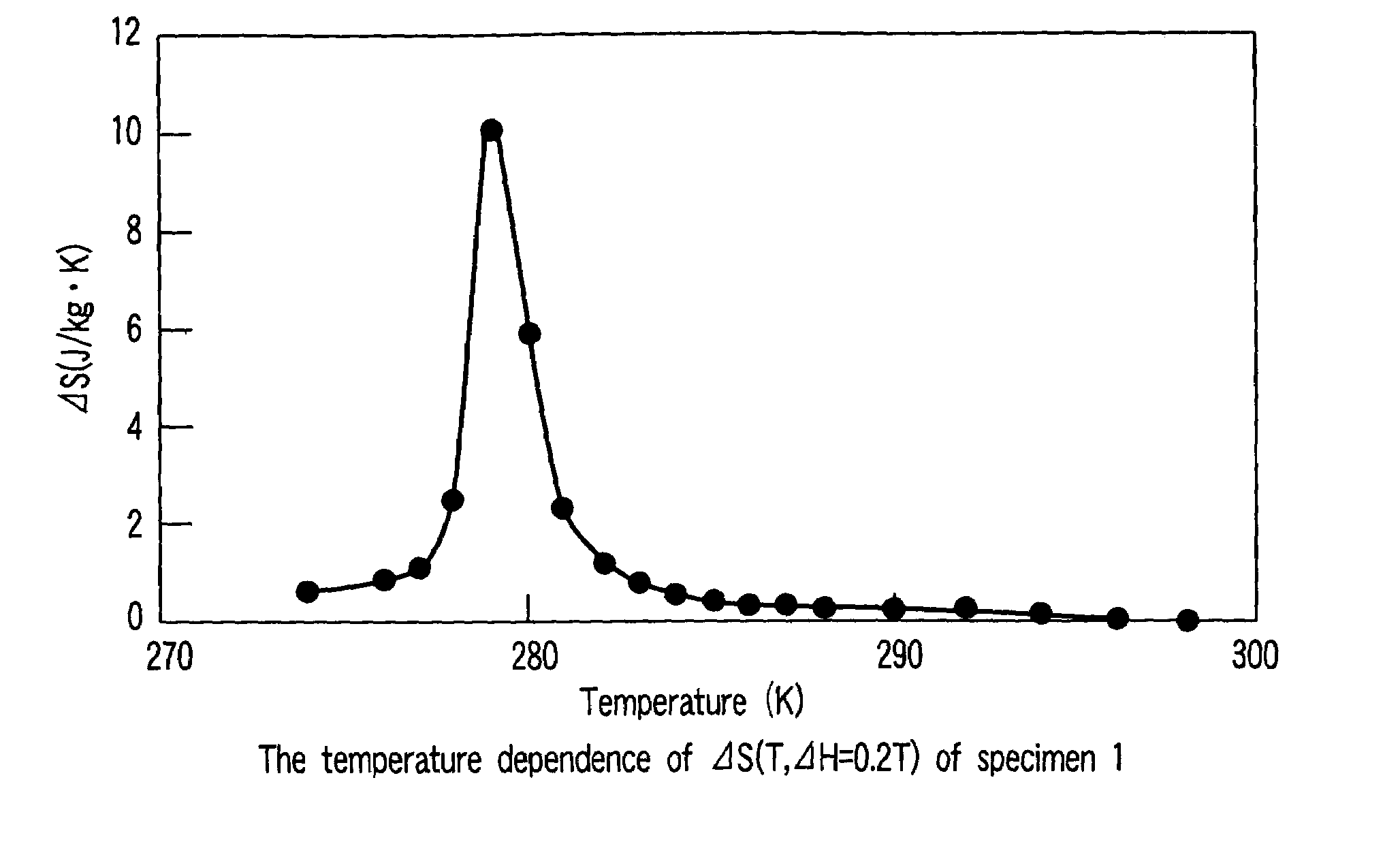
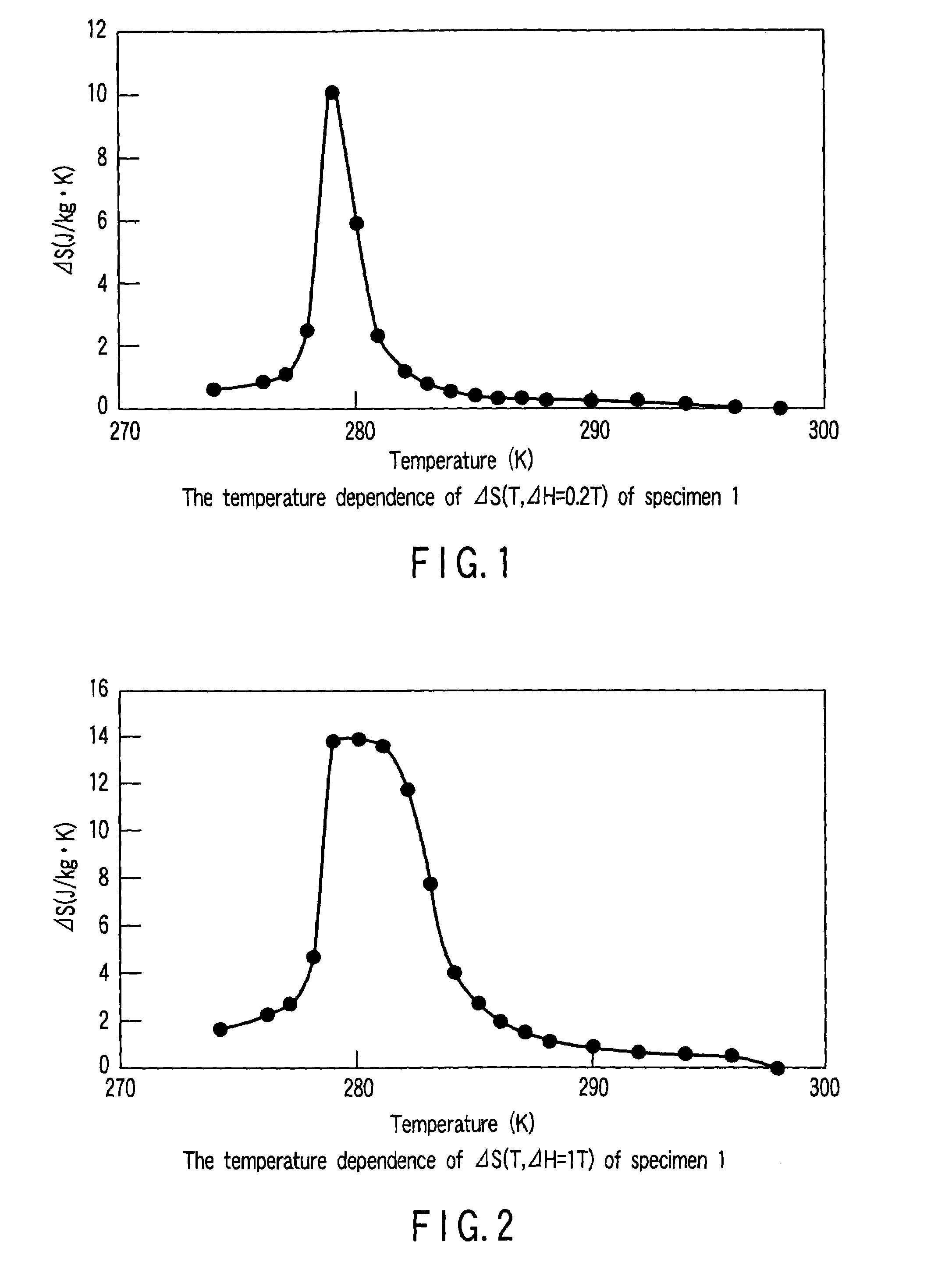
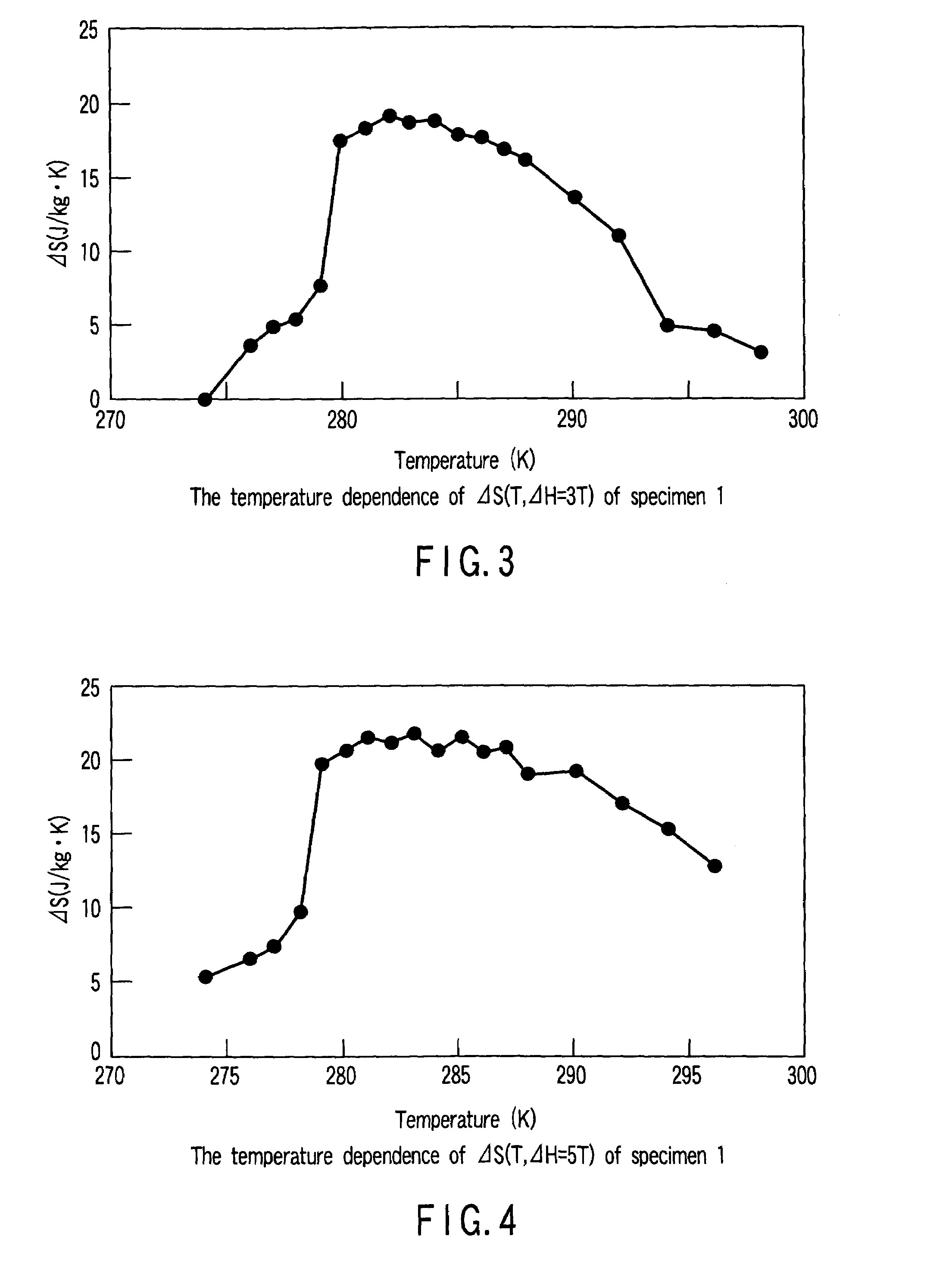
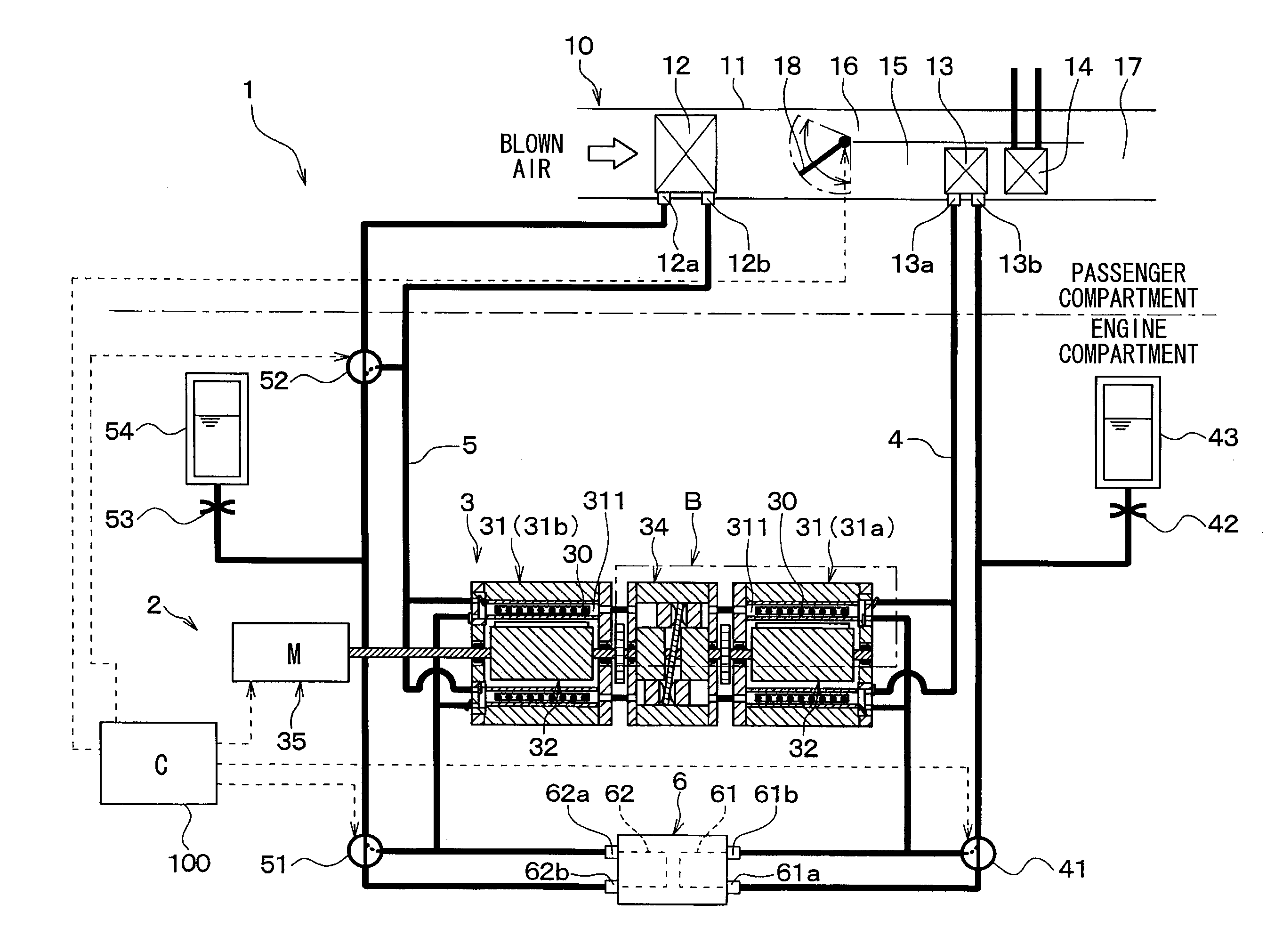
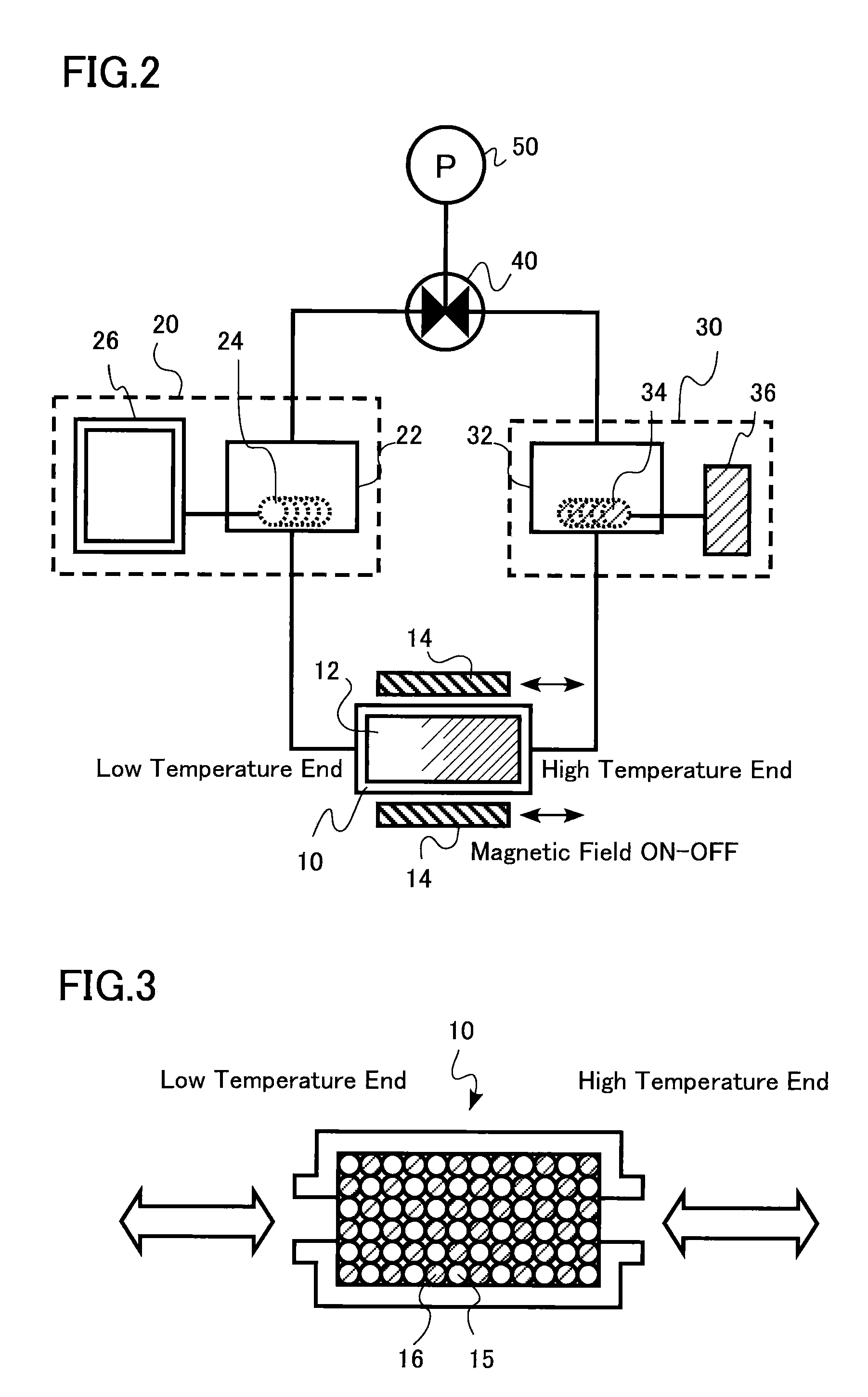
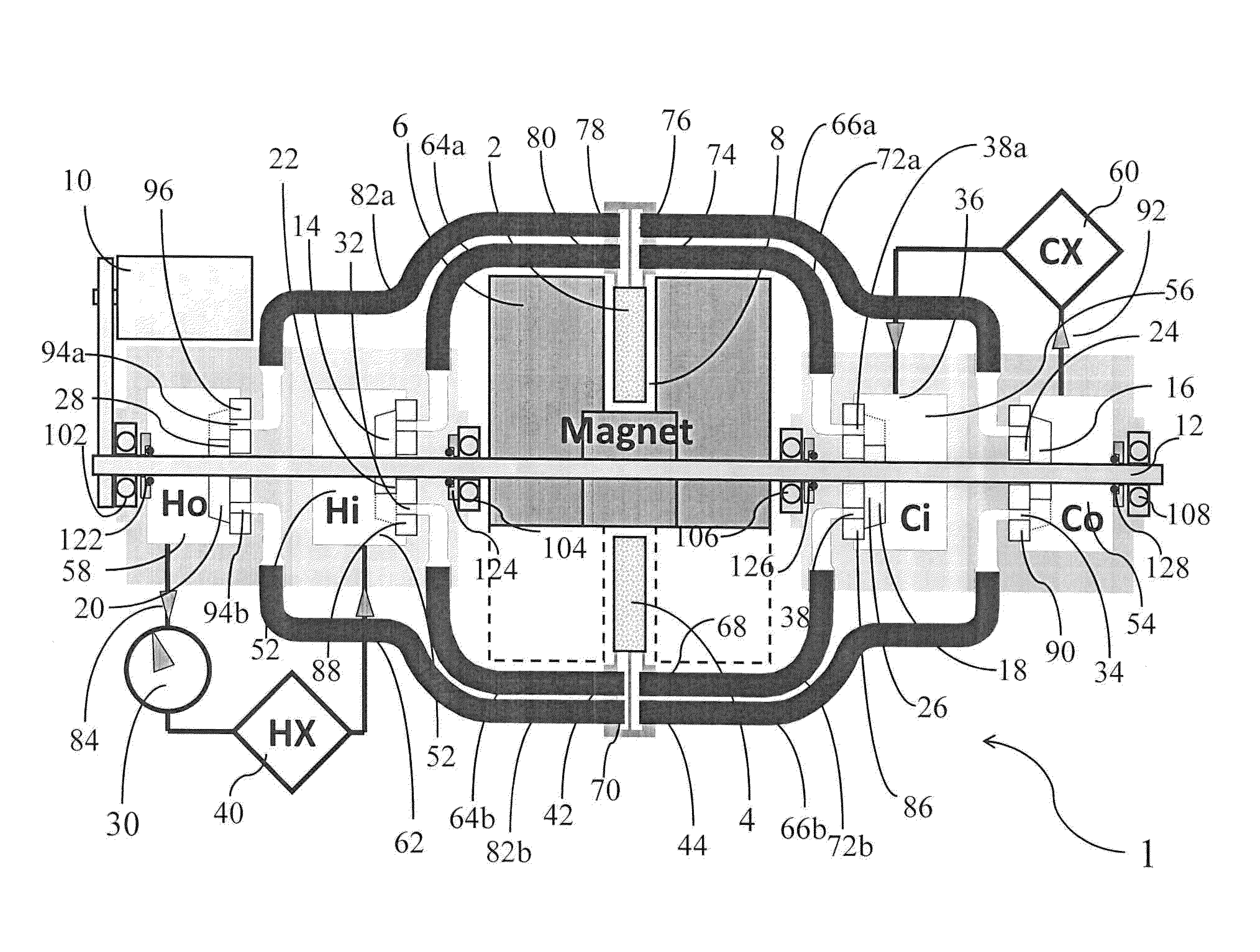
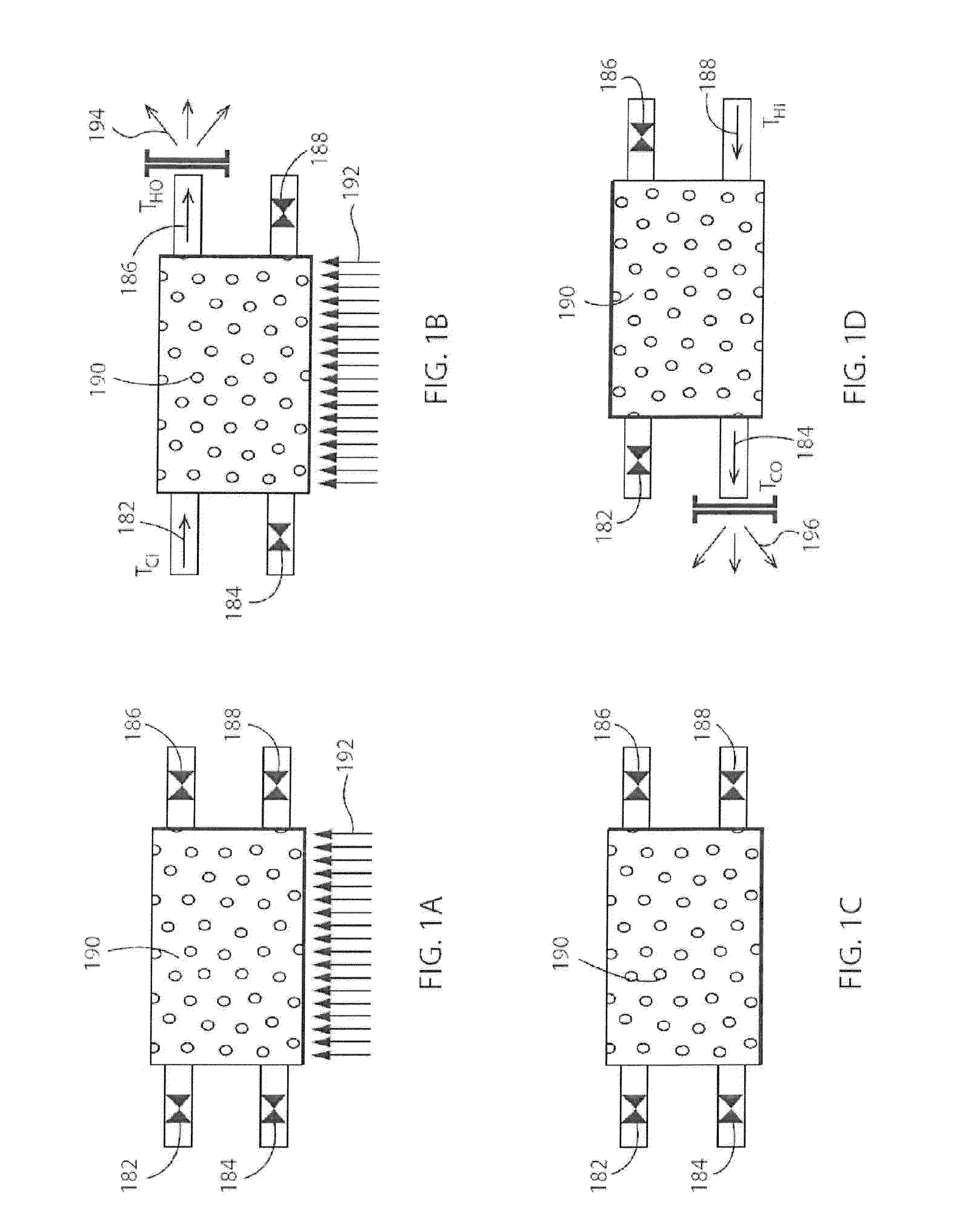
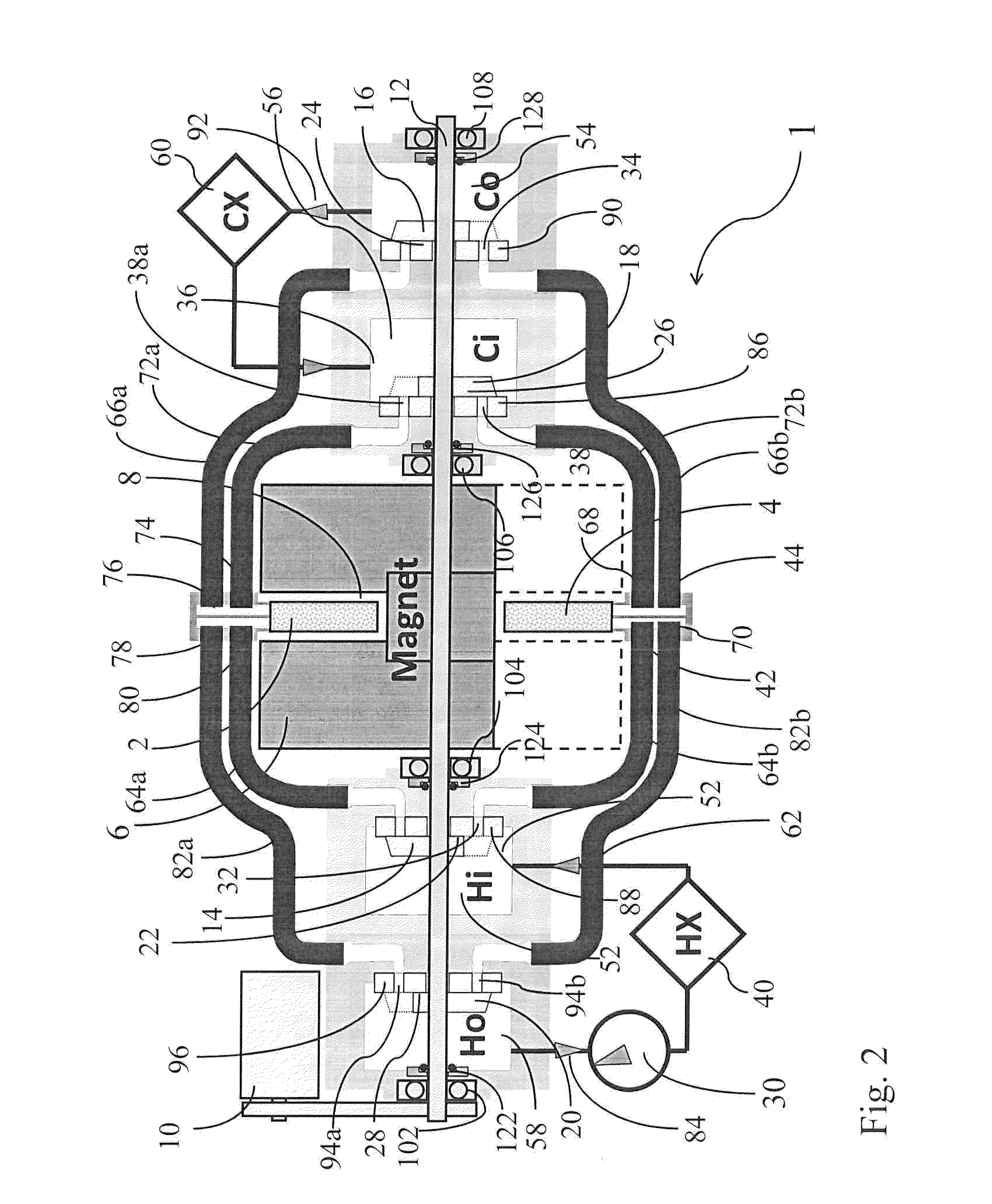
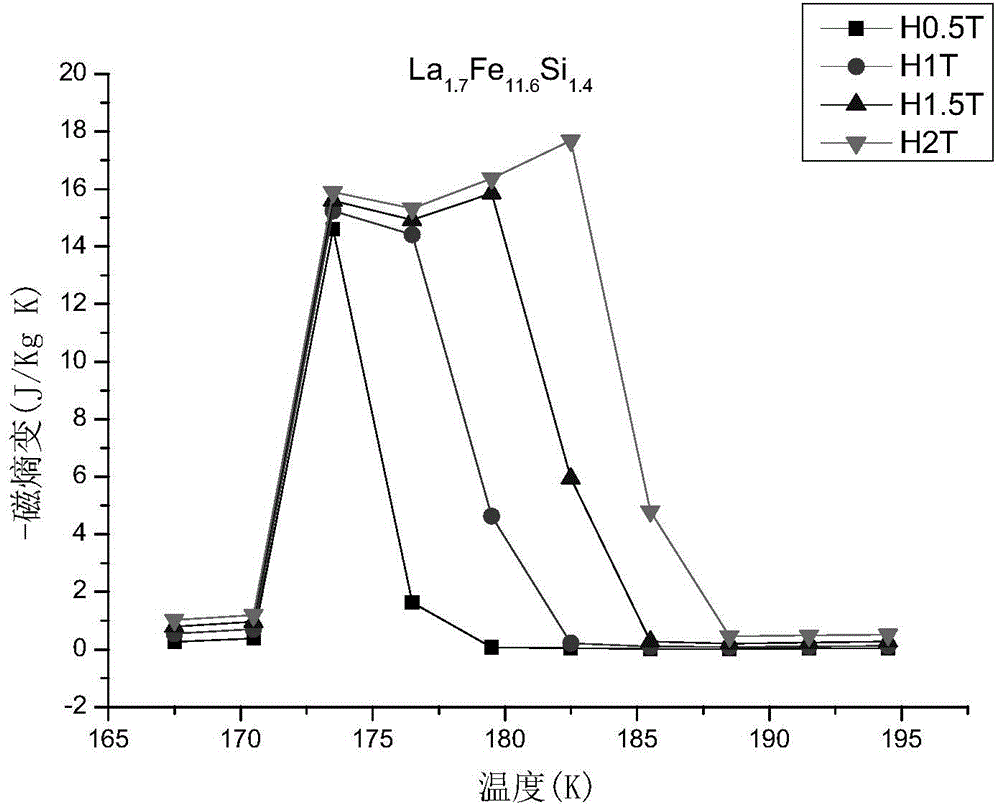
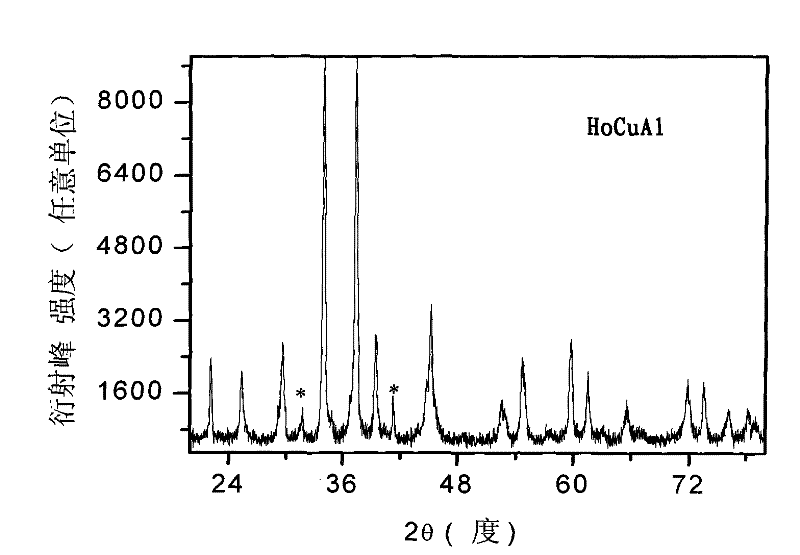
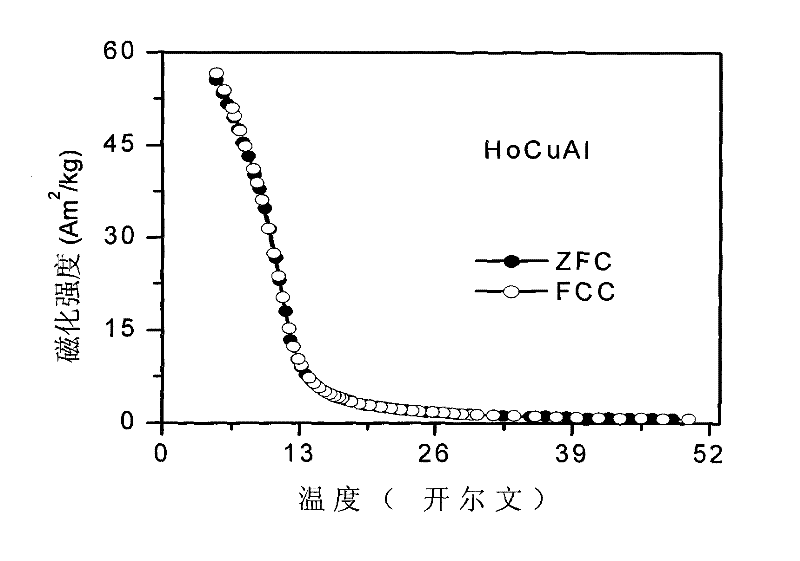
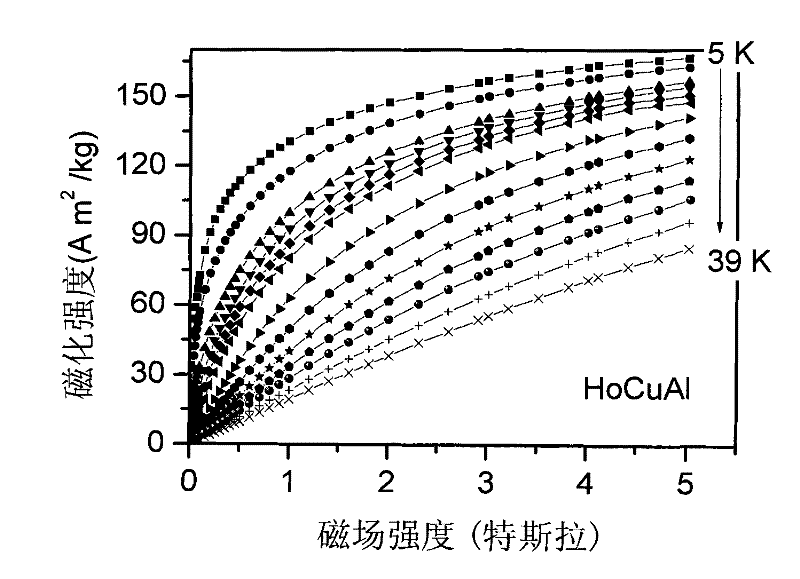
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
693 results about "Magnetic refrigeration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
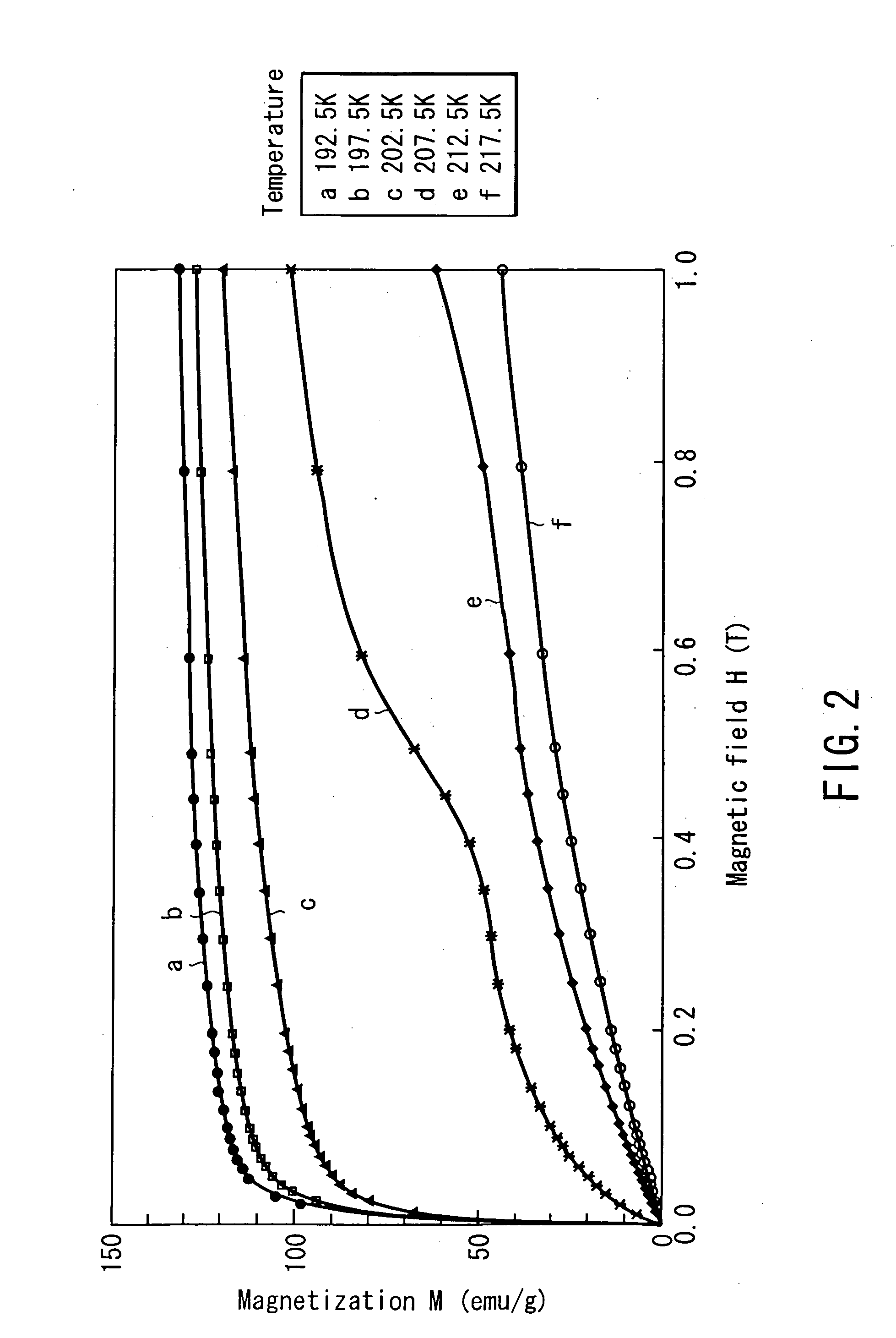
Magnetic refrigeration is a cooling technology based on the magnetocaloric effect. This technique can be used to attain extremely low temperatures, as well as the ranges used in common refrigerators. The effect was first observed by a German physicist Warburg (1881) Subsequently by French physicist P. Weiss and Swiss physicist A. Piccard in 1917. The fundamental principle was suggested by P. Debye (1926) and W. Giauque (1927). The first working magnetic refrigerators were constructed by several groups beginning in 1933. Magnetic refrigeration was the first method developed for cooling below about 0.3K (a temperature attainable by ³He refrigeration, that is pumping on the ³He vapors).
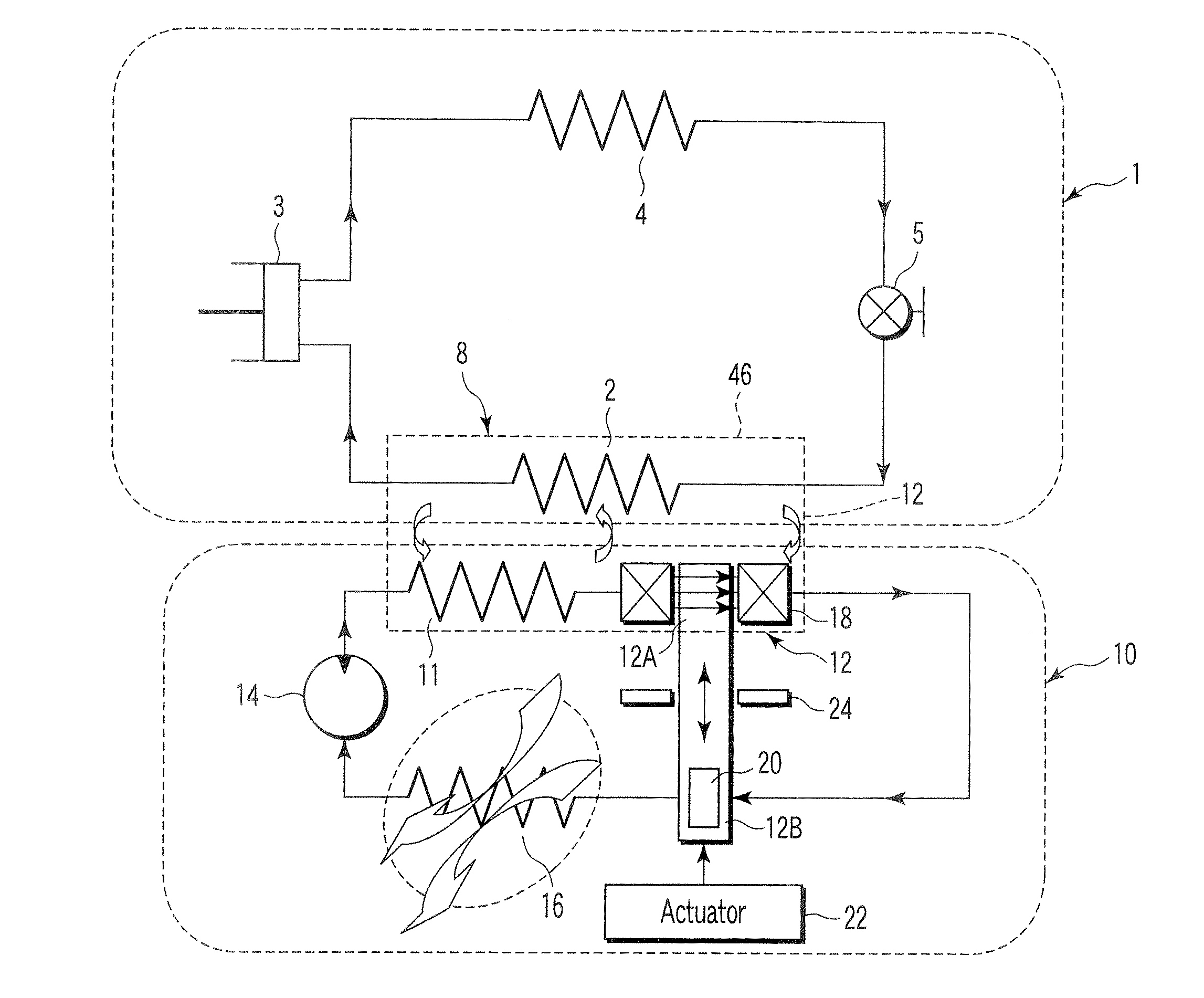
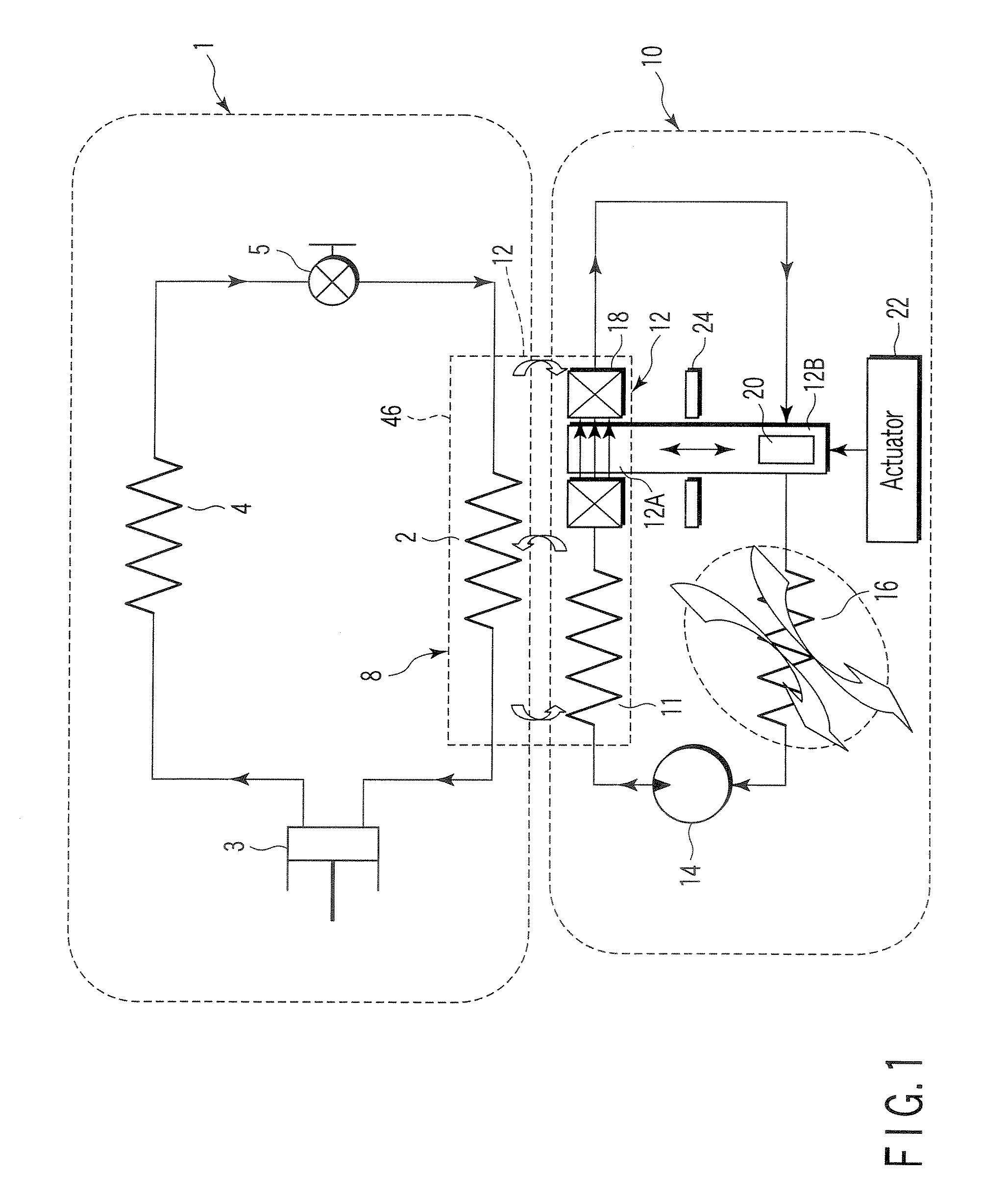
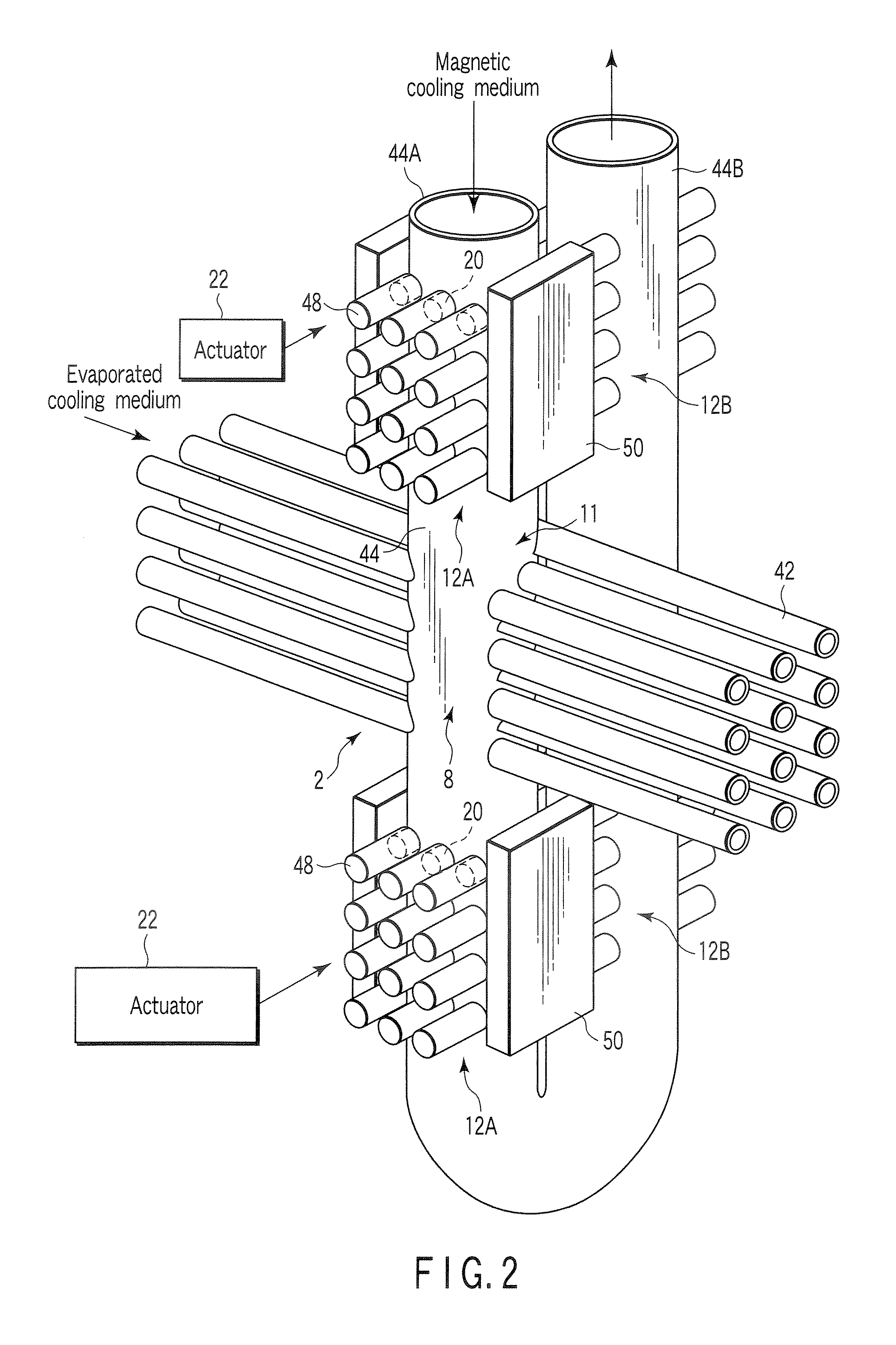
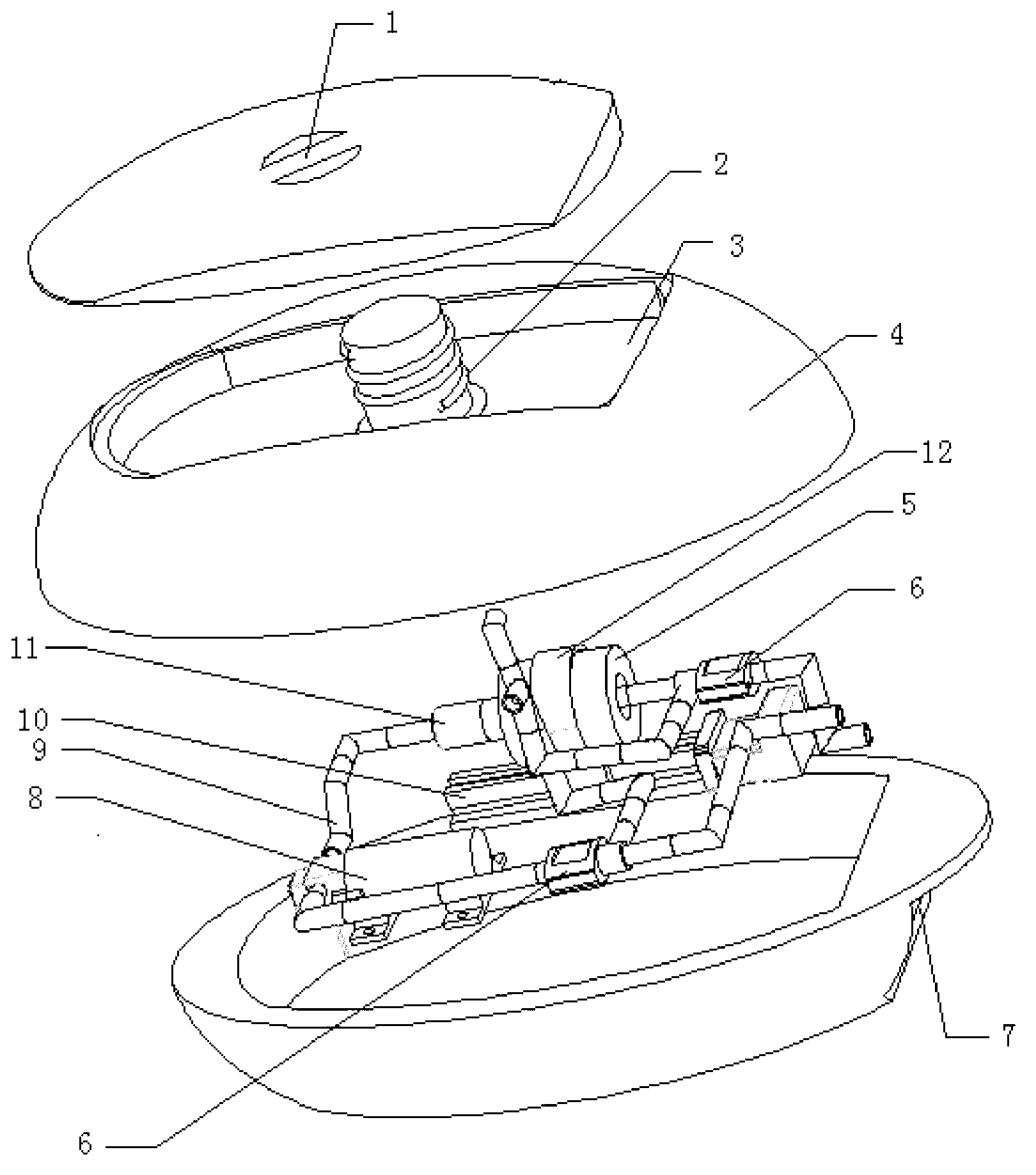
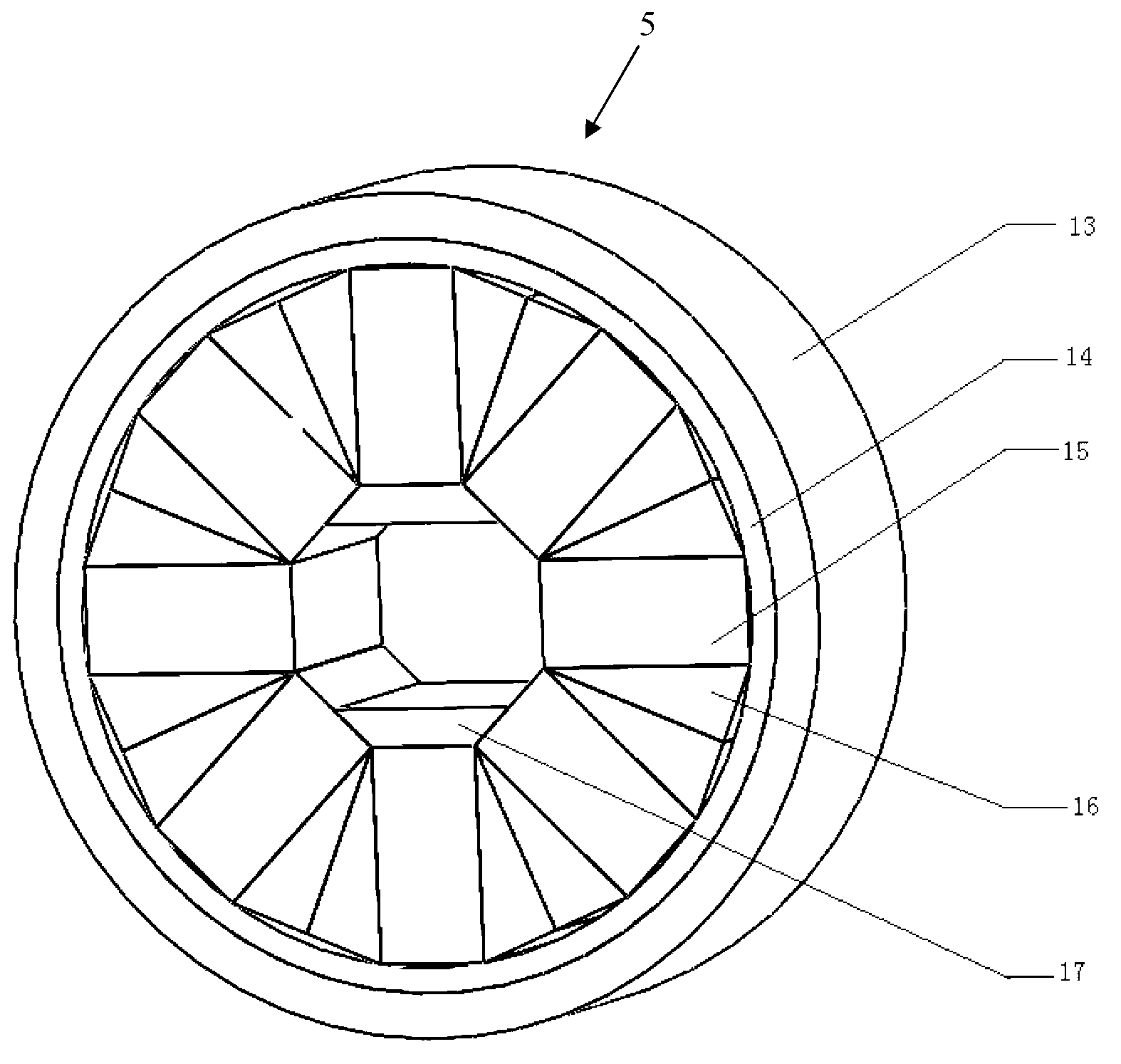
Magnetic refrigeration material and magnetic refrigeration device
InactiveUS20070220901A1Avoid Heat Exchange EfficiencyImprove heat transfer efficiencyTransportation and packagingEnergy efficient heating/coolingOxidation resistantMagnetic refrigeration
A magnetic refrigeration material has magnetic material particles with a magnetocaloric effect and an oxidation-resistant film formed on the surfaces of the magnetic material particles.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Reciprocating and rotary magnetic refrigeration apparatus
InactiveUS6935121B2Increase the magnetic field strengthEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMagnetic effectAtmospheric air
A reciprocating and rotating magnetic refrigeration apparatus adopts a dynamo concept and the design of magnetic supply path and heat transfer unit to alternately magnetize and demagnetize a magnetocaloric material to generate thermo-magnetic effect for cooling. The apparatus includes magnetocaloric material located on the head of stator nose poles, magnetic supply coils surrounding the magnetocaloric material, permanent magnets located on a rotating stator, and a heat transfer unit in contact with the magnetocaloric material. Two adjacent magnetocaloric materials magnetize and demagnetize alternately to alter the temperature and entropy of the magnetocaloric material, and through the heat transfer unit, heat exchange occurs between the magnetocaloric materials and the atmosphere to achieve the cooling effect.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Rotary magnetic refrigeration device and application thereof
InactiveCN101979937AImprove cooling efficiencyImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsThermal insulationMagnetic media
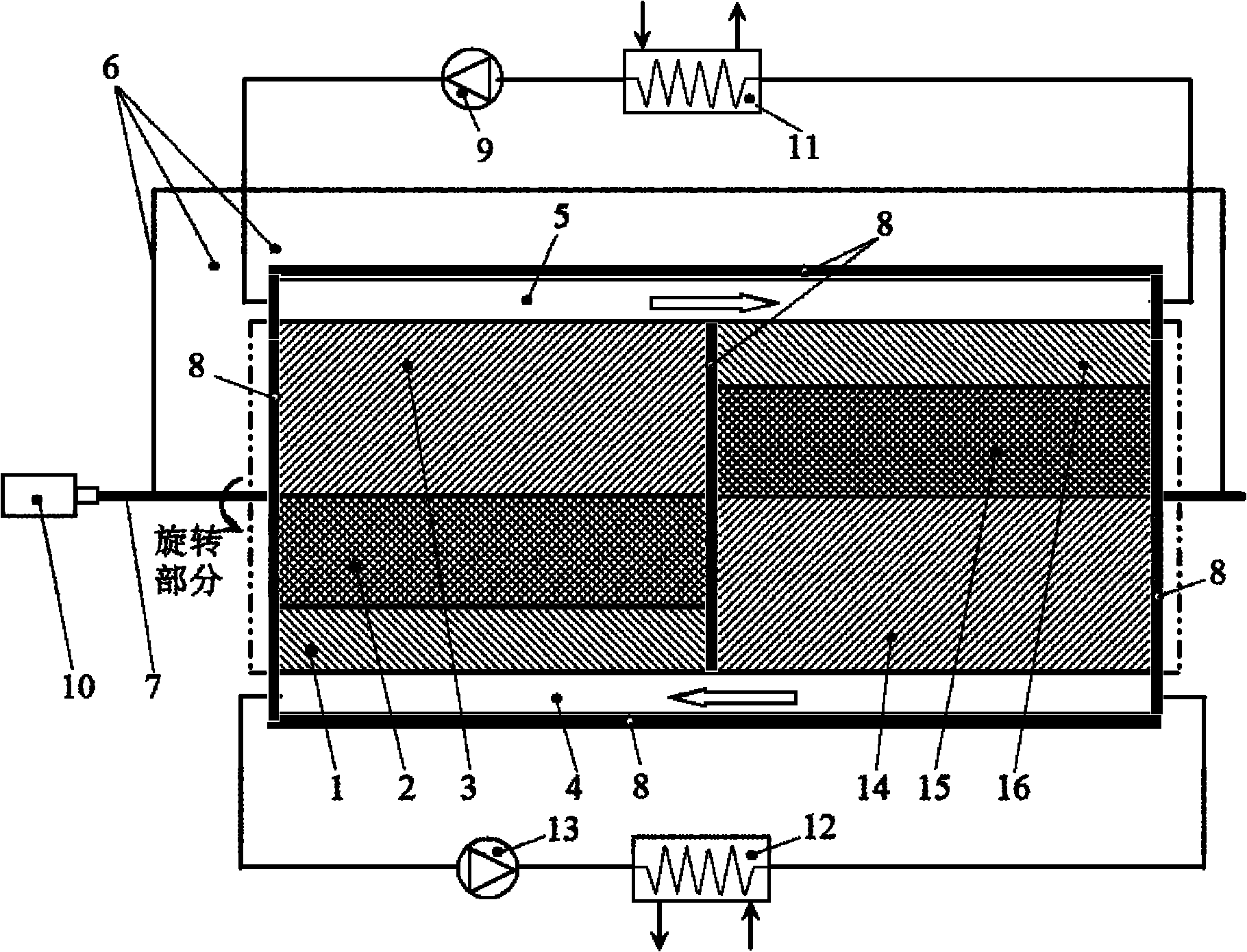
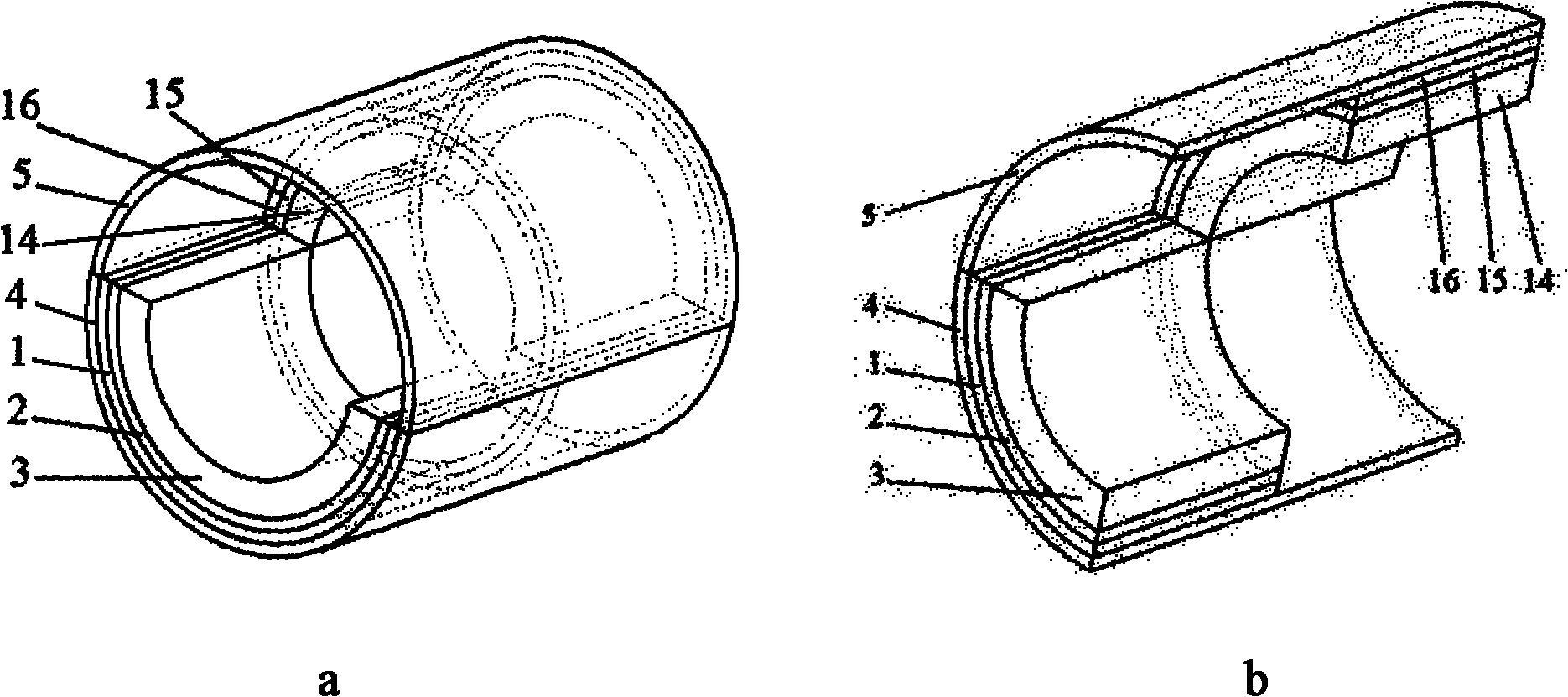
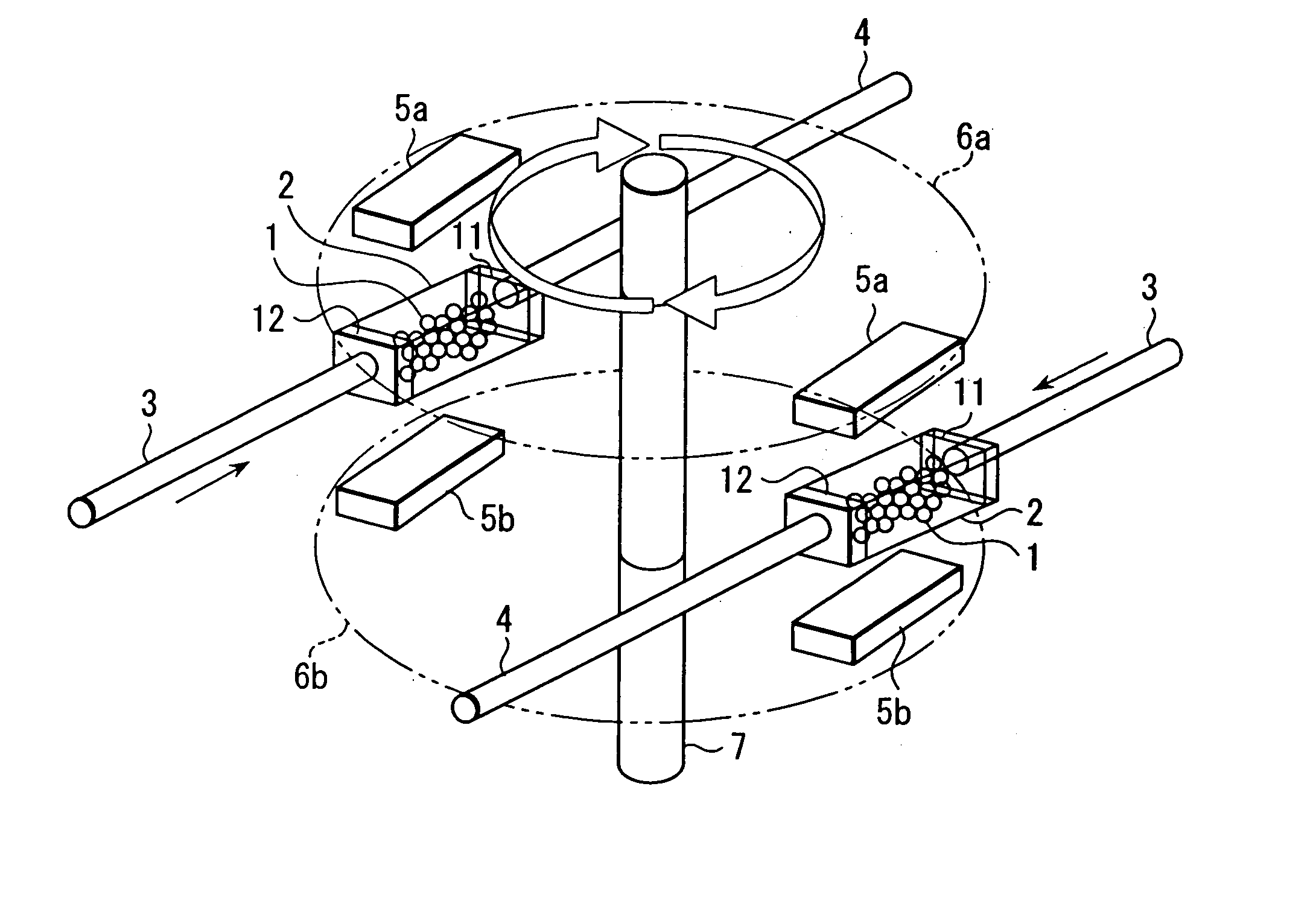
The invention discloses a rotary magnetic refrigeration device. The rotary magnetic refrigeration device comprises a magnetic field source, two active regenerator modules and cold and hot fluid heat exchange channels, and is characterized in that: two packing layers sandwich a magnetic medium in a radial direction so as to form one active regenerator module; the two active regenerator modules are staggered coaxially and axially and arranged at an interval of 180 DEG in the circumferential direction, and pass through an upper half magnetic field region covered with the magnetic field source and a lower half nonmagnetic region alternately when rotating synchronously; A hot fluid channel which is communicated with a high temperature end heat exchanger is statically arranged in the pace of the magnetic field region at the rotating periphery of the active regenerator module; and the cold fluid channel which is communicated with a low temperature end heat exchanger is statically arranged in the space of the nonmagnetic region at the rotating periphery of the active regenerator module, and thermal insulation layers are arranged between the two active regenerator modules in the axial direction, and at the periphery and left and right end faces of the cold and hot fluid channels.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Reciprocating and rotary magnetic refrigeration apparatus
InactiveUS20050120720A1Increase the magnetic field strengthEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMagnetic effectAtmospheric air
A reciprocating and rotating magnetic refrigeration apparatus adopts a dynamo concept and the design of magnetic supply path and heat transfer unit to alternately magnetize and demagnetize a magnetocaloric material to generate thermo-magnetic effect for cooling. The apparatus includes magnetocaloric material located on the head of stator nose poles, magnetic supply coils surrounding the magnetocaloric material, permanent magnets located on a rotating stator, and a heat transfer unit in contact with the magnetocaloric material. Two adjacent magnetocaloric materials magnetize and demagnetize alternately to alter the temperature and entropy of the magnetocaloric material, and through the heat transfer unit, heat exchange occurs between the magnetocaloric materials and the atmosphere to achieve the cooling effect.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration and method for producing thereof
ActiveUS7063754B2Stable magnetic refrigeration cycleLow costCompression machinesInorganic material magnetismHydrogenRoom temperature
The magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration according to the present invention has an NaZn13-type crystalline structure and comprises iron (Fe) as a principal element (more specifically, Fe is substituted for the position of “Zn”) and hydrogen (H) in an amount of 2 to 18 atomic % based on all constitutional elements. Preferably, the magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration preferably contains 61 to 87 atomic % of Fe, 4 to 18 atomic % of a total amount of Si and Al, 5 to 7 atomic % of La. The magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration exhibits a large entropy change in a room temperature region and no thermal hysteresis in a magnetic phase transition. Therefore, when a magnetic refrigeration cycle is configured using the magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration, a stable operation can be performed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic refrigeration system and vehicle air conditioning device
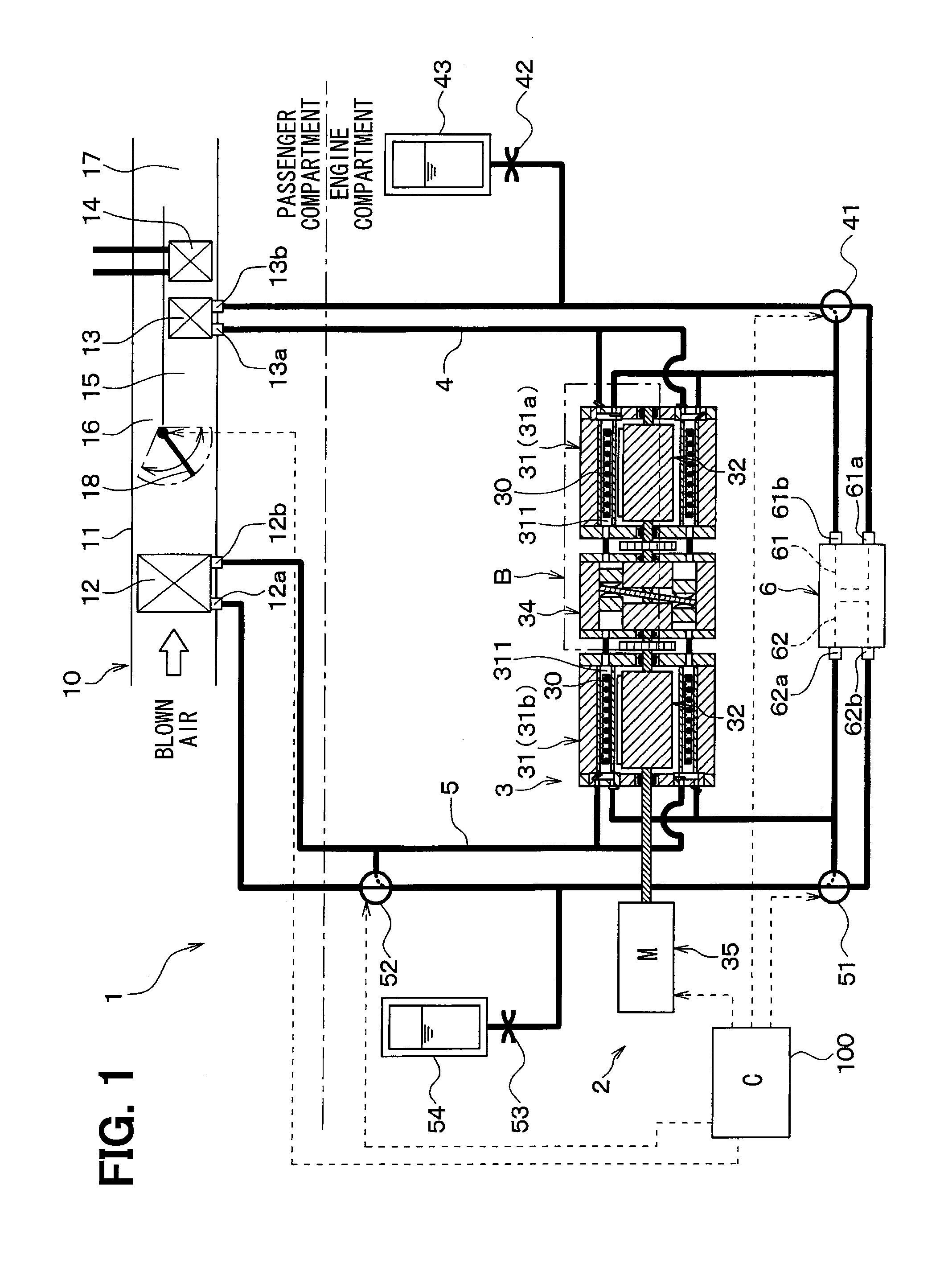
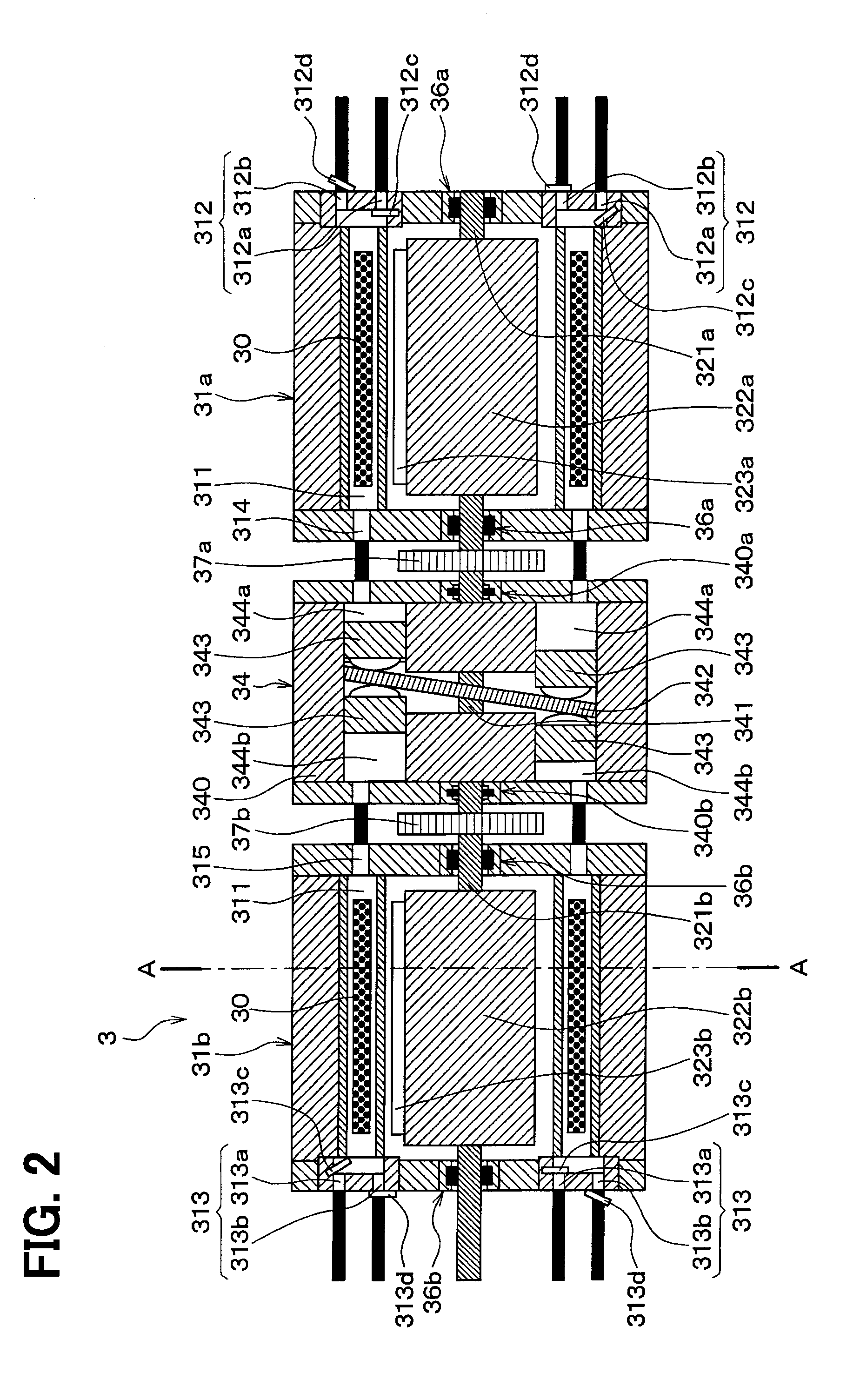
InactiveUS20130298571A1Reduce heat exchangeImprove COPVehicle heating/cooling devicesMachines using electric/magnetic effectsAir conditioningRefrigerant
A magnetic refrigeration system constructed in such a way that a refrigerant transfer part transfers refrigerant from a first refrigerant discharge part of one refrigerant port to a first refrigerant circulation circuit after a magnetic field is applied to a magnetic working material by a magnetic field applying and removing part and that the refrigerant transfer part transfers refrigerant from a second refrigerant discharge part of other refrigerant port to a second refrigerant circulation circuit after the magnetic field is removed from the magnetic working material by the magnetic field applying and removing part.
Owner:DENSO CORP
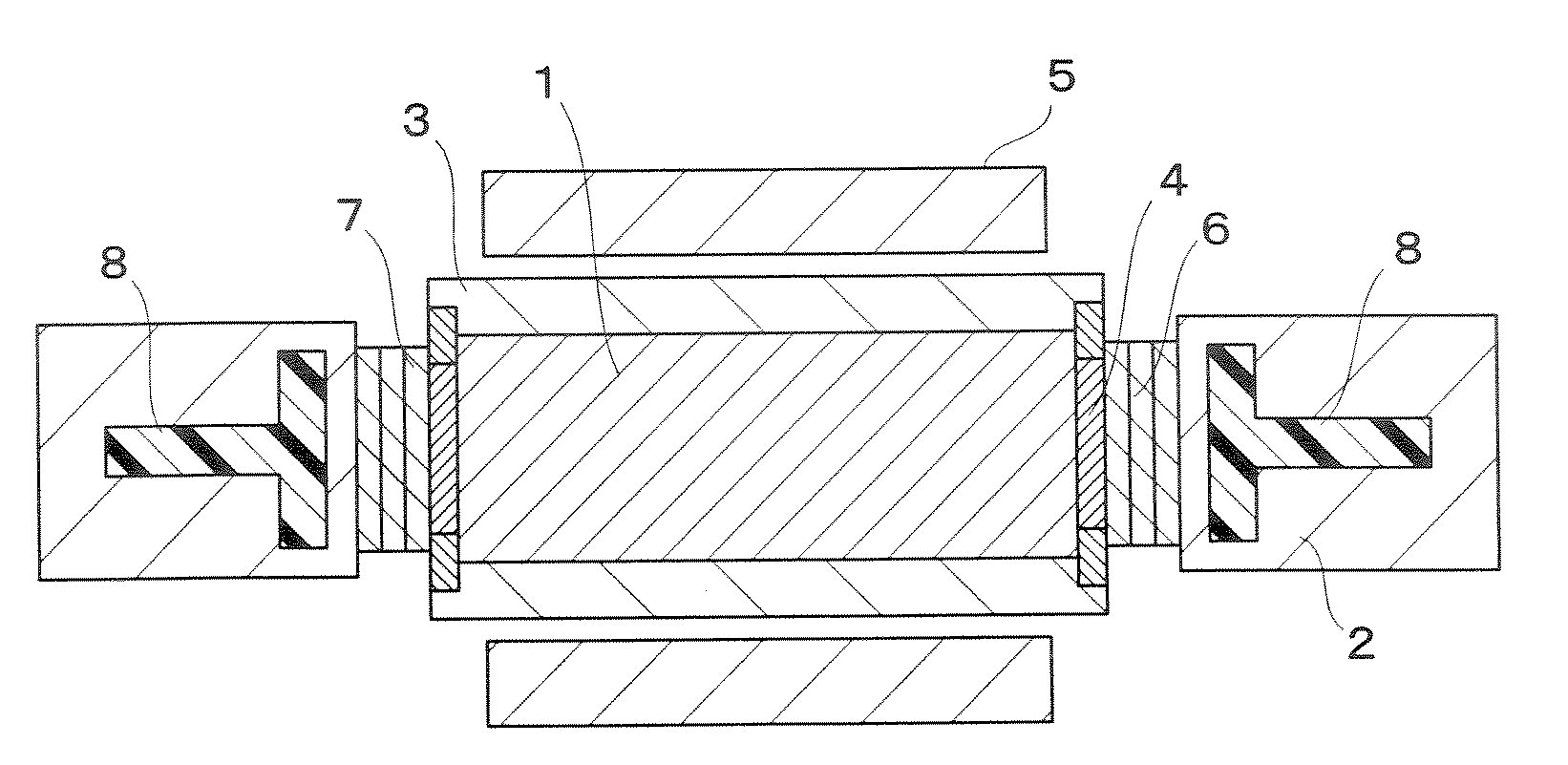
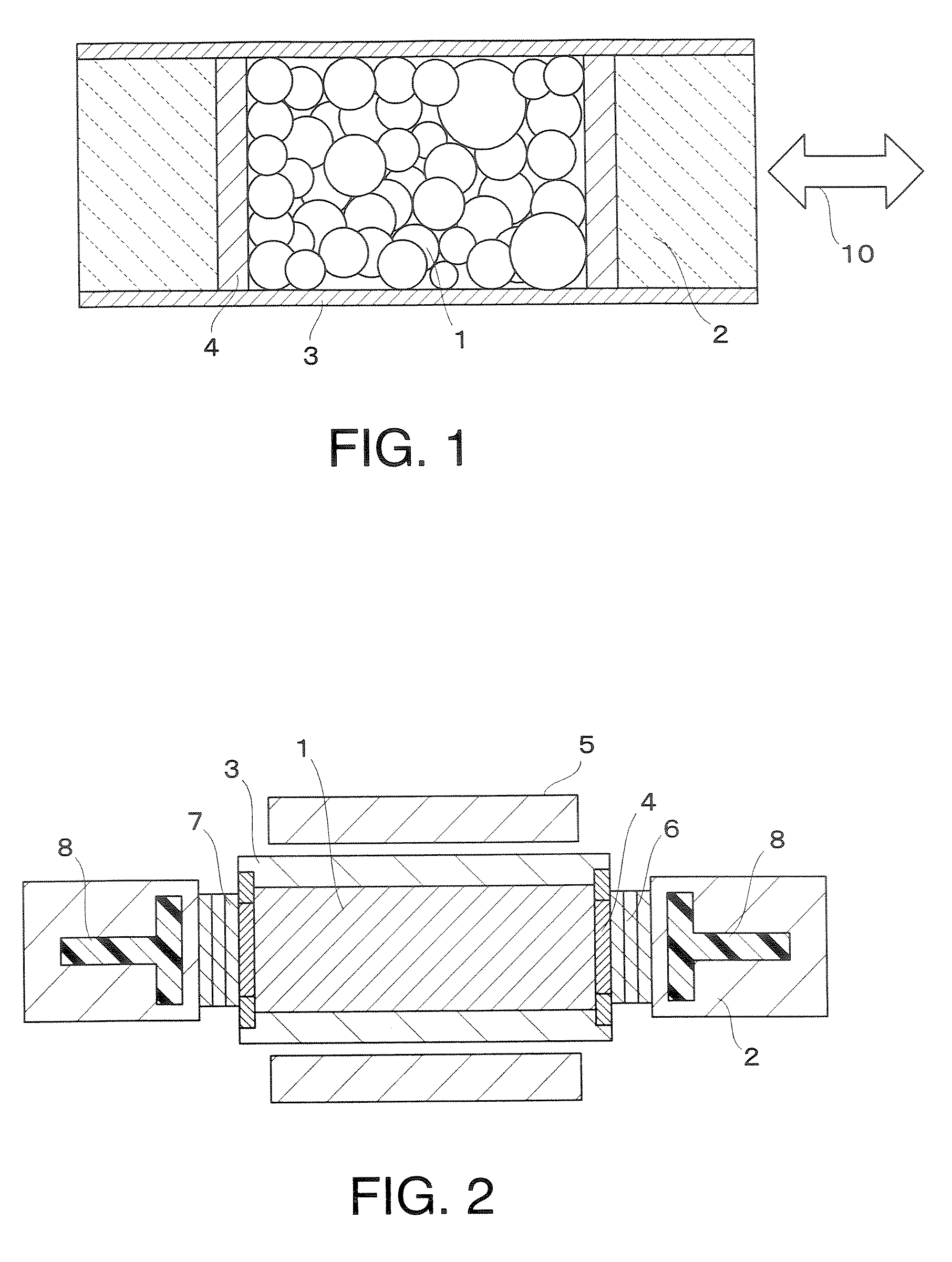
Magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration apparatus, amr bed, and magnetic refrigeration apparatus
InactiveUS20090217674A1Improve cooling efficiencyWide operationEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMagnetic transitionsMaximum diameter
There are provided a magnetic material for a magnetic refrigeration apparatus, which improves magnetic refrigeration efficiency by the wide operation temperature range of it, AMR bed using the magnetic material, and a magnetic refrigeration apparatus. The magnetic material is used for the magnetic refrigeration apparatus using a liquid refrigerant, formed by approximately uniformly blending at least two kinds of magnetic particles having different magnetic transition temperatures, and the magnetic particles exhibit an approximately spherical shape with maximum diameter of 0.3 mm or more to 2 mm or less. The AMR bed is filled with the magnetic particles.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic Refrigeration System With Improved Flow Efficiency
ActiveUS20150168030A1Low efficiencyPromote balance between supply and demandMechanical apparatusMachines using electric/magnetic effectsFluid controlControl valves
A magnetic refrigeration system provides flow-balanced channels between fluid control valves and the magnetocaloric beds to eliminate inefficiencies caused by unequal utilization of the magnetic beds from flow variations.
Owner:ASTRONAUTICS CORPORATION OF AMERICA
Magnetic refrigerating device and magnetic refrigerating method
InactiveUS20080236171A1Reduce heat lossImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMagnetic refrigerationRefrigerant
A magnetic refrigerating device includes: at least one set of double-structured Halbach type magnet including a ring-shaped inner Halbach type magnet and a ring-shaped outer Halbach type magnet which are coaxially arranged one another so that a magnetic field generated by the inner Halbach type magnet is superimposed with a magnetic field generated by the outer Halbach type magnet; a magnetic refrigerant or a magnetic refrigeration working chamber including the magnetic refrigerant therein disposed in a bore space of the inner Halbach type magnet; and a rotating mechanism to rotate the outer Halbach type magnet while the inner Halbach type magnet is stationed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetically refrigerating magnetic material, magnetic refrigeration apparatus, and magnetic refrigeration system
ActiveUS20100058775A1Energy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMaximum diameterEngineering
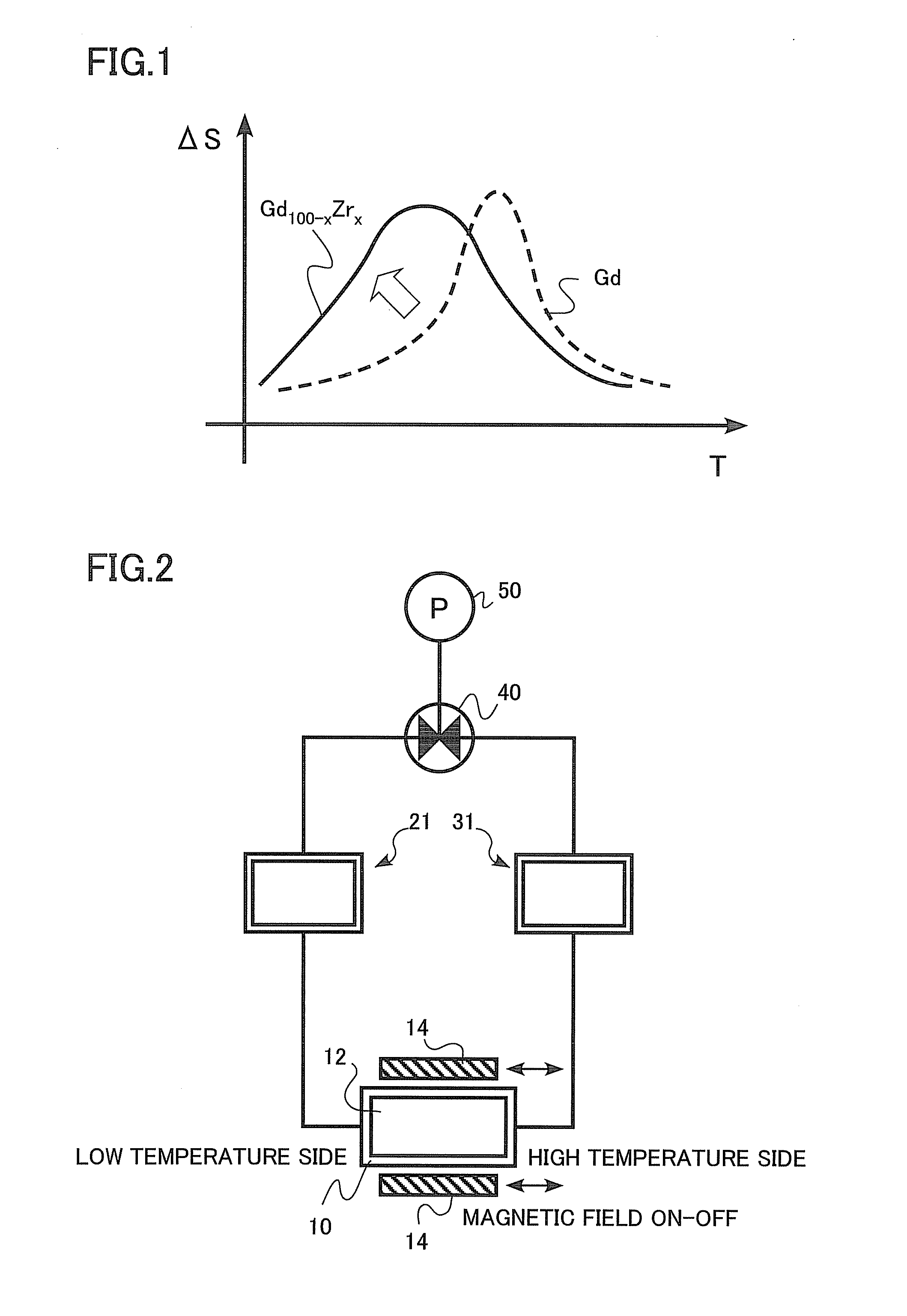
There are provided a magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration improving a magnetic refrigeration efficiency by including a wide operation temperature range and a magnetic refrigeration apparatus and a magnetic refrigeration system using the magnetic material. The magnetically refrigerating magnetic material is formed of a magnetic material shown by a composition formula of Gd100-x-yZrxYy, wherein 0<x<3.4 as well as 0≦y≦13.5, and the magnetic refrigeration apparatus and the magnetic refrigeration system uses the magnetic material.It is preferable that the magnetic material be approximately spherical magnetic particles having a maximum diameter of 0.3 mm or more to 2 mm or less.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic refrigeration control system, and method thereof
InactiveUS20130186107A1Increasing magnetic fieldReduce decreaseEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsCoolant flowControl system
A magnetic refrigeration control system, includes: a first magnetocaloric bed; a pipe, arranged through the first magnetocaloric bed; a coolant, flowing in the pipe; a pump, driving the coolant with a pumping speed; a valve, adjusting a flow period of the flowing coolant; a magnetic module, providing an increasing magnetic field to the first magnetocaloric bed during a magnetization period and providing a decreasing magnetic field to the first magnetocaloric bed during a demagnetization period; and a sensor, detecting a fluid pressure of the coolant flowing in the pipe, the temperature of a refrigerator, and a flowing rate of the coolant flowing in the pipe; and a controller, adjusting the pumping speed, the flow period, the magnetization period, and the demagnetization period according to the temperature, the fluid pressure, and the flowing rate in real time. A magnetic refrigeration control method is also disclosed.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Rereearth-iron base compound magnetic refrigeration material with large magnetic entropy change and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN1450190ALarge magnetic entropy becomes highSuitable for productionEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsRare-earth elementInterstitial compound
The present invention relates to a rare earth-iron base compound magnetic refrigeration material with large magnetic entropy change and its preparation method. Its chemical general formula is La1-xRx(Fe1-yMy)13-zSizX alpha, in which R is more than one rare earth elements and its combination, M is more than one kind of Al, Co and Ga, etc. and its combination, X ix more than one kind of C, H, N andcombination of them, x is 0-0.4, y is 0-0.3, z is 0-3.0 and alpha is 0.3.0. Its preparation method includes the following steps: utilizing direct smelting and annealing treatment to can prepare La1-xRx(Fe1-yMy)13-zSiz and low C-content La1-xRx(Fe1-yMy)13-zSiz alpha gap compound, and utilizing smelting, quickly-quenching and annealing treatment to prepare high C-content La1-xRx(Re1-yMy)13-zSizC alpha gas compound.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic Refrigeration System with Improved Coaxial Valve
InactiveUS20160091227A1Low efficiencyPromote balance between supply and demandMachines using electric/magnetic effectsSustainable buildingsDrive shaftRotary valve
A magnetic refrigeration system provides a rotary valve design that balances the forces needed to seal valve surfaces, reduces influence of wear on leakage, makes assembly and adjustment of the valve easier, reduces potential for bypass flows, reduces stress on and corrosion of the drive shaft, and provides a more compact system.
Owner:ASTRONAUTICS CORPORATION OF AMERICA
Magnetic composite material and method for producing the same
ActiveUS7168255B2Reduce generationSuppress pressure lossEnergy efficient heating/coolingInorganic material magnetismCrystal structureMagnetic refrigeration
The magnetic composite material of the present invention is used as a working substance in the magnetic refrigeration system and comprising at least two phases, including, a first phase composed of an intermetallic compound represented by a general formula: La(Fe(Co, Ni)Si)13, having an NaZn13 type crystal structure, and a second phase is composed of an iron alloy containing Si. The first phase is precipitated in an expansion size of 100 μm or less in average. Preferably, the magnetic composite material contains Fe as a principal component, La in an amount from 4 atomic % to 12 atomic %, Si in an amount from 2 atomic % to 21 atomic %, and Co and Ni in a total amount from 0 atomic % to 11 atomic %, and the total amount of Fe, Co and Ni being from 75 atomic % to 92 atomic %.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
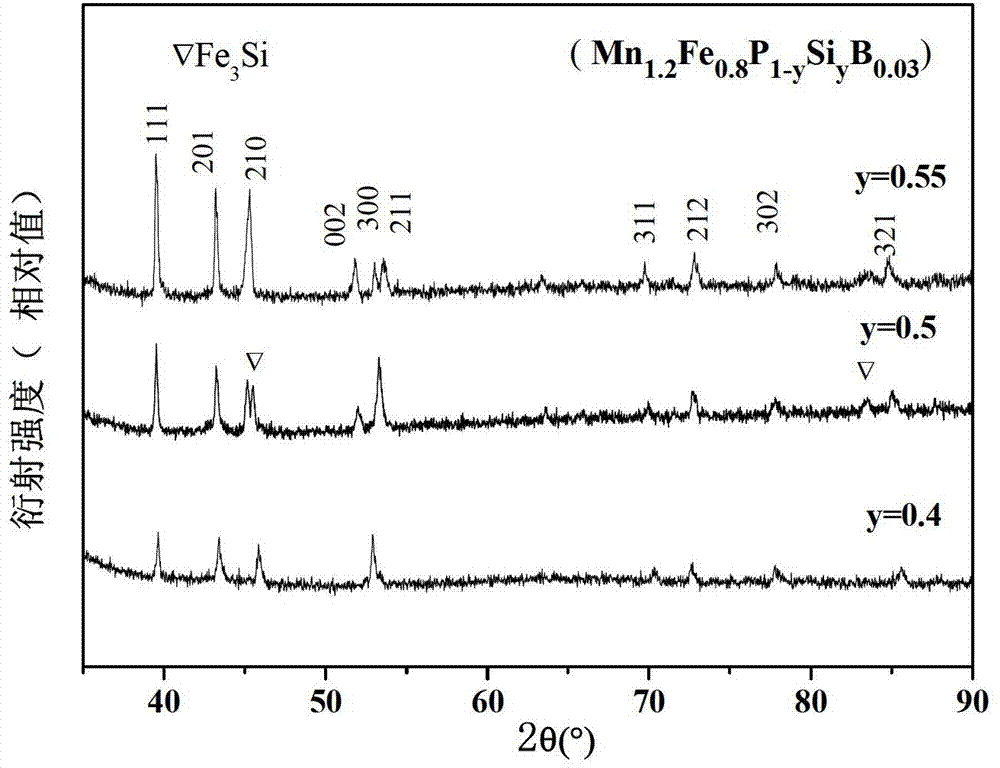
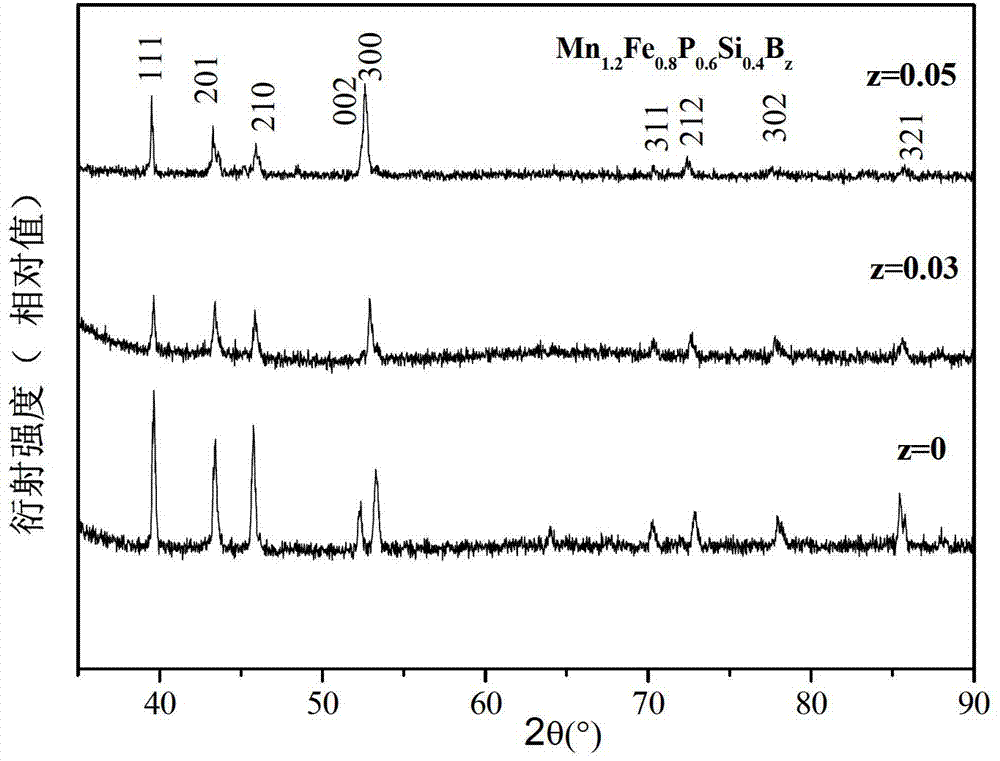
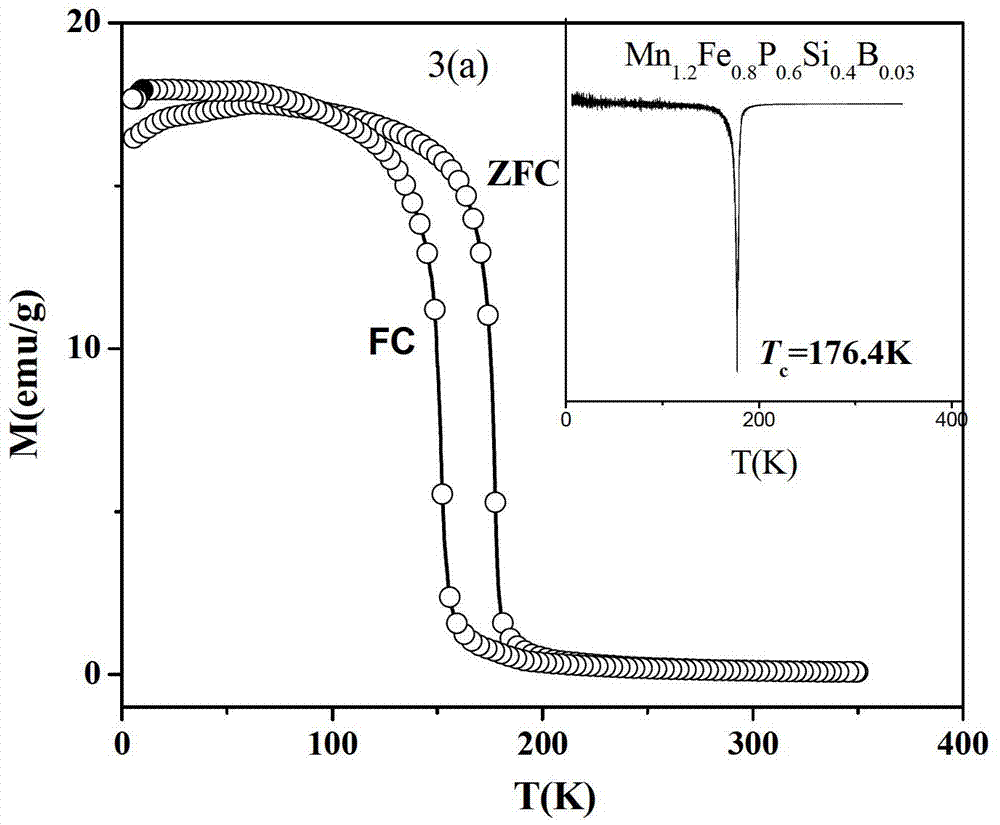
MnFePSi-based room-temperature magnetic refrigeration material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an MnFePSi-based room-temperature magnetic refrigeration material and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the material is Mn1.2Fe0.8P1-ySiyBz, wherein y is greater than or equal to 0.4 and less than or equal to 0.55; and z is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.05. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the Mn, Fe, P, Si and B by mass percent in the formula; (2) filling the prepared powder materials in a ball mill tank under the protection of high-purity argon and capping and sealing the ball mill; (3) calcining the powder obtained from the ball mill under the protection of the argon; and (4) rapidly quenching the melt under the protection of argon after crushing the calcined sample at the melt-spinning speed of 10-20m / s to obtain the belt material, and then annealing and rapidly quenching the belt material in the water to obtain the room-temperature magnetic refrigeration material. The material has simple process and low cost; and in addition, the prepared magnetic refrigeration material has high magnetic entropy and low magnetic lag and heat stagnation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Alloy and method for producing magnetic refrigeration material particles using same
An alloy is used for production of magnetic refrigeration material particles. The alloy contains La in a range of 4 to 15 atomic %, Fe in a range of 60 to 93 atomic %, Si in a range of 3.5 to 23.5 atomic % and at lease one element M selected from B and Ti in a range of 0.5 to 1.5 atomic %. The alloy includes a main phase containing Fe as a main component element and Si, and a subphase containing La as a main component element and Si. The main phase has a bcc crystal structure and an average grain diameter of 20 μm or less.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for preparing magnetic nanosheet
ActiveCN104174855ANarrow particle size distributionMagnetically anisotropicNanotechnologyInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRandom combinationSolid particle
The invention relates to a method for preparing a magnetic nanosheet. During ball milling, solid particles and a surface active agent are added to assist ball milling. The solid particles adopt NaCl, CaCl2, NdCl3, KF, CaF2, NdF3, DyF3, Al2O3, Nd2O3 or random combinations thereof. The surface active agent adopts a cationic, anionic, or non-ionic surface active agent including but not limited to oleic acid, oleylamine and the like. During ball milling, the solid particles work with the surface active agent to stop a nanosheet from being further cold welded and reunited, so that magnetic particles are further crushed, and an ultrathin magnetic nanosheet with a texture is prepared. The thickness of the nanosheet ranges from 10 to 50 nm, and the average thickness is about 20 nm. The magnetic nanosheet with a texture or magnetic anisotropy is used for preparing a high-performance permanent magnet, or for a high-performance soft / hard magnetic coupling magnet and a double (multi) principal phase hard magnetic coupling magnet, or in microwave absorption and the preparation of magnetic refrigeration materials.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite type room temperature magnetic refrigeration system and direction control valve thereof
ActiveCN106481842AImprove efficiencyReduce power consumptionMultiple way valvesMachines using electric/magnetic effectsRoom temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a composite type room temperature magnetic refrigeration system and a direction control valve thereof. The direction control valve comprises a valve body and a valve element which rotate relatively; the valve body is provided with a valve body pump hole, a valve body hot end hole, a valve body liquid storage box hole, a valve body clockwise rotation magnetic hole and a valve body reversion magnetic hole, wherein the valve body pump hole and the valve body hot end hole oppositely extend in the direction of the rotating axis, and the valve body liquid storage box hole, the valve body clockwise rotation magnetic hole and the valve body reversion magnetic hole are formed in a staggered manner in the circumferential direction; the valve element is provided with a valve element pump flow channel and a valve element hot end flow channel which are arranged in a staggered manner in the circumferential direction; when the refrigeration system is in a first heat exchange mode; the valve body pump hole is communicated with the valve body clockwise rotation magnetic hole through the valve element pump flow channel, and the valve body hot end hole is communicated with the valve body reversion magnetic hole through the valve element hot end flow channel; when the refrigeration system is in a second heat exchange mode, the valve body pump hole is communicated with the valve body reversion magnetic hole, and the valve body hot end hole is communicated with the valve body clockwise rotation magnetic hole; and when the refrigeration system is in a first and second non-heat-exchange mode, the valve body pump hole is communicated with the valve body liquid storage box hole. The direction control valve effectively reduces the extra power consumption on the basis of meeting various technical performance indexesof a refrigerating machine, improves the efficiency of the refrigerating machine, and makes the overall structure compact and noise low.
Owner:BAOTOU RES INST OF RARE EARTHS
Magnetic refrigeration material and method of manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20060213580A1Small sizeImprove uniformityCompression machinesInorganic material magnetismProduction rateCrystal structure
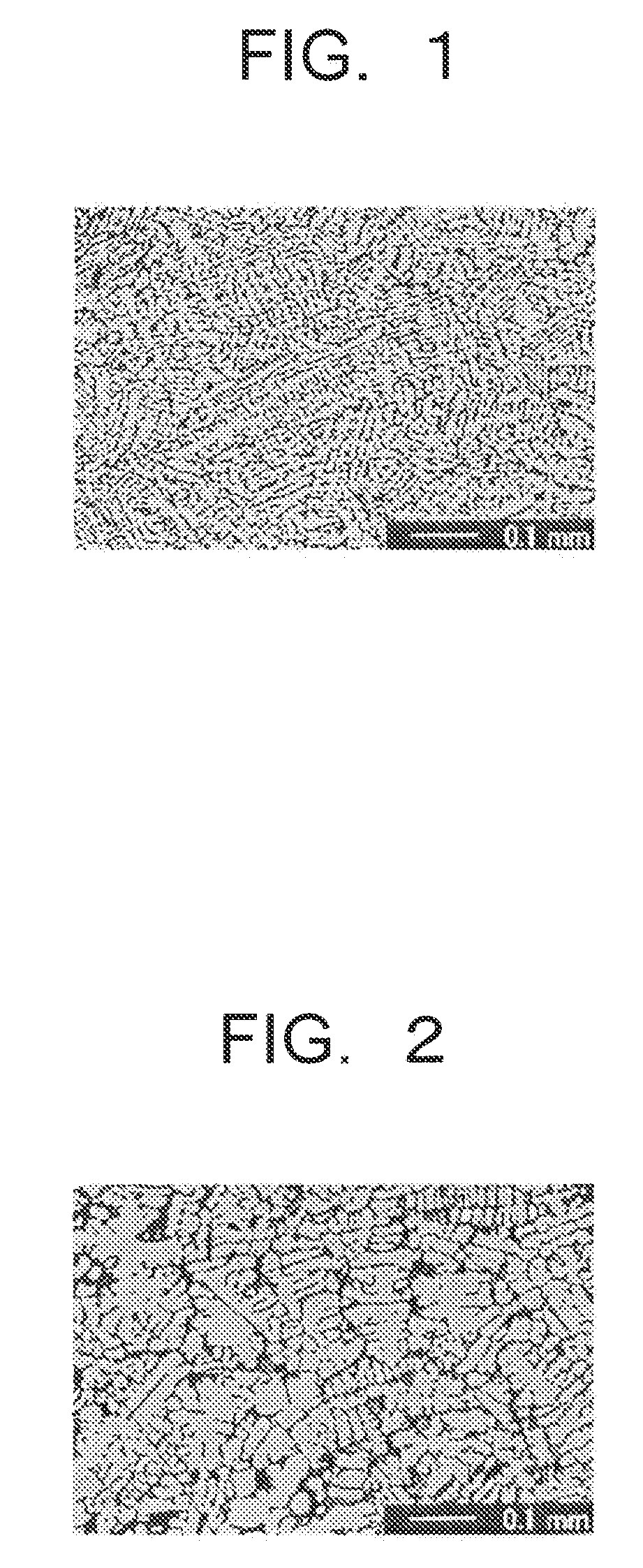
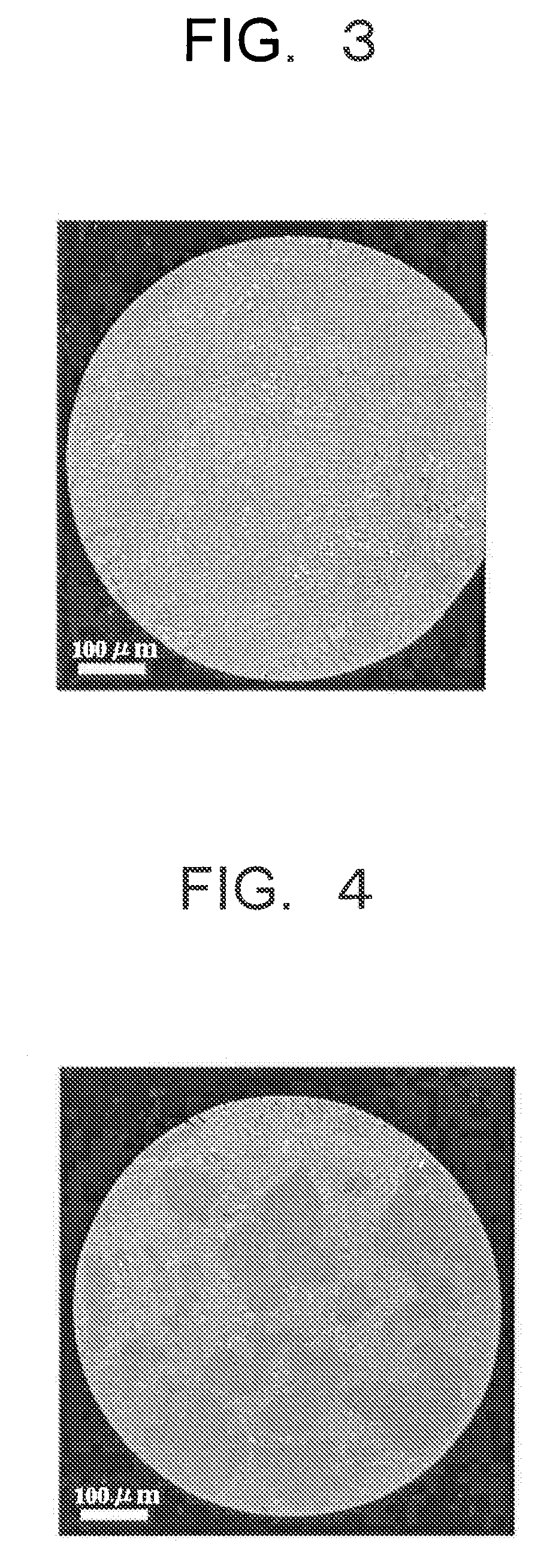
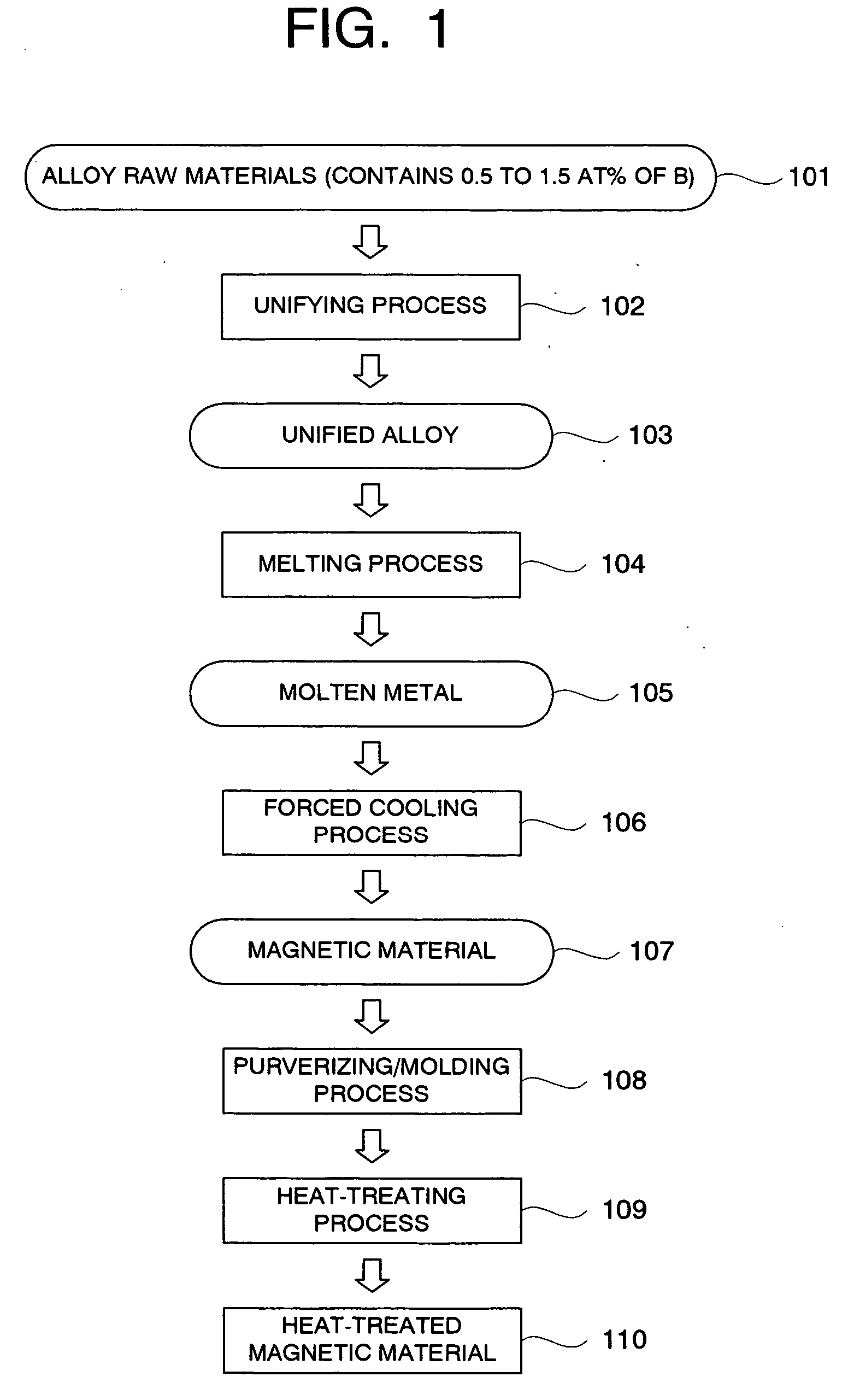
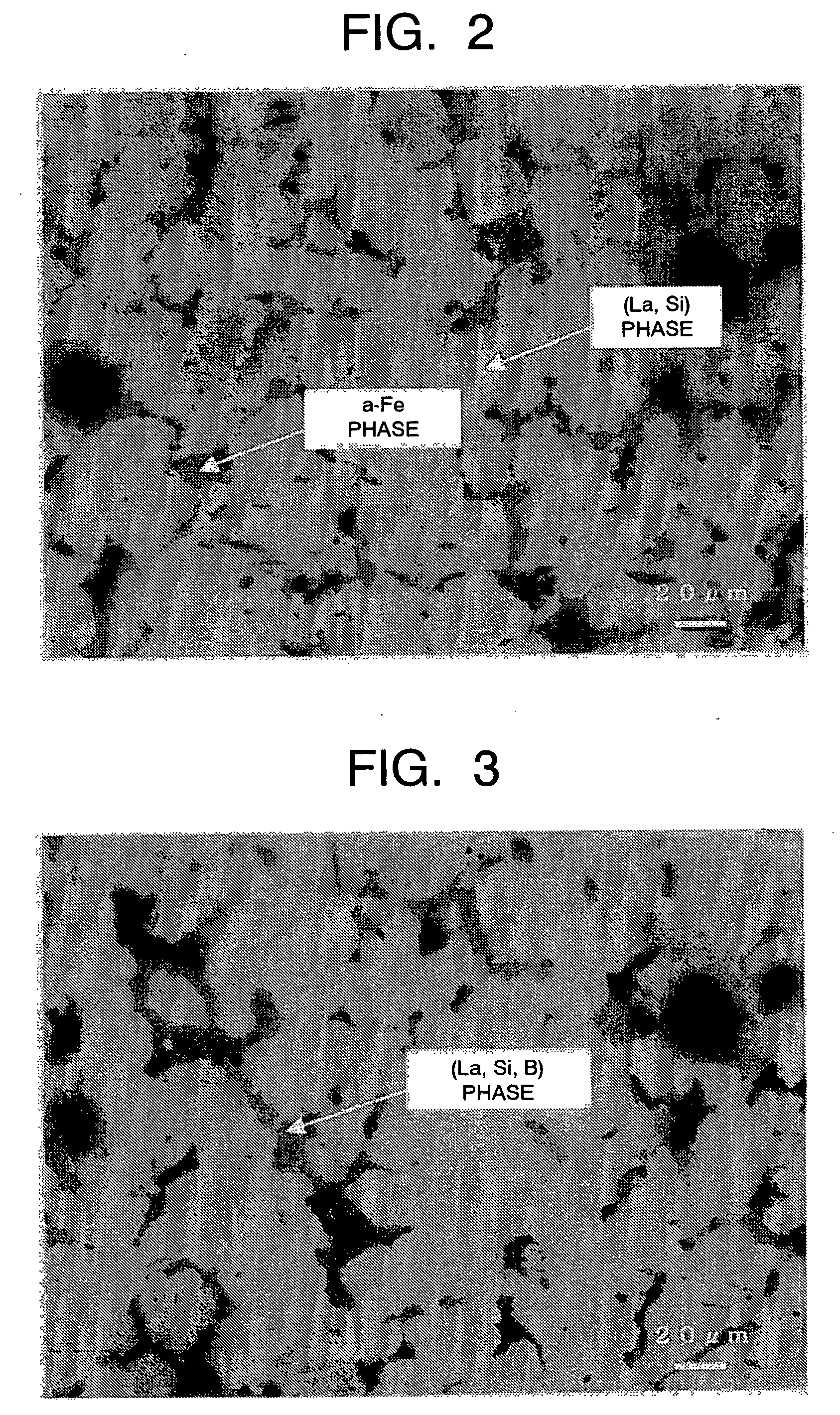
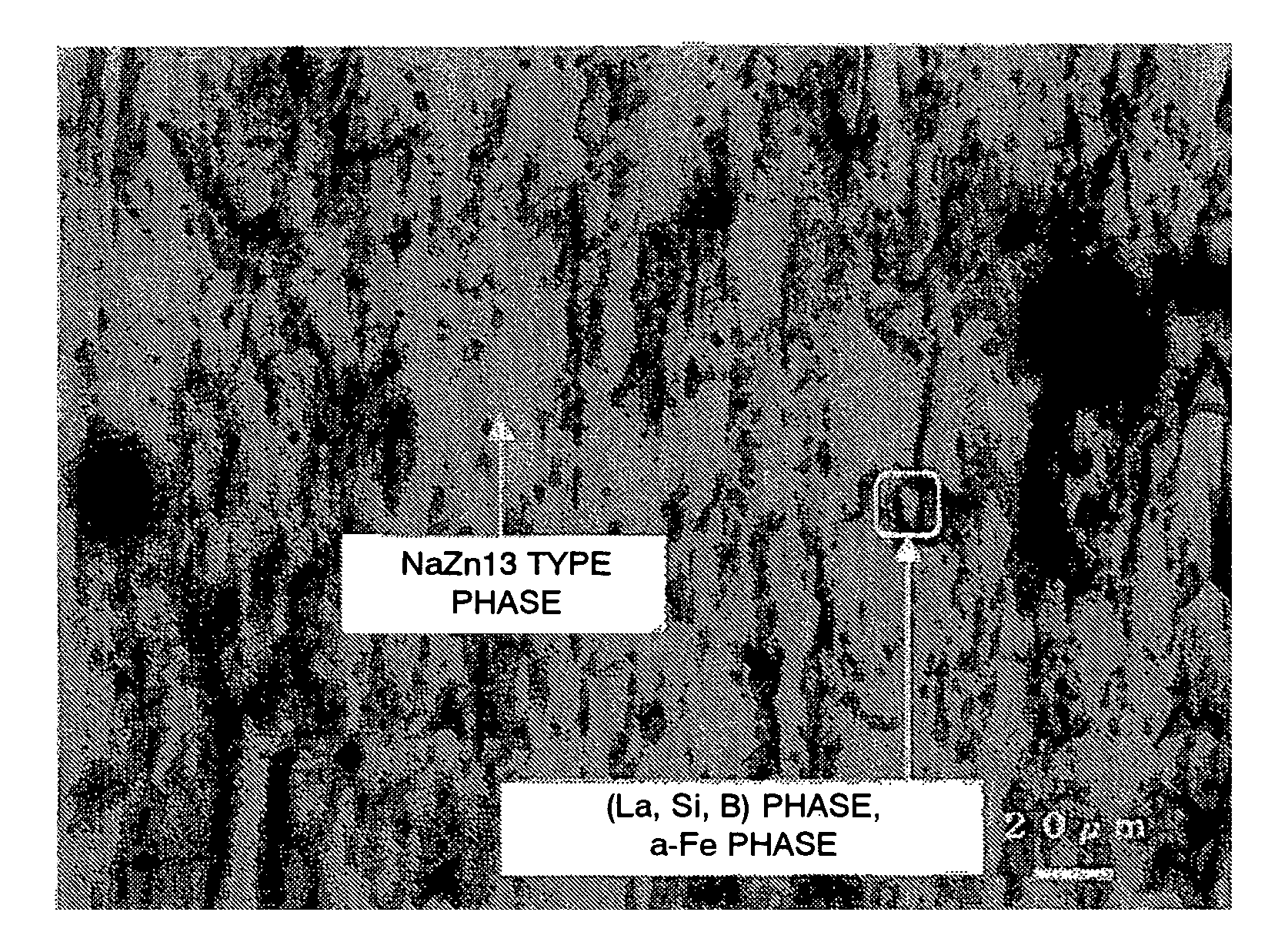
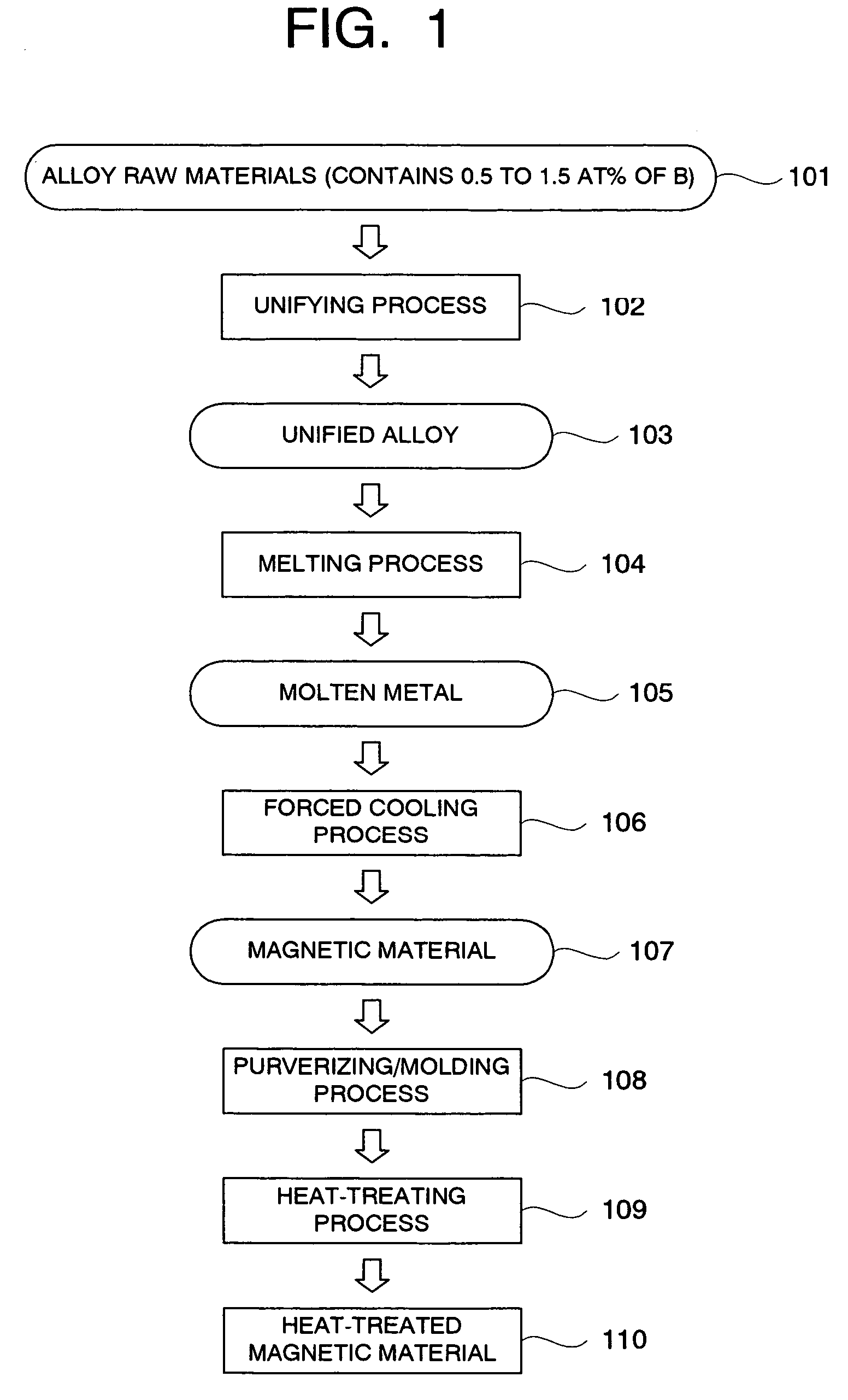
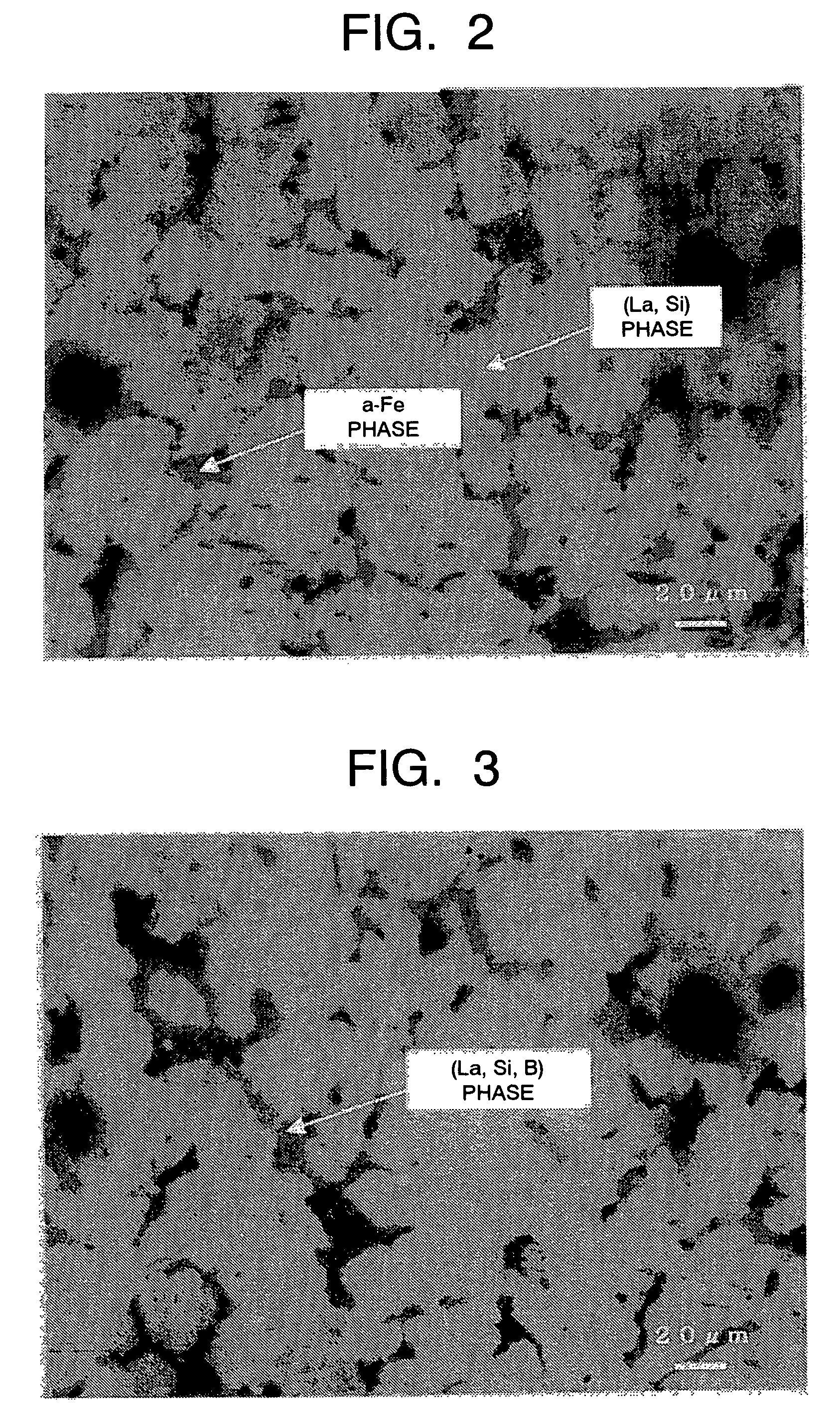
A magnetic material comprising a NaZn13 type crystal structure with uniform and fine microstructure exhibiting excellent characteristics as a magnetic refrigeration material, and a method of manufacturing the magnetic refrigeration material are provided. An alloy composition for forming magnetic material of the NaZn13 type crystal structure was melted comprising 0.5 atomic percent to 1.5 atomic percent of B to molten metal. The molten metal is rapidly cooled and solidified by a forced cooling process. Then, a rapidly cooled alloy having the NaZn13 type crystal structure was obtained. In this manner, magnetic materials comprising the NaZn13 type crystal structure phase, or the NaZn13 type crystal structure phase accompanied with other phases such as α-Fe phase having very small phase regions was manufactured without requiring heat treatment for a long time. As the result, productivity of manufacturing the magnetic refrigeration material is remarkably enhanced.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic material
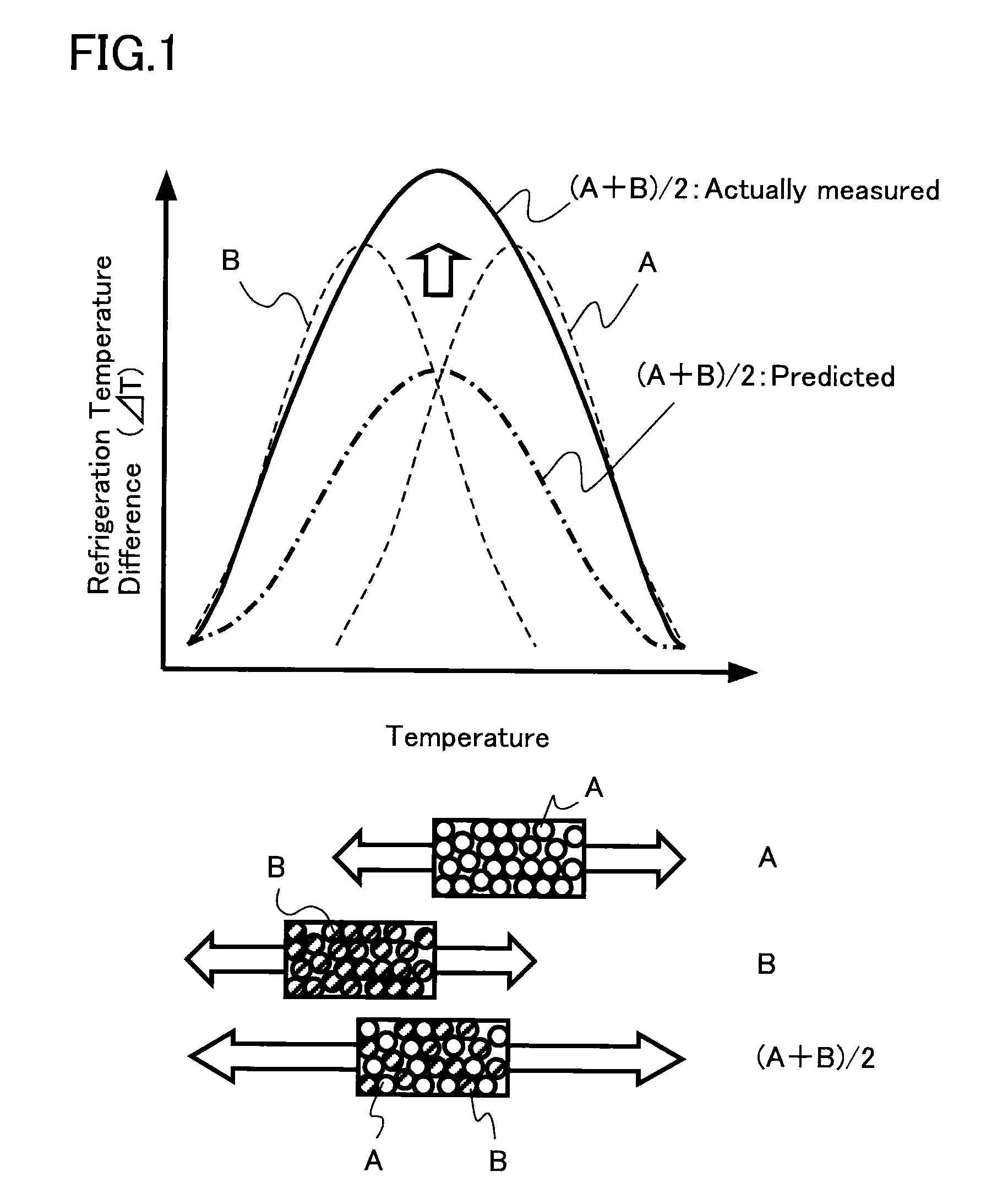
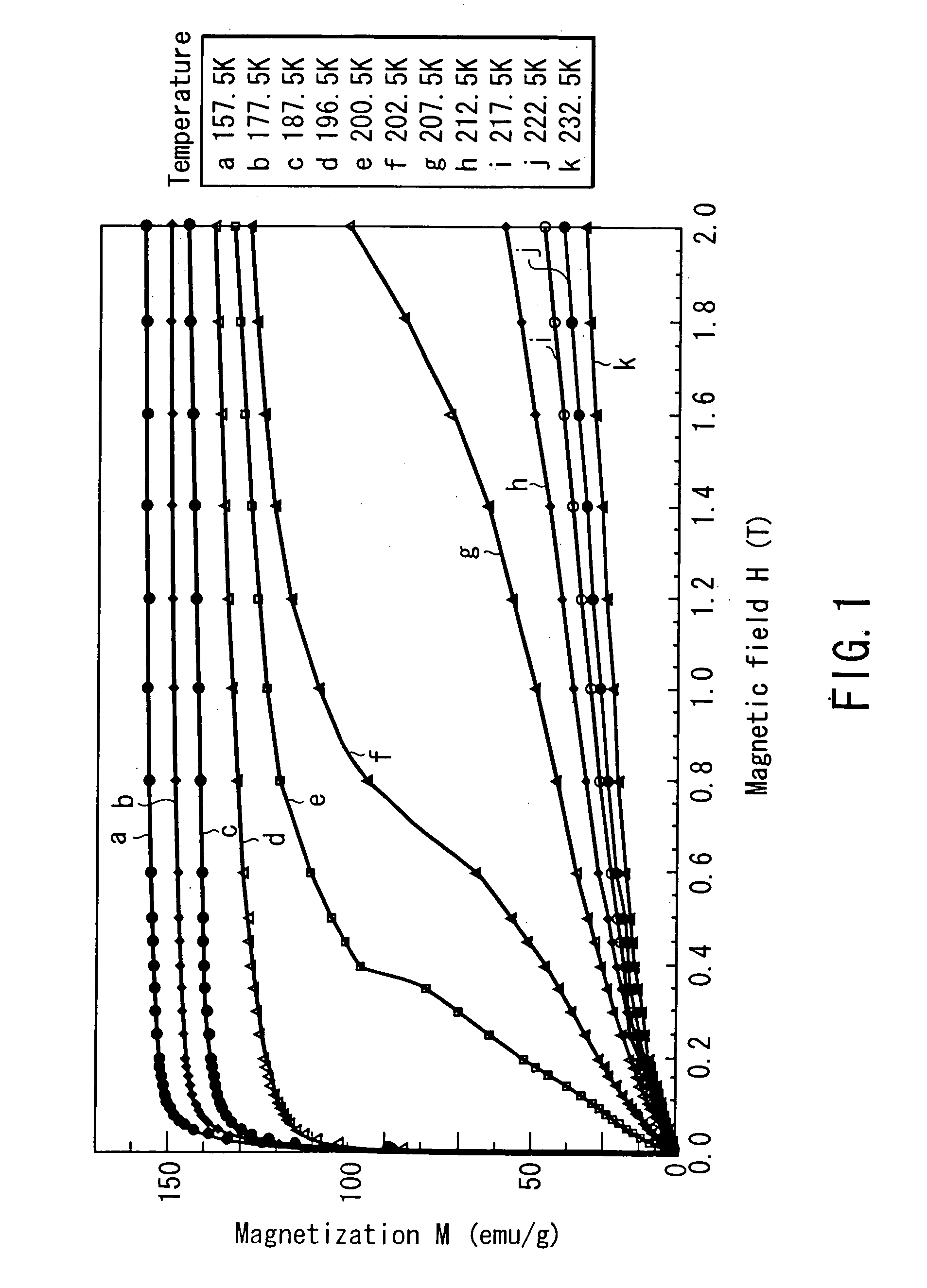
InactiveUS20050000230A1Change level balanceIncreased overall peak widthEnergy efficient heating/coolingInorganic material magnetismDifferential coefficientMagnetization curve
The magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration of the present invention is characterized by exhibiting, in a certain temperature region, preferably, only in part of a temperature region from 200 K to 350 K, an inflection point at which a second order differential coefficient of a magnetization curve changes from positive to negative with respect to a magnetic field, within the range of this magnetic field formed using a permanent magnet unit. This magnetic material of the present invention can generate a low temperature by using a relatively low magnetic field, by transferring the entropy between the electron spin system and the lattice system near the temperature at which an inflection point appears on the magnetization curve. Examples of the magnetic material meeting this condition are La(Fe,Si)13, (Hf,Ta)Fe2, (Ti,Sc)Fe2, and (Nb,Mo)Fe2, each containing 50 to 60 atomic % of transition metals such as Fe.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
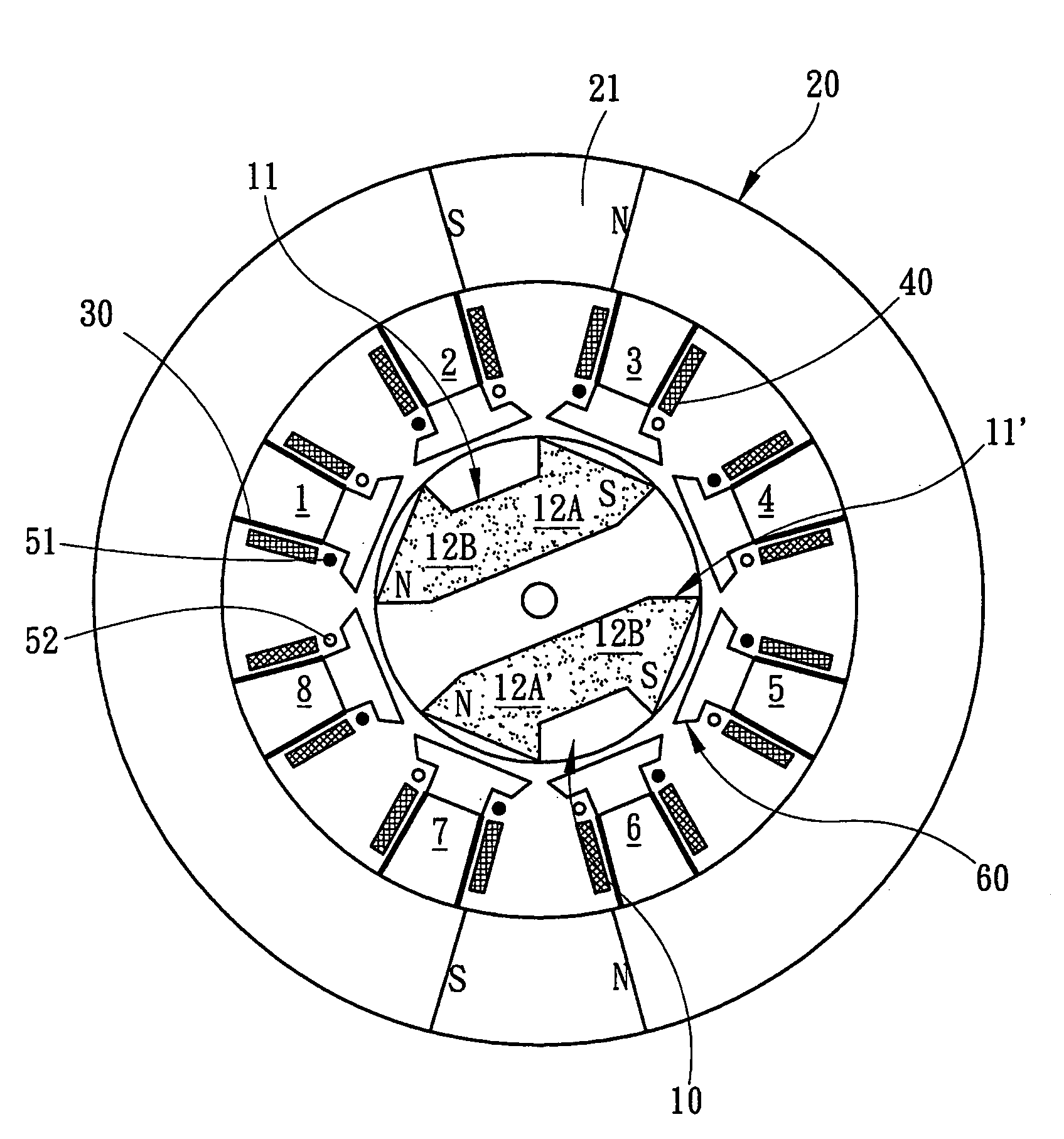
Permanent magnet system for rotary magnetic refrigeration apparatus
InactiveCN101012985AHigh magnetic field strengthReduce volumeEnergy efficient heating/coolingPermanent magnetsMagnetic mediaMetallic materials
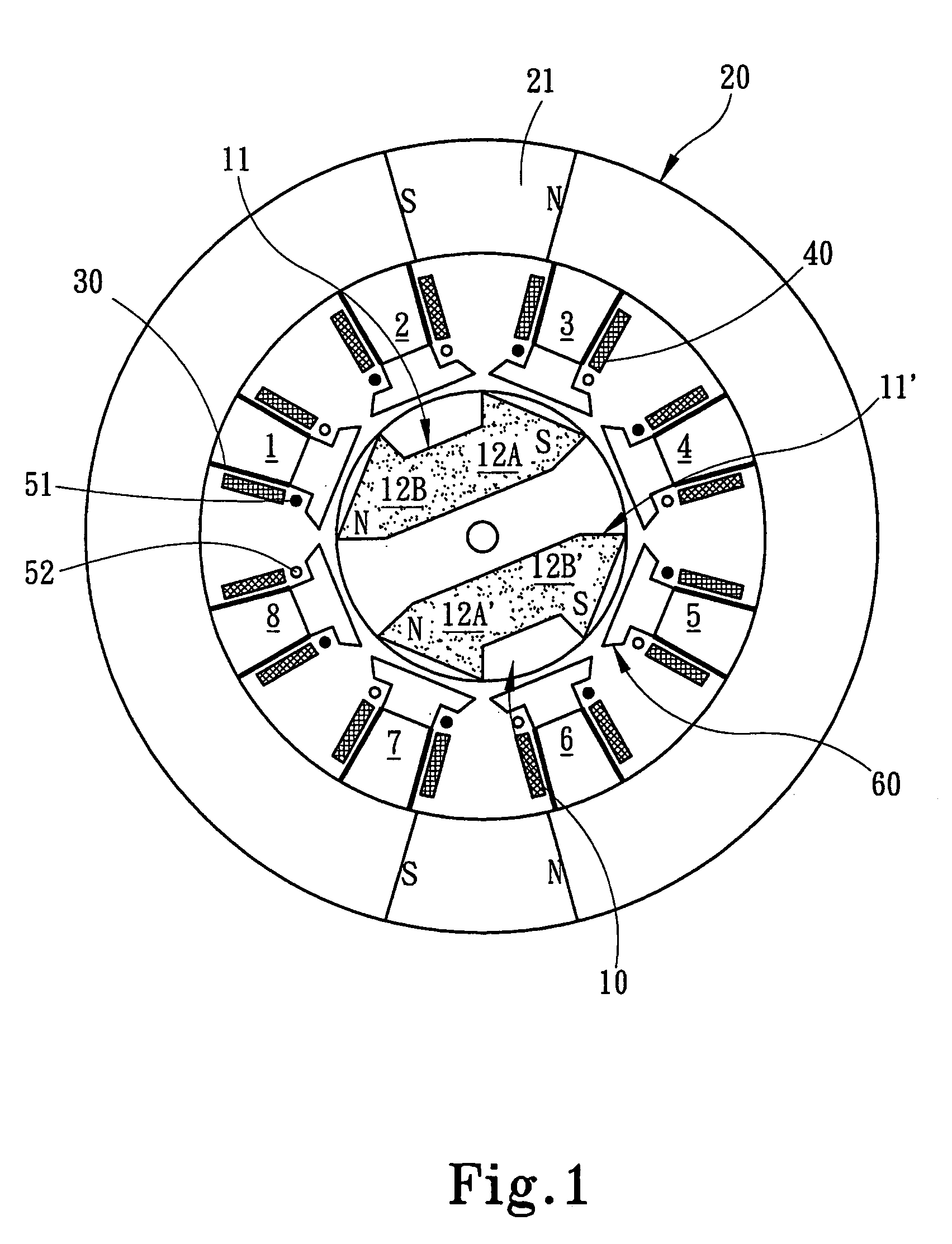
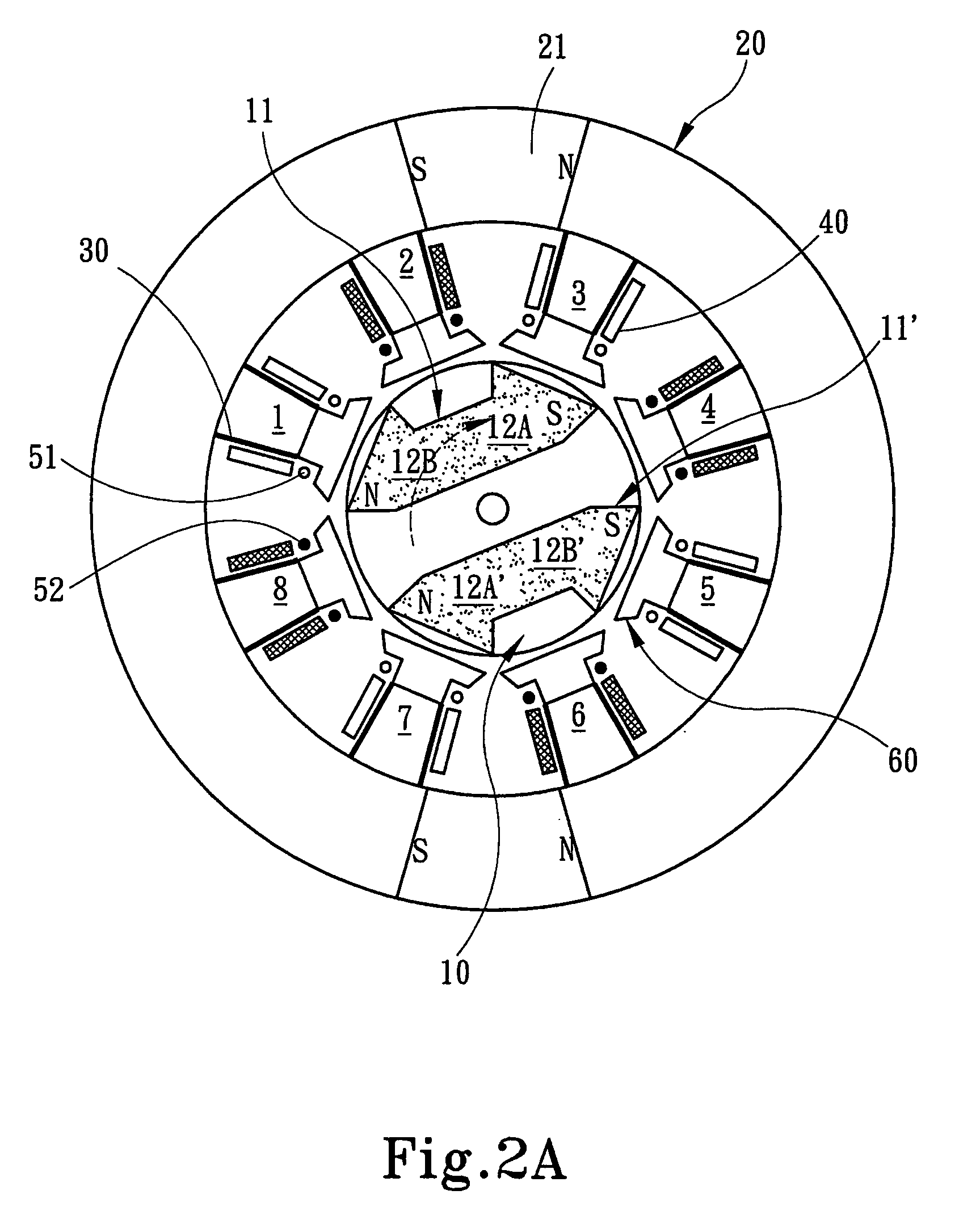
The invention relates to a permanent magnet system used in rotary magnetic refrigerator, wherein, the stator comprises a hollow cylinder permanent magnet and a magnetic conductive polar shoe; the hollow cylinder magnet is assembled symmetry around the central axle of the section of magnet via even permanent magnets; the magnetic direction of permanent magnet is decided by Halbach rotation theory; the magnetic conductive polar shoes are formed by two metals with better magnetic conductivity, while one side face is engaged with the wall of the chamber of permanent magnet, while another side is arc; two magnetic conductive polar shoes are contacted on the wall of chamber at the center of N and S polarities, with 180 degree spatial difference. The rotor comprises a rotary axle, a magnetic conductive iron corn and a magnetic medium; the rotary is cylinder; the iron corn is made from magnetic conductive magnet, as the cylinder with central hole or with cut-off two edges, sheathing the rotary axle while the rotary axle is at the center; two magnetic mediums are mounted on two outer arc faces of magnetic conductive iron corn, while the spatial positions are 180 degree different. The invention can be used as rotational permanent magnetic device.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
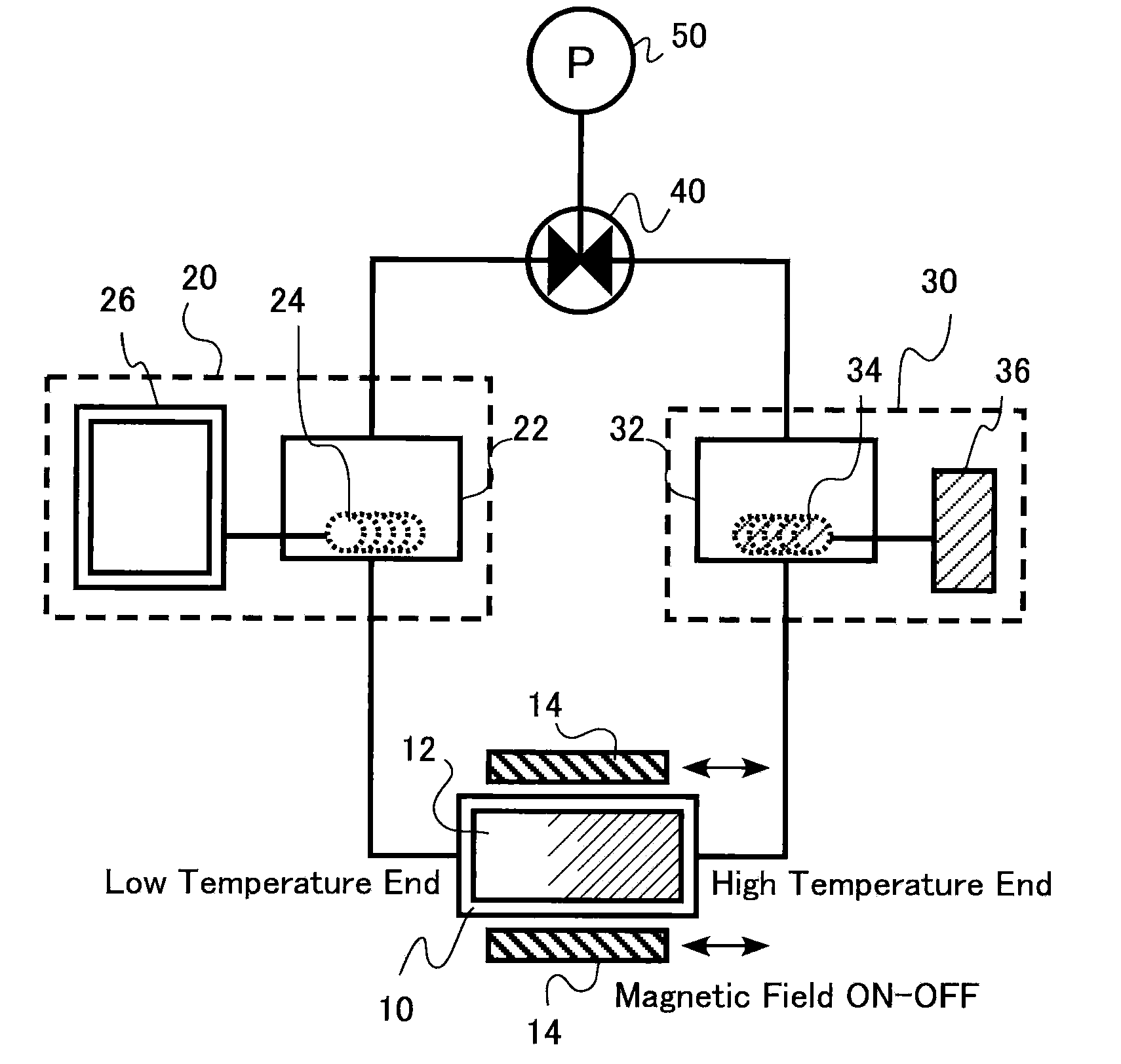
Hybrid magnetic refrigerator
InactiveUS20070240428A1Energy efficient heating/coolingCompression machines with cascade operationNuclear engineeringMagnetic refrigeration
A compact and highly efficient hybrid magnetic refrigerator includes a hybrid refrigerating apparatus wherein an evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle and a heat exchanger of a magnetic refrigeration cycle are thermally connected. The magnetic refrigeration cycle is provided with a magnetic refrigeration unit in which a magnetic substance dissipates and absorbs heat according to the increase and decrease of a magnetic field in order to heat and cool a refrigerant circulating in its vicinity. The heated refrigerant is cooled by the evaporator of the vapor compression refrigeration cycle and the cooled refrigerant is supplied to the heat exchanger cooling the outside air.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Active magnetic regenerator and magnetic refrigeration system
ActiveCN106949673AGive full play to the magnetocaloric effectLarge alternating stressMachines using electric/magnetic effectsSuperheatersMagnetic tension forceEngineering
The invention discloses an active magnetic regenerator and a magnetic refrigeration system. The active magnetic regenerator comprises a shell, a rotating mechanism and a magneto-thermal unit, wherein the rotating mechanism and the magneto-thermal unit are arranged in the shell; the rotating mechanism comprises a rotating part and a fixed support, and the fixed support is arranged on the inner wall of the shell through the rotating part; and the magneto-thermal unit comprises a plurality of plate-shaped magneto-thermal materials which are arranged in parallel, and the magneto-thermal units are arranged on the fixed support. According to the active magnetic regenerator, the magneto-thermal unit is arranged inside the shell through the rotating mechanism, when the direction of an external magnetic field changes, the magneto-thermal unit synchronously rotates with the external magnetic field under the action of magnetic torque so that the direction of the external magnetic field can be always kept in the direction with the smallest demagnetization factor of the magneto-thermal materials, magnetic fields in the magneto-thermal materials are ensured to be maximized, the magneto-thermal effect of the magneto-thermal materials is fully exerted, and the optimal refrigerating performance is obtained. Meanwhile, under the action of the magnetic torque, the magneto-thermal unit rotates, so that large alternating stress is avoided inside the magneto-thermal materials, and the service life of the whole regenerator is prolonged.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reciprocating room temperature magnetic refrigerating machine and refrigerating method
InactiveCN101221001ARealize the cooling effectSimple structureEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsRoom temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a reciprocating room-temperature magnetic refrigerator and a refrigerating method thereof. The magnetic refrigerator mainly comprises a magnetic field source, a magnetic working medium, a heat transmitting liquid circulation pipeline, a heat exchanger and a control unit, wherein, the magnetic field source is mainly composed of a permanent magnet, and the magnetic working medium is arranged in a magnetic refrigeration box. The heat transmitting liquid in the heat transmitting liquid circulation pipeline is circulated according to the heat absorption and release conditions of the magnetic working medium, and the heat transmitting liquid is exchanged through the heat exchanger. The coordination between the parts is controlled by the control unit. The refrigeration method of the magnetic refrigerator is that the refrigeration box in which the magnetic work medium is arranged is arranged in a gas gap of the magnetic field source and the control unit is adopted to control the flowing direction of the heat transmitting liquid at the two ends of the refrigeration box. The invention has simple structure and does not need the use of compressors and complicated mechanical action units and realizes a refrigerating effect at the room temperature.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic refrigerating portable refrigerator and refrigeration method
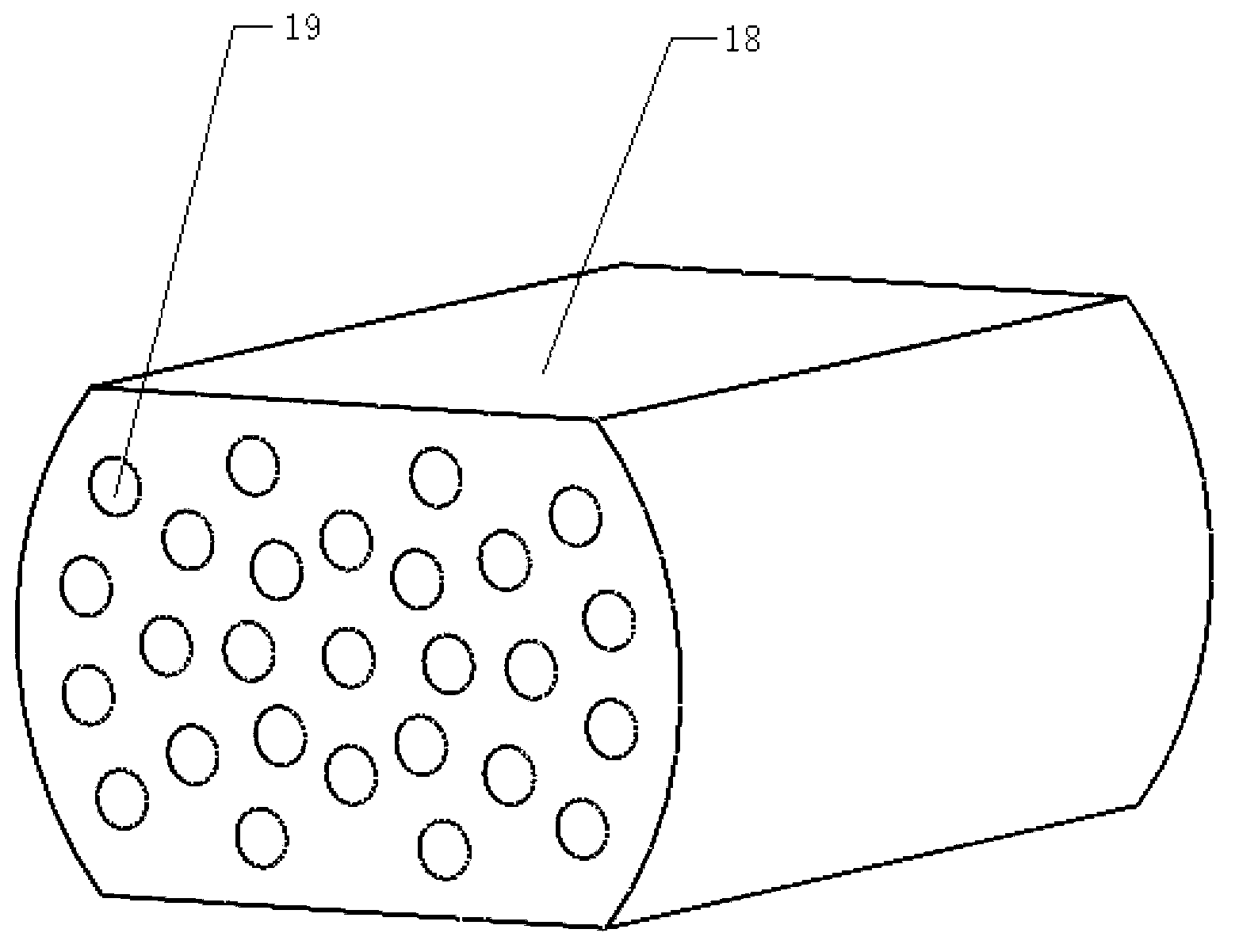
InactiveCN103062973ATo achieve the purpose of coolingSimple and fast operationEnergy efficient heating/coolingDomestic refrigeratorsWaste processingFilling materials
The invention discloses a magnetic refrigerating portable refrigerator and a refrigeration method. The magnetic refrigerating portable refrigerator belongs to the field of domestic electrical appliances and comprises a shell, a storage box arranged in the shell, a permanent magnet group, a magnetic working medium and the like, wherein the permanent magnet group is a tube-shaped body the centre of which is provided with a through hole; and the magnetic working medium is provided with multiple through holes and is closely sleeved in a magnetic working medium shell with a concave slideway. The function of the magnetic refrigeration portable refrigerator is realized by that the magnetic working medium is fixed, straight guide rails drive the permanent magnet to do a reciprocating straight motion relatively to the magnetic working medium, and the magnetic working medium realizes an excitation and demagnetizing process, so that the refrigeration of the refrigerator is realized; the relative movement method of the magnetic working medium and the permanent magnet is simple to operate, relatively stable in motion, and easy to control in the realizing manner; the structure of the magnetic working medium solves the problems that the filling materials is difficult to process and manufacture, and gaps among the filling materials are difficult to guarantee and the like; and a permanent magnet is simple in structure and convenient to process, so that the non-waste processing is realized, and the processing and manufacturing cost is greatly saved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Magnetic refrigeration material and method of manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS7914628B2Improve productivityDecrease productivityCompression machinesInorganic material magnetismProduction rateCrystal structure
A magnetic material comprising a NaZn13 type crystal structure with uniform and fine microstructure exhibiting excellent characteristics as a magnetic refrigeration material, and a method of manufacturing the magnetic refrigeration material are provided. An alloy composition for forming magnetic material of the NaZn13 type crystal structure was melted comprising 0.5 atomic percent to 1.5 atomic percent of B to molten metal. The molten metal is rapidly cooled and solidified by a forced cooling process. Then, a rapidly cooled alloy having the NaZn13 type crystal structure was obtained. In this manner, magnetic materials comprising the NaZn13 type crystal structure phase, or the NaZn13 type crystal structure phase accompanied with other phases such as α-Fe phase having very small phase regions was manufactured without requiring heat treatment for a long time. As the result, productivity of manufacturing the magnetic refrigeration material is remarkably enhanced.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
LaFeSi-based magnetic refrigeration material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104694813AGrain intactMagnetic entropy change does not decreaseHeat-exchange elementsHysteresisStructural phase
The invention discloses a LaFeSi-based magnetic refrigeration material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the refrigeration material is La1+aFe13-b-cCobSicHd and the refrigeration material comprises a NaZn13 structural phase, wherein a is greater than 0 but less than or equal to 1, b is greater than or equal to 0 but less than or equal to 1.2, c is greater than or equal to 1.0 but less than or equal to 1.8 and d is greater than or equal to 0 but less than or equal to 3. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing raw materials according to the chemical formula and smelting in the presence of high-purity inert gas to obtain an alloy ingot with uniform components; annealing the alloy ingot in the presence of high-purity inert gas and then quickly quenching to obtain the La(Fe, Co, Si)13-based block magnetic refrigeration material containing the NaZn13 structural phase; and furthermore, introducing hydrogen into the block magnetic refrigeration material. According to the block magnetic refrigeration material, the forming period of a magnetic thermal phase is obviously shortened. The material before hydrogenation needs not to be mechanically crushed to small particles, and the block can be fully hydrogenated to be saturated. The material has a huge magnetocaloric effect and low hysteresis, so that the material is an ideal near room-temperature magnetic refrigeration working material.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Rare earth-copper-aluminum material for magnetic refrigeration and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102453466AGood magnetic and thermal reversible propertiesLow priceHeat-exchange elementsMagnetic materialsRare earthPhase change
The invention provides a rare earth-copper-aluminum material for magnetic refrigeration and a preparation method thereof. The rare earth-copper-aluminum material for magnetic refrigeration is a compound having a general formula of RCuAl, wherein R represents Ho, Er, Dy, Tb or Gd. The rare earth-copper-aluminum material for magnetic refrigeration has a large magnetic entropy change around respective phase change temperatures of rare earth, copper and aluminum, a large magnetic refrigeration capacity, good thermal and magnetic reversible properties, and a low price, and thus the rare earth-copper-aluminum material for magnetic refrigeration is a very ideal middle / low-temperature zone magnetic refrigeration material.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106906408ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getHigh thermal conductivityHeat-exchange elementsAlloyThermal hysteresis
The invention discloses a LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material and a preparation method and application thereof. The LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material comprises functional body components such as LaFeSi based alloy particles and matrix components such as low-melting-point metal or alloy, and the LaFeSi based alloy particles are bonded and coated by the matrix components to form a bulk material; and the LaFeSi based alloy particles are of a NaZn13 type structure. According to the LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material and the preparation method and application thereof, composite hot pressing is conducted between the cheap and easily-obtained low-melting-point metal or alloy and the LaFeSi based alloy particles, the appropriate low-melting-point components are selected, the pressing pressure, the hot pressing temperature, the pressure maintaining time and the like are adjusted, and thus the high-thermal-conductivity LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material can be obtained; the magnetic entropy change of the LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material is less reduced compared with that before hot pressing, the magnetic hysteresis loss is low, and thermal hysteresis is avoided; and in addition, the process is simple and easy to operate, the process conditions are relatively mild, energy consumption is little, the cost is low, the repeatability is good, and the preparation method can be widely used in preparation of magnetic refrigeration materials.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
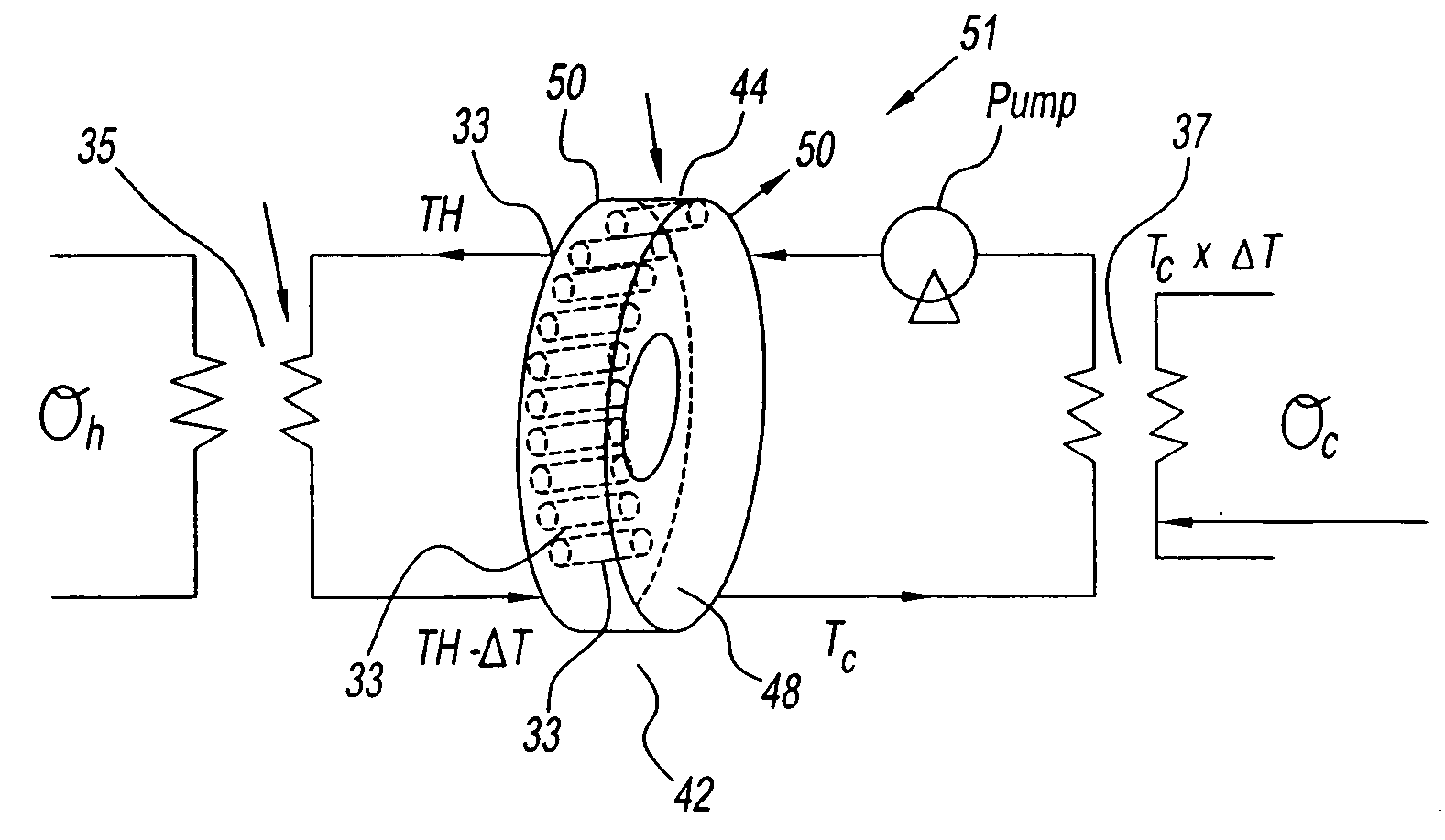
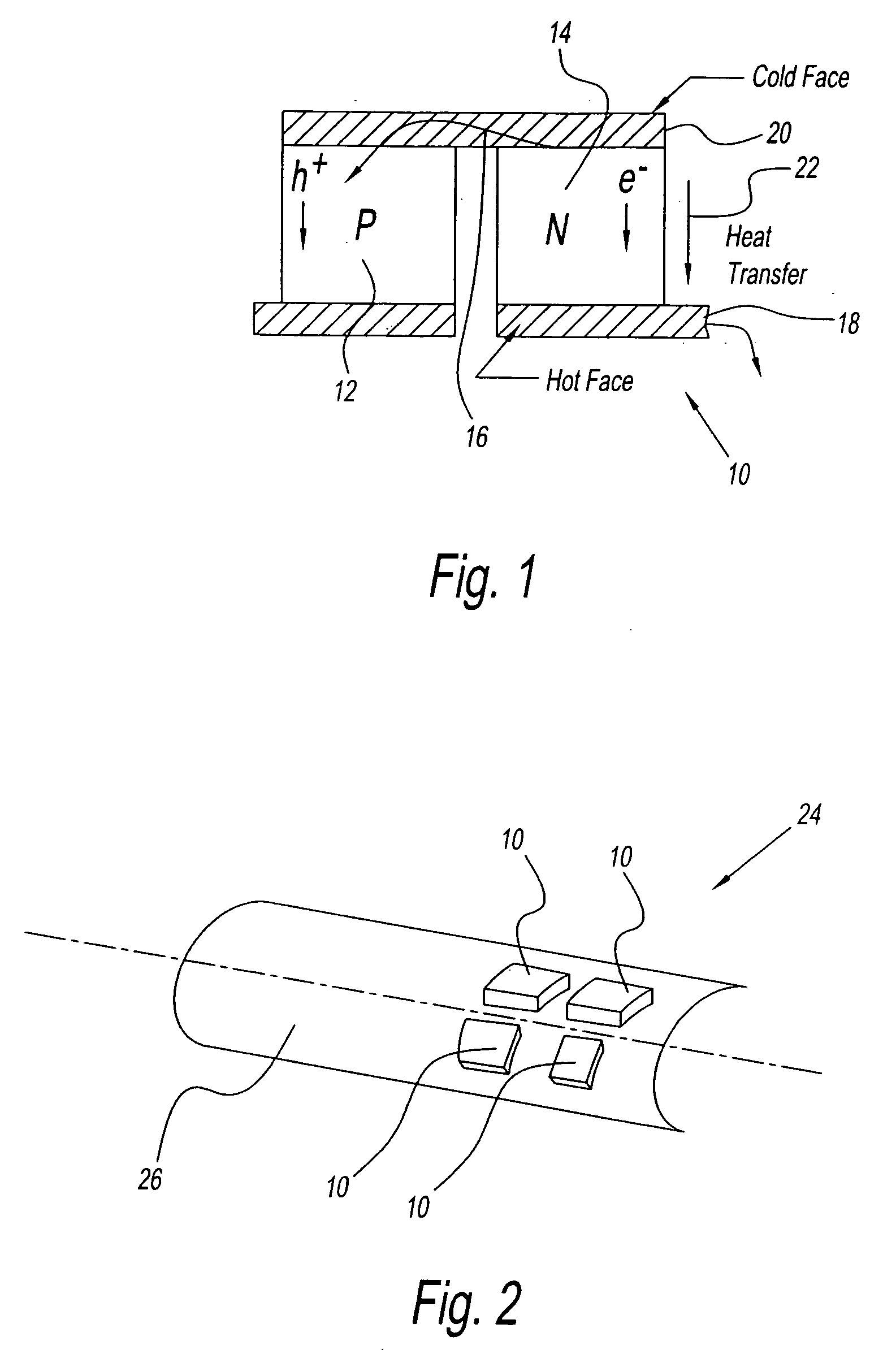
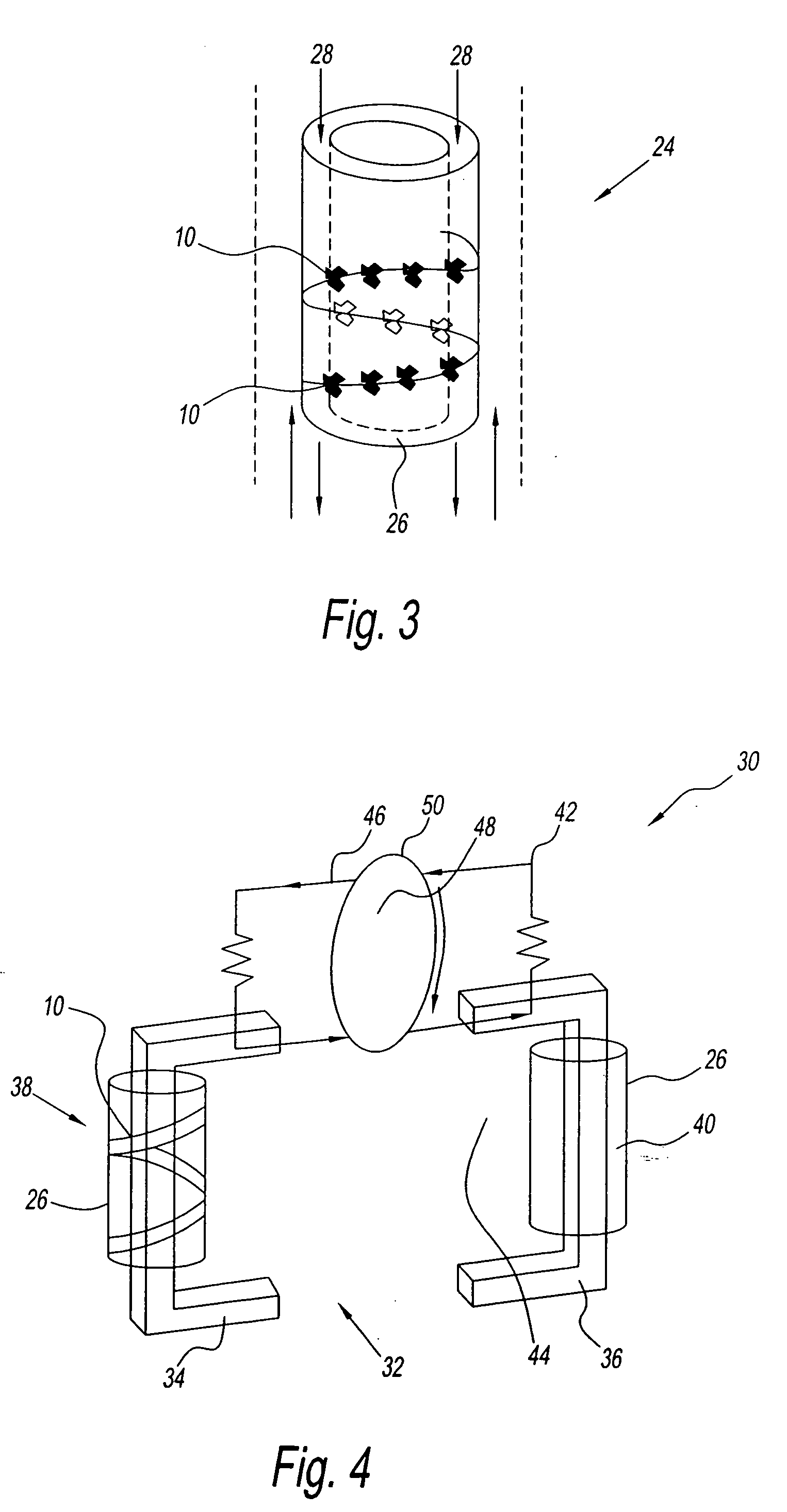
Combination Thermo-Electric and Magnetic Refrigeration System
InactiveUS20090133409A1Energy efficient heating/coolingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRefrigerationMagnetic refrigeration
A refrigeration system has a compartment and a first cooling device. The first cooling device cools the compartment and generates a magnetic field. The refrigeration system also has a second device. The second device uses the generated magnetic field for additional cooling to the compartment.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com