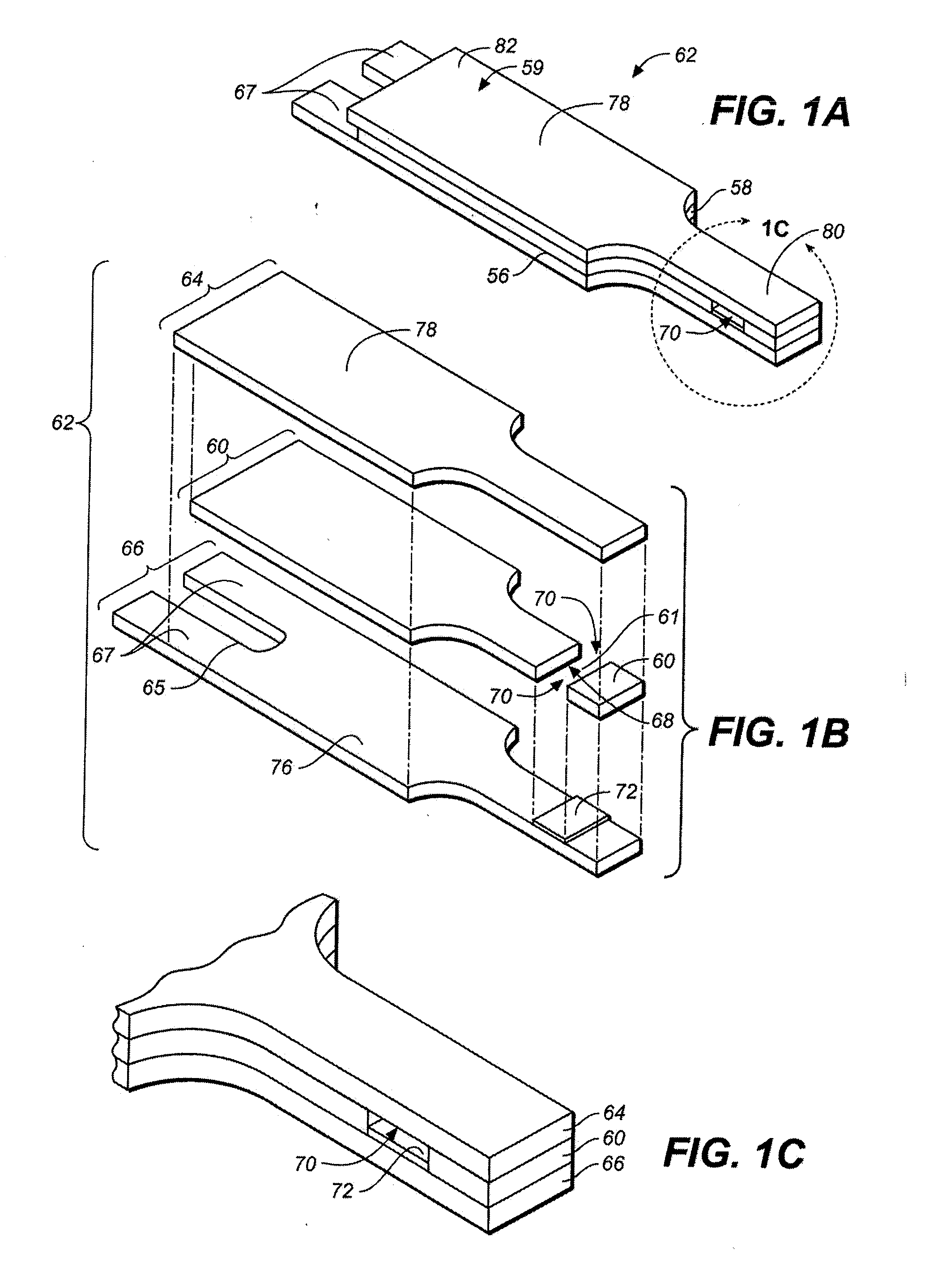
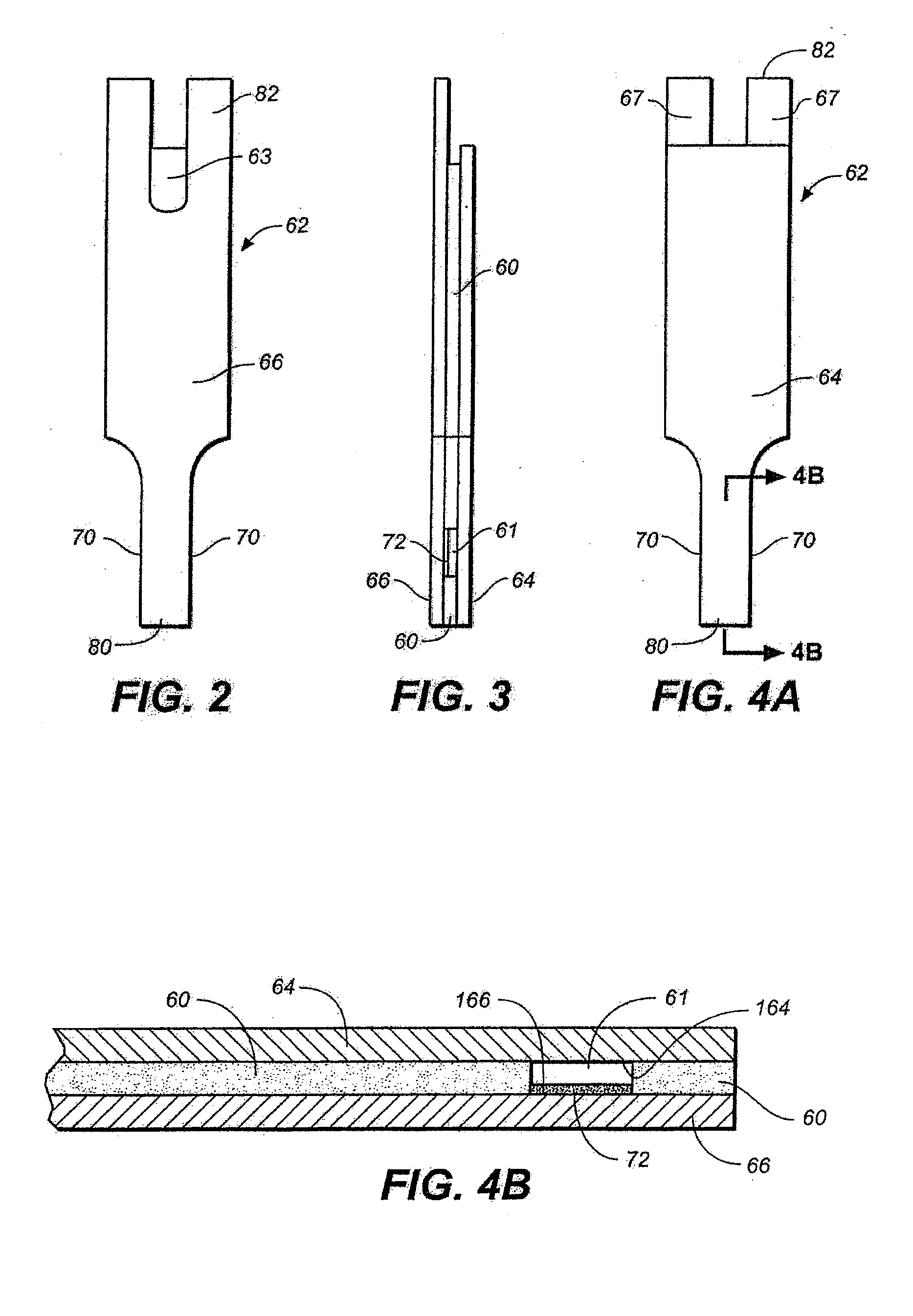
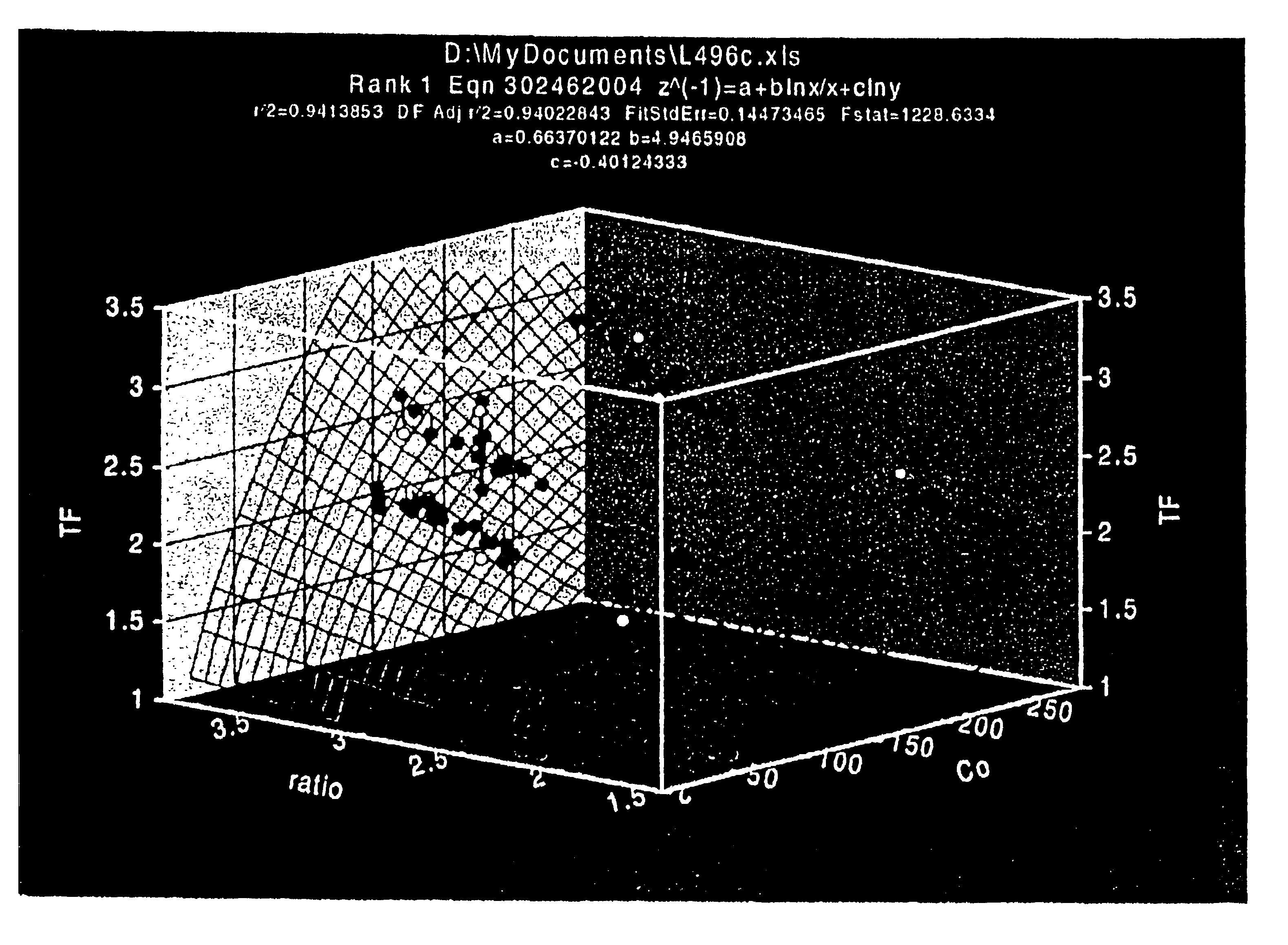
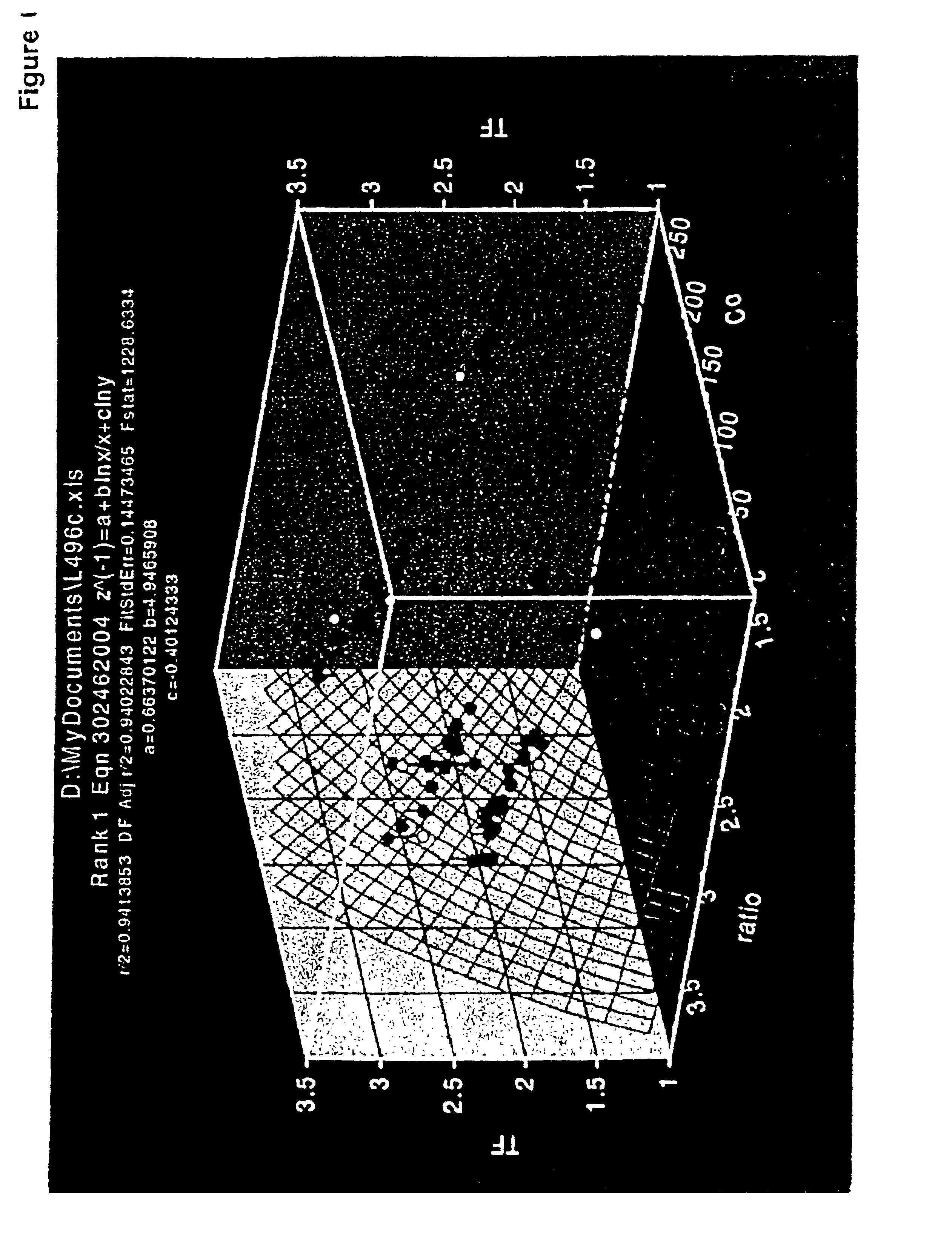
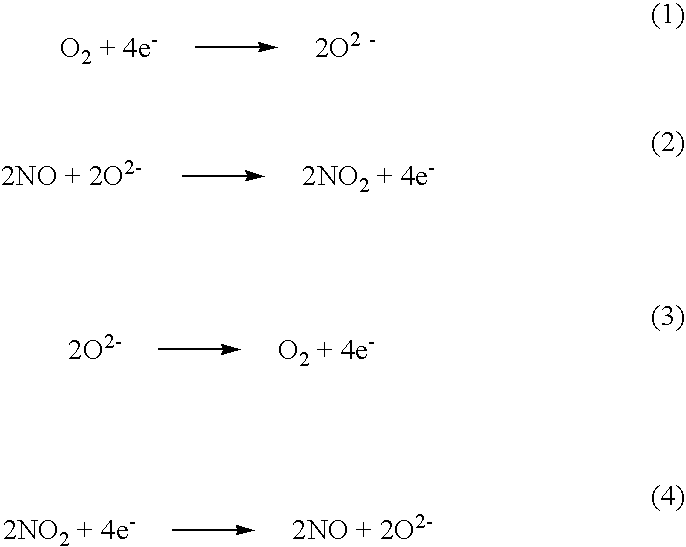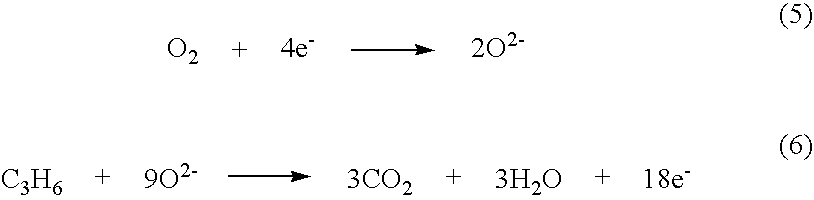Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11343results about "Weather/light/corrosion resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
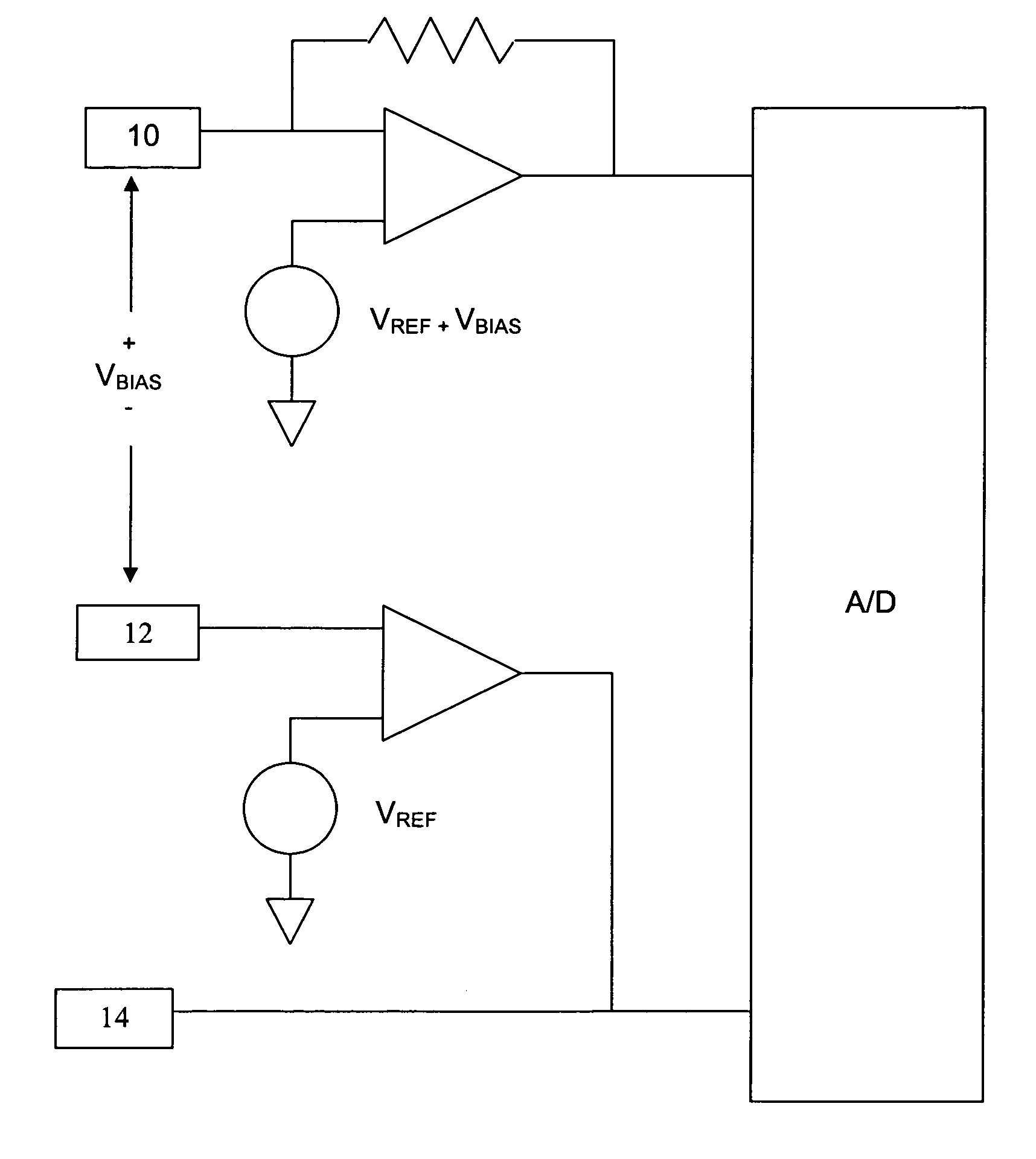
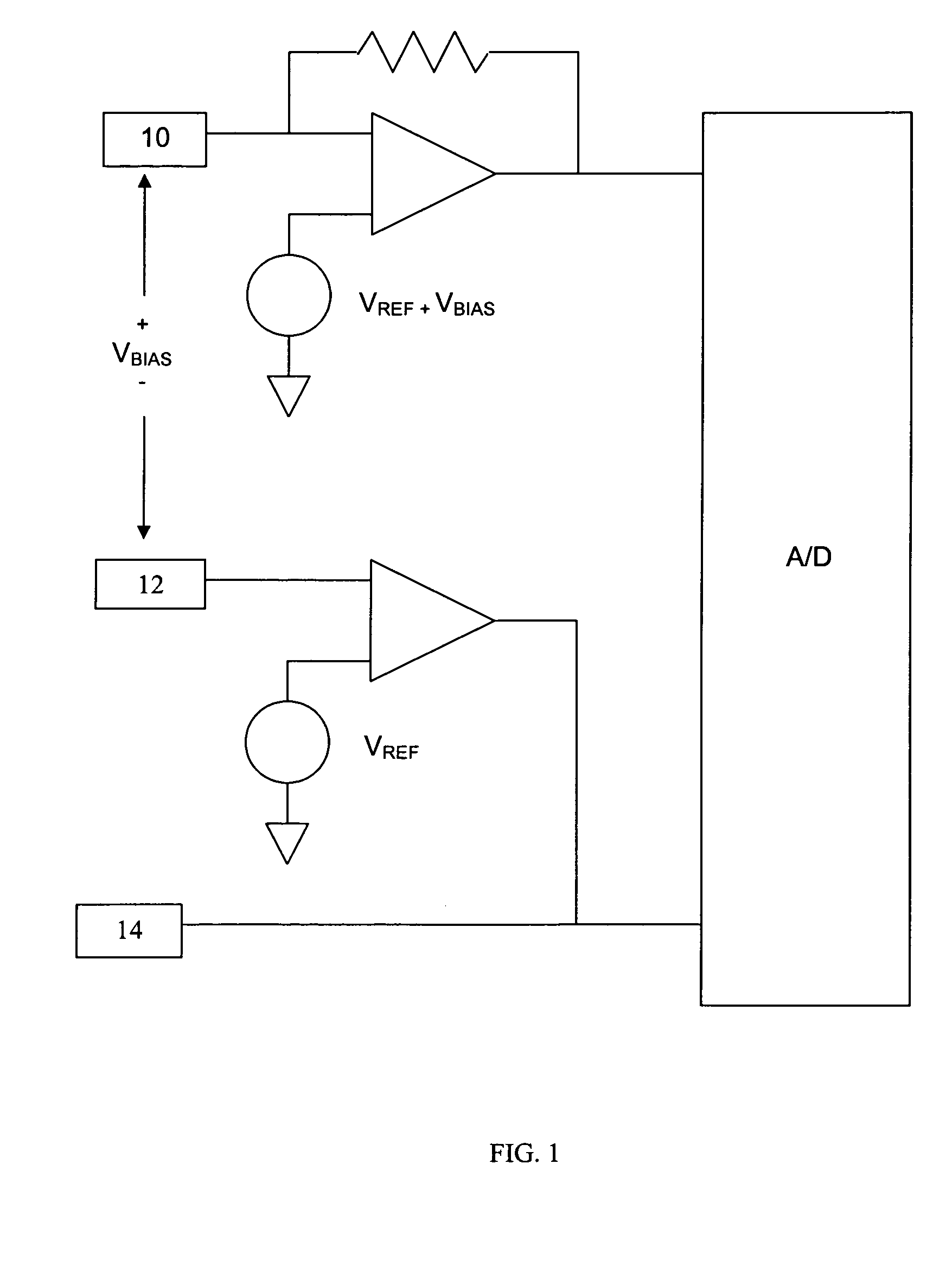
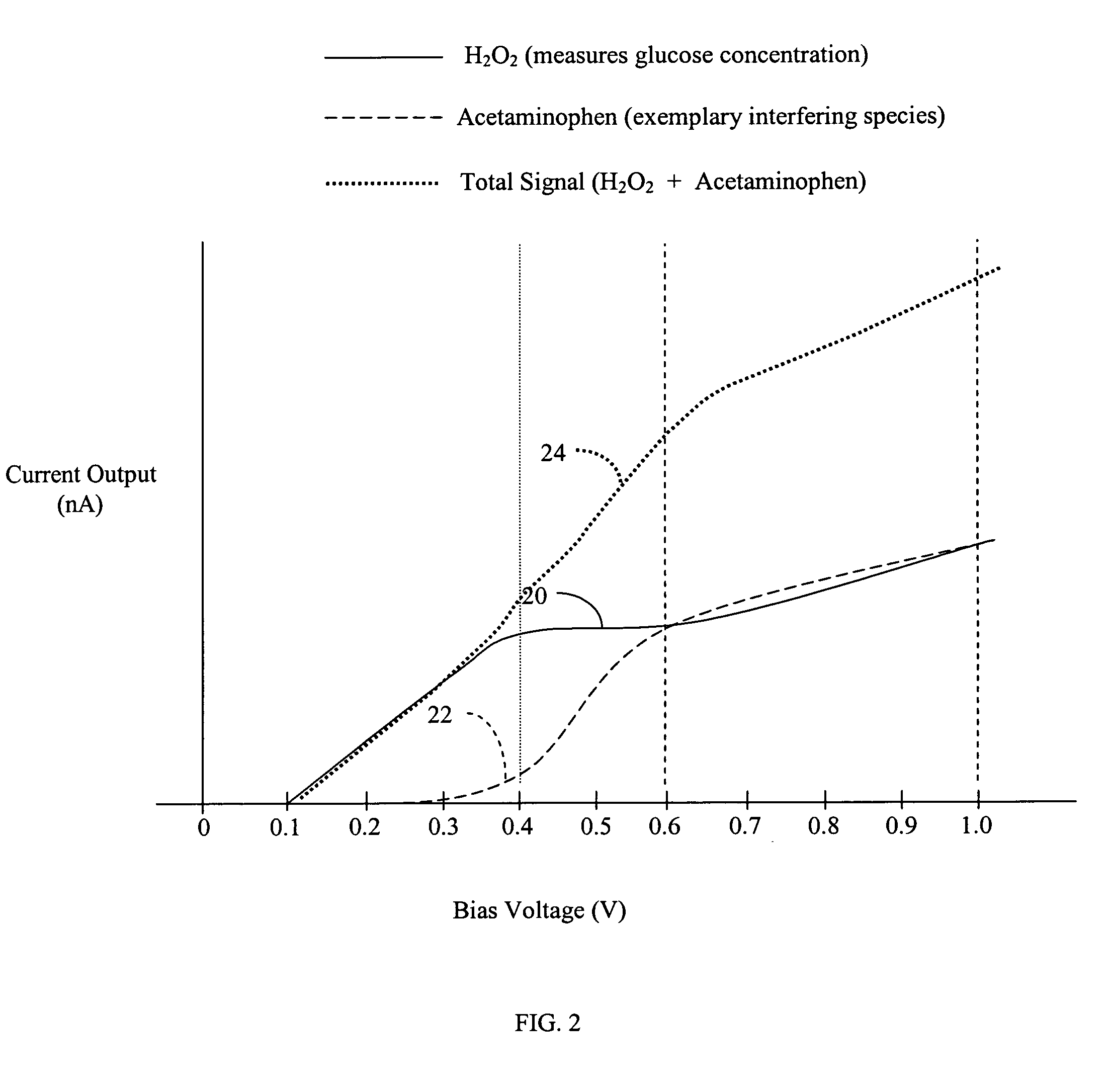
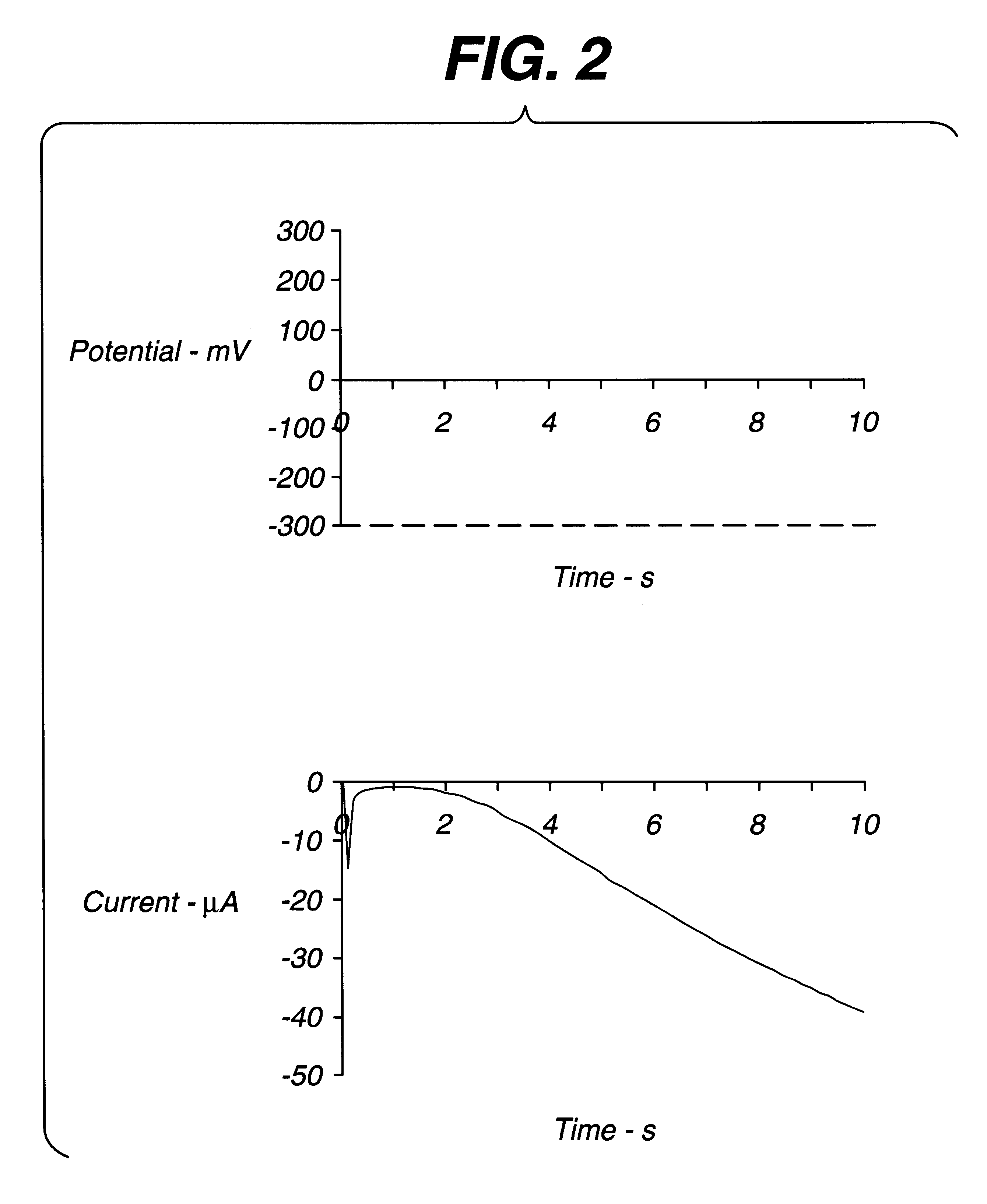
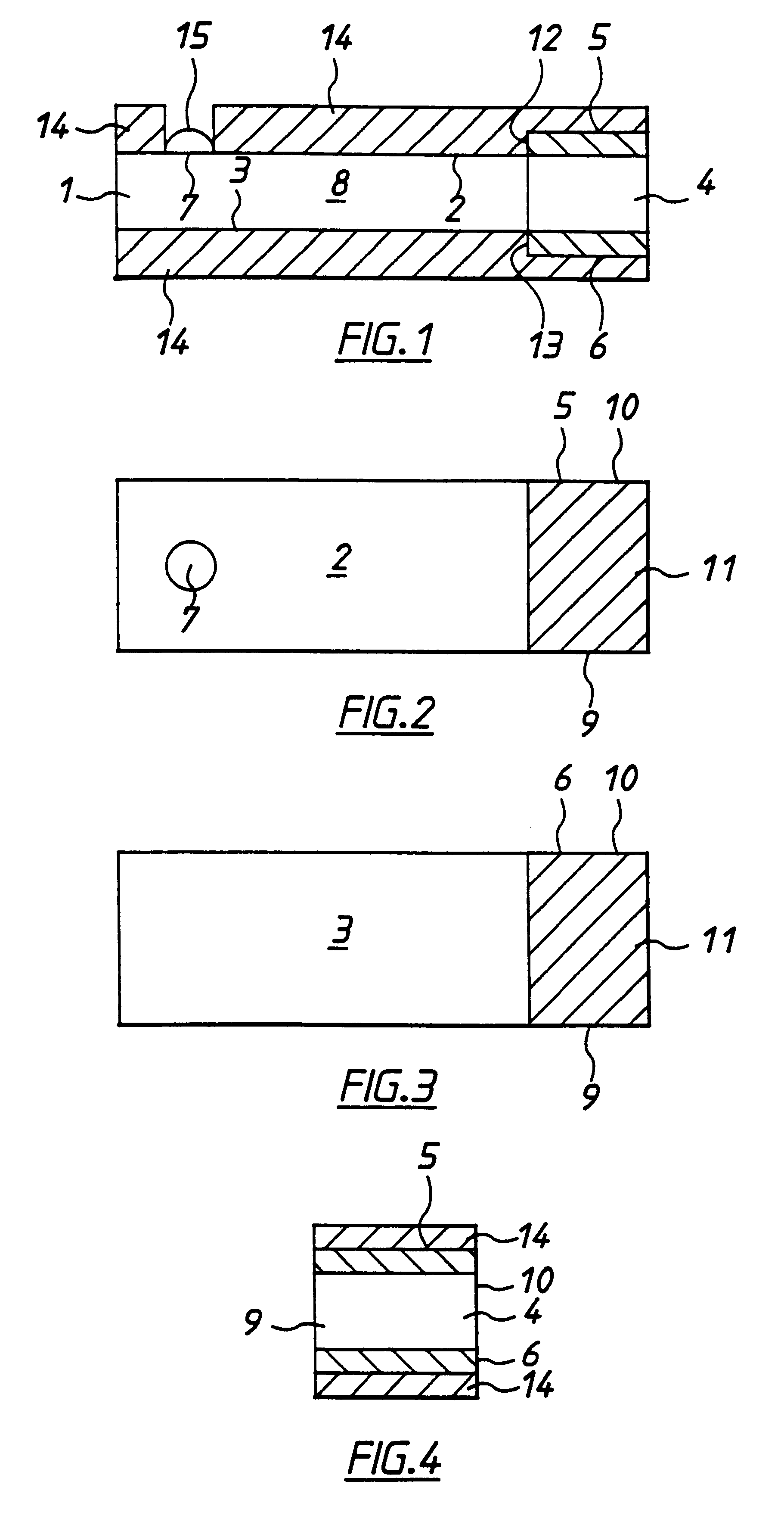
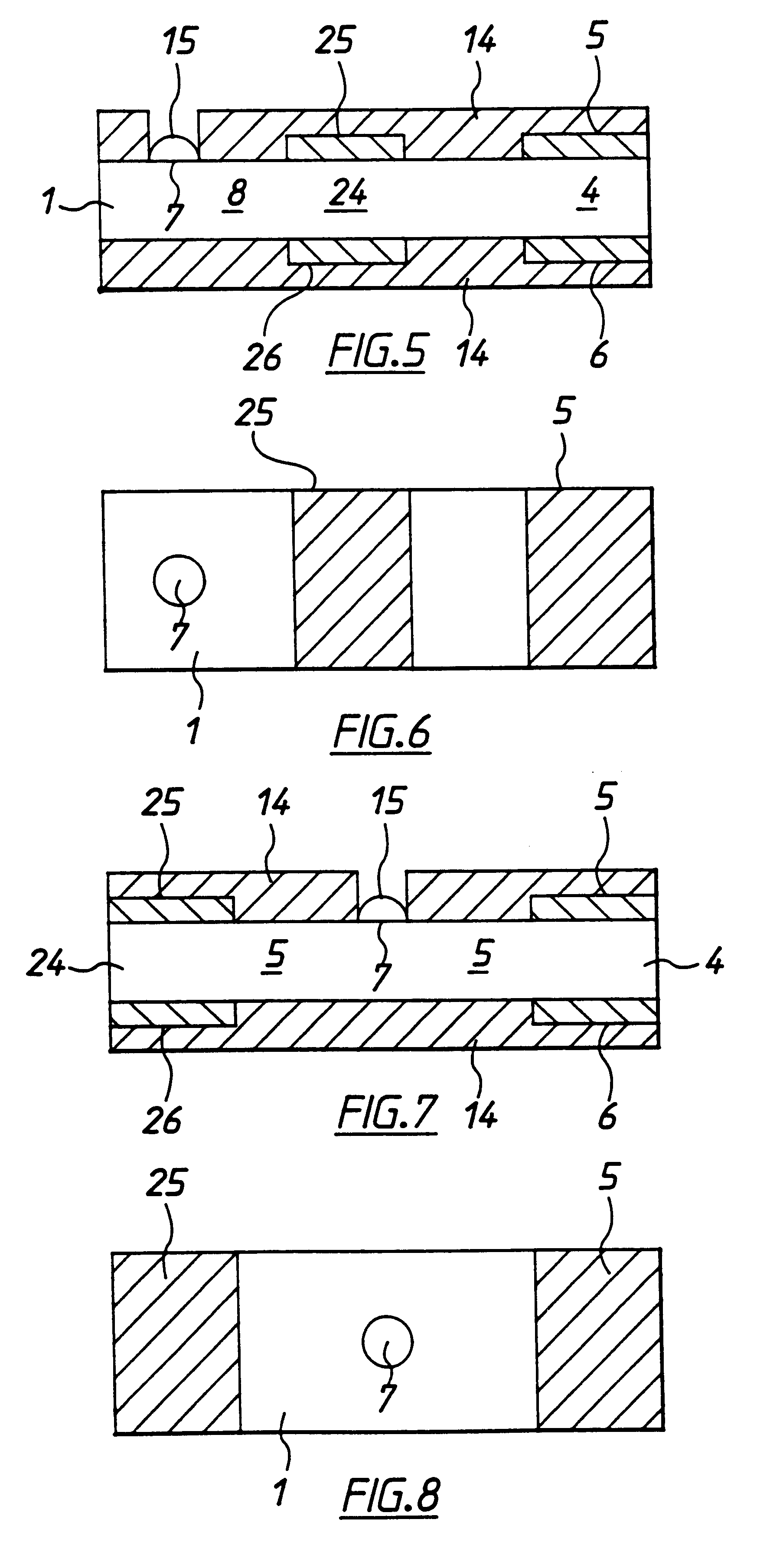
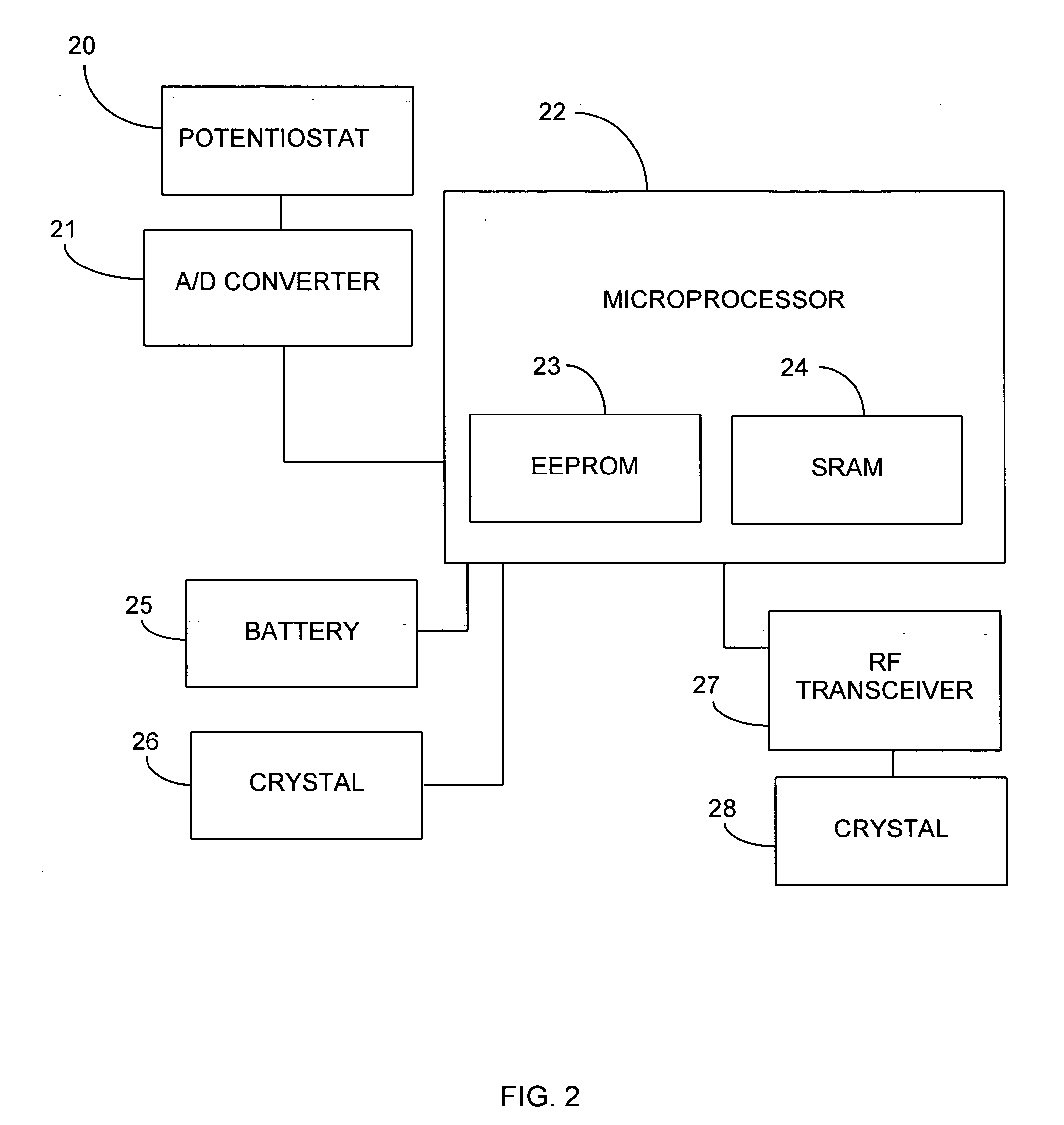
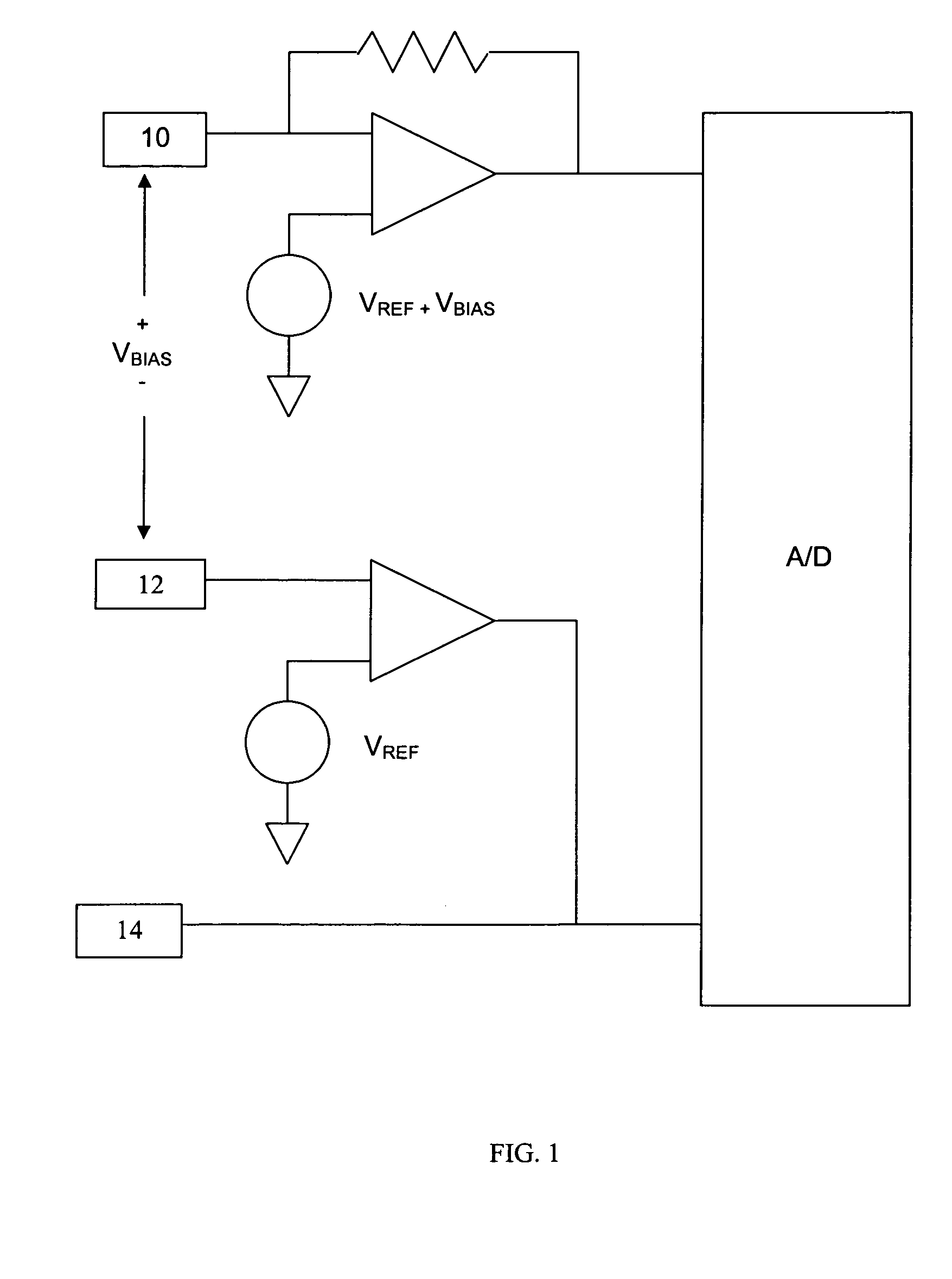
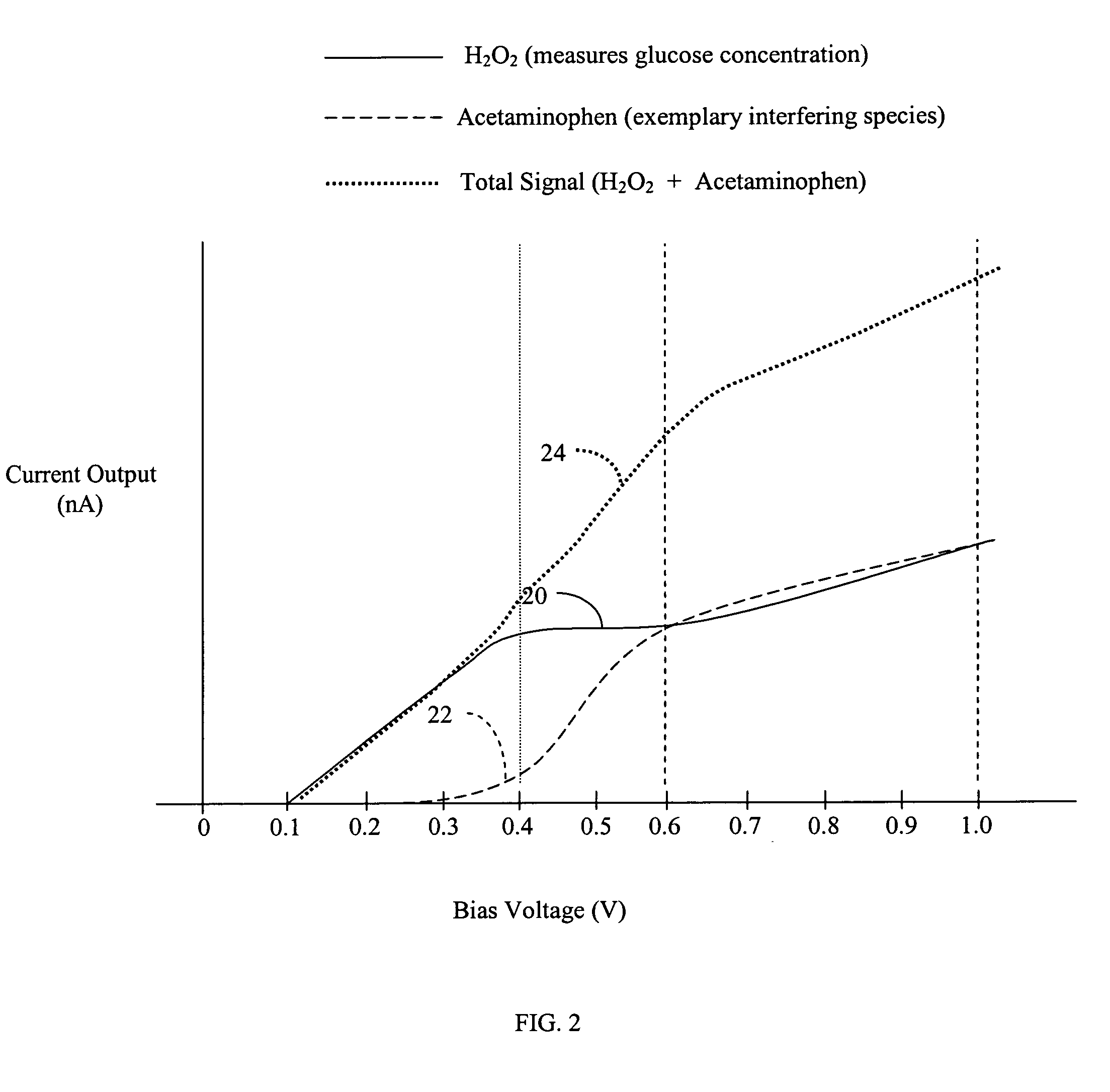
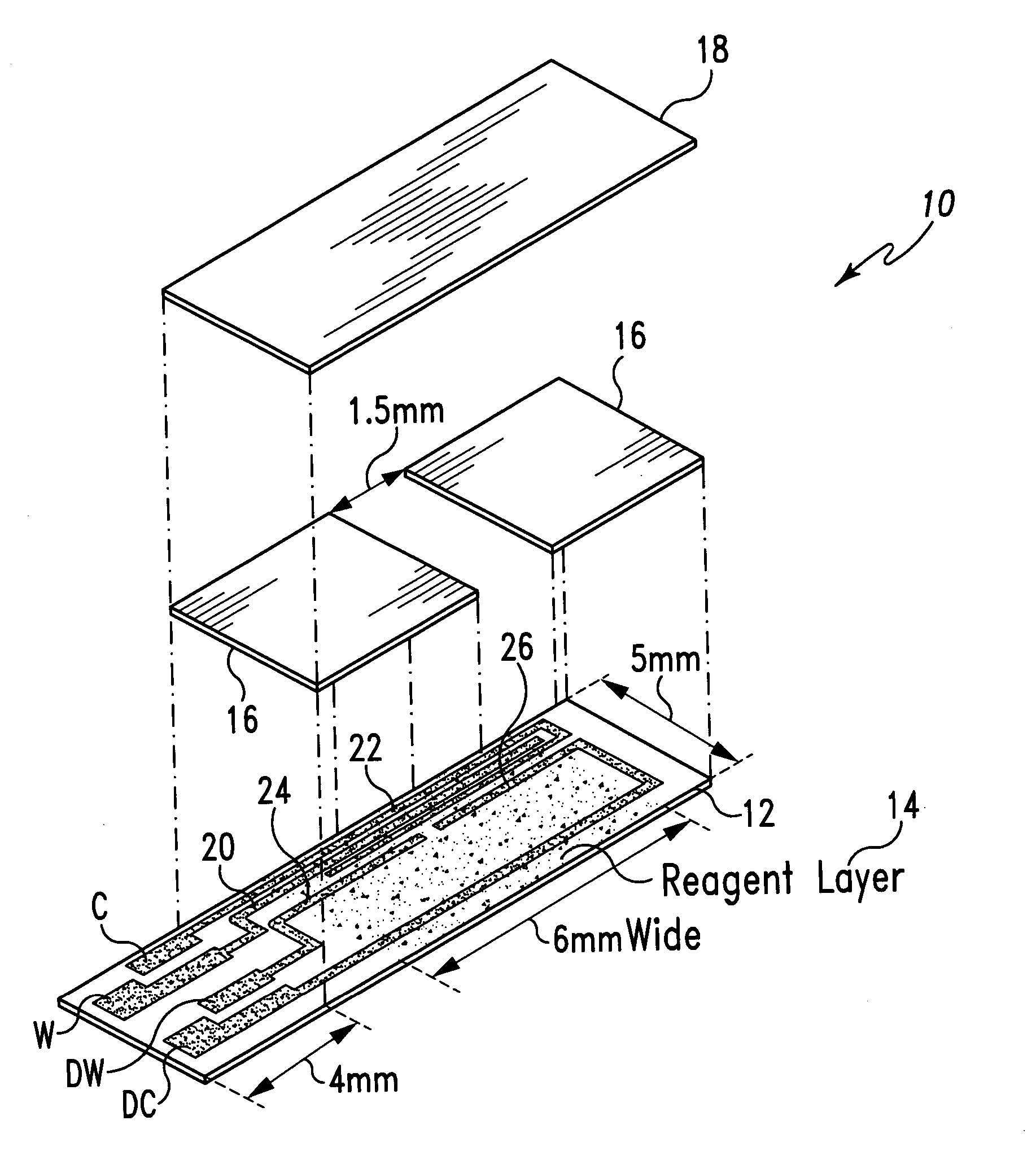
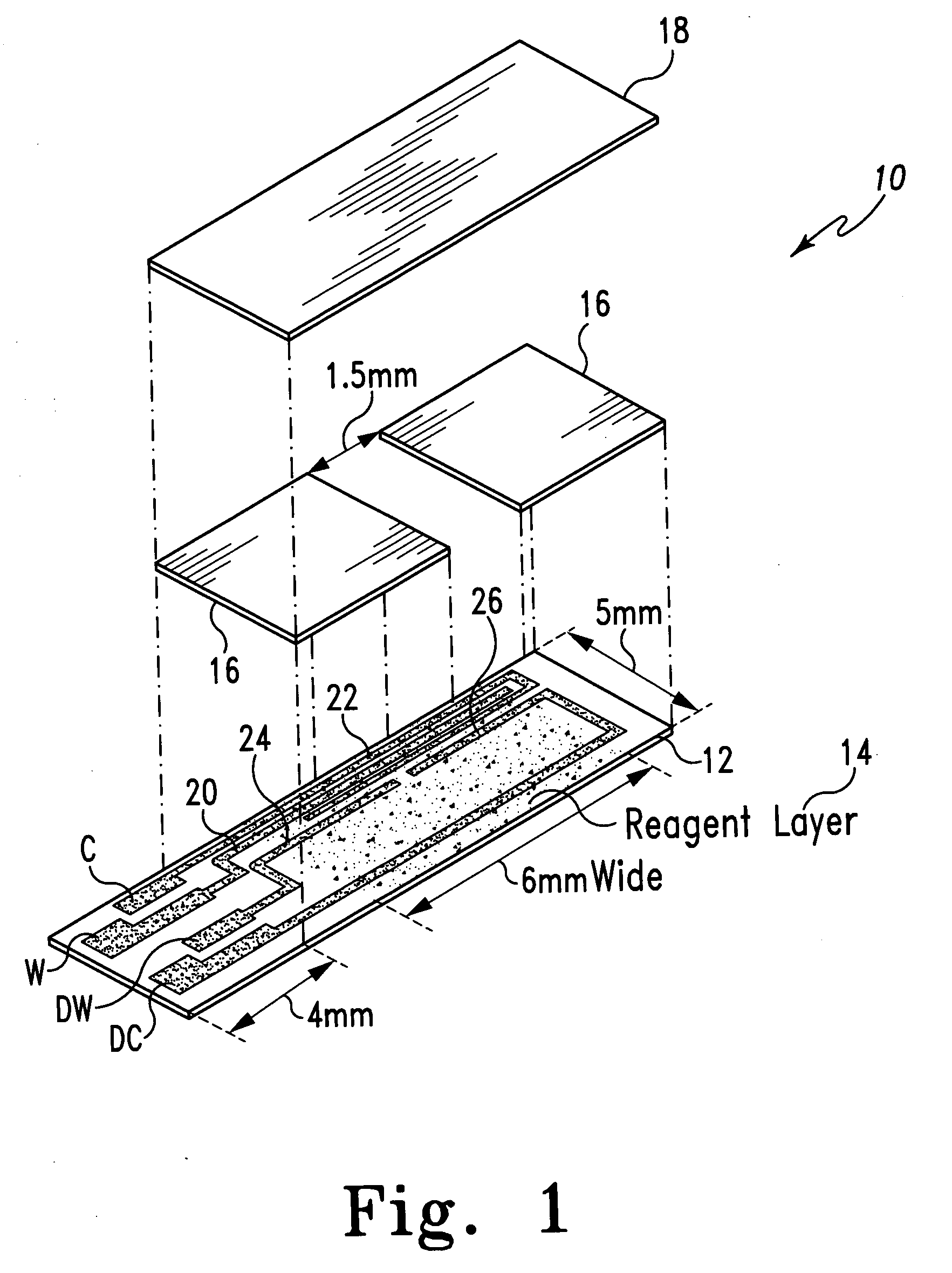
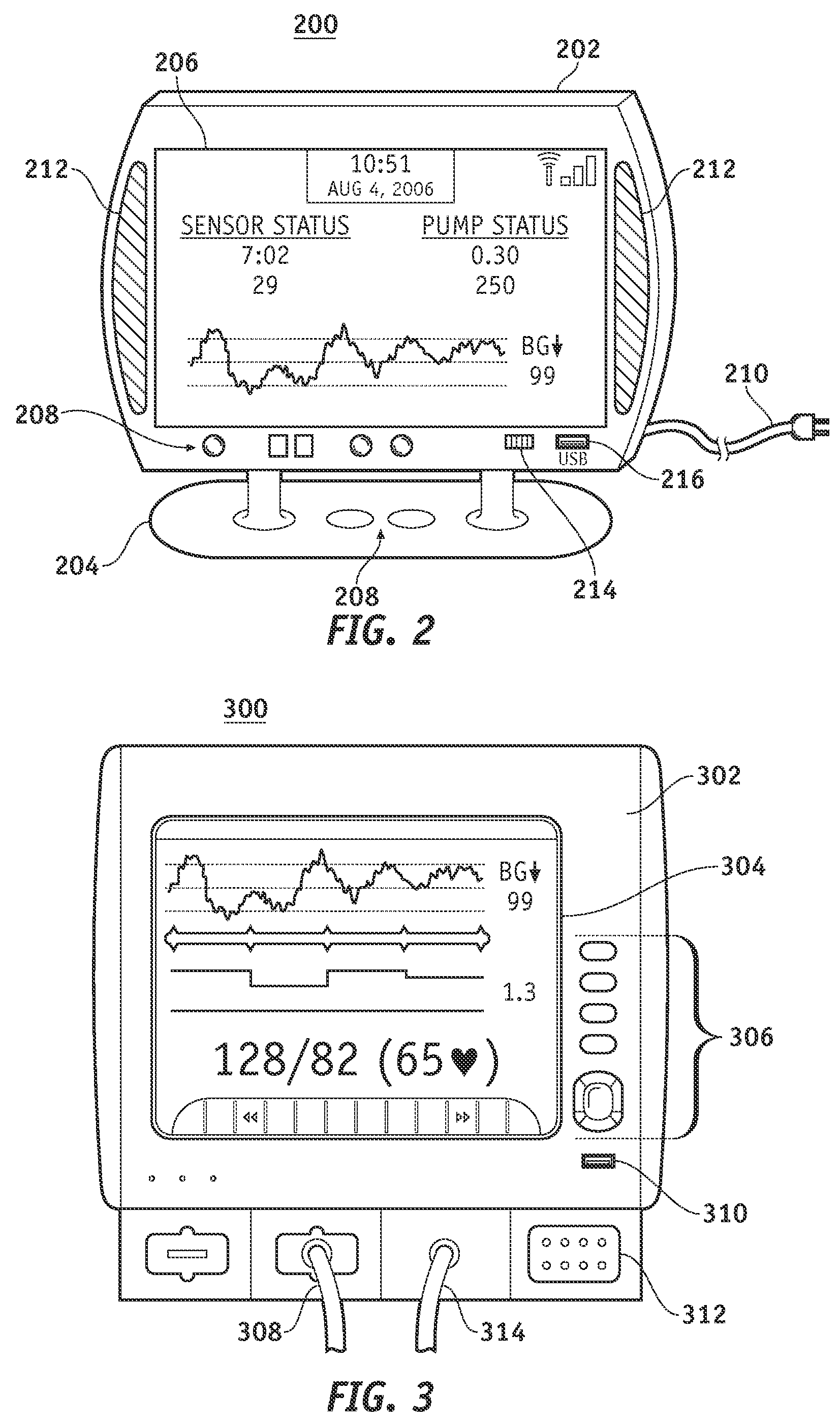
Systems and methods for improving electrochemical analyte sensors
ActiveUS7081195B2Quality improvementReducing and eliminating effectImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteD-Glucose
An analyte-measuring device, particularly an electrochemical sensor, is provided for measuring current values at multiple bias potential settings to assess the quality of the analyte measurement, identify interference in the signal, and calculate substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements. The device and method are suitable for calculating substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements when glucose is the analyte and acetaminophen is an interfering species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensor
ActiveUS20090242425A1Sufficient flow rateReduce the amount requiredImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteVascular Access Devices
Systems and methods of use for continuous analyte measurement of a host's vascular system are provided. In some embodiments, a continuous glucose measurement system includes a vascular access device, a sensor and sensor electronics, the system being configured for insertion into communication with a host's circulatory system.
Owner:DEXCOM
Sample detection to initiate timing of an electrochemical assay
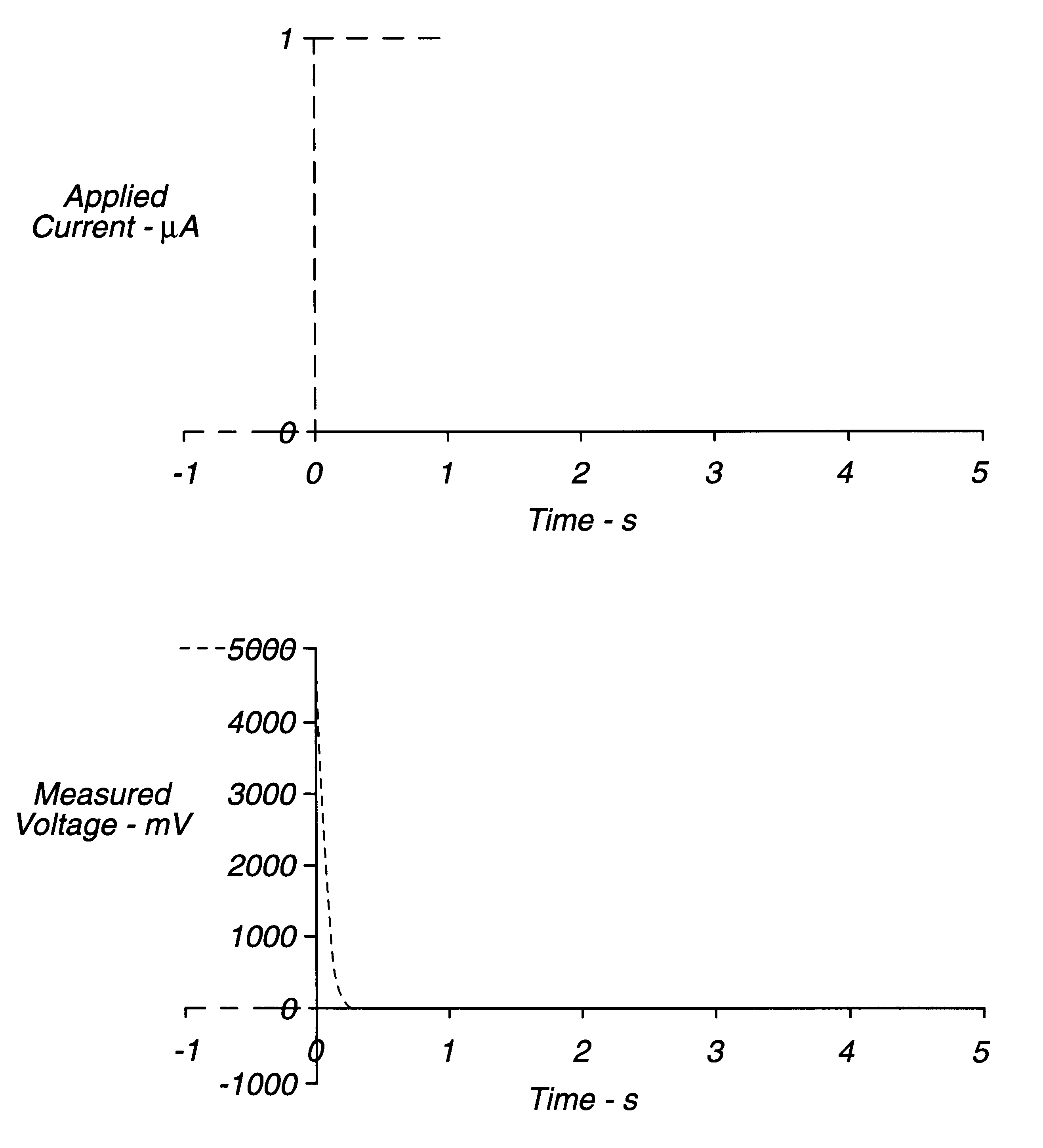
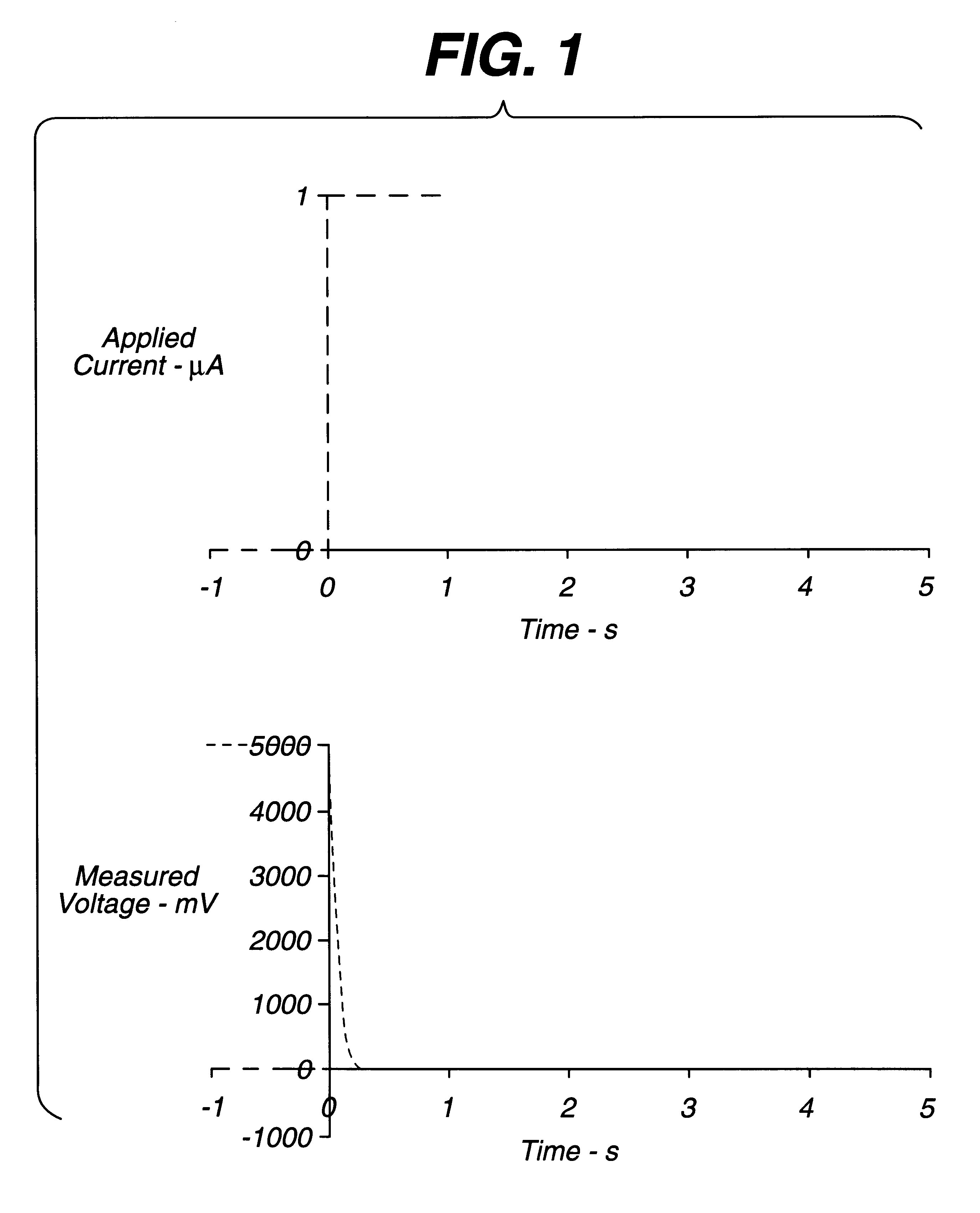
InactiveUS6193873B1Good accuracy and precisionImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalytePotential difference
An electrochemical assay includes a method for determining with great accuracy the time at which an applied sample bridges a gap between the electrodes of an electrochemical cell. The method involves applying a constant small current across the gap, while monitoring the potential difference between the electrodes. The time at which the sample bridges the gap is marked by a sharp drop in the potential. A constant voltage is applied after the sample is detected, and the current and / or charge through the sample is monitored over a period of time. From the measured current or charge, the analyte concentration of interest can be calculated.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Oxygen enhancing membrane systems for implantable devices
ActiveUS20050054909A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImplanted deviceOxygen enhanced
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for increasing oxygen availability to implantable devices. The preferred embodiments provide a membrane system configured to provide protection of the device from the biological environment and / or a catalyst for enabling an enzymatic reaction, wherein the membrane system includes a polymer formed from a high oxygen soluble material. The high oxygen soluble polymer material is disposed adjacent to an oxygen-utilizing source on the implantable device so as to dynamically retain high oxygen availability to the oxygen-utilizing source during oxygen deficits. Membrane systems of the preferred embodiments are useful for implantable devices with oxygen-utilizing sources and / or that function in low oxygen environments, such as enzyme-based electrochemical sensors and cell transplantation devices.
Owner:DEXCOM
Apparatus and methods for performing electrochemical reactions
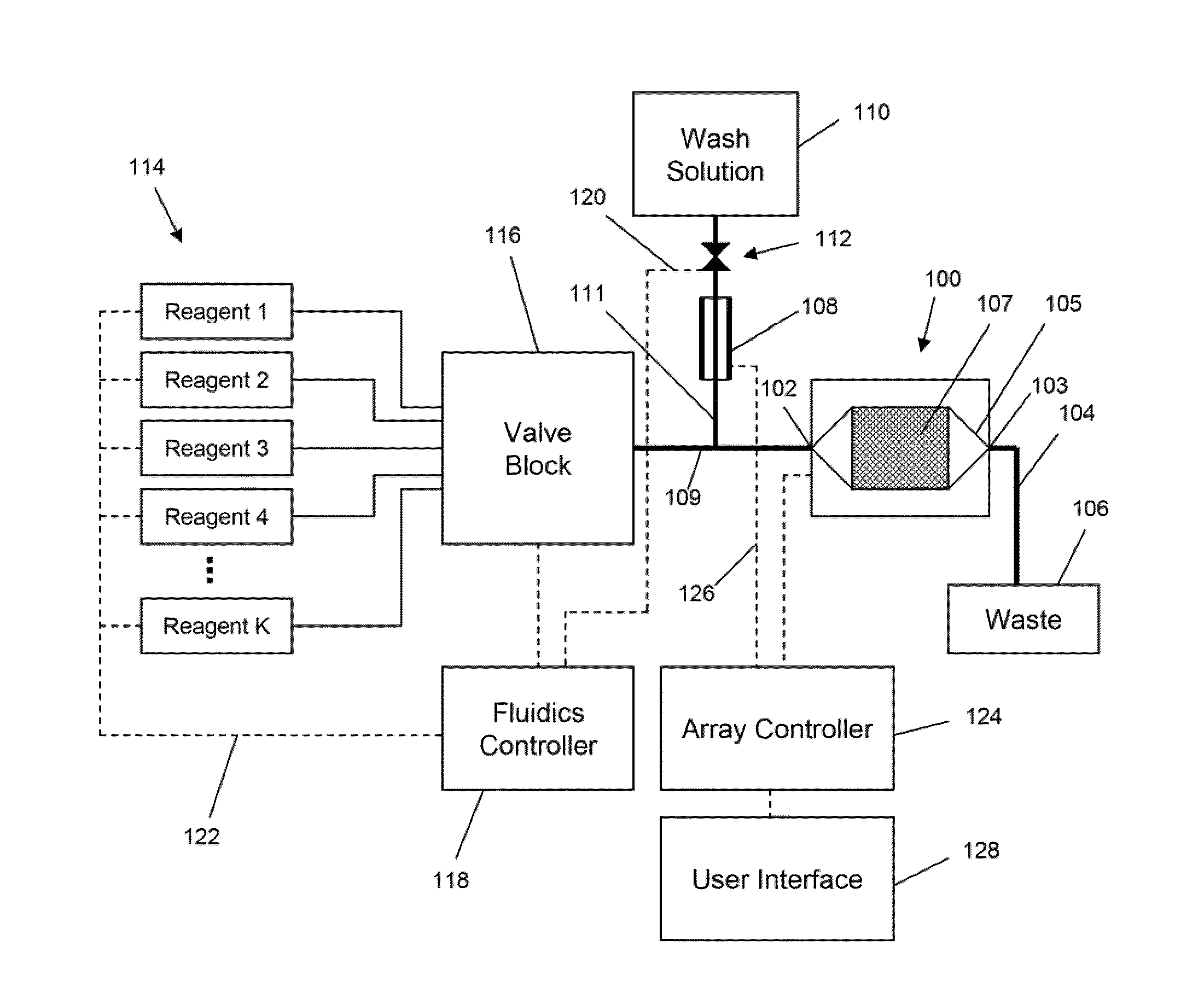
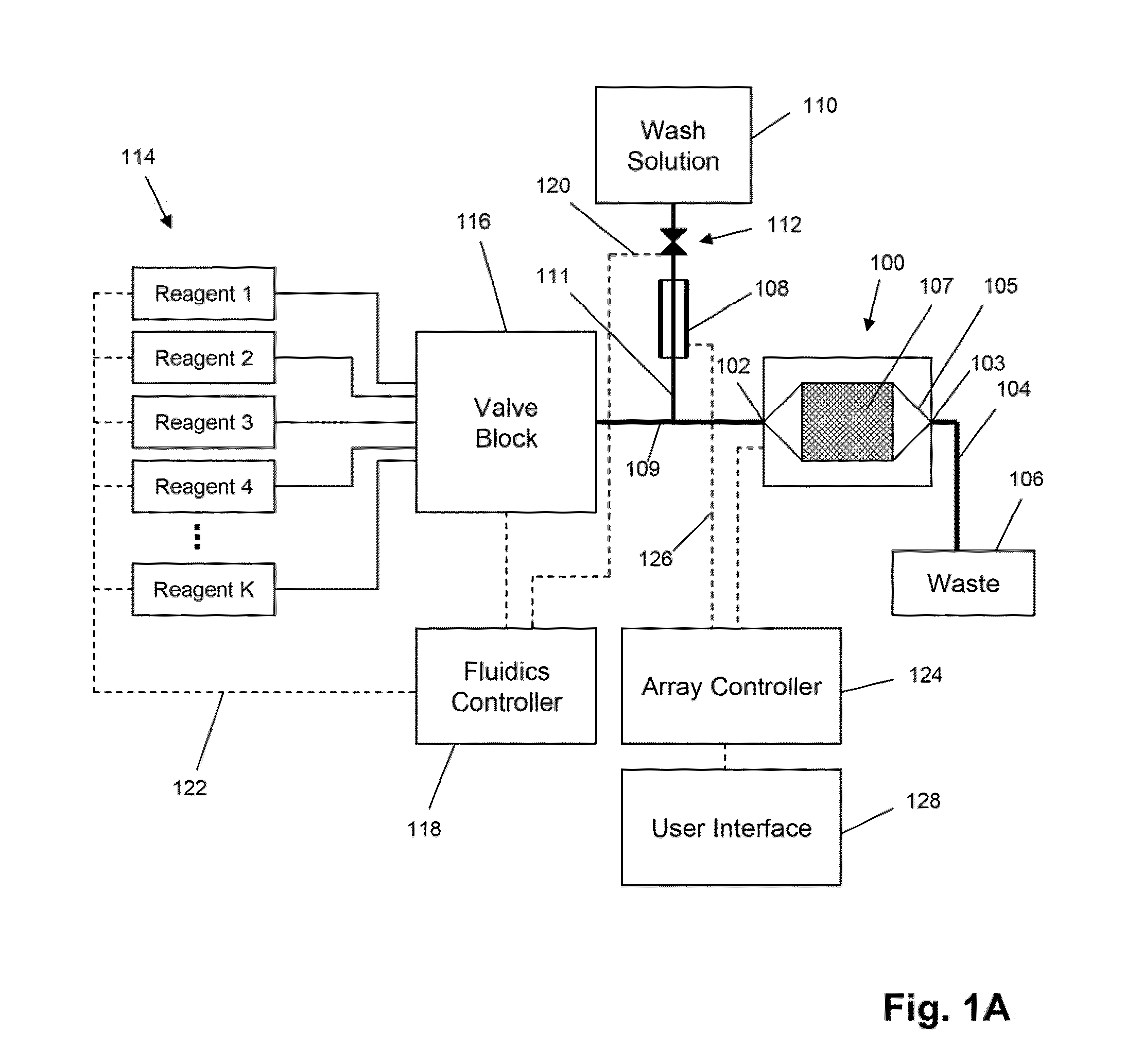
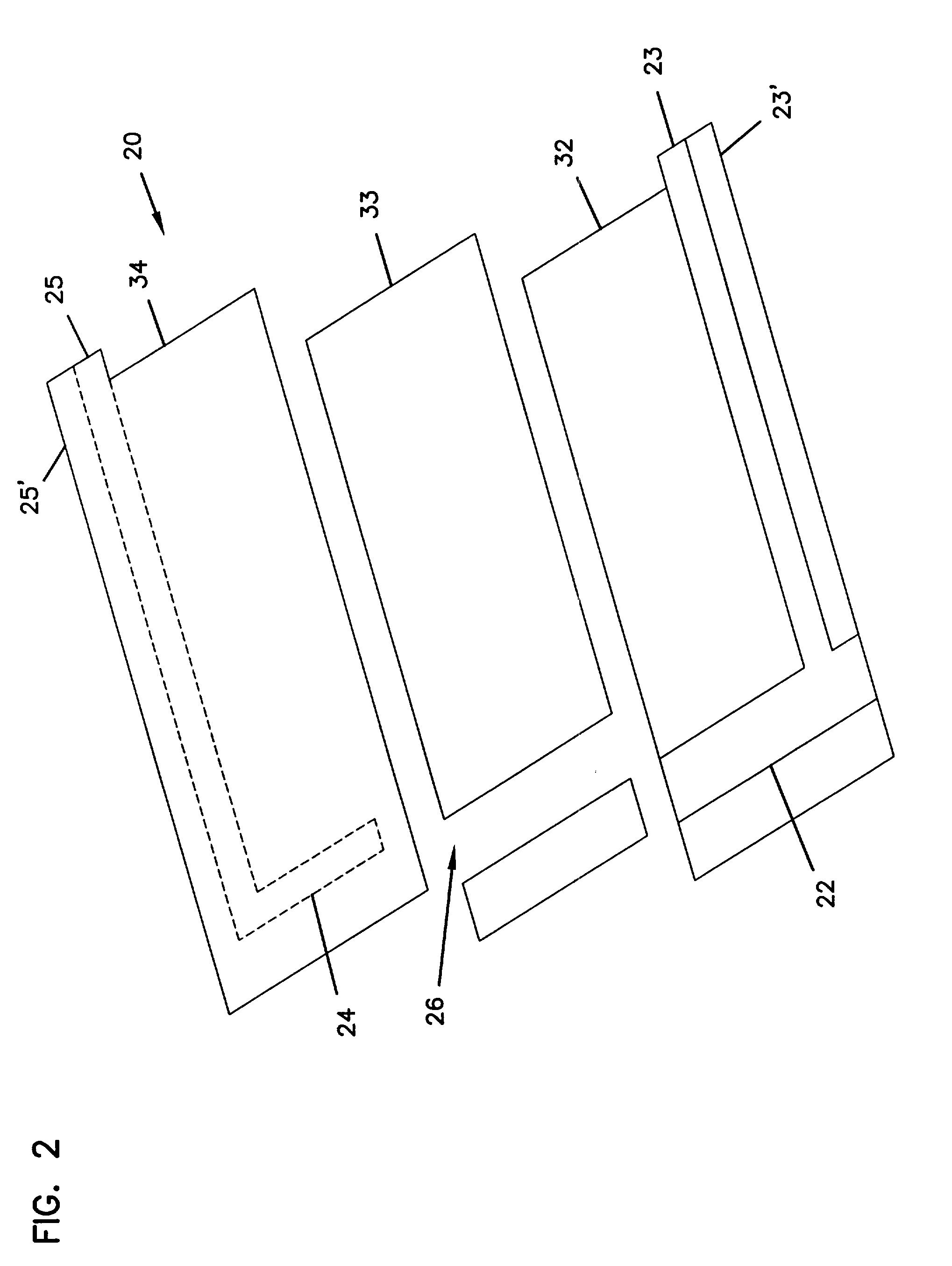
ActiveUS20100300895A1Reduce noiseWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectrochemical responseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention is directed to apparatus and methods for delivering multiple reagents to, and monitoring, a plurality of analytical reactions carried out on a large-scale array of electronic sensors underminimal noise conditions. In one aspect, the invention provides method of improving signal-to-noise ratios of output signals from the electronic sensors sensing analytes or reaction byproducts by subtracting an average of output signals measured from neighboring sensors where analyte or reaction byproducts are absent. In other aspects, the invention provides an array of electronic sensors integrated with a microwell array for confining analytes and / or particles for analytical reactions and a method for identifying microwells containing analytes and / or particles by passing a sensor-active reagent over the array and correlating sensor response times to the presence or absence of analytes or particles. Such detection of analyte- or particle-containing microwells may be used as a step in additional noise reduction methods.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Electrochemical cell
InactiveUS6284125B1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectricityDiffusion
A method for determining the concentration of a reduced (or oxidised) form of a redox species in an electrochemical cell of the kind comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode spaced from the working electrode by a predetermined distance, said method comprising the steps of: (1) applying an electric potential difference between the electrodes; (2) selecting the potential of the working electrode such that the rate of electro-oxidation of the reduced form (or electro-reduction of the oxidised form) of the species is diffusion controlled, (3) selecting the spacing between the working electrode and the counter electrode so that reaction products from the counter electrode arrive at the working electrode; (4) determining current as a function of time after application of the potential and prior to achievement of a steady state; (5) estimating the magnitude of the steady state current, and (6) obtaining from the change in current with time and the magnitude of the steady state current, a value indicative of the diffusion coefficient and / or of the concentration of the reduced form (or the oxidised form) of the species. Also disclosed is an apparatus for determining the concentration of a redox species in an electrochemical cell comprising: an electrochemical cell having a working electrode and a counter (or counter / reference) electrode, means for applying and electric potential difference between said electrodes, means for measuring the change in current with time, and characterised in that the working electrode is spaced from the counter electrode by less than 500 mum.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Increasing bias for oxygen production in an electrode system
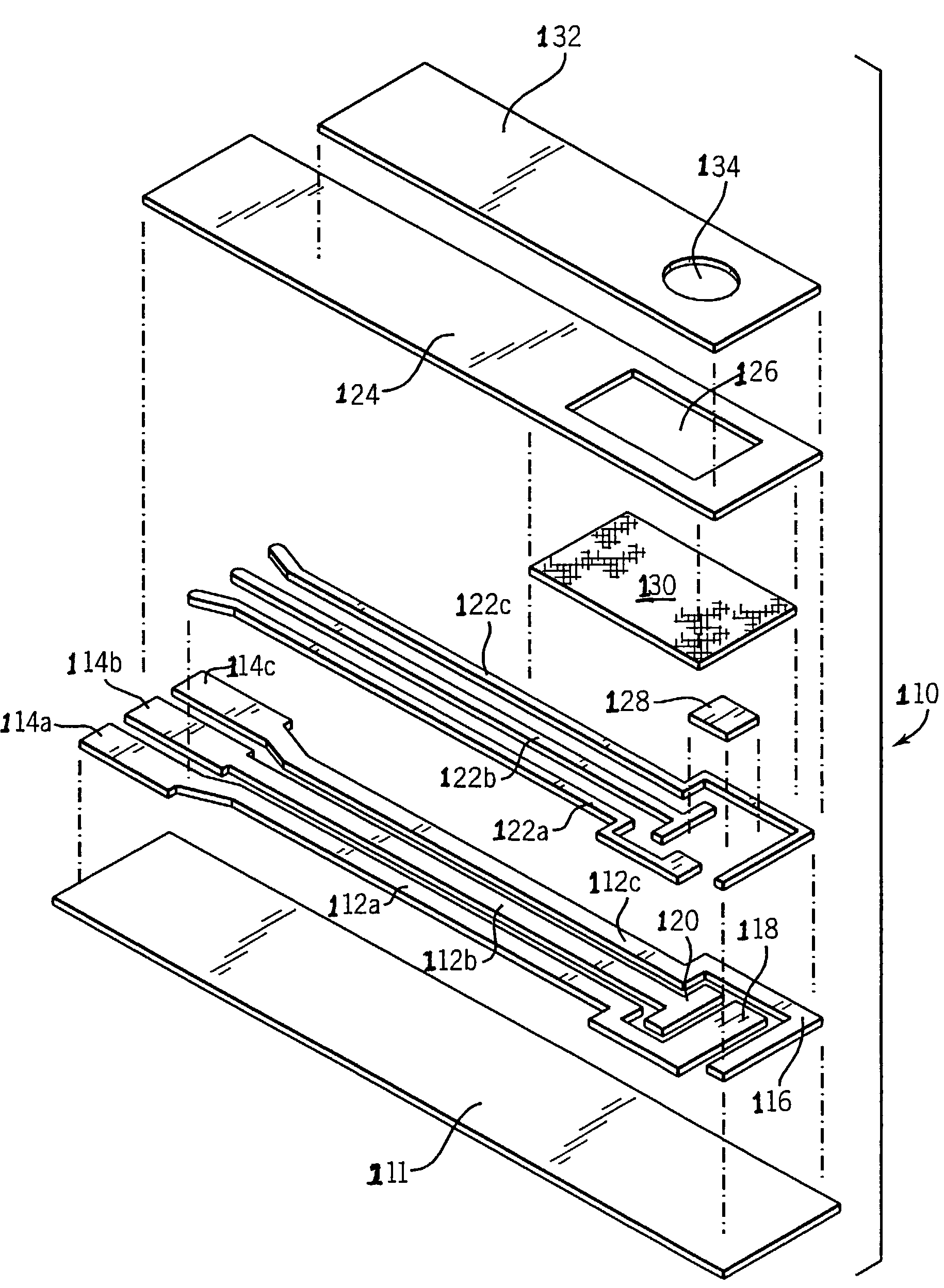
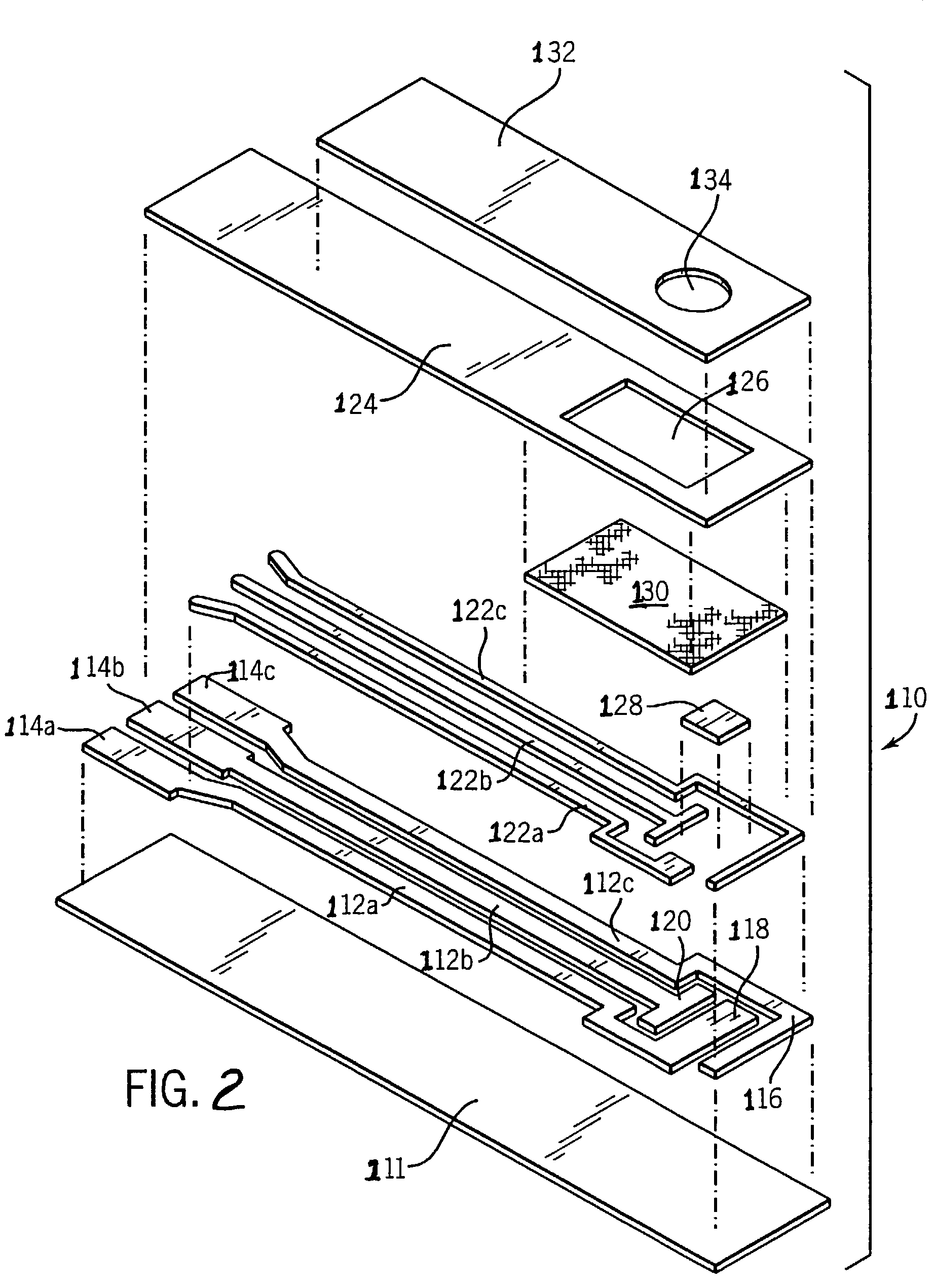
InactiveUS20050056552A1Improve device performanceWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementProcess engineeringOxygen
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for electrochemical sensing. Particularly, the invention relates to optimizing bias settings in an electrode system to increase oxygen production at the working electrode.
Owner:DEXCOM
Electrochemical cell
InactiveUS6413410B1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteElectrochemical biosensor
This invention relates to a biosensor and more particularly to an electrochemical biosensor for determining the concentration of an analyte in a carrier. The invention is particularly useful for determining the concentration of glucose in blood and is described herein with reference to that use but it should be understood that the invention is applicable to other analytic determinations.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
In vitro analyte sensor and methods of use
ActiveUS20070068807A1Easy to fillEasy to recordImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteBiology
In vitro electrochemical sensors that provide accurate and repeatable analysis of a sample of biological fluid are provided. Embodiments include sensors that include a sample chambers having overhangs extending therefrom.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
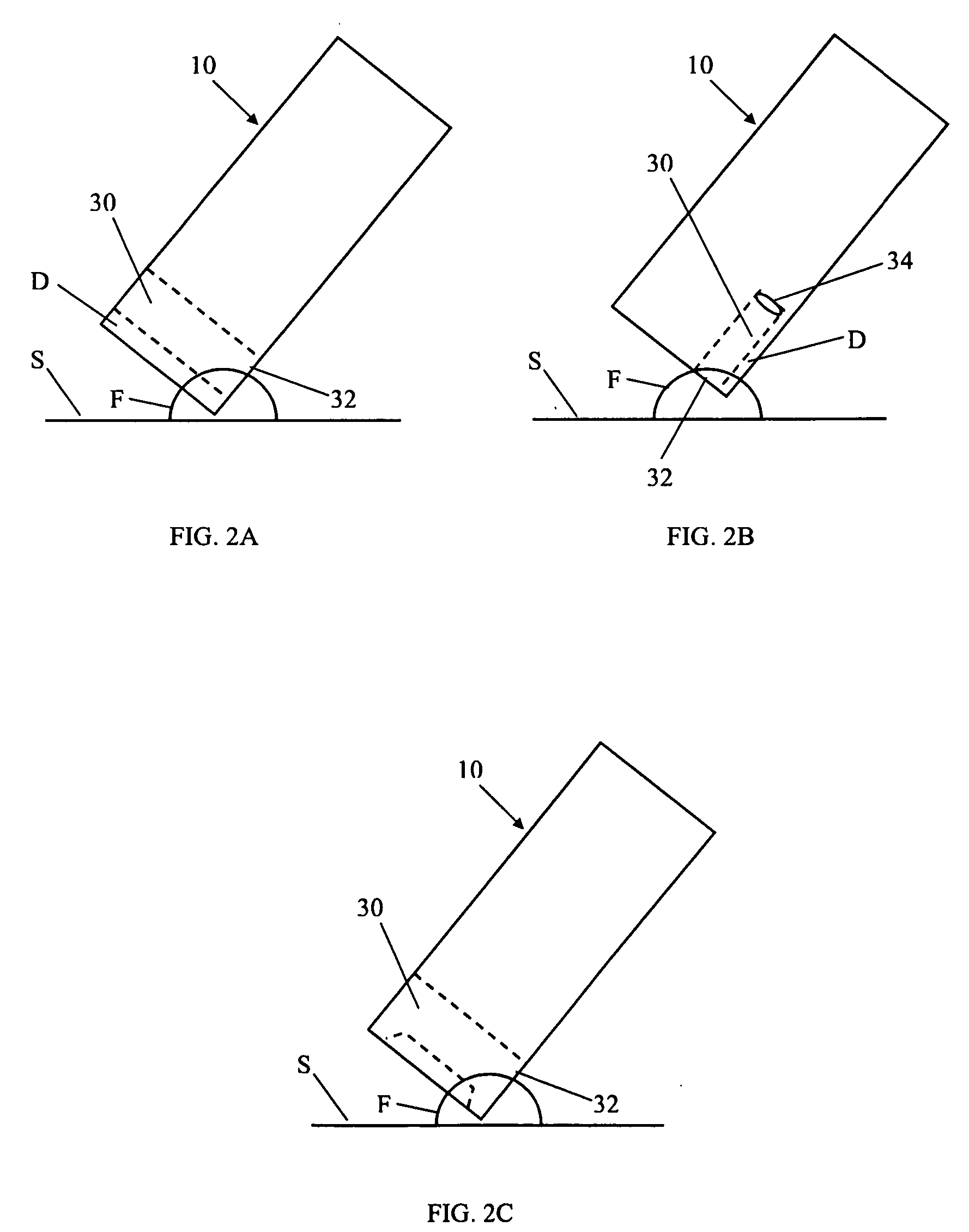
Method and system for detecting age, hydration, and functional states of sensors using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
ActiveUS7985330B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceSpectroscopyEngineering
A method and program prevents a user from bypassing a limit placed on a specified operating life of a sensor by disconnecting and reconnecting the sensor. The present invention checks a characteristic of the sensor to see if the sensor is used prior to the connection of the sensor, and rejects the sensor if the sensor is determined to have been used before. The process of checking the characteristic of the sensor involves performing an Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) procedure and calculating an impedance value. The impedance value can be compared to various threshold values for a variety of purposes including the determination of age, condition, hydration, and stabilization of the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Sensors
ActiveUS20070108048A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBody fluidBiomedical engineering
The subject invention provides devices and methods for the analysis of a body fluid. Embodiments include sensors that are sample-fillable by contacting a corner of the sensor to a sample.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
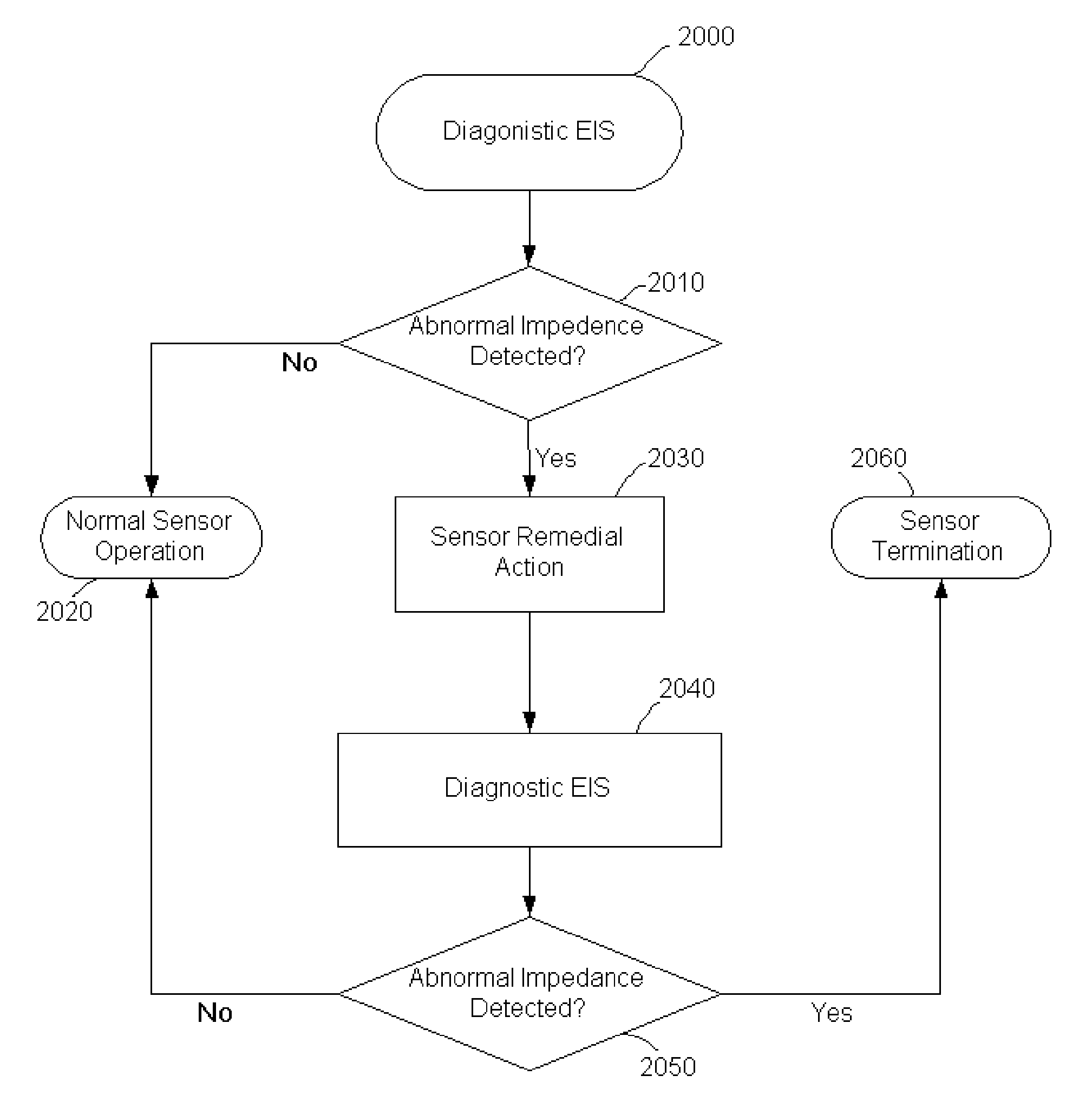
Method and system for remedying sensor malfunctions detected by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
A method and system that enables a user to maintain a sensor in real time. The present invention involves performing a diagnostic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) procedure to measure sensor impedance value in order to determine if the sensor is operating at an optimal level. If the sensor is not operating at an optimal level, the present invention may further involve performing a sensor remedial action. The sensor remedial action involves reversing the DC voltage being applied between the working electrode and the reference electrode. The reversed DC voltage may be coupled with an AC voltage to extend its reach.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Techniques to improve polyurethane membranes for implantable glucose sensors
ActiveUS20060086624A1Easy to makeImmobilised enzymesVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteGlucose sensors
The invention provides an implantable membrane for regulating the transport of analytes therethrough that includes a matrix including a first polymer; and a second polymer dispersed throughout the matrix, wherein the second polymer forms a network of microdomains which when hydrated are not observable using photomicroscopy at 400× magnification or less. In one aspect, the homogeneous membrane of the present invention has hydrophilic domains dispersed substantially throughout a hydrophobic matrix to provide an optimum balance between oxygen and glucose transport to an electrochemical glucose sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Systems and methods for improving electrochemical analyte sensors
ActiveUS20050161346A1Quality improvementReducing and eliminating effectImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteD-Glucose
An analyte-measuring device, particularly an electrochemical sensor, is provided for measuring current values at multiple bias potential settings to assess the quality of the analyte measurement, identify interference in the signal, and calculate substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements. The device and method are suitable for calculating substantially interference-free analyte concentration measurements when glucose is the analyte and acetaminophen is an interfering species.
Owner:DEXCOM
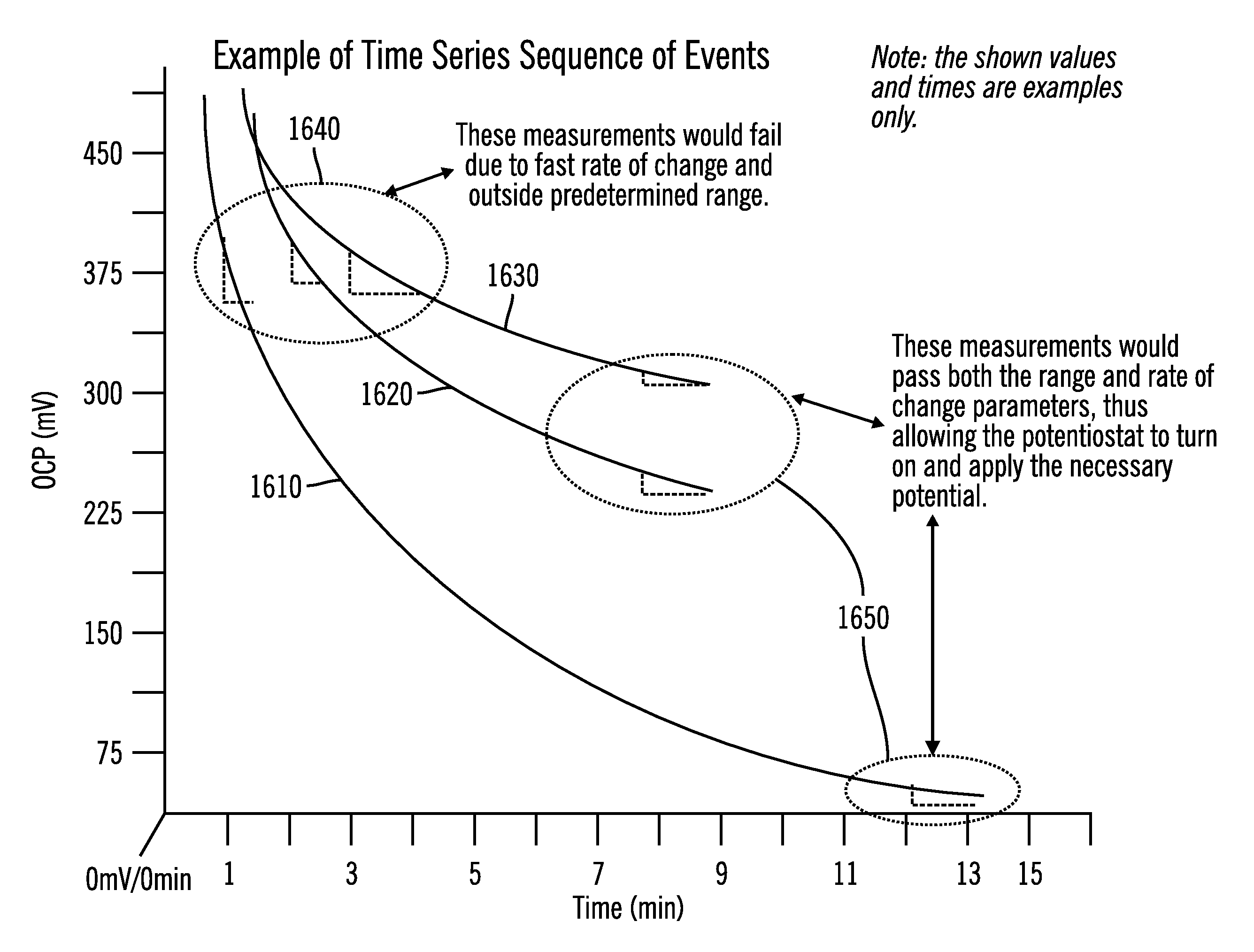
System and method for determining the point of hydration and proper time to apply potential to a glucose sensor
ActiveUS8114269B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPotential measurementGlucose sensors
According to an embodiment of the invention, a method of determining hydration of a sensor having a plurality of electrodes is disclosed. In particular embodiments, the method couples a sensor electronics device to the sensor and measures the open circuit potential between at least two of the plurality of electrodes. Then, the open circuit potential measurement is compared to a predetermined value. In some embodiments, the plurality of electrodes includes a working electrode, a reference electrode, and a counter electrode. In still further embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the reference electrode is measured. In other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the counter electrode is measured. In still other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the counter electrode and the reference electrode is measured.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
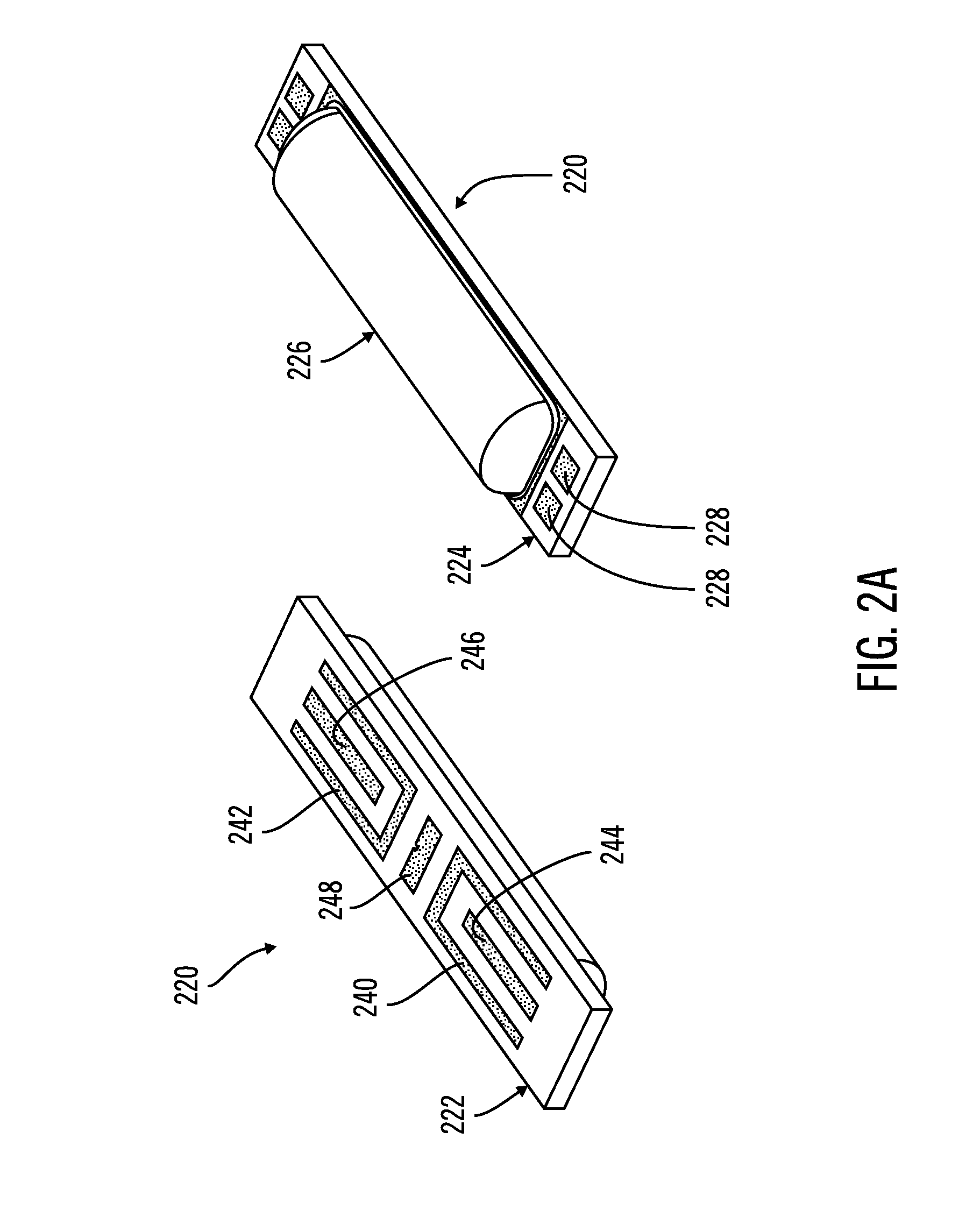
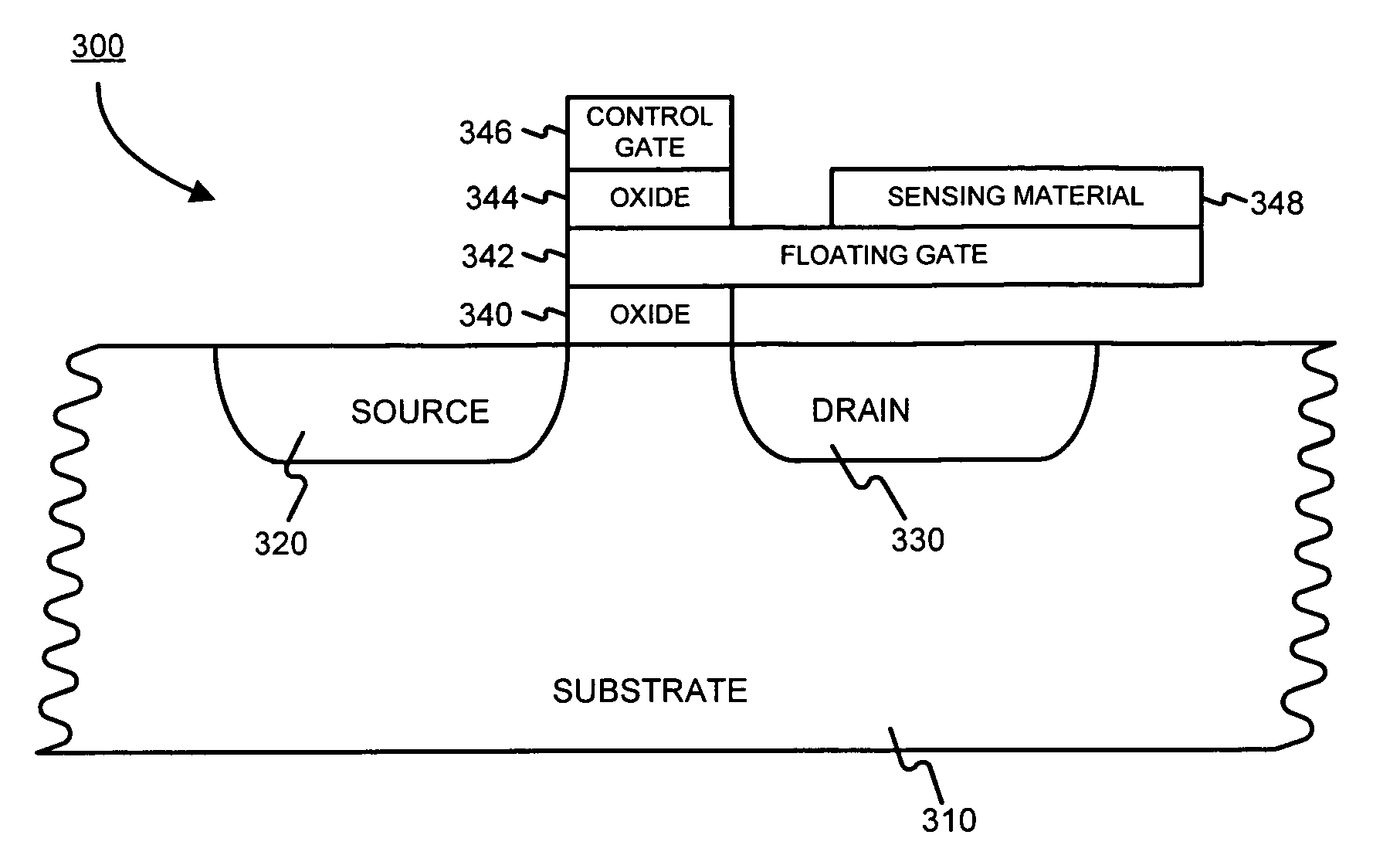
Floating gate field effect transistors for chemical and/or biological sensing
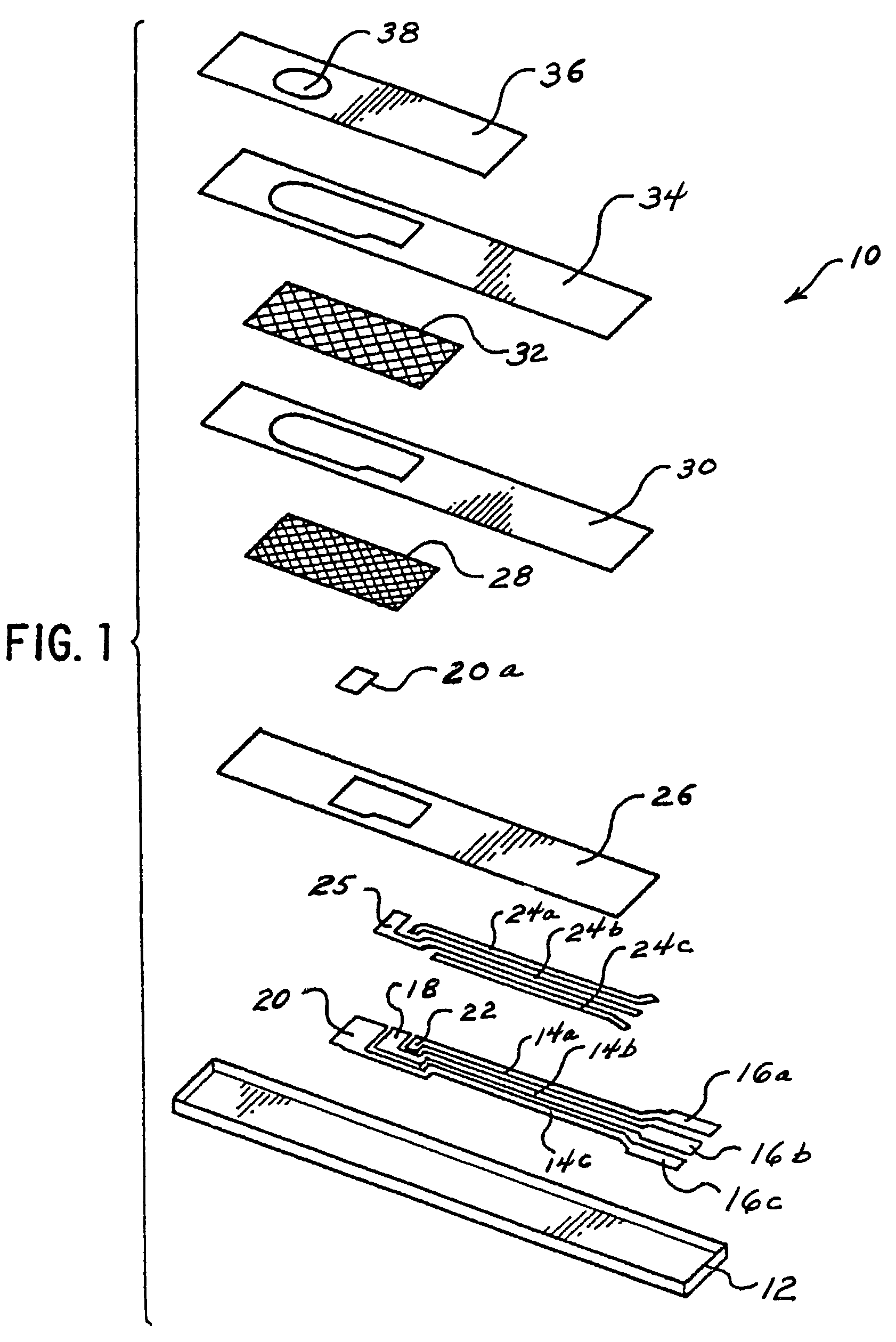
ActiveUS20050230271A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementChemical physicsEngineering
Specific ionic interactions with a sensing material that is electrically coupled with the floating gate of a floating gate-based ion sensitive field effect transistor (FGISFET) may be used to sense a target material. For example, an FGISFET can use (e.g., previously demonstrated) ionic interaction-based sensing techniques with the floating gate of floating gate field effect transistors. The floating gate can serves as a probe and an interface to convert chemical and / or biological signals to electrical signals, which can be measured by monitoring the change in the device's threshold voltage, VT.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
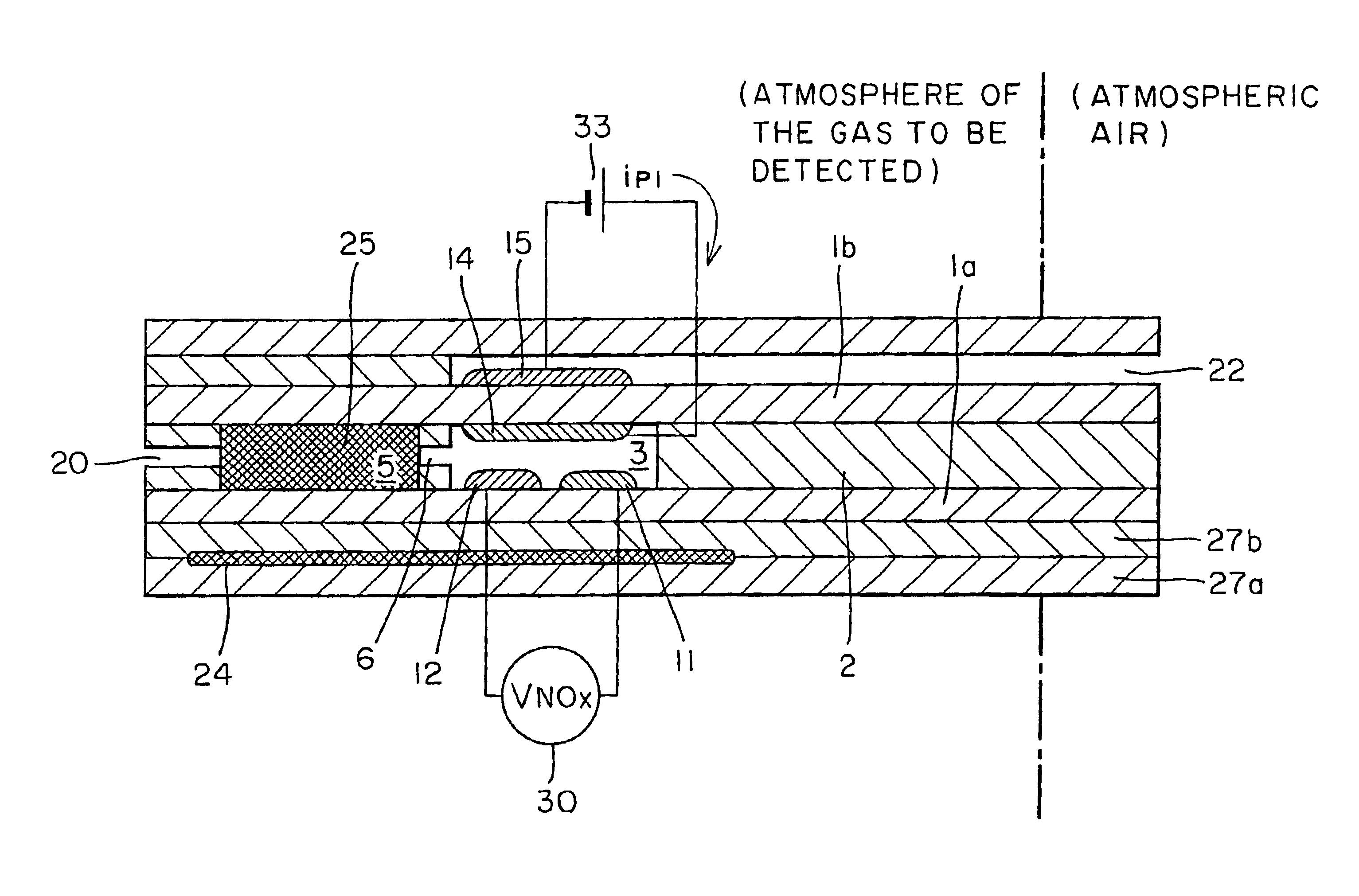
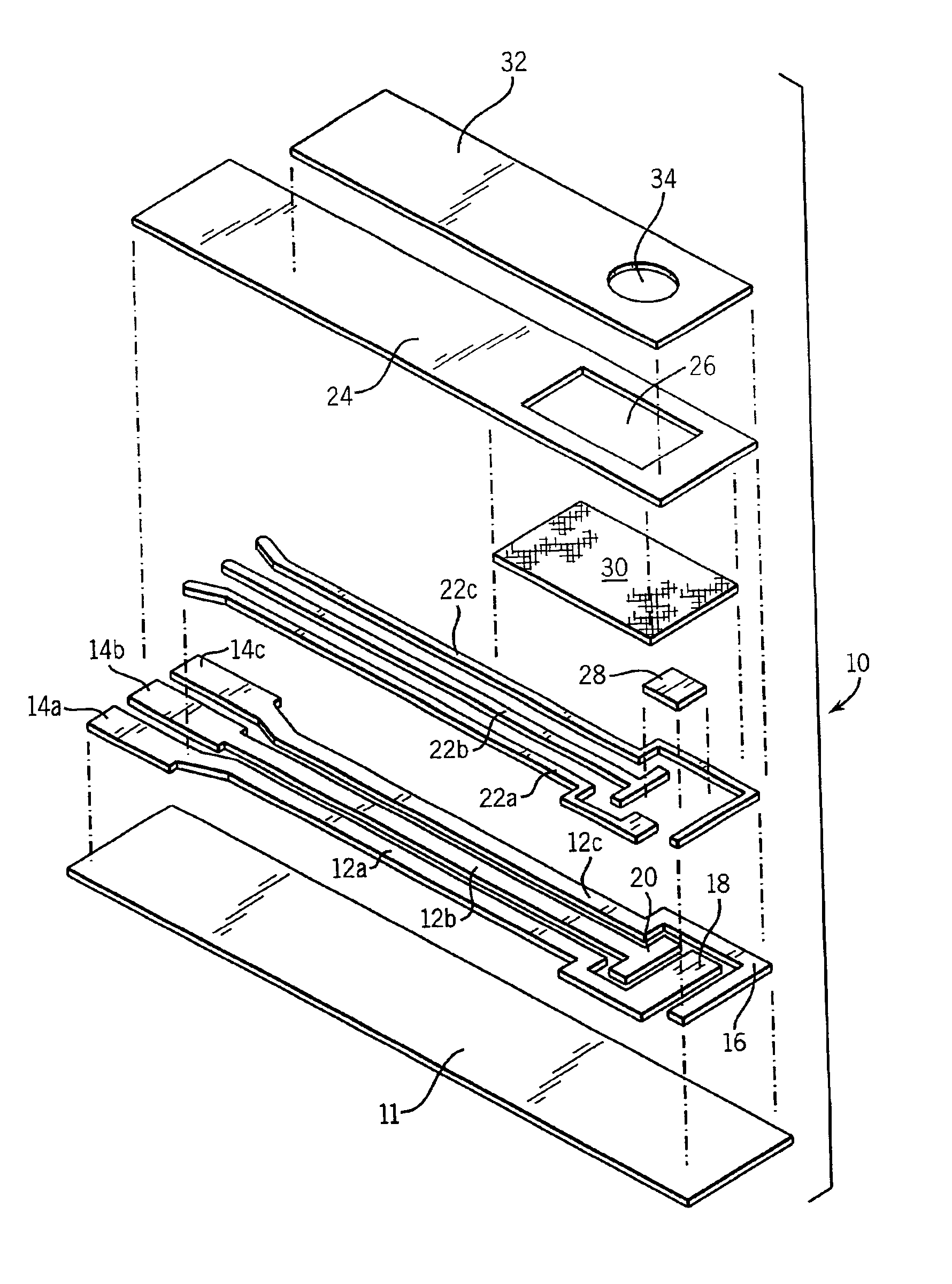
NOx sensor
InactiveUS6773565B2Avoid flowIncreasing active sitesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementNitrogen oxideSingle component
Owner:RIKEN CO LTD
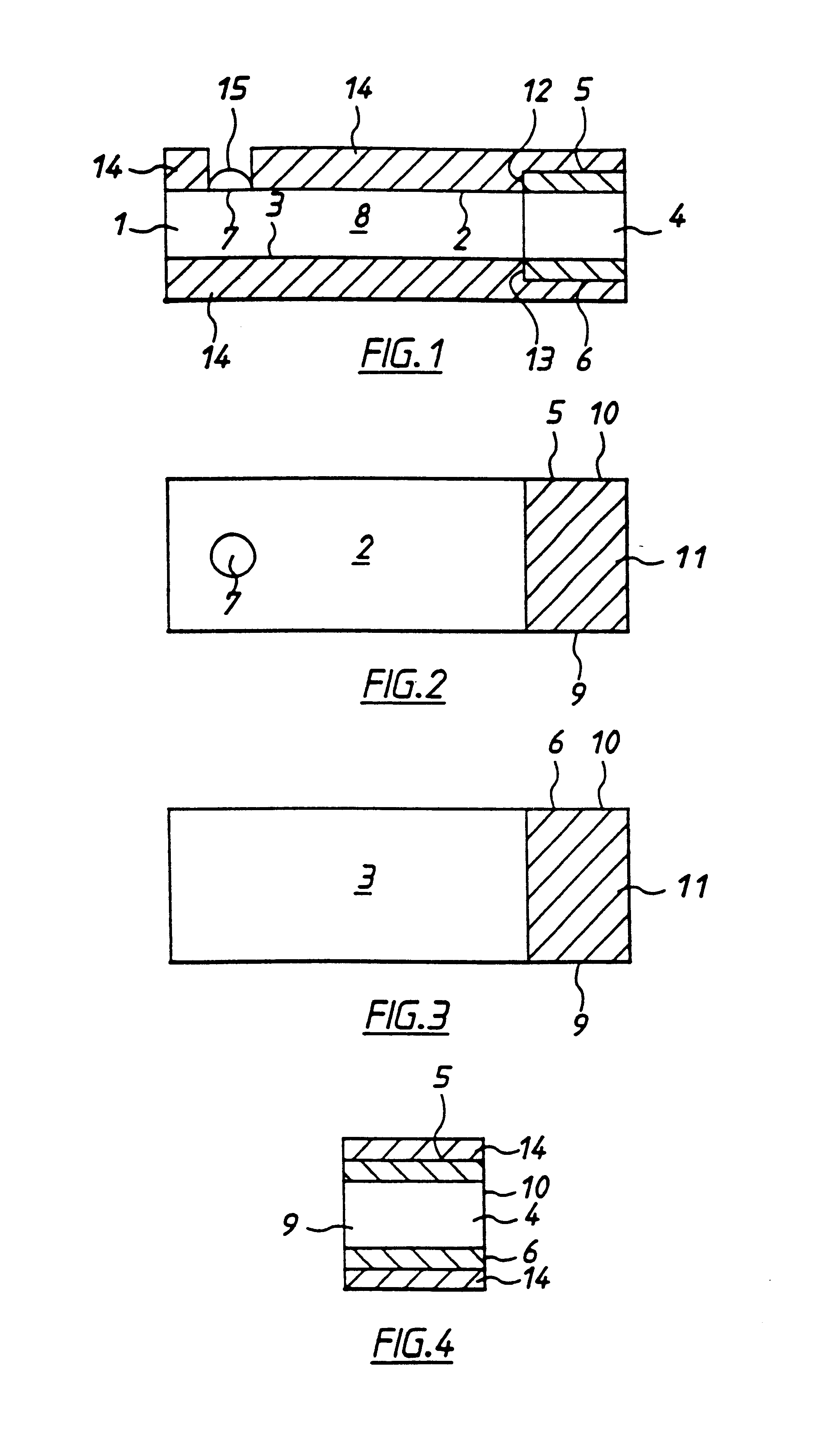
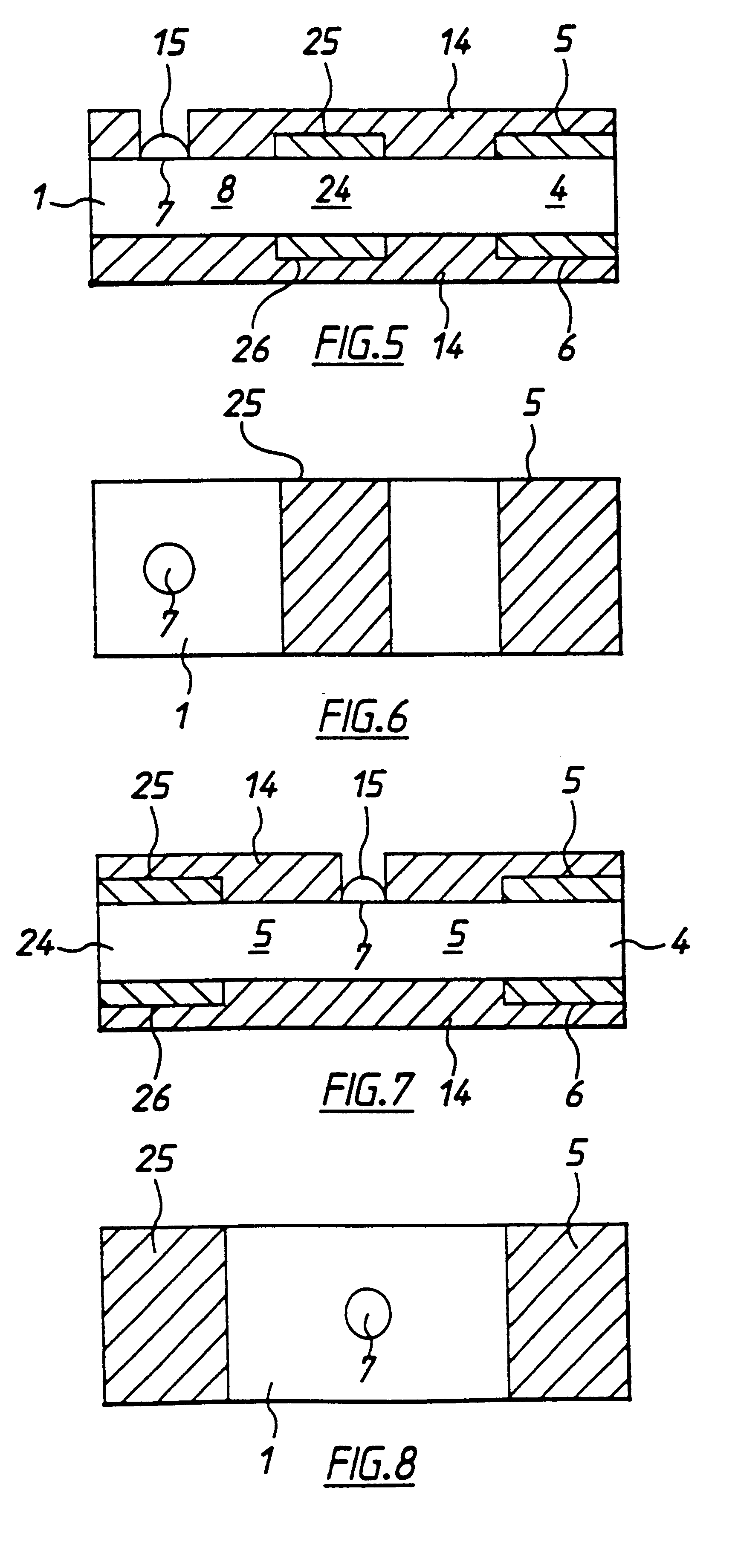
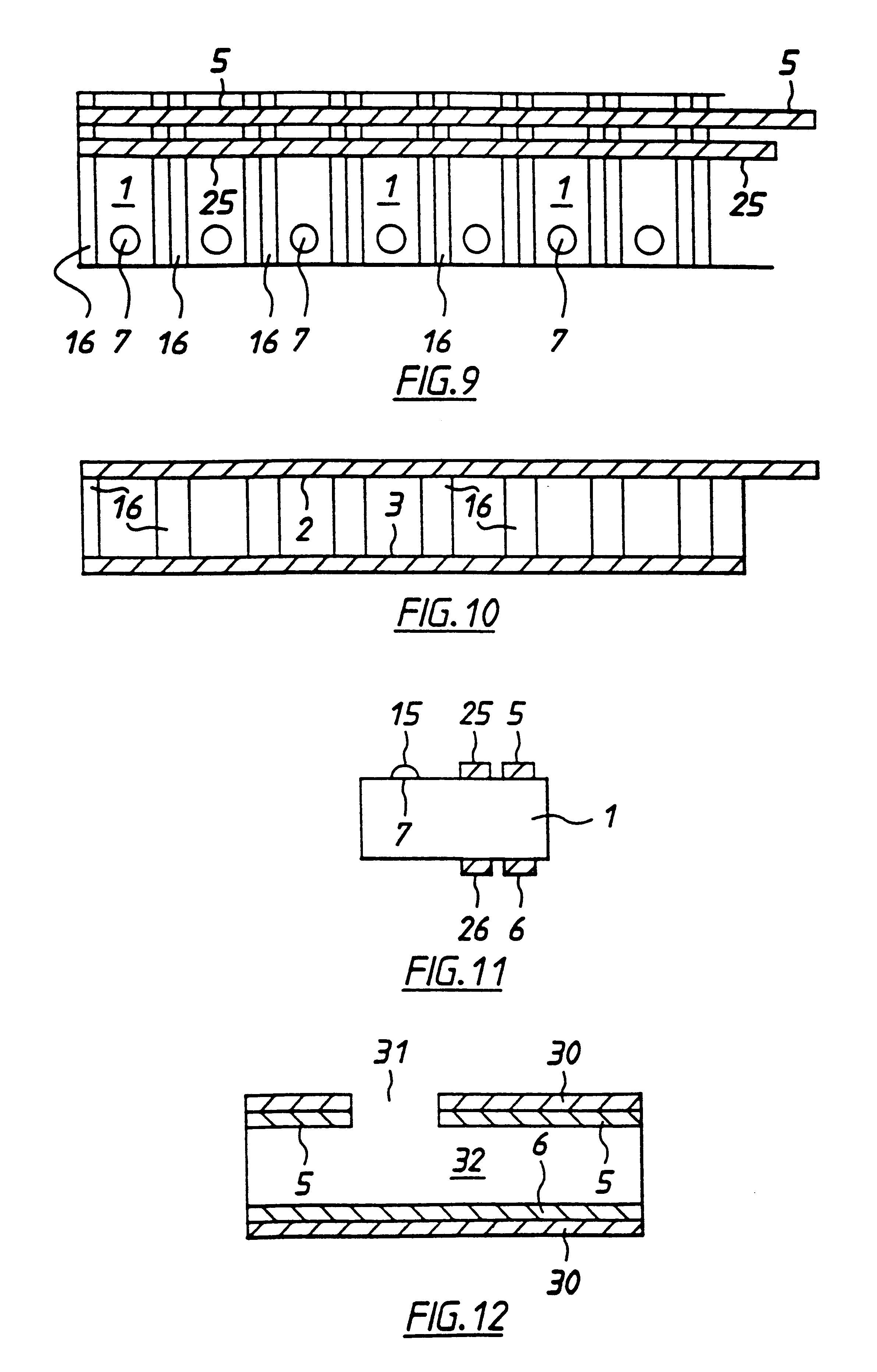
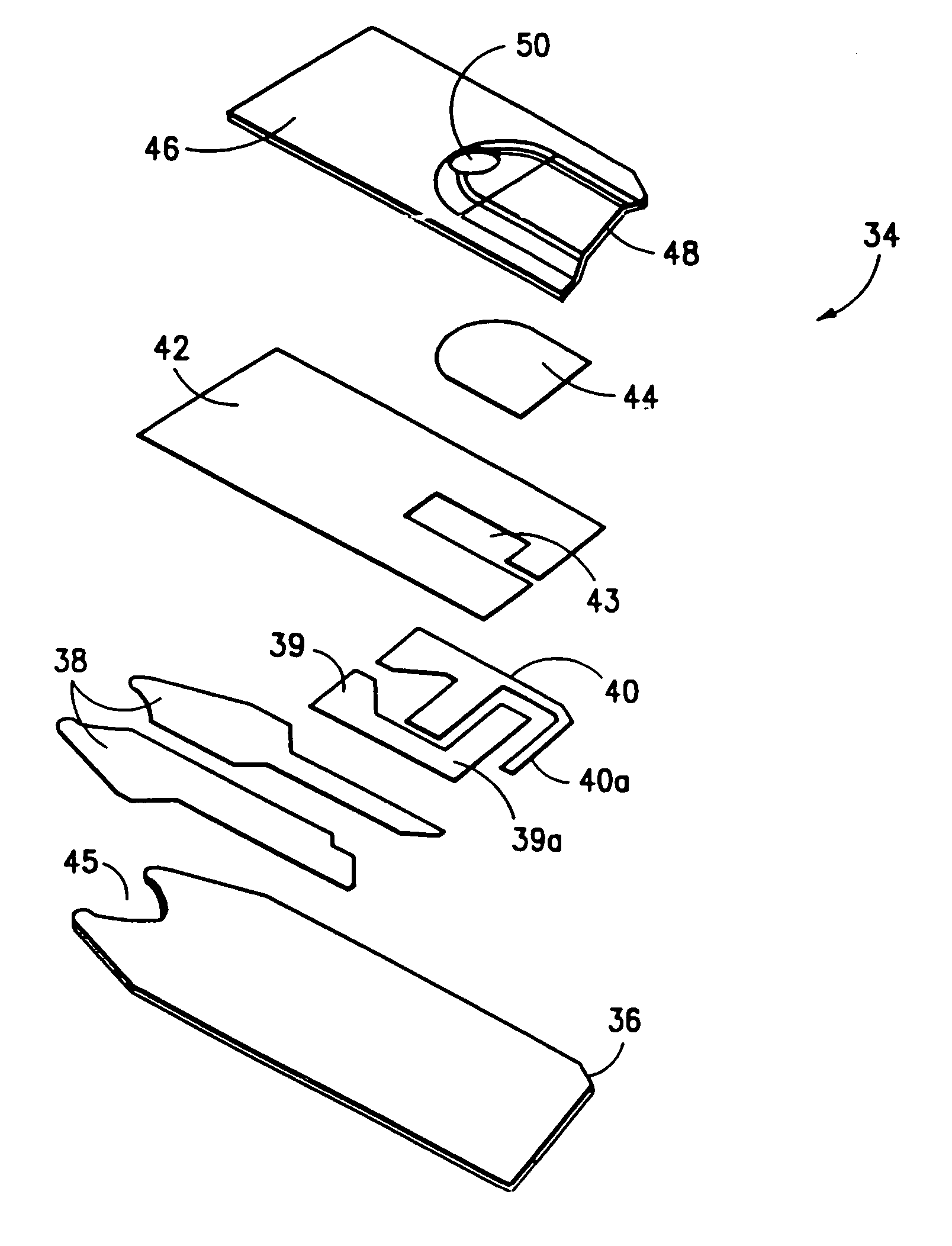
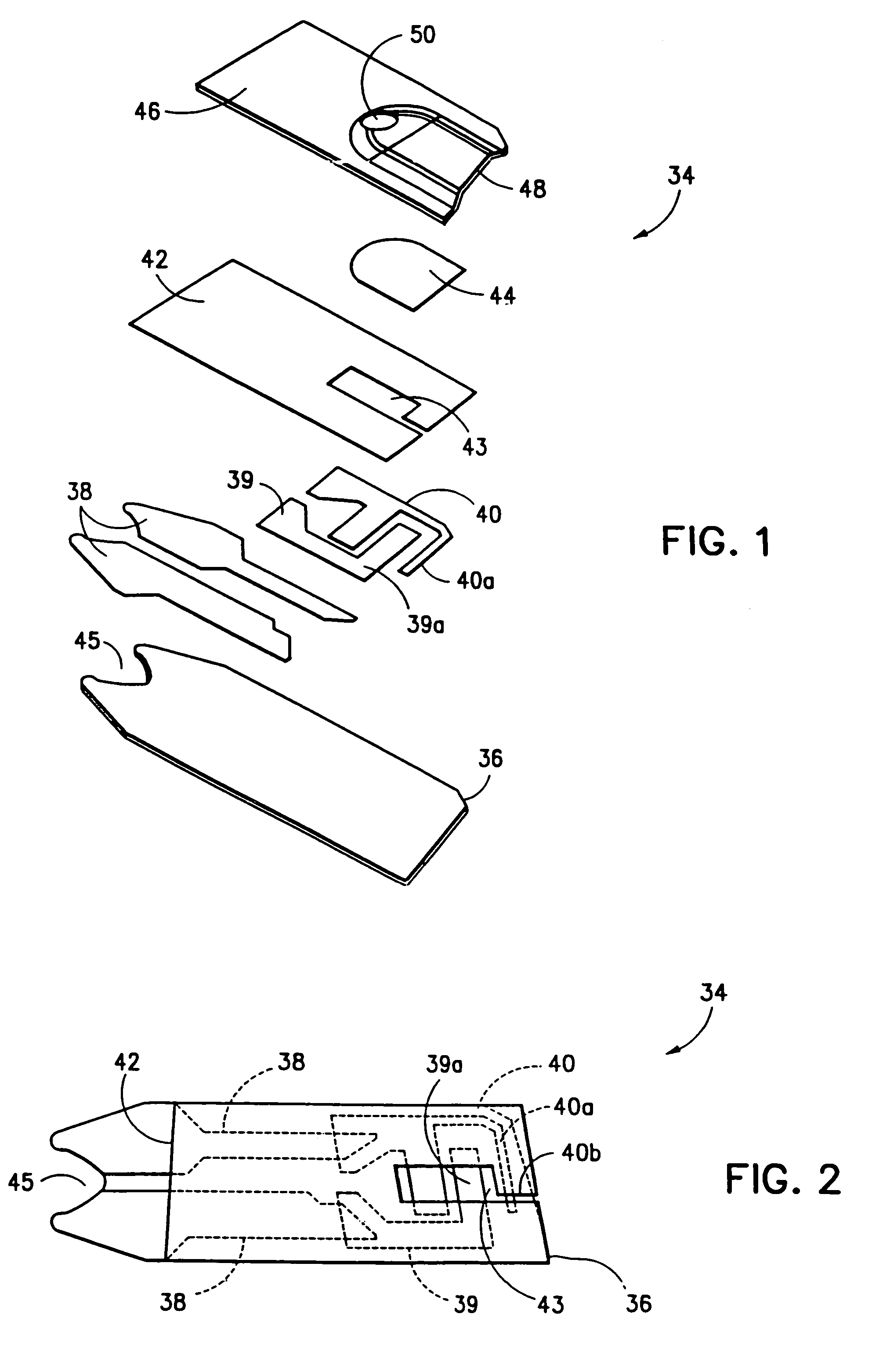
Electrochemical biosensor strip for analysis of liquid samples
InactiveUS6863800B2Easy to transportImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorConcentrations glucose
A biosensor in the form of a strip. In one embodiment, the biosensor strip comprises an electrode support, a first electrode, i.e., a working electrode, a second electrode, i.e., a counter electrode, and a third electrode, i.e., a reference electrode. Each of the electrodes is disposed on and supported by the electrode support. Each of the electrodes is spaced apart from the other two electrodes. The biosensor strip can include a covering layer, which defines an enclosed space over the electrodes. This enclosed space includes a zone where an analyte in the sample reacts with reagent(s) deposited at the working electrode. This zone is referred to as the reaction zone. The covering layer has an aperture for receiving a sample for introduction into the reaction zone. The biosensor strip can also include at least one layer of mesh interposed in the enclosed space between the covering layer and the electrodes in the reaction zone. This layer of mesh facilitates transporting of the sample to the electrodes in the reaction zone. In another embodiment, a biosensor strip can be constructed to provide a configuration that will allow the sample to be introduced to the reaction zone by action of capillary force. In this embodiment, the layer of mesh can be omitted. The invention also provides a method for determining the concentration of glucose in a sample of whole blood by using the biosensor of this invention.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
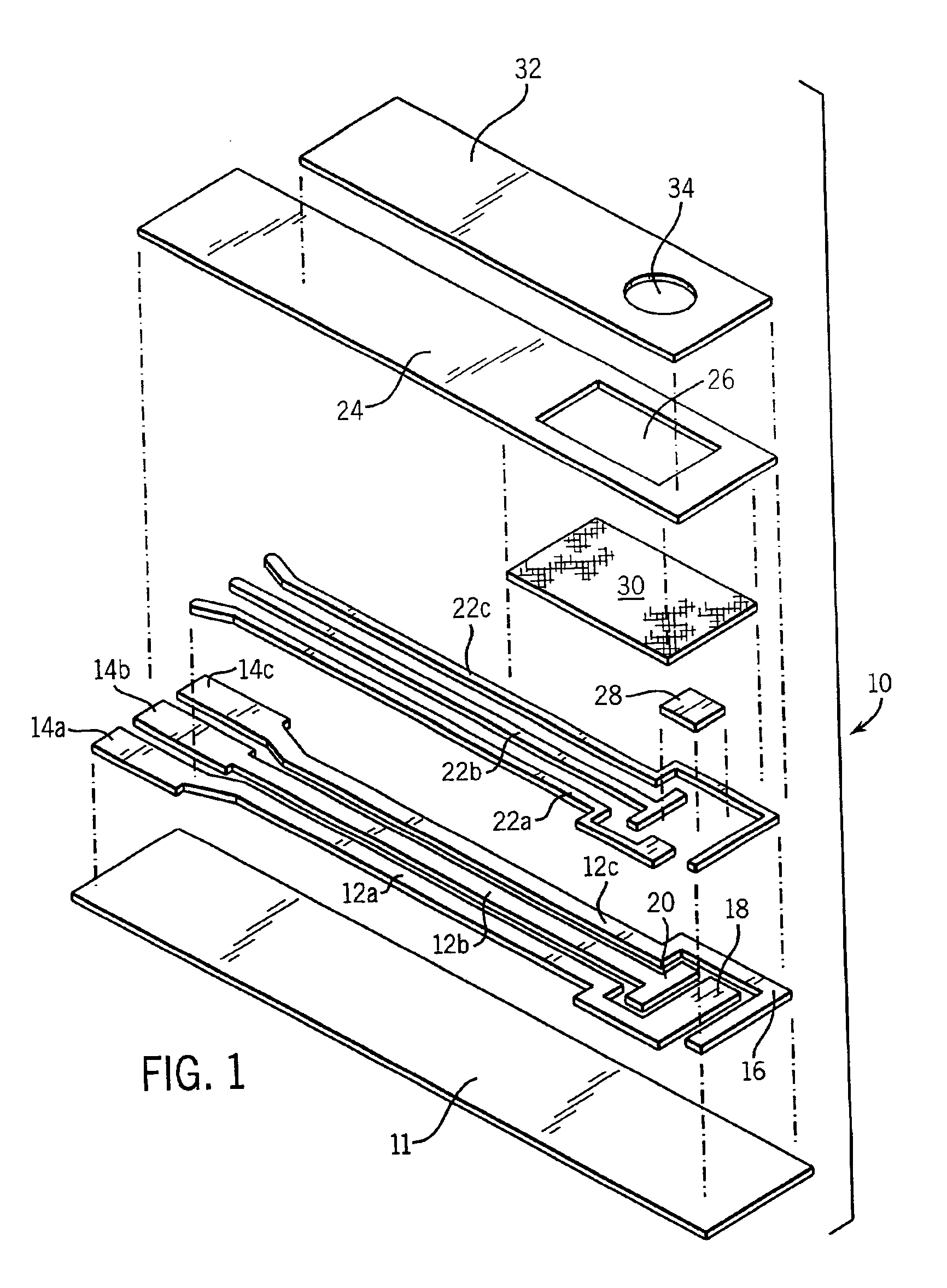
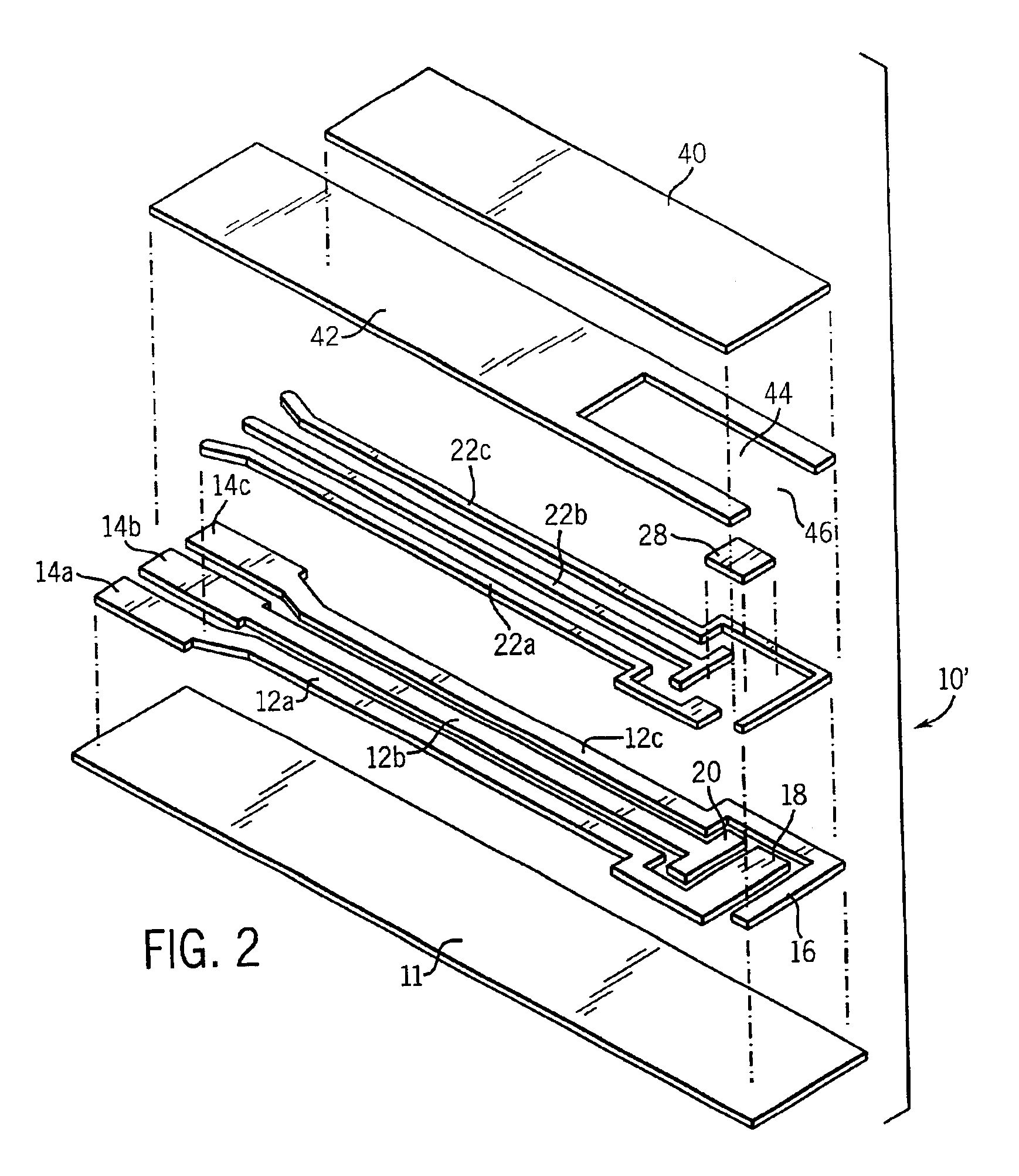
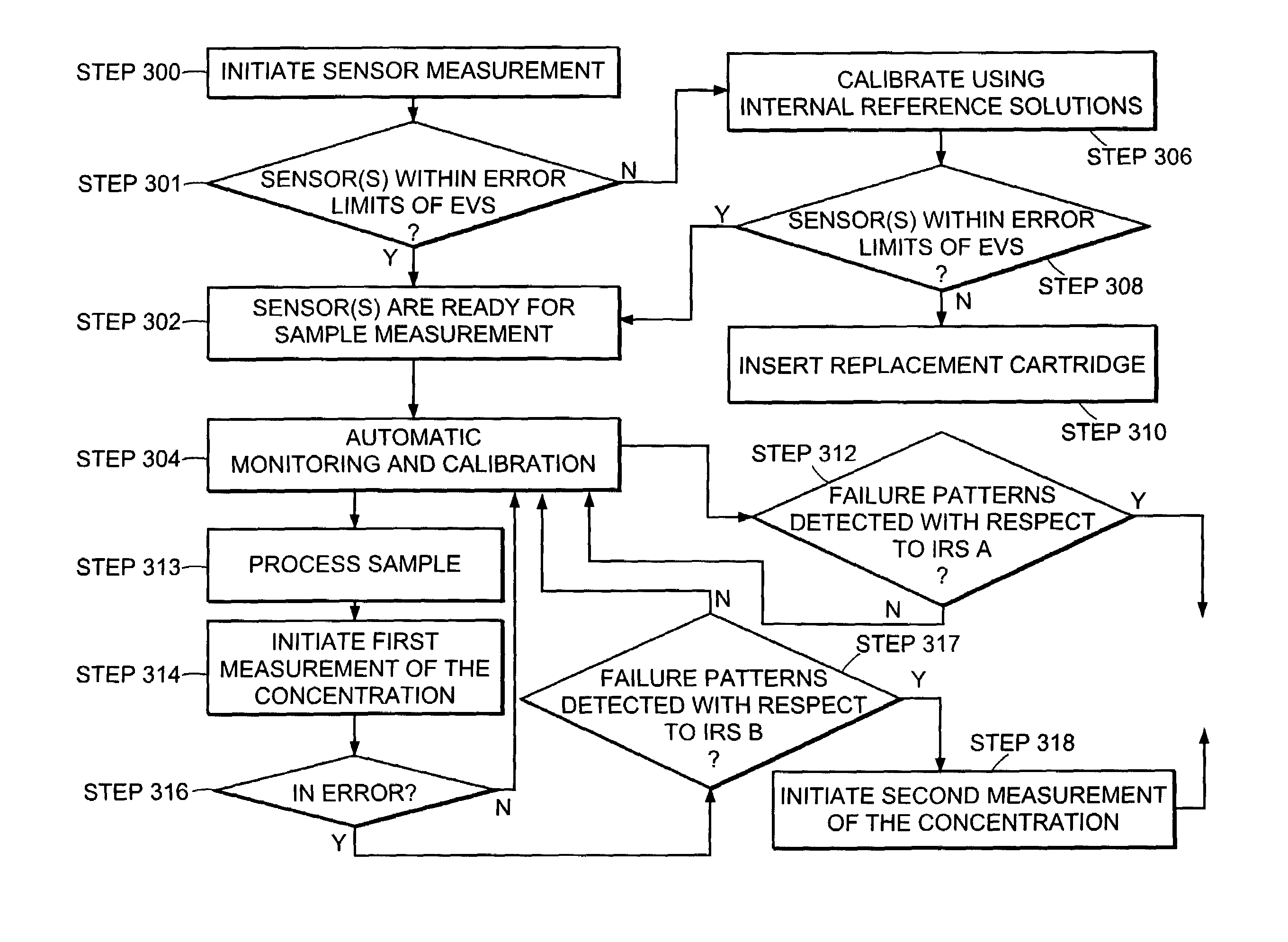
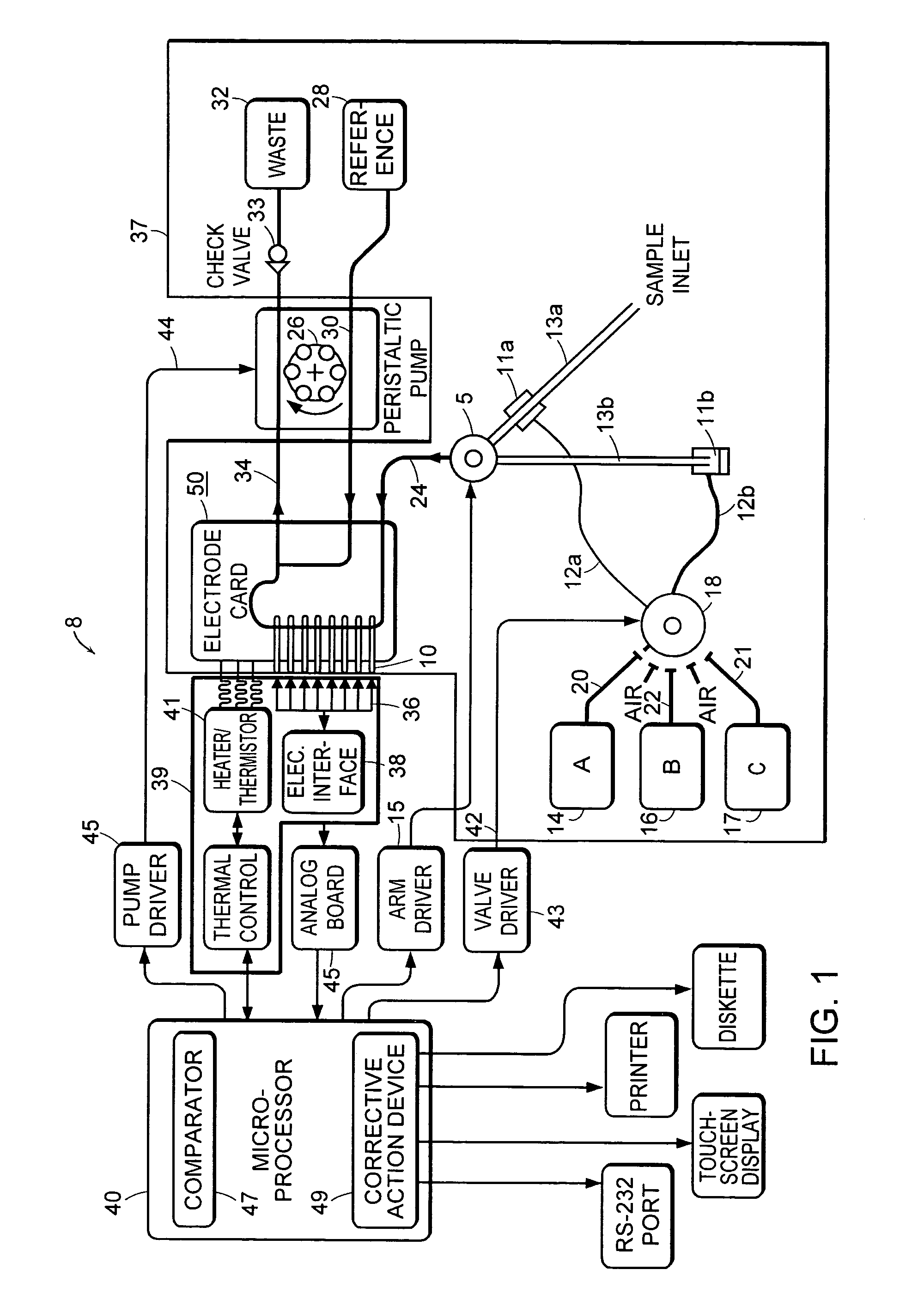
Automated system for continuously and automatically calibrating electrochemical sensors
An electrochemical sensor system that continuously monitors and calibrates the sensors included in the system. The invention also includes a method for determining failure patterns of a sensor and incorporating into an electrochemical sensor system the ability to recognize the failure pattern and initiate remedial action.
Owner:INSTR LAB
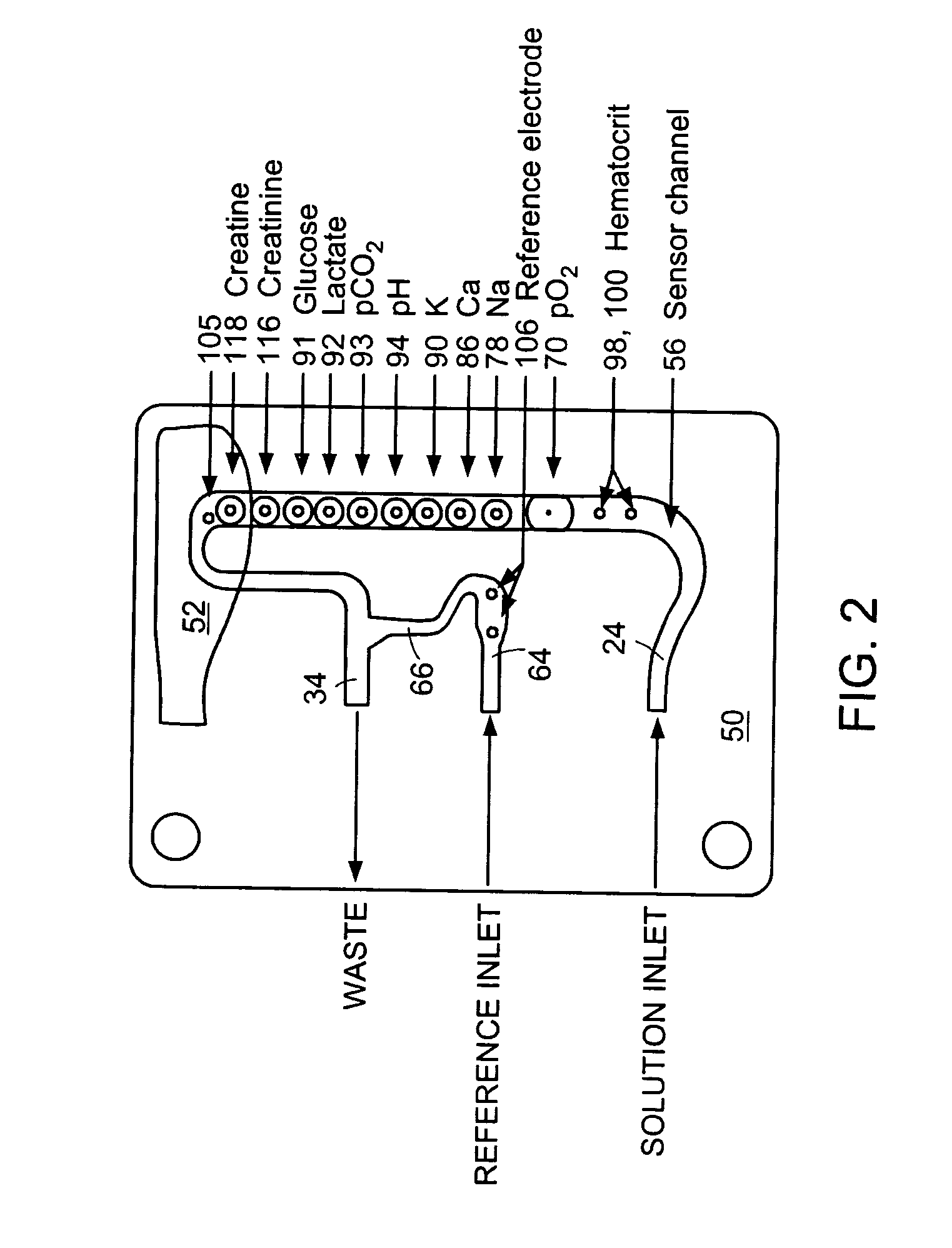
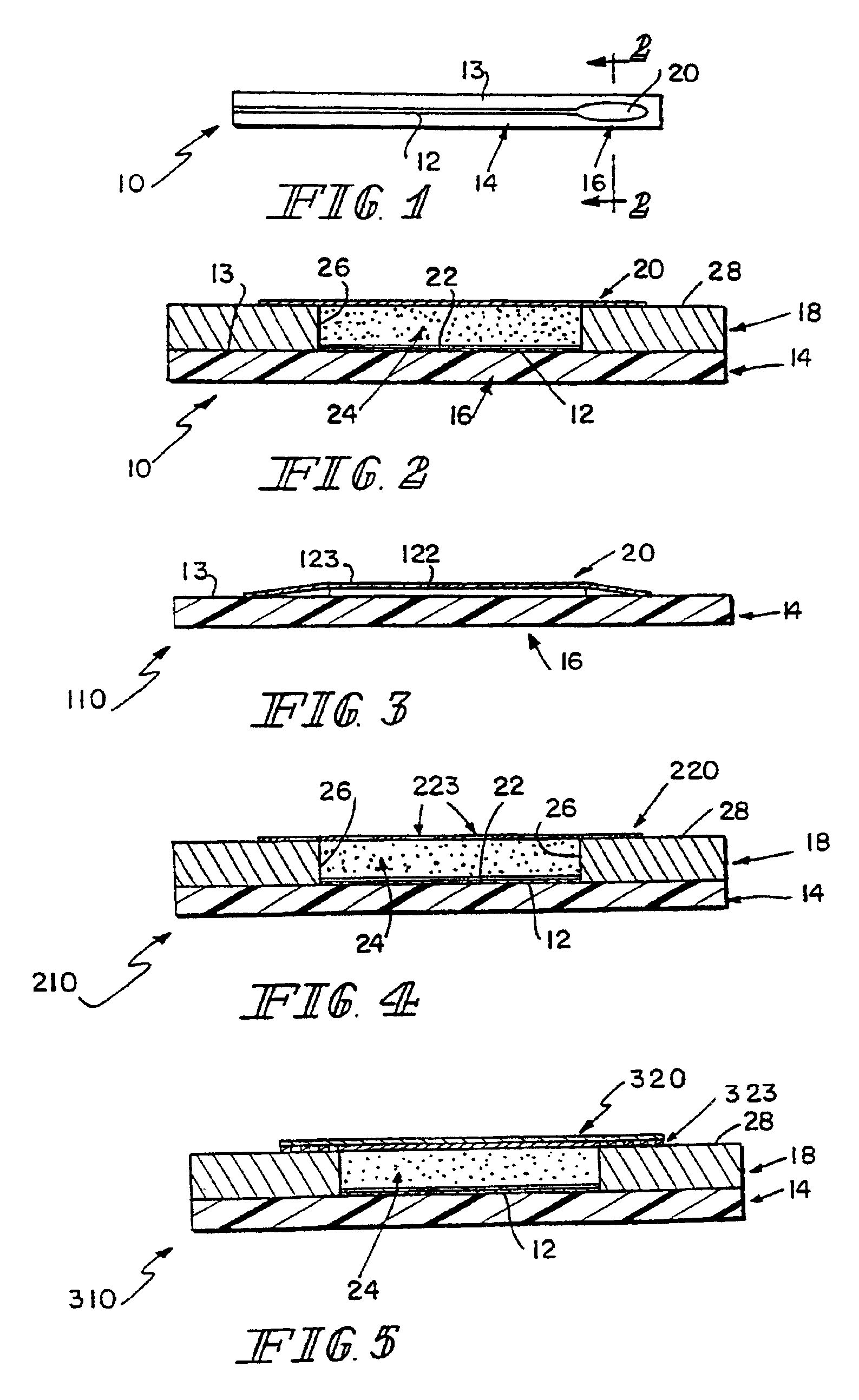
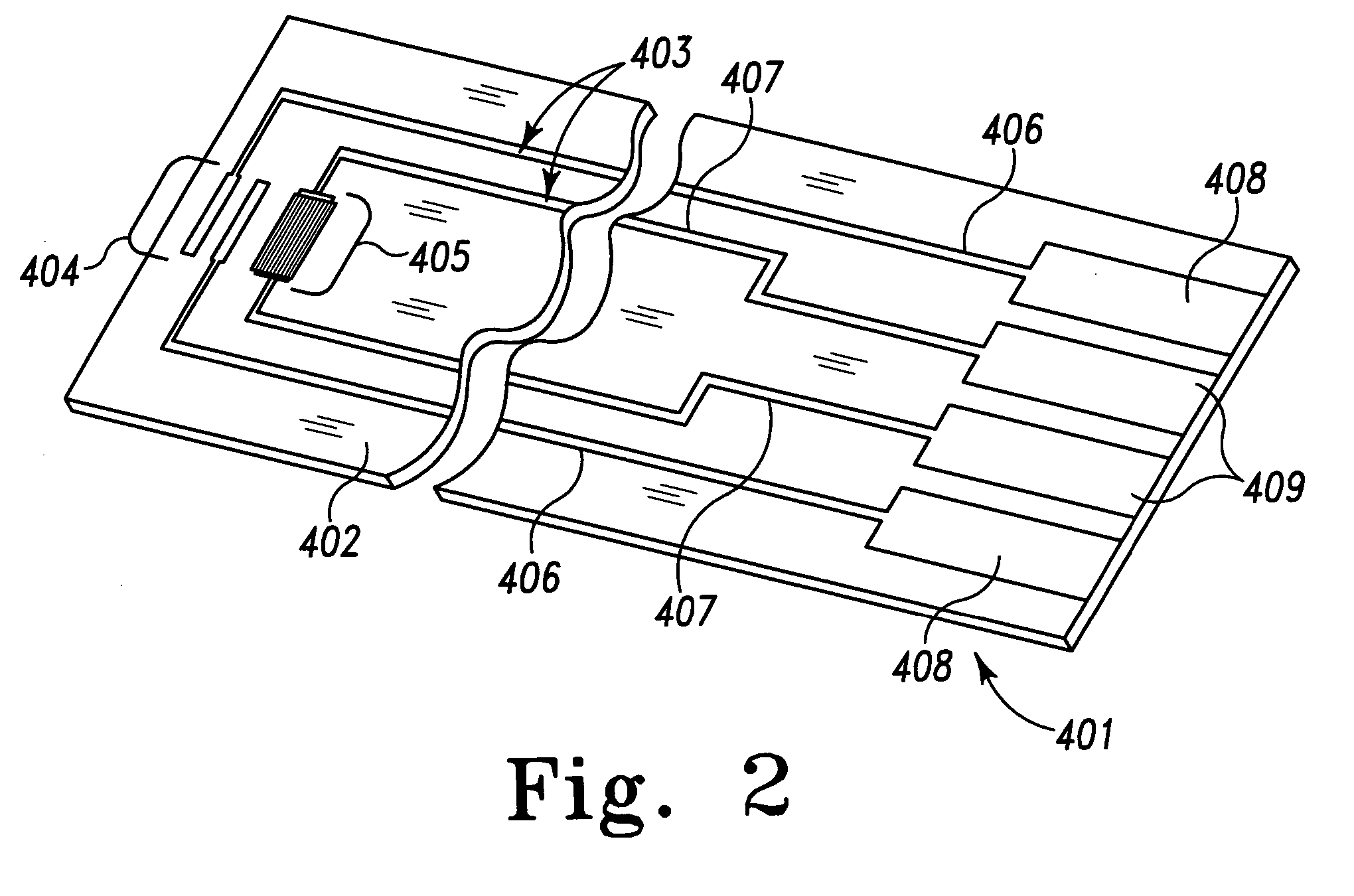
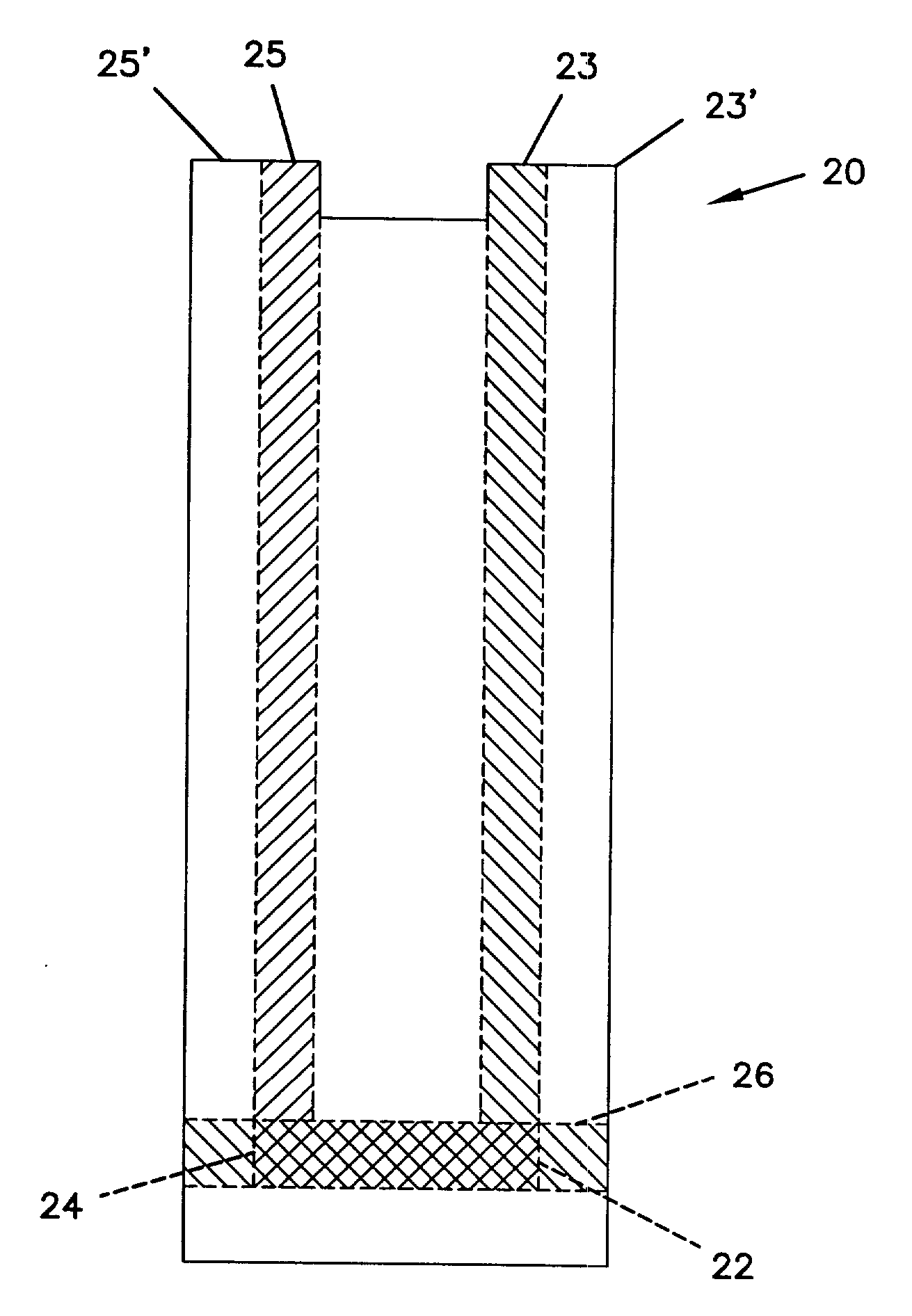
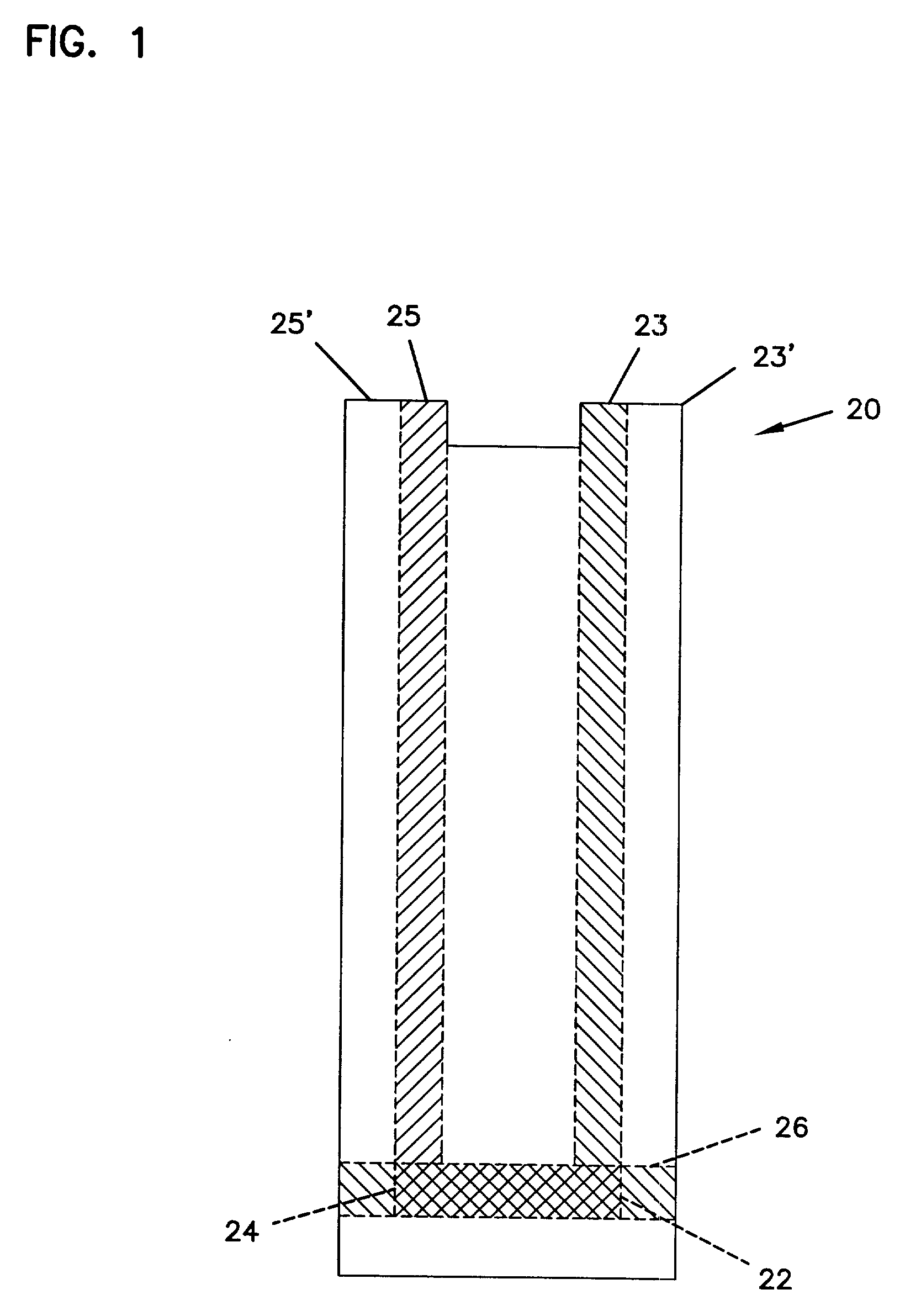
Small volume biosensor for continuous analyte monitoring
InactiveUS7045054B1Increase ratingsMinimize periodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRedox enzymesContinuous analysis
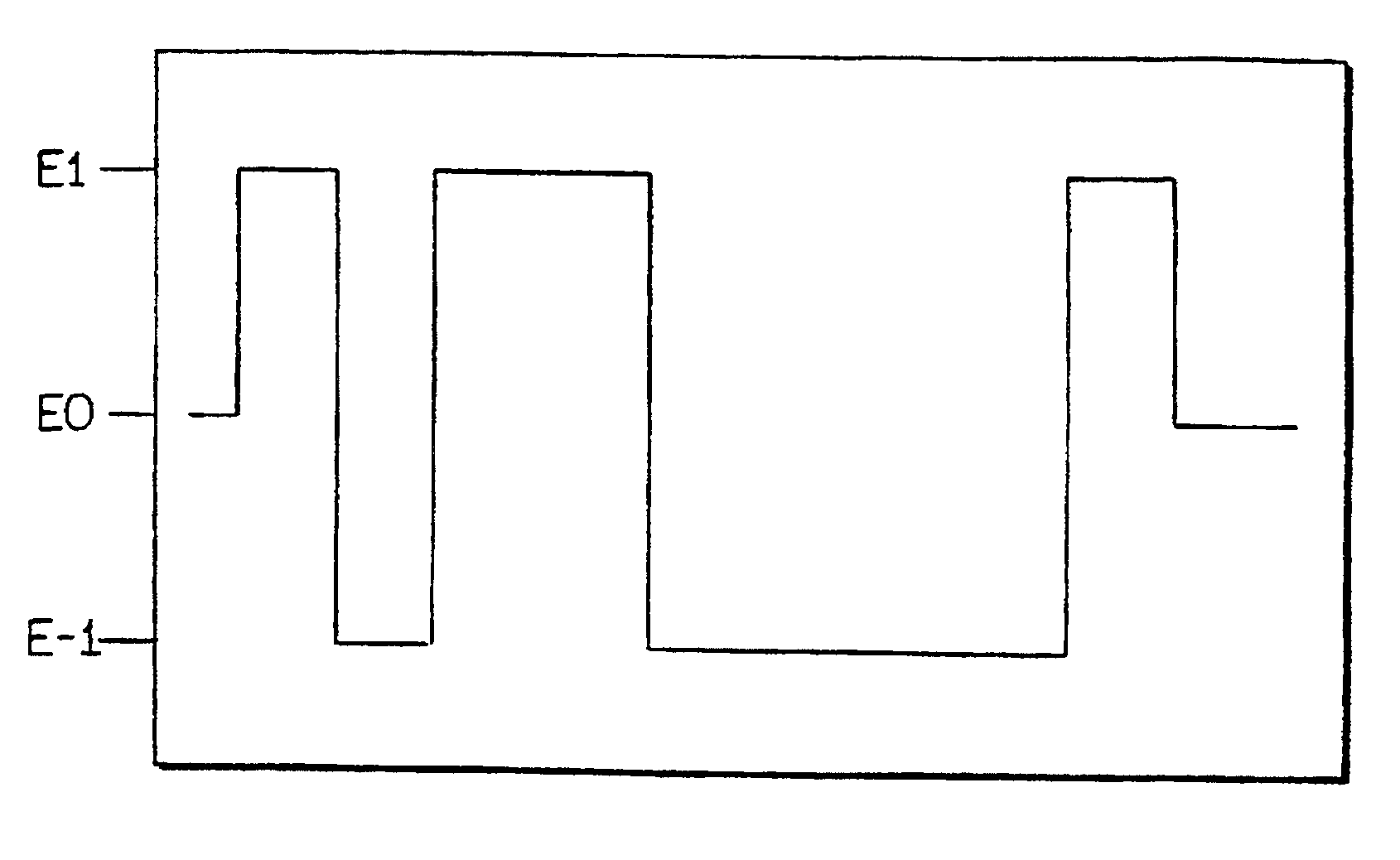
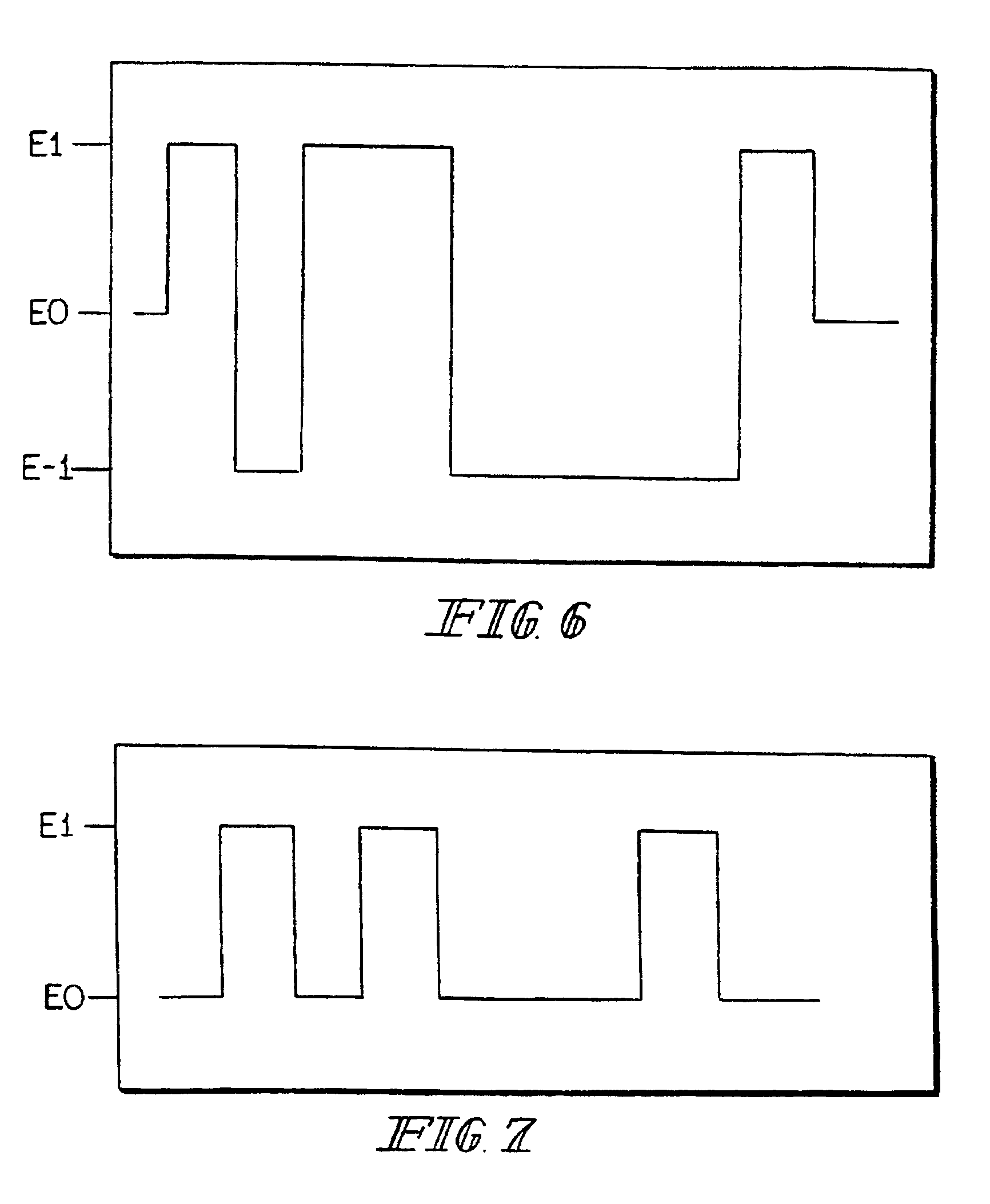
Sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) and a method for detecting an analyte are described. Sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) each have a volume of a hydrophilic medium (24) that retains an amount of analyte proportionate to the concentration of analyte in a biological fluid, electrodes (12) and a redox enzyme in contact with medium (24), and an electron transfer mediator. The fluid contacts sensors (10, 110, 210, 310, 410) and at initially predetermined intervals intermittently applies a potential to electrode (12) sufficient to oxidize the mediator and sensing current through electrode (12) as a function of the duration of the applied potential. The applied mediator oxidizing applied potential is maintained for a period of time sufficient to determine the rate of change of current with time through electrode (12). The current flow is correlated with the current flow for known concentrations of the analyte in medium (24).
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Devices for testing fluid
An improvement is described to disposable devices for performing chemical or biological tests on a sample of fluid, and the method by which such devices perform tests. The power for the device comes from an electrochemical battery, where a portion of the fluid sample itself provides the electrolyte for the battery. Furthermore, the time of diffusion of the fluid into the battery provides the timing signal for activation of the system. Communication between the improved device and an information system is provided by a transponder system built into the device which requires no direct electrical connection. Rather, the device is placed in proximity with a reader which can interrogate the device, obtain the results of the test and if necessary provide power for the device to perform the test, and / or communicate the information. The improvements and methods are particularly applicable to devices for performing in vitro diagnostic tests on a sample of body fluid.
Owner:CROSBY PETER
System and method for measuring an analyte in a sample
ActiveUS20090184004A1Interference minimizationLess of concentration profileImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteConcentrations glucose
Methods of determining a corrected analyte concentration in view of some error source are provided herein. The methods can be utilized for the determination of various analytes and / or various sources of error. In one example, the method can be configured to determine a corrected glucose concentration in view of an extreme level of hematocrit found within the sample. In other embodiments, methods are provided for identifying various system errors and / or defects. For example, such errors can include partial-fill or double-fill situations, high track resistance, and / or sample leakage. Systems are also provided for determining a corrected analyte concentration and / or detecting some system error.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Electrochemical methods and devices for use in the determination of hematocrit corrected analyte concentrations
InactiveUS6890421B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteBlood cell
Methods and devices for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided which correct for errors in the analyte concentration measurement which are due to the hematocrit of the sample.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
System and method for coding information on a biosensor test strip
The present invention provides a test strip for measuring a concentration of an analyte of interest in a biological fluid, wherein the test strip may be encoded with information that can be read by a test meter into which the test strip is inserted.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
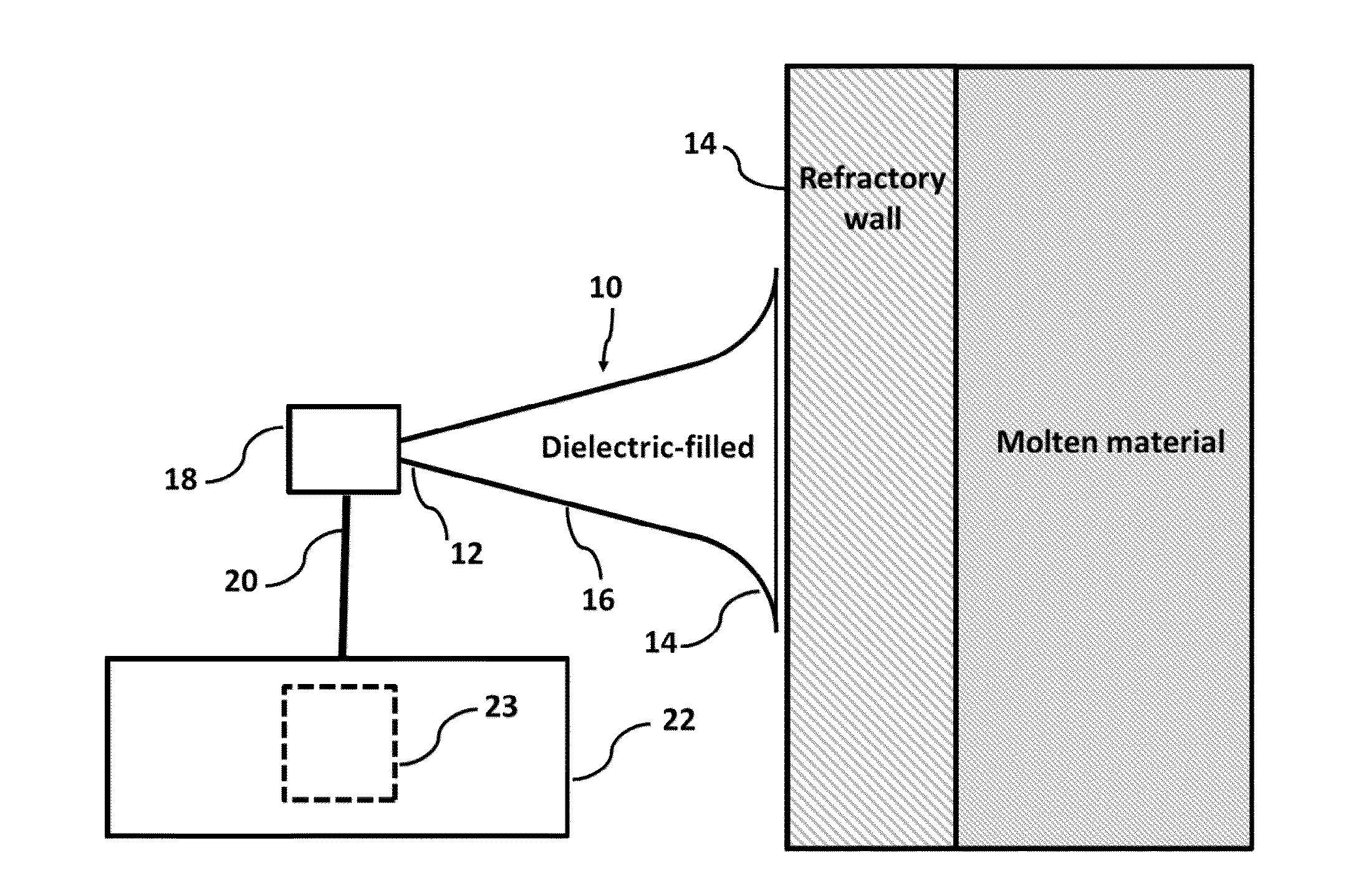
Material erosion monitoring system and method
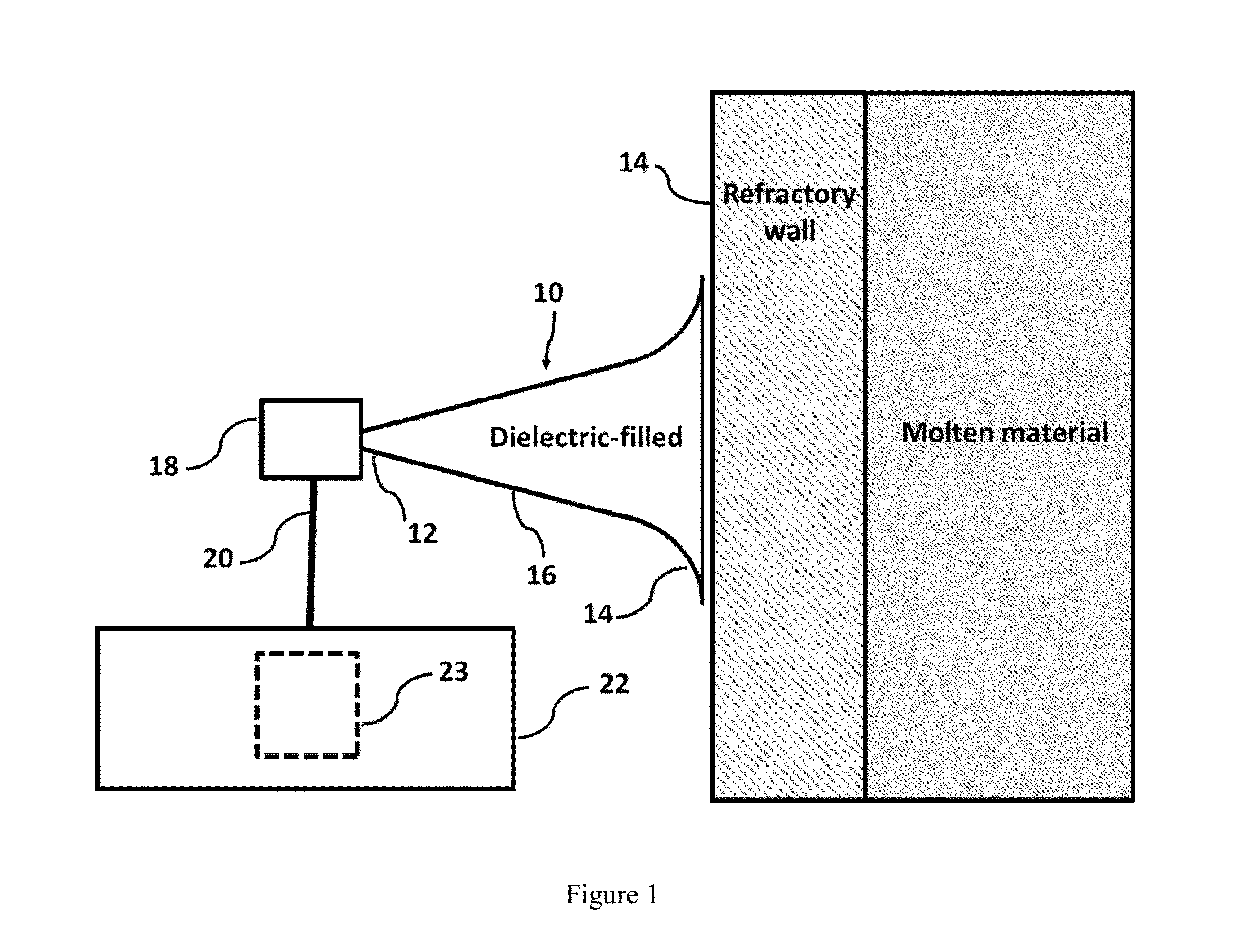
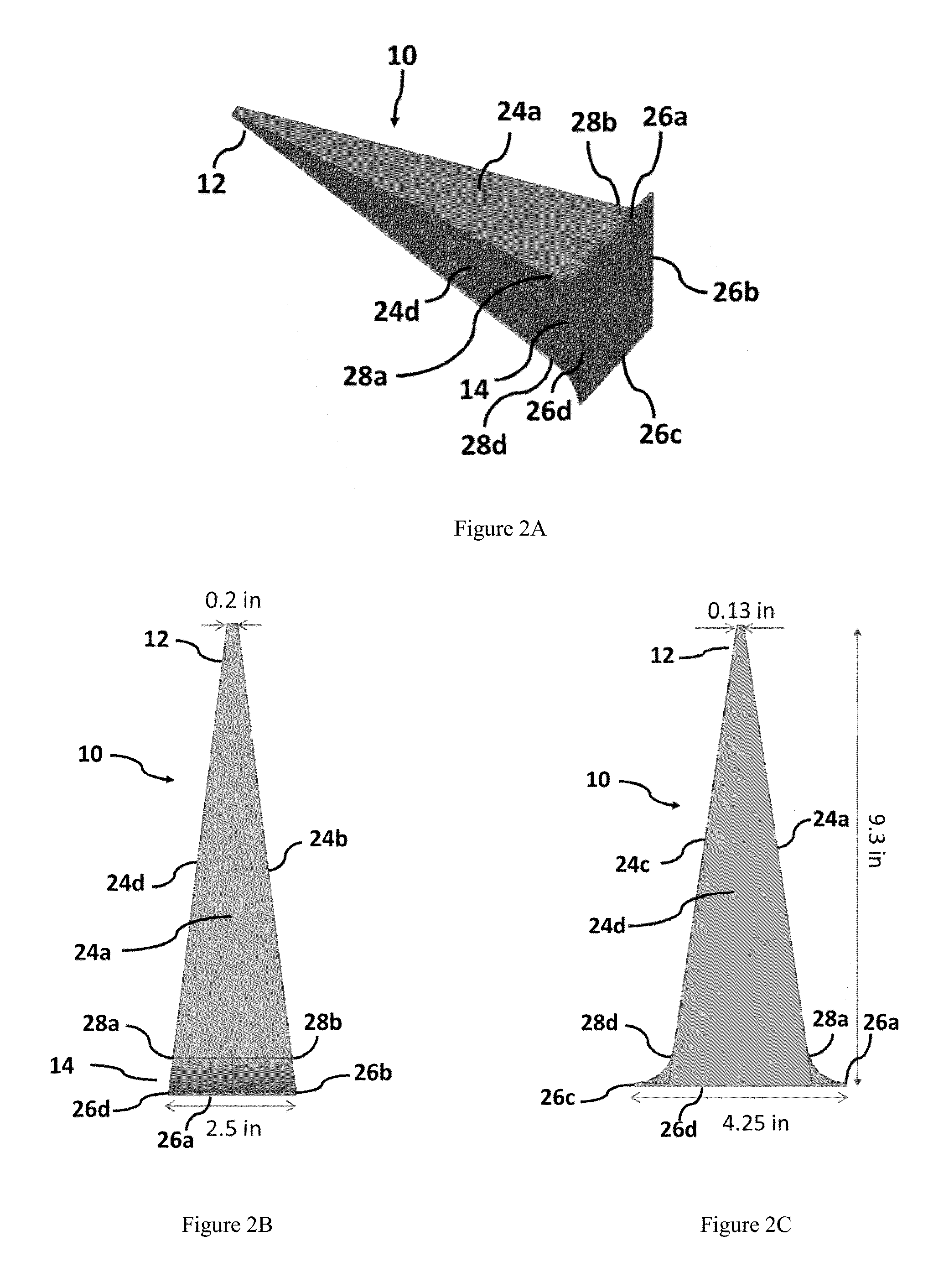
ActiveUS20150276577A1Reduce confusionMultiple EffectsFurnace componentsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial ErosionMonitoring system
Disclosed is an improved system and method to evaluate the status of a material. The system and method are operative to identify flaws and measure the erosion profile and thickness of different materials, including refractory materials, using electromagnetic waves. The system is designed to reduce a plurality of reflections, associated with the propagation of electromagnetic waves launched into the material under evaluation, by a sufficient extent so as to enable detection of electromagnetic waves of interest reflected from remote discontinuities of the material. Furthermore, the system and method utilize a configuration and signal processing techniques that reduce clutter and enable the isolation of electromagnetic waves of interest. Moreover, the launcher is impedance matched to the material under evaluation, and the feeding mechanism is designed to mitigate multiple reflection effects to further suppress clutter.
Owner:PANERATECH
Subnetwork synchronization and variable transmit synchronization techniques for a wireless medical device network
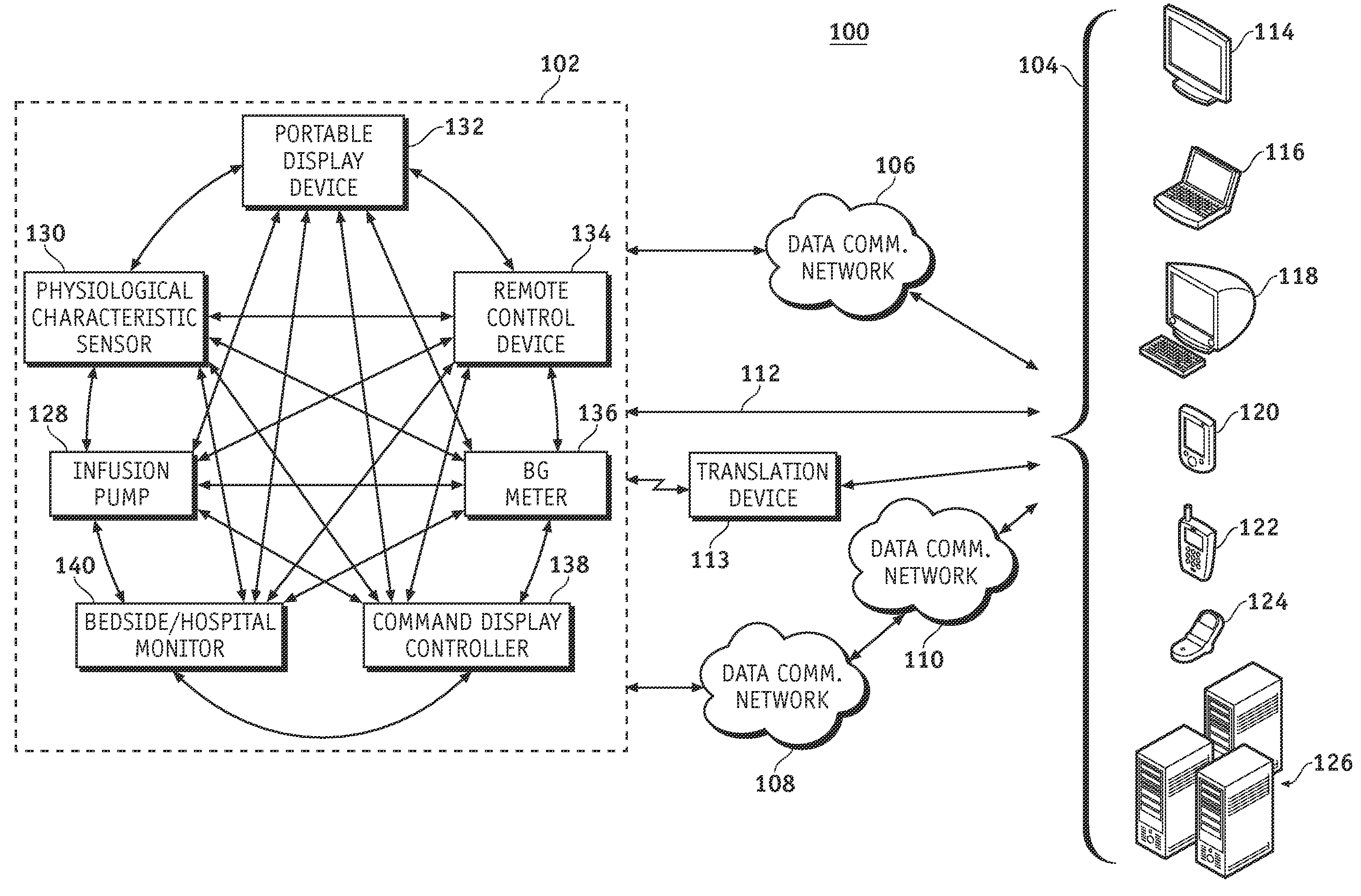
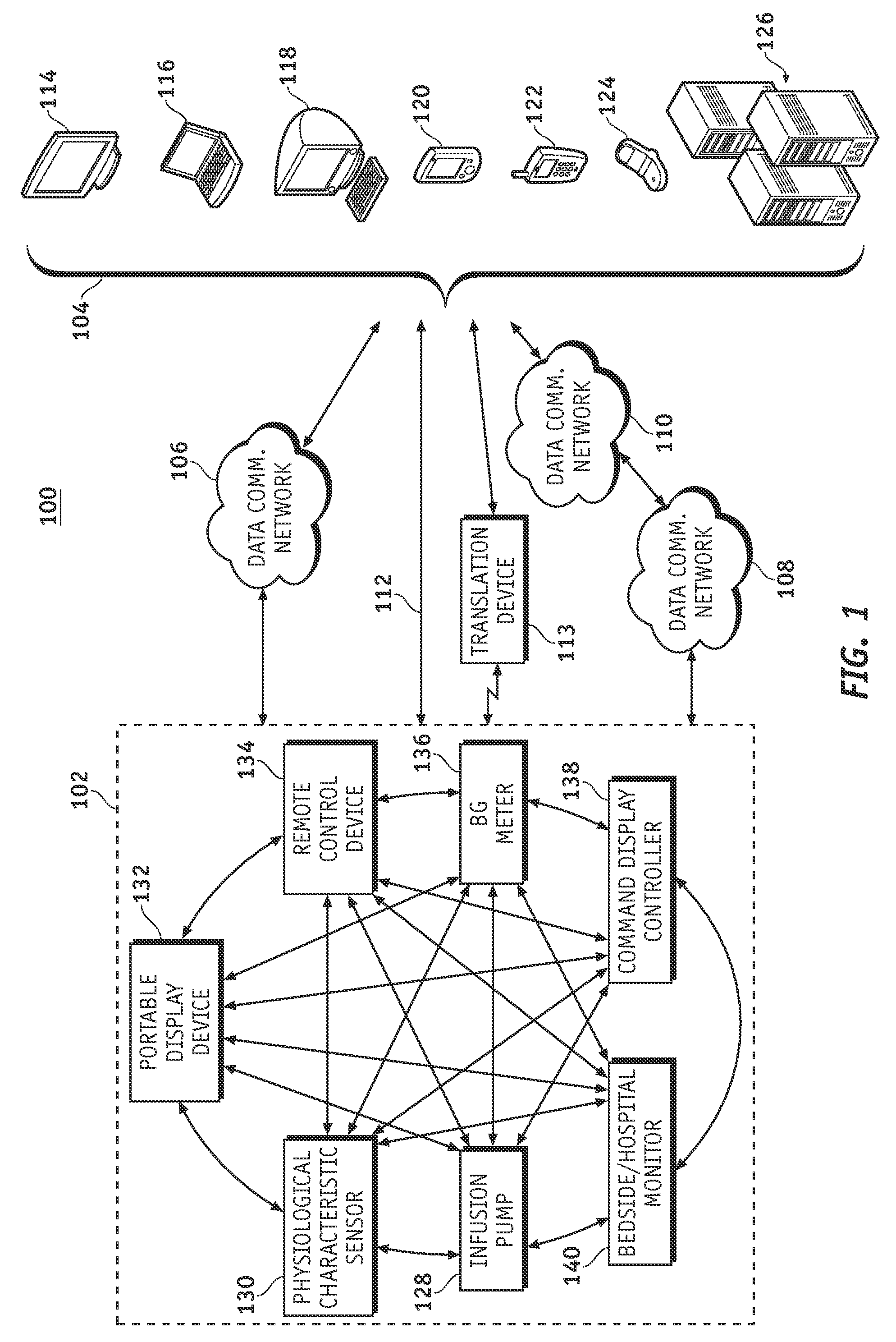
ActiveUS20070251835A1Efficient routingWeather/light/corrosion resistanceDrug and medicationsWireless Application ProtocolFluid infusion
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Electrochemical-sensor design
An electrochemical test sensor adapted to assist in determining the concentration of analyte in a fluid sample is disclosed. The sensor comprises a base that assists in forming an opening for introducing the fluid sample, a working electrode being coupled to the base, and a counter electrode being coupled to the base, the counter electrode and the working electrode being adapted to be in electrical communication with a detector of electrical current, and a sub-element being coupled to the base. A major portion of the counter electrode is located downstream relative to the opening and at least a portion of the working electrode. The sub-element is located upstream relative to the working electrode such that when electrical communication occurs between only the sub-element and the working electrode there is insufficient flow of electrical current through the detector to determine the concentration of the analyte in the fluid sample.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
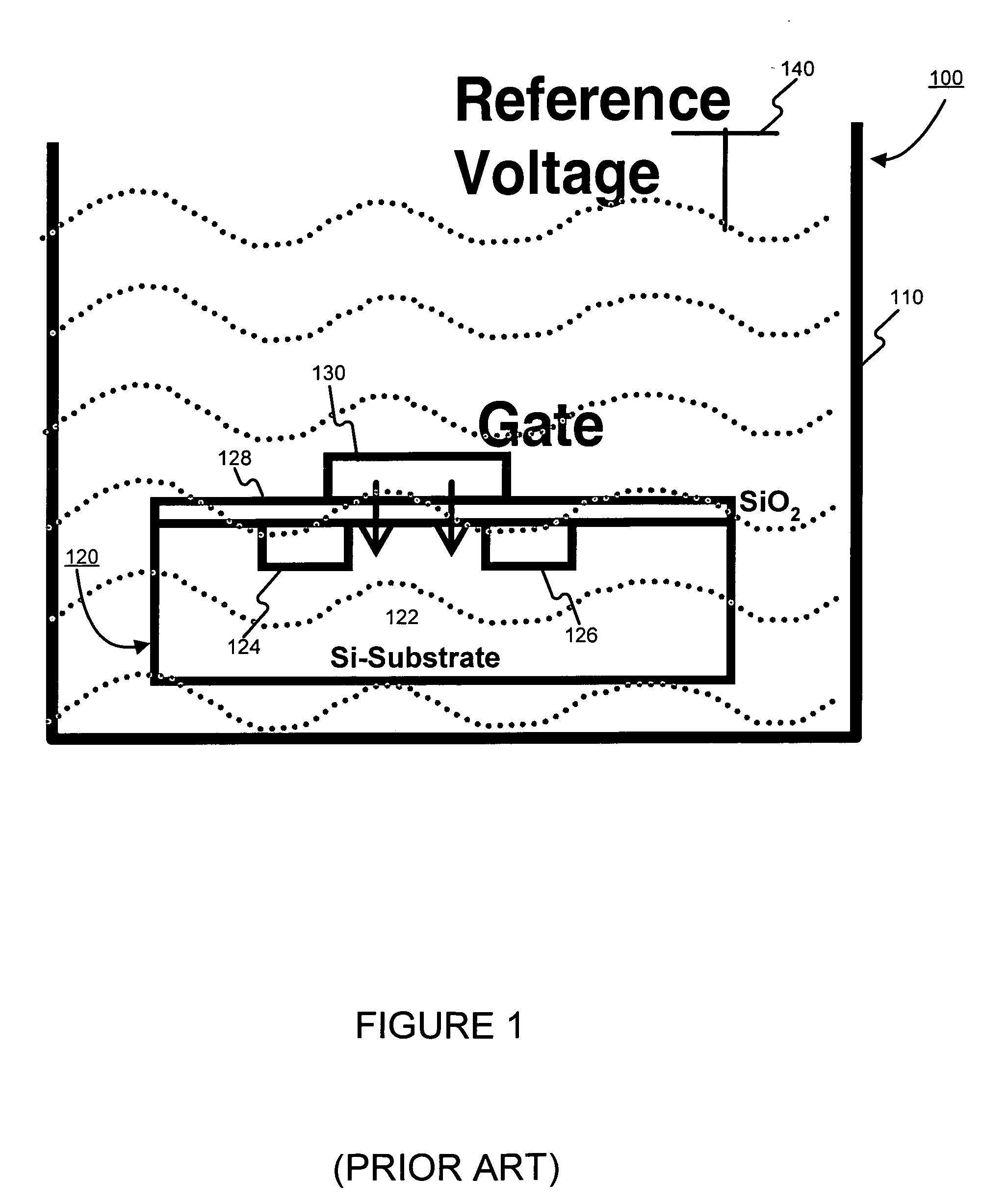
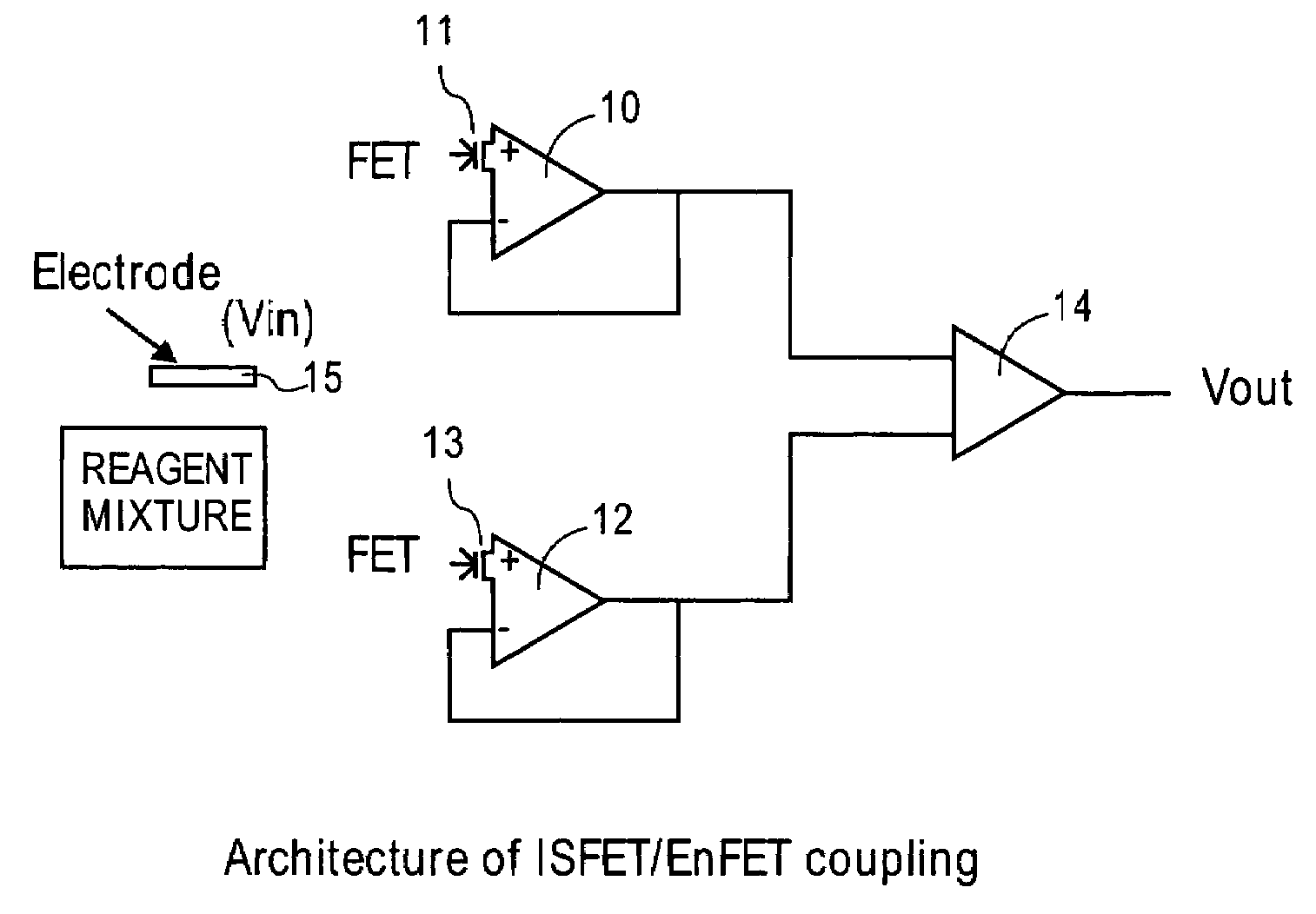
Sensing apparatus and method
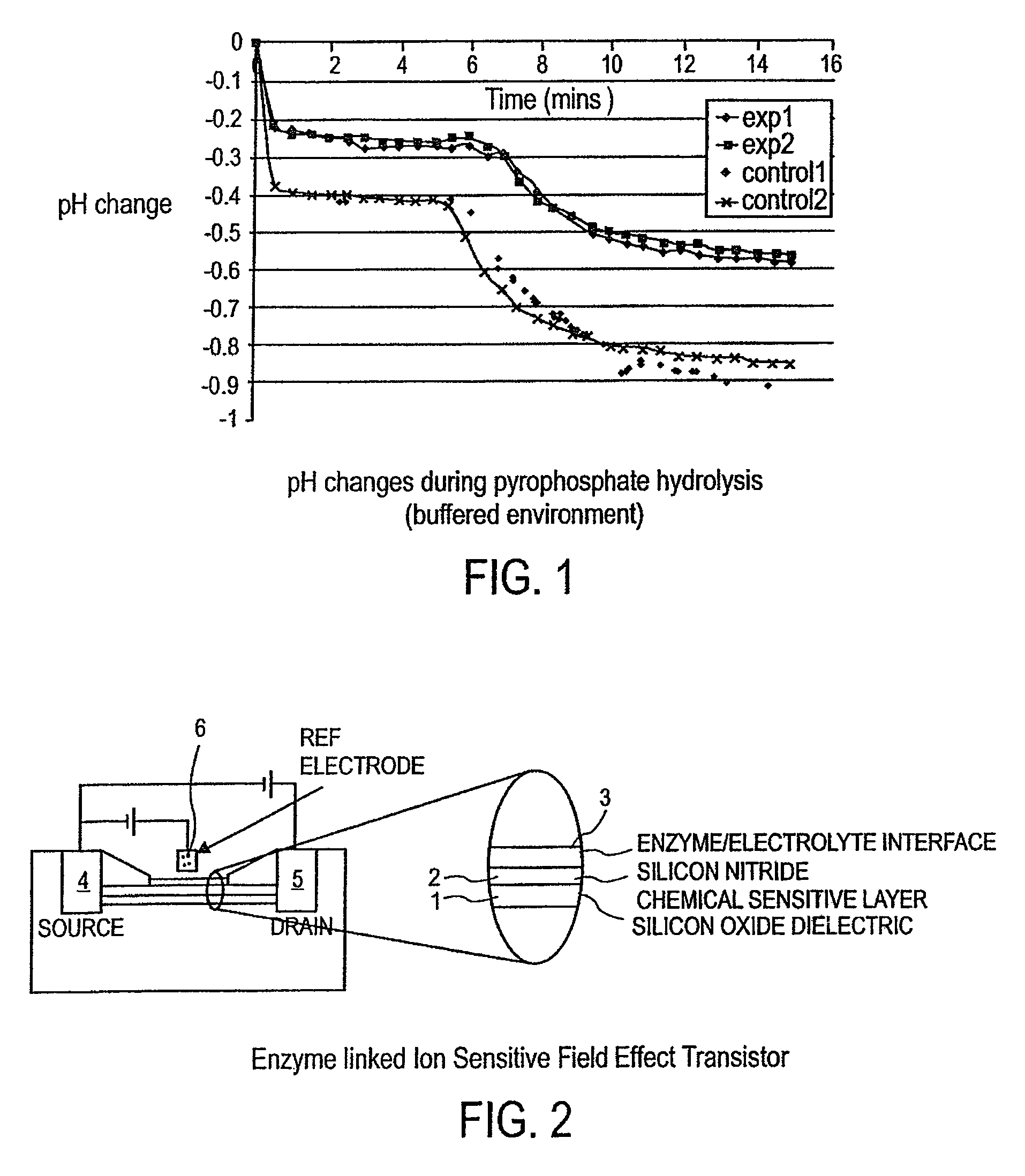
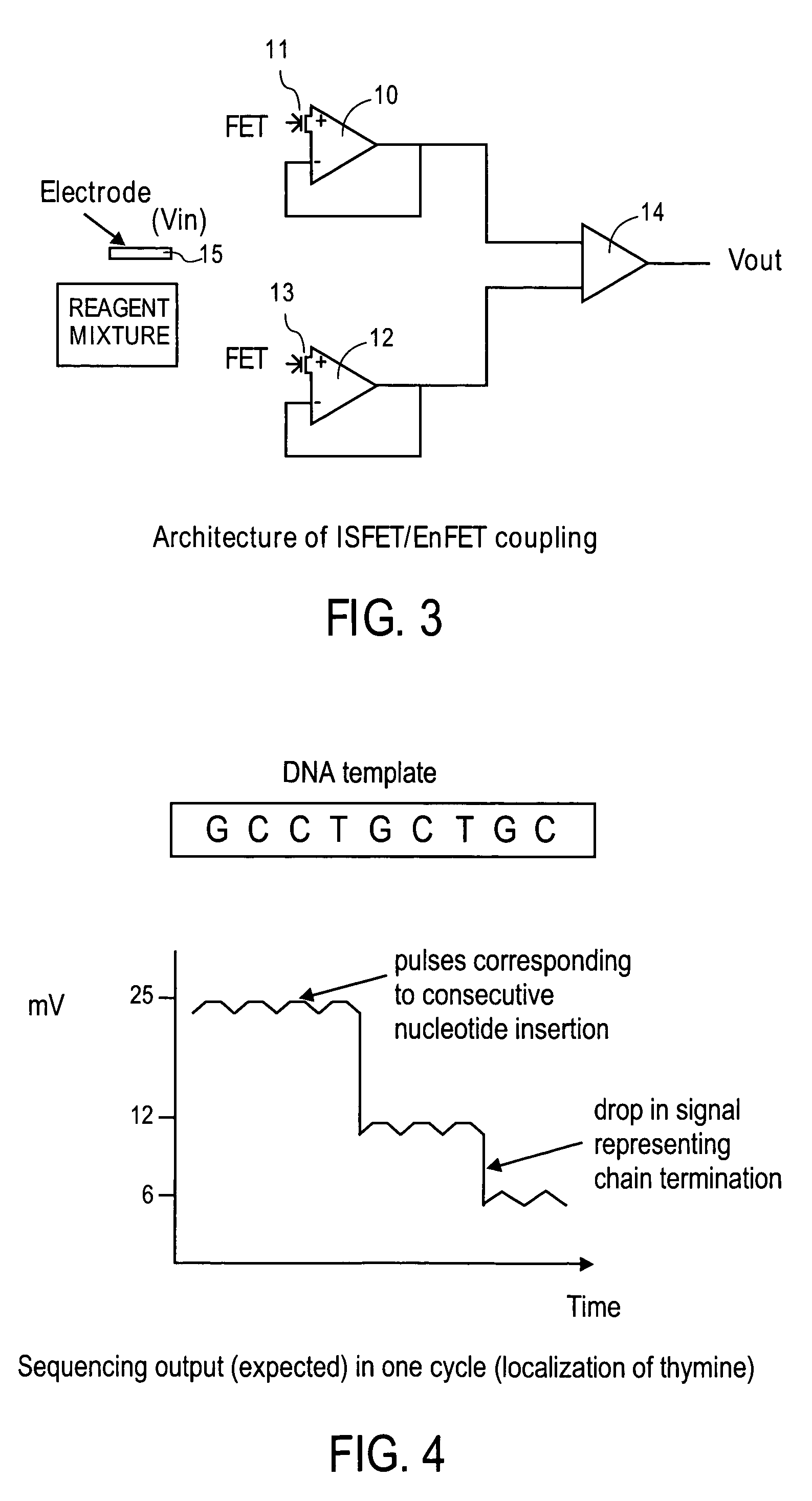
A sensing apparatus comprising an ion sensitive field effect transistor arranged to generate an electrical output signal in response to localized fluctuations of ionic charge at or adjacent the surface of the transistor, and means for detecting the electrical output signal from the ion sensitive field effect transistor, the localized fluctuations of ionic charge indicating events occurring during a chemical reaction.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Small Volume in Vitro Analyte Sensor and Methods
InactiveUS20020148739A2Efficient and reliable methodEfficient methodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBlood serumBiological fluid
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A small volume sensor, and methods of making, for determining the concentration of an analyte, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid, such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. The sensor includes a working electrode and a counter electrode, and can include an insertion monitoring trace to determine correct positioning of the sensor in a connector.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Biosensor having improved hematocrit and oxygen biases
ActiveUS7501053B2Accurate responseDesensitizationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsQuinoneManganese
A biosensor that utilizes a mediator, i.e., an isomer of phenanthroline quinone, 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione, and a metal ion, such as manganese, with an enzyme dependent upon NAD(P)+, such as, for example, glucose dehydrogenase, for improving the hematocrit bias and oxygen bias of biosensors. The electrodes of the biosensors employing this mediator and a metal ion provide an accurate clinical response over a hematocrit range that ranges from about 20% to about 70% and over an oxygen tension range that ranges from about 1 kPa to about 20 kPa.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com