Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1600results about "Compression machines with cascade operation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
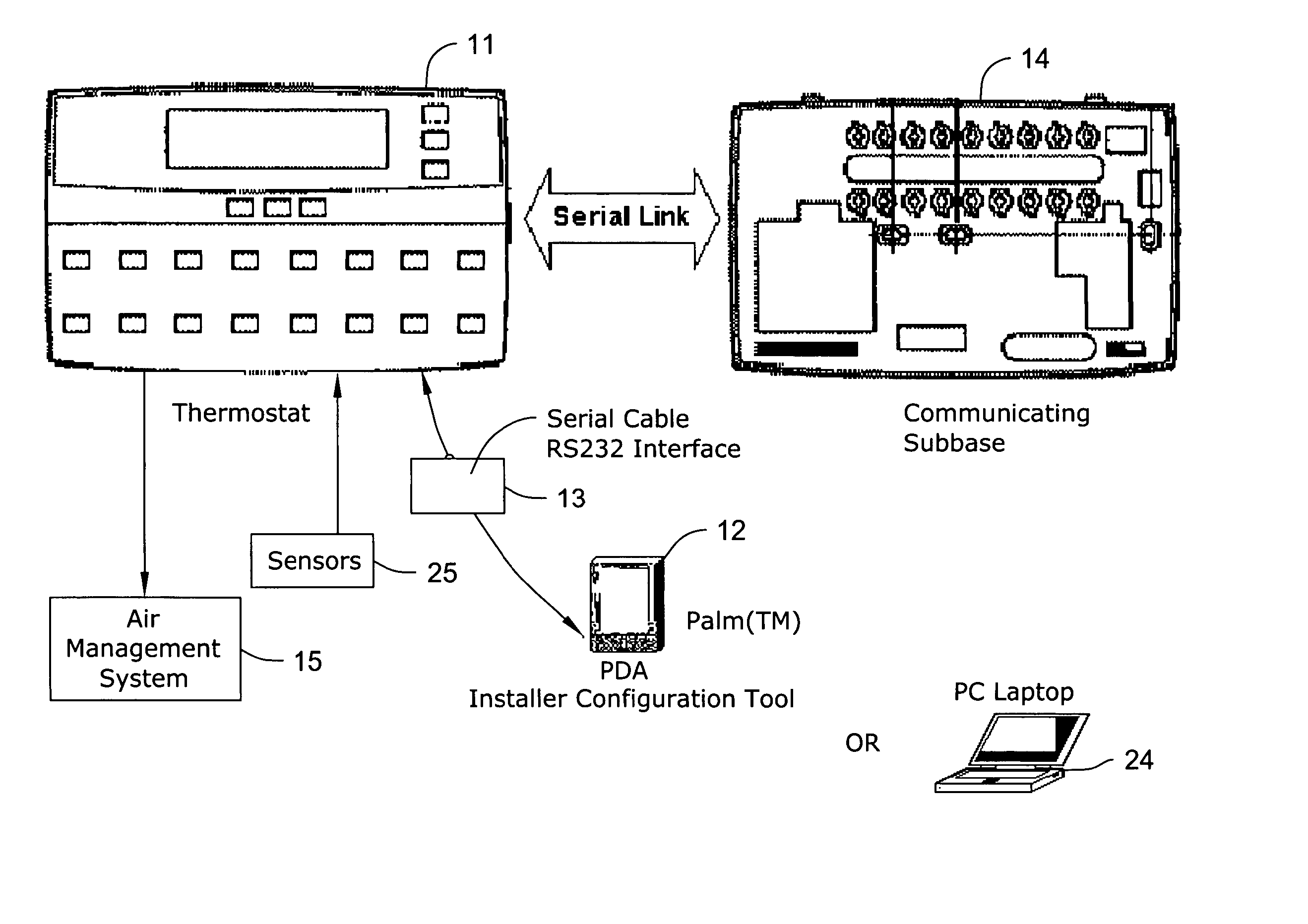
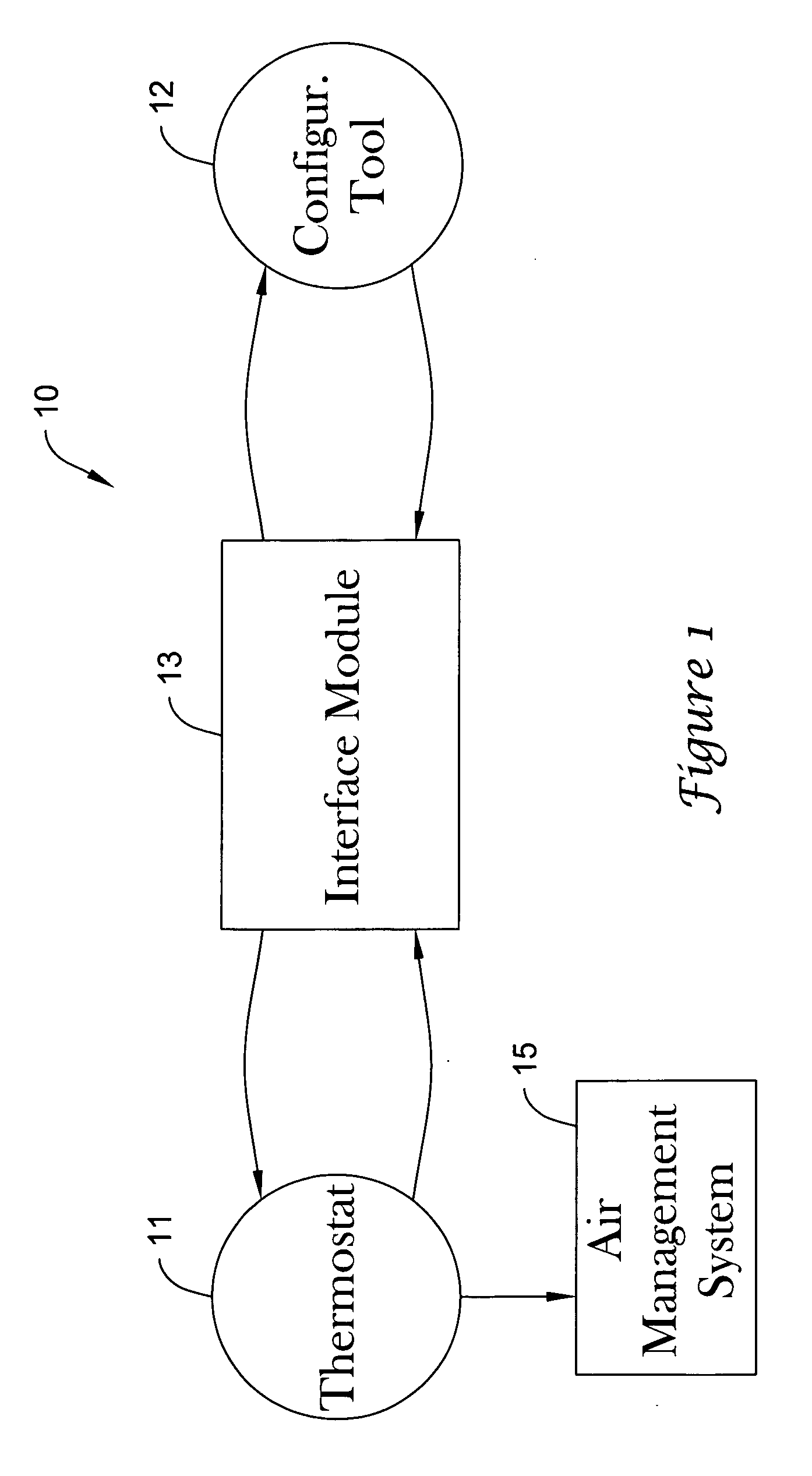
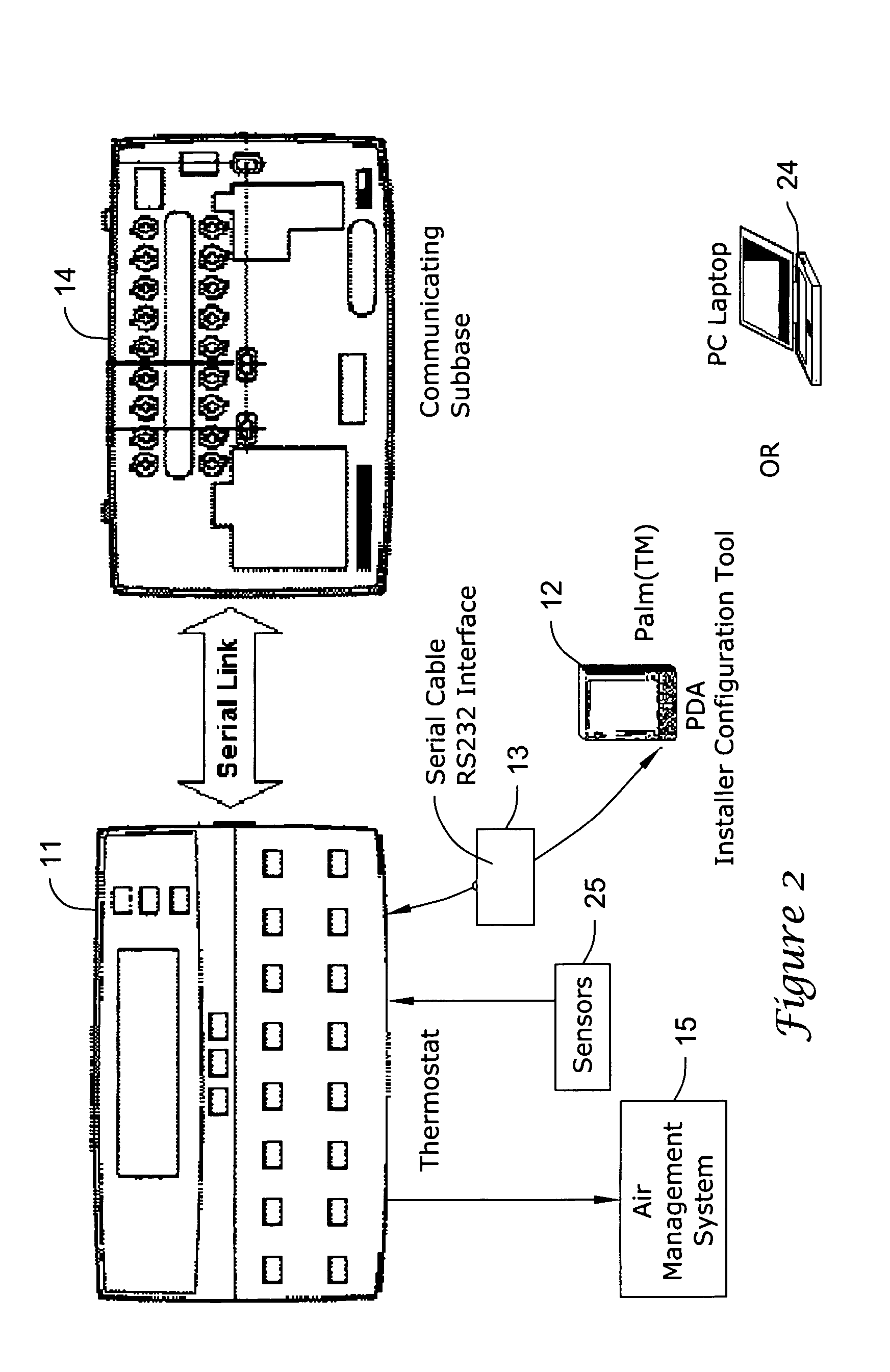
Thermostat having modulated and non-modulated provisions
ActiveUS20050040247A1Quick and efficientEasy to adaptMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsAir managementEngineering
A thermostat providing modulated or analog control of valves or dampers of an air management system. This permits operating a single cooling or heating stage with partially open valves or dampers as needed, since one full stage that is either fully on or off may not be easy to manage for effective air management of a particular type of building, zone or facility. The thermostat may also provide non-modulated control of multi-stage cooling and heating systems. The thermostat may even be used to control a modulated system having more than one stage of cooling or heating.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
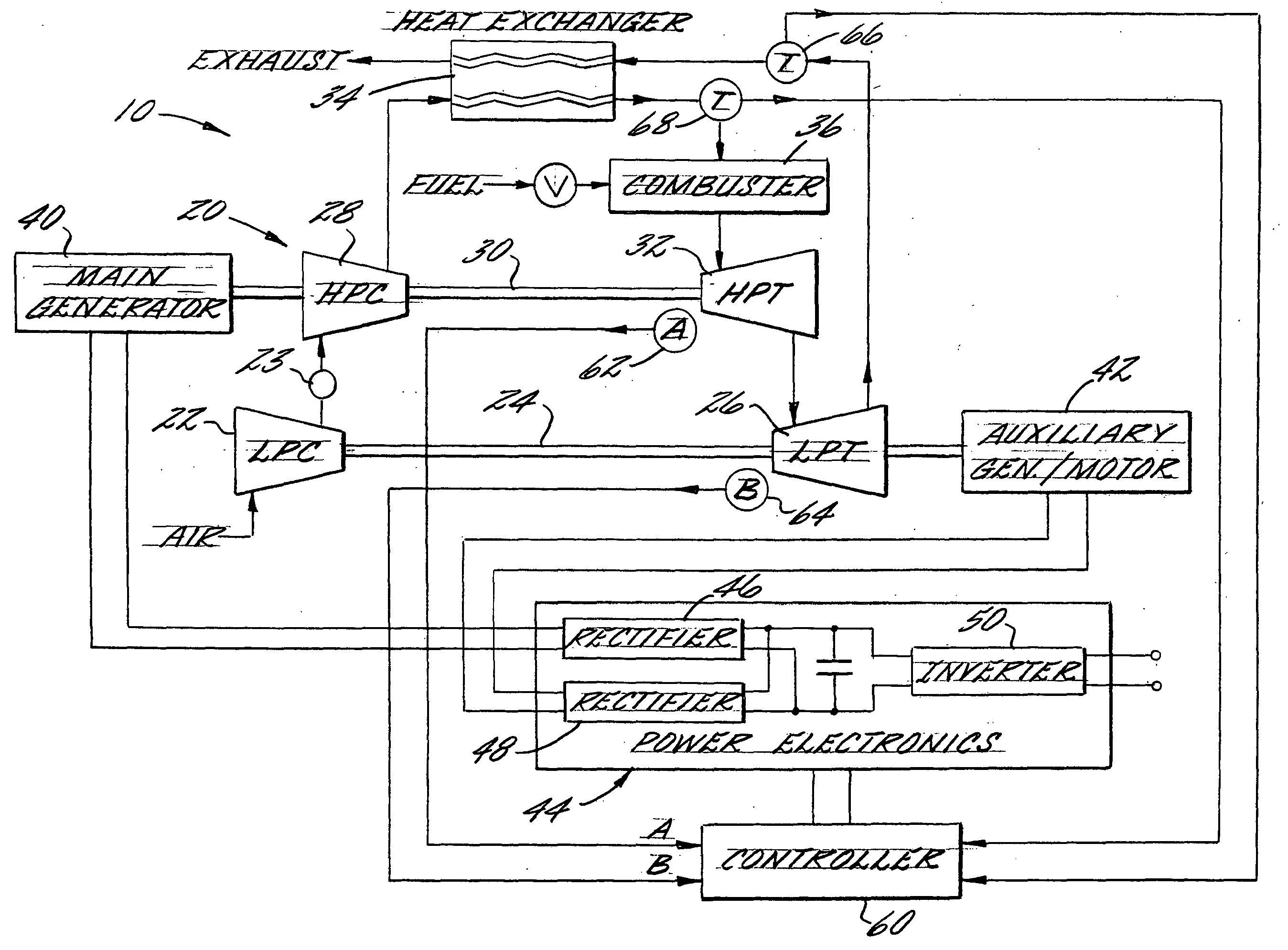
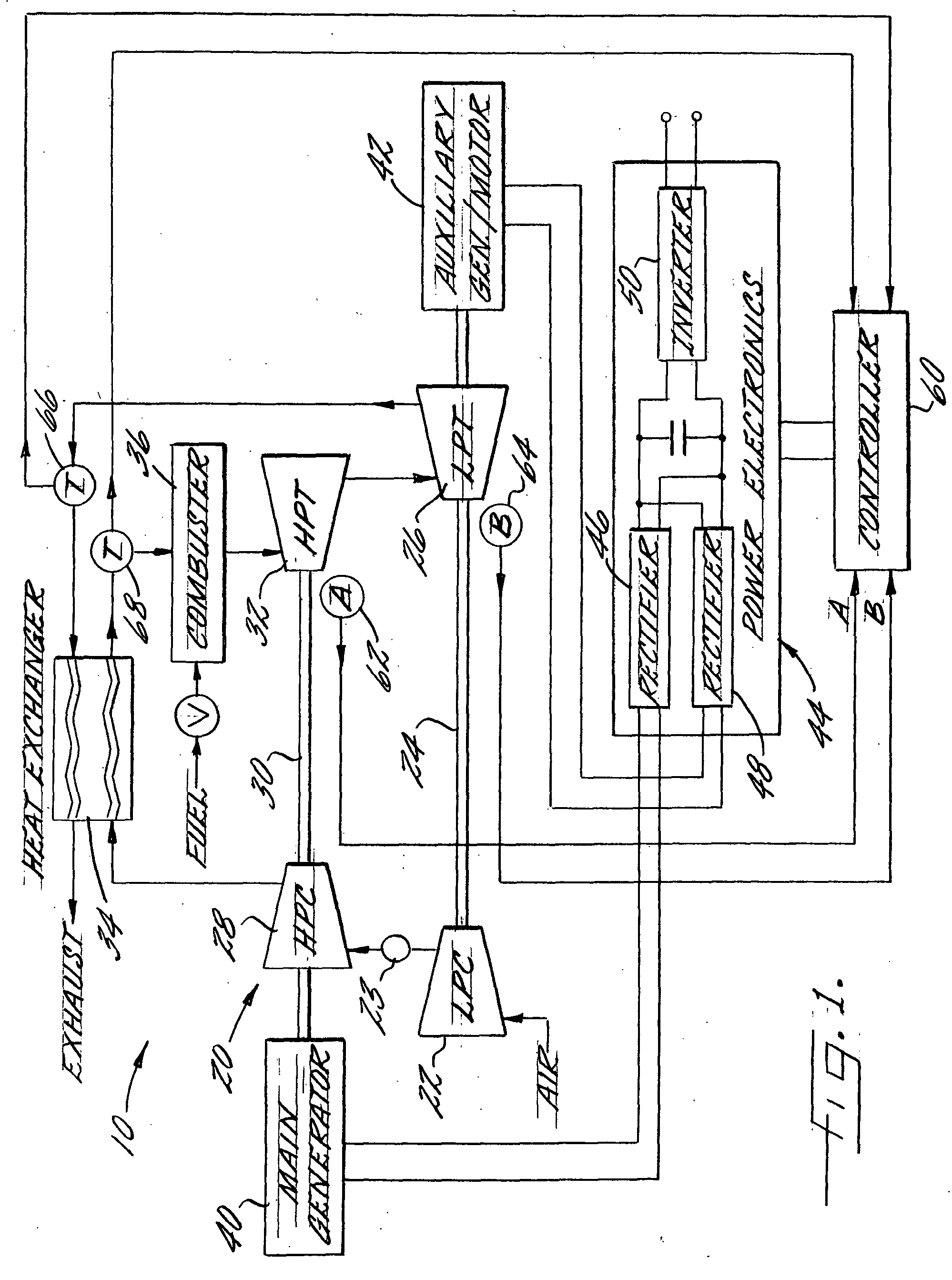
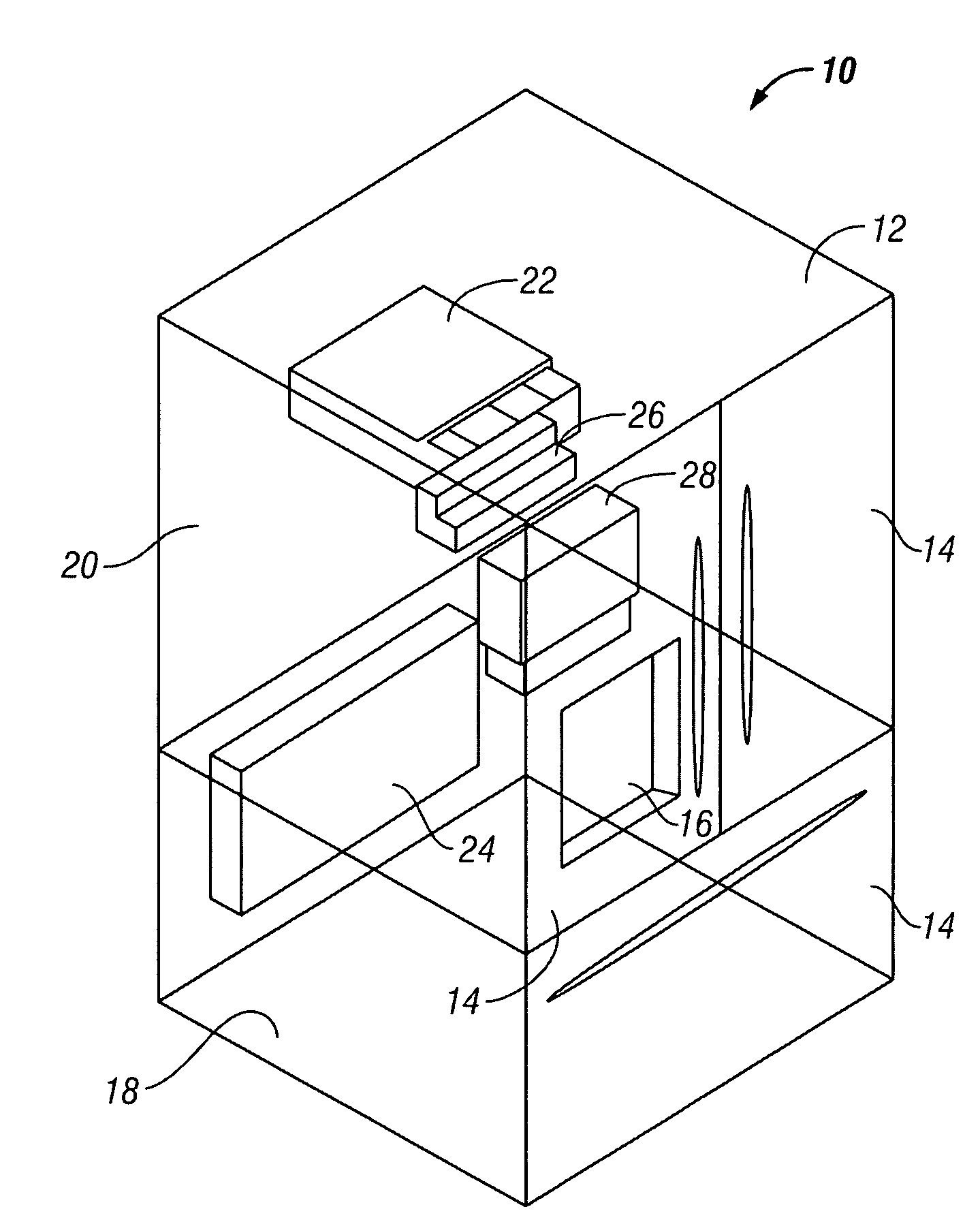
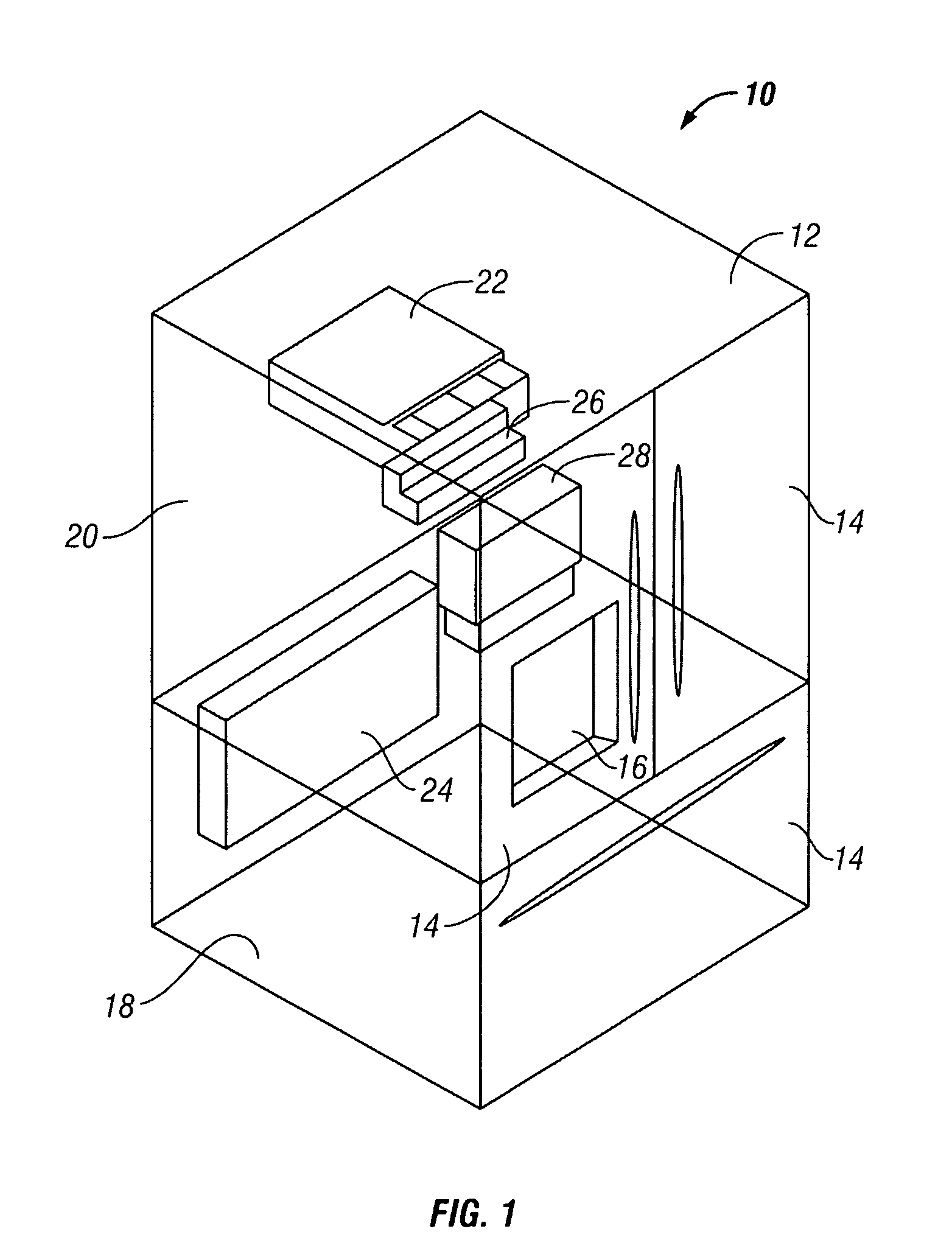
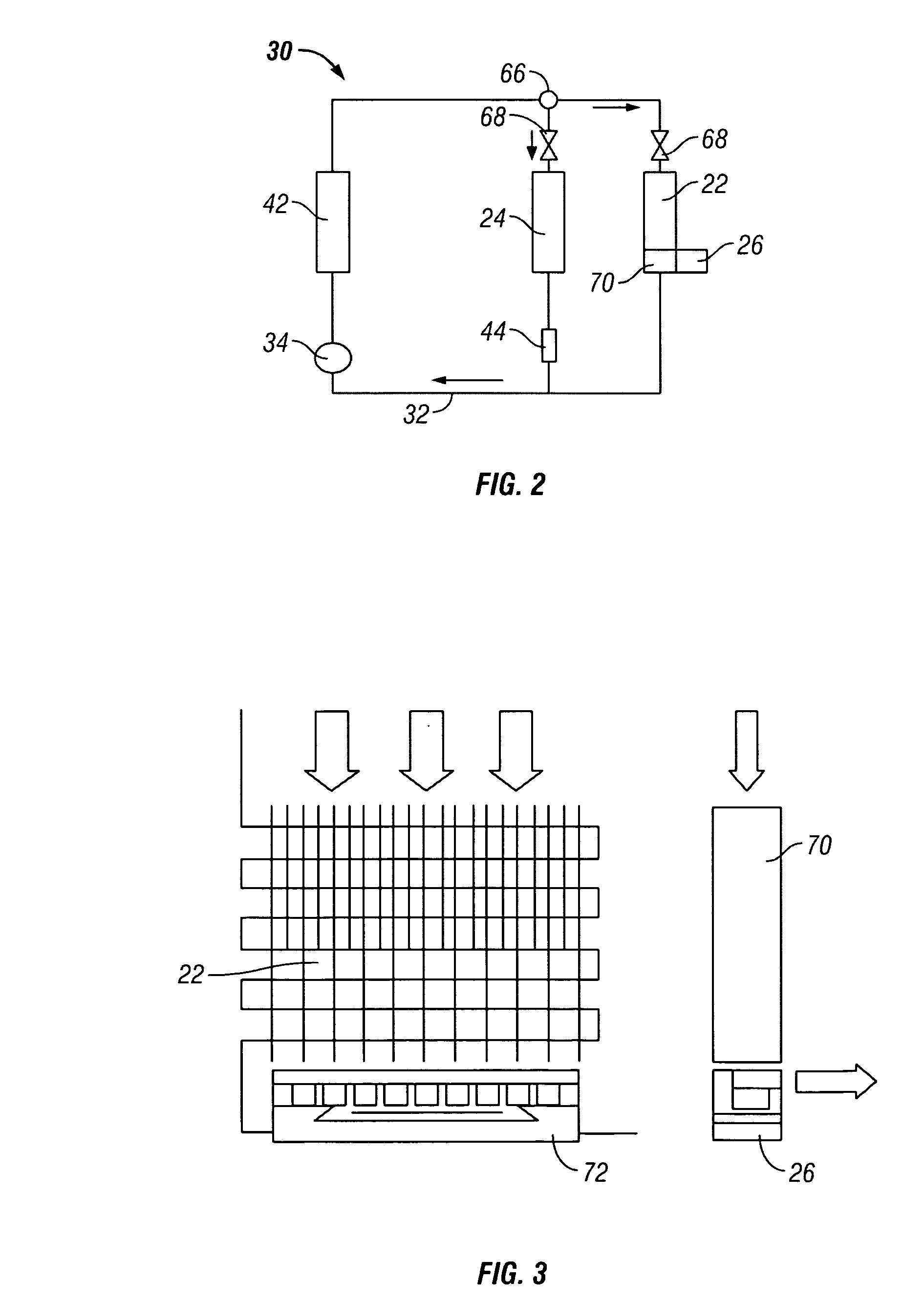
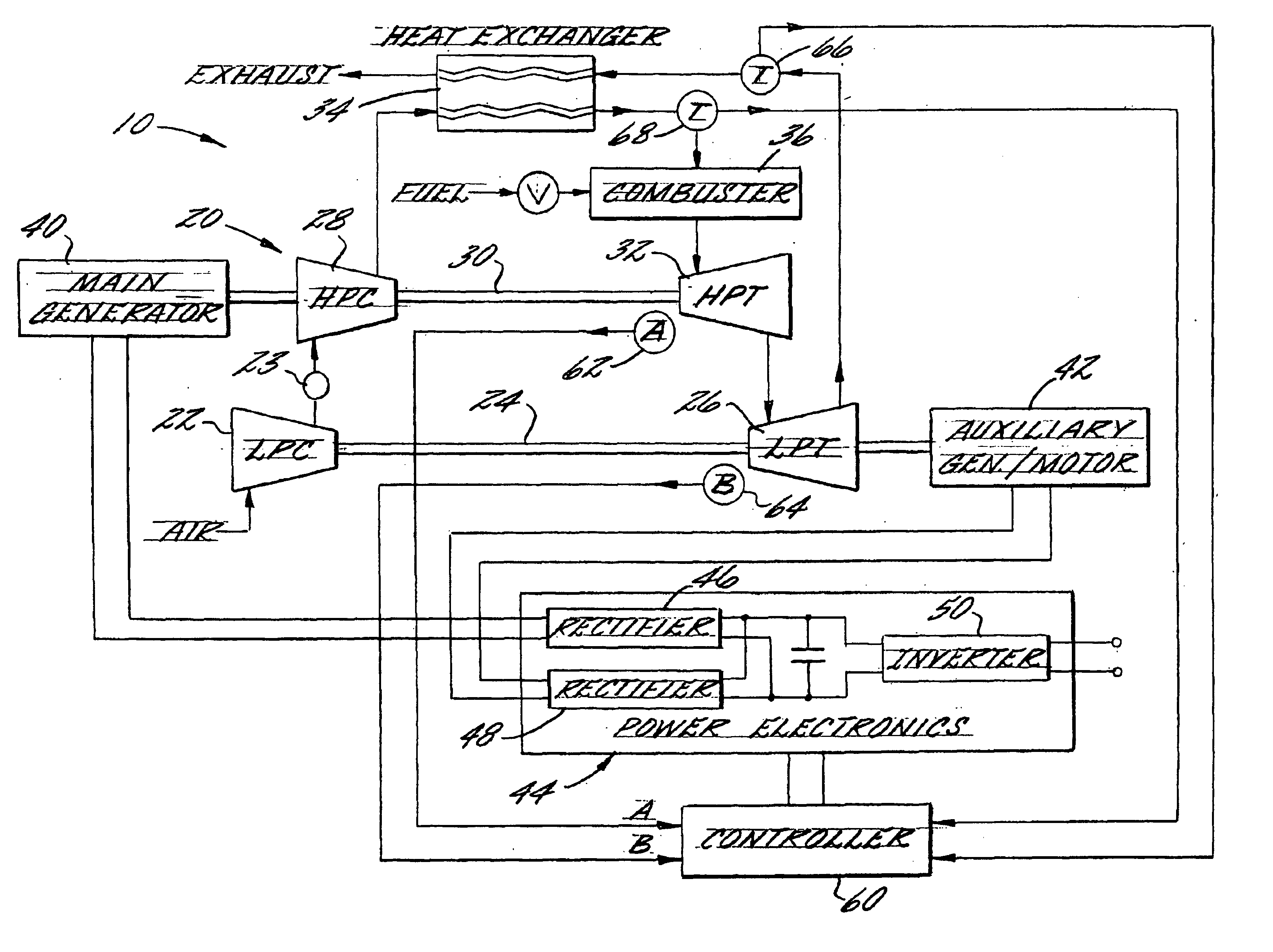
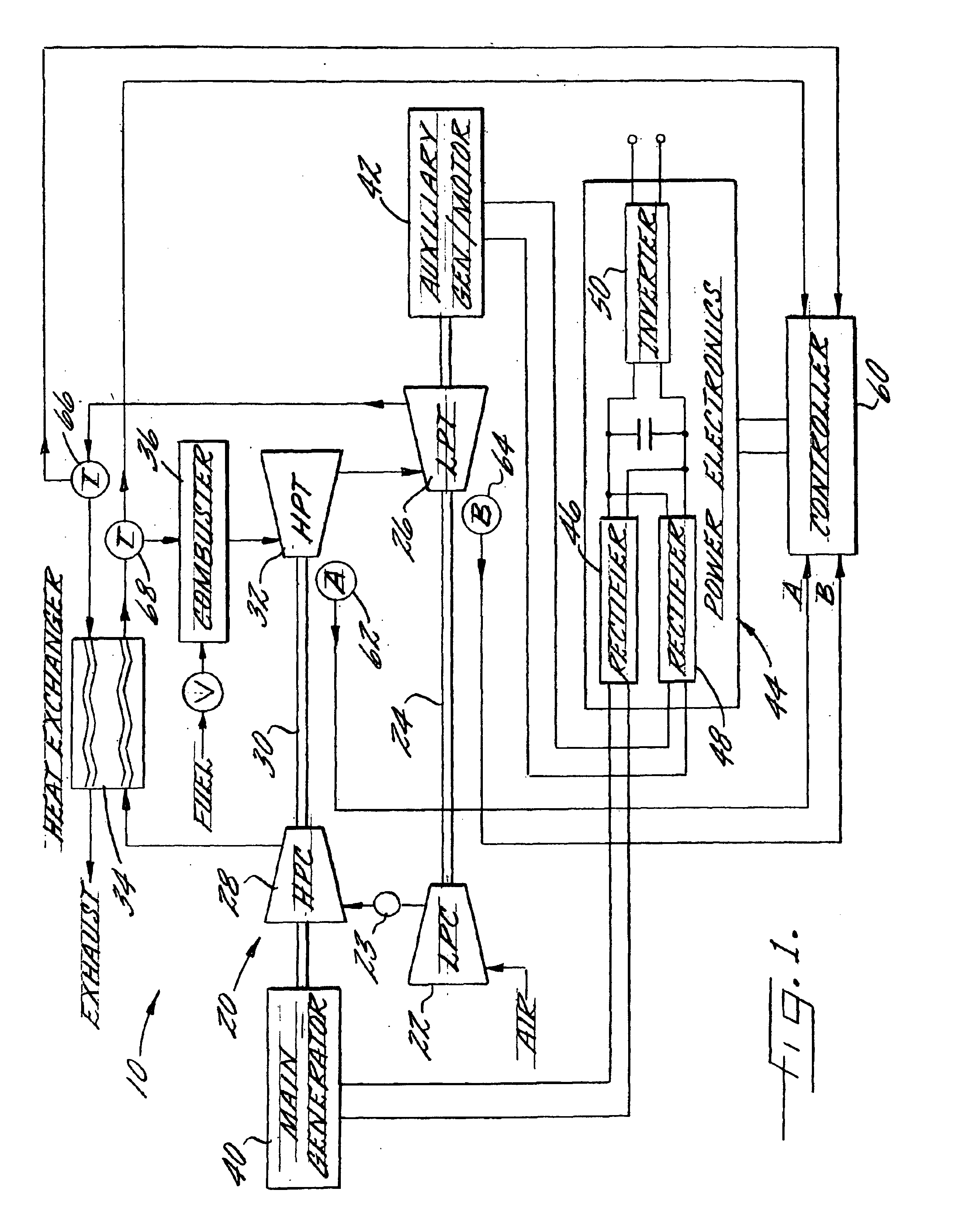
Multi-spool turbogenerator system and control method
ActiveUS20050056021A1Eliminate needMinimize and eliminate needCombustion enginesGas turbine plantsTurbineGas turbines
An electrical power generating system is driven by a multi-spool gas turbine engine including at least first and second spools. The first spool comprises a turbine and a compressor mounted on a first shaft; the second spool has at least a turbine mounted on a second shaft that is not mechanically coupled to the first shaft. A main generator is coupled with one of the spools, and an auxiliary generator / motor is also coupled with one of the spools. Speed control of each of the generators is employed for controlling operation of the engine. The auxiliary generator / motor can operate in either a generation mode to extract power from its spool or a motor mode to inject power into its spool.
Owner:MES INT INC
Method for providing refrigeration
A method for providing refrigeration such as to an insulated enclosure wherein a defined multicomponent refrigerant fluid undergoes a phase change coupled with Joule-Thomson expansion to generate refrigeration over a wide temperature range which may comprise from ambient to low temperatures.
Owner:EDWARDS VACUUM LLC
Ejector cycle system with critical refrigerant pressure
InactiveUS6477857B2Recover energyReduce power consumptionCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEvaporators/condensersEngineeringPressure difference
Owner:DENSO CORP
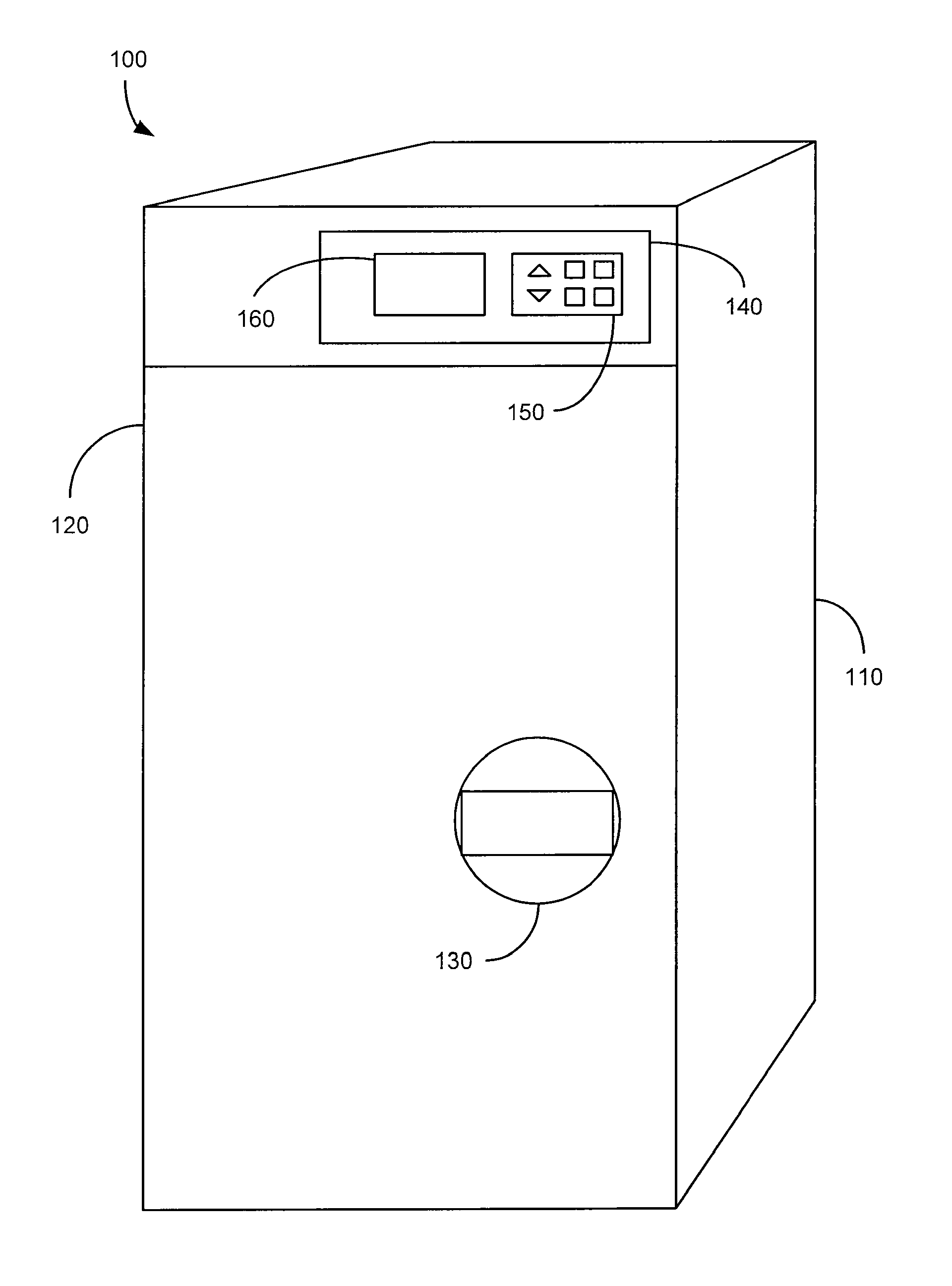
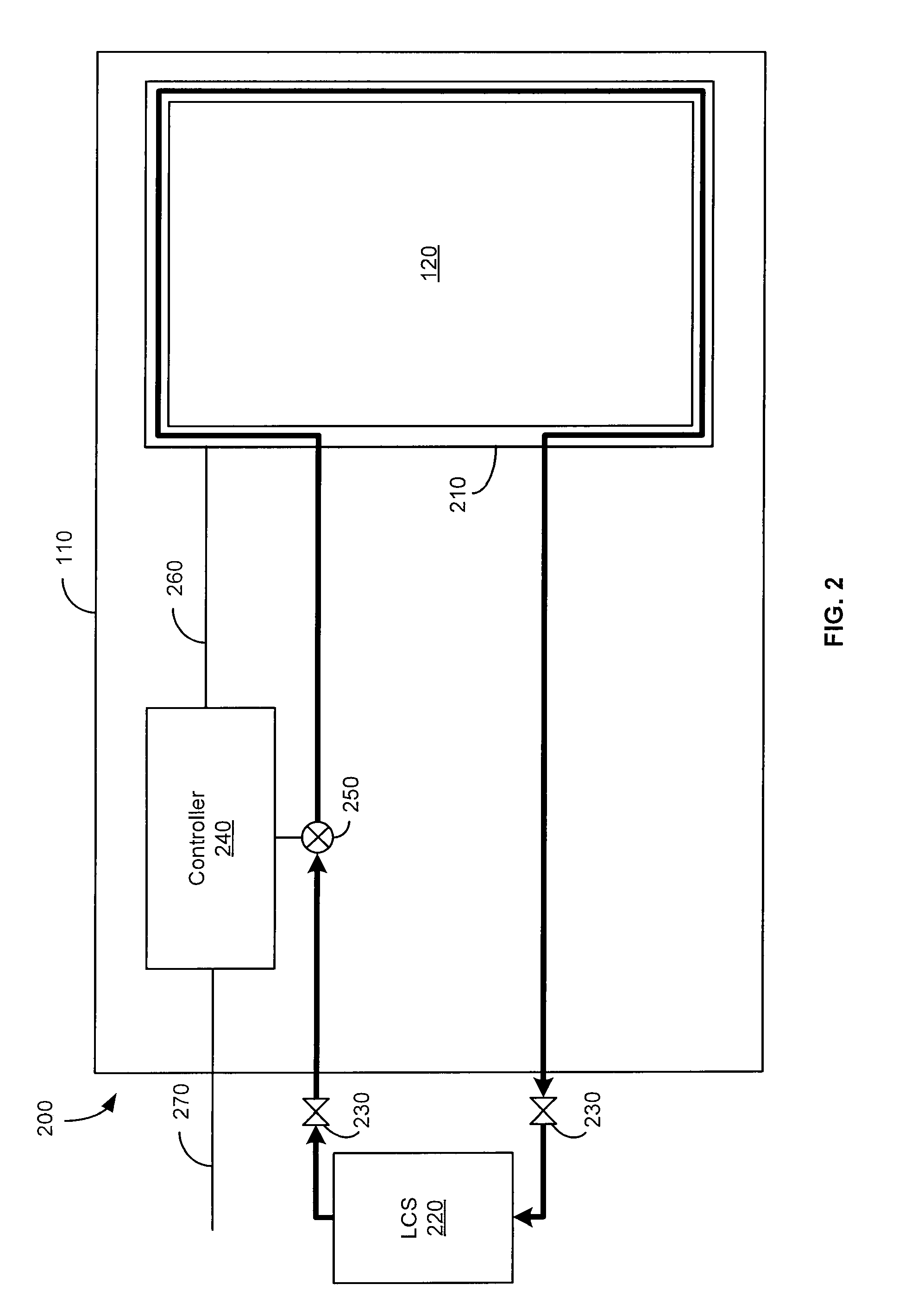
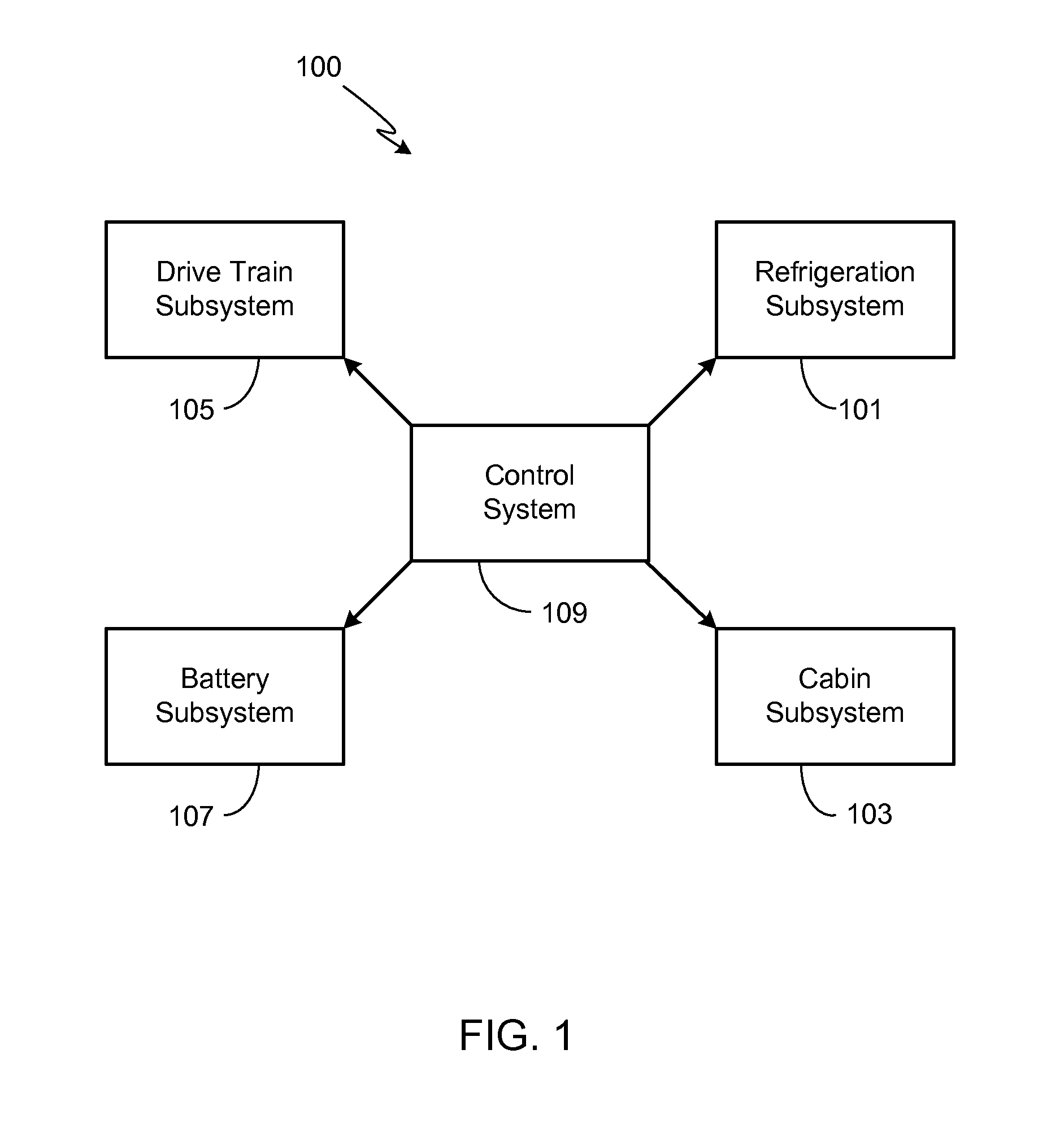
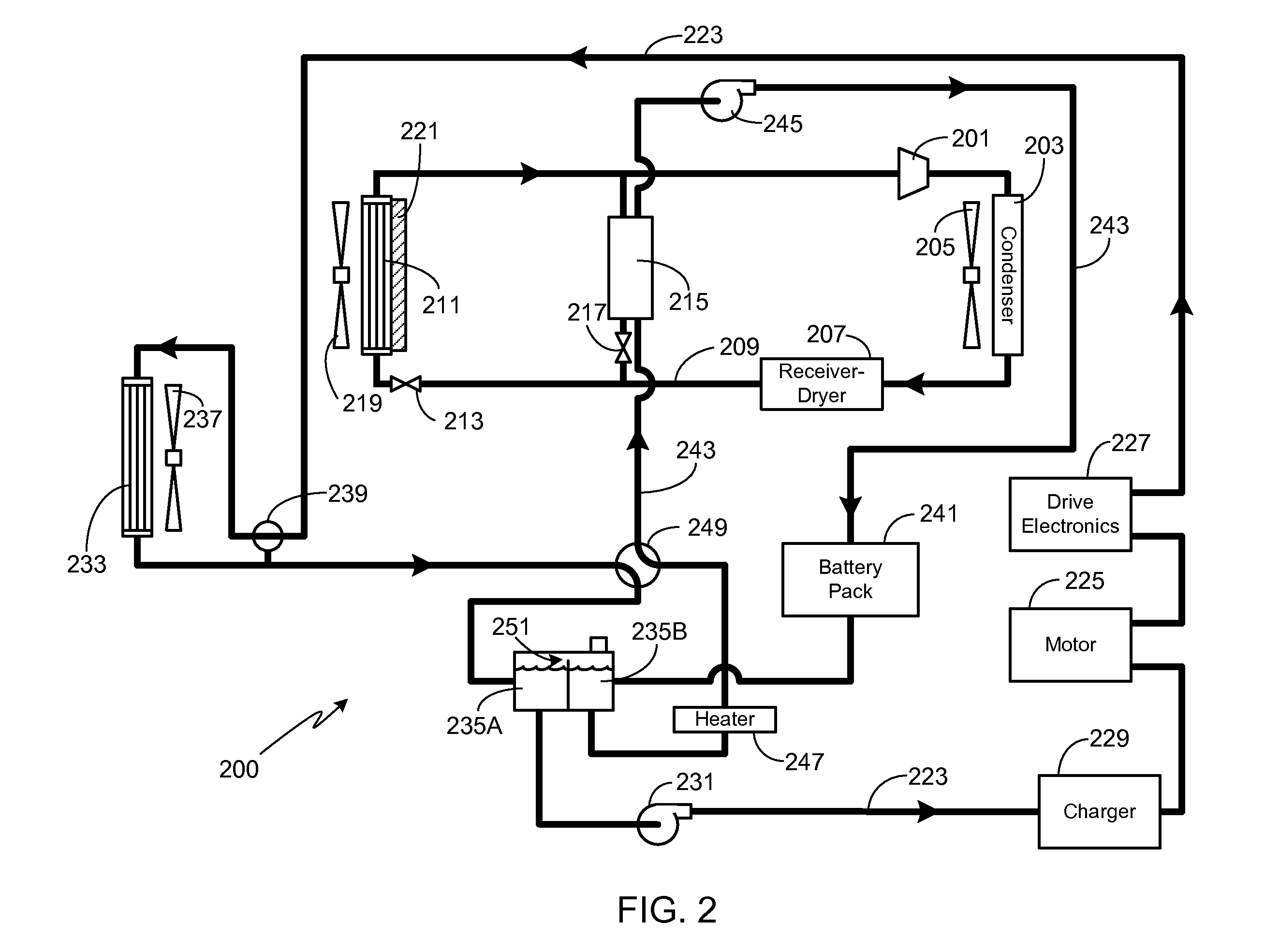
Refrigeration systems and methods for connection with a vehicle's liquid cooling system
An exemplary refrigeration system for cooling food or beverages may use a liquid cooling system of a vehicle. The refrigeration system may include a compartment in which the food or beverages may be placed and removed, a chilled liquid coolant system having a connection through which liquid coolant is received from the liquid cooling system of the vehicle, and a heat exchanger operationally coupled with the chilled liquid coolant system and the compartment to transfer heat from the compartment into the liquid coolant. The refrigeration system may also include a second chilled coolant system through which a second coolant flows and a second heat exchanger operationally coupled with the second chilled coolant system and the compartment to transfer heat from the compartment. The chilled liquid coolant system and the second chilled coolant system may operate together as a cascade cooling system.
Owner:BE AEROSPACE INCORPORATED
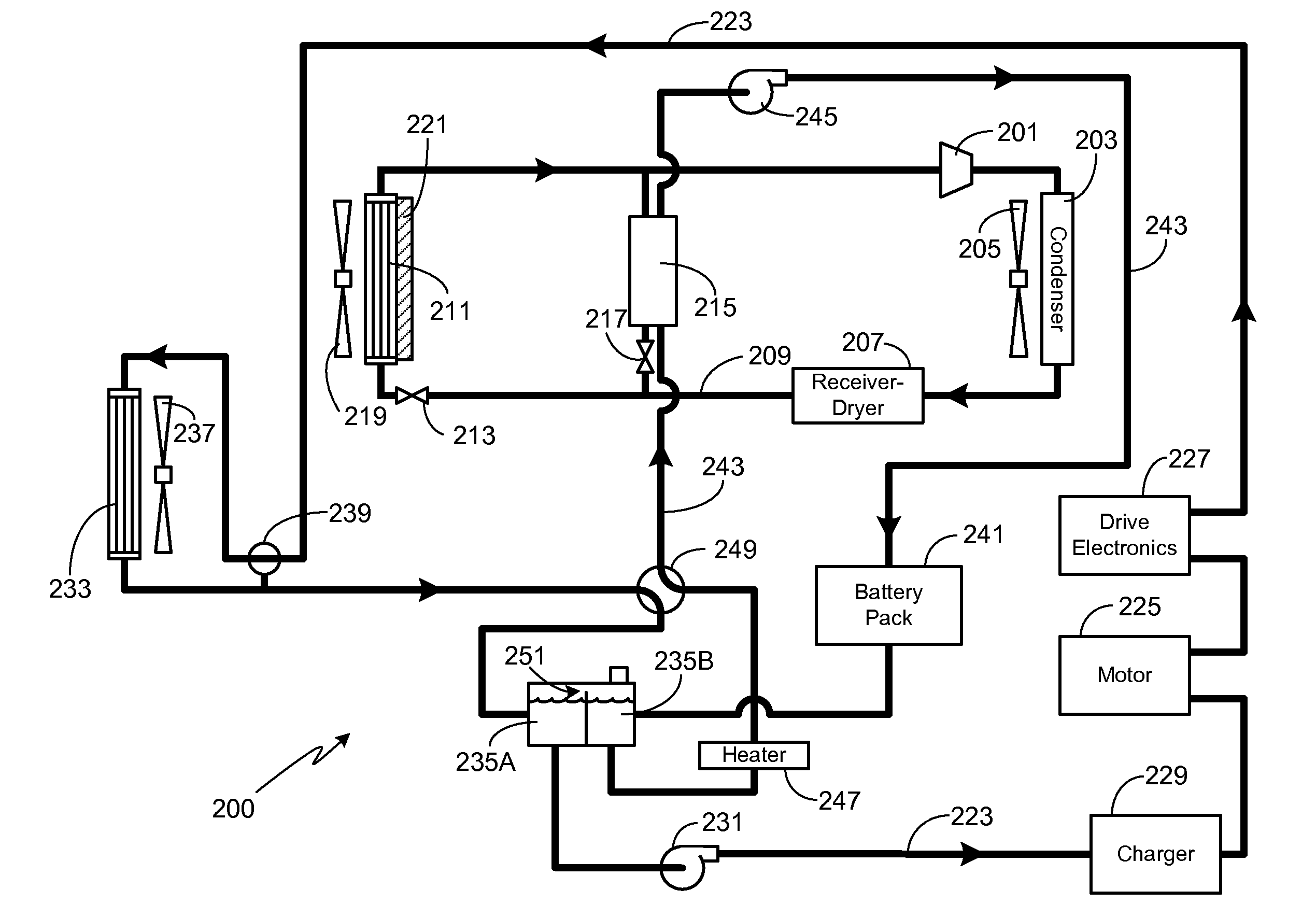
Thermal Management System with Dual Mode Coolant Loops
ActiveUS20110296855A1Power to auxillary motorsCompression machines with reversible cycleNuclear engineeringDual mode
A dual mode, thermal management system for use in a vehicle is provided. At a minimum, the system includes a first coolant loop in thermal communication with a battery system, a second coolant loop in thermal communication with at least one drive train component (e.g., electric motor, power electronics, inverter), and a dual mode valve system that provides means for selecting between a first mode where the two coolant loops operate in parallel, and a second mode where the two coolant loops operate in series.
Owner:TESLA INC
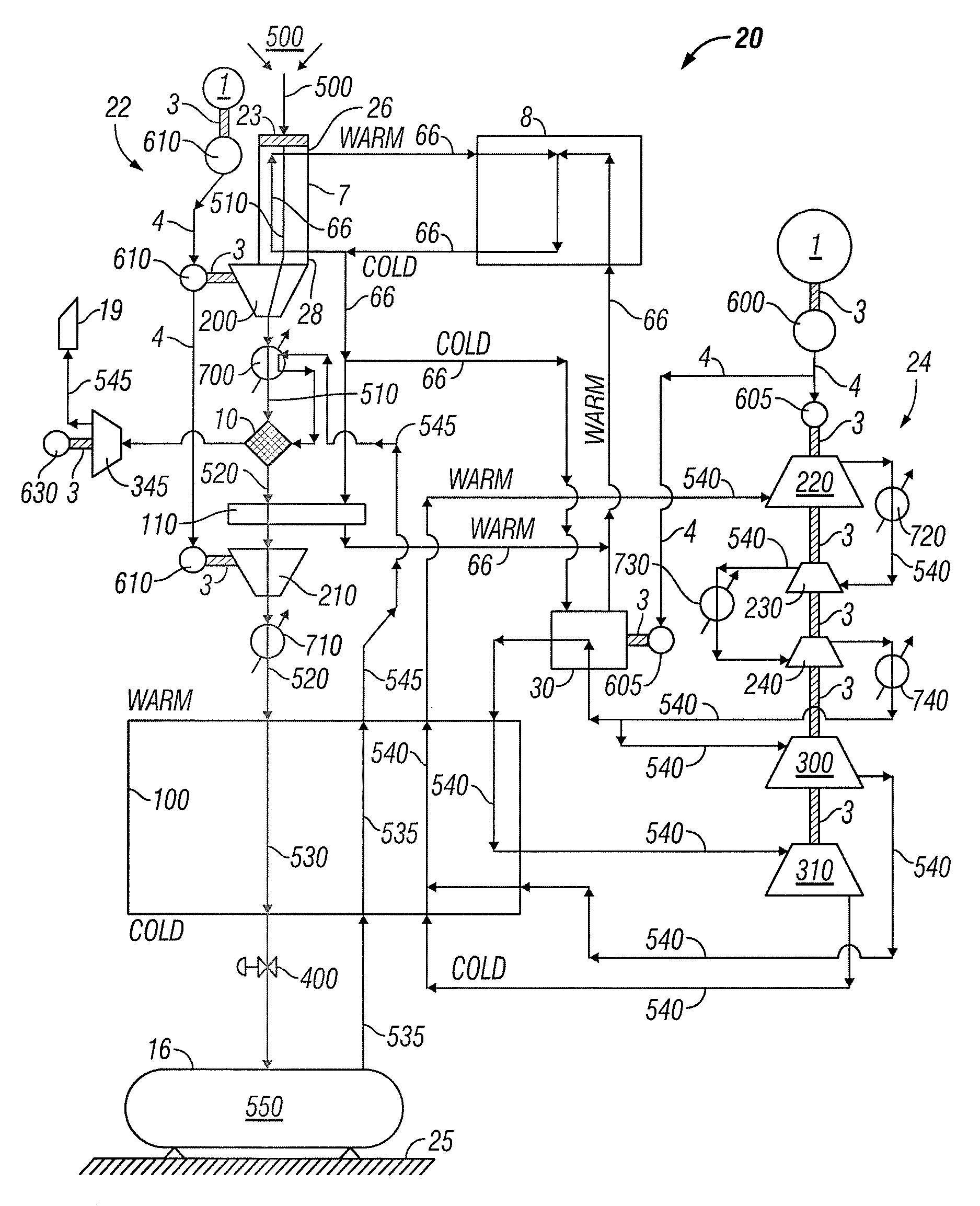
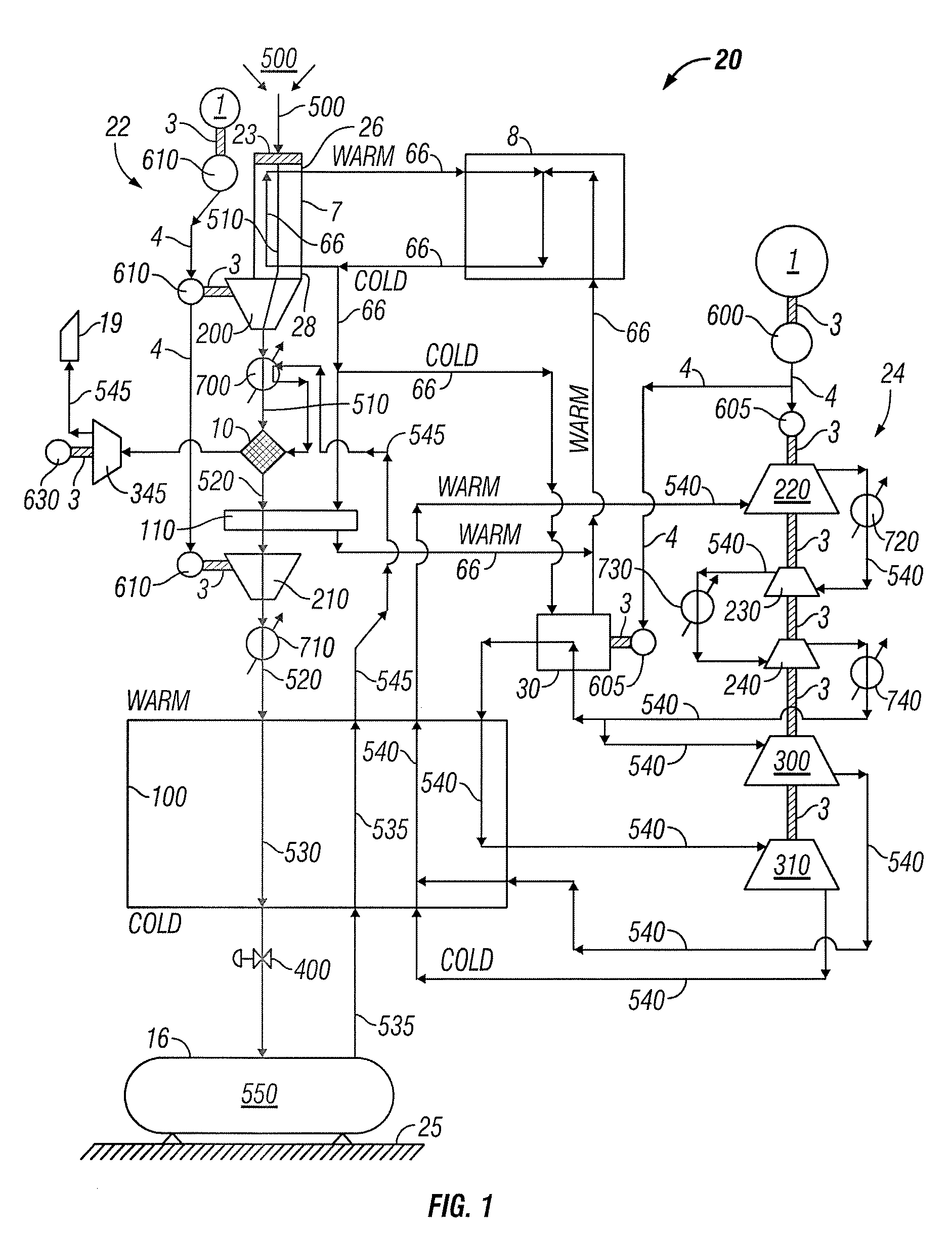
System and method for liquid air production, power storage and power release
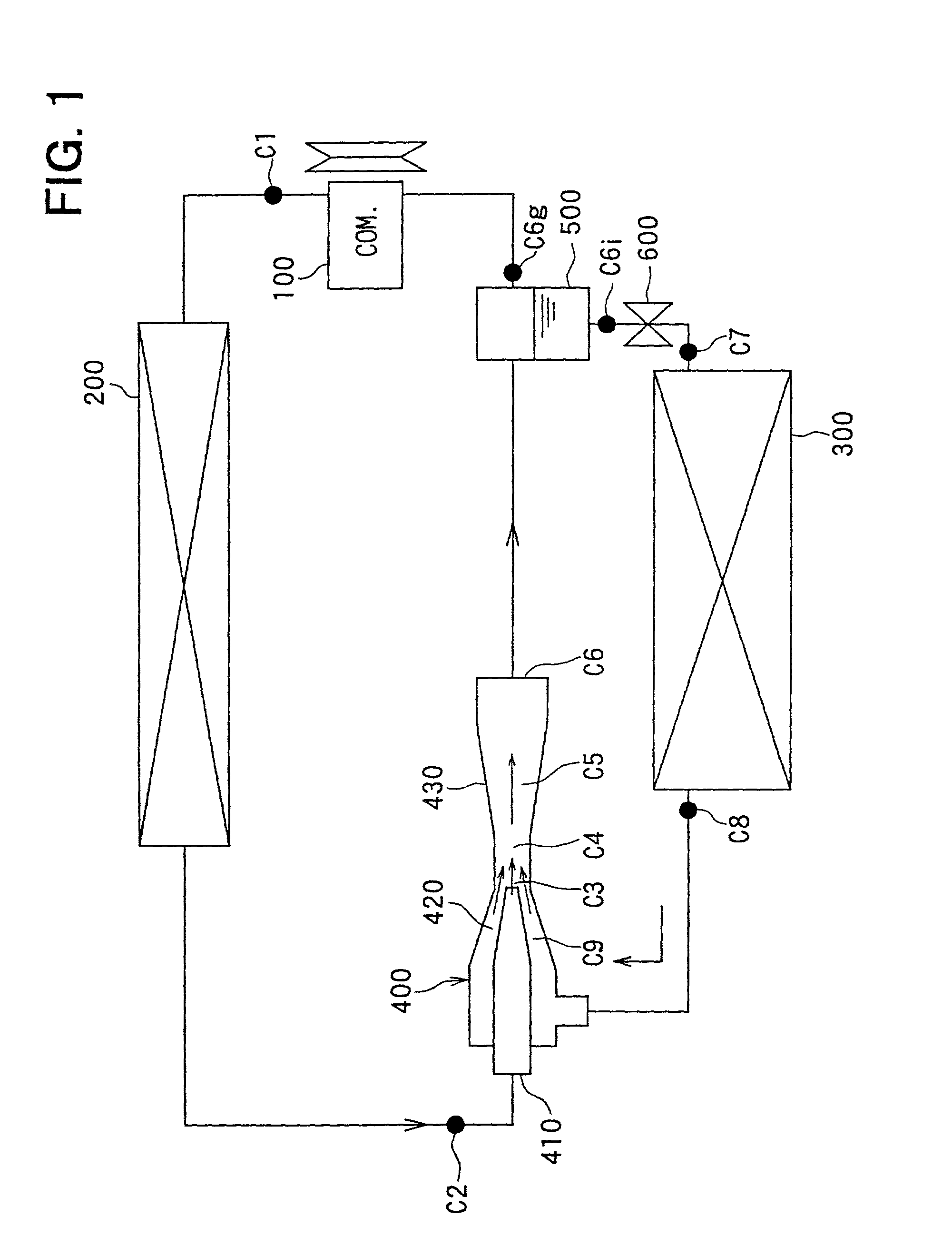
InactiveUS20090293503A1Great energy outputEnergy efficiencySolidificationLiquefactionCombustion chamberEngineering
Systems and methods for storing and releasing energy comprising directing inlet air into a vertical cold flue assembly having an air inlet at or near its top into which inlet air is directed and an exit at or near its bottom. The air is cooled within the cold flue assembly and a portion of moisture is removed from the air within the cold flue assembly. The air is directed out the exit of the cold flue assembly and compressed. The remaining moisture is substantially removed and the carbon dioxide is removed from the air by adsorption. The air is cooled in a main heat exchanger such that it is substantially liquefied using refrigerant loop air, the refrigerant loop air generated by a refrigerant loop process. The substantially liquefied air is directed to a storage apparatus. The refrigerant loop air is cooled by a mechanical chiller and by a plurality of refrigerant loop air expanders. In energy release mode, working loop air warms the released liquid air such that the released liquid air is substantially vaporized, and the released liquid air cools the working loop air such that the working loop air is substantially liquefied. A portion of the released liquid air is directed to the at least one generator and used as bearing air for the at least one generator. The substantially vaporized air is directed to a combustion chamber and combusted with a fuel stream. Combustion gas may be directed from the combustion chamber to at least one expander and expanded in the expander, the expanded combustion gas split into a first portion and a second portion, the first portion being relatively larger than the second portion. The first portion may be directed to a first heat exchanger, and the second portion may be directed to a second heat exchanger such that the second portion heats and substantially vaporizes the released liquid air.
Owner:EXPANSION ENERGY
Hybrid gas liquefaction cycle with multiple expanders
Method for gas liquefaction comprising cooling a feed gas by a first refrigeration system in a first heat exchange zone and withdrawing a substantially liquefied stream therefrom, further cooling the substantially liquefied stream by indirect heat exchange with one or more work-expanded refrigerant streams in a second heat exchange zone, and withdrawing therefrom a further cooled, substantially liquefied stream. At least one of the one or more work-expanded refrigerant streams is provided by compressing one or more refrigerant gases to provide a compressed refrigerant stream, cooling all or a portion of the compressed refrigerant stream in a third heat exchange zone to provide a cooled, compressed refrigerant stream, and work expanding the cooled, compressed refrigerant stream to provide one of the one or more work-expanded refrigerant streams. The flow rate of a work-expanded refrigerant stream in the second heat exchange zone typically is less than the total flow rate of one or more work-expanded refrigerant streams in the third heat exchange zone.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Secondary cooling apparatus and method for a refrigerator
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Multi-spool turbogenerator system and control method
InactiveUS6931856B2Eliminate needMinimize and eliminate needTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionTurbine/propulsion engine startersEngineeringTurbine
An electrical power generating system is driven by a multi-spool gas turbine engine including at least first and second spools. The first spool comprises a turbine and a compressor mounted on a first shaft; the second spool has at least a turbine mounted on a second shaft that is not mechanically coupled to the first shaft. A main generator is coupled with one of the spools, and an auxiliary generator / motor is also coupled with one of the spools. Speed control of each of the generators is employed for controlling operation of the engine. The auxiliary generator / motor can operate in either a generation mode to extract power from its spool or a motor mode to inject power into its spool.
Owner:MES INT INC
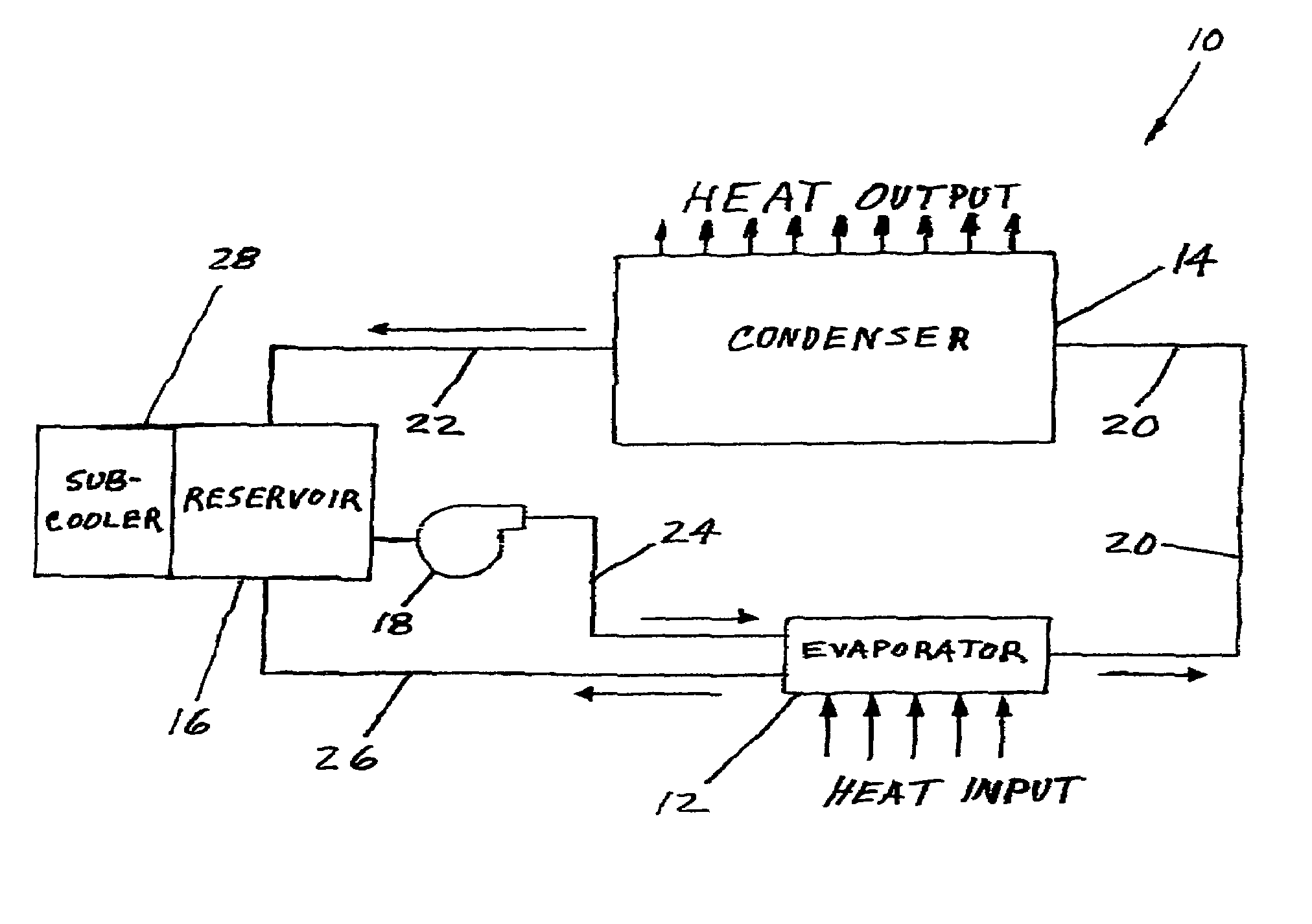
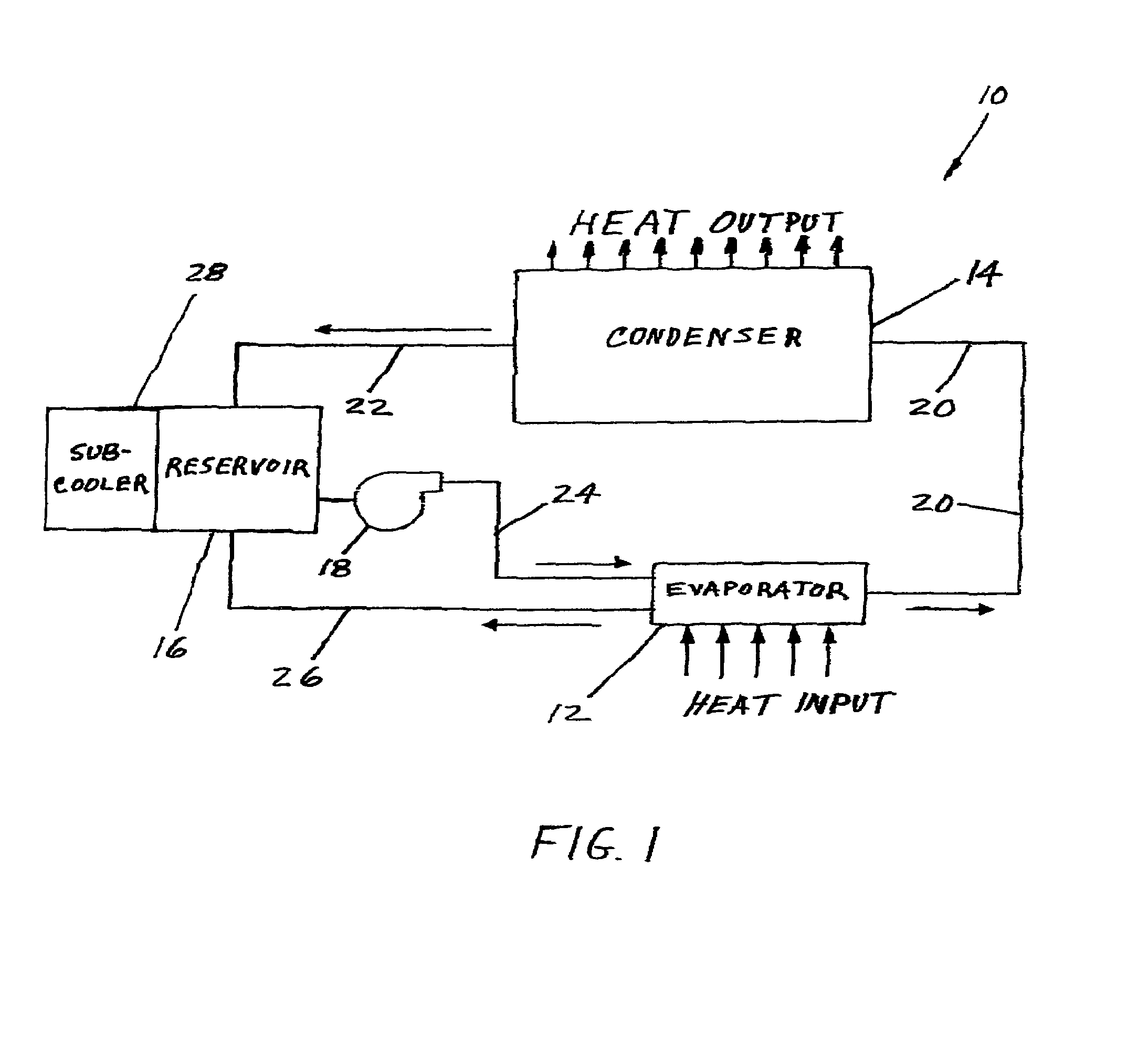
Hybrid capillary cooling apparatus
ActiveUS6990816B1Great heat transport distanceGuaranteed uptimeCosmonautic environmental control arrangementEvaporators/condensersEngineeringChiller
The apparatus is a hybrid cooler which includes one loop within which a heated evaporator forms vapor that moves to a condenser because of the vapor pressure which also drives the liquid condensate from the condenser to a liquid reservoir. A second loop is powered by a mechanical pump that supplies liquid from the reservoir to the evaporator and the second loop also returns excess liquid not vaporized to the reservoir. An optional reservoir cooler can be used to assure that the reservoir temperature and vapor pressure are always lower that the temperatures and pressures of the evaporator and condenser.
Owner:ADVANCED COOLING TECH
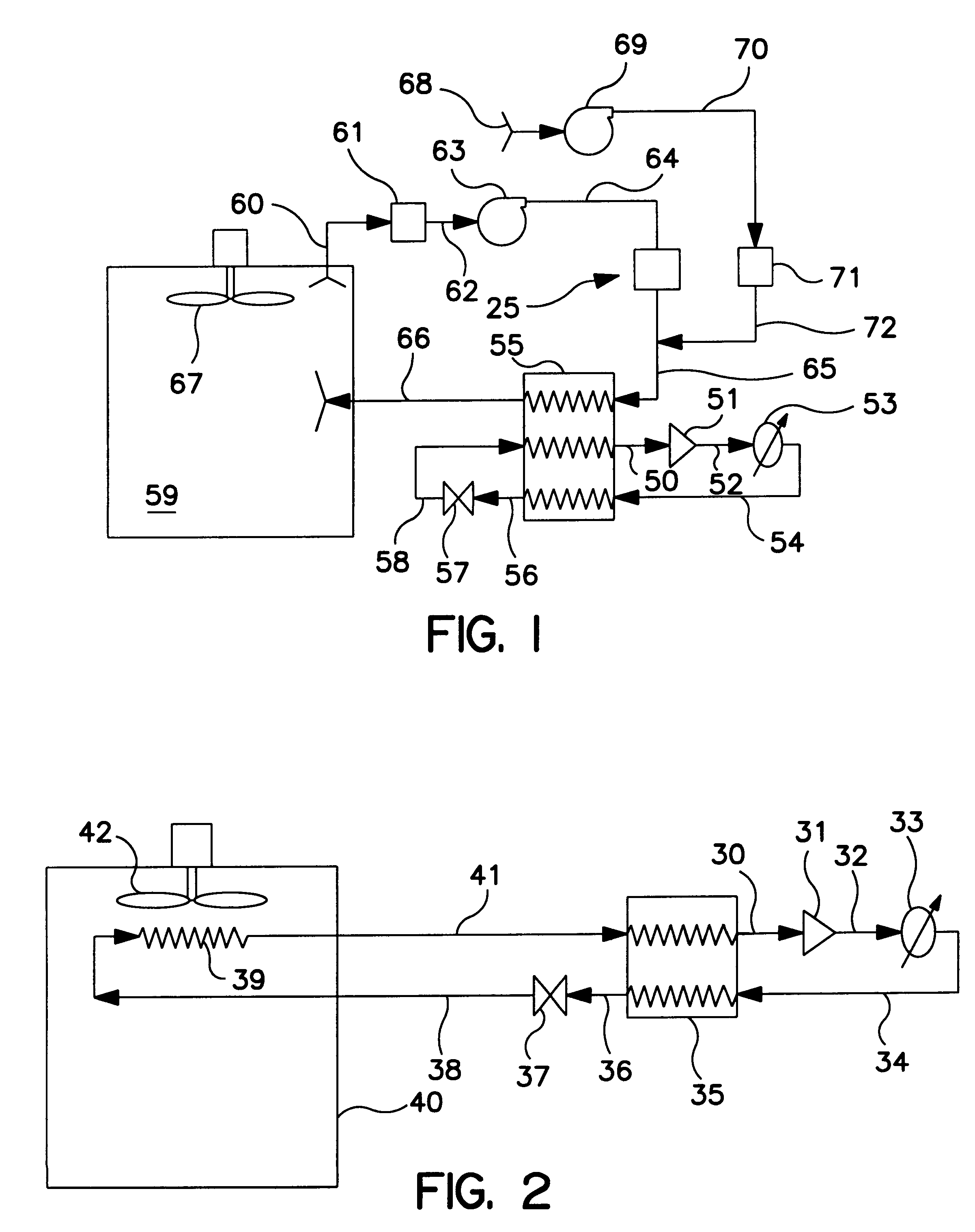
Charge air chiller
InactiveUS20090031999A1Maximum increase in energy efficiencyIncrease boost pressureInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelTurbochargerInlet valve
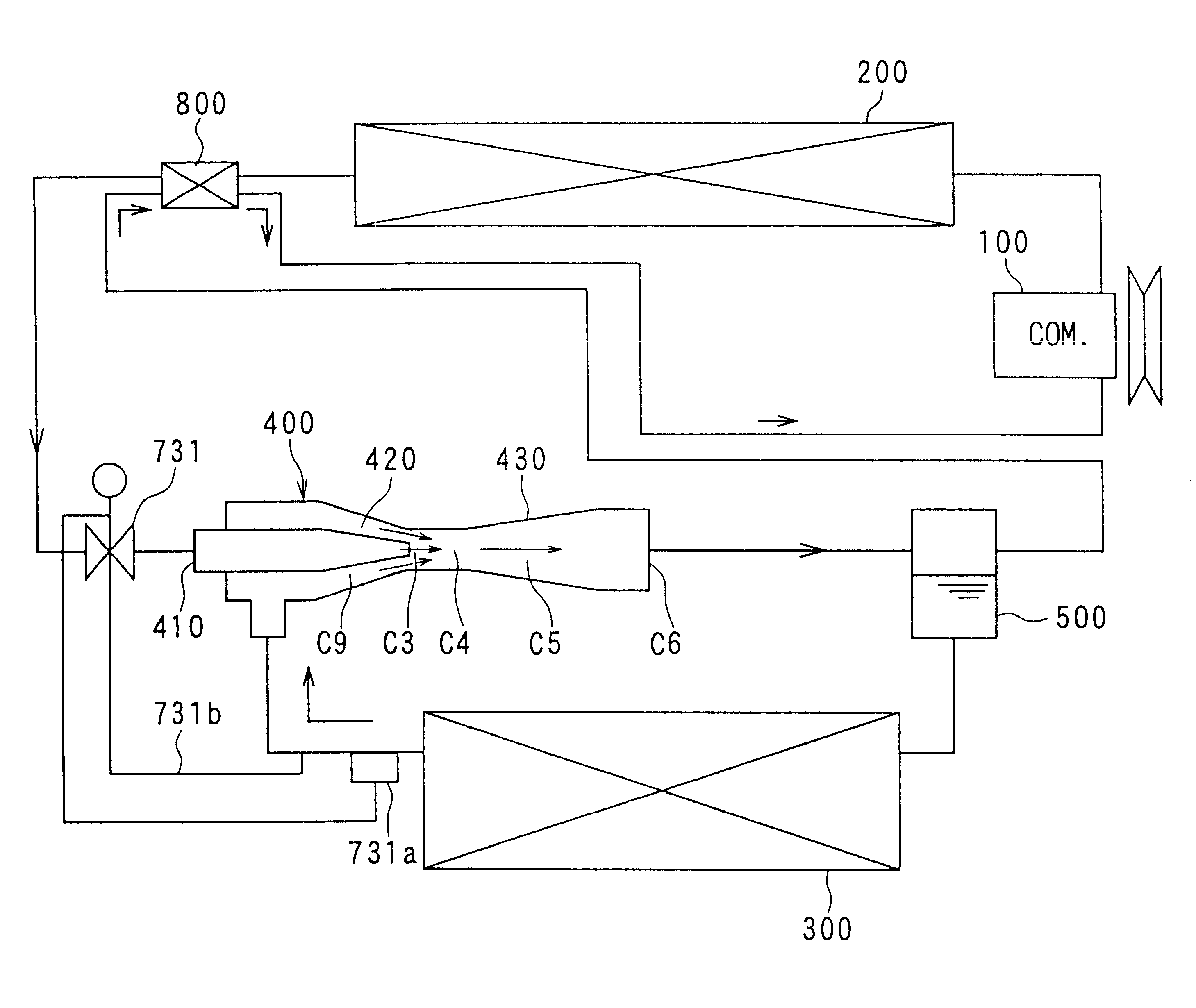
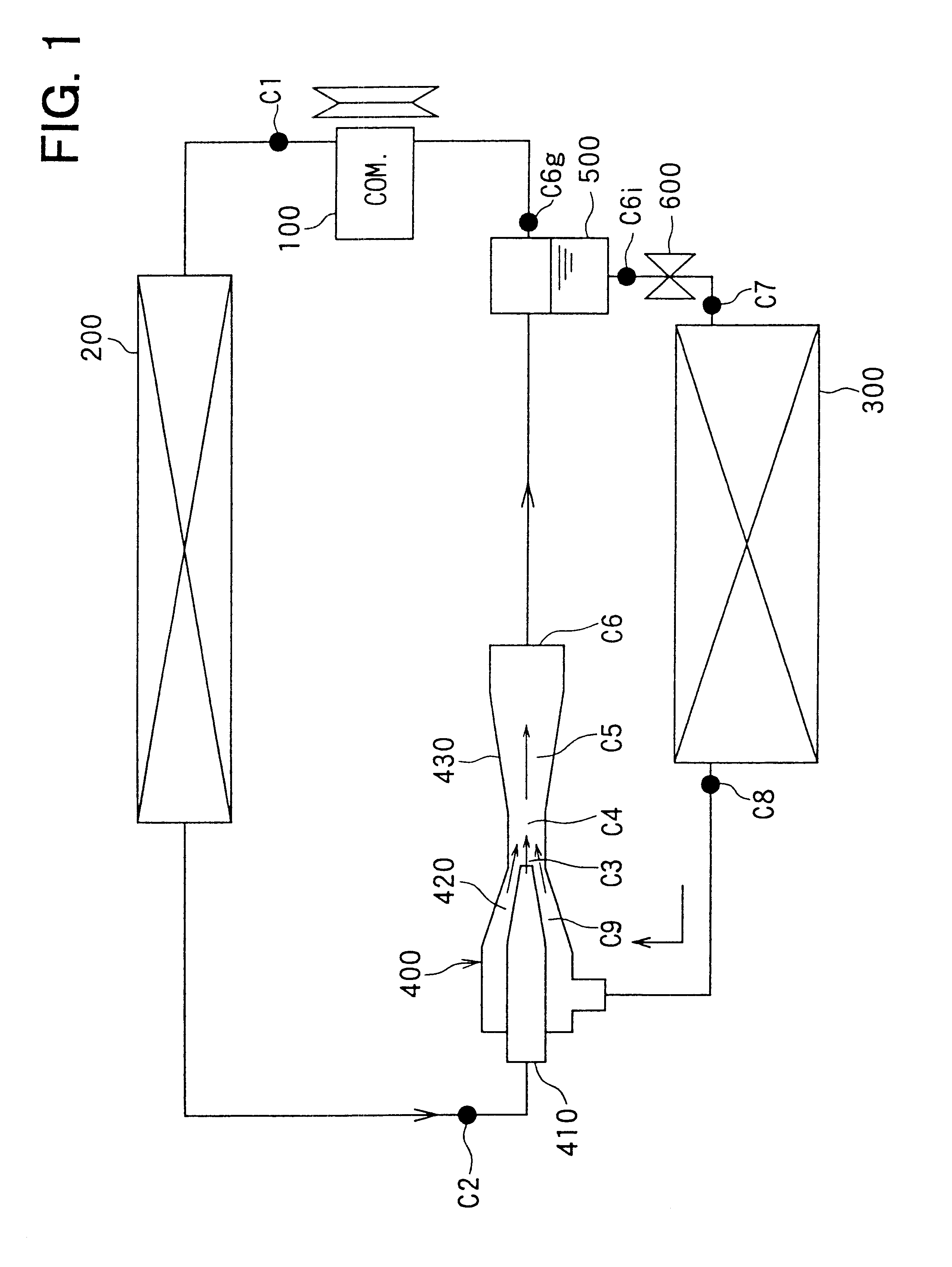
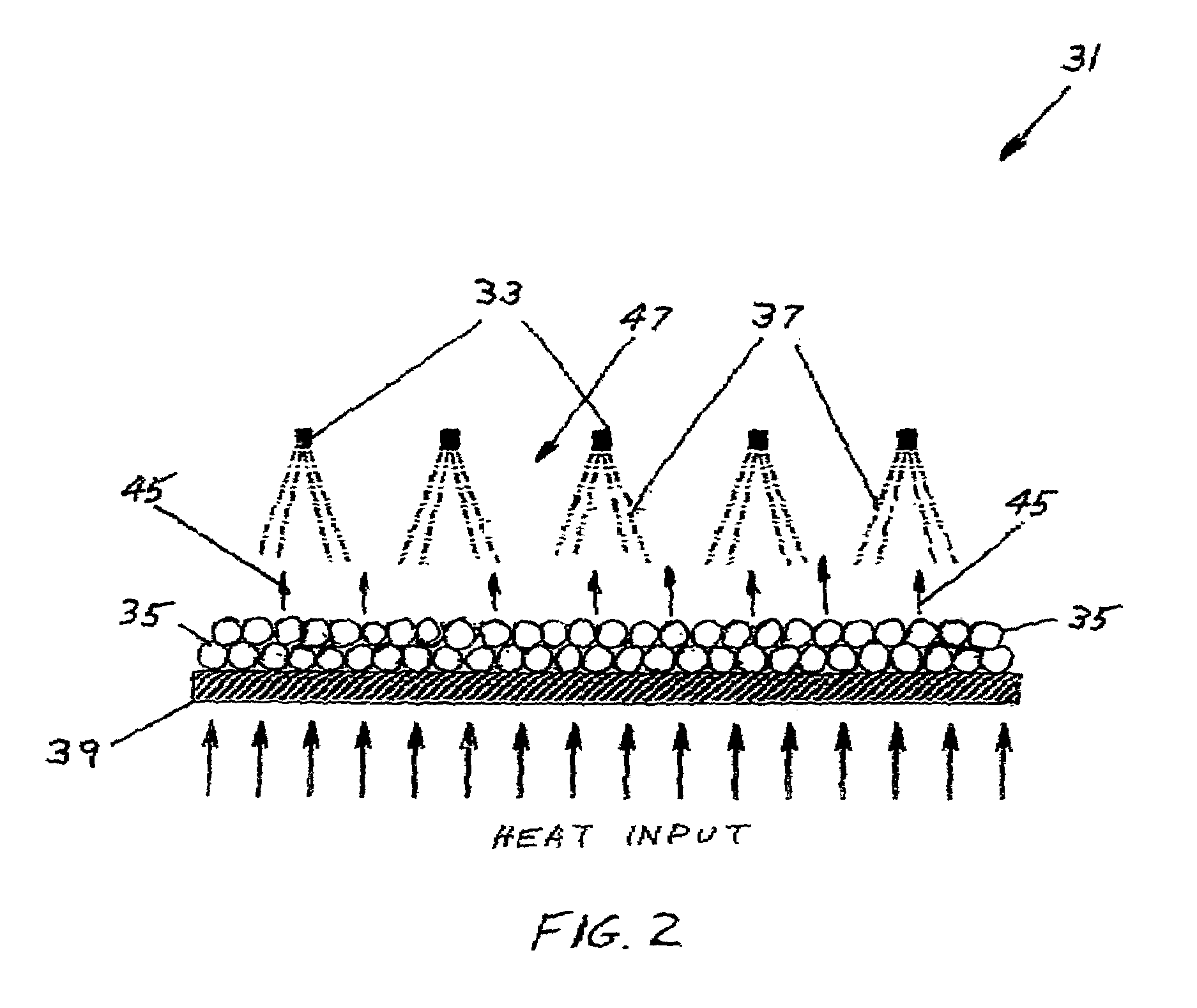
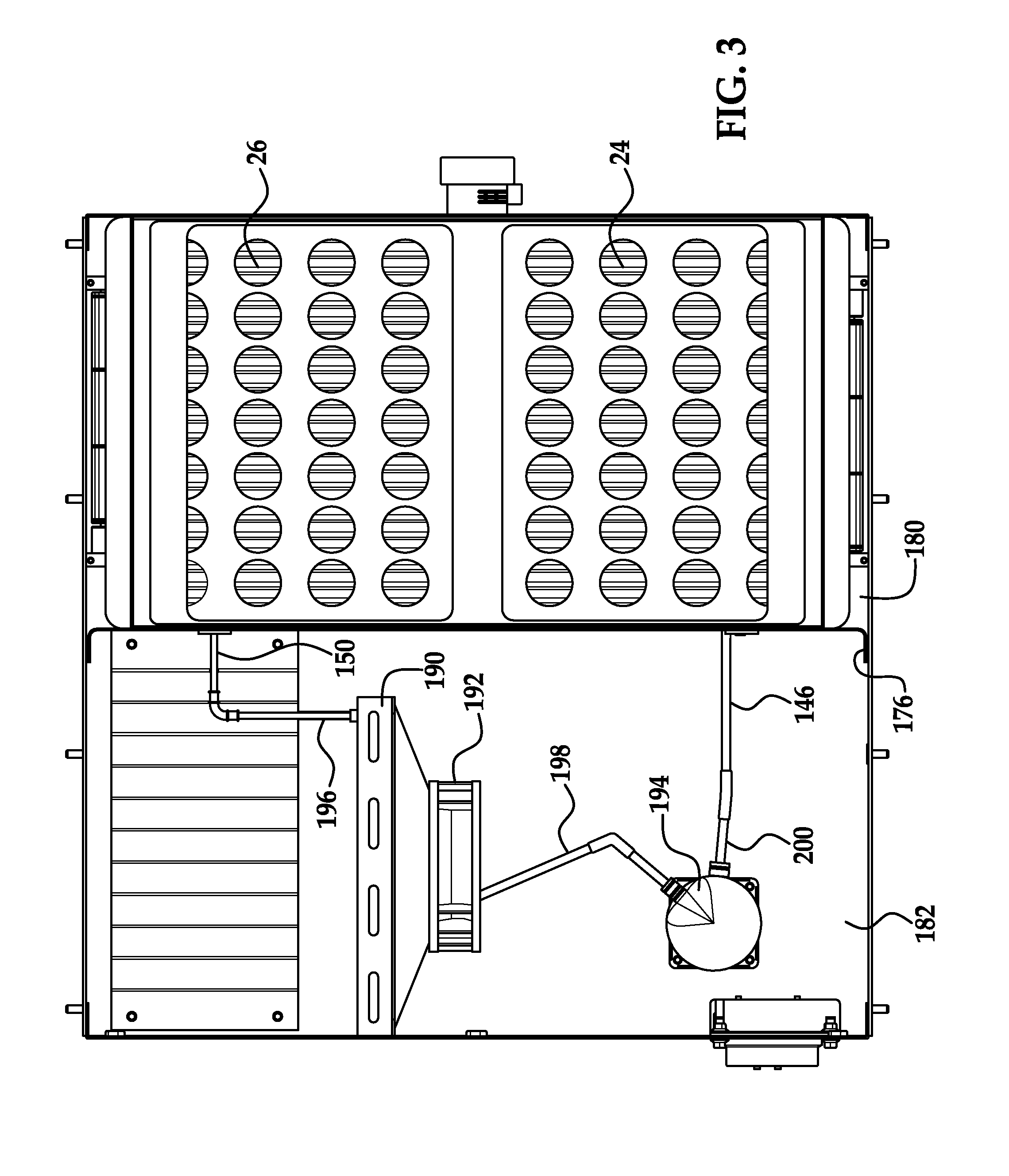
A system for chilling the pressurized charge air to a reciprocating engine is disclosed wherein the chilling is provided by a thermally activated refrigeration cycle powered by waste heat from the engine system. This reduces the required compression power, and also retards knock, making higher compression ratios possible. The chilling system is designed to minimize the amount of chilling required, and also to enable use of compression heat to power the chiller. The disclosed improvement also accommodates exhaust gas recirculation, plus providing activation heat from the exhaust gas, plus Miller cycle timing of the intake valves. Referring to FIG. 1, the charge air from turbocharger 5 is cooled in three stages: heat recovery stage 10; ambient-cooled stage 11; and chilling stage 12. Condensed moisture is removed from the charge air by valve 14 before the charge is supplied to inlet manifold 2.
Owner:ERICKSON DONALD CHARLES
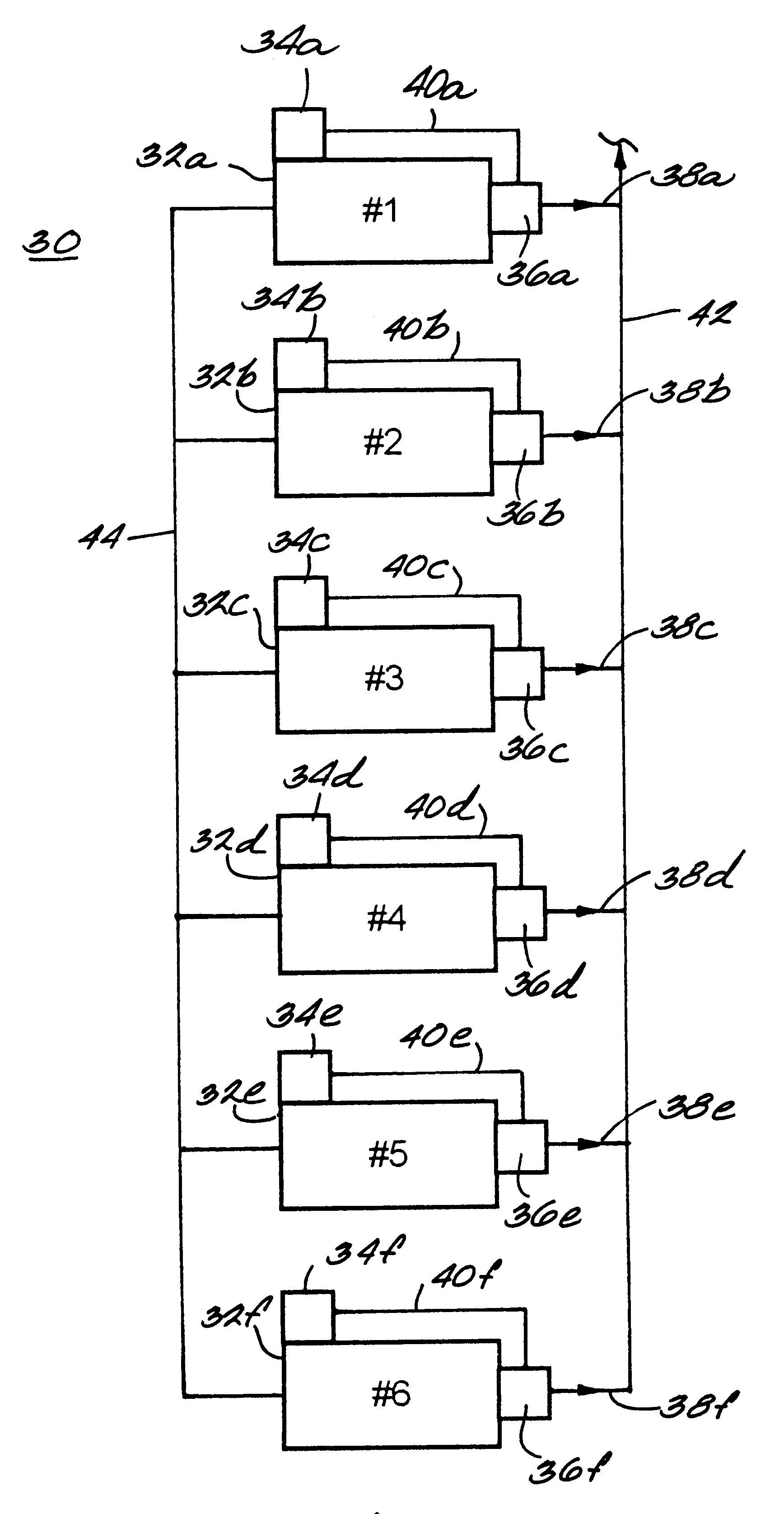
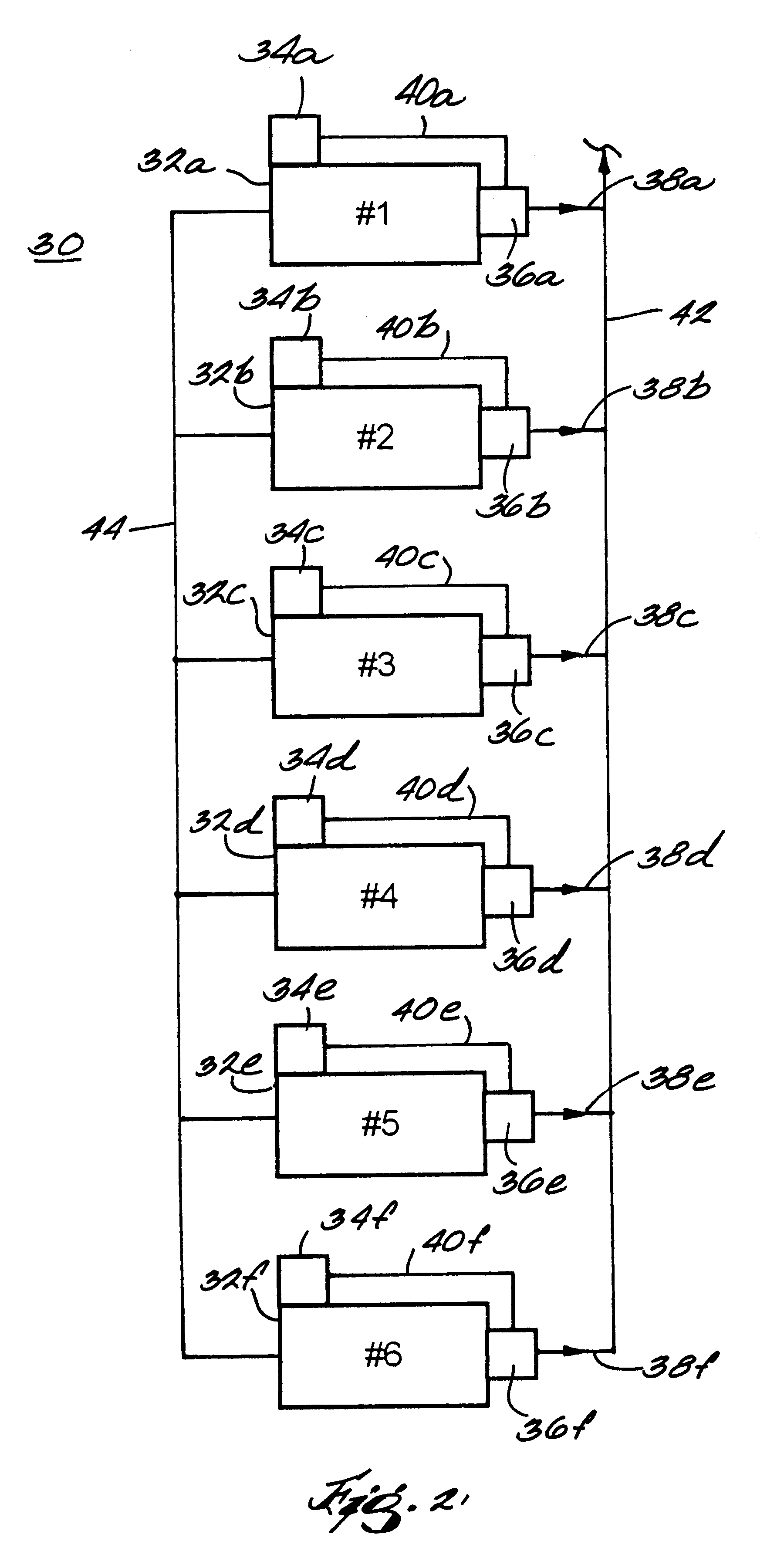
Method for controlling the operation of a compression system having a plurality of compressors
InactiveUS6233954B1Space heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsCompressed fluidRanking
A fluid compression system includes a plurality of compressors, each compressor having a local controller for controlling operation thereof and a sensor for sensing the pressure of compressed fluid discharged therefrom. A method for controlling operation of the fluid compression system includes establishing a set point pressure threshold for loading and unloading each compressor, and assigning a ranking to each compressor for identifying a highest ranked compressor and a lowest ranked compressor, whereby the highest ranked compressor for the compression system initiates all commands for controlling all of the lower ranked compressors in the compression system. The method also includes commencing a loading subroutine including loading the highest ranked unloaded compressor, setting a load delay timer, sensing the pressure of the compressed fluid discharged from the highest ranked compressor, comparing the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and transmitting a load command from the controller of the highest ranked compressor to the controller of the next highest ranked unloaded compressor if the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor remains less than or equal to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and the load delay timer equals zero. The loading subroutine is repeated until the discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor is greater than the set point pressure threshold established therefor.
Owner:INGERSOLL RAND CO
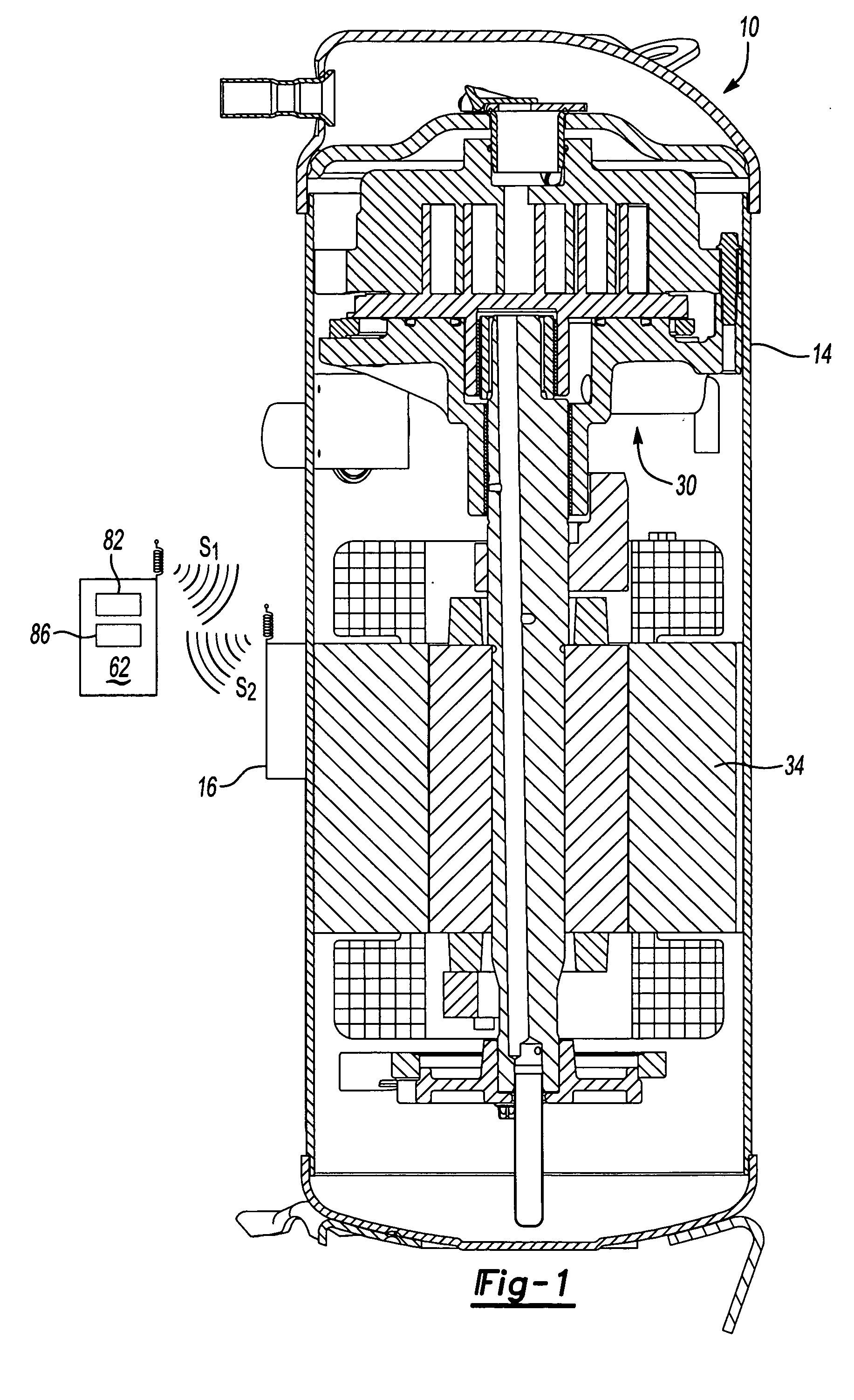
Distributed intelligence control for commercial refrigeration
InactiveUS7270278B2Easy to assembleEasy to installMechanical apparatusEfficient regulation technologiesDistributed intelligenceControl theory
A commercial refrigeration system including a compressor, a condenser, a valve, and an evaporator coil, all of which are in fluid communication. The refrigeration system further including a fixture adapted to be cooled by the evaporator coil, a system controller operable to control operation of the refrigeration system, and a subsystem controller in communication with the system controller. The subsystem controller being operable to monitor at least one parameter of a subsystem having at least one of the compressor, condenser, valve, and fixture, and being further operable to execute a command from the system controller to affect the operation of the subsystem.
Owner:HUSNN
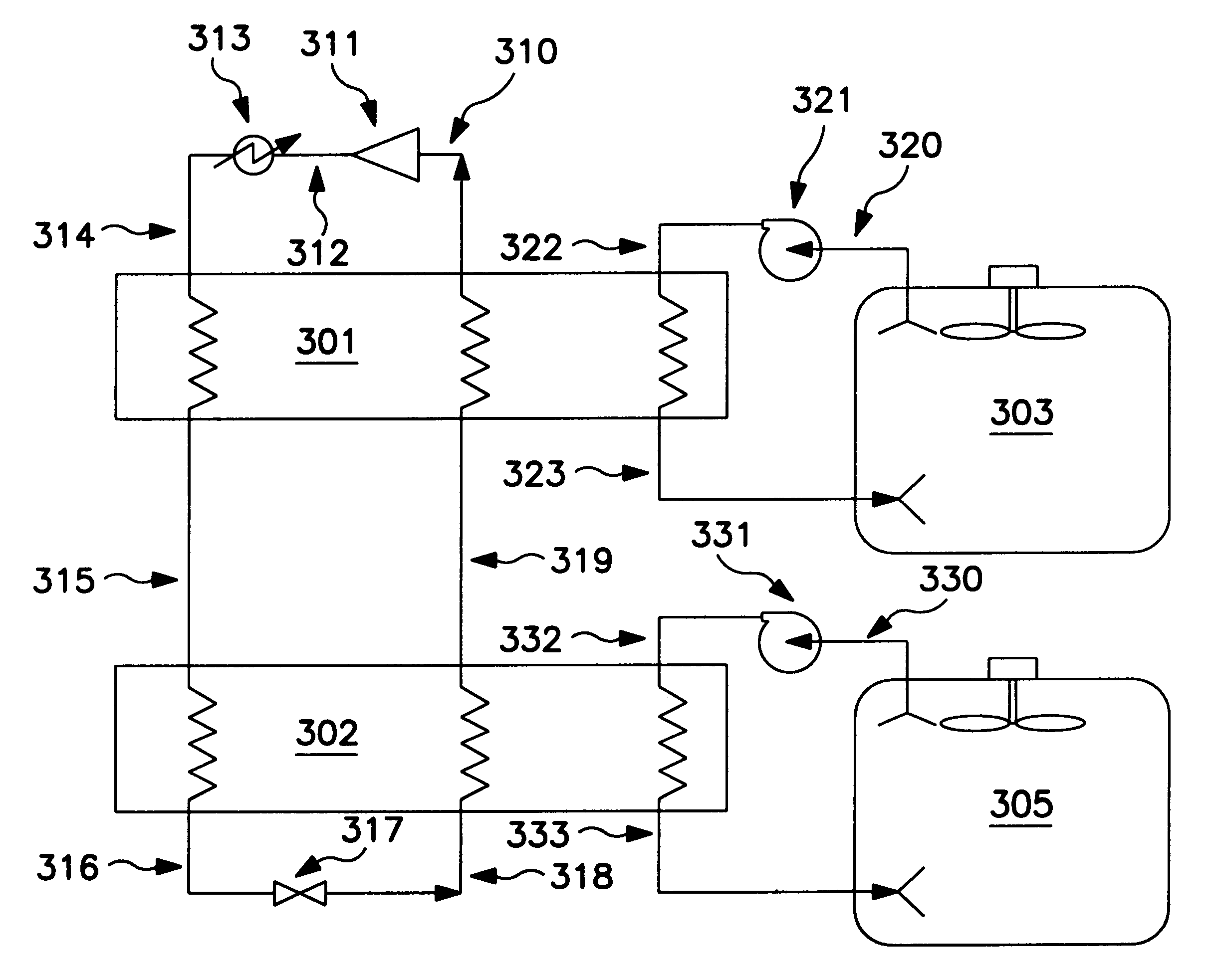
Cooling system for a battery system and a method for cooling the battery system
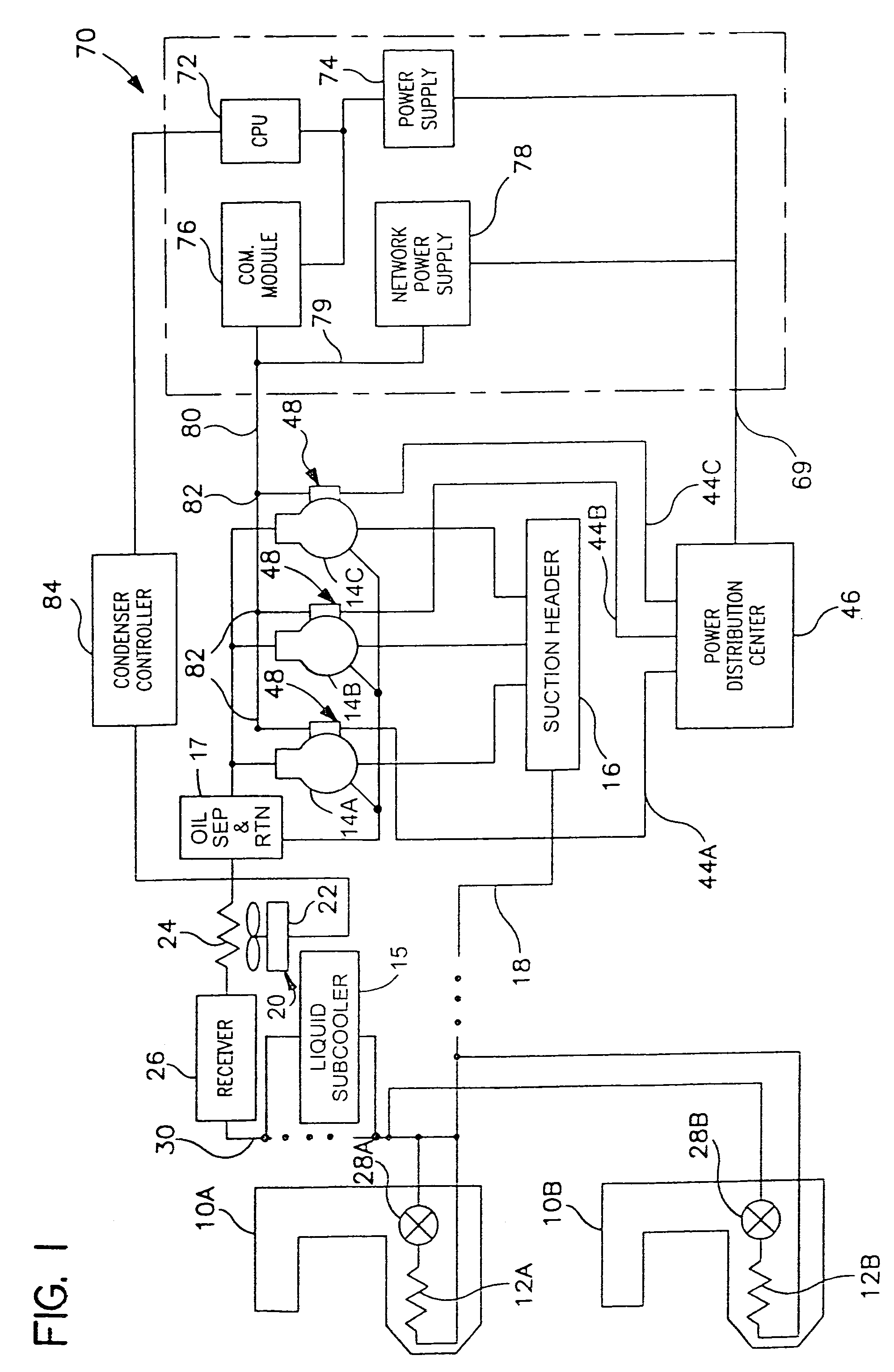
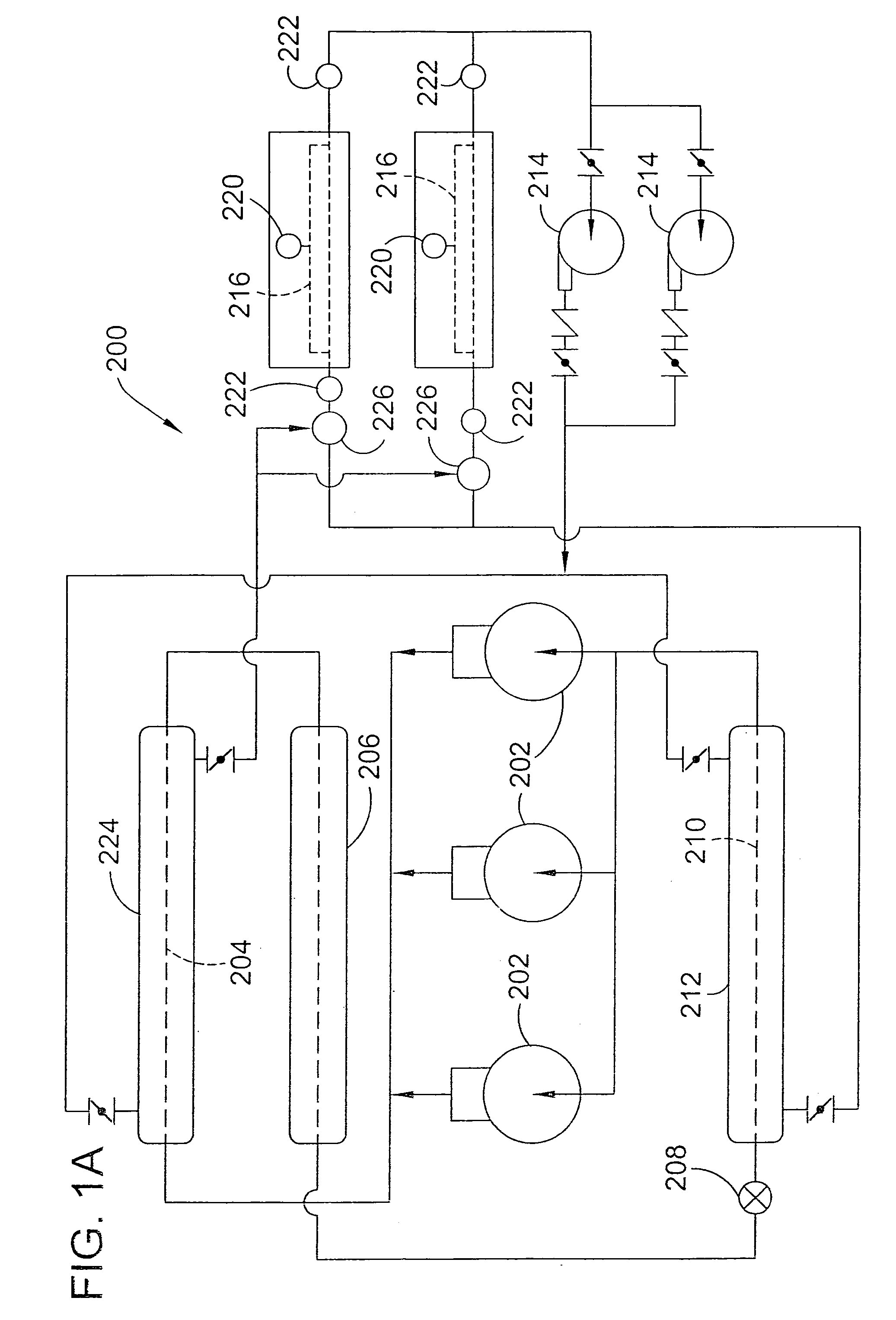
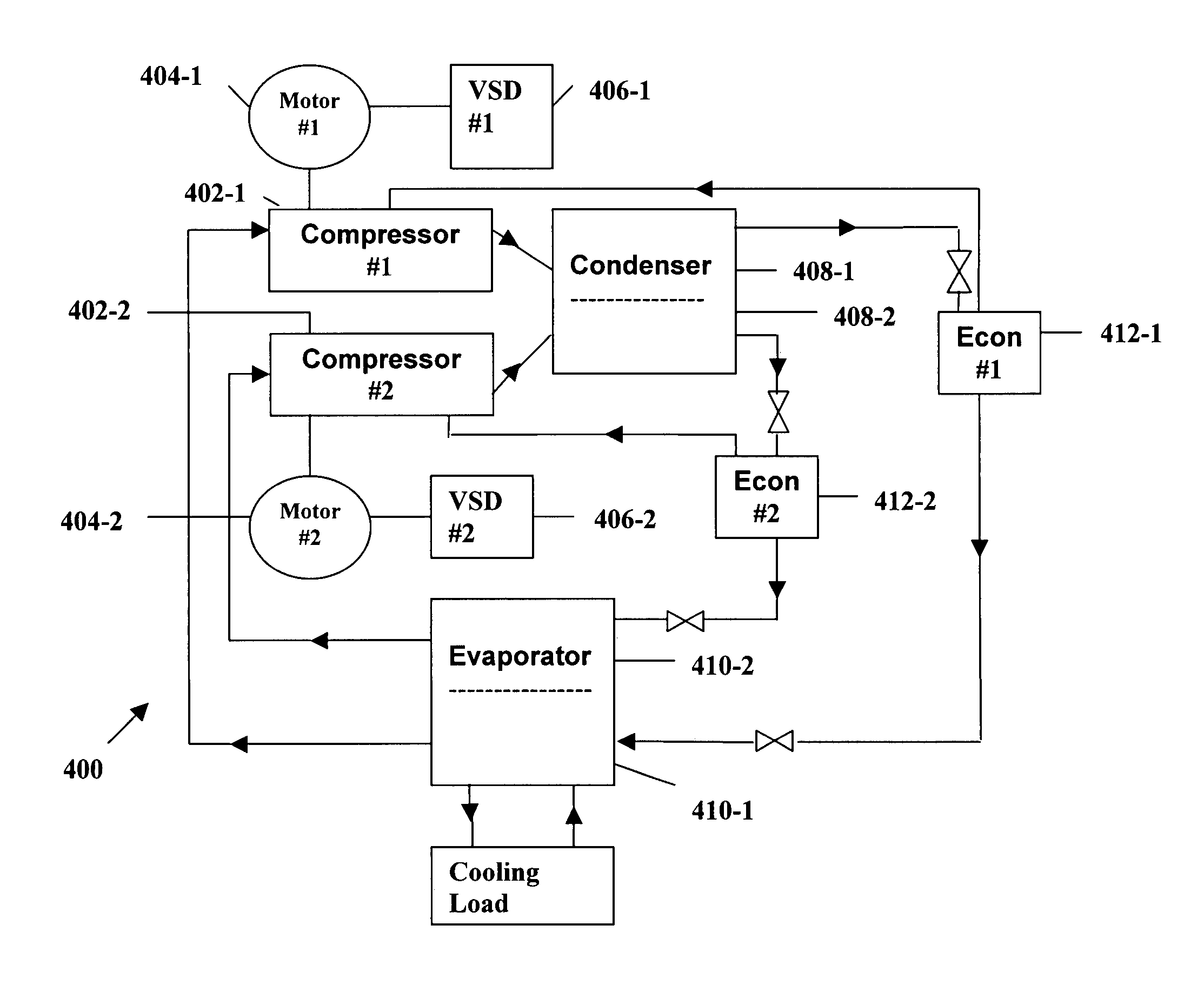
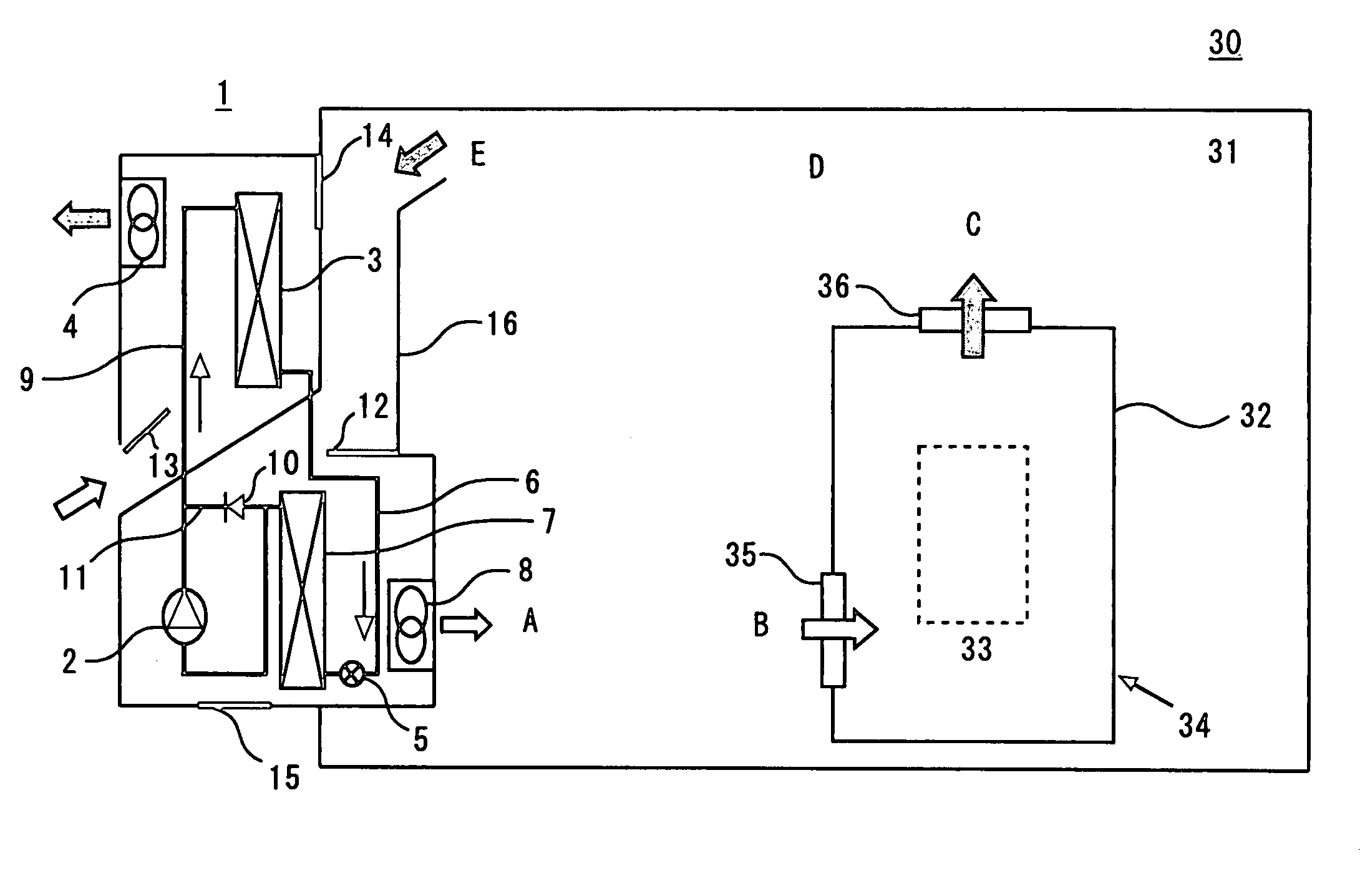
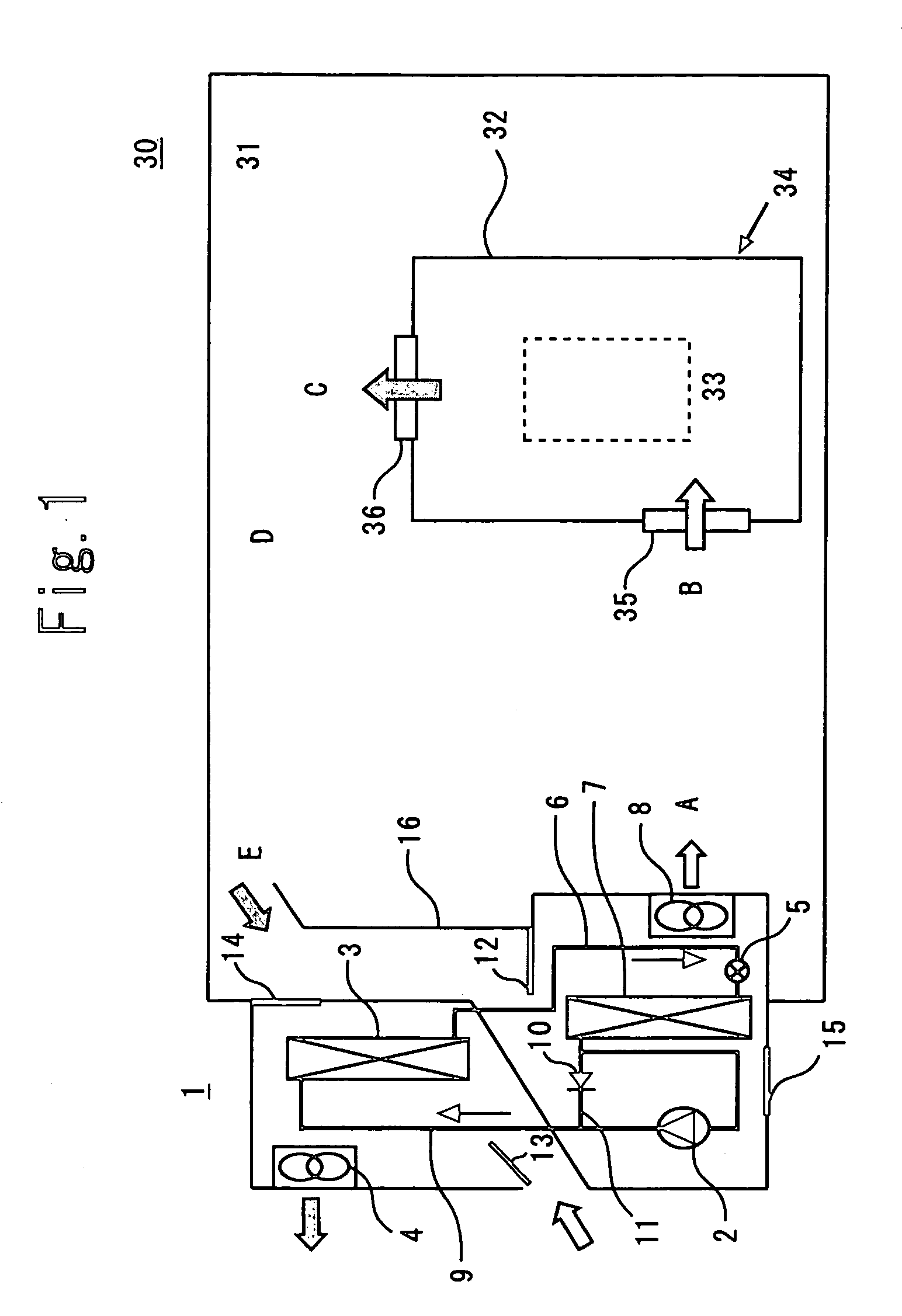
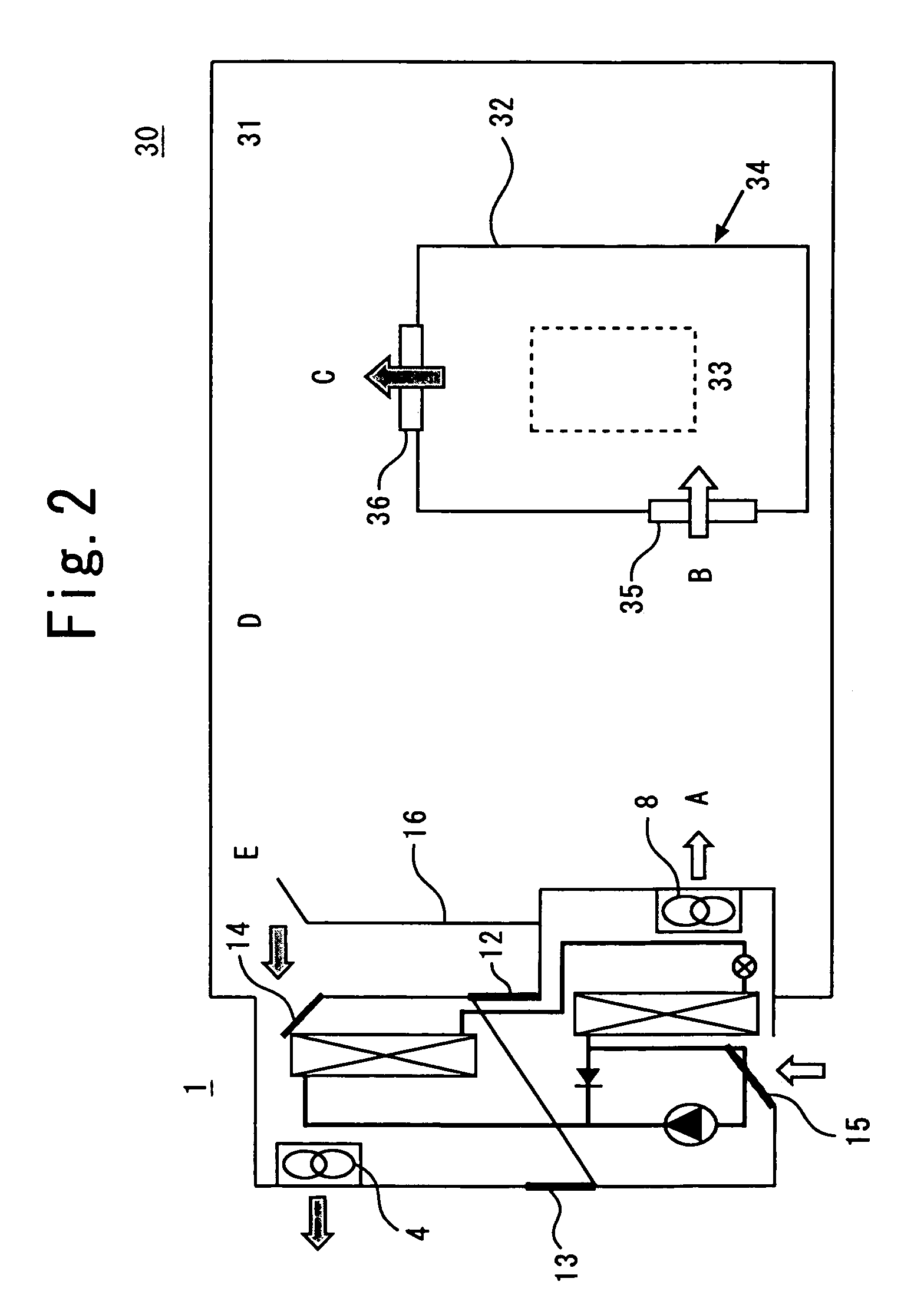
InactiveUS20100275619A1Lower temperature levelDissipate heat energySecondary cellsCompression machines with cascade operationElectrical batteryEngineering
A cooling system for a battery system and a method for cooling the battery system are provided. The cooling system includes a housing having first and second enclosed portions, and a first evaporator and a first evaporator fan disposed in the first enclosed portion that recirculates air in a first closed flow path loop within the first enclosed portion. The first evaporator extracts heat energy from the air in the first closed flow path loop to reduce a temperature level of a first battery module in the first enclosed portion. The cooling system further includes a condenser disposed in the second enclosed portion and fluidly coupled to the first evaporator, which receives heat energy in a refrigerant from the first evaporator and dissipates the heat energy. The cooling system further includes a compressor disposed in the second enclosed portion that recirculates the refrigerant through the first evaporator and the condenser.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Heat pump cycle device
InactiveUS20080041071A1Improve cycle efficiencyPrevent foggingHeat pumpsEvaporators/condensersEngineeringCycle efficiency
A heat pump cycle device includes a compressor for drawing and compressing refrigerant, a first high-pressure heat exchanger located for heating a first fluid circulating in a first fluid circuit using high-pressure refrigerant discharged from the compressor, a second high-pressure heat exchanger for heating a second fluid circulating in a second fluid circuit using the high-pressure refrigerant flowing out of the first high-pressure heat exchanger, a first heating heat exchanger located to heat a third fluid using the first fluid, a second heating heat exchanger located to heat the third fluid using the second fluid, a decompression unit located to decompress the high-pressure refrigerant flowing out of the second high-pressure heat exchanger, and a low-pressure heat exchanger for evaporating low-pressure refrigerant decompressed by the decompression unit. Because the first and second high-pressure heat exchangers are located, cycle efficiency can be improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
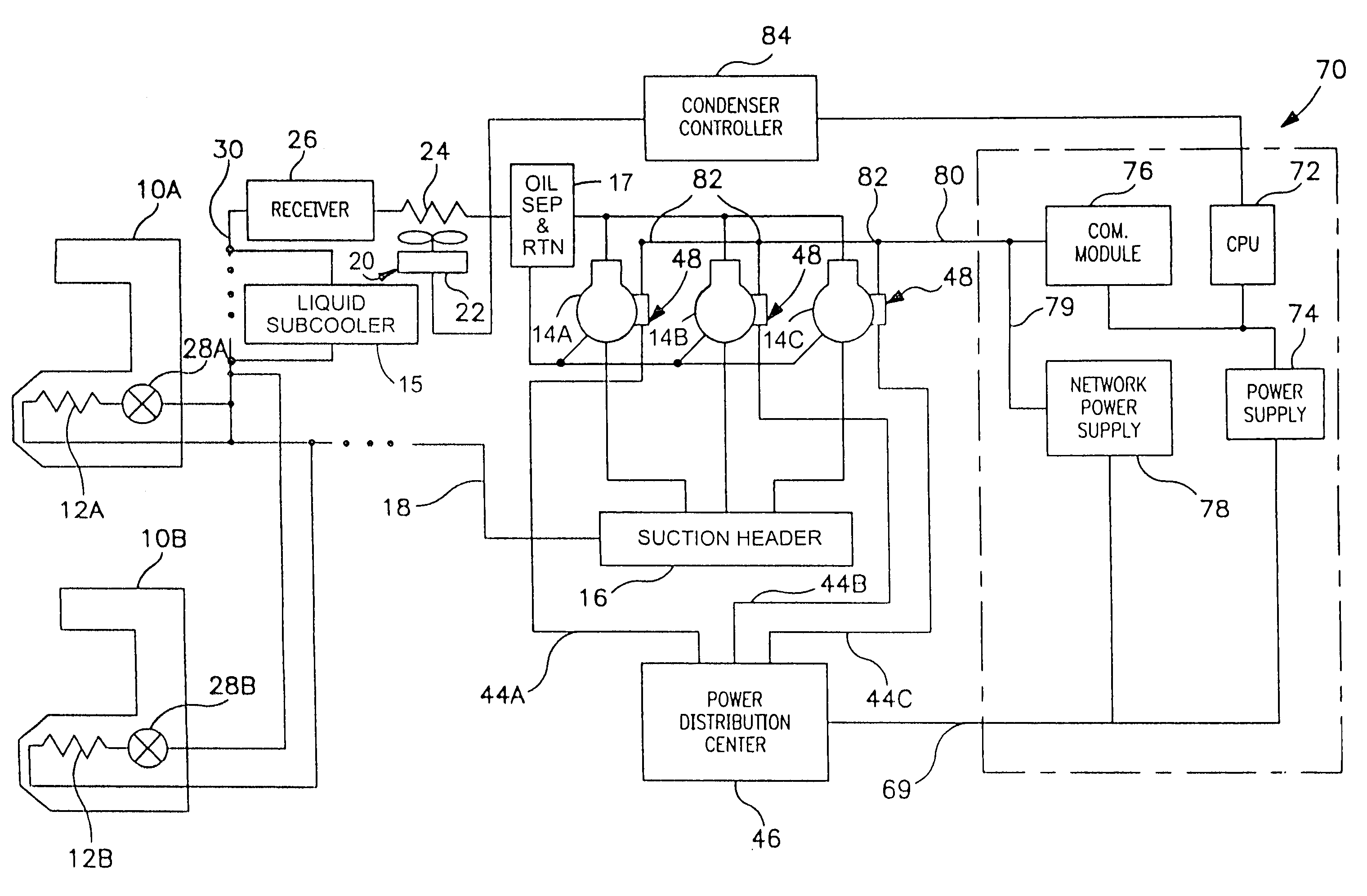
Refrigerating system
InactiveUS6405554B1Improve system reliabilityEasy to implementMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringRefrigerant
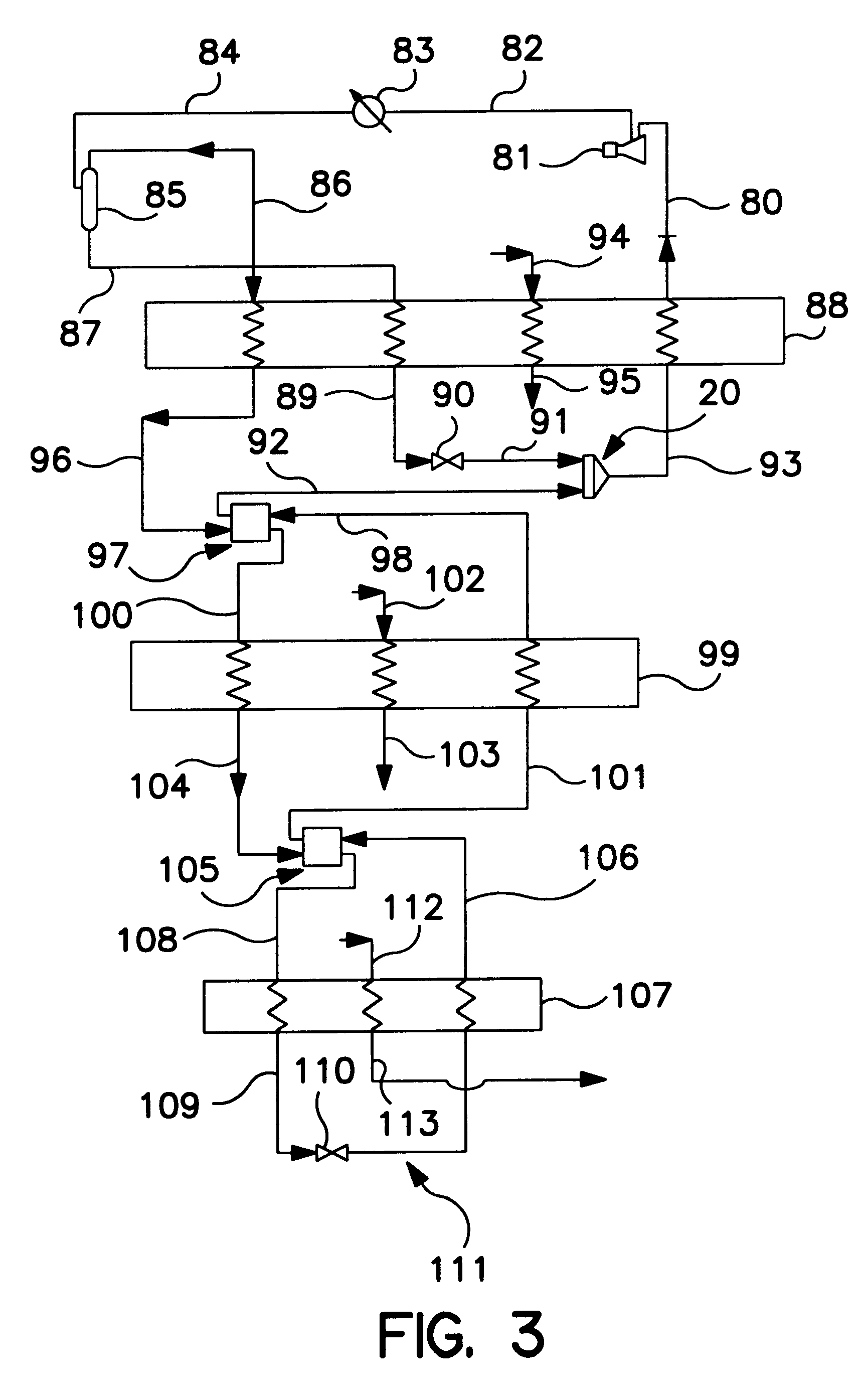
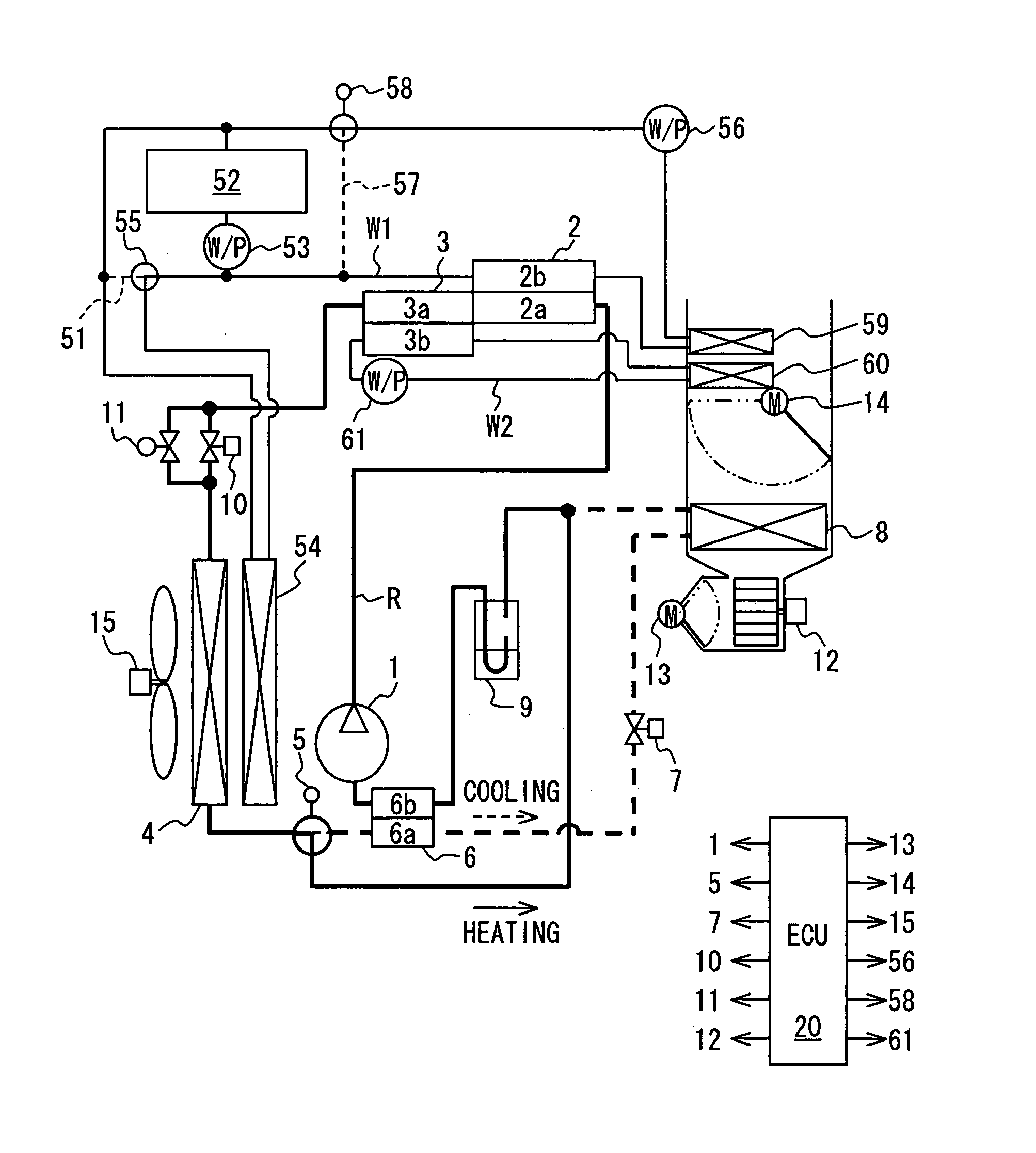
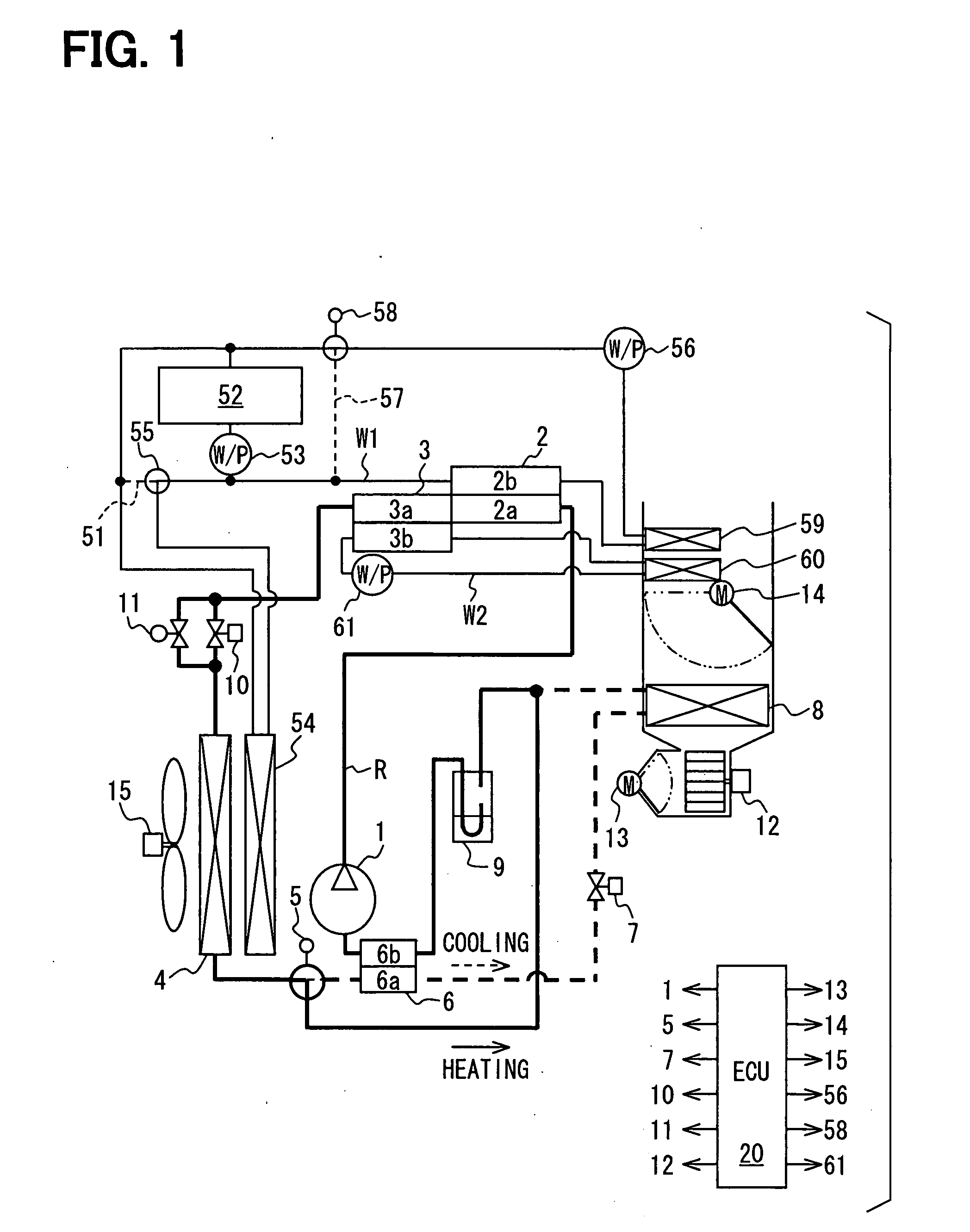
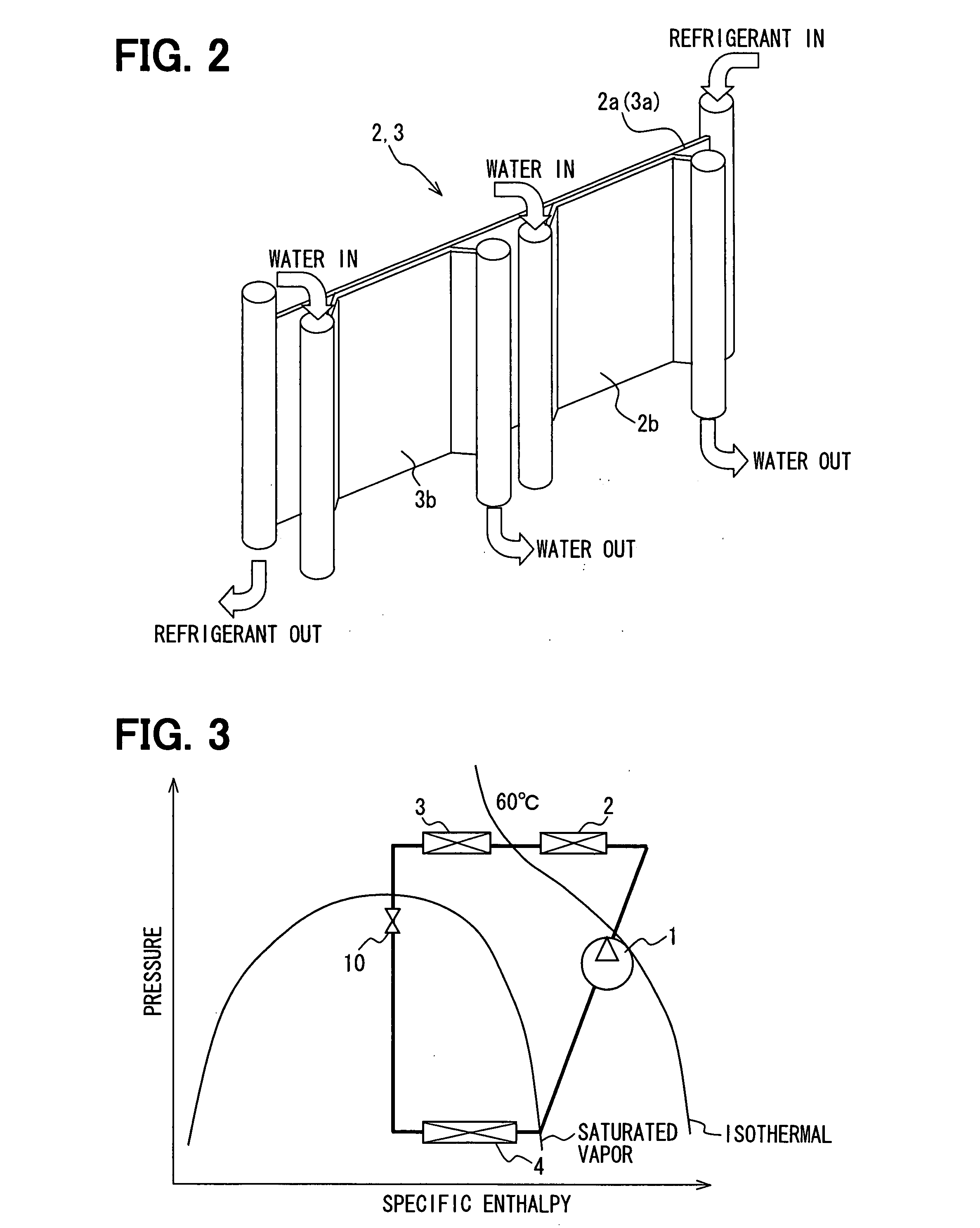
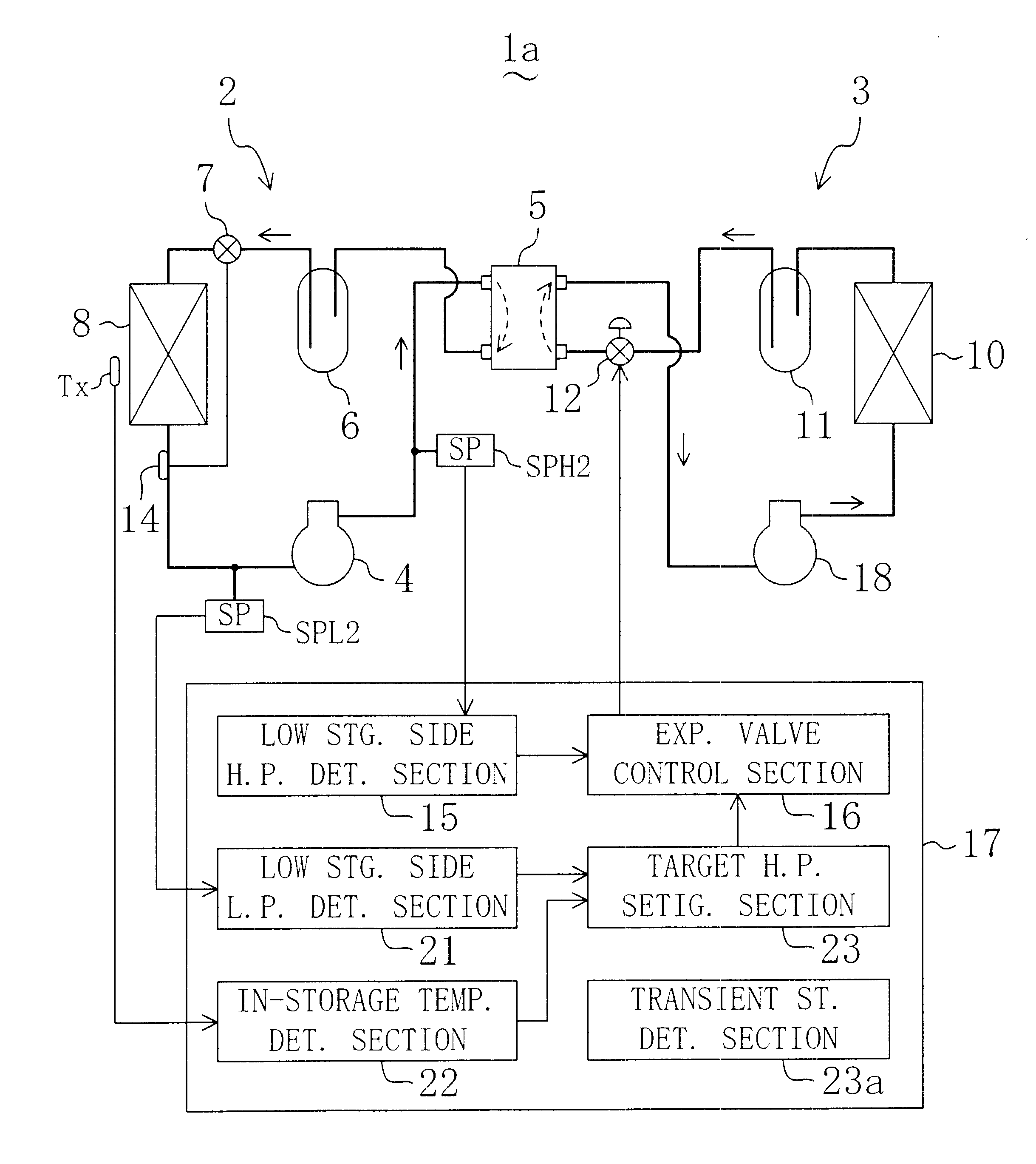
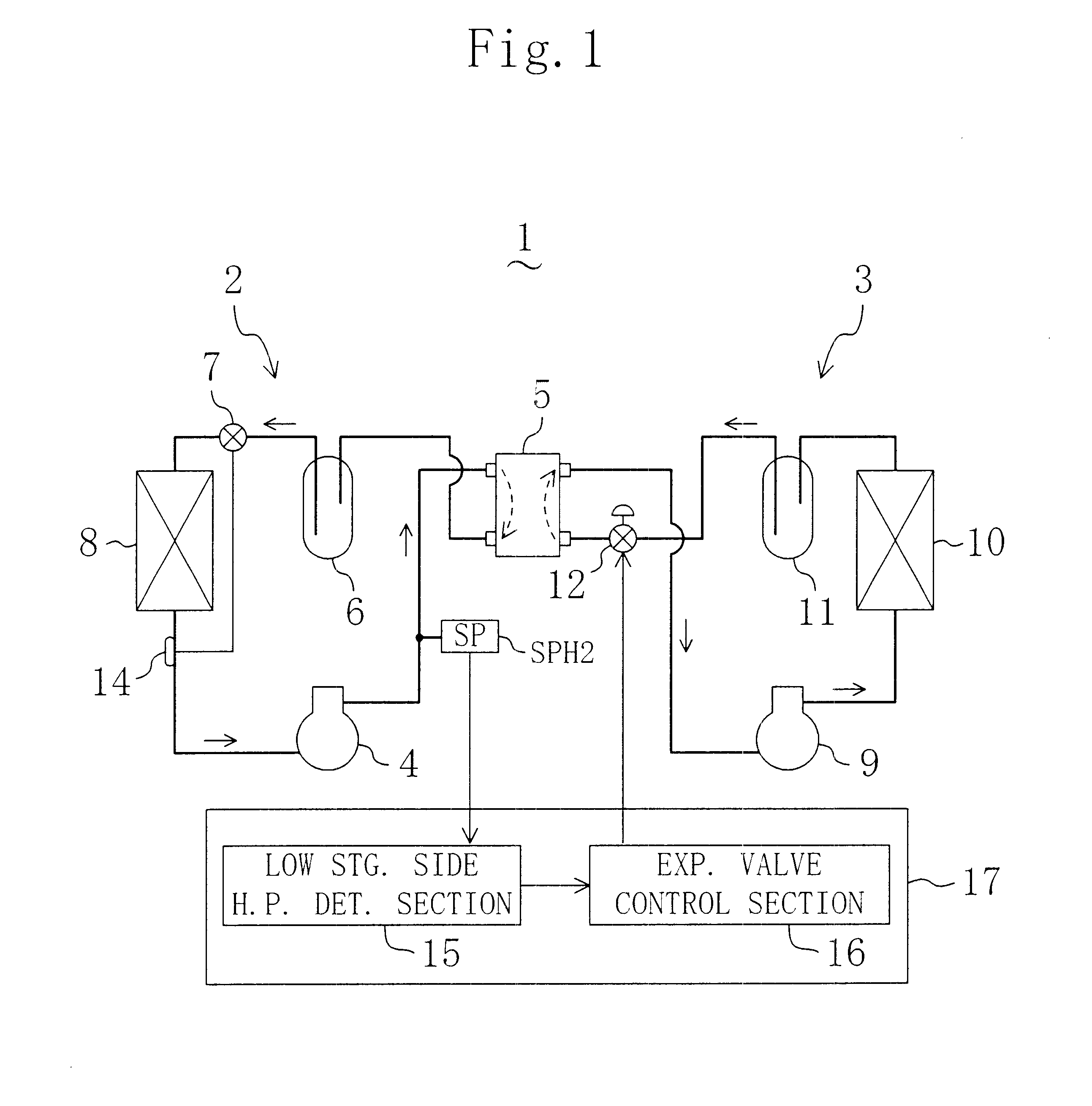
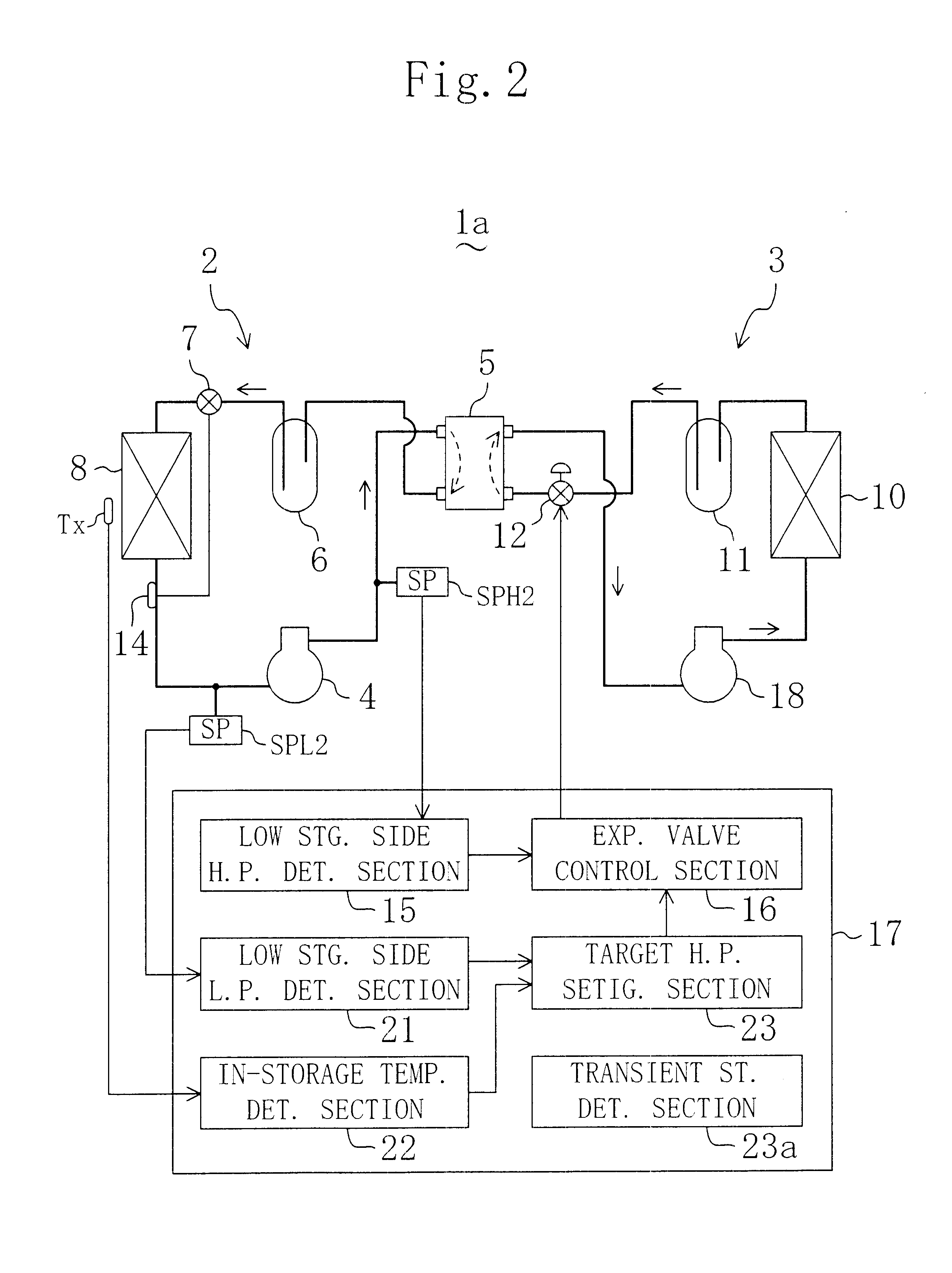
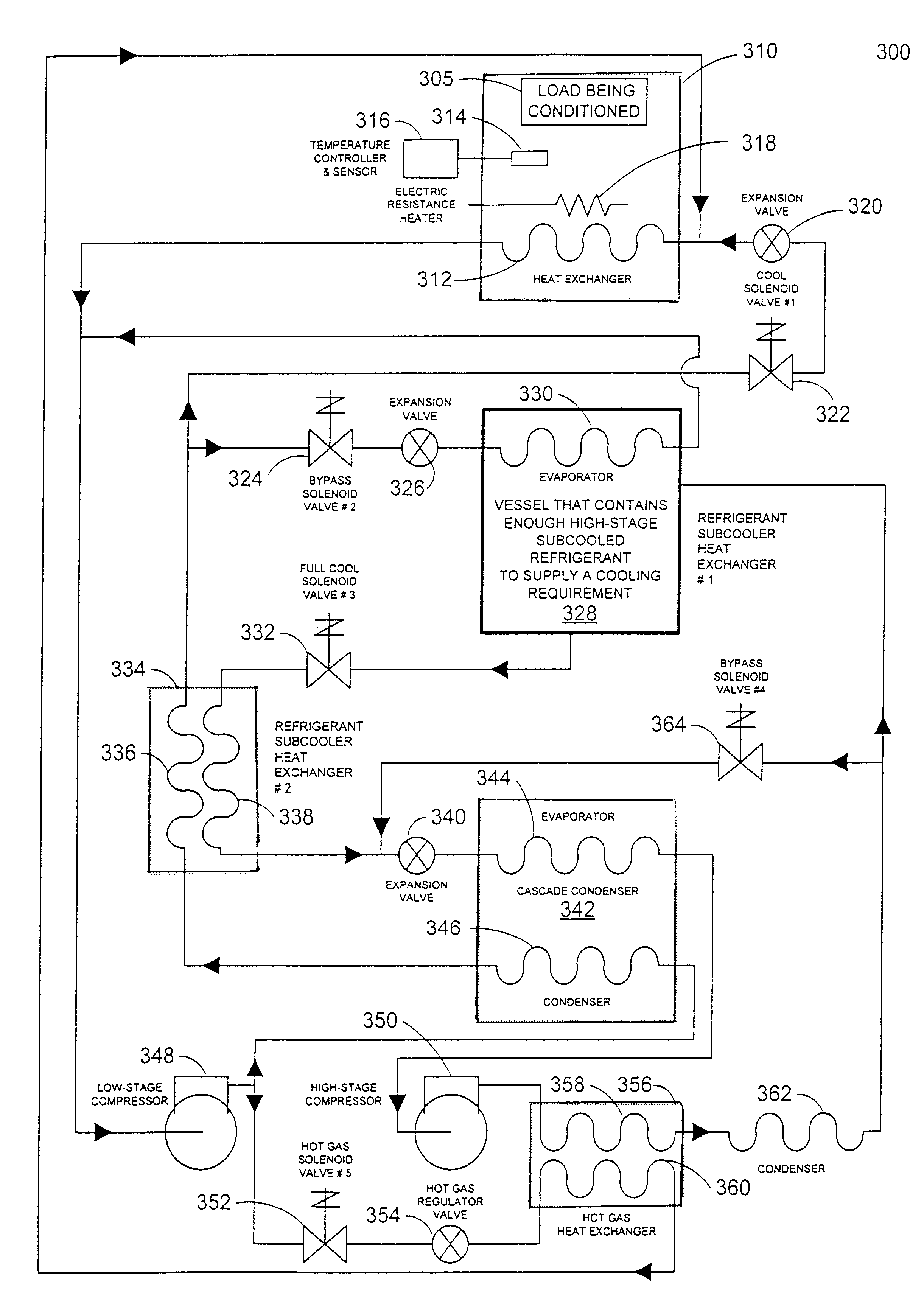
The refrigerating system includes a low stage side refrigerant circuit (2) formed by connecting a low stage side compressor (4), a cascade condenser (5), a low stage side receiver (6), a low stage side expansion valve (7) formed of a temperature-sensitive expansion valve and an evaporator (8) in this order. The system also includes a high stage side refrigerant circuit (3) formed by connecting a high stage side compressor (9), a condenser (10), a high stage side receiver (11), a high stage side expansion valve (12) formed of a motor-operated expansion valve and the cascade condenser (5) in this order. The opening of the high stage side expansion valve (12) is adjusted so that the pressure sensed by a high-pressure sensor (SPH2) for sensing the high pressure in the low stage side refrigerant circuit (2) reaches a predetermined target high pressure.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Control of system coolant to facilitate two-phase heat transfer in a multi-evaporator cooling system
ActiveUS20110056225A1Increase the amount of heatingHigh heat densitySpace heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsElectronic systemsNuclear engineering
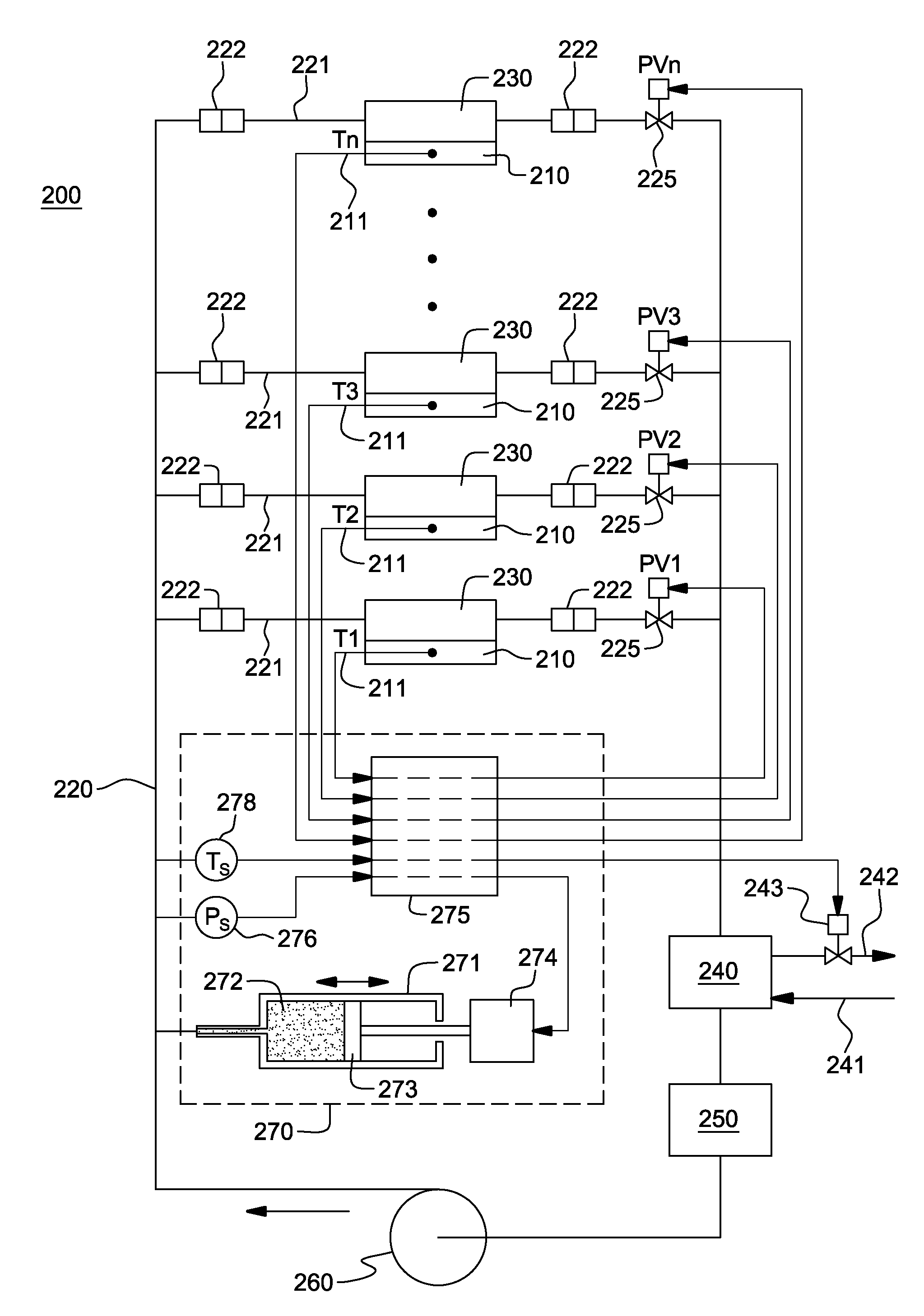
A cooling system and method are provided for facilitating two-phase heat transfer from an electronics system including a plurality of electronic devices to be cooled. The cooling system includes a plurality of evaporators coupled to the electronic devices, and a coolant loop for passing system coolant through the evaporators. The coolant loop includes a plurality of coolant branches coupled in parallel, with each coolant branch being coupled in fluid communication with a respective evaporator. The cooling system further includes a control unit for maintaining pressure of system coolant at a system coolant supply side of the coolant branches within a specific pressure range at or above saturation pressure of the system coolant for a given desired saturation temperature of system coolant into the evaporators to facilitate two-phase heat transfer in the plurality of evaporators from the electronic devices to the system coolant at the given desired saturation temperature.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Packaged chilling systems for building air conditioning and process cooling
InactiveUS20050103032A1Domestic cooling apparatusClimate change adaptationChilled waterHandling system
Disclosed is a packaged chilling system for providing chilled water to an air conditioning system for a building that includes: a duct system; an air handling system; and a water chilling system; wherein: the duct system is in operable communication with a building that has a plurality of rooms, at least one of the rooms having a sensor for detecting the room air temperature in the room, the duct system comprising at least one supply duct for directing low temperature air from the air handling system to the building and at least one return duct for directing high temperature air from the building to the air handling system; the air handling system includes a plurality of air handling units, each air handling unit comprising an air inlet for receiving high temperature air from the building, a cooling coil that includes at least one conduit through which chilled water flows, the cooling coil having multiple passes and positioned for heat transfer contact with the high temperature air, and a fan for increasing the velocity of air in the air handling unit; the water chilling system is installed at a location proximate the building, and is operably connected to the air handling system; and the water chilling system includes a moveable support structure comprising a support base on which a plurality of water chilling system components are affixed, the components including at least one water chiller for lowering the temperature of water from a high temperature to a low temperature. This packaged chilling system may also be used to provide chilled water to industrial processes such as chemical plants, automotive plants, textile mills, paper mills, computer cooling, and factory air-conditioning.
Owner:TAS LTD
Environmental test chamber fast cool down and heat up system
InactiveUS6460355B1Improve energy efficiencyLow calorie contentWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCompression machines with several evaporatorsNuclear engineeringCooling down
An environmental test chamber provides a fast cool down to a temperature of about -125° F. and a fast heat up of an element under test.
Owner:TRIESKEY GUY T
Method and apparatus for controlling temperature for forming ice within an icemaker compartment of a refrigerator
A method of controlling temperature for forming ice within an icemaker compartment of a refrigerator is disclosed. The method includes the steps of activating at least one of the compressor and the coolant pump during an icemaking cycle to provide cooling to the icemaker compartment sufficient to make ice at a first rate, and increasing operation of at least one of the compressor and the coolant pump to provide cooling to the icemaker compartment sufficient to make ice at a second rate, which is faster than the first rate. A related refrigerator is also disclosed.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Cascade refrigeration system with fluoroolefin refrigerant
InactiveUS20120216551A1Lower global warming potentialIncrease capacityCompression machines with cascade operationHeat-exchange elementsEngineeringRefrigeration
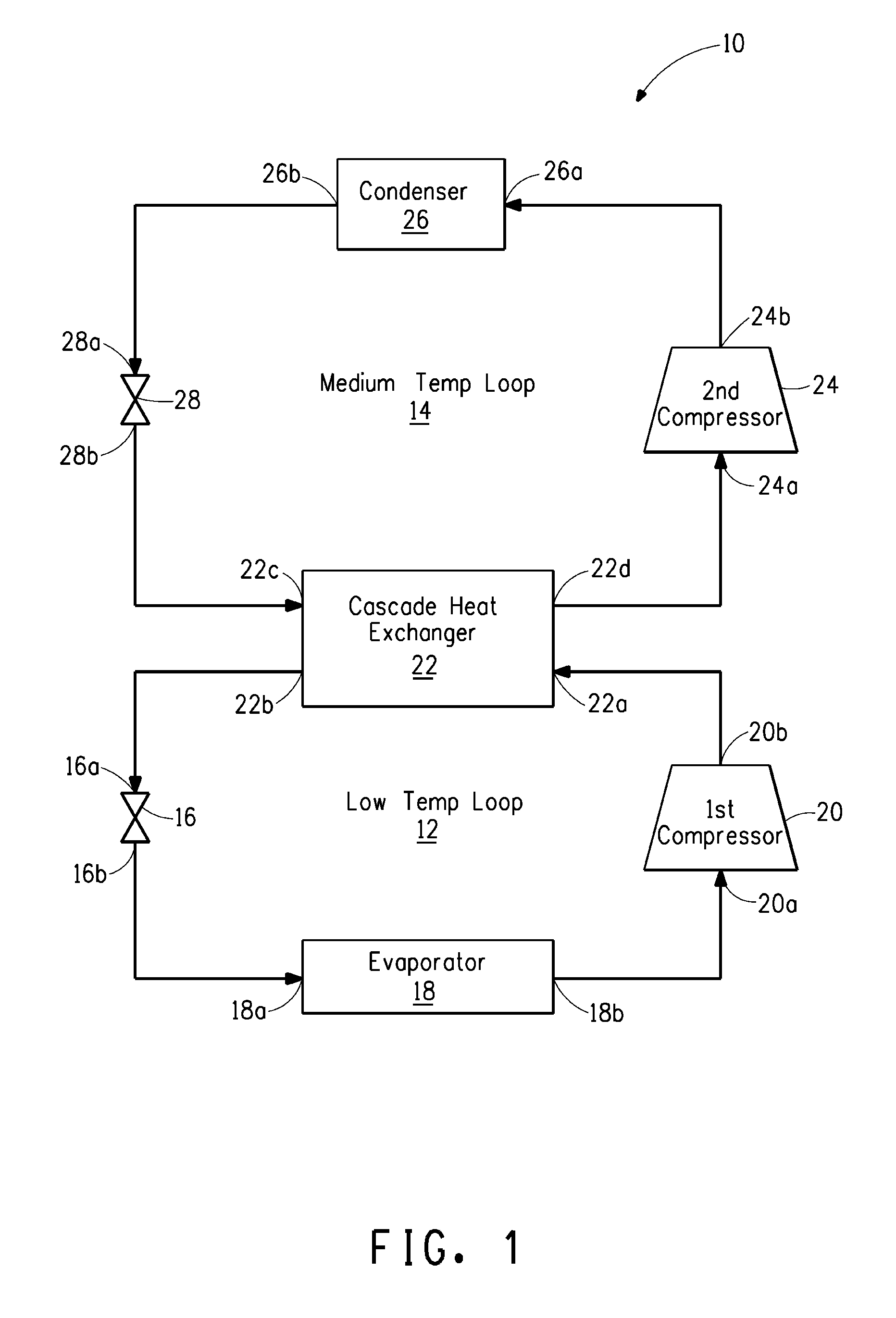
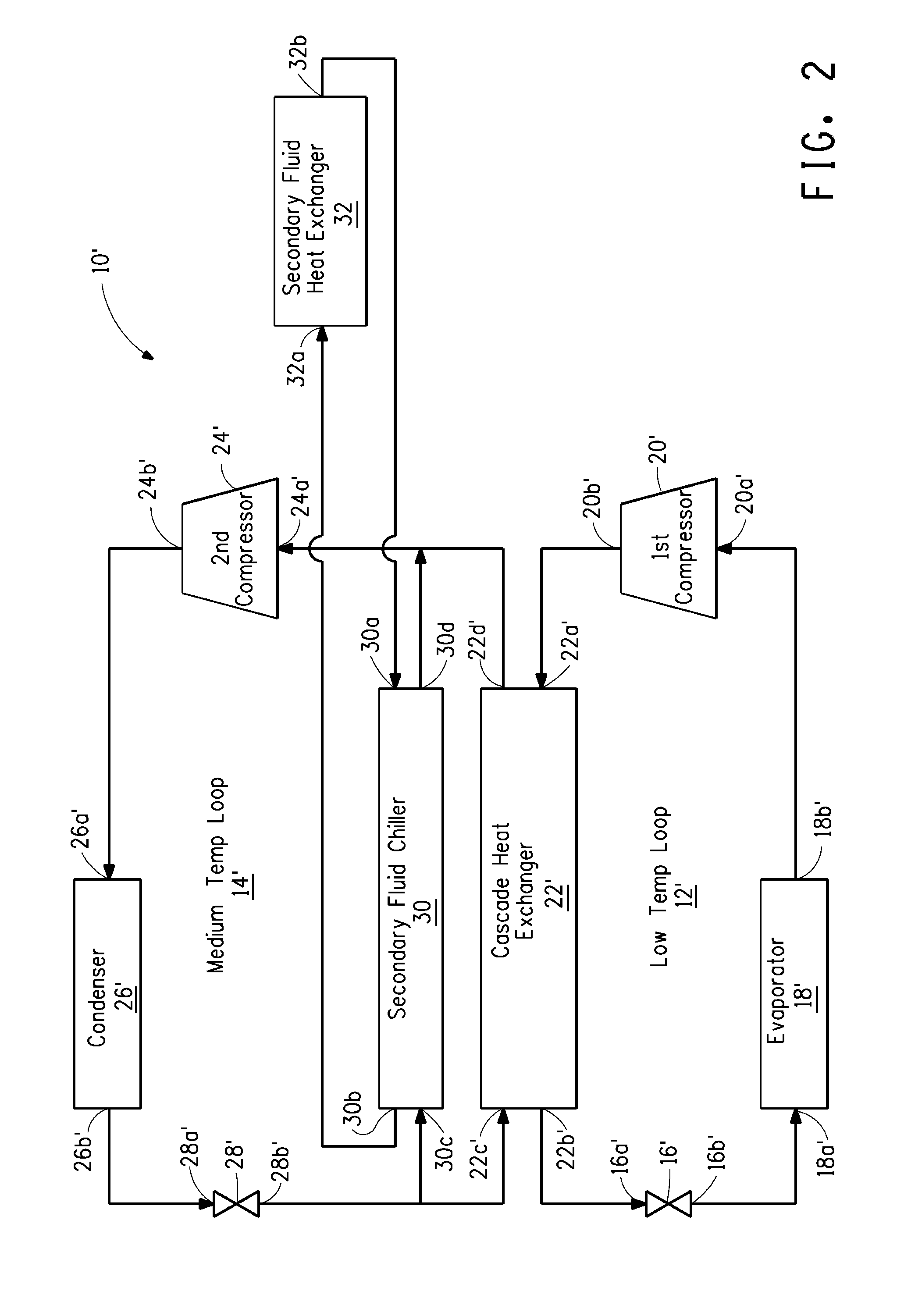
The present invention relates to a cascade refrigeration system which circulates a refrigerant comprising a fluoroolefin therethrough. The cascade refrigeration system includes a low temperature refrigeration loop and a medium temperature refrigeration loop. The fluoroolefin circulates through either loop, or both. In a particular embodiment, the fluoroolefin circulates through the medium temperature loop. In a particular embodiment, where the cascade refrigeration system includes a first and a second cascade heat exchanger, and a secondary heat transfer loop which extends between the first and second cascade heat exchangers, either the first and / or second refrigerant may be, but need not necessarily be, a fluoroolefin.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
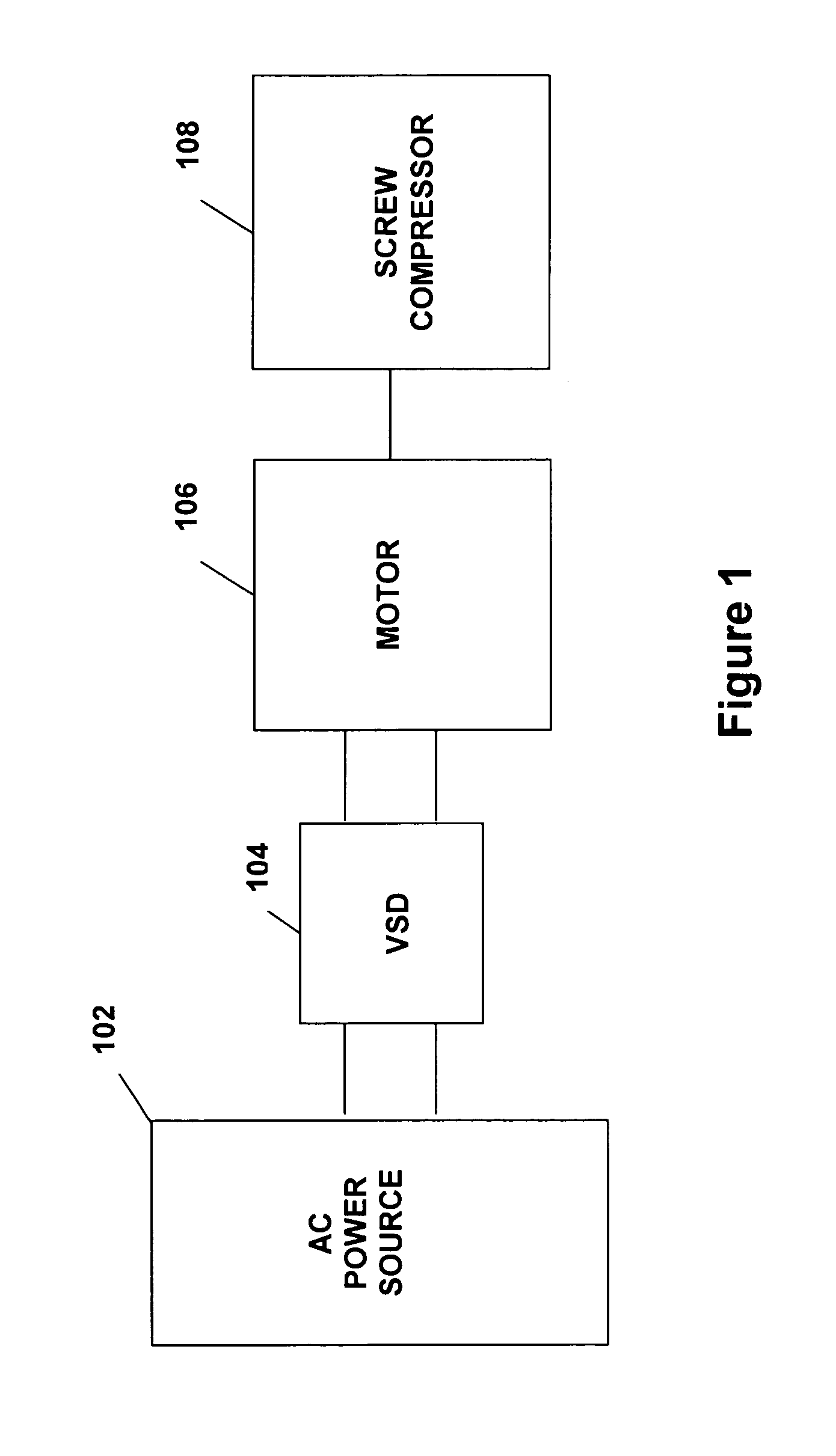
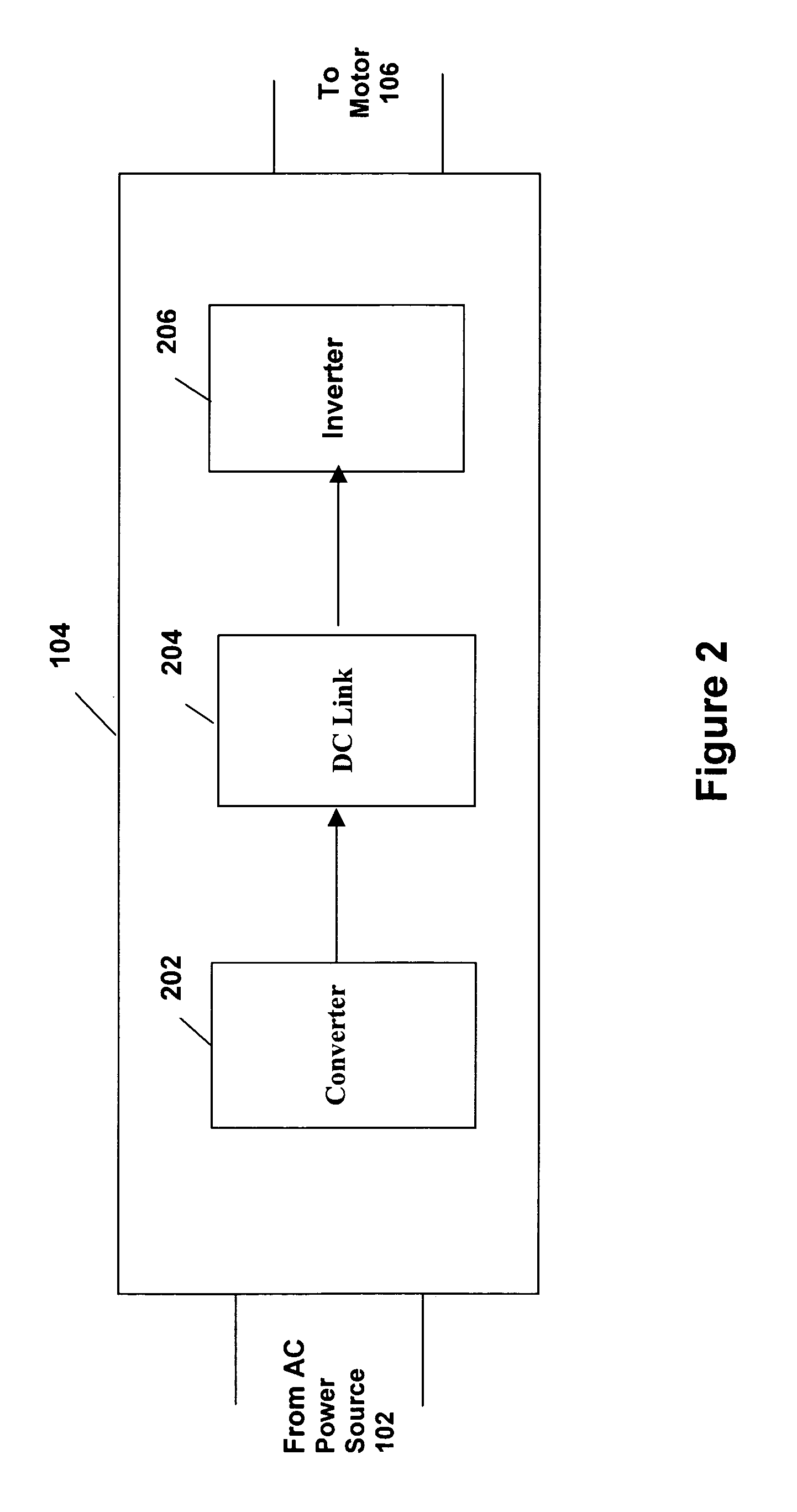
System and method for variable speed operation of a screw compressor
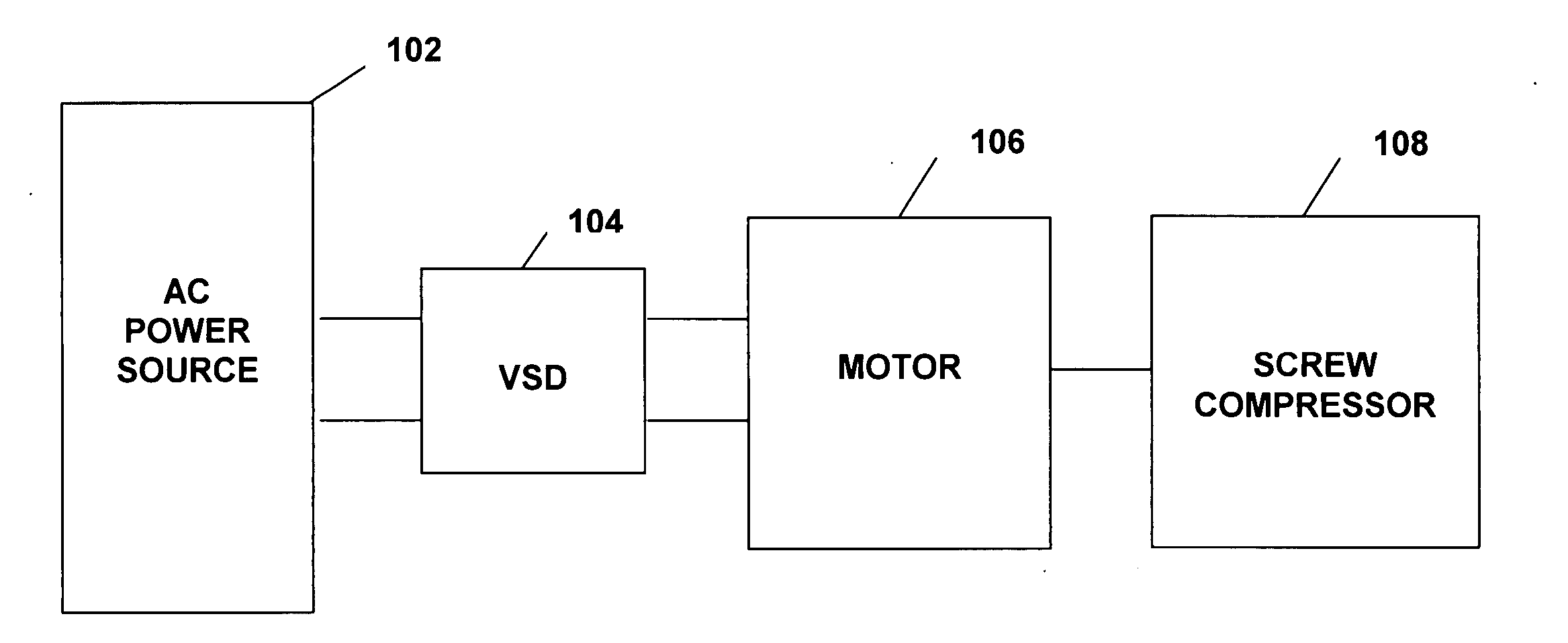
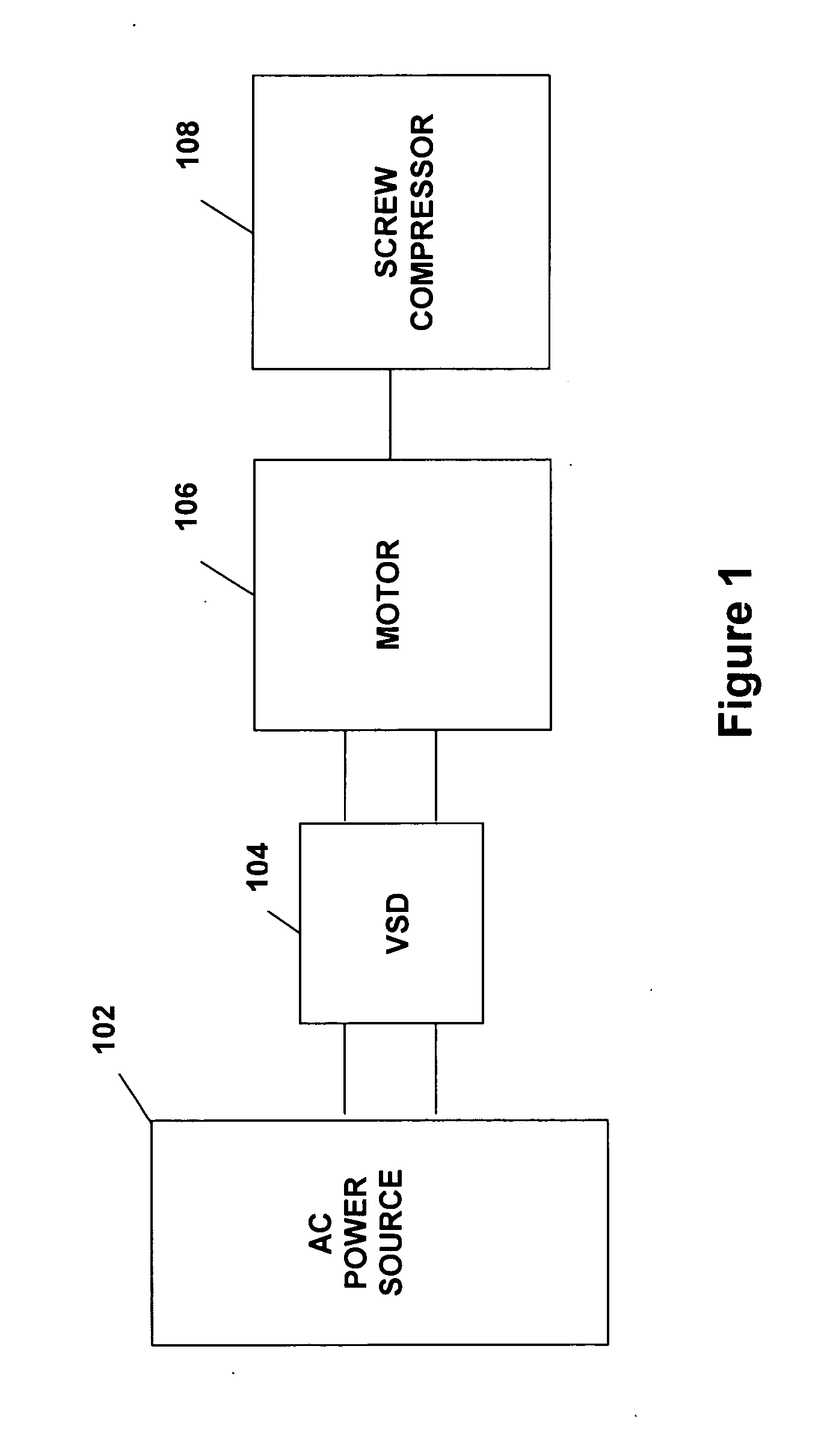
ActiveUS20050188708A1Efficient screw compressor operationReduce gas leakageAC motor controlRotary piston pumpsControl theoryOperating speed
A system and method are provided for variable speed operation of a screw compressor to obtain increased capacity and efficiency. The screw compressor is connected to an induction motor driven by a variable speed drive, wherein the screw compressor has a variable output capacity that is dependent on the output speed of the motor. To obtain increased capacity and efficiency, the screw compressor is operated at a speed greater than the screw compressor's rated speed and does not include a slide valve. The maximum operating speed of the screw compressor, which speed is greater than the rated speed, is related to the maximum operating speed of the motor when operated at a voltage and frequency provided by the variable speed drive that is greater than the motor's rated voltage and frequency in a constant flux or constant volts / Hz mode.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
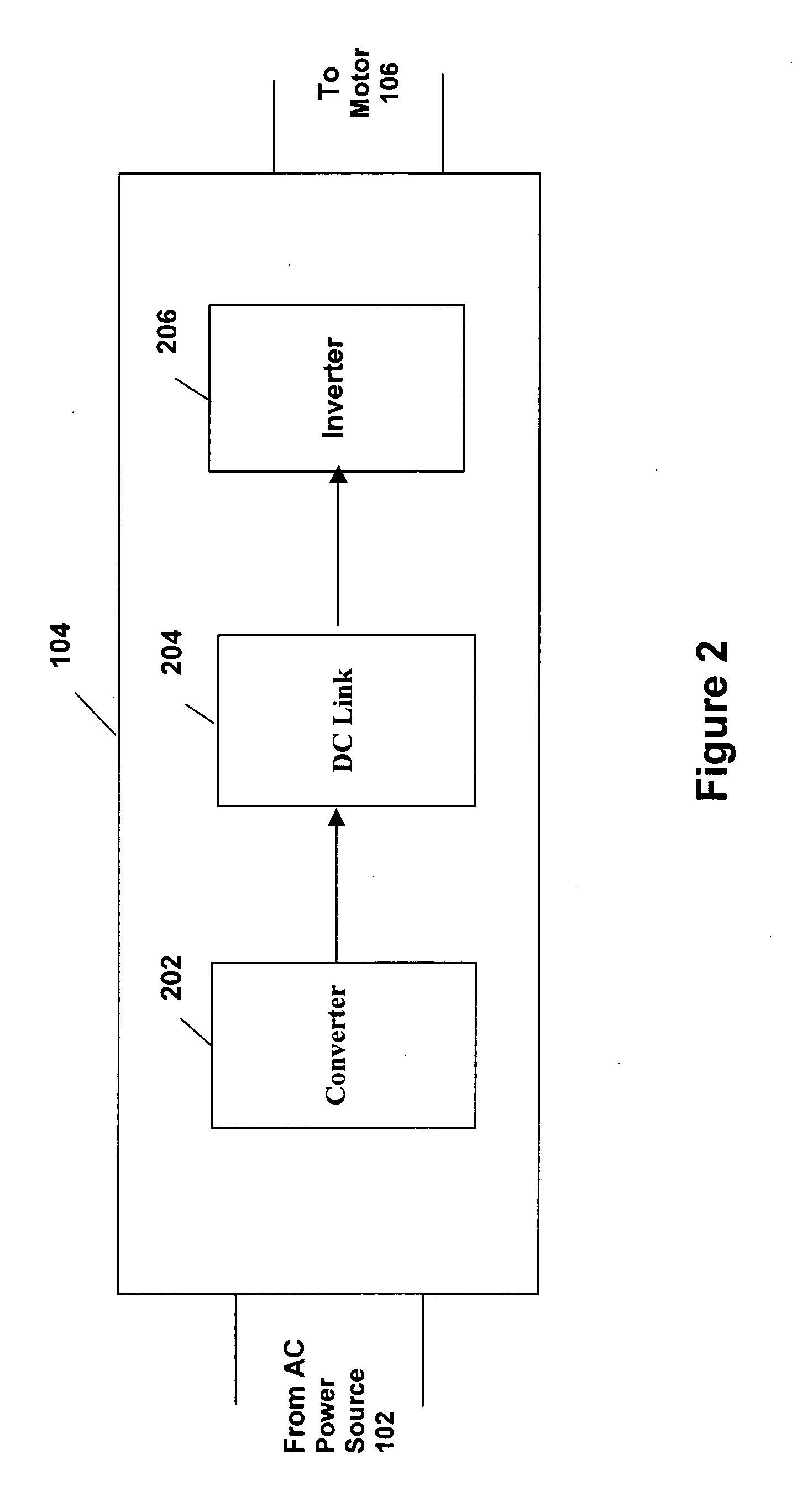
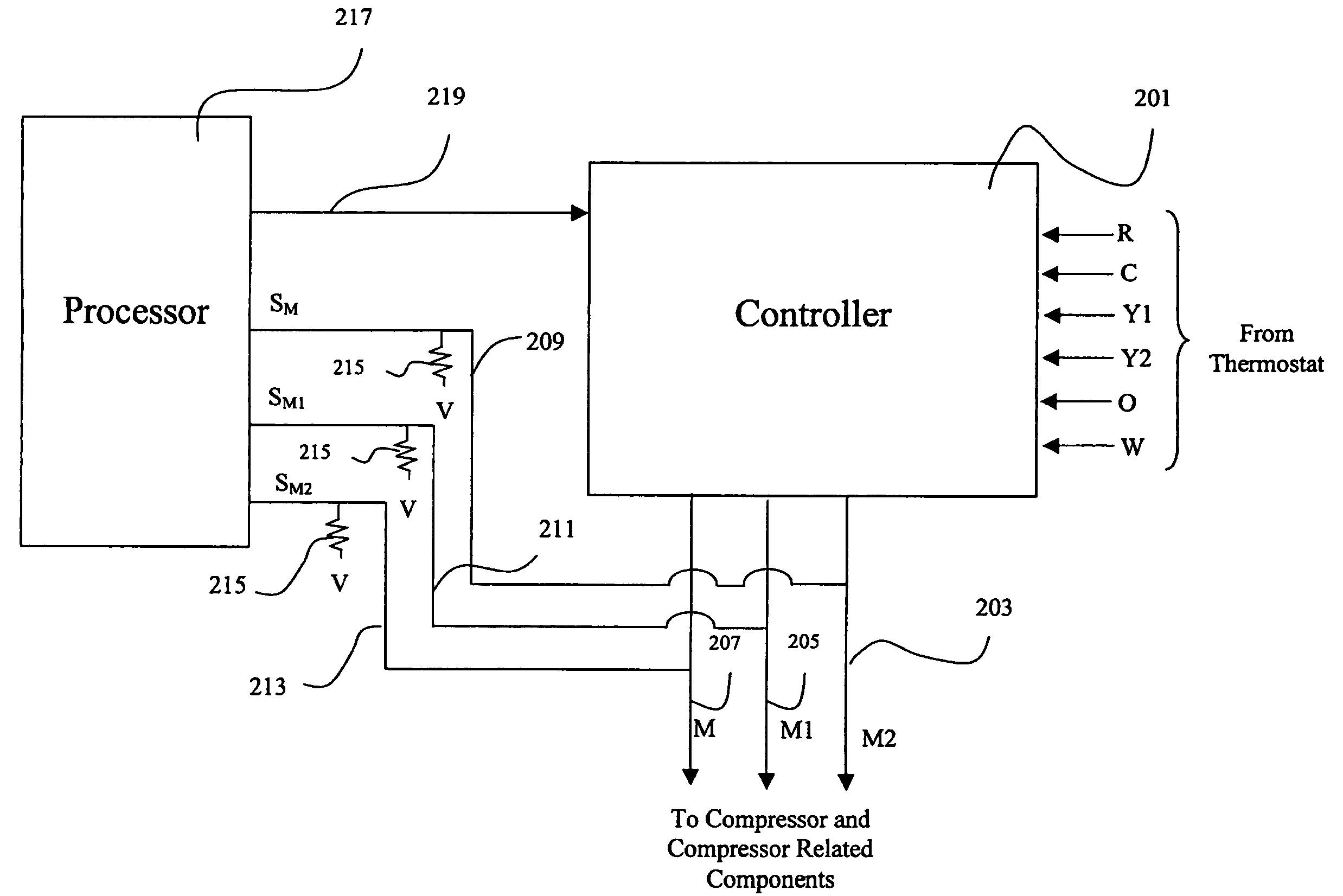
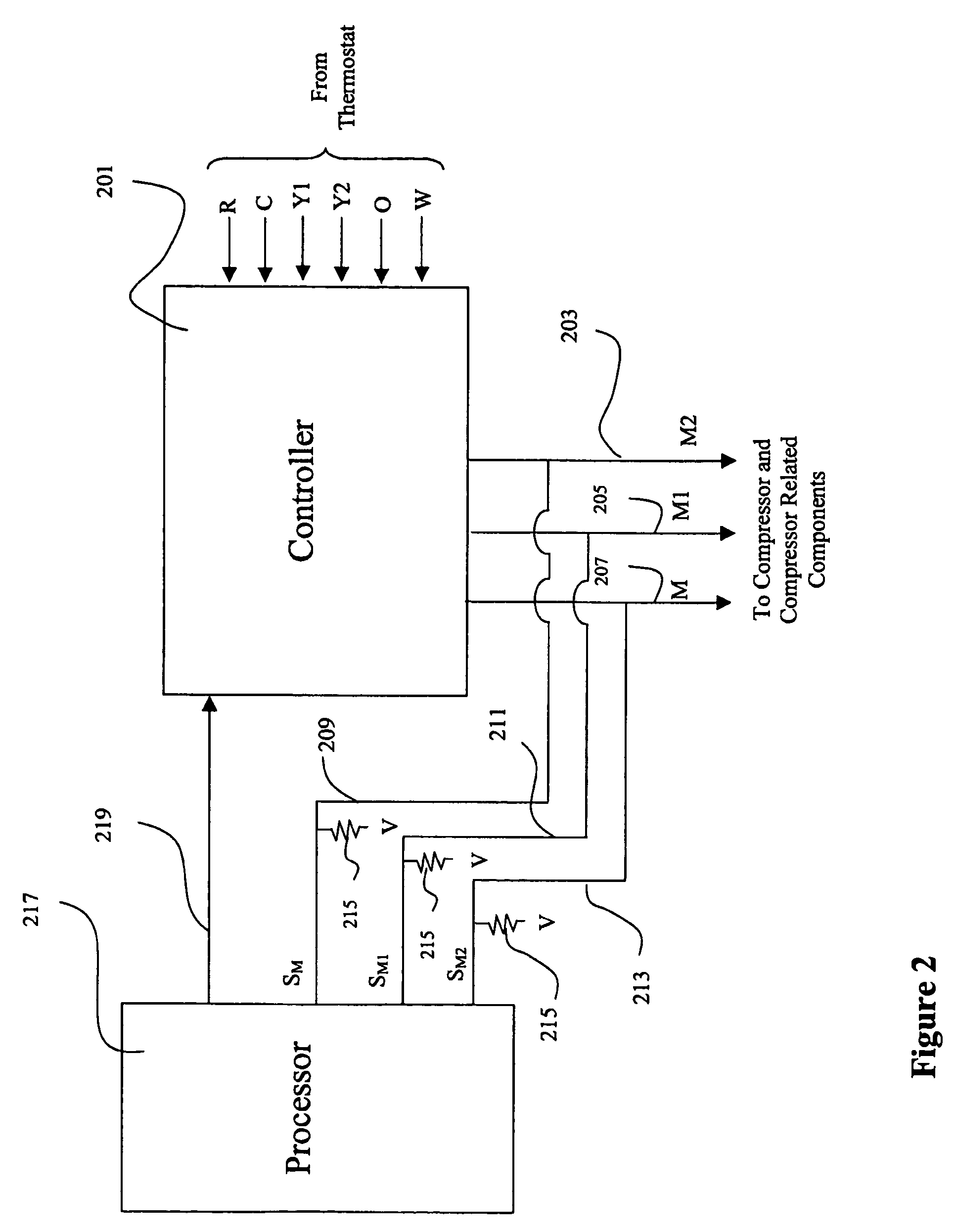
Method and apparatus to sense and control compressor operation in an HVAC system
ActiveUS7562536B2Reduce stepsCompression machines with non-reversible cycleElectric controllersLoad sensingControl theory
An HVAC system and method for configuring a controller to control a compressor including a detection system provided to determine a type of compressor. The detection system includes a processor; and a load sensing circuit connected between the processor and a controller. The controller has a plurality of output connections connectable to a compressor. The load sensing circuit senses whether a load is present on each output connection of the plurality of output connections and provides a load signal to the processor indicating whether a load is present on each output connection. The load signals are processed with the processor to determine the type of compressor is present. The controller is configured to control the compressor in response to the determined type of compressor.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
System and method for variable speed operation of a screw compressor
ActiveUS7096681B2Guaranteed uptimeIncrease rotor speedAC motor controlRotary piston pumpsInduction motorEngineering
A system and method are provided for variable speed operation of a screw compressor to obtain increased capacity and efficiency. The screw compressor is connected to an induction motor driven by a variable speed drive, wherein the screw compressor has a variable output capacity that is dependent on the output speed of the motor. To obtain increased capacity and efficiency, the screw compressor is operated at a speed greater than the screw compressor's rated speed and does not include a slide valve. The maximum operating speed of the screw compressor, which speed is greater than the rated speed, is related to the maximum operating speed of the motor when operated at a voltage and frequency provided by the variable speed drive that is greater than the motor's rated voltage and frequency in a constant flux or constant volts / Hz mode.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
Permanent low cost radio frequency compressor identification
InactiveUS20050232781A1Fast readWrite quicklyRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsRotary piston pumpsEngineeringRadio frequency
Owner:SCROLL TECH
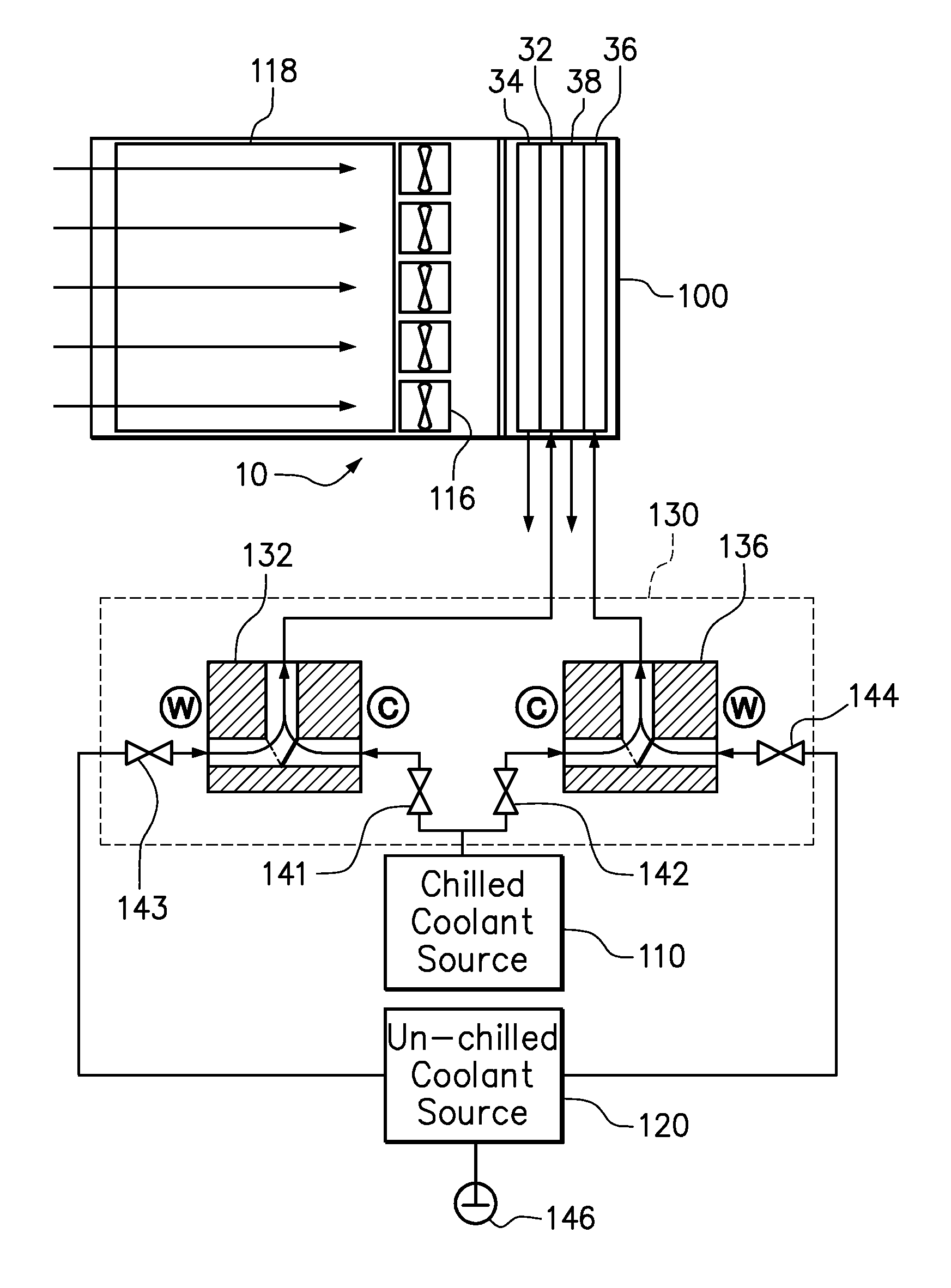
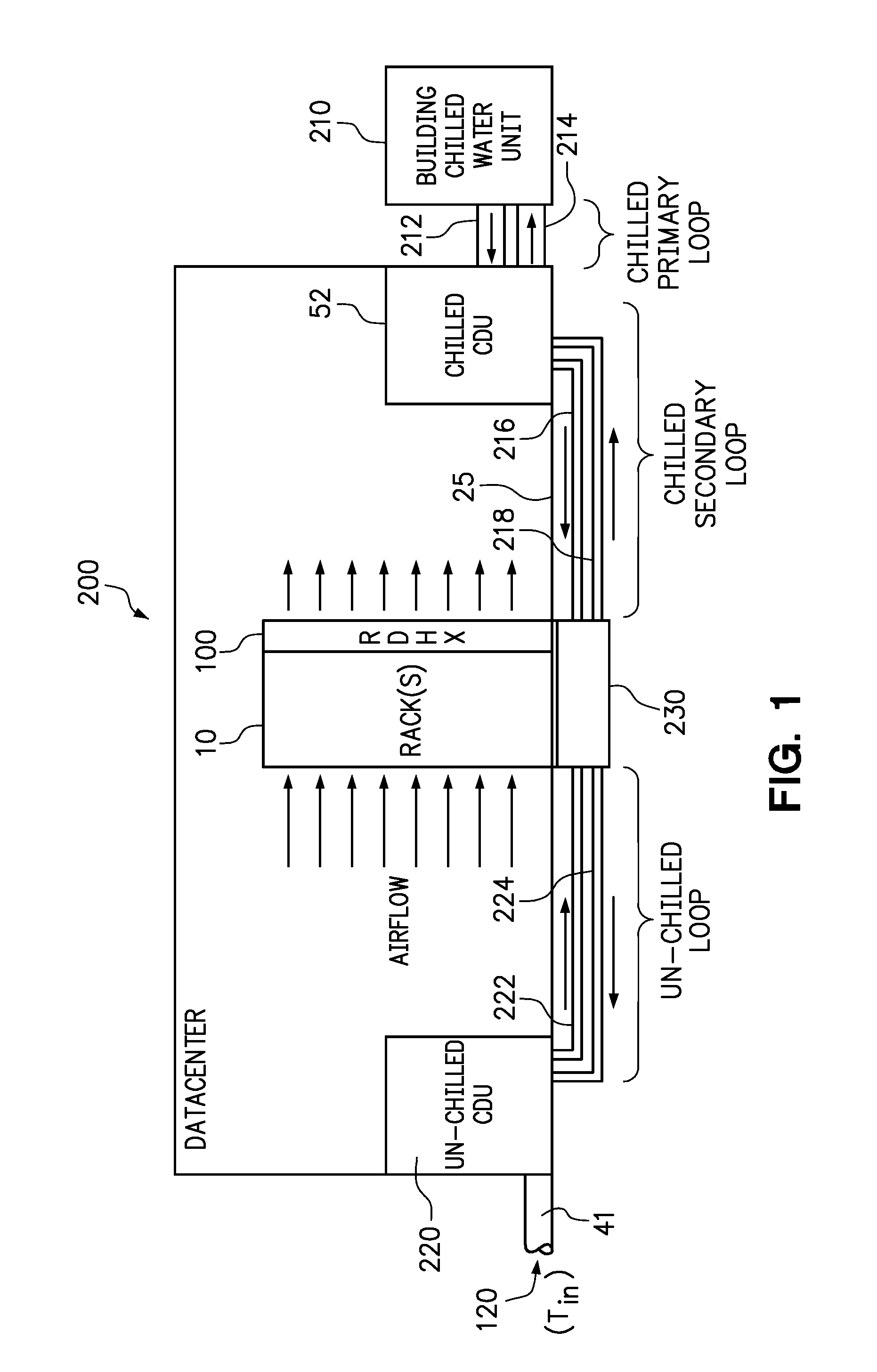
Computer rack cooling using independently-controlled flow of coolants through a dual-section heat exchanger
ActiveUS8789384B2Domestic cooling apparatusCompression machines with cascade operationControl flowNuclear engineering
Embodiments of the present invention include a cooling system and method for cooling a computer rack by circulating liquid coolant through different sections of a rack heat exchanger under separately controlled flow and temperature conditions. In a method according to one embodiment, a first liquid coolant is supplied to a first section of an air-to-liquid heat exchanger. A second liquid coolant is supplied to a second section of the air-to-liquid heat exchanger at a different temperature than the first liquid coolant. Airflow is generated through rack-mounted computer components to the first and second sections of the air-to-liquid heat exchanger. The flow rates of the first and second liquid coolants are independently controlled to enforce a target cooling parameter. The independent operation of the first and second fin tube sections allows for the increased use of un-chilled water without sacrificing heat removal objectives.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
System and method for capacity control in a multiple compressor chiller system
ActiveUS20070056300A1Easy to controlImprove system efficiencyCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCompression machines with cascade operationLiquid temperatureEngineering
A capacity control algorithm for a multiple compressor liquid chiller system is provided wherein the speed and number of compressors in operation are controlled in order to obtain a leaving liquid temperature setpoint. In response to an increase in the load in the chiller system, the algorithm determines if a compressor should be started and adjusts the operating speed of all operating compressors when an additional compressor is started. In response to a decrease in the load in the chiller system with multiple compressors operating, the algorithm determines if a compressor should be de-energized and adjusts the operating speed of all remaining operating compressors when a compressor is de-energized.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
Cooling device
InactiveUS6997006B2Reduce in quantitySimplification of setting workCompression machines with cascade operationRefrigeration devicesPlate heat exchangerEngineering
A cooling system that has a heat exchanger which is housed in one enclosure and is constituted of a plurality of heat exchange modes, and the heat exchanger includes a refrigerant forced circulation mode, a refrigerant natural circulation mode, and a ventilation mode. A temperature detector performs switching to an optimal mode, to thereby cool the inside of the enclosure of a housing accommodating equipment including a heat-generating component.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Ejector cycle system with critical refrigerant pressure
InactiveUS20010025499A1Recover energyReduce power consumptionCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEvaporators/condensersEngineeringPressure difference
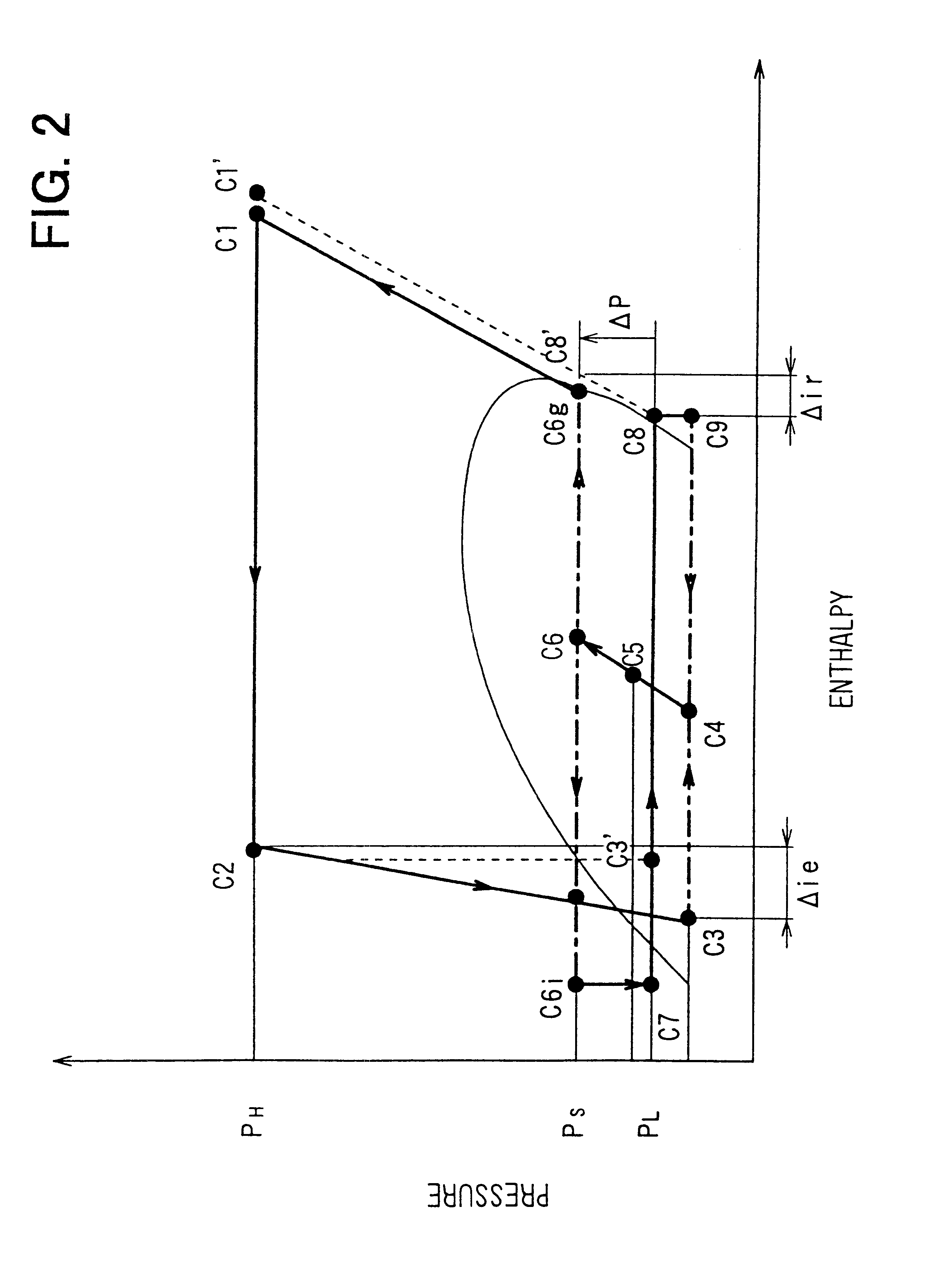
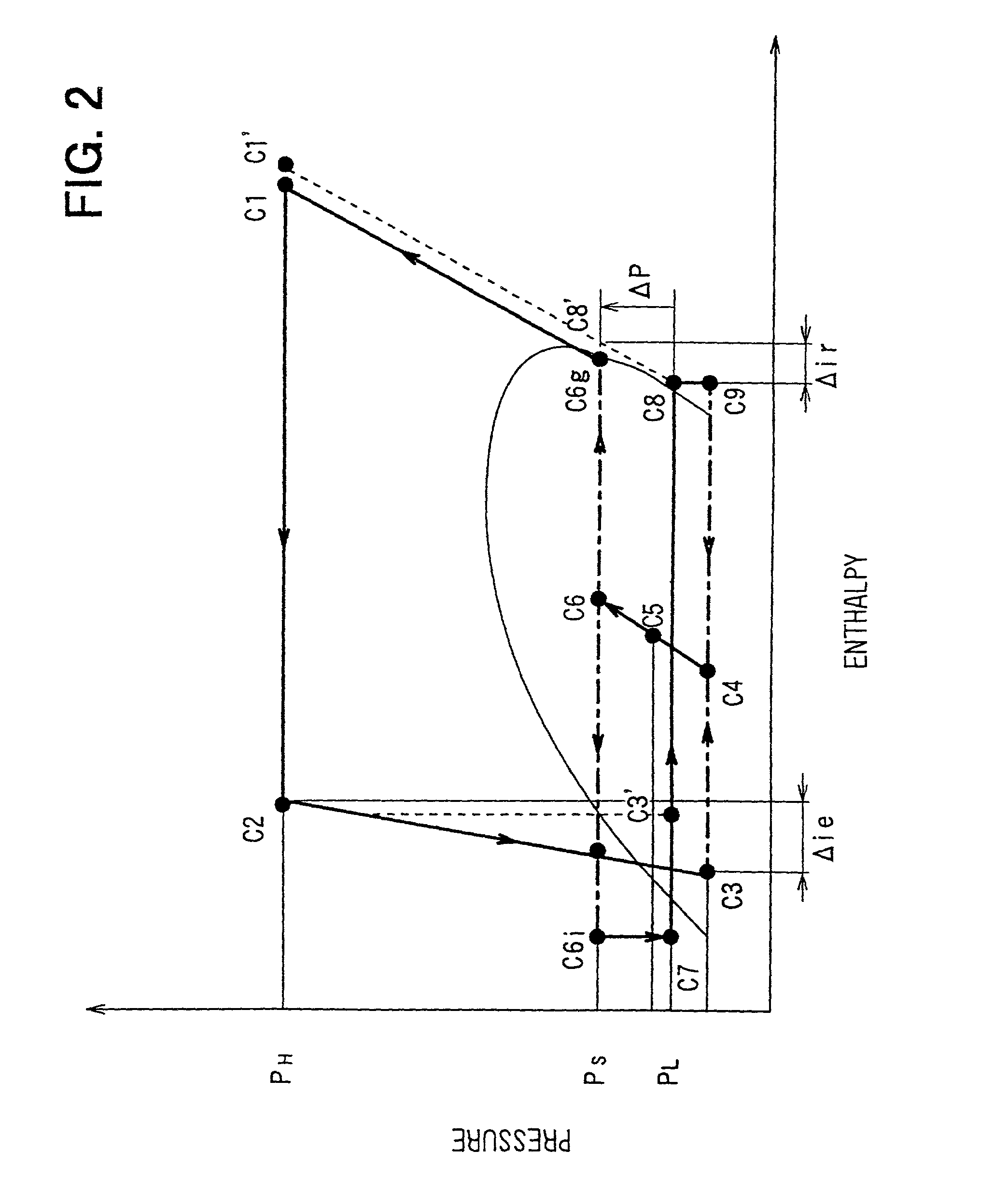
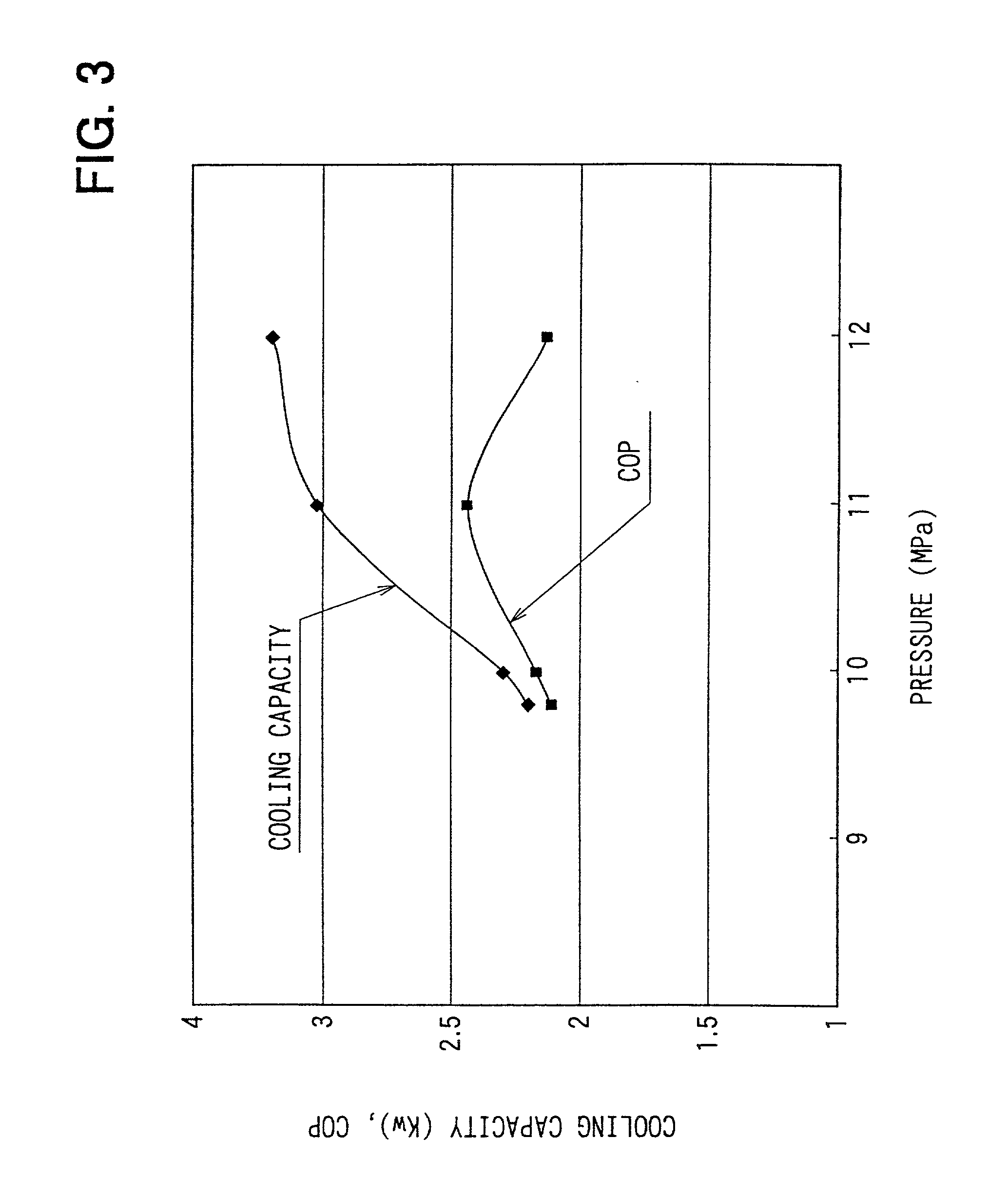
In an ejector cycle system using carbon dioxide as refrigerant, an ejector decompresses and expands refrigerant from a radiator to suck gas refrigerant evaporated in an evaporator, and converts an expansion energy to a pressure energy to increase a refrigerant pressure to be sucked into a compressor. Because refrigerant is decompressed and expanded in a super-critical area, a pressure difference during the decompression operation becomes larger, and a specific enthalpy difference becomes larger. Accordingly, energy converting efficiency in the ejector becomes higher, and efficiency of the ejector cycle system is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com