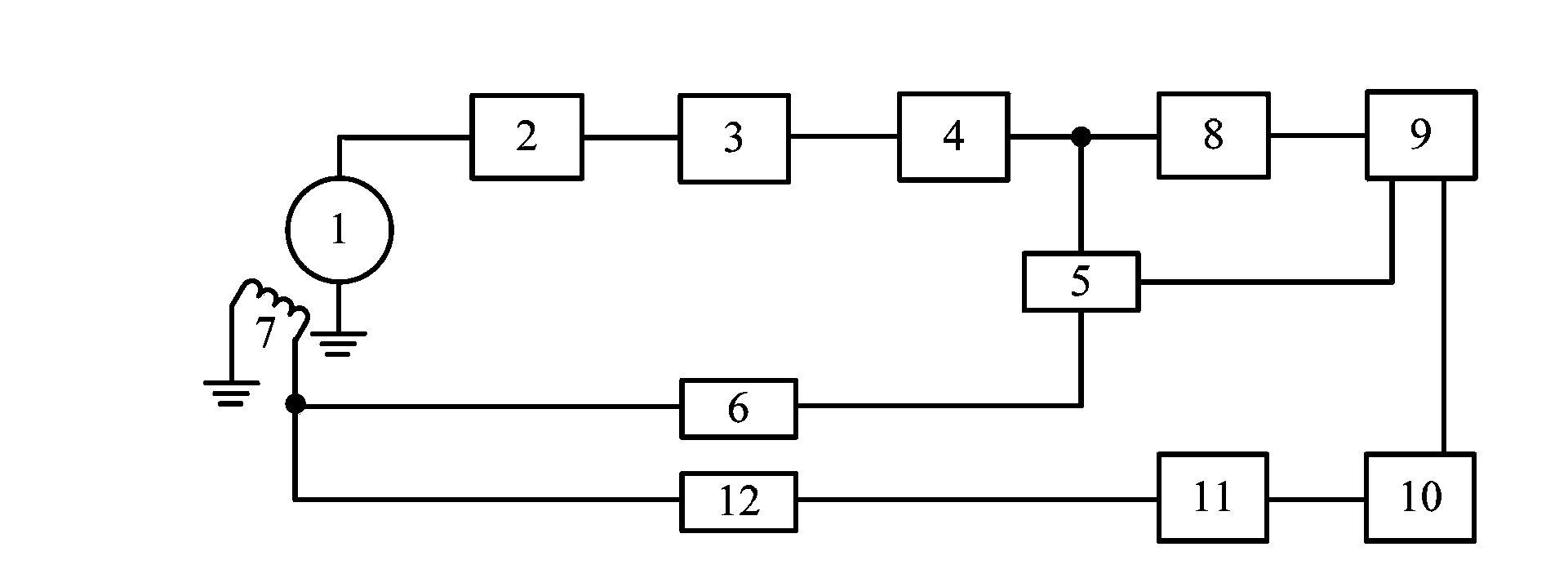
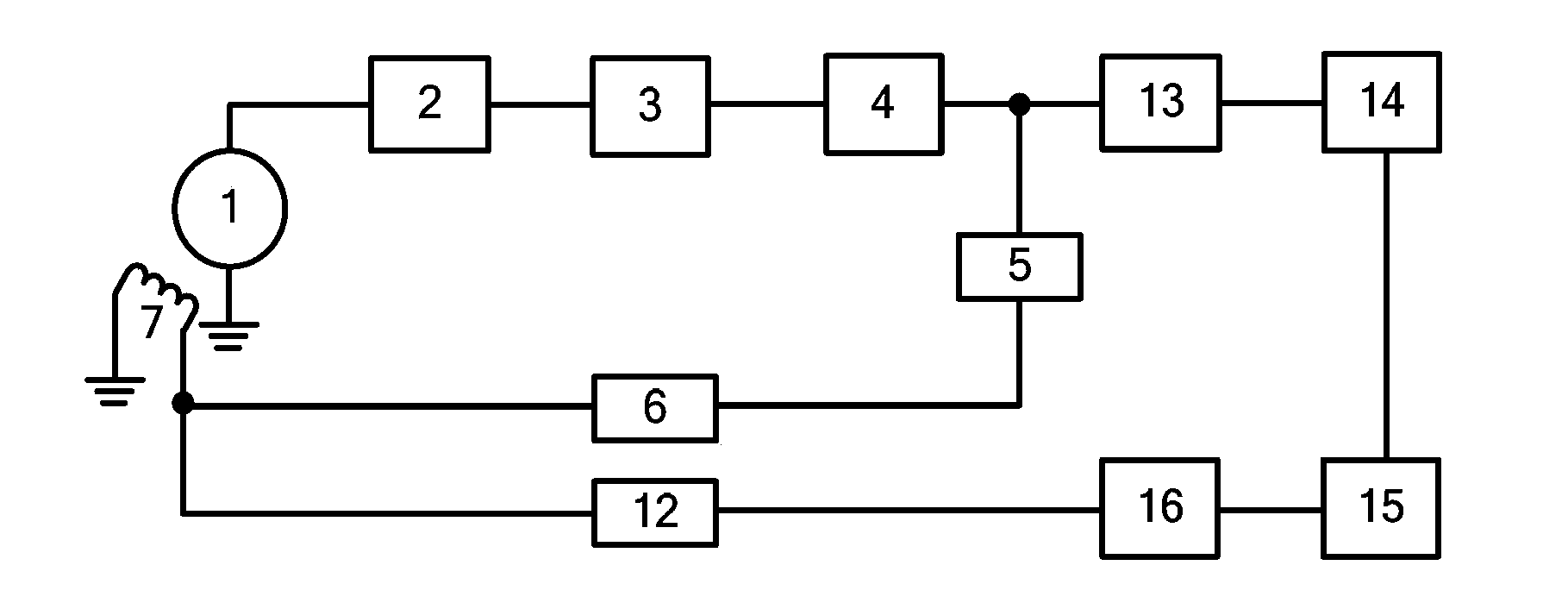
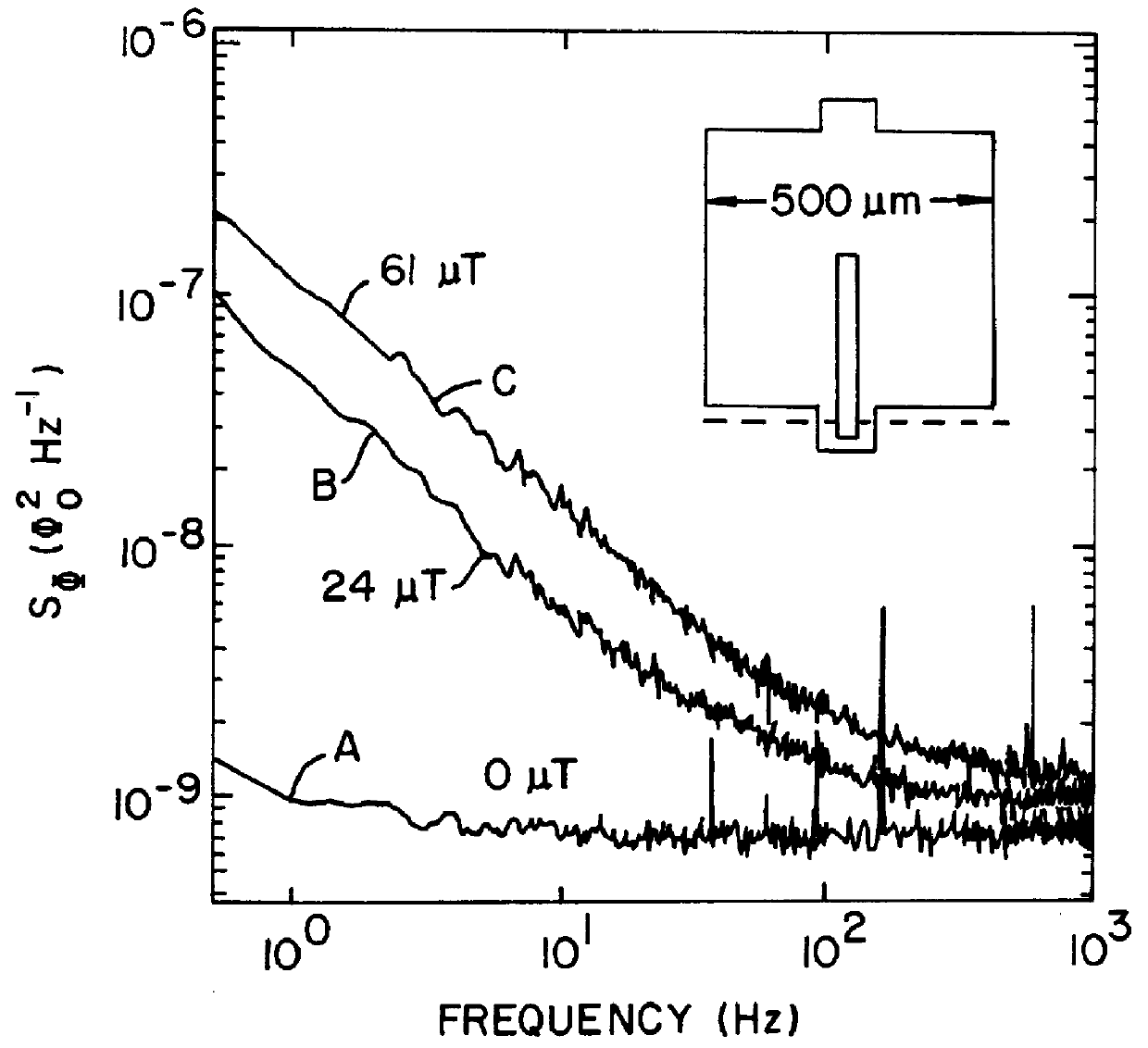
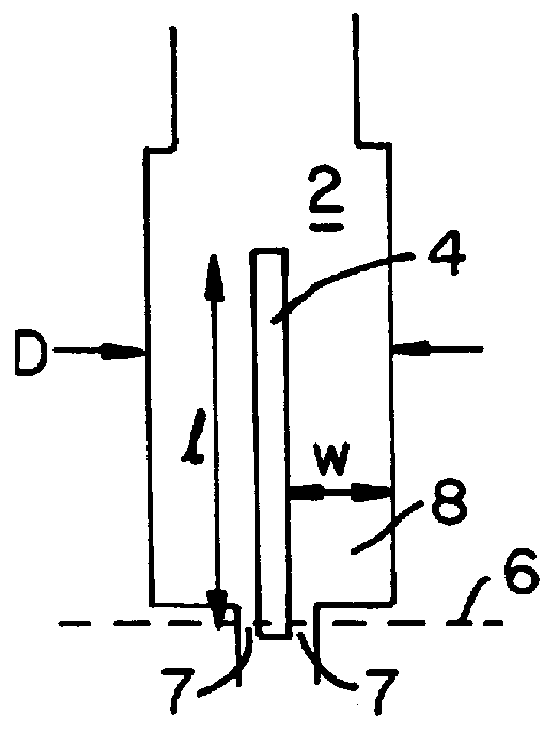
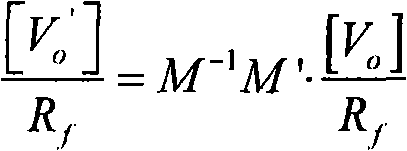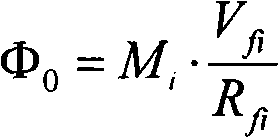Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
472results about "Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
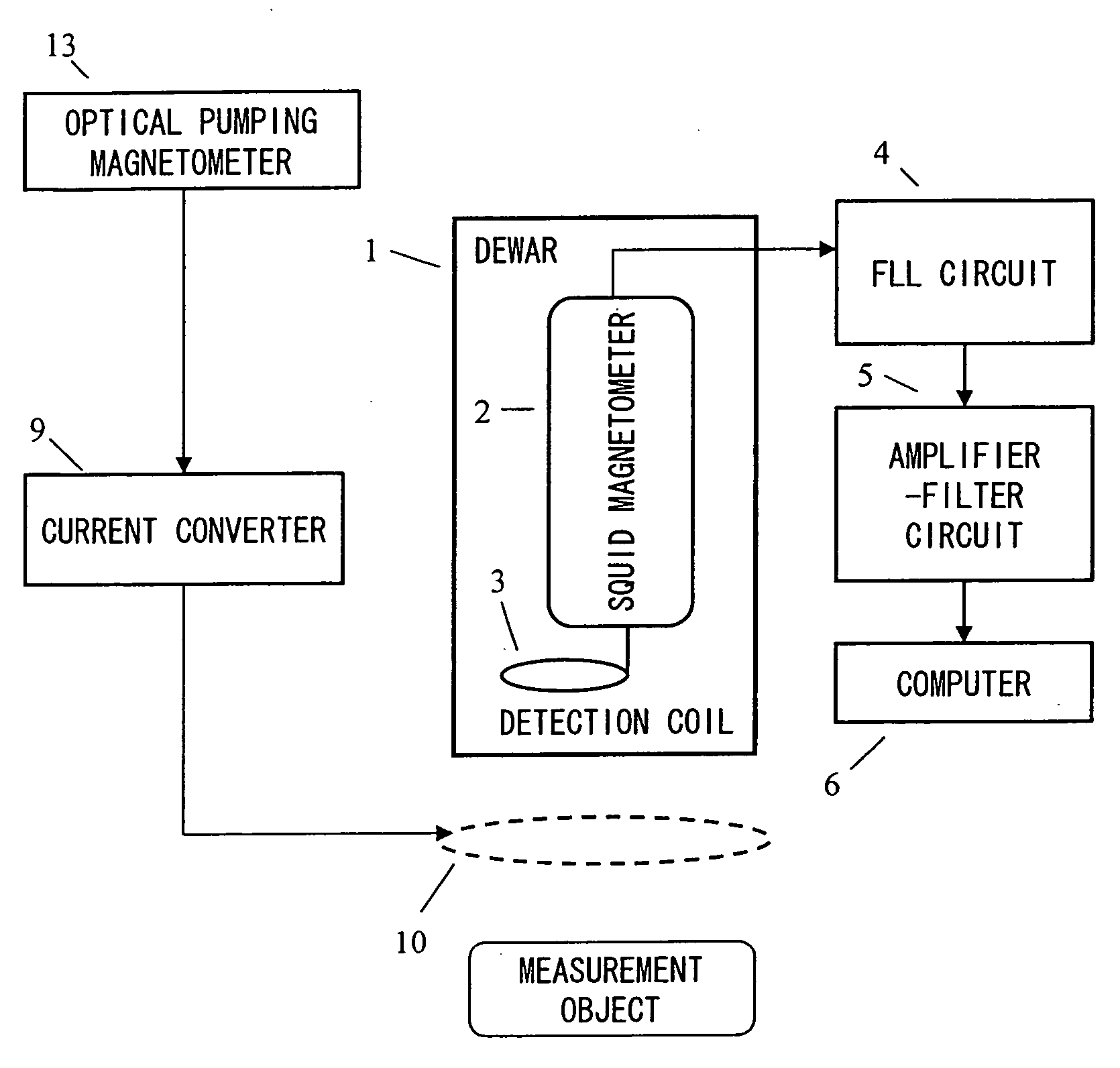
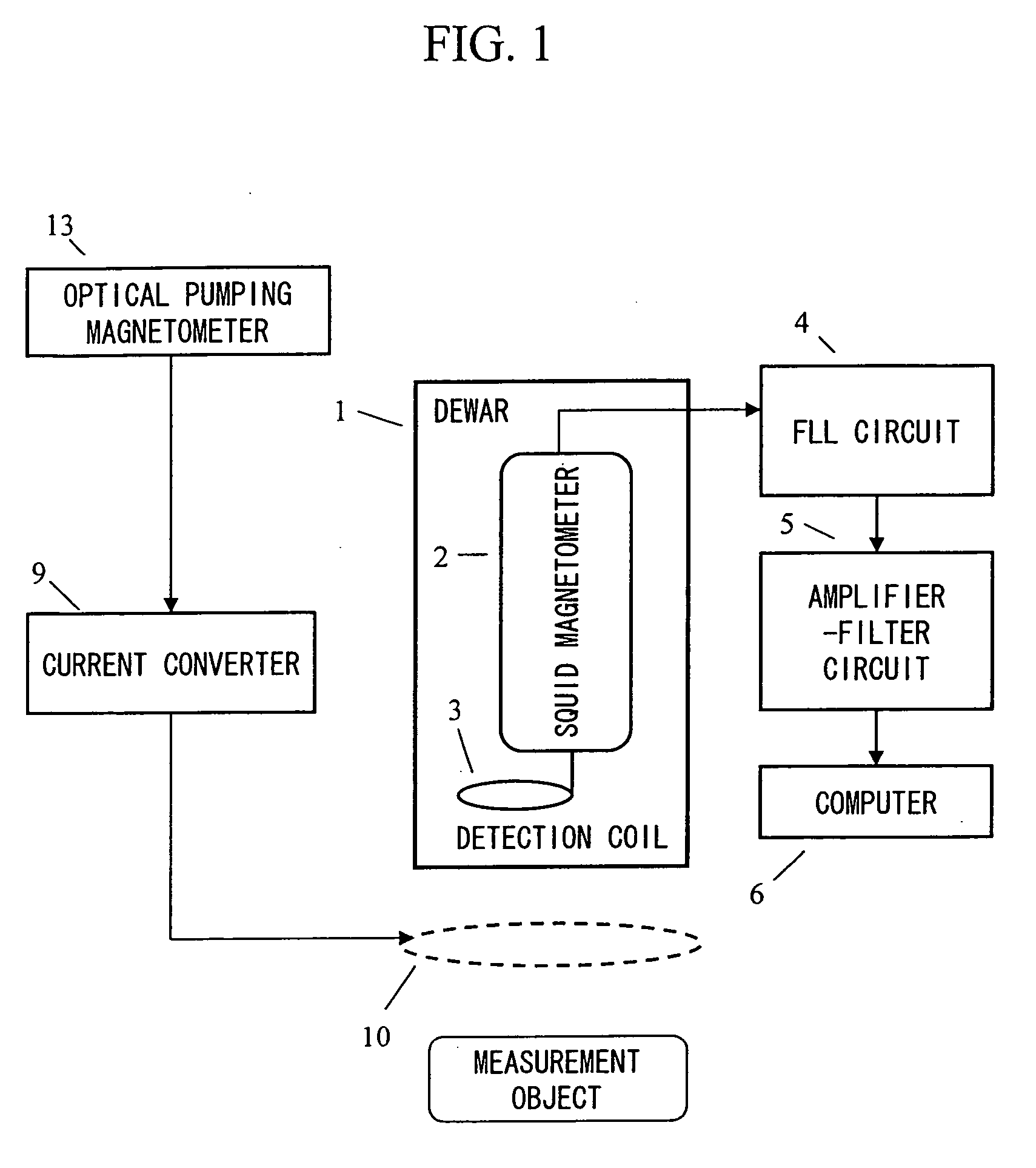
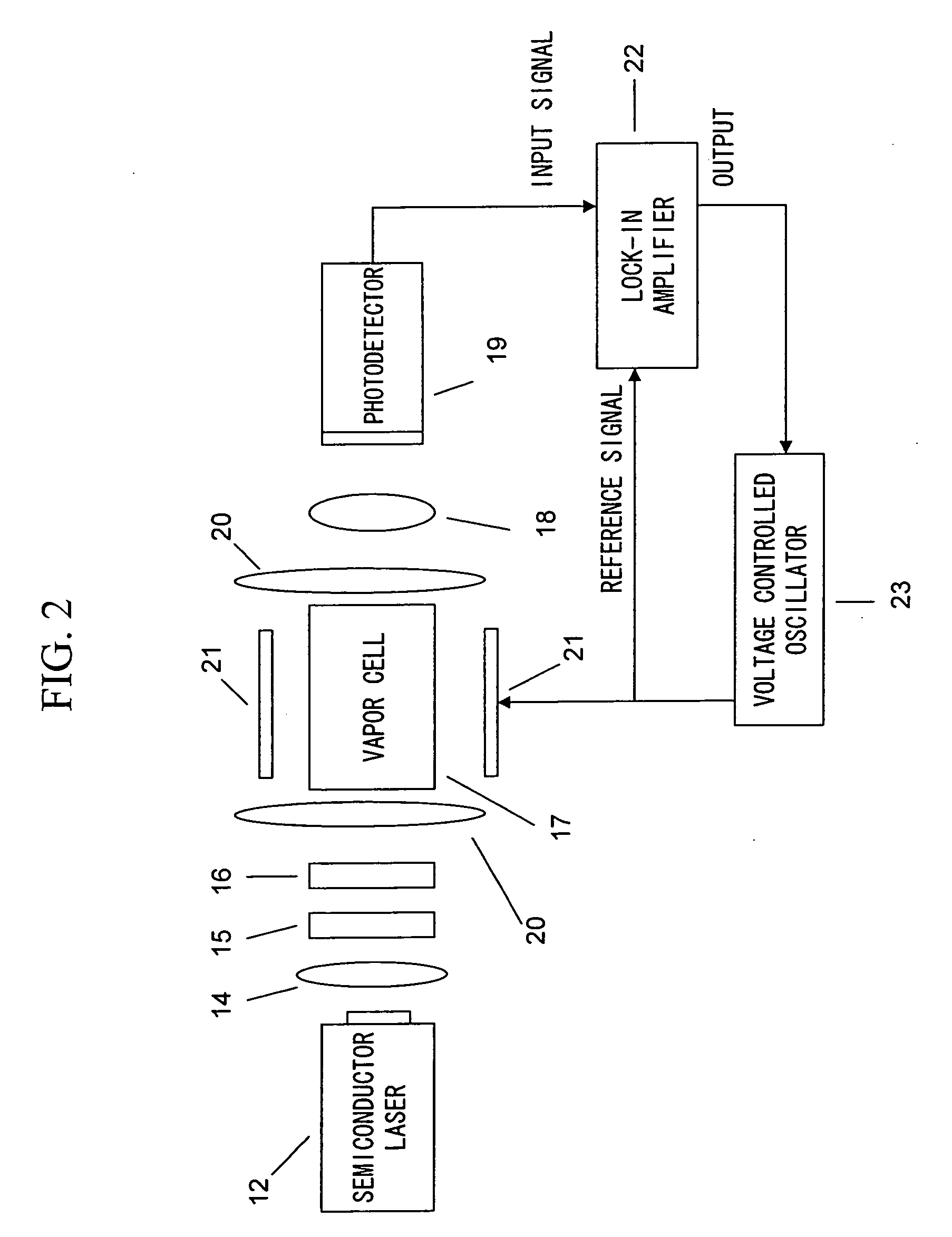
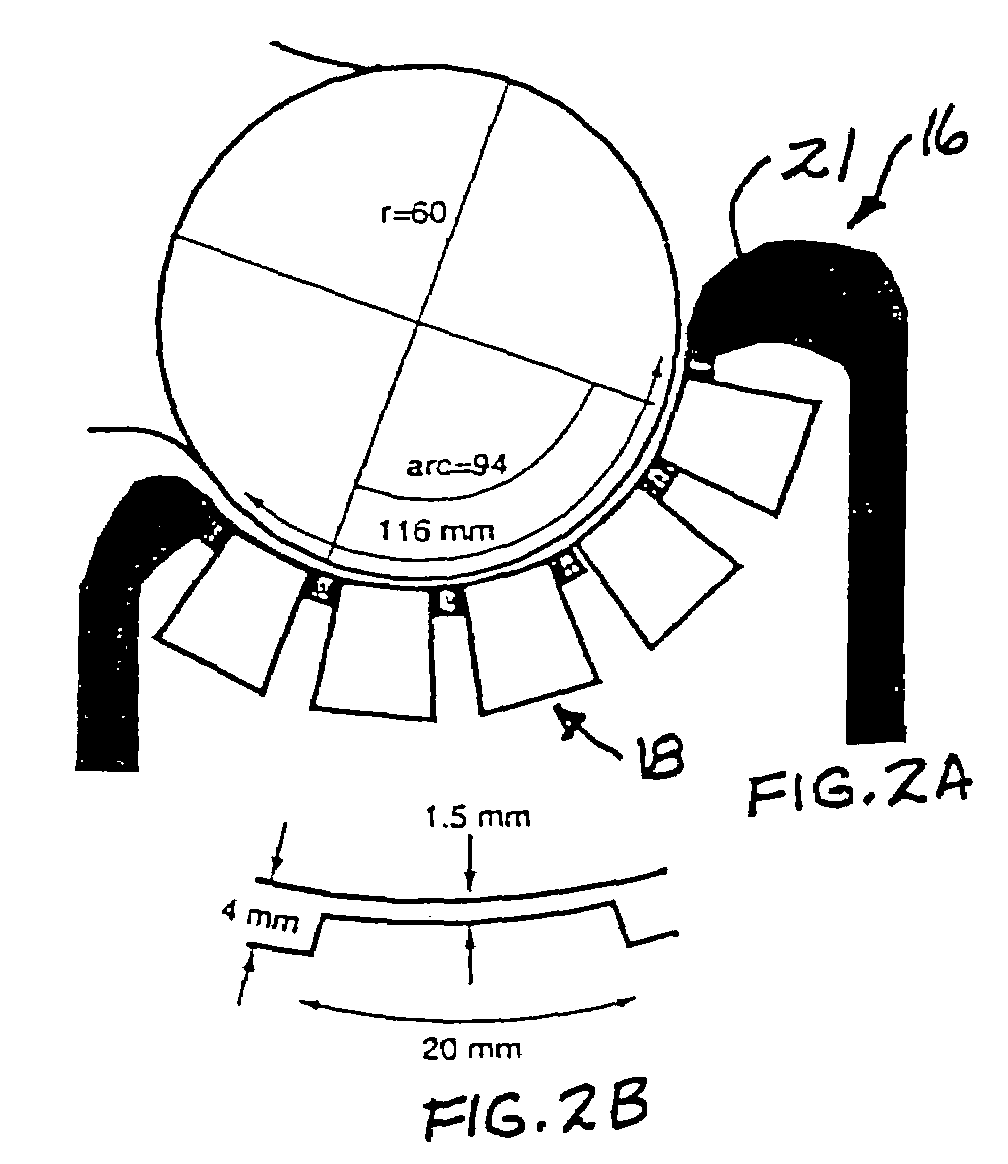
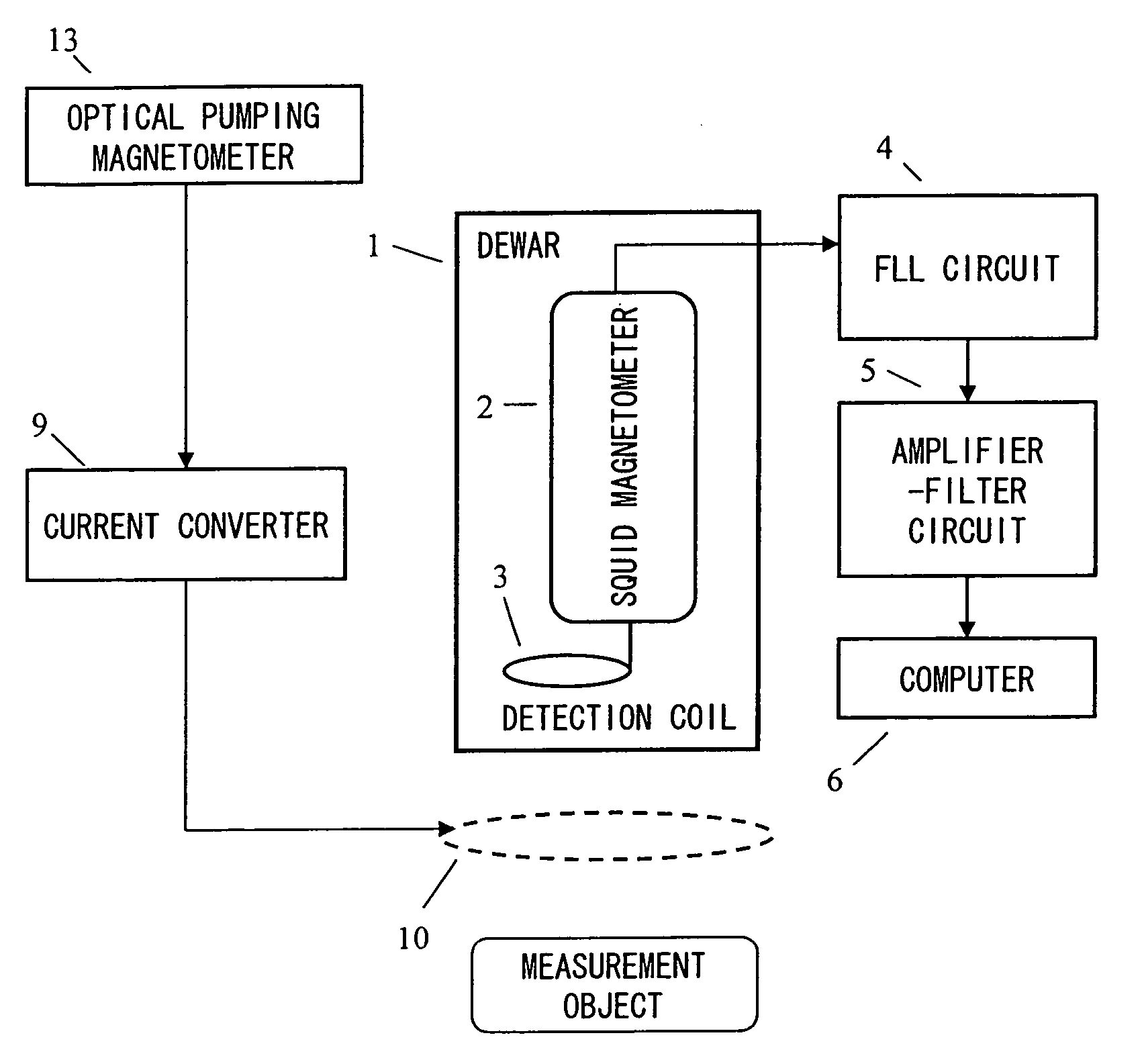
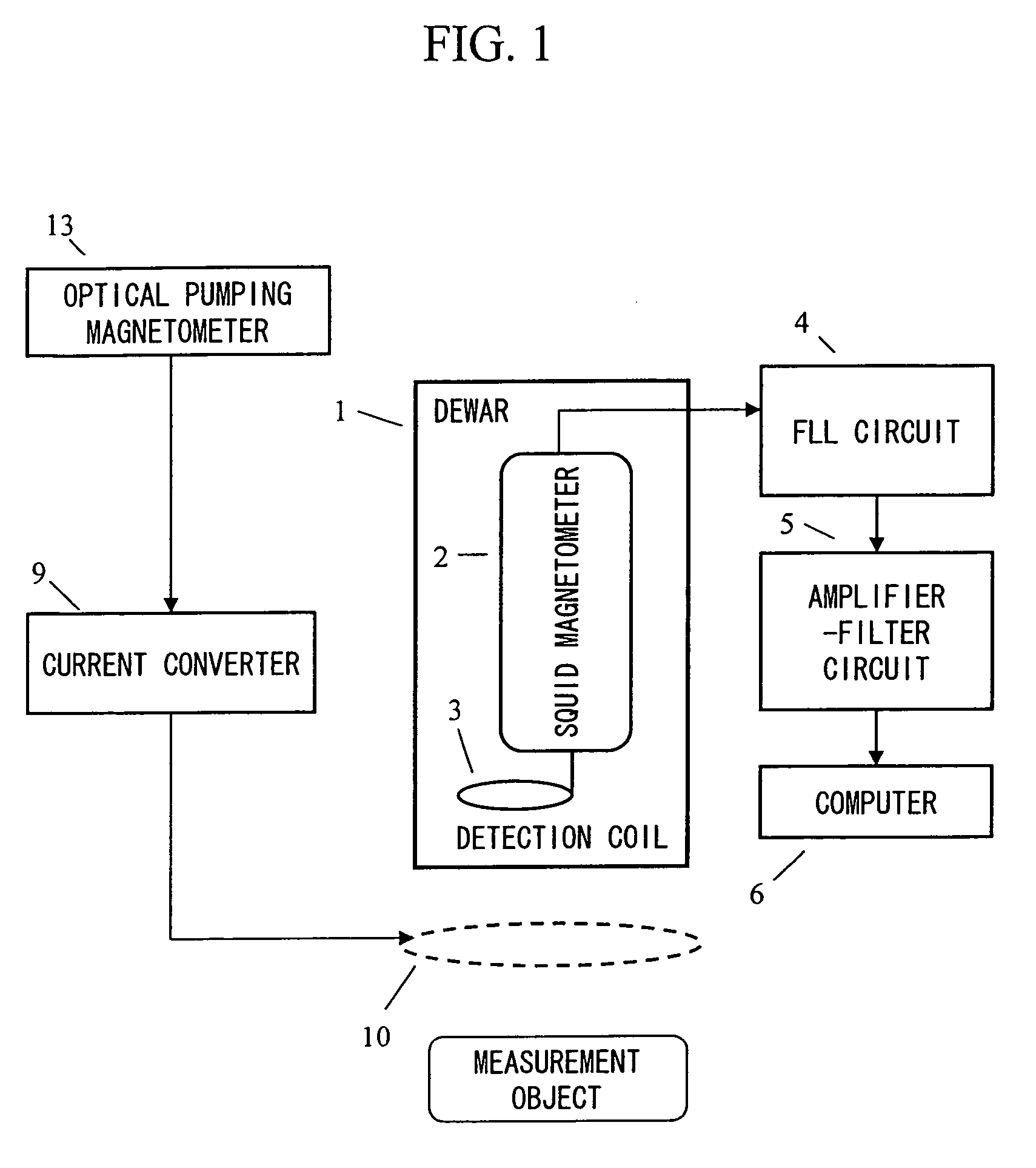
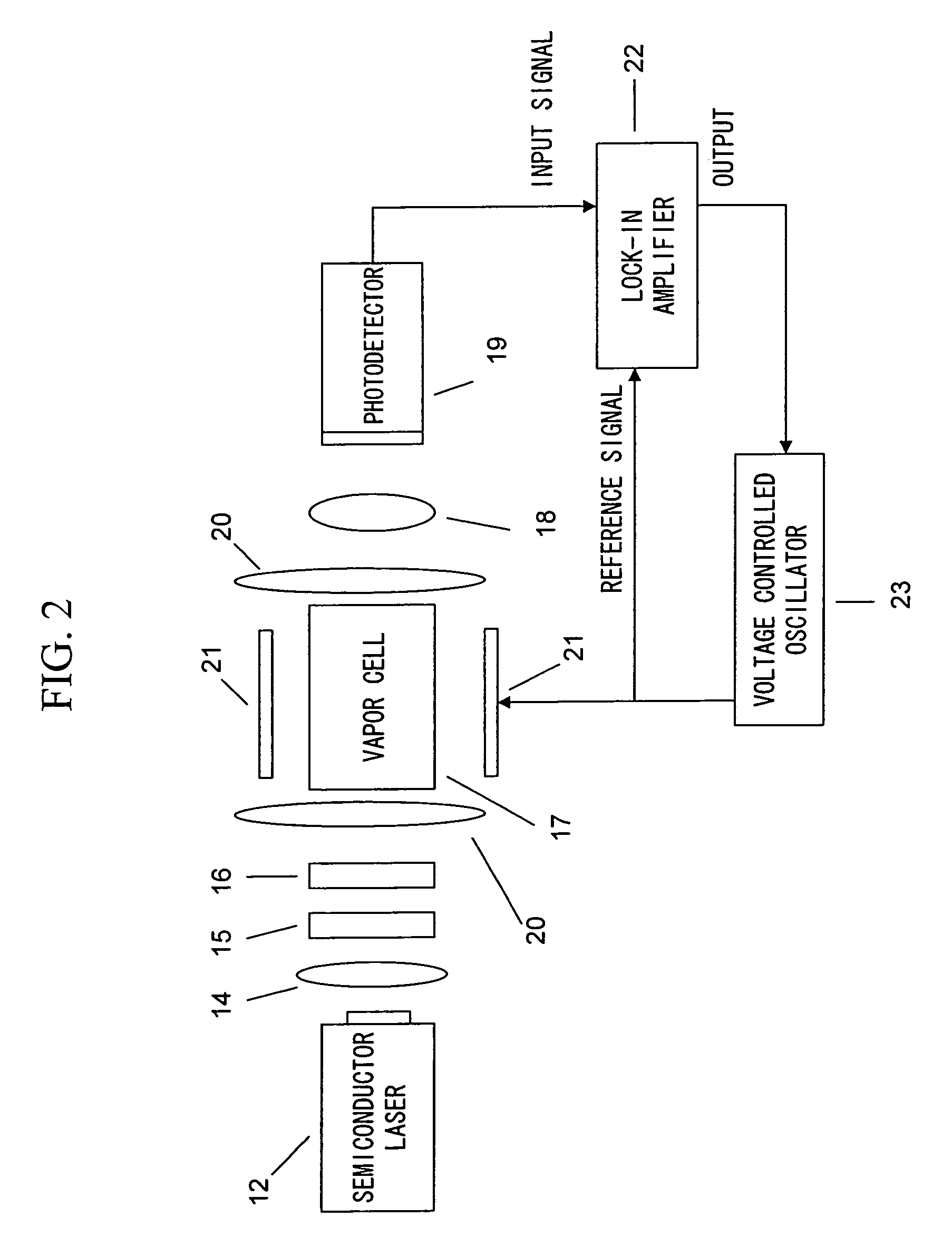
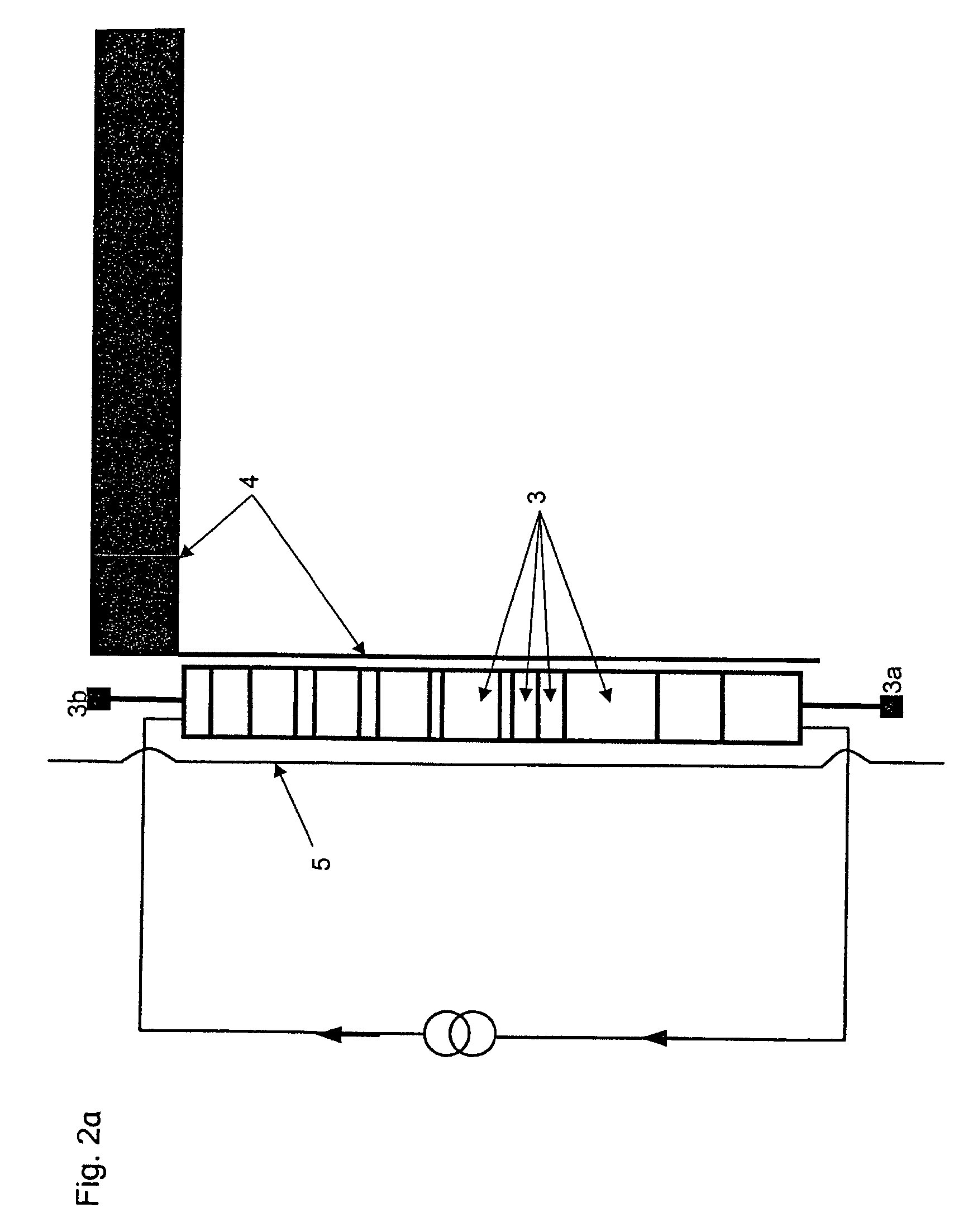
Magnetic field measurement system and optical pumping magnetometer
ActiveUS20070120563A1Reduce magnetic noiseAffect operationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityComing out
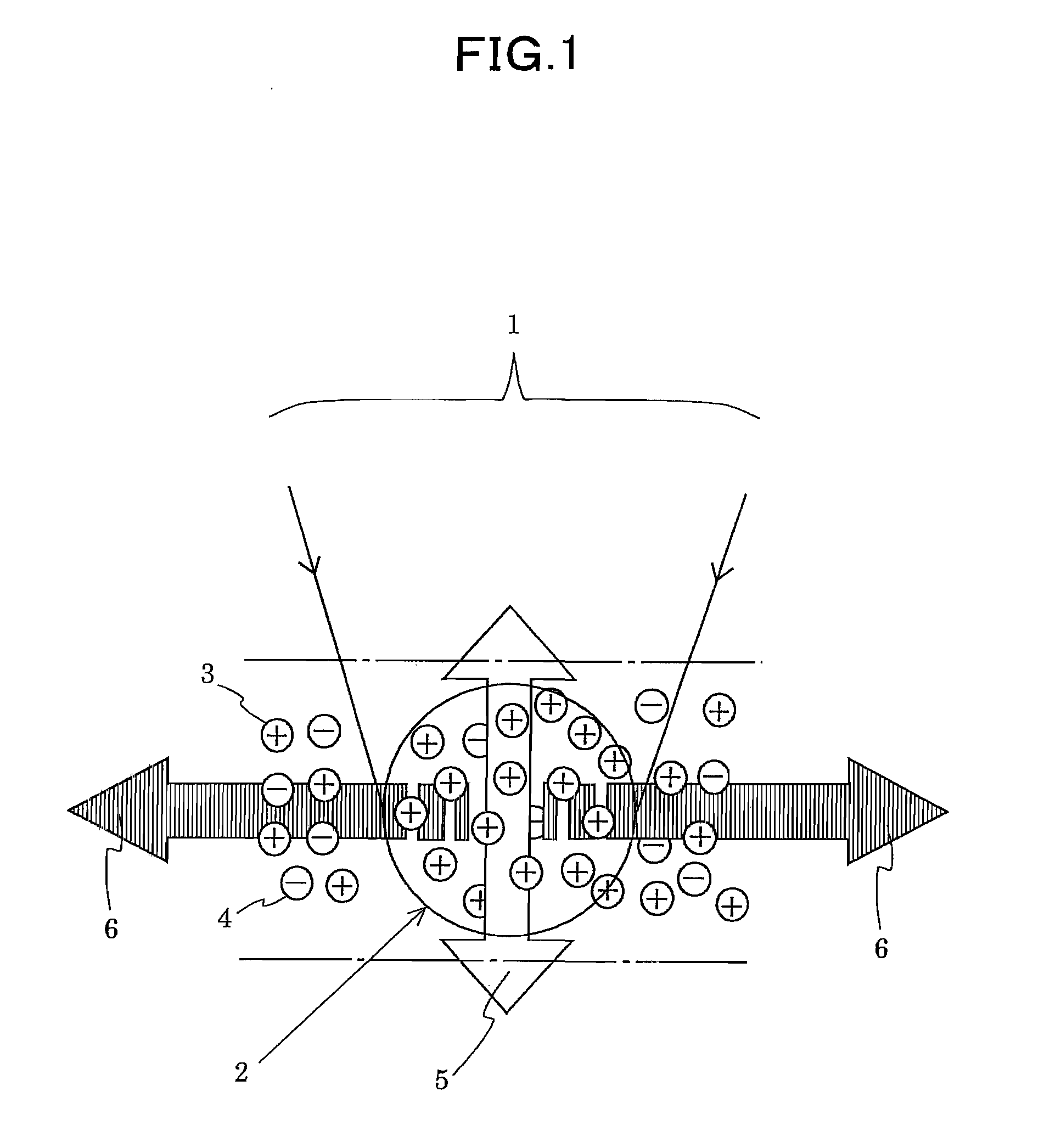
Provided is a highly accurate optical pumping magnetometer, in which a static magnetic field and an oscillating field to be applied to a vapor cell are stabilized. To this end, the optical pumping magnetometer includes: Helmholtz coils for applying a constant static magnetic field to a vapor cell serving as a magnetic field detector; fluxgate magnetometers for detecting environmental magnetic noise in two directions of X-axis direction and Y-axis direction other than Z-axis direction which is a direction for detecting a magnetic field coming out of a measurement object while locating the vapor cell in the center thereof; magnetometer drive circuits for driving the fluxgate magneotometers; current converters for converting outputs of the magnetometer drive circuits into amount of currents; and magnetic field generating coils for generating a magnetic field in a phase opposite to the environmental magnetic noise in the two directions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Device for high-resolution measurement of magnetic fields
InactiveUS6690162B1Superconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field offset compensationFrequency spectrumVoltage drop
A device is proposed for high-resolution measurement, in particular for high-resolution absolute measurement of magnetic fields, having a network (1) of transitions (3) between superconductors (5, 6) which exhibit Josephson effects, called junctions below, the network comprising closed meshes (7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13), denoted by cells below, which in each case have junctions (3), which junctions are connected in a superconducting fashion, and at least three of these cells being connected in a superconducting and / or nonsuperconducting fashion. The object of the invention consists in further developing this device in such a way that it is possible to make absolute measurements of magnetic fields in a highly sensitive fashion. This object is achieved by virtue of the fact that the junctions (3) of the at least three cells (7, 8, 9) can be energized in such a way that a time-variant voltage drops in each case across at least two junctions of a cell, the time average of which voltage does not vanish, and in that the at least three cells are configured differently geometrically in such a way that the magnetic fluxes enclosed by the cells in the case of an existing magnetic field differ from one another in such a way that the frequency spectrum of the voltage response function has no significant Phi0-periodic component with reference to the magnetic flux.
Owner:QEST QUANTENELEKTRONISCHE SYST
High-resolution magnetoencephalography system, components and method
InactiveUS7197352B2Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayMagnetoencephalography
Owner:TRISTAN TECH
Magnetic field measurement system and optical pumping magnetometer
ActiveUS7656154B2Reduce magnetic noiseAffect operationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityComing out
Provided is a highly accurate optical pumping magnetometer, in which a static magnetic field and an oscillating field to be applied to a vapor cell are stabilized. To this end, the optical pumping magnetometer includes: Helmholtz coils for applying a constant static magnetic field to a vapor cell serving as a magnetic field detector; fluxgate magnetometers for detecting environmental magnetic noise in two directions of X-axis direction and Y-axis direction other than Z-axis direction which is a direction for detecting a magnetic field coming out of a measurement object while locating the vapor cell in the center thereof; magnetometer drive circuits for driving the fluxgate magneotometers; current converters for converting outputs of the magnetometer drive circuits into amount of currents; and magnetic field generating coils for generating a magnetic field in a phase opposite to the environmental magnetic noise in the two directions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Multiple SQUID magnetometer
InactiveUS20070241747A1Avoid complicationsHigh sensitivitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesCondensed matter physicsSQUID
Multiple SQUID magnetometers that include at least two SQUID loops, each of which is composed of at least two Josephson Junctions connected in parallel with superconducting wires, are provided. The SQUID loops are fabricated such that they share a common Josephson Junction. Devices and application that employ the multiple SQUID magnetometers are also provided.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
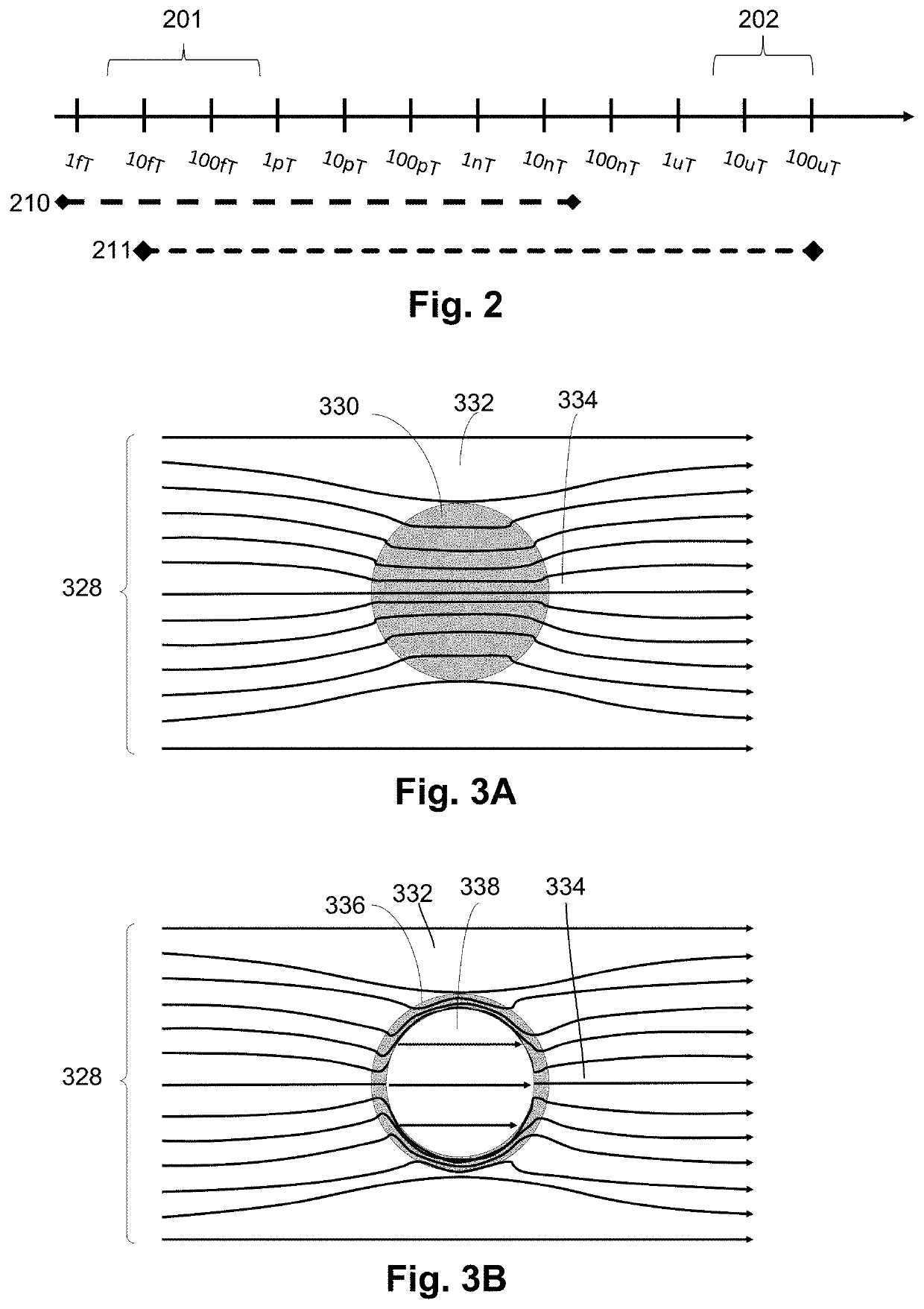
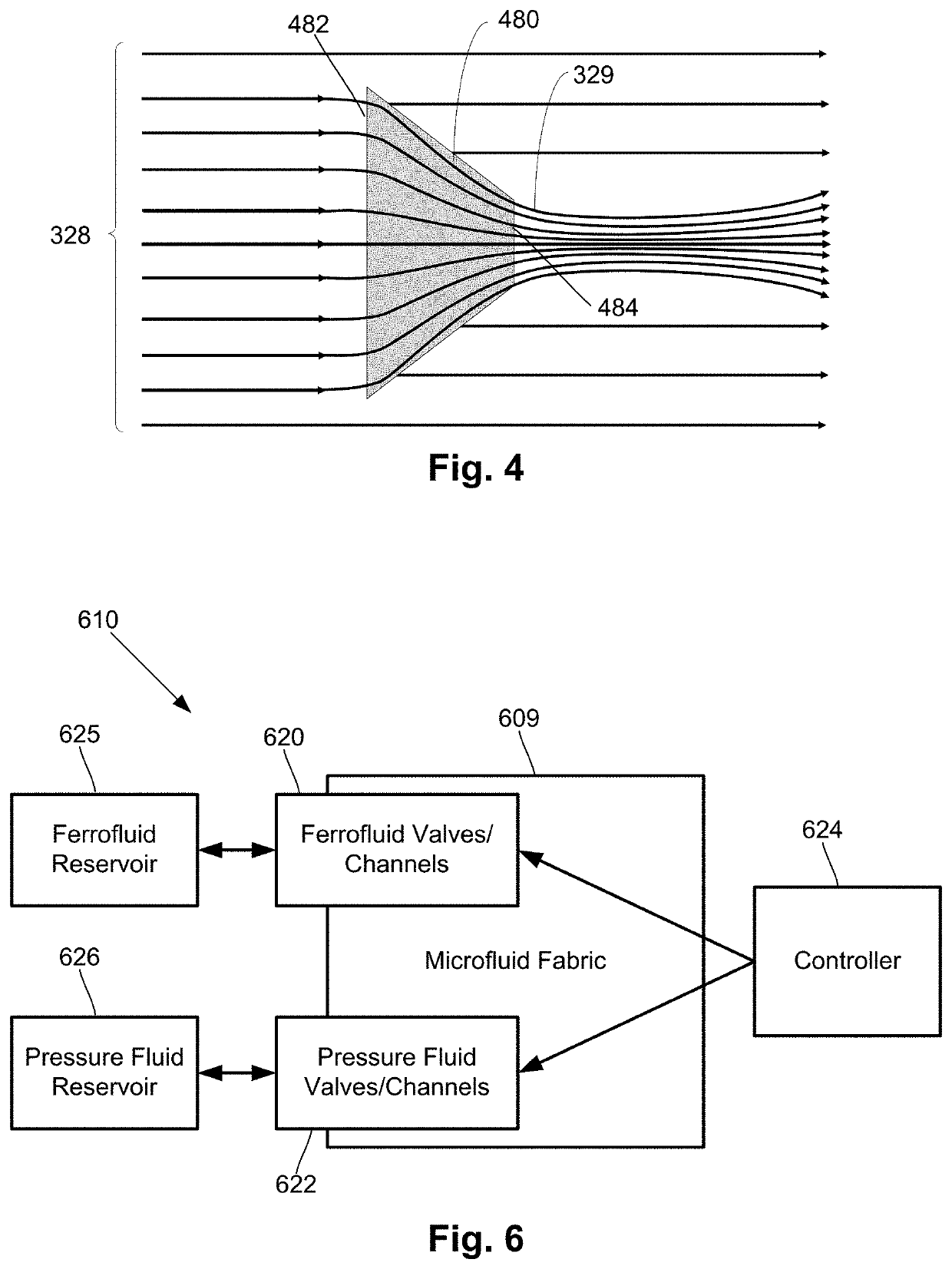
Dynamic magnetic shielding and beamforming using ferrofluid for compact magnetoencephalography (MEG)
ActiveUS20200088811A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetoencephalographyMagnetic shield
A magnetic field measurement system can include at least one magnetometer; and a ferrofluid shield disposed at least partially around the at least one magnetometer. For example, the ferrofluid shield can include a microfluid fabric and a ferrofluid disposed in or flowable into the microfluid fabric. As another example, the ferrofluid shield can include a ferrofluid and a controller configured to alter an arrangement of the ferrofluid within the ferrofluid shield.
Owner:HI LLC
High-sensitivity magnetic measurement device in environment field based on disturbance compensation and realization method thereof
ActiveCN102353911ASimple structureGuaranteed high-sensitivity magnetic field measurementsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectrical measurementsMeasurement deviceIntegrator
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity magnetic measurement device in an environment field based on disturbance compensation and a realization method thereof. In the method, the low-frequency disturbance compensation in an environment magnetic field is realized by a second feedback branch and a second magnetic flux locking loop, wherein the second feedback branch is composed of a second integrator, a low-pass filter, a second feedback resistor and a feedback coil; and the second magnetic flux locking loop is formed based on the second feedback branch. A super-magnetic conduction sensor established based on the method can realize the high-pass response frequency characteristics for the environment field and the low-pass response frequency characteristics for the circuit noise at the same time, ensures the suppression of the influence of environment field disturbance on SQUID (superconducting quantum interference device) magnetic measurement without influencing the weak signal measurement, and avoids the overflow phenomenon. Based on the super-magnetic conduction sensor, the method is suitable for the application environment in which the frequency of the magnetic field signal tobe measured is higher than the disturbance frequency band (DC-30Hz) of the environment field.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Characterization and measurement of superconducting structures
ActiveUS7002174B2High quality factorQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A structure comprising a tank circuit inductively coupled to a flux qubit or a phase qubit. In some embodiments, a low temperature preamplifier is in electrical communication with the tank circuit. The tank circuit comprises an effective capacitance and an effective inductance that are in parallel or in series. In some embodiments, the effective inductance comprises a multiple winding coil of wire. A method that includes the steps of (i) providing a tank circuit and a phase qubit that are inductively coupled, (ii) reading out a state of the phase qubit, (iii) applying a flux to the phase qubit that approaches a net zero flux, (iv) increasing a level of flux applied to the phase qubit, and (v) observing a response of the tank circuit in a readout device.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
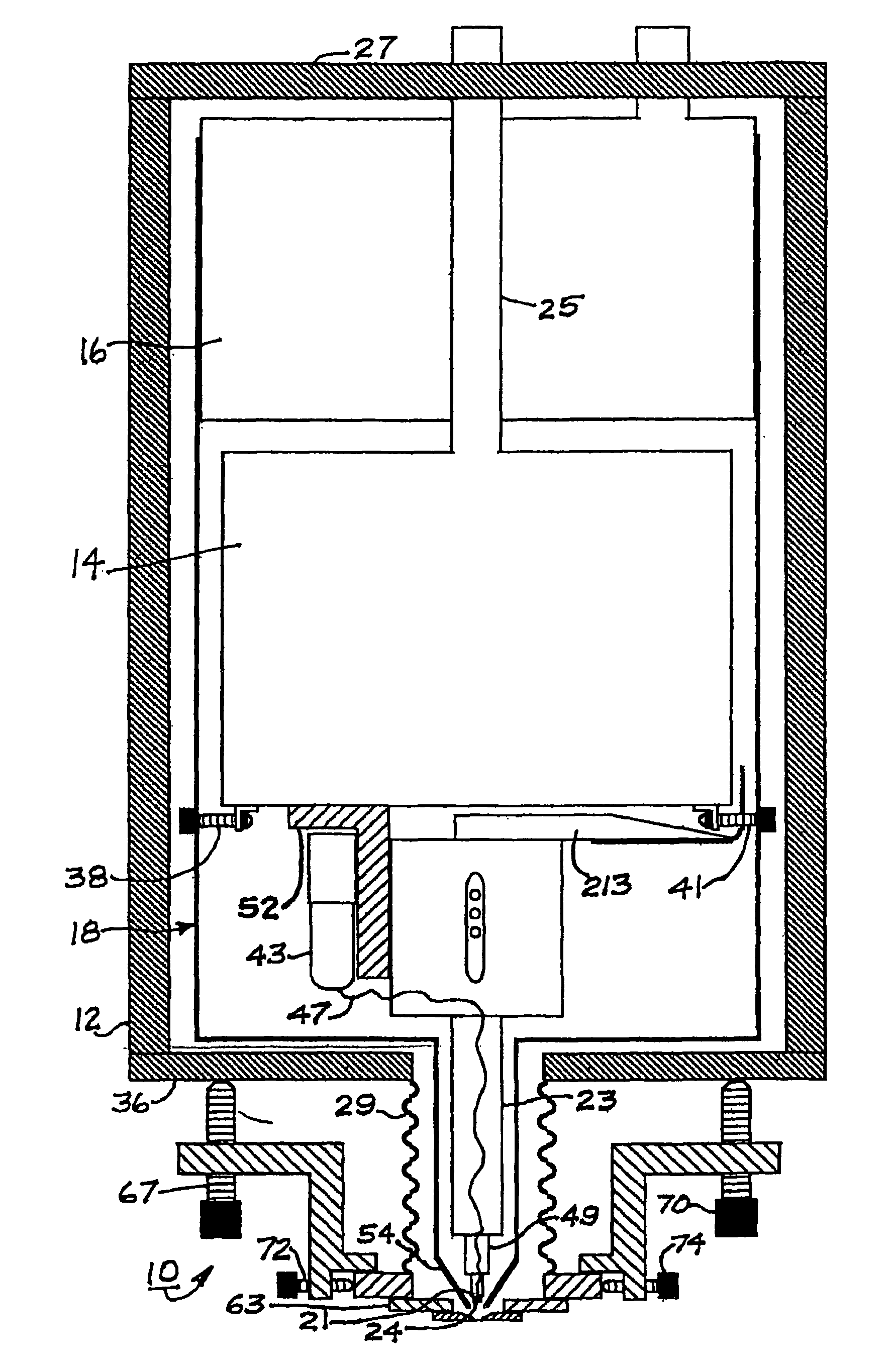
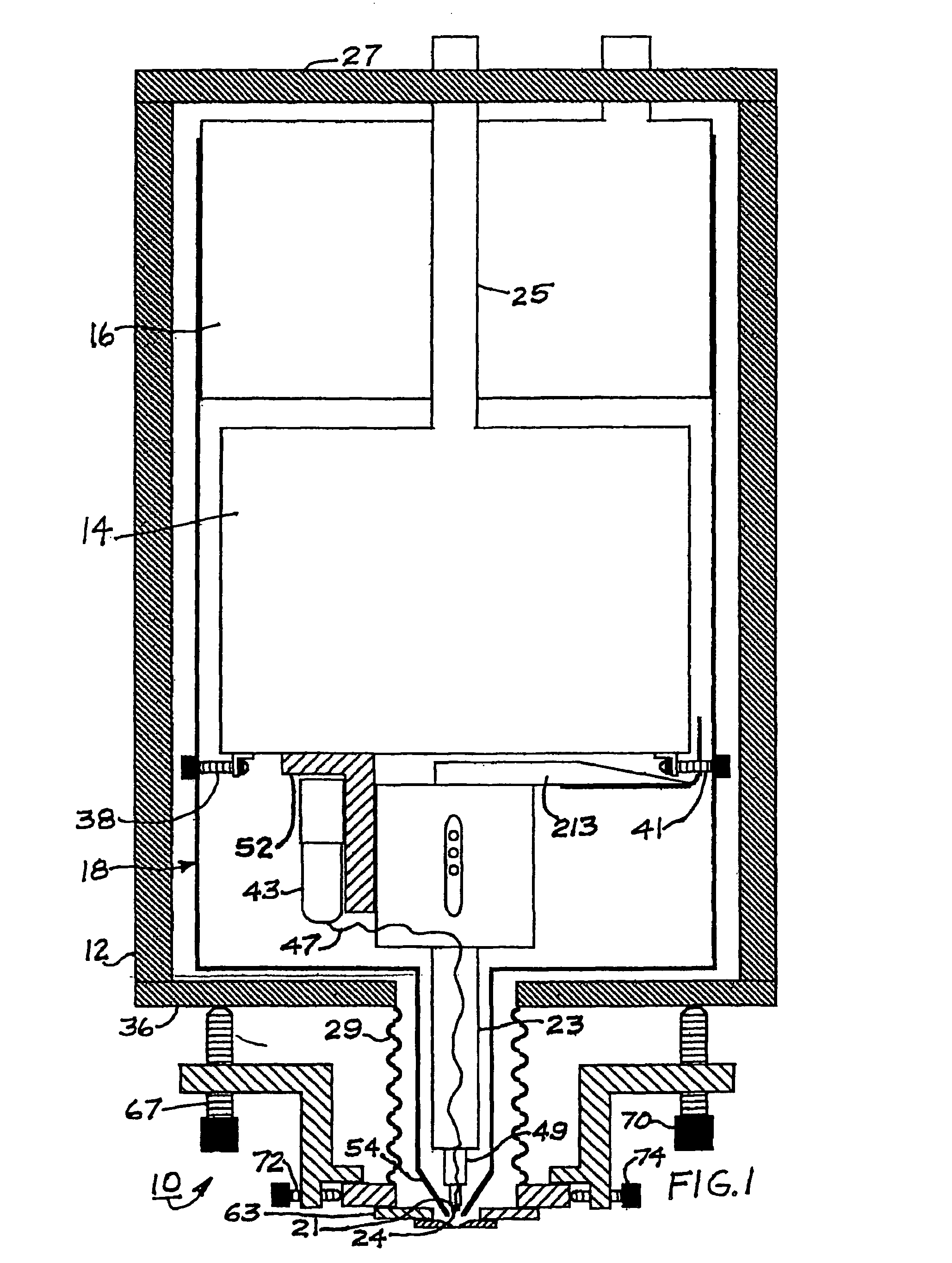
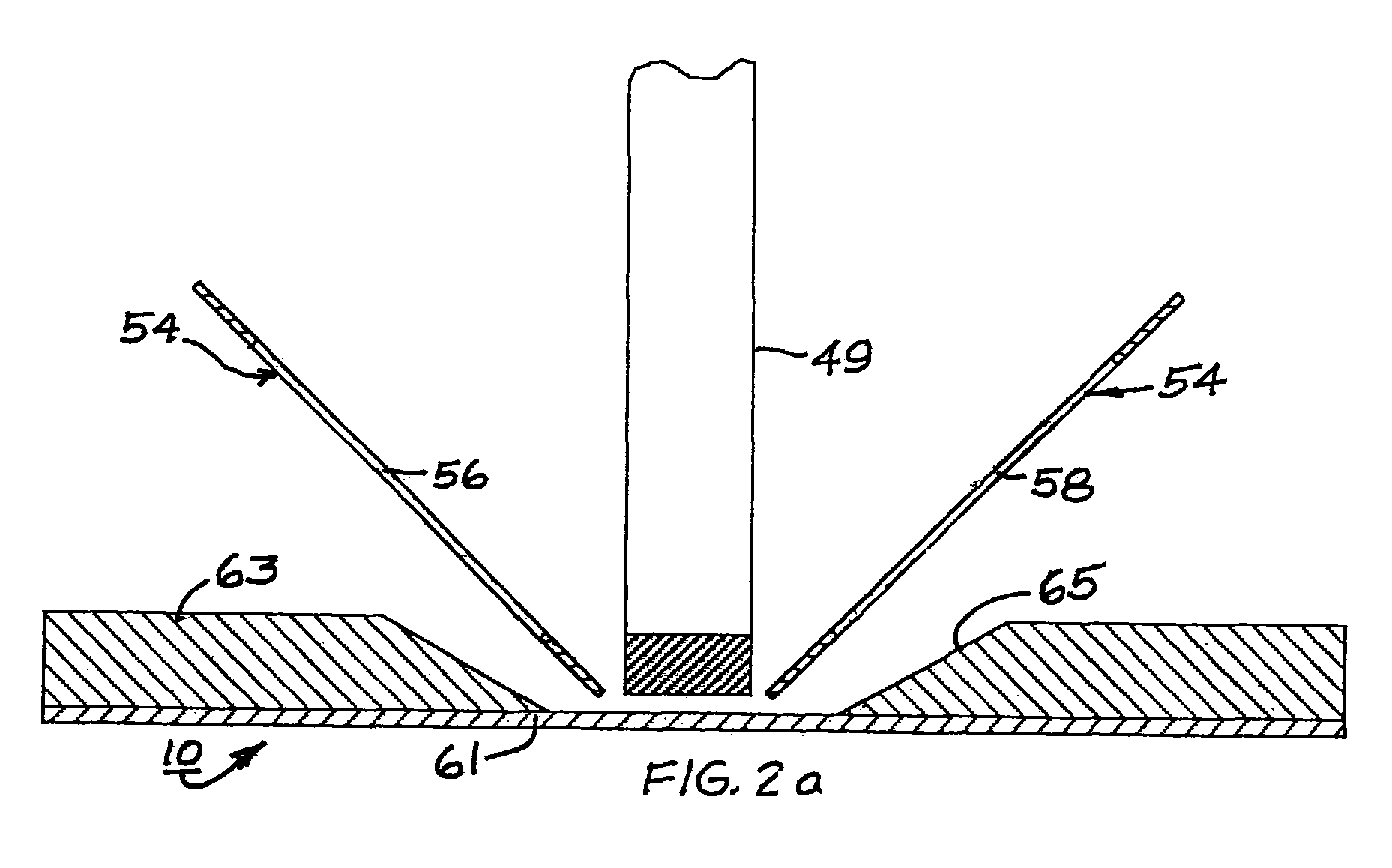
Apparatus and method for cooling a superconducting magnetic assembly
ActiveUS20100248968A1Reduce the amount requiredSimple designSuperconductor detailsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureSuperconducting CoilsEngineering
A superconducting magnet assembly and method of cooling a superconducting magnet assembly. An embodiment of the method of manufacturing a superconducting magnet assembly includes: providing a housing configured about a vacuum reservoir; forming a coil former; surrounding the coil former with a thermal shield; locating the thermal shield in the vacuum reservoir; positioning a superconducting magnet about the coil former, wherein the superconducting magnet is configured about a central core to receive an object; providing a second vacuum reservoir having a cryogen reservoir therein; providing two two-phase heat transfer devices wherein each comprises tubing having an evaporator region and a condenser region; thermally connecting the evaporator region of one of the heat transfer devices with the coil former and / or the superconducting magnet and the evaporator region of the other two-phase heat transfer device with the thermal shield; and thermally connecting a cryocooler to the cryogen reservoir and to the condensing region of both heat transfer devices.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Digitized real-time magnetic field compensation device and method on basis of super-conducting magnetic sensor
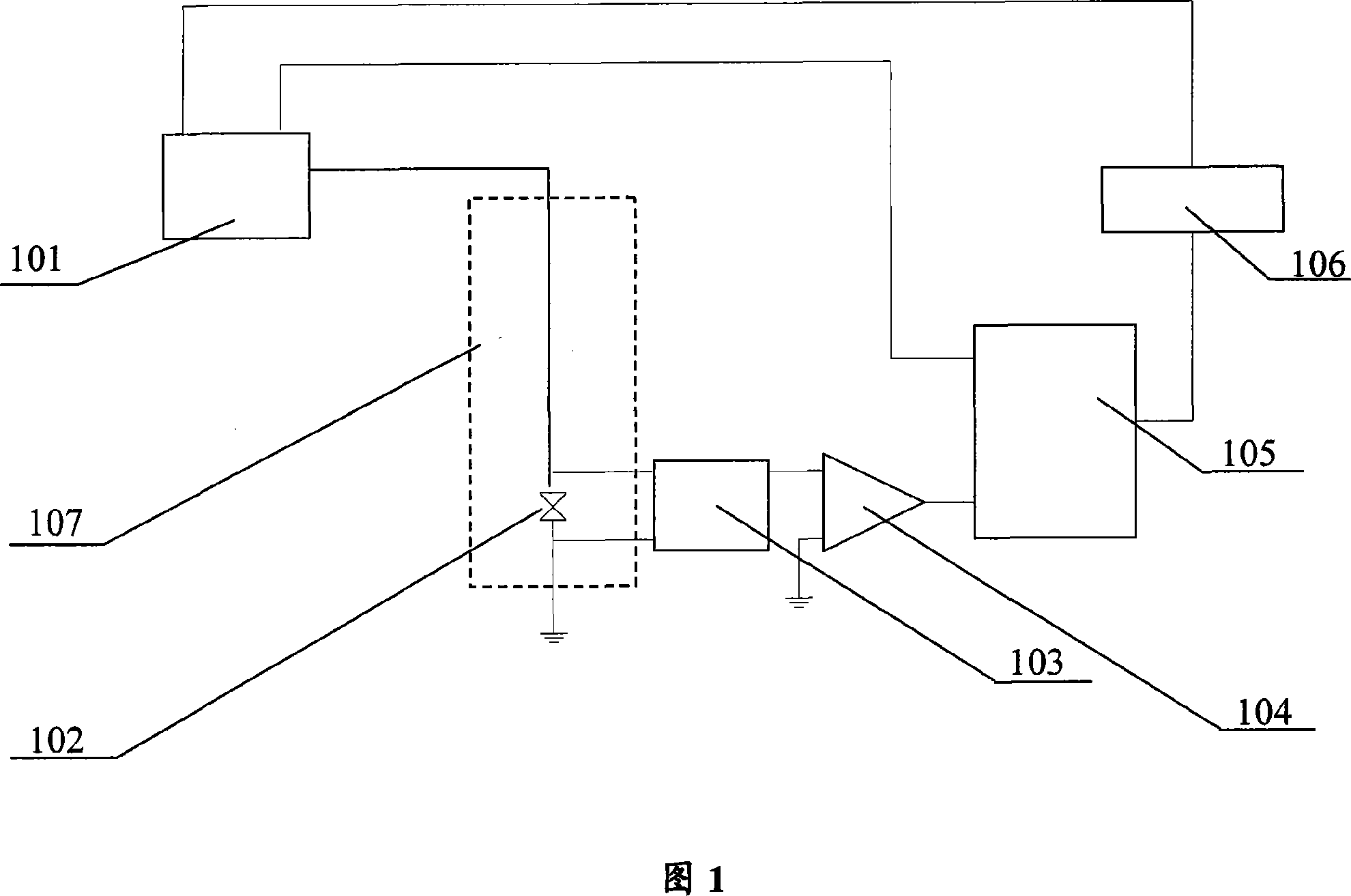
ActiveCN103389478AEasy extractionIncrease flexibilityMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesAnalog-to-digital converterDigitization
The invention relates to a digitized real-time magnetic field compensation device and method on the basis of a super-conducting magnetic sensor. The digitized real-time magnetic field compensation device is characterized by leading in two-stage negative feedback with different passing band characteristics on the basis of a traditional magnetic flux locking ring reading circuit to achieve reading of high-sensitivity to-be-measured magnetic field signals and compensation of low-sensitivity to-be-compensated magnetic field interference, adopting a digital circuit composed of an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a microprocessor, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and accessories thereof to form a magnetic compensation circuit, and adding soft start capable of improving reliability of the magnetic compensation device and a function of automatic direct current offset eliminating of a magnetic flux locking ring. The compensation method is characterized by collecting output signals of the magnetic flux locking ring through the ADC, performing direct current offset elimination, filtering, inversion and integration through the microprocessor and finally outputting signals required by magnetic compensation through the DAC. A SQUID Feedback ring is used for feedback, so that the structure of the magnetic compensation device is greatly simplified, and maintainability, reliability and to-be-compensated signal withdrawing capability of the magnetic compensation device are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-noise SQUID
InactiveUS6023161AReduce noiseNo lossSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesLow noiseBand width
The present invention comprises a high-transition-temperature superconducting device having low-magnitude low-frequency noise-characteristics in magnetic fields comprising superconducting films wherein the films have a width that is less than or equal to a critical width, wC, which depends on an ambient magnetic field. For operation in the Earth's magnetic field, the critical width is about 6 micrometers ( mu m). When made with film widths of about 4 mu m an inventive high transition-temperature, superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) excluded magnetic flux vortices up to a threshold ambient magnetic field of about 100 microTesla ( mu T). SQUIDs were fabricated having several different film strip patterns. When the film strip width was kept at about 4 mu m, the SQUIDs exhibited essentially no increase in low-frequency noise, even when cooled in static magnetic fields of magnitude up to 100 mu T. Furthermore, the mutual inductance between the inventive devices and a seven-turn spiral coil was at least 85% of that for inductive coupling to a conventional SQUID.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
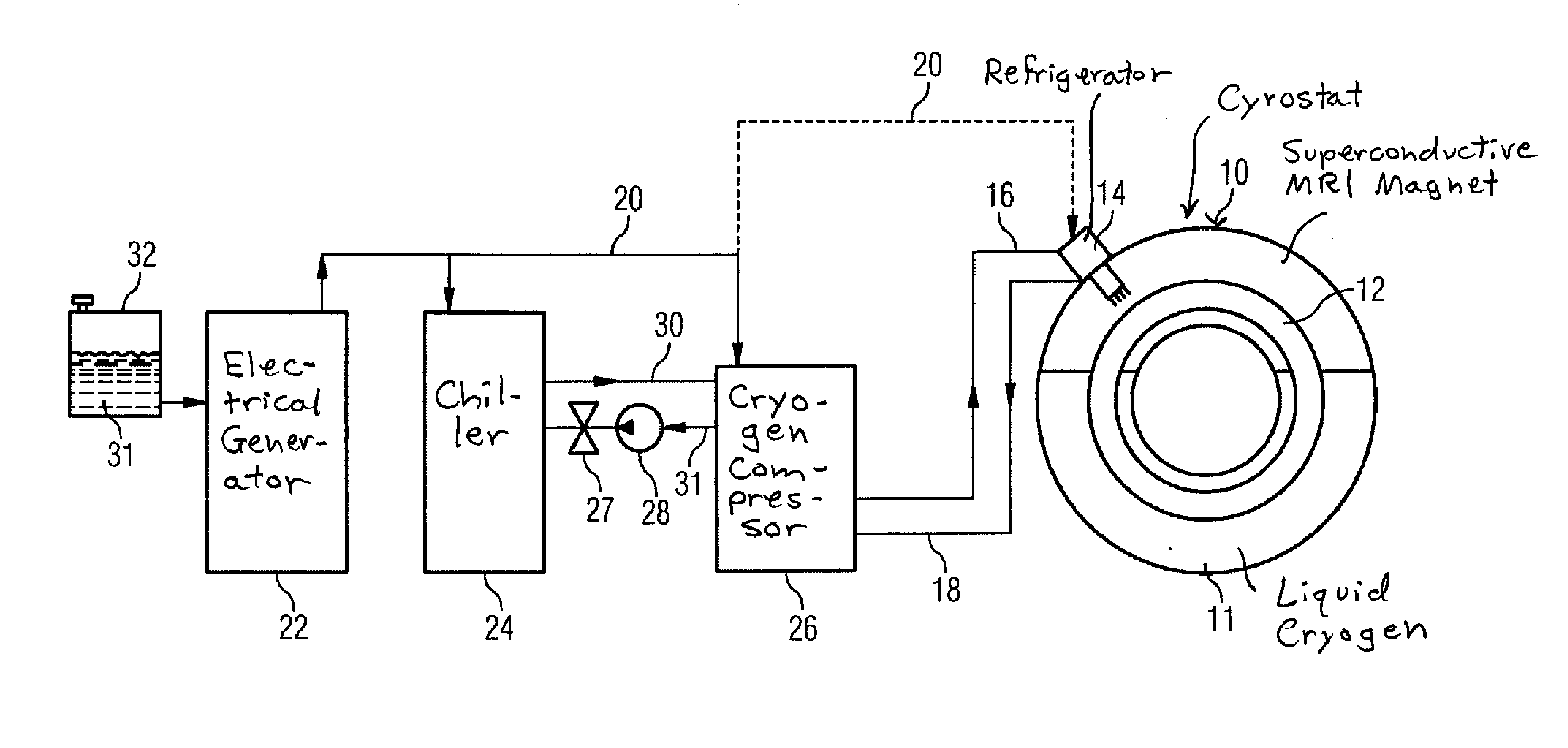
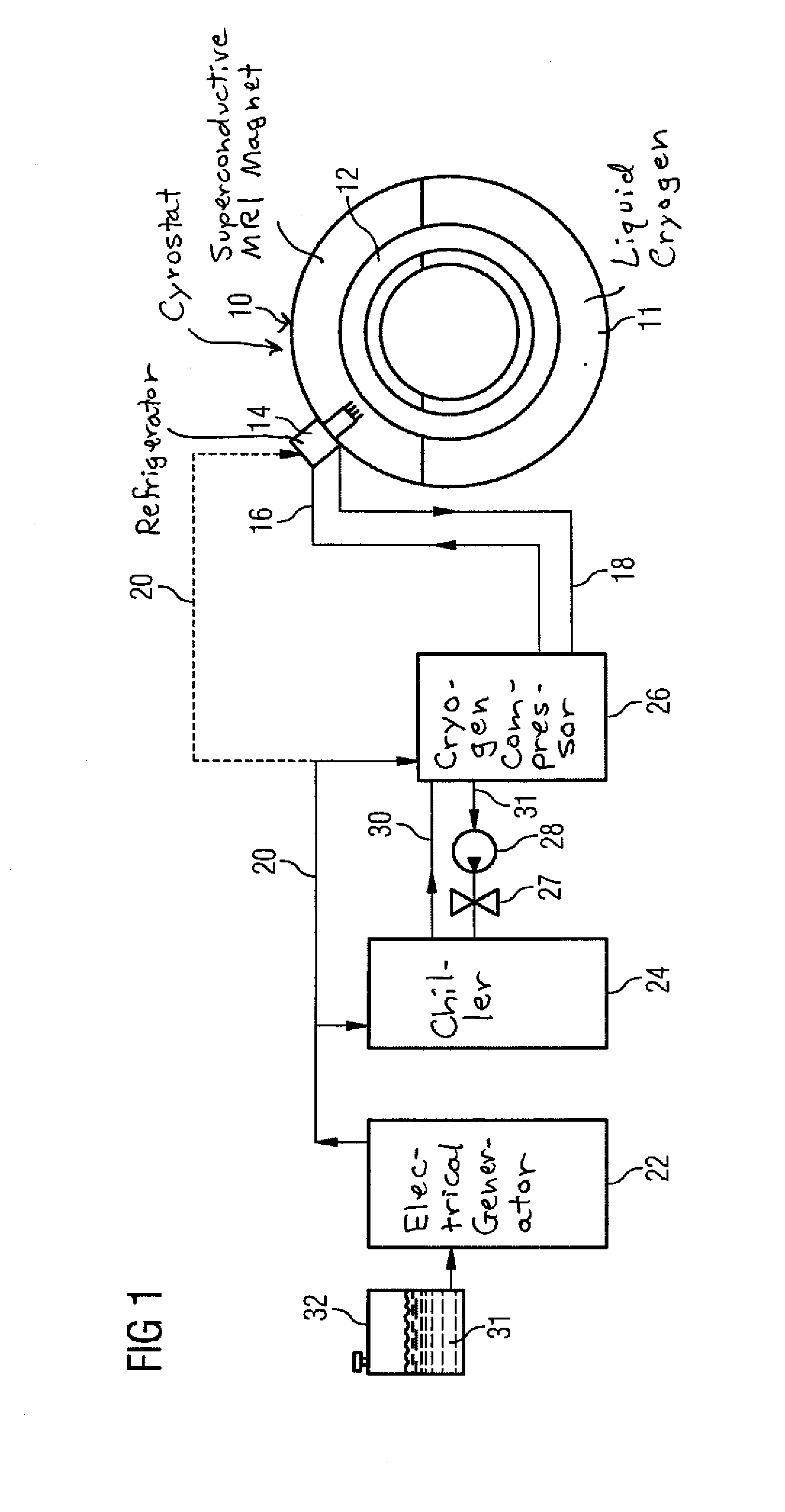
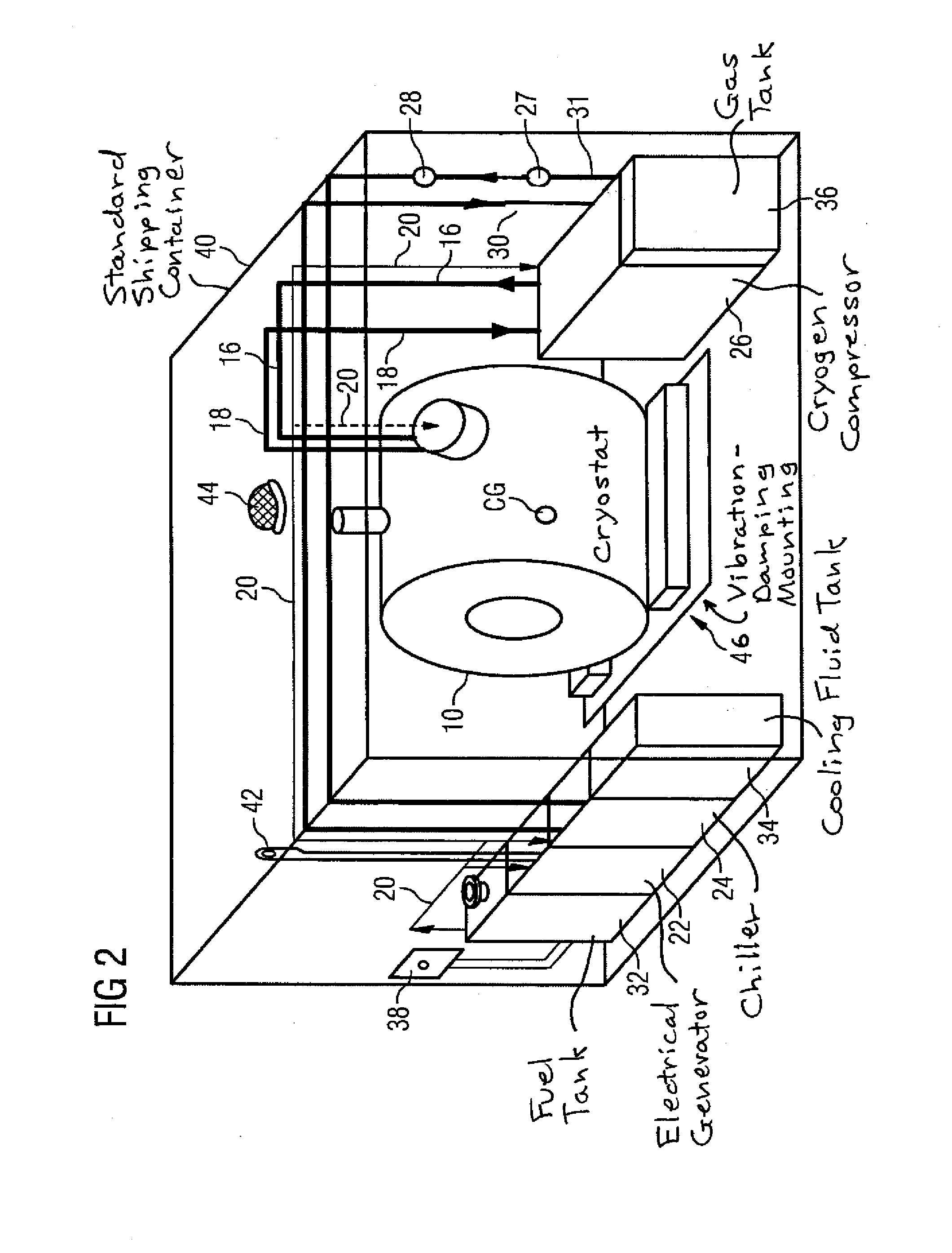
Apparatus and method for transporting cryogenically cooled goods or equipment
InactiveUS20100016168A1Lower the volumeAvoid lostContainer filling methodsSuperconductor detailsActive coolingProcess engineering
In an apparatus and method for transporting cryogenically cooled goods or equipment, a cryostat containing the cryogenically cooled goods or equipment and partially filled with liquid cryogen is provided with a cryogenic refrigerator for active cooling; and auxiliary equipment sufficient to maintain the cryogenic refrigerator in operation, are all mounted on a transportable carrier such that the transportable carrier may be transported with the cryogenic refrigerator in operation without connection of any of the cryostat, refrigerator and auxiliary equipment to any supplies located off of the transportable carrier.
Owner:SIEMENS PLC
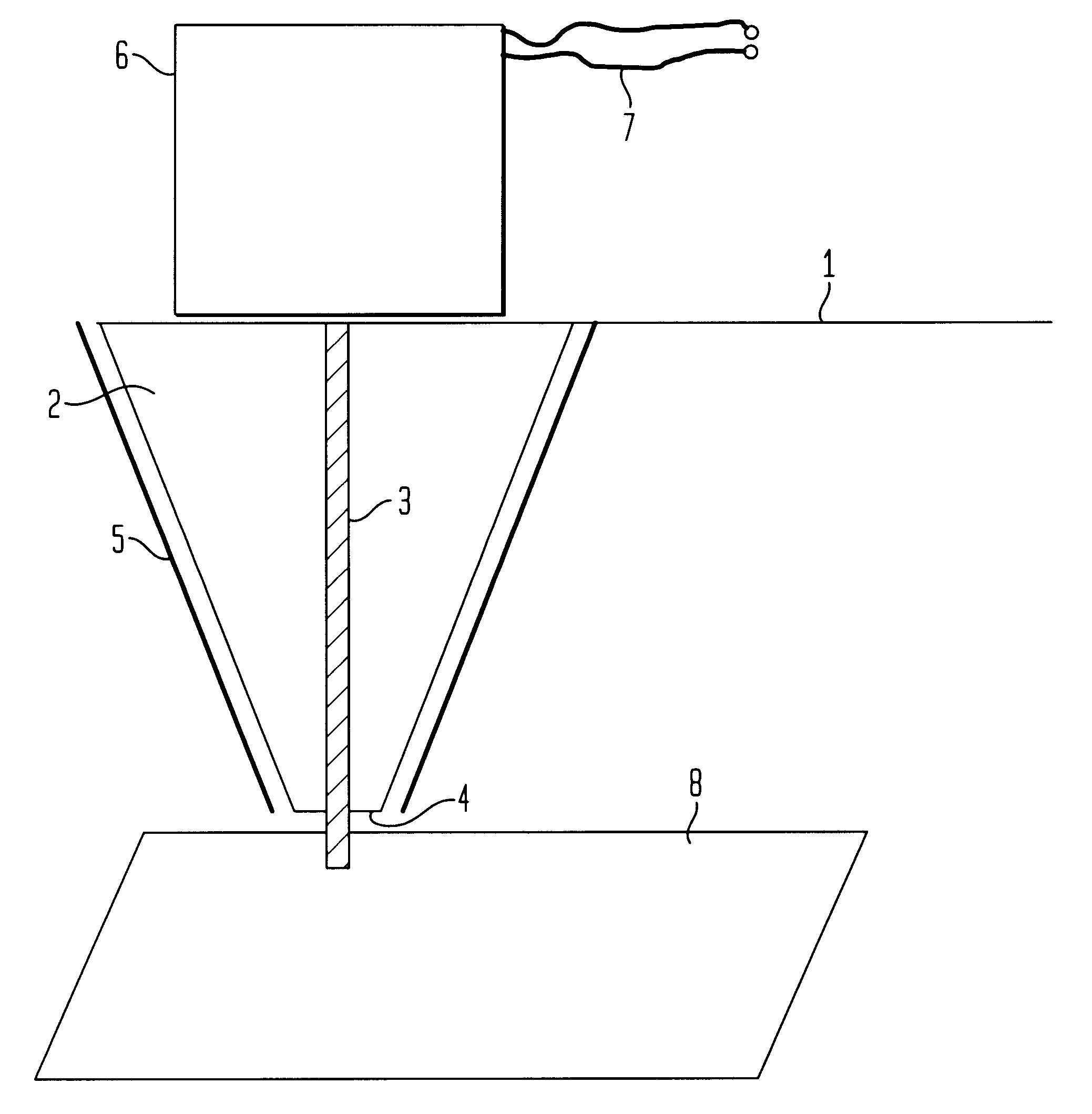
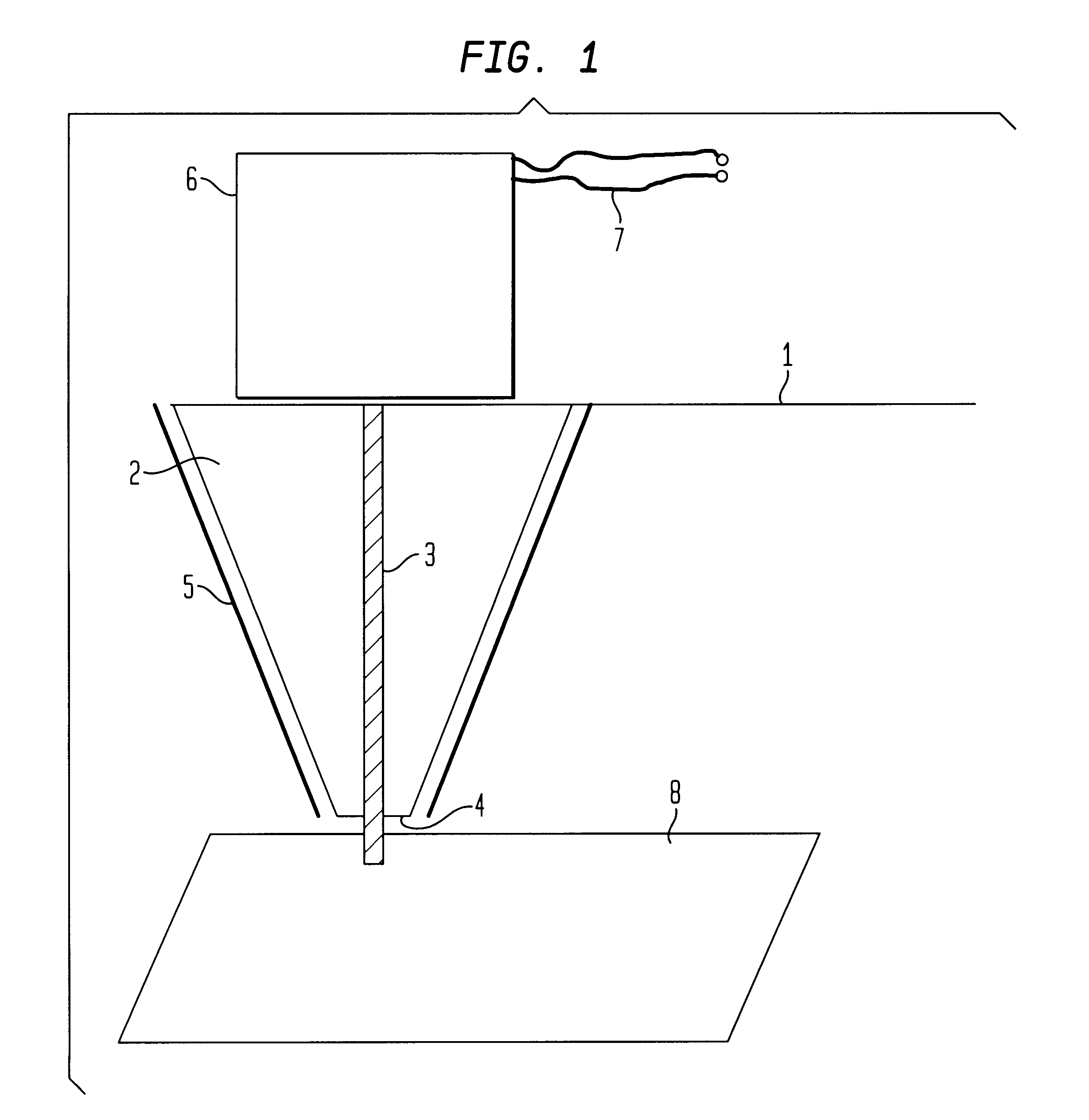
Testing device for magnetic field and magnetic force in three-dimensional space
ActiveCN1632609AReal-time automatic recordingHigh measurement accuracyMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesMagnetic tension forceAutomatic control
This invention relates to a three-dimensional space magnetic field and magnetic force test device. Its controller box of the computer controller and programmable controller is set with a workbench of the part clamper. The workbench is set with longitude moving structure with a level motion structure, which has a vertical motion structure and a magnetic material clamper connection pull sensor in the dangle arm of the vertical motion structure. There are at least one three-dimensional Hall probes rack in the sideway of the magnetic clamper.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Frequency detection system comprising circuitry for adjusting the resonance frequency of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant coil
InactiveUS20060012371A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical conductorResonance
The use of a circuit to adjust the resonance frequency of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant transmit, receive, or transmit and receive coil results in improved performance. The circuit is useful in a frequency detection system, especially in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Superconducting quantum antenna
ActiveUS7369093B2Increase sensitivity-orPointing stableSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsThermal insulationElectromagnetic electron wave
An antenna for electromagnetic waves including a quantum interference filter, at least one low-temperature transistor and primary antenna structures, means for deriving an electromagnetic wave from the circuit, cooling elements and insulating means. The interference filter and the transistor act as active components, the primary antenna structure is connected up to at least one of the active components in such a way that upon incidence of an electromagnetic wave on the primary antenna structure there is present at the output of the at least one active component a conducted electromagnetic wave, and wherein at least one part of the circuit and at least one part of the primary antenna structure are thermally insulated, the thermal insulation is frequency transparent to electromagnetic waves, and the cooling elements are designed to cool down at least one part of the circuit below the transition temperature of at least one of the superconducting materials.
Owner:QEST QUANTENELEKTRONISCHE SYST TUBINGEN GMBH
Apparatus for use in magnetic-field detection and generation devices
InactiveUS6211673B1Improve spatial resolutionWeaken influenceNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic storageEngineering
A magnetic-field-detecting and / or generating apparatus comprises a non-ferromagnetic tip with a longitudinal member of ferromagnetic material embedded in the tip. Further, magnetic-shield means is arranged around the tip. At the end of the longitudinal member a magnetic-field device is arranged. The same principle can be applied to read / write heads for use in magnetic-storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
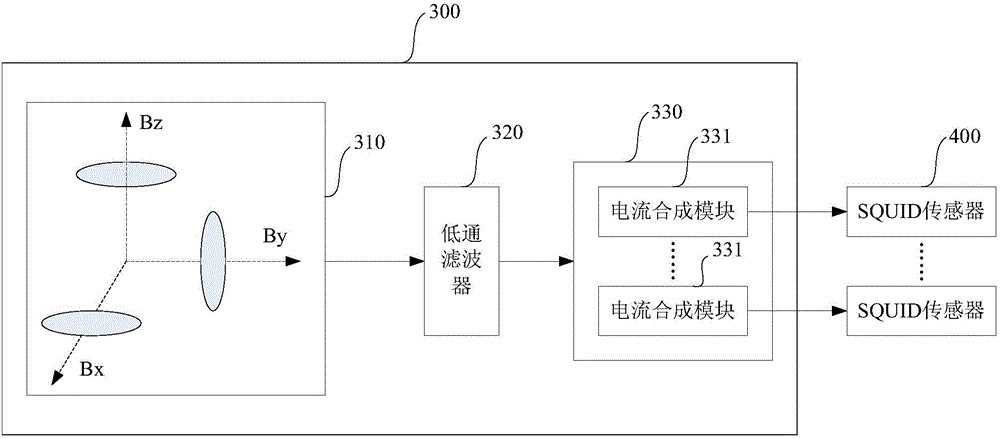
Method for quantitatively calibrating and eliminating crosstalk of SQUID (Superconducting Quantum Interference Device) planar three-shaft magnetometer
ActiveCN101907693AHighly integratedGuaranteed to use optimallyMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectrical measurementsClassical mechanicsMagnetic flux
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Superconducting switch, superconducting magnet and MRI
ActiveUS20130012392A1Maintain strengthThermal efficiencySuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetsSuperconducting CoilsThin membrane
A superconducting switch is provided in which the structural strength of the superconducting switch is kept, and thermal efficiency between a superconducting film and a heater is high when an ON state (superconducting state) and an OFF state (normal conducting state) of the superconducting switch are switched. The superconducting switch includes a substrate, a heater for generating heat by energization, a conductive film, and a MgB2 film evaporated on the conductive film. The heater, the conductive film and the MgB2 film are laminated in this order on one surface of the substrate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Linear voltage response of non-uniform arrays of bi-SQUIDs
InactiveUS9097751B1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesVoltage responseLinearity
An amplifier and method for improving linear response includes a plurality of N bi-SQUIDs. Each bi-SQUID has a non-uniform bi-SQUID parameter βi, described by βi=2πLiIciΦ0 can be defined for each bi-SQUIDs from i=1 to N, where Li is the loop inductance, ic is the critical current, and Φ0 is a flux quantum for each bi-SQUID. The non-uniform bi-SQUIDs can be connected in series or in parallel to establish a Superconducting Quantum Interference Filter (SQIF) array of bi-SQUIDs. Once connected, a mutual inductance between the connected bi-SQUIDs can be established. If the mutual inductance between connected bi-SQUIDs is accounted for, careful manipulation of the critical current or the loop size, or both, of each bi-SQUID can result in extremely uniform behavior (linear response) of the SQIF when considered as a whole, even though the behavior of the element bi-SQUIDs is non-uniform (different βi, parameters).
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Magnetic field measurement apparatus
InactiveUS20020050815A1Reduce weightLow priceMagnetic/electric field screeningSuperconductor detailsEngineeringNon magnetic
A magnetic field measuring apparatus has a magnetic field shielding apparatus including non-magnetic cylindrical members on which high-permeability sheets are located in a state of being partially overlapped with each other. The cylindrical members are located to surround an axis of a first direction concentrically and having a hollow portion, the cylindrical member located on an innermost-side having a first opening at one end of the first direction, a second opening at the other end of the first direction, and a third opening penetrating the cylindrical members in a direction perpendicular to the axis of the first direction. In addition, the magnetic field measuring apparatus has a living-body holder located in an inner-side space of the cylindrical member and a cryostat inserted into the third opening and maintaining SQUID magnetic-flux meters.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus and method for determining magnetic properties of materials
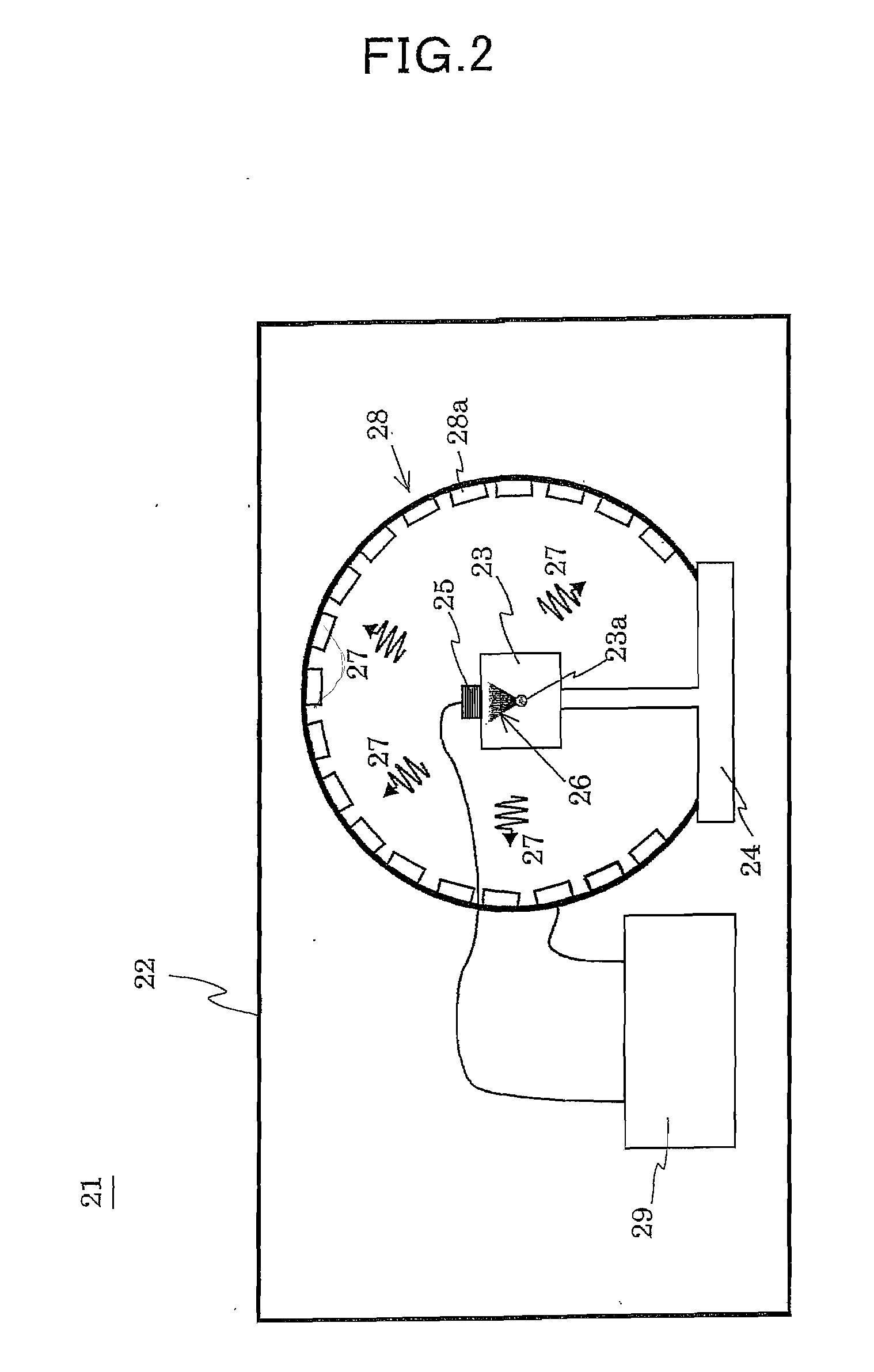
ActiveUS20090201016A1Improve mobilityMaximize signal receptionMagnetisation measurementsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesData acquisitionEngineering
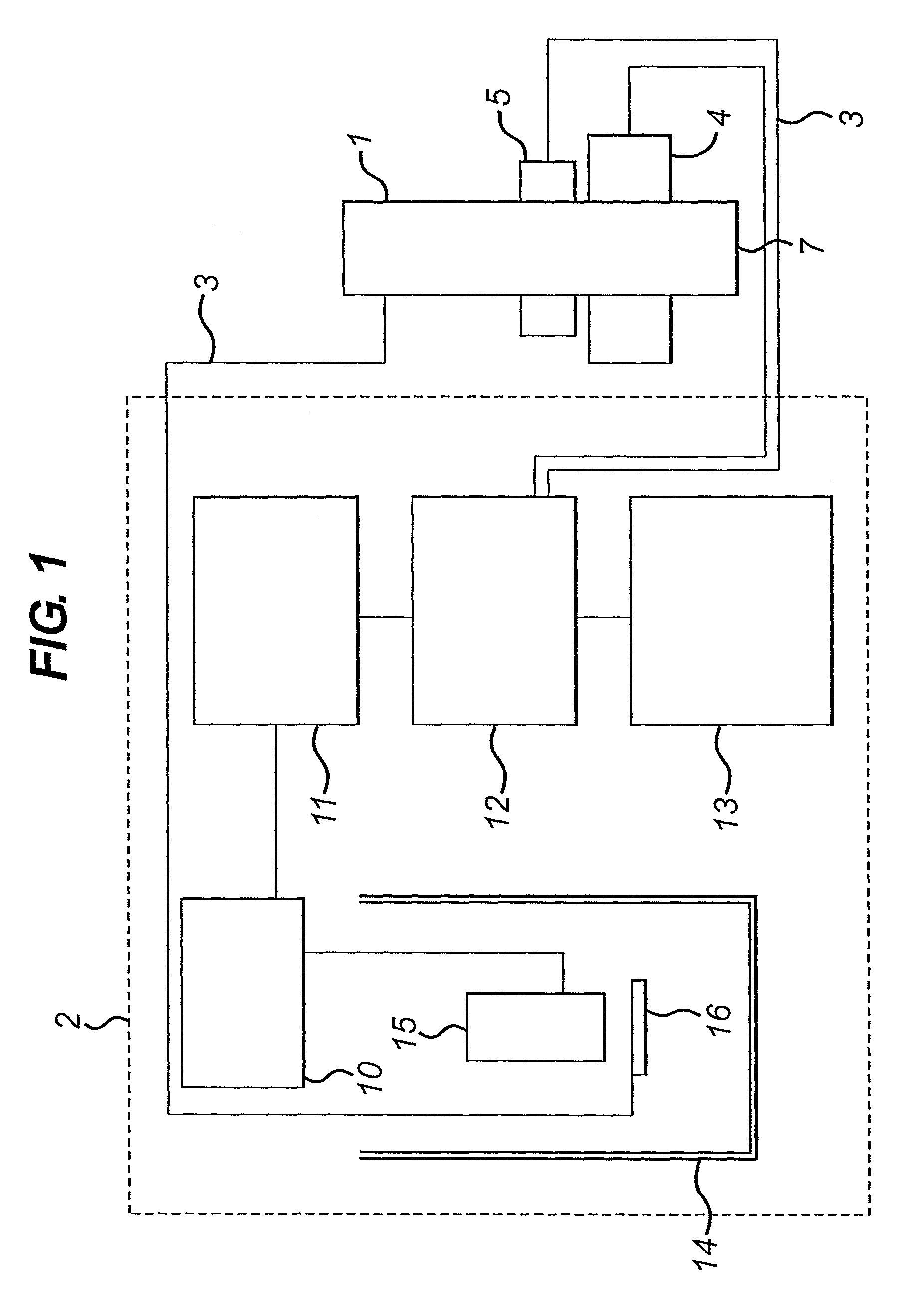
Apparatus for determining magnetic properties of materials comprises a portable probe (1), an equipment trolley (2) holding cryogenics and electronics and connecting cables (3). The probe (1) comprises a drive coil (4) and a correction coil (5), the drive coil (4) being disposed symmetrically with respect to an inner second-order gradiometer sensor coil (8). Electrical connectors in the form of 2-metre long Belden (1192A) microphone cables (3) are used to connect the apparatus on the equipment trolley (2) to the drive coil (4), the correction coil (5) and the sensor coil (8). The drive coil (4) is driven so as to generate a sinusoidally varying magnetic field. The electronics comprise a flux-locked loop (9), a SQUID controller (10), a data acquisition module (11), which captures and processes the signals and a computer (12). A liquid-nitrogen dewar (13) is supported on the equipment trolley (2) and houses a sensitive SQUID detector (14) and a transfer coil (15) made from copper. Possible applications of the apparatus include an intra-operative tool for sentinel lymph node detection in the treatment of breast cancer, and a non-destructive evaluation tool for detecting voids and defects in aluminium and applications in the aeronautics industry.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST +1
Read-out electronics for DC squid magnetic measurements
InactiveUS6420868B1Superconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesMagnetic measurementsEngineering
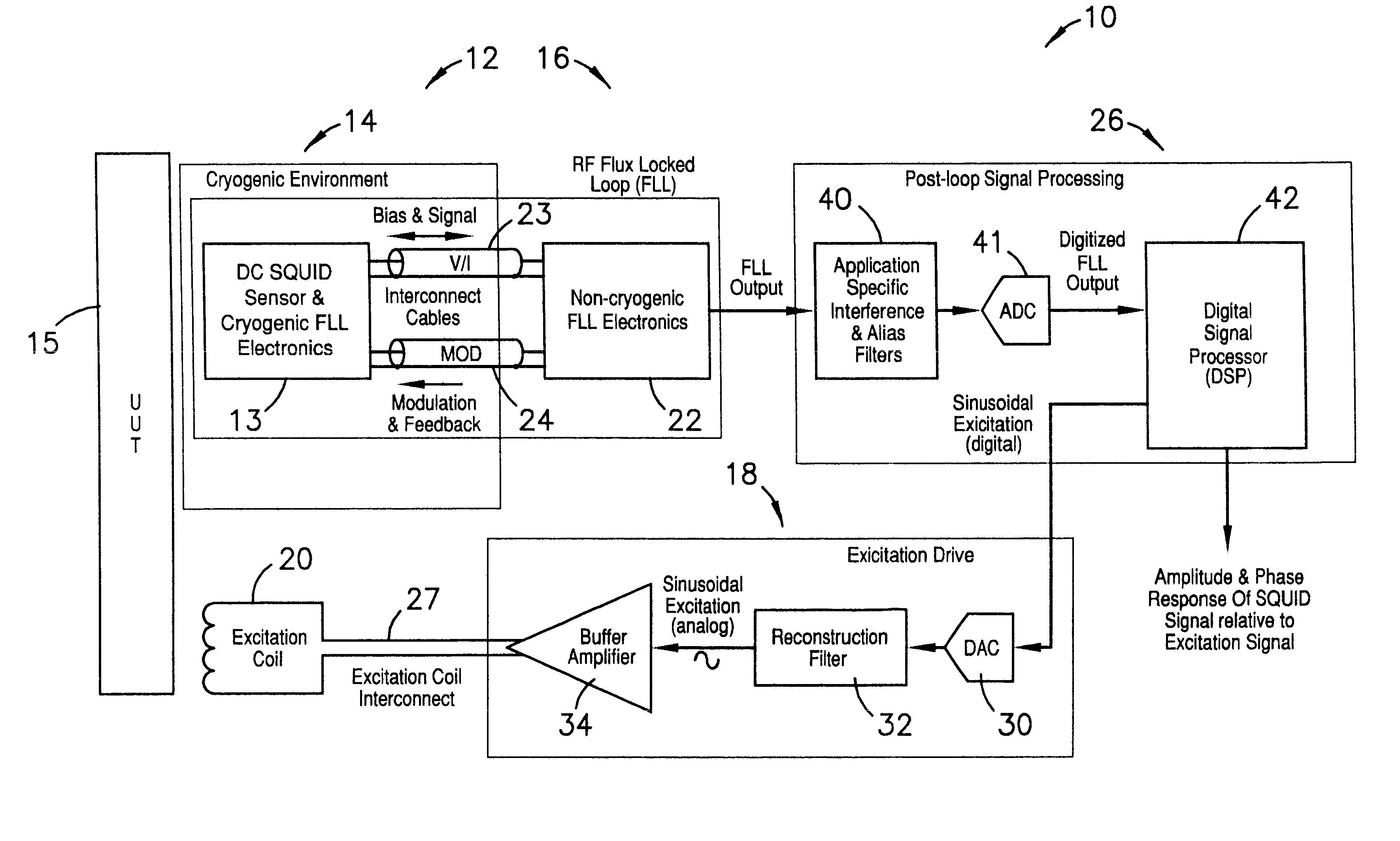
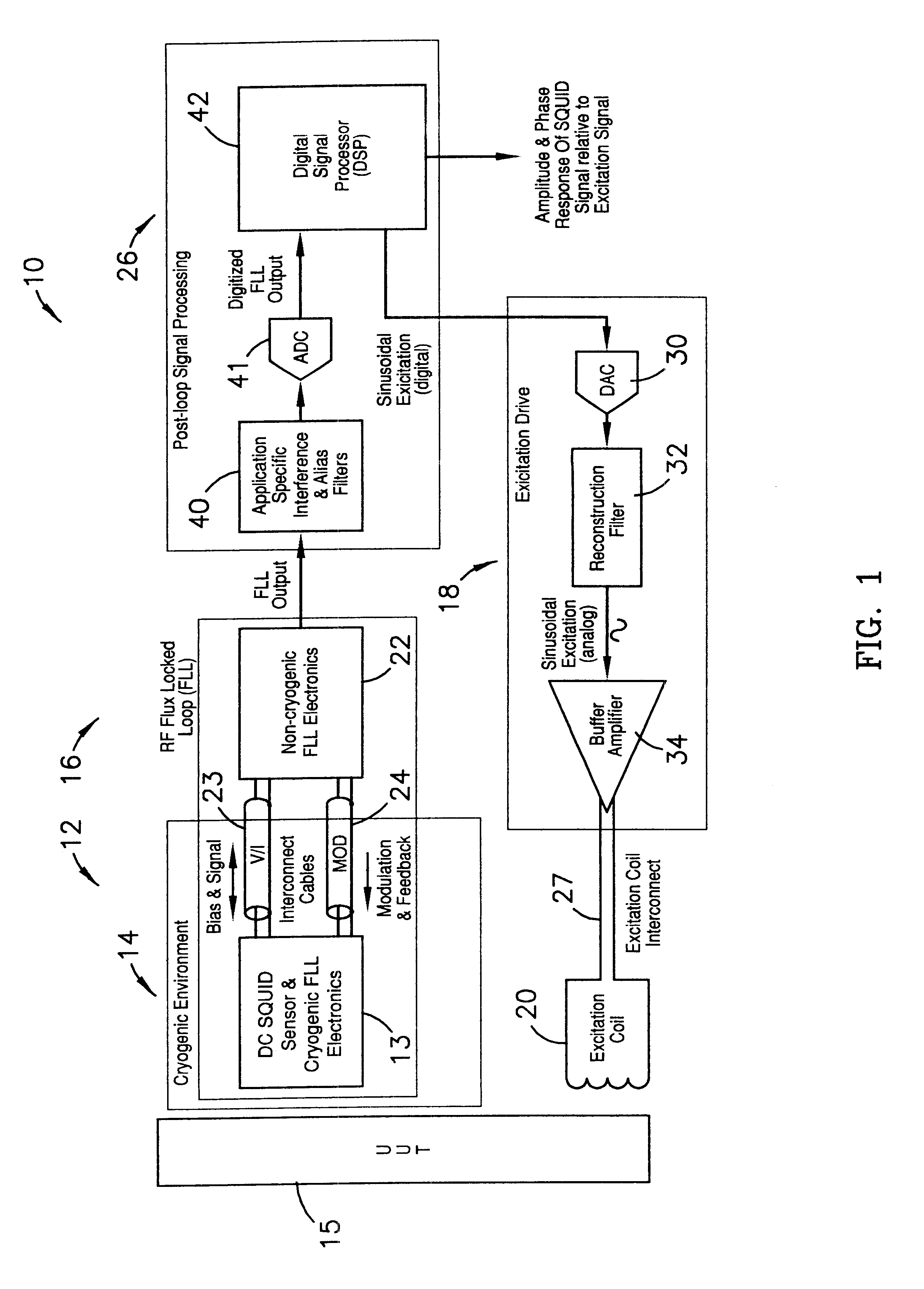
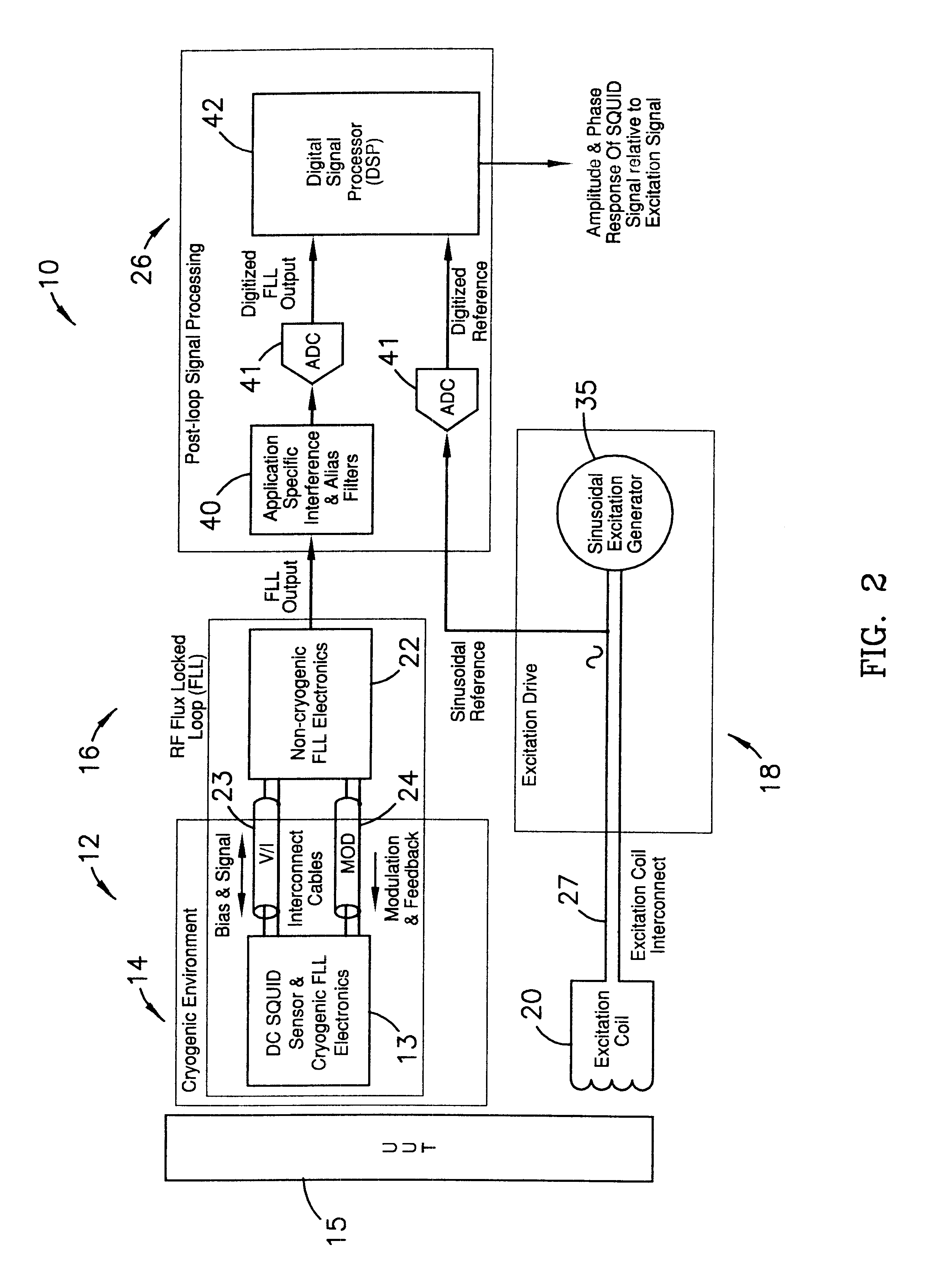
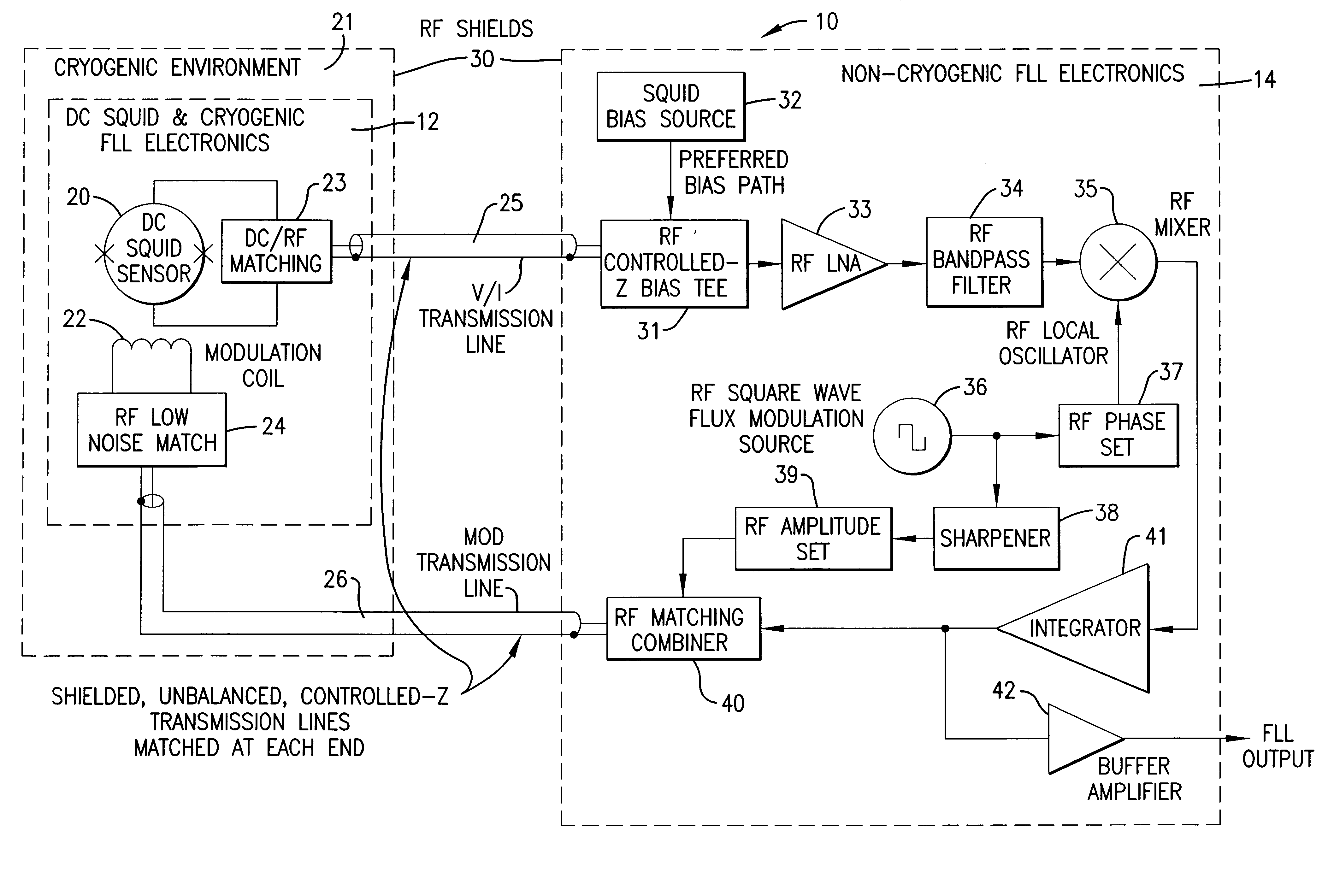
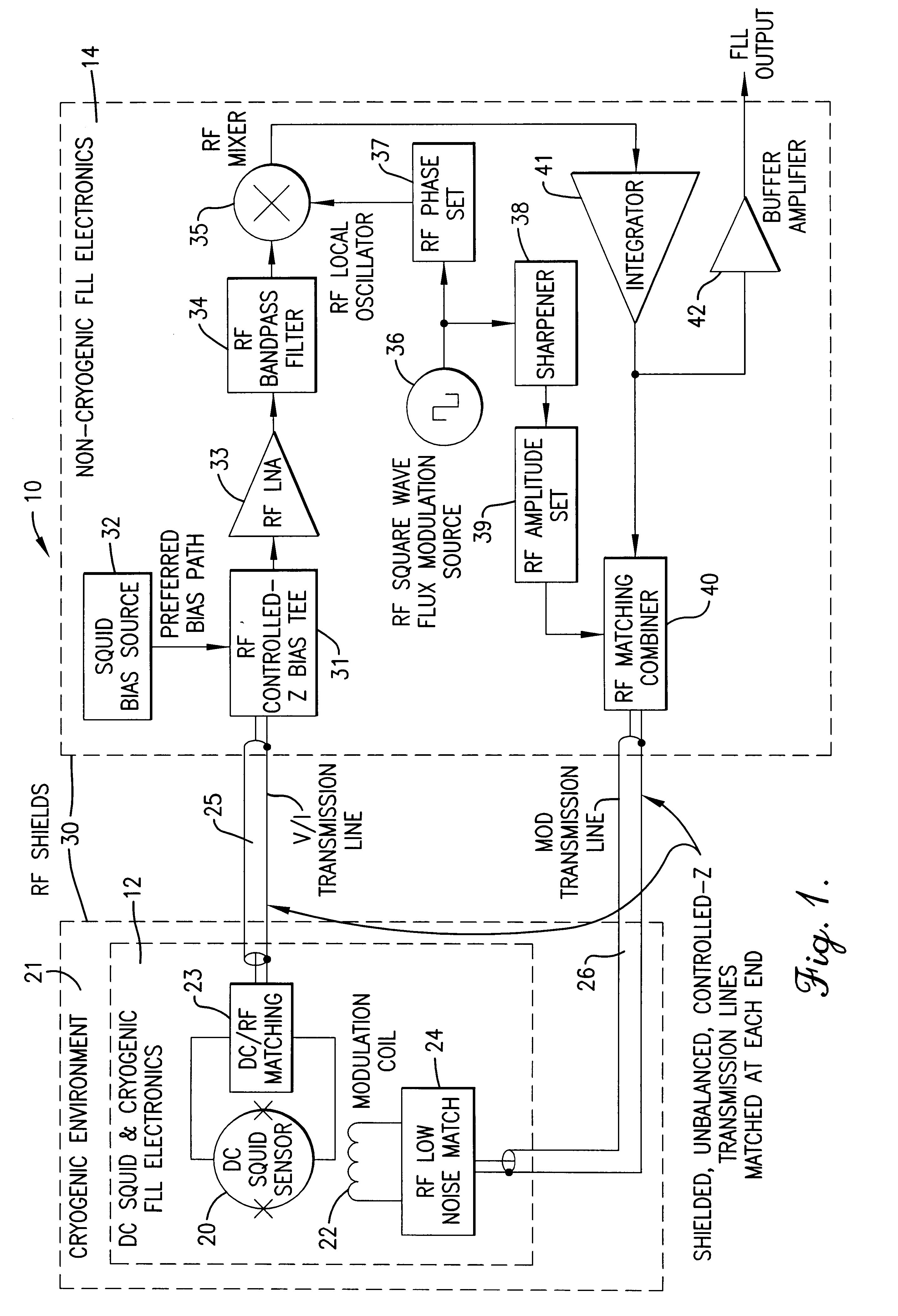
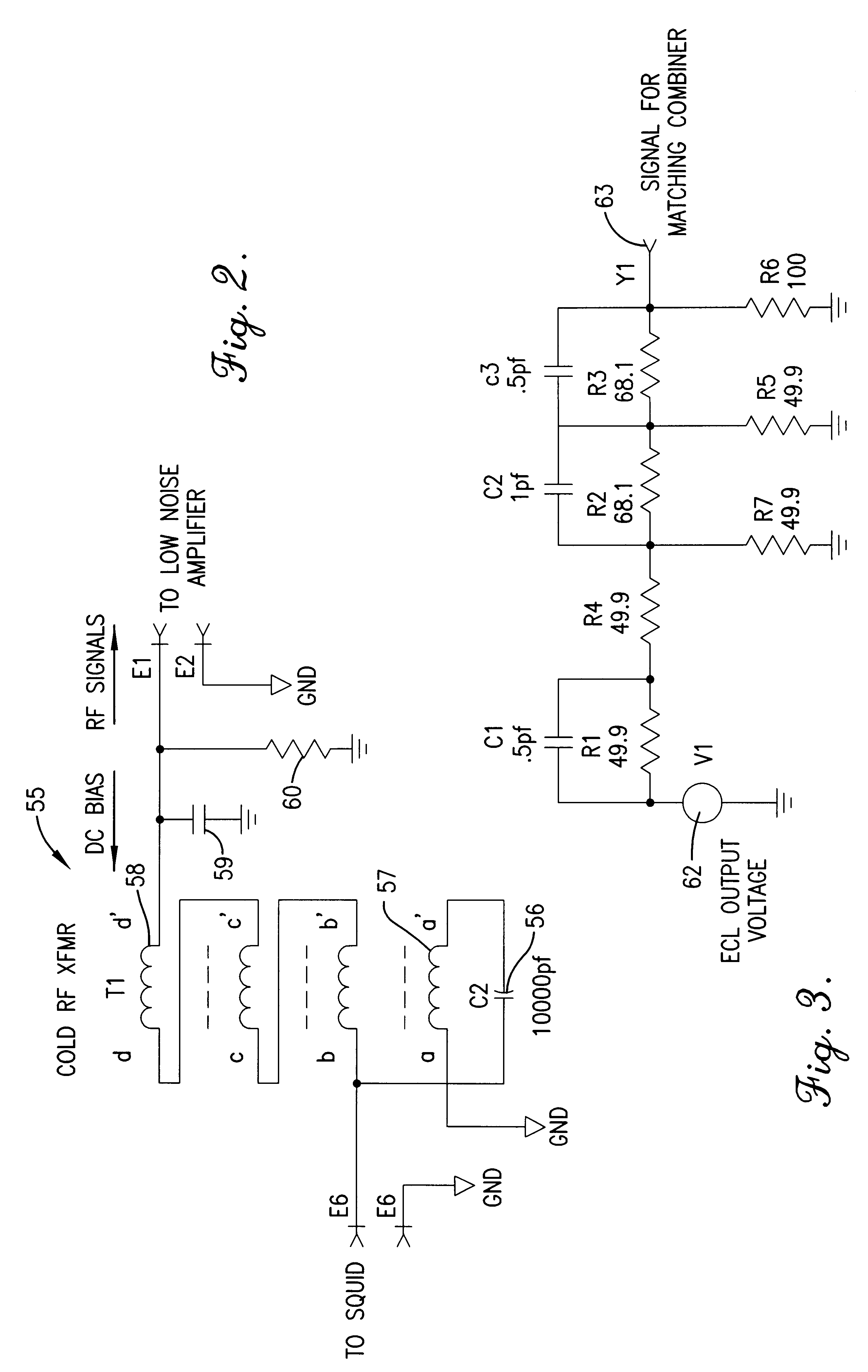
Read-out electronics for DC SQUID sensor systems, the read-out electronics incorporating low Johnson noise radio-frequency flux-locked loop circuitry and digital signal processing algorithms in order to improve upon the prior art by a factor of at least ten, thereby alleviating problems caused by magnetic interference when operating DC SQUID sensor systems in magnetically unshielded environments.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Superconducting quantum interference apparatus and method for high resolution imaging of samples
InactiveUS7002341B2Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringHigh resolution imagingRadiation shield
A method and apparatus performs high resolution imaging. The disclosed apparatus includes a low temperature SQUID sensor mounted in close proximity to a dewar thin window. A radiation shield has an extension surrounding the detection coil.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV +1
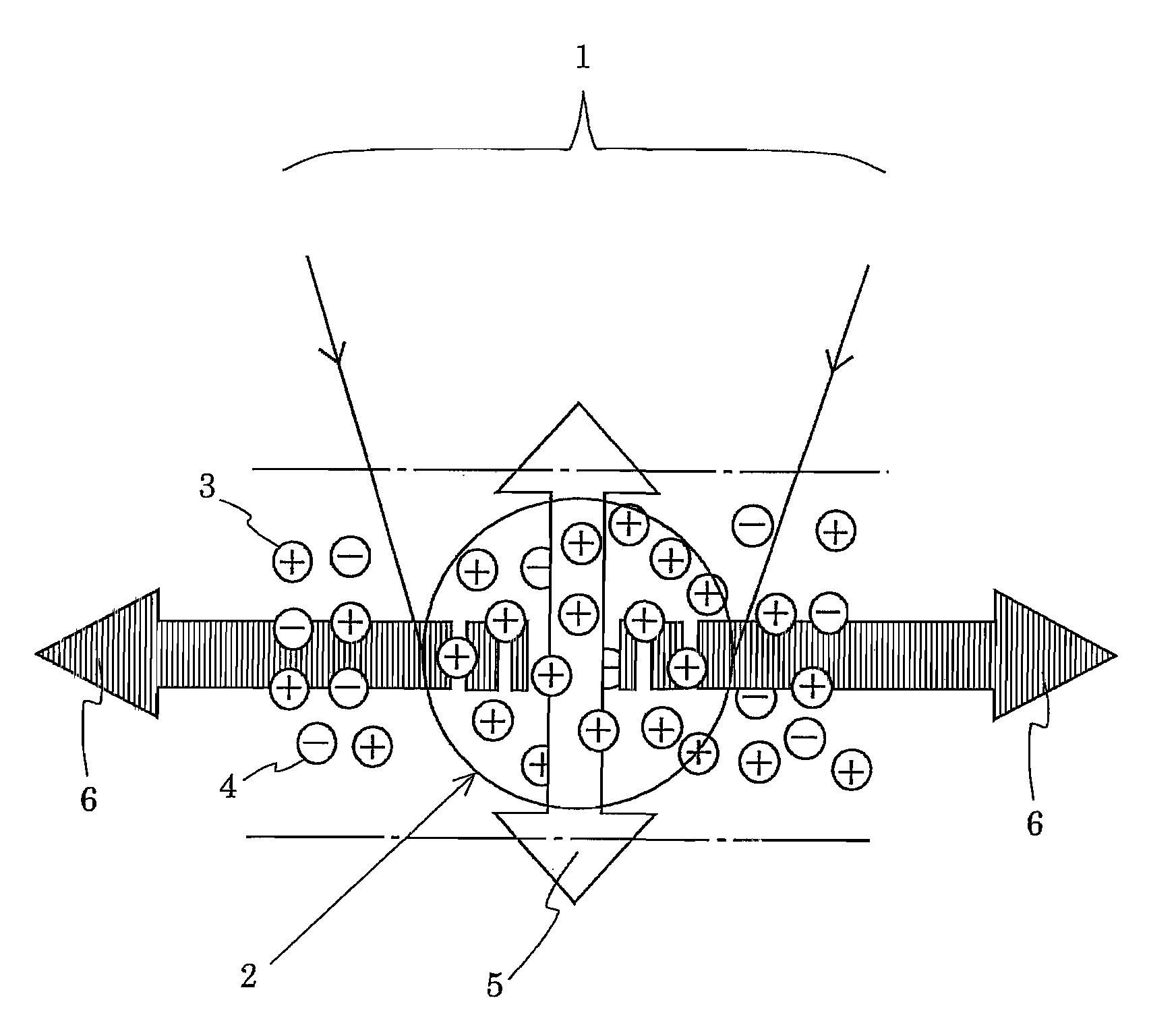
Method of and apparatus for measuring properties of an object with acoustically induced electromagnetic waves
ActiveUS20090221900A1High position resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectromagnetic electron waveProperty value
A measuring method and apparatus in which a measurable object (23) is irradiated with acoustic waves to measure a change in property value of charged particles in the object from electromagnetic waves induced thereby. A part (2) of the measurable object irradiated with an acoustic focused beam (1) is in a charge distribution state in which positive charged particles (3) are greater in number in the part (2) where electromagnetic waves induced by positive charged particles (3) are not canceled by those induced by negative charged particles (4) and where net electromagnetic waves (6) are induced. Since a change in concentration of positive charged particles (3) and / or negative charged particles (4) changes the intensity of electromagnetic waves (6), it is possible to know such a change in concentration of the charged particles from a change in intensity of electromagnetic waves (6).
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
System for magnetic field distortion compensation and method of making same
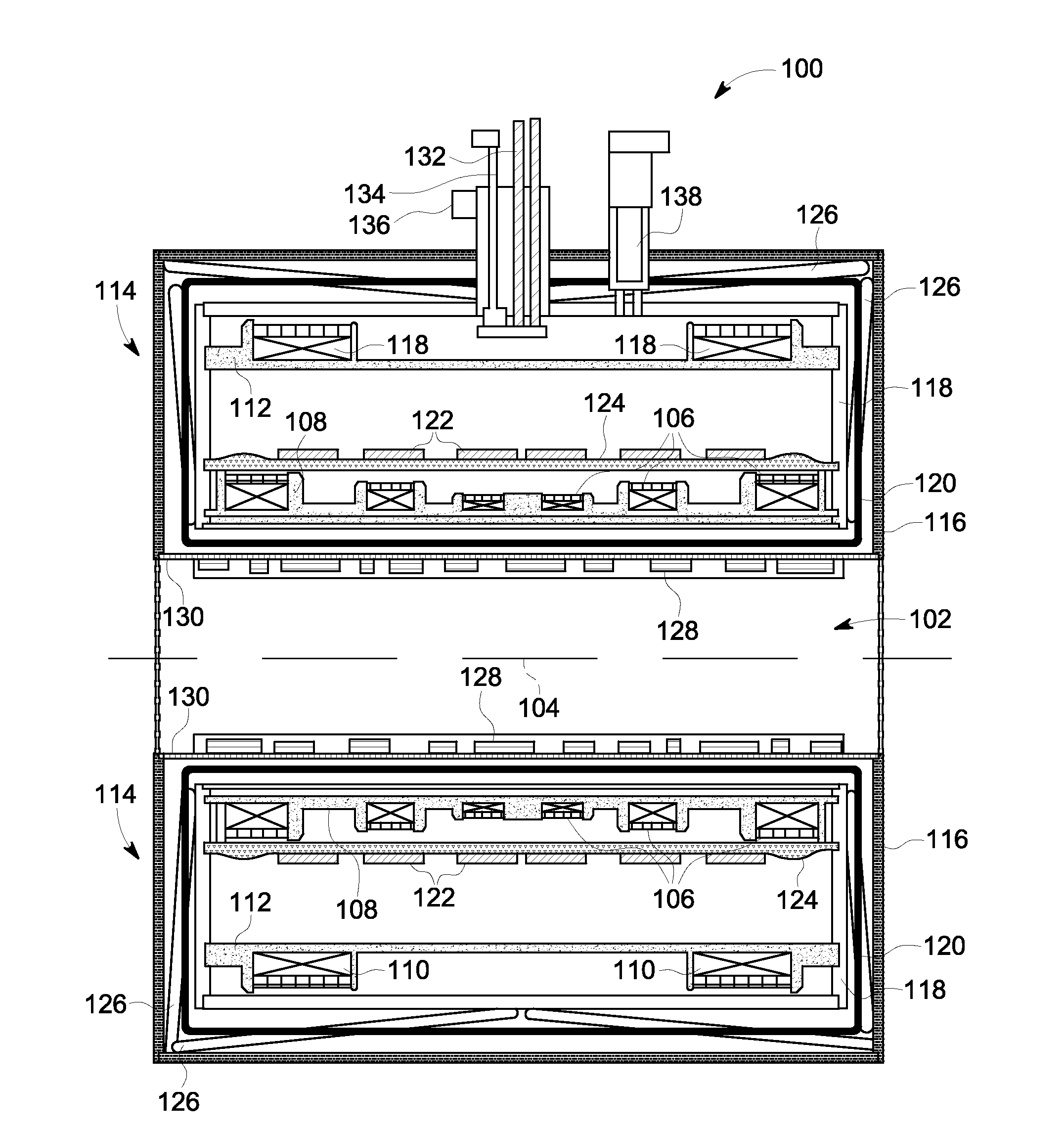
ActiveUS20130157865A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentEngineeringEddy current
A system and method for magnetic field distortion compensation includes a cryostat for a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. The cryostat includes a vacuum casing having a vacuum therein. A cryogen vessel is disposed within the casing, the vessel having a coolant therein. A thermal shield is disposed between the vacuum casing and the cryogen vessel. An eddy current compensation assembly is disposed within the casing. The eddy current compensation assembly includes a plurality of electrically conductive loops formed on one of the vacuum casing, the cryogen vessel, and the thermal shield and constructed to mitigate vibration-induced eddy currents in the MRI system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting magnetic compensation device and method based on predistortion
ActiveCN103616650AImprove stabilityEasy to implementMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDigital signal processingAnalog-to-digital converter
The invention relates to a superconducting magnetic compensation device and method based on predistortion. The superconducting magnetic compensation device based on predistortion is characterized in that the device is composed of a reference magnetic sensor, a magnetic compensation circuit and a compensation coil, the reference magnetic sensor is used for measuring magnetic field signals of an area to be compensated, the magnetic compensation circuit is used for extracting signals of a frequency band to be compensated from the magnetic field signals measured by the reference magnetic sensor, and then the magnetic field of the specific area is compensated through the compensation coil. The compensation method is characterized in that denoising or threshold value judging digital signal processing is conducted in a controller after the measurement value of the external reference magnetic sensor is obtained through an analog-digital converter firstly, then predistortion is conducted selectively on an input signal of an SQUID device by means of a coil, with a feedback factor dozens of times higher than that of the SQUID device, driven by a power amplifier and a feedback resistor through a digital-analog converter, and finally sampling is conducted on output signals of a magnetic flow locking ring and the power amplifier through a synchronous data acquiring device. The superconducting magnetic compensation device is simple in structure, small in size, high in stability and suitable for being used during exercise or in outdoor environments.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
SQUID magnetic sensor measuring sensitivity enhancement method, device and system
ActiveCN105022005AHigh measurement sensitivityMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityLow-pass filter
The invention provides an SQUID magnetic sensor measuring sensitivity enhancement method, device and system. The method comprises the steps that a background magnetic field is converted into electric signals by utilizing a triaxial magnetometer; the background magnetic field comprises an environment magnetic field and a signal magnetic field; the electric signals are conditioned and then main electric signals reflecting the environment magnetic field are acquired; the main electric signals are converted into an environment deduction magnetic field; and the deduction magnetic field is inputted to an SQUID magnetic sensor to counteract magnetic flux generated in the SQUID magnetic sensor by the environment magnetic field. Information of the environment magnetic field is acquired by using the triaxial magnetometer. Certain compensating magnetic flux is generated via a low-pass filter and a current compensating circuit and exactly counteracts magnetic flux of the external environment magnetic field with which the SQUID magnetic sensor is coupled so that the SQUID magnetic sensor is enabled not to respond to high fluctuation of the environment magnetic field, working at a small-range and high-sensitivity mode can be realized, and high-sensitivity detection of weak measured signals can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-resolution magnetoencephalography system, components and method
InactiveUS20040254443A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayMagnetoencephalography
According to certain embodiments of the present invention, there is provided a mounting arrangement for a magnetoencephalography (MEG) system headrest assembly forming a portion of a SQUID dewar and having a fixed headrest and an array of sensors, wherein a sensor array plate positions the sensors relative to the headset. A plurality of first rods interconnecting the array plate and the movable mounting member. A plurality of second rods are fixed at one of their ends relative to the dewar and are connected at their opposite ends to the movable mounting member. Each one of the first and second rods is composed of material expandable and contractible with changes in temperature, whereby the movable mounting member tends to be moved in one direction toward or away from the sensor array plate, and tends to be moved in an opposite direction away from or toward the array plate, resulting in temperature changes affecting the first and second rods, so that the sensor array plate and its sensors maintain a substantially constant spacing between the sensors and the headrest with changes in temperature. A plurality of second rods are fixed at one of their ends relative to the dewar and are connected at their opposite Each one o the rods is composed of material expandible and contractable with changes in temperature, whereby the movable mounting member tends to be moved in one direction toward or away from the sensor array plate, and tends to be moved in an opposite direction away from or toward the array plate resulting in temperature changes affecting the first and second rods, so that the sensor array plate and its sensors maintain a substantially constant spacing between the sensors and and headrest with changes in temperature.
Owner:TRISTAN TECH
Fast flux locked loop
InactiveUS6448767B1Benefit control loop DC stabilityReduce effective amplifier input noiseMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesPulse generation by super conductive devicesElectricityMagnetic measurements
A flux locked loop for providing an electrical feedback signal, the flux locked loop employing radio-frequency components and technology to extend the flux modulation frequency and tracking loop bandwidth. The flux locked loop of the present invention has particularly useful application in read-out electronics for DC SQUID magnetic measurement systems, in which case the electrical signal output by the flux locked loop represents an unknown magnetic flux applied to the DC SQUID.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Superconductive quantum bit measuring system
InactiveCN101059556AReduce noise interferenceAvoid noise disturbanceCurrent/voltage measurementMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesFiberAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a superconductive quantum bit measuring system, comprising a signal source which current signal output is connected with an object Josephson node with two ends respectively connected with two inputs of a low-noise amplifier, while the output of the low-noise amplifier is connected with the positive end of the amplifier, and the negative end of the amplifier is grounded, the output of the amplifier is connected with a stop end of a counter which start end is connected with a synchronous signal output of the signal source, the current signal output of the signal source and the object Josephson node are serially connected with a copper powder filter between, the current signal output of the signal source and the copper powder fiber are serially connected with a RC filter between. The inventive system can effectively reduce noise and meet the demand of superconductive quantum bit measurement.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Popular searches
Sensors Superconductor devices Measurements using magnetic resonance Acoustic wave reradiation Dissimilar materials junction devices Digital storage Detection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonance Magnitude/direction of magnetic fields Computation using non-contact making devices Solid-state devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com