Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
197 results about "Ferrofluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
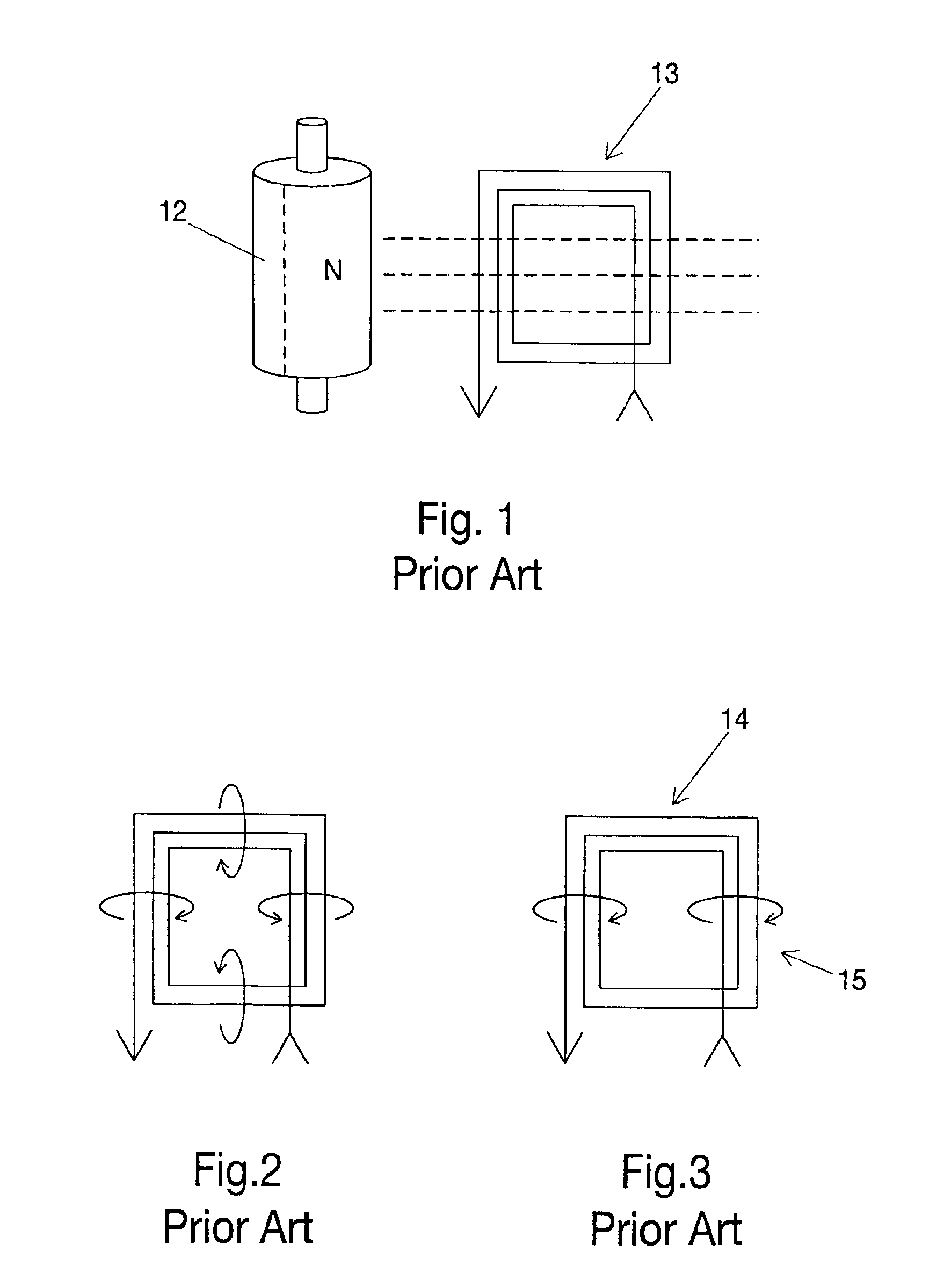
A ferrofluid or ferromagnetic fluid is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field. A process for making a ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell to create liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field. The name ferrofluid was introduced, the process improved, more highly magnetic liquids synthesized, additional carrier liquids discovered, and the physical chemistry elucidated by R. E. Rosensweig and colleagues; in addition Rosensweig evolved a new branch of fluid mechanics termed ferrohydrodynamics.
Coated, resuspendable magnetically responsive, transition metal oxide particles and method for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS6120856AAvoid interferencePromote recoveryMechanical vibrations separationMagnetic materialsCell separationFerroics
The invention relates to an improved method for the manufacture of magnetically responsive particles, also called ferrofluids. The improved method involves a heat treatment step, which may occur at various times during the preparation of the materials, including during subdivision of the magnetic starting material, during the addion of a coating material, after formation of a magnetically responsive particle, or some combination thereof. The materials formed by such a process have numerous advantages over materials formed by other processes, including enhanced salt stability, increased coating uptake, and increased binding capacity. These ferrofluids have applications in a variety of preparative and diagnostic techniques, including immunoassay, cell separations, toxicity testing, food testing, environmental analysis, and MRI.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
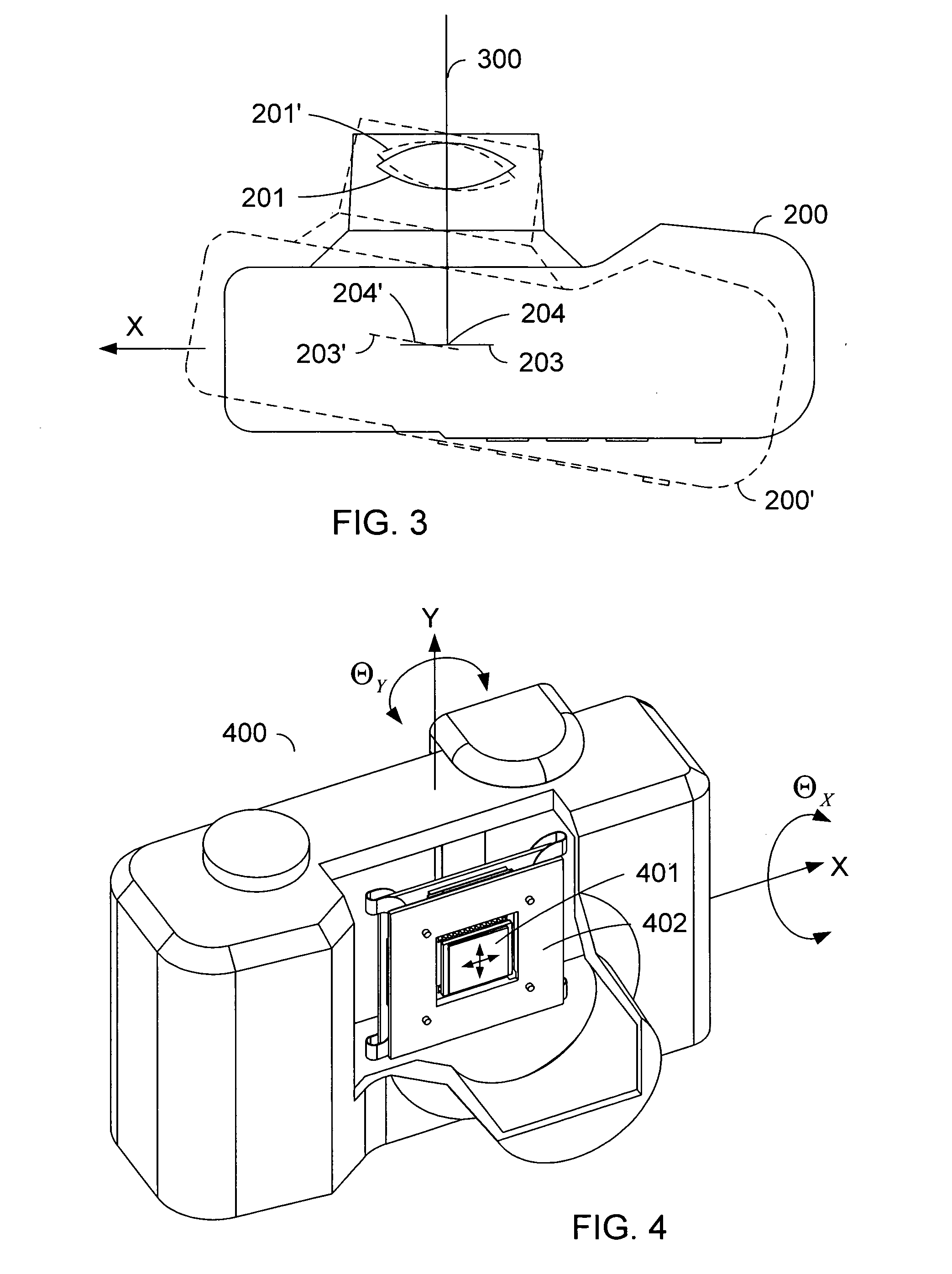
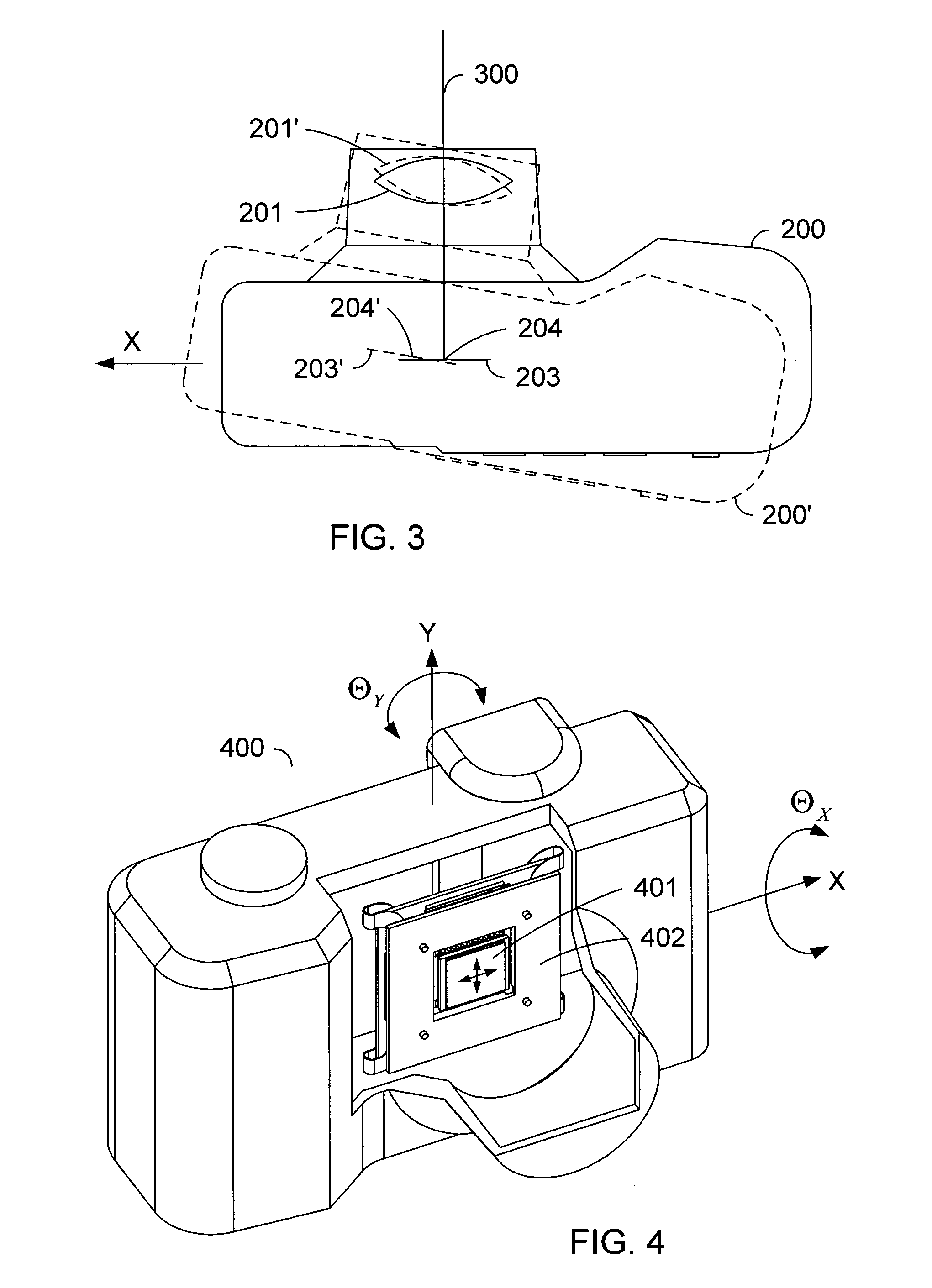
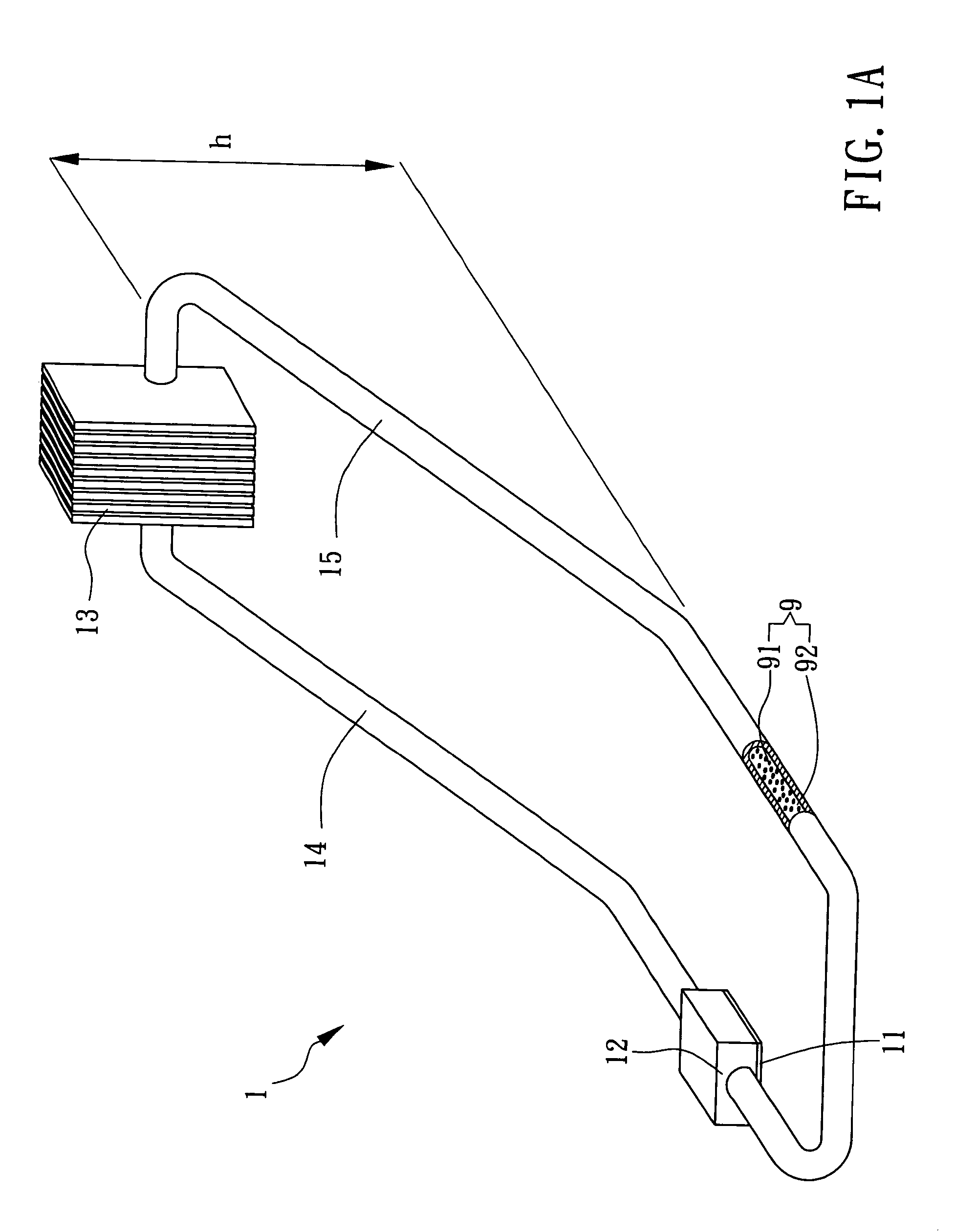
Flexible suspension for image stabilization
InactiveUS20060017815A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImage stabilizationLinear motor
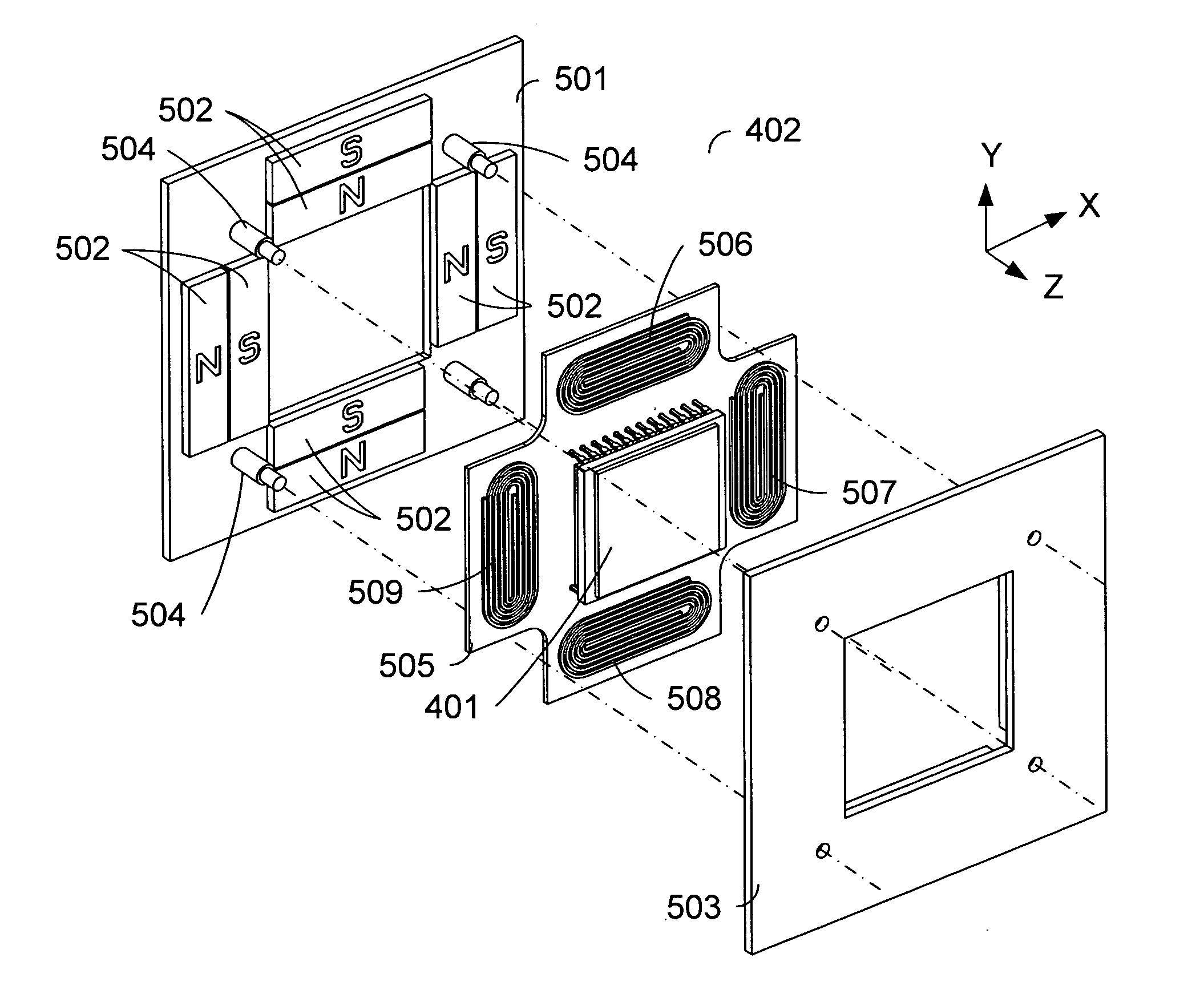
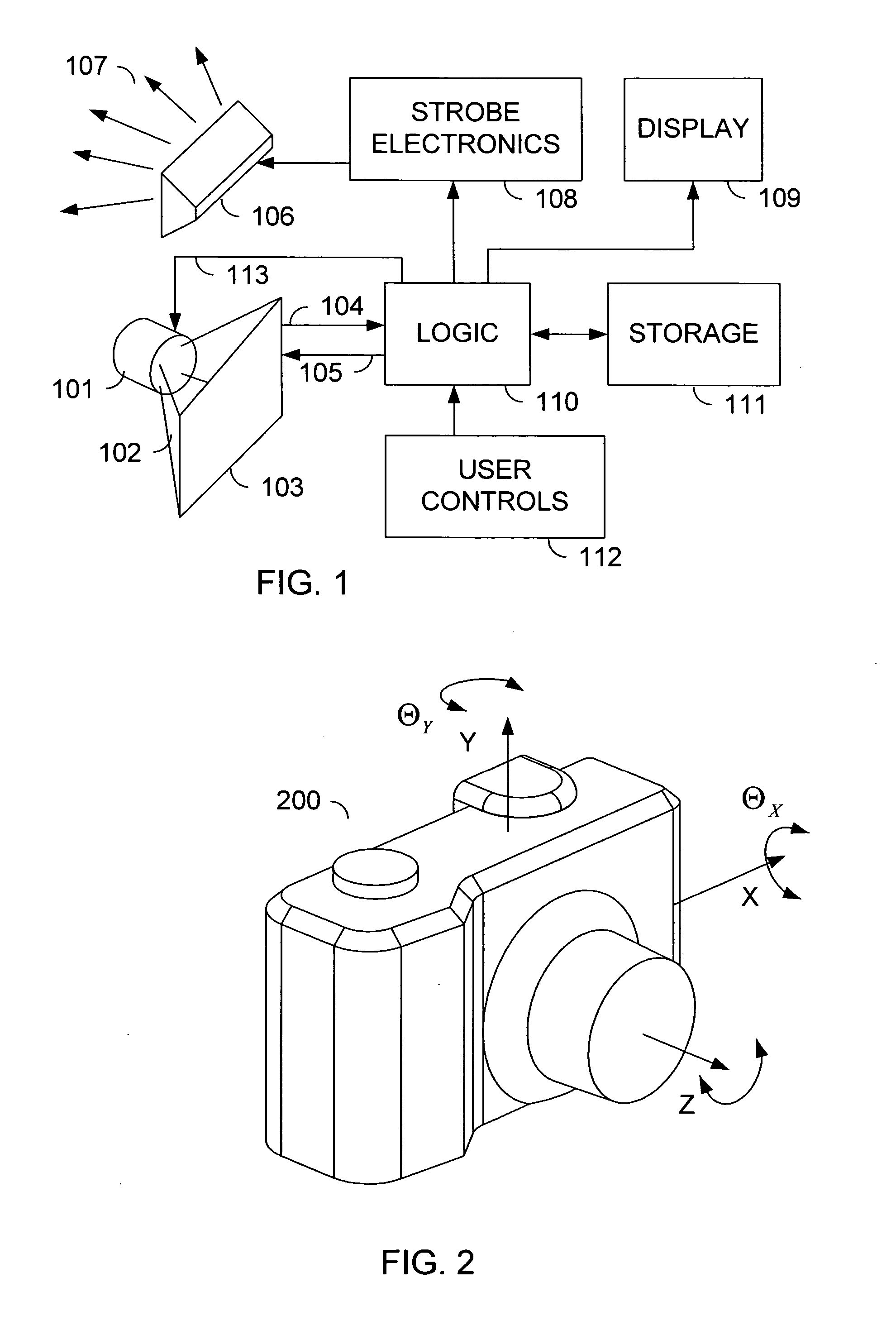
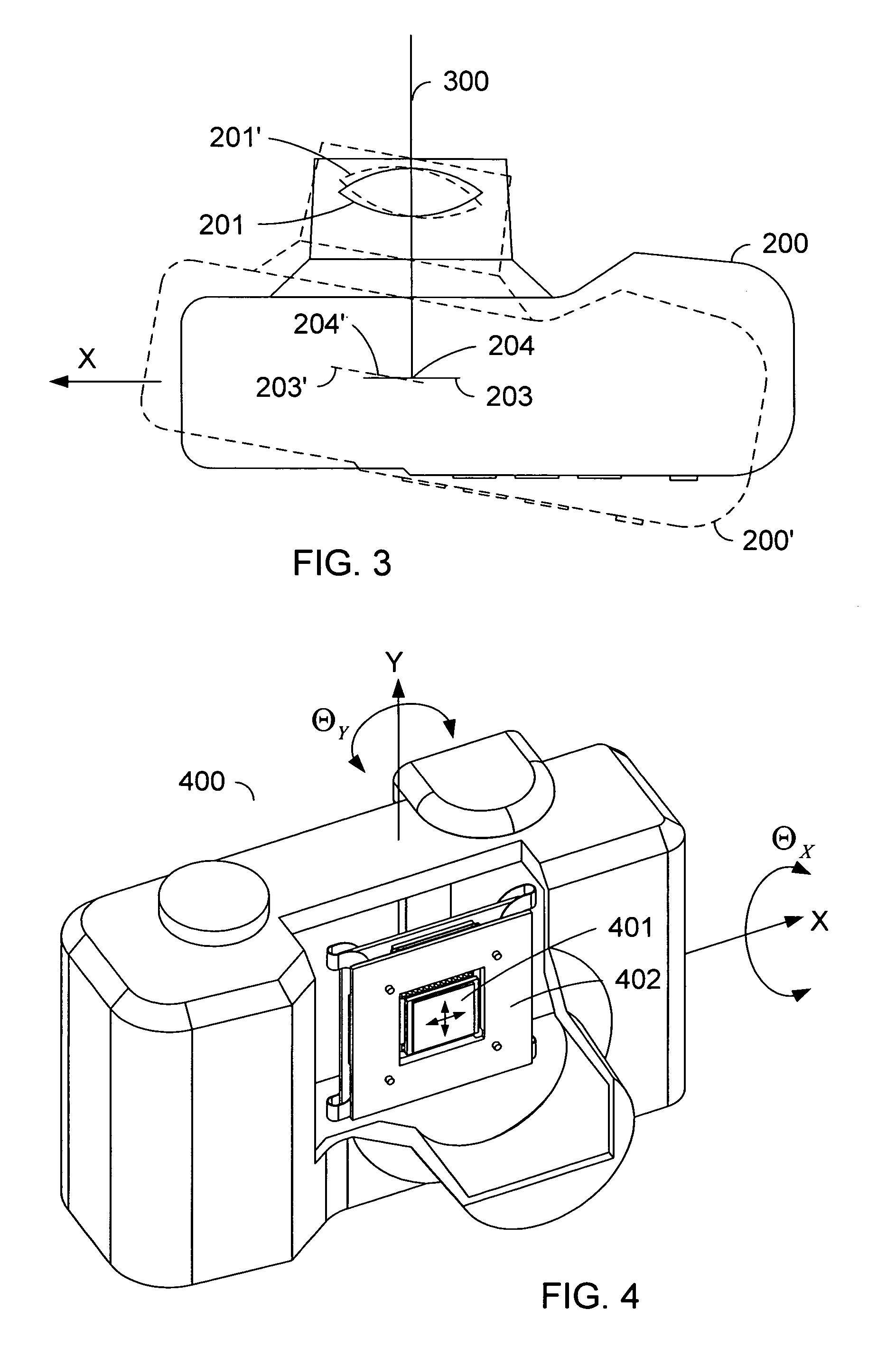
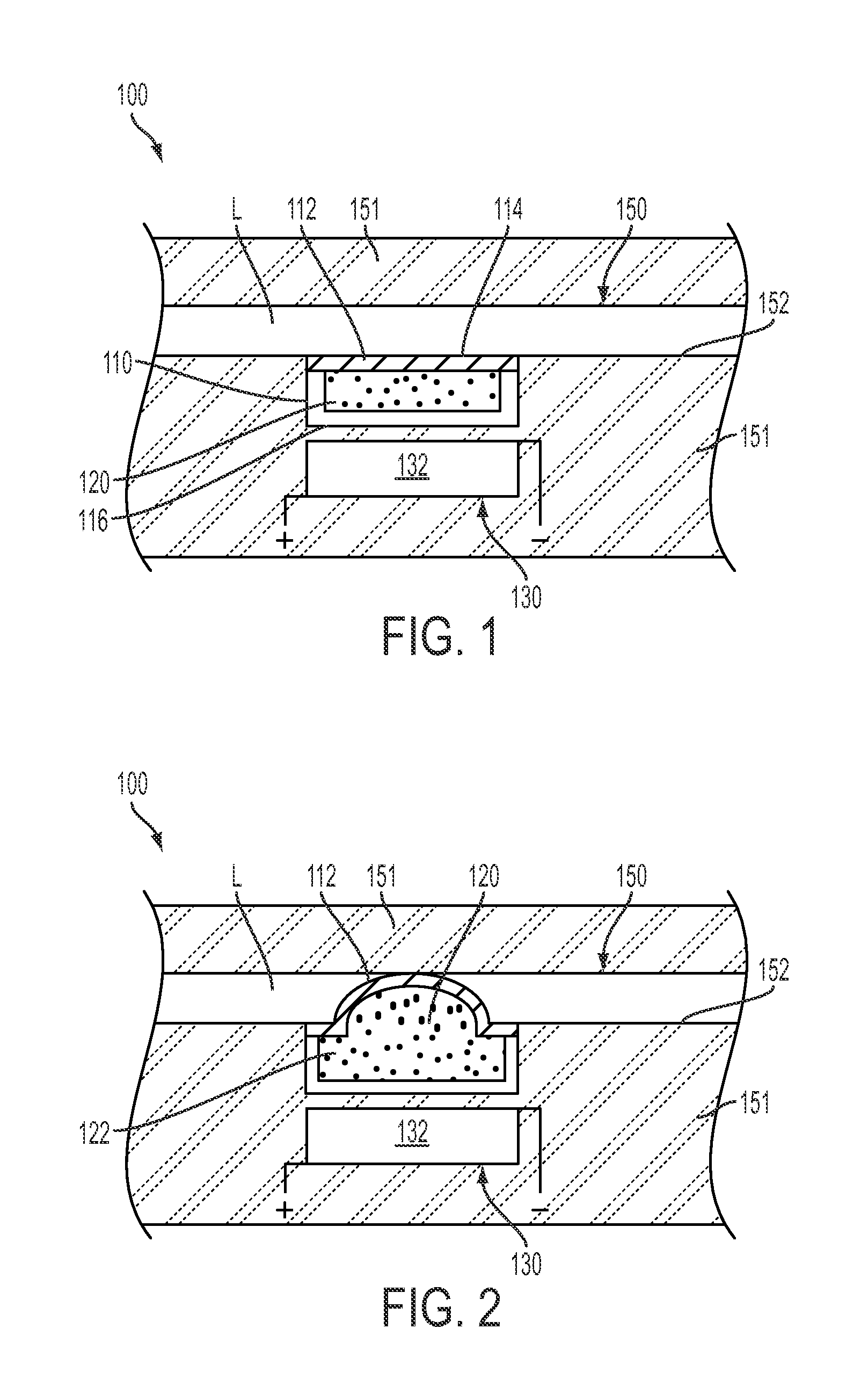
A sensor mounting system for enabling image stabilization in a digital camera is described. An electronic array light sensor is moved in relation to other parts of the camera in response to camera motion. In one embodiment, the sensor is moved by at least one linear motor having a ferrofluid in a gap of the linear motor. Other aspects of the system are described, including methods of heat sinking the sensor, a suspension system, methods of compensating for an effect of temperature on the ferrofluid, and a compact magnet configuration for forming the linear motor and providing feedback as to the position of the sensor.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
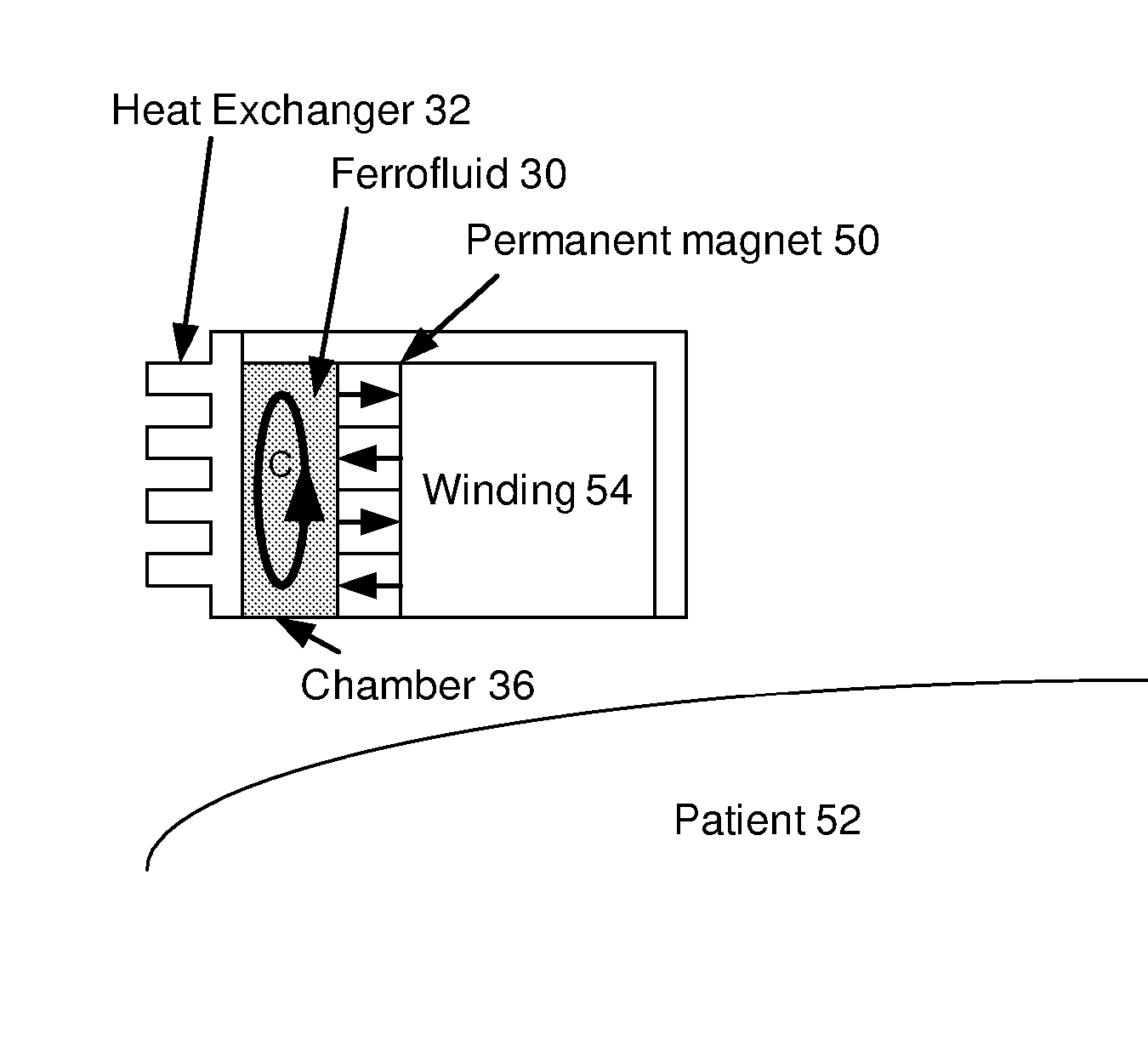
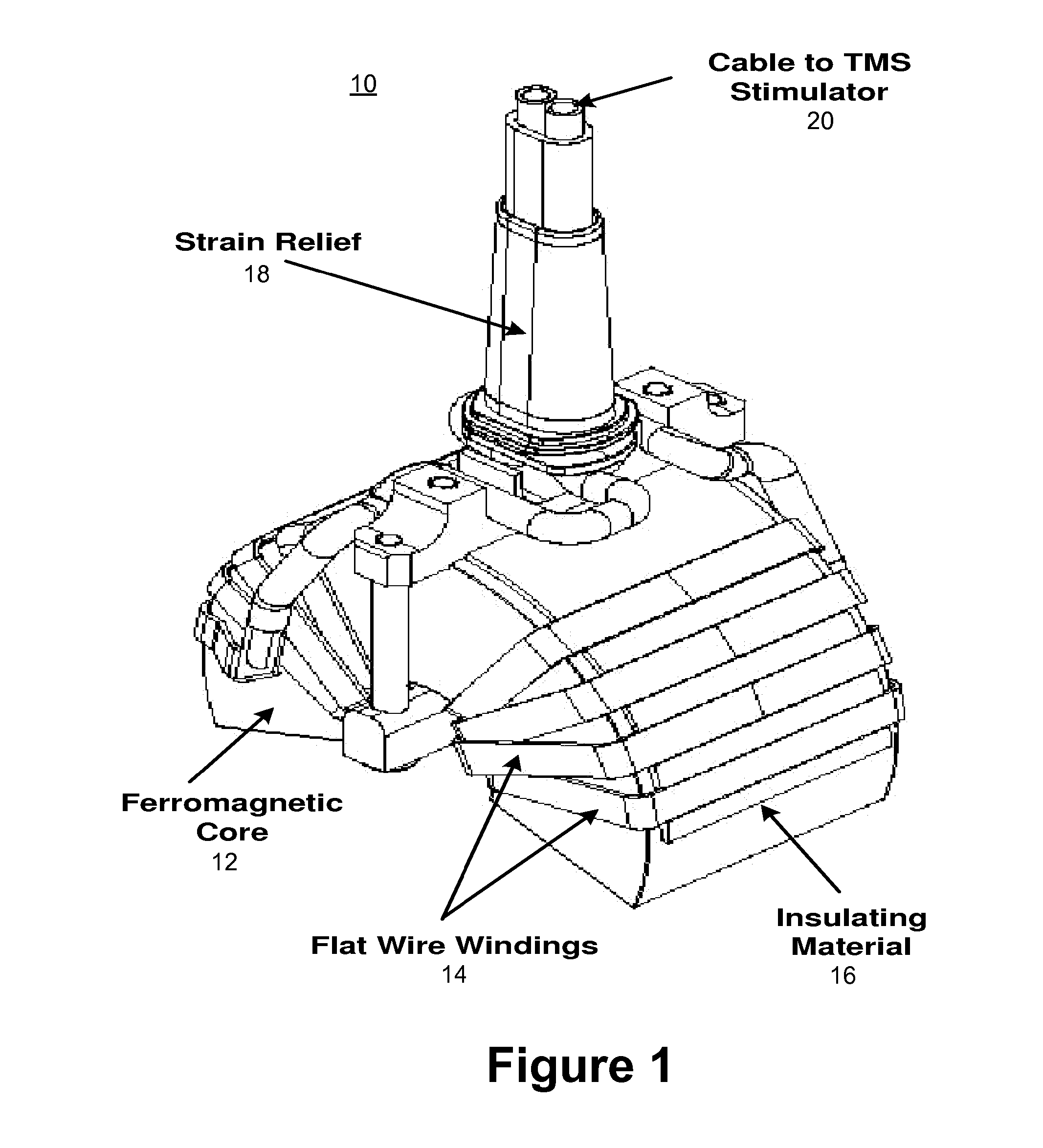
Ferrofluidic cooling and acoustical noise reduction in magnetic stimulators
A ferrofluid chamber has a housing that is adapted to be coupled to a component that generates a magnetic field. A ferrofluid may disposed within the housing for cooling the component via convection of the ferrofluid that is induced by the magnetic field.
Owner:NEURONETICS
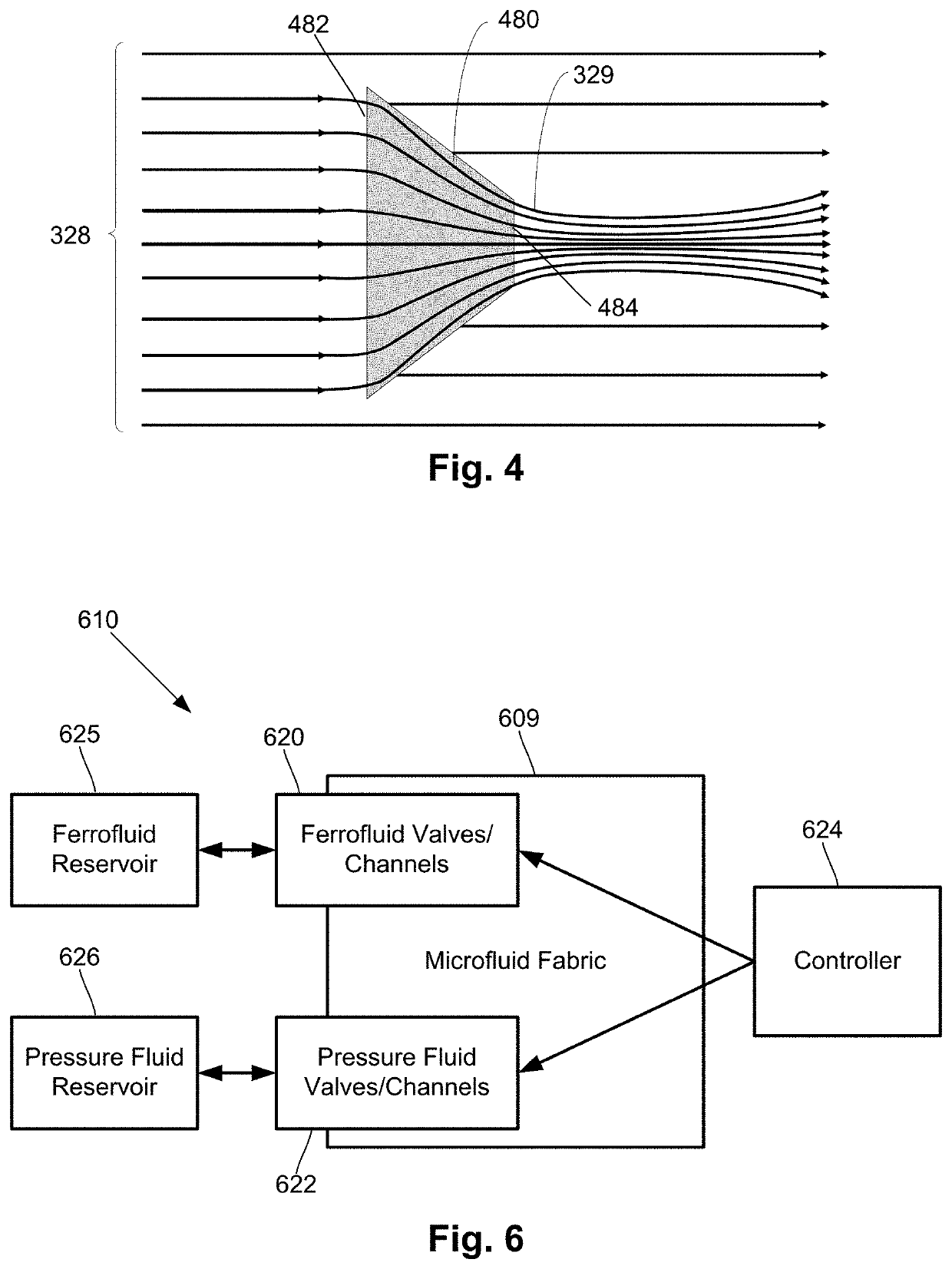
Dynamic magnetic shielding and beamforming using ferrofluid for compact magnetoencephalography (MEG)
ActiveUS20200088811A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetoencephalographyMagnetic shield
A magnetic field measurement system can include at least one magnetometer; and a ferrofluid shield disposed at least partially around the at least one magnetometer. For example, the ferrofluid shield can include a microfluid fabric and a ferrofluid disposed in or flowable into the microfluid fabric. As another example, the ferrofluid shield can include a ferrofluid and a controller configured to alter an arrangement of the ferrofluid within the ferrofluid shield.
Owner:HI LLC
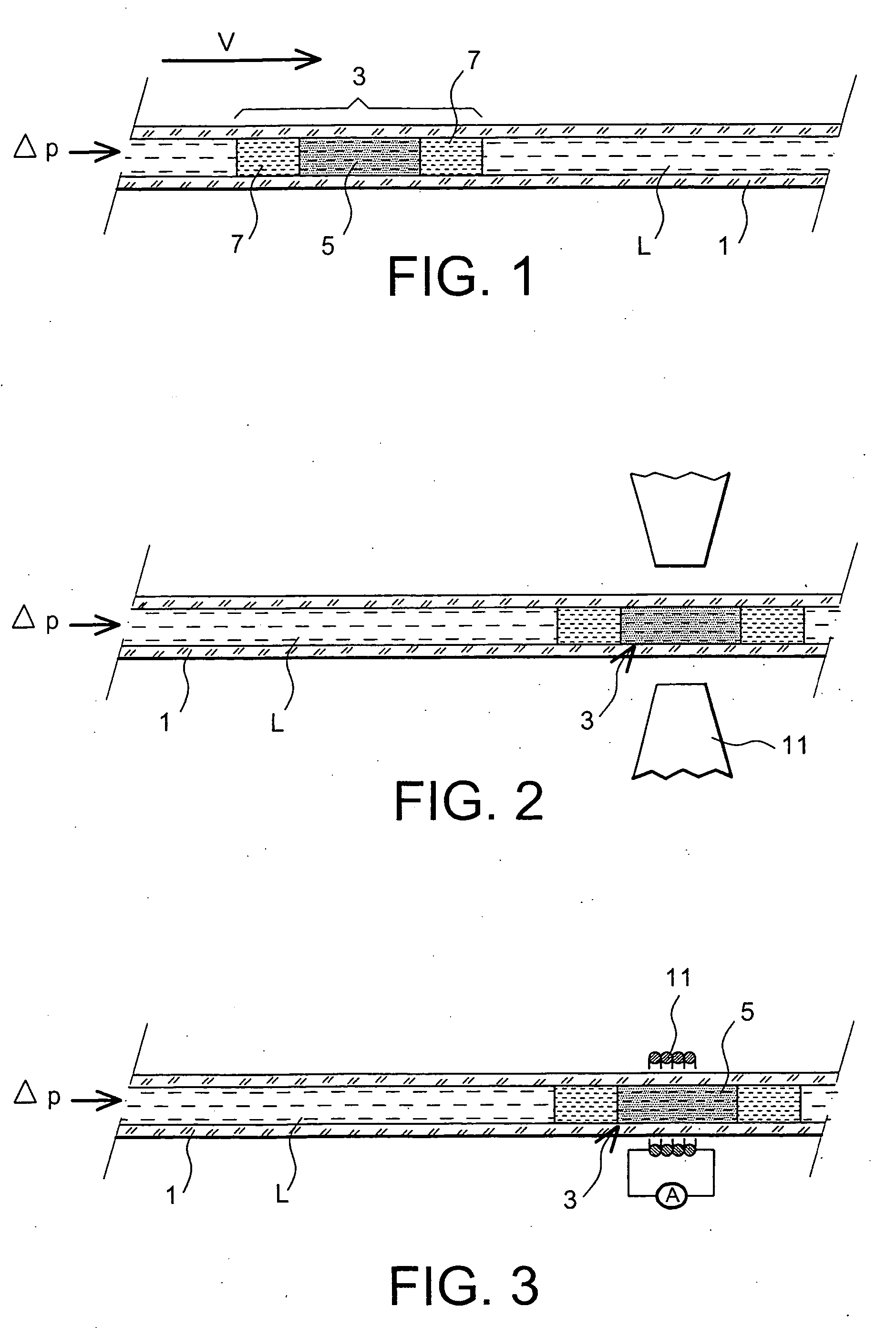
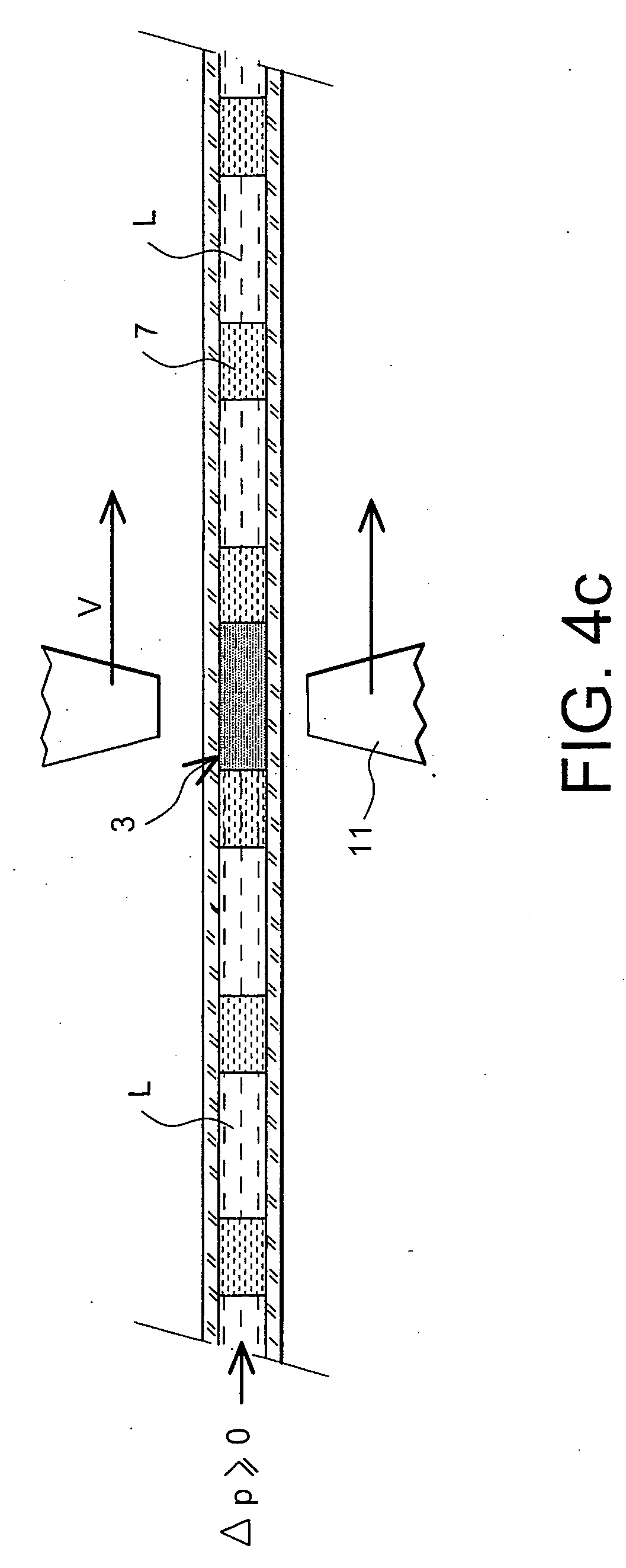
Method for moving a fluid of interest in a capillary tube and fluidic microsystem
InactiveUS20040241693A1Low viscosityGood physical and chemical stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteCapillary channel
The present invention relates to a method for the displacement of an analyte fluid within a capillary microchannel and to a microfluidic system. In particular, it relates to the field of microfluidics, and especially to microfluidic systems. The method comprises steps which consist in introducing at least one ferrofluid train (3) into the said capillary channel (1), the said ferrofluid train (3) comprising a slug of ferrofluid (5) and, placed against at least one of the two ends of the slug of ferrofluid and in contact with it, a slug of liquid (7) immiscible with both the ferrofluid and the analyte fluid; in introducing the said analyte fluid (9) into the said capillary channel, in proximity to the ferrofluid train and on the side having the slug of liquid (7) immiscible with both the ferrofluid and the analyte fluid; and in controlling the analyte fluid displacement within the said capillary channel by the action of a magnetic field on the ferrofluid train, which field is generated by a magnet system placed on the outside of the said capillary channel.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
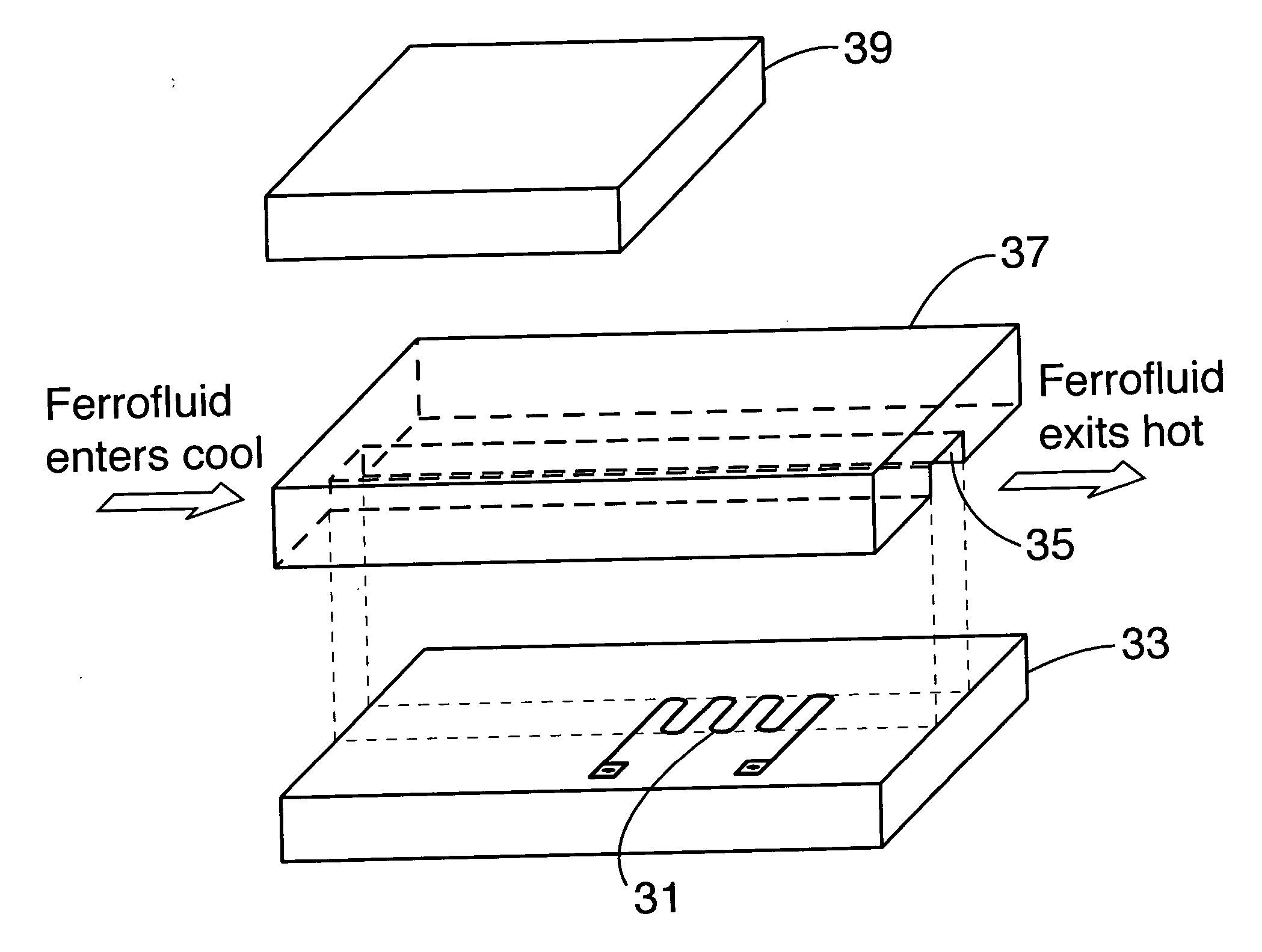
Method and apparatus for removing heat
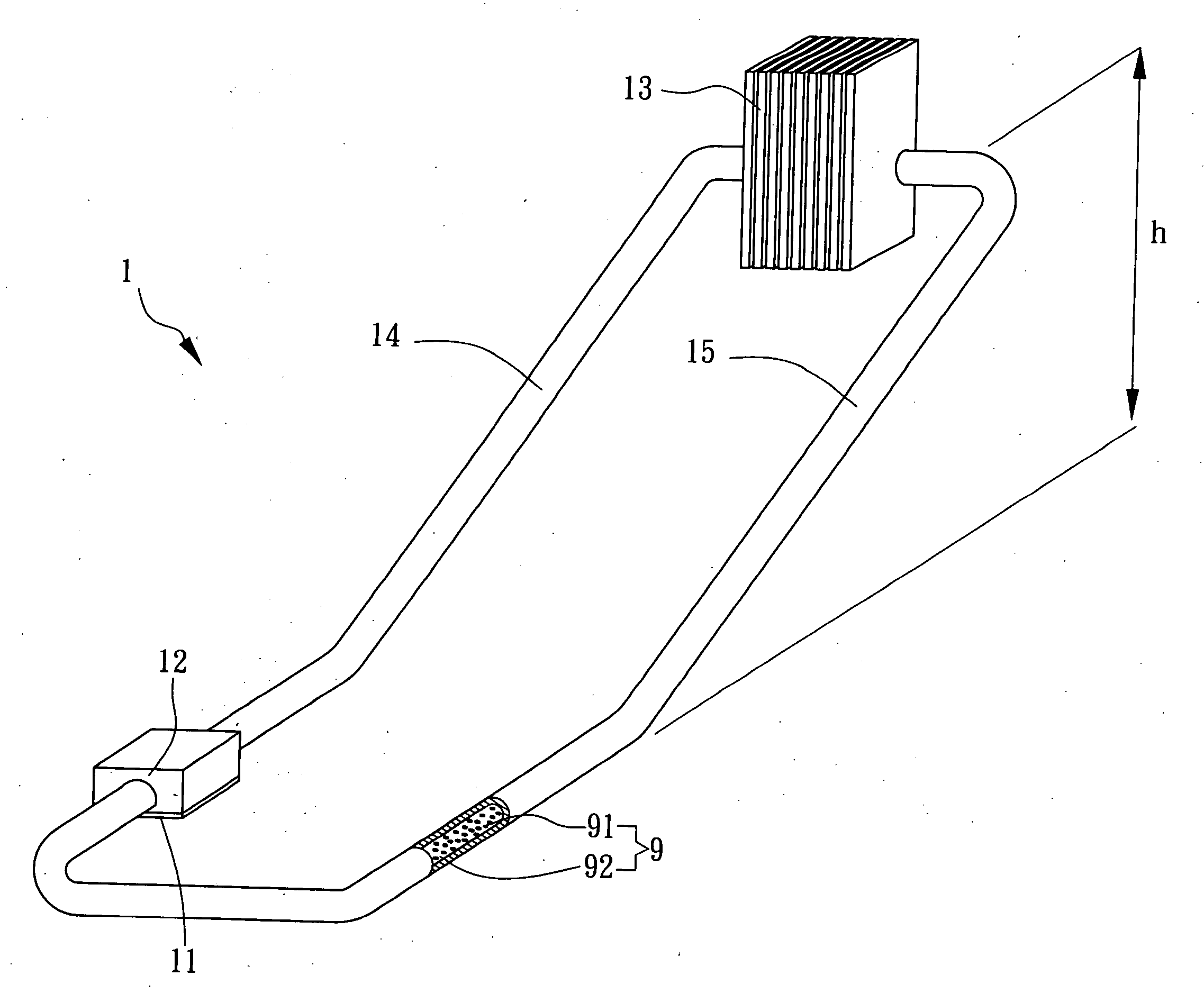
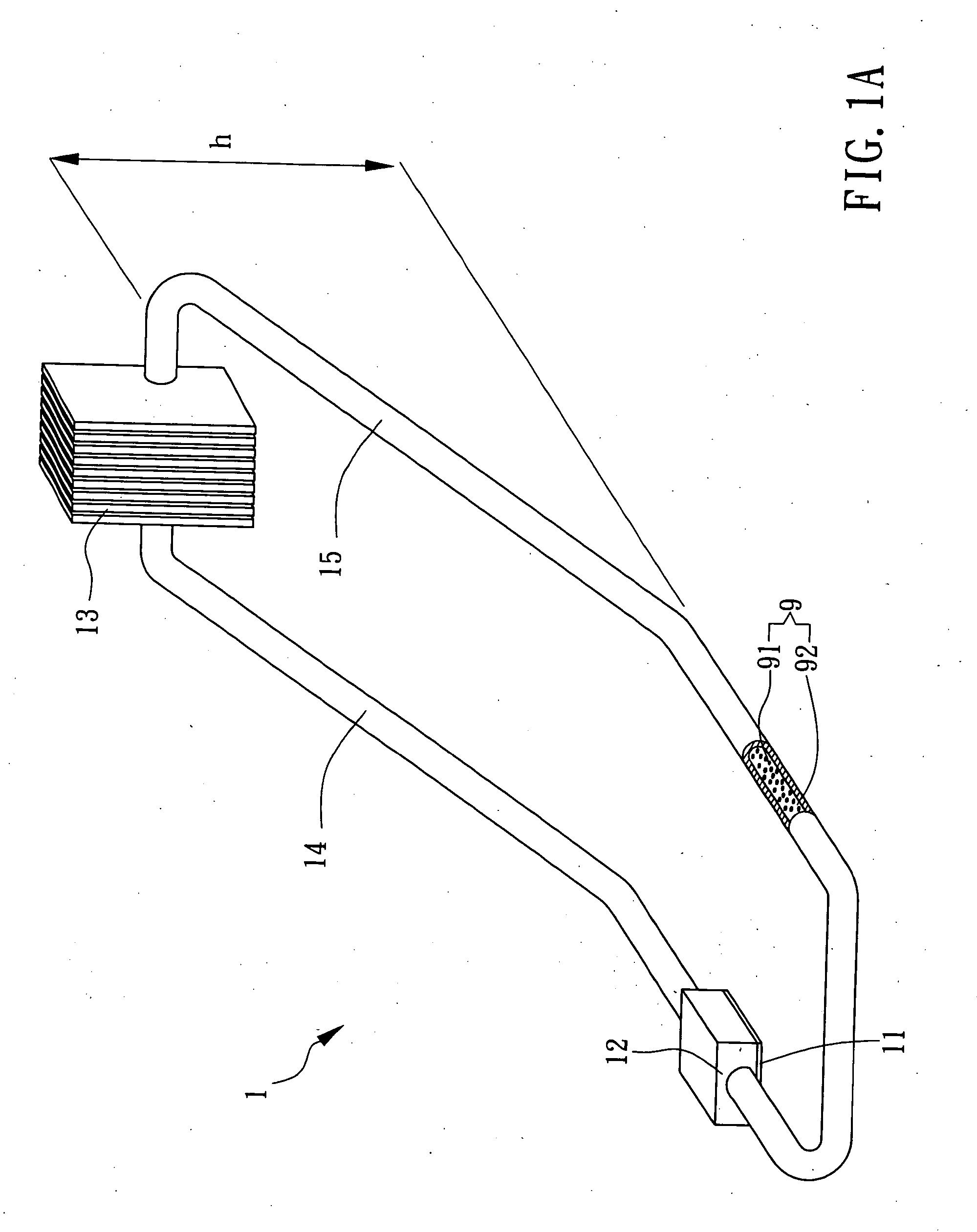
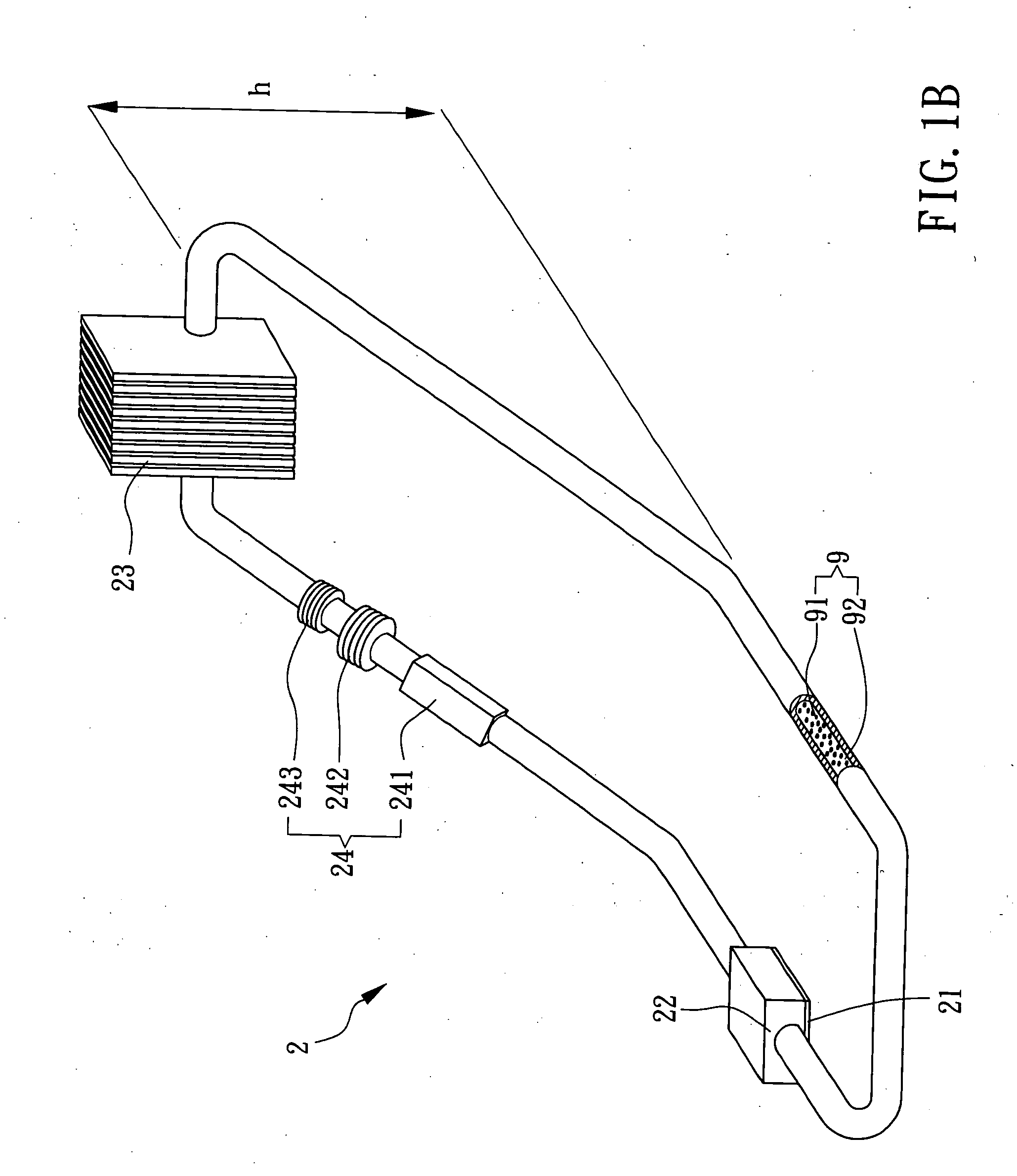
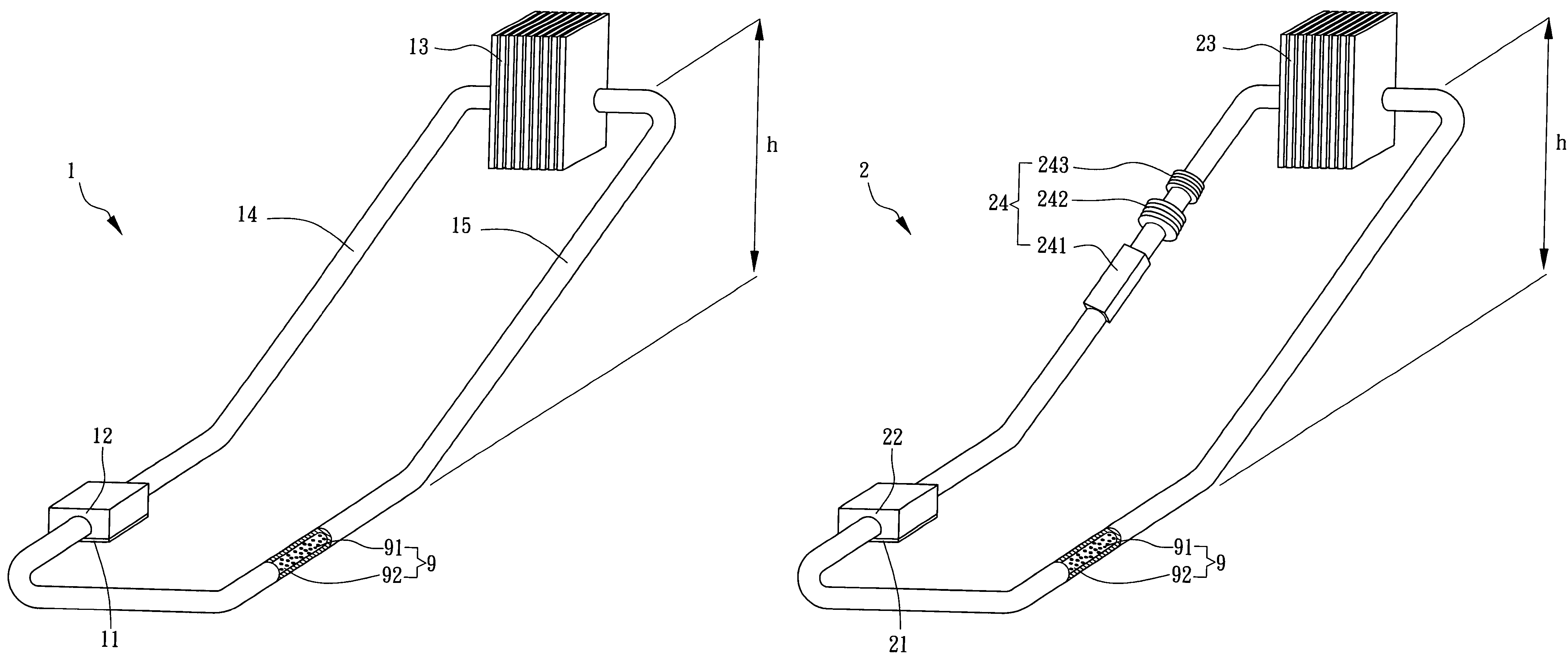
A device includes a liquid metal and a ferrofluid contained in a closed tube. Many electrode groups are connected to the closed tube. A feedback device is connected to the electrode groups. The feedback device switches power to each electrode group in series to circulate the liquid metal and move the ferrofluid in the closed tube.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Electro-optic assemblies and materials for use therein
InactiveUS20050124751A1Non-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesSimple Organic CompoundsPolyelectrolyte
An electro-optic display comprises first and second substrates, and an adhesive layer and a layer of electro-optic material disposed between these substrates, the adhesive layer comprising a mixture of a polymeric adhesive material and an additive selected from a salt, a polyelectrolyte, a polymer electrolyte, a solid electrolyte, a conductive metal powder, a ferrofluid, a non-reactive solvent, a conductive organic compound, and combinations thereof. In one aspect, there is provided an adhesive comprising a mixture of a polymeric adhesive material and an additive selected from a salt, a polyelectrolyte, a polymer electrolyte, a solid electrolyte, and combinations thereof.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Microchannel cooling device with magnetocaloric pumping
InactiveUS20060278373A1Dissipate heat generatedIncrease flow rateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringCooling down
The invention discloses a microchannel cooling device, adapted for dissipating heat generated from an electronic device, which comprises: a heat sink, being arranged on the electronic device and having an inlet, an outlet and a plurality of microchannels embedded thereon for receiving a ferrofluid to flow therein; a condenser, having an outlet connected to the inlet of the heat sink and an inlet connected to the outlet of the heat sink; and a magnetocaloric pump, for providing a magnetic field to the ferrofluid flowing in the heat sink; wherein the magnetocaloric effect (MCE) caused by the working of the magnetic field on the ferrofluid flowing in the heat sink is used for driving the ferrofluid to flow through the plural microchannels of the heat sink while absorbing heat therefrom, and thereafter, the heated ferrofluid flow into the condenser for discharging heat and then the cool-down ferrofluid is guided back to the heat sink to complete a circulation. The invention make use of the high heat transfer performance of the plural microchannels, the nature circulation caused by the loop thermosyphone and the driving of the magnetocaloric pump so as to constitute a cooling device with no mechanically moving elements.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
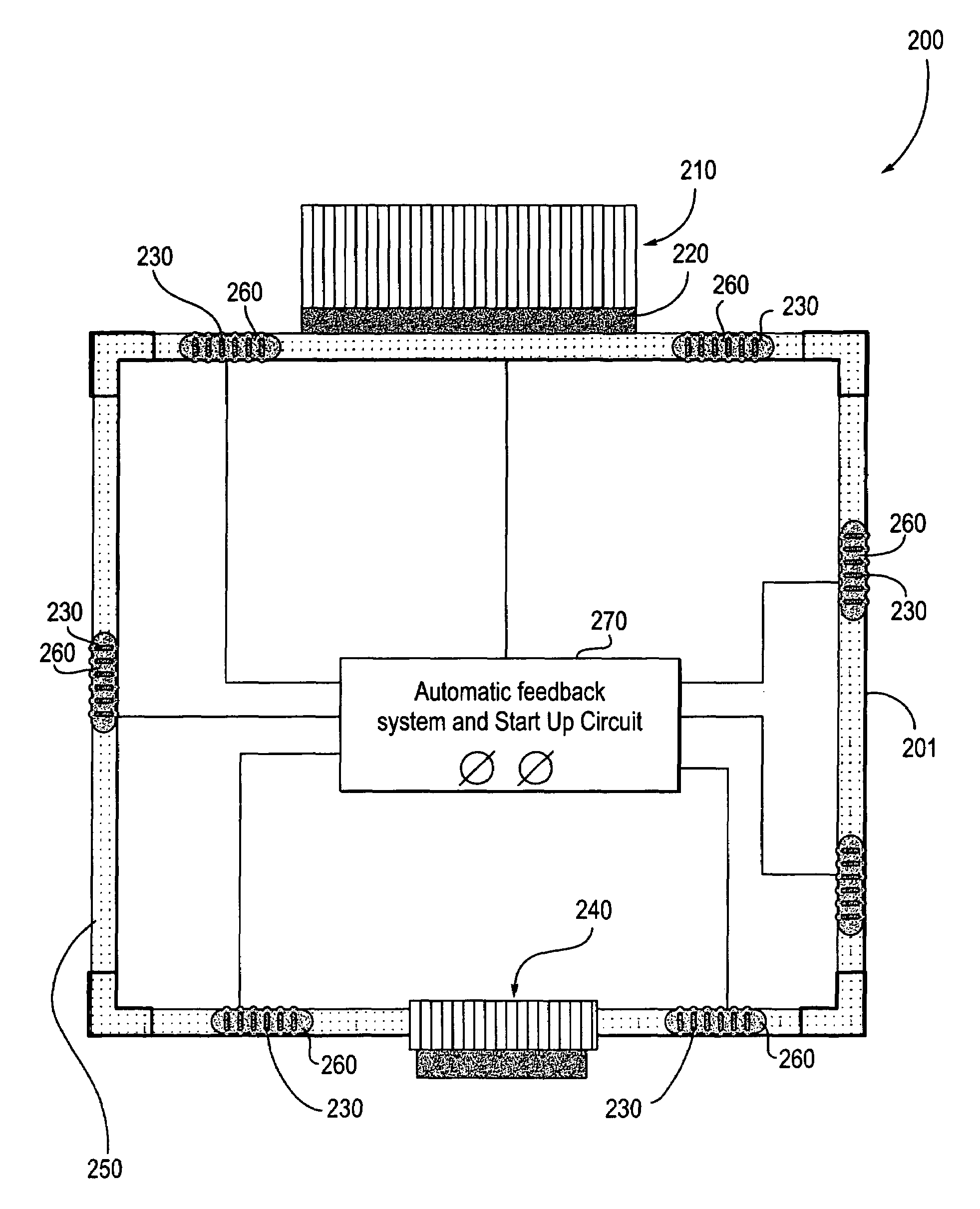
Ellipsoid generator
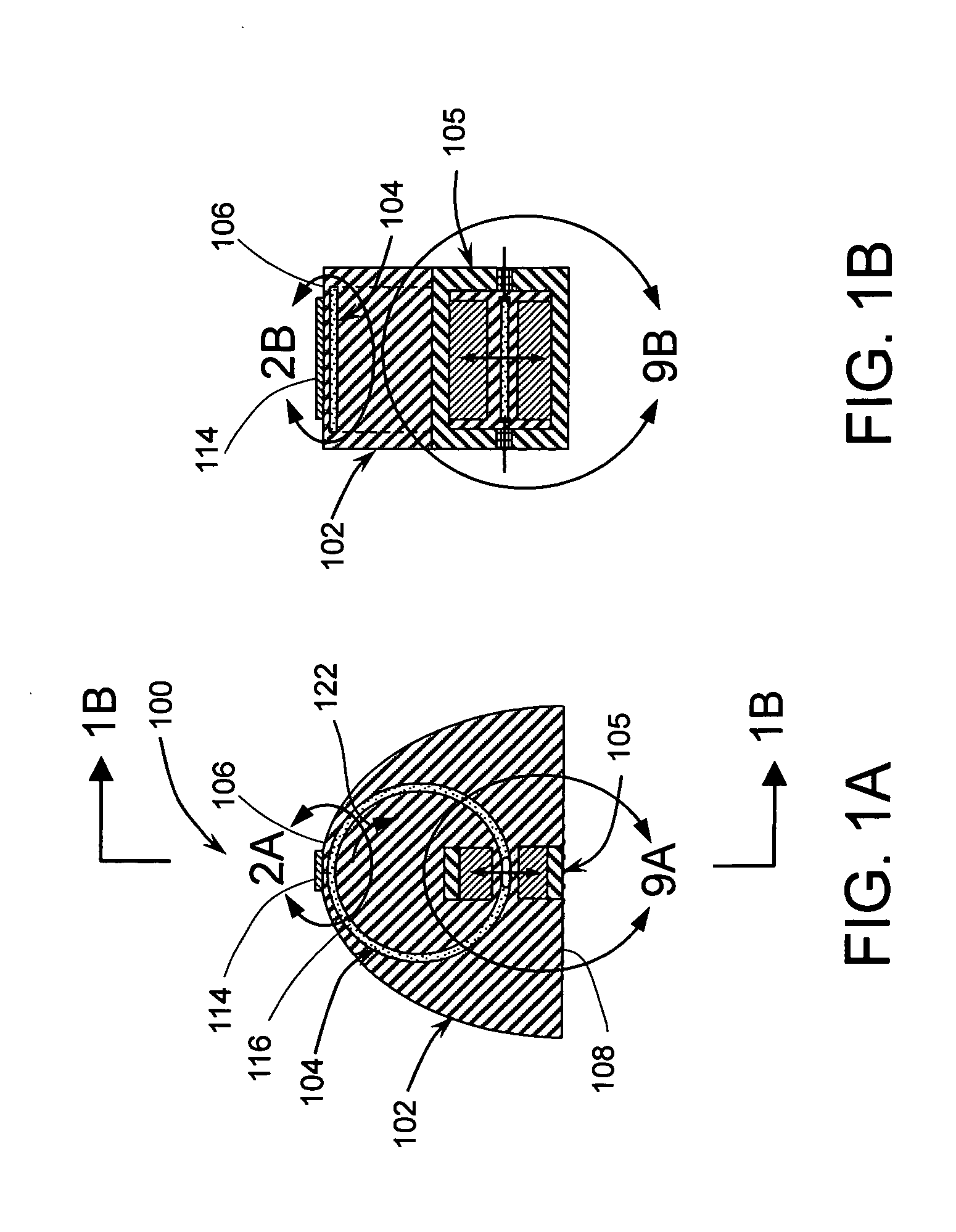
A dynamoelectric device that is highly adaptable to a broad range of applications while providing robust output and energy conversion. The magnetic pole faces of the rotor lie in an ellipsoid. With or without a rotor shaft, the device allows options of either physical connection or contact-less, magnetic coupling. Surrounding the rotor is a brush-less stator having a bobbin-type, axial-centered coil conductor that provides a total capture of magnetic flux emanating from a rotor having an entire surface area of uniform flux density. Devices without a rotor shaft, and those having an air gap filled with ferrofluid, provide a two part generator with remarkable efficiency that is easily waterproofed and mechanically stable.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE INC
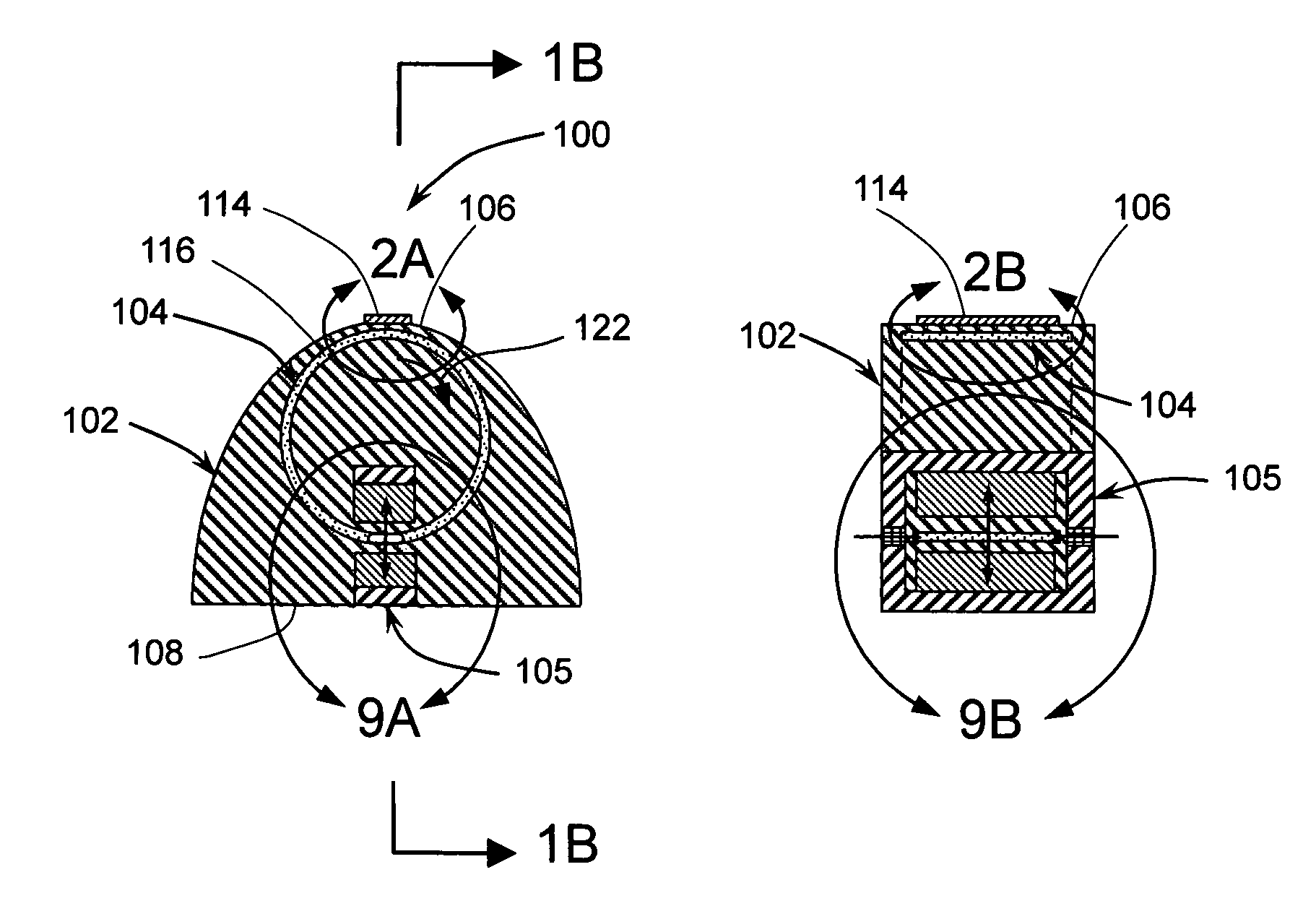
Compositions and method for providing anisotropic conductive pathways and bonds between two sets of conductors
InactiveUS6110399ASimple processImprove electrical contact reliabilityNon-insulated conductorsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesRegular patternElectrical conductor
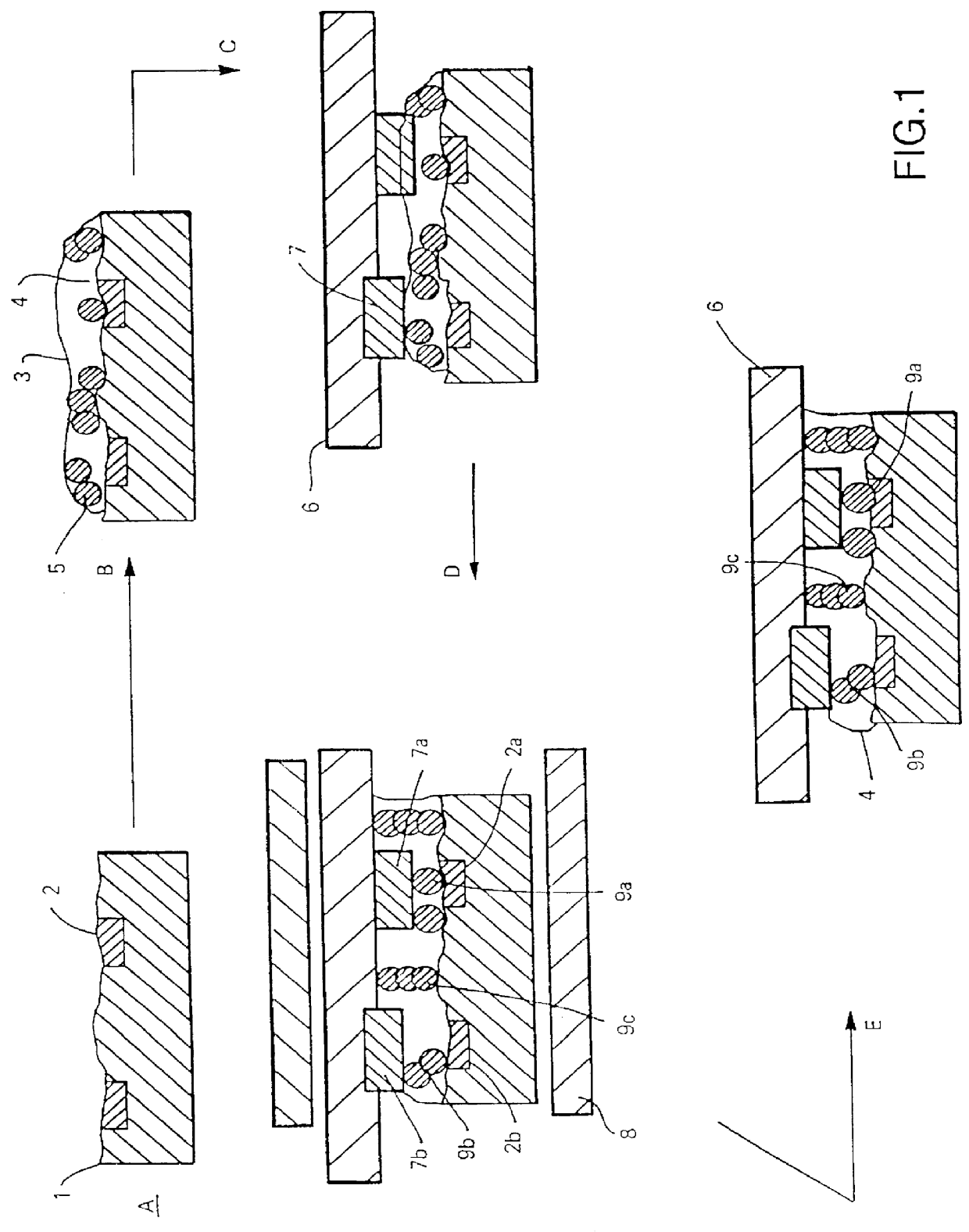
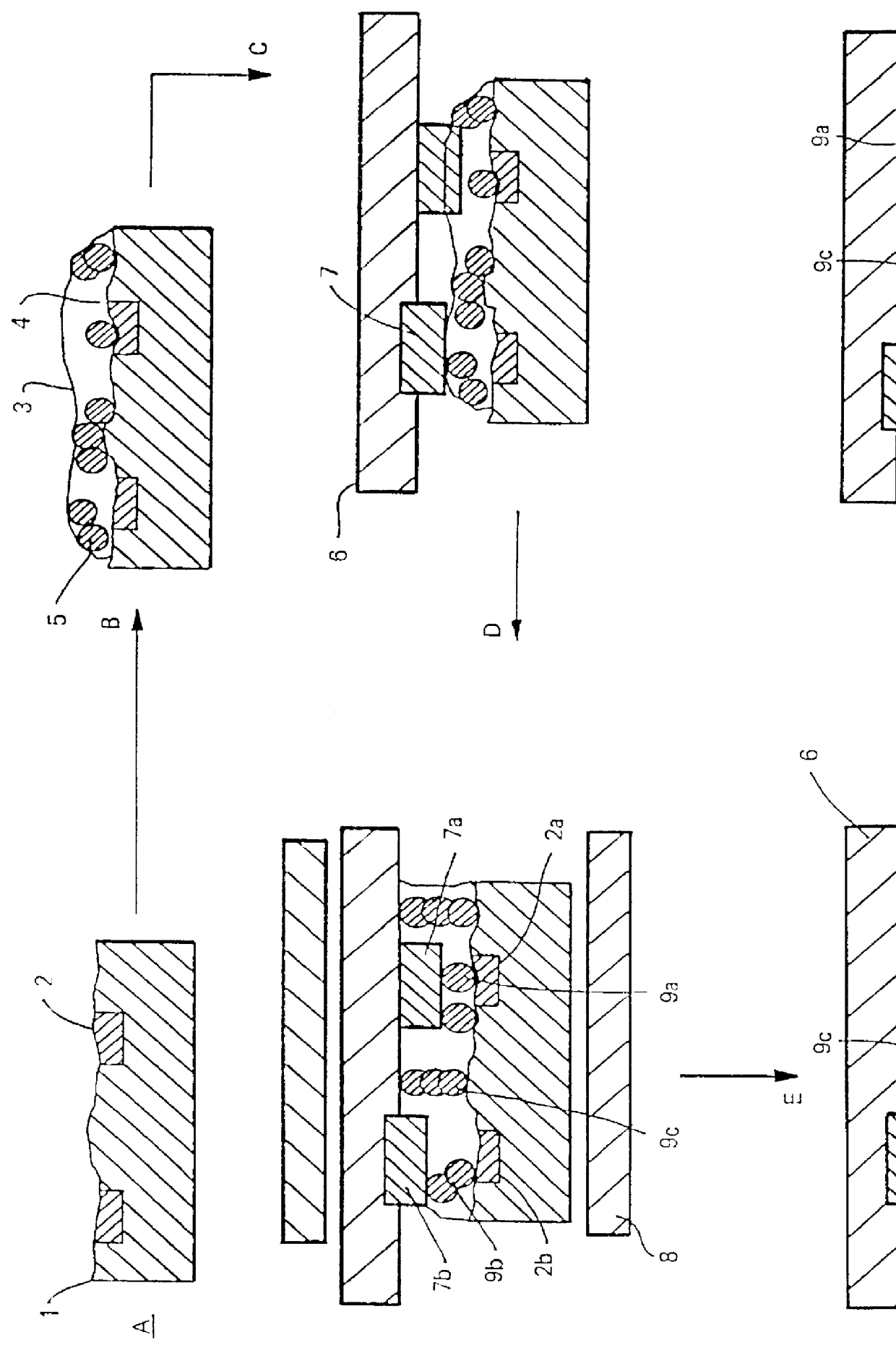
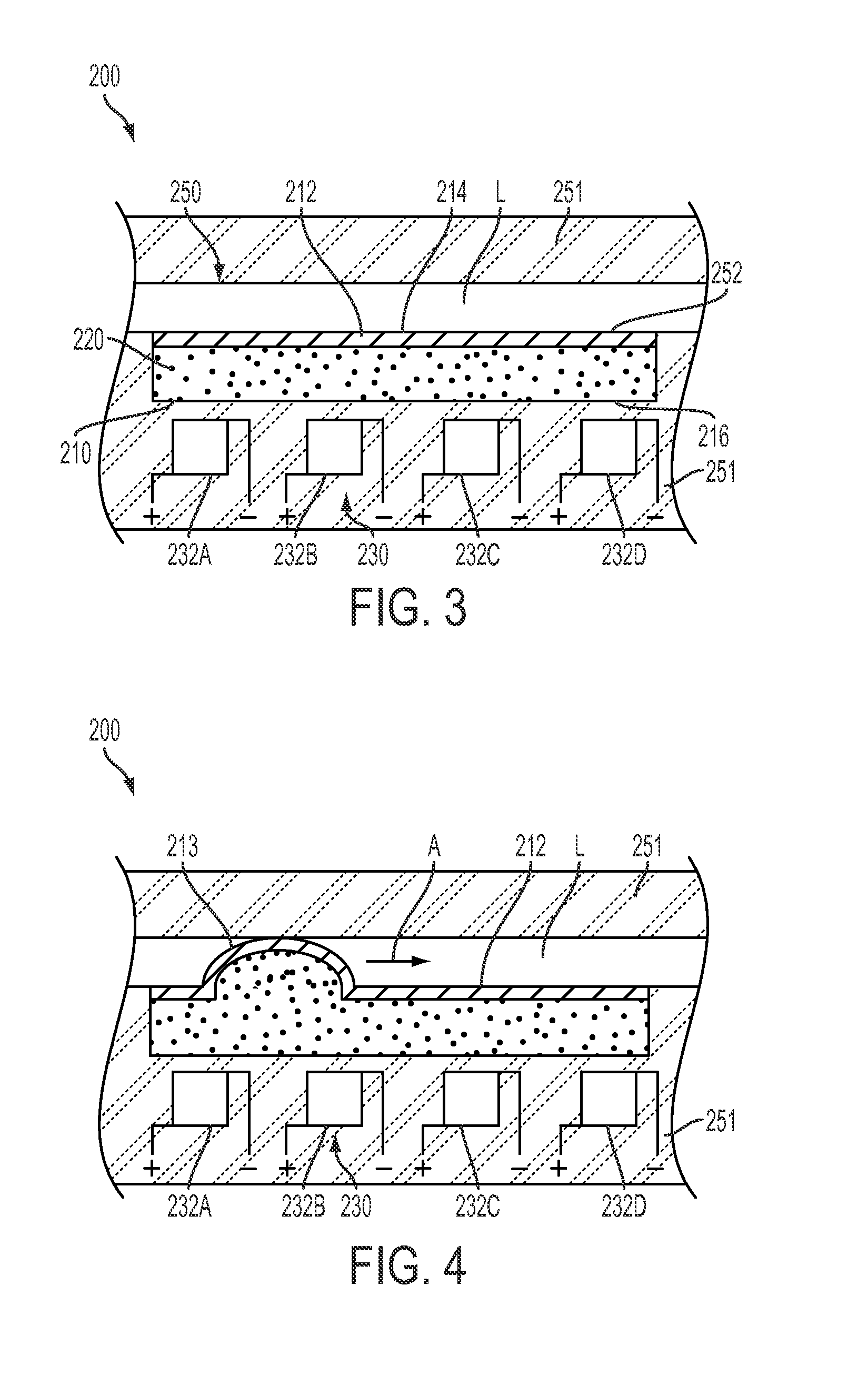
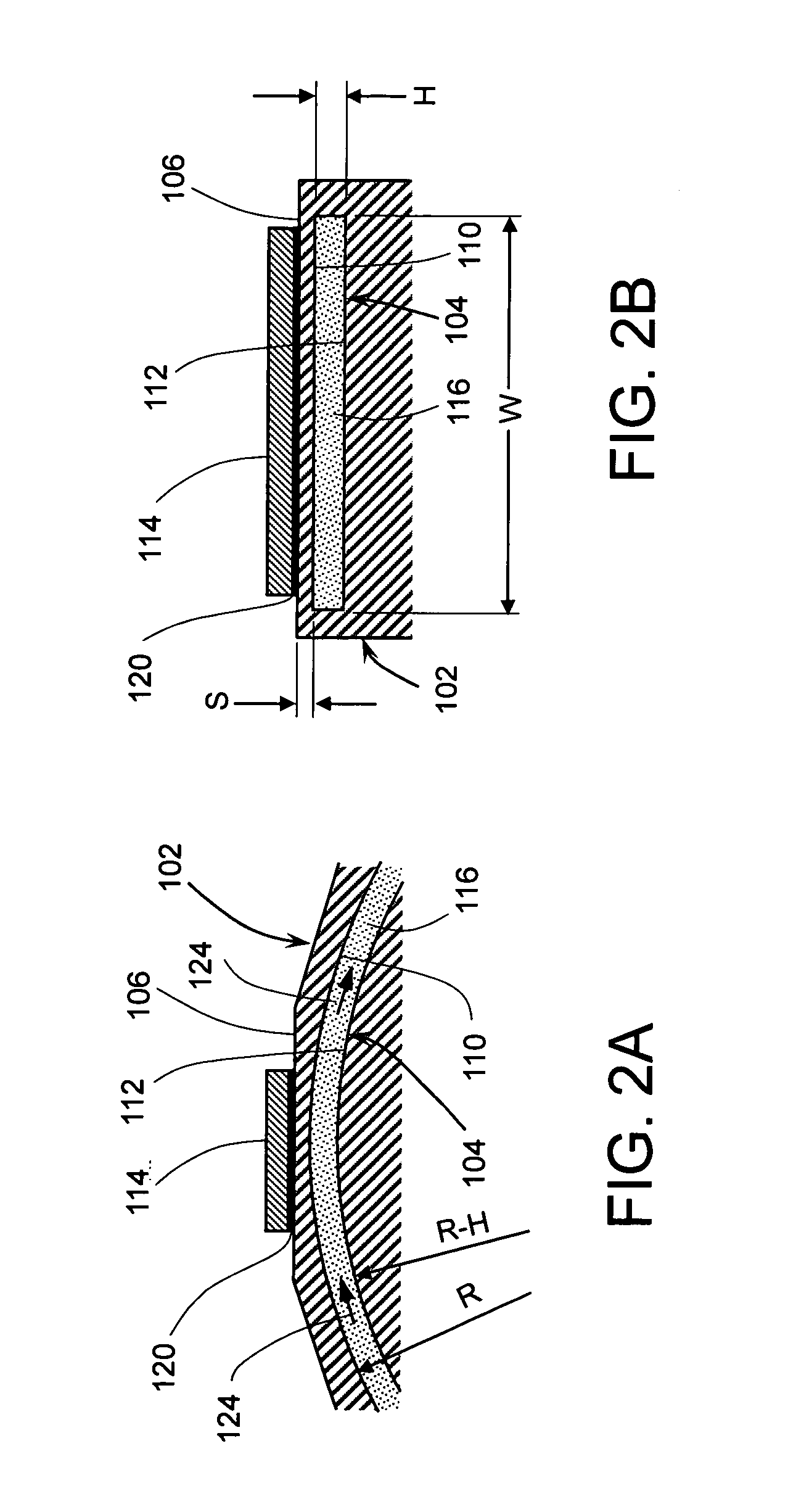
The invention provides a composition (3) comprising: (i) a ferrofluid comprising a colloidal suspension (4) of ferromagnetic particles in a non-magnetic carrier liquid, and (ii) a plurality of electrically-conductive particles (5) having substantially uniform sizes and shapes, dispersed in the ferrofluid. Various types of substantially non-magnetic electrically-conductive particles (5) are described. Application of a substantially uniform magnetic field by magnet means (8) to the composition (3) causes the electrically-conductive particles (5) to form a regular pattern (9). The composition is used for providing anisotropic conductive pathways (9a, 9b) between two sets of conductors (2a, 2b; 7a, 7b) in the electronics industry. The composition may be a curable adhesive composition which bonds the conductors. Alternatively or in addition the electrically-conductive particles may have a latent adhesive property e.g. the particles may be solder particles. The ferrofluid may be a colloidal suspension of ferromagnetic particles in a liquid monomer.
Owner:LOCTITE (R&D) LIMITED
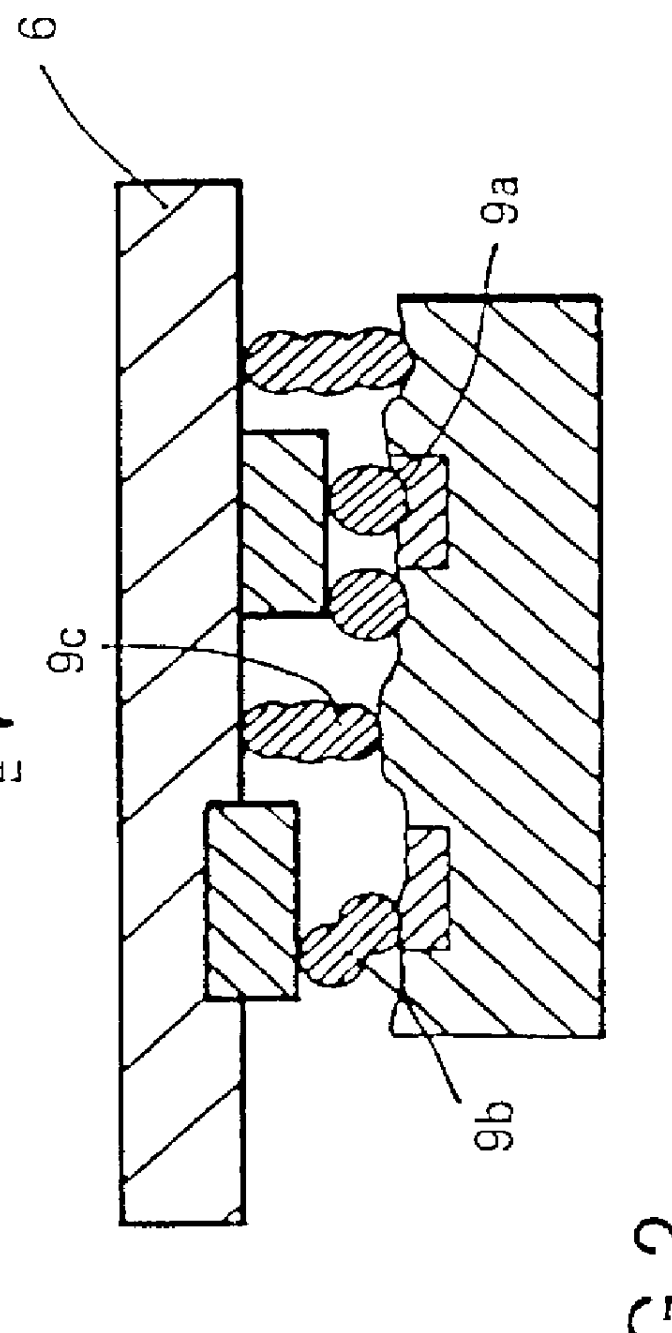
Ultra high vacuum ferrofluidic seals and method of manufacture
A ferrofluid seal incorporates a metal seal comprised of two knife-edges and a flat metal washer is formed between a pole piece and the housing at the axial interface between the parts. One knife edge is machined into the inner face of the housing flange and the other knife edge is machined into the opposing pole piece face. This metal seal effectively seals the pole piece to the housing with a seal suitable for ultra high vacuum applications.
Owner:FEEROTEC USA
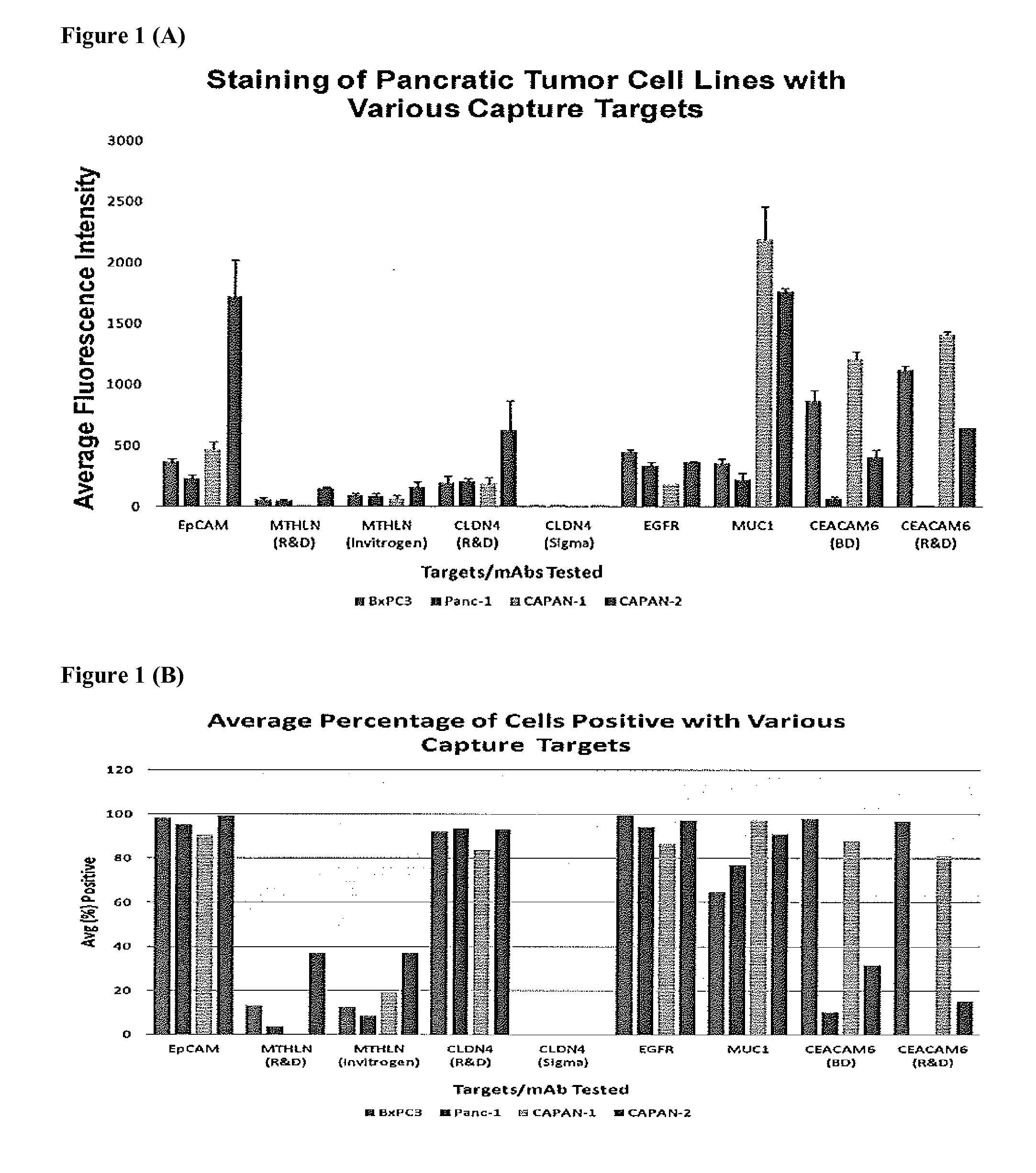
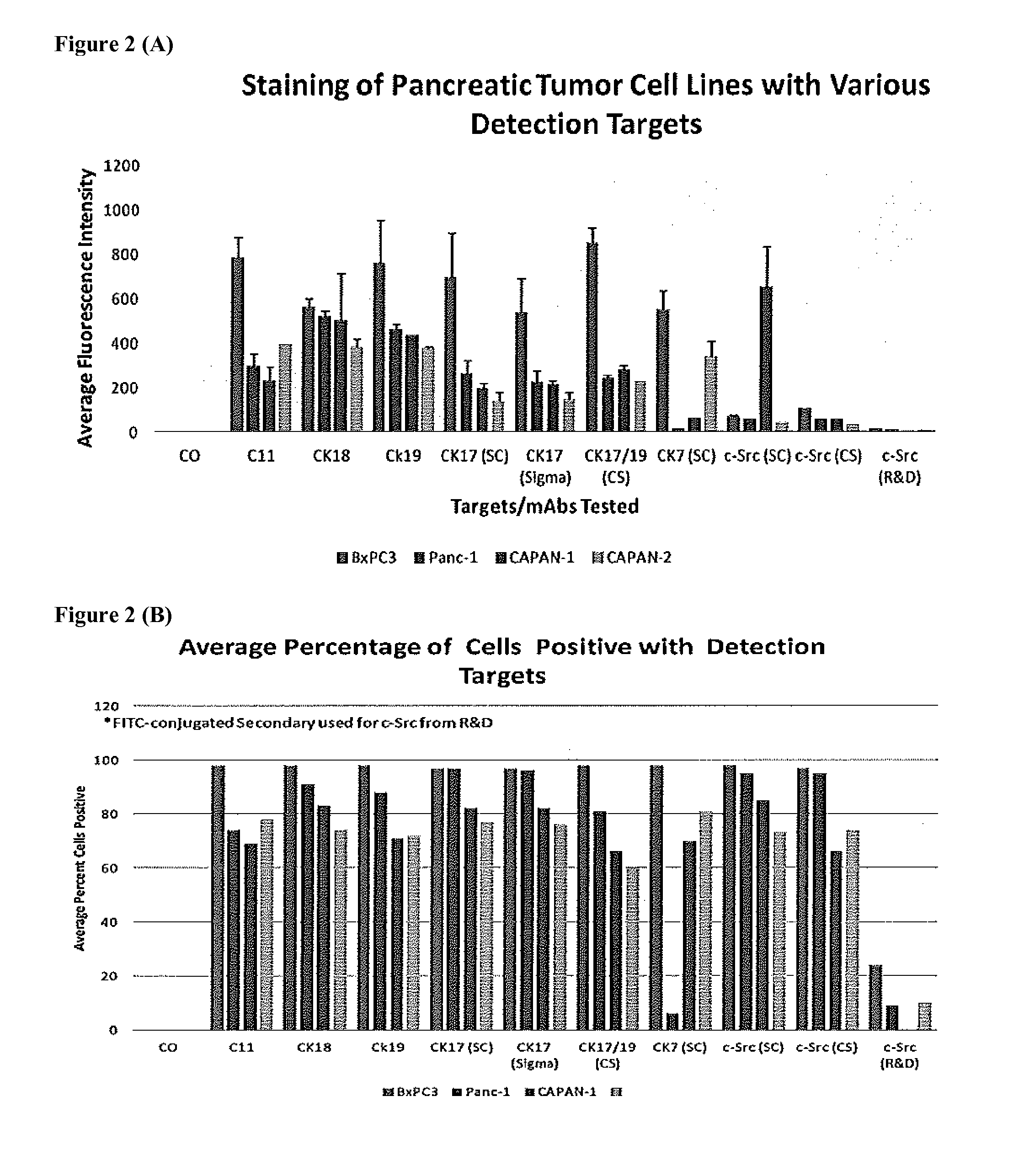
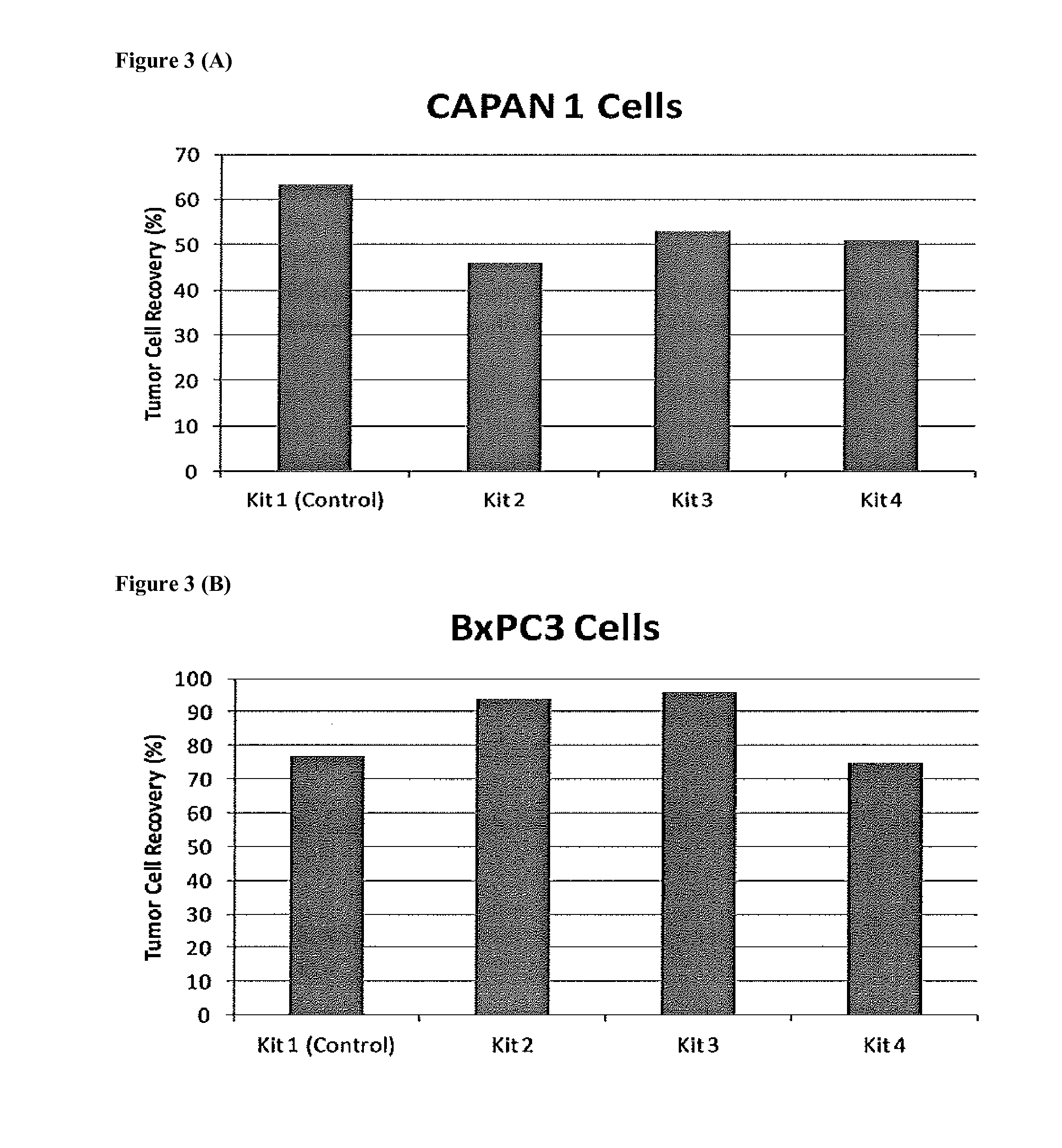
Methods and kits for the detection of circulating tumor cells in pancreatic patients using polyspecific capture and cocktail detection reagents
InactiveUS20120094275A1Easy to detectSufficient binding capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthAntigen
A highly sensitive assay is disclosed which combines immunomagnetic enrichment with multiparameter flow cytometric or image cytometry to detect, enumerate and characterize carcinoma cells in the blood. The present invention incorporates the conjugation of different antibodies to the same ferrofluid. This has the effect of making the ferrofluid polyspecific with respect to the antigens that the ferrofluid will bind. The multiple antibodies present on the same ferrofluid do not appear to block or otherwise interfere with each other. Such ferrofluids have the highly desirable effect of being able to bind specifically to more than one type of cell. The assay is especially useful to enable the capture of CTCs that have low EpCAM expression, but high expression of other tumor markers; Accordingly, the assay facilitates the biological characterization and staging of carcinoma cells.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
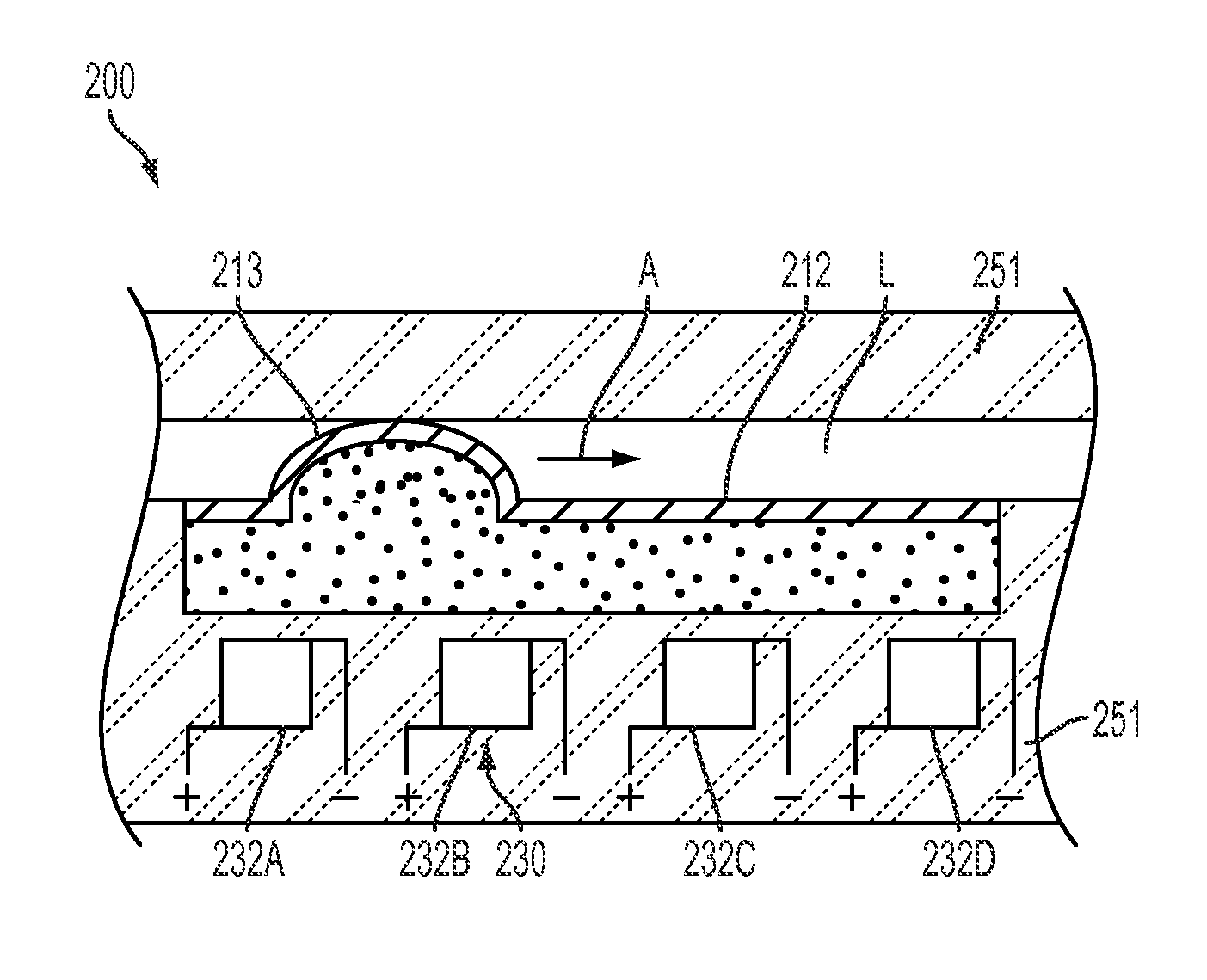
Ferrofluid control and sample collection for microfluidic application
A fluid conveyance system includes a flow passage and a cavity adjacent a side of the flow passage. A wall of the passage includes a flexible section that separates the cavity from the flow passage. The cavity contains a ferrofluidic material. The system further includes at least one magnetic field source positioned adjacent the flow channel. The magnetic field source is operable to move the ferrofluidic material in the cavity to exert a pressure on the flexible section and displace the flexible section into the flow passage to alter the flow of material through the passage. A method of collecting components from a sample volume includes the steps of distributing magnetic particles into the sample volume, capturing the components from the sample volume, and applying a magnetic field to the sample volume to control directional flow of the sample volume.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
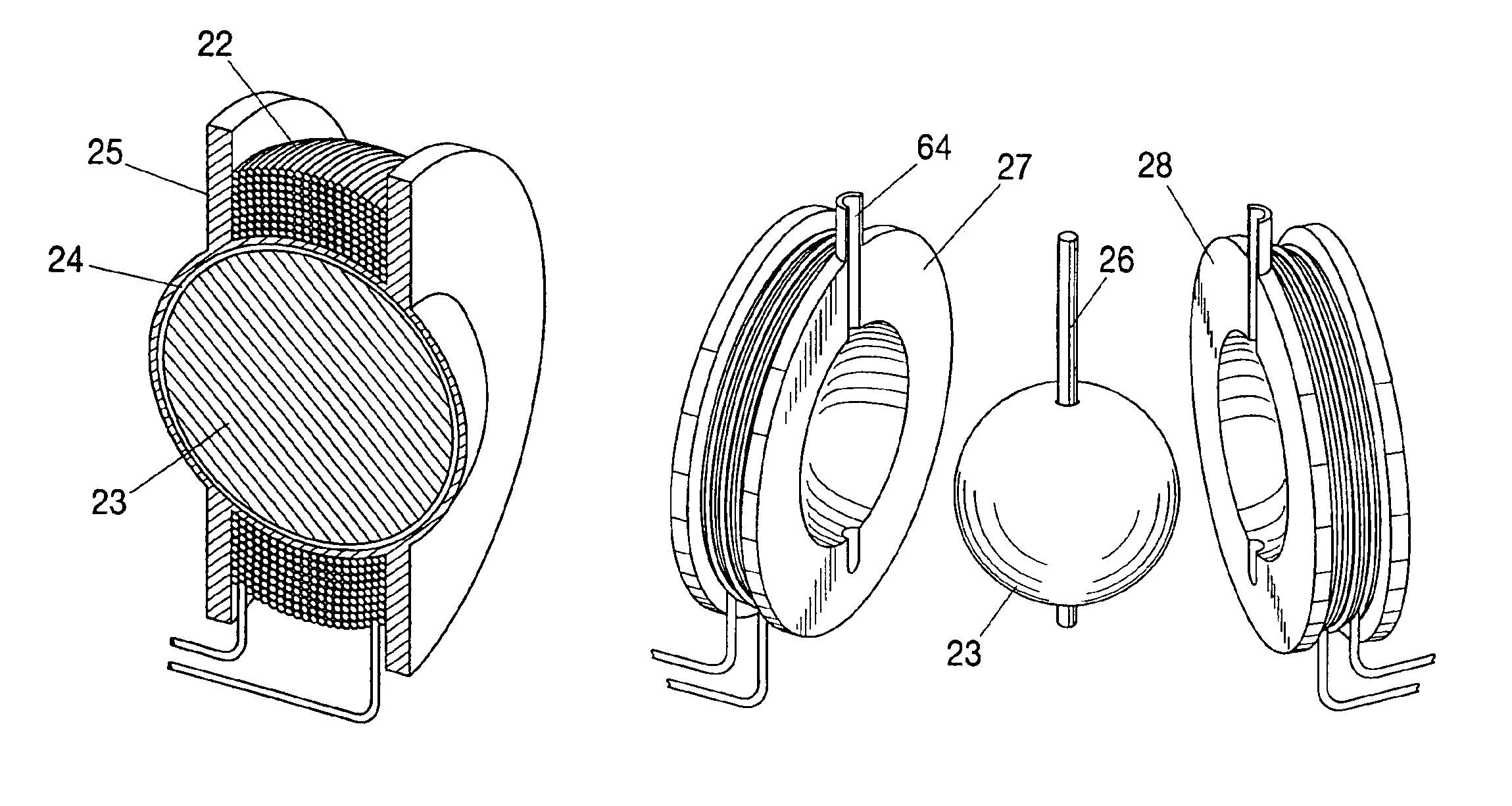
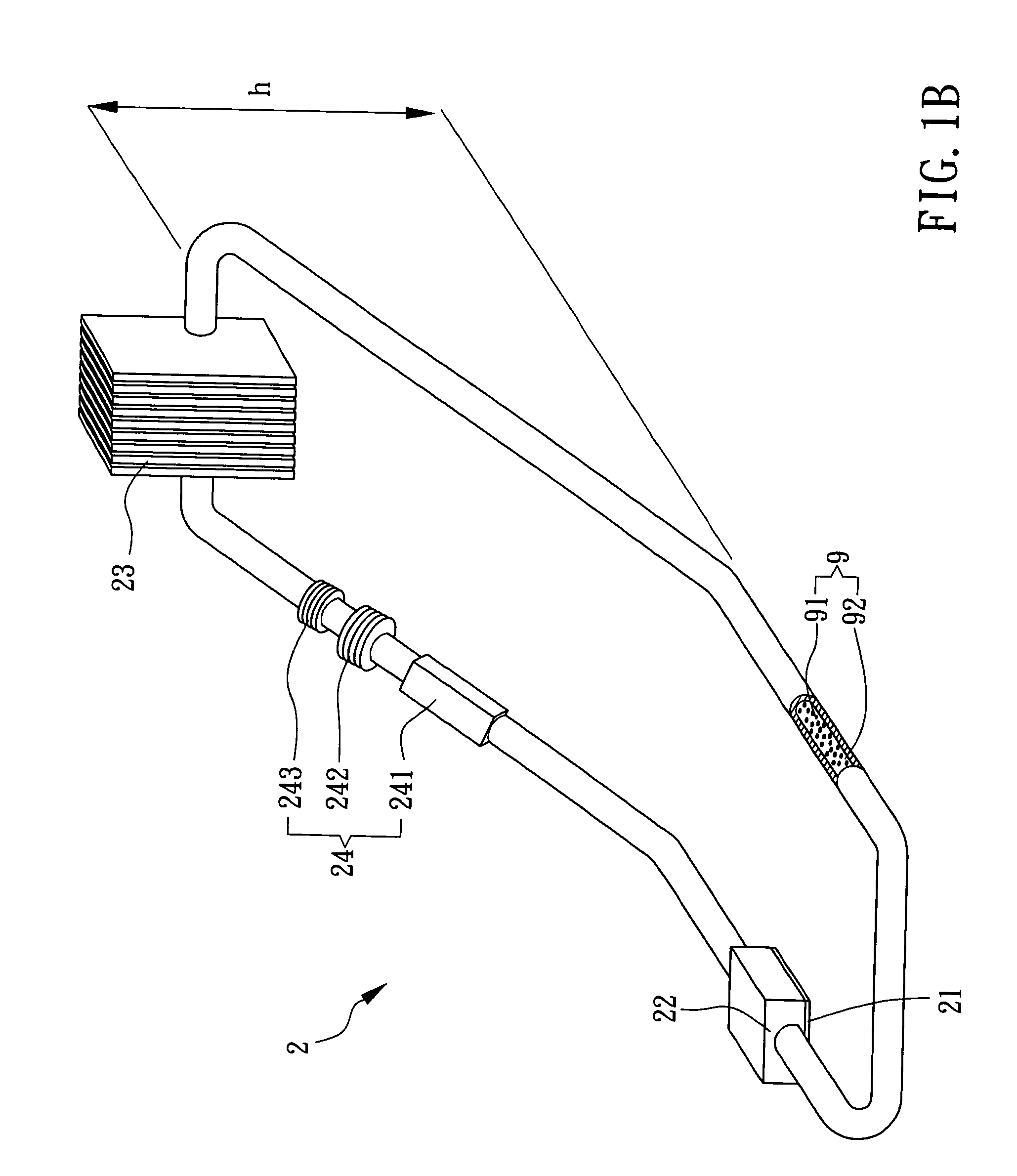
Magnet configuration for image stabilization
A sensor mounting system for enabling image stabilization in a digital camera is described. An electronic array light sensor is moved in relation to other parts of the camera in response to camera motion. In one embodiment, the sensor is moved by at least one linear motor having a ferrofluid in a gap of the linear motor. Other aspects of the system are described, including methods of heat sinking the sensor, a suspension system, methods of compensating for an effect of temperature on the ferrofluid, and a compact magnet configuration for forming the linear motor and providing feedback as to the position of the sensor.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method of compensating for an effect of temperature on a control system
InactiveUS20060018646A1Television system detailsColor television detailsControl systemImage stabilization
A sensor mounting system for enabling image stabilization in a digital camera is described. An electronic array light sensor is moved in relation to other parts of the camera in response to camera motion. In one embodiment, the sensor is moved by at least one linear motor having a ferrofluid in a gap of the linear motor. Other aspects of the system are described, including methods of heat sinking the sensor, a suspension system, methods of compensating for an effect of temperature on the ferrofluid, and a compact magnet configuration for forming the linear motor and providing feedback as to the position of the sensor.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Fault-tolerant permanent magnet machine with reconfigurable stator core slot flux paths
ActiveUS20080238220A1Reduce internal heatMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsMagnetic anisotropyFerrofluid
A permanent magnet (PM) machine has a reconfigurable fault condition mechanism disposed solely within a stator core portion, wherein the mechanism is automatically reconfigurable to reduce fault currents associated with the PM machine during a fault condition. The reconfigurable fault condition mechanism is automatically reconfigurable to also reduce internal heat associated with the PM machine during a fault condition. A method of reconfiguring the fault condition mechanism upon detection of a fault condition includes the steps of 1) selecting the reconfigurable fault condition mechanism from a) a plurality of rotatable magnetically anisotropic cylinders disposed within stator core slots, b) a plurality of ferrofluid-fillable cavities associated with stator core slots, and c) a sliding shield within the stator core; and 2) reconfiguring the fault condition mechanism to automatically reduce fault currents associated with the PM machine upon detection of a fault condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
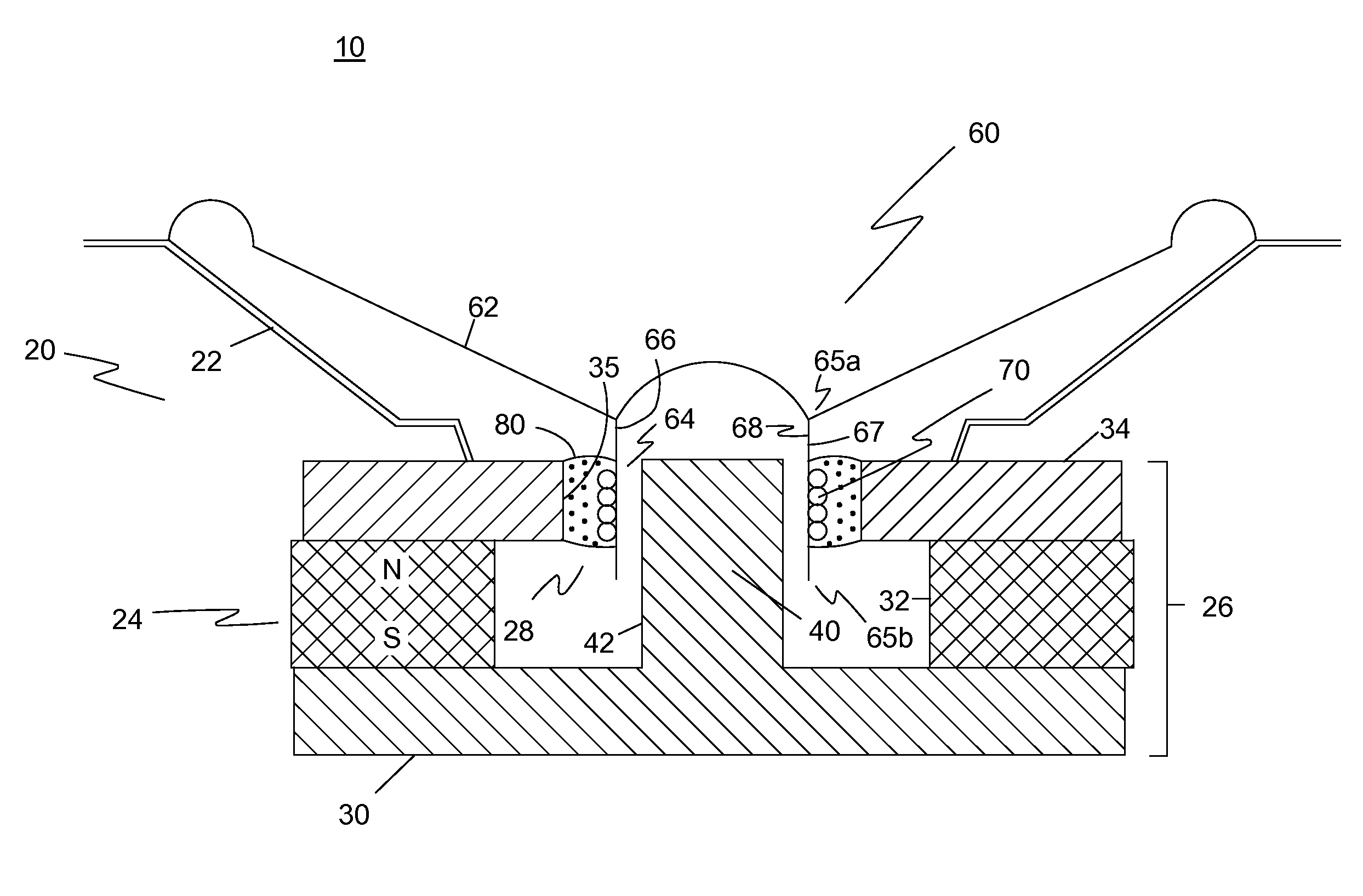
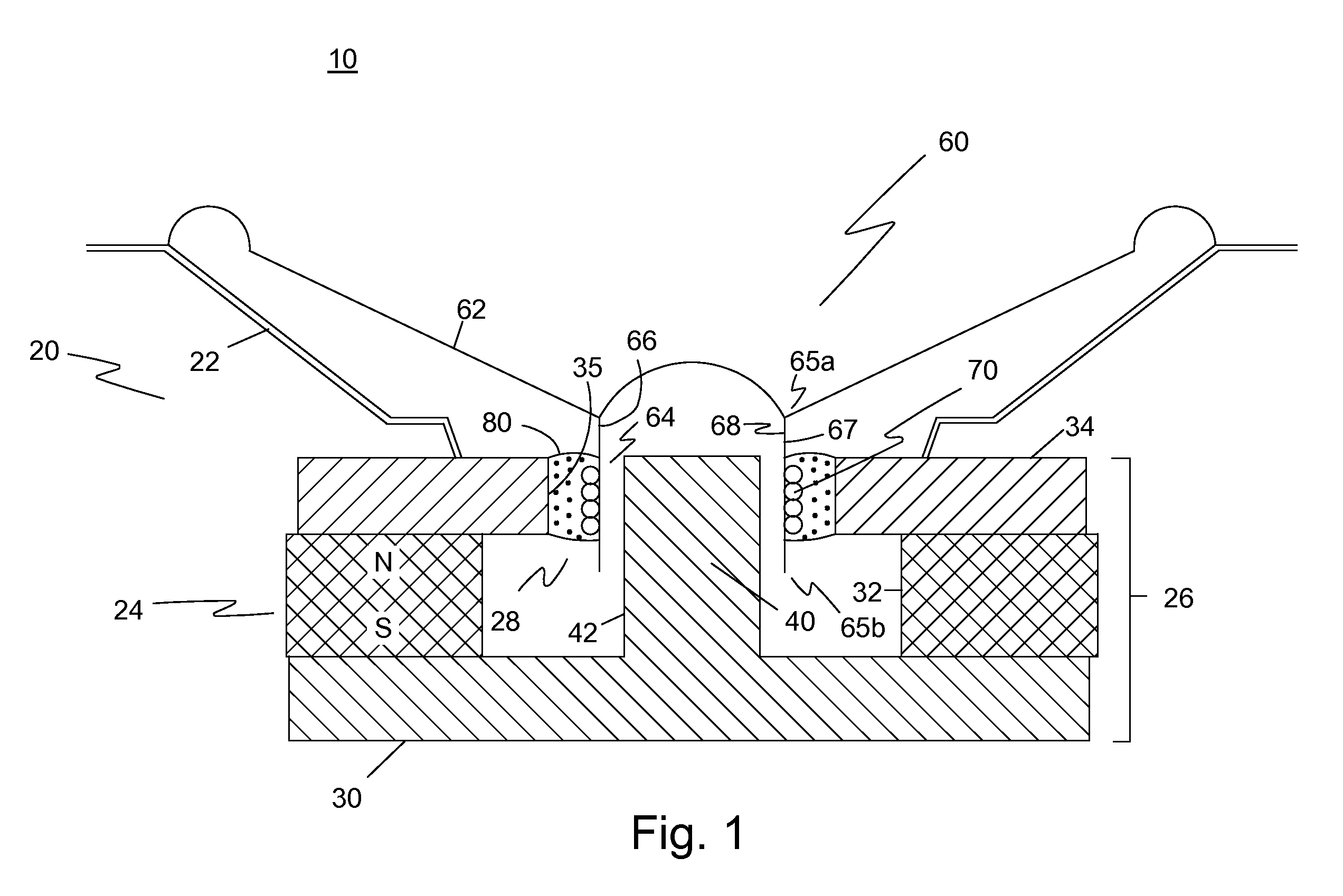
Magnetic actuator using ferrofluid slug
Owner:XEROX CORP
Device of micro vortex for ferrofluid power generator
InactiveUS20060110260A1Improve efficiencyImprove the uniformity of the magnetic fieldPump componentsSteam useRotation velocityEngineering
A ferrofluid power generator with micro vortex generator is disclosed, which is capable of generating an induced current by enabling a ferrofluid having a plurality of magnetic particles to flow in a closed circuit, the device comprising a vortex generator and a induced current unit. The vortex generator further comprises a first inlet, a first outlet and a plurality of cavities, which is capable of accelerating the rotation speed of the magnetic particles by virtue of employing the plural cavities to enable the magnetic particles to rotate while the ferrofluid passing through the plural cavities. The induced current unit is substantially a tube having a second inlet and a second outlet, where the second inlet is coupled to the first outlet of the vortex generator for accepting the ferrofluid with rotating magnetic particles to flow therein and through so as to induce a change of magnetic flux to occur and generate an induced current accordingly.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Magnetic actuator using ferrofluid slug
ActiveUS7204581B2Inexpensive and disposable and easily cleanedLow implementation costClosuresCircuit elementsActuatorFerrofluid
A magnetostatic actuator uses a ferrofluid slug confined in a cylindrical tube which is wrapped in a conducting coil. By applying a current to the coil, a magnetic field is generated inside the coil. The ferrofluid slug may be attracted to the interior of the coil by the interaction of its magnetic moment with the field generated inside the coil. Movement of the ferrofluid slug in response to the magnetic field may be used to actuate various devices, such as a droplet dispenser.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Device of micro loop thermosyphon for ferrofluid power generator
InactiveUS20060110262A1Heat dissipationSave power consumptionPressure pumpsGas turbine plantsThermal energyEngineering
The present invention provides a micro loop thermosyphon cooler, having a thermal absorption unit and a condenser sequentially arranged therein, wherein the condenser is arranged at a position higher than that of the thermal absorption unit by a height. The thermal absorption unit further comprises a microchannel system formed by superimposing a cover on a substrate having a plurality of micro-grooves arranged thereon, so that the microchannel system is capable of allowing a fluid with a plurality of magnetic particles to flow in and through. In this regard the thermal absorption unit is used for absorbing thermal energy and thus enabling the fluid to vaporize and generate bubbles accordingly for elevating and driving the remaining fluid to flow into the condenser for discharging heat. Moreover, the condenser is positioned over the thermal absorption unit by a height while coupled to the outlet of the thermal absorption unit by an inlet thereof via a conduit, and coupled to an inlet of the thermal absorption unit by an outlet thereof via another conduit. In this regard, the condenser is capable of condensing the vaporized fluid and remixing the same with unvaporized fluid passing so as to enable the remixed fluid to flow back to the thermal absorption unit by the action of gravity.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Device of micro loop thermosyphon for ferrofluid power generator
InactiveUS7455101B2Save power consumptionHeat dissipationPressure pumpsGas turbine plantsThermal energyEngineering
The present invention provides a micro loop thermosyphon cooler, having a thermal absorption unit and a condenser sequentially arranged therein, wherein the condenser is arranged at a position higher than that of the thermal absorption unit by a height. The thermal absorption unit further comprises a microchannel system formed by superimposing a cover on a substrate having a plurality of micro-grooves arranged thereon, so that the microchannel system is capable of allowing a fluid with a plurality of magnetic particles to flow in and through. In this regard the thermal absorption unit is used for absorbing thermal energy and thus enabling the fluid to vaporize and generate bubbles accordingly for elevating and driving the remaining fluid to flow into the condenser for discharging heat. Moreover, the condenser is positioned over the thermal absorption unit by a height while coupled to the outlet of the thermal absorption unit by an inlet thereof via a conduit, and coupled to an inlet of the thermal absorption unit by an outlet thereof via another conduit. In this regard, the condenser is capable of condensing the vaporized fluid and remixing the same with unvaporized fluid passing so as to enable the remixed fluid to flow back to the thermal absorption unit by the action of gravity.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
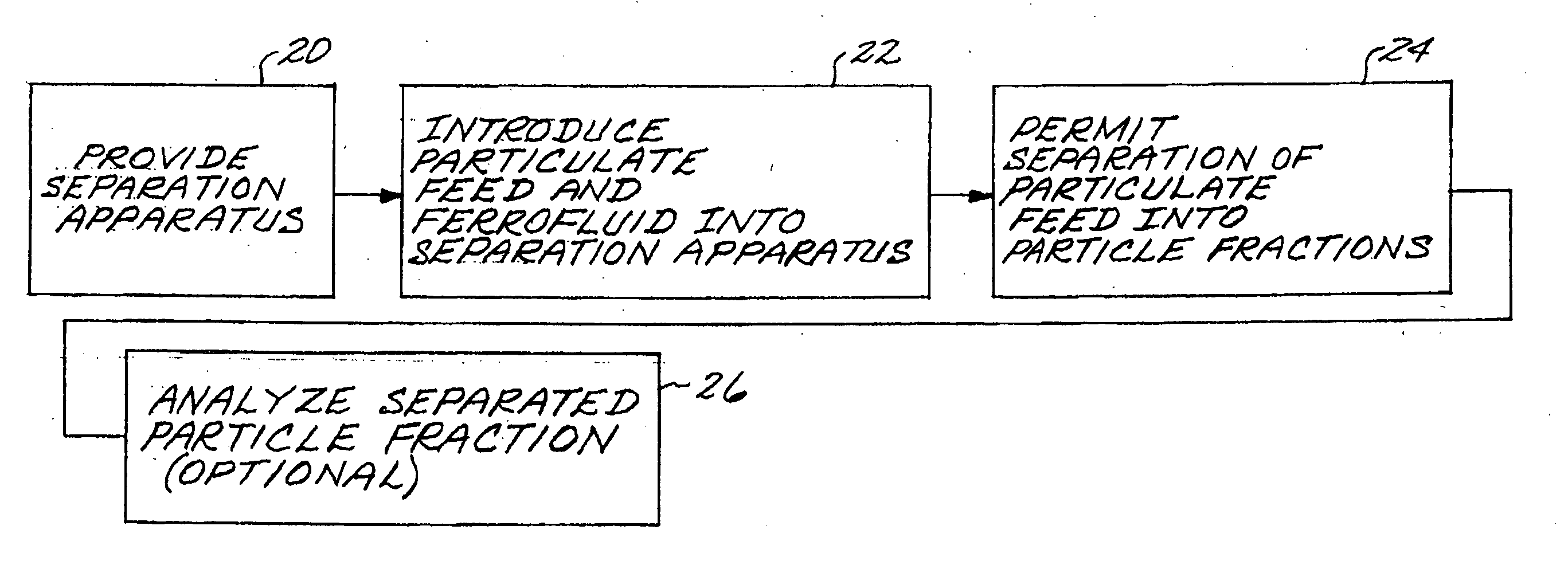
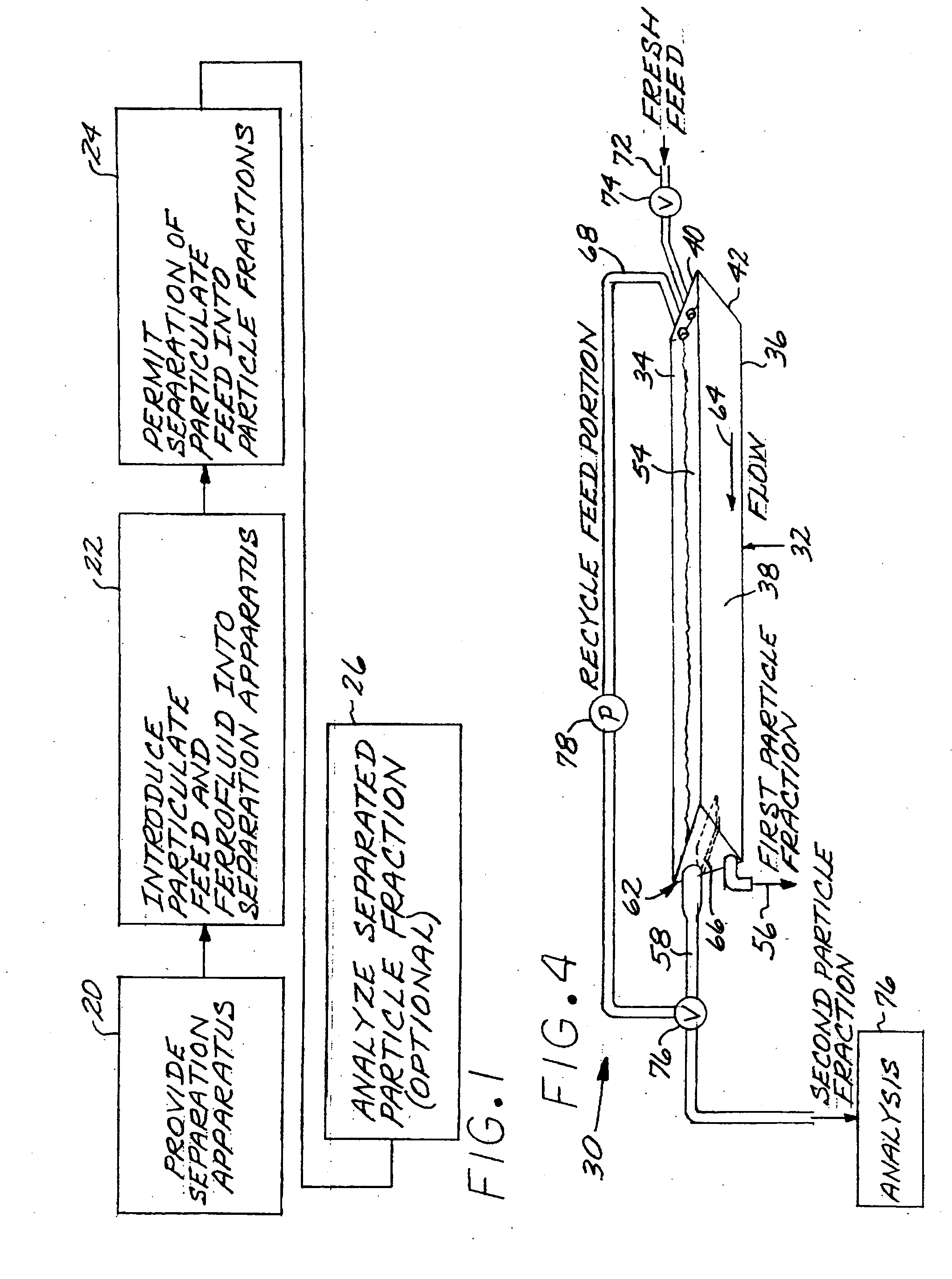
Method for magnetic/ferrofluid separation of particle fractions
InactiveUS20050178701A1Easy to collectEasy to cleanElectrostatic separationHigh gradient magnetic separatorsParticulatesChemical physics
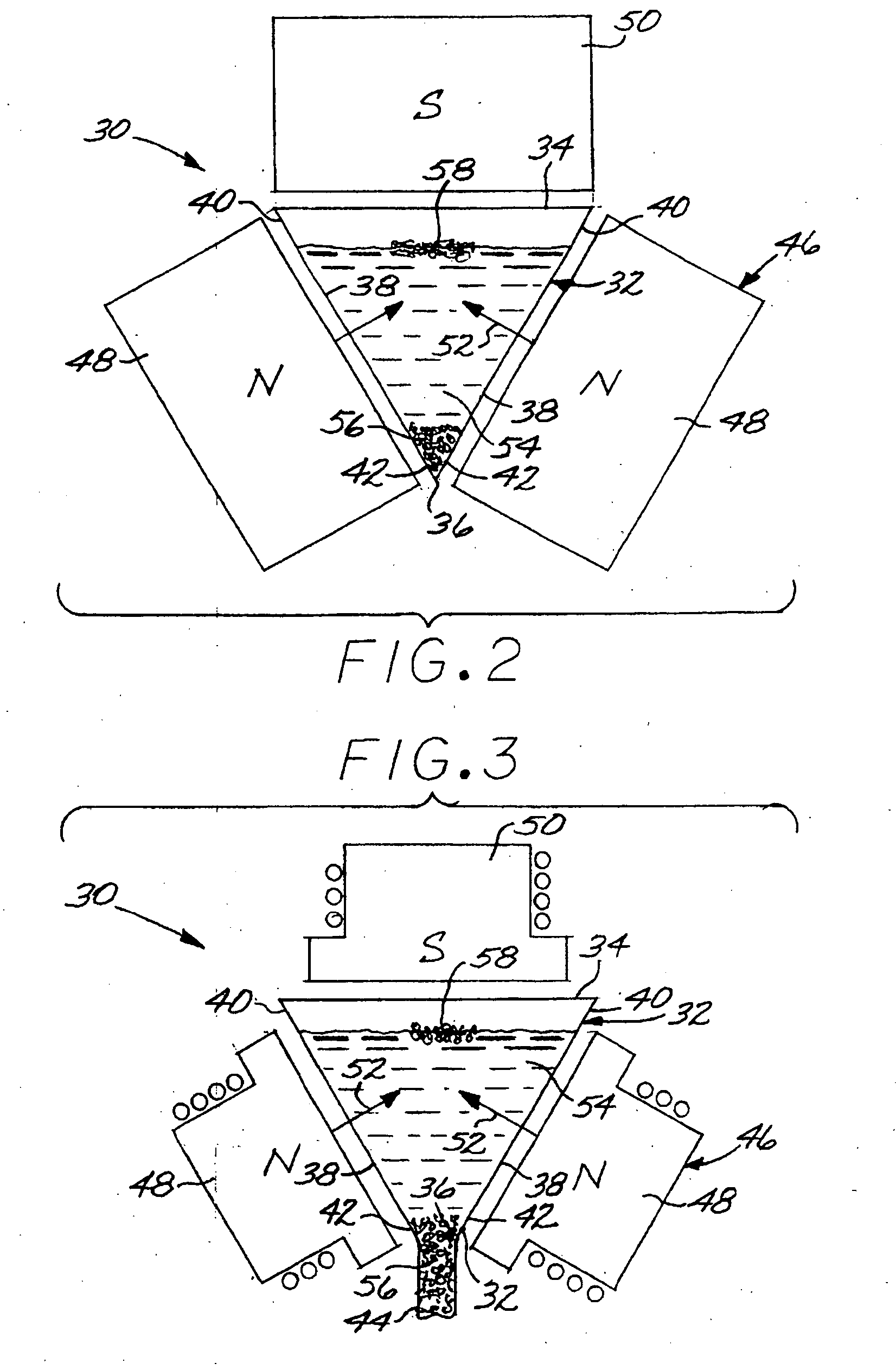
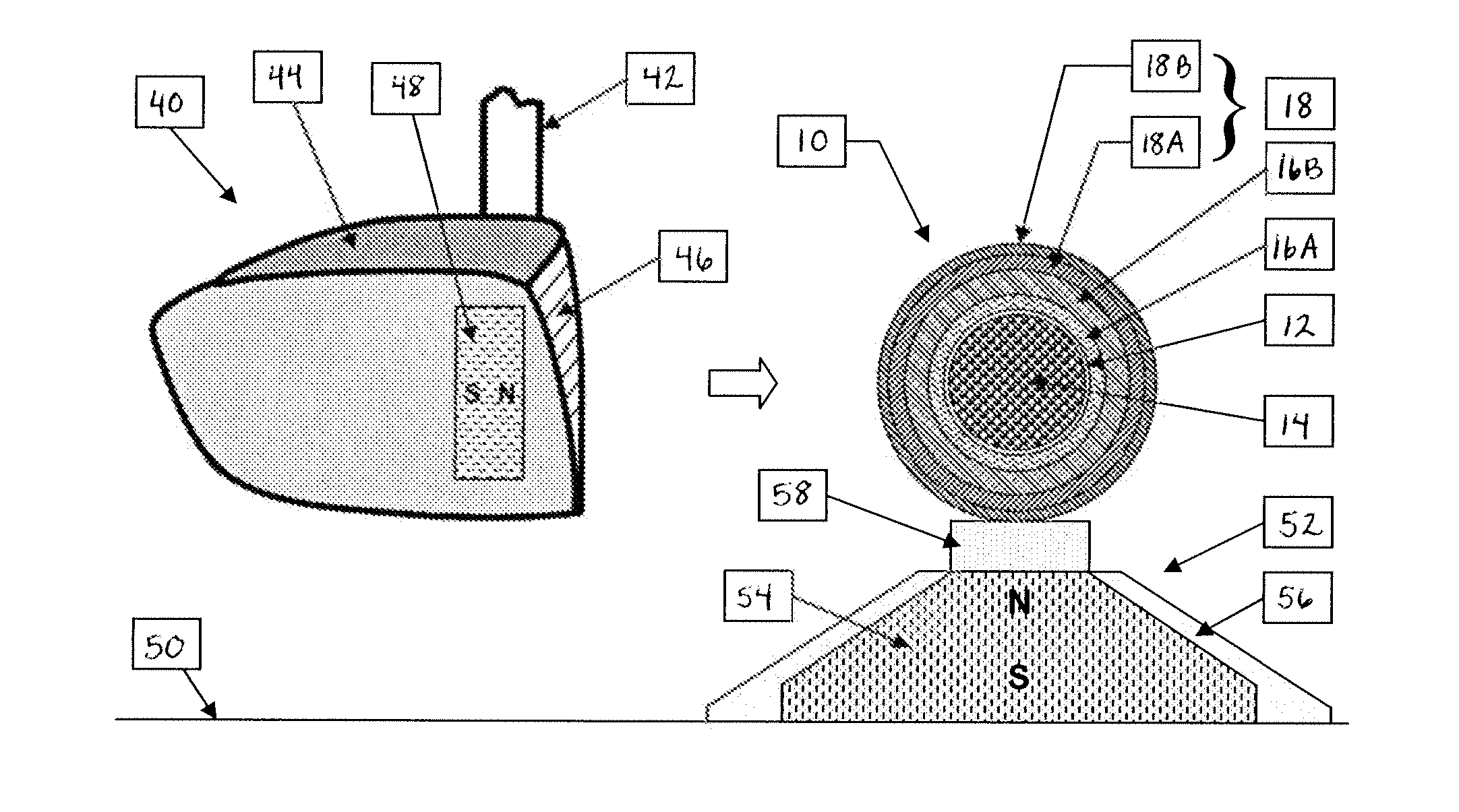
A particulate feed comprising a first particle type and a second particle type is separated by providing a separation apparatus having a separation vessel having a top and a bottom, and wherein the separation vessel includes inwardly sloping side walls. A magnet structure has a first pole positioned exterior of and adjacent to each of the side walls of the separation vessel, and a second pole positioned above the separation vessel. A mixture of the particulate feed and a ferrofluid is introduced into the separation vessel, and the particulate feed is separated into a first particle fraction comprising a majority of the first particle type, which sinks in the separation vessel, and a second particle fraction comprising a majority of the second particle type which floats in the separation vessel.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for delivering a catheter to a target in the brain of a patient and guide wire for a microcatheter for insertion in the brain of a patient
The movement of catheters and guide wires for catheters with the aid of magnets is known from the field of cardiology. Conventional magnets are, as a result of their size, not suited to being inserted into the brain of patient, because the vessels there are smaller than the cardiac vessels. To enable the navigation methods proven in cardiology also to be used in neurology, the invention provides a microcatheter having a guide wire, which features magnetic nanoparticles. The magnetic nanoparticles can be provided in the form of a ferrofluid or also as diamond nanoparticles in powder form. This enables navigation of the guide wire and thus ultimately of the catheter in the brain from the outside by way of magnetic fields.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
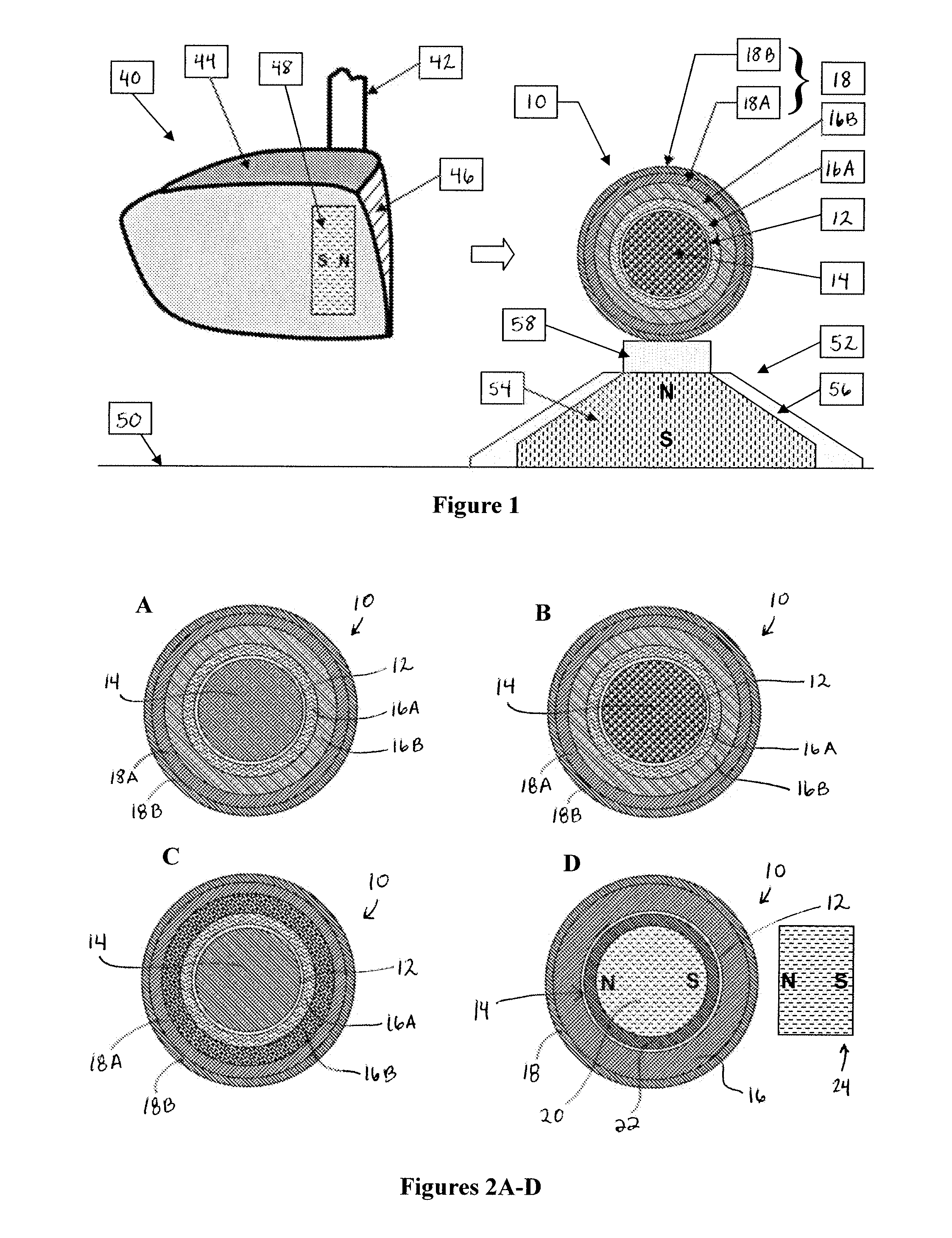
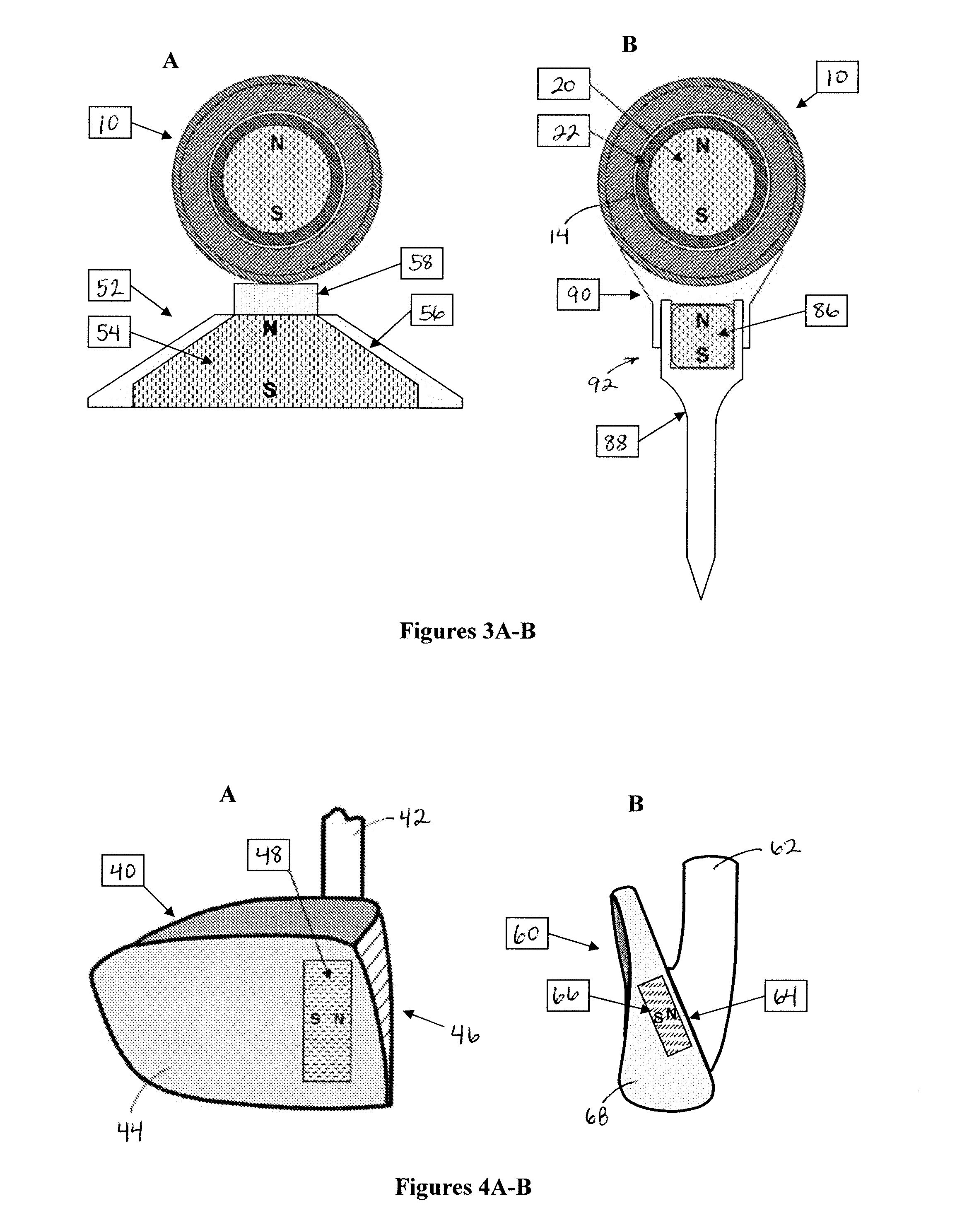
Adaptive golf ball
InactiveUS20080045358A1Improve the level ofChanging manufacturabilityGolf teesGymnastic exercisingElastomerEngineering
The present invention relates to a smart golf ball comprised of one or more mantle layers juxtaposed between an inner core and outer cover, where the core, the mantle layer(s), and / or the cover are further comprised of a ferrofluid, a magnetorheological fluid, an inverse magnetorheological fluid, and / or a magnetorheological elastomer, in any of its construction. These nano-engineered materials make possible a golf ball with heretofore-unprecedented levels of adaptive play.
Owner:VANDELDEN JAY
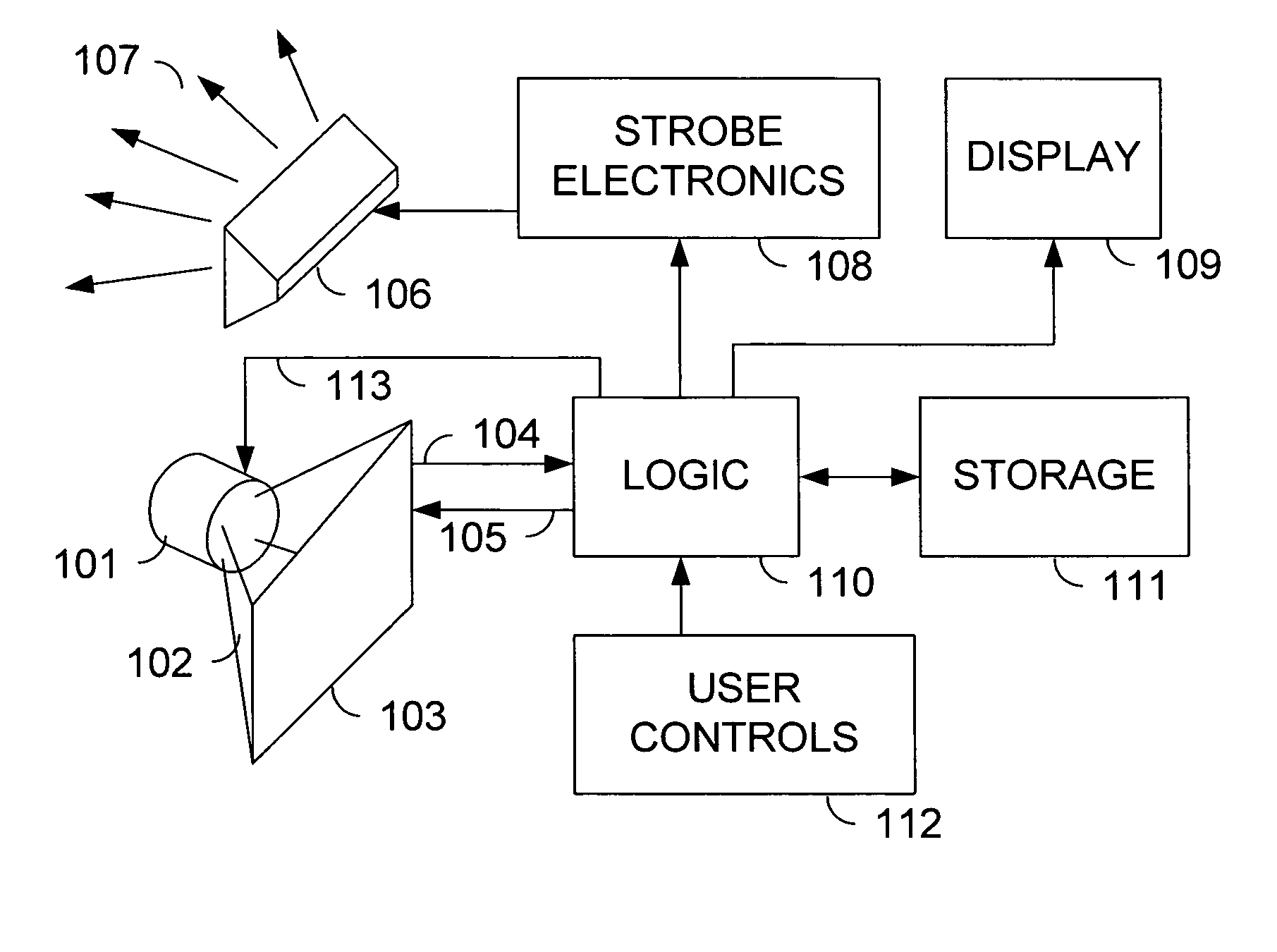
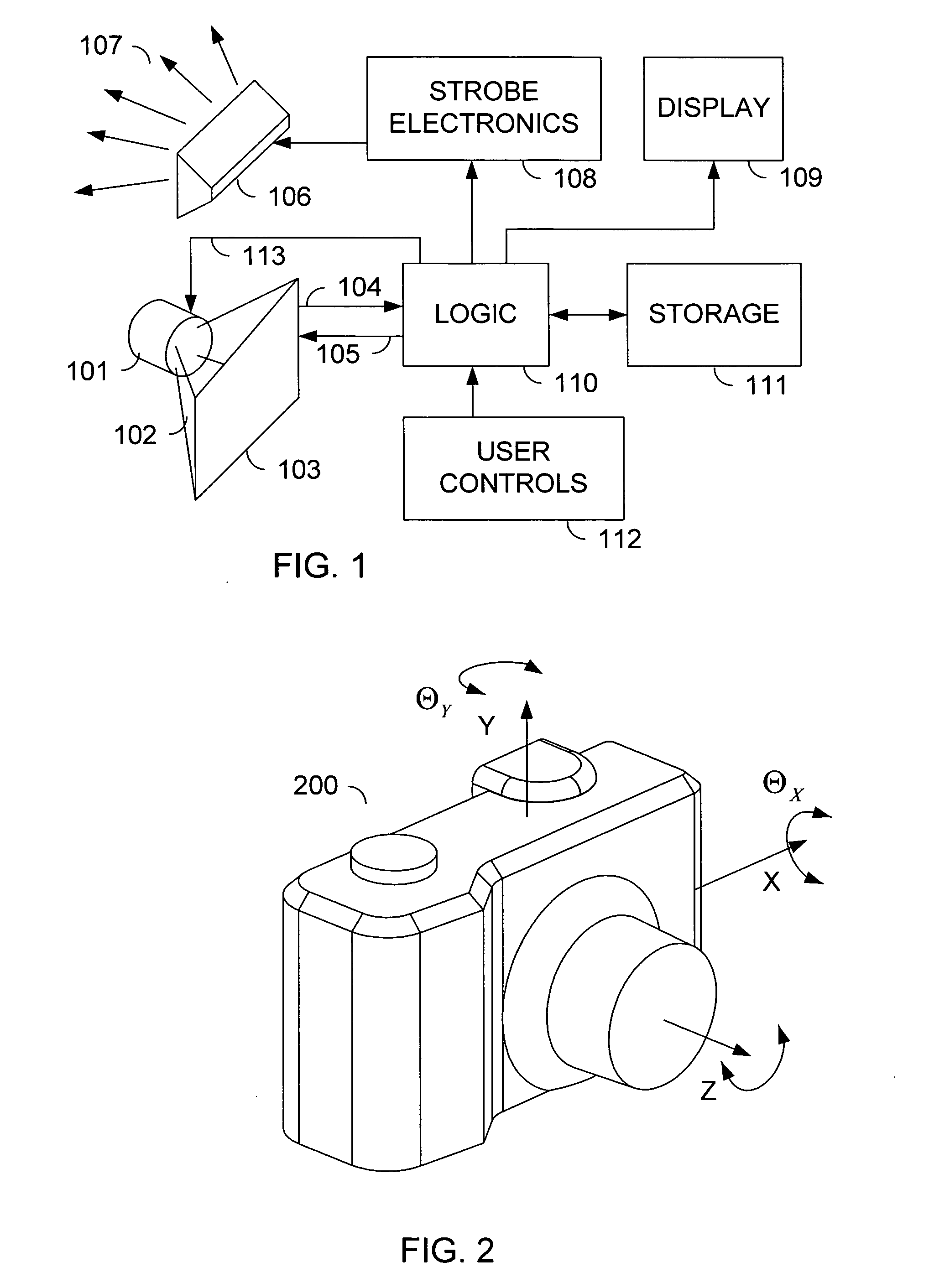
Ferrofluid Centered Voice Coil Speaker
ActiveUS20070189577A1Reduce volatilityReduce magnetizationMicrophonesLoudspeakersEngineeringLoudspeaker
An audio speaker has a driver unit having a support frame with a central portion forming a magnetic structure defining an annular gap around a central magnetic post, a vibration system having a diaphragm and a voice coil, the voice coil is attached to one side of the diaphragm where the vibration system is fixed to the support frame and where the voice coil is movably mounted in the annular gap, and a magnetic fluid disposed in the annular gap only in a space between one side of the voice coil and a surface of the annular gap having a higher magnetic flux density.
Owner:FERROTEC MATERIAL TECH CORP
Fault-tolerant permanent magnet machine with reconfigurable flux paths in stator back iron
ActiveUS20080238217A1Reduce internal heatMagnetic circuit stationary partsEnergy production using magneto-hydrodynamic generatorsMagnetic anisotropyFerrofluid
A permanent magnet (PM) machine has a fault condition mechanism disposed within a back iron of the stator portion, the mechanism operational to automatically reduce fault currents associated with the PM machine during a fault condition. The fault condition mechanism disposed within the stator back iron is reconfigurable to automatically reduce internal heat associated with the PM machine during a fault condition. A method of reconfiguring the PM machine upon detecting a fault condition includes the steps of 1) selecting the reconfigurable fault condition mechanism from a) a plurality of magnetically anisotropic rotatable cylinders, b) a plurality of ferrofluid-filled cavities, and c) a dual-phase material selectively embedded within the stator core; and 2) reconfiguring the fault condition mechanism to automatically reduce fault currents or internal heat associated with the PM machine upon detection of a fault condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Reflecting mirrors shaped with magnetic fields
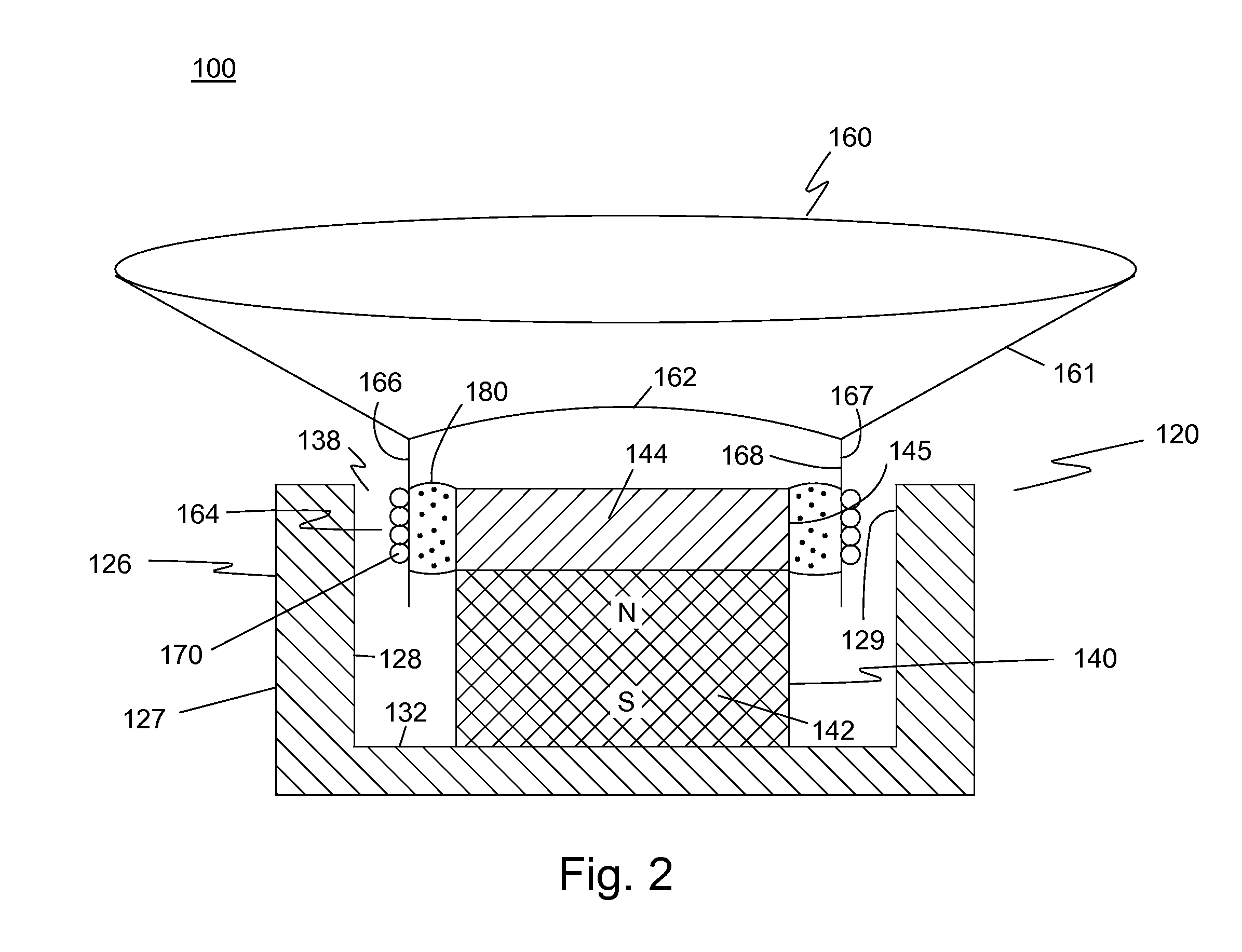
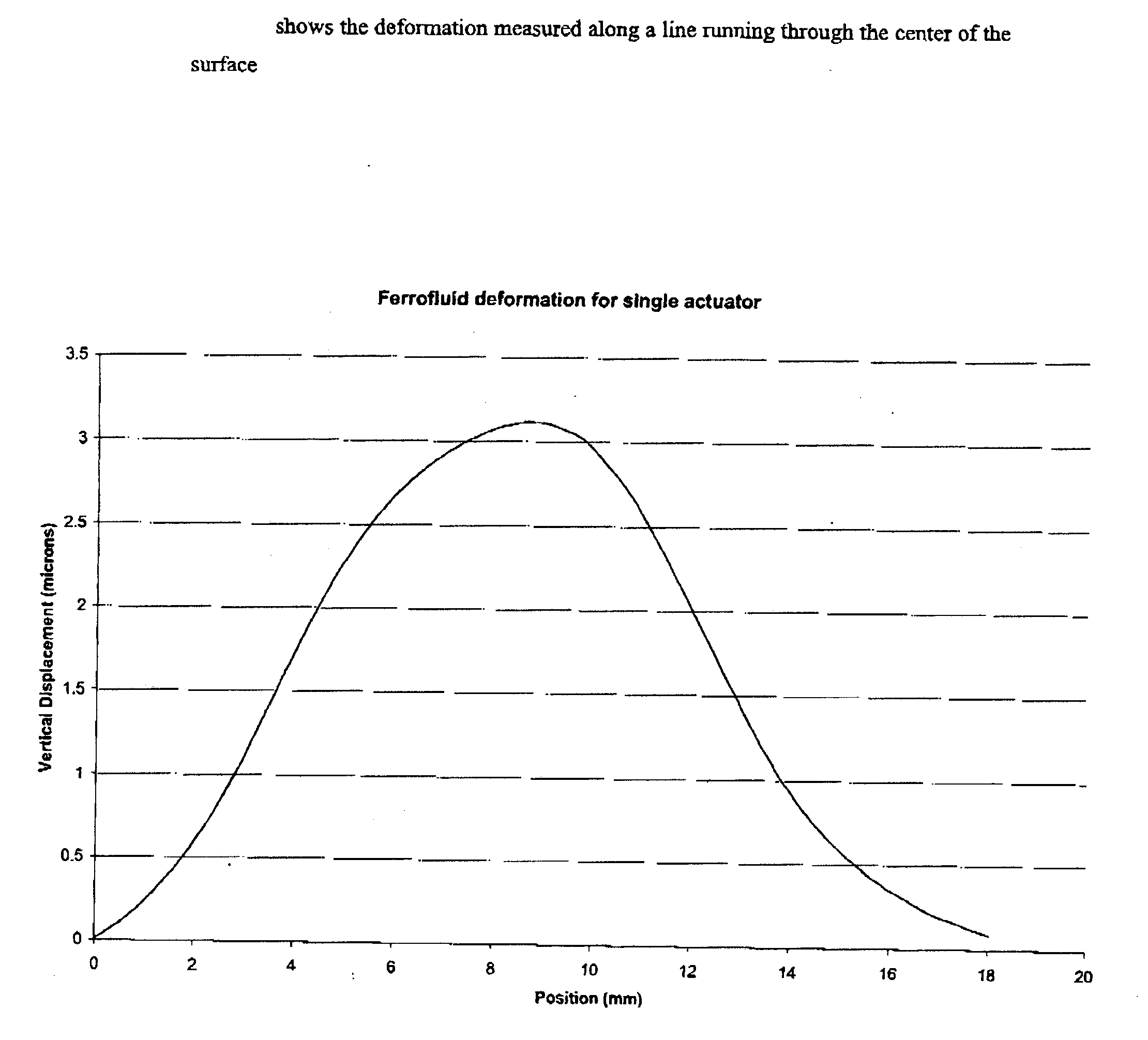
InactiveUS20040008430A1Less expensiveQuick modificationMirrorsMagnetic liquidsReflective layerLiquid surfaces
This invention relates to a new type of reflective optical element made of a fluid that responds to a force if subjected to a magnetic field. As a consequence, one can impose any shape one wants to the reflecting surface by generating an appropriate magnetic field geometry with permanent magnets, electromagnets or a combination of permanent magnets and electromagnets, or the like. A preferred embodiment uses a ferromagnetic fluid made of water containing ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Liquid ferromagnetic surfaces thus obtained were successfully shaped using magnetic fields. In another preferred embodiment, to modify the reflectivity of the optical element, a reflective layer, such as a nano-engineered silver reflecting surface, is deposited on the surface of the magnetically sensitive fluid. The surface of the reflecting layer can therefore be warped by applying a magnetic field to the fluid. Coated or uncoated magnetically deformable liquid surfaces with reflective layers allows one to make inexpensive and versatile high-quality reflecting mirrors having complex shapes. The shapes of the reflecting surfaces can be changed within short time periods by changing the shapes of the magnetic fields.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Method for preparing conducting polymer micro-nanofibers in magnetic spinning mode
ActiveCN104911719AArranged in an orderly mannerIncrease productionElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureFilament/thread formingMicro nanoFiber
The invention discloses a method for preparing conducting polymer micro-nanofibers in a magnetic spinning mode. The method comprises the steps that 1, a magnetic spinning device is built, wherein the magnetic spinning device comprises a rotary collection disc with a permanent magnet; 2, a spinning precursor solution is prepared, wherein magnetic nano particles, high-molecular polymer and conducting polymer are mixed and dissolved in an organic solvent solution; 3, the magnetic spinning device is utilized for preparing conducting polymer micro-nano complex fibers, wherein the spinning precursor solution is injected into a feeding device, the feeding device is started, liquid drops on an opening of a spinning nozzle forms a jet flow under the effect of magnetic field force to be connected with the permanent magnet to be a bridge, a brushless direct-current motor is started to drive the collection disc to rotate, the ferrofluid jet flow is continuously pulled out under the effect of magnetic field force, and conducting polymer micro-nanofibers are wound and formed among vertical supporting columns of the collection disc. The method does not need the high voltage effect, reduces the production cost and potential safety hazards, is suitable for large-scale production and has the good application prospect, and the fibers are distributed in order.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
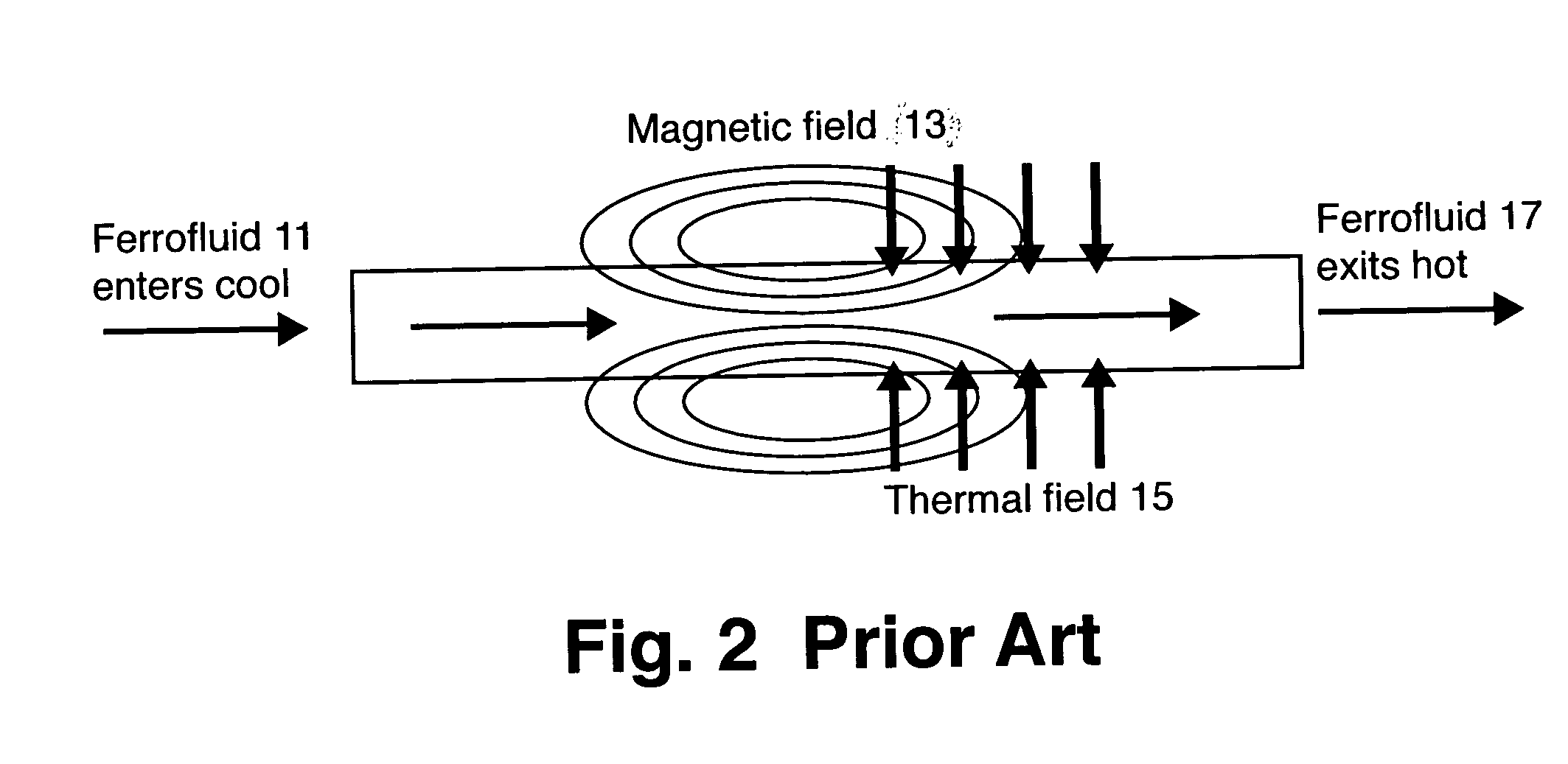
Magnetocaloric pump for microfluidic applications
A microfluidic magnetocaloric pump. The magnetic and thermal properties of a ferrofluid such as MnZnFe2O4 nanoparticles in an oil- or water-based medium are allowed to interact with a magnetic field that is partially coincident with a thermal gradient. As the ferrofluid heats, it loses its attraction to the magnetic field and is displaced by cooler fluid. The micropump produces fluid propulsion with no moving mechanical parts while requiring only 35 mW power and operation at a temperature of only 40-80° C.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Thermal interface device
InactiveUS20110180238A1High removal rateLittle powerSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMagnetic tension forceLiquid metal
The invention is for an apparatus and method for removal of waste heat from heat-generating components including high-power solid-state analog electronics such as being developed for hybrid-electric vehicles, solid-state digital electronics, light-emitting diodes for solid-state lighting, semiconductor laser diodes, photo-voltaic cells, anodes for x-ray tubes, and solids-state laser crystals. Liquid coolant is flowed in one or more closed channels having a substantially constant radius of curvature. Suitable coolants include electrically conductive liquids (including liquid metals) and ferrofluids. The former may be flowed by magneto-hydrodynamic effect or by electromagnetic induction. The latter may be flowed by magnetic forces. Alternatively, an arbitrary liquid coolant may be used and flowed by an impeller operated by electromagnetic induction or by magnetic forces. The coolant may be flowed at very high velocity to produce very high heat transfer rates and allow for heat removal at very high flux.
Owner:VETROVEC JAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com