Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
214results about How to "Less" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Data caching based on data contents
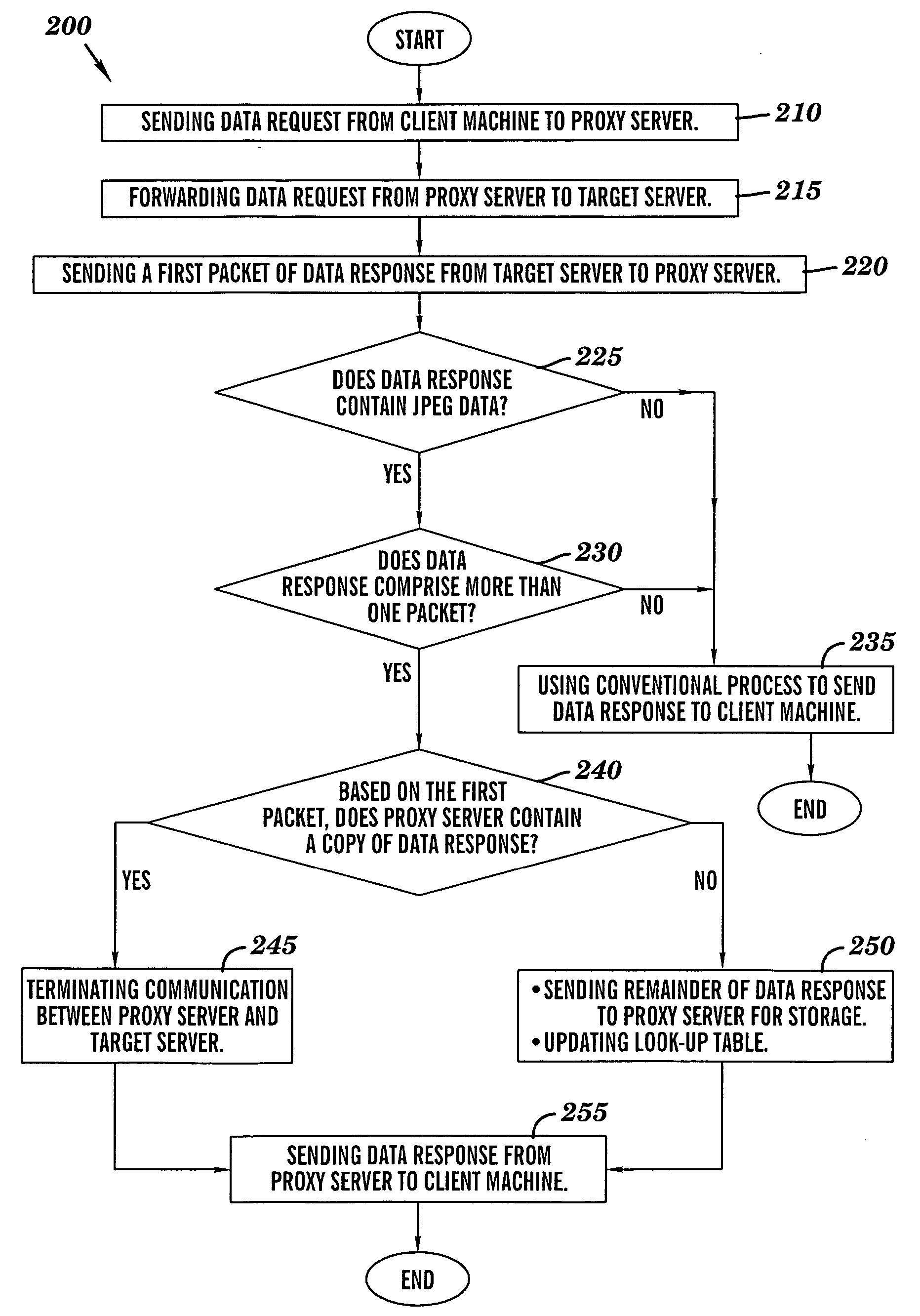
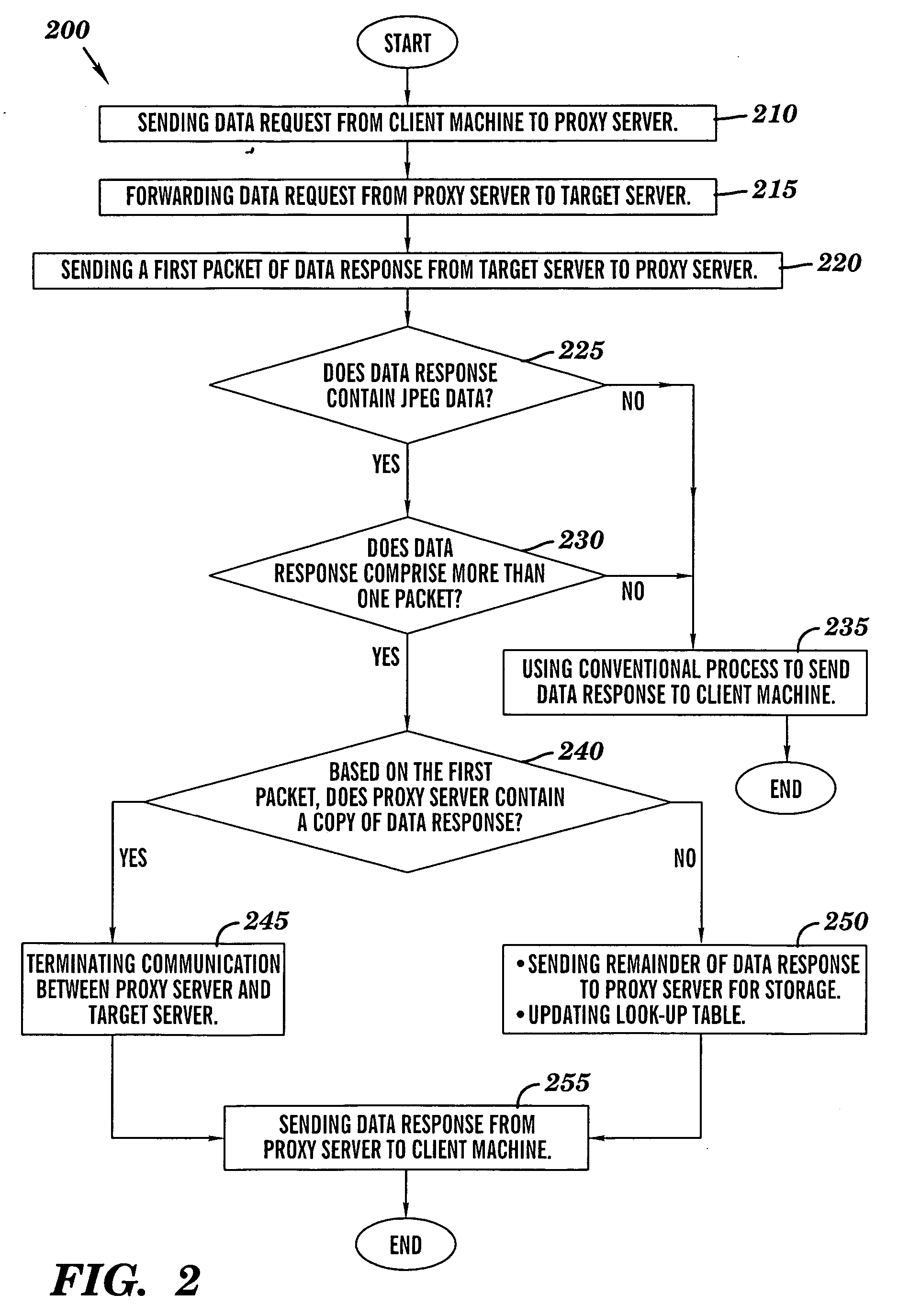
ActiveUS20060167969A1LessMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData contentClient machine
A novel method and structure in which data caching is based on data contents. The method comprises the steps of (a) sending a data request from a processing circuit to a target server; (b) in response to the target server receiving the data request, sending a first response portion of a data response from the target server to the processing circuit; and {circle around (c)} in response to the processing circuit receiving the first response portion, using the processing circuit to examine the first response portion so as to determine whether the processing circuit contains a copy of the data response; and (d) in response to the processing circuit determining that the processing circuit contains a copy of the data response, sending the copy of the data response from the processing circuit to a client machine.
Owner:TWITTER INC
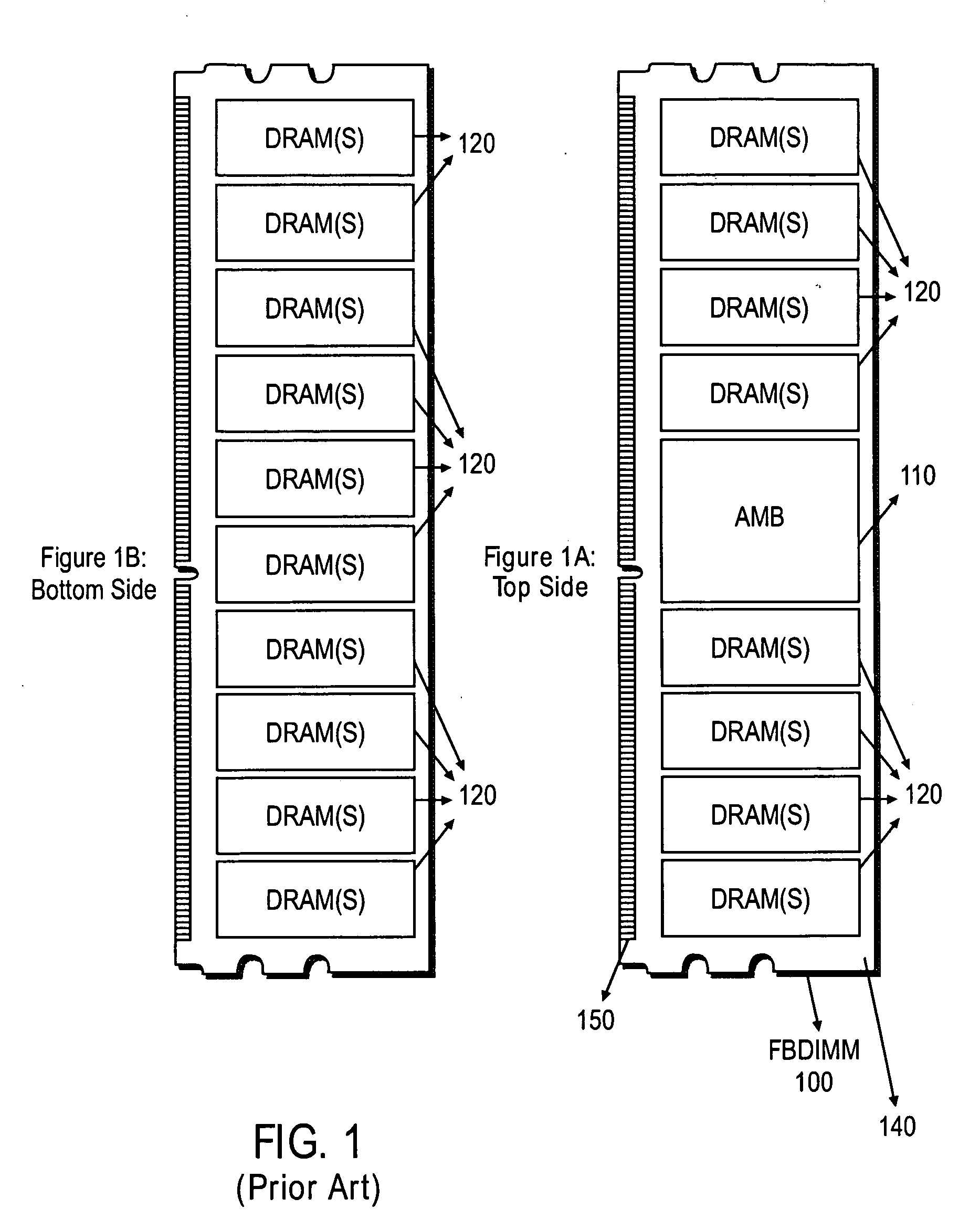
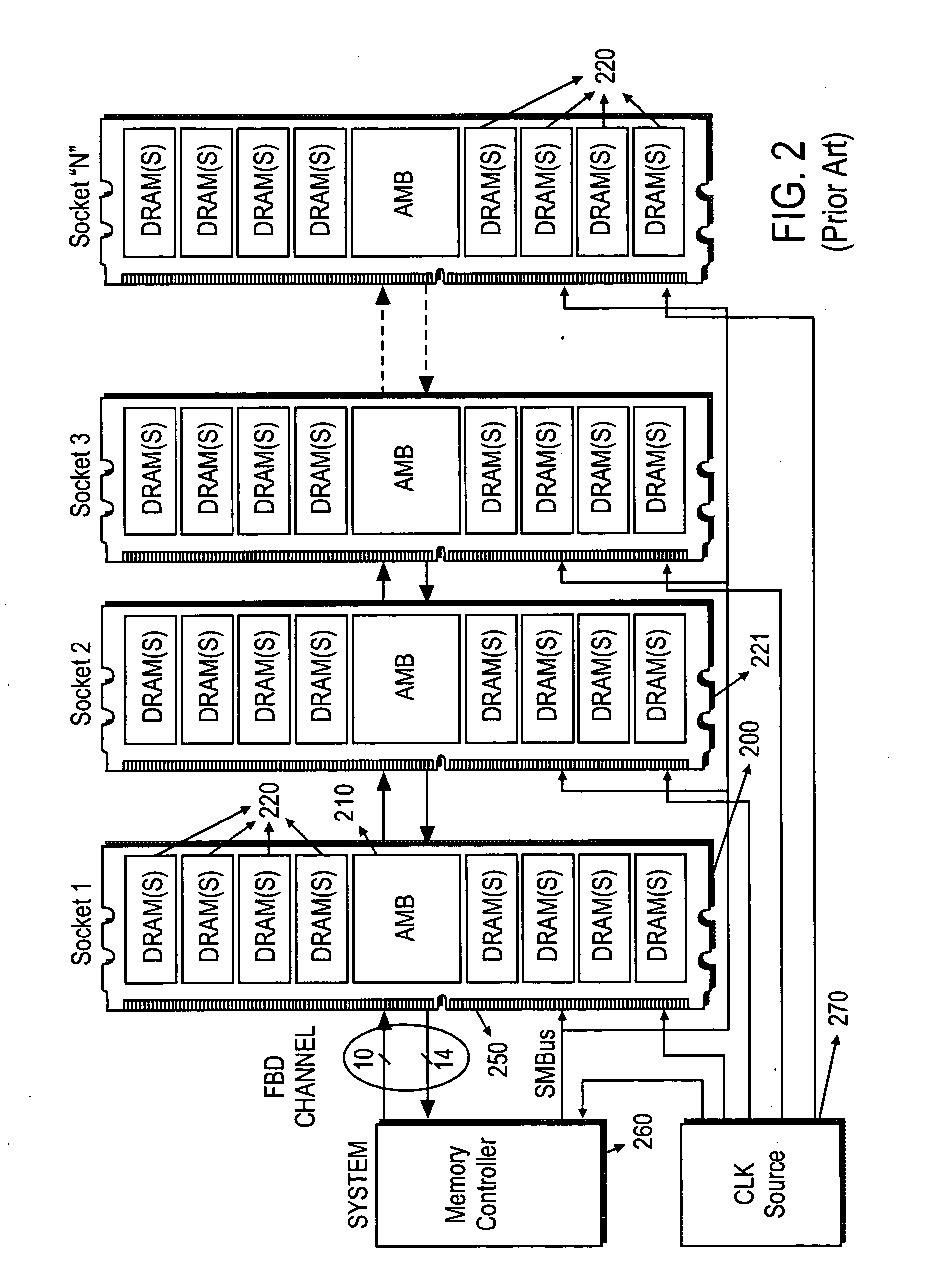
Memory supermodule utilizing point to point serial data links
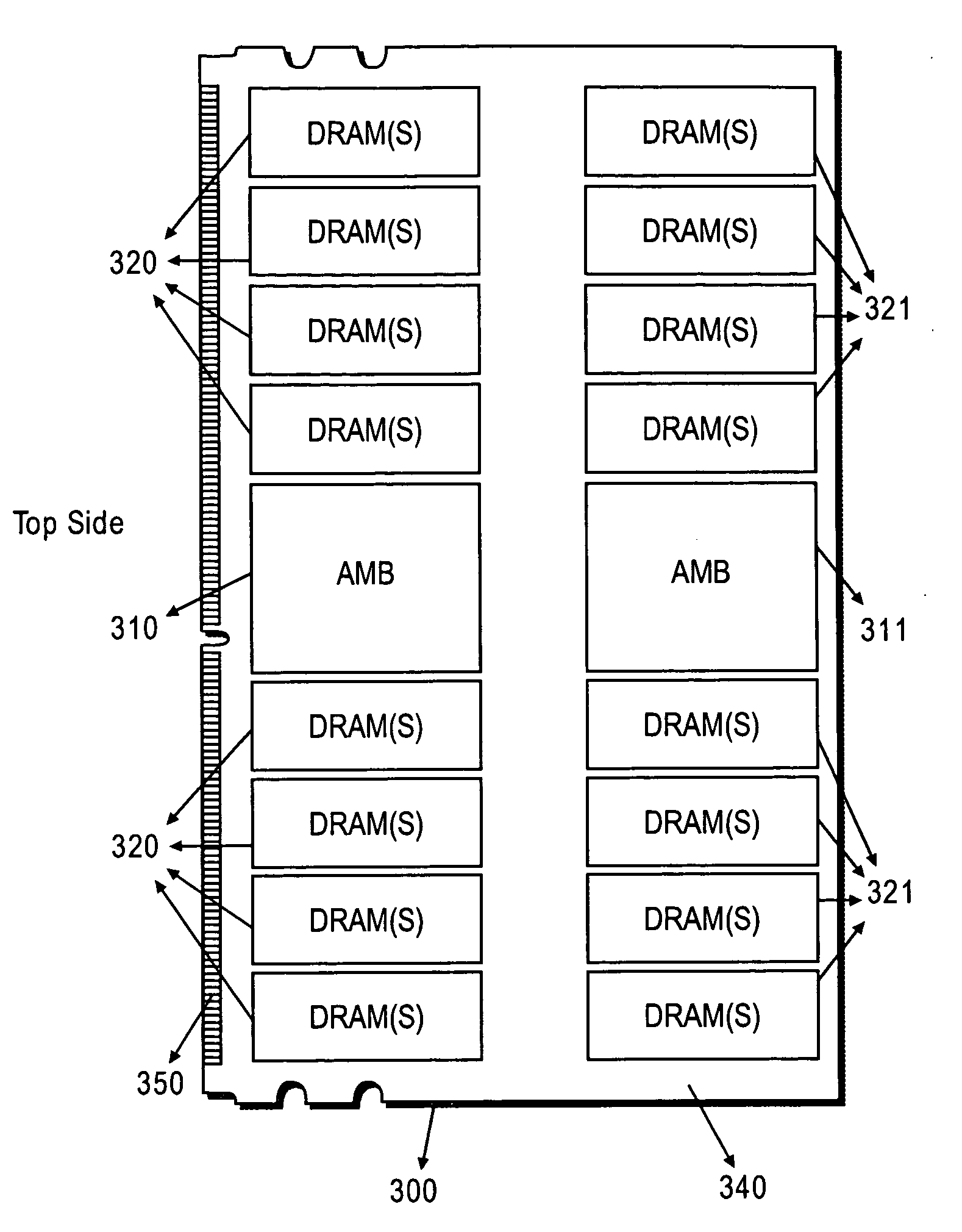
InactiveUS20080002447A1Lower heightLess board spaceFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsContact padMemory module
A memory supermodule containing two or more memory modules disposed on a common circuit board. Also, a memory supermodule comprising two or more memory modules, each module comprising a circuit board, the circuit boards connected by a flexible circuit. All modules in a supermodule share a single set of contact pads for establishing signal connection with a system in which the supermodule is used.
Owner:SMART MODULAR TECH
Multiple outlet air path for a clothes dryer
ActiveUS7020985B2Accelerated dryingLessDrying machines with non-progressive movementsTextiles and paperEngineeringDrying time
A clothes dryer has a heat source, preferably a heat pump, a rotating drum, and means to generate flow of air from the heat source to an inlet in the drum. At least two outlets are separated from each other in the drum to enable higher air flow rates without increase in pressure drop, resulting in reduced drying time.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Methods, systems and devices for neuromodulating spinal anatomy
ActiveUS20100292769A1Minimizing complicationMinimize side effectsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSide effectSpinal anatomy
Devices, systems and methods for treating pain or other conditions while minimizing possible complications and side effects. Treatment typically includes electrical stimulation and / or delivery of pharmacological or other agents with the use of a lead or catheter. The devices, systems and methods provide improved anchoring which reduces migration of the lead yet allows for easy repositioning or removal of the lead if desired. The devices, systems and methods also provide for simultaneous treatment of multiple targeted anatomies. This shortens procedure time and allows for less access points, such as needle sticks to the epidural space, which in turn reduces complications, such as cerebral spinal fluid leaks, patient soreness and recovery time. Other possible complications related to the placement of multiple devices are also reduced.
Owner:TC1 LLC
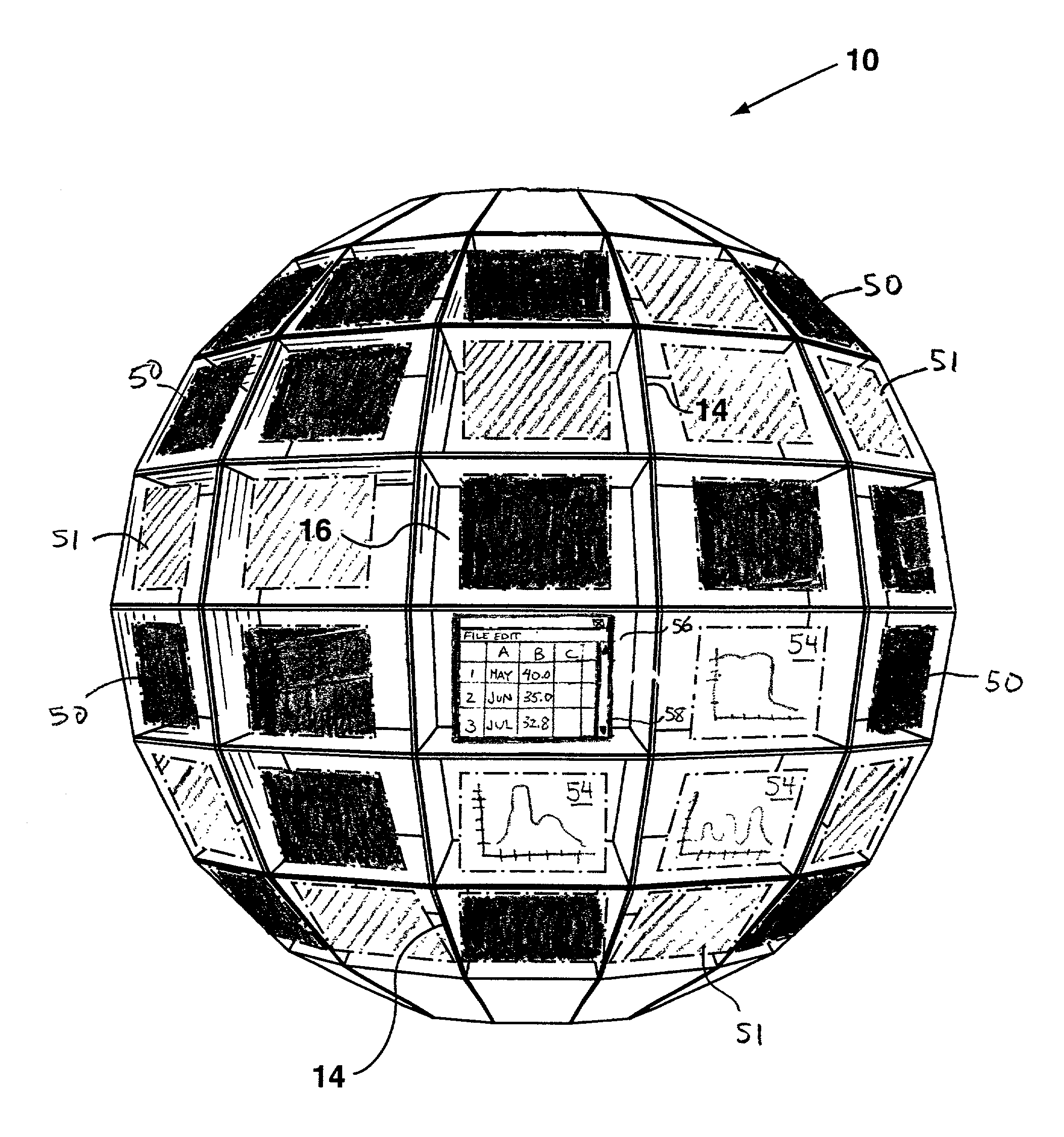
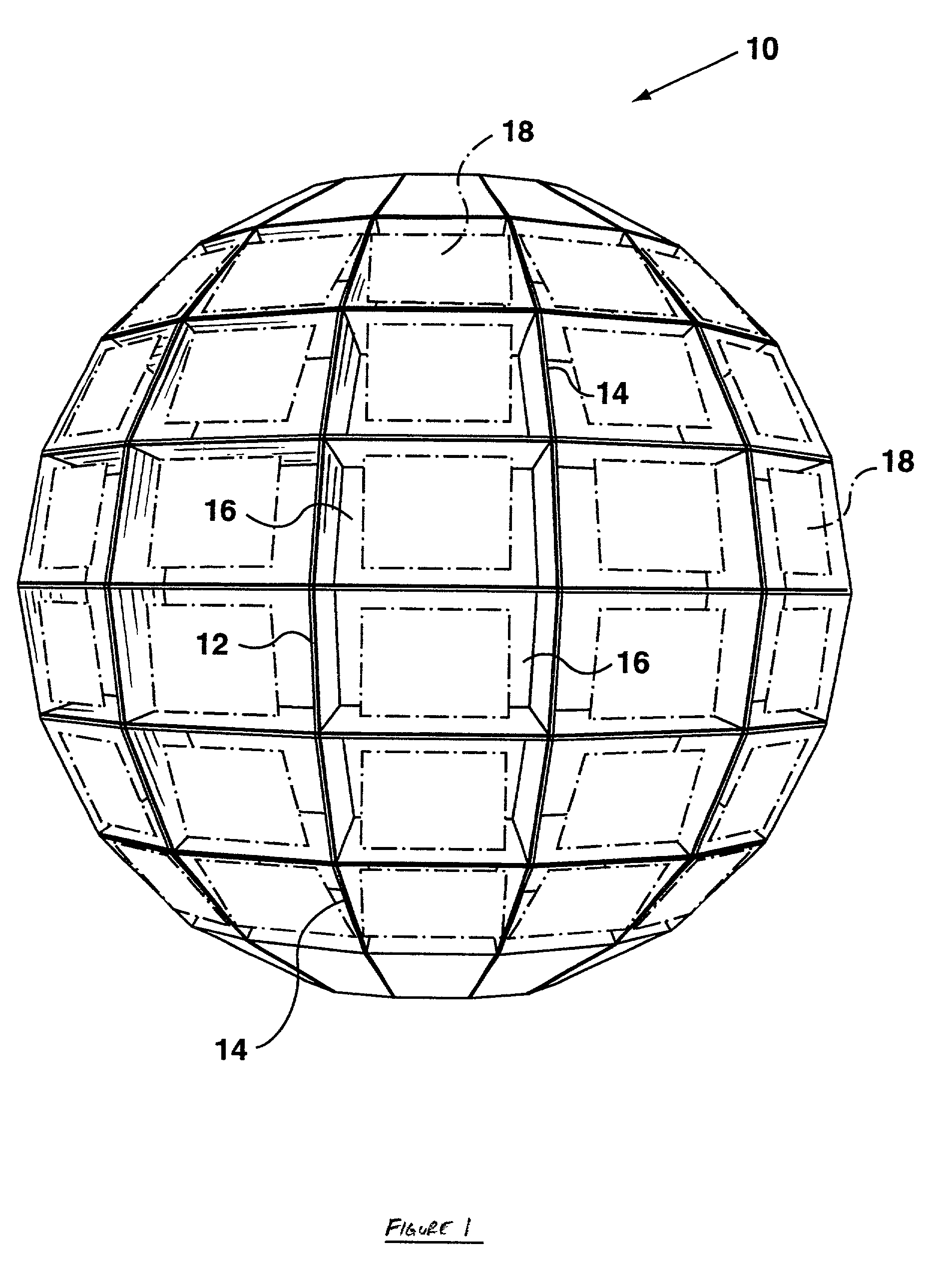
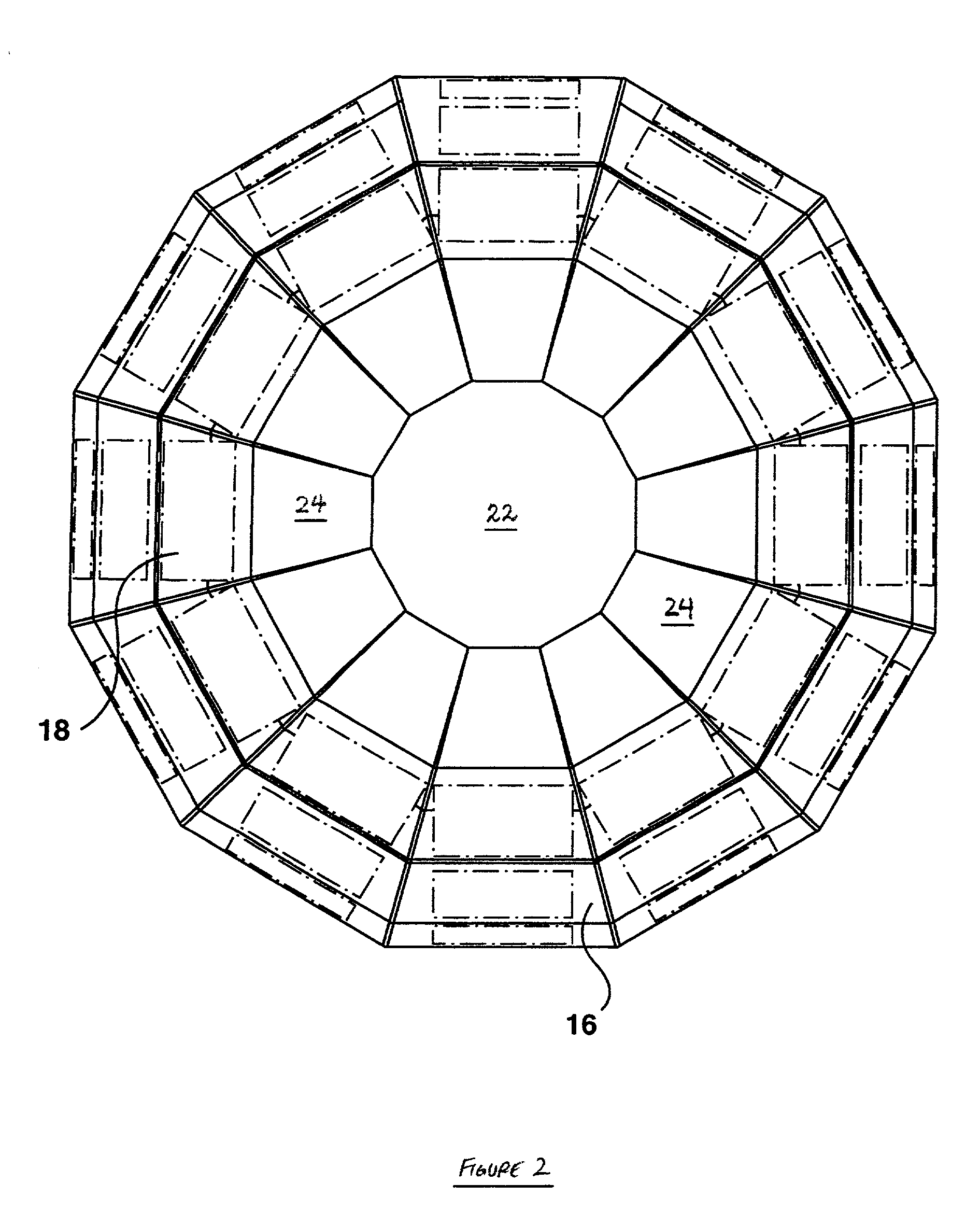
Method of representing information on a three-dimensional user interface
ActiveUS7412650B2Facilitate representation of dataHigh level of abstractionSpecial data processing applicationsDigital output to display deviceColor-codingColor code
The present invention relates to a method of representing information on a three-dimensional user interface having multiple portals, in which data is associated with each of the portals. A symbolic marker is associated with each of the portals according to a pre-specified scheme, and displayed in the respective portals. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the symbolic marker is a colored marker. By color-coding the portals, data associated with the portals can be classified into a number of categories to provide the user with a summary of the data on the three-dimensional user interface at a high level of abstraction. The three-dimensional user interface may be adapted to update the colored markers more efficiently, and to display them using less computing resources than would be required if more memory-sensitive visual cues were displayed.
Owner:VIZIBLE CORP
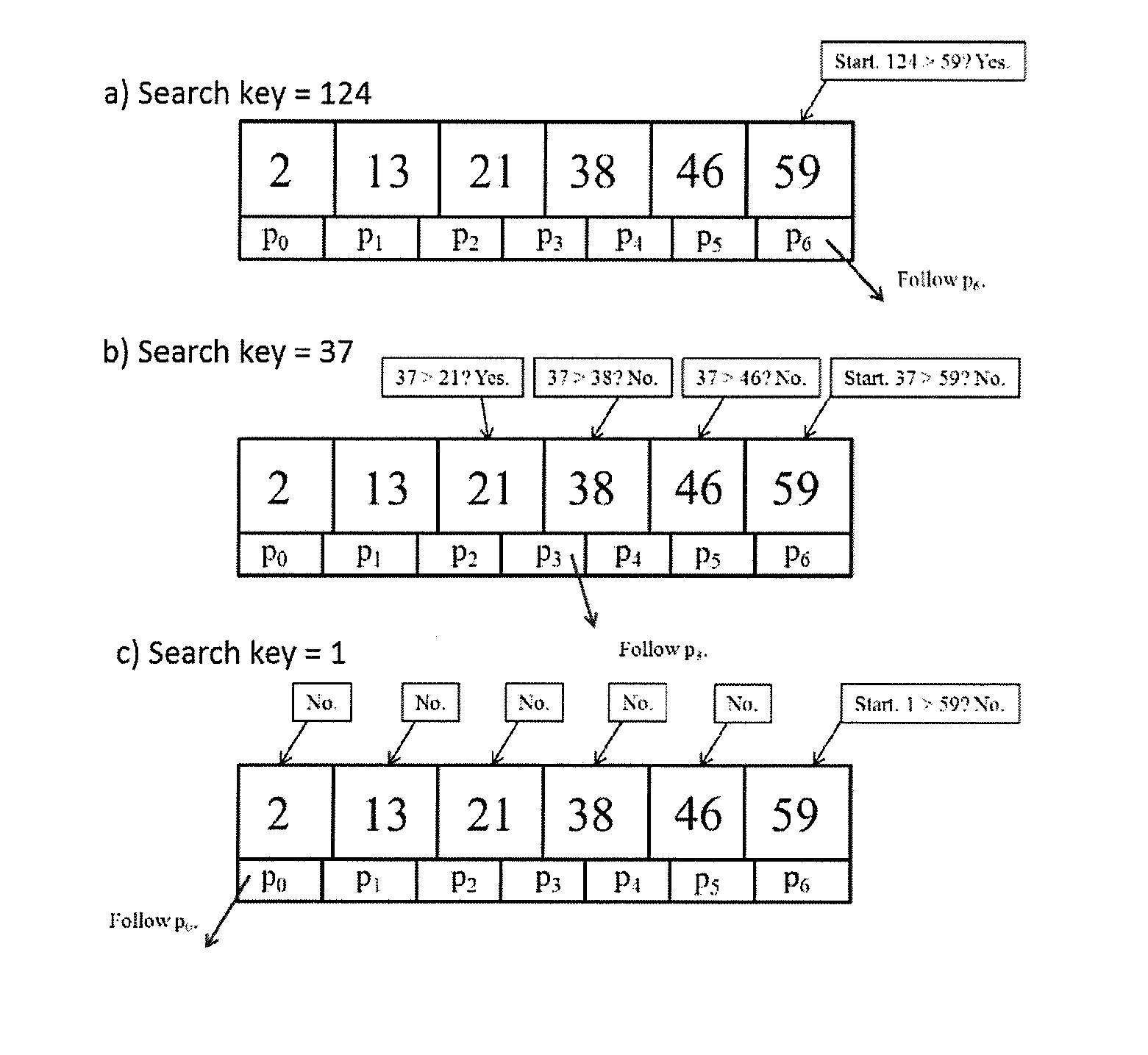
Indexing based on key ranges
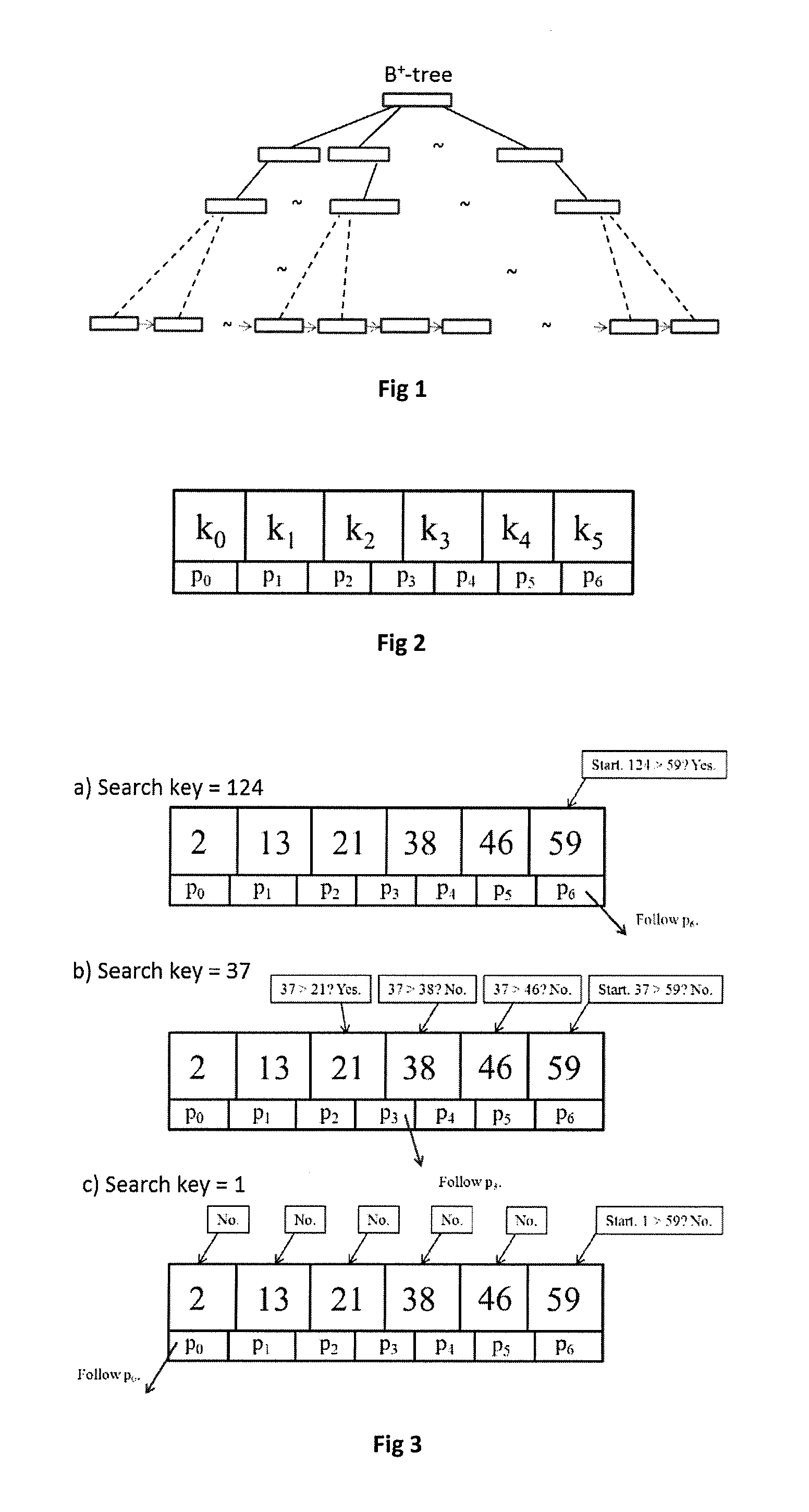
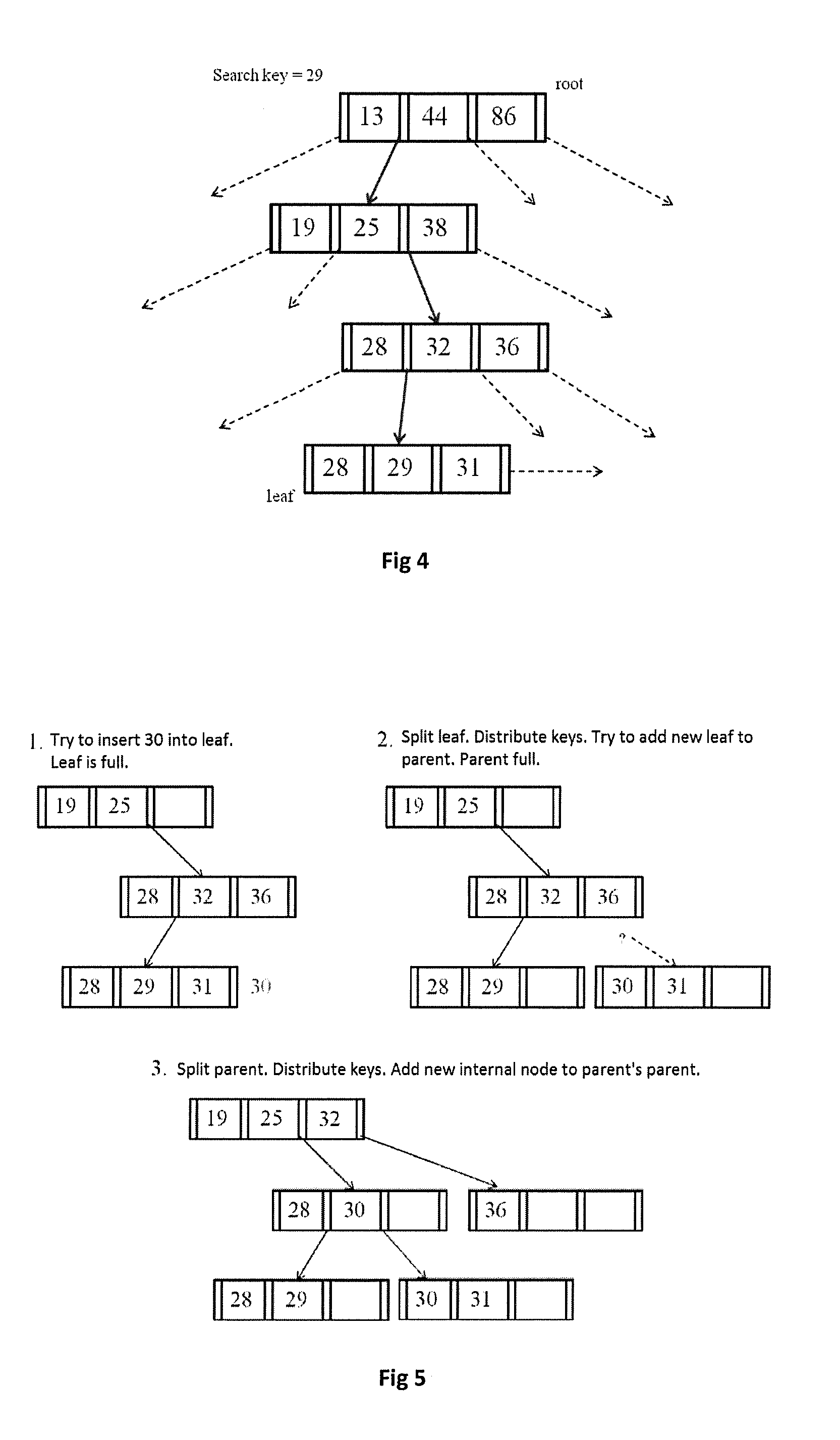
InactiveUS20130297613A1Fast executionLessDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsOne passTheoretical computer science
The present invention is a fast indexing technique that builds an indexing structure based on multi-level key ranges typically for large data storage systems. The invention is explained based on the B+-tree. It is designed to reside in main memory. Point searches and range searches are helped by early termination of searches for non-existent data. Range searches can be processed depth-first or breath-first. One group of multiple searches can be processed with one pass on the indexing structure to minimize total cost. Implementation options and strategies are explained to show the flexibility of this invention for easy adaption and high efficiency. Each branch of any level has exact and clear key boundaries, so that it is very easy to build or cache partial index for various purposes. The inventive indexing structure can be tuned to speed up queries directed at popular ranges of index or index ranges of particular interest to the user.
Owner:MONMOUTH UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and related methods for turbine cooling
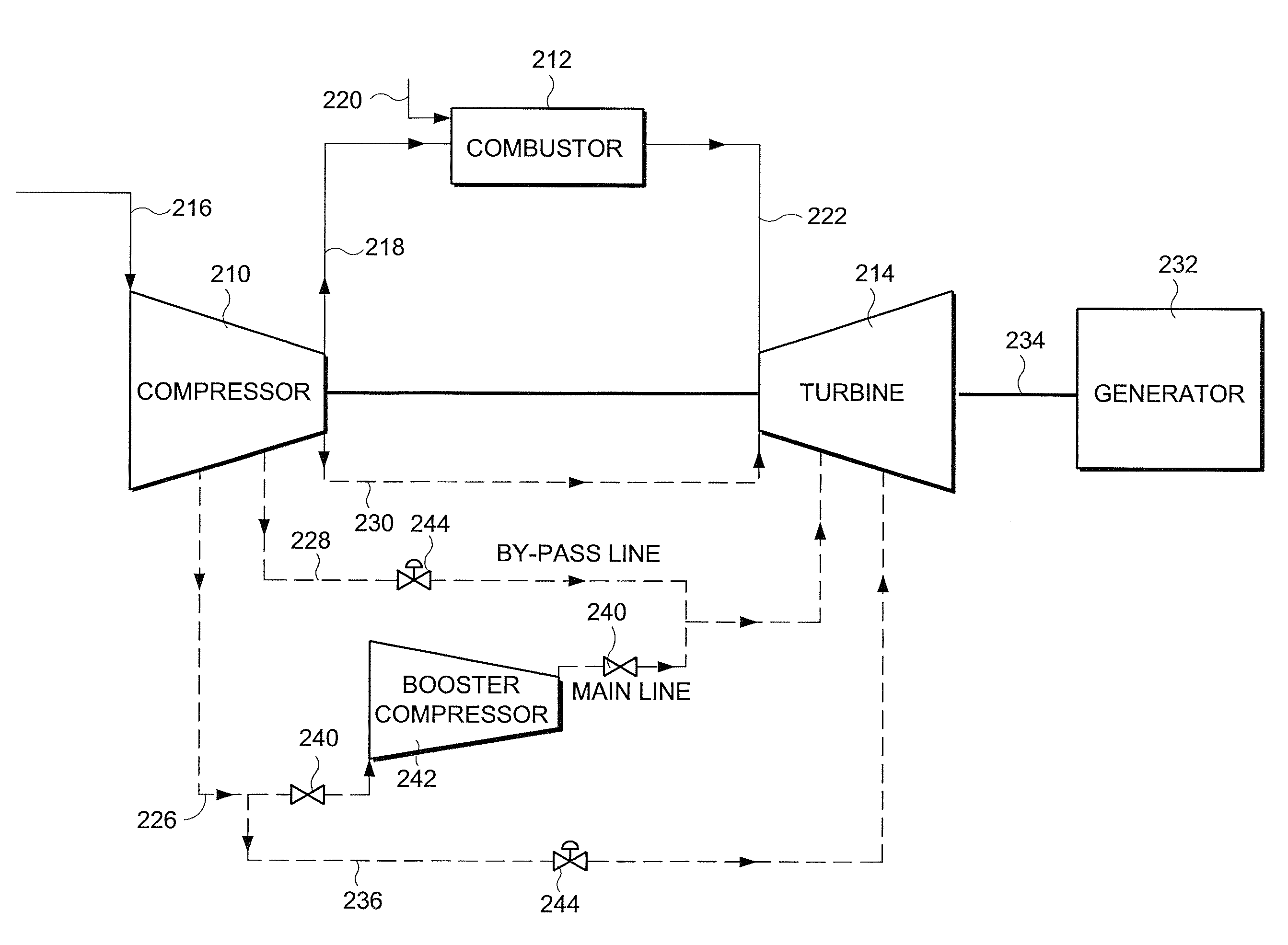
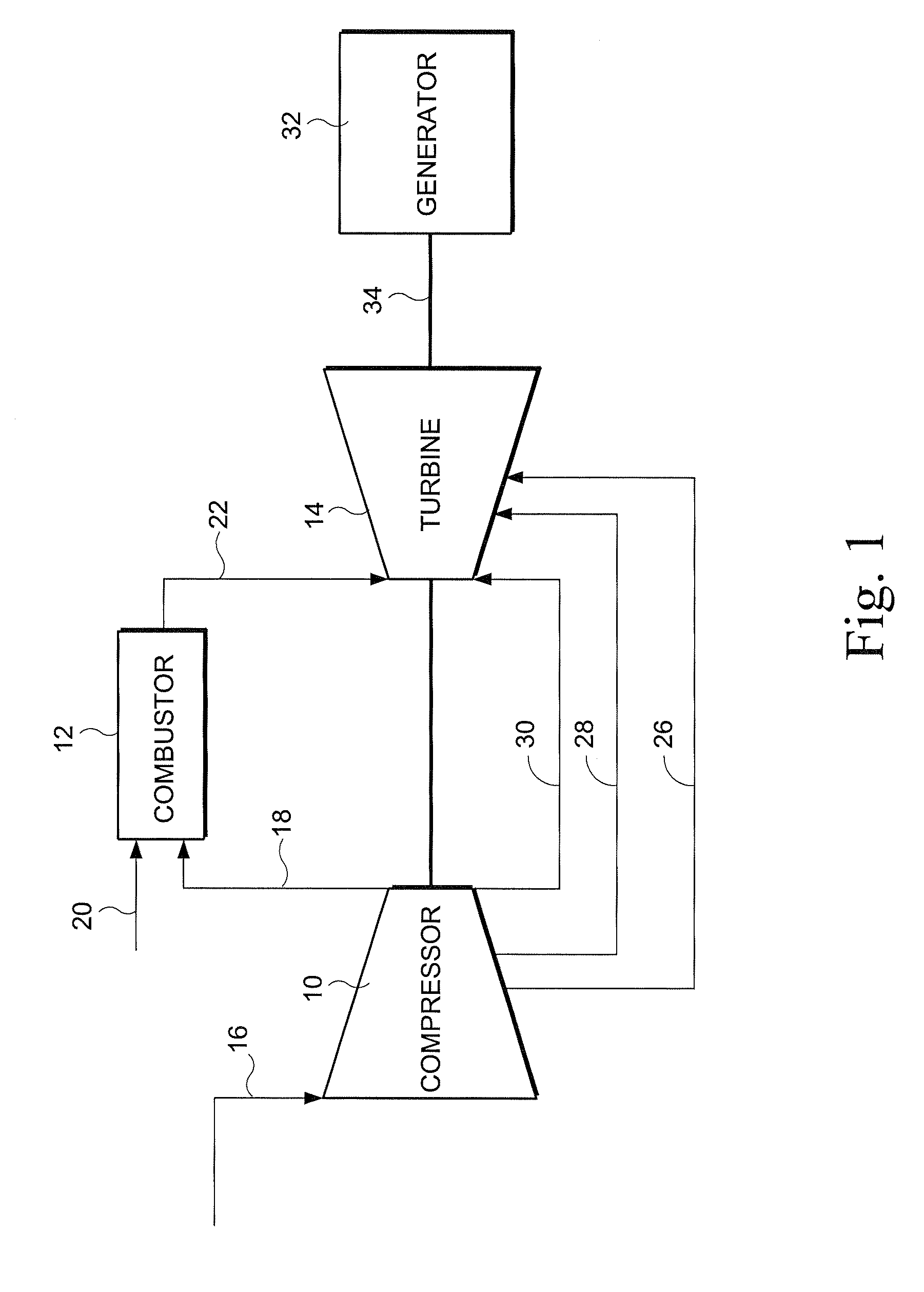
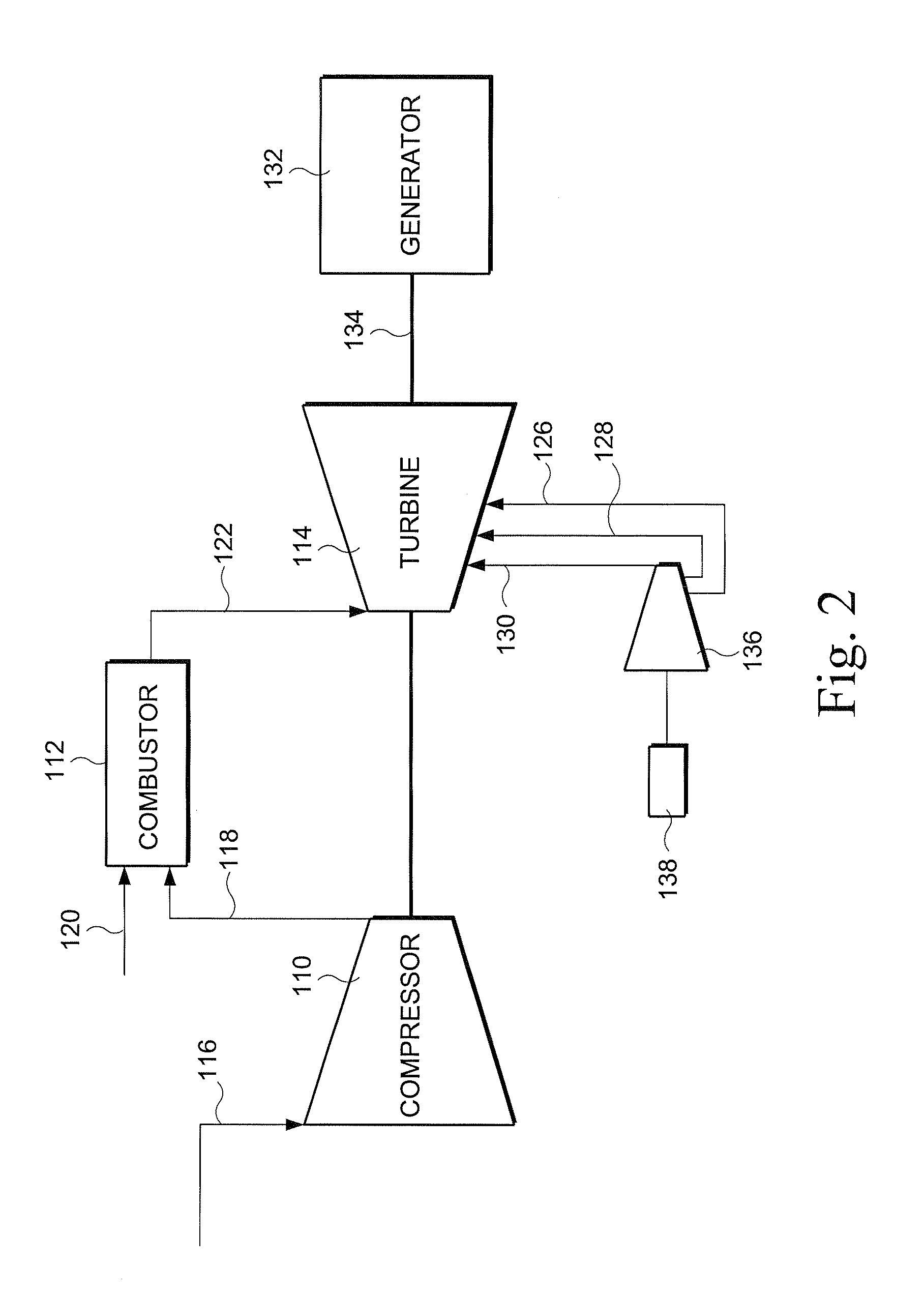
InactiveUS20090196736A1LessIncrease mass flowPump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingTurbineGas turbines
An apparatus and a method for cooling and / or sealing a gas turbine by selectively boosting the pressure of air extracted at a lower extraction stage is provided. The pressure of the extracted air is boosted by an external compressor before it becomes available for cooling and / or sealing the turbine components. A bypass line includes a higher extraction stage providing air for cooling the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
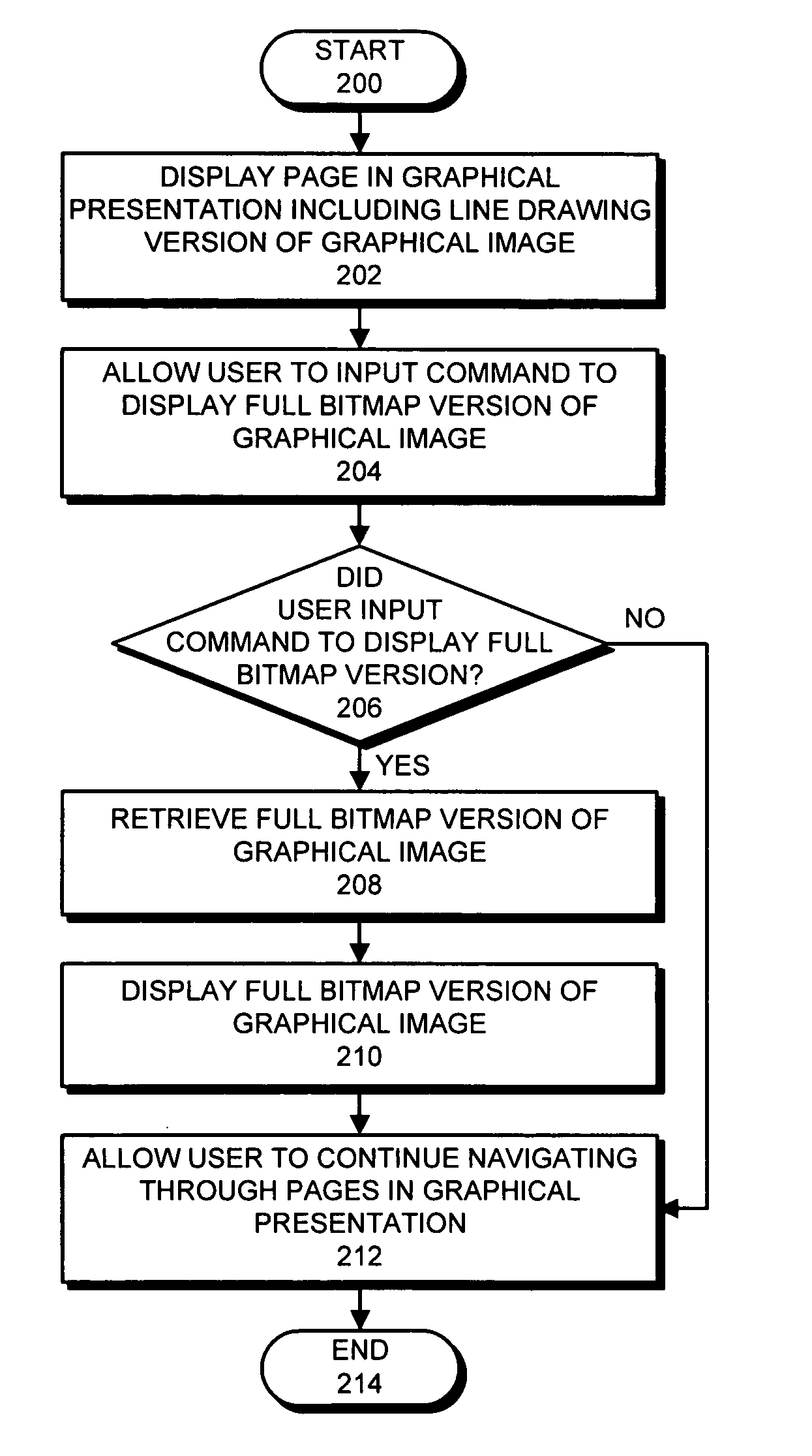
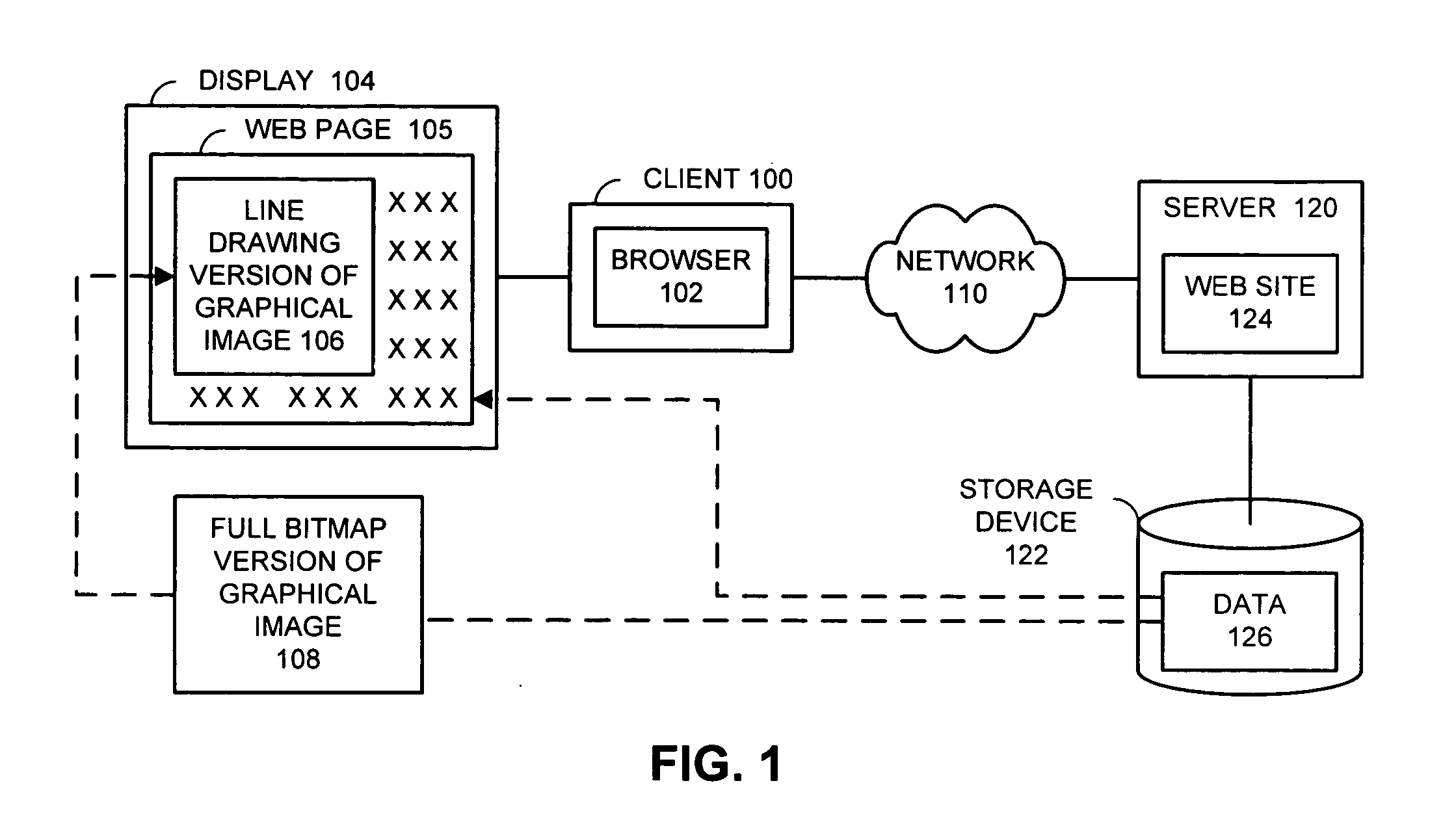
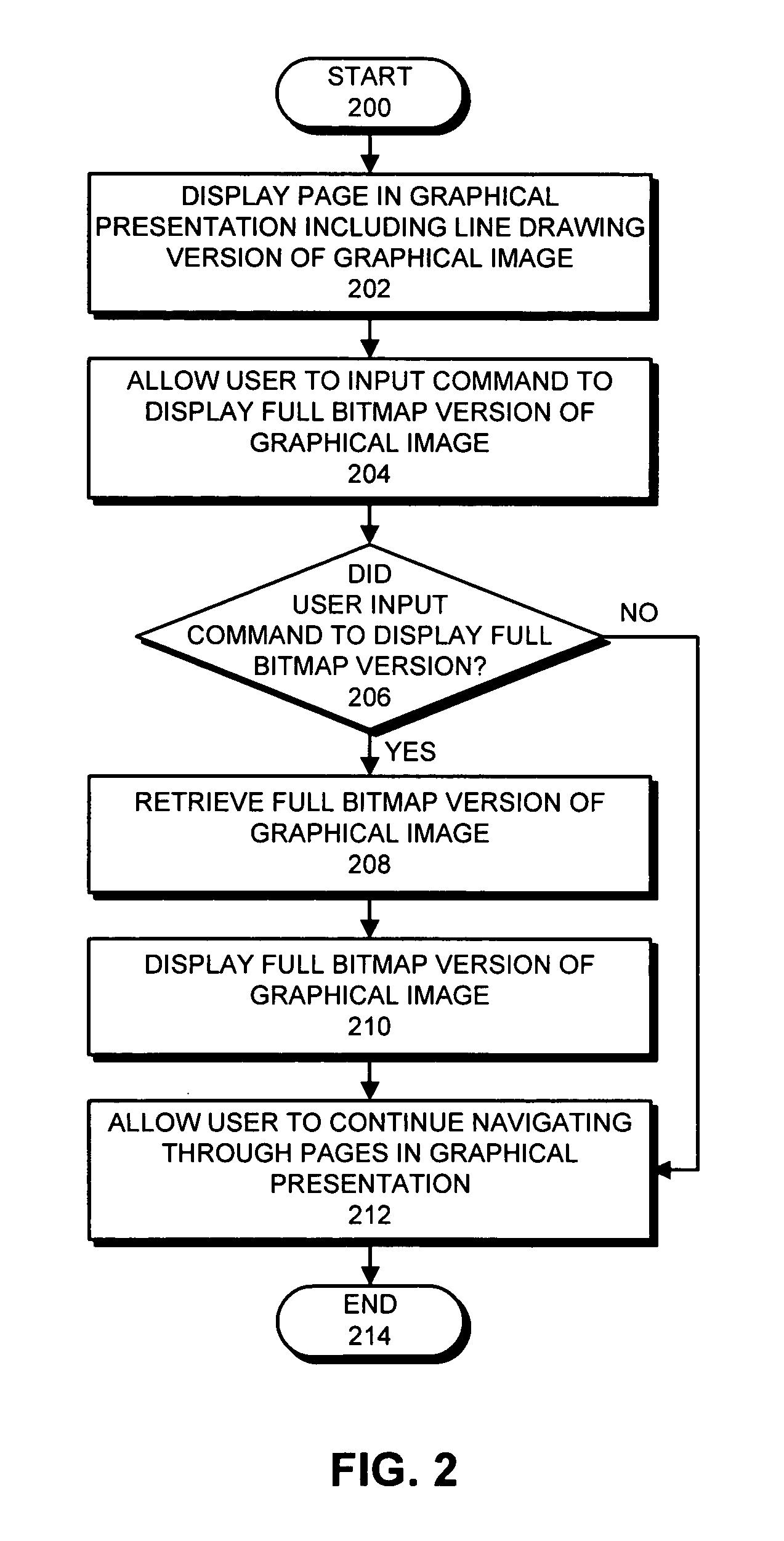
Method and apparatus for facilitating substitution of digital images with line drawings
InactiveUS20050183039A1Facilitate substitutionLessDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsUser input
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates substitution of a full bitmap version of a graphical image with a line drawing version of the graphical image in a graphical presentation. The system operates by displaying a page in the graphical presentation, which includes the line drawing version of the graphical image. Next, the system allows a user to input a command to display the full bitmap version of the graphical image. If the user inputs the command, the system retrieves the full bitmap version of the graphical image, and displays the full bitmap version of the graphical image. Note that displaying the line drawing version of the graphical image requires less data to be retrieved than displaying the full bitmap version of graphical image. Consequently, loading the line drawing version of the graphical image takes less time than loading the full bitmap version. Another embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates substitution of a full bitmap version of a graphical image with a line drawing version of the graphical image in a graphical presentation. The system receives the full bitmap version of the graphical image, and then produces the line drawing version of the graphical image from the full bitmap version of the graphical image. Next, the system inserts the line drawing version of the graphical image into a page in the graphical presentation, and then links the full bitmap version of the graphical image into the graphical presentation so that selecting the line drawing version of the graphical image causes the full bitmap version of the graphical image to be displayed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Multipart chew toy
InactiveUS7063044B2LessSofter chew portionsOther apparatusTaming and training devicesEngineeringCompanion animal
Owner:HARTZ MOUNTAIN THE
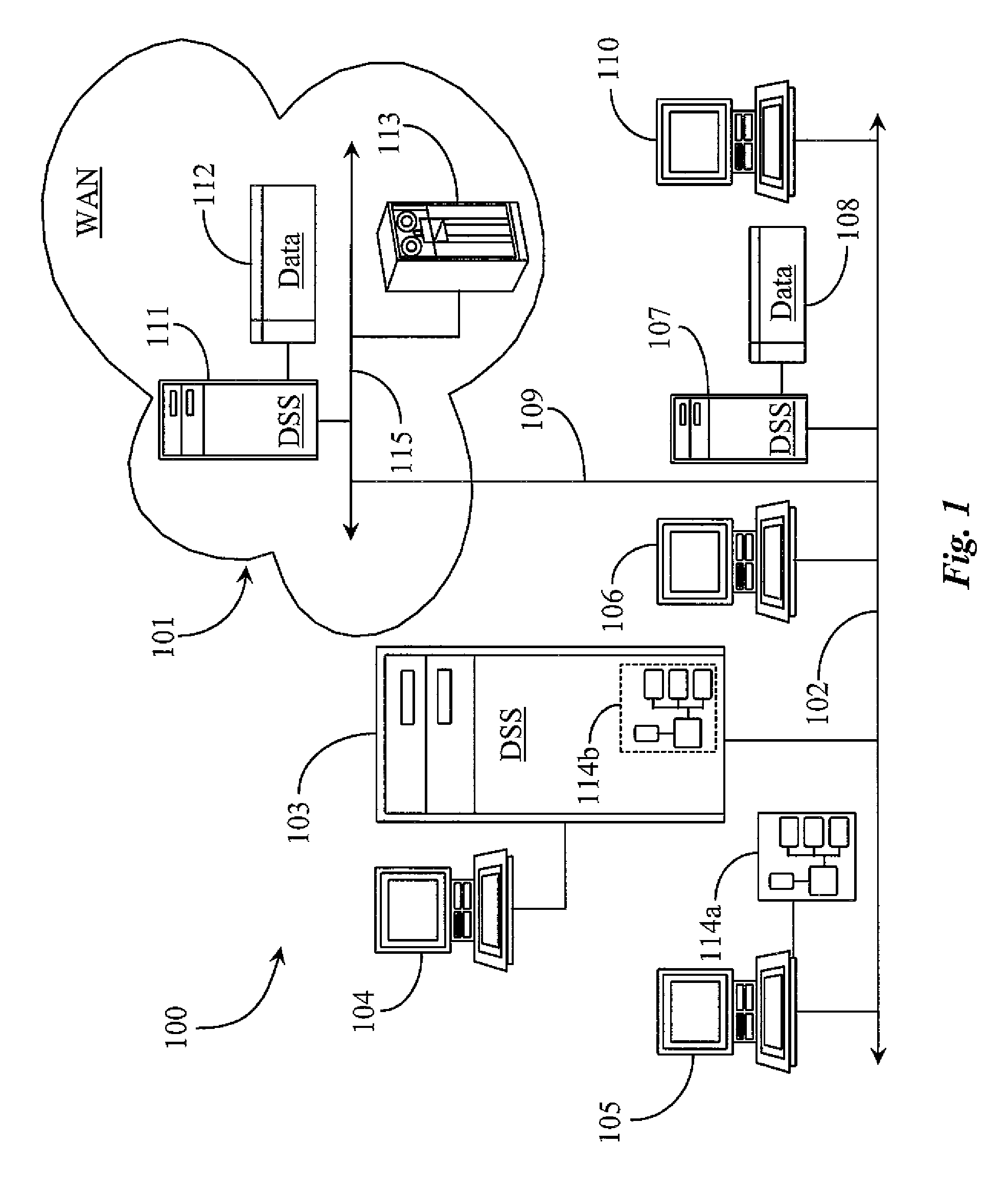
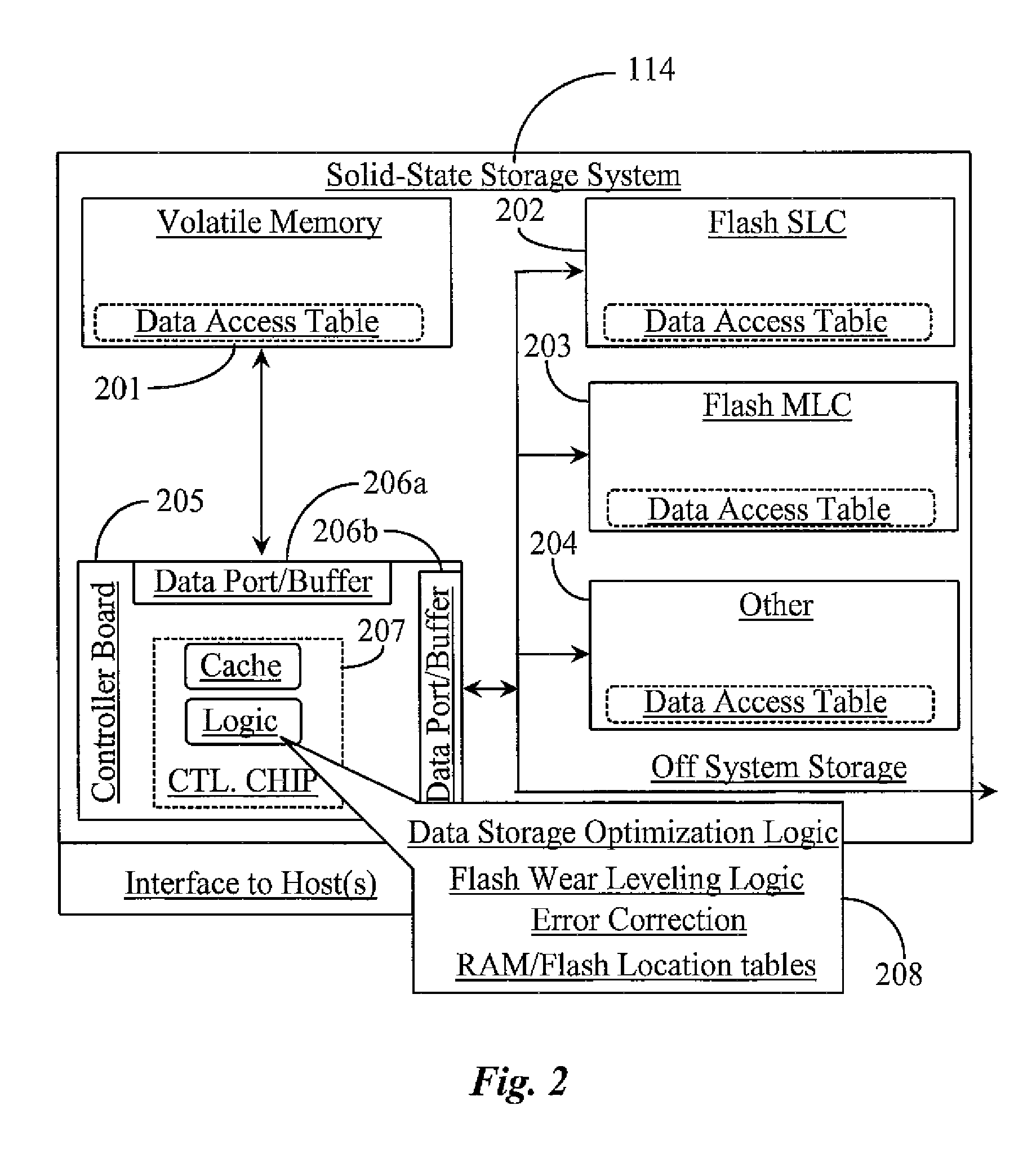
Priority Ordered Multi-Medium Solid-State Storage System and Methods for Use
InactiveUS20110191523A1Low costIncrease write speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-state storageTracking data
A hierarchical data-storage system has a volatile storage medium, a first non-volatile storage medium, and a controller including a ranking engine tracking data writes to each of the memory mediums. Each medium is associated with a pre-set capacity threshold, and the controller, upon the volatile medium reaching its pre-set threshold, identifies one or more blocks of data as least-frequently written to the volatile medium, copies the data in those blocks to the non-volatile medium, and marks those blocks as available for new data writes, and the controller, upon the non-volatile medium reaching its pre-set threshold, identifies one or more blocks of data as least-frequently written to the non-volatile medium, and marks those blocks as available for new data writes from the volatile medium.
Owner:DATARAM MEMORY
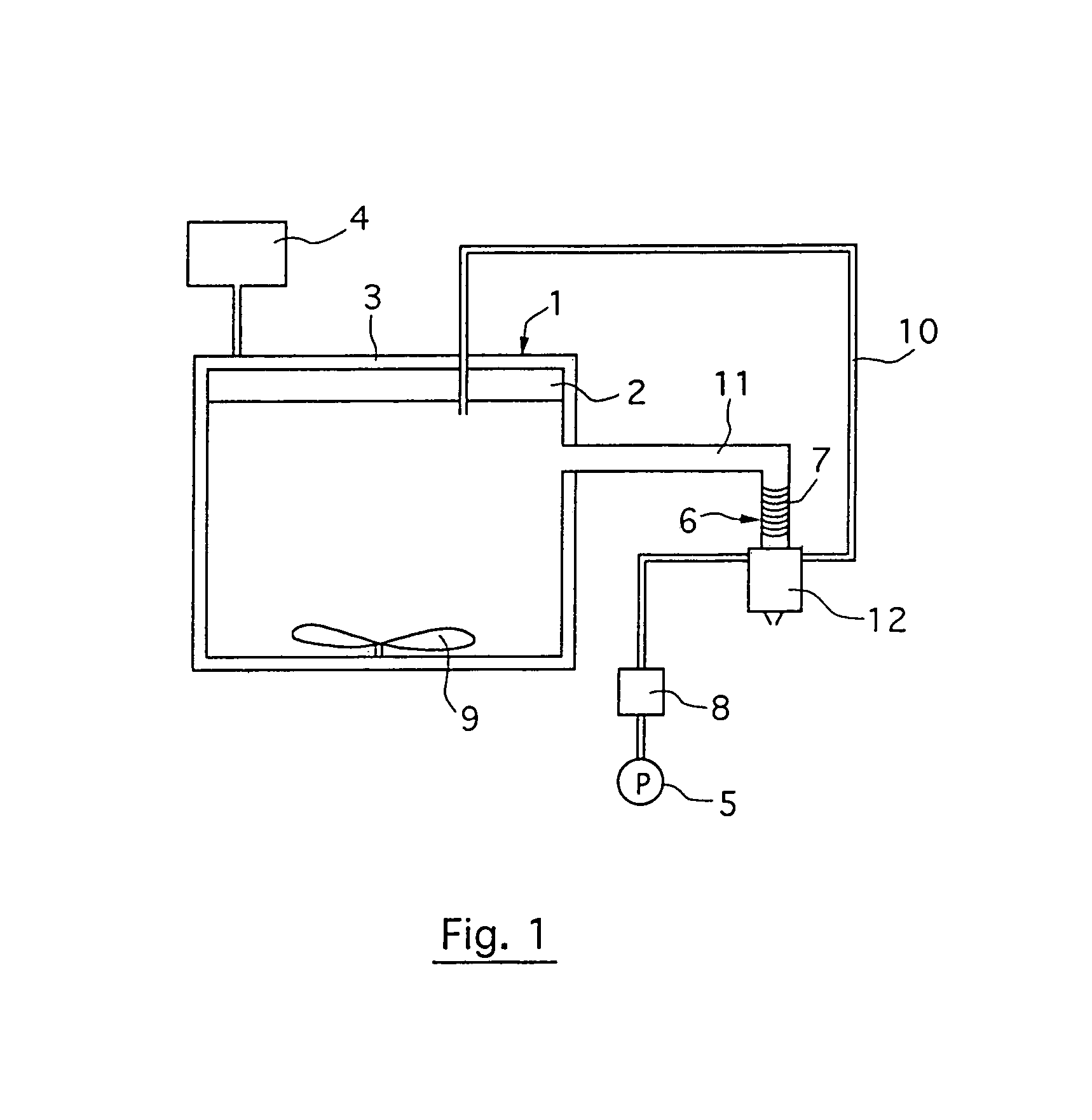
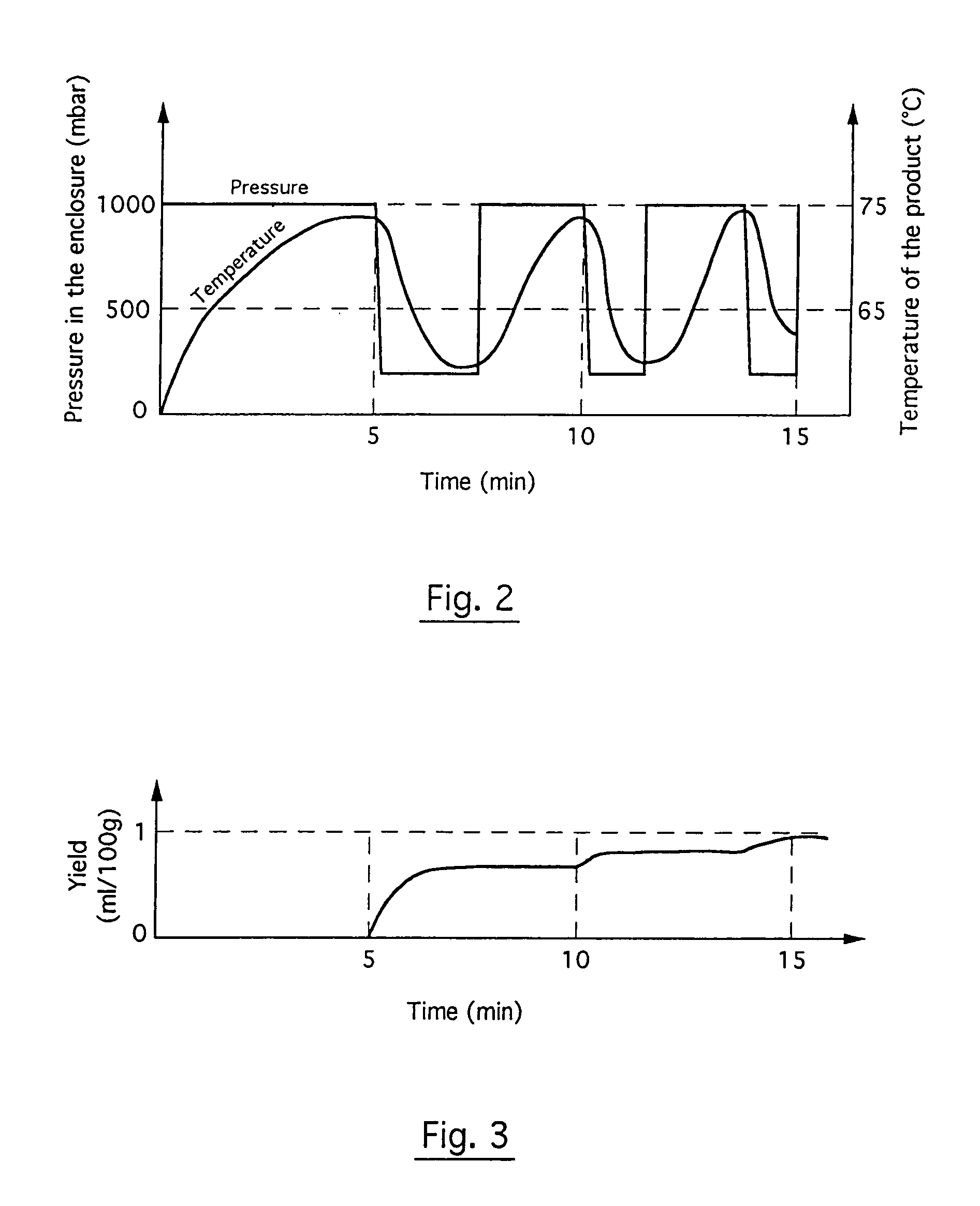
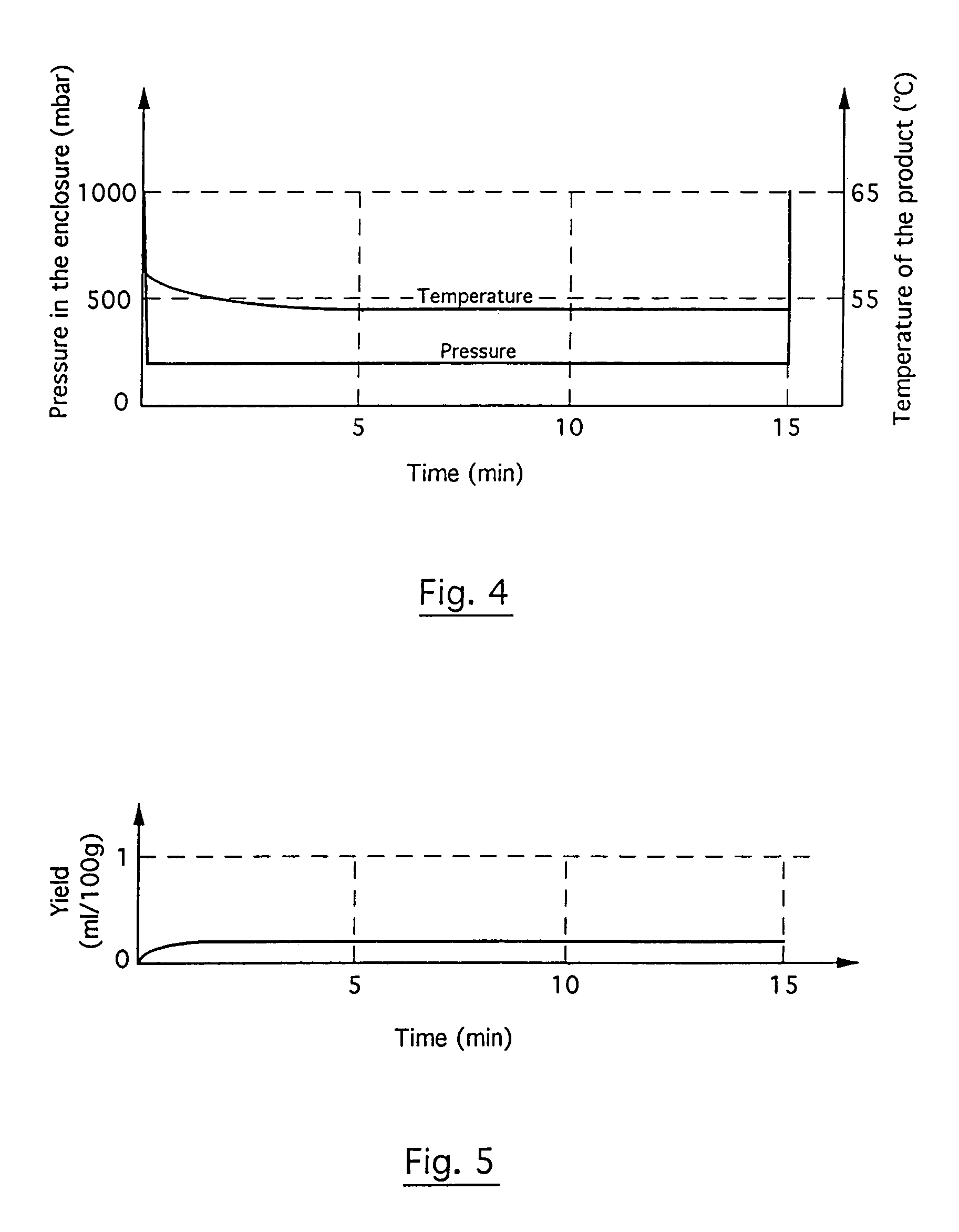
Method and plant for solvent-free microwave extraction of natural products
InactiveUS7001629B1LessIncrease in factorBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDough treatmentSolventSolvent free
A microwave extraction method involves the steps of placing biological material in an enclosure without any solvent whatsoever and exposing the solvent-free biological material to microwave radiation to free at least some of the natural product, and then separating any residual biological material from the extracted natural product. Additionally, the microwave extraction method involves the steps of applying reduced pressure in the enclosure during the microwave radiation stage and heating the enclosure during at least most of the microwave radiation stage to compensate for the temperature drop resulting from water evaporation from the biological material.
Owner:AMADEITE
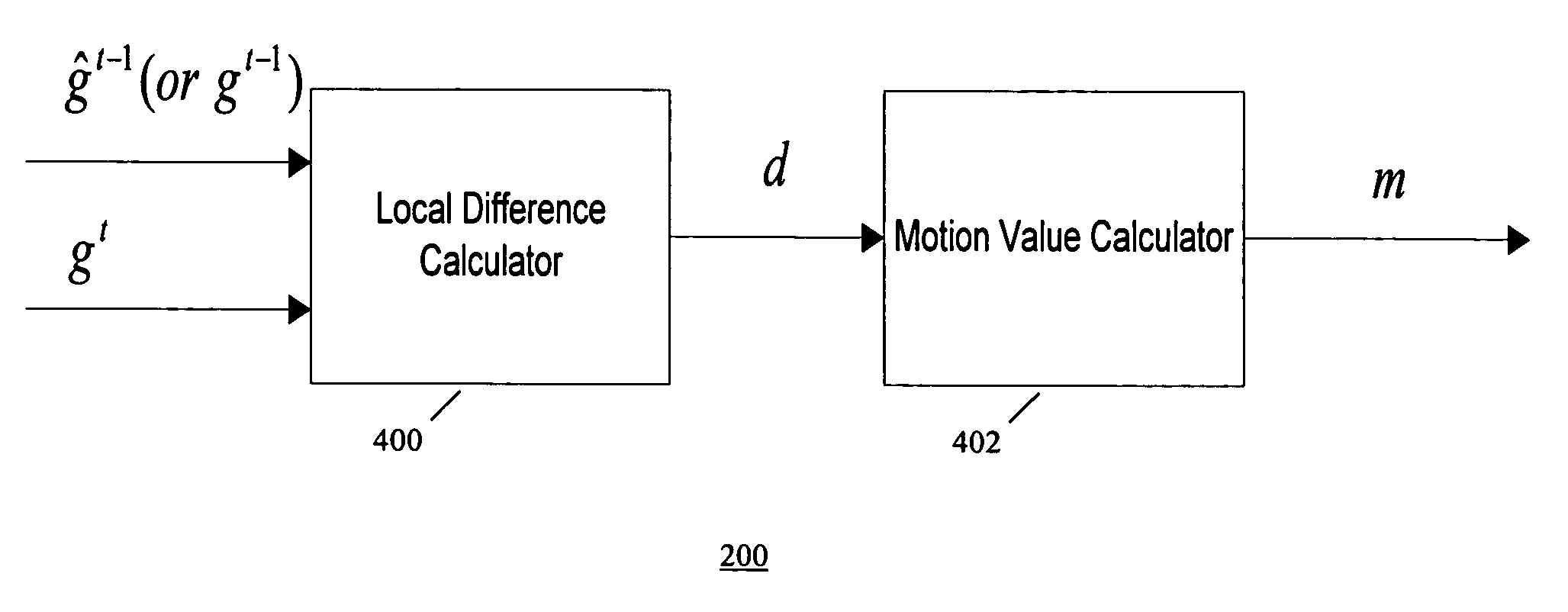
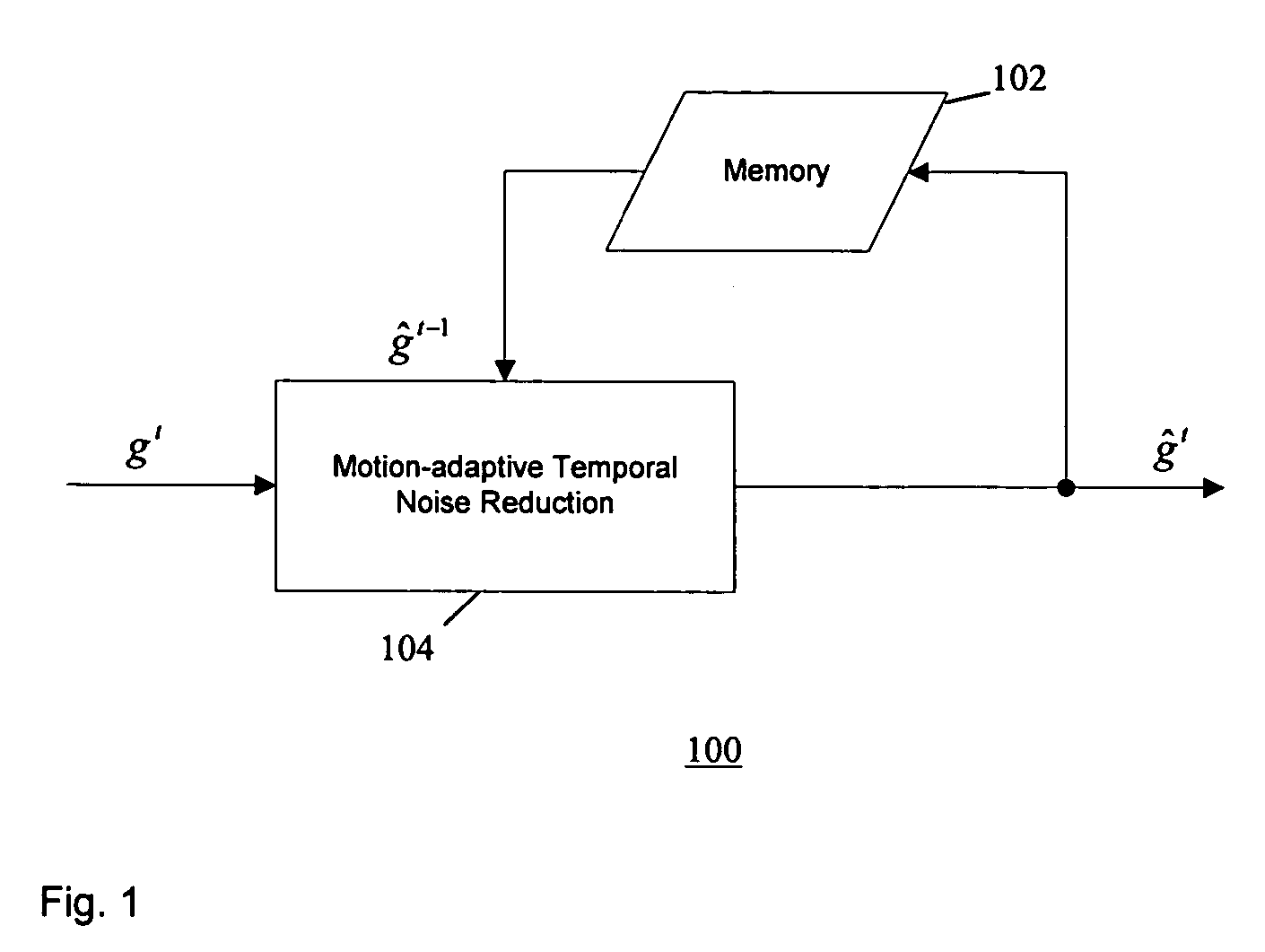
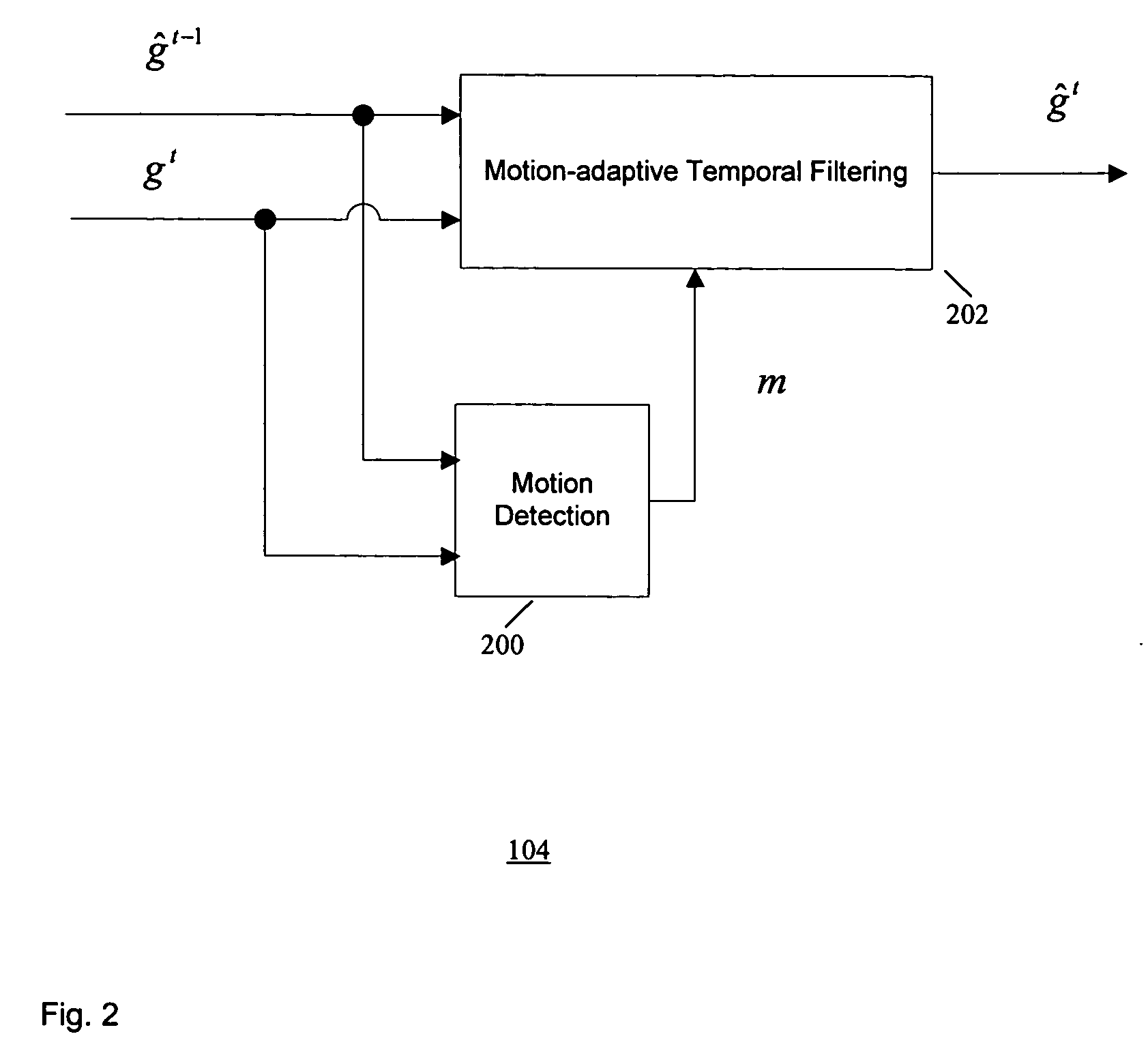
Method of temporal noise reduction in video sequences
InactiveUS20060139494A1LessMaintain performanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionVideo sequence
A motion-adaptive temporal noise reducing method and system for reducing noise in a sequence of video frames is provided. Temporal noise reduction is applied to two video frames, wherein one video frame is the current input noisy frame, and the other video frame is a previous filtered frame stored in memory. Once the current frame is filtered, it is saved into memory for filtering the next incoming frame. A motion-adaptive temporal filtering method is applied for noise reduction. Pixel-wise motion information between the current frame and the previous (filtered) frame in memory is examined. Then the pixels in the current frame are classified into motion region and non-motion region relative to the previous (filtered) frame. In a non-motion region, pixels in the current frame are filtered along the temporal axis. In a motion region, the temporal filter is switched off to avoid motion blurring.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
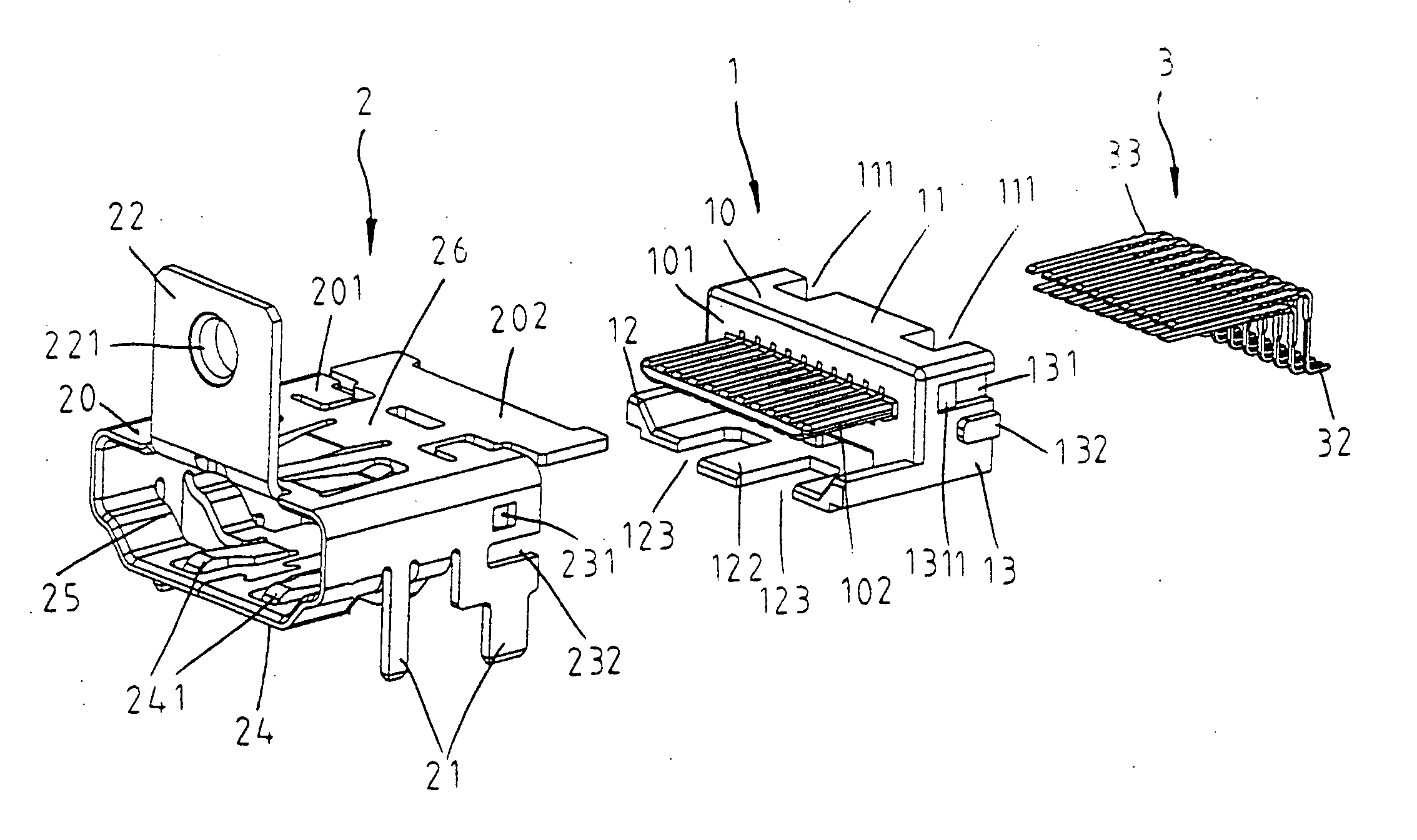
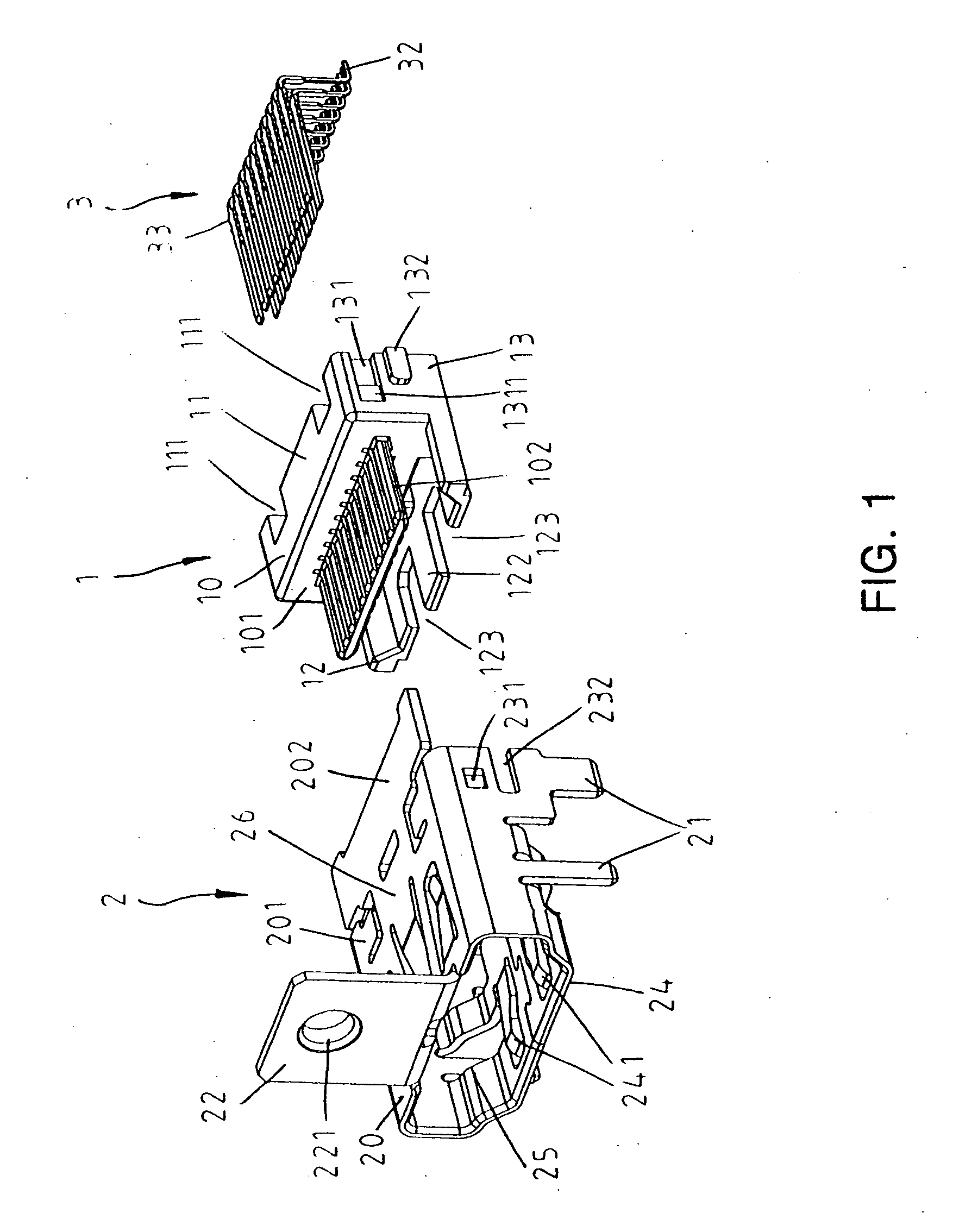
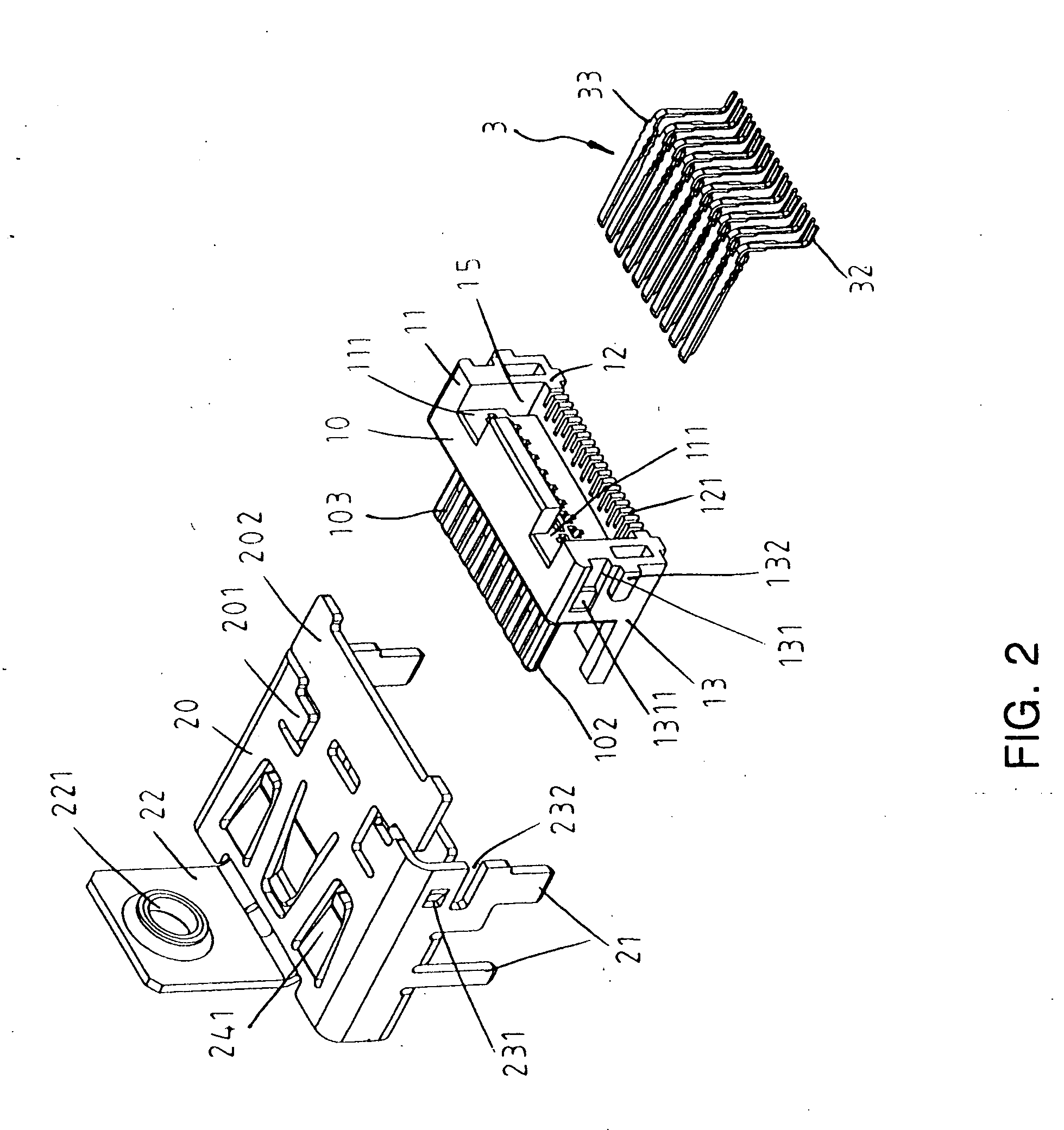
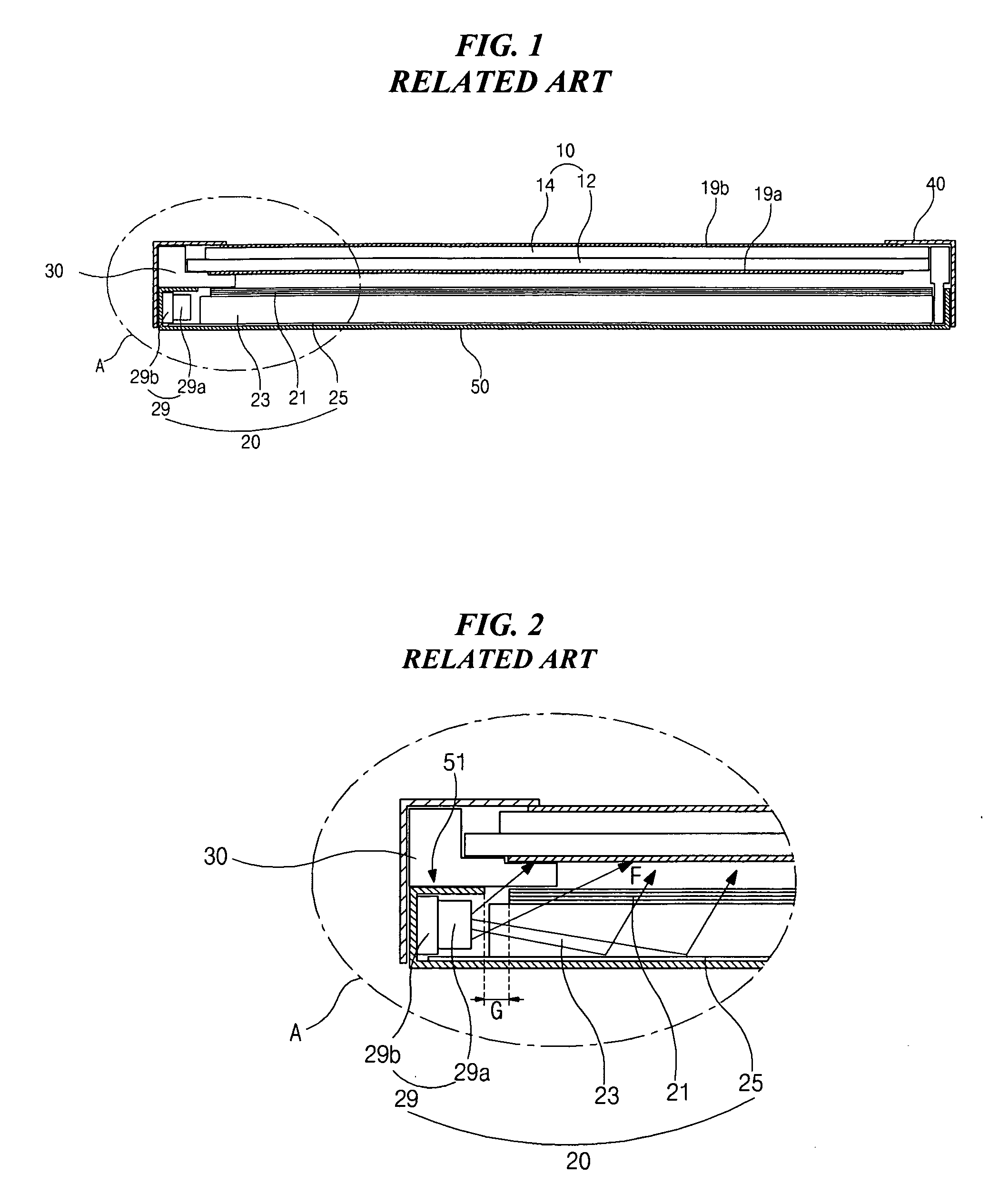
HDMI connector
InactiveUS20050186843A1Quality improvementHigh fidelity video signalTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsEngineeringFront edge
The present invention provides a high definition multimedia interface (HDMI) connector with various types through combinations of the outer metallic shells and the inner terminal modules of the HDMI connector. The outer metallic shell may exhibit various types including with or without the presence of flange on the front edge of said outer metallic shell and with or without the application of the surface mount technology (SMT) to the solder pins. Therefore, the HDMI of the present invention is applicable to provide different types of connector to fulfill market requirements through the combinations of different types of module.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
Backlight unit and liquid crystal display module including the same
InactiveUS20100165241A1LessAvoid problemsOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
A backlight unit for a display device includes a light guide plate; a reflective sheet under the light guide plate; a lamp at least one side of the light guide plate and providing a light into the light guide plate; and an optical sheet disposed on the light guide plate and including a first lenticular sheet, the first lenticular sheet including a base film for diffusing the light through the light guide plate, a first lenticular lens disposed on a front surface of the base film and having a half-cylinder shape and a first printing pattern on at least one edge of a rear surface of the base film.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
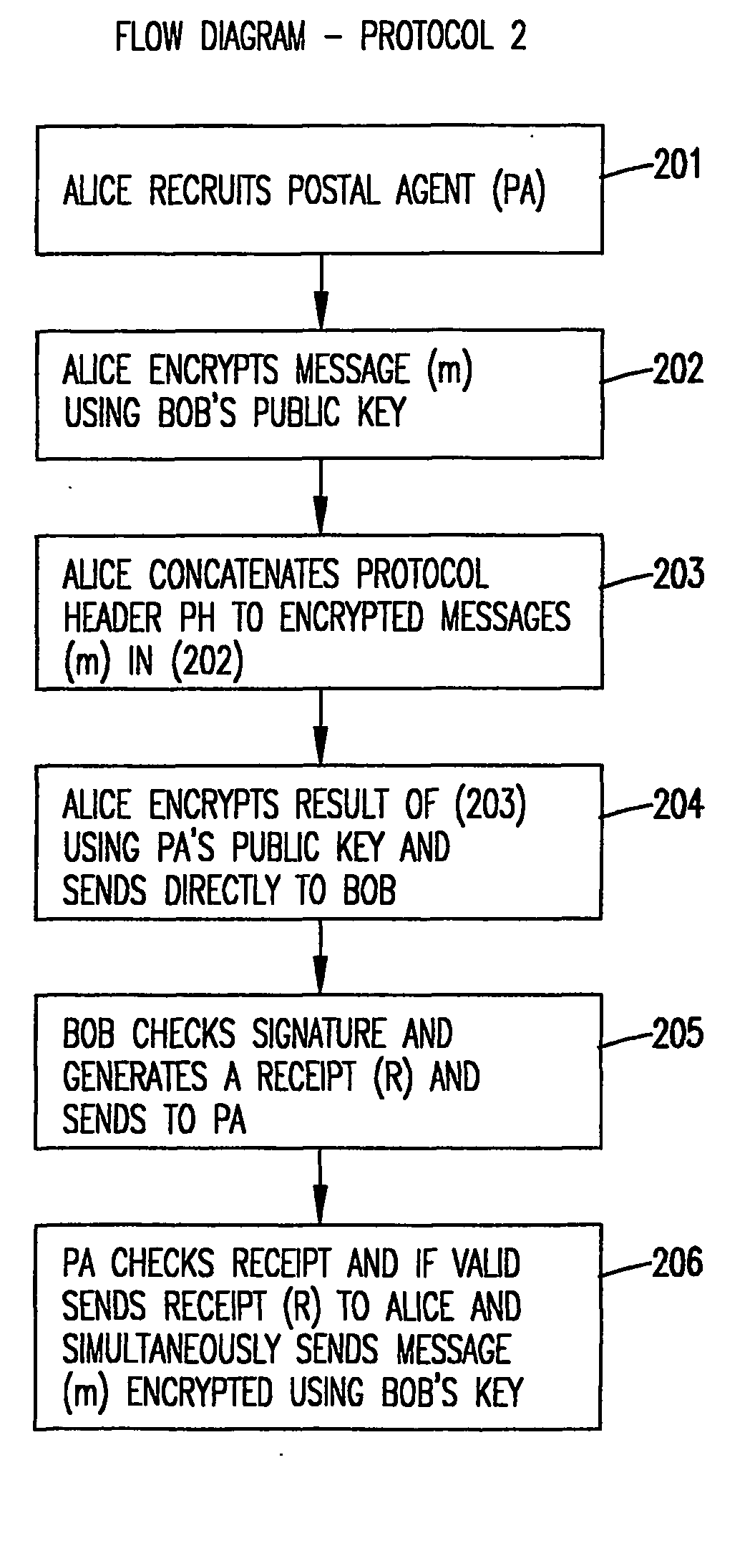
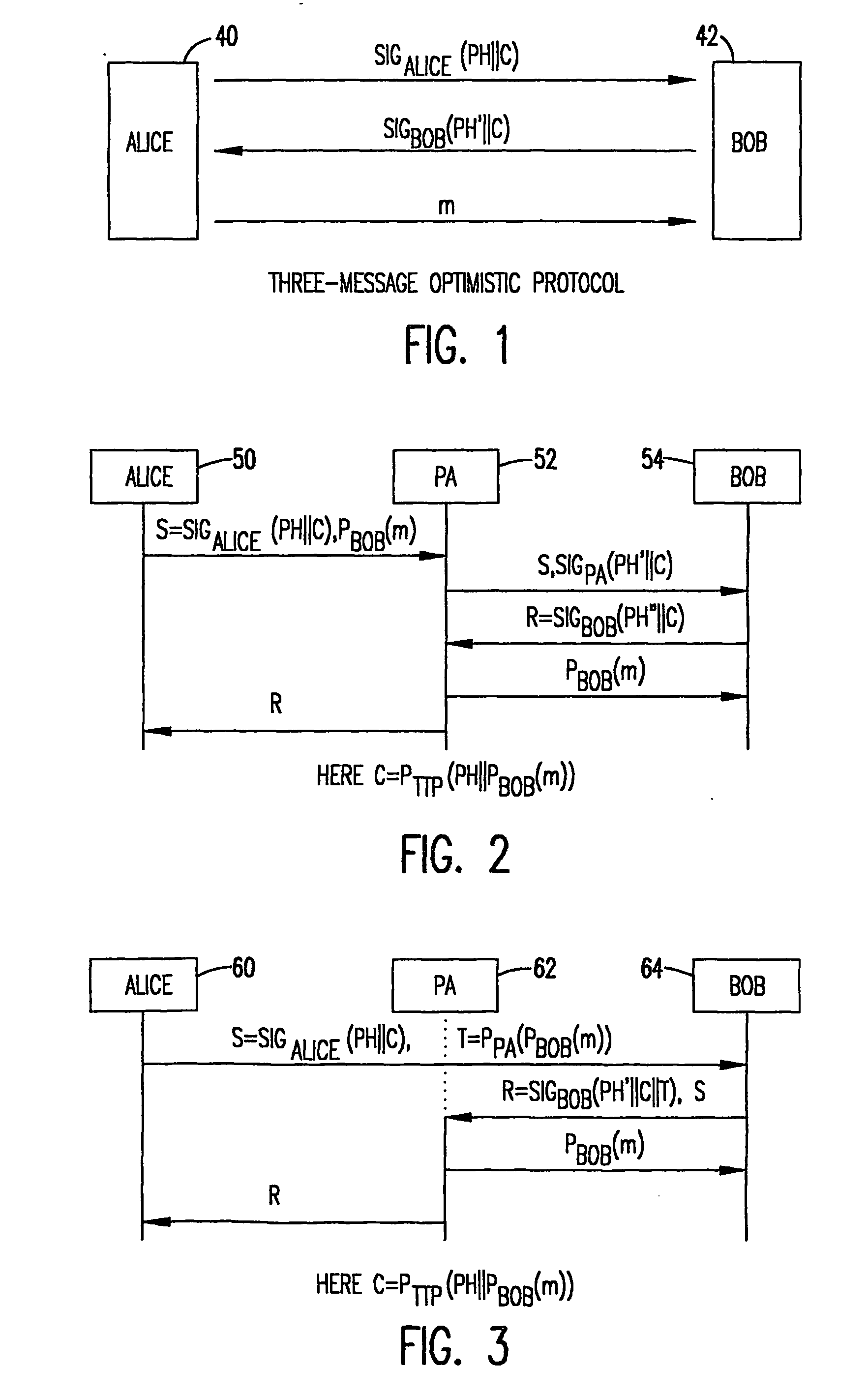
Intermediated delivery scheme for asymmetric fair exchange of electronic items
InactiveUS20040073790A1ConfidenceHard and expensiveKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationElectronic informationAsymmetry
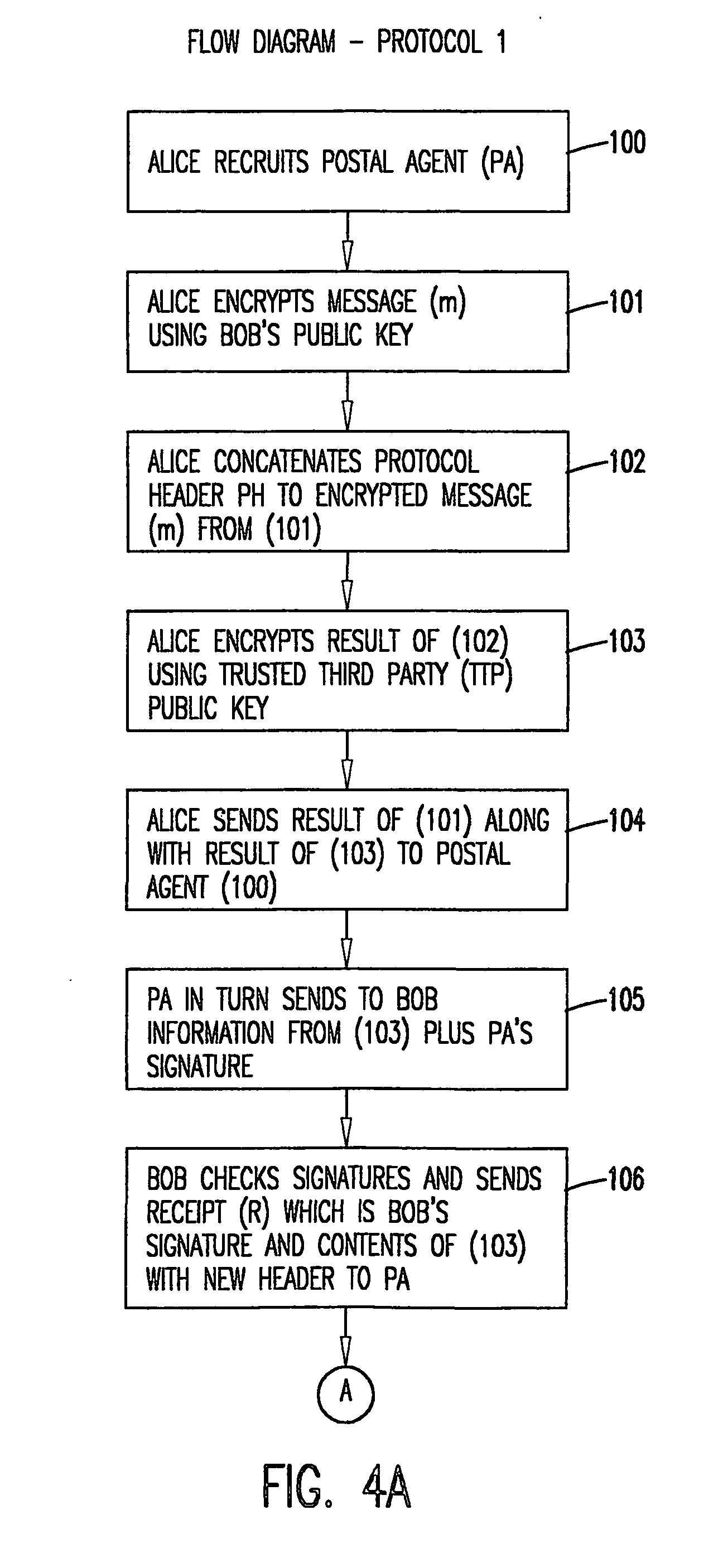
A methodology and system is used to facilitate the exchange of valued electronic information in a confidential, fair, and efficient manner. Either of two protocols can be employed that used encryption and electronic signatures to effectively guarantee origin and identity of sender and receiver in the exchange of valued information and requires timely response by both sender and receiver. The protocols rely upon one or a plurality of postal agents (servers) to provide secured online exchange of the information by arranging an efficient validation of the required signatures and information being exchanged between the sender and receiver. In the event of a breakdown in the exchange between sender and receiver, the use of a trusted third party (TTP) allows for fair and pre-agreed arbitration based upon the encrypted information and electronic signatures of the sender and receiver. The method does not require the use of the TTP unless a dispute arises.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Hybrid drive train for a motor vehicle and method for operating the hybrid drive train
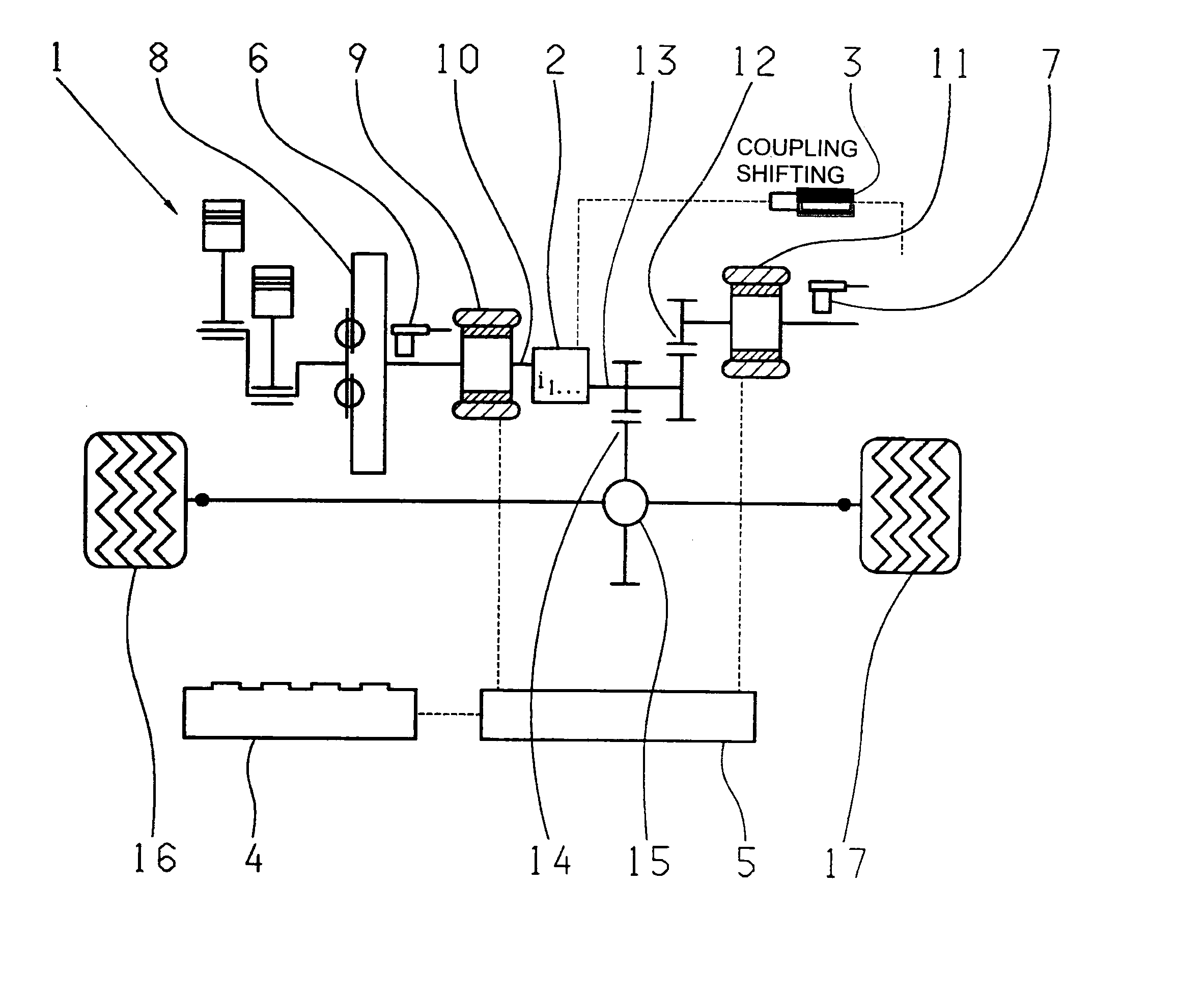
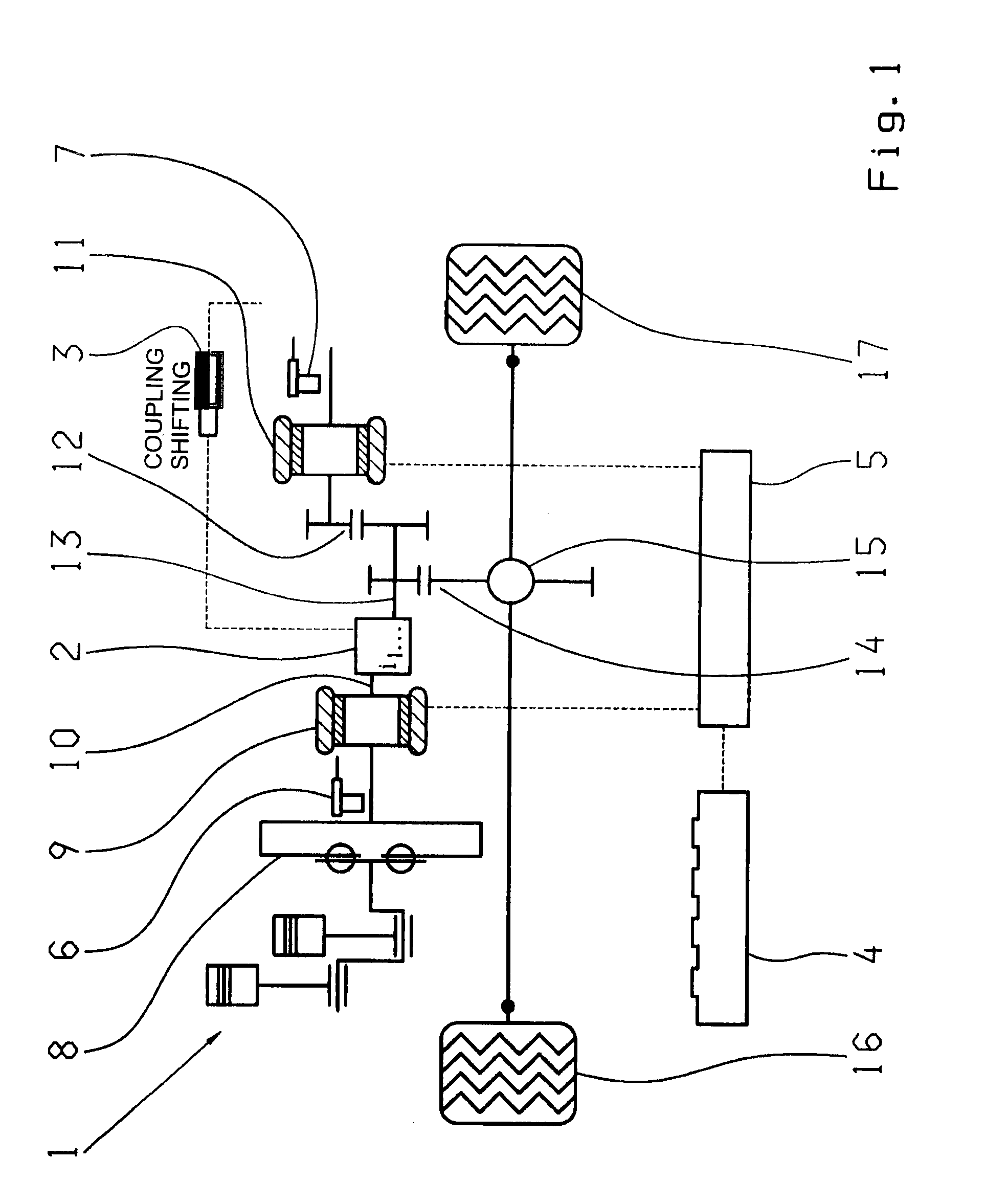
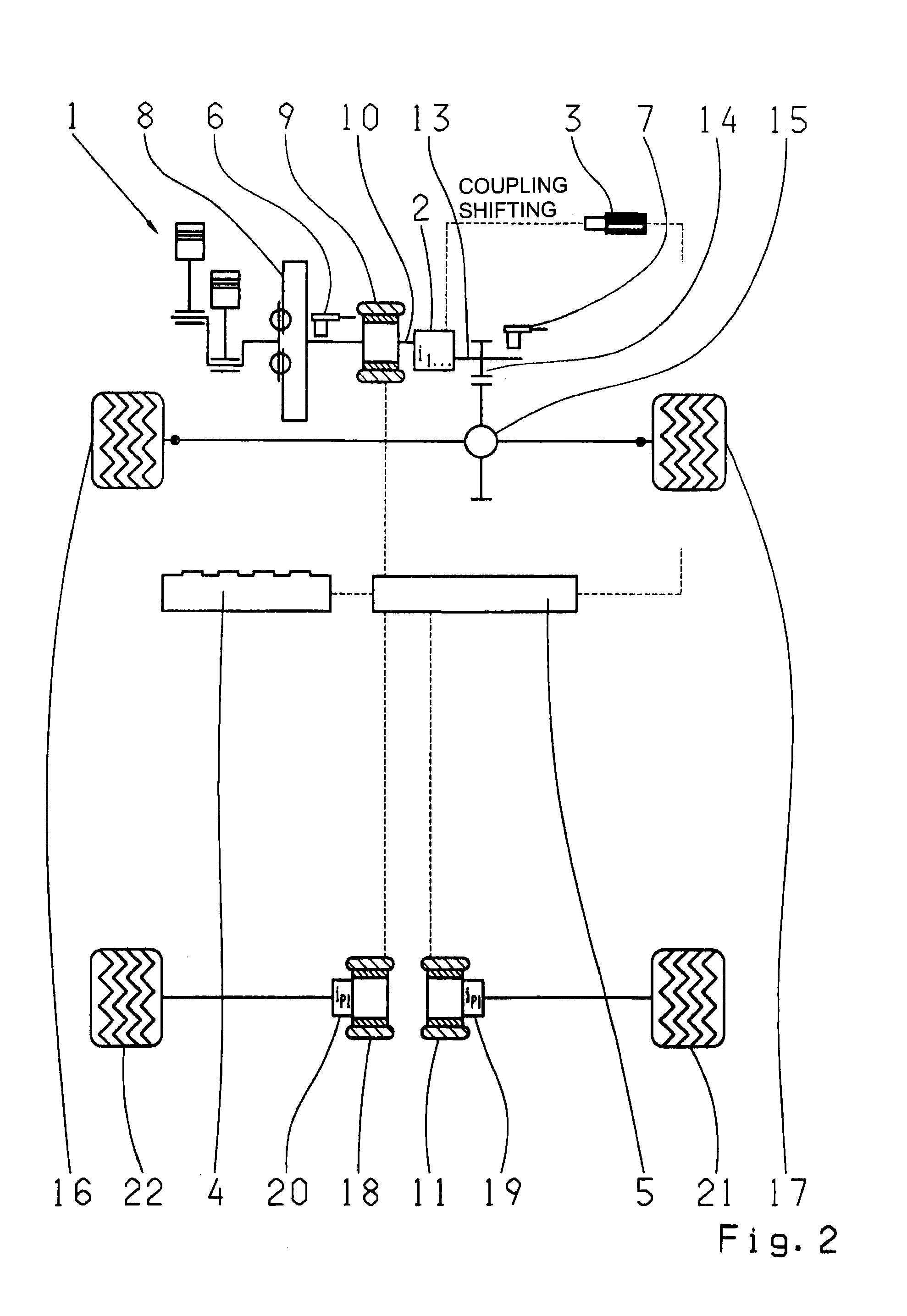
InactiveUS20110098151A1Simple engagementLessElectric propulsion mountingToothed gearingsMobile vehicleElectric machine
A hybrid drive train for a motor vehicle which comprises an combustion engine, at least two electric machines, a multi-gear transmission with transmission input and output shafts, a shift actuator, at least one energy storage device and a control unit arranged such that the combustion engine and the rotor of the first electric machine are connected to the transmission input shaft, and the transmission output shaft is connected either permanently or via a gearwheel arrangement or a chain or toothed-belt drive mechanism to at least one wheel or to a differential of a first vehicle axle. The rotor of the second electric machine is connected either permanently or via a chain or toothed-belt drive mechanism, either to at least one wheel or to a differential of the first vehicle axle, or to at least one wheel or to a differential of a second vehicle axle.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
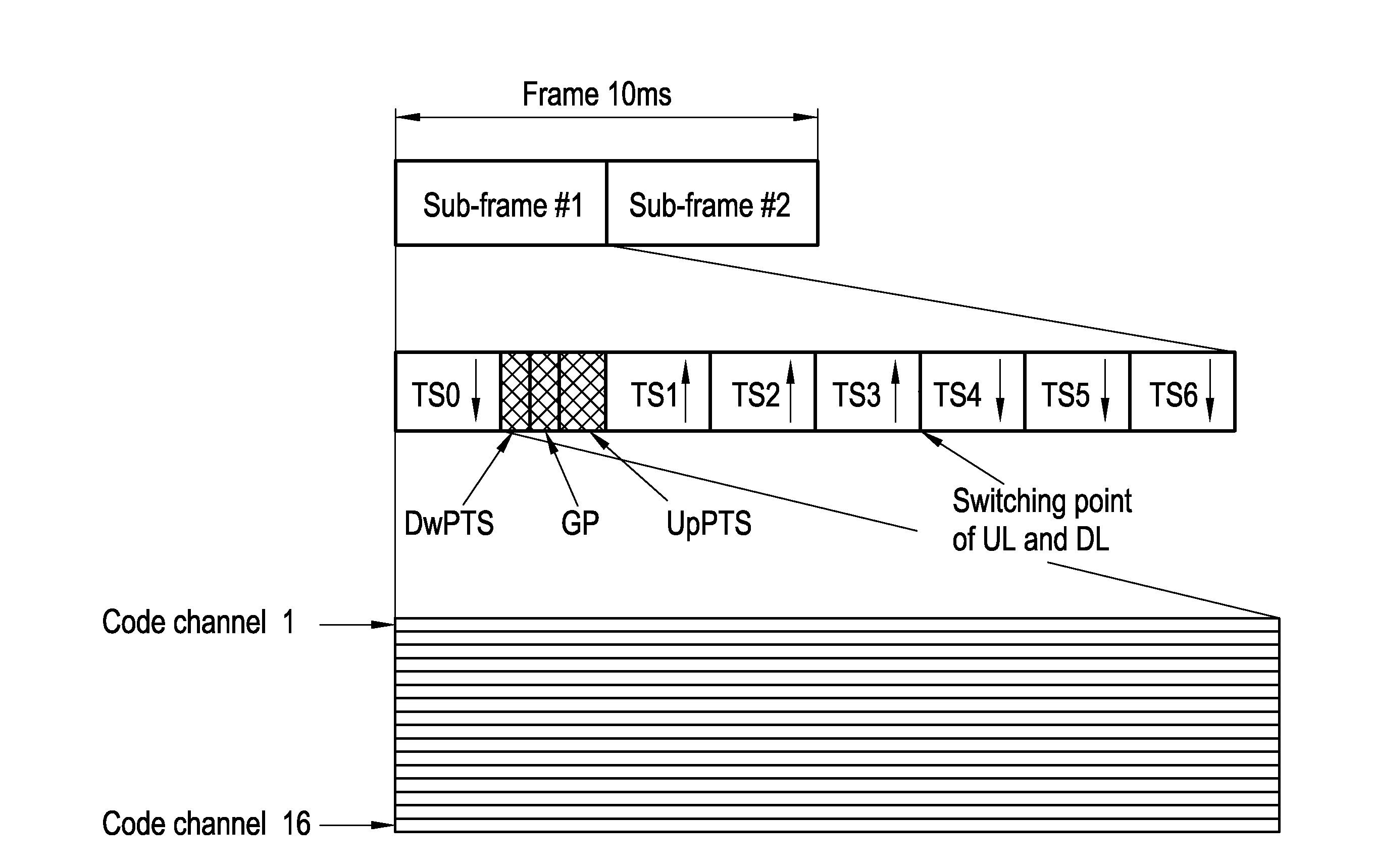
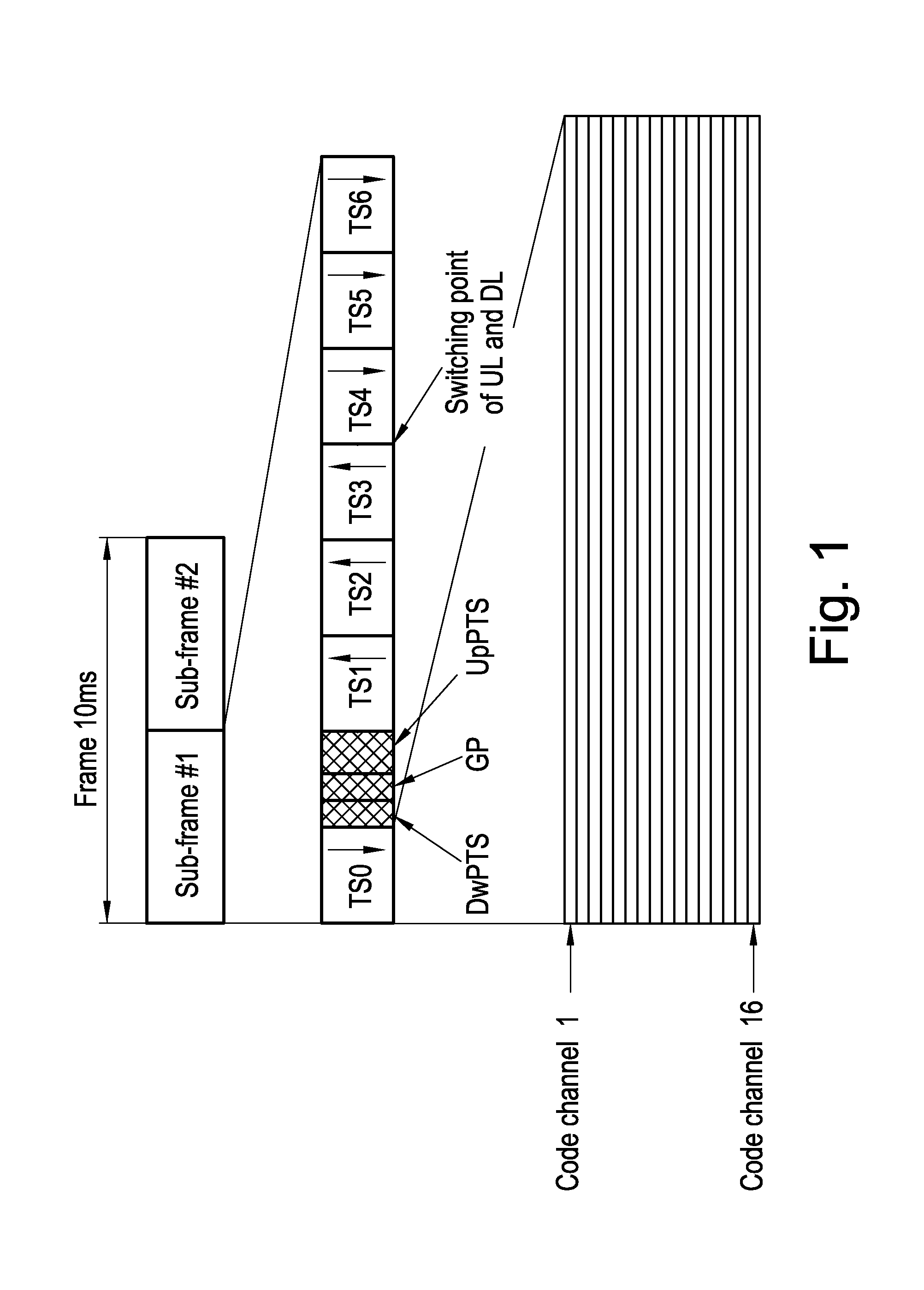
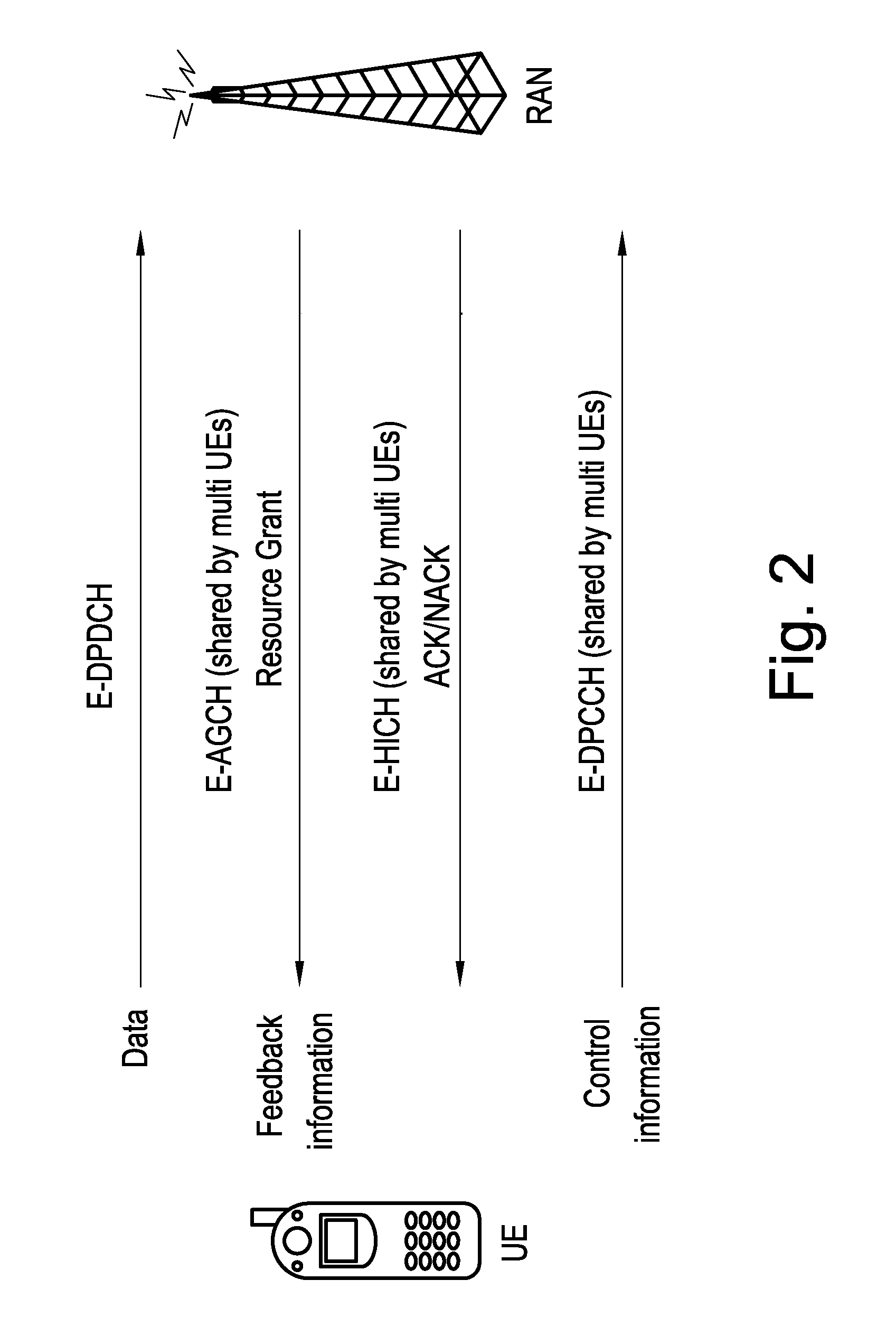
Method for resource unit allocation for wireless communiciation, subscriber station and base station
InactiveUS20100177741A1Reduce power consumptionLessRadio transmissionMultiplex code allocationMultiplexingResource allocation
A method for wireless communication between a base station and a plurality of subscriber stations is described wherein a communication capacity is partitioned in resource units at least by code multiplexing, which resource units are distributed by the base station over said devices, wherein data from each subscriber station is spread by means of a signature sequence, characterized in that multiple resource units assigned to a common subscriber station have the same signature sequence.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Method for producing aqueous dispersion of thermoplastic resin microparticles and toner for electrophotography
The present invention provides a method for producing an aqueous dispersion of thermoplastic resin microparticles containing considerably less residual solvent remaining in resin particles, and a toner for electrophotography containing considerably less residual solvent. A self-water-dispersible thermoplastic resin is swollen using an organic solvent having a boiling point lower than 100° C., which does not dissolve but can swell the self-water-dispersible thermoplastic resin, to produce a swollen material and the resulting swollen material is dispersed into an aqueous medium in the form of microparticles to produce an initial aqueous dispersion, and then the organic solvent is removed from the initial aqueous dispersion to prepare a dispersion. A toner for electrophotography contains microparticles obtained by separating microparticles of the self-water-dispersible thermoplastic resin from the aqueous dispersion of thermoplastic resin microparticles and drying the microparticles.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Latent stabilization of bioactive agents releasable from implantable medical articles
InactiveUS20080154241A1Improve stabilityLessPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsOphthalmologyActive agent
Implantable medical articles comprising natural biodegradable polysaccharides are described. The polysaccharides can provide desirable release properties, and can also be degraded into products that can act as an excipient in the presence of the bioactive agent. In some aspects, the articles are ocular implants formed of a matrix of natural biodegradable polysaccharides. These ocular implants include a bioactive agent that can be released within the eye to treat an ocular condition or indication.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Set associative repair cache systems and methods
InactiveUS20060080572A1Reduce sizeLessError detection/correctionStatic storageMemory addressParallel computing
The present invention facilitates scaling of memory devices and operation thereof by employing a set associative repair cache system to correct or repair identified faulty memory cells. A repair cache region router 602 compares a repair region portion of a memory address to repair cache regions to identify a matching repair cache region. Then, a local repair location router 603 compares a repair address portion of the memory address to a local repair location addresses particular to the matching repair cache region to identify a matching local repair address. If a matching local repair address is identified, a repair component 606 provides access to a repair data location according to the matching local repair address and the matching repair cache region. Otherwise, a main memory 604 provides access to a memory location according to the memory address. Other systems and methods are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Memory efficient use of dynamic data structures used to manage sparsely accessed data
ActiveUS8819386B1LessEfficient data structureMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationShardDynamic data structures
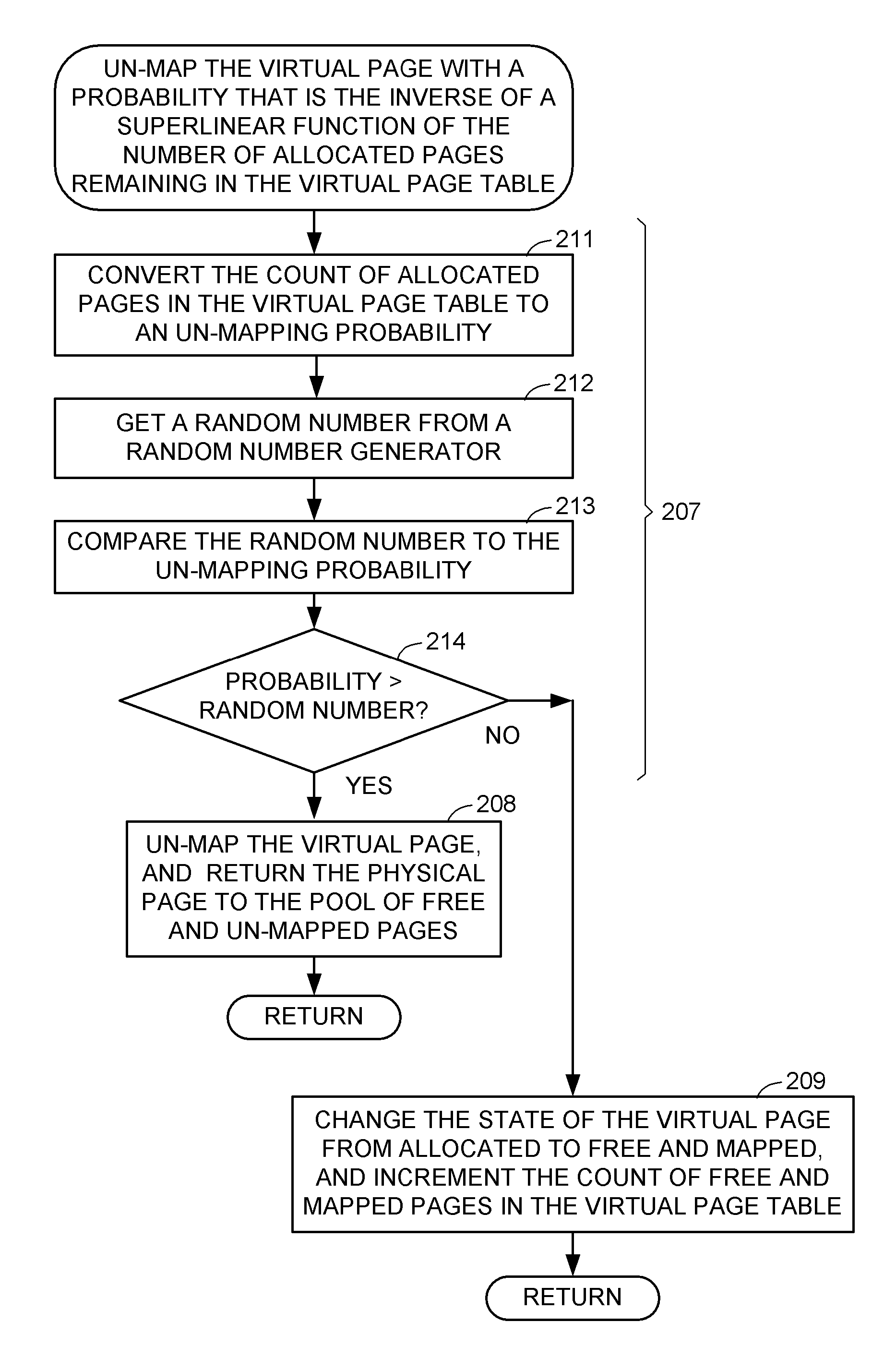
When a dynamic data structure is used for managing sparsely accessed data stored in memory of a digital computer, pages of the memory are dynamically allocated and de-allocated to respective portions of the dynamic data structure so that the pages become distributed over the portions of the dynamic data structure and the de-allocated pages include free pages that are mapped in the dynamic data structure and free pages that are not mapped in the dynamic data structure. To reduce memory fragmentation and recover memory, upon de-allocating a page of memory from a portion of the data structure, a determination is made whether or not to un-map the de-allocated page from the portion of the dynamic data structure so that un-mapping of the de-allocated page has a probability that is the inverse of a superlinear function of the number of allocated pages in the portion of the dynamic data structure.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Compressing a signal that represents a physical attribute
ActiveUS20180075622A1LessEfficiently obtainedCode conversionImage codingImproved methodComputer science
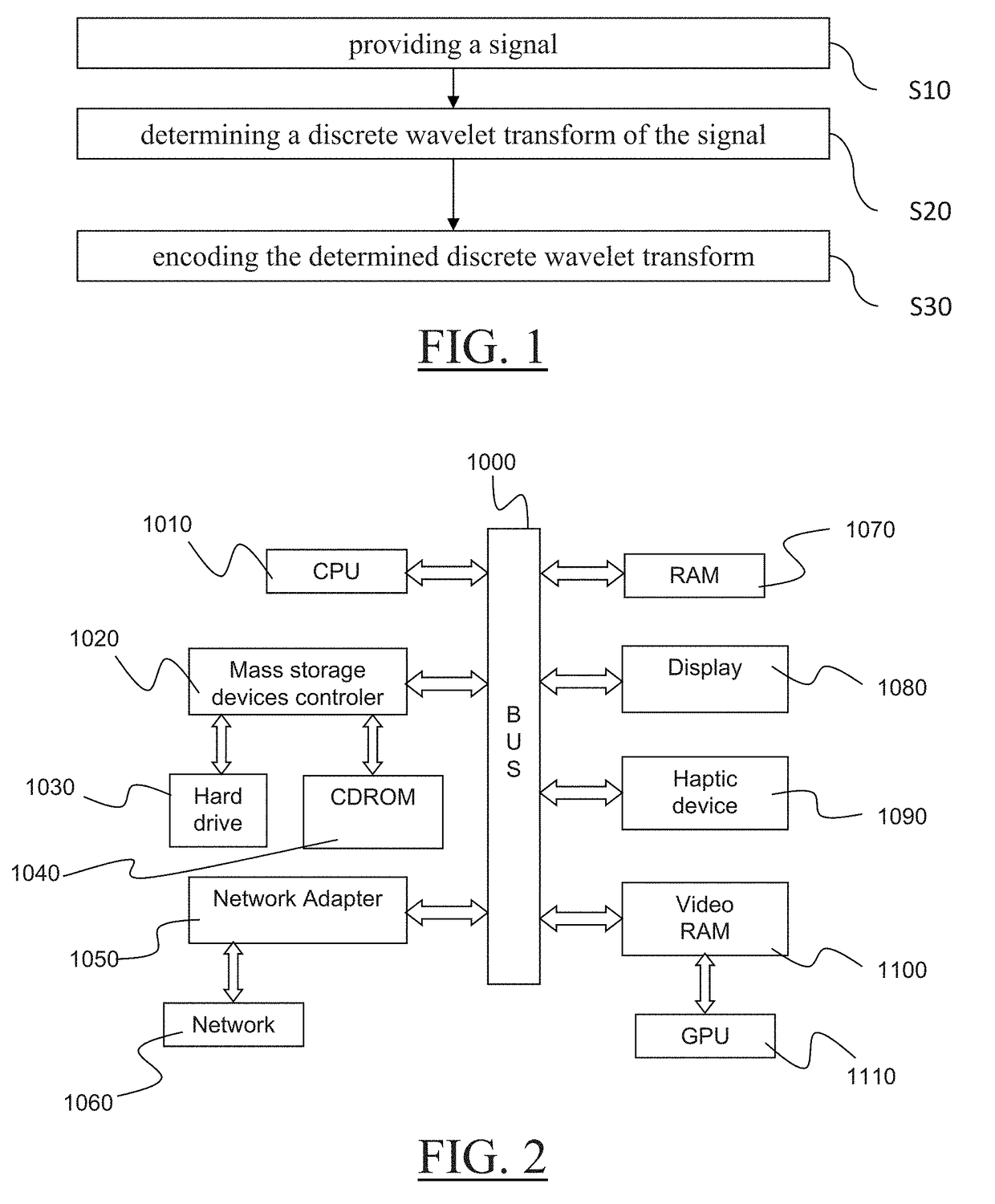
The invention notably relates to a computer-implemented method for compressing data representing values of a physical attribute in a predetermined space. The method comprises providing a signal that includes a mapping from leaf cells of a hierarchical subdivision of the predetermined space each onto a respective coefficient representative of a value of the physical attribute at the respective leaf cell. The method also comprises determining a discrete wavelet transform of the signal and encoding the determined discrete wavelet transform. The method provides an improved way to compress a modeled object that represents a real object.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
System and method for performance analysis and classification of losses for solar power systems
InactiveUS20160190984A1LessFinancial impact of lossPhotovoltaic monitoringElectric devicesEngineeringSolar power
The invention provides a system and method for analyzing and classifying the losses of a photovoltaic array. The system and method compares expected power output and to actual power output and can determine a photovoltaic string, combiner, or inverter is generating less power than expected due to at least one of snow cover, soiling, and inverter clipping. The system and method can then determine an amount of power lost during a period of time the photovoltaic string, combiner, or inverter is experiencing snow cover, soiling, or inverter clipping and determine a value of the amount of power lost during the period of time. Various user interfaces enable a user to view one or more reasons why a PV string, combiner or inverter is generating less power than expected and the value of the amount of power lost.
Owner:ALSO ENERGY
Semiconductor wafer cleaning systems and methods
InactiveUS20040050405A1Improve efficiencyMinimized chemical usageDrying solid materials with heatReconditioning/cleaning record carriersEngineeringDelivery system
An immersion processing system is provided for cleaning wafers with an increased efficiency of chemical use. Such a system advantageously uses less cleaning enhancement substance that may be provided as gas, vapor or liquid directly to a meniscus or wafer / liquid / gas bath interface so as to effectively modify surface tensions at the meniscus with minimized chemical usage. Such a delivery system design may be applied for single wafer processing or for processing multiple wafers together within a single liquid bath vessel. For single wafer processing, in particular, cleaning enhancement substance can be delivered along one or both major sides of the wafer, preferably at the meniscus that is formed as the wafer and liquid are relatively moved, while a processing vessel usable for such single wafer processing may itself be designed with a minimized size to accommodate a single wafer. By reducing the vessel volume, chemical usage for any processing chemicals that are to be provided within a liquid bath may also be advantageously reduced.
Owner:TEL EPION
Differential steering application for trailer spotter vehicles
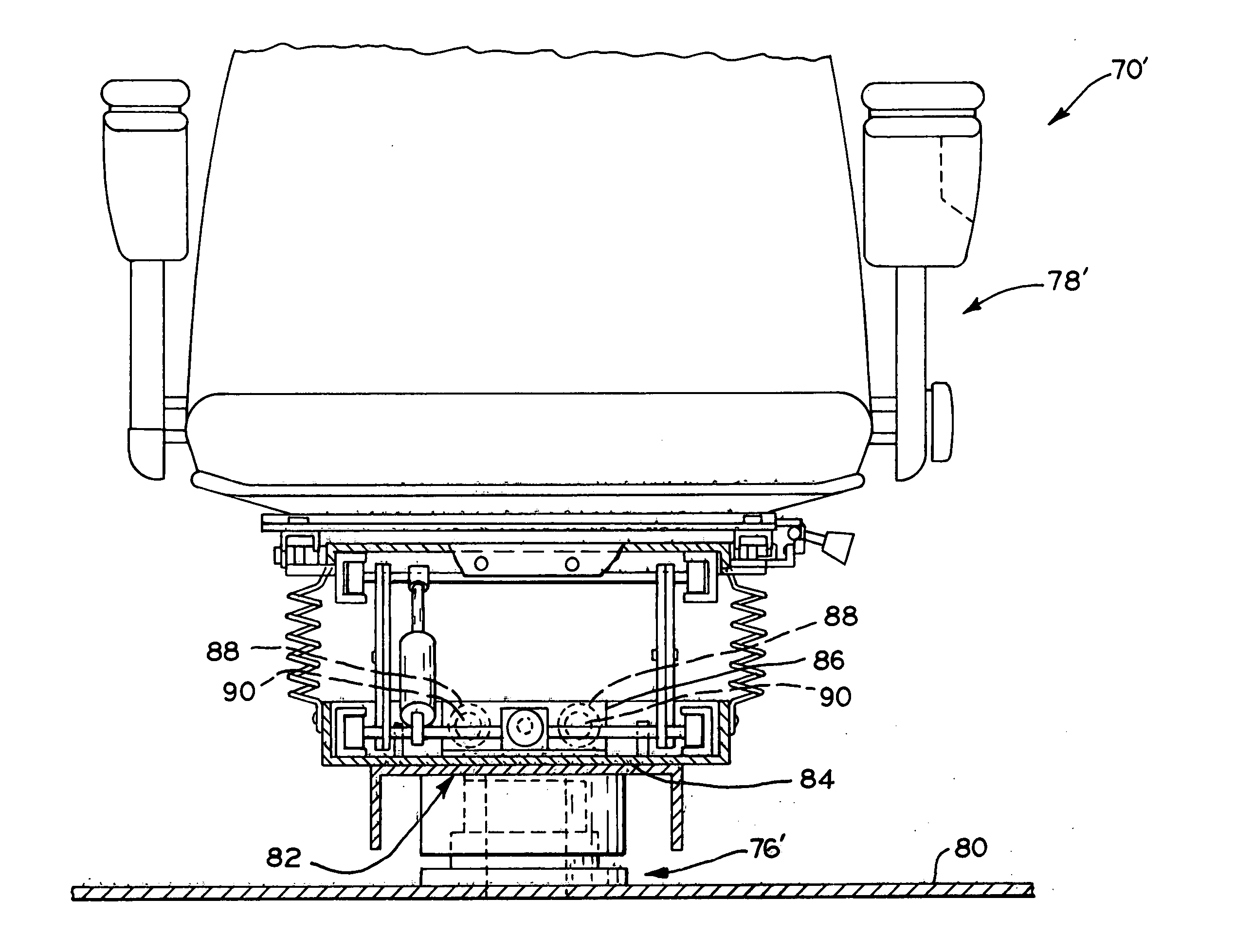
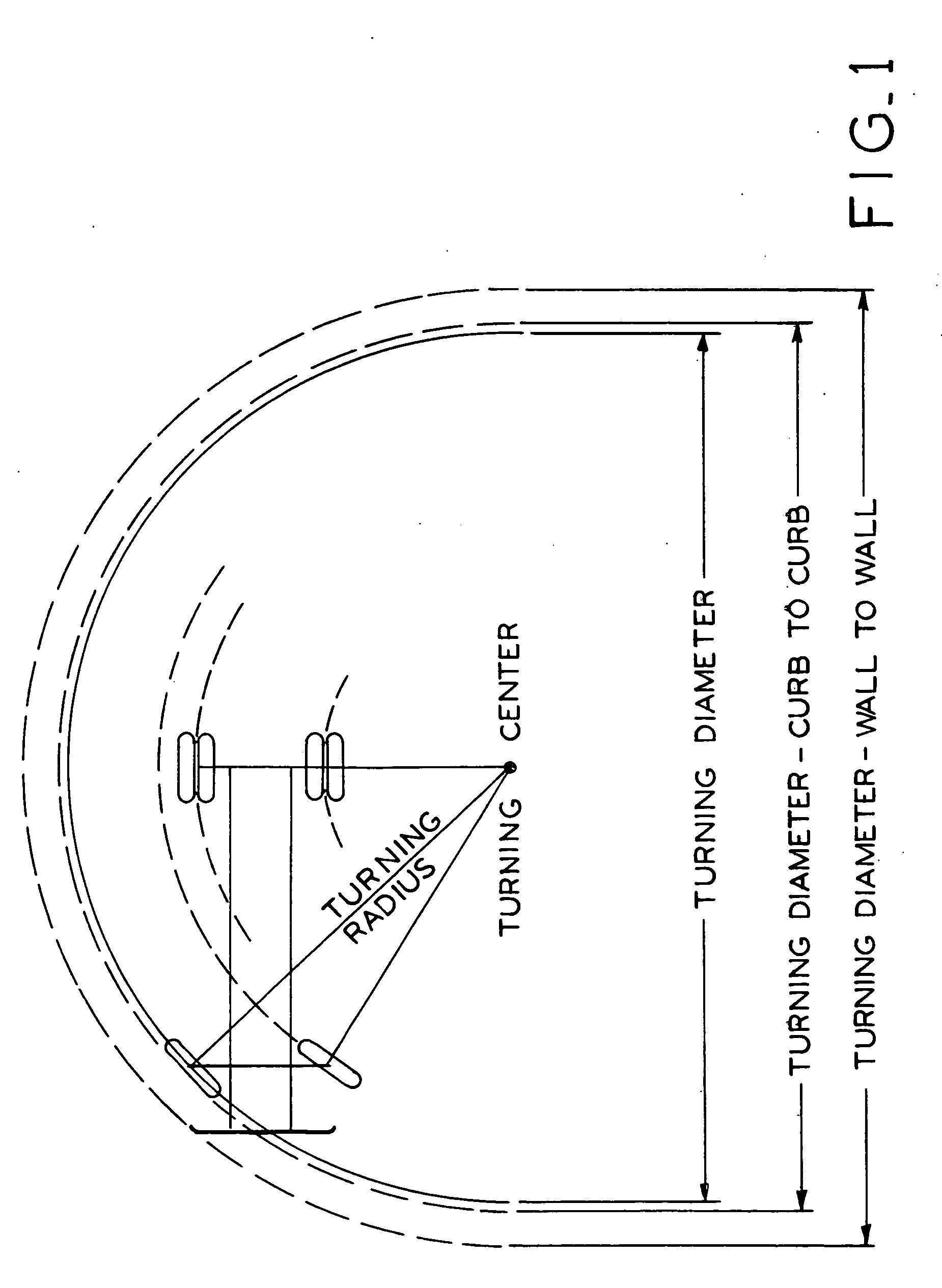
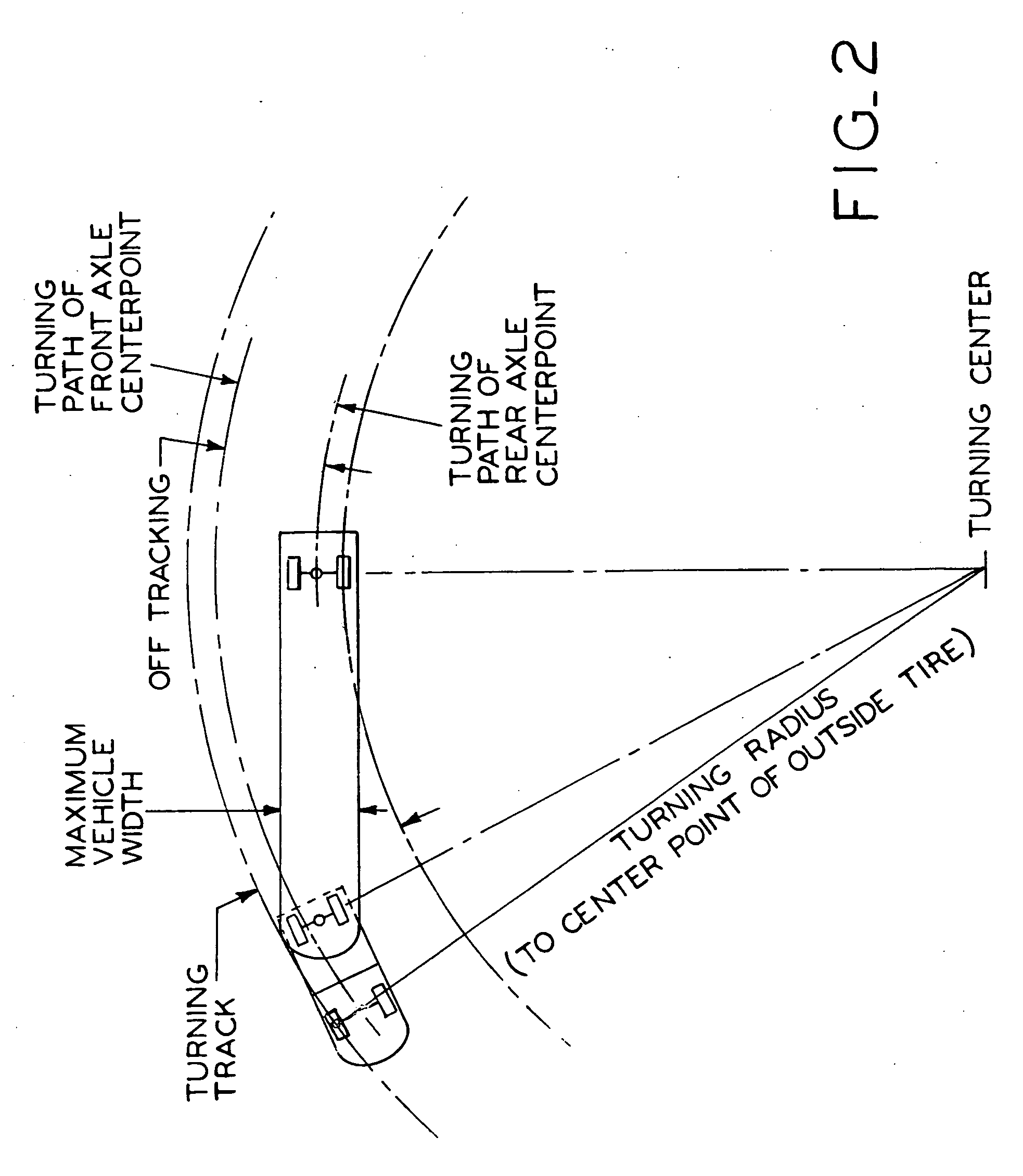
InactiveUS20060207822A1Reduce the overall diameterMinimal effortVehicle seatsVehicle mounted steering controlsVehicle frameHydraulic pump
A trailer spotter vehicle having a seat and a control console which are relatively rotatable with respect to the vehicle frame, and a differential drive system which permits the vehicle to turn within a very small turning radius. The rotatable seat and control console allow the operator to steer the vehicle without having to substantially turn their body or use mirrors to observe the path of the vehicle. To drive the vehicle in a forward direction, hydraulic pumps transmit pressurized hydraulic fluid to the trailer spotter wheels to rotate them in a first direction. In order to drive the vehicle in reverse, the flow of hydraulic fluid to the wheels is reversed to rotate the wheels in an opposite direction. To pivot the vehicle, the first wheel is driven in the first direction and the second wheel is driven in the opposite direction.
Owner:TAYLOR KERMIT O
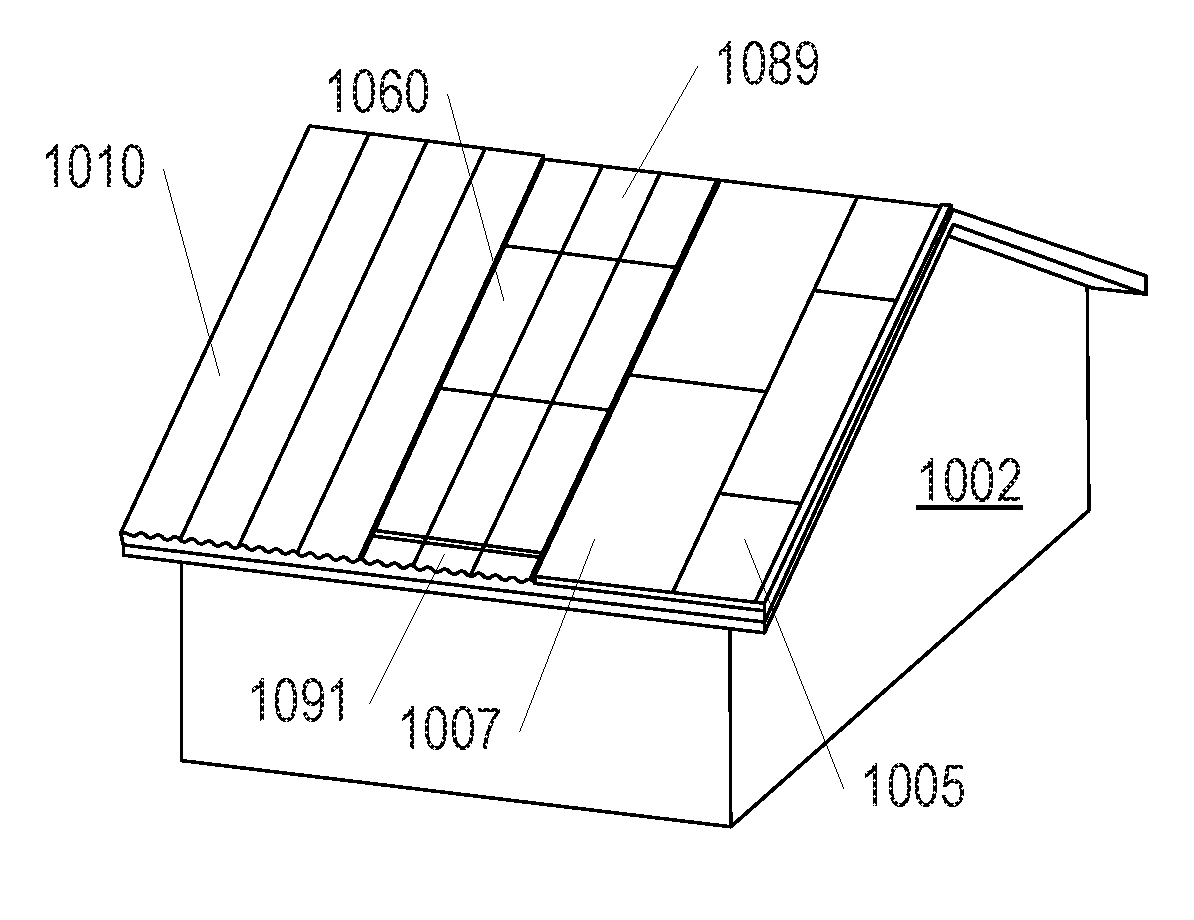
Building integrated photovoltaic roofing assemblies and associated systems and methods
ActiveUS20170237390A1Reduce the differenceEasy to replacePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectrical and Electronics engineeringPhotovoltaics
Owner:TESLA INC
Electrochemical systems and methods for operating an electrochemical cell with an acidic anolyte
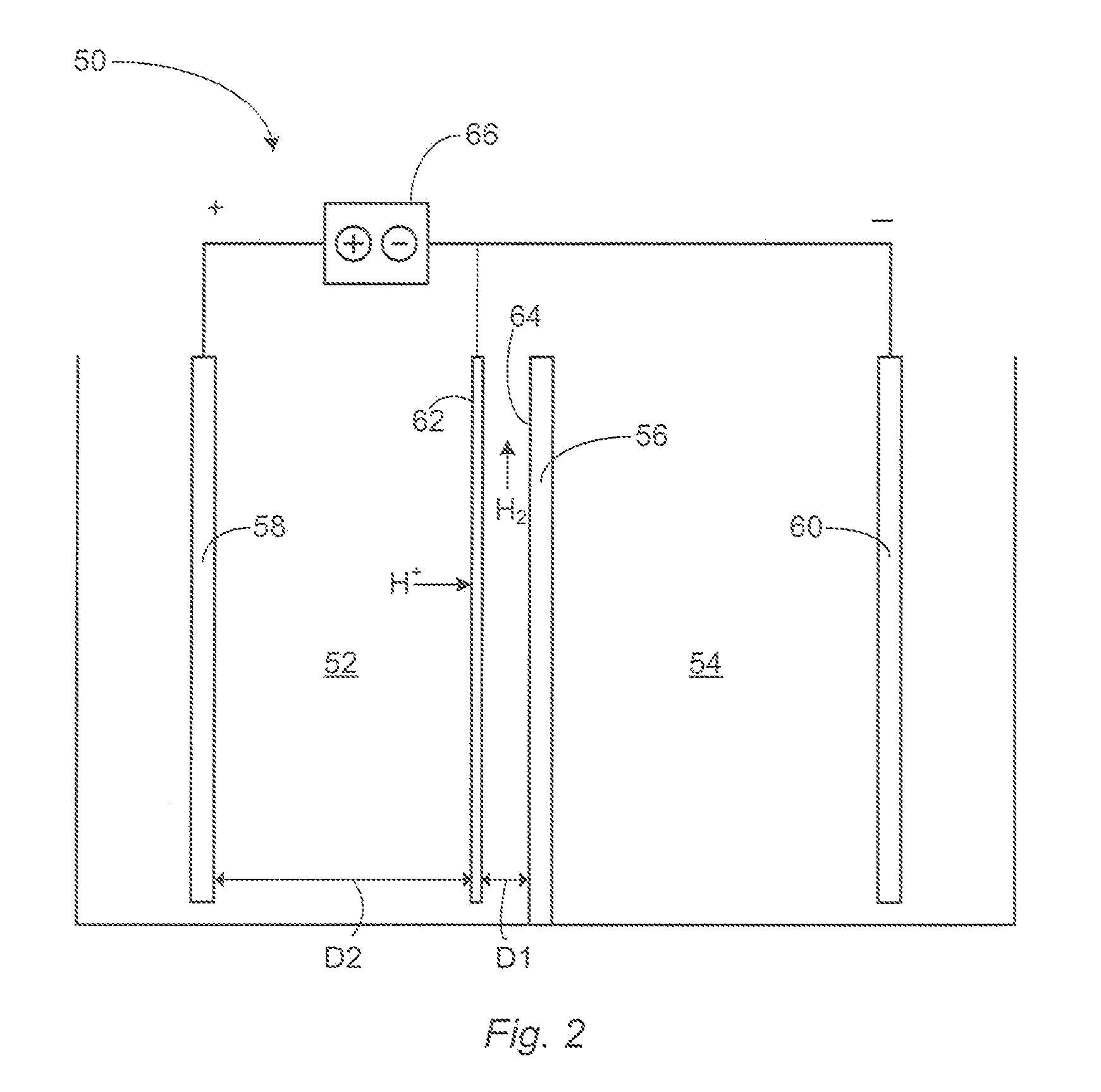
ActiveUS20120085658A1Cut surfaceObstruction is producedCellsWater treatment parameter controlHydrogenCeramic membrane
An electrochemical cell having a cation-conductive ceramic membrane and an acidic anolyte. Generally, the cell includes a catholyte compartment and an anolyte compartment that are separated by a cation-conductive membrane. While the catholyte compartment houses a primary cathode, the anolyte compartment houses an anode and a secondary cathode. In some cases, a current is passed through the electrodes to cause the secondary cathode to evolve hydrogen gas. In other cases, a current is passed between the electrodes to cause the secondary cathode to evolve hydroxyl ions and hydrogen gas. In still other cases, hydrogen peroxide is channeled between the secondary cathode and the membrane to form hydroxyl ions. In yet other cases, the cell includes a diffusion membrane disposed between the secondary cathode and the anode. In each of the aforementioned cases, the cell functions to maintain the pH of a fluid contacting the membrane at an acceptably high level.
Owner:ENLIGHTEN INNOVATIONS INC
Fiber configurations for wellbore treatment compositions
ActiveUS20200040254A1LessLow fluid viscosityFluid removalDrilling compositionCelluloseFiber structure
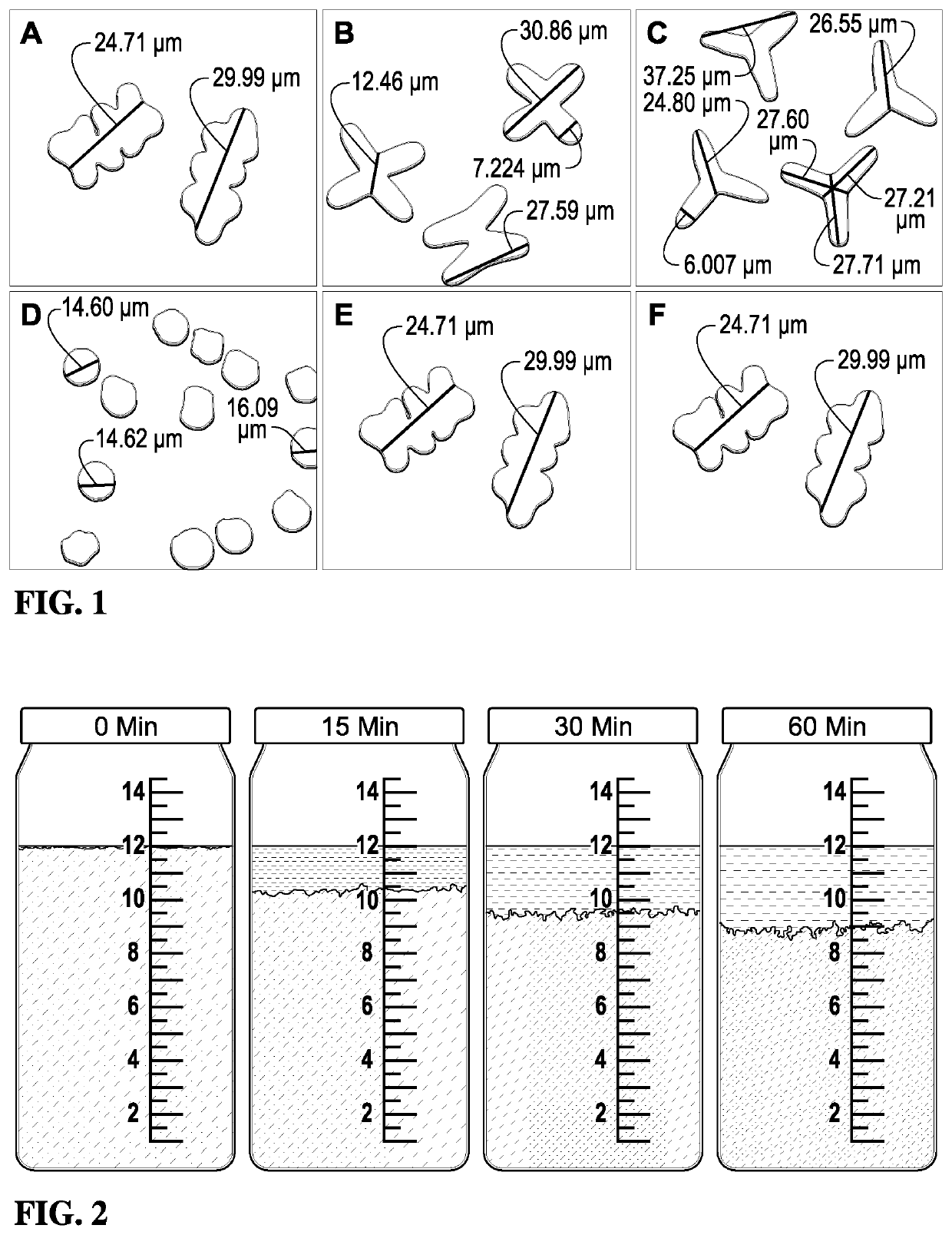
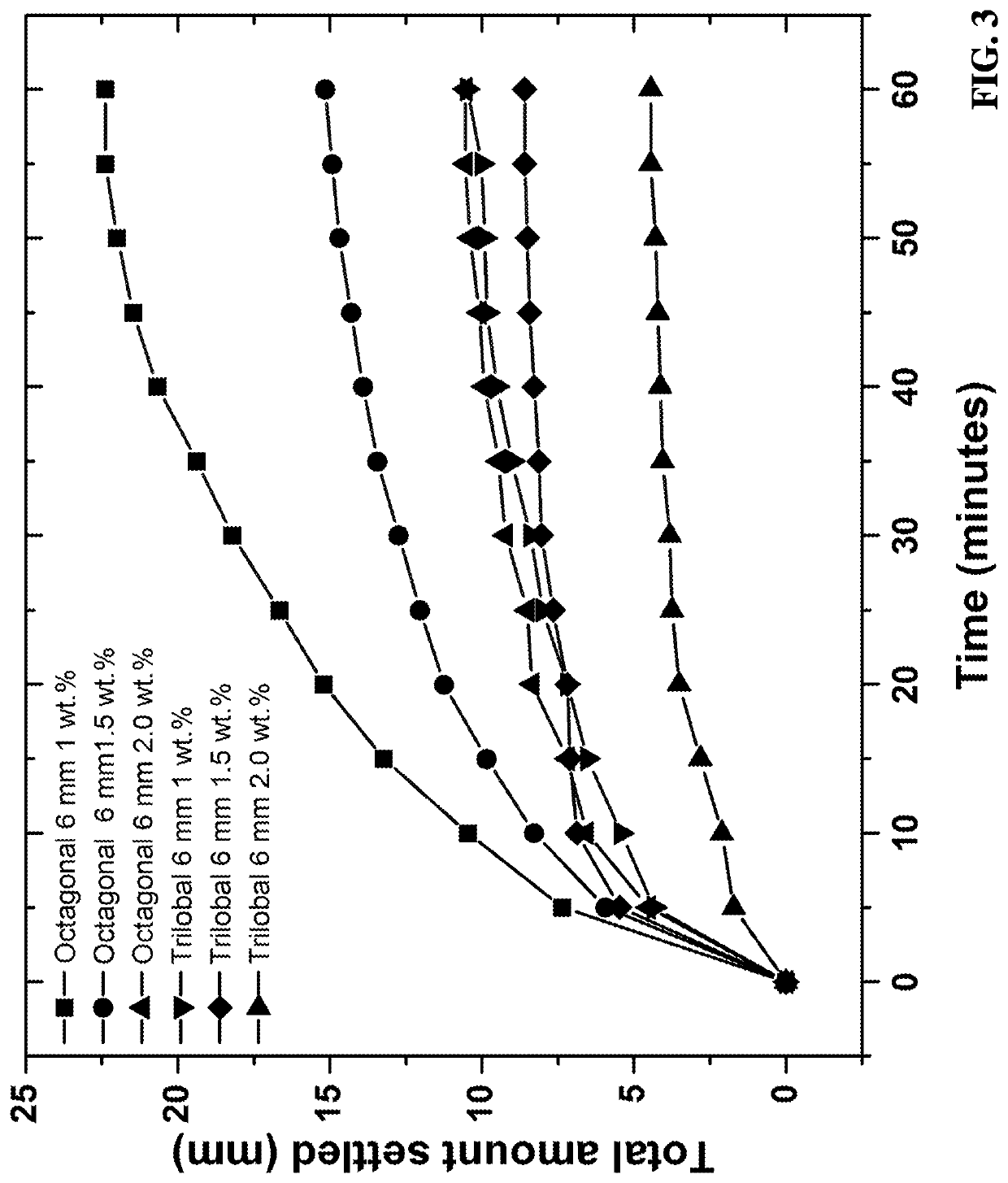
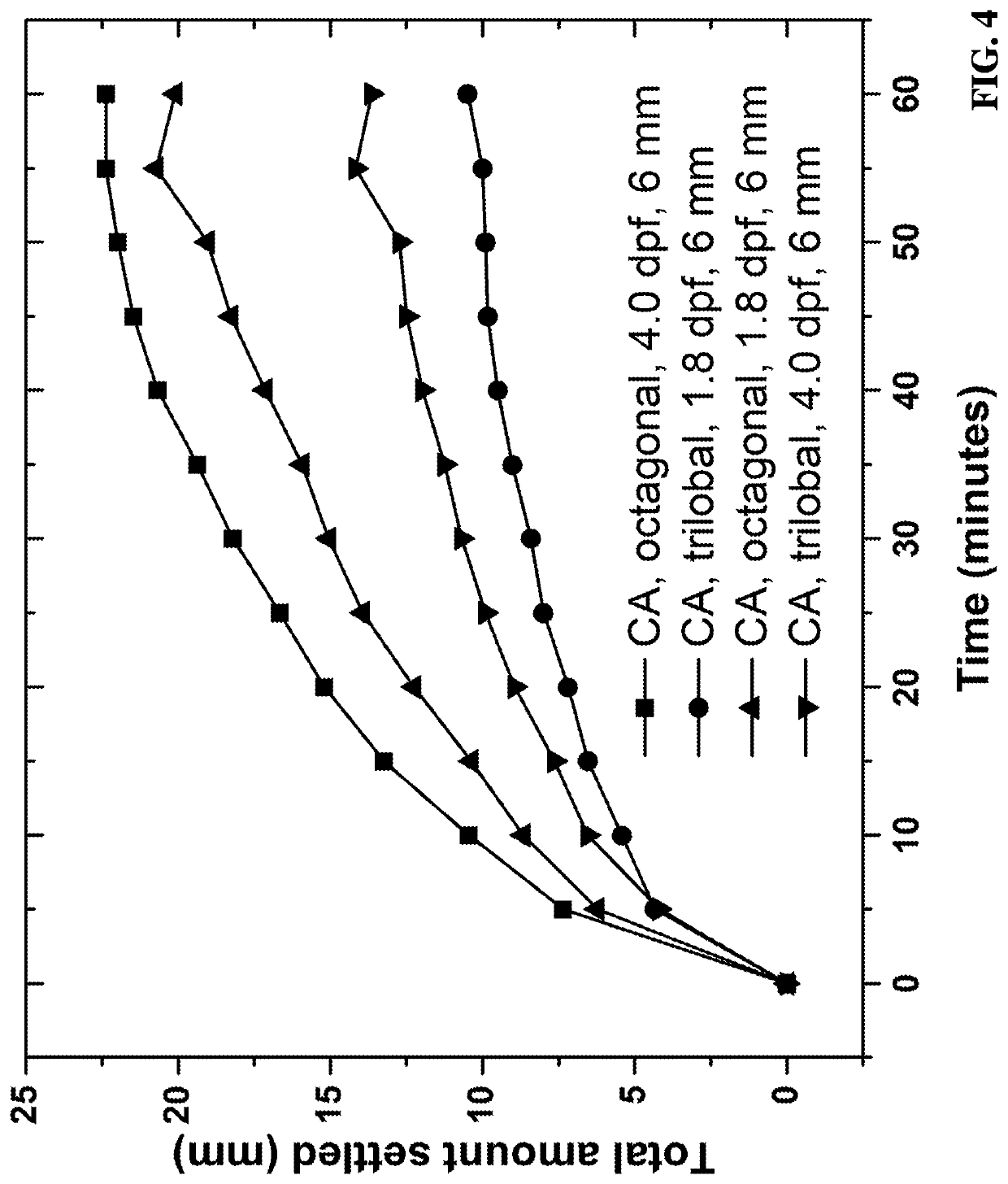
Suspension of proppants in hydraulic fracturing applications can be strongly affected by the cross-sectional shapes and lengths of the fibers present in the wellbore treatment compositions. For instance, it has been observed that crimped cellulose ester fibers with a trilobal cross-section and an optimized length can provide enhanced suspension of proppants in aqueous fracturing fluids. Furthermore, the present invention demonstrates that non-round cellulose ester fibers can provide superior proppant suspension properties relative to polylactic acid fibers with a round cross-section.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
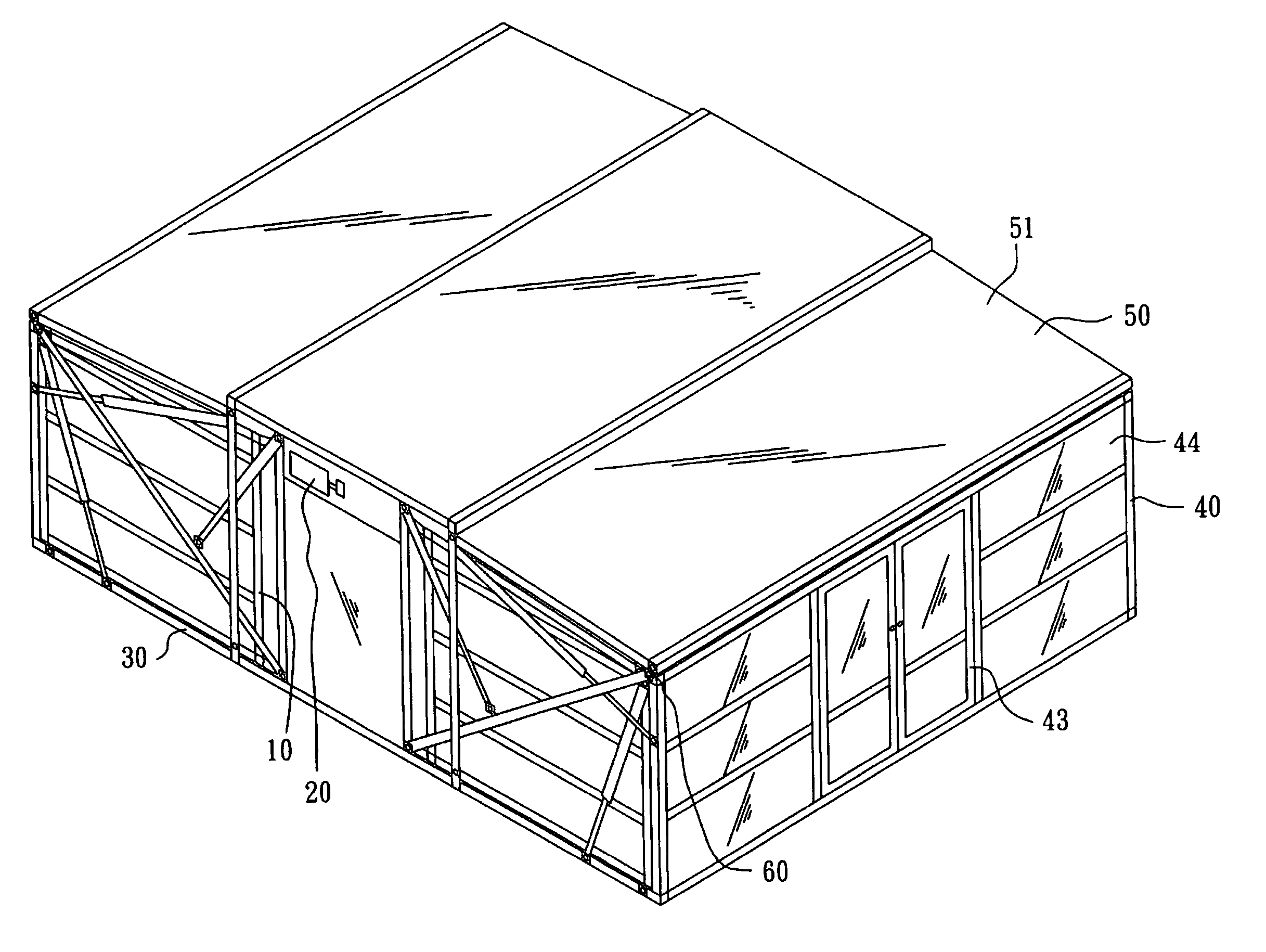
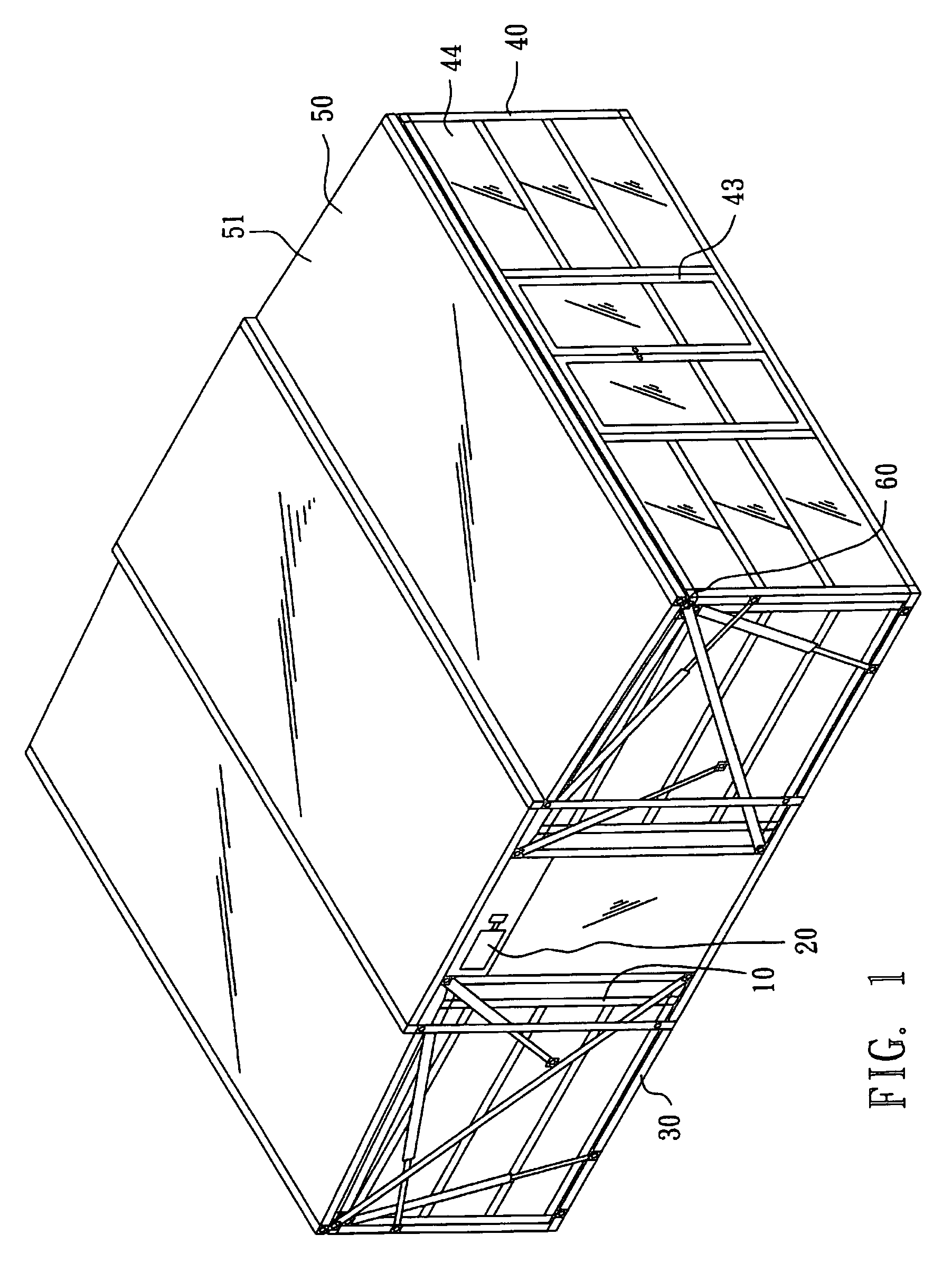
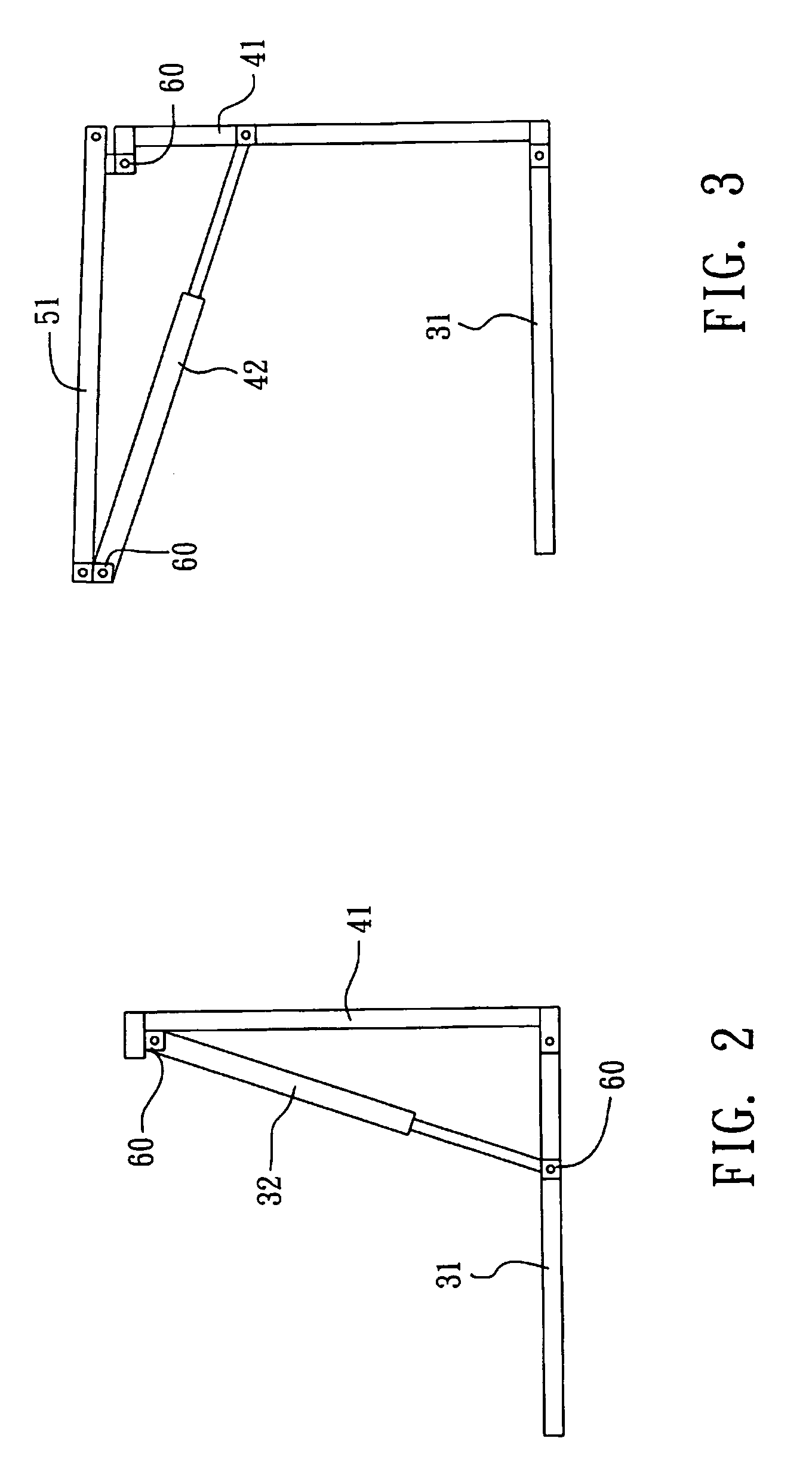
Retrievable combinational house
A retrievable combinational house comprising a main body to store following items, at least one motor to expand and retrieve the combination, at least one floor part, at least one wall part and at least one roof part; when the combination expands, the motor expands the roof part, the wall part and the floor part in series to double the area, while retrieval, the motor retrieves the floor parts, the wall parts and the roof parts in reverse order into the main body.
Owner:LIN SHENG I
Building integrated photovoltaic system for tile roofs
ActiveUS20180115275A1Reduce the differenceSimplify replacement capability of photovoltaicPhotovoltaic supportsRoof covering using tiles/slatesRoof tileEngineering
Building integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) systems provide for solar panel arrays that can be aesthetically pleasing to an observer, with minimal visible difference between photovoltaic and non-photovoltaic areas of the BIPV system. BIPV systems can be incorporated as part of roof surfaces as built into the structure of the roof, particularly as roofing tiles that have photovoltaic elements embedded or incorporated into the body of the roofing tiles. BIPV systems can also include mimic or dummy tiles that appear similar to tiles with photovoltaic elements, but do not collect solar energy. In some configurations, the appearance of BIPV tile roof systems can be generally uniform to an observer at ground level, where the blending and distribution of photovoltaic and non-photovoltaic elements generate a consistent and elegant appearance that camouflages any differences between photovoltaic tile or non-photovoltaic tiles.
Owner:TESLA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com