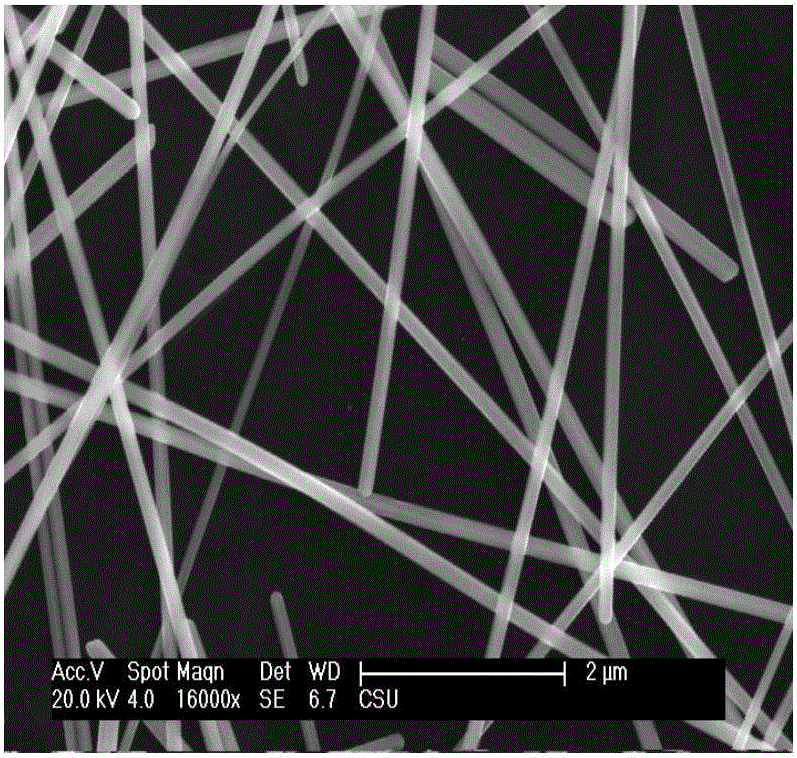
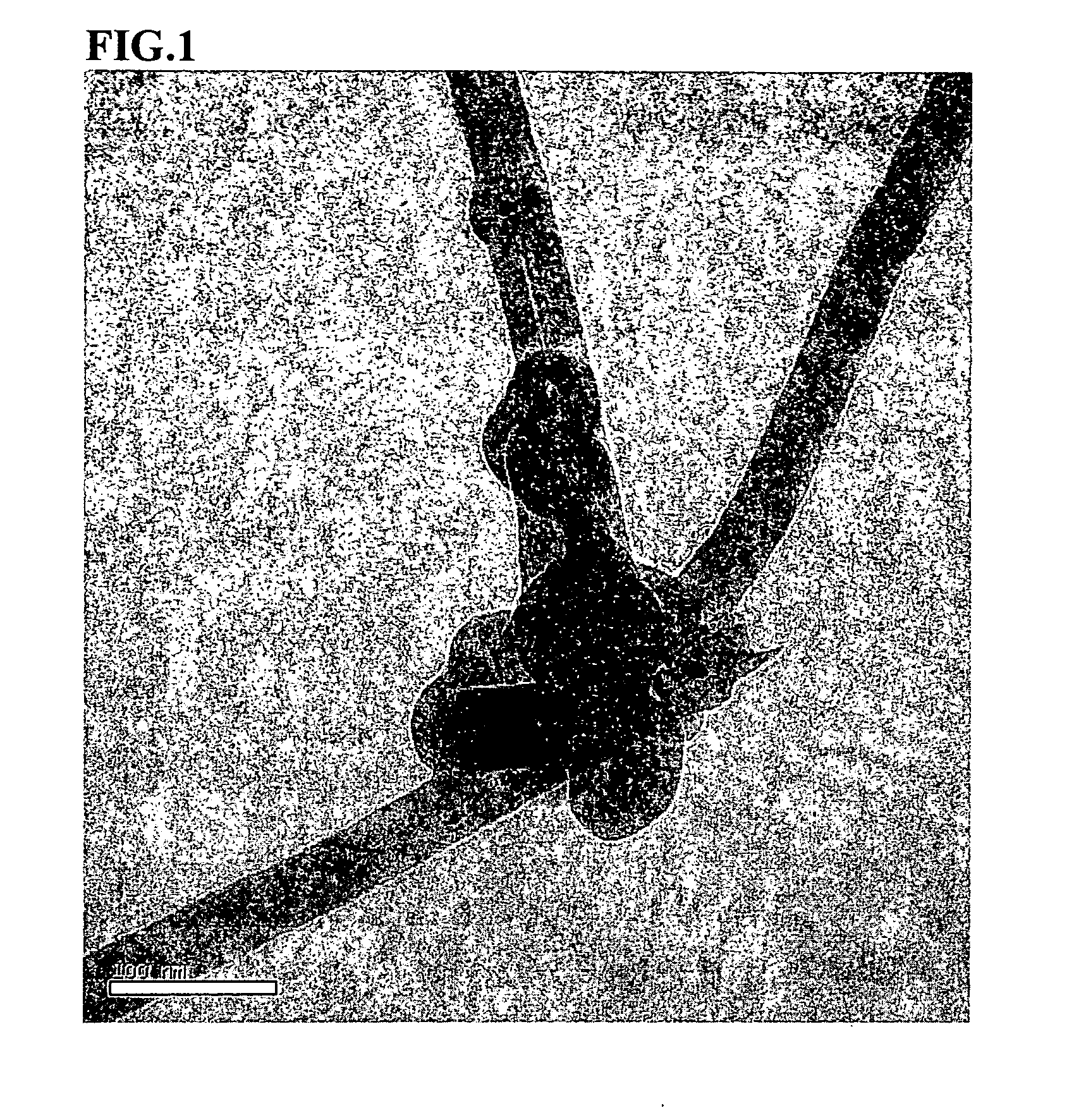
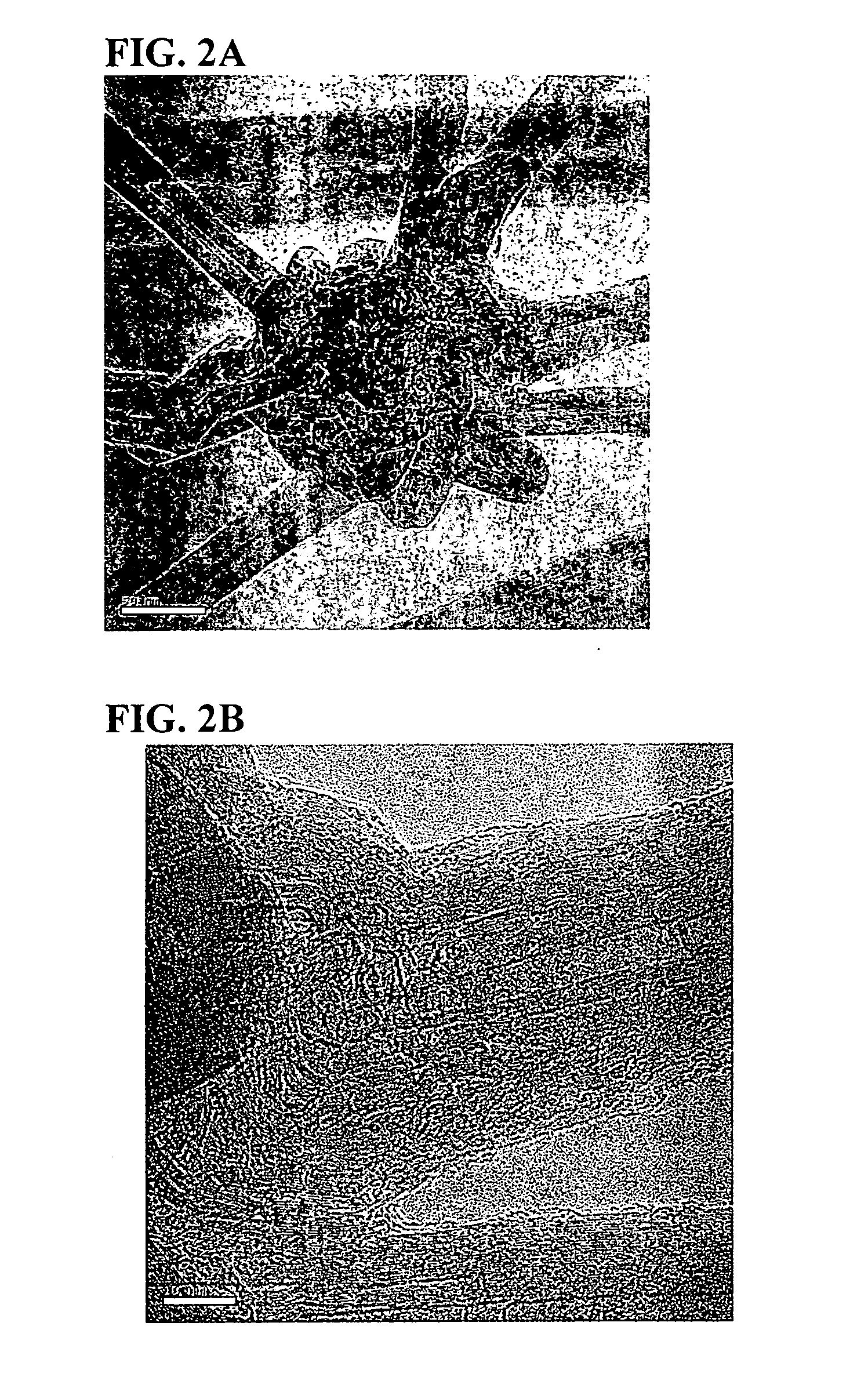
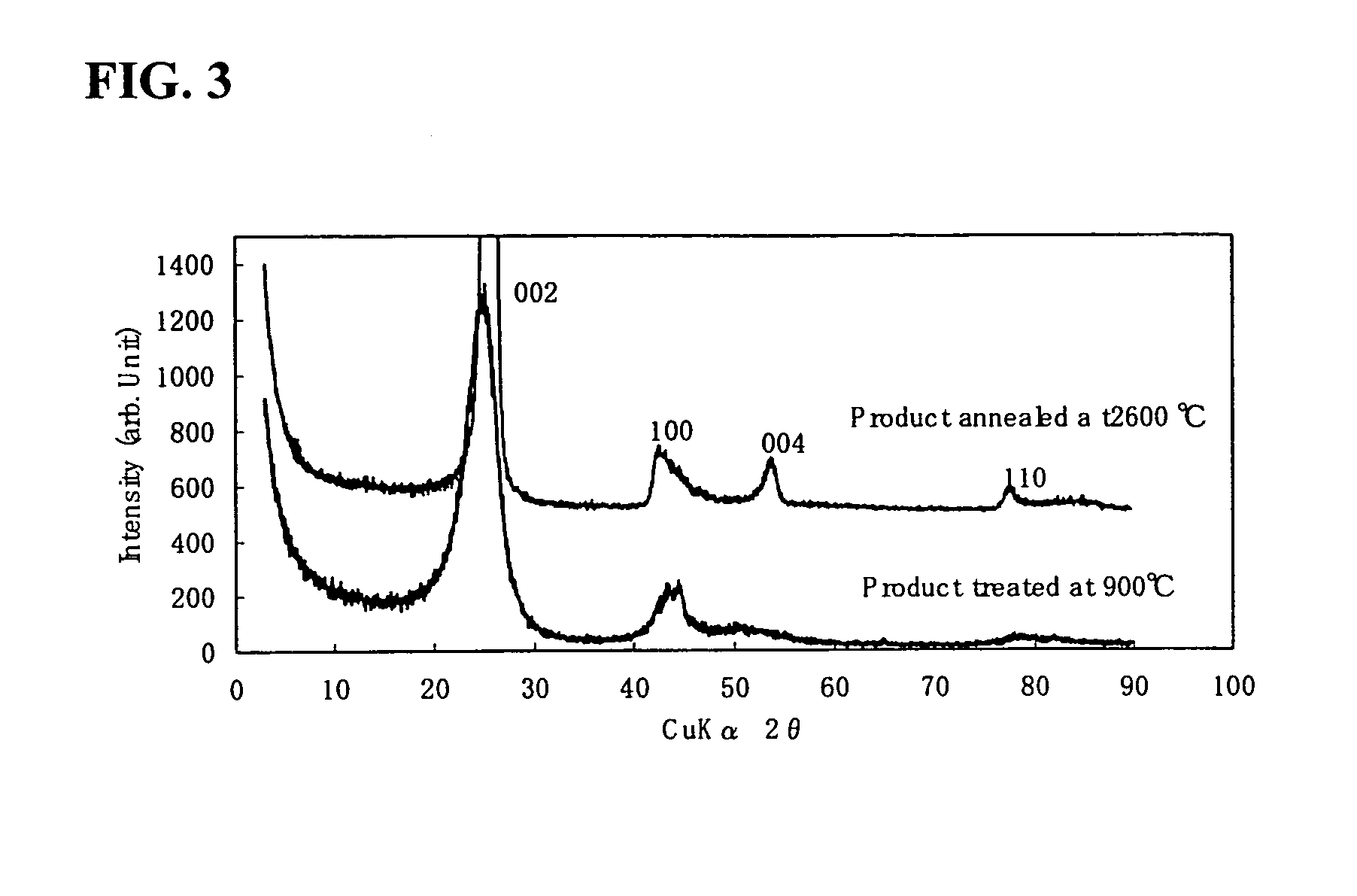
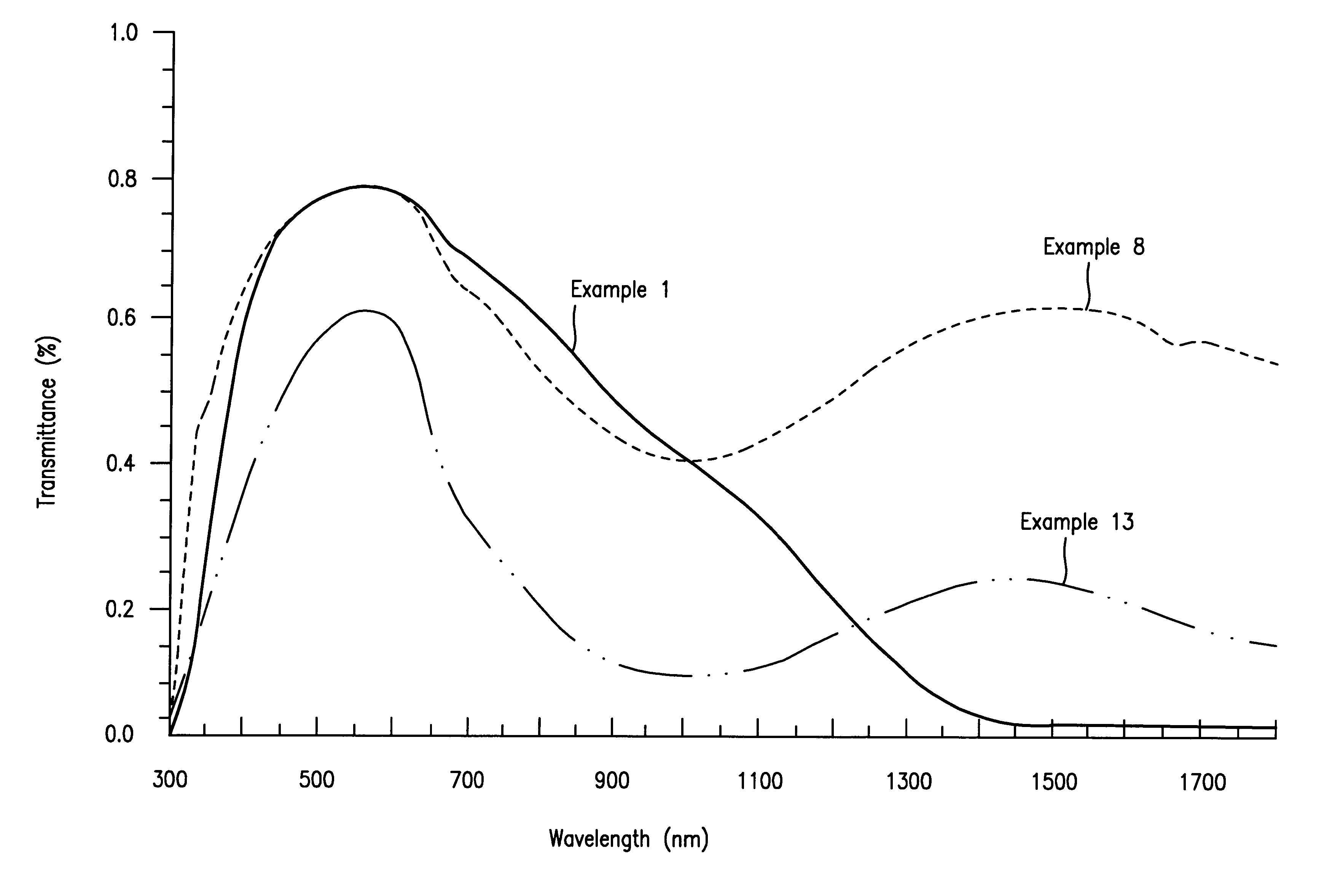
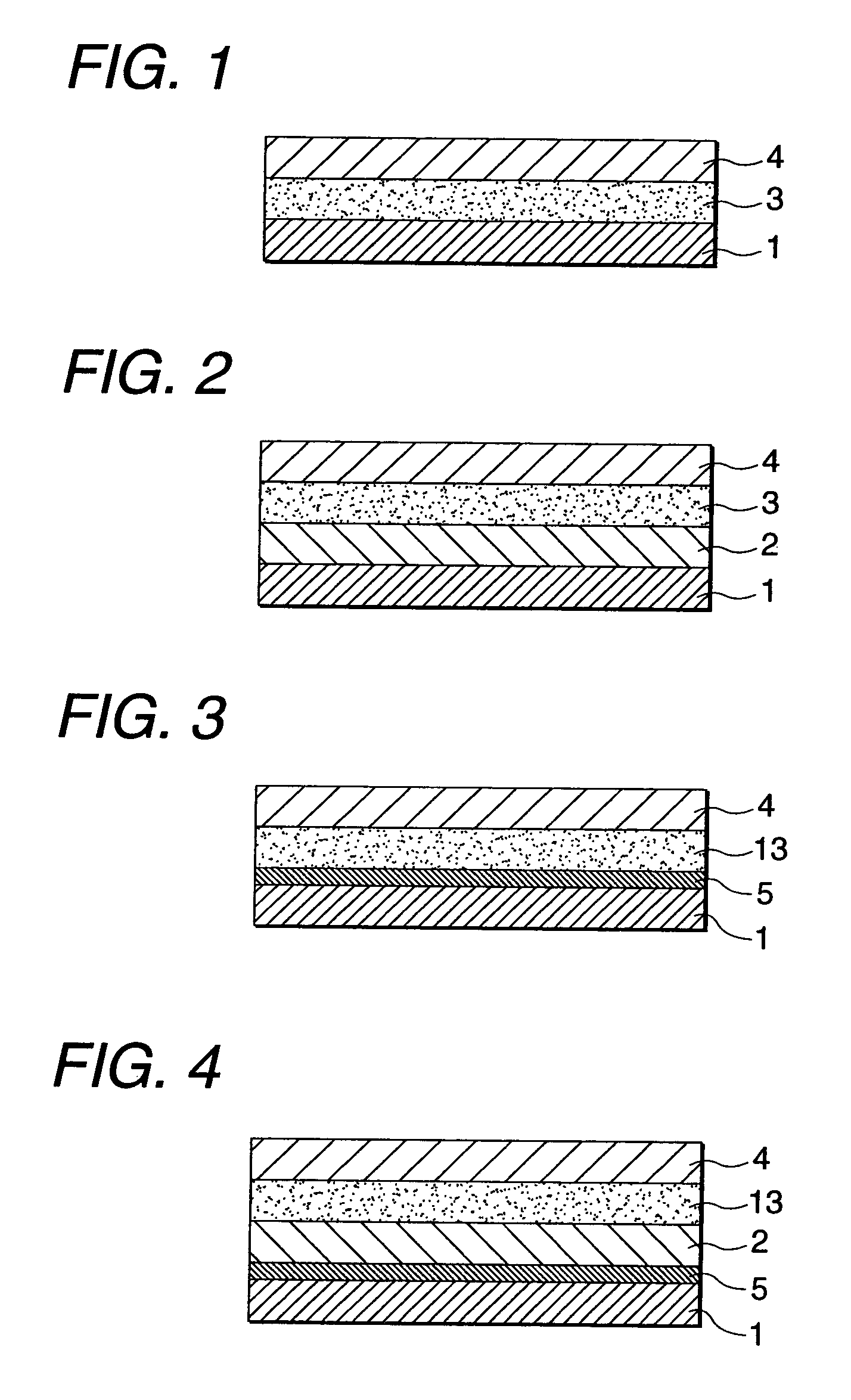
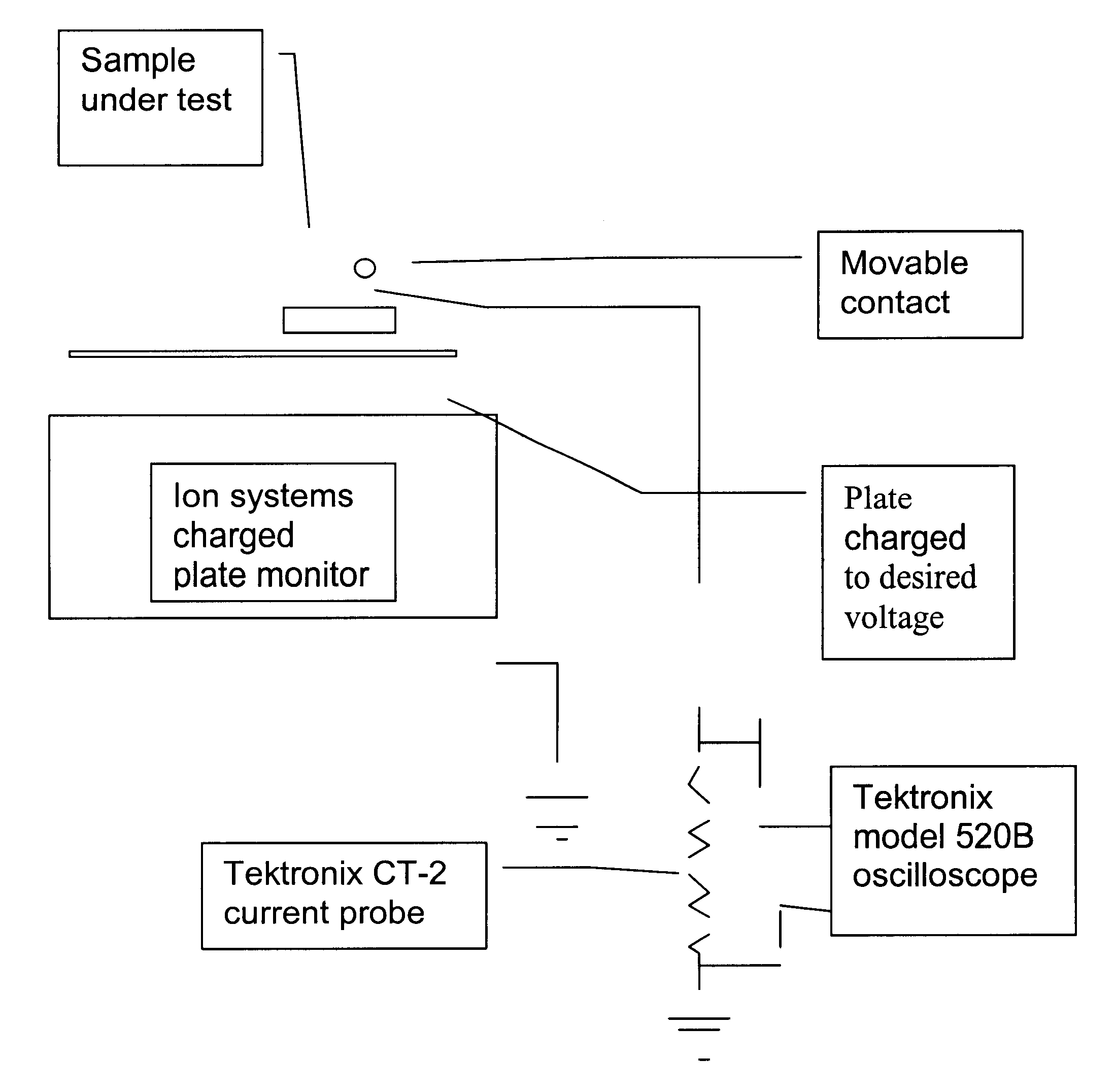
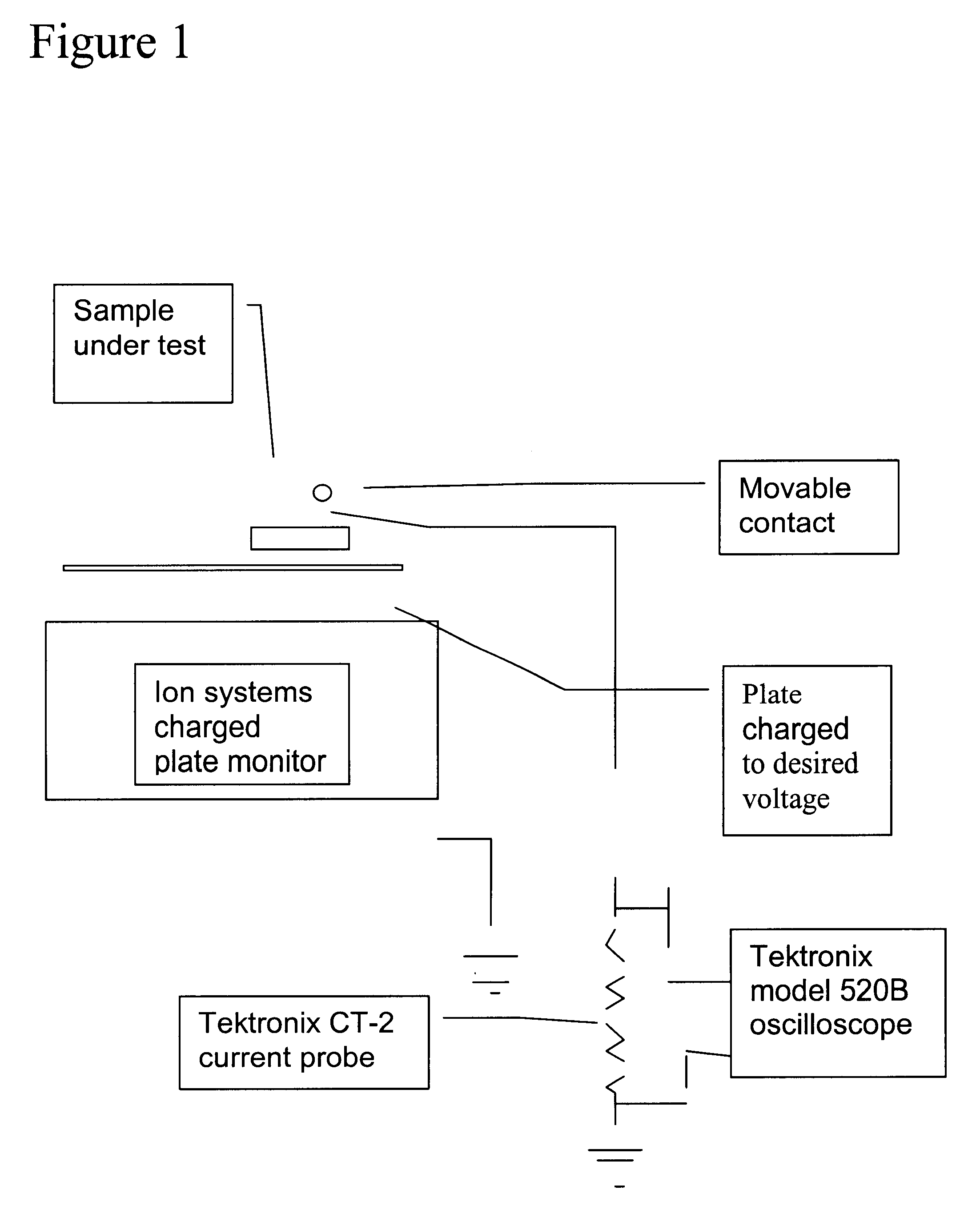
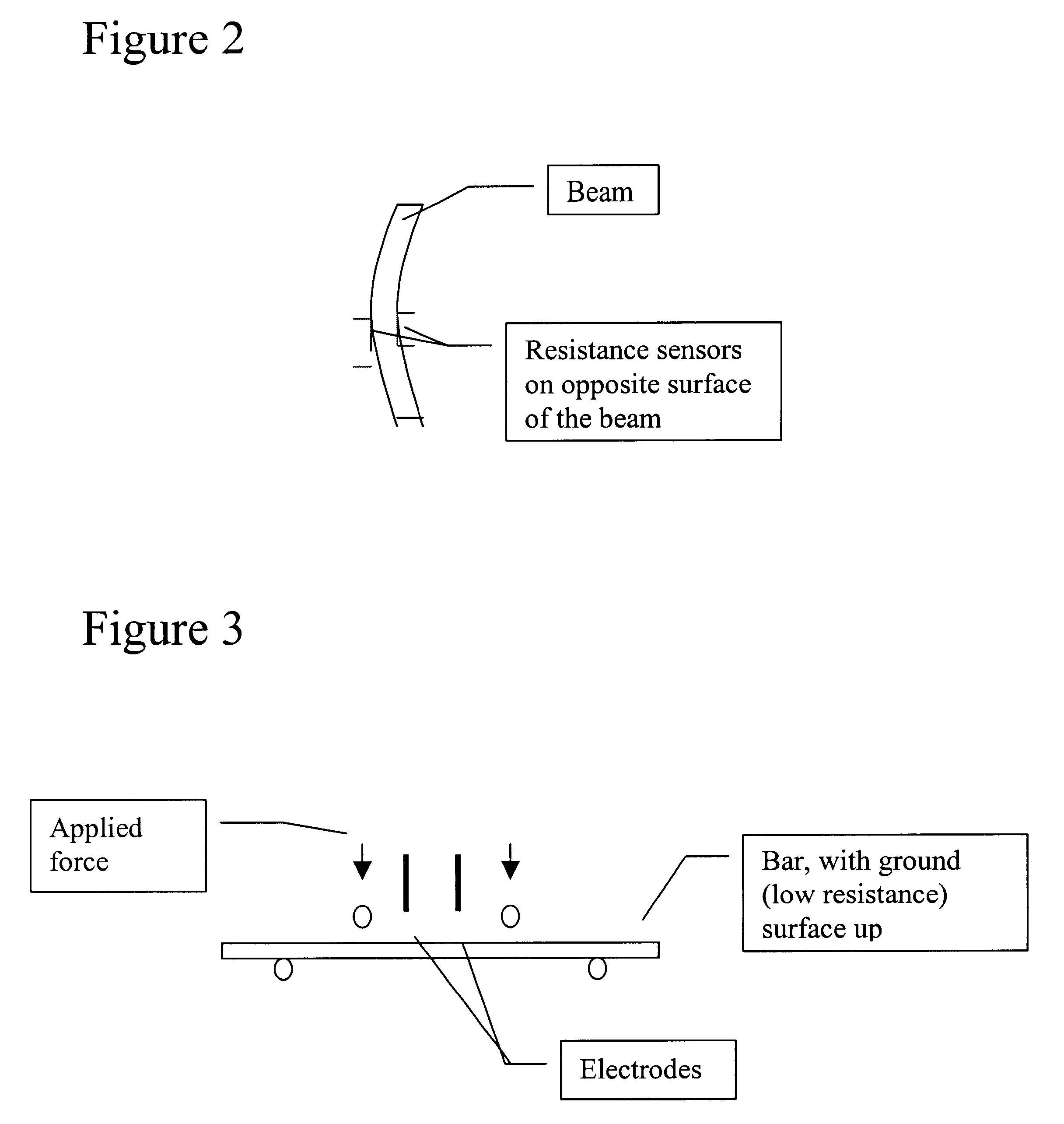
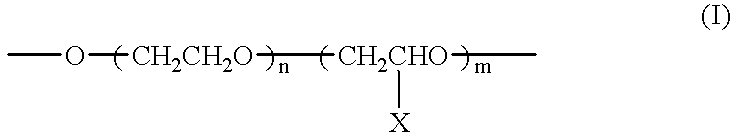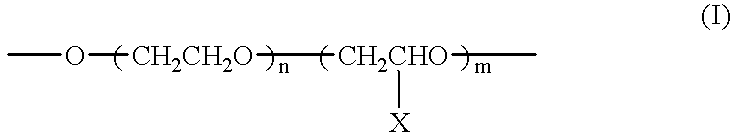Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1096 results about "Surface resistivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
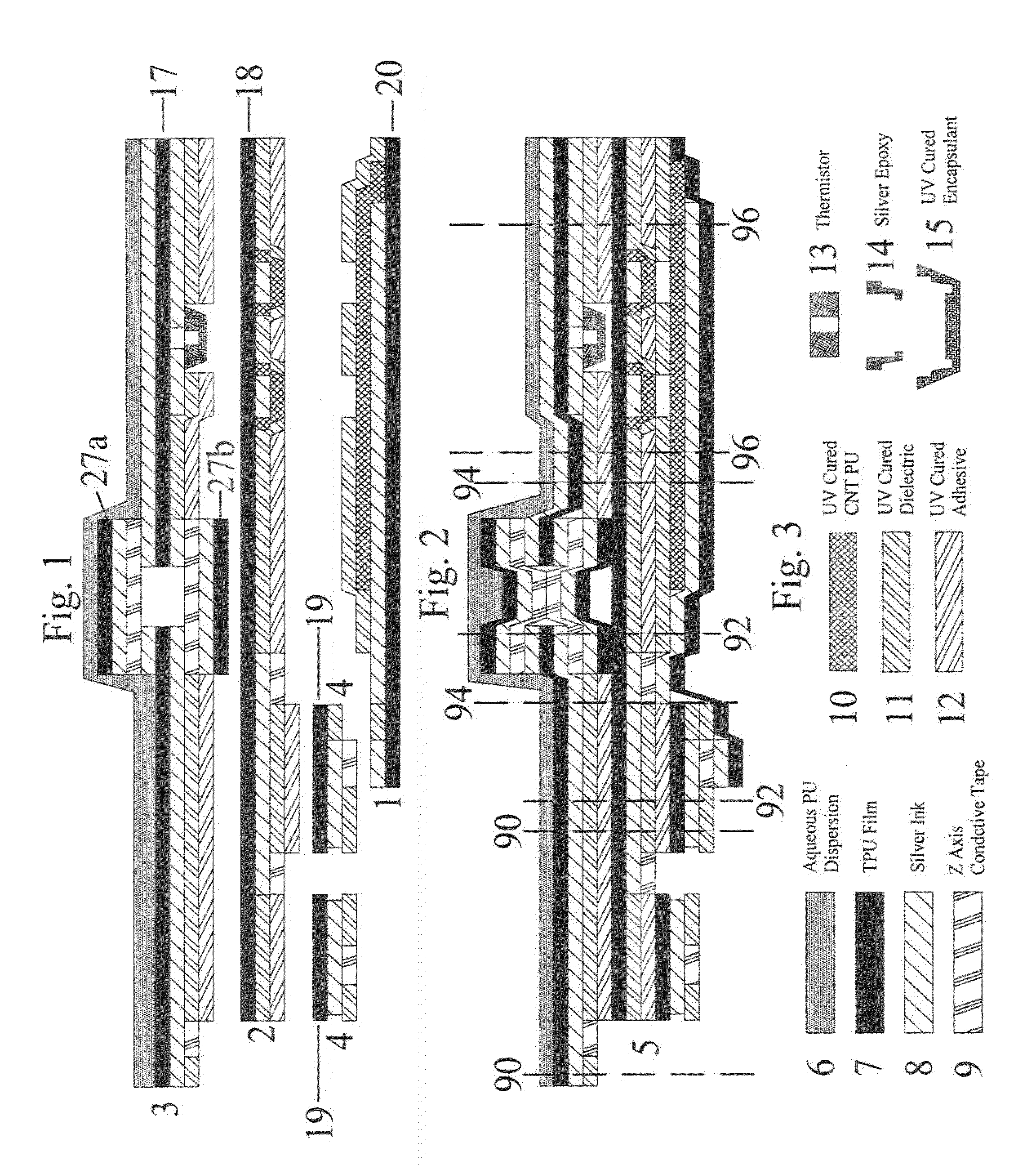
Surface resistivity refers to the resistance experienced by the leakage of current along the surface of coat/insulating material.
Transparent conductive film and coating composition therefor
InactiveUS20060263588A1High transparencyImproved and well controllable electrical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsPolymer scienceCarbon fibers
The disclosed is a transparent conductive film that includes a matrix and carbon fibrous structures added to the matrix, wherein the carbon fibrous structures comprise carbon fibers, each having an outside diameter of 15-100 nm, and wherein the carbon fibrous structures each comprise a granular part at which two or more carbon fibers are bound to each other, and wherein the granular part is concurrently produced in a growth process for the carbon fibers. When the transparent conductive film is formed at a thickness of 0.1-5 μm on a glass substrate, it shows a surface resistivity of not more than 1.0×1012Ω / □, and a total light transmittance of not less than 30%. A coating composition for the conductive transparent film is prepared by using a media mill equipped with beads having an average diameter of 0.05-1.5 mm to disperse the carbon fibrous structures into the liquid resinous composition.
Owner:MITSUI & CO LTD +1
Coating solution for forming a film for cutting off solar radiation and the film formed therefrom
InactiveUS6319613B1Low costReduce heat radiationOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsSurface resistivityNear infrared radiation
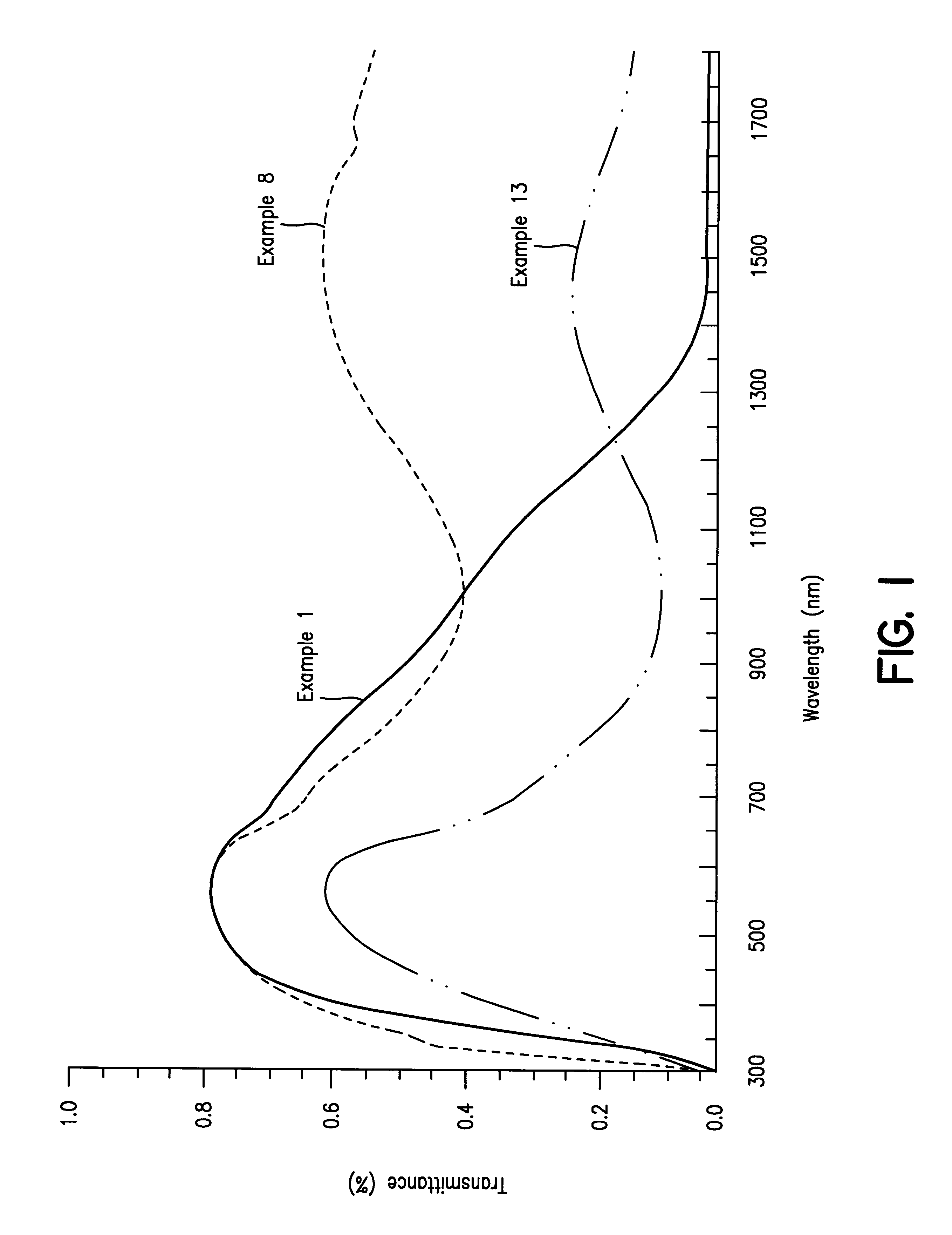
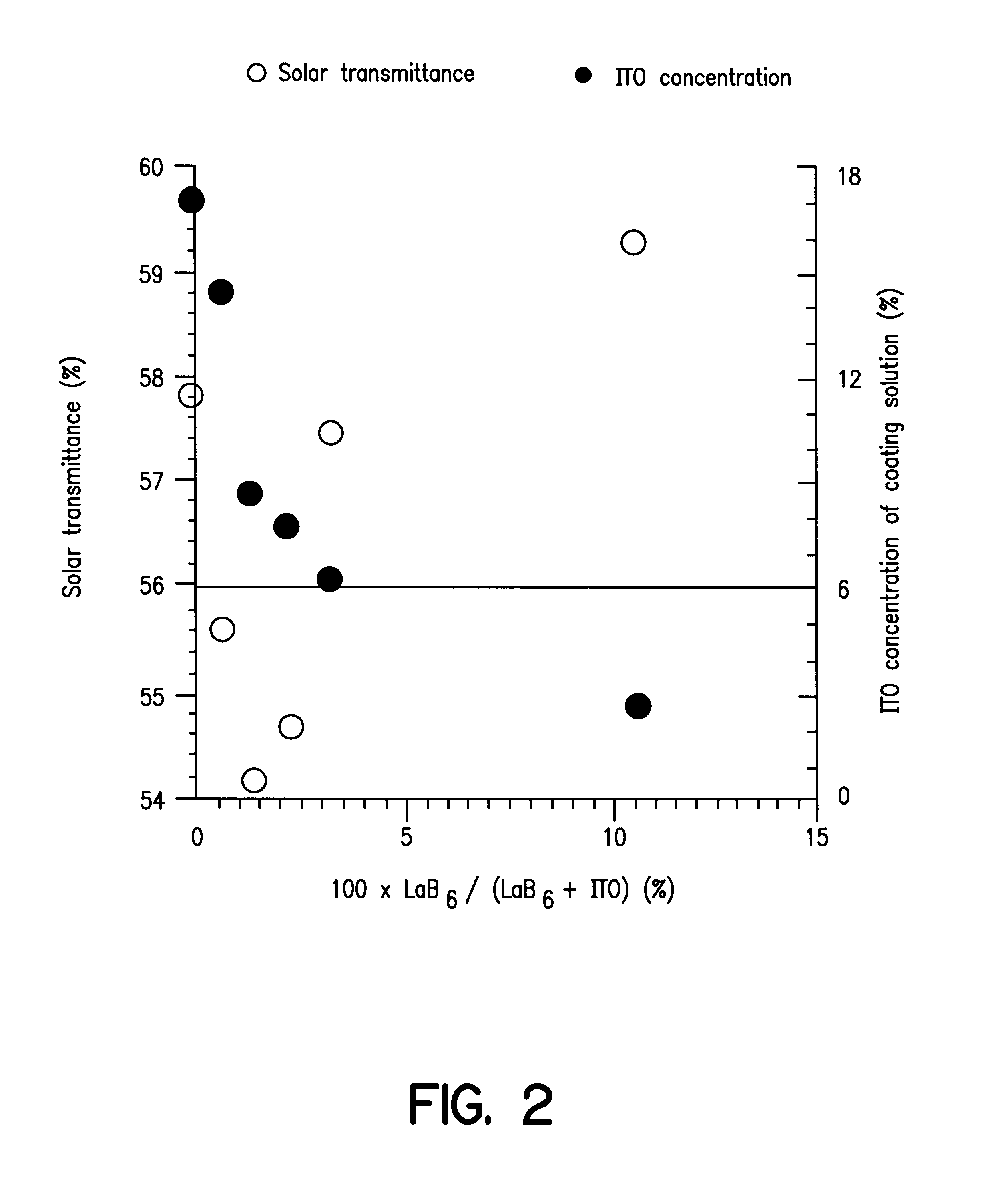
A solution for forming a film having a high transmittance and a low reflectivity for visible light, a low transmittance for near infrared radiation, and a surface resistivity of at least 106 ohms / square. It contains fine particles of a hexaboride of Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Th, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Sr or Ca, and fine particles of ITO or ATO in a weight ratio of from 0.1:99.9 to 90:10. Also disclosed is a film formed on at least one side of a resin film as a base, for cutting off solar heat radiation.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Silicone rubber for composite insulator and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a silicone rubber for a composite insulator, wherein the silicone rubber comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of methyl vinyl silicone rubber A, 50-70 parts of methyl vinyl silicone rubber B, 25-50 parts of fumed silica, 100-130 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 1-6 parts of silane coupling agent, 0.2-2 parts of ultraviolet absorber, 2-6 parts of zinc oxide, 0.5-3 parts of triethanolamine, 0.2-1 parts of stearic acid, 0.5-2 parts of hydrogen-containing silicone oil, 0.2-1 parts of vinyl silicone oil, 0.5-3 parts of color masterbatch rubber, 2-6 parts of hydroxyl silicone oil and 0.5-1 parts of vulcanizing agent. The silicone rubber provided by the invention can achieve the following performances: the tensile strength is larger than 4 MPa; the breaking elongation is larger than 350%; the peel strength is larger than or equal to 12 KN.m<-1>; the shore hardness is 60+ / -5 degrees; the thermal aging tensile strength retention is larger than or equal to 90%; the anti-creep track passes a grade of 1A4.5; the flame retardance reaches a grade of FV-0; the average static contact angle is larger than 105 degrees; the electrical surface resistivity is larger than 2*10<15> omega; the dielectric constant is smaller than 3.8; and the dielectric loss angle tangent is smaller than 0.01.
Owner:PINGGAO GRP +2
Resin composition and jig for use in transportation
InactiveUS6344513B1Excellent static charge dissipating performanceLittle changeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial tyresFiberCarbon fibers
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
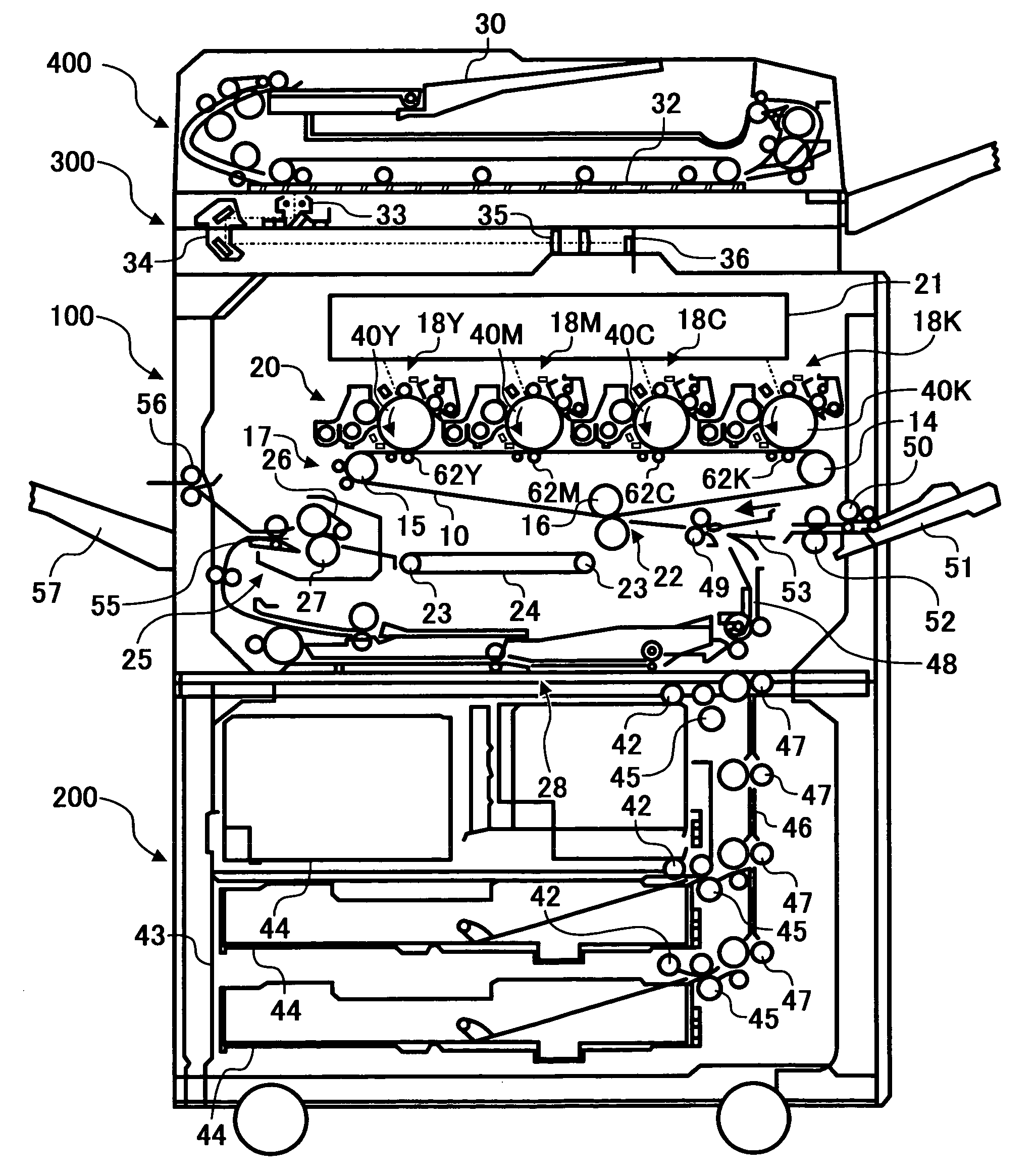
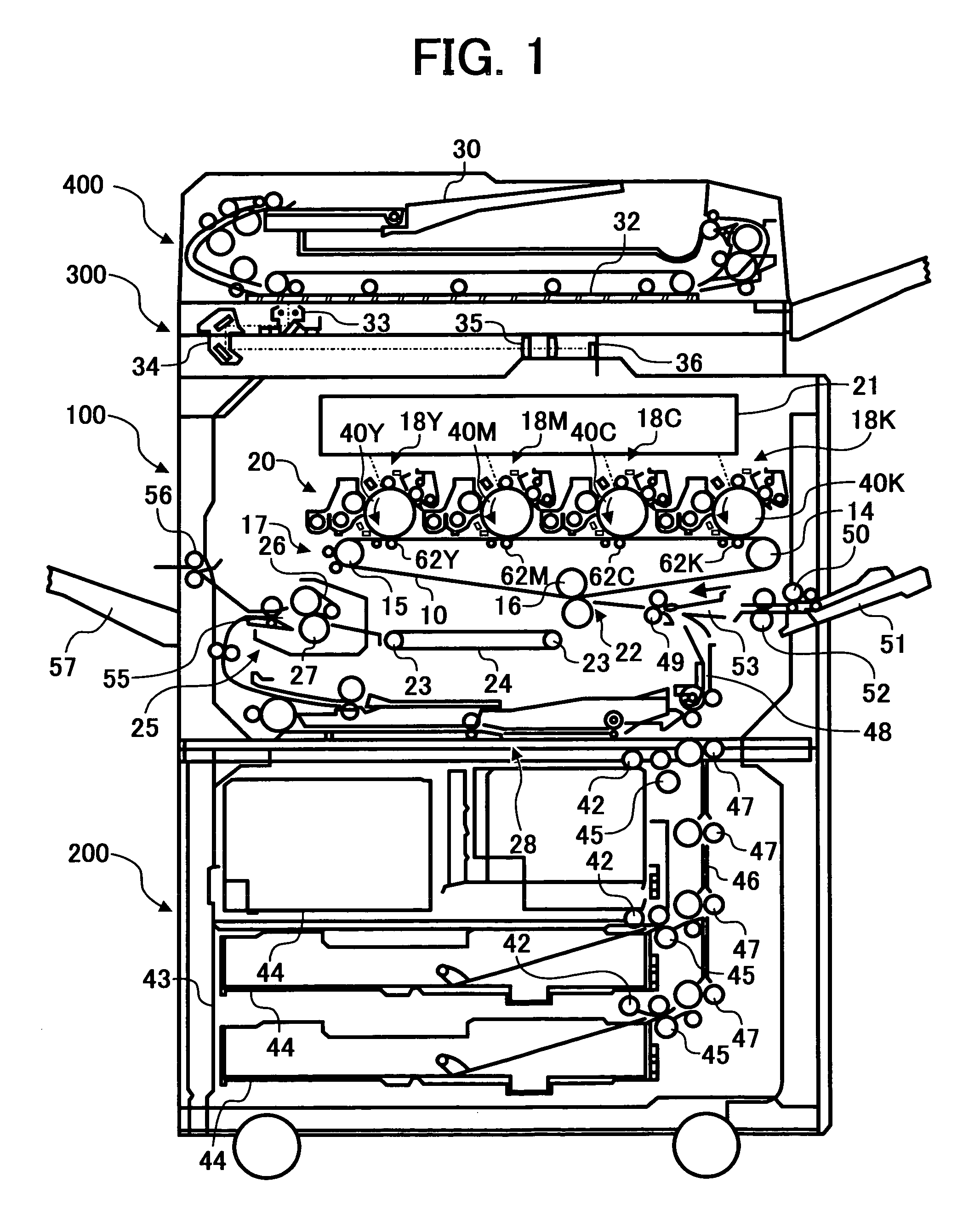
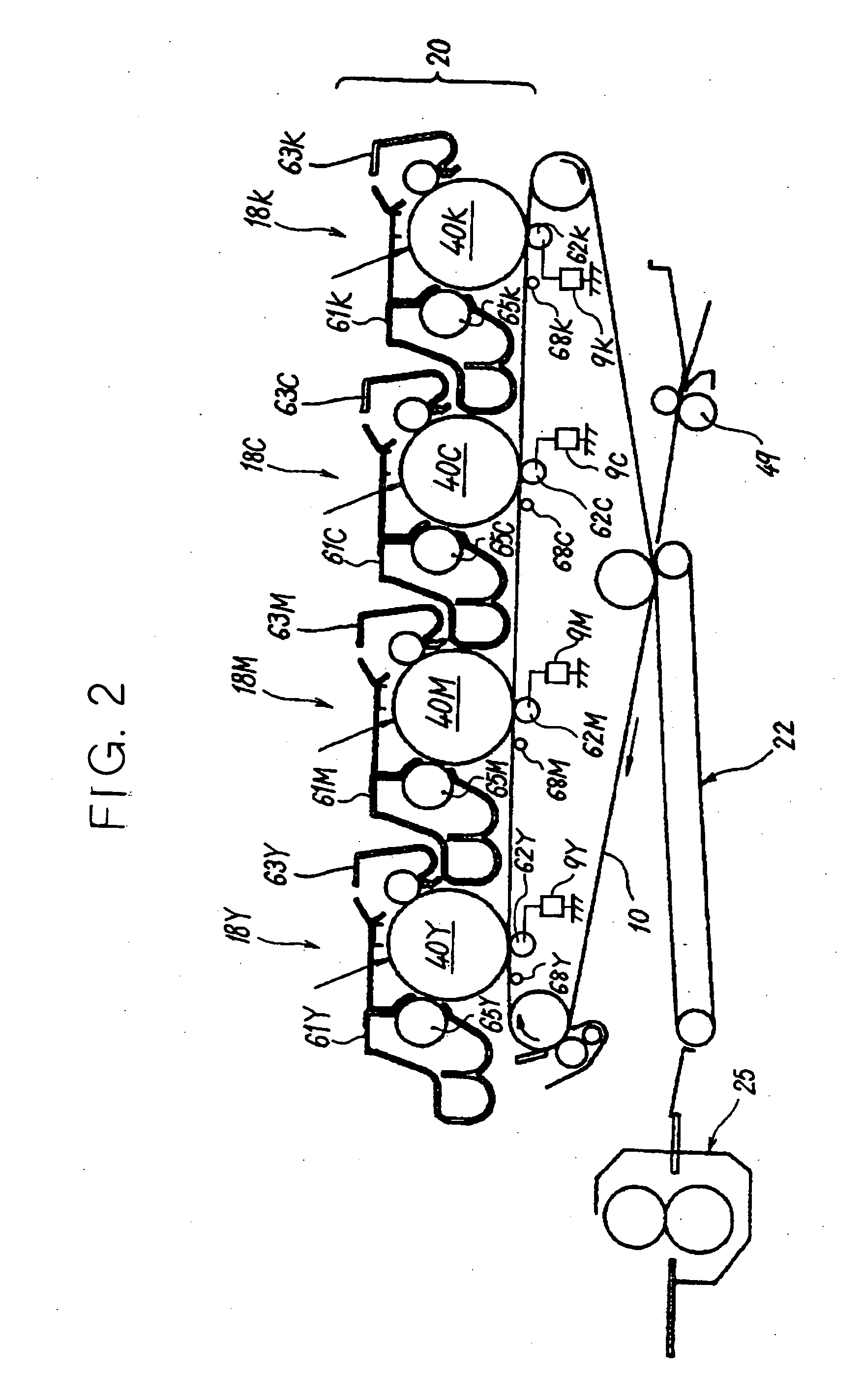
Intermediate image transfer device for a color image forming apparatus
ActiveUS7003238B2Irregular image transferElectrographic process apparatusColor imageIntermediate image
An intermediate image transfer type of image forming apparatus of the present invention includes an image carrier, an intermediate image transfer body, primary image transferring means for transferring a toner image from the image carrier to the intermediate image transfer body, and secondary image transferring means for transferring the toner image from the intermediate image transfer body to a sheet. When the surface resistivity of the intermediate image transfer body is measured by a method that repeatedly applies a voltage of 200 V for 60 seconds to the intermediate image transfer body and grounds the intermediate image transfer body for 10 seconds 1,000 consecutive times, a difference in absolute value between the logarithm of the first time of measurement and that of the thousandth time of measurement is 0.5 log Ω / □ or below.
Owner:RICOH KK
Panel-type input device, method of manufacturing panel-type input device, and electronic apparatus having panel-type input device
ActiveUS20090201268A1Improve surface resistivityReduce thicknessContact member manufacturingConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive polymerConductive coating
A panel-type input device including a pair of electrode plates, each electrode plate having a substrate and a conductive coat provided on a surface of the substrate, the conductive coat of each electrode plate being formed from a conducting polymer. The conductive coat of each electrode plate includes a detecting area adapted to detect a touch input and an inoperative area disposed adjacent to the detecting area, the inoperative area having a surface resistivity higher than a surface resistivity of the detecting area. A parallel electrode pair adapted to apply a voltage to the conductive coat is formed in the detecting area, and conductors connected to the parallel electrode pair are formed in the inoperative area. The inoperative area insulates the conductors from the detecting area.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
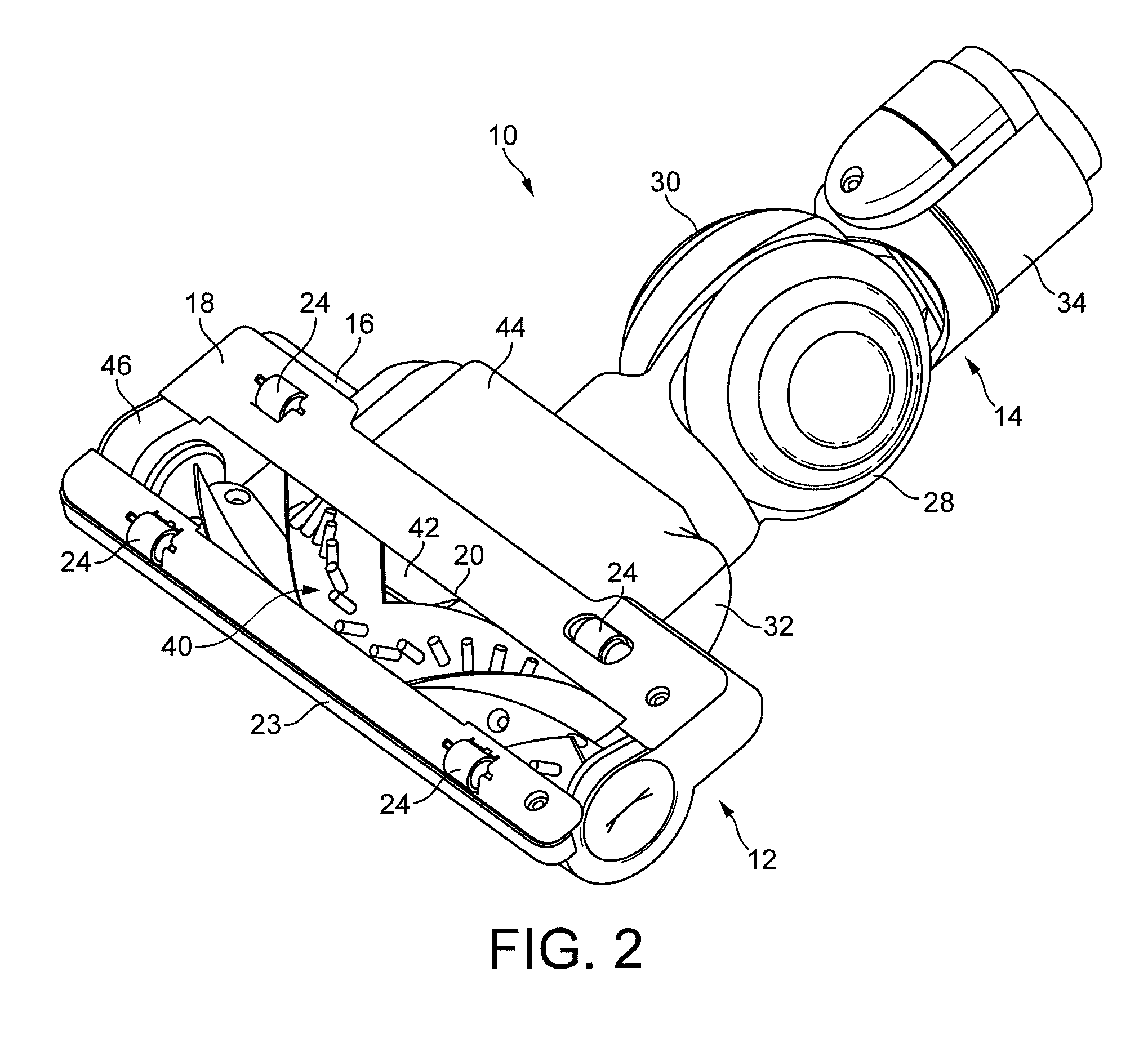
Cleaner head
Agitating apparatus for a surface treating appliance includes a rotatable body having an outer surface comprising an electrically conductive pile formed from filaments having a surface resistivity in the range from 1×10−5 to 1×1012 Ω / sq.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Water polyurethane electric conduction paint containing carbon nano-tube and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101165127AImprove dispersion uniformityNo subsidencePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEmulsion paintsPolyesterCarbon nanotube
The present invention belongs to the field of chemical technology, and is especially one kind of conducting water soluble polyurethane paint containing carbon nanotube and its preparation process. The conducting paint is prepared through the first modifying carbon nanotube chemically for the surface to carry hydroxyl group, carboxyl group or amino group; the subsequent introducing to polyester polyol or isocyanate terminated polyurethane pre-polymer through chemical bonding and self-emulsifying to prepare water soluble polyurethane dispersoid containing carbon nanotube; and final adding deionized water and assistants through high speed stirring to obtain the conducting paint. The conducting paint can form coating with volume resistivity of 1x10<-5>-4x10<-4. ohm.cm, surface resistivity of 1x10<-1>-2x10<2> ohm, adhesion of 0 grade, shielding effectiveness of 70-85 dB, and long term stability, and has wide application.
Owner:SHANGHAI SAFEGREEN TECH
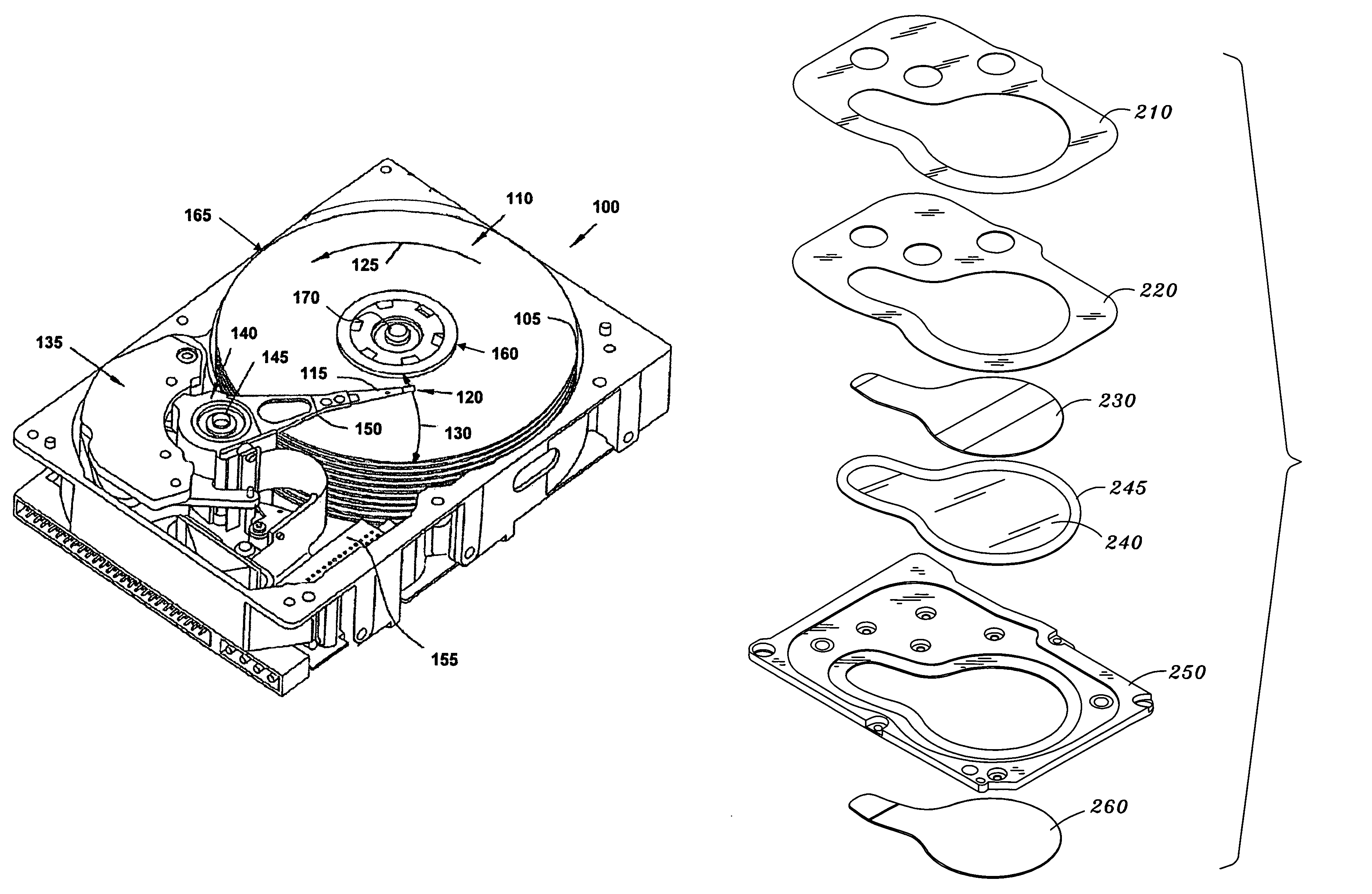
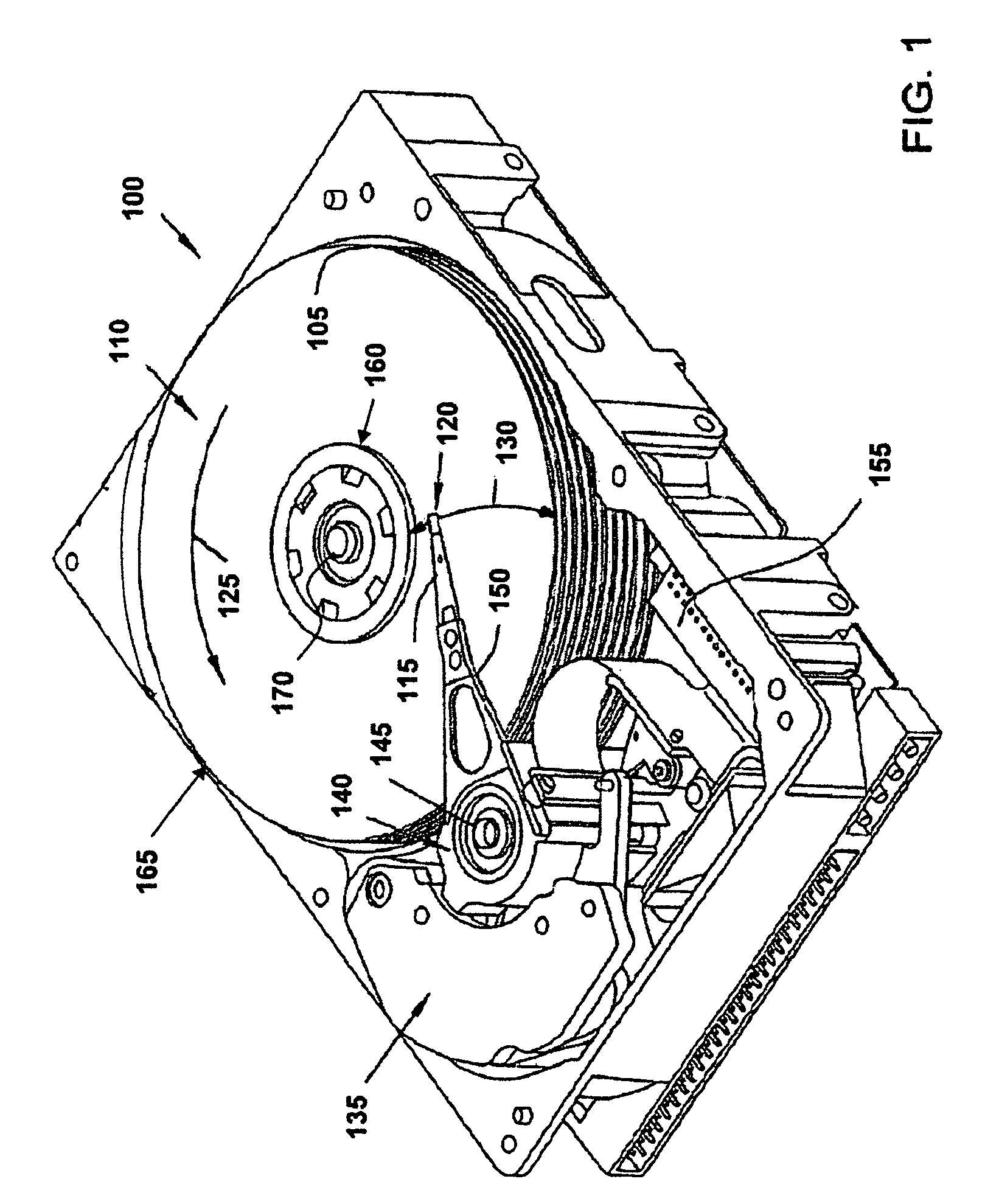
Disk drive cover having a see-through insert including an electrically conductive material
InactiveUS7605999B1Apparatus modification to store record carriersUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionIndium tin oxideSurface resistivity
A disk drive includes an opaque cover secured to a base, where the opaque cover has an opening. A see-through insert, which includes an electrically conductive material, is affixed to the opaque cover over the opening. The electrically conductive material may be a coating applied to the see-through insert which, in one embodiment is a polymer coating having a certain surface resistivity. Alternatively, the coating's ESD-dissipative properties may be due to the presence of sputtered gold, sputtered indium tin oxide or a metal film. The electrically conductive material may alternatively be embedded in the see-through insert.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
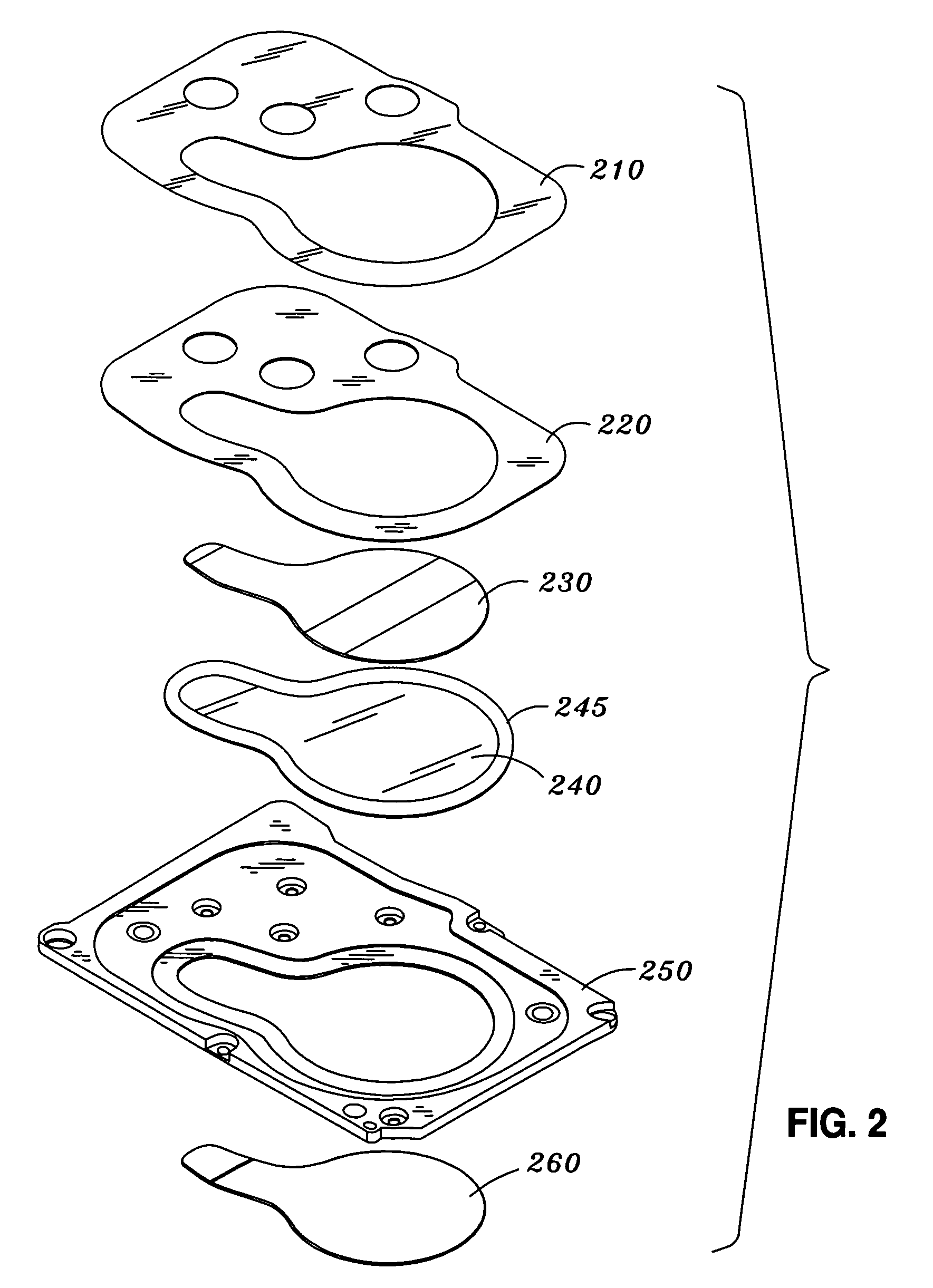
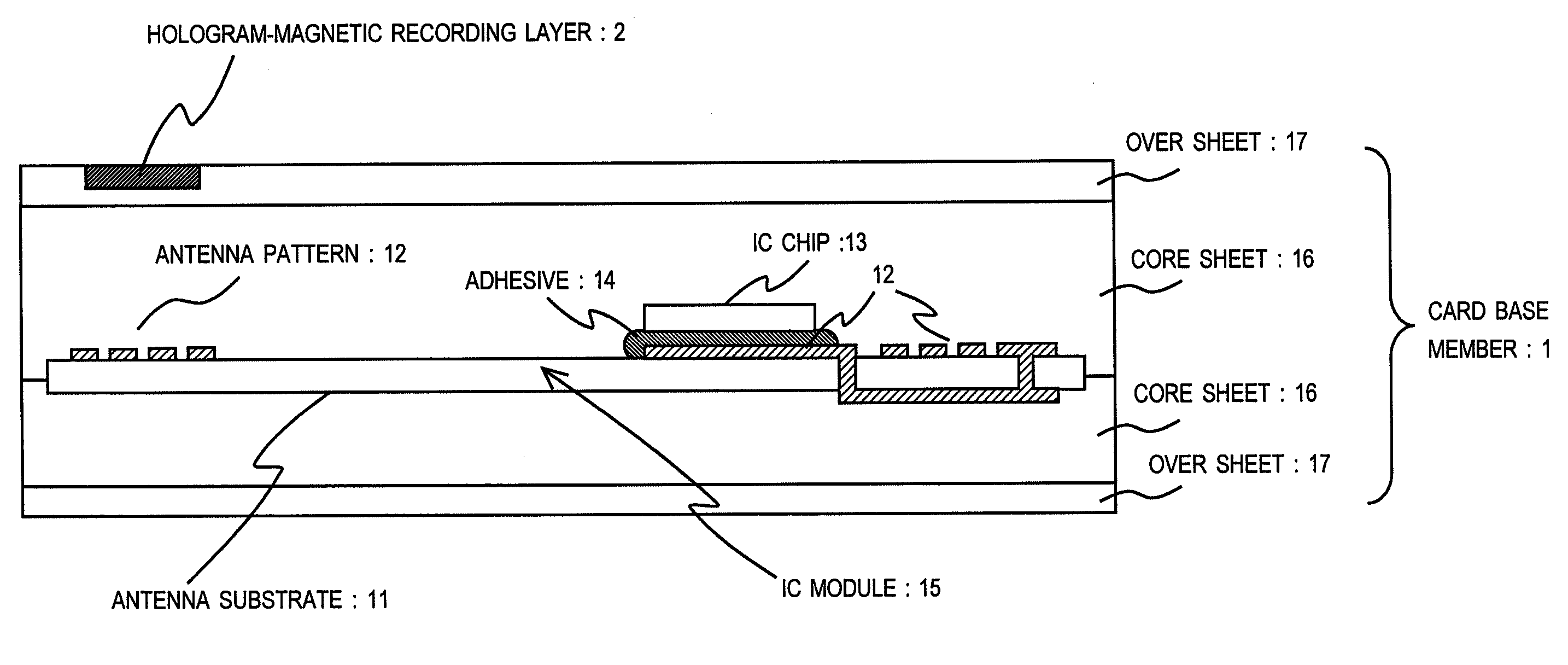
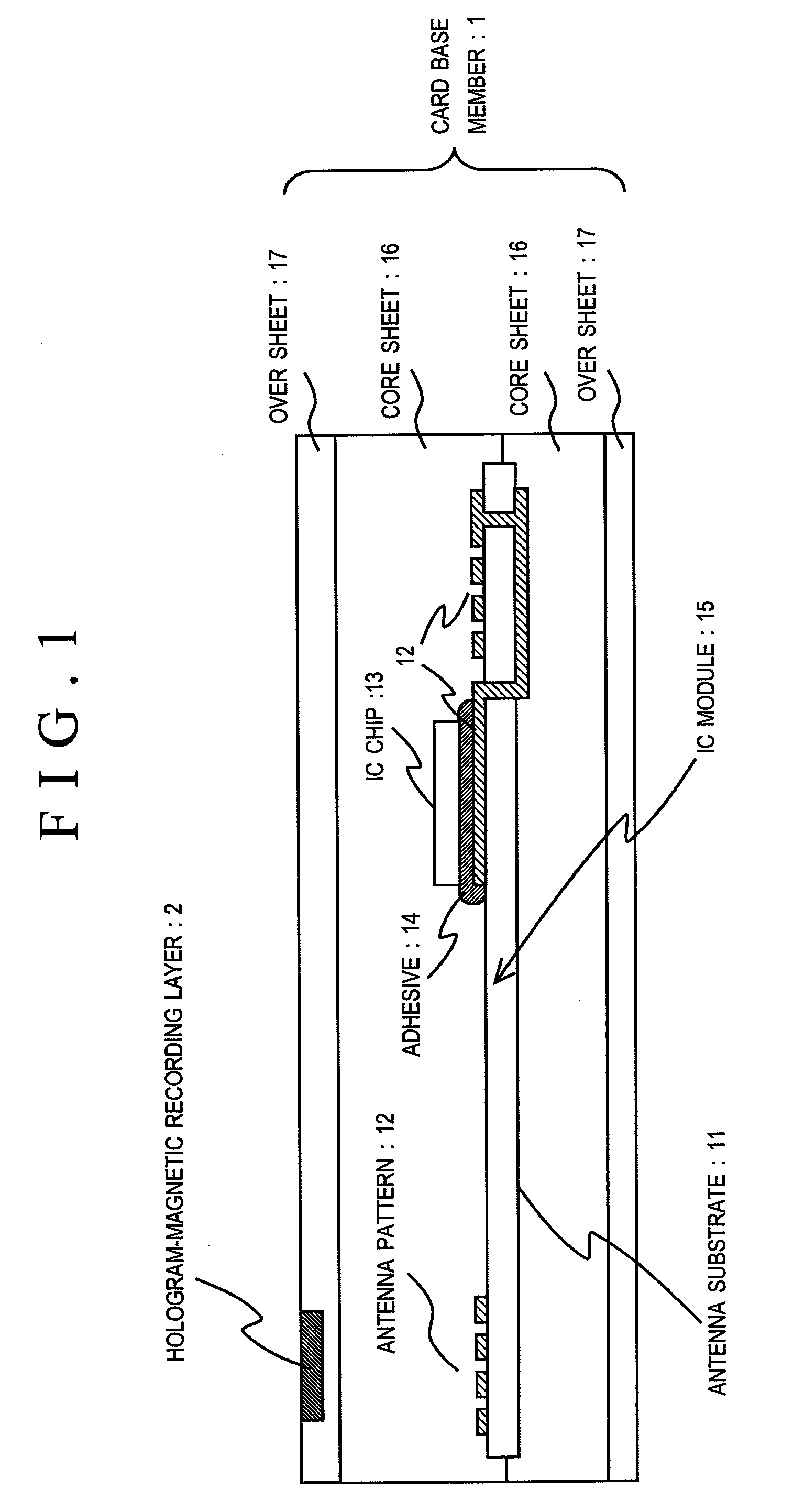
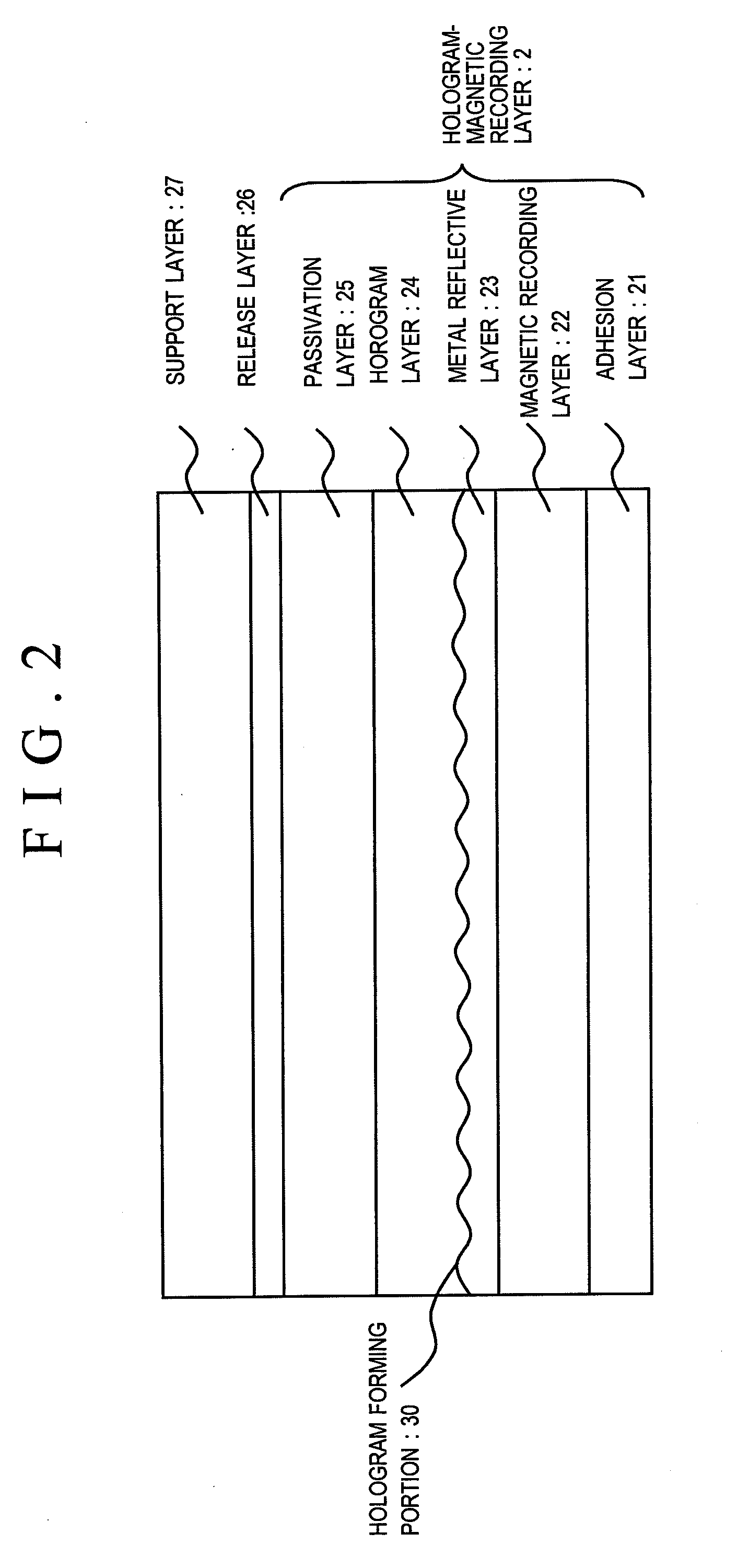
Non-contact type IC card
InactiveUS20090250521A1Prevent electrostatic discharge failureCurrent is limitedDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSurface resistivityContact type
There is provided a non-contact type IC card that prevents electrostatic discharge failure of an IC chip embedded in an IC card.A non-contact type IC card includes at least a magnetic recording layer, a metal reflective layer, and a hologram layer, which are sequentially laminated on a card base member, and an antenna and an IC chip connected to the antenna that are embedded in the card base member. The metal reflective layer is made of a material of which electric conductivity is smaller than 28.9×106 / Ωm, or is composed of a thin film of which surface resistivity is 7.02 (Ω / □) or more.
Owner:KYODO INSATU KK KYODO PRINTING CO LTD
Production method of silver nanowire transparent conductive film
ActiveCN104992752AWide applicabilityLow costConductive layers on insulating-supportsCable/conductor manufactureConductive coatingSurface resistivity
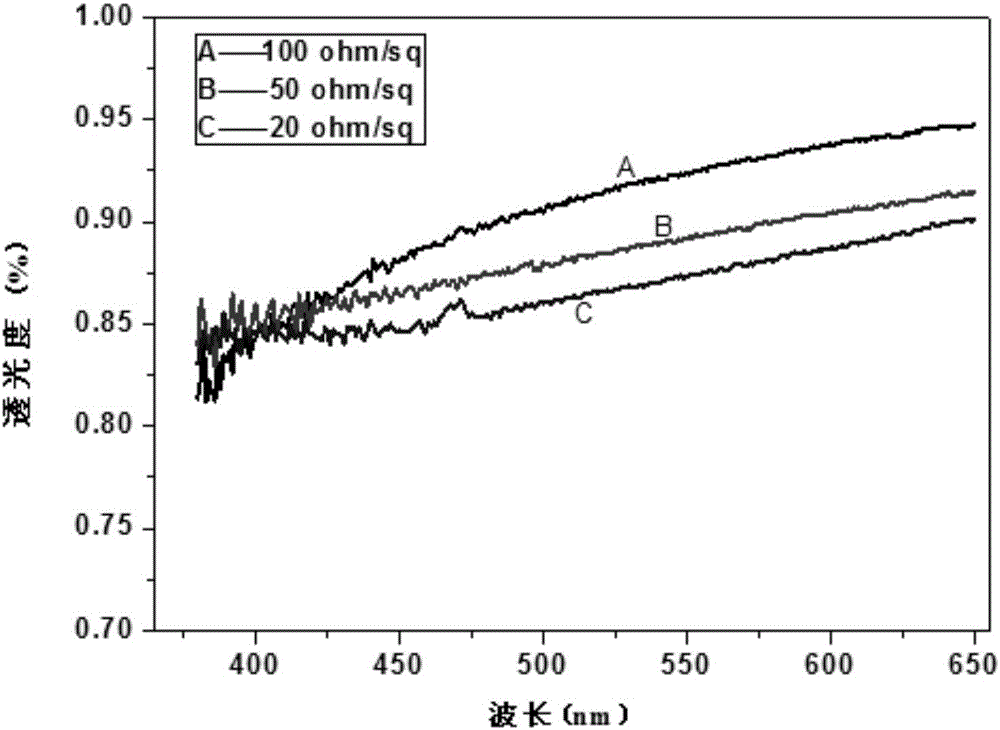
The invention provides a production method of a silver nanowire transparent conductive film. The production method comprises the steps of: preparing a silver nanowire coating liquid, and coating the silver nanowire coating liquid on a base material sheet to obtain a silver nanowire conductive coating; coating an oxide sol on the upper surface of the silver nanowire conductive coating to obtain an oxide protective layer; and forming the silver nanowire transparent conductive film on the base material sheet after baking and curing. The transmittance of the silver nanowire transparent conductive film prepared by adopting the method can reach 85 to 91%, the haze of the same is less than or equal to 2%, the surface resistivity of the same ranges from 10 to 200ohm / sq, and the surface hardness of the same ranges from 6 to 8H.
Owner:城步新鼎盛电子科技有限公司 +1
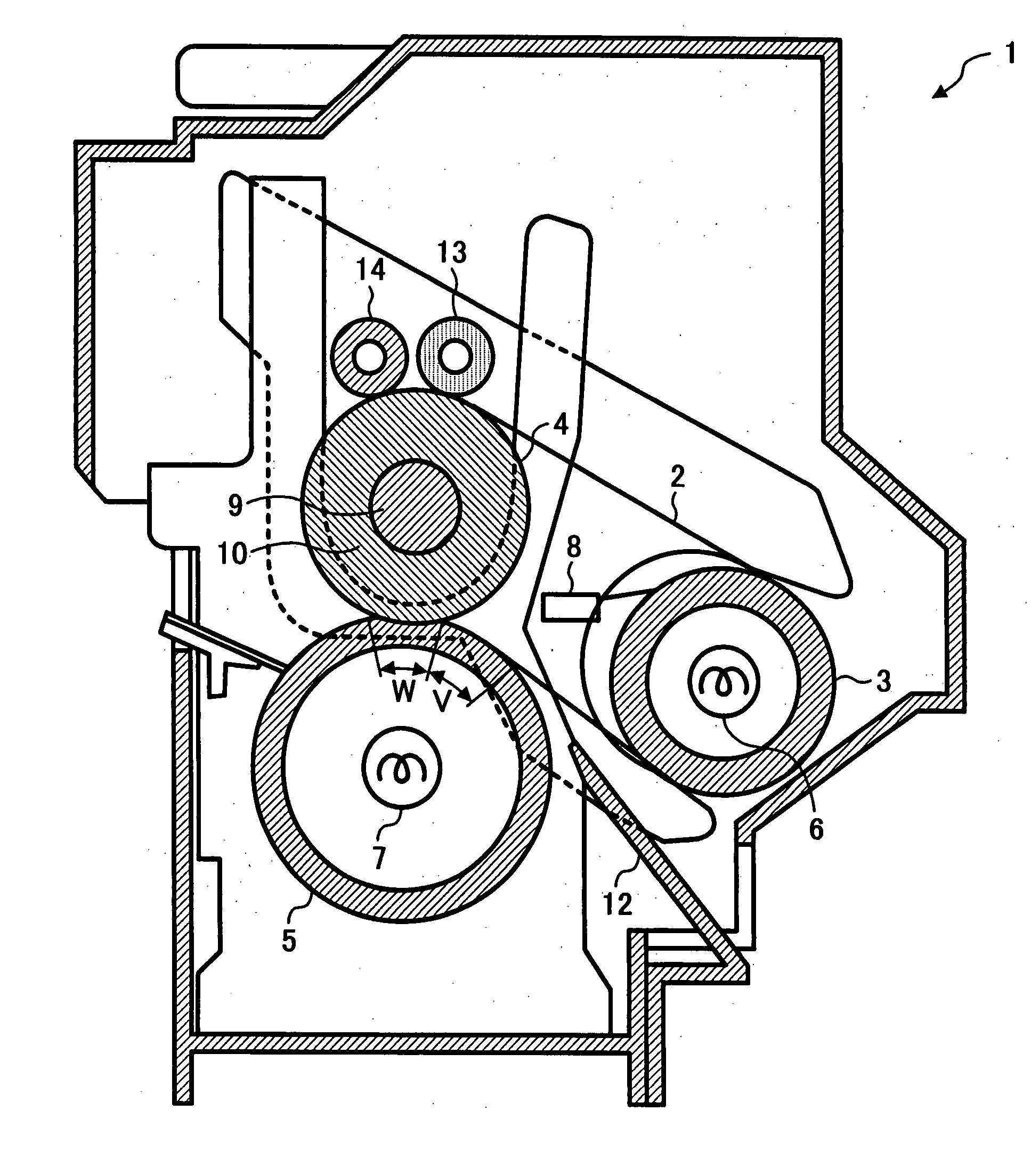
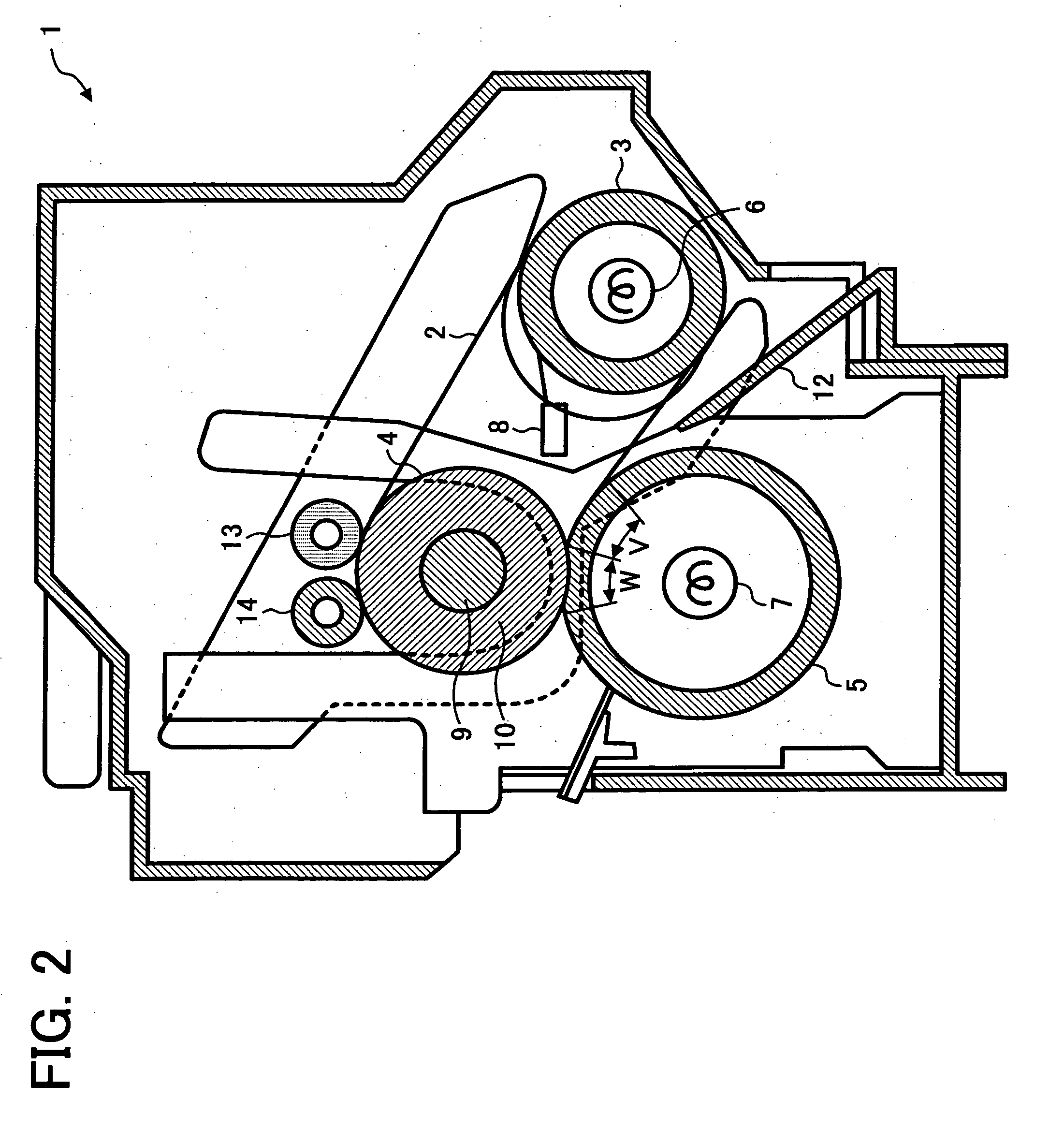
Method for evaluating changes in resistance of electric resistance member and image forming apparatus using same
InactiveUS20050013636A1Improve image qualityWithout transfer defectResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrographic process apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceSurface resistivity
A method for evaluating an electric resistance member of an image forming apparatus which can maintain good image quality, without the occurrence of transfer defects such as insufficient transfer, even in a long-term use. An intermediate transfer belt of the image forming apparatus, which is evaluated based on a fluctuation characteristic of the resistivity in a period of continuous voltage application, is used. The absolute value Δρs of the amount of changes in the surface resistivity of the intermediate transfer belt within 2 seconds to 100 seconds from the beginning of voltage application is 0.3 [Log(Ω / )] or less, when the surface resistivity ρs is measured by applying a voltage of 500 V. The absolute value Δρv of the amount of changes in the volume resistivity within 2 seconds to 100 seconds from the beginning of voltage application is 0.5 [Log(Ω·cm)] or less, when the volume resistivity ρv is measured by applying a voltage of 200 V.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image forming apparatus and fixing apparatus for fixing toner image by using belt
An image forming apparatus includes an image forming mechanism configured to form a visible image using toner on a recording sheet according to input image data and a fixing mechanism configured to fix the visible image onto the recording sheet. The fixing mechanism includes a first roller, a second roller, a belt, and a third roller. The first roller is configured to rotate. The second roller includes inside a first heater and is configured to rotate. The belt is looped over the first and second rollers. The third roller is arranged opposite to the first roller via the belt, includes inside a second heater, and has a surface resistivity not higher than 1.0×106 Ω-cm under a voltage of 10 V. The third roller applies a pressure to the belt and the first roller and rotates in conjunction with a movement of the first roller via the belt.
Owner:RICOH KK
Coating materials and methods for enhanced reliability
ActiveUS20160013329A1Reduce trafficHigh surface resistanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPotential induced degradationMoisture
Glass coating materials and methods are disclosed for the coating of glass substrates used in the manufacturer of photovoltaic solar modules such that the coating enhances the reliability of the module by reducing its susceptibility to potential induced degradation (PID). Coating materials are disclosed that reduce soiling on the front surface of the glass; that increase the surface resistivity of the glass and that repel moisture and that seal the surface from the ingress of moisture. Further electrically conductive coatings are disclosed that reduce the electric field between the front and back surfaces of the glass and hence reduce ion mobility within the glass and transport from the interior glass surface to the solar cell. There are additional configuration choices for fine tuning associated with separately optimizing the exterior and interior glass coating. Finally, coating processes and methods are disclosed for coating glass substrates with the disclosed materials.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet
InactiveUS6998175B2Avoid YieldAvoid breakingSynthetic resin layered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface resistivitySurface roughness
A heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet which, even when used for temporarily fixing electronic parts having poor resistance to static electricity, such as magnetic heads, is effective in preventing the yield of such electronic parts from being reduced by electrostatic breakage, while ensuring its functions of adhesiveness before heating and peelability after heating. The heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet comprises a substrate and formed on at least one side thereof a heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer containing heat-expandable microspheres, wherein the heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer has a surface resistivity of 1012 Ω / □ or lower. In this heat-peelable pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet, the heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer before heating may have a center line average surface roughness of 2 μm or less and a maximum surface roughness of 5 μm or less. The adhesive sheet may have a rubber-like organic elastic layer interposed between the substrate and the heat-expandable pressure-sensitive adhesive layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
ESD dissipative ceramics
InactiveUS6669871B2Minimize grain growthLow resistivityHeads using thin filmsConductive materialStructural reliabilityFlexural strength
This invention relates to a dense ceramics having ESD dissipative characteristics, tunable volume and surface resistivities in semi-insulative range (10.sup.3 -10.sup.11 Ohm-cm), substantially pore free, high flexural strength, light colors, for desired ESD dissipation characteristics, structural reliability, high vision recognition, low wear and particulate contamination to be used as ESD dissipating tools, fixtures, load bearing elements, work surfaces, containers in manufacturing and assembling electrostatically sensitive microelectronic, electromagnetic, electro-optic components, devices and systems.
Owner:COORSTEK INC
Transparent conductors and methods for fabricating transparent conductors
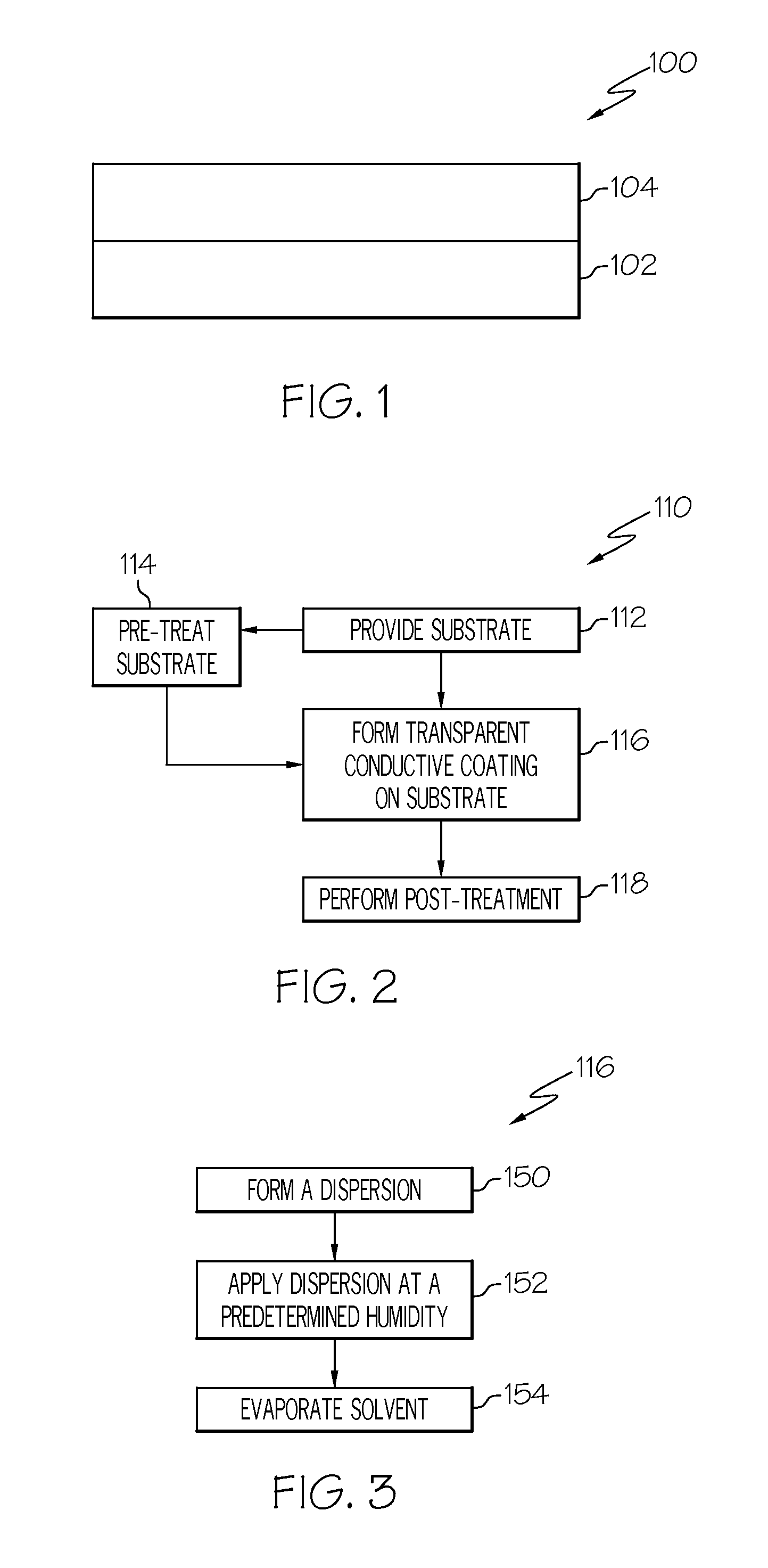
Transparent conductors and methods for fabricating transparent conductors are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, a method for fabricating a transparent conductor comprises forming a dispersion comprising a plurality of conductive components and a solvent, applying the dispersion to a substrate in an environment having a predetermined atmospheric humidity that is based on a selected surface resistivity of the transparent conductor, and causing the solvent to at least partially evaporate such that the plurality of conductive components remains overlying the substrate.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
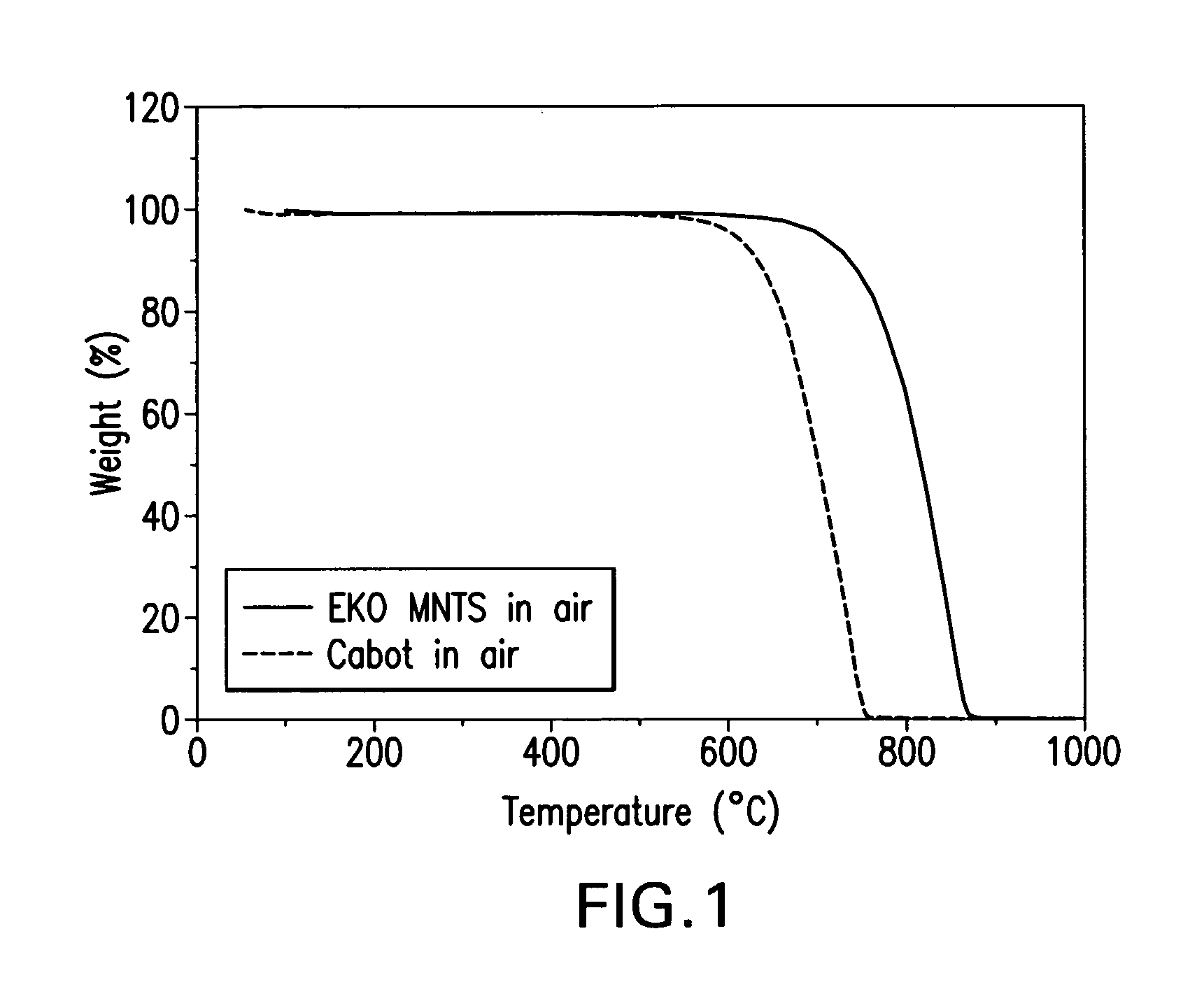
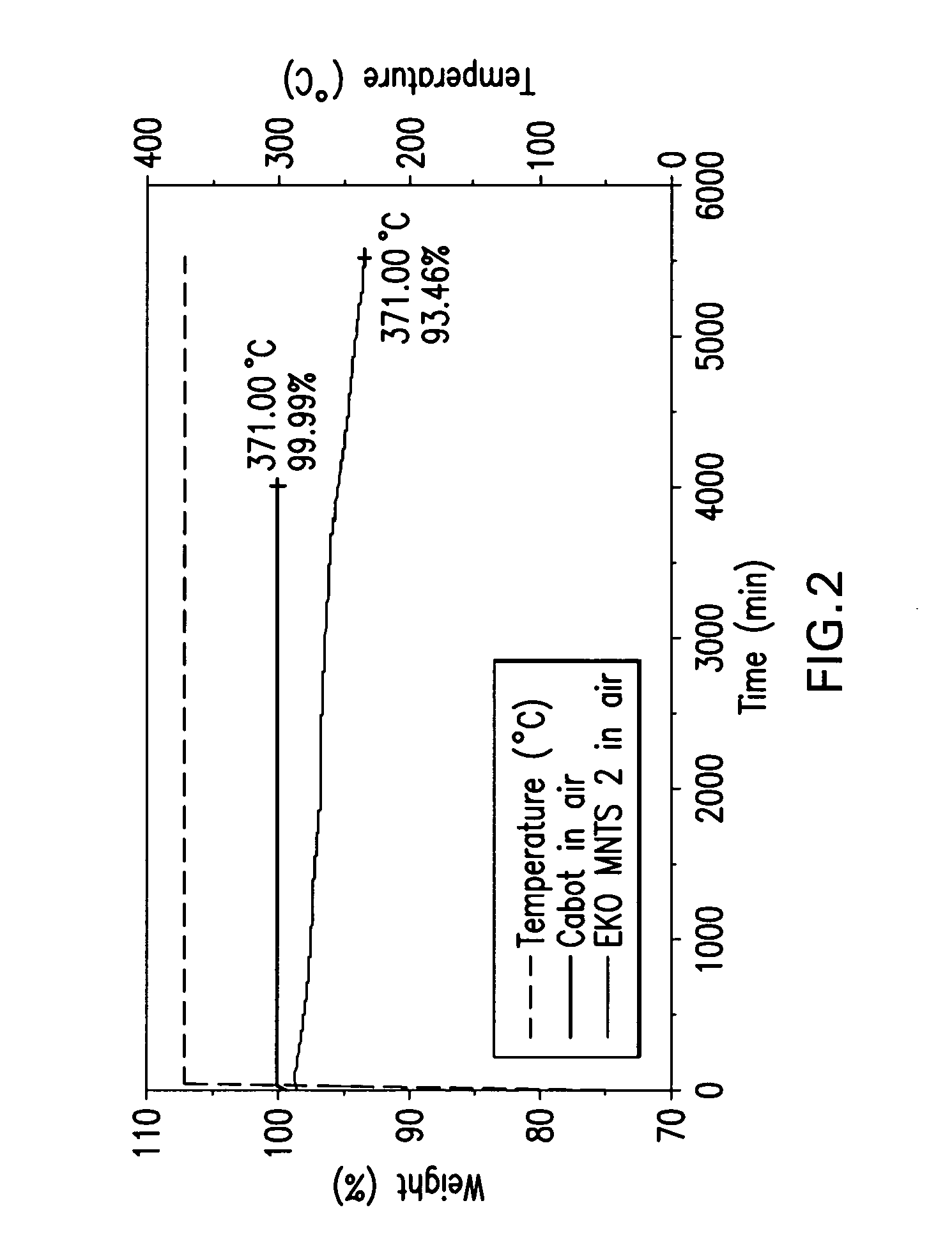
Electrically conductive coatings with high thermal oxidative stability and low thermal conduction
InactiveUS20050191493A1Material nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsConductive coatingSurface resistivity
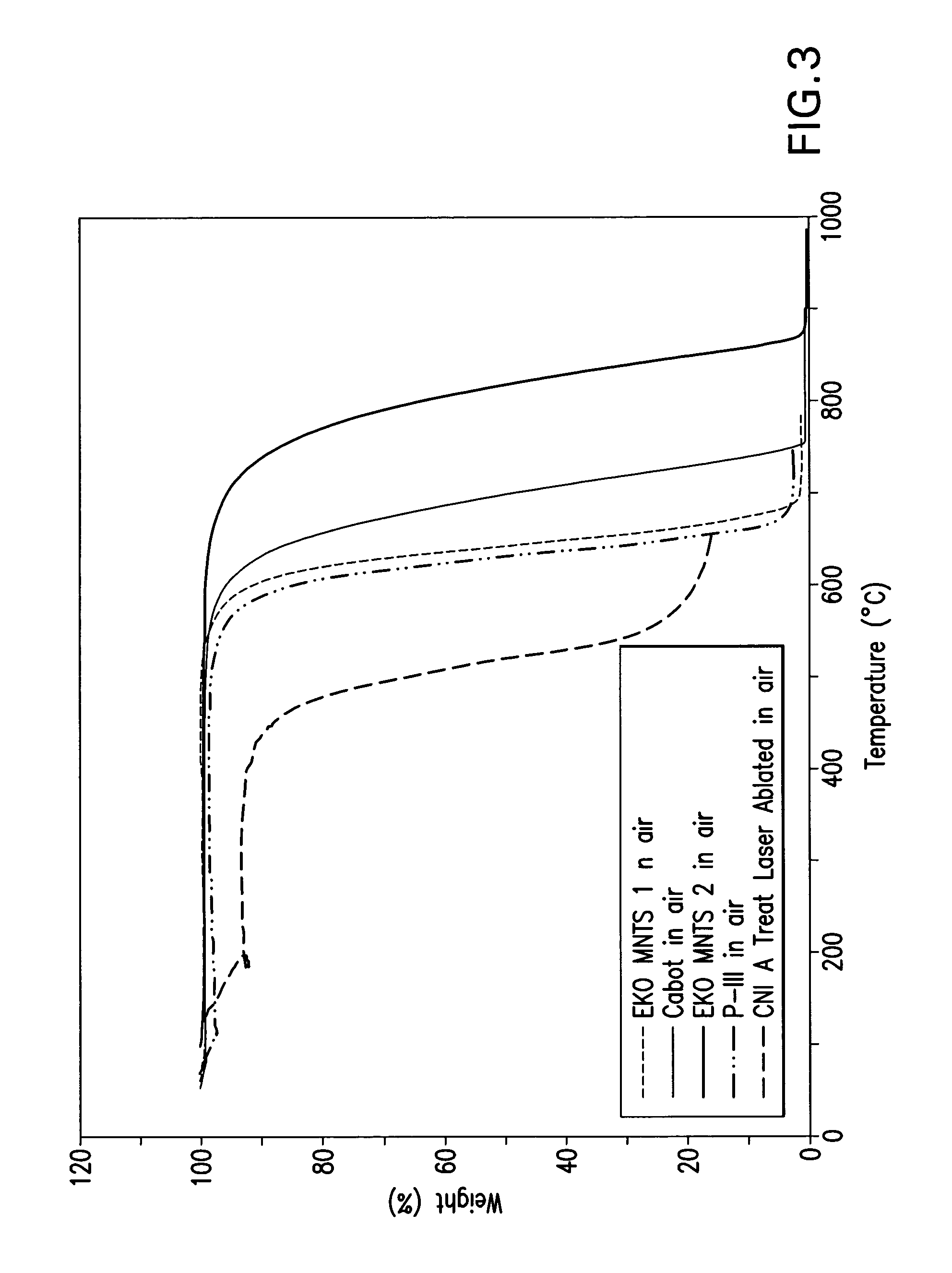
The present invention is directed to electrically conductive coatings of carbon that have high thermal oxidative stability and low thermal conduction. Coatings of the invention provide a surface resistivity to the coated substrate of 102 ohms / square, and preferably 10−2 ohms / square. Coatings also provide the coated article increased thermal oxidative stability as compared to the uncoated article and articles coated with convention materials like carbon black and metals, as well as low thermal conduction. The invention is also directed to substrates possessing conductive coatings, methods of utilizing the coated substrates, and to methods of forming the coatings of the invention.
Owner:EIKOS
Endless belt for image-forming apparatuses, and image-forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060172097A1Increase resistanceImprove stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageElastomerImaging quality
There are provided an endless belt for image-forming apparatuses comprising a molded product produced from a blended mixture containing a thermoplastic elastomer, a thermoplastic resin and a conductive substance, the said endless belt having properties satisfying the following formulae (1), (2) and (3): SR(100V) / SR(500V)<VR(100V) / VR(250) (1) SR(100V) / SR(500V)≦30 (2) 8≦VR(100V) / VR(250V)≦100 (3) wherein SR(100V) represents a surface resistivity as measured by applying a voltage of 100V to the endless belt for 10 sec, SR(500V) represents a surface resistivity as measured by applying a voltage of 500V to the endless belt for 10 sec, VR(100V) represents a volume resistivity as measured by applying a voltage of 100V to the endless belt for 10 sec, and VR(250V) represents a volume resistivity as measured by applying a voltage of 250V to the endless belt for 10 sec. The endless belt for image-forming apparatuses is excellent in flexibility, chemical resistance, dimensional stability, electric resistivity and external environmental stability of these properties, is inexpensive, and is capable of achieving a high image quality and a high durability.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
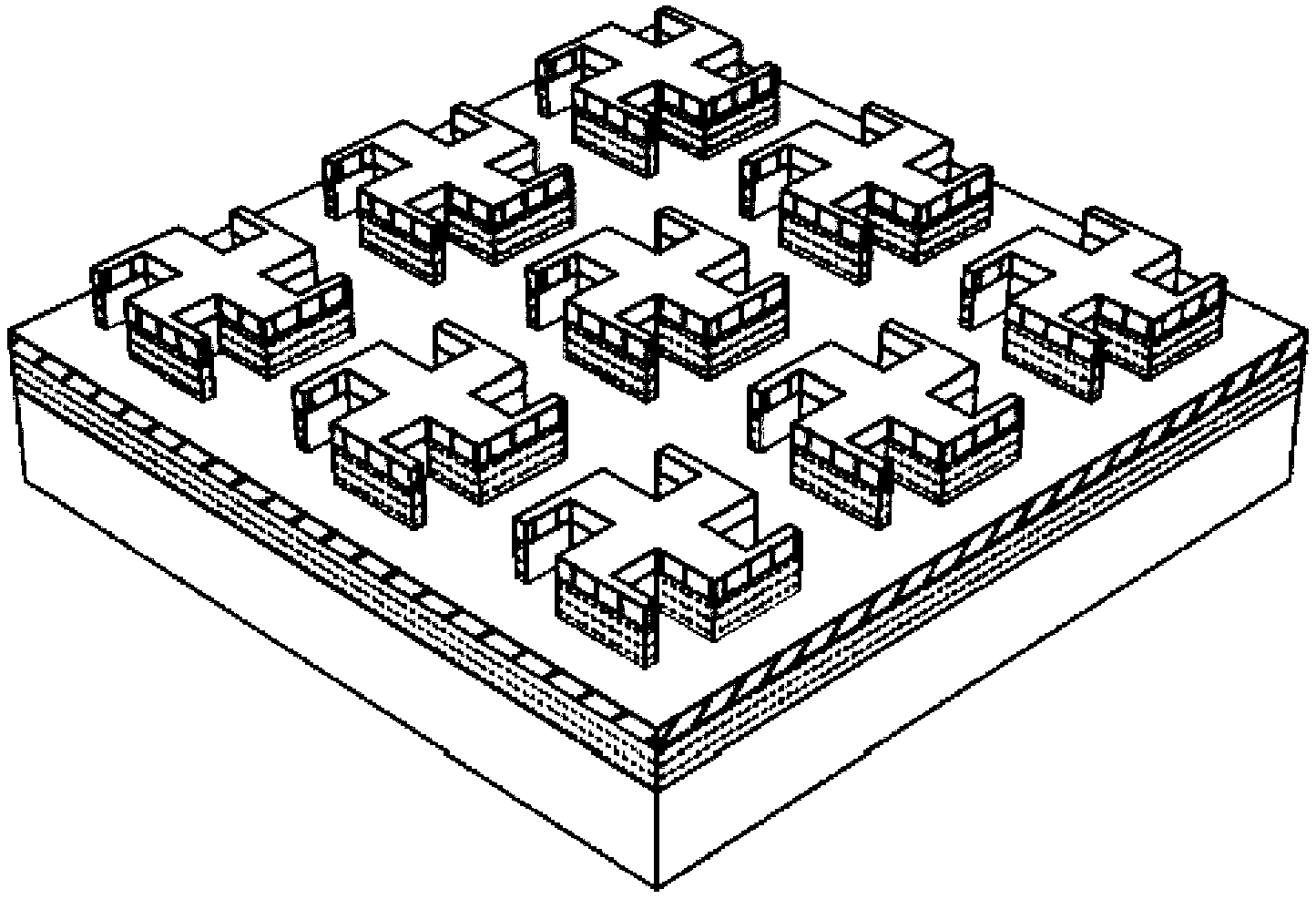
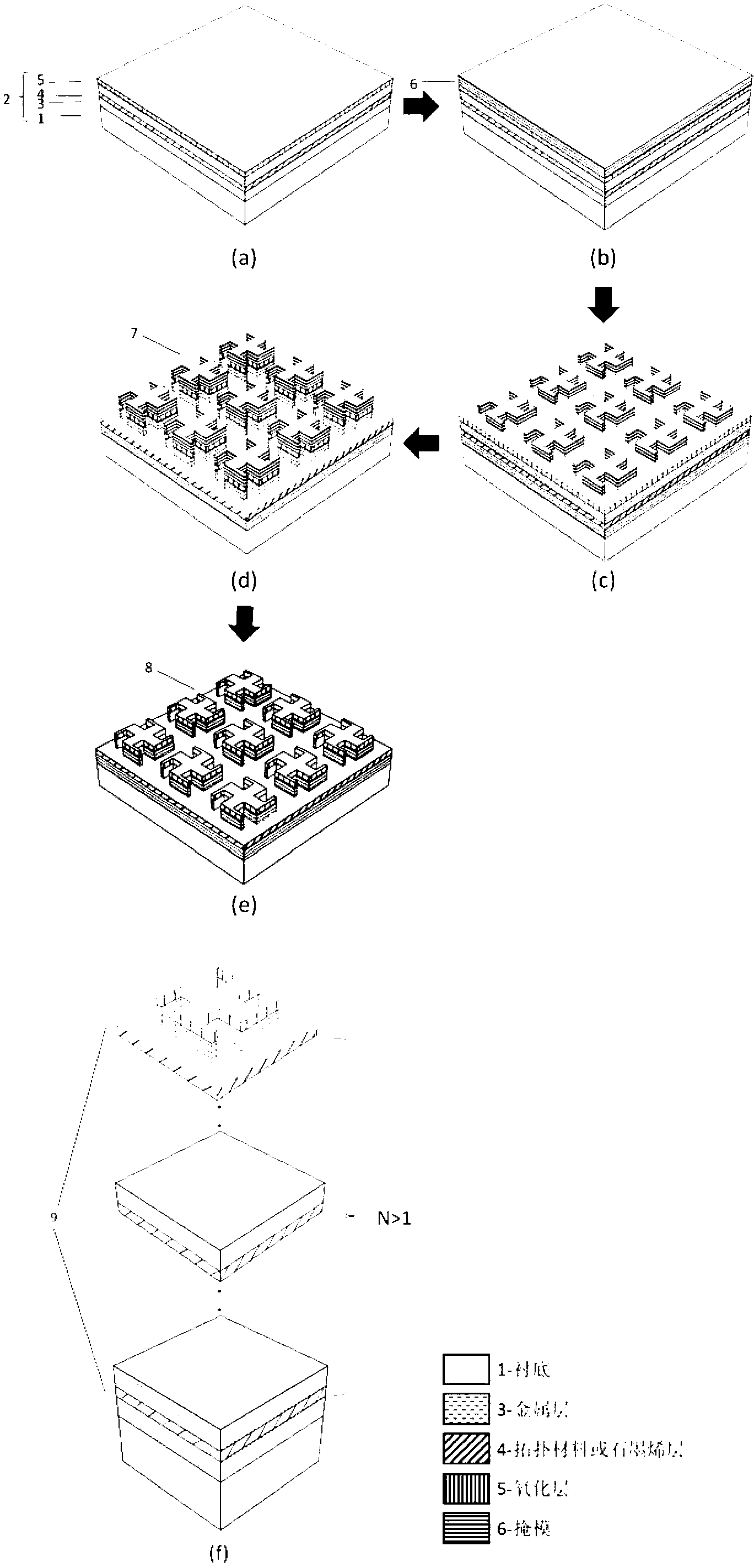
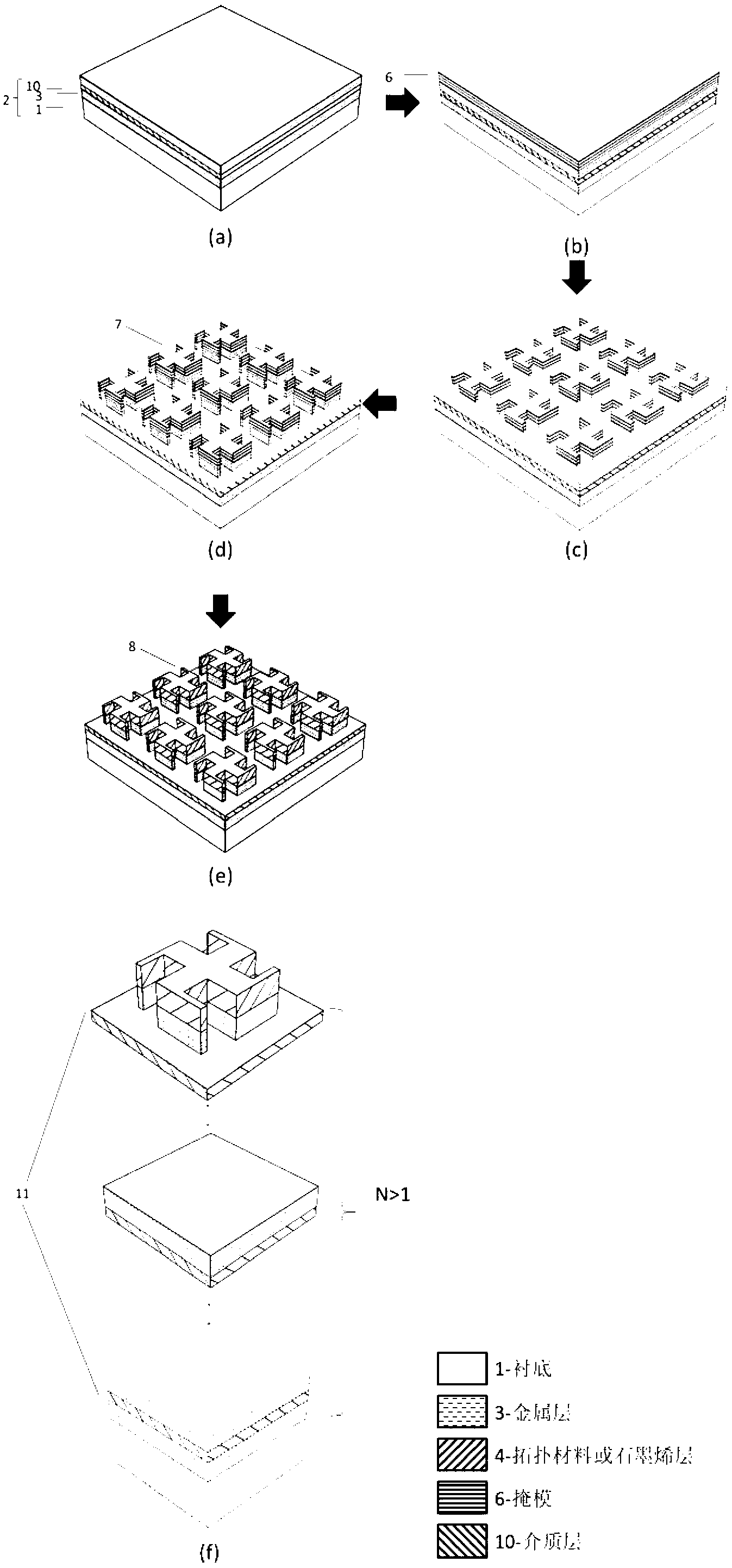
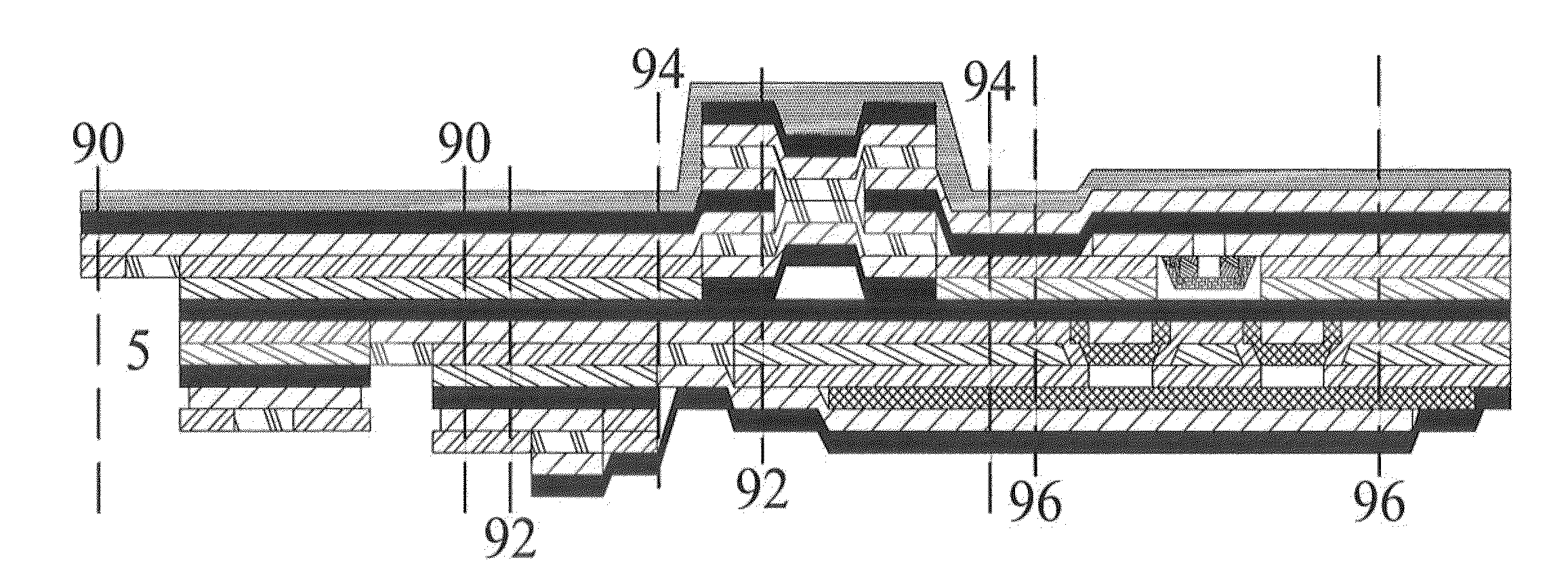
Tunable microwave-absorbing artificial electromagnetic metamaterial based on topology/graphene
The invention provides a tunable microwave-absorbing artificial electromagnetic metamaterial based on a topology / graphene material. Through the introduction of the topology material or the graphene material into the microwave-absorbing artificial electromagnetic metamaterial, the resonant frequency corresponding to an absorption peak is changed, so that the frequency band of an absorption spectrum is tunable; and therefore, the problem that the frequency band of the microwave-absorbing artificial electromagnetic metamaterial is too narrow and untunable is solved. With the adoption of the tunable microwave-absorbing artificial electromagnetic metamaterial based on the topology / graphene material, the dielectric coefficient and the surface resistivity of the topology material or the graphene material can be changed through control on an external electric field, temperature or thickness of the topology material or the graphene material; and in such a way, the microwave-absorbing artificial electromagnetic metamaterial with the tunable working frequency band is further realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Antistatic adhesion-resistant slippery linear low density polyethylene composition and method of making the same
ActiveCN101012322AGuaranteed performanceMeet production requirementsLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The invention discloses an antistatic blocking resistant smooth linear low-density polyethylene composition based on LLDPE as base, which comprises the following parts: 0.05-0.2% opening agent, 0.05-0.3% smooth agent, 0.05-0.3% antistatic agent, 0.05-0.2% anti-oxidant and 0.05-0.2% manufacturing and heat stabilizer, wherein the opening agent contains inorganic blocking resistant agent or organic opening agent; the smooth agent is amide, soap or organic silicane; the main auxiliary anti-oxidant is hindered phenol and phosphorus anti-oxidant; the antistatic agent adopts composite pattern of non-ionic typed antistatic agent and ion-typed antistatic agent. The making method compress the following steps: adopting LLDPE as base; adding blended auxiliary material into graining stage; or graining auxiliary agent into mother grain; adding mother grain; manufacturing specific material.
Owner:SINOPEC YANGZI PETROCHEM
Flexible sensing material containing carbon nanotubes
ActiveUS20120258302A1Improve conductivityReduce conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsCarbon nanotubeSurface resistivity
The present invention relates to a flexible sensing material made from (a) at least one flexible polymeric layer and (b) at least one conductive, curable coating layer containing about 0.01 wt. % to about 5 wt. % of multi-walled carbon nanotubes having a diameter of greater than about 4 nm, about 10 wt. % to about 99 wt. % of an aliphatic urethane acrylate and about 0.1 wt. % to about 15 wt. % of a photoinitiator, wherein the weight percentages are based on the weight of the formulation, wherein the coating layer is curable by exposure to radiation and wherein the cured coating layer has a surface resistivity of about 102Ω / □ to about 1010Ω / □. The inventive sensing material may prove useful for sensing one or more of pressure, temperature and moisture and find use in a wide variety of applications.
Owner:COVESTRO LLC
Antistatic gloves and process for making same
InactiveUS20080306200A1Desirable antistatic propertyDesirable propertyGlovesConjugated diene hydrocarbon coatingsPolymer scienceAntistatic agent
The present invention is directed to antistatic elastomeric articles and methods of making the same. The articles can be single layered or multilayered. The single layered articles possess desirable antistatic properties and desirable properties of comfort and feel. The multilayered articles have an outermost layer / surface that possesses desirable antistatic properties and an innermost layer / surface that exhibits desirable properties of comfort and feel. In preferred embodiments, the elastomeric articles are made form a nitrile / natural rubber blend. Articles of the present invention have antistatic properties measured as having a surface resistivity below about 1014 Ω / sq and a static decay time of less than about 60 seconds.
Owner:ALLEGIANCE CORP
Electromagnetic wave shielding material, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20110122596A1Reduce resistanceFree from damageMagnetic/electric field screeningSynthetic resin layered productsLine widthSurface resistivity
The present invention is to provide an electromagnetic wave shielding material including a transparent substrate and a convex pattern layer composed of a conductive composition formed in a prescribed pattern on the transparent substrate, wherein the conductive composition contains conductive particles and a binder resin; and in observation of a transverse cross section of the convex pattern layer by electron microscopic photography, at least a part of the conductive particles has a fused continuation and a method for manufacturing the same. The electromagnetic wave shielding material and the method for manufacturing the same include a configuration capable of achieving a lower surface resistivity in an electromagnetic wave shielding material which is required to achieve a much more reduction in a line width of the pattern, specifically, a reduction to a line width of not more than 30 μm, and more preferably not more than 15 to 20 μm and a treatment method capable of reducing the surface resistivity by an easy and short-time treatment.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Electromagnetic-shielding light-diffusing sheet
InactiveUS20070116916A1Satisfactory performanceHigh light transmittanceDiffusing elementsLayered productsSurface resistivityEngineering
A subject for the invention is to provide an electromagnetic-shielding light-diffusing sheet which has satisfactory electromagnetic shielding performance, attains a large transmitted-light amount, and can emit even diffused light having reduced unevenness of luminance. The invention relates to an electromagnetic-shielding light-diffusing sheet comprising a light-diffusing sheet main body and, laminated on at least one side thereof, a light-transmitting electroconductive layer having a surface resistivity of 105 Ω / □ or lower.
Owner:TAKIRON CO LTD
Sound dampening foam
InactiveUS20050042437A1Improve sound insulationLow areal densityLayered productsSound producing devicesSurface resistivityAverage size
A closed-cell foam comprises at least about 50 weight percent thermoplastic polymer and from about 5 to about 50 weight parts of particles dispersed in the thermoplastic polymer per 100 weight parts of the thermoplastic polymer. The particles have an average size in the longest dimension of from about 5 to about 300 microns. If the particles are electrically conductive, then the foam has a surface resistivity of at least about 1×106 ohms. The foam is useful in sound dampening applications.
Owner:SEALED AIR CORP
Electrostatic dissipative foams and process for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20150274924A1Increase elasticityStay flexibleShielding materialsLayered productsPolymer scienceConductive polymer
The present invention relates to the development of electrostatic dissipative (ESD) electronic packaging materials based on the electrically conducting nanofiller decorated polyurethane foams and also describes a process for the preparation of the same. More specifically it relates to the development of electrically conducting foams by providing a coating of 0.003 to 2.97 vol % loading of electrically conducting materials (like conducting polymers, functionalized carbon nanotubes, graphene analogues etc) over / onto otherwise electrically insulating surface of foams. The combination of low density, mechanical flexibility, resilience and surface conductivity collectively contribute towards their excellent shock absorption and static charge dissipation capabilities. In particular, these foams display surface resistivity value <109 ohm / sq and static charge dissipation time <0.5 sec, which clearly demonstrate their potential for electronic packaging applications. Besides, these foams could also be useful for antistatic dust filters, clean-room / medical apparels, static-free footwear, static dissipative upholstery items, antistatic / dissipative floorings / tiles etc.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Matrix tray with tacky surfaces
InactiveUS6926937B2Widen meansSufficient forceEnvelopes/bags making machinerySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolyetherimidePolybutylene terephthalate
A tray for handling and retaining a plurality of small components comprising a rigid body portion with a plurality of pockets formed therein. Each of the pockets has an elastomeric contact surface for contacting and retaining a component. The contact surface may be formed from a thermoplastic material having a surface energy between 20 dyne / cm and 100 dyne / cm, and a surface electrical resistivity of between about 1×104 ohms / square and 1×1012 ohms / square. The material for the contact portion may be urethane, polybutylene terephthalate, polyolefin, polyethylene terephthalate, styrenic block co-polymer, styrene-butadiene rubber, polyether block polyamide, or polypropylene / crosslinked EDPM rubber. The body portion may be formed from acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene, polycarbonate, urethane, polyphenylene sulfide, polystyrene, polymethyl methacrylate, polyetherketone, polyetheretherketone, polyetherketoneketone, polyether imide, polysulfone, styrene acrylonitrile, polyethylene, polypropylene, fluoropolymer, polyolefin, or nylon. The body portion may have a peripheral border region and a downwardly projecting skirt portion to facilitate stacking of multiple trays.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Preparation method for antistatic super hydrophobic composite coating
ActiveCN101792633ASimple and fast operationMild conditionsVegetal fibresElectrically-conductive paintsCarbon nanotubePolymer SMA
The invention discloses a preparation method for antistatic super hydrophobic composite coating, comprising the following steps: dissolving 0.2-2 parts of styrene-maleic anhydride alternate copolymer by weight into 20-1000 parts of solvent by weight, adding 1 part of carbon nanotube by weight and then evenly mixing, adding 0-26 parts of ammonia water and 0.2-2 parts of silicate ester or titanate compound by weight, stirring and mixing to enable silicate ester or titanate compound to perform hydrolysis reaction, adding 0.1-2 parts of silicate ester or titanate compound and 0.02-0.5 part of fluorine containing silane coupling agent by weight, evenly mixing and spraying on base materials, carrying out aging and thermal treatment to obtain stable antistatic super hydrophobic composite coating. The invention has simple operation and mild condition, the carbon nanotube can be directly used without the need of any chemical modification, the obtained composite coating has good hydrophobicity,the static contact angle and rolling angle between the composite coating and water are respectively larger than 150 degrees and less than 3 degrees, and the surface resistivity is 106-1011 omega, thus meeting the requirement of antistatic transparent coating and having wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com