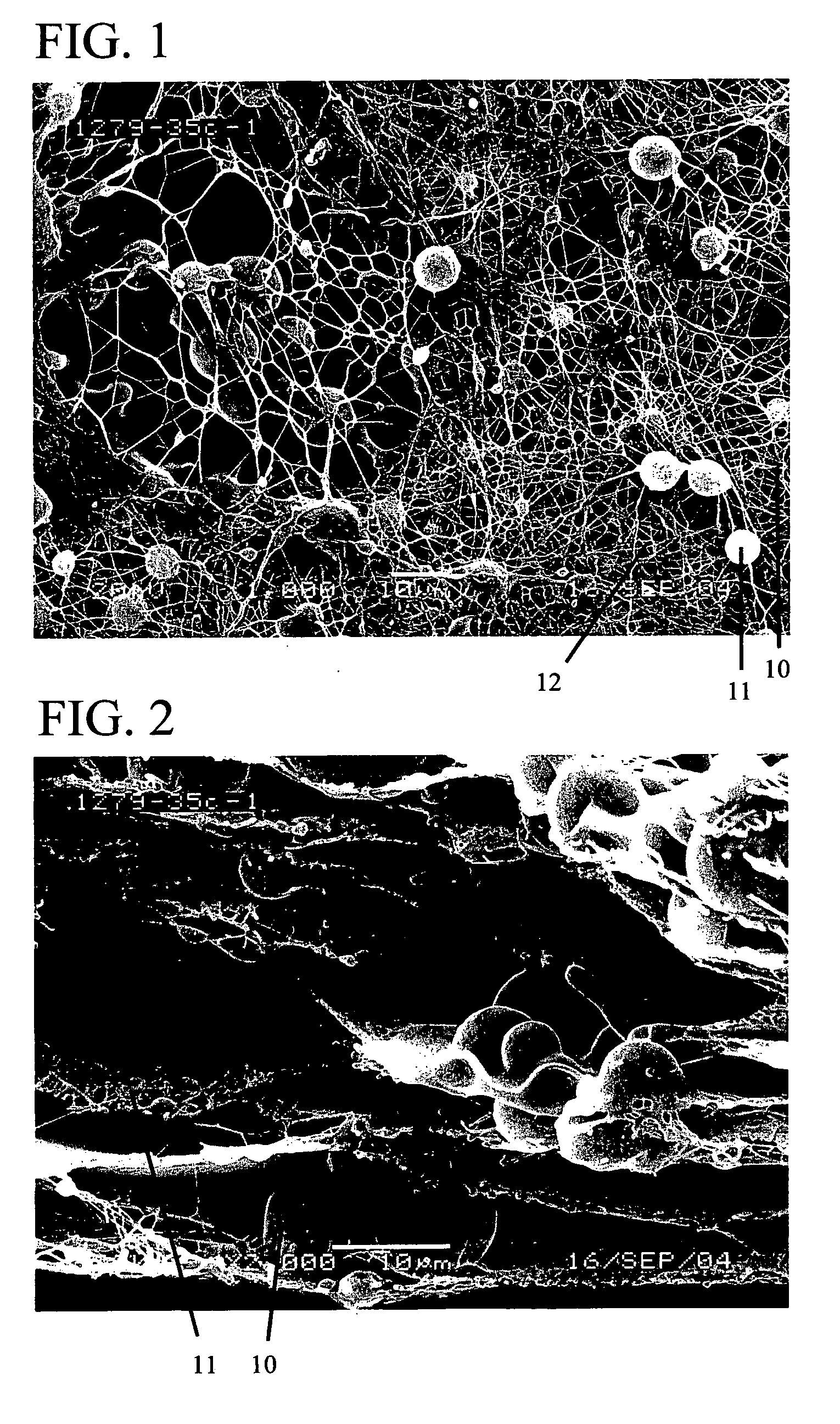
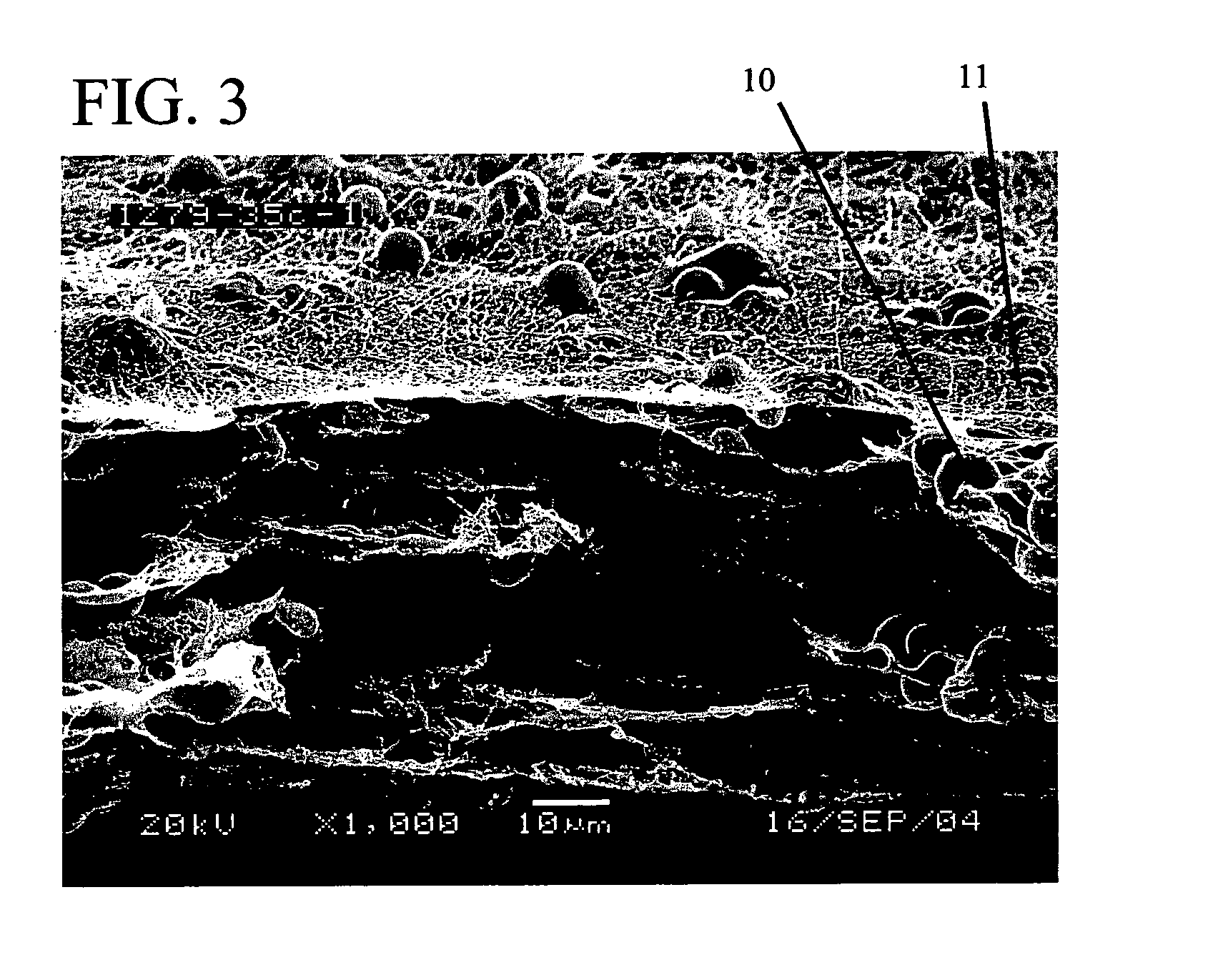
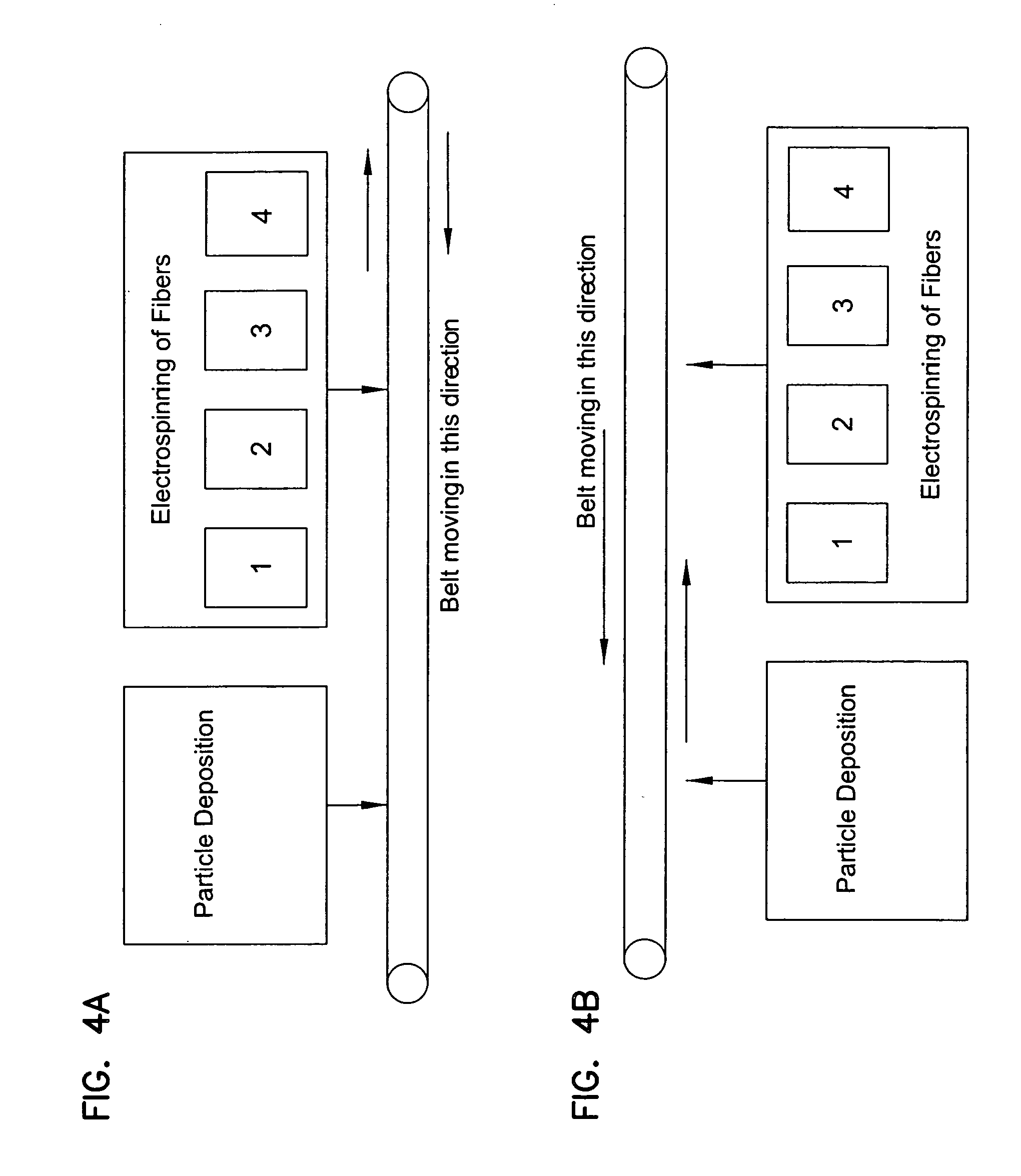
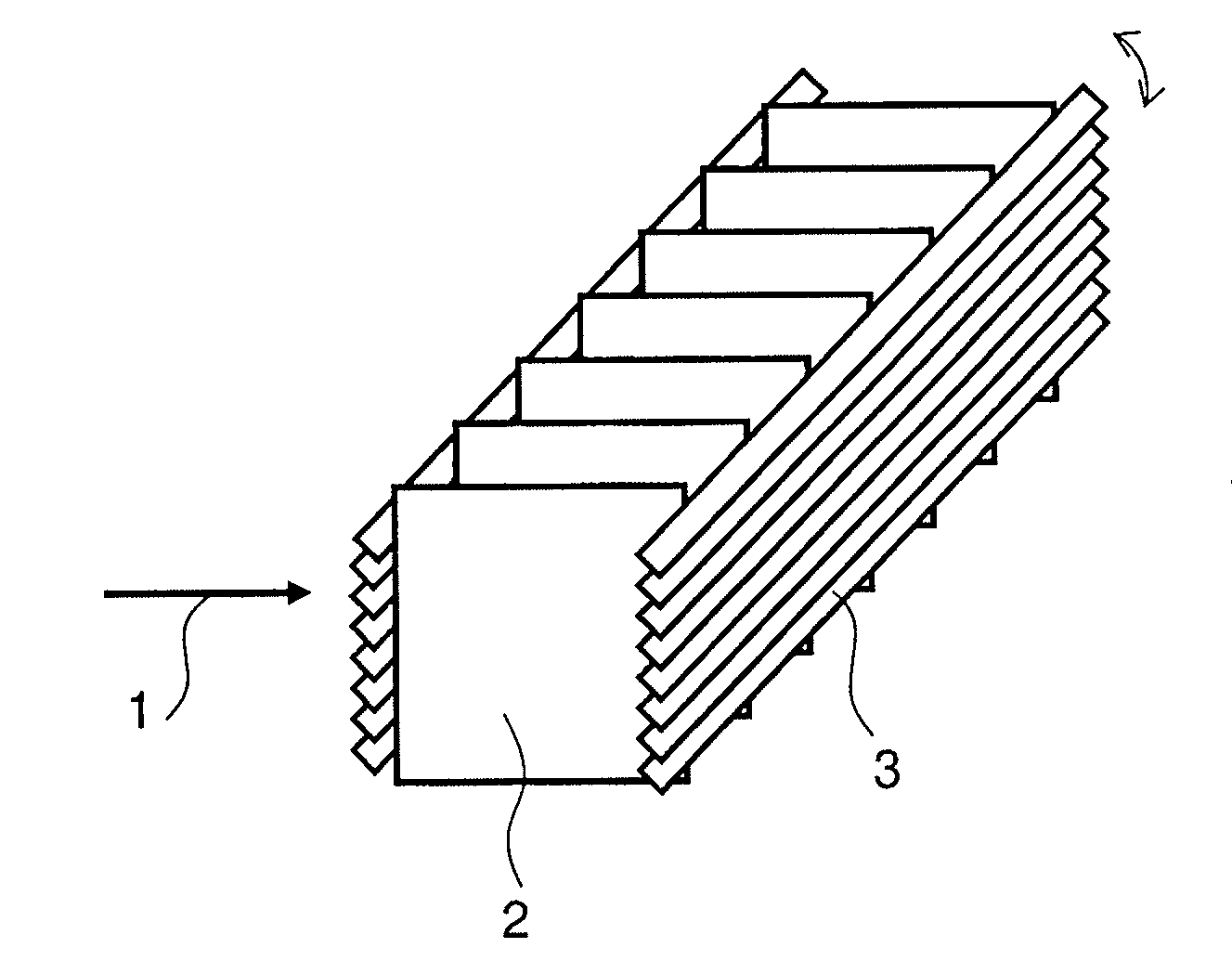
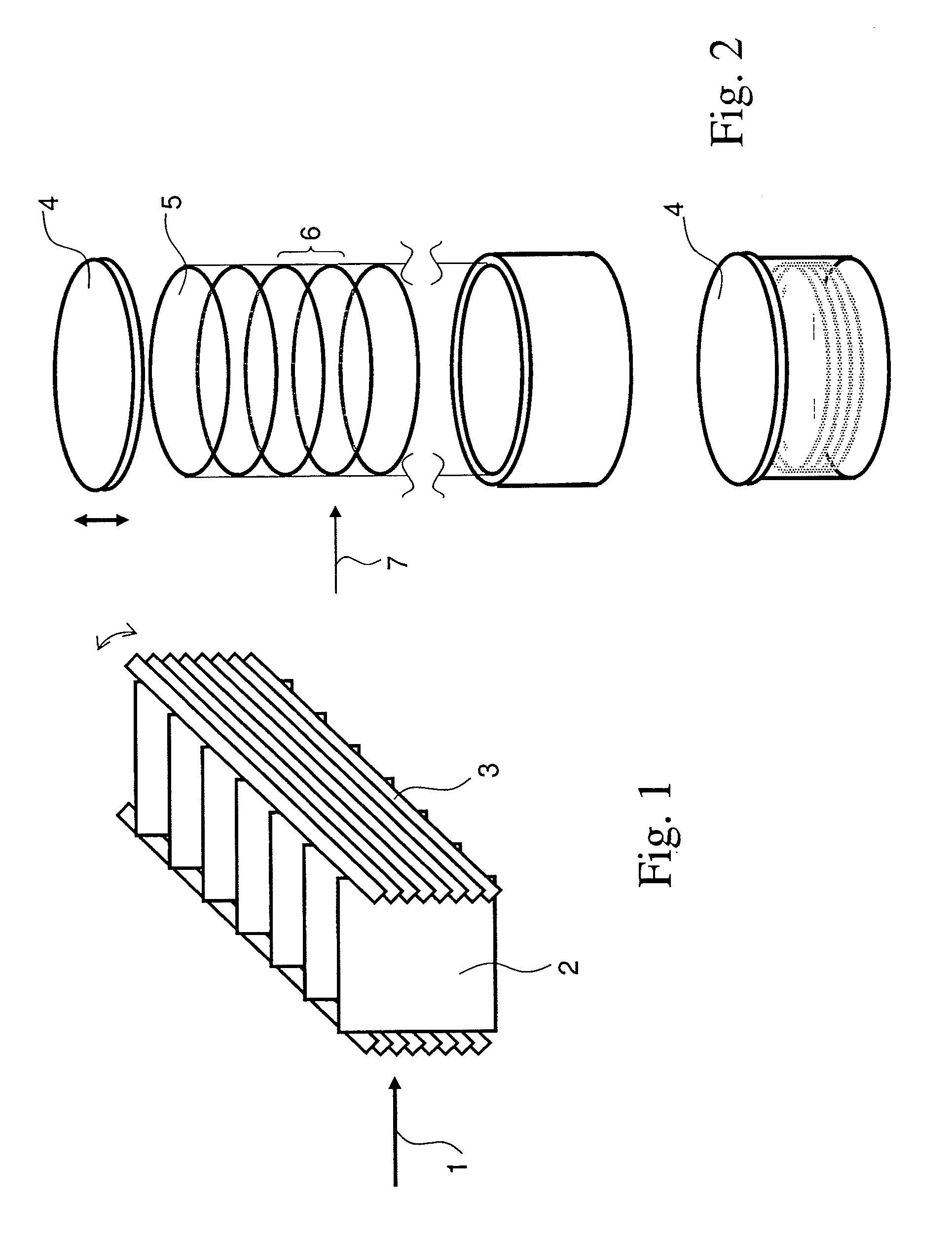
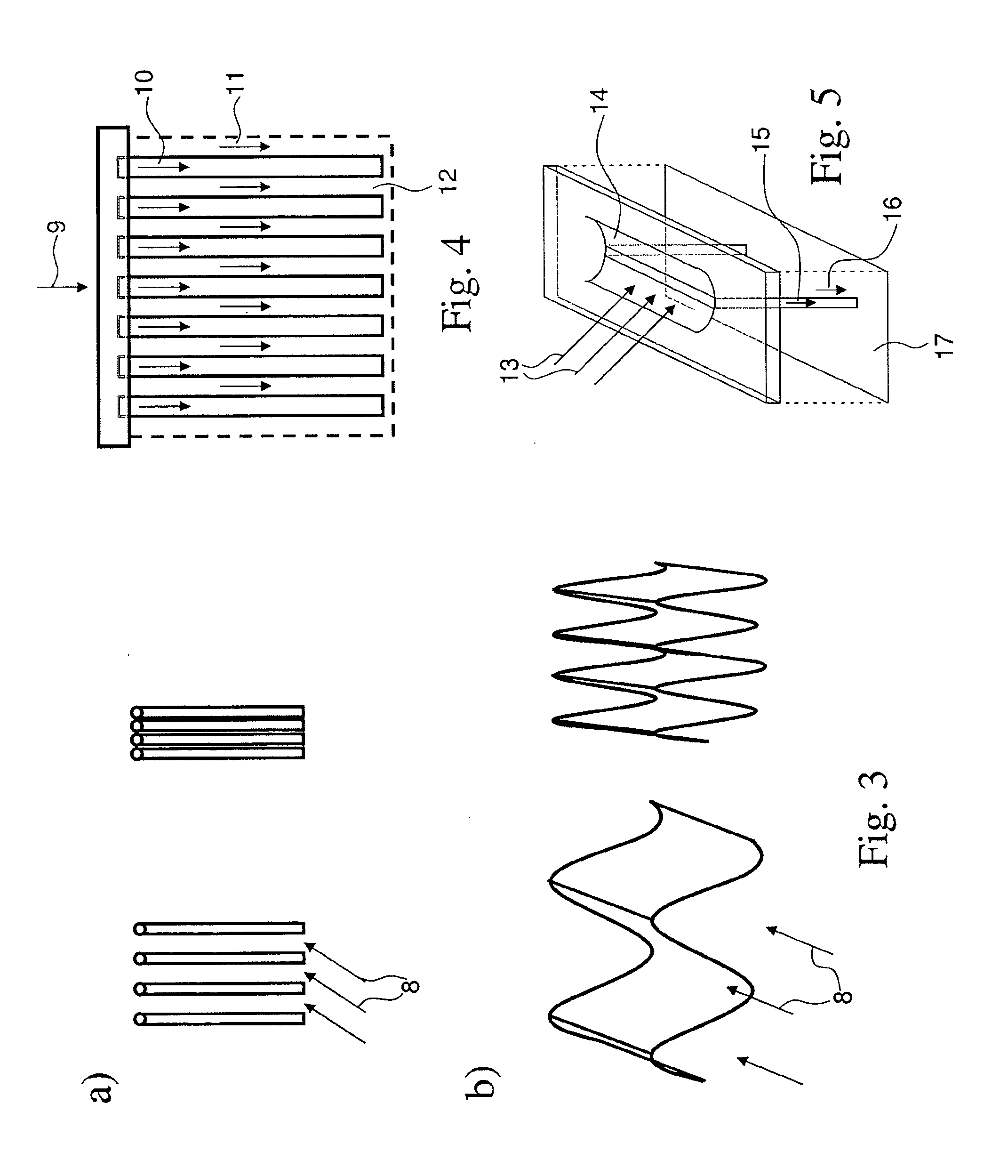
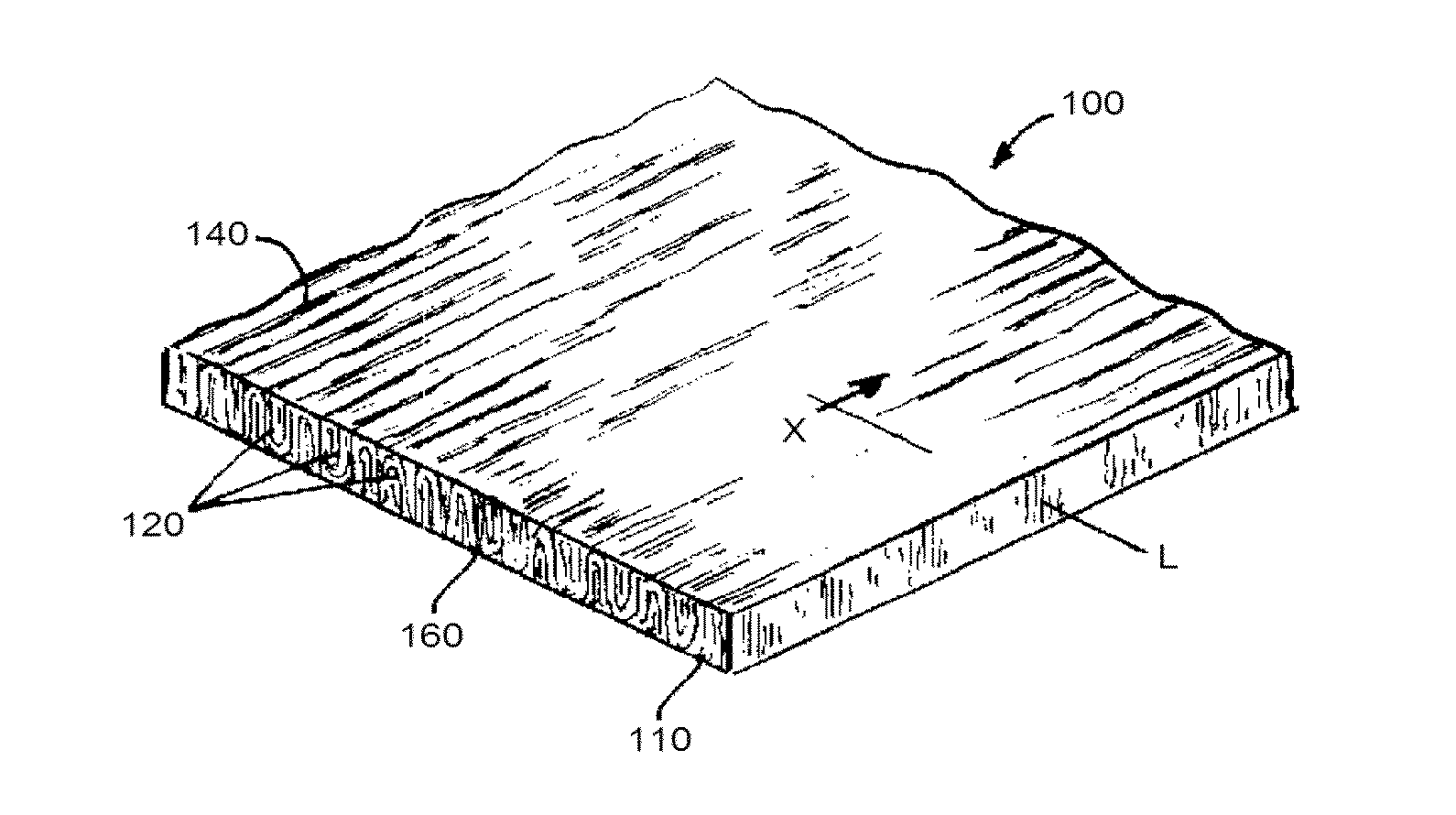
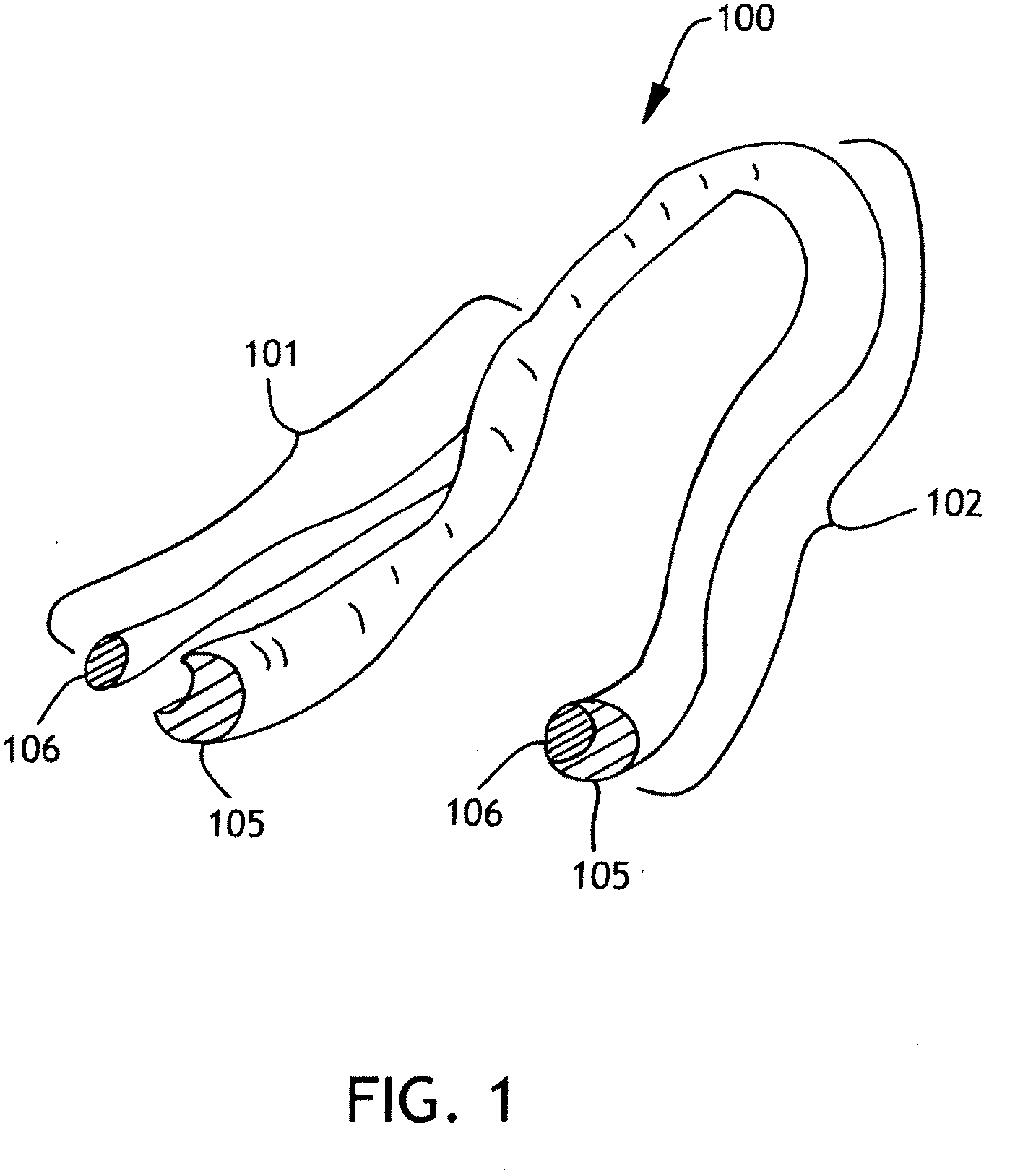
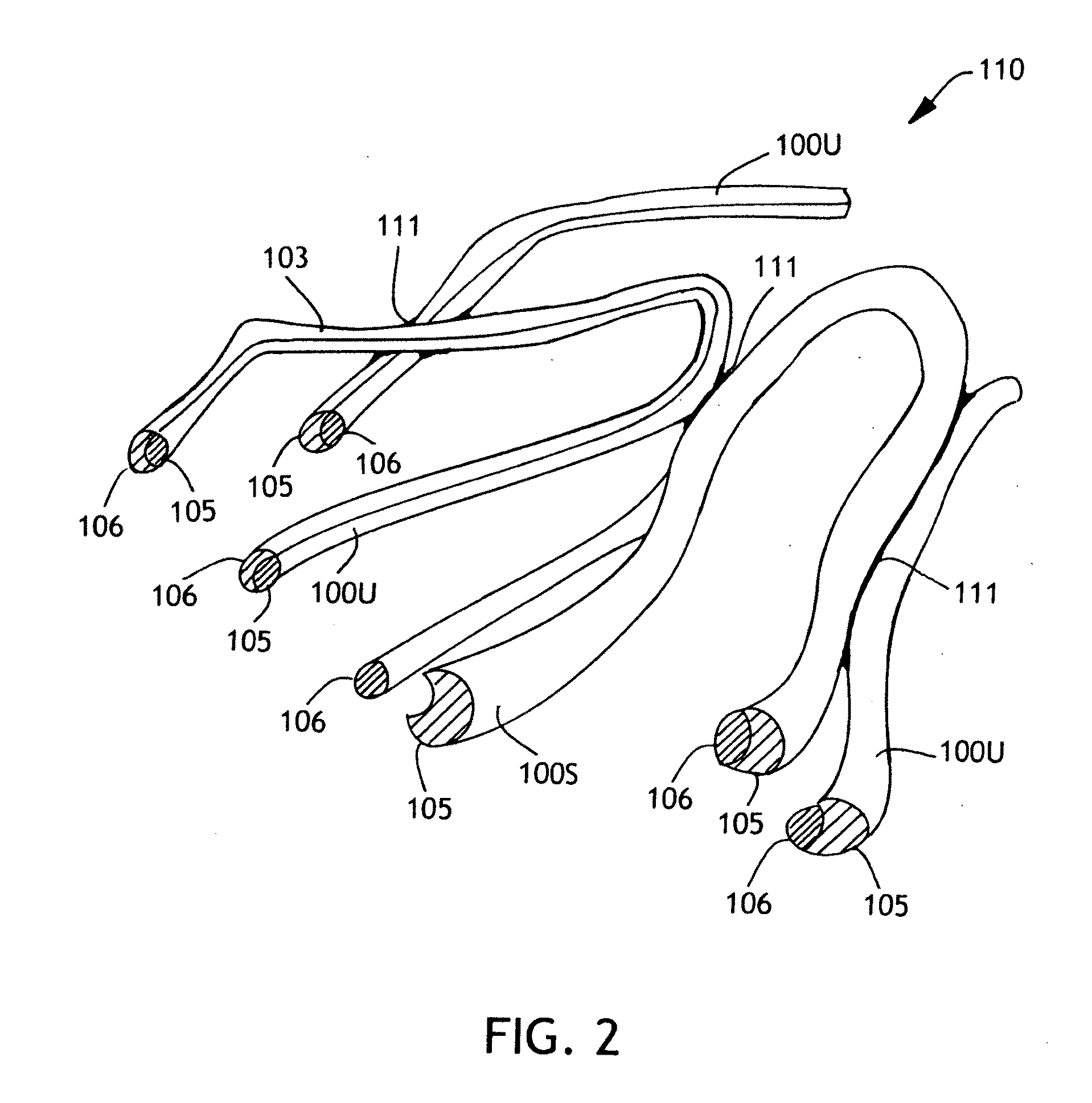
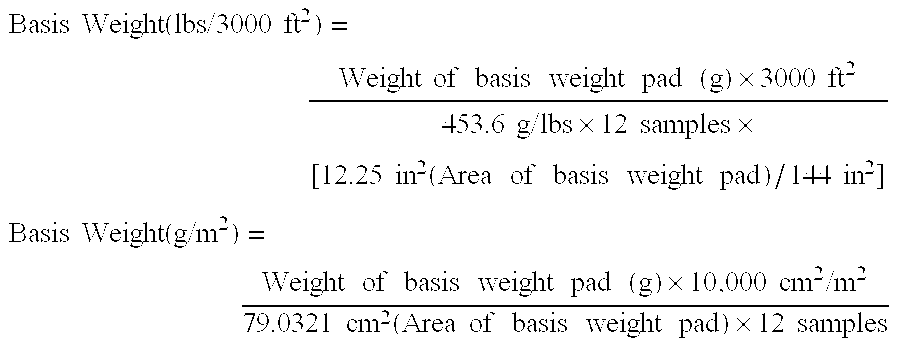Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2488 results about "Fiber structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The basic structure of an optical fiber consists of three parts; the core, the cladding , and the coating or buffer. The basic structure of an optical fiber is shown in figure 2-9. The core is a cylindrical rod of dielectric material. Dielectric material conducts no electricity. Light propagates mainly along the core of the fiber.
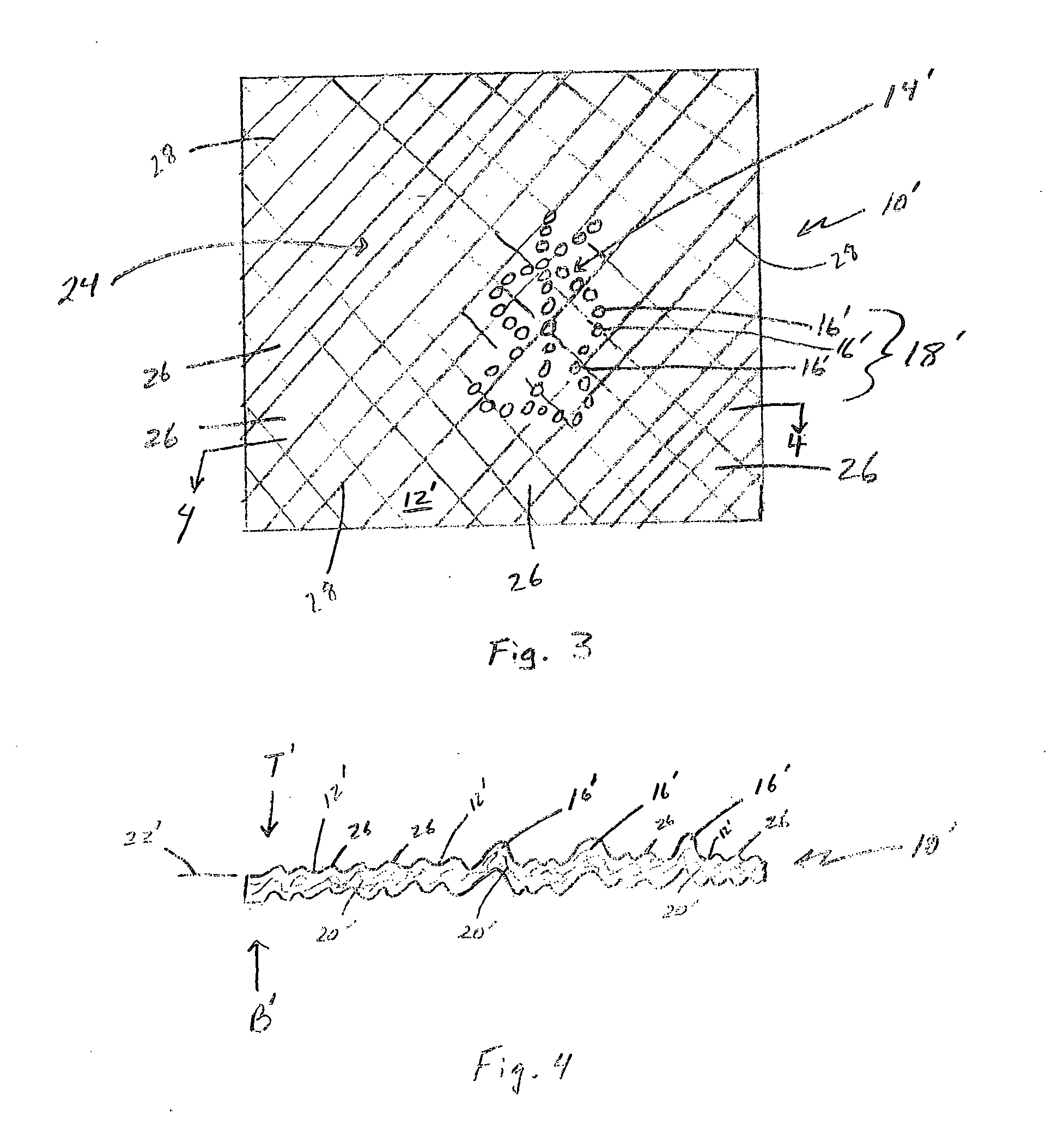
Process for making unitary fibrous structure comprising randomly distributed cellulosic fibers and non-randomly distributed synthetic fibers
InactiveUS7067038B2High densityNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceRepeat pattern
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Topically applied clotting material
A composition, system, articles and method for the enhancement of clotting in wounds with extravascular blood flow, especially where the surface of the tissue has been broken is described. The system consists of biotolerable, porous particulates applied to the surface of a wound with liquid blood thereon. The porous nature of the particulate material, either free-flowing or packaged or restrained on or in a surface, enhances clotting. Chemical or biochemical agents, such as additional clotting agents, therapeutic agents, antibiotics, clot strengthening agents (such as fibrous structural materials), and the like may optionally be included on, with or within the porous particles. The particles may comprise such diverse materials as organics, metallics, inorganics, ceramics, and the like, both natural and artificial. It is generally preferred that the pore size distribution lies within a general range, and this range may vary from animal to animal and condition to condition, but generally falls within about 0.5 to 1000 nanometers or 3,000 to 200,000 Daltons.
Owner:MEDAFOR
Organic devices having a fiber structure
ActiveUS20060013549A1Final product manufactureOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOrganic devicesFiber structure
A photoactive fiber is provided, as well as a method of fabricating such a fiber. The fiber has a conductive core including a first electrode. An organic layer surrounds and is electrically connected to the first electrode. A transparent second electrode surrounds and is electrically connected to the organic layer. Other layers, such as blocking layers or smoothing layers, may also be incorporated into the fiber. The fiber may be woven into a cloth.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Pleated filter with monolayer monocomponent meltspun media
ActiveUS7947142B2Lower overall pressure dropEfficient captureDispersed particle filtrationLaminationFilter mediaEngineering
A pleated filter is made from a monocomponent monolayer nonwoven web of continuous monocomponent meltspun partially crystalline and partially amorphous oriented fibers of the same polymeric composition that are bonded to form a coherent and handleable web having a Gurley Stiffness of at least 100 mg and which further may be softened while retaining orientation and fiber structure. Rows of pleats are formed in the nonwoven web, and the web is cut to a desired size and shape to provide a pleated filter element containing a self-supporting porous monocomponent monolayer matrix of fibers bonded to one another at least some points of fiber intersection and having an average initial submicron efficiency of at least 15% at a 1.52 meters / sec face velocity. The filter element is deformation resistant without requiring stiffening layers, bicomponent fibers, adhesive or other reinforcement in the filter media layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
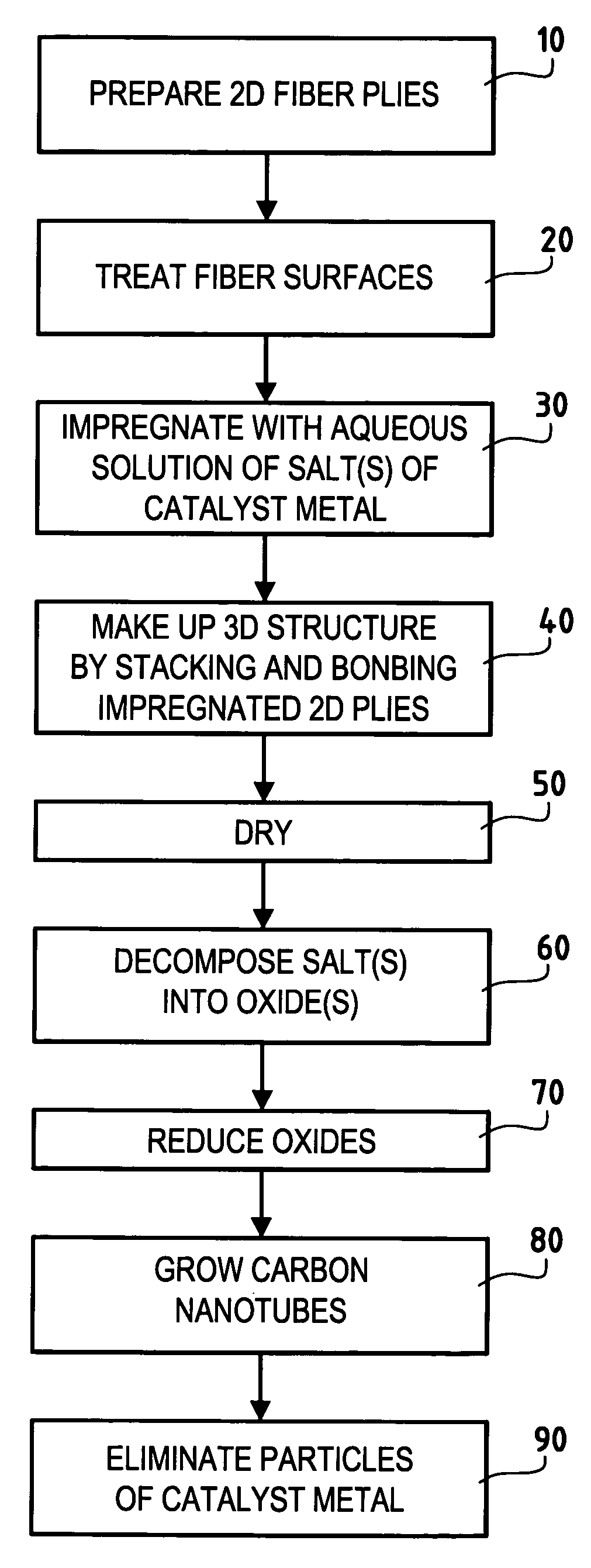
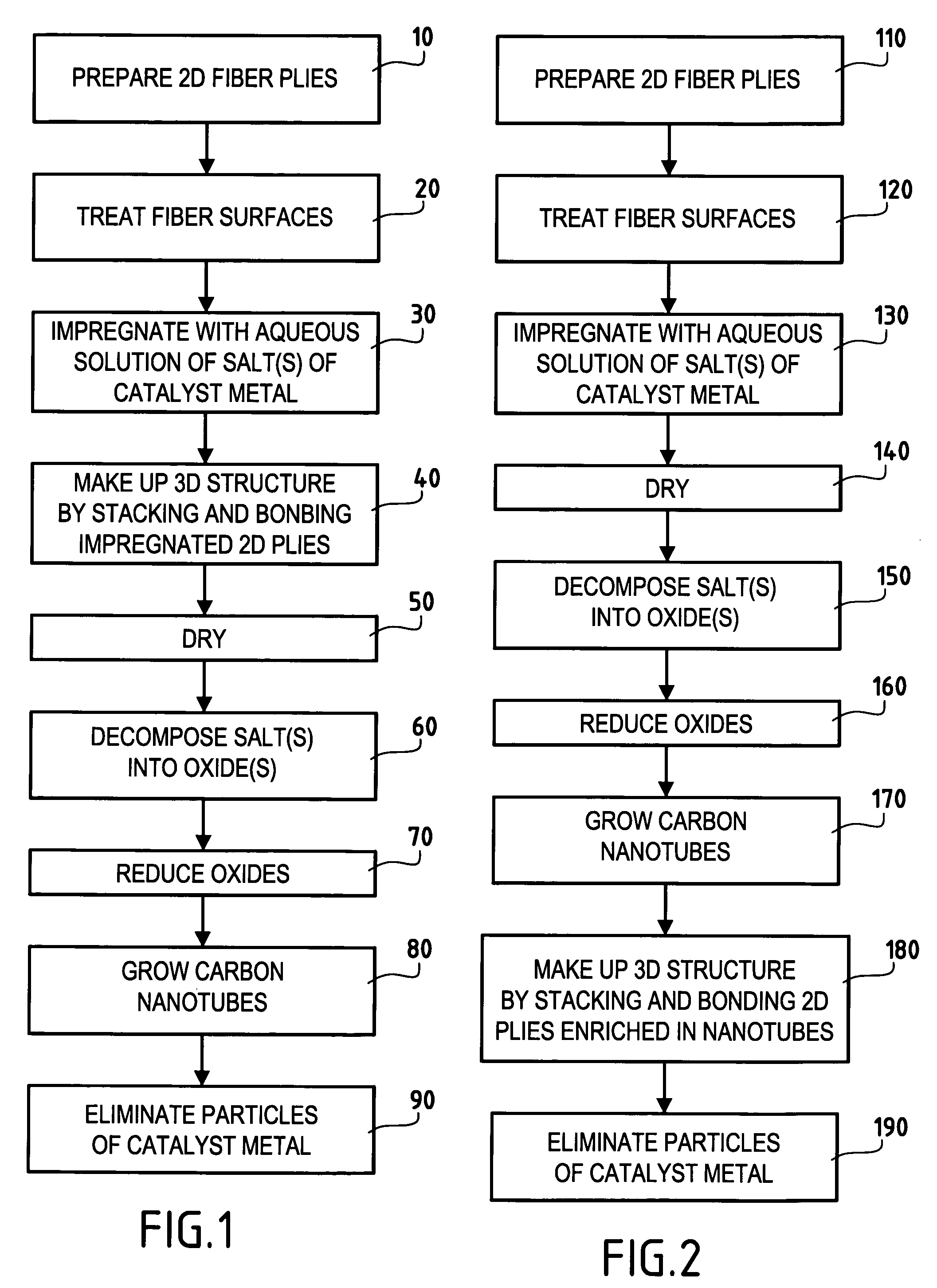
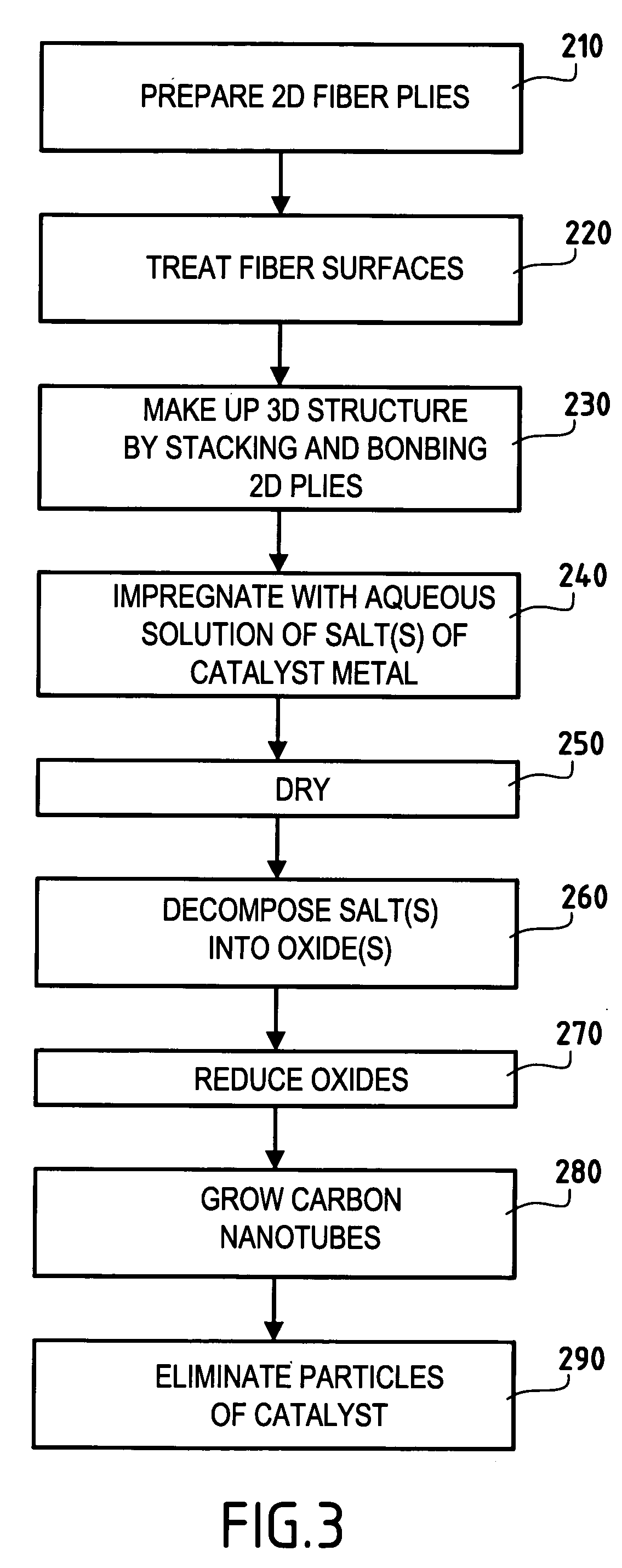
Three-dimensional fiber structure of refractory fibers, a method of making it, and thermostructural composite materials, in particular friction parts, made therefrom
ActiveUS20050176329A1Improve propertiesEasy to prepareMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon fibresMetallurgyCarbon nanotube
Carbon nanotubes are incorporated in the fiber structure by growing them on the refractory fibers of the substrate so as to obtain a three-dimensional substrate made of refractory fibers and enriched in carbon nanotubes. The substrate is densified with a matrix to form a part of composite material such as a friction part of C / C composite material.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
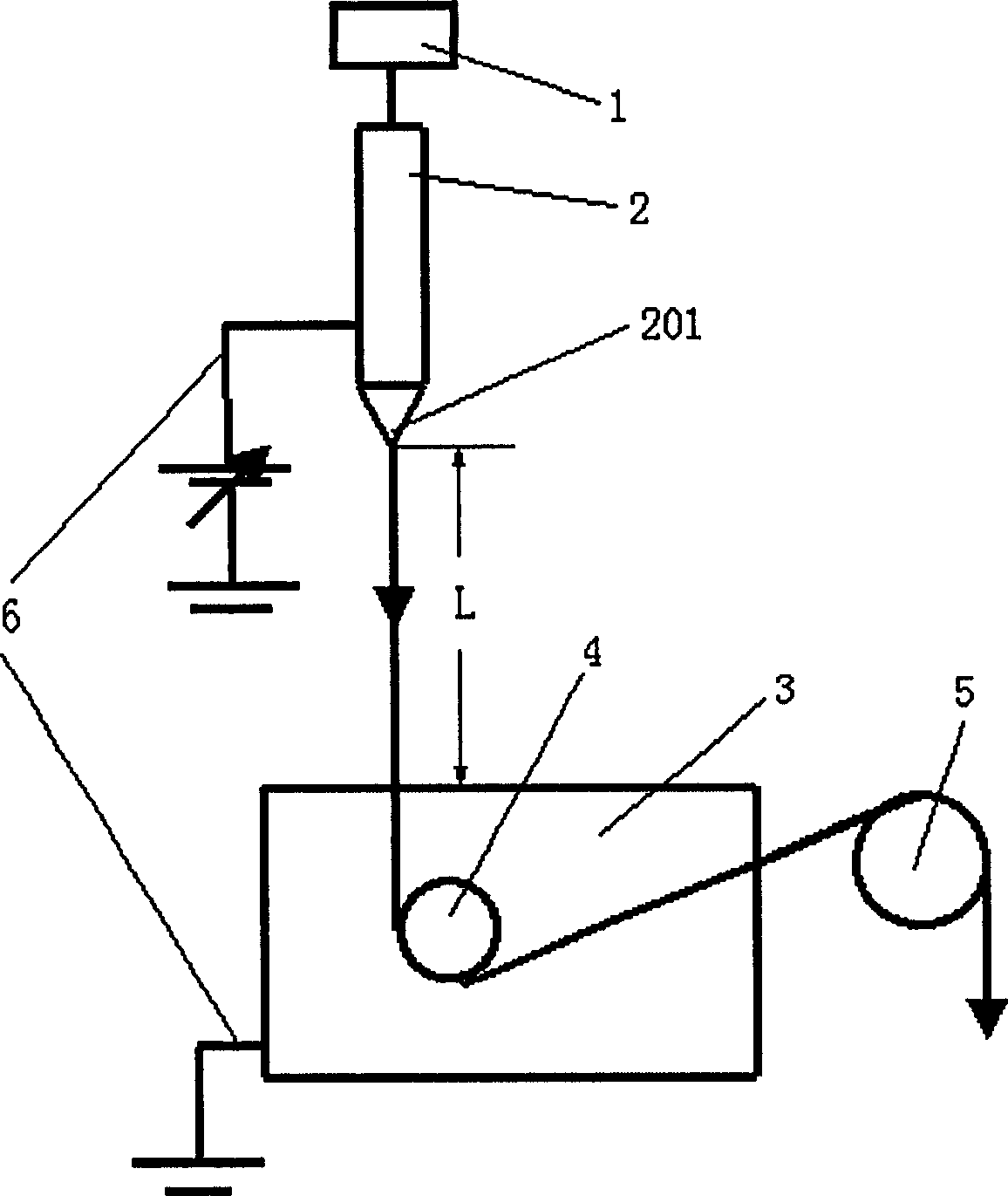
Static spinning device and its industrial use
InactiveCN1715463AHigh speedImprove mechanical propertiesFilament/thread formingElectrospinningMagnification
The present invention provides electrostatic spinning apparatus and its industrial application. The apparatus includes polymer solution conveying machine, spinning nozzle device connected to the outlet of the polymer solution conveying machine, spinning bath below the spinning nozzle device, fiber turning guide roller set inside the spinning bath and electrodes set on the spinning nozzle device and the spinning bath. The apparatus of the present invention is used in spinning polymer, and has greatly raised wet spinning speed, great fiber drafting magnification, well oriented fiber molecule chain, compact fiber structure, greatly raised mechanical performance of fiber, wide solvent selecting range, simplified electrostatic spinning equipment, raised solvent recovering rate and less environmental pollution caused by the solvent.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Reduced solidity web comprising fiber and fiber spacer or separation means
ActiveUS20060230731A1Improve filtering effectEnhance layeringCombination devicesOther chemical processesParticulatesFiltration
A web can comprise a substantially continuous fiber mass and a separation means dispersed into the fiber. The web having a preferred thickness resulting from forming a polymer material and a particulate into a fine fiber layer can have a variety of end uses. A filtration media can include a structure comprising such a web of fine fiber and a substantial volume of particulate embodiment of the separation means. The resulting fine fiber structure provides an improved filtration medium having substantial depth, thickness, and a layered structure. The improved properties of the web results from inclusion of the separation or spacer particulate.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Heat spreader and semiconductor device and package using the same
InactiveUS7067903B2Improve thermal conductivityLarge thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPolymer adhesiveCeramic
A semiconductor device and package has a heat spreader directly disposed on the reverse surface of the semiconductor device. This heat spreader includes a diamond layer or a layer containing diamond and ceramics such as silicon carbide and aluminum nitride. The heat spreader is directly formed on a substrate for the semiconductor device. In particular, the heat spreader is composed of a diamond layer and one or two metal or ceramic members, which are bonded to the diamond layer with one or two polymer adhesive layers. This diamond layer has a fiber structure across the thickness or a microcrystalline structure. Cilia are formed on a surface of the diamond layer facing the one or two metal or ceramic members.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
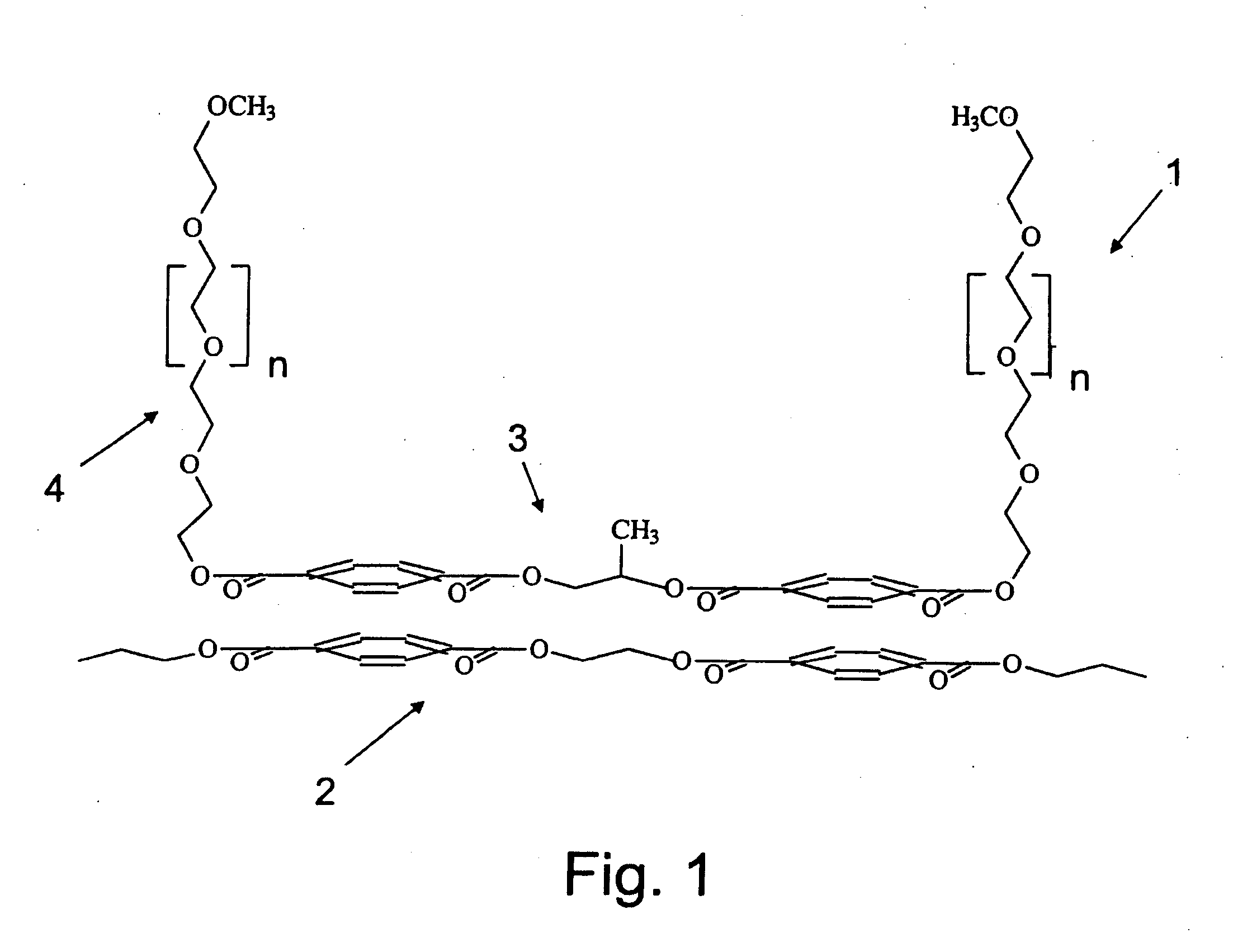
Transparent conductive film and coating composition therefor
InactiveUS20060263588A1High transparencyImproved and well controllable electrical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsPolymer scienceCarbon fibers
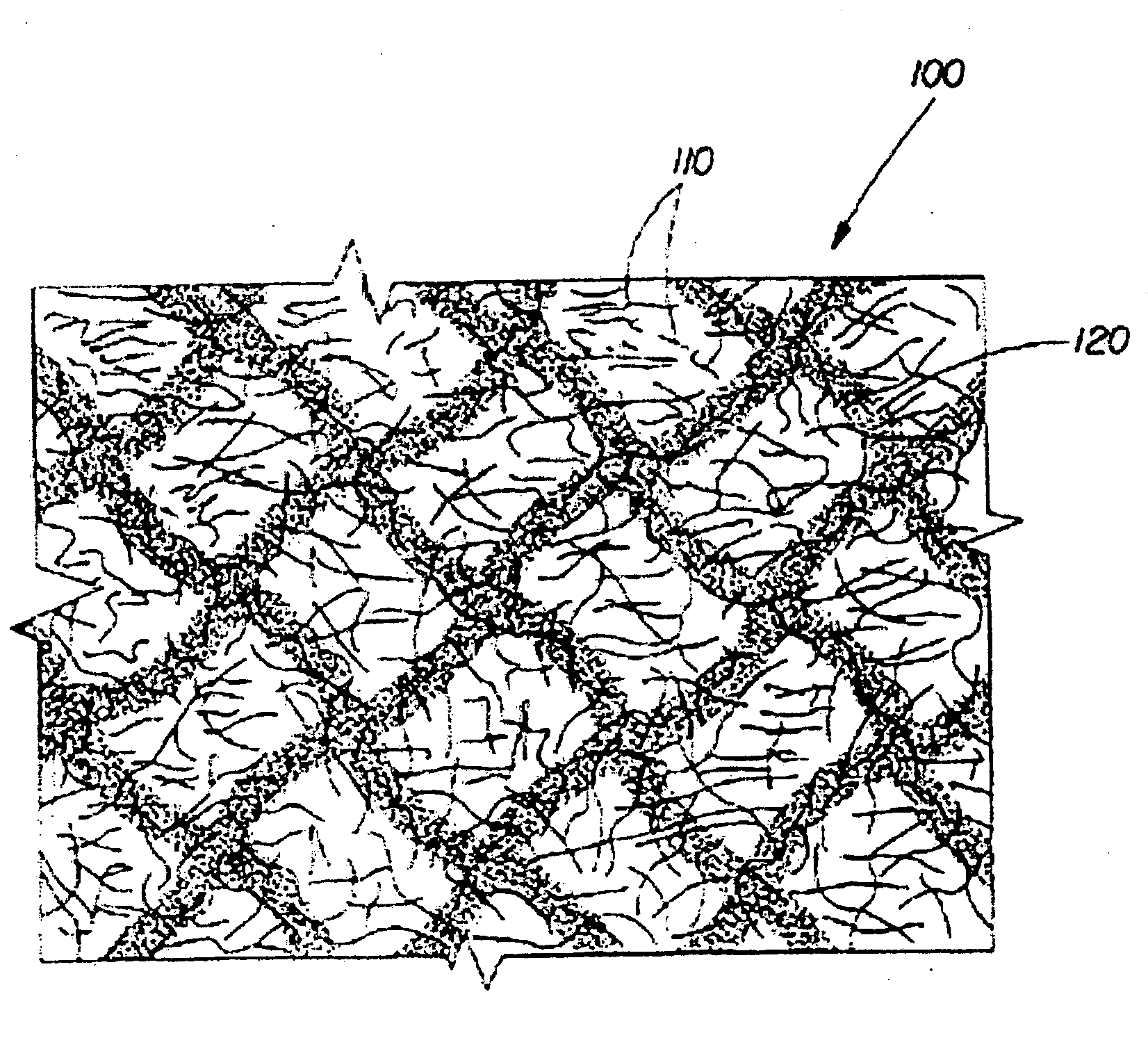
The disclosed is a transparent conductive film that includes a matrix and carbon fibrous structures added to the matrix, wherein the carbon fibrous structures comprise carbon fibers, each having an outside diameter of 15-100 nm, and wherein the carbon fibrous structures each comprise a granular part at which two or more carbon fibers are bound to each other, and wherein the granular part is concurrently produced in a growth process for the carbon fibers. When the transparent conductive film is formed at a thickness of 0.1-5 μm on a glass substrate, it shows a surface resistivity of not more than 1.0×1012Ω / □, and a total light transmittance of not less than 30%. A coating composition for the conductive transparent film is prepared by using a media mill equipped with beads having an average diameter of 0.05-1.5 mm to disperse the carbon fibrous structures into the liquid resinous composition.
Owner:MITSUI & CO LTD +1
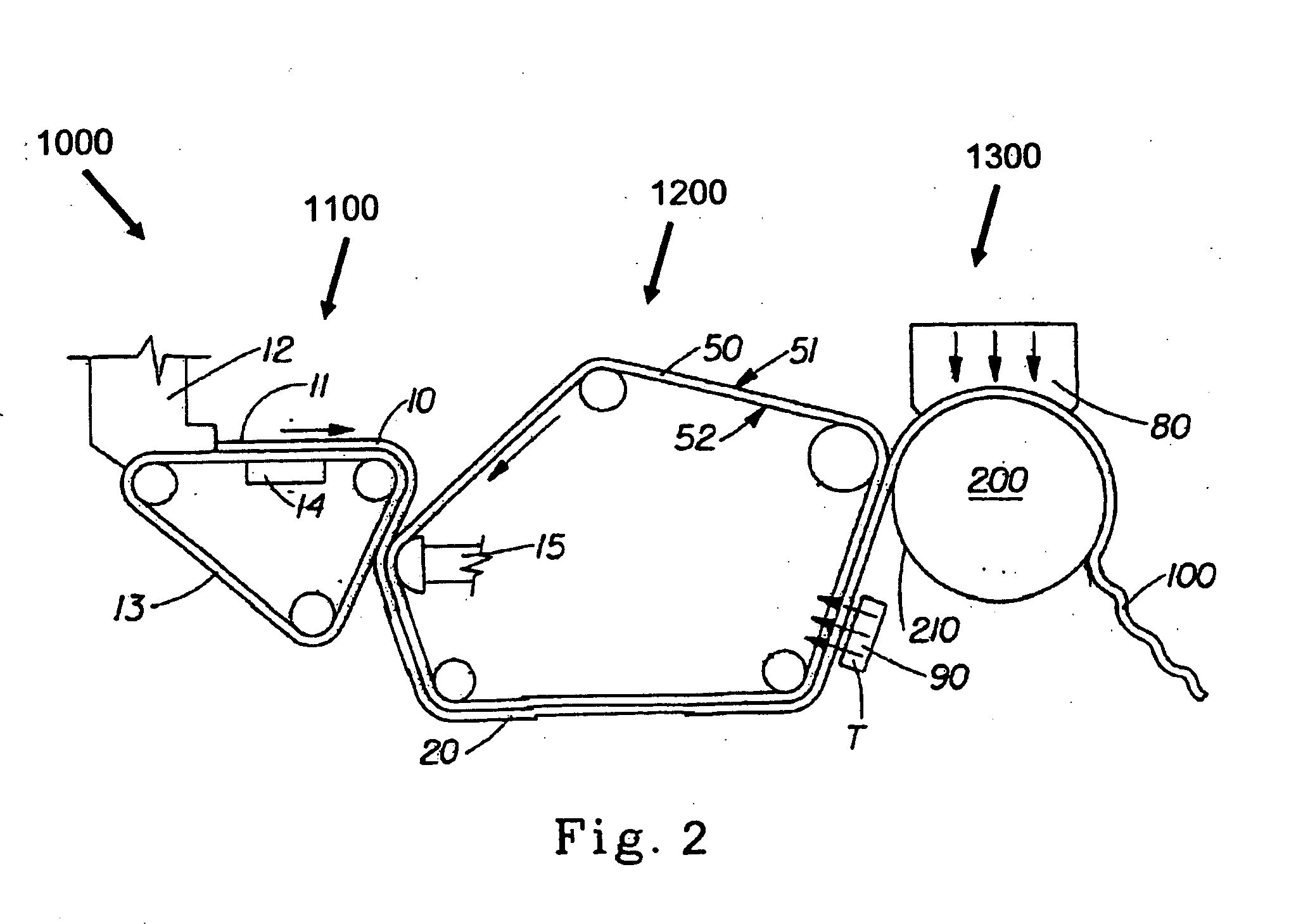
Vascular closure device
ActiveUS20090171388A1Minimize potential for infectionFilament/thread formingAntiinfectivesVascular closure deviceVascular device
A biocompatible material may be configured into any number of implantable medical devices including a vascular closure device. The vascular closure device includes a fibrous structure formed from at least one randomly oriented fiber, the randomly oriented fiber comprising at least one polymer, and at least one agent, in therapeutic dosage, incorporated into at least one of the fibrous structure and the at least one randomly oriented fiber.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Amine containing fibrous structure for adsorption of co2 from atmospheric air
InactiveUS20120076711A1Eliminate needMaterial nanotechnologyExhaust apparatusCarbon dioxideReversible adsorption
A structure is disclosed containing a sorbent with amine groups that is capable of a reversible adsorption and desorption cycle for capturing CO2 from a gas mixture wherein said structure is composed of fiber filaments wherein the fiber material is carbon and / or polyacrylonitrile.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Fiber-based carpet cushion with added resilience from vertically oriented fiber construction
ActiveUS20110311758A1Increase elasticityImprove the immunityLayered productsWoven fabricsParallel fiberEngineering
A fiber pad having a core non-woven layer is disclosed. The core layer can have an upper surface and a lower surface. The core layer can comprise at least one fiber layer. The at least one fiber layer can comprise a plurality of parallel fibers. Selected groups of the parallel fibers can be folded into desired pleated configurations. Optionally, the core layer can comprise post-consumer carpet materials.
Owner:COLUMBIA INSURANCE CO
High bulk strong absorbent single-ply tissue-towel paper product
ActiveUS20050067126A1Increase in sizeIncrease in caliperNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperEngineeringFiber structure
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
High performance filter media with internal nanofiber structure and manufacturing methodology
ActiveUS20070021021A1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesIndividual molecule manipulationFiberFilter media
High performance filter media and manufacturing methodology provides nanofibers of diameter less than 1 μm incorporated and processed into internal structure of a filter medium dominantly composed of coarse fibers of diameter greater than 1 μm, to change the internal media structure.
Owner:FLEETGUARD INC
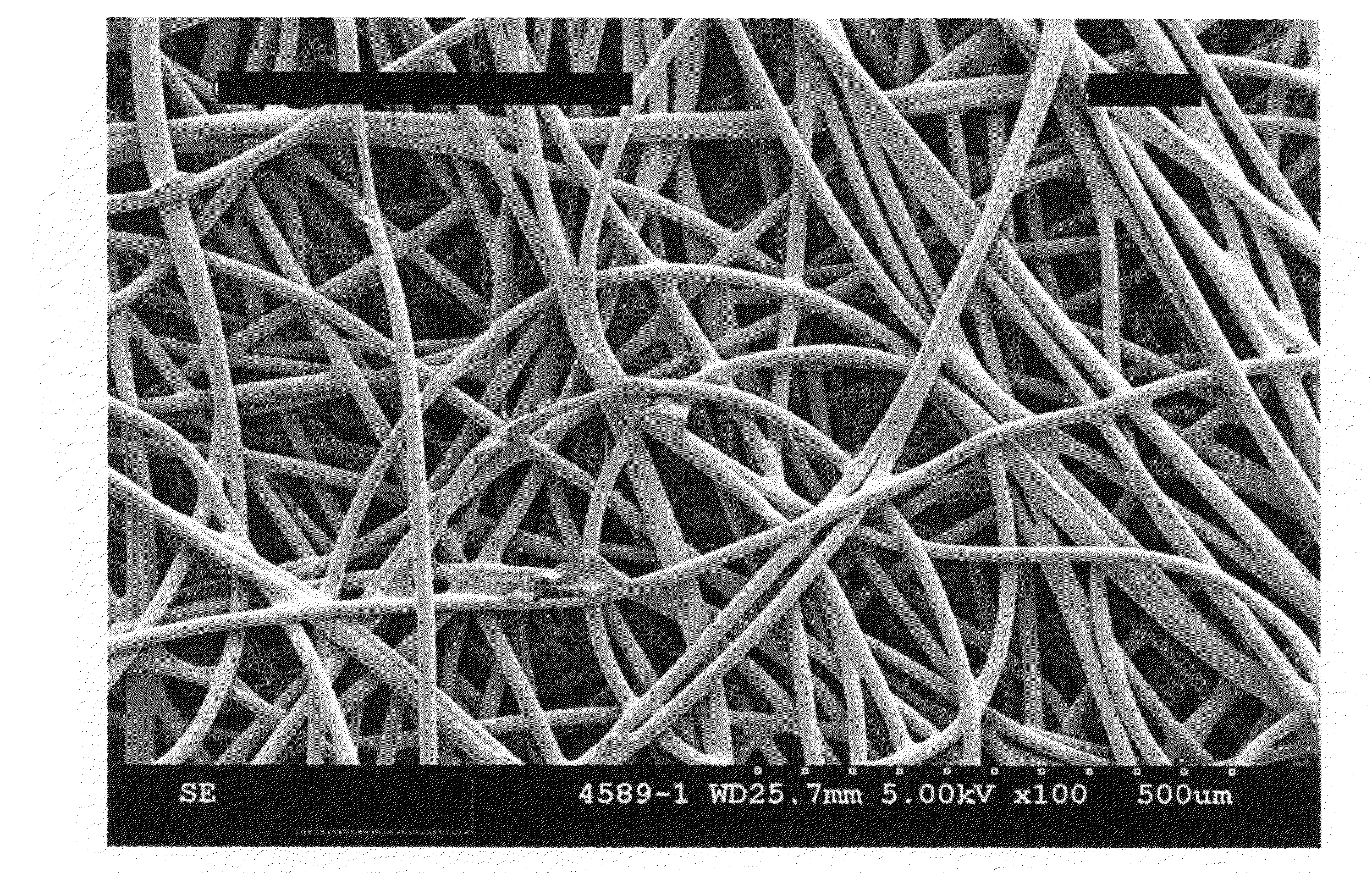
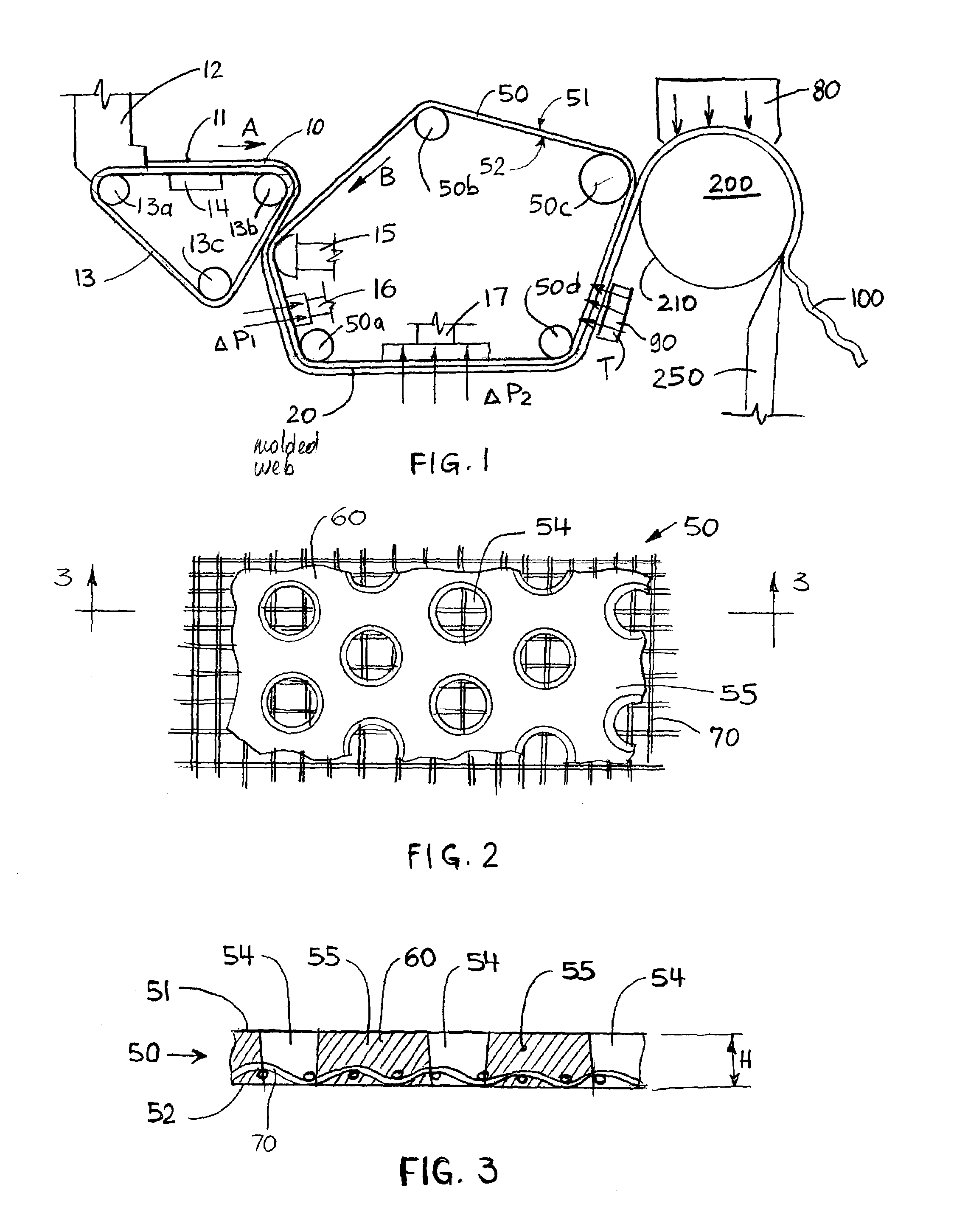
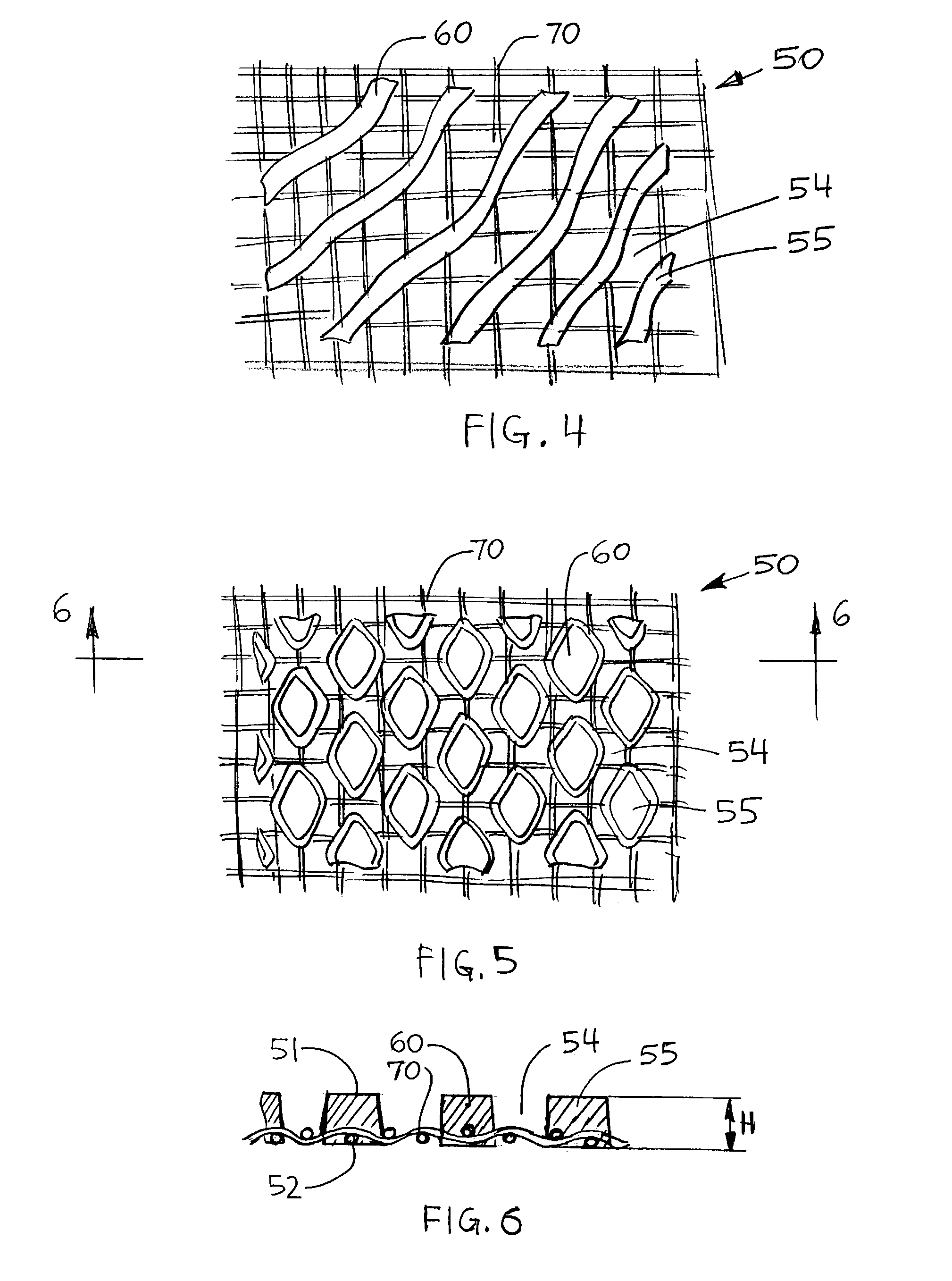
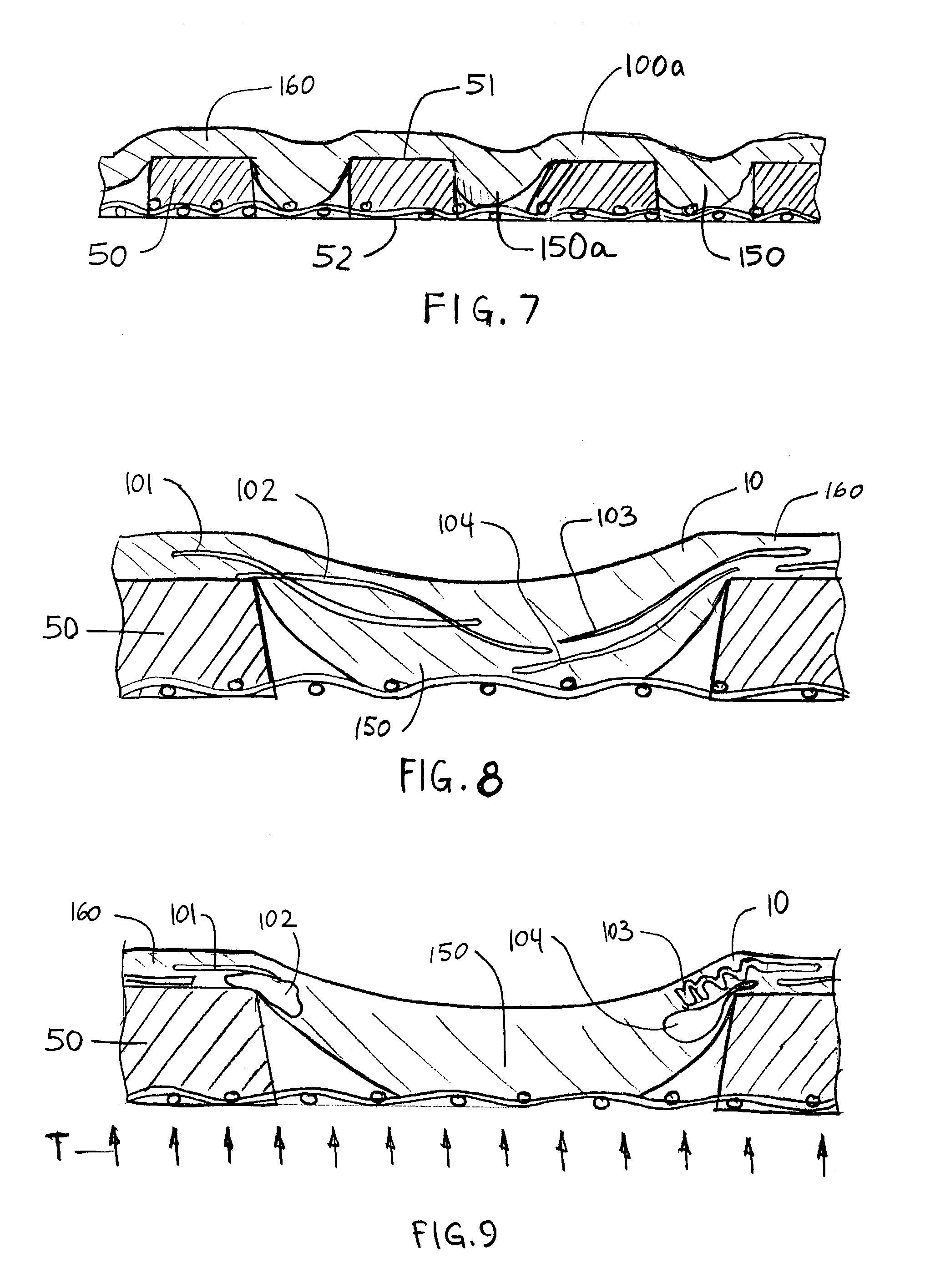
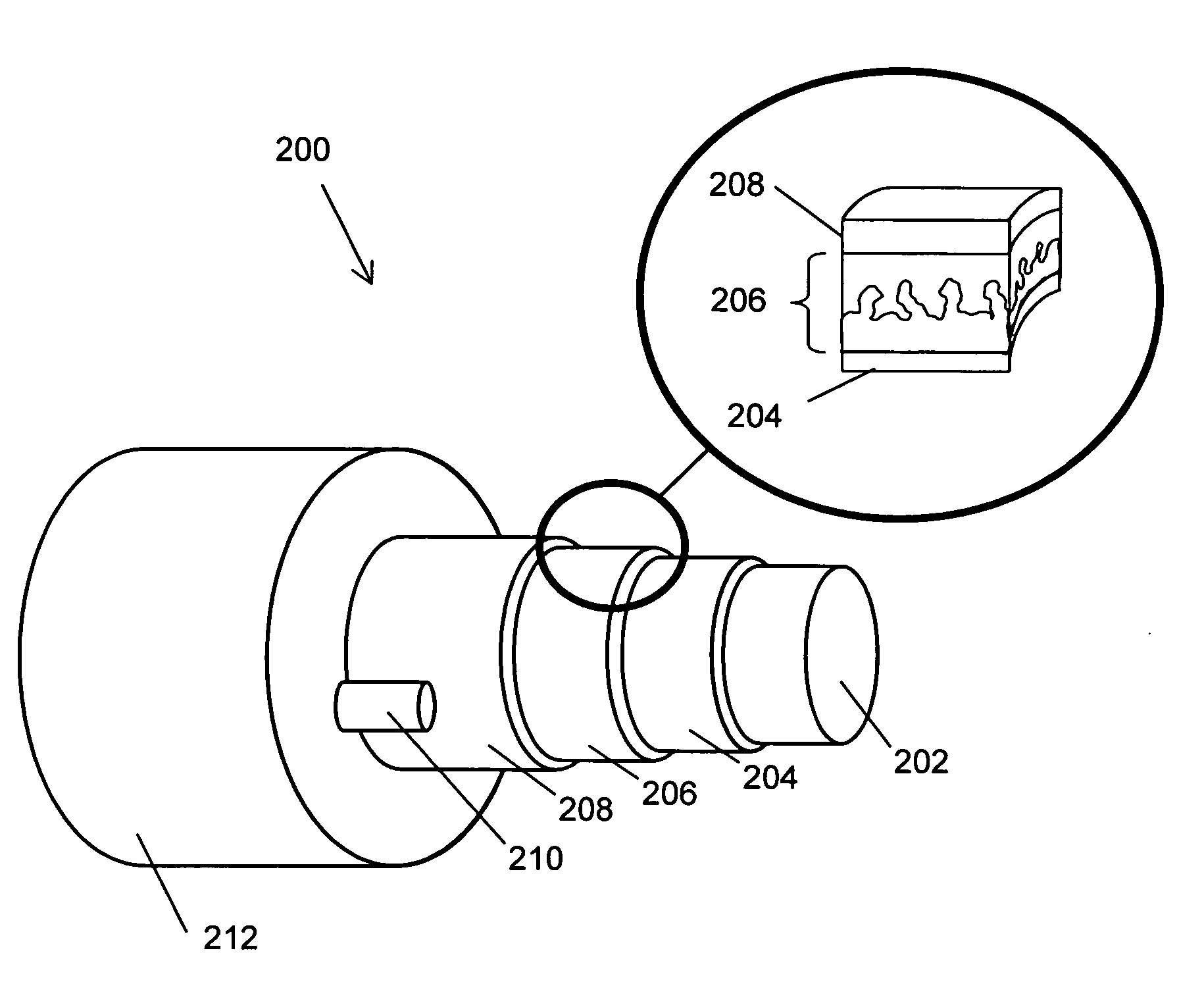
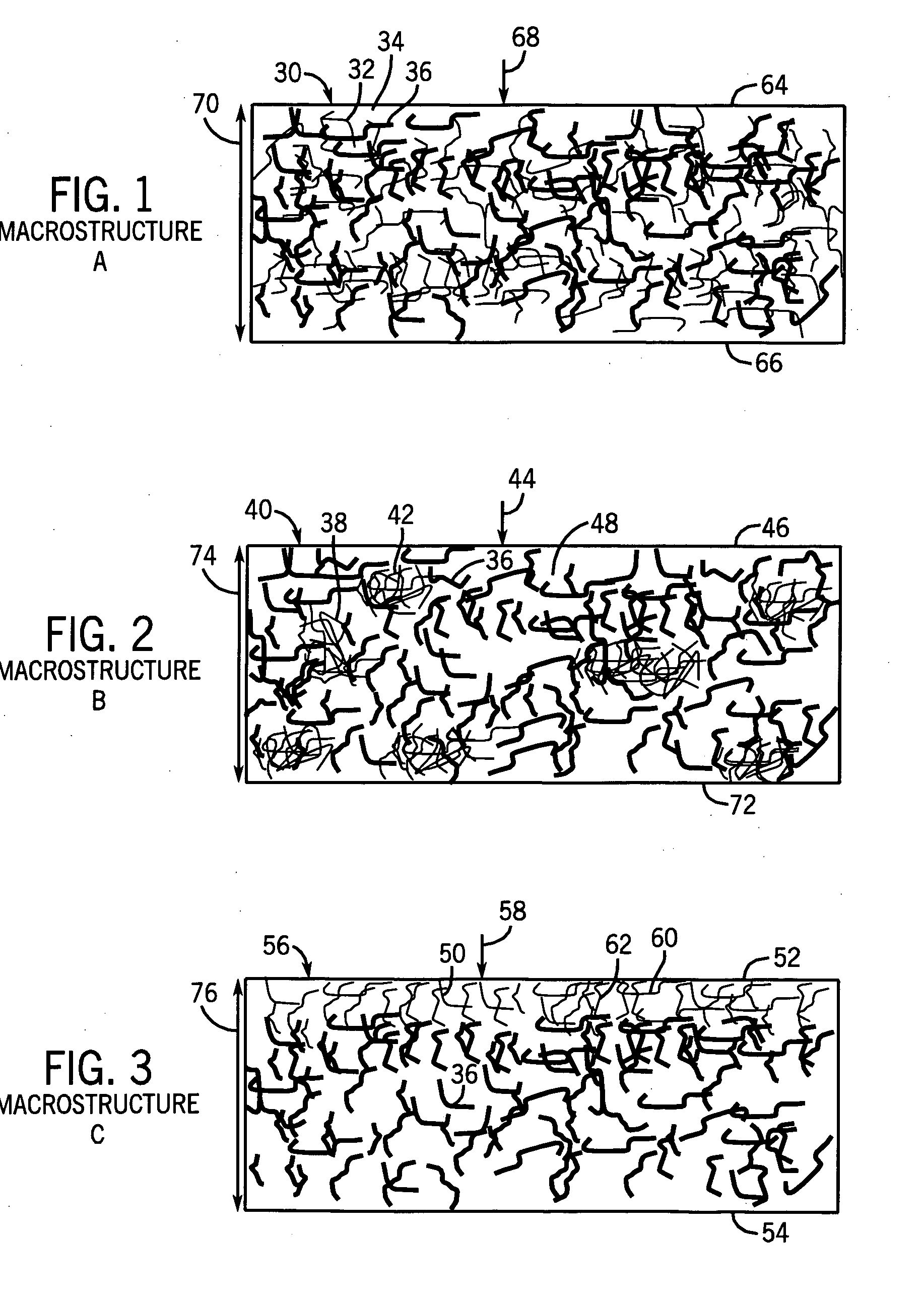
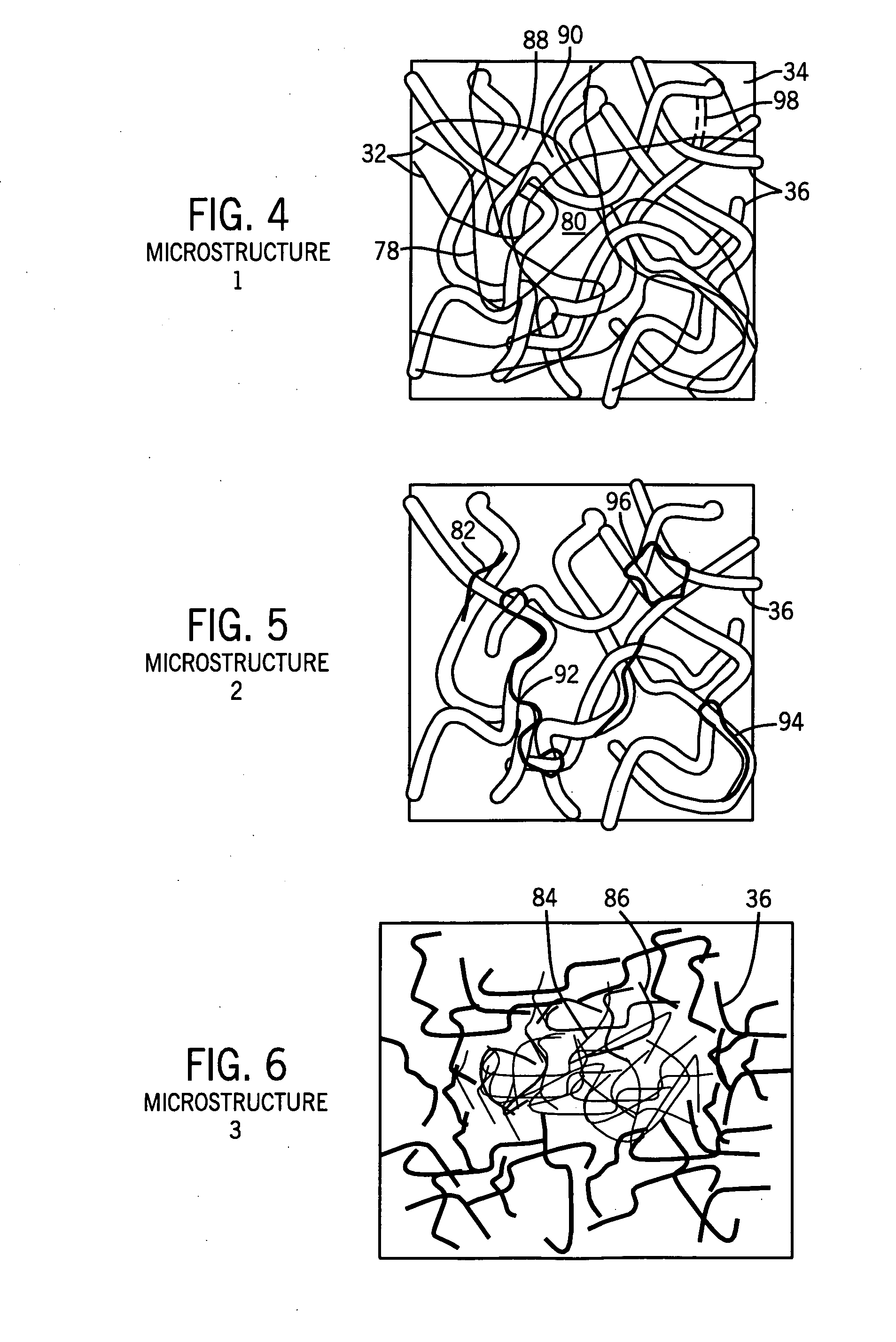
Fibrous structures comprising a design and processes for making same
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for forming a fibrous structure comprising synthetic fibers and hydrophilizing agents
InactiveUS20070232178A1Natural cellulose pulp/paperWater-repelling agents additionEngineeringFiber structure
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Dissection handpiece and method for reducing the appearance of cellulite
ActiveUS20100228182A1Prevent removalIncrease kinetic energyElectrotherapyAnti-cellulite devicesWound healingSkin treatments
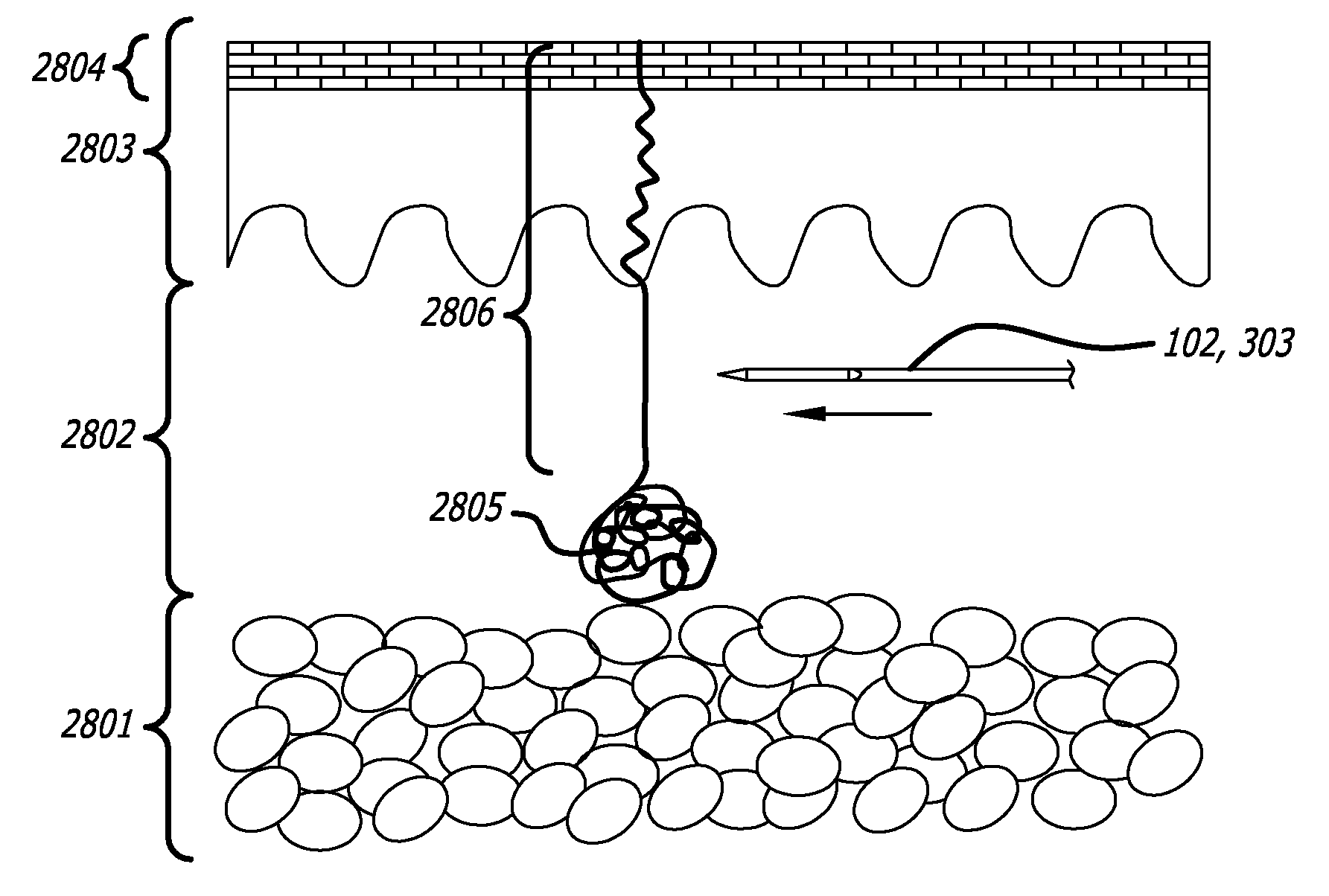
A dermatological skin treatment device is provided. The device comprises a handpiece and a cutting tool, wherein the tool is inserted through the conduit and percutaneously inserted into a tissue disposed within a recessed area of the handpiece. The device and method cut the fibrous structures under the skin that cause cellulite at an angle substantially parallel to the surface of the skin and replace these structures with a non-cellulite forming structure by deploying a highly fibrous mesh through a single needle hole to create a highly fibrous layer directly or through wound healing processes.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
Fibre structure of carbon nano tube/nano oxide nano composite material and preparation method and use thereof
The invention relates to a fiber structure of nanometer composite material of carbon nanometer pipe / nanometer oxide or polymer / carbon nanometer pipe / nanometer oxide. Disperse the front drive body of the carbon nanometer pipe and nanometer oxide into a polymer solution, so as to obtain a dispersion liquid; then, perform electric filature to obtain a polymer / carbon nanometer pipe / nanometer oxide with a front drive body of nanometer fiber structure. The front drive body of the nanometer oxide can be converted into a nanometer oxide with such methods as hydrothermal process, high-temperature process or microwave process and etc. The polymer can be kept or eliminated through such methods as high-temperature process or solvent fractionating and etc, in order to obtain the nanometer fiber of carbon nanometer pipe / nanometer oxide. The fiber composed of the composite material fiber structure, or films made of the fiber can be utilized in the fields of sewage process, air purification, solar energy battery and antibiotic material and etc.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dynamically Tunable Fibrillar Structures
A multi-mode adhesive is disclosed comprising a plurality of fibers connected to a backing material where applying an external influence causes a change in properties of the plurality of fibers or backing. This change in properties causes the multi-mode adhesive to change from one level of adhesive strength to another. The multimode adhesive may be used for a variety of novel applications, from adhesives that can be detached remotely to medical adhesives with adhering and non-adhering modes.
Owner:LIVNE OREN
Molded elements
InactiveUS20070254145A1High texture impressionImprove textureSynthetic resin layered productsMedical applicatorsPolymer scienceFiber structure
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Nonwoven fibrous structure comprising synthetic fibers and hydrophilizing agent
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Conductive composite particle, method of manufacturing the same, electrode using the same, lithium ion secondary battery
In a manufacturing method of a conductive composite particle, a conductive composite particle is manufactured that is formed of an active material particle having a region capable of electrochemically inserting and desorbing lithium and a carbon layer joined to the particle surface. In the carbon layer, fine metal particles are dispersed. This method has the following three steps. In the first step, a polymer material containing the metal element composing the fine metal particles is prepared. In the second step, the active material particle surface is coated with the polymer material containing the metal element. In the third step, a carbon layer having a porous structure including a fibrous structure is formed as the surface layer section from the polymer material by a treatment where the active material particle coated with the polymer containing the metal element is heated in an inert atmosphere to carbonize the polymer material.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wiping sheet
InactiveUS20060009106A1Improve wiping effectPromote stratificationCarpet cleanersFloor cleanersNonwoven fabricFiber structure
A wiping sheet is provided, which presents excellent in handling during wiping, high wiping ability for greasy dirt, and less liquid remains on an object after wiping. A wiping sheet having a fiber structure (such as a woven fabric, a knitted fabric and a nonwoven) is obtained, which includes an ultrafine fiber layer containing ultrafine fibers having a fineness of at most 0.9 dtex which result from at least two types of ultrafine fiber-generating conjugate fibers, at least one conjugate fiber giving ultrafine fibers containing a modified vinyl alcohol resin, and the other conjugate fibers giving ultrafine fibers containing another resin(s). The ultrafine fibers can be obtained by a first splittable conjugate fiber including a component containing the modified vinyl alcohol resin and a second splittable conjugate fiber composed of components of other resins. In the ultrafine fiber layer, the fibers are preferably bonded by thermoadhesive resin-containing ultrafine fibers.
Owner:DAIWABO HLDG +1
Gypsum wood fiber structural insulated panel arrangement
InactiveUS20080245007A1Low costHigh tensile strengthBuilding componentsMesh reinforcementCellulose fiber
A generally planar, structural insulated panel for building construction includes a pair of outer facings disposed on opposed surfaces of a plastic foam core. Both of the outer facings are gypsum cellulose fiber board such as gypsum wood fiber board. Disposed on the exterior surface of the gypsum wood fiber board on the exterior surface and between another expanded polystyrene insulation panel is a weather resistant barrier that is fastened to the gypsum wood fiber board. The exterior surface of the second insulation panel is fastened to the gypsum wood fiber board by mechanical fasteners. The insulation panels are then coated with a basecoat which has an embedded mesh reinforcement and then a finishing coat is applied to the base coating. Vinyl or aluminum metal siding can be fastened to the structural assembly by G screw fasteners or other mechanical fasteners.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Fibrous structures
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Medical chitosan fibre and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101250759AHigh molecular weightEnough aminoFilament manufactureArtificial filament washing/dryingAcetic acidBrute force
The invention relates to medical chitosan fiber in the textile processing field and a preparing method thereof, the method for preparing spinning fluid comprises the following steps: arranging the chitosan powder in glacial acetic acid water solution and slowly dissolving by stirring under the condition of controlling temperature and time, wherein the dissolution temperature is 10-30DEG C, the dissolution time is 10-48h, and the stirring speed is 60-180r / min, wherein the chitosan powder occupies 3%-10%, dissolvent glacial acetic acid occupies 1%-5% and the other is water in the spinning raw materials, the chitosan content is more than 99.9% in chitosan fiber, and the chitosan fiber has higher molecular weight, sufficient amido, steady fiber structure, and good antibacterial property, brute force and hygiene security property.
Owner:HISMER BIO TECH
Composite of support matrix and collagen, and process for producing support substrate and composite
InactiveUS20060216320A1Improve tensile propertiesAdequate Young 's modulusLigamentsMusclesSupport matrixCylindroma
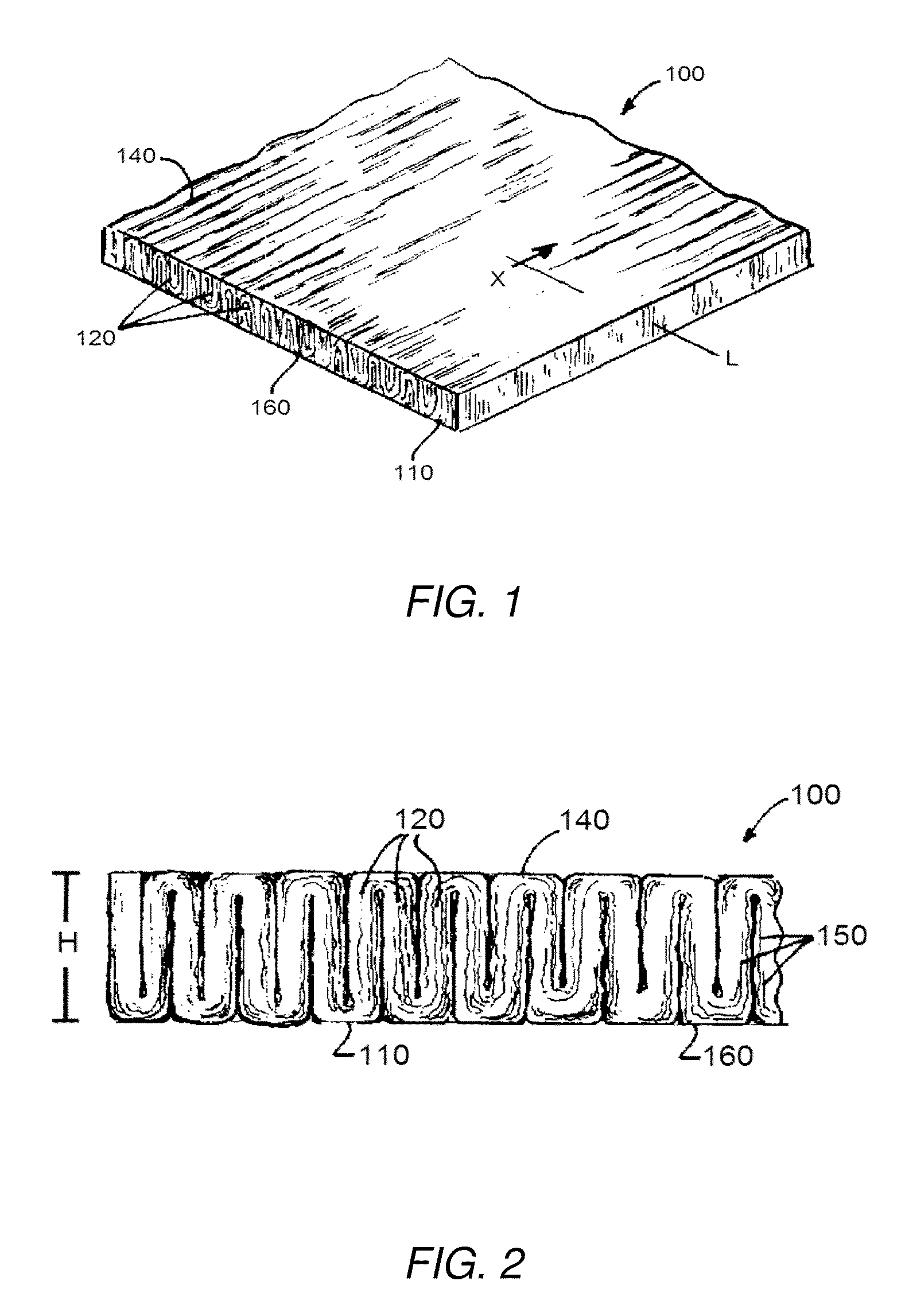
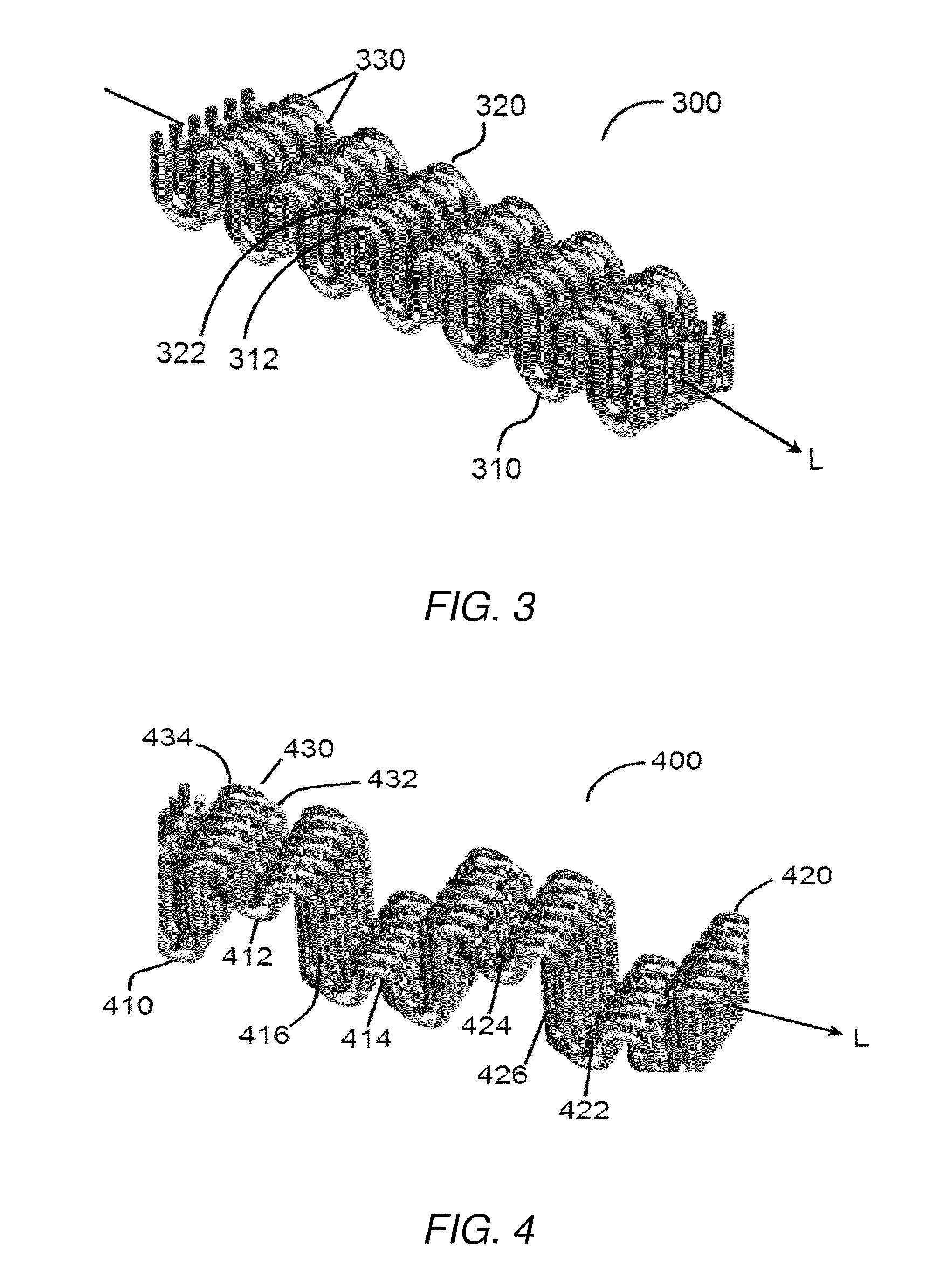
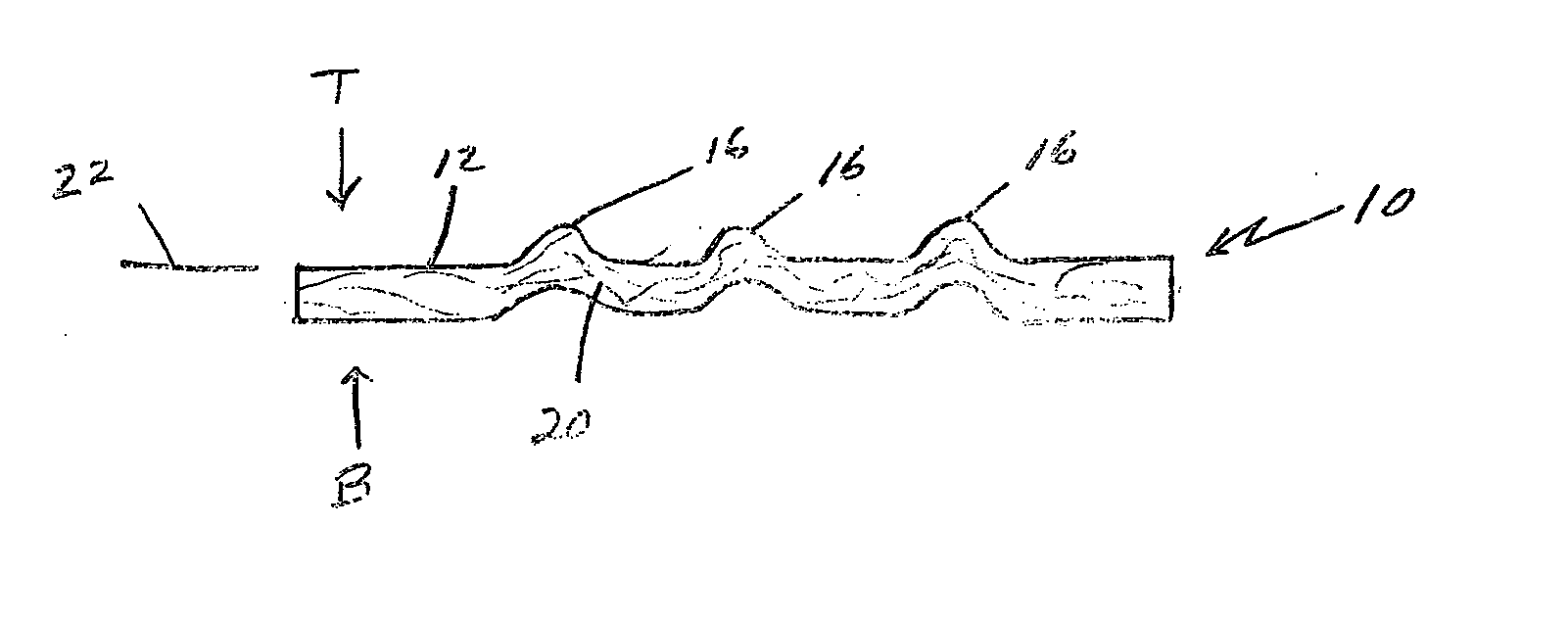
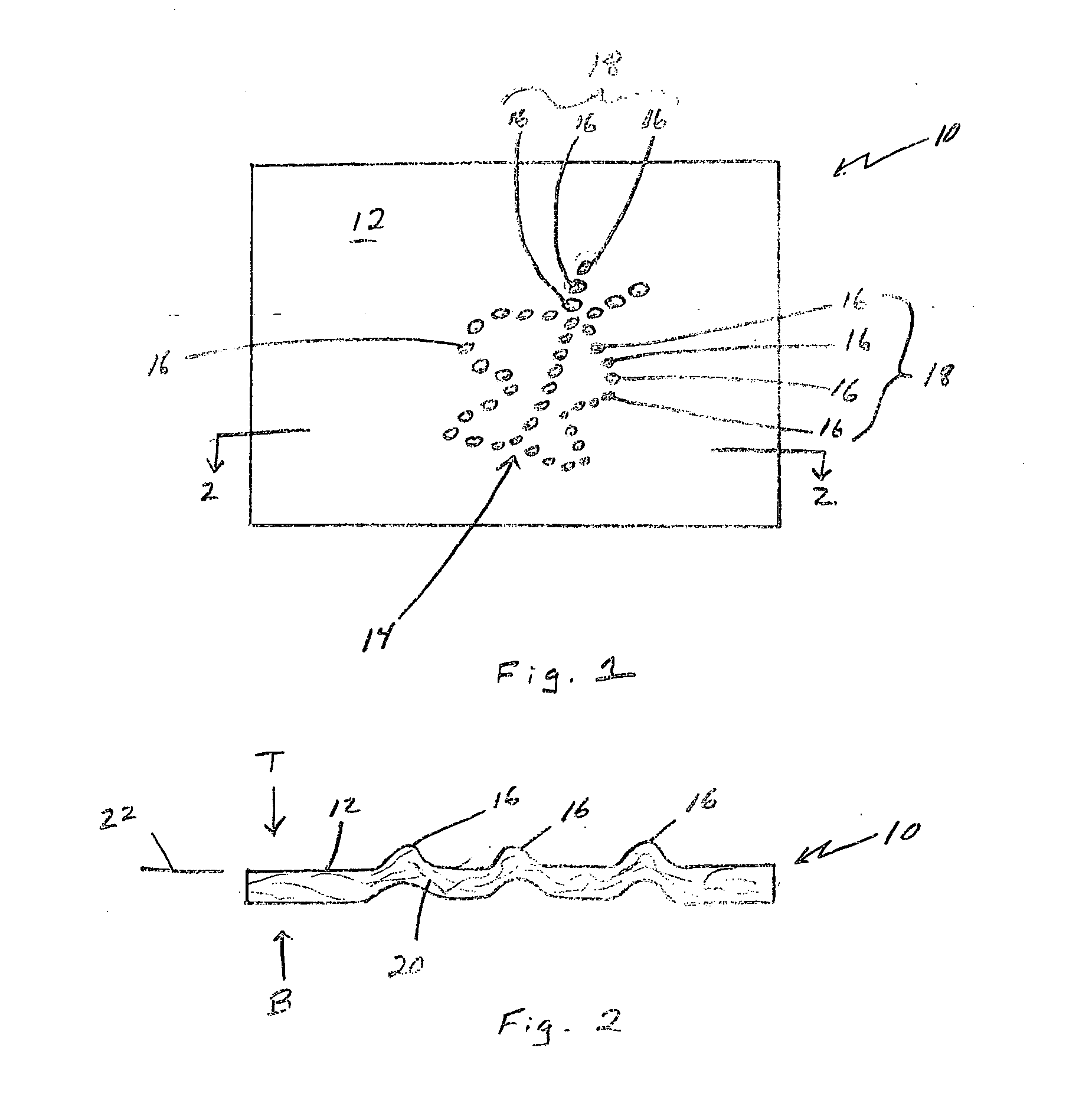
A cylindrical body is produced which is composed of a fiber structure with a basis weight of 1-50 g / m2 and having a diameter of 0.5-50 mm and a bellows-shaped section, wherein the crest-to-crest spacing of the bellows-shaped section is no greater than 2 mm and the crest-to-valley depth of the bellows-shaped section is 0.01-1 mm; collagen is added to the cylindrical body to produce a composite comprising the cylindrical body and collagen.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Cigarette Filter Comprising a Carbonaceous Fiber
The invention provides a cigarette filter including at least one filter segment having one or more composite fiber structures imbedded therein, the composite fiber structure including a carrier fiber and an adsorbent fiber, the adsorbent fiber including an adsorbent material. The filter can include one or more segments of fibrous tow material, with the one or more composite fiber structures imbedded within the fibrous tow, the composite fiber structure including a carrier fiber and a carbonaceous fiber.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Nonwoven web and filter media containing partially split multicomponent fibers
ActiveUS20100159770A1Improve filtration efficiencyLower overall pressure dropLayered productsWoven fabricsFilter mediaEngineering
The present invention provides a nonwoven web prepared from multicomponent fibers which are partially split. The partially split multicomponent fibers have at least one component of the multicomponent fiber separated from the remaining components of the multicomponent fiber along a first section of the longitudinal length of the multicomponent fibers. Along a second section of the longitudinal length of the multicomponent fibers the components of the multicomponent fibers remain together as a unitary fiber structure. In addition, part of the second section of the multicomponent fibers is bonded to part of a second section of an adjacent multicomponent fiber.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Polypropylene fibrous elements and processes for making same
InactiveUS20110104493A1High elongationImprove spinnabilityMixingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsPolymer scienceFiber structure
Polypropylene fibrous elements and more particularly polypropylene microfiber fibrous elements, fibrous structures including polypropylene fibrous elements, and processes for making same are provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com