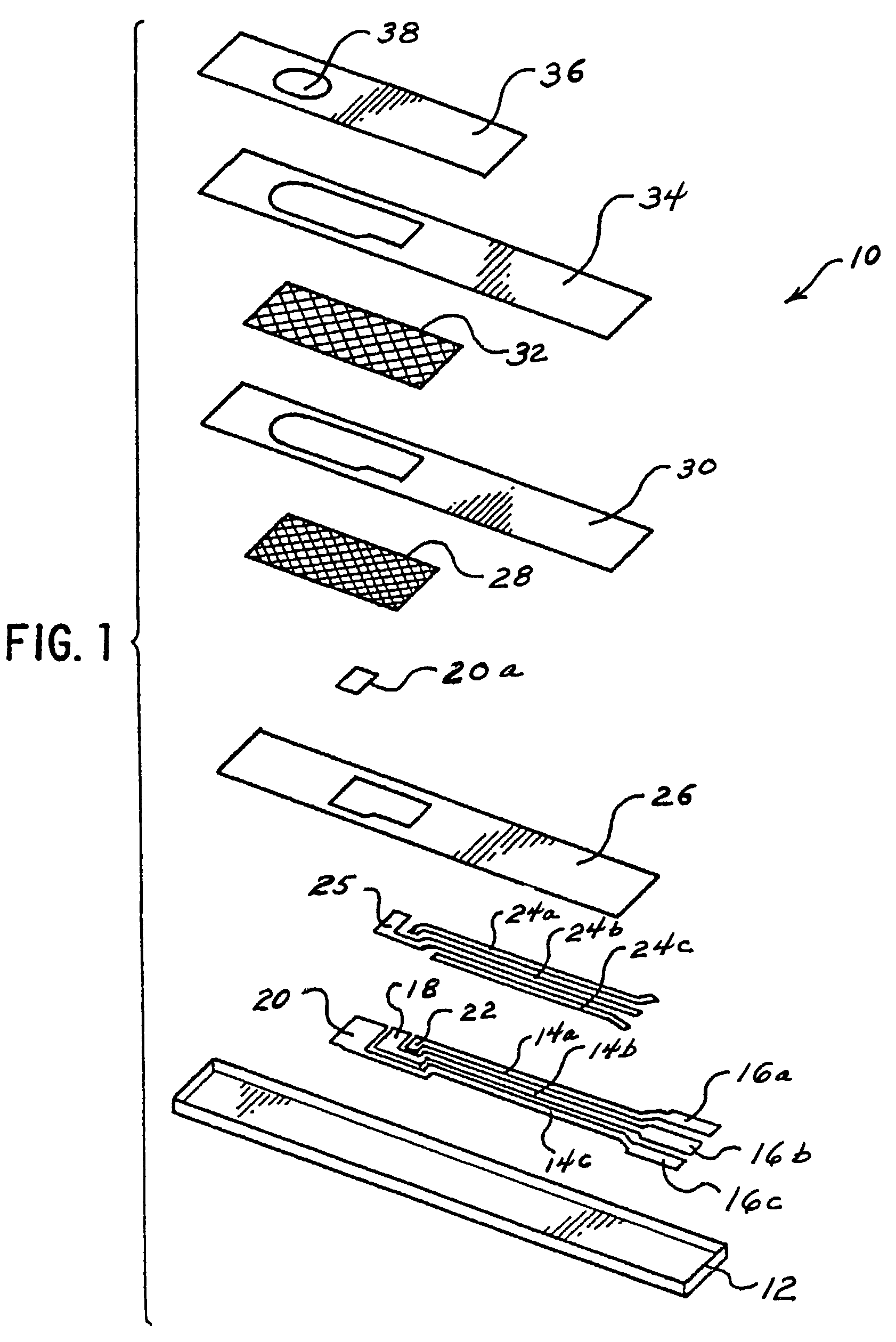
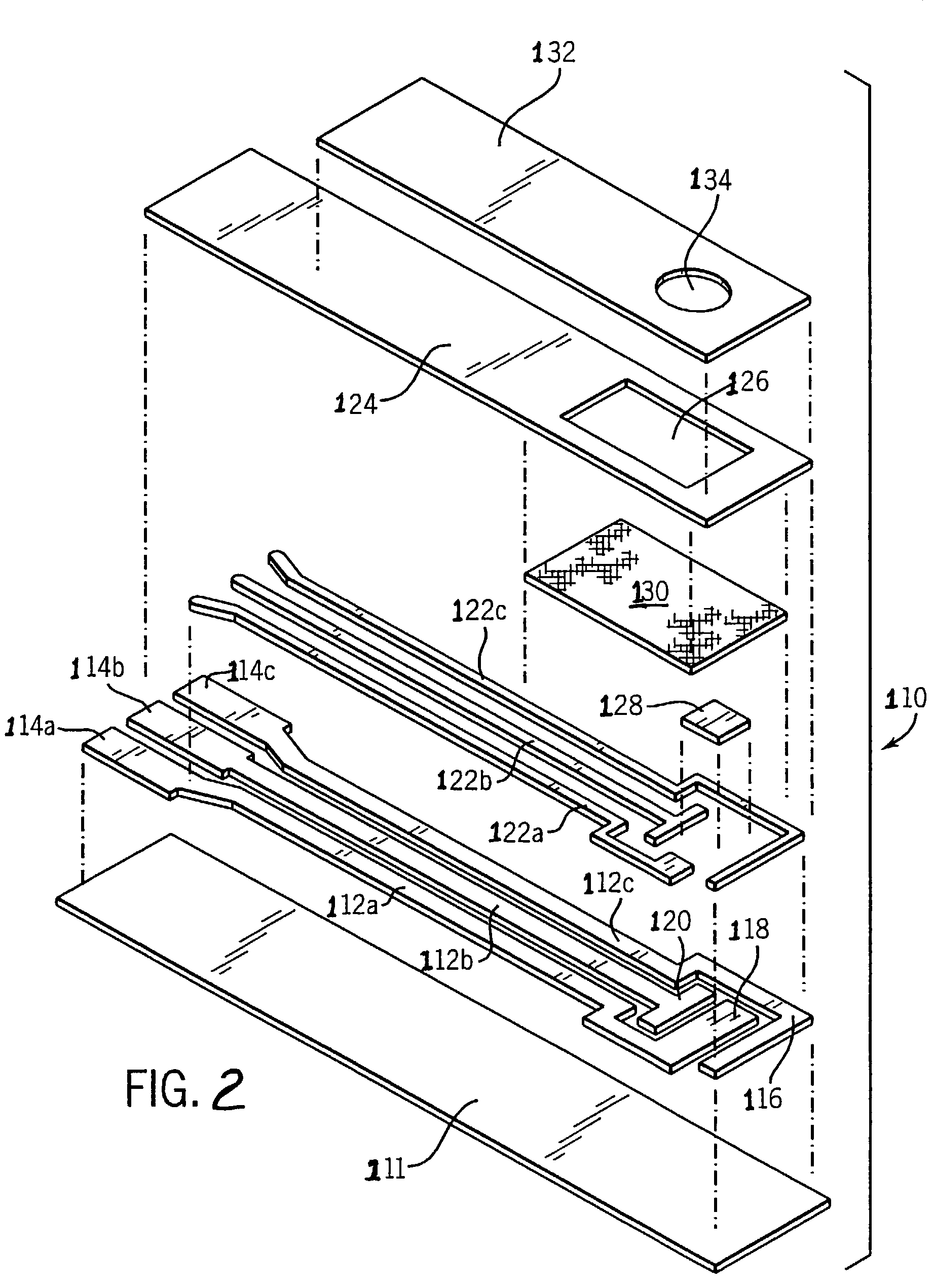
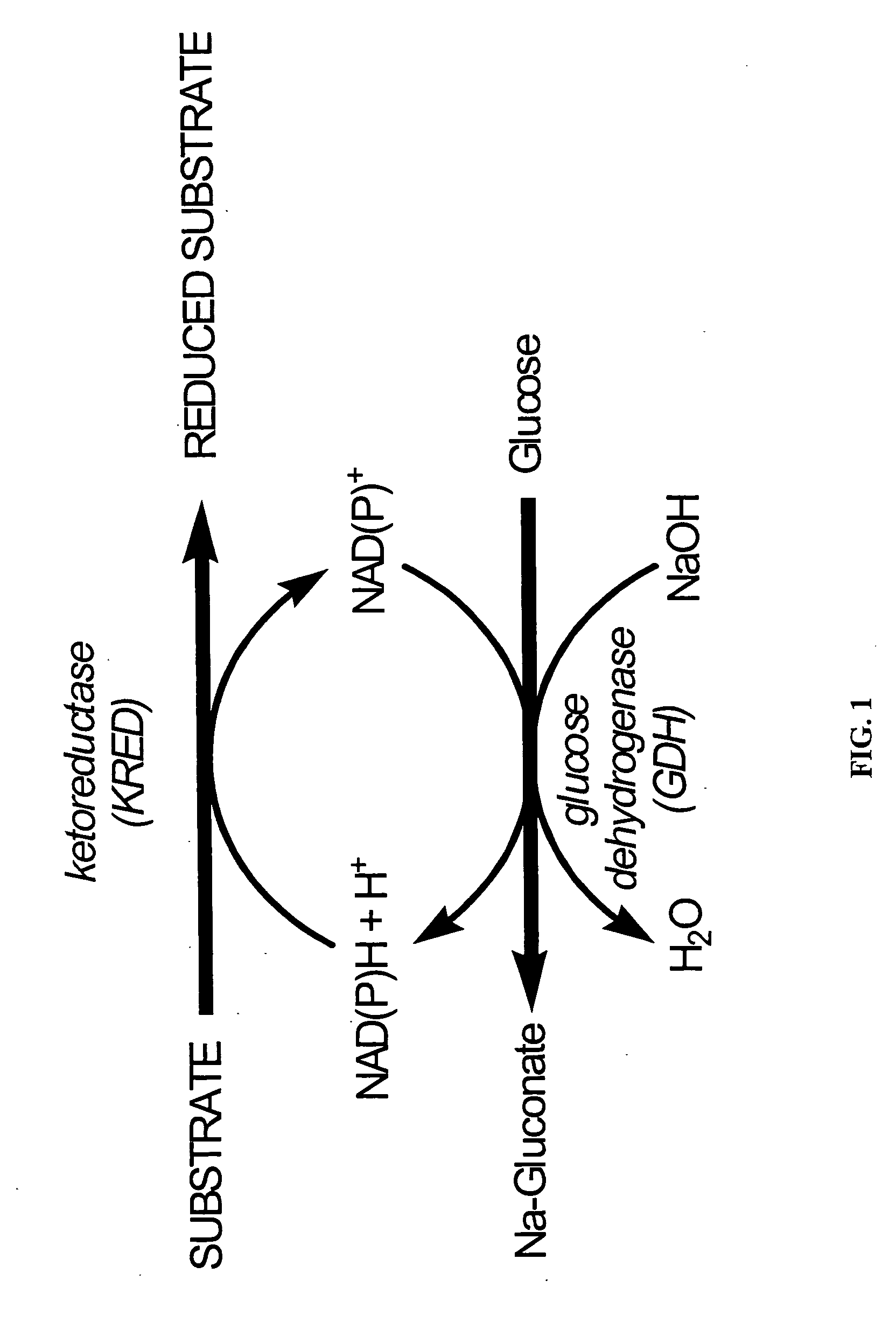
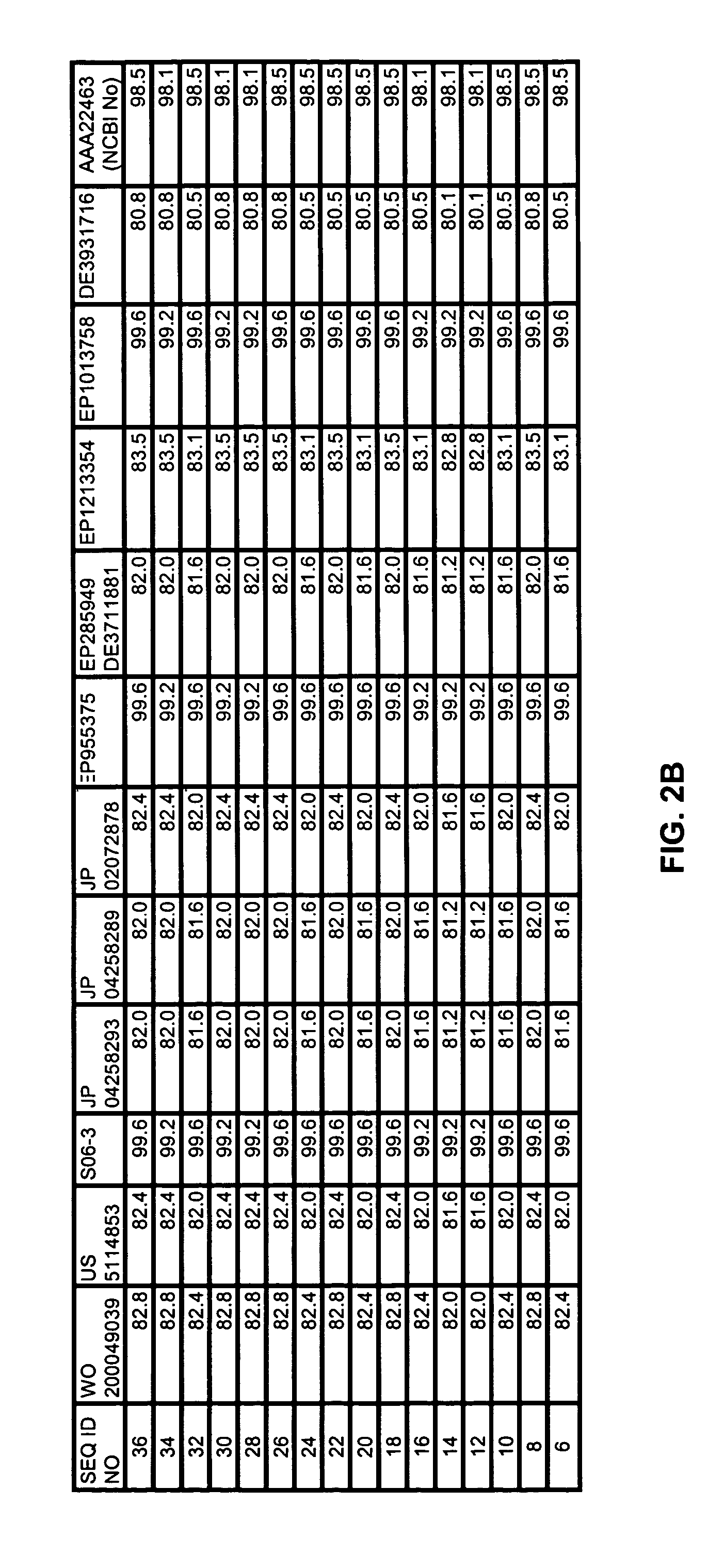
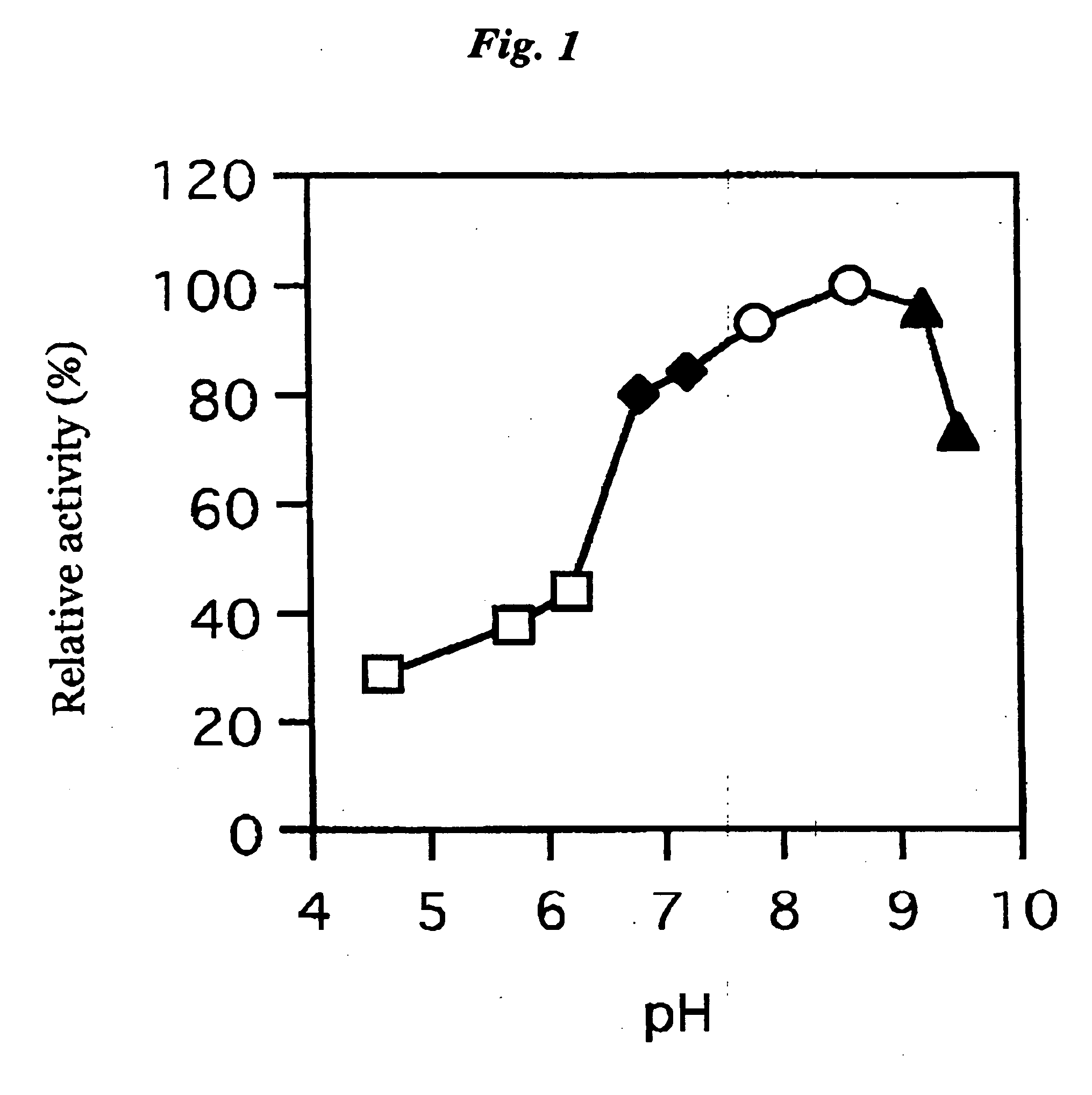
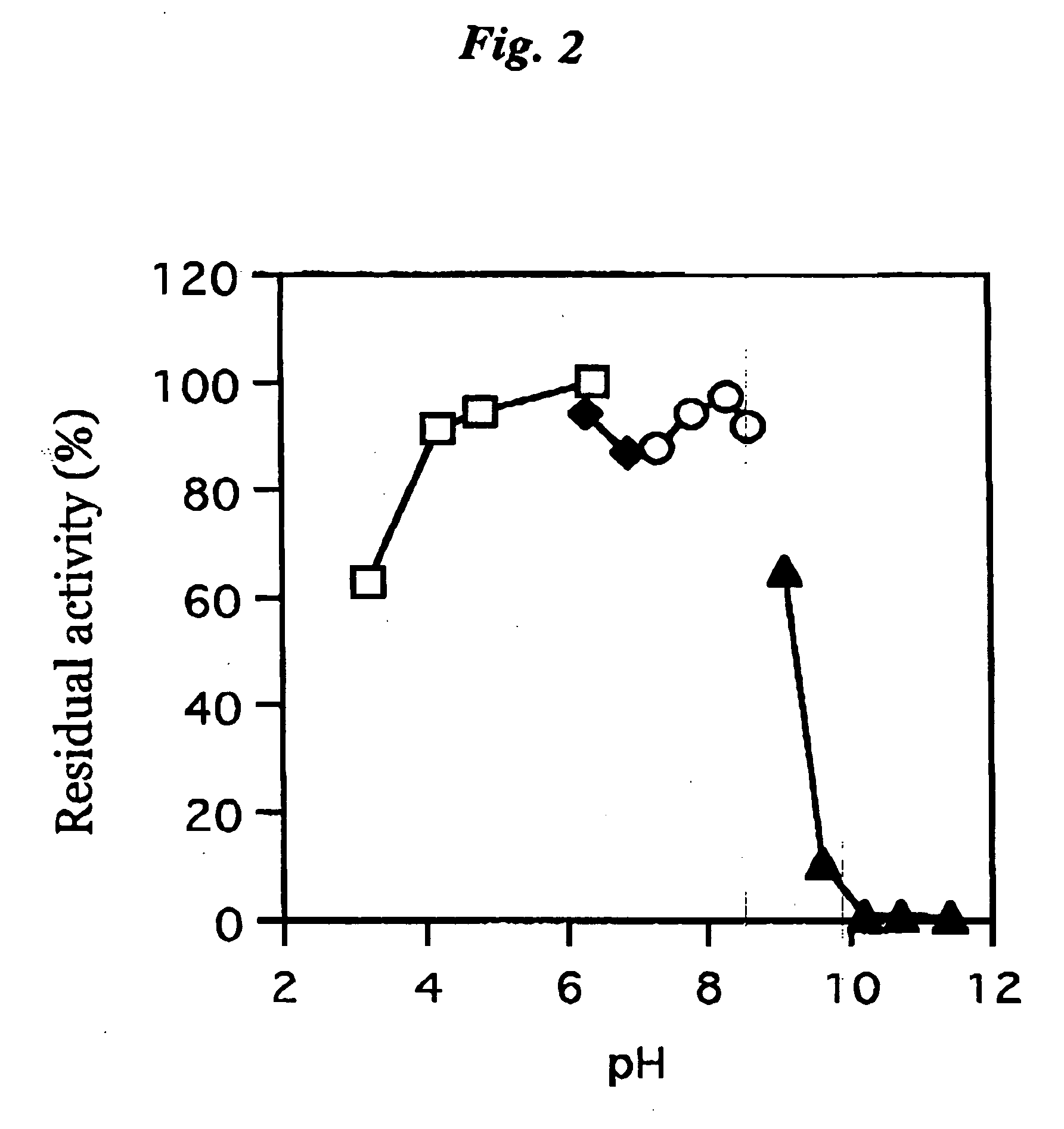
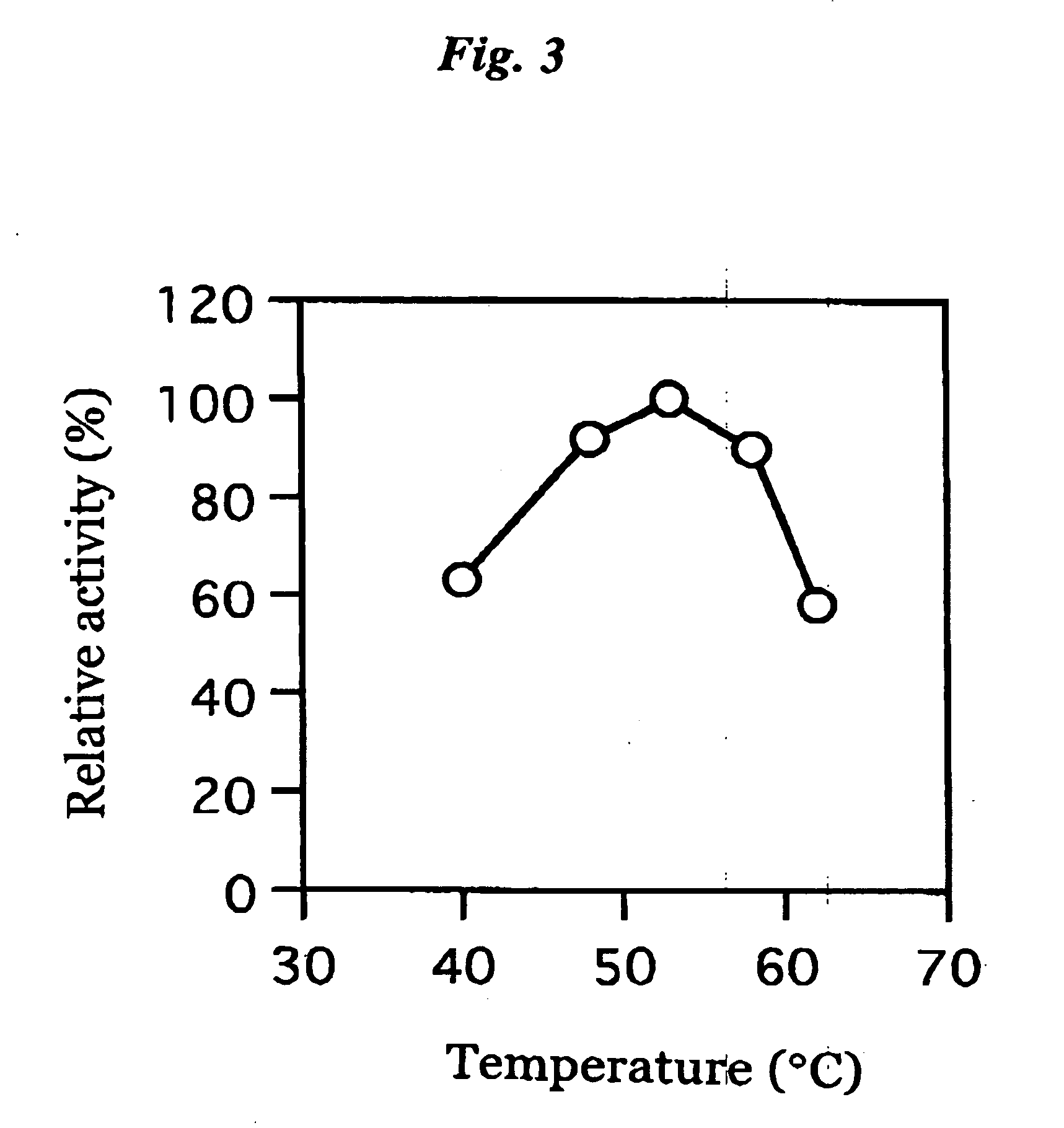
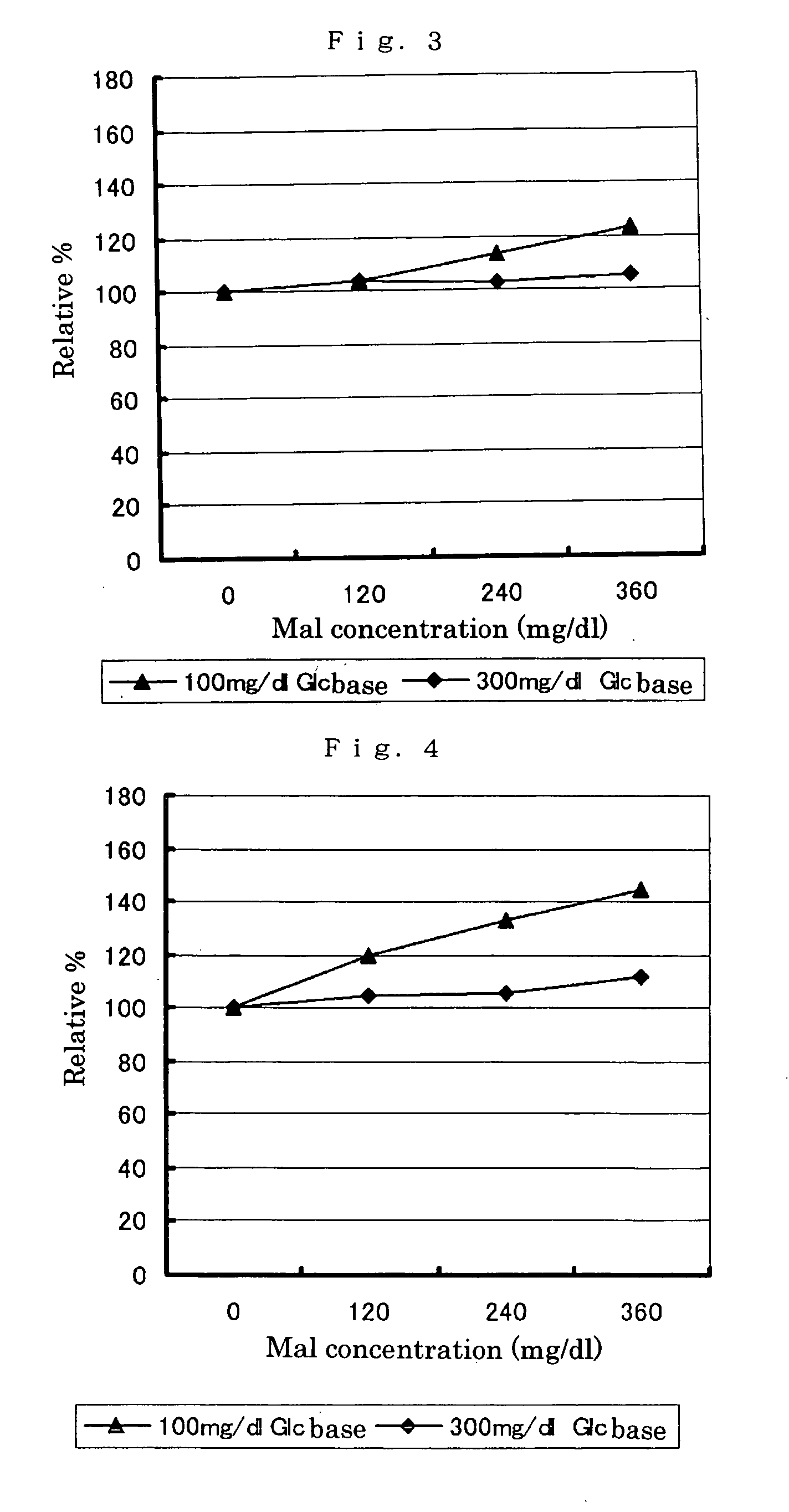
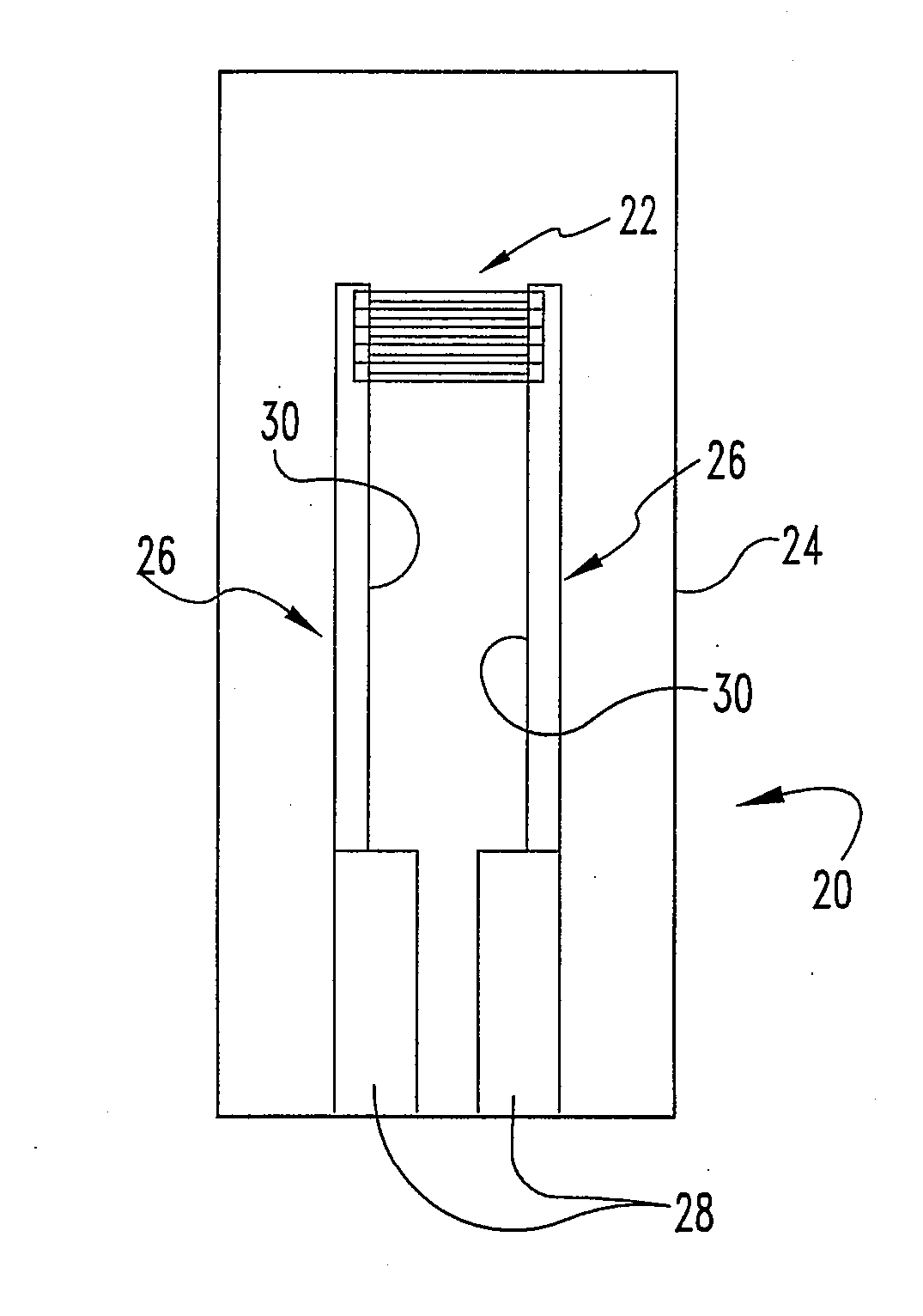
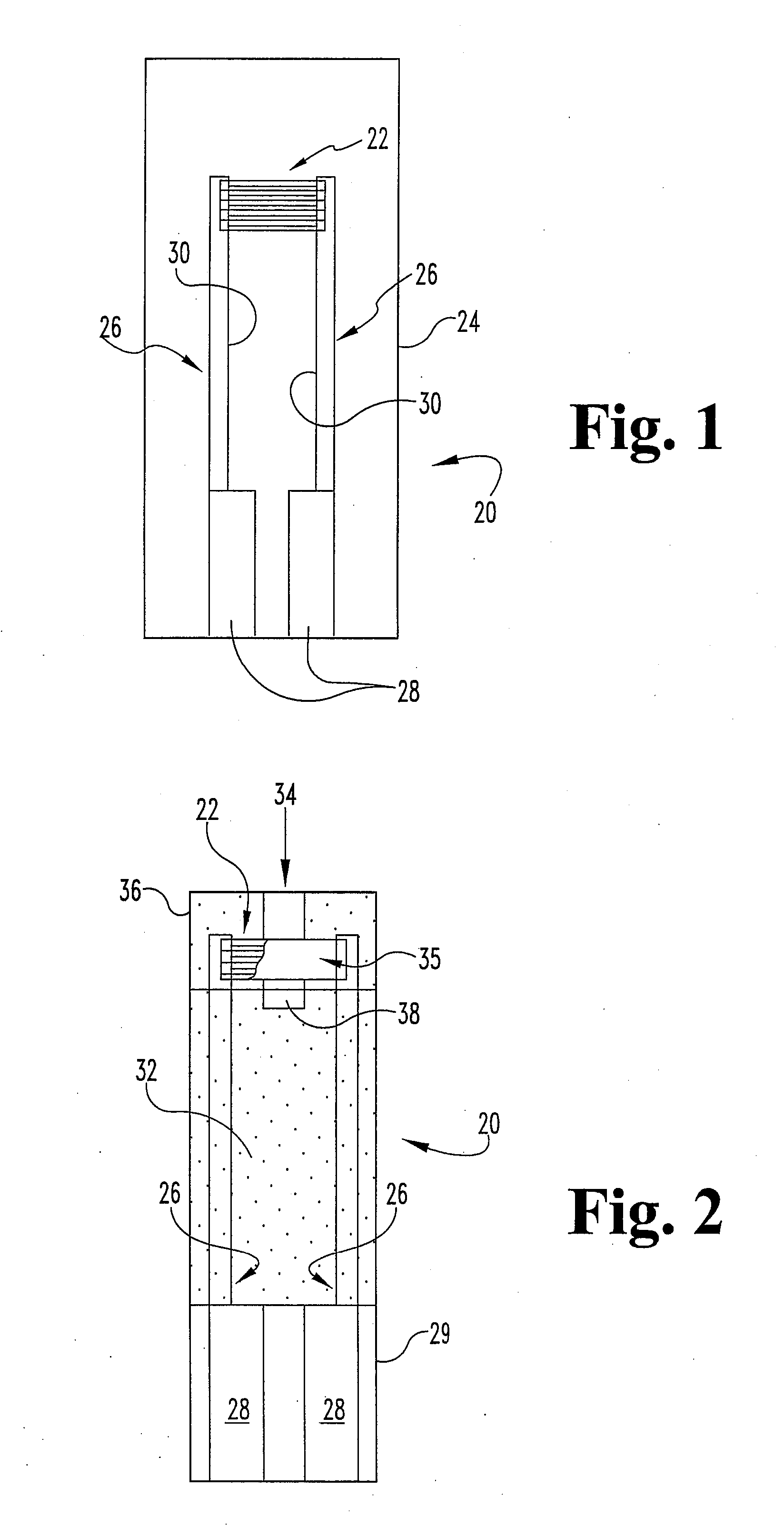
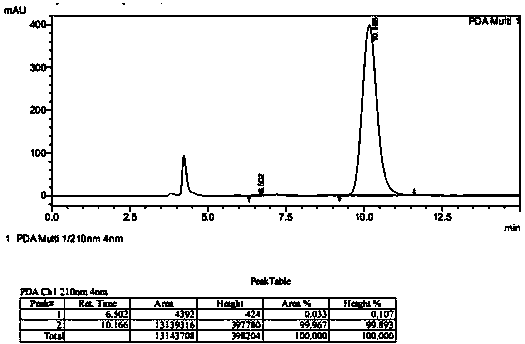
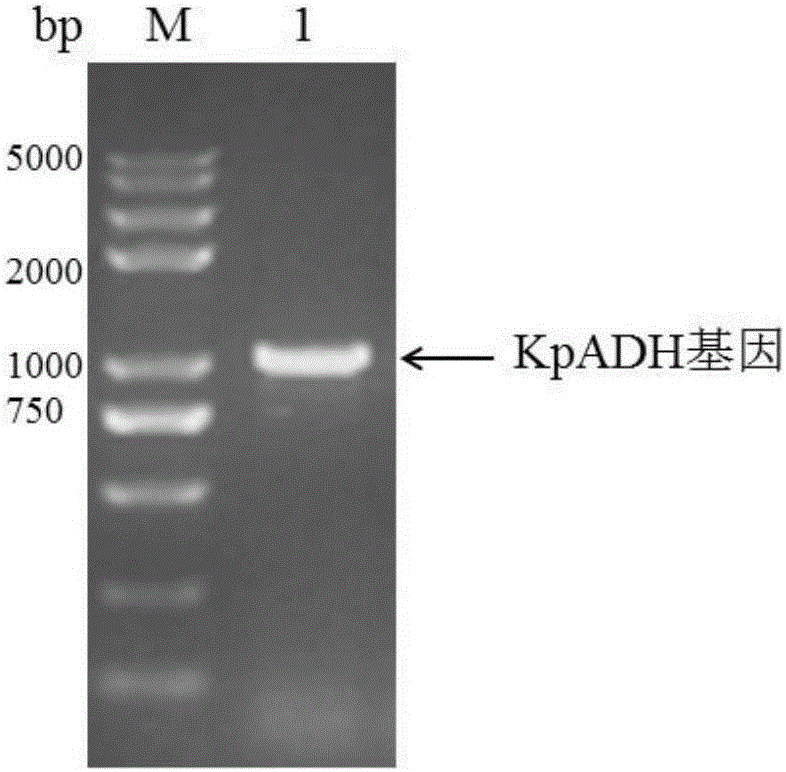
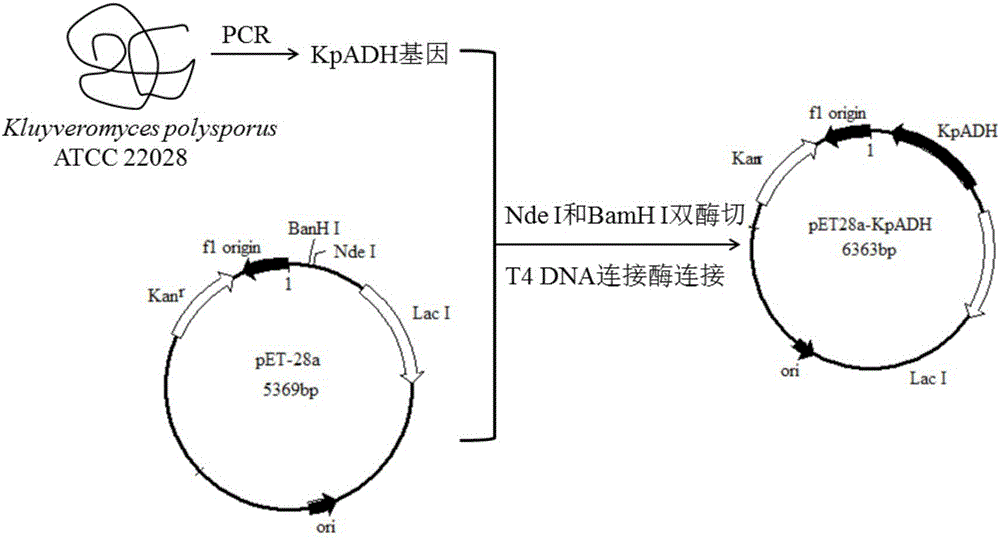
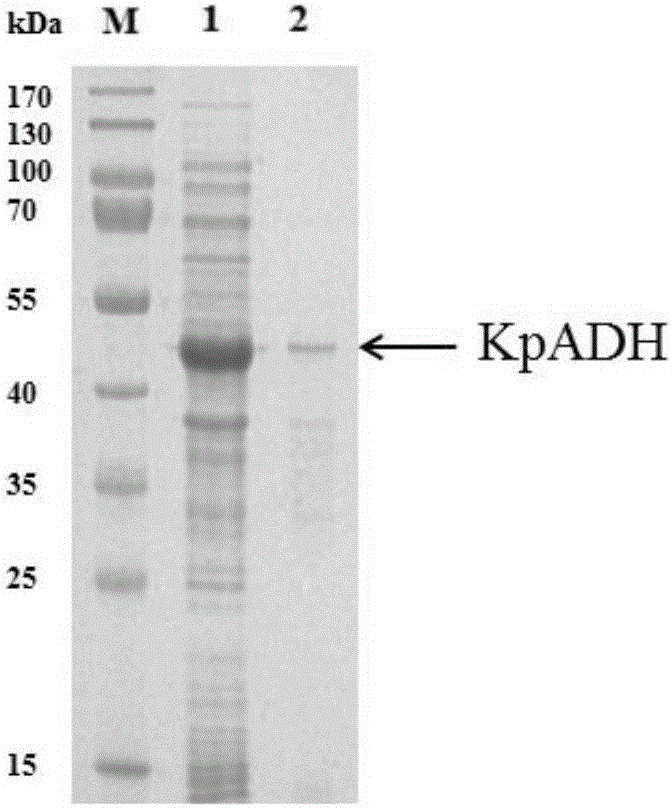
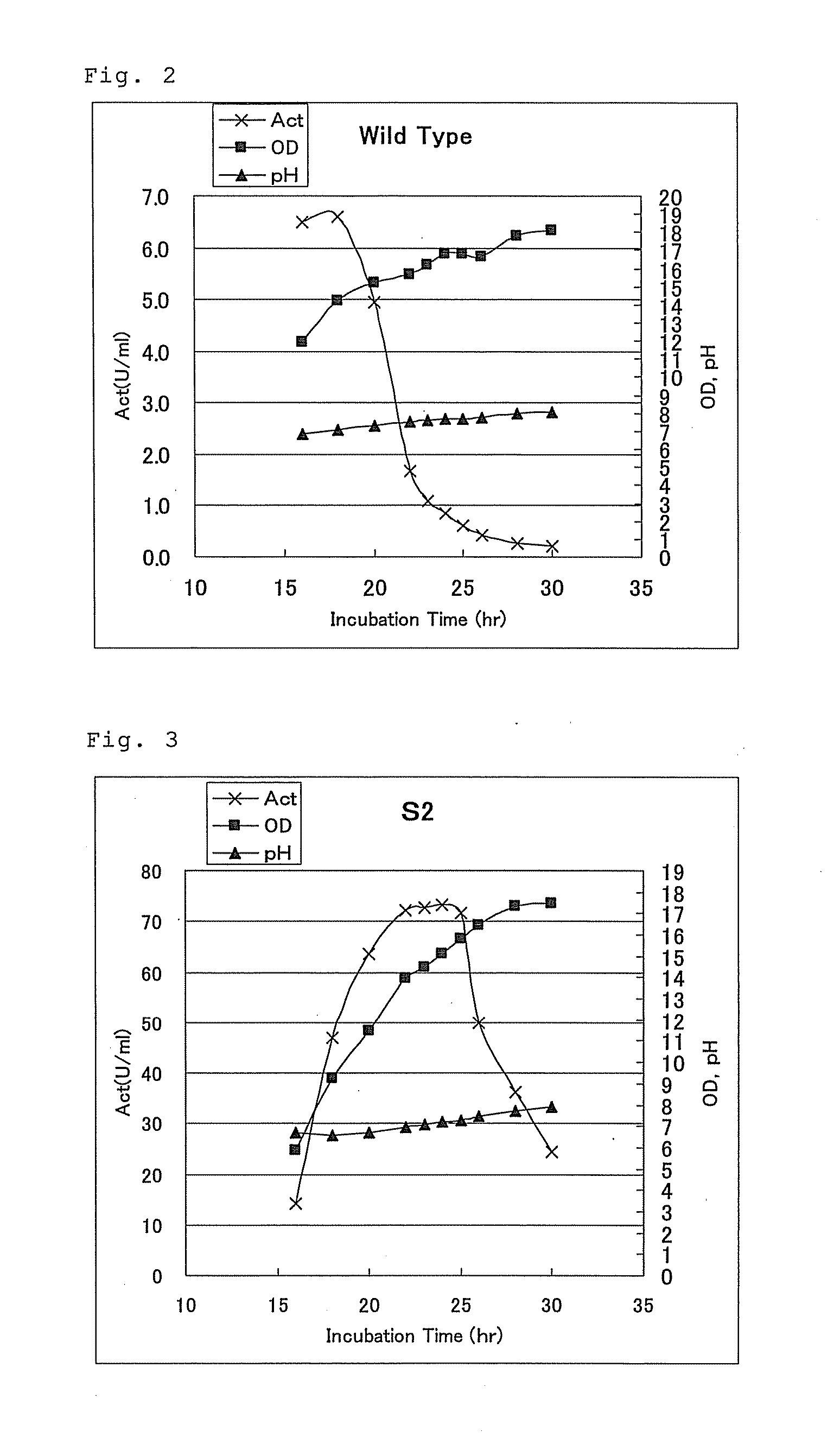
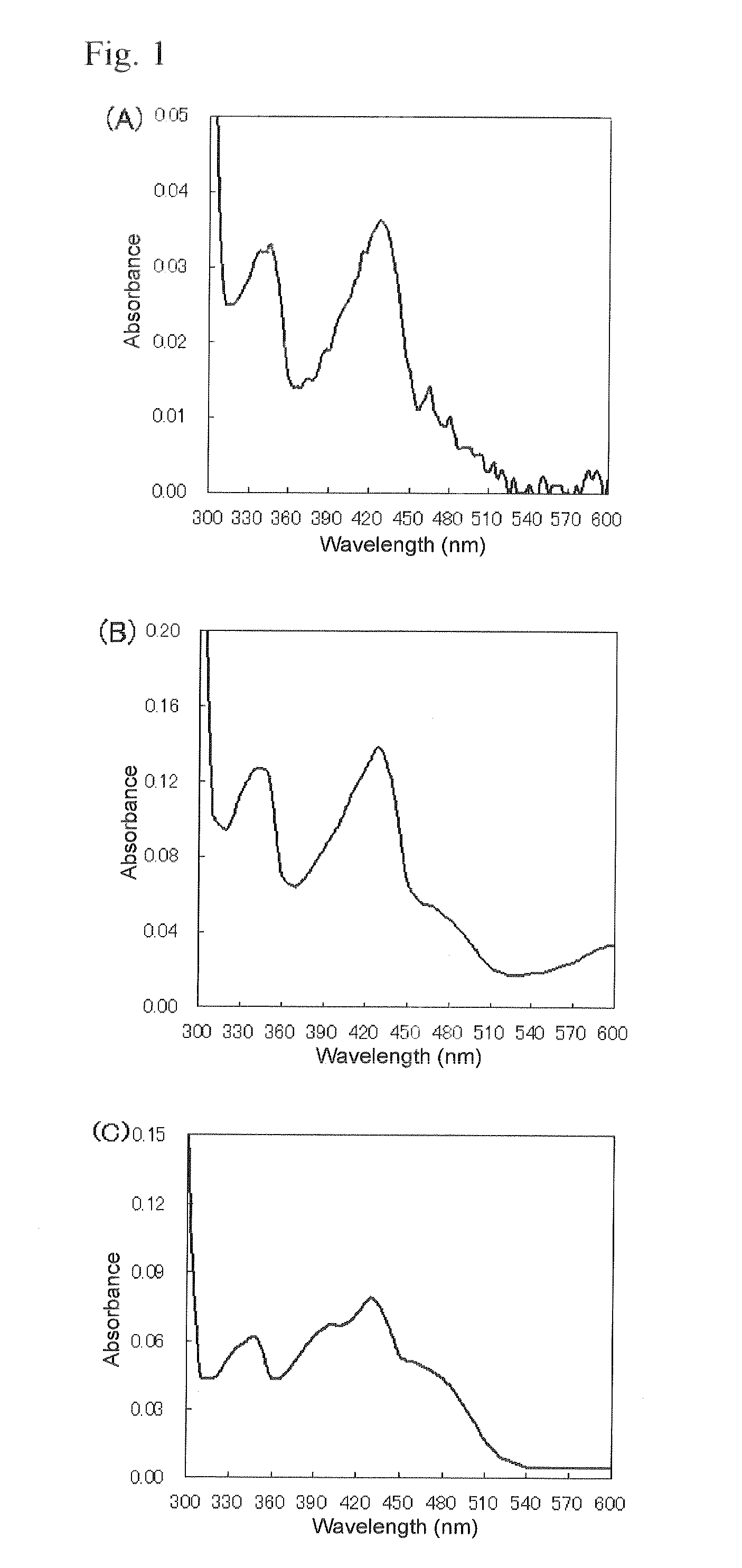
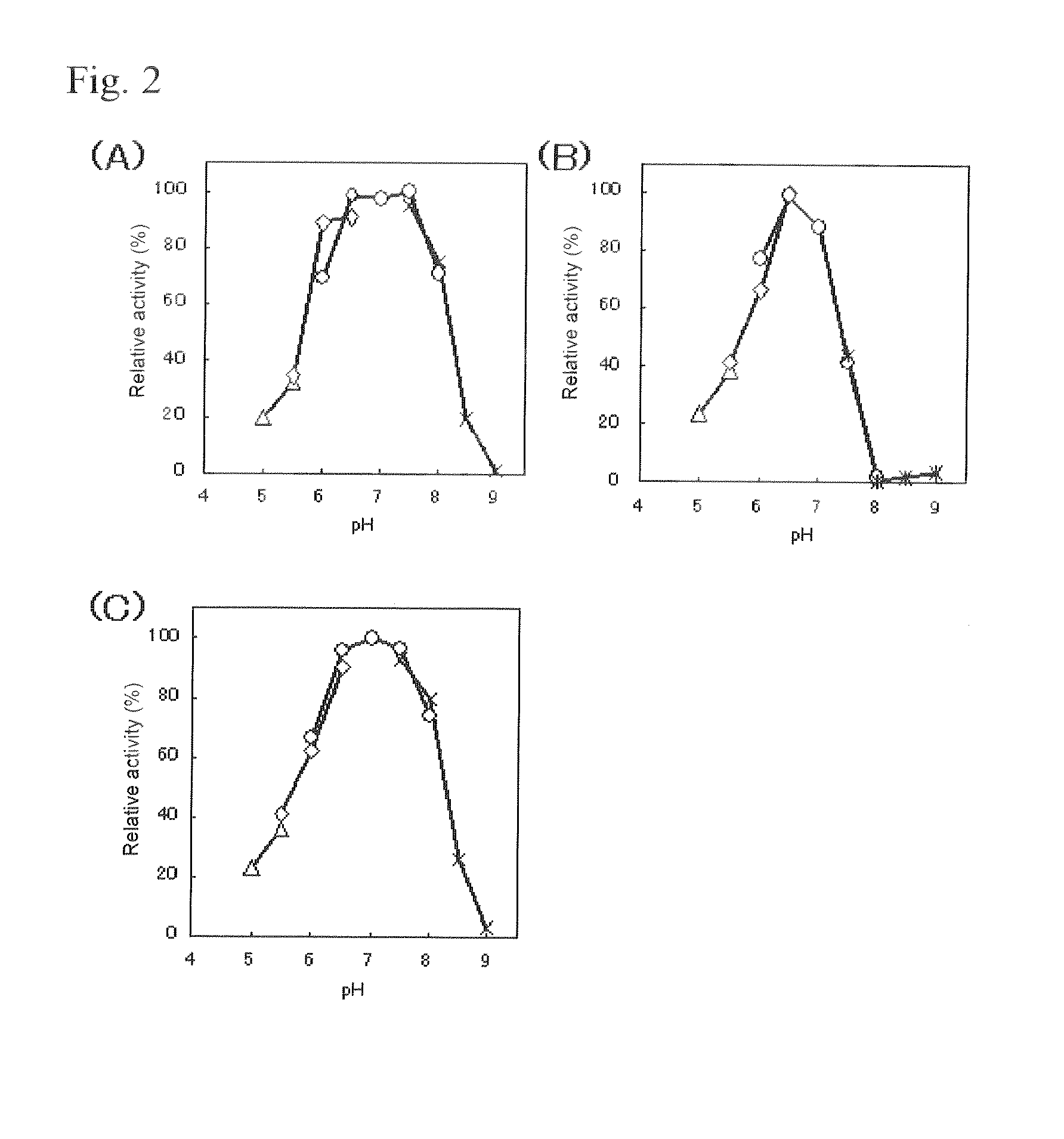
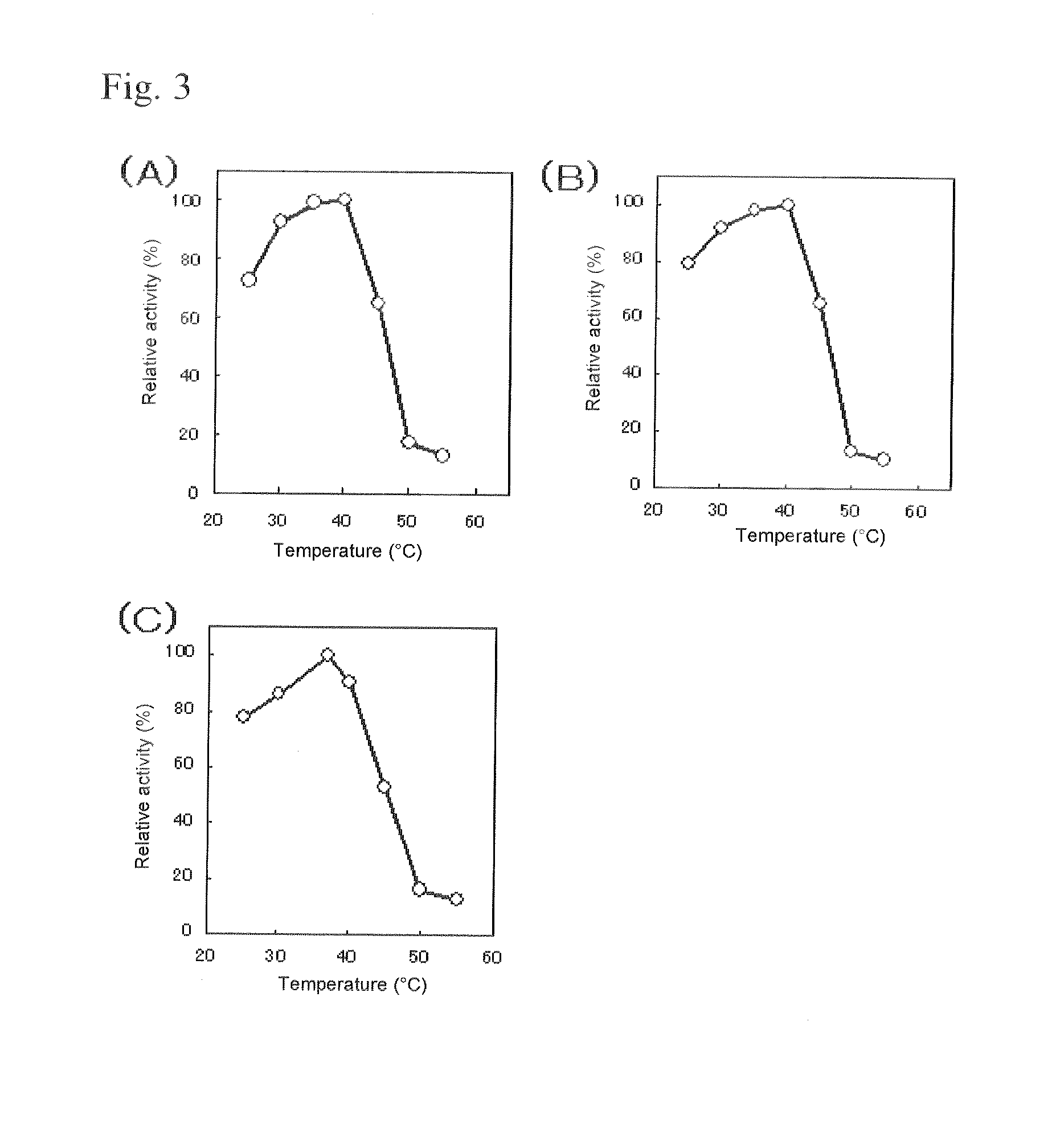
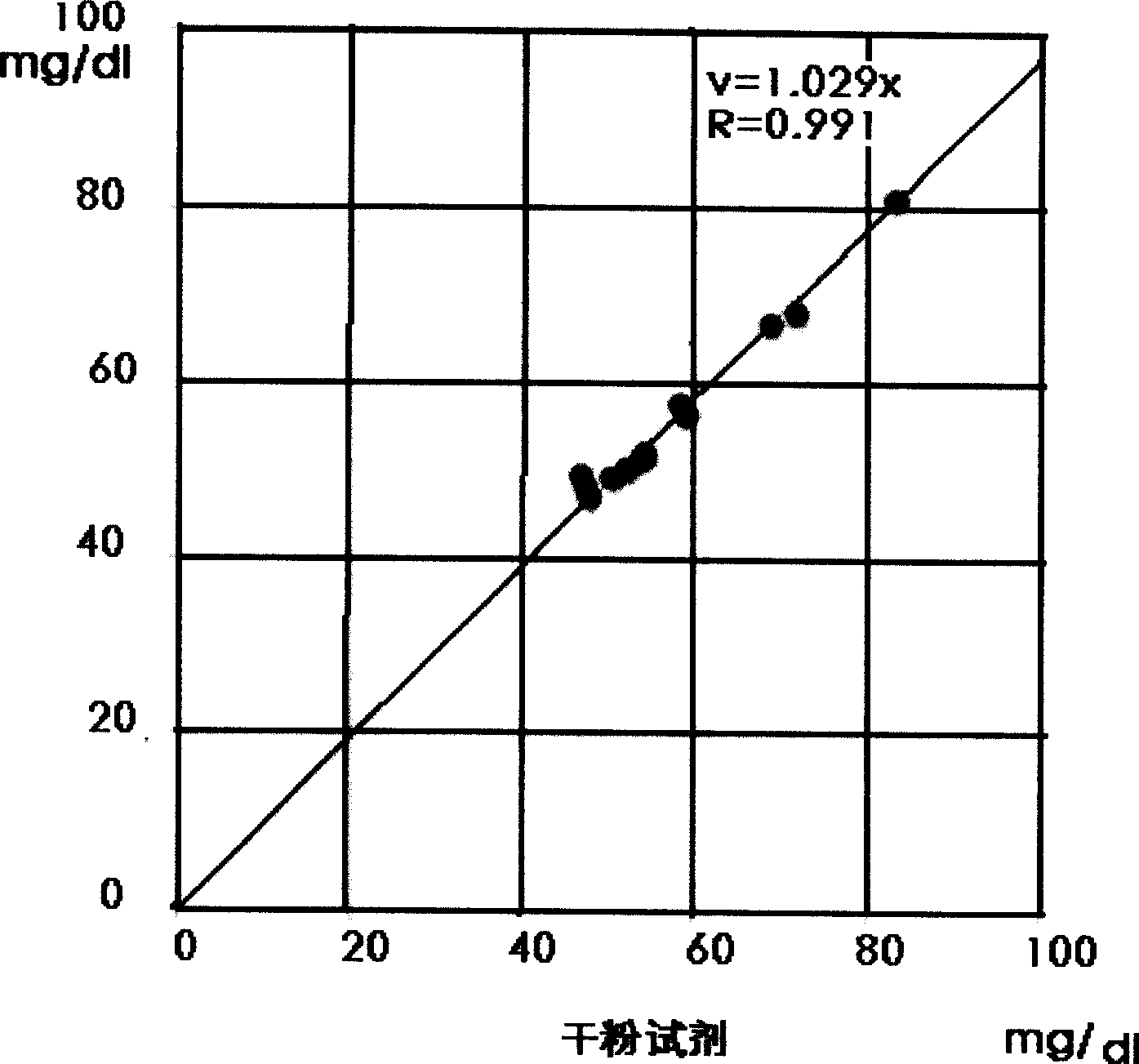
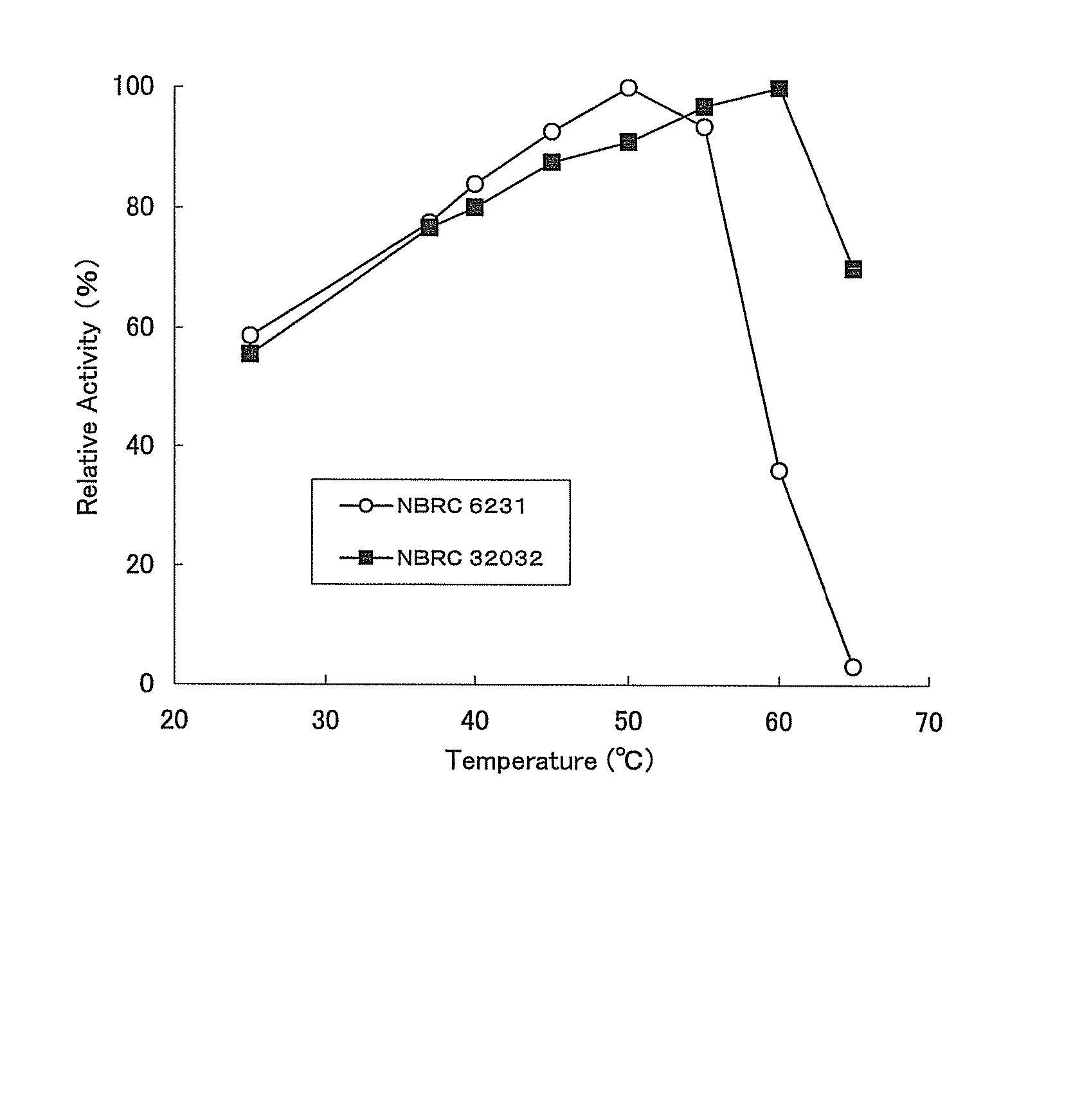
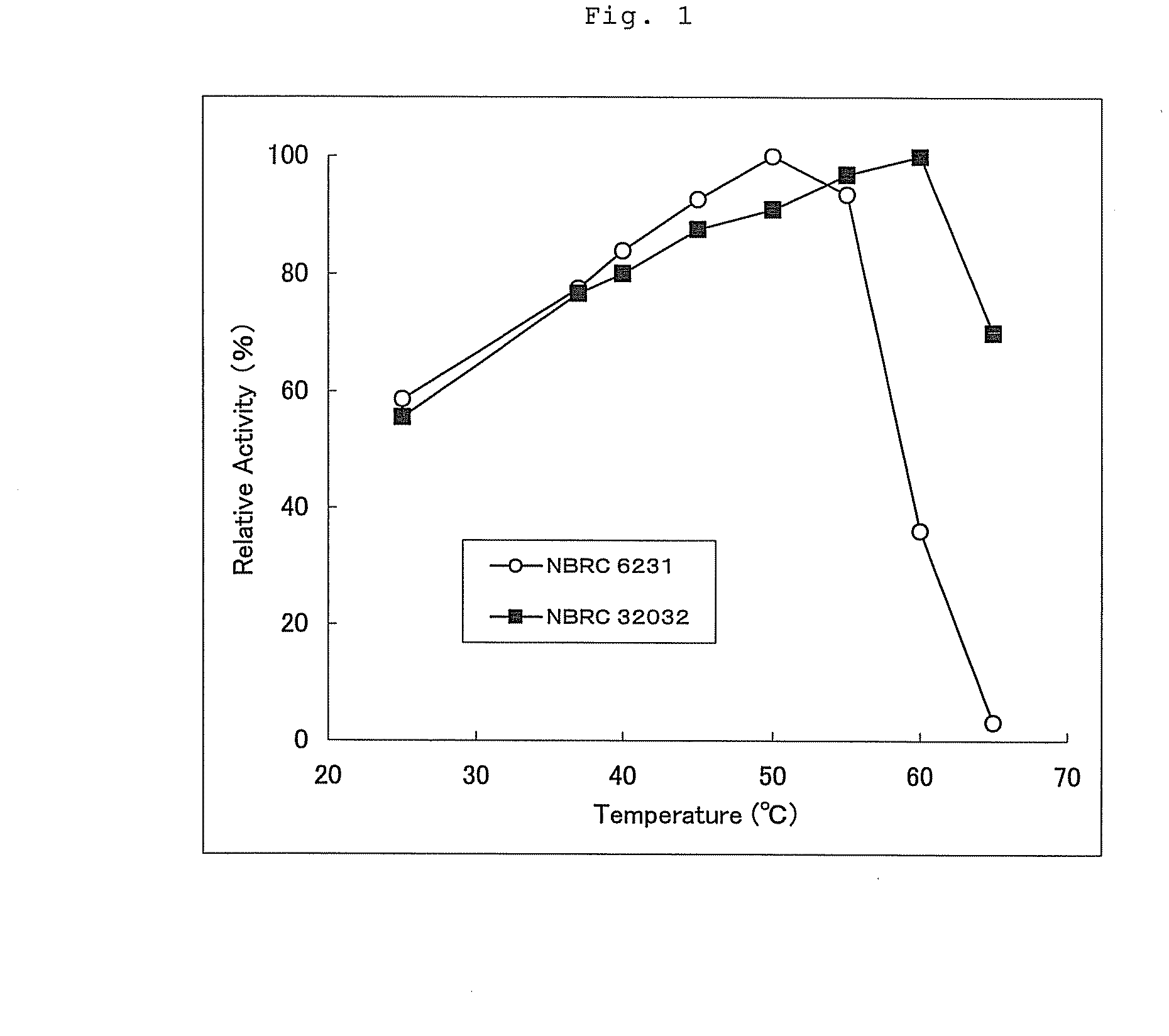
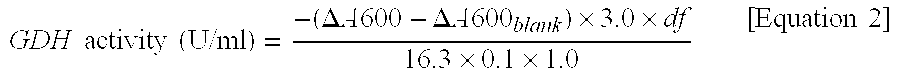Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
311 results about "Glucose dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glucose sensor
InactiveUS7005048B1Avoid separationImprove reliabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerElectricity
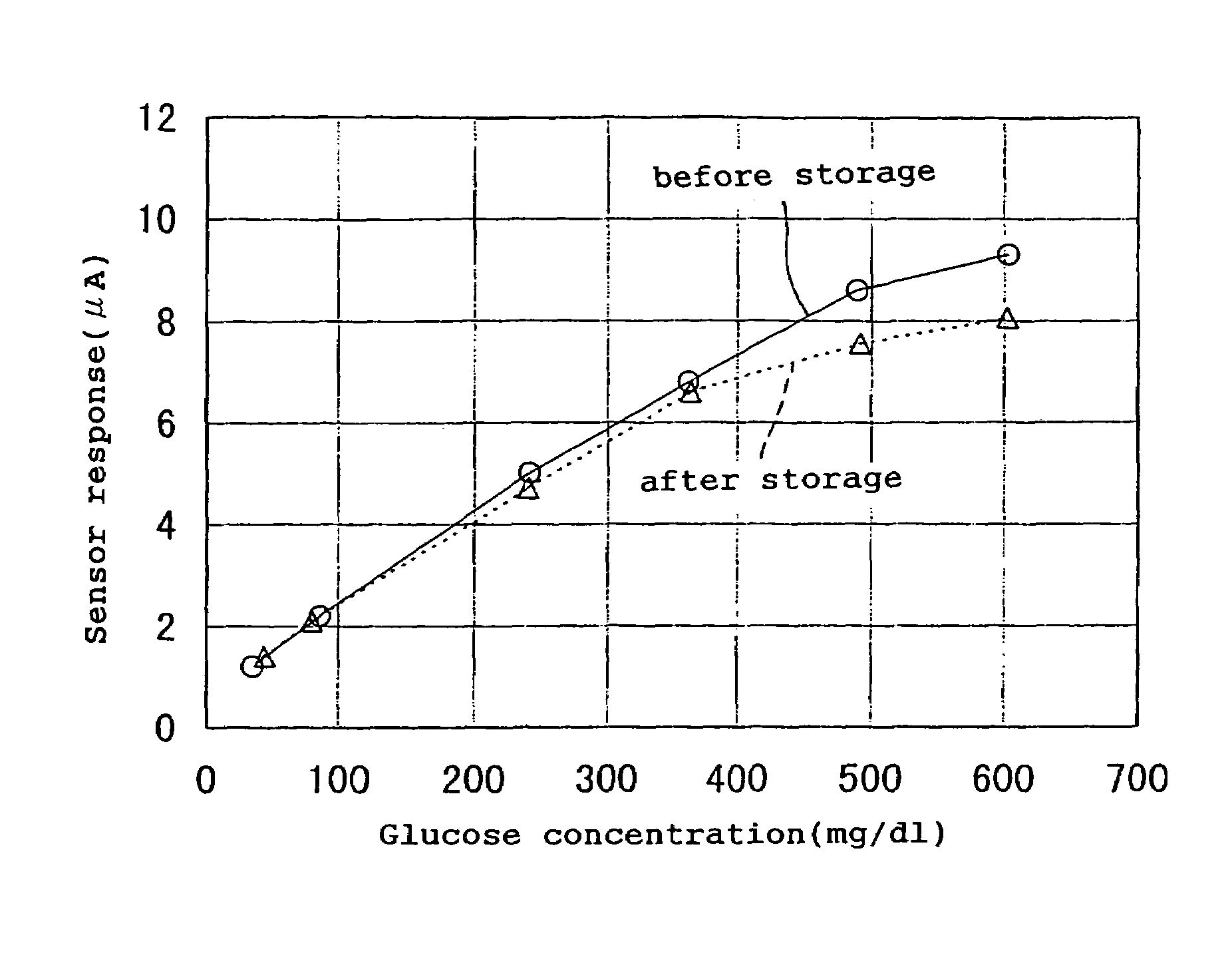
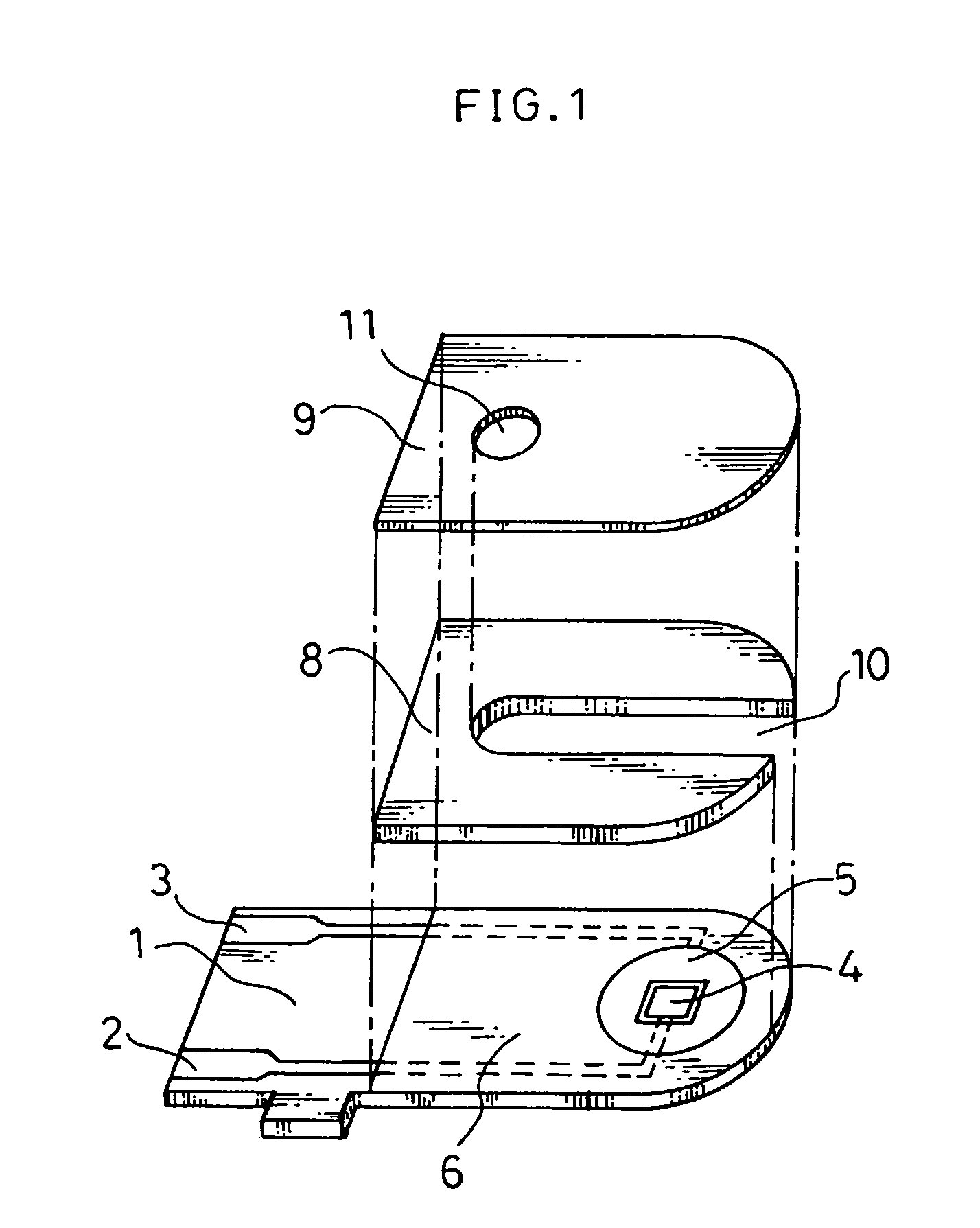
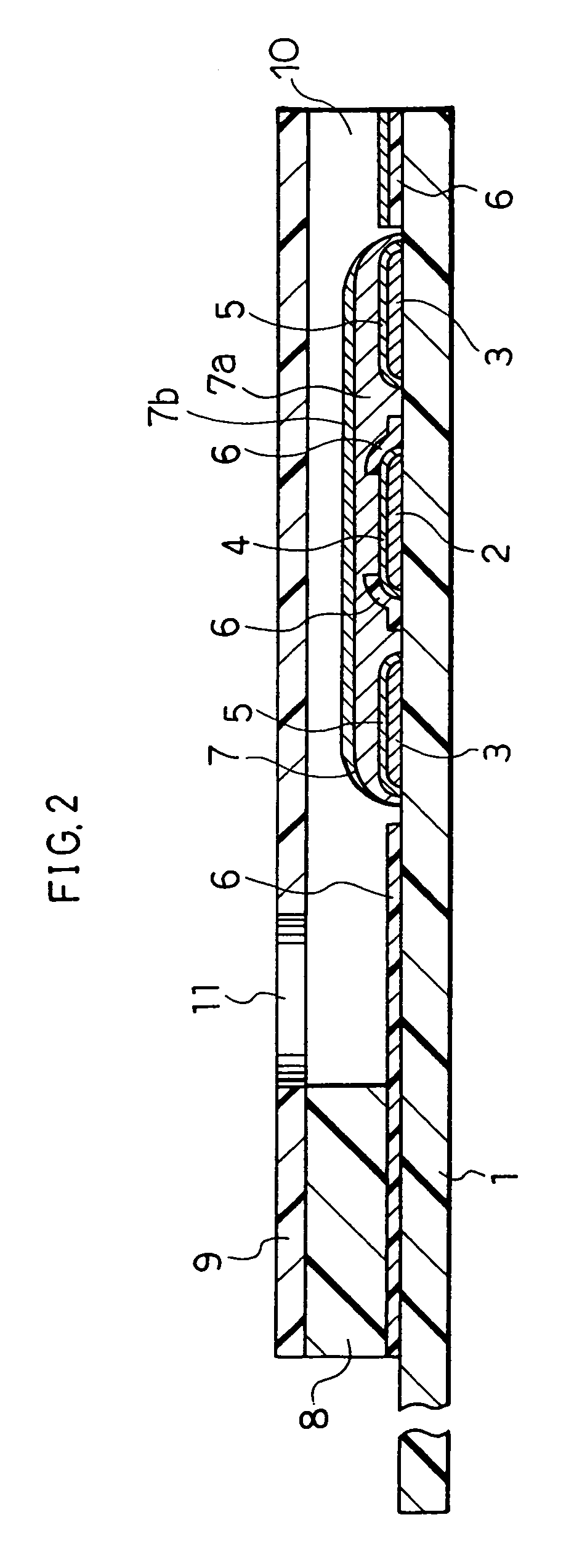
The present invention provides a high-performance glucose sensor having excellent storage stability and an improved response characteristic. This sensor comprises: an electrically insulating base plate; an electrode system including at least a working electrode and a counter electrode formed on the base plate; and a reaction layer containing at least pyrrolo-quinoline quinone dependent glucose dehydrogenase, formed in contact with or in the vicinity of the electrode system, and the reaction layer contains at least one kind of additive selected from the group consisting of gluconic acid and salts thereof.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Biosensor having improved hematocrit and oxygen biases
ActiveUS7501053B2Accurate responseDesensitizationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsQuinoneManganese
A biosensor that utilizes a mediator, i.e., an isomer of phenanthroline quinone, 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione, and a metal ion, such as manganese, with an enzyme dependent upon NAD(P)+, such as, for example, glucose dehydrogenase, for improving the hematocrit bias and oxygen bias of biosensors. The electrodes of the biosensors employing this mediator and a metal ion provide an accurate clinical response over a hematocrit range that ranges from about 20% to about 70% and over an oxygen tension range that ranges from about 1 kPa to about 20 kPa.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Glucose dehydrogenase polypeptides and related polynucleotides
ActiveUS20050095619A1Increase dehydrogenase activityImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaNucleotideWild type
The present invention is directed to glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) polypeptides that have enhanced GDH activity and / or thermostability relative to the backbone wild-type glucose dehydrogenase polypeptide. In addition, the present invention is directed to a polynucleotide that encodes for the GDH polypeptides of the present invention, to nucleic acid sequences comprising the polynucleotides, to expression vectors comprising the polynucleotides operatively linked to a promoter, to host cells transformed to express the GDH polypeptides, and to a method for producing the GDH polypeptides of the present invention.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Coenzyme-binding glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20060063217A1The process is convenient and fastImprove accuracyFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGlucose sensorsPhenanthroline
The present invention provides a microorganism-derived soluble coenzyme-binding glucose dehydrogenase which catalyzes a reaction for oxidizing glucose in the presence of an electron acceptor, has an activity to maltose as low as 5% or less, and is inhibited by 1,10-phenanthroline. The invention also provides a method for producing the coenzyme-binding glucose dehydrogenase, and a method and a reagent for measuring employing the coenzyme-binding glucose dehydrogenase. According to the invention, the coenzyme-binding glucose dehydrogenase can be applied to an industrial field, and a use becomes possible also in a material production or analysis including a method for measuring or eliminating glucose in a sample using the coenzyme-binding glucose dehydrogenase as well as a method for producing an organic compound. It became also possible to provide a glucose sensor capable of accurately measuring a blood sugar level. Therefore, it became possible to provide an enzyme having a high utility, such as an ability of being used for modifying a material in the fields of pharmaceuticals, clinical studies and food products.
Owner:PHC CORP
Forms of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7132270B2Increased substrate specificityImprove propertiesFungiBacteriaMutated proteinGlucose polymers
The present invention relates to improved variants of soluble pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)-dependent glucose dehydrogenases (s-GDH), to genes encoding mutated s-GDH, to mutant proteins of s-GDH with improved substrate specificity for glucose, and to different applications of these s-GDH variants, particularly for determining concentrations of sugar, especially of glucose in a sample.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
E. coli transformant, method for producing flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase using the same, and mutant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20130309750A1Accurate measurementEfficiently obtainedBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
A flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH) with high substrate specificity for D-glucose. A gene encoding a mutant FAD-GDH with its N-terminal region, containing an amino acid sequence corresponding to MKITAAIITVATAFASFASA that exists in the N-terminal region, deleted from the amino acid sequence of a wild-type FAD-GDH derived from Mucor is introduced into E. coli to obtain an E. coli transformant. Subsequently, this E. coli transformant is cultured to obtain an FAD-GDH with a specific N-terminal region deleted. The transformant allows the production of a large amount of GDH in a short time as compared with the original microorganism. An FAD-GDH that is less susceptible to the effects of dissolved oxygen and allows accurate measurement of glucose even in the presence of sugar compounds other than glucose in a sample.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenases, a method for producing a flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase, and yeast transformant used for the same
A heat-resistant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase having a high substrate specificity for D-glucose, an method for producing the same, and a transformant used for the same. A flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase gene encoding a flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase derived from Mucor is introduced into yeast, Zygosaccharomyces, to obtain a transformant. Subsequently, the yeast transformant is cultured to obtain a flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase from the culture. The heat-resistant flavin-bound glucose dehydrogenase is less susceptible to the effects of dissolved oxygen and allows accurate measurement of glucose even in the presence of sugar compounds other than glucose in a sample.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Carbon nano tube modified blood sugar biosensor
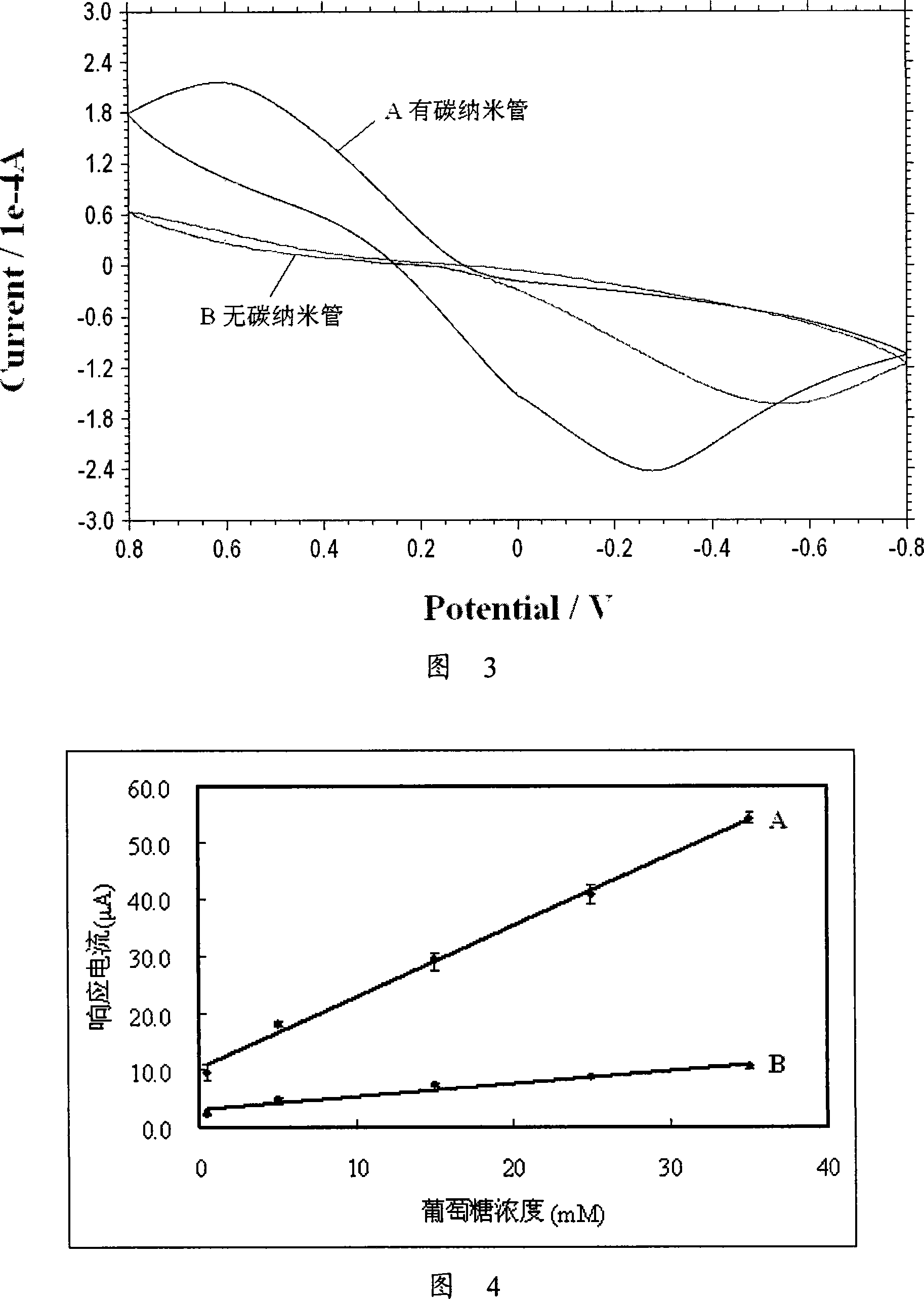
InactiveCN101101273AImprove responsivenessIncreased contact surface areaDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsQuinoneConcentrations glucose
The invention provides a blood sugar biosensor of carbon nanometer tube, it includes floor, three electrode system, insulation, forming the reaction lumen body around three electrode system, setting the conversion zone in the reaction lumen body, laying over the cover plate on the reaction lumen body, the conversion zone includes, enzyme and electron transport agent, the enzyme is the glc dh pyrrole and quinone for coenzyme. The transducer's corresponding sensitivity improves evidently, it has not infection for measuring the dextrose deepness in the blood with the oxygen pressure, thickness in the measuring site and oxygen content of blood sample. The invention has the excellence of easy manufacture artwork, low cost, suited to volume-produce and the low sample quantity etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Modified flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20080220460A1Reduce heat-inactivationDecreasing amount of usedFungiBacteriaFlavin adenine dinucleotideGlucose sensors
Object: An object of the present invention is to provide a more practically advantageous enzyme usable as a reagent for measuring blood glucose than the known enzymes used as blood glucose sensors.Method for Achieving the Object: A modified flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent glucose dehydrogenase (FADGDH) with more improved heat stability than FADGDH derived from wild-type FADGDH, the modified FADGDH being derived from preferably a eukaryote, more preferably a filamentous fungus, and furthermore preferably an Aspergillus fungus, and, for example, those having a primary structure with at least one amino acid substituted, deleted, inserted or added to FADGDH having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID Nos. 2 or 46 in the sequence table.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Method for enhancing stability of a composition comprising soluble glucose dehydrogenase (GDH)
InactiveUS20080003628A1Optimal blood glucose levelImprove the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansD-GlucoseGlucose polymers
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing stability of a composition comprising soluble glucose dehydrogenase (GDH). Soluble GDH is preferably FAD-dependent GDH derived from filamentous fungus, and the best effect is observed in FAD-GDH derived from A. oryzae or FAD-GDH derived from A. terreus. According to the invention, in a composition comprising soluble glucose dehydrogenase (GDH), stability of GDH can be enhanced by coexisting the enzyme with one or more compounds selected from amino acids and sugars which are not substrate of the enzyme, thus expected to enhancing a measurement accuracy of glucose.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Method for enhancing stability of a composition comprising soluble glucose dehydrogenase (GDH)
InactiveUS20080090278A1Optimal blood glucose levelImprove the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansD-GlucoseGlucose polymers
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing stability of a composition comprising soluble glucose dehydrogenase (GDH). Soluble GDH is preferably FAD-dependent GDH derived from filamentous fungus, and the best effect is observed in FAD-GDH derived from A. oryzae or FAD-GDH derived from A. terreus. According to the invention, in a composition comprising soluble glucose dehydrogenase (GDH), stability of GDH can be enhanced by coexisting the enzyme with one or more compounds selected from amino acids and sugars which are not substrate of the enzyme, thus expected to enhancing a measurement accuracy of glucose.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Modified glucose dehydrogenase gene
InactiveUS20100323378A1Maintain good propertiesReduced activityFungiSugar derivativesNucleotideWild type
[Object] To provide an FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase having a higher specificity for glucose.[Means for Resolution] A modified glucose dehydrogenase (GLD) which includes a substitution of at least one amino acid residue selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues at positions 37, 69, 72, 73, 76, 78, 102, 217, 228, 240, 356, 407, 424, 437, 527, and 530 in an amino acid sequence of a wild-type FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase (GLD) represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, and has a decreased ratio of activity for xylose / activity for glucose as compared with the wild-type GLD; a polynucleotide encoding the modified GLD; a recombinant vector containing the polynucleotide; a transformed cell produced by using the recombinant vector; etc.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Modified pyrroloquinoline quinone (pqq) dependent glucose dehydrogenase excellent in substrate specificity
InactiveUS20070105173A1Action propertyProcess stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiWild typePyrroloquinoline quinone
PQQGDH having an improved substrate specificity or having an improved specific activity in an assay system using ferricyanide ion as a mediator is provided. Modified PQQGDH having the enhanced substrate specificity by introducing an amino acid mutation in a particular region of PQQGDH, and a method of enhancing the specific activity compared with a wild type in the assay system using the ferricyanide ion as the mediator by deleting, substituting, or adding one or more amino acids in an amino acid sequence of the wild type pyrroloquinoline quinone dependent glucose dehydrogenase.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Coenzyme-linked glucose dehydrogenase and polynucleotide encoding the same
ActiveUS8691547B2Maintain good propertiesLow activity toward maltoseAnimal cellsBacteriaNucleotidePolynucleotide
The present invention provides members that produce on a large scale a coenzyme-linked glucose dehydrogenase which has excellent substrate-recognizing ability toward glucose while providing low action on maltose. The present invention relates to a polynucleotide encoding a soluble coenzyme-linked glucose dehydrogenase that catalyzes the oxidation of glucose in the presence of an electron acceptor and has an activity toward maltose of 5% or lower; a polypeptide encoded by the nucleotide sequence of the polynucleotide; a recombinant vector carrying the polynucleotide; a transformed cell produced using the recombinant vector; a method for producing a polypeptide comprising culturing the transformed cell and collecting from the cultivated products a polypeptide that links to FAD to exert the glucose dehydration activity; a method for determination of glucose using the polypeptide; a reagent composition for determination of glucose; and a biosensor.
Owner:PHC CORP
Biosensor with improved analyte specificity
ActiveUS20090246808A1Strong specificityInterference minimizationOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrochemical biosensorAnalyte
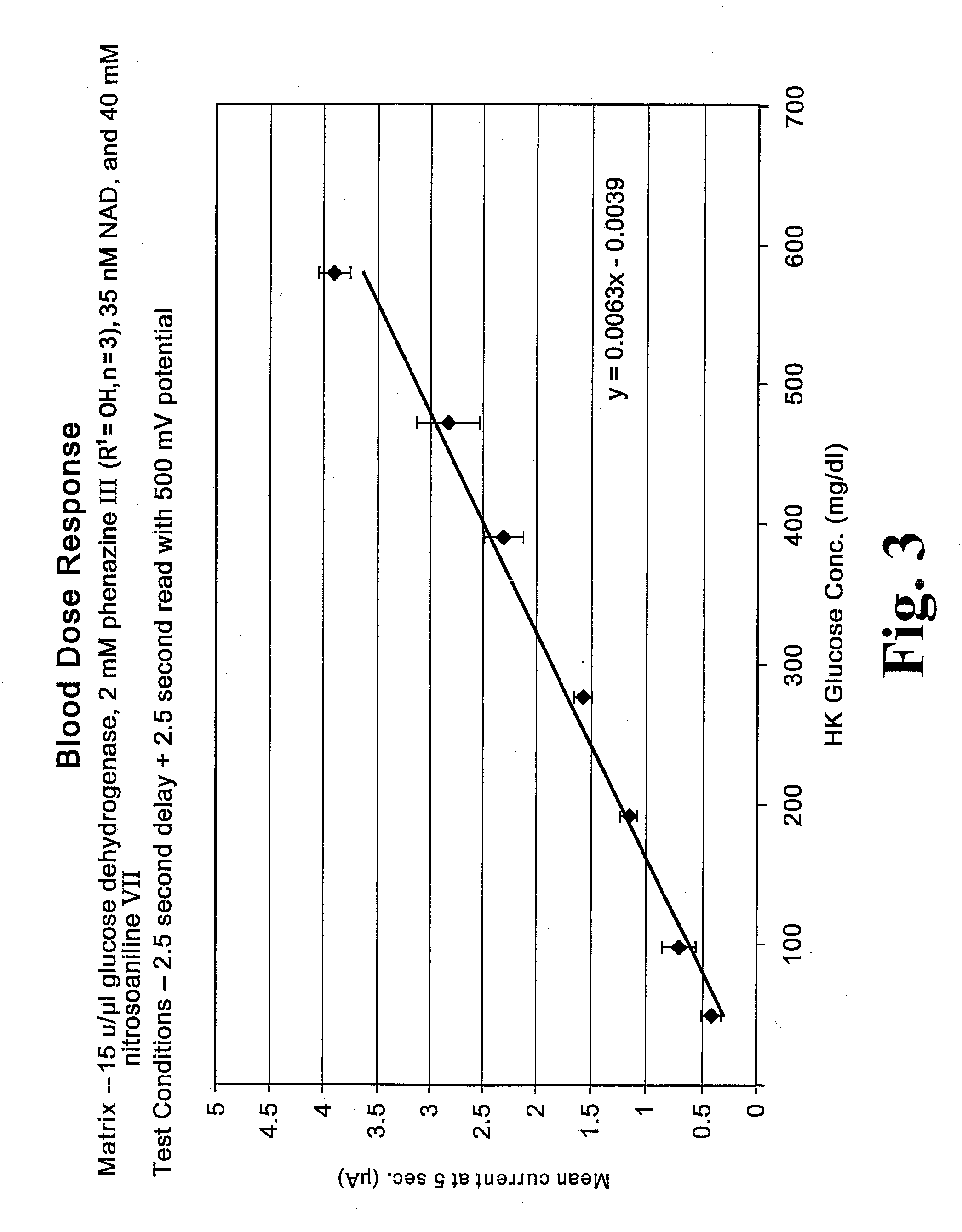
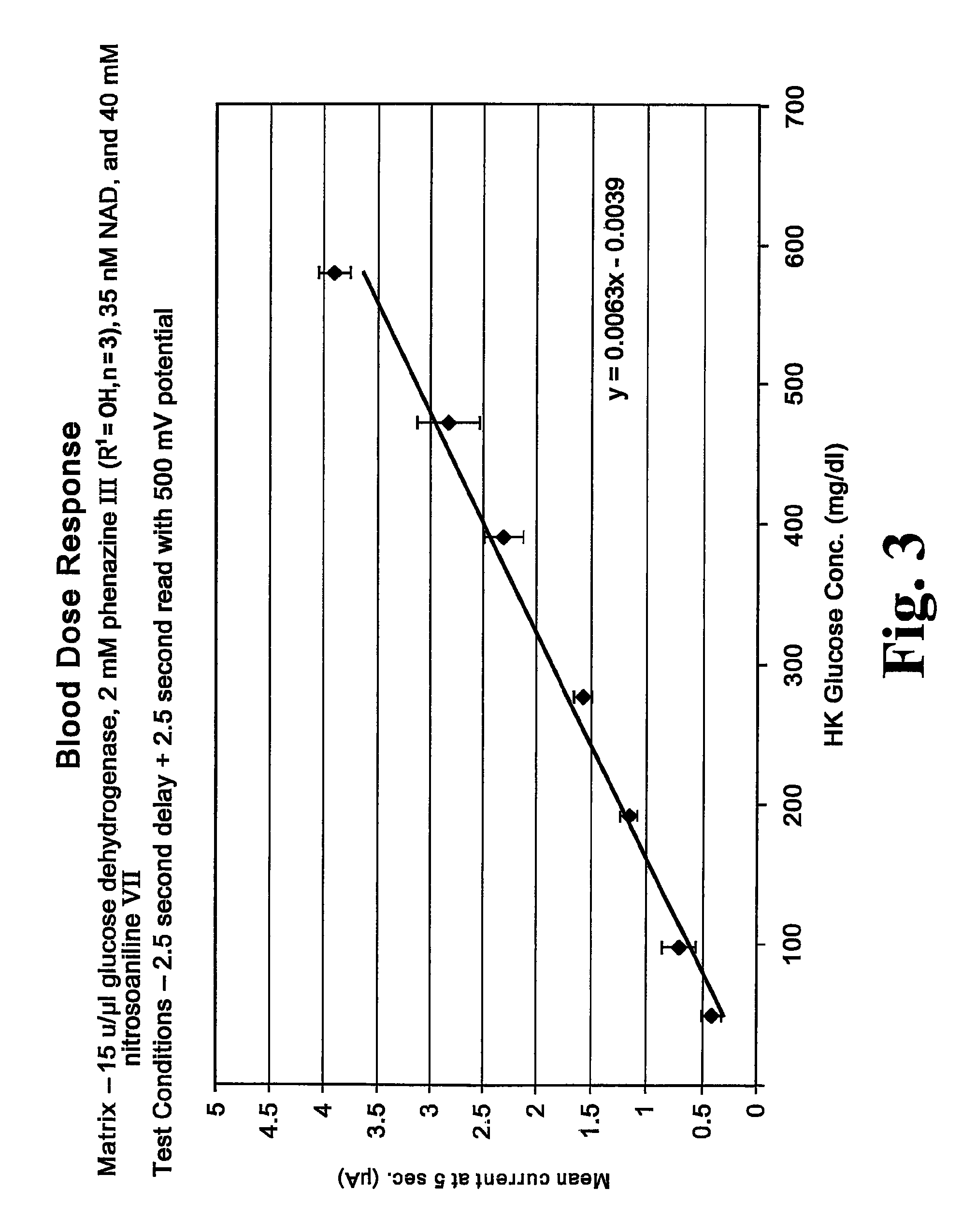
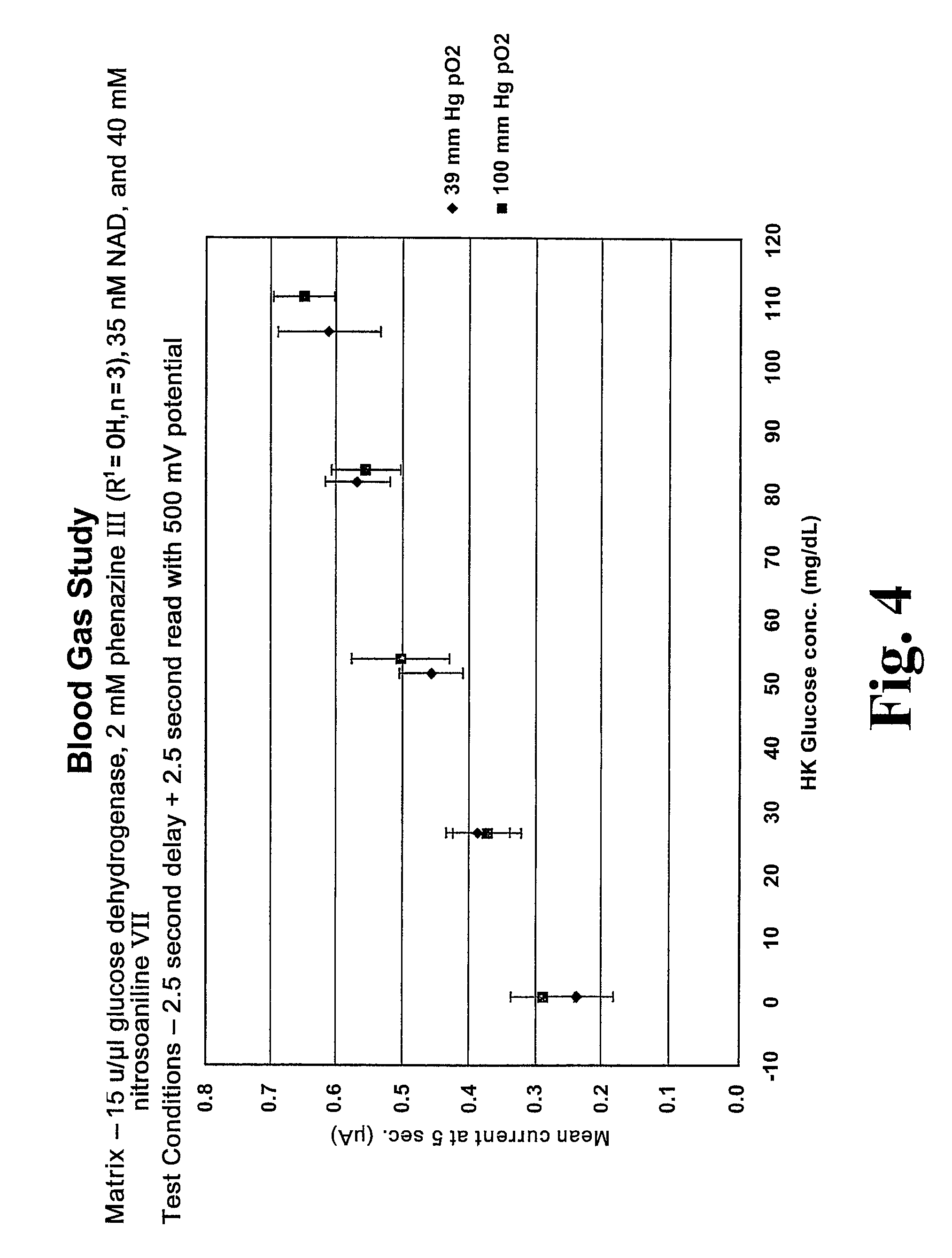
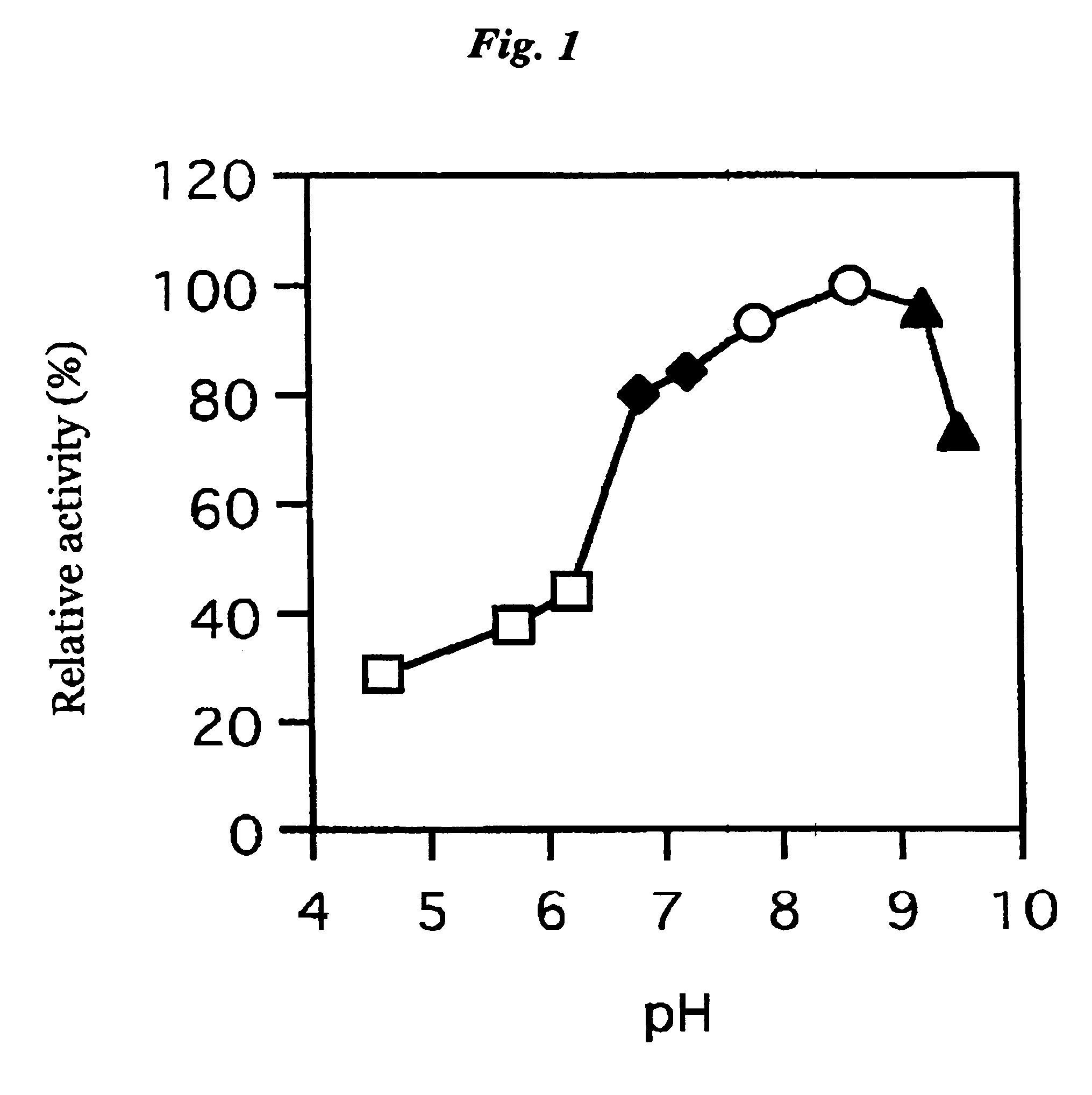
A chemistry matrix for use in determining the concentration of an analyte in a biological fluid includes a glucose dehydrogenase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, an alkylphenazine quaternary salt, and / or a nitrosoaniline. The chemistry matrix is used with an electrochemical biosensor to determine the concentration of an analyte after a reaction occurs within the biosensor, at which time an analysis is completed to determine the concentration. A method of determining the concentration of an analyte using the chemistry matrix of glucose dehydrogenase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, an alkylphenazine quaternary salt, and / or a nitrosoaniline is another aspect that is described. The method also further features test times of five seconds or less. Methods utilizing the new chemistry matrix can readily determine an analyte such as blood glucose at concentrations of from about 20-600 mg / dL at a pH of from about 6.5 to about 8.5.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Preparation method and application of paper-based self-power supply biosensor
InactiveCN104535626AReduce evaporationReduce adsorptionMaterial electrochemical variablesCarbon nanotubeCatalytic effect
A preparation method and an application of a paper-based self-power supply biosensor are provided. The invention discloses a three-dimensional hollow channel microfluidic paper chip adapter sensor having the advantages of simple operation, low cost and self-power supply and successfully used for on-site detection. The sensor successfully introduces a biofuel cell into a three-dimensional hollow channel microfluidic paper chip, utilizes a catalytic effect of a biological fuel cell cathode and anode on a substrate to voluntarily generate an electrical signal, and gets rid of limits on external power supply equipment. The biofuel cell anode prepared by growing gold improves the conductivity of the electrodes, and glucose dehydrogenase is immobilized on the anode; the biofuel cell cathode adopts a carbon nanotube-platinum nano composite material for catalyzing oxygen to reduce, and glucose is used as a fuel; mutual recognition between an adapter and heavy metal ions is generated on the gold-anode; the current intensity is detected by an electrochemical workstation, and thus the heavy metal ions in water are detected.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Glucose biosensor and method
ActiveUS7955484B2The result is accurateMinimize interference from dissolved oxygenImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsD-GlucoseGlucose polymers
A system for more accurately measuring glucose in a sample includes a first glucose-sensing electrode incorporating a quantity of glucose oxidase, a second glucose-sensing electrode incorporating a quantity of PQQ-glucose dehydrogenase, a reference electrode, and means for selecting between a first glucose measurement made with the first glucose-sensing electrode and a second glucose measurement made with the second glucose-sensing electrode.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
Matrix composition with alkylphenazine quaternary salt and a nitrosoaniline
ActiveUS8008037B2Strong specificityInterference minimizationOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrochemical biosensorAnalyte
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Coenzyme-binding glucose dehydrogenase
Owner:PHC CORP
Biological preparation method of intermediate of atazanavir
InactiveCN103468757AImprove reaction efficiencyGreen biotransformation processFermentationBenzeneSolvent
The invention relates to a biological preparation method of an intermediate of atazanavir. (S)-tertiary butyl (4-chloro-3-carbonyl-1-benzene butyl-2-yl) carbamic acid ester is taken as a substrate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of adding the substrate, a cosolvent and glucose into a reactor, stirring uniformly, weighing ketoreductase powder, glucose dehydrogenase and cofactor, dissolving in a water phase buffered solution with pH of 8-9, adding the obtained mixed solution into the reactor, stirring, controlling the temperature to be at 32DEG C-34 DEG C, and beginning reacting, wherein at the beginning of the reaction, the mass volume ratio concentration of the substrate is 0.05-0.2g / ml, and the mass ratio of the added ketoreductase to cofactor to glucose to the substrate is (0.02-0.03):(0.001-0.005):(0.8-1.2):1. Compared with the prior art, the biological preparation method realizes more environment-friendly and mild biological conversion process with high reaction efficiency, and has important application value.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
Oxygen electrode
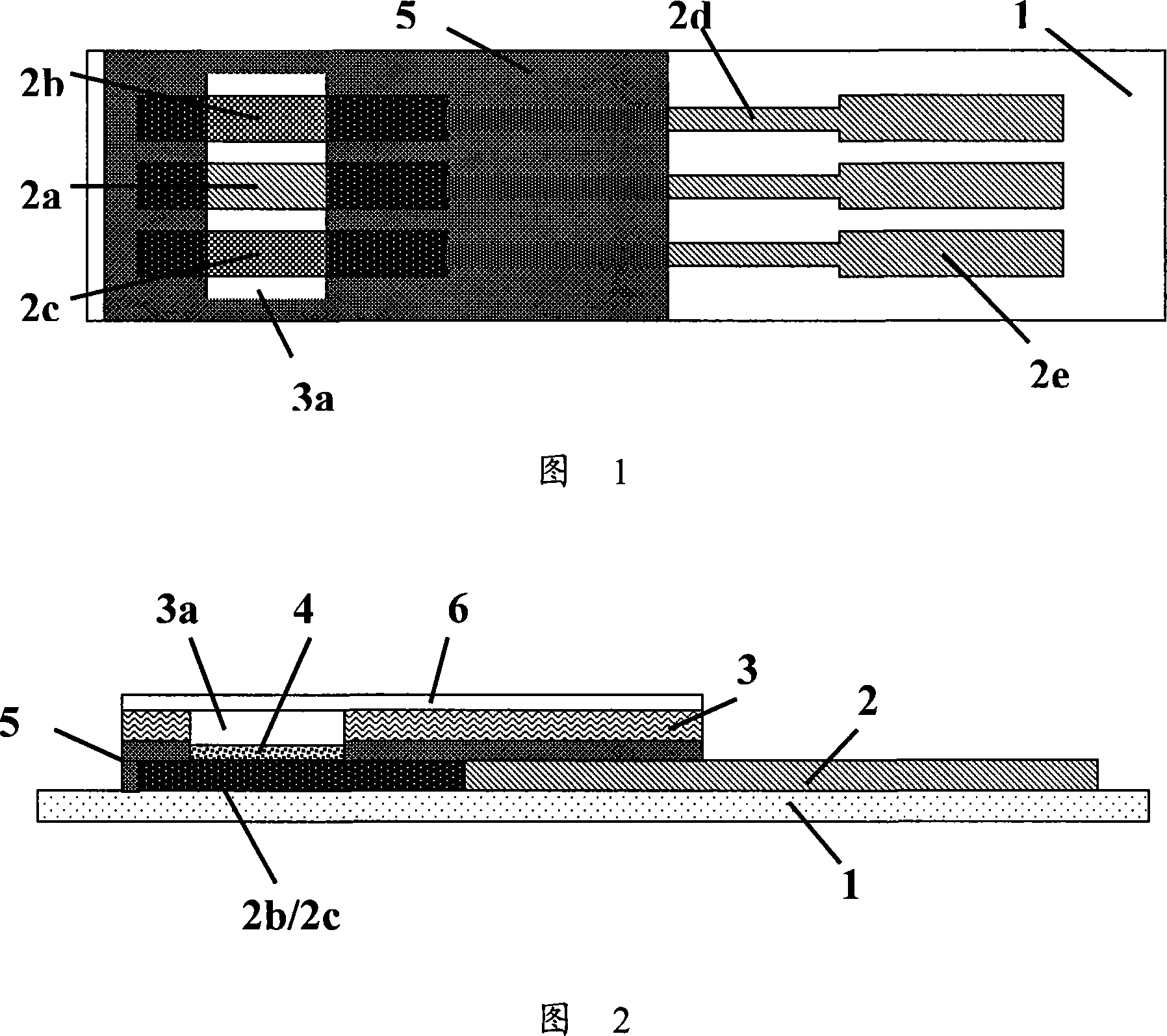
InactiveUS20050067278A1High responseIncrease valueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzyme electrodeOxidoreductase
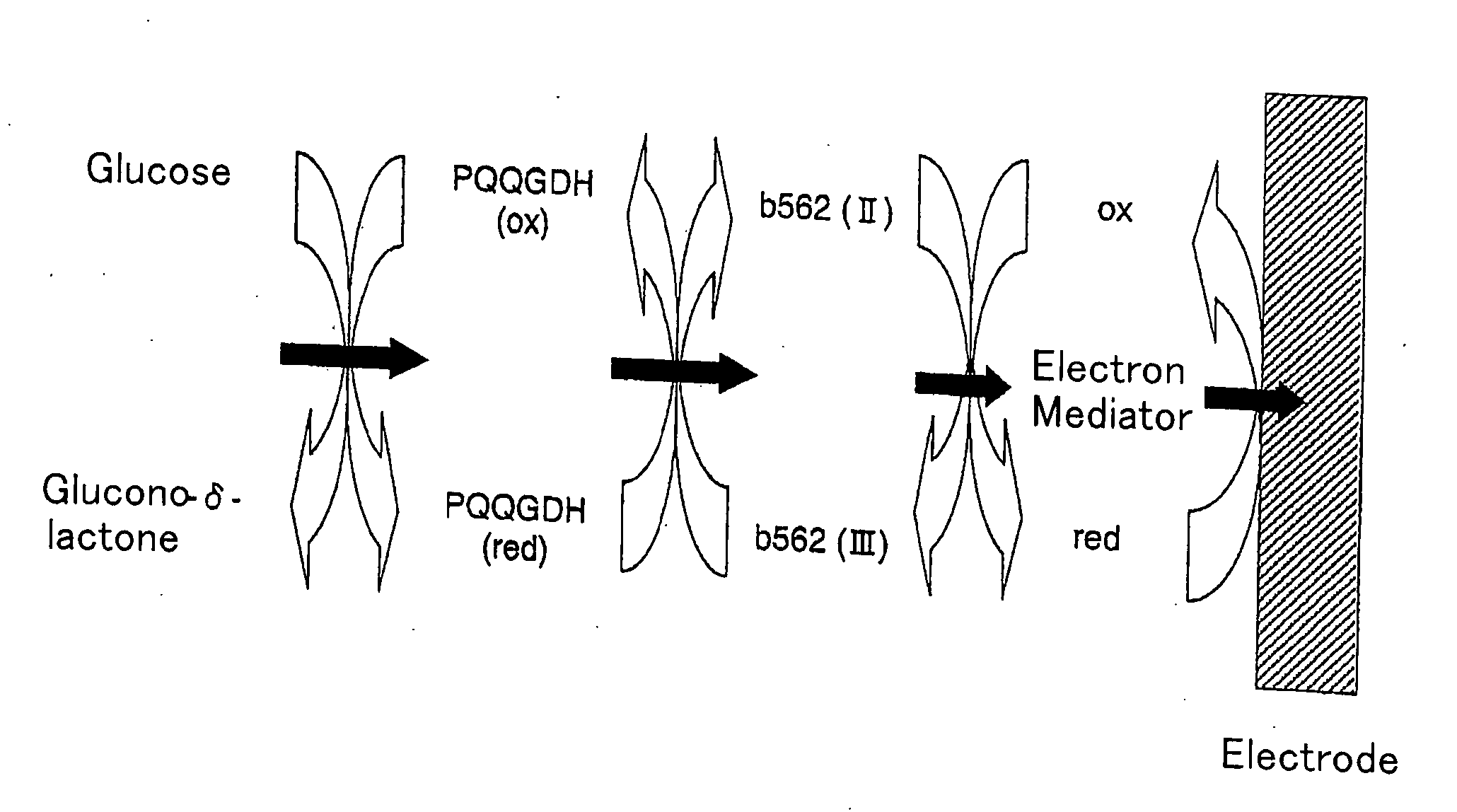
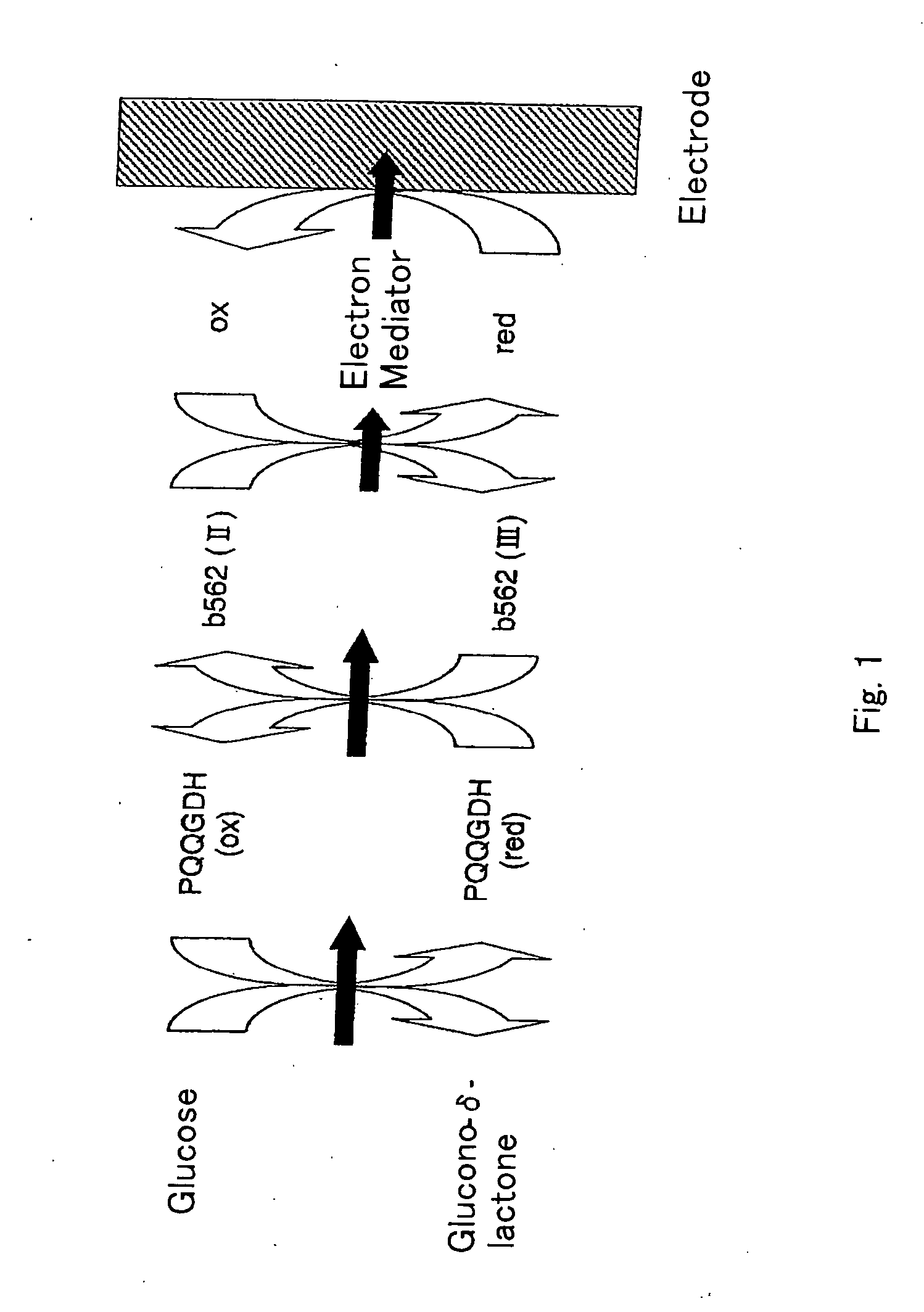
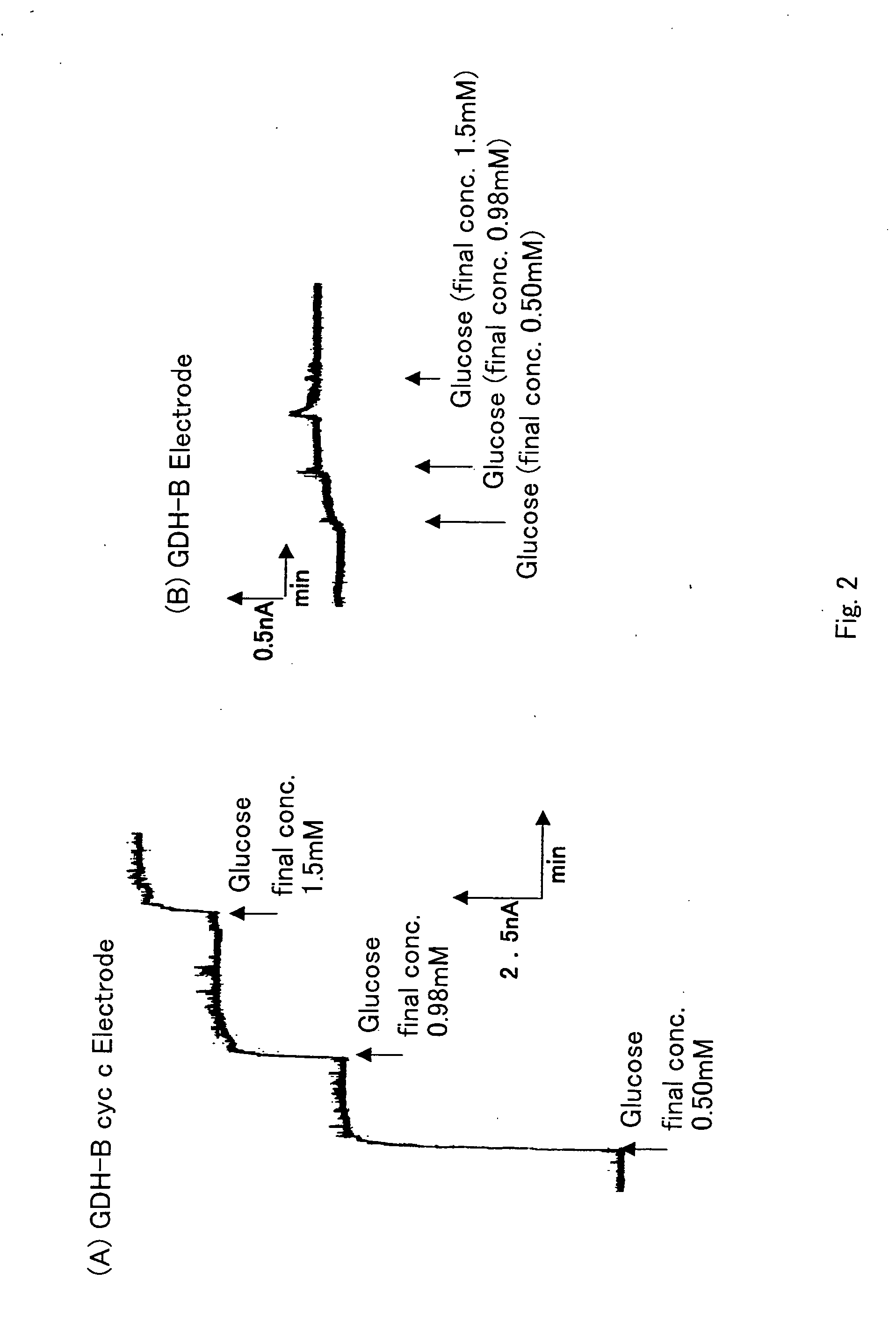
Disclosed is an enzyme electrode having an oxidoreductase (for instance, glucose oxidase, cholesterol oxidase, fructosylamine oxidase and glucose dehydrogenase) and an electron-transfer protein (for instance, cytochrome C, cytochrome b562 and cytochrome c551), as well as a sensor utilizing the enzyme electrode as working electrode. The enzyme electrode of the invention can provide high response current values.
Owner:SODE
Alcohol dehydrogenase, gene and recombinase thereof, and application of alcohol dehydrogenase in synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol
InactiveCN105936909AImprove expression levelIncrease enzyme activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringDiaryl ketoneGenus Kluyveromyces
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase, a gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant respectively containing the gene, a recombinase of the alcohol dehydrogenase, and an application of the alcohol dehydrogenase in asymmetric reduction synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase is from Kluyveromyces sp. CCTCCM2011385, has a carbonyl group reduction function, and also has a hydroxy group oxidation function. Extra addition of glucose dehydrogenase and other enzymes used for cofactor circulation is not needed when the alcohol dehydrogenase is used in the reduction of diaryl ketone into the chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a biocatalyst, and the alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages of high catalysis efficiency, mild reaction conditions, easy product recovery and low cost, so the alcohol dehydrogenase has very good application and exploitation prospect in the production of antihistamine medicines.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for highly expressing recombinant glucose dehydrogenase derived from filamentous bacterium
InactiveUS20080014611A1Efficient productionMore practicalBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyFungus
The present invention provides a method for highly expressing a recombinant FAD-GDH protein derived from filamentous fungi, protein obtained by the method, and a regent for measuring glucose using the protein. According to the invention, the FAD-GDH can be highly expressed by altering DNA sequence coding for a signal peptide of FAD-GDH gene isolated from Aspergillus oryzae. FAD-GDH can be stably produced by adjusting pH of 7.1 to 7.3 during culture production.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, method for producing flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase, and glucose measurement method using thereof
ActiveUS20140287445A1Increased substrate specificityImprove stabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEscherichia coliHeat stability
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase (FAD-GDH), which in addition to having high substrate specificity and adequate desirable heat stability, is suitable for efficient production, preferably using E. coli, yeast or molds and the like as host cells. The FAD-GDH has amino acid substitutions at positions equivalent to one or more locations selected from the group consisting of position 213, position 368 and position 526 in the amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 8. The FAD-GDH is acquired from a culture by inserting a gene encoding the FAD-GDH into host cells such as E. coli. A preferable example of the FAD-GDH is FAD-GDH, in which a signal peptide region present in an N-terminal region has been deleted from the amino acid sequence of Mucor-derived FAD-GDH, and which has the aforementioned amino acid substitutions. The FAD-GDH can be preferably used in clinical diagnosis.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenases
ActiveUS20110318810A1Accurate measurementAccurate blood glucose levelSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismLactose
A flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase with a high substrate specificity for D-glucose. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase which is derived from a microorganism belonging to the genus Mucor. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase has a low reactivity for maltose, D-galactose and D-xylose compared to its reactivity for D-glucose, and therefore is relatively unaffected by these saccharide compounds. The flavin-binding glucose dehydrogenase is also relatively unaffected by dissolved oxygen, and allows accurate measurement of glucose amounts even in the presence of saccharide compounds other than glucose in samples.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing with recombinant carbonyl reductase
InactiveCN102618590AAvoid inhibitionImprove conversion abilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEthyl butyrate
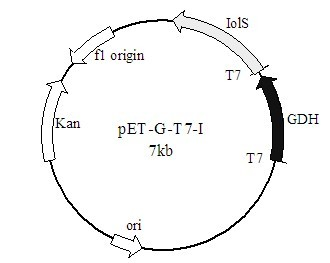
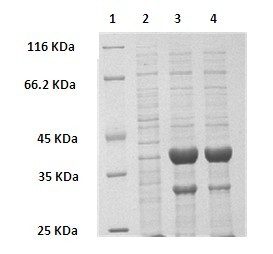
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing recombinant carbonyl reductase, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning gene segments of carbonyl reductase (IolS) and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from bacillus subtilis CGMCC NO.1.1508, expressing an IolS gene and a GDH gene in series by adopting a dual-starter method to construct a recombinant plasmid pET24a-G-T7-I, and introducing the plasmid into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); and under the condition of not adding or adding a small amount of NADP+cofactors, performing biotransformation by taking a cell-free extract of the escherichia coli recombinant plasmid as a catalyst, 2-oxo-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and glucose as a substrate to obtain (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, wherein the enantiomeric excess value of the product is higher than 99.5 percent. In the method, IolS and GDH are co-expressed, so that efficient regeneration of an intra-cellular cofactor NADP(H) is realized, production cost is lowered, and a good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Double reagent for detecting sialic acid liquid by stable enzyme method and use thereof
ActiveCN101469344AEasy to useLittle difference between bottlesMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseNeuraminidase
The invention relates to a double reagent, in particular to a liquid double reagent for determining sialic acid by an enzyme method and application thereof. The technical proposal of the liquid double reagent comprises: the steady liquid double reagent for determining the sialic acid by the enzyme method consists of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises 0.01 to 50KU / L of neuraminidase, 0.1 to 50KU / L of lactate dehydrogenase, and 25 to 100mmol / L of buffer liquid; and the reagent 2 comprises 0.1 to 50KU / L of N-acetyleuraminic acid aldolase, 0.05 to 5mmol / L of reducing coenzyme NADH, 0.1 to 10000U / L of glucose dehydrogenase, 0.1 to 500mmol / L of glucose, and 5 to 100mmol / L of the buffer liquid. The liquid double reagent has the advantages that the liquid double reagent has convenient use, does not need a dissolving solution to redissolve, has small difference among bottles, ensures that the packaging of the liquid double reagent can adapt to various automatic biochemical analyzers, can avoid secondary pollution, and simplify a production technology method.
Owner:上海微鸿企业管理有限公司
Alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to synthesis of chiral biaryl alcohols
InactiveCN108359649AHigh stereoselectivityIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholMutant
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and an application thereof to synthesis of chiral biaryl alcohols, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant has excellent catalytic activity and stereoselectivity and can be used for efficient catalysis for preparation of a series of R-configuration and S-configuration chiral biaryl alcohols. Alcohol dehydrogenase can be applied to synthesis of various chiral biaryl alcohol intermediates of antihistamine drugs by being coupled with glucose dehydrogenase or formate dehydrogenase. Compared withthe existing reports, a method for preparing the chiral biaryl alcohols from alcohol dehydrogenase through asymmetric catalytic reduction has the advantages of simple operation, high substrate concentration, complete reaction and high product purity, and has broad industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Coenzyme-Linked Glucose Dehydrogenase and Polynucleotide Encoding the Same
ActiveUS20120122130A1Maintain good propertiesReduced activityFungiBacteriaNucleotideGlucose polymers
The present invention provides members that produce on a large scale a coenzyme-linked glucose dehydrogenase which has excellent substrate-recognizing ability toward glucose while providing low action on maltose. The present invention relates to a polynucleotide encoding a soluble coenzyme-linked glucose dehydrogenase that catalyzes the oxidation of glucose in the presence of an electron acceptor and has an activity toward maltose of 5% or lower; a polypeptide encoded by the nucleotide sequence of the polynucleotide; a recombinant vector carrying the polynucleotide; a transformed cell produced using the recombinant vector; a method for producing a polypeptide comprising culturing the transformed cell and collecting from the cultivated products a polypeptide that links to FAD to exert the glucose dehydration activity; a method for determination of glucose using the polypeptide; a reagent composition for determination of glucose; and a biosensor.
Owner:PHC CORP
Novel glucose dehydrogenase
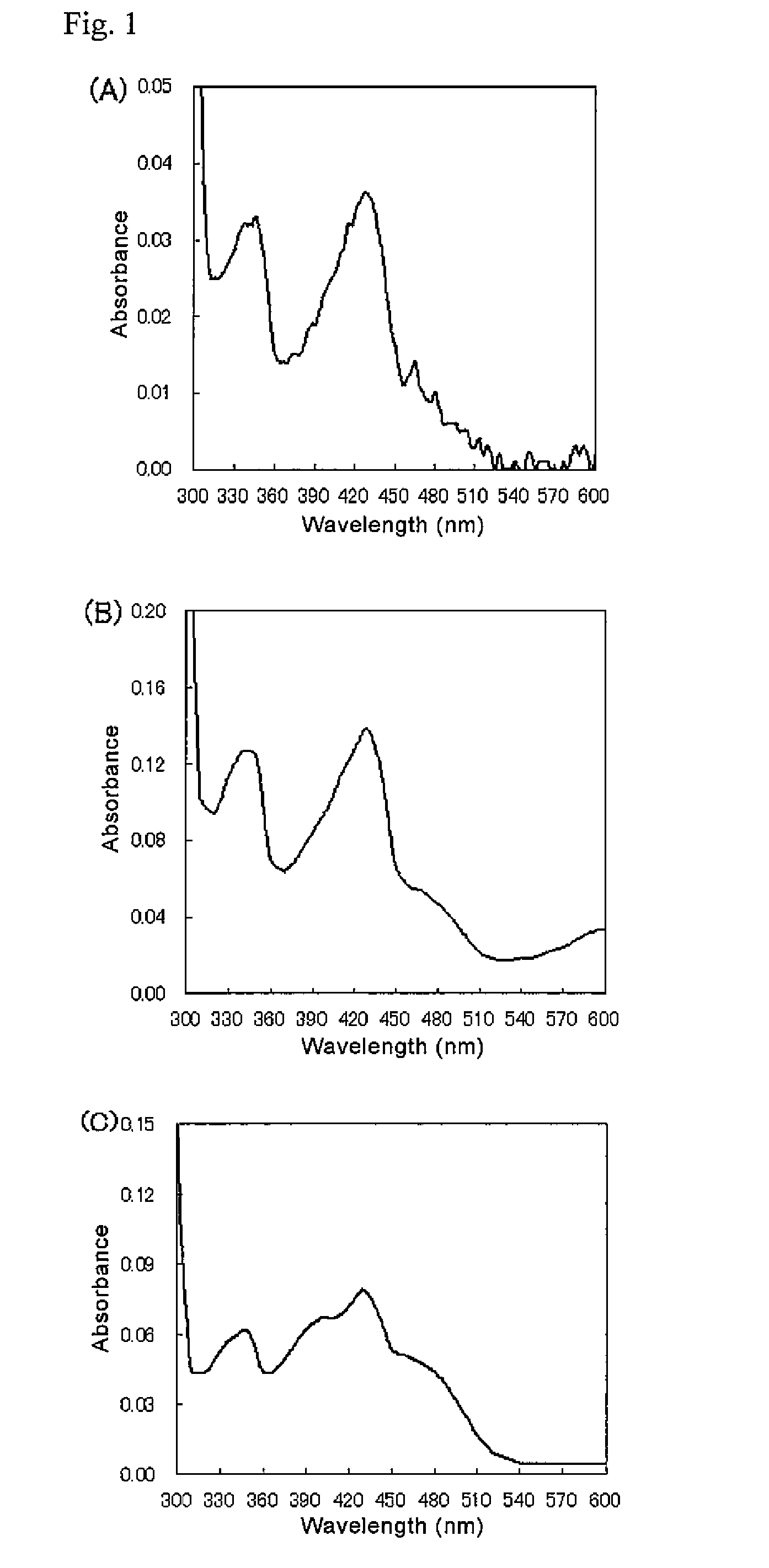
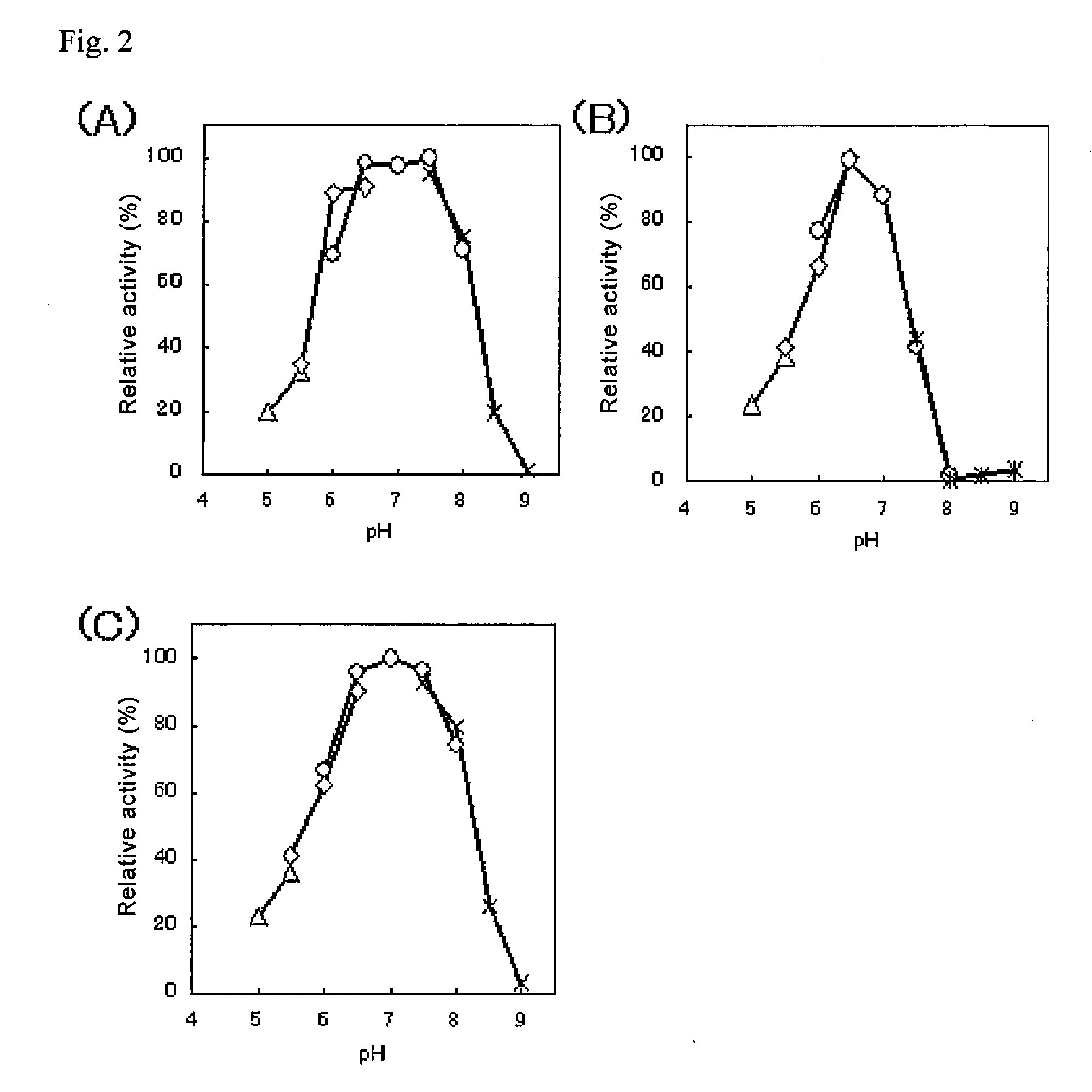
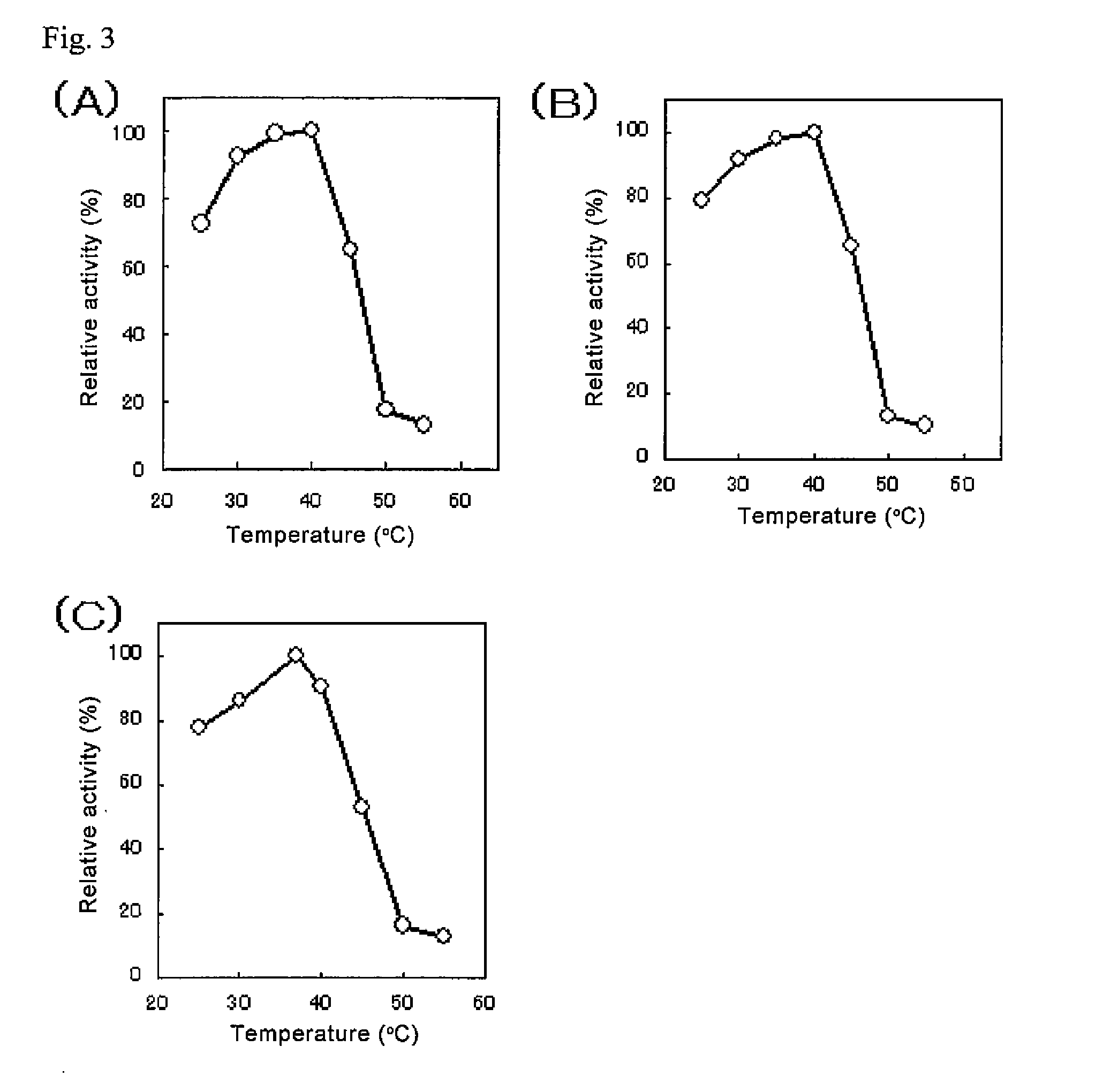
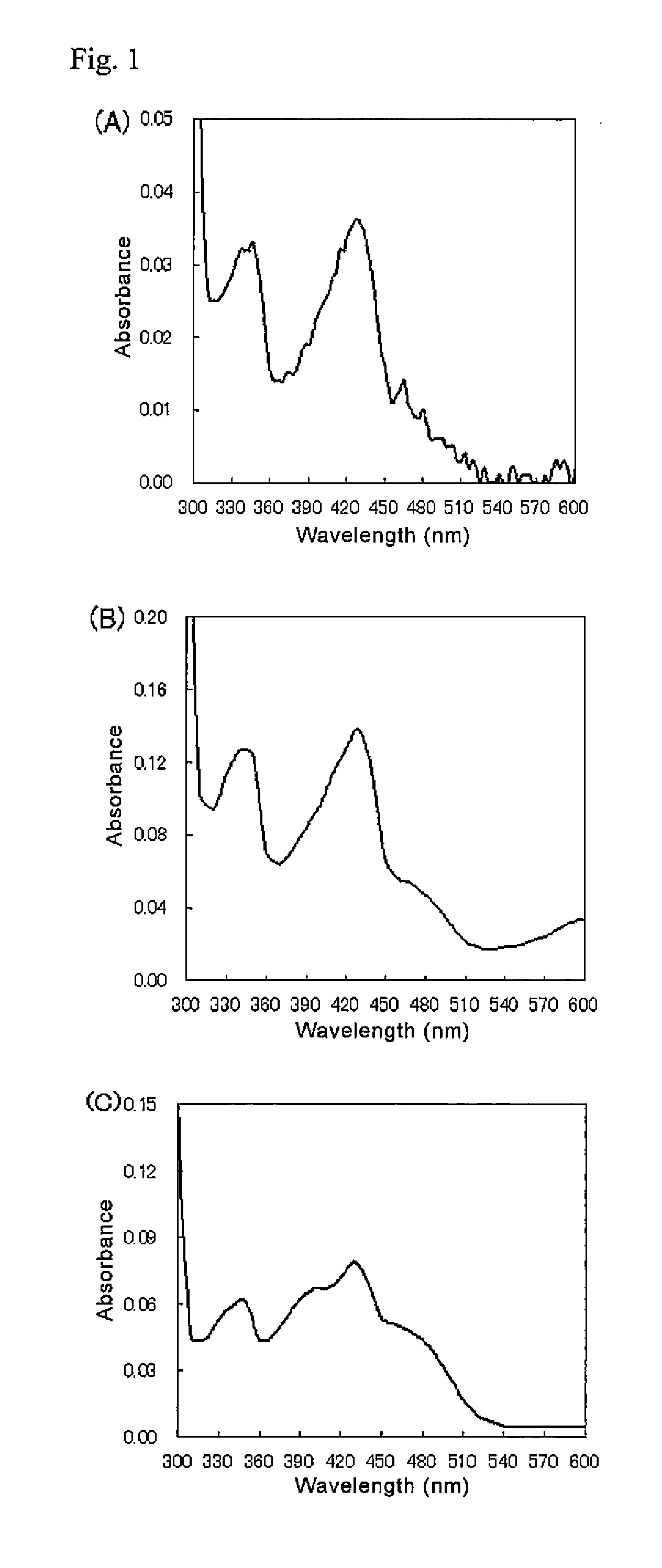
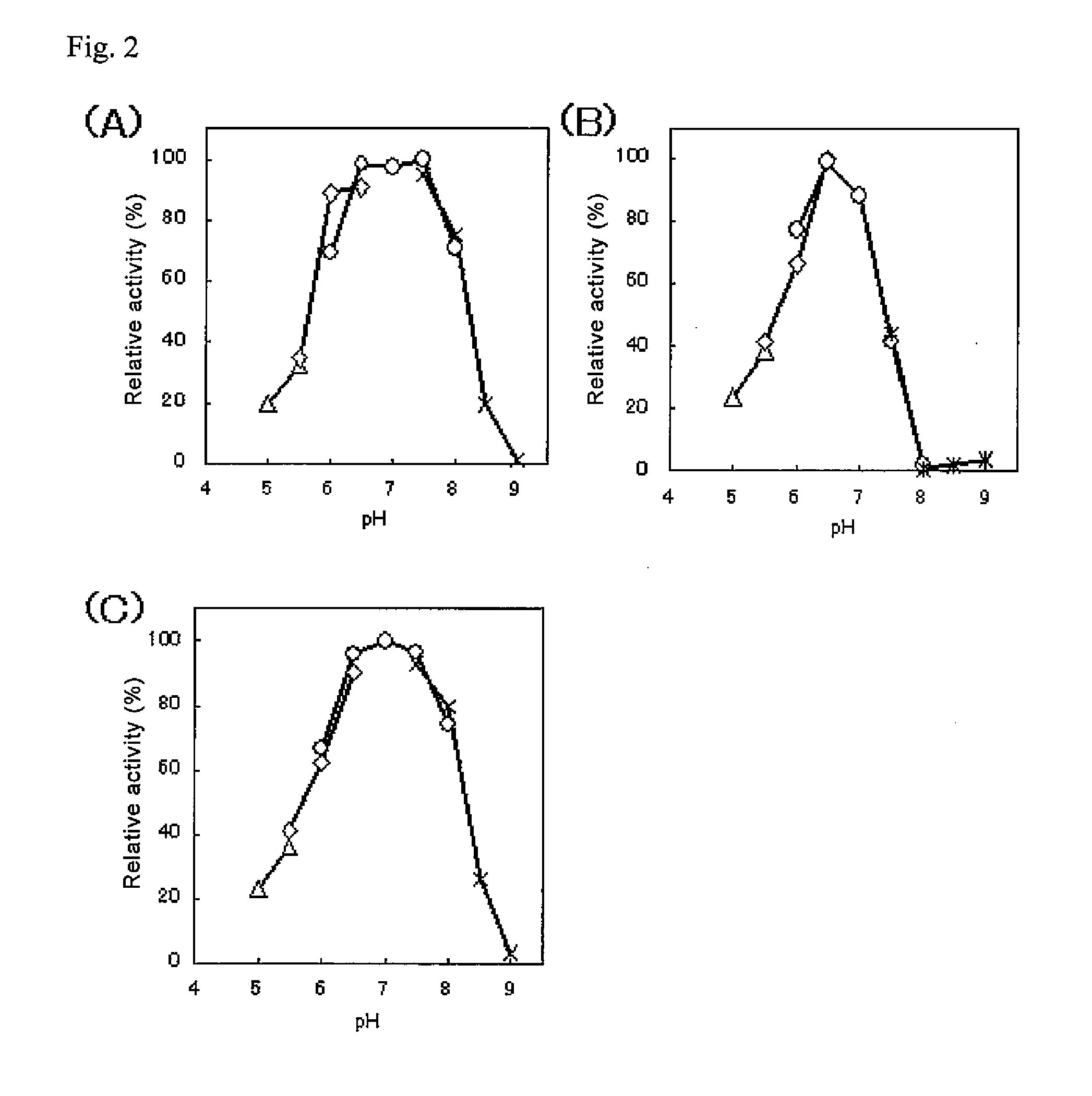
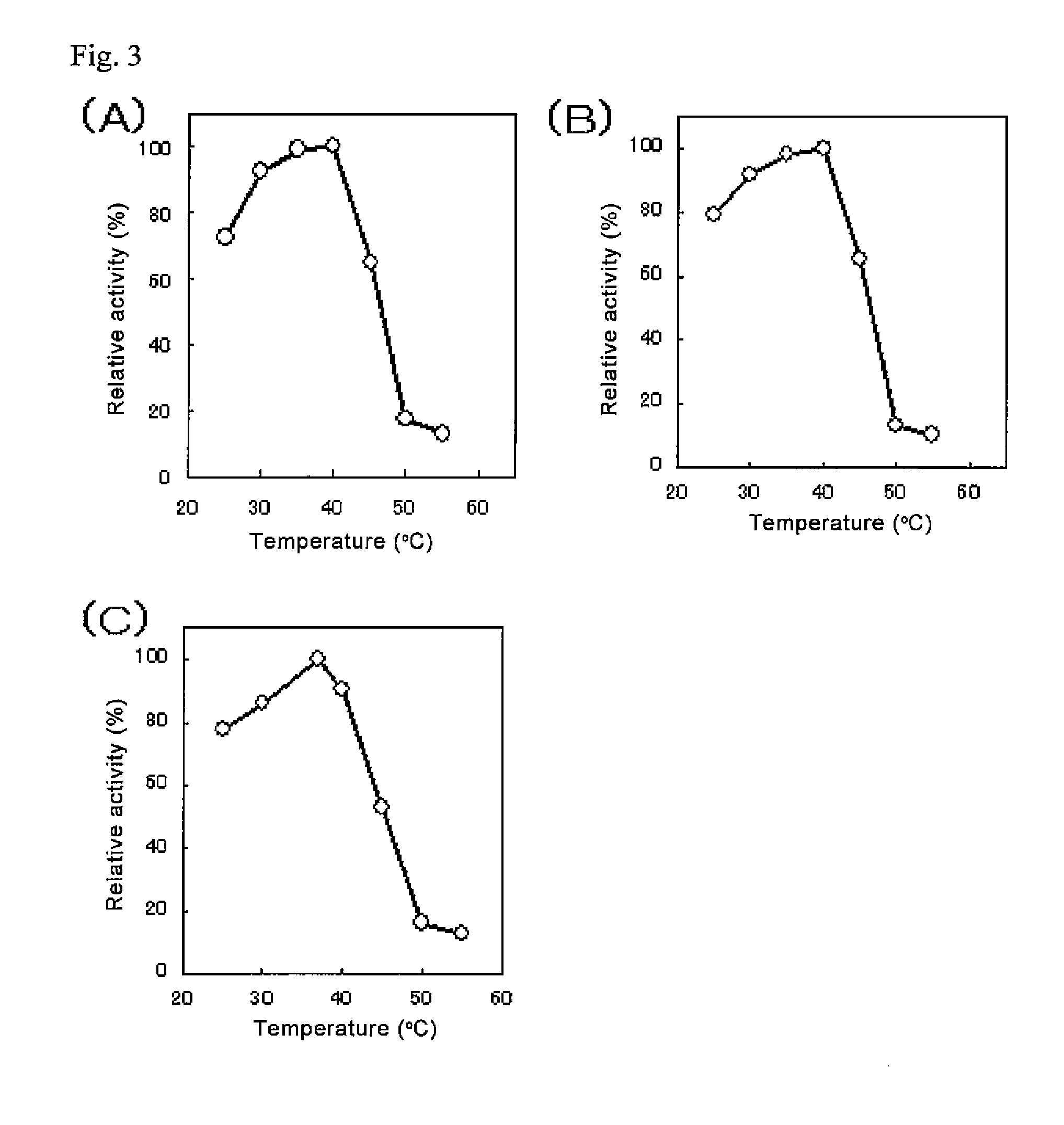
The present invention provides glucose dehydrogenase which is excellent in heat resistance and substrate specificity and is not affected by dissolved oxygen. Specifically, the present invention relates to glucose dehydrogenase characterized by being derived from an eukaryotic organism and keeping 90% or more activity after being treated with heat at 55° C. for 15 minutes in a liquid form compared with the activity before being treated.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com