Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4595results about How to "Less expensive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
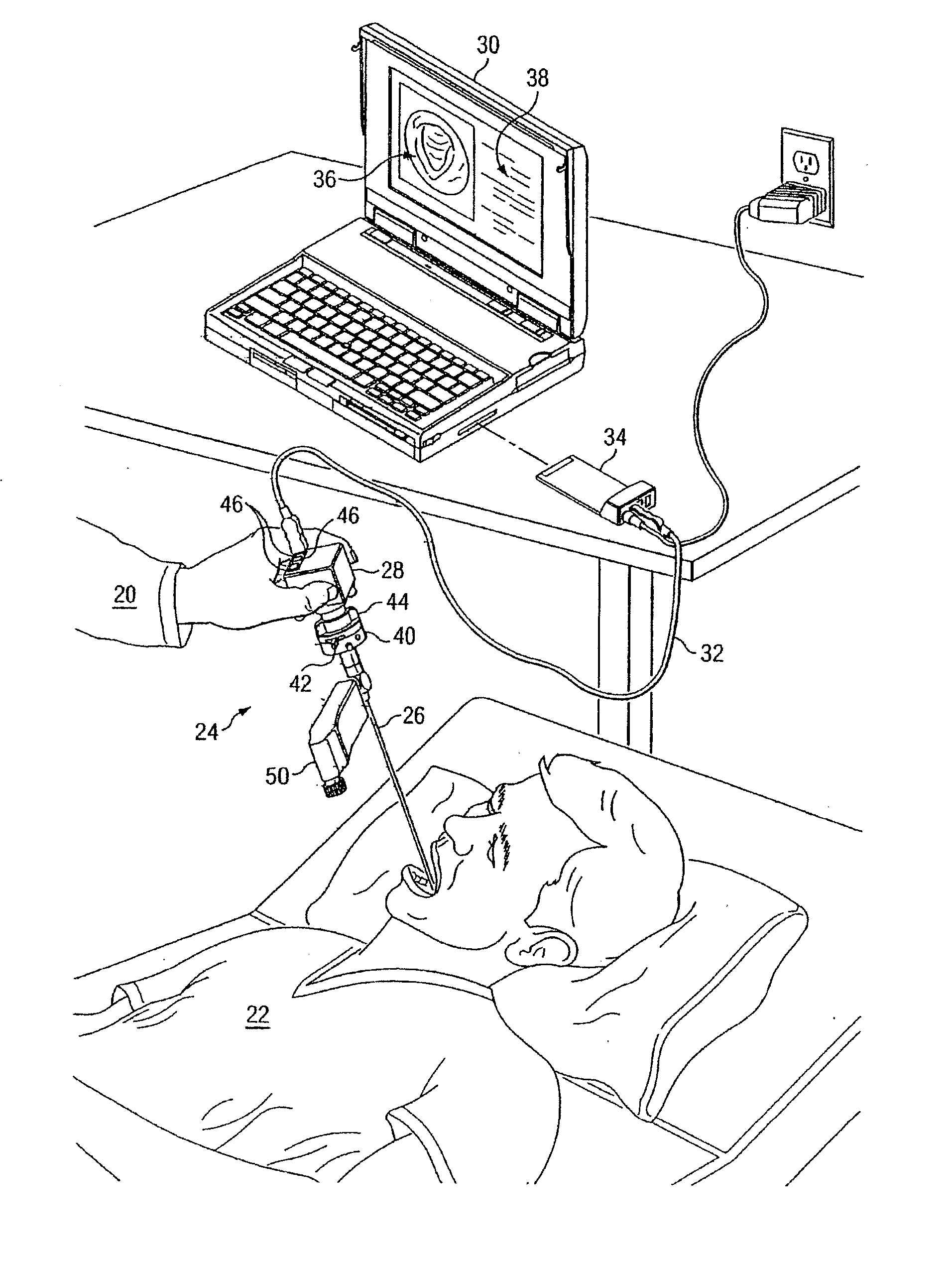
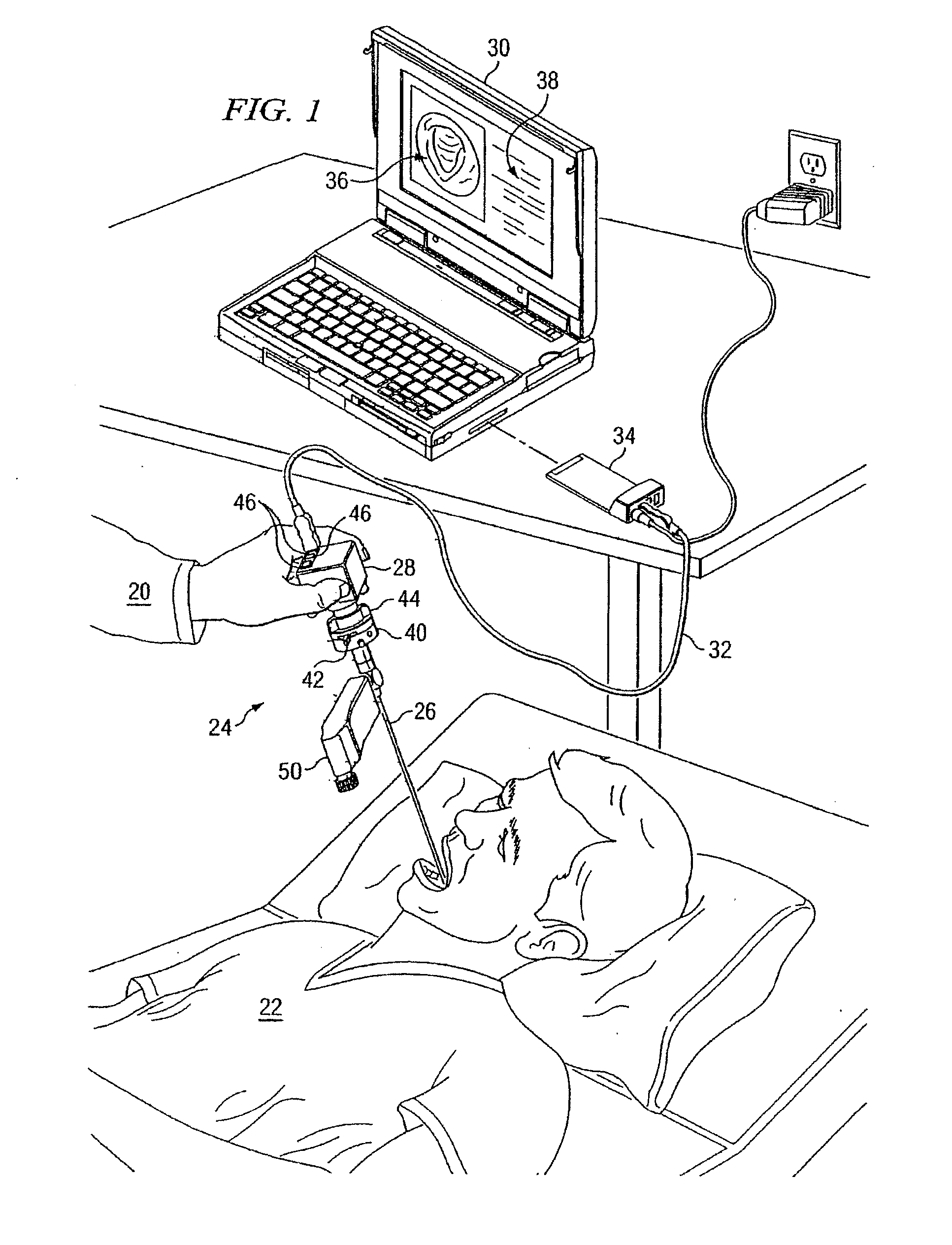
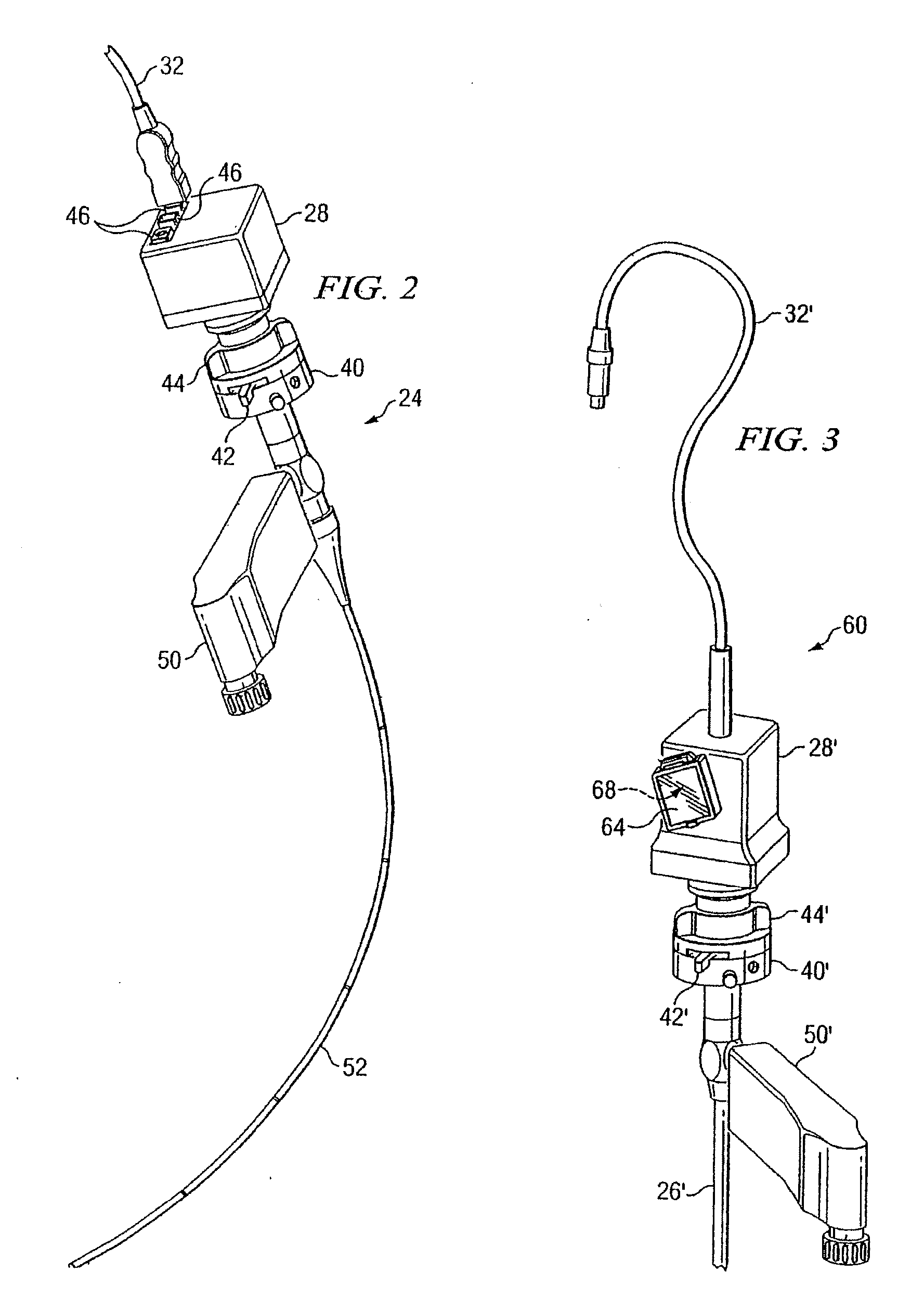
Endoscopic digital recording system with removable screen and storage device
InactiveUS20100145146A1Easy to transportImprove versatilitySurgeryEndoscopesDocking stationDigital recording
A medical imaging recording and viewing system adapted for use interchangably with a variety of endoscopes. The system includes a portable hand-held device that may be removably placed within a cradle affixed to the endoscope. An interface between an image acquisition device of the endoscope and the portable device permits images to be transmitted to and stored within the portable device. The portable device also may include a viewing screen to permit a user to view the images. A docking station may receive the portable device for transferring images to a separate viewing device and for recharging the battery of the portable device.
Owner:ENVISIONIER MEDICAL TECH
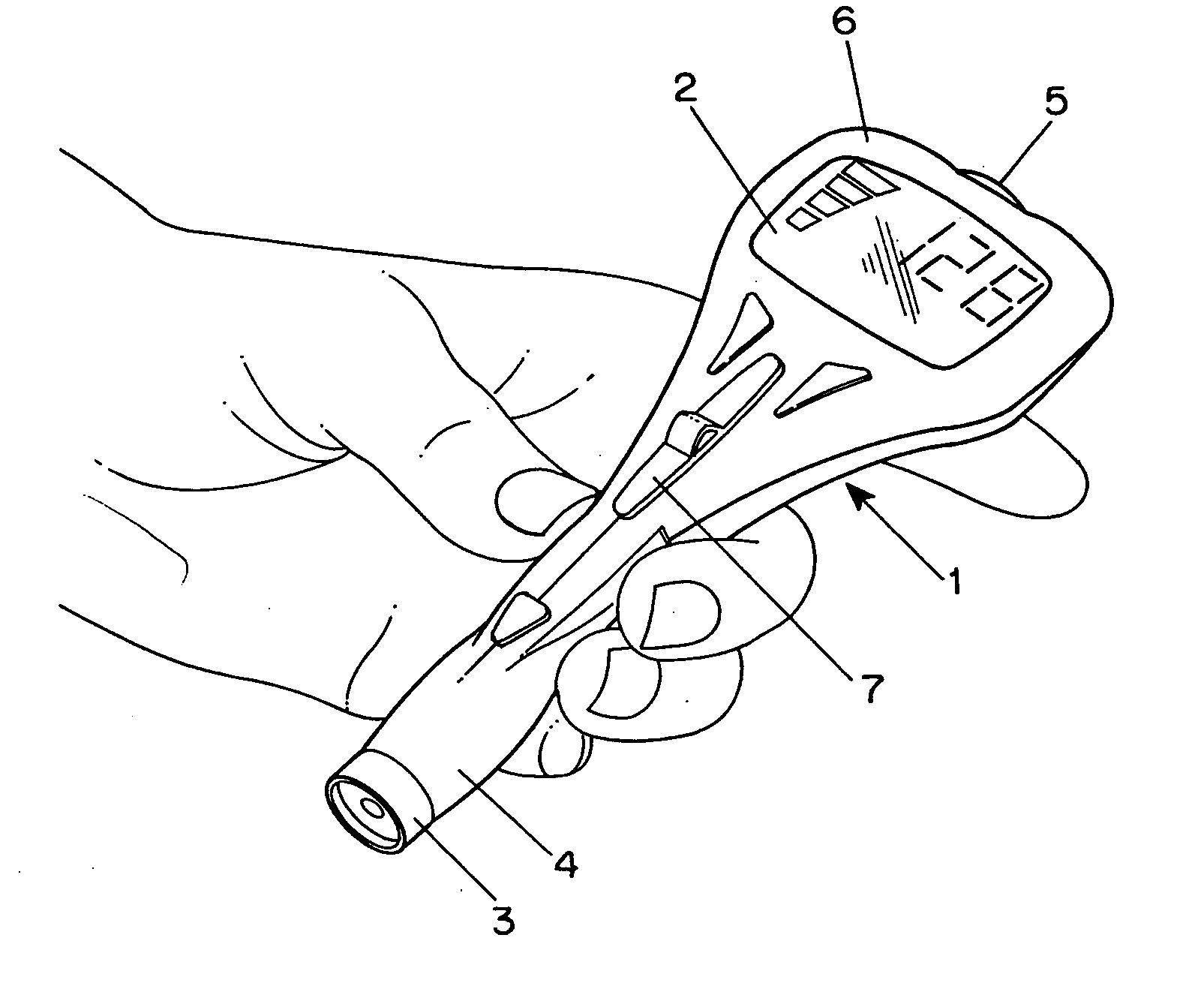
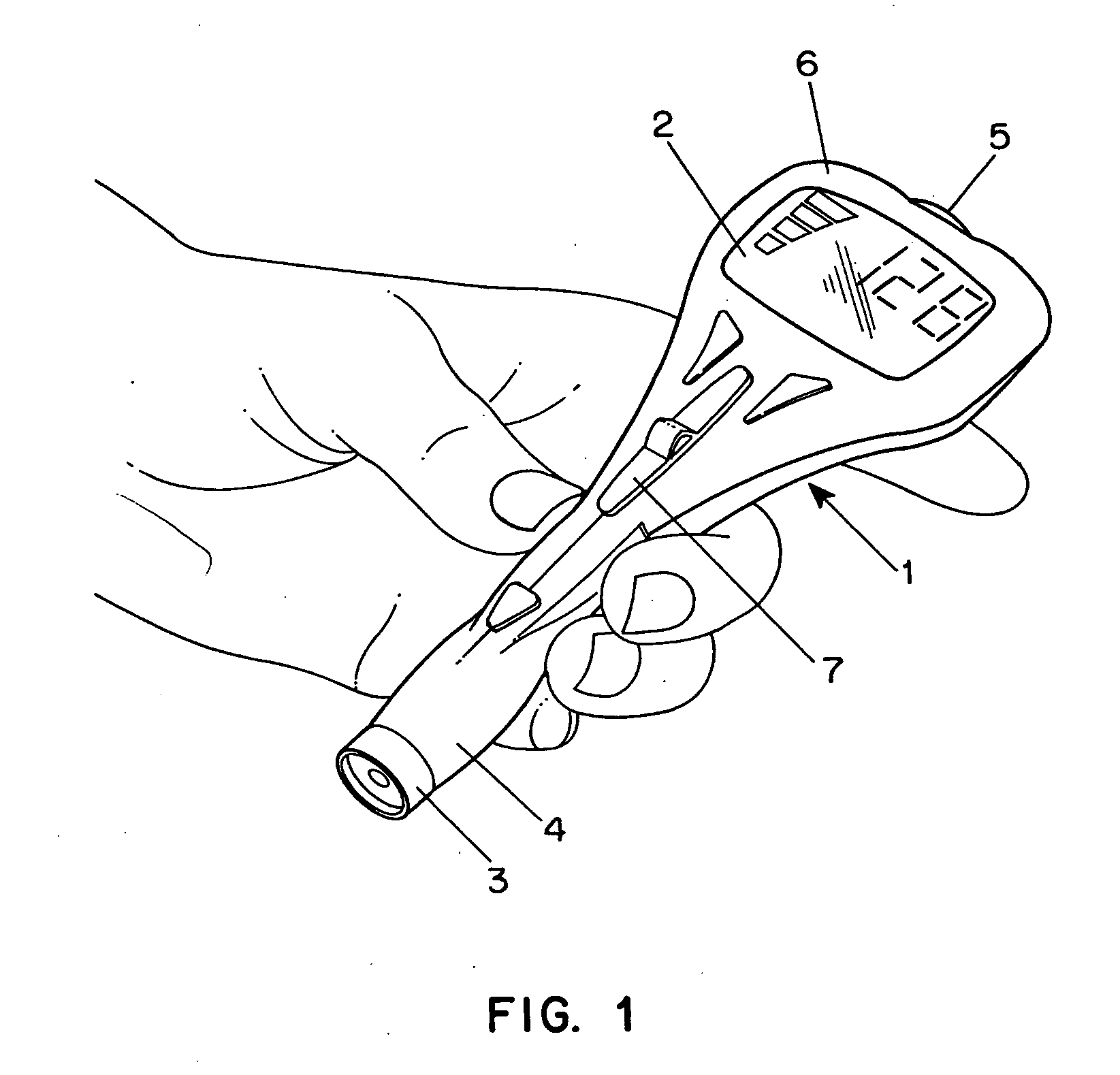
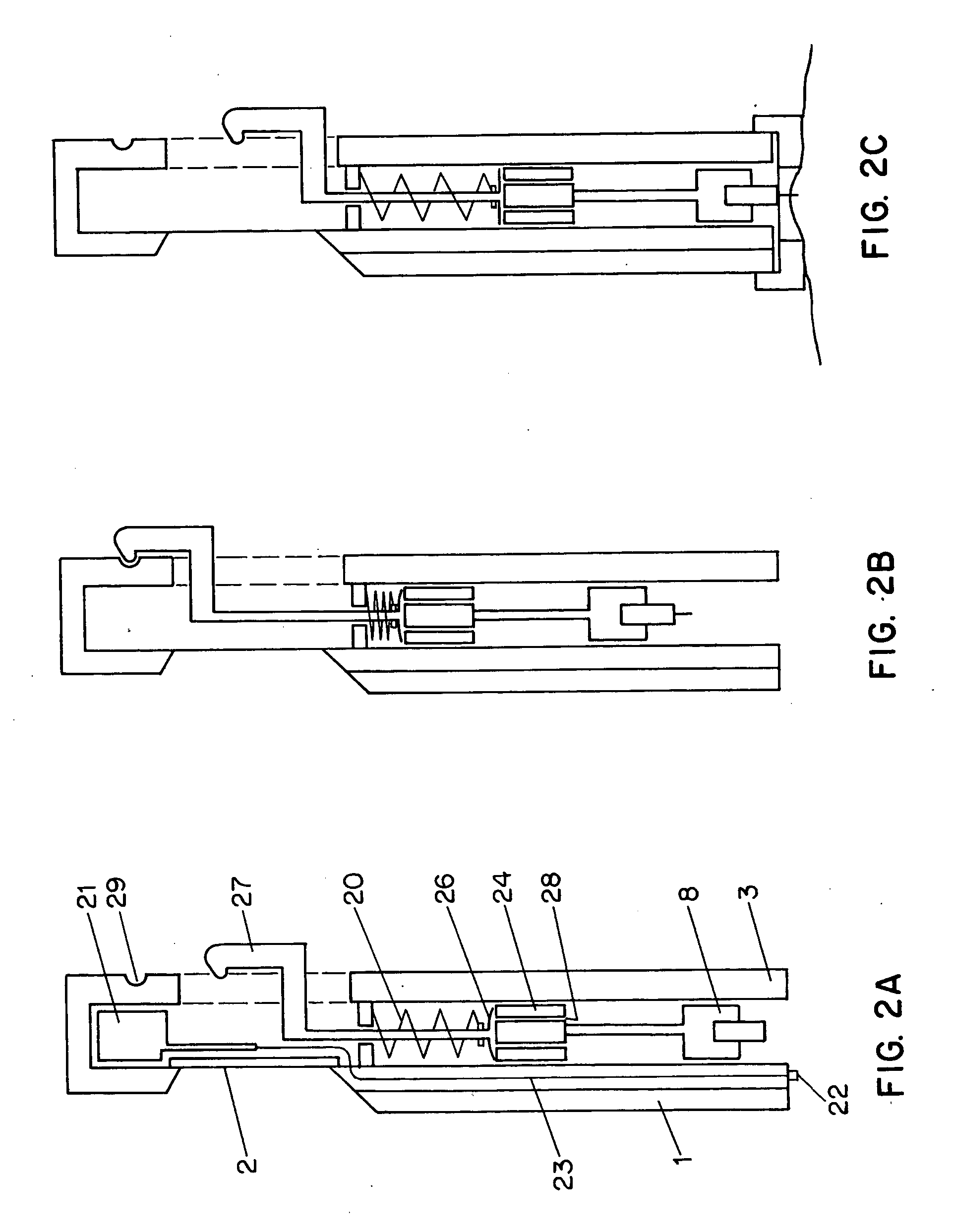
Combined lancet and electrochemical analyte-testing apparatus
InactiveUS20020130042A1Easy to takeReduces and eliminates disposal issueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteDisplay device
An apparatus for detection and quantitation of an electrochemically-detect- able analyte, such as glucose, in blood or interstitial fluid includes a meter unit, a lancet and an electrochemical sensor. Of these components, the meter is preferably reusable, while the lancet and the electrochemical sensor are preferably incorporated in assemblies intended for single-use. The meter unit has a housing, within which a lancet is engaged with a mechanism for moving then lancet; a connector disposed within the housing for engaging an electrochemical sensor specific for the analyte and transmitting a signal indicative of the amount of analyte, and a display operatively-associated with a connector for displaying the amount of the analyte to user. The electrochemical sensor is adapted for detection of a particular analyte. In addition, the electrochemical sensor has an absorptive member for uptake of a sample of blood or interstitial fluid. In one version, the lancet moves from a initial position to a piercing position in which skin of the user is pierced and optionally back to a retracted position. The electrochemical sensor is disposed such that the absorptive member takes up a sample from the pierced skin of the user when it is pierced by the lancet without movement of the apparatus. In an alternative version, the lancet is a hollow cannula through which blood or interstitial fluid is transported from the puncture site to an absorbent portion of the electrochemical sensor. In either version, the apparatus provides single-step operation in which sample acquisition and analysis occur as a result of the single action of pressing the apparatus against the users skin.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
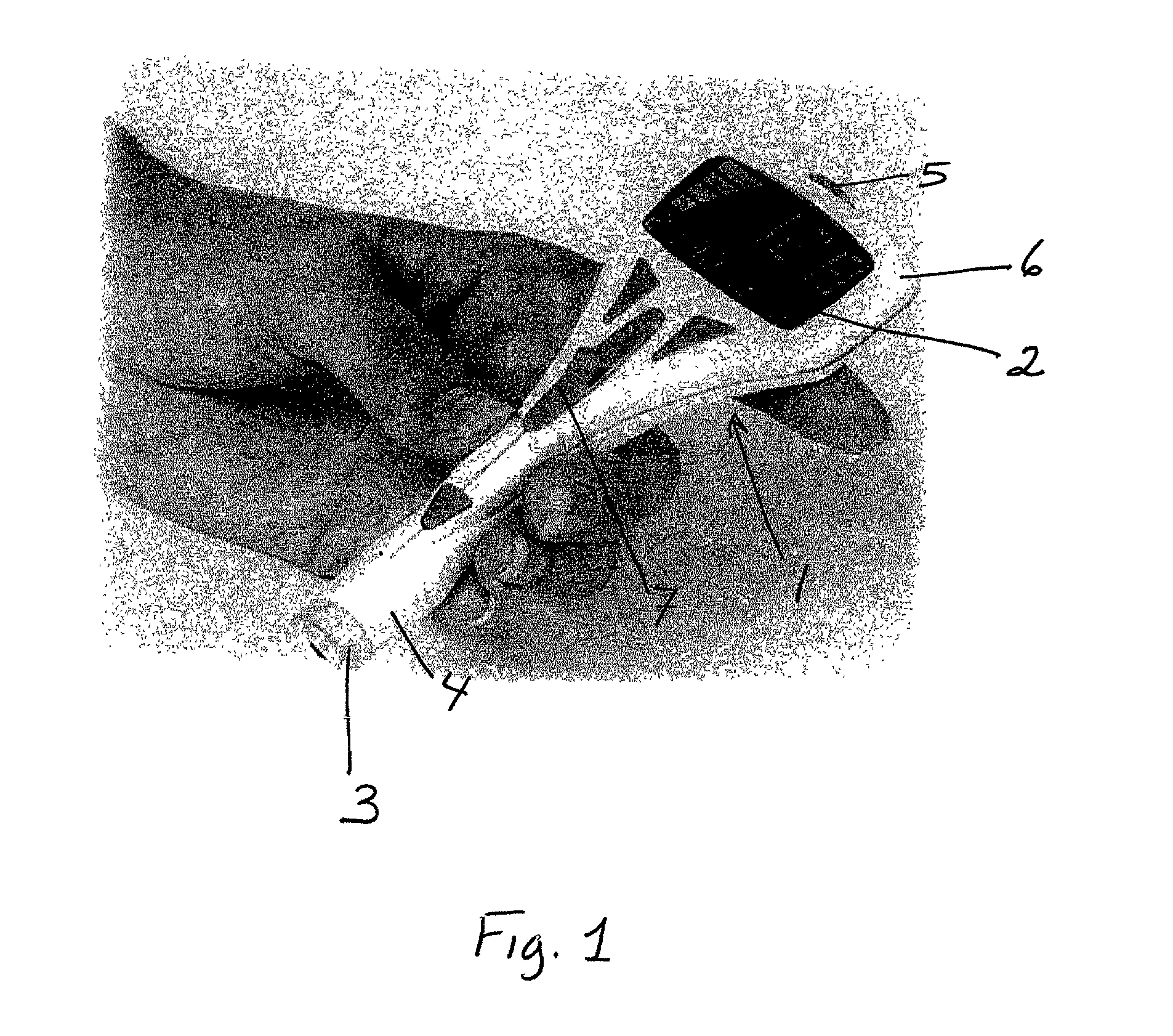
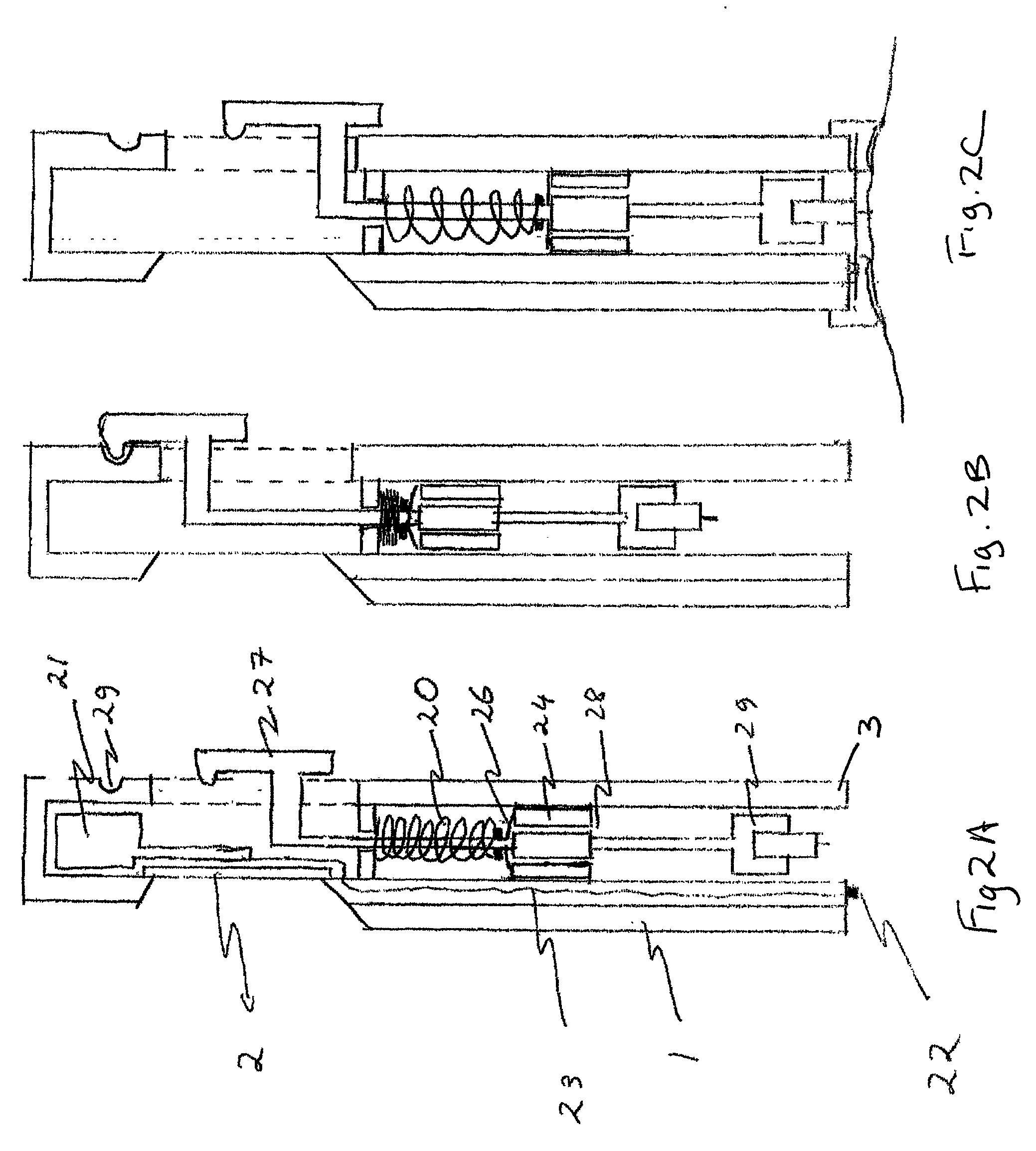
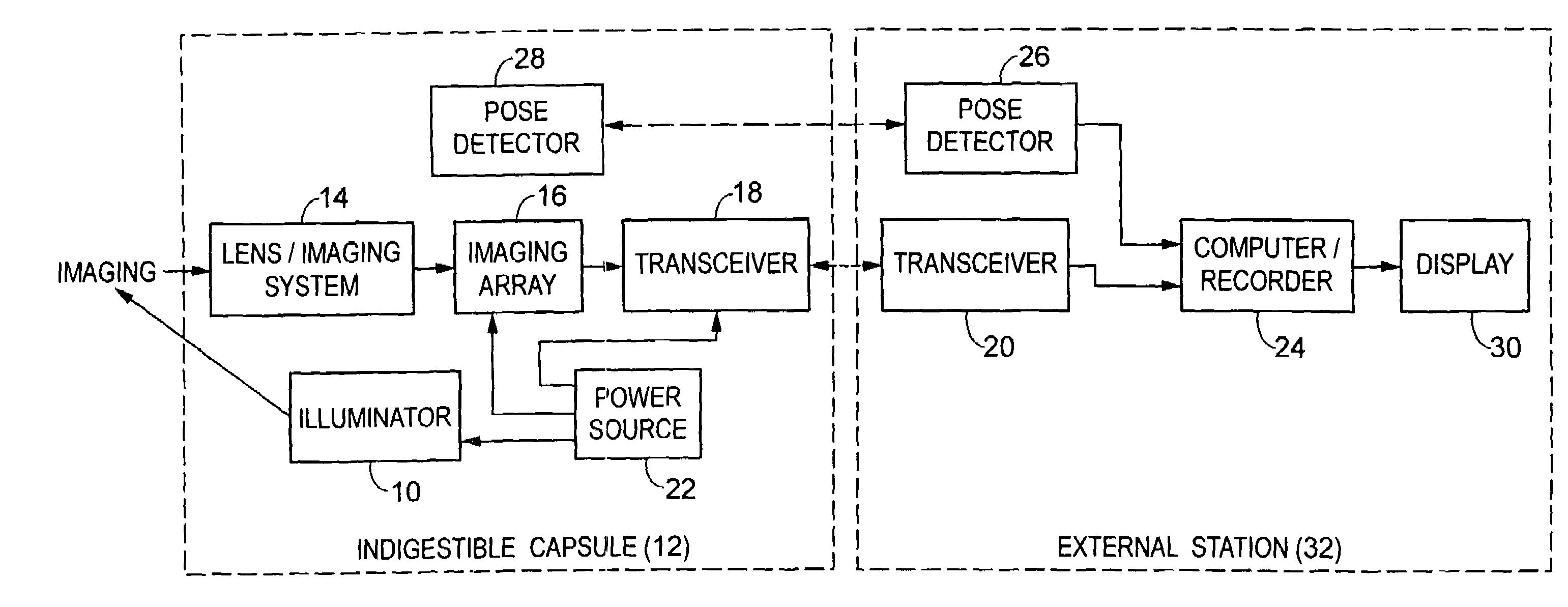
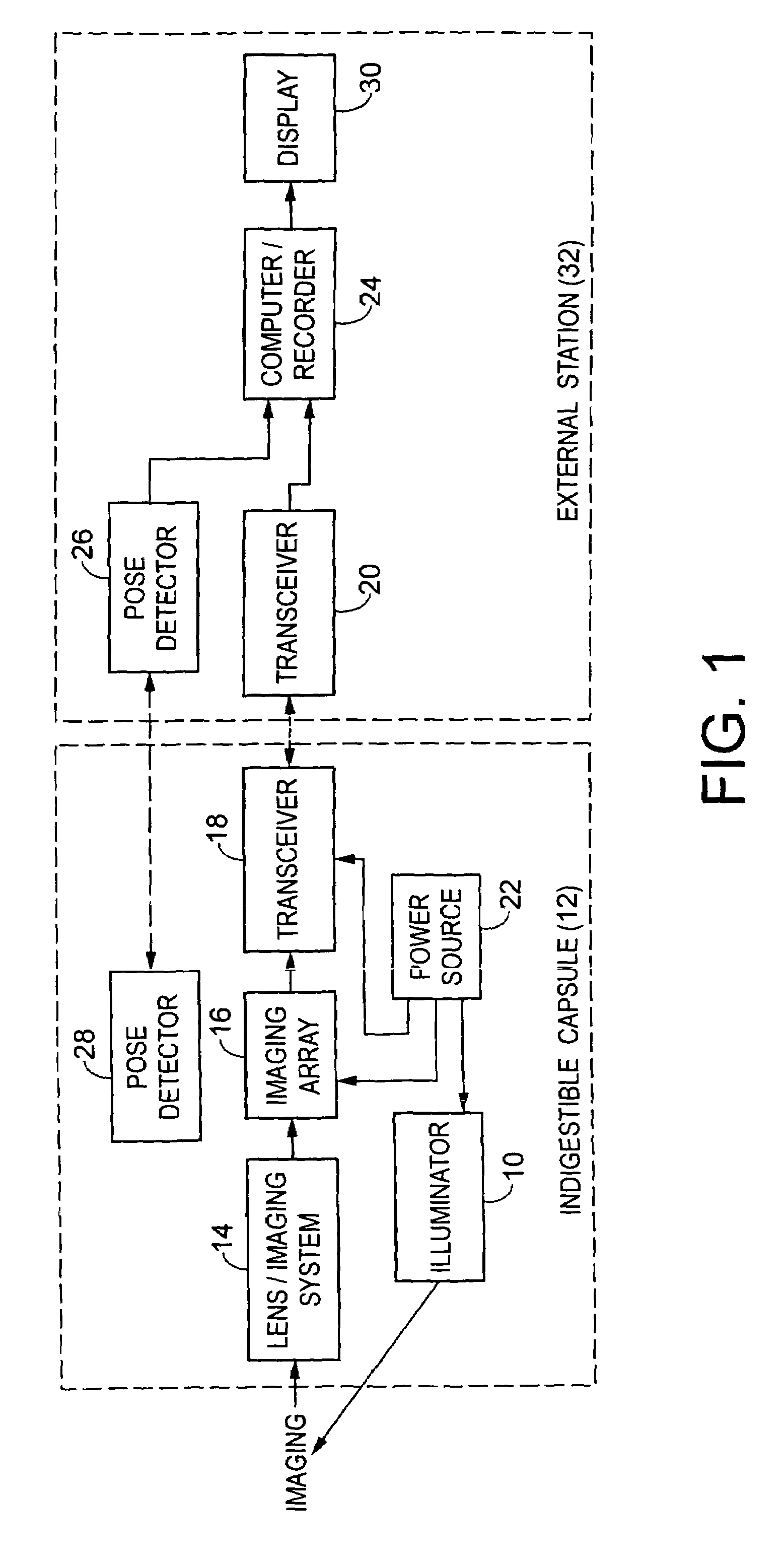
Miniature ingestible capsule
A miniature ingestible imaging capsule having a membrane defining an internal cavity and being provided with a window is provided. A lens is disposed in relation to said window and a light source disposed in relation to the lens for providing illumination to outside of the membrane through the window. An imaging array is disposed in relation to the lens, wherein images from the lens impinge on the imaging array. A transmitter is disposed in relation to the imaging array for transmitting a signal from the imaging array to an associated transmitter outside of the membrane. The lens, light source imaging array, and transmitter are enclosed within the internal cavity of the capsule.
Owner:NAIR PADMANABHAN P +1
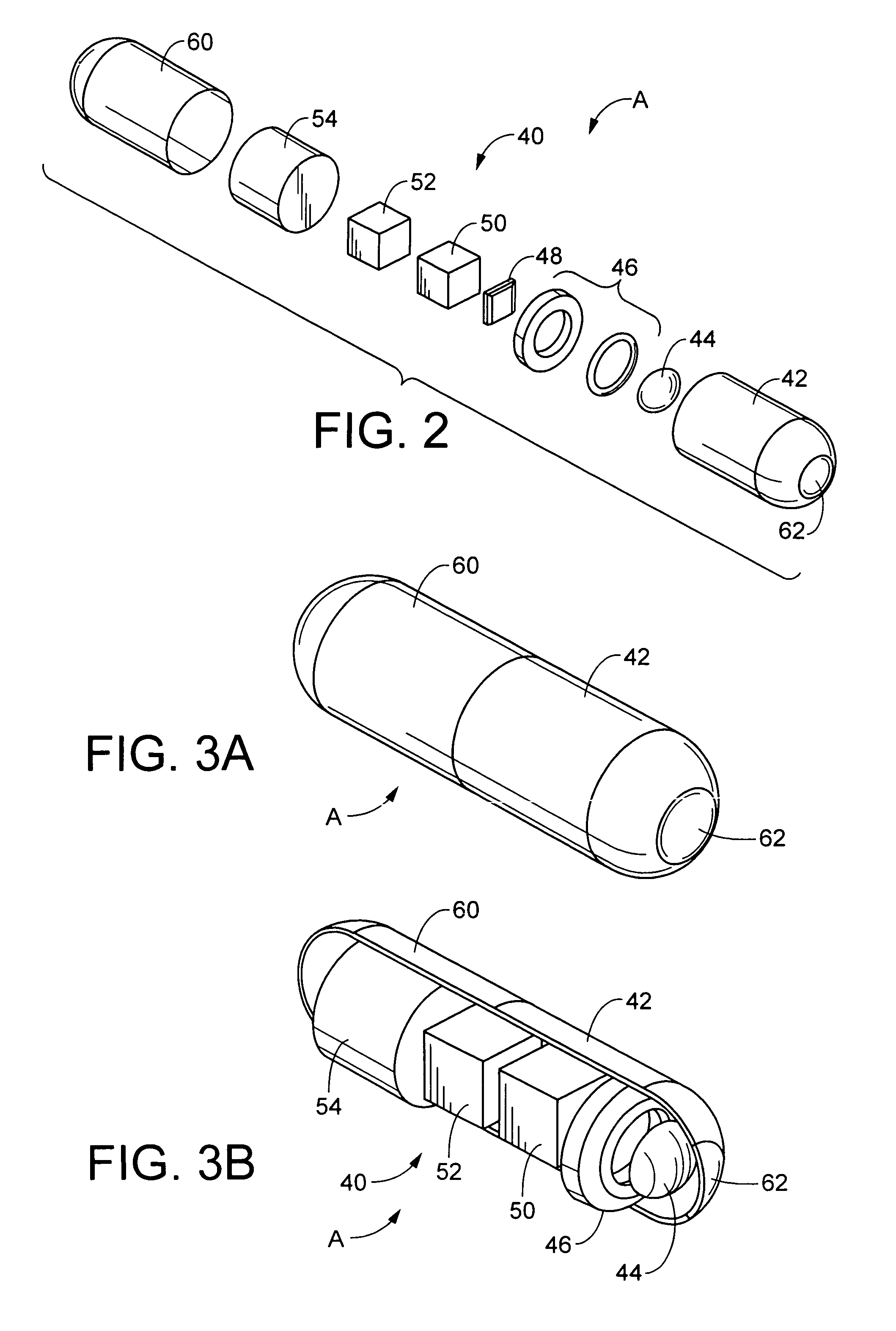
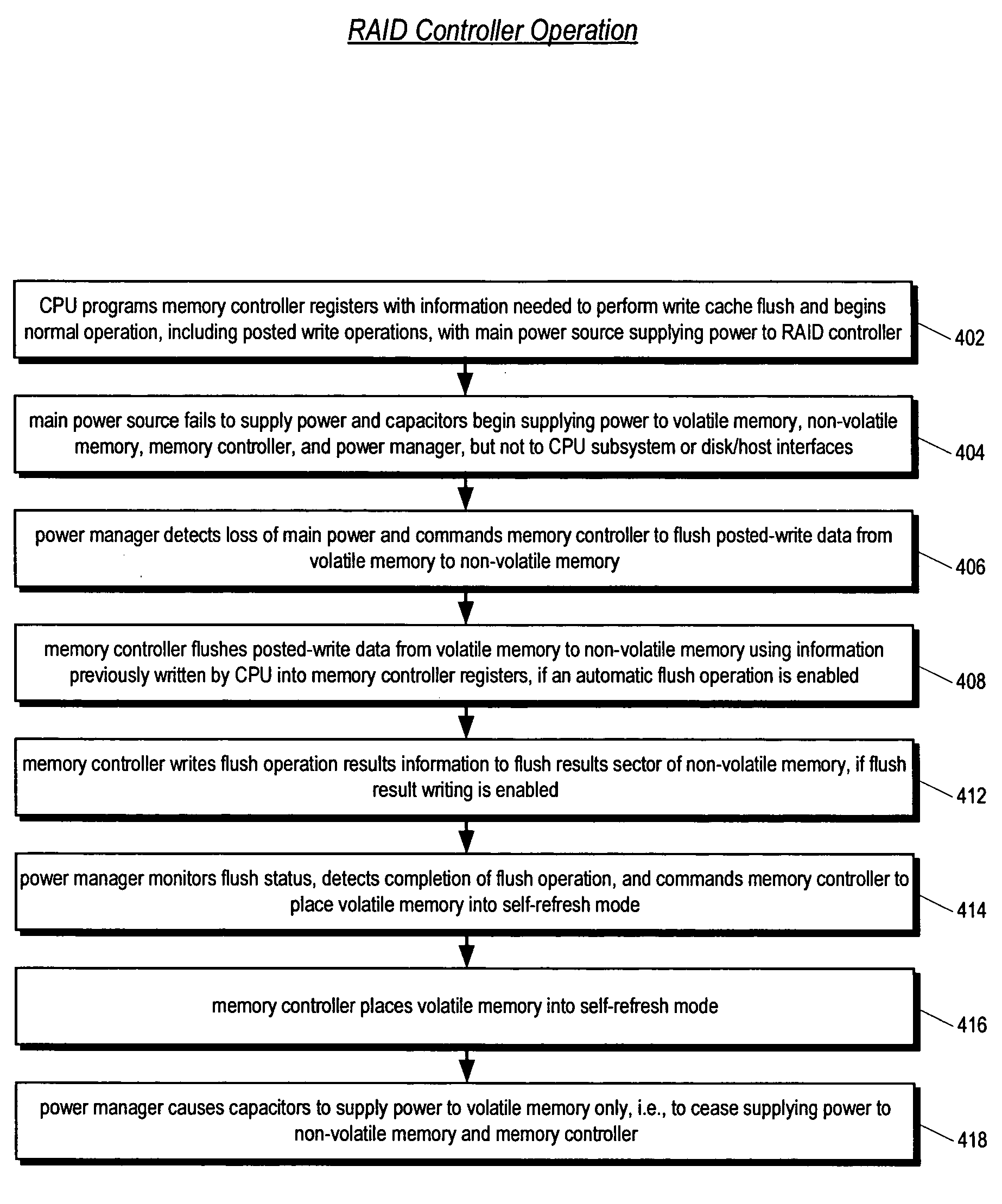
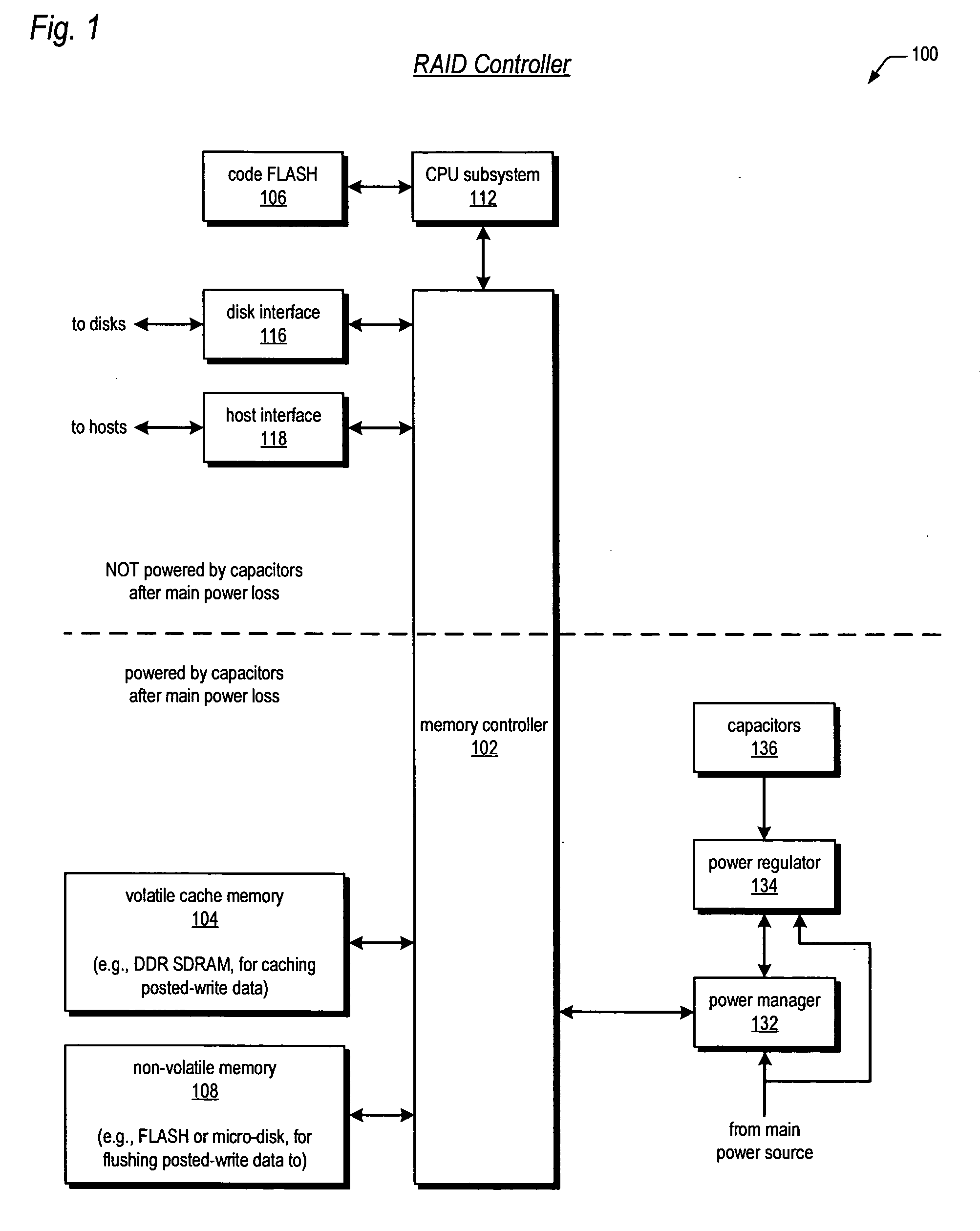
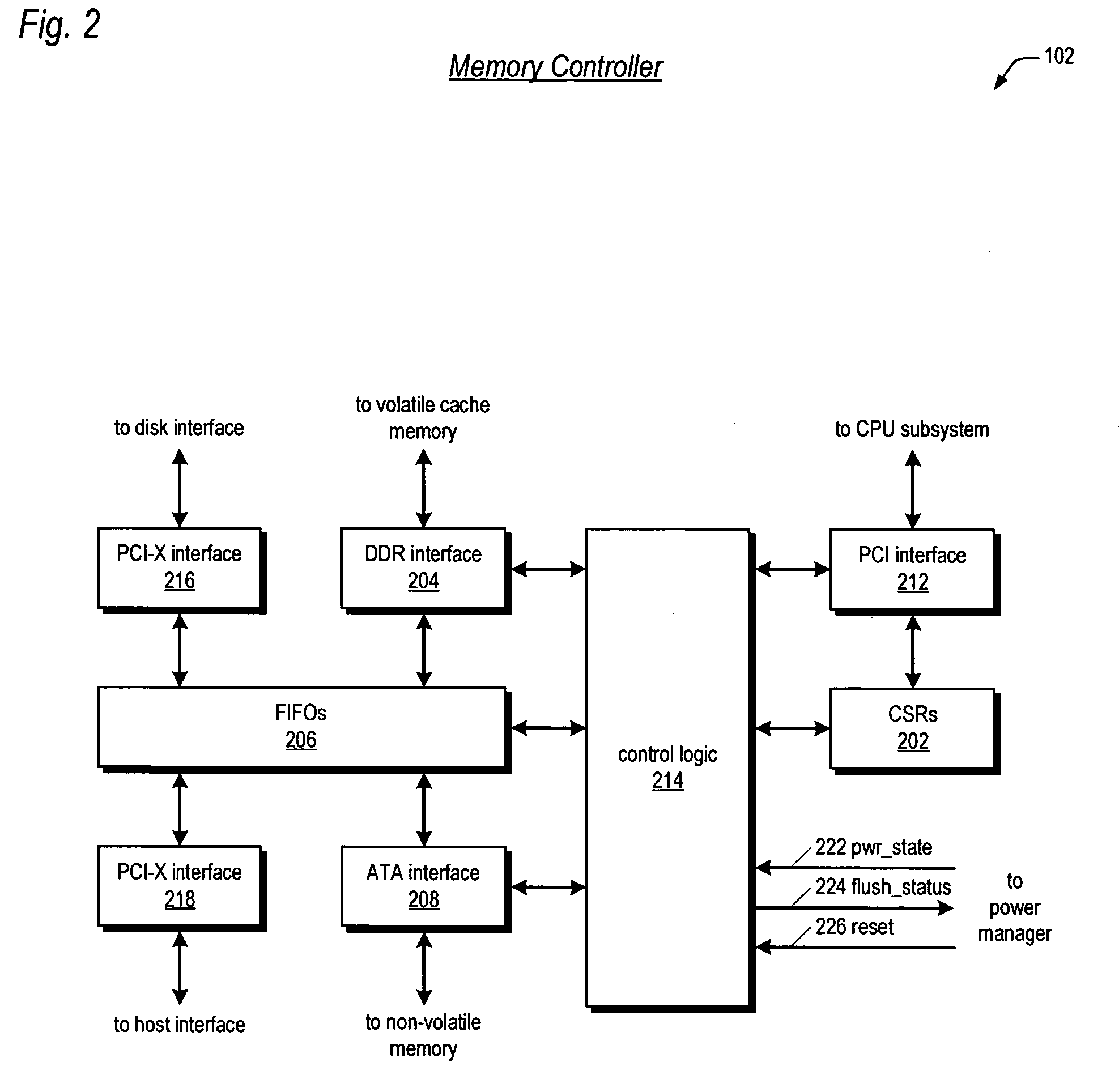
Raid controller using capacitor energy source to flush volatile cache data to non-volatile memory during main power outage
InactiveUS20060015683A1Reduces amount of energy storage capacity requirementLess expensiveEnergy efficient ICTMemory loss protectionRAIDStored energy
A write-caching RAID controller is disclosed. The controller includes a CPU that manages transfers of posted-write data from host computers to a volatile memory and transfers of the posted-write data from the volatile memory to storage devices when a main power source is supplying power to the RAID controller. A memory controller flushes the posted-write data from the volatile memory to the non-volatile memory when main power fails, during which time capacitors provide power to the memory controller, volatile memory, and non-volatile memory, but not to the CPU, in order to reduce the energy storage requirements of the capacitors. During main power provision, the CPU programs the memory controller with information needed to perform the flush operation, such as the location and size of the posted-write data in the volatile memory and various flush operation characteristics.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
Solar cell and method of manufacture
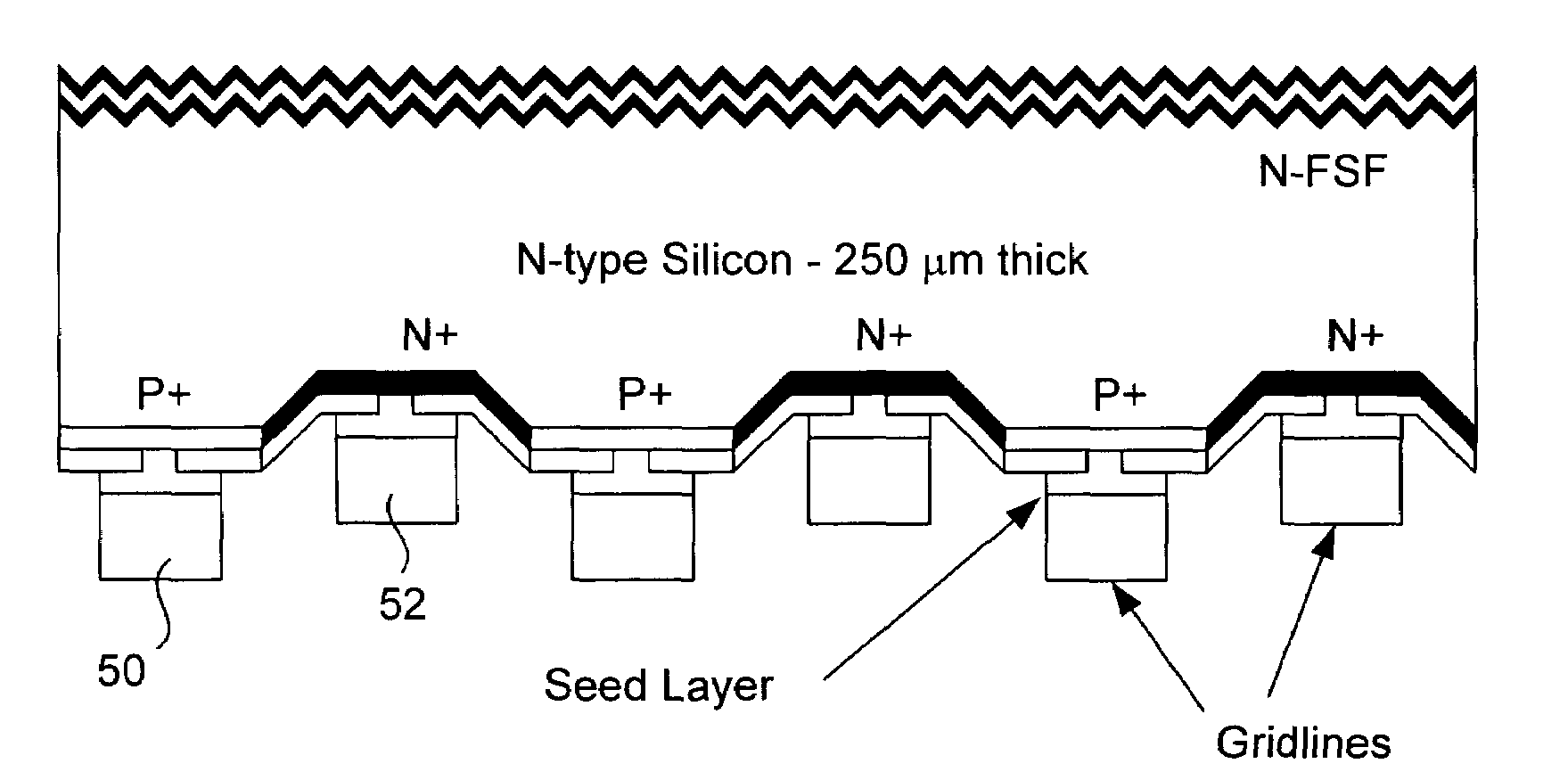
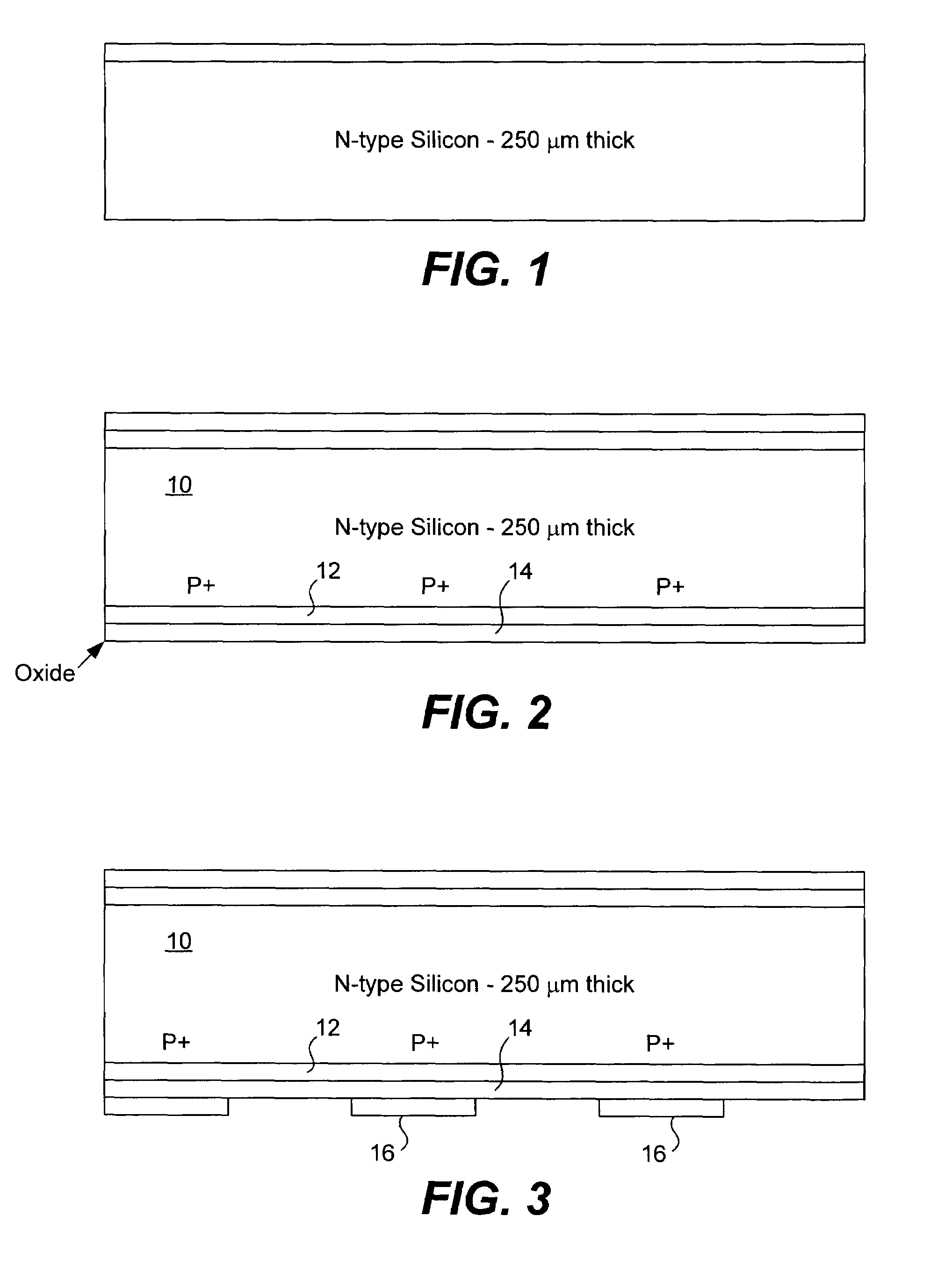
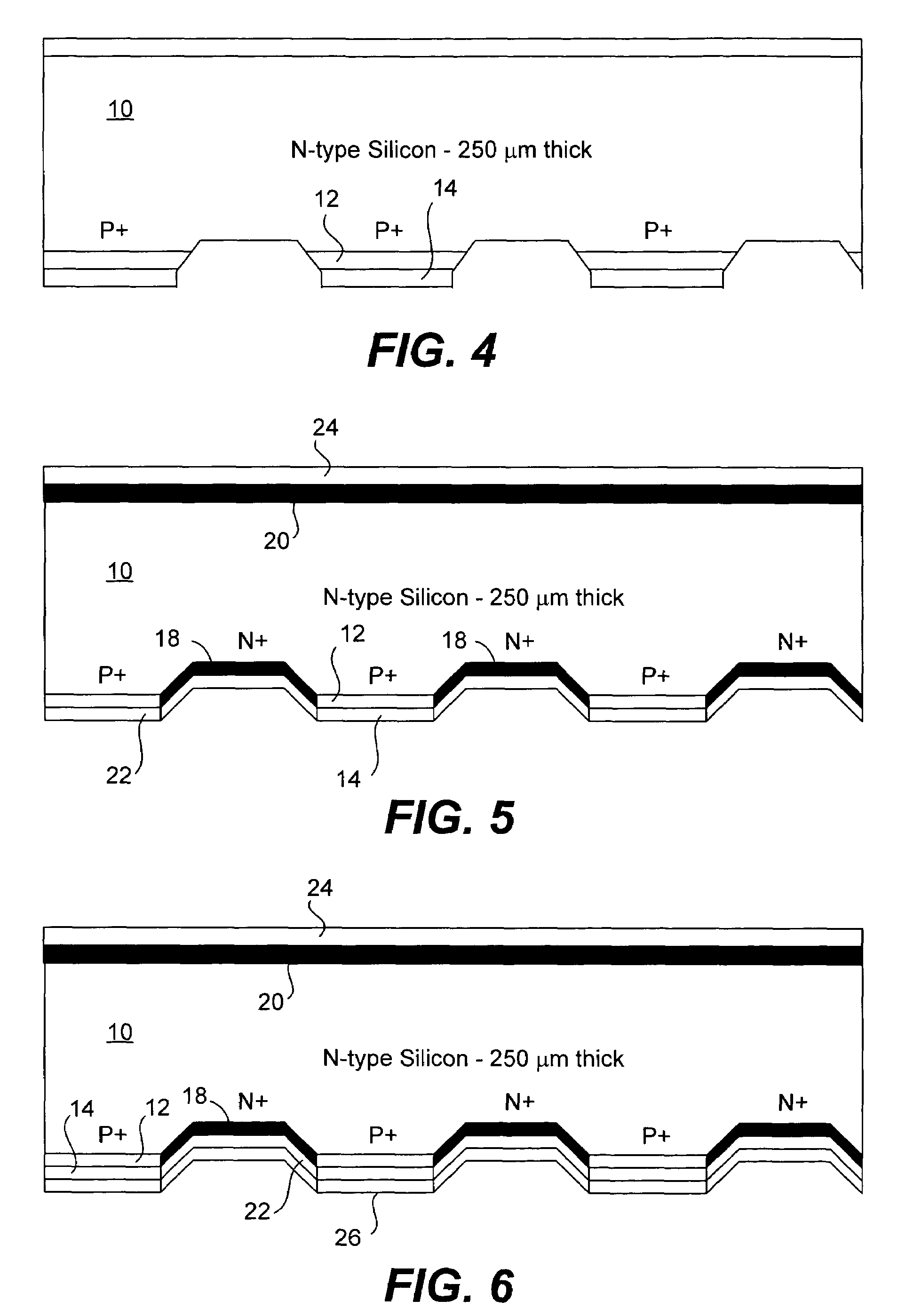
ActiveUS7339110B1Easy to manufactureLess expensiveFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSilicon oxide
A solar cell that is readily manufactured using processing techniques which are less expensive than microelectronic circuit processing. In preferred embodiments, printing techniques are utilized in selectively forming masks for use in etching of silicon oxide and diffusing dopants and in forming metal contacts to diffused regions. In a preferred embodiment, p-doped regions and n-doped regions are alternately formed in a surface of the wafer in offset levels through use of masking and etching techniques. Metal contacts are made to the p-regions and n-regions by first forming a seed layer stack that comprises a first layer such as aluminum that contacts silicon and functions as an infrared reflector, second layer such titanium tungsten that acts as diffusion barrier, and a third layer functions as a plating base. A thick conductive layer such as copper is then plated over the seed layer, and the seed layer between plated lines is removed. A front surface of the wafer is preferably textured by etching or mechanical abrasion with an antireflection layer provided over the textured surface. A field layer can be provided in the textured surface with the combined effect being a very low surface recombination velocity.
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD +1
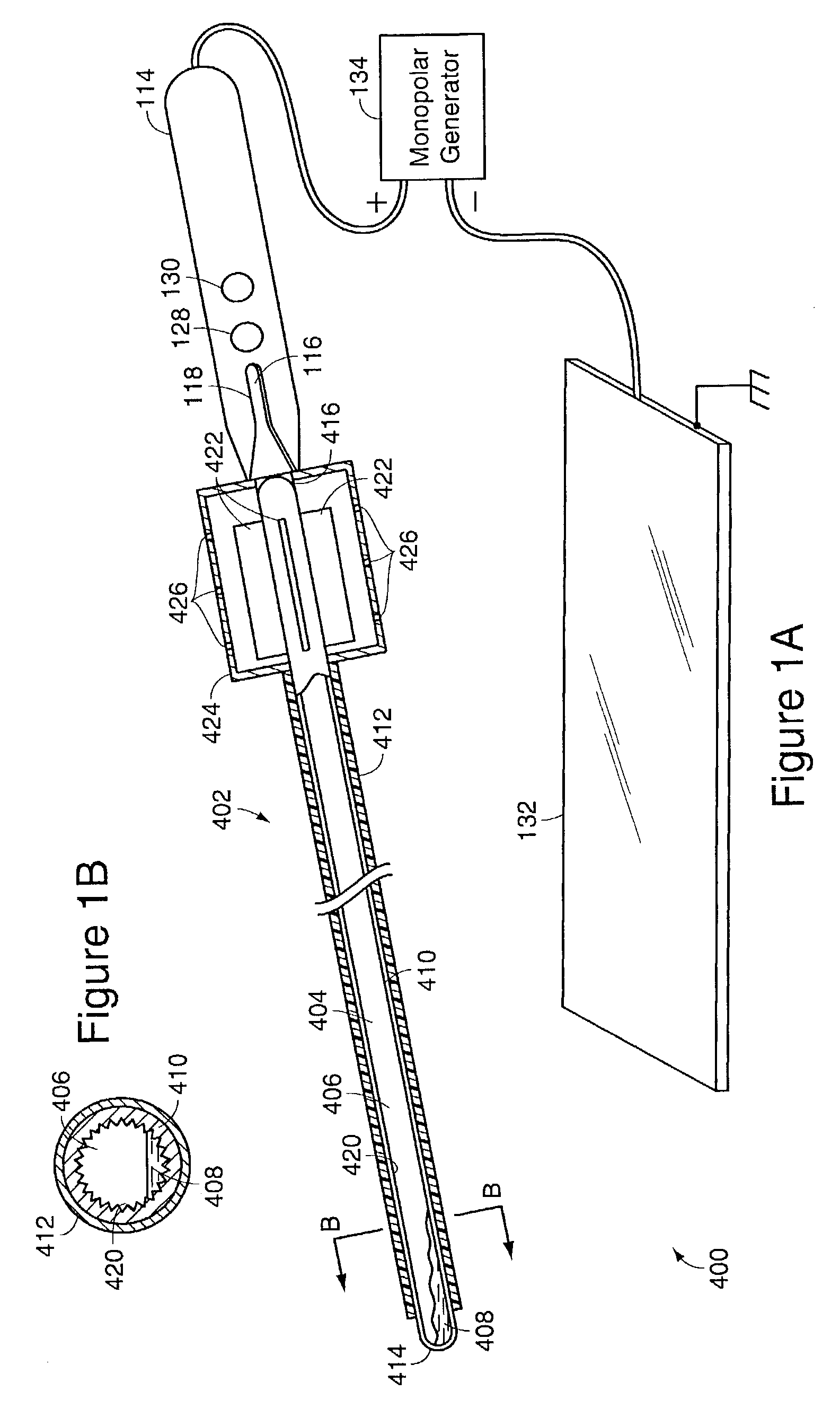
Electrosurgery with cooled electrodes
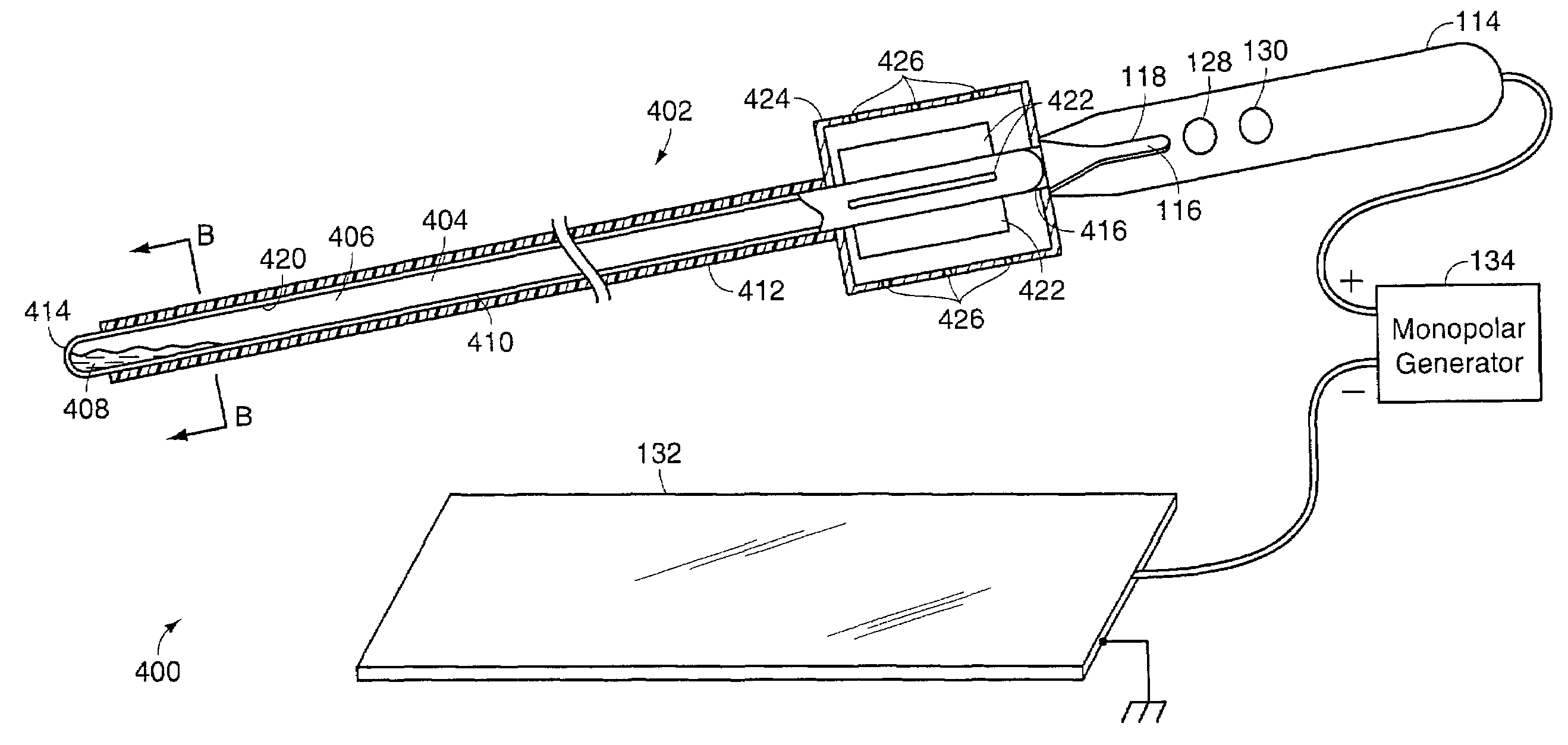
InactiveUS7074219B2Avoid insufficient heatingPractical for saleSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsElectricityElectrosurgery
A cooled electrosurgical system includes an electrosurgical device having at least one electrode for applying electrical energy to tissue. In one embodiment, the electrode includes an internal cavity in which a cooling medium such as water is contained. The internal cavity is closed at both ends of the device such that the cooling medium is contained within the electrode at the surgical site such that the cooling medium does not contact the tissue being treated. The electrosurgical device has an electrode and a heat pipe to conduct heat from the electrodes where substantially all heat conducted from the electrode through the heat pipe is dissipated along the length of the heat pipe. The heat pipe can have a thermal time constant less than 60 seconds and preferably less than 30 seconds.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Bubbler assembly and method for vapor flow control
InactiveUS20120304935A1Mitigate and overcomeLess expensiveUsing liquid separation agentMixing methodsSource materialEngineering
Disclosed is a bubbler assembly. The bubbler assembly includes a vessel configured to contain a liquid source material and its vapor. It also includes a carrier gas supply line, a downstream end of which discharges in a lower portion of the vessel, and a gas outlet line, an upstream end of which is in fluid communication with an upper portion of the vessel. The gas outlet line includes a constriction. The bubbler assembly further includes a pressurizing gas supply line, a downstream end of which discharges in either the upper portion of the vessel or in the gas outlet line at a point upstream of the constriction.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Digital imaging system and method using multiple digital image sensors to produce large high-resolution gapless mosaic images
InactiveUS20090268983A1Avoid smallNot easy to produceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayCamera lens
A digital imaging system and method using multiple cameras arranged and aligned to create a much larger virtual image sensor array. Each camera has a lens with an optical axis aligned parallel to the optical axes of the other camera lenses, and a digital image sensor array with one or more non-contiguous pixelated sensors. The non-contiguous sensor arrays are spatially arranged relative to their respective optical axes so that each sensor images a portion of a target region that is substantially different from other portions of the target region imaged by other sensors, and preferably overlaps adjacent portions imaged by the other sensors. In this manner, the portions imaged by one set of sensors completely fill the image gaps found between other portions imaged by other sets of sensors, so that a seamless mosaic image of the target region may be produced.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Gas-phase reactor and system having exhaust plenum and components thereof
ActiveUS20150267301A1Less complexLess expensiveElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseProcess engineering
An improved exhaust system for a gas-phase reactor and a reactor and system including the exhaust system are disclosed. The exhaust system includes a channel fluidly coupled to an exhaust plenum. The improved exhaust system allows operation of a gas-phase reactor with desired flow characteristics while taking up relatively little space within a reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
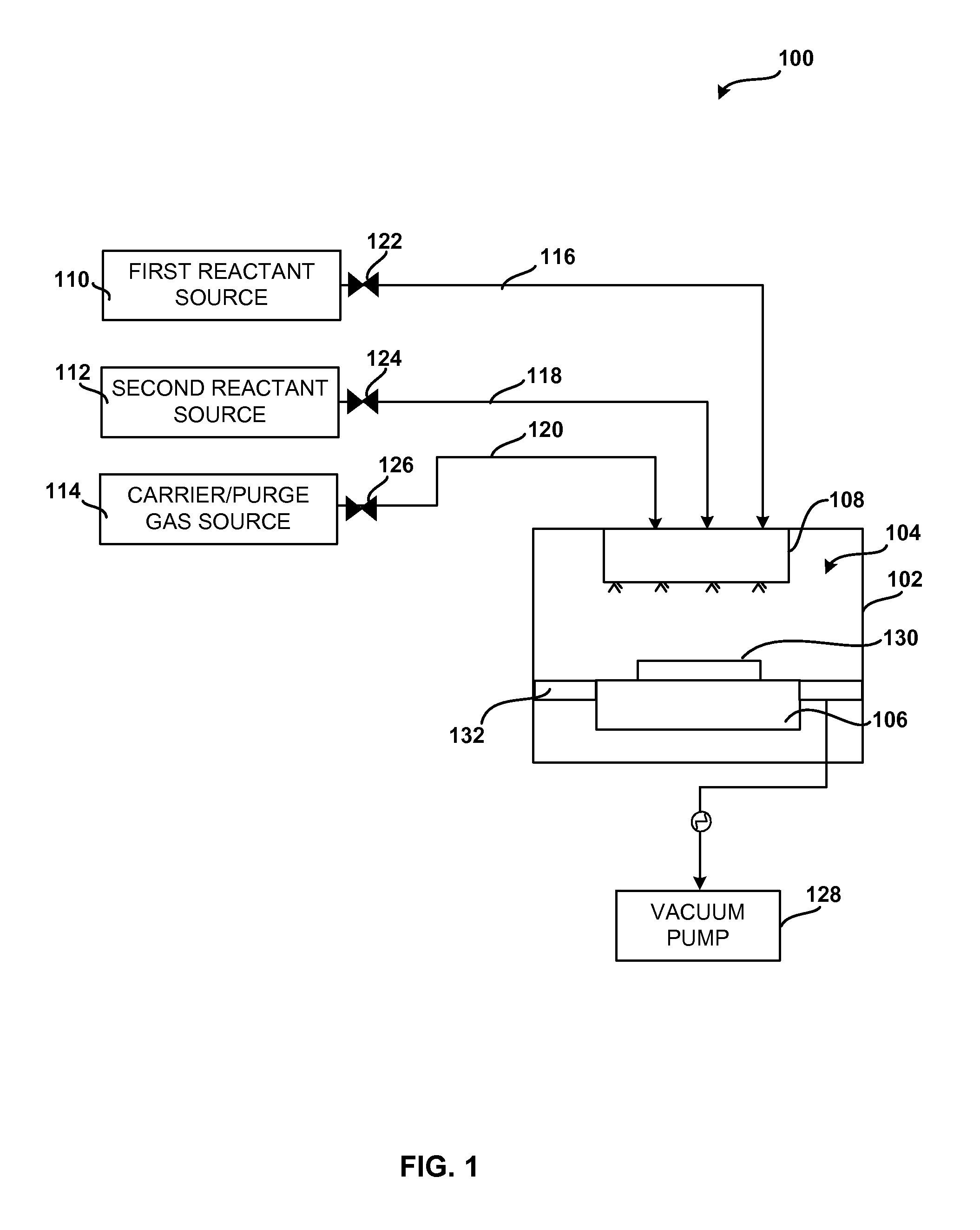
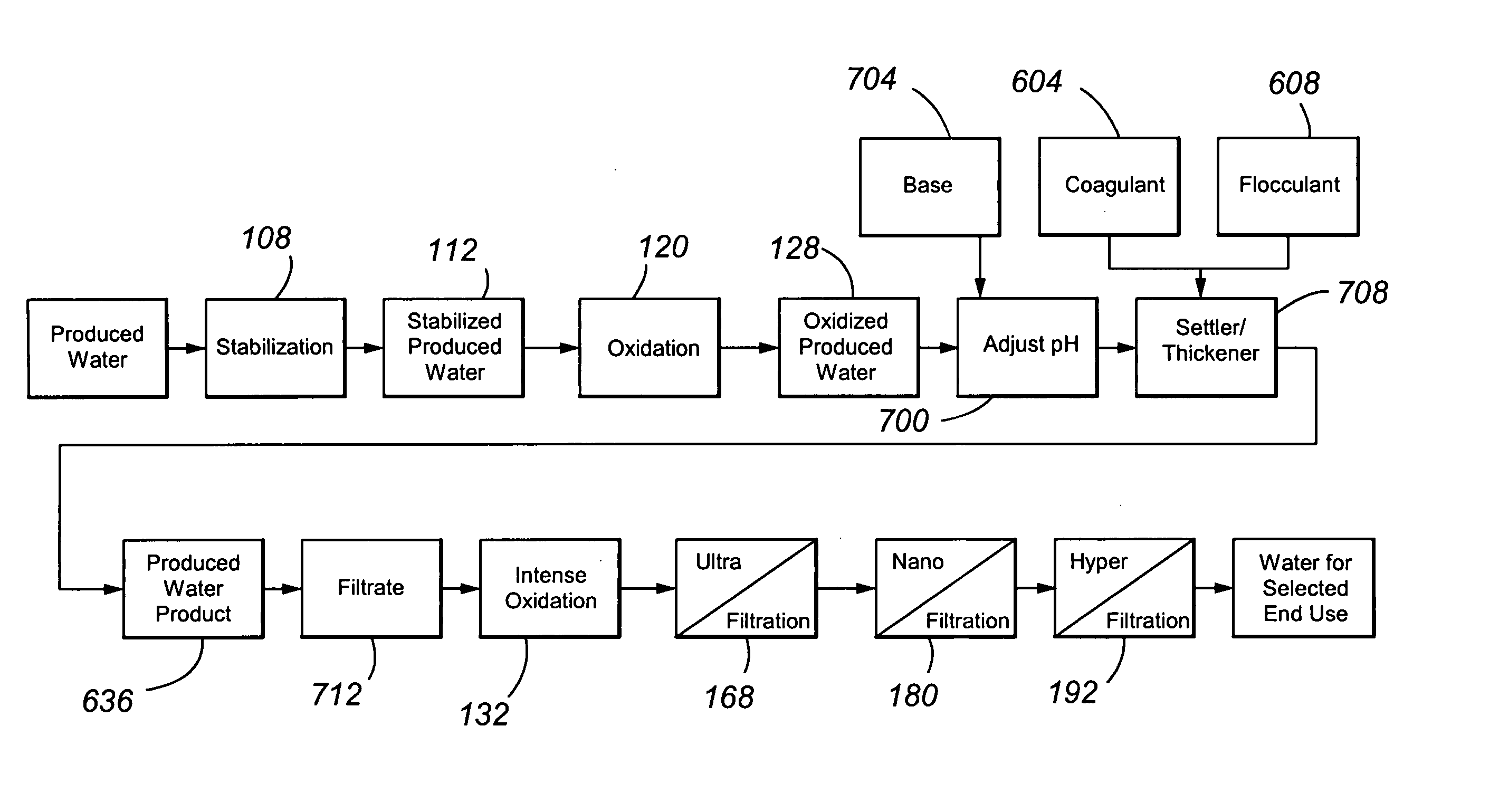
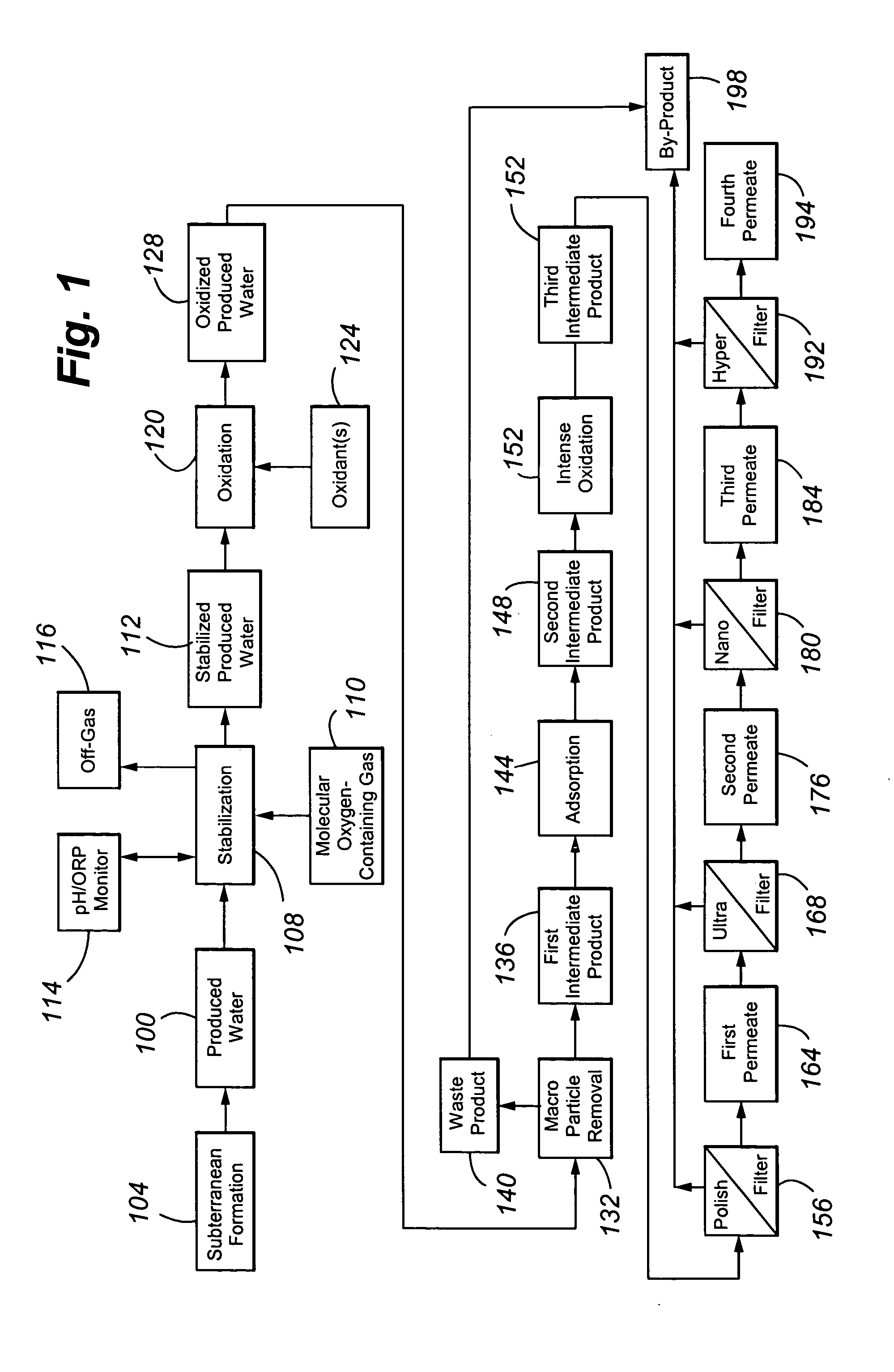
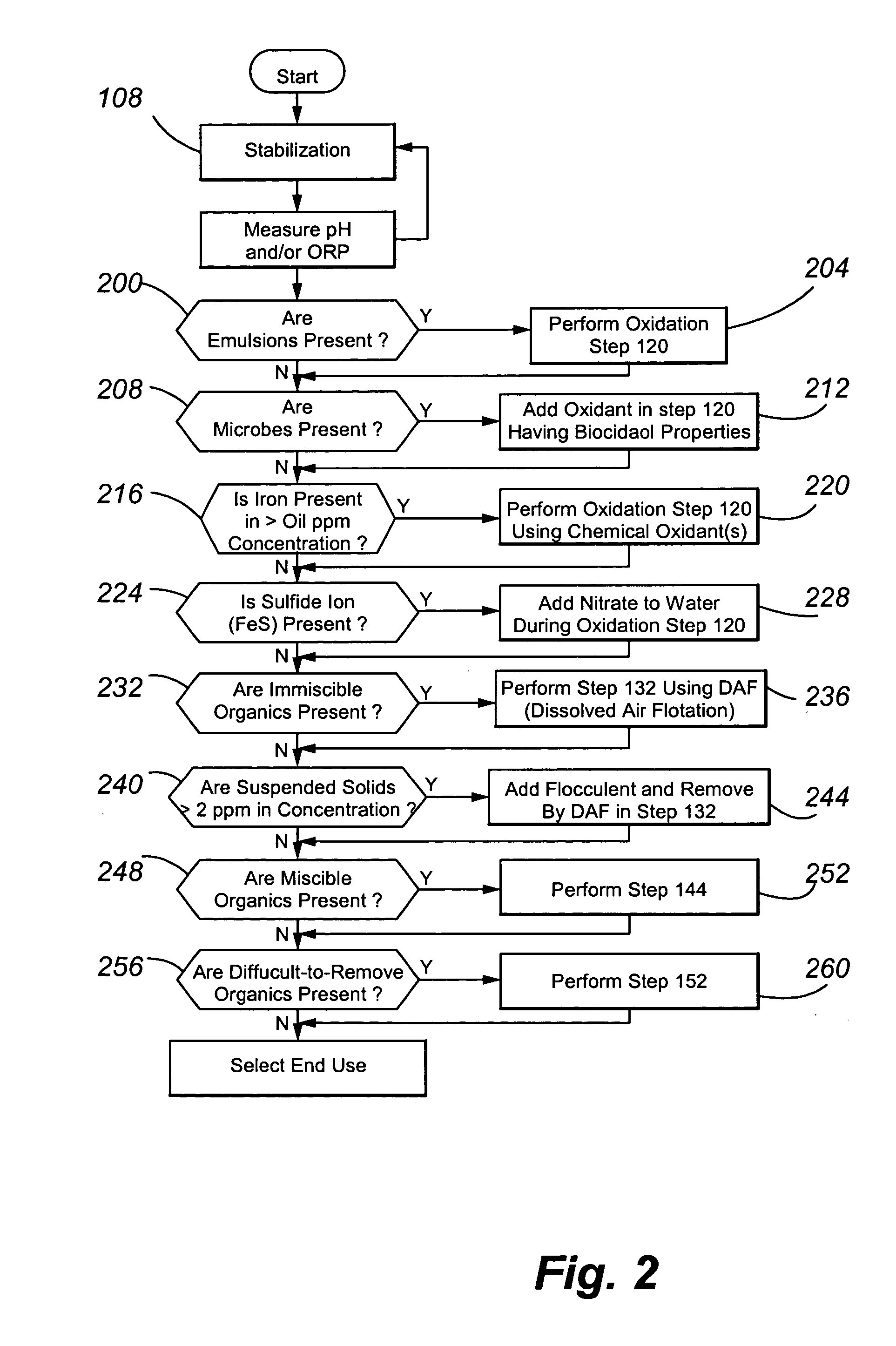
Treating produced waters
InactiveUS20070102359A1Complicate purificationIncrease ratingsUltrafiltrationTreatment involving filtrationEmulsionUnit operation
The present invention is directed to various sets of unit operations for treating aqueous effluents and logic for designing and effecting the treatment. The unit operations include stabilization of subterranean waters, sequential oxidation steps to alter selected target materials, oxidation to break up emulsions prior to removal of the emulsion components, and intense oxidation to break up difficult-to-remove organic target materials.
Owner:HW PROCESS TECH
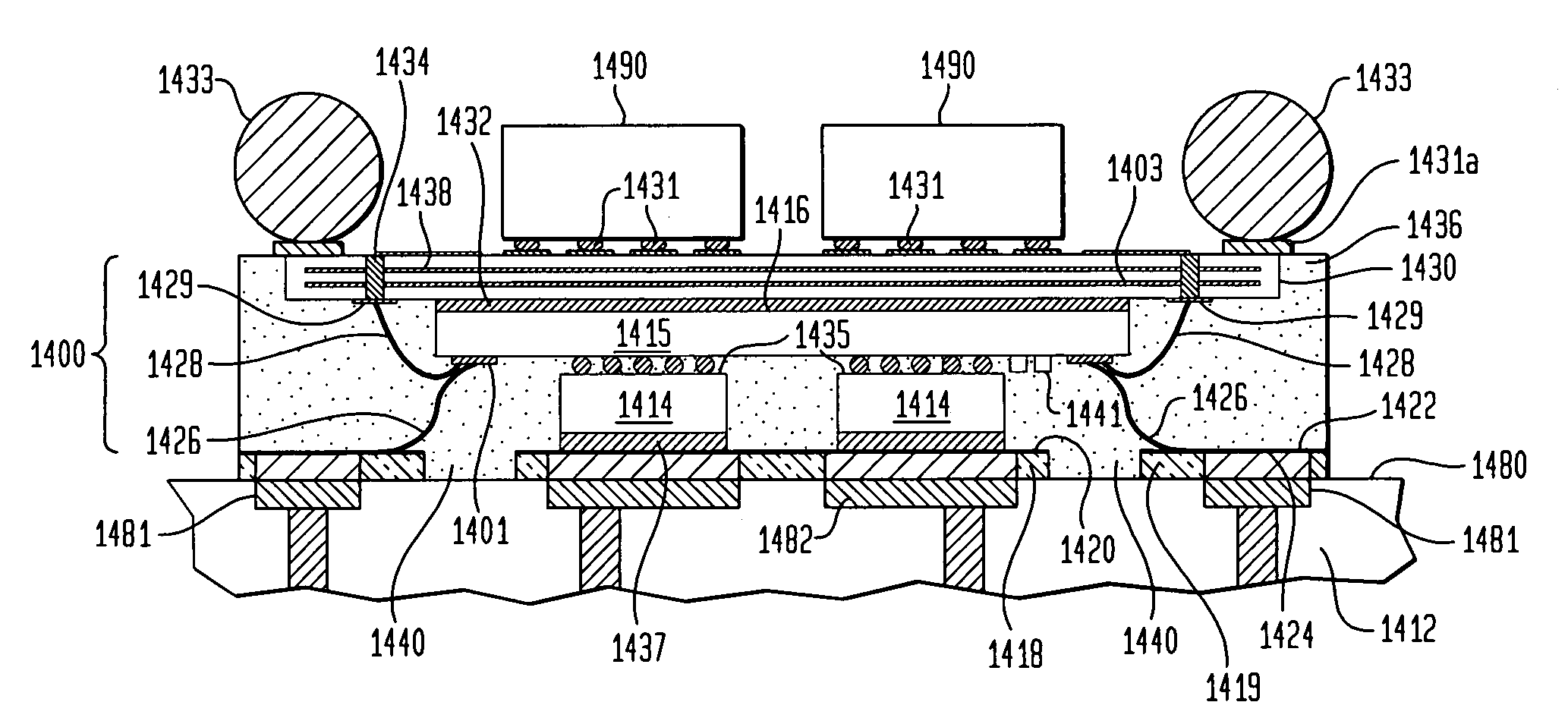
Polyaxial bone screw with torqueless fastening
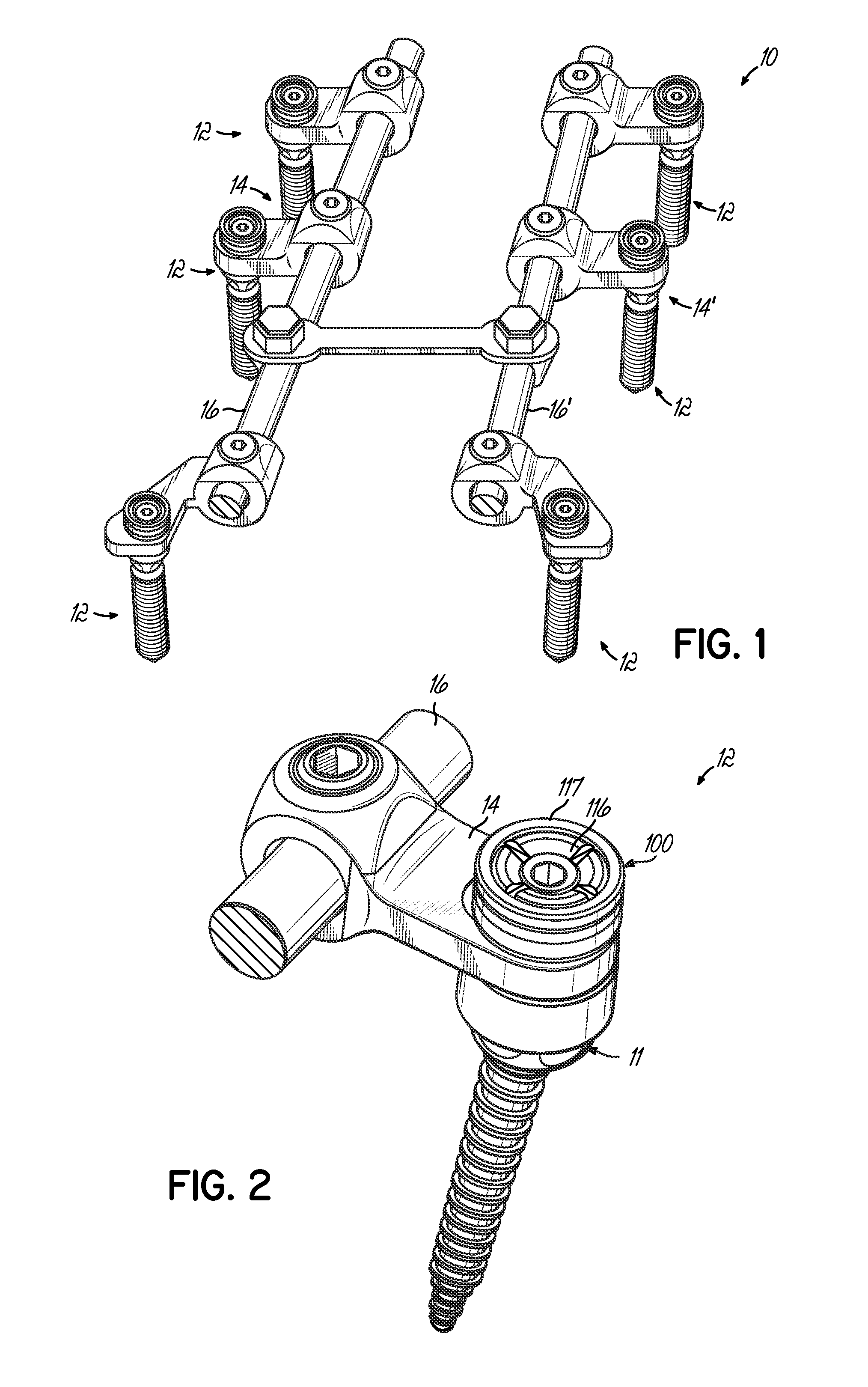
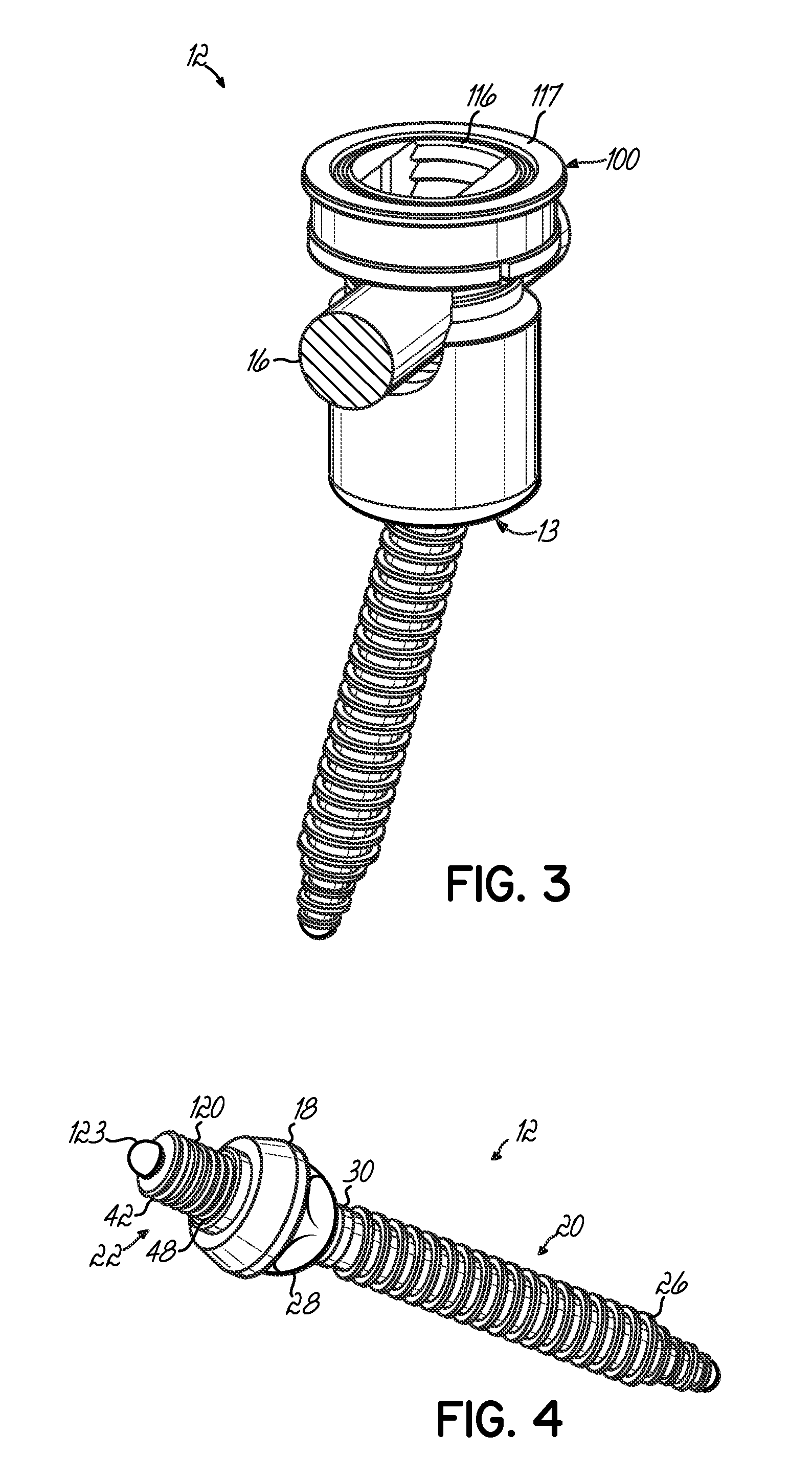
ActiveUS20050070899A1Avoid disassemblyLarge caliberSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBiomedical engineeringBone screws
An adjustable spinal fixation system is composed of a collection of anchoring assemblies attached, via a variety of connectors, to spine-stabilizing rods. The anchoring assemblies include a linking member attached in a ball-and-socket fashion to a bone-engaging member that is adapted to engage a spinal bone of a patient. The linking member joins one of the included connectors to an associated bone-engaging member. The connectors are selectively attached to one of the stabilizing rods. The anchoring assemblies each include a support collar and a split retention ring that cooperate to allow adjustment of the bone-engaging member and corresponding connector during surgery. When surgery is complete, a linear engaging fastener cooperates with the support collar and split retention ring to maintain the relative position of the entire fixation system, preventing unwanted movement between the system components.
Owner:SPINAL
Method of preparing nano-structured surface coatings and coated articles
InactiveUS7892606B2Improve adhesionMore readily manufacturableMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCross-linkNano structuring
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Methods for valuing and placing advertising
Disclosed are methods for valuing and placing advertising segments on the basis of competitive bidding. Publishers having available ad space make that space (segments) available to an intermediary. The intermediary accepts bids from potential advertisers, ranks the bids and awards advertising segments to the bidders according to the rankings. Payments for the placement of advertising may be made on a per-display basis, or on a per click-through or per transaction basis for internet applications. Under these methods, virtually every advertiser will have some level of access to the available ad space. The intermediary continuously updates its lists of available ad space according to numbers and amounts of bids so that, over time, the lists themselves are representative of the rankings of the most popular ad space. The intermediary also continuously organizes and updates the advertising material it receives according to subject matter for access by potential consumers.
Owner:TALEGON GALIP
High frequency chip packages with connecting elements
InactiveUS7176506B2Reduce packaging costsLow impedance connectionImpedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFlexible circuitsSurface mounting
A radio frequency chip package is formed by assembling a connecting element such as a circuit board or flexible circuit tape having chips thereon with a bottom plane element such as a lead frame incorporating a large thermally-conductive plate and leads projecting upwardly from the plane of the plate. The assembly step places the rear surfaces of the chips on the bottom side of the connecting element into proximity with the thermal conductor and joins the conductive traces on the connecting element with the leads. The resulting assembly is encapsulated, leaving terminals at the bottom ends of the leads exposed. The encapsulated assembly may be surface-mounted to a circuit board. The leads provide robust electrical connections between the connecting element and the circuit board.
Owner:TESSERA INC
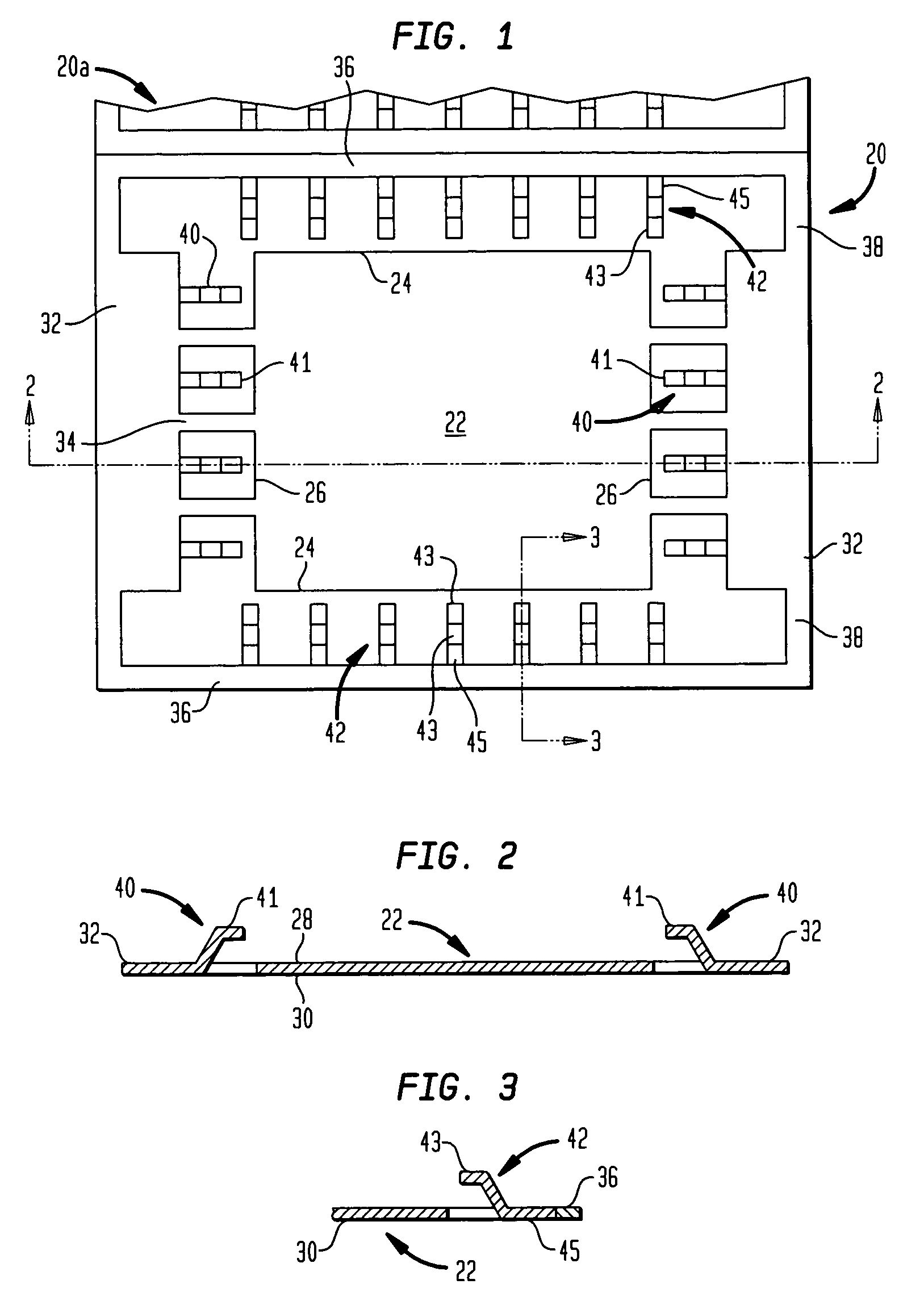
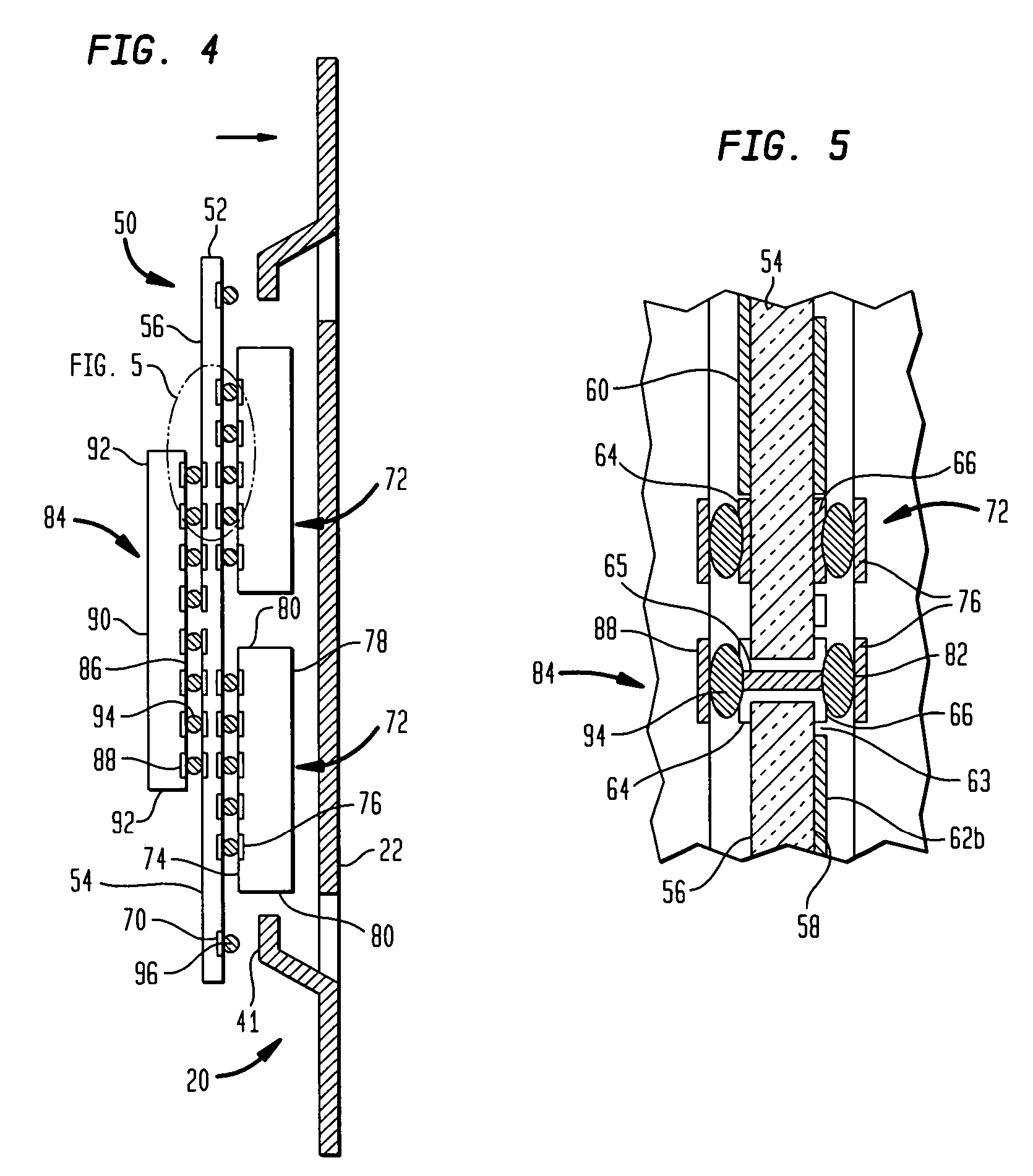
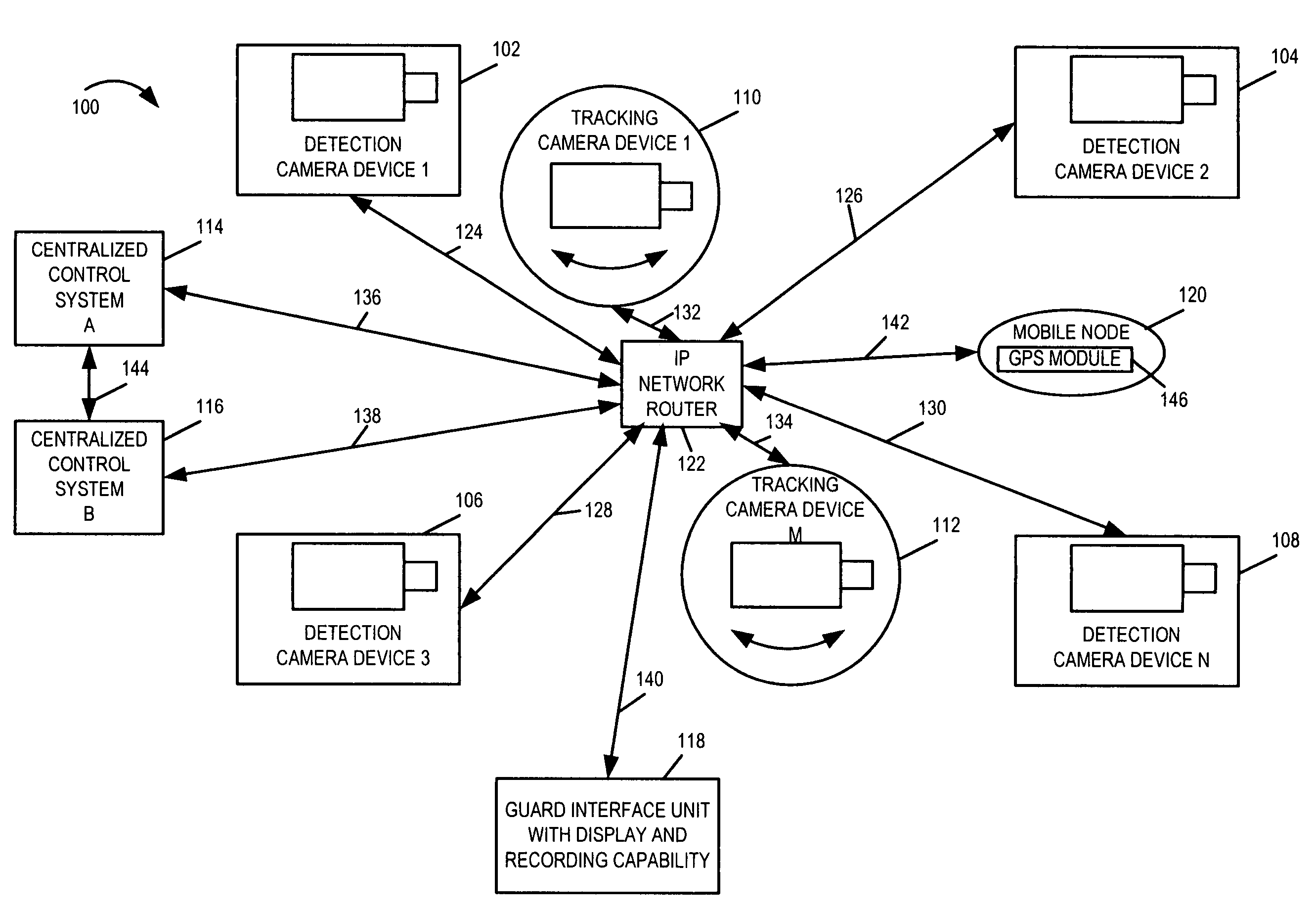
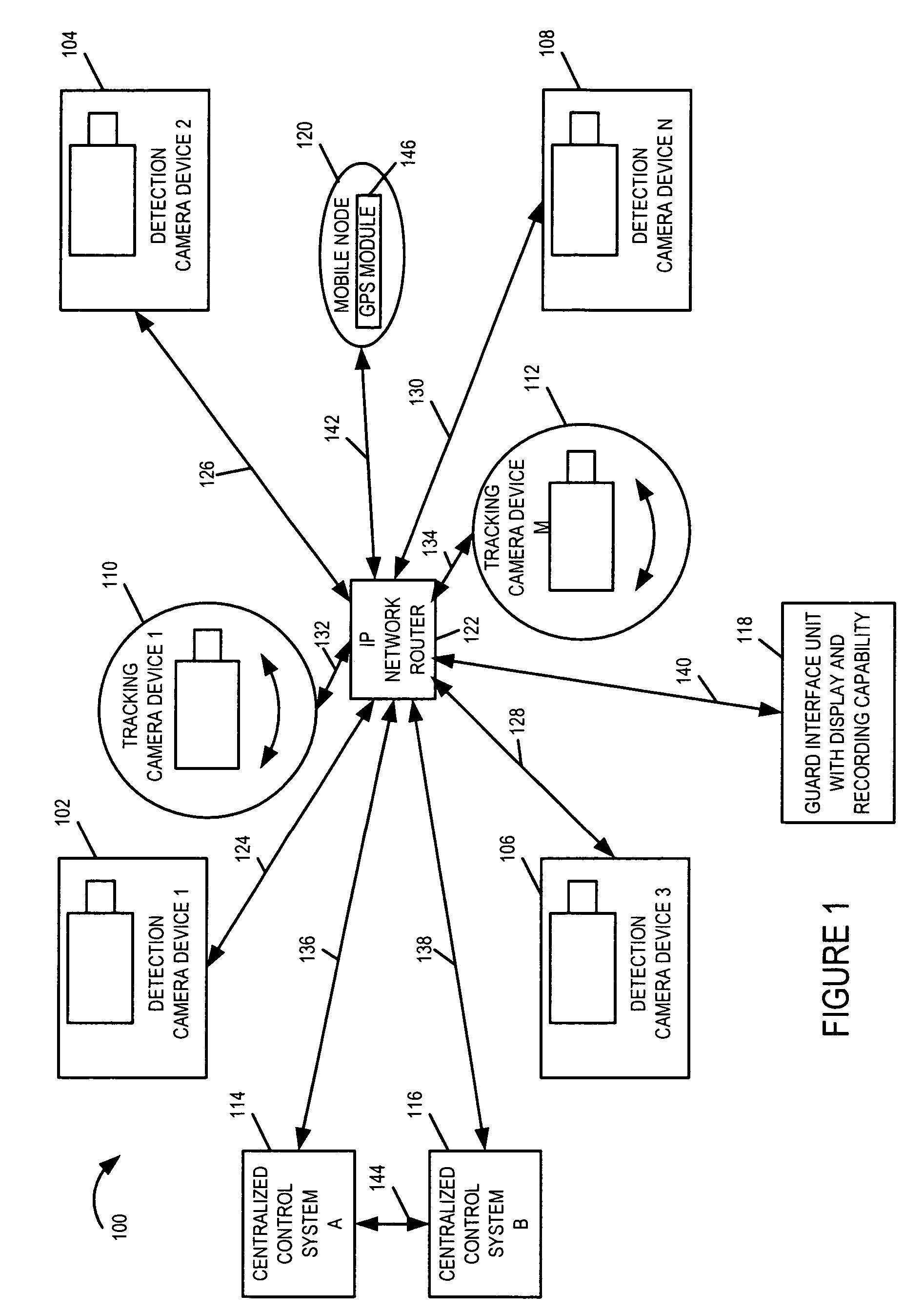
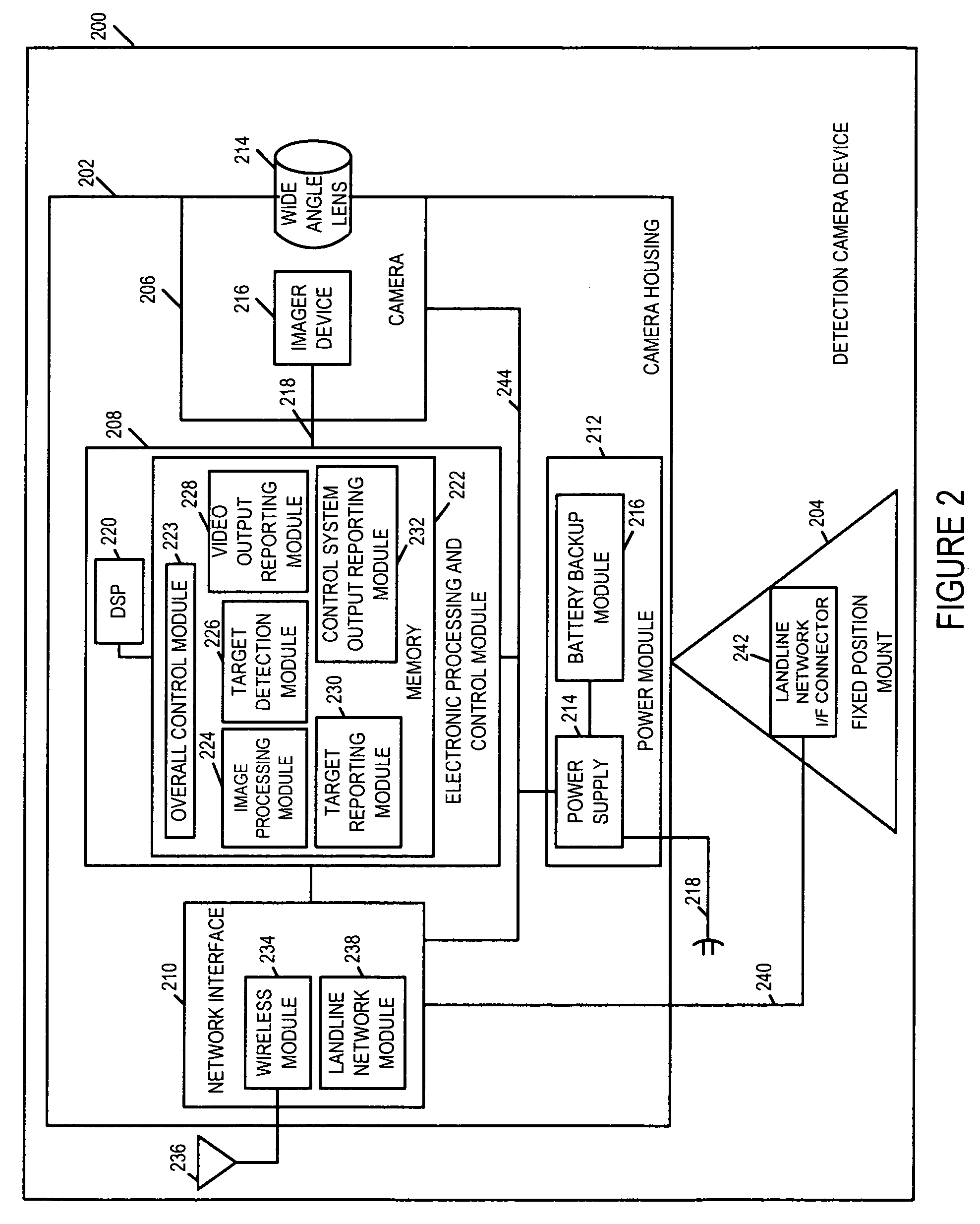
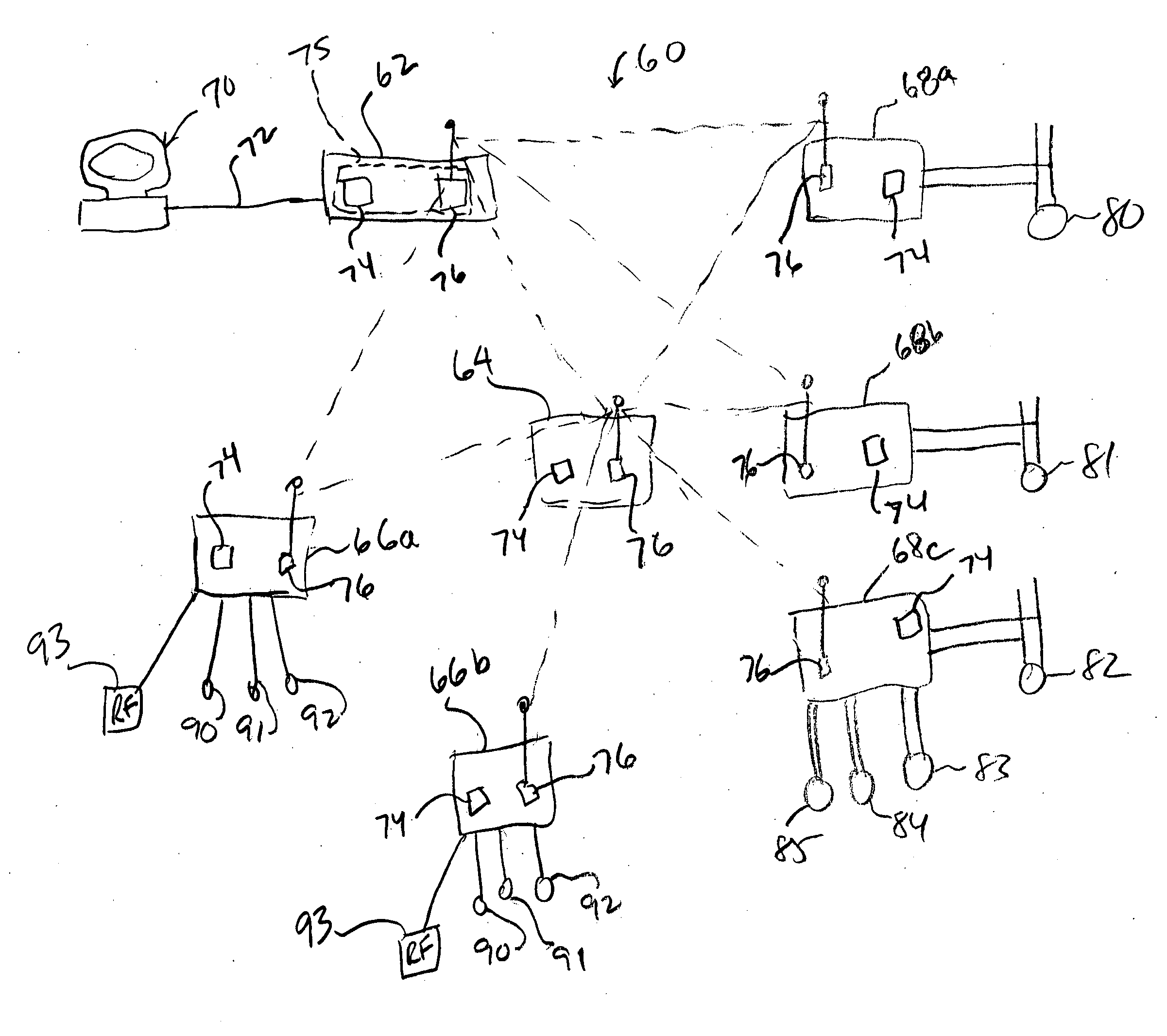
Methods and apparatus for a wide area coordinated surveillance system
ActiveUS20070039030A1Improve abilitiesHigh resolution imageTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionControl system
A coordinated surveillance system uses a larger number of fixed low resolution detection smart camera devices and a smaller number of pan / tilt / zoom controllable high resolution tracking smart camera devices. The set of detection cameras provide overall continuous coverage of the surveillance region, while the tracking cameras provide localized high resolution on demand. Each monitor camera device performs initial detection and determines approximate GPS location of a moving target in its field of view. A control system coordinates detection and tracking camera operation. A selected tracking camera is controlled to focus in on, confirm detection, and track a target. Based on a verified detection, a guard station is alerted and compressed camera video is forwarded to the guard station from the camera(s). The guard station can direct a patrol guard to the target using GPS coordinates and a site map. Redundancy is provided by using multiple control units, each able to handle the full load in the event of failure. Camera devices vote on the status of the control units. A failed detection camera device can be temporarily replaced by a tracking camera device in a back-up mode of operation thus maintaining full overall basic coverage of the surveillance region.
Owner:SIGHTLOGIX
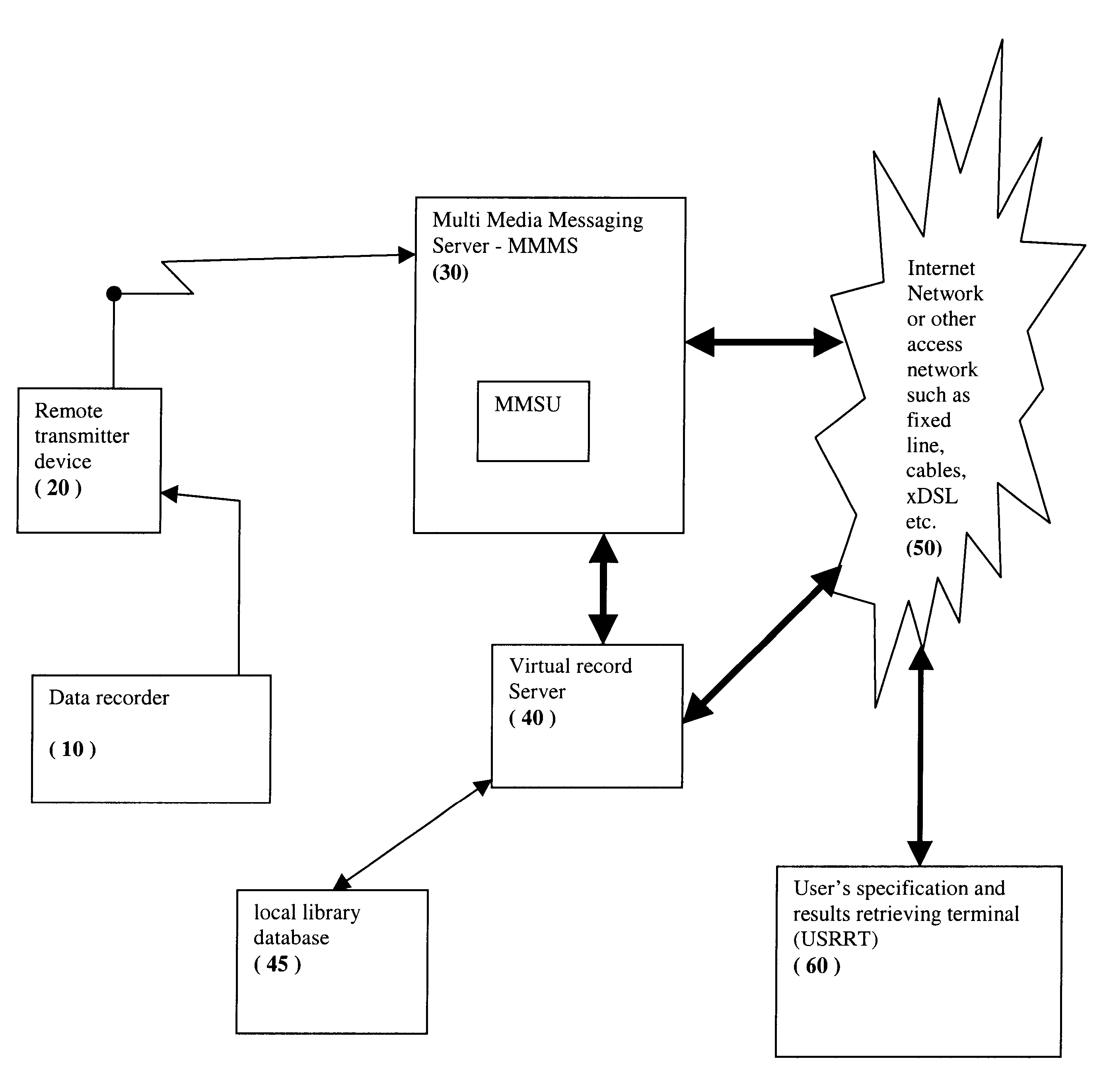
System and method for interleaving of material from database and customized audio-visual material
InactiveUS6912544B1Less expensiveEliminate needData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTime transferMultimedia storage
A system and method for real-time transfer of multimedia material from a remote device to a centralized multi-media storage unit, wherein the multimedia material is combined with extrinsic material to generate a virtual record. A user selects specifications and instructions via a remote terminal for retrieving the extrinsic material from external databases and interleaving the retrieved extrinsic material to the multimedia material provided by the user. Iteration of the selecting of user specifications and instructions and the interleaving process is performed until a final virtual record is produced which is satisfactory to the user.
Owner:COMVERSE
Polyaxial bone screw with torqueless fastening
ActiveUS7335201B2Avoid disassemblyReduce the overall diameterSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBiomedical engineeringBone screws
Owner:SPINAL
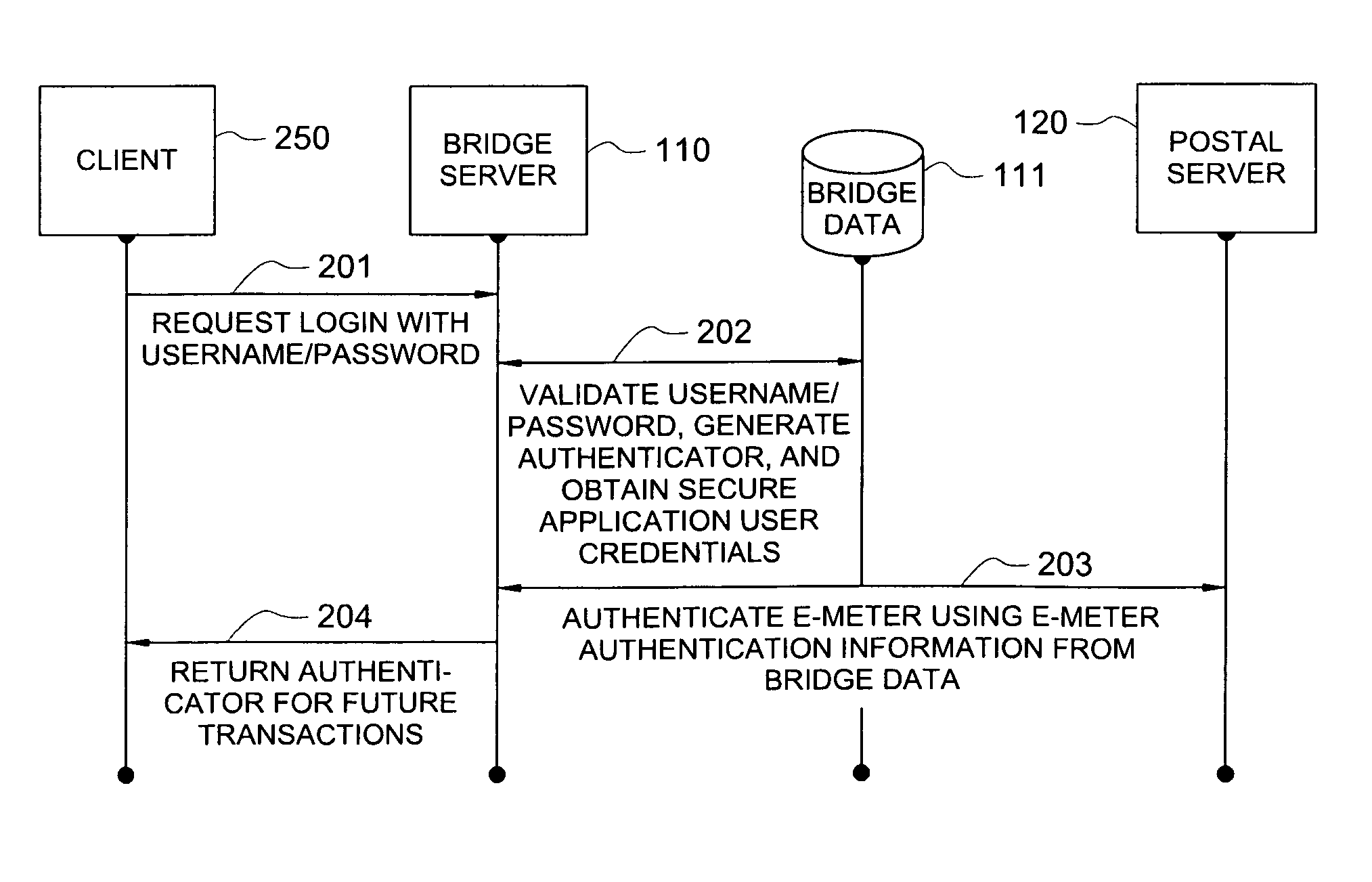
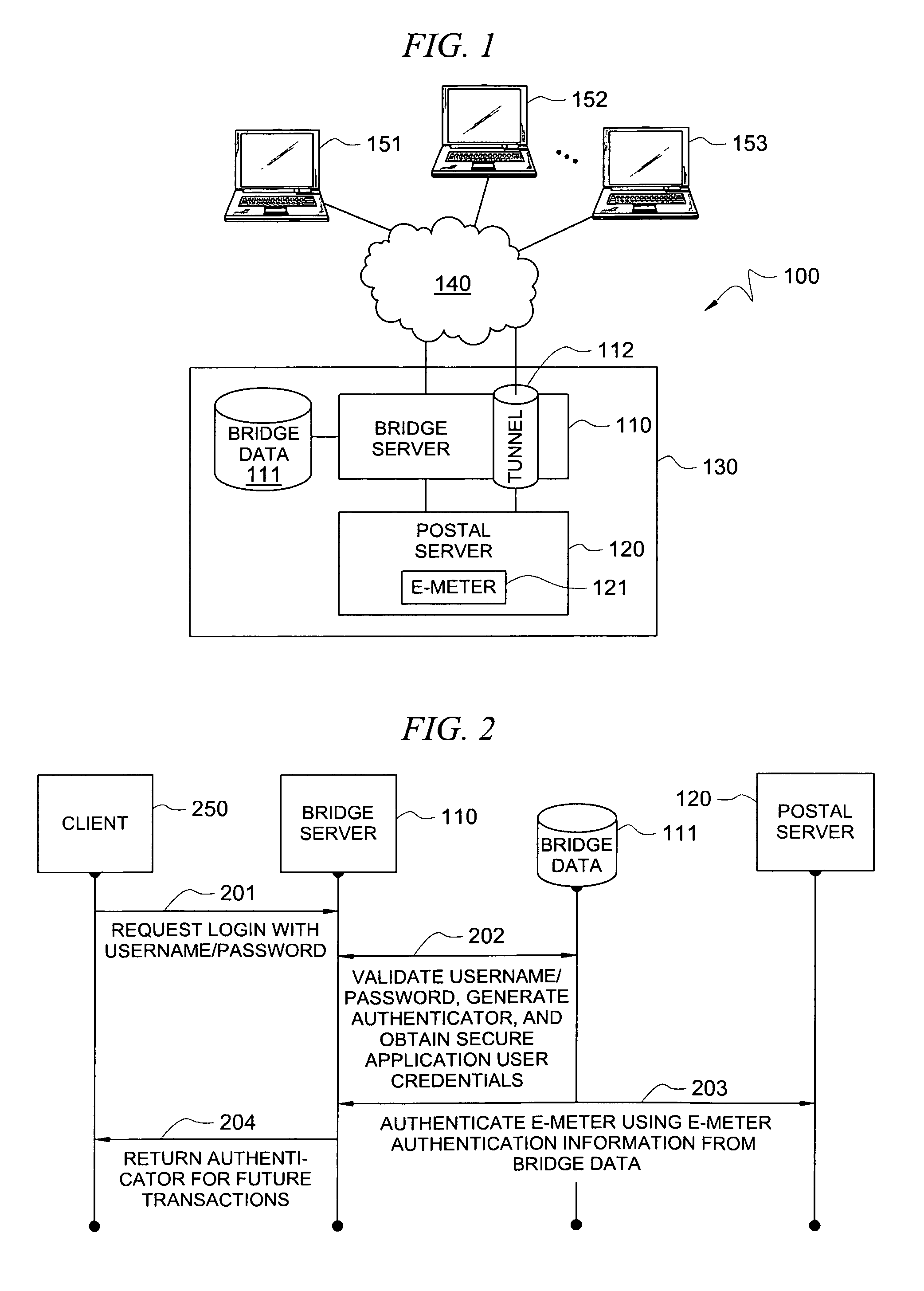
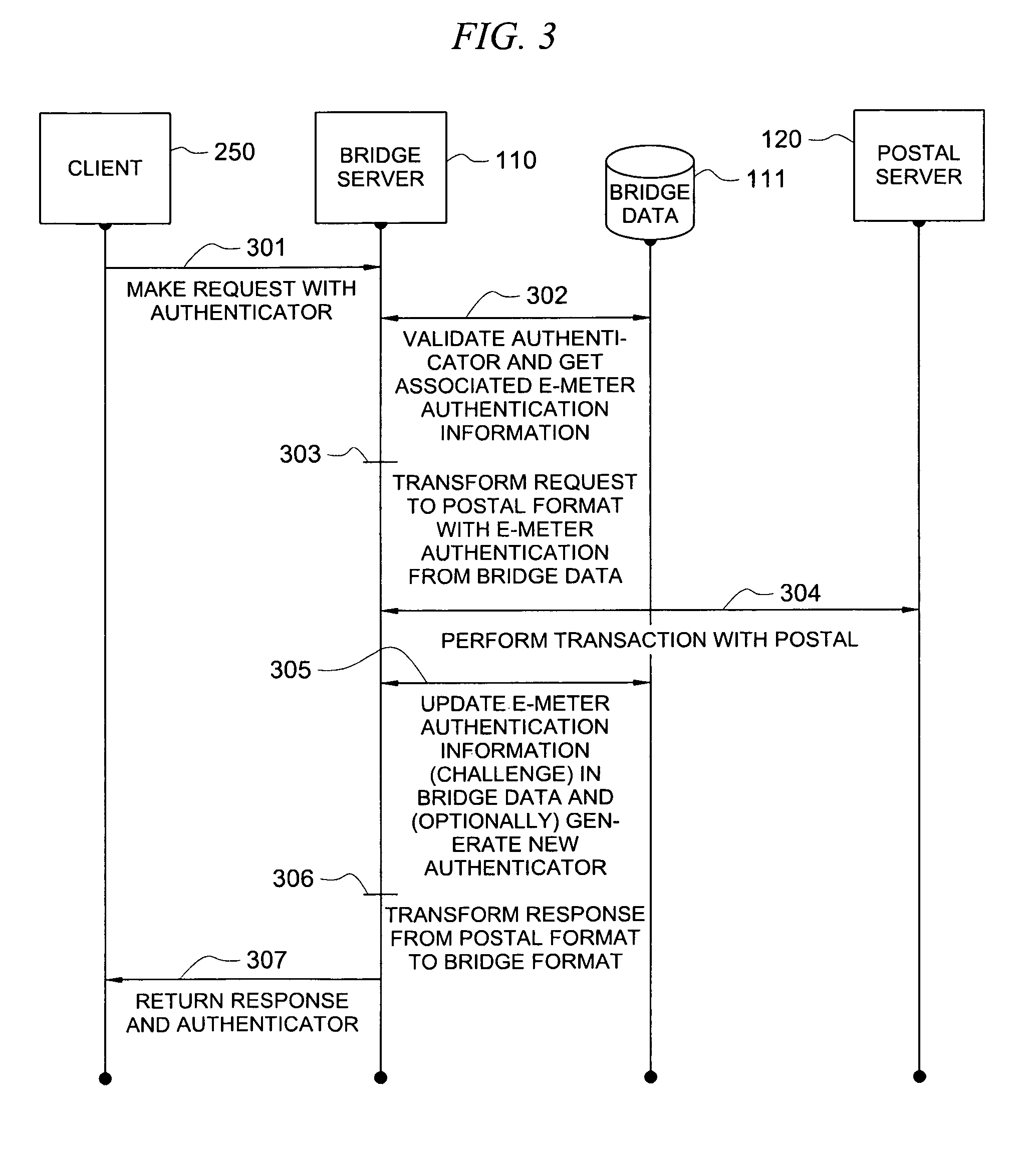
Secure application bridge server
ActiveUS8046823B1Easy to implementConvenient to accommodateDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsApplication serverCryptographic protocol
Systems and methods are provided which implement a bridge server to provide user access to one or more secure applications. A bridge server of embodiments is disposed between a user and a secure application and invokes bridge server security protocols with respect to the user and secure application security protocols with respect to the secure application. In operation according to embodiments, client applications will link into a bridge server, the user will be authenticated by the bridge server, and a valid user will be correlated to an account of the secure application by the bridge server. Bridge servers of embodiments facilitate providing features with respect to secure application user access unavailable using the secure application security protocols.
Owner:AUCTANE INC
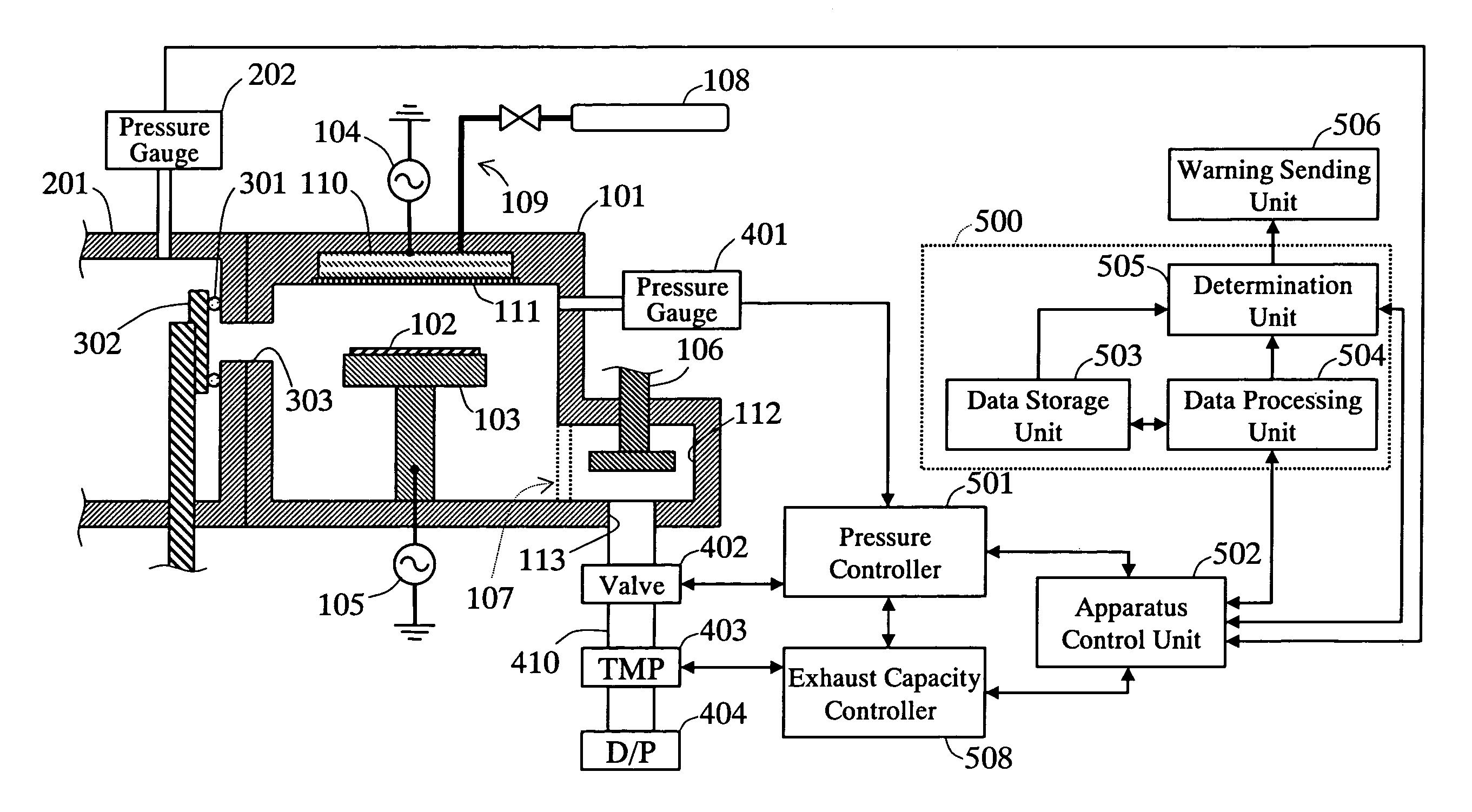
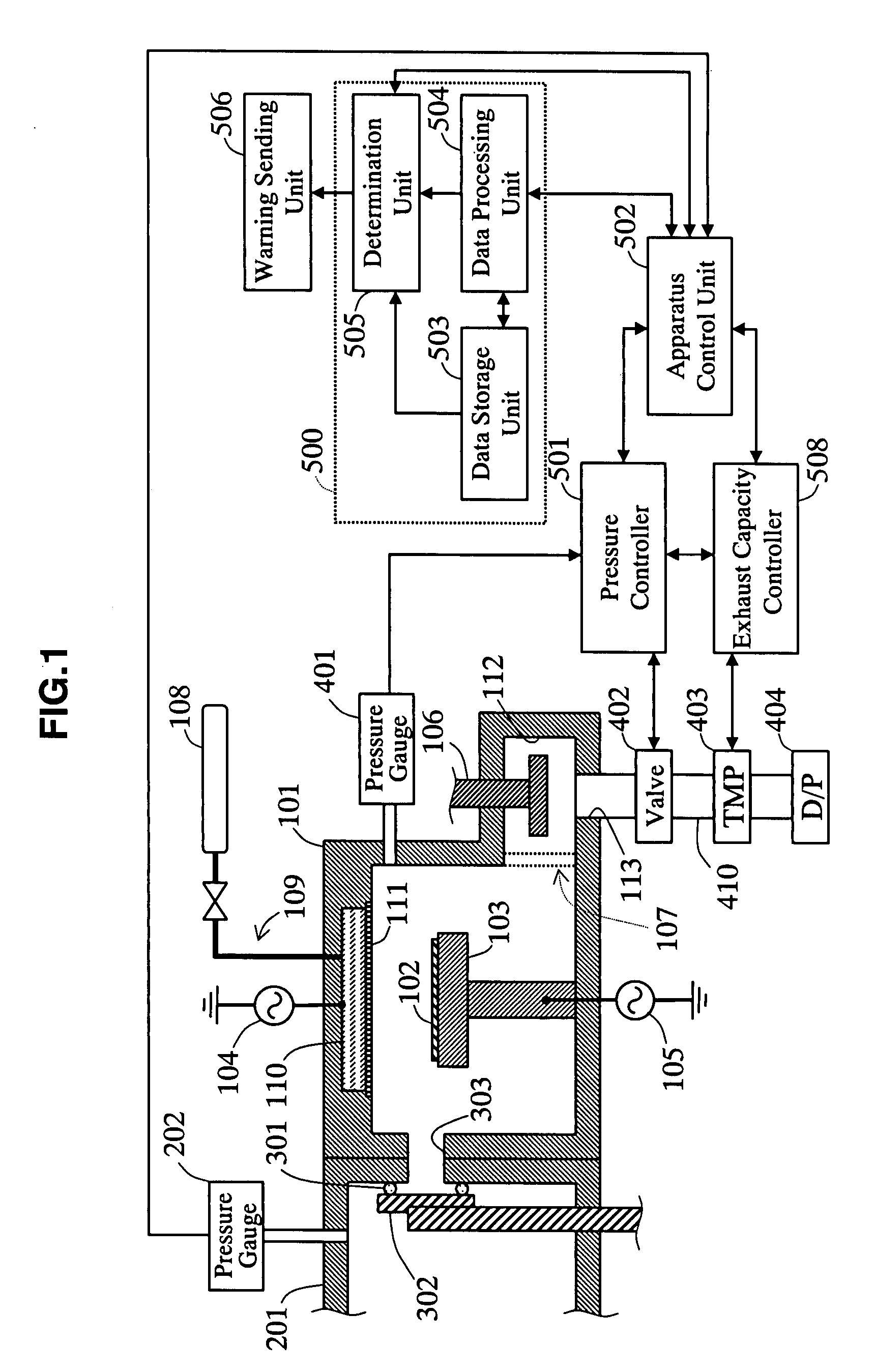
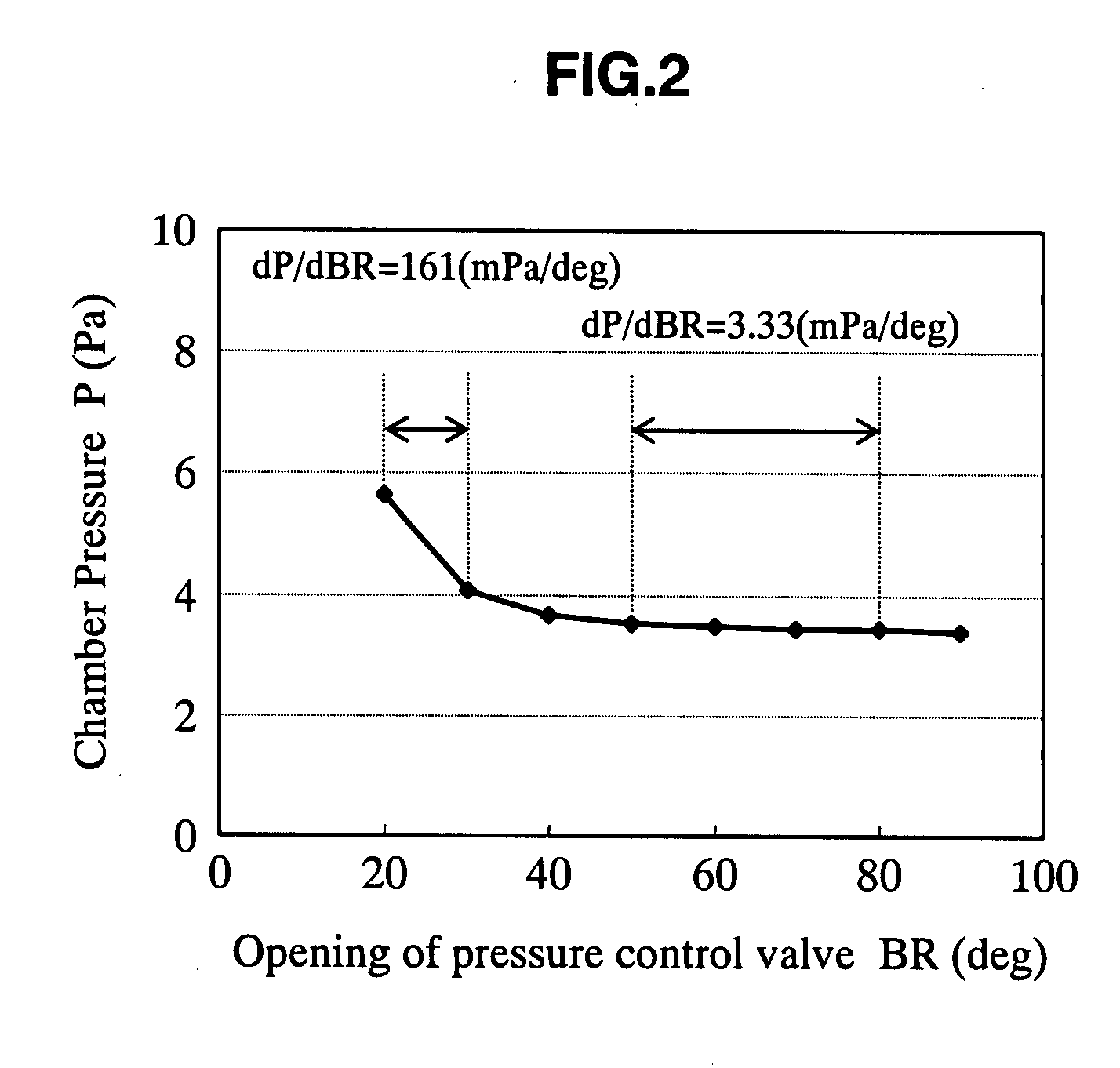
Plasma processing apparatus, method for detecting abnormality of plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
InactiveUS20080067146A1Reliable detectionLess expensiveLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesPlasma processingAirflow
The plasma processing apparatus relating to the present invention is provided with a process chamber, a pressure measuring unit for measuring the pressure inside of the process chamber and a pump for exhausting a gas in the process chamber. A pressure control valve for maintaining the pressure inside of the process chamber to a predetermined pressure by regulating an opening based on a measured value of the pressure measuring unit is provided between the pump and the process chamber. An exhaust capacity controller sets up the exhaust capacity in a state that the variation of the opening of the pressure control valve in response to the pressure fluctuation inside of the process chamber is large. A computing unit detects very small pressure fluctuation based on the variation of the opening of the pressure control valve. In results, enabling reliable detection of a very small gas flow fluctuation and pressure fluctuation by a less expensive method independent of process conditions.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of and apparatus in a filter tipping machine for manipulating a web
InactiveUS6229115B1More reliableLess expensiveCigarette manufactureLaser beam welding apparatusFiberAdhesive
A running web of tipping paper (one side of which is coated with a film of adhesive) in a filter cigarette making machine is subdivided into discrete uniting bands and / or is perforated by resorting to a single source or to two discrete sources of coherent radiation. Each source is associated with a control unit which initiates the emission of short-lasting flashes of coherent radiation. Such radiation is caused to impinge upon a diffractive focusing lens which focuses coherent radiation upon one or more masks having openings for coherent radiation which is to sever the web along transversely extending linear zones and / or to provide the web with desired arrays of perforations. The perforations permit atmospheric air to enter the column of tobacco smoke in a filter cigarette wherein the tobacco-containing portion and the filter mouthpiece are united by a perforated adhesive-coated uniting band.
Owner:HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG
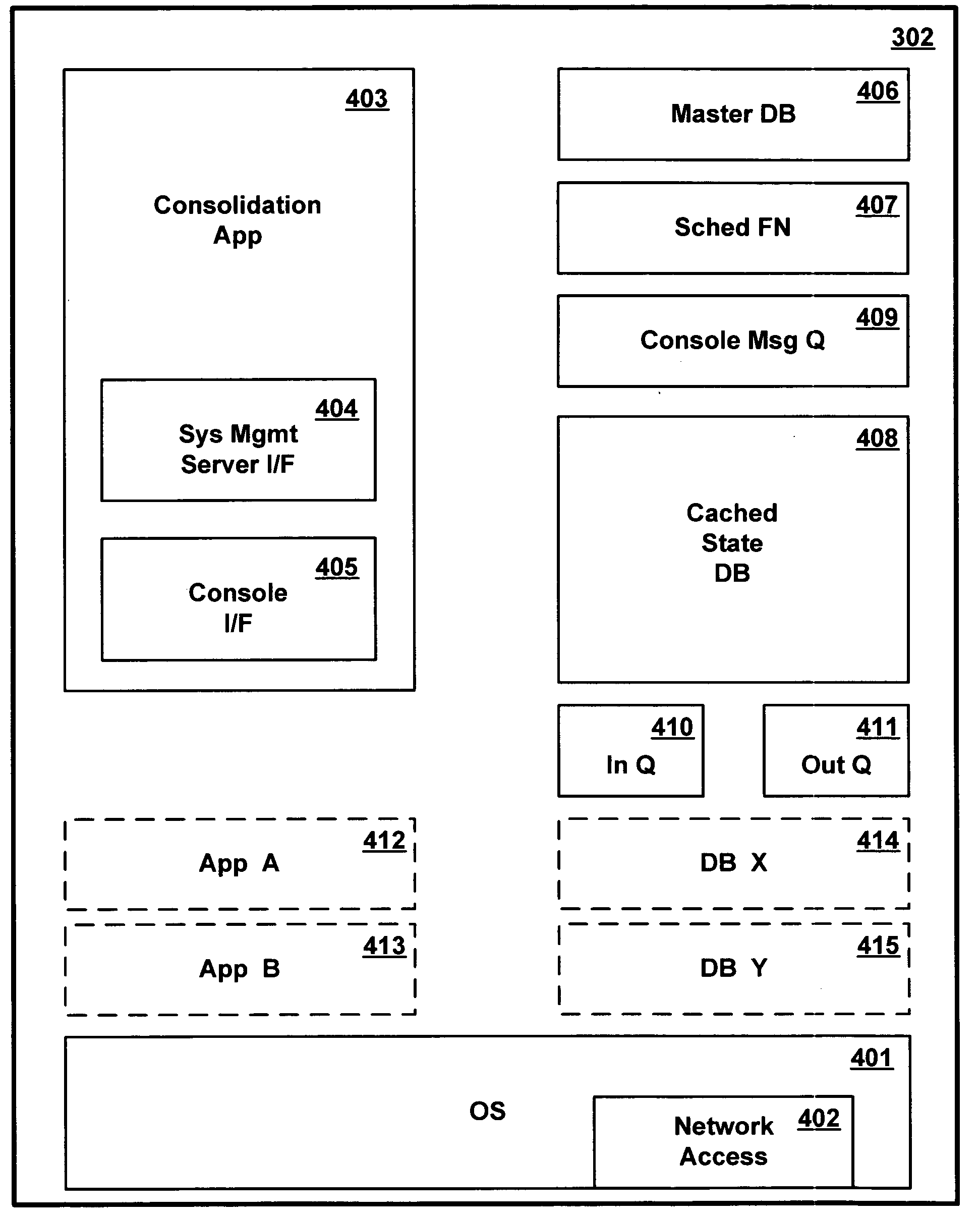
Method and apparatus for managing multiple data processing systems using existing heterogeneous systems management software
InactiveUS20050102683A1Less expensiveMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsPublic interfaceData processing system
A common consolidation management application provides an interface to the multiple different system management software applications and at least one user input console. An adapter in each of the system management software applications supports communication with the consolidation application. A system administrator issues requests to different system management software applications using a common interface provided by the consolidation application. The consolidation application can be installed over an existing complex of computer systems managed by different management applications, without modifying the managed systems or replacing the management applications.
Owner:IBM CORP
Touch panel display system with illumination and detection provided from a single edge
InactiveUS20050248540A1Accurately detect user 's touchEasy to operateCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsTriangulationTouch panel
A touch panel that has a front surface, a rear surface, a plurality of edges and an interior volume. An energy source is positioned in proximity to a first edge of the touch panel and is configured to emit energy that is propagated within the interior volume of the touch panel. A diffusing reflector is positioned in proximity to the front surface of the touch panel for diffusively reflecting at least a portion of the energy that escapes from the interior volume. At least one detector is positioned in proximity to the first edge of the touch panel and is configured to detect intensity levels of the energy that is diffusively reflected across the front surface of the touch panel. Preferably, two detectors are spaced apart from each other in proximity to the first edge of the touch panel, to allow calculation of touch locations using simple triangulation techniques.
Owner:SMART TECH INC (CA)
Substrate lift mechanism and reactor including same
ActiveUS20190051555A1Easy to maintain and process substrateReduce amount of timeElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSusceptor
A substrate support assembly suitable for use in a reactor including a common processing and substrate transfer region is disclosed. The substrate support assembly includes a susceptor and one or more lift pins that can be used to lower a substrate onto a surface of the susceptor and raise the substrate from the surface, to allow transfer of the substrate from the processing region, without raising or lowering the susceptor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Combined lancet and electrochemical analyte-testing apparatus
InactiveUS20050011759A1Easy to takeReduces and eliminates disposal issueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTissue fluidDisplay device
An apparatus for detection and quantitation of an electrochemically-detectable analyte, such as glucose, in blood or interstitial fluid includes a meter unit, a lancet and an electrochemical sensor. Of these components, the meter is preferably reusable, while the lancet and the electrochemical sensor are preferably incorporated in assemblies intended for single-use. The meter unit has a housing, within which a lancet is engaged with a mechanism for moving then lancet; a connector disposed within the housing for engaging an electrochemical sensor specific for the analyte and transmitting a signal indicative of the amount of analyte, and a display operatively-associated with a connector for displaying the amount of the analyte to user. The electrochemical sensor is adapted for detection of a particular analyte. In addition, the electrochemical sensor has an absorptive member for uptake of a sample of blood or interstitial fluid. In one version, the lancet moves from a initial position to a piercing position in which skin of the user is pierced and optionally back to a retracted position. The electrochemical sensor is disposed such that the absorptive member takes up a sample from the pierced skin of the user when it is pierced by the lancet without movement of the apparatus. In an alternative version, the lancet is a hollow cannula through which blood or interstitial fluid is transported from the puncture site to an absorbent portion of the electrochemical sensor. In either version, the apparatus provides single-step operation in which sample acquisition and analysis occur as a result of the single action of pressing, the apparatus against the users skin.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Wireless server based text to speech email
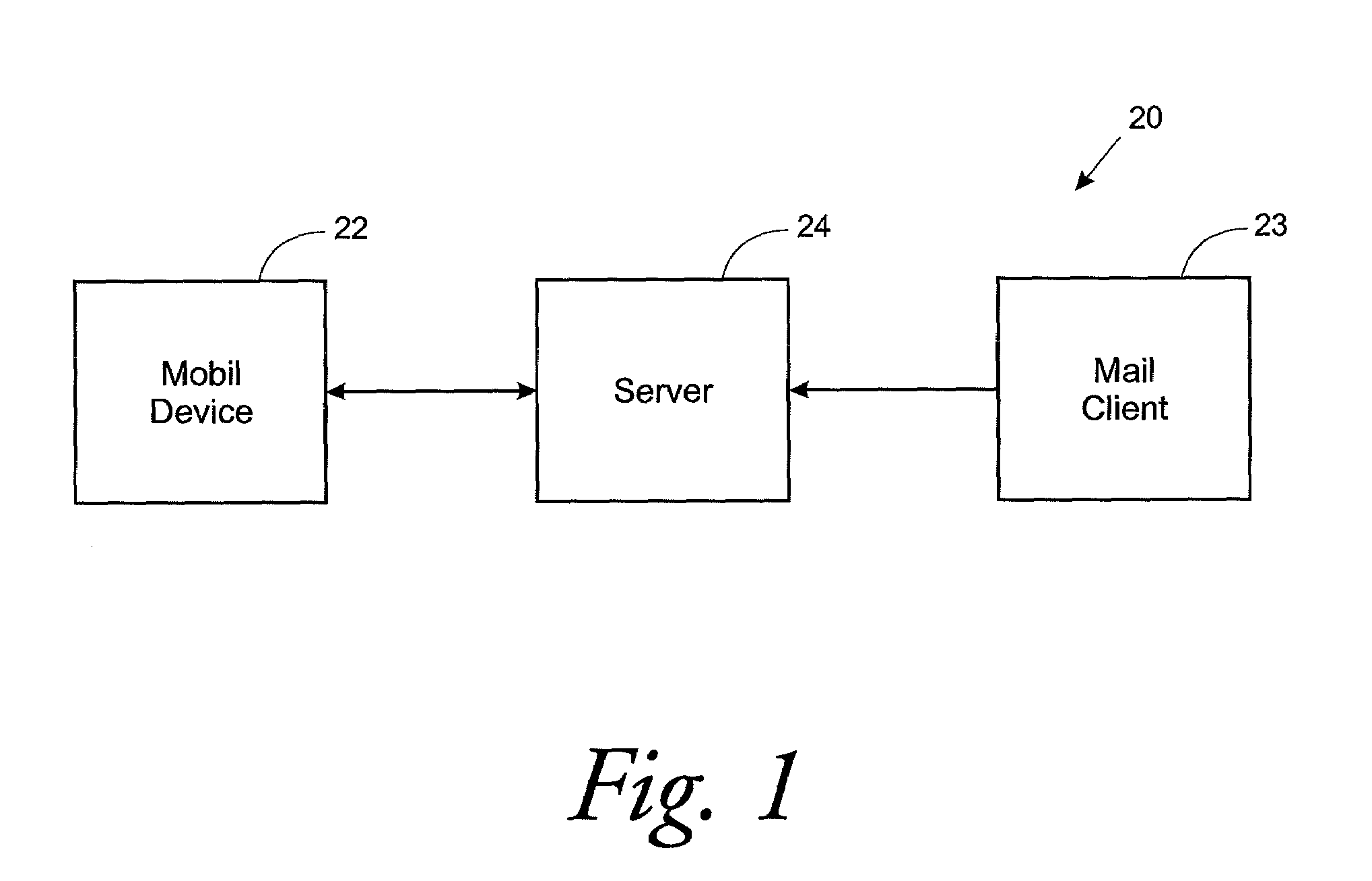
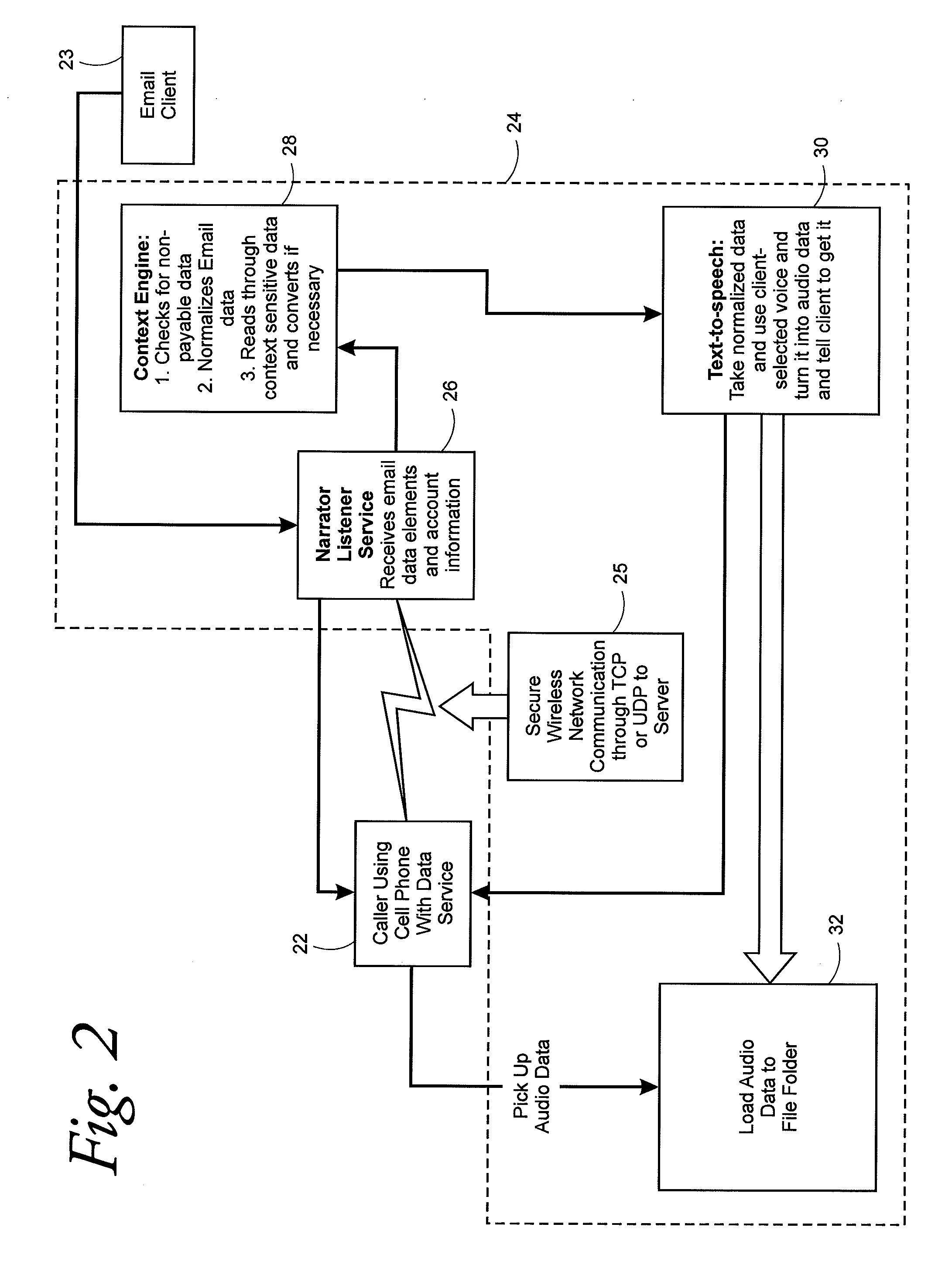
ActiveUS20080262846A1Function increaseLess complicatedInformation formatContent conversionMobile deviceCellular telephone
An email system for mobile devices, such as cellular phones and PDAs, is disclosed which allows email messages to be played back on the mobile device as voice messages on demand by way of a media player, thus eliminating the need for a unified messaging system. Email messages are received by the mobile device in a known manner. In accordance with an important aspect of the invention, the email messages are identified by the mobile device as they are received. After the message is identified, the mobile device sends the email message in text format to a server for conversion to speech or voice format. After the message is converted to speech format, the server sends the messages back to the user's mobile device and notifies the user of the email message and then plays the message back to the user through a media player upon demand.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Lanthanide-based catalyst composition for producing cis-1,4-polydienes
InactiveUS7008899B2Easy to processHigh viscosityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystLanthanide
A catalyst composition that is the combination of or the reaction product of ingredients comprising (a) a lanthanide compound, (b) an organoaluminum hydride, and (c) a tin halide compound.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Integrated semiconductor circuits on photo-active Germanium substrates
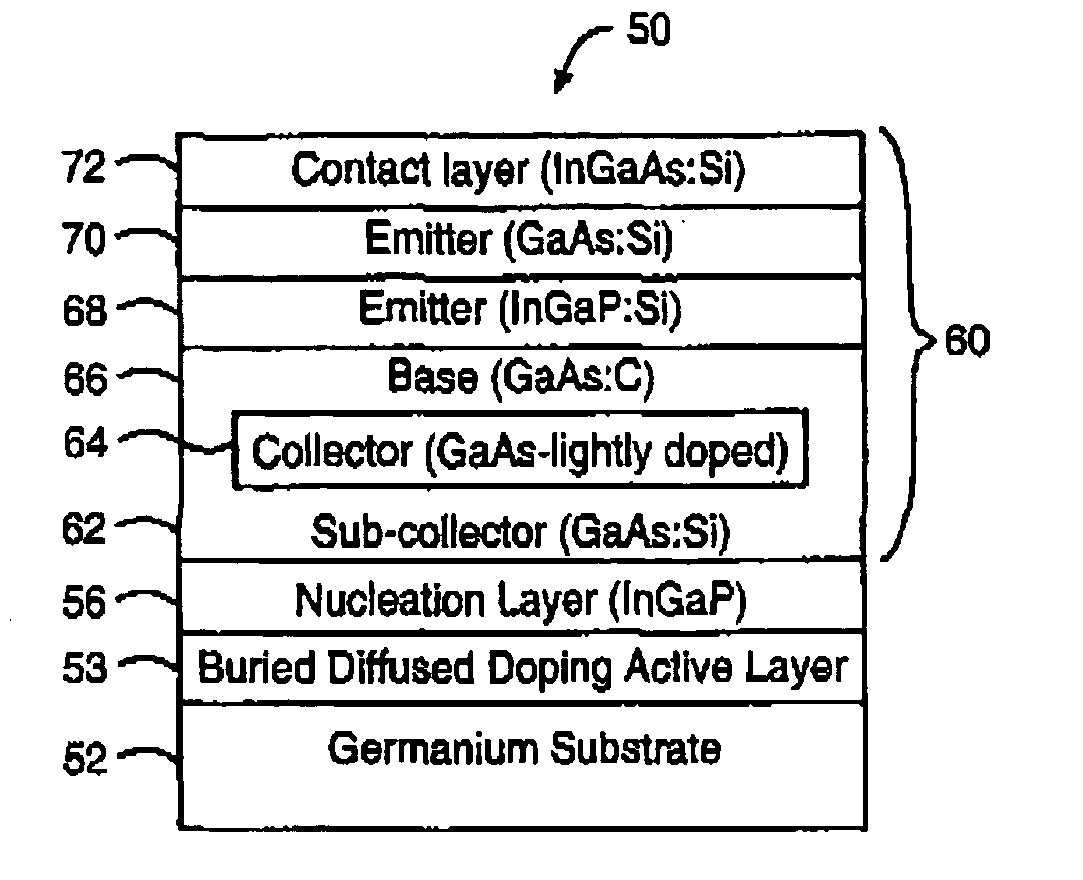
InactiveUS20050110041A1Less expensiveSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A semiconductor device having at least one layer of a group III-V semiconductor material epitaxially deposited on a group III-V nucleation layer adjacent to a germanium substrate. By introducing electrical contacts on one or more layers of the semiconductor device, various optoelectronic and microelectronic circuits may be formed on the semiconductor device having similar quality to conventional group III-V substrates at a substantial cost savings. Alternatively, an active germanium device layer having electrical contacts may be introduced to a portion of the germanium substrate to form an optoelectronic integrated circuit or a dual optoelectronic and microelectronic device on a germanium substrate depending on whether the electrical contacts are coupled with electrical contacts on the germanium substrate and epitaxial layers, thereby increase the functionality of the semiconductor devices.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Enamel coated bullet, method of making an enamel coated bullet
ActiveUS9254503B2Reduces barrel depositsLess expensiveAmmunition projectilesLiquid surface applicatorsSufficient timeLacquer thinner
Owner:WARD TYLER
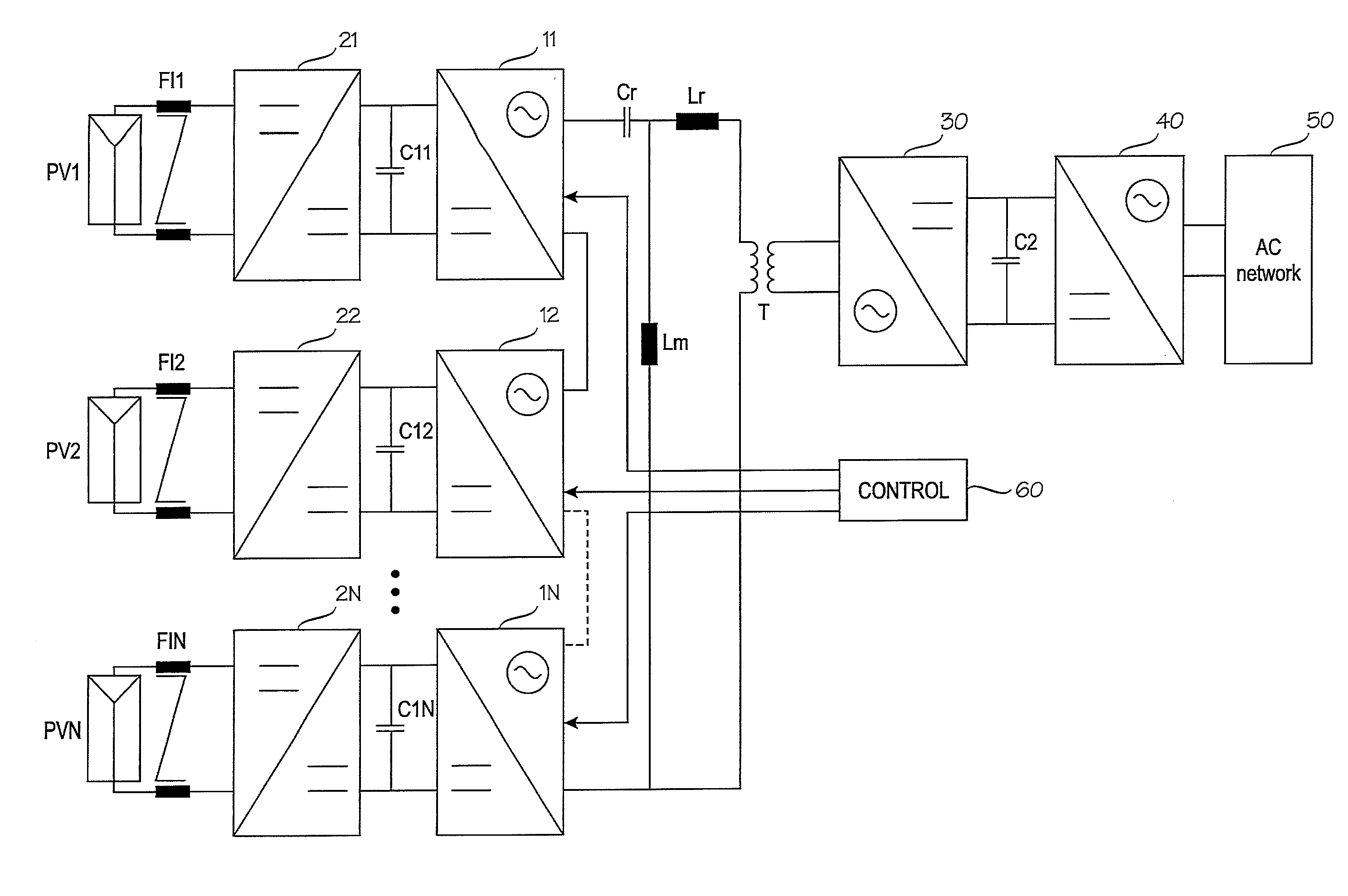
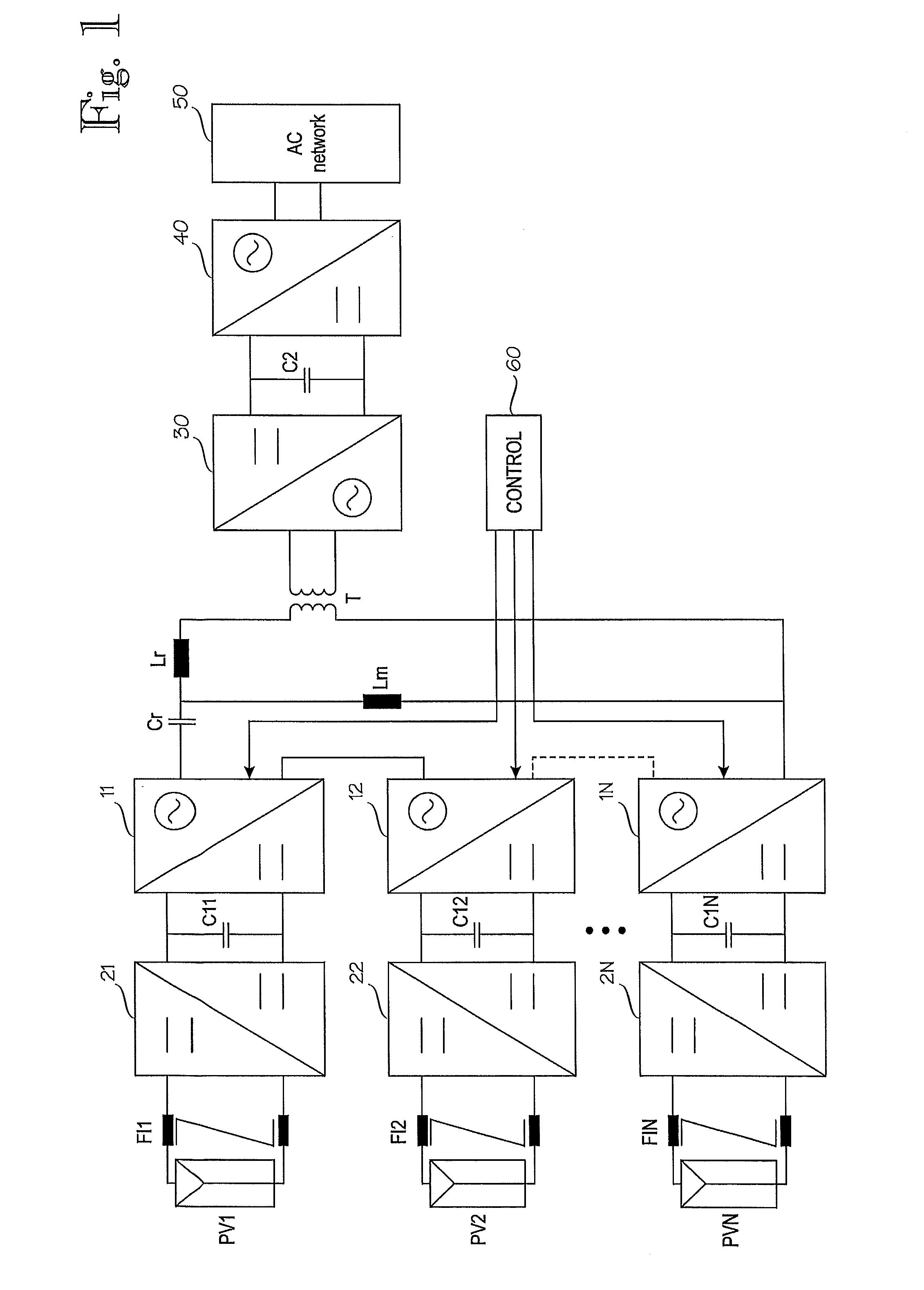
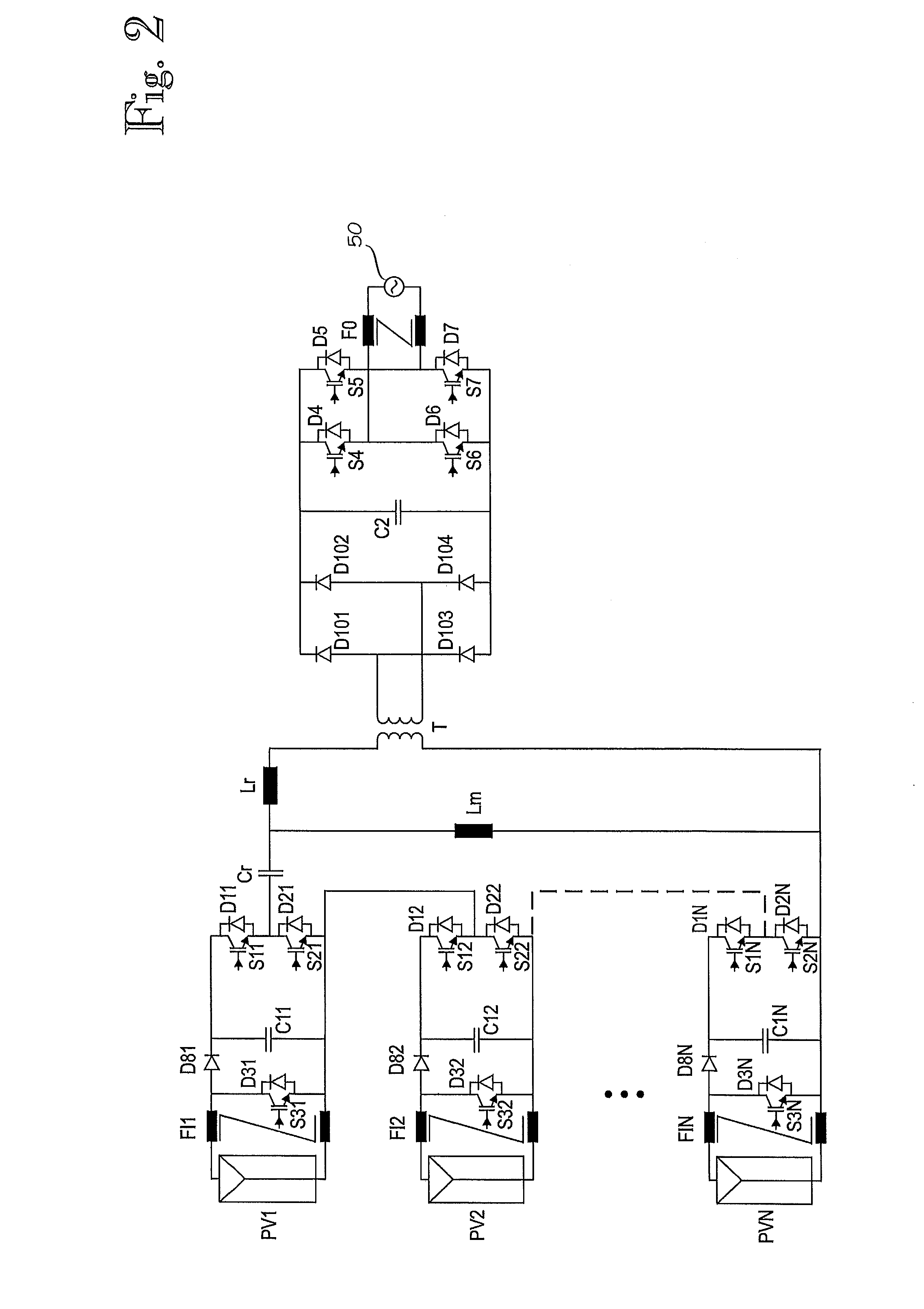
Method for controlling single-phase dc/ac converters and converter arrangement
ActiveUS20100244575A1More compactLess expensiveDc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationTransverterControl theory
A method is disclosed for controlling single-phase DC / AC converters, along with a converter arrangement having at least two single-phase DC / AC converters. A controller is provided which can control the at least two single-phase DC / AC converters, and an isolation transformer, wherein outputs of the at least two single-phase DC / AC converters are cascade-connected with each other and an input of the isolation transformer. The controller is configured to control the at least two single-phase DC / AC converters to deliver power from their inputs to their outputs by turns.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Wireless architecture and support for process control systems
InactiveUS20050276233A1Easy to changeEasy to configureNetwork topologiesElectric testing/monitoringCommunication AnalysisTelecommunications
A wireless communication system for use in a process environment uses mesh and possibly a combination of mesh and point-to-point communications to produce a wireless communication network that can be easily set up, configured, changed and monitored, thereby making a wireless communication network that is less expensive, and more robust and reliable. The wireless communication system allows virtual communication paths to be established and used within the process control system in a manner that is independent of the manner in which the wireless signals are sent between different wireless transmitting and receiving devices within the process plant, to thereby operate in a manner that is independent of the specific messages or virtual communication paths within the process plant. Still further, communication analysis tools are provided to enable a user or operator to view the operation of the wireless communication network to thereby analyze the ongoing operation of the wireless communications within the wireless communication network.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com