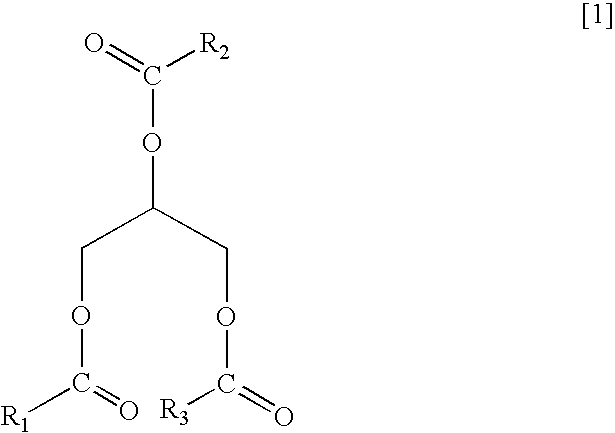
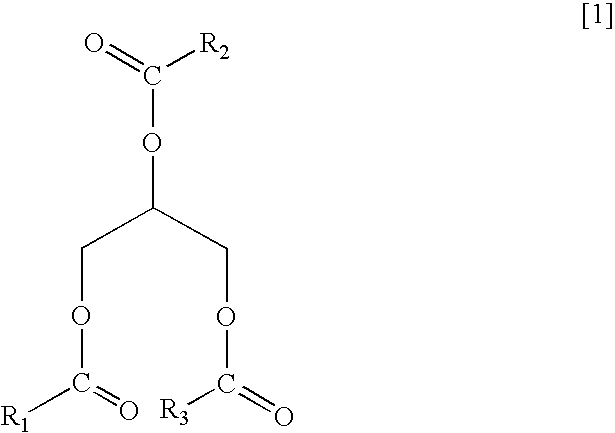
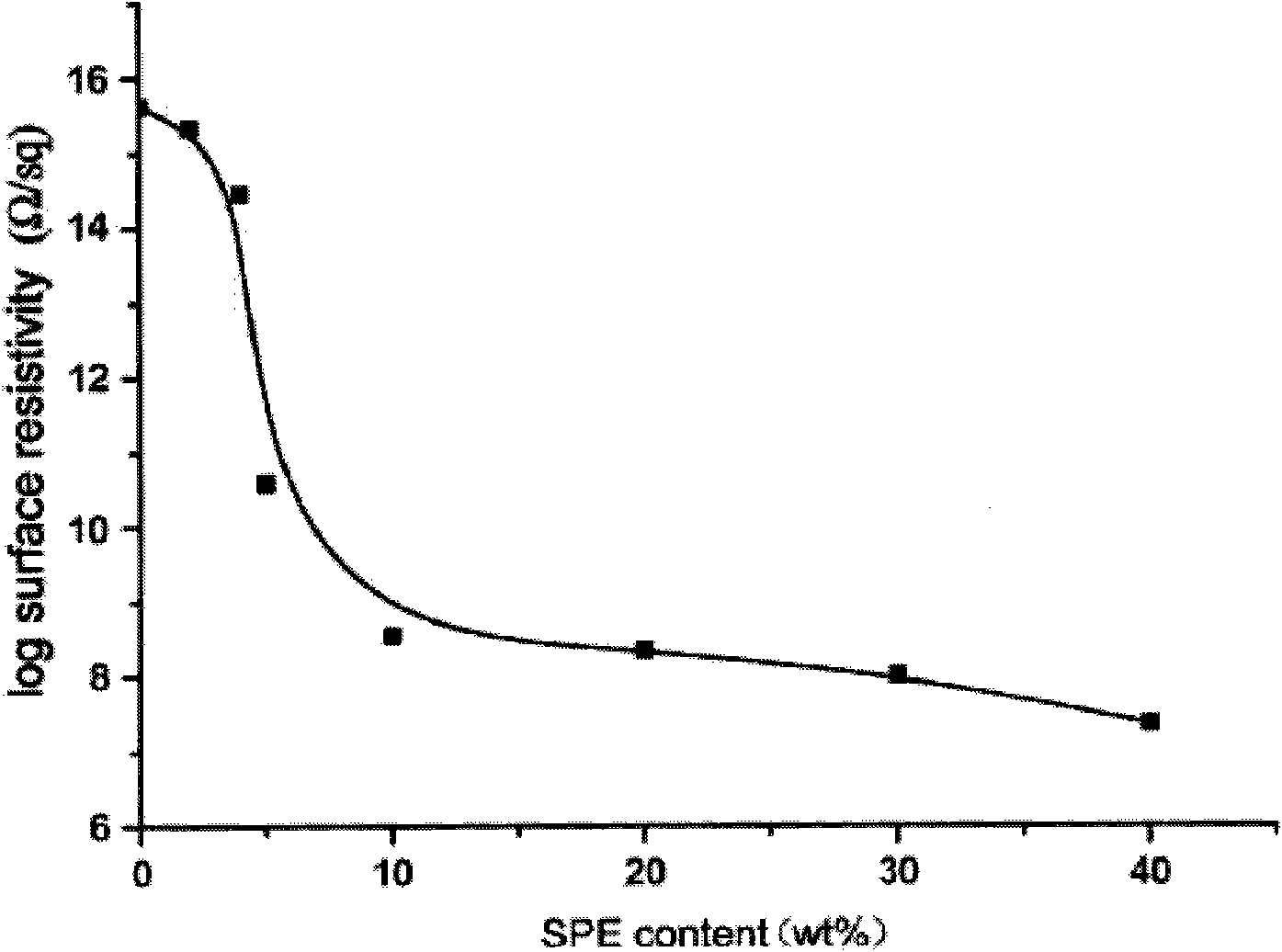
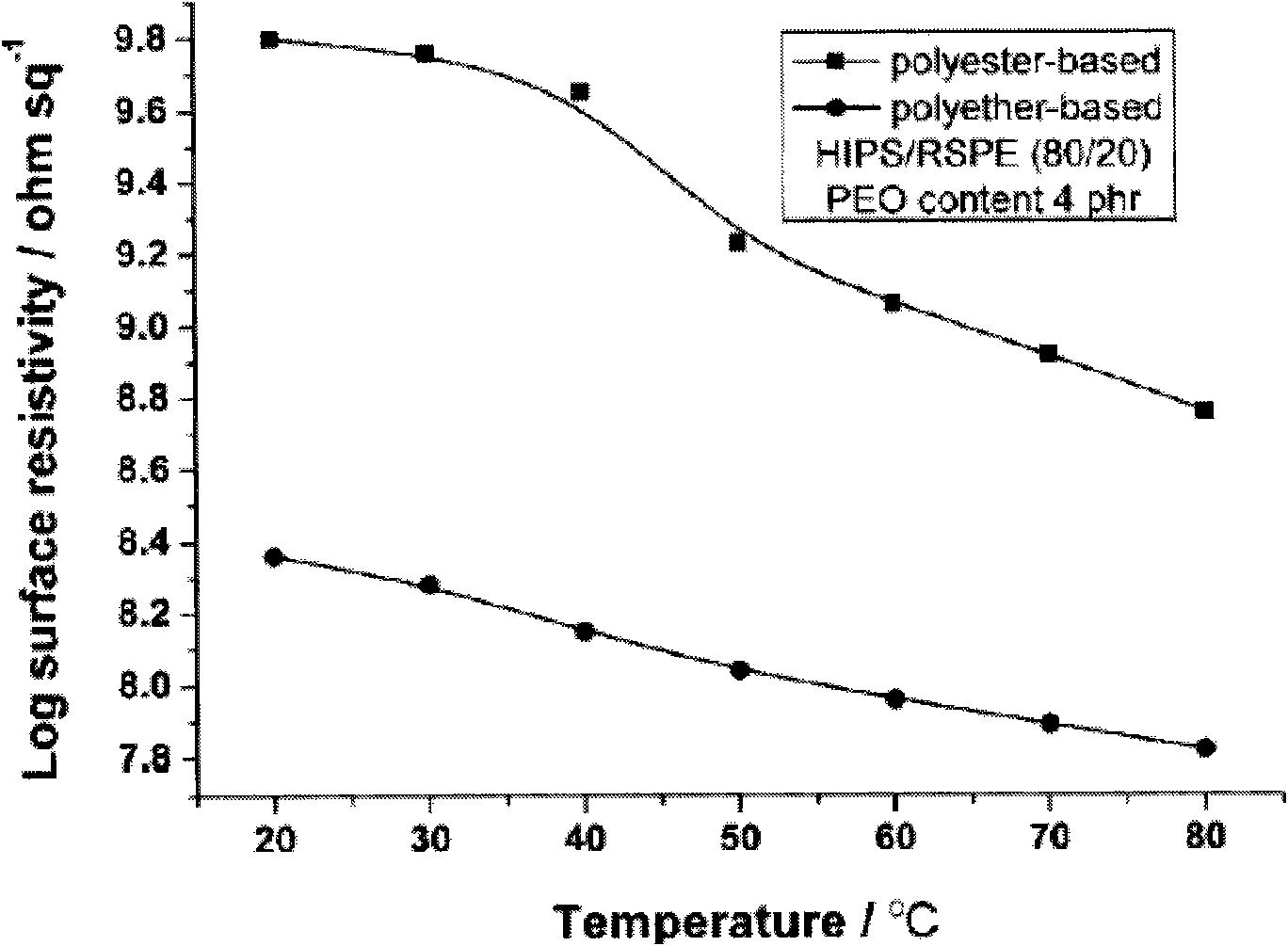
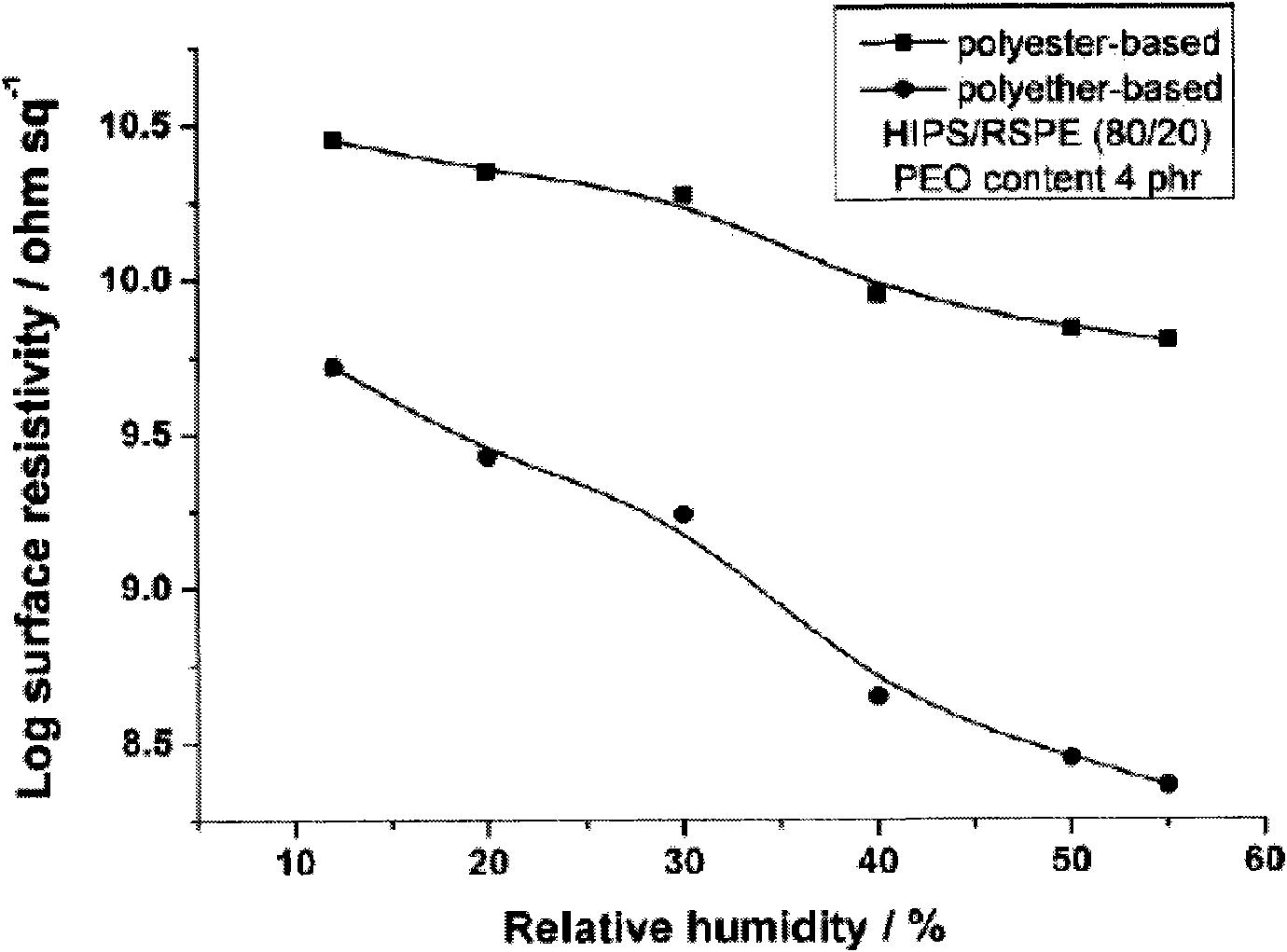
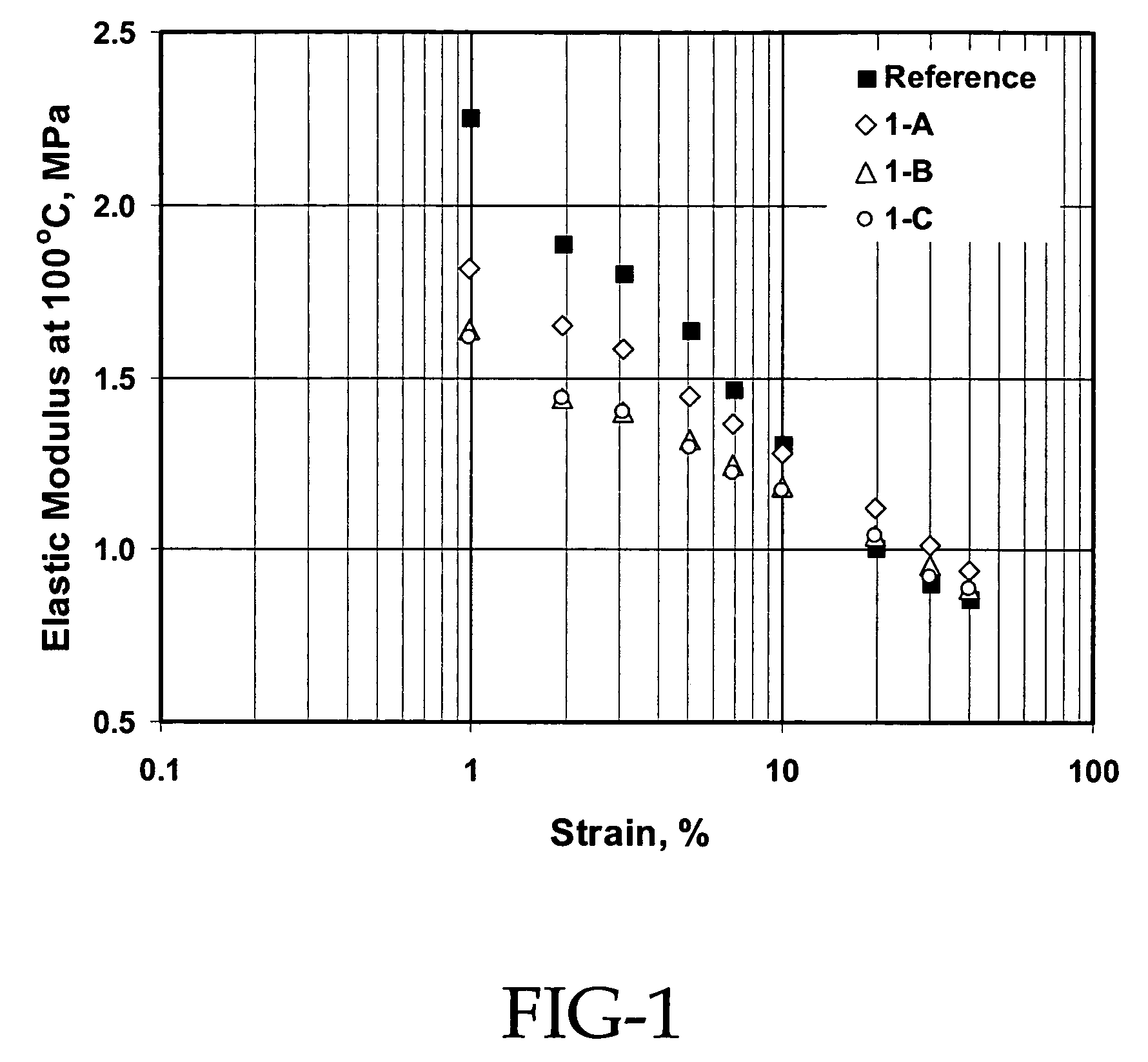
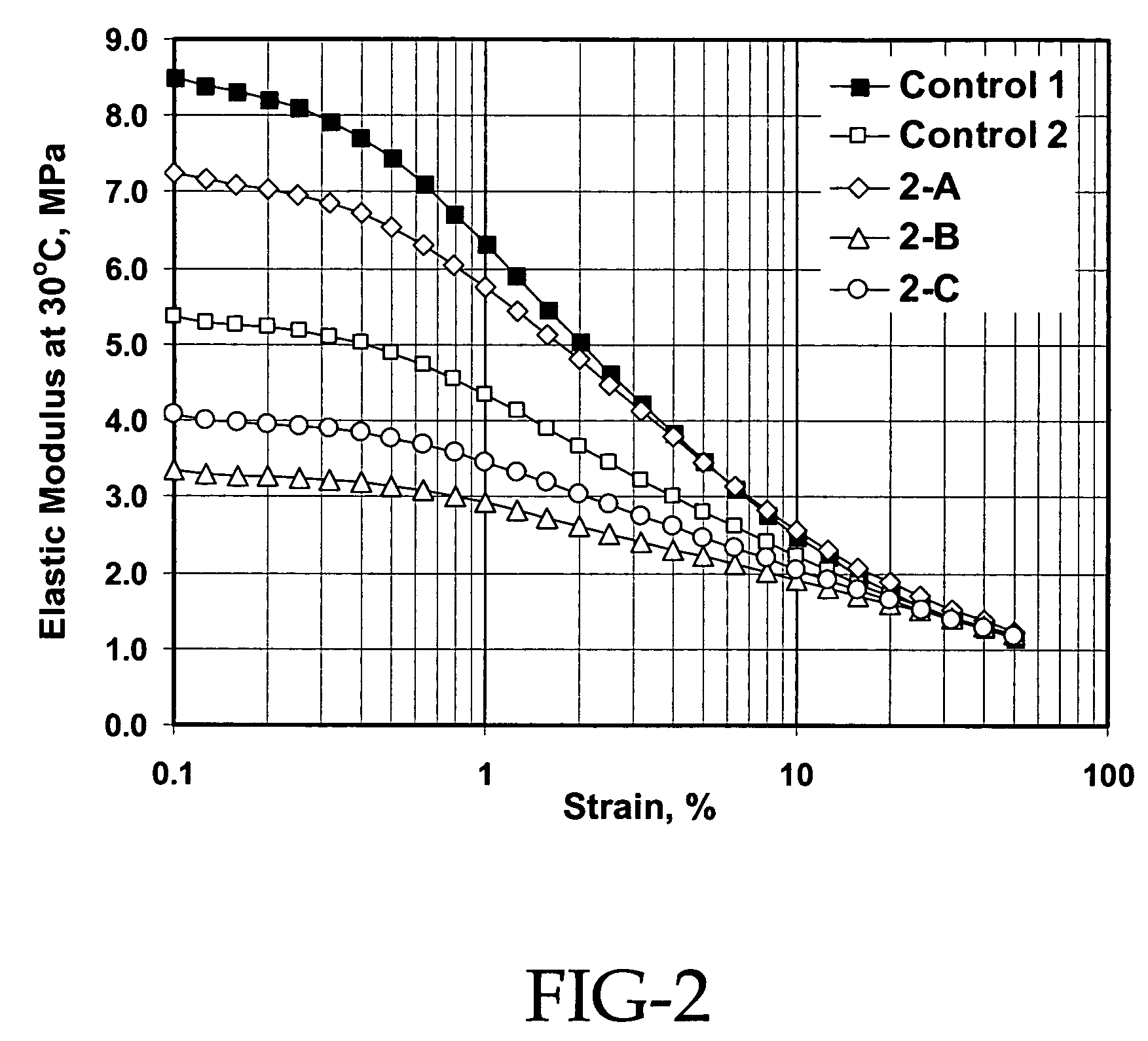
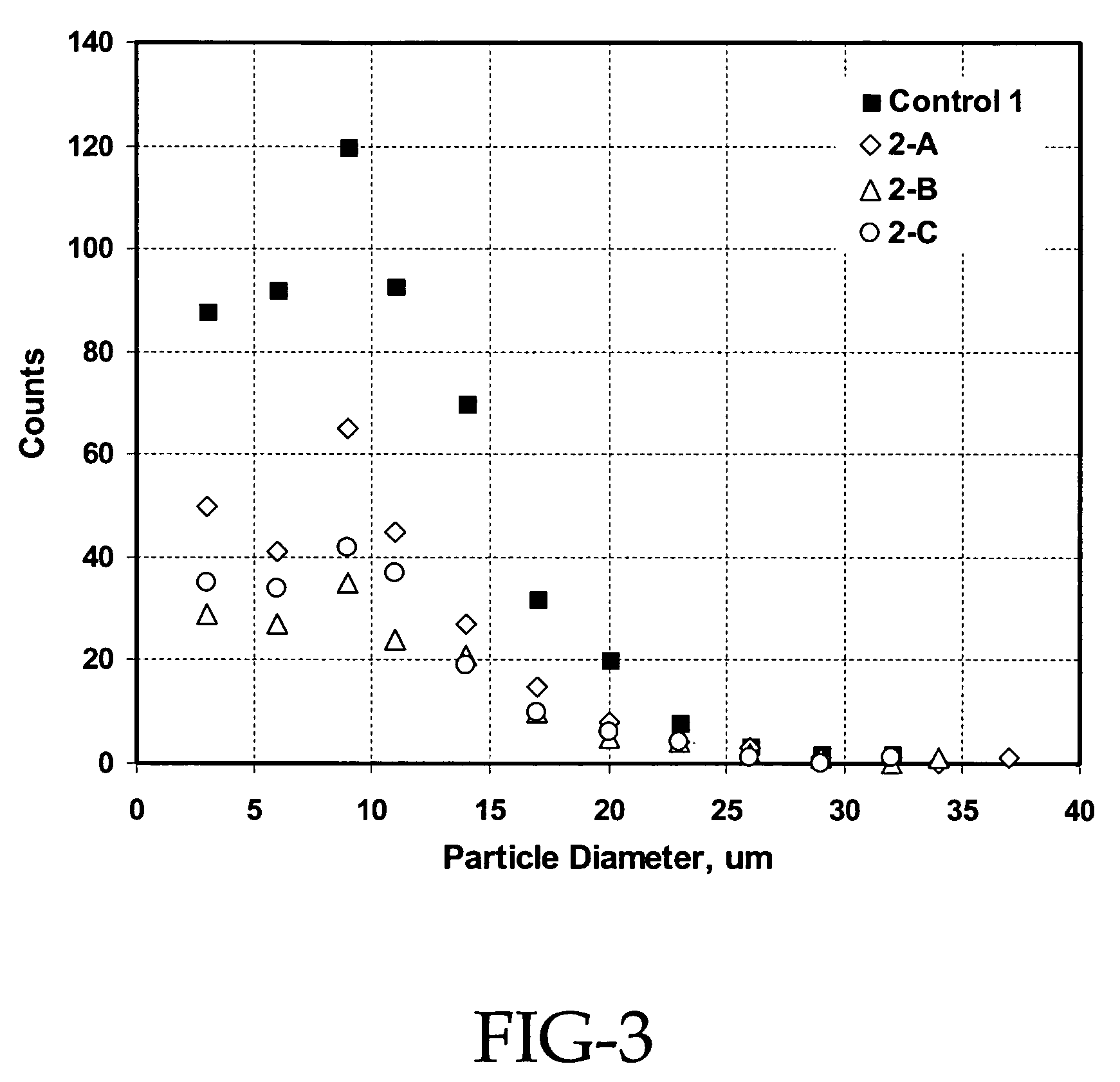
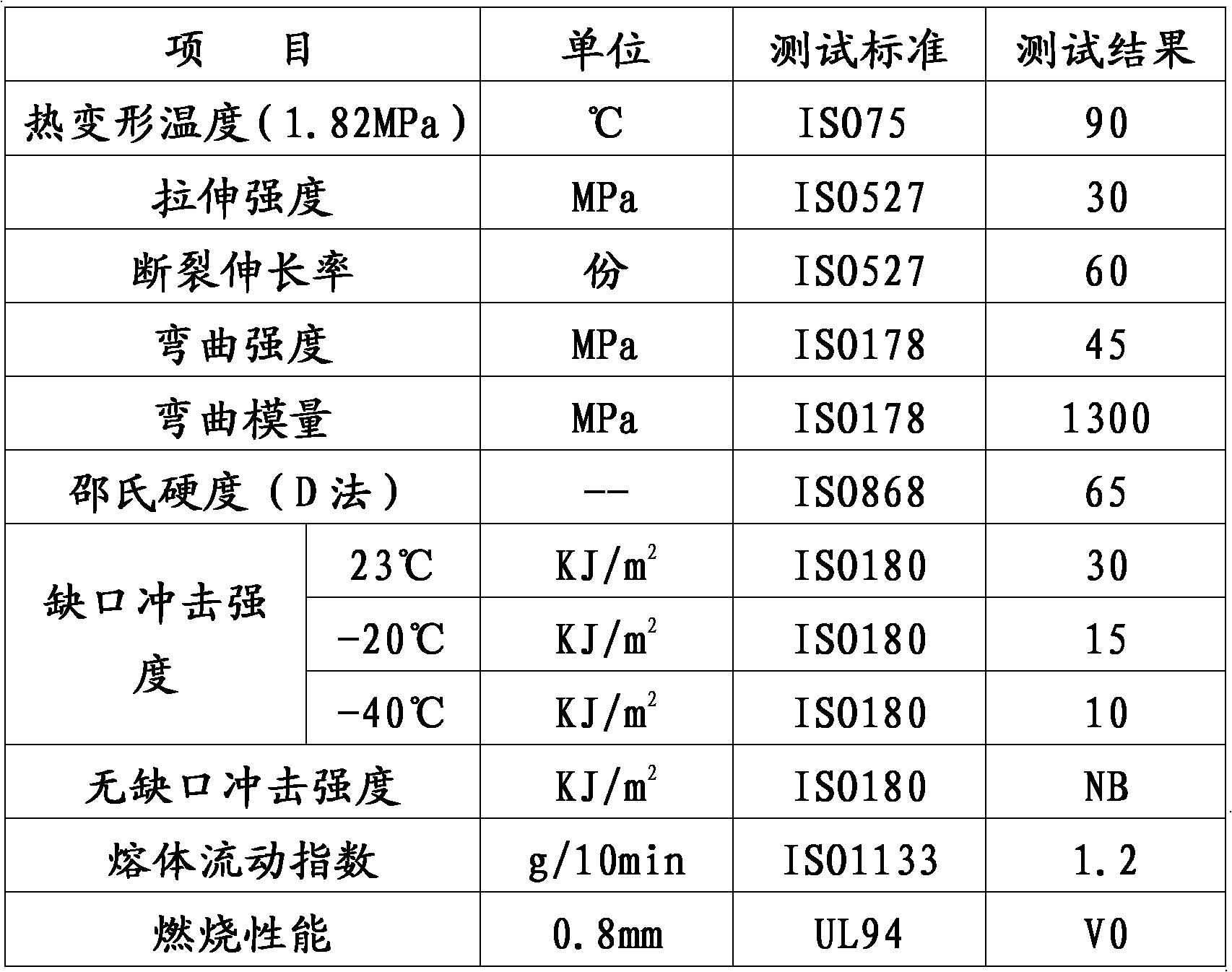
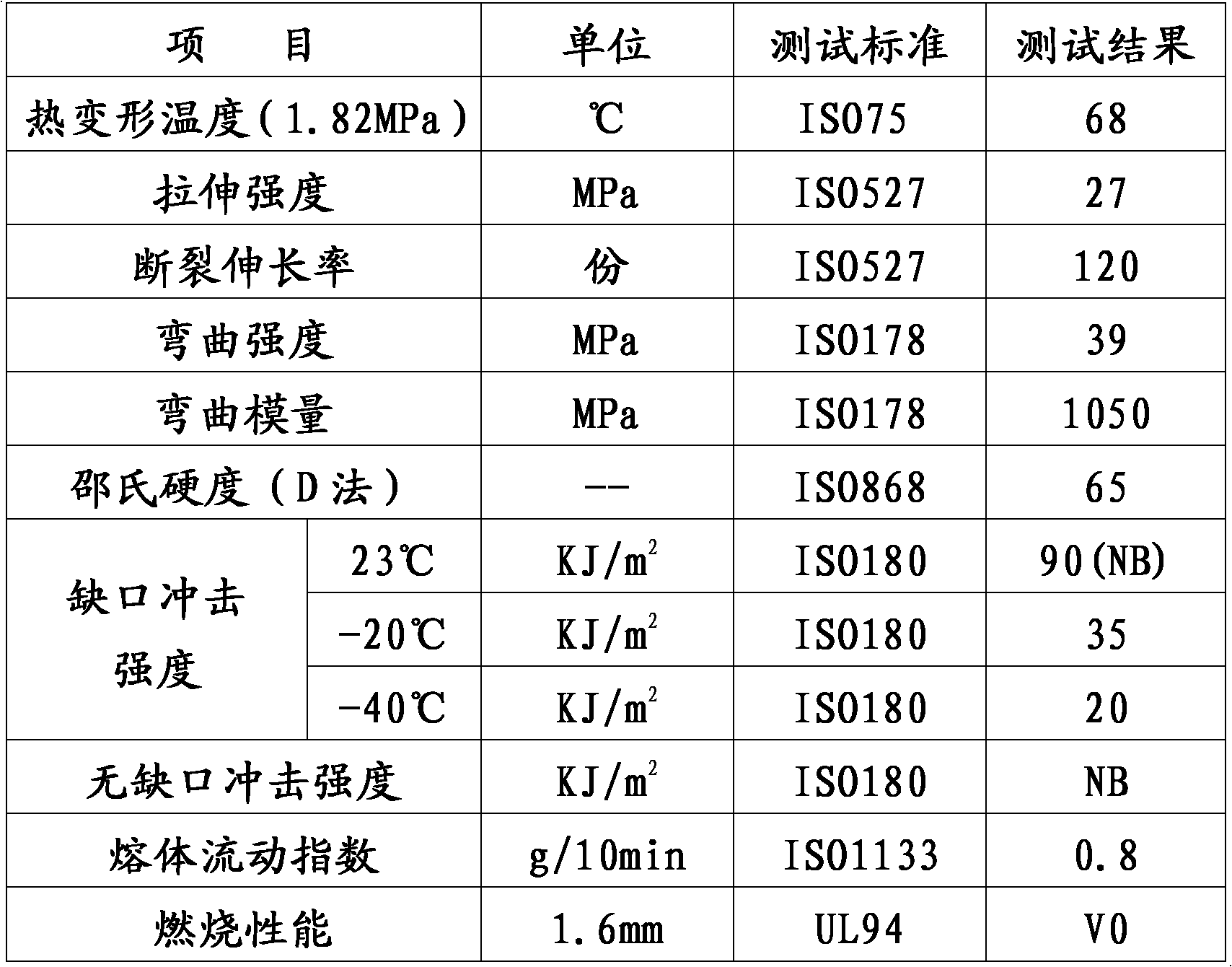
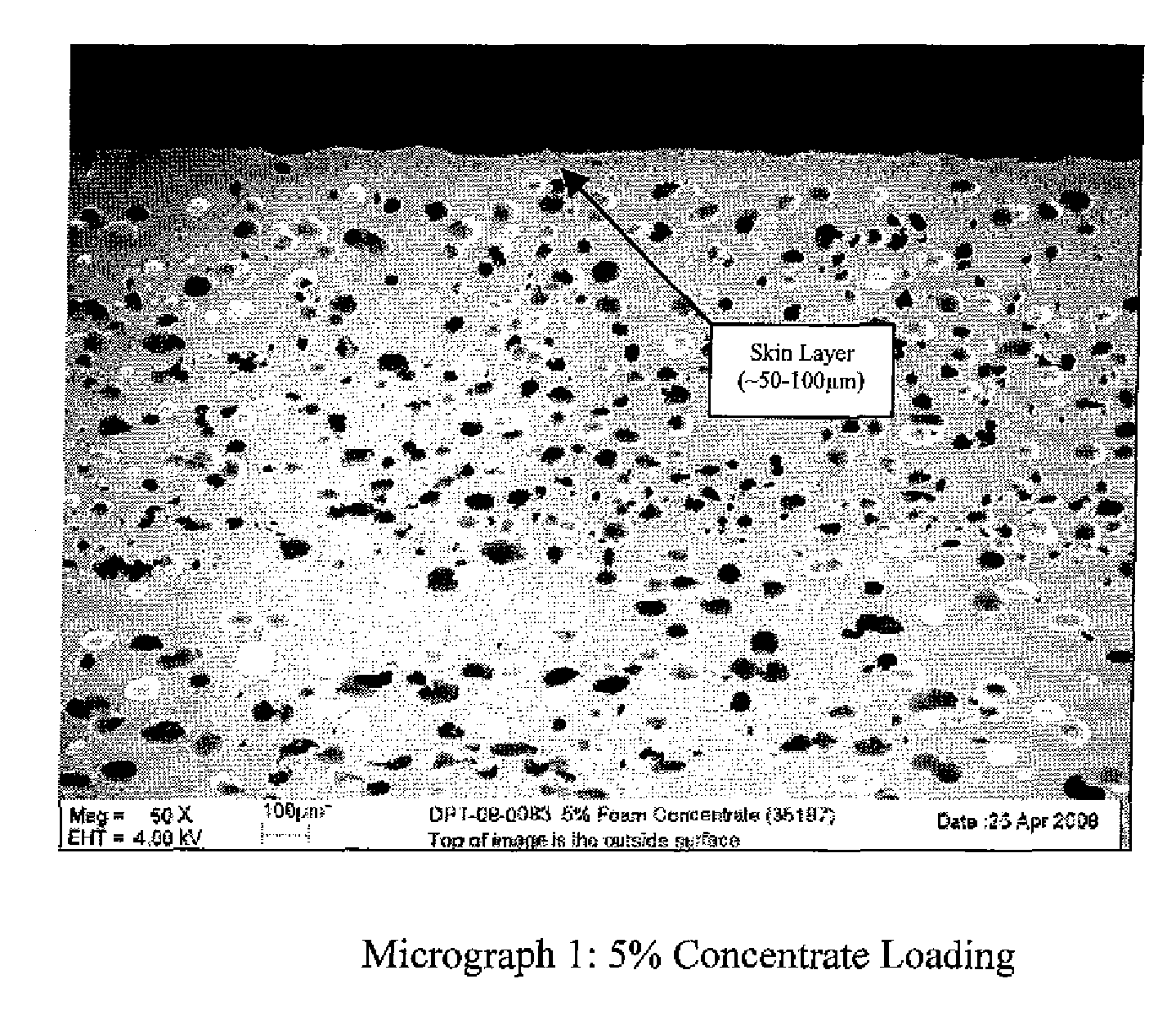
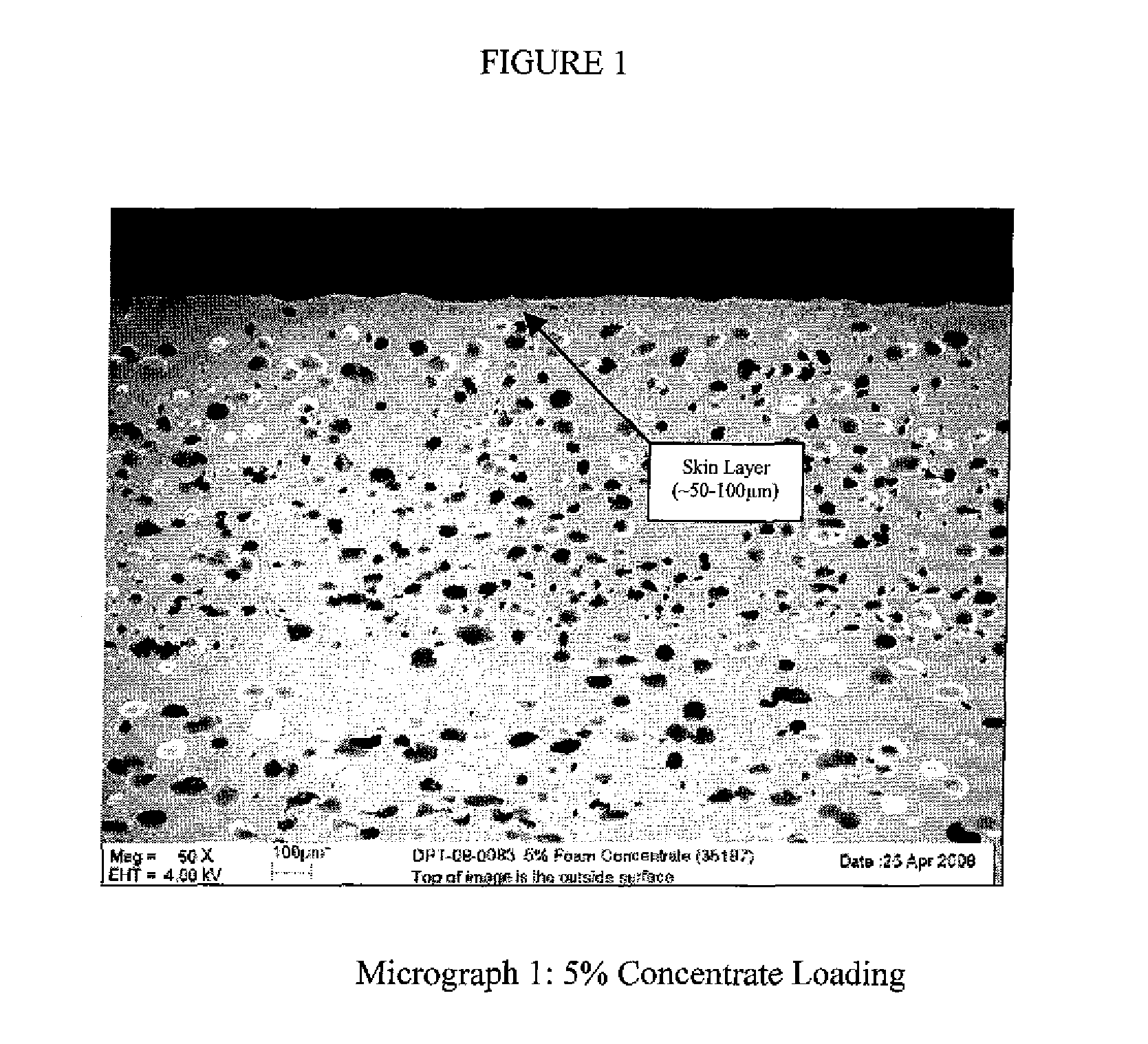
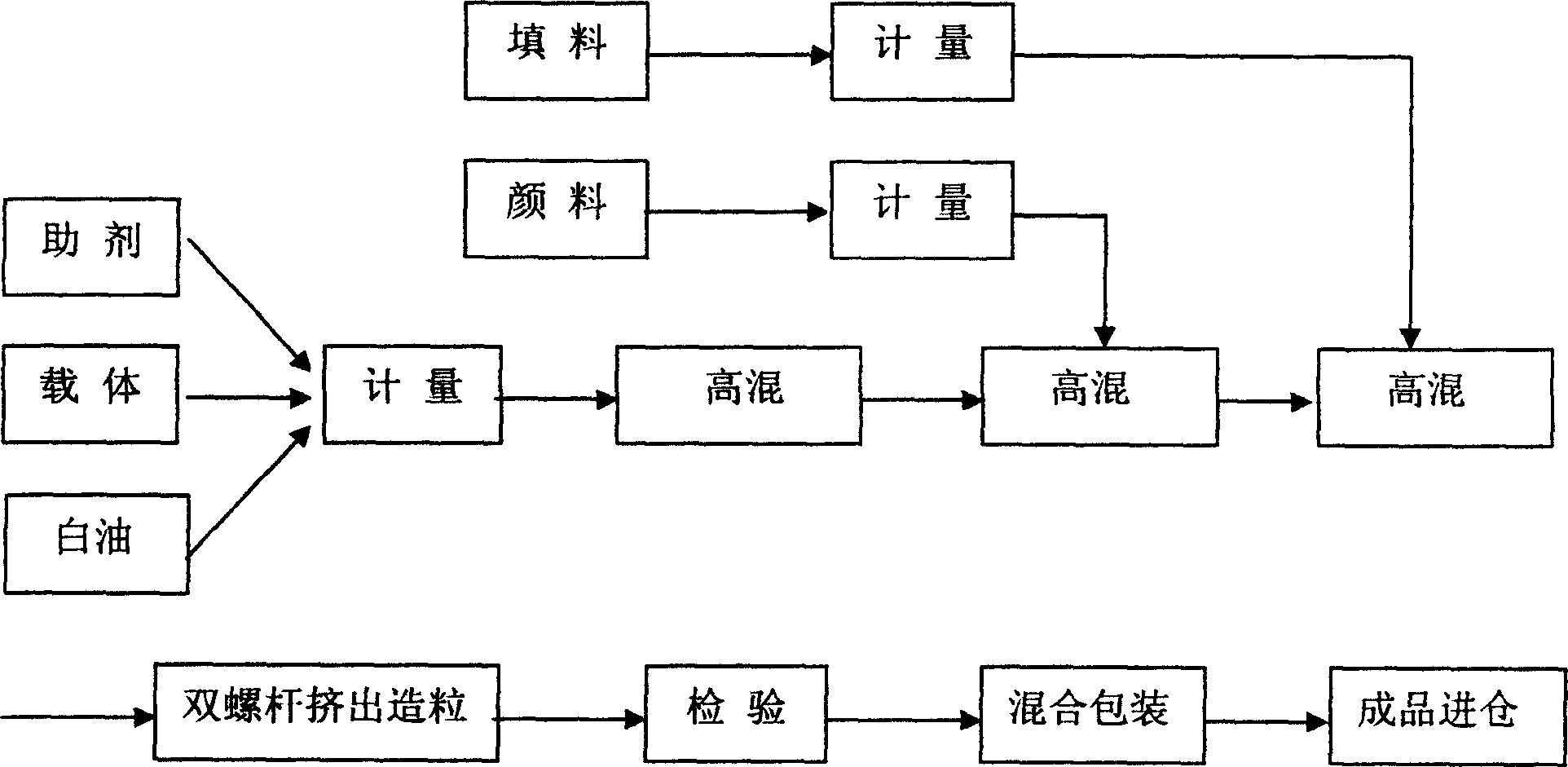
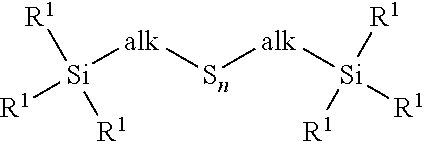Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8036 results about "Masterbatch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
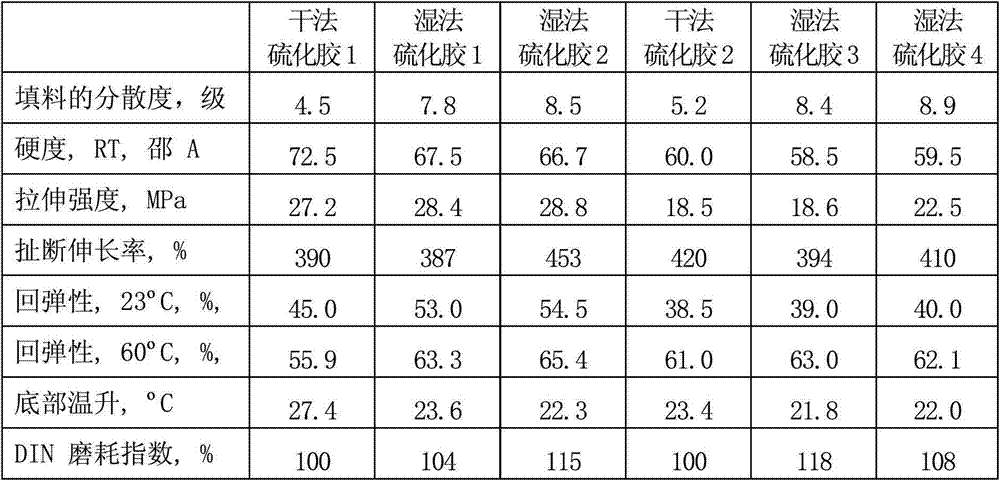
Masterbatch (MB) is a solid or liquid additive for plastic used for coloring plastics (color masterbatch) or imparting other properties to plastics (additive masterbatch). Masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of pigments and/or additives encapsulated during a heat process into a carrier resin which is then cooled and cut into a granular shape. Masterbatch allows the processor to colour raw polymer economically during the plastics manufacturing process.
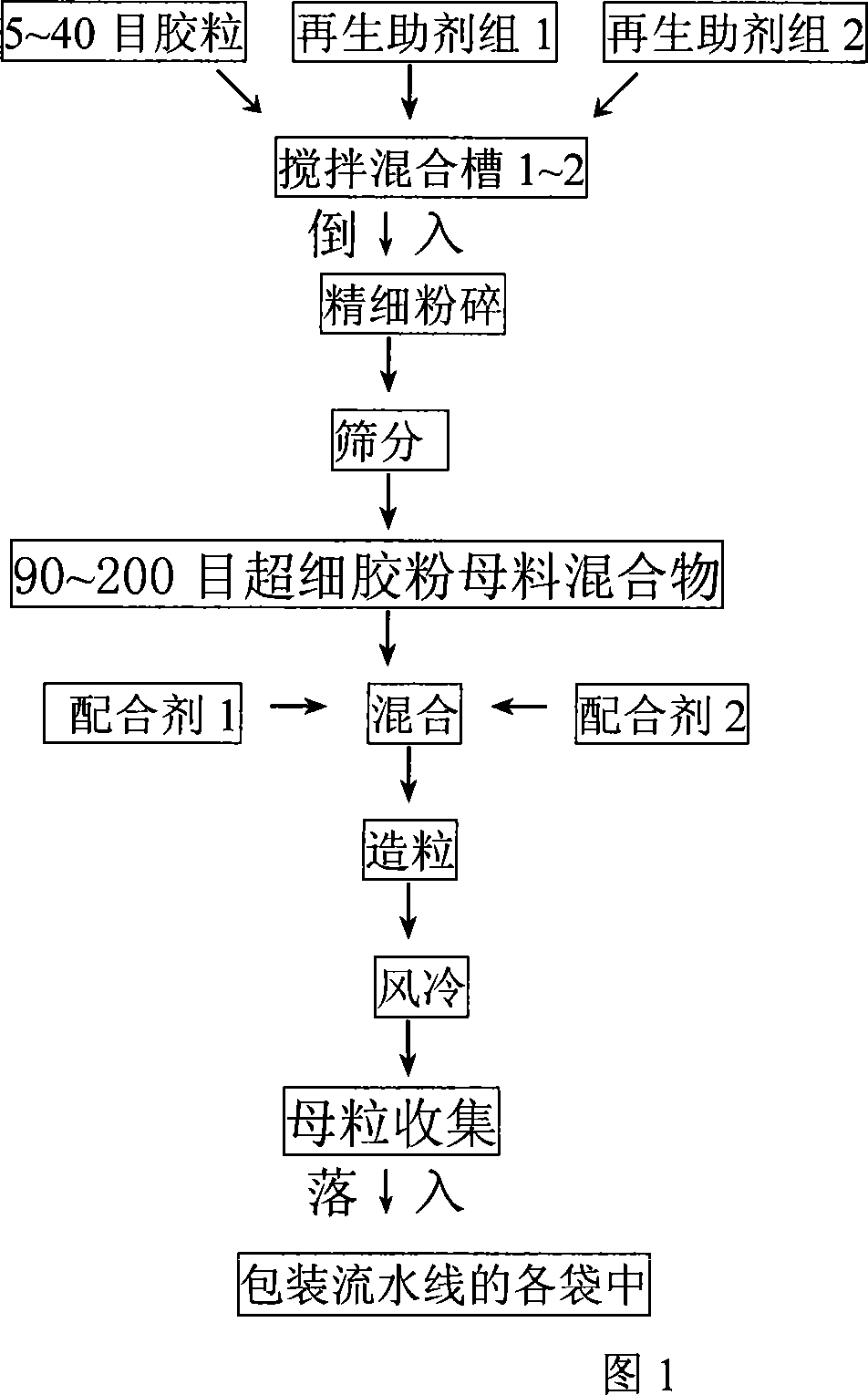
Reproduction new method for waste elastomer and plastic
InactiveCN101041725AThe ratio is roughly constantReduce or eliminate the impact of flow fluctuationsPlastic recyclingElastomerEngineering
The invention discloses a new regenerating method of waste elastics and plastic, which comprises the following steps: 1. blending waste elastics or / and plastic with grain size between 5 and 80 order and non-polluted regenerative adjuvant according to proportion; placing into the manufacturing machine; grinding; sieving; heating to desulfurize; bulking; soaping; emulsifying; kneading; pressing; graining; obtaining composite product 1 with mother material or mother particle or mother gel of plastic elastic powder; 2. weighing product 1 and non-polluted mating agent into mixing machine according to proportion; kneading; blending evenly; pressing; graining; obtaining the product 2 of mother material or mother particle or mother gel with 5-95% waste elastic or / and plastic.
Owner:陈书怡 +1
Method and apparatus for producing and treating novel elastomer composites
InactiveUS6929783B2Facilitate controlling and changing operating parameterImprove economyLiquid degasificationSpecial tyresParticulatesMasterbatch
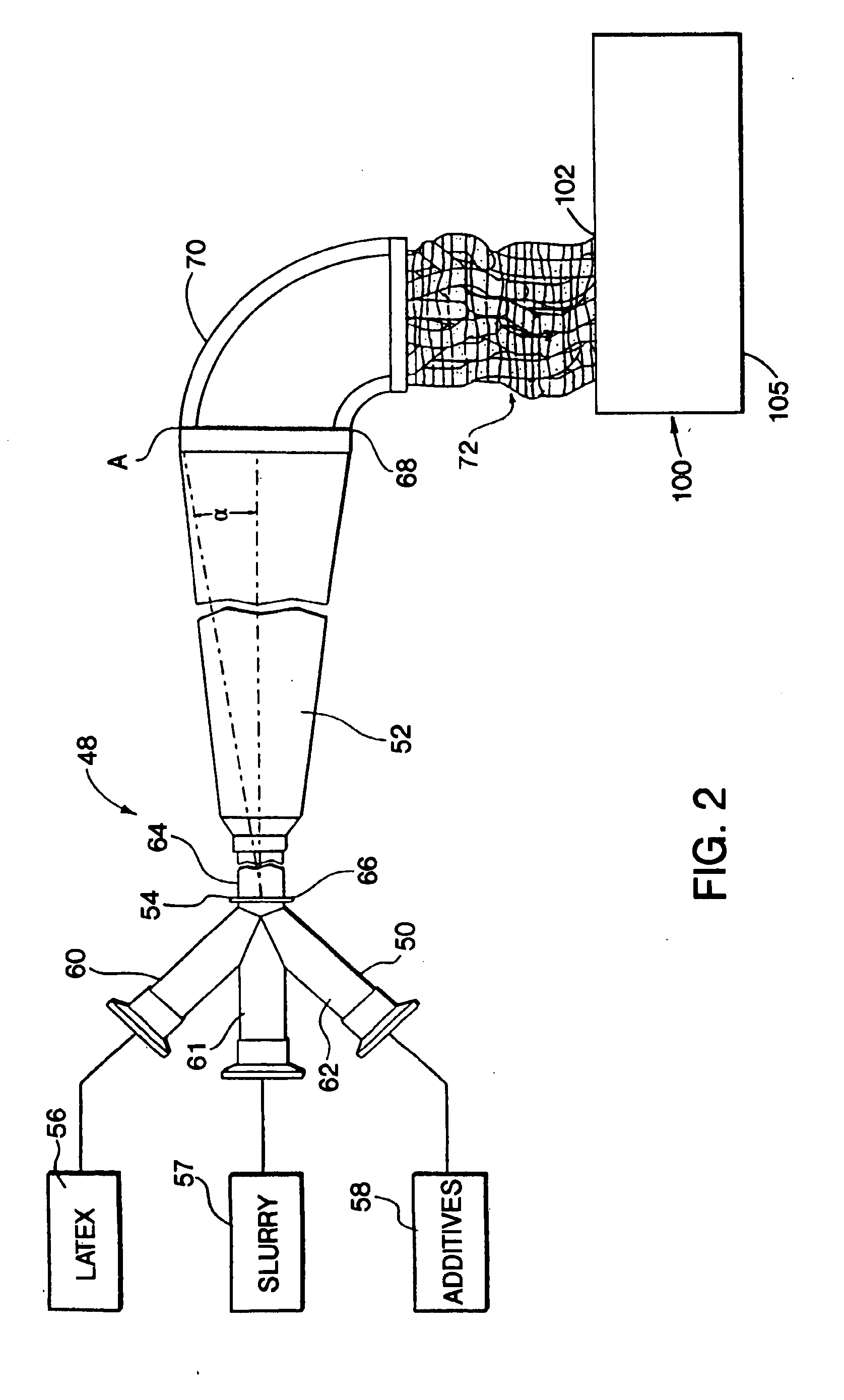
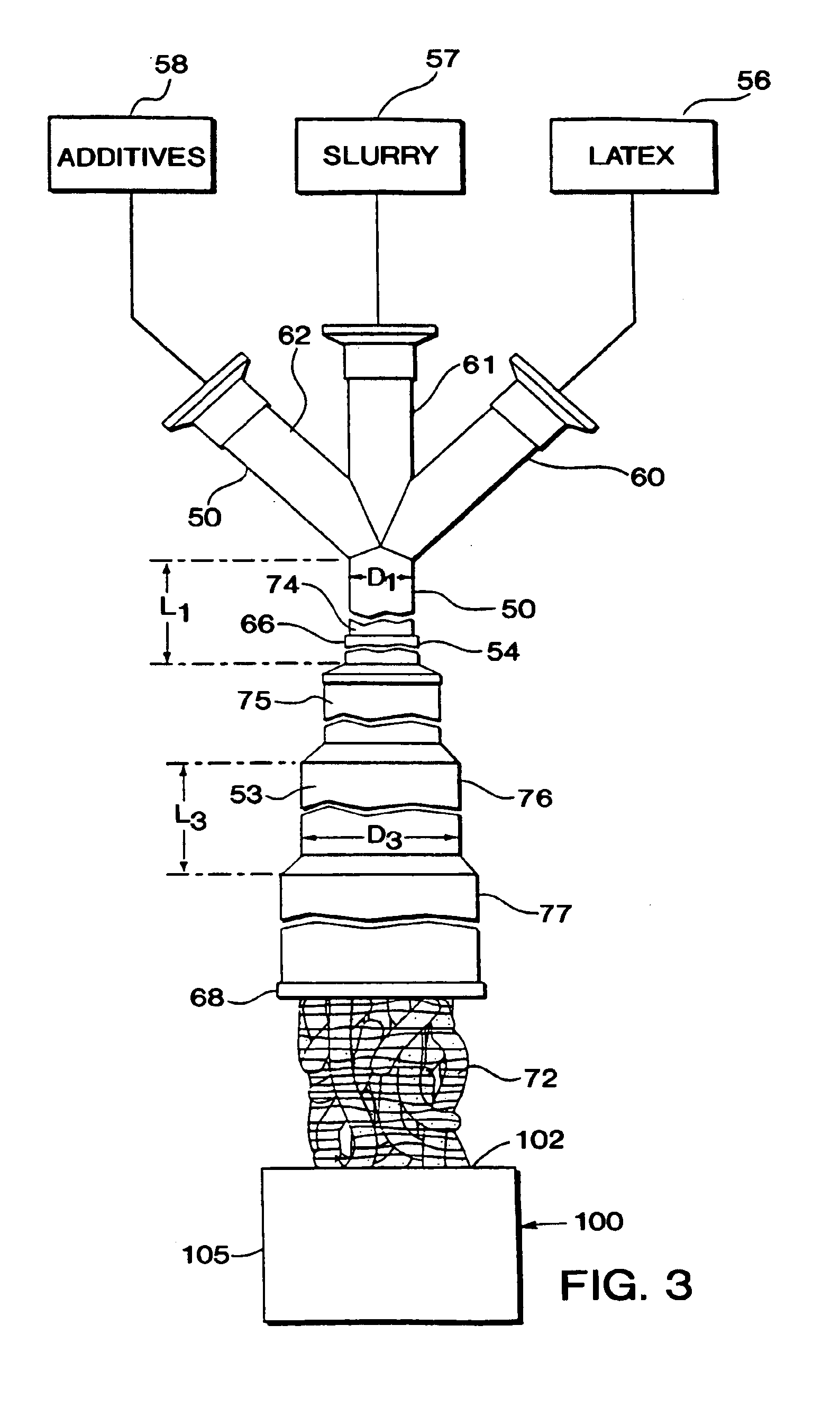
Elastomer masterbatch is processed in a continuous compounder having multiple parallel elongate rotors axially oriented in an elongate processing chamber. Optionally, additional materials are compounded into the masterbatch, e.g., additives, other elastomeric compositions, etc. Preferably, the masterbatch then is further processed in an open mill. Excellent control of Mooney Viscosity is achieved.In certain preferred embodiments, elastomer composites are produced by novel continuous flow methods and apparatus in which fluid streams of particulate filler and elastomer latex are fed to the mixing zone of a coagulum reactor to form a coagulated mixture in semi-confined flow continuously from the mixing zone through a coagulum zone to a discharge end of the reactor. The particulate filler fluid is fed under high pressure to the mixing zone, such as to form a jet stream to entrain elastomer latex fluid sufficiently energetically to substantially completely coagulate the elastomer with the particulate filler prior to the discharge end without need of adding acid or salt solution or other coagulation step. The coagulated elastomer and particulate filler composite is fed into the aforesaid continuous compounder for processing and control of its moisture level and Mooney Viscosity. Novel elastomer composites are produced. Such novel elastomer composites combine material properties and characteristics, such as choice of filler, elastomer, level of filler loading, moisture level, Mooney Viscosity, balance between molecular weight and amount of bound rubber, and macro-dispersion not previously achieved.
Owner:CABOT CORP
High-content red phosphorus flame-retardant master batch
The invention provides a high-content red phosphorus flame retardant master batch, which is essentially prepared by the raw materials with the following weight ratio: 40-90 parts of red phosphorus, 5-20 parts of carrier, 5-50 parts of synergist, 0.5-3 parts of lubricant and 0.5-5 parts of dispersant. Compared with the microcapsule red phosphorus flame retardant, the master batch has the main beneficial effects of solving the safety problems of flammability, inconvenient transport, and the like of the product, effectively solving the problem of bad compatibility between red phosphorus and resin, being able to be directly injected with the carrier, and the like to produce finished product, reducing energy waste, reducing the dust in the production process and improving production environment. Compared with the existing red phosphorus flame retardant master batch with low content of phosphorus, the master batch reduces a half of the using addition amount in rubber injection, which can effectively reduce production cost, reduce the matter property influence of the finished product and improves the quality of the finished product.
Owner:黄华昌
Method of manufacturing a golf ball
The present invention relates to an industrially beneficial method of manufacturing golf balls which includes the steps of pre-preparing a masterbatch of an unsaturated carboxylic acid and / or a metal salt thereof by mixing an unsaturated carboxylic acid and / or a metal salt thereof with a rubber material, preparing a rubber composition that contains the rubber material by using the masterbatch, and employing a material obtained by molding the rubber composition under heat as a golf ball component. The masterbatch is composed of:(A) from 20 to 100 wt % of a modified polybutadiene obtained by a modification reaction wherein a polybutadiene having a vinyl content of from 0 to 2%, a cis-1,4 bond content of at least 80% and an active end is modified at the active end with at least one type of alkoxysilane compound, and(B) from 80 to 0 wt % of a diene rubber other than Ingredient A.such that ingredients A and B are included in a combined amount of 100 wt %, and(C) an unsaturated carboxylic acid and / or a metal salt thereof.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Oxidized grapheme/carbon black rubber nanocomposite and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an oxidized grapheme / carbon black rubber nanocomposite and preparation method thereof, which belongs to the field of rubber nanocomposite technology. The nanocomposite comprises the following basic compositions by mass: 100 parts of diene series rubber matrix, 0.5-5 parts of oxidized grapheme, 30-70 parts of hard carbon black of average particle size 11-30nm, 1-10 parts of plasticizer, 6-10 parts of activator, 0.5-4 parts of anti-aging agent, 1-4 parts of sulfuration promoter and 1-6 parts of insoluble sulphur; oxidized grapheme modifier. The oxidized grapheme powder is dispersed in deionized water for ultrasound, and a natural rubber emulsion is added, and masterbatch after flocculation, washing and drying is mixed uniformly with other additives, after sulfuration, the product is obtained. The oxidized grapheme / carbon black rubber nanocomposite has the advantages of excellent processing performance and obviously reduced dynamic themogenesis, thereby improving the usage life of tyre.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Appearance-improving spraying-free aesthetic resin and its preparation method
The invention relates to an appearance-improving spraying-free aesthetic resin and its preparation method. The resin comprises the following components by weight part: 90 of matrix resin, 0.1-2.0 of a lubricant, 0.1-1.0 of an antioxidant, and 10-30 of a magnetic metallic pigment masterbatch, which consists of the following components by weight part: 100 of the matrix resin, 1.0-20 of a magnetic metallic pigment, 1.0-30 of a pearlescent pigment, 0.1-2.0 of the lubricant, 0.1-1.0 of the antioxidant. The preparation method includes: preparing the magnetic metallic pigment masterbatch; and mixingthe above raw materials, then conducting mixing, extrusion, bracing, cooling, and pelletizing, thus obtaining the aesthetic resin. The aesthetic resin of the invention can effectively improve the affinity of an aluminum powder pigment and a plastic substrate, mitigate flow marks and weld lines that appear during injection molding or extrusion of aluminum powder pigment-containing aesthetic resin,and simultaneously strengthens the metal effect a made piece, greatly reduces consumption of the aluminum powder pigment, and saves cost. The present invention is green and environmental aesthetics resin instead of traditional paint scheme provides technical support. The aesthetic resin and the preparation method provided in the invention provide technical support for green and environmentally friendly aesthetic resin to substitute traditional paint spraying schemes.
Owner:SHANGHAI KUMHO SUNNY PLASTICS
Preparation method of polyamide/nano montmorillonite masterbatch
The present invention is preparation process of polyamide / nanometer montmorillonite base material. The polyamide / nanometer montmorillonite base material comprising montmorillonite 1-30 wt% and polyamide 70-99 wt% is prepared with deionized water in 9-15 times the weight of montmorillonite as the intercalating agent, and through mixing purified montmorillonite with deionized water to form slurry, adding molten polyamide, blending at 210-300 for 10-60 min, and pelletizing. The polyamide / nanometer montmorillonite base material has simple preparation process, low production cost and high stripping performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Silicone rubber for composite insulator and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a silicone rubber for a composite insulator, wherein the silicone rubber comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of methyl vinyl silicone rubber A, 50-70 parts of methyl vinyl silicone rubber B, 25-50 parts of fumed silica, 100-130 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 1-6 parts of silane coupling agent, 0.2-2 parts of ultraviolet absorber, 2-6 parts of zinc oxide, 0.5-3 parts of triethanolamine, 0.2-1 parts of stearic acid, 0.5-2 parts of hydrogen-containing silicone oil, 0.2-1 parts of vinyl silicone oil, 0.5-3 parts of color masterbatch rubber, 2-6 parts of hydroxyl silicone oil and 0.5-1 parts of vulcanizing agent. The silicone rubber provided by the invention can achieve the following performances: the tensile strength is larger than 4 MPa; the breaking elongation is larger than 350%; the peel strength is larger than or equal to 12 KN.m<-1>; the shore hardness is 60+ / -5 degrees; the thermal aging tensile strength retention is larger than or equal to 90%; the anti-creep track passes a grade of 1A4.5; the flame retardance reaches a grade of FV-0; the average static contact angle is larger than 105 degrees; the electrical surface resistivity is larger than 2*10<15> omega; the dielectric constant is smaller than 3.8; and the dielectric loss angle tangent is smaller than 0.01.
Owner:PINGGAO GRP +2
Continuous manufacturing method of rubber masterbatch and rubber masterbatch prepared by same
ActiveCN103113597AGood physical and mechanical propertiesQuality improvementMasterbatchPolymer science
The invention relates to a continuous manufacturing method of rubber masterbatch and rubber masterbatch prepared by the continuous manufacturing method. The invention discloses the continuous manufacturing method of rubber masterbatch. The continuous manufacturing method of rubber masterbatch comprises the following steps of: 1) adding stuffing into rubber liquor, and stirring to form a rubber / stuffing / solvent mixture; 2) feeding the rubber / stuffing / solvent mixture in step 1) to a flocculator, wherein the rubber / stuffing / solvent mixture is contacted and mixed with one or more of nitrogen, steam, stuffing aqueous slurry and oil, and flocculating to obtain a mixture of a rubber / stuffing compound and the solvent; and 3) removing the solvent and drying the mixture to obtain rubber / stuffing masterbatch. The invention further relates to masterbatch prepared by the method and a rubber product prepared by the masterbatch. Compared with the flocculating technology in current wet-method mixing, as no special requirements are posed to rubber and stuffing, the application range is wider. In addition, the manufacturing method is continuous in production process, efficient, low in energy consumption and less in labor, so that the cost is lower. Meanwhile, masterbatch prepared by the method is quite excellent in processability, physical and mechanical properties and product quality.
Owner:EVE RUBBER RES INST
Melt-blown polypropylene material as well as preparation method and application thereof
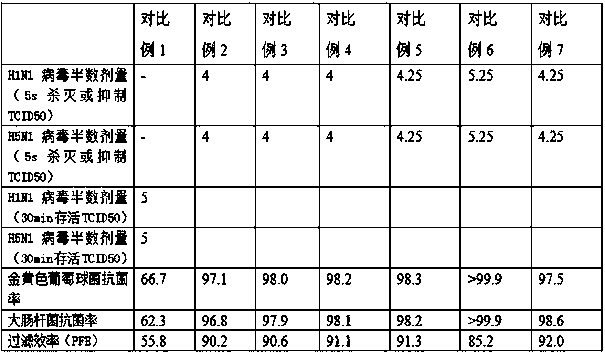
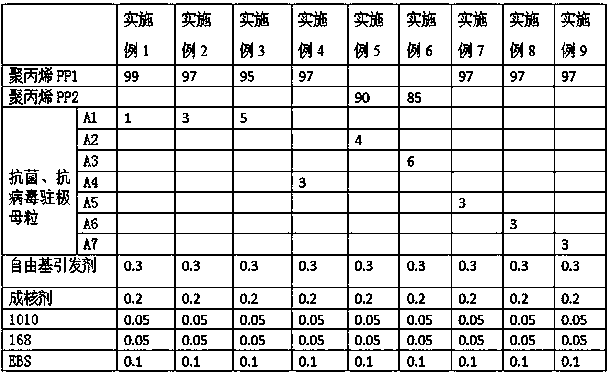
ActiveCN111393754AReach killImprove filtration efficiencyDispersed particle filtrationNon-woven fabricsMasterbatchNonwoven fabric
The invention discloses a melt-blown polypropylene material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The melt-blown polypropylene material comprises the following components: 80-99 parts of polypropylene resin; 0.5 to 10 parts of antibacterial and antiviral electret masterbatch; 0.1 to 1 part of a free radical initiator; 0.1 to 0.5 part of a nucleating agent; 0.01 to 3 parts of anantioxidant; 0-3 parts of a lubricant. According to the invention, inorganic antibacterial and antiviral particles are introduced into melt-blown polypropylene; the material is endowed with intrinsicantibacterial and antiviral characteristics; after the melt-blown non-woven fabric is prepared, when viruses and bacteria are filtered, the viruses and bacteria remain on the melt-blown layer, the nano material on the composite material can rapidly wrap the viruses and bacteria, attack the bacteria and viruses, synergistically destroy the structure of the bacteria and viruses and block electron transfer of the bacteria and viruses, so that the effects of killing the viruses and bacteria and the like are achieved, and the material has excellent antibacterial performance and antiviral performance and high filtering efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU KINGFA SCI & TECH ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD +2
Hydrophobic additive for use with fabric, fiber, and film
The present invention relates to a hydrophobic additive for use with fabric, fiber, and film. One aspect of the present invention comprises a master batch composition for use in preparing a non-woven fabric in order to increase the hydrophobicity of the non-woven fabric. In one embodiment, the master batch composition includes a polymer and a lipid ester. The lipid ester comprises from 10 wt. % to 40 wt. % of the master batch. The fabric, when including the master batch composition, has a contact angle ranging from 100° to 125° when measured according to test method ASTM D2578.
Owner:TECHMER PM
Process for the production of polyester nanocomposites
InactiveUS20080315453A1Increase polyester molecular weightHigh molecular weightMaterial nanotechnologyRotary stirring mixersCompound aMasterbatch
A method for dispersing sepiolite-type clay particles in a polyester matrix by melt-compounding a mixture of: sepiolite-type clay, at least one linear polyester oligomer, and at least one polyester polymer to produce a nanocomposite composition; and, optionally, subjecting said nanocomposite composition to solid state polymerization to increase polyester molecular weight. Further described is a method for preparing a polyester nanocomposite composition from a masterbatch, comprising melt-compounding a mixture of: sepiolite-type clay, at least one polyester oligomer, and at least one polyester polymer to produce a nanocomposite composition containing a greater concentration of sepiolite-type clay than is desired in the final resin composition; optionally, subjecting said nanocomposite composition to solid state polymerization to increase the polyester molecular weight; and further melt compounding said nanocomposite composition with polyester polymer and, optionally, additional ingredients.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
All-weather persistent antistatic master batch capable of being subjected to thermoplastic processing and antistatic composite material
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of macromolecular composite materials and particularly relates to an all-weather persistent antistatic master batch capable of being subjected to thermoplastic processing and an antistatic composite material. The antistatic master batch is prepared by forming of a low-dissociation-energy compounding agent, a processing auxiliary agent and thermoplastic macromolecular resin containing polar groups through macromolecular thermoplastic processing equipment at the temperature of 25-300 DEG C; and the mass ratio of the compounding agent to the thermoplastic macromolecular resin is equal to (1:10)-(1:50). The invention also discloses the antistatic composite material which is obtained after the persistent antistatic master batch and a macromolecular base material are formed through the thermoplastic processing equipment. The antistatic composite material has the characteristics that: 1. the antistatic composite material has light color and dyeability; 2. The master batch of the antistatic composite material and the compounding agent are wider in selection range, low in cost and easy to obtain, and the production process is simple, safe and non-hazardous; and 3. the influence of the ambient environment on the antistatic performance of the antistatic composite material is less, and the antistatic performance is persistent.
Owner:浙江三和塑料有限公司
Polyolefin masterbatch and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polyolefin masterbatch and a preparation method thereof. The polyolefin masterbatch comprises the following components by weight percent: 20-70% of carrier, 0.01-70% of toner, 0-40% of dispersant, 0.1-10% of foaming agent, 0-10% of crosslinking agent, 0-2% of heat stabilizer and 0-40% of filler. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using the components to dose in proportion, mixing, using a double-screw extruder or internal mixer to melt and blend, then granulating, and drying to obtain the masterbatch disclosed by the invention, wherein the masterbatch can be columnar, beaded, flaky or round according to different granulating ways. When the polyolefin masterbatch provided by the invention is used in polyolefin extrusion, spinning and the coloring of the injection molding product, the masterbatch has good dispersibility and color stability.
Owner:广东波斯科技股份有限公司
Graphene/carbon black thermoplastic resin master batch with high dispersibility and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a graphene / carbon black thermoplastic resin master batch with high dispersibility and a preparation method thereof. The graphene / carbon black compound in the master batch is formed in an electrostatic self-assembly manner, and comprises 10-50% of graphene, 5-20% of carbon black, 0.5-10% of surfactant, 10-65% of carrier resin and 2-10% of assistant. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) compounding and dispersing graphene by adopting the surfactant to control the positive electricity of the graphene surface; (2) forming a stable graphene / carbon black compound from the modified graphene and carbon black with positive electricity through electrostatic incorporation in a self-assembly manner; (3) preparing the graphene / carbon black thermoplastic resin master batch with high dispersibility by matching with a solution blended process, a melt-blending method and an in-situ polymerization method; (4) adding the assistant to extrude and pelletize, so as to prepare the graphene / carbon black / thermoplastic resin master batch particles after processing the master batch. By adopting the obtained master batch, the problems of difficult charging of graphene powder, uneven dispersion, dust pollution, unstable product performance and the like are solved.
Owner:XIAMEN KNANO GRAPHENE TECH CORP
High temperature self-crosslinking halogen-free flame retardant cable insulation material or sheath material and method for preparing high temperature self-crosslinking halogen-free flame retardant cable insulation material or sheath material
ActiveCN103012940AReduce manufacturing costPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesElastomerPolymer science
The invention discloses a high temperature self-crosslinking halogen-free flame retardant cable insulation material or sheath material. The cable insulation material or sheath material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of ethylene and copolymer thereof and / or ethylene propylene diene monomer, 0-20 parts of compatilizer, 20-250 parts of halogen-free flame retardant, 0-5 parts of antioxidant, 0-5 parts of lubricating agent, 0.01-5 parts of peroxide crosslinking agent, 0-40 parts of polymer elastomer, 0-3 parts of coupling agent and 0-20 parts of color masterbatch; and the ethylene and the copolymer thereof are selected from one or a plurality of the following materials of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer, ethylene-ethyl acrylate and the like. The high temperature peroxide crosslinking agent crosslinks under the temperature condition of above 150 DEG C only, during a cable material mixing extrusion and insulating layer or sheath layer formation process, chemical crosslinking or micro-crosslinking cannot be caused, but the high temperature peroxide crosslinking agent generates a crosslinking function when the temperature is higher than 150 DEG C in the case of fire, so that the production cost is lowered.
Owner:SHENZHEN WOER HEAT SHRINKABLE MATERIAL +1
Silica containing rubber composition
InactiveUS7307121B2Great tractionReduce rolling resistanceSpecial tyresPretreated surfacesElastomerHysteresis
This invention discloses a method for preparing rubber compositions that exhibit unique combinations of properties that are desirable for tire tread applications for enhanced snow / ice and wet traction, low rolling resistance and increased treadwear performance in comparison with conventional silica compounds. Specifically, a high reactively silane coupling agent, such as a mercaptosilane, is used in combination with a silane coupling typically used for silica tread compounds such as bis(triethoxylsilylpropyl)disulfide to treat silica pellets in a hydrocarbon solvent at elevated temperatures. The treated silica is then blended with solution elastomer cement in a hydrocarbon solvent. The deposited reactive silanes partially react with the elastomer molecules forming a layer of polymer grafted on the silica surfaced. This structure significantly improves the silica retention during the steam stripping operation. Almost 100% (99+%) silica retention has been achieved by this invention. After solvent removal from steam stripping, the treated silica / elastomer mixer is dewatered and dried using conventional equipment such as shaker screens, expellers and expanders to form a well-dispersed silica masterbatch. This technique results in silica compounds with excellent silica dispersion and increased filler-polymer interaction, hence enhanced compound performance such as better physical properties, more desirable dynamic properties (low hysteresis at high temperatures and high hysteresis at low temperatures) and increased abrasion resistance.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Filler masterbatch used for increasing polarity of polypropylene and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a filler masterbatch used for increasing the polarity of polypropylene and a preparation method thereof. The filler masterbatch is characterized by comprising the following components by weight percent: 50%-79% of inorganic filler, 15%-30% of carrier, 5%-17% of polar additive and 1%-3% of processing additive; and the polar additive is one or more of thermoplastic polyurethane resin (TPU), maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene, epoxy resin, ethylene acrylate, ethylene vinyl acetate, polyether amine and polybutylene polyol. In the preparation method of the invention, the added carrier can not improve the polarity of polypropylene, the inorganic filler is used to increase the rigidity of the material; the key is to introduce the polar additive with high unipolarity, thus the filler masterbatch used for increasing the polarity of polypropylene can be prepared; when the filler masterbatch is combined with the polypropylene material for production, the surface polarity of the filled and modified polypropylene material can be increased, the surface energy of the filled and modified polypropylene can be reduced, the dimension stability can be increased, the modified polypropylene material can have good paint adhesion and the material can be used to form exterior trimming parts such as bumpers and interior trimming parts such instrument panels.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +3
Flame-retardant PP/nylon corrugated tube composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102050993AImprove flame retardant performanceImprove high temperature resistanceProcedure AgentsManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a corrugated tube material and particularly discloses a flame-retardant PP (Polypropylene) / nylon corrugated tube composite material and a preparation method thereof, aiming to overcome the shortcomings in the prior art that the mechanical property of the PP corrugated tube is bad, the nylon corrugated tube is not flame-retardant, the stability is bad, and the service lifeis short. The material disclosed by the invention comprises the following substances by weight percentage: 47-75 of PP, 3-40 of nylon, 5-30 of flame retardant, 5-20 of compatilizer, 1-40 of flexibilizer, 0-10 of filling master batches, 0.2-1.5 of heat stabilizer, and 0.2-1.5 of processing agent. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: the filling master batches are firstly preparedand then added into a twin-screw extruder to melt and mix with other materials, and pelletings are extruded out to prepare the flame-retardant PP / nylon composite material. The invention has the advantages of favorable flame-retardant property, excellent high-temperature resistance, friction resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, long service life, high surface glossiness, high electrical insulativity, simple manufacturing technology, and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI KINGFA SCI & TECH +1
Dry-Coated Oxygen-Scavenging Particles and Methods of Making Them
InactiveUS20070020456A1Reduce in quantityReduce and eliminate hazeLiquid surface applicatorsOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideHigh concentrationMasterbatch
Heterogeneous oxygen-scavenging particles are formed by dry coating activating component particles onto oxidizable component particles, largely through a succession of mechanical motions. The component particles are repeatedly mixed, compressed, and sheared. Smaller activating component particles coat the surface of larger oxidizing component particles by force-induced contact, while irregularities are removed by abrasion among the particles. The oxygen-scavenging particles can be blended together with a base polymer into a masterbatch having a higher concentration than required for use as an active barrier to oxygen permeation. The masterbatch can be diluted with the same or a compatible polymer to form the active barrier.
Owner:MULTISORB TECH INC
Processes for making silane, hydrophobated silica, silica masterbatch and rubber products
ActiveUS8357733B2No lossImprove securitySilicon organic compoundsPigmenting treatmentMasterbatchPolymer science
The present invention provides a process for making silica-filled rubber masterbatch using silica hydrophobated with a trimethoxy silane coupling agent that is soluble in an alcohol-water solution containing at least about 70 wt % water. One embodiment uses a mixture of trimethoxy silanes, one or more of which react with rubber to bond the silica to the rubber, and one or more of which do not react with rubber, but do hydrophobate the silica. Hydrophobated silica is mixed with latex polymer and incorporated into rubber during coagulation of the latex, which is preferably coagulated with calcium chloride. The present invention further provides a process for making the trimethoxy silane coupling agents. Preferred trimethoxy silane coupling agents include bis-(3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)-disulfide and bis-(3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)-tetrasulfide. Rubber products, particularly tires, compounded with the inventive silica masterbatch can be processed for a long time before scorching because the silica masterbatch provides a long scorch time.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO +1
Foamed polyvinylidene fluoride structure
InactiveUS20120045603A1Improve impact resistanceImprove hysteresisLayered productsFlexible pipesHysteresisFoaming agent
The invention relates to a foamed fluoropolymer, preferably a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) structure, such as from Kynar® resins. The foamed structure is continuous self-supporting, sized, and has a dense skin. The foamed structure is manufactured in a process using foaming agents and nucleating agents. The structure is sized into a specific shape during the manufacturing process—requiring a good melt viscosity of the PVDF foam. In one process, a master batch containing the nucleating agent is used. The foamed article could be a sheet, film, profile, tube, pipe, article, rod foam-core structure, or other self-supporting shape. Foamed tubes, pipes, rods, sheets and conduit are especially useful. The foamed structure of the invention provides added value by being lighter weight, more flexible, and more impact resistant than a comparable non-foamed PVDF structure. It also has increased hysteresis, increased insulation properties, reduced dielectric constant, and increased compressibility.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Natural-like multifunctional color batch and use thereof
The present invention features that the color concentrate is prepared with main carrier resin A, matched carrier resin X, compatizer, pigment, inorganic stuffing, antistatic agent, light stabilizer, antioxidant and pigment lubricating dispersant. The main carrier resin an and the matched carrier resin X, which has obviously different compatibility and smelting behavior from that of the basic resin B in the product, may constitute alloy carrier resin. The said materials may be altered to result in various decoration effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGHENGCHANG CHEM IND
Highly-transparent ultraviolet-resistant energy-saving film and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a highly-transparent ultraviolet-resistant energy-saving film and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of composite films synthesized by compounding polymer and inorganic nano-particles and aiming at overcoming the defects that the prior film has low visible light transmission and high production cost. The highly-transparent ultraviolet-resistant energy-saving film comprises the following components by the weight percent: 50-99.8 of organic polymer, 0.2-50 of metal-oxide nano-particles and 0-39.9 of polymer auxiliary agent. The highly-transparent ultraviolet-resistant energy-saving film is prepared by a solution mixing method or a solution-melting mixing method; with the solution mixing method, the organic polymer and the metal-oxide nano-particles are dispersed in dispersing medium to prepare film preparing stock solution, and the film preparing stock solution is used for preparing the energy-saving film on a substrate; with the solution-melting mixing method, the mixture of the organic polymer and the metal-oxide nano-particles is dried to prepare master batch, and the master bath is mixed with the organic polymer and the polymer auxiliary agent to prepare the energy-saving film. The highly-transparent ultraviolet-resistant energy-saving film has high visible light transmission, good ultraviolet resistance and energy-saving effect, simple preparation process and low cost, thereby being suitable for industrial production.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Method for preparing high-strength heat-resistant and cold-resistant modified polypropylene pipe
ActiveCN102966801AImprove toughnessGood strength performanceRigid pipesMasterbatchEngineering plastic
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-strength heat-resistant and cold-resistant modified polypropylene pipe. The pipe is formed by the following steps of: extruding an outer layer, a middle transition layer and an inner wall layer onto the same one mold through three extruders, fusing and compounding. The outer layer of the pipe consists of modified polypropylene, an impact-resistant modifying agent, an antibacterial agent, a light stabilizer, an antioxygen, a compatibilizer, nanometer materials, a tackifier and a color masterbatch in parts by weight; the middle transition layer of the pipe consists of engineering plastics, the modified polypropylene, the compatibilizer, the a tackifier and the color masterbatch in parts by weight; and the inner wall layer of the pipe consists of the engineering plastics, the modified polypropylene, the compatibilizer, a fortifier, a filler, the nanometer materials and the color masterbatch in parts by weight. Compared with traditional similar pipes, the operating temperature of the pipe prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is improved by 30-70 DEG C; the cold-resistant temperature is lowered by minus 15-minus 30 DEG C; the pressure-resistant property is improved by 30-50 percent; the creep resistance is improved by 100-200 percent; the service life is prolonged by 10-20 years; and the wall thickness of the pipe is reduced by 20-50 percent.
Owner:HONGYUE PLASTIC GROUP
Biodegradable Polyester Compositions
InactiveUS20090162683A1High impact strengthHigh transparencySynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingMasterbatchBiodegradable polyester
The present invention relates to a biodegradable polyester composition having excellent transparency and impact strength, in particular to a biodegradable polyester composition comprising polylactic acid and a metal alkyl sulfonate as impact modifier as well as to a masterbatch composition useful in the preparation of the biodegradable polyester composition, and to films, sheets, profiles or moulded articles made thereof.
Owner:SUKANO FINANCE AG
High electrical property and low corrosion flame retardant reinforcing nylon material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high electrical property and low corrosion flame retardant reinforcing nylon material and a preparation method thereof, aiming at solving the defects of low electrical property and high corrosion caused by red phosphorus based flame retardant added into flame retardant reinforcing nylon in the prior art. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the high electrical property and low corrosion flame retardant reinforcing nylon material disclosed by the invention has the formulation (by weight percent): (1) 40-65% of nylon 66 resin, (2) 10-20% of red phosphorus based flame retardant masterbatch, (3) 1-5% of compatilizer, (4) 3-10% of synergistic compound flame retardant system, (5) 0.5-5% of acid absorbent, (6) 0.1-0.5% of antioxidant, (7) 0.2-0.8% of lubricating agent and (8) 10-30% of glass fiber; and the reinforcing nylon material can be prepared by mixing all the components in a high-speed mixing machine for 1-2min and then putting into a twin-screw extruder for extrusion and pelleting. The flame retardant reinforcing nylon material is excellent in the electrical property, low in corrosion (extremely low in corrosion for equipment and a mould) as well as high in fluidity, heat resistance and cost performance, and is capable of meeting the requirements of electrical and electronic appliances such as a temperature controller, a contactor, a circuit breaker and the like as well as domestic appliance products.
Owner:GUANGDONG WAYLAM ENG PLASTICS
Glass fibre reinforced nylon colorful heat insulation stripe for al-alloy door & window and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101307147ADifficult to disperseSolve easy discolorationDoors/windowsMasterbatchGlass fiber
The invention discloses a glass fiber reinforced nylon colored insulated strip used for an aluminum alloy door and window. The compositions by weight portion of the glass fiber reinforced nylon colored insulated strip are: 100 portions of nylon resin, 5 to 50 portions of glass fibers, 0 to 50 portions of inorganic filler, 5 to 25 portions of toughening agent, 0.3 to 5 portions of coupling agent, 0.3 to 5 portions of dispersing lubricant, 0.2 to 5 portions of antioxidant, 0.1 to 1 portion of light stabilizer, 0.1 to 1 portion of heat stabilizer and 2 to 10 portions of colored masterbatch. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the colored insulated strip. The glass fiber reinforced nylon colored insulated strip solves the problems that the masterbatch and the filler are difficult to disperse and nylon 66 is easy to change color during the processing procedure; the insulated strip products have various colors, superior performance and beautiful appearance; and the glass fiber reinforced nylon colored insulated strip realizes perfect matching with the window color, can achieve the beautility effect, meets and enlarges the demand of clients and the market, and is favorable for promotion, use and development of the glass fiber reinforced nylon 66 insulated strip.
Owner:FOSHAN NANHAI YILE ENG PLASTICS
Oxygen scavenging composition
InactiveUS20060069197A1Delayed action of absorptionPromote formationSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialPolyesterAlloy
The present invention provides an Oxygen scavenging composition as a concentrate master batch to act as active and passive barrier, said composition comprising a resin carrier which is an alloy of PET with PTN, or PBN or PBT, mixed micron sized and nano-sized iron particles, an alkali metal bisulphate and ascorbate, a metal halide and additives. The iron particle mixture with a particle size in the range of 1 to 50 micron along with nano sized iron particles of 5 to 50 nanometers (nm) having an additional enhanced rate of oxygen absorption. The oxygen scavenging composition also includes metal halide and ascorbates and bisulphates of alkali metals. The oxygen scavenging composition of the present invention as a master batch in a polyester carrier resin containing barrier, color and U.V. light absorbing additives is used in food packaging applications of human consumption, especially those oxygen sensitive food items including alcoholic beverages, fruit beverages etc, where the oxygen permeation levels are to be maintained at very low levels.
Owner:TAMMAJI KULKARNY SANJAY +1
Environmental-friendly synthetic organosilicon leather and method for producing same
ActiveCN102174262AImprove plasticityEasy to shapeTextile/flexible product manufactureTextiles and paperVulcanizationDecomposition
The invention relates to environmental-friendly synthetic organosilicon leather and a method for producing the same. The synthetic organosilicon leather comprises vinyl polysiloxane gum, white carbon black, a structured treatment agent, a plastifying agent, an inhibitor, hydrogen containing silicone oil, a platinum catalyst and silicone rubber masterbatch. The method for producing the synthetic organosilicon leather comprises the following steps: mixing the raw materials to obtain solid mixed silicone rubber through vulcanization via addition, rolling the solid mixed silicone rubber by a multi-roll rolling machine to fit textile-based fabric, heating and vulcanizing to form the synthetic organosilicon leather. The environmental-friendly synthetic organosilicon leather is efficiently produced with a simple process and can be produced on a large scale. The produced synthetic organosilicon leather has good mechanical properties and excellent characteristics of being resistant to high andlow temperature, weathering aging and physical inertia, is easy to cut and sew and is waterproof and breathable. The combustion and decomposition product of the synthetic organosilicon leather contains no harmful substance, can be recycled and accords with environmental protection requirements.
Owner:东莞市贝特利新材料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com