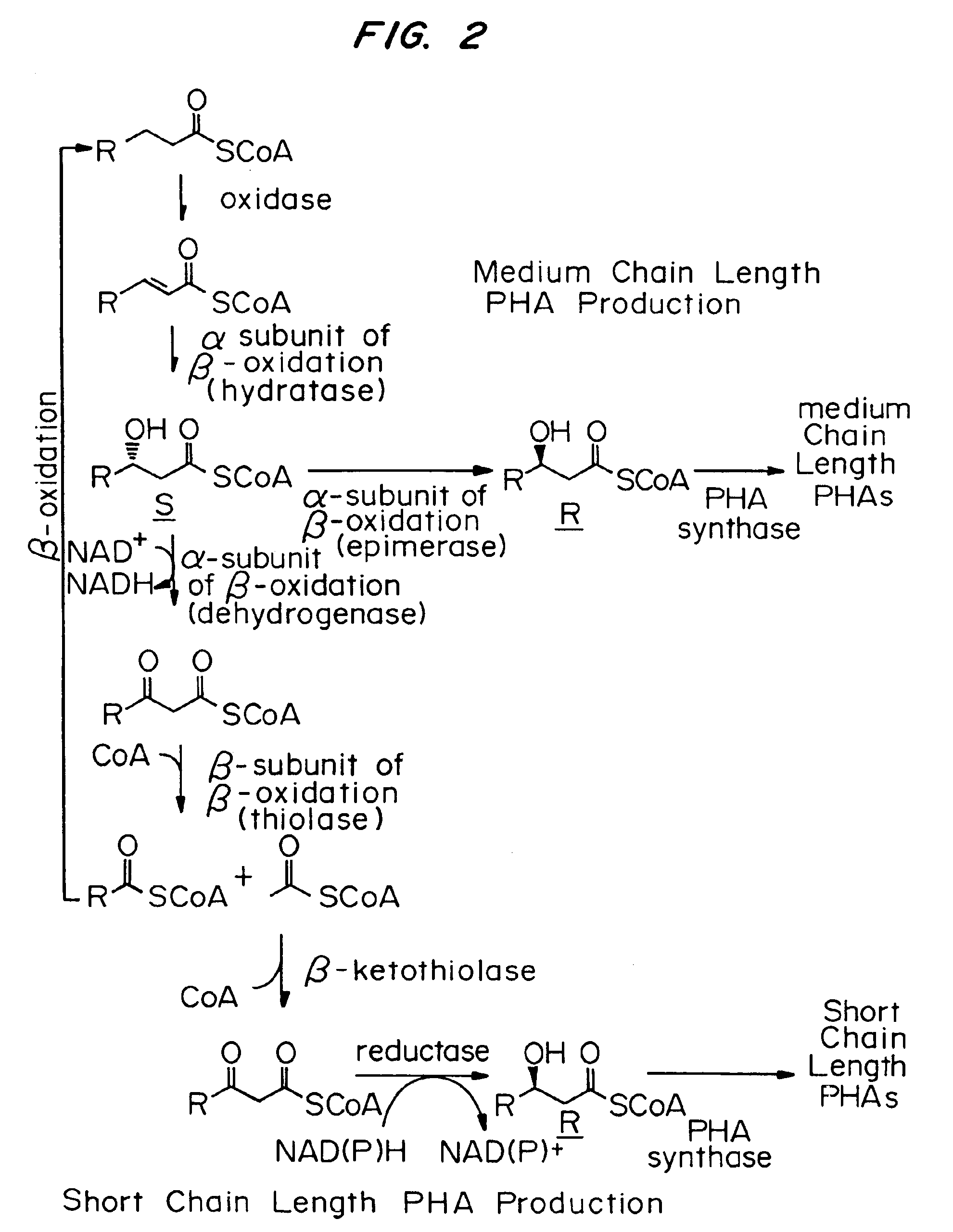
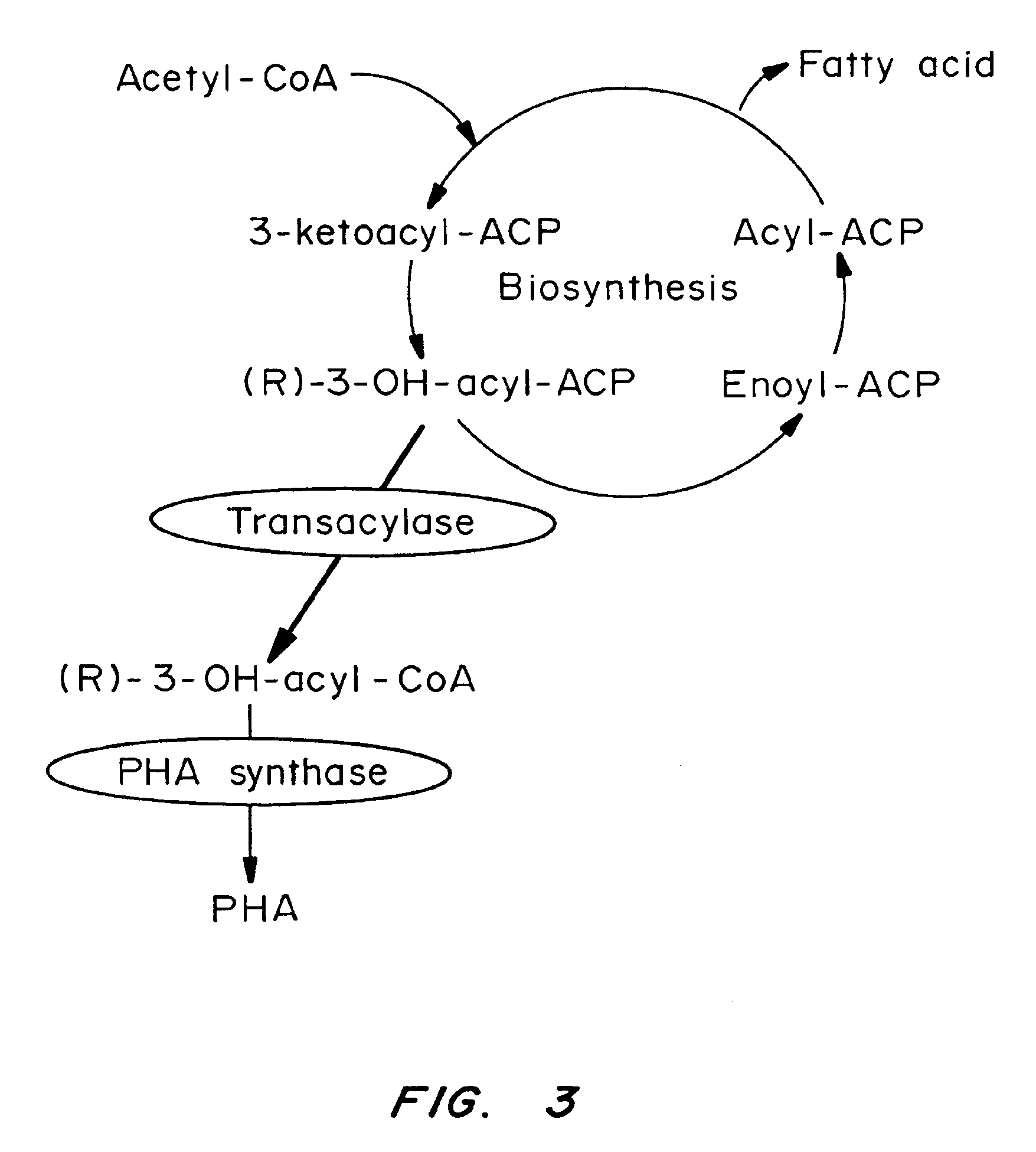
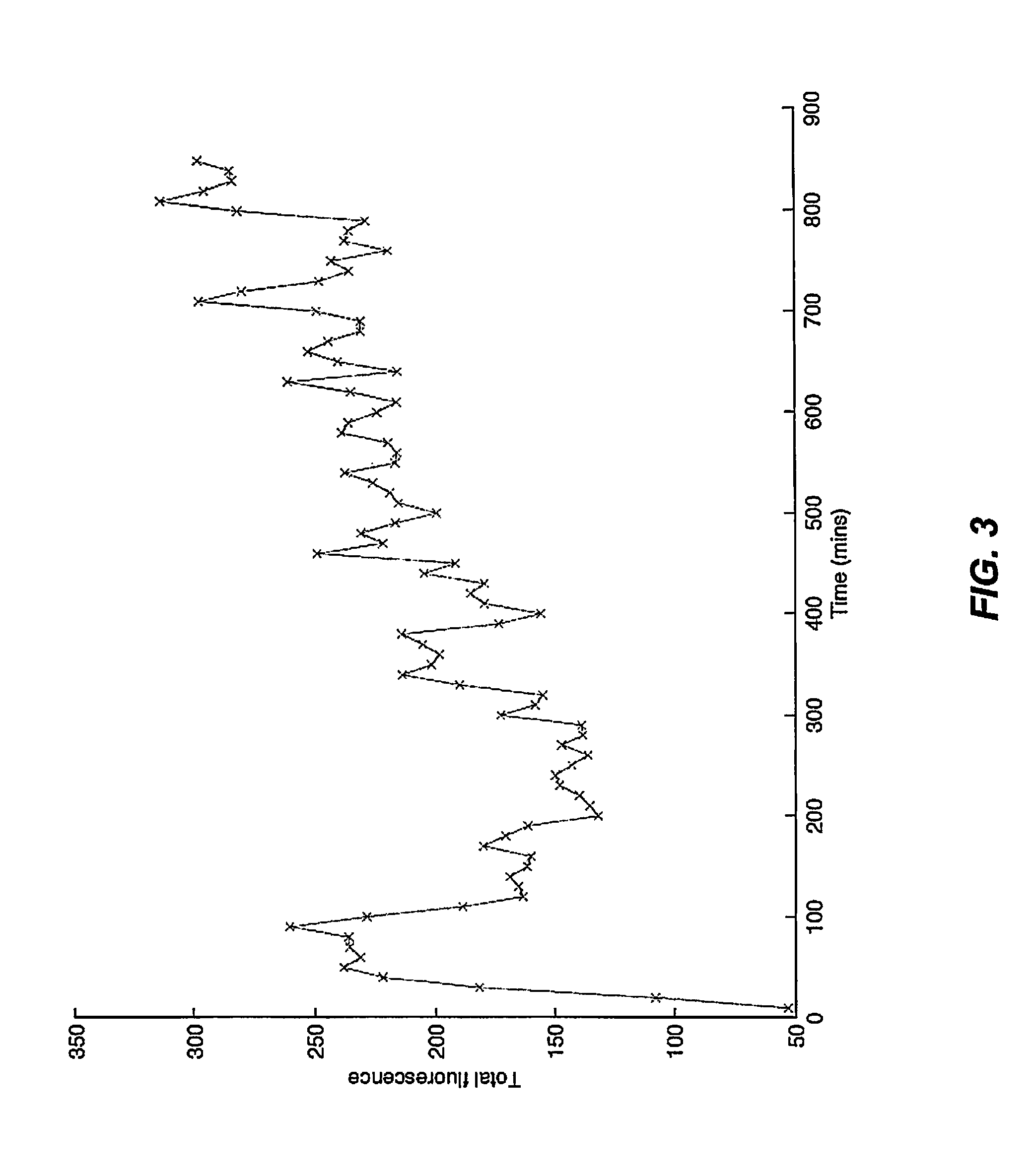
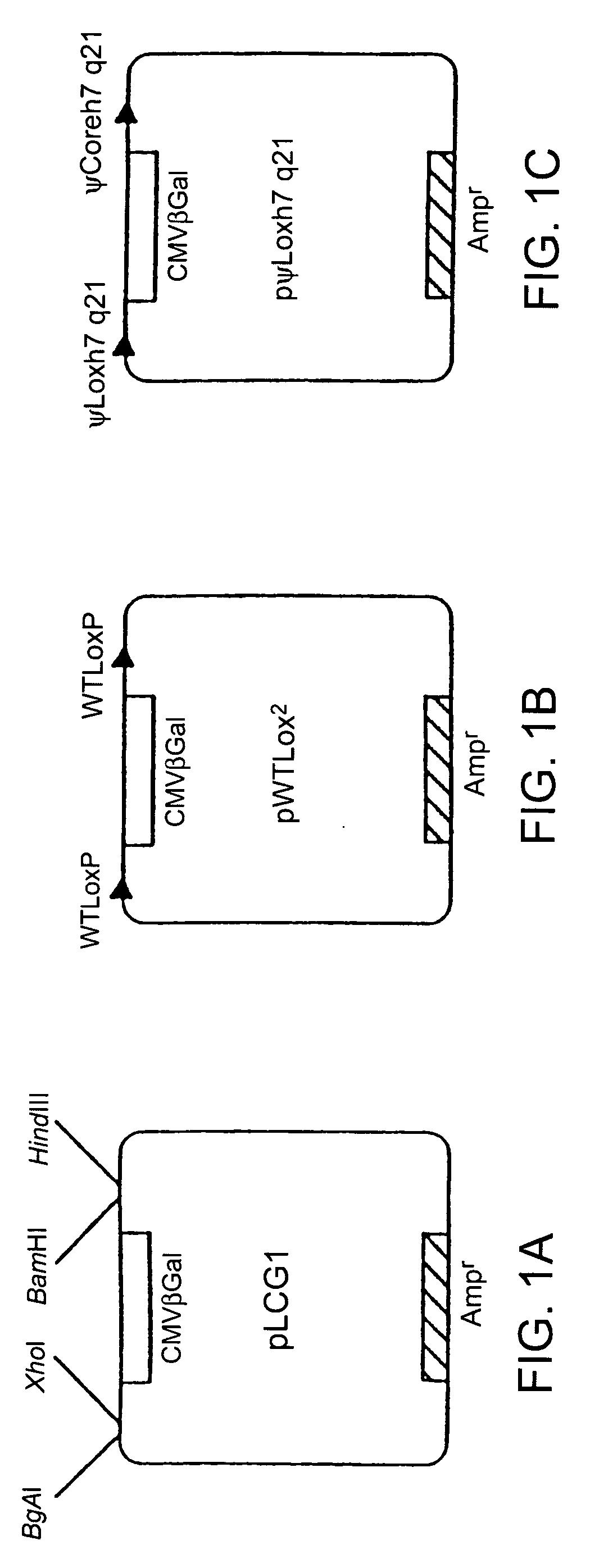
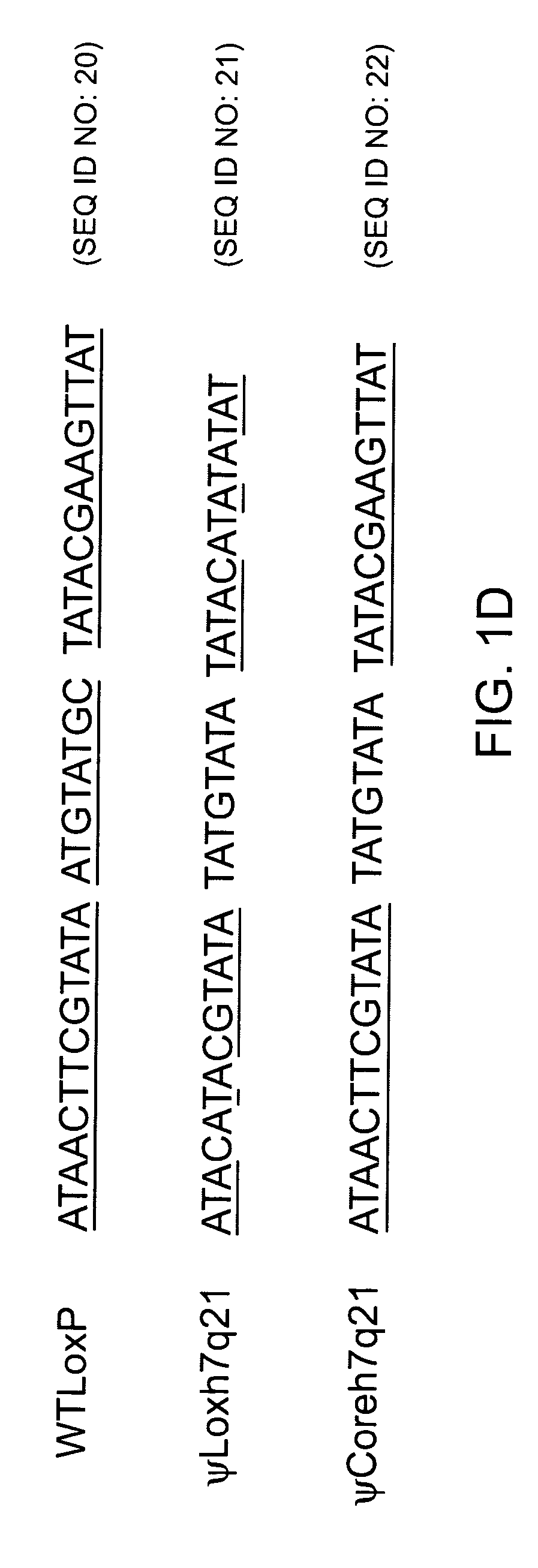
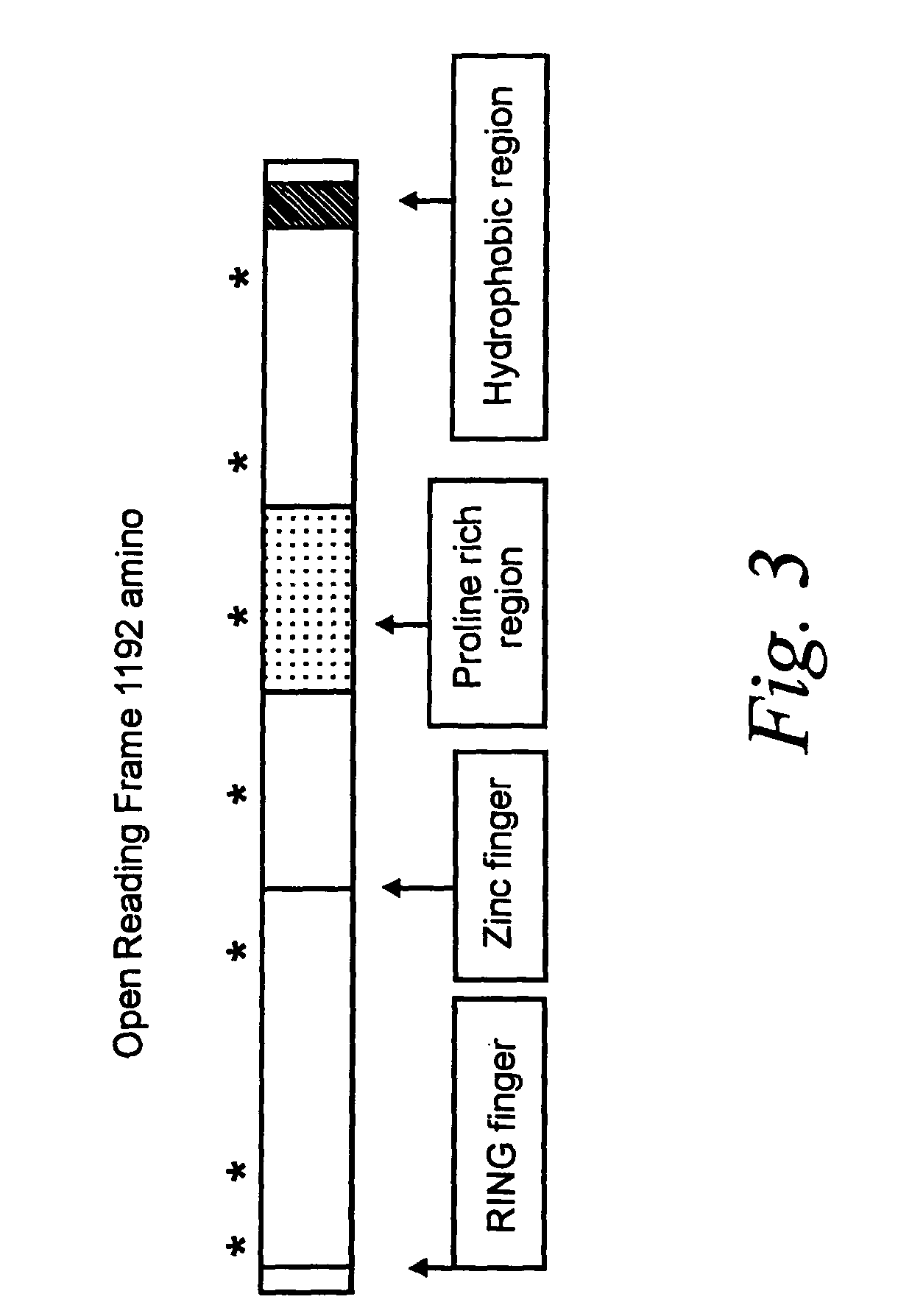
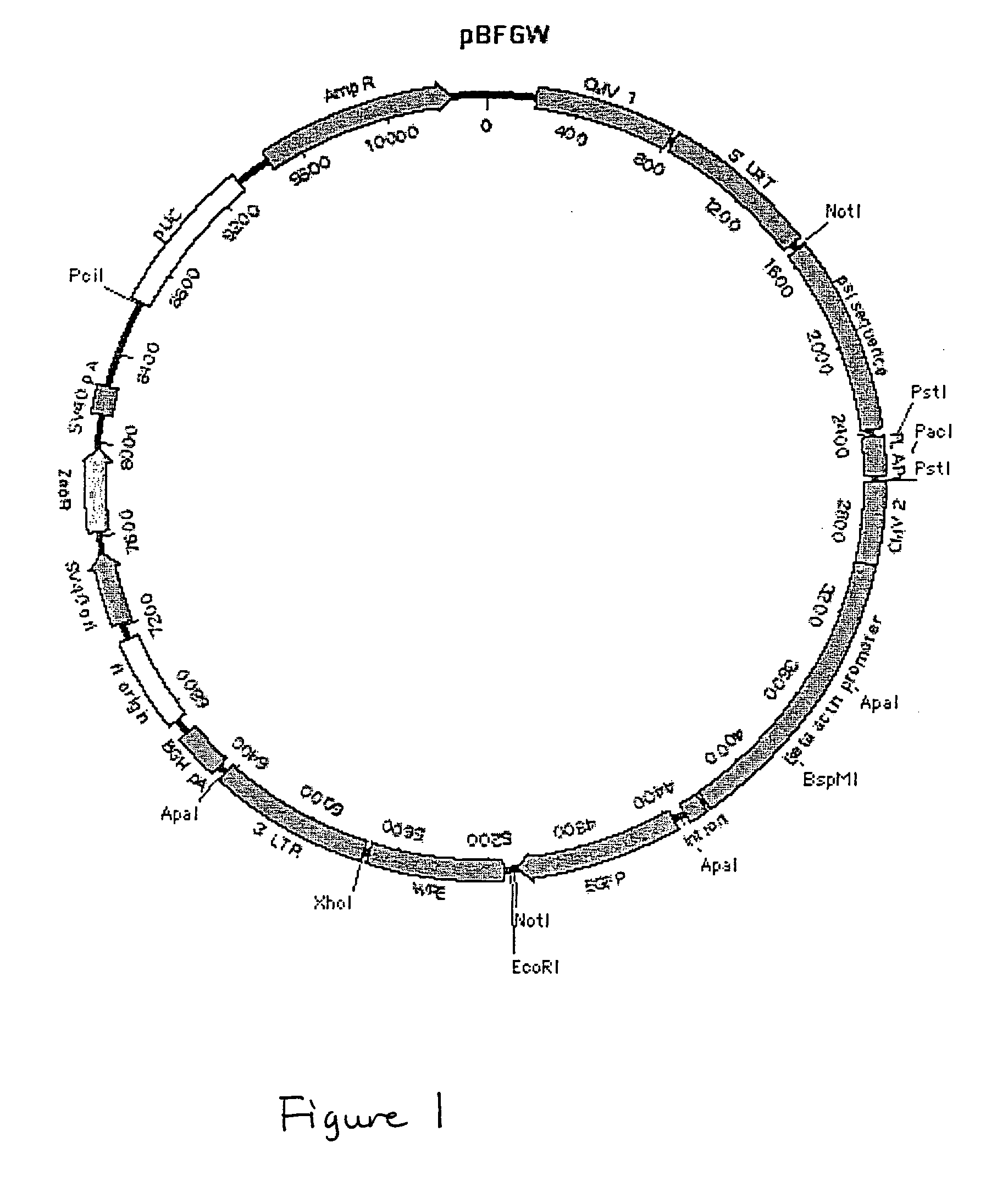
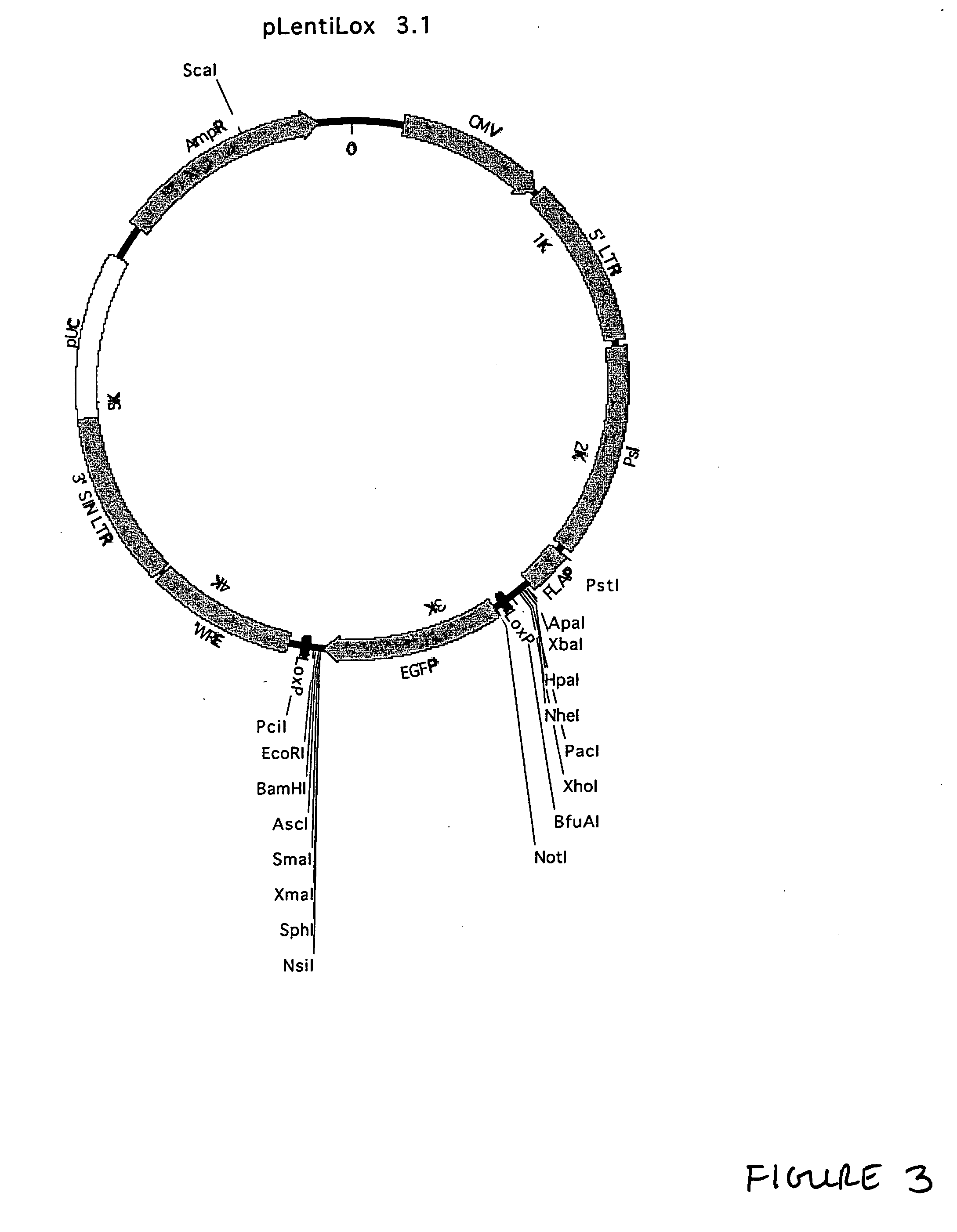
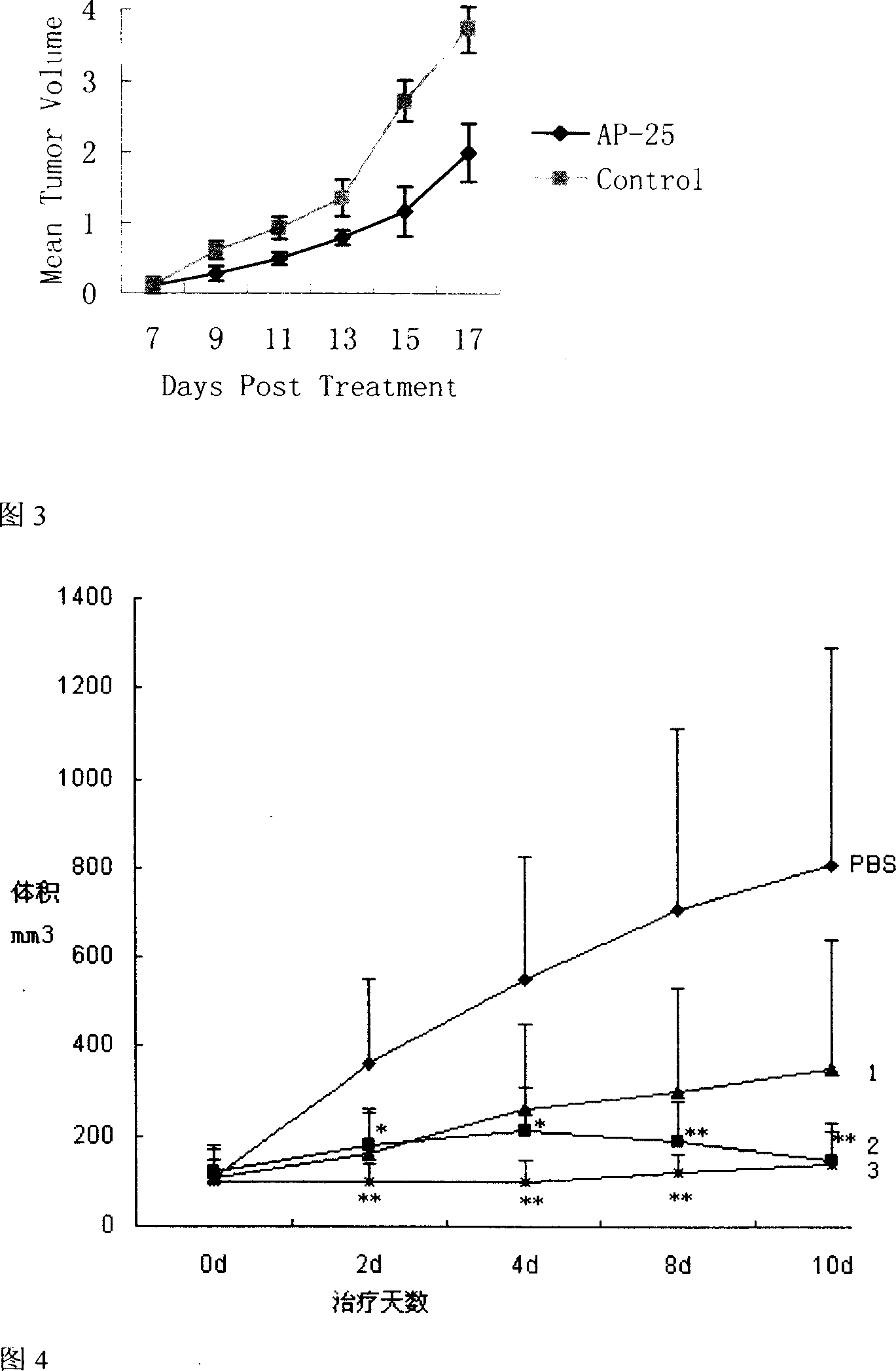
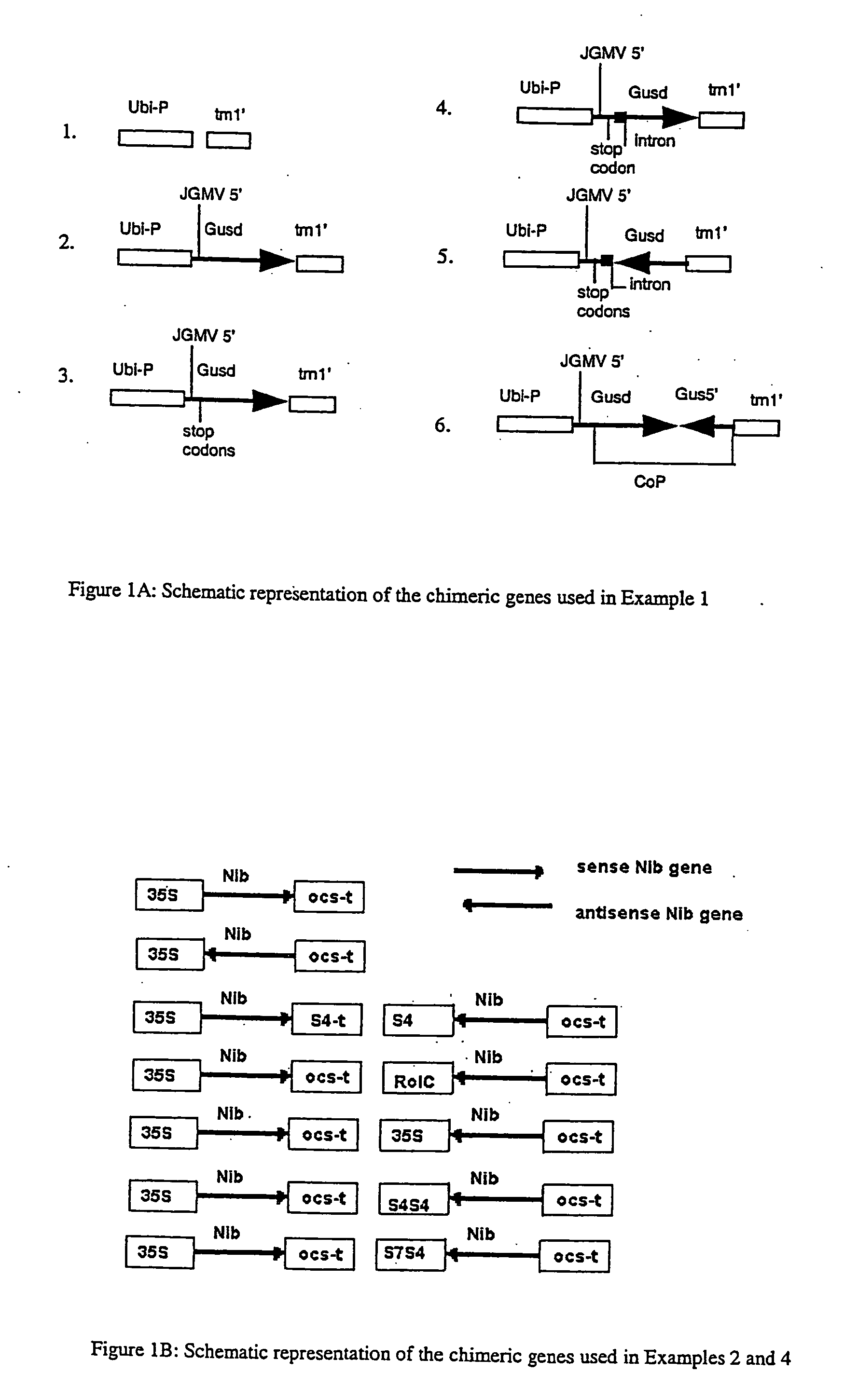
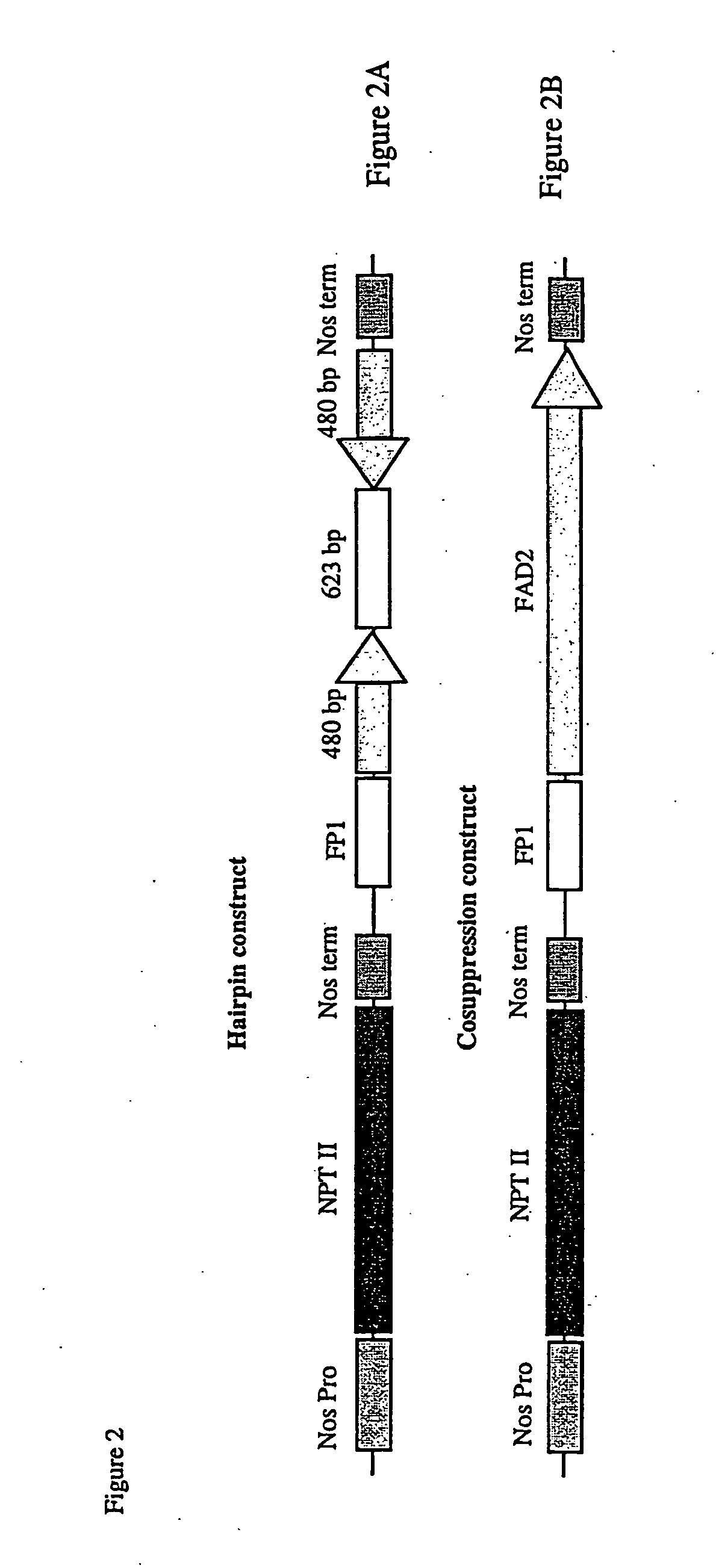
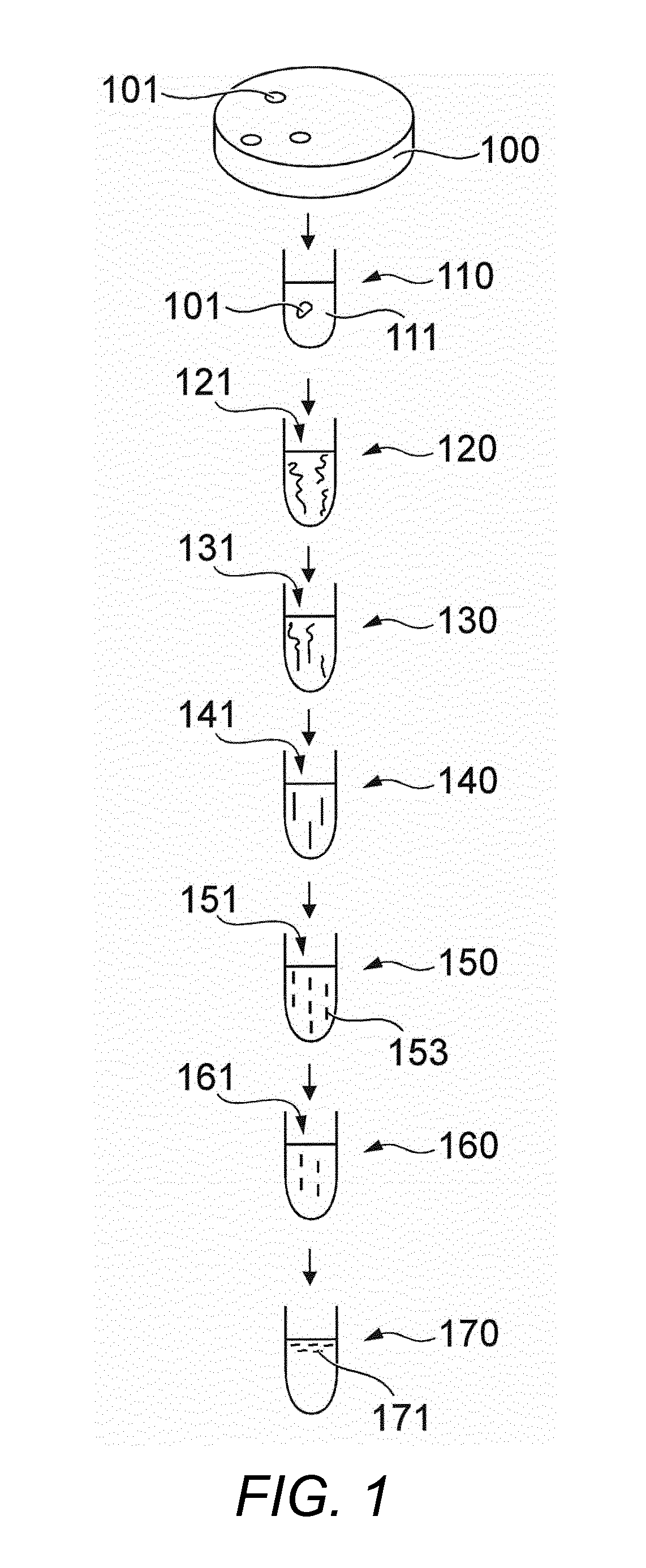
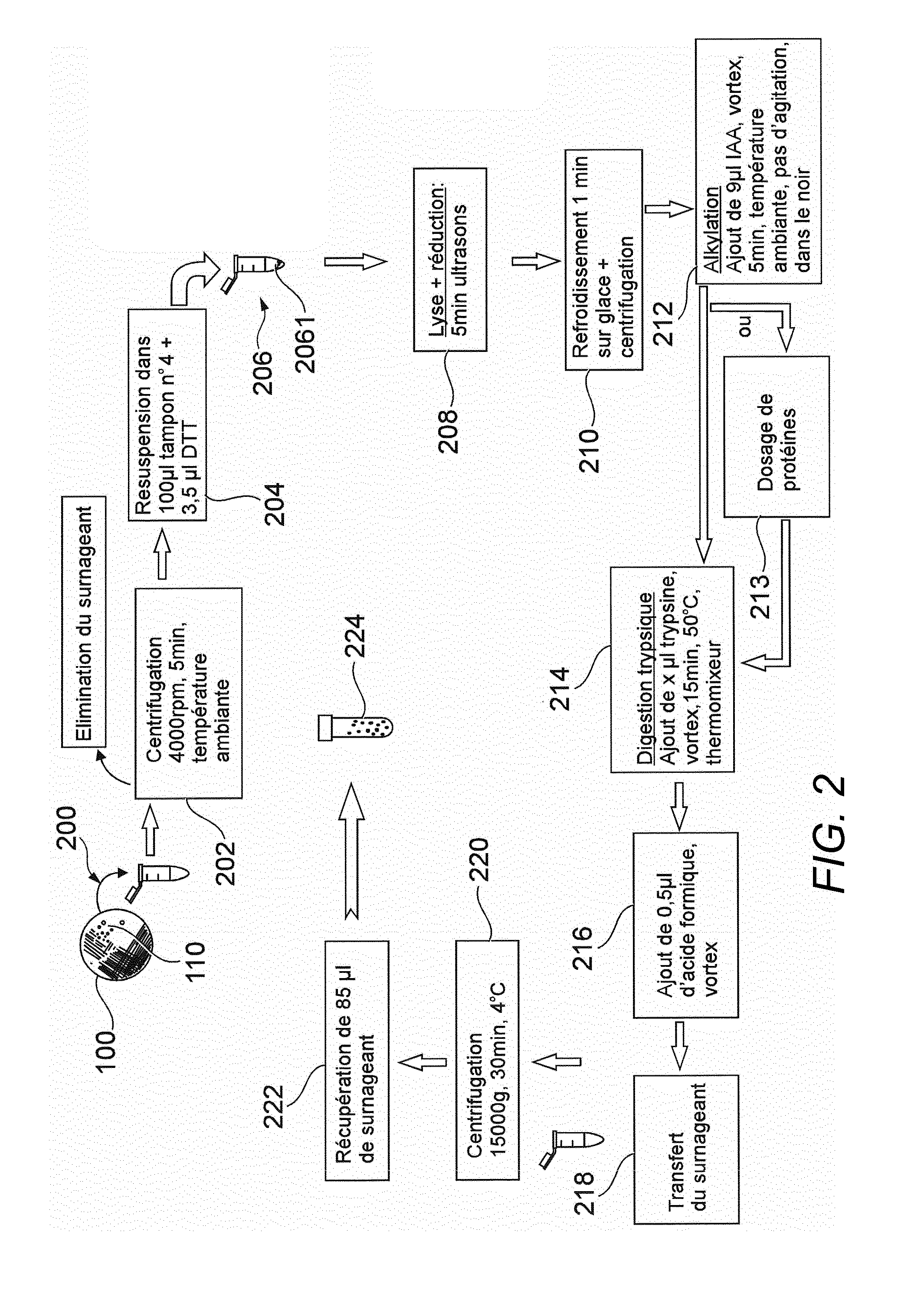
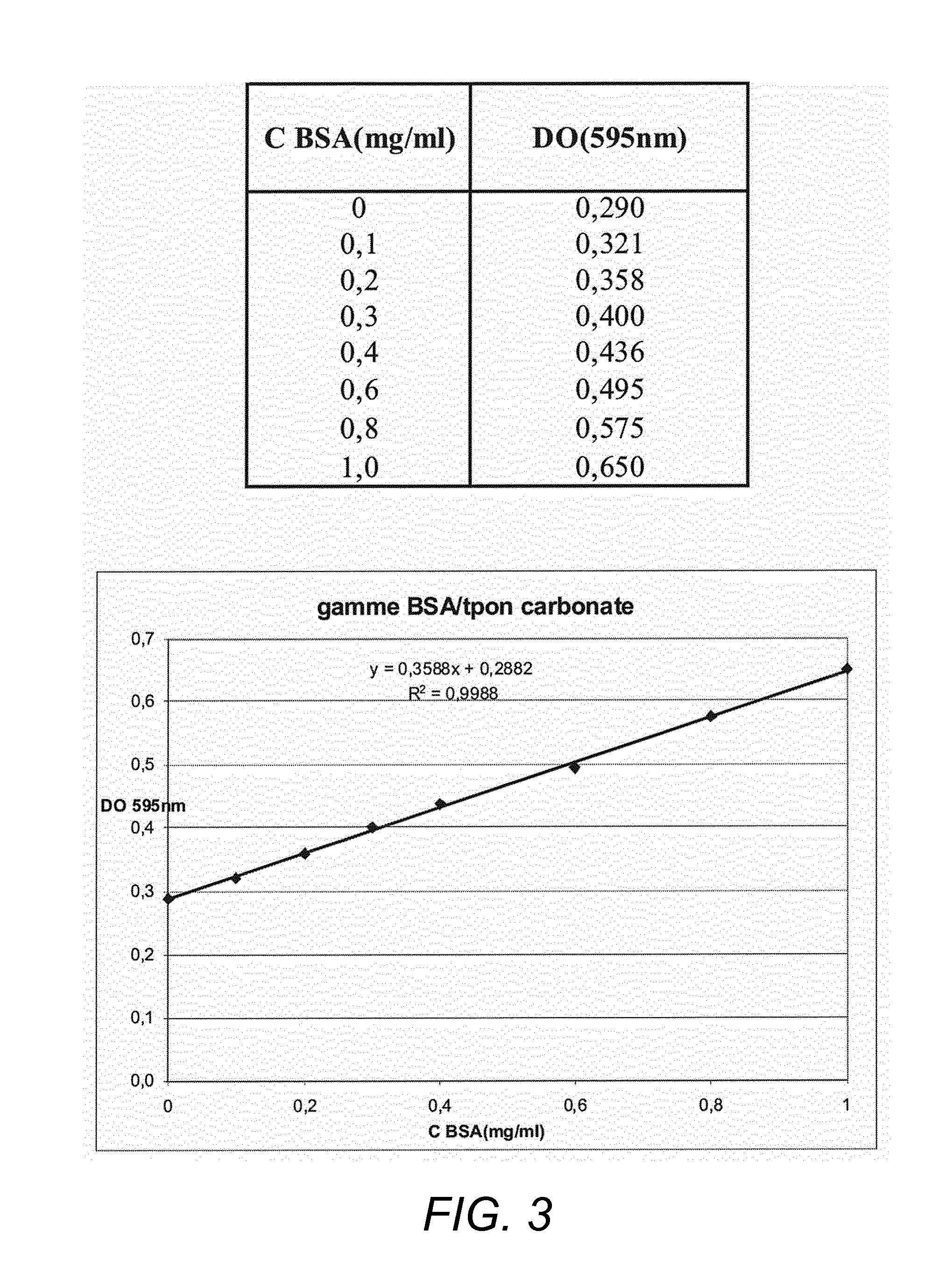
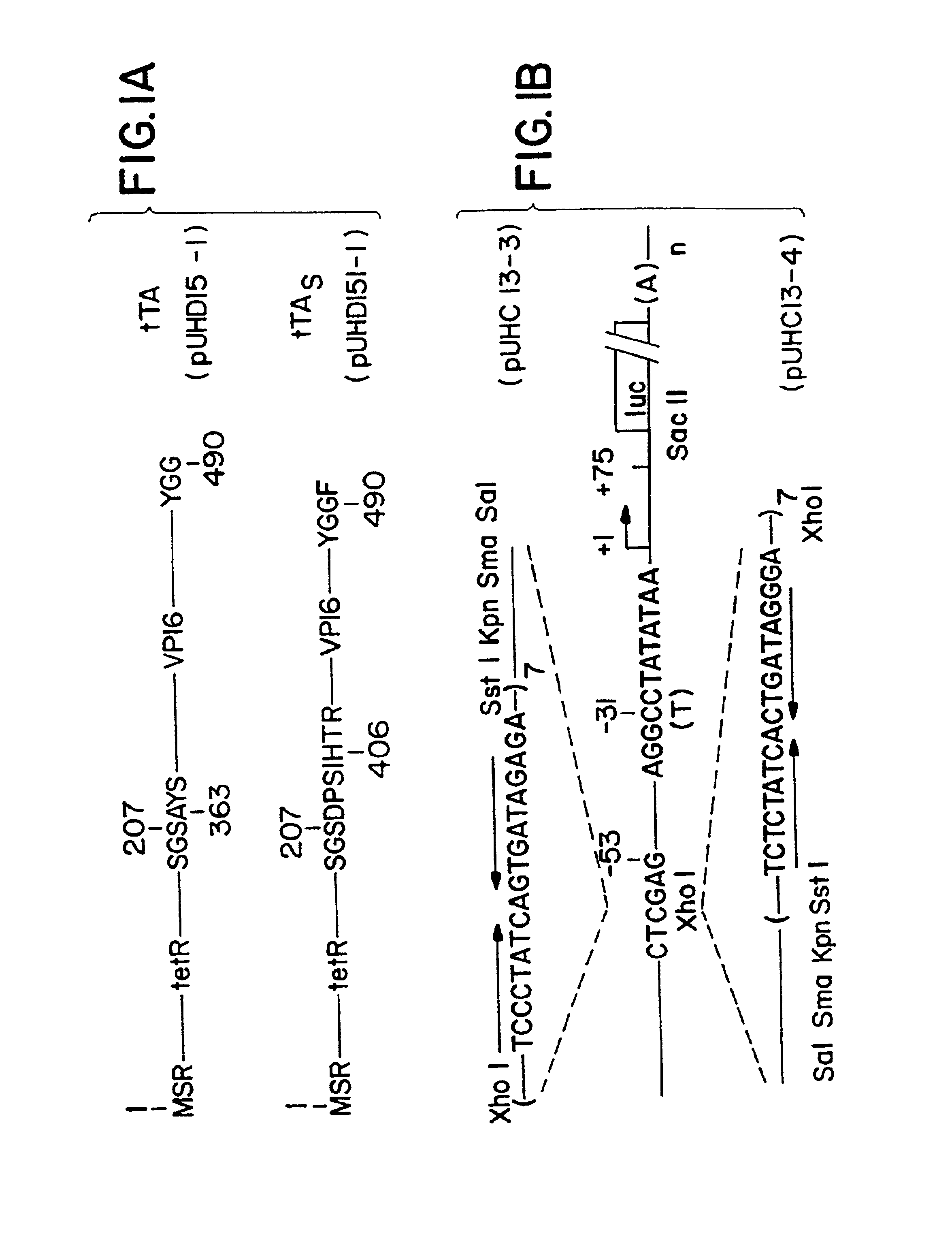
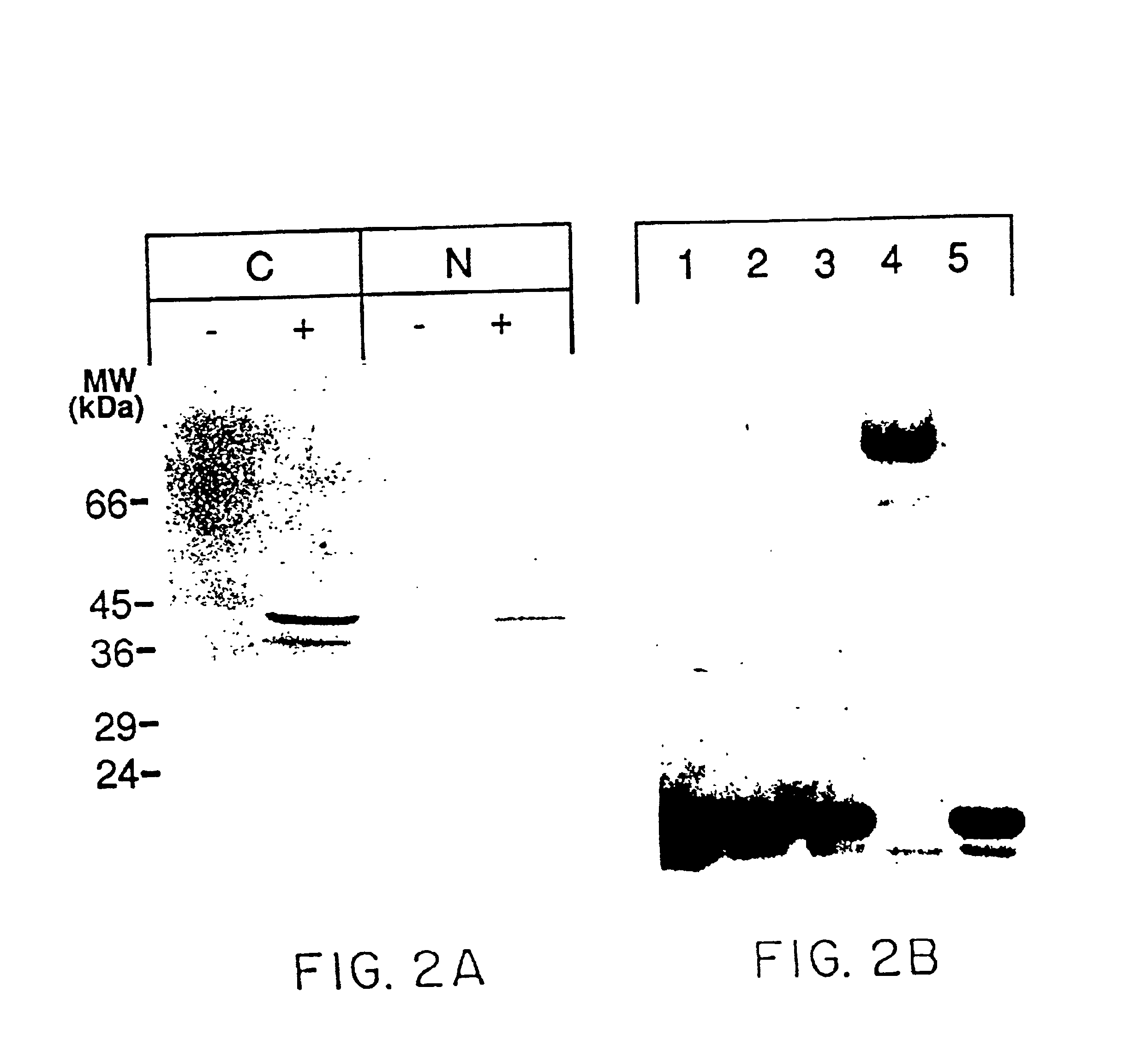
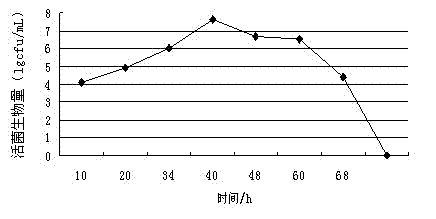
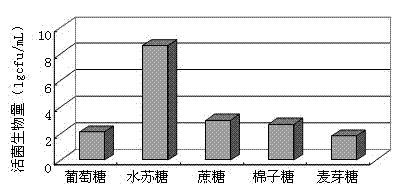
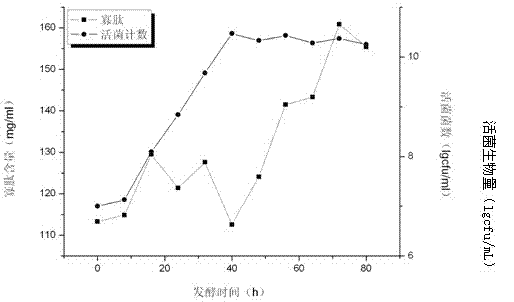
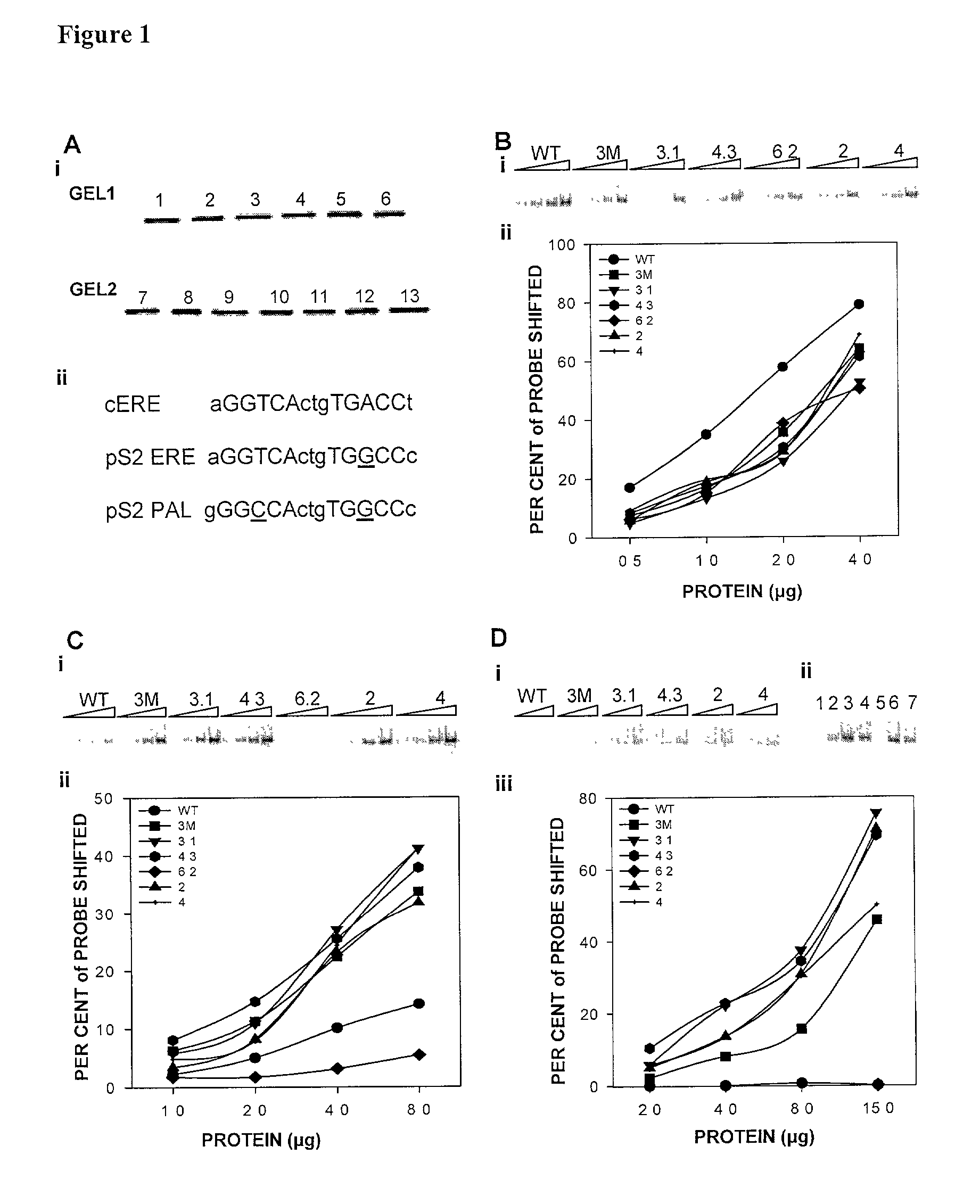
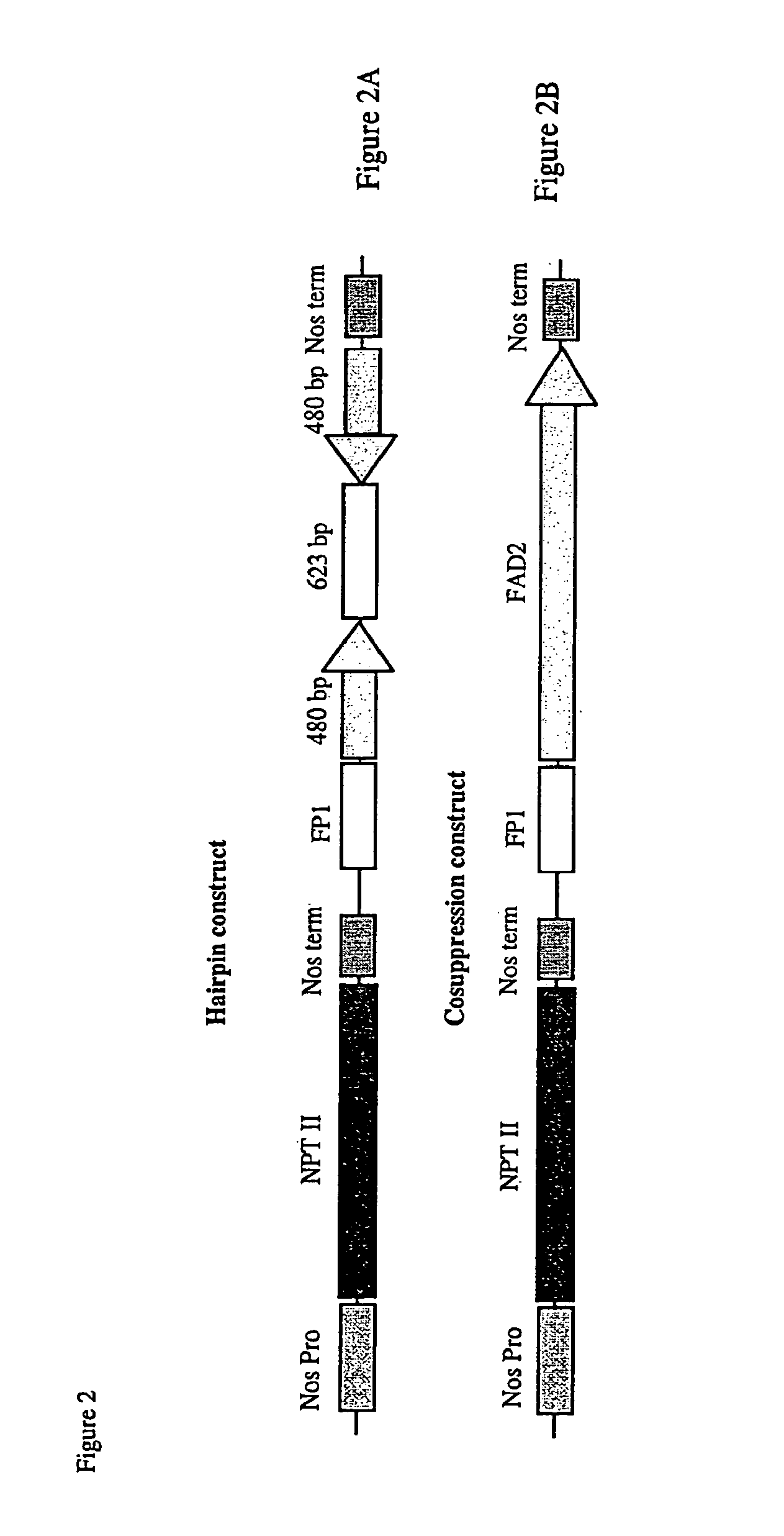
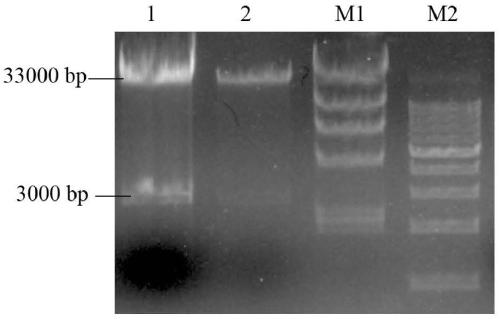
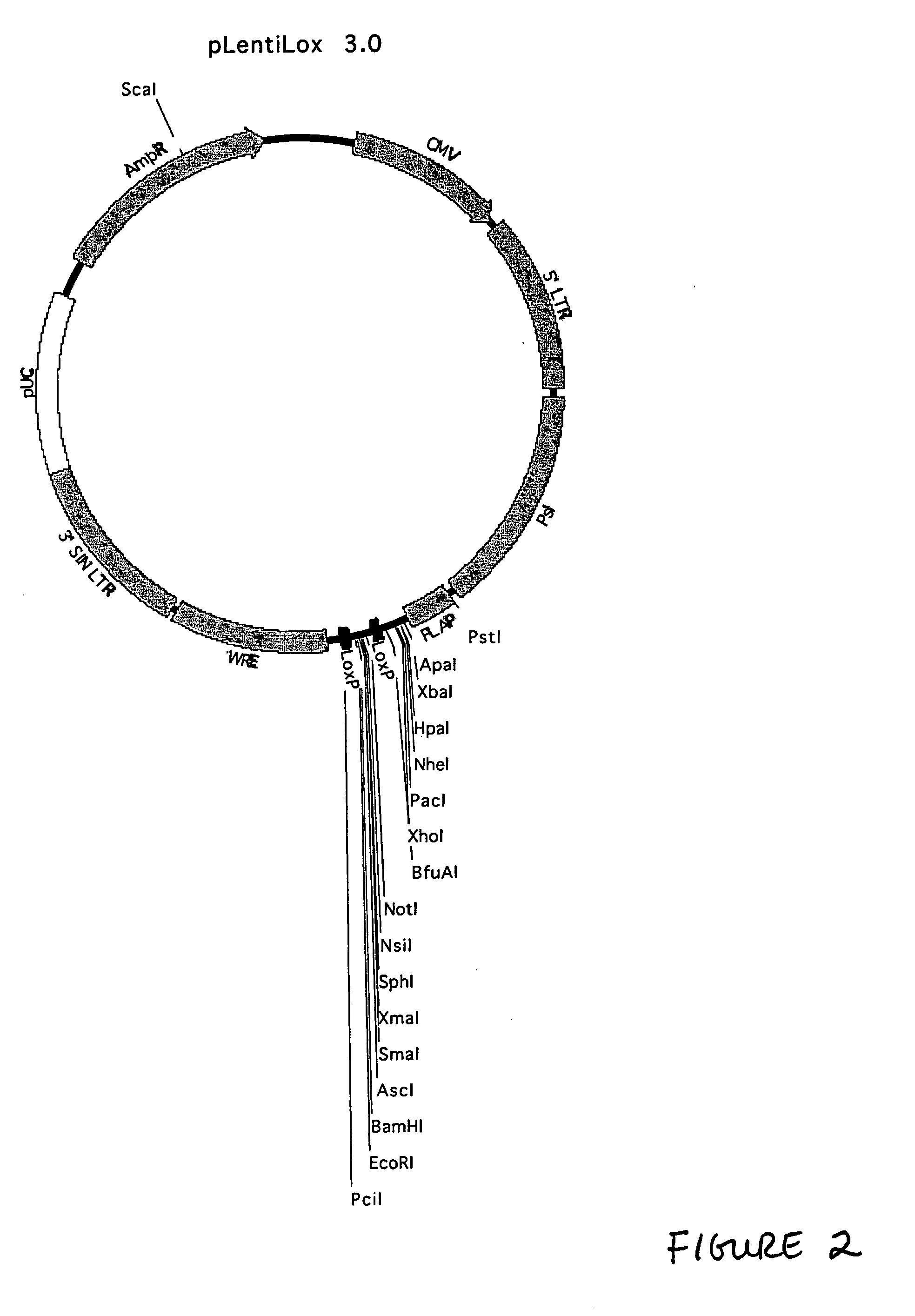Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
204 results about "Eucaryotic cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A eukaryotic cell is a cell that contains membrane-bound compartments in which specific metabolic activities take place. Most important among these compartments is the nucleus, which houses the eukaryotic cell's DNA.
Methods and compositions for genomic modification
InactiveUS20040203152A1Genetic material ingredientsStable introduction of DNAEucaryotic cellSite-specific recombination
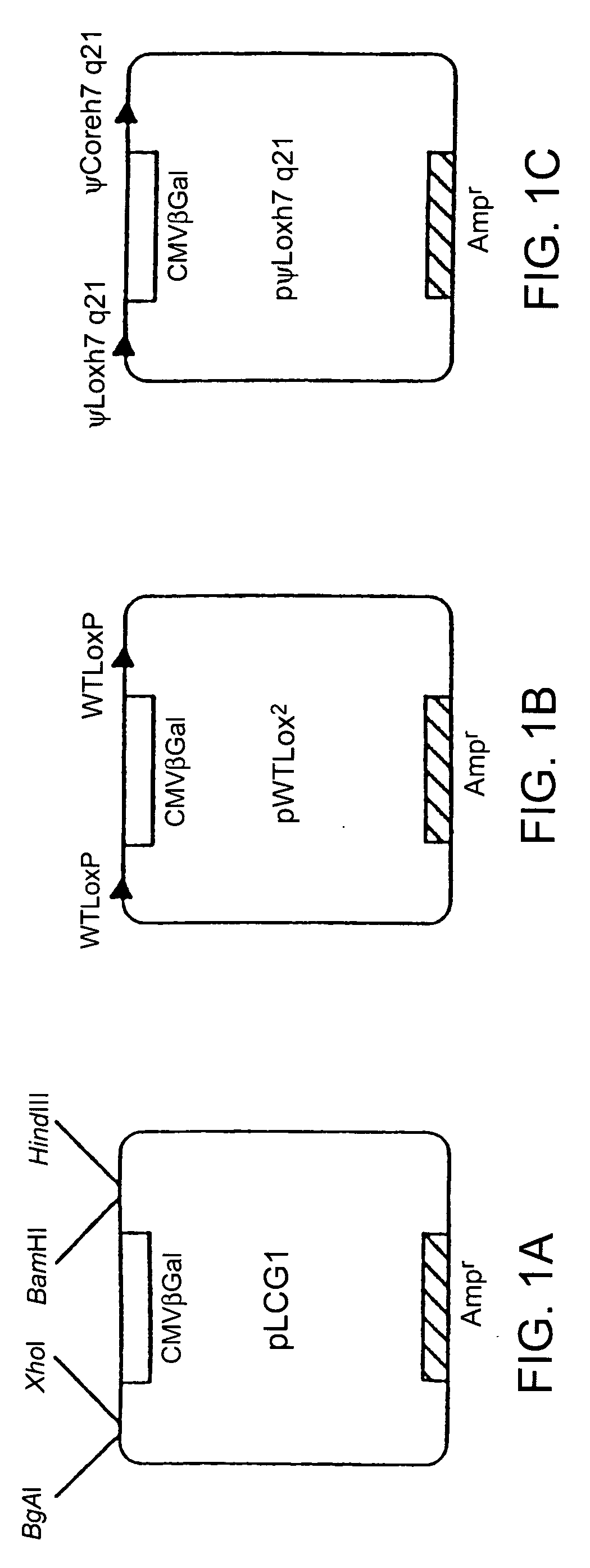
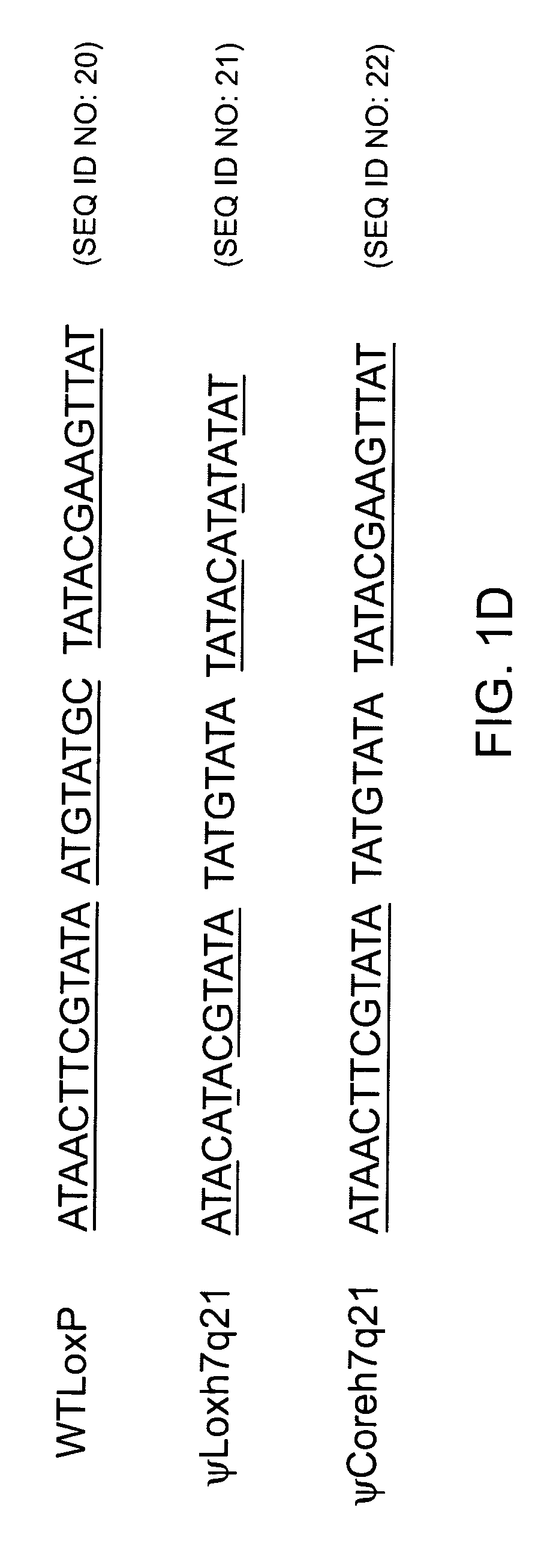
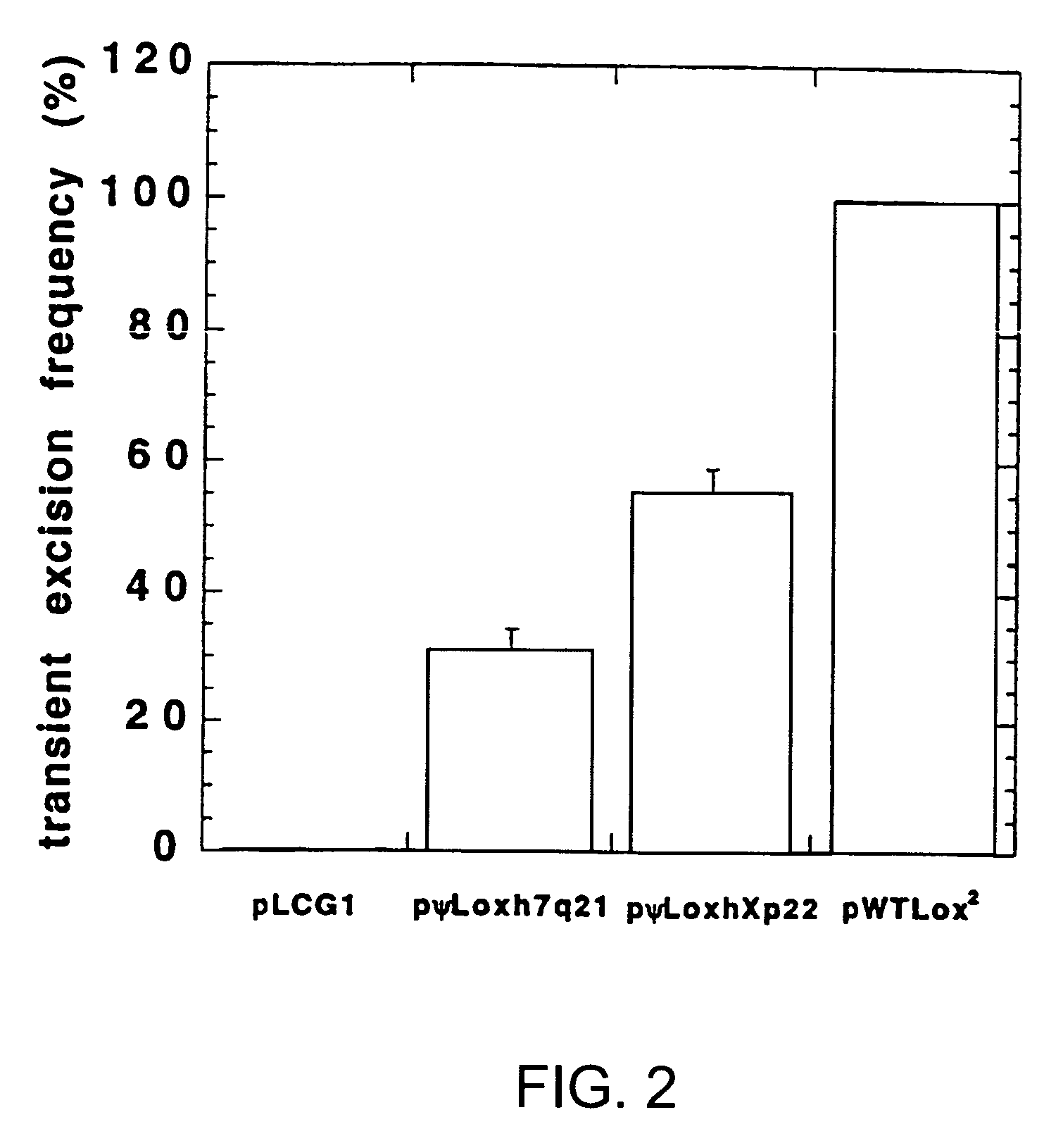
The present invention provides methods of site-specifically integrating a polynucleotide sequence of interest in a genome of a eucaryotic cell, as well as, enzymes, polypeptides, and a variety of vector constructs useful therefore. In the method, a targeting construct comprises, for example, (i) a first recombination site and a polynucleotide sequence of interest, and (ii) a site-specific recombinase, which are introduced into the cell. The genome of the cell comprises a second recombination site. Recombination between the first and second recombination sites is facilitated by the site-specific recombinase. The invention describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors, and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
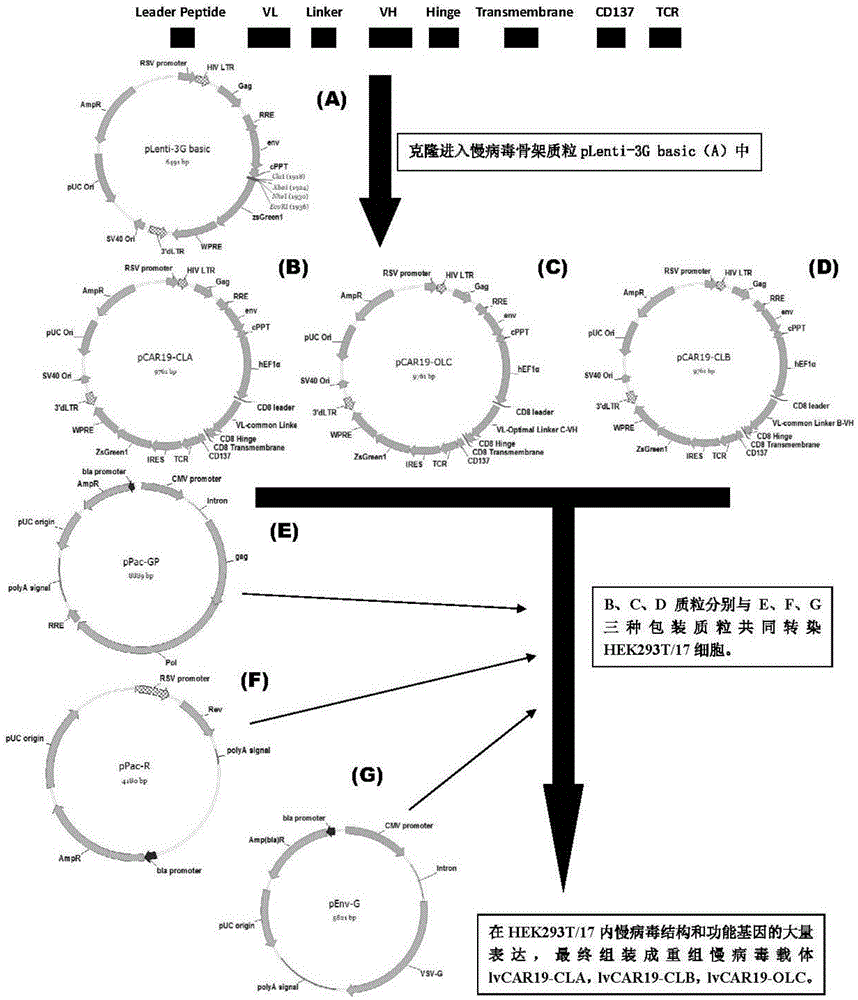
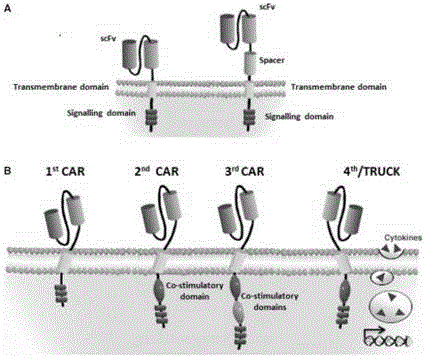
CAR-T transgene vector based on replication defective recombinant lentivirus and construction method and application of CAR-T transgene vector
ActiveCN105602992ASignificant effectPromote secretionGenetic material ingredientsFermentationEucaryotic cellAmpicillin
The invention discloses a CAR-T transgene vector based on replication defective recombinant lentivirus. The CAR-T transgene vector comprises an original nuclear replicon pUCOri sequence, a resistance gene AmpR sequence containing ampicillin, a virus replicon SV40 Ori sequence, a lentivirus packaging cis element, ZsGreen1 green fluorescent protein, an IRES ribosome binding sequence, a human EF1 alpha promoter , a chimeric antigen receptor of second-generation CAR or third-generation CAR and a regulating element, wherein the original nuclear replicon pUCOri sequence is used for plasmid replication; the resistance gene AmpR sequence is used for massively proliferating target strains; the virus replicon SV40 Ori sequence is used for enhancing replication in eukaryocyte; the lentivirus packaging cis element is used for lentivirus packaging; the ZsGreen1 green fluorescent protein is used for expressing green fluorescent for eukaryocyte; the IRES ribosome binding sequence is used for jointly transcribing and expressing protein; the human EF1 alpha promoter is used for conducting eukaryotic transcription on antigen receptor genes; the chimeric antigen receptor is used for forming the second-generation CAR or the third-generation CAR integrating recognition, transfer and start; the regulating element is used for enhancing expression efficiency of transgenes and used after eWPRE-enhanced type woodchuck hepatitis b virus is transcribed. Besides, the invention further discloses a construction method and application of the vector. By means of the CAR-T transgene vector and the construction method and application of the vector, secretion of cell factors and an in vitro killing effect of CAR-T cells can be remarkably improved, and the clinical treatment effect is remarkable.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNICAR THERAPY BIOPHARM TECH CO LTD
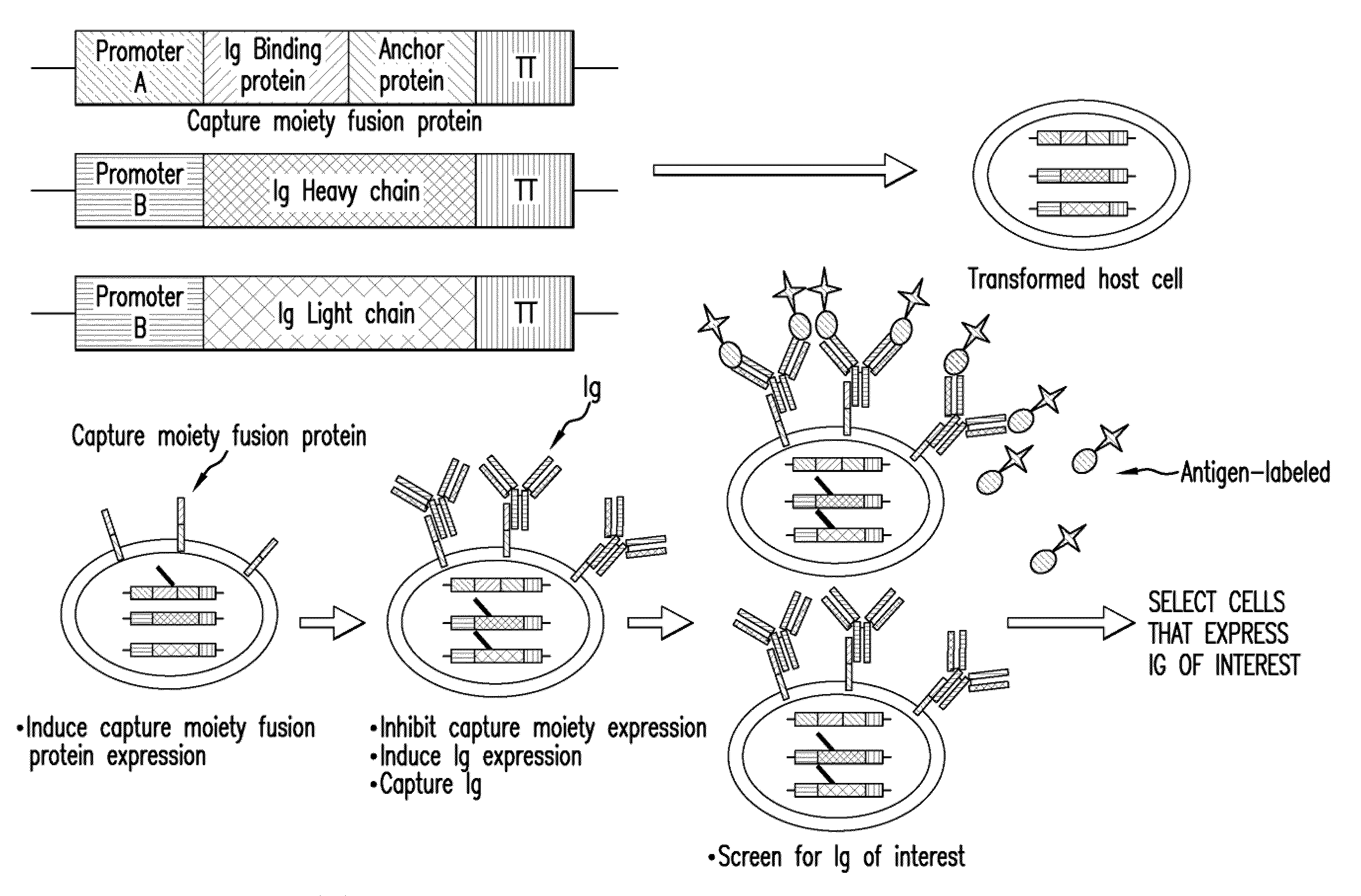
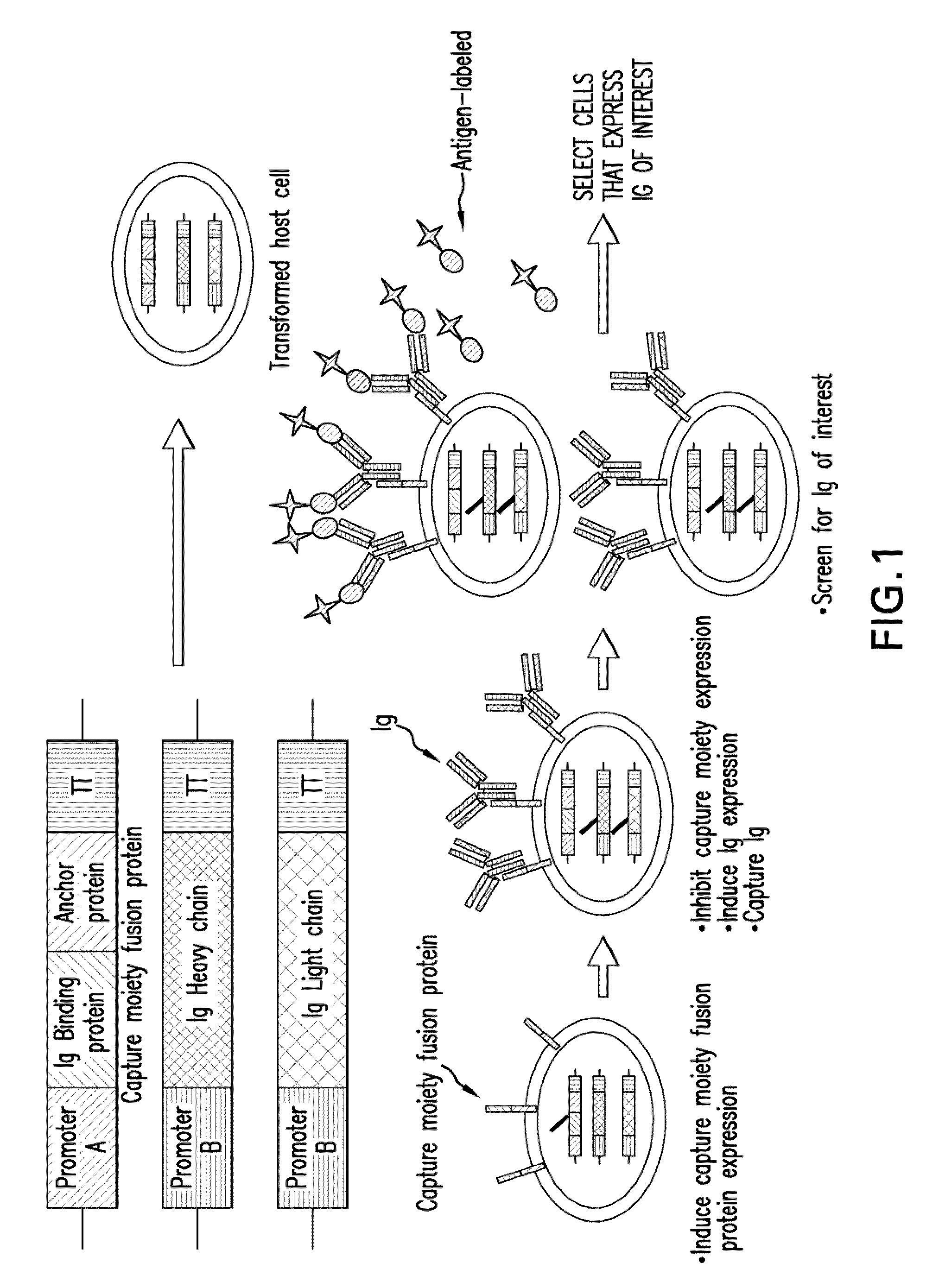
Surface Display of Whole Antibodies in Eukaryotes
ActiveUS20100009866A1Stabilize cytoplasmic mRNAImprove translation efficiencyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningYeastAntigen
Methods for display of recombinant whole immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin libraries on the surface of eukaryote host cells, including yeast and filamentous fungi, are described. The methods are useful for screening libraries of recombinant immunoglobulins in eukaryote host cells to identify immunoglobulins that are specific for an antigen of interest.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Signal for targeting molecules to the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum
Owner:NEWVA CAPITAL PARTNERS LP
Delivery, engineering and optimization of systems, methods and compositions for sequence manipulation and therapeutic applications
ActiveCN105164264AAvoid off-target bindingAvoid side effectsSenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseVector system
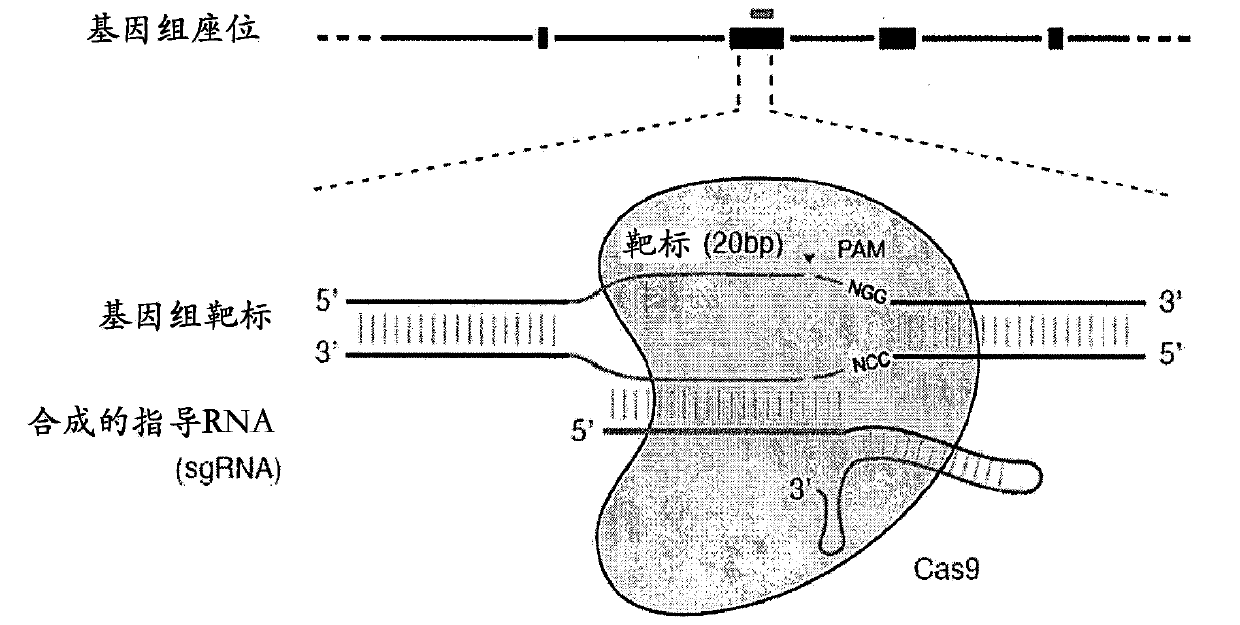
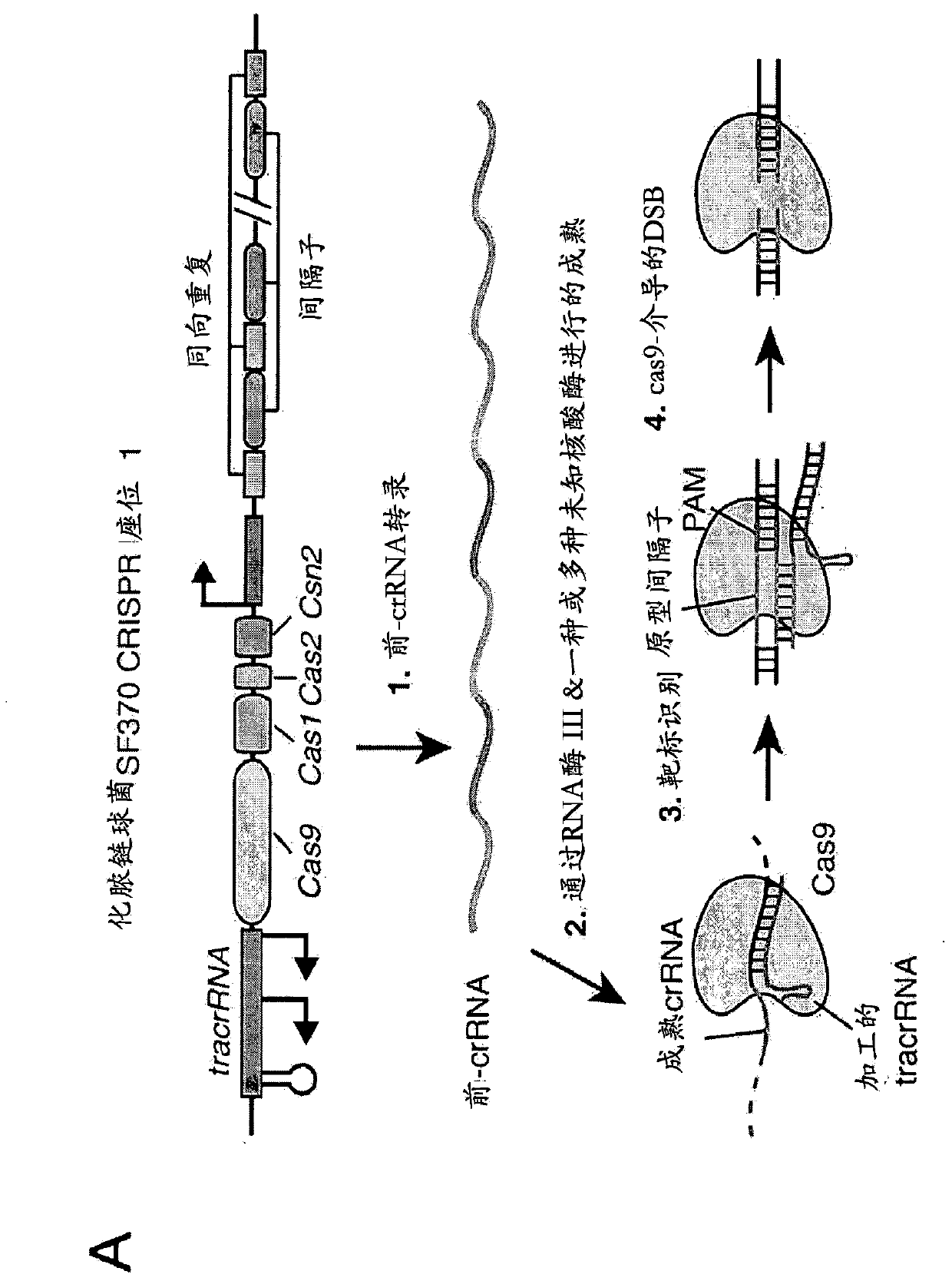
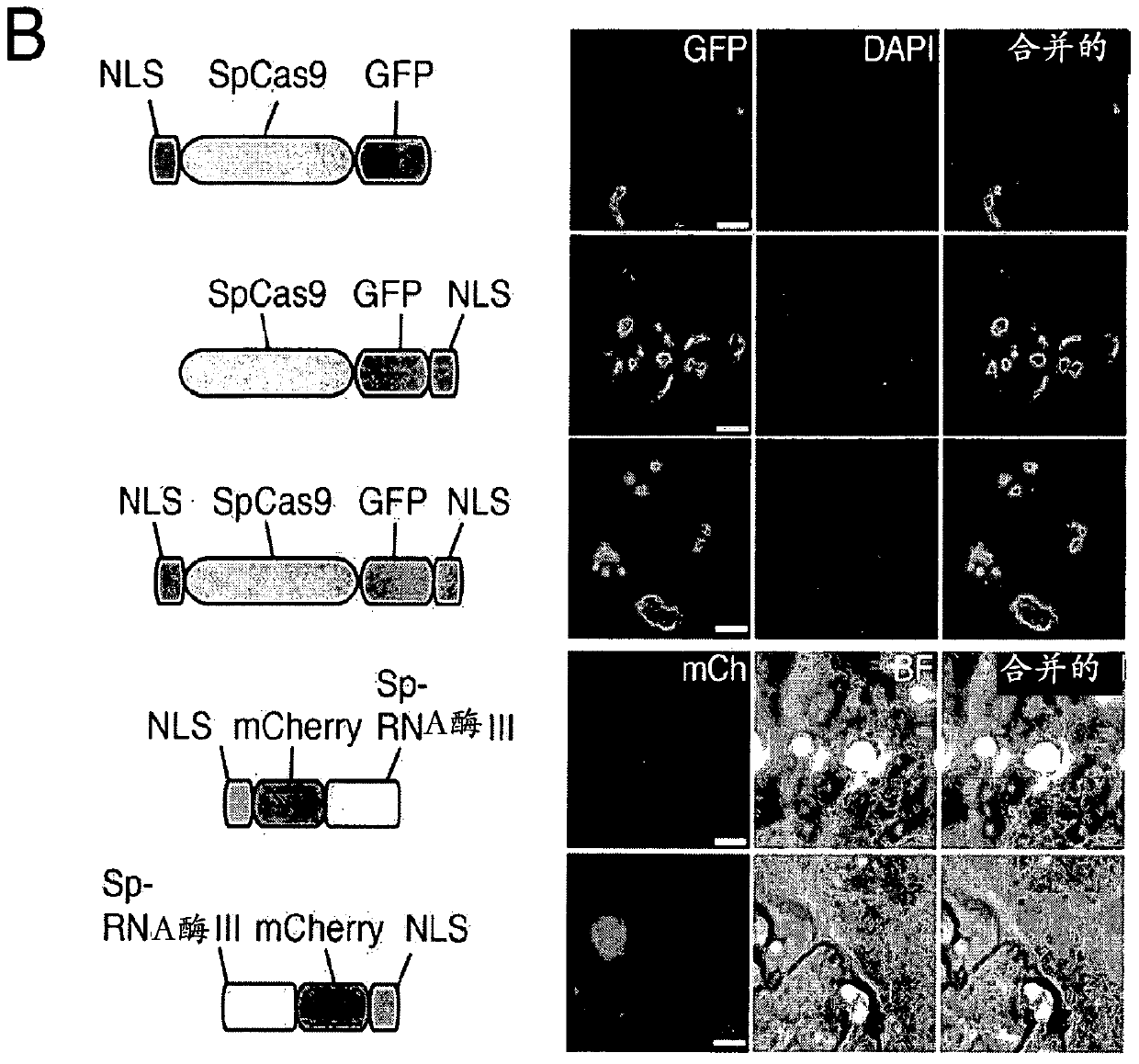
The invention provides for delivery, engineering and optimization of systems, methods, and compositions for manipulation of sequences and / or activities of target sequences. Provided are deliver systems and tissues or organ which are targeted as sites for delivery. Also provided are vectors and vector systems some of which encode one or more components of a CRISPR complex, as well as methods for the design and use of such vectors. Also provided are methods of directing CRISPR complex formation in eukaryotic ceils to ensure enhanced specificity for target recognition and avoidance of toxicity and to edit or modify a target site in a genomic locus of interest to alter or improve the status of a disease or a condition.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
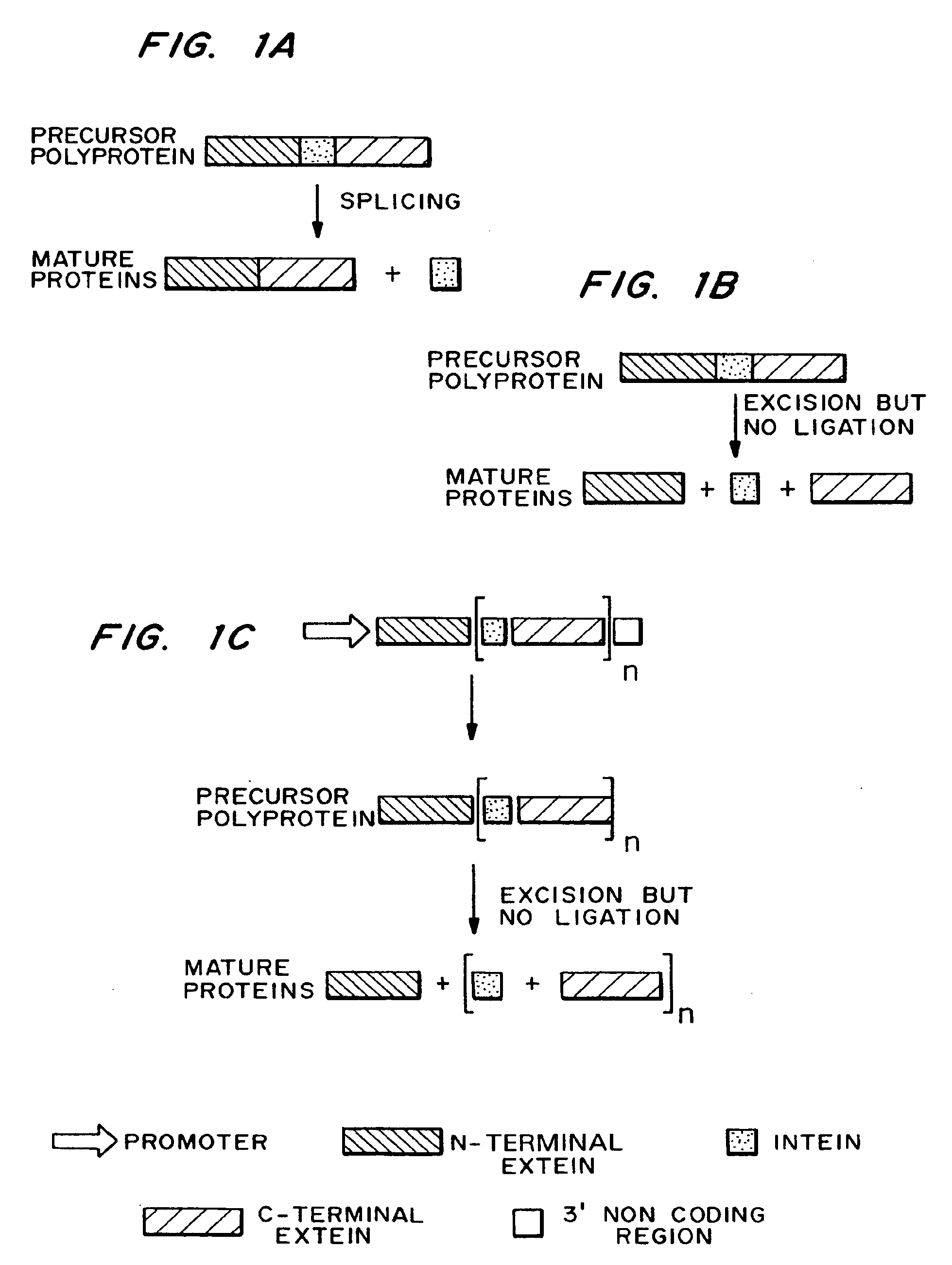
Multi-gene expression constructs containing modified inteins
InactiveUS7026526B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPoly-A RNA
Methods and constructs for the introduction of multiple genes into plants using a single transformation event are described. Constructs contain a single 5′ promoter operably linked to DNA encoding a modified intein splicing unit. The splicing unit is expressed as a polyprotein and consists of a first protein fused to an intein fused to a second protein. The splicing unit has been engineered to promote excision of all non-essential components in the polyprotein but prevent the ligation reactions normally associated with protein splicing. Additional genetic elements encoding inteins and additional proteins can be fused in frame to the 5′-terminus of the coding region for the second protein to form a construct for expression of more than two proteins. A single 3′ termination sequence, such as a polyadenylation sequence when the construct is to be expressed in eucaryotic cells, follows the last coding sequence. These methods and constructs are particularly useful for creating plants with stacked input traits, illustrated by glyphosate tolerant plants producing BT toxin, and / or value added products, illustrated by the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in plants.
Owner:METABOLIX
Method for introducing antisense oligonucleotides into eucaryotic cells
InactiveUS20060147514A1Efficient deliveryInduce cytotoxicityOrganic active ingredientsFungiLipid formationEucaryotic cell
The present invention relates to a method for introducing one or more antisense oligonucleotides into one or more eucaryotic cells using one or more lipid formulations comprising one or more cationic lipids of Formula I and optionally at least one neutral lipid. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for introducing one or more antisense oligonucleotides into one or more eucaryotic cells using a lipid formulation comprising dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide (DDAB) and at least one neutral lipid, especially dioleylphosphatidylethanolamine (DOPE). The invention also relates to kits for carrying out the invention, compositions for carrying out the invention, and compositions formed while carrying out the invention. Further, the present invention relates to a method for inhibiting or preventing cell growth or proliferation, and a method for inhibiting or preventing expression of one or more proteins.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
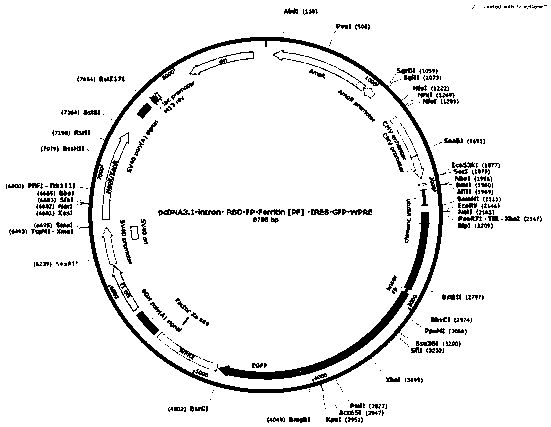
Novel coronavirus S protein two-region subunit nano vaccine based on pyrococcus furiosus ferritin
ActiveCN111217919AMultimerizationOvercoming the disadvantage of insufficient immunogenicitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsEucaryotic cellNeutralising antibody
The invention discloses a novel coronavirus S protein double-region subunit nano vaccine based on pyrococcus furiosus ferritin. The virus receptor binding domain (RBD) and fusion peptide (FP) are usedtogether as a double antigen, and are connected with pyrococcus furiosus ferritin (PF_Ferritin) to from a fusion protein RBD-FP-PF_Ferritin to realize antigen multimerization; and then an eukaryoticcell expression system is used for expressing, and a 24-mer nano antigen can be formed through self-assembly of PF_Ferritin. The scheme can overcome the shortcoming of insufficient immunogenicity of RBD monomers, the obtained vaccine can significantly increase the level of a neutralizing antibody against the virus of a host, and the produced antibody has the ability to strongly block the virus from invading target cells. In addition, the vaccine of the invention is simple in preparation method, is easy to purify, and is high in safety, and the vaccine can be relatively quickly applied to clinical trials.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
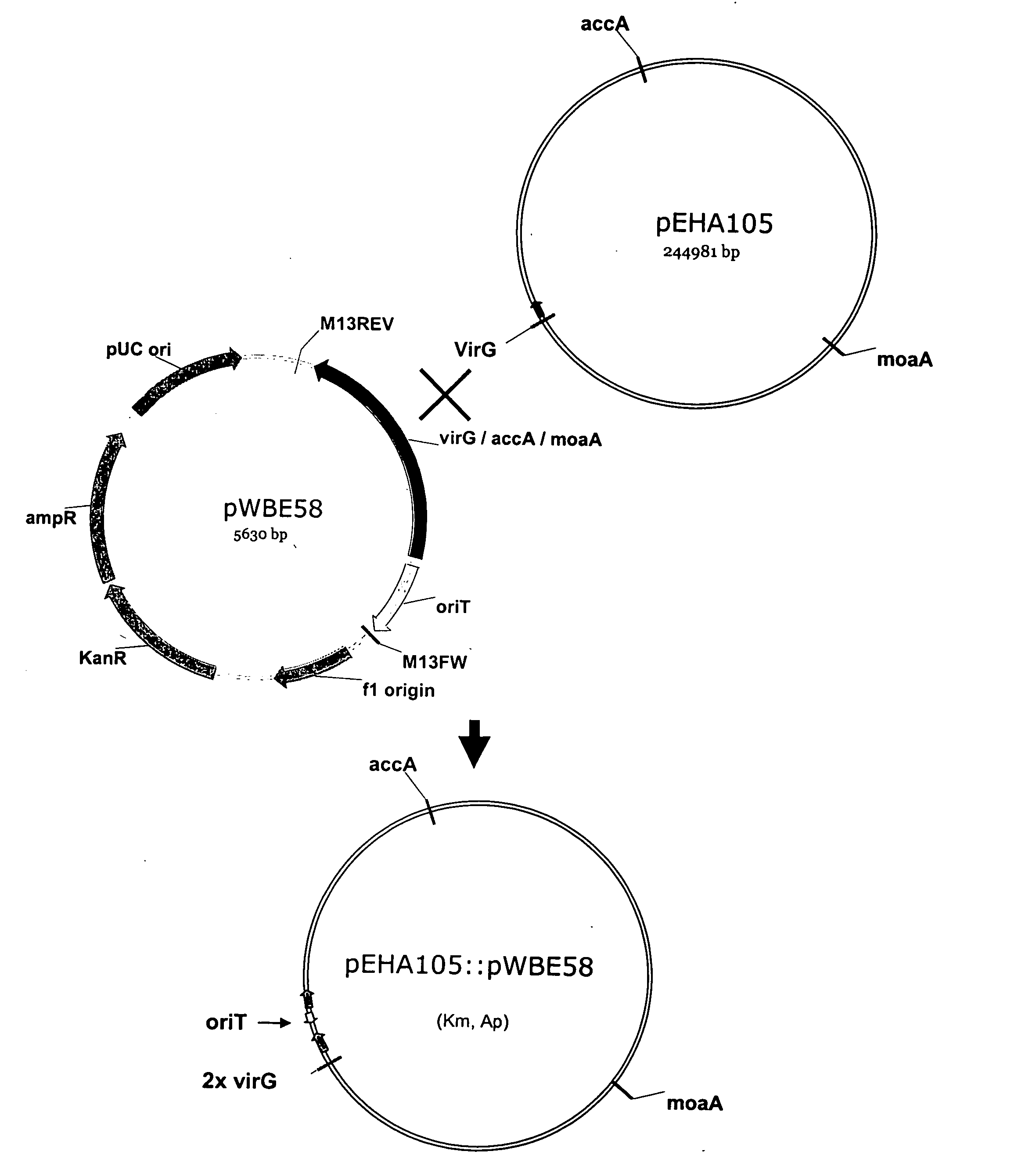
Biological gene transfer system for eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20050289672A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPlant cell
This invention relates generally to technologies for the transfer of nucleic acids molecules to eukaryotic cells. In particular non-pathogenic species of bacteria that interact with plant cells are used to transfer nucleic acid sequences. The bacteria for transforming plants usually contain binary vectors, such as a plasmid with a vir region of a Ti plasmid and a plasmid with a T region containing a DNA sequence of interest.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Host cells with artificial endosymbionts
The present invention is directed generally to eukaryotic cells comprising single-celled organisms that are introduced into the eukaryotic cell through human intervention and which transfer to daughter cells of the eukaryotic cell through at least five cell divisions, and methods of introducing such single-celled organisms into eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides methods of using such eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides single-celled organisms that introduce a phenotype to eukaryotic cells that is maintained in daughter cells. The invention additionally provides eukaryotic cells containing magnetotactic bacteria.
Owner:BELL BIOSYST
Methods and compositions for genomic modification
InactiveUS7361641B2Genetic material ingredientsStable introduction of DNAEucaryotic cellSite-specific recombination
The present invention provides methods of site-specifically integrating a polynucleotide sequence of interest in a genome of a eucaryotic cell, as well as, enzymes, polypeptides, and a variety of vector constructs useful therefore. In the method, a targeting construct comprises, for example, (i) a first recombination site and a polynucleotide sequence of interest, and (ii) a site-specific recombinase, which are introduced into the cell. The genome of the cell comprises a second recombination site. Recombination between the first and second recombination sites is facilitated by the site-specific recombinase. The invention describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors, and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method of contactless magnetic electroporation
This invention provides a novel method of tissue electroporation that eliminates the need for electrodes that conduct electricity to the tissues. This invention creates electric currents and fields sufficient for porating cell membranes for improving the delivery of polynucleotides such as plasmid and linear DNA and RNA constructs, and polypeptides such as antigen protein constructs into mammalian eucaryotic cells purely by magnetic field pulses that does not require the use of contacting electrodes to conduct electric or ionic current. This invention thus provides a method for improving transfection and immunogenicity of pharmaceutical substances without direct contact with a living body, and may be called magnetopermeabilization. A concomitant aspect of the invention is the method by which a drug such as a solution containing DNA is delivered to a targeted tissue bed that is optimal in conjunction with magnetopermeabilization for maximal transgene expression and drug effect.
Owner:INOVIO PHARMA
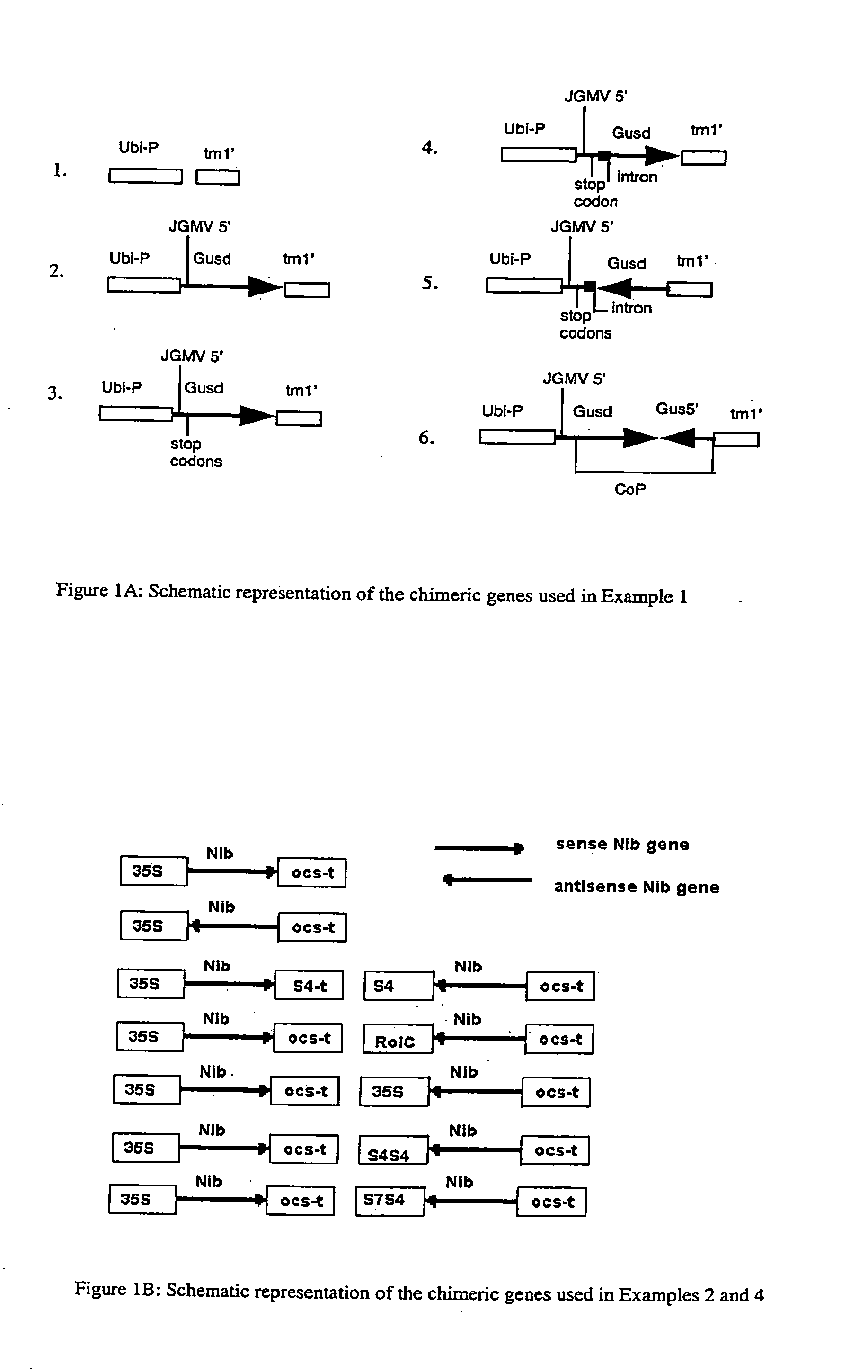
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20060178335A1Reducing phenotypic expressionGenetic material ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionEucaryotic cellAntisense RNA
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eucaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by introducing chimeric genes encoding sense and antisense RNA molecules directed towards the target nucleic acid, which are capable of forming a double stranded RNA region by base-pairing between the regions with sense and antisense nucleotide sequence or by introducing the RNA molecules themselves. Preferably, the RNA molecules comprises simultaneously both sense and antisense nucleotide sequence.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
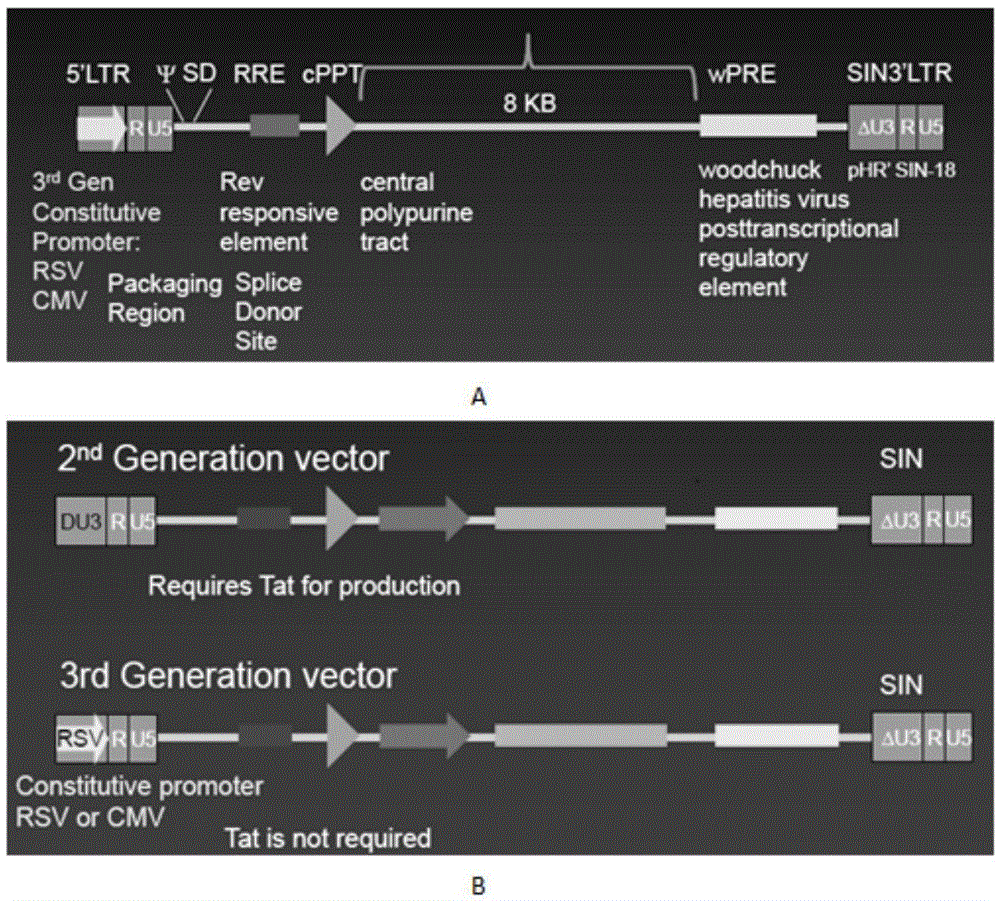
Lentiviral Vectors That Provide Improved Expression And Reduced Variegation After Transgenesis
The present invention provides new lentiviral vectors that include an anti-repressor element (ARE) and, optionally, a scaffold attachment region (SAR). The lentiviral vectors provide expression of a heterologous nucleic acid in at least 50% of the cells of multiple cell types when used for lentiviral transgenesis. In certain embodiments of the invention the heterologous nucleic acid encodes an RNAi agent such as an shRNA. The invention further provides transgenic nonhuman animals generated using a lentiviral vector that includes an ARE and optional SAR. In addition, the invention provides a variety of methods for using the vectors including for achieving gene silencing in eukaryotic cells and transgenic animals, and methods of treating disease. The invention also provides animal models of human disease in which one or more genes is functionally silenced using a lentiviral vector of the invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Mammalian cell surface DNA receptor
The present invention relates to novel mammalian DNA-R proteins and genes that encode such proteins. The invention is directed toward the isolation and characterization of mammalian DNA-R proteins. The invention specifically provides isolated complementary DNA copies of mRNA corresponding to rat and human homologues of a mammalian DNA-R gene. Also provided are recombinant expression constructs capable of expressing the mammalian DNA-R genes of the invention in cultures of transformed prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as such cultures of transformed cells that synthesize the mammalian catecholamine receptor proteins encoded therein. The invention also provides methods for screening compounds in vitro that are capable of binding to the mammalian DNA-R proteins of the invention, and further characterizing the binding properties of such compounds in comparison with known DNA-R agonists and antagonists. Improved methods of pharmacological screening are provided thereby.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
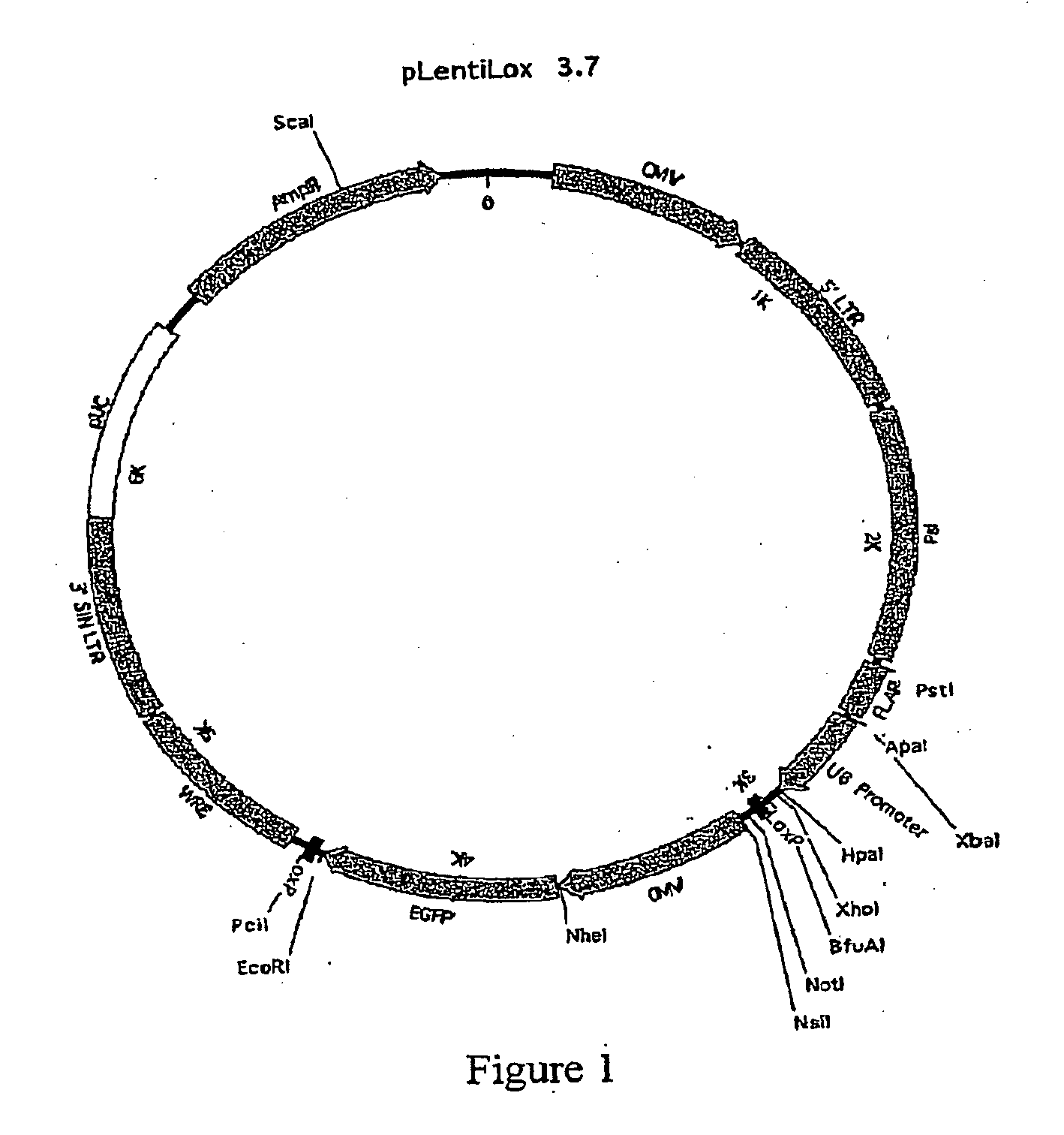
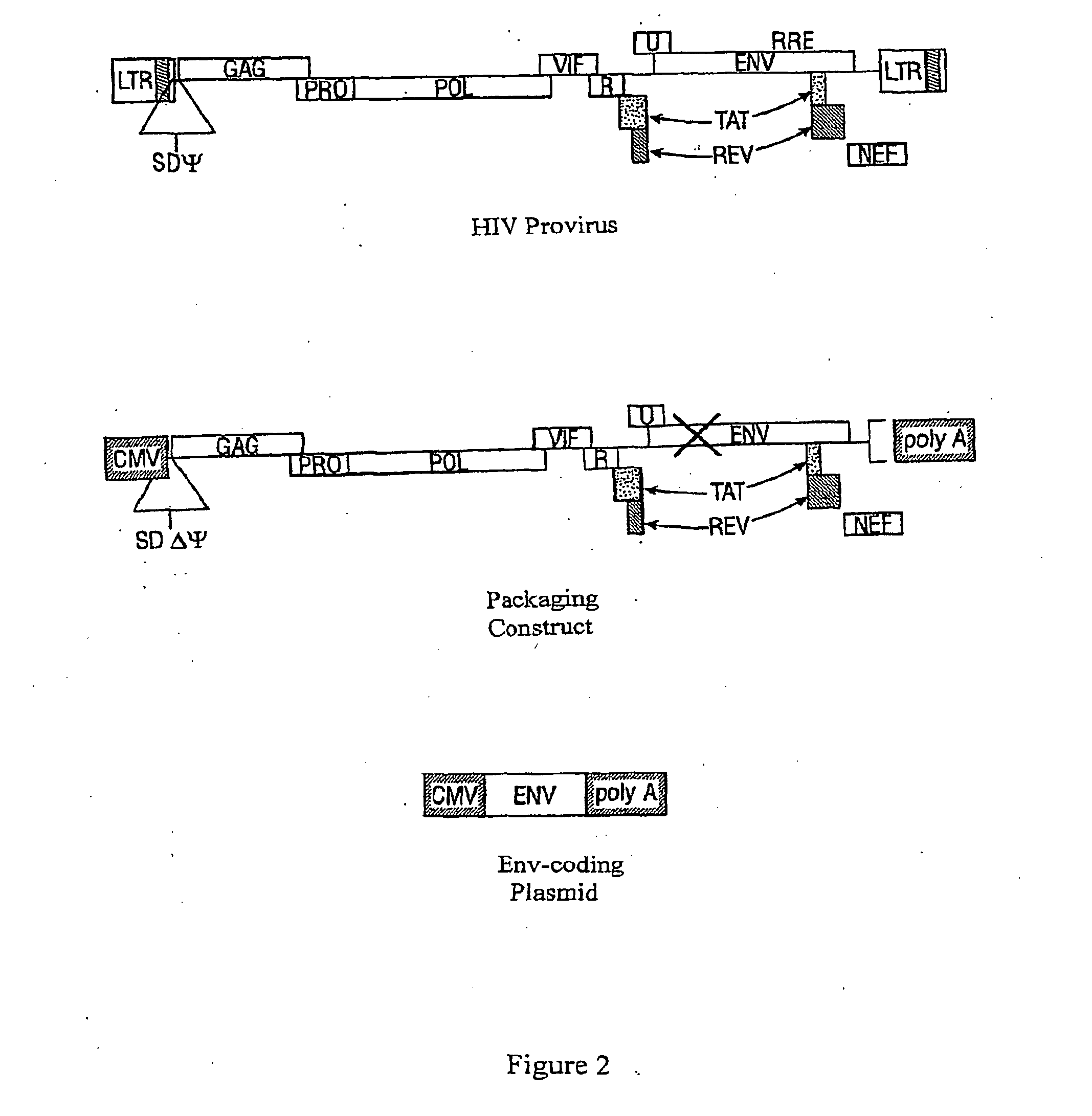
Lentiviral vectors, related reagents, and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides new lentiviral vectors, including lentiviral transfer plasmids and infectious lentiviral particles. Lentiviral vectors of the invention were designed to offer a number of desirable features including reduced size, convenient cloning sites (including multiple cloning sites and sites for particularly useful restriction enzymes), loxP sites, self-inactivating LTRs, etc. Certain of the vectors are optimized for expression of reporter genes and / or for expression of siRNAs or shRNAs within eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides three and four plasmid lentiviral expression systems. In addition, the invention provides a variety of methods for using the vectors including gene silencing in cells and transgenic animals, and methods of treating disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Highly effective polypeptide for inhibiting angiogenesis, physical chemistry modifying method and application thereof
InactiveCN101143894APrevent proliferationLittle side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesIon exchangeGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a high-performance angiogenesis inhibitor and a production method, which belongs to the field of the biological engineering pharmaceutical technology or protein polypeptide drugs. The invention designs a high-performance angiogenesis inhibitor RGD-ED with integrin compatibility, the inhibitor contains angiogenesis inhibition polypeptide isoleucine-valine-arginine-arginine-alanine-aspartate-arginine-alanine-alanine-valine-proline, and one or two ends of the inhibitor are respectively connected with polypeptides containing arginine-glycin-aspartate sequence. The RGD-ED of the invention can be synthesized. By the method of genetic engineering, the invention also expresses one of RGD-Eds in escherichia coli or other eukaryotic cells, and the RGD-ED is obtained by carrying out the separation, dissolution and renaturation of inclusion body protein and separation and purification by ion exchange chromatography. All the polypeptide sequences of the invention are modified by Polyethylene Glycol (PEG), heparin, dextran, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), polyglycol-poly (amino acid) copolymer, palmitic acid, colominic acid and liposome, which includes liposome (REV), drying liposomal (DRV) and multivesicular liposome (Mvl). In vivo and in vitro experiments, the synthetic polypeptide sequence, product of genetic engineering and modified product of the invention can notably increase the effects of inhibiting the growth of endothelial cells, inhibiting angiogenesis and resisting tumor of the present angiogenesis inhibitors, and moreover, the high-performance angiogenesis inhibitor can be used as a drug curing solid tumors and rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Biological gene transfer system for eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20050289667A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPlant cell
This invention relates generally to technologies for the transfer of nucleic acids molecules to eukaryotic cells. In particular non-pathogenic species of bacteria that interact with plant cells are used to transfer nucleic acid sequences. The bacteria for transforming plants usually contain binary vectors, such as a plasmid with a vir region of a Ti plasmid and a plasmid with a T region containing a DNA sequence of interest.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20070078105A1Reducing phenotypic expressionGenetic material ingredientsGenetic engineeringEucaryotic cellAntisense RNA
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eucaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by introducing chimeric genes encoding sense and antisense RNA molecules directed towards the target nucleic acid, which are capable of forming a double stranded RNA region by base-pairing between the regions with sense and antisense nucleotide sequence or by introducing the RNA molecules themselves. Preferably, the RNA molecules comprises simultaneously both sense and antisense nucleotide sequence.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for obtaining peptides
ActiveUS20150087003A1Provide stabilityHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsEucaryotic cellCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Tetracycline-regulated transcriptional activator fusion proteins
InactiveUS6914124B2Avoid developmentEfficient workFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEucaryotic cellTET repressor
A method for regulating expression of a tet operator-linked gene in a cell of a subject is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method involves introducing into the cell a nucleic acid molecule encoding a tetracycline-controllable transactivator (tTA), the tTA comprising a Tet repressor operably linked to a polypeptide which directly or indirectly activates transcription in eucaryotic cells; and modulating the concentration of a tetracycline, or analogue thereof, in the subject. Alternatively, in another embodiment, the method involves obtaining the cell from the subject, introducing into the cell a first nucleic acid molecule which operatively links a gene to at least one tet operator sequence, introducing into the cell a second nucleic acid molecule encoding a tTA, to form a modified cell, administering the modified cell to the subject, and modulating the concentration of a tetracycline, or analogue thereof, in the subject. The first and second nucleic acid molecule can be within a single molecule (e.g., in the same vector) or on separate molecules.
Owner:TET SYST
Preparation method of spirulina extract
The invention discloses an extraction method of a spirulina organism, which comprises the following three steps: a fermentation preprocessing step: super macro pulverizing spirulina fine powders, and adding a complex medium to carry out fermentation to prepare fermentation basic solution; a fermentation step: inoculating eosinophilic spirulina bifidobacterium with the fermentation basic solution, and carrying out fermentation to prepare fermentation liquor; and a fermentation postprocessing step: carrying out thallus removal and enzyme inactivation on the fermentation liquor, concentrating, and drying to prepare a spirulina main chemical componet extract. According to the invention, a process combining a super macro pulverization physical method and a bifidobacterium fermentation biological method is adopted for processing spirulina fine powder, so that the unpleasant fishy smell of the spirulina can be effective removed, and the taste of an end product is improved; an eucaryotic cell structure of the spirulina can be effectively damaged, and the contained protein is disassociated, so that the extraction rate of the protein is improved; the high protein can be completely resolved to translate into oligopeptides, and the content of the oligopeptides is improved, so that the end product is easy to absorb and utilize; and the method is simple and convenient to operate, has low cost and little environment pollution.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
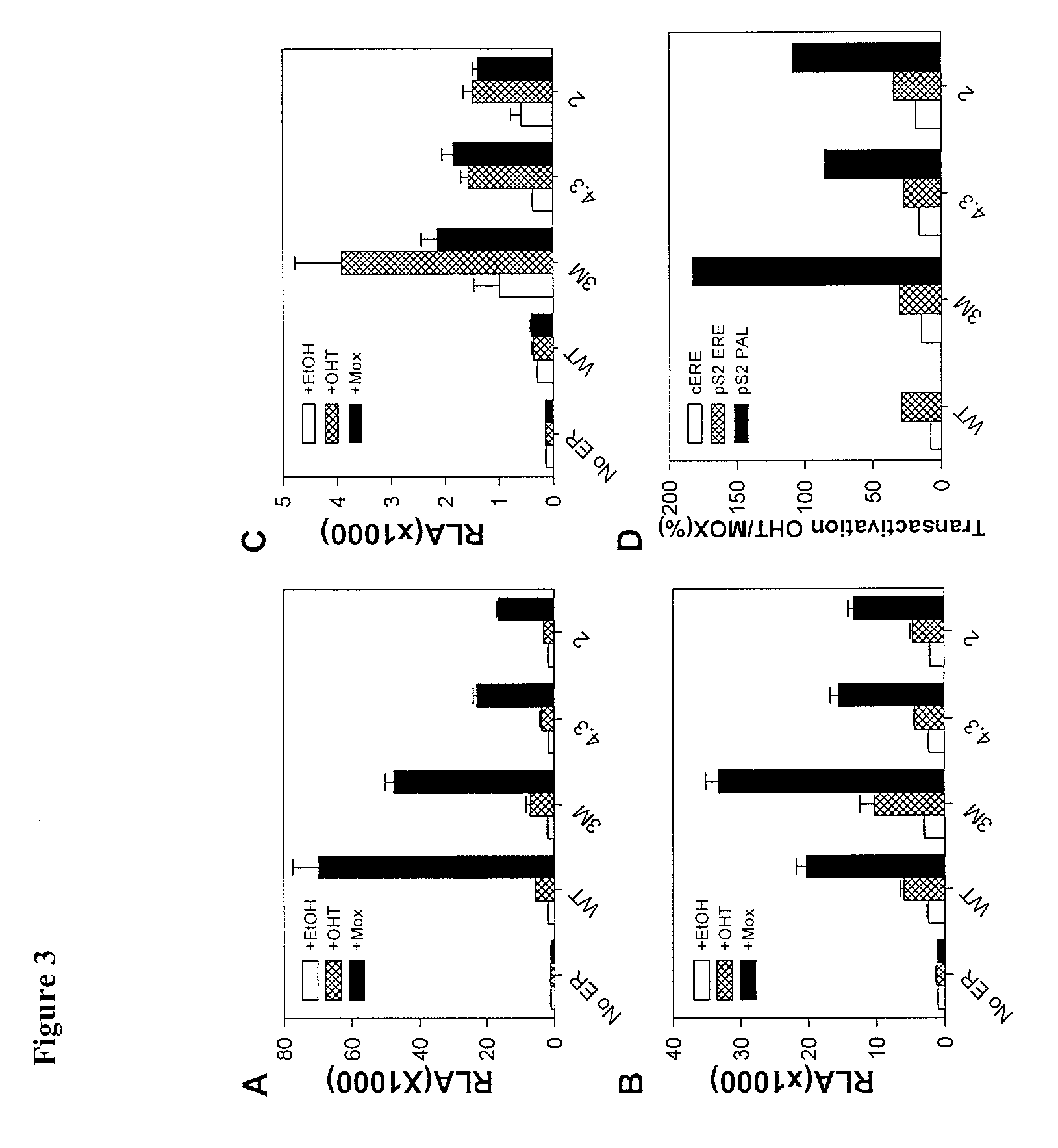
Tamoxifen and 4-hydroxytamoxifen-activated system for regulated production of proteins in eukaryotic cells
ActiveUS7153685B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsEucaryotic cell4-hydroxytamoxifen
Novel tamoxifen inducible and ICI 182,780 repressible expression systems comprising mutant estrogen receptors and mutant estrogen response element are disclosed. Such systems have a wide variety of applications, including gene therapy and in vivo and in vitro expression, as well as their use in transgenic animals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
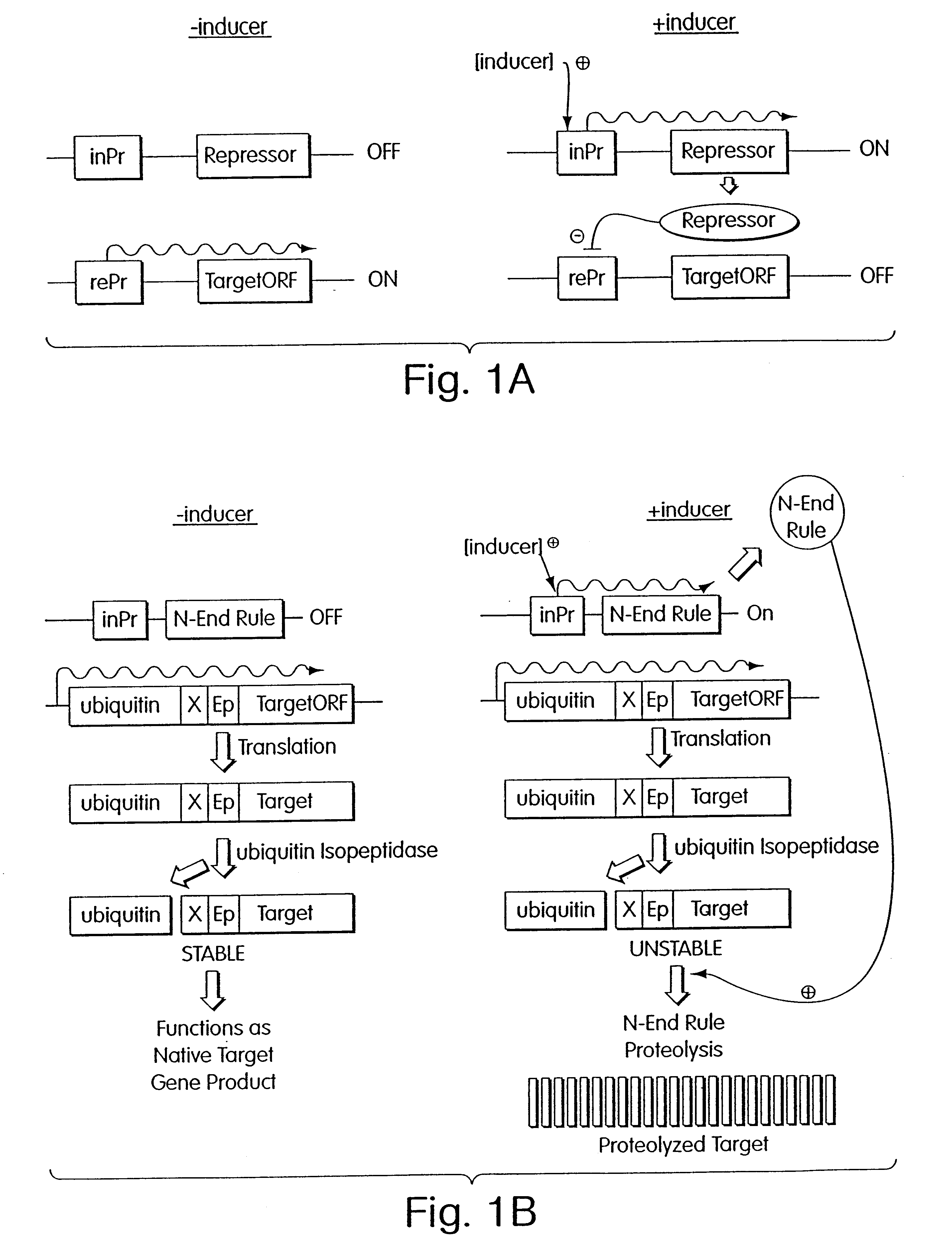
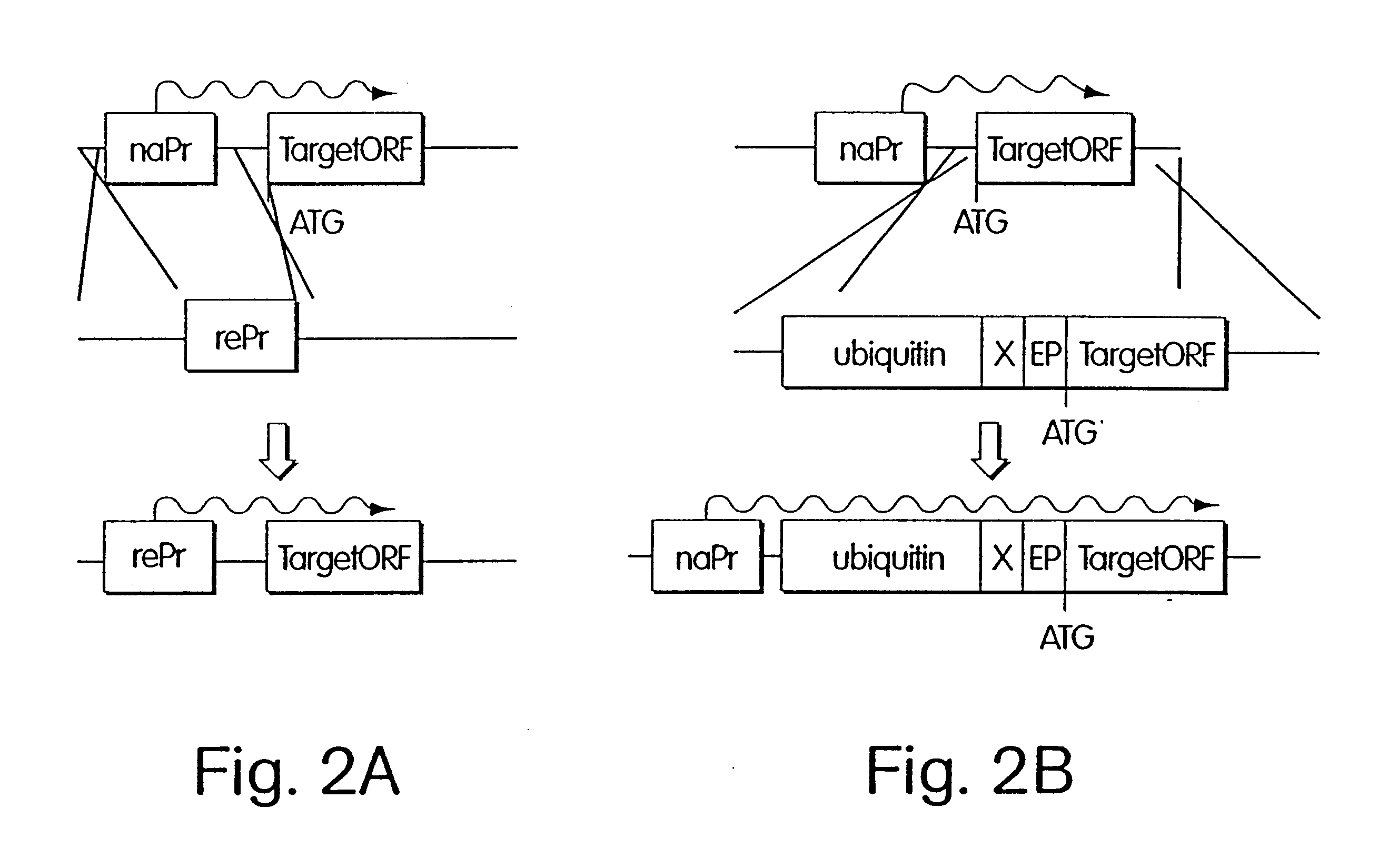
Inducible methods for repressing gene function
InactiveUS6576469B1Rapid and effective meanRapid and reliable repressionVectorsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEucaryotic cellFunction method
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods and means for obtaining modified phenotypes
InactiveUS20080104732A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesEucaryotic cellAntisense RNA
Methods and means are provided for reducing the phenotypic expression of a nucleic acid of interest in eucaryotic cells, particularly in plant cells, by introducing chimeric genes encoding sense and antisense RNA molecules directed towards the target nucleic acid, which are capable of forming a double stranded RNA region by base-pairing between the regions with sense and antisense nucleotide sequence or by introducing the RNA molecules themselves. Preferably, the RNA molecules comprises simultaneously both sense and antisense nucleotide sequence.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Three component chimeric antisense oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20030083477A1Reduce errorsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEucaryotic cellBiological activation
The invention provides a class of oligonucleotide that is optimized to target a specific RNA for RNAse H degradation and to be itself resistant to degradation within in plasma and within eukaryotic, especially mammalian cells. The oligonucleotides of the invention contain no naturally occurring 5'->3'-linked nucleotides. Rather, the invention provides oligonucleotides having two types of nucleotides: 2'-deoxyphosphorothioate, which activate RNase H, and 2'-modified nucleotides, which do not. The linkages between the 2'-modified nucleotides can be phosphodiesters, phosphorothioate or P-ethoxyphosphodiester. Activation of RNAse H is accomplished by a contiguous, RNAse H-activating region, which contains between three and five 2'-deoxyphosphorothioate nucleotides to activate bacterial RNAse H and between five and ten 2'-deoxyphosphorothioate nucleotides to activate eukaryotic and, particularly, mammalian RNAse H. Protection from degradation is accomplished by making the 5' and 3' terminal bases highly nuclease resistant and, optionally, by placing a 3' terminal blocking group.
Owner:WOOLF TOD MITCHELL +1
Method for establishing recombinant adenovirus vector with Africa swine fever EP153R and P54 gene coexpression and packaging adenovirus
PendingCN109735567AEnhance immune responseViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsGene coexpressionMultiple cloning site
The invention provides a method for establishing a recombinant adenovirus vector with Africa swine fever EP153R and P54 gene coexpression and packaging adenovirus and belongs to the technical field ofgene engineering. According to the adenovirus vector of coexpression of the EP153R gene and the P54 gene, with a pShuttle-CMV eukaryotic expression vector as a basis, the CTLA4, EP153R and P54 genesare introduced at multiple cloning sites. The invention further provides recombinant adenovirus with coexpression of the EP153R and P54 genes. The established pAD-Shuttle-CMV-CTLA4-EP153R-P54 vector is used for achieving the adenovirus packaging process, the adenovirus which can directly infect animals or eukaryocyte is obtained, the aim of coexpression of the EP153R and P54 genes in eukaryocyte is achieved, and the basis is laid for research on adenovirus vaccines of coexpression of the EP153R and P54 genes.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
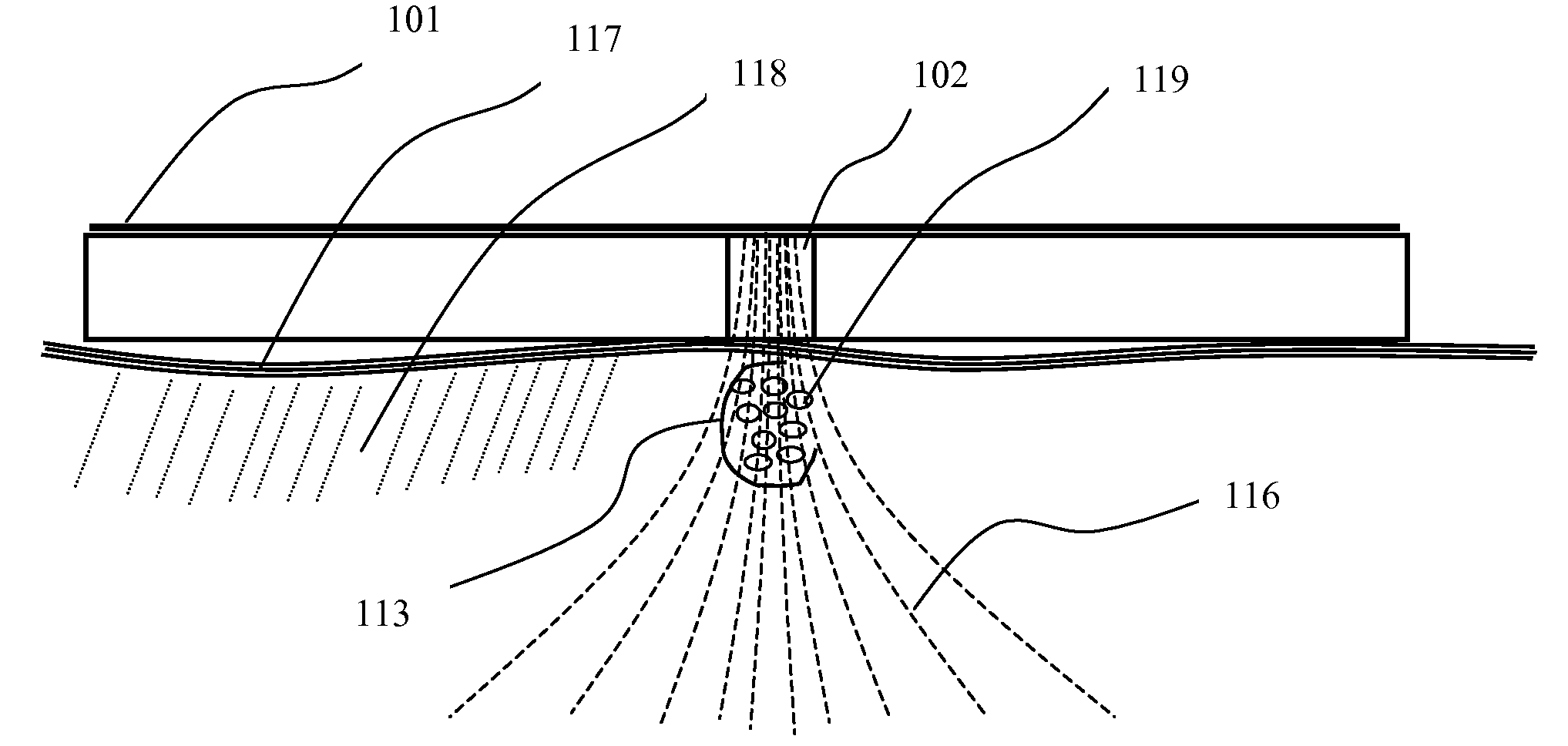
Vector mediated organelle transfection
ActiveUS20070011759A1High expressionFunction increaseSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsEucaryotic cellDNA construct
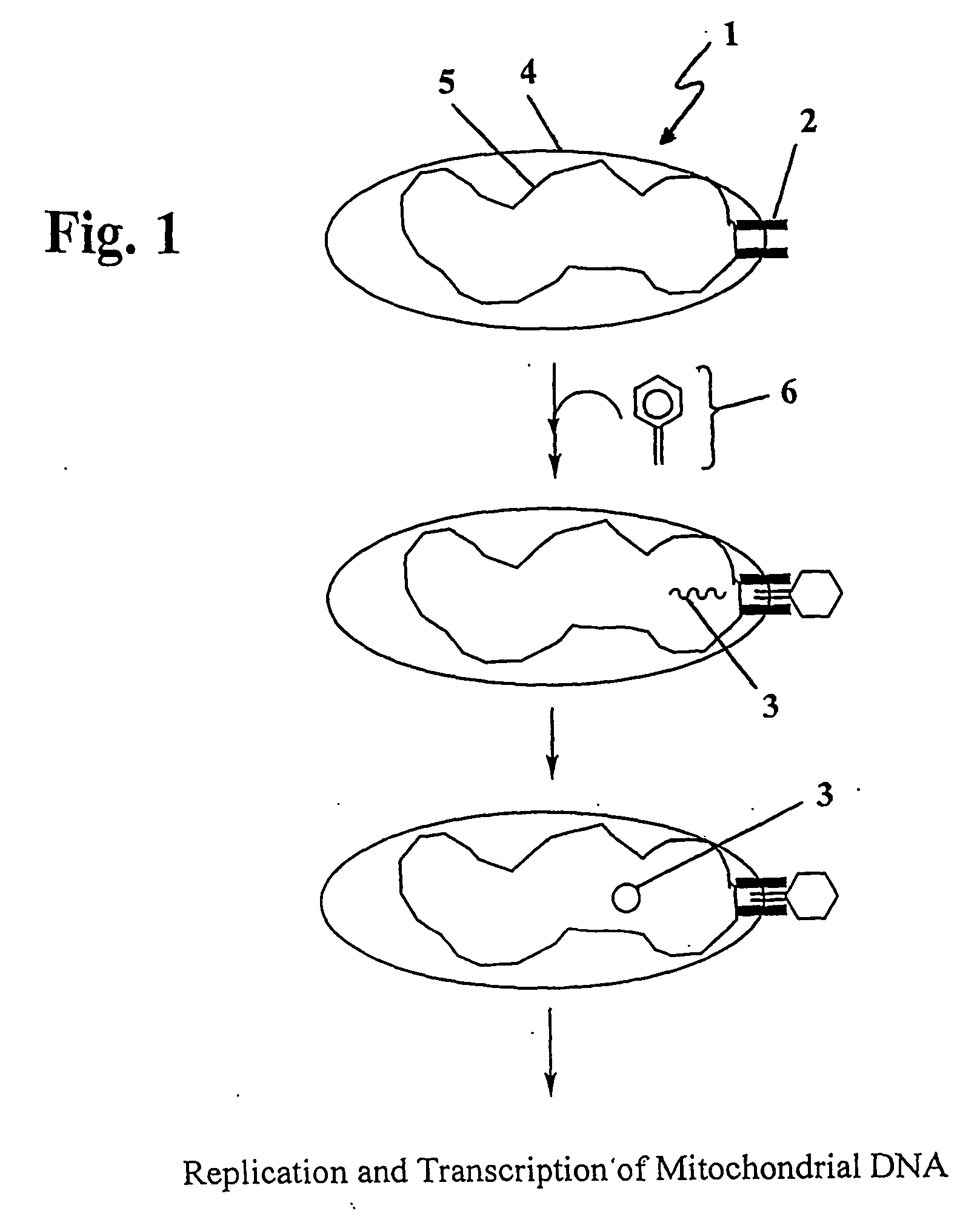
The present invention provides compositions and methods for direct transfection of mitochondria and chloroplast DNA in living cells. More particularly, the present invention is based on the use of viral vectors that specifically bind to receptors uniquely found on the target organelle. In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, a eukaryotic cell containing an organelle (1) that has been modified to express a viral receptor (2) on the organelle's surface is provided. A viral vector (6) comprising a desired recombinant DNA construct (3) is introduced into the cytosol of the cell, wherein the viral vector binds to its receptor and introduces the recombinant DNA into the interior of the organelle.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Construction of EP153R and EP402R gene co-expression recombinant adenovirus vector and adenovirus packaging method
InactiveCN109652449ADirect infectionEnhance immune responseViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesMultiple cloning siteCloning Site
The invention provides construction of an EP153R and EP402R gene co-expression recombinant adenovirus vector and a adenovirus packaging method, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. Based on a pShuttle-CMV eukaryotic expression vector, an EP153R gene and EP402R gene overexpression adenovirus vector pAD-Shuttle-CMV-CTLA4-EP153R-EP402R is introduced with CTLA4, EP153R and EP402Rgenes at multiple cloning sites. The invention also provides recombinant adenovirus for co-expressing EP153R and EP402R genes, and the adenovirus packaging process is achieved by utilizing the constructed pAD-Shuttle-CMV-CTLA4-EP153R-EP402R vector to obtain the adenovirus capable of directly infecting animal or eukaryotic cells, thereby achieving the purpose of co-expressing EP153R and EP402R genes in eukaryotic cells, and laying a foundation for researching the adenovirus vaccine for achieving the co-expression of EP153R and EP402R genes.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com