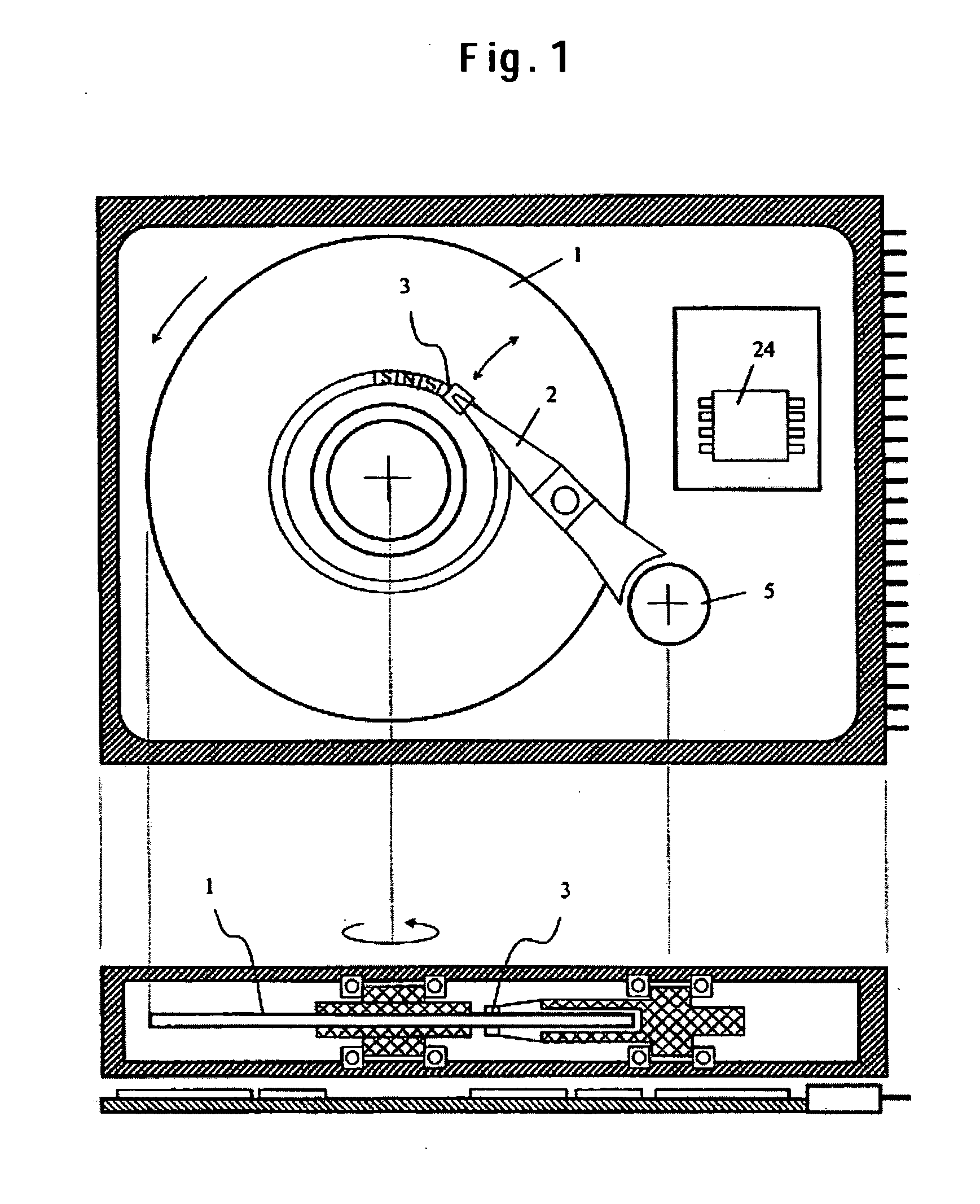
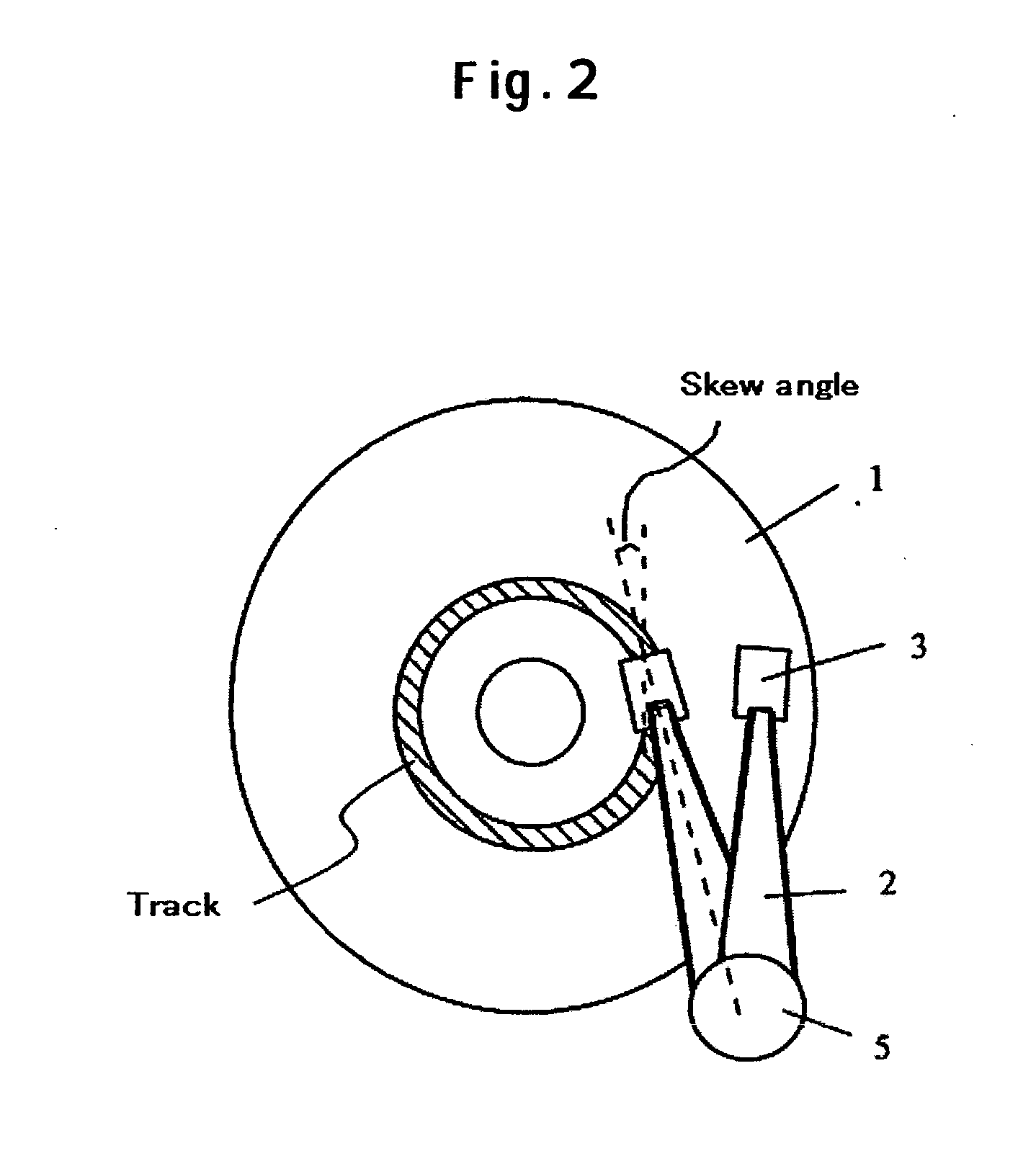
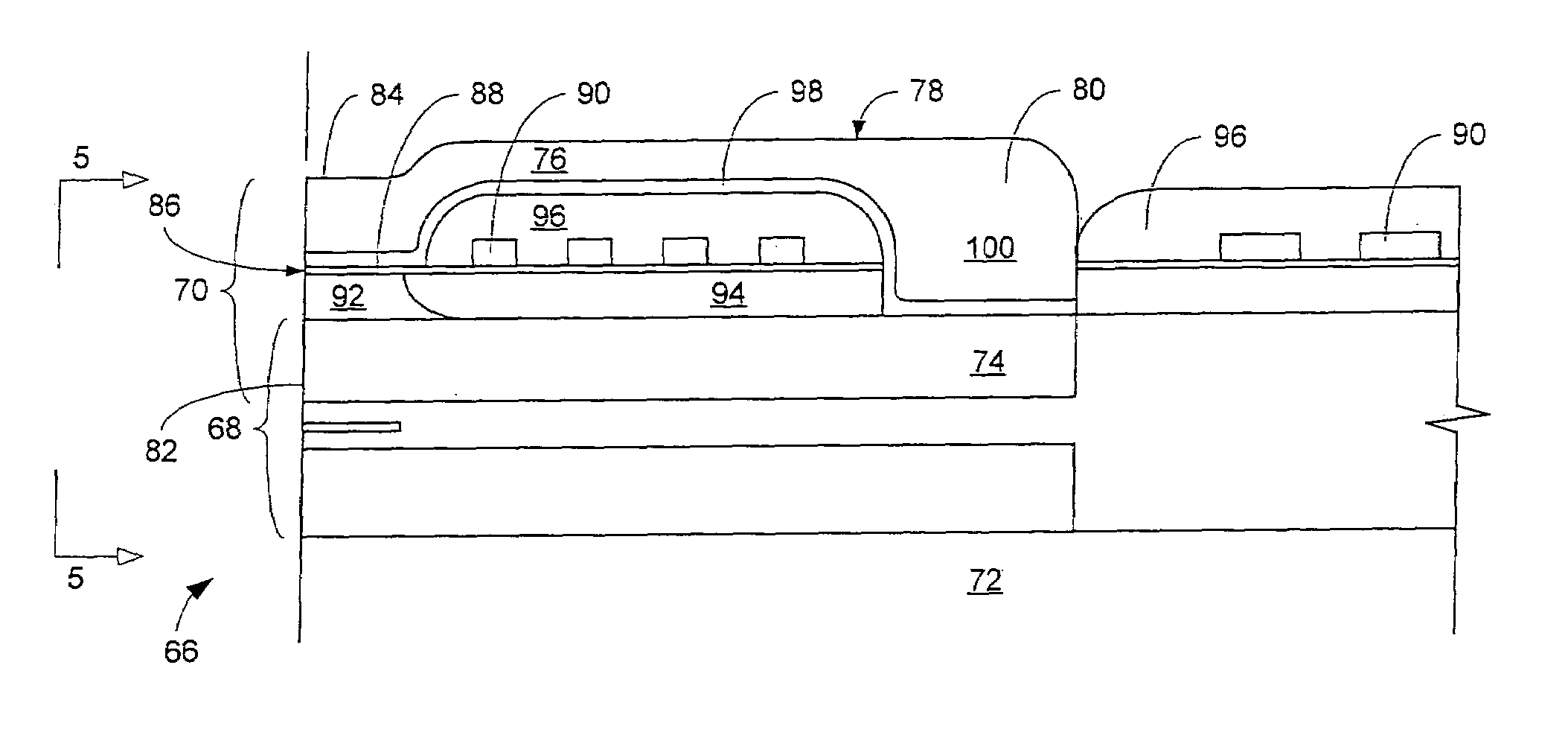
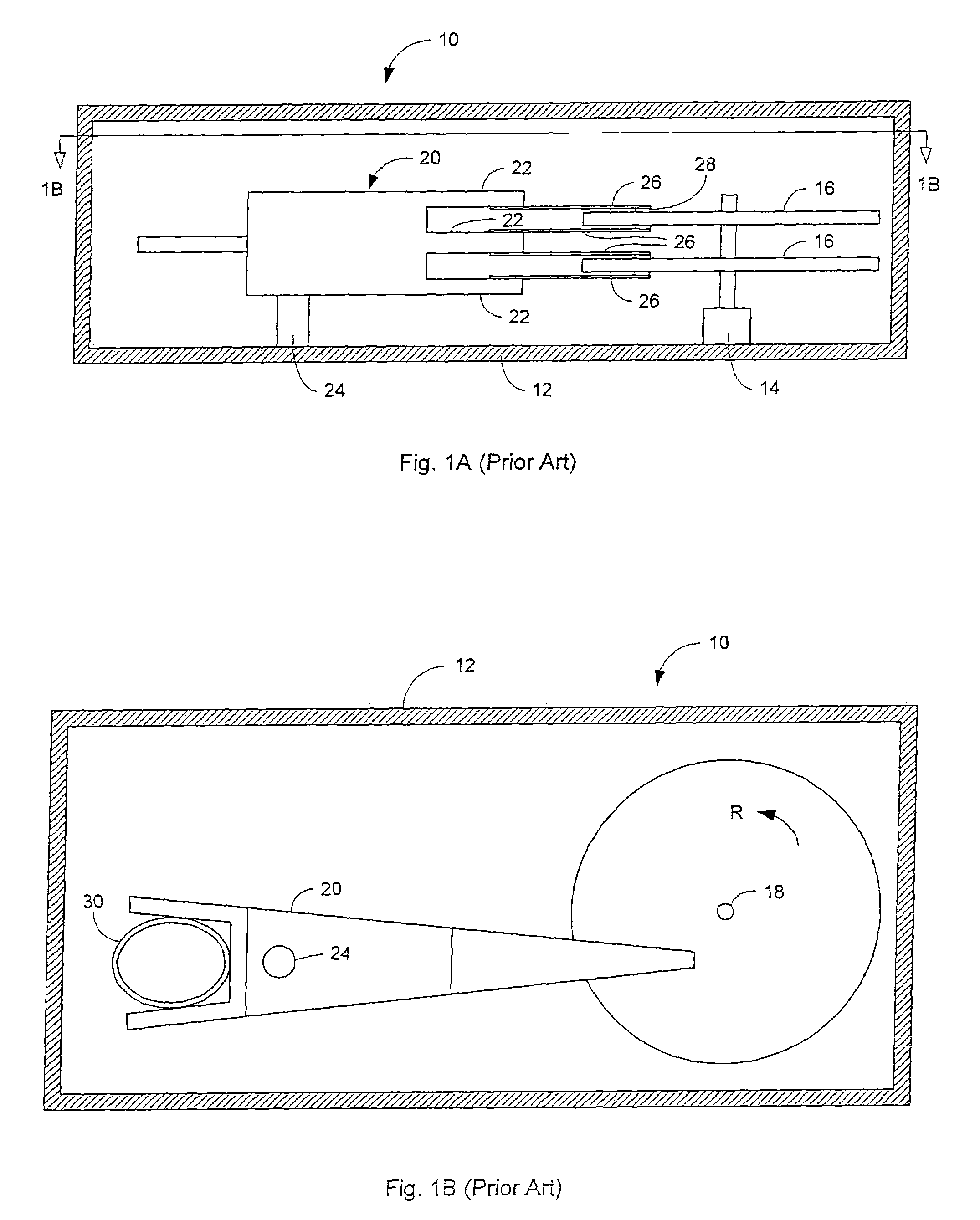
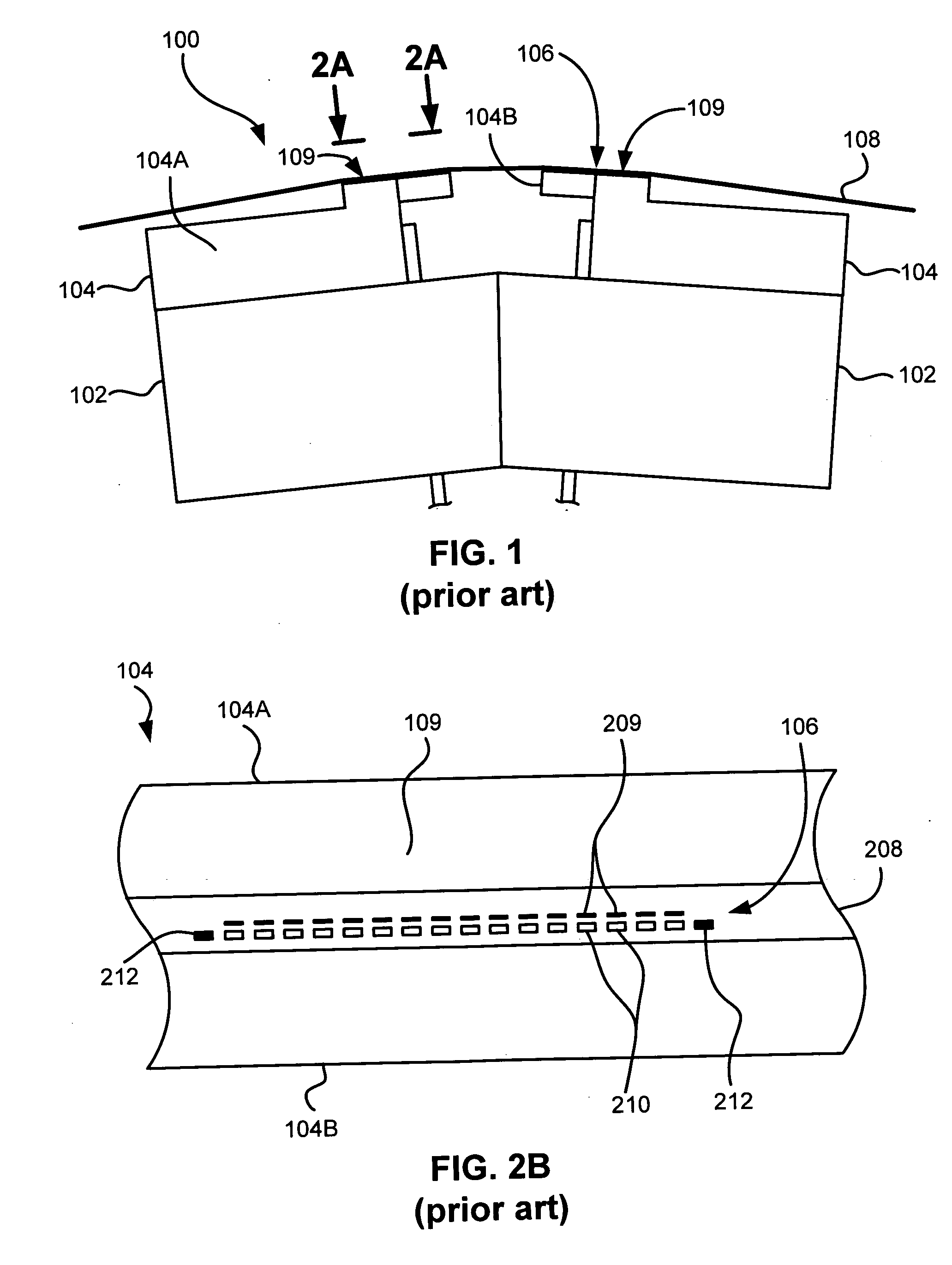
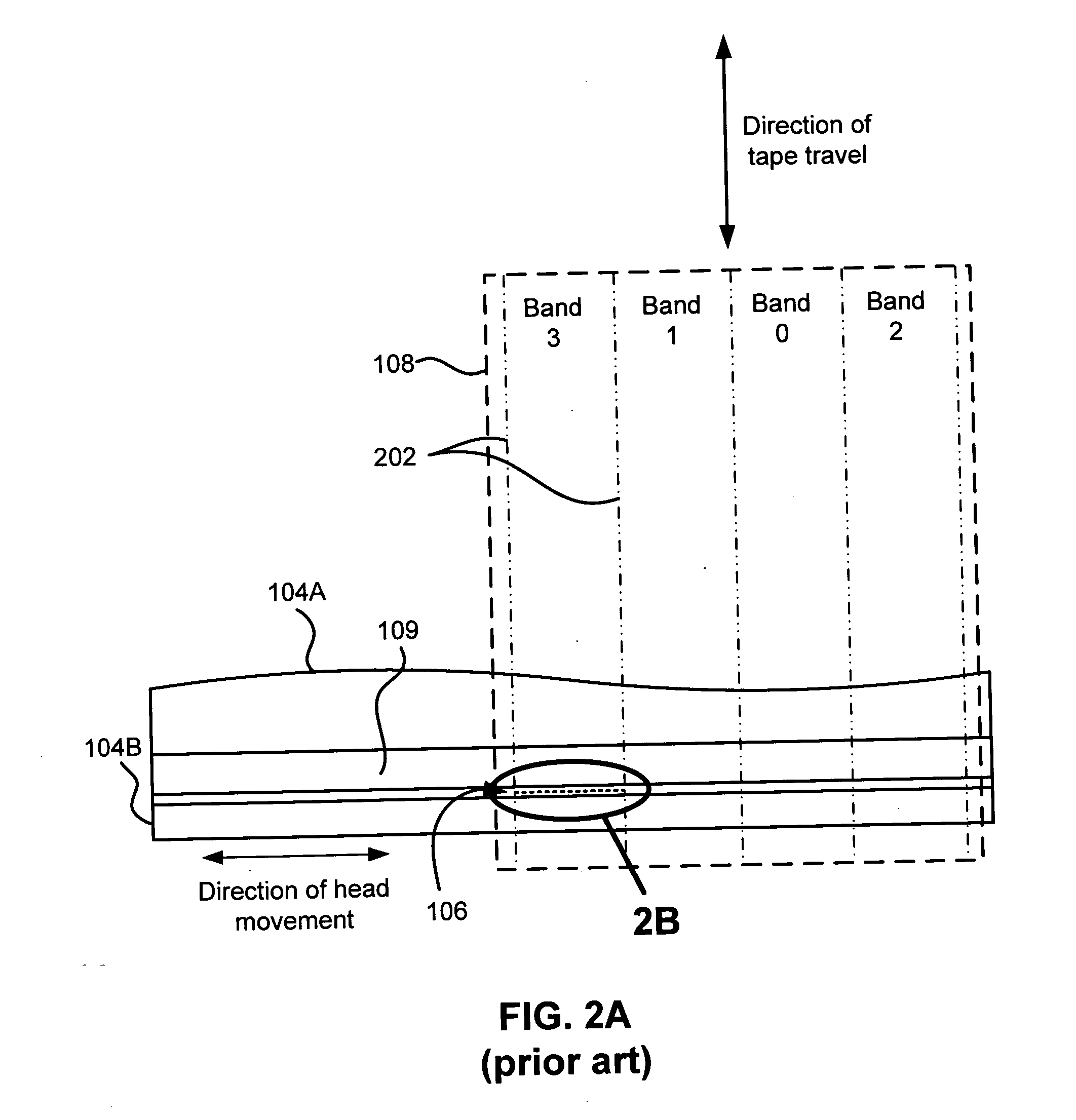
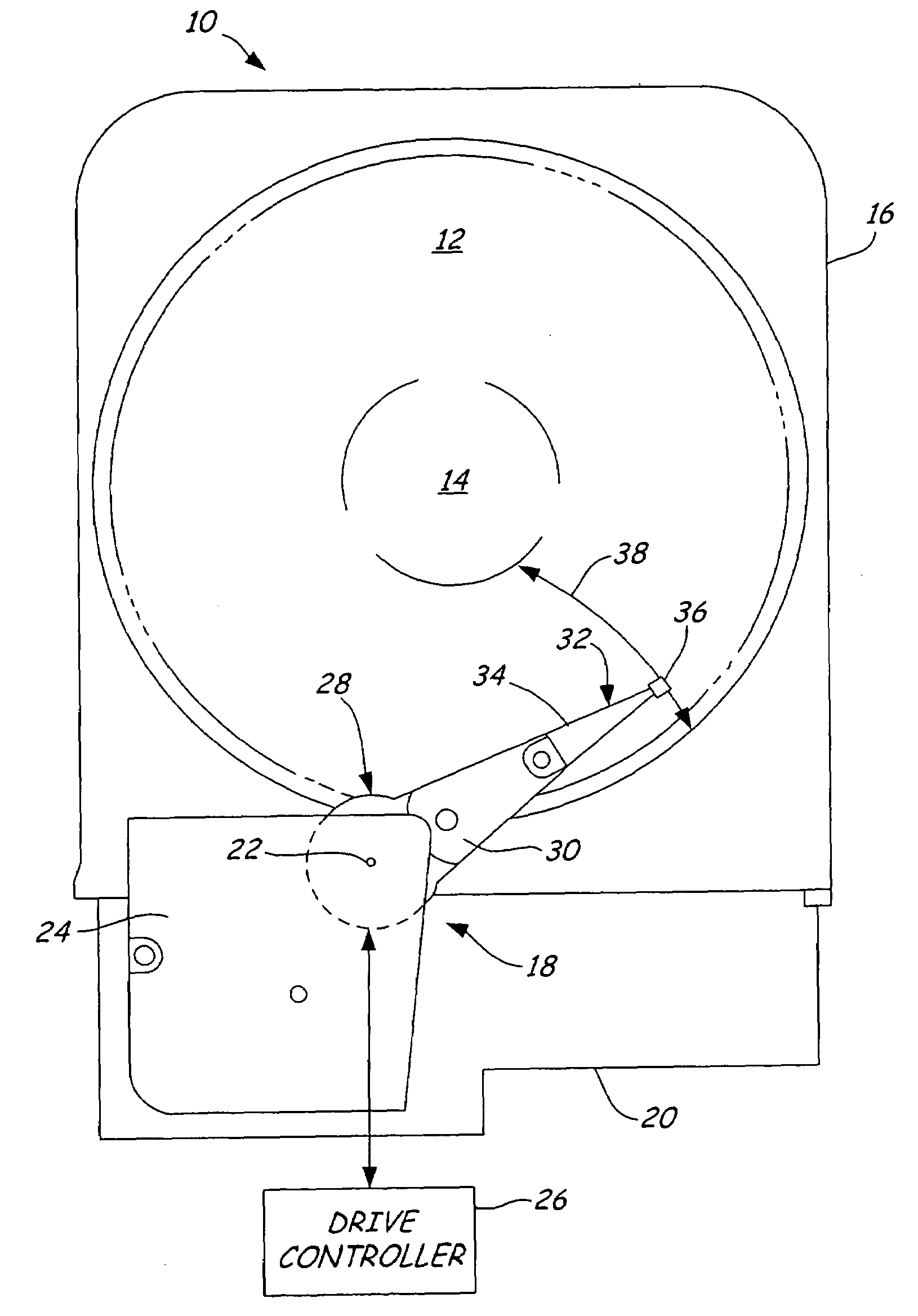
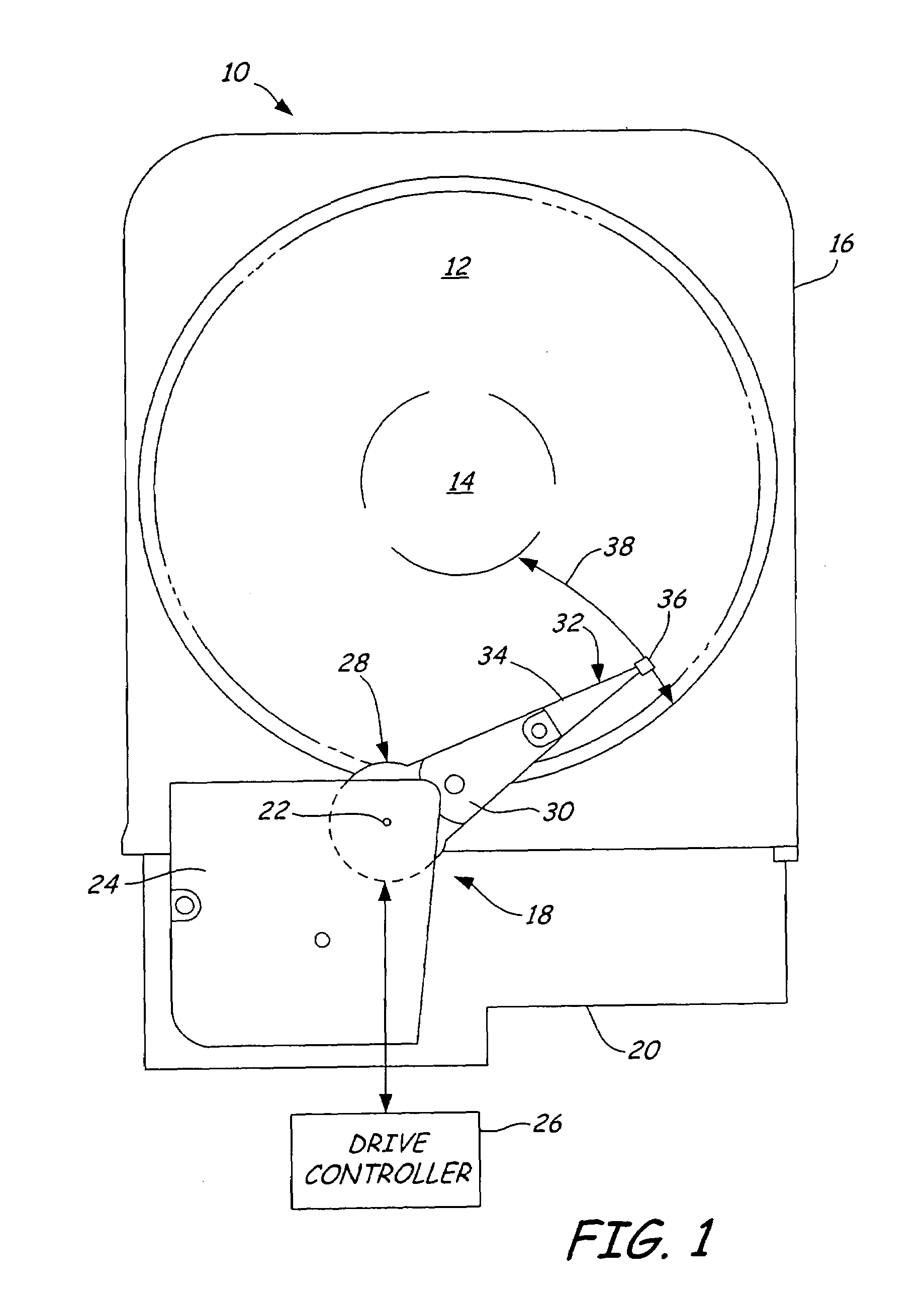
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1327 results about "Magnetic media" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
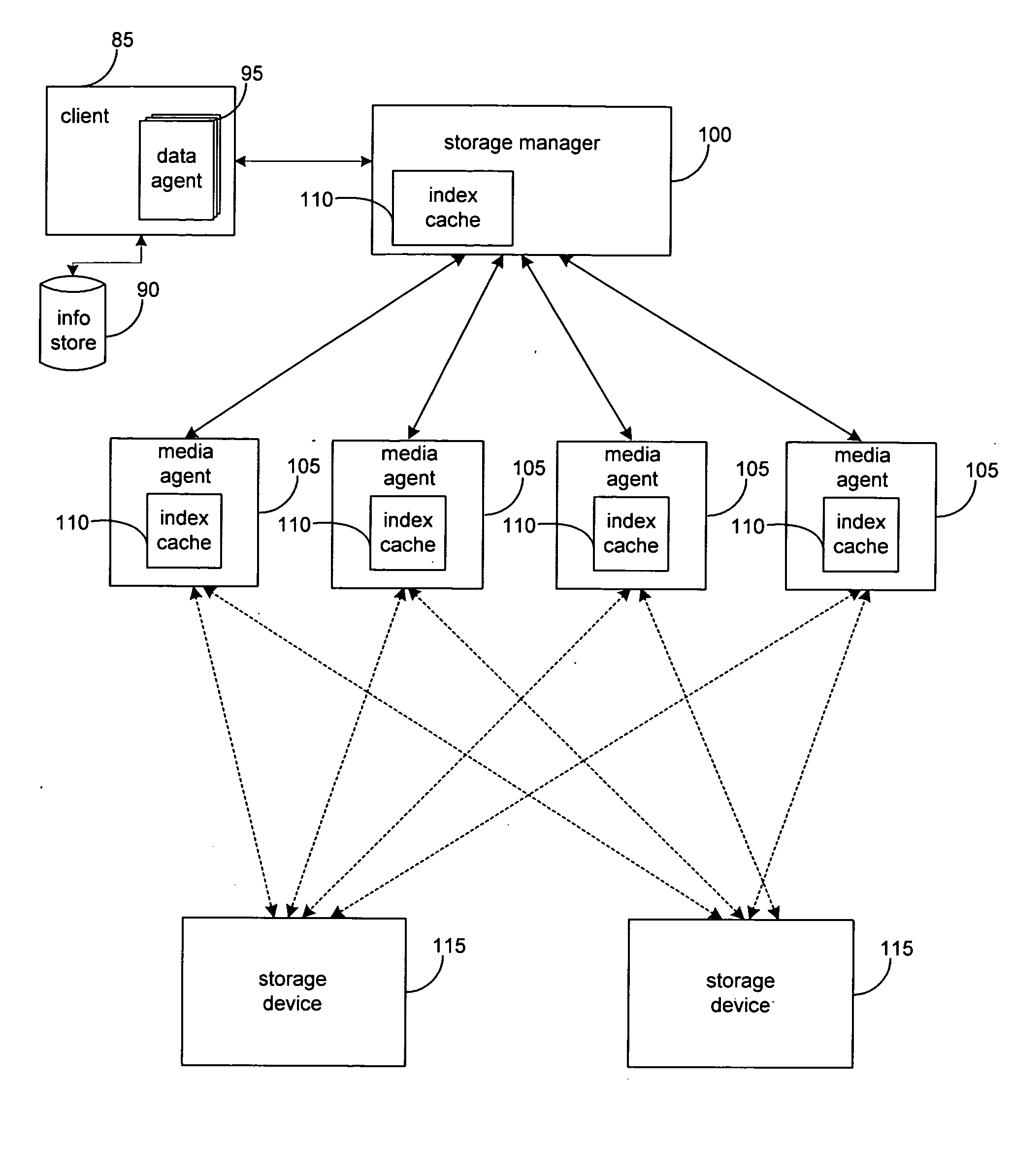
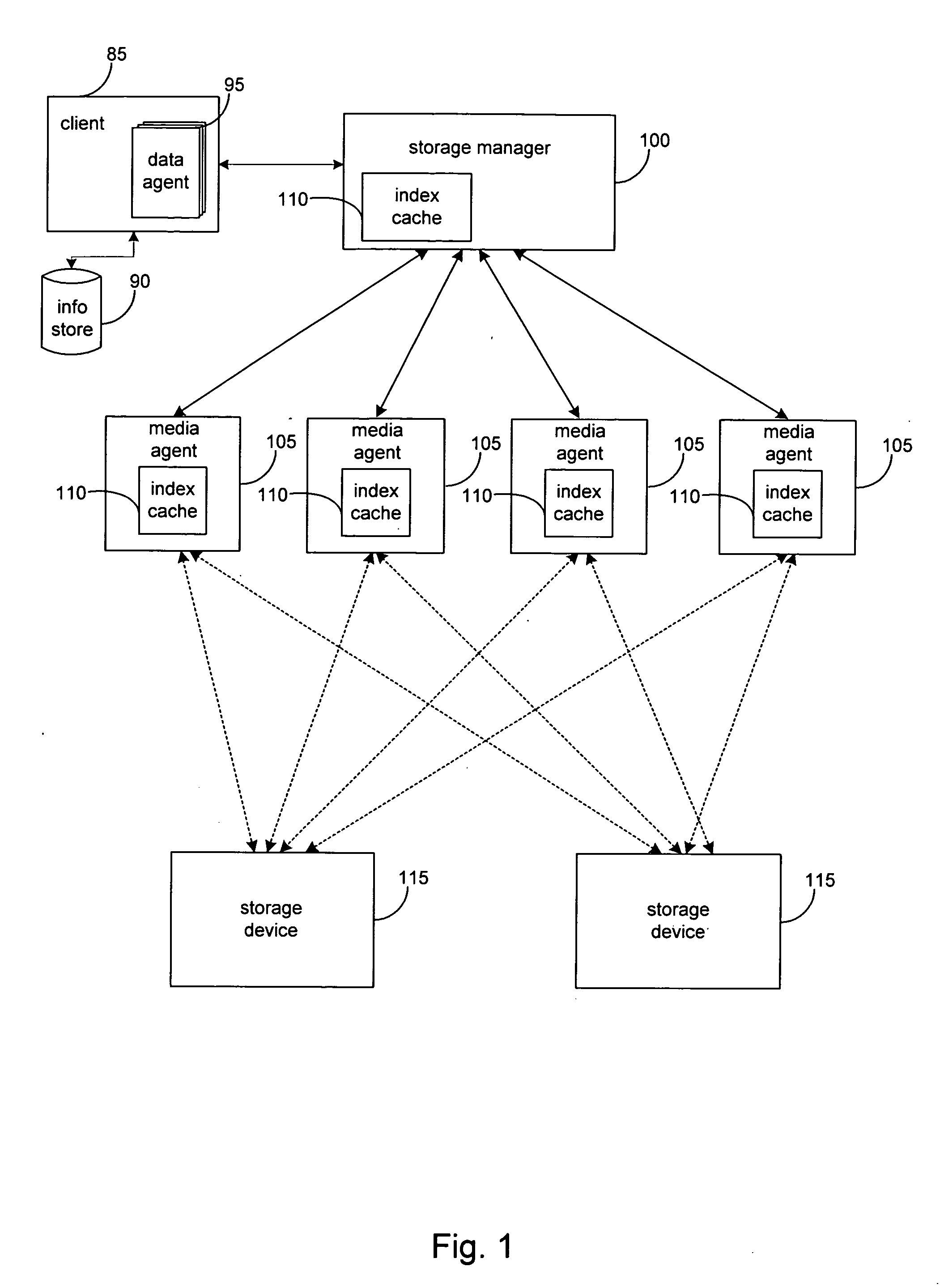
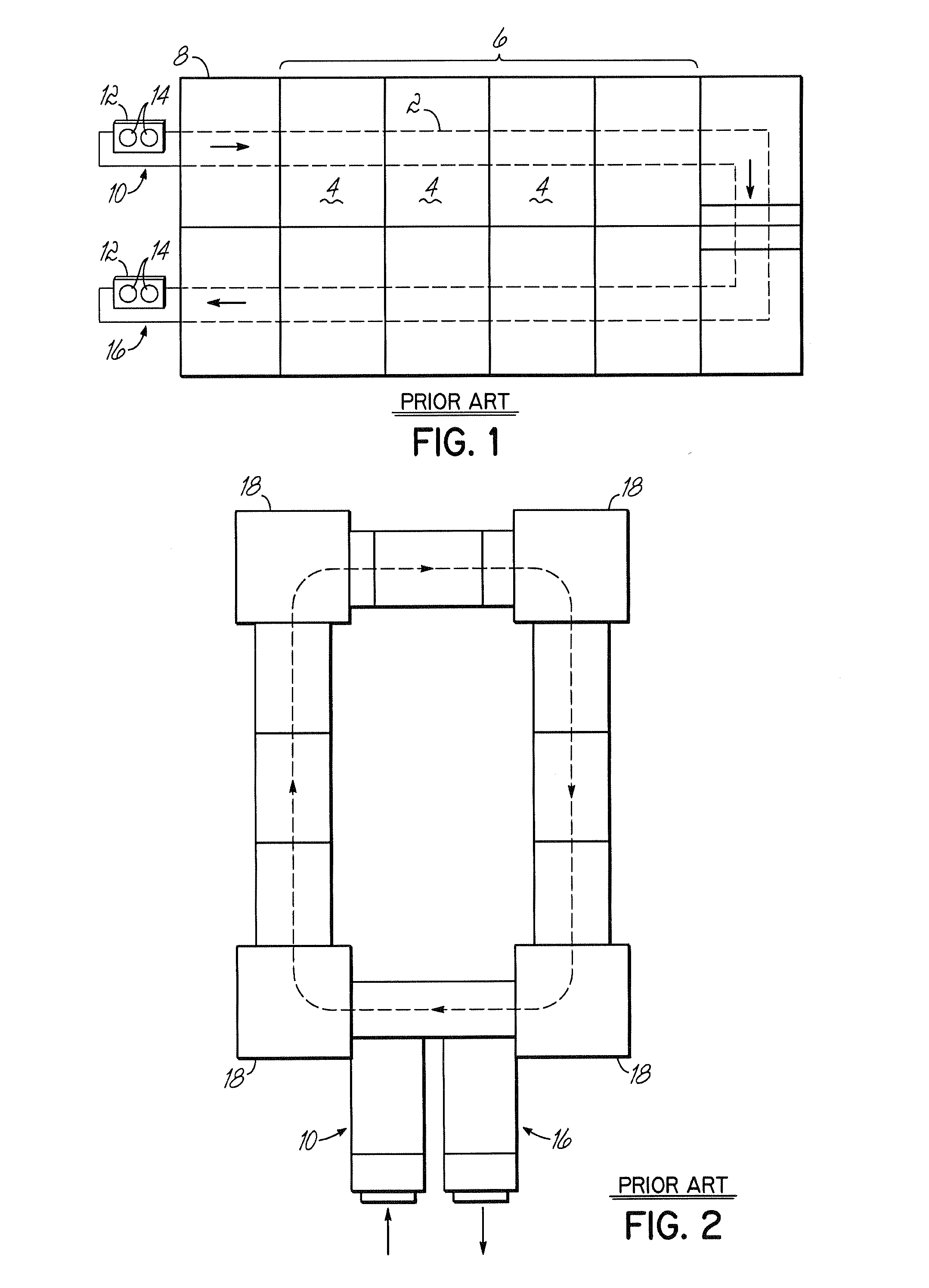
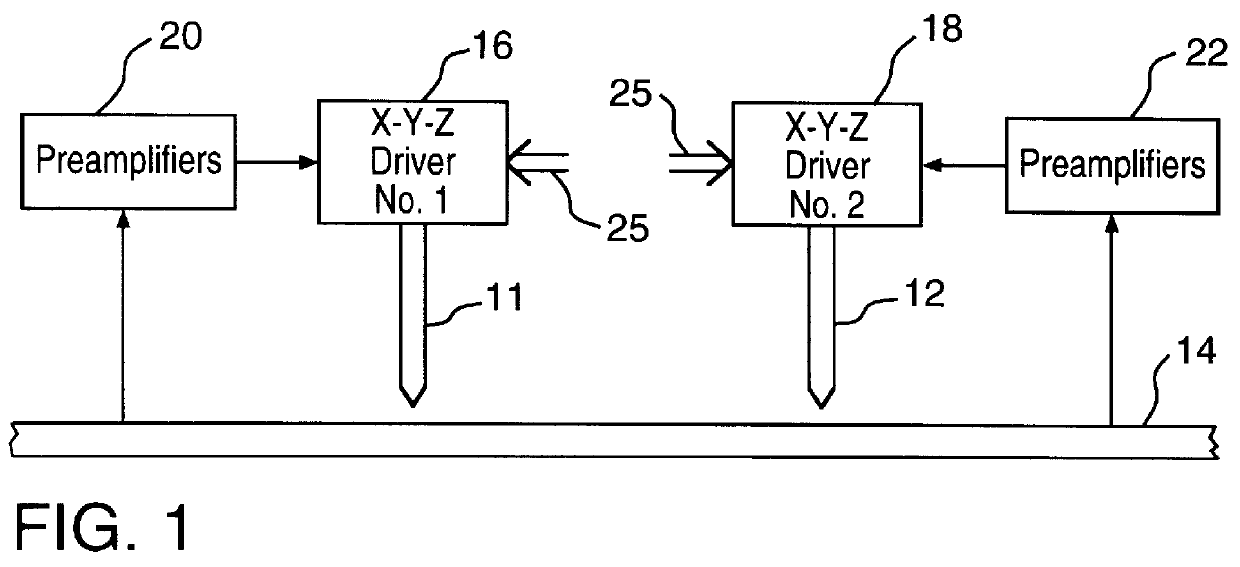
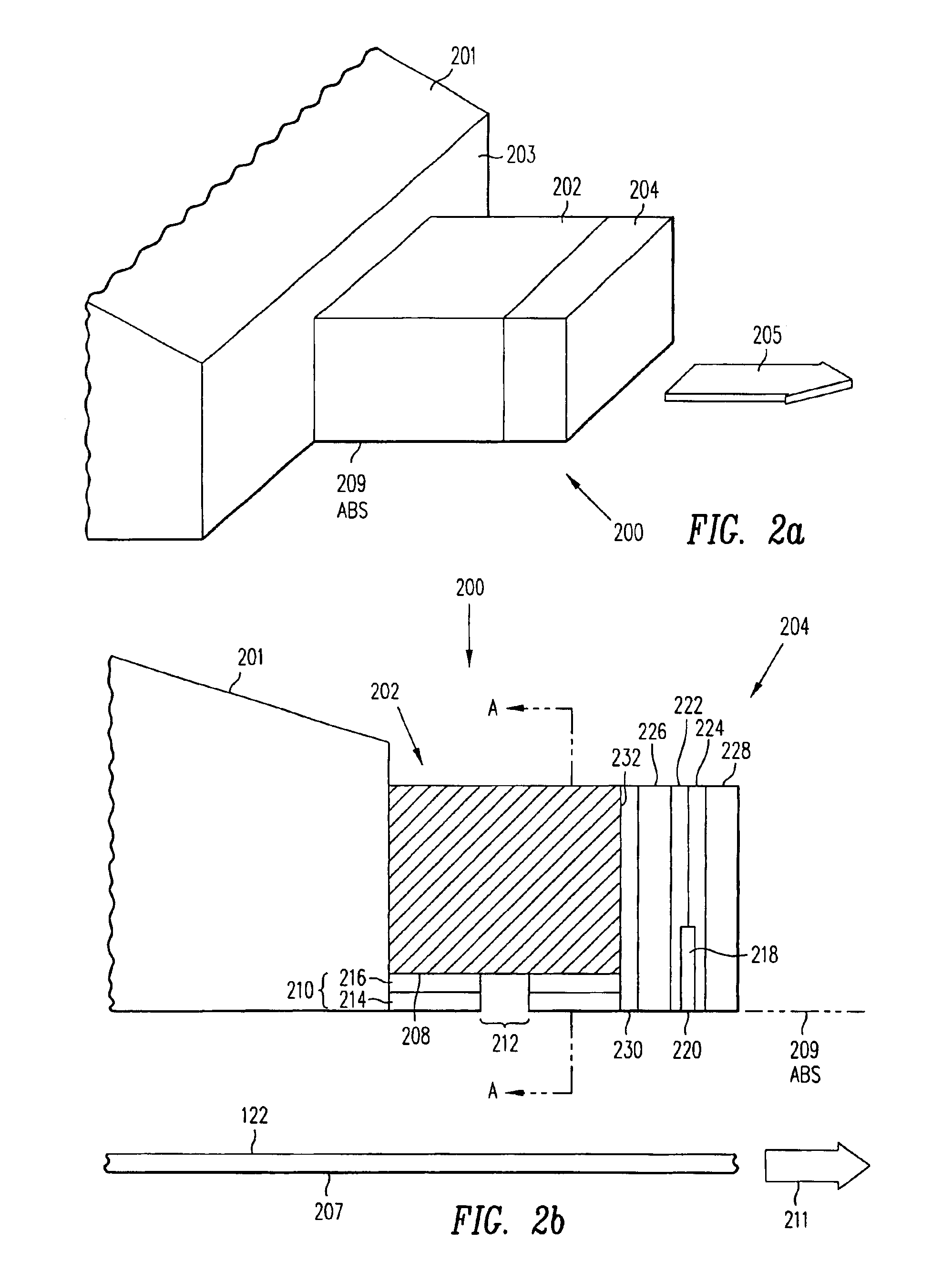
System and method for dynamically sharing storage volumes in a computer network
InactiveUS20050033756A1Data processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersMagnetic mediaDistributed computing
A computerized method for dynamically sharing a magnetic media volume in a network, the method comprising removing, in response to a volume sharing request, an association between a first media management component and the magnetic media volume, and associating, according to a set of selection logic, a second media management component with the magnetic media volume.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
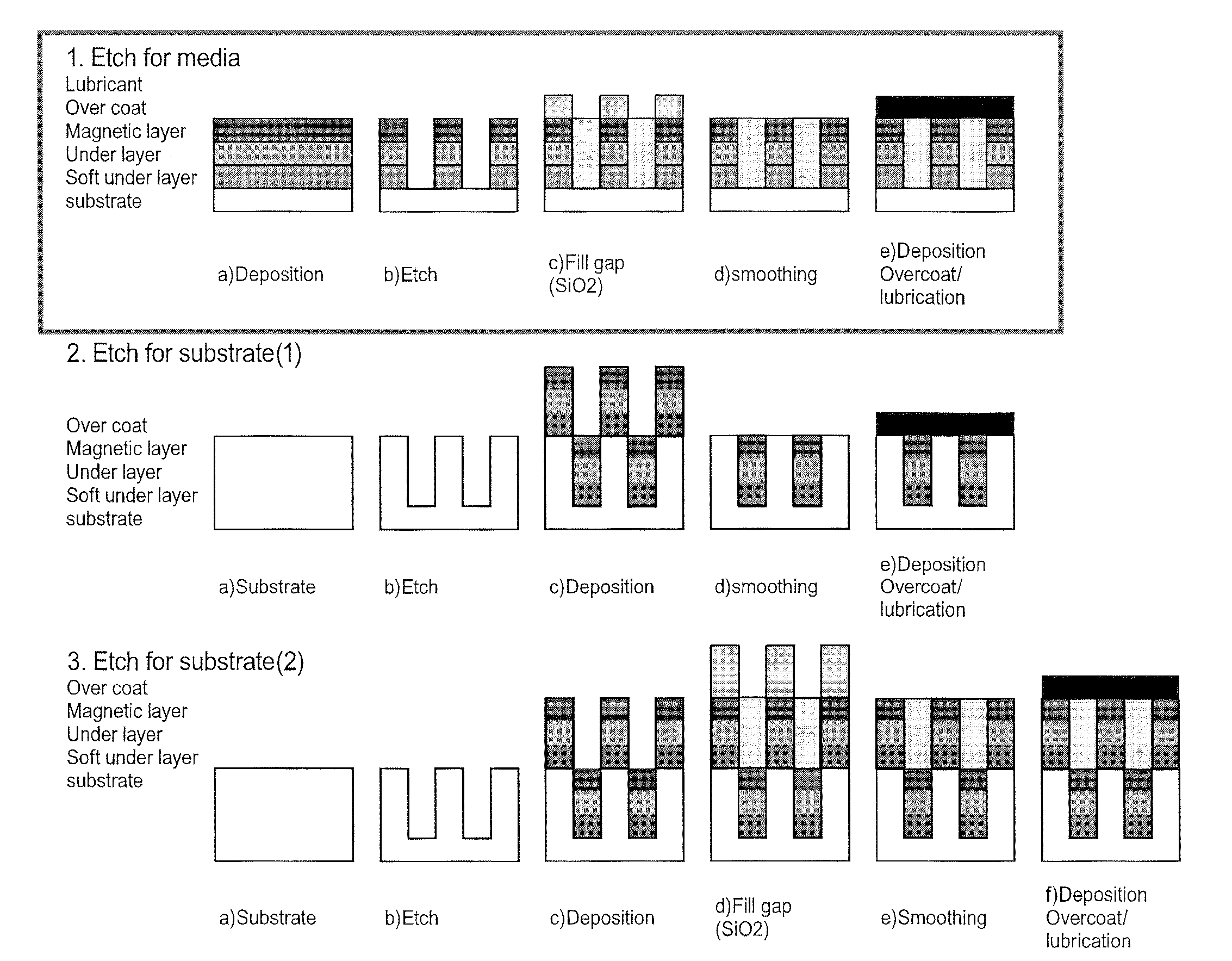
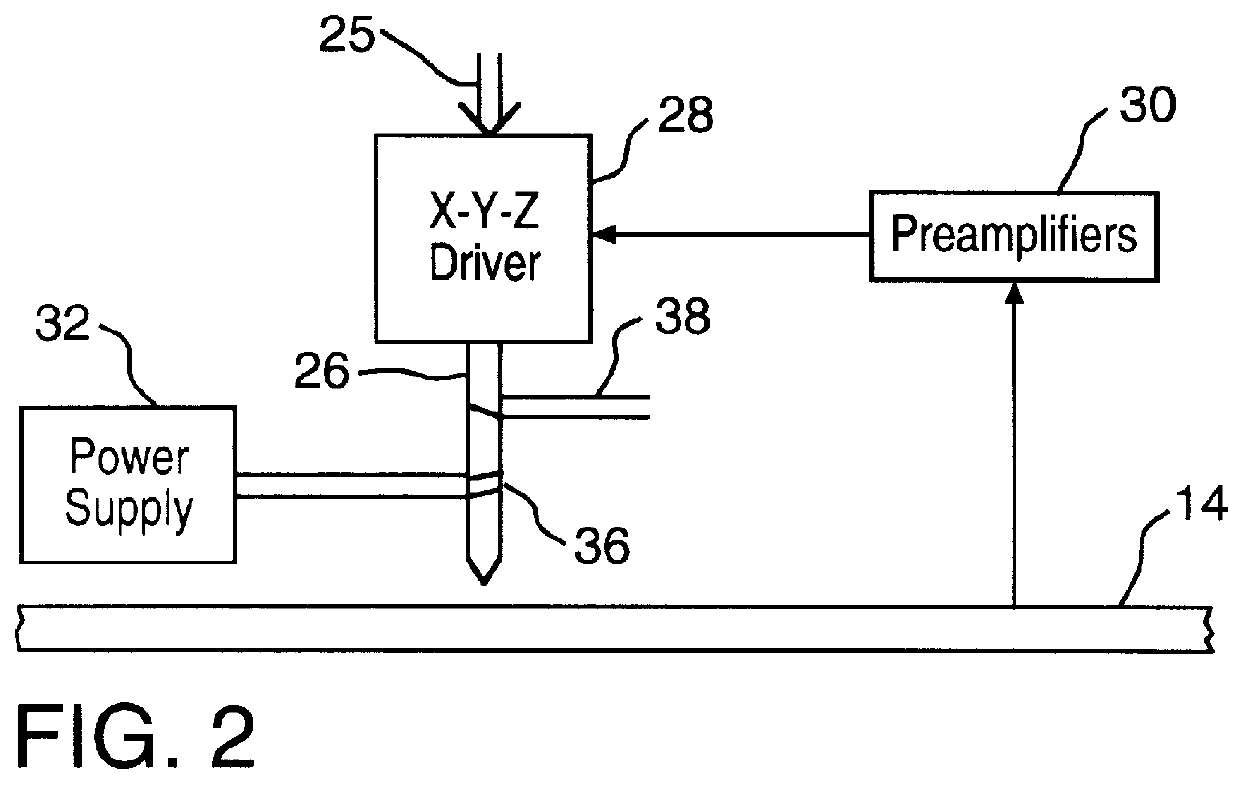
System for Fabricating a Pattern on Magnetic Recording Media
InactiveUS20120223048A1Easy to useReduce system footprintLiquid surface applicatorsDecorative surface effectsHard disc driveMagnetic media
An inline processing system for patterning magnetic recording layers on hard discs for use in a hard disc drive. Discs are processed on both sides simultaneously in a vertical orientation, in round plate-like holders called MDCs. A plurality (as many as 10) discs are held in a dial carrier of the MDC, and transferred from one process station to another. The dial carrier of the MDC may be rotated and / or angled at up to 70° from normal in each process station, so that one or a plurality of process sources may treat the discs simultaneously. This configuration provides time savings and a reduction in the number and size of process sources needed. A mask enhancement process for patterning of magnetic media, and a filling and planarizing process used therewith, are also disclosed.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
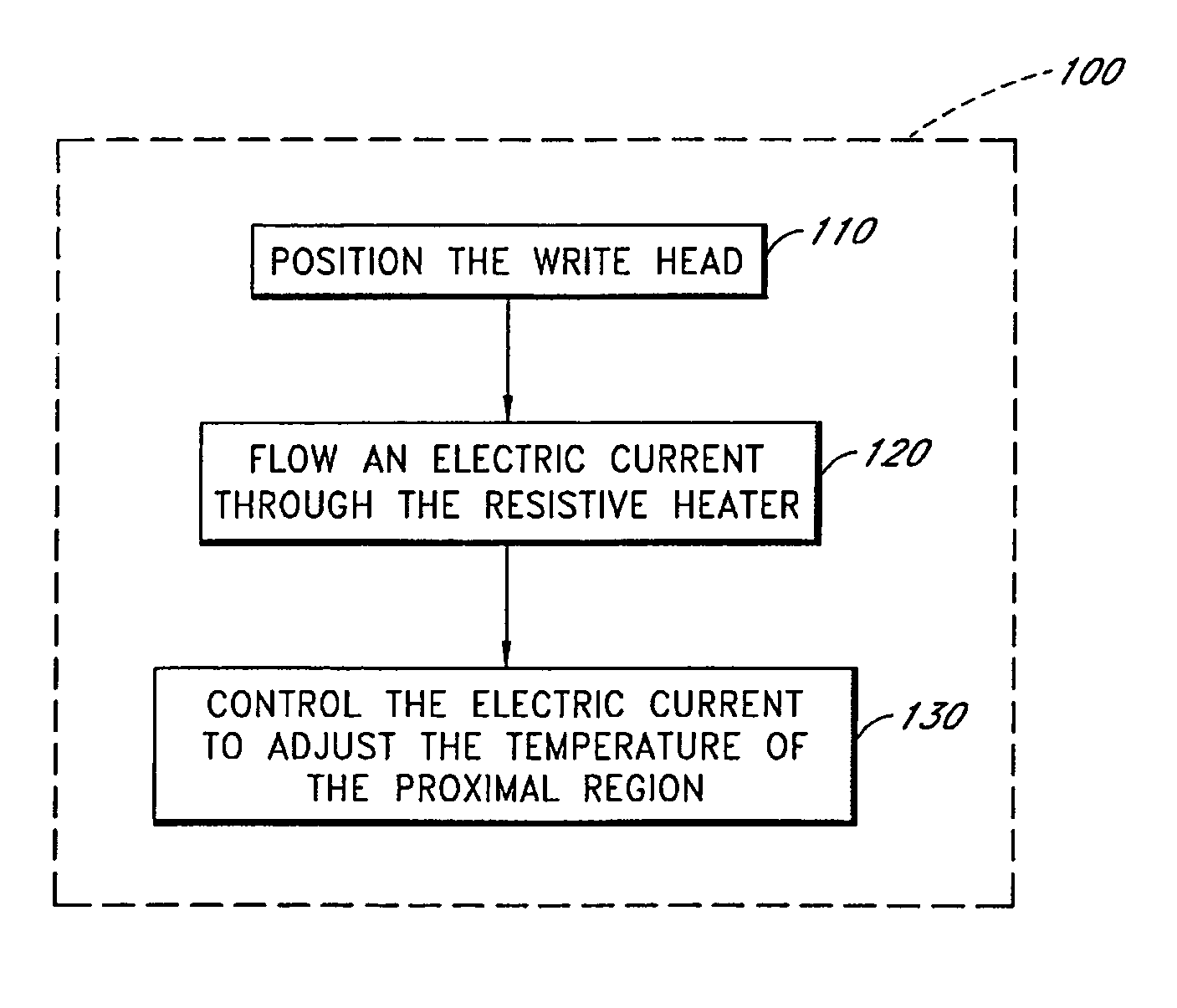
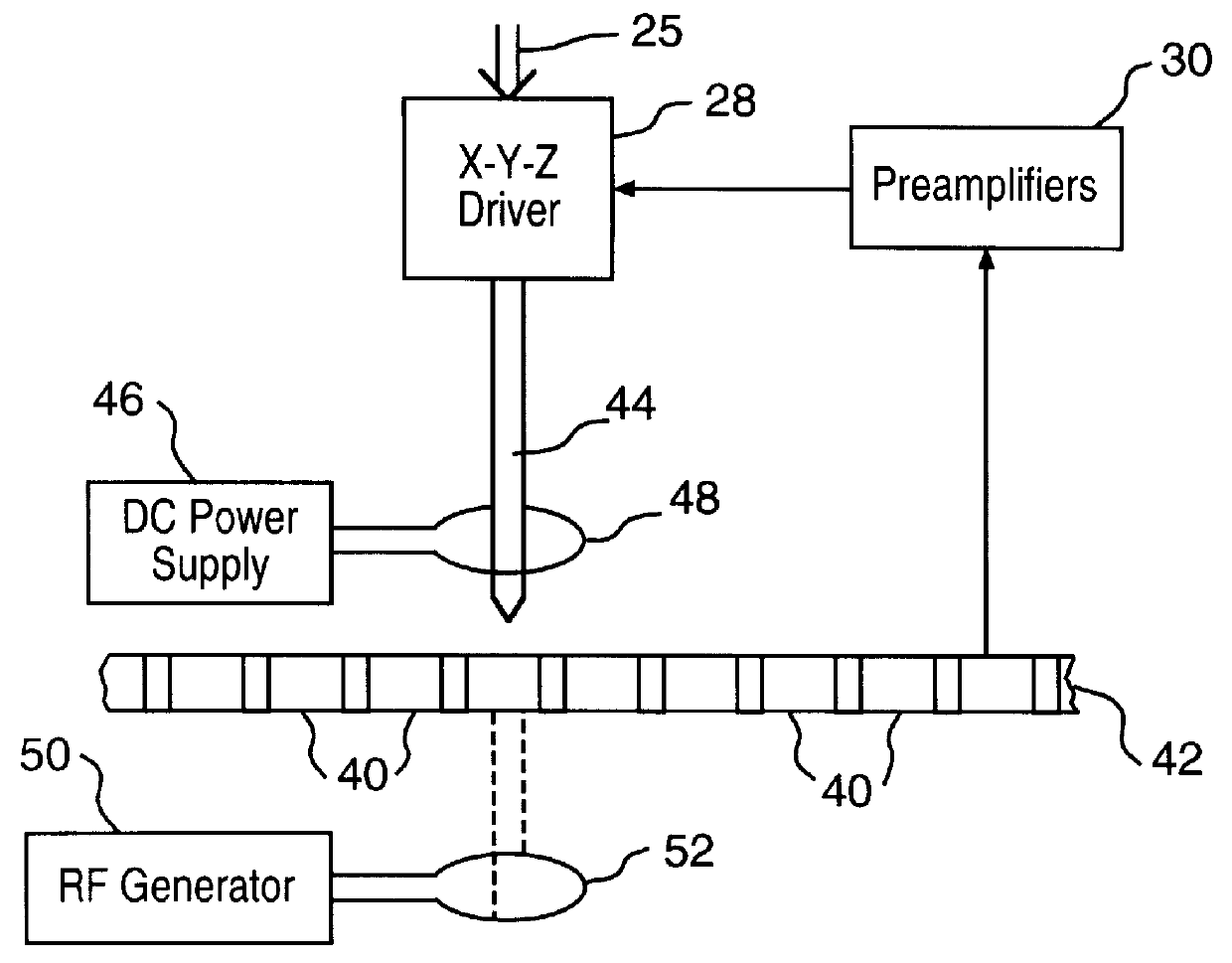
Method of using a magnetic write head having an internal heater
A method adjusts a flying-height distance between a magnetic write head and a magnetic medium. The method includes positioning the write head in a location spaced from the magnetic medium by the flying-height distance. The write head includes a magnetic yoke and a proximal region in proximity to the magnetic medium. The write head further includes a resistive heater and at least a portion of the resistive heater is within the magnetic yoke and is in proximity to the proximal region. The resistive heater is configured to heat the proximal region. The proximal region has a coefficient of thermal expansion. The proximal region is configured to expand and to contract in response to a temperature of the proximal region. The method further includes flowing an electric current through the resistive heater. The method further includes controlling the electric current to adjust the temperature of the proximal region to selectively expand and contract the proximal region and thereby control the flying-height distance. Controlling the electric current includes pulsing the electrical current and adjusting a time interval between pulses.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
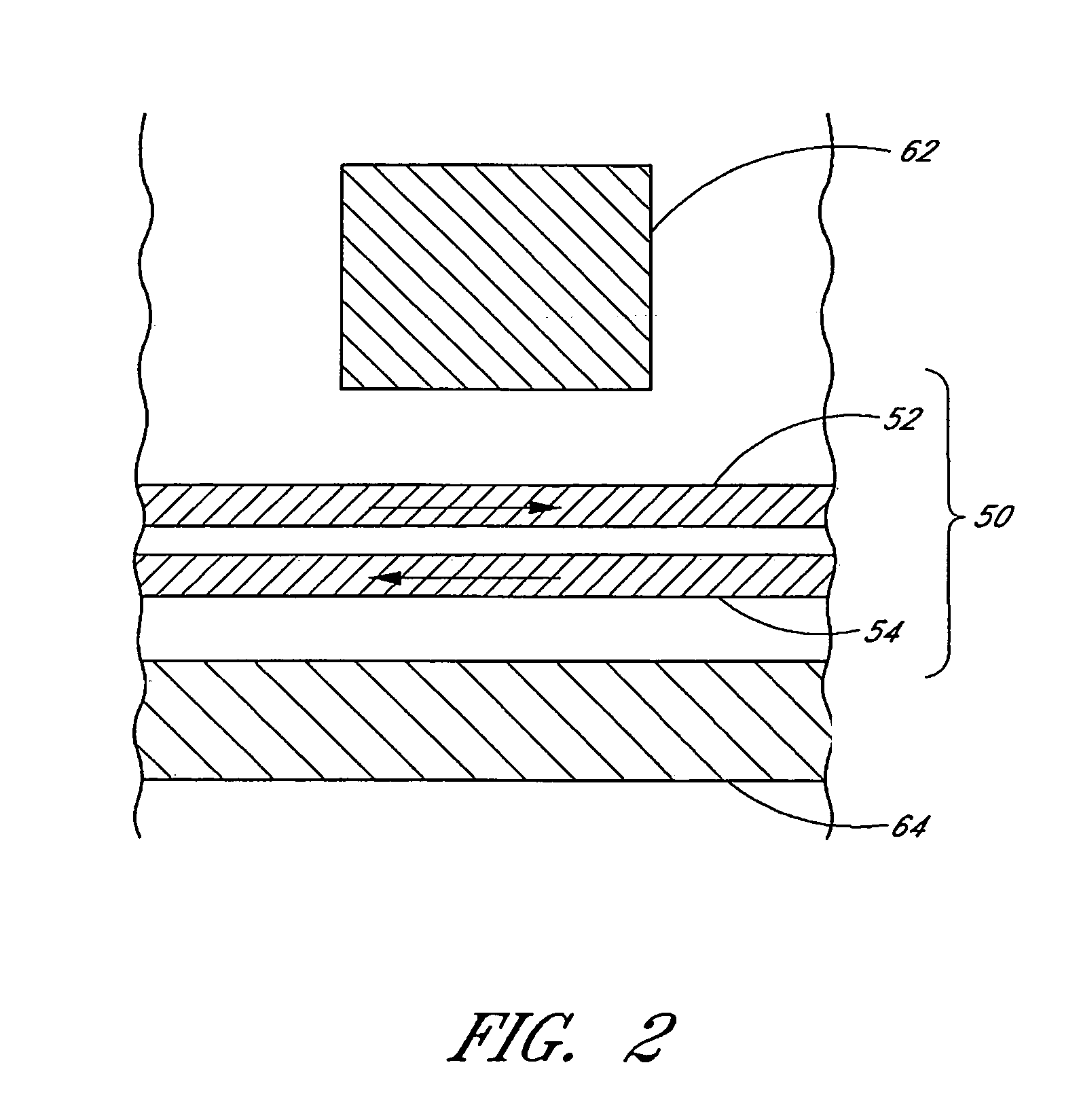
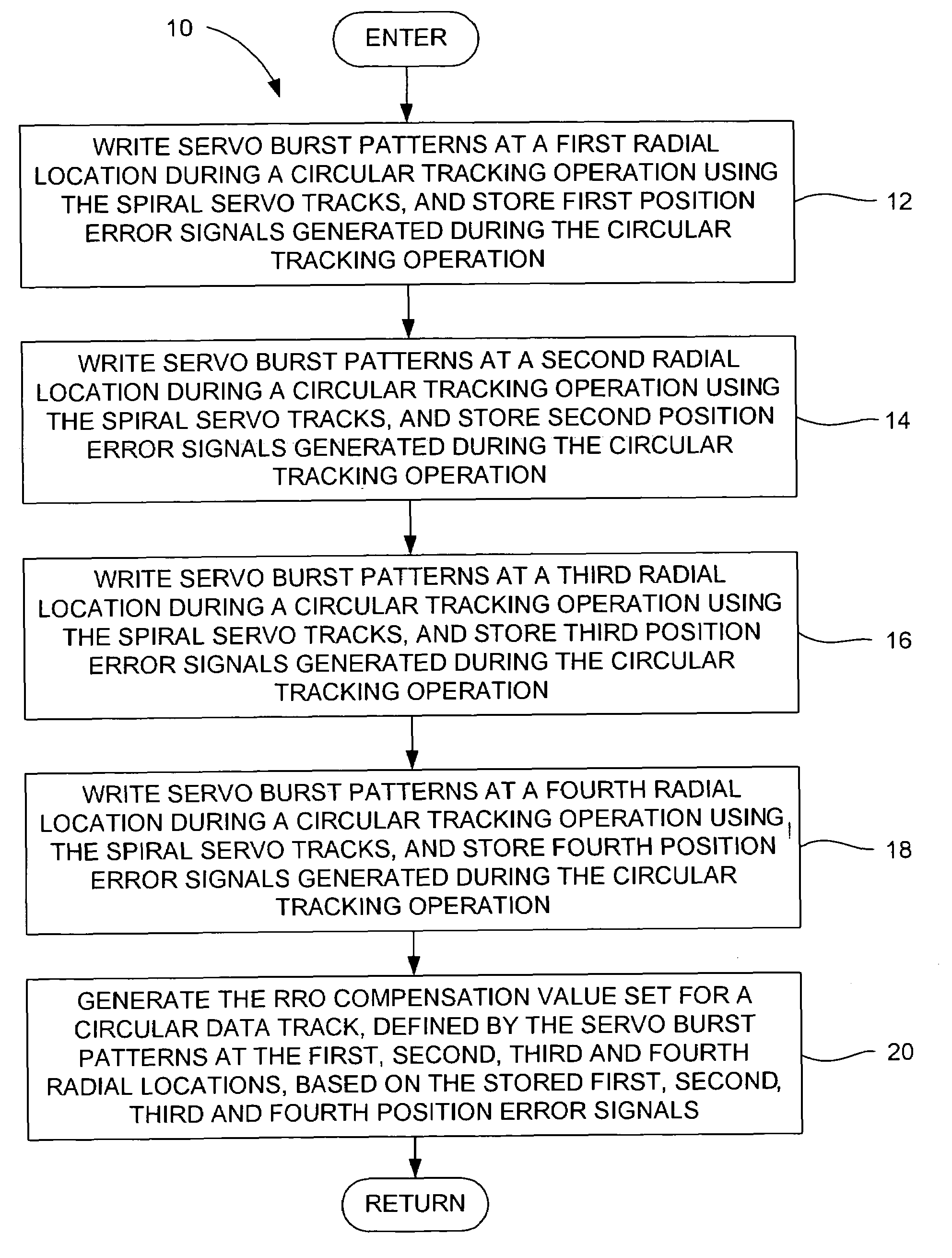
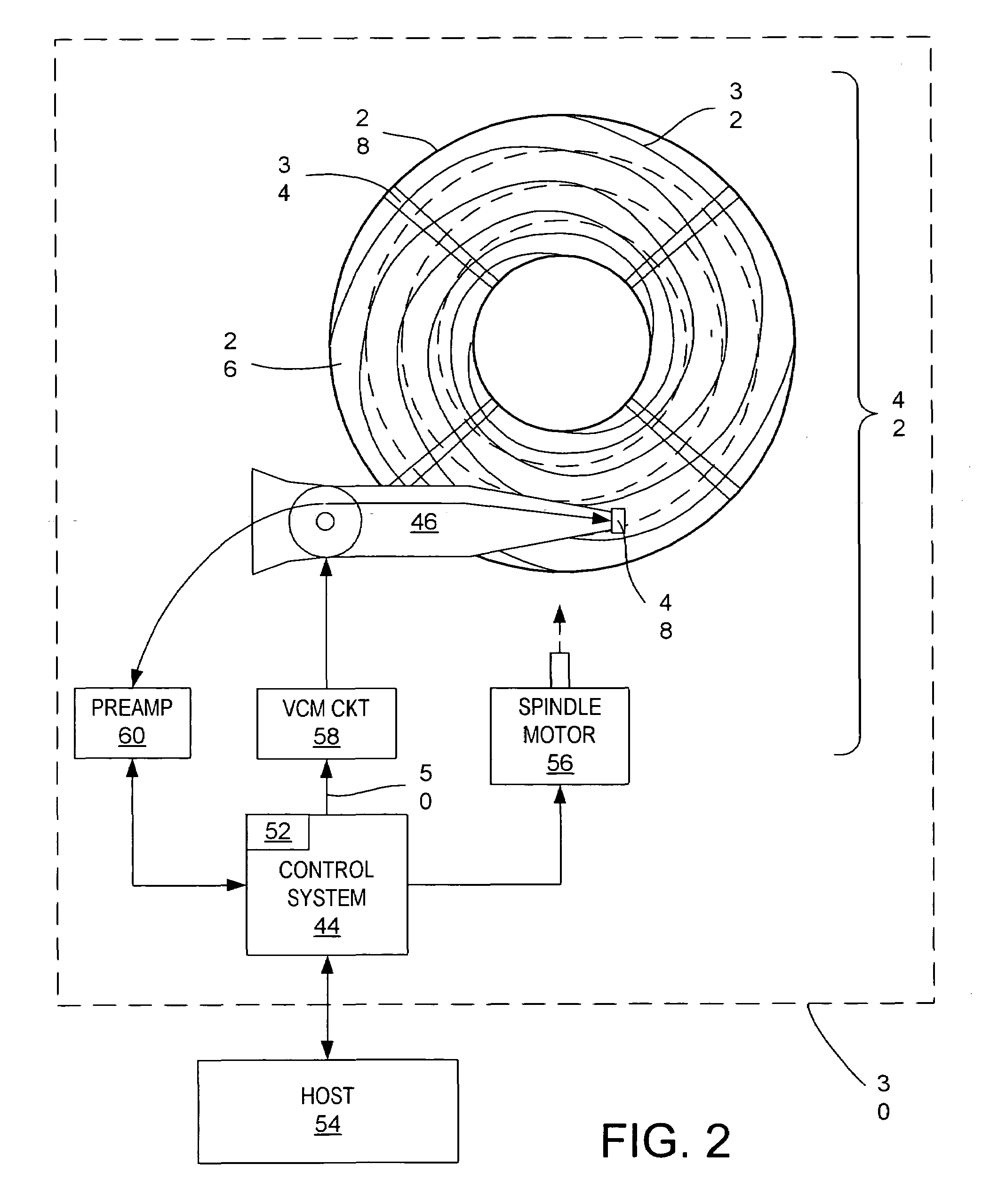
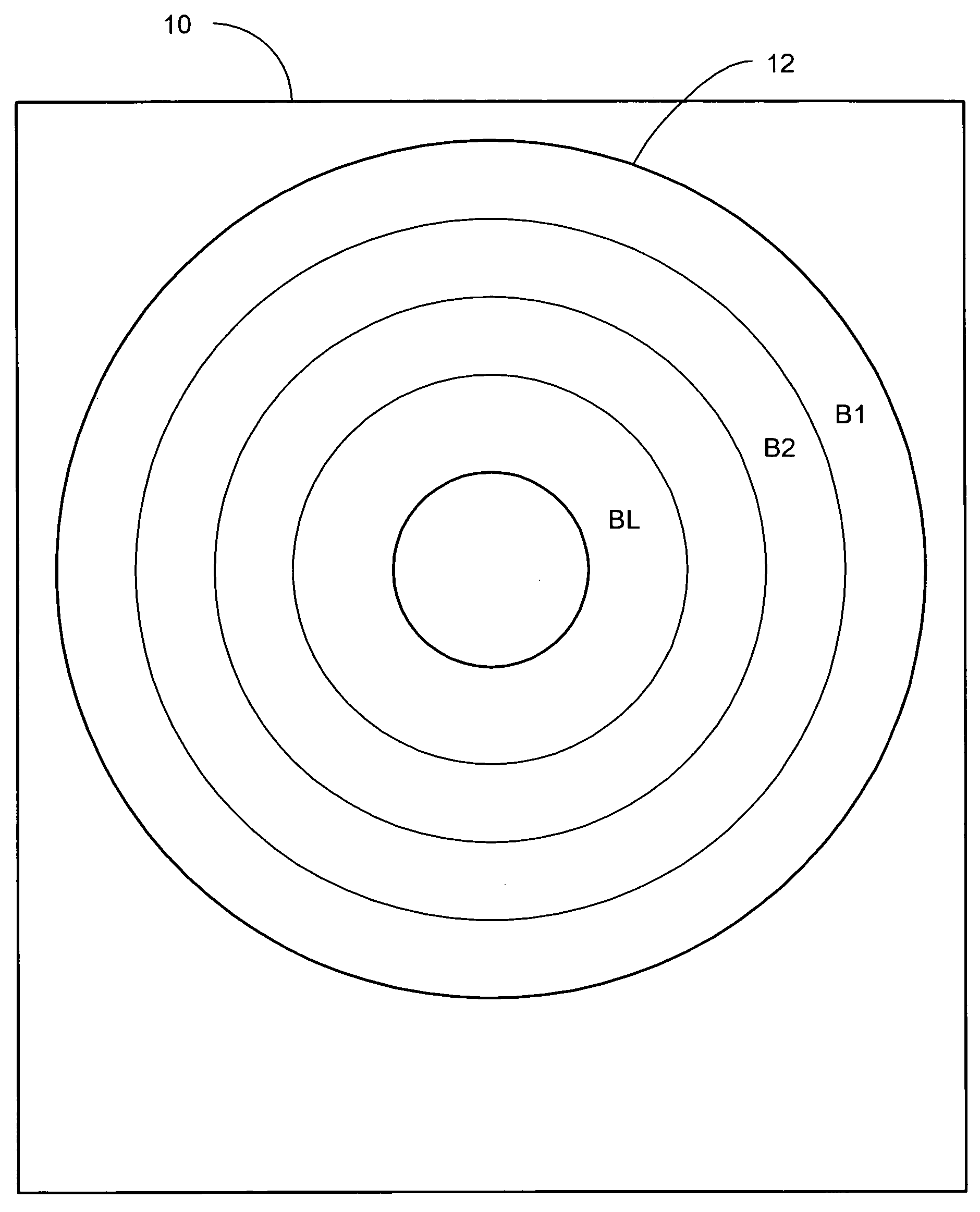
Determining repeatable runout cancellation information using PES information generated during self servo-writing operations
Disclosed is a method for generating a repeatable runout (RRO) compensation value set for a circular track on a magnetic medium on a surface of a disk in a disk drive. The magnetic medium has a plurality of previously written spiral servo tracks for providing position information during a self servo-writing operation. In the method, servo burst patterns are written at a plurality of radial locations on the magnetic data storage surface during circular tracking operations using the spiral servo tracks, and respective position error signals generated during the circular tracking operations are stored. The servo burst patterns at the plurality of radial locations define a circular data track. The RRO compensation value set for the circular data track may be generated based on the respective stored position error signals generated during the circular tracking operations for writing the servo burst patterns at the plurality of radial locations.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
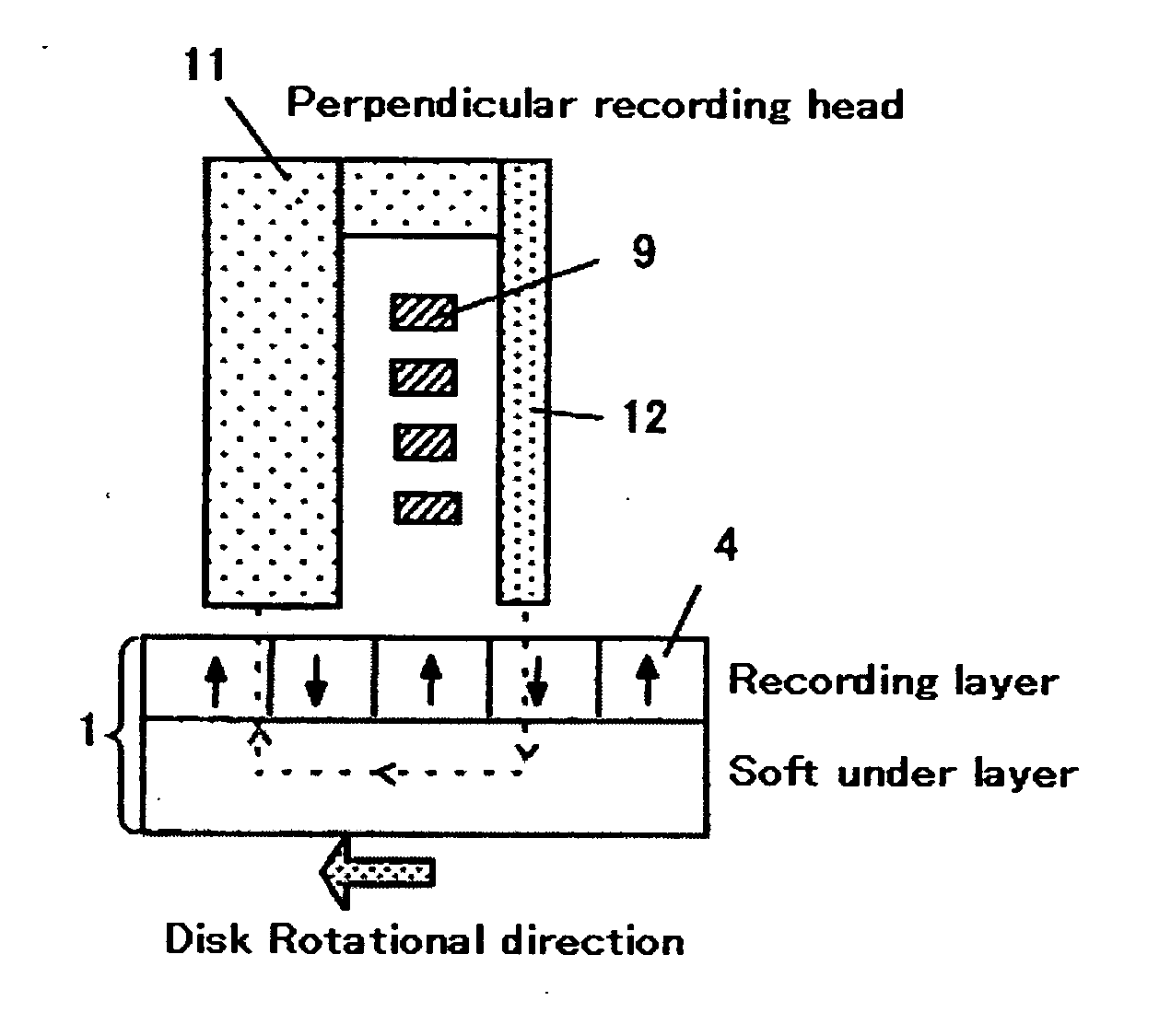
Magnetic recording head for perpendicular recording, fabrication process, and magnetic disk storage apparatus mounting the magnetic head
InactiveUS20050141137A1Improving recording magnetic field gradientIncreasing the thicknessManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsMagnetic field gradientMagnetic media
Embodiments of the invention provide a perpendicular magnetic writing head with a suppressed effective track width to be written on a magnetic medium while increasing writing magnetic field gradient. In one embodiment a trailing side shield is disposed by way of a gap film to a main pole of a perpendicular writing magnetic head. A gap distance (Gt) on a trailing side of the main pole and a gap distance (Gs) on a lateral side of the main pole is defined as Gt<Gt, and a thickness (Gd) from an air bearing surface of the shield is made equal to or less than a throat height. Alternatively, the thickness of Gd on the side of the main pole is reduced to less than that on the trailing side of the main pole. Further, for preventing defoliation of the shield upon fabrication of the air bearing surface, a thickness for a portion away from the main pole is increased.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method for making high speed, high areal density inductive write structure
InactiveUS7007372B1Excellent magnetic propertiesIncrease coverageDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingMagnetic mediaMagnetic poles
An inductive write element is disclosed for use in a magnetic data recording system. The write element provides increased data rate and data density capabilities through improved magnetic flux flow through the element. The write element includes a magnetic yoke constructed of first and second magnetic poles. The first pole includes a pedestal constructed of a high magnetic moment (high Bsat) material, which is preferably FeRhN nanocrystalline films with lamination layers of CoZrCr. The second pole includes a thin inner layer of high Bsat material (also preferably FeRhN nanocrystalline films with lamination layers of CoZrCr), the remainder being constructed of a magnetic material capable of being electroplated, such as a Ni—Fe alloy. An electrically conductive coil passes through the yoke between the first and second poles to induce a magnetic flux in the yoke when an electrical current is caused to flow through the coil. Magnetic flux in the yoke produces a fringing field at a write gap whereby a signal can be imparted onto a magnetic medium passing thereby.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Multilayer structure with high perpendicular anisotropy for device applications
ActiveUS20110293967A1Improve performanceLow costMagnetic measurementsPretreated surfacesPerpendicular anisotropyMagnetic media
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and Hc are enhanced in magnetic devices with a Ta / M1 / M2 seed layer where M1 is preferably Ti, and M2 is preferably Cu, and including an overlying (Co / Ni)X multilayer (x is 5 to 50) that is deposited with ultra high Ar pressure of >100 sccm to minimize impinging energy that could damage (Co / Ni)X interfaces. In one'embodiment, the seed layer is subjected to one or both of a low power plasma treatment and natural oxidation process to form a more uniform interface with the (Co / Ni)X multilayer. Furthermore, an oxygen surfactant layer may be formed at one or more interfaces between adjoining (Co / Ni)X layers in the multilayer stack. Annealing at temperatures between 180° C. and 400° C. also increases Hc but the upper limit depends on whether the magnetic device is MAMR, MRAM, a hard bias structure, or a perpendicular magnetic medium.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing with a probe on erasable magnetic media
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing on an erasable magnetic medium include using a micromachined mechanism having two probes for writing to the medium. Use of the two probe embodiment eliminates the need to change the magnetic orientation of the probe. In another embodiment, a single probe is provided which is heated to the vicinity of its Curie temperature to enable the magnetic orientation of the probe to be switched. The probe may be heated to its Curie temperature through the use of a heating element or a focused laser. In another embodiment of the present invention, either the magnetic orientation of the probe or the magnetic orientation of the medium may be switched through the combination of a static magnetic field, a radio frequency magnetic field and, under certain circumstances, the magnetic field of the probe. In all cases, the writing techniques enable information to be written to a magnetic medium in a manner which enables the information to be erased and the medium rewritten.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
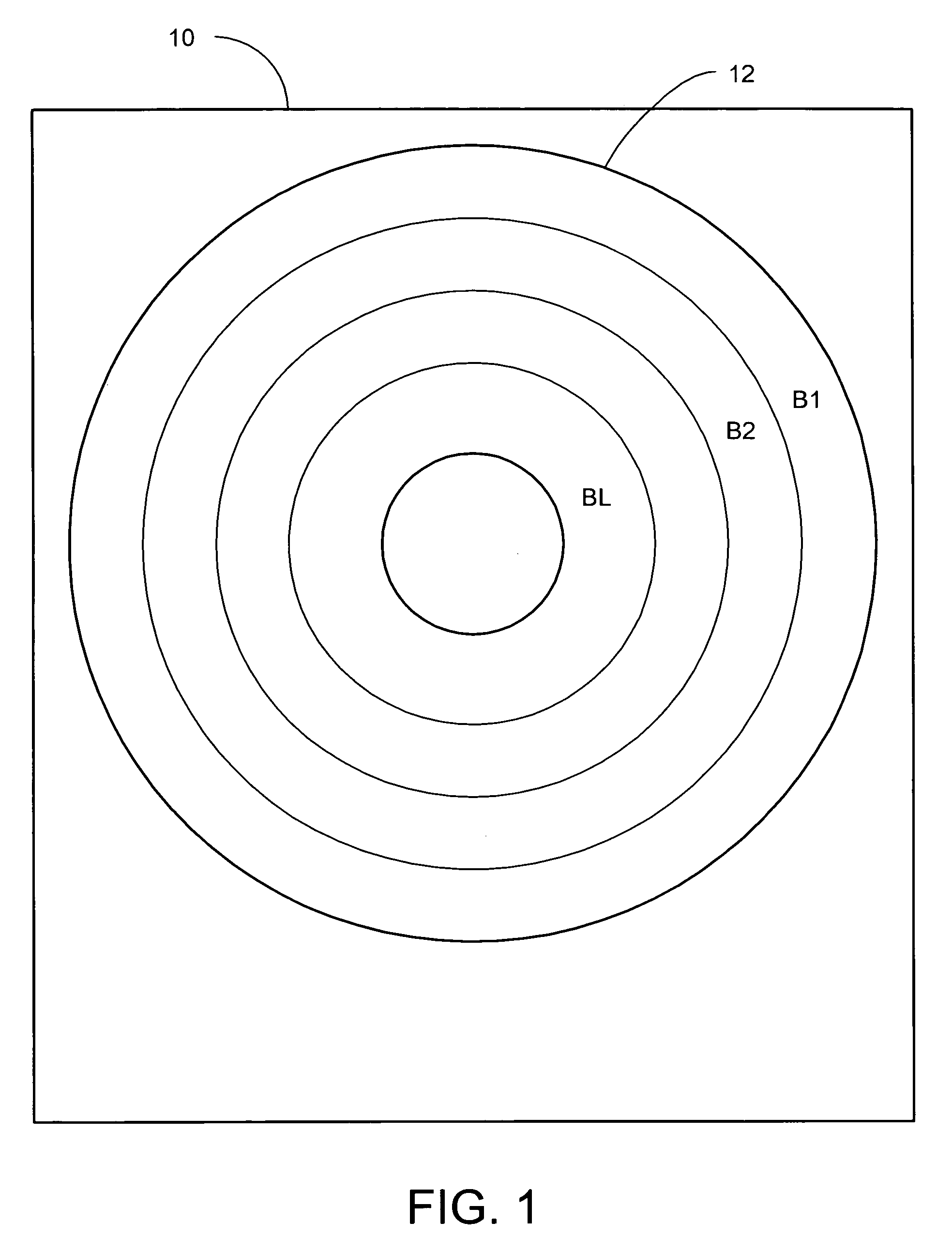
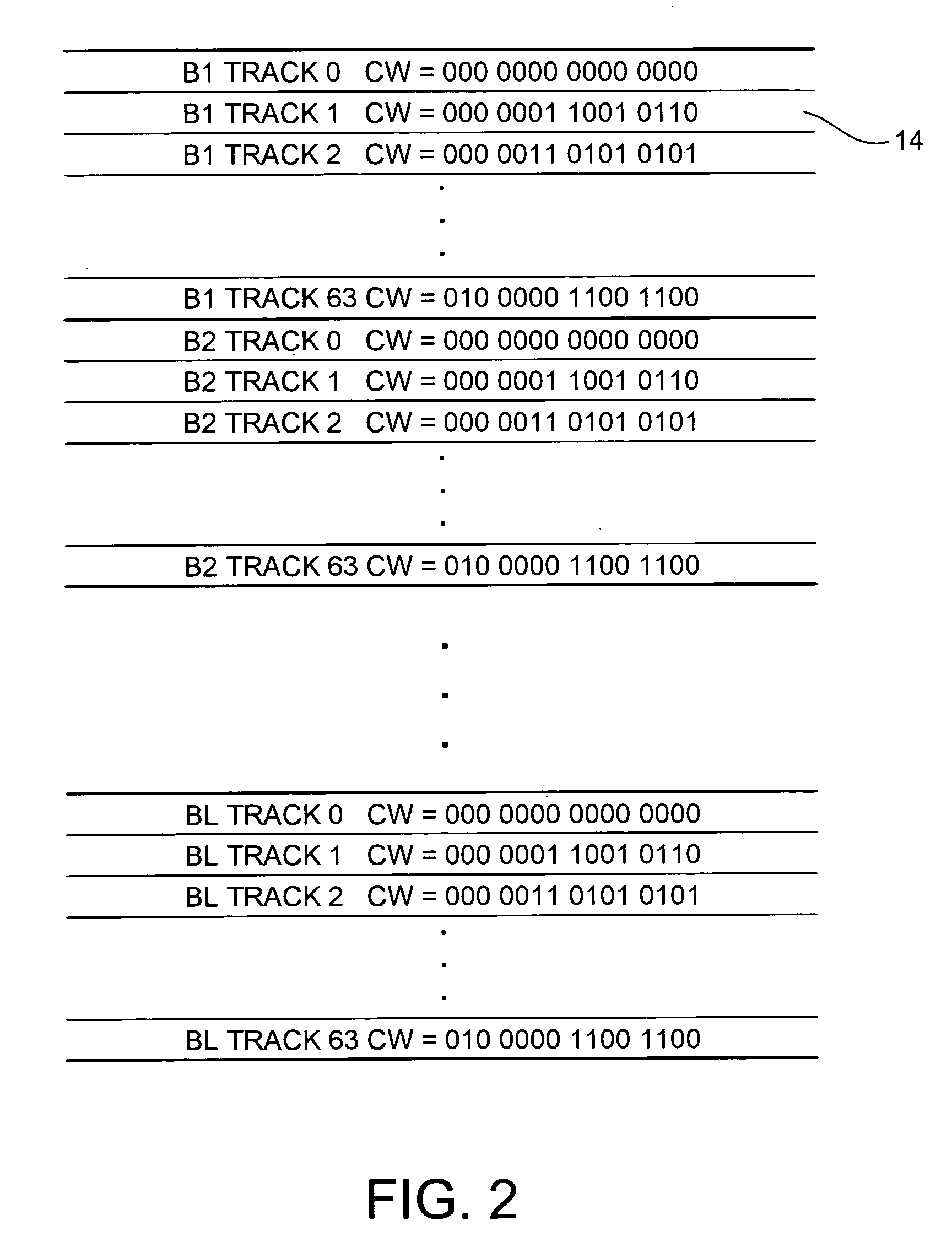
Track identification codewords having multiple bit error correction capability and generalized gray code property
InactiveUS7099095B1Record information storageIndividual digits conversionMagnetic mediaComputer science
The present invention may be embodied in a disk drive comprising a rotating magnetic media having tracks identified by binary codewords, and in a related method. Each track codeword for a particular track within a contiguous band of tracks differs from a track codeword for an adjacent track within the contiguous band of tracks by a defined number of bits, and differs from a track codeword for a nonadjacent track within the contiguous band of tracks by at least the defined number of bits. The defined number N of bits is greater than four such that at least two bit errors may be corrected when reading a track codeword.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
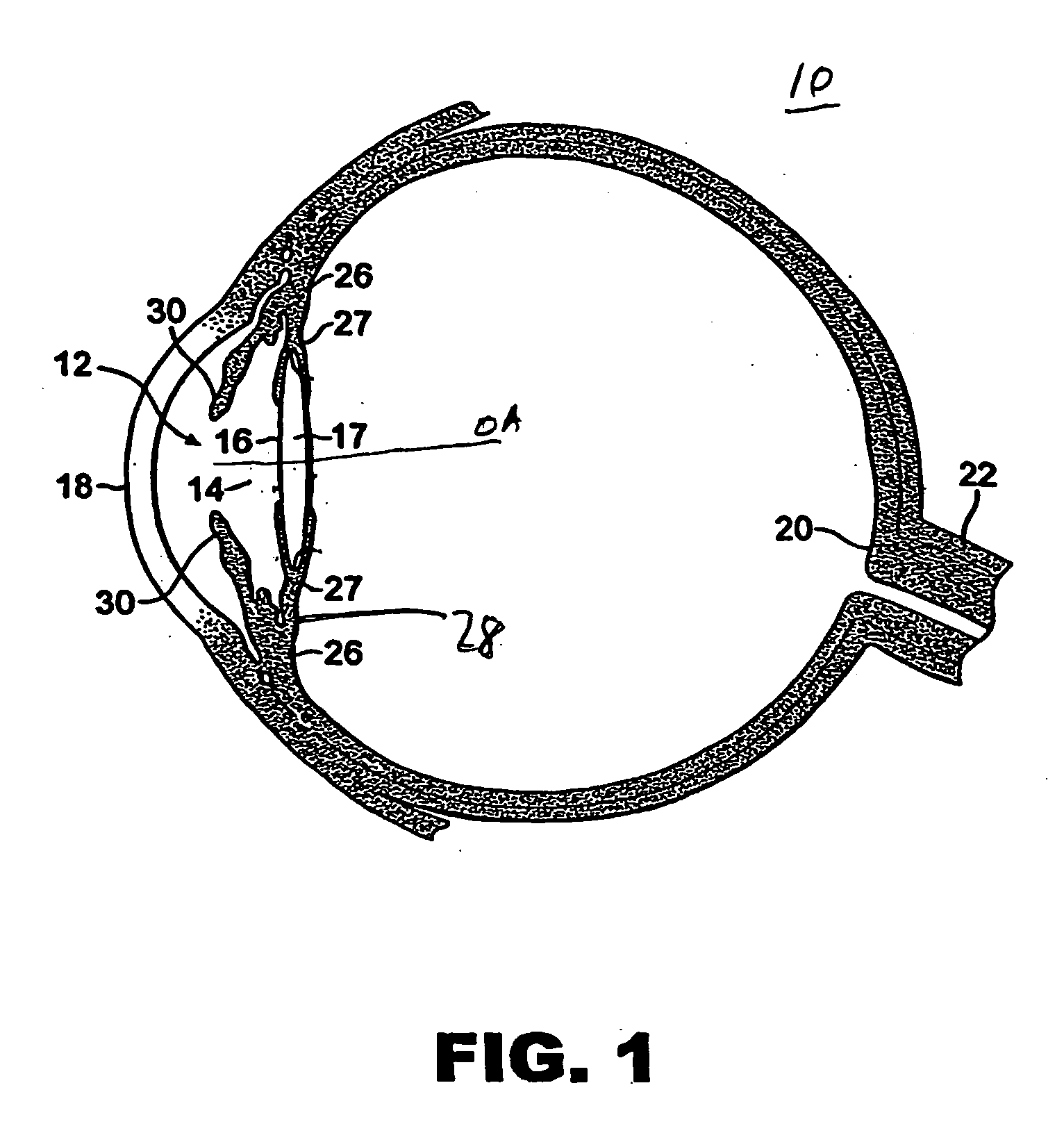
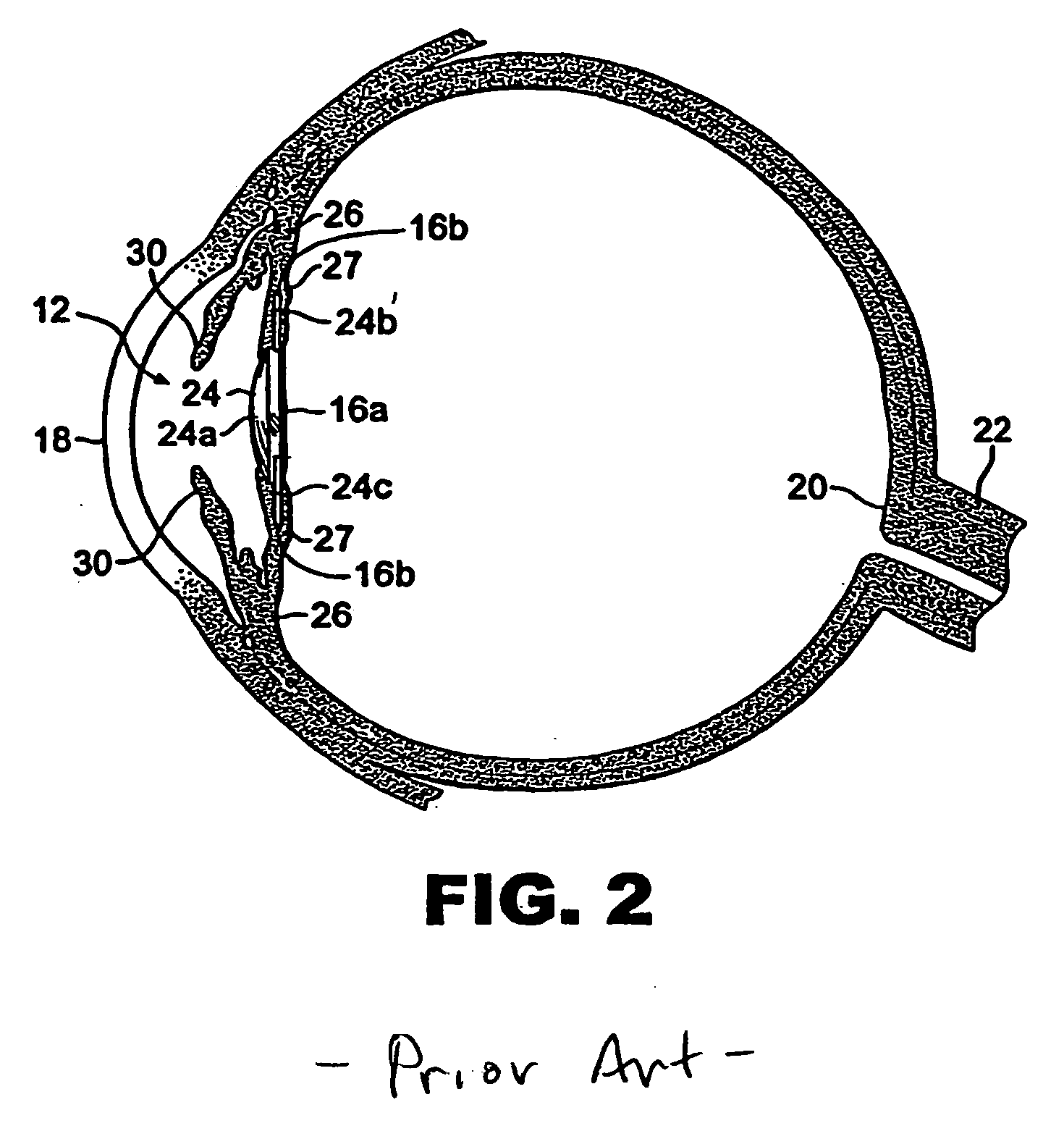
Accommodative intraocular lens
InactiveUS20070118216A1Reduce in quantityImprove reliabilityIntraocular lensIntraocular lensMagnetic media
An intraocular lens (IOL) comprising an apparatus capable of changing power in response to ciliary body movement. An IOL is provided that comprises a first optical power element, and a second optical power element. The second optical power element is mechanically coupled to the first optical power element, and at least one of the first optical power element and the second optical power element is mechanically coupled to at least one magnet, such that a magnetic field applied to the at least one magnet causes the first optical element and the second optical element to displace relative to one another. The optical power elements may be surfaces or lens, the magnetic medium may be liquid, gel or solid.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
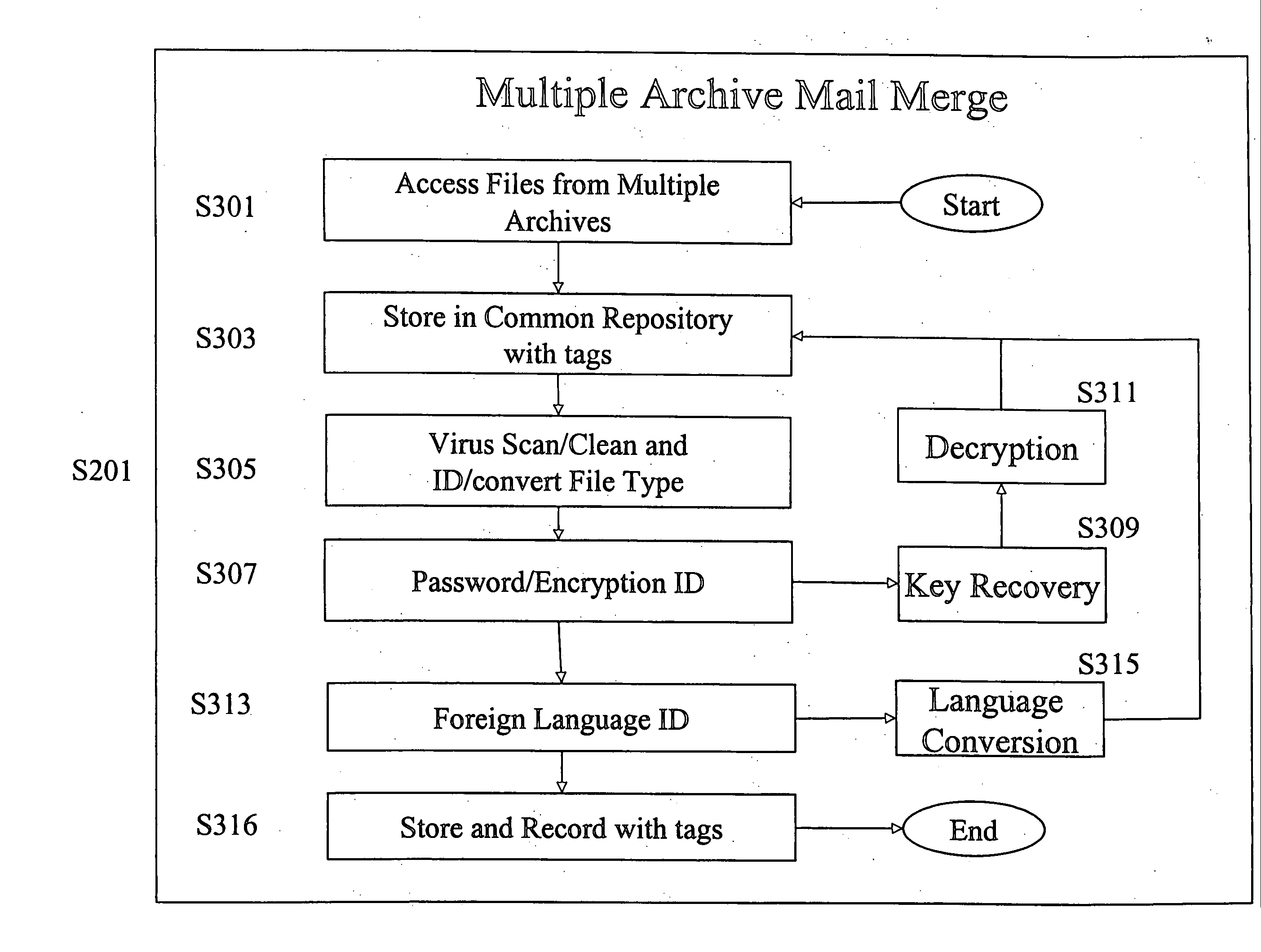
Electronic archive filter and profiling apparatus, system, method, and electronically stored computer program product
InactiveUS20050066190A1Low costEasy to handleDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringTagged Image File FormatConfigfs
A software-based electronic data discovery tool which accesses multiple electronic archives; copies files and their meta-data into a common repository; vertically de-duplicates and tags the files; horizontally de-duplicates and tags the files; filters and tags the files against a one or more sets of predetermined compliance and privileged criteria identified by one or more parties associated with a specific electronic data discovery procedure; profiles and tags select results; and produces a variety of reports and excerpts. Production is at least one of printing on paper, transferring to magnetic media, or other processes. Files that are selected for profiling and production are then rendered in TIFF or another related format and stored in a common file. All files are identified with a digital “finger print” and complete chain-of-custody information.
Owner:CRICKET TECH
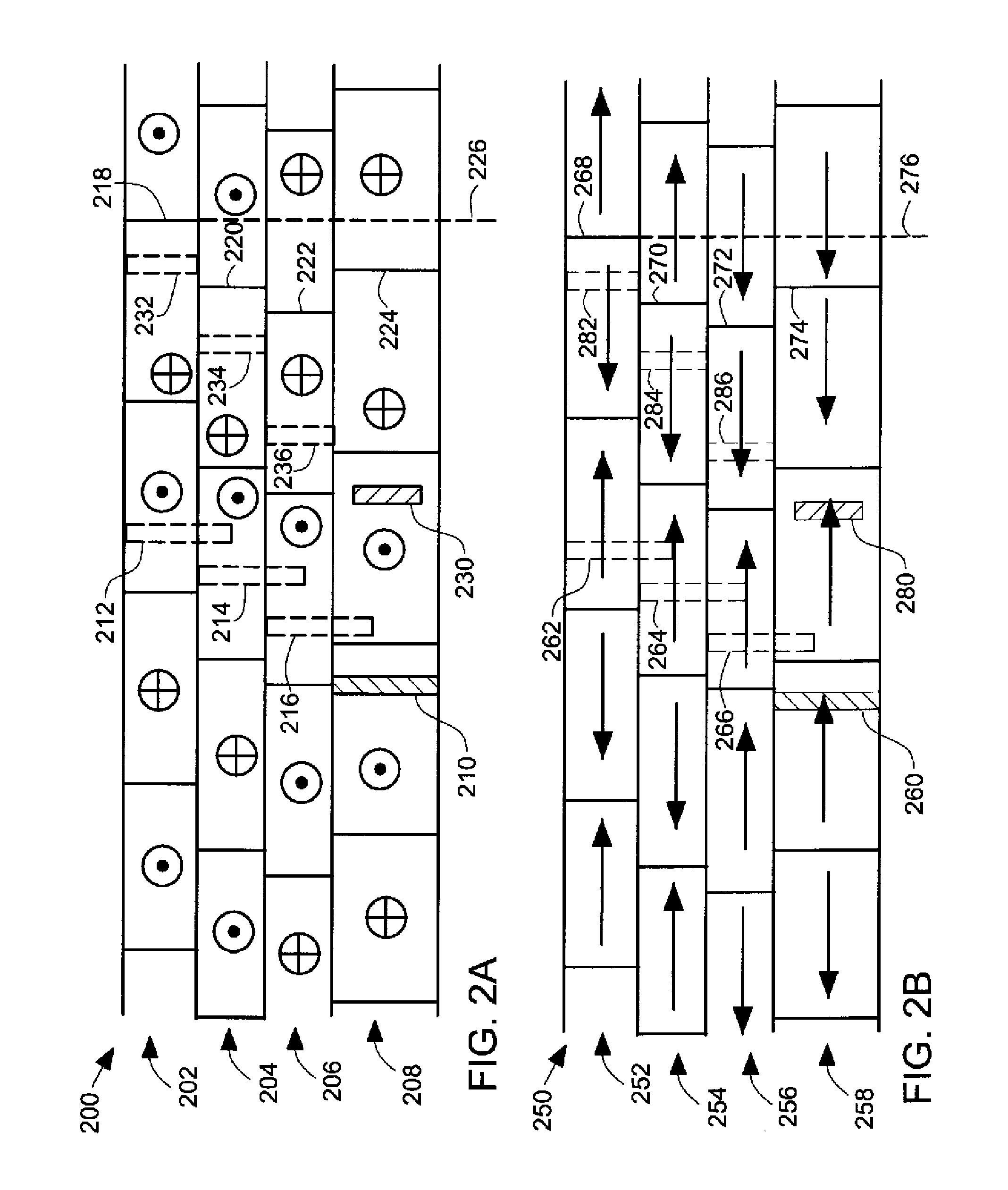
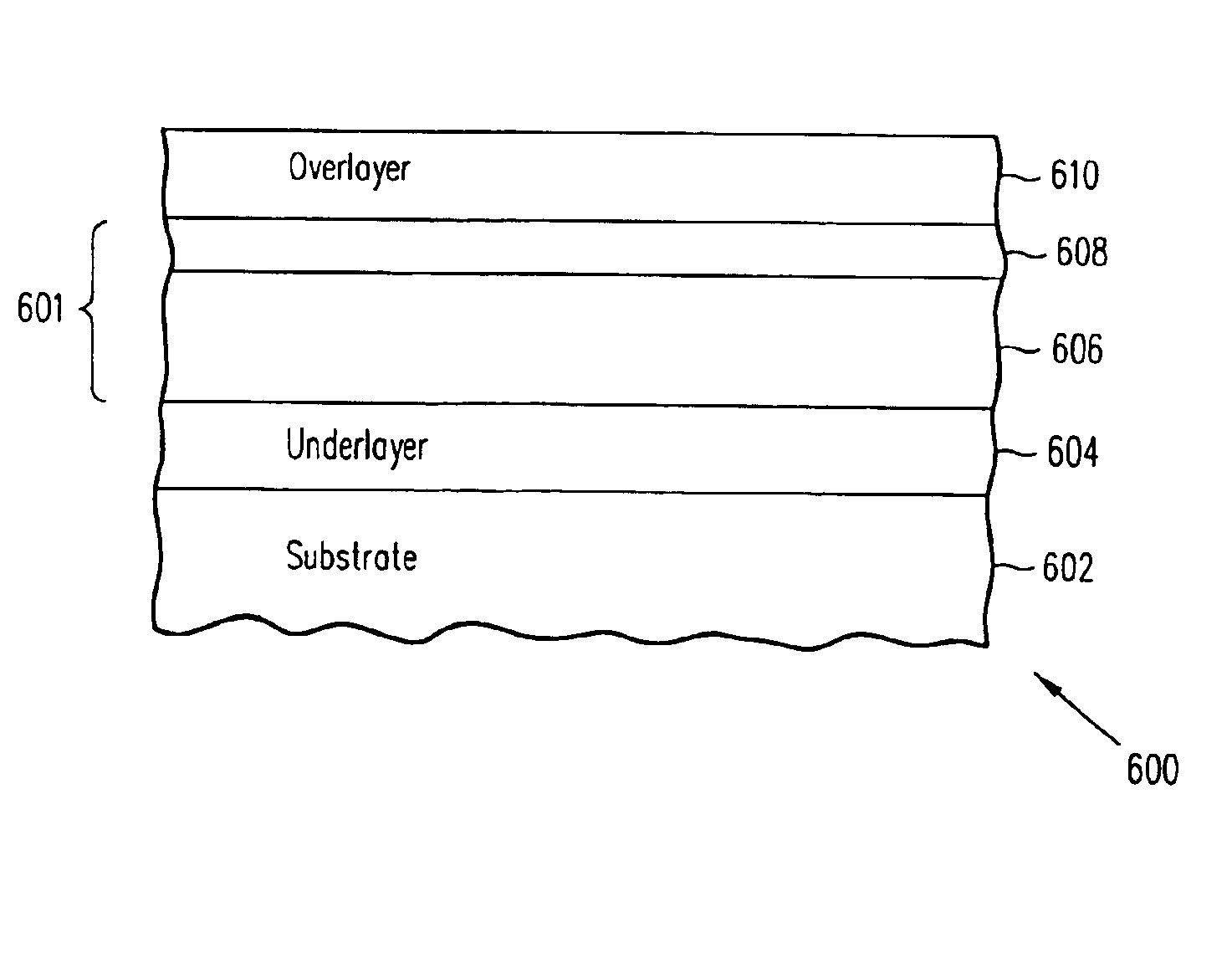
Magnetic media with improved exchange coupling
InactiveUS6899959B2Easy and fast switchingImprove thermal stabilityDifferent record carrier formsRecord information storageInter layerMagnetic media
A magnetic recording medium includes a substrate, an underlayer, a lower magnetic layer formed on the underlayer, an intermediate layer, and an upper magnetic layer formed on the intermediate layer. The intermediate layer is typically Ru, and promotes antiferromagnetic coupling between the upper and lower magnetic layers. The upper and lower magnetic layers are typically Co alloys. The lower magnetic layer has a high saturation magnetization Ms to promote high exchange coupling between the upper and lower magnetic layers. The dynamic coercivity of the lower magnetic layer is lower than the exchange field to ensure rapid switching of the lower magnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thin-film magnetic head with near-field-light-generating layer
ActiveUS20070139818A1Improve reliabilityLow coercivityCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideMagnetic mediaBiomedical engineering
A thin-film magnetic head that has a configuration in which the element-formed surface and the opposed-to-medium surface are perpendicular to each other, and a light source is sufficiently distanced from the medium surface is provided. The head comprises at least one near-field-light-generating layer for heating a part of a magnetic medium during write operation by generating a near-field light, having a shape tapered toward a head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and comprising a near-field-light-generating portion having a light-received surface and a tip reaching the head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and the light-received surface being sloped in respect to the element-formed surface and being provided in a position where an incident light propagating from a head end surface opposite to the opposed-to-medium surface can reach at least a part of the light-received surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
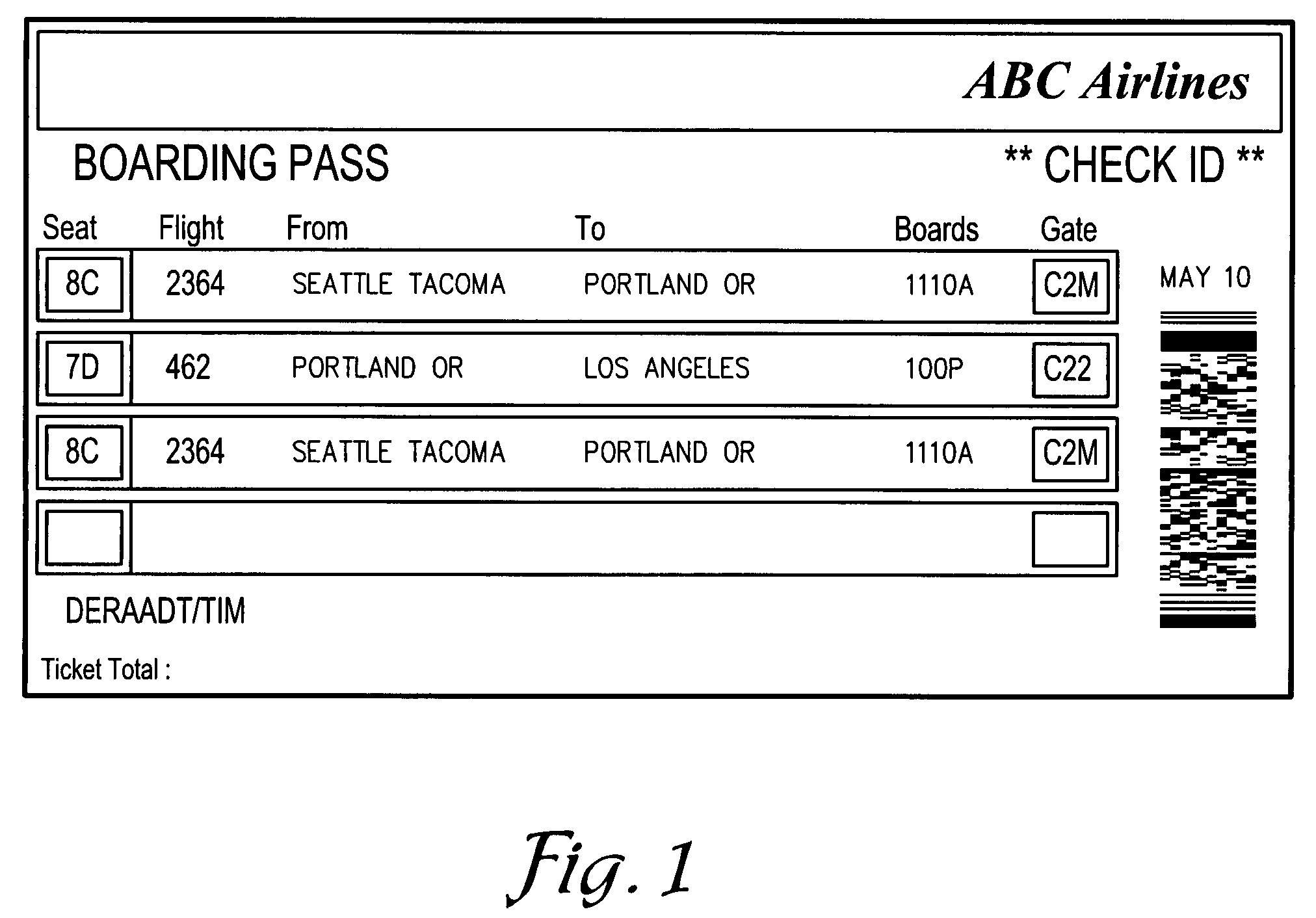
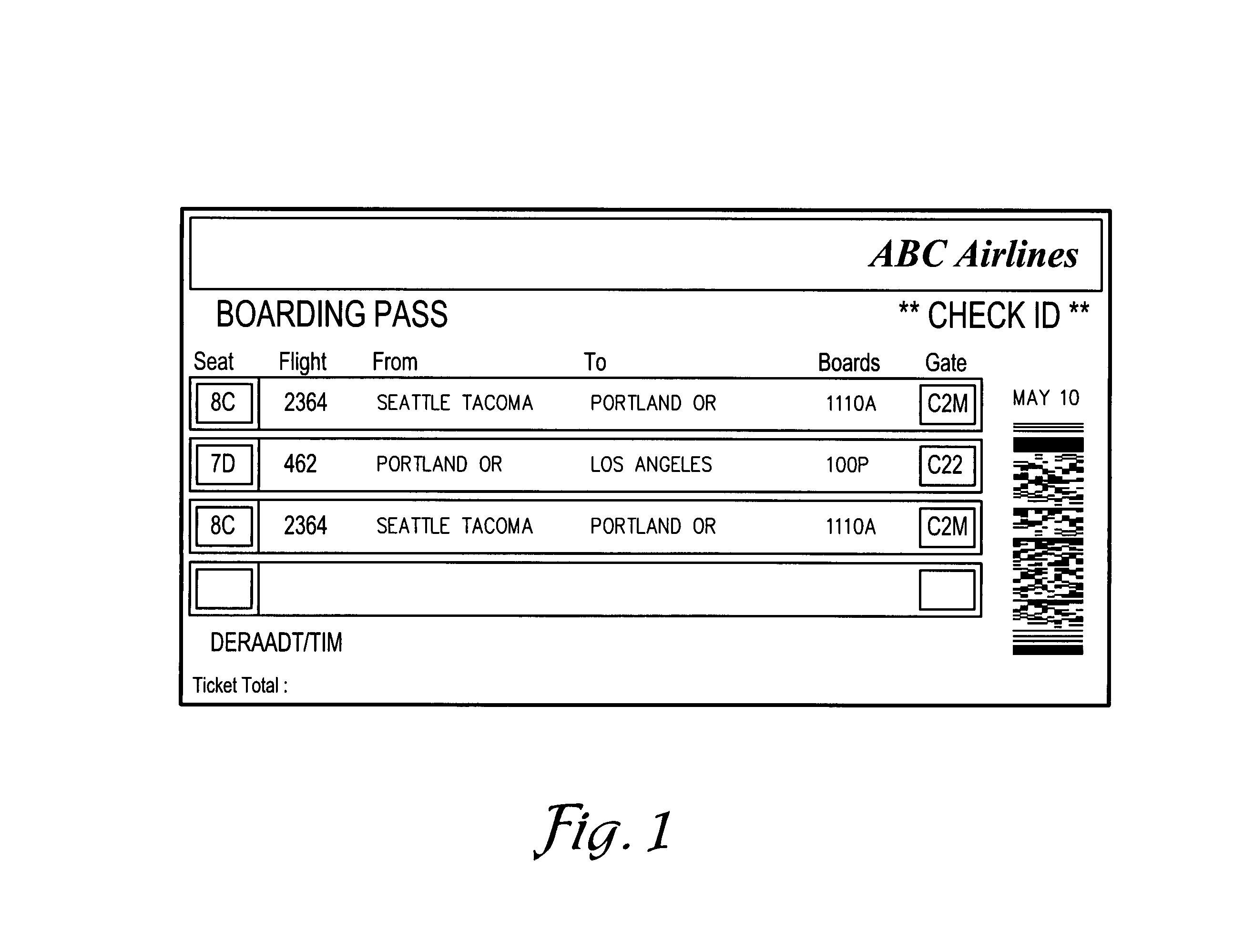
Method of selecting and storing airline ticket data
A method is provided for receiving a data stream of an airline ticketing reservations computer, striping-away data bits included for the ordering and identifying and reading and writing of the data stream on magnetic media and selecting and converting the remaining data into multi-dimensional symbology or bar code for printing onto airline ticket and / or boarding documents.
Owner:PETERSON STANLEY K
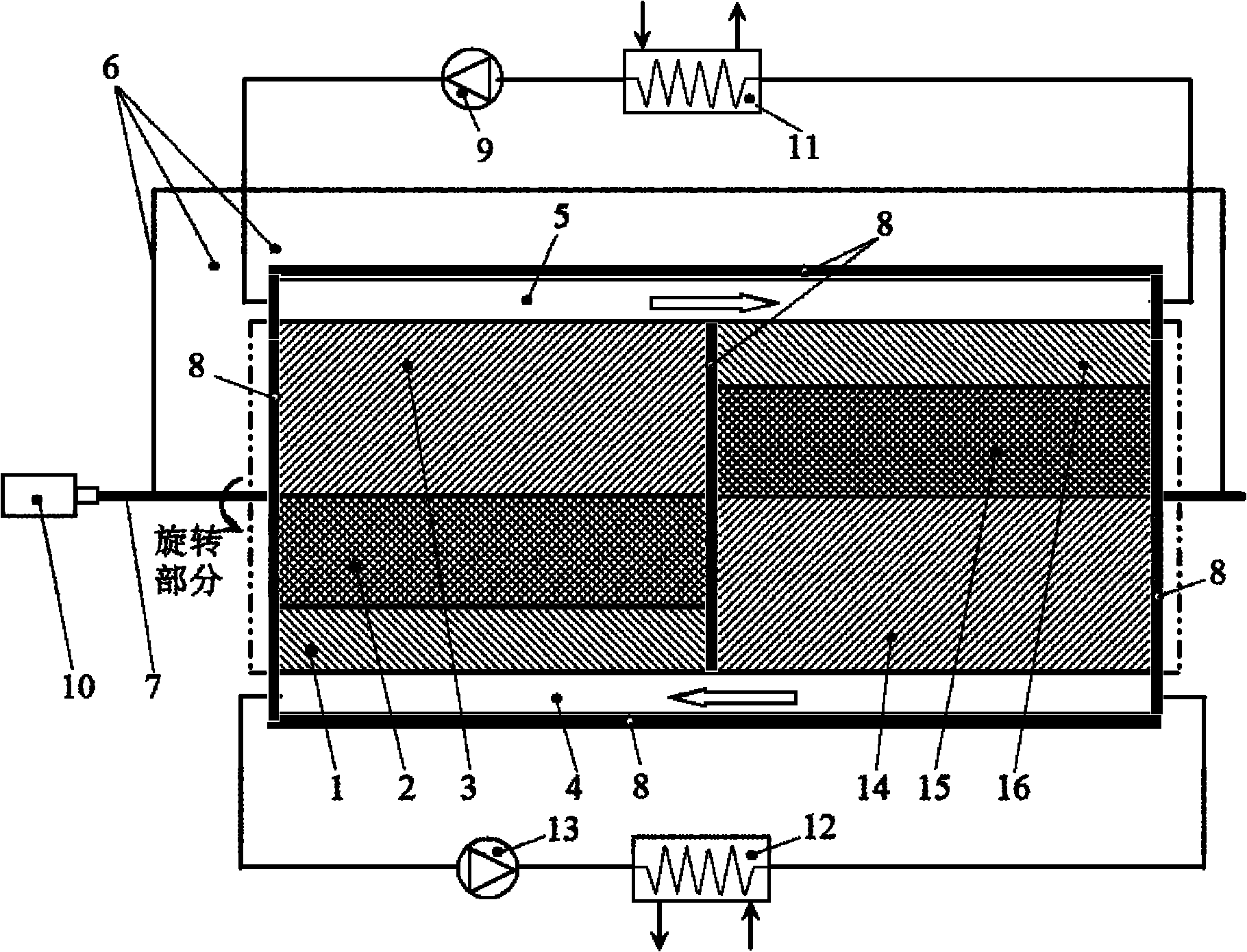
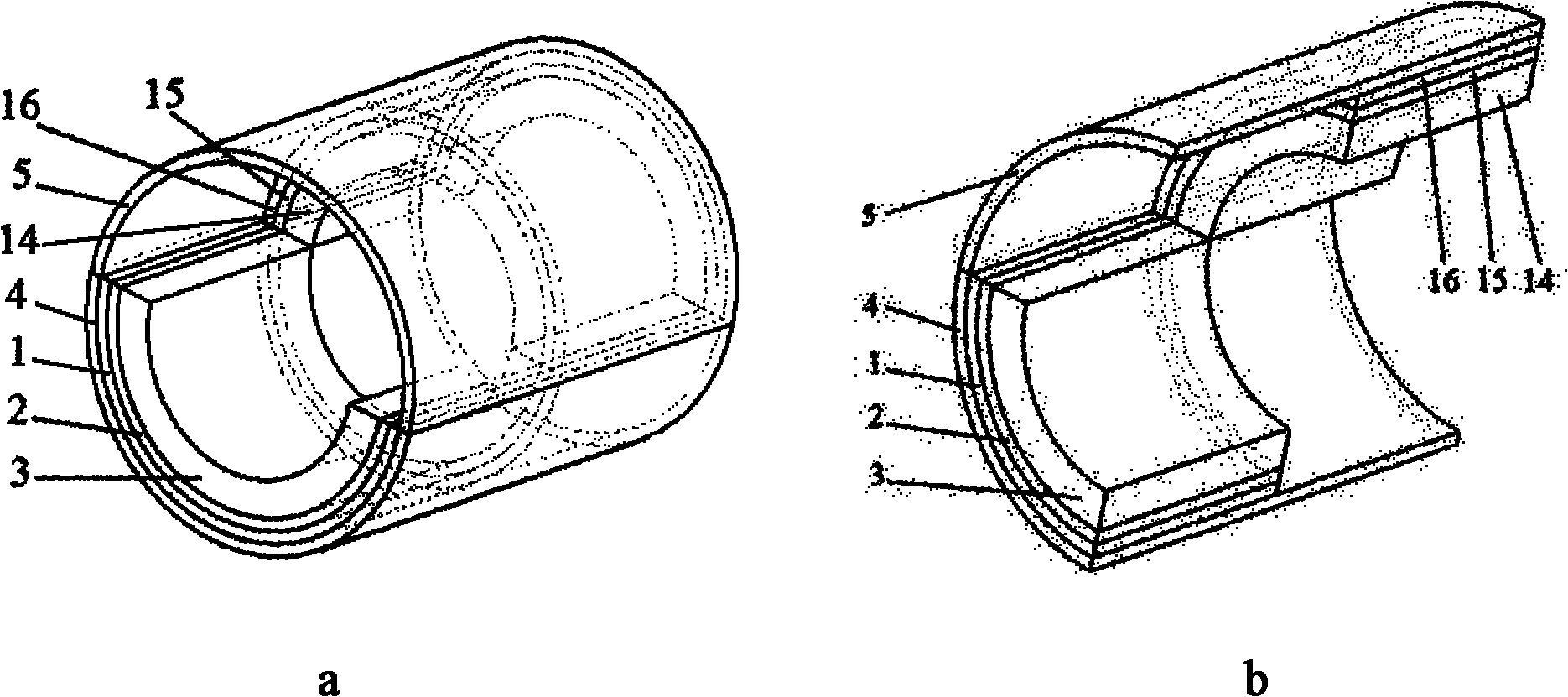
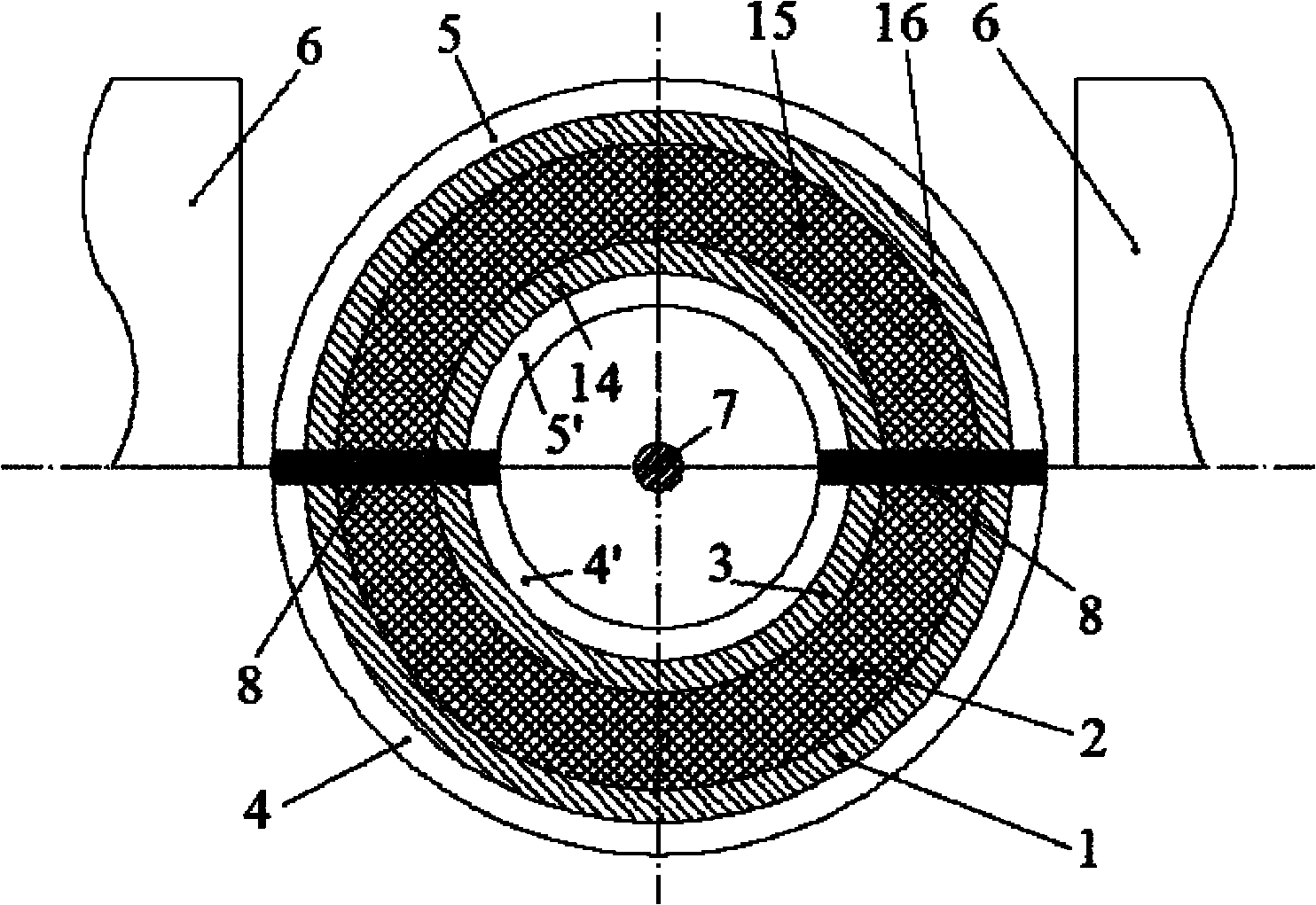
Rotary magnetic refrigeration device and application thereof
InactiveCN101979937AImprove cooling efficiencyImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsThermal insulationMagnetic media
The invention discloses a rotary magnetic refrigeration device. The rotary magnetic refrigeration device comprises a magnetic field source, two active regenerator modules and cold and hot fluid heat exchange channels, and is characterized in that: two packing layers sandwich a magnetic medium in a radial direction so as to form one active regenerator module; the two active regenerator modules are staggered coaxially and axially and arranged at an interval of 180 DEG in the circumferential direction, and pass through an upper half magnetic field region covered with the magnetic field source and a lower half nonmagnetic region alternately when rotating synchronously; A hot fluid channel which is communicated with a high temperature end heat exchanger is statically arranged in the pace of the magnetic field region at the rotating periphery of the active regenerator module; and the cold fluid channel which is communicated with a low temperature end heat exchanger is statically arranged in the space of the nonmagnetic region at the rotating periphery of the active regenerator module, and thermal insulation layers are arranged between the two active regenerator modules in the axial direction, and at the periphery and left and right end faces of the cold and hot fluid channels.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
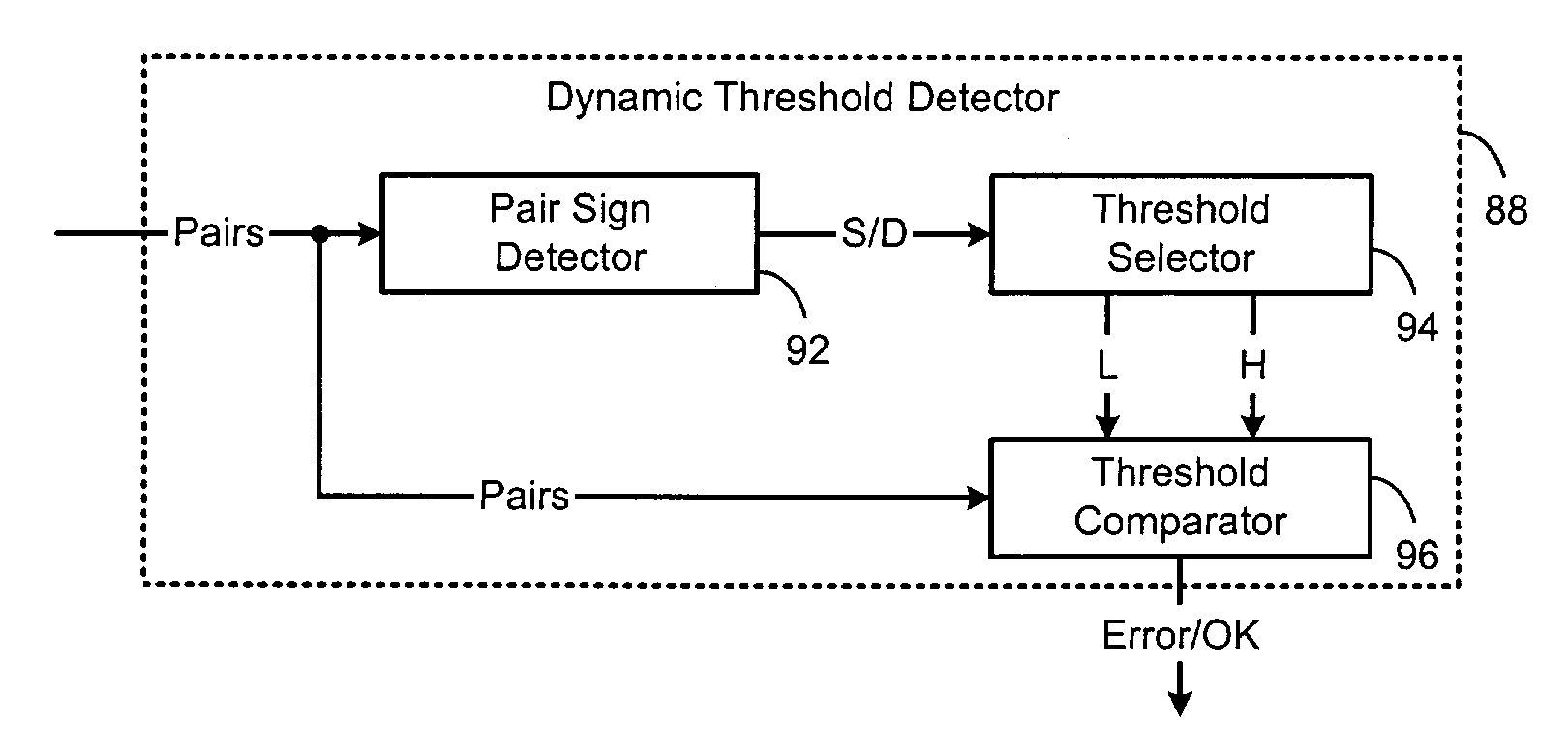
Method for checking the quality of servo gray codes
ActiveUS7113356B1Poor reception qualityModification of read/write signalsRecord information storageMagnetic mediaMagnetic storage
A dynamic threshold detector for a servo writer / detector in a magnetic storage system with a magnetic medium comprises a detector that receives data from the magnetic medium and that selects one of a first condition and a second condition based on at least one of an amplitude, a sign and bit transitions of the data. A threshold selector selects a first set of thresholds when the first condition is selected by the detector and a second set of thresholds when the second condition is selected by the detector. The data includes pairs of numbers with a first number and a a second number each having one of a positive sign and a negative sign and wherein the detector selects the first condition when the signs of the pairs are the same and the second condition when the signs of the pairs are different.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
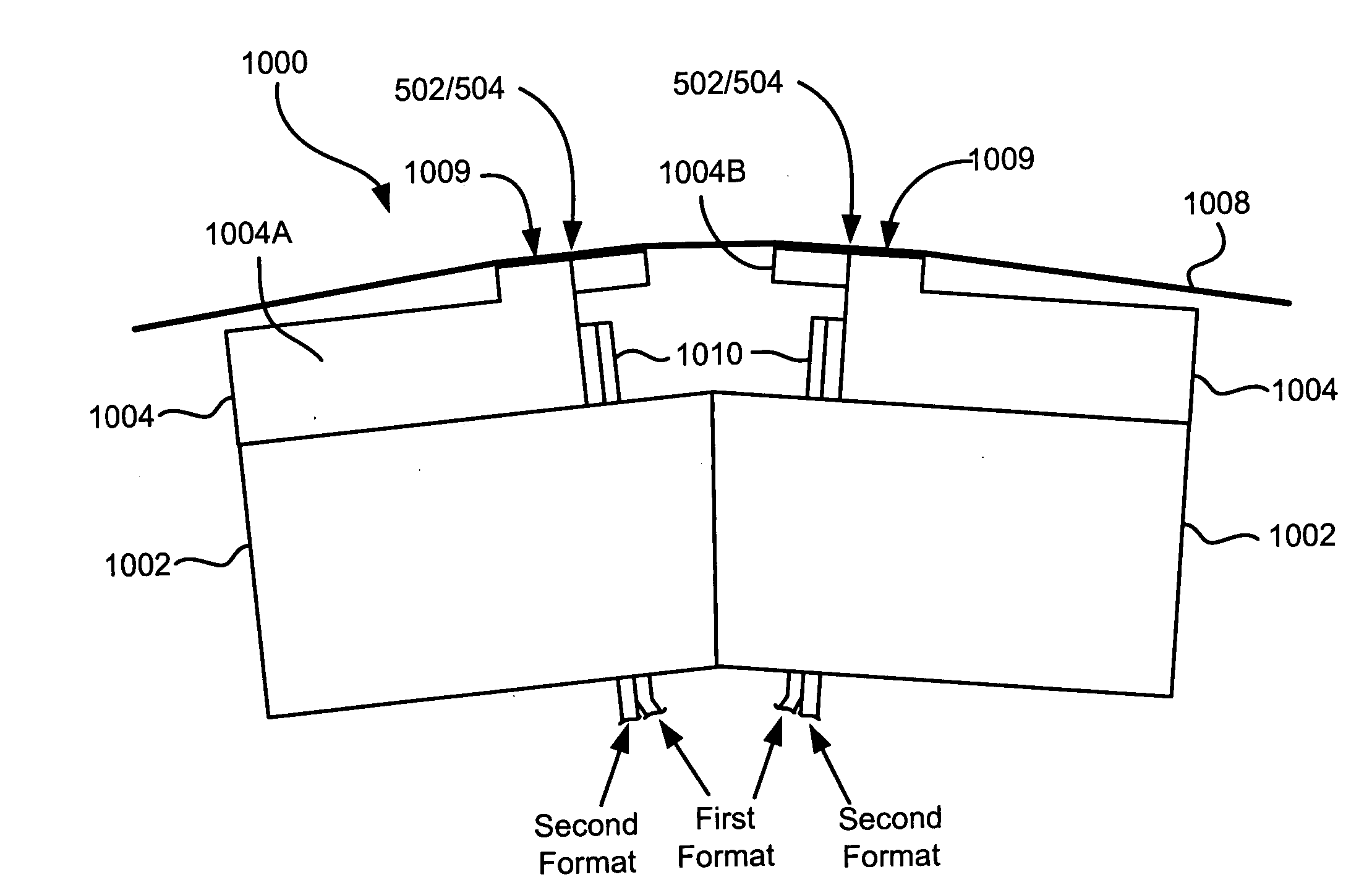
Multi-format magnetic head
A magnetic head includes a first array of elements associated with a first data format and a second array of elements associated with a second data format, the elements being selected from a group consisting of readers, writers, and combinations thereof. The first and second arrays of elements are adjacent each other in a direction transverse to a direction of travel of a magnetic medium over the head.
Owner:IBM CORP
High frequency assisted writing
InactiveUS7256955B2Easy to switchHigh frequency magnetic fieldRecord information storageDigital recordingMagnetic mediaElectrical current
Data is written to a magnetic media, by applying a magnetic write field to the magnetic media with a write pole, in conjunction with a high frequency magnetic field, to the magnetic media to assist writing to the magnetic media. The high frequency magnetic field is generated by applying a specific write current waveform to the magnetic writer, resulting in the generation of a high frequency magnetic write field.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method of fabricating a glass magnetic hard drive disk platter using filamentation by burst ultrafast laser pulses
ActiveUS20150118522A1Reduce manufacturing costExtreme precisionMagnetic materials for record carriersGlass furnace apparatusHard disc driveNon ablative
A non-ablative method and apparatus for making an economical glass hard disk (platter) for a computer hard disk drive (HDD) using a material machining technique involving filamentation by burst ultrafast laser pulses. Two related methods disclosed, differing only in whether the glass substrate the HDD platter is to be cut from has been coated with all the necessary material layers to function as a magnetic media in a computer's hard drive. Platter blanks are precisely cut using filamentation by burst ultrafast laser pulses such that the blank's edges need not be ground, the platter's geometric circularity need not be corrected and there is no need for further surface polishing. Thus the platters can be cut from raw glass or coated glass. As a result, this method reduces the product contamination, speeds up production, and realizes great reductions in the quantity of waste materials and lower production costs.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR TECH
Heating device and magnetic recording head for thermally-assisted recording
InactiveUS20050190496A1Extended stayEfficient heatingRecord information storageSpecial recording techniquesLeading edgeMagnetic media
A heating device for a magnetic recording head includes first and second separating layers, the first separating layer having preferably a higher or equal thermal resistance than the first separating layer, and a heater formed between the first and second separating layers. A magnetic recording head for recording on magnetic medium includes a heating device which generates a heat spot on the magnetic medium which is larger than a magnetic track width, and / or heats a portion of the magnetic recording head which is on a leading edge side of a write gap in the magnetic recording head.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Heating device and magnetic recording head for thermally-assisted recording
InactiveUS7262936B2High densityEfficient heatingRecord information storageSpecial recording techniquesLeading edgeMagnetic media
A heating device for a magnetic recording head includes first and second separating layers, the first separating layer having preferably a higher or equal thermal resistance than the first separating layer, and a heater formed between the first and second separating layers. A magnetic recording head for recording on magnetic medium includes a heating device which generates a heat spot on the magnetic medium which is larger than a magnetic track width, and / or heats a portion of the magnetic recording head which is on a leading edge side of a write gap in the magnetic recording head.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
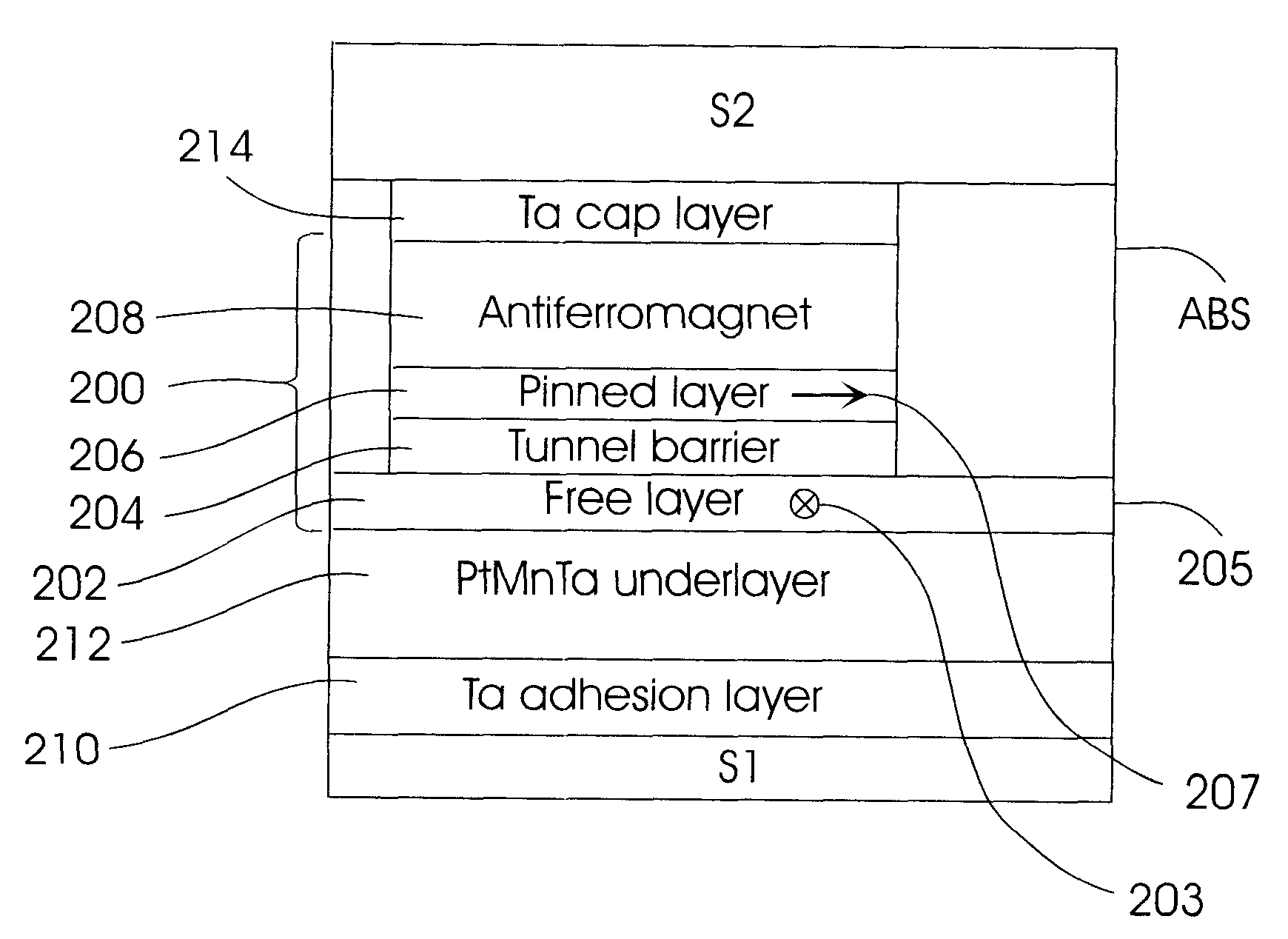
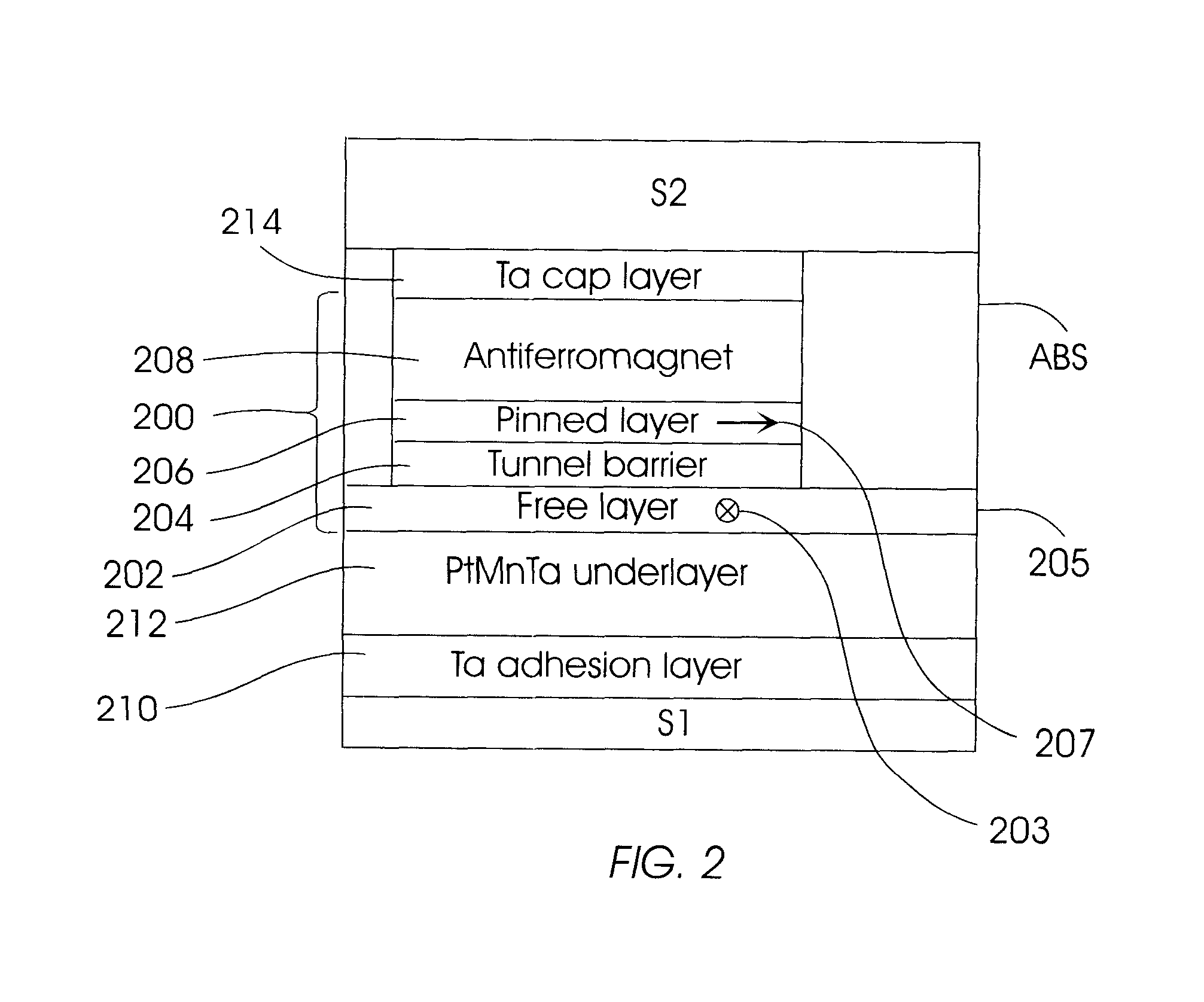
Magnetic tunnel junction device with bottom free layer and improved underlayer
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device usable as a magnetic memory cell or magnetoresistive sensor, such as a MTJ read head for magnetic recording, has the free ferromagnetic layer located on the bottom of the device, the bottom free layer being formed on a special underlayer. The MTJ read head may be a flux-guided head that uses the free layer as a flux guide for directing magnetic flux from the magnetic media to the sensing region of the MTJ. The special underlayer for the growth of the free layer is an alloy comprising Mn, one of Pt, Ni, Ir and Os, and an additive X selected from Ta, Al, Ti, Cu, Cr and V. Without the additive, the underlayer alloy is antiferromagnetic. The additive is present in an amount sufficient to render the alloy to have no magnetic ordering, i.e., it is neither antiferromagnetic nor ferromagnetic, but without substantially affecting the preferred crystalline texture and unit cell size so that the underlayer is well-suited as a growth-enhancing underlayer for the free layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
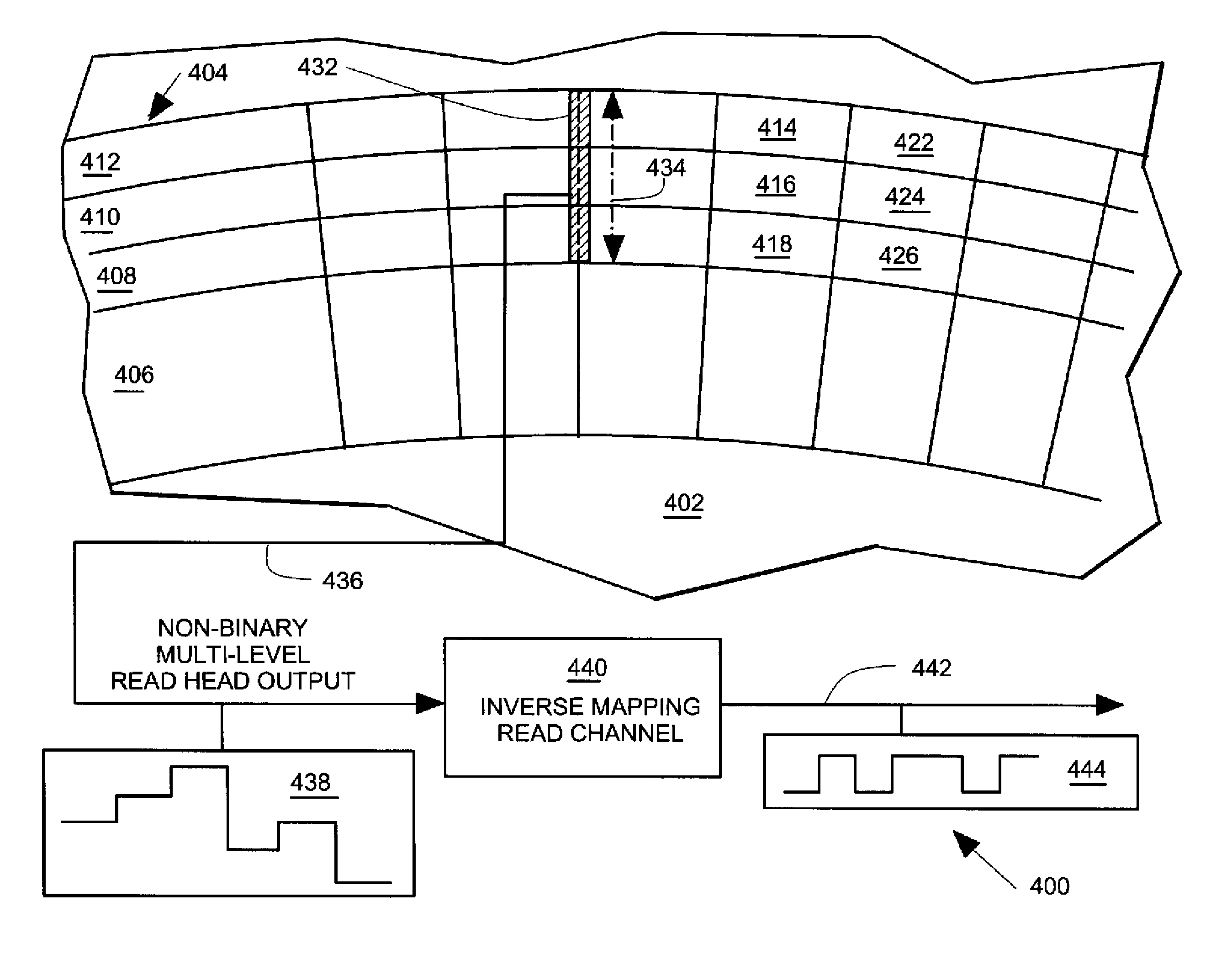
Multi-level recording on shingled coherent magnetic media
InactiveUS7982994B1Effective widthRecord information storageAnalogue recordingMagnetic mediaRecording media
A data storage system includes recording media with a shingled track pattern of multiple data tracks in which mapped data bits are recorded. The mapped data are coherently aligned with one another across the multiple data tracks. A read head has an effective read head width that extends across the multiple data tracks and that is aligned to coherently read the mapped data bits. A read head output includes a non-binary multi-level amplitude summation of the mapped data bits.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
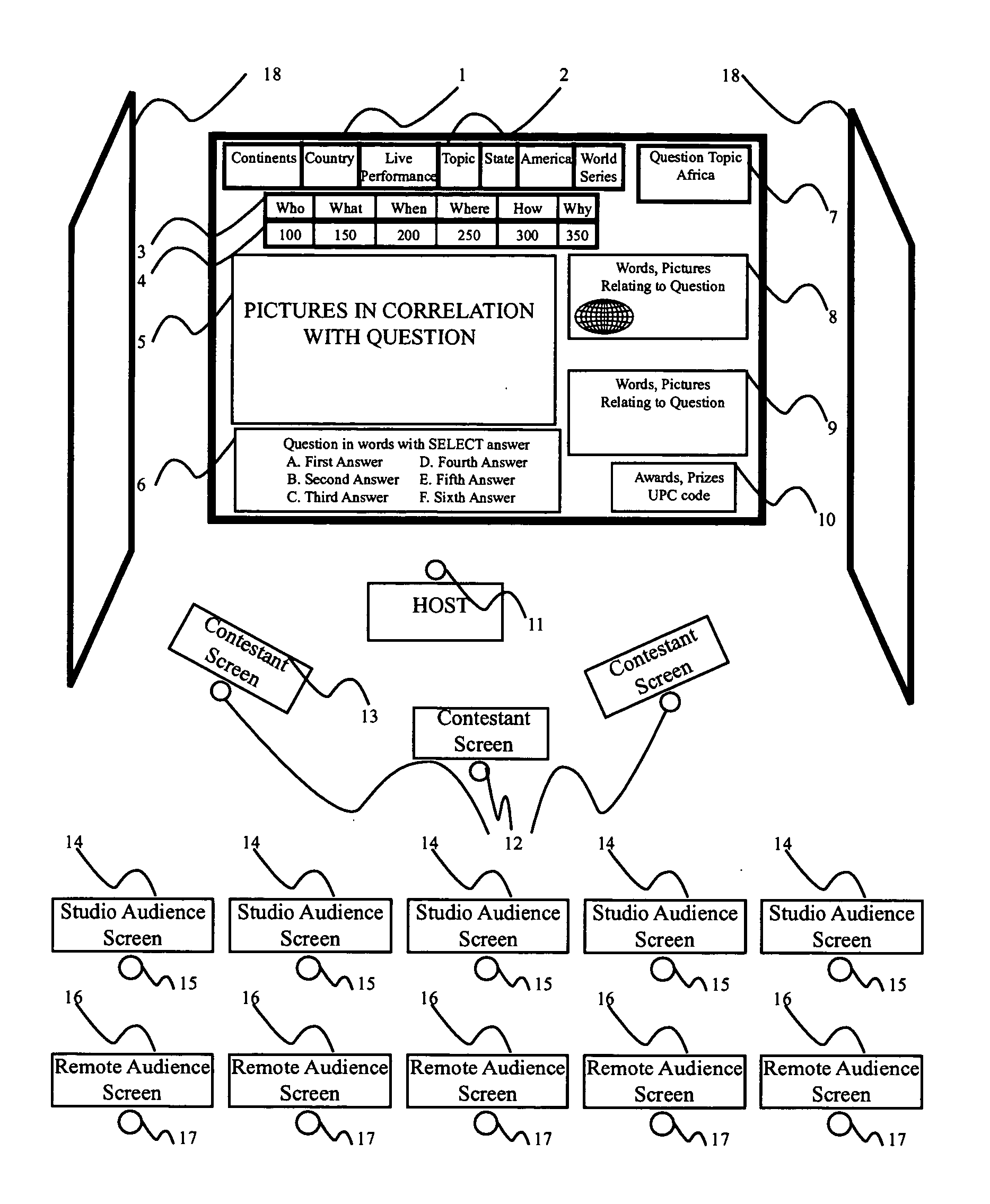
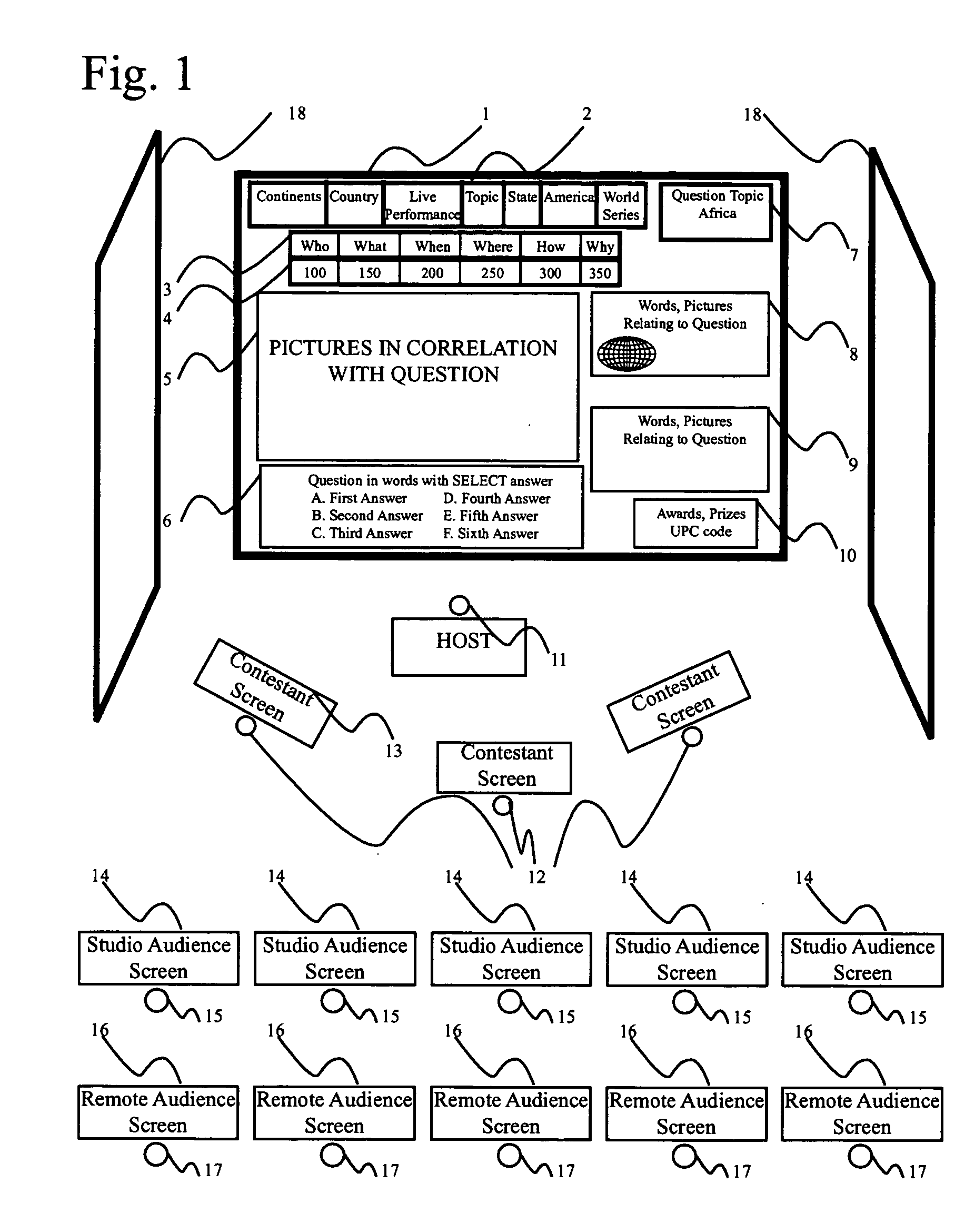
Geography game show
A multi-media geography game show allows real time participation of contestants, live show audience participants and remote TV viewers having Internet connections. Answers to questions related to geography provided within an allotted time period qualify participants for monetary or material rewards, together with learning credits. The learning credits may be converted to college credits by taking appropriate validation tests from accredited educational institutions that have made arrangements with the geography game show. The responses of contestants, live show audience participants and remote TV viewers, as well as the rewards and the leaning credits, are electronically processed and appropriate credits are issued using print outs or magnetic media.
Owner:MCHUGH GARNET
Dual spin-orbit torque oscillator in magnetic recording
ActiveUS10210888B1Reduce critical currentQuality improvementMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsHeads using thin filmsIn planeMagnetic media
The present disclosure generally relates to data storage devices, and more specifically, to a magnetic media drive employing a magnetic recording head. The head includes a main pole, a trailing shield, and an oscillator located between the main pole and the trailing shield. The oscillator is disposed at a media facing surface (MFS). The oscillator includes a spin-torque layer sandwiched between two distinct spin Hall layers. The two distinct spin Hall layers generate spin-orbit torque (SOT) that induces in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer, and both in-plane precessions are in the same direction. The same-direction in-plane precessions on opposite surfaces of the spin-torque layer reduce the critical current of the oscillation of the oscillator, leading to high quality recording.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
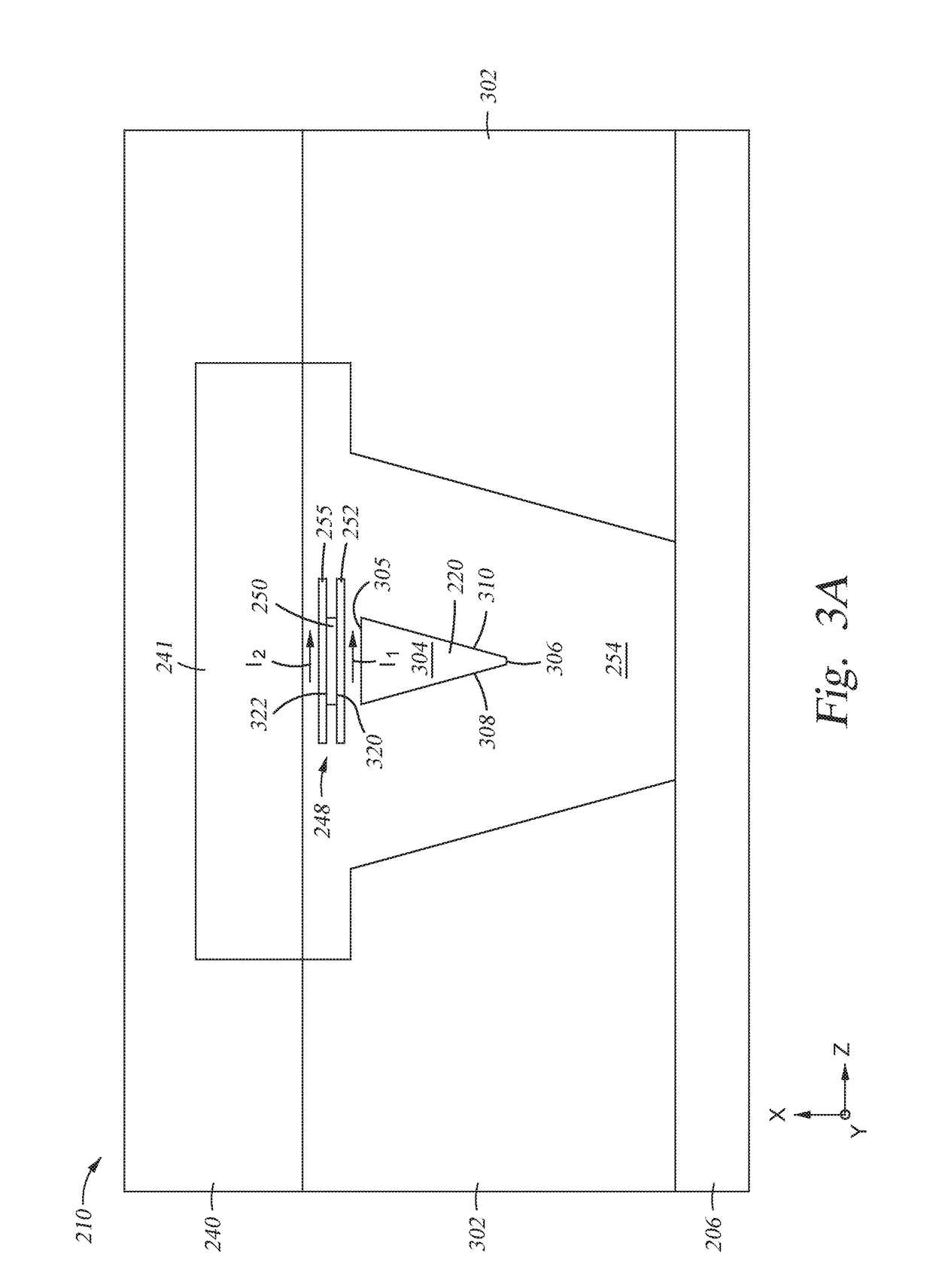
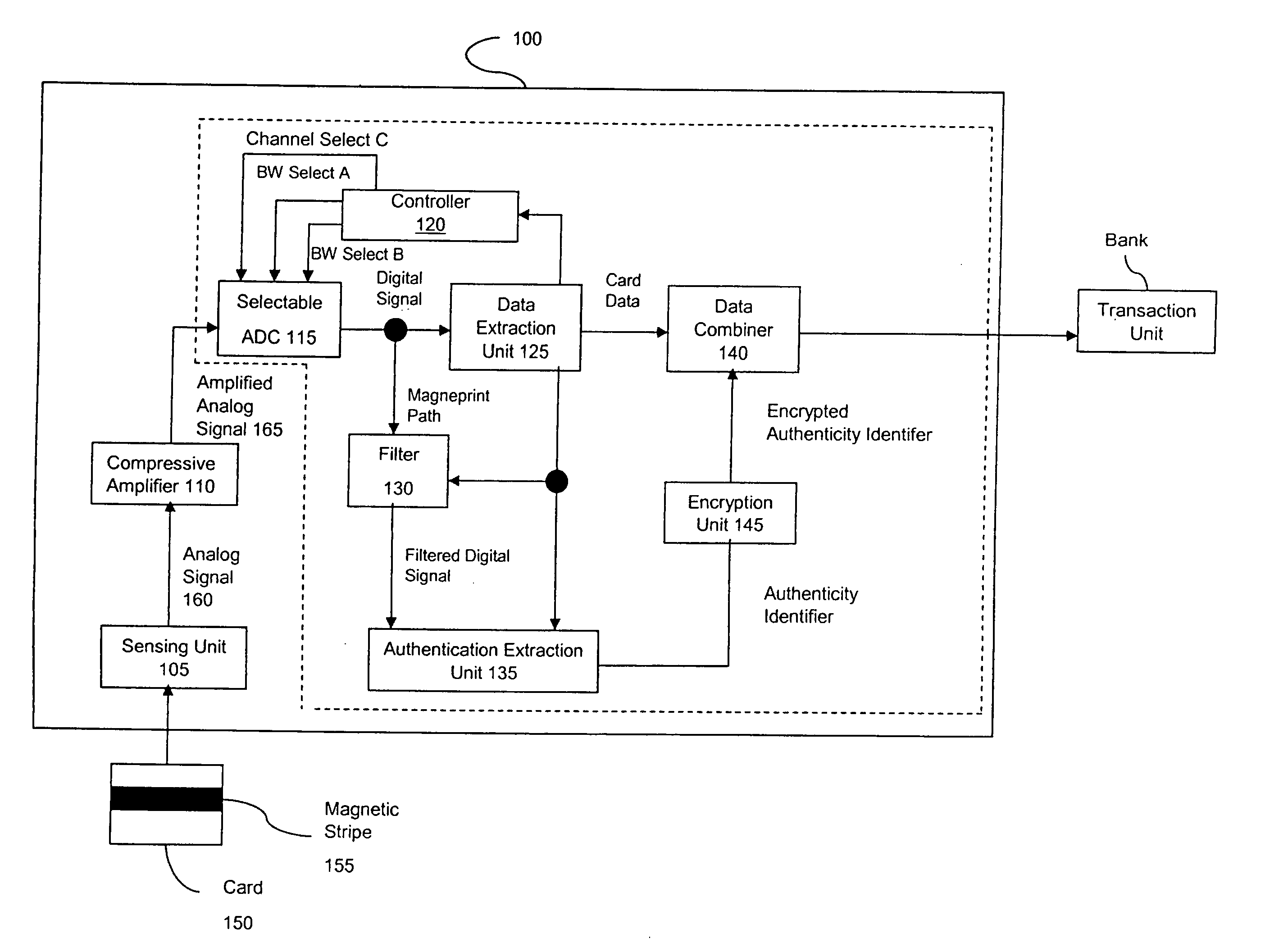
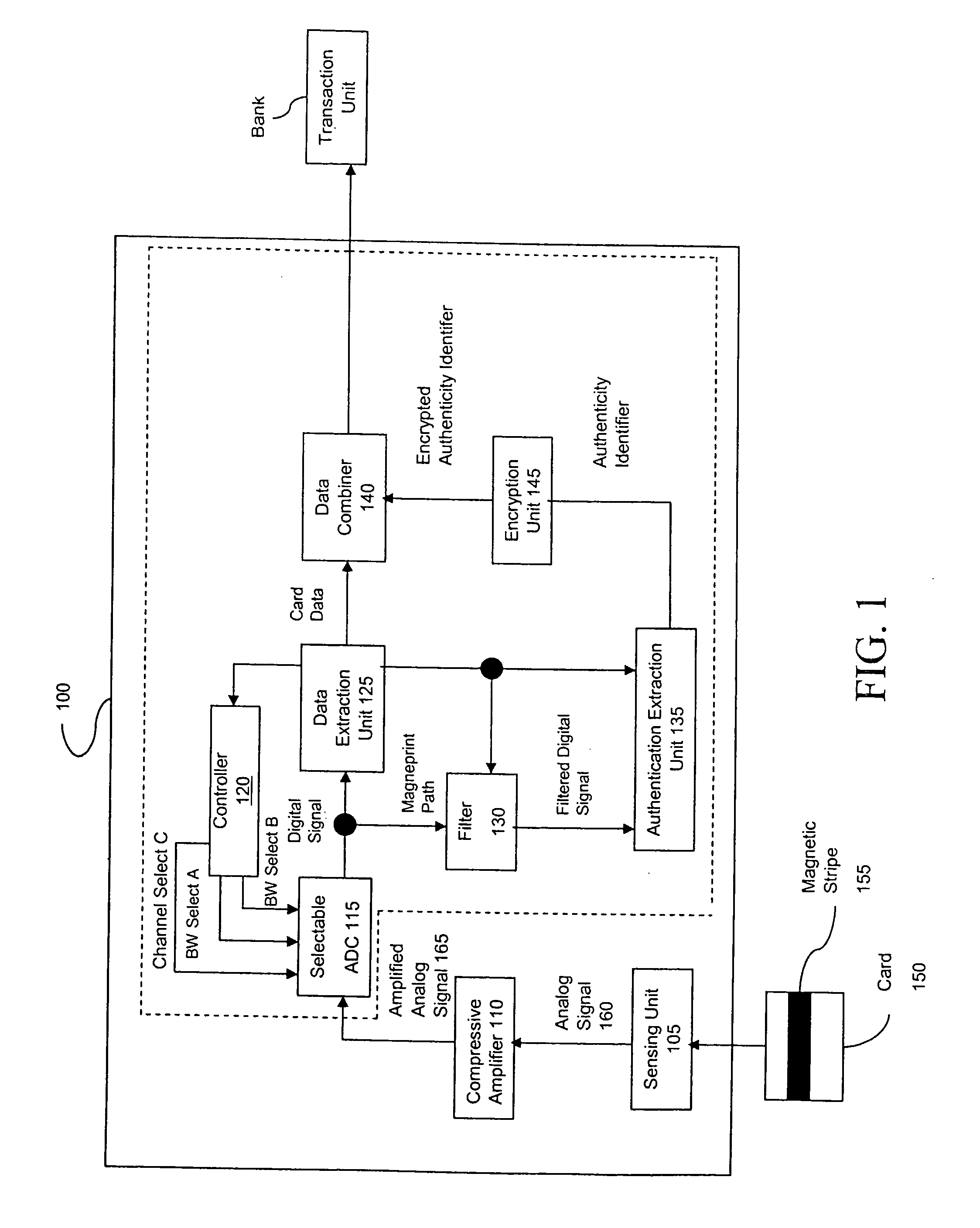
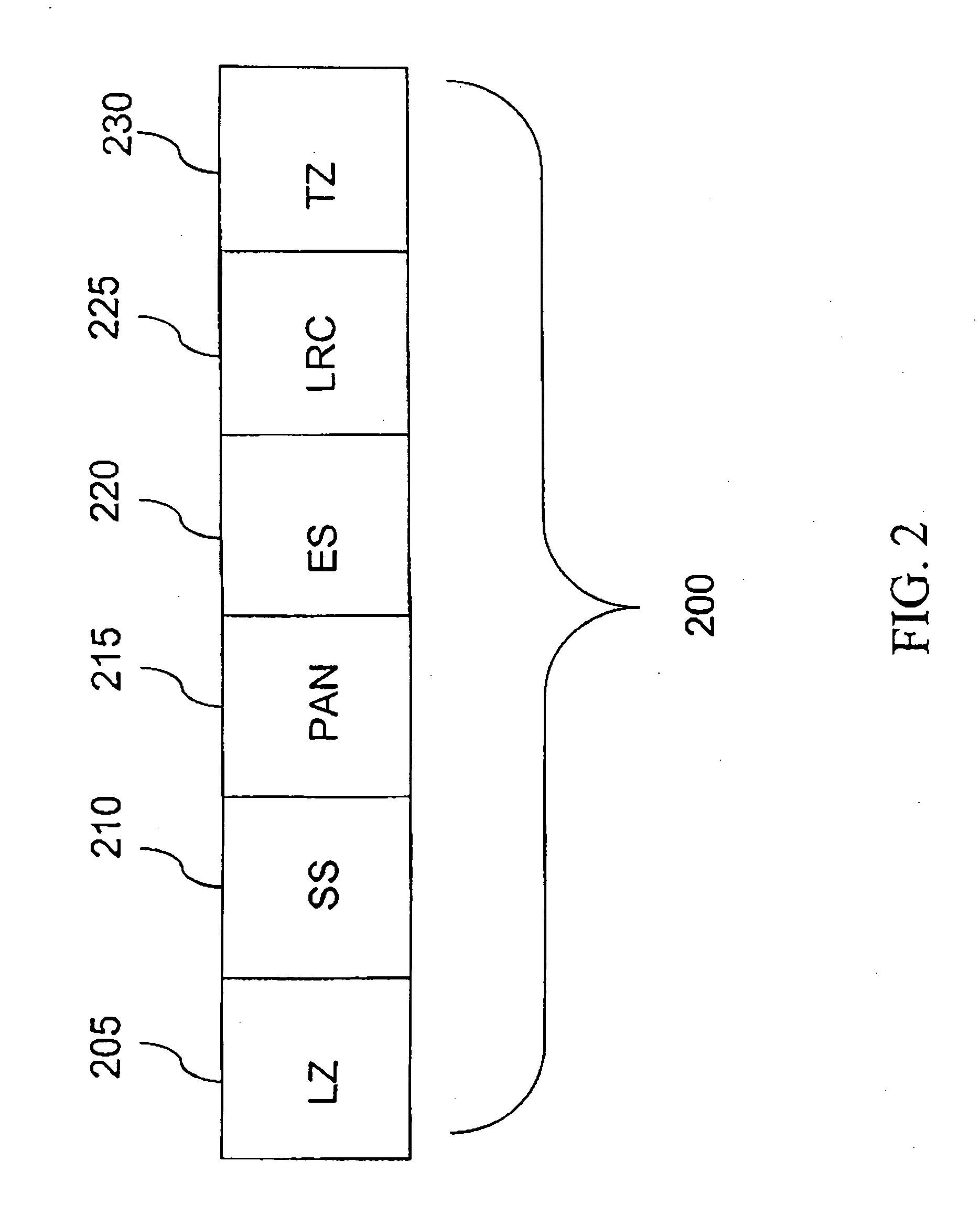
Method and apparatus for authenticating a magnetic fingerprint signal using compressive amplification
InactiveUS20050218229A1Effective and reliable in operationPaper-money testing devicesPayment architectureMagnetic mediaEngineering
A system for verifying the authenticity of data contained in a magnetic medium using the remanent noise characteristics of the magnetic medium. In one embodiment, the invention includes a sensing unit configured to generate a signal indicative of the sensed magnetic field and an amplifier. The amplifier is in communication with the sensing unit, is configured to amplify signals having amplitudes less than a threshold by at least a first factor and configured to amplify signals having amplitudes greater than the threshold by at most a second factor. The first factor is greater than the second factor. The invention also includes an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) in communication with the amplifier and configured to digitize the analog signal, a filter in communication with the ADC configured to attenuate the portion of the digitized signal indicative of the stored data, a data extraction unit in communication with the ADC and the filter, which is configured to measure bit duration and peak location and an authentication extraction unit in communication with the filter and the data extraction unit, which is configured to extract a set of scaled samples representative of the remanent noise characteristic.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
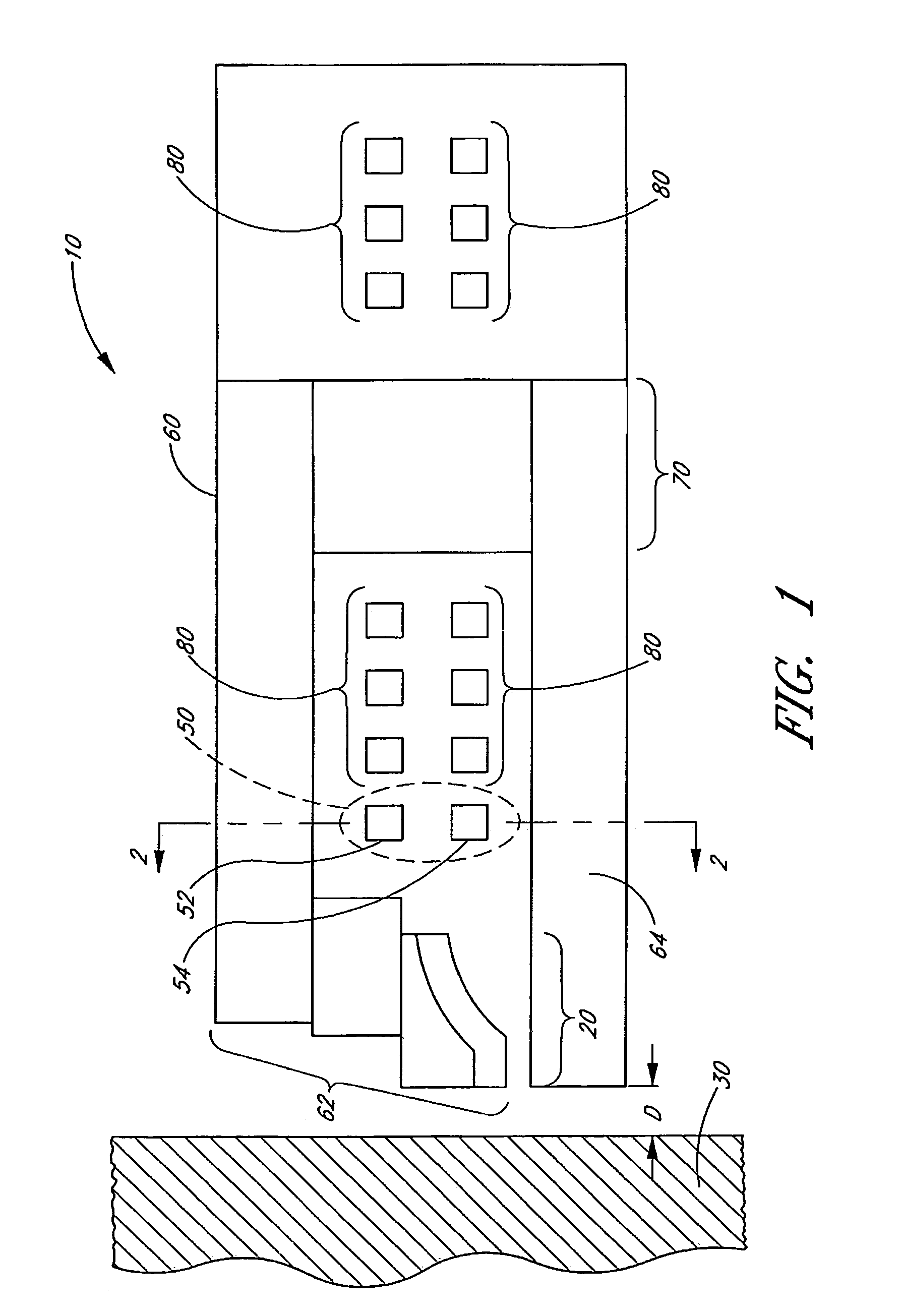
Low friction tape head and system implementing same
InactiveUS20120008234A1Manufacture head surfaceManufacturing heads with multiple gapsMagnetic mediaMechanical engineering
A magnetic data storage system according to one embodiment includes a magnetic head; and guides on opposite sides of the magnetic head for directing a magnetic medium over the magnetic head. The magnetic head includes: outer portions each having a tape bearing surface and an array of transducers selected from a group consisting of readers and writers; and a central portion positioned between the outer portions, the central portion having a tape bearing surface and an array of transducers selected from a group consisting of readers and writers. An inner edge of each of the tape bearing surfaces of the outer portions is adapted for skiving air from the magnetic medium when the magnetic medium travels in a direction from the central portion towards the respective outer portion. The guides are oriented to direct the magnetic medium to fly over a leading one of the outer portions, engage a leading edge of the tape bearing surface of the central portion, and engage an inner edge of the tape bearing surface of a trailing one of the outer portions.
Owner:IBM CORP
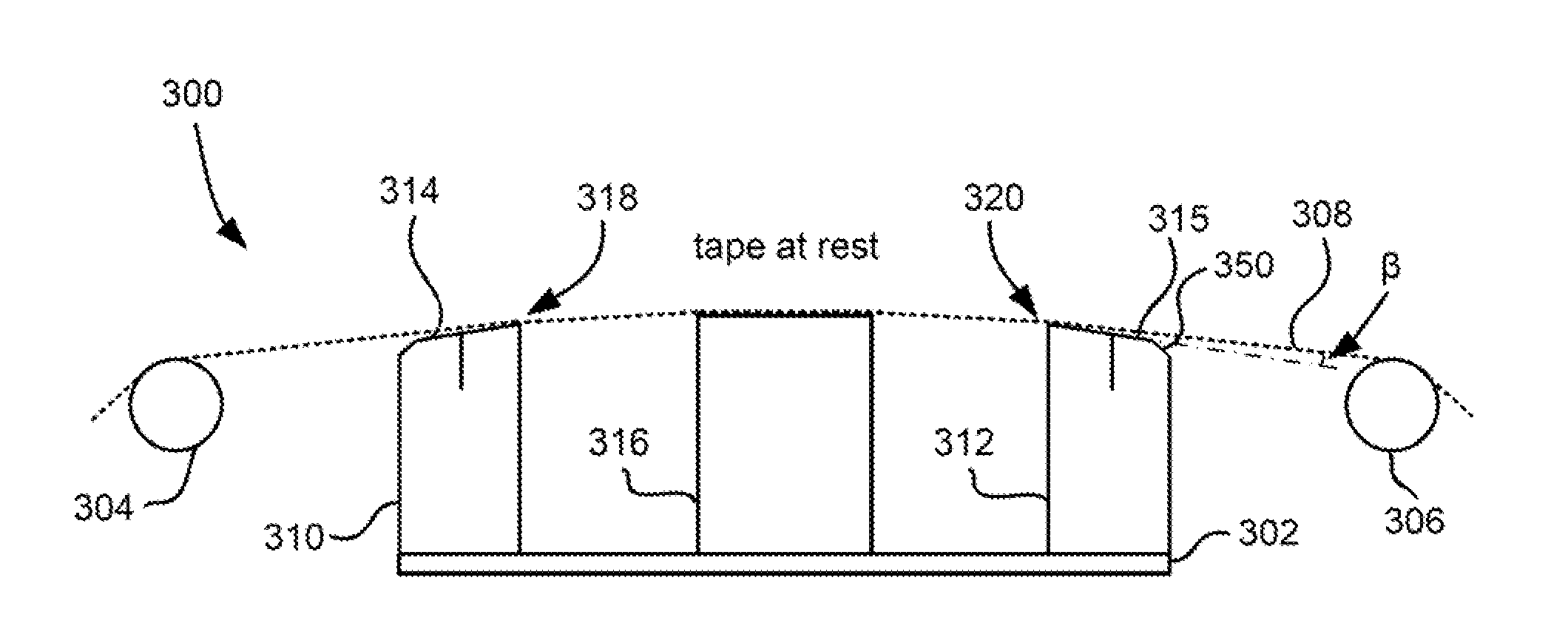
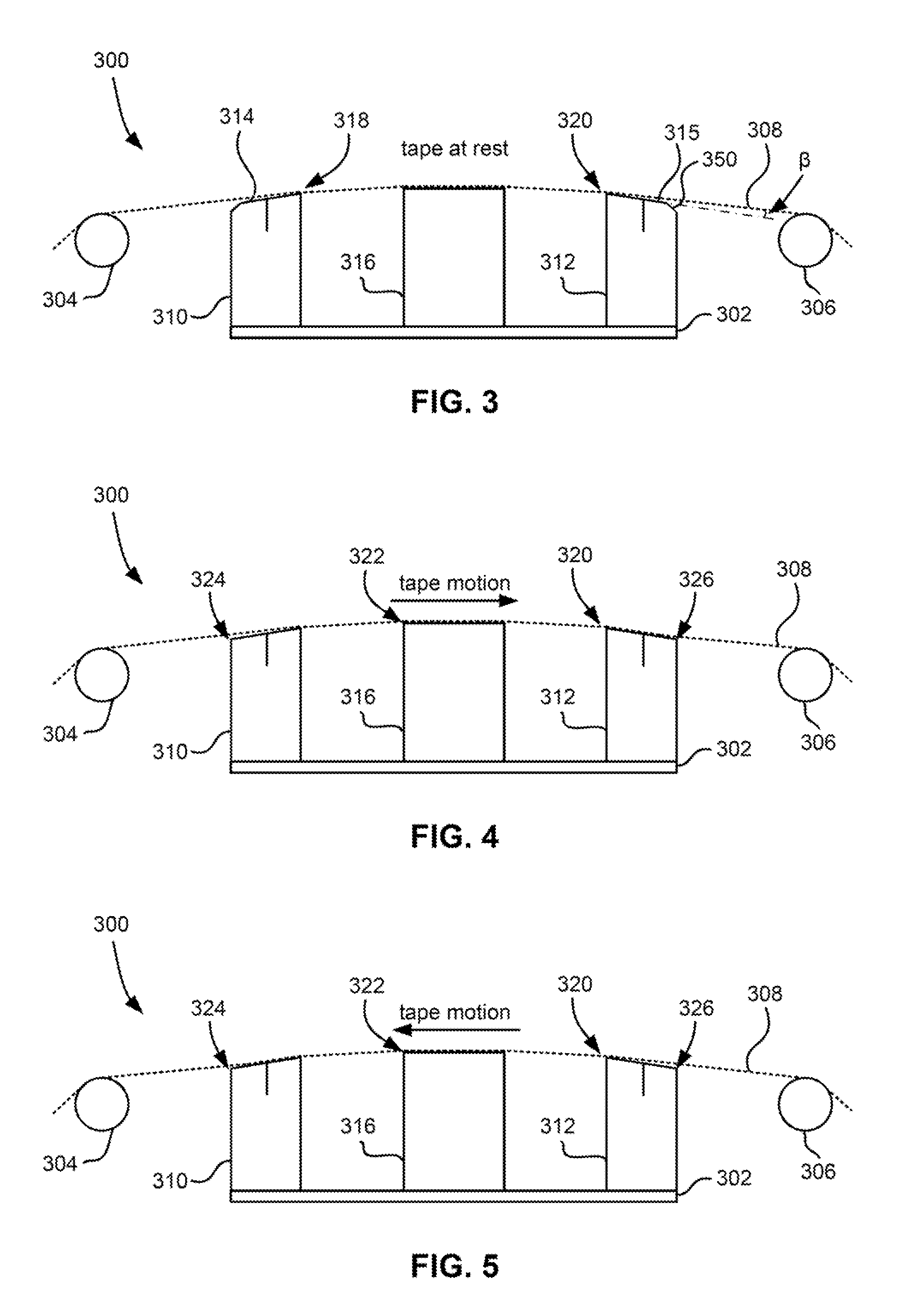
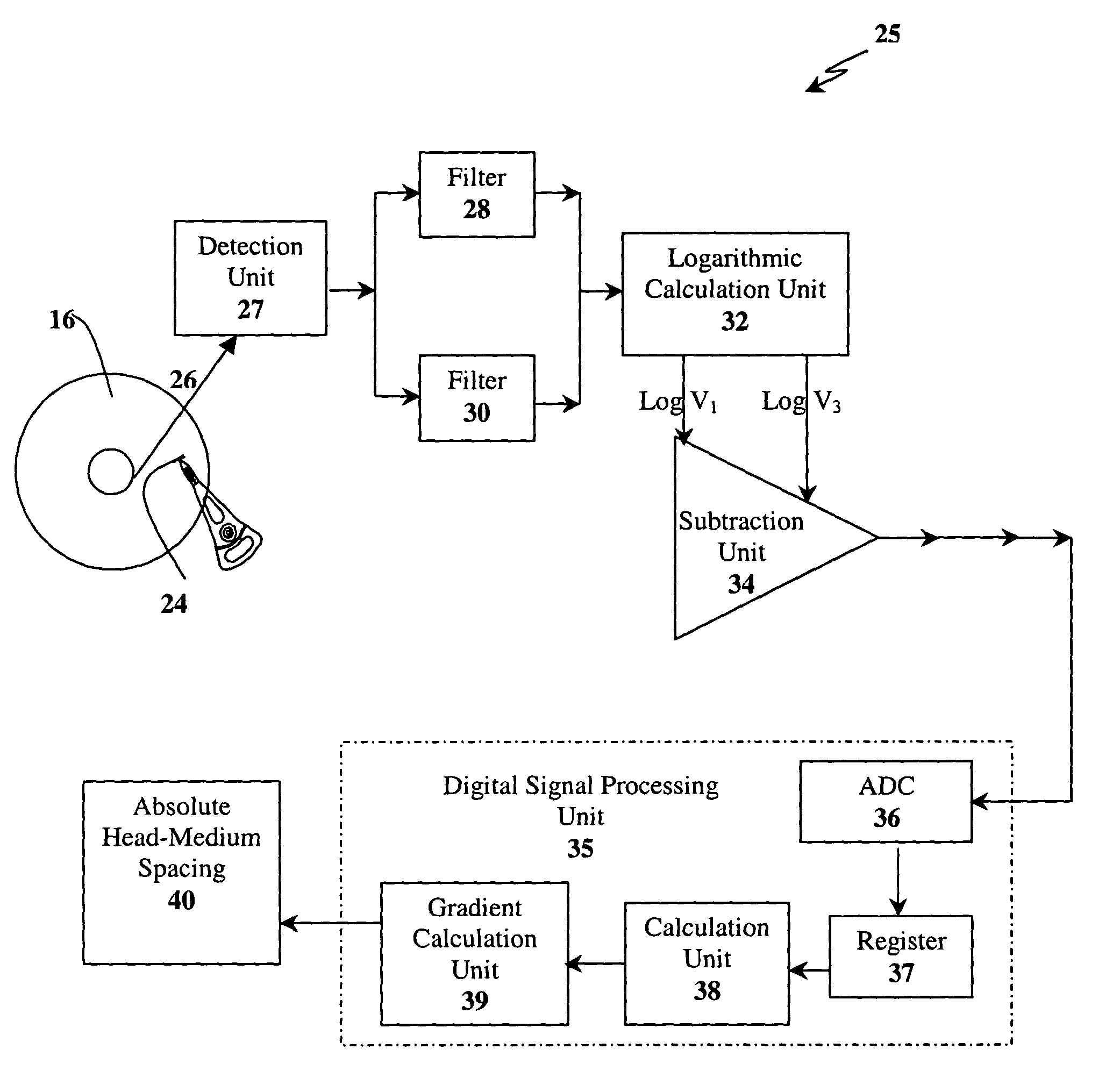
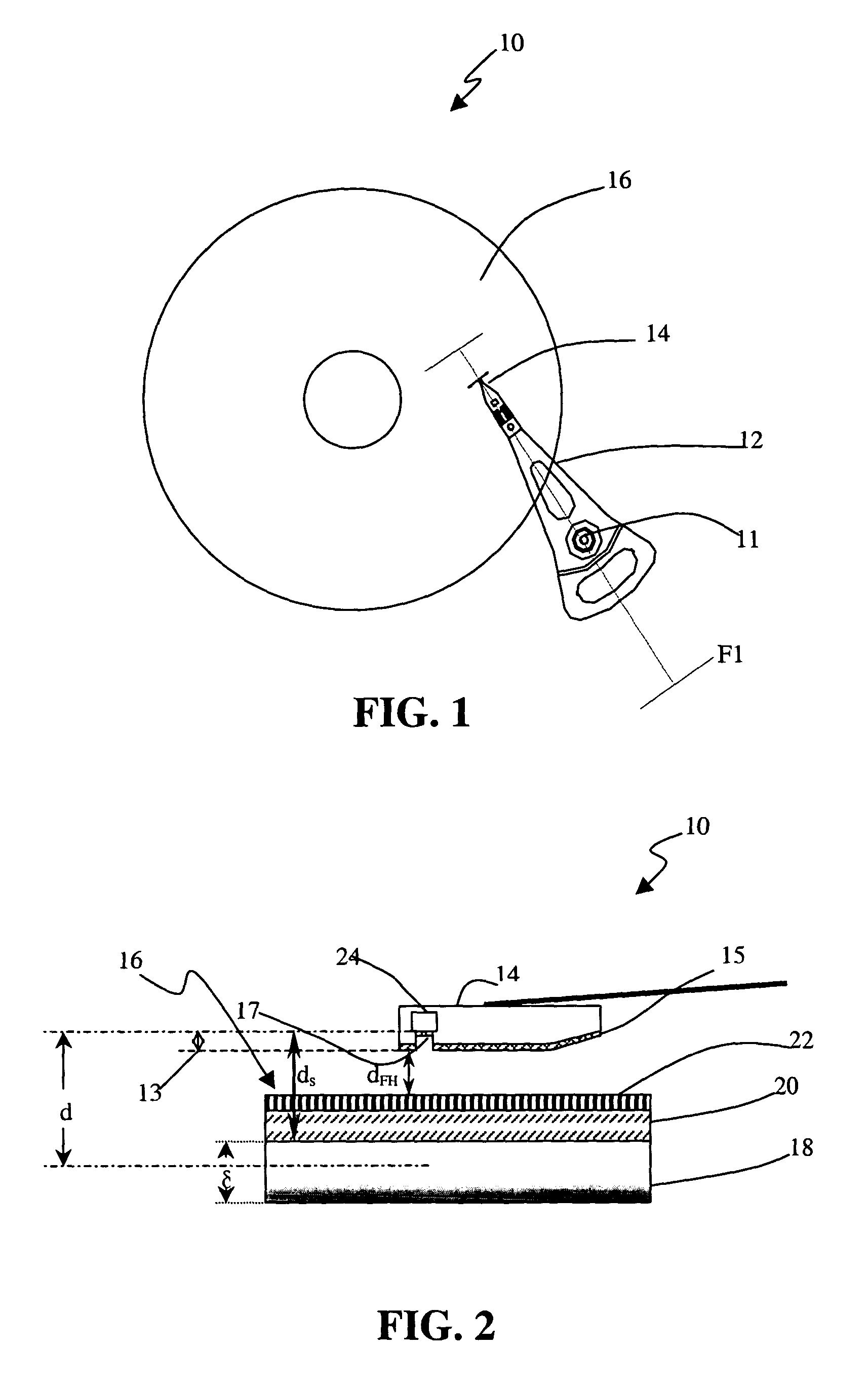
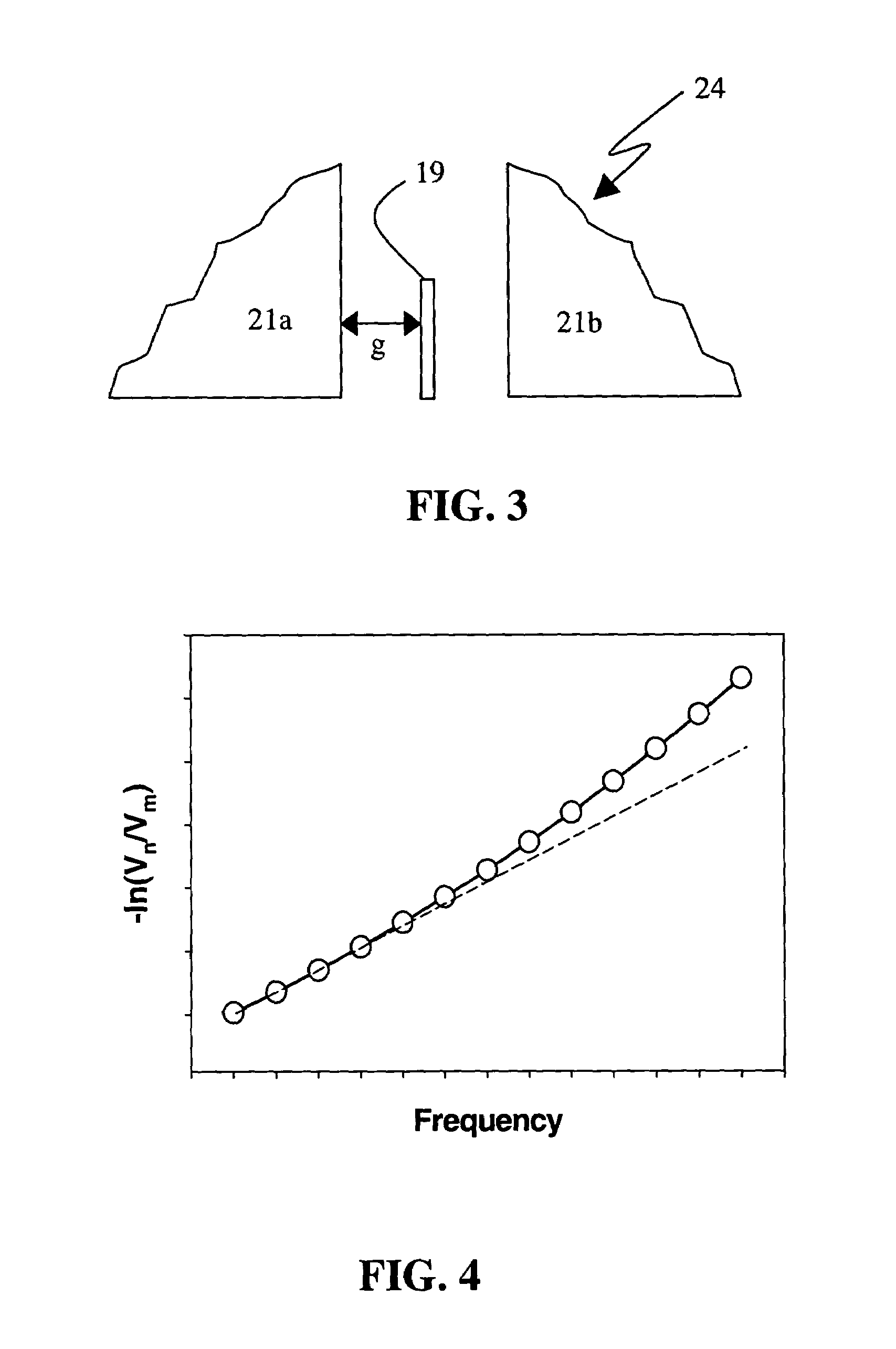
Method and implementation of in-situ absolute head medium spacing measurement
InactiveUS7016131B2Error minimizationError of of lengthDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storagePrecodingHarmonic
In a method based on readback signal for in-situ measuring of absolute head-medium spacing, a pre-encoded pattern in the magnetic medium on a disk has at least two harmonics with amplitudes such that a linear function of the logarithmic ratio of the spacing loss-term is formed in relation to testing frequencies. This linear function is applied to determine the absolute head-medium spacing directly through the multiplication of gradient of the linear function and the linear velocity between the head and the medium of the disk drive.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
‘Thermal spring’ magnetic recording media for writing using magnetic and thermal gradients
InactiveUS6881497B2Avoid thermal instabilityRapid coolingSoldering apparatusRecord information storageMagnetic gradientMagnetic media
A thermal spring magnetic medium is provided having first and second stacks providing two exchange coupled ferromagnetic layers having different Curie temperatures. The first stack has a high magneto-crystalline anisotropy, a relatively low saturation magnetization and a low Curie temperature. The second stack has a relatively low magneto-crystalline anisotropy, a high saturation magnetization and a high Curie temperature. Preferably the first stack includes an alloy of Fe—Pt or Co—Pt, and the second stack includes an allow of Co—Pt or Co—Pd. A disk drive system having the novel medium is also provided.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Dead on demand disk technology
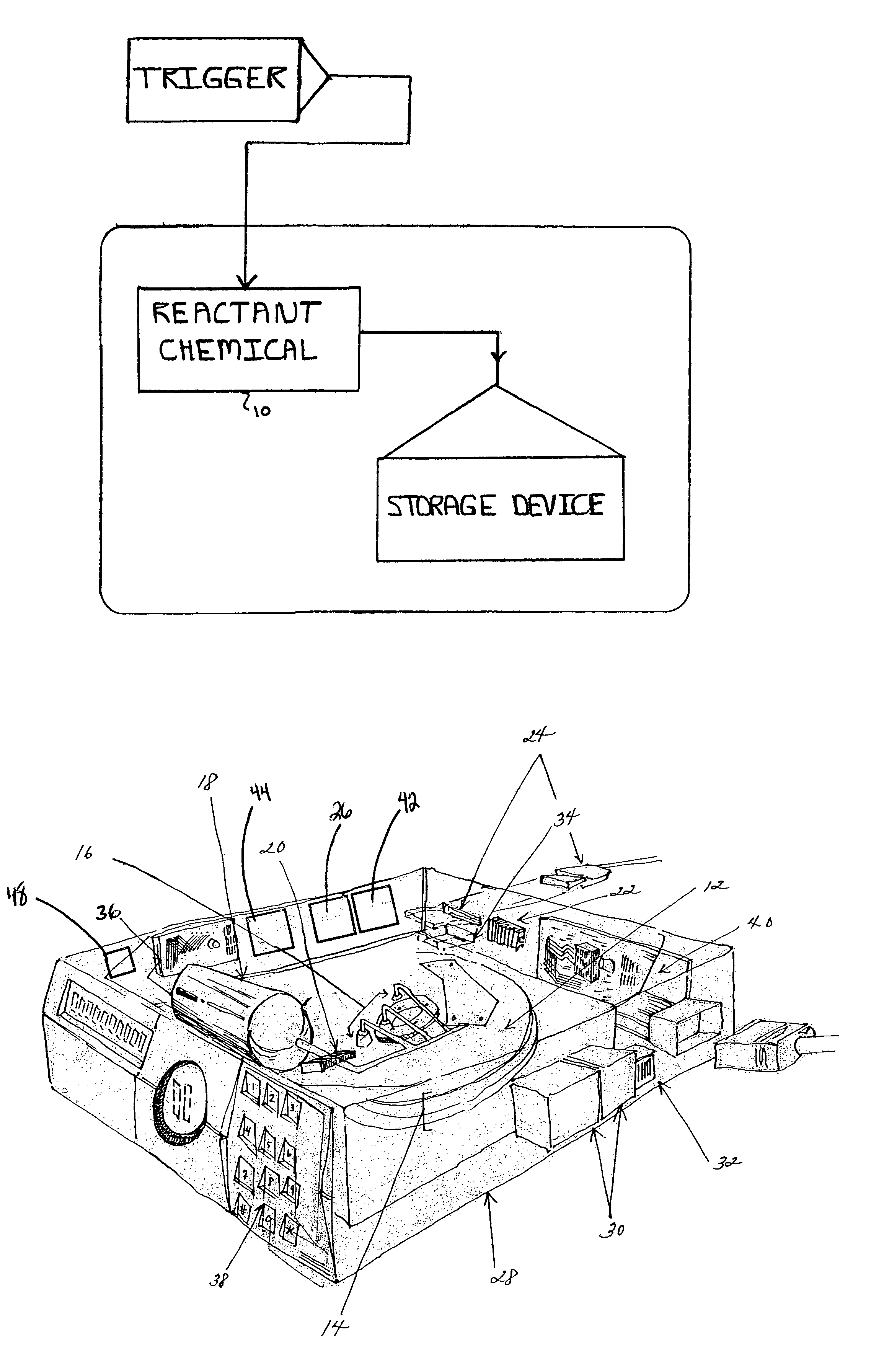
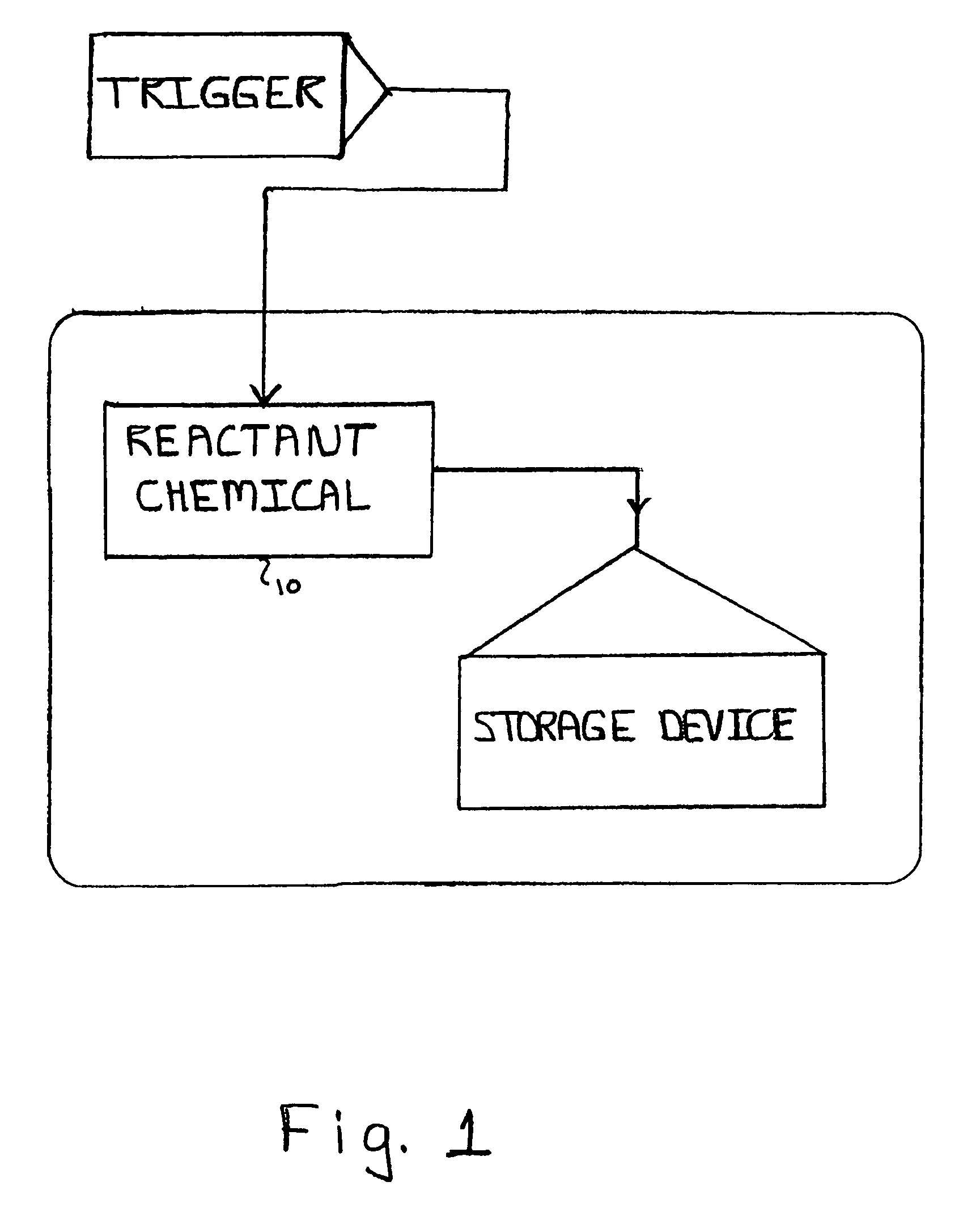
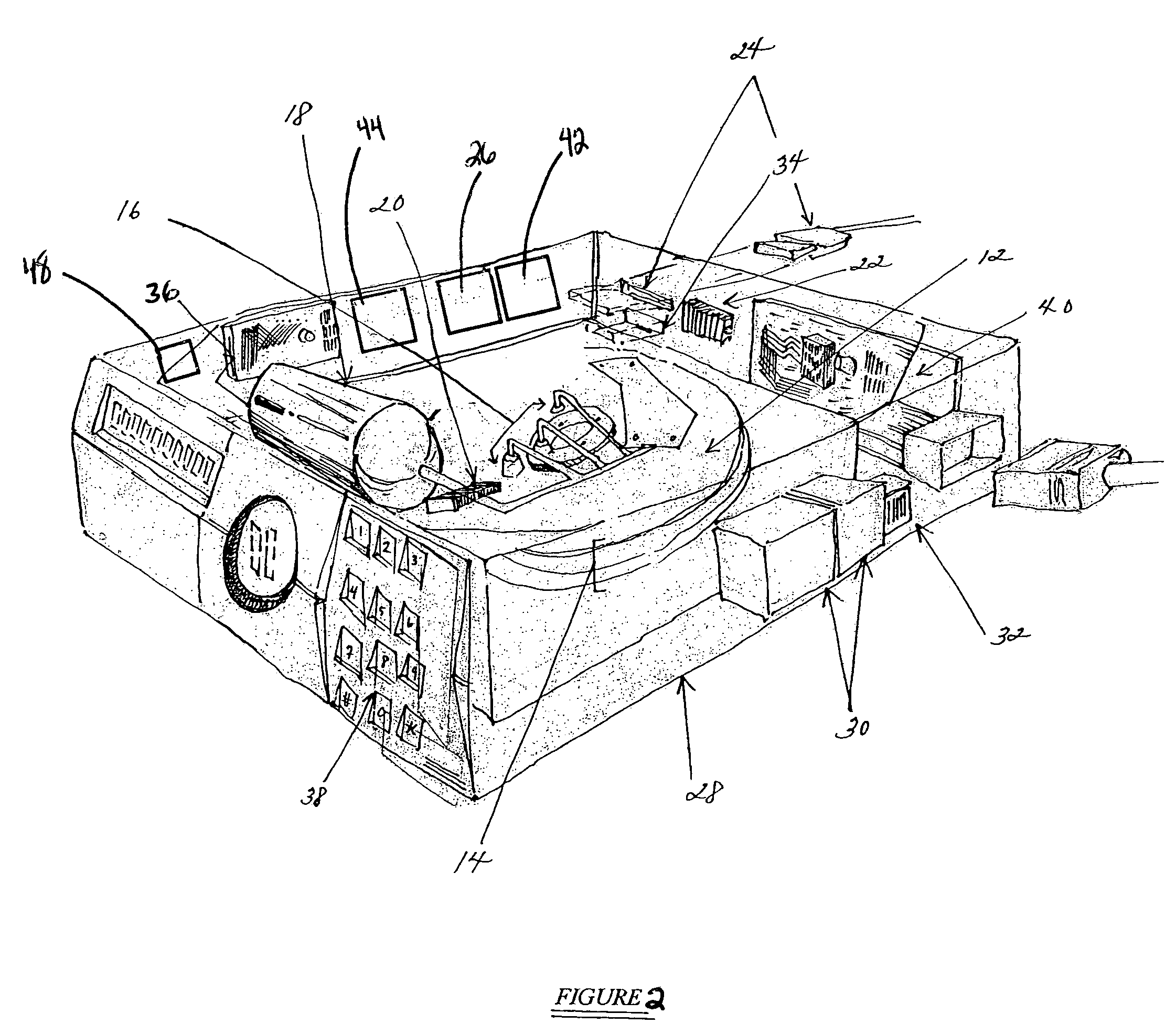
InactiveUS7099110B2Avoid retrievingApparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionMagnetic mediaData storing
The present invention relates to a system and method for permanently and generally instantaneously destroying at least the data contained on magnetic data storage media upon the occurrence of certain events. Unauthorized access to data stored on magnetic media is prevented by destruction of the media with a reactant chemical. This approach may be initiated as a response to tampering or intentionally by using any one of several triggering interfaces described herein. Destruction of the media is quick and permanent, rendering the data unrecoverable even to aggressive recovery procedures.
Owner:ENSCONCE DATA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com