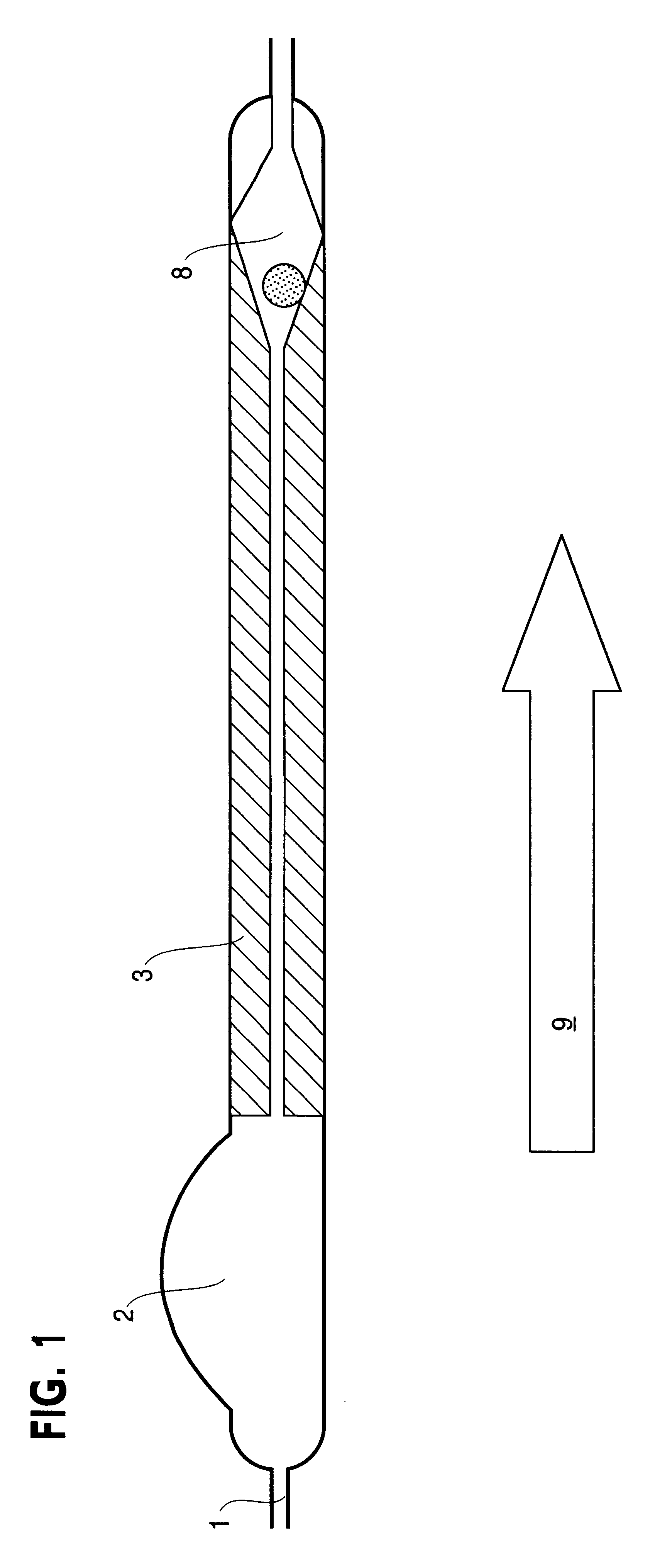
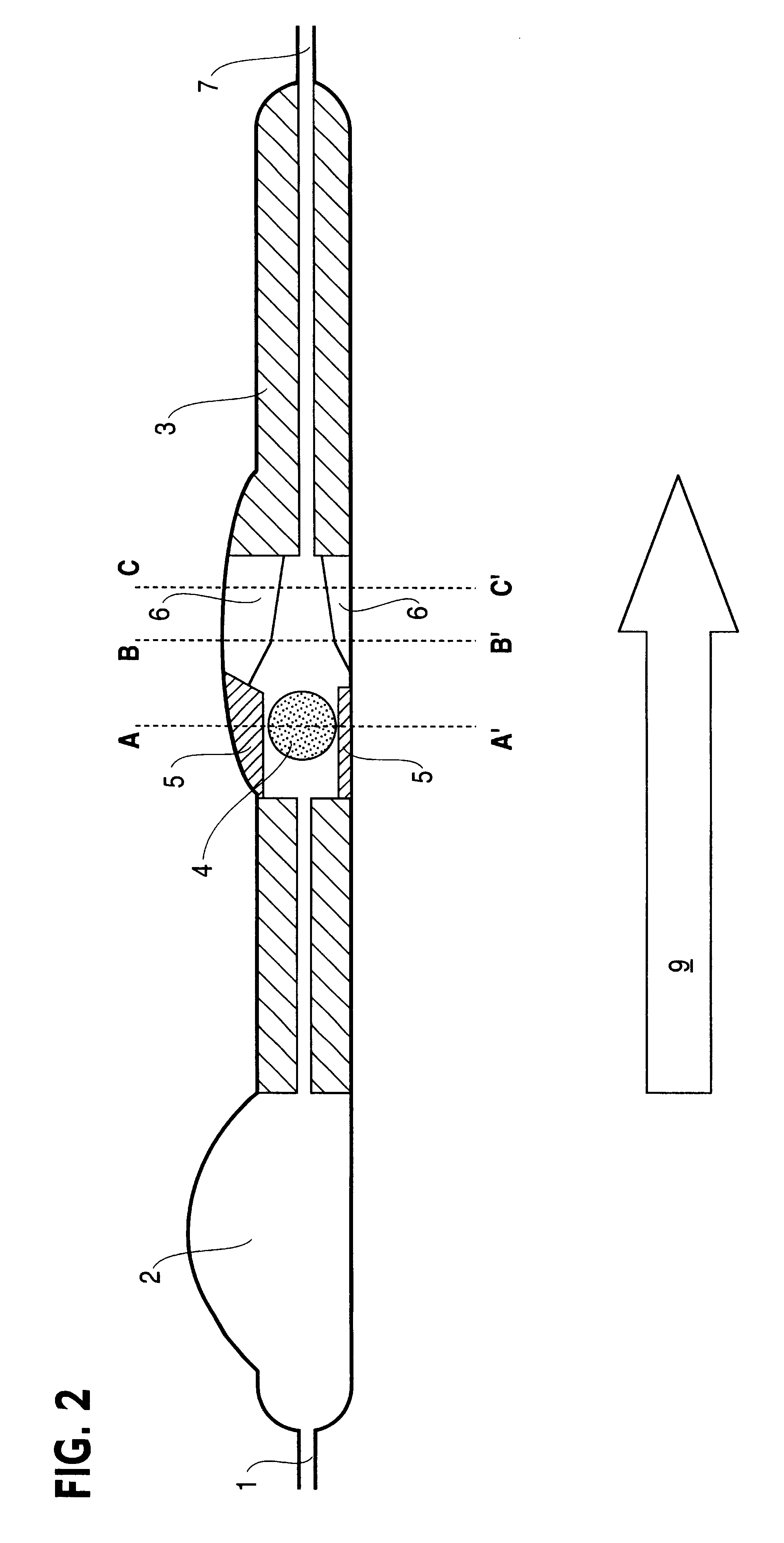
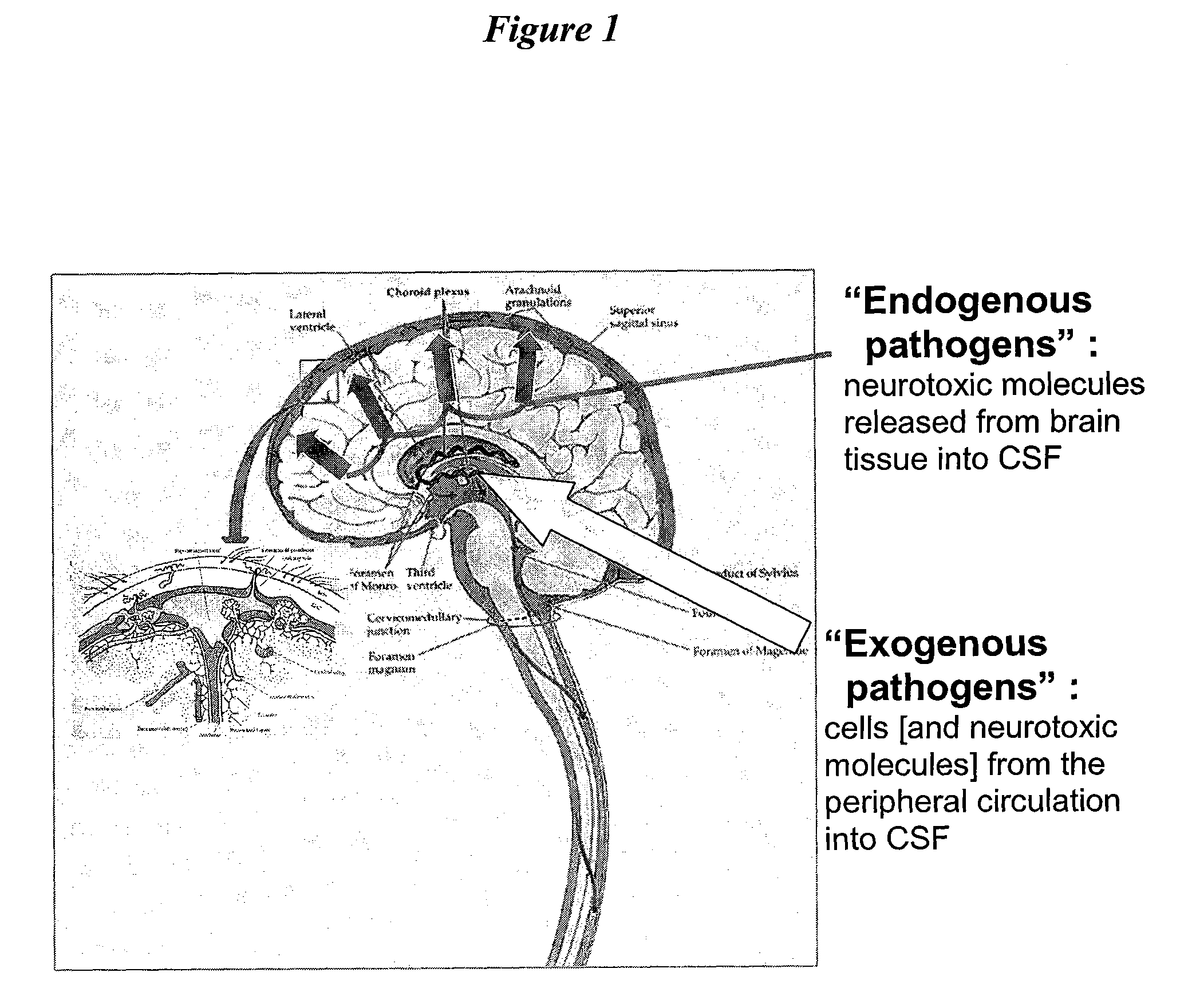
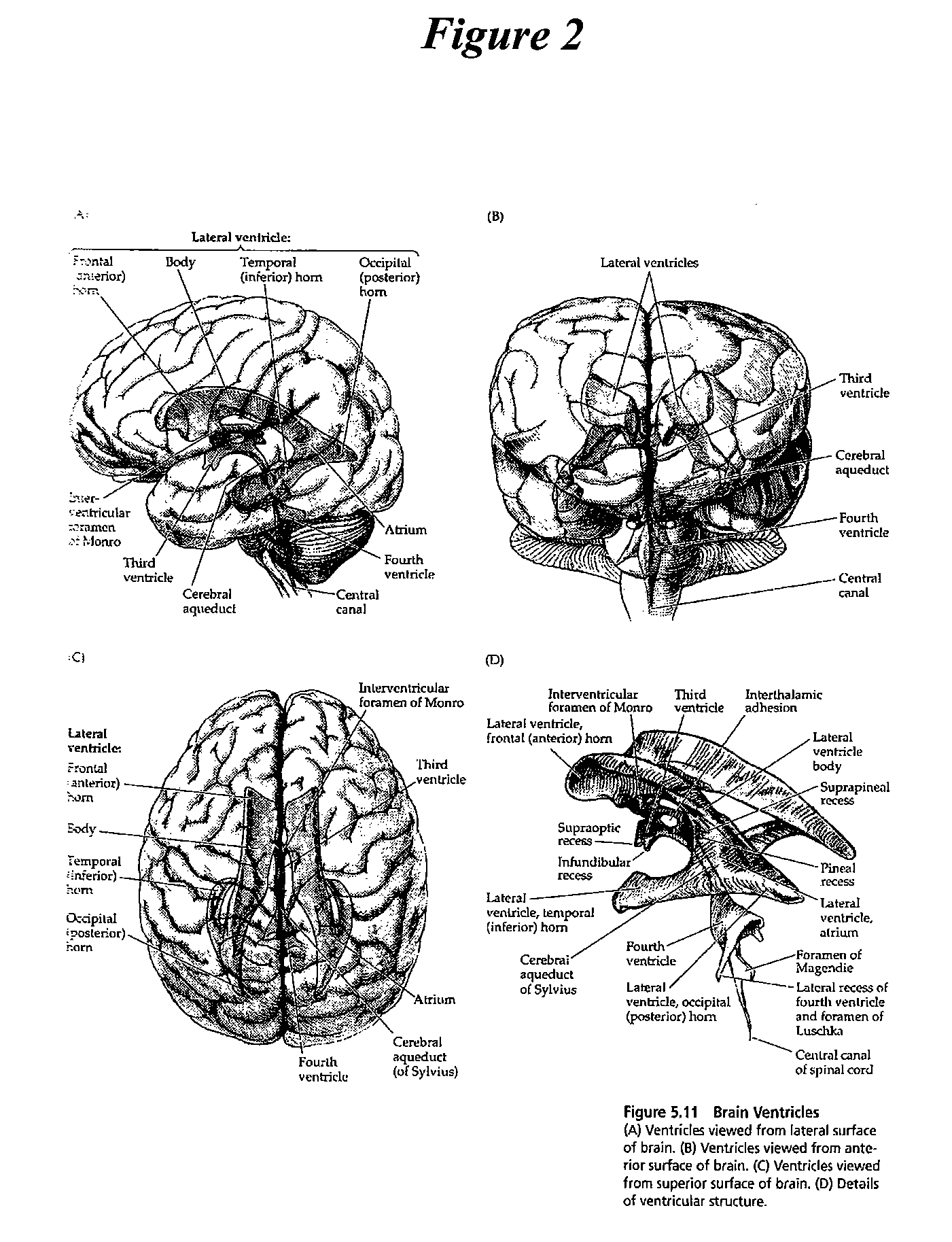
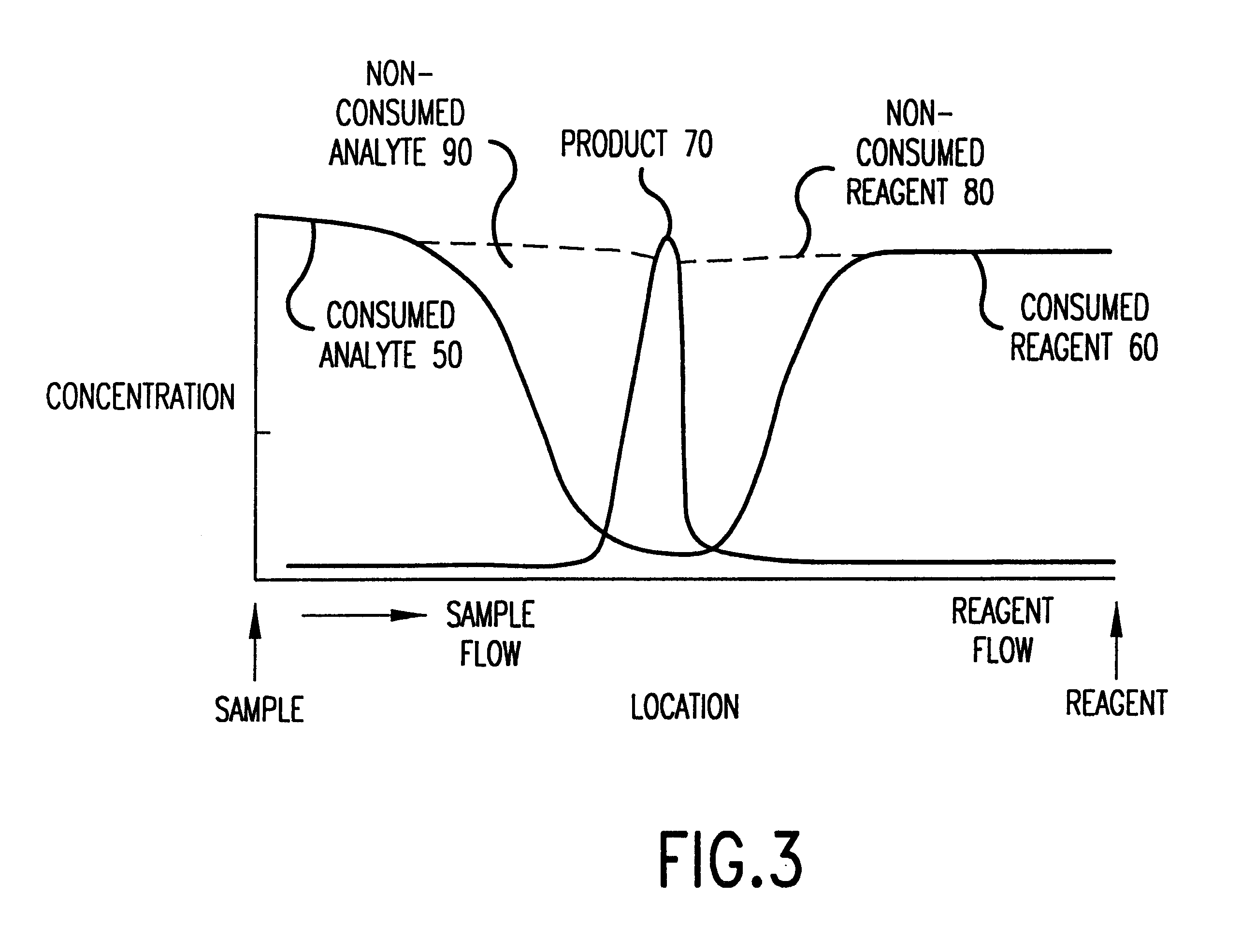
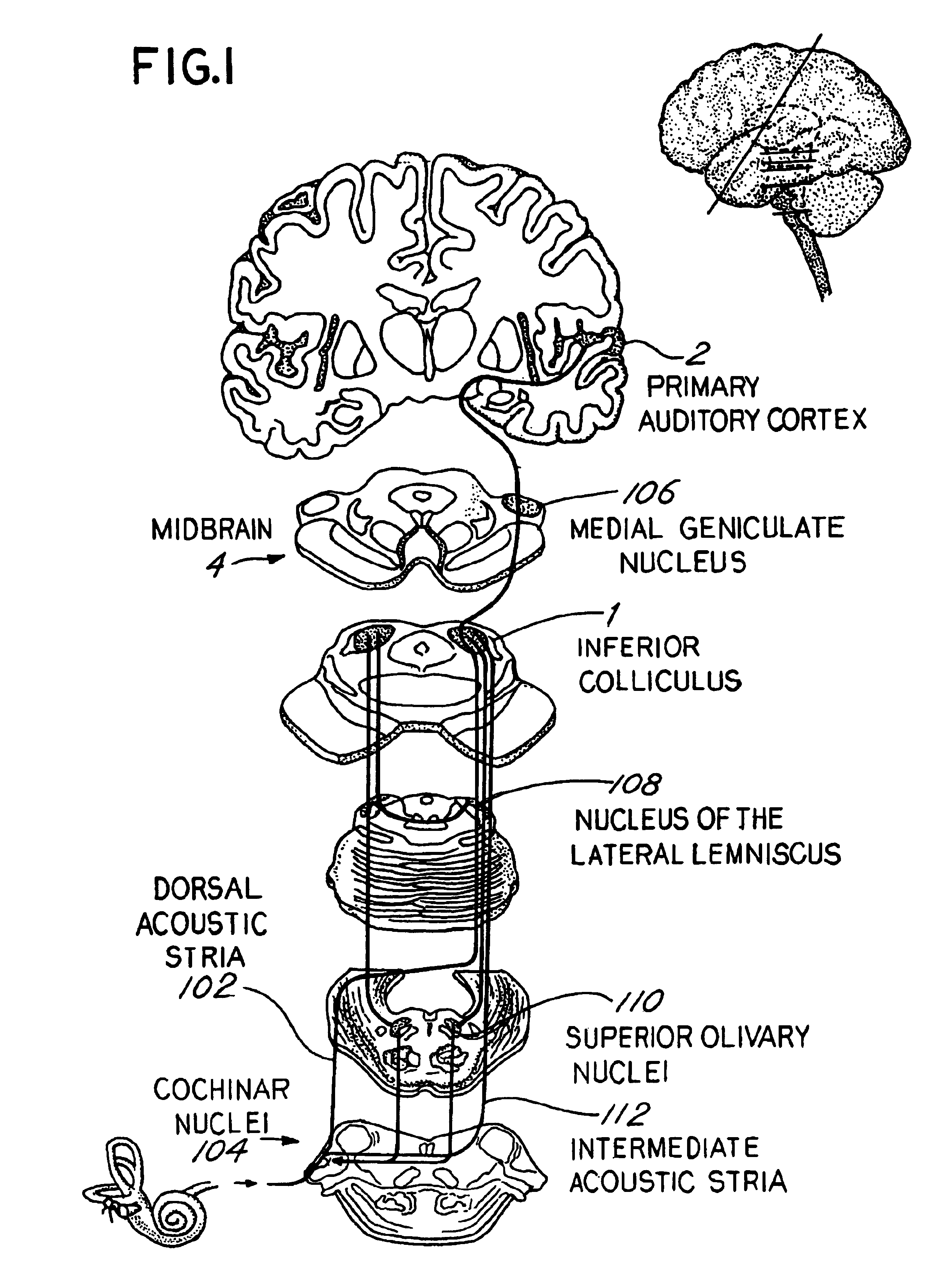
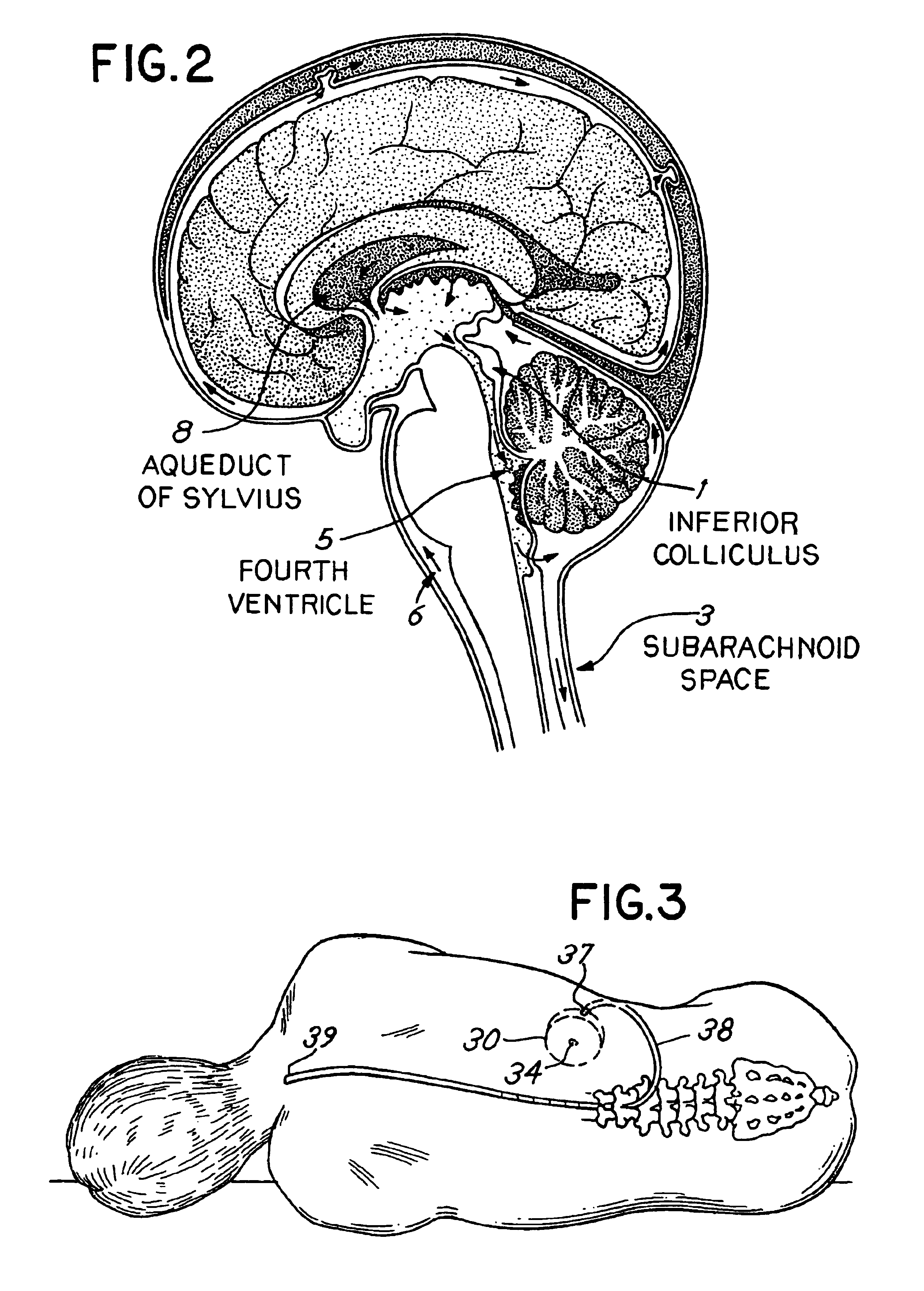
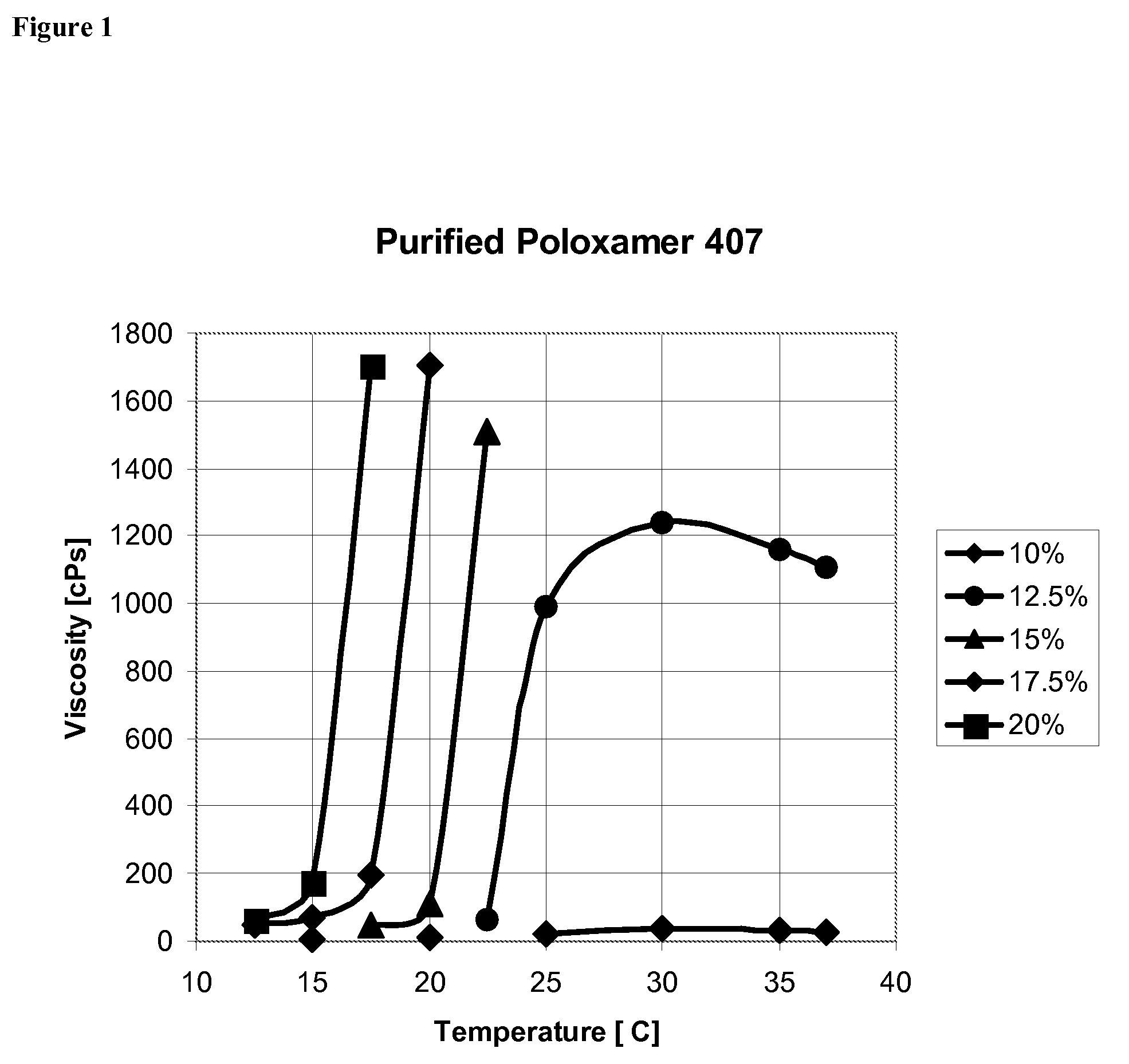
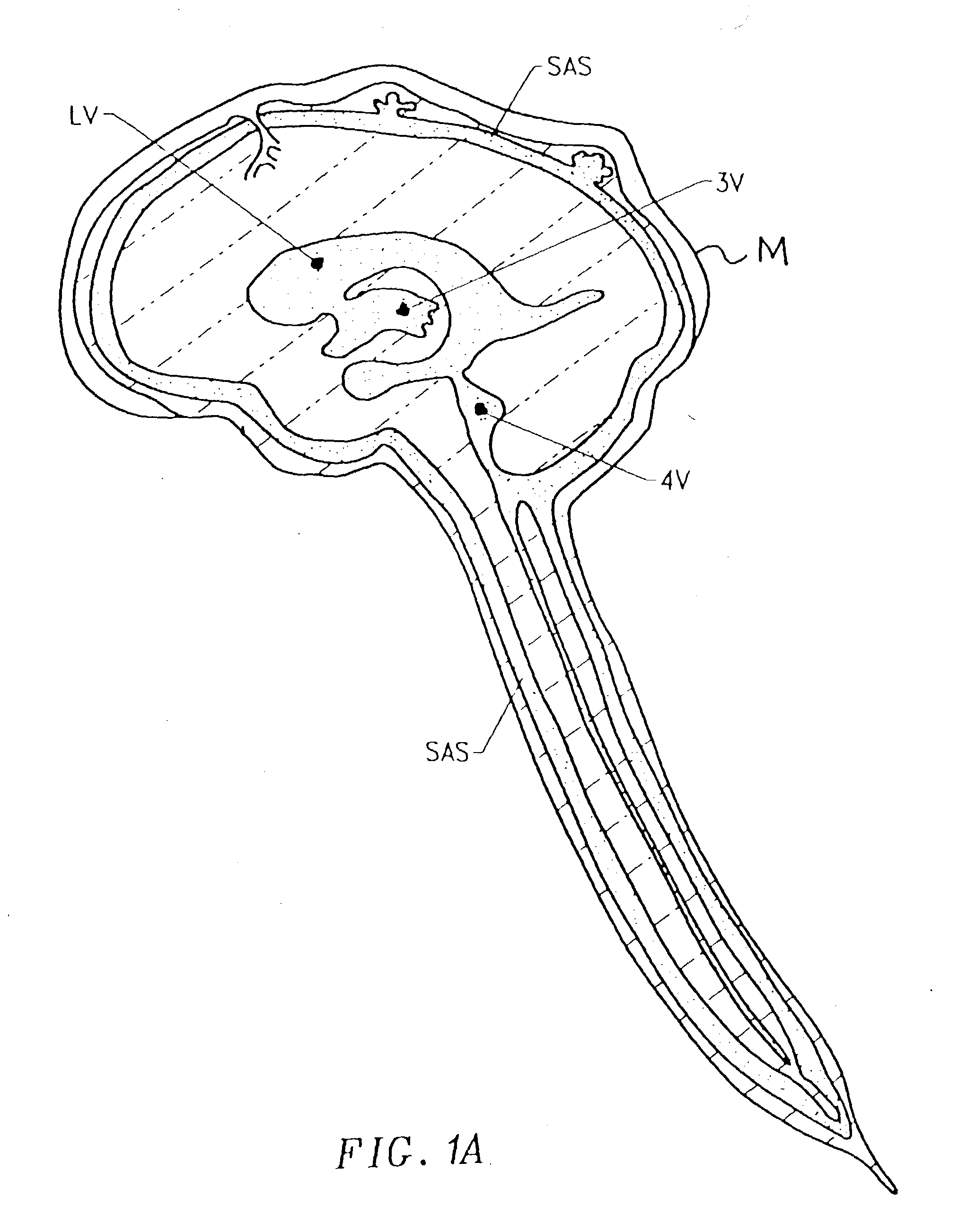
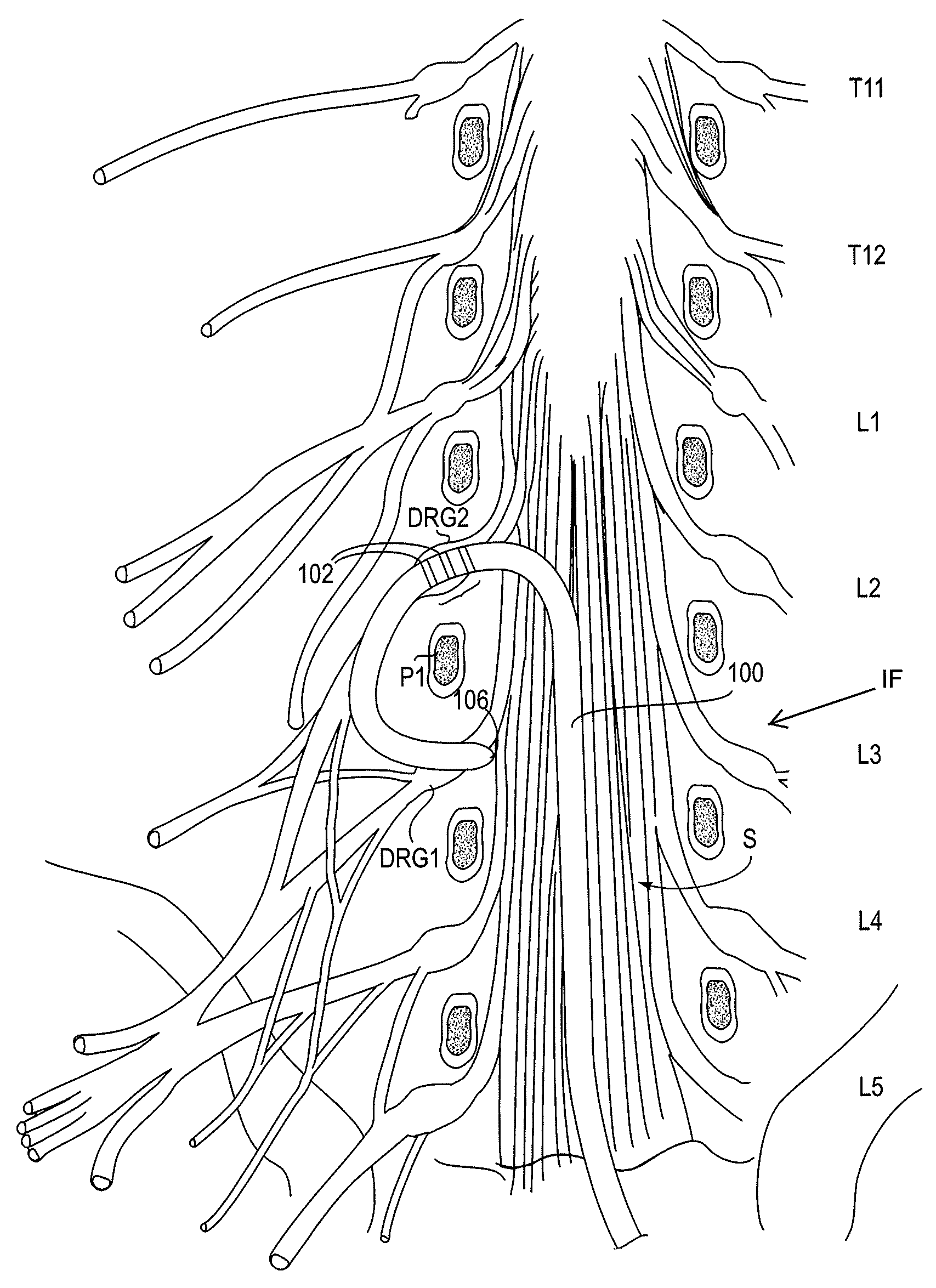
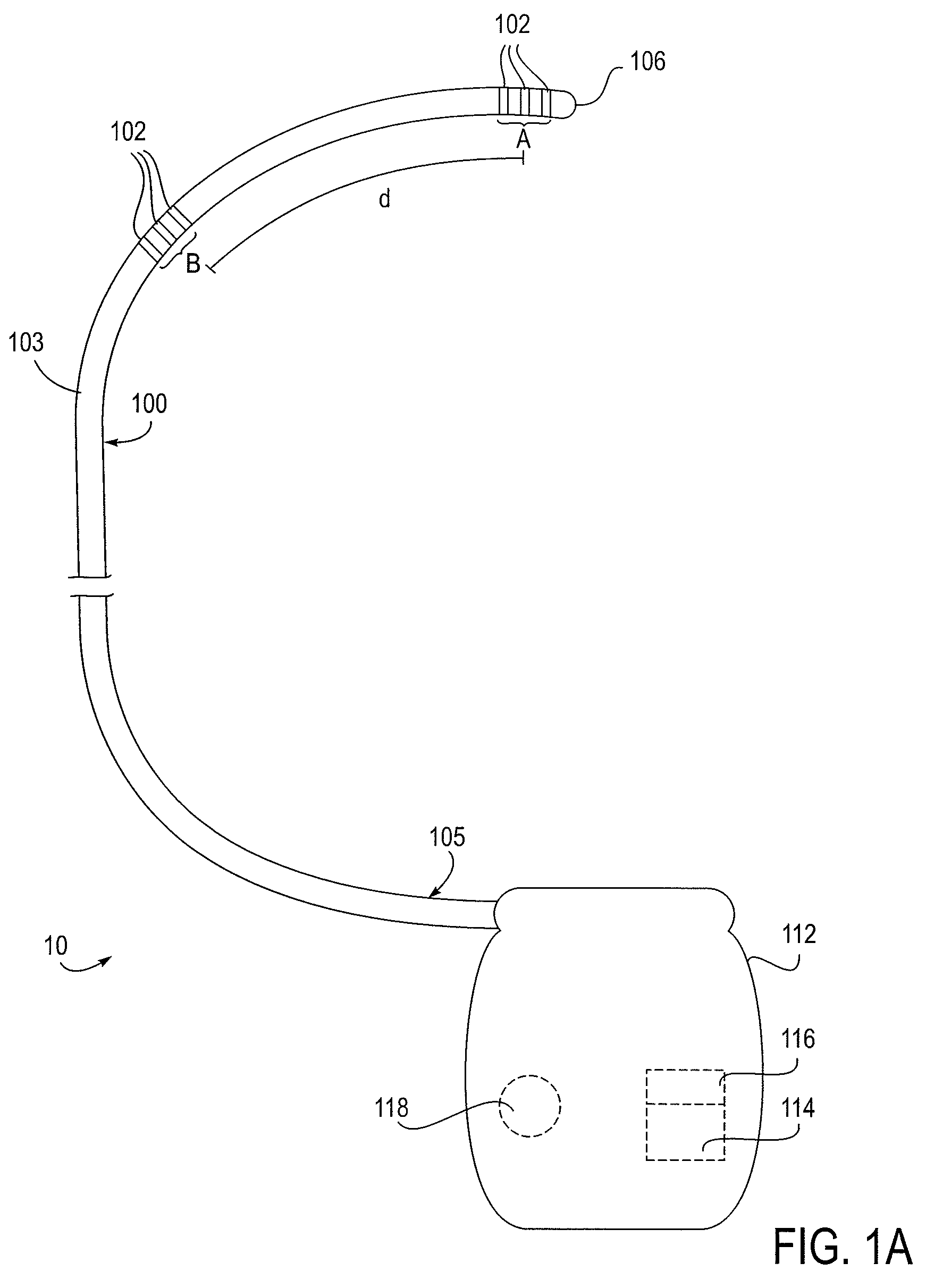
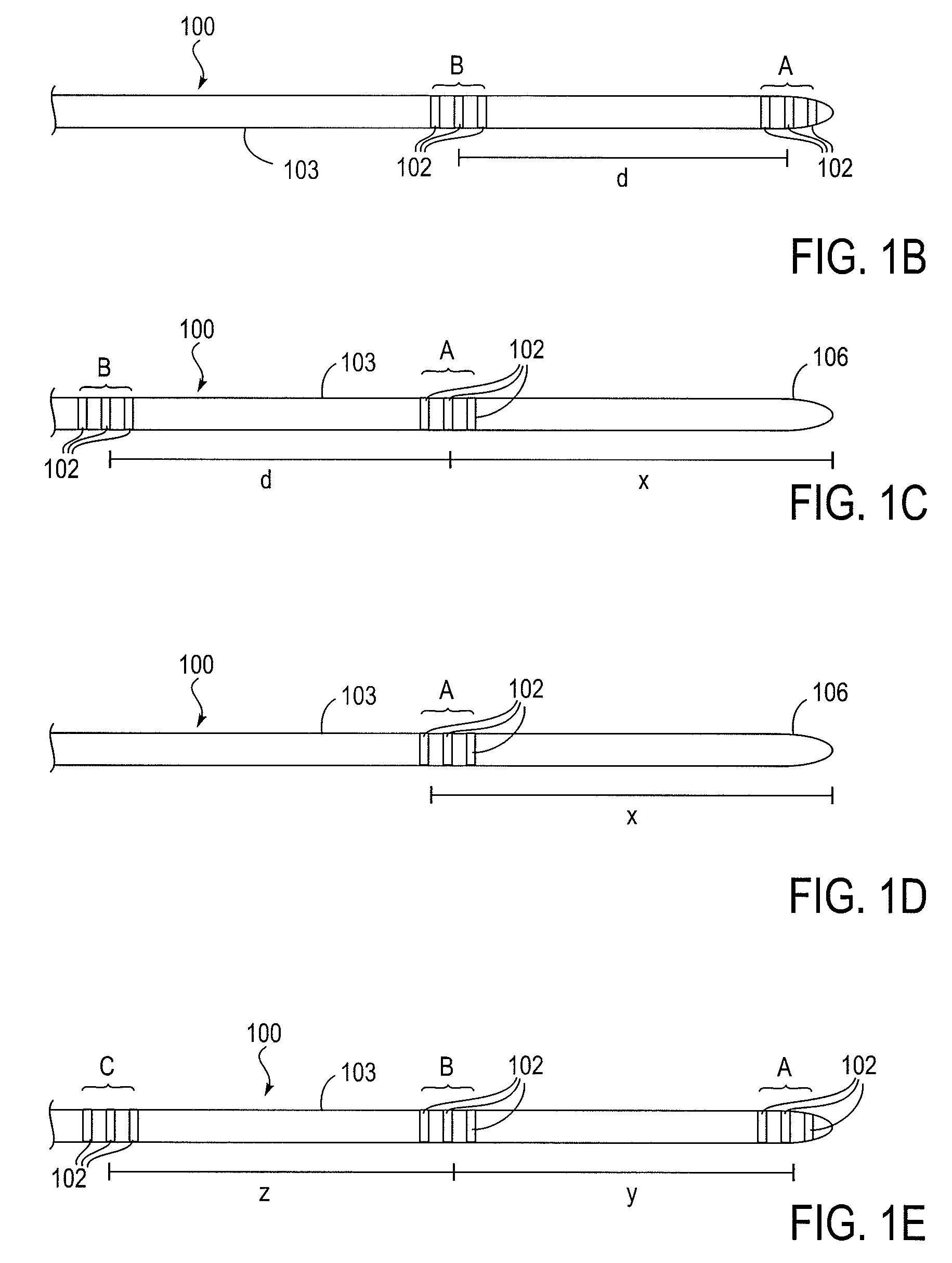
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
129 results about "Cerebral Spinal Fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cerebral Spinal Fluid: Cerebral spinal fluid is a clear watery fluid that flows within the brain and in the subarachnoid space in the meninges, which surround the central nervous system.
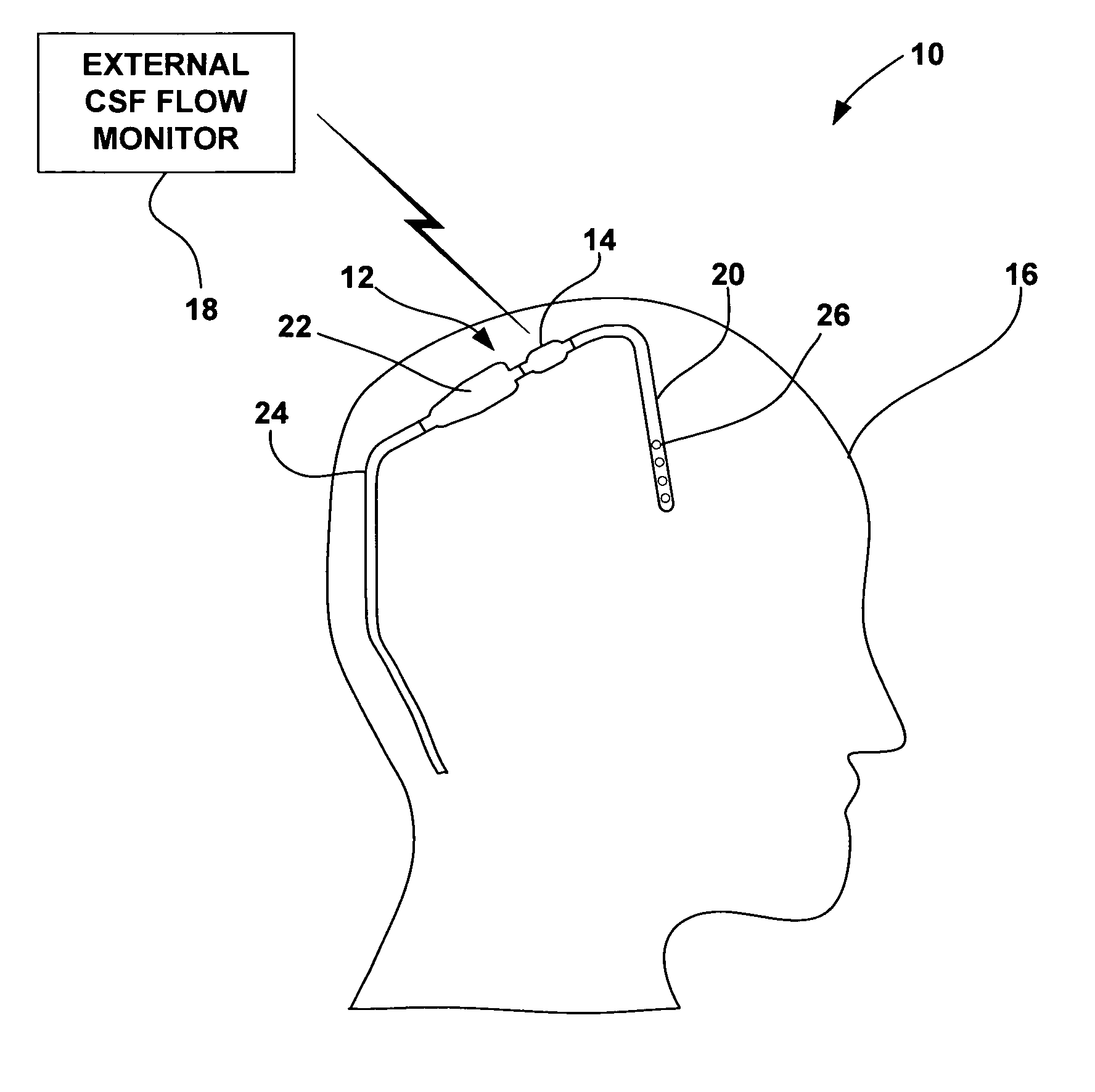
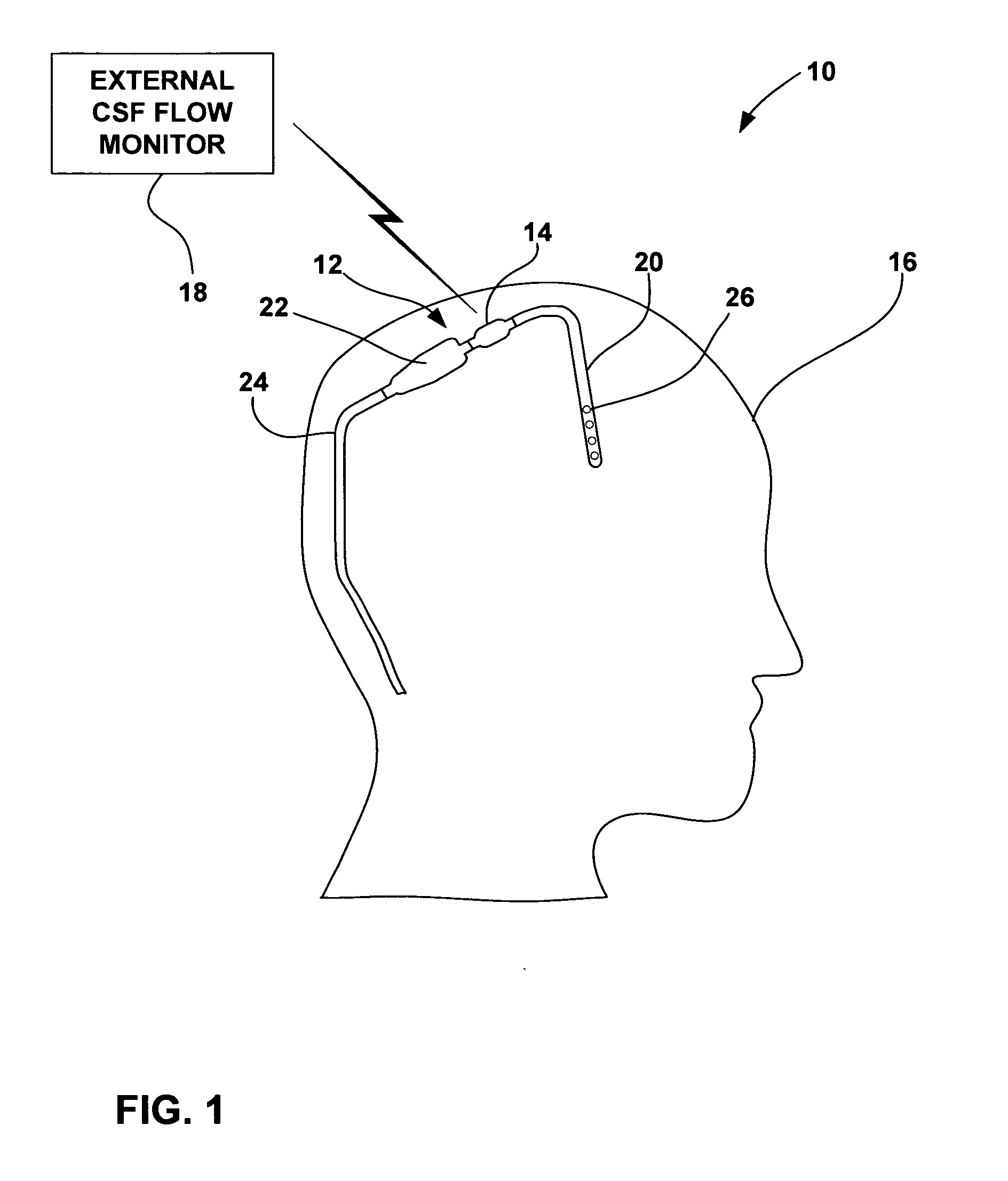
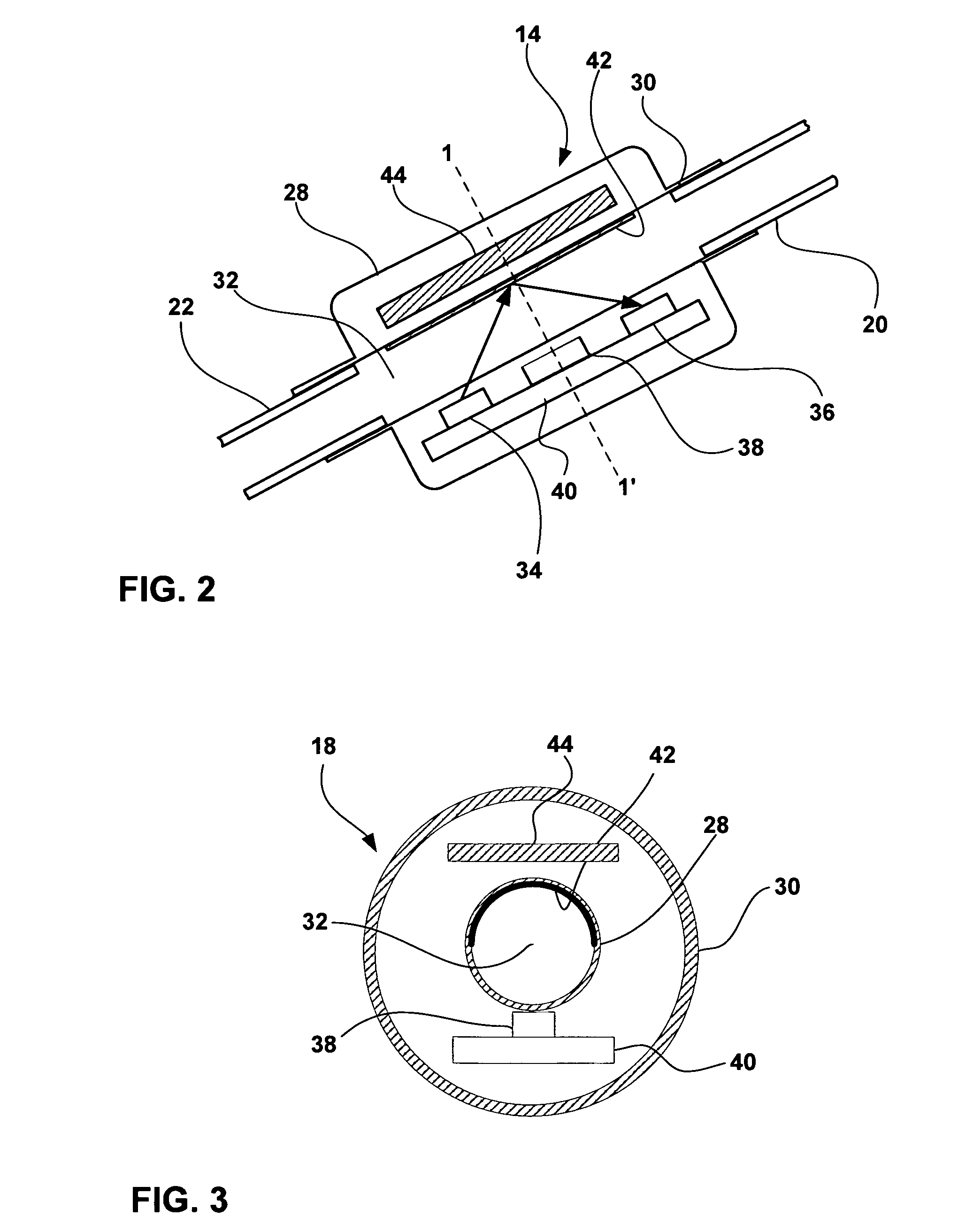
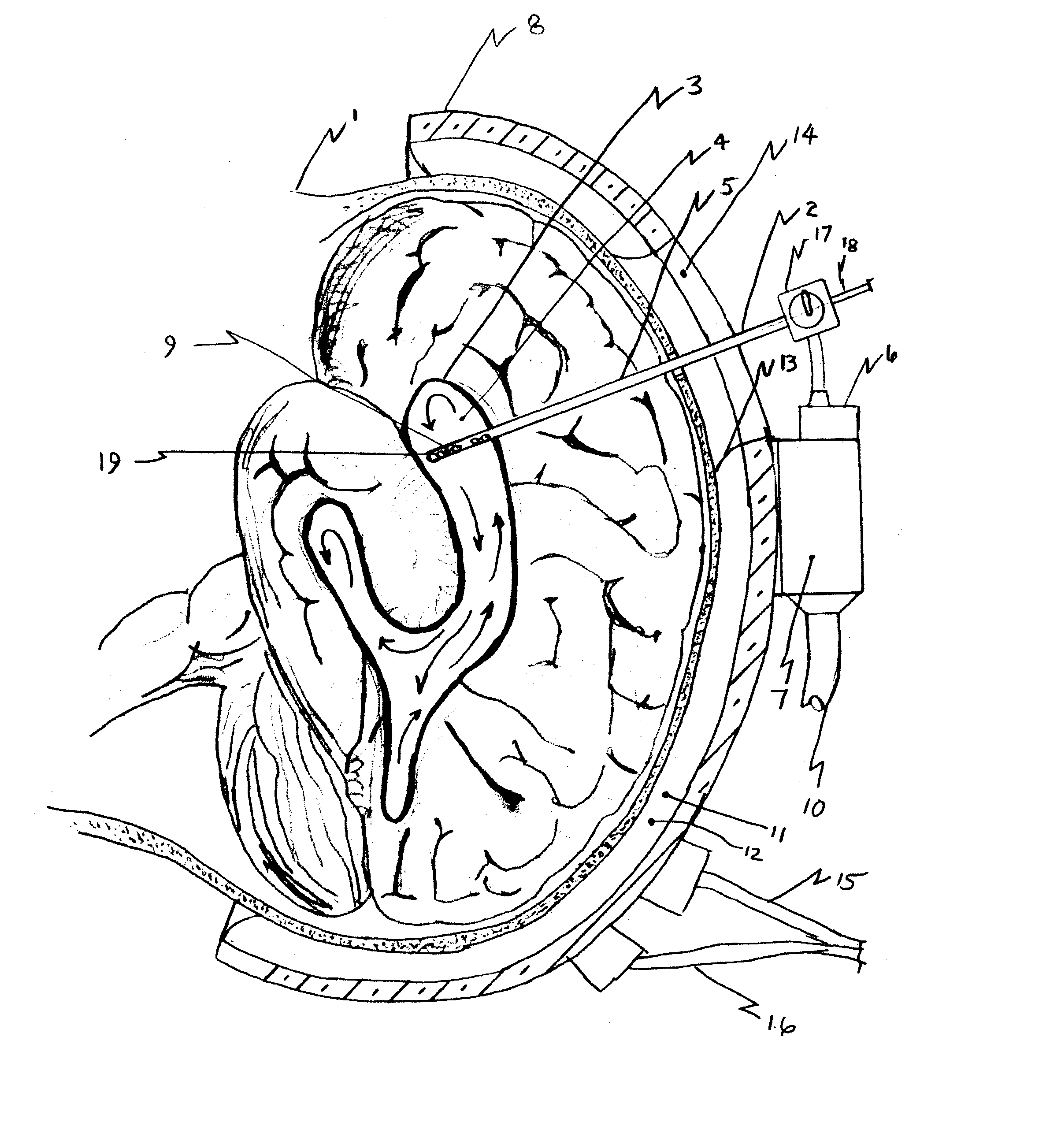
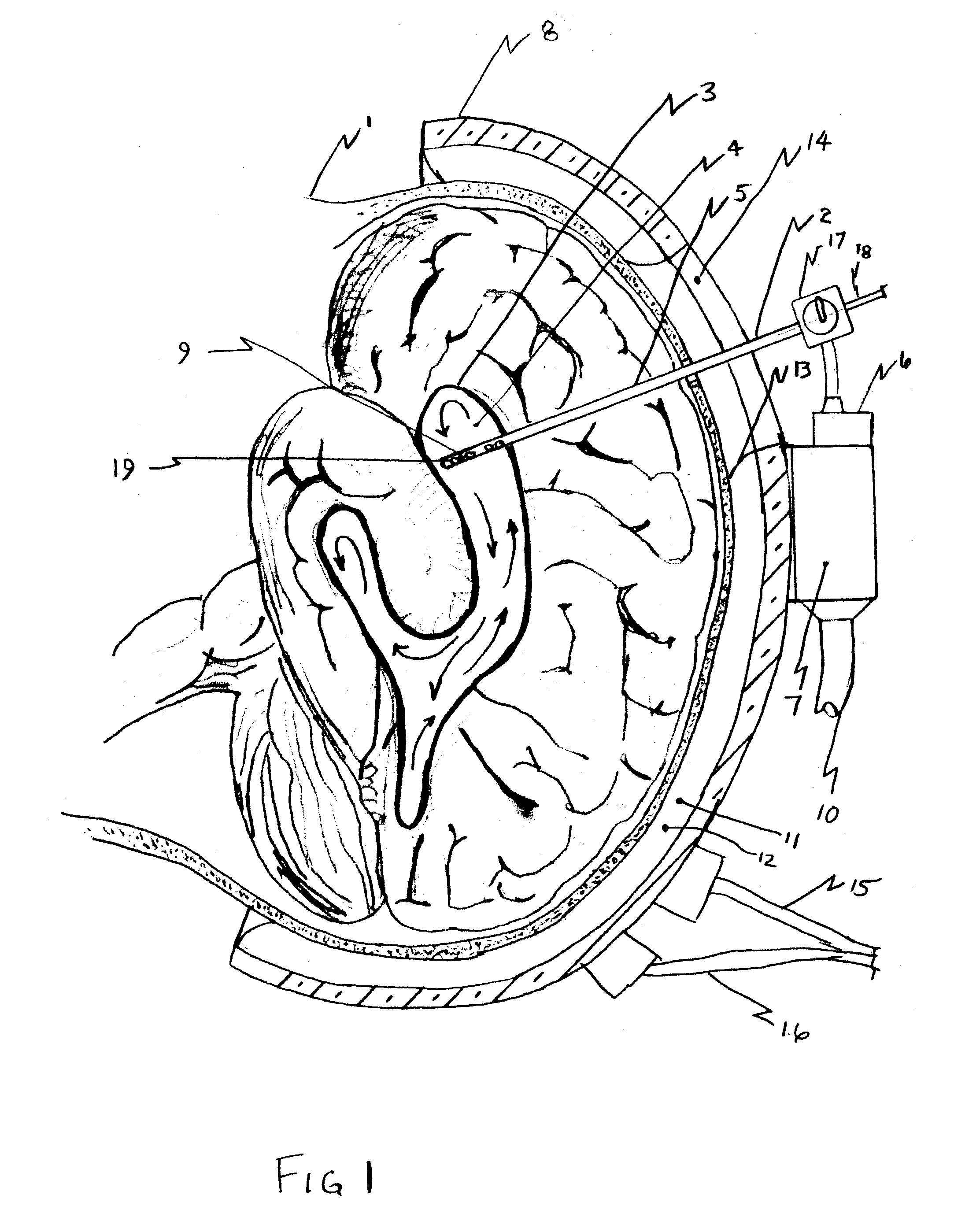
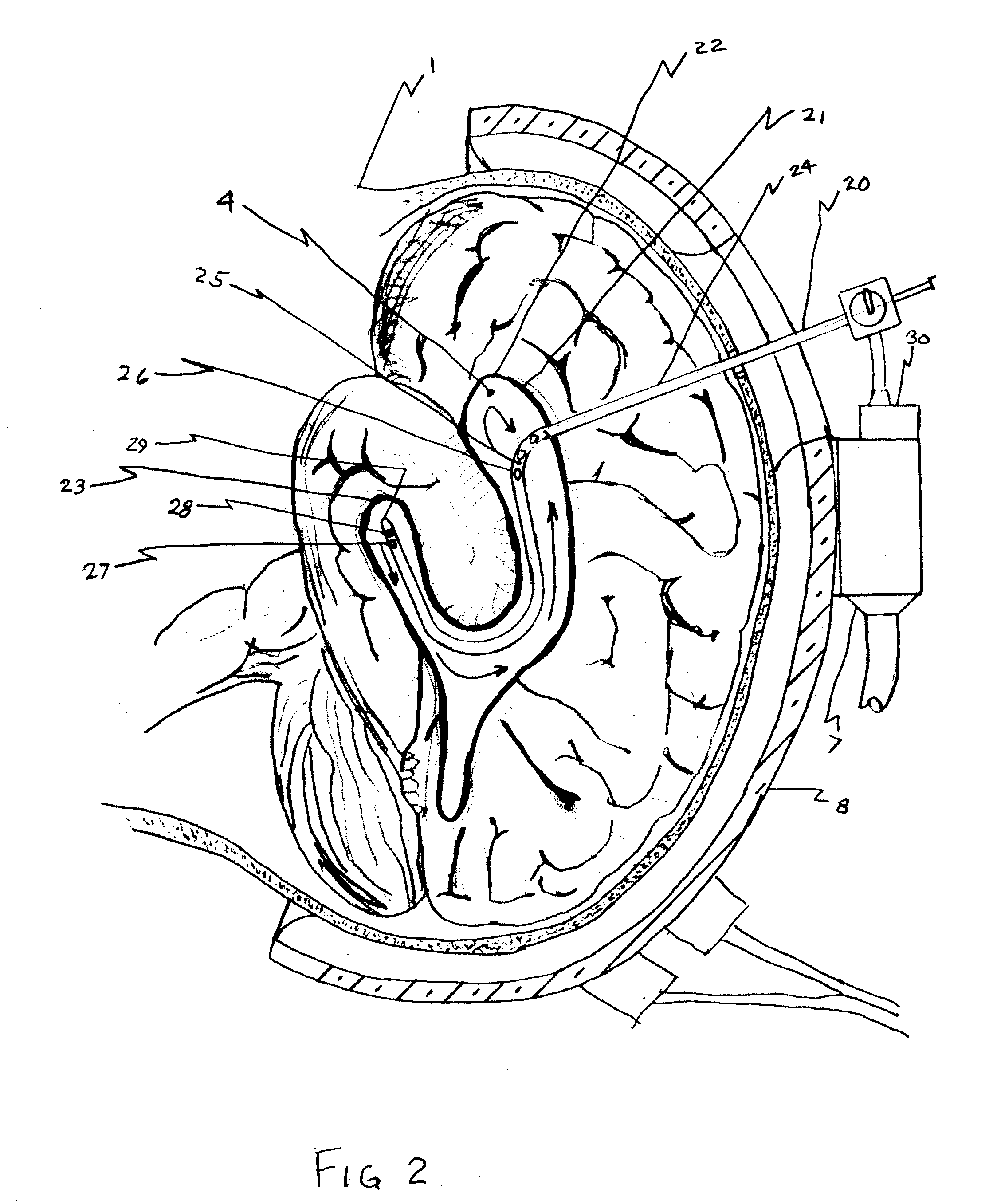
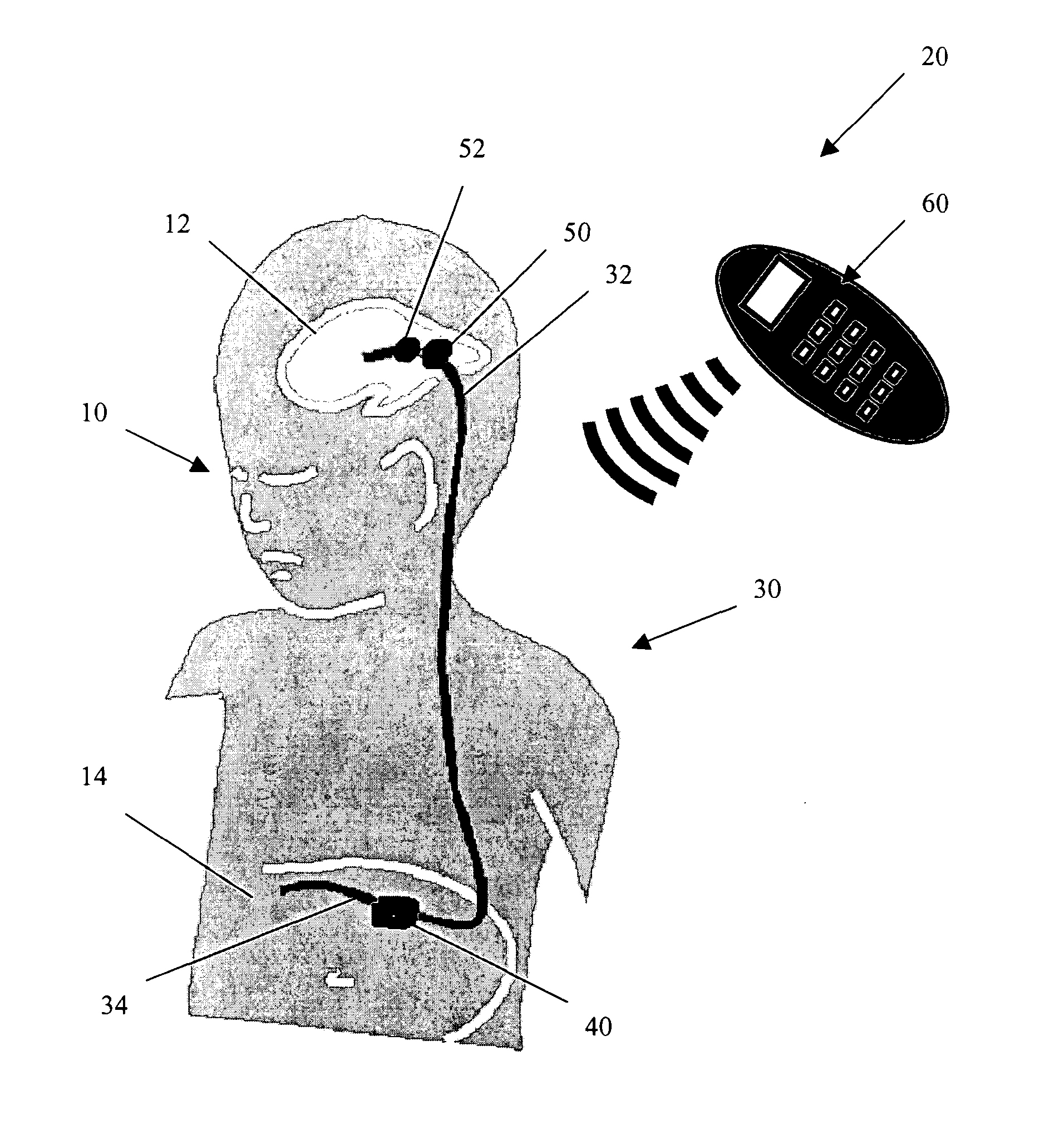
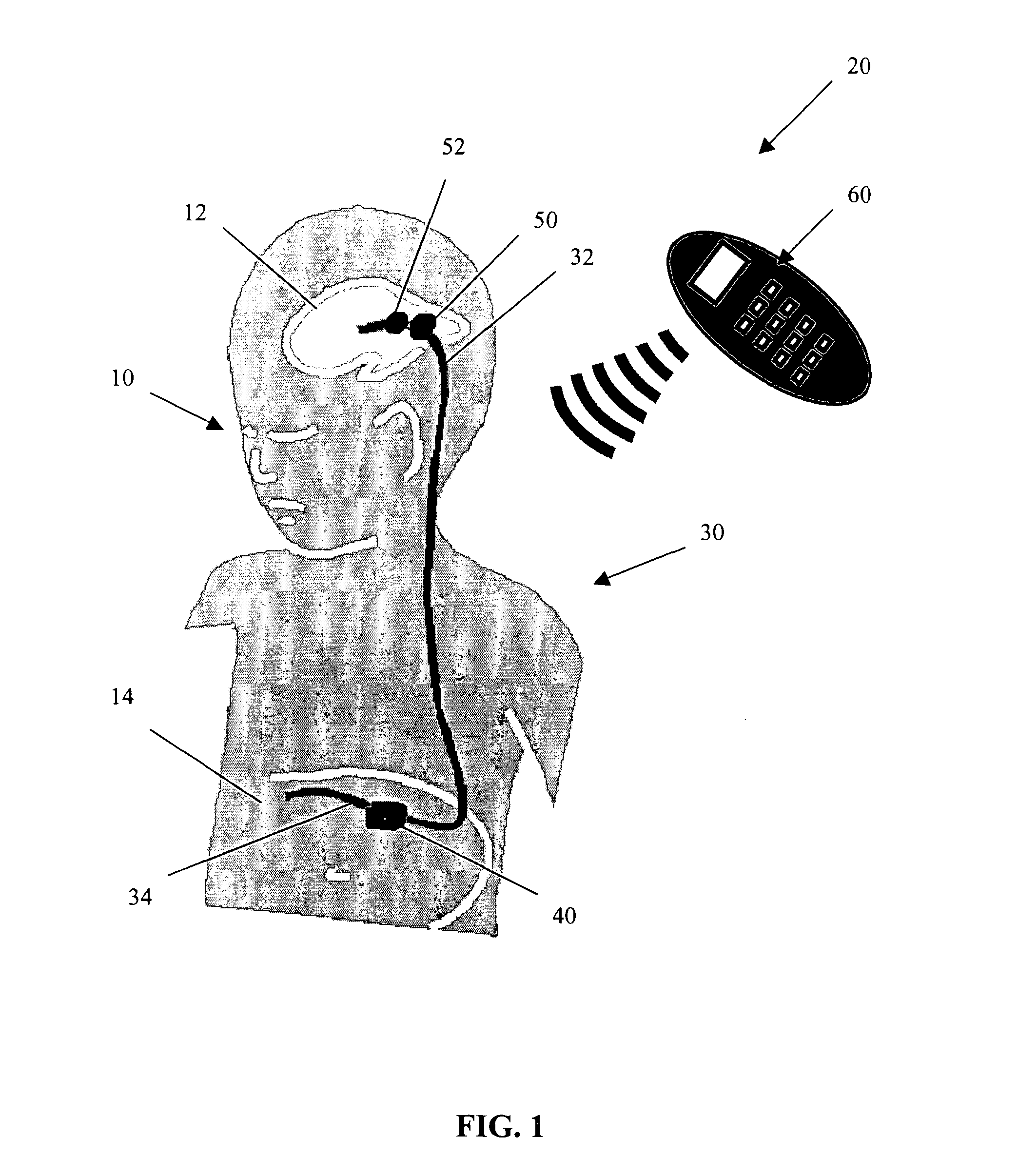
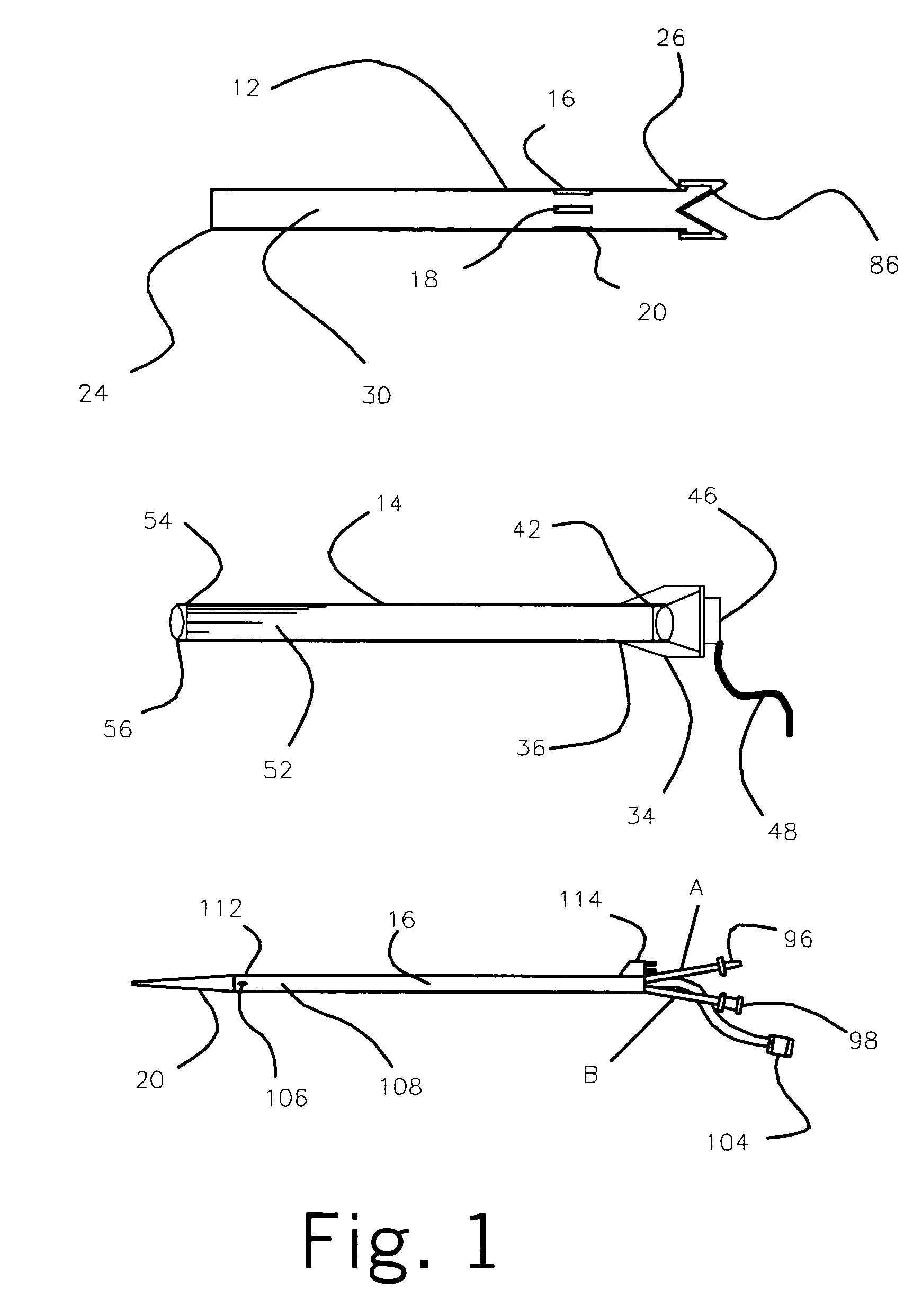
Cerebral spinal fluid flow sensing device
InactiveUS20060020239A1Evaluate performance of ventricular shuntEnsure correct executionWound drainsEndoradiosondesFlow transducerCsf shunt
The disclosure is directed to an implantable device for sensing CSF flow through an implantable ventricular shunt. The sensing device is implanted with the CSF shunt, and includes a flow sensor to sense flow rate or shunt blockage. The sensing device is either placed within or adjacent to the fluid path through the shunt. The sensing device transmits the sensed flow rate to an external monitoring device by wireless telemetry. The sensing device may be integrally formed as part of the shunt, or clamped onto a portion of the shunt, in which case the sensing device may be resusable. An external monitor receives the transmitted flow signal and presents information based on the flow signal. The sensing device may be inductively powered or include its own power supply.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
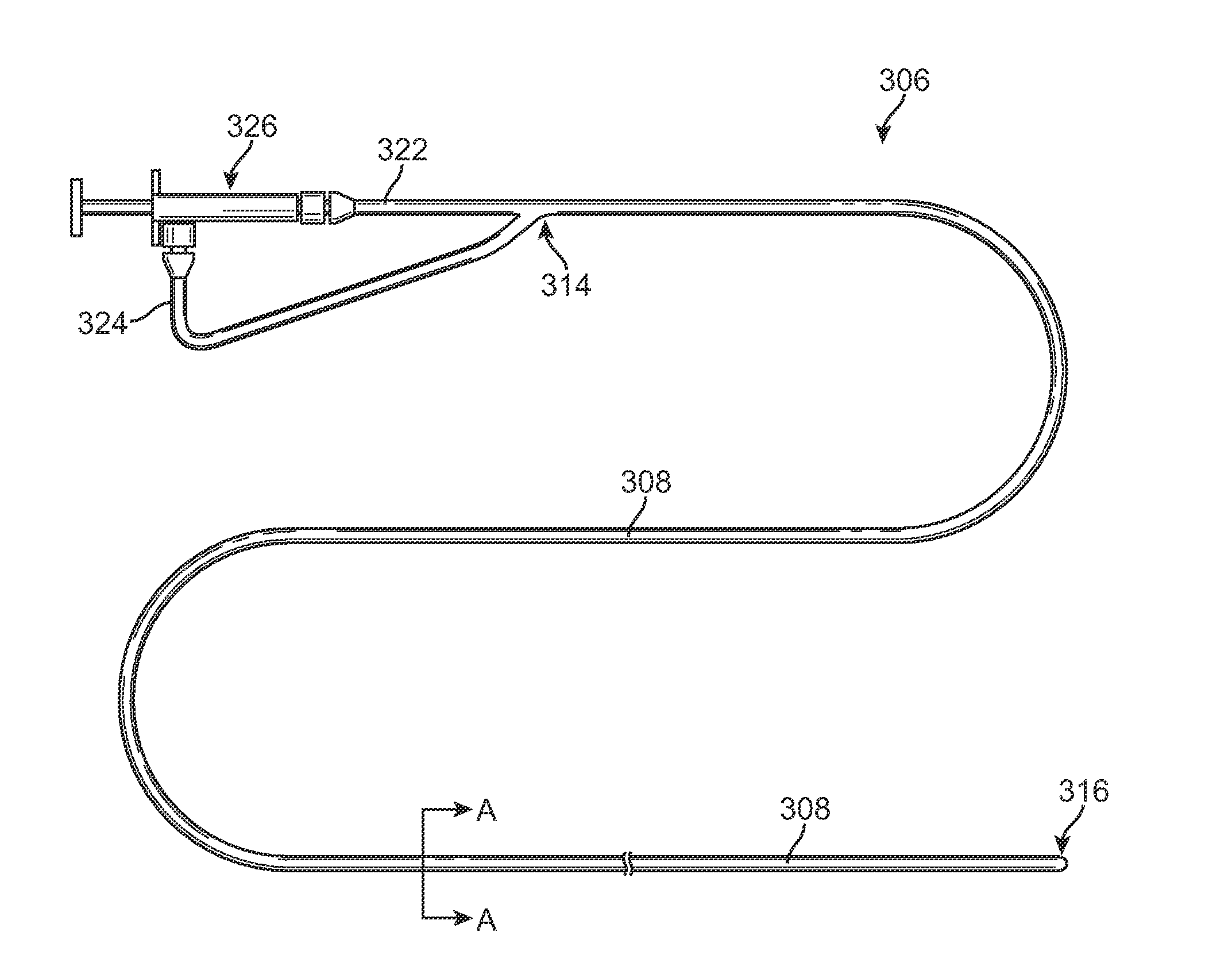
Methods for Simultaneous Injection and Aspiration of Fluids During a Medical Procedure
Methods for simultaneous injection and aspiration of fluids during a medical procedure are disclosed. Embodiments include methods for operating medical devices within the subarachnoid space of the spinal column to gain access to the ventricles of the brain, as well as the surrounding cranial subarachnoid space. A dual lumen constant volume aspiration catheter is disclosed that injects a volume of injectable fluid to break up an obstruction within the brain or cranial subarachnoid space while simultaneously aspirating a same volume of aspirated fluid from the treatment site. Methods hereof include constant volume re-circulation of cerebral spinal fluid to and from a treatment area within one of the brain and the surrounding cranial subarachnoid space, which may be desirable during a ventriculostomy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
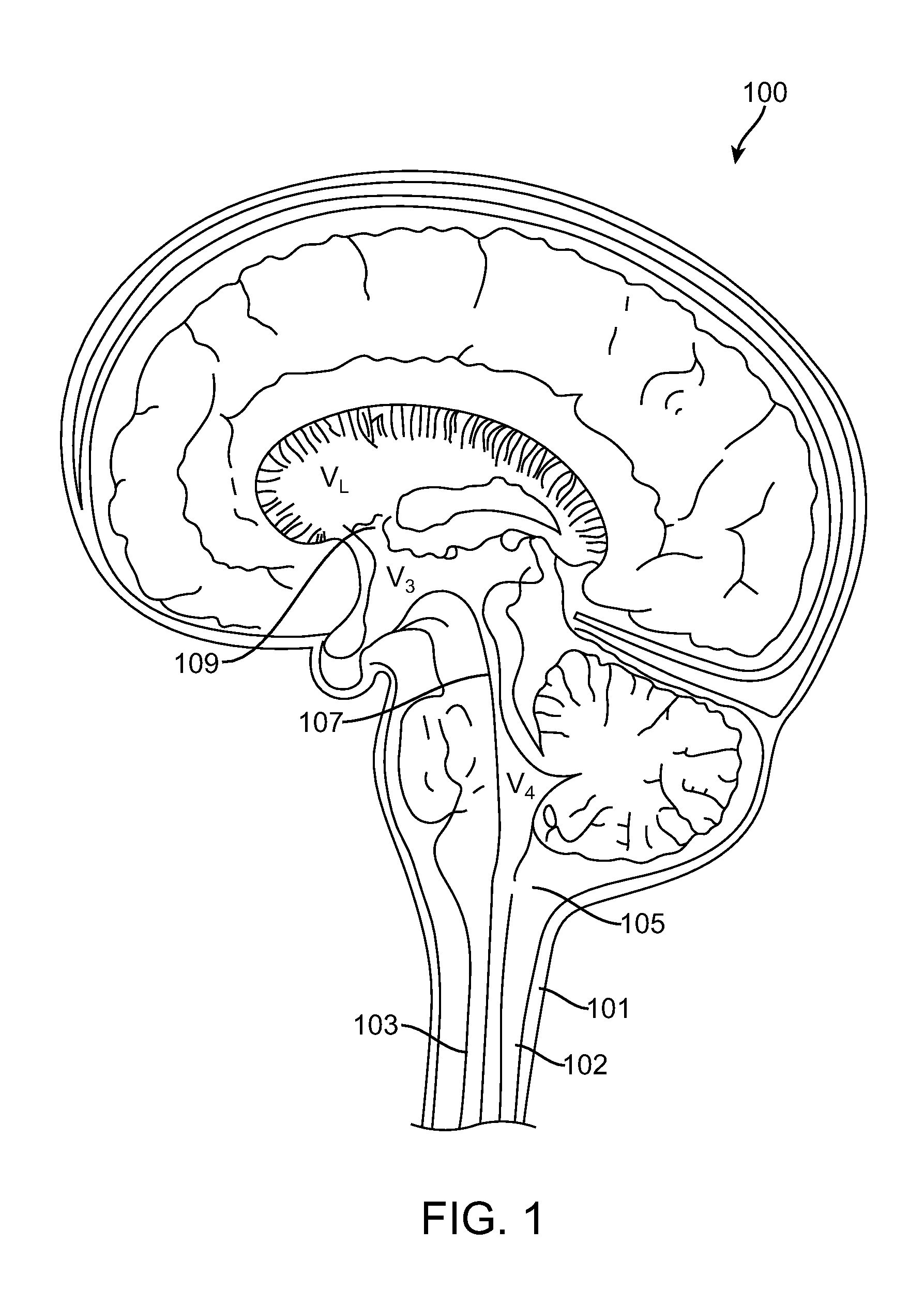
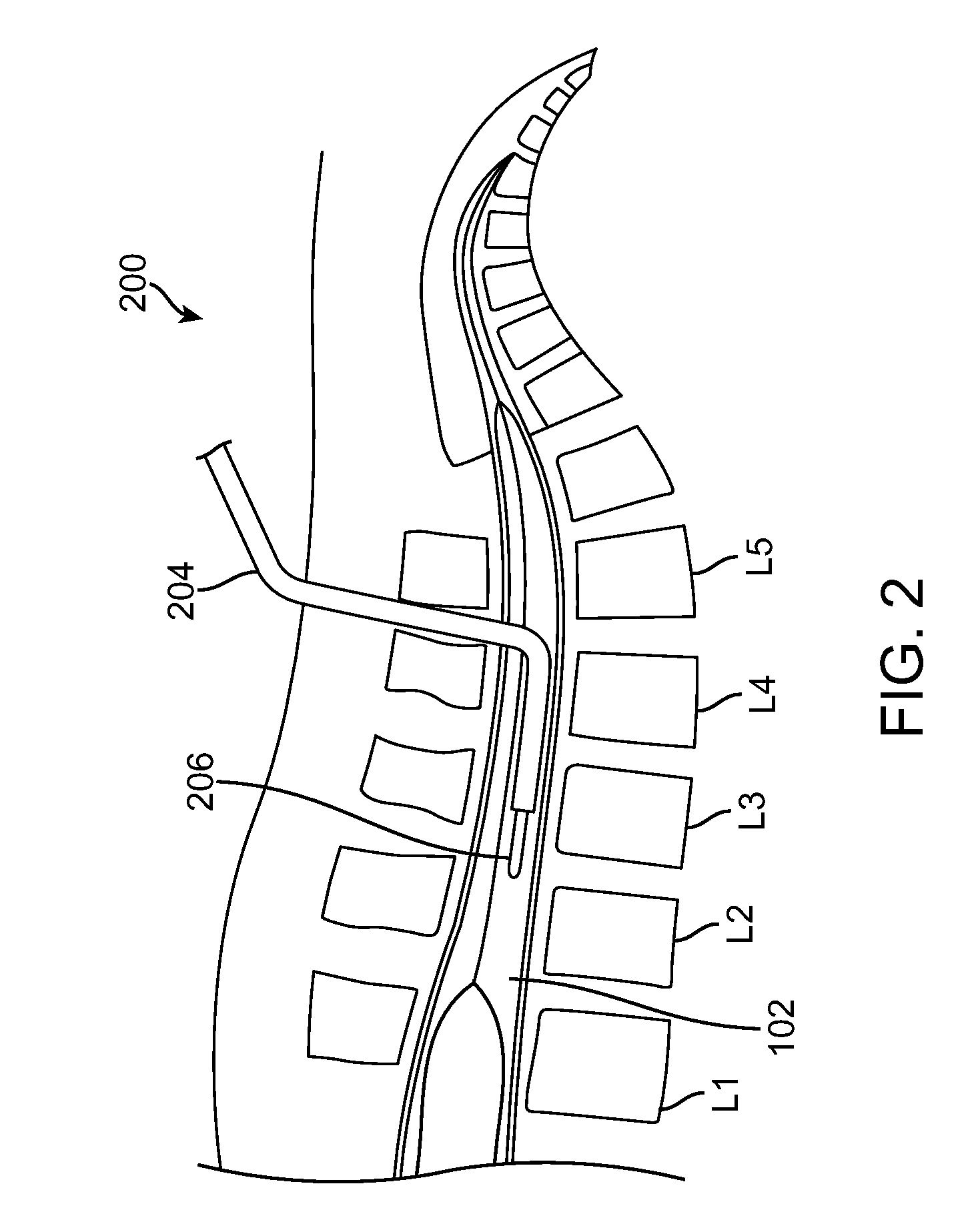
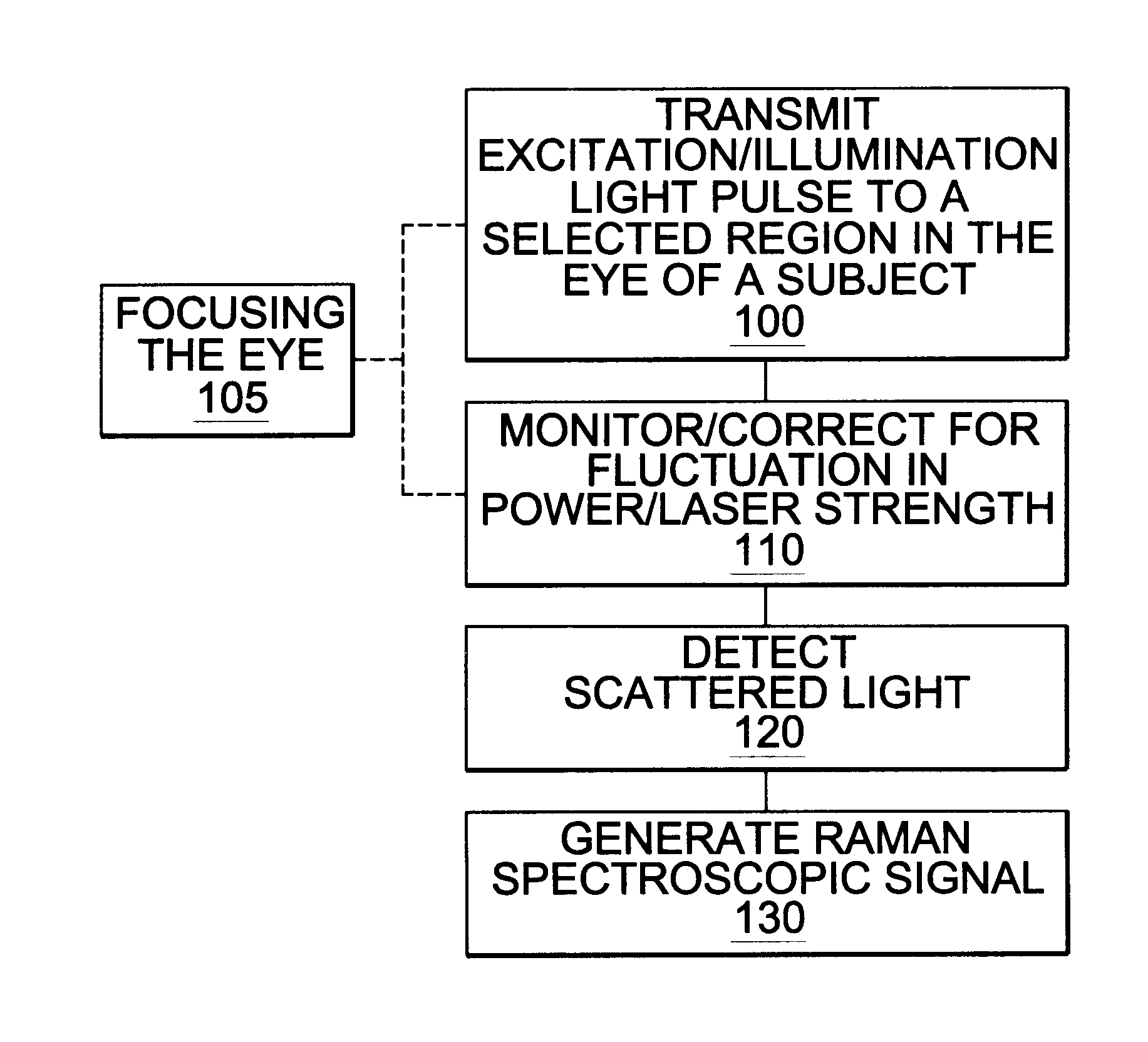
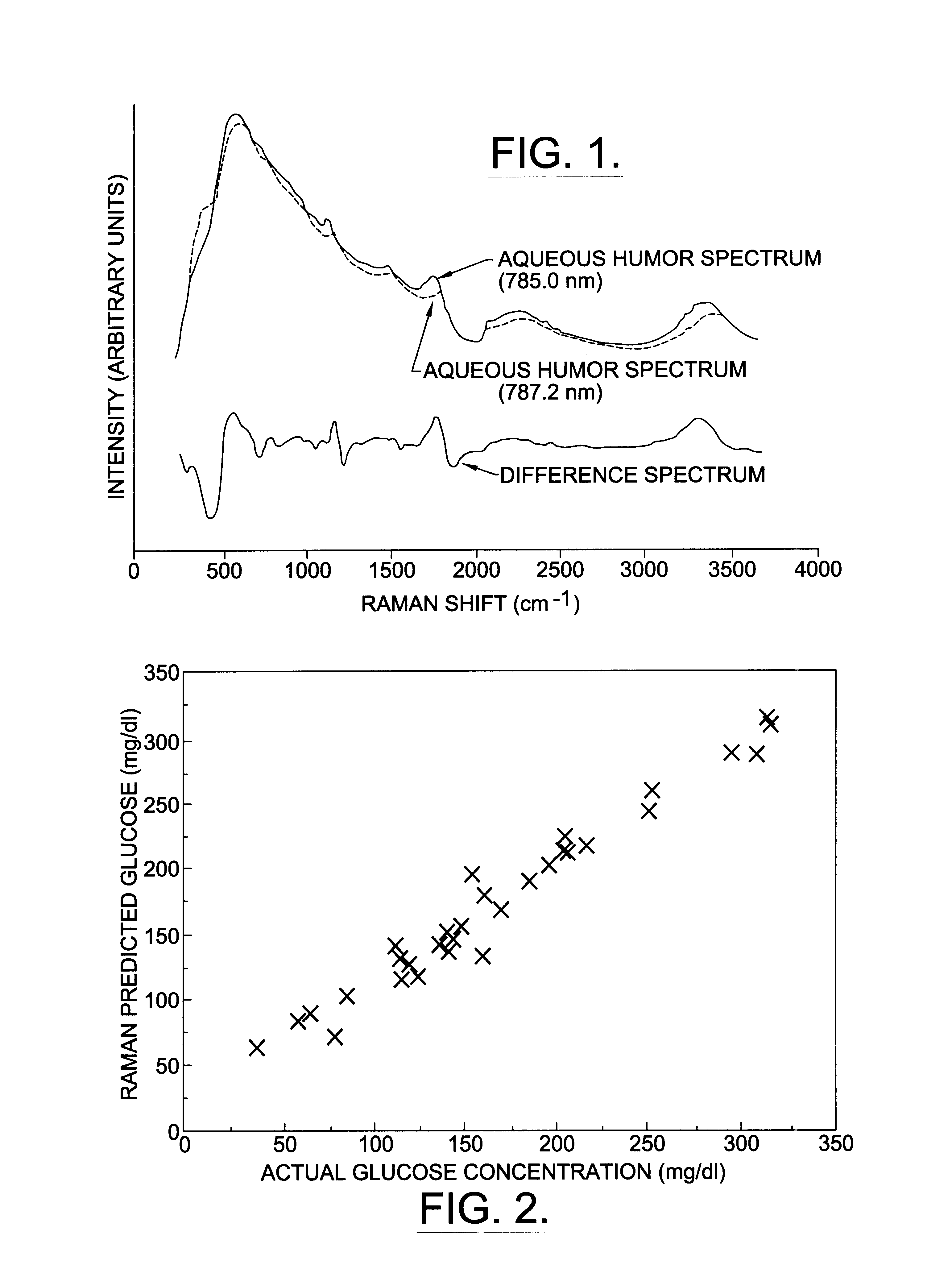
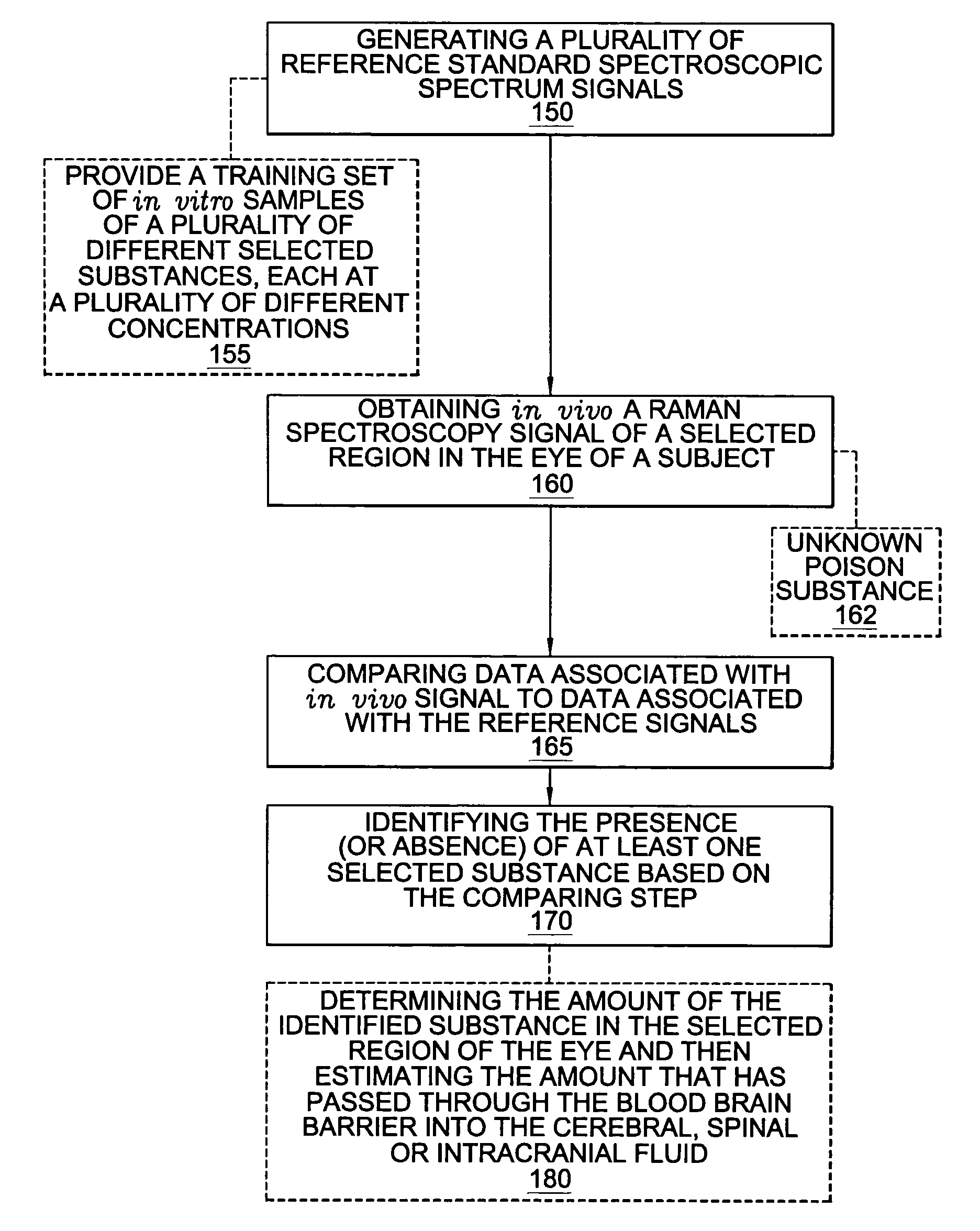
Assessing blood brain barrier dynamics or identifying or measuring selected substances or toxins in a subject by analyzing Raman spectrum signals of selected regions in the eye
InactiveUS6574501B2Reduced energy/density exposure ratingImproved margin of safetyRaman scatteringDiagnostic recording/measuringConjunctivaNon invasive
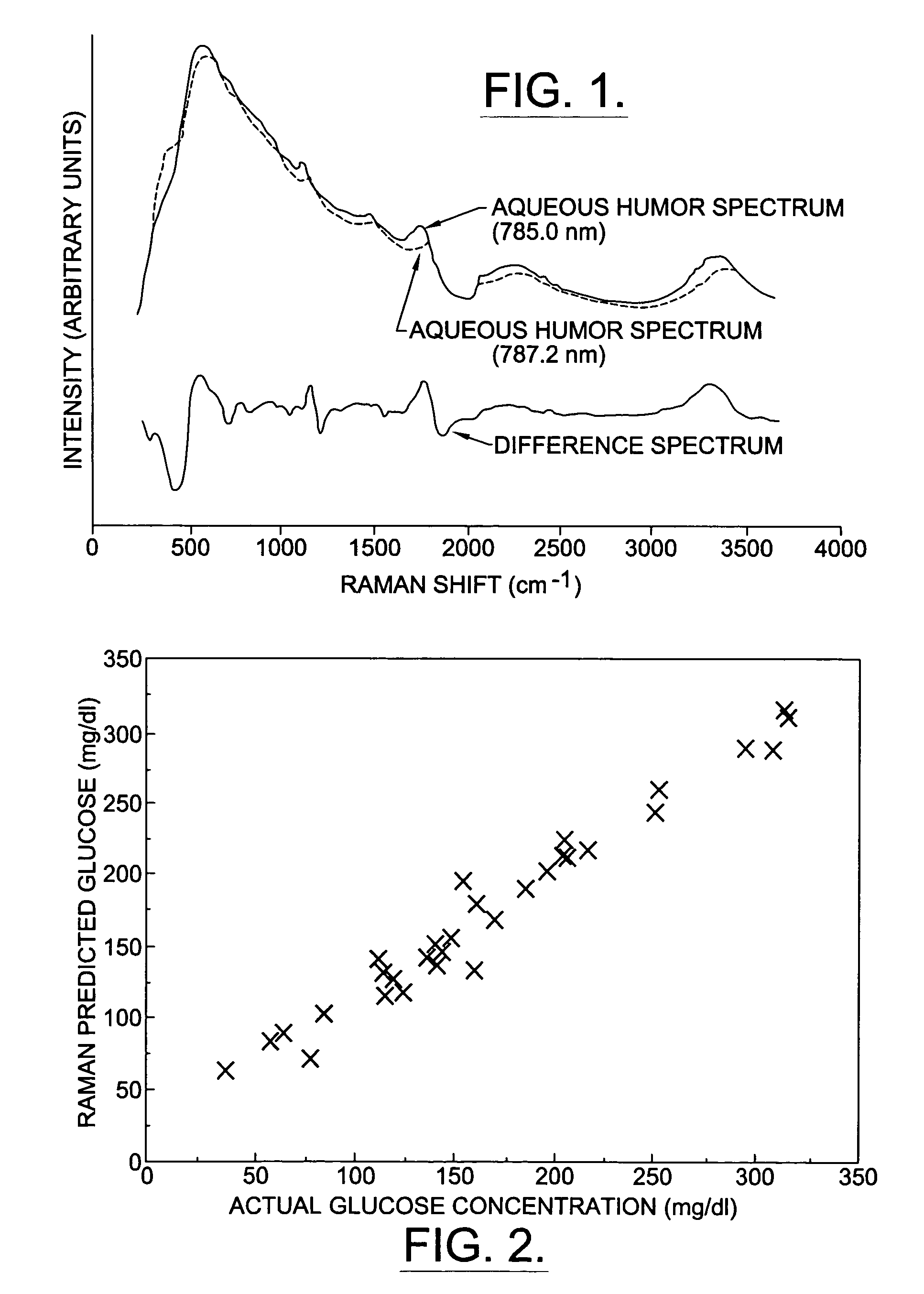
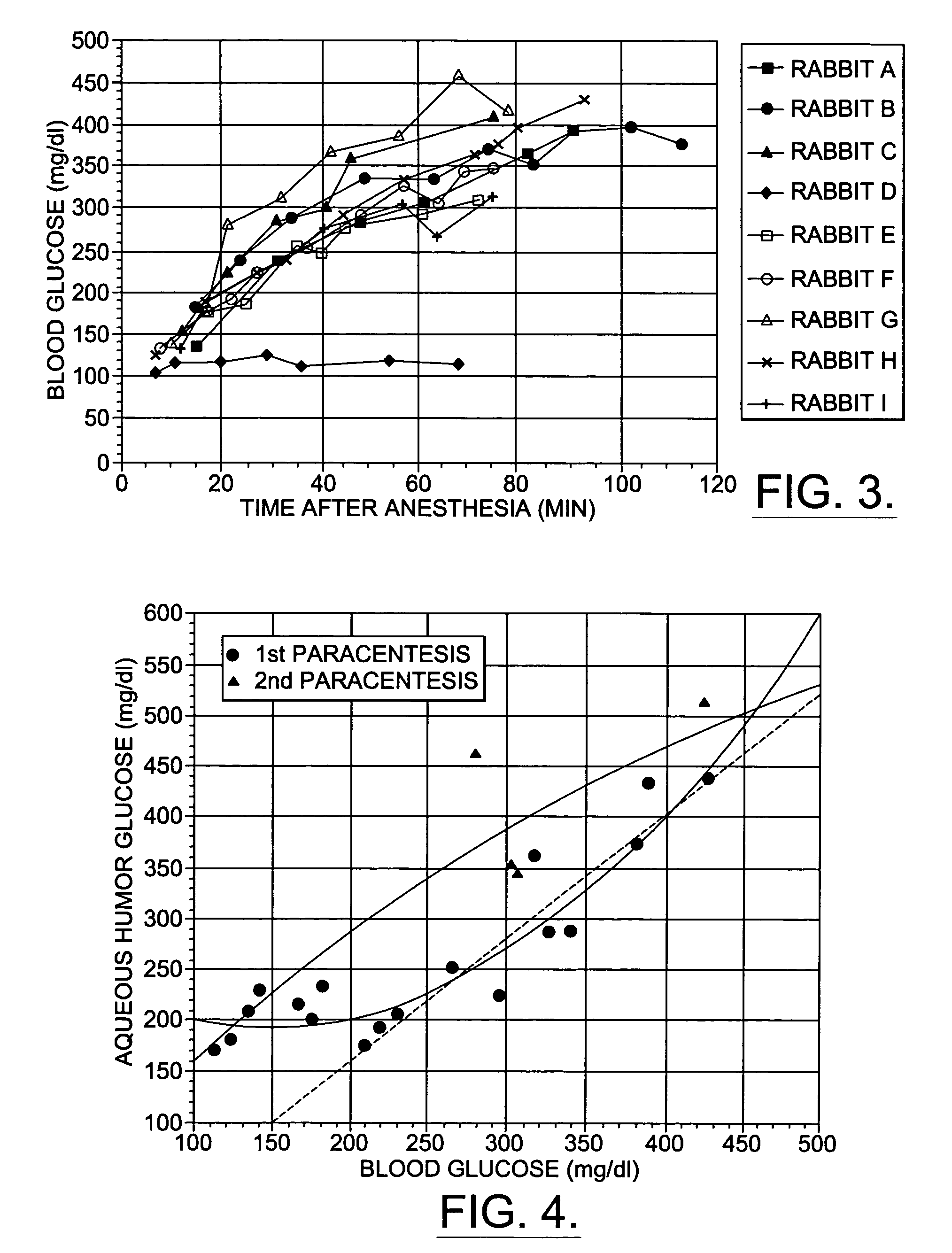
A non-invasive method for analyzing the blood-brain barrier includes obtaining a Raman spectrum of a selected portion of the eye and monitoring the Raman spectrum to ascertain a change to the dynamics of the blood brain barrier. Also, non-invasive methods for determining the brain or blood level of an analyte of interest, such as glucose, drugs, alcohol, poisons, and the like, comprises: generating an excitation laser beam (e.g., at a wavelength of 600 to 900 nanometers); focusing the excitation laser beam into the anterior chamber of an eye of the subject so that aqueous humor, vitreous humor, or one or more conjunctiva vessels in the eye is illuminated; detecting (preferably confocally detecting) a Raman spectrum from the illuminated portion of the eye; and then determining the blood level or brain level (intracranial or cerebral spinal fluid level) of an analyte of interest for the subject from the Raman spectrum. In certain embodiments, the detecting step may be followed by the step of subtracting a confounding fluorescence spectrum from the Raman spectrum to produce a difference spectrum; and determining the blood level and / or brain level of the analyte of interest for the subject from that difference spectrum, preferably using linear or nonlinear multivariate analysis such as partial least squares analysis. Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES +1
Multipath Stimulation Hearing Systems
A prosthetic hearing system is described that provides multi-path stimulation of the patient auditory system. A mechanical stimulation component applies mechanical stimulation signals to cerebral tissue such as the dura mater, cerebrospinal fluid, vestibular structures, etc. using multiple separate mechanical stimulation channels. And an electrical stimulation component provides electrical stimulation of auditory neural tissue of the patient user.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Assessing blood brain barrier dynamics or identifying or measuring selected substances, including ethanol or toxins, in a subject by analyzing Raman spectrum signals
InactiveUS7398119B2Fast “ triage ” assessmentReliable and faster treatment decisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationNon invasivePhysics
A non-invasive method for analyzing the blood-brain barrier includes obtaining a Raman spectrum of a selected portion of the eye and monitoring the Raman spectrum to ascertain a change to the dynamics of the blood brain barrier.Also, non-invasive methods for determining the brain or blood level of an analyte of interest, such as glucose, drugs, alcohol, poisons, and the like, comprises: generating an excitation laser beam at a selected wavelength (e.g., at a wavelength of about 400 to 900 nanometers); focusing the excitation laser beam into the anterior chamber of an eye of the subject so that aqueous humor, vitreous humor, or one or more conjunctiva vessels in the eye is illuminated; detecting (preferably confocally detecting) a Raman spectrum from the illuminated portion of the eye; and then determining the blood level or brain level (intracranial or cerebral spinal fluid level) of an analyte of interest for the subject from the Raman spectrum. In certain embodiments, the detecting step may be followed by the step of subtracting a confounding fluorescence spectrum from the Raman spectrum to produce a difference spectrum; and determining the blood level and / or brain level of the analyte of interest for the subject from that difference spectrum, preferably using linear or nonlinear multivariate analysis such as partial least squares analysis. Apparatus for carrying out the foregoing methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Methods and apparatus for delivering a drug influencing appetite for treatment of eating disorders
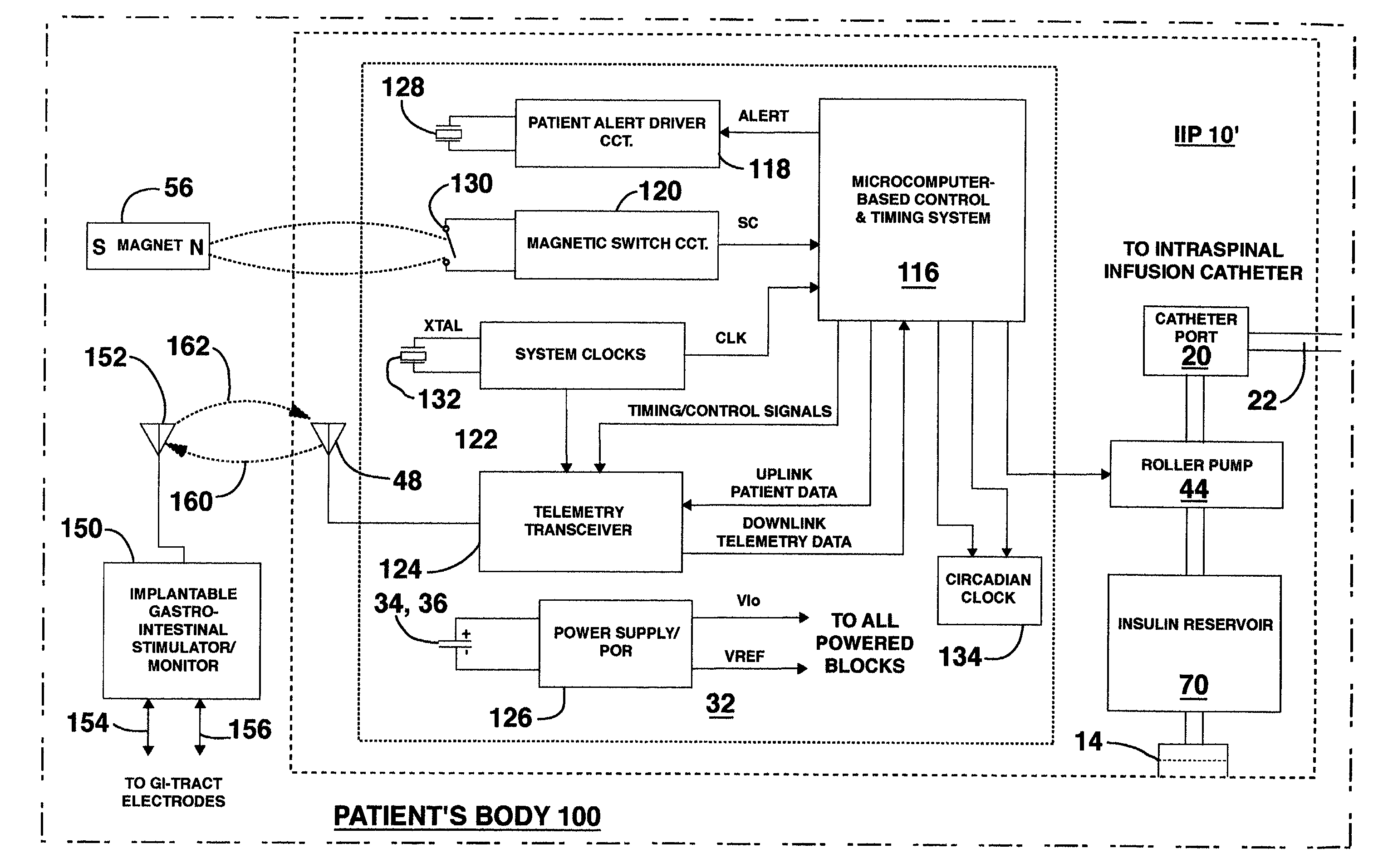
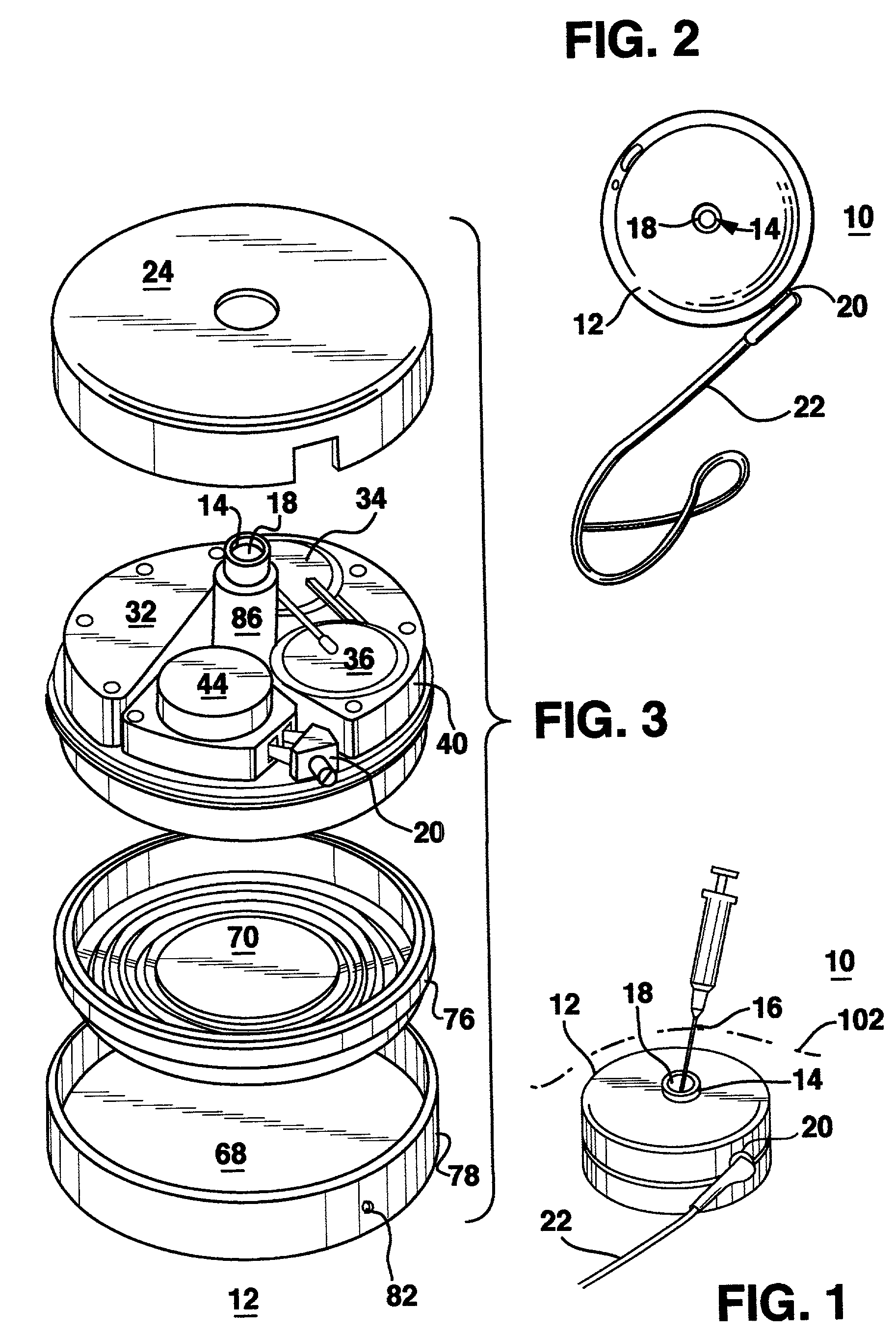
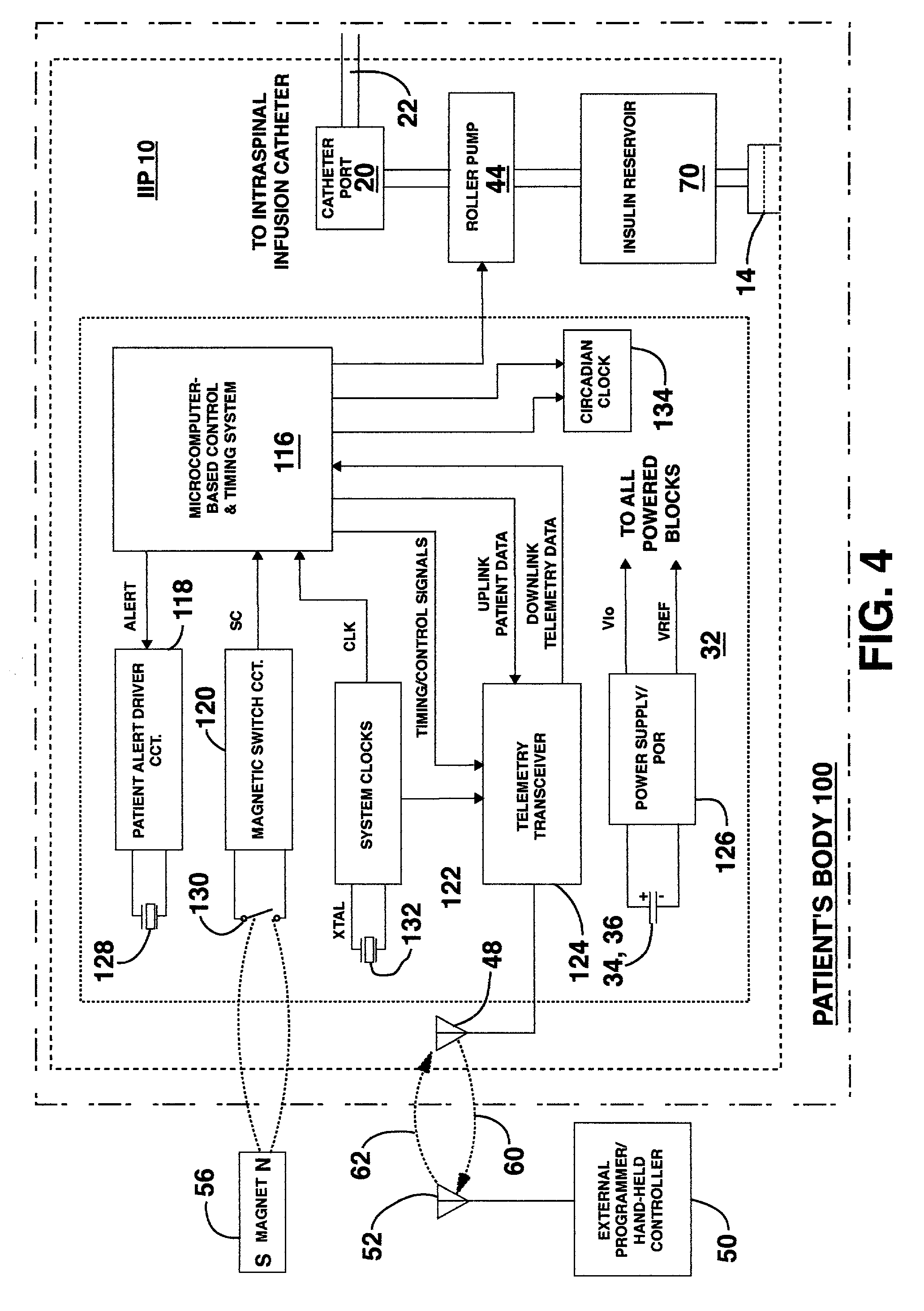
Methods and systems for treating patients suffering from eating disorders, e.g. obesity, through the dispensation of a drug by an implantable infusion pump (IIP) delivering drug into the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) at a site of the intrathecal space in amounts and at times effective to suppress the patient's appetite through interaction of the drug transported through the CSF with receptors in the brain. Delivery of a programmed drug dosage is preferably by one of time-out of programmed time(s) of day, a command received from the patient, or a trigger signal developed from a sensed GI tract signal accompanying peristalsis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods, systems and devices for neuromodulating spinal anatomy
ActiveUS20100292769A1Minimizing complicationMinimize side effectsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSide effectSpinal anatomy
Devices, systems and methods for treating pain or other conditions while minimizing possible complications and side effects. Treatment typically includes electrical stimulation and / or delivery of pharmacological or other agents with the use of a lead or catheter. The devices, systems and methods provide improved anchoring which reduces migration of the lead yet allows for easy repositioning or removal of the lead if desired. The devices, systems and methods also provide for simultaneous treatment of multiple targeted anatomies. This shortens procedure time and allows for less access points, such as needle sticks to the epidural space, which in turn reduces complications, such as cerebral spinal fluid leaks, patient soreness and recovery time. Other possible complications related to the placement of multiple devices are also reduced.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Uniform selective cerebral hypothermia
InactiveUS20030130651A1Surgical instrument detailsIntravenous devicesCooling chamberTemperature difference
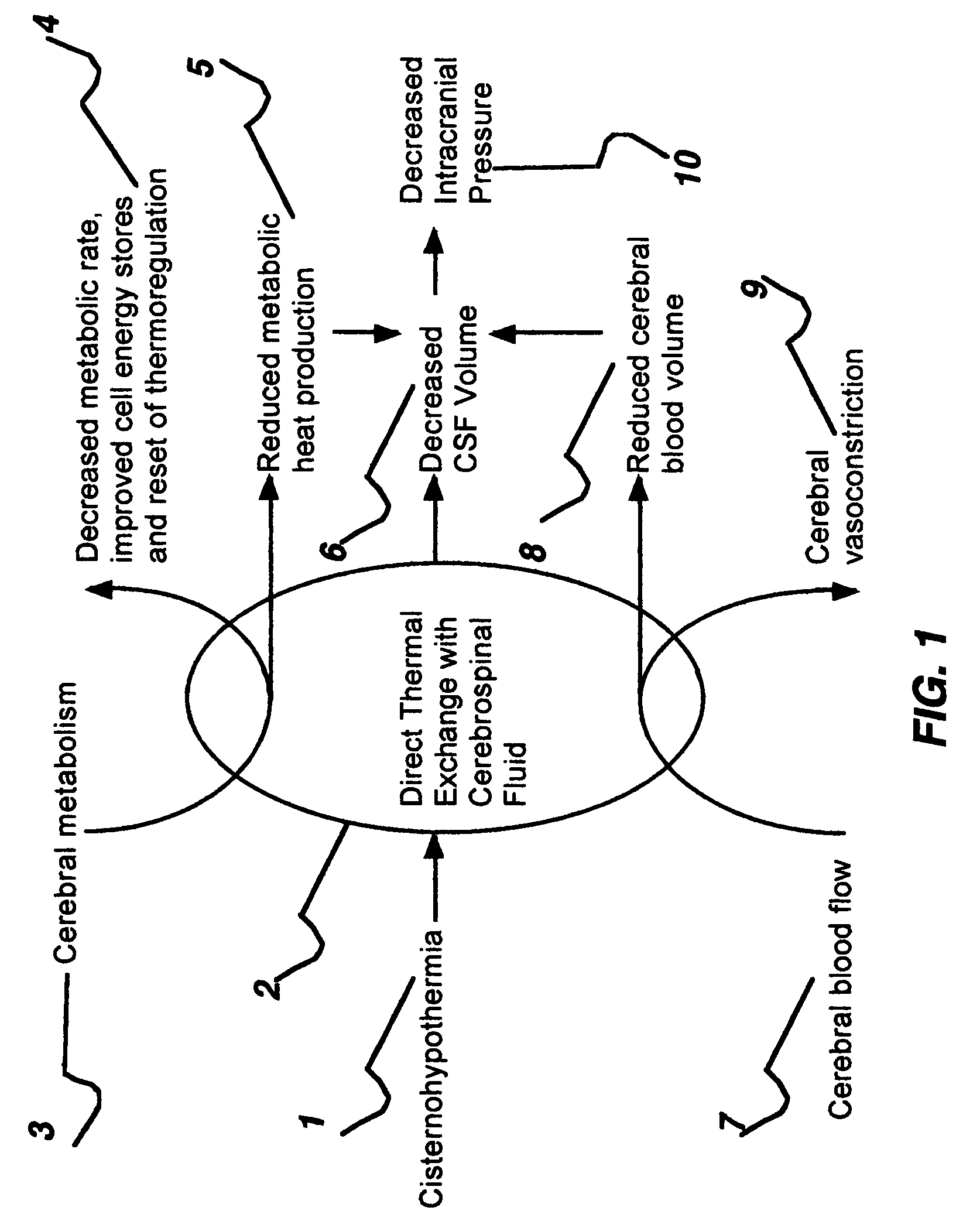
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for uniform selective cerebral hypothermia. The apparatus includes a brain-cooling probe, a head-cooling cap, a body-heating device and a control console. The brain-cooling probe cools the cerebrospinal fluid within one or more brain ventricles. The brain-cooling probe withdraws a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid from a ventricle into a cooling chamber located ex-vivo in close proximity to the head. After the cerebrospinal fluid is cooled it is then reintroduced back into the ventricle. This process is repeated in a cyclical or continuous manner. The head-cooling cap cools the cranium and therefore cools surface of the brain. The combination of ventricle cooling and cranium cooling provides for whole brain cooling while minimizing temperature gradients within the brain. The body-heating device replaces heat removed from the body by the brain-cooling probe and the head-cooling cap and provides for a temperature difference between the brain and the body where the brain is maintained a temperature lower than the temperature of the body.
Owner:MEDCOOL
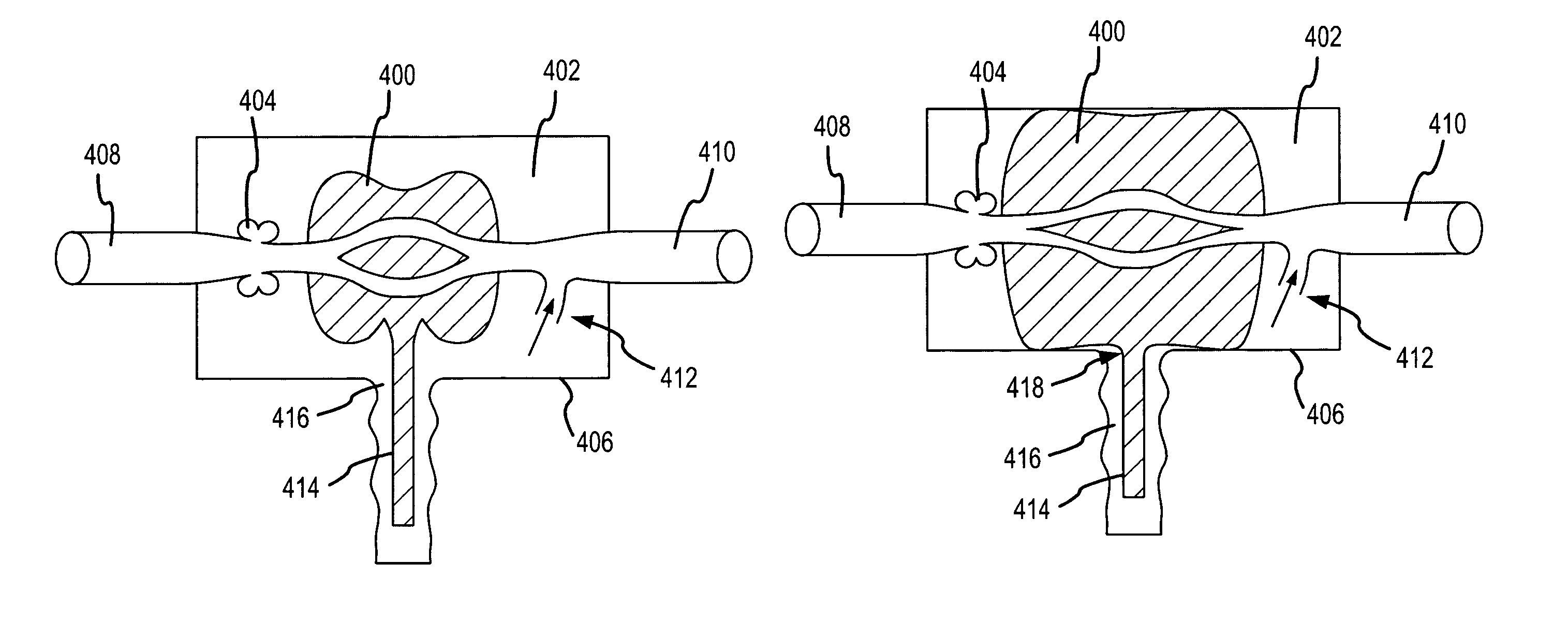
Systems and methods for increasing cerebral spinal fluid flow
InactiveUS7185649B2Decreasing intracranial and intraocular pressureReduce pressureElectrocardiographyBreathing filtersVeinCerebrospinal fluid
In one embodiment, the invention provides a device for decreasing intracranial or intraocular pressures. The device comprises a housing having an inlet opening and an outlet opening that is adapted to be interfaced with a person's airway. The device further includes a valve system that is operable to regulate respiratory gas flows through the housing and into the person's lungs during spontaneous or artificial inspiration. The valve system assists in lowering intrathoracic pressures during each inspiration to repetitively lower pressures in the venous blood vessels that transport blood out of the head to thereby reduce intracranial or intraocular pressures.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Device for the treatment of hydrocephalus
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricular catheter for insertion into the brain ventricle so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle. The system also comprises a sinus sagittalis catheter for insertion into the sinus sagittalis for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into sinus sagittalis. A shunt main body is connected at one end thereof to the brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to the sinus sagittalis catheter. The shunt main body can provide fluidic communication between the brain ventricle catheter and the sinus sagittalis catheter. The system further comprises a tubular flow passage restricting member defined within the shunt main body. The tubular flow passage restricting member defines a resistance to flow of 8-12 mm Hg / ml / min.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
Cerebrospinal Fluid Purification System
The present invention provides methods and systems for conditioning cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The methods provide for efficiently removing target compounds from CSF. The systems provide for a multilumen flow path and exchange of a majority volume portion of CSF in the CSF space. The removal and / or delivery of specific compounds can be tailored to the pathology of the specific disease. The removal is targeted and specific, for example, through the use of specific size-exclusion thresholds, antibodies against specific toxins, and other chromatographic techniques, as well as delivery and / or removal of targeted therapeutic agents. The invention finds use as a diagnostic, therapeutic and drug delivery platform for a variety of diseases affecting the CNS by accessing the CSF space. Exemplified disease conditions treatable by the present CSF processing systems and methods include, but are not limited to: Cerebral Vasospasm, Guillain Bane Syndrome, illustrating multi-lumen lumbar approach Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington's, Multiple Sclerosis, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury, Traumatic Brain Injury, Stroke, Cancer affecting the brain or spinal cord, Prion disease, Encephalitis from various causes, Meningitis from various causes, diseases secondary to enzymatic or metabolic imbalances, Biological Warfare, etc. For the first time, the present invention offers patients a disease-modifying, disruptive technology treatment platform that addresses the known disease pathogenesis of a number of neurologic conditions to which there are presently limited and ineffective treatment options.
Owner:NEUROFLUIDICS
CNS gene delivery using peripheral administration of aav vectors
ActiveUS20100130594A1Safe and convenientSuitable as therapeuticOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGene deliveryTherapeutic protein
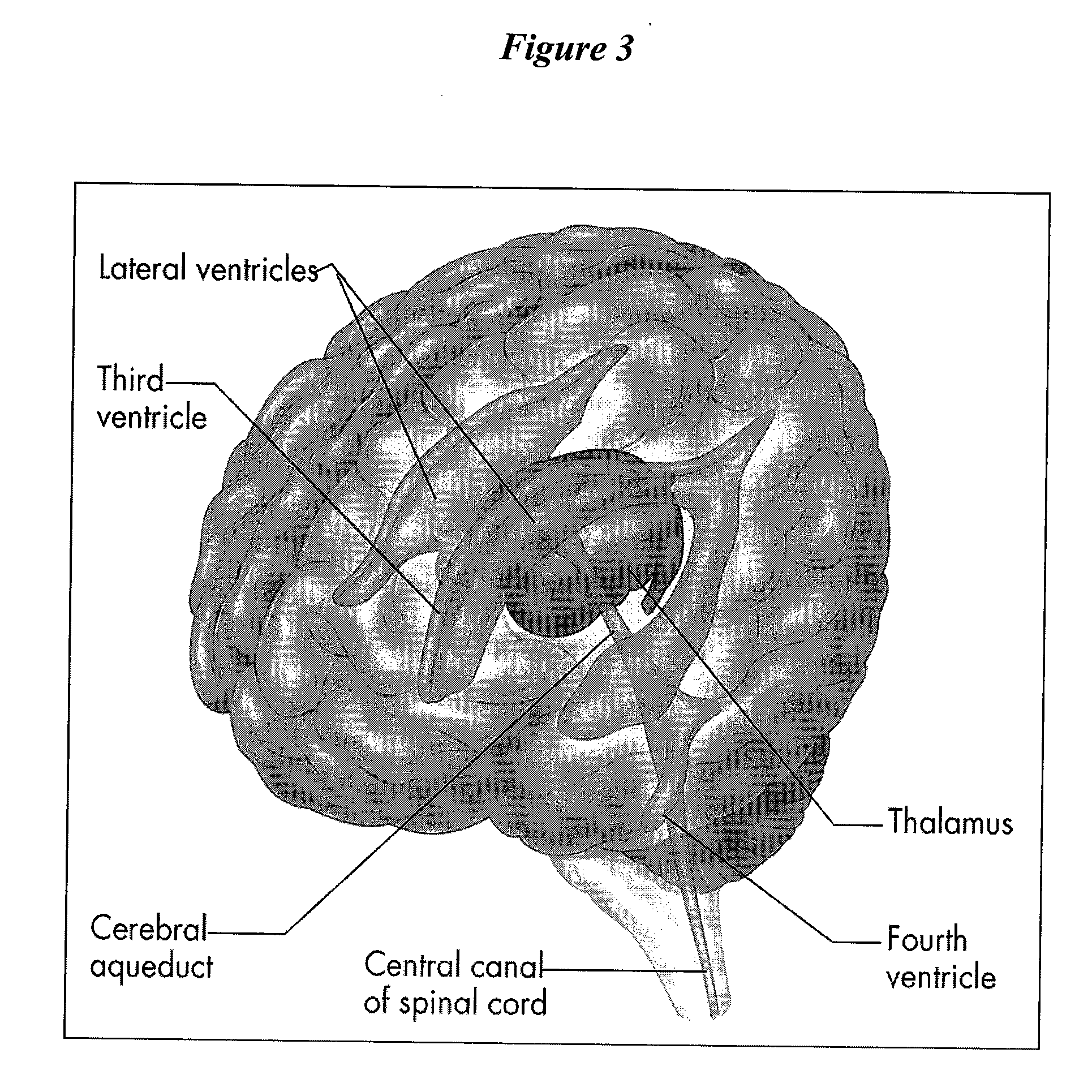
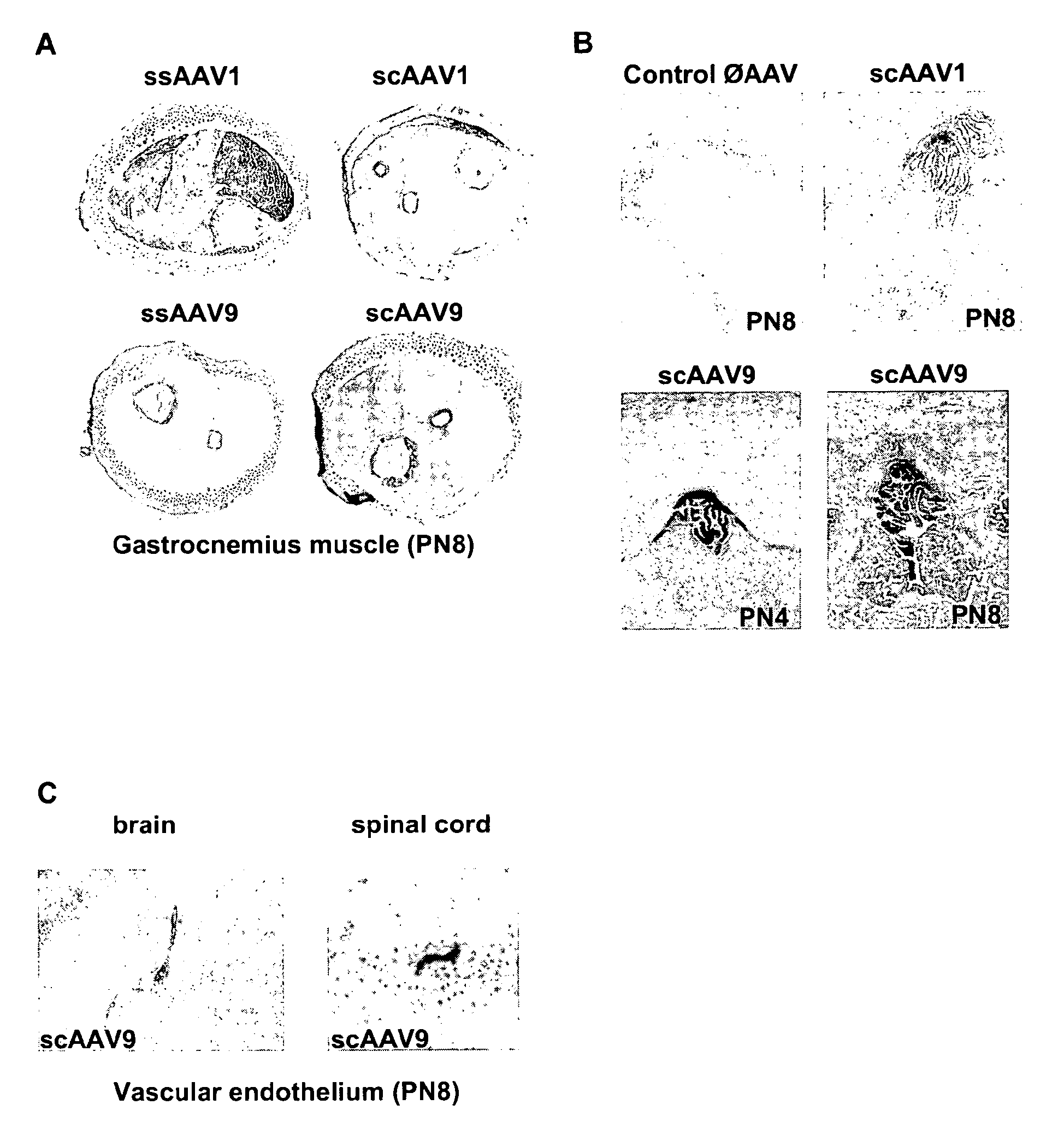
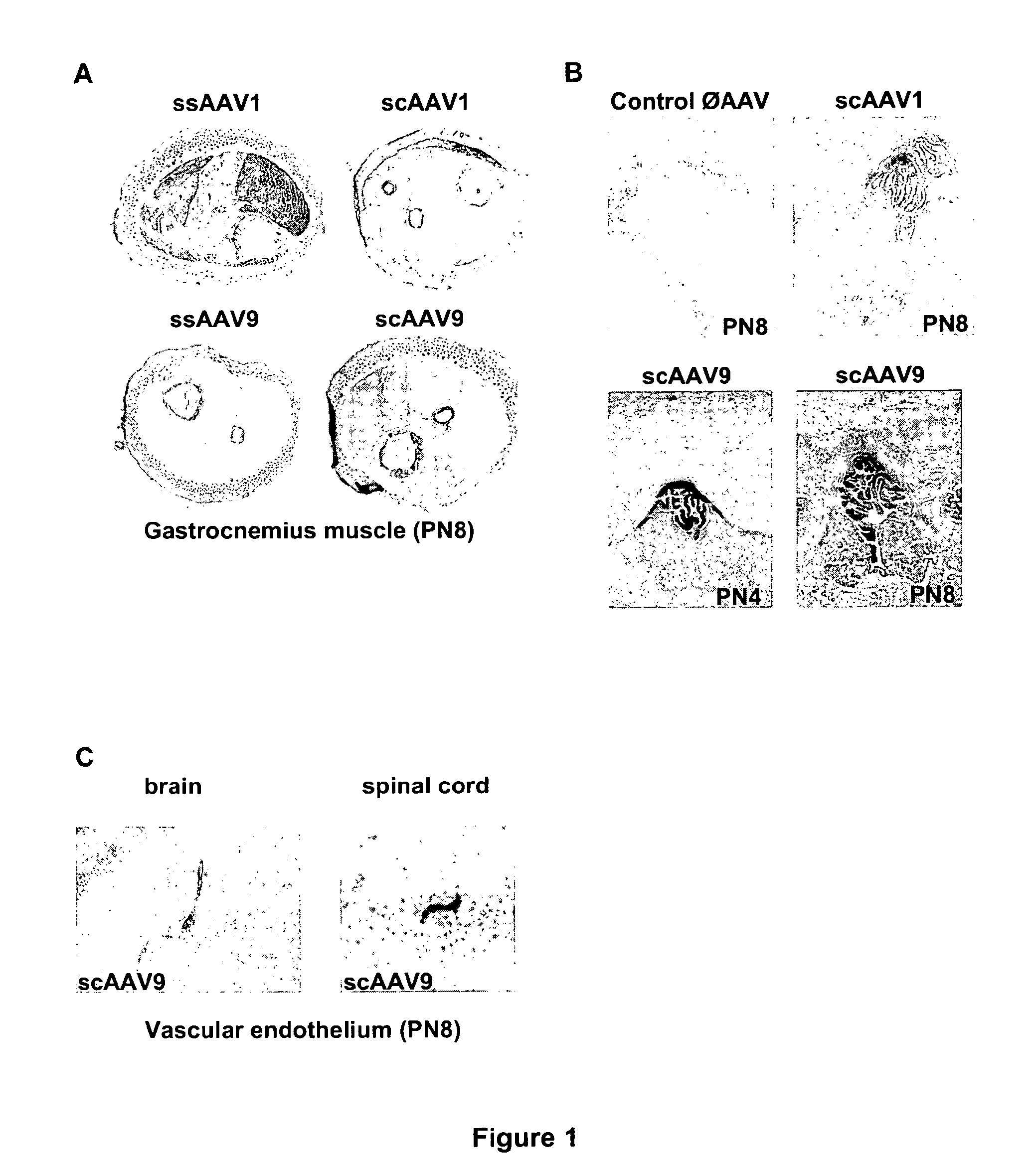
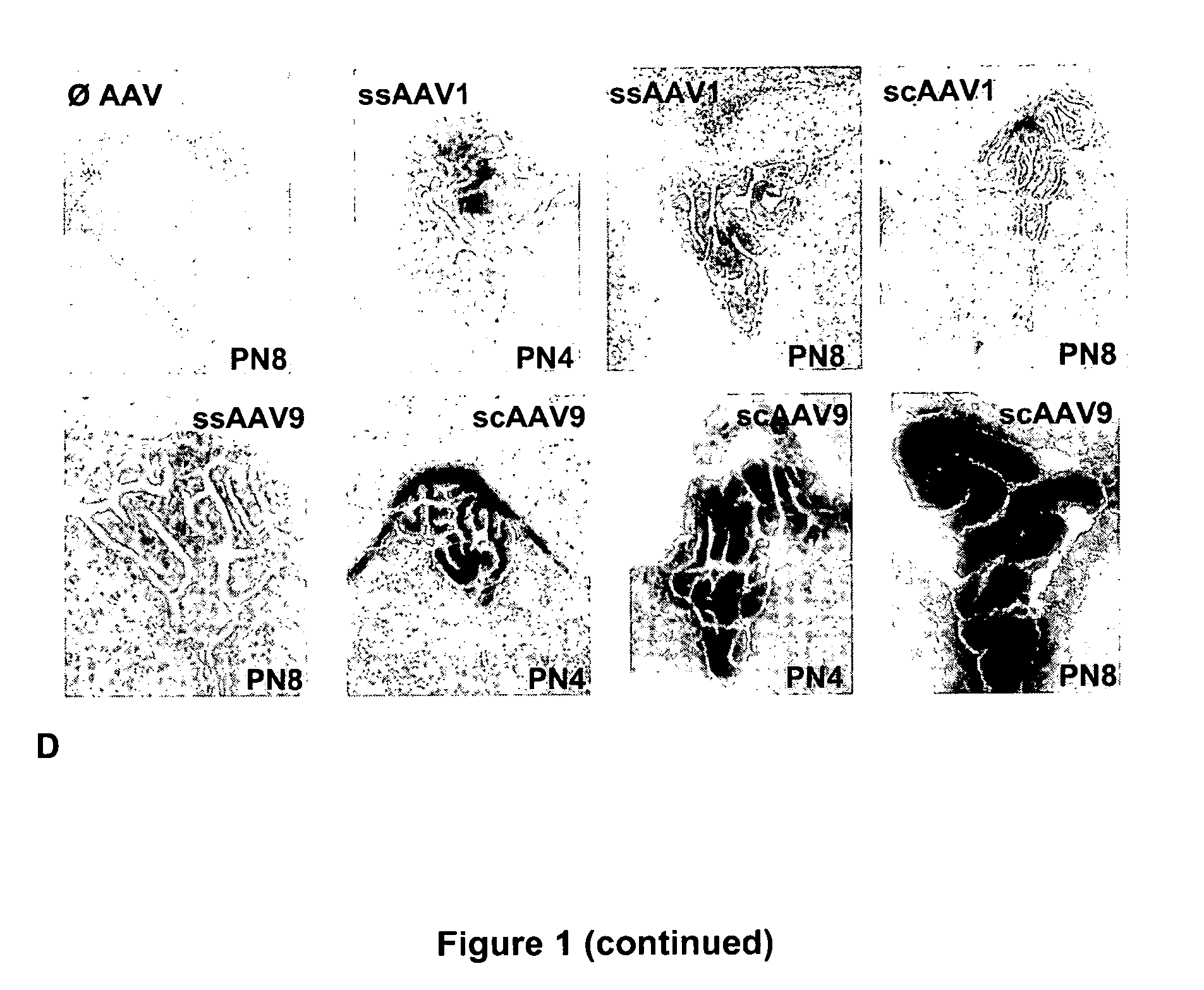
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the delivery of therapeutic proteins to the CNS using recombinant AAV vectors. More specifically, the invention relates to compositions and methods for delivering proteins into the cerebrospinal fluid of mammalian subjects through peripheral administration of AAV vectors. The invention may be used to treat various disorders of the central nervous system, including degenerative diseases and motor neuron diseases.
Owner:GENETHON +1
Histogram segmentation of FLAIR images
ActiveUS20030009098A1Automatically measuring the volume of tissueThe classification result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisFluid-attenuated inversion recoveryLeukoaraiosis
A method for classifying tissue in a magnetic resonance image. and particularly for measuring a volume of pathological tissue such as white tissue hyperintensity (leukoaraiosis) in the brain based on the segmentation of the intensity histogram of fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images is described. A magnetic resonance image of the brain of a subject is acquired, and a pixel intensity histogram is constructed from the image. A statistically-based regression analysis is applied to the histogram to determine upper and lower threshold values, which define different types of brain tissue, particularly normal brain, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), or lesion.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method and device for detecting analytes in fluids
InactiveUS6602719B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh concentrationBlood plasma
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Method for treating severe tinnitus
A method for treating severe tinnitus is disclosed. The method of the present invention comprises implanting a catheter into a patient and administering a drug formulation or fluid comprising a therapeutic agent intrathecally into the patient's cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
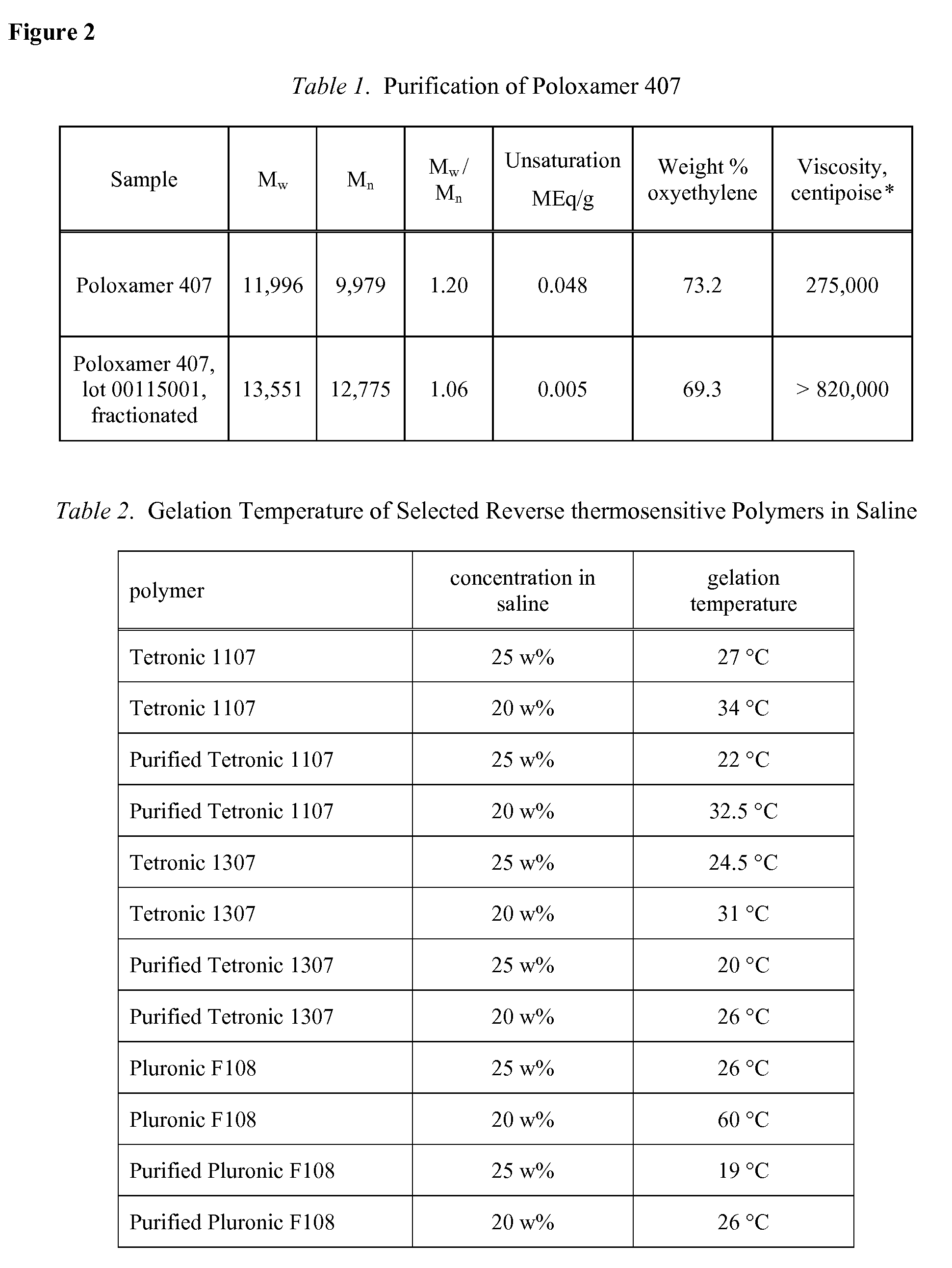
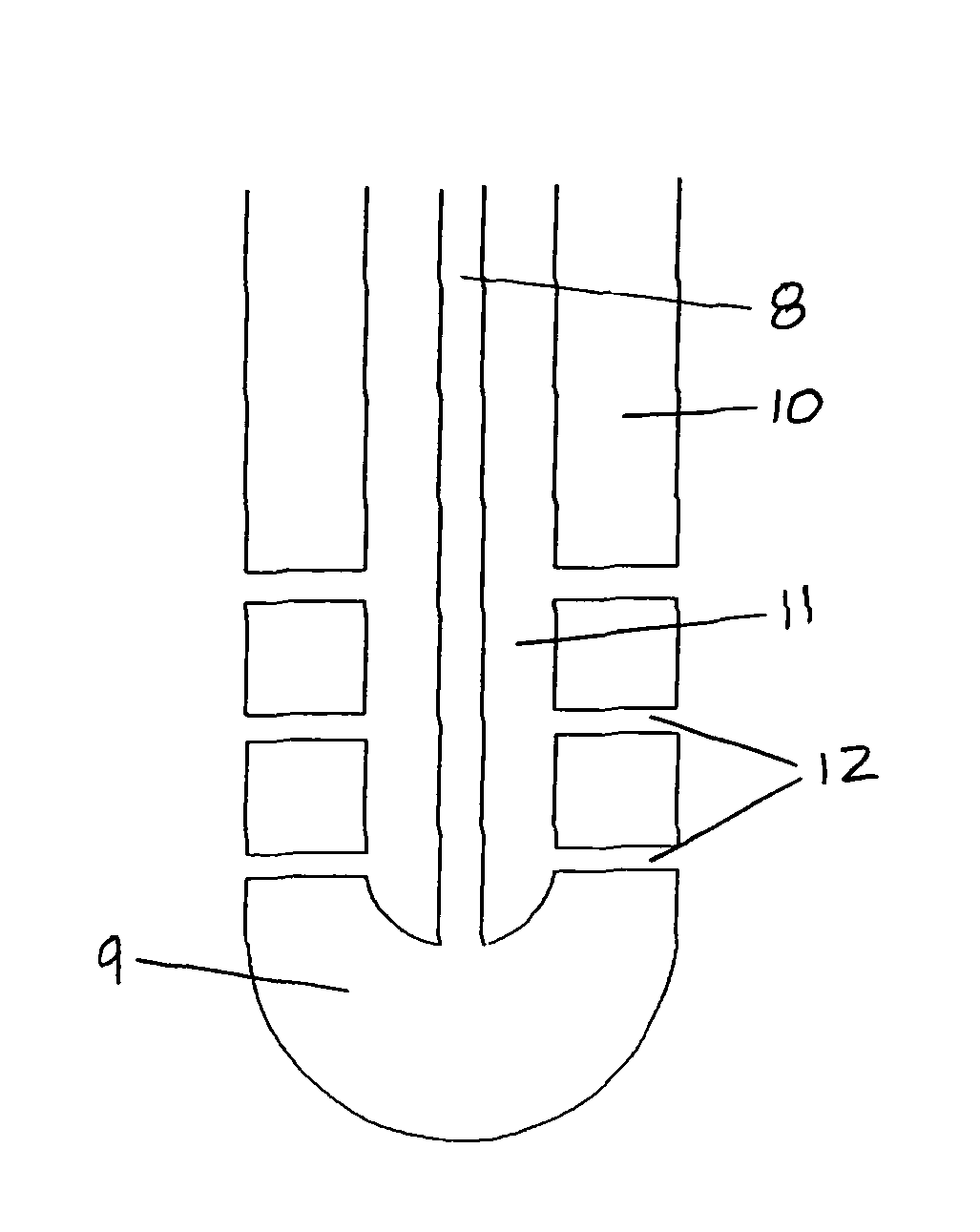
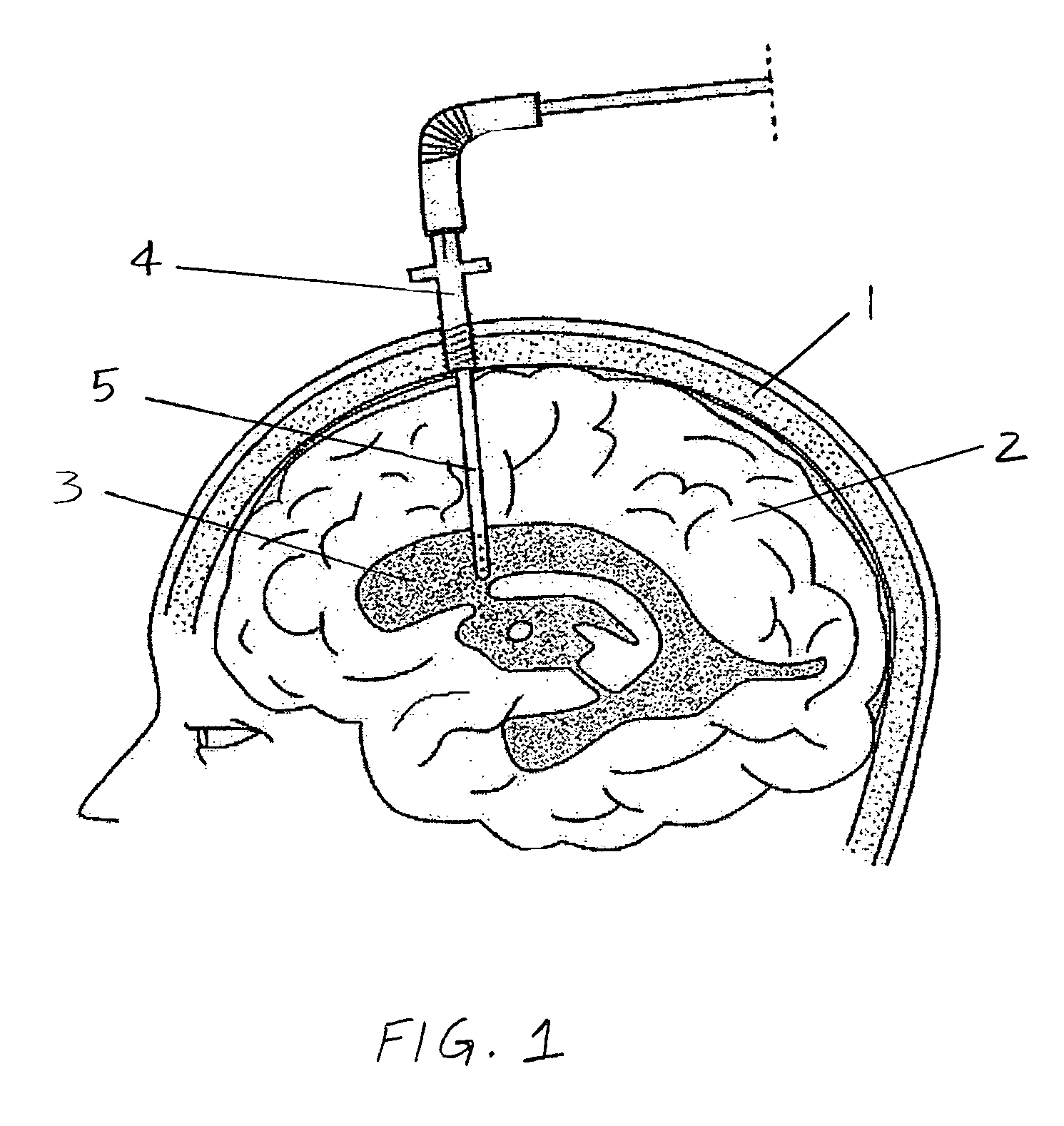
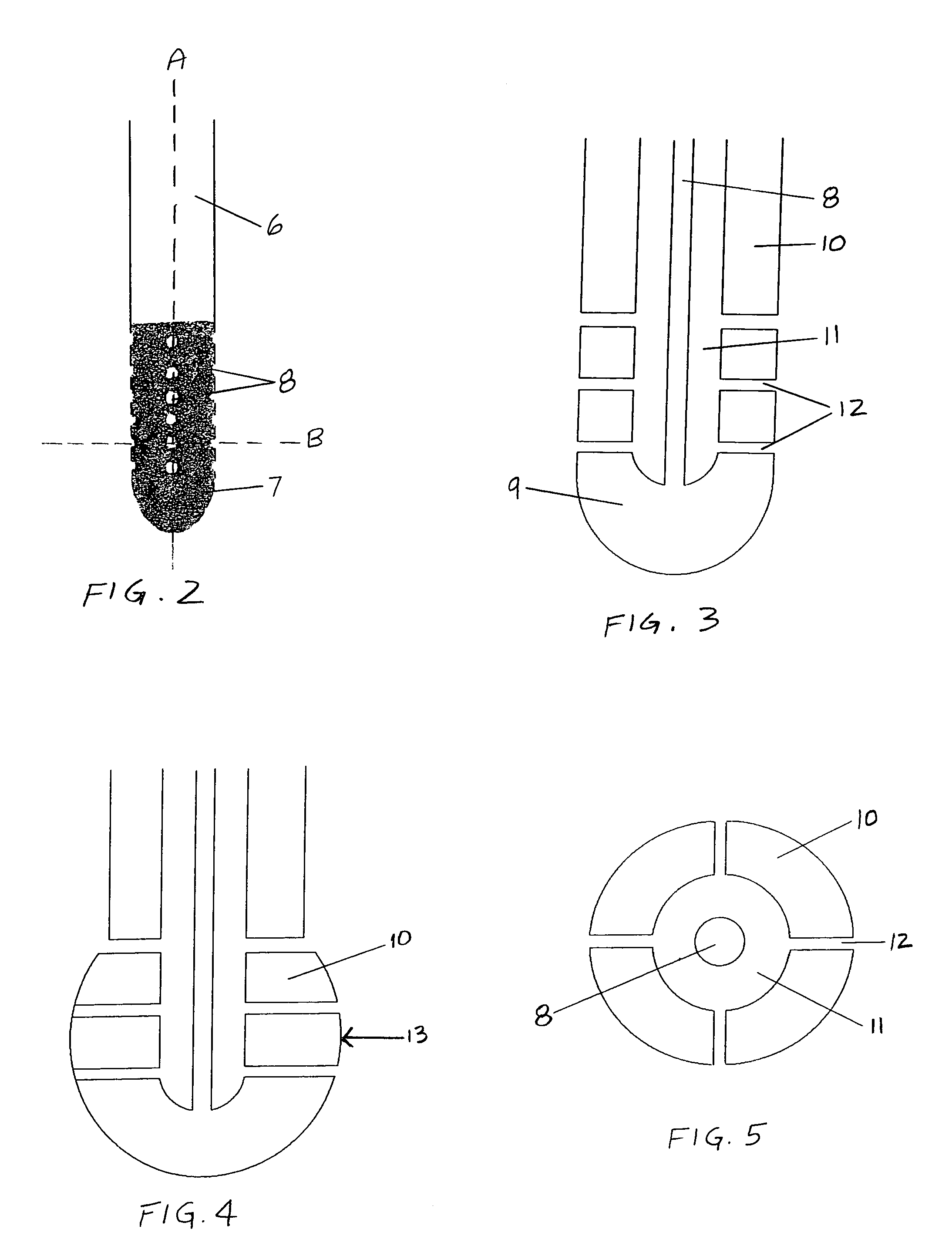
Use of Reverse Thermosensitive Polymers to Control Biological Fluid Flow Following a Medical Procedure
InactiveUS20080208163A1Reduce riskFacilitate and control injectionMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFistulaHeat sensitive
One aspect of the present invention relates to a method to control biological fluid flow at a site in a mammal by use of an in situ formed polymer plug. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to a method to control bleeding following a catheterization procedure, a method to control leakage of cerebral spinal fluid following a lumbar puncture, a method to seal a fistula, or a method to control the flow of serous fluid after a lymphadenectomy. In certain embodiments, the polymer plug is generated in situ by temperature changes, pH changes or ionic interactions. In certain embodiments, the polymer plug comprises at least one optionally purified reverse thermosensitive polymer.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
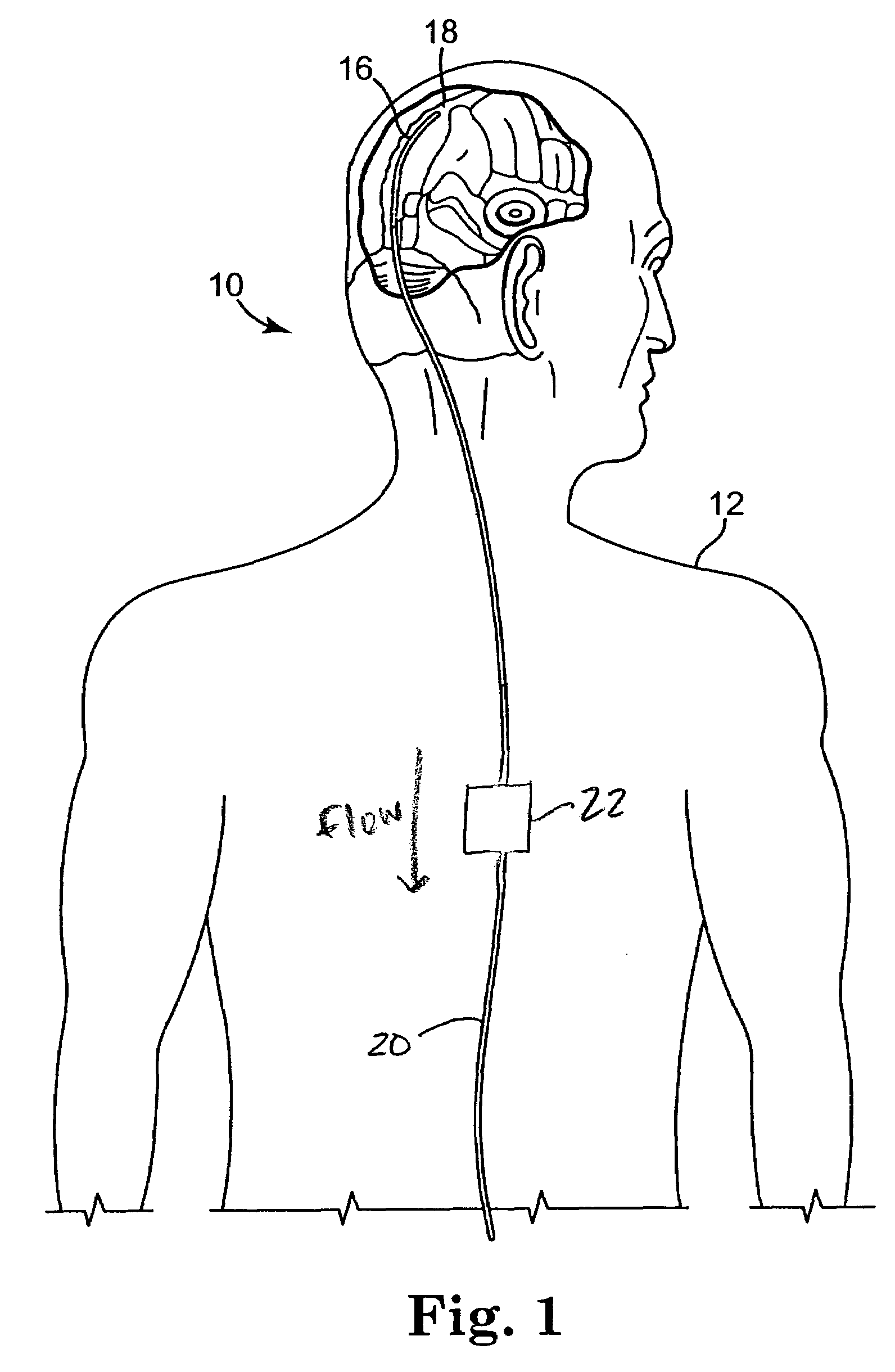
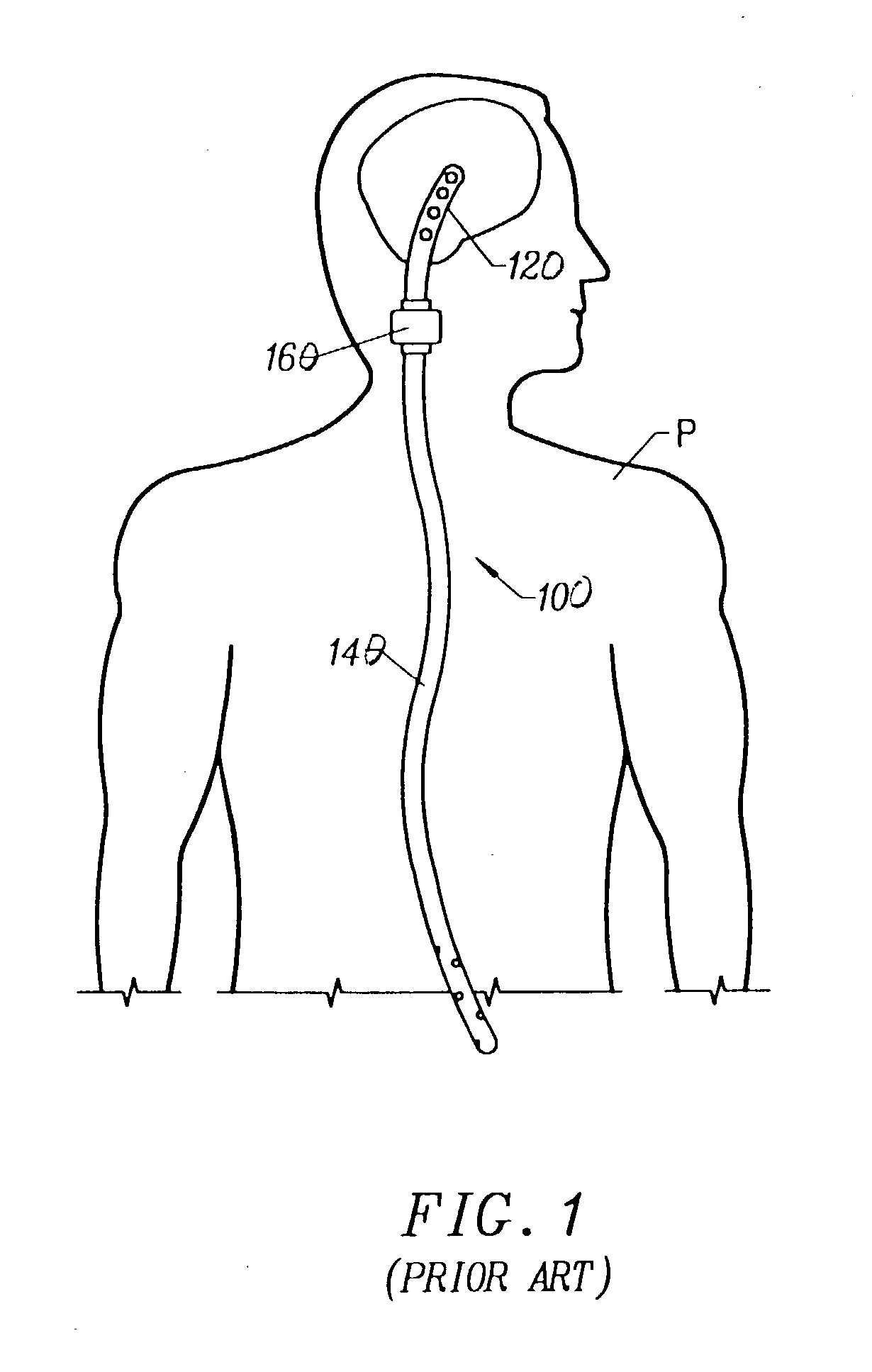
Central nervous system cooling catheter
ActiveUS8123789B2Reduce riskHigh riskSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingHemolysisWhole body
The invention provides a method and apparatus for performing selective hypothermia to the brain and spinal cord for injury protection without the need for systemic cooling. A flexible catheter is inserted into the cerebral lateral ventricle or spinal subdural space. The catheter has lumens with a heat transfer element. The lumens of the catheter circulate a coolant and communicate at the distal heat transfer element for transfer of heat from the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore a method of maintaining catheter patency and providing blood clot hemolysis and drainage is also provided through the use of ultrasonic and / or laser energy delivered through the catheter.
Owner:KHANNA ROHIT
Method and apparatus for managing normal pressure hydrocephalus
InactiveUS20050055009A1Increased and decreased resistanceReduce resistanceWound drainsMedical devicesVentricular volumePhysician attending
An adjustable drainage system for regulating cerebrospinal fluid flow in a hydrocephalus patient where the drainage rate is adjusted in response to ventricular volume variations in the patient. The system includes an adjustable valve and a volume sensor that can be periodically energized with an external system controller device by the patient or attending physician to determine when, or if, a change in the ventricular volume has occurred. The system enables the user to adjust the valve's resistance in response to changes in the ventricular volume using the controller device so that a target ventricular volume can be achieved. Also provided is a method of continuously draining cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial cavity of the patient using the system of the present invention.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
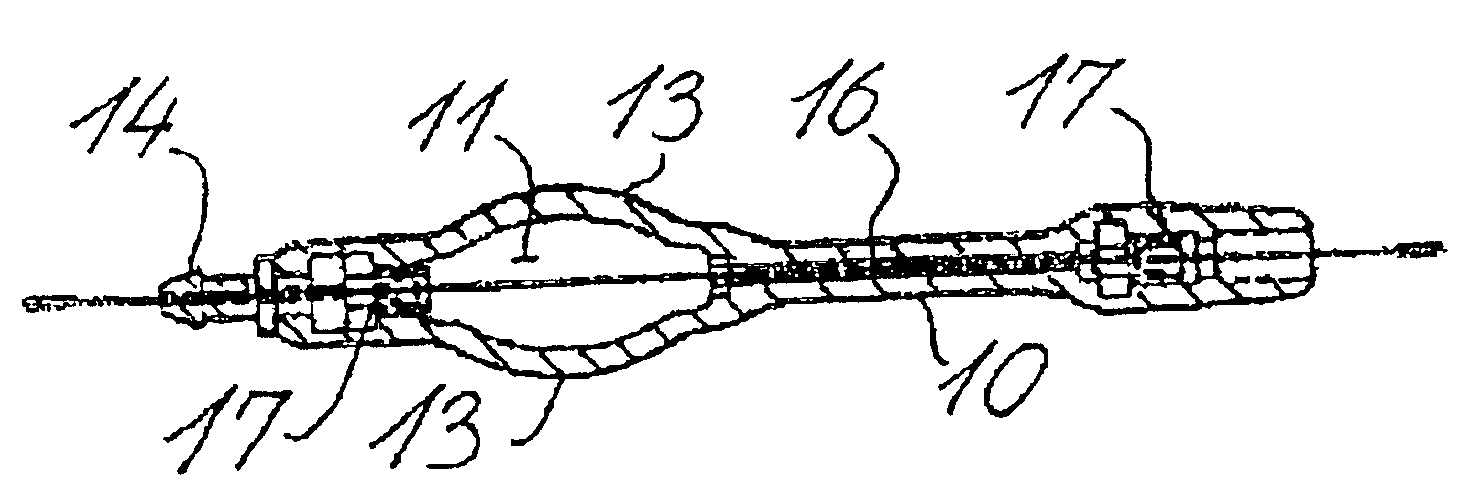
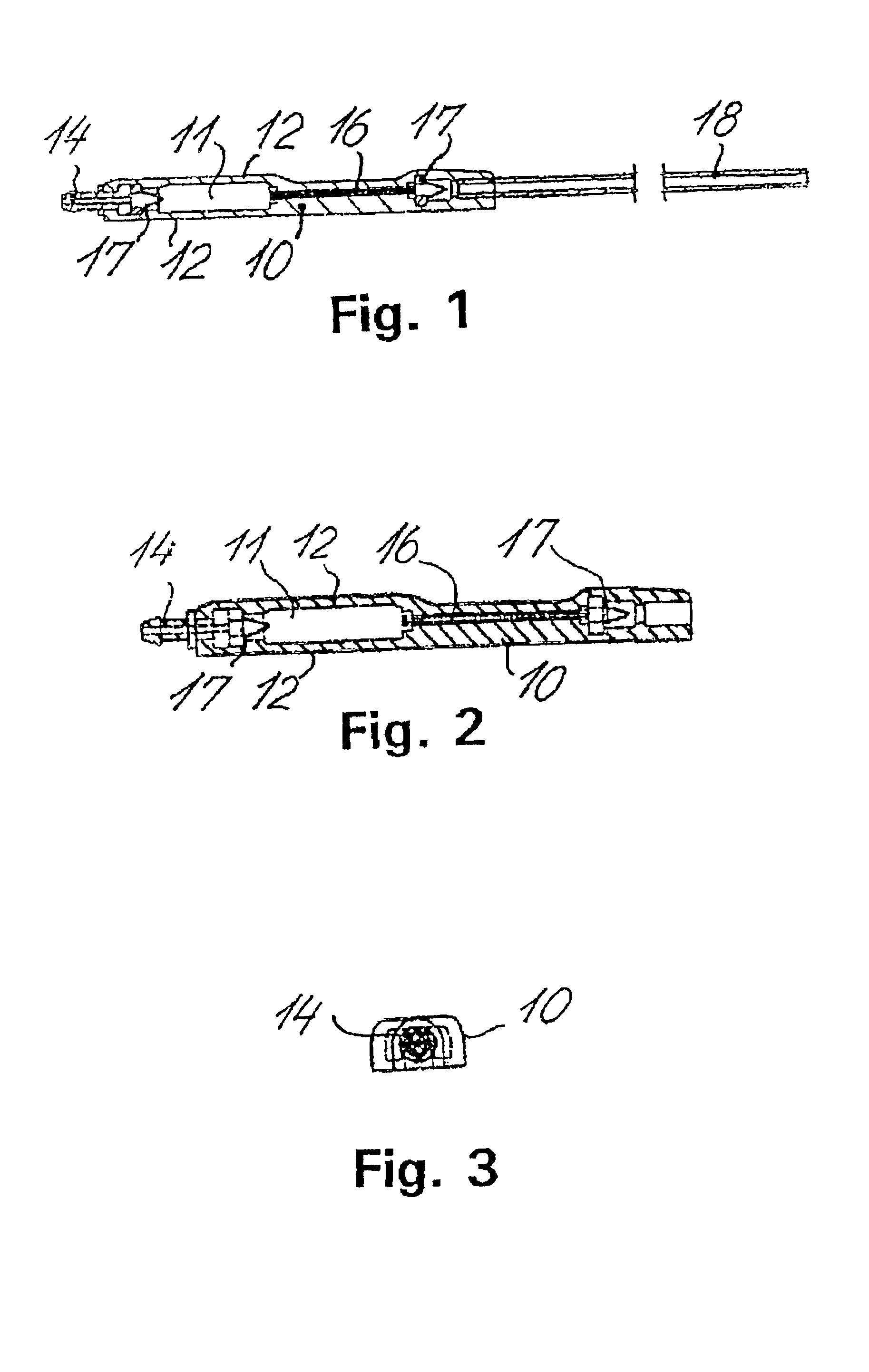
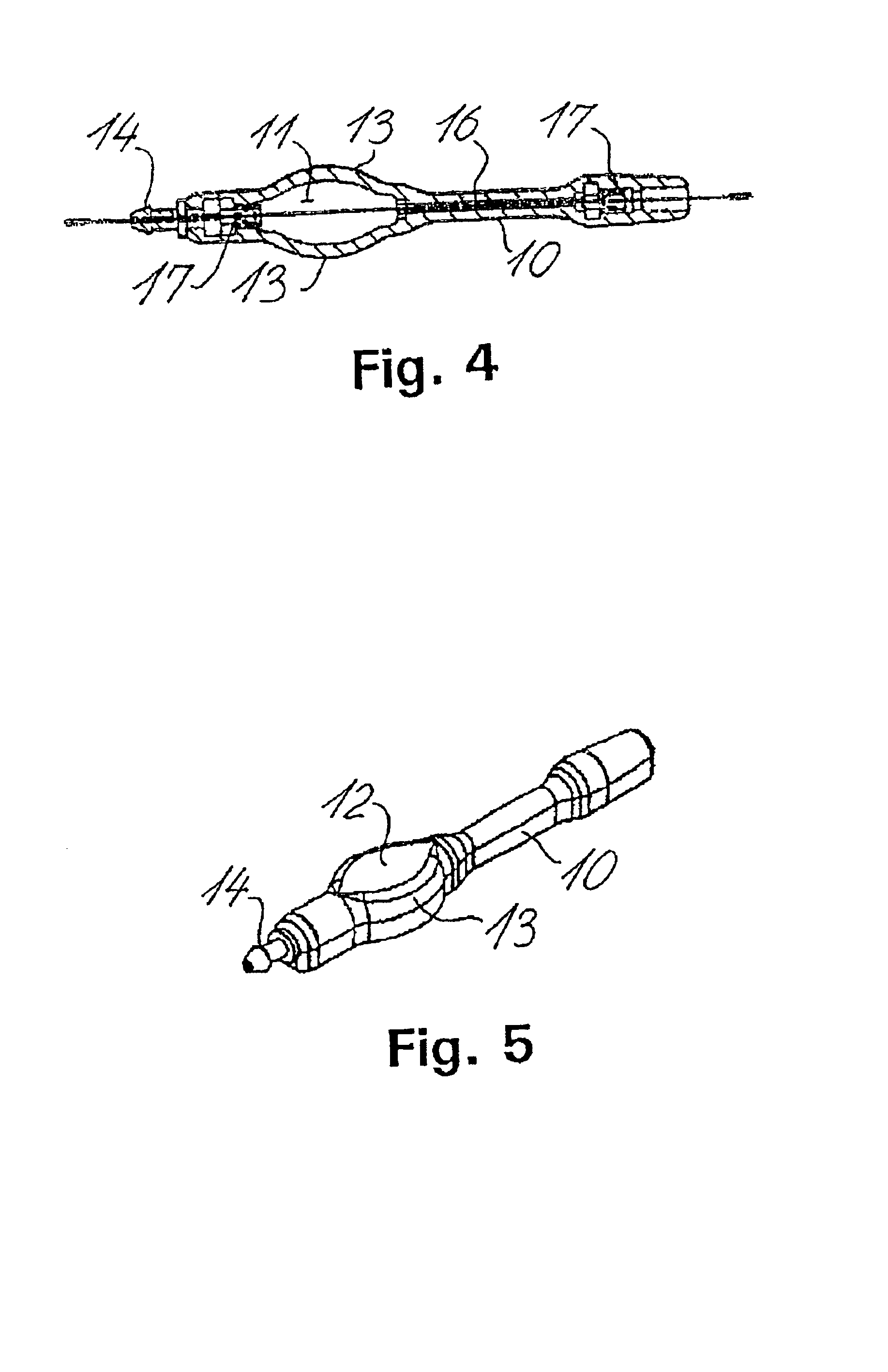
Implantable cerebral spinal fluid drainage device and method of draining cerebral spinal fluid
The invention provides a drainage system that includes a ventricular catheter, a drainage catheter, and a positive displacement pump that can function to actively drain CSF from the ventricles of the brain of a patient. Methods of using a drainage system in accordance with the invention are also provided, as well as kits.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
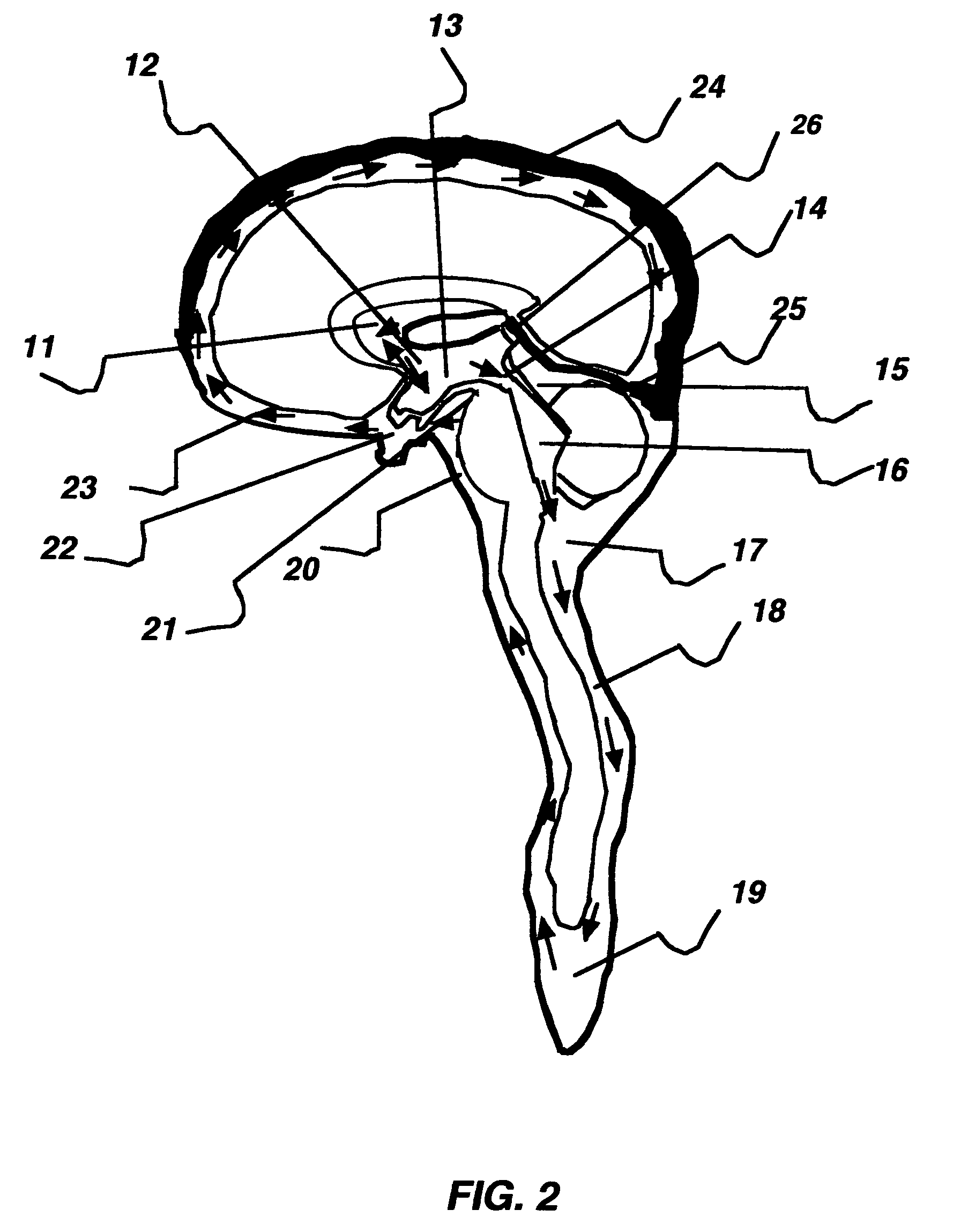
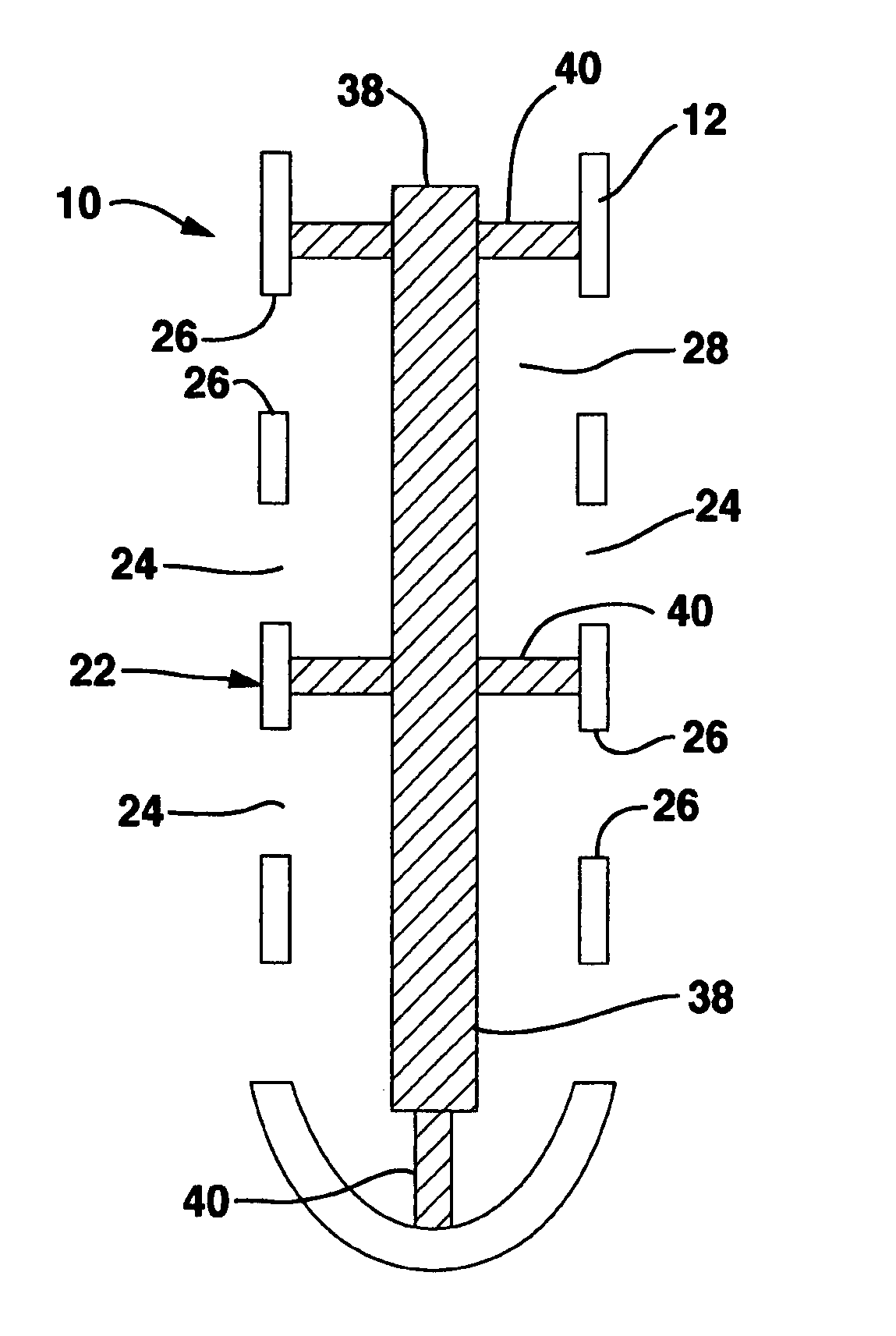
Fluid shunt system and a method for the treatment of hydrocephalus
InactiveUS6905474B2Lower resistanceInhibit posture changesWound drainsMedical devicesFlow diverterBrain Ventricle
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricle catheter (15) to insert into the brain ventricle (21) so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle, a sinus catheter (18) to insert into the sinus sagittalis system (22) for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into the sinus sagittalis system, a shunt body member (10) connected at one end thereof to said brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to said sinus catheter system to provide fluidic communication between said brain ventricle catheter (15) and said sinus catheter (18), and a flow restriction (16) defined within the shunt body member (10) to maintain a resistance to fluid flow of the shunt system of less than 8 mm Hg / ml / min, such as 2-7 or 4-6 and preferably about 5 mm Hg / ml / min. When the shunt system is implanted the shunt body member (10) is placed subcutaneously on top of the calvarium of a patient, behind the coronal suture on one of side of the sagittal suture. One end of each of the catheters (15, 18) is then connected to a respective end of the shunt body member (10), and a second end of each catheter is inserted in the right ventricle (21) and in the sinus sagittalis system (22), respectively, via holes bored in the scull (19).
Owner:CSF DYNAMICS
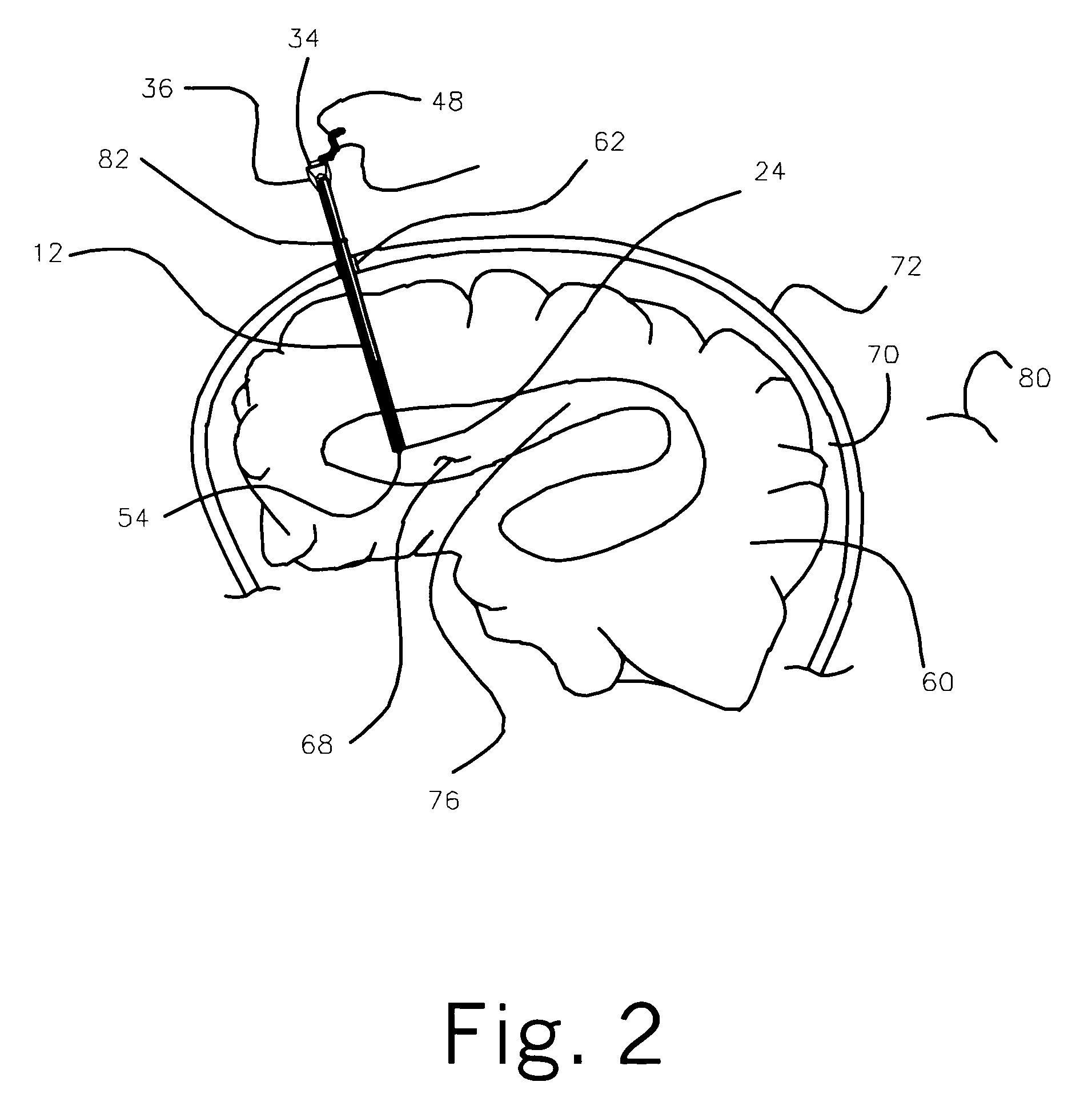
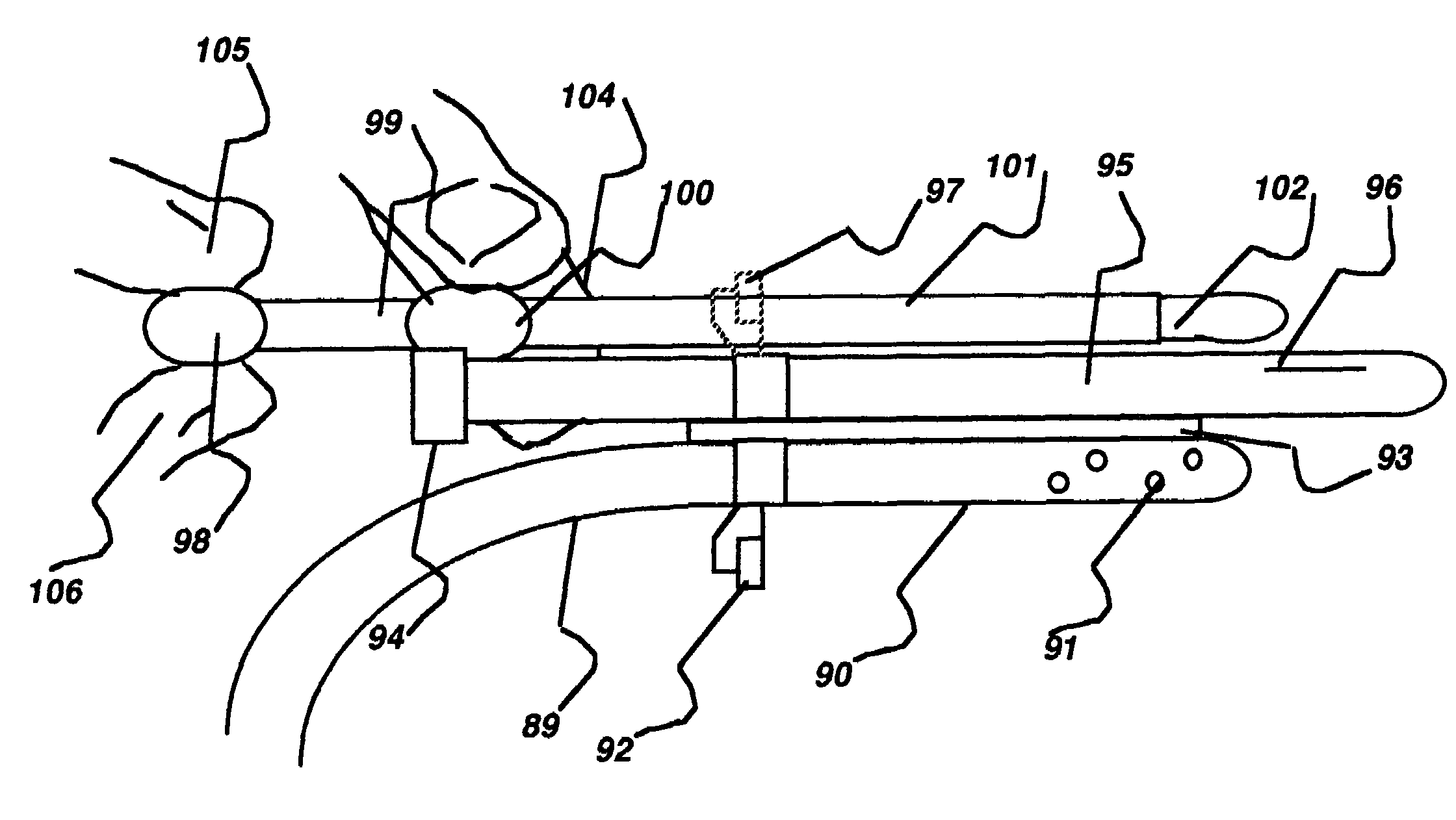
Medical device and method for temperature control and treatment of the brain and spinal cord
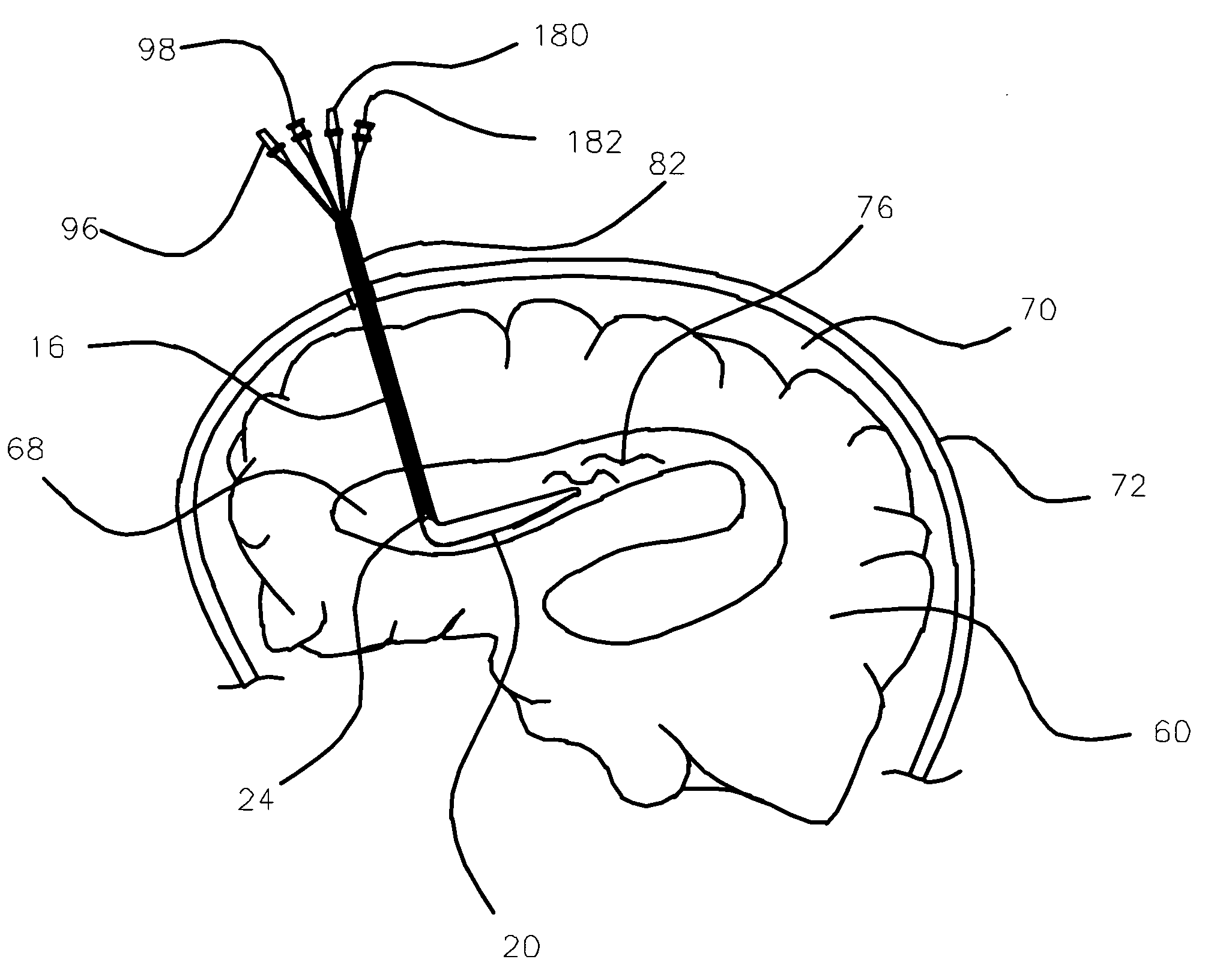
ActiveUS7004961B2Rapid and accurate insertionFast transferUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSubarachnoid space
The invention provides a medical device having a thermister for temperature measurement, irrigation / aspiration ports for fluid exchange and application of therapeutic modalities, a pressure manometer for pressure measurement, and an external system for control of temperature, pressure, and flow rate. When applied to the central nervous system (CNS), this device can be used in hypothermia or hyperthermia applications, the exchange of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), the application of treatment modalities, and the insertion of a ventriculostomy or ventriculostomy-like unit. When applied to spinal cord applications, this device can provide temperature control and a method for application of treatment modalities by using a venting device placed in the space surrounding the spinal cord, a device with similar instrumentation to measure temperature and pressure. A device for ultrasound localization of the CNS device is described. A device for a fiber optic endoscope for visualization and localization is also described. Method of using the devices in treating patients suffering from cardiac arrest, circulatory arrest, exsanguination, head or neck trauma, strokes, tumors and other intracranial diseases are disclosed. In the case of hypothermia treatment of the brain, rapid cooling using principles of convection and conduction will be applied to the lateral ventricle and subarachnoid and / or subdural space simultaneously where the neurons are located in close proximity.
Owner:WONG EDWARD +2
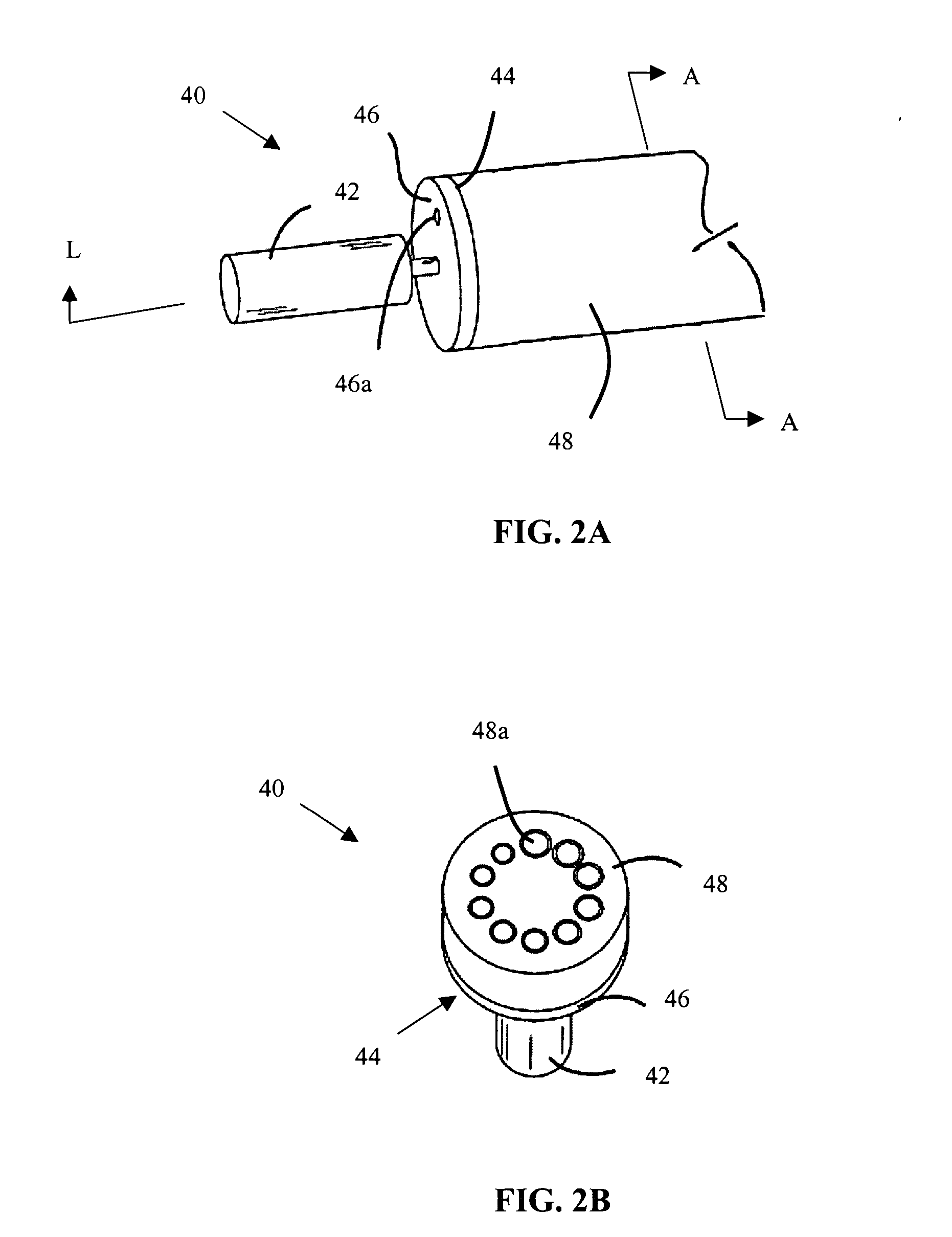
Systems and methods for flow detection and measurement in CSF shunts
InactiveUS20040068201A1Reduce concentrationIncrease productionWound drainsDiagnostic recording/measuringNormal intracranial pressureCsf shunt
Devices and methods for removing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from a CSF space of a patient at relatively constant flow rates for patients having normal intracranial pressures, e.g. patients not suffering from hydrocephalus. The devices and methods provide drainage paths which permit the removal of CSF at relatively low flow rates, usually below 0.2 ml / day, at normal intracranial pressures, e.g. an intracranial pressure between -170 mm of H2O in upright patients and 200 mm of H2O in reclining patients. The removal of CSF at relatively low, constant rates is particularly suitable for treating Alzheimer's disease and other conditions related to the presence of toxic and / or pathogenic substances in the CSF.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Methods, systems and devices for neuromodulating spinal anatomy
ActiveUS9259569B2Minimally invasivePromote migrationSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSide effectSpinal anatomy
Devices, systems and methods for treating pain or other conditions while minimizing possible complications and side effects. Treatment typically includes electrical stimulation and / or delivery of pharmacological or other agents with the use of a lead or catheter. The devices, systems and methods provide improved anchoring which reduces migration of the lead yet allows for easy repositioning or removal of the lead if desired. The devices, systems and methods also provide for simultaneous treatment of multiple targeted anatomies. This shortens procedure time and allows for less access points, such as needle sticks to the epidural space, which in turn reduces complications, such as cerebral spinal fluid leaks, patient soreness and recovery time. Other possible complications related to the placement of multiple devices are also reduced.
Owner:TC1 LLC
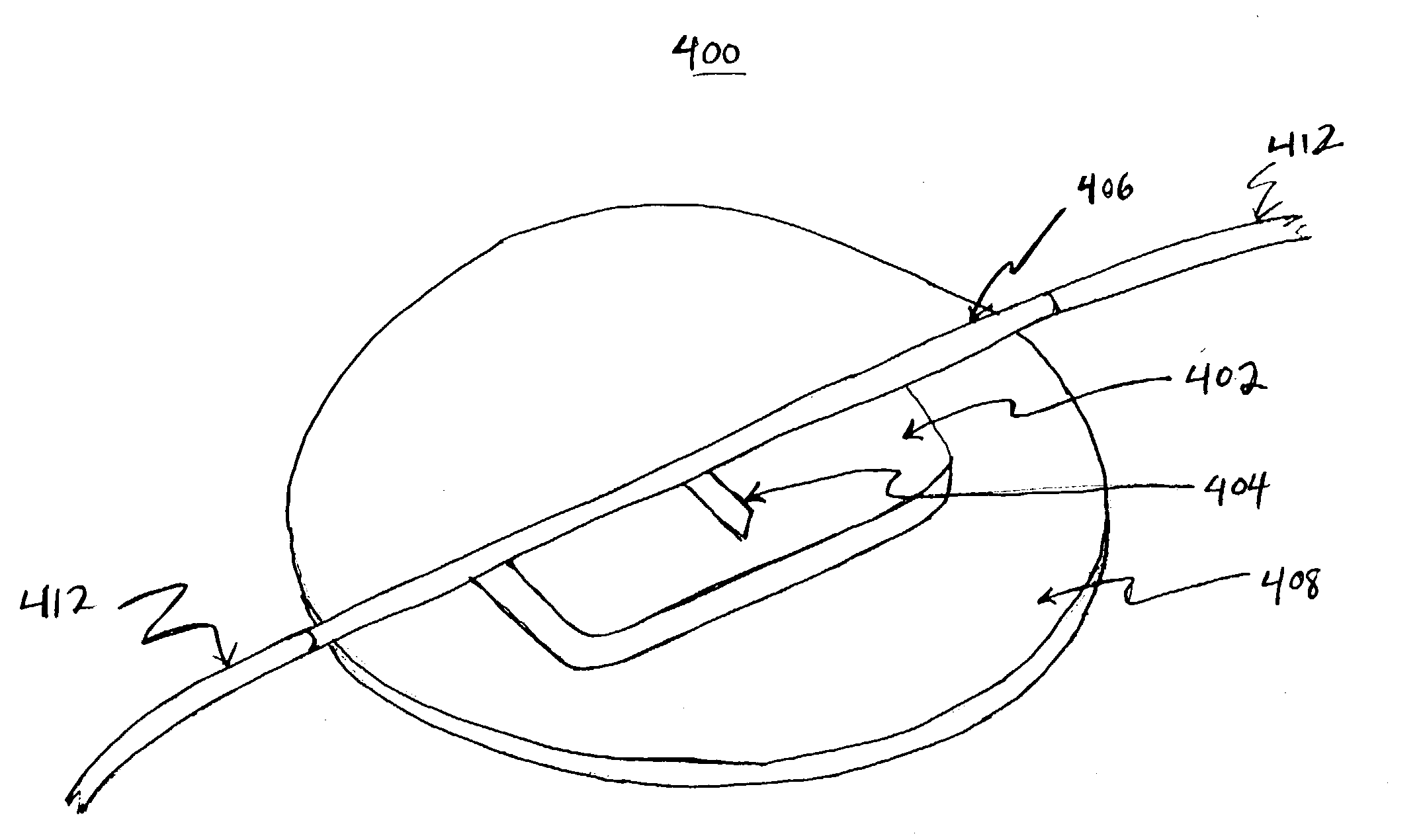
Methods for assessing fluid flow through a conduit
A method for assessing fluid flow in a conduit includes sensing the fluid flow with a sensor and generating data from the sensor that relates to the sensed fluid flow. The data is output from the sensor and filtered so that it may be interpreted to characterize the fluid flow. The conduit may be a prosthesis such as stent, a stent-graft or a prosthetic vascular graft and the flow may be any body fluid such as blood, bile, or cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:ALIO
Apparatus and method for hypothermia and rewarming by altering the temperature of the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain
ActiveUS7318834B2Rapid cooling/rewarmingReduce riskTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingVentricular cathetersCistern
The invention relates to a method for hypothermia and rewarming of the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. In one embodiment, cooling and rewarming of the cerebrospinal fluid is accomplished by applying cooling and rewarming elements externally placed in contact with the skin overlying the cerebrospinal fluid cisterns at the back of the head and spine regions of a patient. In another embodiment, hypothermia and rewarming is accomplished using a double barrel ventricular catheter placed within the lateral ventricles with one catheter used for heat exchange and the other for drainage of excess cerebrospinal fluid. In yet another embodiment of the invention, hypothermia and rewarming is accomplished using a loop catheter with fluid running through the loop placed in the lateral ventricles.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
Occlusion resistant hydrocephalic shunt
An occlusion resistant medical shunt, particularly a hydrocephalic shunt, is provided for implantation into a mammal. The shunt has an elongate wall structure configured as a tube having a lumen therethrough and a proximal end for receipt of bodily fluids. The bodily fluids, such as cerebrospinal fluid, flows through the shunt to a distal end for discharge of the bodily fluids. The wall structure of the shunt generally includes a biocompatible medical device material. The shunts of the present invention further include one or more occlusion resistant materials to resist occlusion of the lumenal passage in the shunt.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of detecting or diagnosing of a neurodegenerative disease or condition
InactiveUS20060141541A1Unknown materialsDisease diagnosisNeuro-degenerative diseaseAutoantibody production
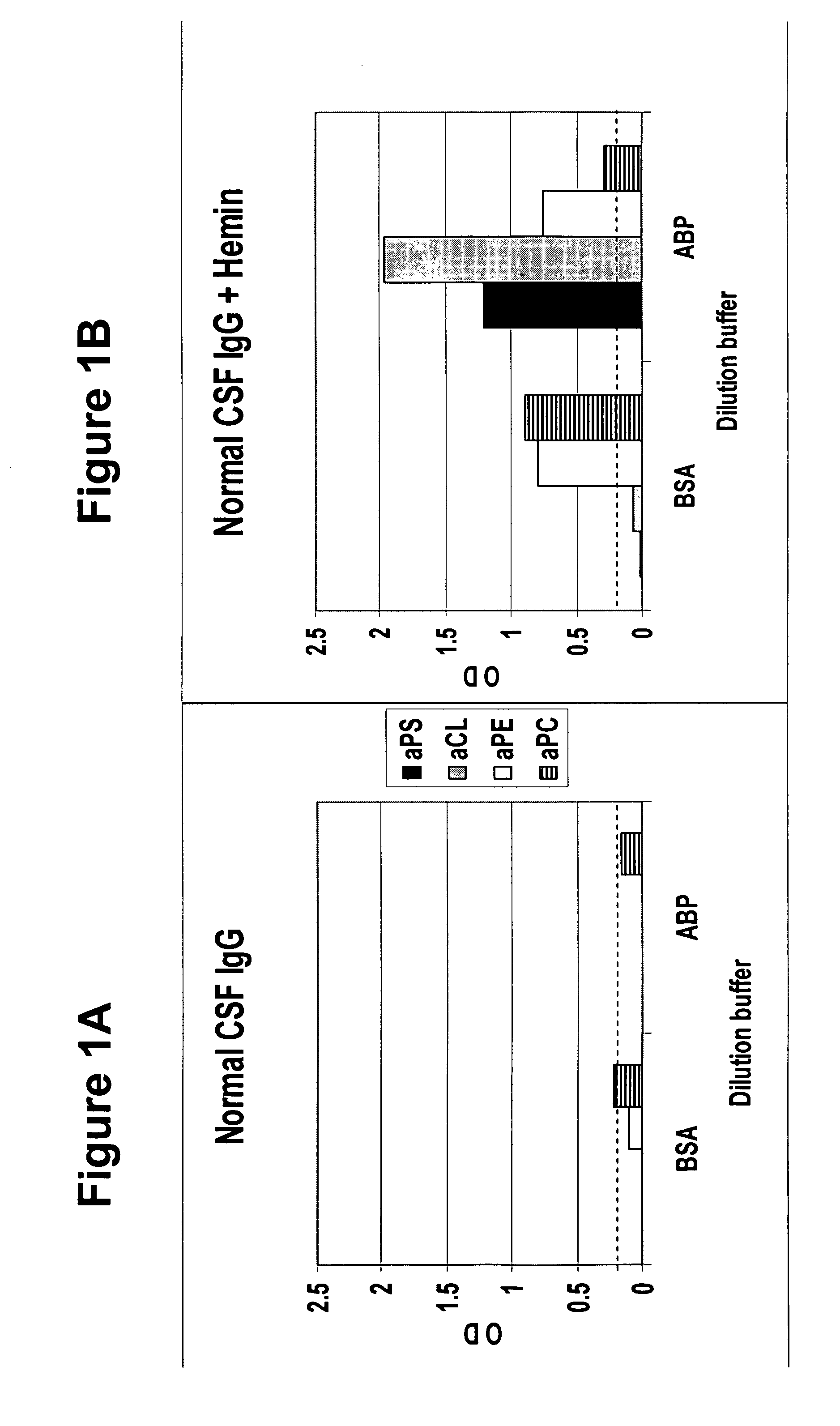
A neurodegenerative disease or condition is diagnosed in a subject by obtaining a sample of cerebral spinal fluid from the subject and assaying the sample by an assay method that detects the presence of at least one antiphospholipid autoantibody in the sample, wherein an elevated level of at least one antiphospholipid autoantibody in the sample of cerebral spinal fluid correlates with a neurodegenerative disease or condition in the subject. The neurodegenerative disease or condition may also be diagnosed by assaying a sample of cerebral spinal fluid to detect nitrosylated antibodies, wherein an elevated level of nitrosylated antibodies correlates with a neurodegenerative disease or condition in said subject. A neurodegenerative disease or condition is also detected or diagnosed by assaying a first sample of cerebral spinal fluid from the subject to determine a level of at least one autoantibody having a selected specificity, treating a second sample of cerebral spinal fluid with an oxidizing agent and assaying the oxidized second sample to determine a level the at least autoantibody having the selected specificity, and comparing the level of the at least one autoantibody in the first sample with the level of the at least one autoantibody in the oxidized second sample, wherein a lack of increase in the level of the at least one autoantibody in the oxidized second sample as compared to the level of the at least one autoantibody in the first sample correlates with a neurodegenerative disease or condition in said subject.
Owner:REDOX REACTIVE REAGENTS LLC
Cerebral spinal fluid shunt evaluation system
A method for evaluating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow rate in a CSF shunt applied to a patient for transmitting the CSF between first and second locations of the patient includes applying temperature sensors to the CSF shunt for determining a flow rate of the CSF through the shunt to provide a determined CSF flow rate and applying an error correction sensor to the patient for providing an error correction signal. The determined CSF flow rate is adjusted in accordance with the error correction signal to provide a corrected CSF flow rate. The sensor can be a temperature sensor such as a thermistor. The CSF is cooled and a temperature value of the CSF is measured in accordance with the cooling. A time value is determined in accordance with the temperature value and the CSF flow rate is determined in accordance with the time value.
Owner:NEFF INDIVIDUAL JANINE +1
Method and device for reducing secondary brain injury
InactiveUS6929656B1Preventing secondary brain injuryTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingBrain coolingCerebral Spinal Fluid
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for reducing secondary brain injury. The apparatus includes a brain-cooling probe and a control console. The brain-cooling probe cools the brain to prevent secondary injury by cooling the cerebrospinal fluid within one or more brain ventricles. The brain-cooling probe withdraws a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid from a ventricle into a cooling chamber located ex-vivo in close proximity to the head. After the cerebrospinal fluid is cooled it is then reintroduced back into the ventricle. This process is repeated in a cyclical or continuous manner in order to achieve and maintain a predetermined brain ventricle temperature lower than normal body temperature. The apparatus and method disclosed provides effective brain ventricle cooling without the need to introduce extra-corporeal fluids into the brain.
Owner:MEDCOOL
Method for detecting cell proliferative disorders
InactiveUS6291163B1Fast and reliable and sensitive and non-invasive screeningHigh copy numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCervical tissuePolymerase L
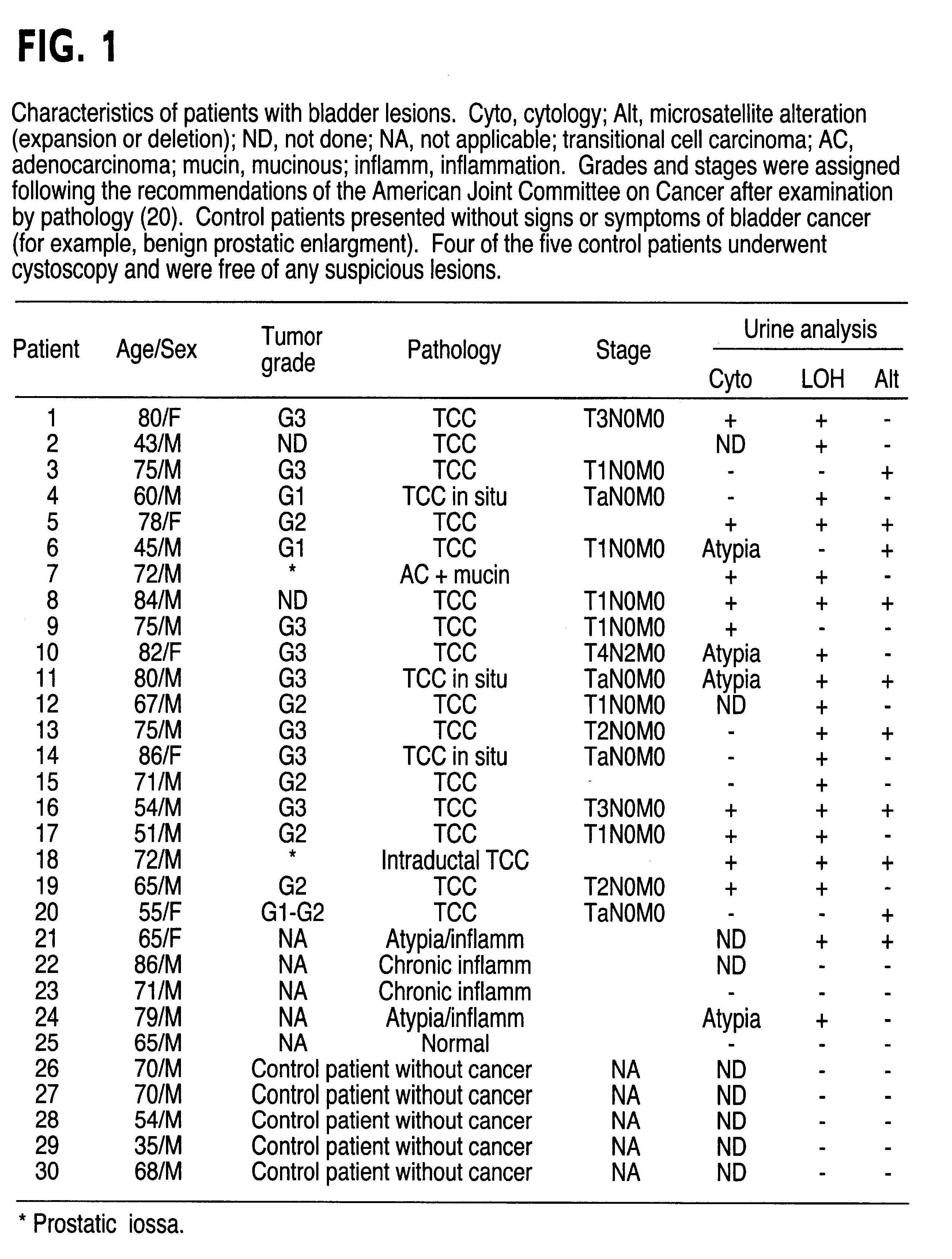
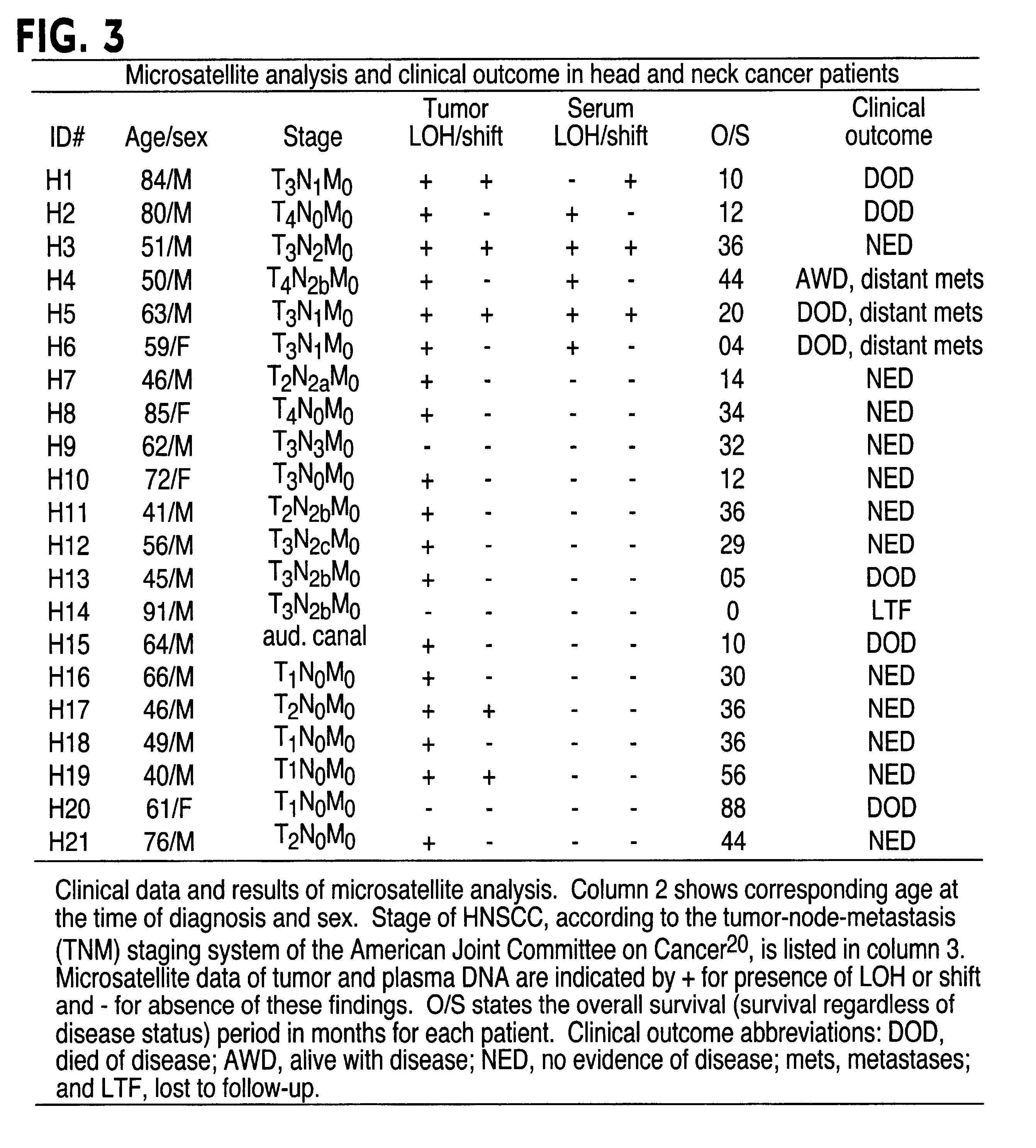
The present invention relates to the detection of a cell proliferative disorder associated with alterations of microsatellite DNA in a sample. The microsatellite DNA can be contained within any of a variety of samples, such as urine, sputum, bile, stool, cervical tissue, saliva, tears, or cerebral spinal fluid. The invention is a method to detect an allelic imbalance by assaying microsatellite DNA. Allelic imbalance is detected by observing an abnormality in an allele, such as an increase or decrease in microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. An increase can be detected as the appearance of a new allele. In practicing the invention, DNA amplification methods, particularly polymerase chain reactions, are useful for amplifying the DNA. DNA analysis methods can be used to detect such a decrease or increase. The invention is also a method to detect genetic instability of microsatellite DNA. Genetic instability is detected by observing an amplification or deletion of the small, tandem repeat DNA sequences in the microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. The invention is also a kit for practicing these methods.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com