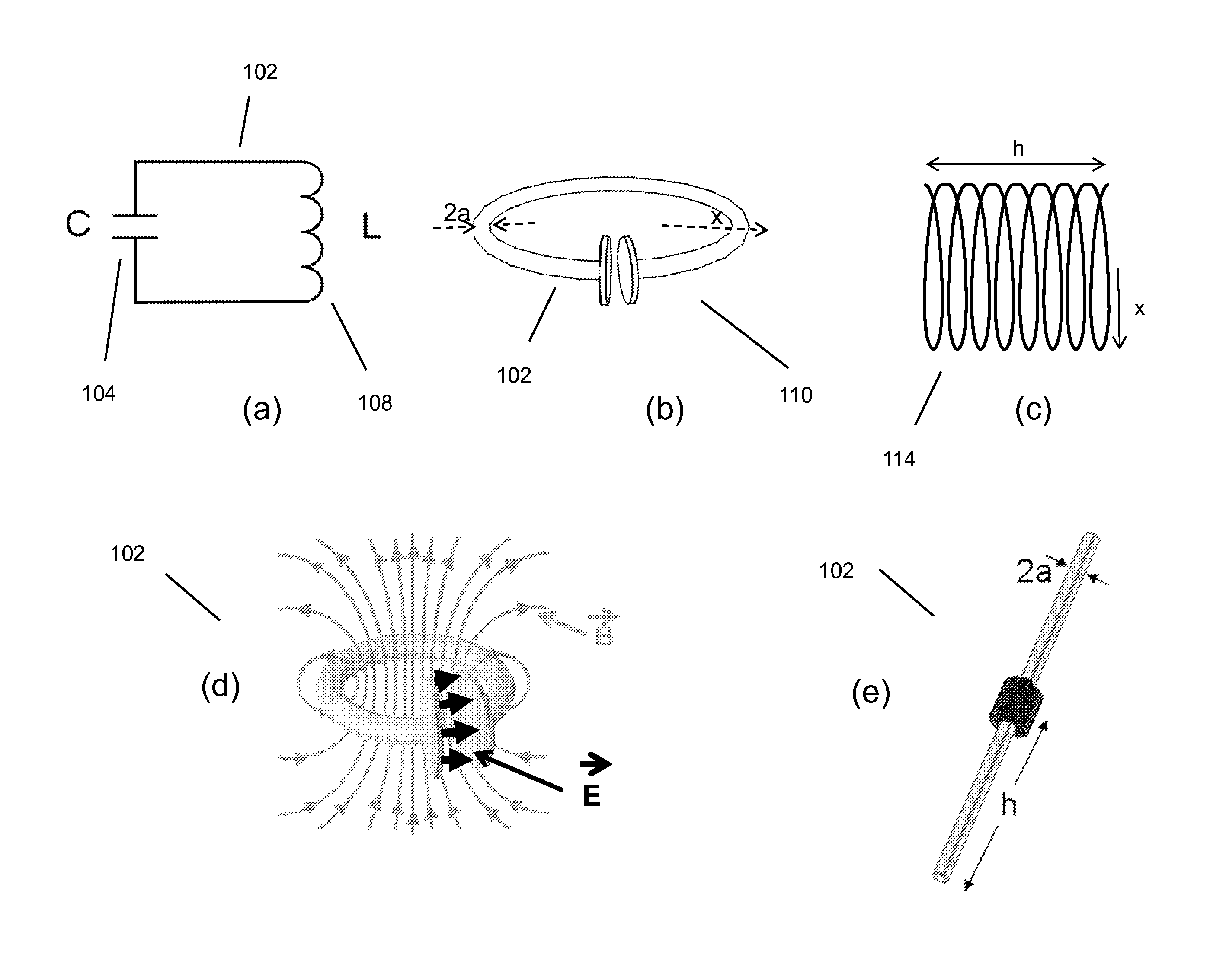
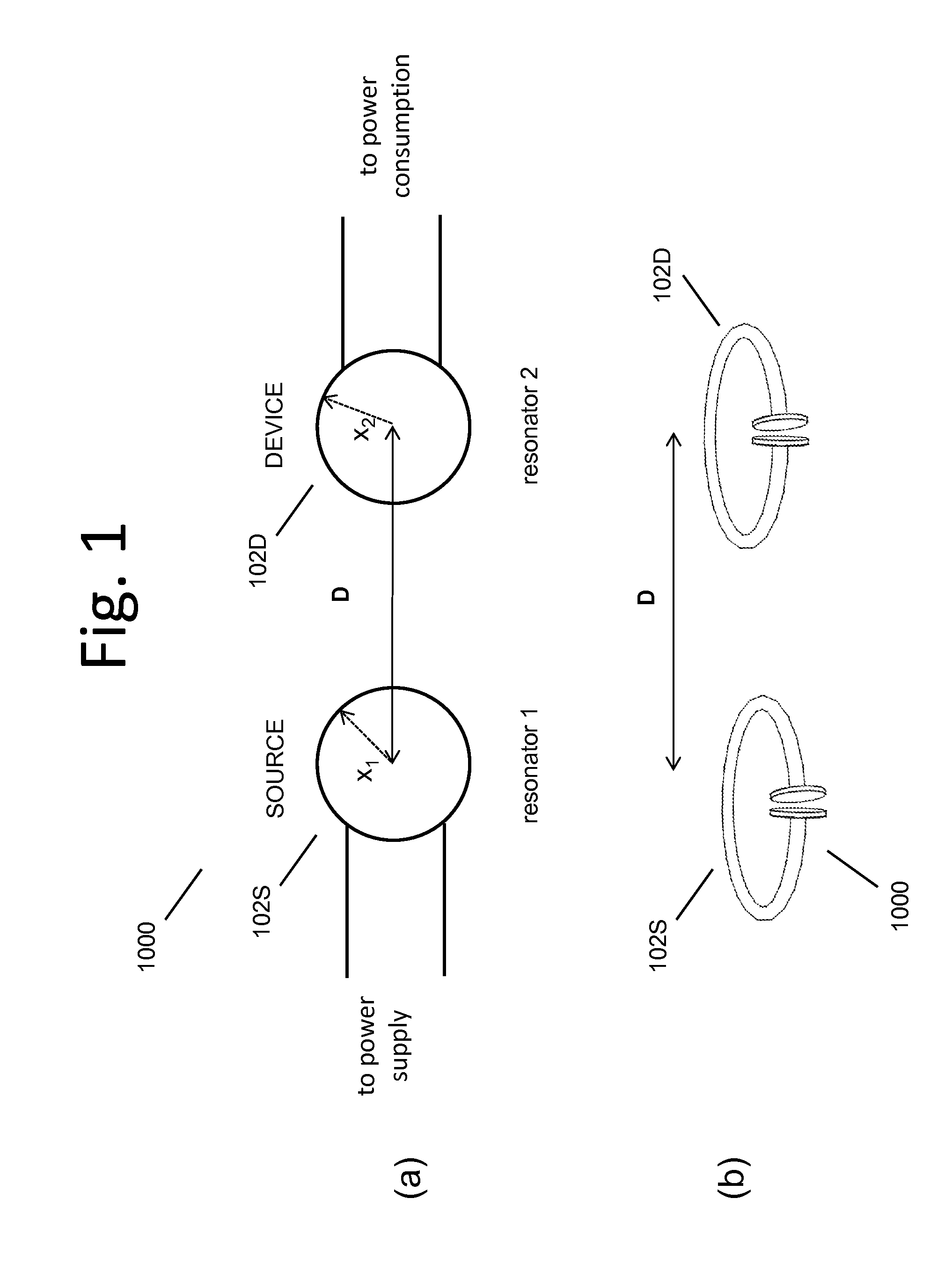
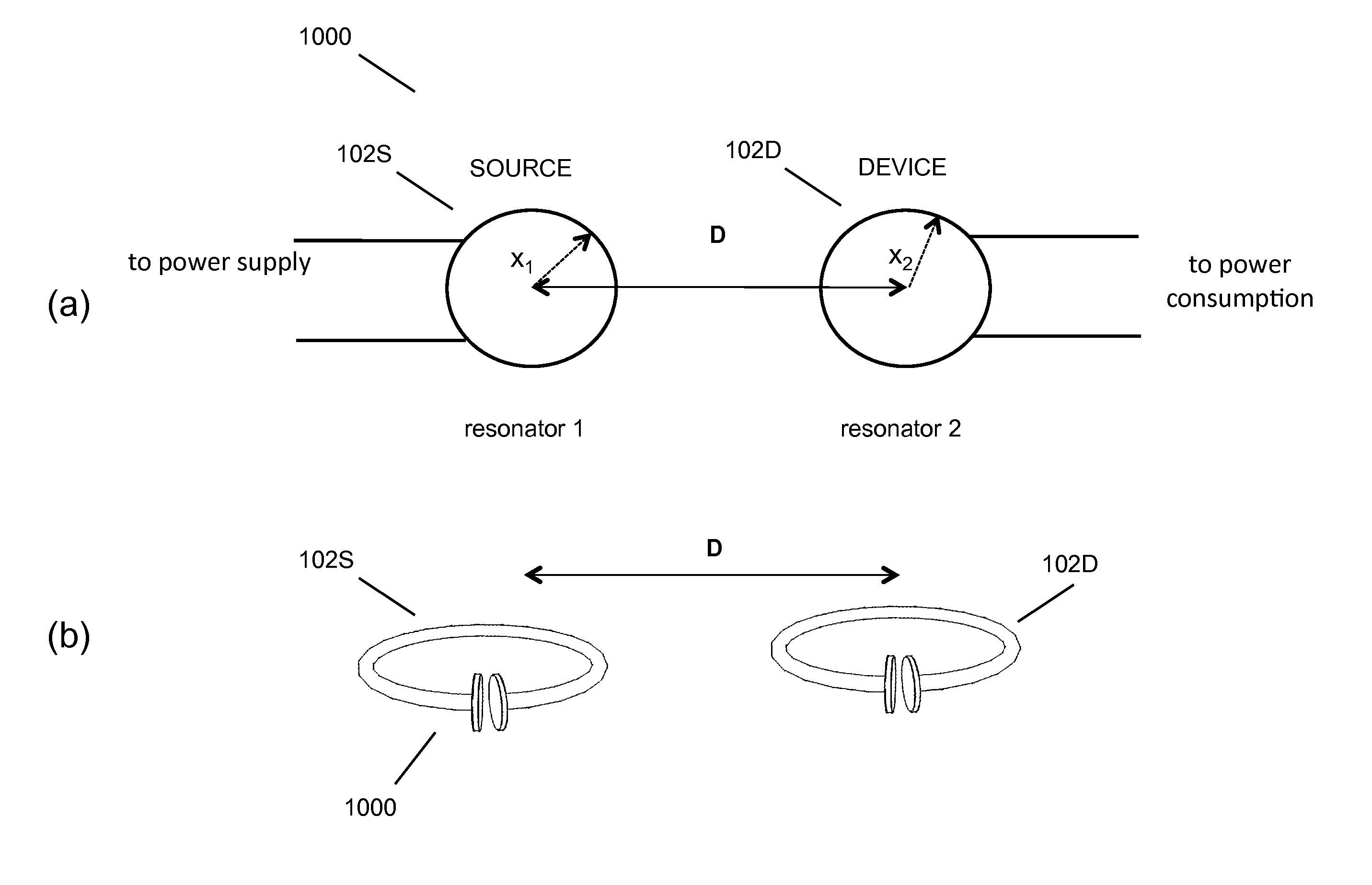
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
201 results about "Oscillating magnetic field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An oscillating magnetic field is applied to make the nickel parts move from side to side, in turn swinging the head and tail and creating movement - essentially, swimming.
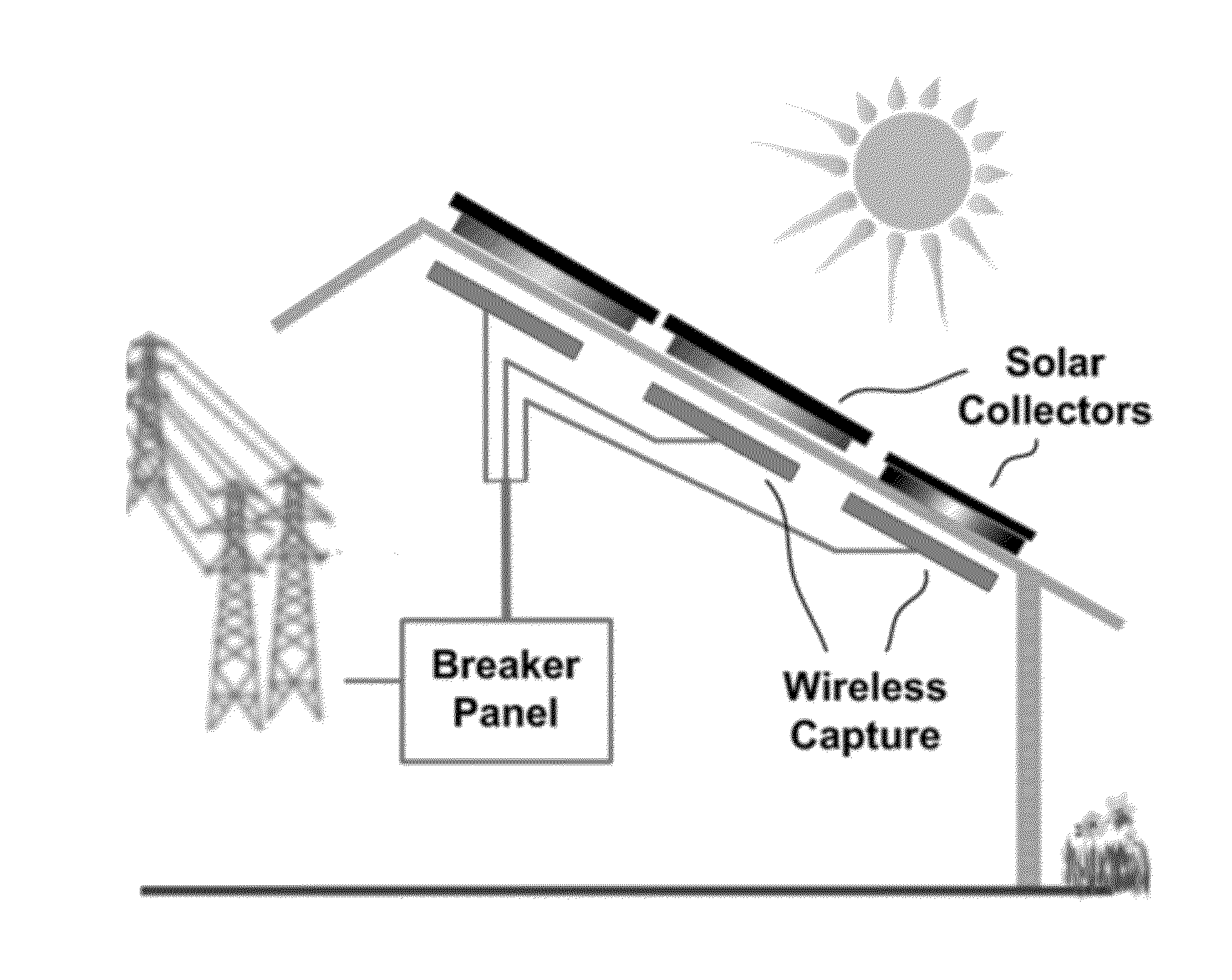
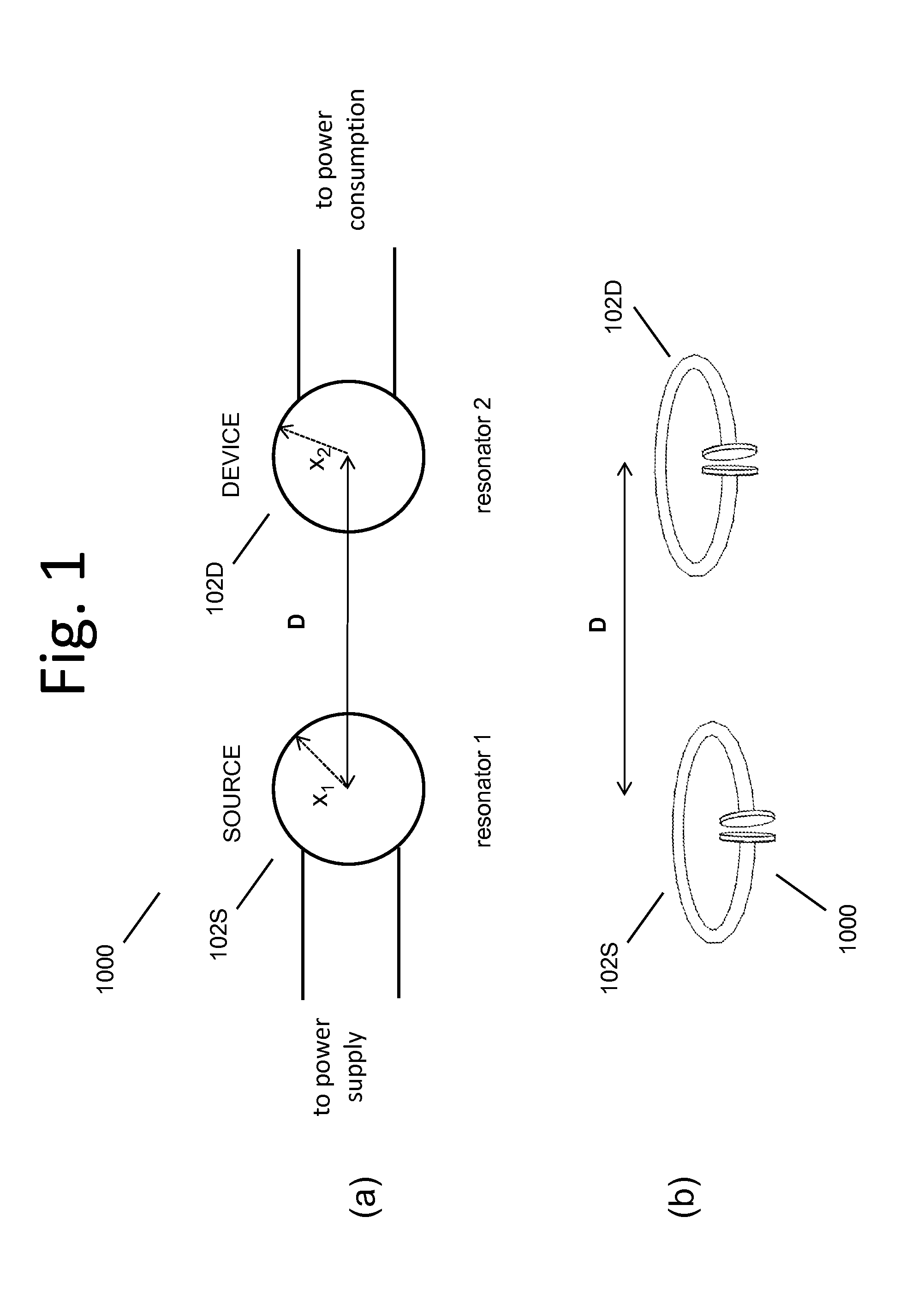
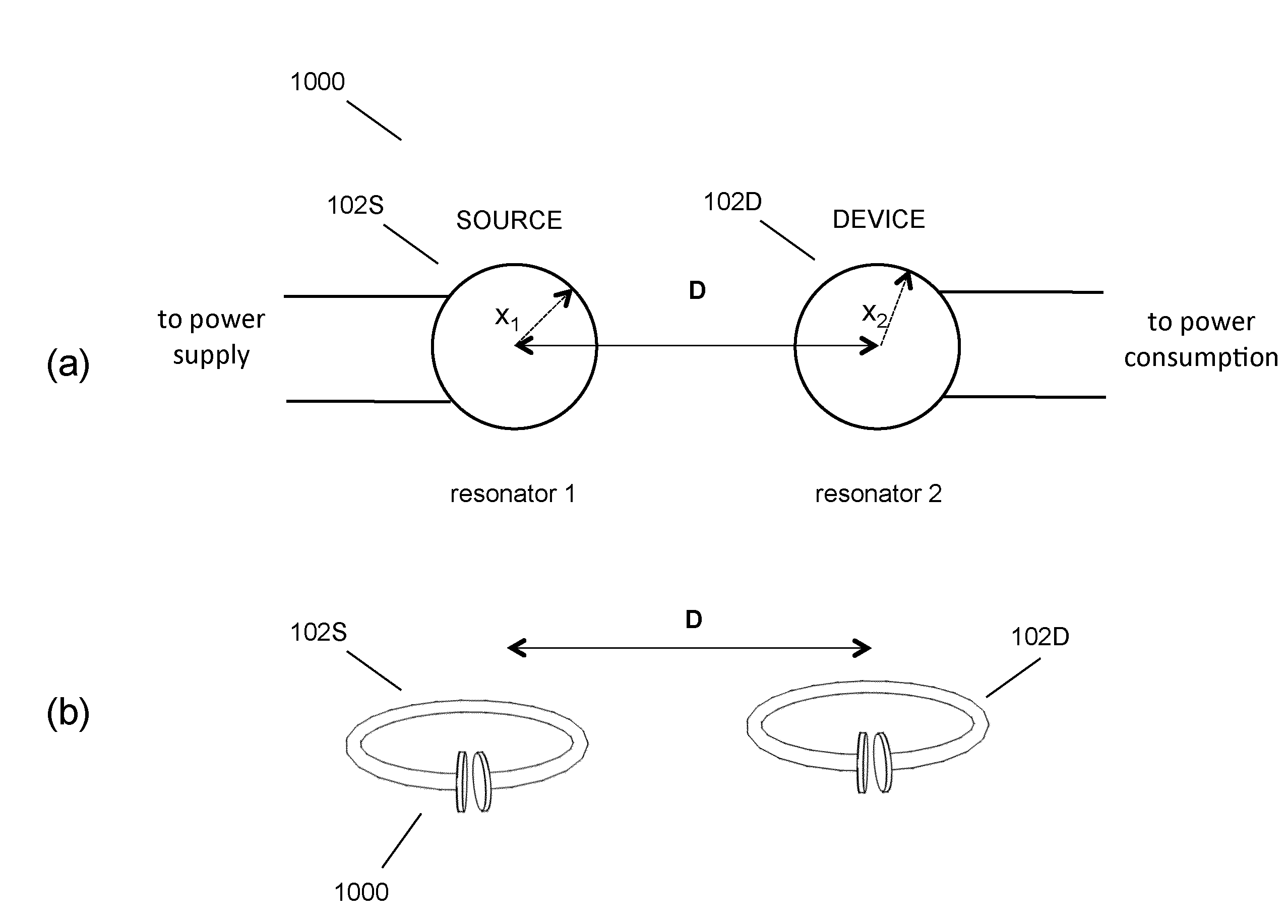
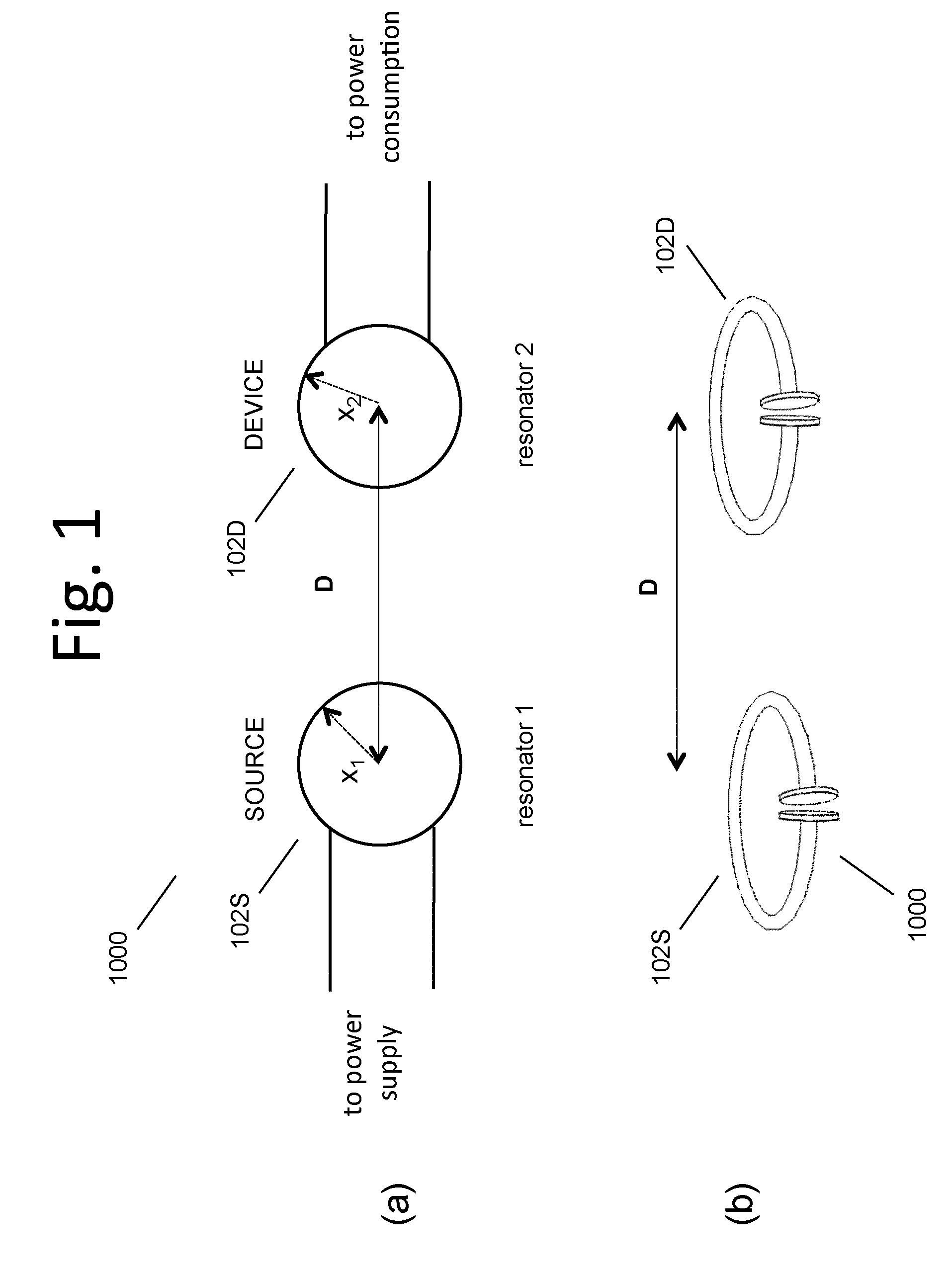
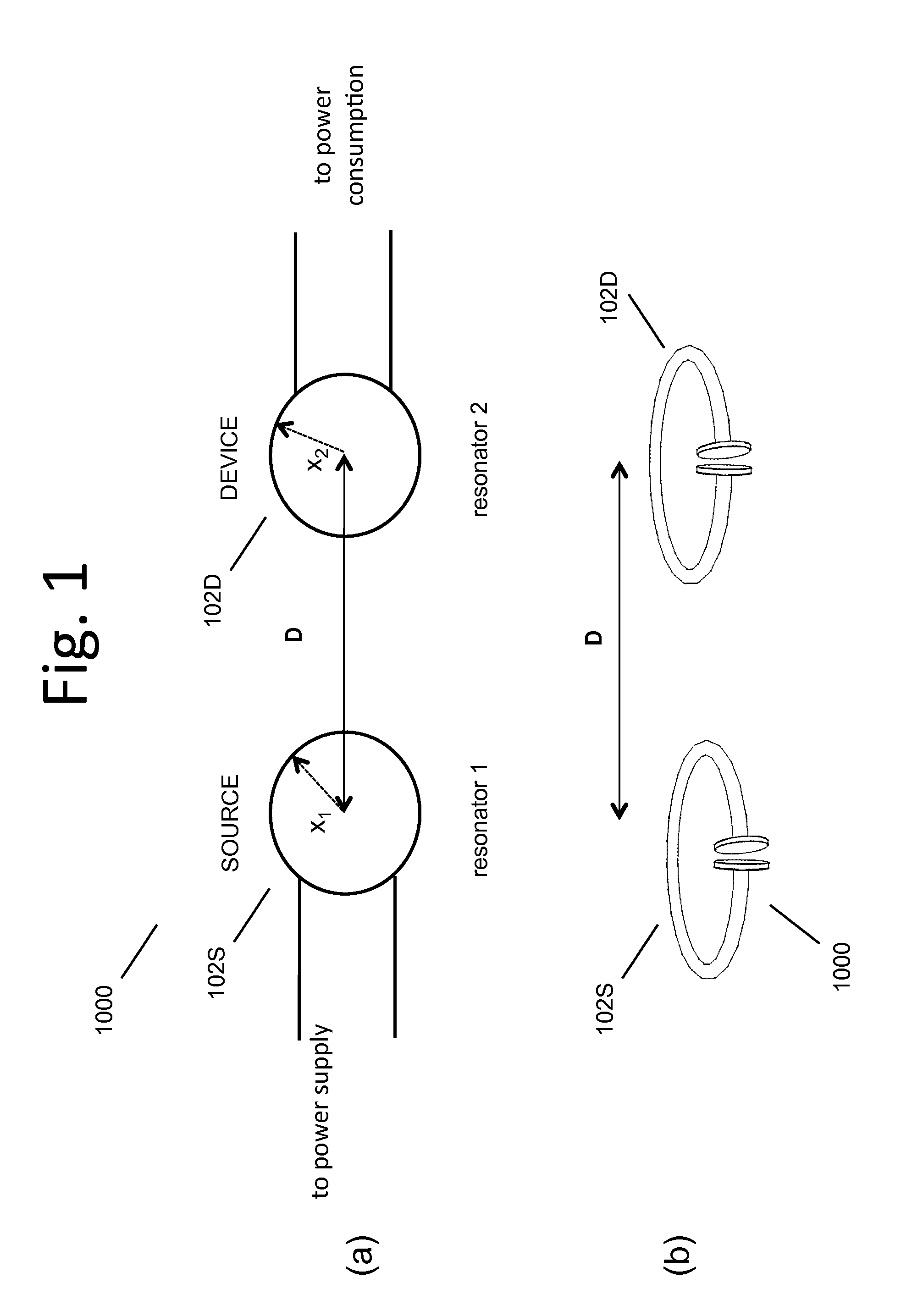
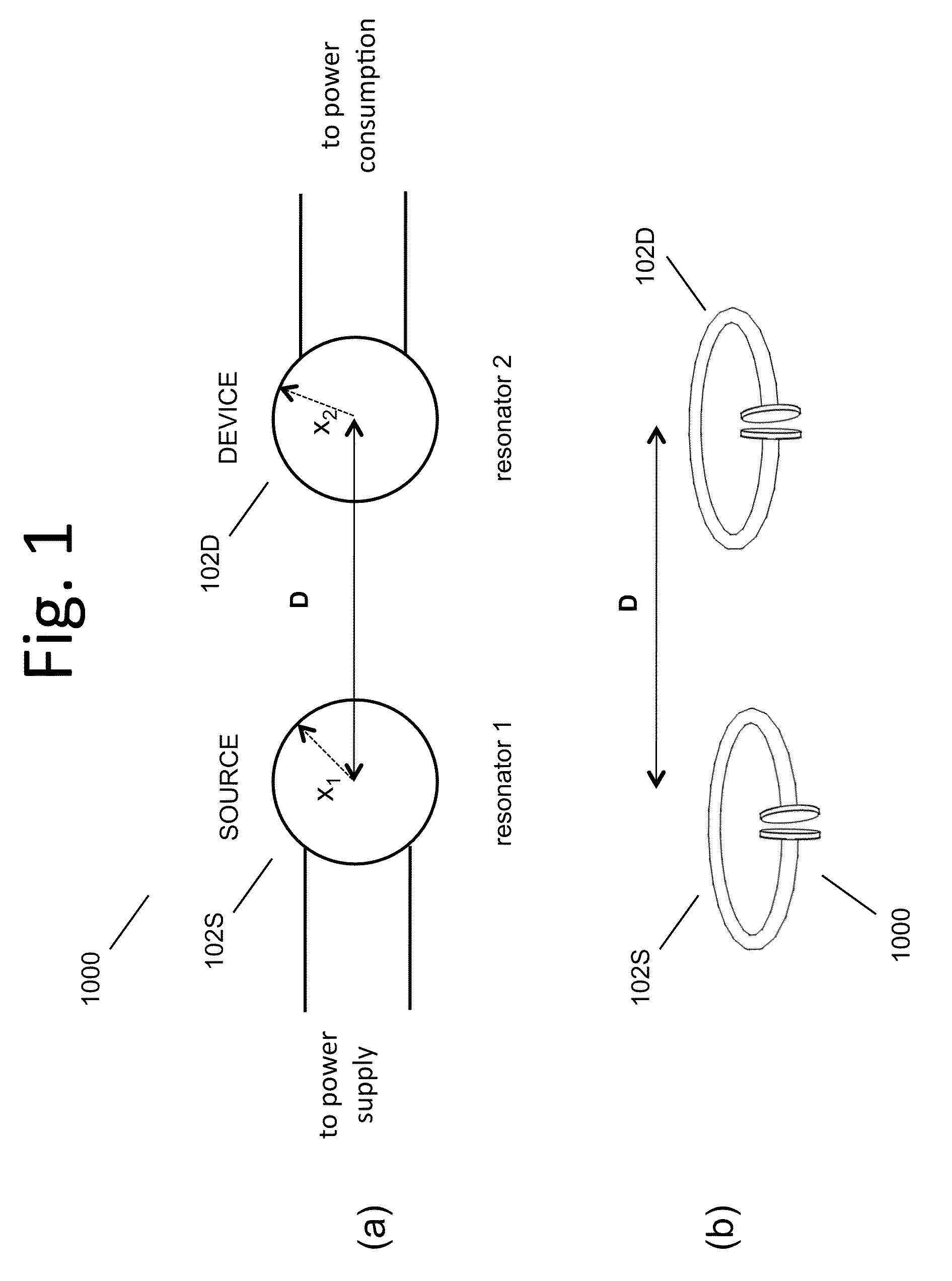
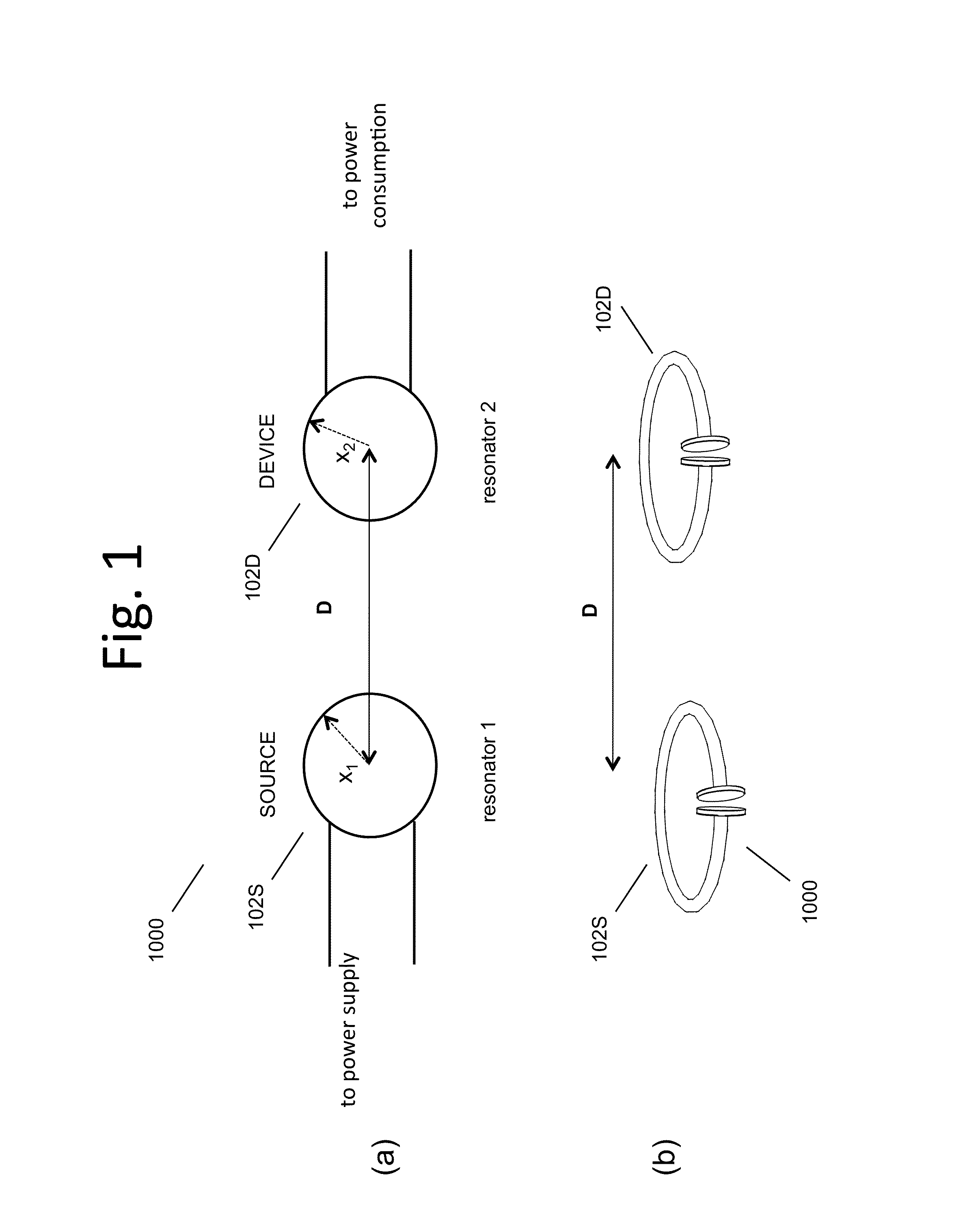
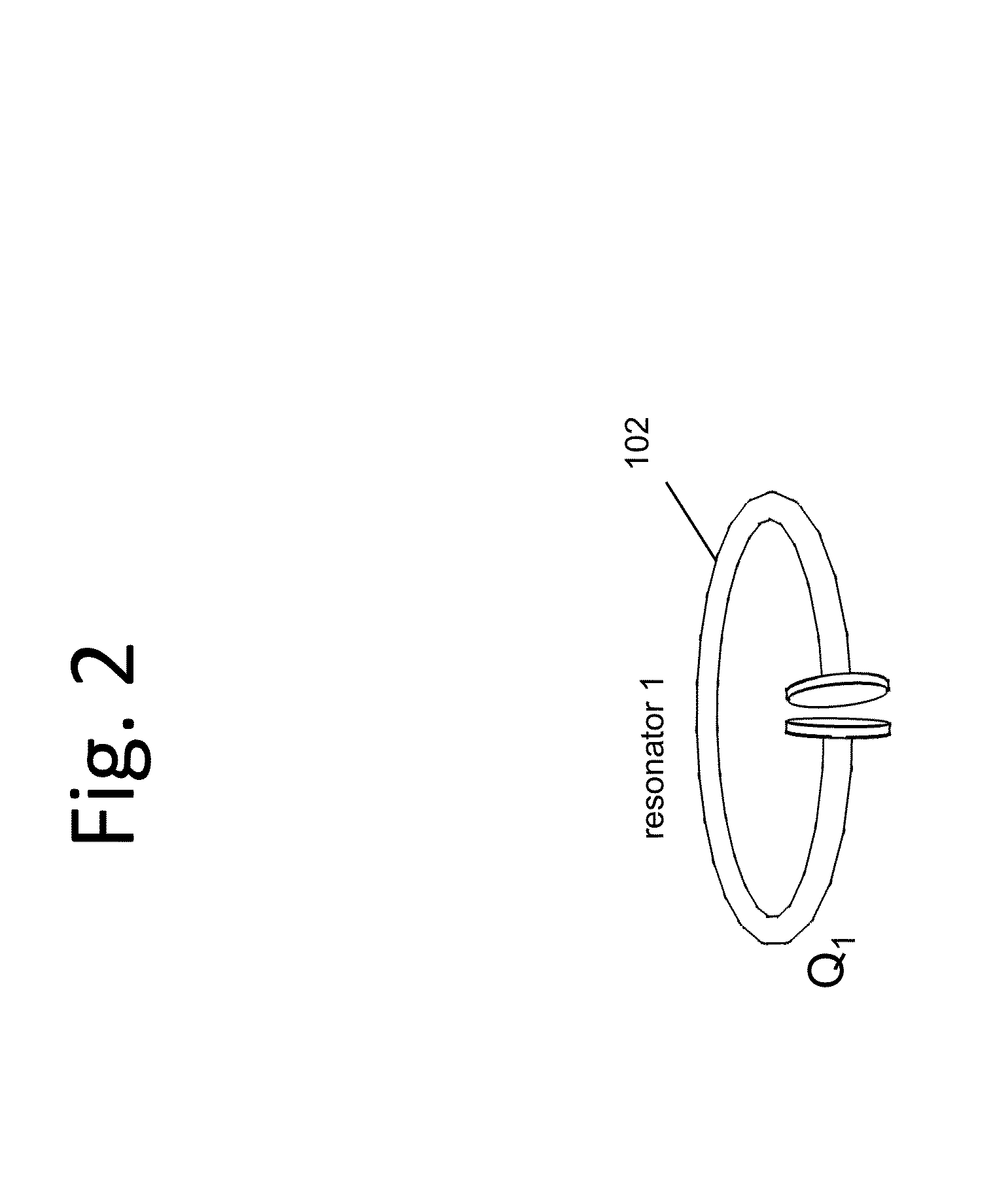
Wireless energy transfer for photovoltaic panels
ActiveUS20120098350A1Reduce cost and complexityMitigate factor drivingMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionElectric power transmissionEnergy transfer
Described herein are improved configurations for a wireless power transfer involving photovoltaic panels. Described are methods and designs that use electric energy from a photovoltaic module to energize at least one wireless energy source to produce an oscillating magnetic field for wireless energy transfer. The source may be configured and tuned to present an impedance to a photovoltaic module wherein said impedance enables substantial extraction of energy from said photovoltaic module.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless power transfer within a circuit breaker
InactiveUS20120091820A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCharging stationsElectric forceTransmitted power
A wireless power service panel source includes power and control circuitry that receives power from a wired power connection at a position in a service panel, and generates an electronic drive signal at a frequency, f, and a source magnetic resonator configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field in response to the electronic drive signal, wherein the source magnetic resonator is configured to wirelessly transmit power to sensors in other positions within the service panel.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer using repeater resonators
ActiveUS20110095618A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferCircuit authenticationMultiple-port networksEnergy transferElectricity
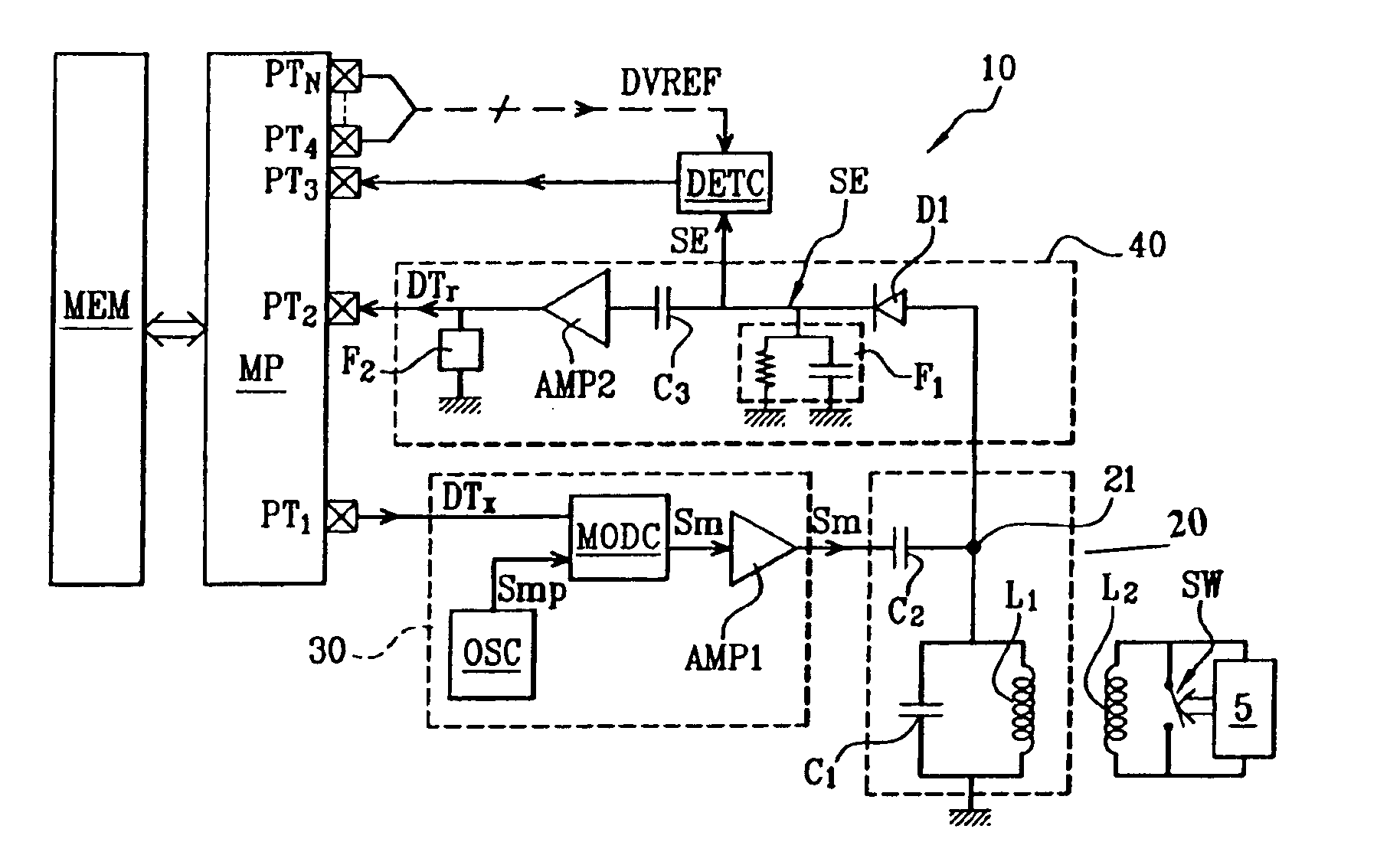
Described herein are improved configurations for a device for wireless power transfer that includes a conductor forming at least one loop of a high-Q resonator, a capacitive part electrically coupled to the conductor, and a power and control circuit electrically coupled to the conductor, the power and control circuit providing two or more modes of operation and the power and control circuit selecting how the high-Q resonator receives and generates an oscillating magnetic field.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Foreign object detection in wireless energy transfer systems
ActiveUS20130069441A1Improve detection rateNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemEnergy transferForeign object
A wireless energy transfer system includes a foreign object debris detection system. The system includes at least one wireless energy transfer source configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field. The foreign object debris may be detected by at least one field gradiometer positioned in the oscillating magnetic field. The voltage of the at least one field gradiometer may be measured using readout circuitry and a feedback loop based on the readings from the gradiometers may be used to control the parameters of the wireless energy source.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless powered television
ActiveUS20120091795A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsElectric power systemElectric power
A wireless power system for powering a television includes a source resonator, configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field, and at least one television component attached to at least one device resonator, wherein the at least one device resonator is configured to wirelessly receive power from the source resonator via the oscillating magnetic field when the distance between the source resonator and the at least one device resonator is more than 5 cm, and wherein at least one television component draws at least 10 Watts of power.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Mechanically removable wireless power vehicle seat assembly
ActiveUS20130221744A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationHigh conductivityElectric power
Described herein are improved capabilities for a system and method for wireless energy distribution to a mechanically removable vehicle seat, comprising a source resonator coupled to an energy source of a vehicle, the source resonator positioned proximate to the mechanically removable vehicle seat, the source resonator generating an oscillating magnetic field with a resonant frequency and comprising a high-conductivity material adapted and located between the source resonator and a vehicle surface to direct the oscillating magnetic field away from the vehicle surface, and a receiving resonator integrated into the mechanically removable vehicle seat, the receiving resonator having a resonant frequency similar to that of the source resonator, and receiving wireless energy from the source resonator, and providing power to electrical components integrated with the mechanically removable vehicle seat.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer using repeater resonators
ActiveUS8587155B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksRailway vehiclesEnergy transferEngineering
Described herein are improved configurations for a lighting system with wireless power transfer that includes a source high-Q magnetic resonator coupled to a power source and generating an oscillating magnetic field, at least one device high-Q magnetic resonator configured to convert said oscillating magnetic field to electrical energy used to power a light coupled to the at least one device resonator, and at least one repeater resonator, larger than the device resonator, wherein the repeater resonator is positioned further from the source resonator than the device resonator and improves the power transfer efficiency between the source resonator and the device resonator.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer with feedback control for lighting applications
ActiveUS20100201203A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreMultiple-port networksEnergy transferElectricity
Described herein are improved configurations for a wireless lighting power transfer method including providing a source having a source resonator that includes a high-Q source magnetic resonator coupled to a power source, providing a device having a device resonator that includes a high-Q device magnetic resonator, distal from the source resonator, the device including a light emitting part electrically coupled to the device resonator, providing a signaling capability between the source and the device, signaling a state of the device to the source using the signaling capability, and energizing the source to generate an oscillating magnetic field according to the state of the device.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer in lossy environments
ActiveCN102439669AShort coupling timeLow intrinsic lossMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy transferCapacitance
Described herein are improved configurations for a wireless power transfer for electronic devices that include at least one source magnetic resonator including a capacitively- loaded conducting loop coupled to a power source and configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field and at least one device magnetic resonator, distal from said source resonators, comprising a capacitively-loaded conducting loop configured to convert said oscillating magnetic fields into electrical energy, wherein at least one said resonator has a keep-out zone around the resonator that surrounds the resonator with a layer of non-lossy material.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Induction charging for an aerosol delivery device
An aerosol delivery device is provided that includes at least one housing enclosing a reservoir configured to retain an aerosol precursor composition, and a heating element controllable to activate and vaporize components of the aerosol precursor composition. The aerosol delivery device also includes a power source connected to and configured to provide power to an electrical load that includes the heating element, and an induction receiver connected to the power source, the induction receiver including a resonant receiver coupling device in which an alternating current is induced when exposed to an oscillating magnetic field, and a rectifier configured to convert the alternating current to a direct current from which the power source is rechargeable.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
Control for an induction-based aerosol delivery device
An aerosol delivery device is provided that includes a substrate configured to carry an aerosol precursor composition, and includes an induction transmitter, induction receiver and control component. The induction transmitter is configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field. The induction receiver is positioned in proximity to the substrate, and configured to generate heat when exposed to the oscillating magnetic field and thereby vaporize components of the aerosol precursor composition. The control component is configured to direct current to the induction transmitter to drive the induction transmitter to generate the oscillating magnetic field, with the control component being configured to direct the current according to a zero voltage switching (ZVS) inverter topology.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
Series relayed wireless power transfer in a vehicle
InactiveUS20140265555A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferElectromagnetic wave systemRailway vehiclesElectric power transmissionEnergy transfer
Described herein are improved capabilities for a system and method for wireless energy distribution across a vehicle compartment of defined area, comprising a source resonator coupled to an energy source of a vehicle and generating an oscillating magnetic field with a frequency, and at least one repeater resonator positioned along the vehicle compartment, the at least one repeater resonator positioned in proximity to the source resonator, the at least one repeater resonator having a resonant frequency and comprising a high-conductivity material adapted and located between the at least one repeater resonator and a vehicle surface to direct the oscillating magnetic field away from the vehicle surface, wherein the at least one repeater resonator provides an effective wireless energy transfer area within the defined area.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Self-regulating transcutaneous energy transfer
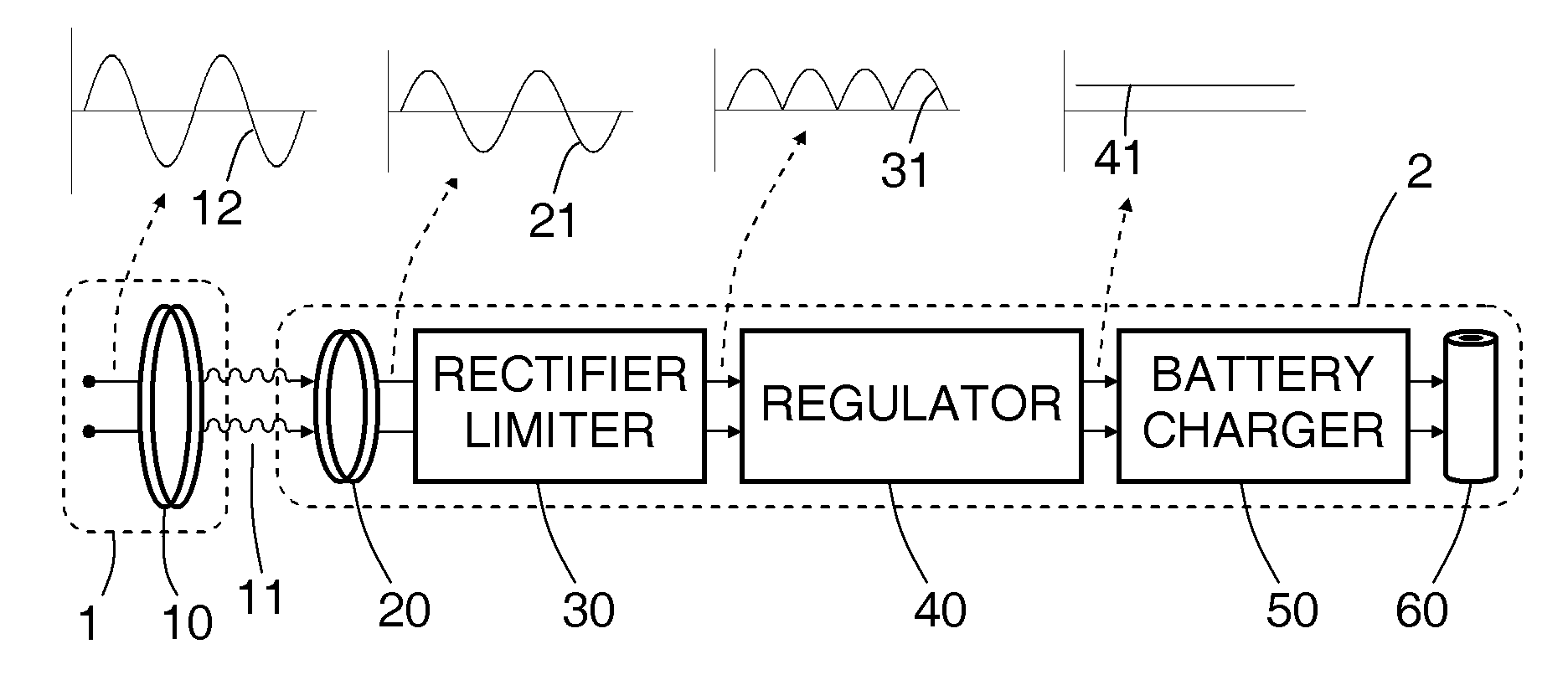
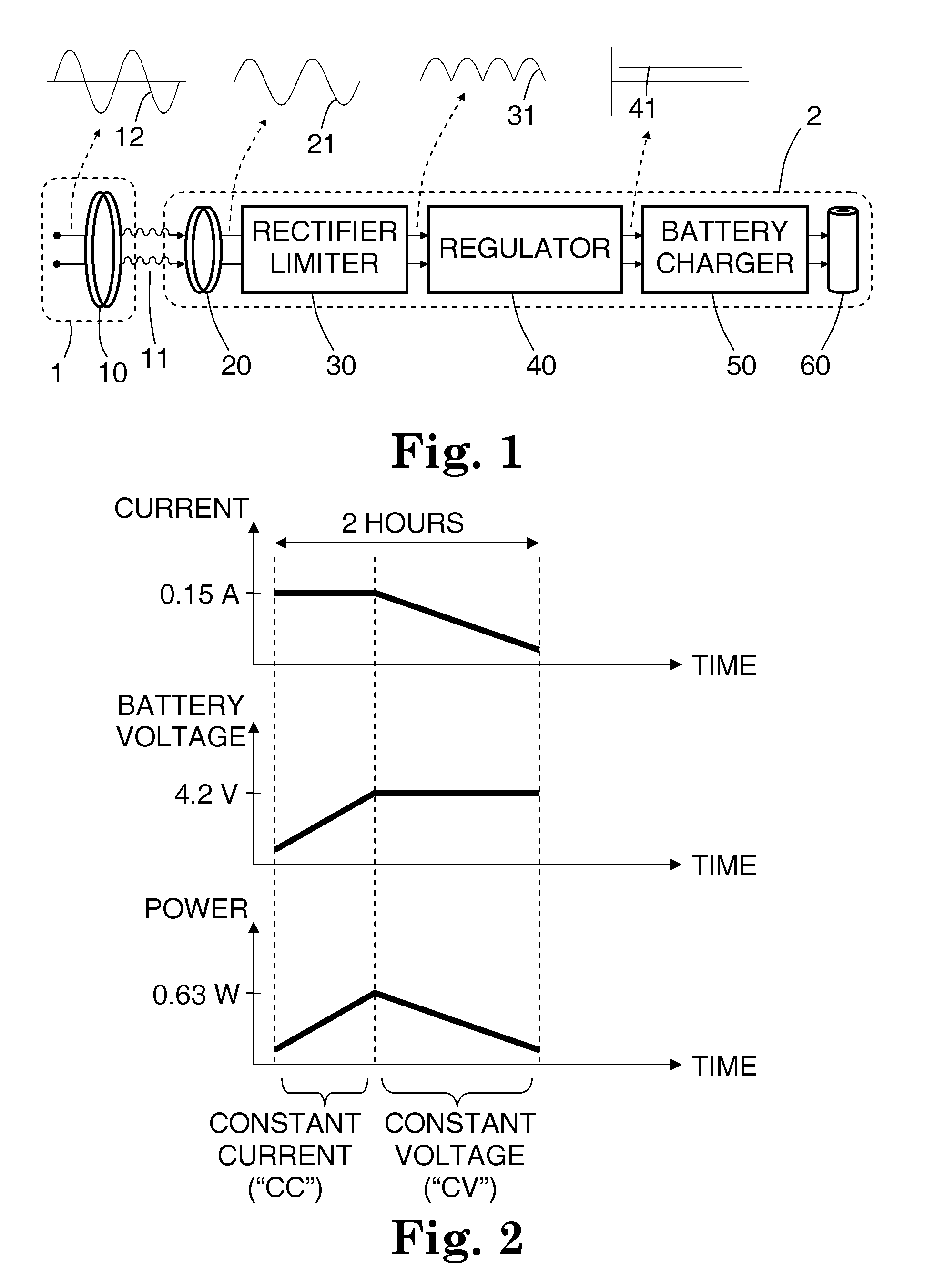
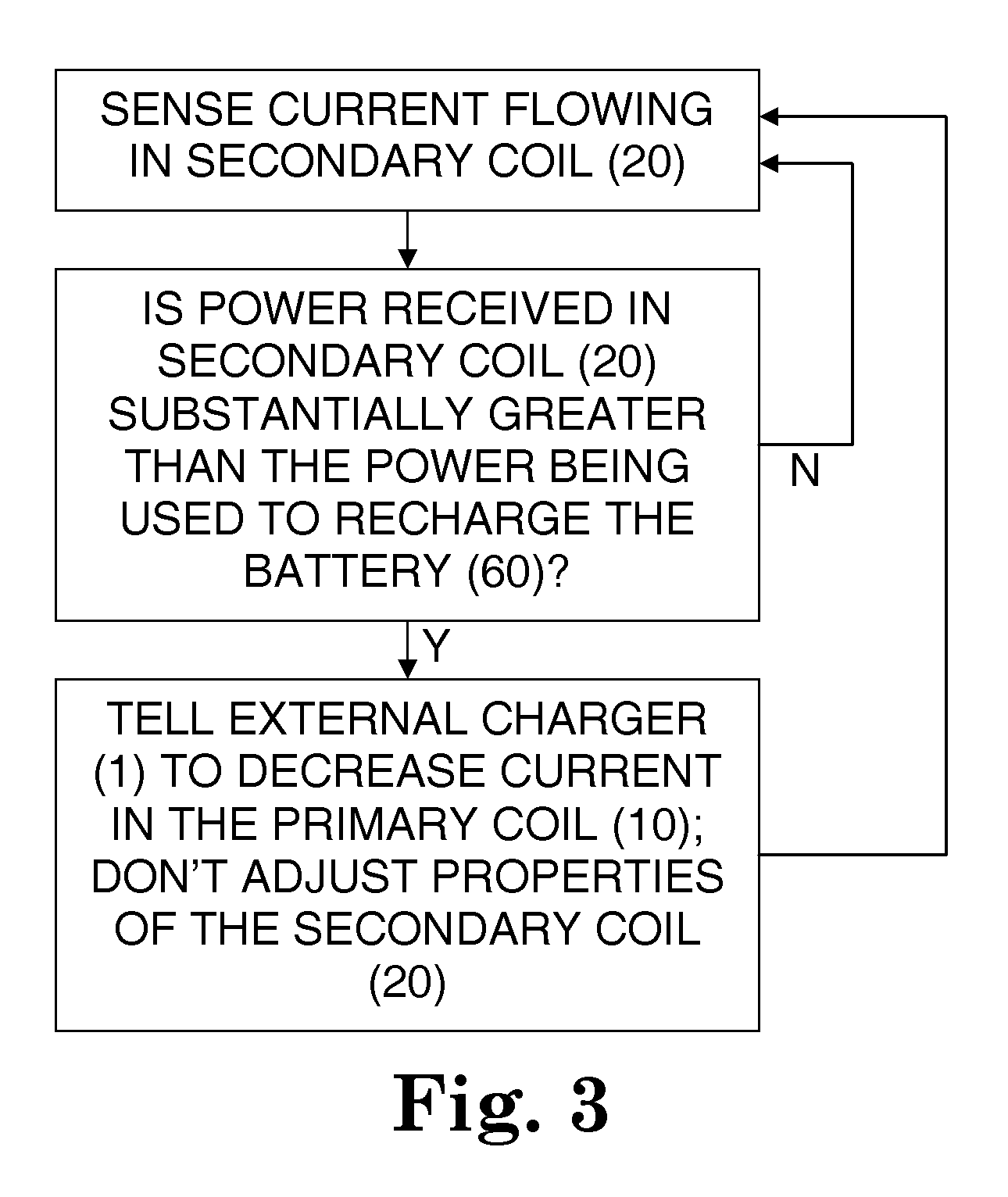
A rechargeable battery system and method are disclosed, in which an implantable medical device (IMD) regulates its transfer of energy from a separate charger unit. For recharging, a charger unit is brought into proximity to the implanted device. An oscillating current is generated in a primary coil, located in the charger. By inductive coupling through an oscillating magnetic field, an alternating current is generated in a secondary coil, which is implanted in or near the implanted device. The alternating current then passes through a half-wave or full-wave rectifier to form a one-sided current, then passes through a regulator to form an essentially direct current, which is in turn directed to the rechargeable battery in the implanted device. The secondary coil has a controllable damped resonant frequency, which can be dynamically tuned away from the driving frequency of the primary coil by a variable resistor and / or by varying a duty cycle of a rapidly switched electrical element. If a control loop in the implant senses that more power is being received at the second coil than is actually being used to recharge the battery, the control loop temporarily changes the variable resistance. When this happens, the resonant frequency of the secondary coil is detuned slightly away from the driving frequency, so that less of the incoming power is absorbed by the secondary coil. Alternatively, the secondary coil may be temporarily short-circuited. With less or no excess power entering the circuitry of the implant, the problem of overheating is mitigated.
Owner:ST CROIX MEDICAL
Position insensitive wireless charging
ActiveUS8963488B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferCircuit authenticationMultiple-port networksAudio power amplifierEngineering
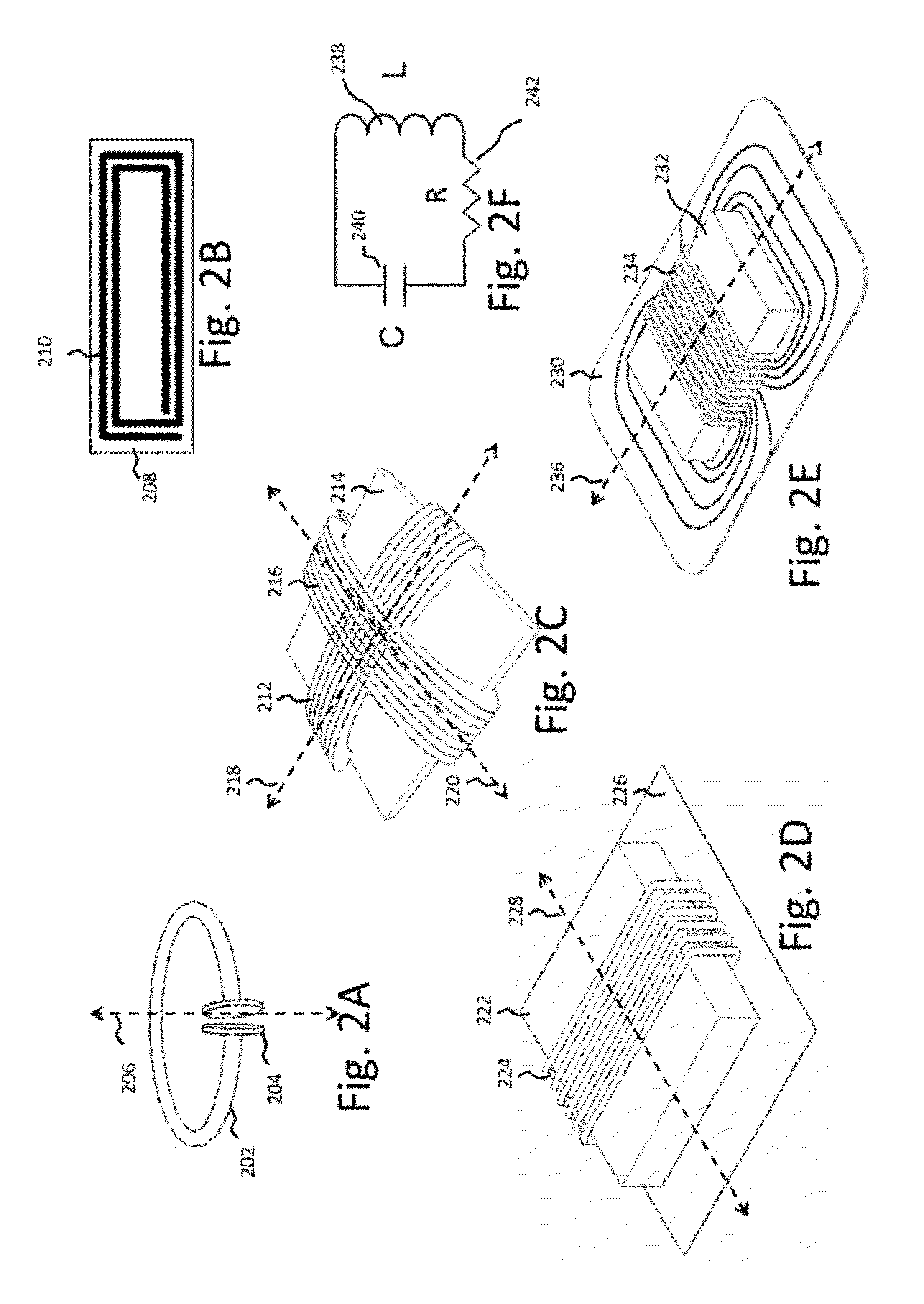
A wireless charging pad includes a capacitively-loaded conducting loop source resonator, with a characteristic size, L1, connected to a switching amplifier and configured to generate an oscillating magnetic field, wherein the conducting loop comprises multiple turns circumscribing an area, the conducting loop does not extend into the center of the circumscribed area, the source resonator delivers useful power to at least one device resonator with a characteristic size, L2, and where L1 is larger than L2.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Induction-based aerosol delivery device
An aerosol delivery device is provided that includes a substrate configured to carry an aerosol precursor composition, and a resonant transformer including a transmitter coupling device and a resonant receiver coupling device that is positioned in proximity to the substrate. The aerosol delivery device also includes a pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter configured to drive the resonant transformer. The PWM inverter includes a bridge circuit coupled to the transmitter coupling device, and a PWM controller embodied as an integrated circuit and configured to output a PWM signal to the bridge circuit configured to drive the transmitter coupling device to generate an oscillating magnetic field and induce an alternating voltage in the resonant receiver coupling device when exposed to the oscillating magnetic field. The alternating voltage causes the resonant receiver coupling device to generate heat and thereby vaporize components of the aerosol precursor composition.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
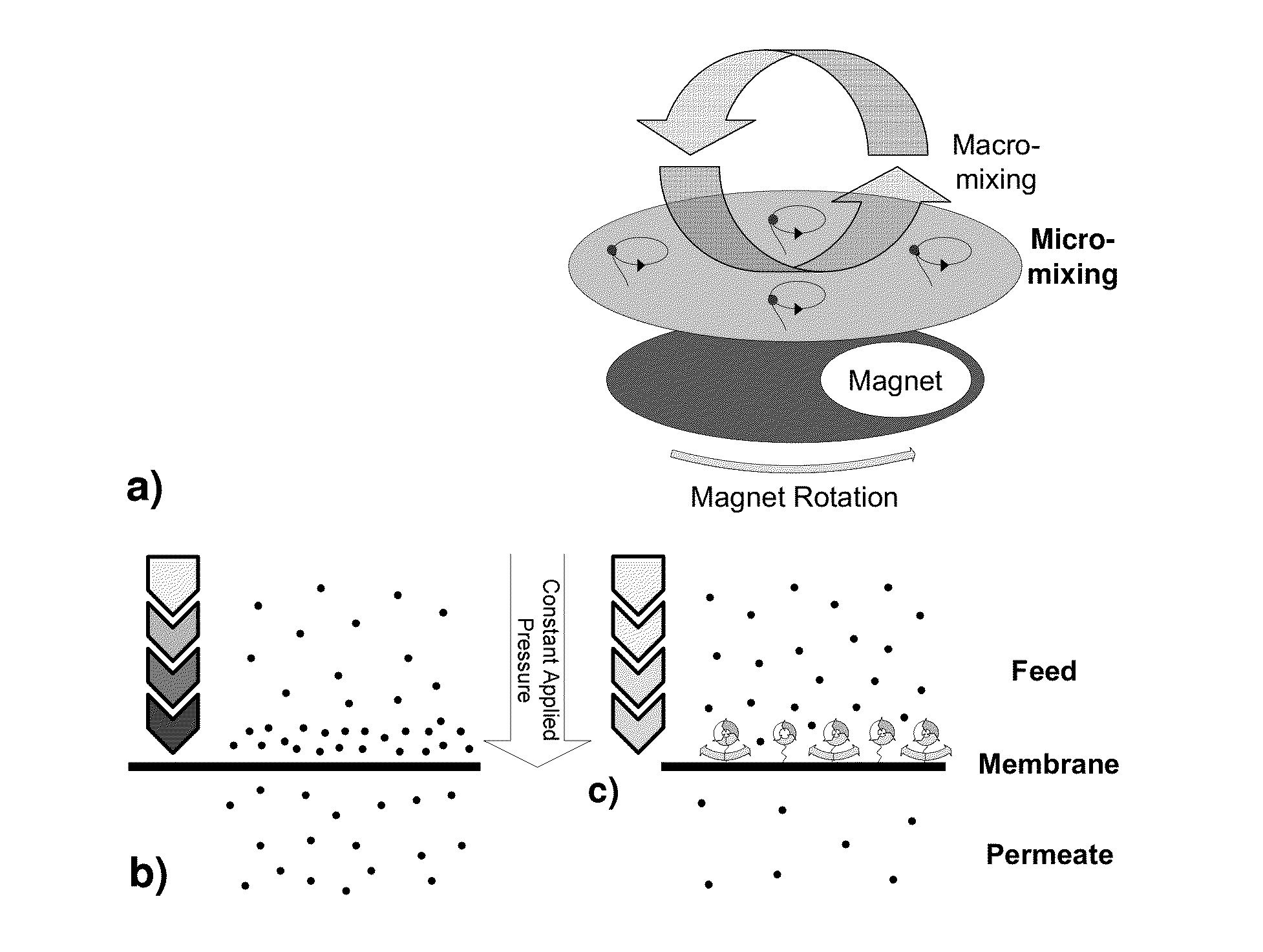
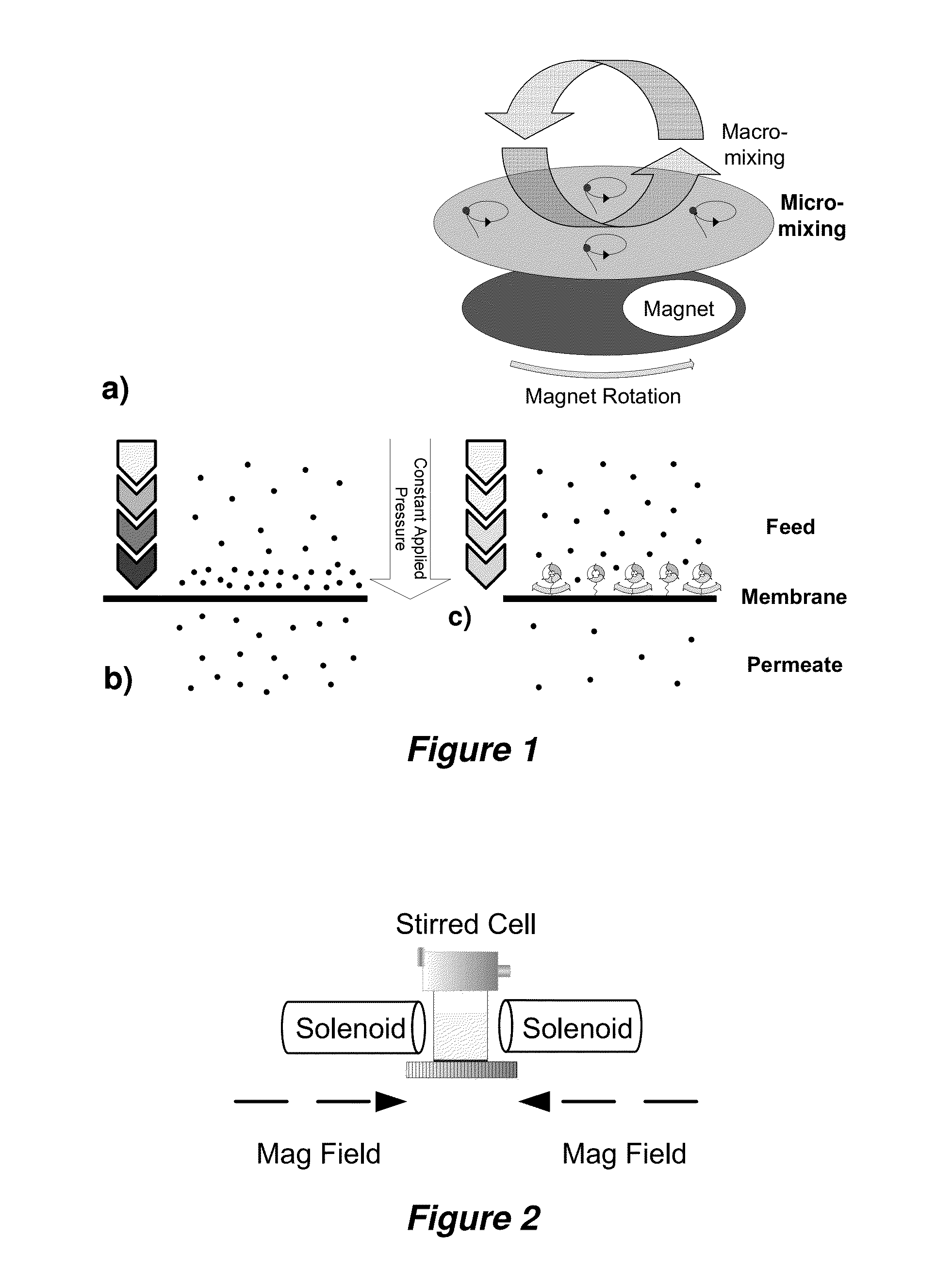
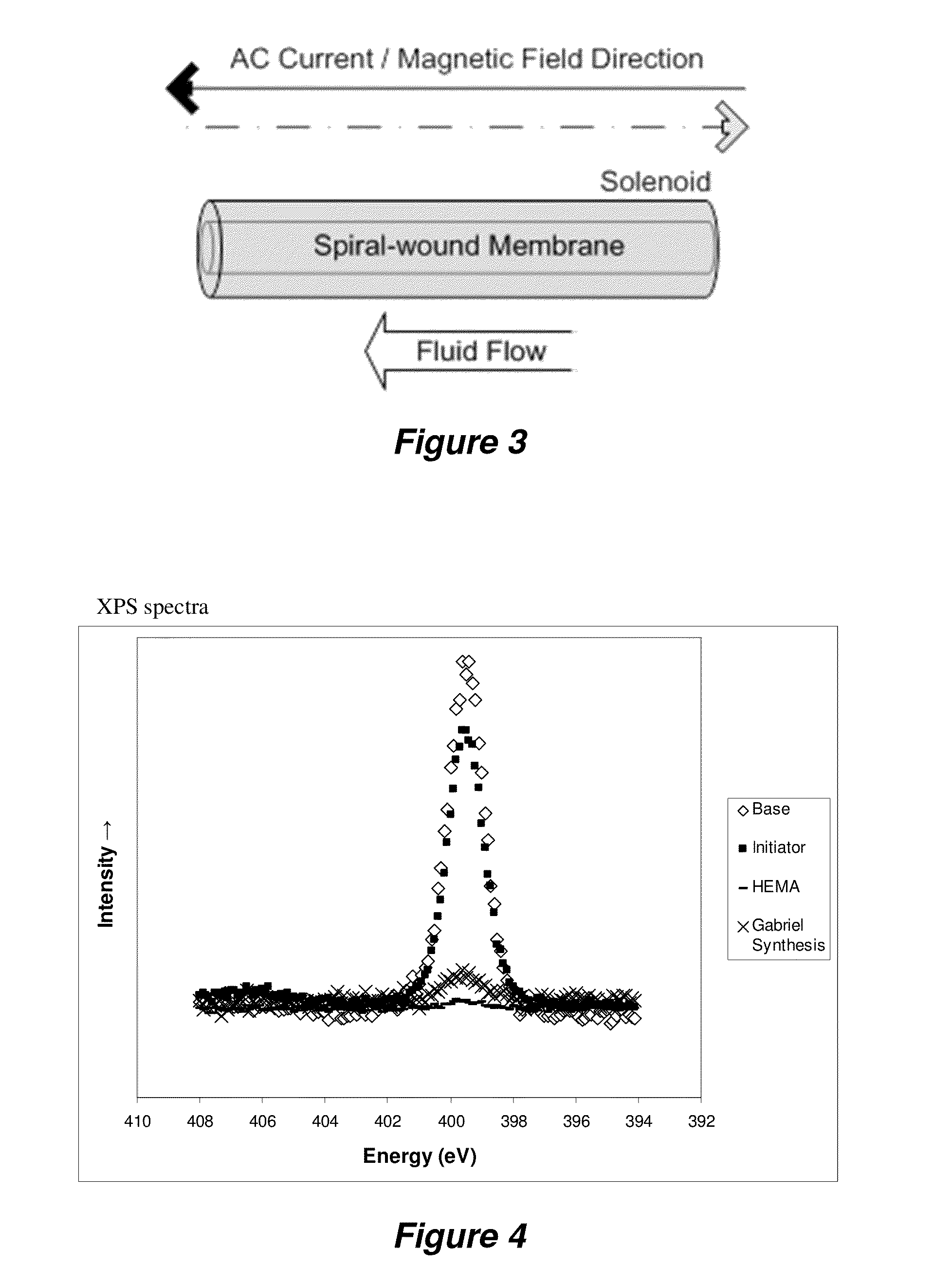
Magnetically responsive membranes
ActiveUS20140231351A1Low purityReduced effectivenessMembranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisPolymer scienceHydrophilic polymers
The invention provides permeable magnetically responsive filtration membranes that include a filtration membrane polymer base suitable for fluid filtration; hydrophilic polymers conjugated to the surface of the filtration membrane polymer; and magnetic nanoparticles affixed to the ends of a plurality of the hydrophilic polymers, wherein the hydrophilic polymers are movable with respect to the surface of the filtration membrane polymer surface in the presence of an oscillating magnetic field.
Owner:LEHRSTUHL FUR TECHN CHEM II UNIV DUISBURG ESSEN +2
Mechanically removable wireless power vehicle seat assembly
ActiveUS9318922B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationHigh conductivityElectric power
Described herein are improved capabilities for a system and method for wireless energy distribution to a mechanically removable vehicle seat, comprising a source resonator coupled to an energy source of a vehicle, the source resonator positioned proximate to the mechanically removable vehicle seat, the source resonator generating an oscillating magnetic field with a resonant frequency and comprising a high-conductivity material adapted and located between the source resonator and a vehicle surface to direct the oscillating magnetic field away from the vehicle surface, and a receiving resonator integrated into the mechanically removable vehicle seat, the receiving resonator having a resonant frequency similar to that of the source resonator, and receiving wireless energy from the source resonator, and providing power to electrical components integrated with the mechanically removable vehicle seat.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Non-contact integrated circuit reader comprising a low power consumption active standby mode
InactiveUS6905074B2Current consumptionEasy to monitorNear-field transmissionMemory record carrier reading problemsEngineeringLow power dissipation
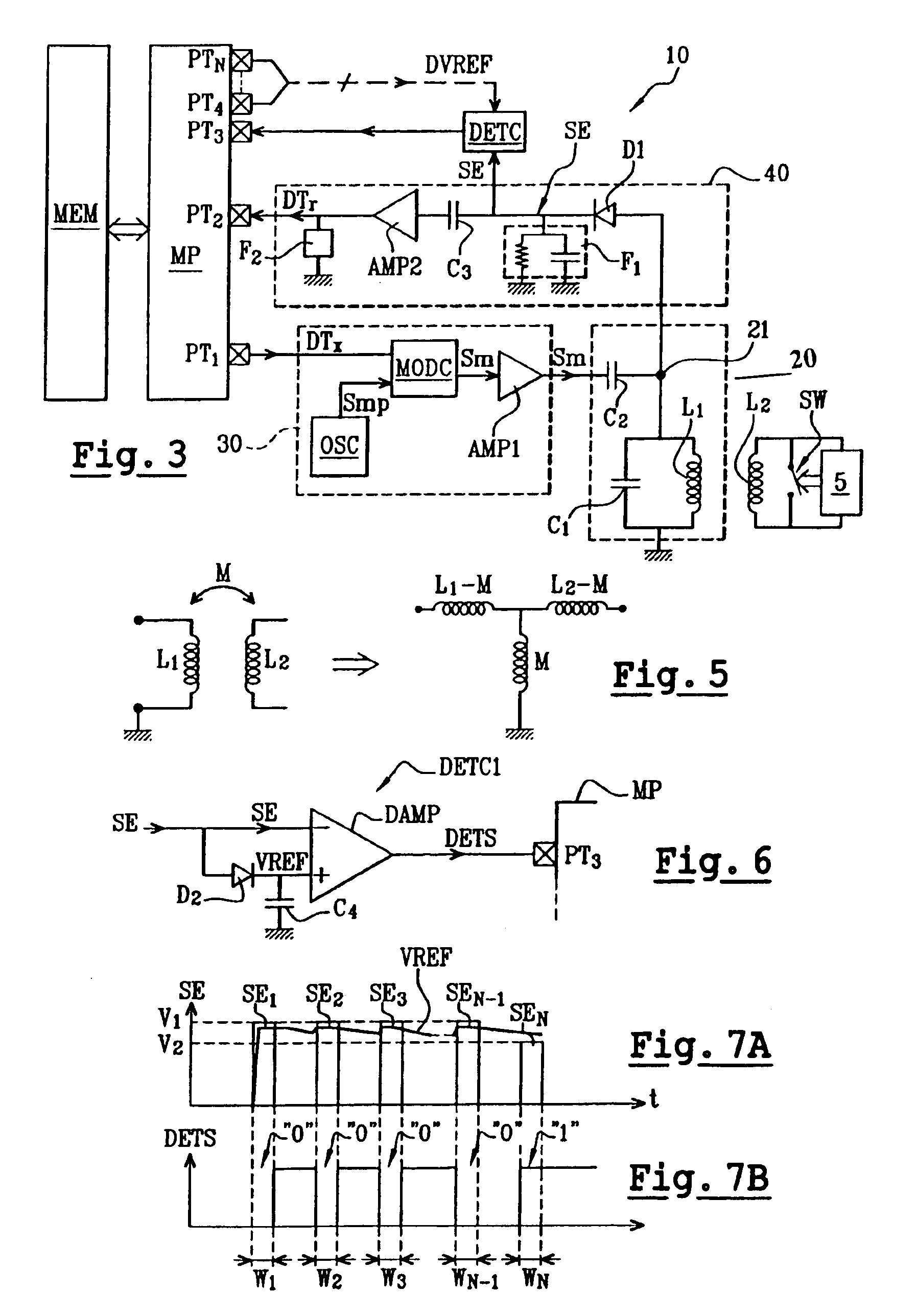
A contactless integrated circuit reader includes an antenna coil for emitting an oscillating magnetic field, and circuitry for detecting the presence of a contactless integrated circuit within a communication perimeter of the reader without receiving an identification message. The detection circuitry include circuitry for emitting short magnetic field pulses, circuitry for extracting from the antenna coil an envelope signal having envelope pulses corresponding to the magnetic field pulses, and circuitry for monitoring the amplitude of the envelope pulses, arranged for detecting a variation in the amplitude of the envelope pulses representative of the entry of the contactless integrated circuit into the communication perimeter of the reader.
Owner:VERIMATRIX INC
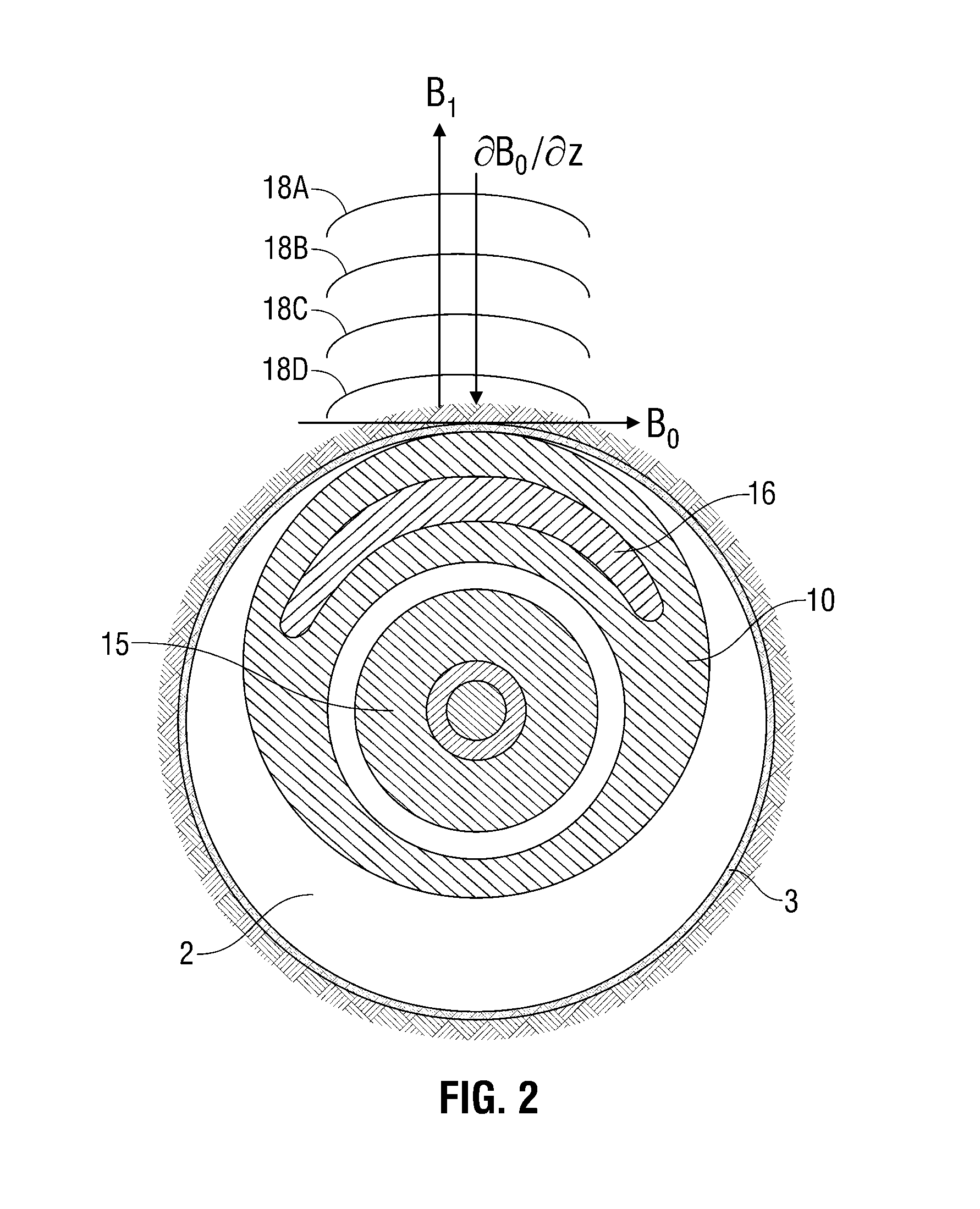
Method and apparatus for acquiring high resolution spectral data or high definition images in inhomogeneous environments
InactiveUS20100001727A1High definitionReduce complicationsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData treatment
A method and apparatus for treating a sample for acquiring high-definition magnetic resonance images (MRI images) or high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra even in the presence of magnetic field distortions within one or multiple scans. The spatial nature and temporal dependence of the field inhomogeneities are determined a priori using any of several literature procedures. A static or oscillating magnetic field gradient is applied on the sample so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with different resonance frequencies. A phase- and amplitude-modulated radiofrequency (RF) pulse is applied in unison with the magnetic field gradient so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with a homogeneous excitation / inversion profile. The nature of the spatially-selective RF irradiation is tailored in such a way that, when added on top of the effects of the inhomogeneities, the spins' evolution phases and their signal amplitudes at the time of the acquisition become independent of the inhomogeneities. The spin signals thus created are captured and decoded, so as to obtain the spins' response as if the inhomogeneity was not present. The collected data is processed to a suitable rearrangement and Fourier analysis procedure to retrieve a final undistorted image or spectrum. The magnetic field gradient can be oscillated to impose this kind of inhomogeneity corrections on multiple spatial dimensions sequentially, or simultaneously.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
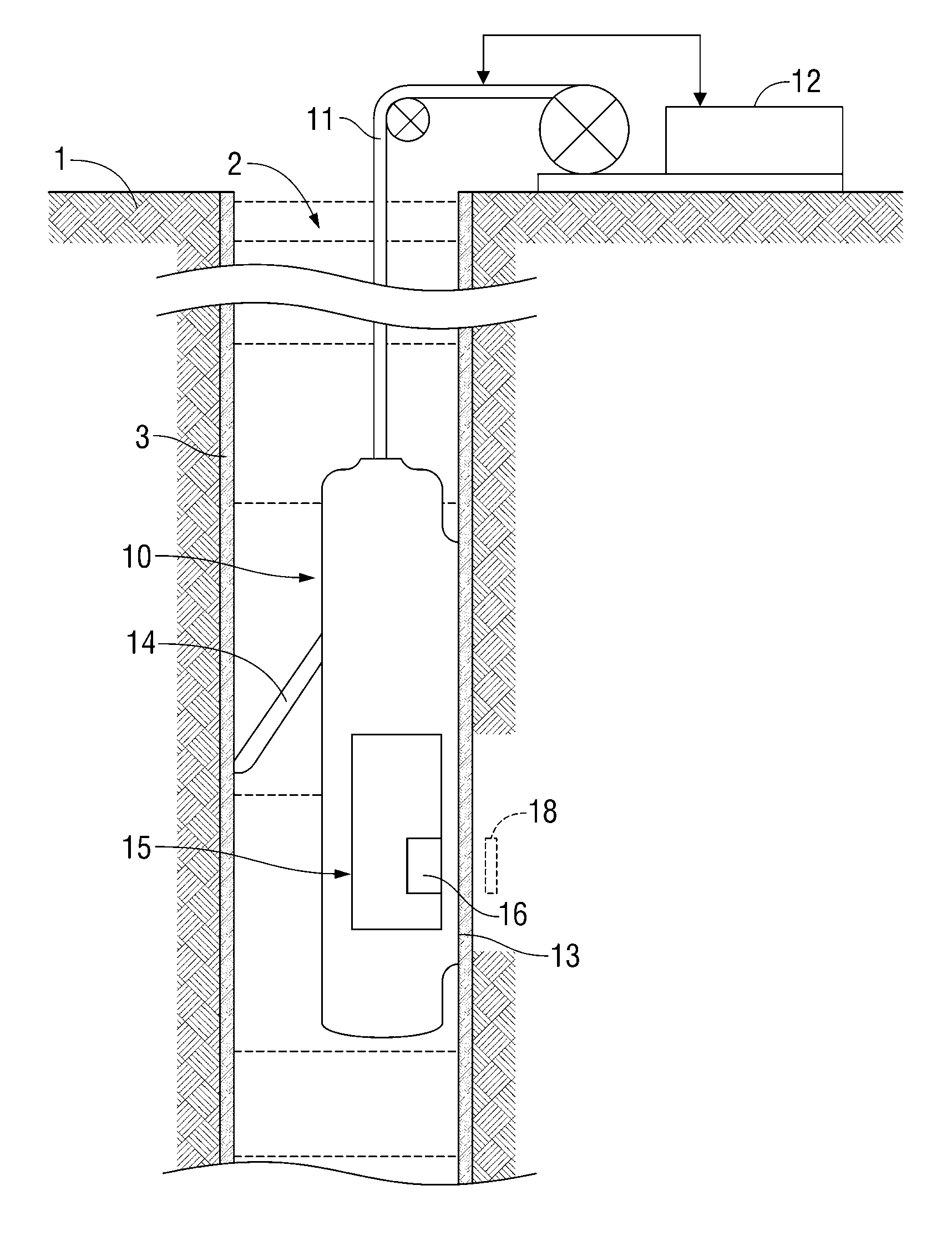
System and method for emulating nuclear magnetic resonance well logging tool diffusion editing measurements on a bench-top nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for laboratory-scale rock core analysis
InactiveUS20110234220A1Increase displacementPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWell loggingLaboratory scale
A laboratory NMR methodology (and corresponding laboratory apparatus) defines a sample volume. The method stores downhole tool data corresponding to a hydrocarbon-bearing sample collected from a given subsurface formation. The downhole tool data includes parameters pertaining to magnetic fields used by a downhole tool during a suite of NMR measurements of the given subsurface formation. The sample is positioned in the sample volume of the laboratory apparatus, which applies a static magnetic field in the sample volume. Furthermore, the laboratory apparatus applies a suite of NMR measurements to the sample volume to thereby determine a property of the sample. The NMR measurements of the suite each include a pulse sequence of oscillating magnetic field in conjunction with a pulsed-mode gradient field. The pulsed-mode gradient field is based on the stored downhole tool data corresponding to the sample. A laboratory NMR methodology for optimizing downhole NMR measurements is also described.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus and methods for analyzing fluids extracted from earth formation
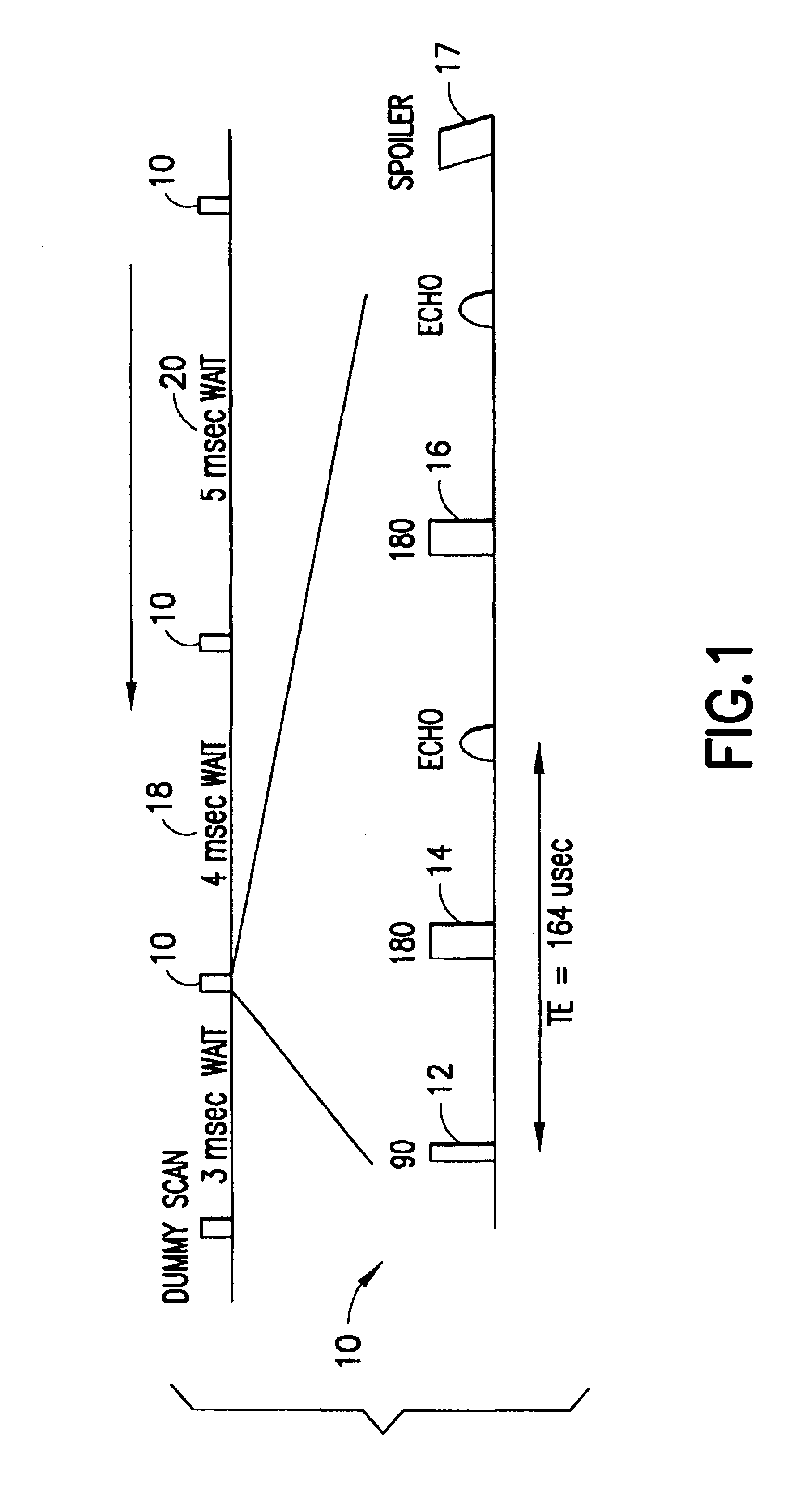
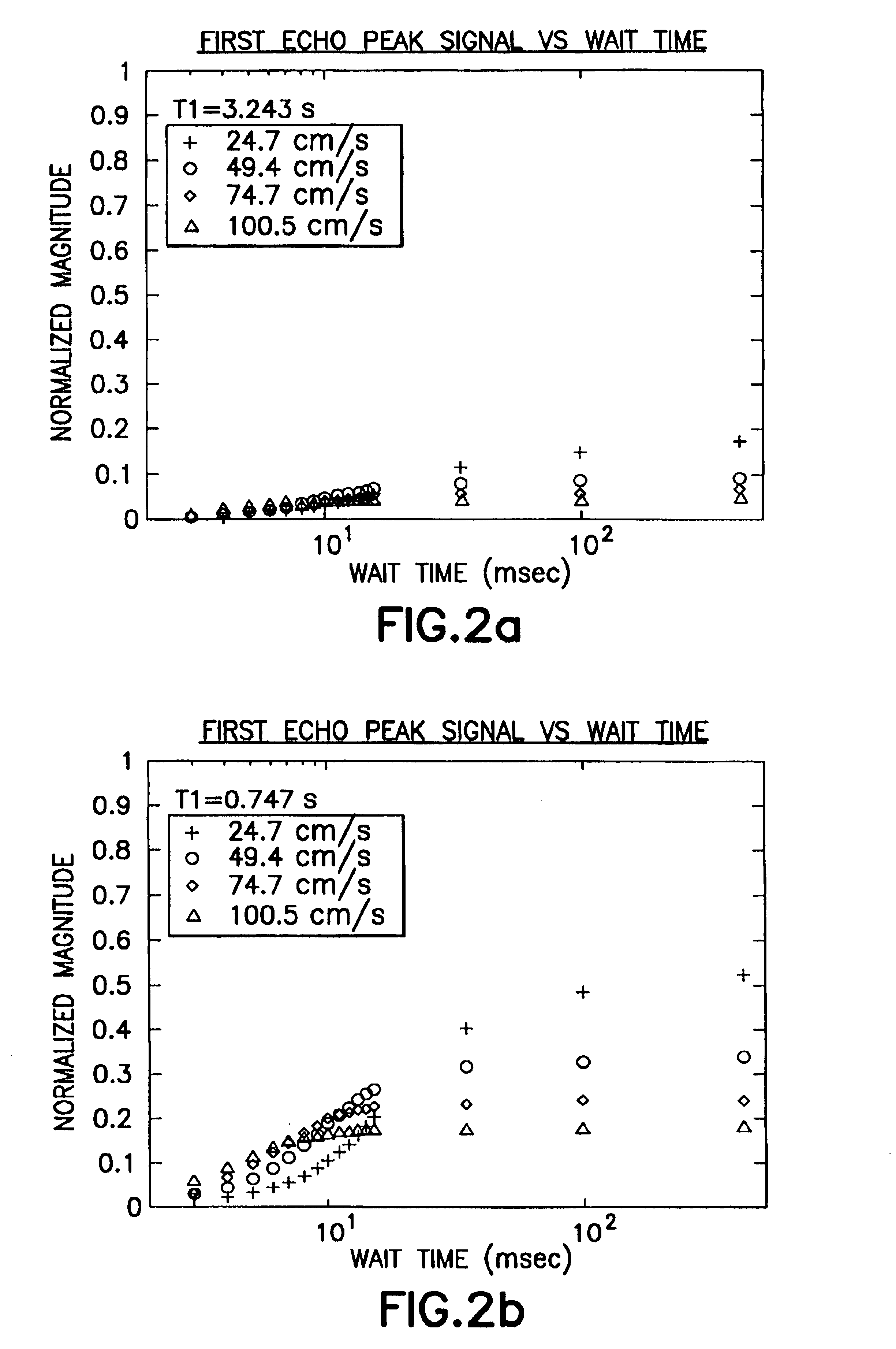
InactiveUS6841996B2Readily apparentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWaiting time
The present invention discloses a method and apparatus to make a nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on a flowing fluid using varied wait times. In one method, NMR measurements are made by: a) flowing the fluid through a static magnetic field; b) applying a group of oscillating magnetic field pulses to the flowing fluid, wherein the group of pulses is comprised of an initial pulse and one or more refocusing pulses; c) detecting magnetic resonance signals from the flowing fluid; d) after a wait time, repeating (b) and (c) one or more times, wherein at least two of the repetitions have varied wait times; and e) analyzing the detected magnetic resonance signals to extract information about the flowing fluid. Further, varied wait time measurements may be useful in determining the flow rate of the sample.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for acquiring high resolution spectral data or high definition images in inhomogeneous environments
InactiveUS7944206B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData treatment
A method and apparatus for treating a sample for acquiring high-definition magnetic resonance images (MRI images) or high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra even in the presence of magnetic field distortions within one or multiple scans. The spatial nature and temporal dependence of the field inhomogeneities are determined a priori using any of several literature procedures. A static or oscillating magnetic field gradient is applied on the sample so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with different resonance frequencies. A phase- and amplitude-modulated radiofrequency (RF) pulse is applied in unison with the magnetic field gradient so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with a homogeneous excitation / inversion profile. The nature of the spatially-selective RF irradiation is tailored in such a way that, when added on top of the effects of the inhomogeneities, the spins' evolution phases and their signal amplitudes at the time of the acquisition become independent of the inhomogeneities. The spin signals thus created are captured and decoded, so as to obtain the spins' response as if the inhomogeneity was not present. The collected data is processed to a suitable rearrangement and Fourier analysis procedure to retrieve a final undistorted image or spectrum. The magnetic field gradient can be oscillated to impose this kind of inhomogeneity corrections on multiple spatial dimensions sequentially, or simultaneously.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
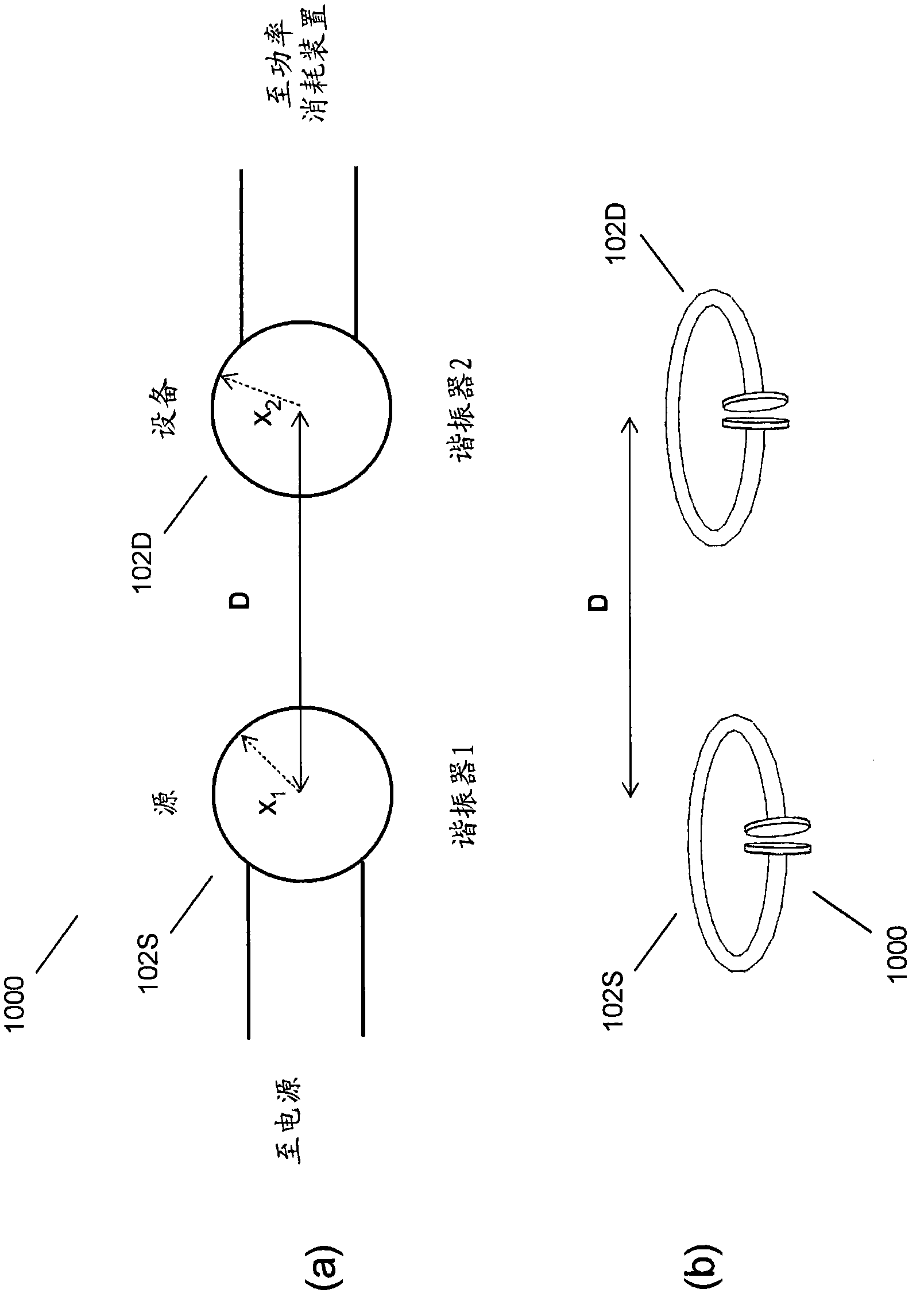
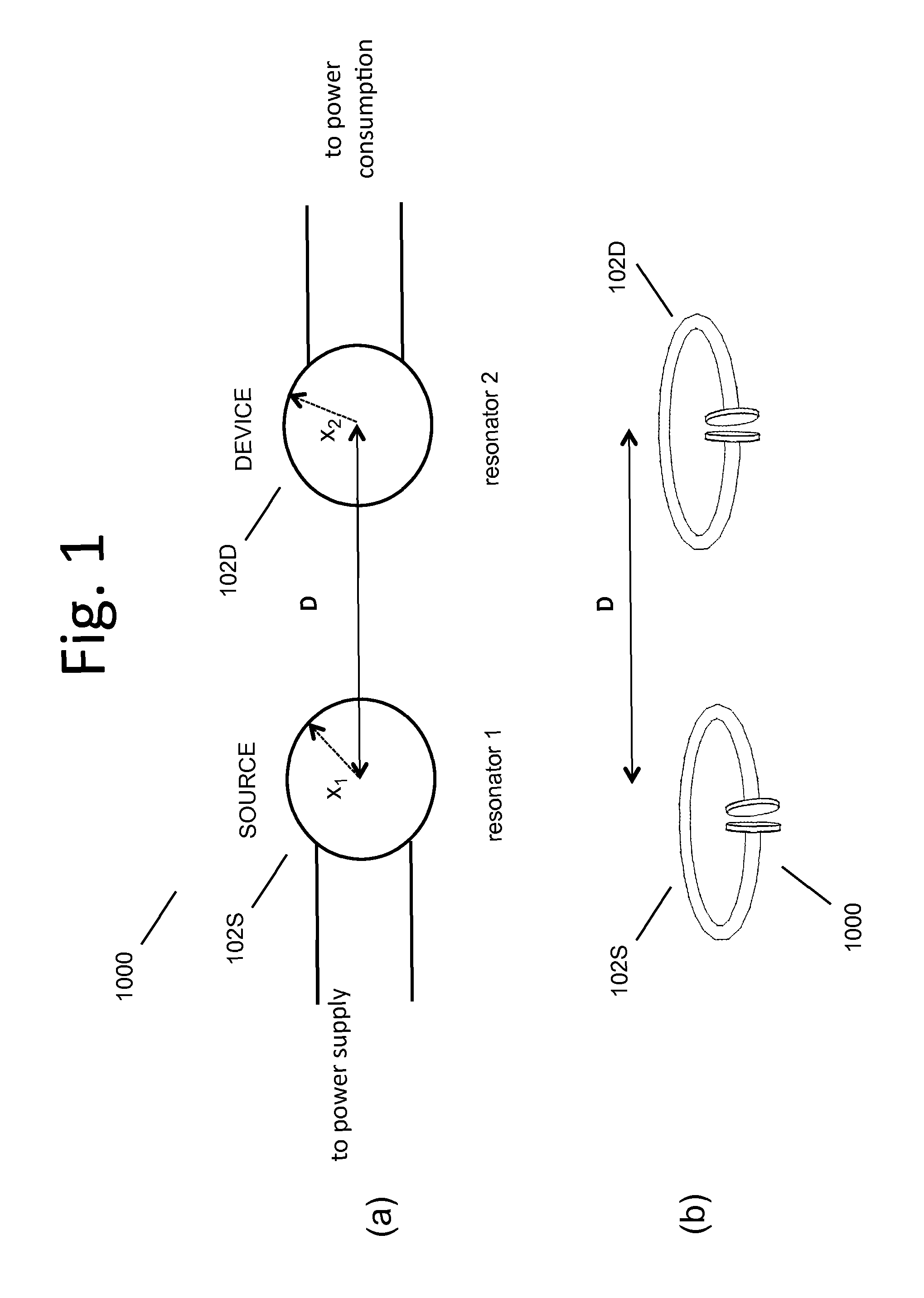
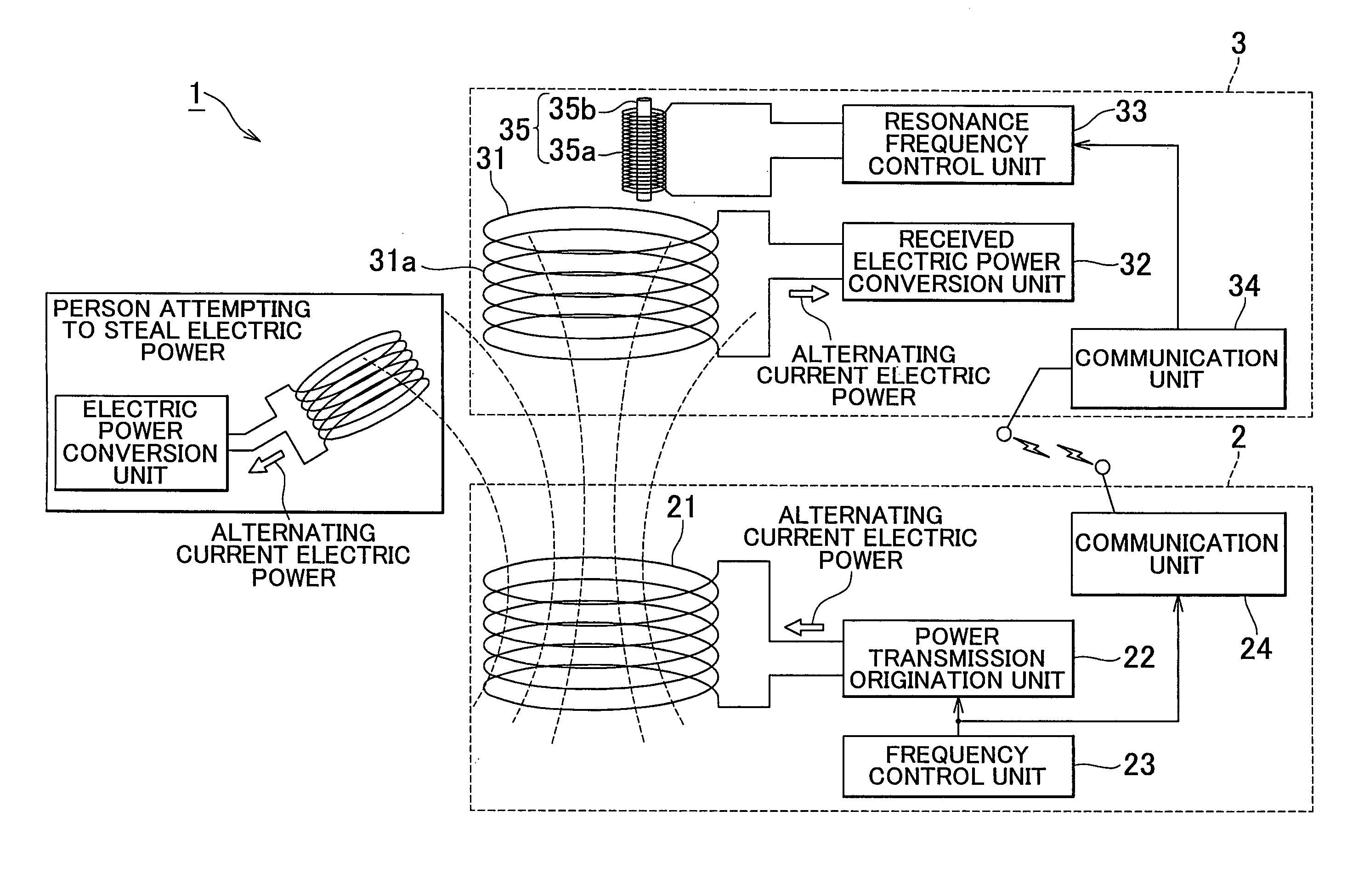
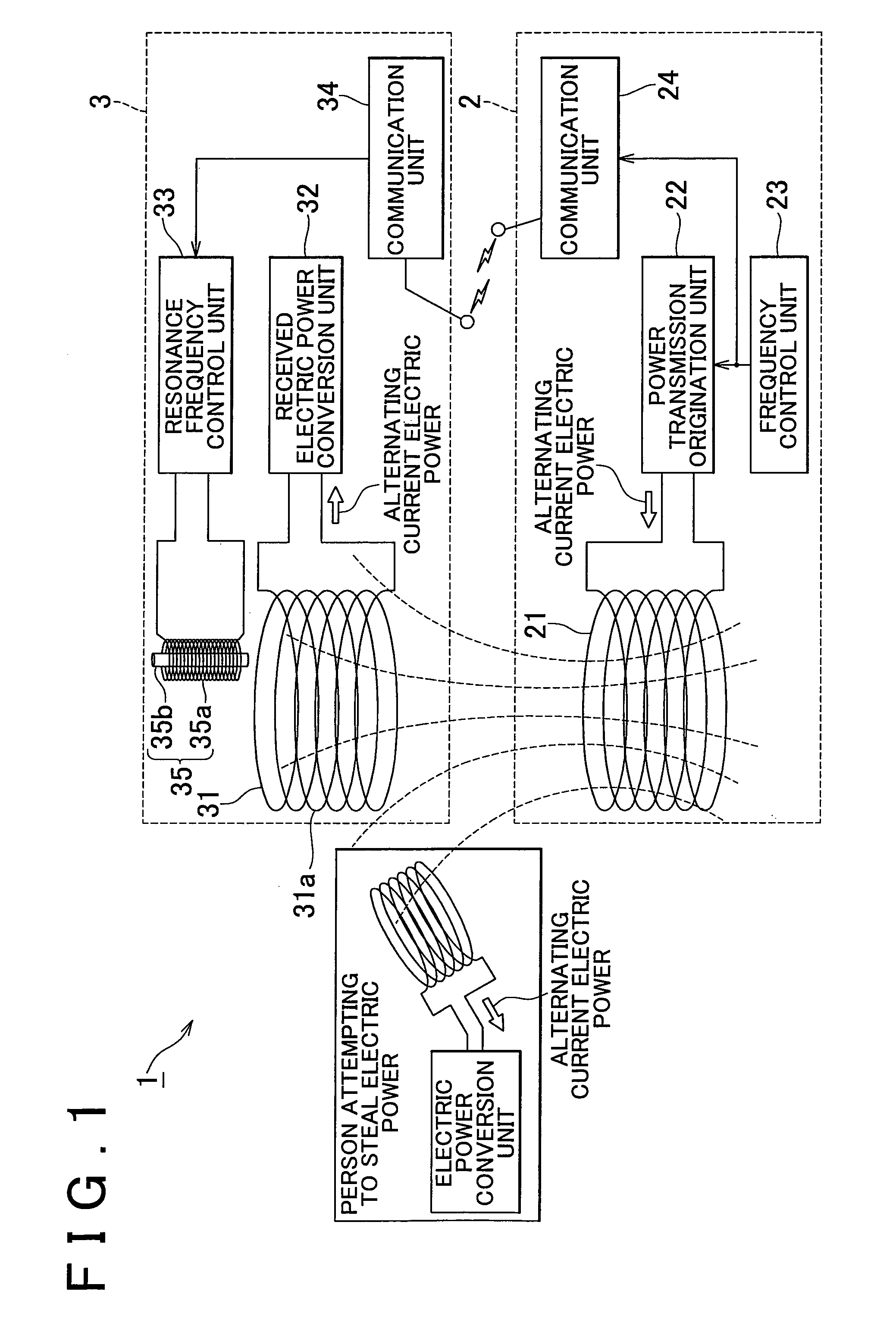
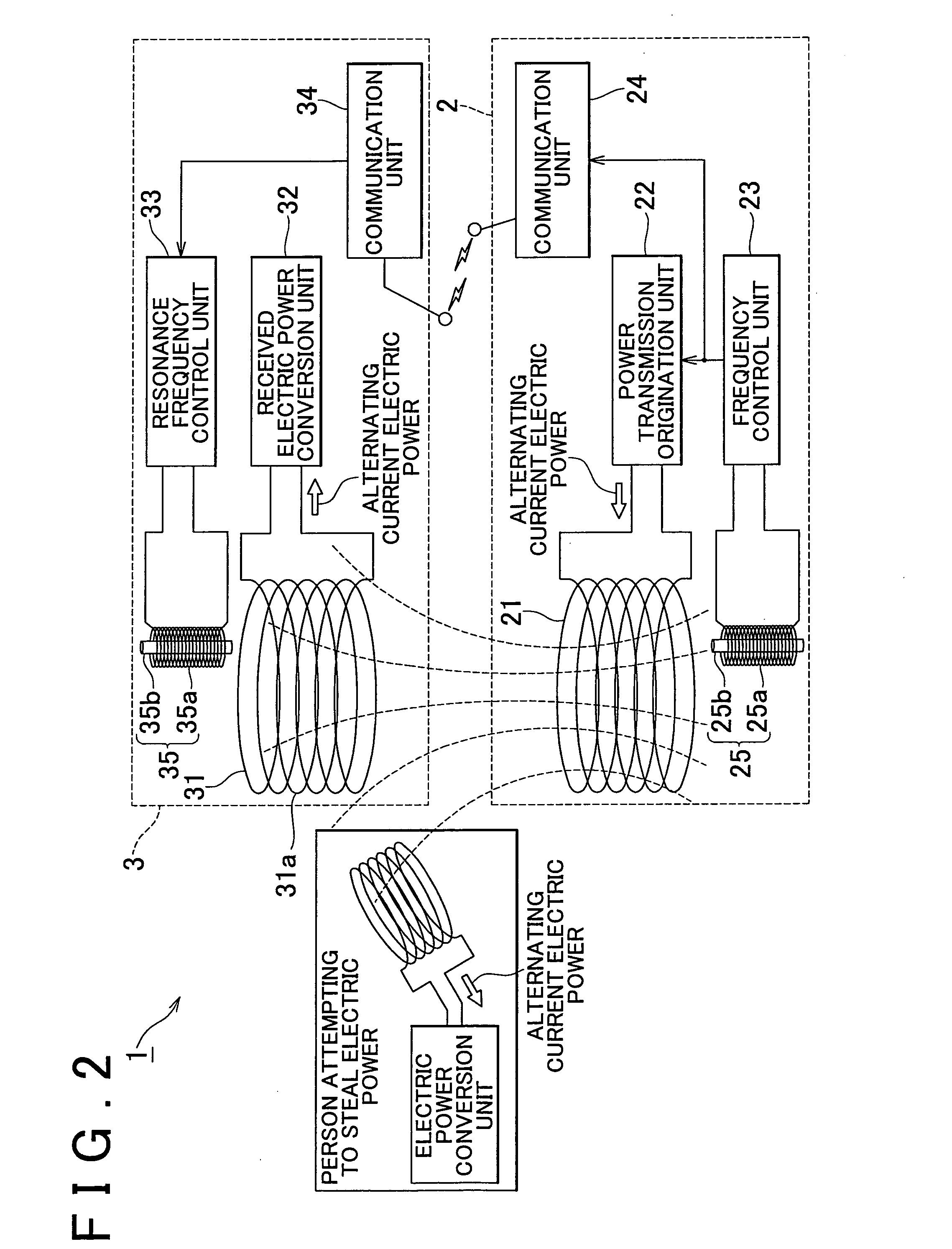
Wireless energy transfer device
ActiveUS20110121658A1Suppressing theftElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersEnergy transferElectric power transmission
A wireless energy transfer device (1) includes: a power transmission unit (2) that generates an oscillating magnetic field or oscillating electric field; a power reception unit (3), which is provided with a receiving antenna (31), and which converts the oscillating magnetic field or the oscillating electric field of the power transmission unit (2) to electric power by the receiving antenna (31); and an electric power theft suppression unit that suppresses the theft of energy with the oscillating magnetic field or the oscillating electric field of the power transmission unit (2).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel gauge for fuel cartridges
ActiveUS20050115312A1Reactant parameters controlContainer/cavity capacity measurementCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Fuel gauges for fuel supplies for fuel cells are disclosed. Each fuel gauge has a property that is readable by an electrical circuit. These properties are related to the remaining fuel in the fuel supplies. These properties include, but are not limited to, electrical capacitance, magnetic, semi-conducting resistance, bi-metal resistance, and oscillating magnetic field. These fuel gauges are functional at any fuel supply orientation.
Owner:INTELLIGENT ENERGY LTD
Atomic force microscope and method for determining properties of a sample surface using an atomic force microscope
ActiveUS20050081609A1Reduced tip wearReduce wearNanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsAtomic force microscopyAtomic force acoustic microscopy
A method for determining properties of a sample surface using an atomic force microscope includes applying a first voltage between the sample and a probe, moving the probe towards the surface of the sample, and stopping movement of the probe towards the surface of the sample when current in the probe is initially detected. An oscillating magnetic field is applied to the probe such that the probe obtains stable contact with the surface of the sample.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fuel gauge for fuel cartridges
InactiveUS7117732B2Reactant parameters controlVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsCapacitanceFuel cells
Fuel gauges for fuel supplies for fuel cells are disclosed. Each fuel gauge has a property that is readable by an electrical circuit. These properties are related to the remaining fuel in the fuel supplies. These properties include, but are not limited to, electrical capacitance, magnetic, semi-conducting resistance, bi-metal resistance, and oscillating magnetic field. These fuel gauges are functional at any fuel supply orientation.
Owner:INTELLIGENT ENERGY LTD
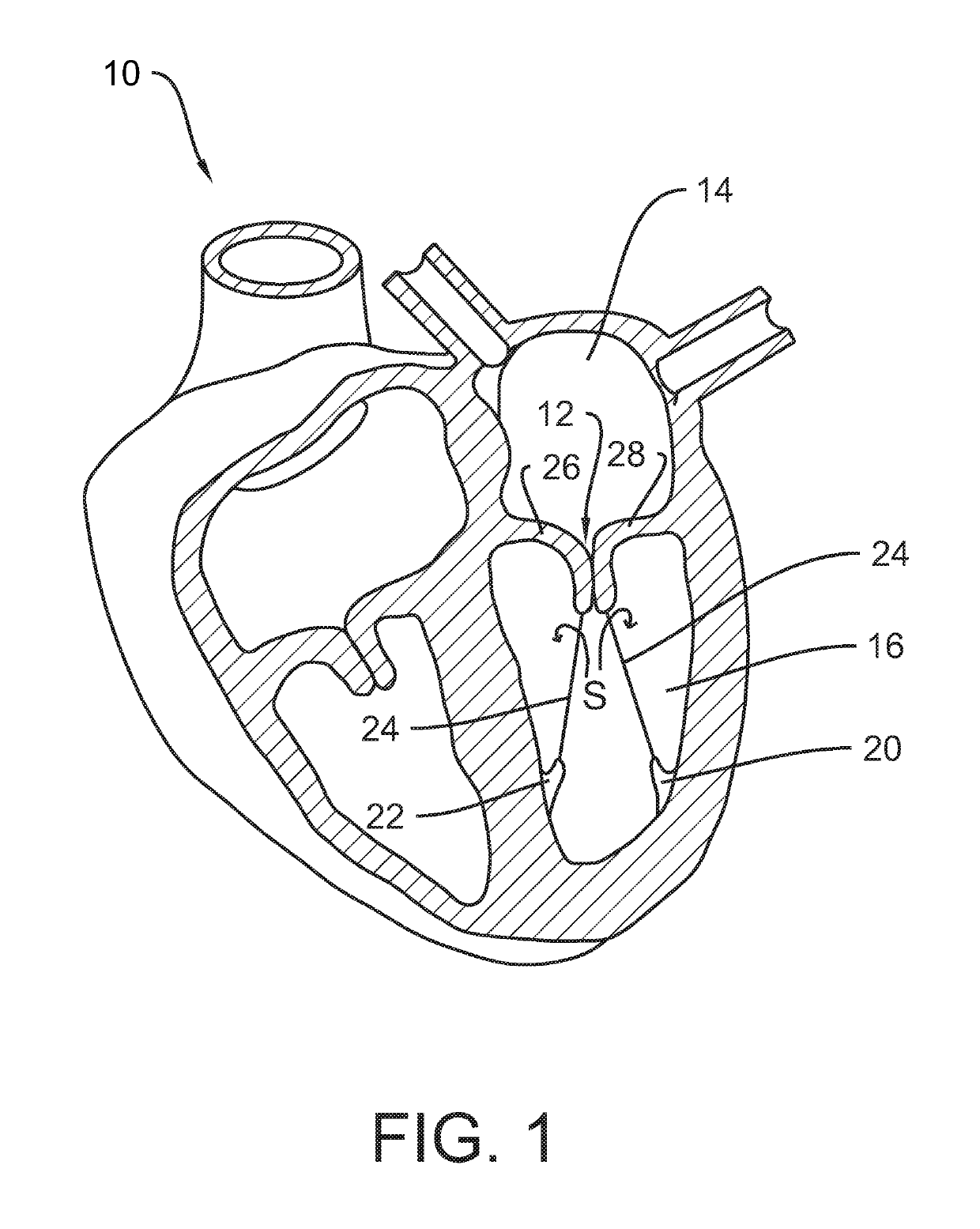
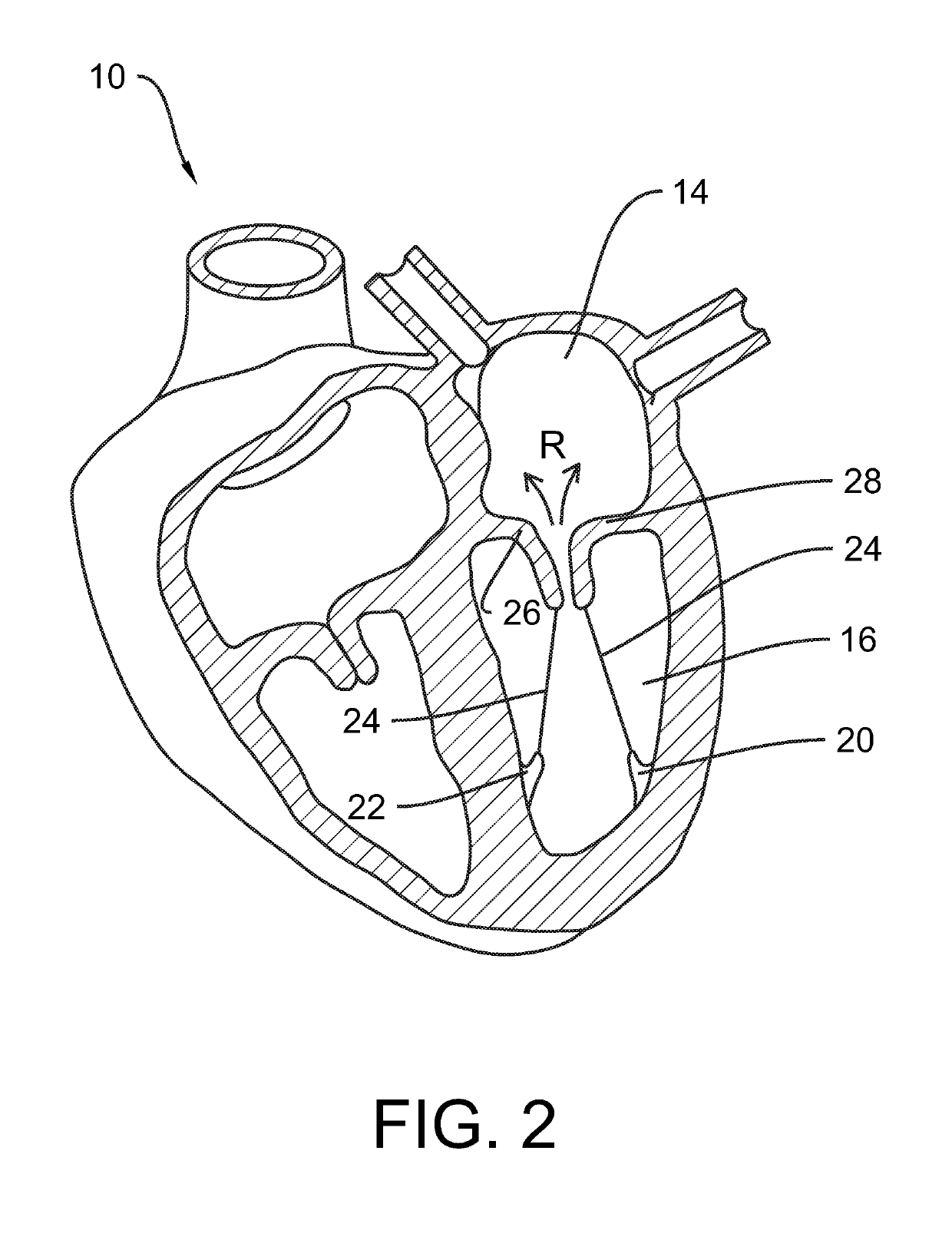
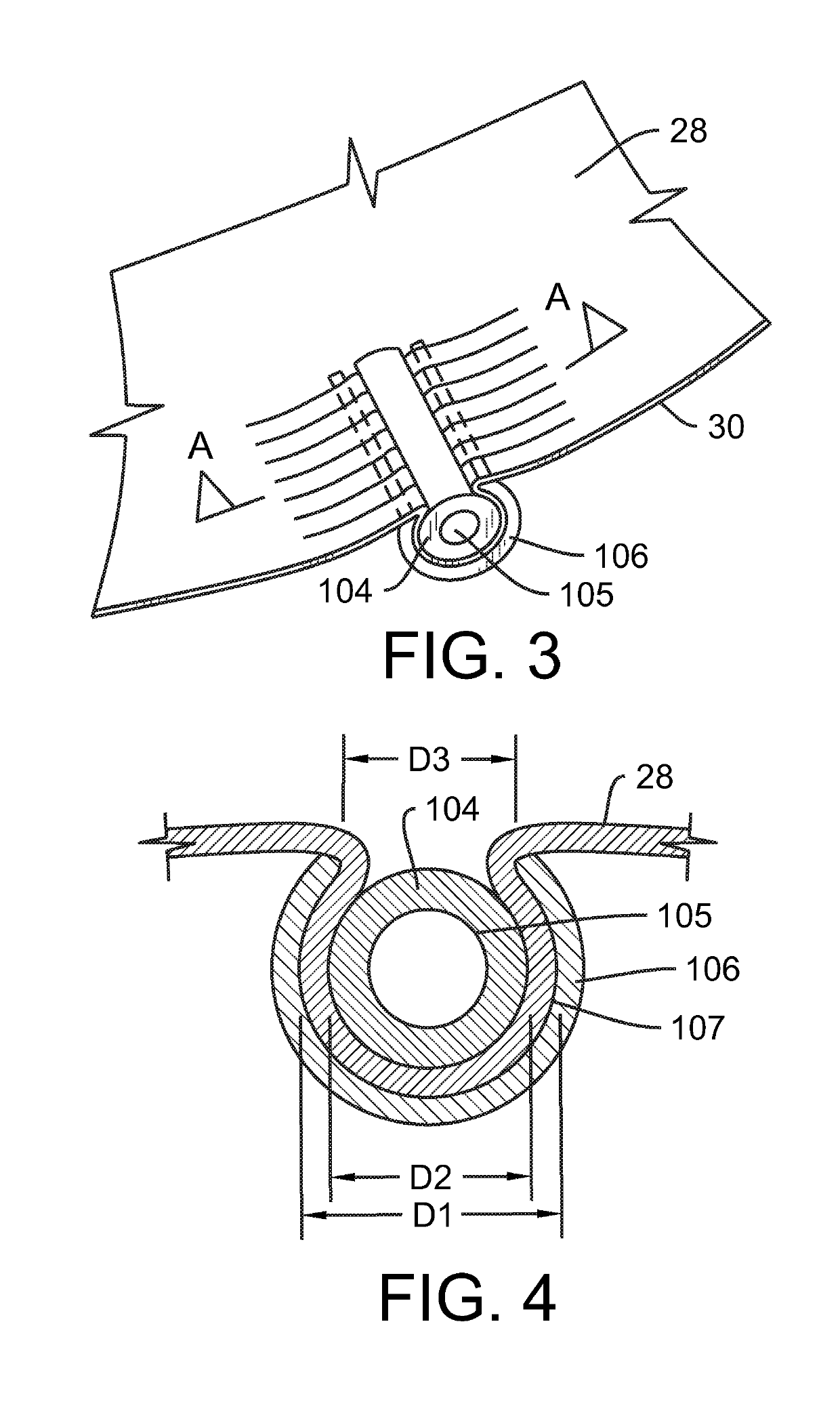
System and method for valve activation
A method for improving the function of a valve in the heart of a patient, comprising attaching, to a leaflet of the valve, an element that is responsive to a magnetic field; positioning, outside of the heart of the patient, a coil connected to a source of electric energy; activating the source of electric energy to provide an oscillating current in the coil; and thereby providing an oscillating magnetic field through the coil to effect movement of the element and the leaflet.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
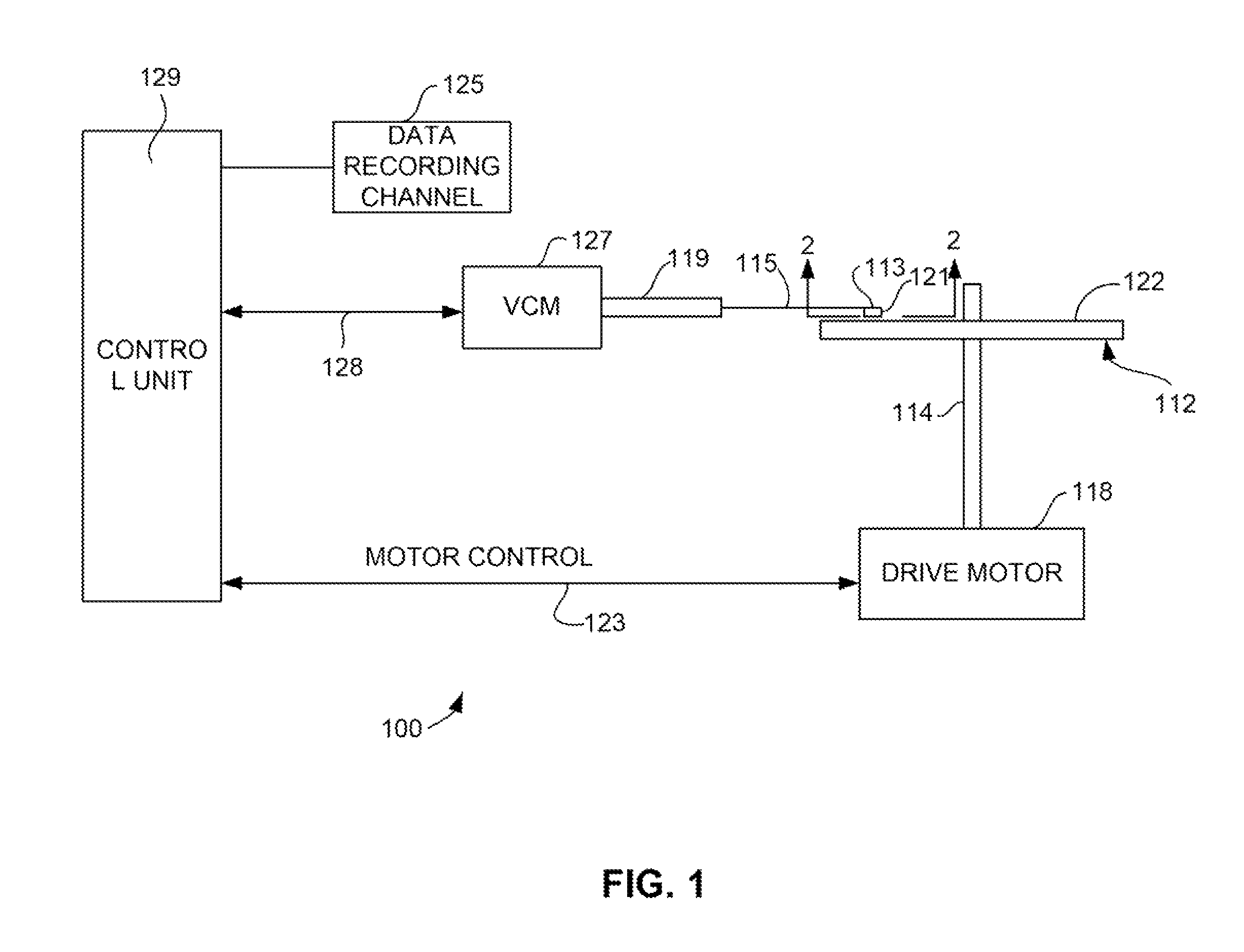
Magnetic recording head with adjacent track interference suppresion by novel microwave-assisted magnetic recording element
ActiveUS8553362B2Reduces magnetic resonance of magneticEasy to writeManufacture head surfaceManufacturing heads with multiple gapsMagnetic mediaEngineering
A magnetic write head for magnetic data recording that incorporates a novel magnetic oscillation generator stricture that sets up a magnetic oscillation in the magnetic media for improving writing and that also narrows the write width and reduces adjacent track interference by suppressing writing in regions outside of the desired data track. The magnetic oscillation generating structure includes a centrally disposed magnetic assist element that generates an oscillating magnetic field that oscillates in a direction that will assist the write pole in writing to the magnetic medium. The magnetic oscillation generating structure also includes first and second magnetic non-assist elements at either side of the assist element. The non-assist elements generate a magnetic field that oscillates in a second direction that is opposite to the first direction, which counteracts the magnetic write assist from the centrally disposed magnetic assist element and acts to suppress writing in these side regions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
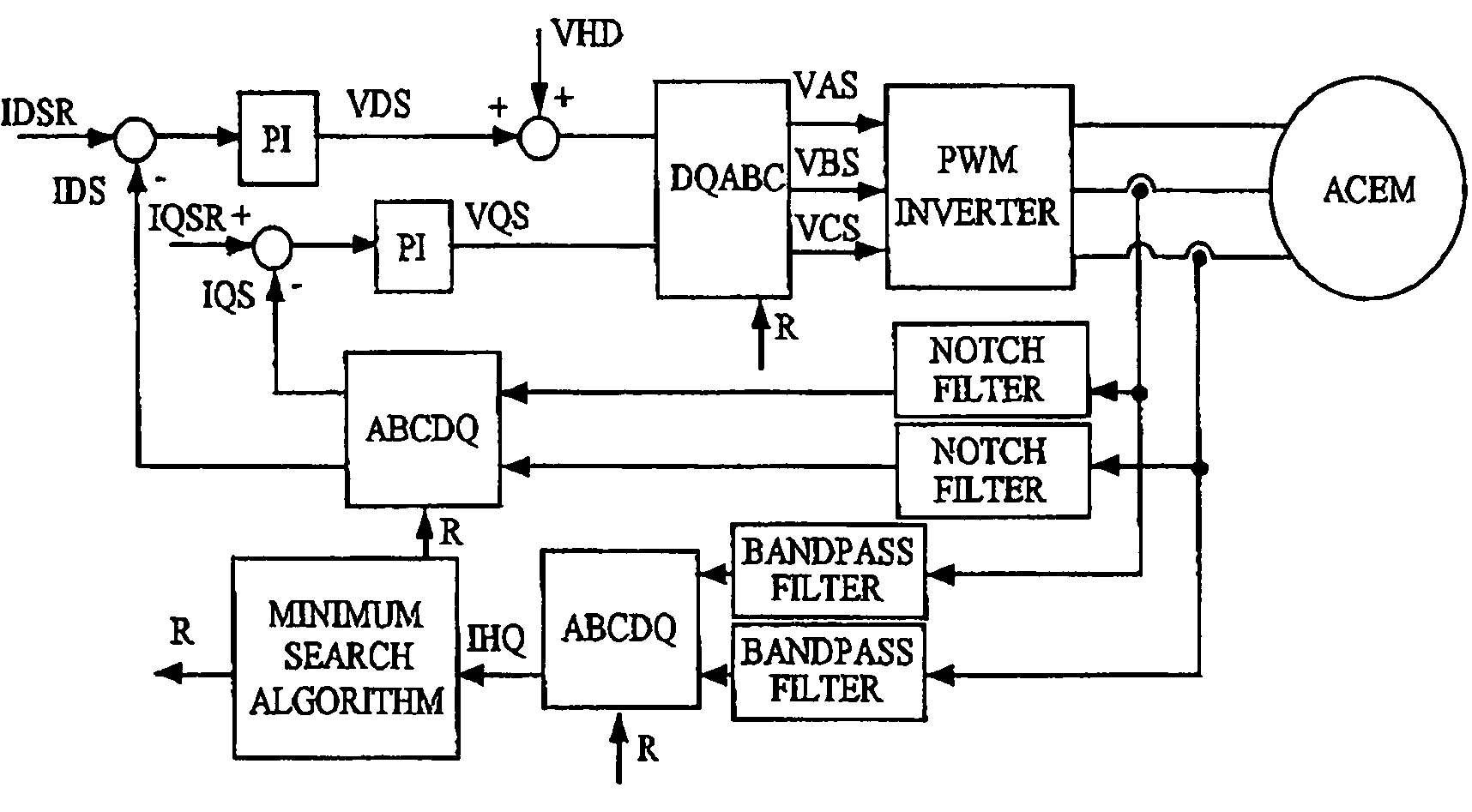
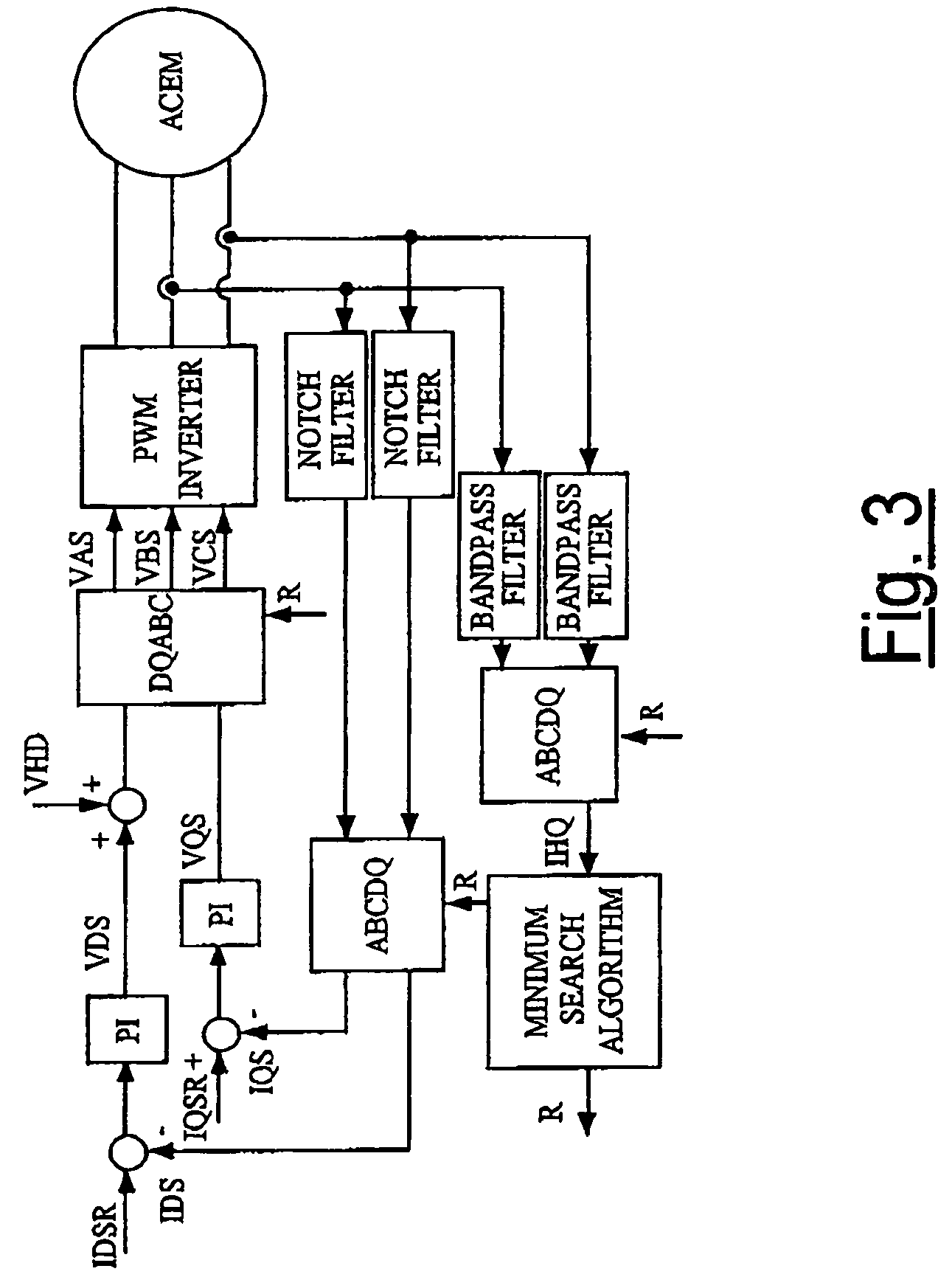
Control system and method for electric drives with a.c. motors
InactiveUS7180262B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersControl systemElectric drive
A vector-control system and method of a “sensorless” type for electric drives with a.c. motors is based upon generation of an oscillating magnetic field and upon measurement of the deviation, with respect to said oscillating field, of the flux generated thereby on account of anisotropy, whether natural or induced, of the magnetic structure of the machine.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CATANIA
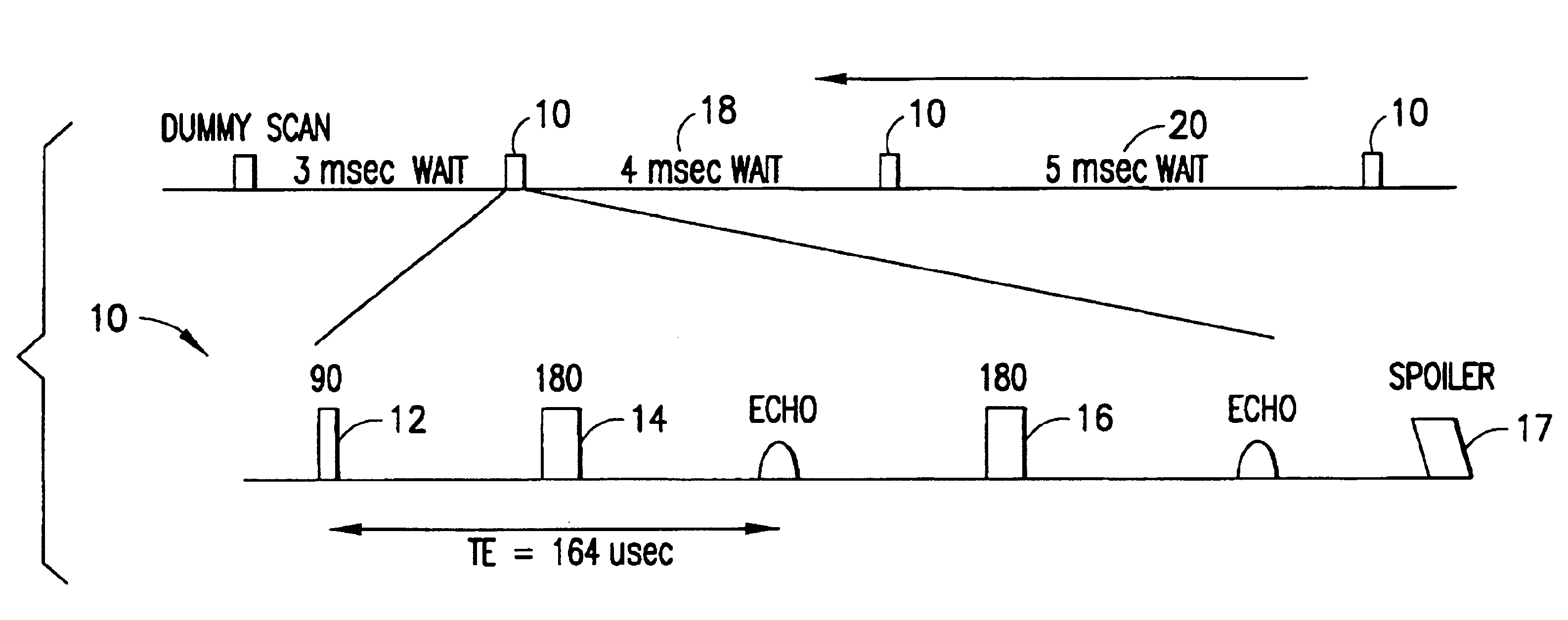
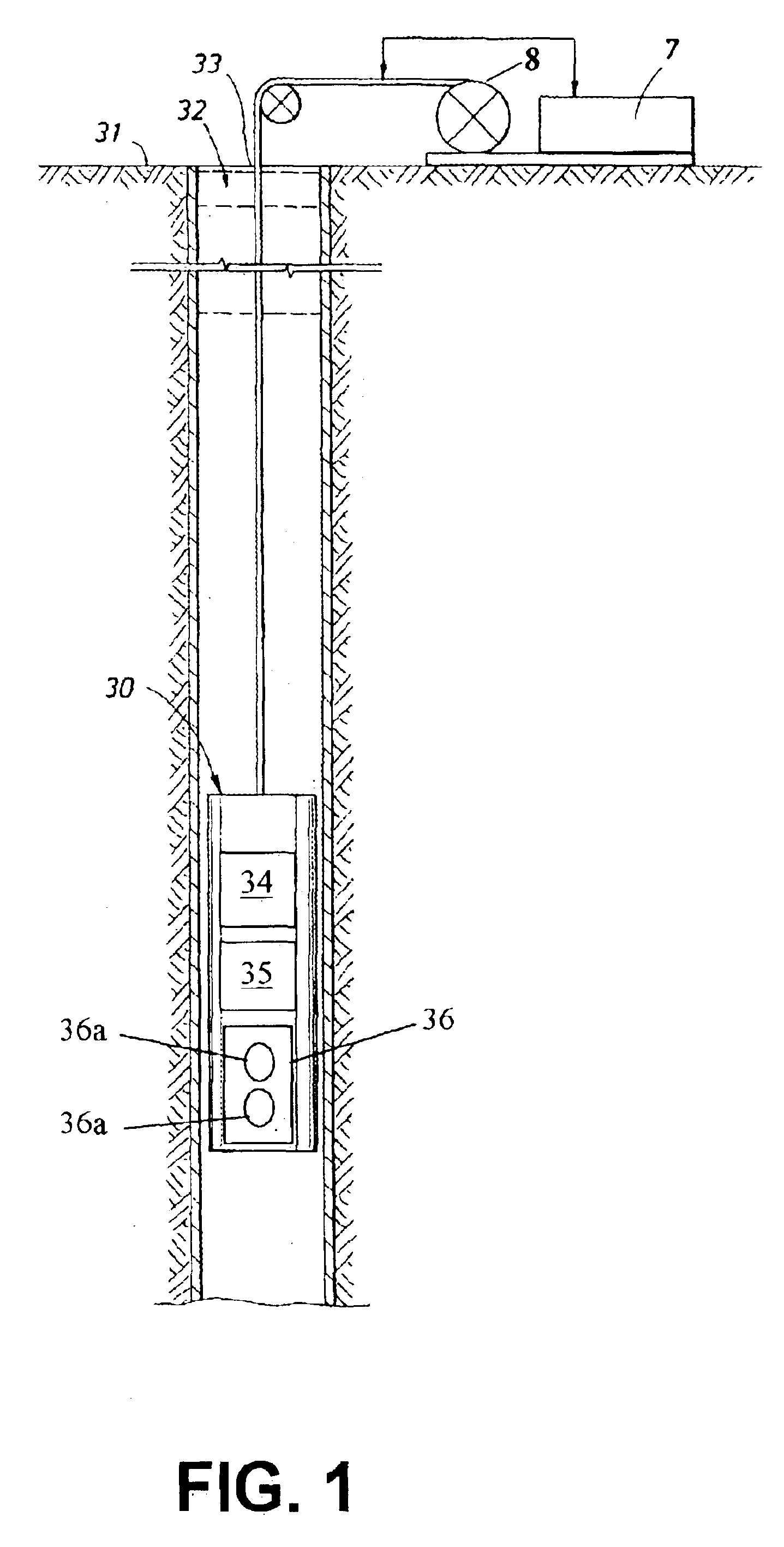
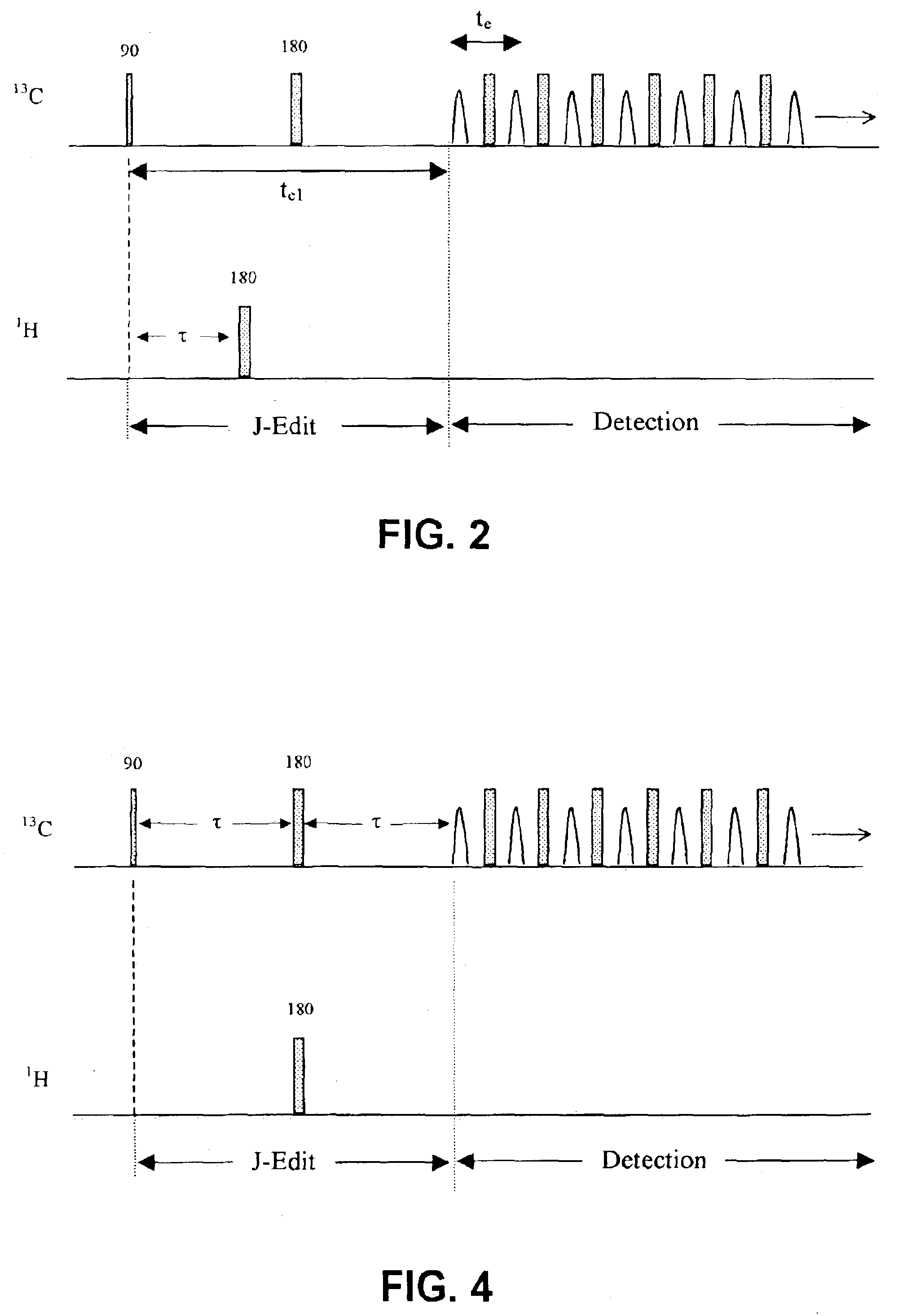
Apparatus and methods for J-edit nuclear magnetic resonance measurement
ActiveUS6958604B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance measurements includes inducing a static magnetic field in a formation fluid sample; applying an oscillating magnetic field to the fluid sample according to a preparation pulse sequence that comprises a J-edit pulse sequence for developing J modulation; and acquiring the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements using a detection sequence, wherein the detection sequence comprises at least one 180-degree pulse. The method may further include acquiring the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements a plurality of times each with a different value in a variable delay in the J-edit pulse sequence; and analyzing amplitudes of the plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements as a function of the variable delay to provide J coupling information.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com