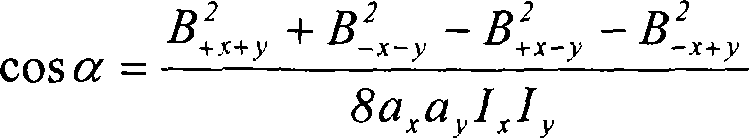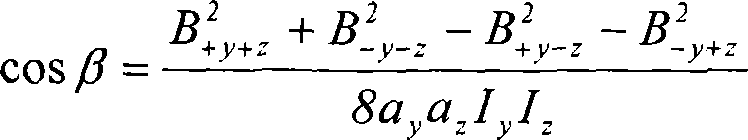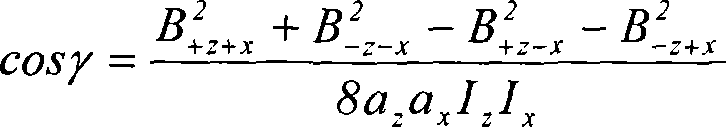Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
361 results about "Gradiometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gradiometer measures the gradient (numerical rate of change) of a physical quantity, such as a magnetic field or gravity.
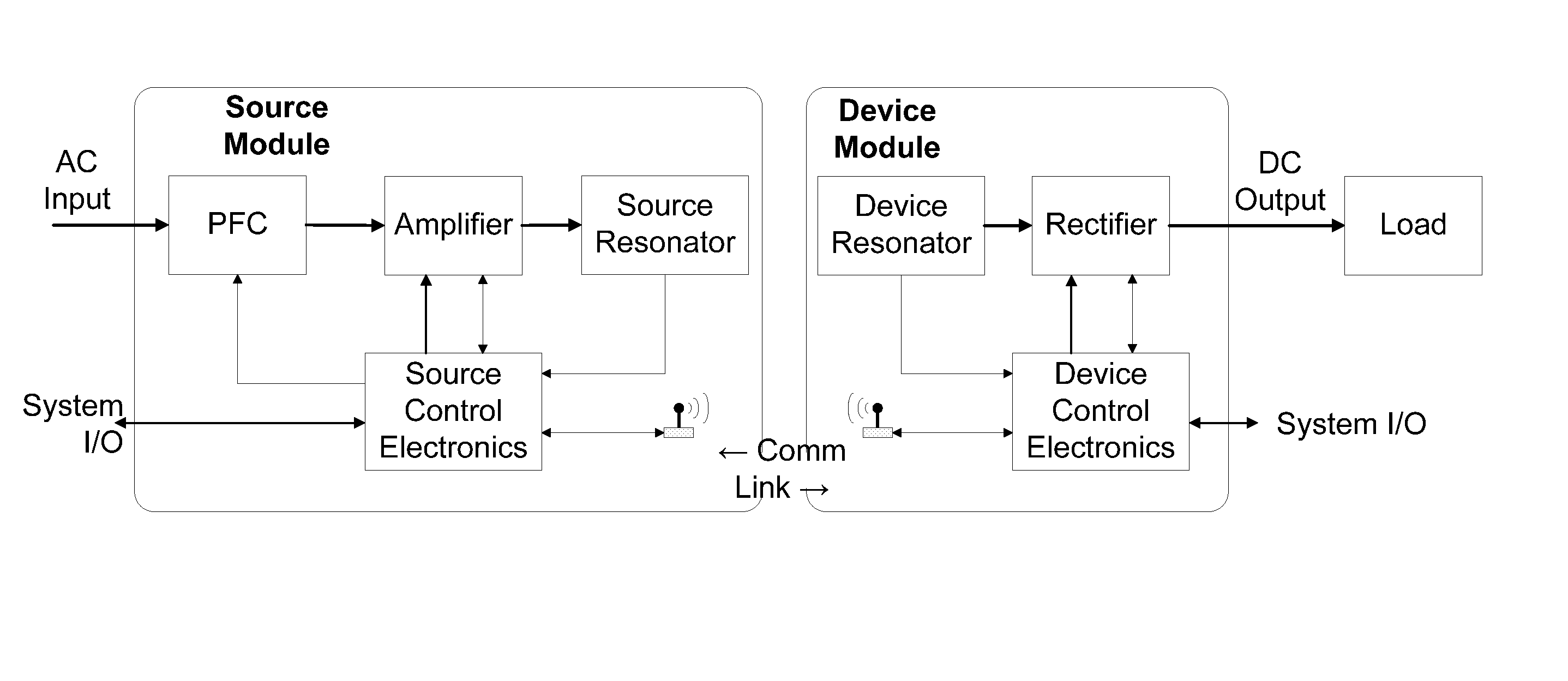
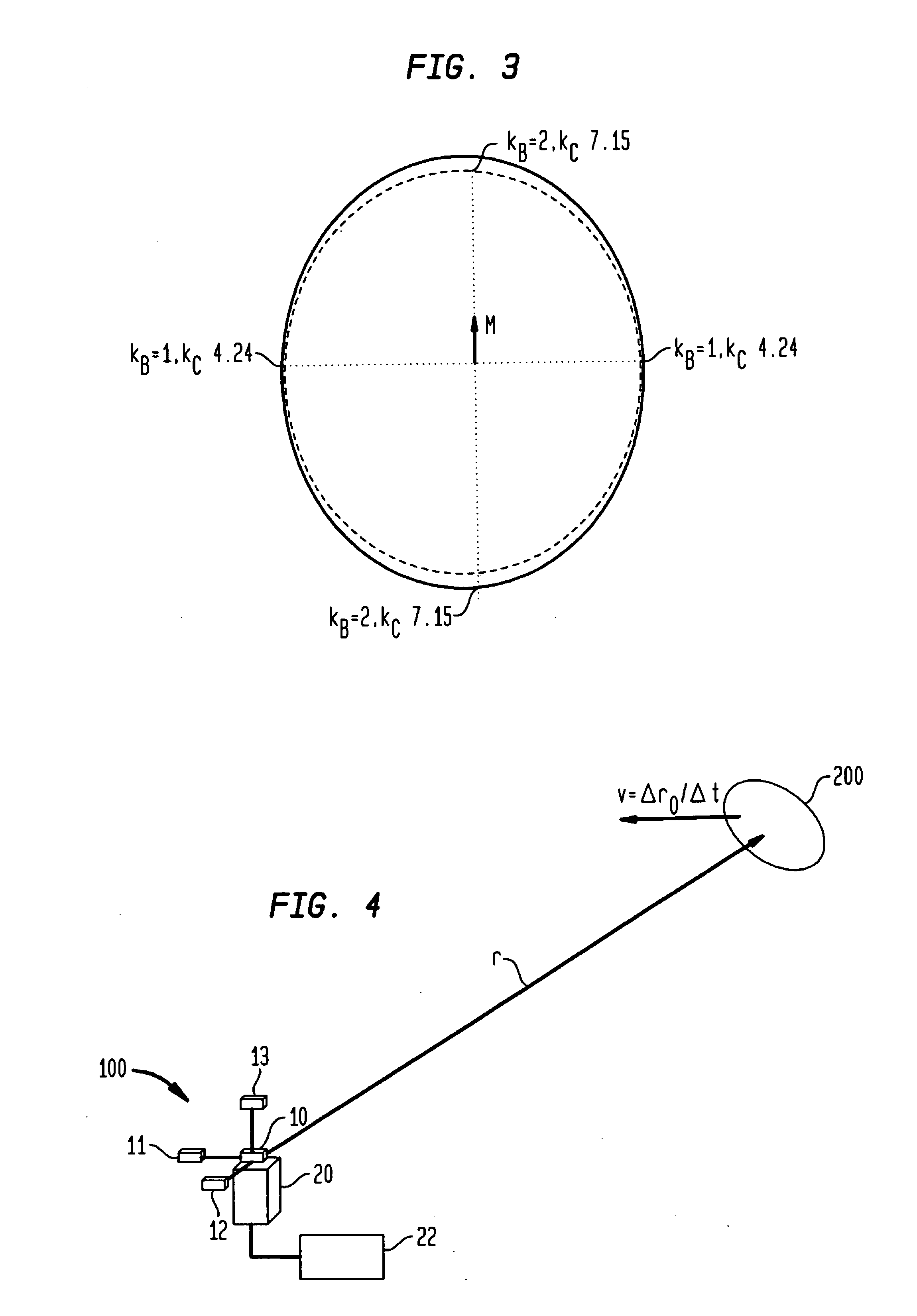
Foreign object detection in wireless energy transfer systems
ActiveUS20130069441A1Improve detection rateNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemEnergy transferForeign object
A wireless energy transfer system includes a foreign object debris detection system. The system includes at least one wireless energy transfer source configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field. The foreign object debris may be detected by at least one field gradiometer positioned in the oscillating magnetic field. The voltage of the at least one field gradiometer may be measured using readout circuitry and a feedback loop based on the readings from the gradiometers may be used to control the parameters of the wireless energy source.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer with improved linearity and sensitivity and method for gravity gradient sensing
ActiveUS20060207326A1Improve linearityReduce sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGravitational wave measurementAccelerometerOperability
A cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer sensitive to off-diagonal components of the gradient tensor includes, for each gradient axis, a pair of closely matched angular accelerometers coupled by superconducting circuitry, including sensing circuits designed to minimize the sensitivity of the instrument to angular acceleration of the platform at which the angular accelerometers are mounted; and a mode-splitting circuitry designed to reduce a nonlinear coupling of angular acceleration to the output of the gravity gradiometer and to attain the operability of the instrument in a broader range in the frequency domain.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
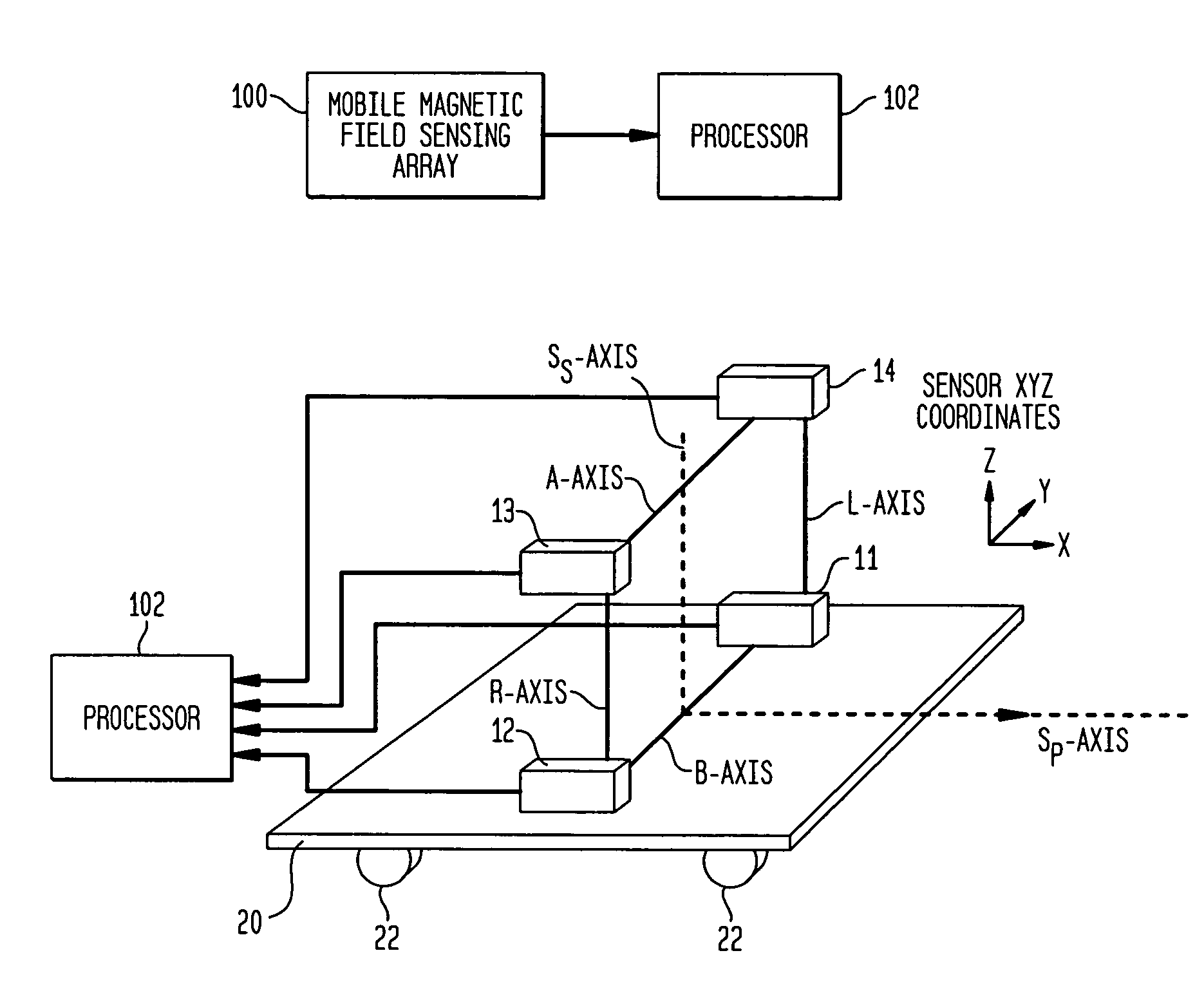
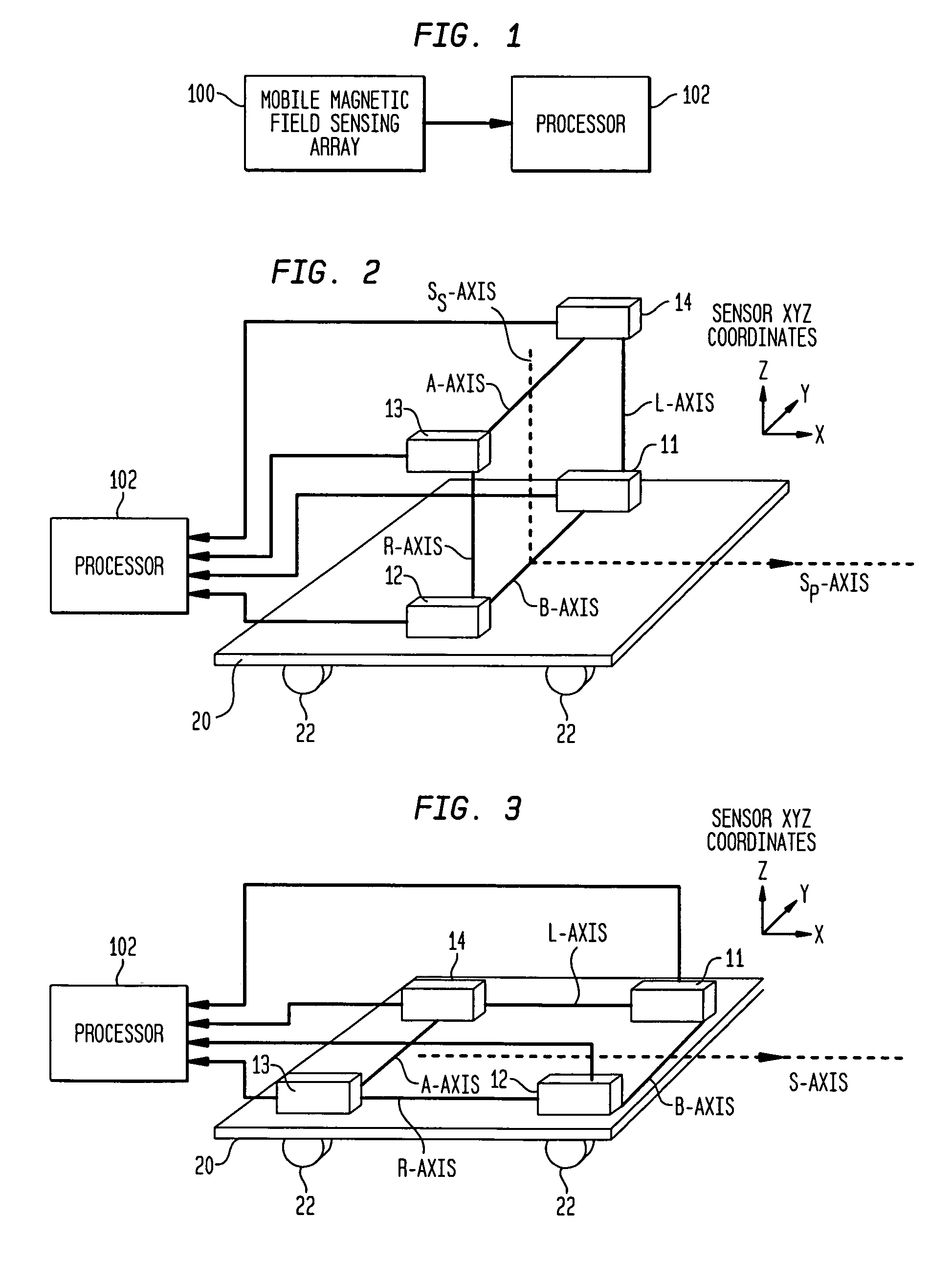
System and method using magnetic anomaly field magnitudes for detection, localization, classification and tracking of magnetic objects
InactiveUS7932718B1Easy to detectImprove classificationMagnetic gradient measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic dipoleGradiometer
A magnetic anomaly sensing system and method uses at least four triaxial magnetometer (TM) sensors with each of the TM sensors having X,Y,Z magnetic sensing axes. The TM sensors are arranged in a three-dimensional array with respective ones of the X,Y,Z magnetic sensing axes being mutually parallel to one another. The three-dimensional array defines a geometry that forms at least one single-axis gradiometer along each of the X,Y,Z magnetic sensing axes. Information sensed by the TM sensors is to generate scalar magnitudes of a magnetic anomaly field measured at each of the TM sensors, comparisons of the scalar magnitudes to at least one threshold value, distance to a source of the magnetic anomaly field using the scalar magnitudes when the threshold value(s) is exceeded, and a magnetic dipole moment of the source using the distance.
Owner:USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY THE
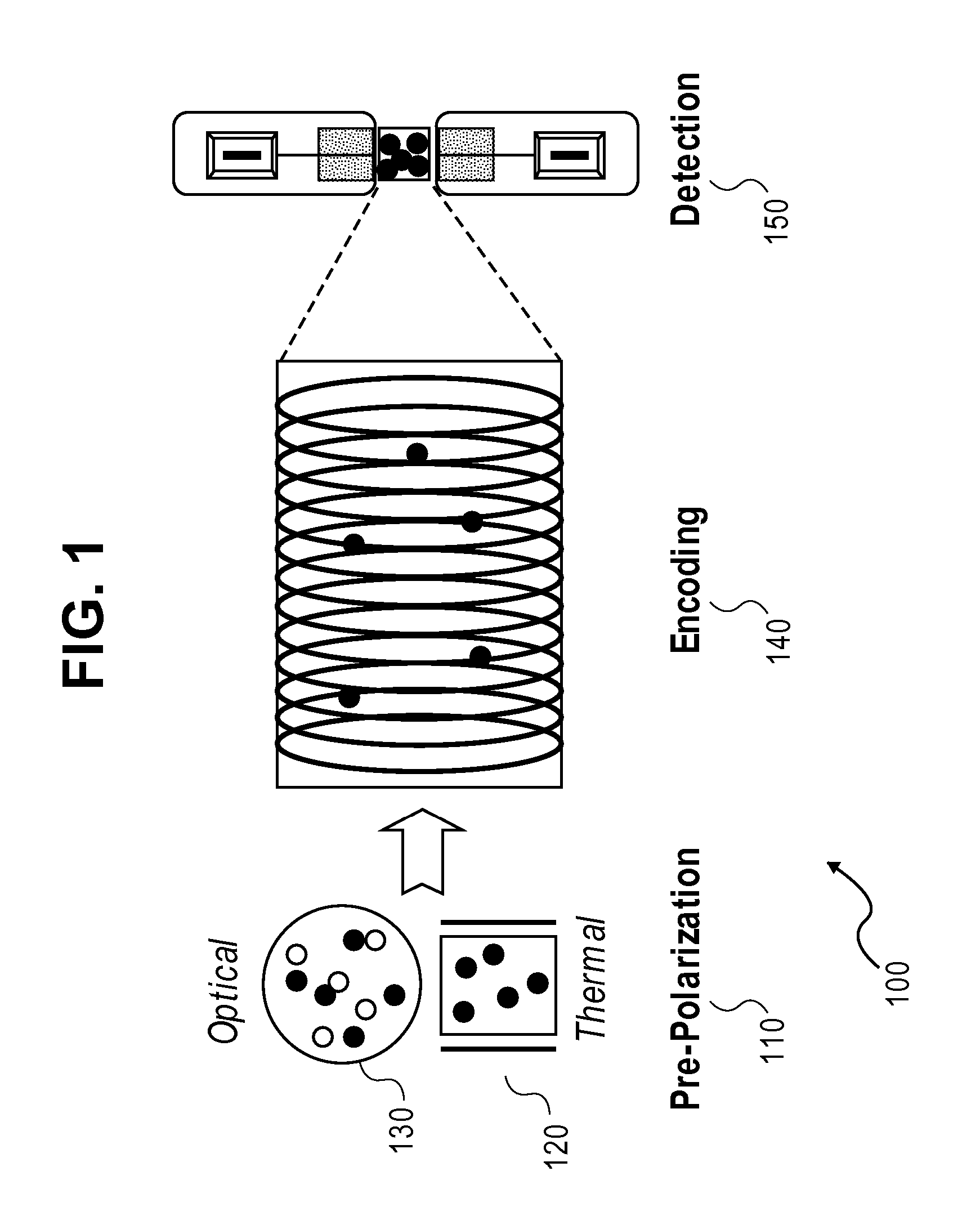
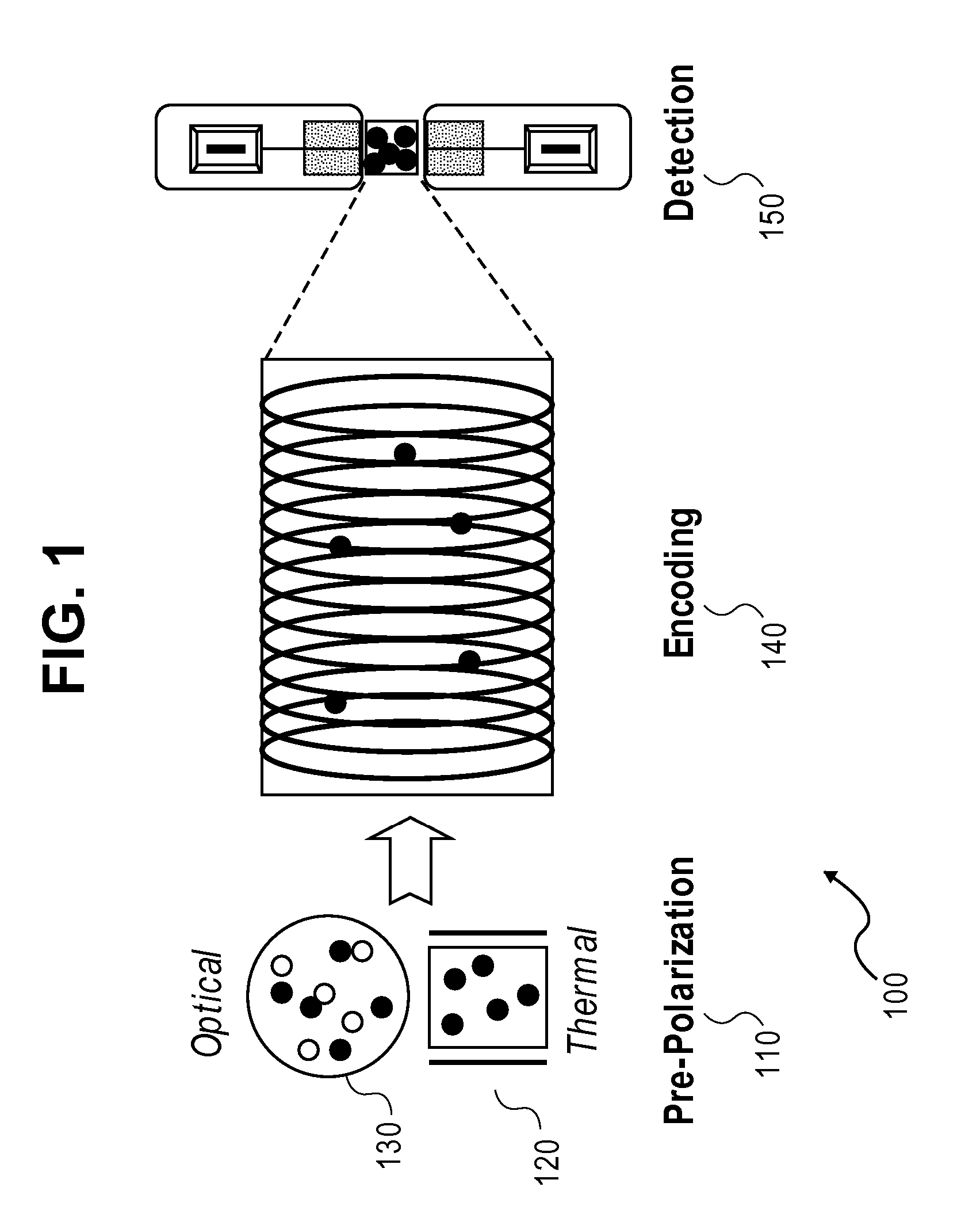
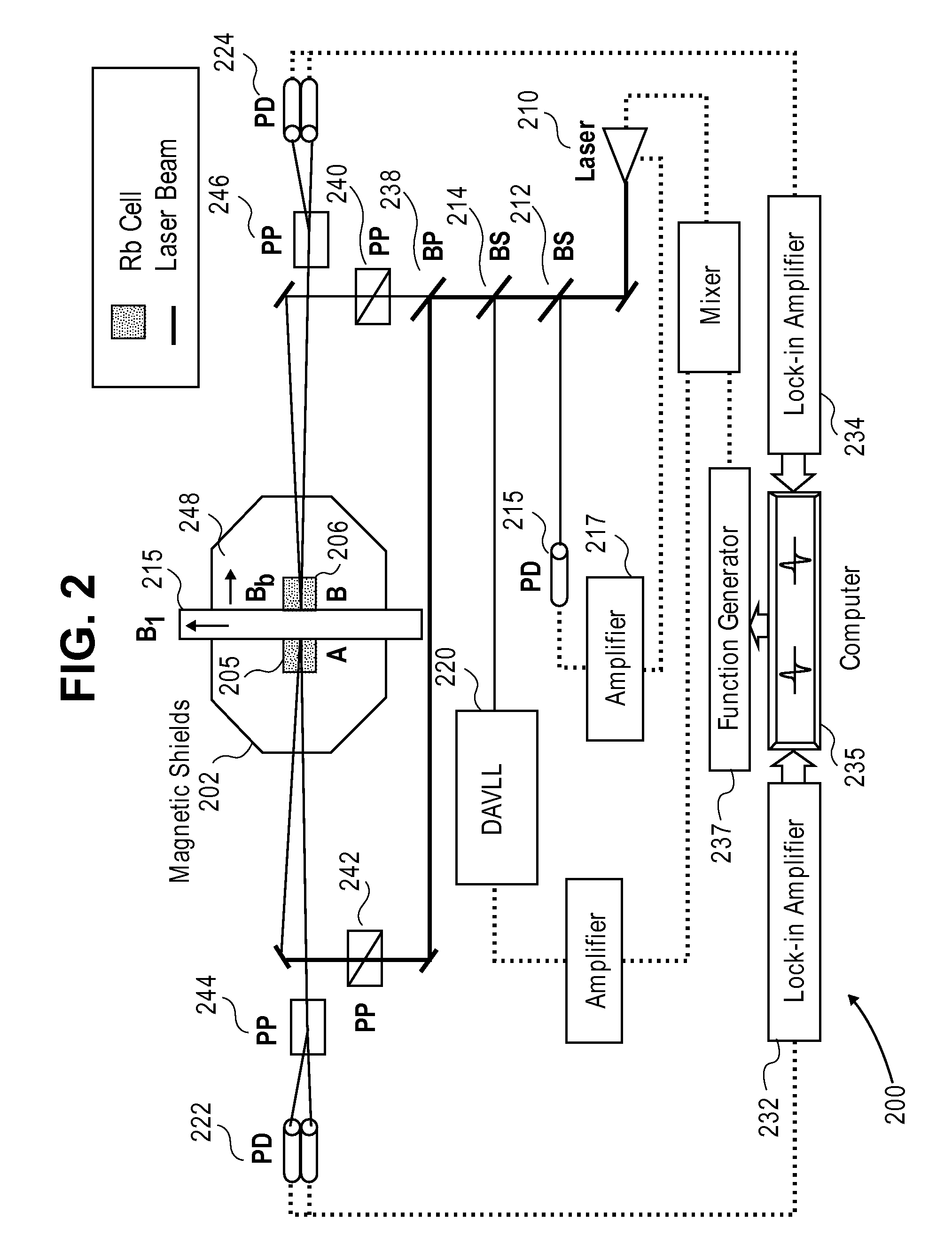
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS20070205767A1Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSingle polarizationGradiometer
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Gravity gradiometer
ActiveUS7360419B2Improve featuresStatic/dynamic balance measurementGravitational wave measurementHigh stiffnessRoom temperature
A gravity gradiometer having quadrupole responders in which a mass quadrupole is supported by a torsional spring forming a flexure allowing rotation of the mass quadrupole about its center of mass. The flexure can be a pair of spaced apart posts. The flexure can be made from glassy metal having at room temperature a high elastic limit, high stiffness, high strength and low internal damping. The flexure can alternatively be a web made of glassy metal.
Owner:GEDEX
Gravity gradiometry
InactiveUS6837106B2Reduces linear accelerationsEfficient separationSeismologyGravitational wave measurementMobile vehicleSystems design
A gravity gradiometer is combined with a two-stage actively controlled isolation system. The gravity gradiometer and two stage isolation system may then be mounted within (or on) a mobile vehicle such as, for example, an aircraft. It has been recognized by the inventors herein that the accelerations imparted to an aircraft during normal operations can be separated through system design into two relatively distinct regimes within the frequency domain. The invention provides a first isolation mount, which forms part of the isolation system, to isolate accelerations (and resulting translations) falling within a first of the two frequency regimes. The second isolation mount, which is mounted to the first isolation mount, isolates accelerations falling within the second of the two frequency regimes. A gravity gradiometer can then be mounted to the second isolation mount. As a result of housing the gravity gradiometer within the nested isolation system (a combination of the first and second isolation mounts), the gravity gradiometer is substantially isolated from the accelerations experienced by the mobile vehicle. Consequently, gravity gradients measured by the gravity gradiometer are relatively noise free and provide heretofore-unobtainable accuracy.
Owner:GEDEX
Magnetic gradiometer incorporating global feedback
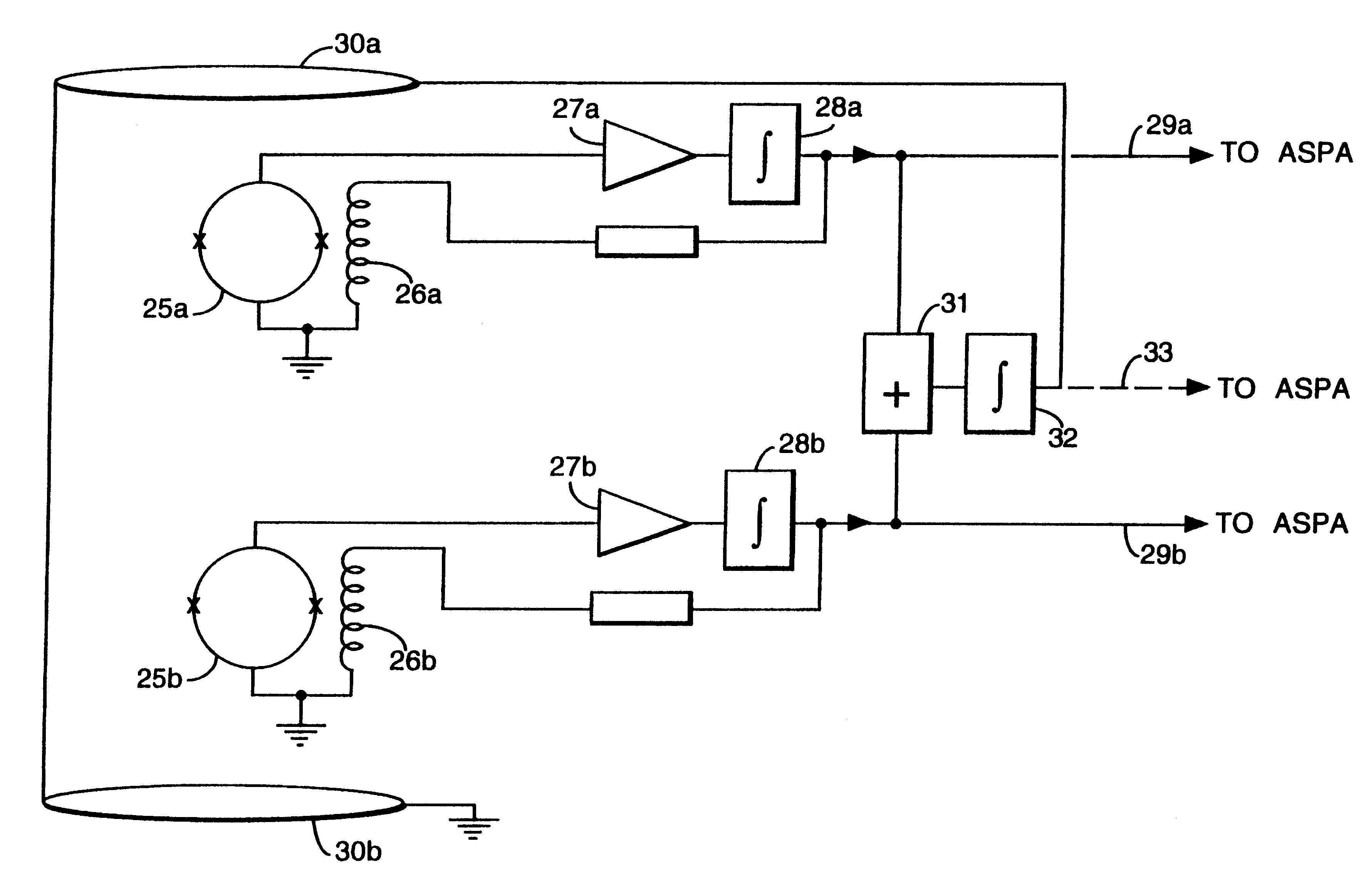
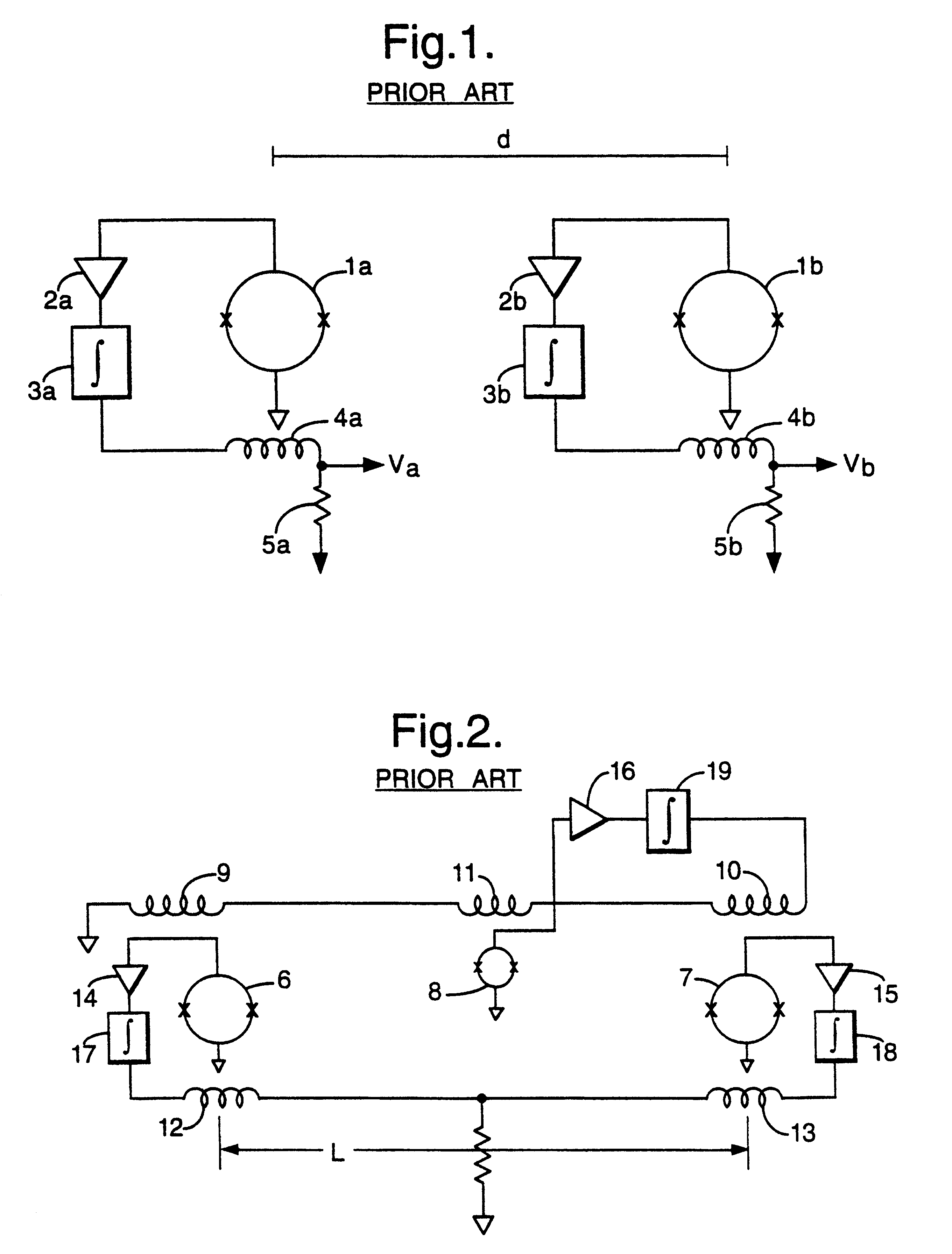
InactiveUS6339328B1Minimizing energySufficient dynamic rangeMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic field gradientGradiometer
A gradiometer for measuring properties of a magnetic field and in particular, for measuring magnetic field gradient components, comprising at least two magnetic sensors wherein at least two of the magnetic sensors are arranged to sense the magnetic field component in substantially the same direction. The magnetic sensors may be super conducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometers, Hall probes, flux gates or magneto-resistive magnetometers. The gradiometer also includes a computer processor loaded with an adaptive signal-processing algorithm, for performing adaptive signal balancing of the magnetometer outputs. In a preferred embodiment the gradiometer may comprise at least eight magnetometers in a three-dimensional arrangement, and a set of three orthogonal global feedback coils, one for each direction x, y, z, such that the five independent magnetic field gradient components may be measured. The gradiometer may also be used to measure second or higher order magnetic field gradient components.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Three-axial magnetometer correcting method and three-axial magnetic gradient correcting method
InactiveCN101251584AImprove work efficiencyReasonable designElectrical measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic gradientMagnetic disturbance
The invention relates to a magnetometer correcting method and a magnetic gradiometer correcting method, in particular to a three axis magnetometer correcting method and a three axis magnetic gradiometer correcting method. Under the conditions of no standard three-axis coil, no standard magnetic field and no normalized three-axis magnetometer, the invention corrects the error and carrier magnetic interference generated due to the inconsistent nonorthogonality, interaxial coupling and sensitivity of the three axis magnetometer and the three axis magnetic gradiometer. The invention adopts an ordinary three-axis coil, a scalar quantity magnetometer and a high precision current source to form a correcting device which has the correcting precision at the same order of magnitude as the single axis test precision of a corrected three axis magnetometer. The invention does not need to turn a corrected three axis magnetometer and a corrected three axis magnetic gradiometer during correcting, thereby having a simple operation process and high correcting precision and improving the test precision of magnetic field vector by the three axis magnetometer and the three axis magnetic gradiometer.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Gradiometer-based flux qubit for quantum computing and method therefor
InactiveUS6984846B2Intrinsic robustnessHigh quality factorQuantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsGradiometerFlux qubit
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Magnetic screening system
InactiveUS20060197523A1Improve processing speedLess incidenceElectric/magnetic detectionMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsHigh rateObject store
A magnetic screening system uses directional gradiometers with high resolution and accuracy to measure magnetic field signatures of target objects (e.g., gun, knife, cell phone, keys) in a volume of interest. The measured signatures can be compared to signatures of known objects stored in a local database. Various mathematical processes may be used to identify or classify target object signatures. In a network of magnetic screening systems, the magnetic screening systems can transmit signatures to a central signature database, and a management computer can share the central signature database with all of the magnetic screening systems on the network. The magnetic screening system can operate in multiple modes, such as a tracking mode, measurement mode, and self-test mode. Through use of unique processes and designs, the magnetic screening system can achieve a high rate of processing persons for target objects.
Owner:ASSURANCE TECH CORP
Cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer with improved linearity and sensitivity and method for gravity gradient sensing
ActiveUS7305879B2Improve linearityReduce sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGravitational wave measurementAccelerometerOperability
A cross-component superconducting gravity gradiometer sensitive to off-diagonal components of the gradient tensor includes, for each gradient axis, a pair of closely matched angular accelerometers coupled by superconducting circuitry, including sensing circuits designed to minimize the sensitivity of the instrument to angular acceleration of the platform at which the angular accelerometers are mounted; and a mode-splitting circuitry designed to reduce a nonlinear coupling of angular acceleration to the output of the gravity gradiometer and to attain the operability of the instrument in a broader range in the frequency domain.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
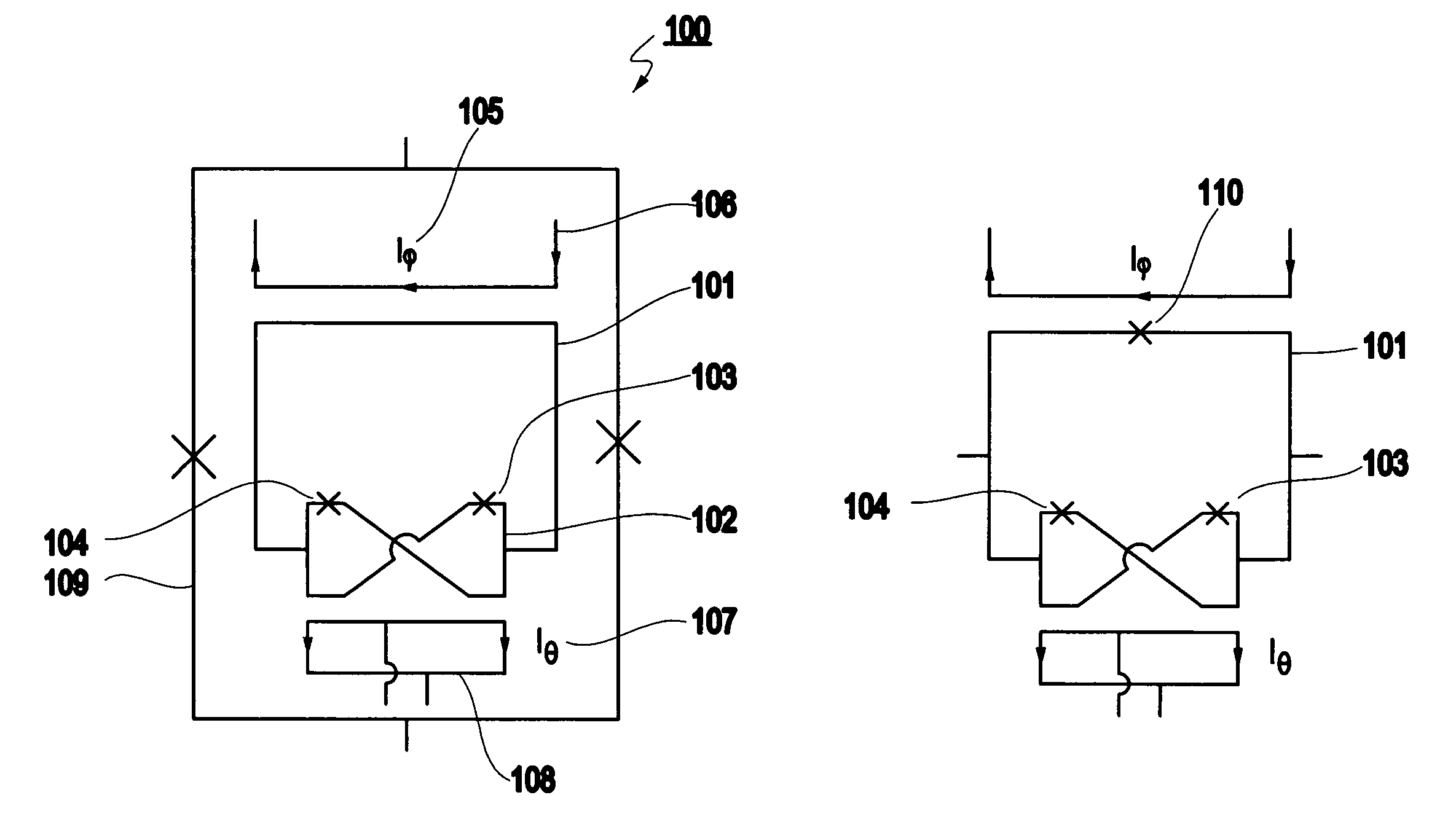
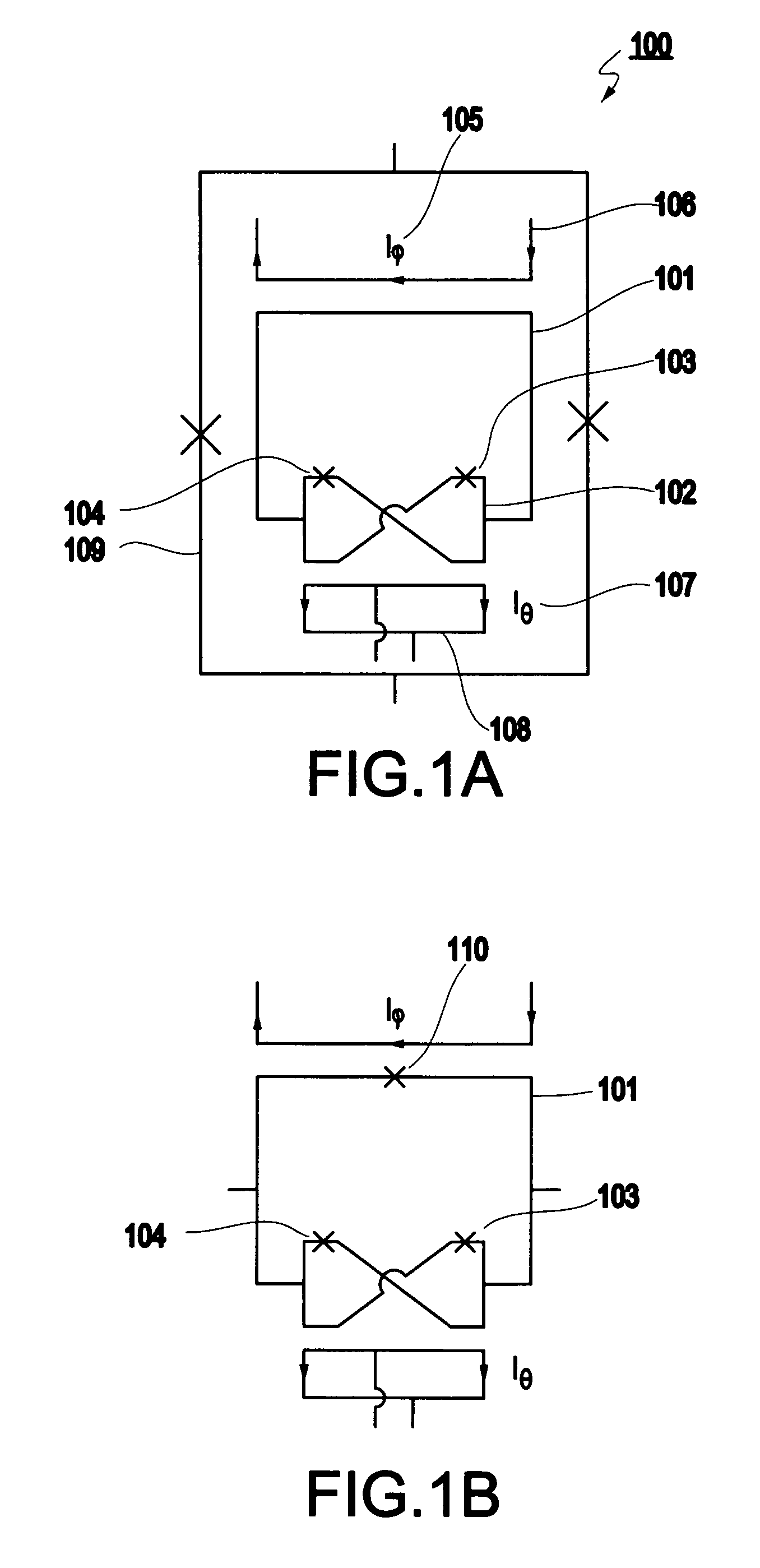
Gravity Gradiometer
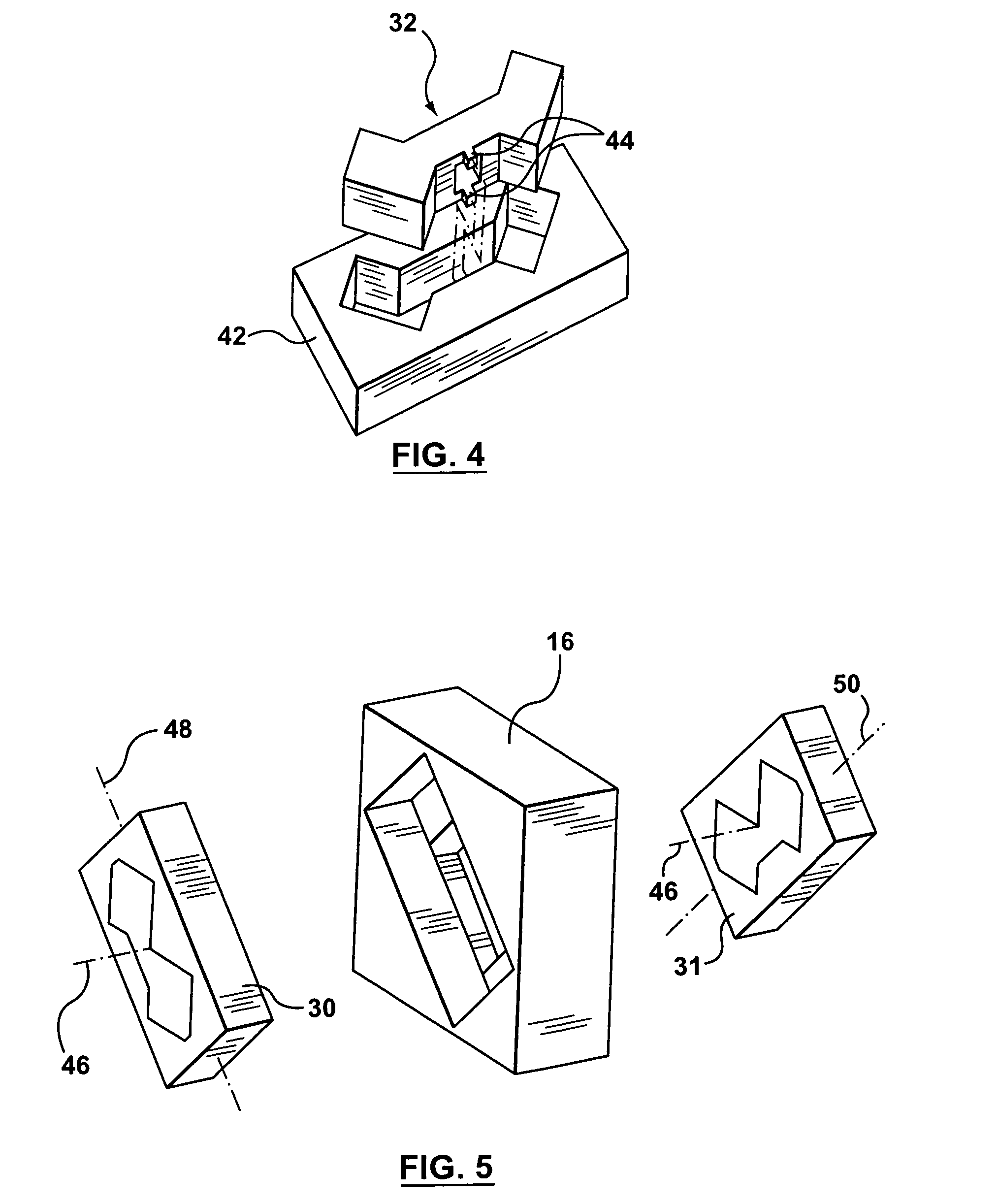
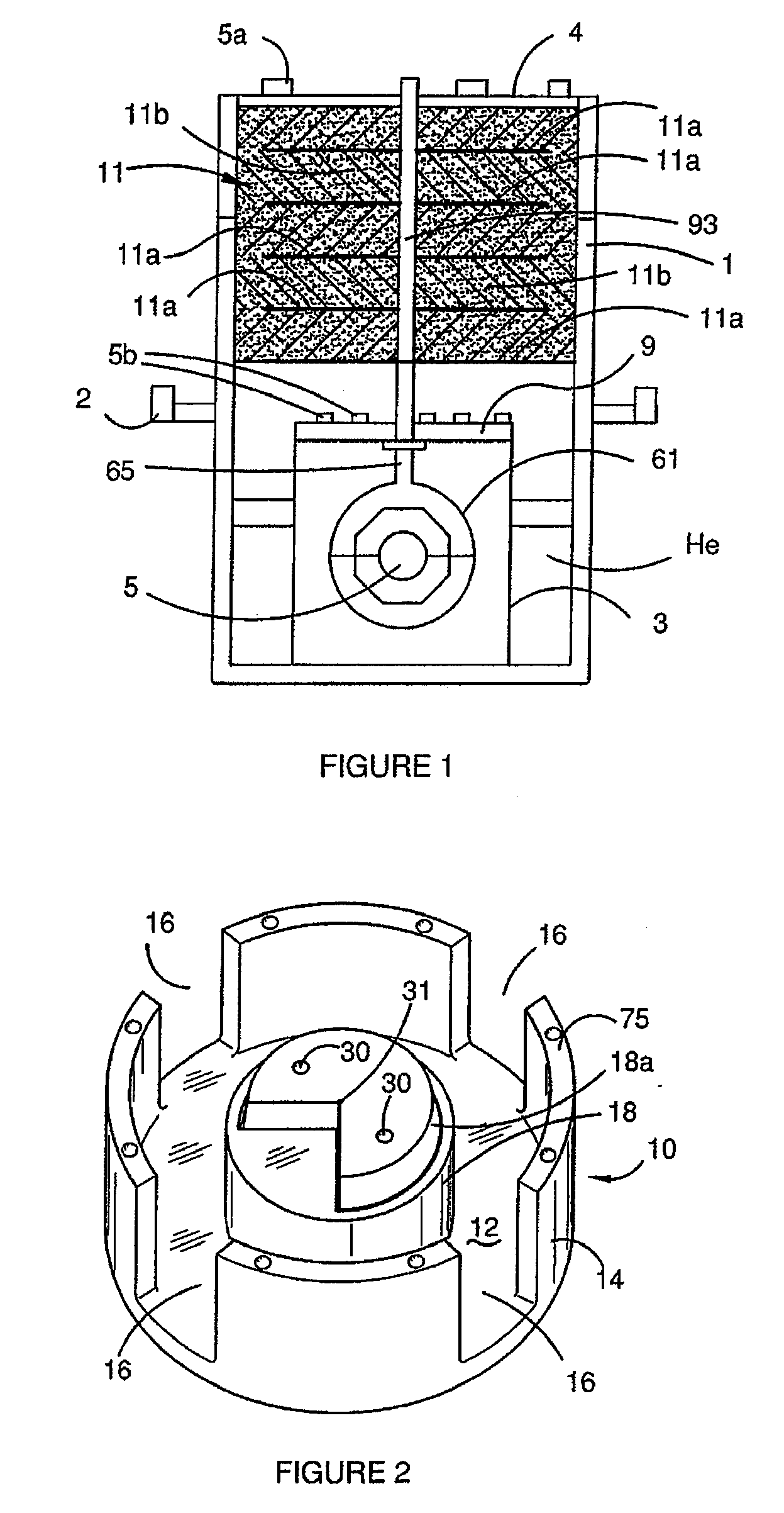
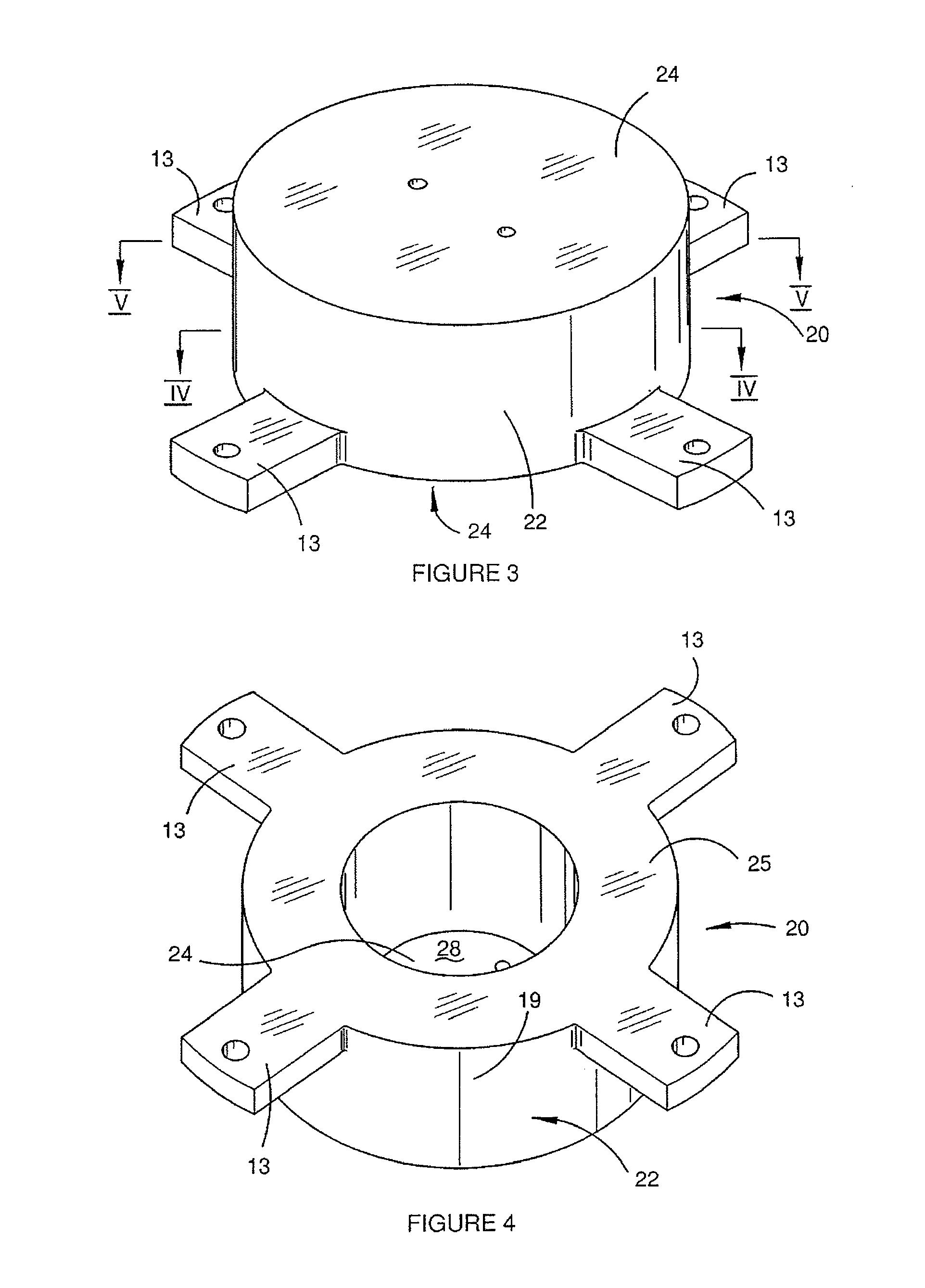
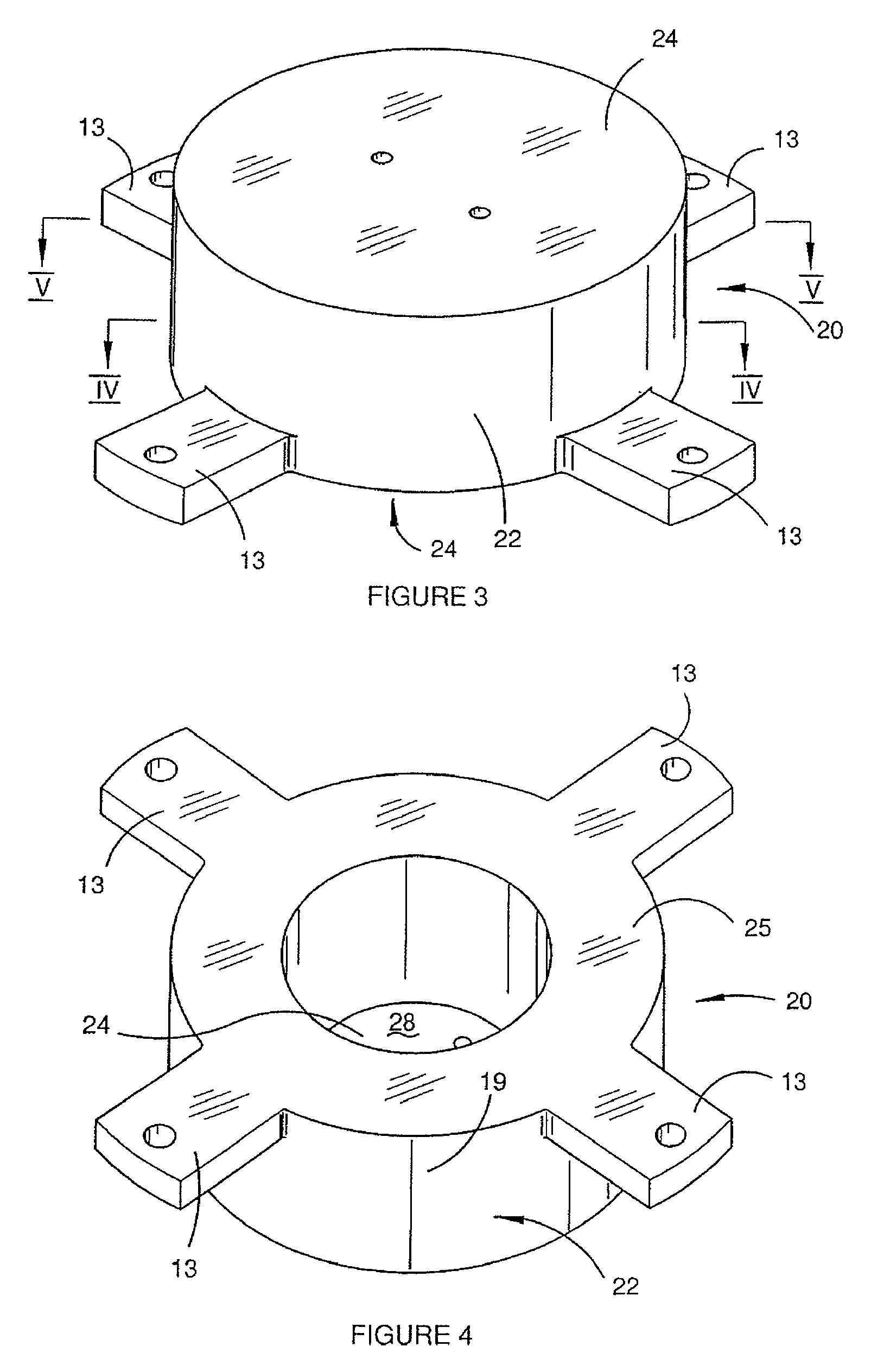
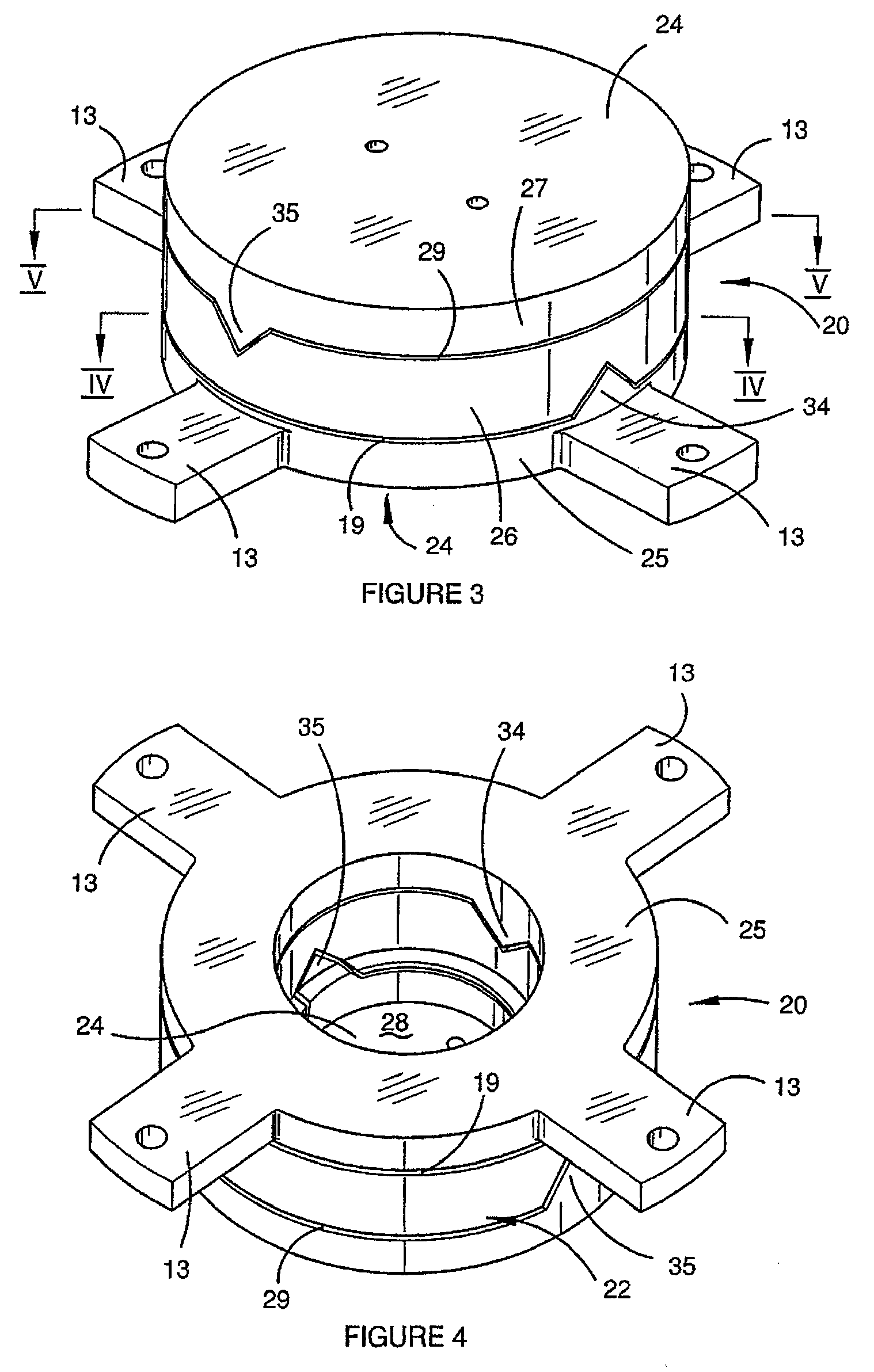
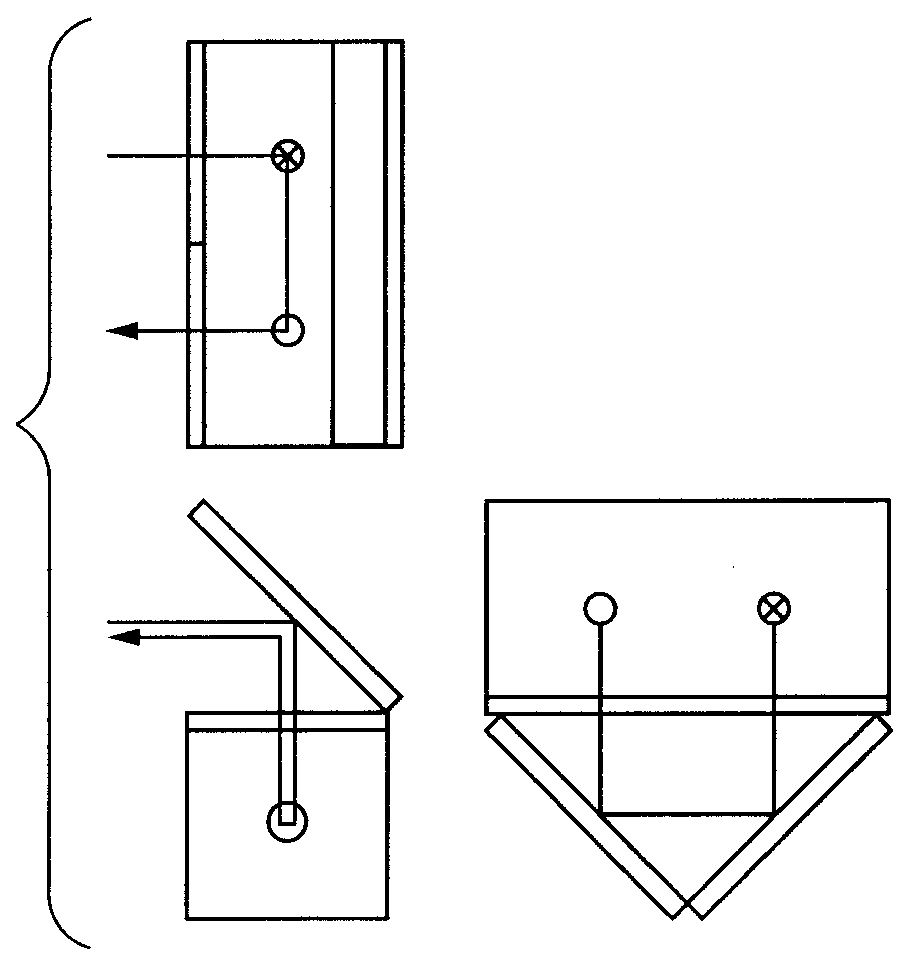
InactiveUS20080122435A1Save spaceInaccurate spacingUsing electrical meansPlumb lines for surveyingTransducerEngineering
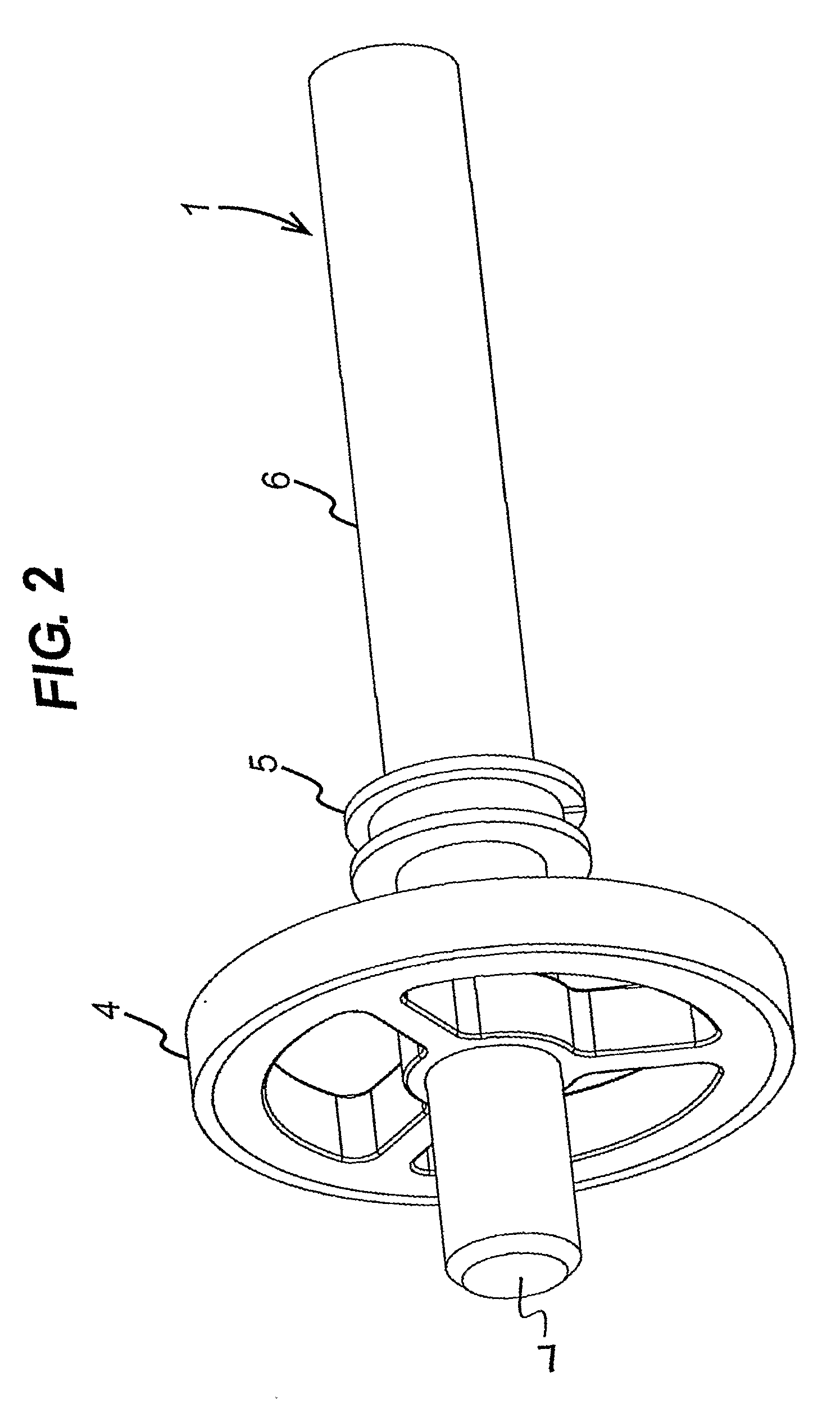
A gradiometer is disclosed which has a pair of sensor bars 41, 43 supported in housings 45, 47. Transducers 71 are located adjacent the bars 41, 43 to detect movement of the bars in response to the gravity gradient tensor. At least one of the transducers 71 comprises a first coil 510 and a second coil 516 arranged in parallel and a switch 362 for proportioning current between the coils 510 and 516 so as to create a virtual coil at a position D between the coils 510 and 516.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Gravity Gradiometer
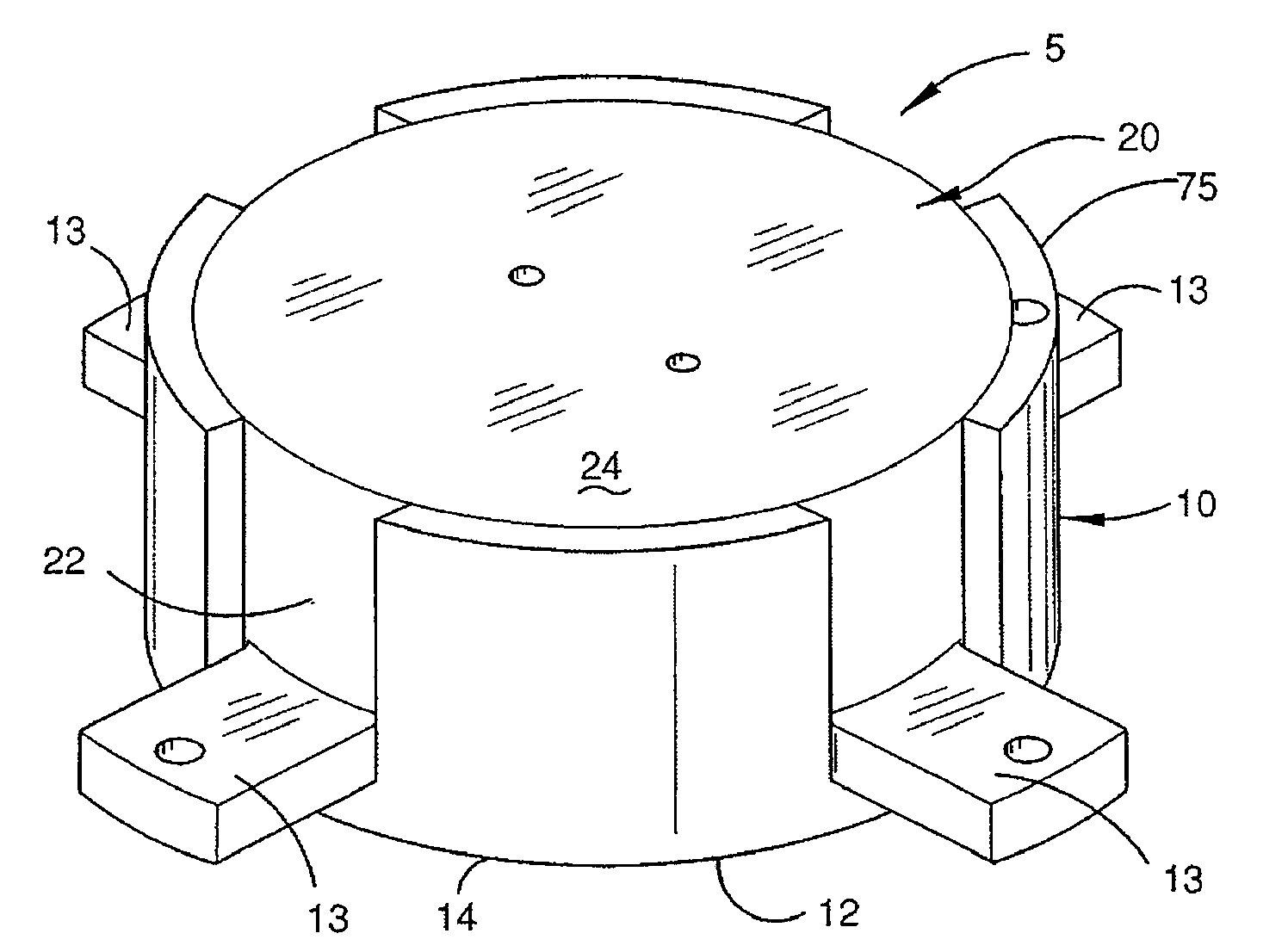
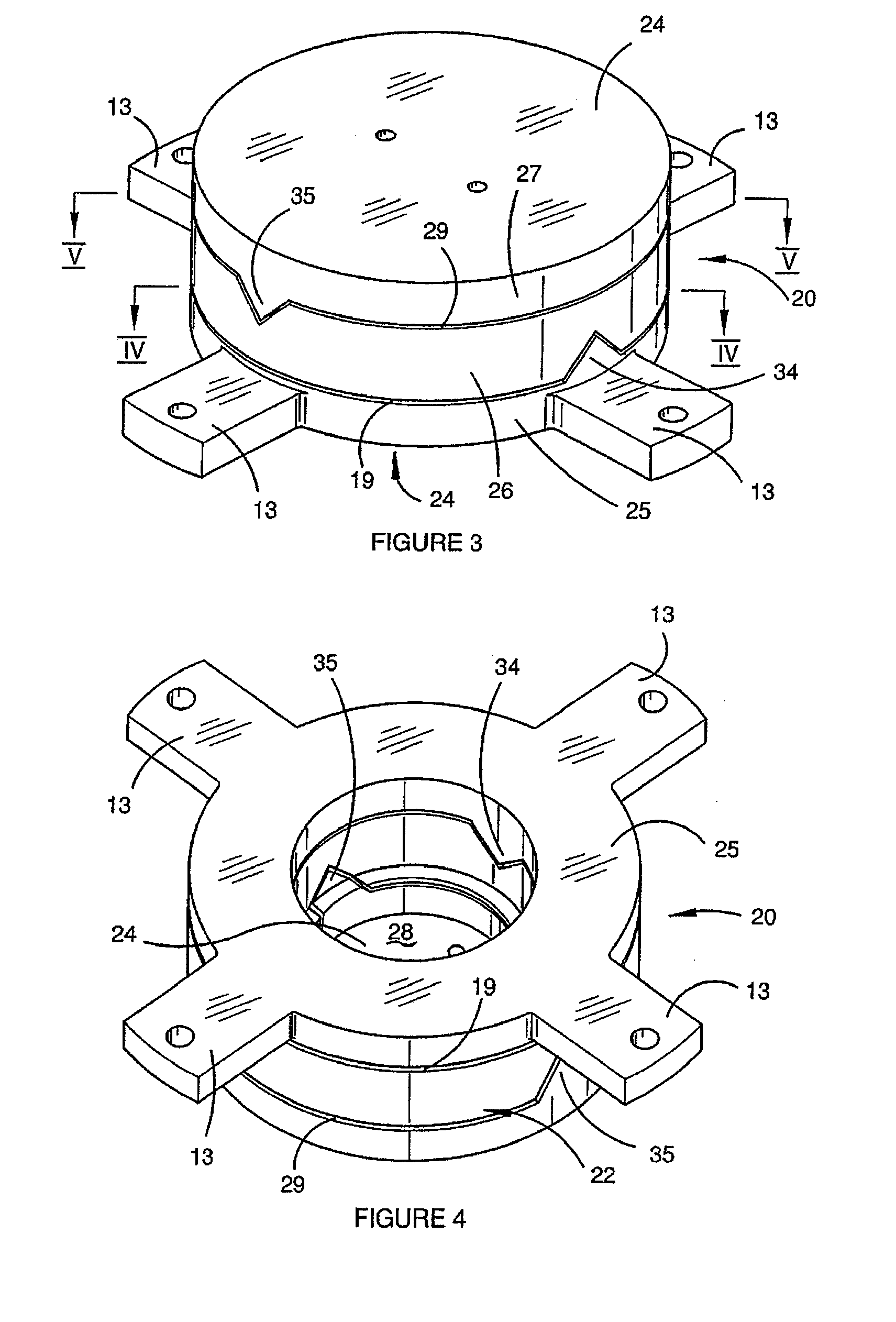
A gravity gradiometer is disclosed which has a sensor in the form of bars (41 and 42) which are supported on a mounting (5) which has a first mount section (10) and a second mount section (20). A first flexure web (33) pivotally couples the first and second mount sections about a first axis. The second mount has a first part (25), a second part (26) and a third part (27). The parts (25 and 26) are connected by a second flexure web (37) and the parts (26 and 27) are connected by a third flexure web (35). The bars (41 and 42) are located in housings (45 and 47) and form a monolithic structure with the housings (45 and 47) respectively. The housings (45 and 47) are connected to opposite sides of the second mount section 20. The bars (41 and 42) are connected to their respective housings by flexure webs (59). Transducers (71) are located in proximity to the bars for detecting movement of the bars to in turn enable the gravitational gradient tensor to be measured. A calibration sensor is provided for sensing whether the masses are balanced at room temperature so the balance of the masses can be adjusted by adjustable screws to balance the masses for cryogenic operation of the gradiometer. The calibration sensor comprises a resonant circuit (400, 410) and an oscillator (414). The resonant circuit includes a capacitor (400) which is formed by part of the sensor mass and a space plate (405).
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Gradient-based single well ranging system for sagd application
ActiveUS20150268371A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsElectromagnetic fieldGradiometer
A tool, method and system for ranging between two wellbores. The target wellbore includes a conductive member disposed within a portion of the target wellbore. An investigative wellbore includes an electromagnetic gradiometer positioned within the wellbore, as well as emitter electrode and return electrode spaced apart along an investigative wellbore, preferably in the process of being drilled. The position of the emitter electrode and the return electrode are selected to optimize current transmission to the target wellbore in order to enhance the electromagnetic field emanating from the conductive member at a desired point along the conductive member. Where the electrodes and gradiometer are carried by a drill string, gap subs are positioned along the drill string to minimize conduction of current along the drill string therebetween. In some embodiments, the gradiometer is positioned between the emitter and return electrodes.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
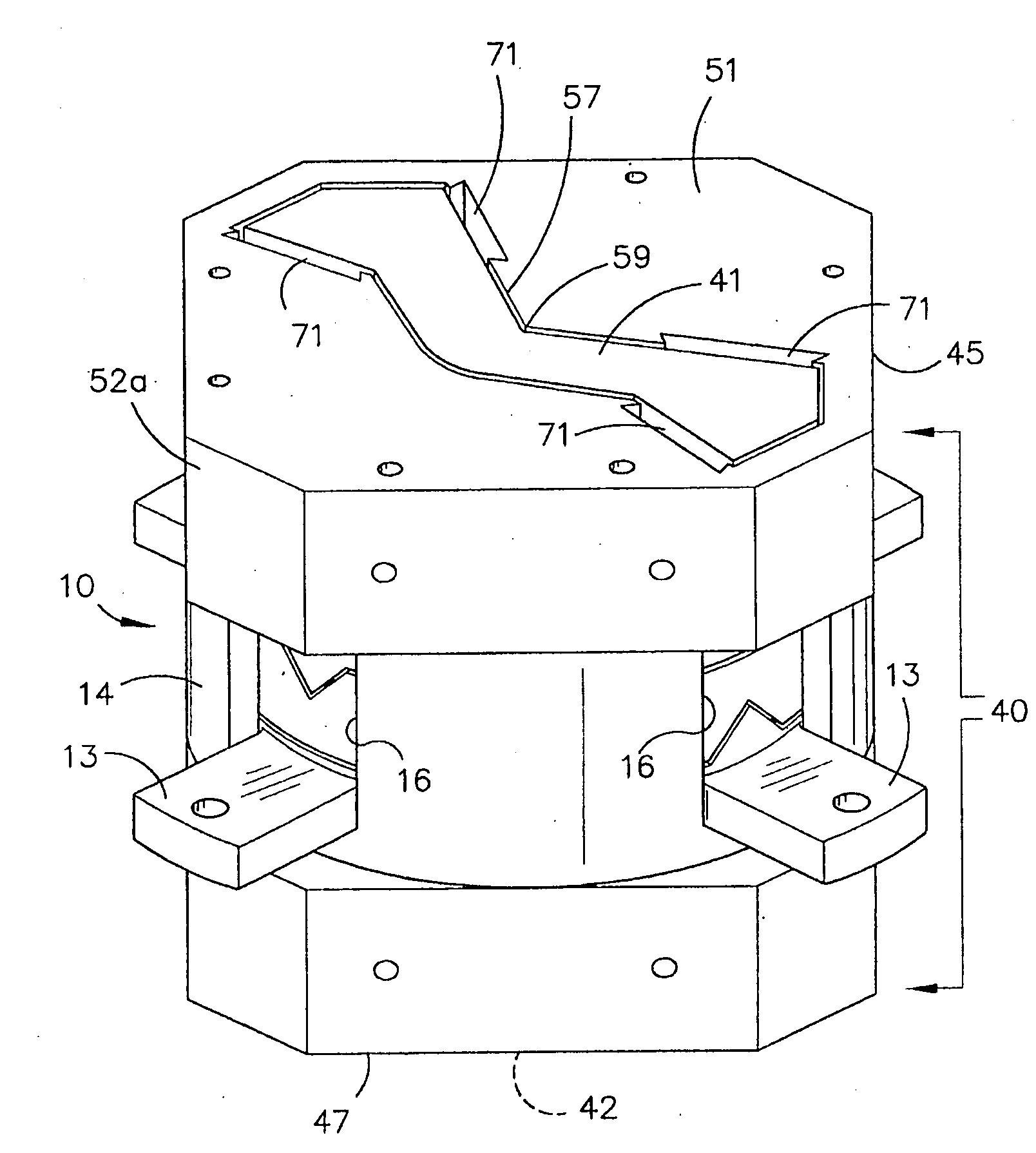
Gravity Gradiometer
ActiveUS20080115376A1Promote sportsAcceleration measurementPlumb lines for surveyingCouplingGradiometer
The present invention provides a gravity gradiometer for measuring components of the gravity gradient tensor. The gravity gradiometer comprises at least one sensor mass for movement in response to a gravity gradient and a pivotal coupling enabling the movement of the at least one sensor mass about an axis. Further, the gravity gradiometer comprises a constant charge capacitor that is arranged so that the movement of the at least one sensor mass generates a change in a voltage across the constant charge capacitor.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS7573264B2Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceProton NMRSingle polarization
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Gravity Gradiometer
ActiveUS20080116905A1Reduce noiseResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention provides a gravity gradiometer for measuring components of the gravity gradient tensor. The gravity gradiometer comprises at least one sensor mass for movement in response to a gravity gradient and a sensor and actuator unit for generating an electrical signal in response to the movement of the at least one sensor mass and for influencing the movement of the at least one sensor mass. The gravity gradiometer also comprises an electronic circuit for simulating an impedance. The electrical circuit is arranged for amplifying the electrical signal received from the sensor and actuator unit and for directing an actuating signal to the sensor and actuator unit. The electronic circuit comprises a differential amplifiers having first and second amplifier input terminals and an amplifier output terminal and impedances Z1, Z2, Z3, at least one of the impedances have an imaginary impedance component.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
Gravity Gradiometer
ActiveUS20080115377A1Testing/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesPlumb lines for surveyingEngineeringCapacitor
The present invention provides a method of tuning properties of a gravity gradiometer for measuring components of the gravity gradient tensor. The gravity gradiometer comprises a pair of first and second transversely arranged sensor masses that are arranged for movement about an axis and relative to each other in response to a gravity gradient. The gravity gradiometer further comprises first and second capacitors for sensing and influencing the movement of the first and second sensor masses. The method comprising applying a bias voltage to at least one of the capacitors for generating an electrostatic force which acts on one of the sensor masses and thereby influences the movement of that sensor mass.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
Gravity Gradiometer
A gravity gradiometer is disclosed which comprises a pair of sensor masses 41, 43 arranged in housings 45, 47. Transducers 71 are provided for measuring movement of the sensor masses in response to the gravity gradient tensor. The masses are supported for movement by a flexure web 59 between the mass and a support and a stop comprises a pair of abutment services 554, 555 and 558, 559 defined by a cut 550 prevent movement of the sensor masses 41, 43 beyond the elastic limit of the flexure web 59.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Gravity Gradiometer
InactiveUS20080120858A1Less-expensive to manufacturePrecision productionPlumb lines for surveyingIncline measurementTransformerTransducer
A gravity gradiometer is disclosed which has sensor masses in the forms of bars 41 and 43 arranged orthogonal to one another and transducers for providing an output signal indicative of movement of the bars in response to changes in the gravity gradient tensor. The transducers are formed from thin film structure having a first layer forming a fine pitch coil 510 and a second layer forming a coarse pitch coil 511. The layers are separated by an insulating layer. The coarse pitch coil 511 forms a transformer for stepping up the current flowing through the fine pitch coil 510 and the coarse pitch coil 511 supplies current to a SQUID device 367.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Gravity Gradiometer
A gravity gradiometer is disclosed which has a sensor in the form of bars (41 and 42) which are supported on a mounting (5) which has a first mount section (10) and a second mount section (20). A first flexure web (33) pivotally couples the first and second mount sections about a first axis. The second mount has a first part (25), a second part (26) and a third part (27). The parts (25 and 26) are connected by a second flexure web (37) and the parts (26 and 27) are connected by a third flexure web (35). The bars (41 and 42) are located in housings (45 and 47) and form a monolithic structure with the housings (45 and 47) respectively. The housings (45 and 47) are connected to opposite sides of the second mount section 20. The bars (41 and 42) are connected to their respective housings by flexure webs (59). Transducers (71) are located in proximity to the bars for detecting movement of the bars to in turn enable the gravitational gradient tensor to be measured.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
System and method for measuring a magnetic gradient field
ActiveUS10088535B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEfficient detectionMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic field gradientPhotodetector
A system and method is described to measure the magnetic field gradient using an optically pumped magnetometer configured as an intrinsic gradiometer. Atoms are prepared in a freely precessing coherent superposition of the magnetically sensitive hyperfine ground states in two or more physically separated locations. A probe laser beam is used to interrogate atoms in both locations. As the probe light beam passes through the coherent atoms, optical sidebands are self-generated at the ground state hyperfine frequency of the magnetically sensitive states. Each of the two sets of atoms produces distinct sidebands at a frequency separation proportional to the magnetic field experienced by each set of atoms. The probe light is captured using a photodetector. The self-generated probe optical sidebands interfere to produce a beat note whose frequency is proportional to the magnetic field gradient between the two sets of atoms. Measuring the frequency of the beat note therefore provides an accurate reading of the magnetic field gradient. An optical filter or a polarizer can be additionally used to remove the central frequency of the probe light, thus removing the noise produced by the residual probe beam.
Owner:QUSPIN
Gravity Gradiometer
ActiveUS20080115578A1Reduce external impactIncrease in sizeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPlumb lines for surveyingCouplingTransducer
The present invention provides a gravity gradiometer which comprises at least one sensor mass suspended by a coupling which enables movement of the at least one sensor mass about an axis in response to a gravity gradient. Further, the gravity gradiometer comprises at least one transducer for generating an electrical signal in response to the movement of the at least one sensor mass relative to a component of the transducer and for influencing the movement of the at least one sensor mass. The gravity gradiometer also comprises electrical circuitry for receiving the electrical signal from the at least one transducer and for directing an actuating signal to the at least one transducer so that in use the at least one transducer functions as sensor and actuator.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
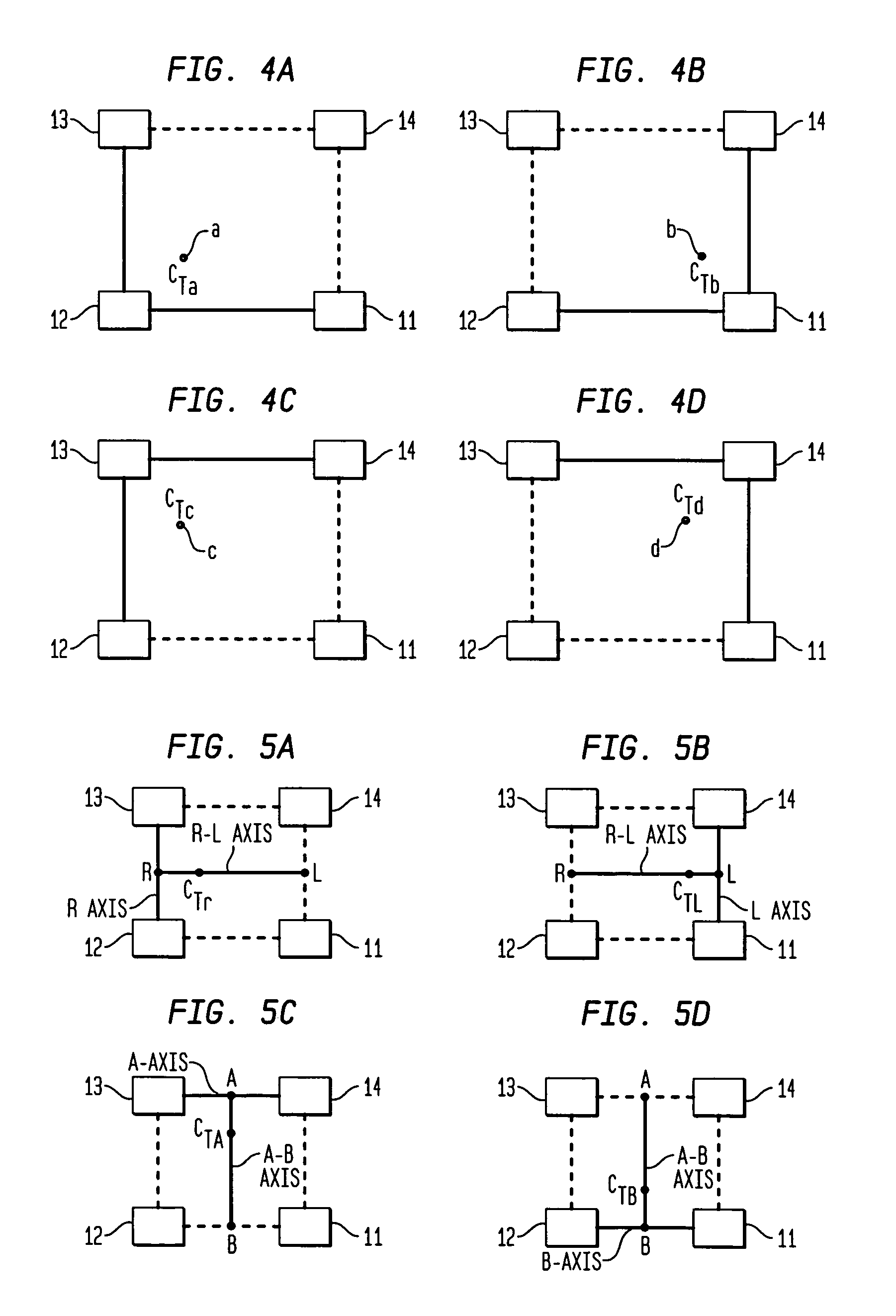
Magnetic anomaly homing system and method using rotationally invariant scalar contractions of magnetic gradient tensors
InactiveUS7038458B1Electric/magnetic detectionMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic gradientGuidance control
A magnetic anomaly homing system and method utilize an array of four triaxial magnetometer (TM) sensors coupled to a non-magnetic platform. The four TM sensors are positioned at the vertices of a rectangular parallelogram. The magnetic field sensed at the four TM sensors is processed to generate complete gradient tensors and corresponding scalar gradient contractions thereof for four two-axis gradiometers formed by the array. The scalar gradient contractions define guidance control parameters used to steer the platform toward the magnetic anomaly.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
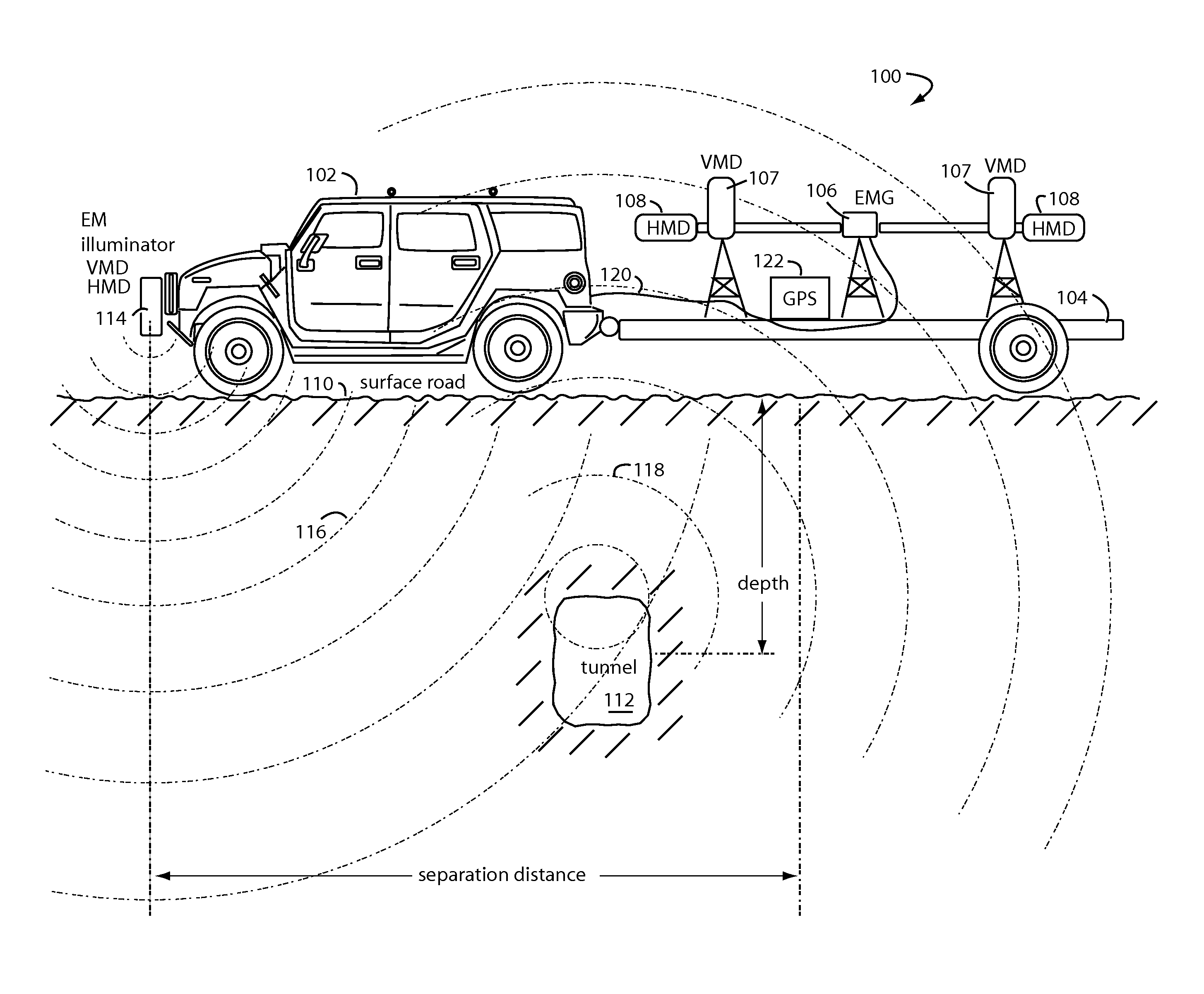
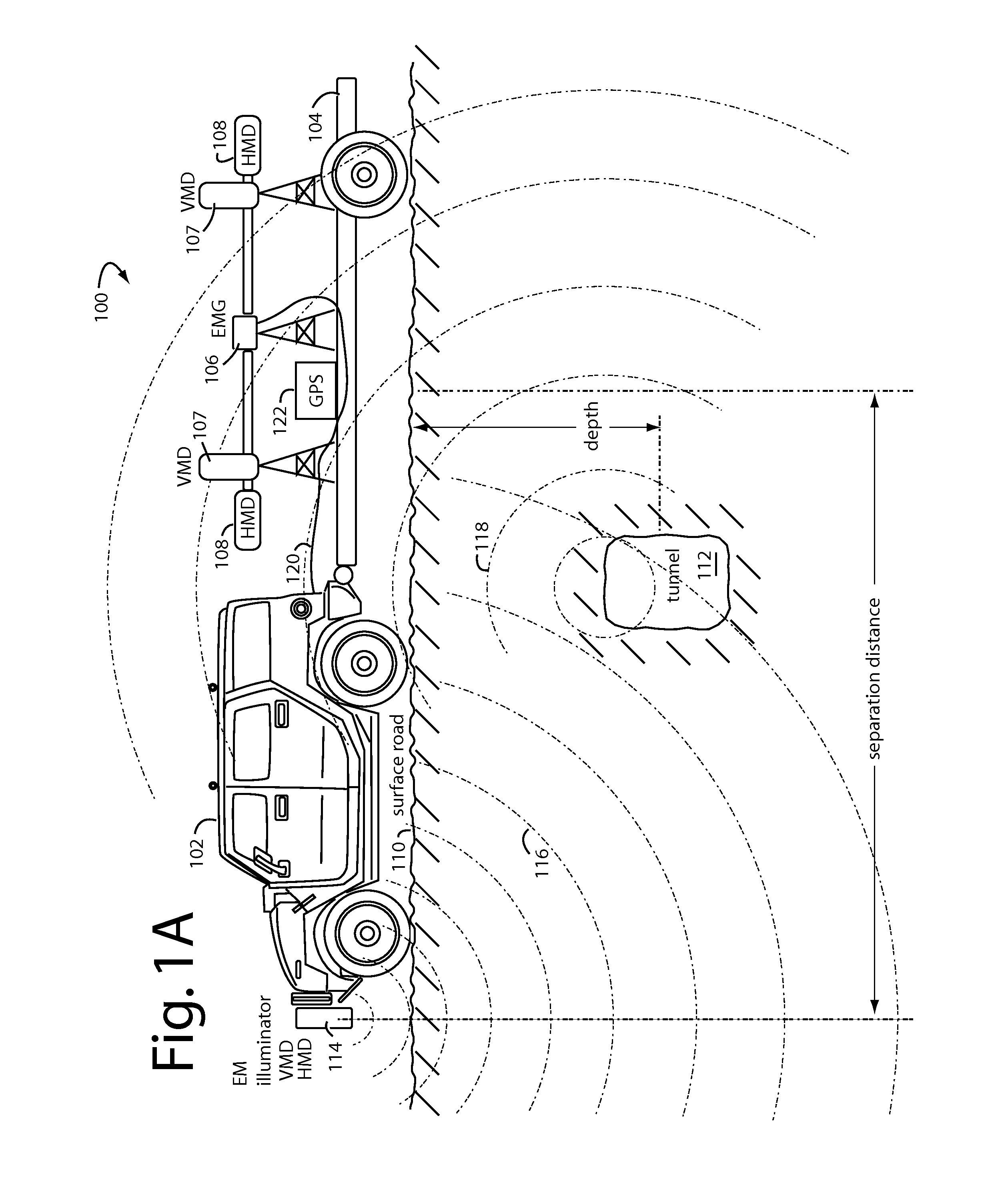
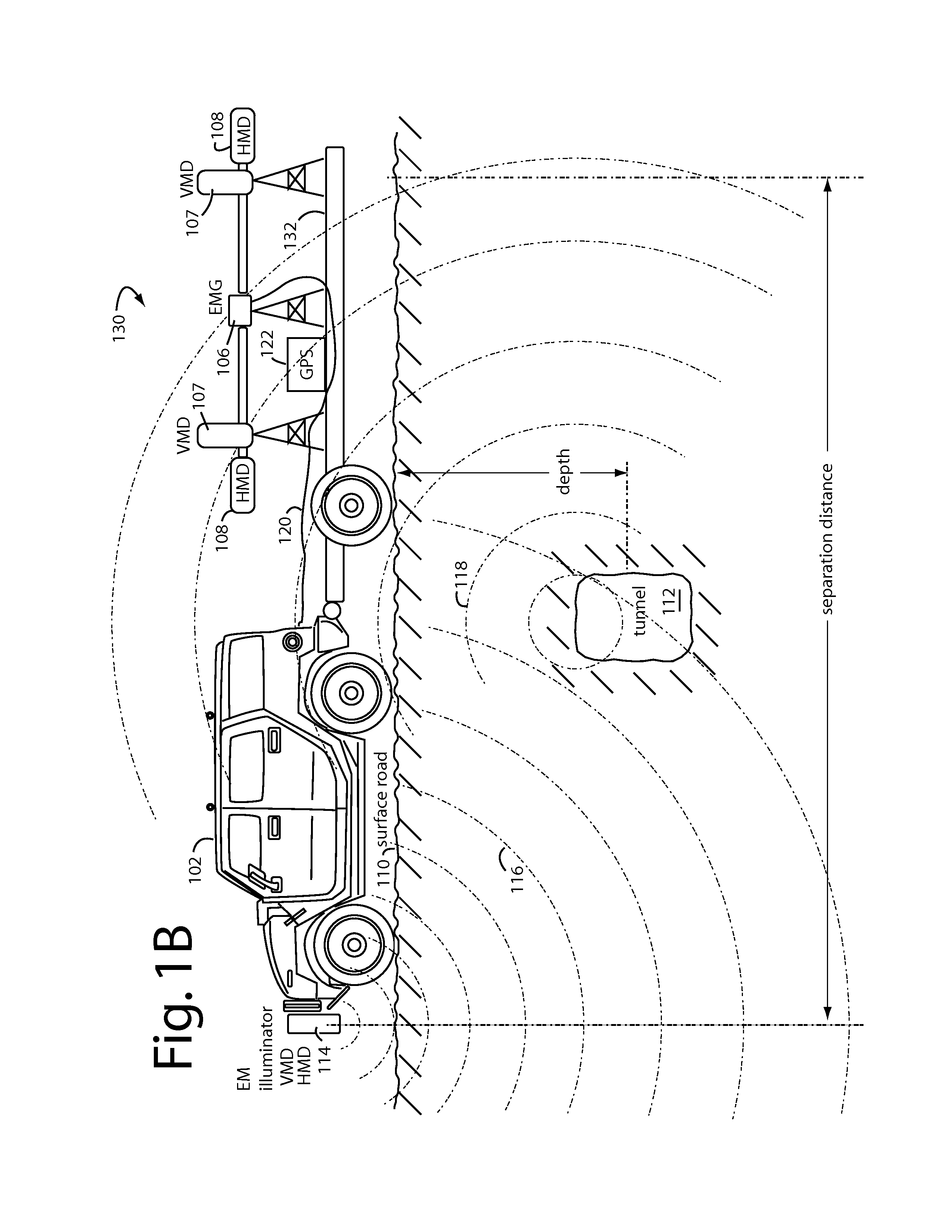
Underground anomalies detection vehicle and trailer
InactiveUS7675289B1Detection using electromagnetic wavesElectric/magnetic detection for transportAnomaly detectionTrackway
A system for detection of linear underground anomalies passing under surface roads comprises an electromagnetic (EM) gradiometer mounted on a vehicle trailer. A transmitter is mounted to the front bumper of a car or vehicle towing the trailer and provides carrier synchronization information to the EM-gradiometer. An opportunistic radio station can be used as an illuminator. The transmitter or ground wave from an opportunistic radio station directs radio waves down into the ground where objects like linear underground anomalies and their equipment will produce reflections and scattered waves. These reflections will have phase angles and magnitudes that can be interpreted for characterizing information about the linear underground anomalies. Each EM-gradiometer measurement is tagged with GPS location information and then stored in a database. Subsequent passes over the same roadways and tracks are compared (change detection) to the earlier stored data. New linear underground anomalies and features become very obvious in these comparisons.
Owner:STOLAR
Magnetic gradiometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS9383419B2Magnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesLight beamSignal source
A gradiometer in which a probe beam for reading sequentially passes through two magnetic field measurement regions to obtain signals according to magnetic flux densities of the respective regions is formed using an optically pumped magnetometer. In particular, in a gradiometer using a high sensitivity optically pumped magnetometer, a geometric arrangement enabling obtainment of a large signal from a dipole moment as a signal source is defined.
Owner:CANON KK
Gravity Gradiometer System
InactiveUS20090064778A1Not been mechanism for accuratelyReduce the impactGravitational wave measurementEngineeringGradiometer
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
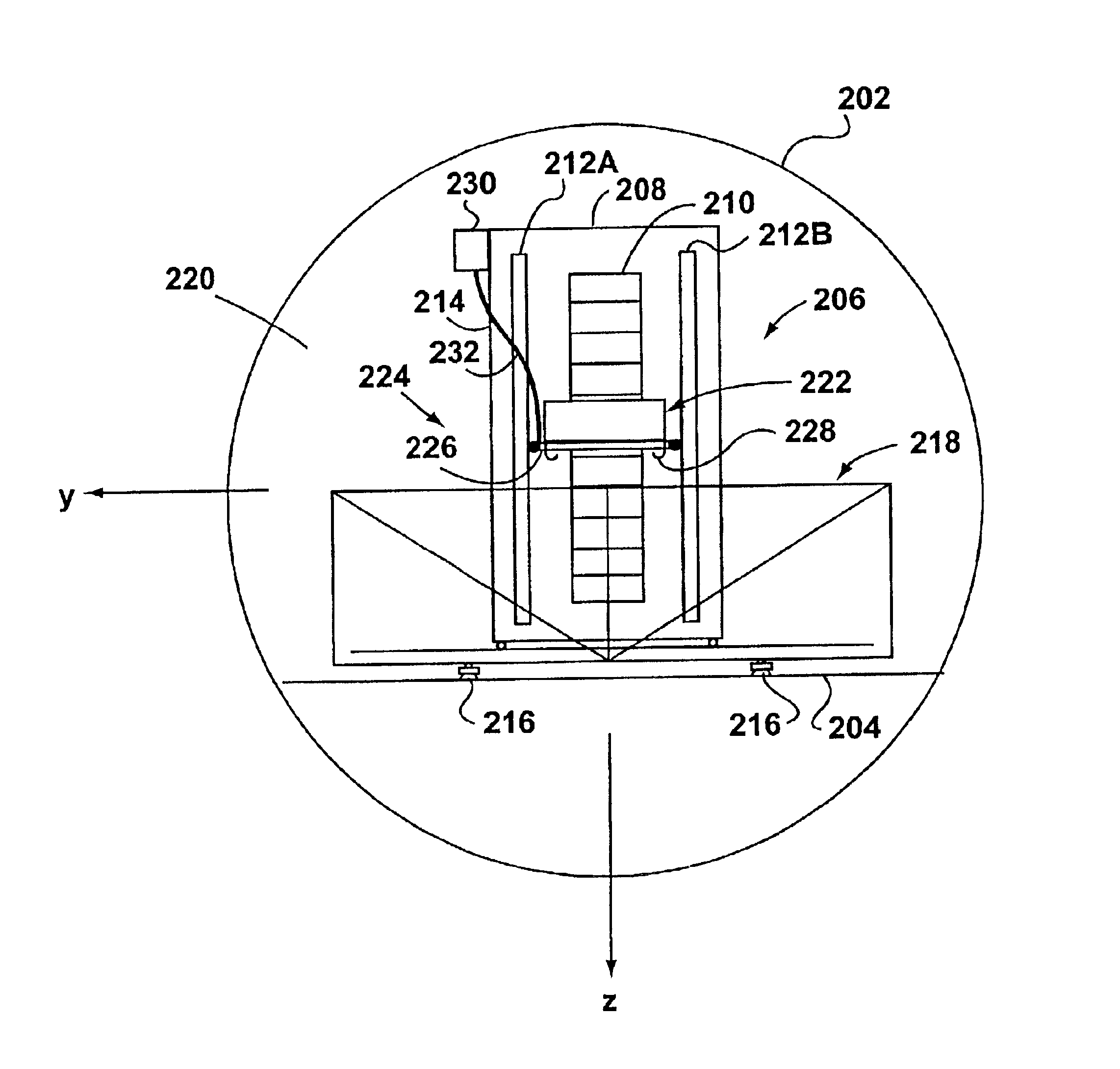
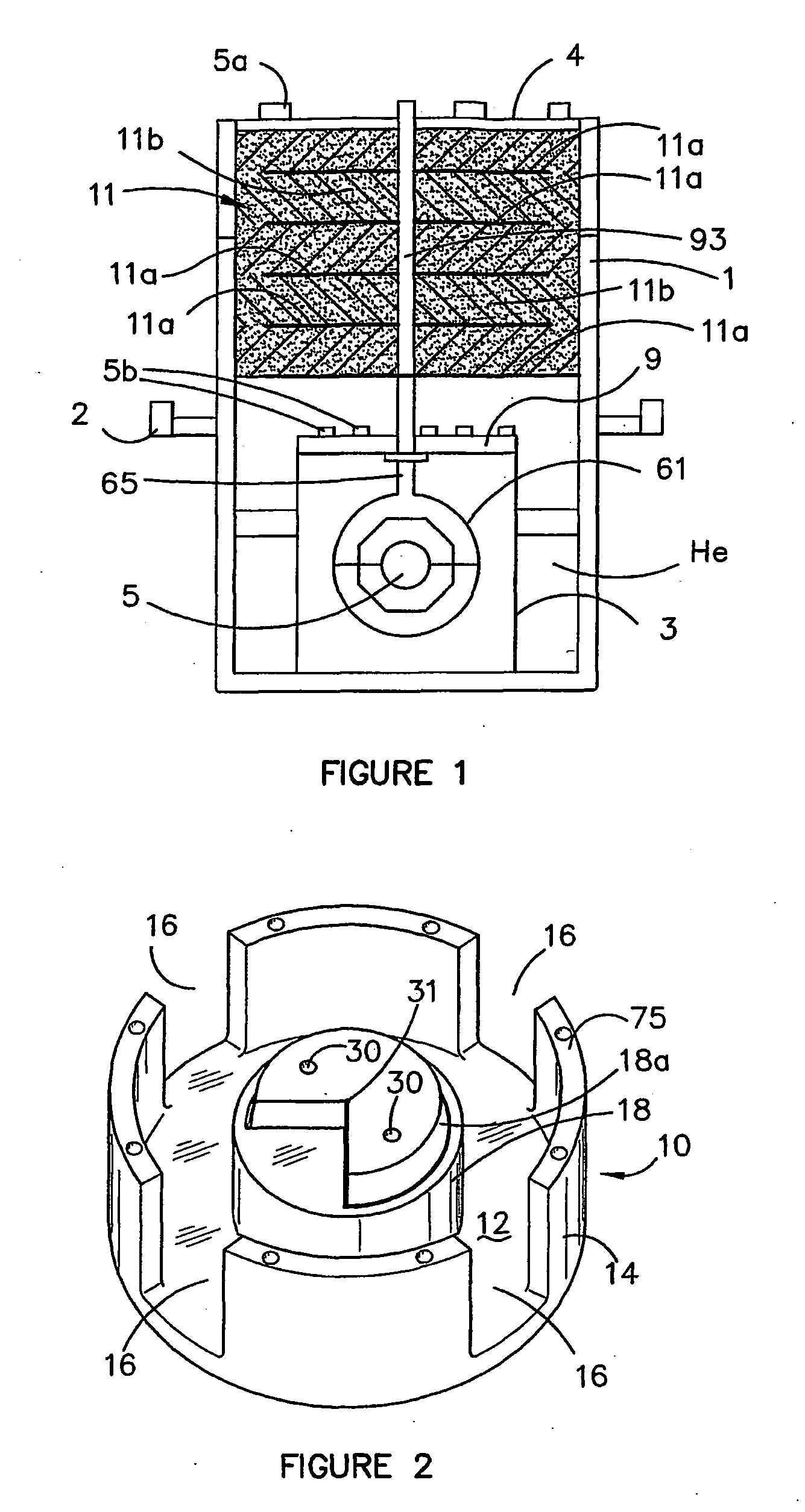
Apparatus and method for determining magnetic properties of materials
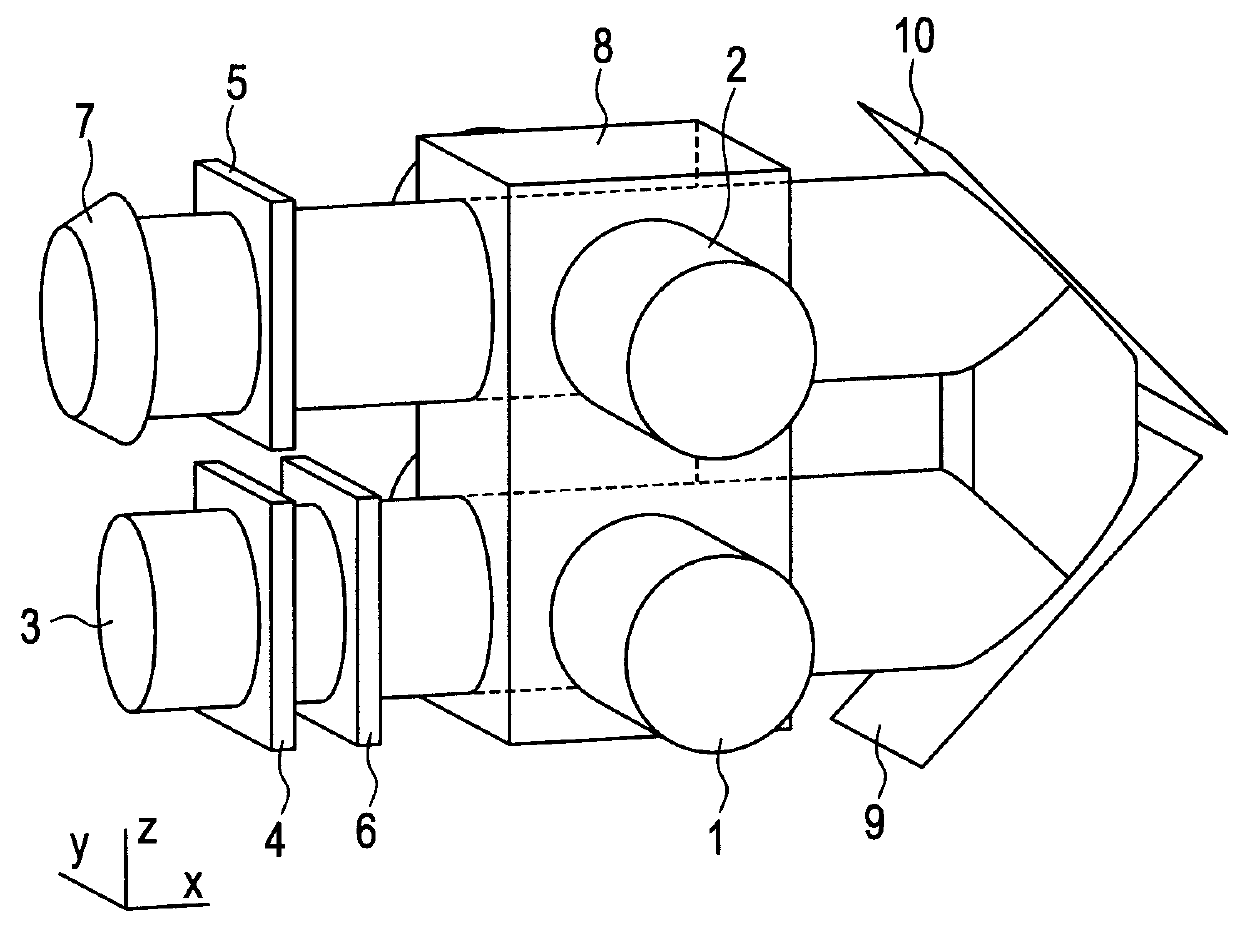
ActiveUS20090201016A1Improve mobilityMaximize signal receptionMagnetisation measurementsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesData acquisitionEngineering
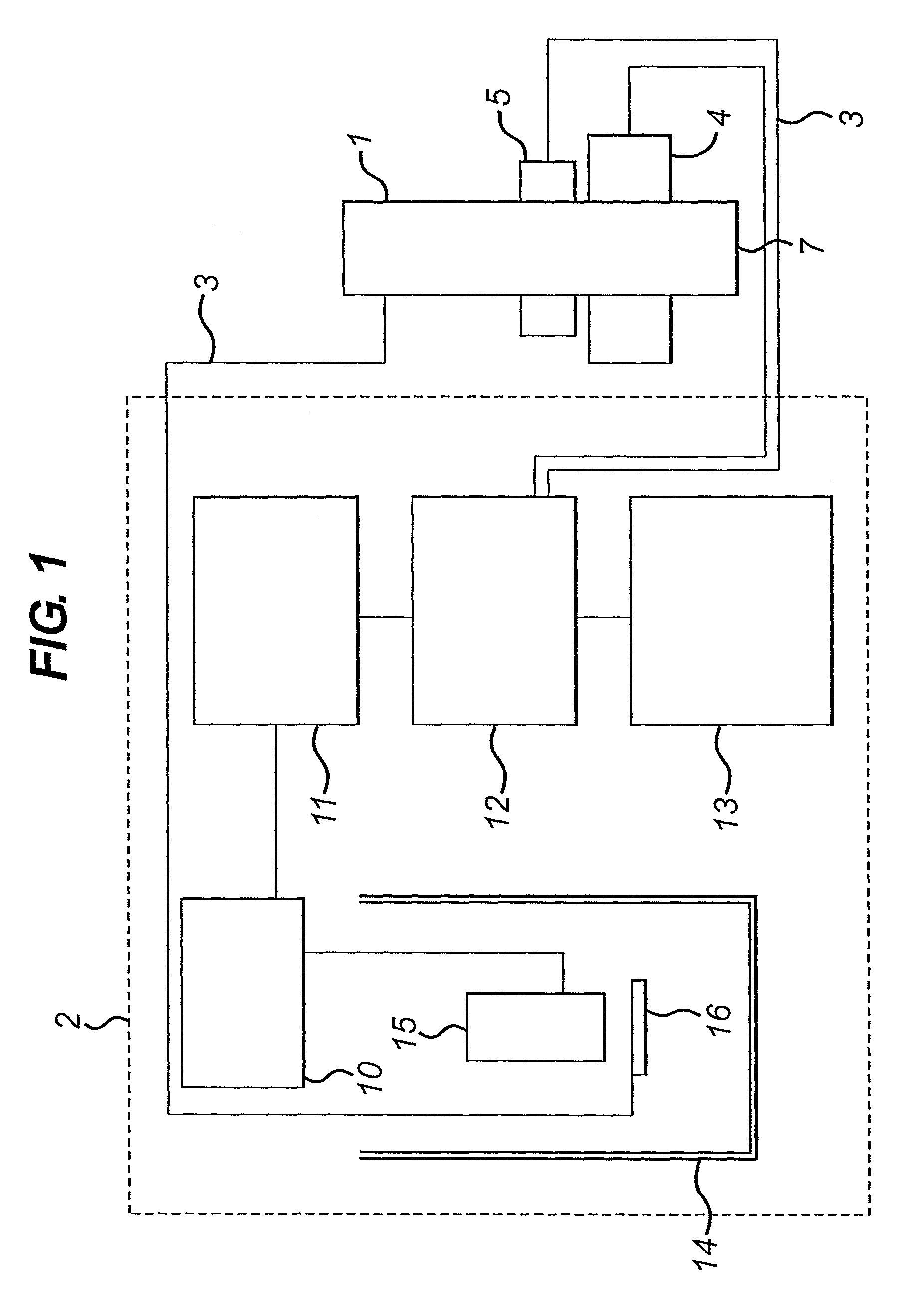
Apparatus for determining magnetic properties of materials comprises a portable probe (1), an equipment trolley (2) holding cryogenics and electronics and connecting cables (3). The probe (1) comprises a drive coil (4) and a correction coil (5), the drive coil (4) being disposed symmetrically with respect to an inner second-order gradiometer sensor coil (8). Electrical connectors in the form of 2-metre long Belden (1192A) microphone cables (3) are used to connect the apparatus on the equipment trolley (2) to the drive coil (4), the correction coil (5) and the sensor coil (8). The drive coil (4) is driven so as to generate a sinusoidally varying magnetic field. The electronics comprise a flux-locked loop (9), a SQUID controller (10), a data acquisition module (11), which captures and processes the signals and a computer (12). A liquid-nitrogen dewar (13) is supported on the equipment trolley (2) and houses a sensitive SQUID detector (14) and a transfer coil (15) made from copper. Possible applications of the apparatus include an intra-operative tool for sentinel lymph node detection in the treatment of breast cancer, and a non-destructive evaluation tool for detecting voids and defects in aluminium and applications in the aeronautics industry.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST +1
System for high-resolution measurement of a magnetic field/gradient and its application to a magnetometer or gradiometer
InactiveUS20050052650A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTotal internal reflectionImage resolution
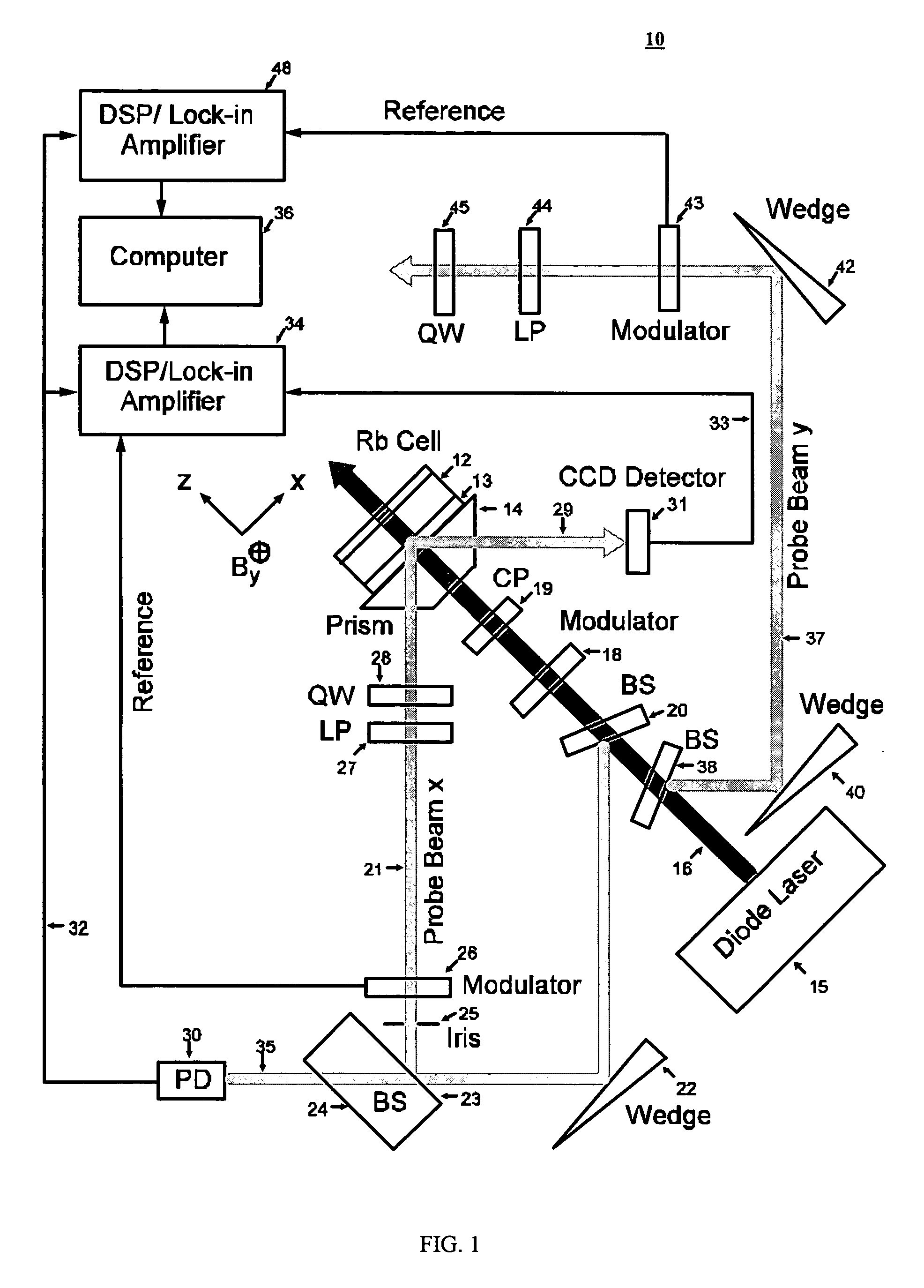
The present invention relates to a method and system for high spatial resolution measurement of a magnetic field or gradient. The method determines Zeeman polarization at a submicron distance from cell surfaces of an optical pumping cell using two laser beams. A strong pump beam produces Zeeman polarization in the vicinity of surfaces inside the optical pumping cell. The Zeeman polarization precesses around the magnetic field that is to be measured and is probed by the evanescent wave of a weak probe beam. The precessing Zeeman polarization can be monitored by measuring reflectivity of the probe beam at an interface between the active medium and the cell. The polarization can be used to measure the magnetic field or gradient. In one embodiment a second probe beam in the yz-plane is incident on the same position as the pump beam and the first probe beam that is in the xz-plane. Both probe beams undergo total internal reflection at an interface between the cell surface and the active medium. The reflectivities of the two probe beams are measured, from which the x, y and z components of the magnetic field can be determined simultaneously.
Owner:WU ZHEN
Spherical feedback tricomponent fluxgate magnetic full-tenser gradiometer
InactiveCN102928885AAvoid mutual interferenceStable working conditionElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationUniform fieldClosed loop
The invention relates to a spherical feedback tricomponent fluxgate magnetic full-tenser gradiometer. Three mutually perpendicular crossed enameled wire winding slots are carved on the surface of a spherical non-conductive material, and more than three tricomponent fluxgate sensors are mounted in the sphere and connected with a triaxial spherical feedback coil to form a closed loop through a control circuit so as to further form the tricomponent fluxgate magnetic full-tenser gradiometer. Compared with the prior art, the uniform field generated by the spherical coil is larger than that generated by other feedback coils; under the same uniformity, the spherical feedback coil occupies the minimum volume; the plurality of fluxgate sensors are placed in one triaxial spherical coil, the fluxgate is in a stable working state in the environment close to zero magnetism, so that mutual interference of the feedback coils during feedback of each fluxgate is avoided, the calibration is facilitated, the baseline distance is greatly shortened, and the system precision is improved. The spherical feedback tricomponent fluxgate magnetic full-tenser gradiometer is particularly suitable for being used in aeronautical, aerospace and other space-limited environments and has a wider application range.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com