Magnetocaloric pump for microfluidic applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment
Cooling Embodiment
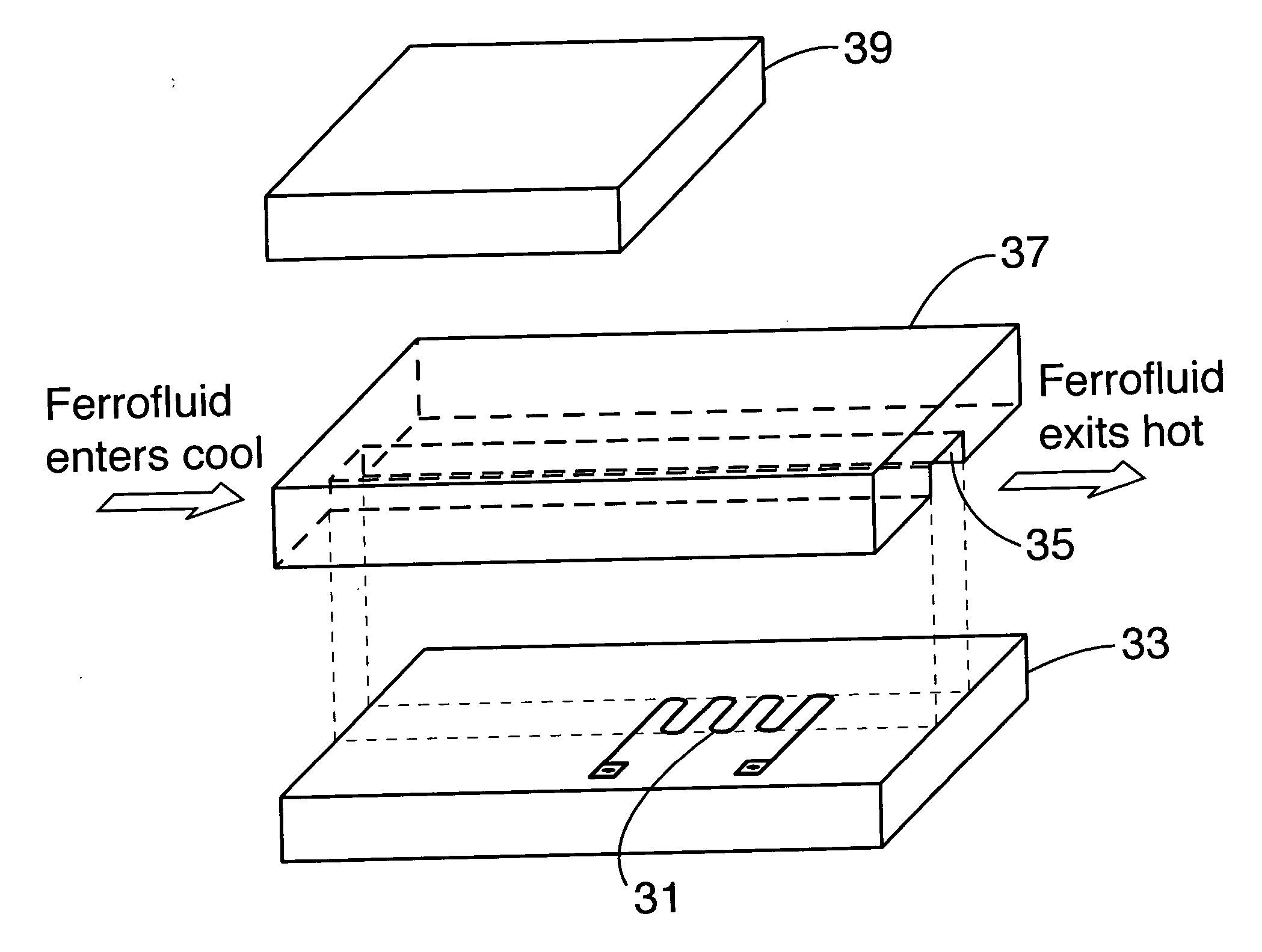
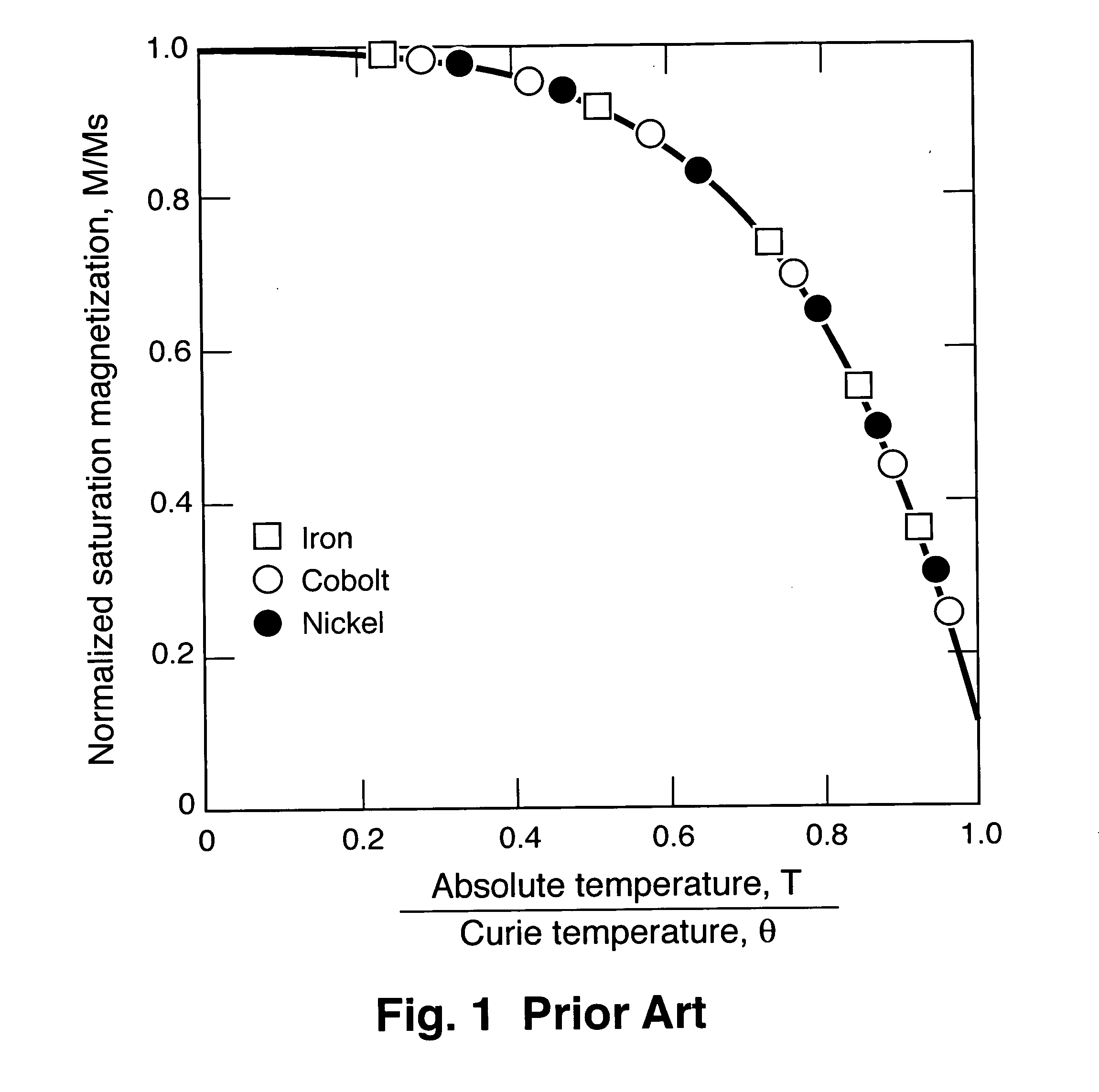
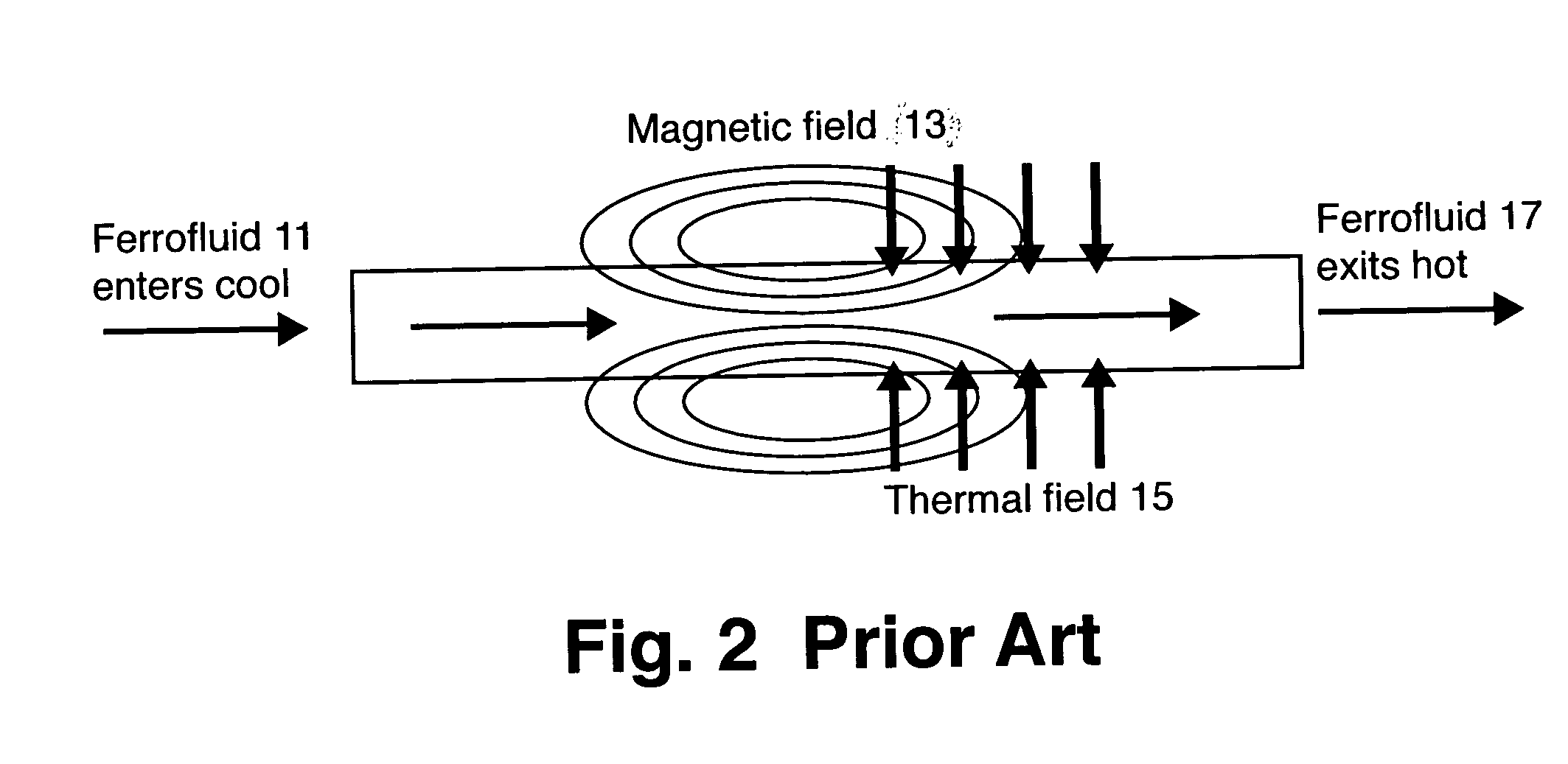
[0046] The basic principle for cooling is exactly the same as the pump except now the fluid acts as a convective heat exchanger taking heat away from a hot component, represented by the thermal field in FIG. 2 or the heat source in FIG. 6. As in the pump embodiment, cool fluid is attracted to the magnet. The hot component heats the fluid which subsequently loses it's attraction to the magnetic field and is displaced by cooler fluid. Subsequently, the pump is now acting as a heat pump removing heat from the hot component. The advantage of such an approach is 1) no moving mechanical parts and 2) self regulating control. As the hot component increases in temperature, the fluid flow will increase naturally, increasing the heat removal rate.
[0047] All electromagnetic actuators have coincident magnetic and thermal fields. The maximum operating torque of electric actuators is limited due to thermal constraints on the coils. Using this invention, it is possible to cool an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com