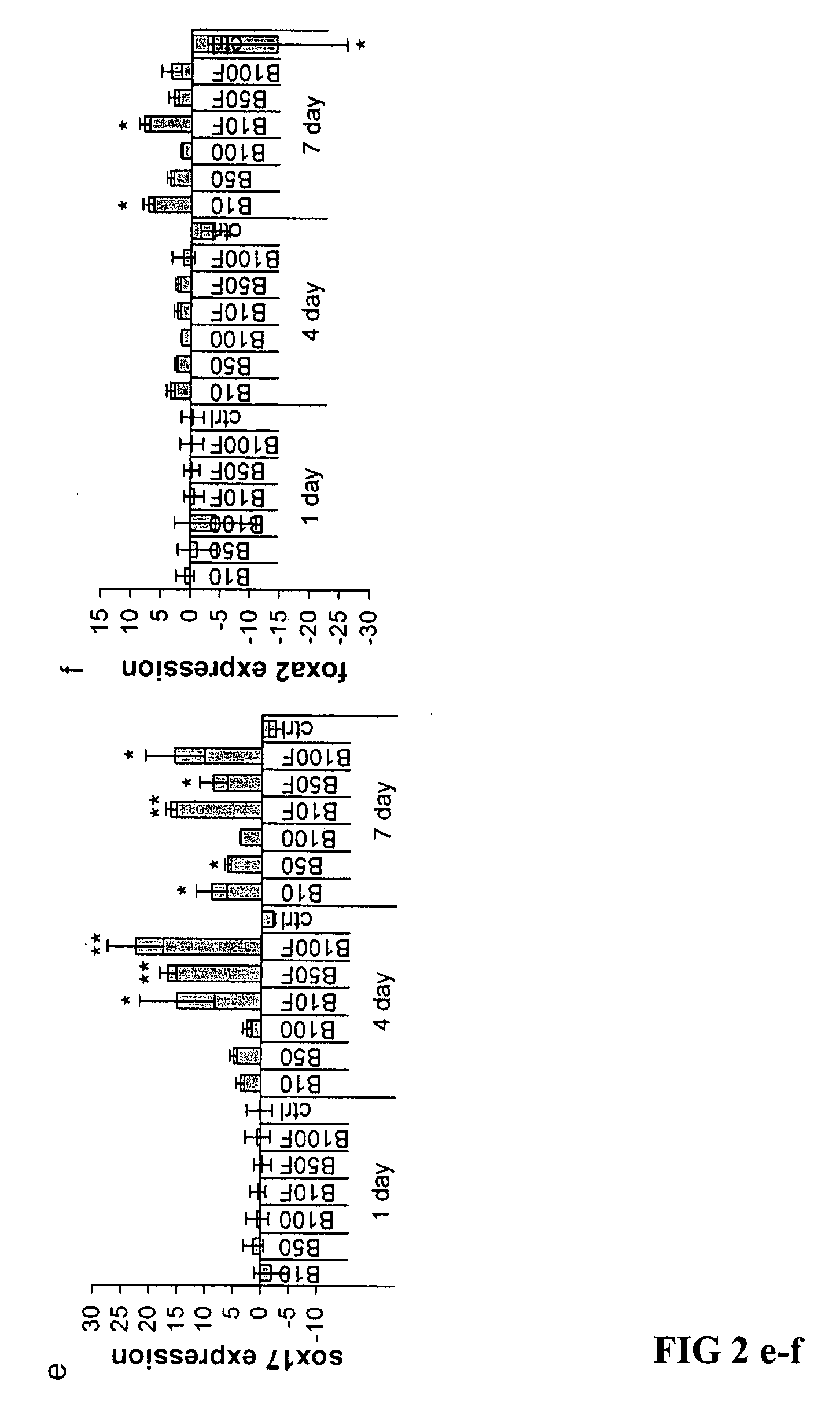
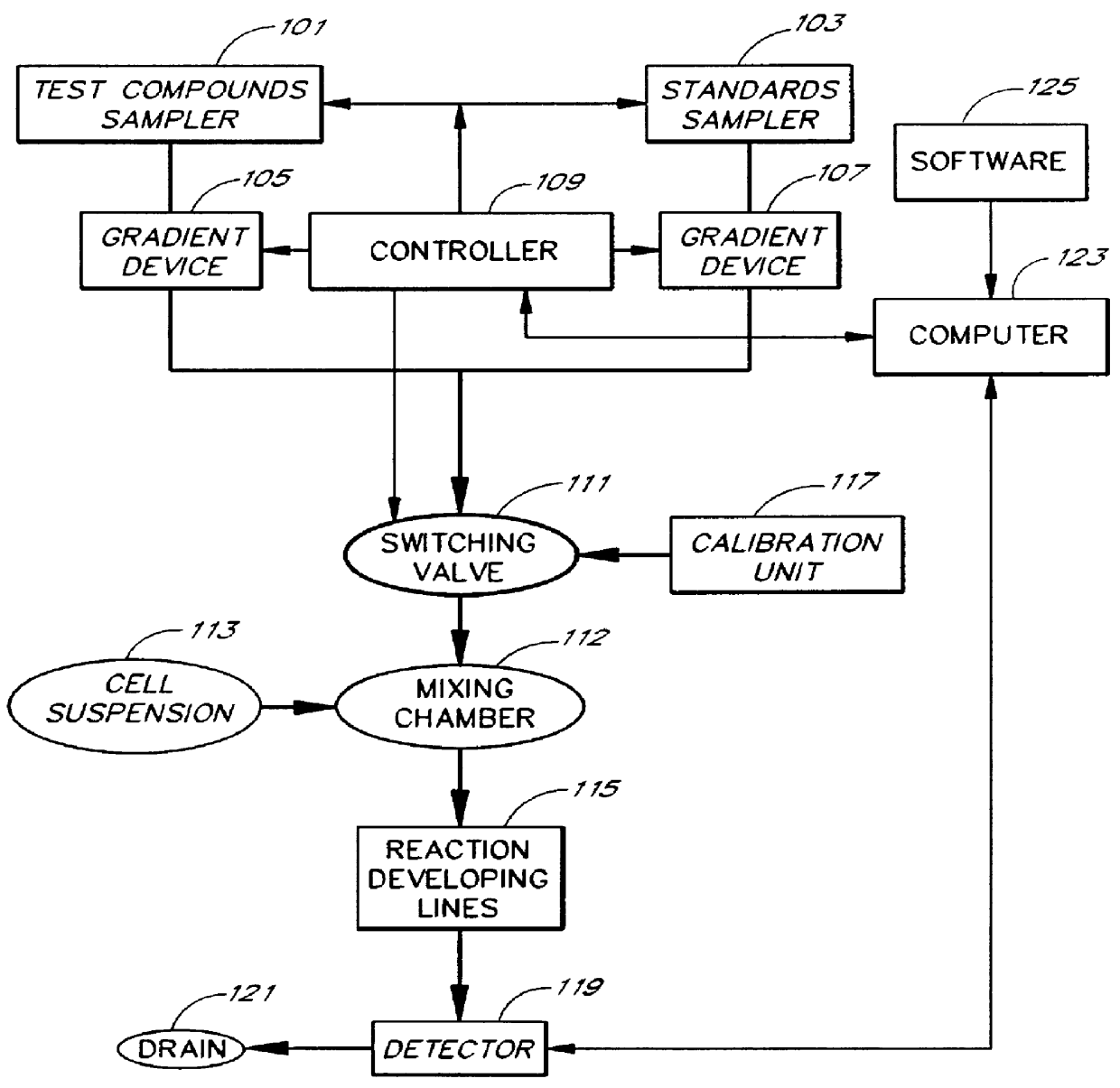
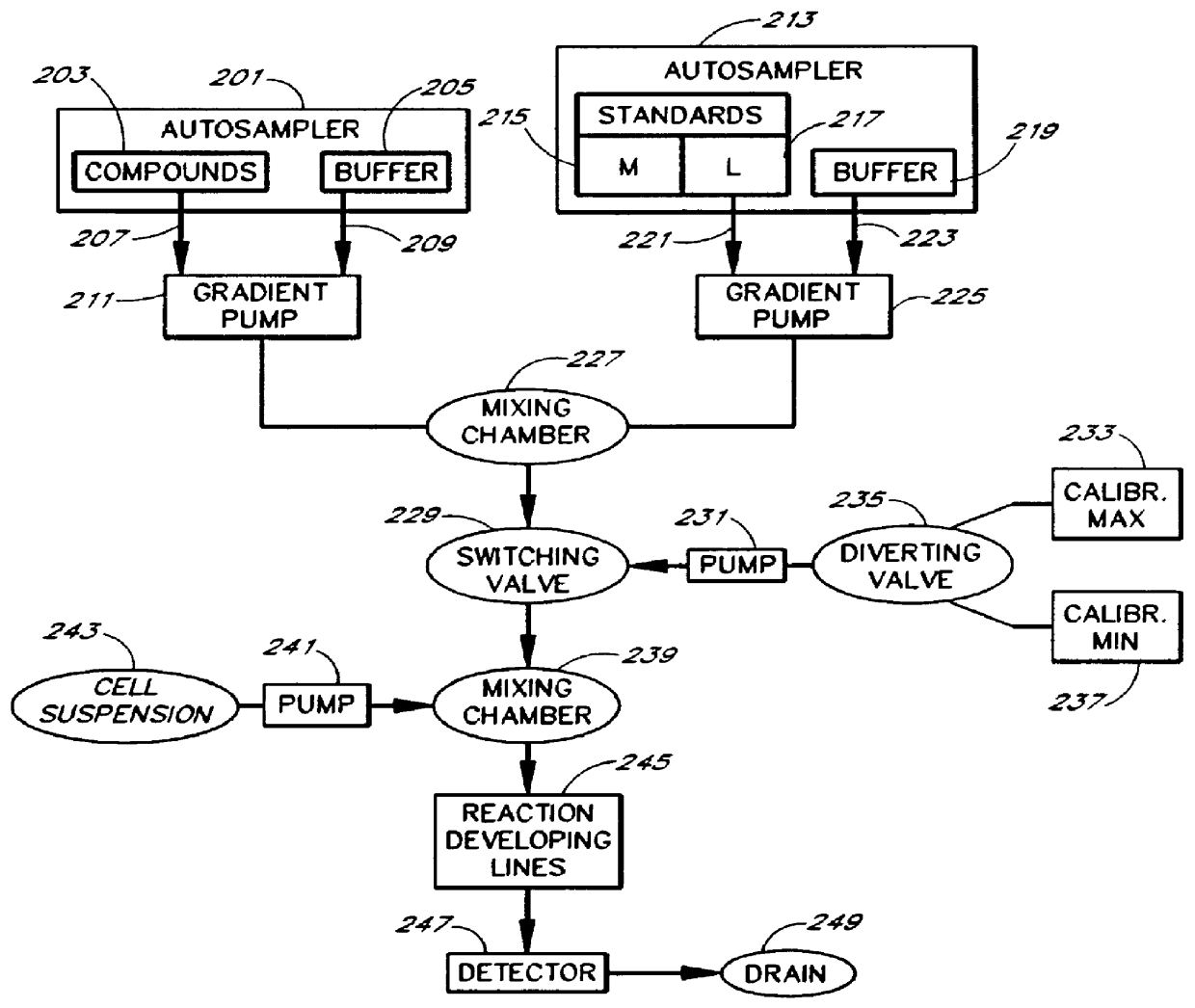
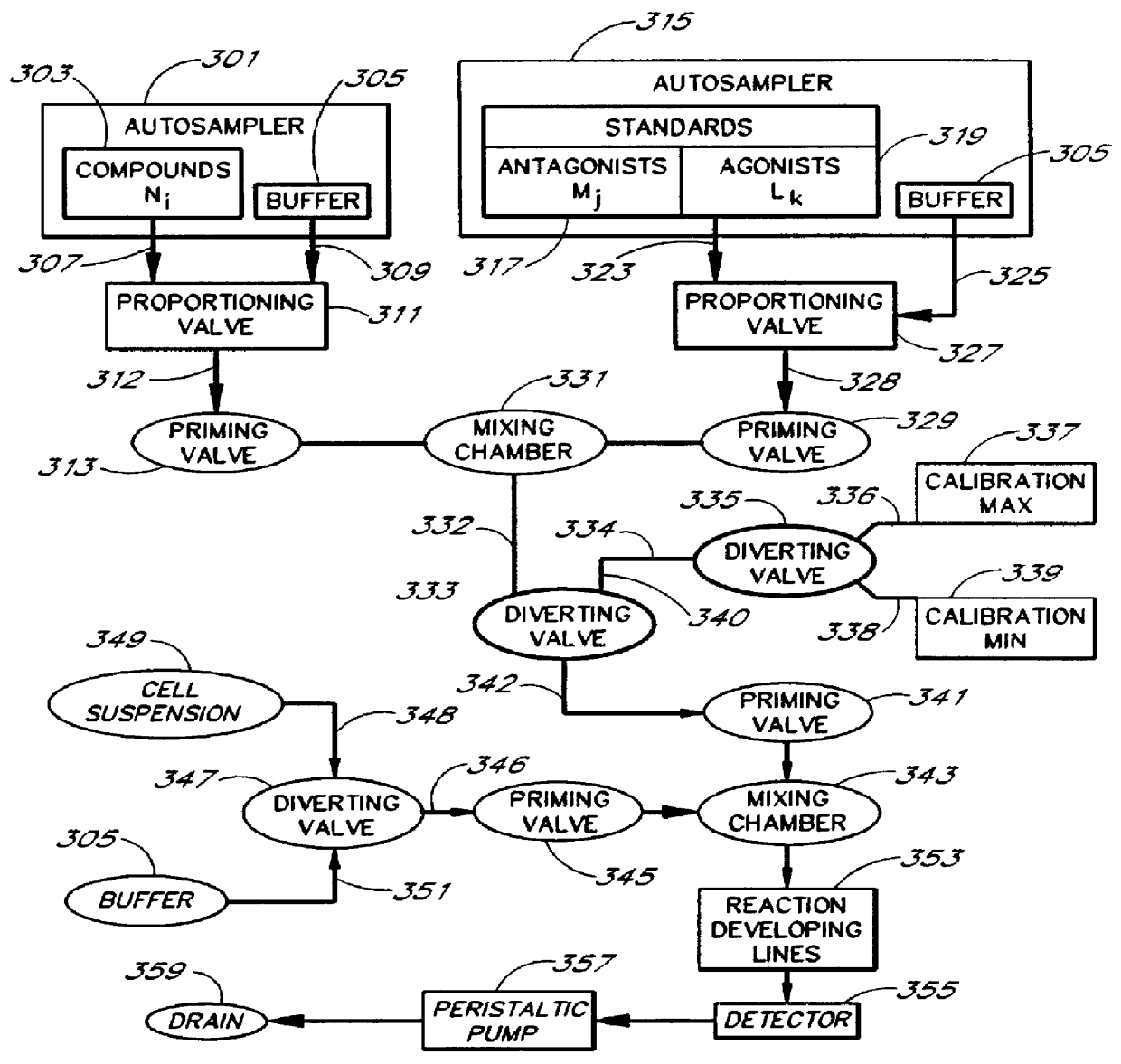
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1319 results about "Cell type" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cell type is a classification used to distinguish between morphologically or phenotypically distinct cell forms within a species. A multicellular organism may contain a number of widely differing and specialized cell types, such as muscle cells and skin cells in humans, that differ both in appearance and function yet are genetically identical. Cells are able to be of the same genotype, but different cell type due to the differential regulation of the genes they contain. Classification of a specific cell type is often done through the use of microscopy (such as those from the cluster of differentiation family that are commonly used for this purpose in immunology). Recent developments in single cell RNA sequencing facilitated classification of cell types based on shared gene expression patterns. This has led to the discovery of many new cell types in e.g. mouse cortex, hippocampus, dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord.
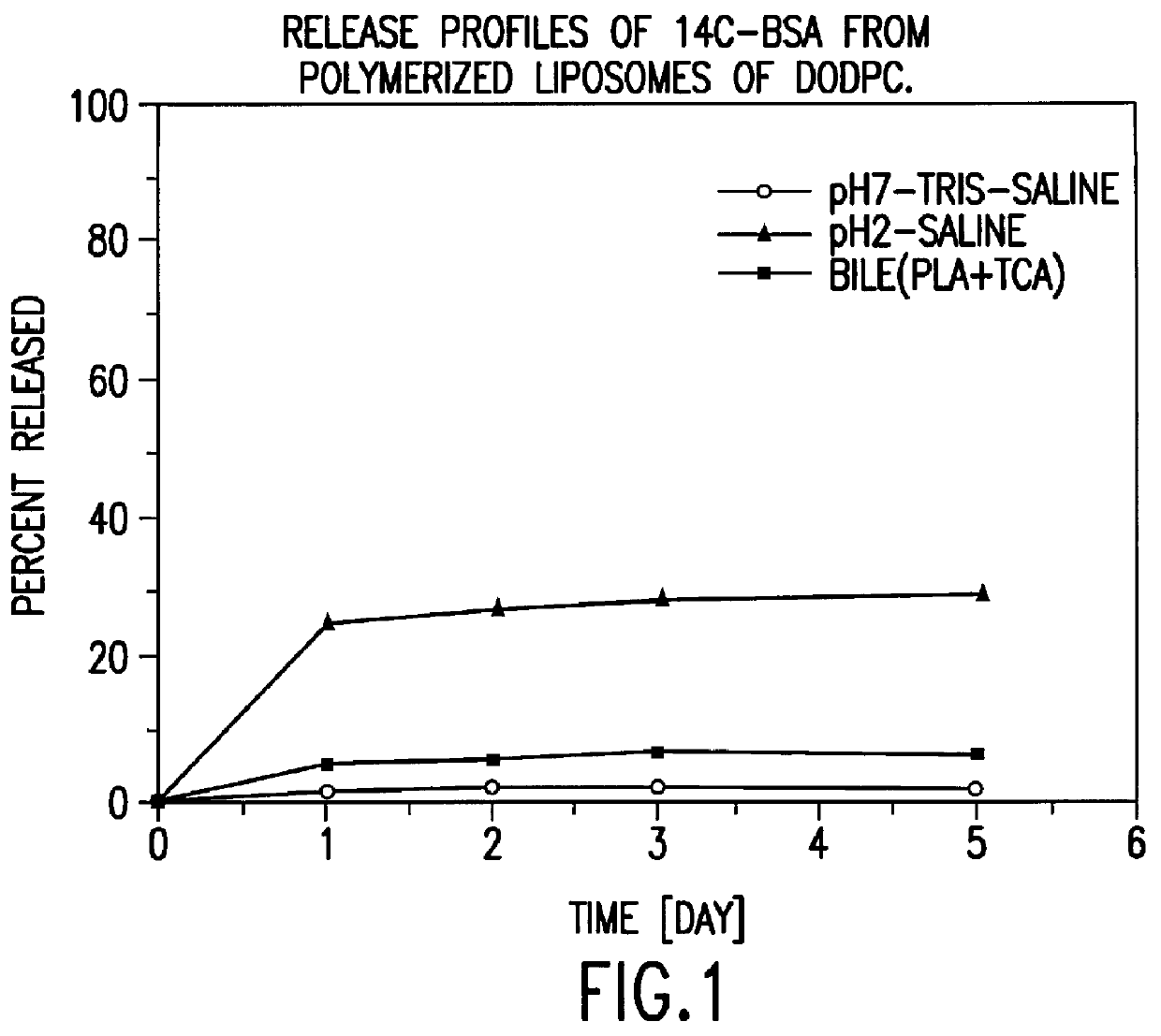
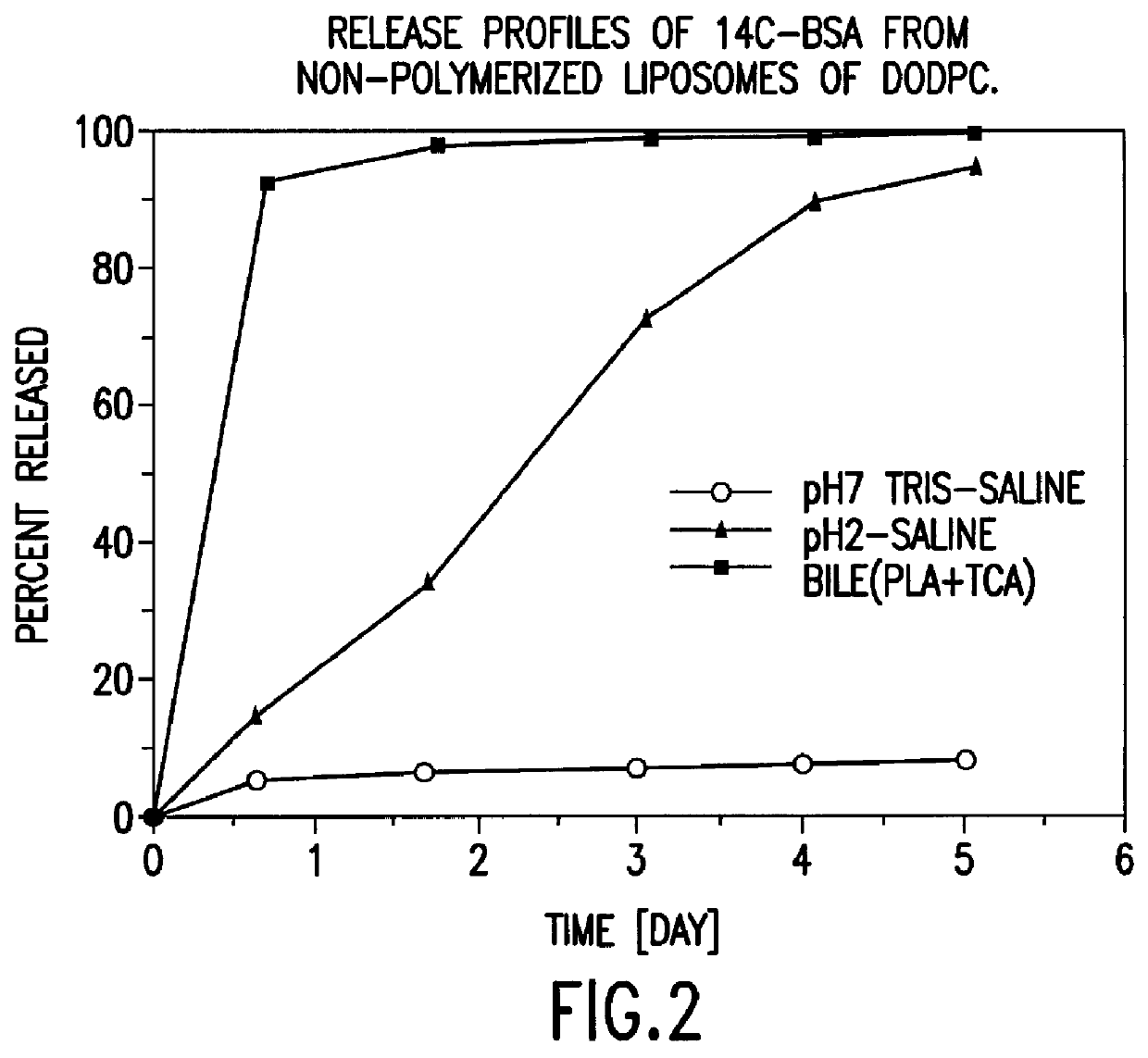
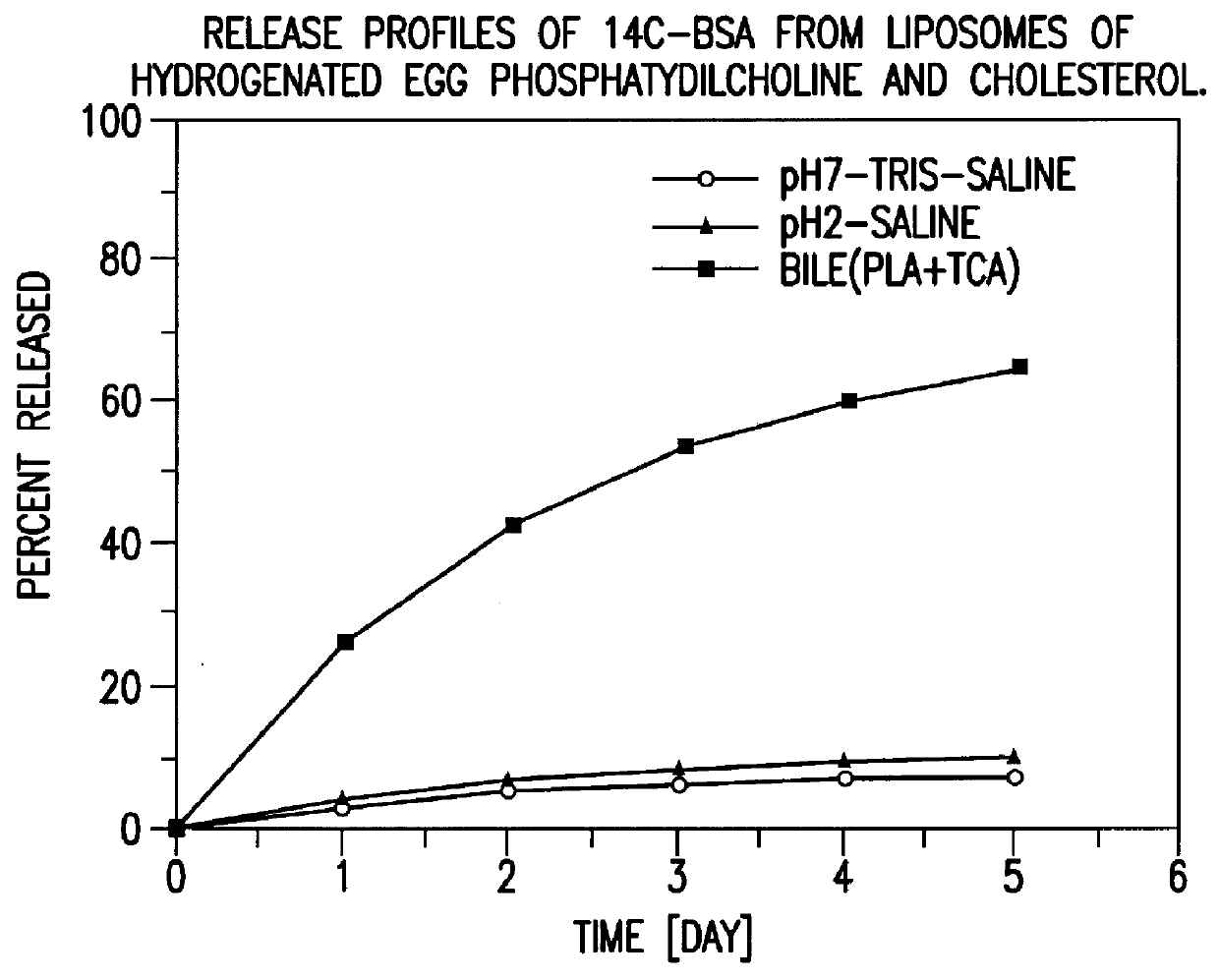
Polymerized liposomes targeted to M cells and useful for oral or mucosal drug delivery
InactiveUS6060082ALessContainment leakBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell typeLiposome
The present invention relates to targeted polymerized liposomes for oral and / or mucosal delivery of vaccines, allergens and therapeutics. In particular, the present invention relates to polymerized liposomes which have been modified on their surface to contain a molecule or ligand which targets the polymerized liposome to a specific site or cell type. More particularly, the invention relates to the use of polymerized liposomes modified to contain a carbohydrate or lectin on their surface.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
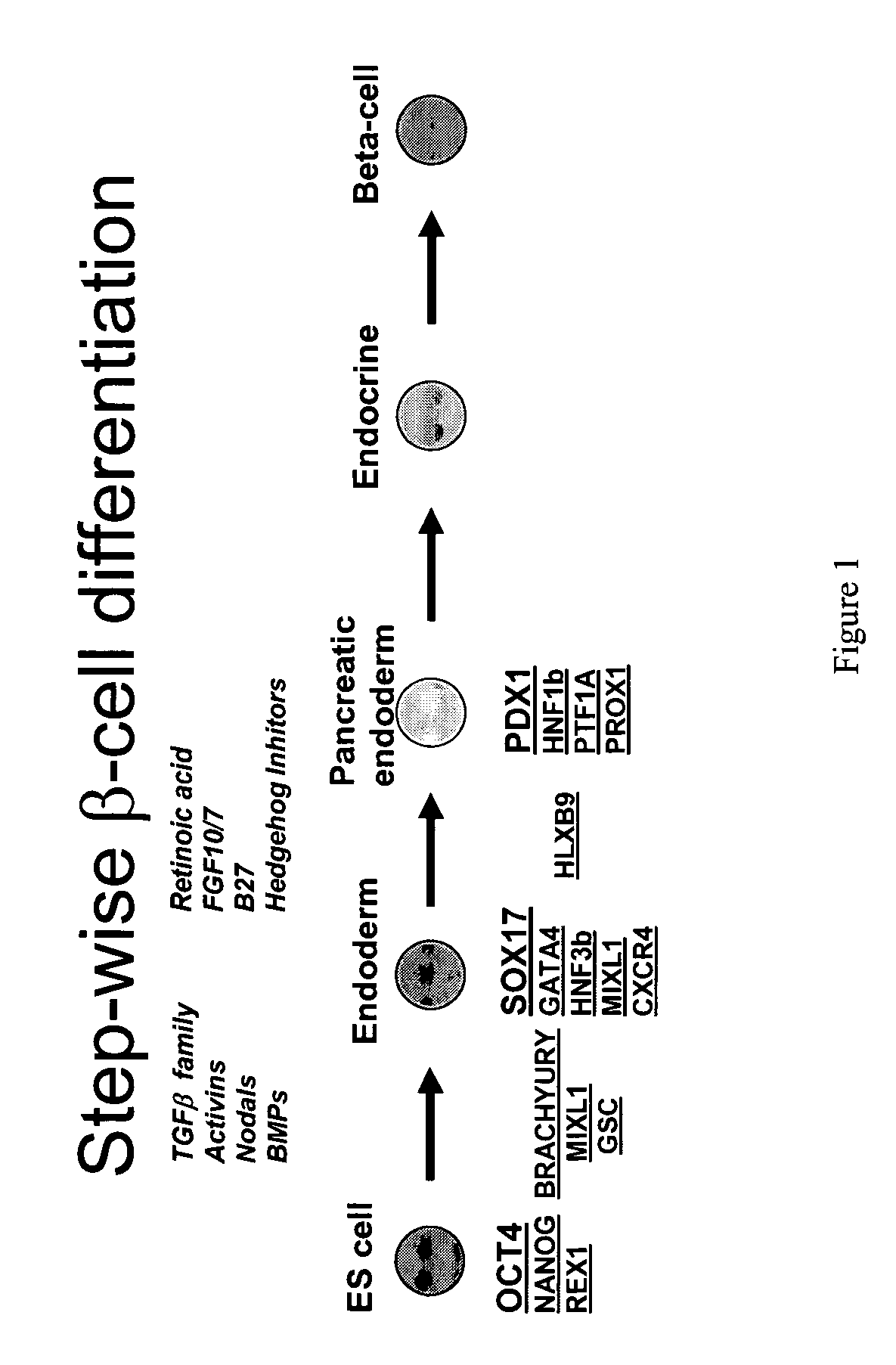
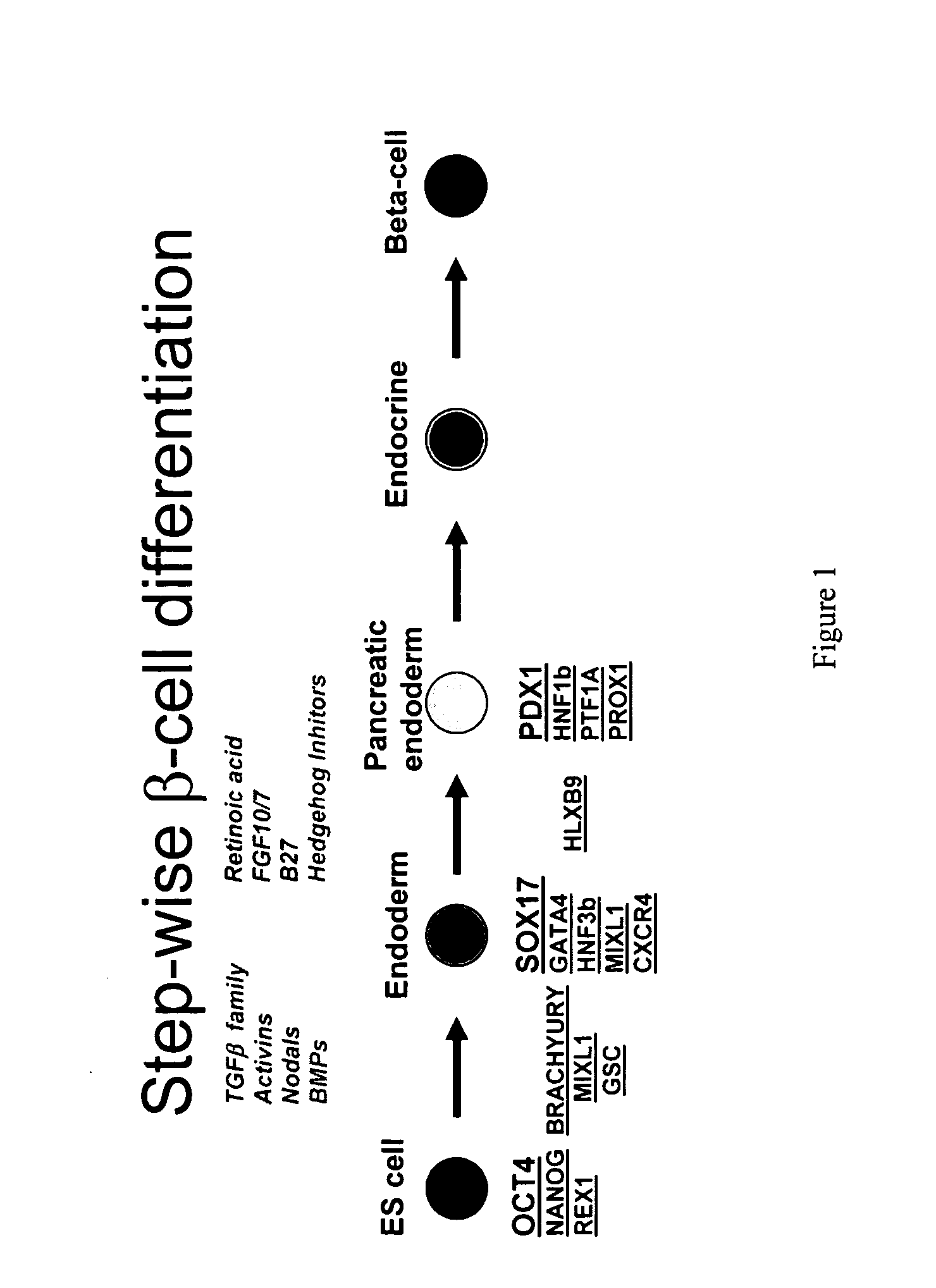
PDX1 expressing endoderm
InactiveUS20050266554A1Increase differentiationIncrease productionGastrointestinal cellsDiagnosticsGerm layerCell type
Disclosed herein are cell cultures comprising PDX1-positive endoderm cells and methods of producing the same. Also disclosed herein are cell populations comprising substantially purified PDX1-positive endoderm cells as well as methods for enriching, isolating and purifying PDX1-positive endoderm cells from other cell types. Methods of identifying differentiation factors capable of promoting the differentiation of endoderm cells, such as PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells and PDX1-negative definitive endoderm cells, are also disclosed.
Owner:CYTHERA
Integrated nucleic acid assays
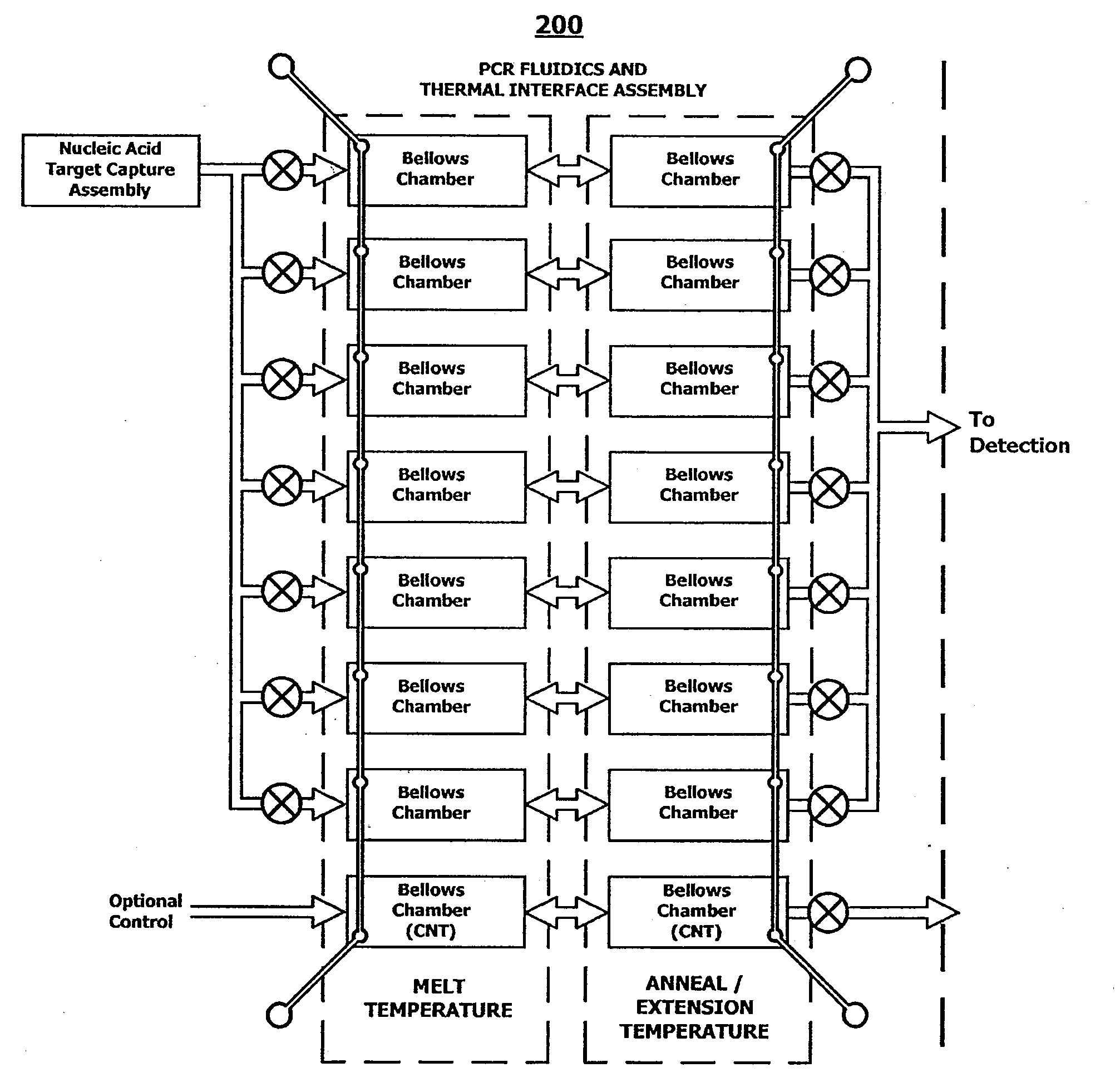
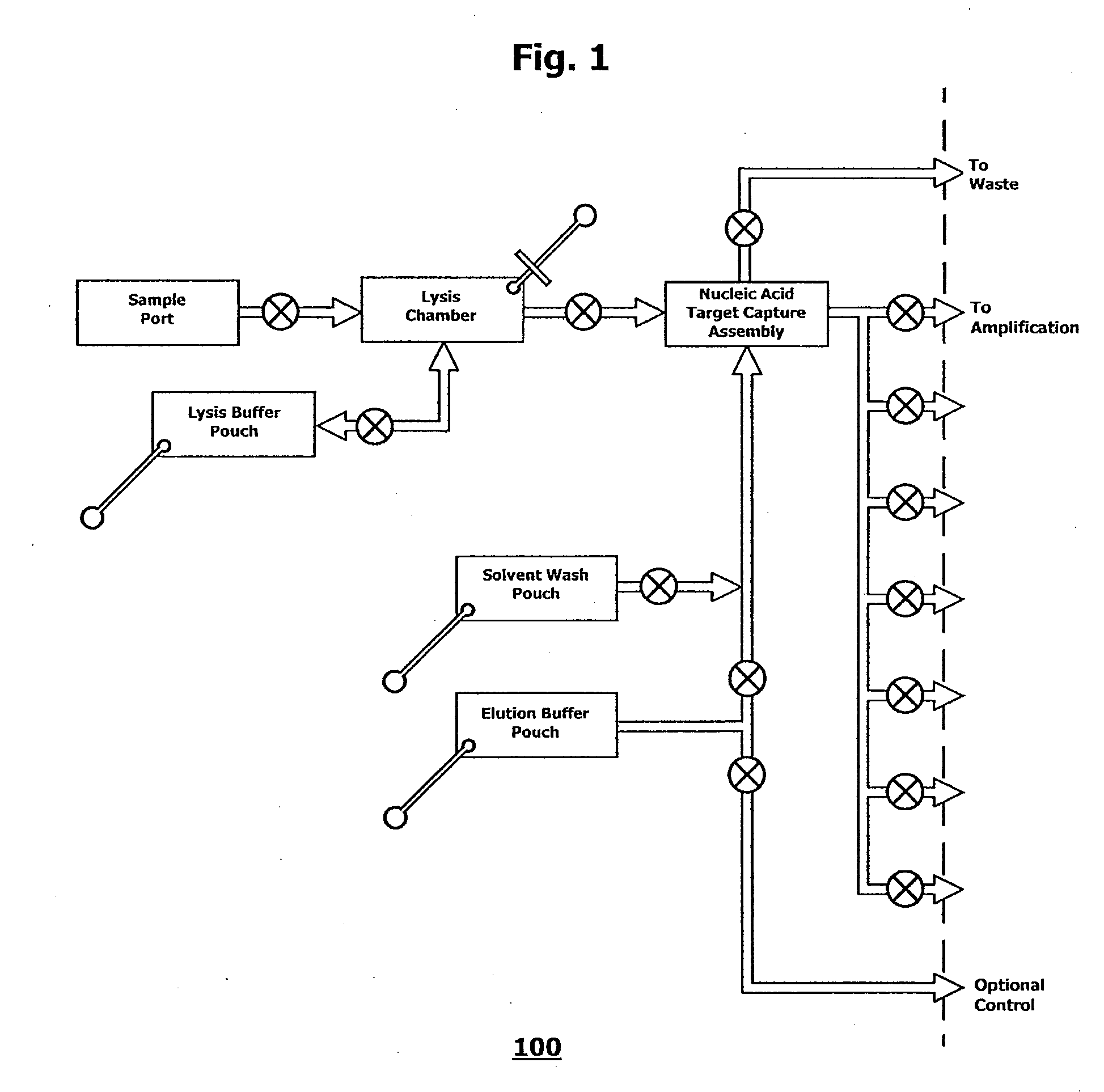
ActiveUS20090148933A1Reduce pervasive dangerEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusCancer cellAssay
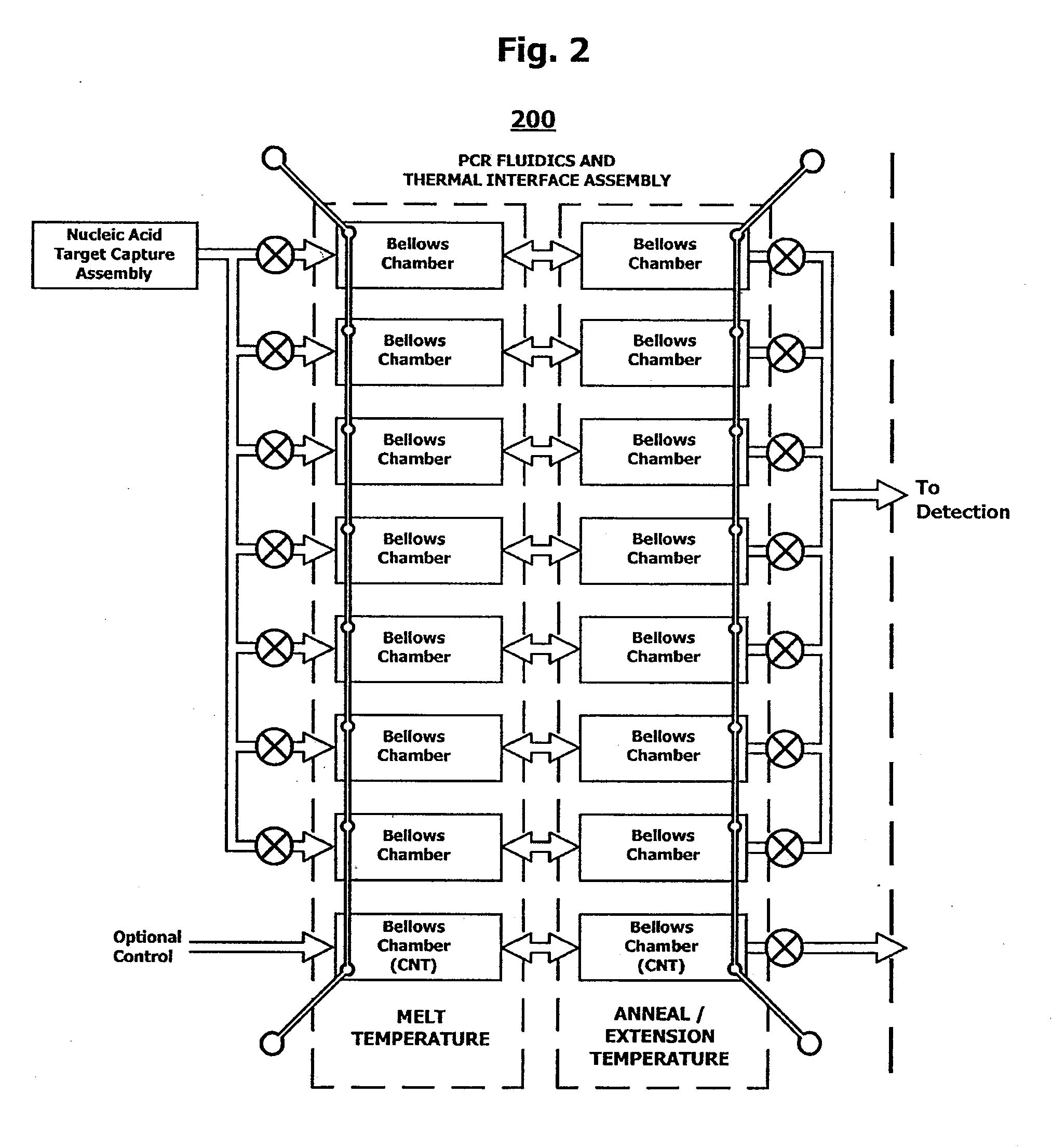
Integrated microfluidic cartridges for nucleic acid extraction, amplification, and detection from clinical samples are disclosed. The devices are single-entry, sanitary, and disposable. The devices enable simplex or multiplex nucleic acid target detection, as for example: assay panels for multiple infectious agents, or assay panels for cancerous cell types. Methods for use of microfluidic cartridges in a fully automated, pneumatically controlled apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Placental derived stem cells and uses thereof
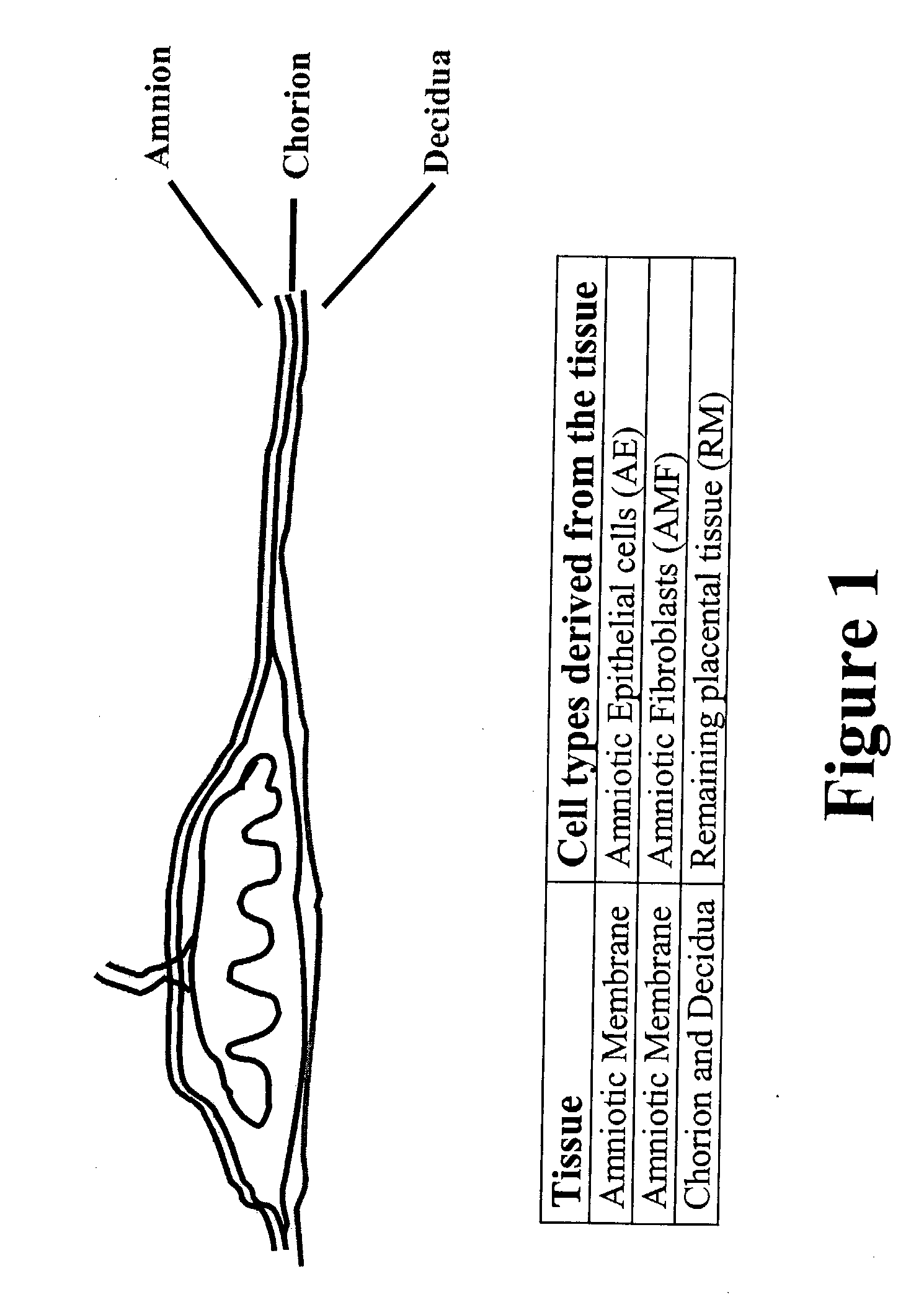
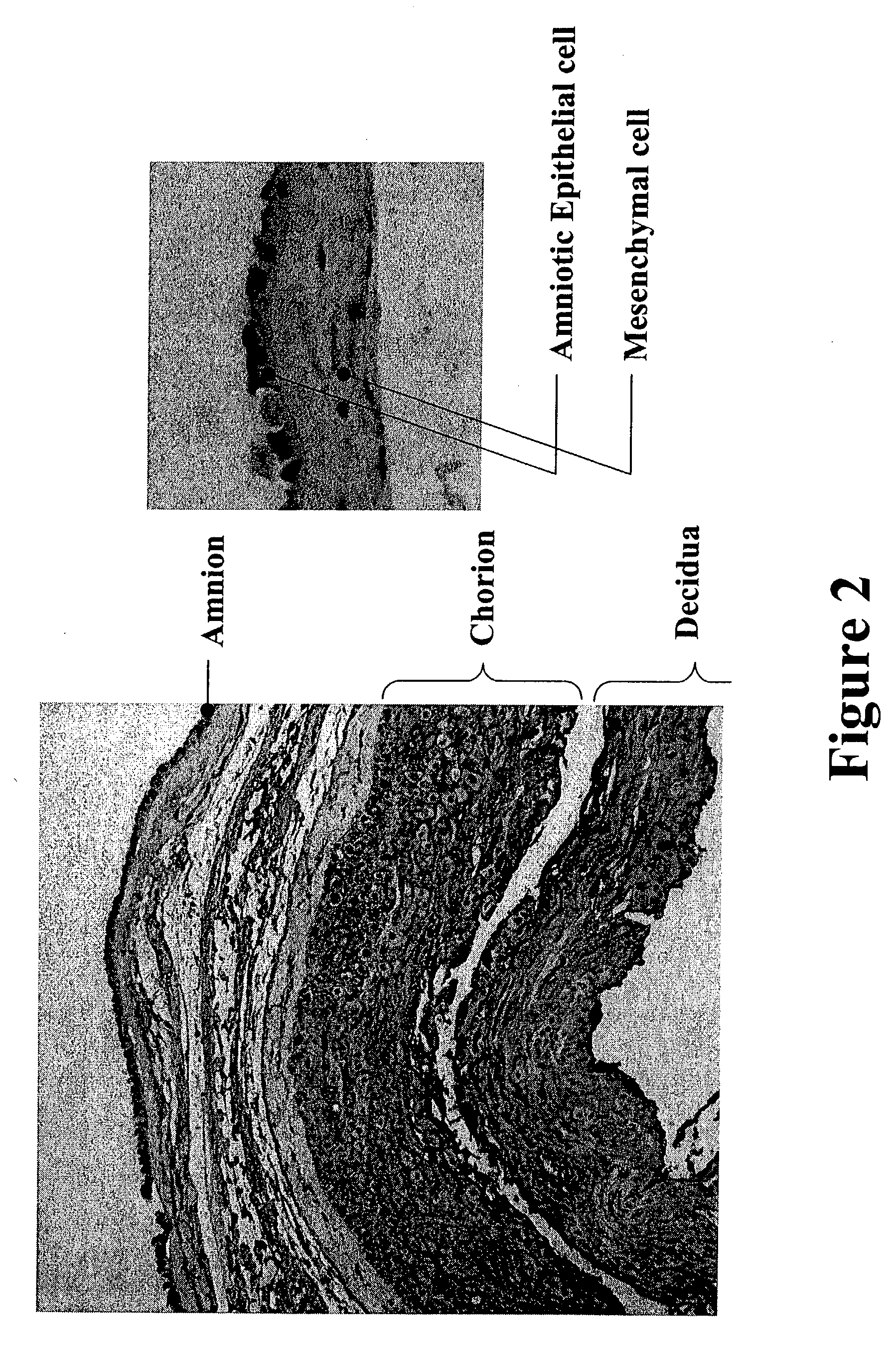
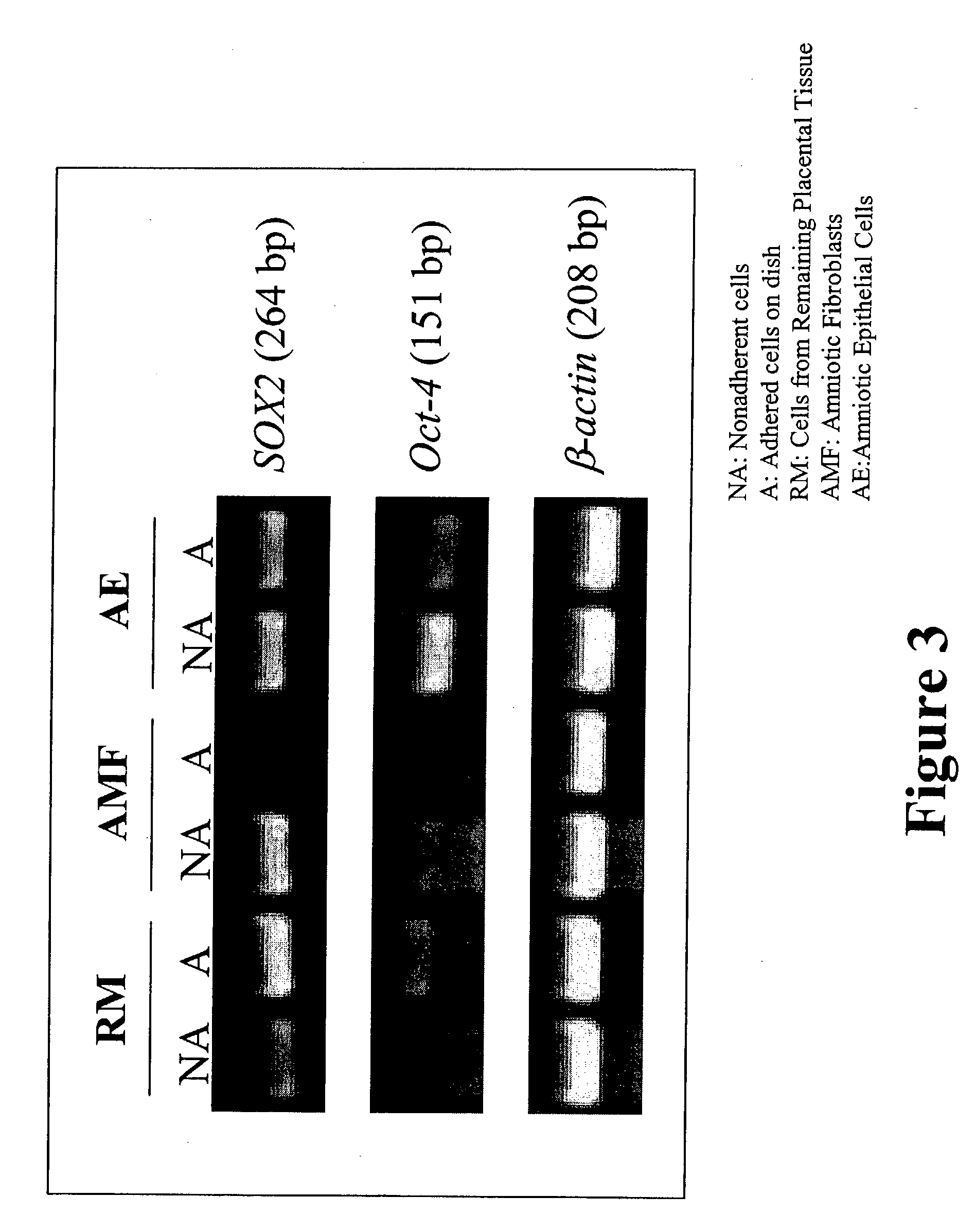
The present invention features novel placental derived stem cells and provides methods and compositions for the therapeutic uses of placental derived stem cells or placental derived stem cells that have been induced to differentiate into a desired tissue type into a recipient host in amounts sufficient to result in production of the desired cell type, i.e., hepatic, pancreatic, neuronal, or nervous tissue.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
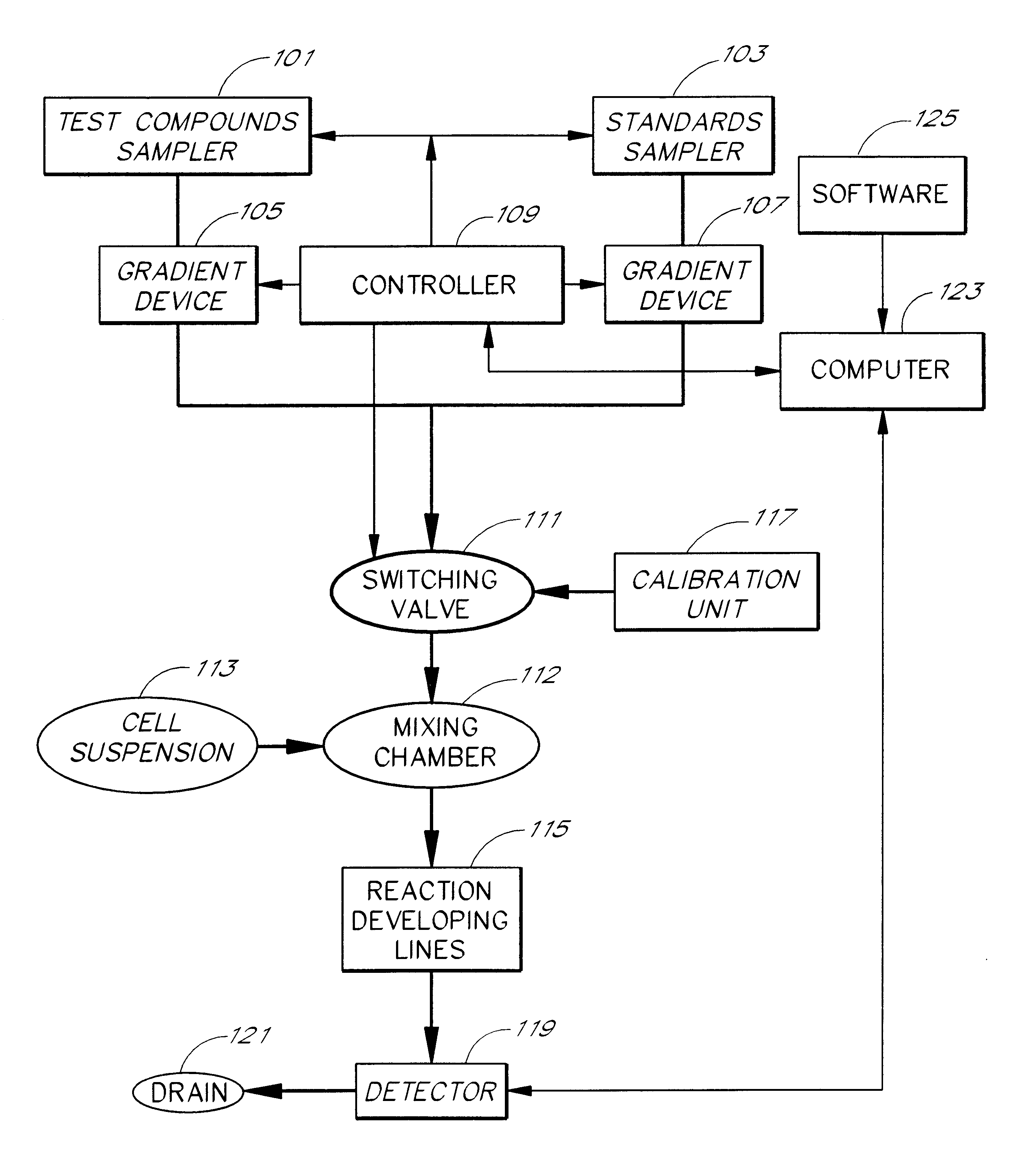
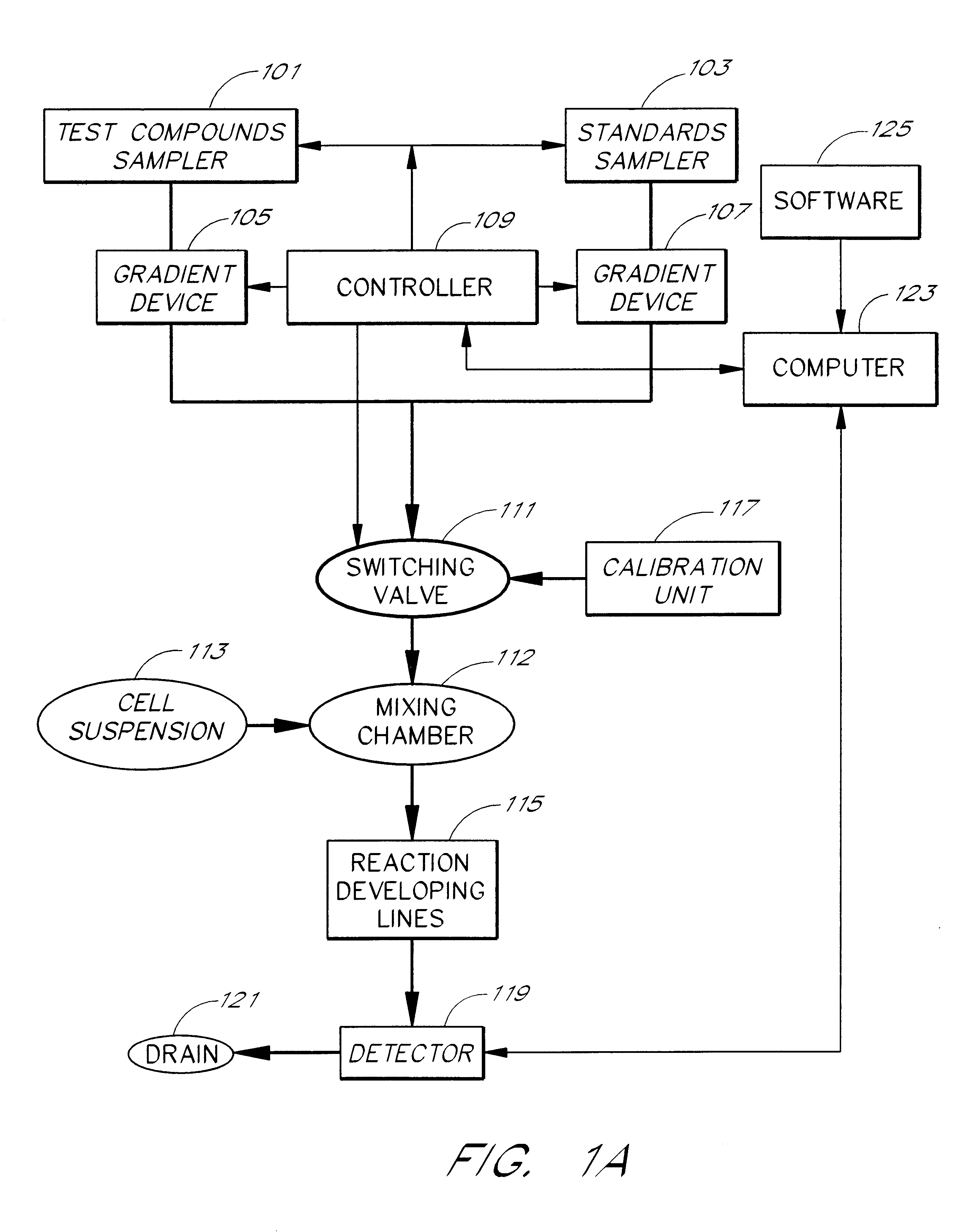
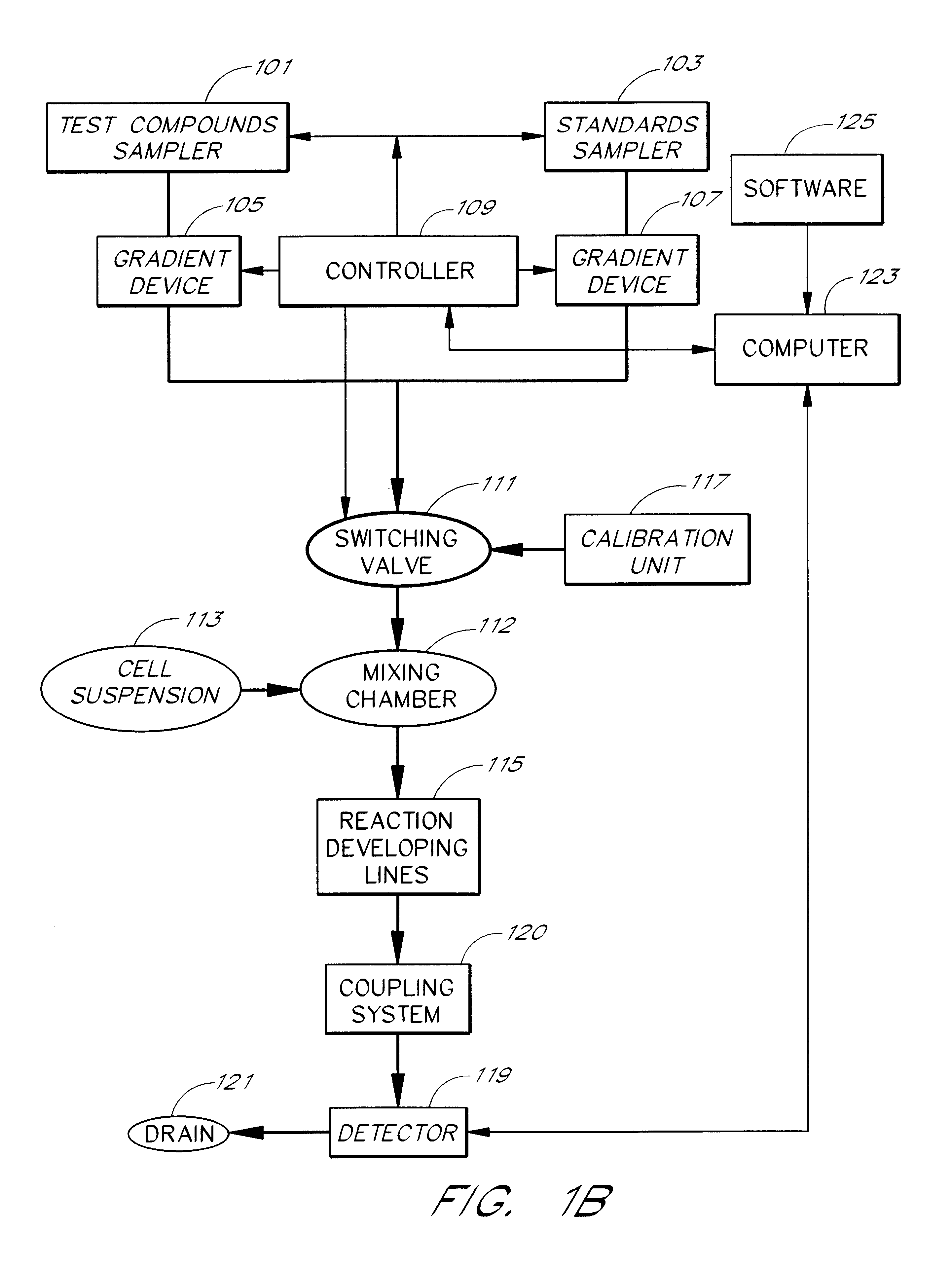
Cell flow apparatus and method for real-time of cellular responses
InactiveUS6280967B1Quick filterIncrease the number ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningMeasurement testCell type
An apparatus and method for real-time measurement of a cellular response of a test compound or series of test compounds (303) on a flowing suspension of cells (349), in which a homogeneous suspension of each member of a series of cell types (349) is combined with a concentration of a test compound (303), directed through a detection zone (355), and a cellular response of the living cells is measured in real time as the cells in the test mixture are flowing through the detection zone (355). The apparatus may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds, and is capable of real-time variation of concentrations of test and standard compounds and generation of dose / response profiles within a short time span.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
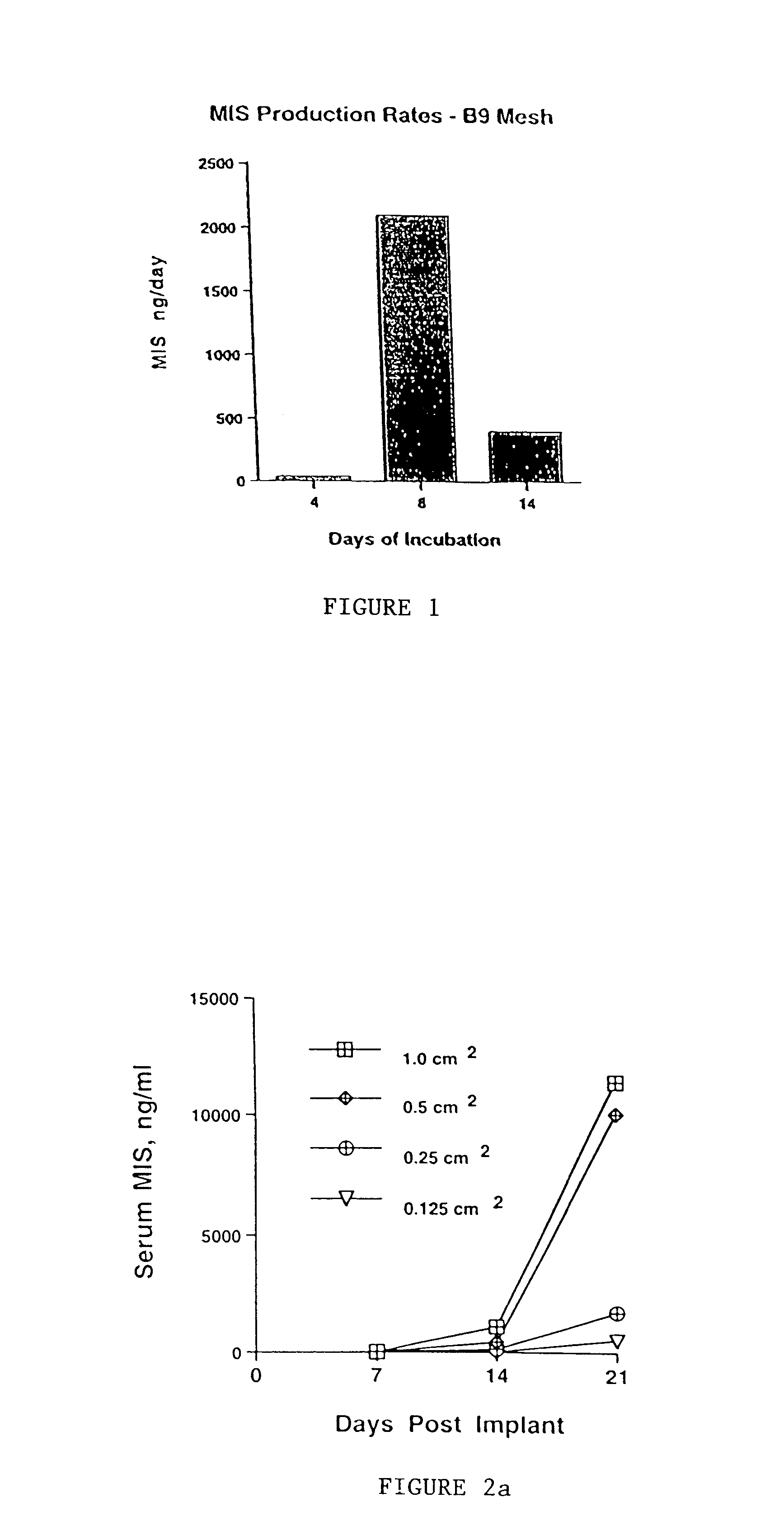
Delivery of therapeutic biologicals from implantable tissue matrices
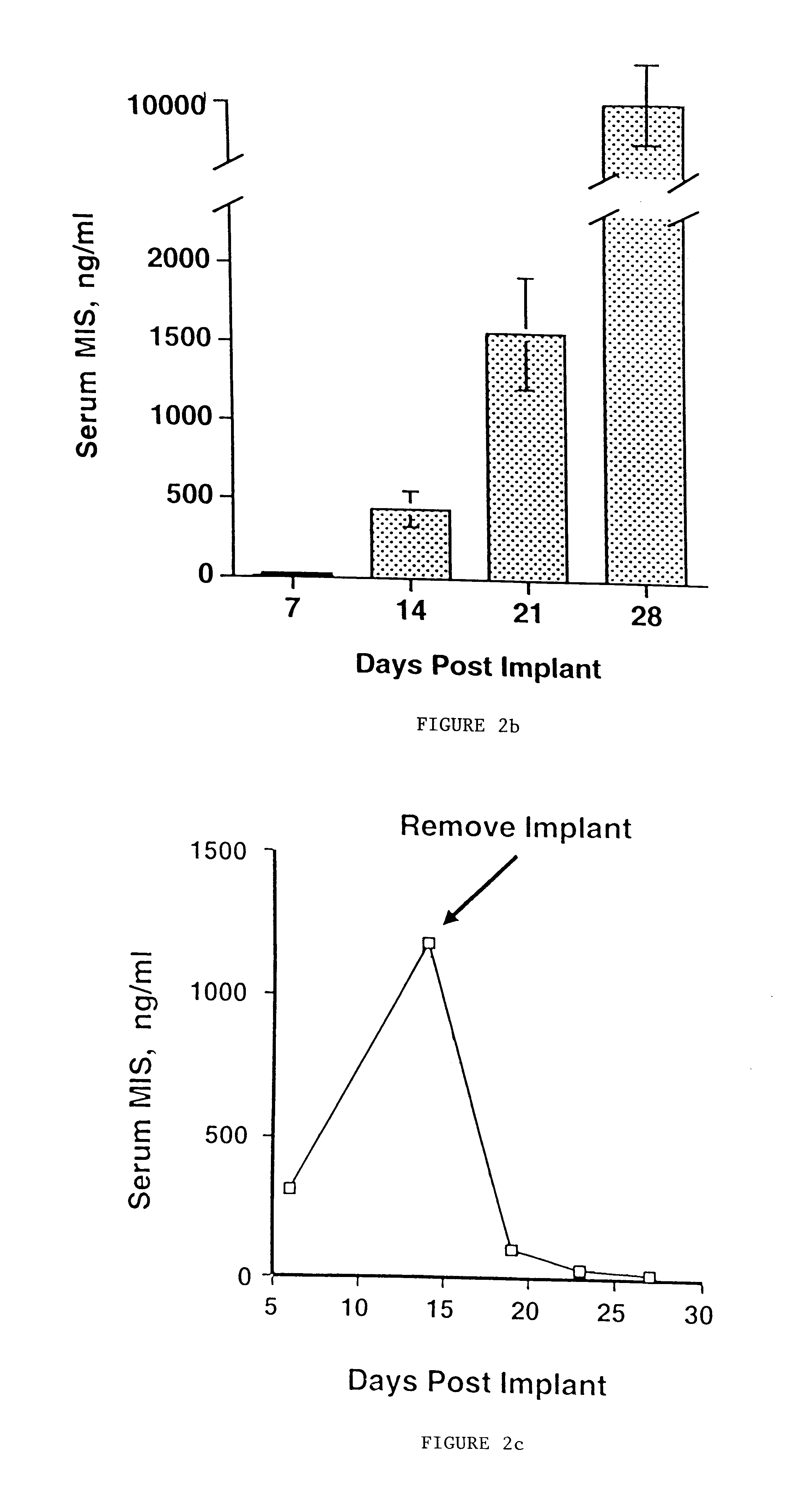
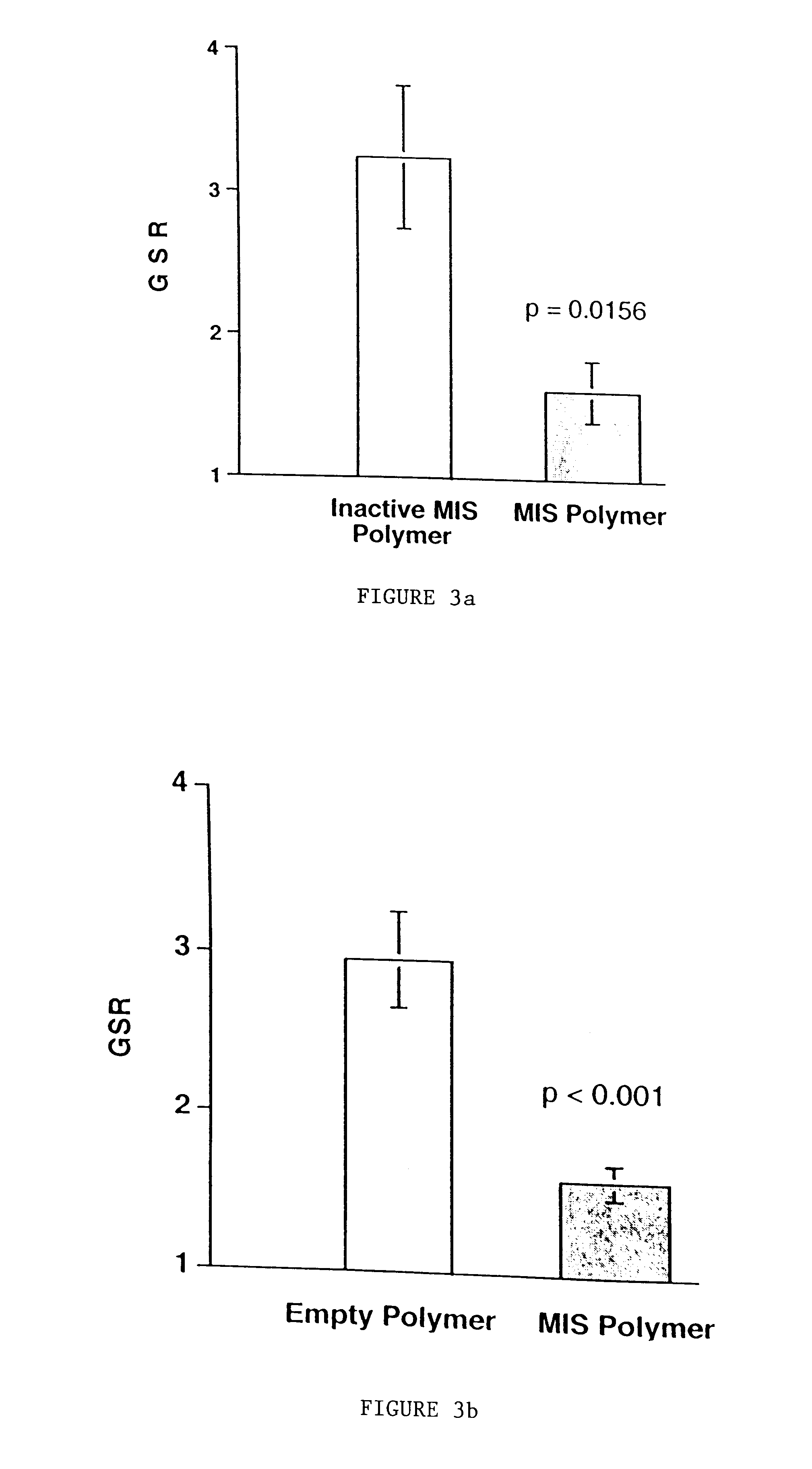
Normal cells, such as fibroblasts or other tissue or organ cell types, are genetically engineered to express biologically active, therapeutic agents, such as proteins that are normally produced in small amounts, for example, MIS, or other members of the TGF-beta family Herceptin(TM), interferons, andanti-angiogenic factors. These cells are seeded into a matrix for implantation into the patient to be treated. Cells may also be engineered to include a lethal gene, so that implanted cells can be destroyed once treatment is completed. Cells can be implanted in a variety of different matrices. In a preferred embodiment, these matrices are implantable and biodegradable over a period of time equal to or less than the expected period of treatment, when cells engraft to form a functional tissue producing the desired biologically active agent. Implantation may be ectopic or in some cases orthotopic. Representative cell types include tissue specific cells, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Matrices can be formed of synthetic or natural materials, by chemical coupling at the time of implantation, using standard techniques for formation of fibrous matrices from polymeric fibers, and using micromachining or microfabrication techniques. These devices and strategies are used as delivery systems via standard or minimally invasive implantation techniques for any number of parenterally deliverable recombinant proteins, particularly those that are difficult to produce in large amounts and / or active forms using conventional methods of purification, for the treatment of a variety of conditions that produce abnormal growth, including treatment of malignant and benign neoplasias, vascular malformations (hemangiomas), inflammatory conditions, keloid formation, abdominal or plural adhesions, endometriosis, congenital or endocrine abnormalities, and other conditions that can produce abnormal growth such as infection. Efficacy of treatment with the therapeutic biologicals is detected by determining specific criteria, for example, cessation of cell proliferation, regression of abnormal tissue, or cell death, or expression of genes or proteins reflecting the above.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Identication of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and/or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and virues
InactiveUS6881825B1Reduce deliveryFacilitating uptakeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionIn vivoCell type
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of the peptides, and methods of use for the peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Identification of peptides that facilitate uptake and cytoplasmic and/or nuclear transport of proteins, DNA and viruses
The present invention relates to internalizing peptides which facilitate the uptake and transport of cargo into the cytoplasm and nuclei of cells as well as methods for the identification of such peptides. The internalizing peptides of the present invention are selected for their ability to efficiently internalize cargo into a wide variety of cell types both in vivo and in vitro. The method for identification of the internalizing peptides of the present invention comprises incubating a target cell with a peptide display library, isolating peptides with internalization characteristics and determining the ability of said peptide to internalize cargo into a cell.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Method and apparatus for assay of electrochemical properties
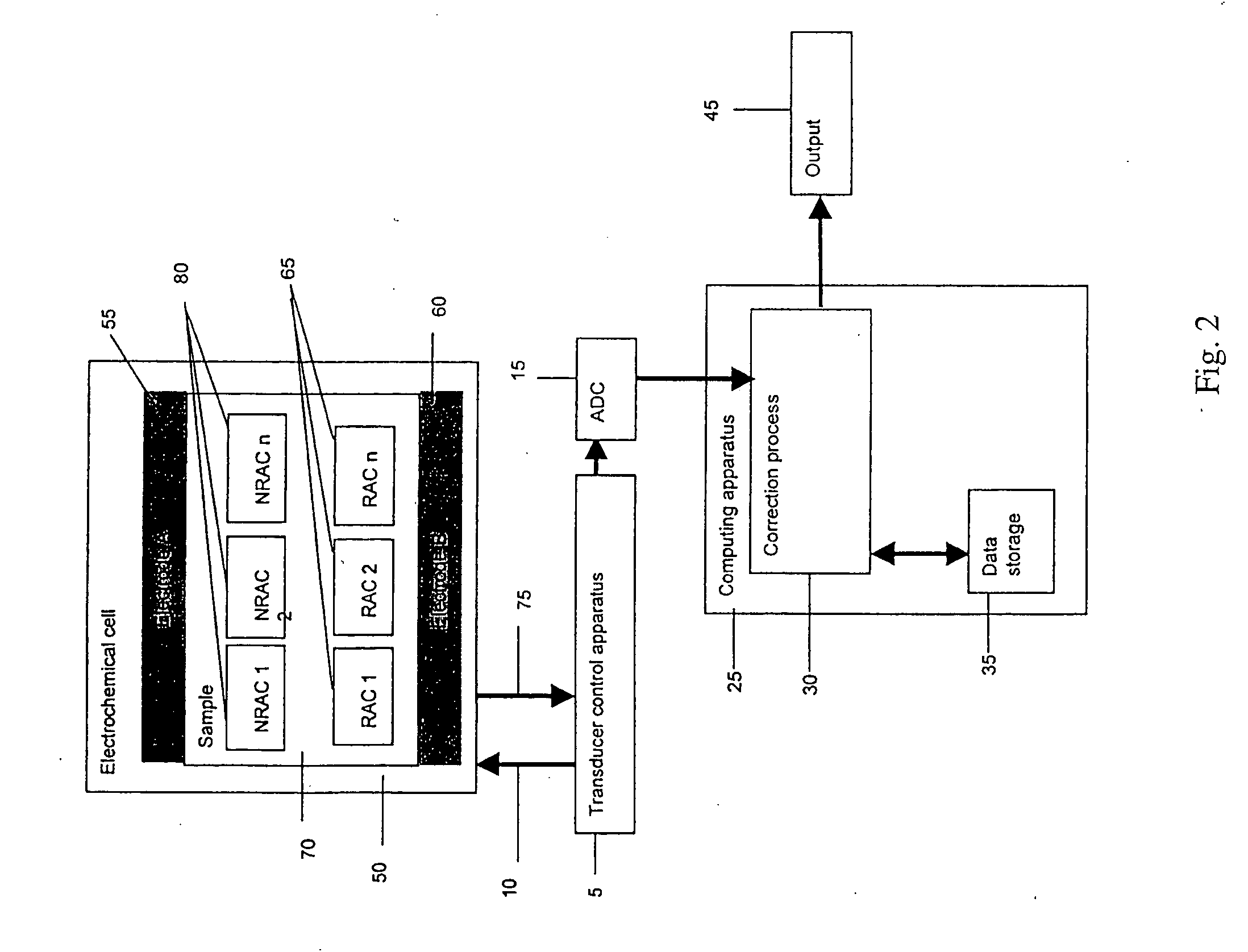
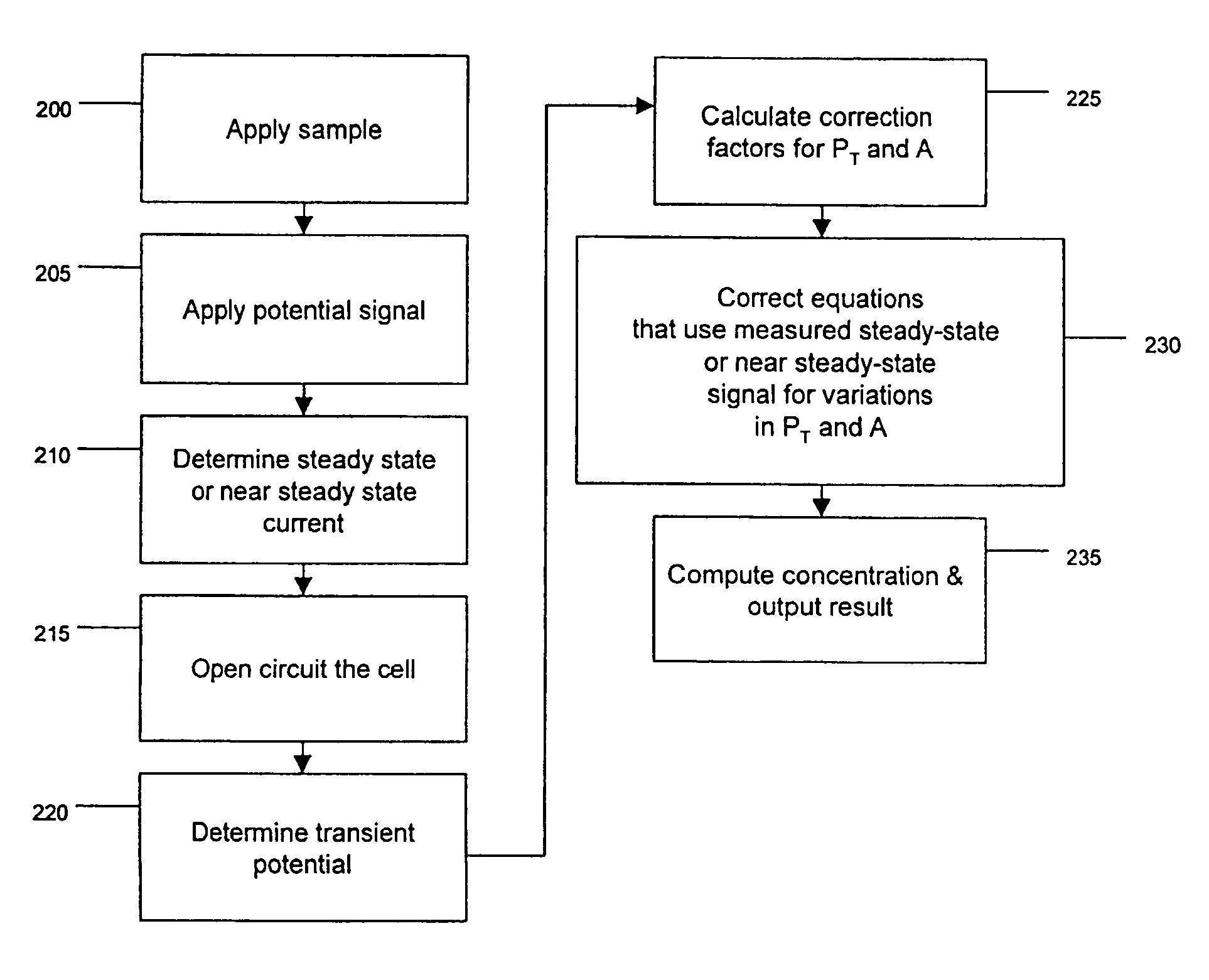
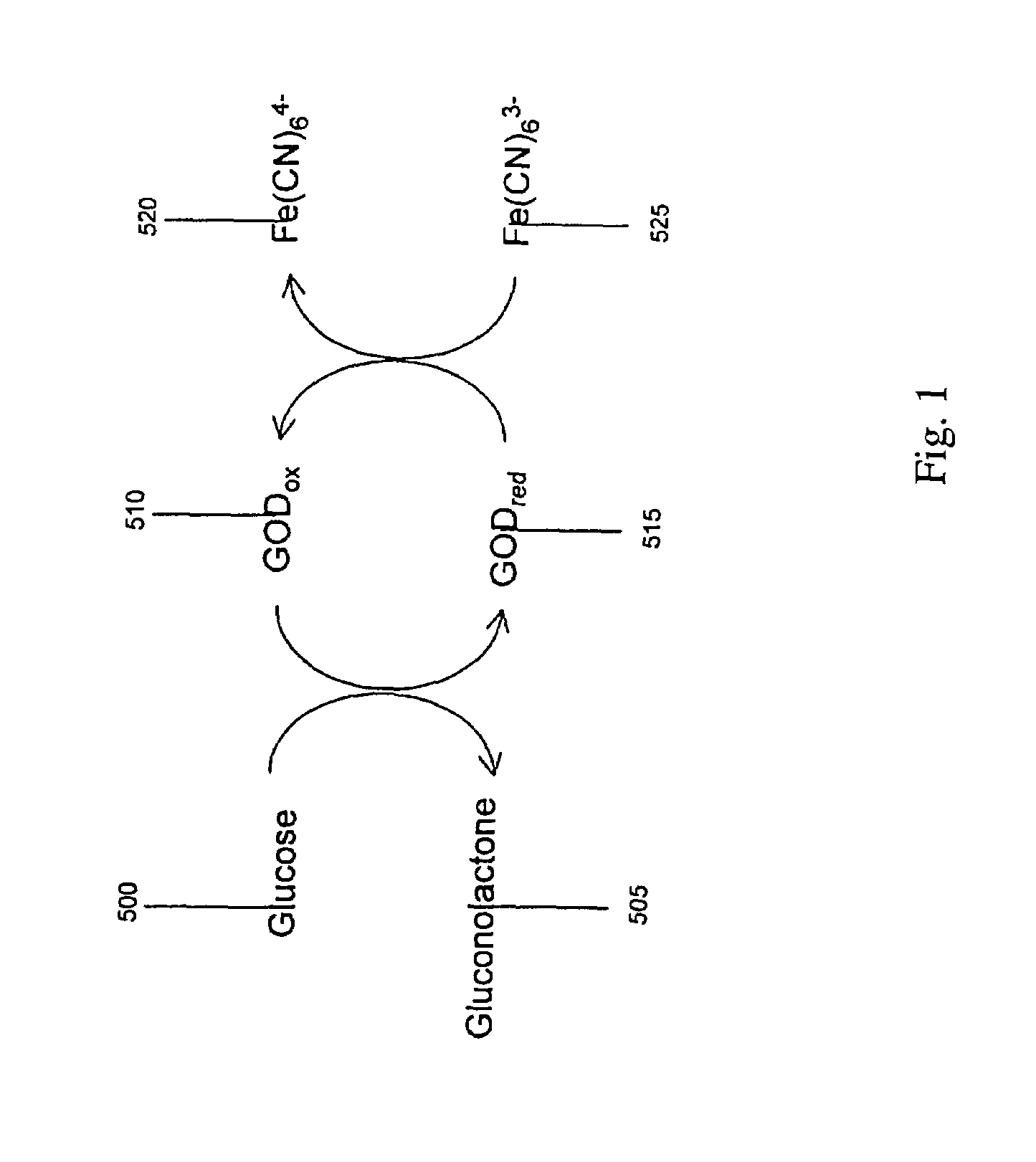
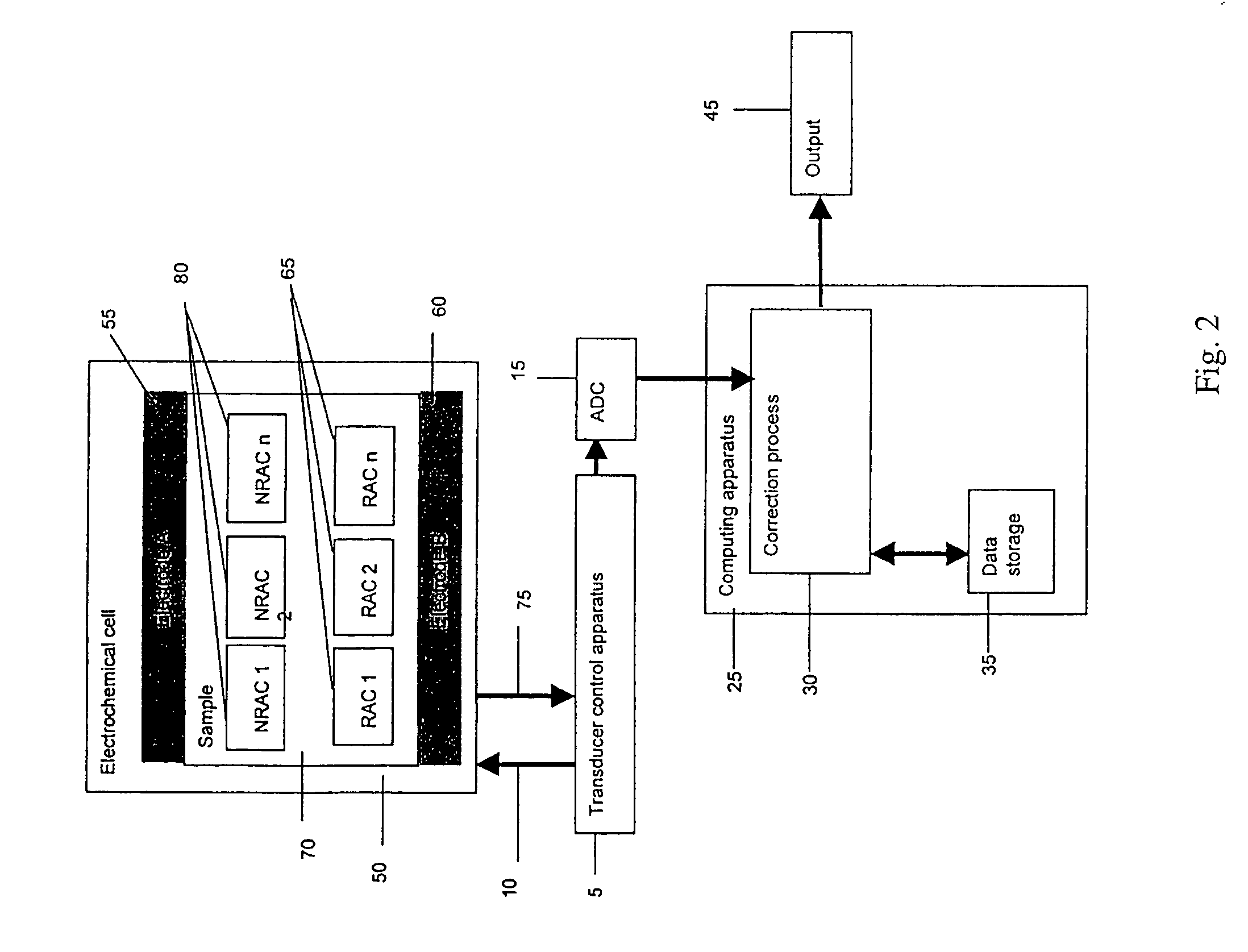
ActiveUS20050109637A1Easy to measureImprove accuracyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementHand heldApplied potential
The presence of a select analyte in the sample is evaluated in an an electrochemical system using a conduction cell-type apparatus. A potential or current is generated between the two electrodes of the cell sufficient to bring about oxidation or reduction of the analyte or of a mediator in an analyte-detection redox system, thereby forming a chemical potential gradient of the analyte or mediator between the two electrodes After the gradient is established, the applied potential or current is discontinued and an analyte-independent signal is obtained from the relaxation of the chemical potential gradient. The analyte-independent signal is used to correct the analyte-dependent signal obtained during application of the potential or current. This correction allows an improved measurement of analyte concentration because it corrects for device-specific and test specific factors such as transport (mobility) of analyte and / or mediator, effective electrode area, and electrode spacing (and as a result, sample volume), without need for separate calibration values. The analysis can be performed using disposable test strips in a hand held meter, for example for glucose testing.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Methods for the production of ips cells using non-viral approach
ActiveUS20100003757A1Promote generationExpand the populationGenetically modified cellsVirus peptidesVector elementCell type
Methods and composition of induction of pluripotent stem cells and other desired cell types are disclosed. For example, in certain aspects methods for generating essentially vector-free induced pluripotent stem cells are described. Furthermore, the invention provides induced pluripotent stem cells and desired cell types essentially free of exogenous vector elements with the episomal expression vectors to express differentiation programming factors.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
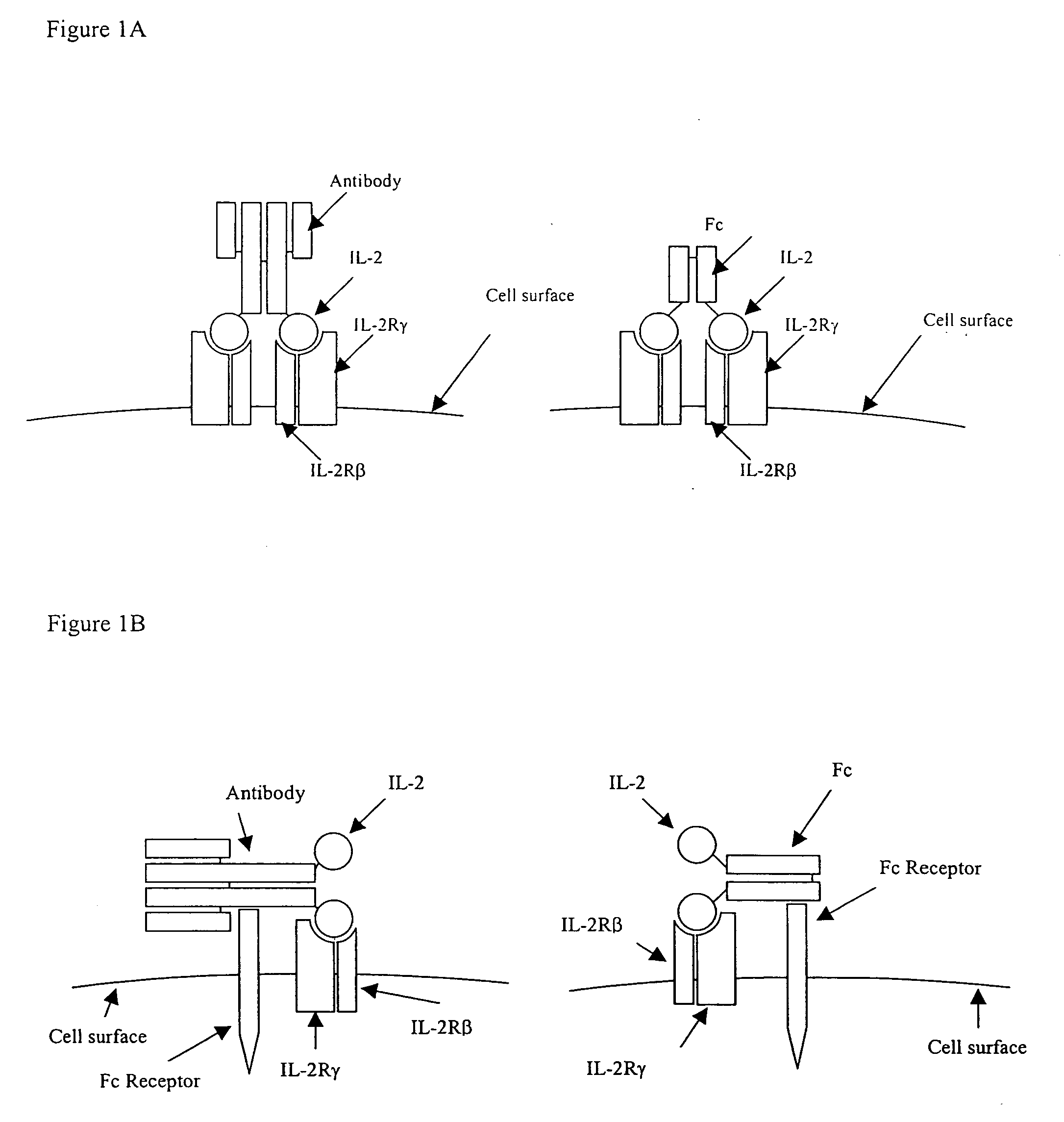
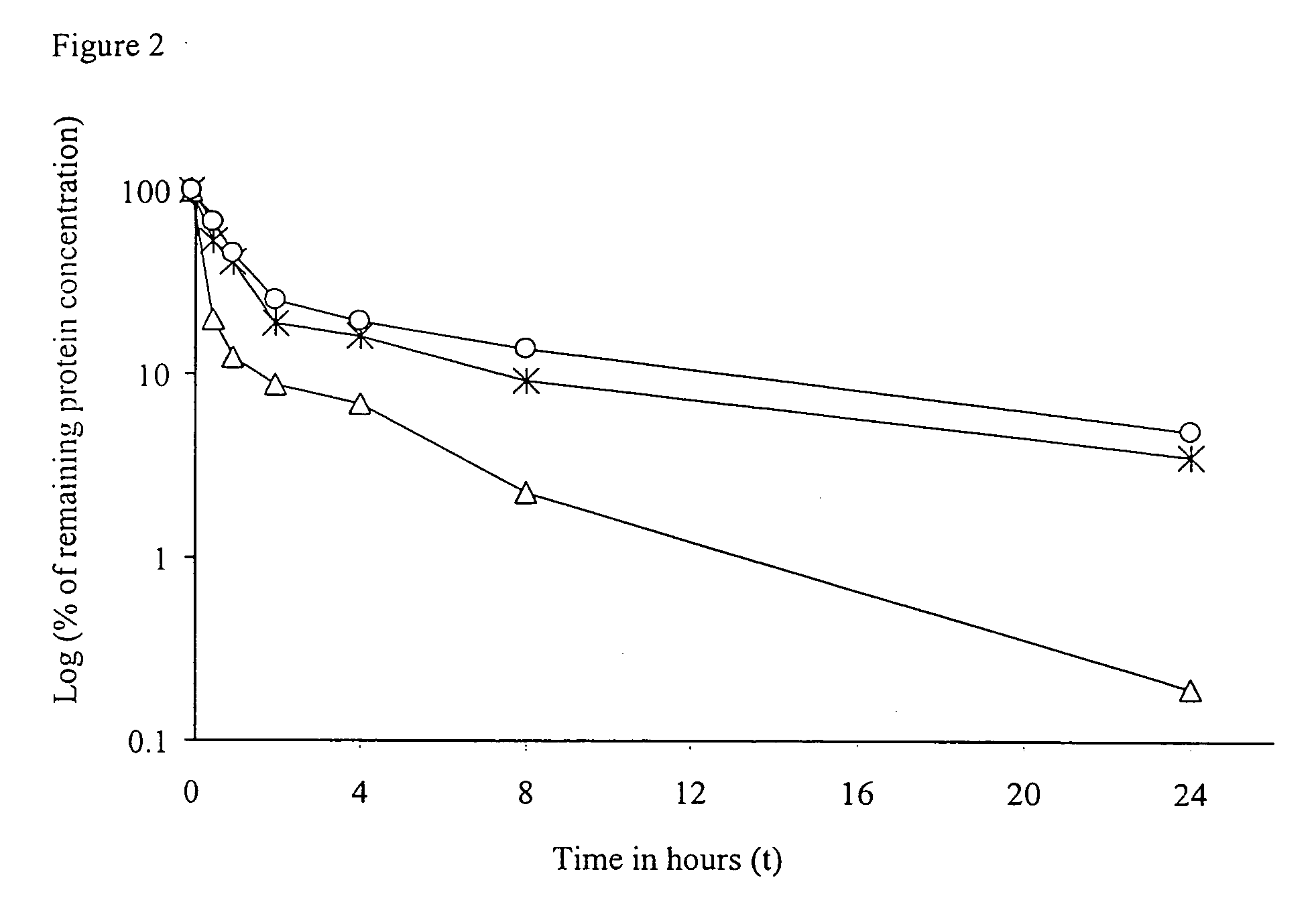
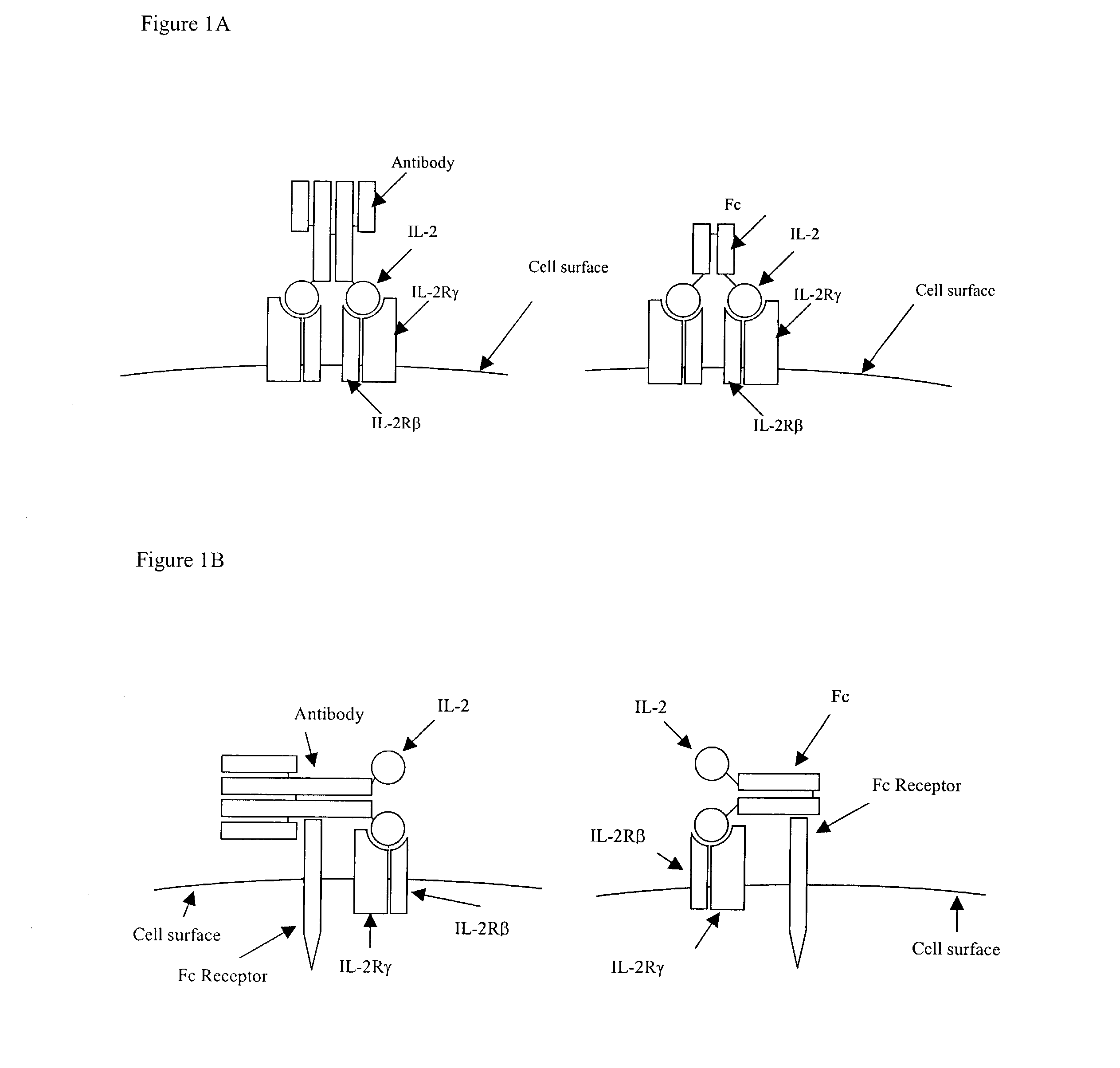
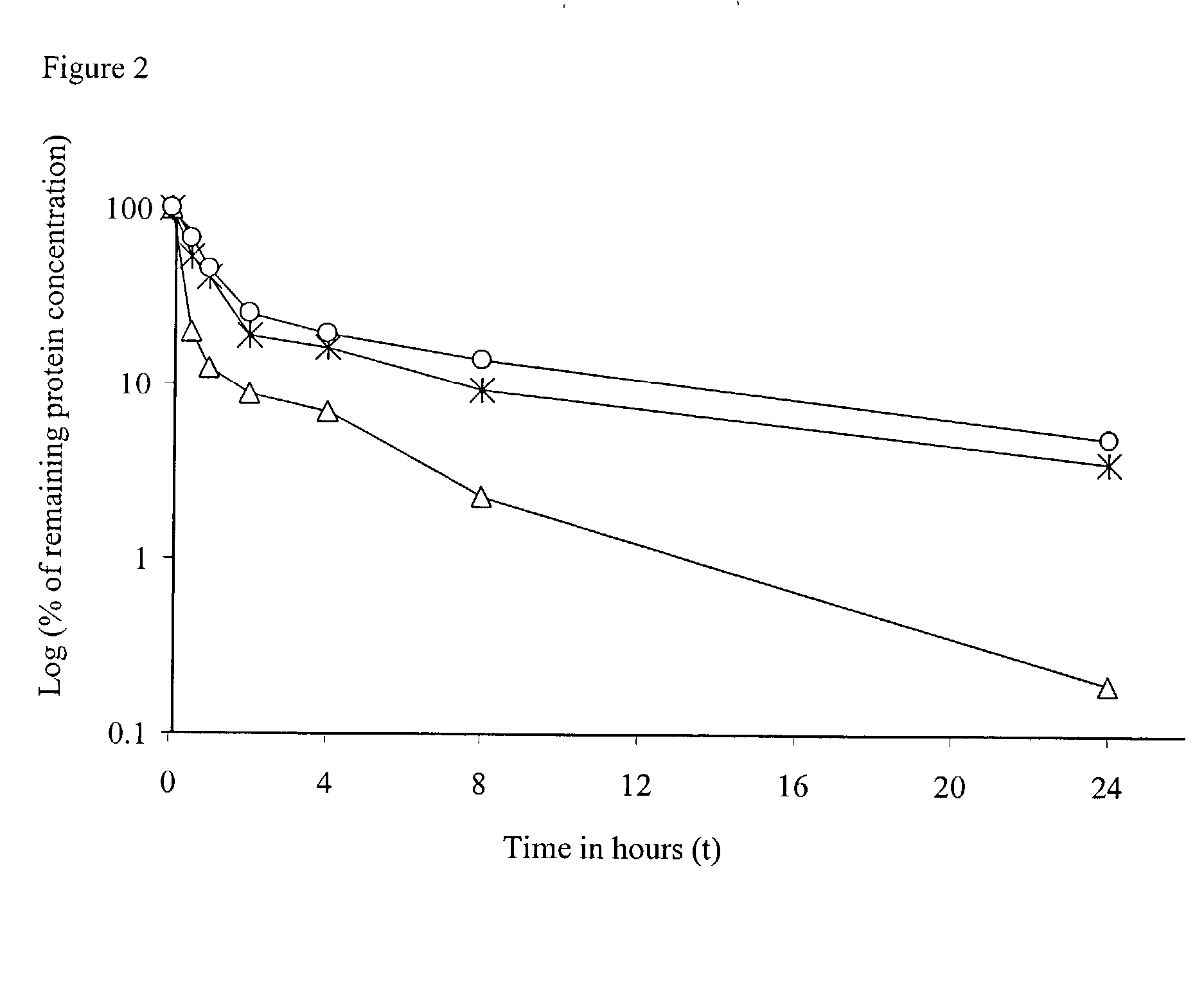
IL-2 fusion proteins with modulated selectivity
The invention provides cytokine fusion proteins with an increased therapeutic index, and methods to increase the therapeutic index of such fusion proteins. The fusion proteins of the invention are able to bind to more than one type of cytokine receptor expressed on cells and also bind to more than one cell type. In addition, the fusion proteins of the invention exhibit a longer circulating half-life in a patient's body than the corresponding naturally occurring cytokine.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
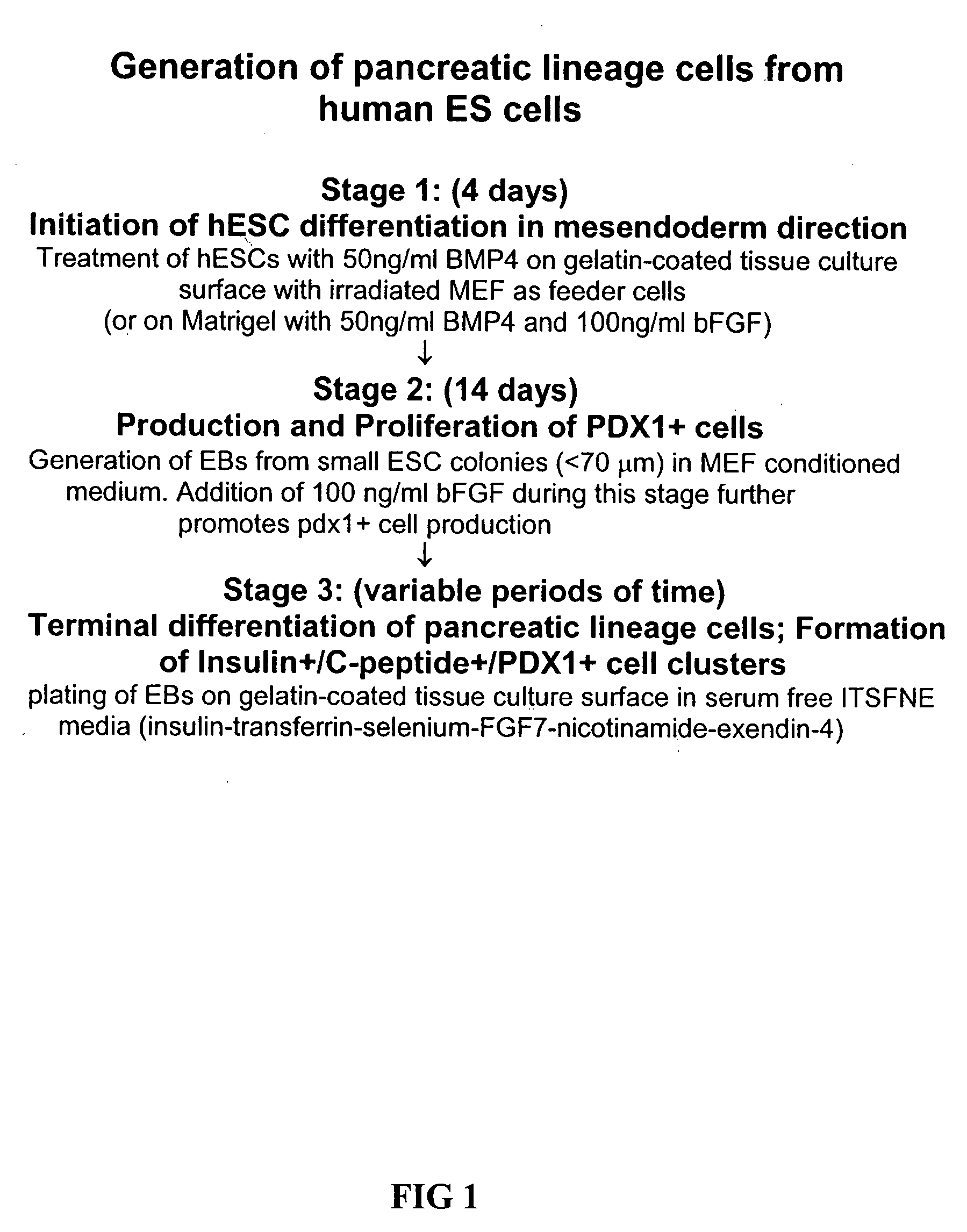
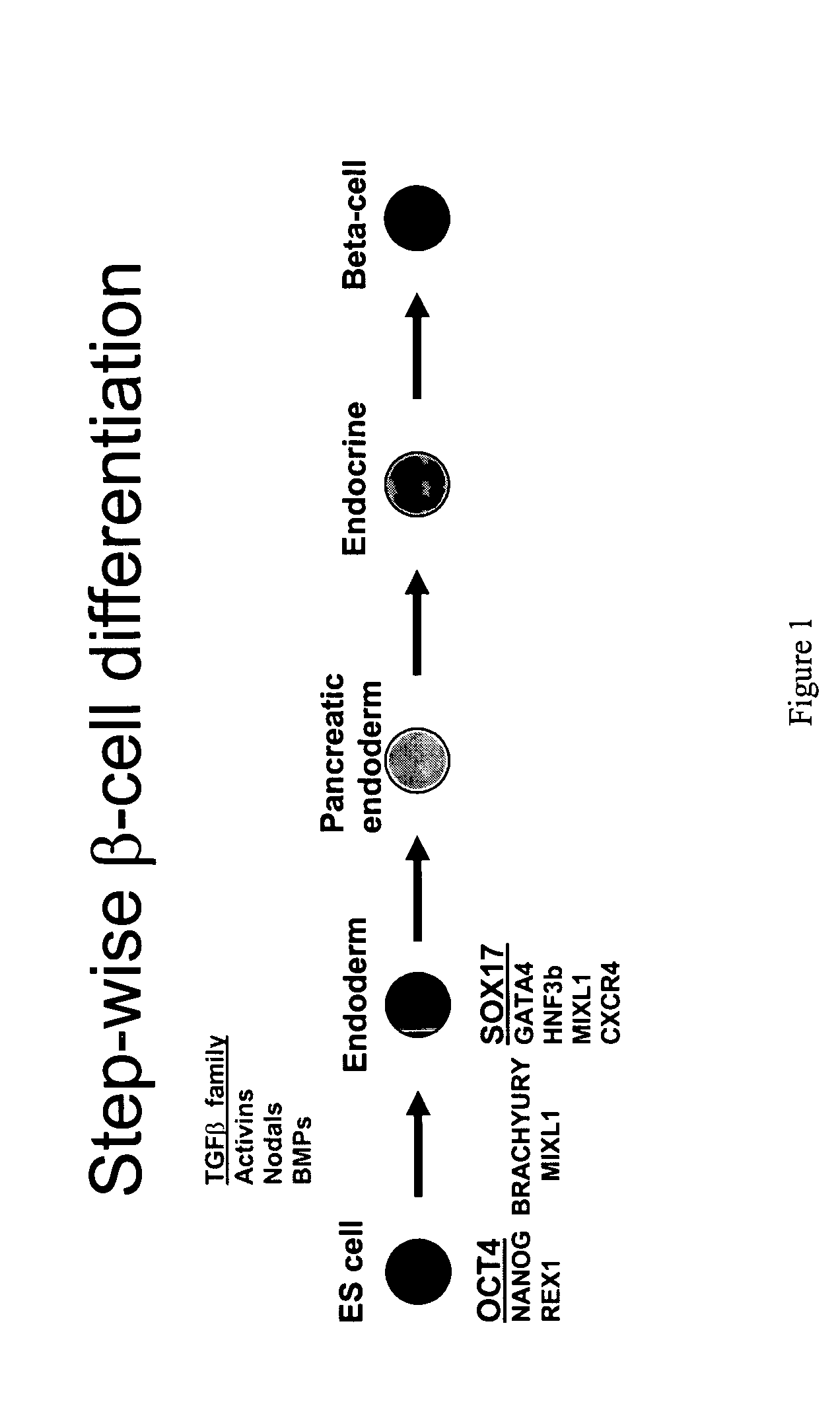
Method of differentiating stem cells into cells of the endoderm and pancreatic lineage
InactiveUS20070259423A1Promote differentiationMass productionPancreatic cellsCulture processPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Methods are described to more efficiently produce cells of the endoderm and pancreatic lineage from mammalian pluripotent stem cells. These methods provide a simple, reproducible culture protocol using defined media components to enable consistent, large-scale production of pancreatic cell types for research or therapeutic uses.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for compound profiling of living cells
InactiveUS6096509AQuick filterBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell typeTEST Mixture
An apparatus and method for real-time measurement of a cellular response of a test compound or series of test compounds (303) on a flowing suspension of cells (349), in which a homogeneous suspension of each member of a series of cell types (349) is combined with a concentration of a test compound (303), directed through a detection zone (355), and a cellular response of the living cells is measured in real time as the cells in the test mixture are flowing through the detection zone (355). The apparatus may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds, and is capable of real-time variation of concentrations of test and standard compounds and generation of dose / response profiles within a short timespan.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Method and apparatus for assay of electrochemical properties
ActiveUS7501052B2Easy to measureImprove accuracy and precisionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHand heldApplied potential
The presence of a select analyte in the sample is evaluated in an an electrochemical system using a conduction cell-type apparatus. A potential or current is generated between the two electrodes of the cell sufficient to bring about oxidation or reduction of the analyte or of a mediator in an analyte-detection redox system, thereby forming a chemical potential gradient of the analyte or mediator between the two electrodes After the gradient is established, the applied potential or current is discontinued and an analyte-independent signal is obtained from the relaxation of the chemical potential gradient. The analyte-independent signal is used to correct the analyte-dependent signal obtained during application of the potential or current. This correction allows an improved measurement of analyte concentration because it corrects for device-specific and test specific factors such as transport (mobility) of analyte and / or mediator, effective electrode area, and electrode spacing (and as a result, sample volume), without need for separate calibration values. The analysis can be performed using disposable test strips in a hand held meter, for example for glucose testing.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
PDX1-expressing dorsal and ventral foregut endoderm
Disclosed herein are cell cultures comprising dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells and methods of producing the same. Also disclosed herein are cell populations comprising substantially purified dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells as well as methods for enriching, isolating and purifying dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells from other cell types. Methods of identifying differentiation factors capable of promoting the differentiation of dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells, are also disclosed.
Owner:CYTHERA
Self-Assembling Cell Aggregates and Methods of Making Engineered Tissue Using the Same
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
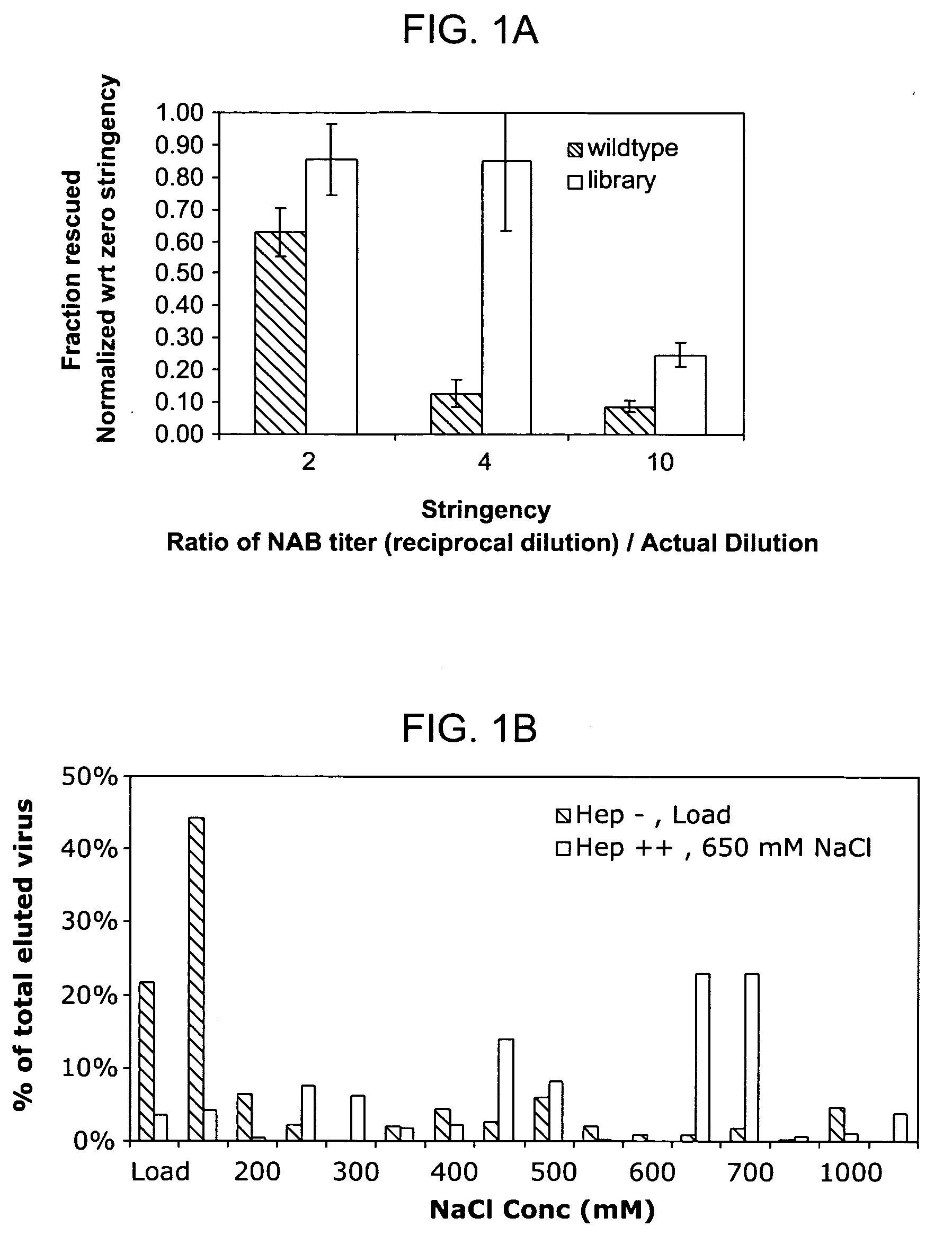
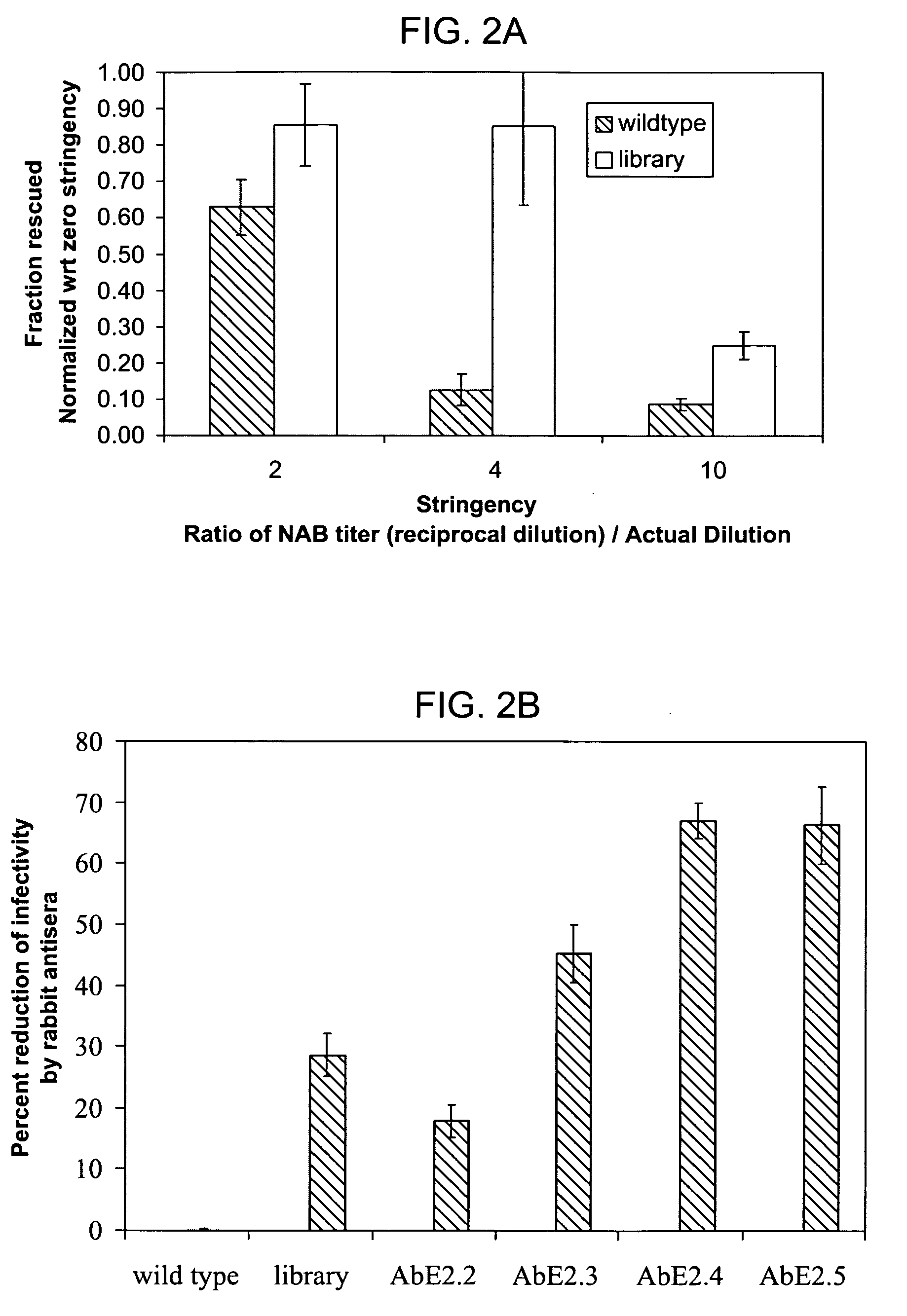
ActiveUS20050053922A1Reduce the binding forceAltered infectivityAntibacterial agentsVirusesReassortant VirusesNeutralizing antibody
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE GENE THERAPEUTICS +1
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7297539B2Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerFiber
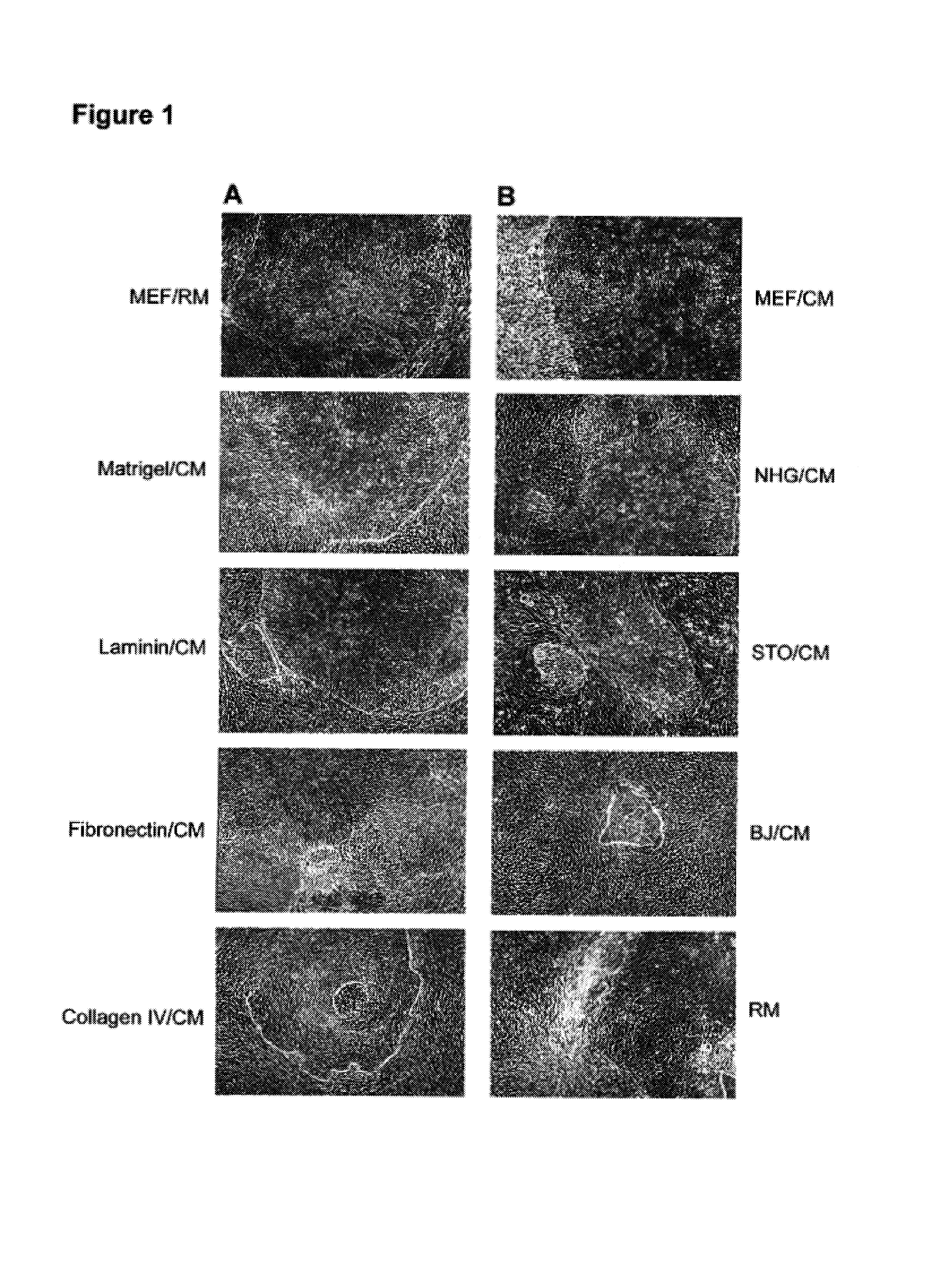
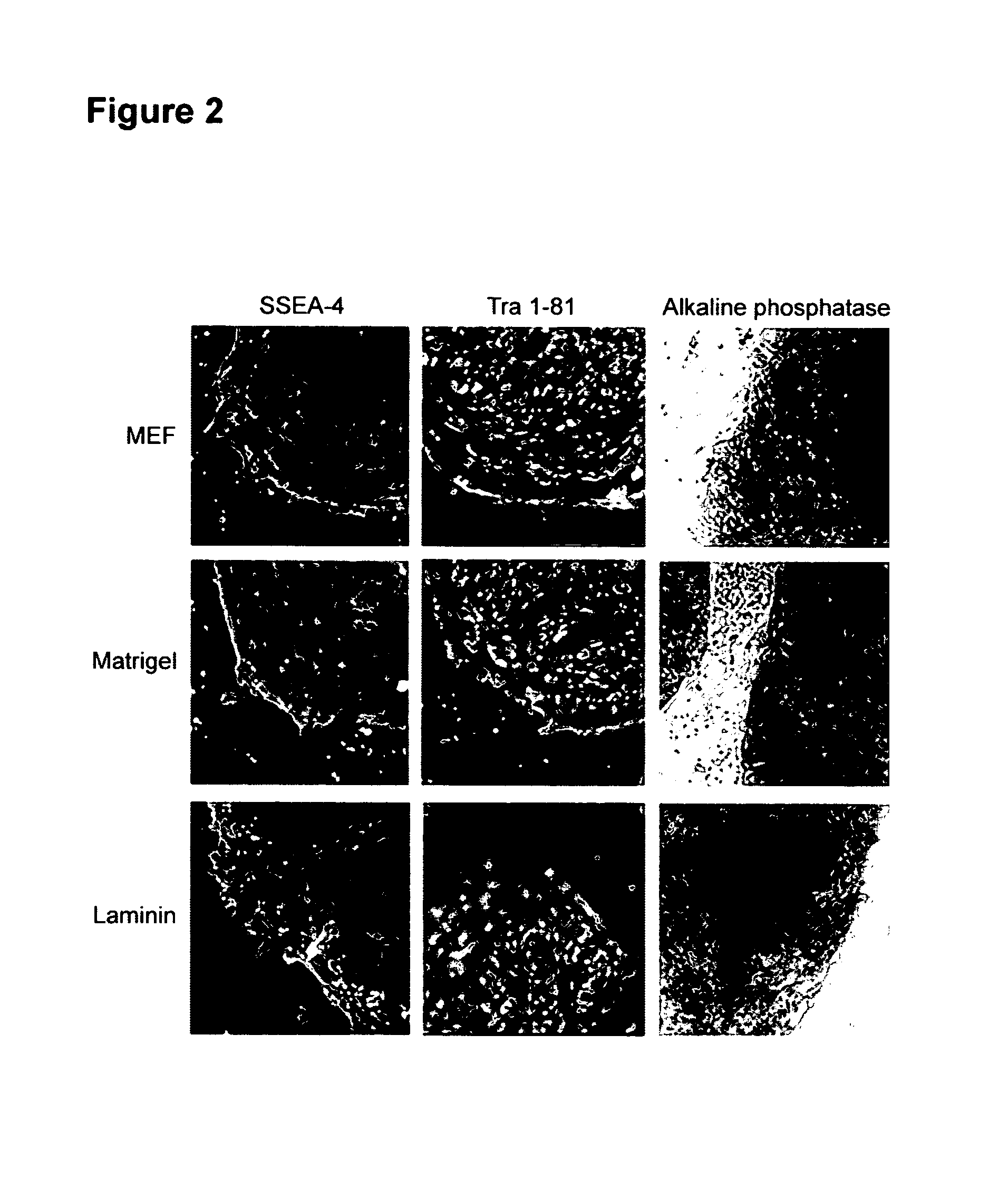
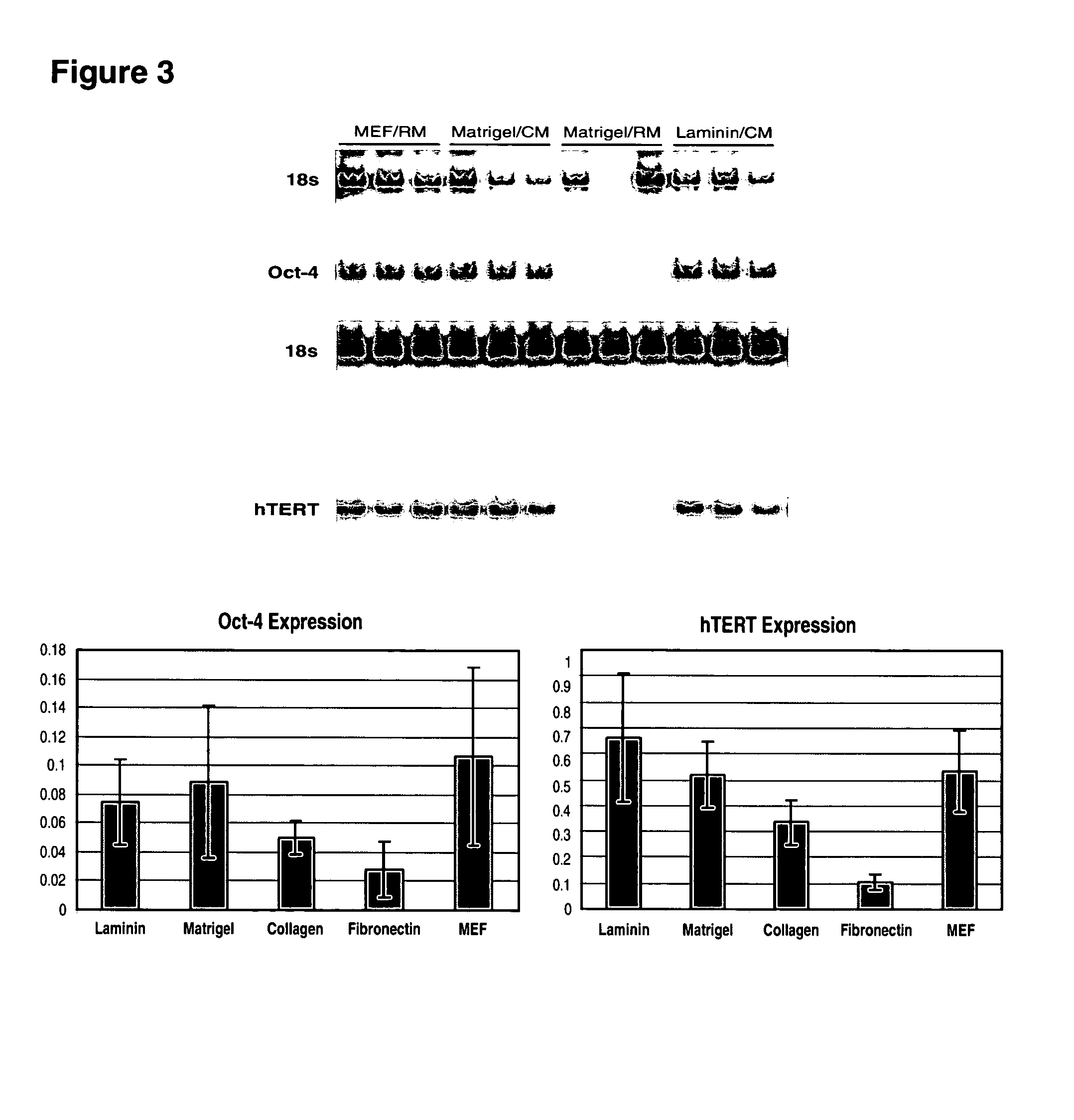
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for identifying a fetal cell
InactiveUS20100304978A1High expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCandidate Gene Association StudyTrophoblast
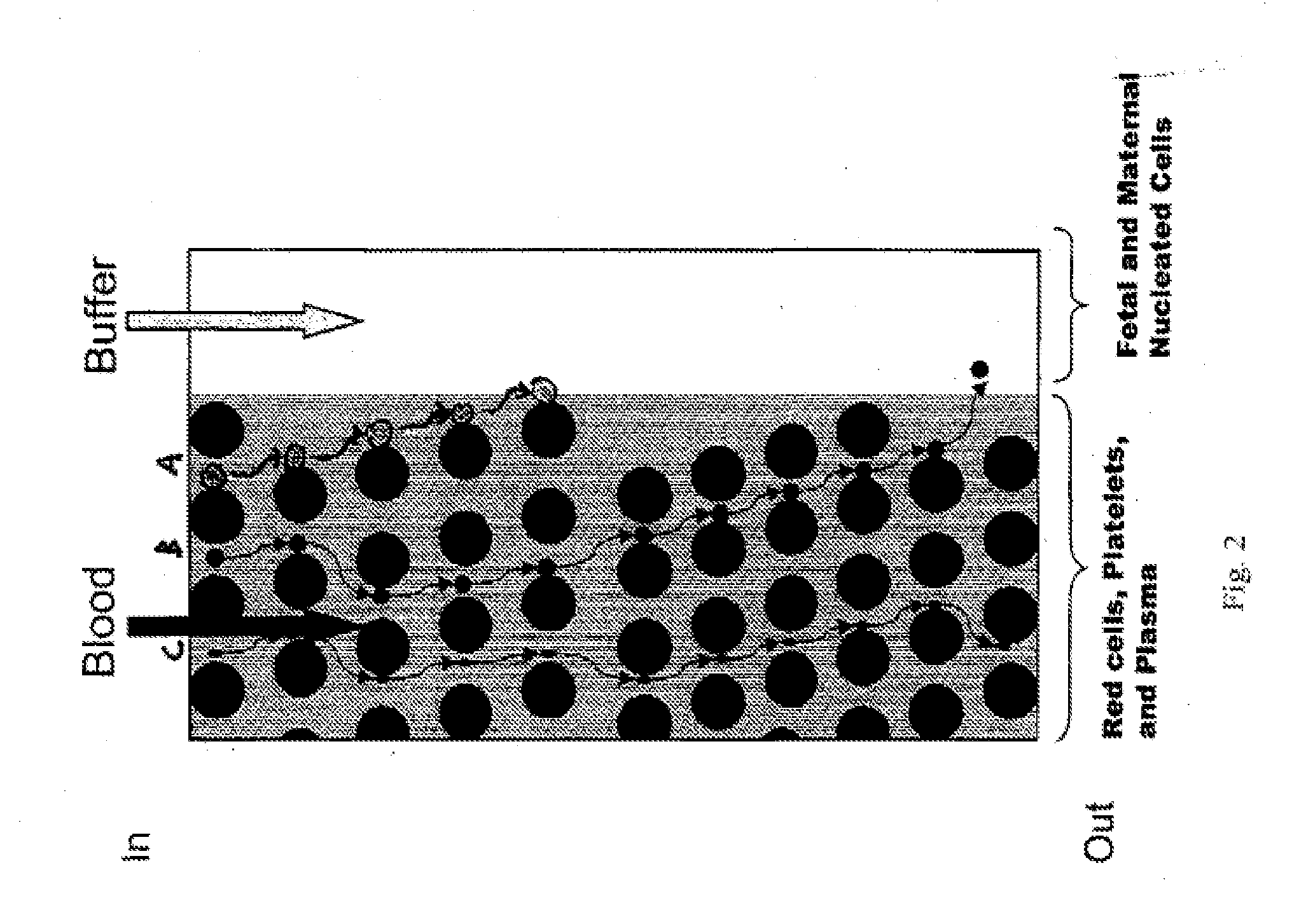
The present invention provides methods and compositions for specifically identifying a fetal cell. An initial screening of approximately 400 candidate genes by digital PCR in different fetal and adult tissues identified a subset of 24 gene markers specific for fetal nucleated RBC and trophoblasts. The specific expression of those genes was further evaluated and verified in more defined tissues and isolated cells through quantitative RT-PCR using custom Taqman probes specific for each gene. A subset of fetal cell specific markers (FCM) was tested and validated by RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in blood samples from non-pregnant women, and pre-termination and post-termination pregnant women. Applications of these gene markers include, but are not limited to, distinguishing a fetal cell from a maternal cell for fetal cell identification and genetic diagnosis, identifying circulating fetal cell types in maternal blood, purifying or enriching one or more fetal cells, and enumerating one or more fetal cells during fetal cell enrichment.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Visual-servoing optical microscopy
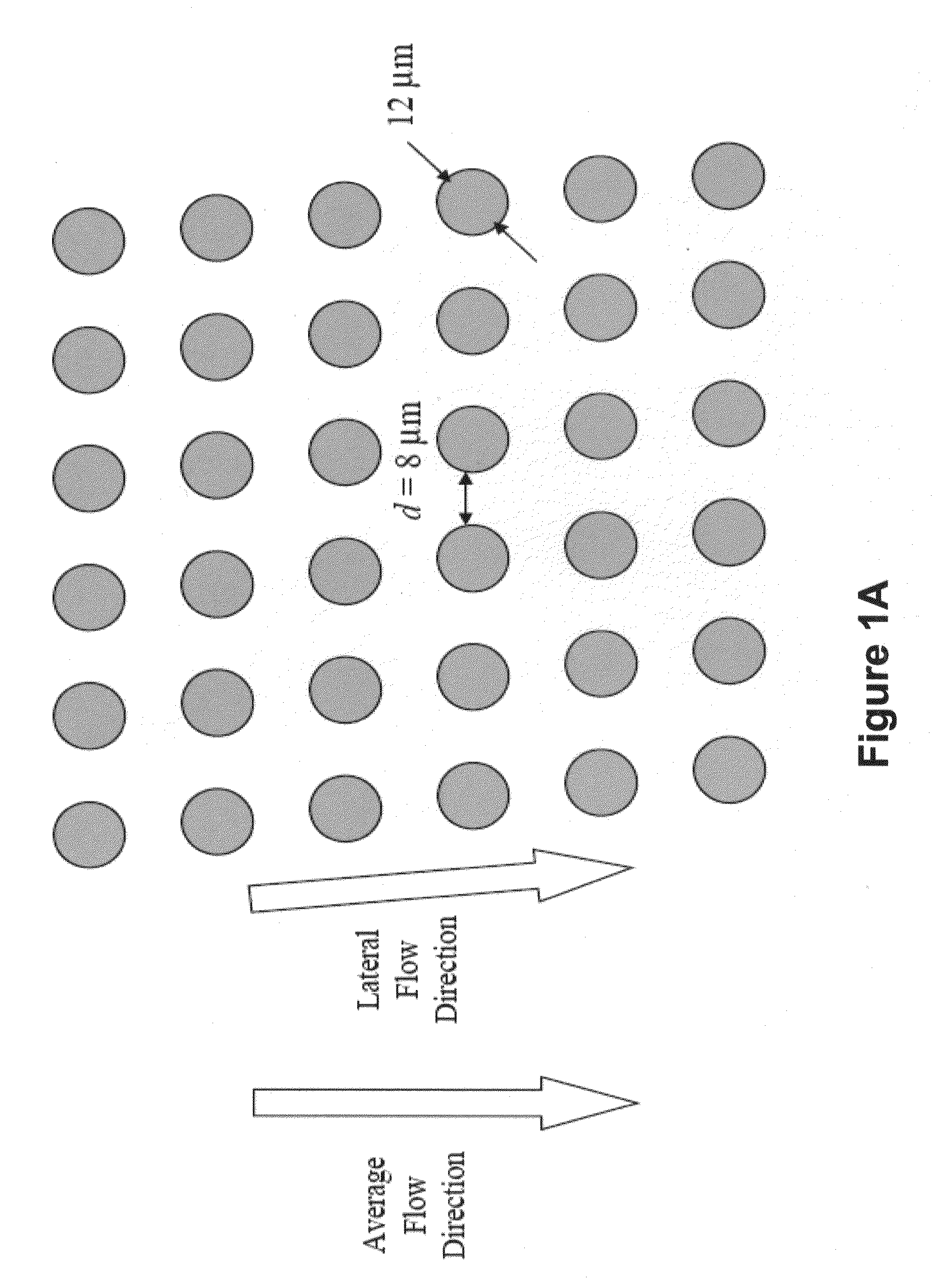
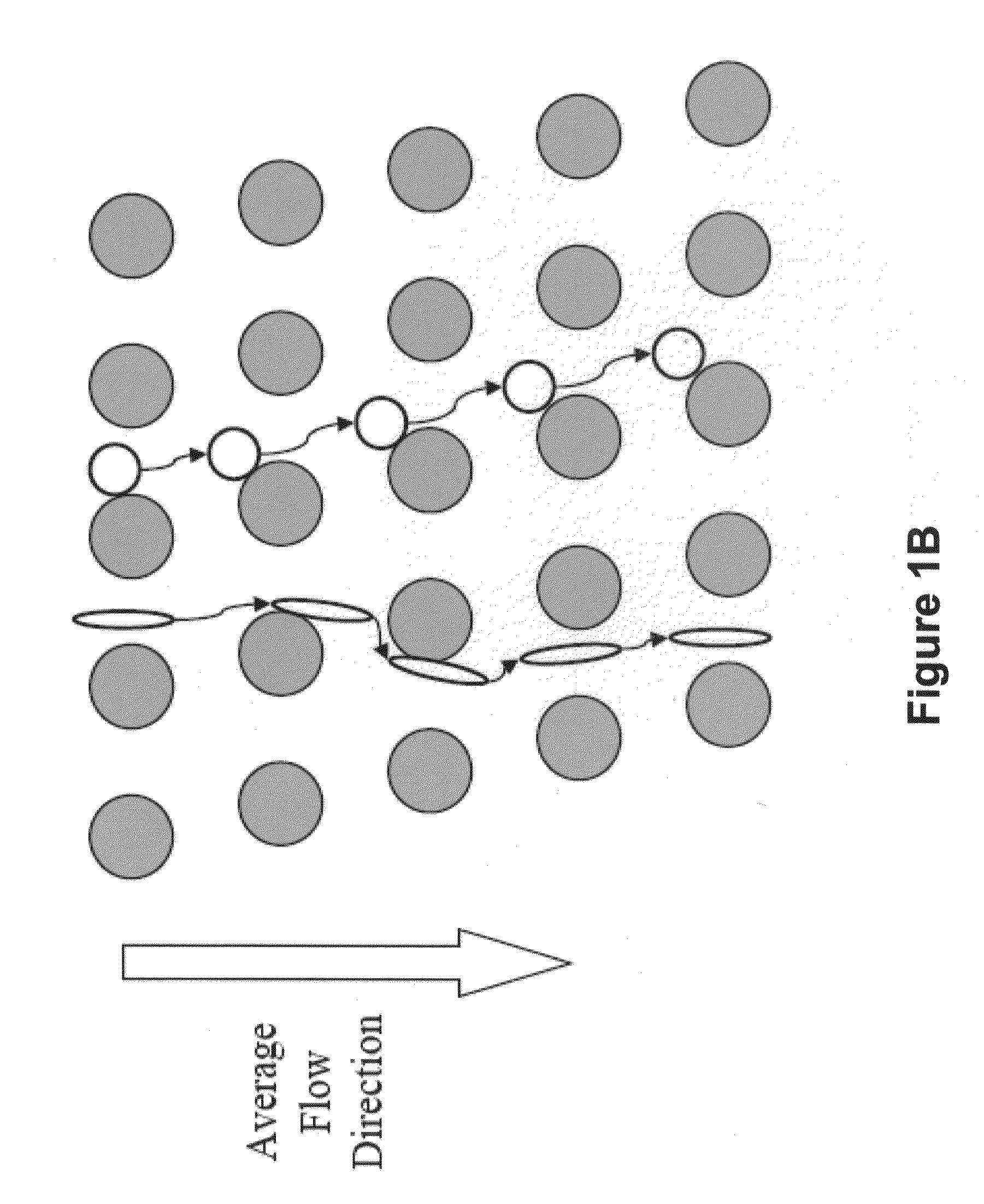
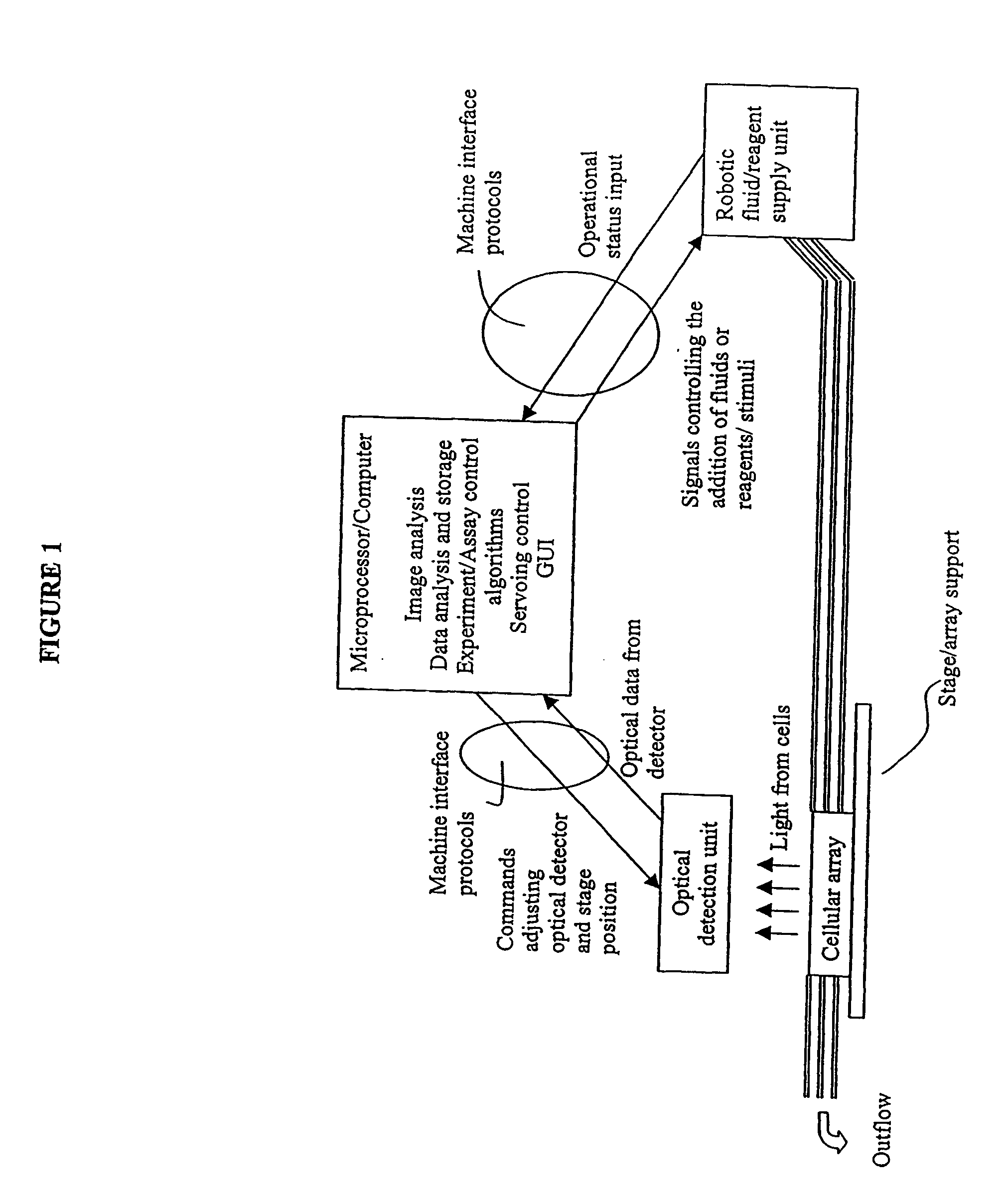
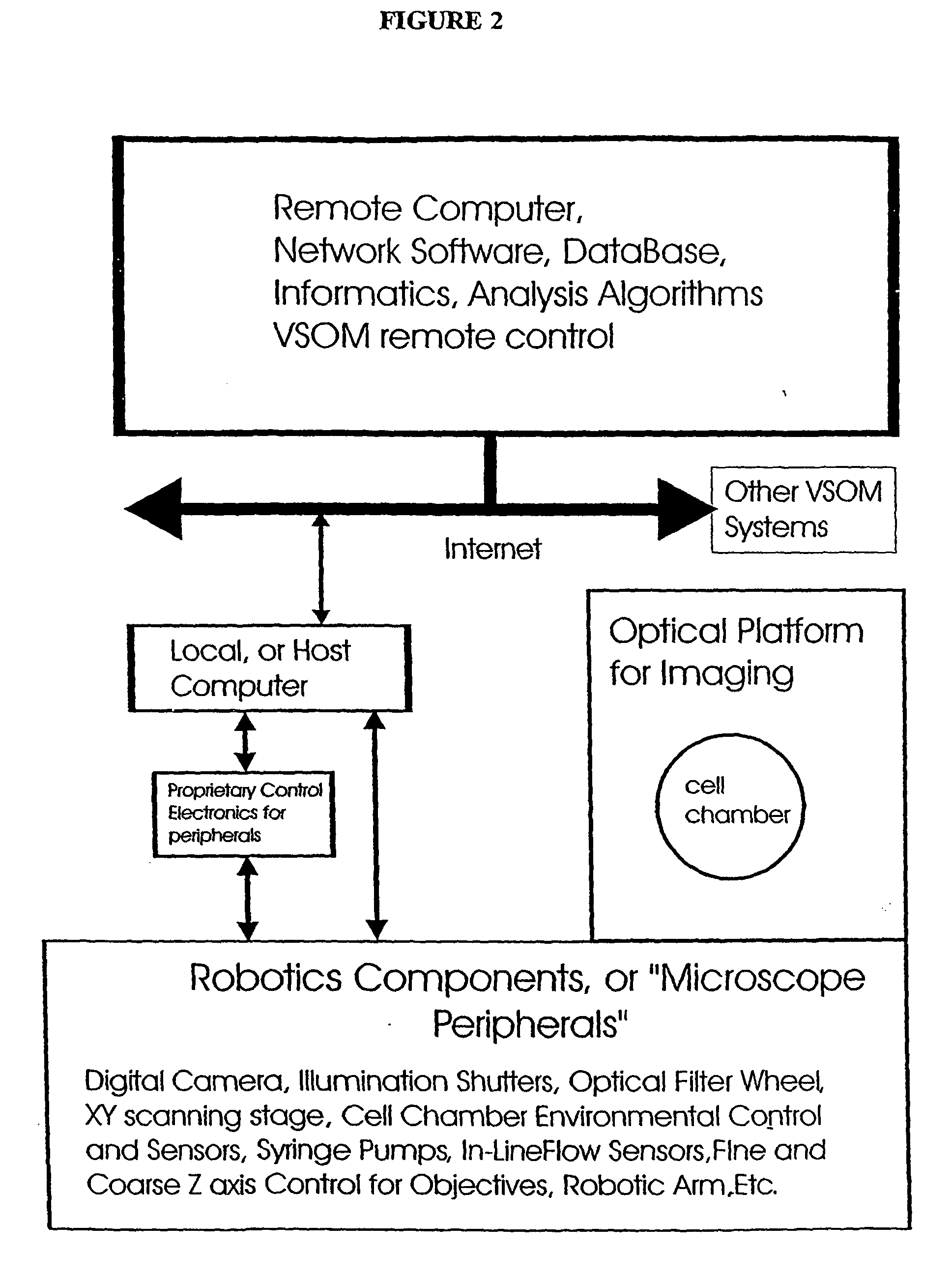
InactiveUS20040029213A1Close monitoringOptimize culture conditionsImage enhancementImage analysisCell typeCell stimulation
The present invention provides methods and devices for the knowledge-based discovery and optimization of differences between cell types. In particular, the present invention provides visual servoing optical microscopy, as well as analysis methods. The present invention provides means for the close monitoring of hundreds of individual, living cells over time: quantification of dynamic physiological responses in multiple channels; real-time digital image segmentation and analysis; intelligent, repetitive computer-applied cell stress and cell stimulation; and the ability to return to the same field of cells for long-term studies and observation. The present invention further provides means to optimize culture conditions for specific subpopulations of cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cell seeded expandable body
InactiveUS20050096731A1Promote regenerationAugment tissue repairStentsSurgeryInsertion stentBody cavity use
Devices, systems and methods for treating medical conditions using cell therapy via body lumens. Localized delivery is achieved with the use of a stent-like expandable body seeded with cells. The expandable body is expanded to contact at least a portion of the inner walls of the body lumen and the cells, cellular products and / or other therapeutic agents are delivered to the surrounding tissue. The therapeutic benefit provided is dependent on the type of cells used and the features of the expandable body.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
Intracellular delivery of biological effectors
InactiveUS6960648B2Improve concentrationTo promote metabolismOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell typeBiological membrane
Owner:XIGEN
Kits for Prenatal Testing
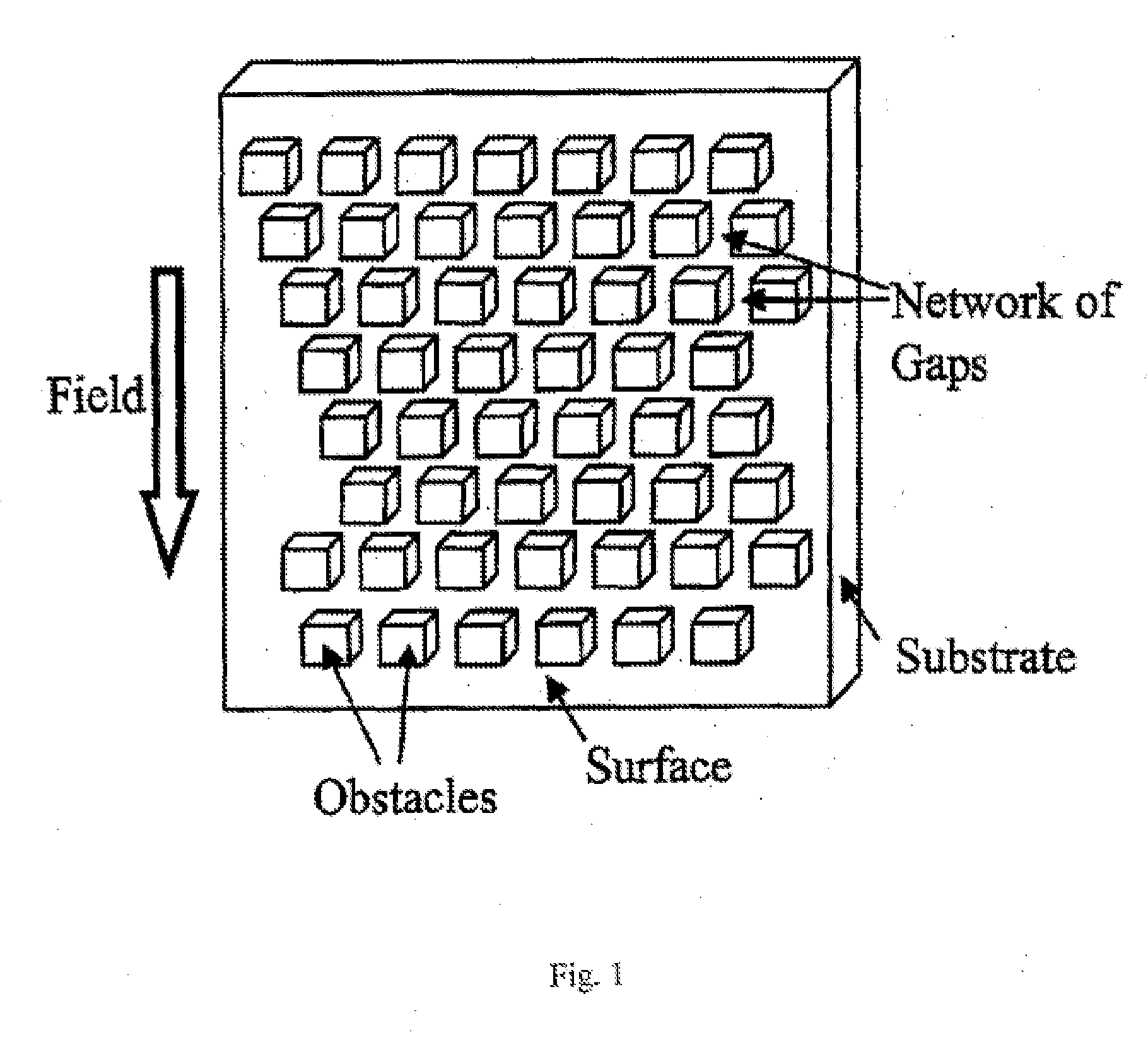
The invention relates to a kit for prenatal testing comprising a size-based separation module which enriches a first cell type from a maternal blood sample found in vivo in a pregnant female at a concentration of less than 1% of all blood cells, and a set of instructions for analyzing said one or more enriched cells to make a prenatal diagnosis. In some embodiments, the size-based separation module can comprise a plurality of obstacles to selectively direct the one or more cells of the first cell type in a first direction away from one or more cells of a second cell type.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
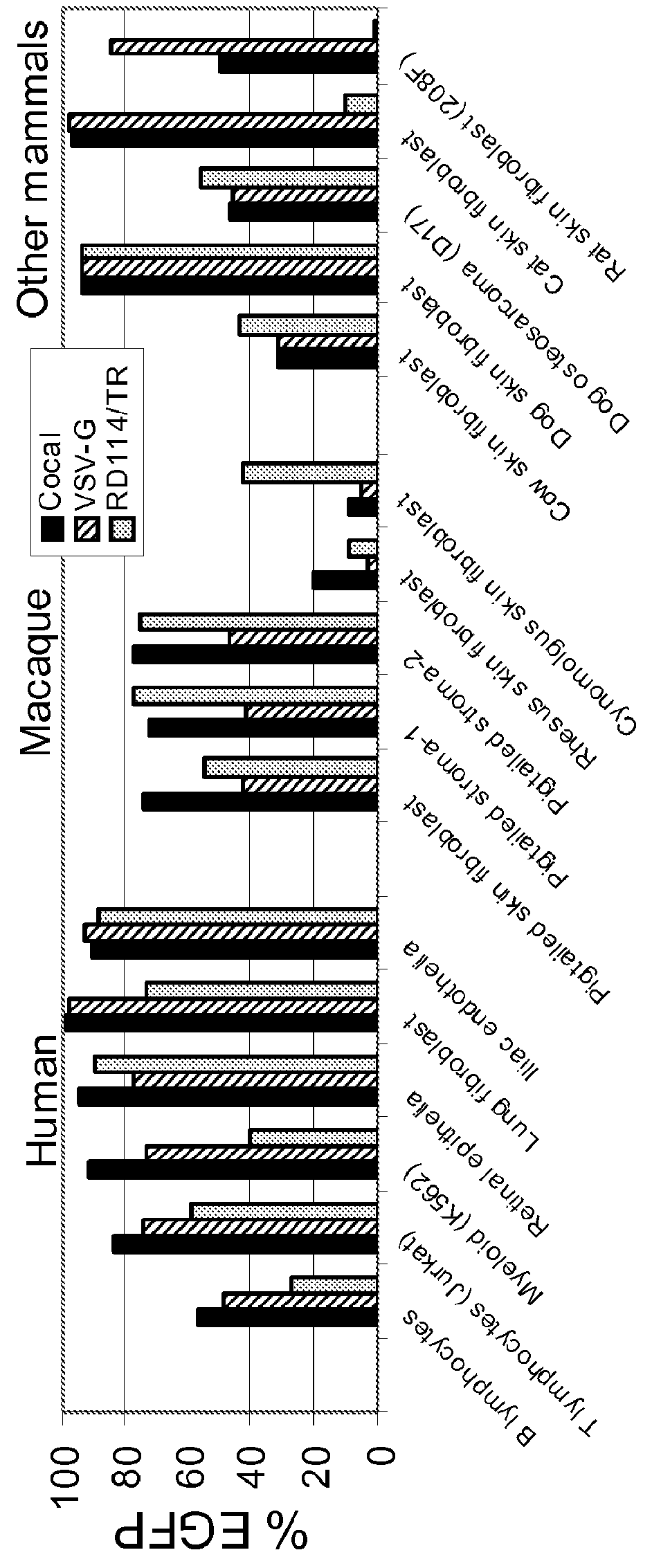
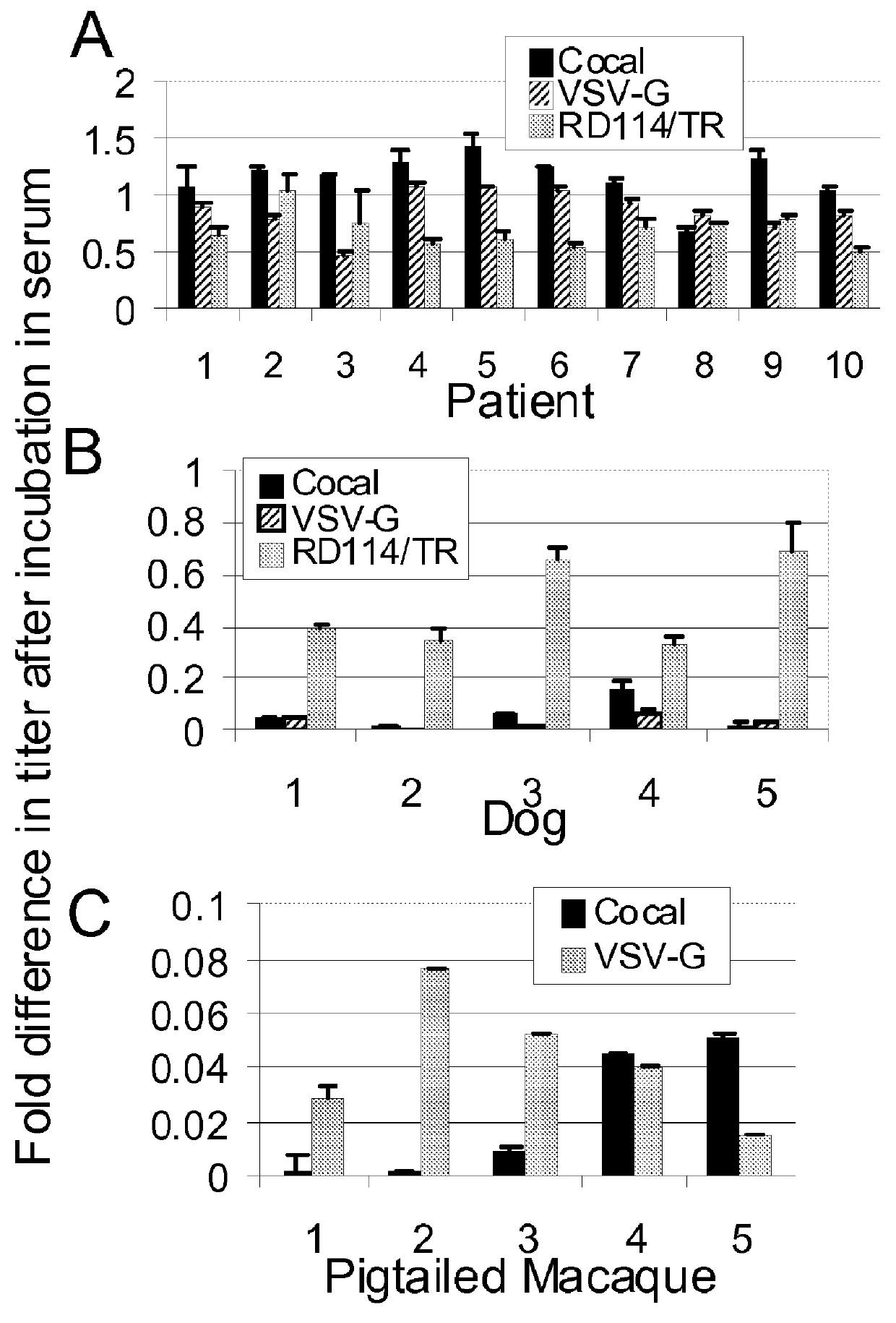
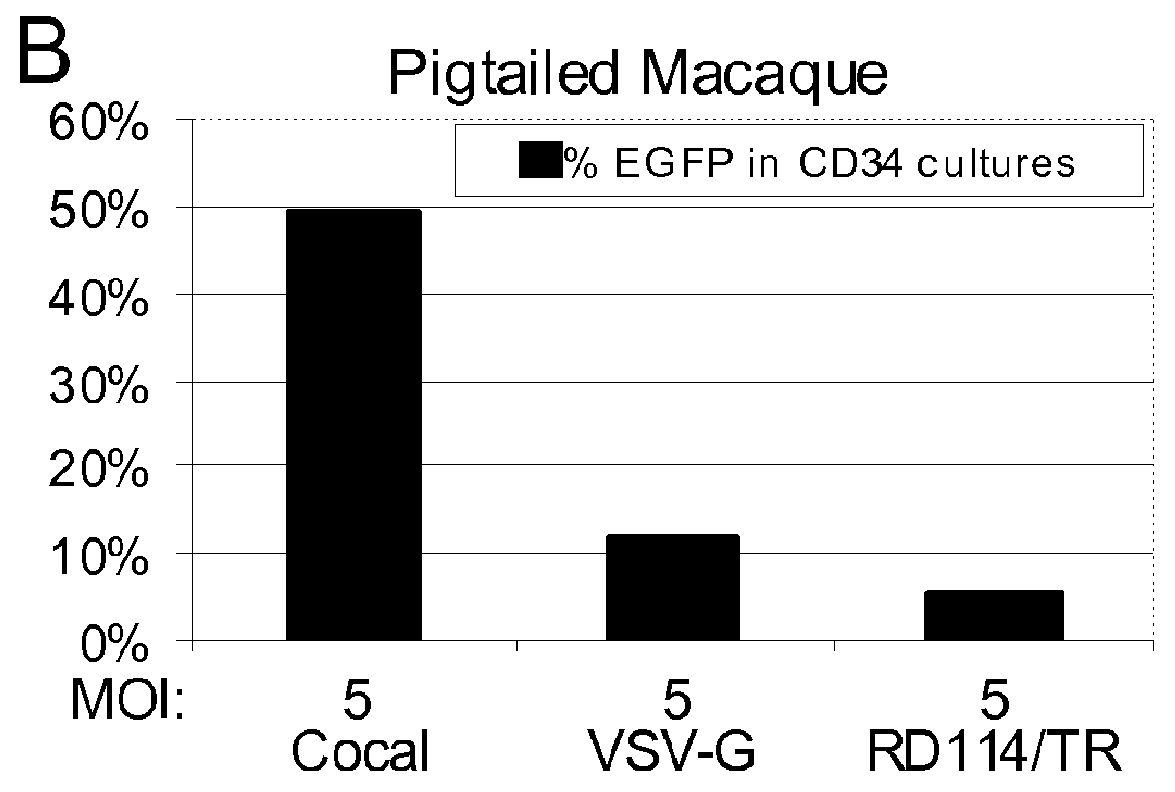
Cocal vesiculovirus envelope pseudotyped retroviral vectors
InactiveUS20120164118A1Increase serum stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideCocal vesiculovirusVirus-Retrovirus
Provided herein are Cocal vesiculovirus envelope pseudotyped retroviral vectors that exhibit high titers, broad species and cell-type tropism, and improved serum stability. Disclosed Cocal vesiculovirus envelope pseudotyped retroviral vectors may be suitably employed for gene therapy applications and, in particular, for the ex vivo and in vivo delivery of a gene of interest to a wide variety of target cells.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
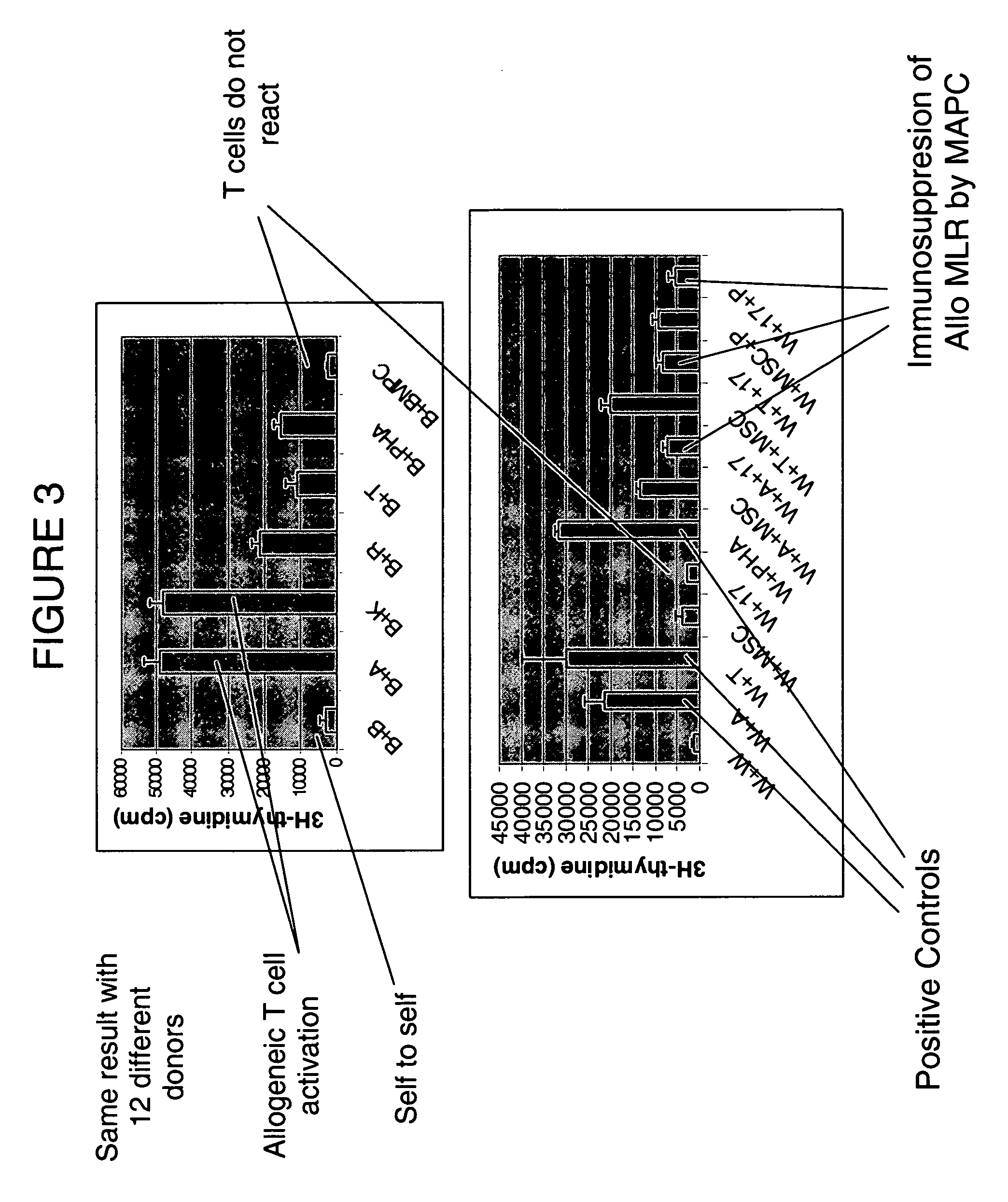
Immunomodulatory properties of multipotent adult progenitor cells and uses thereof
Isolated cells are described that are not embryonic stem cells, not embryonic germ cells, and not germ cells. The cells can differentiate into at least one cell type of each of at least two of the endodermal, ectodermal, and mesodermal lineages. The cells do not provoke a harmful immune response. The cells can modulate immune responses. As an example, the cells can suppress an immune response in a host engendered by allogeneic cells, tissues, and organs. Methods are described for using the cells, by themselves or adjunctively, to treat subjects. For instance, the cells can be used adjunctively for immunosuppression in transplant therapy. Methods for obtaining the cells and compositions for using them also are described.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY +1
IL-2 fusion proteins with modulated selectivity
The invention provides cytokine fusion proteins with an increased therapeutic index, and methods to increase the therapeutic index of such fusion proteins. The fusion proteins of the invention are able to bind to more than one type of cytokine receptor expressed on cells and also bind to more than one cell type. In addition, the fusion proteins of the invention exhibit a longer circulating half-life in a patient's body than the corresponding naturally occurring cytokine.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Definitive endoderm
ActiveUS20050158853A1Enough timeGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm layerCell type
Disclosed herein are cell cultures comprising definitive endoderm cells and methods of producing the same. Also disclosed herein are cell populations comprising substantially purified definitive endoderm cells as well as methods for enriching, isolating and purifying definitive endoderm cells from other cell types.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
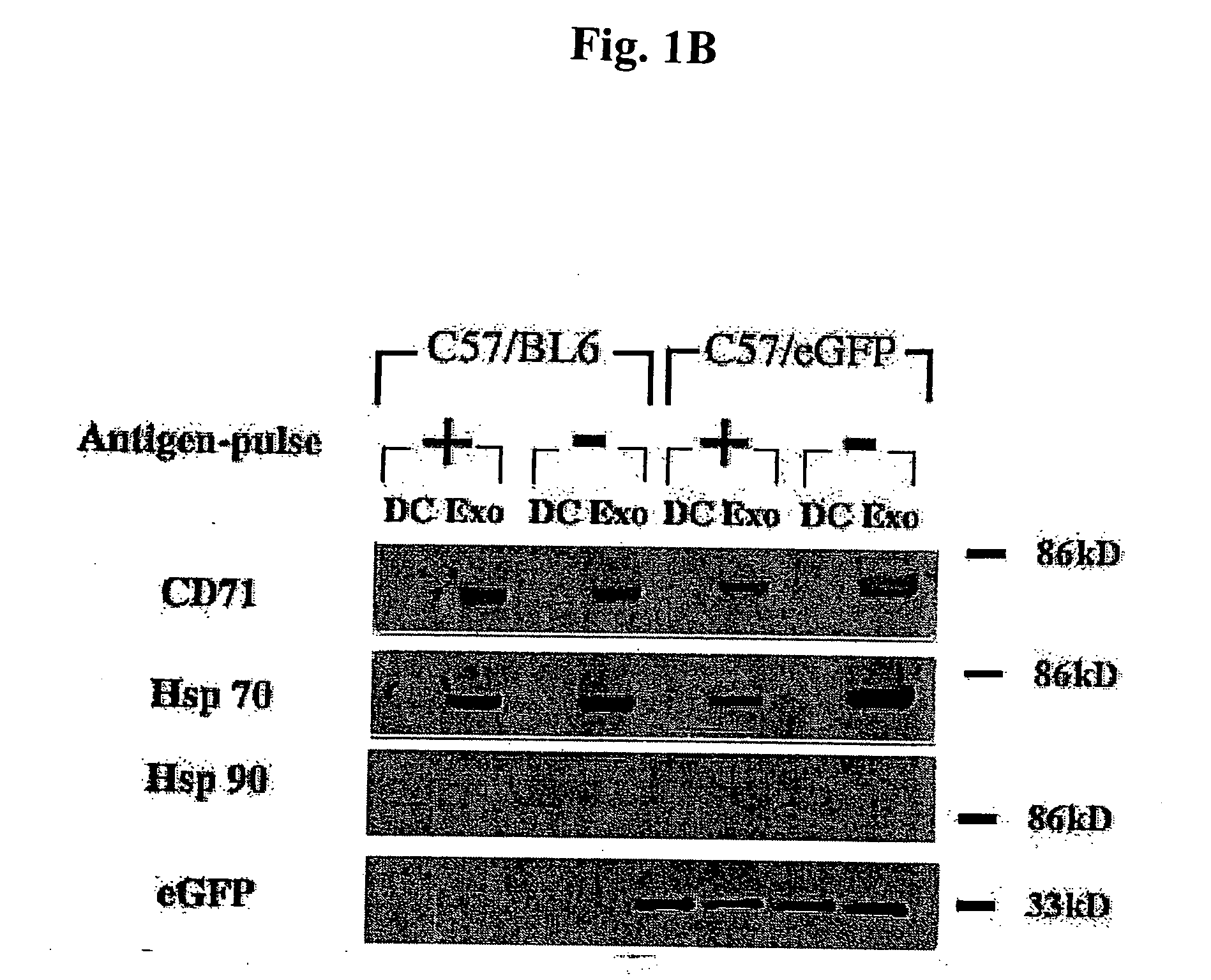
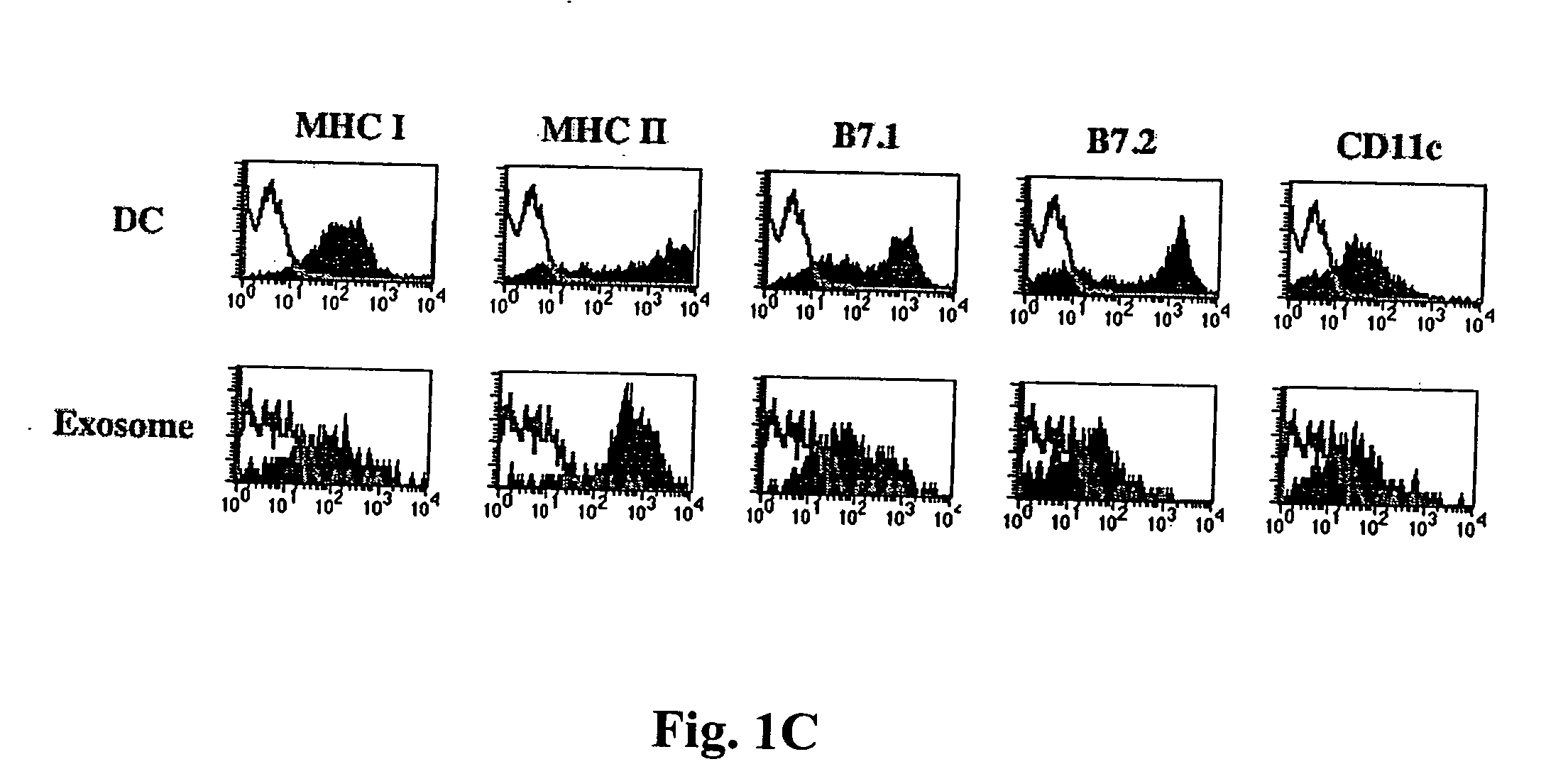
Immunosuppressive exosomes
InactiveUS20060116321A1Suppress undesirable immune responseStimulate immune responseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCytokine SuppressionDendritic cell
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in mediating an immunosuppressive reaction. The compositions of the invention comprise exosomes having immunosuppressive activity. Such exosomes may be derived from a variety of different cell types, including antigen presenting cells such as dendritic cells and macrophages. Prior to isolation of exosomes, the cells may be genetically engineered to express molecules capable of enhancing the immunosuppressive activity of said exosomes and / or may be exposed to one or more agents, such as cytokines or cytokine inhibitors, which are also capable of enhancing the immunosuppressive activity of exosomes. The present invention also relates to the use of such exosomes for the treatment of diseases and disorders associated with undesirable activation of the immune system. The present invention also includes exosomes isolated directly from serum that have been shown to be immunosuppressive.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF THE +1
Buffer solution for electroporation and a method comprising the use of the same
InactiveUS20050064596A1High transfection efficiencyReduce cell deathPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsElectroporationIon
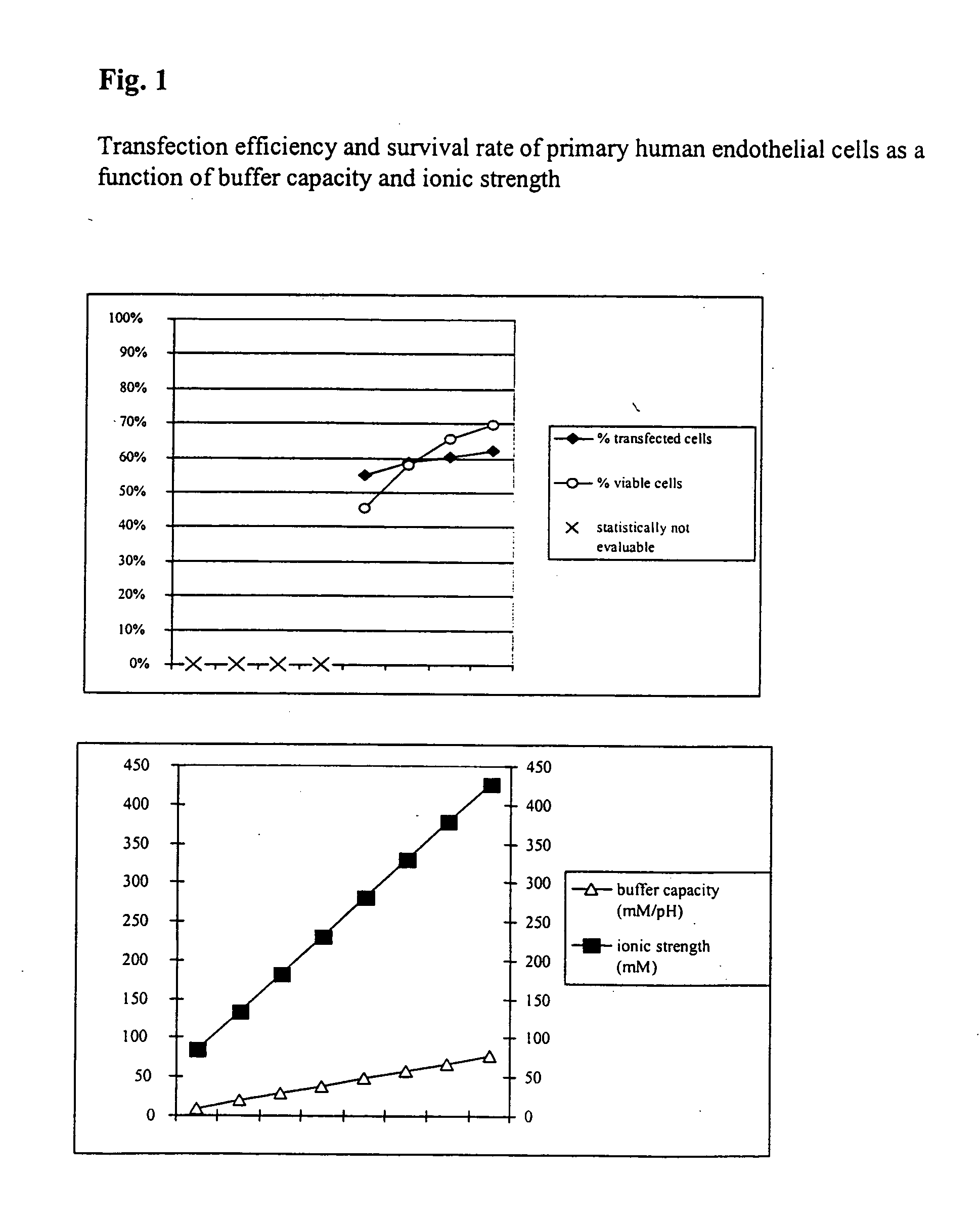
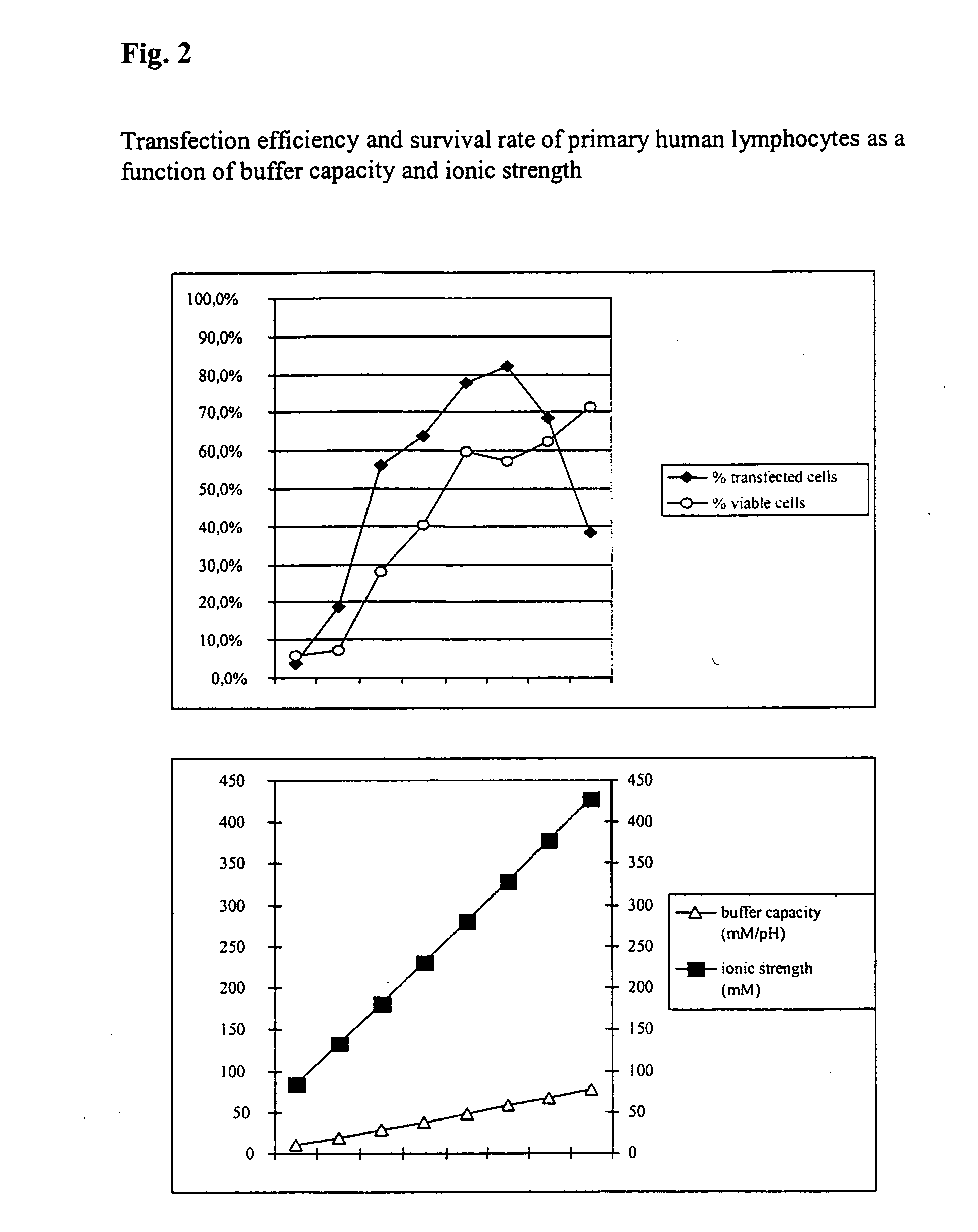
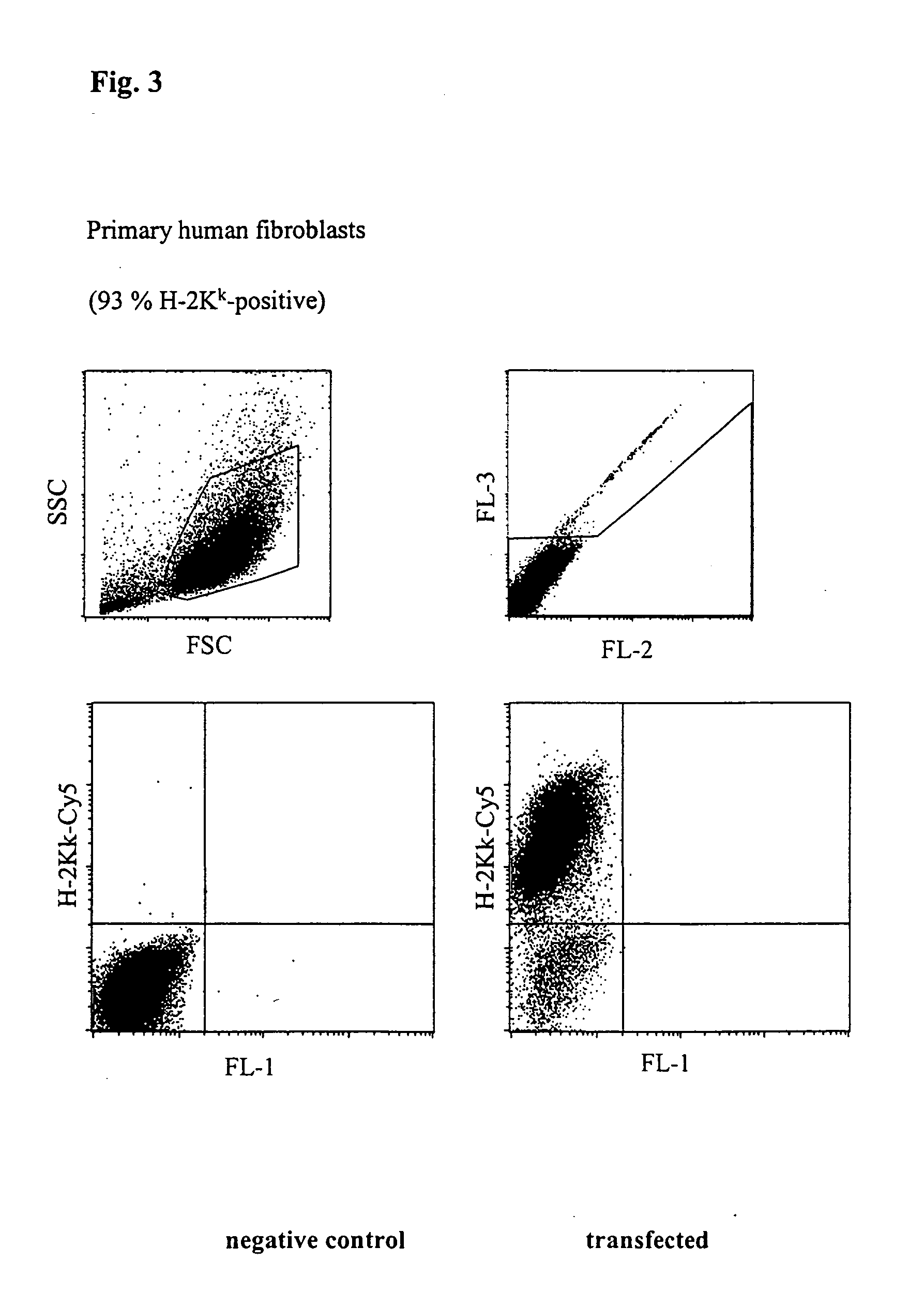
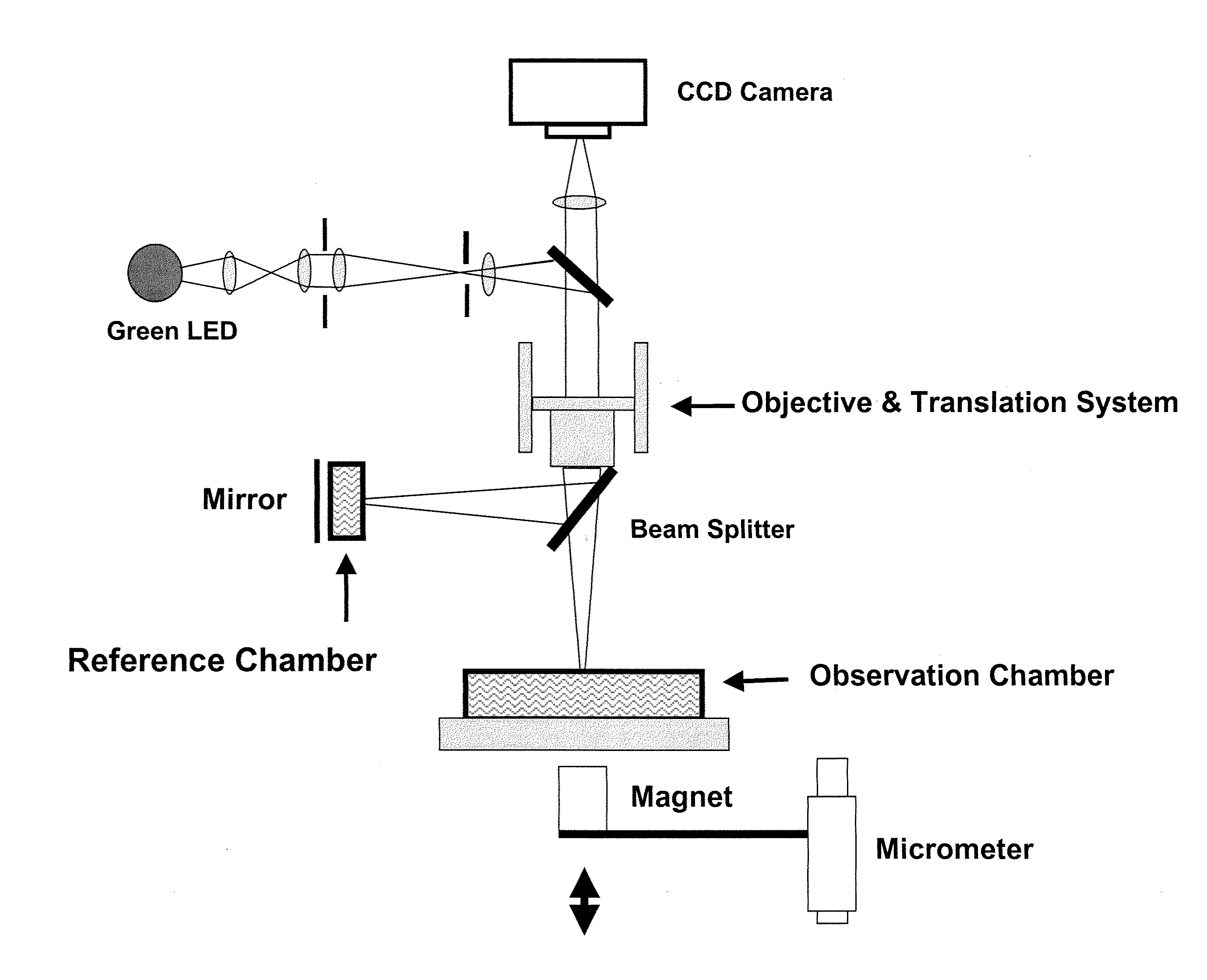
The invention relates to a buffer solution for suspending animal or human cells and for dissolving biologically active molecules in order to introduce said biologically active molecules into the cells using an electric current and to a method for introducing biologically active molecules into animal or human cells using an electric current and a buffer solution. The inventive buffer solution has a buffering capacity of at least 20 mmol*I−1*pH−1 and an ionic strength of at least 200 mmol*I−1 during a change to the pH value from pH 7 to pH 8 and at a temperature of 25° C. The use of a buffer solution of this type in the corresponding method allows biologically active molecules to be introduced into animal and human cells with a high degree of transfection efficiency and at the same time a low cell mortality. Different cell types, in particular dormant and actively dividing cells of low activity, can be successfully transfected in said buffer solution.
Owner:LONZA COLOGNE
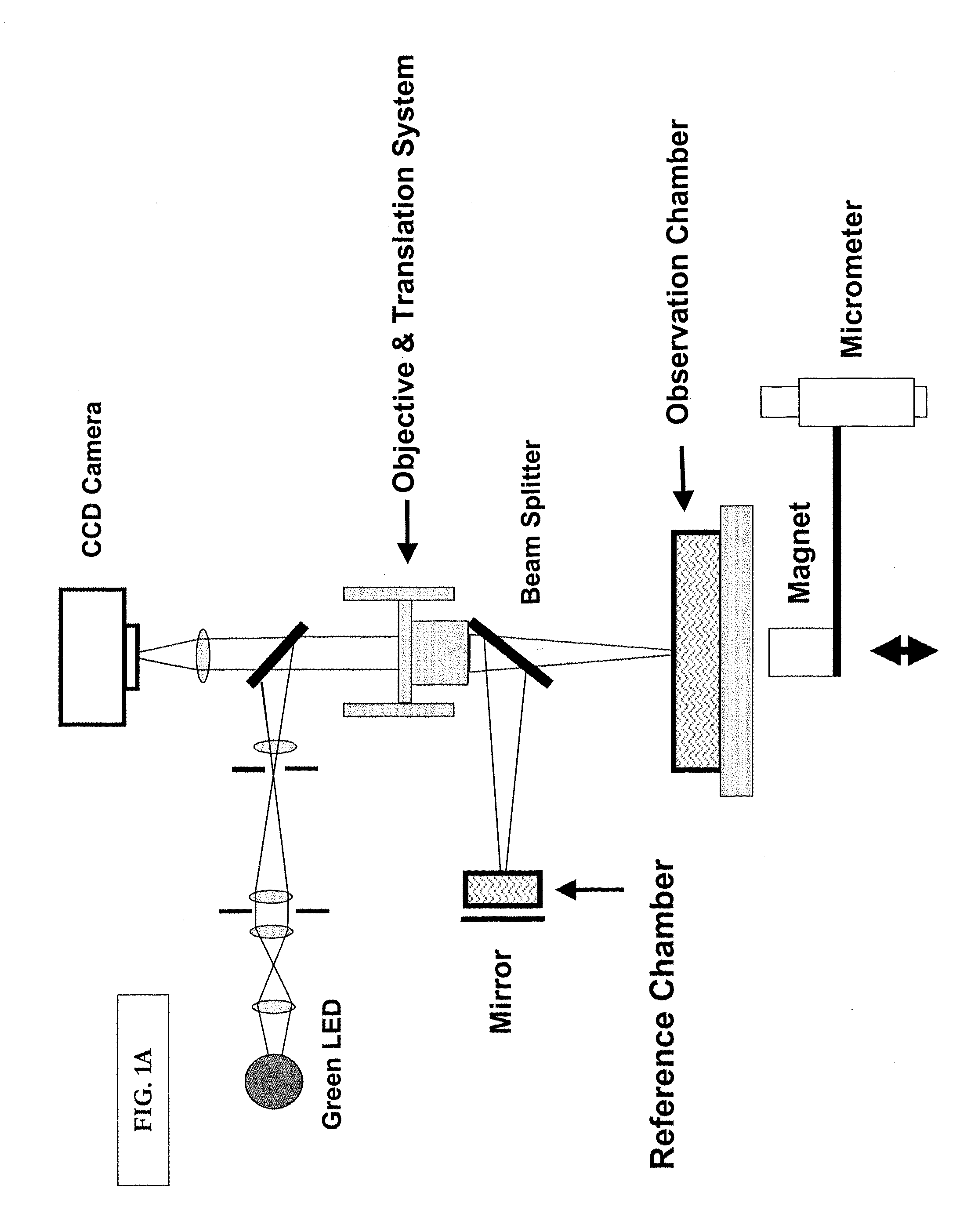
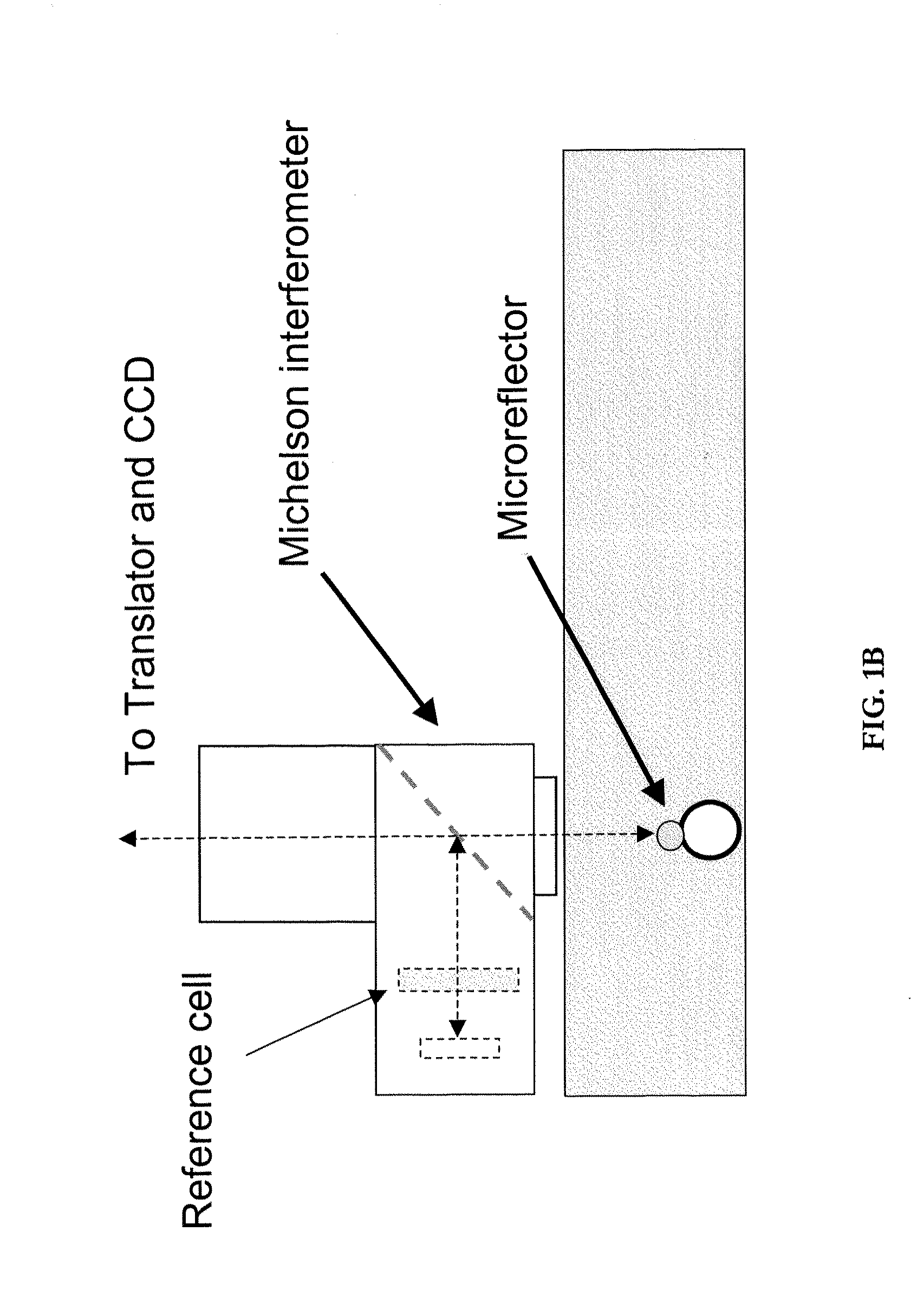
Optical cytometry
The present invention provides optical systems and methods for determining a characteristic of a cell, such as cell type, cellular response to a biochemical event, biological state and the like. The methods typically involve using interferometry to observe membrane properties in a cell and then use this information to determine one or more characteristics of a cell. The methods of the invention are useful for applications such as drug screening as well as diagnostic techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com