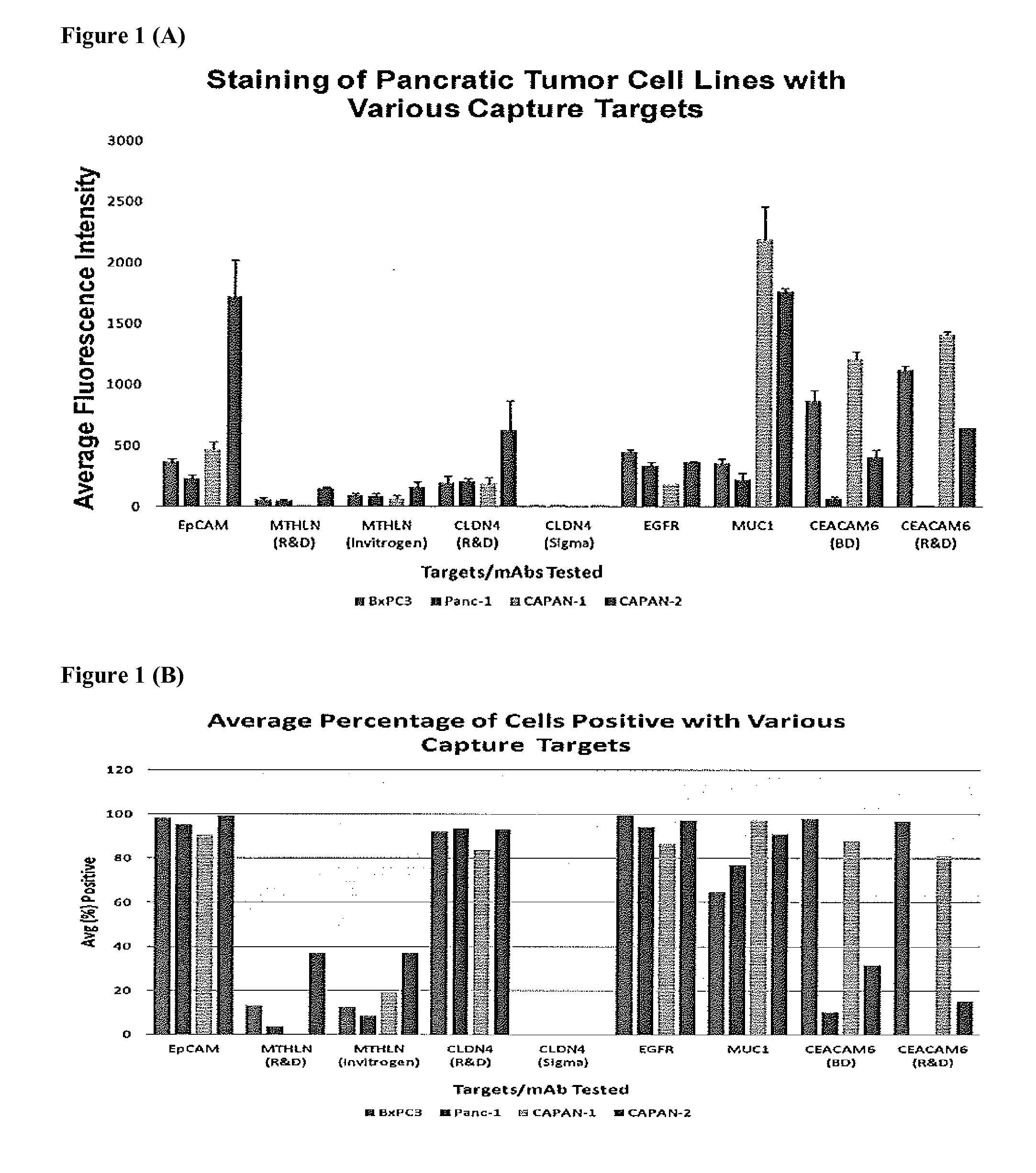
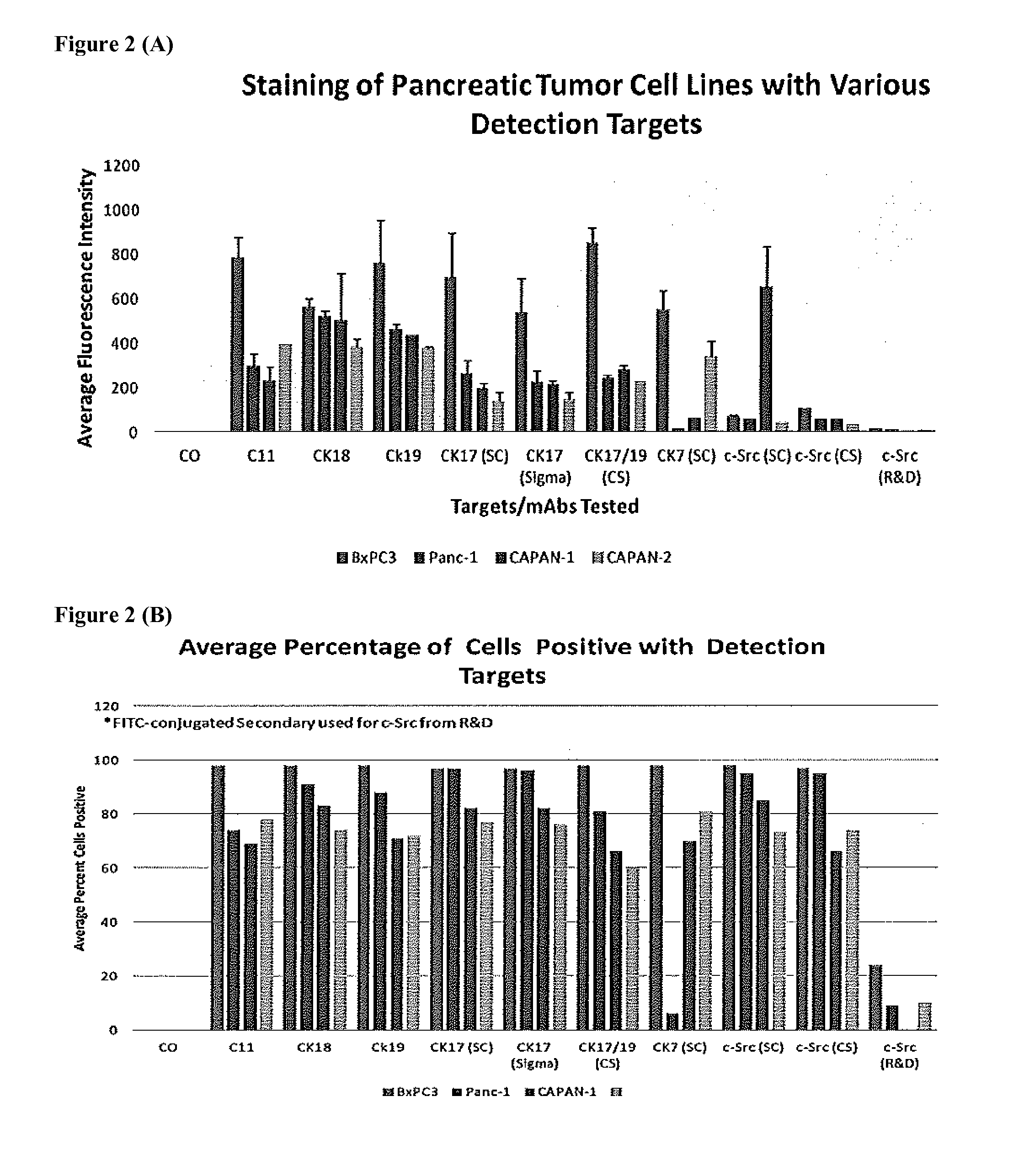
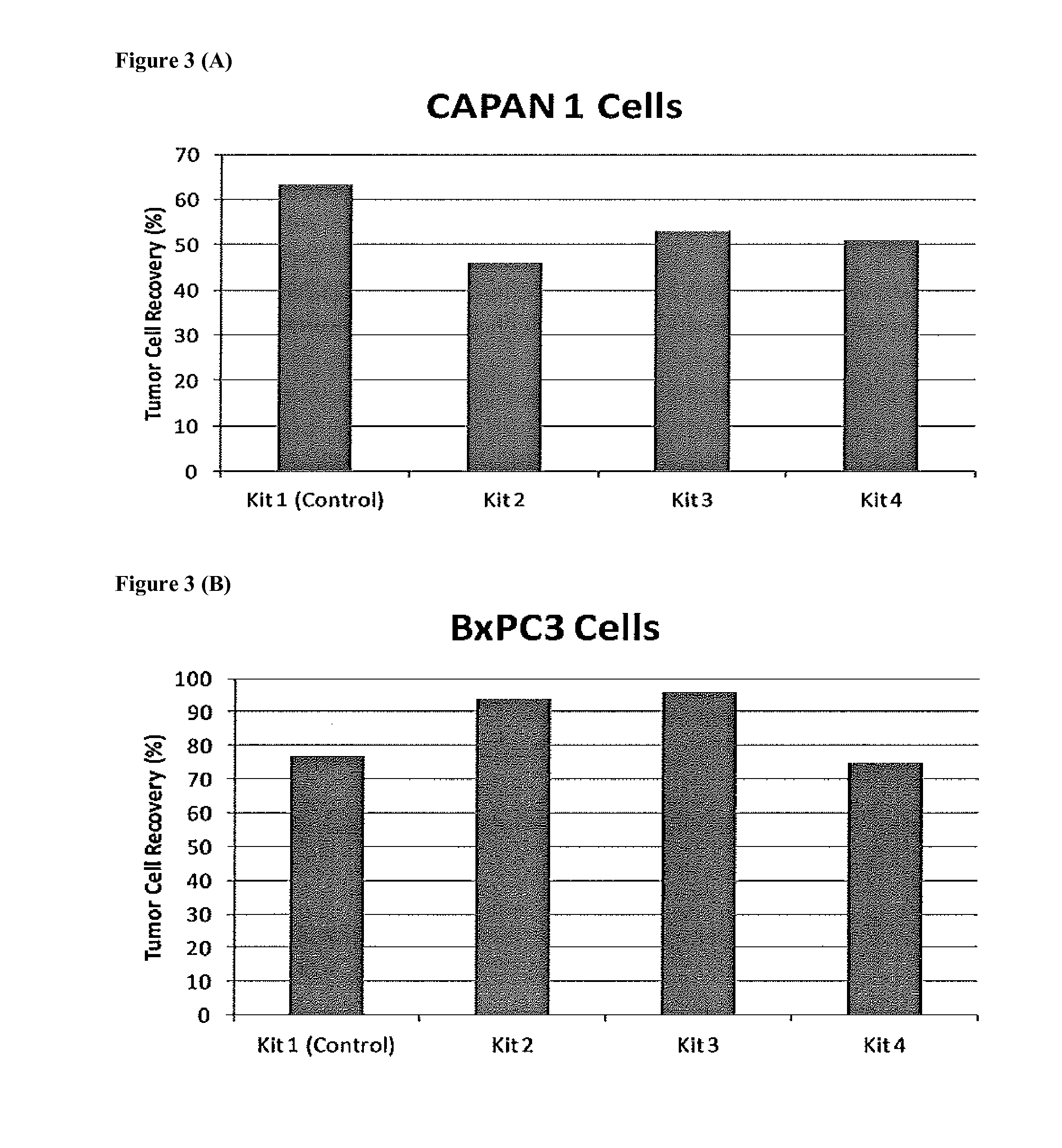
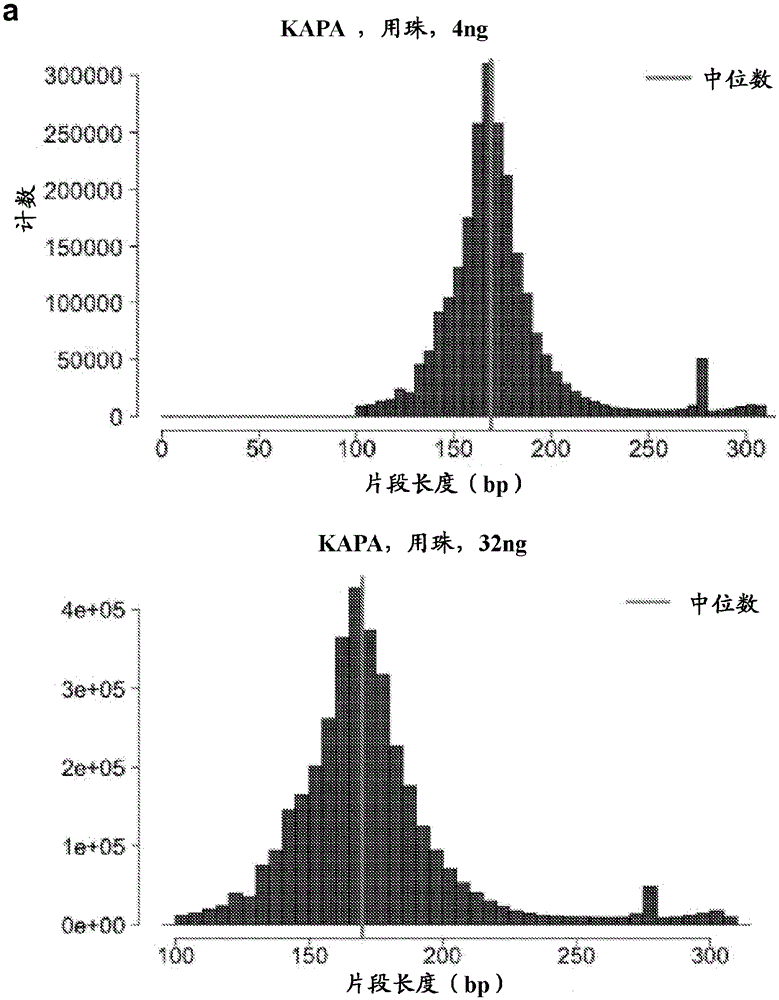
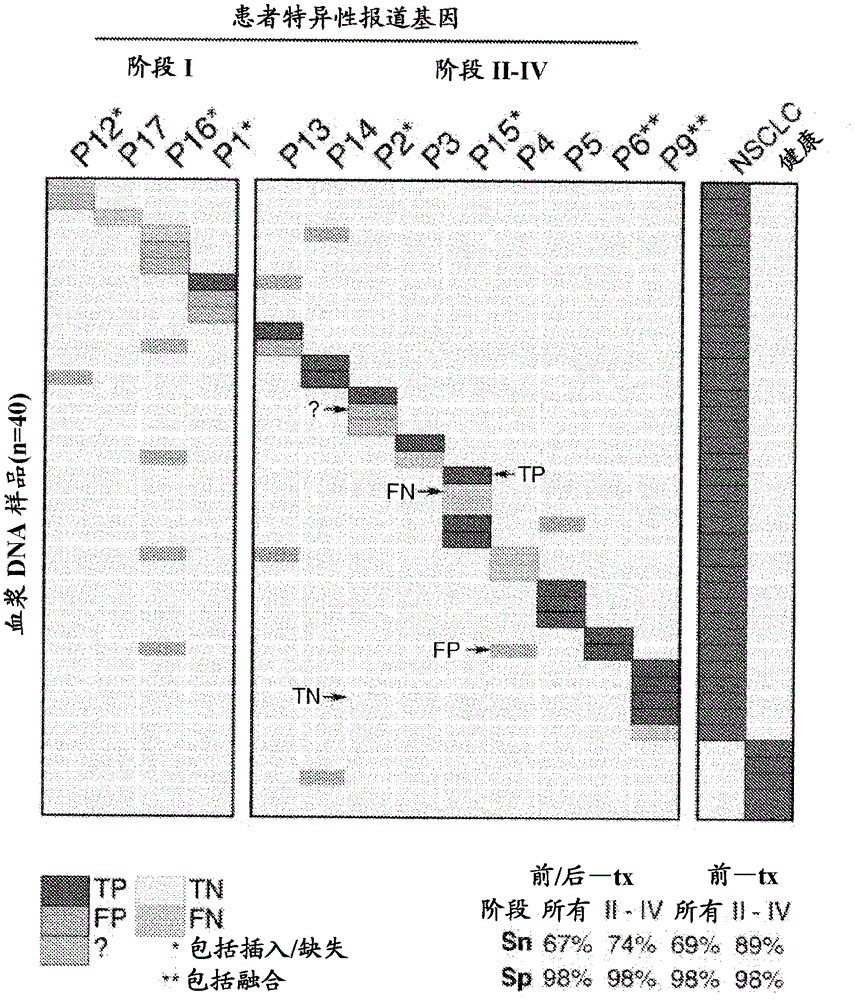
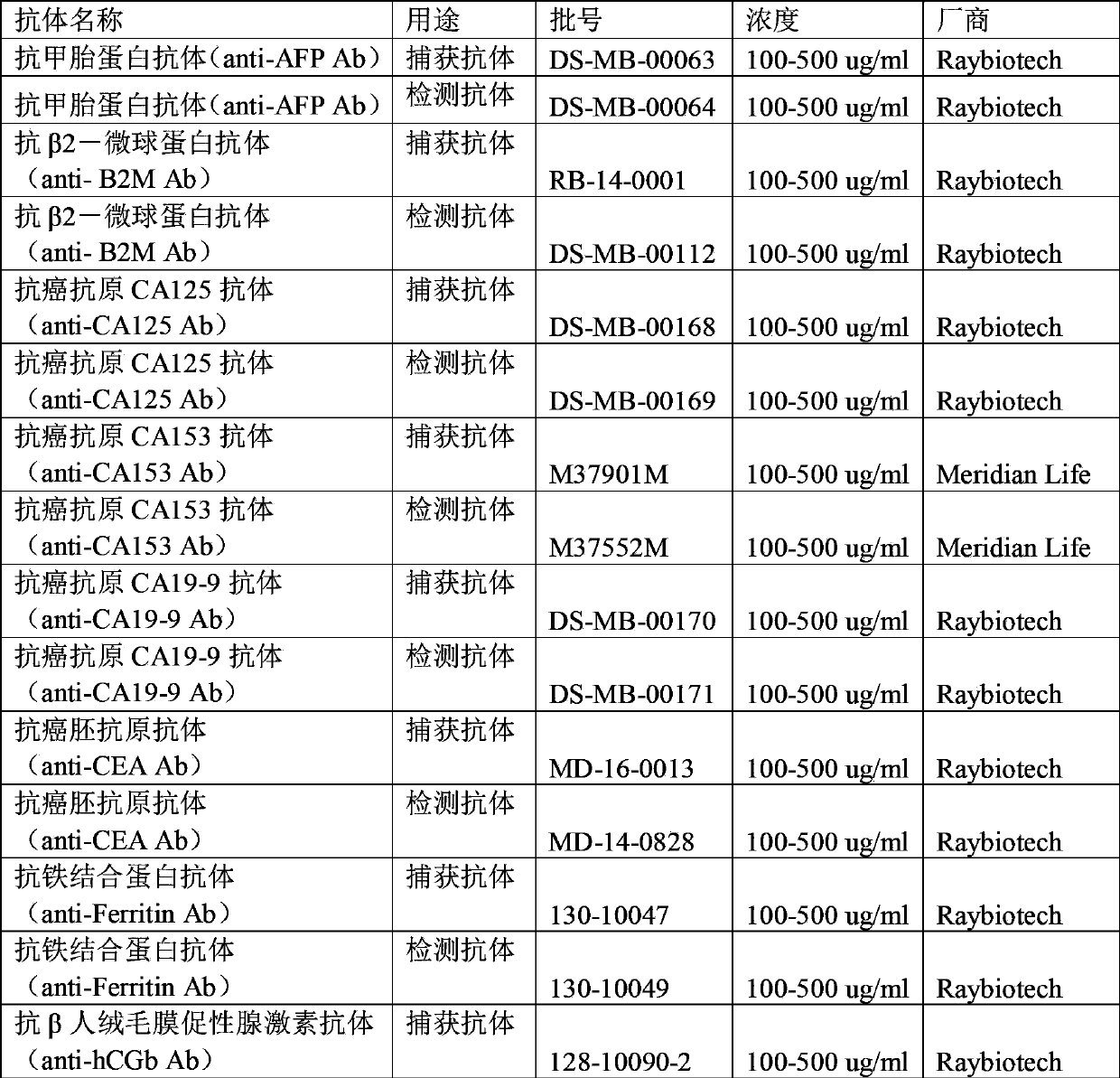
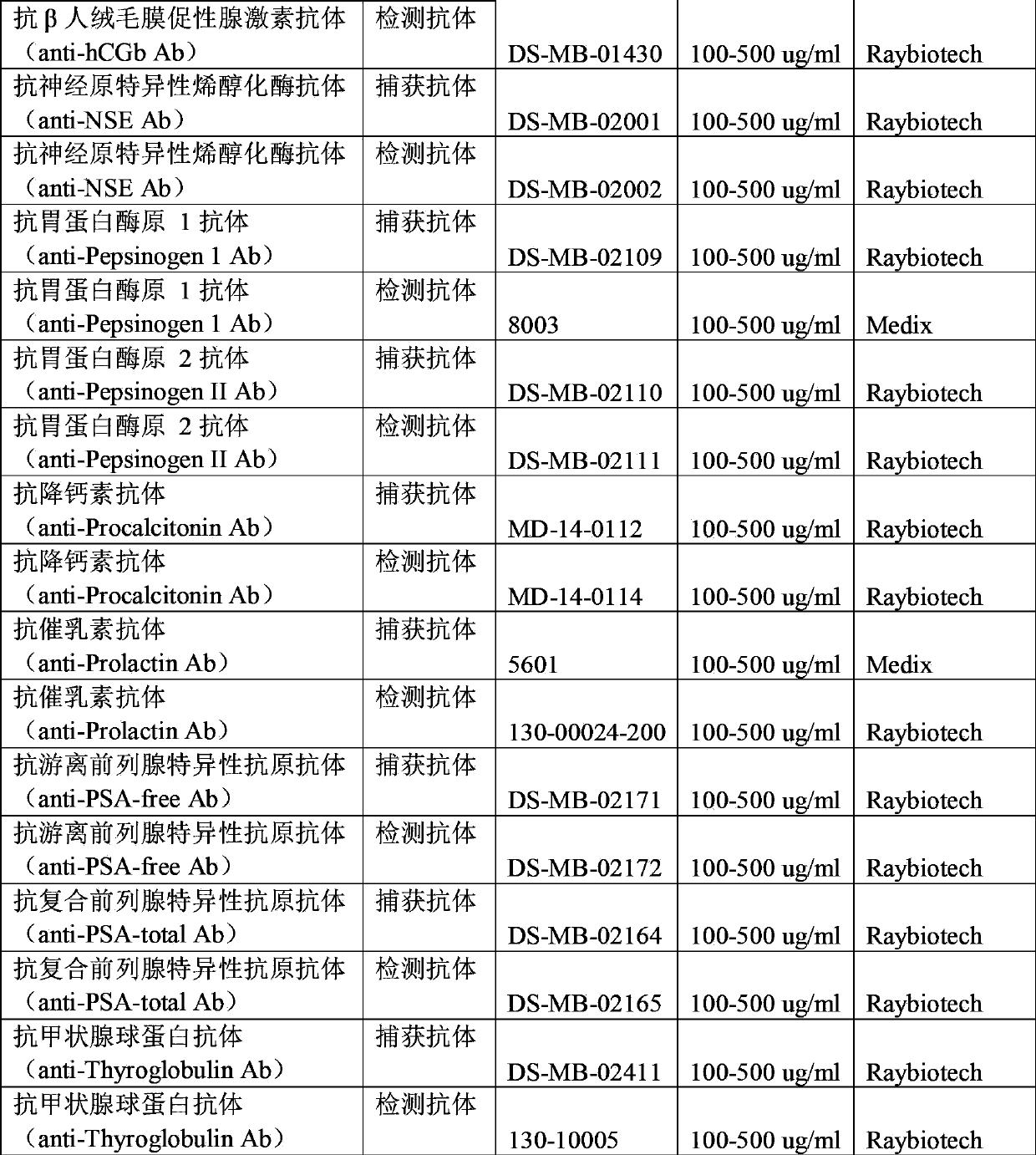
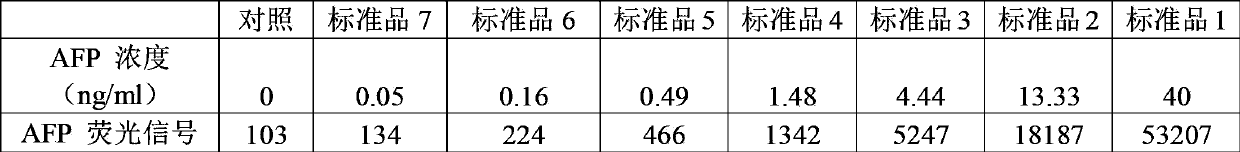
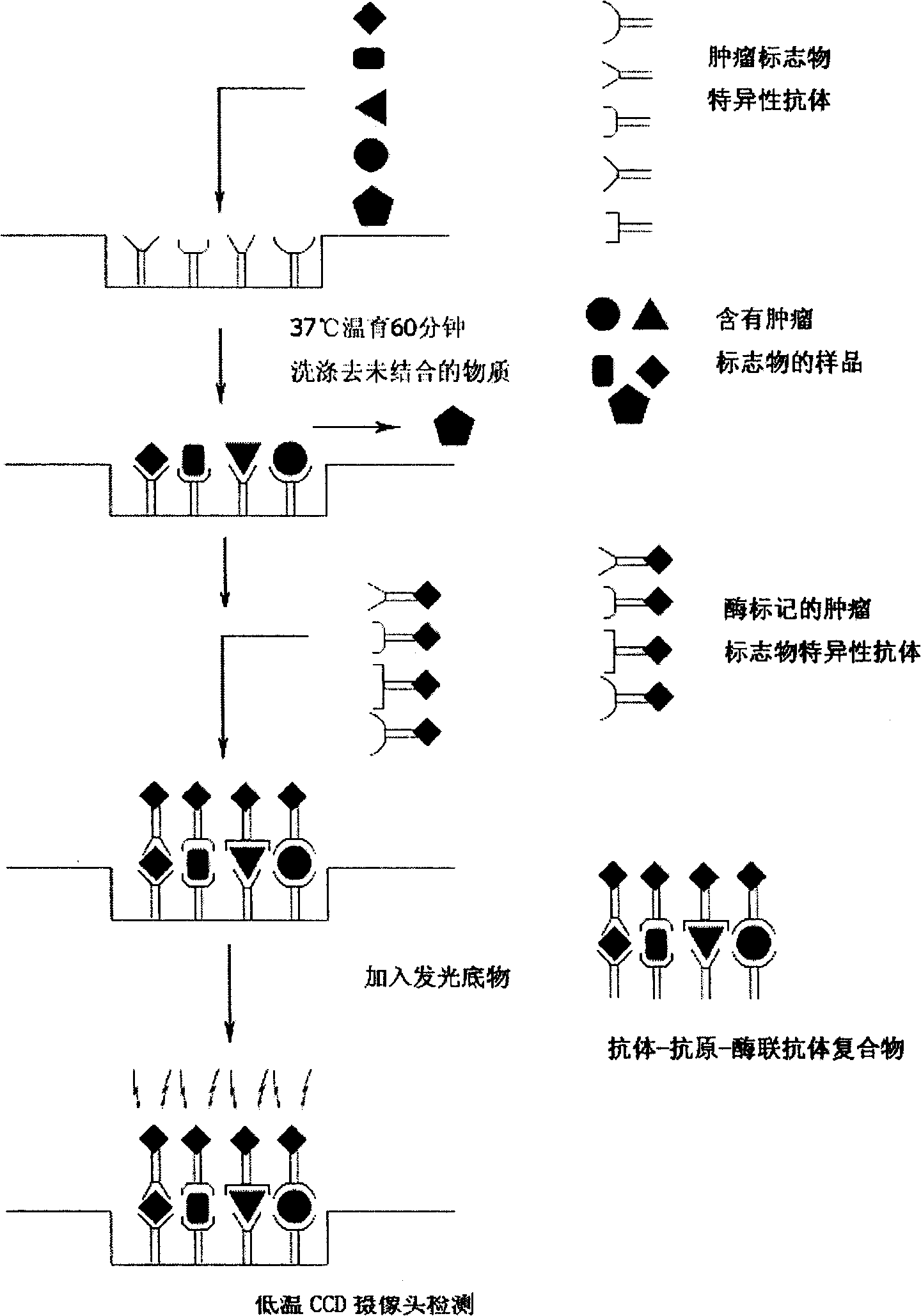
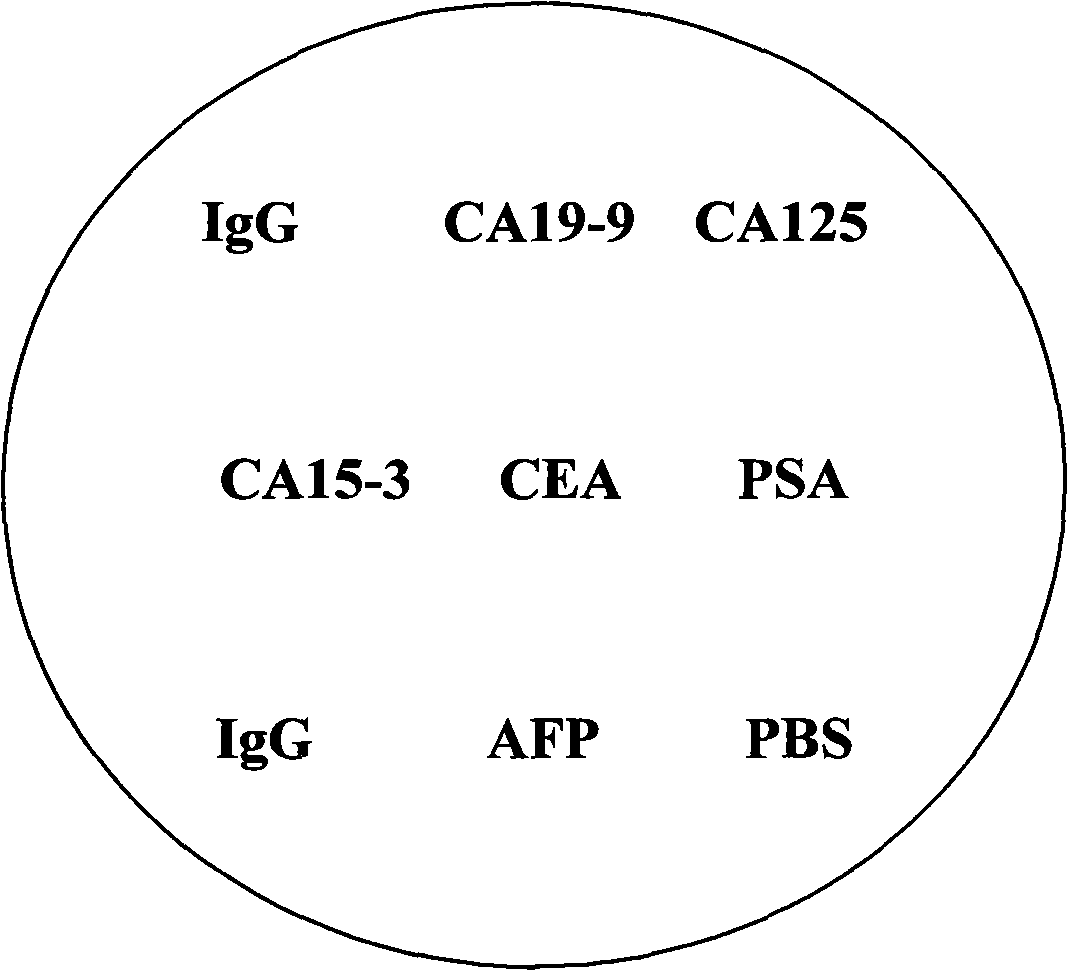
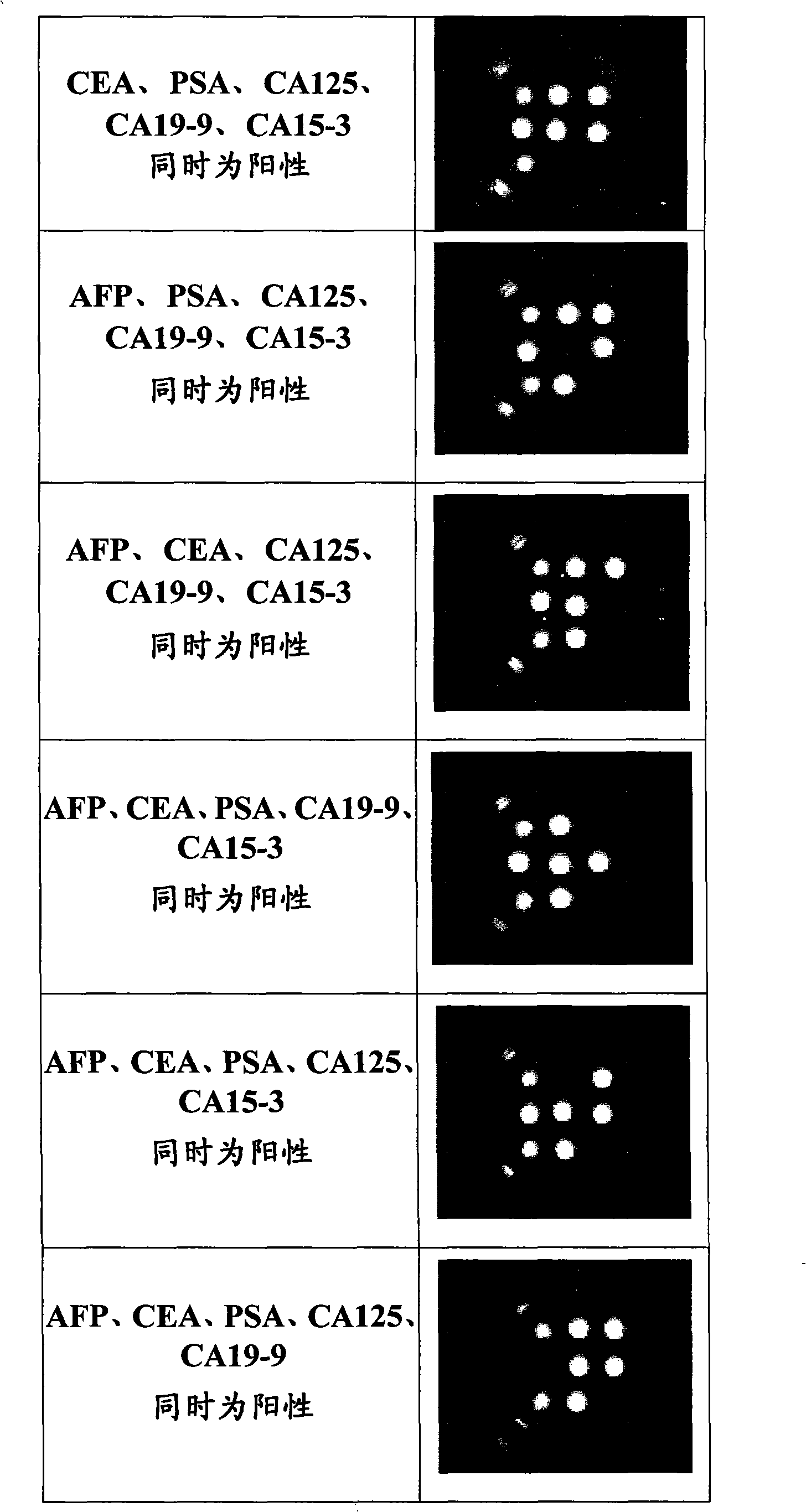
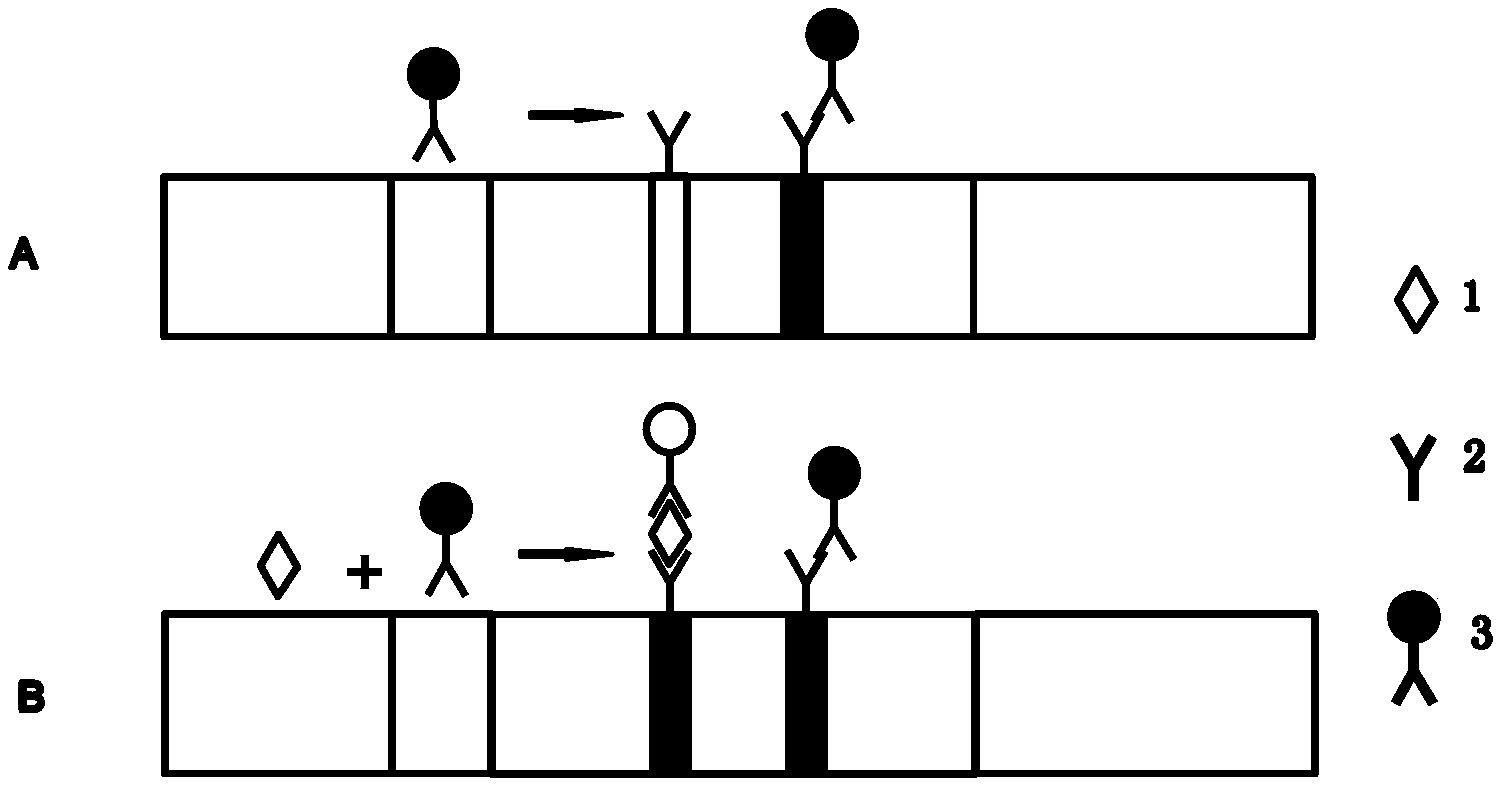
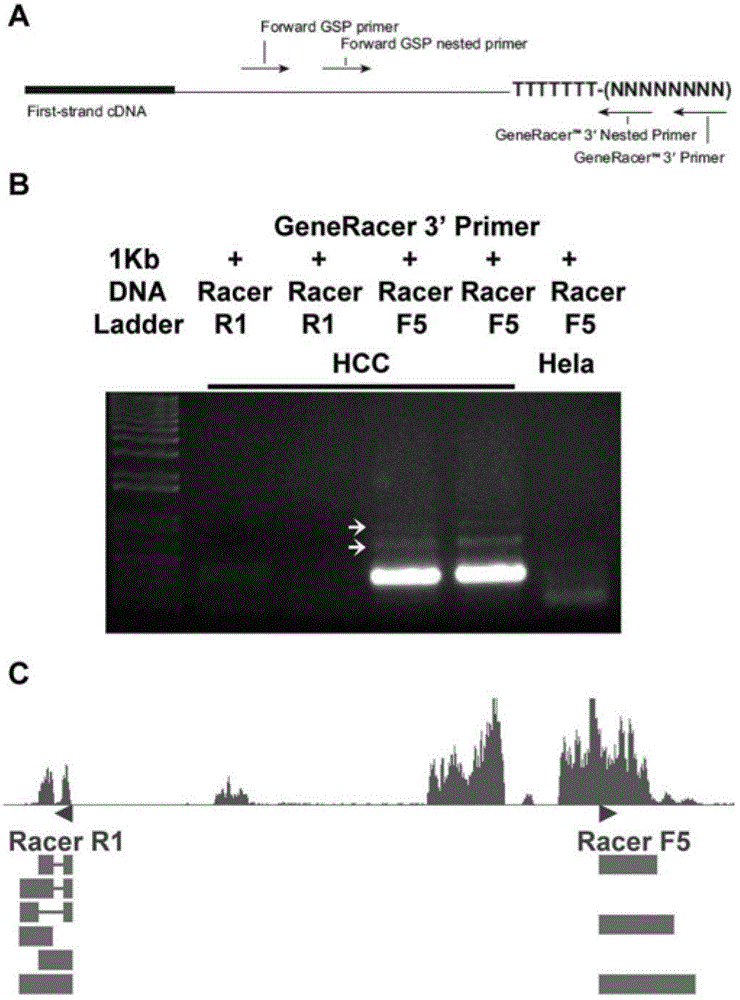
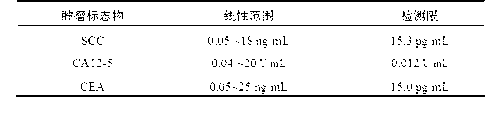
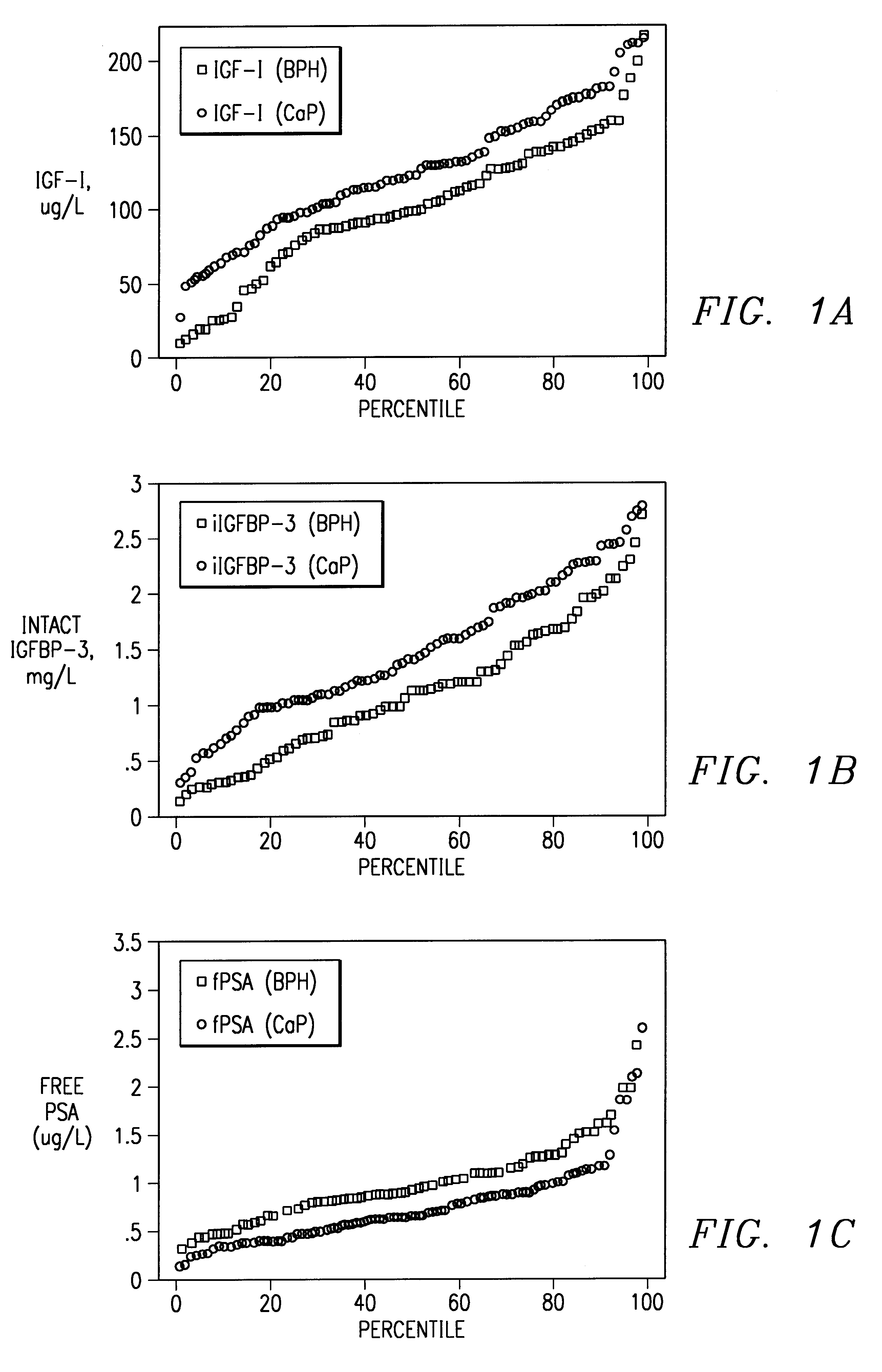
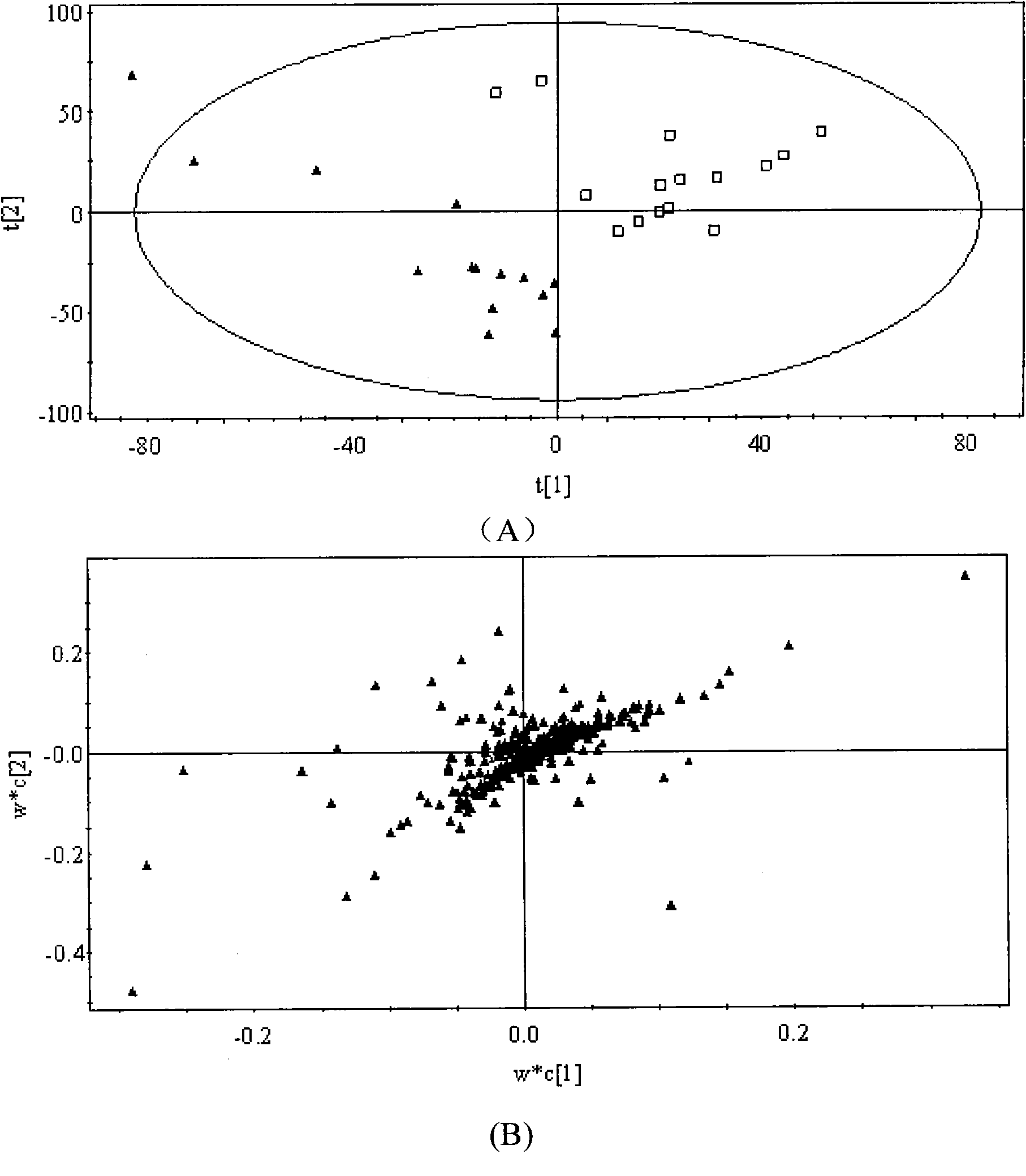Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1276 results about "Tumor marker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
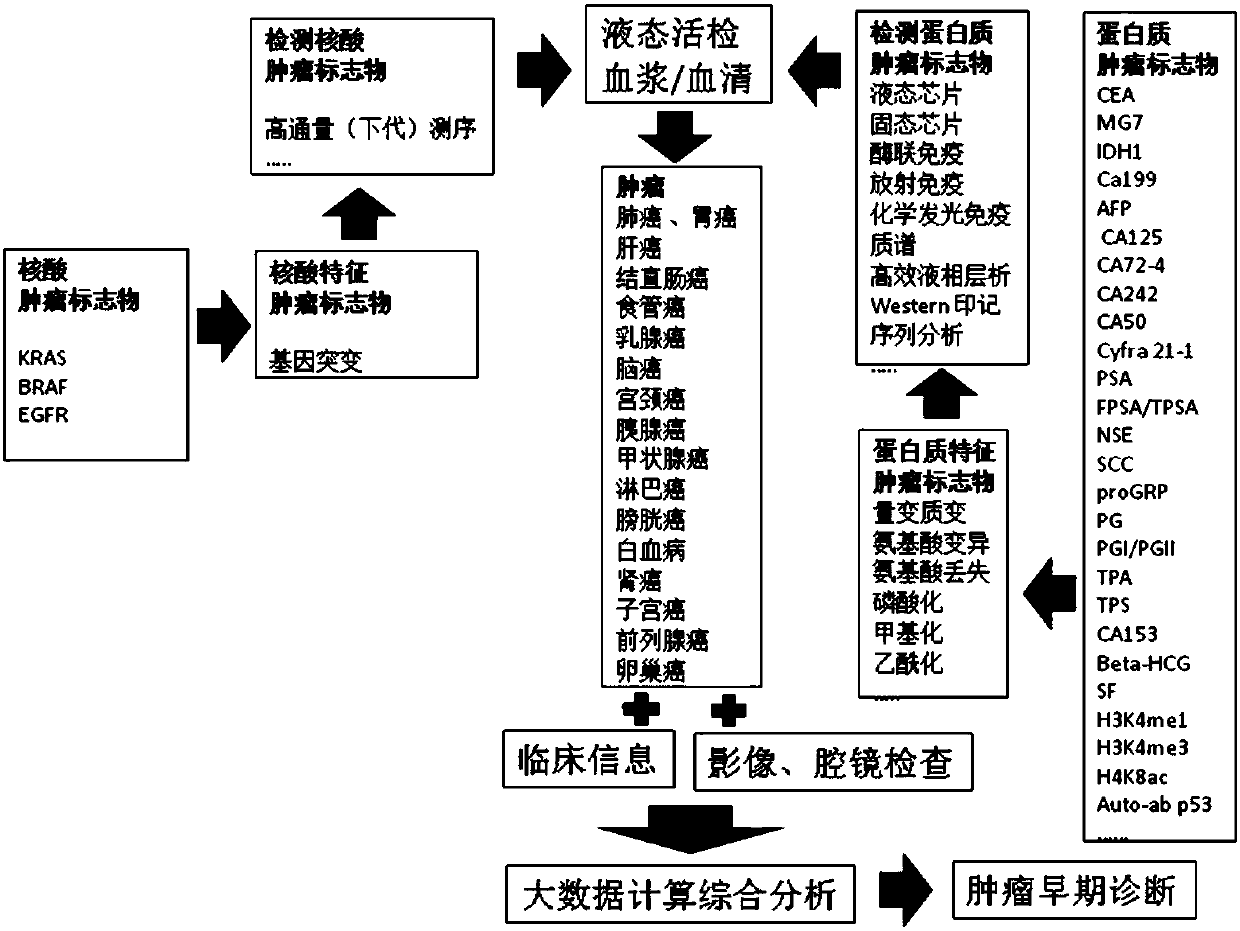
A tumor marker is a biomarker found in blood, urine, or body tissues that can be elevated by the presence of one or more types of cancer. There are many different tumor markers, each indicative of a particular disease process, and they are used in oncology to help detect the presence of cancer. An elevated level of a tumor marker can indicate cancer; however, there can also be other causes of the elevation (false positive values).
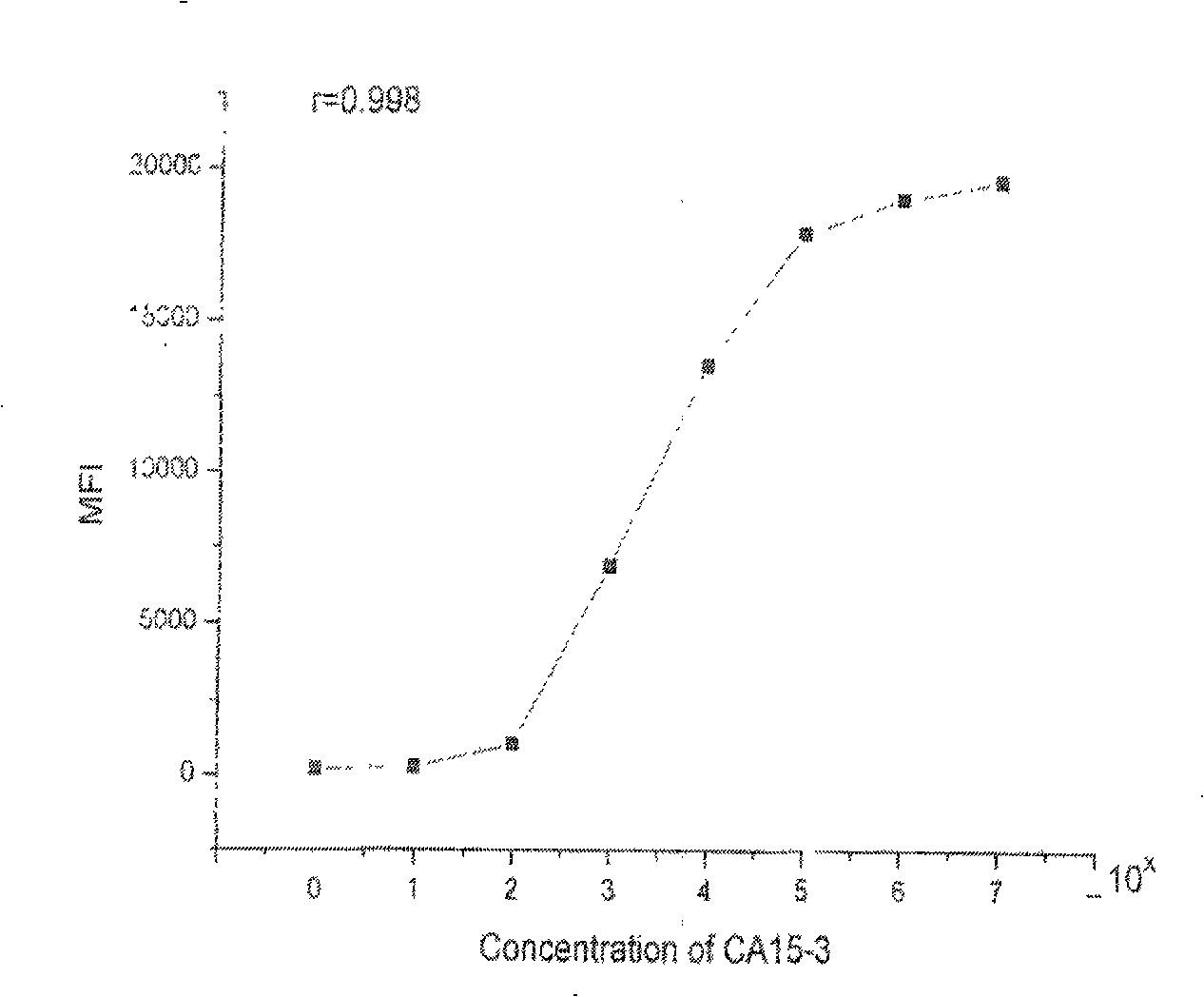
Liquid phase chip for joint detection of multiple tumor markers and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a liquid phase chip for joint detection of multiple tumor markers and a preparation method thereof. The liquid phase chip comprises micro-balloons of a coupled antibody (at least two of the followings: AFP, CEA, CA125, CA153, CA19-9, CA242, CA72-4, PSA, HGH, Beta-HCG), corresponding biotin-labeled detection antibodies, streptavidin phycoerythrin and vegetable hydrosol or polysaccharide hydrosol which has a solute content of 1-10 wt per thousand and does not contain protein. The preparation of the liquid phase chip comprises refining and purification of hydrosol, coupling between captured antibodies and micro-balloons, preparation of biotin-labeled antibodies, dispersing the coupled micro-balloons into the vegetable hydrosol or the polysaccharide hydrosol, and the like. The liquid phase chip has the advantages of stable performance, good micro-balloon dispersivity, long preservation time, fast and convenient use and operation, small amount of samples in use, high detection sensitivity, wide linear scope and low detection cost, can detect ten tumor markers at most at one time, and requires a cost which is a quarter of the total fee of conventional methods.
Owner:HENAN YUKANG BIOTECH
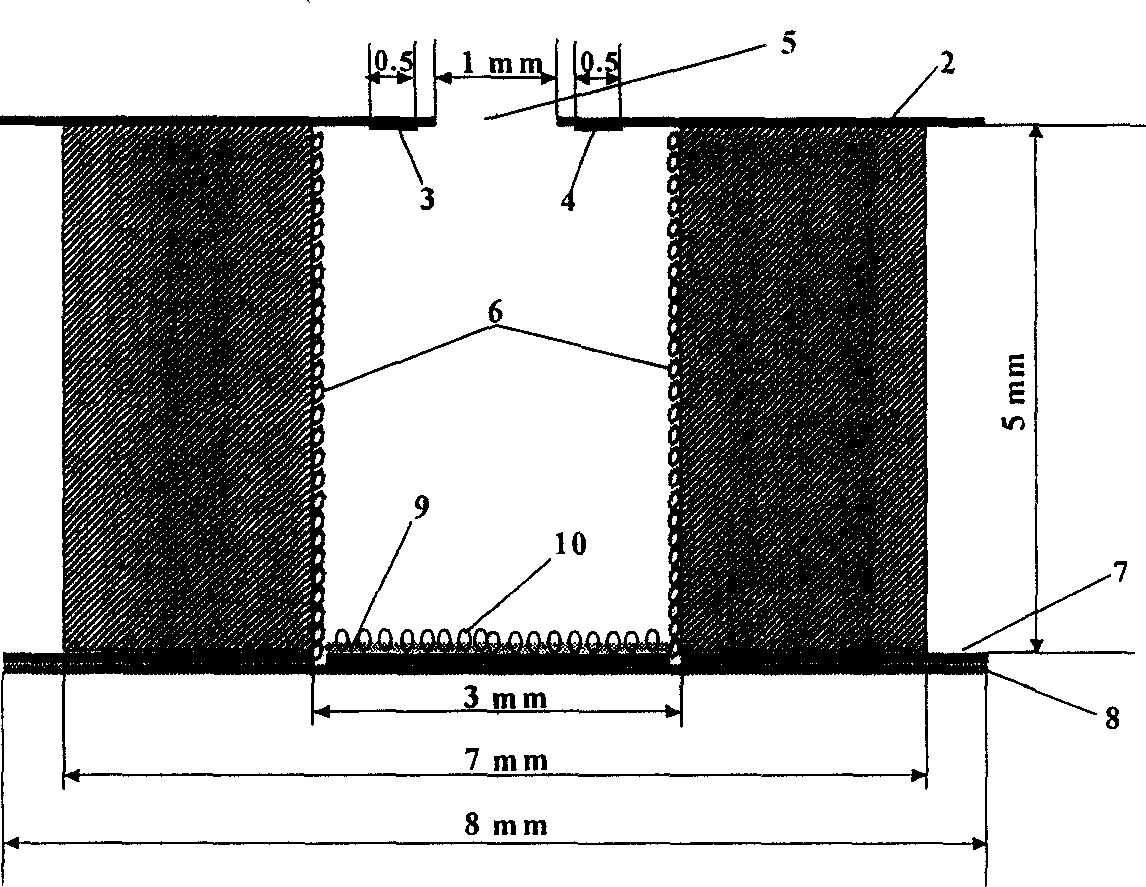
Electrochemcial immunoassay for tumor marker and small size immunoassay chip
InactiveCN1614405ARapid separation-free assayAvoid pollutionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingAntigenContact free
An electrochemical method for determining immunity of tumor marker includes forming microreaction cell, placing reference and counter electrode above it and fixing antigen molecular functioning film at pool bottom, connecting enzyme labelled antibody to pool bottom at time of only proper quantity of horseradish peroxidase to label tumor marker antibody, obtaining cataltyic current on working electrode by contacting free immune matter with electronic media and having positive ratio of the current to antigen. The microvolume immune determining chip is also disclosed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
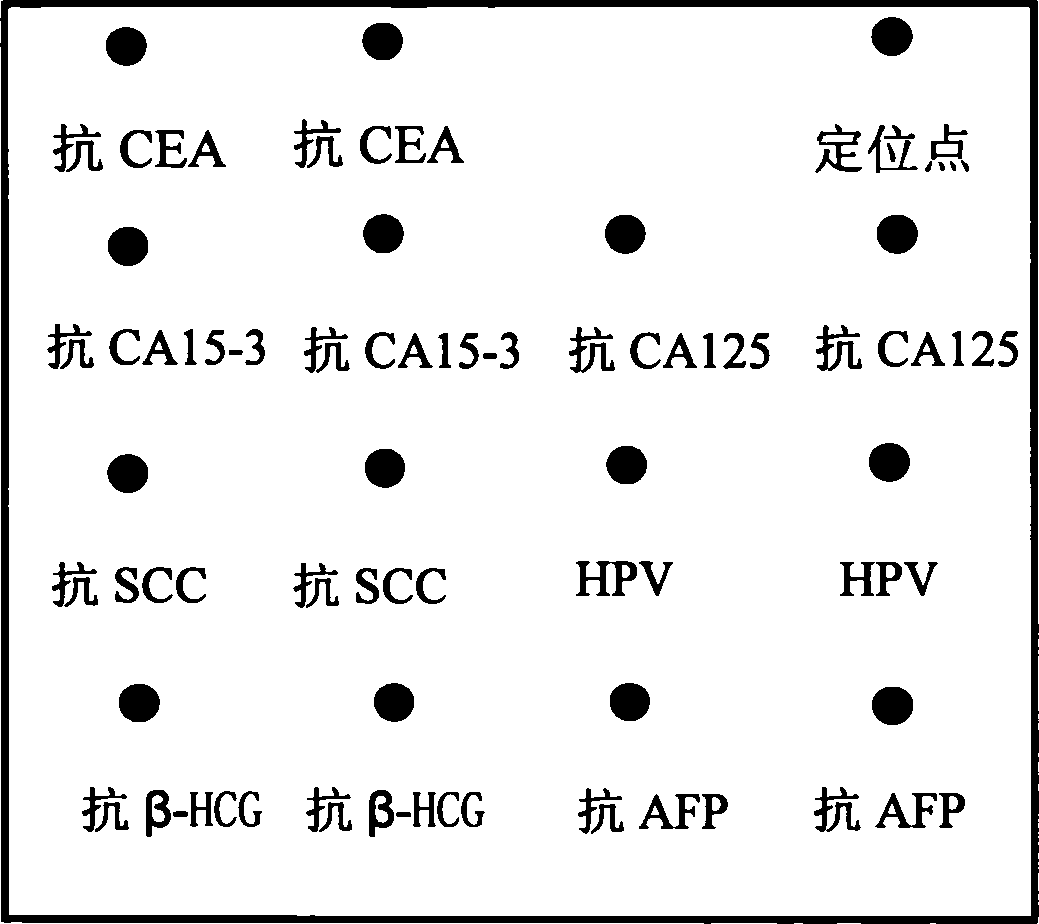
Reaction plate and protein chip kit for integrated detection of multiple gynecologic tumor markers
InactiveCN1880960AChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceColor/spectral properties measurementsCarbohydrate antigenGynecologic Tumor
The invention discloses an integral detecting reacting board and protein chip agent box of Carcinoembryonic antigen,CEA, 15-3 CA15-3(Carbohydrate Antigen 15-3,CA15-3), CA 125 (Cancer antigen 125,CA125), Squamous cell carcinoma antigen,SCC, Human papillomavirus antibody,HPVAb, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, beta-HCG and alpha-fetoprotein,AFP, wherein the reacting hole board contains base and reacting hole on the base; the reacting hole contains 2-384 sample holes, 2-200 standard sample holes; the fixing phase carrier is set on the bottom of each reacting hole, which is covered by seven antigen or antibody molecule arrays with anti-CEA, anti-CA15-3,anti-CA125,anti-SCC,HPV,anti- beta-HCG,anti-AFP.
Owner:汪宁梅
Fluorescent silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20130039848A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAntibacterial agentsDiseaseCellular component
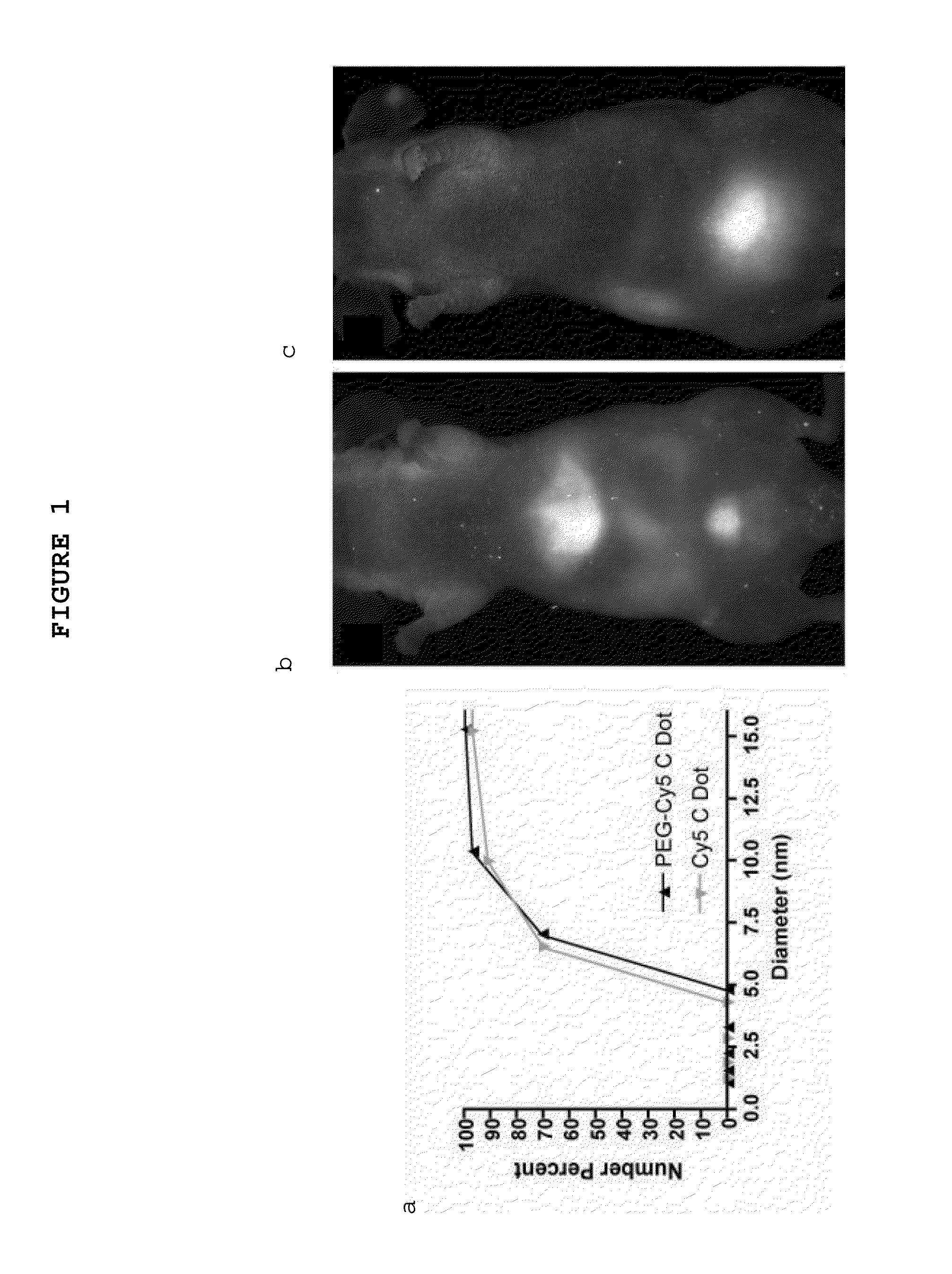
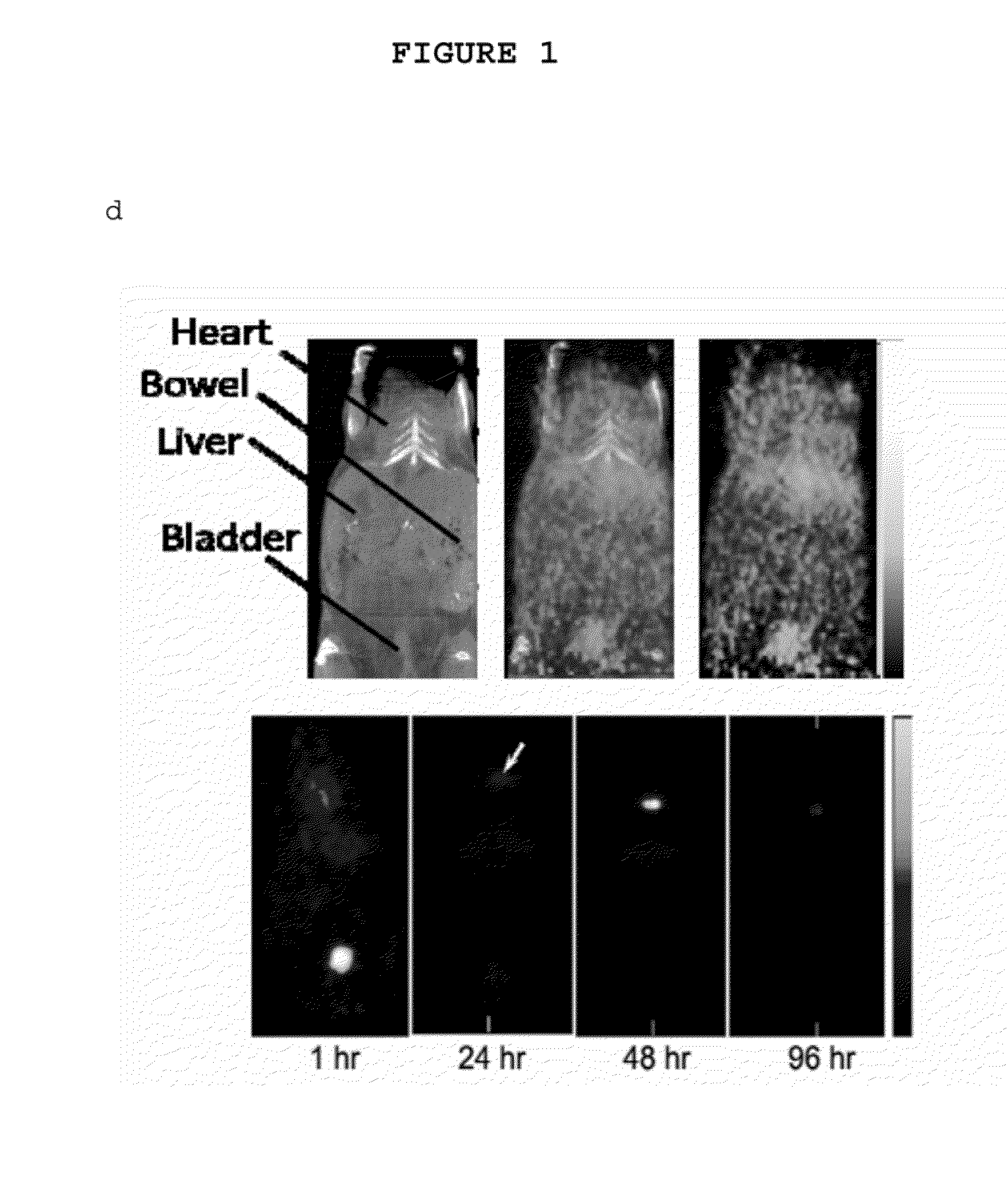
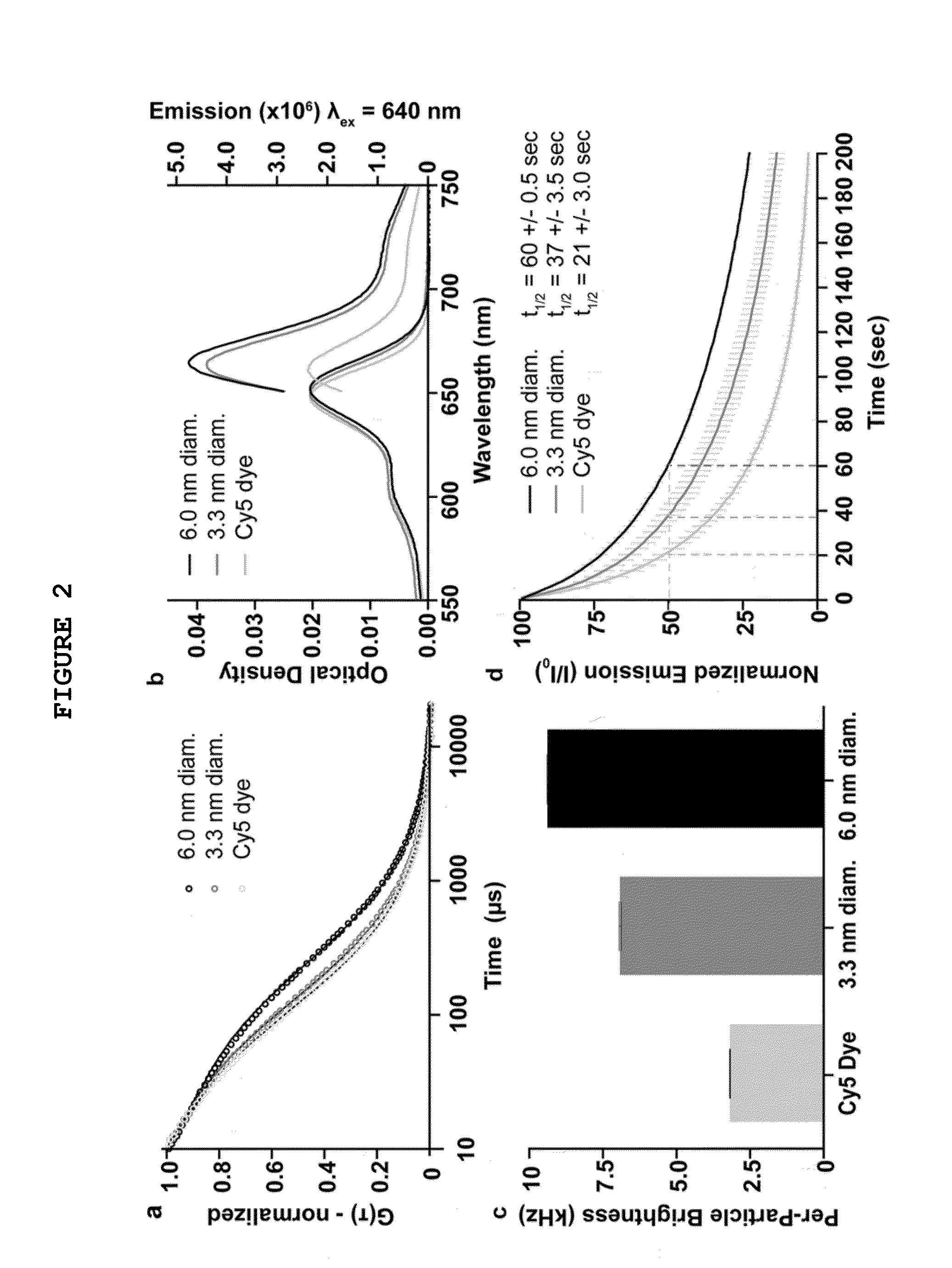
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as polyethylene glycol) (PEG) The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo The nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker A therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle Radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle to permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by various imaging techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
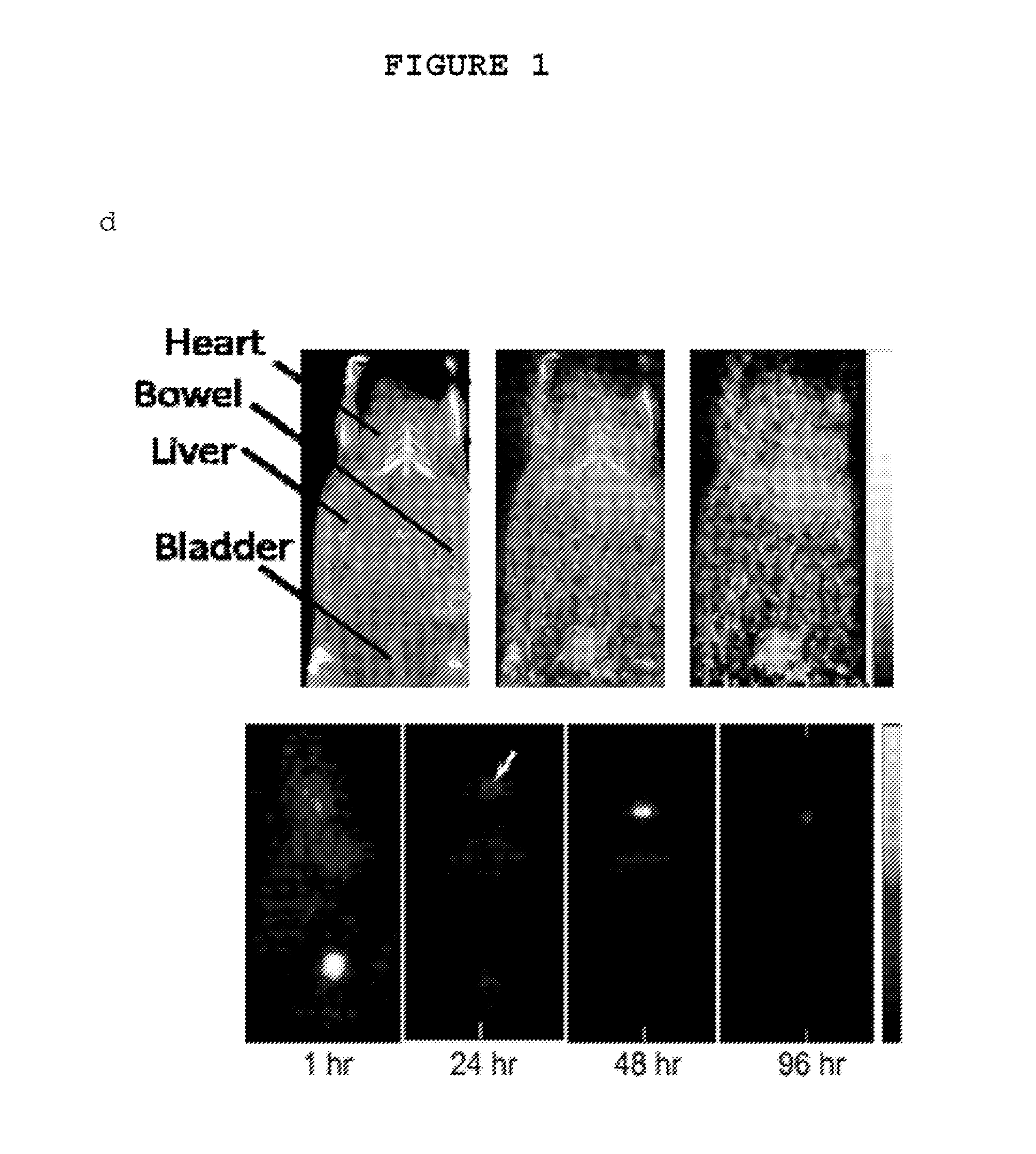
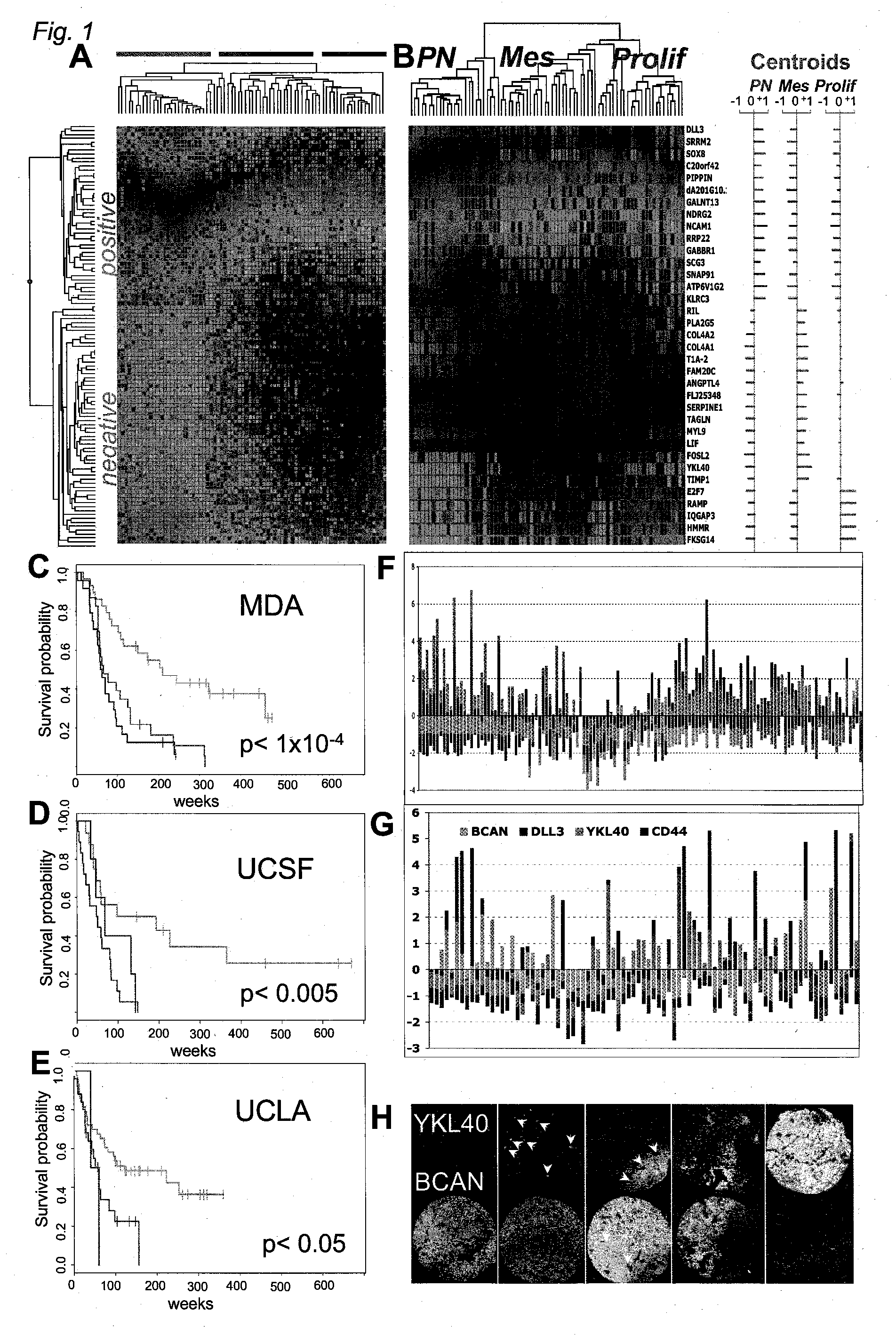
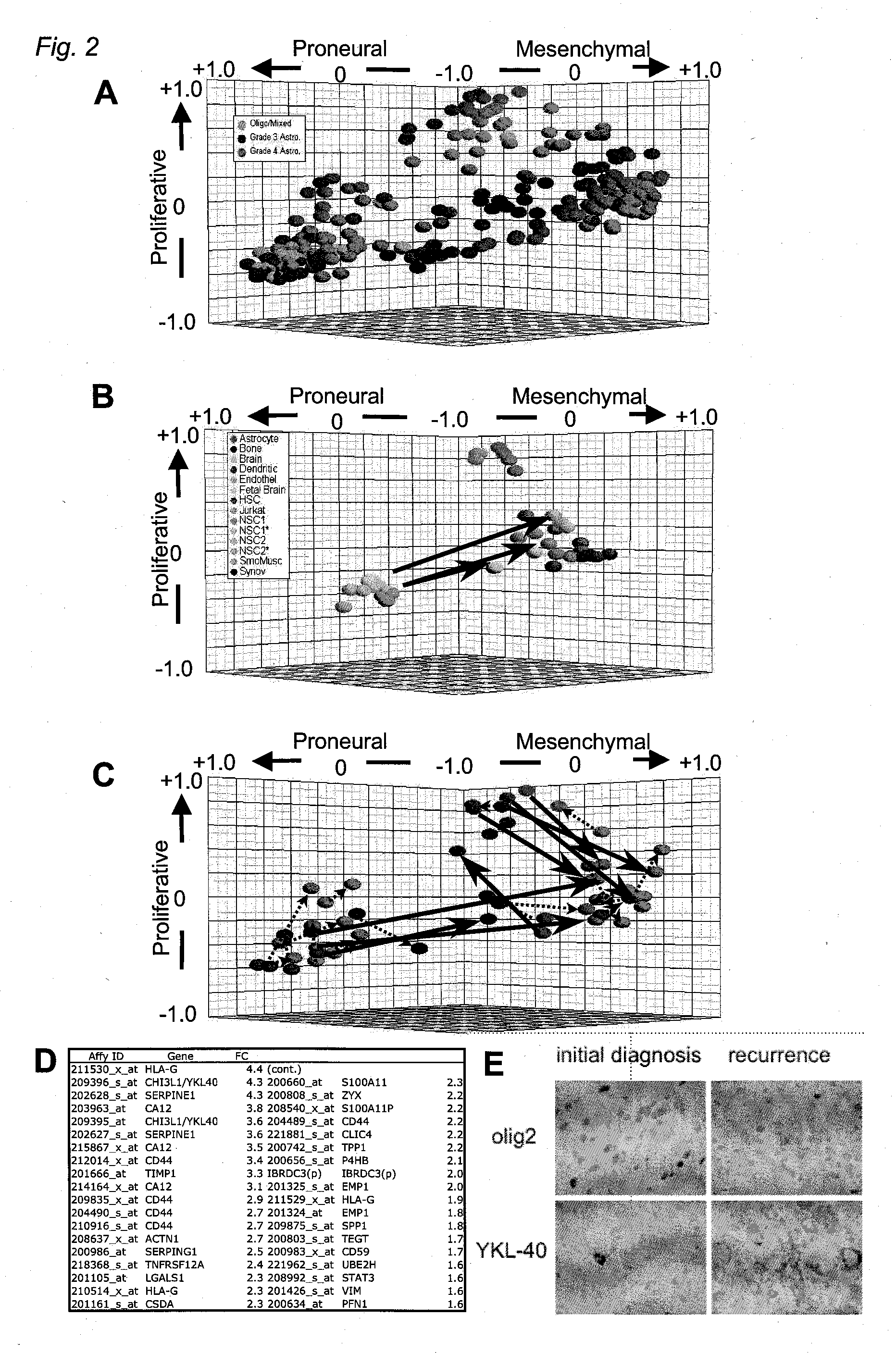
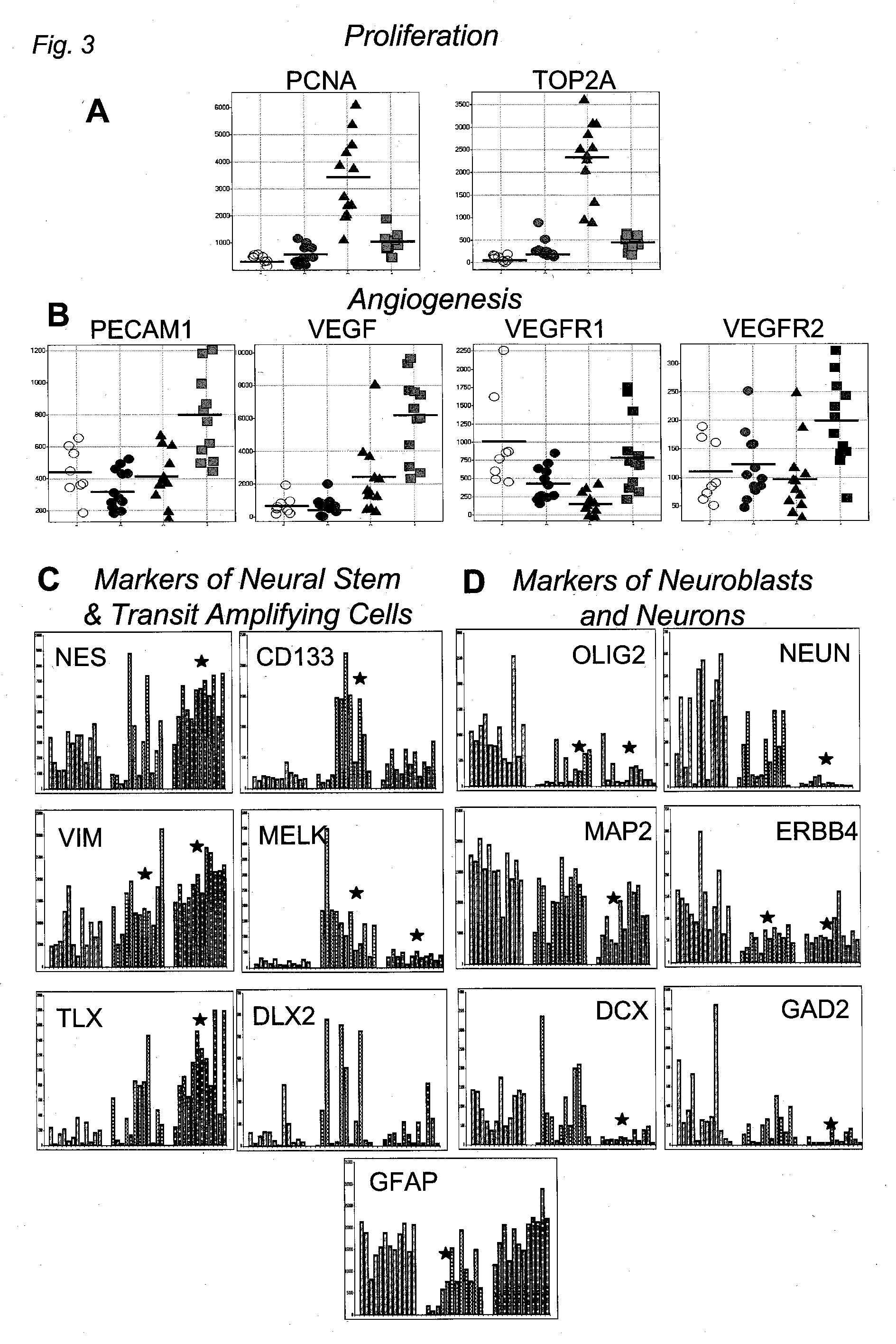
Method for Diagnosing, Prognosing and Treating Glioma
InactiveUS20070141066A1Long median patient survivalShort overall survivalHeavy metal active ingredientsCompound screeningAbnormal tissue growthAnti mitotic
The invention provides generally a method of monitoring, diagnosing, prognosing and treating glioma. Specifically, the invention provides for three (3) prognostic subclasses of glioma, which are differentially associated with activation of the akt and notch signaling pathways. Tumor displaying neural or proneural PN lineage markers (including notch pathway elements) show longer median patient survival, while the two remaining tumor markers Prolif and Mes are associated with shortened survival. Tumors classified in this manner may also be treated with the appropriate PN- Prolif- or Mes-therapeutic corresponding to the subclassification in combination with anti-mitotic agents, anti-angiogenic agents, Akt antagonists, and neural differentiation agents. Alternatively, the invention also provides for method of prognosing and diagnosing glioma with a two-gene model based on the expression levels of PTEN and DLL3.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140248210A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryCellular componentDisease
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer. The nanoparticle has a range of diameters including between about 0.1 nm and about 100 nm, between about 0.5 nm and about 50 nm, between about 1 nm and about 25 nm, between about 1 nm and about 15 nm, or between about 1 nm and about 8 nm. The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound. The nanoparticle also exhibits high biostability and biocompatibility. To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo. In order to target a specific cell type, the nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand, which is capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker. In one embodiment, a therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle. To permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by not only optical fluorescence imaging, but also other imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomography (CT), bioluminescence imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
Method for stimulating an immune response
InactiveUS6977073B1Stimulating directed immune responseStimulate immune responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsAbnormal tissue growthHematopoietic cell
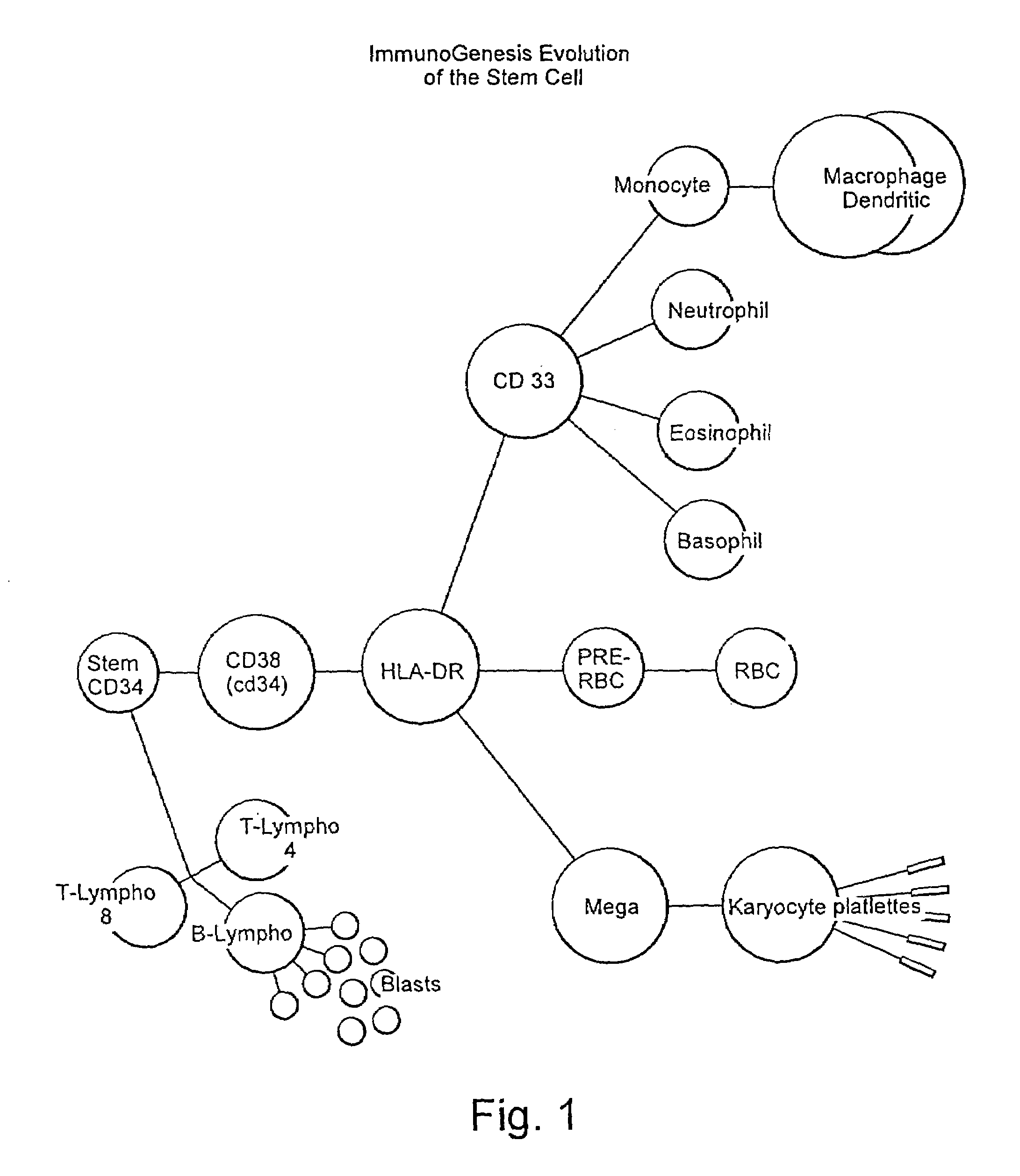
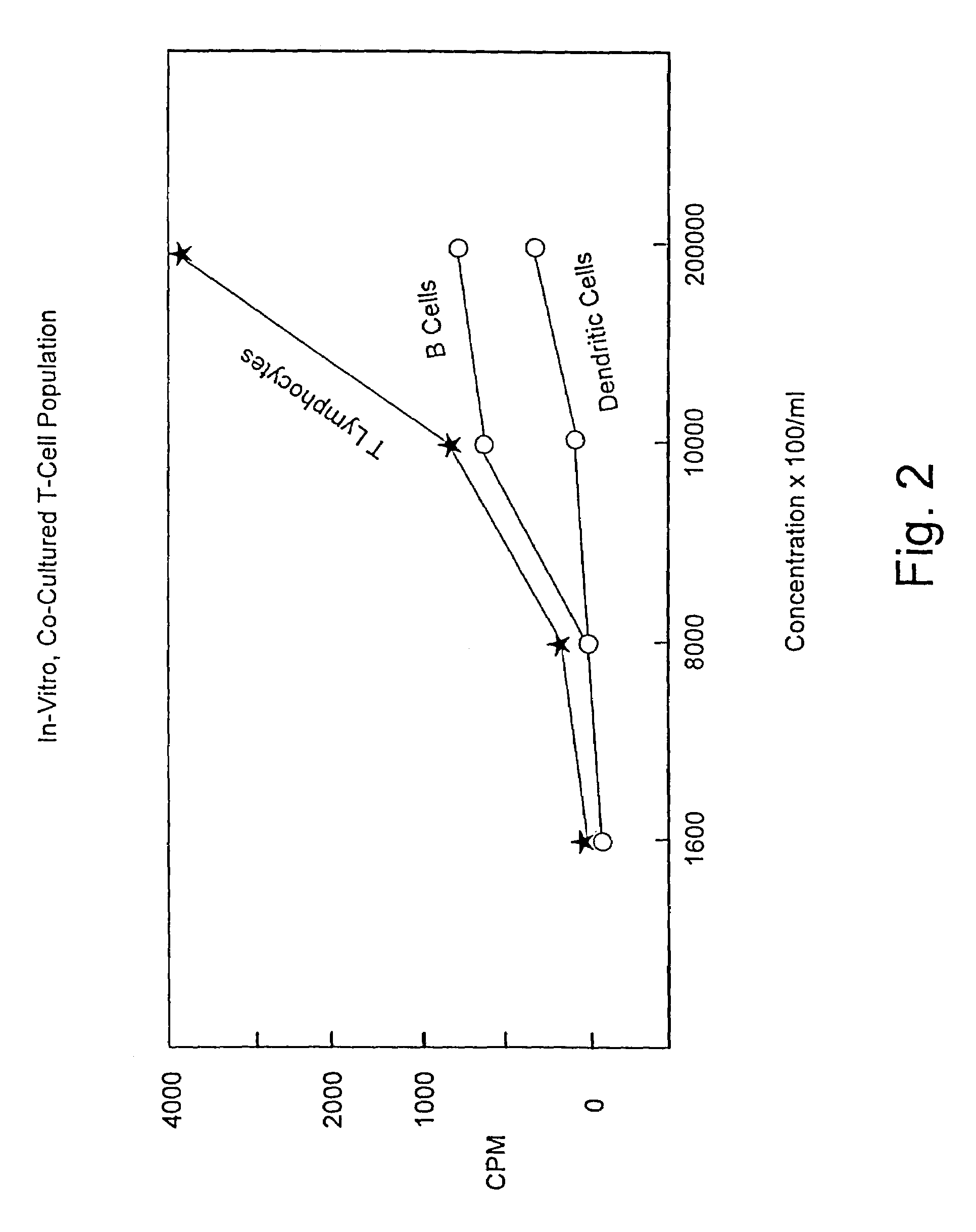
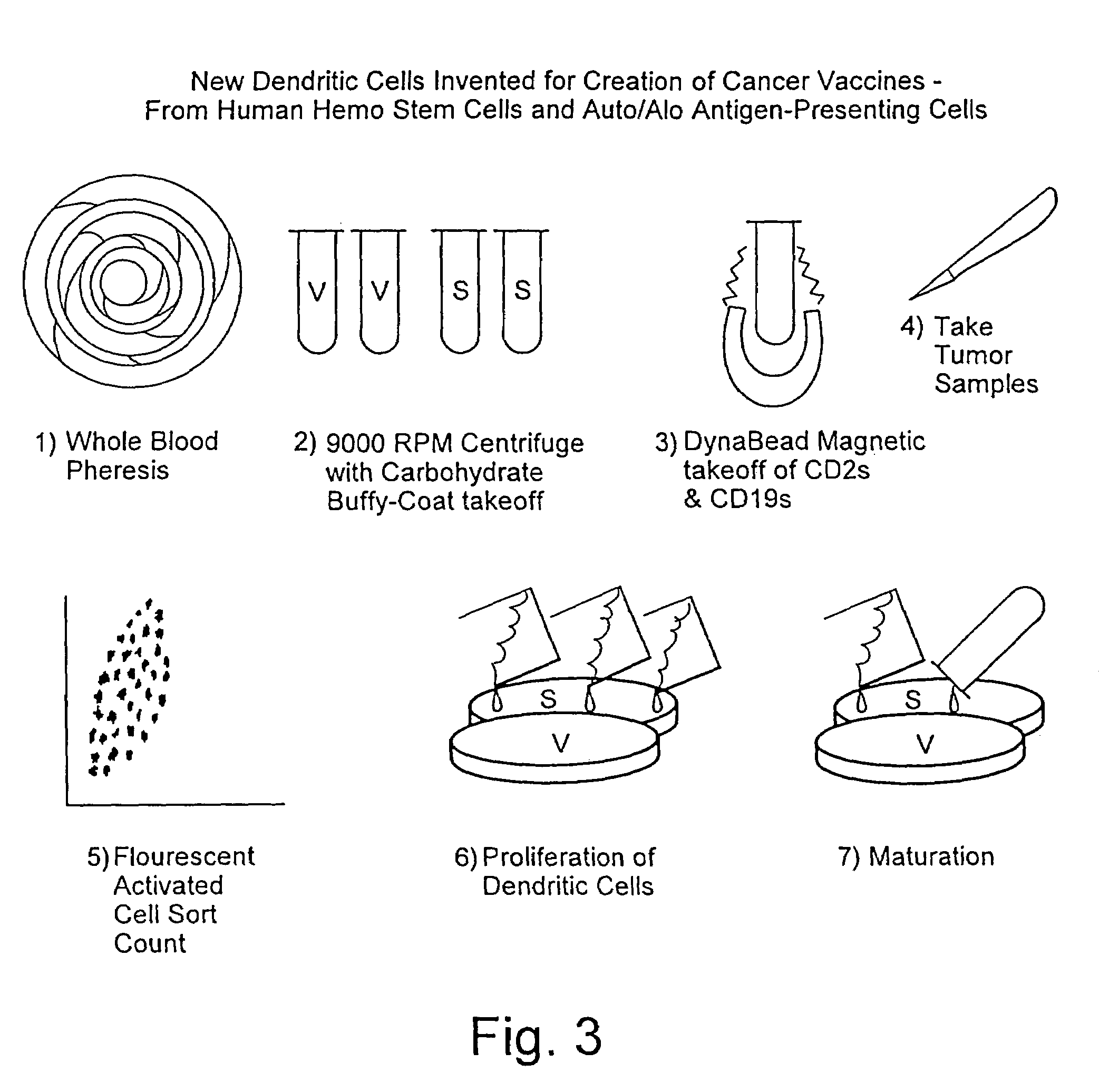
A method is described whereby dendritic cells derived from the CD34+ and CD 34−hematopoietic cell lineages are directed to become programmable antigen presenting cells. The programmed cells may be pulsed with tumor cell RNA or tumor cell RNA expression products. The protocol provides for directing the maturation of dendritic cells to become antigen presenting cells. The protocol further provides for isolating tumor cell RNA from biopsy material that has been prepared in paraffin block storage. The directed dendritic cell is provided with a plurality of tumor markers by using tumor RNA in toto, the poly A+RNA fraction or the expression product of such RNA. Once activated the dendritic cells are incubated with T4 and T8 lymphocytes to stimulate and sensitize the T lymphocytes which upon introduction either into a donor host or a nondonor recipient will provide immune response protection.
Owner:CEZAYIRLI CEM
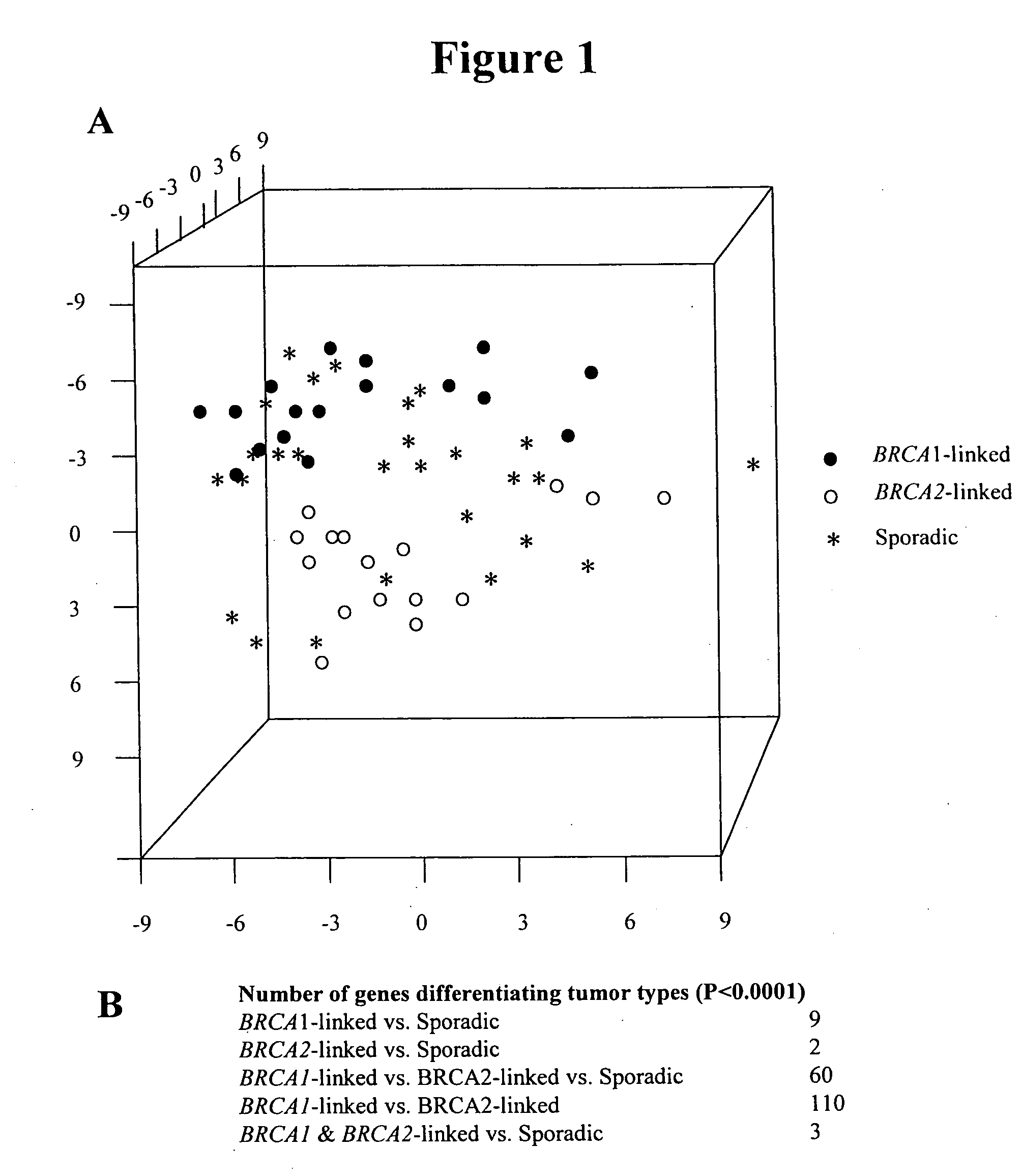
Identification of ovarian cancer tumor markers and therapeutic targets
The present disclosure provides methods for classifying ovarian tumors into BRCA1-type, BRCA2-type or non-BRCA-type tumor types by measuring expression levels of a plurality of disclosed ovarian tumor markers. The markers disclosed herein are useful in the diagnosis, staging, detection, and / or treatment of ovarian cancer. Also provided are methods of selecting a treatment regimen by selecting the tumor type. Ovarian cancer-linked logarithmic expression ratios and kits for diagnosis, staging, and detection of ovarian cancer using are also provided.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING +1
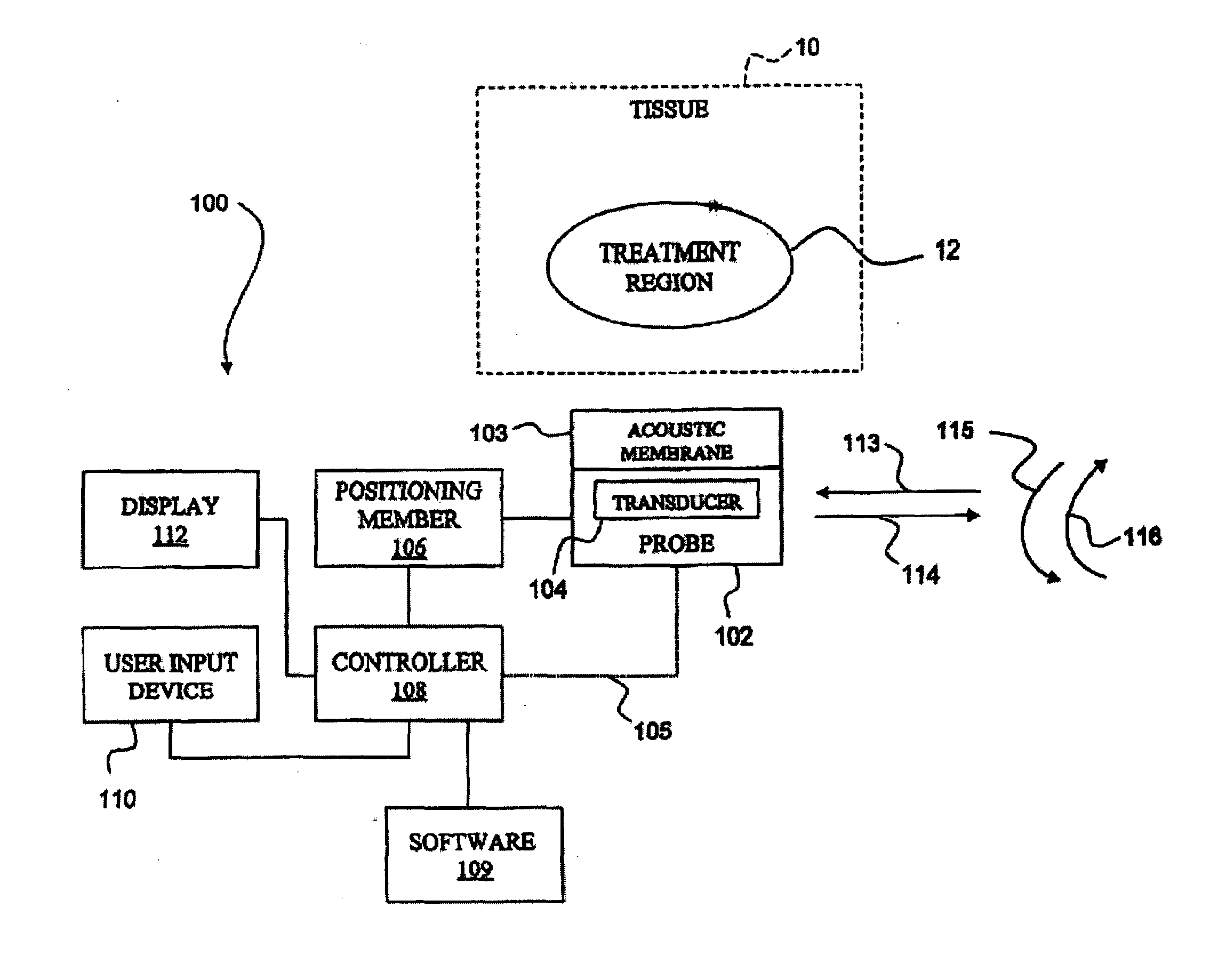
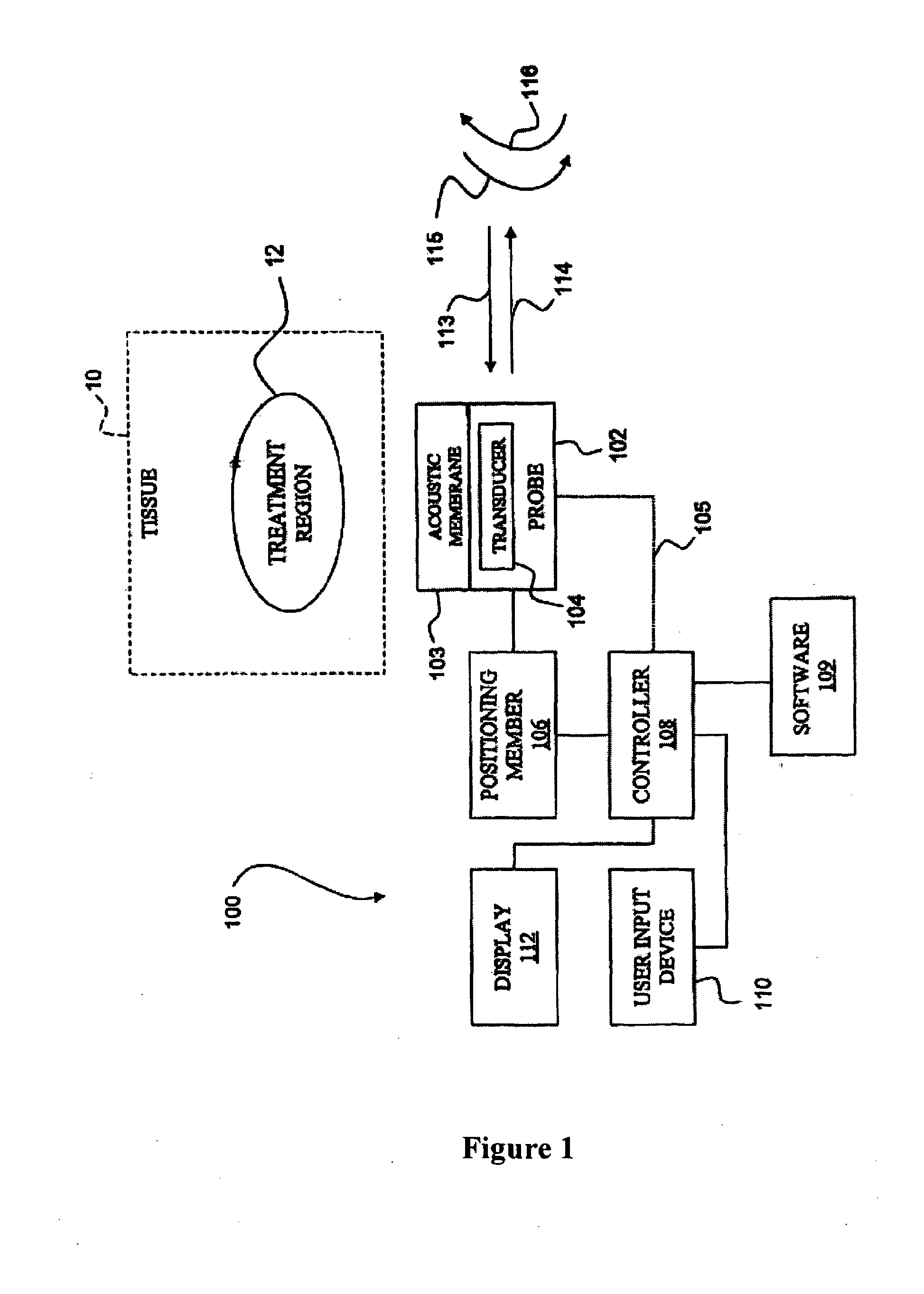
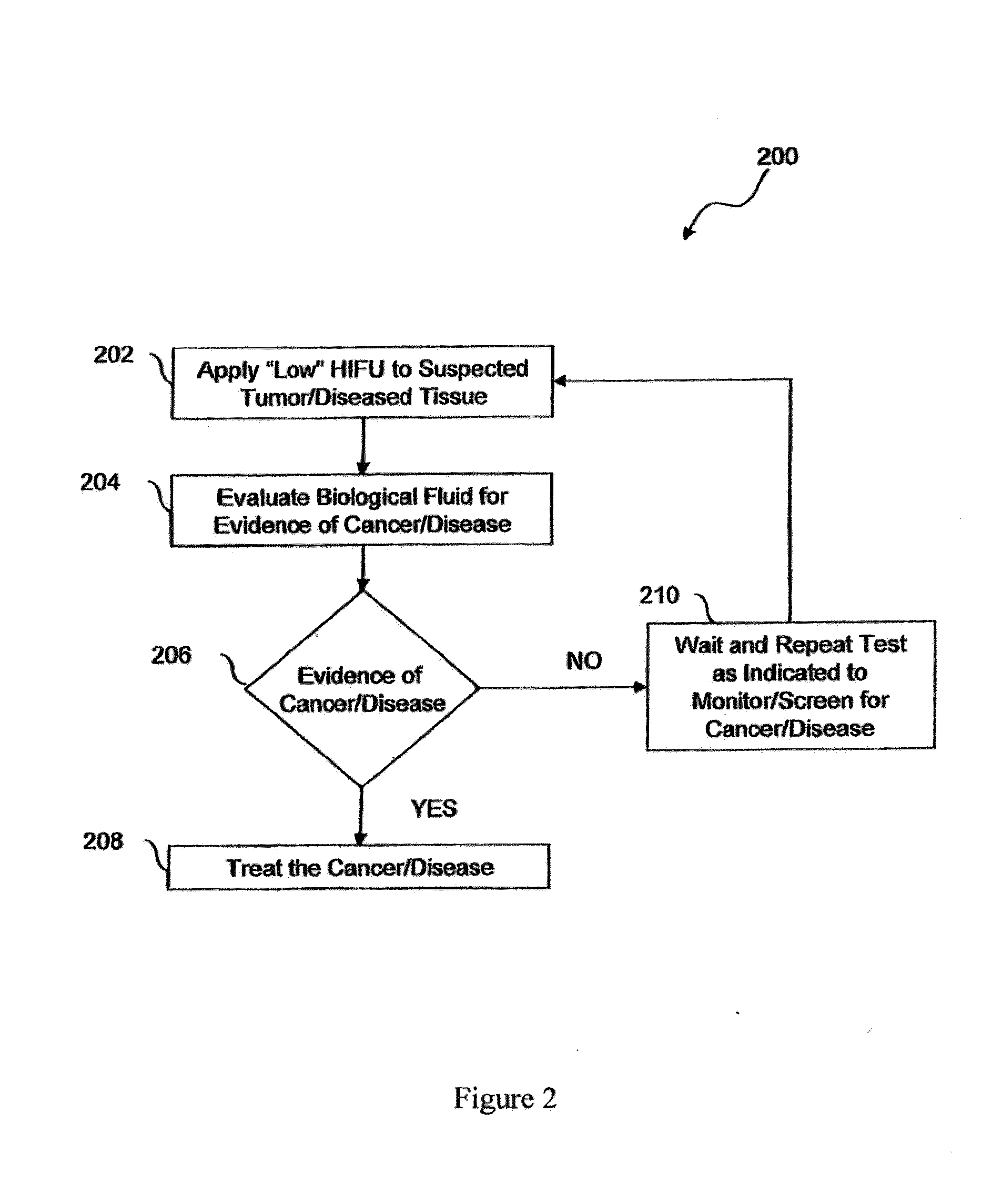
Method of diagnosis and treatment of tumors using high intensity focused ultrasound
InactiveUS20100092424A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRadiologyHigh intensity
A method of diagnosis and treatment of tumors using High Intensity Focused Ultrasound is provided. The method of diagnosing the presence of a tumor in a patient comprises the steps of subjecting a tumor to high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) to cause the tumor cells to release cellular material and evaluating the cellular material for a tumor marker. The method of treating a tumor in a patient can also comprise the step of subjecting a tumor to high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) to provoke an immune response.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Method of age management
InactiveUS20130317315A1Medical devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringApproaches of managementMedicine
A method of age management, by consulting with a patient, performing comprehensive testing on the patient, determining the physiological, functional, and biological age of the patient, and recommending and performing treatments based on the physiological, functional, and biological age of the patient. The performing comprehensive testing is further defined as performing a test of standard plus functional medicine testing, complete hormonal panel, infectious disease panel, tumor markers panel, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ONE LIFE HEALTH
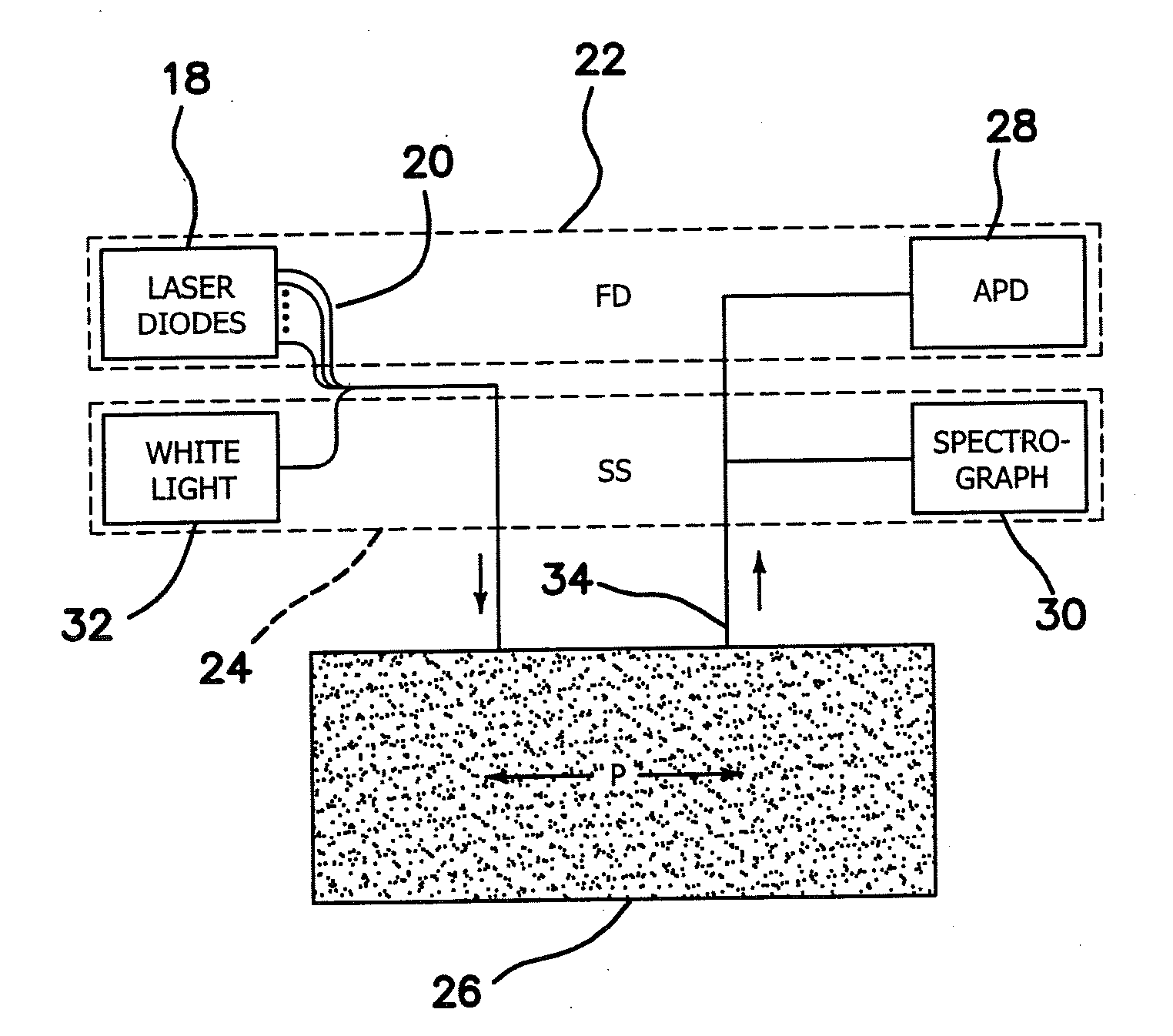
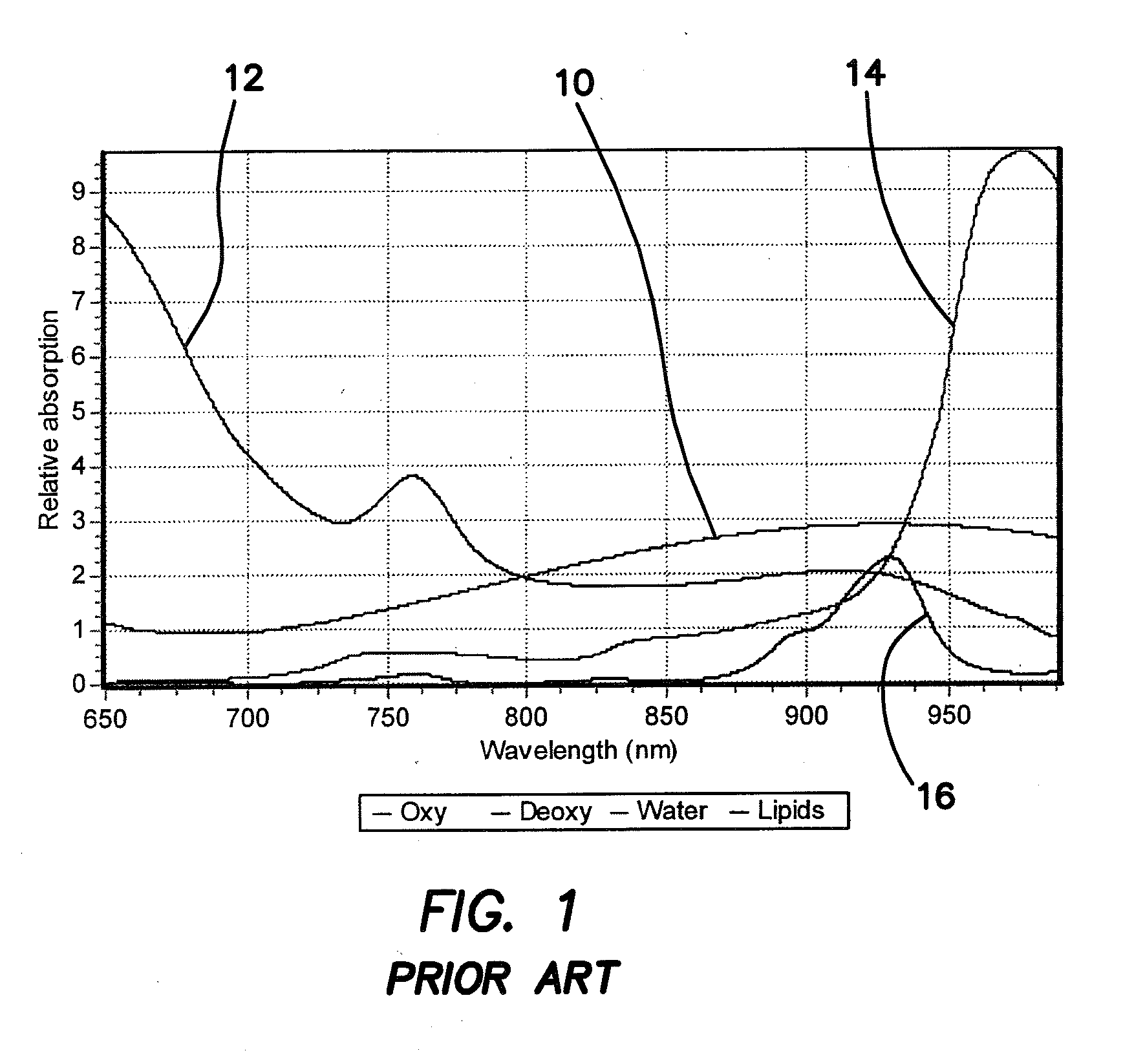
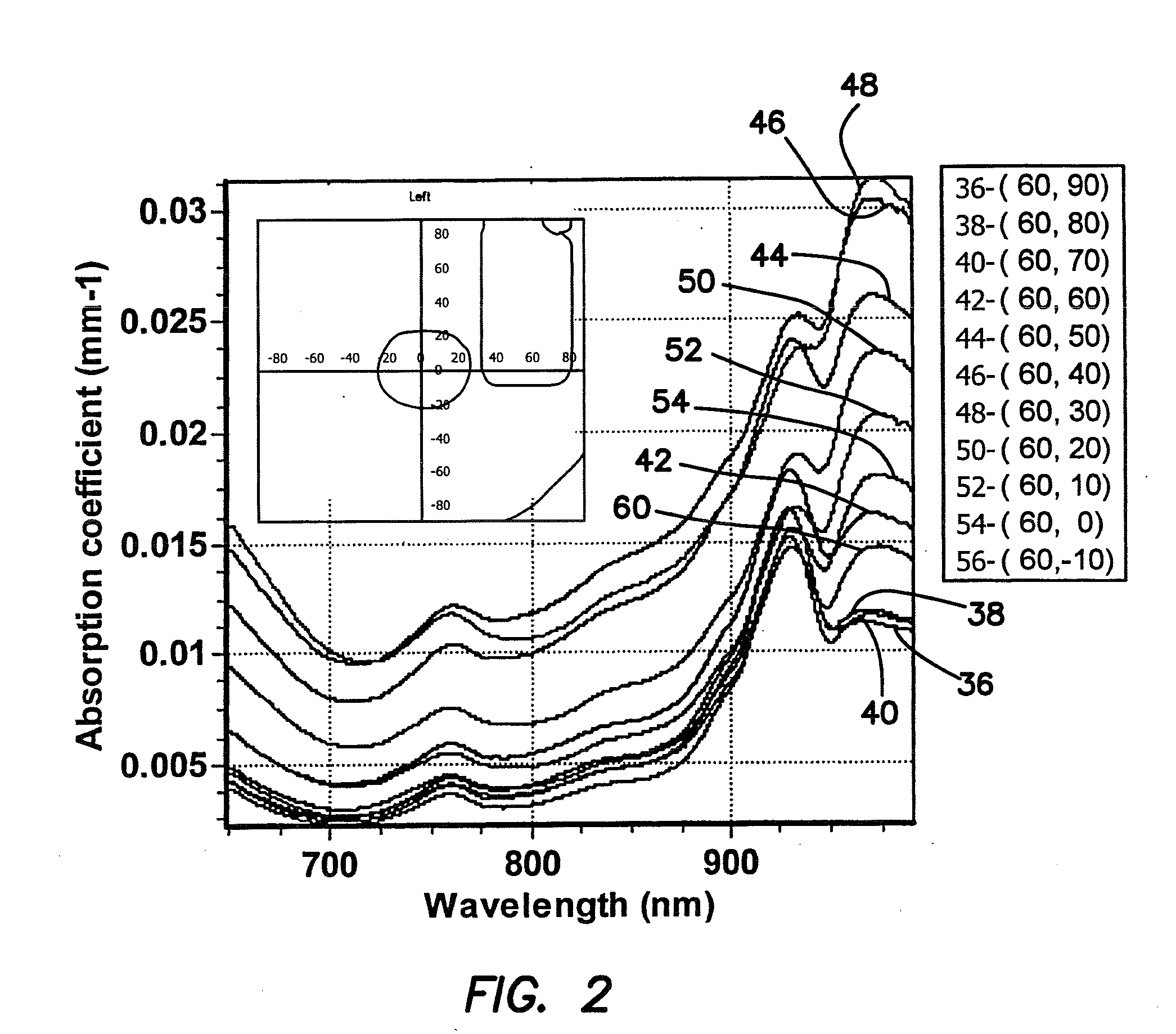
Method and apparatus for the determination of intrinsic spectroscopic tumor markers by broadband-frequency domain technology
InactiveUS20080009748A1Less expensiveDiagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansAbnormal tissue growthMedicine
The illustrated embodiment is an improvement in a method of optically analyzing tissue in vivo in an individual to obtain a unique spectrum for the tissue of the individual, the improvement including the steps of optically measuring the tissue of the individual to obtain a spectrum of an optical parameter, and identifying a spectral signature specific to a metabolic or physiologic state in the tissue of the individual with a unique spectrum for the tissue by considering only the spectral differences between a first metabolic or physiologic state of the tissue of the individual and one or more other metabolic or physiologic states of the tissue of the individual such that identification of the spectral signature is self-referencing with respect to intra-individual metabolic or physiologic variations. The method also includes separating benign and malignant lesions only using the shape or a characteristic of the spectrum.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
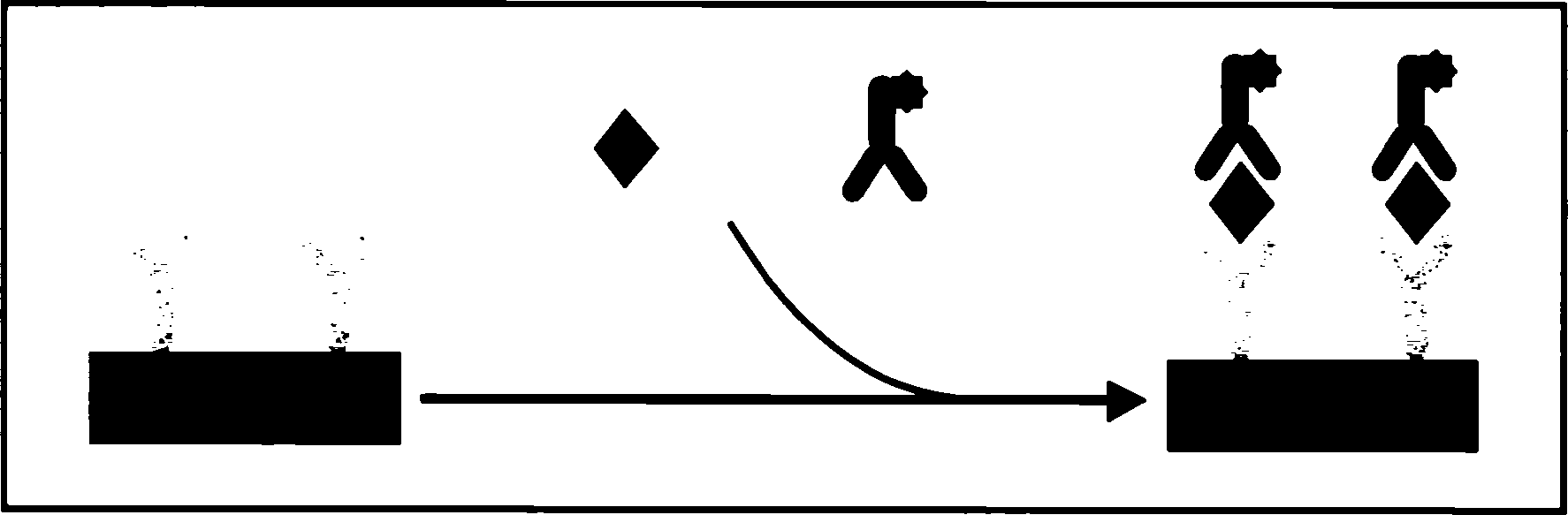
Fluorescence immune chromatography test paper and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN101526534AHigh sensitivityOvercome the easy-to-quench defectBiological testingFiberAntigen
The invention relates to fluorescence immune chromatography test paper which is formed by mutually and sequentially overlapping a sample pad, a combination pad, an antibody carrying film and water absorbing paper on a lining board with adhesive, wherein the combination pad is coated with a fluorescence material antibody 1 composite, a fluorescence-marked material is fluorescein granules or fluorescence material converted by rare earth, the antibody carrying film is a cellulose nitrate film or a nylon film and is respectively connected with an antibody 2 and the T line and the C line of a secondary antibody, the fluorescence material is fluorescein granules or the fluorescence granules converted by the rare earth, and the fluorescein granules are selected from isosulfocyanic acid fluorescein or tetramethyl isosulfocyanic acid rhodamine or tetraethyl rhodamine, and the surface of the fluorescence-marked material is aminated and combined with the antibody by cross-linking reaction. The fluorescence quantitative measuring system is used for detecting the fluorescence strength of the areas of the T line and the C line, and the quantitative detection is completed by the standard curve of the antigen concentration. The invention is suitable for the immune detection of tumor marked objects of urinal fiber-connected protein, and the like.
Owner:沈鹤柏
Ultrasound system for disease detection and patient treatment
InactiveUS6589173B1High diagnostic sensitivityEasy to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDiseaseProstate cancer
A device and method of detection and treatment of a solid cancer tumor, for example prostate cancer. In a diagnostic method, ultrasound is used to extract a cancer tumor marker from interstitial fluid into a coupling medium. In a method for treating a solid tumor, ultrasound is used to deliver one or more drugs from the coupling medium directly to the site of the tumor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and kits for the detection of circulating tumor cells in pancreatic patients using polyspecific capture and cocktail detection reagents
InactiveUS20120094275A1Easy to detectSufficient binding capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthAntigen
A highly sensitive assay is disclosed which combines immunomagnetic enrichment with multiparameter flow cytometric or image cytometry to detect, enumerate and characterize carcinoma cells in the blood. The present invention incorporates the conjugation of different antibodies to the same ferrofluid. This has the effect of making the ferrofluid polyspecific with respect to the antigens that the ferrofluid will bind. The multiple antibodies present on the same ferrofluid do not appear to block or otherwise interfere with each other. Such ferrofluids have the highly desirable effect of being able to bind specifically to more than one type of cell. The assay is especially useful to enable the capture of CTCs that have low EpCAM expression, but high expression of other tumor markers; Accordingly, the assay facilitates the biological characterization and staging of carcinoma cells.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Identification and use of circulating nucleic acid tumor markers
ActiveCN105518151AMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisCancers diagnosisCancer therapy
Methods for creating a selector of mutated genomic regions and for using the selector set to analyze genetic alterations in a cell-free nucleic acid sample are provided. The methods can be used to measure tumor-derived nucleic acids in a blood sample from a subject and thus to monitor the progression of disease in the subject. The methods can also be used for cancer screening, cancer diagnosis, cancer prognosis, and cancer therapy designation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Antibody chip kit for diagnosis of various tumors
ActiveCN103869068AImprove adsorption capacityImprove stabilityMaterial analysisBiotin-streptavidin complexPositive control
The invention relates to an antibody chip kit for diagnosis of various tumors. The kit includes an antibody chip, a tumor marker standard substance mixture, a biotin-labeled tumor marker detection antibody mixture, and a fluorescein Cy3-labeled streptavidin, wherein the antibody chip includes a substrate, 16 kinds of tumor marker specific antibodies fixed on the surface of the substrate, and two kinds of positive controls, and the tumor marker standard substance mixture is a freeze-dried mixture obtained by mixing 16 kinds of standard tumor marker standard substances together according to a certain amount. The kit can detect 16 clinical commonly used tumor markers, overcomes the defects of complicated operation, single detection index, low sensitivity and the like in the prior art, has the advantages of being cheap, convenient, sensitive, accurate, high in throughput, and less in amount of samples, and can be popularized and large-scaled in common laboratories.
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU +1
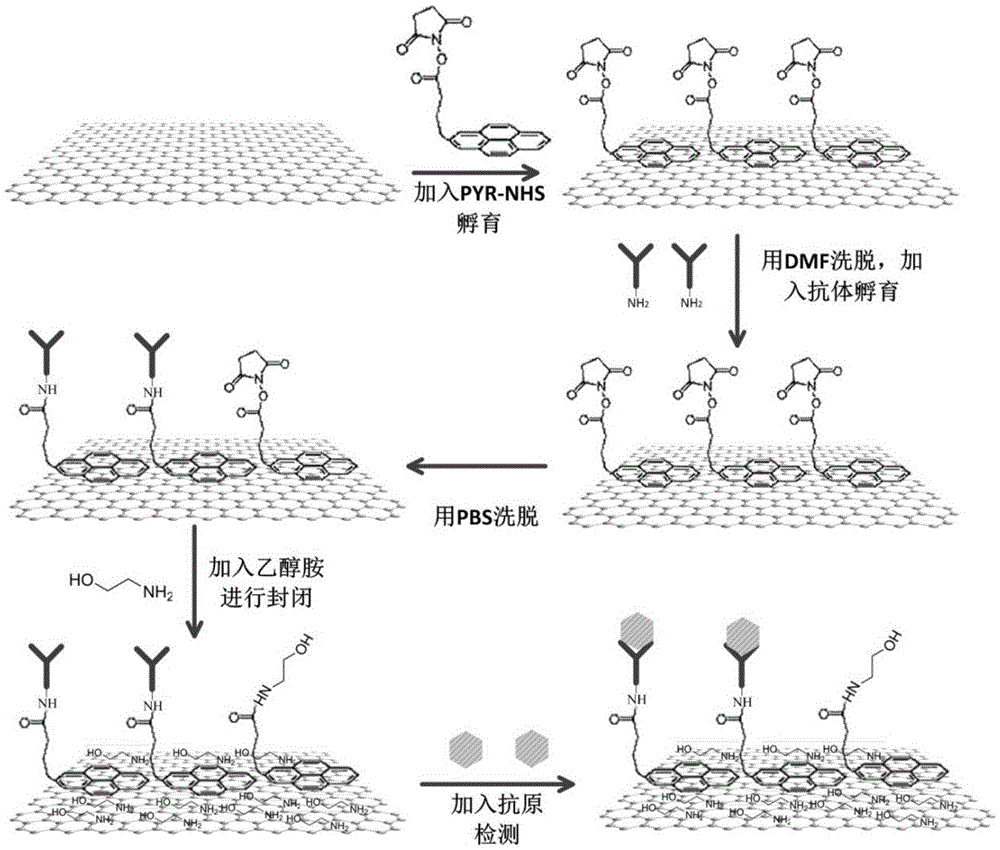
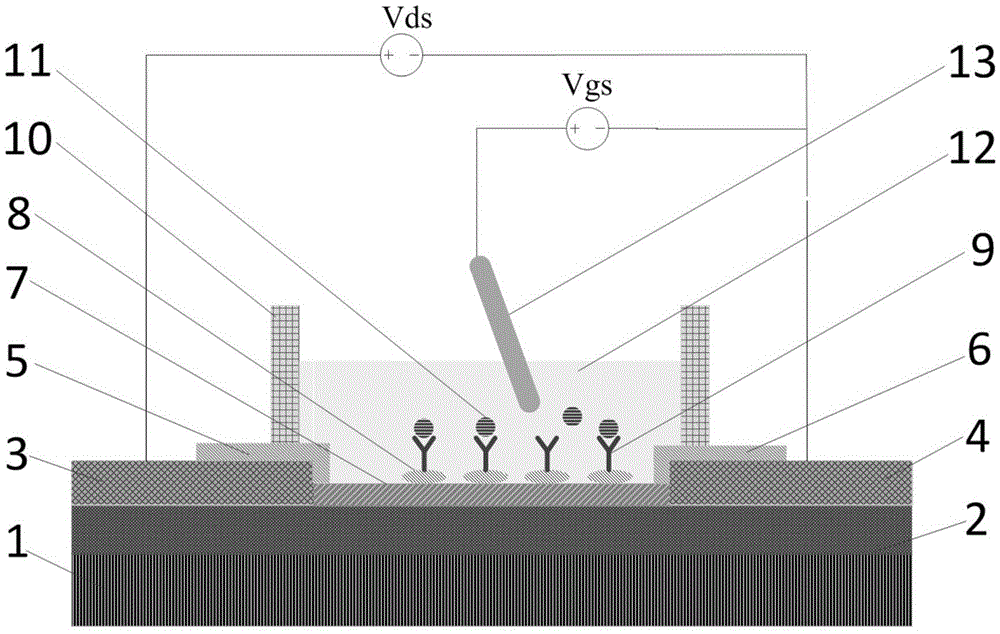
Non-covalently modified graphene field effect transistor-based tumor marker detection sensor and production method thereof
InactiveCN105651845ALittle influence on electrical characteristicsGood electrical propertiesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInsulation layerMetal electrodes
The invention relates to a non-covalently modified graphene field effect transistor-based tumor marker detection sensor and a production method thereof. The sensor comprises a silica substrate, a graphene channel and a reaction chamber. The production method comprises the following steps: making a metal electrode, carrying out wet transfer on graphene, making the graphene channel and a protection insulation layer of the graphene channel, and modifying the surface of graphene in a non-covalent mode. The sensor has the advantages of convenient making process, simple modification process, easy operation, and high sensitivity and good specificity in application; and the making method can also be used to make most of biosensors of capture probes with amino groups, and the sensor is used to detect target molecules.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systemic detection method of tumor marker and application thereof
InactiveCN107727865AReduce the burden onAccurate measurementBiological testingProtein tumor markersNucleic acid sequencing
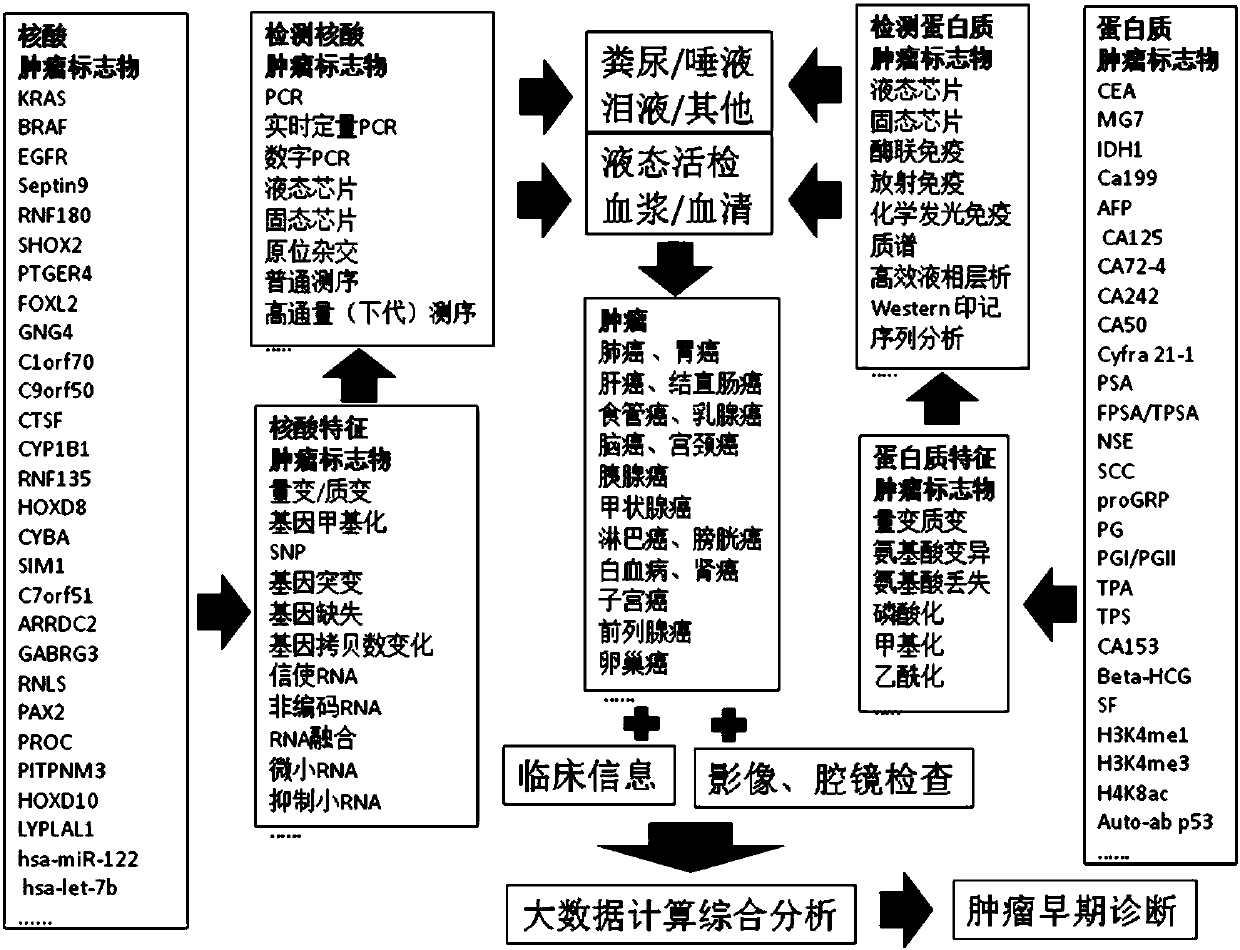
The invention provides a systemic detection method of a tumor marker and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) providing a sample from a checking object, wherein the checking object is a person; 2) detecting the sample of step 1), wherein in the detection step, whether various protein tumor markers exist or not is determined by utilizing high-throughput nucleic acid sequencing and determination comprising polygene mutation, polygene methylation, a plurality of micro RNAs (Ribonucleic Acid) and the like and utilizing a protein chip. According to the systemic detection method of the tumor marker and the application thereof, the different tumor markers are subjected to systemic detection including DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), RNA, protein and the like, so that thesensitivity of early-stage detection of the tumors is improved.
Owner:BIOCHAIN BEIJING SCI & TECH
Preparation of three-dimensional photoelectrochemical paper chip and application of three-dimensional photoelectrochemical paper chip in tumor detection
The invention discloses a preparation method for a three-dimensional photoelectrochemical paper chip and a method for measuring six tumor markers in a sample through a photoelectrochemical sensor. A hydrophobic region and a hydrophilic region are formed on paper by adopting a wax printing technology; a corresponding reference electrode and working electrodes are printed on the paper through proper ink; a working region is functionalized for antigen recognition; the prepared paper chip is folded to form a three-electrode system; a buffering solution containing ascorbic acid is dropwise added into a reaction region; under the irradiation of an ultraviolet lamp, the high-sensitivity detection on an object to be measured is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
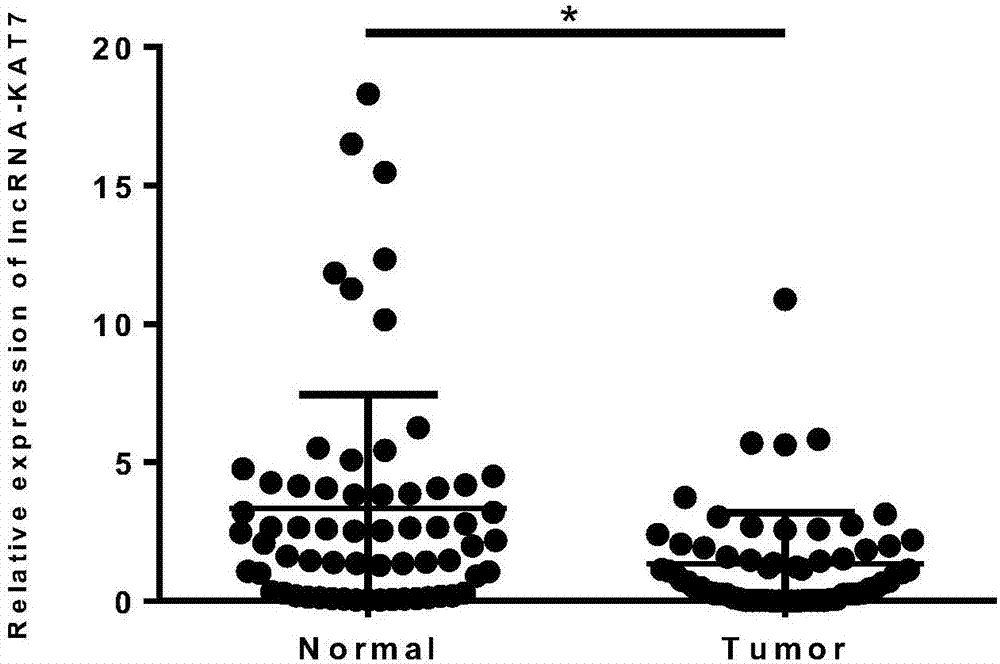
Tumor marker related to colorectal cancer and application
ActiveCN107043823AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLymphatic SpreadNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a tumor marker related to colorectal cancer and application. The tumor marker is lncRNA (long noncoding RNA) and is located on the seventeenth chromosome of chr17: 47785696-47797422, a nucleotide sequence of the lncRNA is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is named as lncRNA-KAT7. According to the lncRNA-KAT7 sequence, specific real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR primer can be designed and synthesized to be used for preparing preparation for colorectal cancer diagnosis or treating effect prediction. By means of the real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR preparation, expression level of lncRNA-KAT7 is detected in colorectal cancer clinical case specimen, expression of the lncRNA-KAT7 in the colorectal cancer is found to be obviously reduced, the lncRNA-KAT7 has obvious statistic significance (p<0.05), and low expression of the lncRNA-KAT7 in the colorectal cancer is closely related to colorectal tumor differentiation, T staging, invasion and metastasis. The result shows that the lncRNA-KAT7 can serve as the tumor marker of the colorectal cancer and can be used for preparing preparation or kits applied to auxiliary diagnosis, treating effect prediction and prognosis of the colorectal cancer.
Owner:CHENZHOU NO 1 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
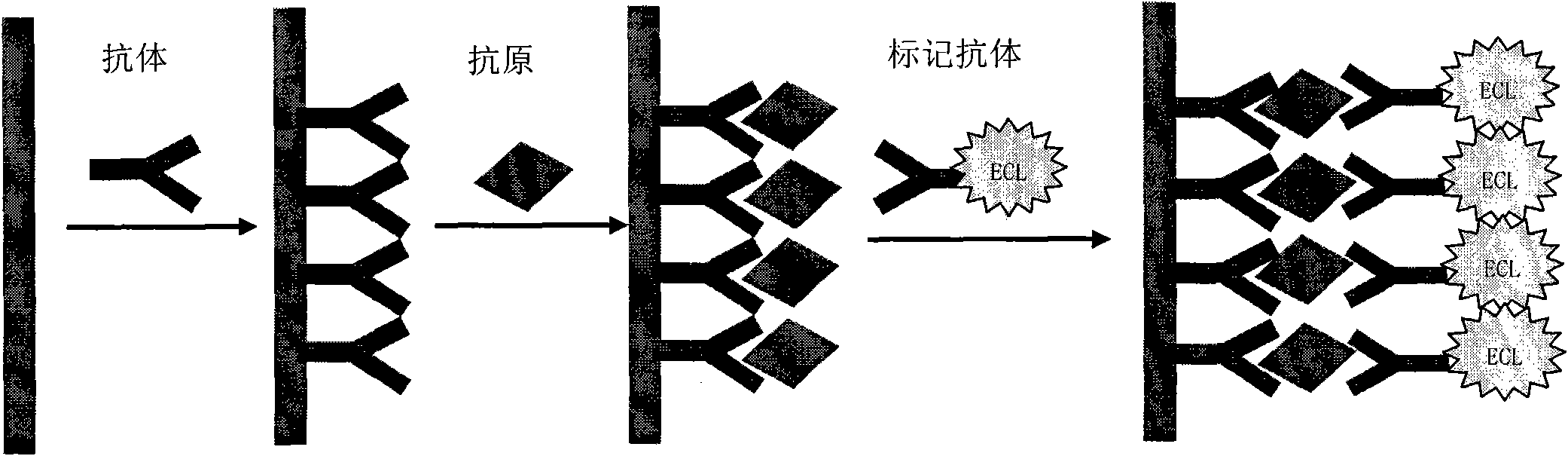
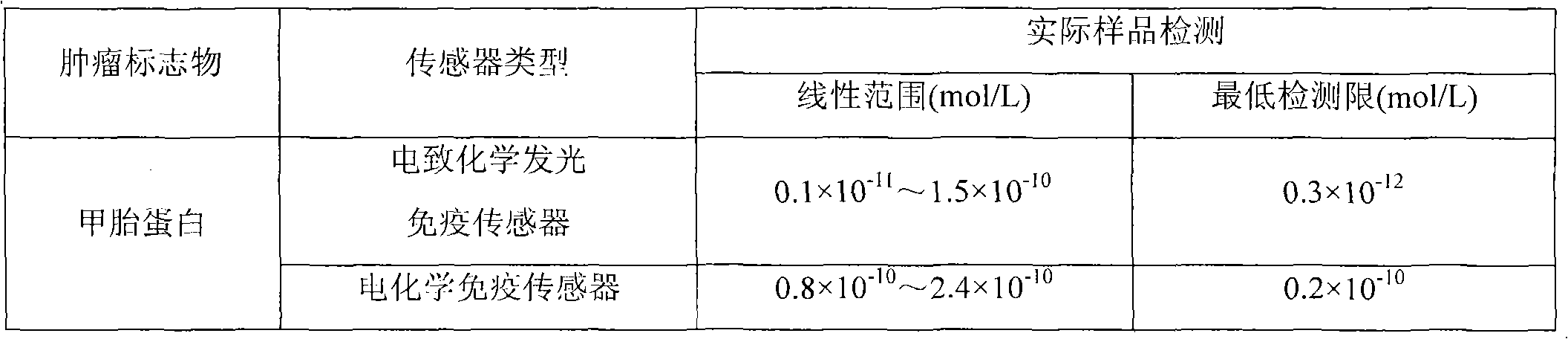
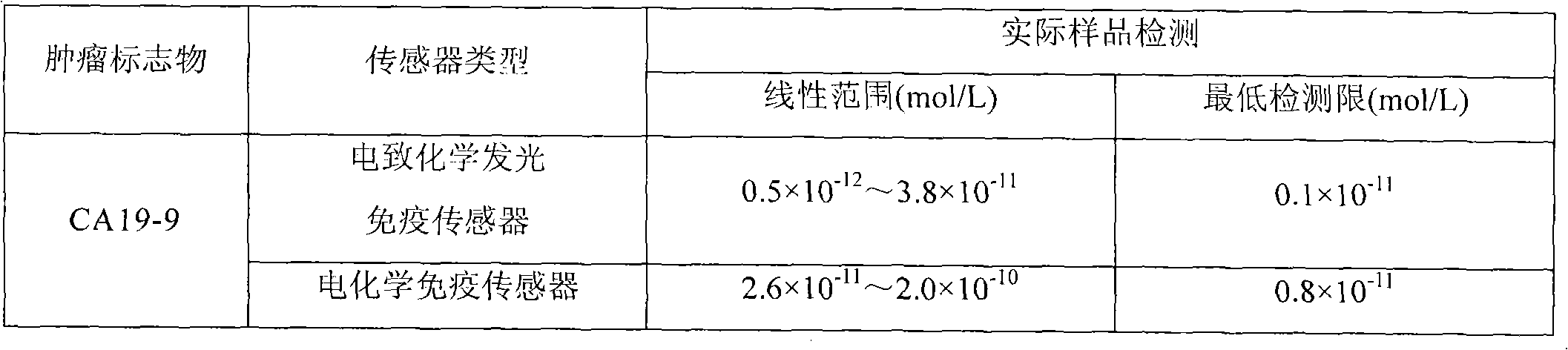
Research and application of electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for detecting tumor markers
InactiveCN102072954AIncreased sensitivityHigh selectivityAnalysis by electrical excitationQuantum dotTumor marker
The invention discloses a method for researching and applying an electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for detecting tumor markers. An electrode preparation method (shown in attached drawings as schematic diagrams) comprises the following steps of: selecting a tumor marker with higher clinical morbidity for detection; preparing a quantum dot nano-material solution; and preparing the electrochemiluminescent immunosensor by modifying an antibody onto an electrode surface by using an electrode surface modification technology. A method for detecting the tumor markers comprises the following step of connecting a modified electrode to an electrochemiluminescent instrument so as to detect a tumor marker in a sample. The electrode provided by the invention has strong specificity and high sensitivity and can reach ng level; and moreover, the time required for completing a basic detection process is short, and the cost is low. The method for detecting the tumor markers through the electrode has the advantages that: the operation is fast and simple, and both reactions and results are automatically completed and recorded by the instrument.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Micro array-ELISA detecting kit for detecting six tumor markers
The present invention relates to a six-item tumor labeling material micro array (Array)-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection kit, in particular to a six-item tumor labeling material micro array (Array)-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection kit which is used for detecting the characteristic protein which has an indicating function to the liver cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer and other tumor diseases.
Owner:BEIJING BGI GBI BIOTECH +1
Method and device for rapidly and quantitatively detecting tumor marker with immunochromatography test strip marked by quantum dots
InactiveCN103364550AHigh detection sensitivityEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceTreatment effectFluorescence
The invention relates to a method and a device for rapidly and quantitatively detecting a tumor marker with an immunochromatography test strip marked by quantum dots. The method comprises the following steps of: replacing collaurum particles by using quantum dots as a signal marker, coupling with an antibody corresponding to the tumor marker to be tested, and spraying or directly coating on a conjugate releasing pad, wherein the antibody on another site corresponding to the tumor marker and a second antibody are coated on a nitrocellulose membrane to form a T line and a C line respectively; assembling a sample pad, a combining pad, a reaction membrane and a water absorbing pad according to a certain sequence to prepare the immunochromatography test strip; detecting qualitatively and quantitatively according to fluorescent stripes presented on the T line and the C line and the strength of fluorescence; and providing a quantum dot fluorescence immune detection device. The detection device is simple, the operation is simple and rapid, the time consumption for detection is short, and the result judgment is easy. The method and device are particularly suitable for early-stage screening, diagnosis, judgment prediction and prognosis of the tumor markers in households, communities, hospitals and the like, and evaluation of treatment effect and followed observation of high risk groups.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
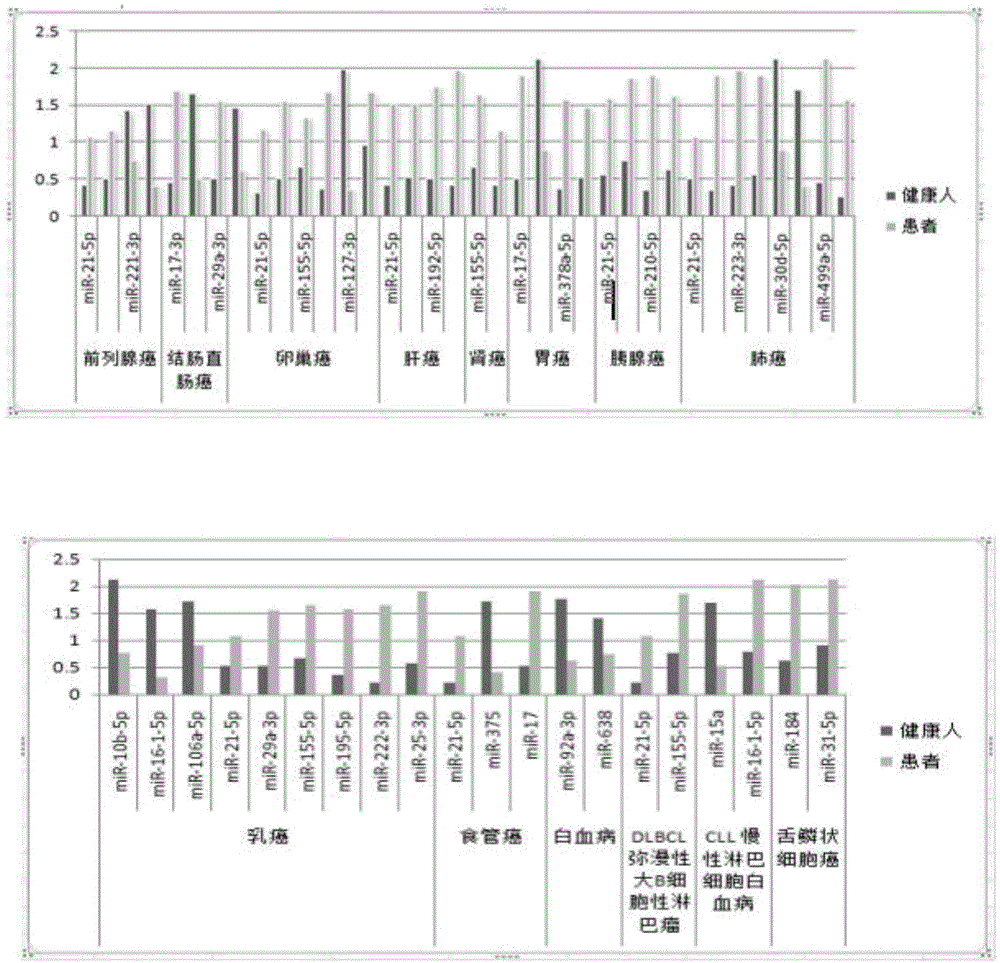
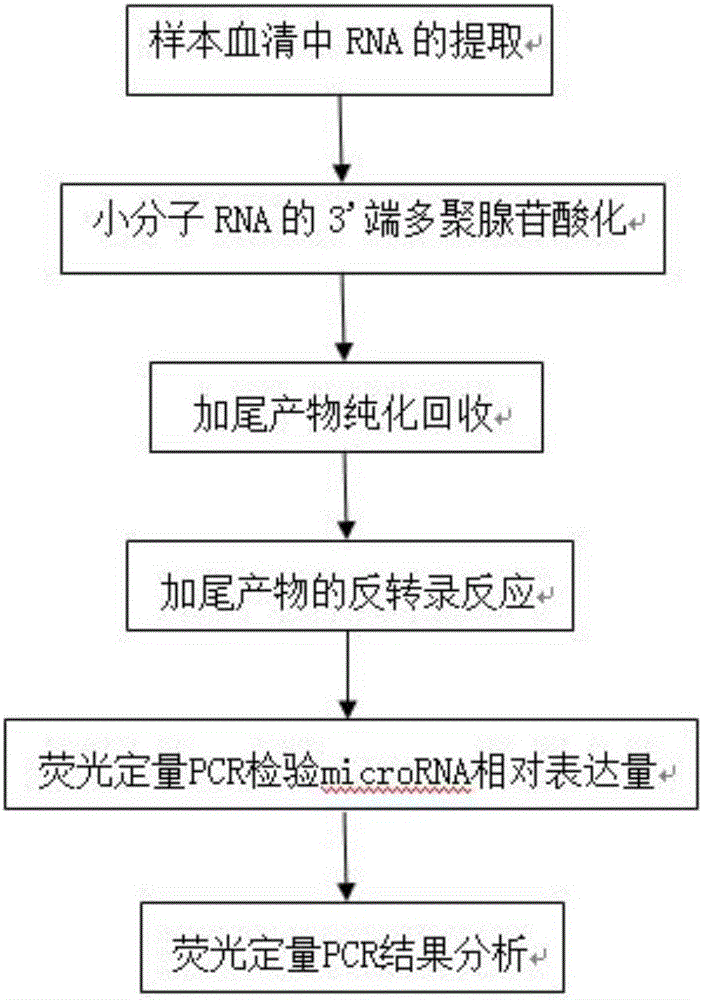
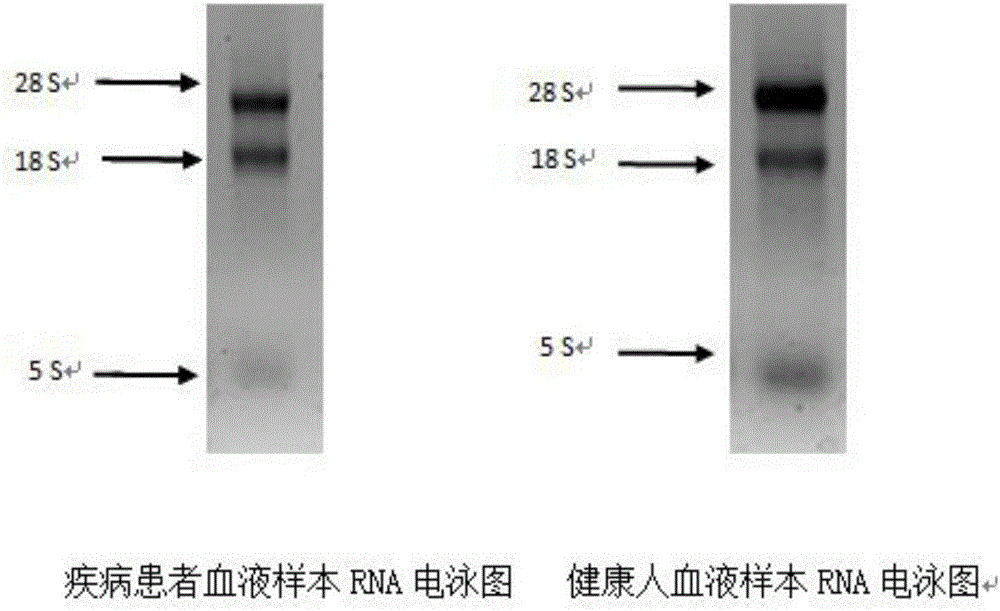
Kit for auxiliary diagnosis of multiple tumors by taking micro ribonucleic acid (RNA) combination as tumor marker, and detection method of kit
PendingCN105950768AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPoly-A RNAIndividualized treatment
The invention relates to a kit for auxiliary diagnosis of multiple tumors by taking a micro ribonucleic acid (RNA) combination as a tumor marker, and a detection method of the kit. The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and oncology. The detection method comprises the steps of (1) extracting RNA from serum; (2) carrying out polyadenylation on the 3' end of micro RNA; (3) purifying and recovering a tailing product; (4) carrying out an inverse transcription reaction on the tailing product; (5) testing the relative expression of the micro RNA by means of a fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction); (6) analyzing the result of the fluorescent quantitative PCR. The kit has the characteristics of high conservative property, space-time specificity, stability, tissue specificity and the like, and plays an important role in the aspects such as disease pathogenesis research, early diagnosis, individualized treatment and prognosis; furthermore, the kit is simple to operate, convenient in material obtaining, safe and noninvasive, and is conveniently used for screening of a great deal of diseases.
Owner:JIANGSU YINUOWAN CELL CLINIC CO LTD
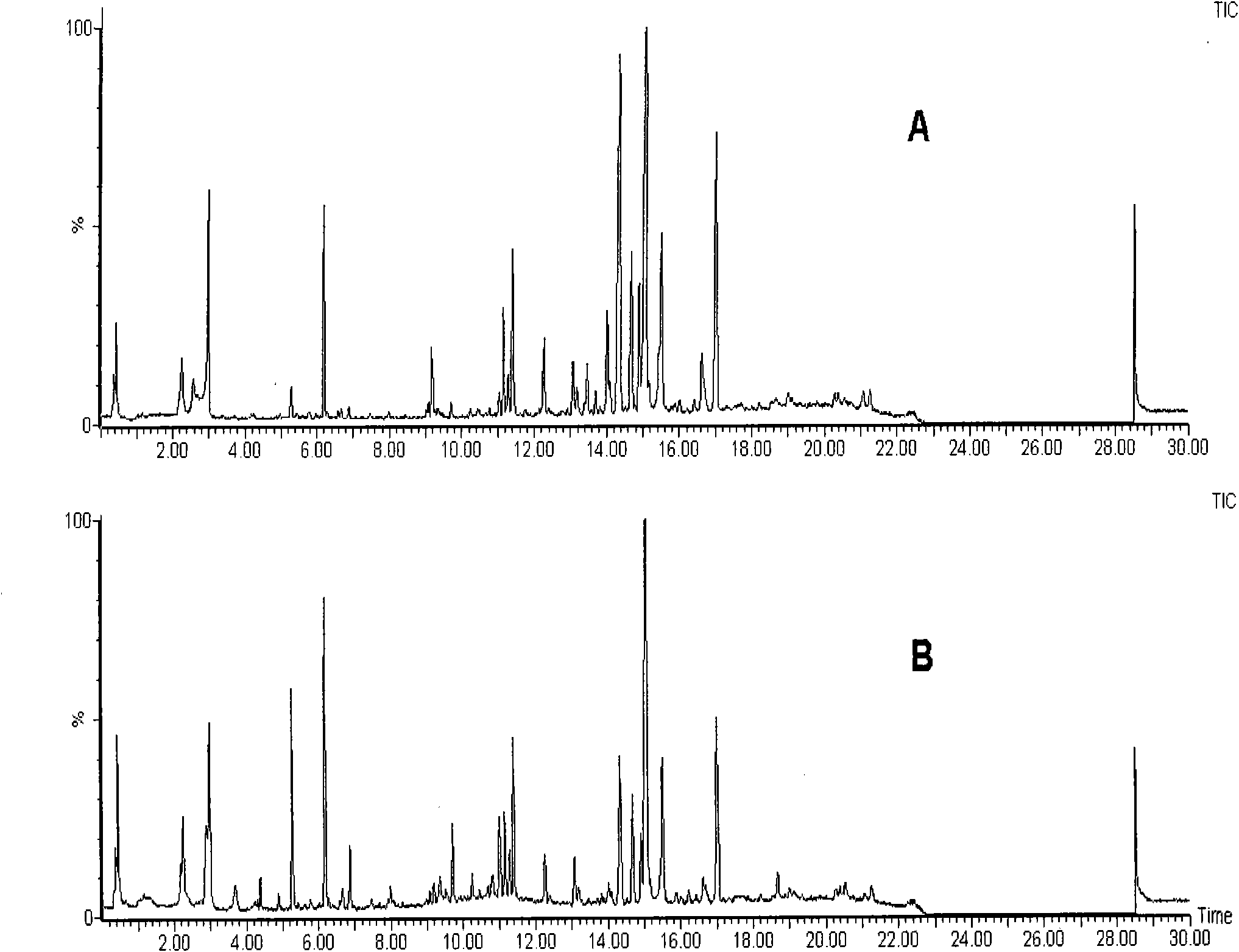
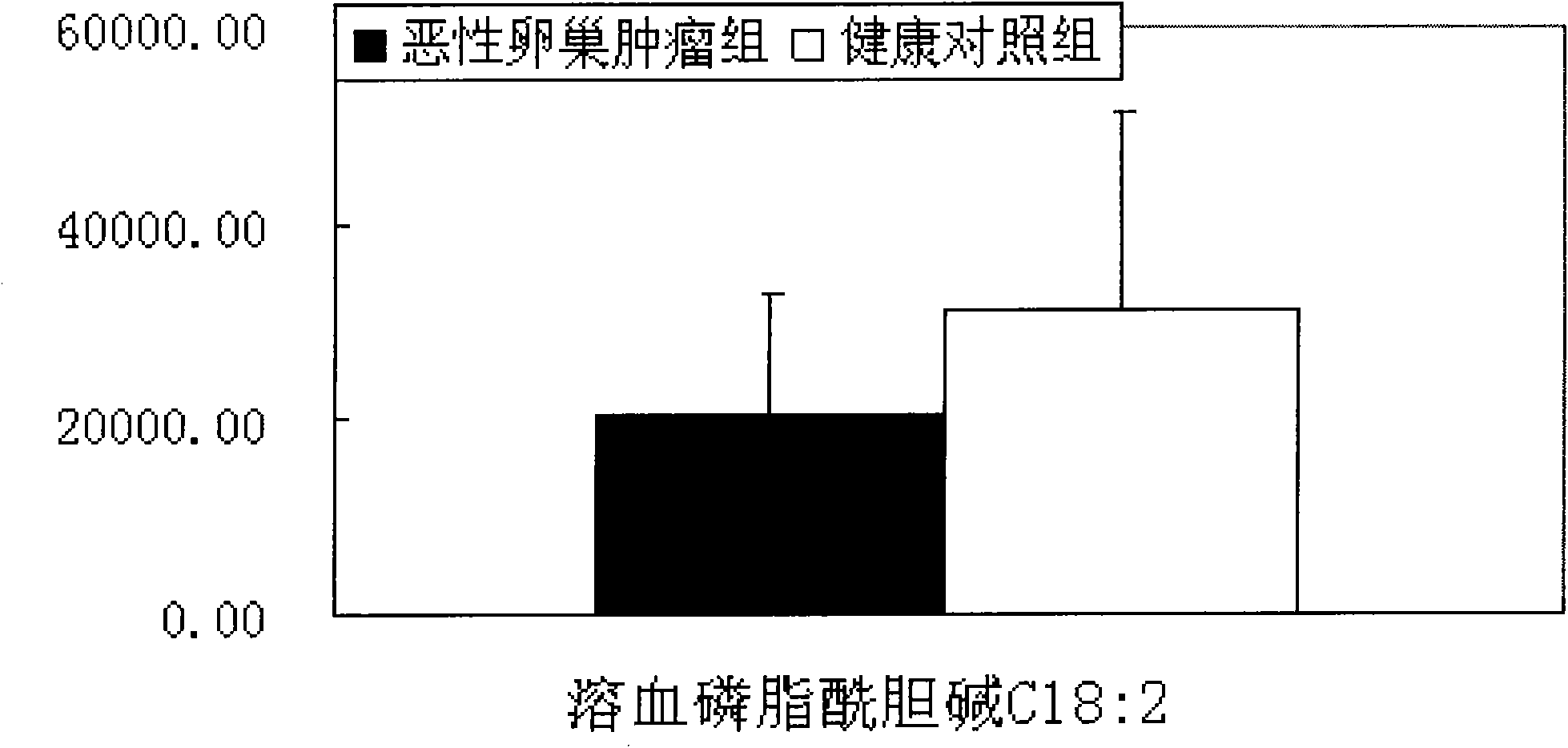
Method for screening malignant ovarian tumor markers from blood serum metabolic profiling
InactiveCN101769910AReduce human errorAvoid human errorComponent separationBiological testingMultivariate statisticsScreening method
The invention discloses a method for screening malignant ovarian tumor markers according to blood serum metabolic profiling. In the method, the Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-mass spectrometry technology is employed to analyze blood serum to obtain blood serum metabolic profiling; then the multivariate statistics method is employed to analyze data concerning malignant ovarian tumor and blood serum metabolic profiling of healthy people, so as to screen maker spectrums. The screening method of the invention features good repeatability and good forecasting property of the screened markers. Proven by discriminant classification analysis, the screening method enjoys an average forecasting precision rate of 90.90% and a positive relevance ratio of 82.65%.The maker spectrum covering multiple compounds can be obtained in a single analysis, which indicates that the marker is suitable for high flux analysis and enjoys the prospect of being promoted to large-scale sample screening and clinical application.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +4
Male multi-tumor marker detection protein chip and kit thereof
InactiveCN101603966AChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingProtein markersProstate cancer
The invention discloses a male multi-tumor marker detection protein chip and a kit thereof. The chip comprises a substrate, protein markers distributed in an array type and point coatings of contrasts, wherein the substrate is a glass substrate or a film substrate; and the tumor markers and the point coatings of the contrasts are seven protein markers of AFP, CEA, NSE, CYFRA21-1, CA19-9, tPSA and SCC-ag, a positive contrast and a negative contrast which are uniformly distributed and latticed on the substrate. A reaction result of various indexes can be obtained only through one reaction by utilizing the protein chip, and the following tumors can be simultaneously screened: primary liver cancer, prostatic cancer, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. The invention is particularly suitable for the general examination of malignant tumors of male asymptomatic groups and high risk groups.
Owner:上海裕隆生物科技有限公司
Long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and application method thereof
ActiveCN103146693ADeep meaningFar-reaching promotionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExpression vectorRNA interference
The invention relates to a newly cloned full-length sequence of a long chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) gene and an application method thereof. The gene can be detected in a separation sample by methods including a hybrid method or an amplification method; and the gene can be used as a tumor marker, in particular a marker of liver cancer. According to the gene sequence, a real-time quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer and an in situ hybridization probe are designed and synthesized; and by detecting the expression level of the long chain non-coding RNA in a liver cancer clinical case sample, expression of the long chain non-coding RNA in liver cancer is up-regulated remarkably, and prognosis of patients with liver caner with high expression of long chain non-coding RNA is poorer. According to the gene sequence, a RNA eukaryotic expression vector in a short hairpin structure for closing the expression of the long chain non-coding RNA by RNA interference is designed and synthesized; and the expression of the long chain non-coding RN in a liver cancer cell line A is inhibited successfully by using the vector.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Sandwich type electrochemical immunosensor, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102980925AHigh sensitivityWide detection rangeMaterial electrochemical variablesImmune profilingEngineering
The invention relates to an electrochemical immunosensor, a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to a sandwich type electrochemical immunosensor constructed by a marker based on dumbbell type Pt-Fe3O4 nano particles serving as a second antibody, a preparation method thereof, and application of the electrochemical immunosensor prepared by using the method in measurement of tumor markers. The electrochemical immunosensor is high in accuracy, stability, reproducibility and sensitivity, can quickly and conveniently perform immunoassay detection and can be used for clinical analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Insulin-like growth factor system and cancer
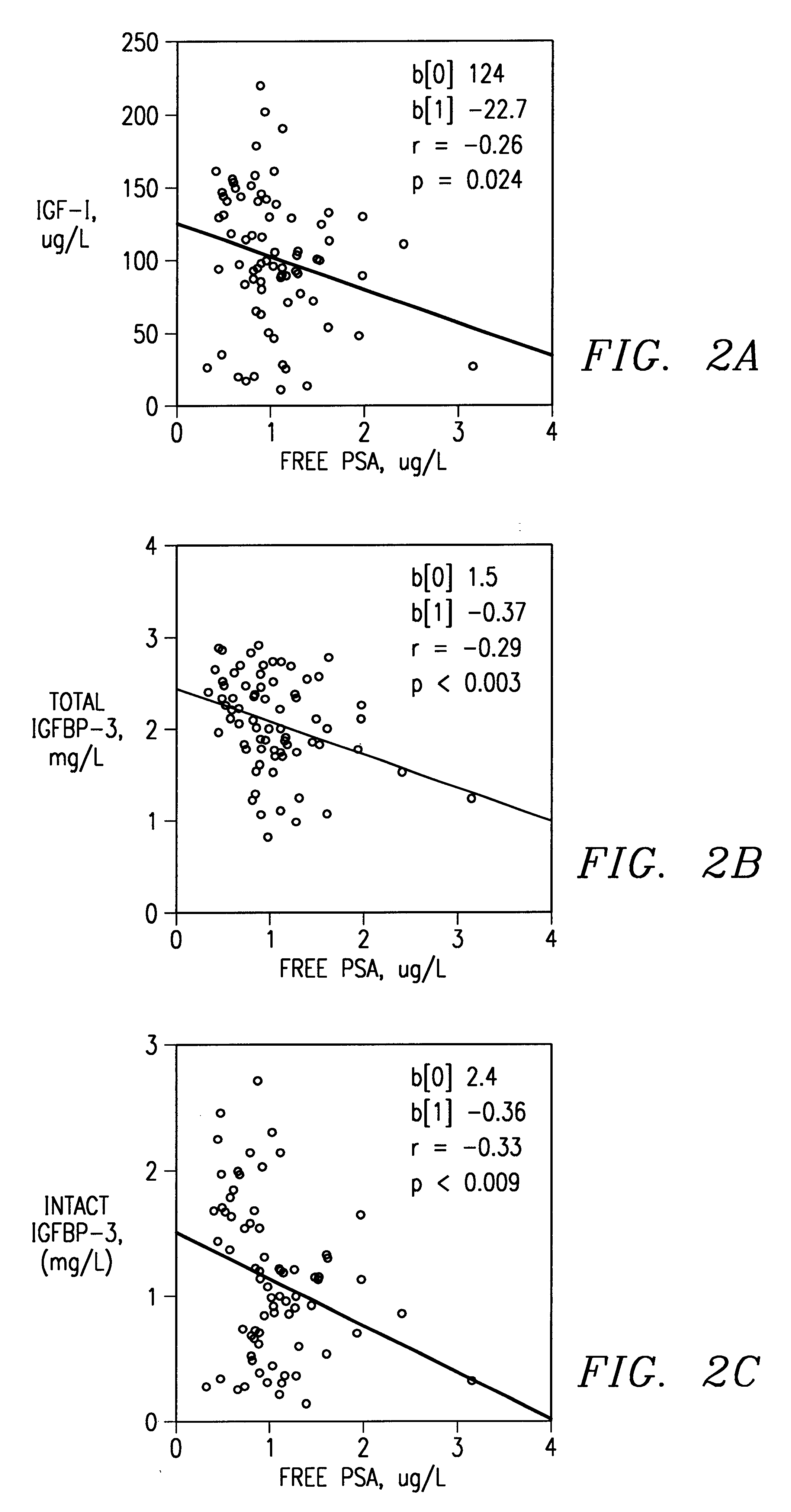
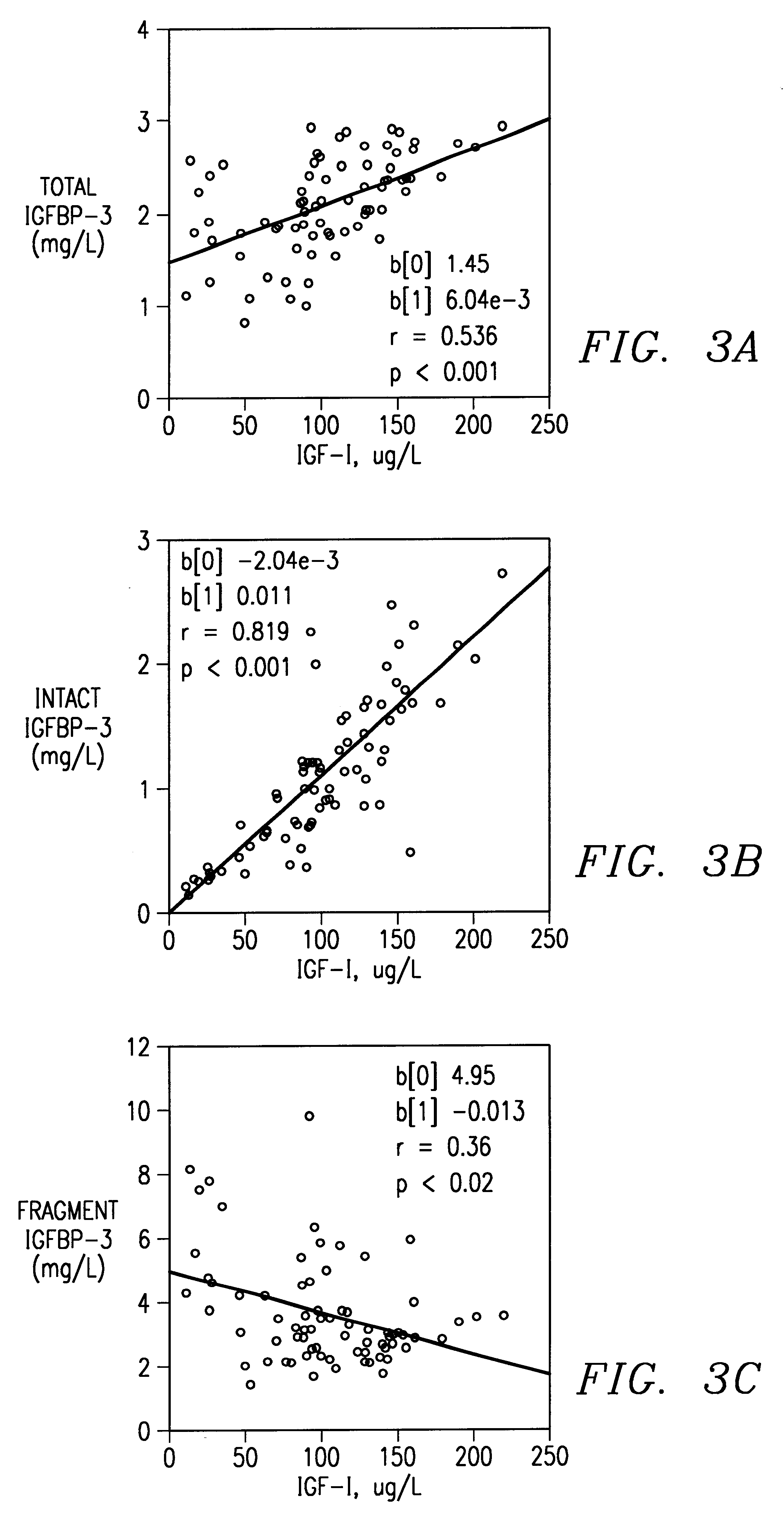
InactiveUS6448086B1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInsulin-like growth factorAntigen
Method of monitoring or diagnosing disease conditions, including disease of the prostate, that involve measuring a combination of tumor markers and at least one component of the IGF axis. The invention is exemplified with prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia, the tumor marker prostate specific antigen, and the insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
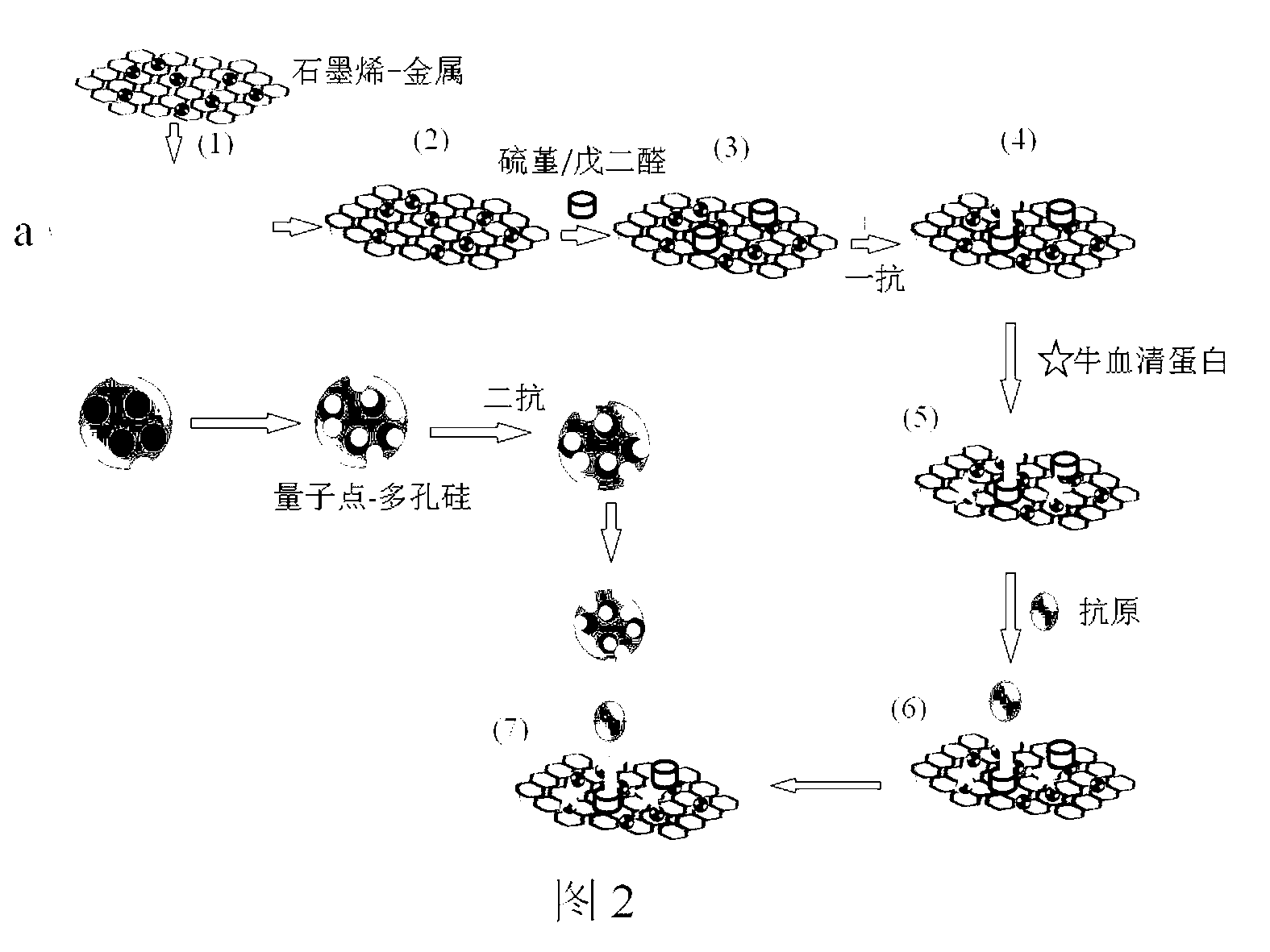
Preparation method and application of composite nano material paper chip electrochemical luminescence immunosensor
InactiveCN103018231AFast diagnostic monitoringHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenComputer printing
The invention discloses a method for researching and applying a paper chip electrochemical luminescence immunosensor for detecting tumor marker by using a composite nano material. The paper chip and sensor preparation method (see the schematic diagram in the attached figure) mainly comprises the steps of printing designed channel patterns on a piece of chromatographic paper by using a printer; heating the wax printed chromatographic paper by using an electronic temperature controller; preparing a graphene-metal composite nano material and a quantum dot-porous silicon nano material; modifying the nano material on the paper chip; connecting an antibody to the paper chip modified by the nano material; after antigen specificity identification, carrying out antigen specificity identification on the antibody marked by a luminescent material so as to make the electrochemical luminescence immunosensor; and detecting an electrochemical luminescence signal with the combination of the processed paper chip with a screen-printed electrode. The sensor is strong in specificity detection and high in sensitivity, and the sensitivity can be of ng grade; the diagnosis and monitoring speed is fast, and the time for accomplishing one basic detection process is shorter; and a film electrode at the bottom of the sensor can be repeatedly used for multiple times, so that the cost is low.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com