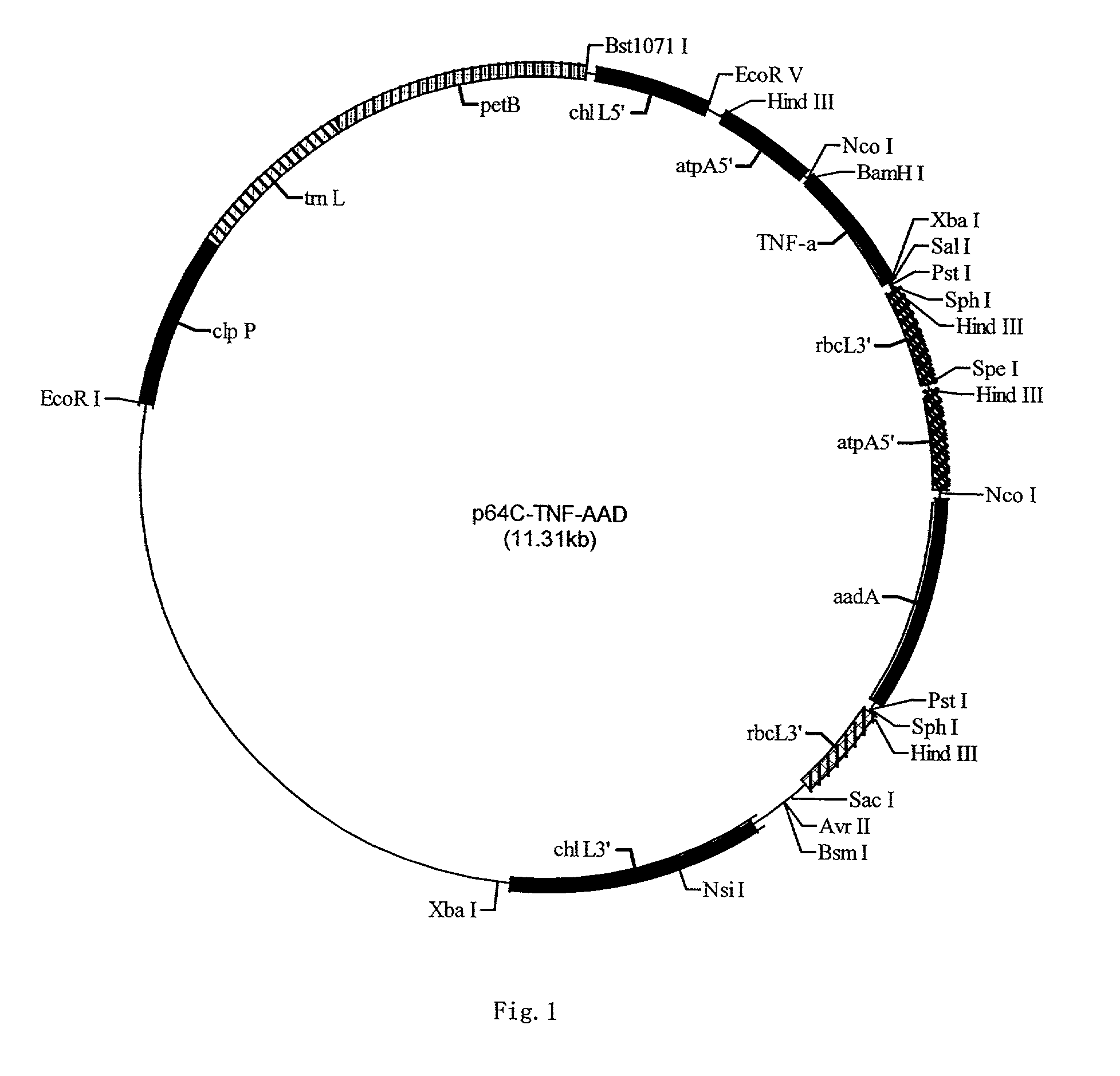
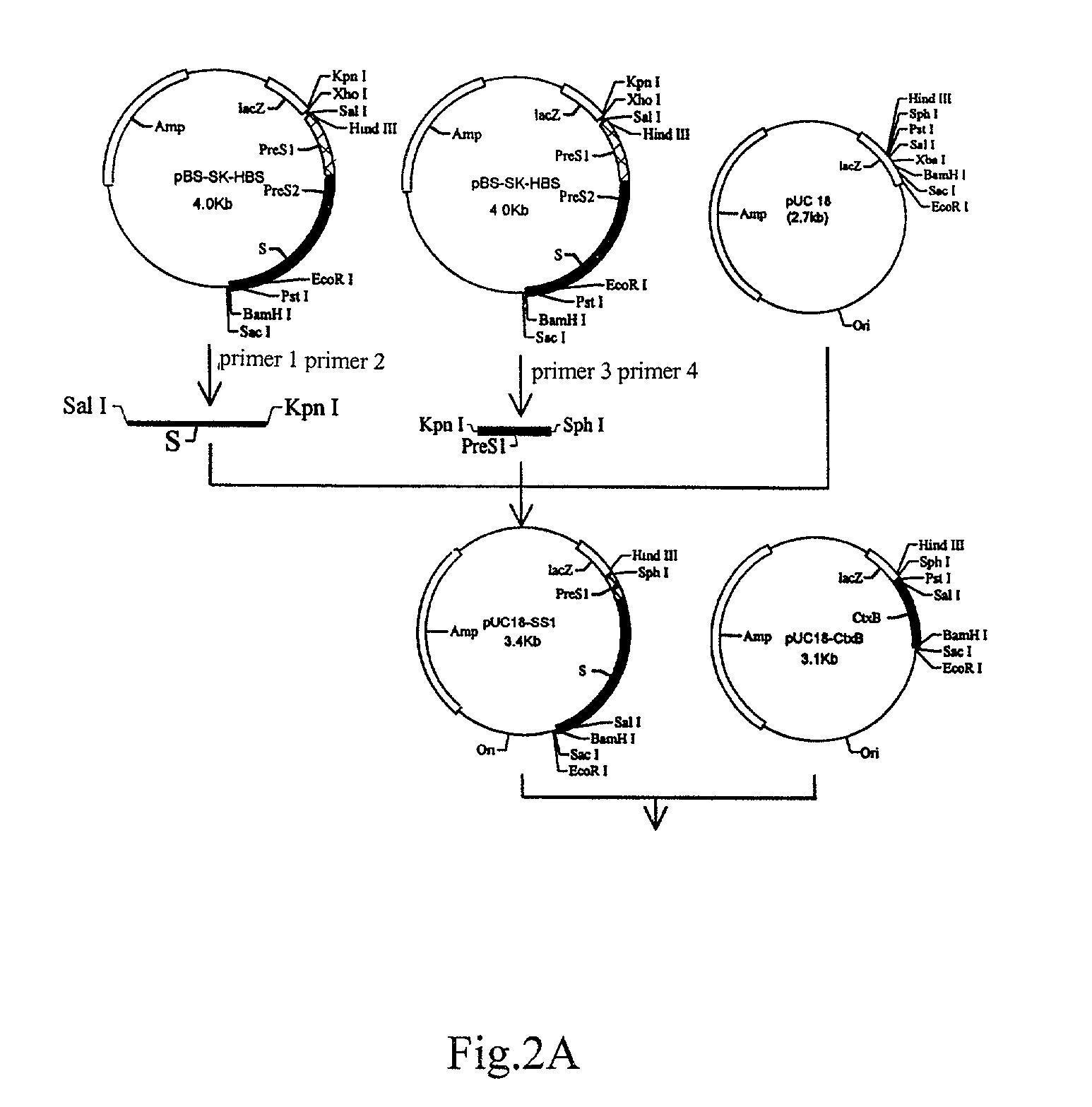
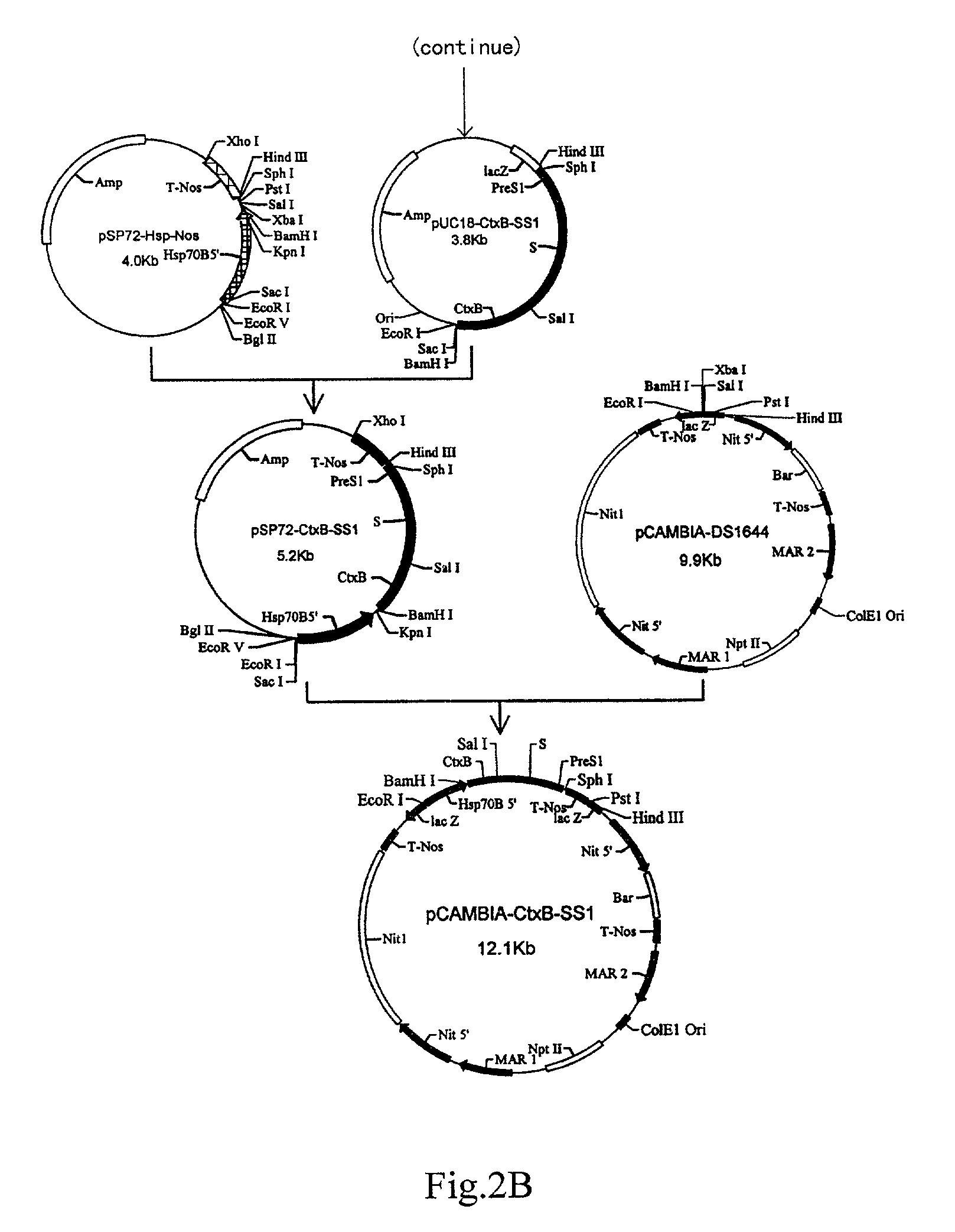
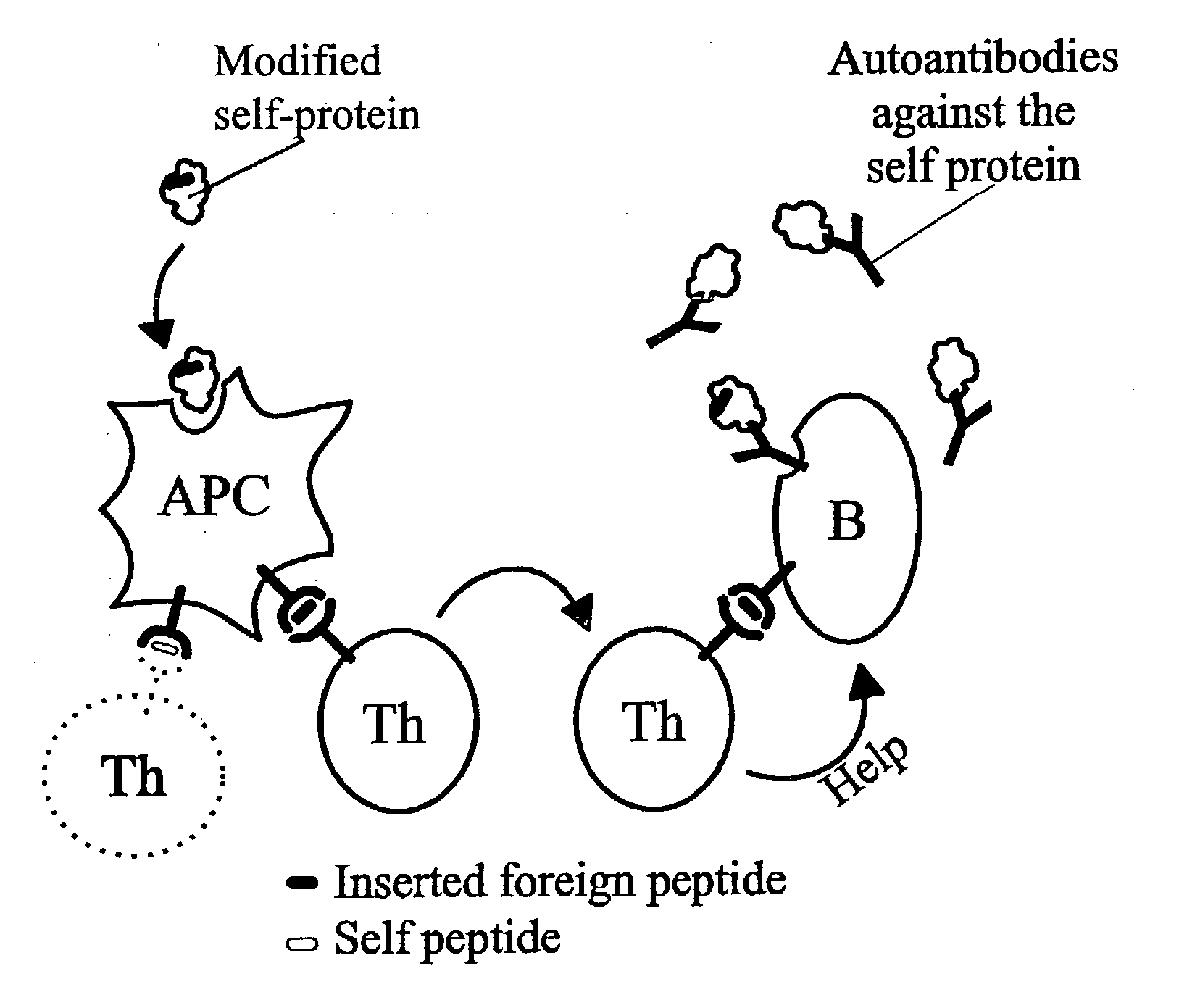
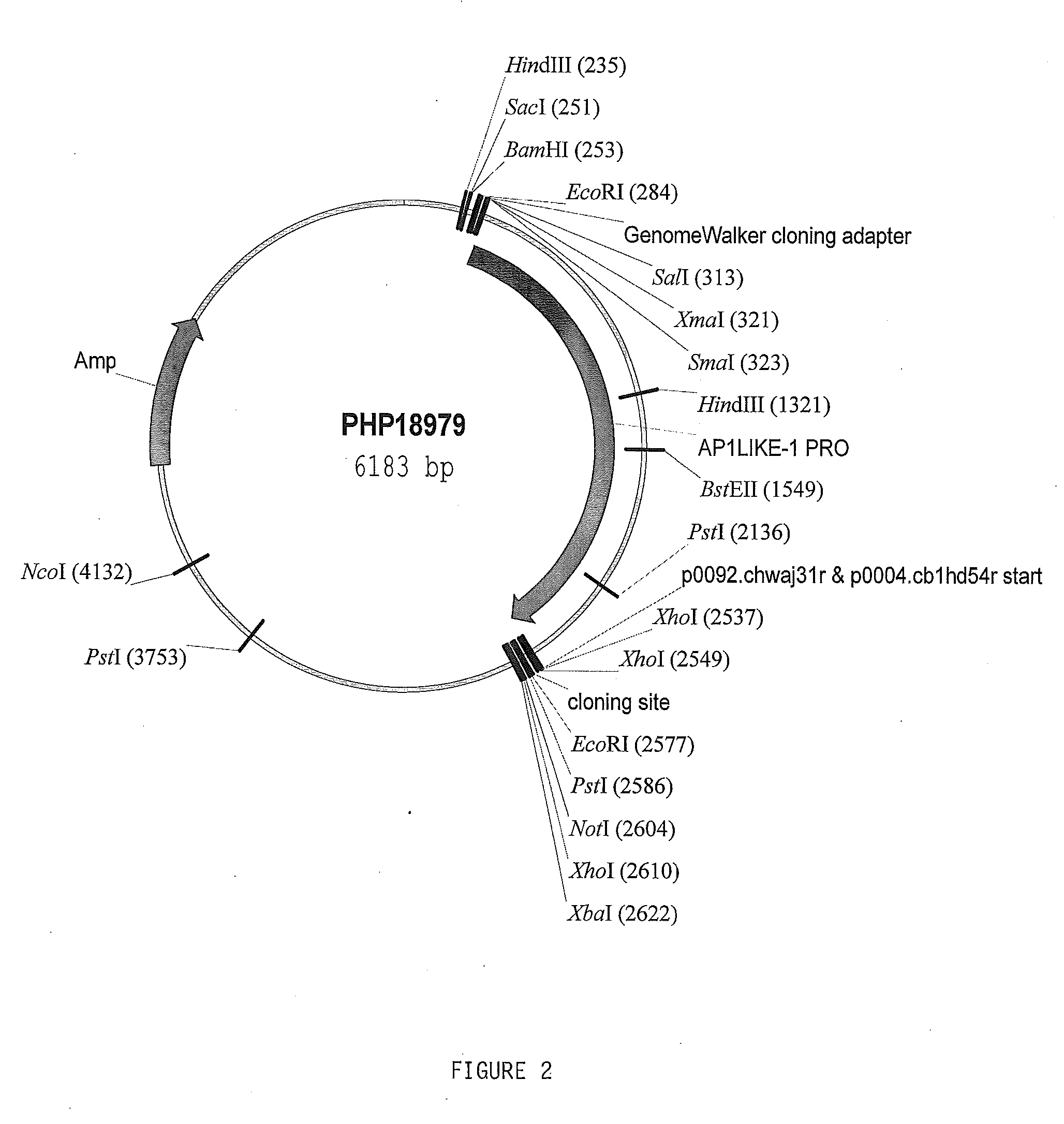
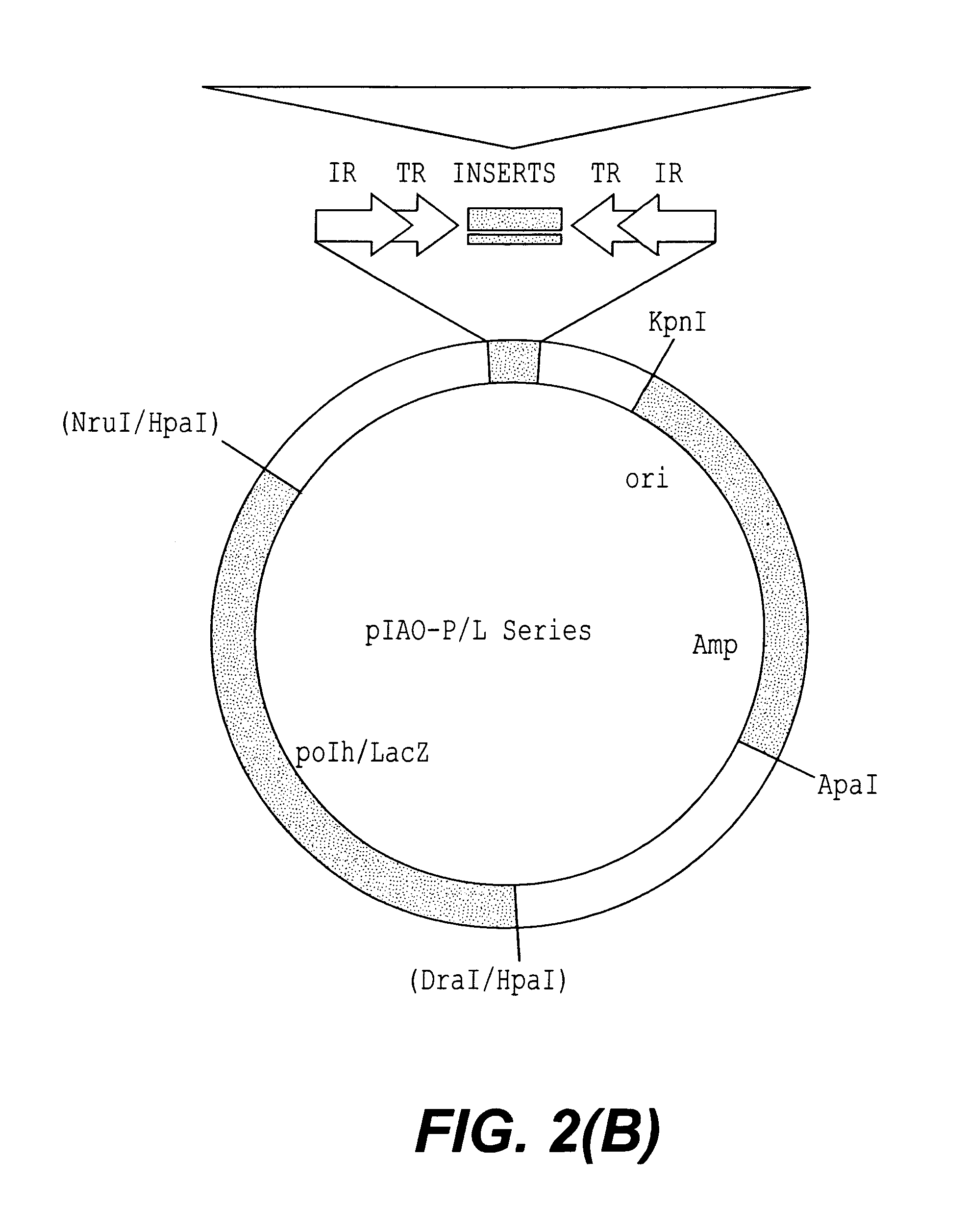
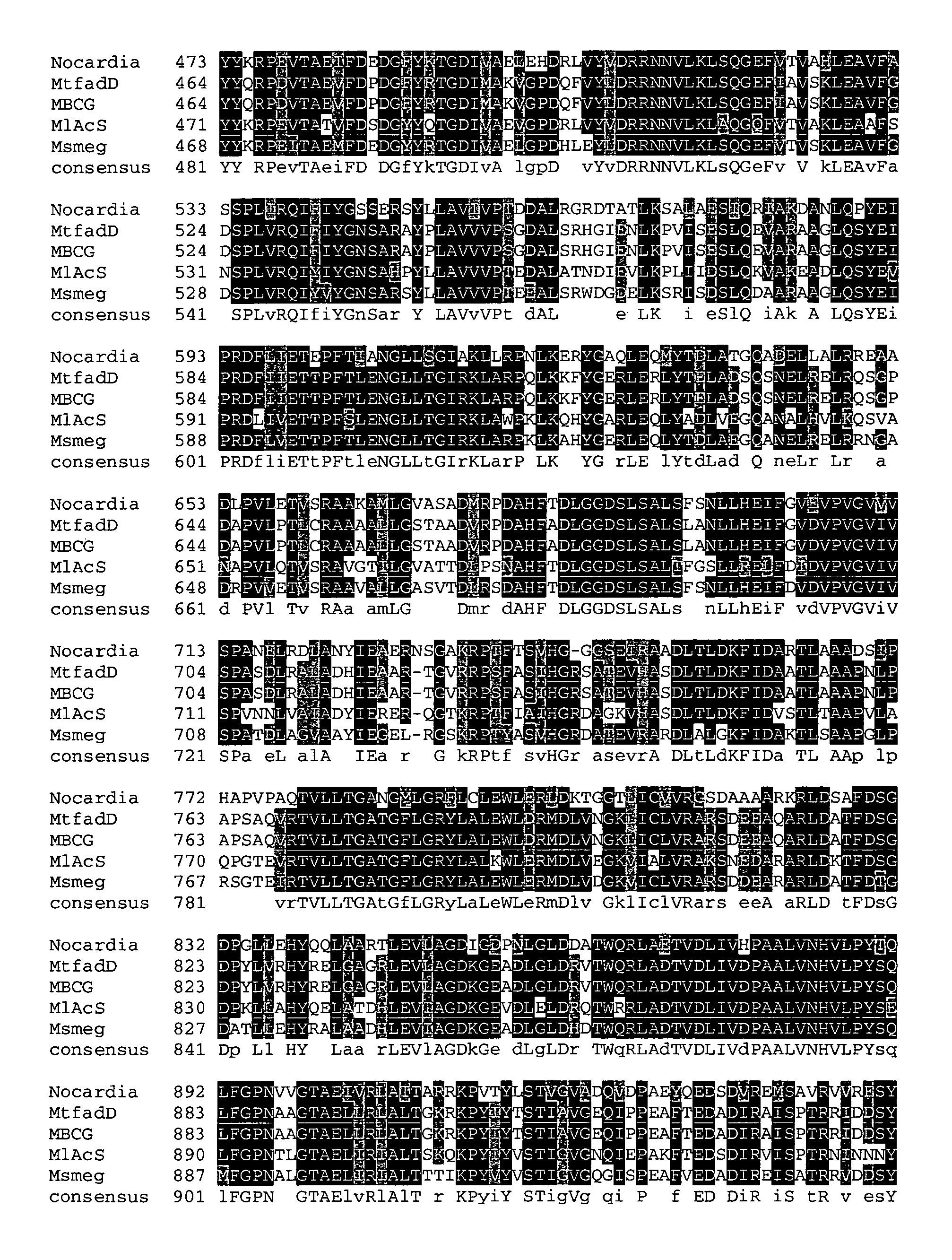
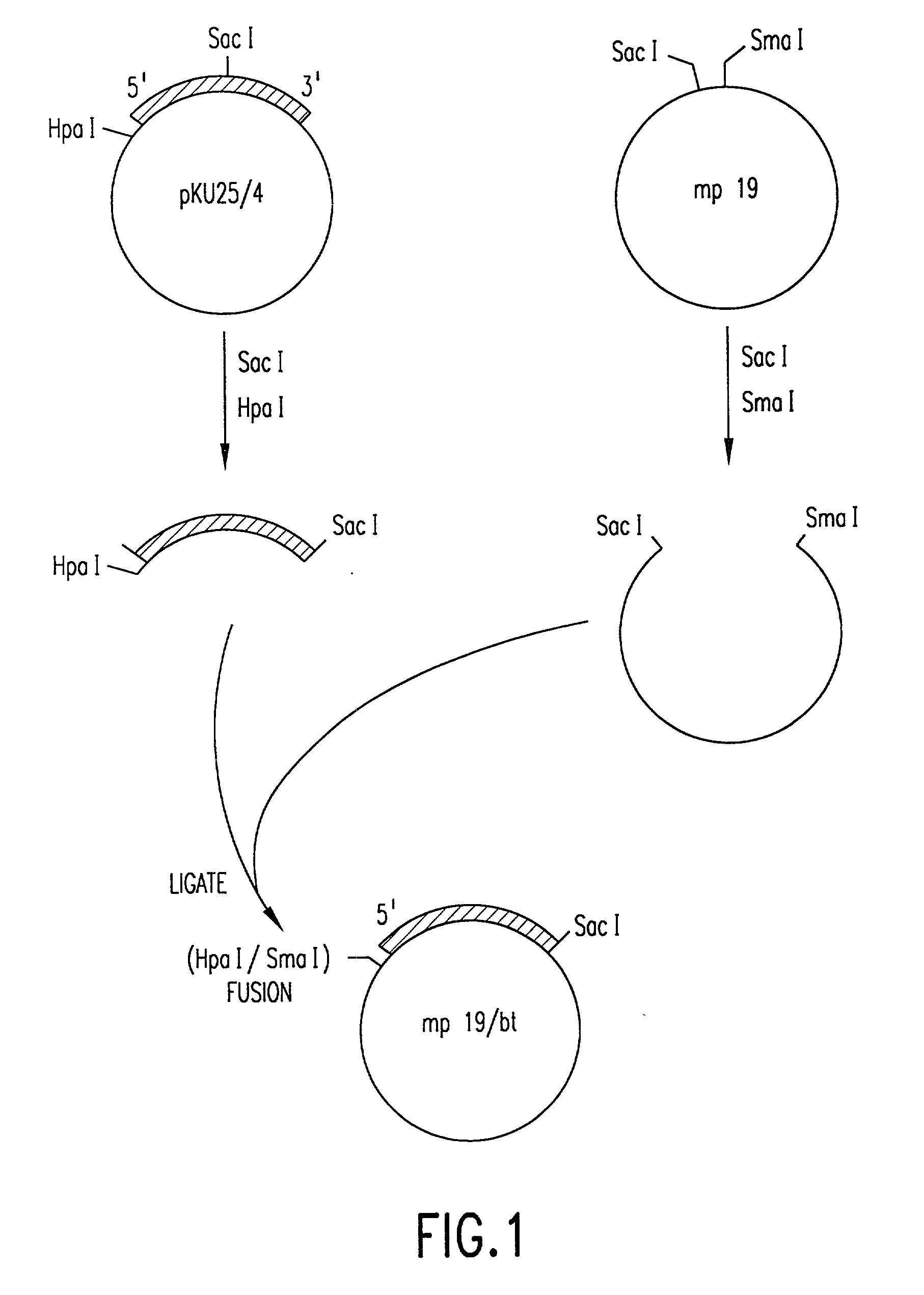
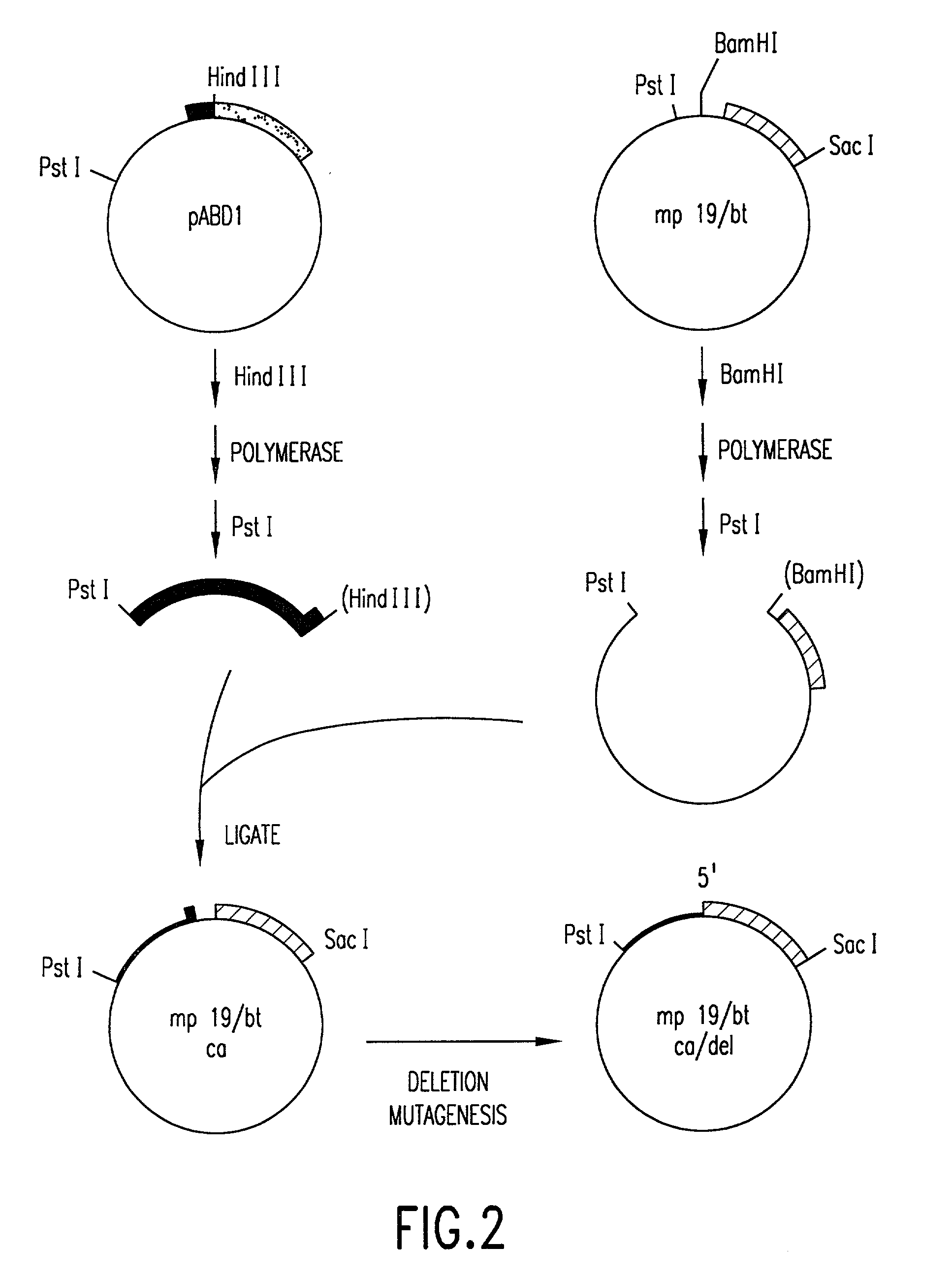
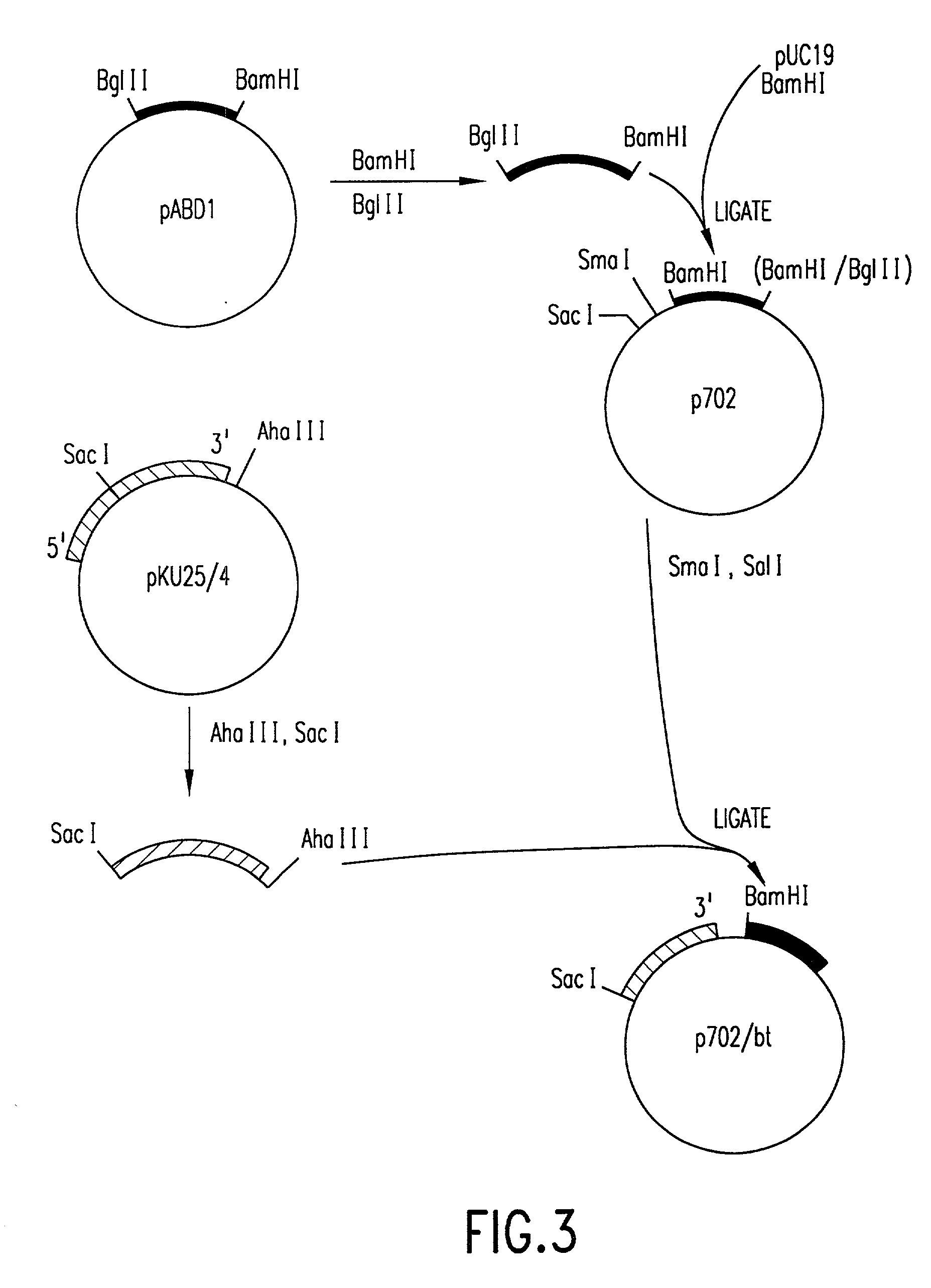
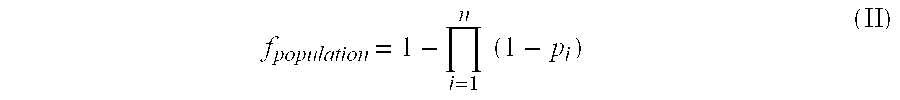Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
552 results about "Transformed cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transformation method for plants
InactiveUS6140553AImprove conversion efficiencyIncreasing frequency of stable transformationBryophytesSugar derivativesCell divisionDNA Integration
A process for integrating a DNA fragment into the genome of a cell of a monocotyledonous plant, the process comprising the steps of: 1) incubating, prior to contacting with the DNA fragment, a culture of untransformed monocotyledonous plant cells on a medium comprising a plant phenolic compound, for a period of time sufficient to stimulate cell division and enhance competence for integration of foreign DNA; and 2) contacting the untransformed cells with the DNA fragment under conditions in which the DNA fragment is taken up by the untransformed cells and is stably integrated in the genome of the untransformed cells, to generate transformed cells.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
Transgenic dunaliella salina as a bioreactor
Disclosed is a method for making a bioreactor comprising a foreign target gene, special selectable markers and Dunaliella Salina as host. It is prepared by the genetic transformation techniques that include introducing a foreign target gene into the cells of Dunaliella Salina and screening the transformed cells of Dunaliella Salina. The bioreactor of the present invention can be used as a safe and cheap production system for proteins of pharmaceutical interest including vaccines, especially oral products, in a large scale, because the cells of Dunaliella Salina are easy of genetic manipulation in preparation of the bioreactor, nontoxic and edible for humans and animals, and harmless to the environment.
Owner:XUE LEXUN +1
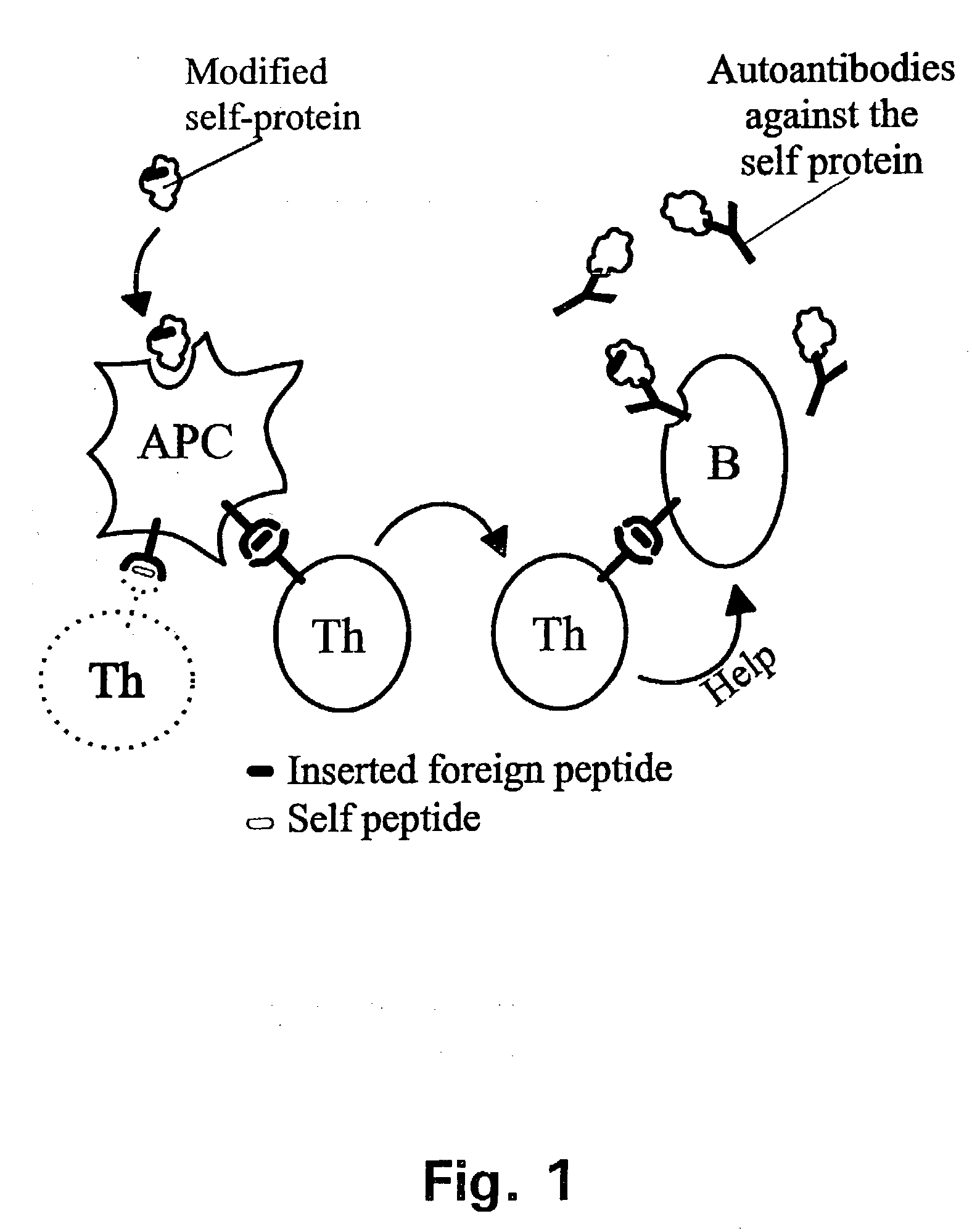
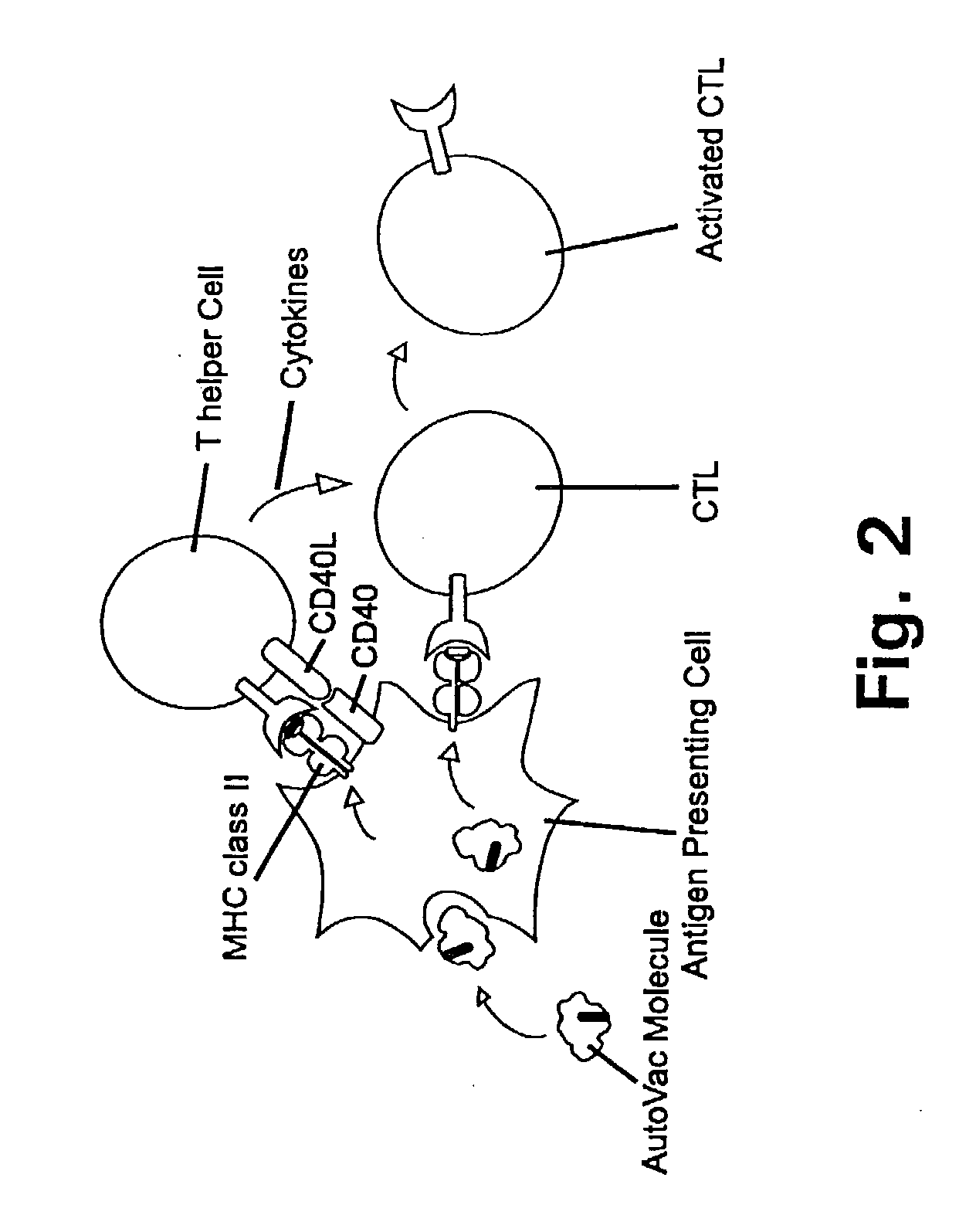
Novel methods for therapeutic vaccination
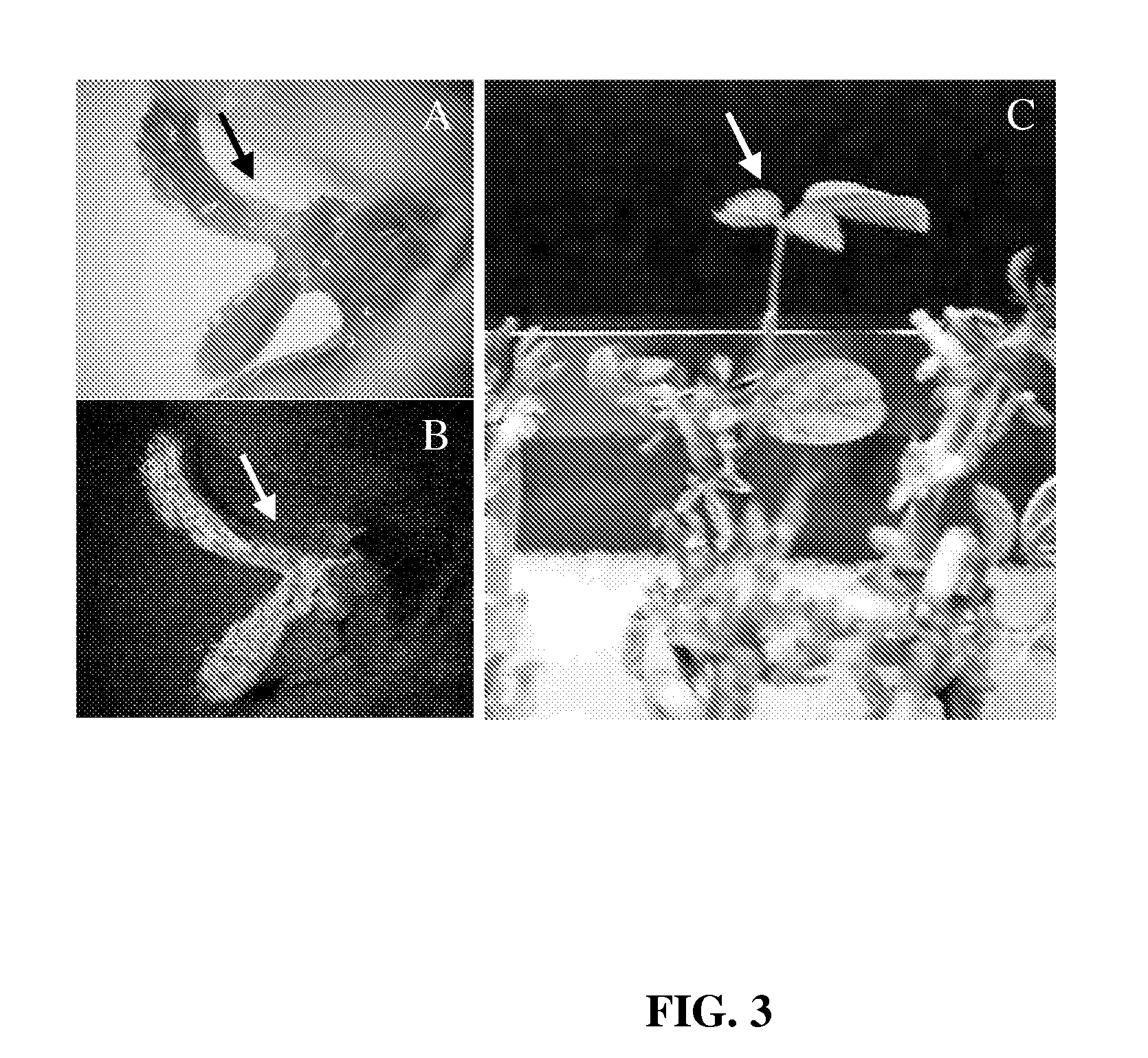
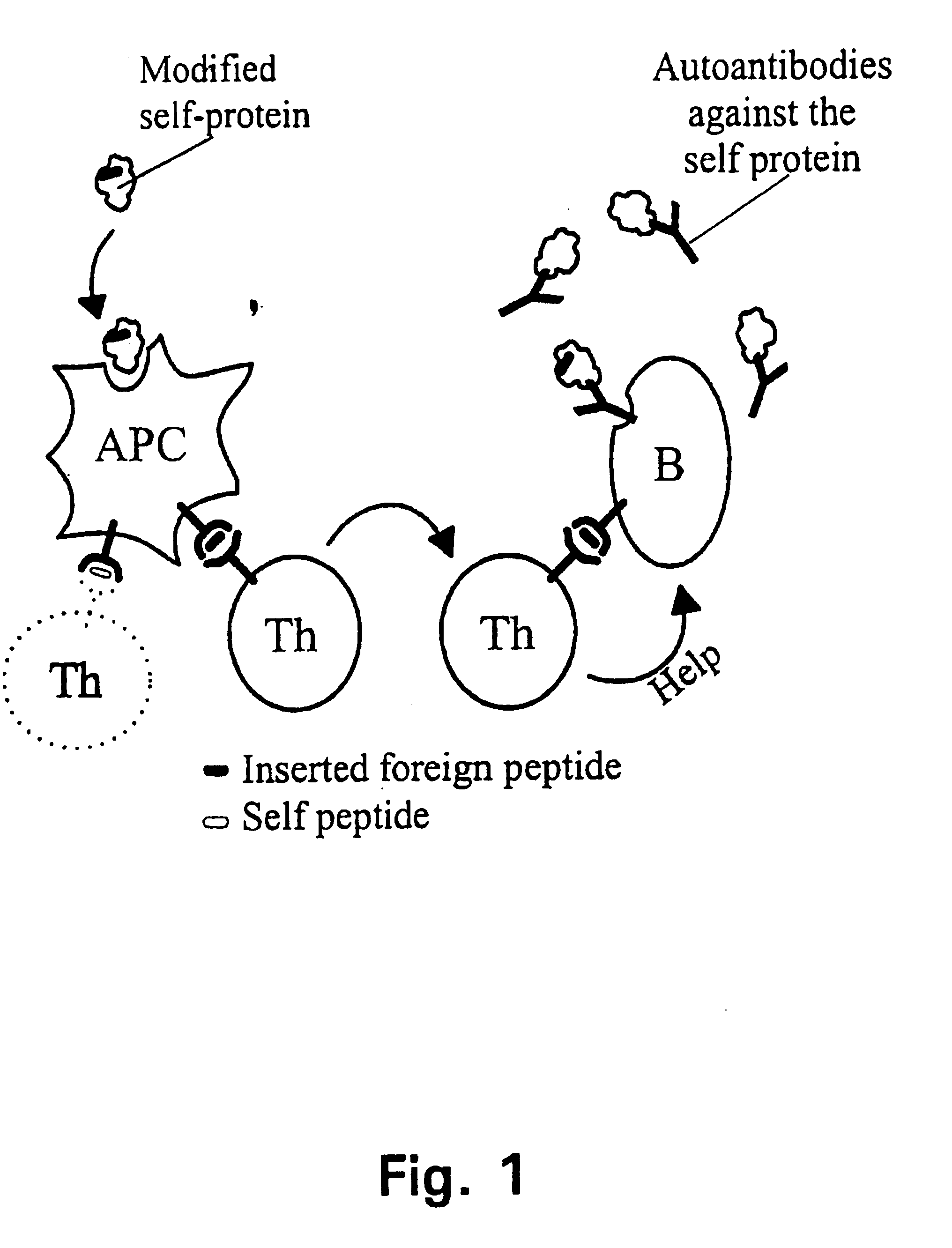
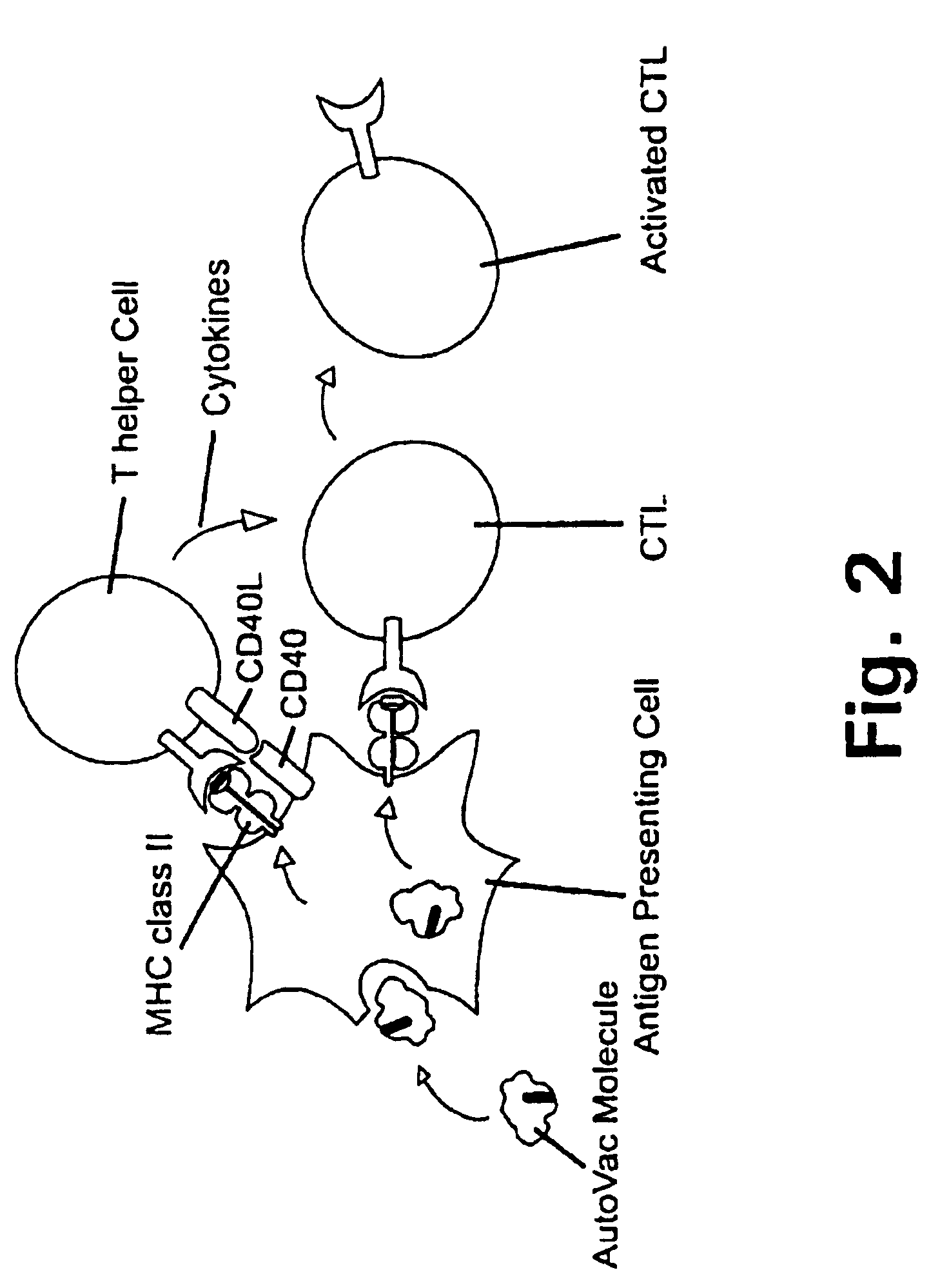
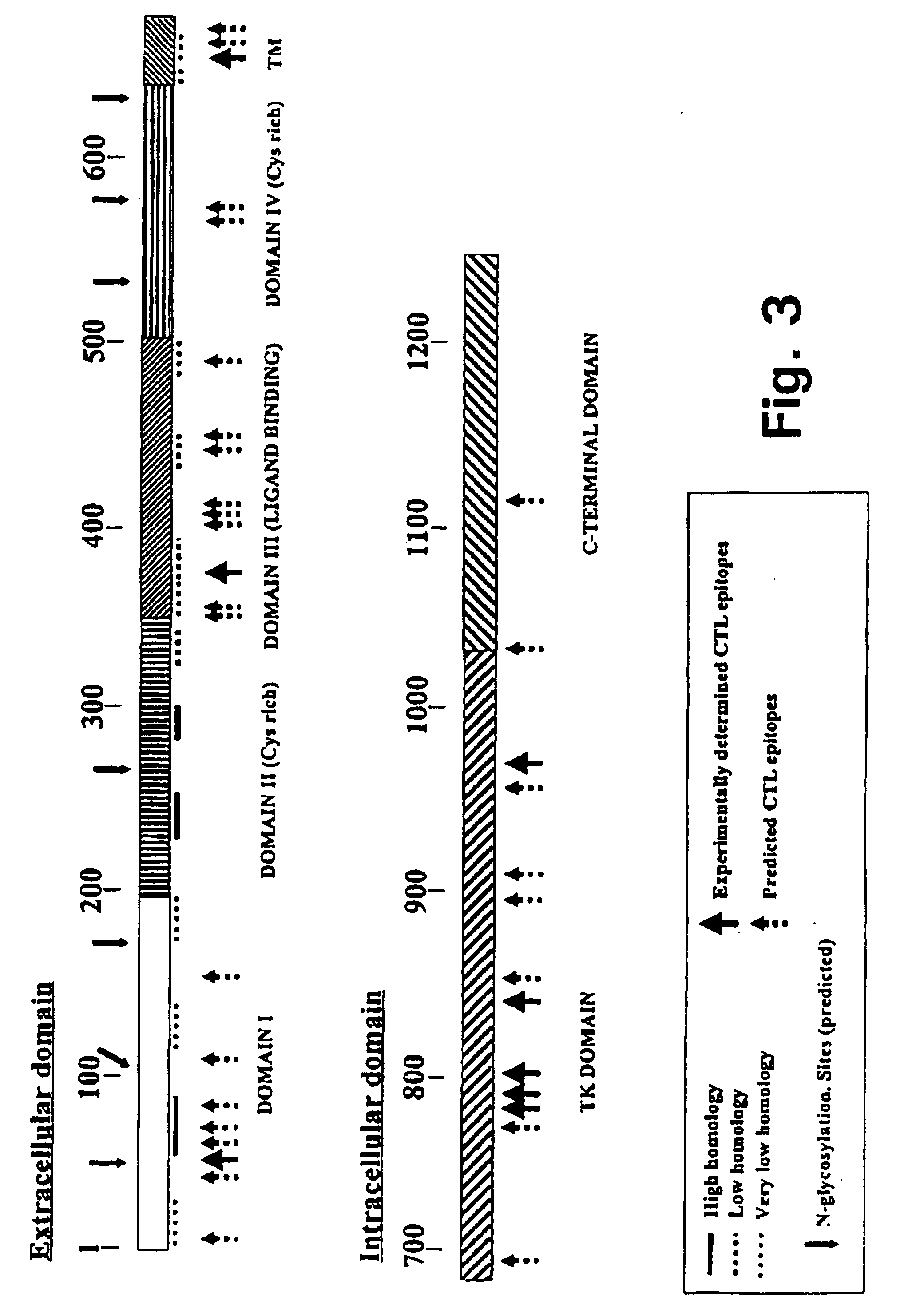
A method is disclosed for inducing cell-mediated immunity against cellular antigens. More specifically, the invention provides for a method for inducing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte immunity against weak antigens, notably self-proteins. The method entails that antigen presenting cells are induced to present at least one CTL epitope of the weak antigen and at the same time presenting at least one foreign T-helper lymphocyte epitope. In a preferred embodiment, the antigen is a cancer specific antigen, e.g. PSM, Her2, or FGF8b. The method can be exercised by using traditional polypeptide vaccination, but also by using live attenuated vaccines or nucleic acid vaccination. The invention furthermore provides immunogenic analogues of PSM, Her2 and FGF8b, as well as nucleic acid molecules encoding these analogues. Also vectors and transformed cells are disclosed. The invention also provides for a method for identification of immunogenic analogues of weak or non-immunogenic antigens.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Method for selection of transformed cells
ActiveUS20080120739A1Growth inhibitionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesSelect agentDirect production
The invention provides methods for the selection of transgenic cells. The invention relates to the unexpected finding that cells expressing a gene conferring tolerance to auxin-like herbicides such as dicamba may be directly selected from non-transgenic cells using auxin-like herbicides as a selective agent. In this manner, plants exhibiting tolerance to auxin-like herbicides can be directly produced without the need for separate selectable markers.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Novel methods for therapeutic vaccination
A method is disclosed for inducing cell-mediated immunity against cellular antigens. More specifically, the invention provides for a method for inducing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte immunity against weak antigens, notably self-proteins. The method entails that antigen presenting cells are induced to present at least one CTL epitope of the weak antigen and at the same time presenting at least one foreign T-helper lymphocyte epitope. In a preferred embodiment, the antigen is a cancer specific antigen, e.g. PSM, Her2, or FGF8b. The method can be exercised by using traditional polypeptide vaccination, but also by using live attenuated vaccines or nucleic acid vaccination. The invention furthermore provides immunogenic analogues of PSM, Her2 and FGF8b, as well as nucleic acid molecules encoding these analogues. Also vectors and transformed cells are disclosed. The invention also provides for a method for identification of immunogenic analogues of weak or non-immunogenic antigens.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
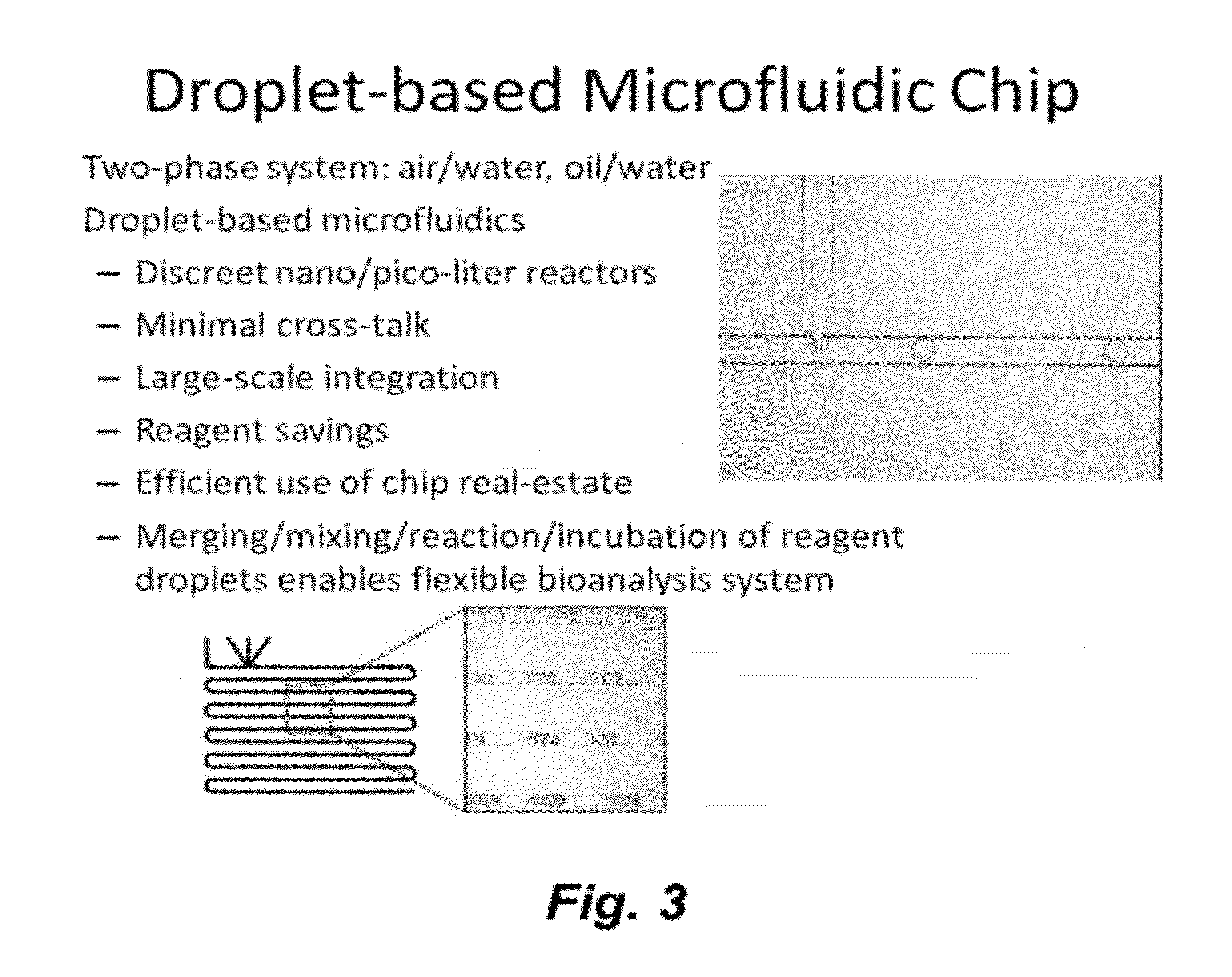
Microfluidic platform for synthetic biology applications
ActiveUS20120258487A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologySynthetic biology
This invention provides methods and compositions for assembling biological constructs (e.g., plasmids, transformed cells, etc.). In certain embodiments the methods involve encapsulating separate components of said biological construct each in a fluid droplet confined in a fluid channel; optionally mixing droplets from different fluid channels to for a sequenced order of droplets carrying different components of said biological construct in a channel or chamber; and optionally combining two or more droplets each containing different components of said biological construct to permit said components to react with each other in one or more reactions contributing to the assembly of said biological construct.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
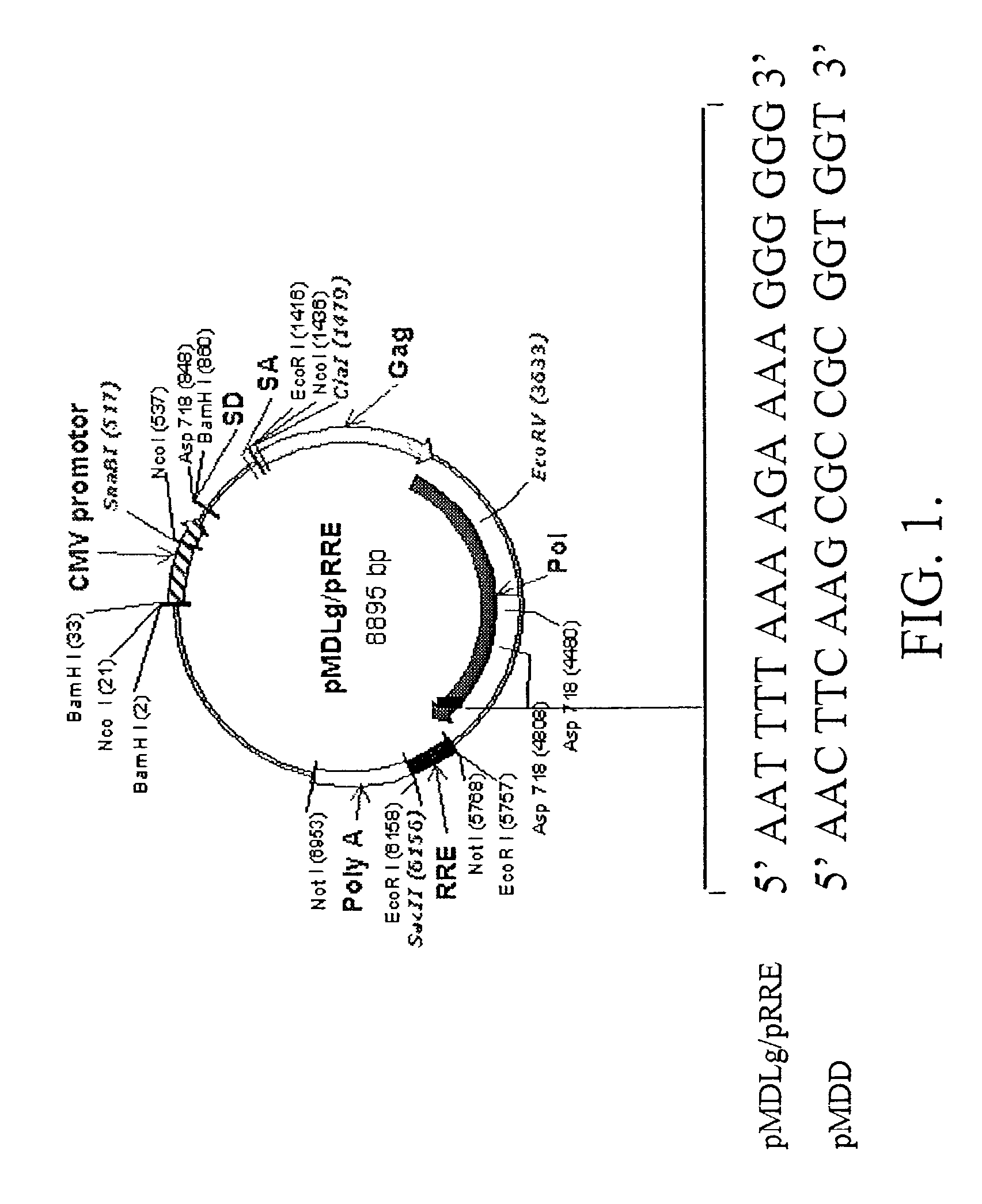
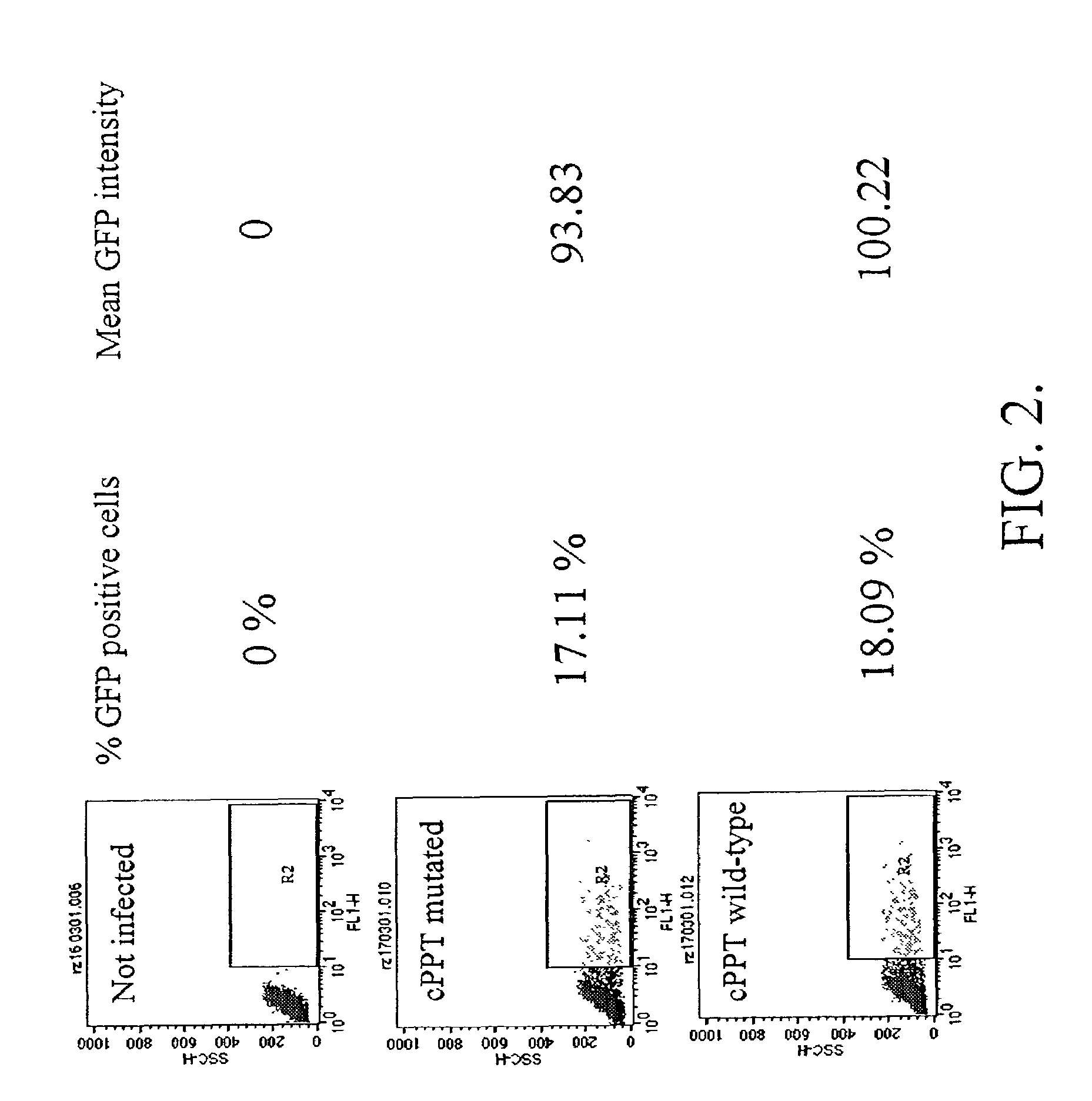
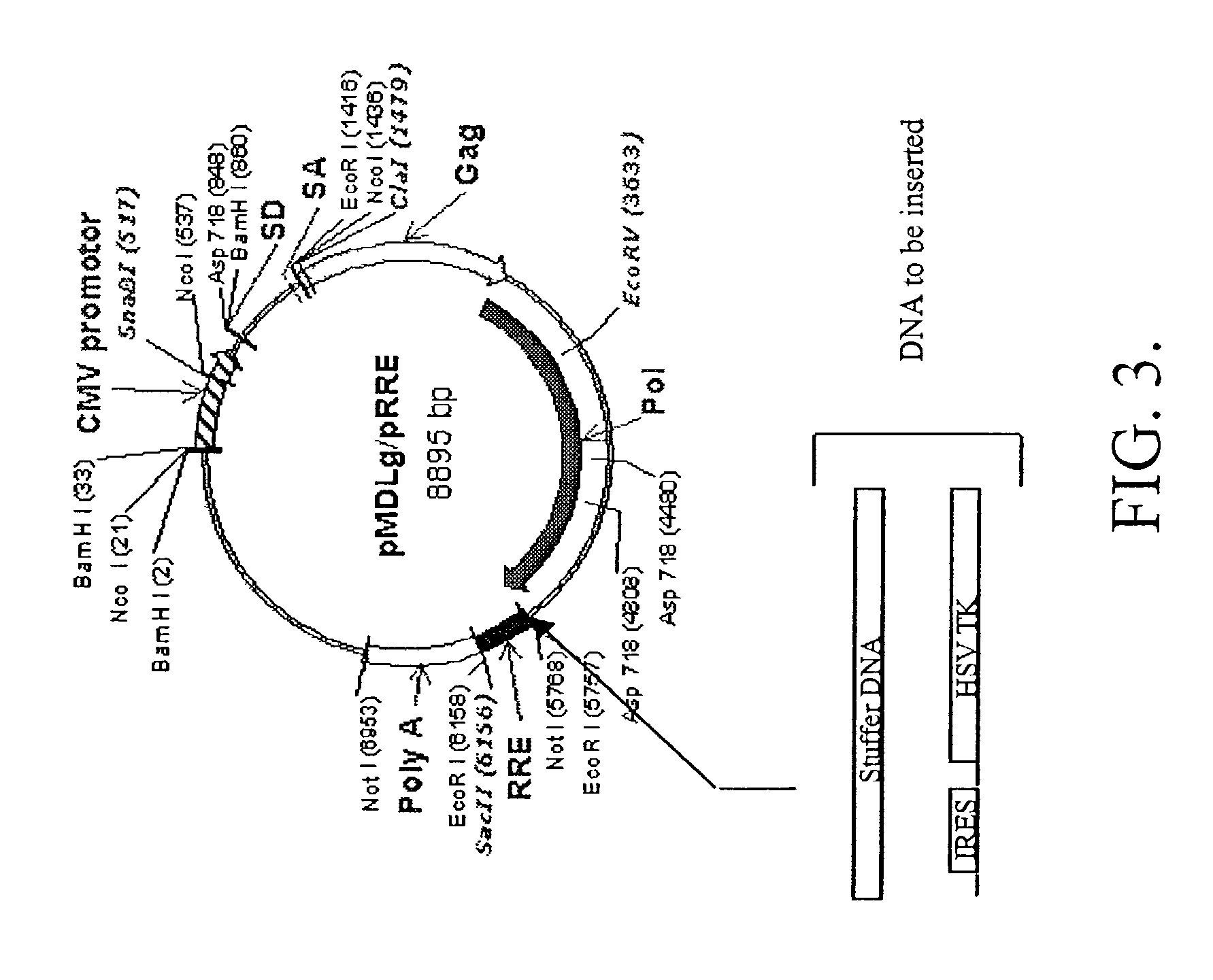
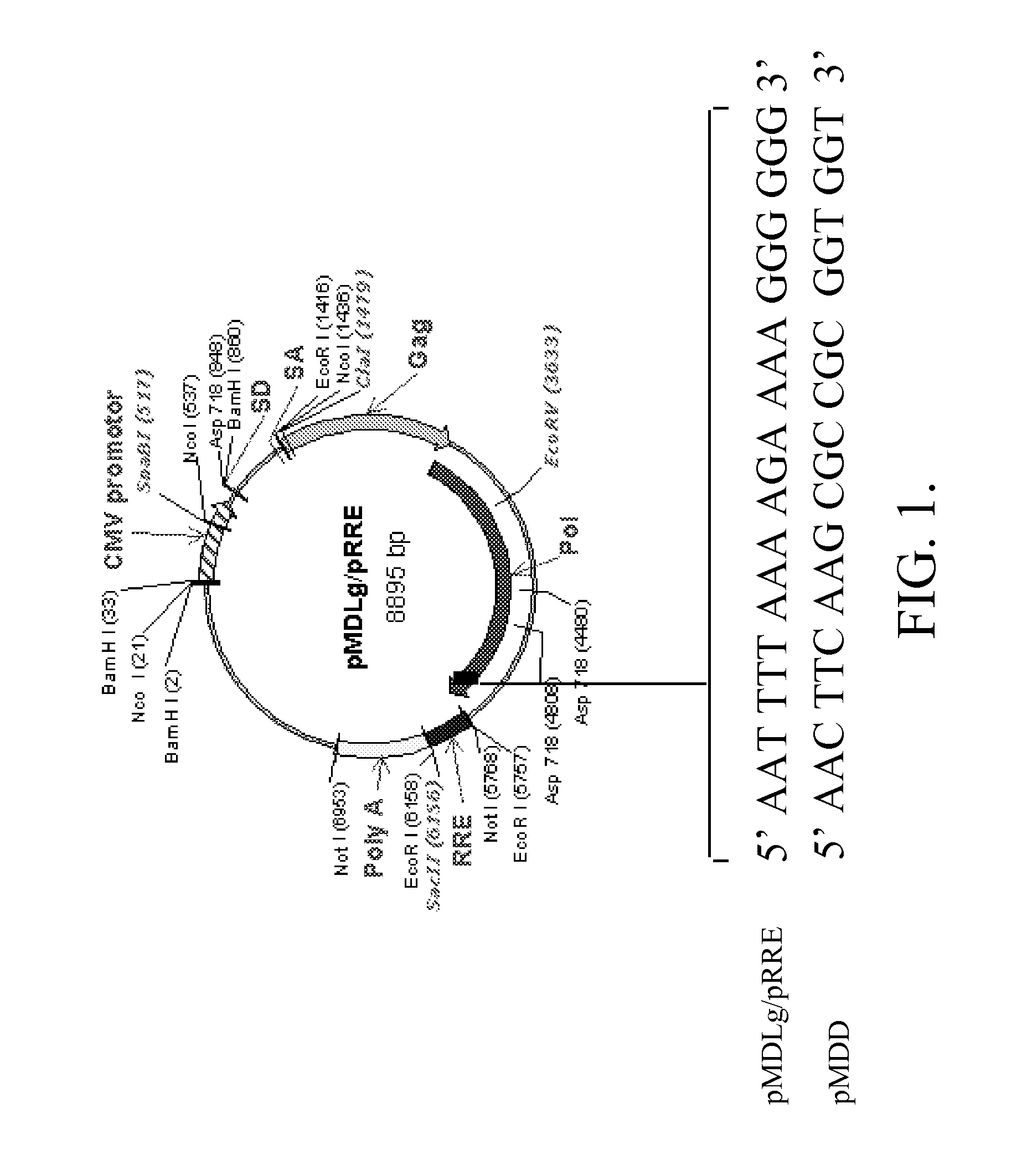
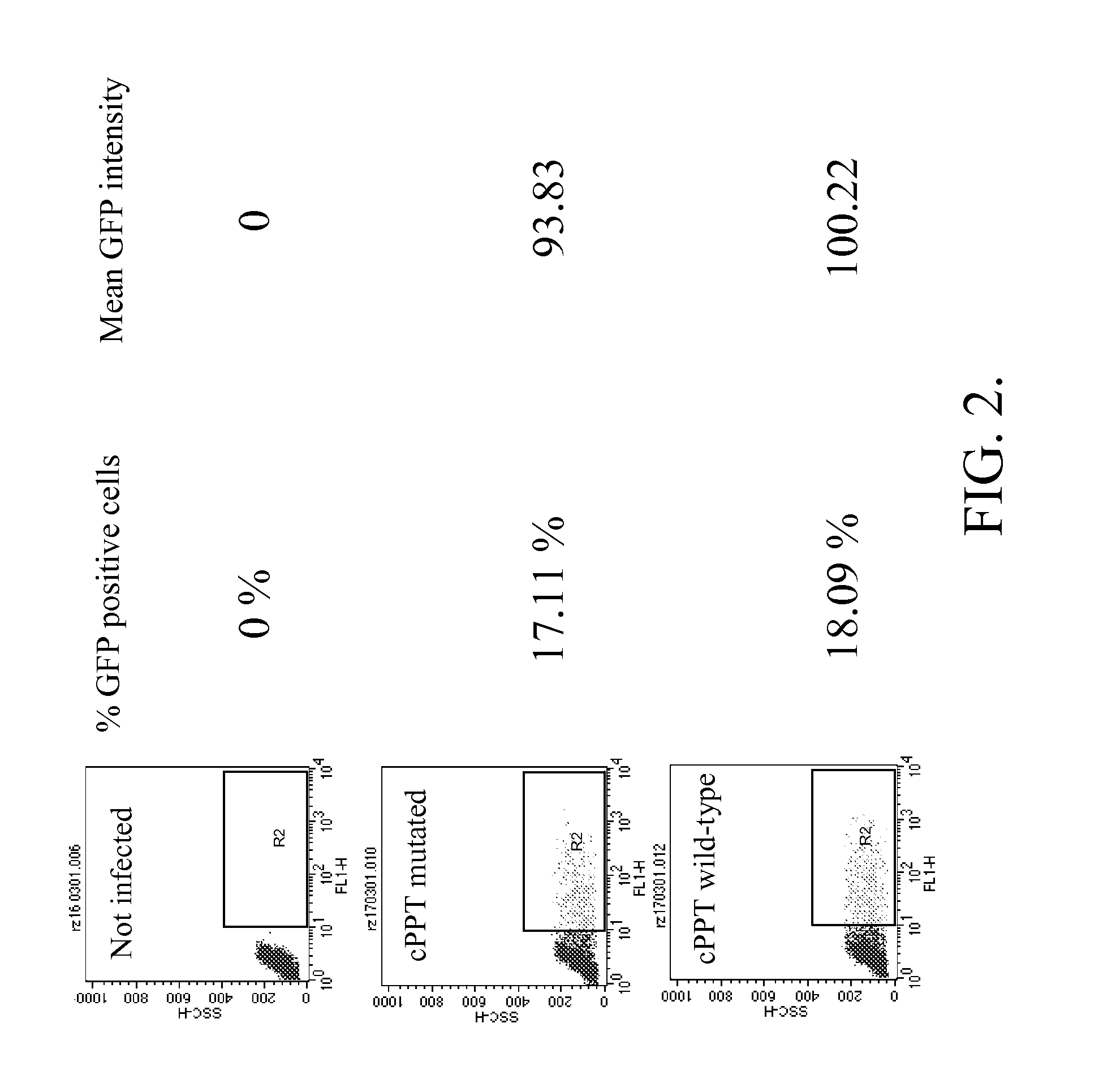
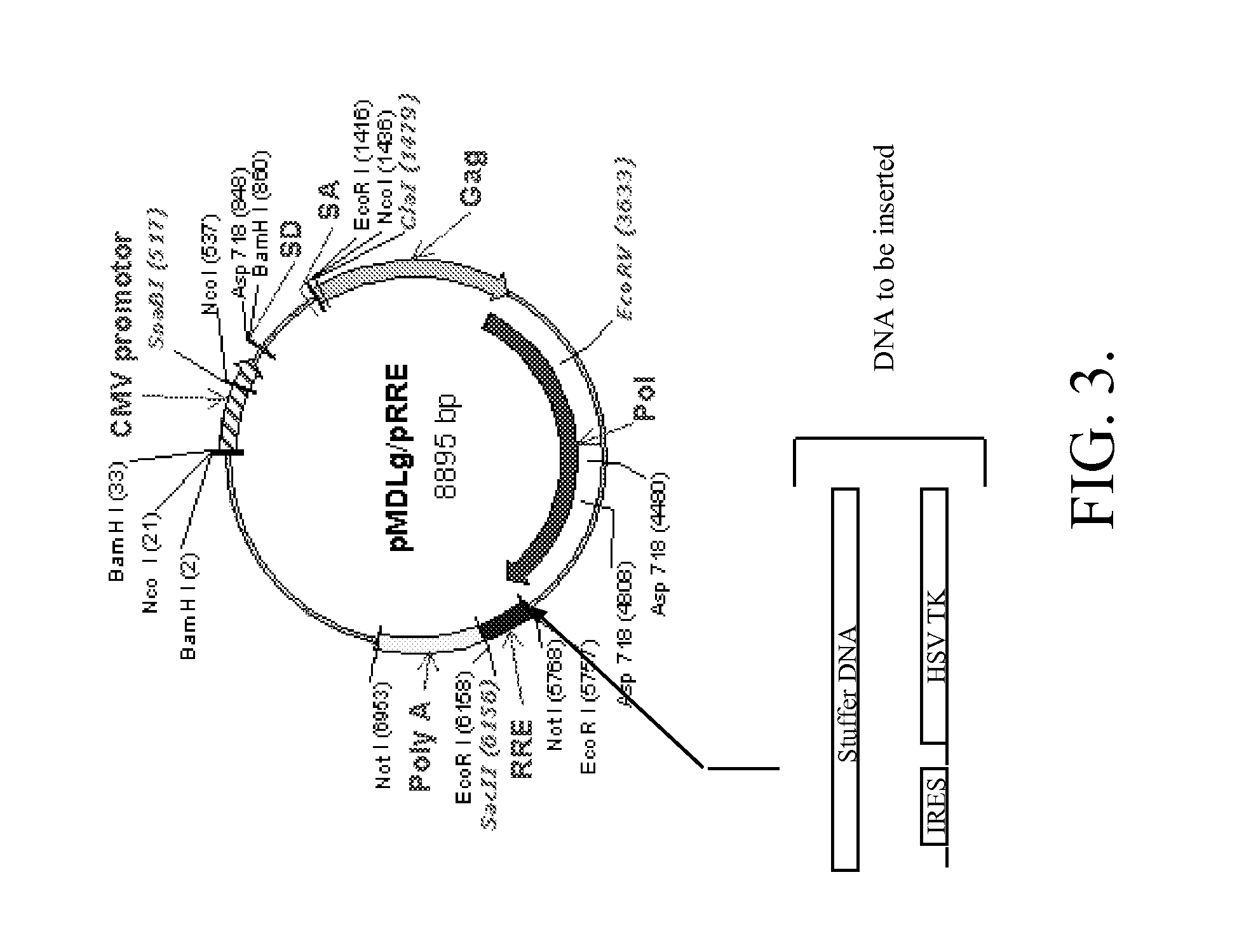
Methods and compositions relating to improved lentiviral vector production systems
ActiveUS7629153B2Increasing its biosafetySafe transfection and transductionVectorsGenetic material ingredientsTranscriptional Regulatory ElementsTransgene
The present invention provides HIV-derived lentivectors which are multiply modified to create highly safe, efficient, and potent vectors for expressing transgenes for gene therapy. The lentiviral vectors comprise various combinations of an inactive central polypurine tract, a stuffer sequence, which may encode drug susceptibility genes, and a mutated hairpin in the 5′ leader sequence that substantially abolishes replication. These elements are provided in conjunction with other features of lentiviral vectors, such as a self-inactivating configuration for biosafety and promoters such as the EF1α promoter as one example. Additional promoters are also described. The vectors can also comprise additional transcription enhancing elements such as the wood chuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element. These vectors therefore provide useful tools for genetic treatments for inherited and acquired disorders, gene-therapies for cancers and other disease, the creation of industrial and experimental production systems utilizing transformed cells, as well as for the study of basic cellular and genetic processes.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
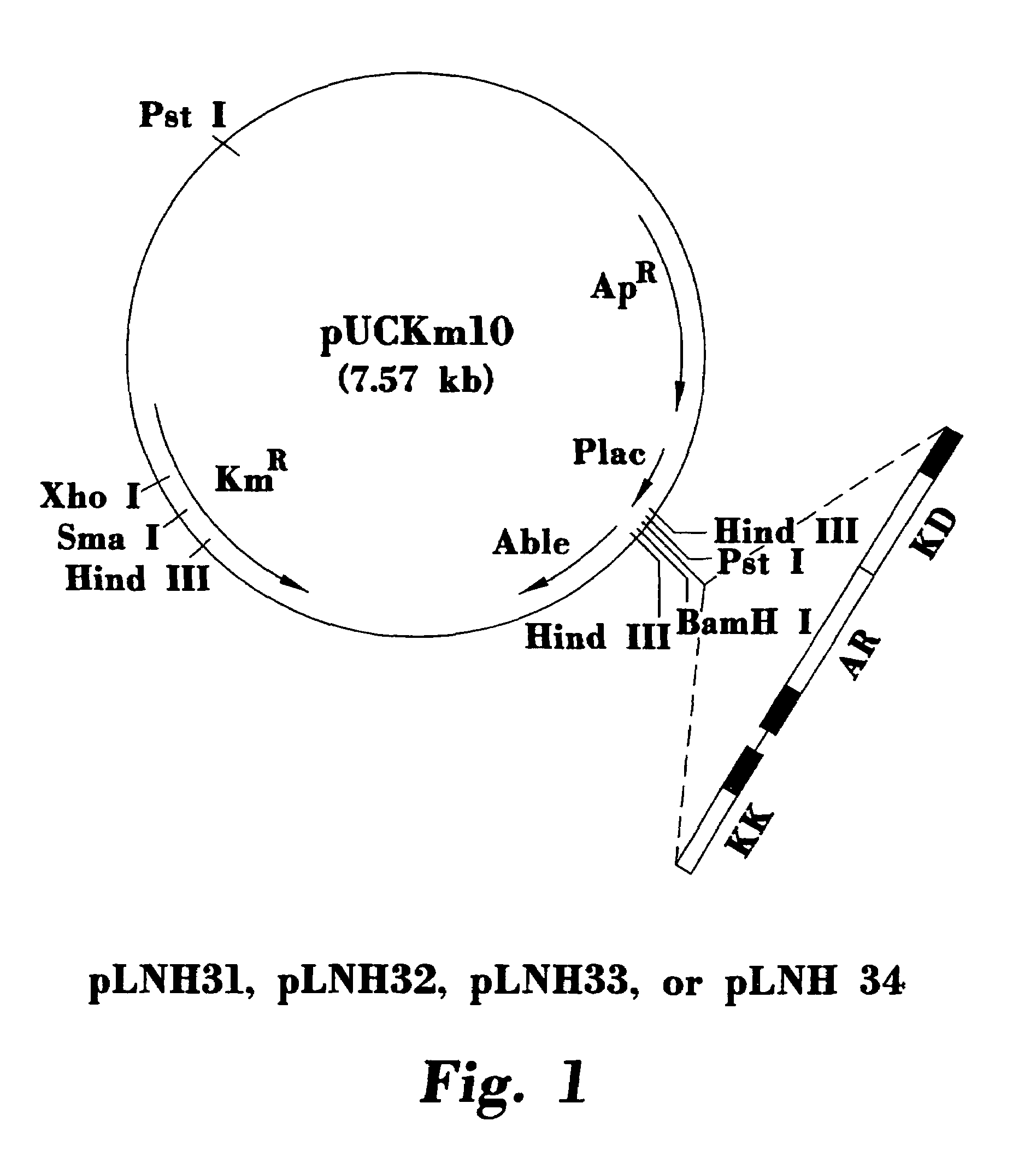
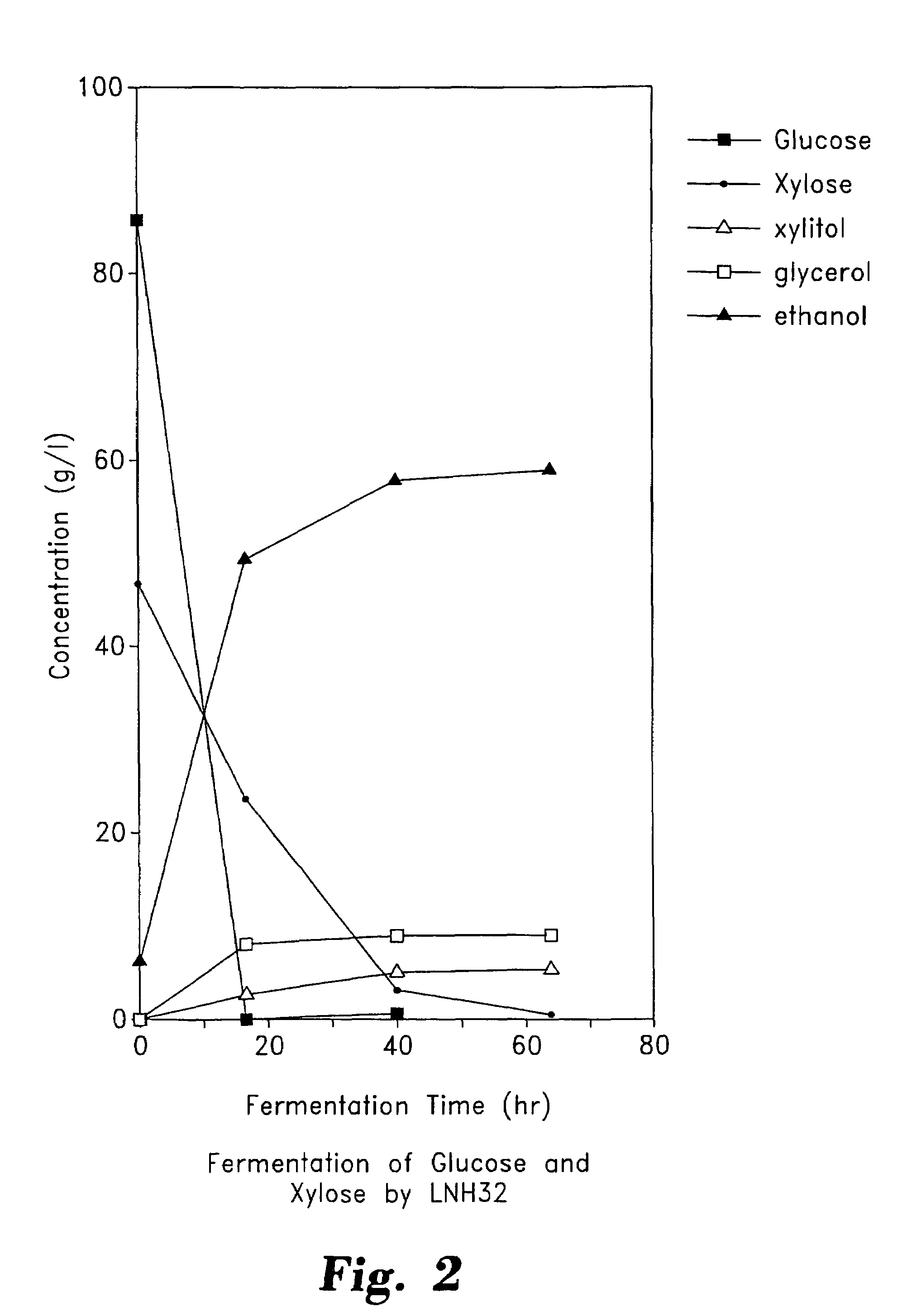
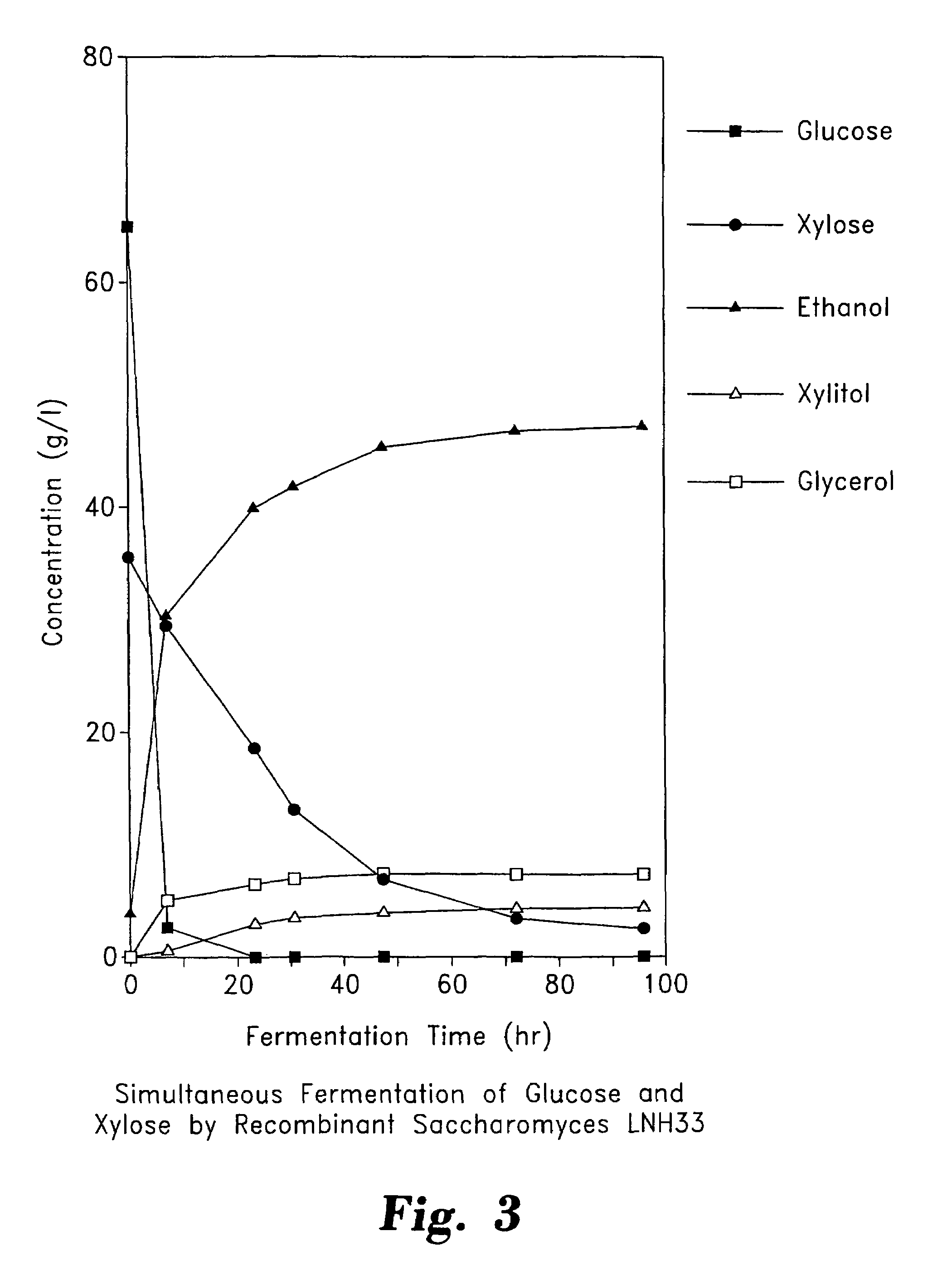
Stable recombinant yeasts for fermenting xylose to ethanol
InactiveUS7527927B1Easy to keepIncrease lossFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyXylitol dehydrogenase
Described are recombinant yeast which ferment xylose to ethanol and which maintain their ability to do so when cultured for numerous generations in non-selective media. The preferred yeast contain multiple copies of integrated genes encoding xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase fused to promoters which are non-glucose inhibited and which do not require xylose for induction. Also described are preferred methods for integrating multiple copies of exogenous DNA into host cells by transforming cells with replicative / integrative vectors, and then replicating the cells a number of times under selective pressure to promote retention of the vector in subsequent generations. The replicated vectors thus serve to integrate multiple copies of the exogenous DNA into the host cells throughout the replication / selection phase. Thereafter the selective pressure can be removed to promote loss of the vector in subsequent generations, leaving stable integrants of the exogenous DNA.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
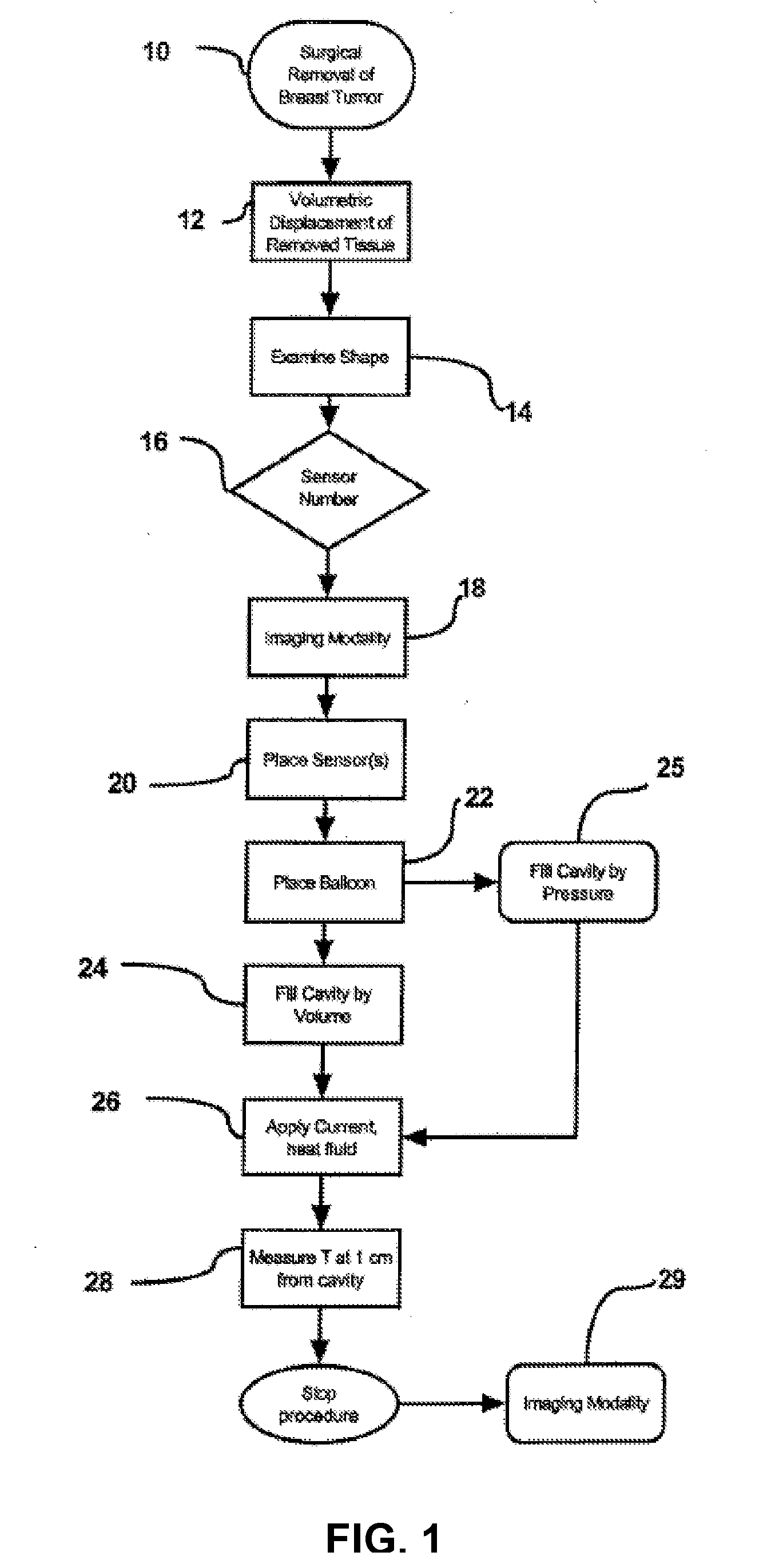
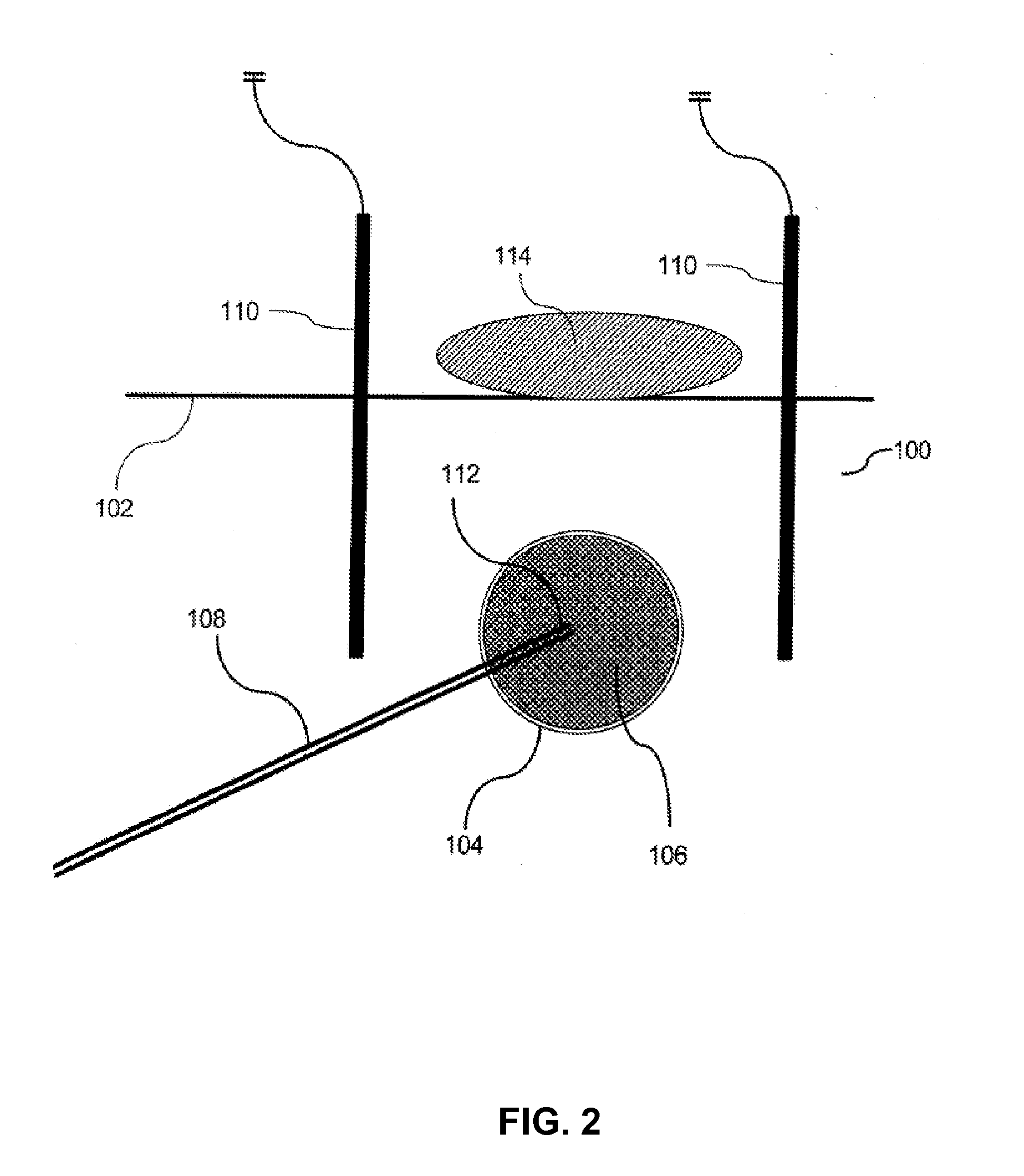
High temperature thermal therapy of breast cancer
A method is described for preventing breast cancer recurrence after surgical removal of a breast cancer mass. Specifically, the method is thermal treatment of breast tissue surrounding a cavity after lumpectomy for breast cancer. Delivery of a heated fluid is through a balloon catheter to the cavity generated after lumpectomy with the goal of ablating the surrounding tissue, including transformed cells that were not removed through surgery. A balloon and controller were designed for this application.
Owner:THERMATOME
Methods and compositions relating to improved lentiviral vector production systems
ActiveUS8900858B2Increasing its biosafetySafe transfection and transductionVectorsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseTranscriptional Regulatory Elements
The present invention provides HIV-derived lentivectors which are multiply modified to create highly safe, efficient, and potent vectors for expressing transgenes for gene therapy. The lentiviral vectors comprise various combinations of an inactive central polypurine tract, a stuffer sequence, which may encode drug susceptibility genes, and a mutated hairpin in the 5′ leader sequence that substantially abolishes replication. These elements are provided in conjunction with other features of lentiviral vectors, such as a self-inactivating configuration for biosaftey and promoters such as the EF1α promoter as one example. Additional promoters are also described. The vectors can also comprise additional transcription enhancing elements such as the wood chuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element. These vectors therefore provide useful tools for genetic treatments for inherited and acquired disorders, gene-therapies for cancers and other disease, the creation of industrial and experimental production systems utilizing transformed cells, as well as for the study of basic cellular and genetic processes.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Enhancing inorganic carbon fixation by photosynthetic organisms
A method of enhancing inorganic carbon fixation by a photosynthetic organism. The method is effected by transforming cells of the photosynthetic organism with an expressible polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide having a bicarbonate transporter activity. Preferably, the polynucleotide further includes a plant promoter. Sequences and constructs for implementing the method are also described.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Methods for lyophilizing competent cells
This invention relates to a method for producing cells which are competent for transformation and which may be stably stored for extended periods of time at various temperatures. The method involves growing cells in a growth conducive medium, rendering said cells competent, and lyophilizing said competent cells. The invention further relates to competent cells produced by such a method, to methods of transforming said cells with a DNA molecule, and to a method of producing a desired protein or polypeptide from said transformed cells.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Transformation of soybean
InactiveUS20090049567A1Improved shoot productionShorten the timeOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureGlycineTarget tissue
The present invention relates to improved methods for the incorporation of DNA into the genome of a soybean (Glycine max) plant utilizing meristematic cells of primary or higher leaf nodes as target tissue by means of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and subsequent regeneration of the transformed cells into a whole plant.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
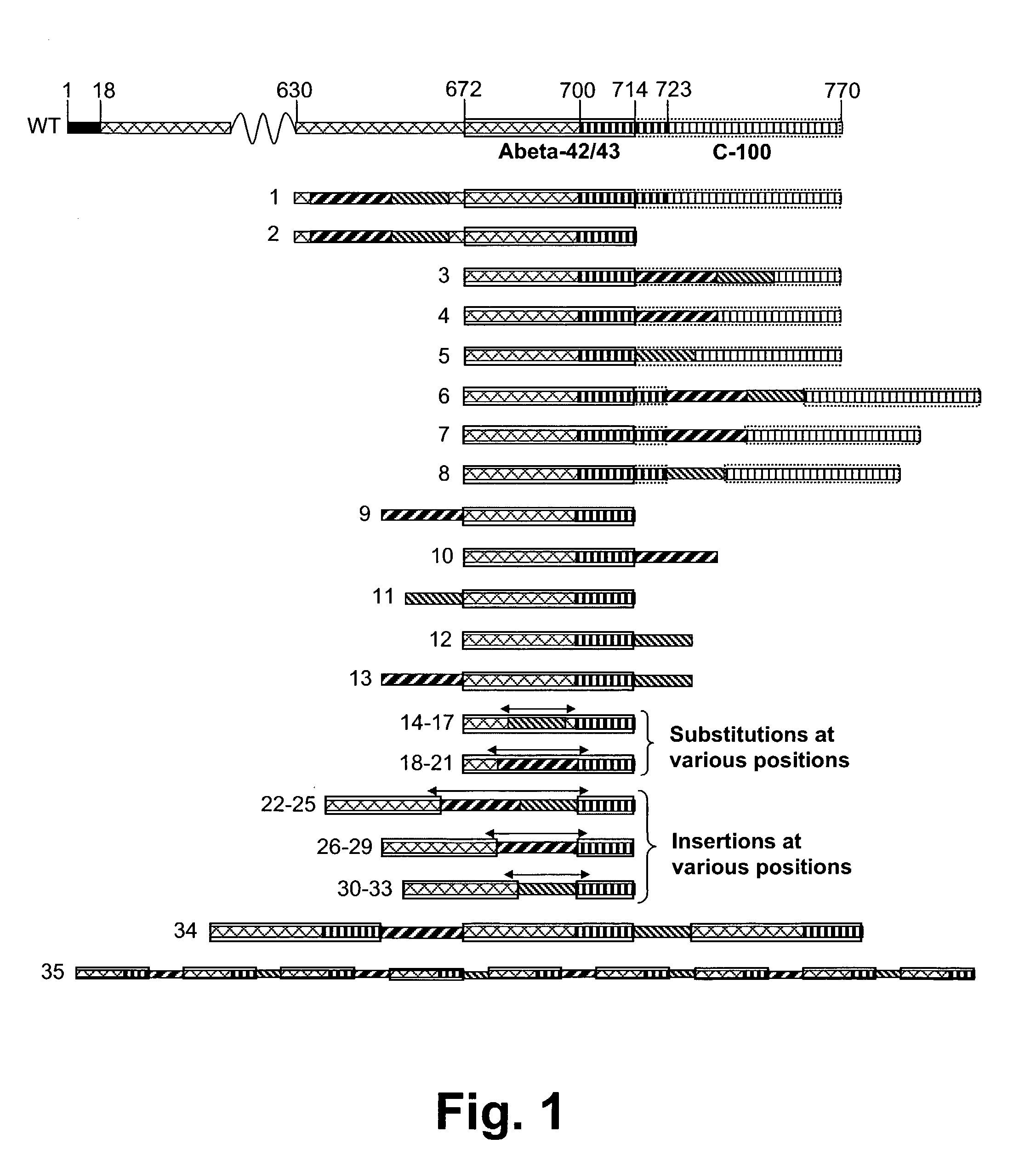
Novel method for down-regulation of amyloid
Disclosed are novel methods for combatting diseases characterized by deposition of amyloid. The methods generally rely on immunization against amyloid precursor protien (APP) or beta amyloid (Abeta). Immunization is preferably effected by administration of analogues of autologous APP or Abeta, said analogues being capable of inducing antibody production against the autologous amyloidogenic polypeptides. Especially preferred as an immunogen is autologous Abeta which has been modified by introduction of one single or a few foreign, immunodominant and promiscuous T-cell epitopes. Also disclosed are nucleic acid vaccination against APP or Abeta and vaccination using live vaccines as well as methods and means useful for the vaccination. Such methods and means include methods for the preparation of analogues and pharmaceutical formulations, as well as nucleic acid fragments, vectors, transformed cells, polypeptides and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
Early-inflorescence-preferred regulatory elements and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070136891A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleic acid sequencingNucleotide sequencing
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of isolated nucleotide sequences in a plant. The compositions are novel nucleic acid sequences for regulatory elements providing expression preferentially in the inflorescence meristem and developing floral tissues. Methods for expressing an isolated nucleotide sequence in a plant using the regulatory sequences are also provided, as well as expression constructs, vectors, and transformed cells and plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
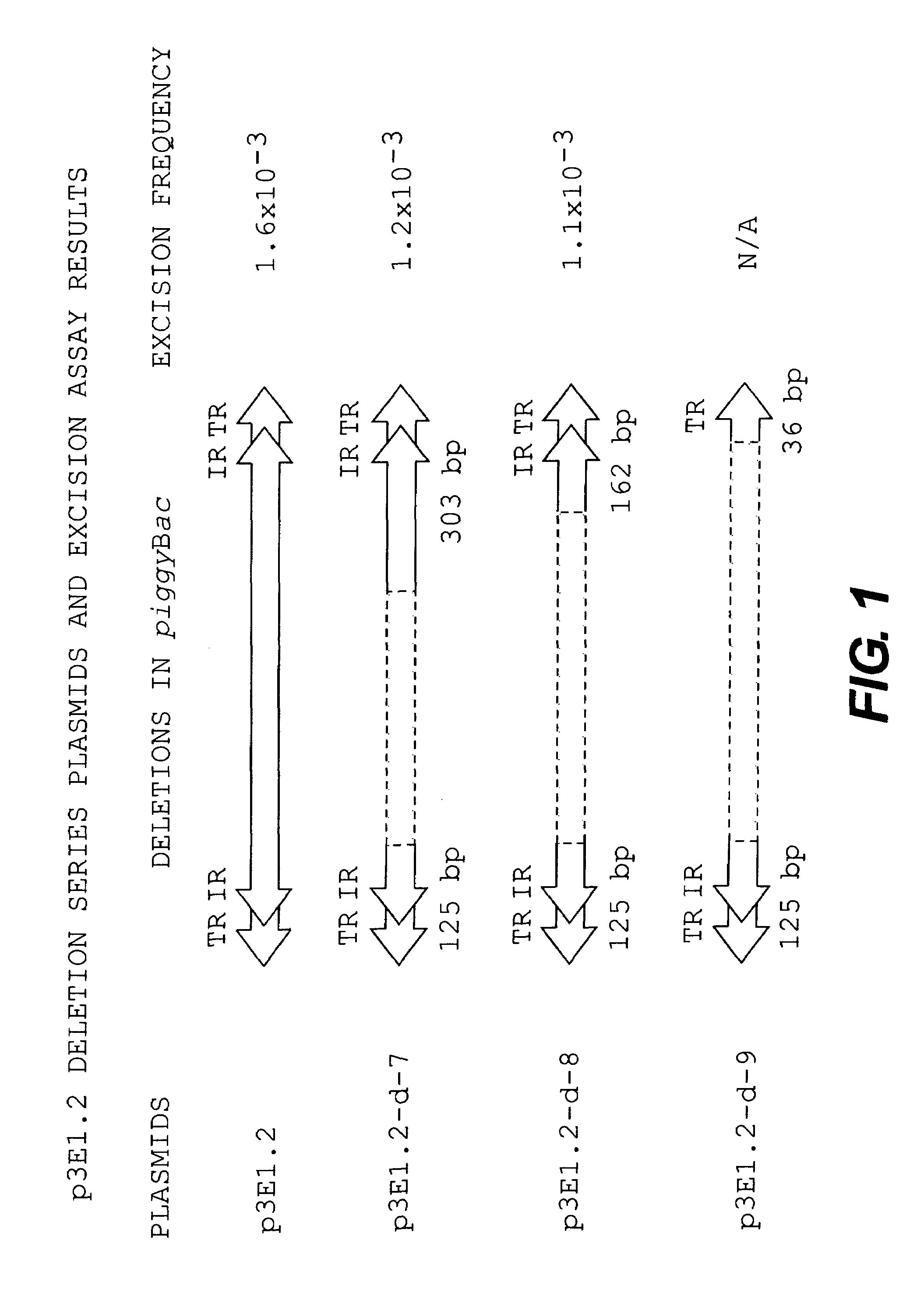
Methods and compositions for transposition using minimal segments of the eukaryotic transformation vector Piggybac
InactiveUS7105343B1Inserting DNA molecules into cells is enhancedEasy to insertSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNATransformation cellGene transfer
The present invention provides efficient transfer of genes into host cells or embryos to transform the cells or embryos by transposition vectors using the minimal amount of nucleotide sequences in the transposon piggyBac required for gene transfer. The transformed cells or embryos may also be developed into transgenic organisms.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
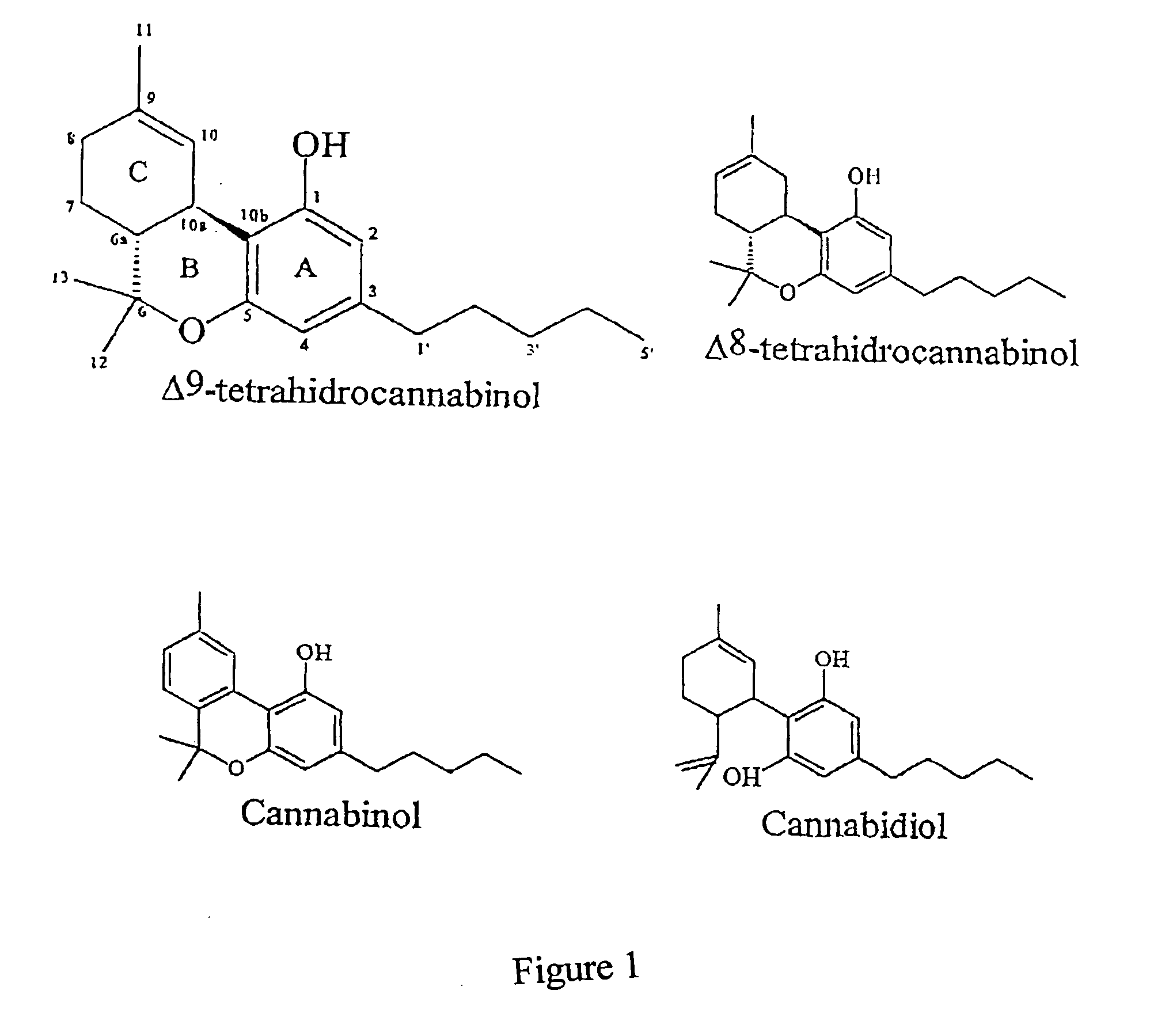
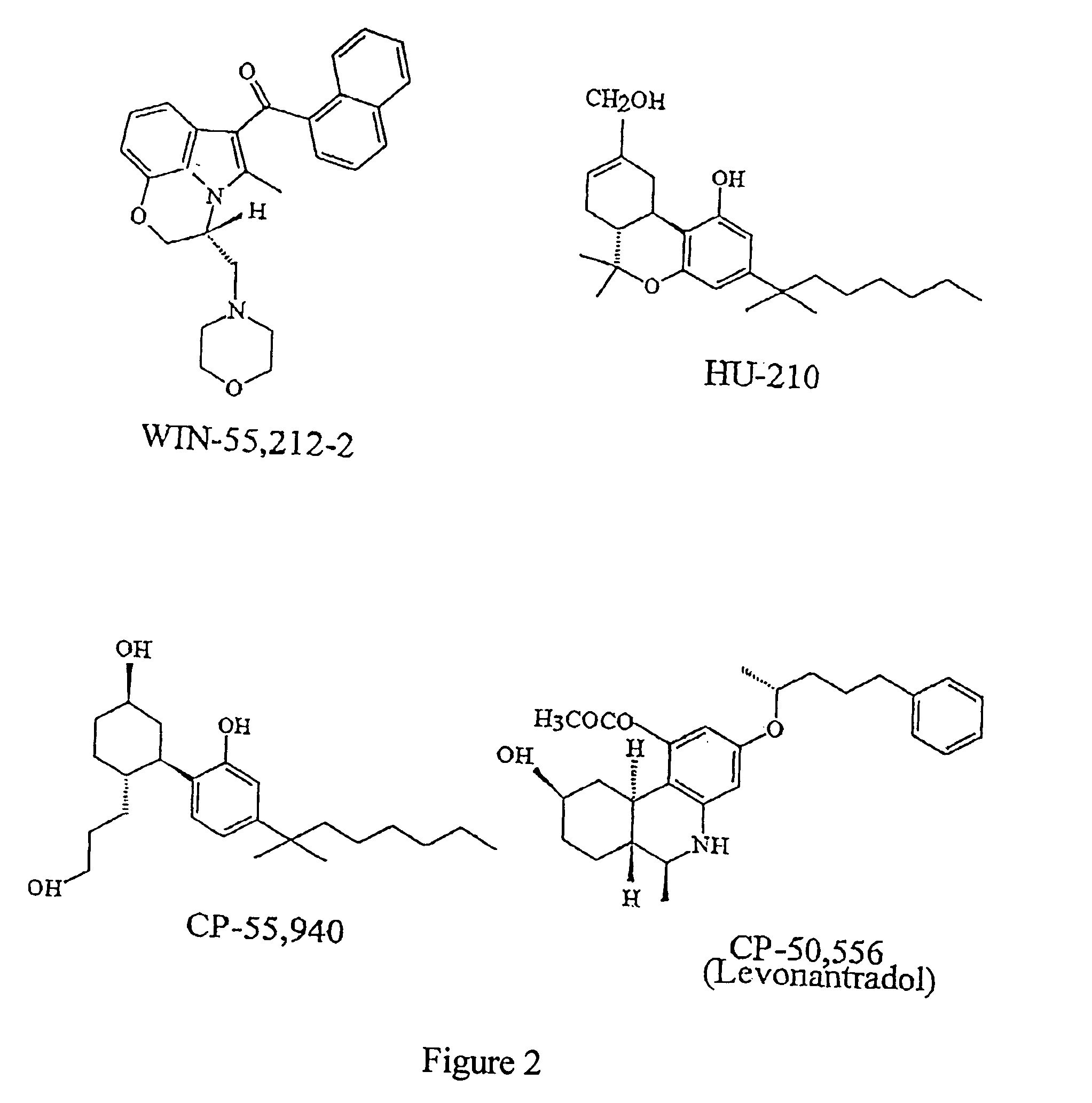
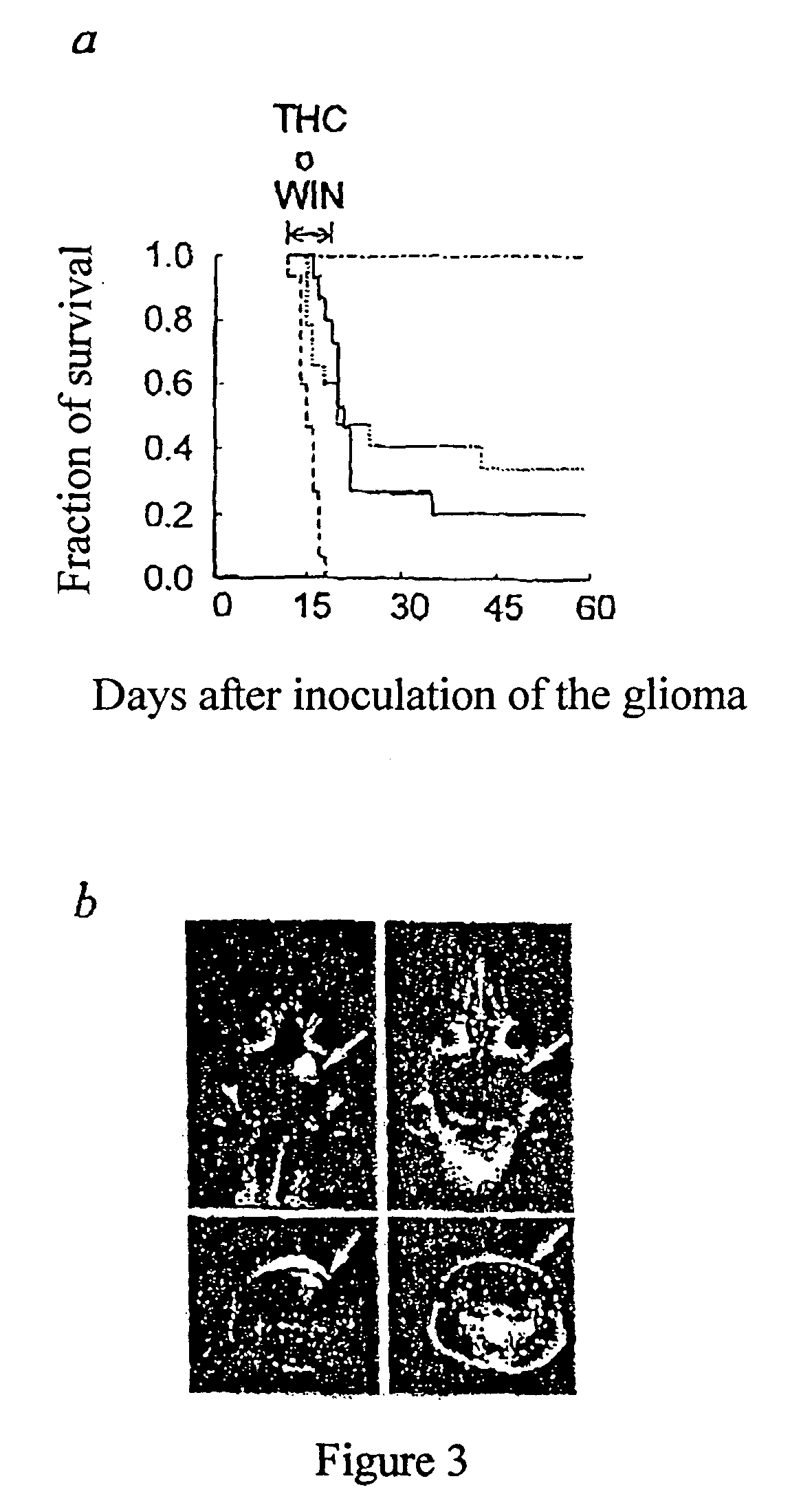
Therapy with cannabinoid compounds for the treatment of brain tumors
InactiveUS20040039048A1Lacking appreciable side effectHighly effective in treatmentBiocideAmide active ingredientsSide effectCannabinoid
Owner:GUZMAN PASTOR MANUEL +2
Methods for stable transformation of plants
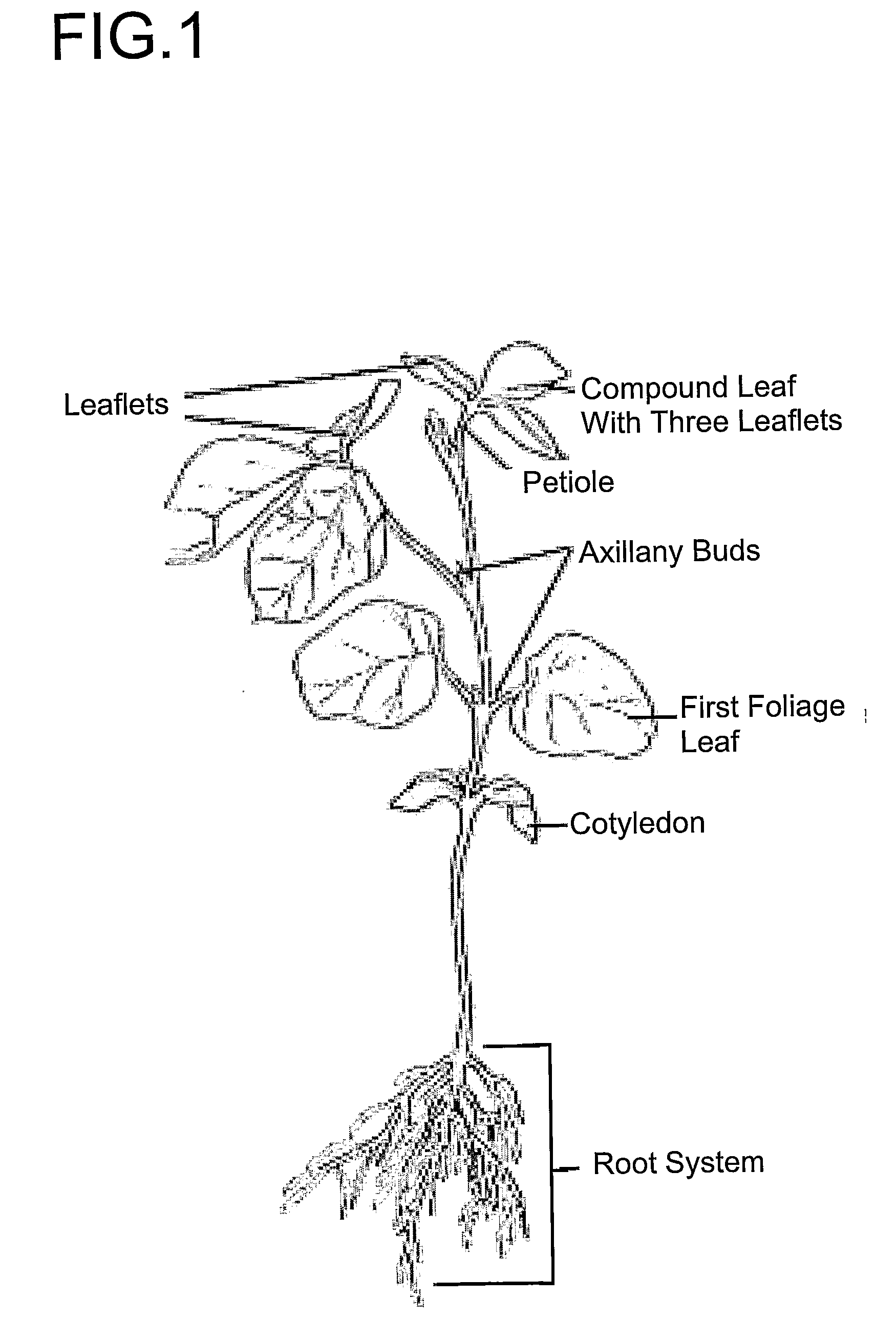
InactiveUS6858777B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove transformation efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationAxillary budNicotiana tabacum
Multiple shoot structures are induced from plant tissues (e.g., shoot apices or axillary buds on an artificial medium) to produce multiple shoot cultures. These multi-shoot cultures are then transformed by known transformation methods. Plants are subsequently regenerated from the transformed cells. Crops that may be efficiently transformed by this method include plants normally recalcitrant to transformation such as sugar beet, sunflower, soybean, cotton, tobacco, tomato, peanuts, melons, watermelon, squash, Brassica, and pepper.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Carboxylic acid reductase polypeptide, nucleotide sequence encoding same and methods of use
The invention provides the nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence for the enzyme carboxylic acid reductase isolated from bacteria. Expression cassettes, vectors, transformed cells, and variants are also provided as methods for use of recombinant biocatalytic reagents in production of synthetic, aromatic, aliphatic and alicyclic aldehydes and alcohols.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Insecticidal cotton plant cells
InactiveUS20010026939A1Sufficient efficiencyClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacillus thuringiensisPlant cell
Cotton cells are transformed with a chimeric gene that expresses in the cells a polypeptide having substantially the insect toxicity properties of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein. The transformed cells are regenerated into plants that are toxic to the larvae of lepidopteran insects.
Owner:RICE DOUGLAS +7
Expression of foreign sequences in plants using transactivation system
InactiveUS20050114920A1High expressionOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellNucleic acid sequencing
A transactivation system and method for producing a foreign polypeptide of interest in cells of a host plant is disclosed. The transactivation system has two components. It has genetically transformed cells of the host plant having integrated in their nuclear genome, an inactive or silenced foreign nucleic acid sequence, which is capable of encoding, upon its activation, the foreign polypeptide of interest; and a recombinant RNA viral vector capable of infecting the cells of the host plant and encoding therein a factor for activating or facilitating the expression of inactive or silenced foreign nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:IBIO
Mutant Forms of Fas Ligand and Uses Thereof
The invention provides for DNA encoding Fas ligand muteins and chimeras and the proteins encoded thereby. The invention further includes the use of DNA and vectors to produce transformed cells expressing the mutant or chimeric Fas ligand. When the Fas ligand of the invention is a non cleavable form, the cells expressing the Fas ligand are useful in vitro for identifying Fas expressing cells or in vivo for reducing populations of Fas expressing cells. Thus, in other embodiments, the present invention is also directed to a method for treating a patient, for example a mammal, for autoimmune disease or transplant rejection by administering a Fas ligand therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent is a polypeptide, a polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide or a small molecule. The polypeptides include full-length Fas ligand polypeptide, or a biologically active variant, derivative, portion, fusion or peptide thereof.
Owner:CHU KETING
Method of screening multiply transformed cells using bicistronic expression of fluorescent proteins
A method of screening multiply transformed / transfected cells to identify those cells expressing at least two peptides or proteins of interest. The method comprising: 1. Simultaneously or sequentially transforming a cell with at least two different expression cassettes in which the gene of interest is linked via an IRES to a fluorescent marker gene. Each marker gene is different. 2. Providing conditions in which expression of the genes will occur. 3. Identifying cells expressing proteins by detecting the different fluorescent signals.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
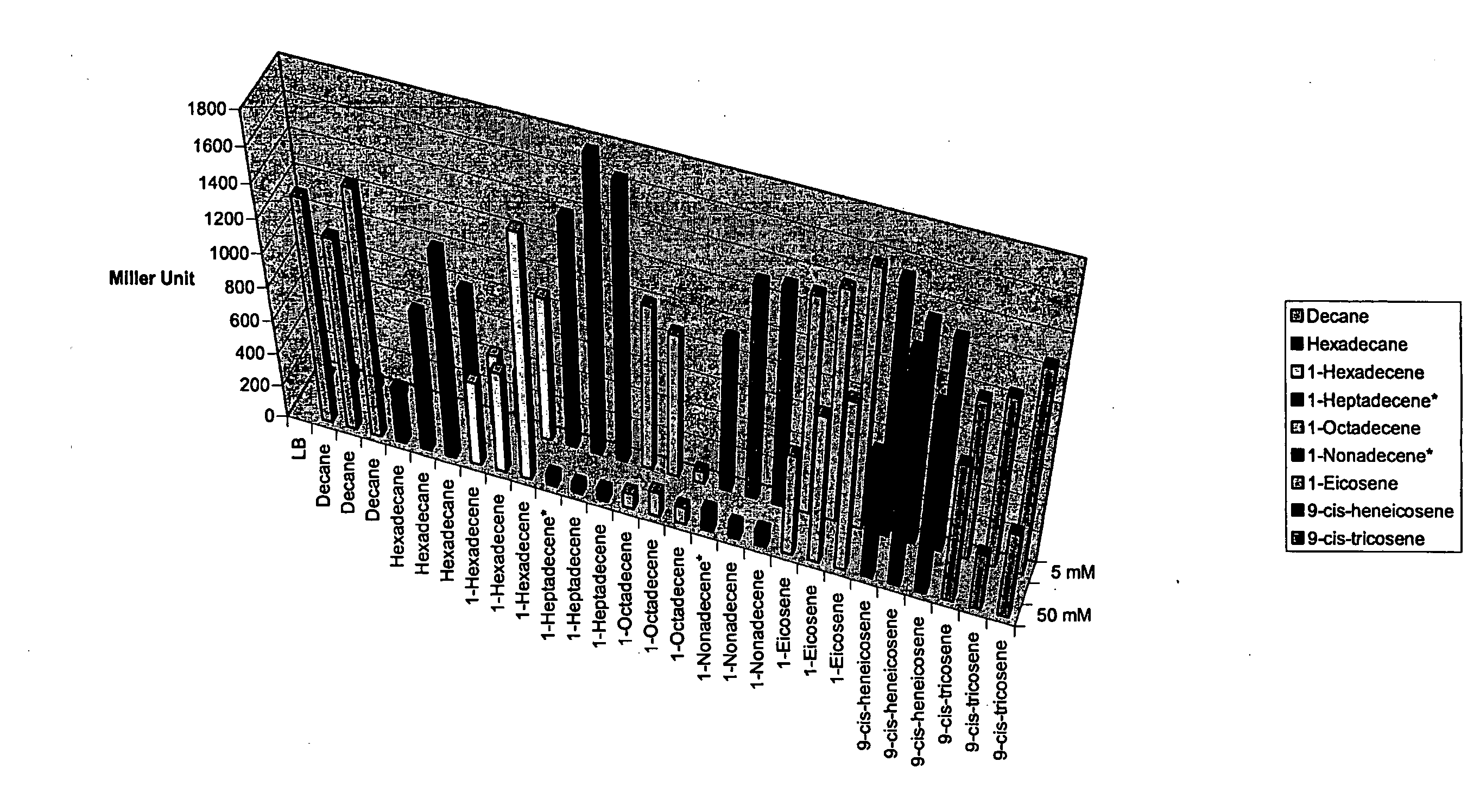
Methods and Compositions for Identification of Hydrocarbon Response, Transport and Biosynthesis Genes
InactiveUS20080293060A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiosynthetic genesResponse element
Disclosed is a method using an alkane response element (ARE) from, e.g., Acinetobacter spp. to (i) identify and clone hydrocarbon biosynthesis genes, (ii) identify and clone hydrocarbon transporter genes (iii) identify and clone hydrocarbon response genes. Screening cells were developed that expressed a transcriptional activator, e.g., alkR, and included a reporter gene, e.g., GFP operatively linked to an ARE promoter, e.g., the alkM promoter. The cells were transformed with libraries from organisms capable of hydrocarbon biosynthesis. Transformed cells that expressed the reporter gene harbored library-derived genes involved in one or more of the above-mentioned processes; and these genes were isolated from the cells using standard molecular biology techniques. Additional systems were designed wherein screening cells also expressed a gene identified in the original screen, e.g., an additional hydrocarbon pathway gene, e.g., an enhancer.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
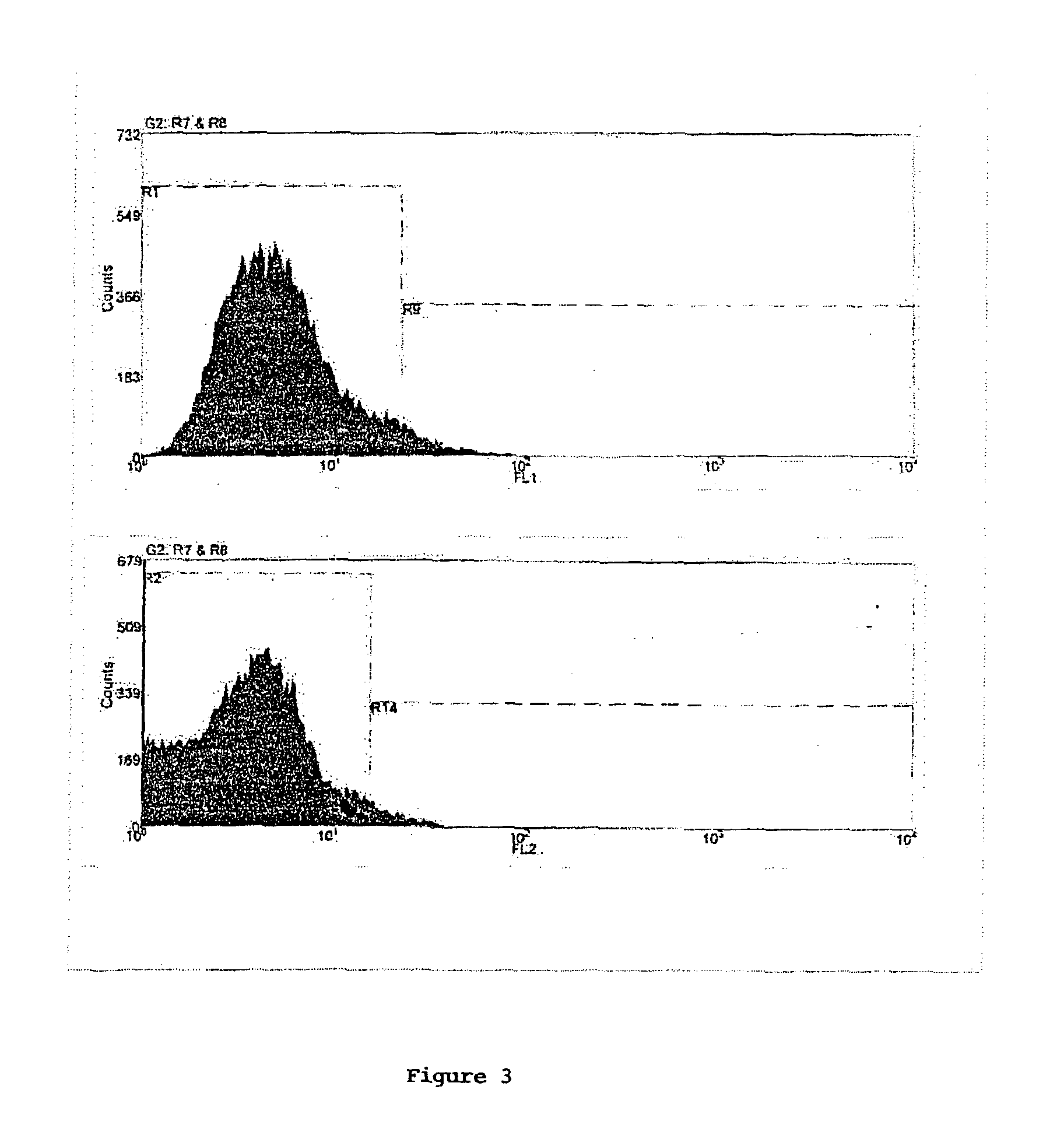
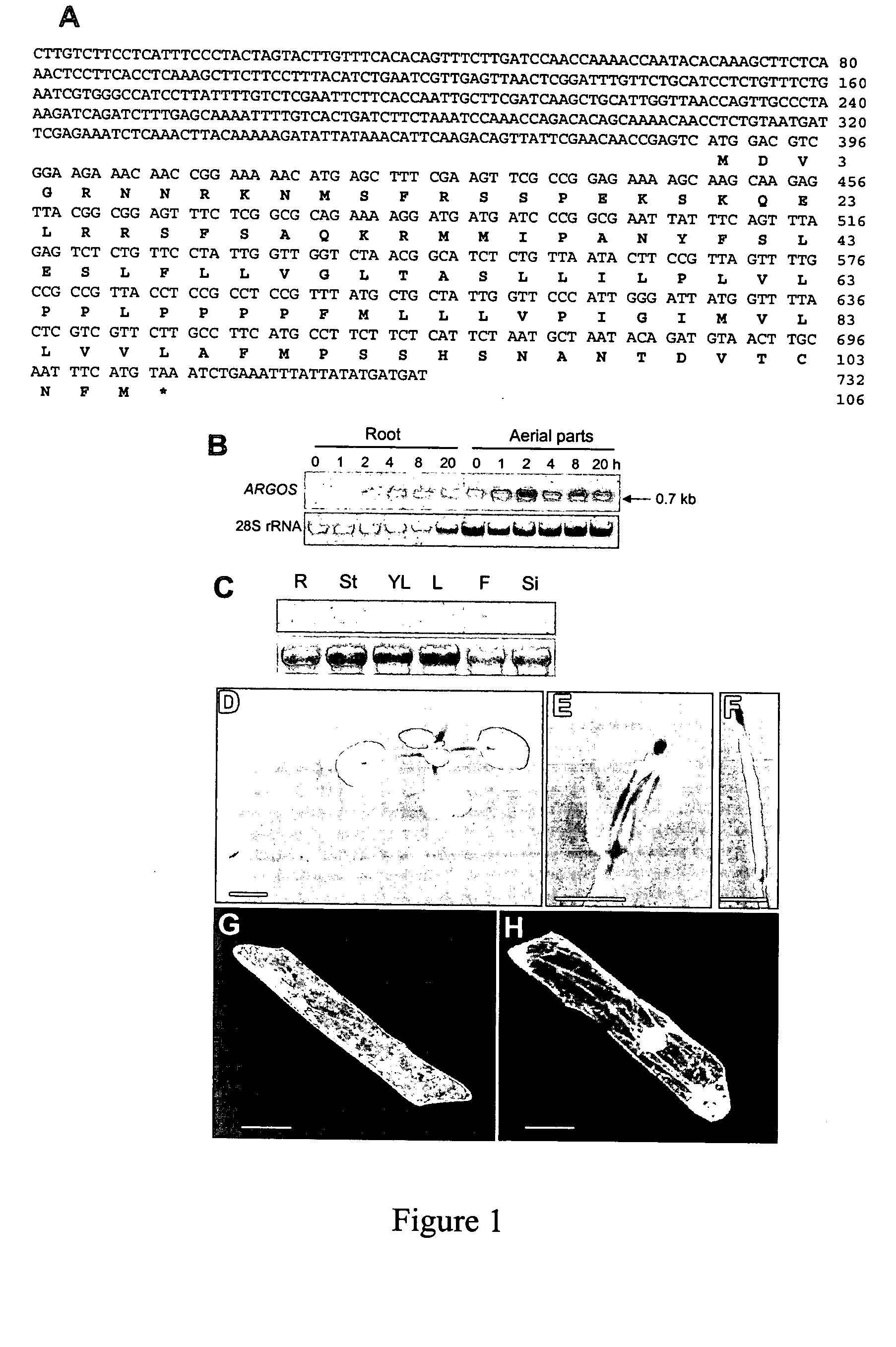
Arabidopsis argos, a novel gene involved in organ development
The present invention is directed to a novel auxin-inducible gene, ARGOS, that is involved in organ development, including size control, in plants. Methods of influencing this development are also described, as are transformed cells and transgenic plants comprising the described sequences.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
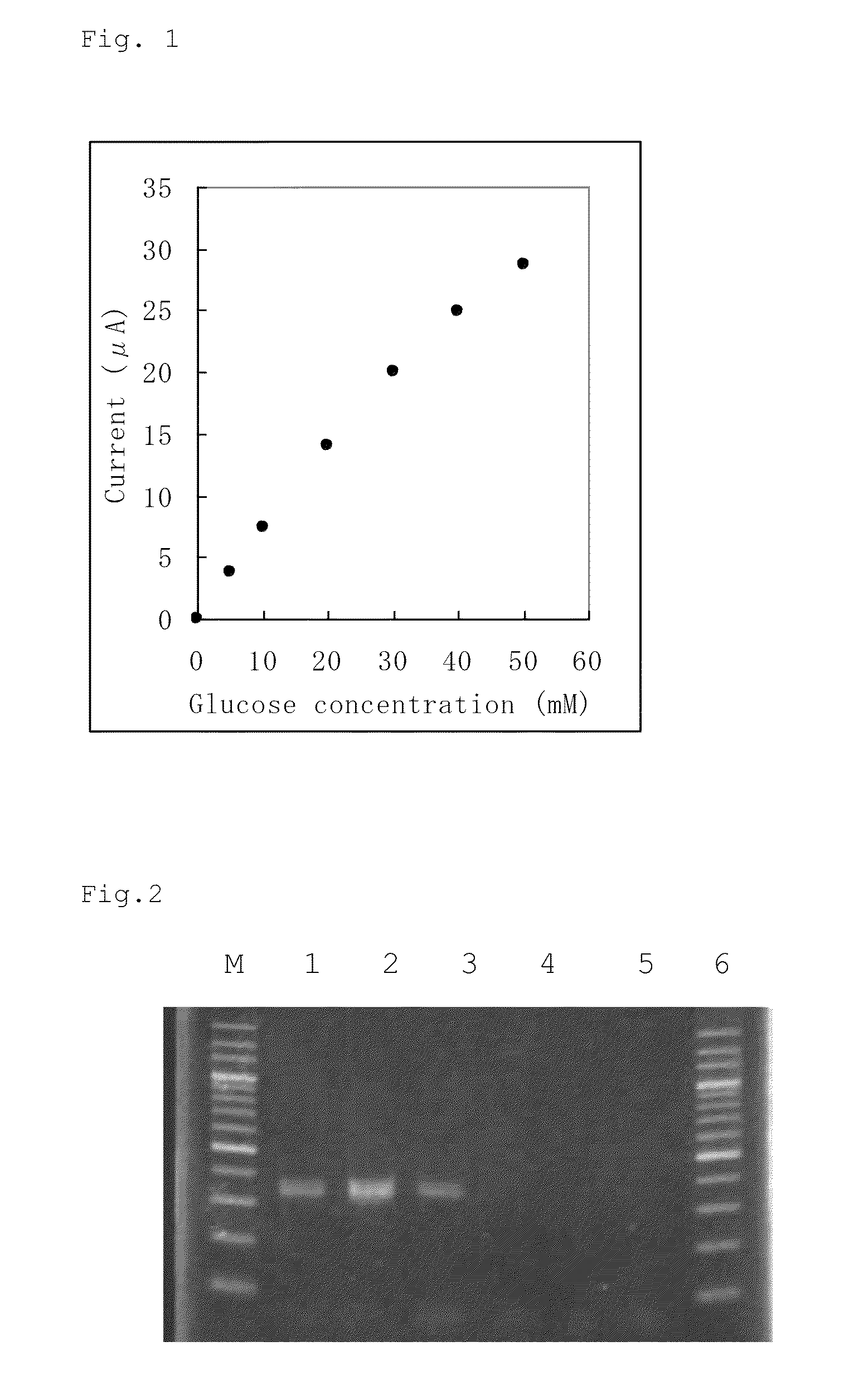
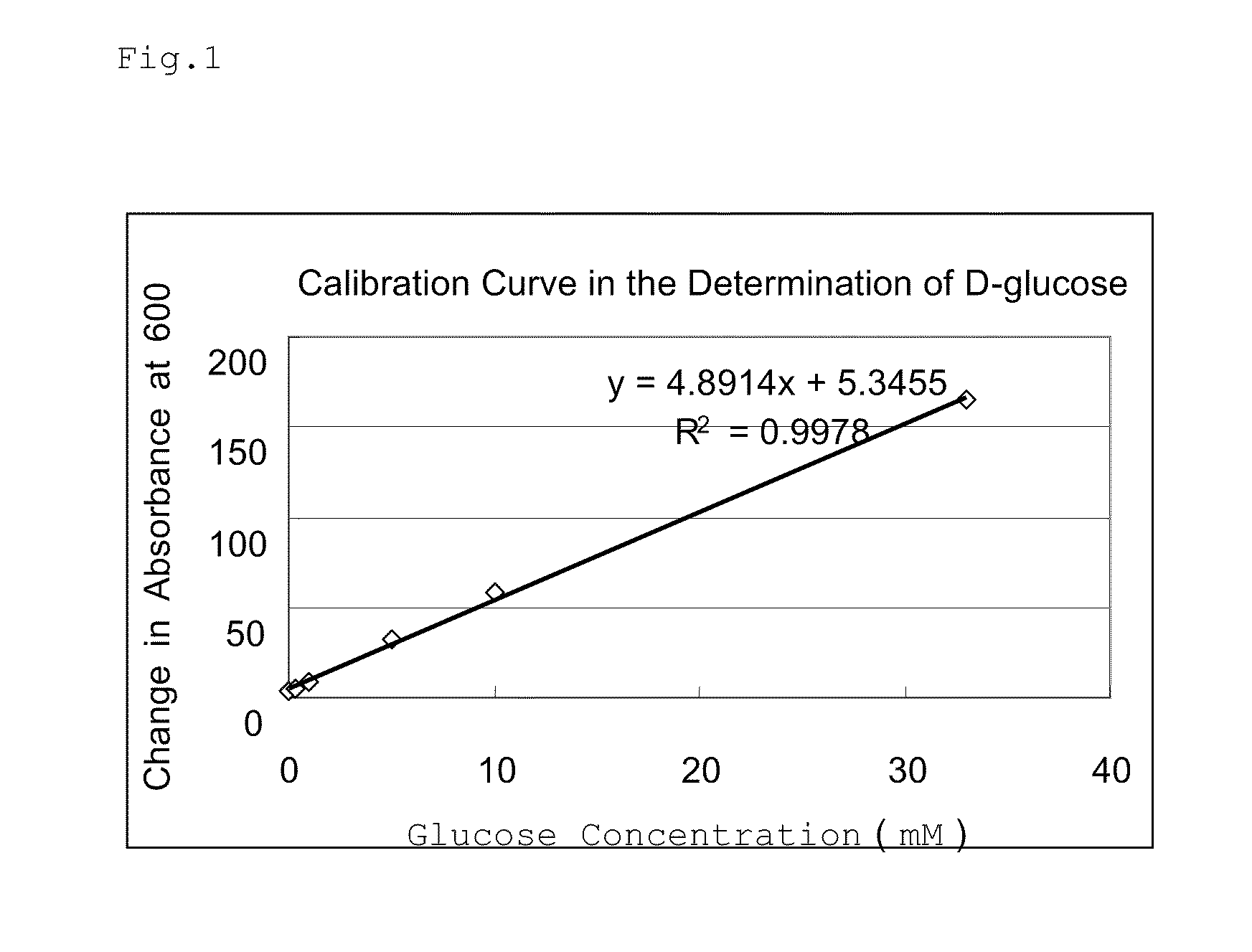
FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase gene
InactiveUS8492130B2Maintain good propertiesEasy to identifyBacteriaSugar derivativesNucleotidePolynucleotide
An object of the present invention is to provide: a novel gene (polynucleotide) encoding an FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase having excellent properties that it has excellent reactivity to glucose, excellent thermal stability, and excellent substrate-recognition performance and also has a low activity for maltose; a process for the production of the enzyme using a transformant cell transfected with the gene; and a method for the determination of glucose, a reagent composition for use in the determination of glucose, a biosensor for use in the determination of glucose and others, each characterized by using the enzyme obtained. The invention relates to a polynucleotide encoding an FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase, comprising a polypeptide containing an amino acid sequence: X1-X2-X3-X4-X5-X6 (wherein X1 and X2 independently represent an aliphatic amino acid residue; X3 and X6 independently represent a branched amino acid residue; and X4 and X5 independently represent a heterocyclic amino acid residue or an aromatic amino acid residue); and others.
Owner:PHC CORP
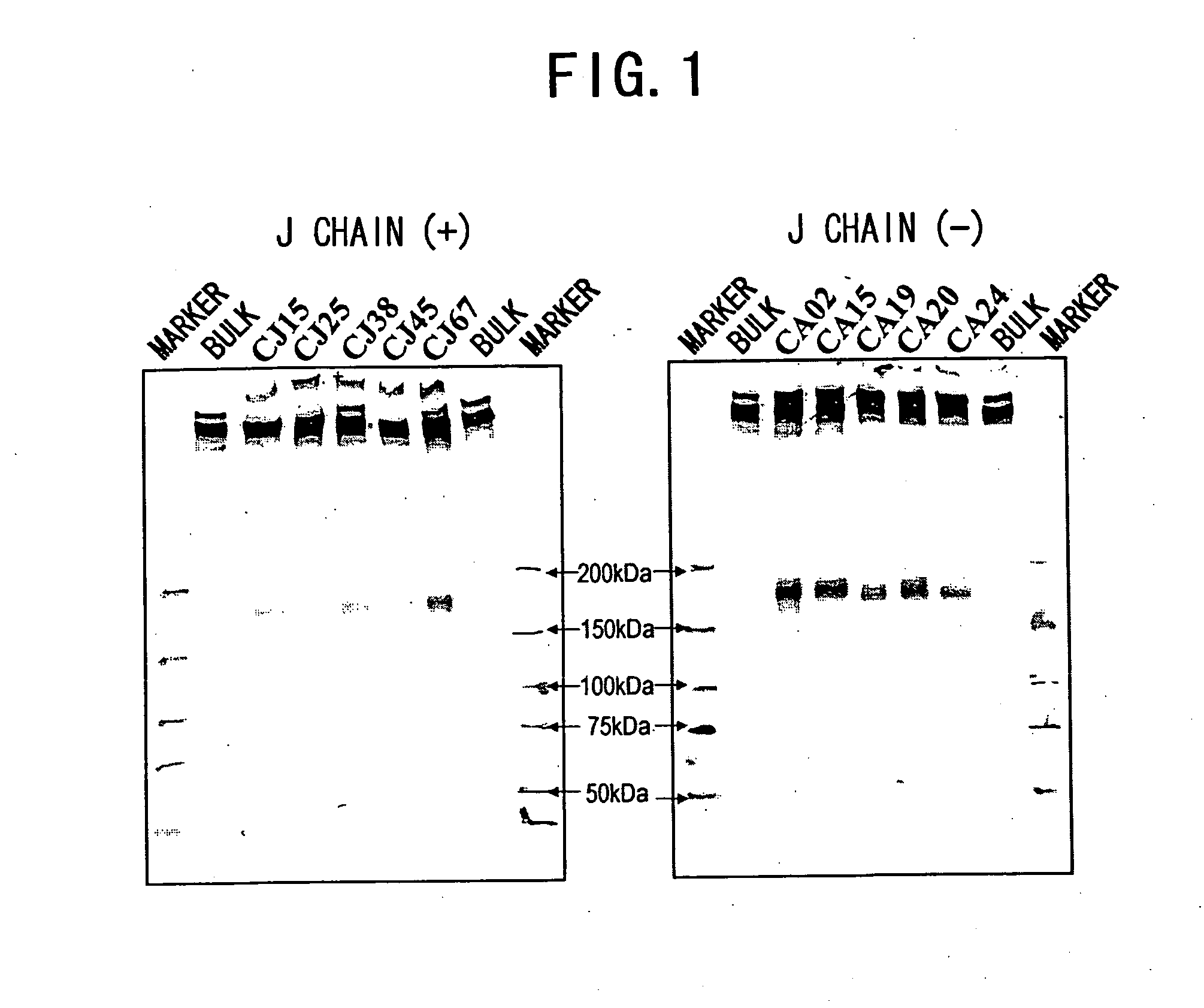
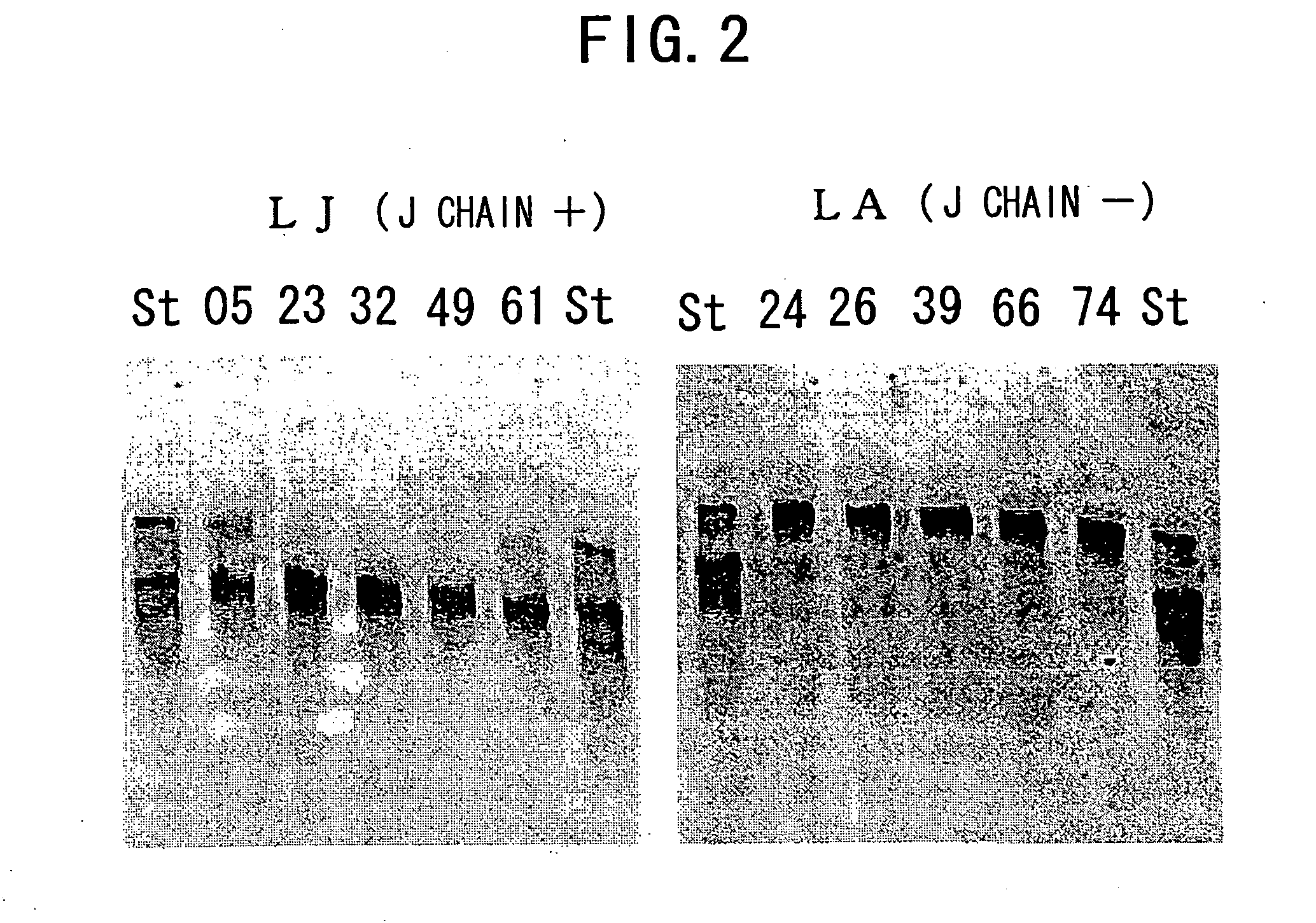
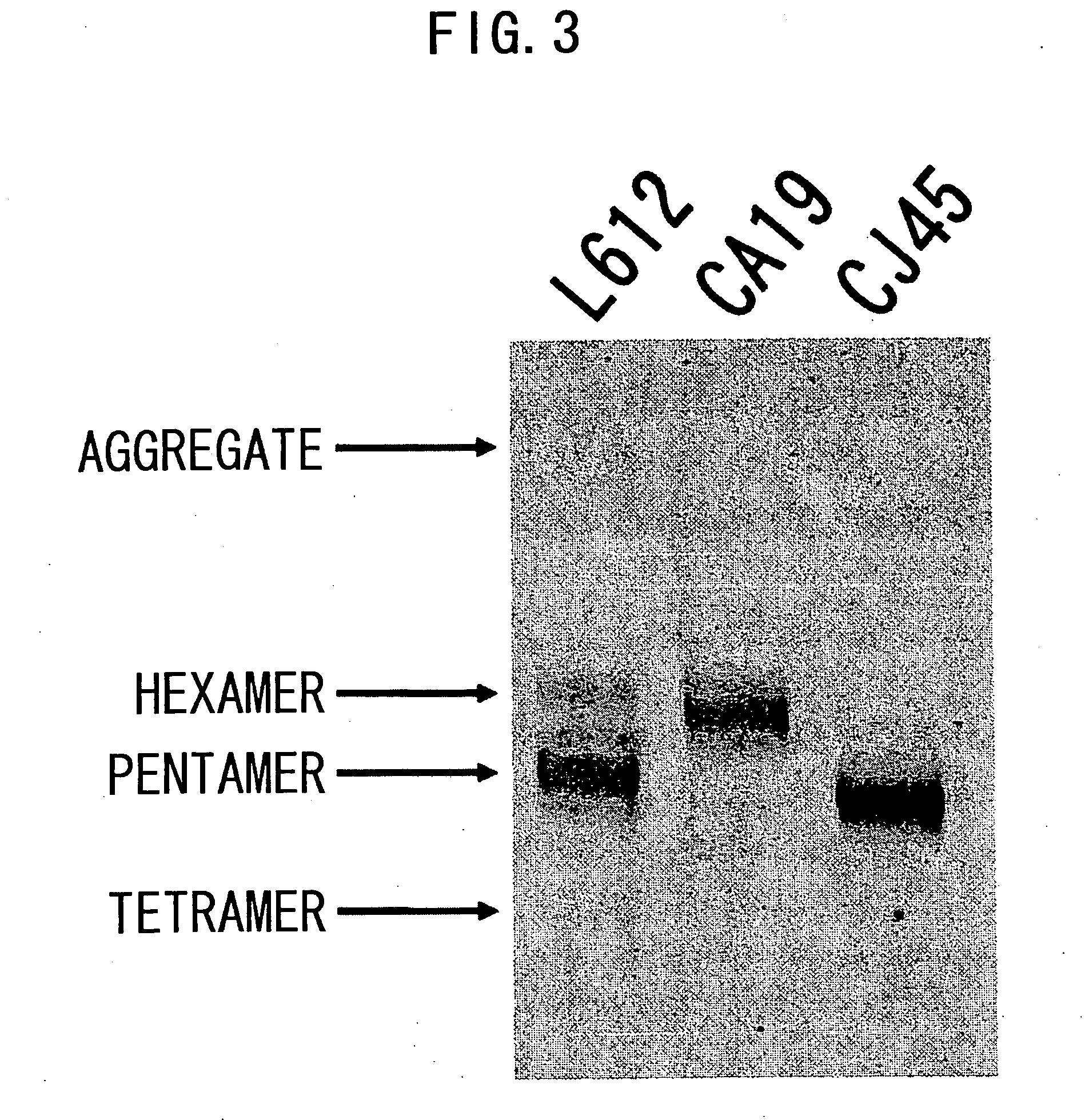
IGM production by transformed cells and methods of quantifying said IgM production
ActiveUS20070154469A1High IgM activityImprove safety and efficacyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesPentamerPolymeric IgM
IgM can be obtained in the form of a pentamer by placing the genes encoding the H, L, and J chains on the same vector to transform appropriate host cells. The gene encoding the J chain may be introduced by co-transfection. When no J chain is expressed, the IgM is produced as a hexamer. The transformants obtained according to the present invention achieve a high yield of IgM. The present invention also provides methods which enable separation and quantification of polymeric IgM.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Modified glucose dehydrogenase gene
InactiveUS20100323378A1Maintain good propertiesReduced activityFungiSugar derivativesNucleotideWild type
[Object] To provide an FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase having a higher specificity for glucose.[Means for Resolution] A modified glucose dehydrogenase (GLD) which includes a substitution of at least one amino acid residue selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues at positions 37, 69, 72, 73, 76, 78, 102, 217, 228, 240, 356, 407, 424, 437, 527, and 530 in an amino acid sequence of a wild-type FAD-conjugated glucose dehydrogenase (GLD) represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, and has a decreased ratio of activity for xylose / activity for glucose as compared with the wild-type GLD; a polynucleotide encoding the modified GLD; a recombinant vector containing the polynucleotide; a transformed cell produced by using the recombinant vector; etc.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Methods for transforming immature maize embryos
InactiveUS7057089B2Promote embryogenic-tissue formationSmall sizeStable introduction of DNAFermentationEmbryogenesisGenetically modified maize
Methods are provided for transforming freshly isolated, immature maize embryos and for producing transgenic maize plants. The methods comprise obtaining immature embryos from a maize plant, contacting the embryos with an auxin-depleted or phytohormone-depleted transformation support medium and introducing a nucleotide construct into cells from the embryos prior to subjecting the embryos to conditions which promote embryogenic-tissue formation. The methods additionally comprise identifying or selecting transformed cells and regenerating such cells into transformed maize plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Mammalian cell surface DNA receptor
The present invention relates to novel mammalian DNA-R proteins and genes that encode such proteins. The invention is directed toward the isolation and characterization of mammalian DNA-R proteins. The invention specifically provides isolated complementary DNA copies of mRNA corresponding to rat and human homologues of a mammalian DNA-R gene. Also provided are recombinant expression constructs capable of expressing the mammalian DNA-R genes of the invention in cultures of transformed prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as such cultures of transformed cells that synthesize the mammalian catecholamine receptor proteins encoded therein. The invention also provides methods for screening compounds in vitro that are capable of binding to the mammalian DNA-R proteins of the invention, and further characterizing the binding properties of such compounds in comparison with known DNA-R agonists and antagonists. Improved methods of pharmacological screening are provided thereby.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com