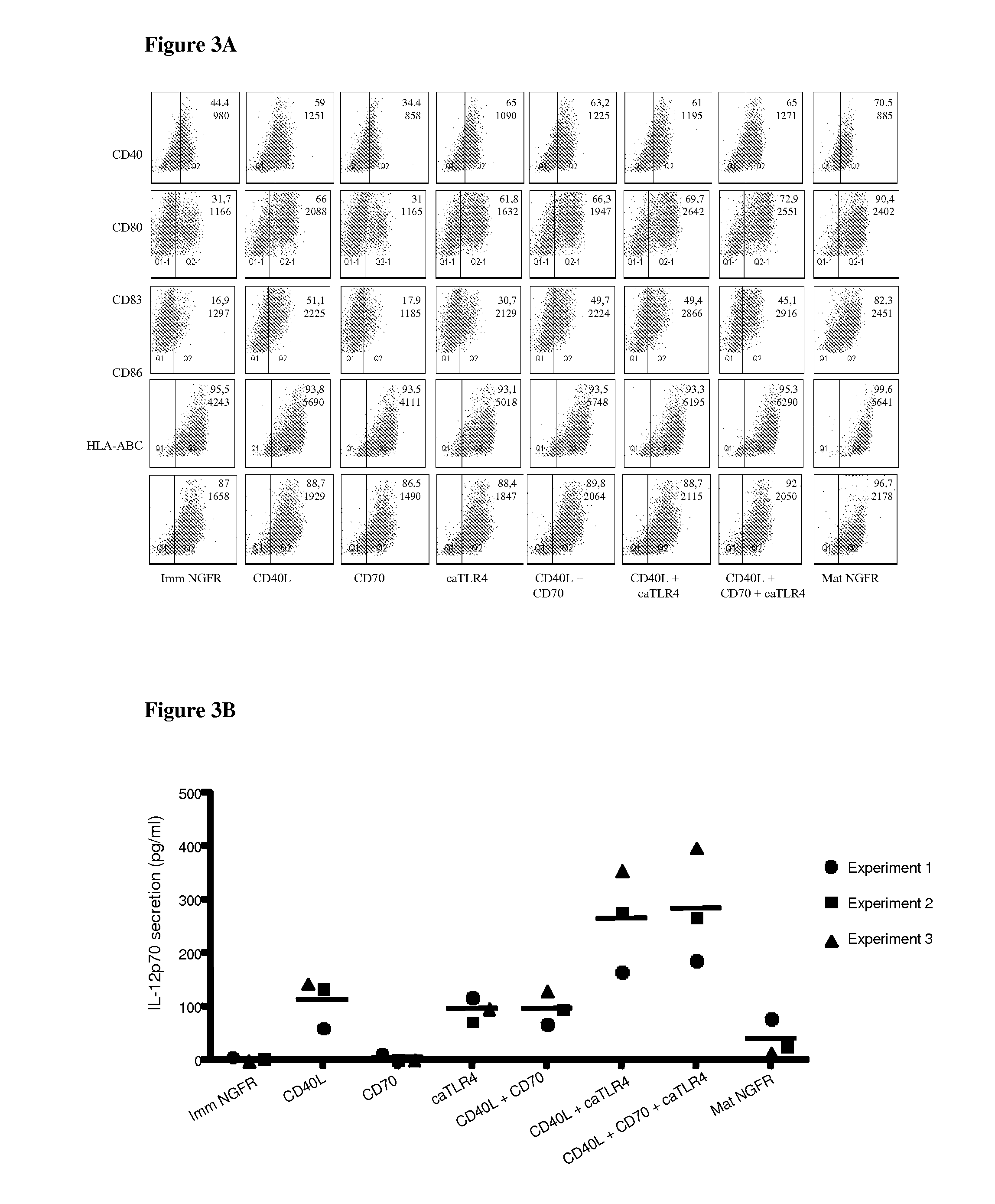
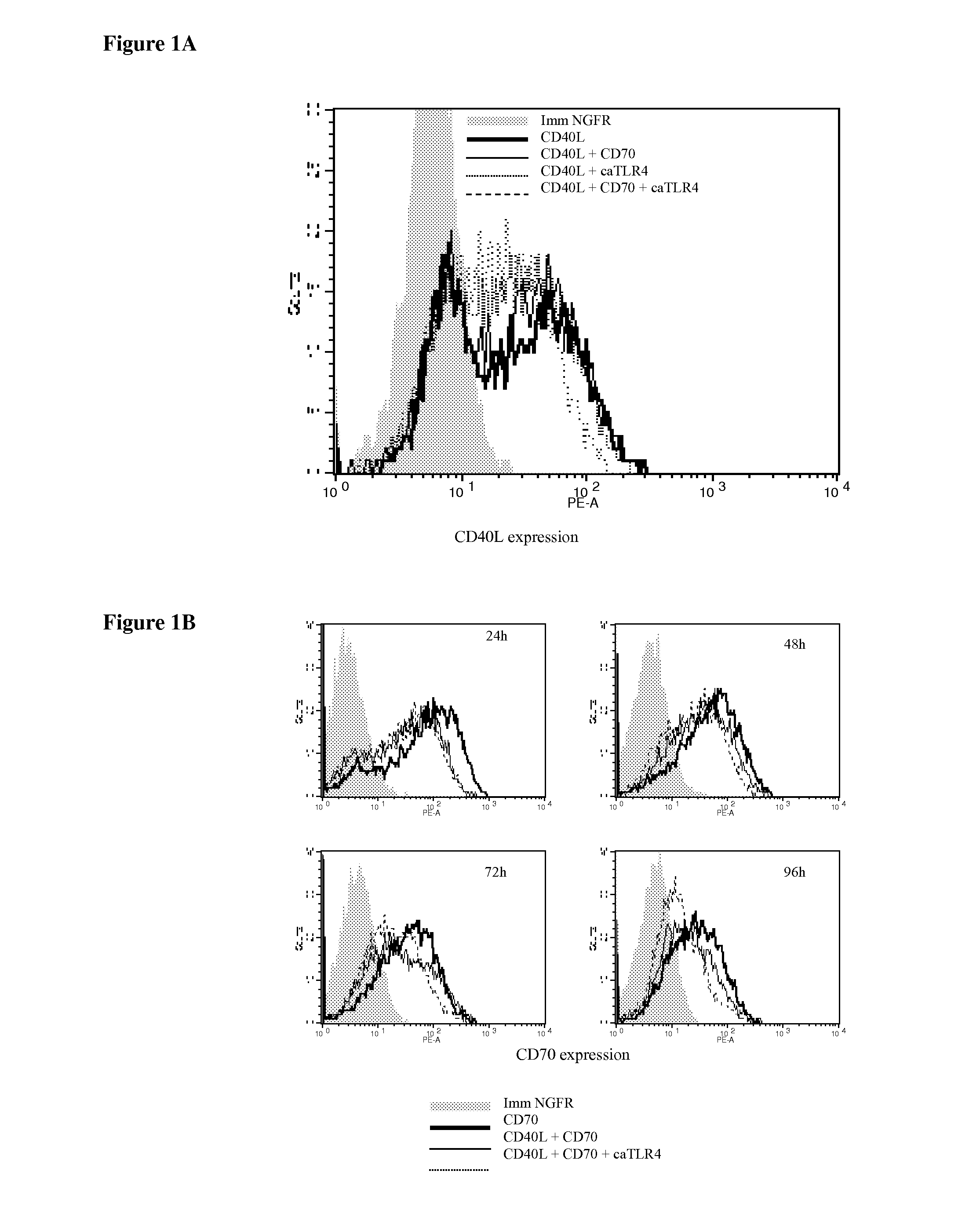
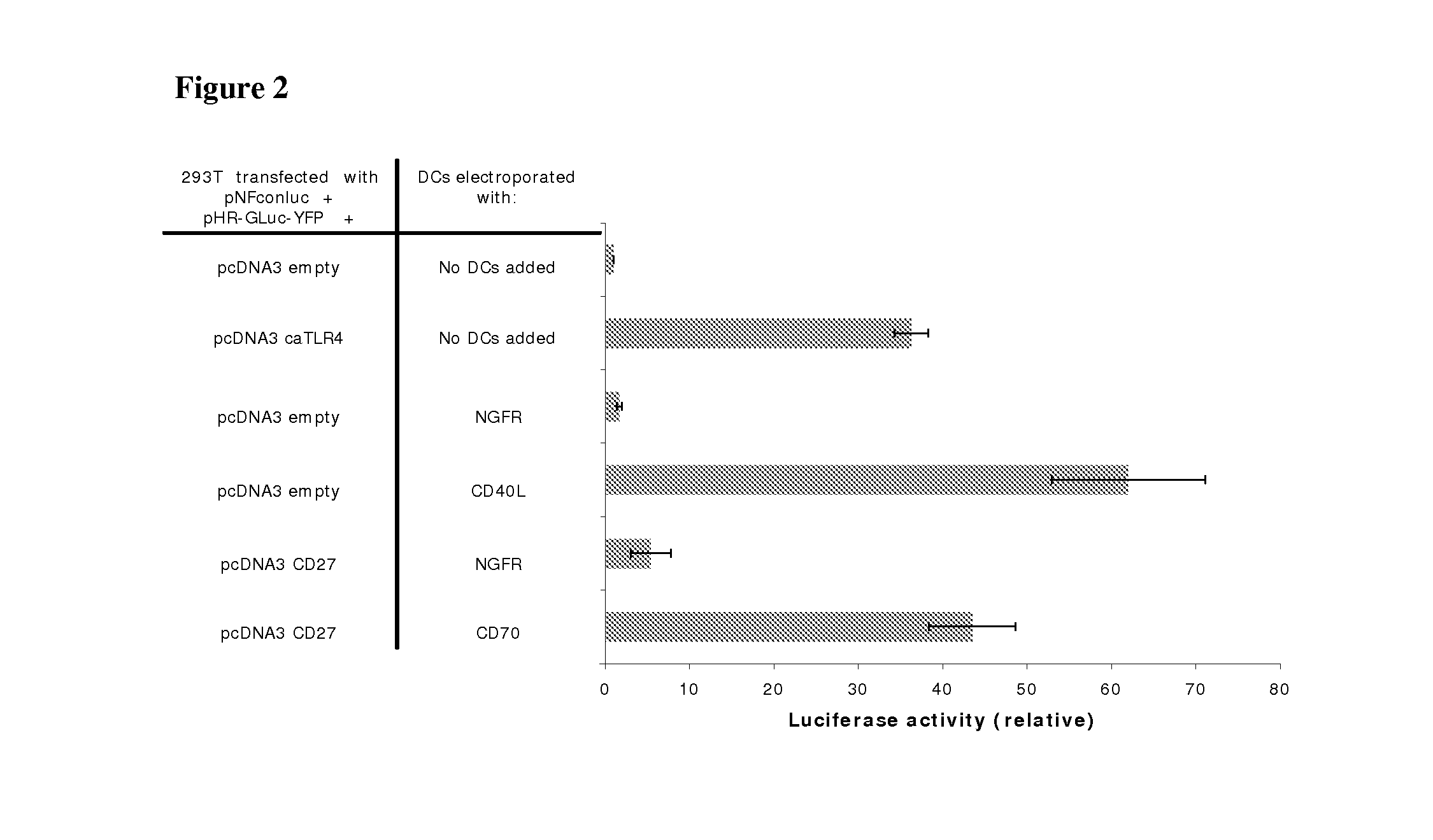
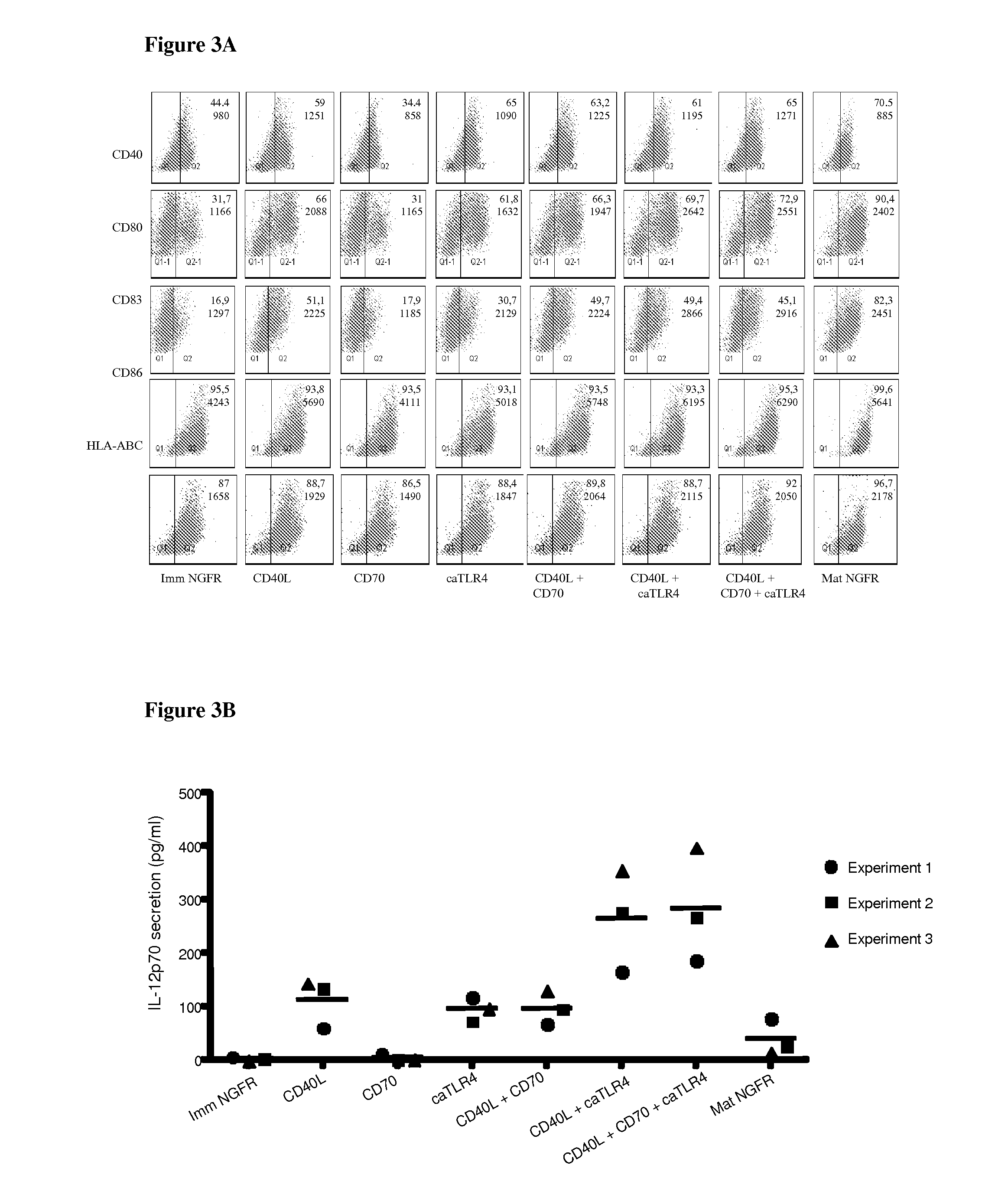
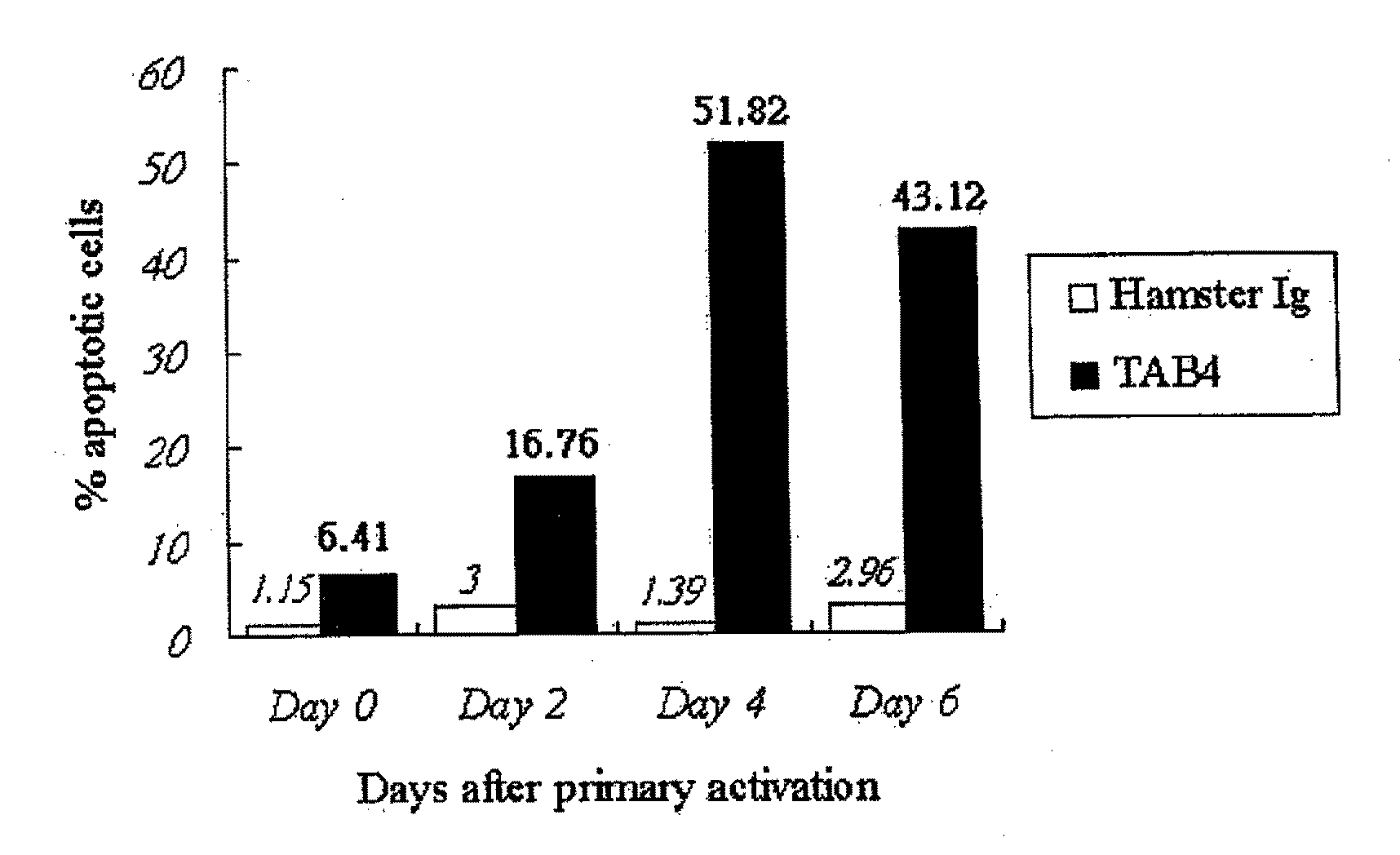
With the current invention, we provide new methods of enhancing the T-cell stimulatory capacity of human dendritic cells (DCs) and their use in cancer vaccination. The method comprises the introduction of different molecular adjuvants to human DCs through transfection with at least two mRNA or DNA molecules encoding markers selected from the group of: CD40L, CD70, constitutively active TLR4 (caTLR4), IL-12p70, EL-selectin, CCR7 and / or 4-1 BBL; or in combination with inhibition of SOCS, A20, PD-L1 and / or STAT3 expression, for example through siRNA transfection. We could show a clear increase in the immunostimulatory capacity of DCs obtained in this way, enabling them to elicit an unexpectedly high T-cell immune response in vitro. Introduction of at least two of the above molecules, in combination with a tumor-specific antigen enables the DCs to elicit a significant host-mediated T-cell immune response in vivo against the tumor antigen and thus makes them very attractive in the manufacturing of anti-cancer vaccines.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Treatment and prophylaxis
ActiveUS20110020270A1Stimulating and enhancing hematopoiesisAvoid adjustmentOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseWhite blood cell
This invention discloses the use of an E-selectin antagonist and a mobilizer of hematopoietic stem cells or progenitor cells in methods and compositions for treating or preventing immunocompromised conditions resulting from medical treatment. The present invention is particular relevant for prophylaxis and / or treatment of hematopoeitic disorders including neutropenia, agranulocytosis, anemia and thrombocytopenia in individuals receiving or proposed to receive treatments that target rapidly dividing cells or that disrupt the cell cycle or cell division.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Linkable Lewis X Analogs
InactiveUS20080300220A1Improve abilitiesHigh bonding strengthBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSialyl LexTreatment choices
Disclosed herein is a class of linkable tetrasaccharide compounds that includes the amino phenyl glycoside of sialyl Lewis X (SLeX) and related analogs. These compounds have conjugatable nucleophilic groups, making them useful in preparing multimeric SLeX compositions. In particular, the disclosed SLeX compounds can be used to prepare selectin binding ligand conjugates by linking them to a reporter moiety, such as a contrast agent, a radiodiagnostic agent, or a cytotoxic or chemotherapeutic agent. The SLeX compounds and conjugates of the invention exhibit binding to selectin that is similar to native Sialyl LeX, and are, therefore, useful for diagnosing and treating selectin-mediated disorders and related conditions.
Owner:BRACCO SUISSE SA
Pan-selectin inhibitor with enhanced pharmacokinetic activity
Compounds, compositions and methods are provided for treatment of diseases or complications associated therewith, in which a selectin plays a role. More specifically, particular glycomimetics and uses thereof are described. For example, use of particular glycomimetics for treating sickle cell disease or a cancer involving a selectin, or complications associated with either, is described.
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
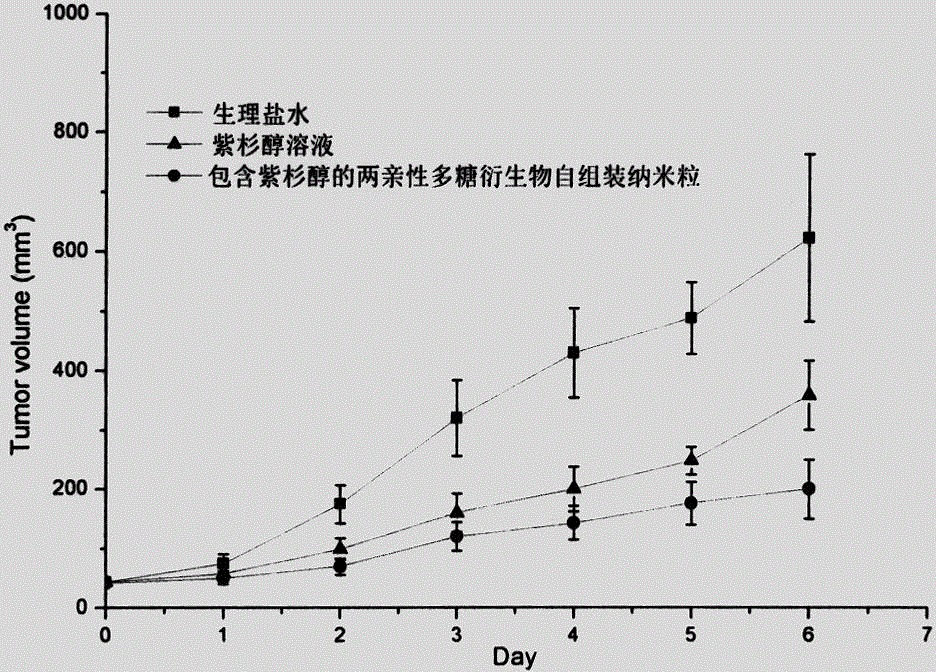
Amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier for targeting tumor new blood vessels as well as preparation and application of pharmaceutical composition of amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier
ActiveCN104971353AImprove stabilityImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWater insolubleVascular endothelium
The invention relates to an amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier for targeting tumor new blood vessels. According to the derivative, a polysaccharide skeleton is coupled with functional polypeptide targeting E-selectin by virtue of a disulfide bond to ensure that polysaccharide has amphipathy, and is assembled into nano particles for targeting the tumor new blood vessels after carrying an antitumor drug or a tumor new blood vessel inhibitor in an aqueous medium. The nano particles deliver medicines to the tumor new blood vessels in an active targeting manner by virtue of the high affinity between the functional polypeptide targeting the E-selectin and the E-selectin on the surface of the tumor new blood vessels, then a disulfide bond connecting arm can be specifically degraded by a strong reducing environment in endothelial cells of the tumor new blood vessels to cause that the functional polypeptide targeting the E-selectin is separated from polysaccharide, and the medicines are quickly released to treatment target points, so that the concentration of free medicines at tumor new blood vessel parts can be significantly improved and the antitumor curative effect is enhanced. An auxiliary material can be used as a carrier for water-insoluble, indissolvable or amphiphilic antitumor drugs and the tumor new blood vessel inhibitor, and is administrated by injecting into blood vessels or muscles, or is administrated orally or externally. The amphiphilic polysaccharide derivative carrier provided by the invention is simple in preparation method, mature in process and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Enhancing the T-cells stimulatory capacity of human antigen presenting cells and their use in vaccination
With the current invention, we provide new methods of enhancing the T-cell stimulatory capacity of human dendritic cells (DCs) and their use in cancer vaccination. The method comprises the introduction of different molecular adjuvants to human DCs through transfection with at least two mRNA or DNA molecules encoding markers selected from the group of: CD40L, CD70, constitutively active TLR4 (caTLR4), IL-12p70, EL-selectin, CCR7 and / or 4-1 BBL; or in combination with inhibition of SOCS, A20, PD-L1 and / or STAT3 expression, for example through siRNA transfection. We could show a clear increase in the immunostimulatory capacity of DCs obtained in this way, enabling them to elicit an unexpectedly high T-cell immune response in vitro. Introduction of at least two of the above molecules, in combination with a tumor-specific antigen enables the DCs to elicit a significant host-mediated T-cell immune response in vivo against the tumor antigen and thus makes them very attractive in the manufacturing of anti-cancer vaccines.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
Modulators of p-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1
InactiveUS20100080819A1Induce depletionInduce of inductionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
Multimeric compounds that bind to P-Selectin Glycoprotein 1 (PSGL-1) on the surface of T cells or natural killer (NK) cells can be used to induce T cell or NK cell depletion and / or to induce T cell or NK cell apoptosis. The multimeric compounds and methods of the invention can be used to control unwanted T cell- or NK cell-mediated immune responses in conditions such as inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, transplant rejection, and allergic diseases.
Owner:ABGENOMICS COOPERATIEF U A
Synthesis, activity and application for 1,1 dimethylol-tetrahydro-beta-carboline-3-formyl-GYIGSR
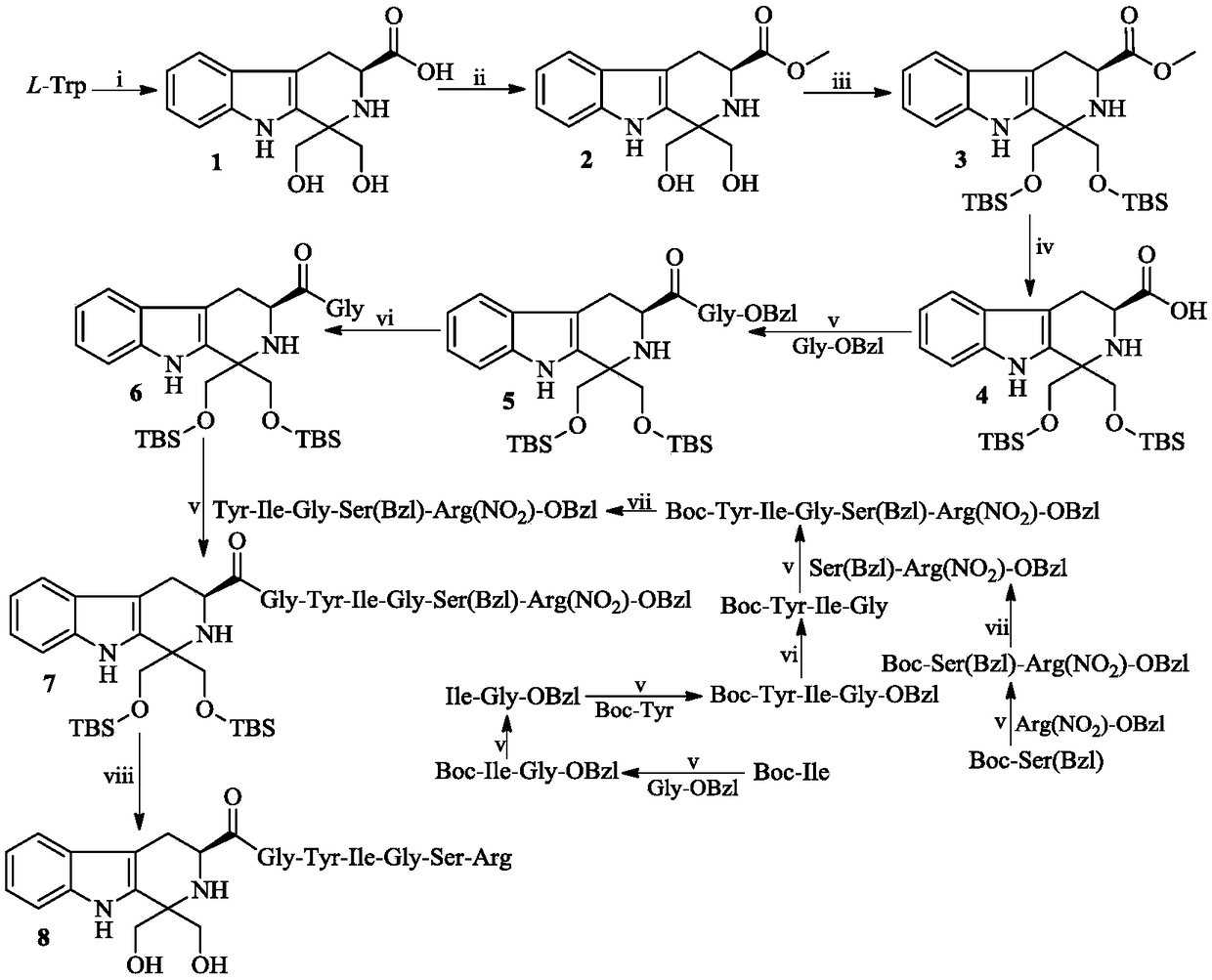
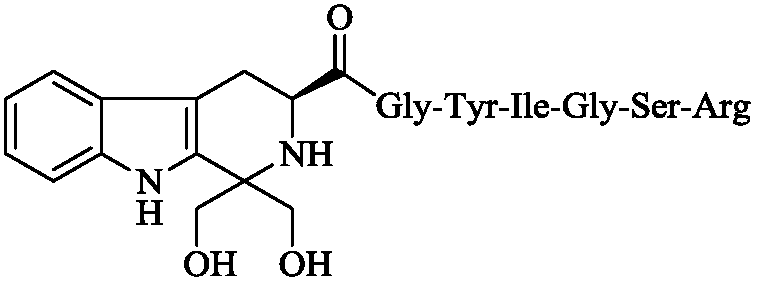
ActiveCN109134603AInhibit expression activityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsVenous bloodSelectin
The invention discloses a (3S) -1, 1-Dihydroxymethyl-Tetrahydro-Beta-Carboline-3-Formyl-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Gly-Ser-Arg, discloses a preparation method thereof, discloses the anti-arterial thrombosis activity, discloses the anti-venous thrombosis activity, discloses the activity of inhibiting the GPIIb / IIIa expression, and discloses the activity of inhibiting the P-selectin expression in vivo. Therefore,the invention discloses the application in preparing anti-arterial thrombosis medicine, the application in preparing the anti-venous thrombosis medicine, the application in preparing the GPIIb / IIIa antagonist and the application in preparing P-selectin antagonist. The formulas are shown in the decription.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com