Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3473 results about "Electrode pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
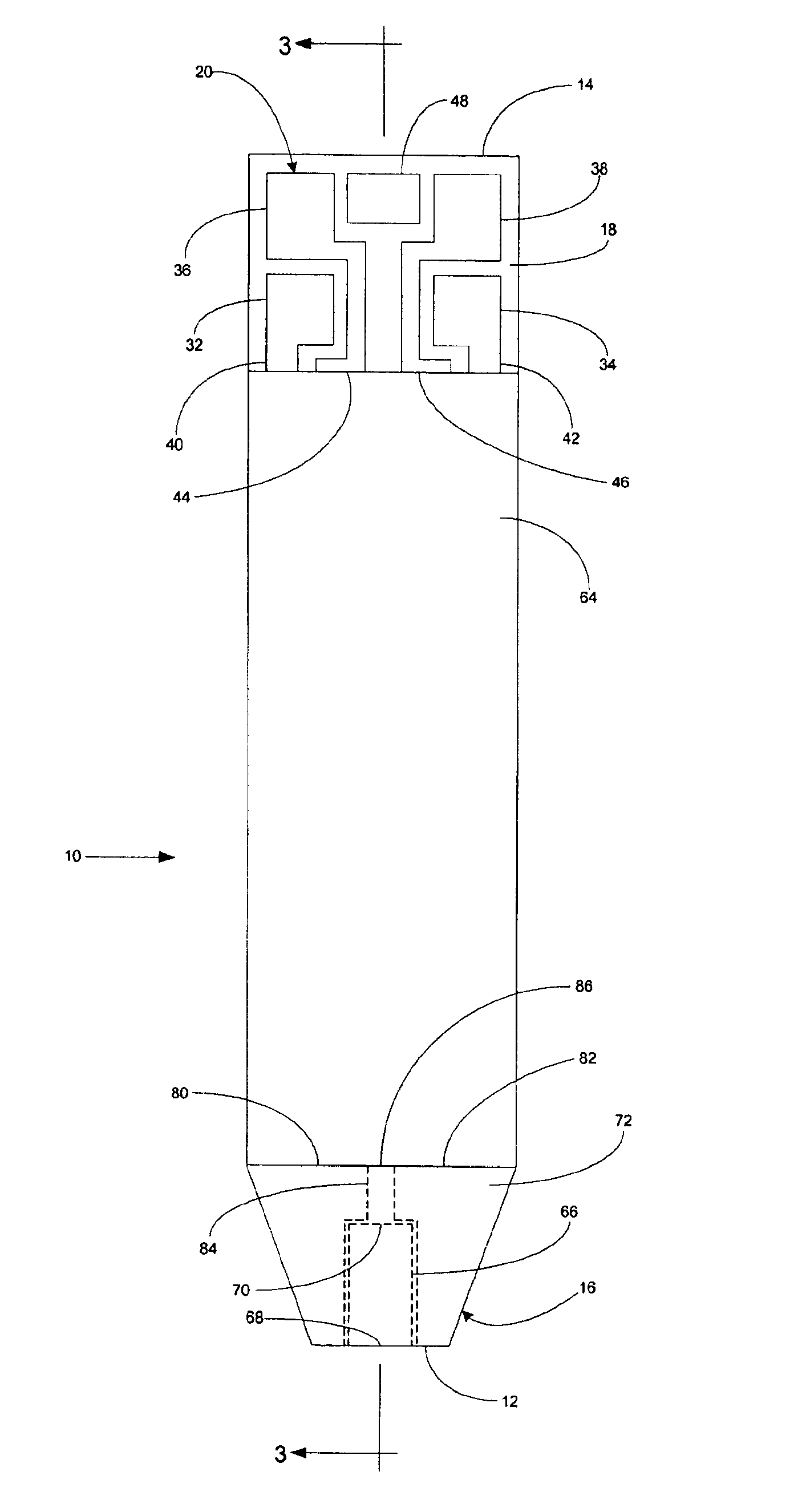
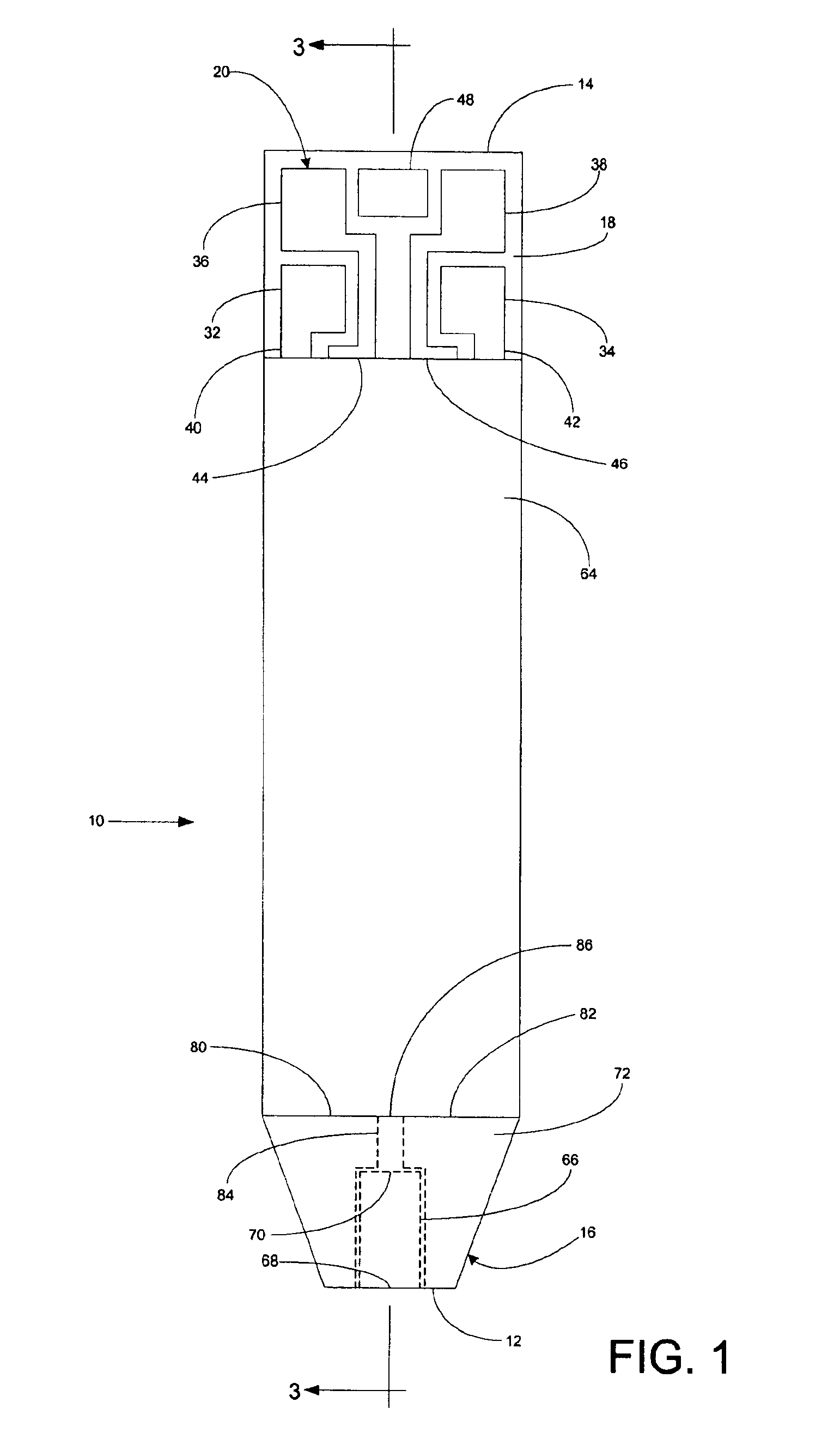
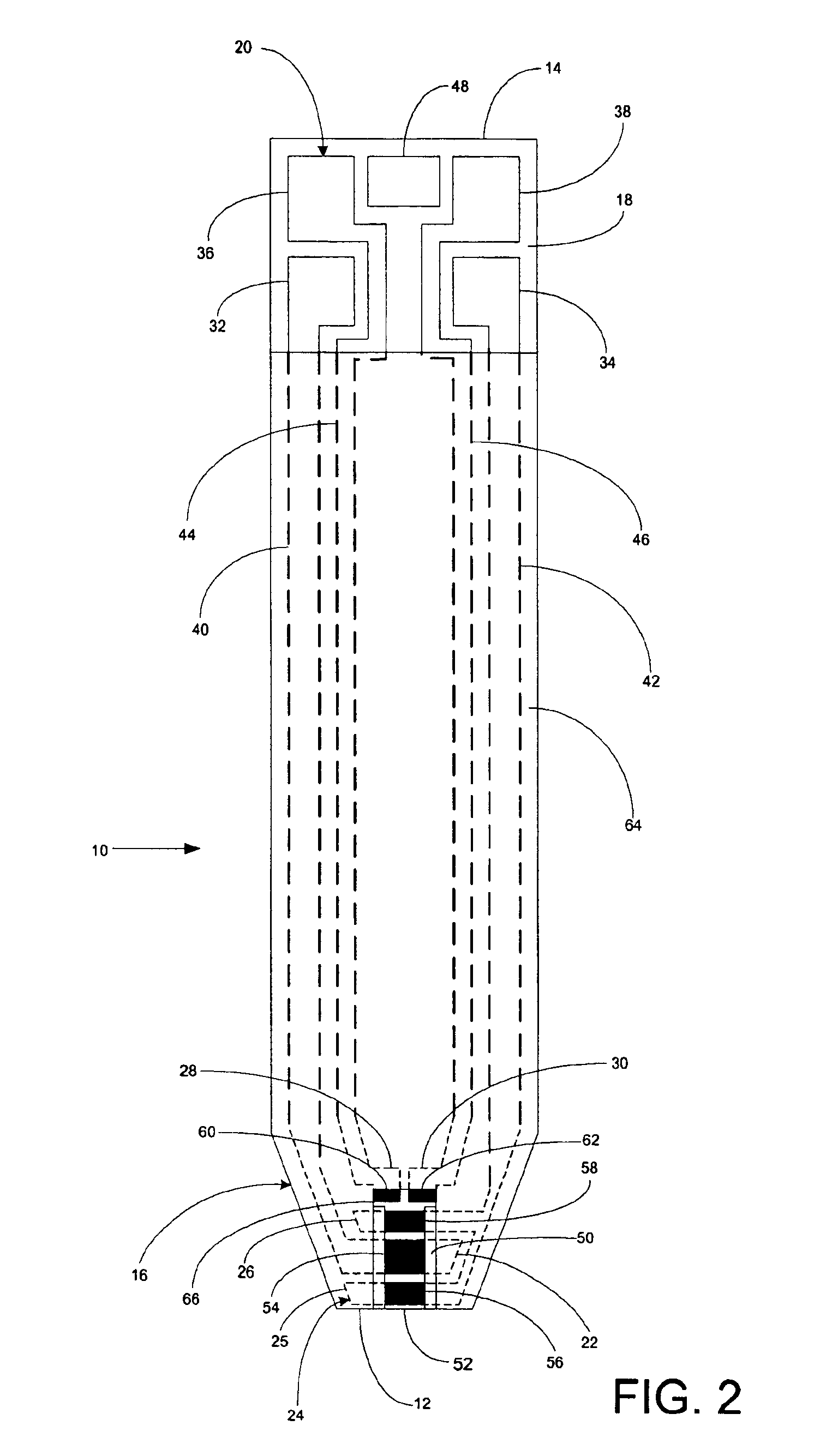
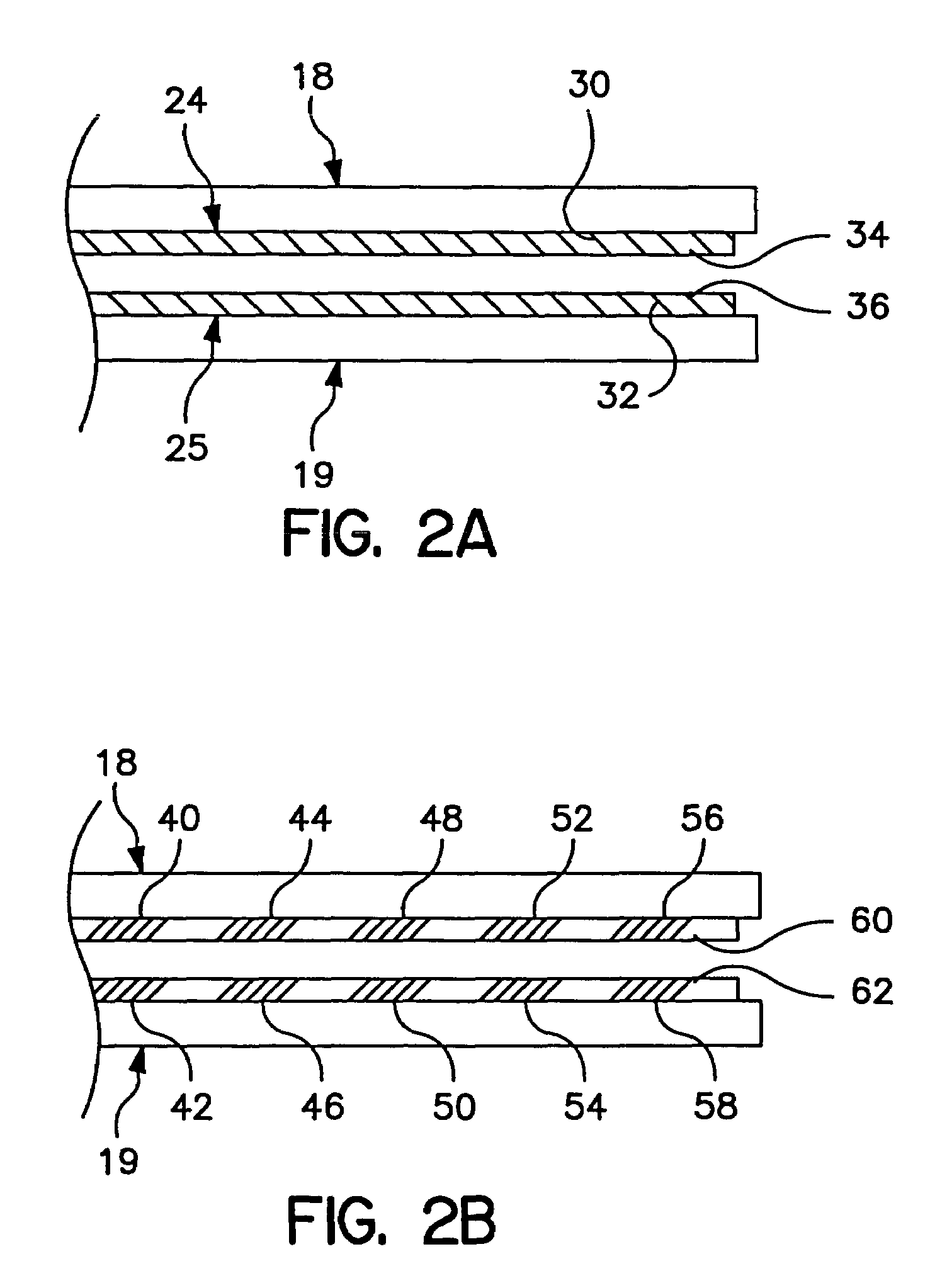
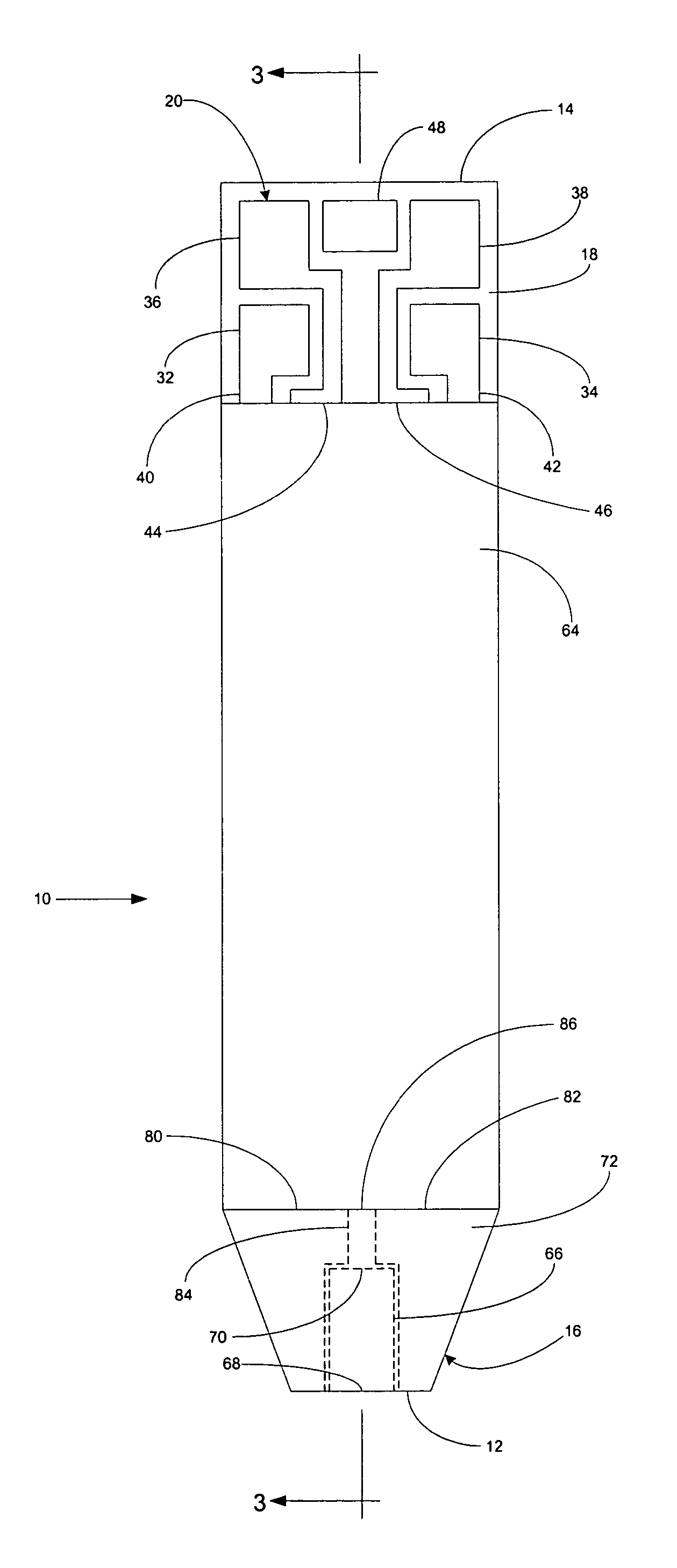
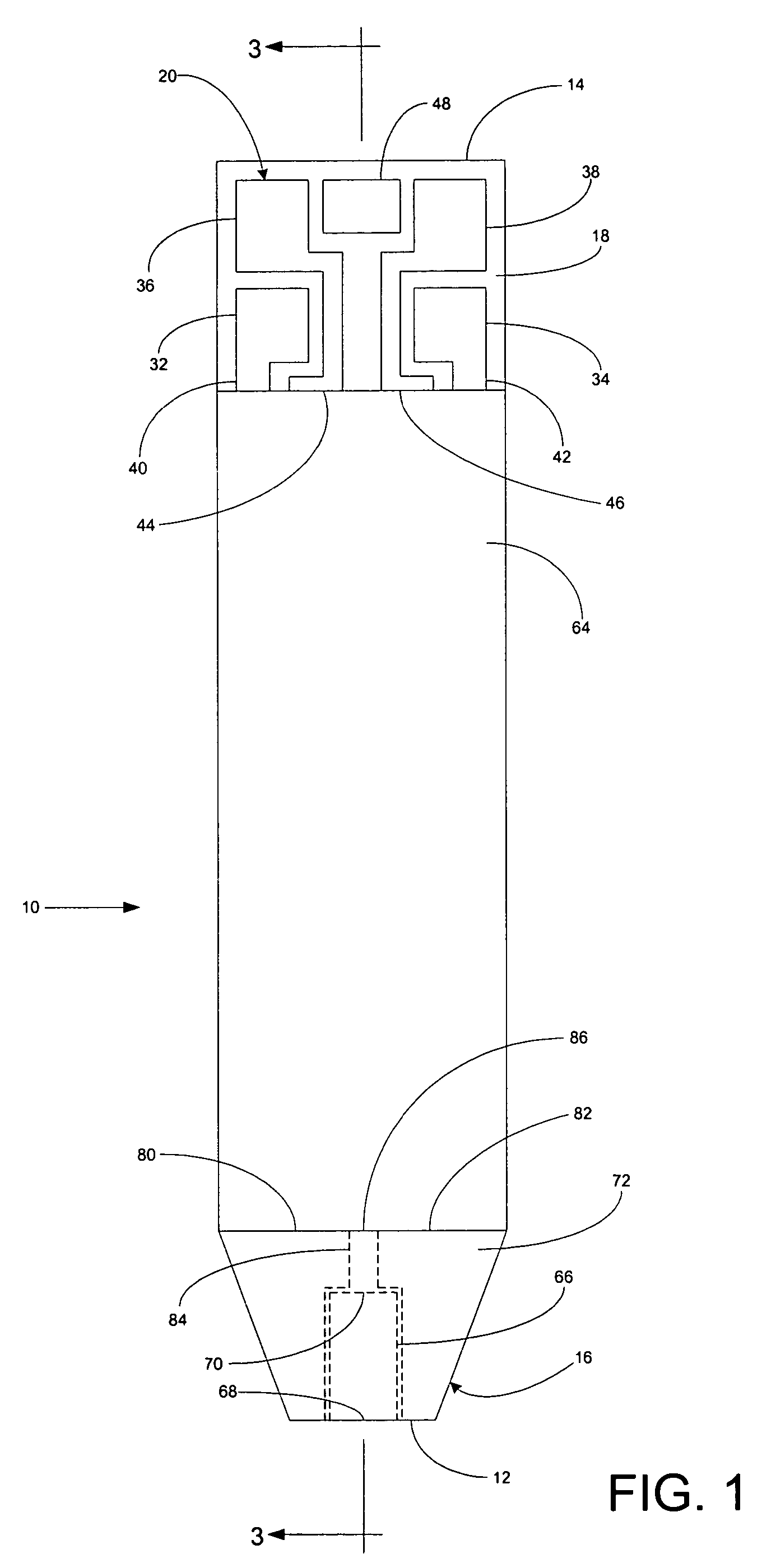
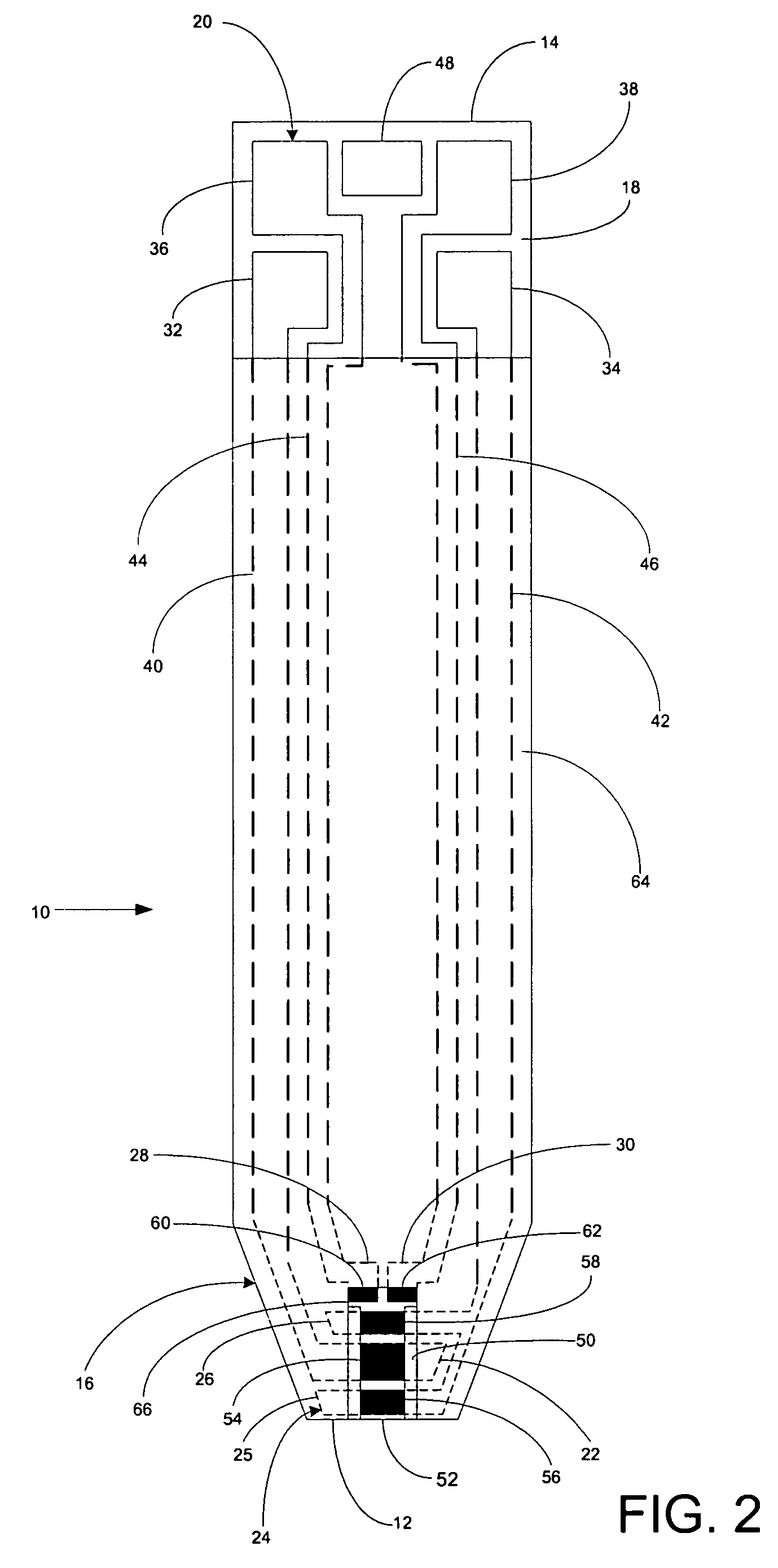
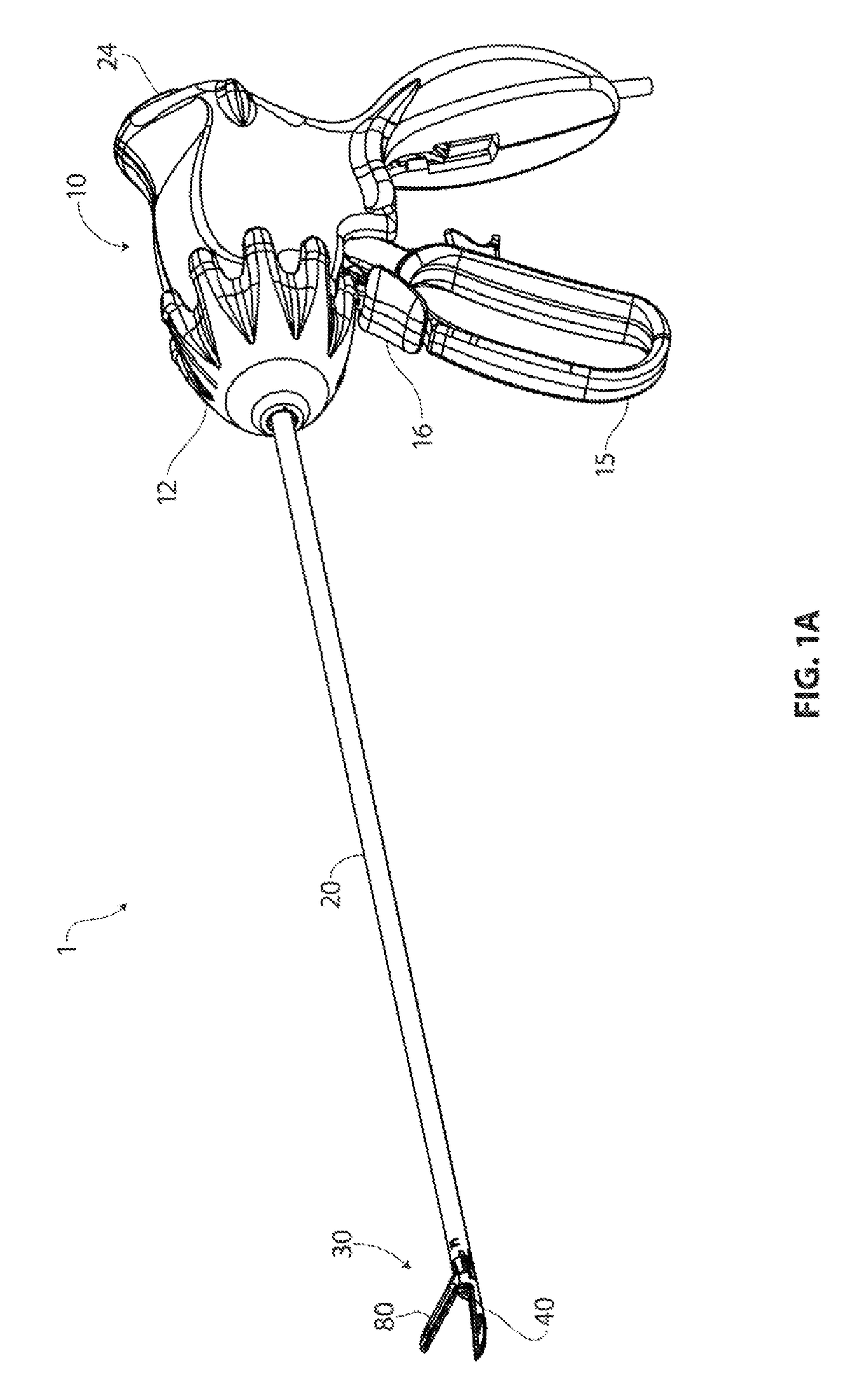
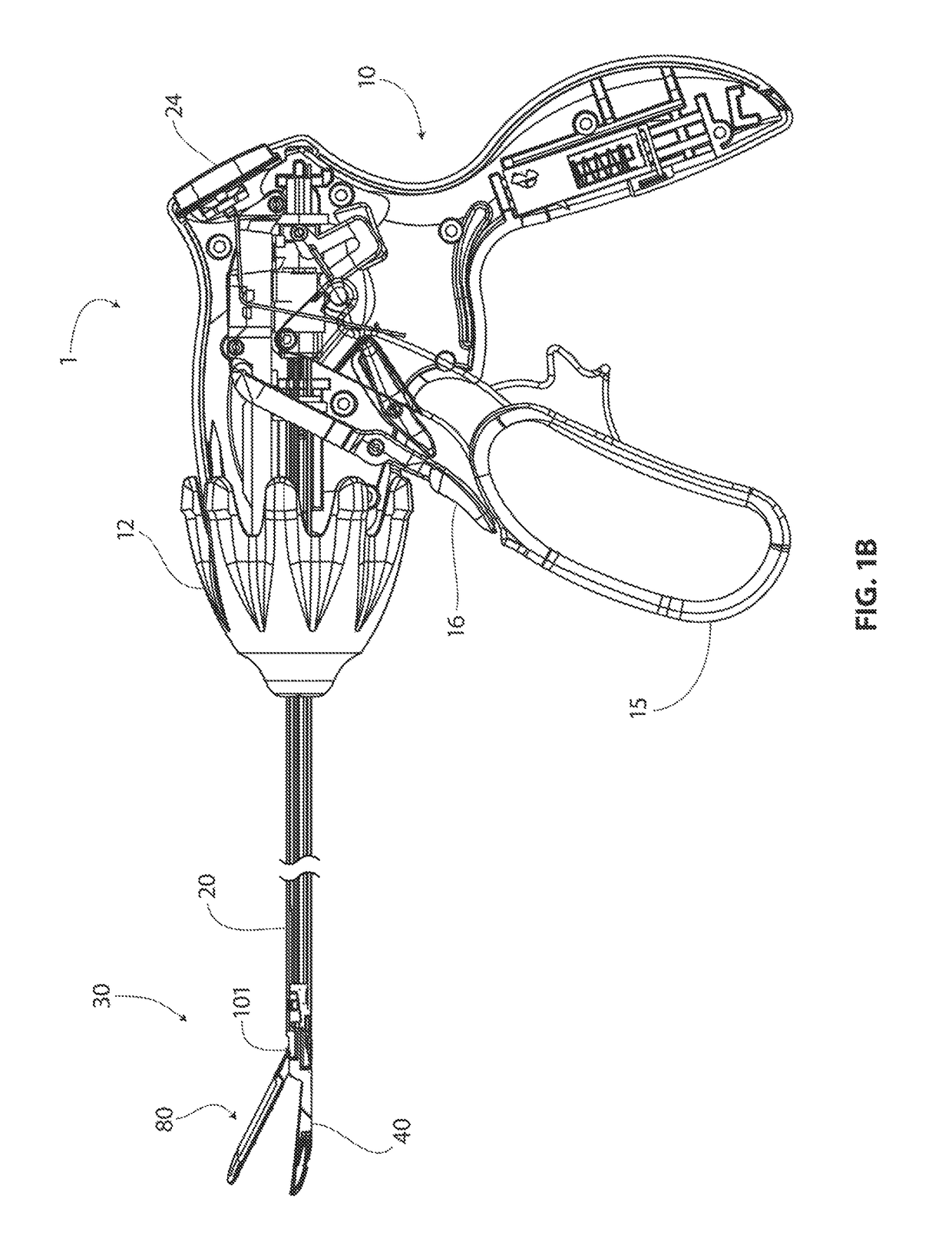
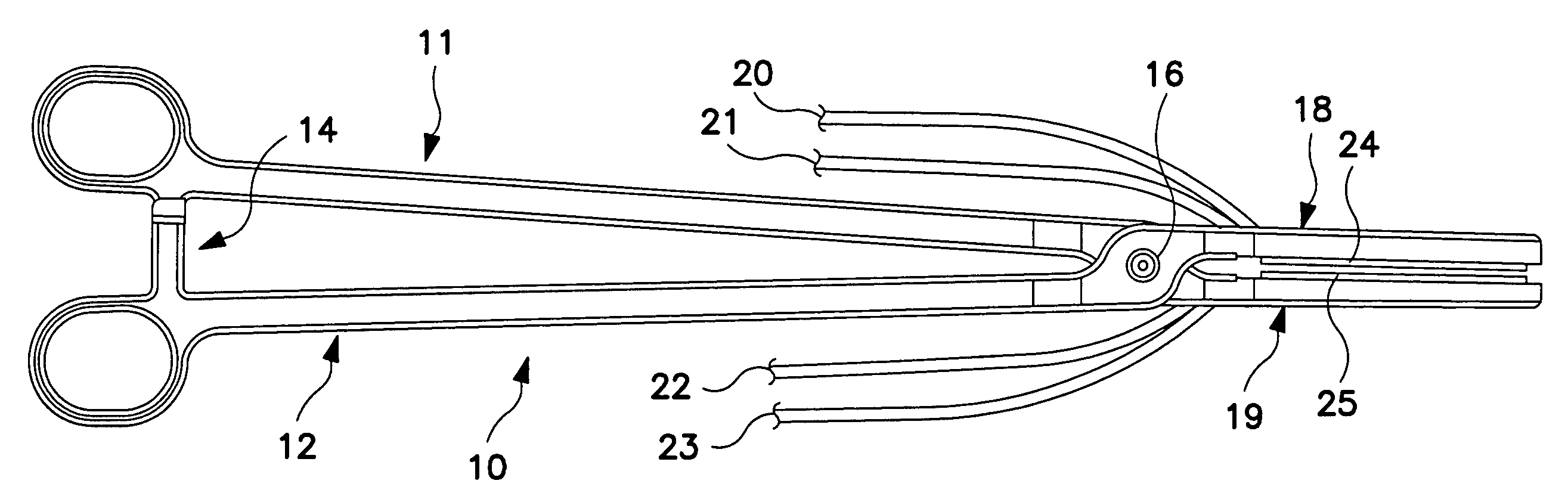
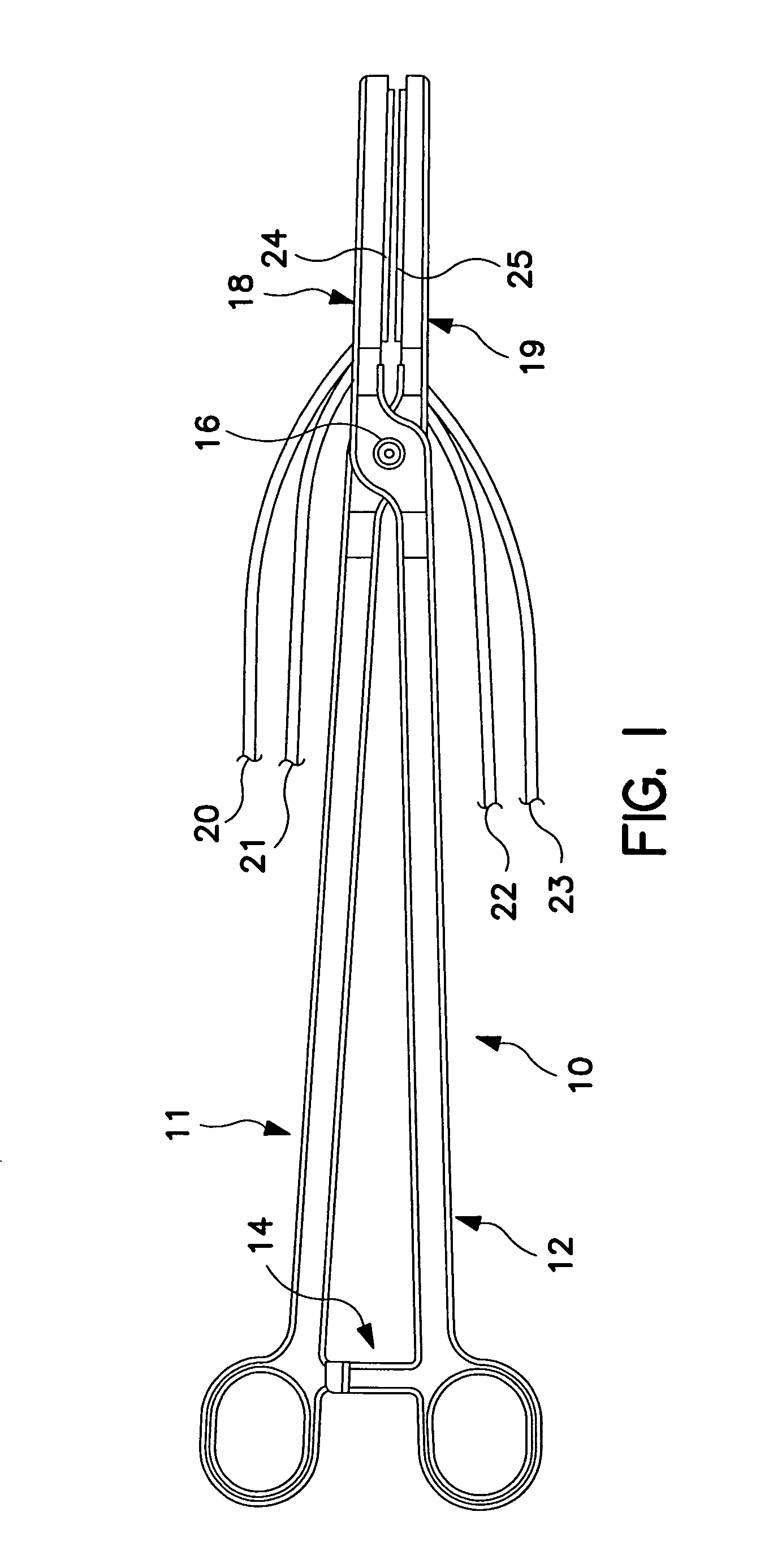
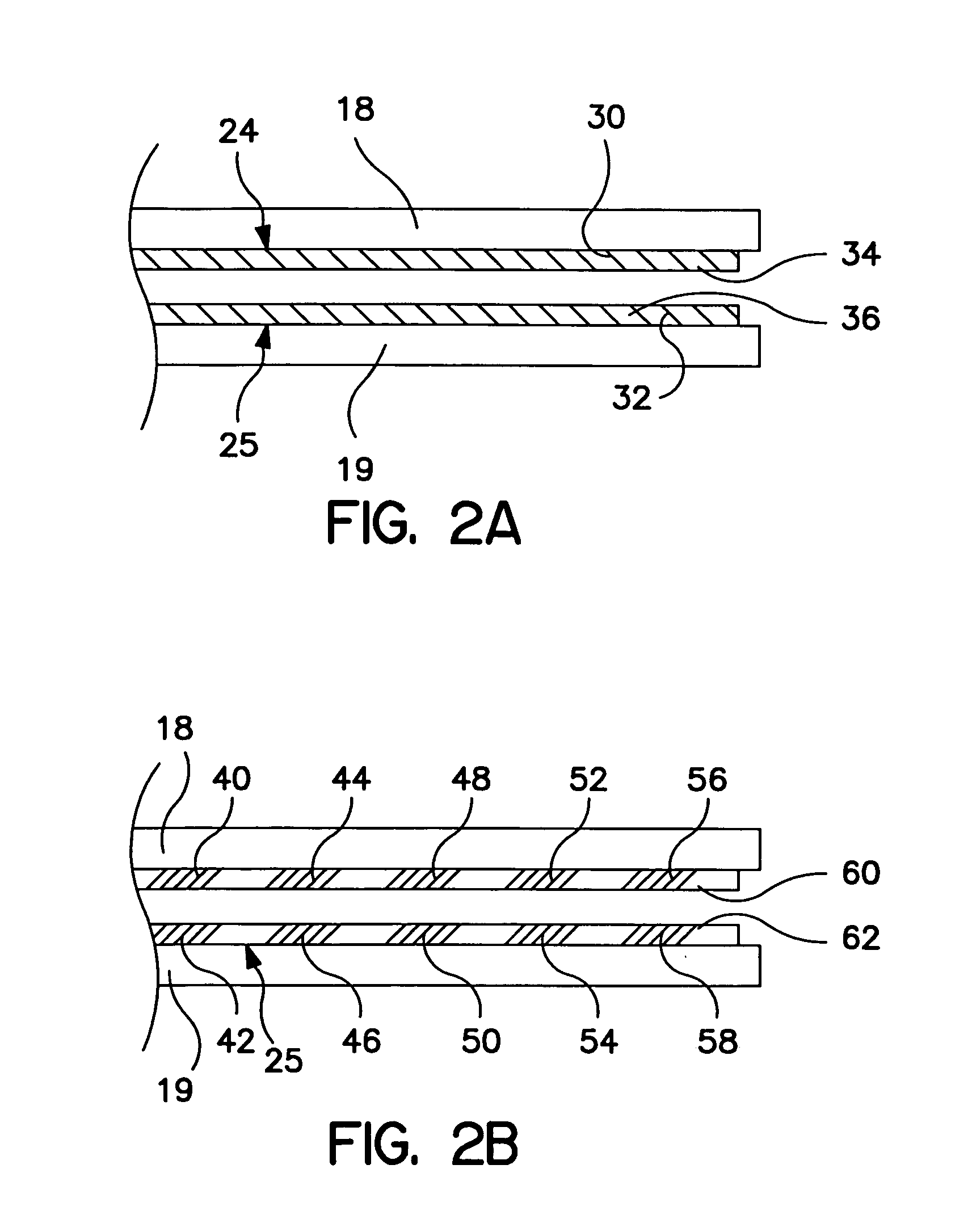
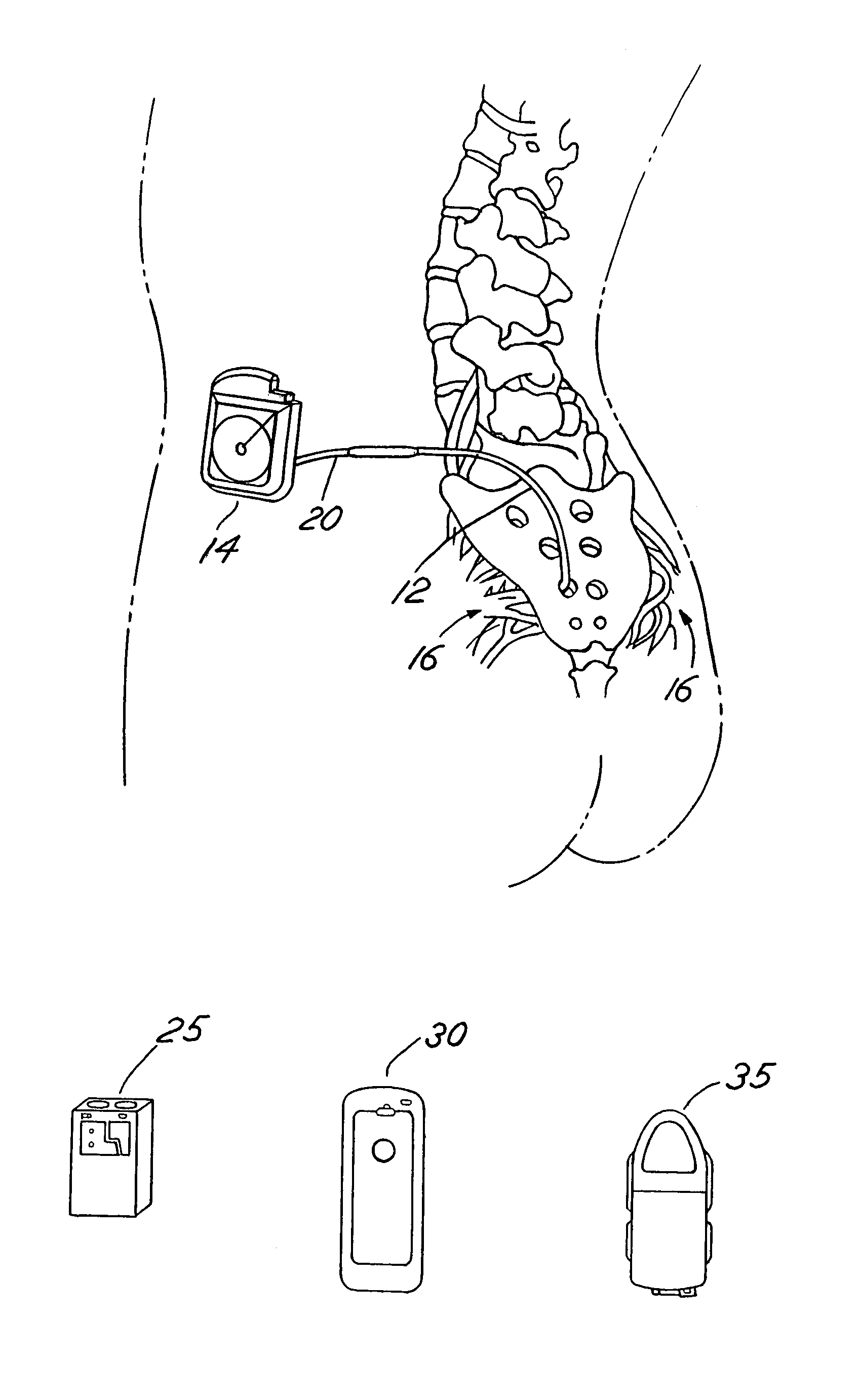
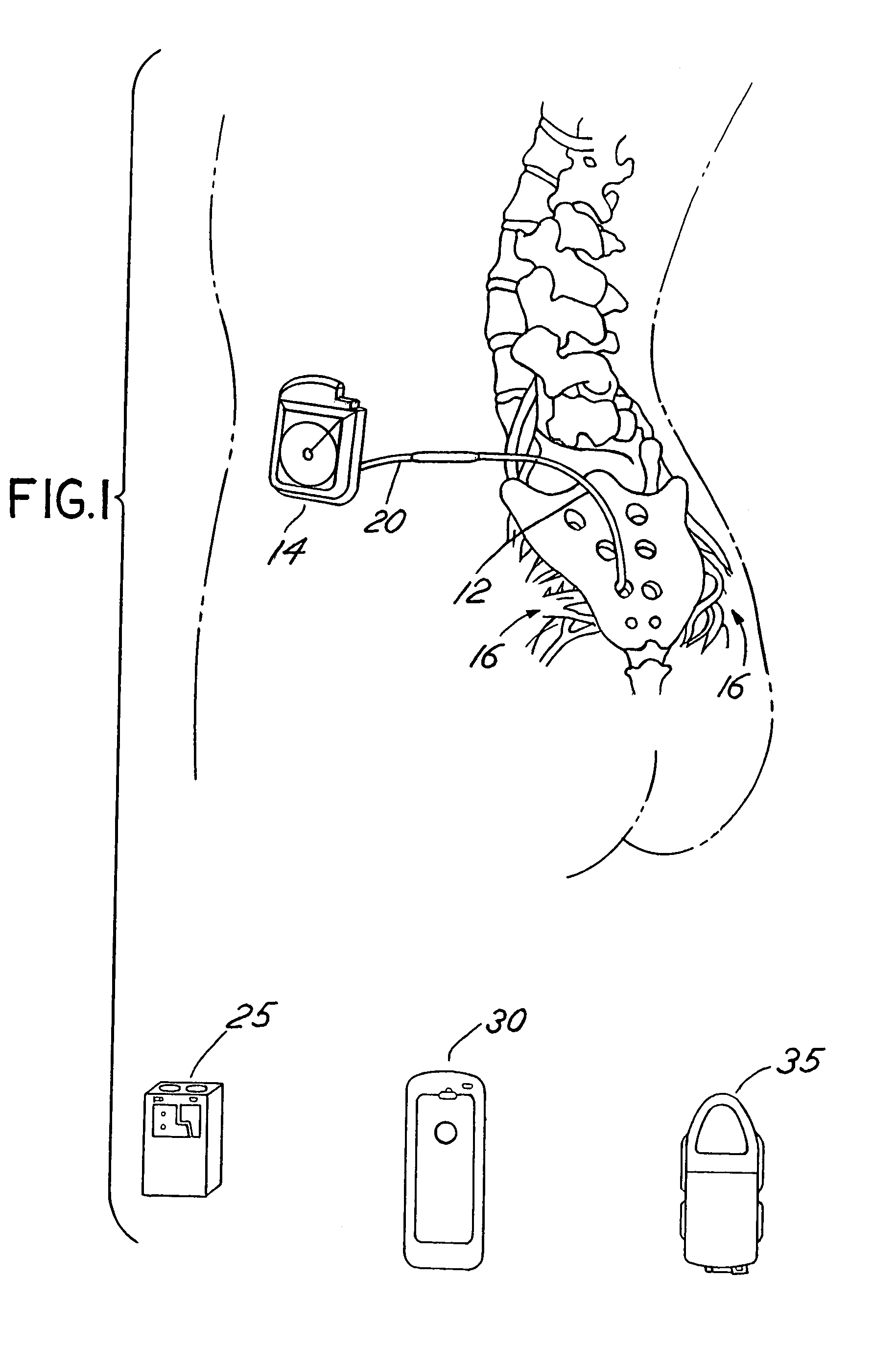
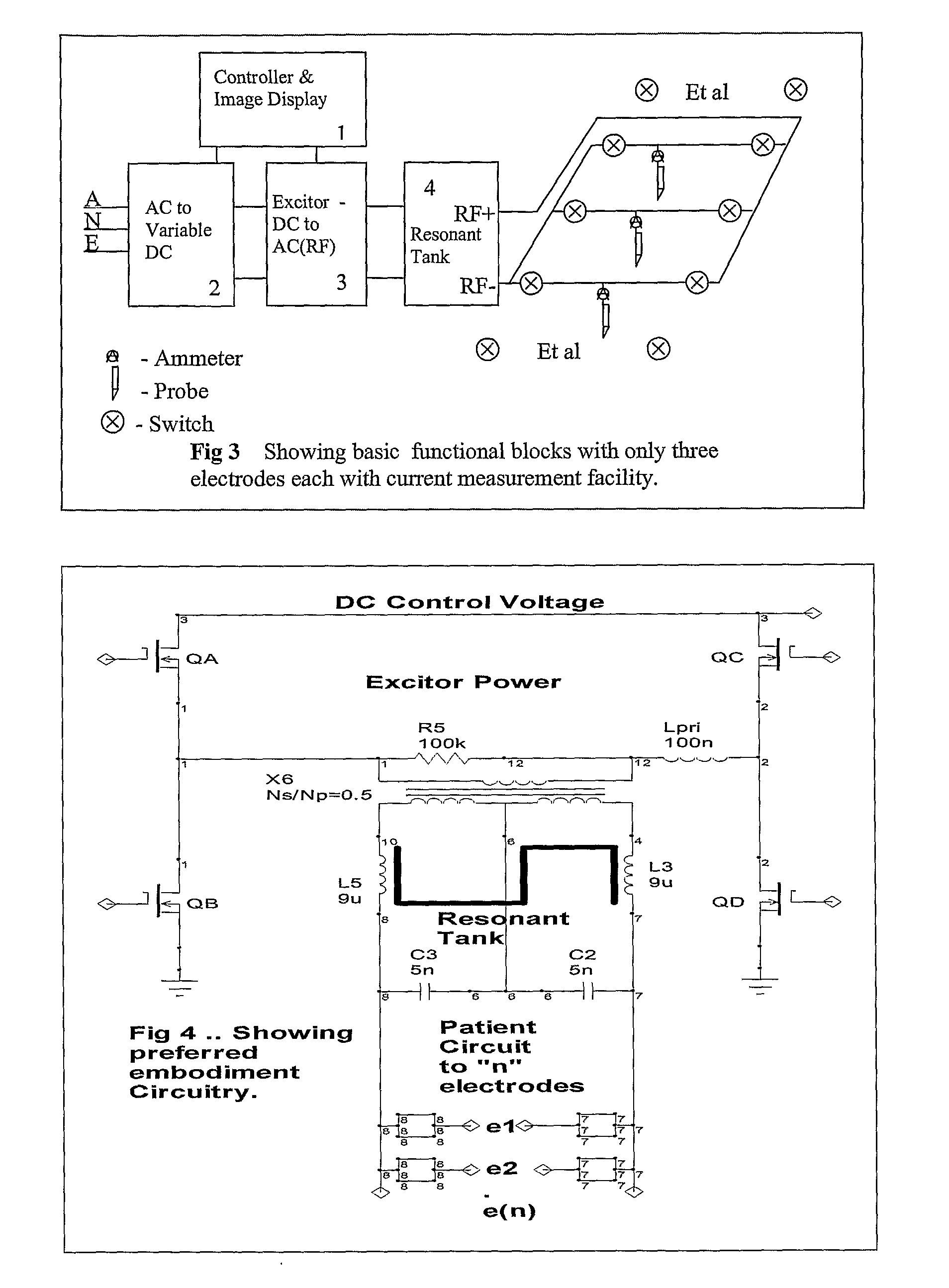
Implantable monitor
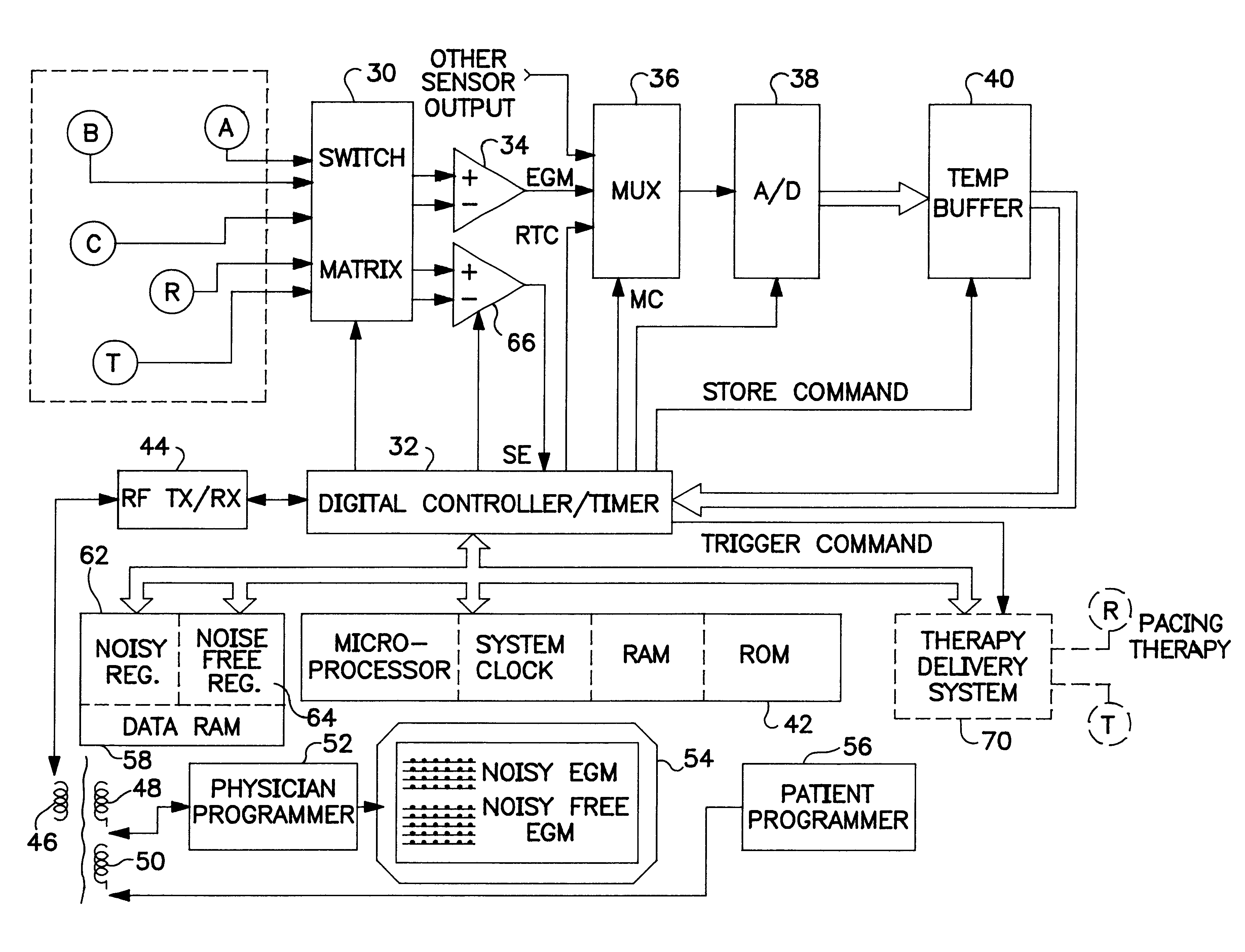
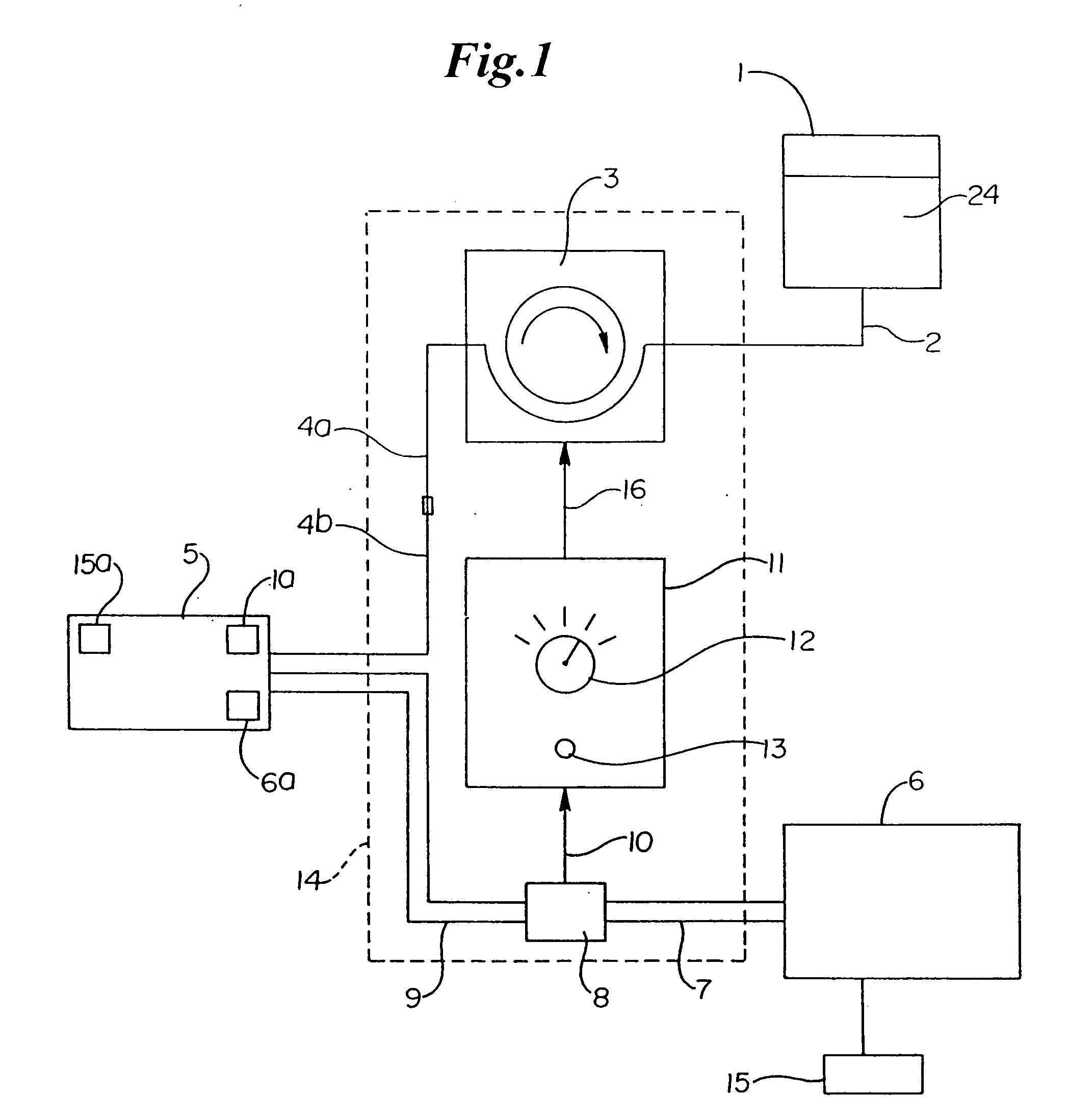
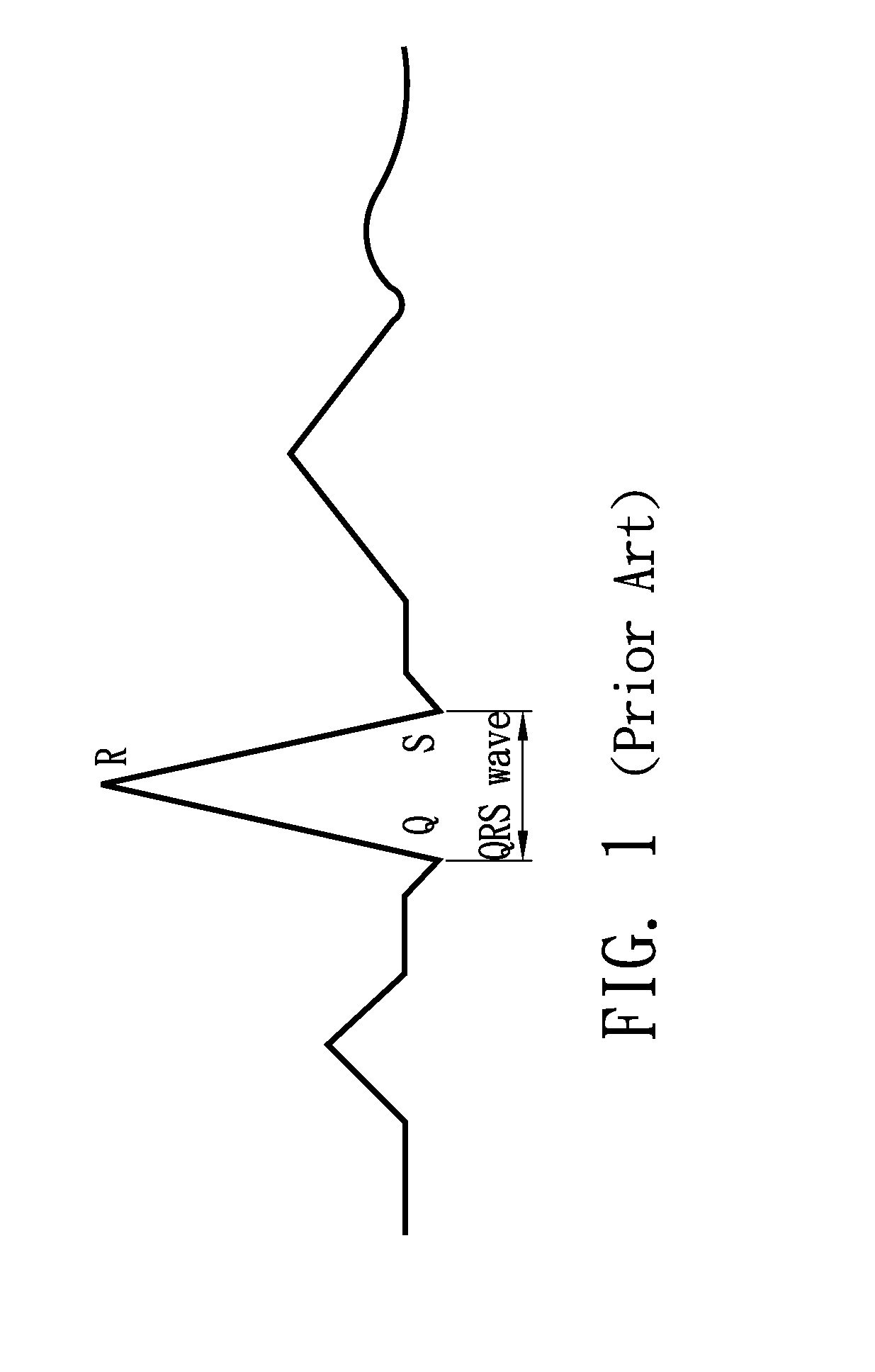
An implantable medical device (IMD) capable of monitoring physiologic data, distinguishing relatively noisy and noise free physiologic data, and recording noisy and relatively noise free segments of physiologic data in separate memory registers of a limited memory for retrieval and analysis at a later time. Preferably the physiologic data comprises the sampled EGM of the heart detected from sense electrode pairs that are implanted in the patient at sites where extraneous electrical noise, e.g., electromyographic signals, are also capable of being detected. The sense electrode pairs can constitute one or both sense electrodes located on or adjacent to the atrial and / or ventricular heart chambers and coupled to the IMD by a lead body or sense electrode pairs that are located remotely from the heart, e.g. at a subcutaneous implantation site of the IMD. A plurality of noisy EGM episode data registers store a corresponding plurality of noisy EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis and another plurality of noise free EGM episode data registers to store a corresponding plurality of relatively noise free EGM episode data sets on a FIFO basis. Any form of discrimination of noisy data from relatively noise free data can be employed at the time of recording, but because the stored EGM episode data sets are subsequently viewed and analyzed by a physician, discrimination with absolute certainty is not required, and the physician can alter the detection criteria to fine tune it.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
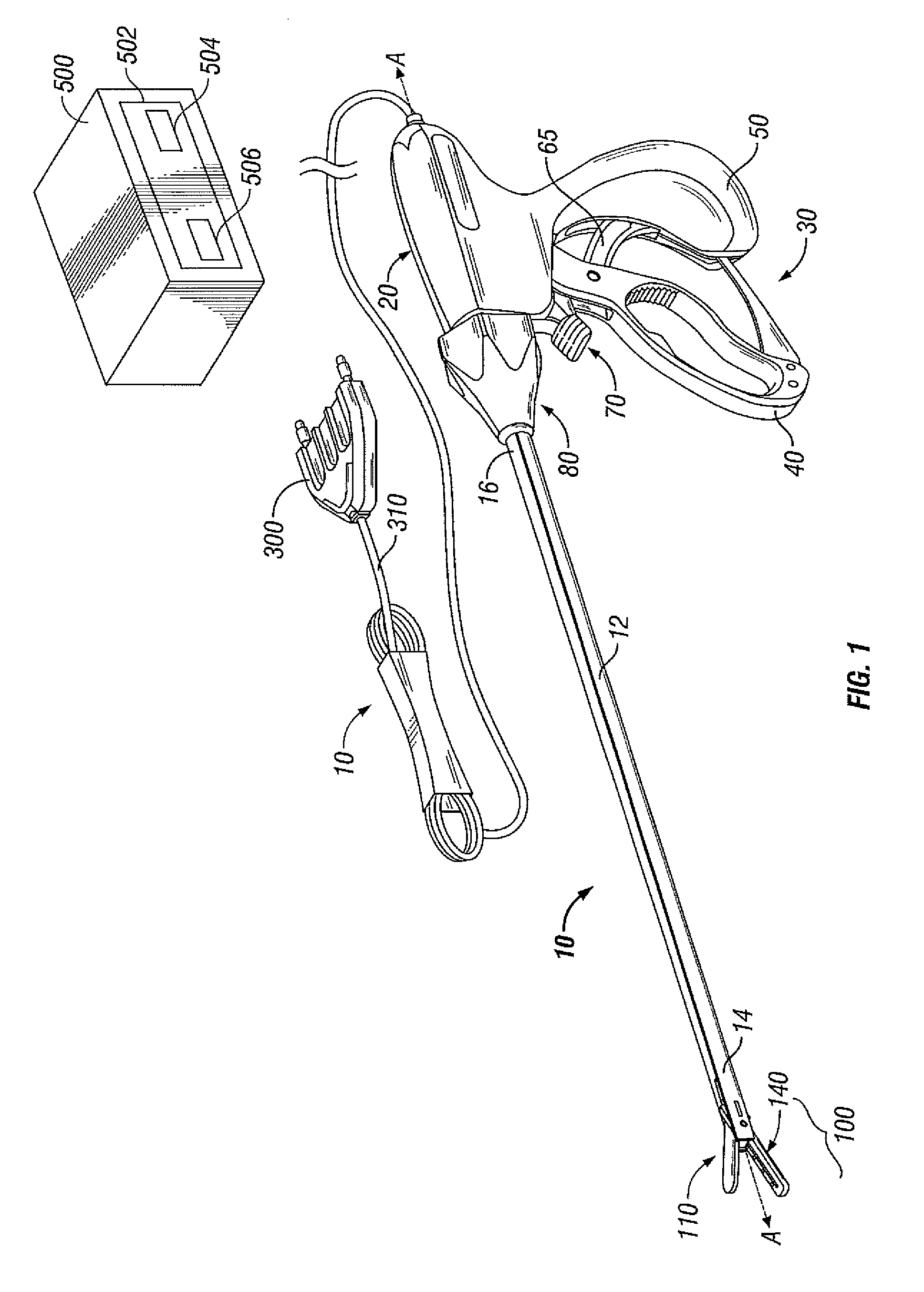
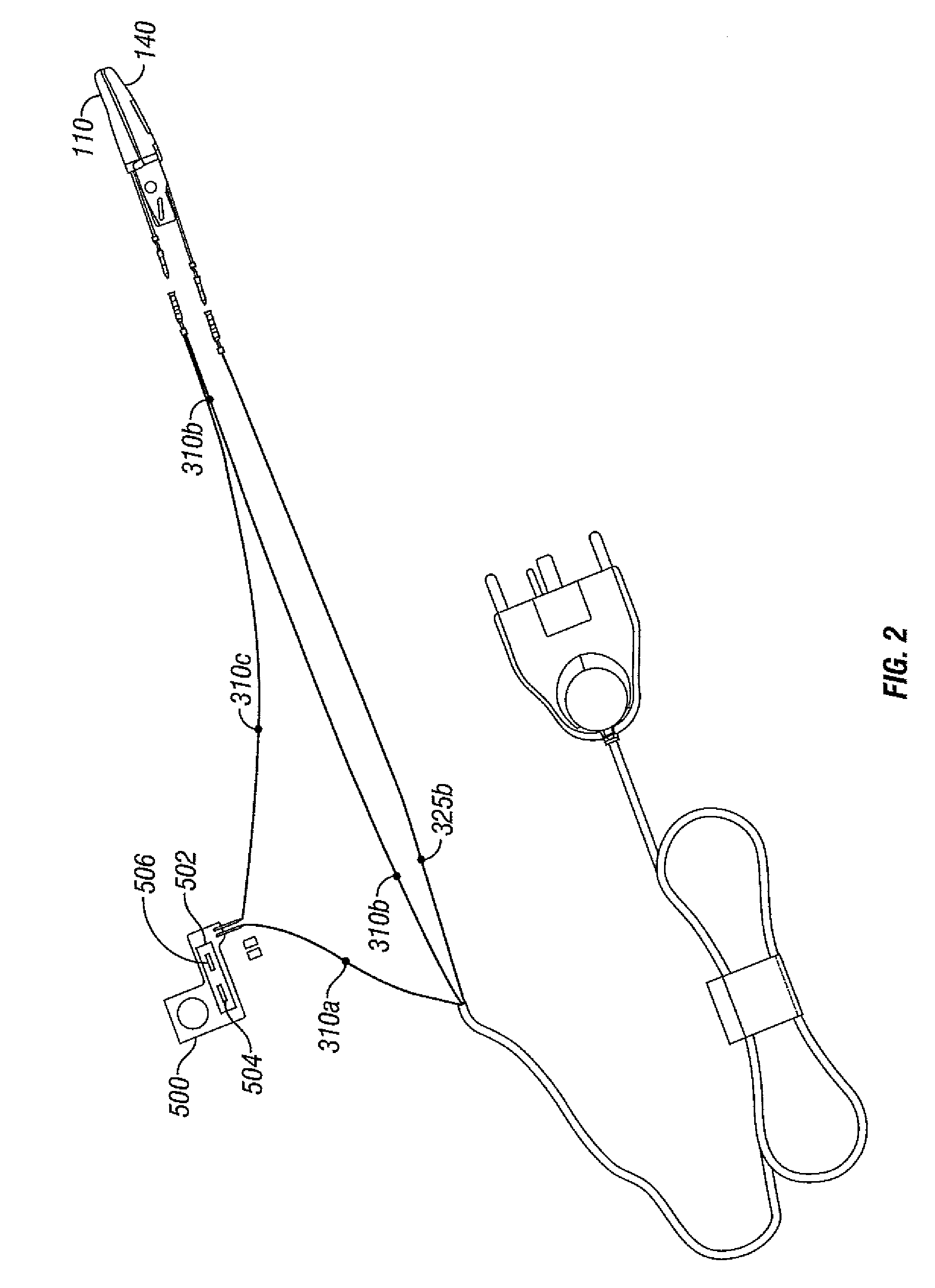
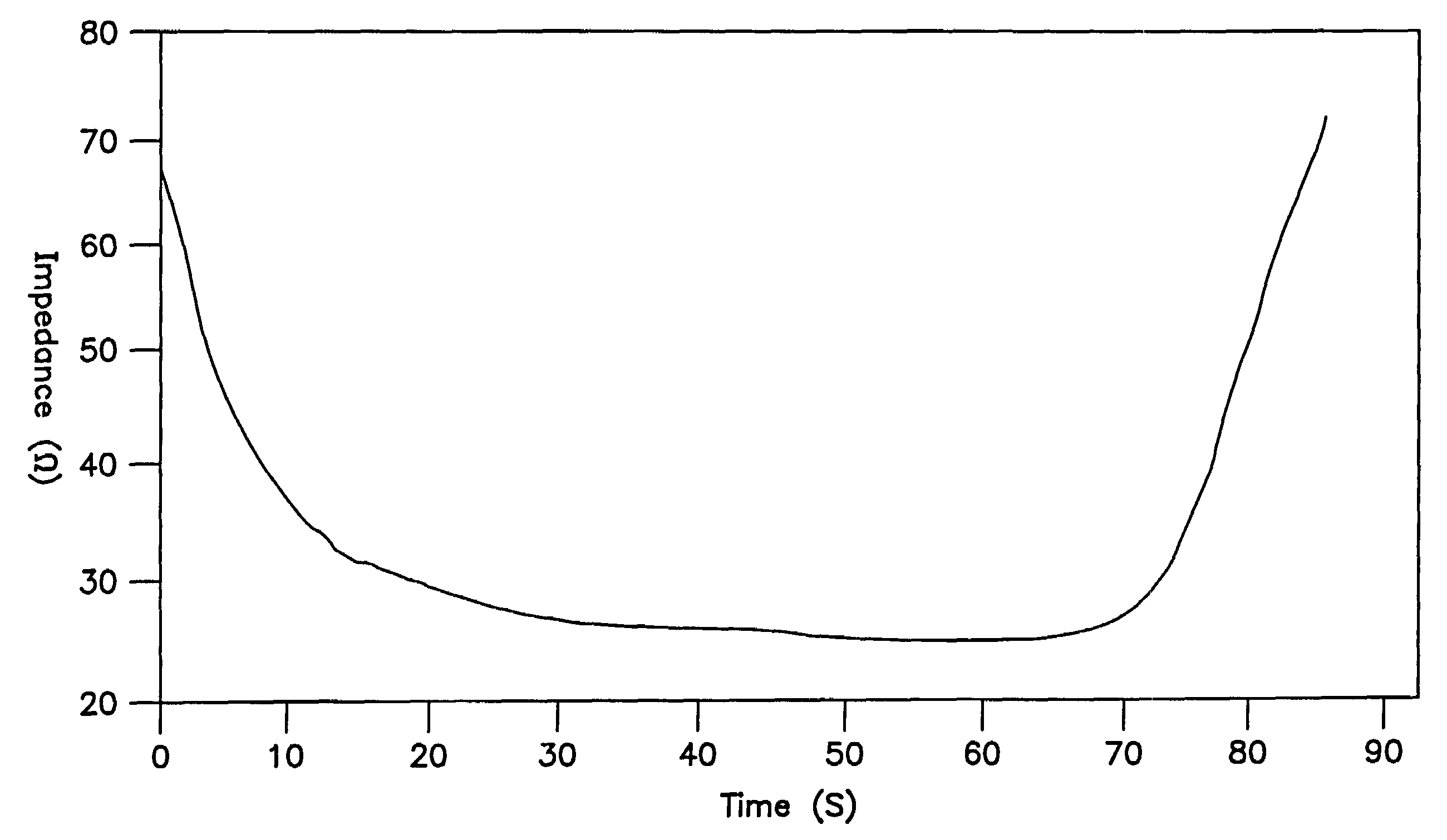
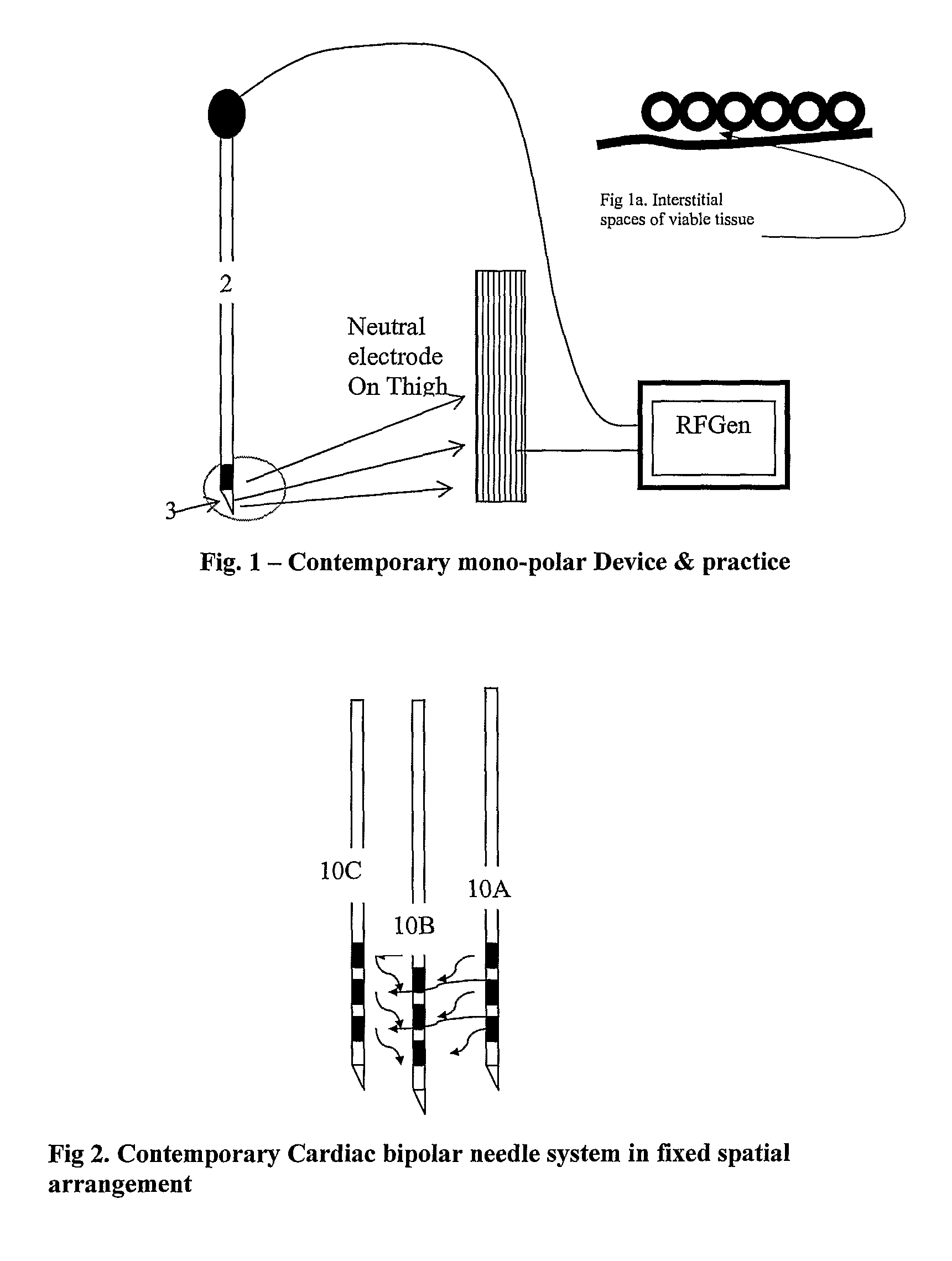
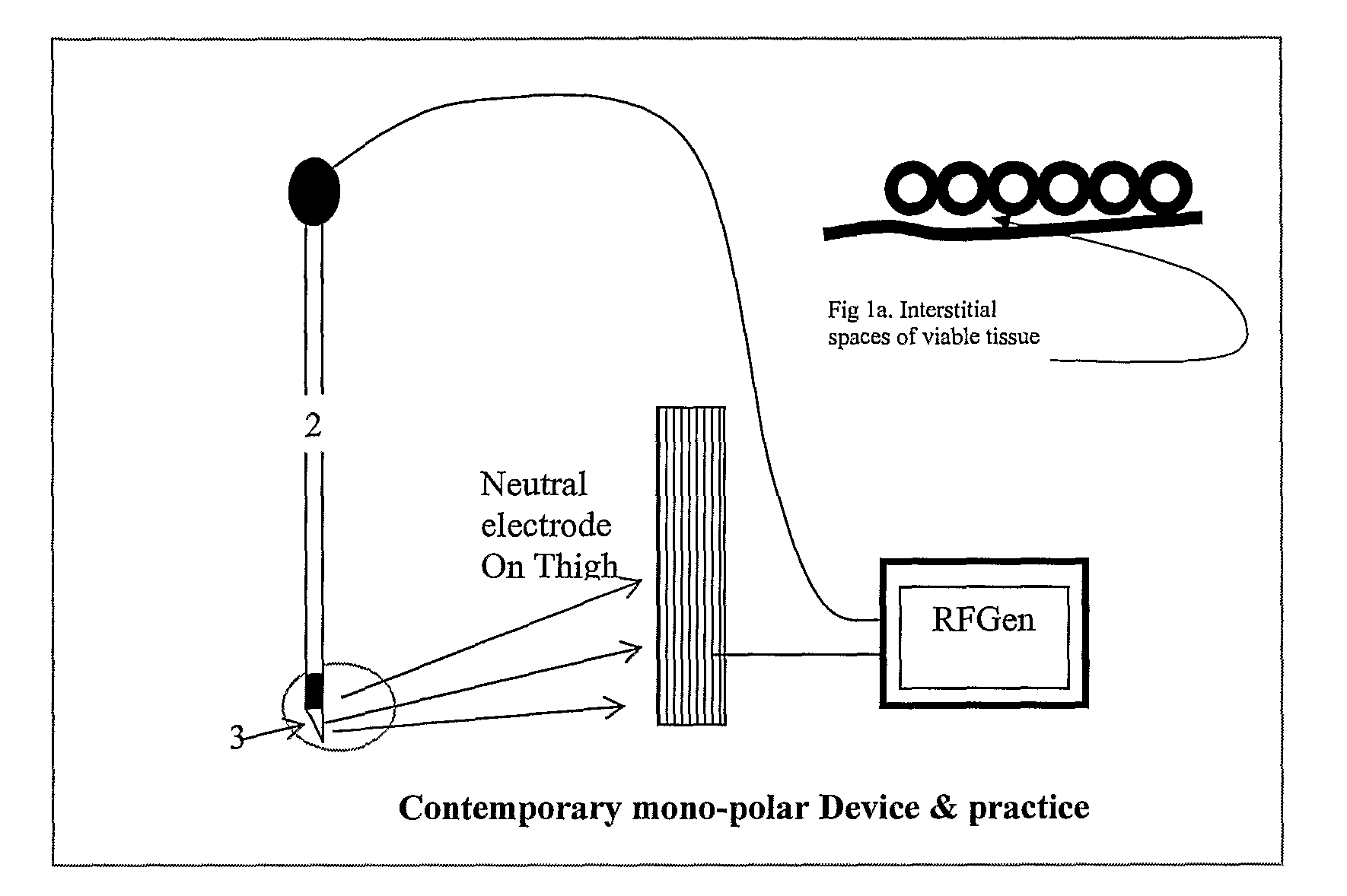
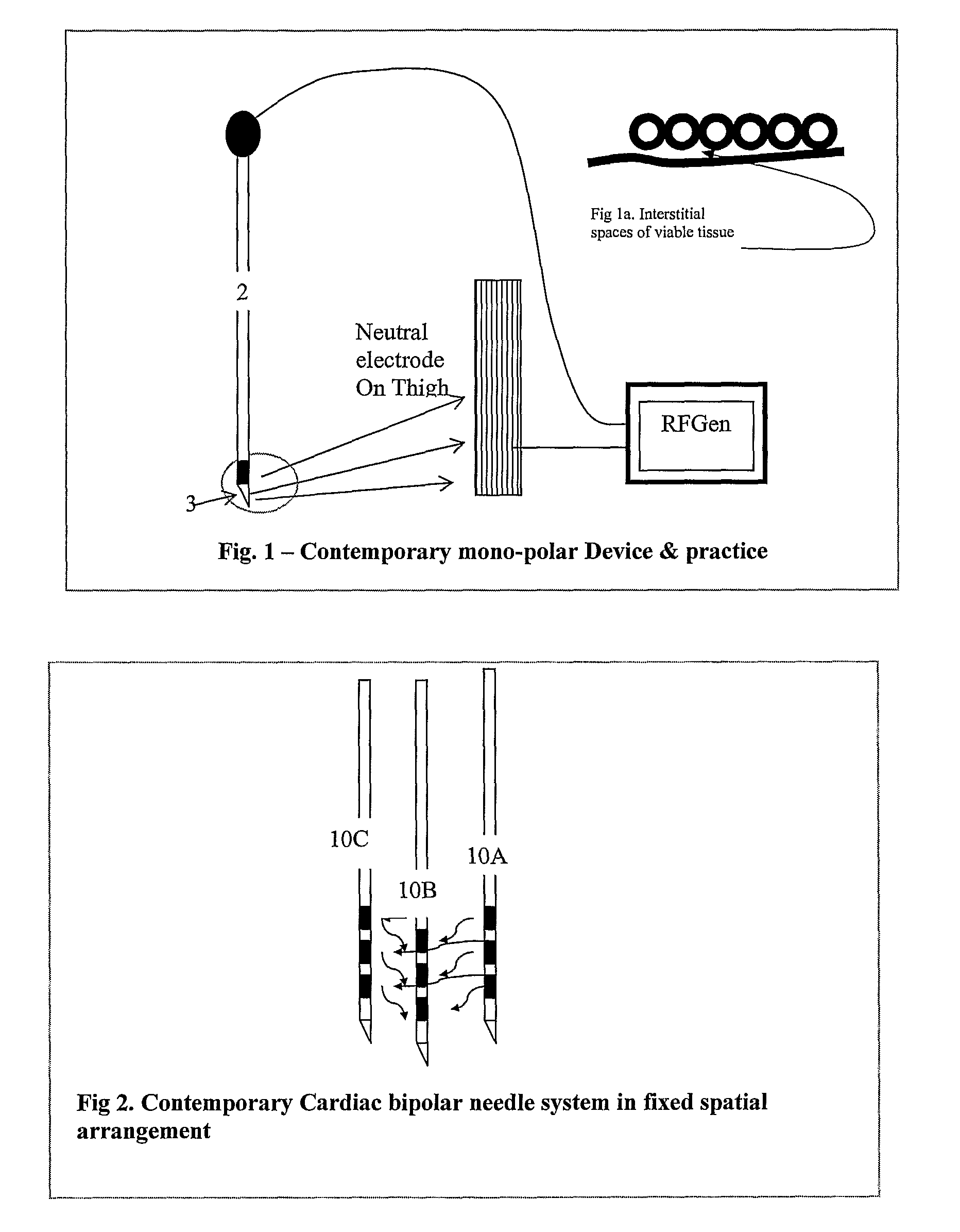
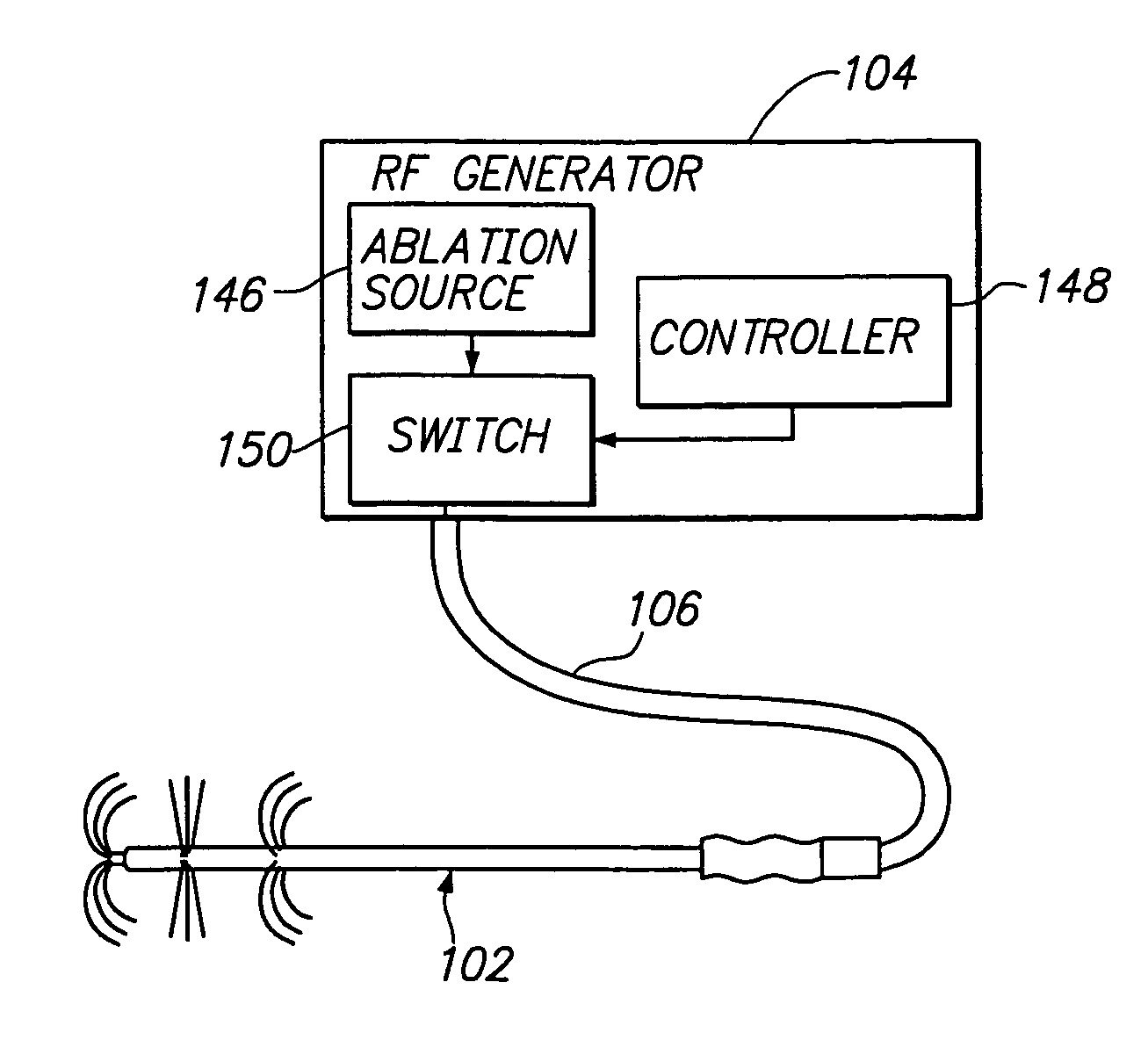
Ablation system and method of use
InactiveUS6989010B2Simple systemImproving impedanceDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringPlateau
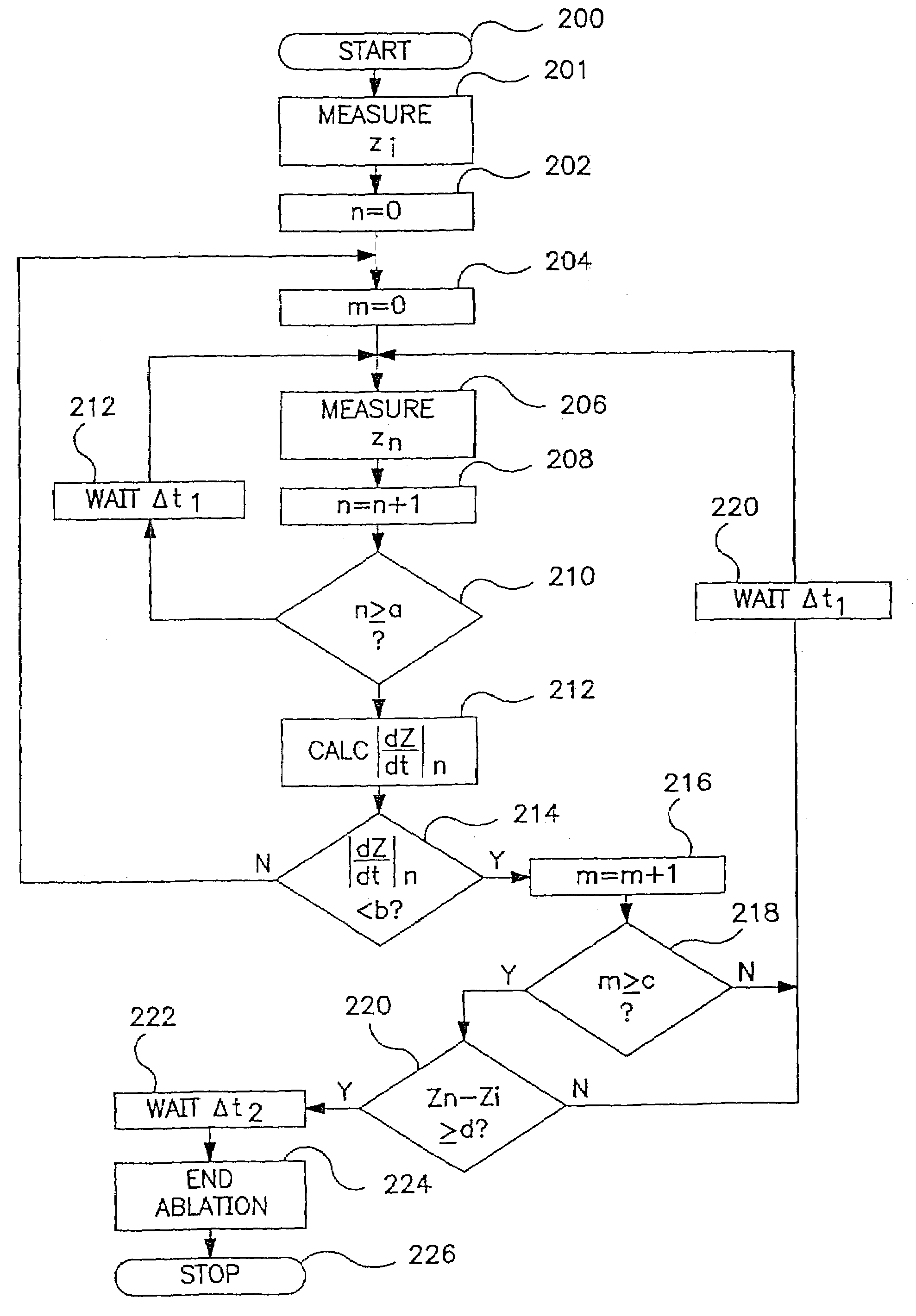
A system and method for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the impedance of the tissue to be ablated. Rather than attempting to detect a desired drop or a desired increase impedance, completeness of a lesion is detected in response to the measured impedance remaining at a stable level for a desired period of time, referred to as an impedance plateau. The mechanism for determining transmurality of lesions adjacent individual electrodes or pairs may be used to deactivate individual electrodes or electrode pairs, when the lesions in tissue adjacent these individual electrodes or electrode pairs are complete, to create an essentially uniform lesion along the line of electrodes or electrode pairs, regardless of differences in tissue thickness adjacent the individual electrodes or electrode pairs.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
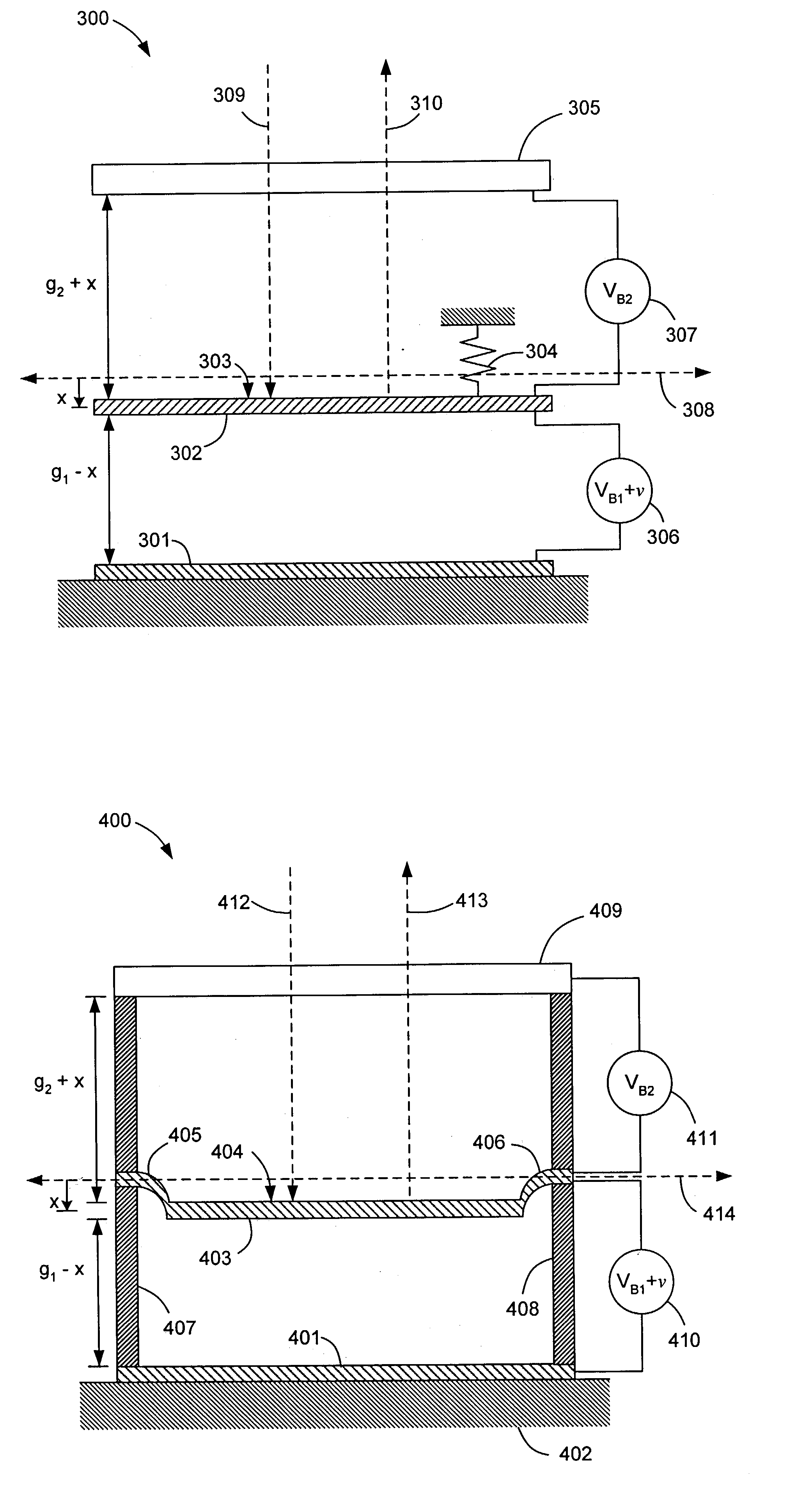
Differentially-driven MEMS spatial light modulator
InactiveUS20040008396A1Non-linear opticsOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorElectrostatic actuator
A MEMS SLM and an electrostatic actuator associated with a pixel in an SLM. The actuator has three electrodes: a lower electrode; an upper electrode fixed with respect to the lower electrode; and a center electrode suspended and actuable between the upper and lower electrodes. The center electrode is capable of resiliently-biasing to restore the center electrode to a non-actuated first equilibrium position, and a mirror is operably connected to the center electrode. A first voltage source provides a first bias voltage across the lower and center electrodes and a second voltage source provides a second bias voltage across the upper and center electrodes, with the first and second bias voltages determining the non-actuated first equilibrium position of the center electrode. A third voltage source provides a variable driver voltage across one of the lower / center and upper / center electrode pairs in series with the corresponding first or second bias voltage, to actuate the center electrode to a dynamic second equilibrium position.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
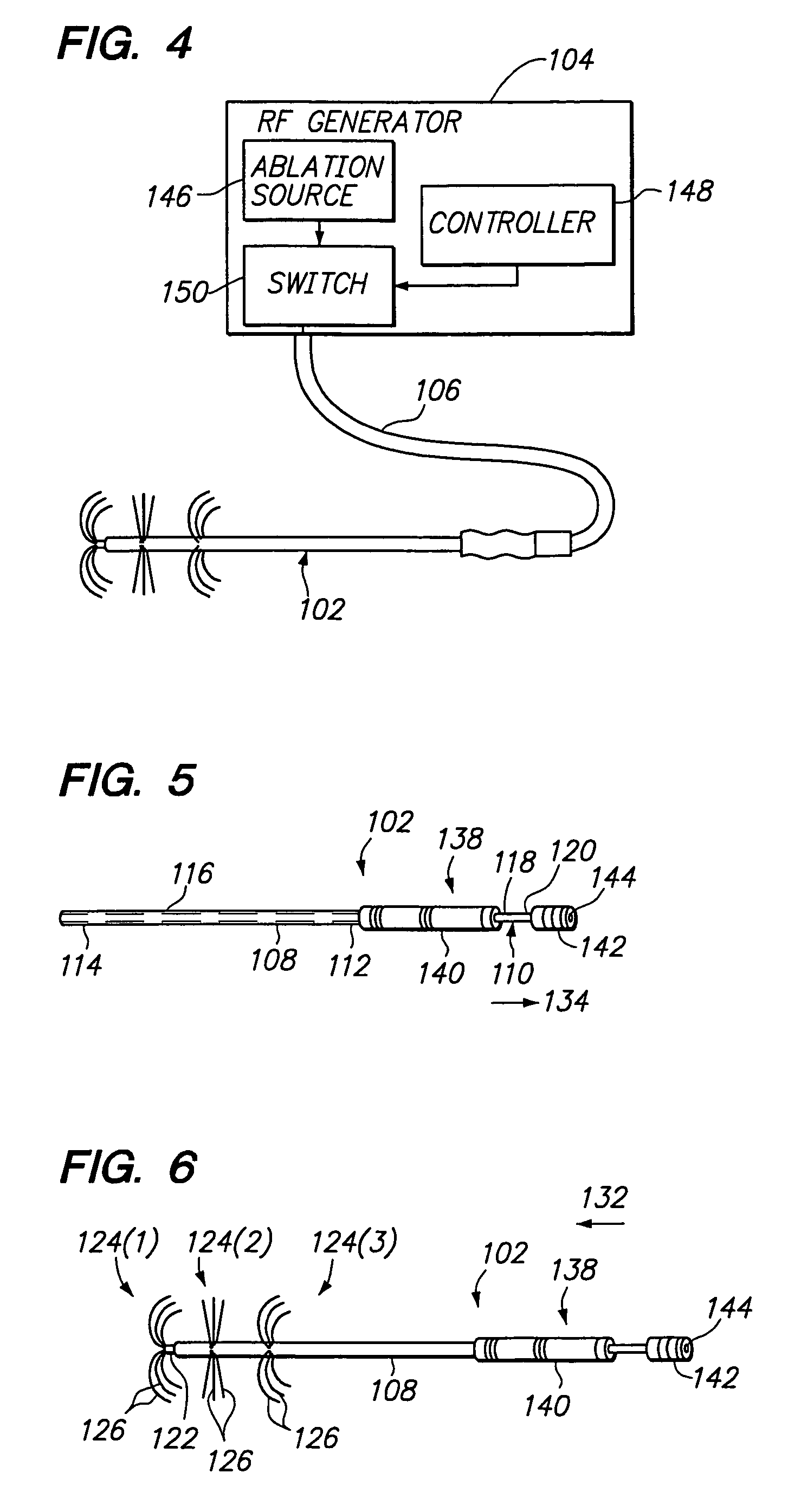
Multi-zone bipolar ablation probe assembly
ActiveUS20050080409A1Efficient ablationAdd dimensionSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequencyElectrode pair
A medical probe assembly, tissue treatment system, and method are provided for ablating tissue. The probe assembly comprises an elongated member and electrode elements mechanically coupled to the distal end of the elongated member. The electrode elements are configurable as two bipolar electrode pairs with a common electrode element. At least one of the electrode elements comprises a plurality of electrodes (such as, e.g., needle electrodes) radially extendable from the elongated member. An ablation source, such as a radio frequency source, can be connected to the probe assembly in order to convey ablation energy to the electrode pairs, either simultaneously or sequentially.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Systems and methods for blood glucose sensing
InactiveUS6946299B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical conductorGlucose polymers
A system for measuring a glucose level in a blood sample includes a test strip and a meter. The test strip includes a sample chamber, a working electrode, a counter electrode, fill-detect electrodes, and an auto-on conductor. A reagent layer is disposed in the sample chamber. The auto-on conductor causes the meter to wake up and perform a test strip sequence when the test strip is inserted in the meter. The meter uses the working and counter electrodes to initially detect the blood sample in the sample chamber and uses the fill-detect electrodes to check that the blood sample has mixed with the reagent layer. The meter applies an assay voltage between the working and counter electrodes and measures the resulting current. The meter calculates the glucose level based on the measured current and calibration data saved in memory from a removable data storage device associated with the test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
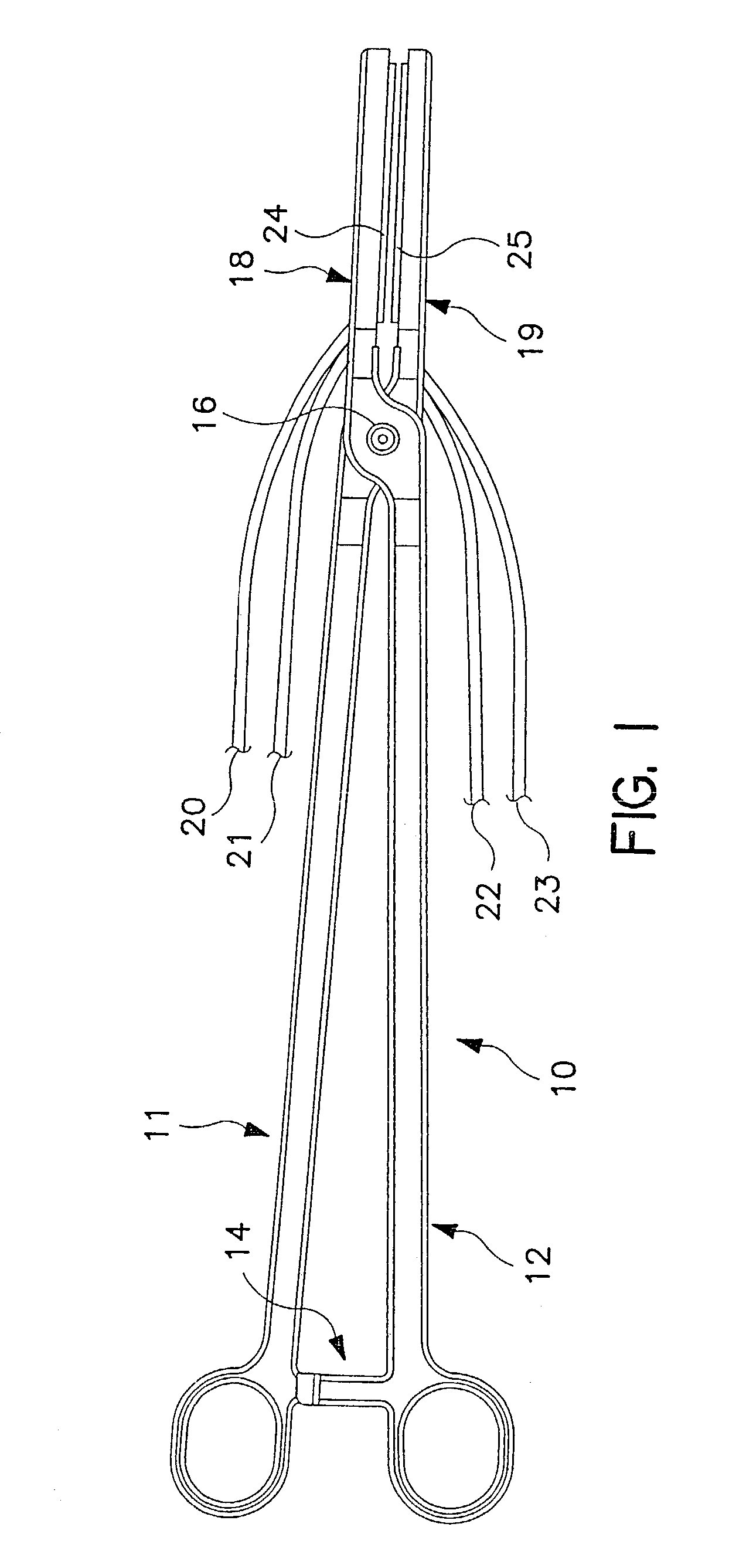
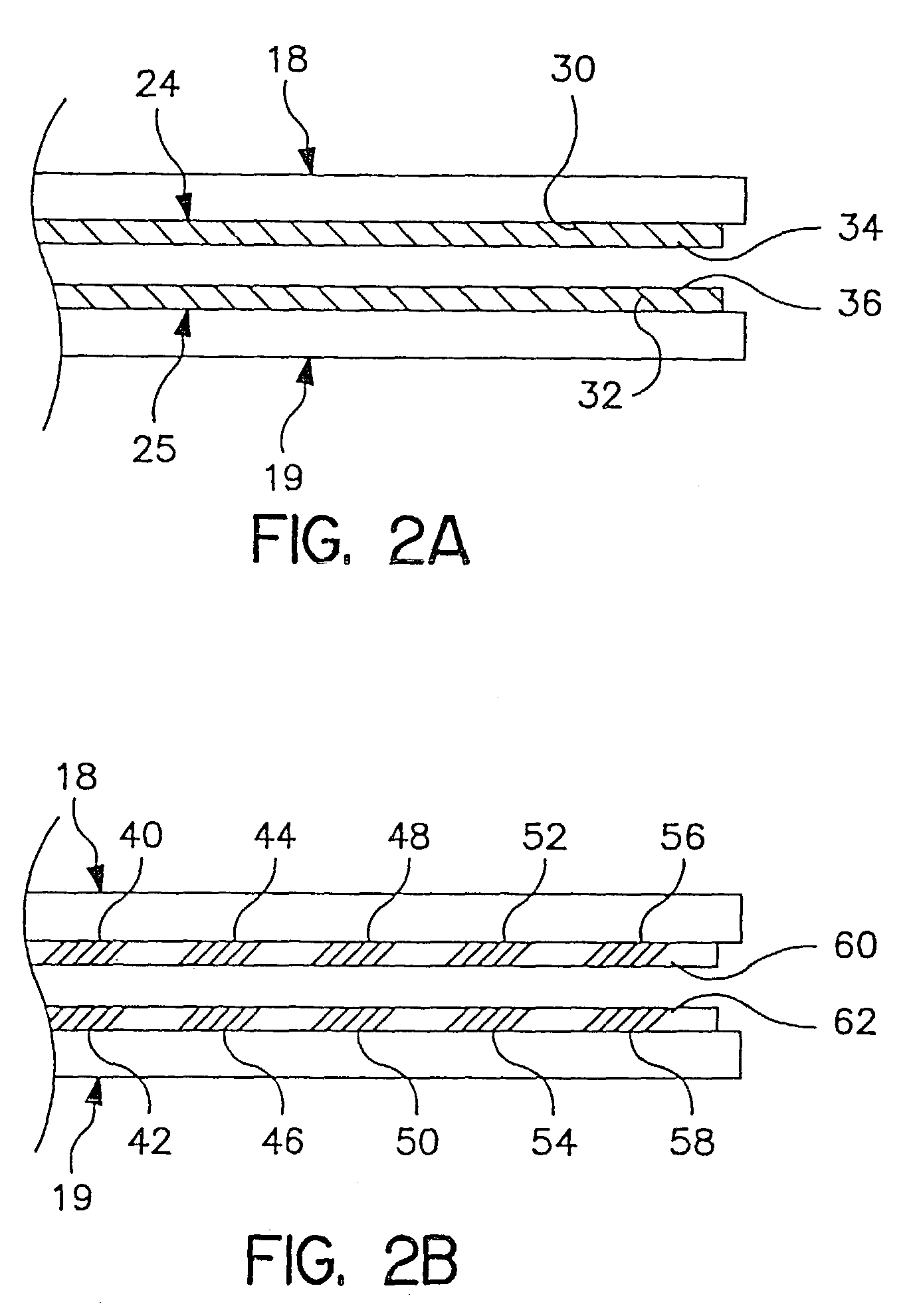
End Effector Assembly for Electrosurgical Devices and System for Using the Same
A bipolar forceps is provided and includes a housing having one or more shafts that extend therefrom that operatively support an end effector assembly at a distal end thereof. The end effector assembly includes first and second jaw members. A tissue sealing plate disposed on each of the jaw members is provided. The tissue sealing plates is configured to support a plurality of electrodes thereon and arranged in vertically opposing pairs along the length of the jaw members. The plurality of electrodes is adapted to independently connect to an electrosurgical energy source such that each vertically opposing electrode pairs form an independently controllable electrical circuit when tissue is held between the jaw members. A control system having one or more algorithms for independently controlling and / or monitoring the delivery of electrosurgical energy from the electrosurgical energy source to the plurality of electrodes is also provided.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Ablation system
A system for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the impedance of the tissue to be ablated. Rather than attempting to detect a desired drop or a desired increase impedance, completeness of a lesion is detected in response to the measured impedance remaining at a stable level for a desired period of time, referred to as an impedance plateau. The mechanism for determining transmurality of lesions adjacent individual electrodes or pairs may be used to deactivate individual electrodes or electrode pairs, when the lesions in tissue adjacent these individual electrodes or electrode pairs are complete, to create an essentially uniform lesion along the line of electrodes or electrode pairs, regardless of differences in tissue thickness adjacent the individual electrodes or electrode pairs.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for blood glucose sensing
InactiveUS7160251B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical conductorElectrode pair
A system for measuring a glucose level in a blood sample includes a test strip and a meter. The test strip includes a sample chamber, a working electrode, a counter electrode, fill-detect electrodes, and an auto-on conductor. A reagent layer is disposed in the sample chamber. The auto-on conductor causes the meter to wake up and perform a test strip sequence when the test strip is inserted in the meter. The meter uses the working and counter electrodes to initially detect the blood sample in the sample chamber and uses the fill-detect electrodes to check that the blood sample has mixed with the reagent layer. The meter applies an assay voltage between the working and counter electrodes and measures the resulting current. The meter calculates the glucose level based on the measured current and calibration data saved in memory from a removable data storage device associated with the test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20110132542A1Improve uniformityReduce device sizeElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A plasma processing apparatus includes an upper electrode that is installed within a processing chamber so as to face a lower electrode, supplies a gas through a plurality of gas supply holes provided in a facing surface and is vertically movable; a cover body installed above the upper electrode so as to airtightly seal a top opening of the processing chamber; a multiple number of gas exhaust holes provided in the facing surface; a ring-shaped member that is arranged along a circumference of the upper electrode, is vertically movable along with the upper electrode, and forms, at a lowered position, a processing space surrounded by the lower electrode, the upper electrode and the ring-shaped member; a multiplicity of gas supply holes opened in an inner wall of the ring-shaped member; and a plurality of gas exhaust holes opened in an inner wall of the ring-shaped member.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
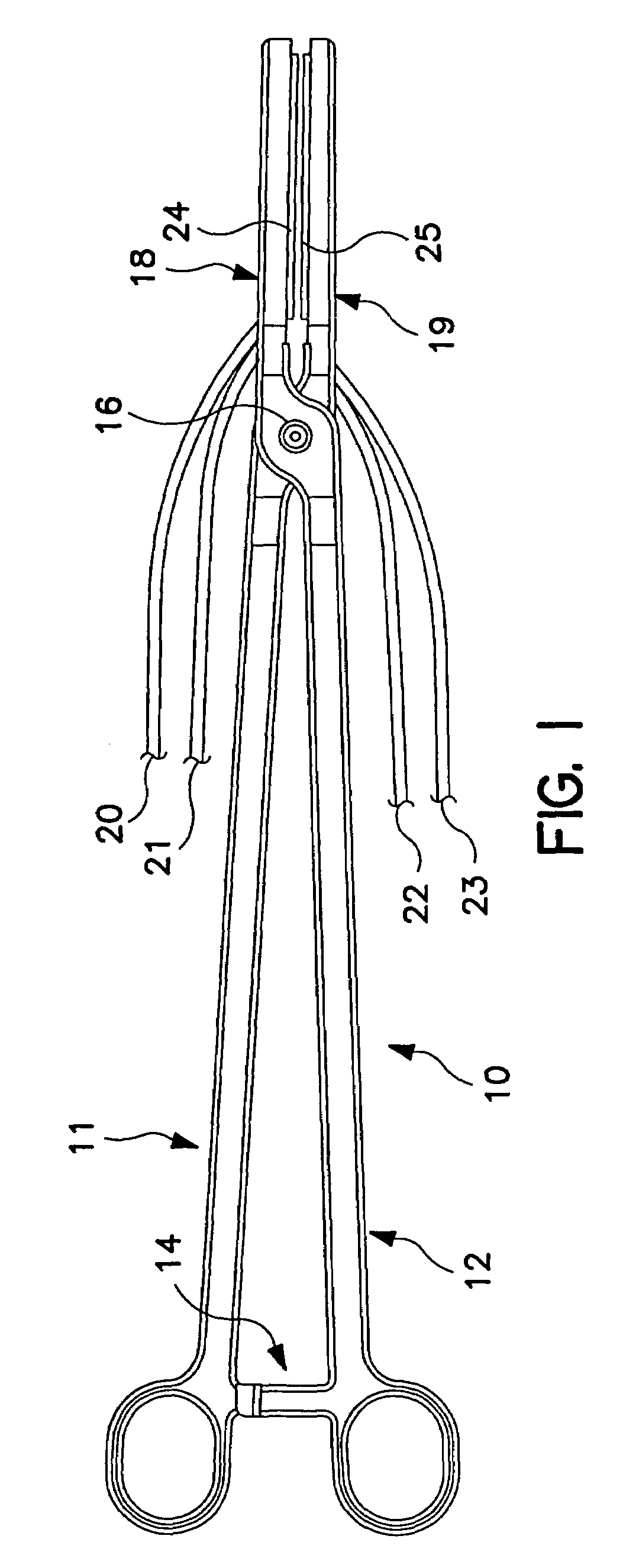
Fluid-assisted medical devices, systems and methods
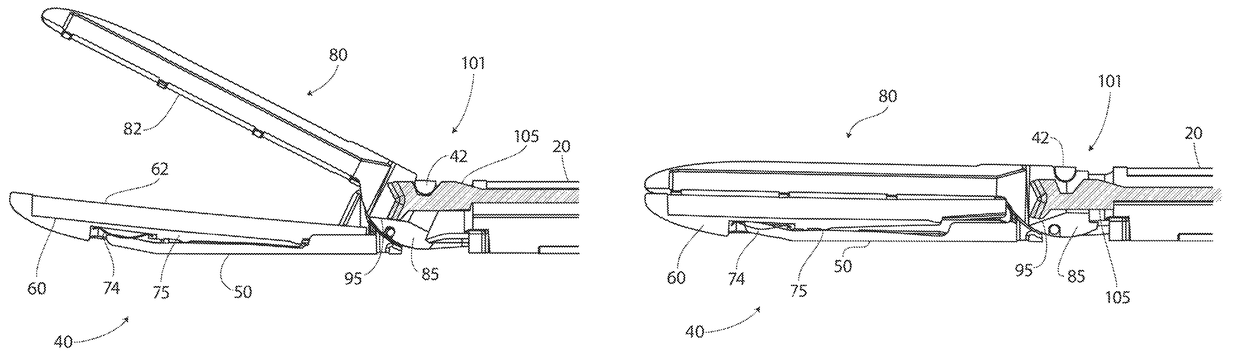
A medical device (5) is provided which comprises a catheter tube having a distal end and a lumen, and configured to assist in applying tamponage to a bleeding source in a gastrointestinal tract when flexed. A catheter tip having a catheter tip outer surface is assembled with the tube adjacent the distal end of the tube. The catheter tip comprises a probe body comprising an electrically insulative material, at least one electrode pair located on the probe body which comprises a first electrode spaced from a second electrode, and a fluid distribution manifold to direct a fluid from inside the probe body towards the tip outer surface. The manifold comprises a central passage within the probe body and a plurality of lateral passages which extend from the central passage towards the tip outer surface. An extendable injection needle is housed within the central passage to provide treatment to tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
Ablation system and method of use
A system and method for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the impedance of the tissue to be ablated. Rather than attempting to detect a desired drop or a desired increase impedance, completeness of a lesion is detected in response to the measured impedance remaining at a stable level for a desired period of time, referred to as an impedance plateau. The mechanism for determining transmurality of lesions adjacent individual electrodes or pairs may be used to deactivate individual electrodes or electrode pairs, when the lesions in tissue adjacent these individual electrodes or electrode pairs are complete, to create an essentially uniform lesion along the line of electrodes or electrode pairs, regardless of differences in tissue thickness adjacent the individual electrodes or electrode pairs. Complete or partial submersion in a fluid of the ablating portion of the ablation device may be detected prior to, during or following an ablation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
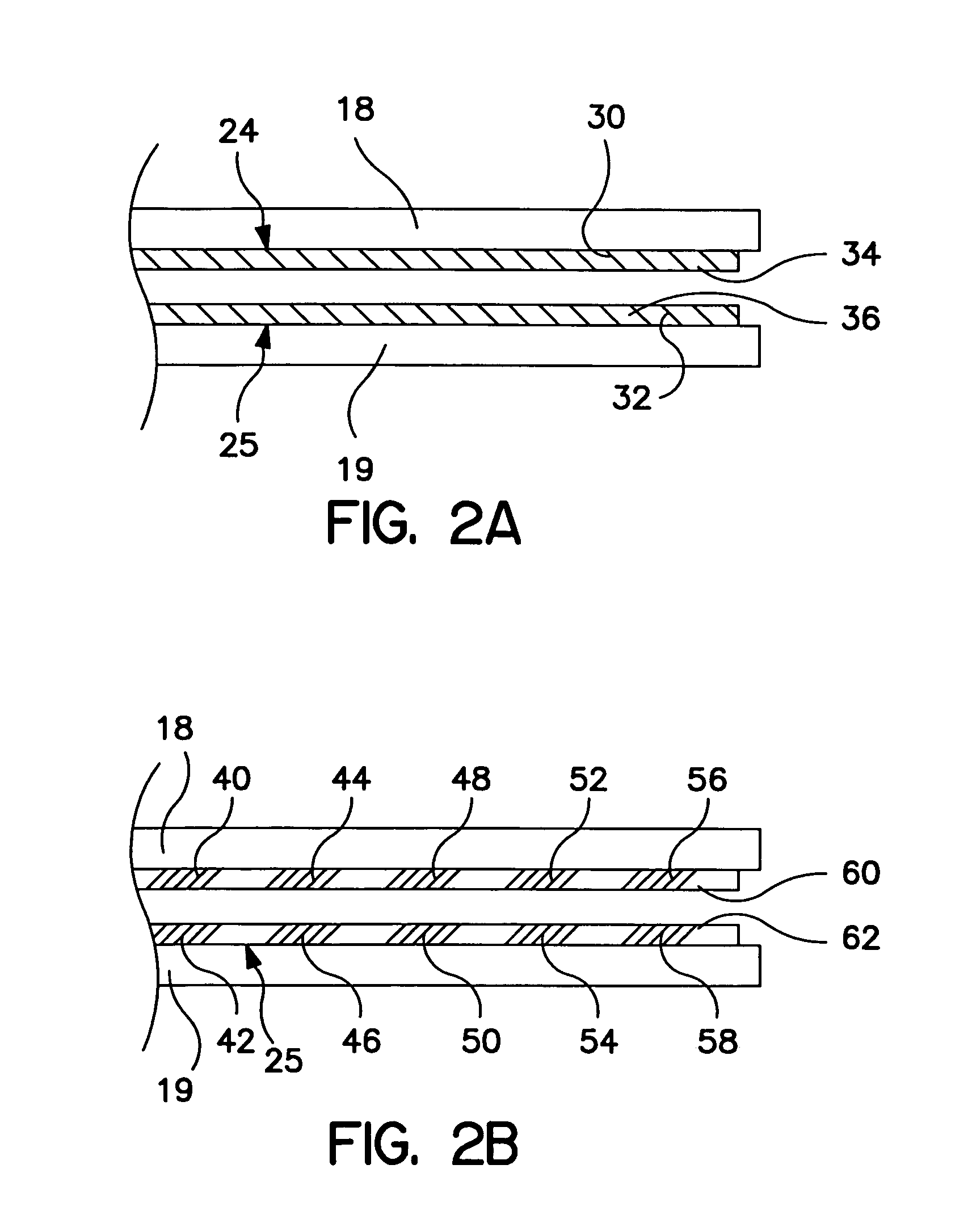
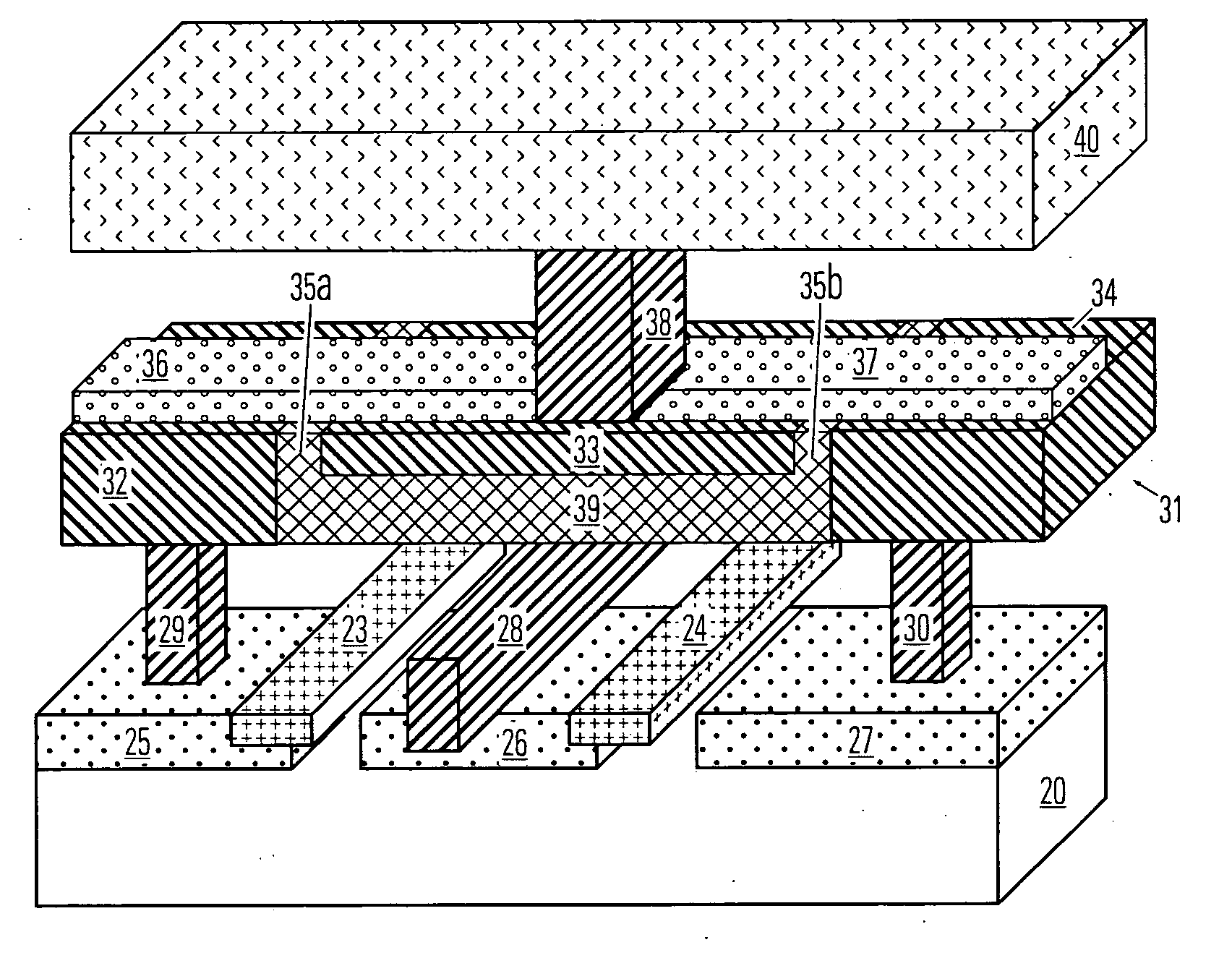
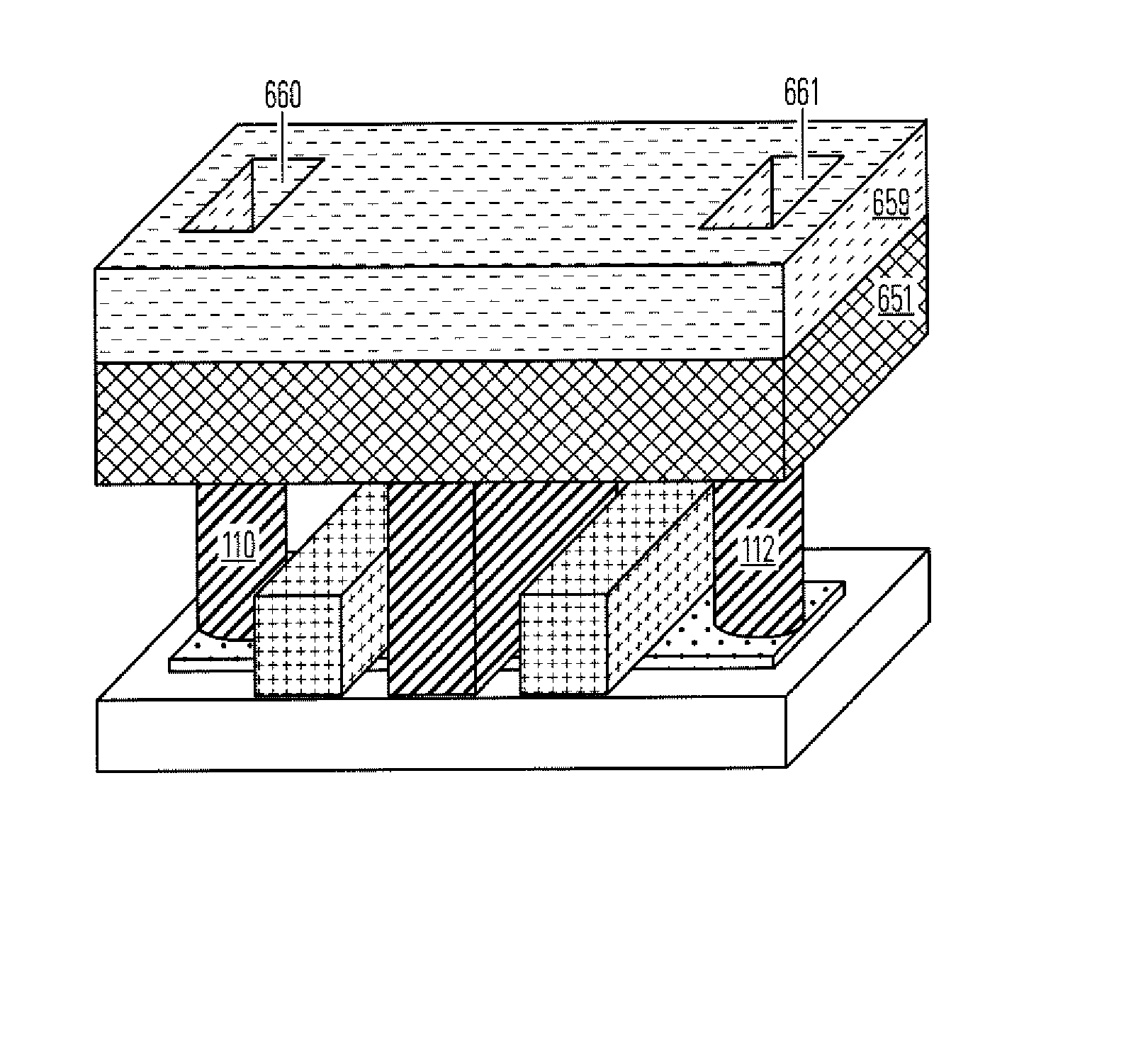
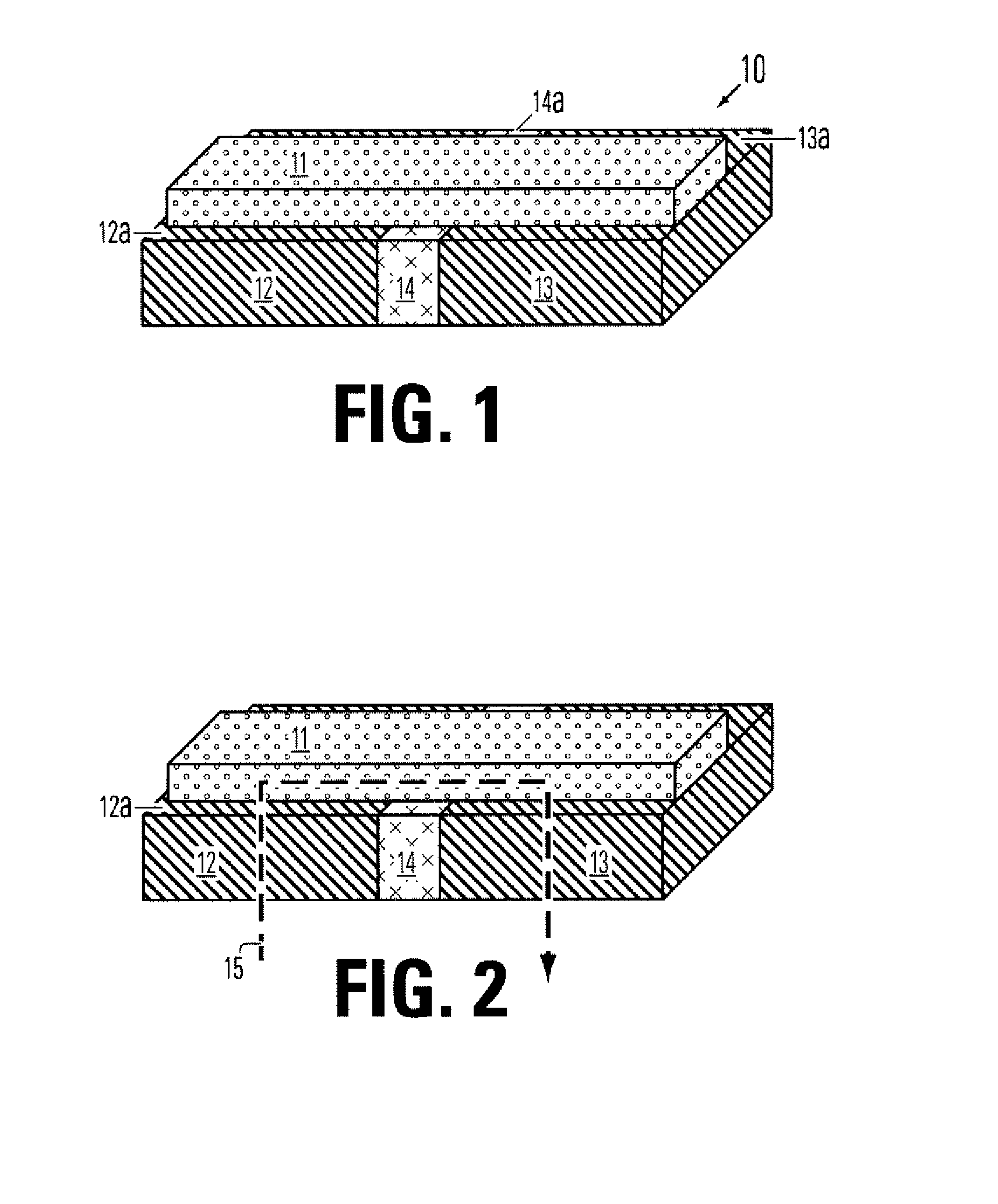
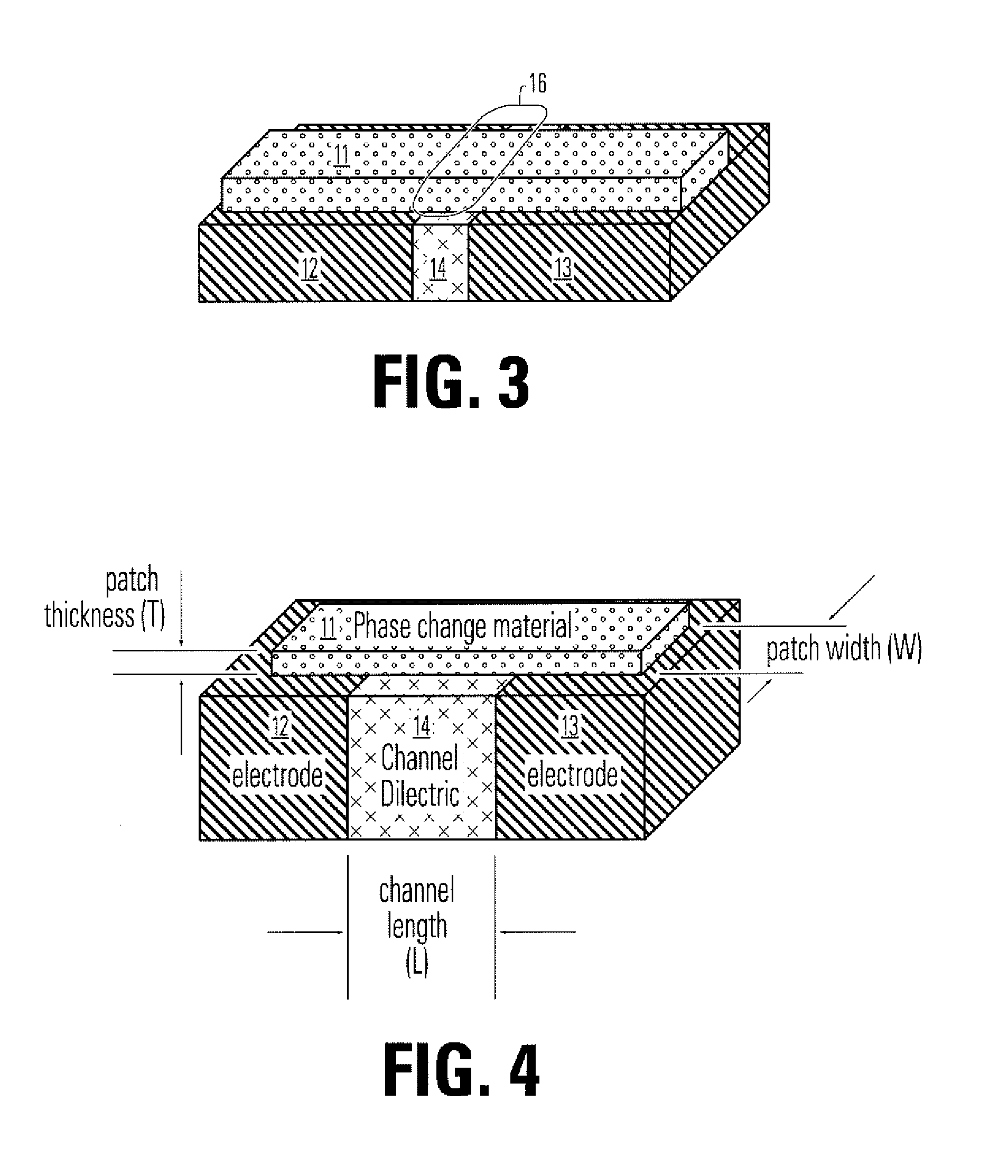
Thin film plate phase change RAM circuit and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060284157A1Simple structureReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesBit linePhase-change memory
A memory device comprising a access circuits, an electrode layer over the access circuits, an array of phase change memory bridges over the electrode layer, and a plurality of bit lines over the array of phase change memory bridges. The electrode layer includes electrode pairs. Electrode pairs include a first electrode having a top side, a second electrode having a top side and an insulating member between the first electrode and the second electrode. A bridge of memory material crosses the insulating member, and defines an inter-electrode path between the first and second electrodes across the insulating member.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
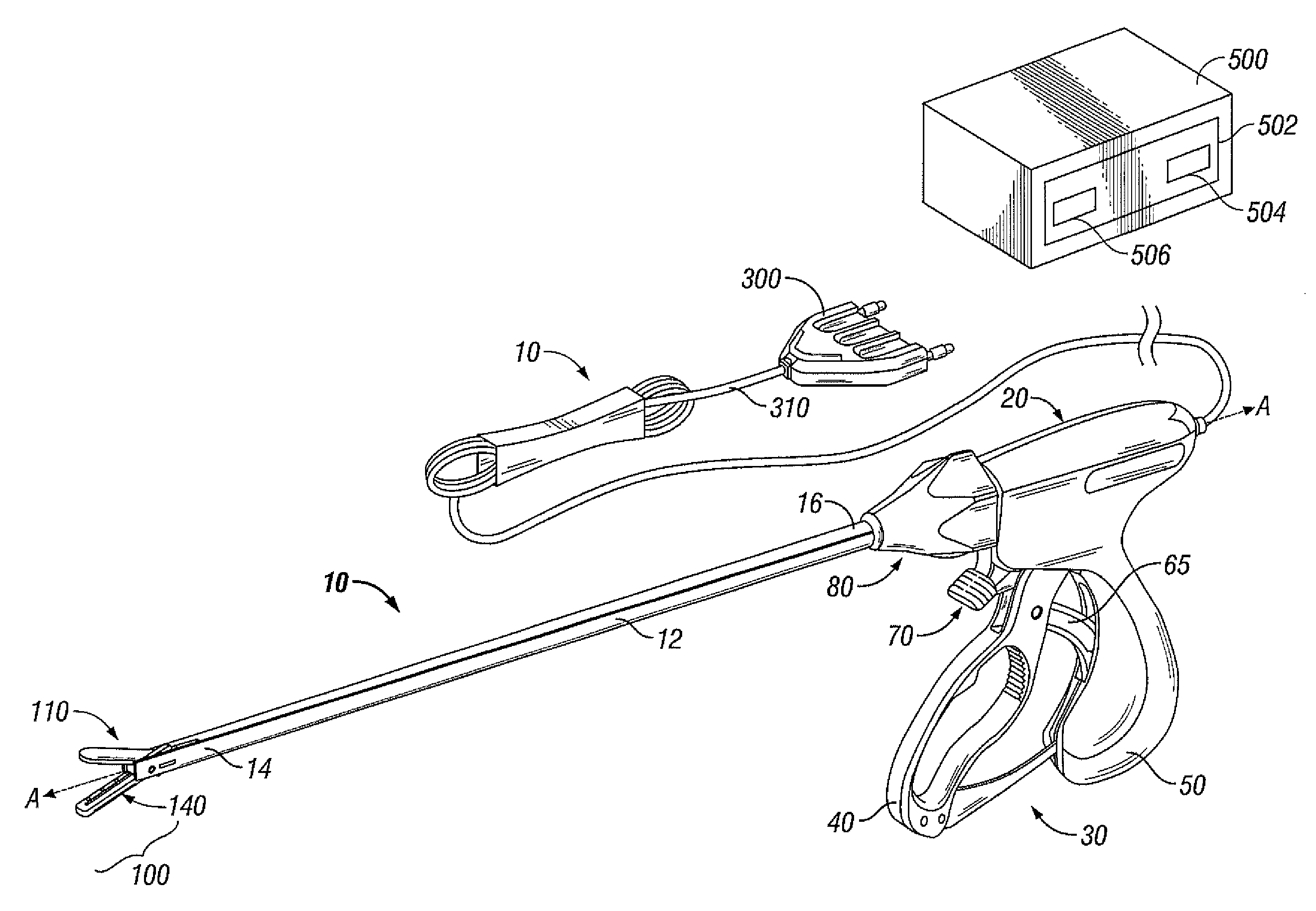
Laparoscopic radiofrequency surgical device
ActiveUS9918778B2High strengthPrevent movementDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingBipolar electrosurgeryPERITONEOSCOPE
Embodiments of the disclosed technology relate to a bipolar electrosurgical device for a laparoscopic environment, as well as methods for the use of such a device. Embodiments of the device may include a set of opposing jaws comprising at least one bipolar electrode pair disposed thereon, the set of jaws configured to deliver radiofrequency energy to a target tissue. Embodiments of the set of jaws, when closed, may have a diameter no greater than about 5 mm. The device may further include a shaft with a diameter that may be no greater than about 5 mm. Each of the jaws has a tissue-facing surface of each jaw that may include a complementary self-aligning configuration with respect to the longitudinal axis of the other jaw. Embodiments of the device may further include a pinless rotation assembly formed from rotatably cooperative features of the first jaw and the second jaw that connect the jaws together and enable the jaw set to pivot between an open position and a closed position.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
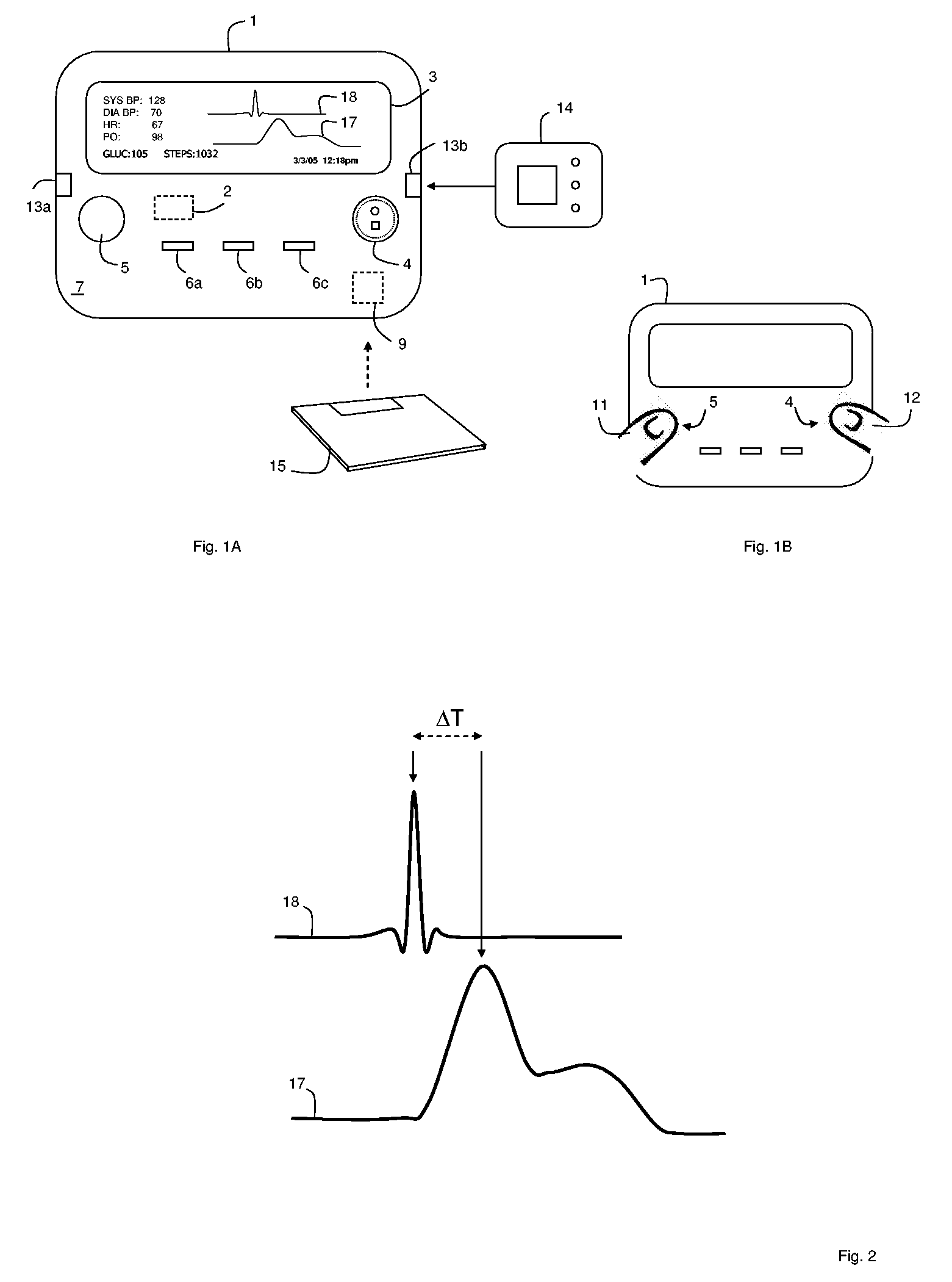
Hand-held monitor for measuring vital signs
InactiveUS20060009698A1Easily perform throughout dayGood blood pressureElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsOptical radiationPhotodetector
The invention provides a monitor for measuring blood pressure and other vital signs from a patient without using a cuff. The monitor features a housing with a first surface that, in turn, supports a first sensor. The first sensor features: i) an optical system with one or more light sources (e.g., LEDs or laser diodes) that generate optical radiation, and a photodetector oriented to collect radiation after it irradiates the patient and in response generate an optical signal; and ii) a first electrode. A second sensor features a second electrode paired with the first electrode that collects an electrical signal from the patient. A microprocessor in electrical communication with the first and second sensor receives the optical and electrical signals and processes them with an algorithm to determine systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Owner:TRIAGE WIRELESS
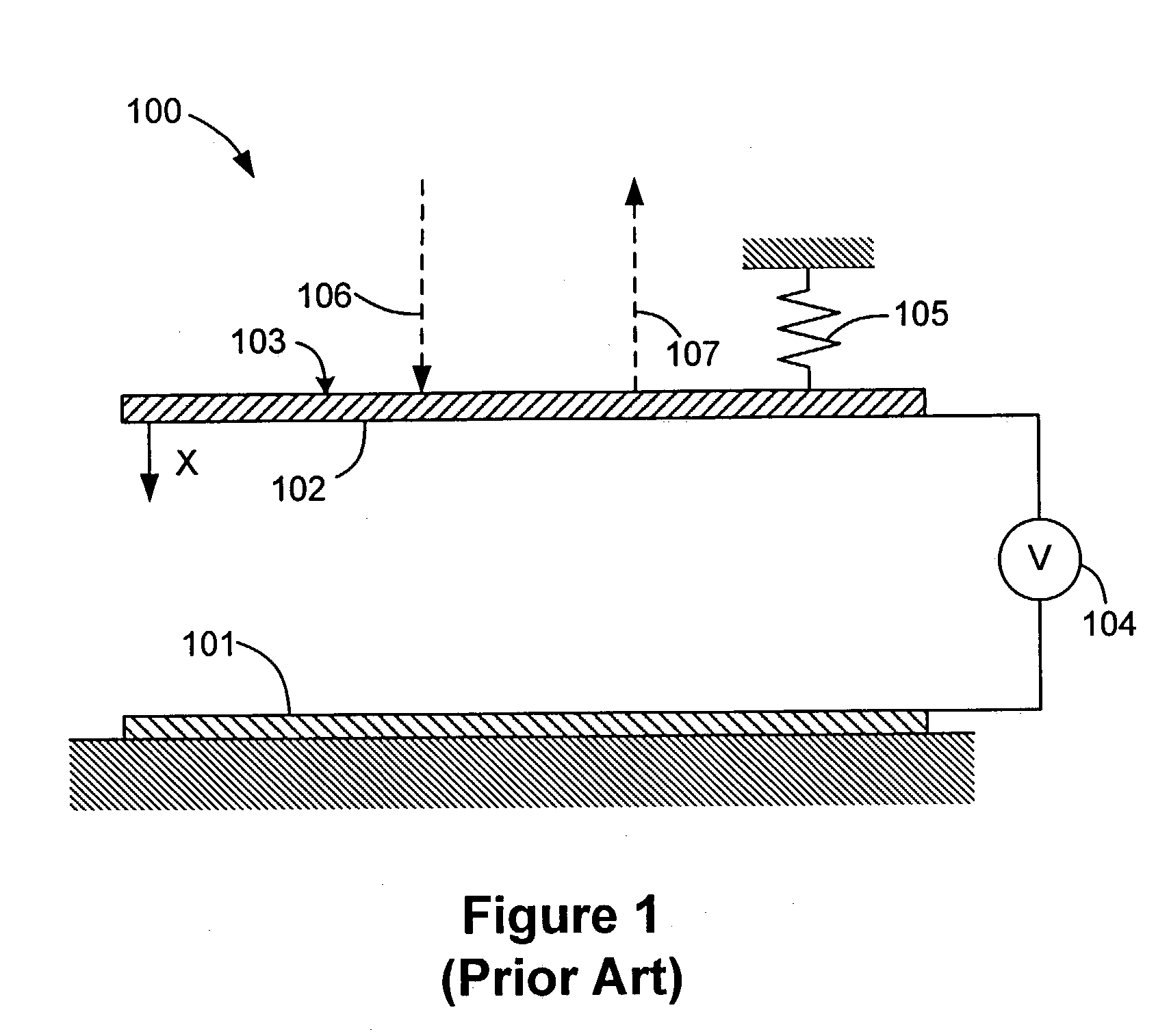
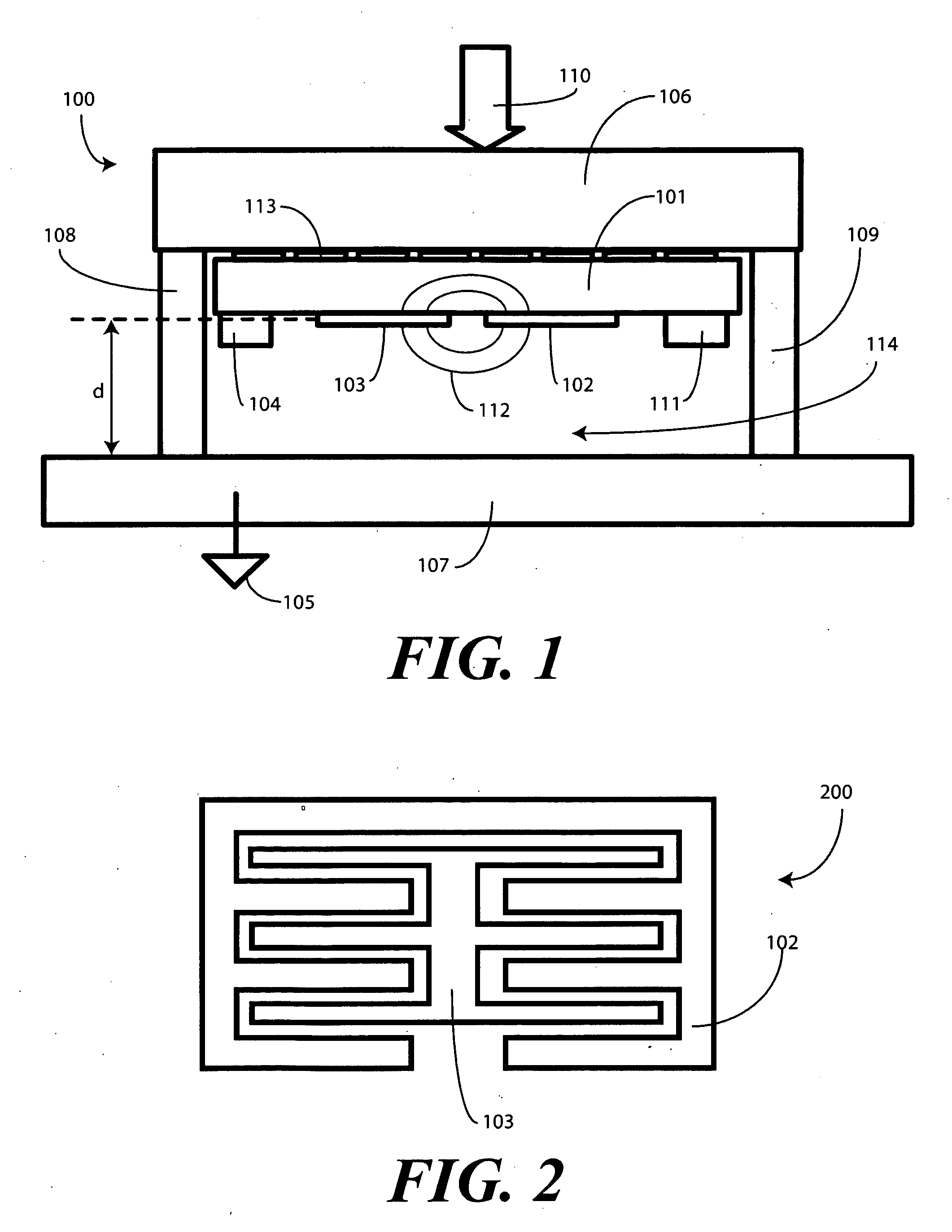
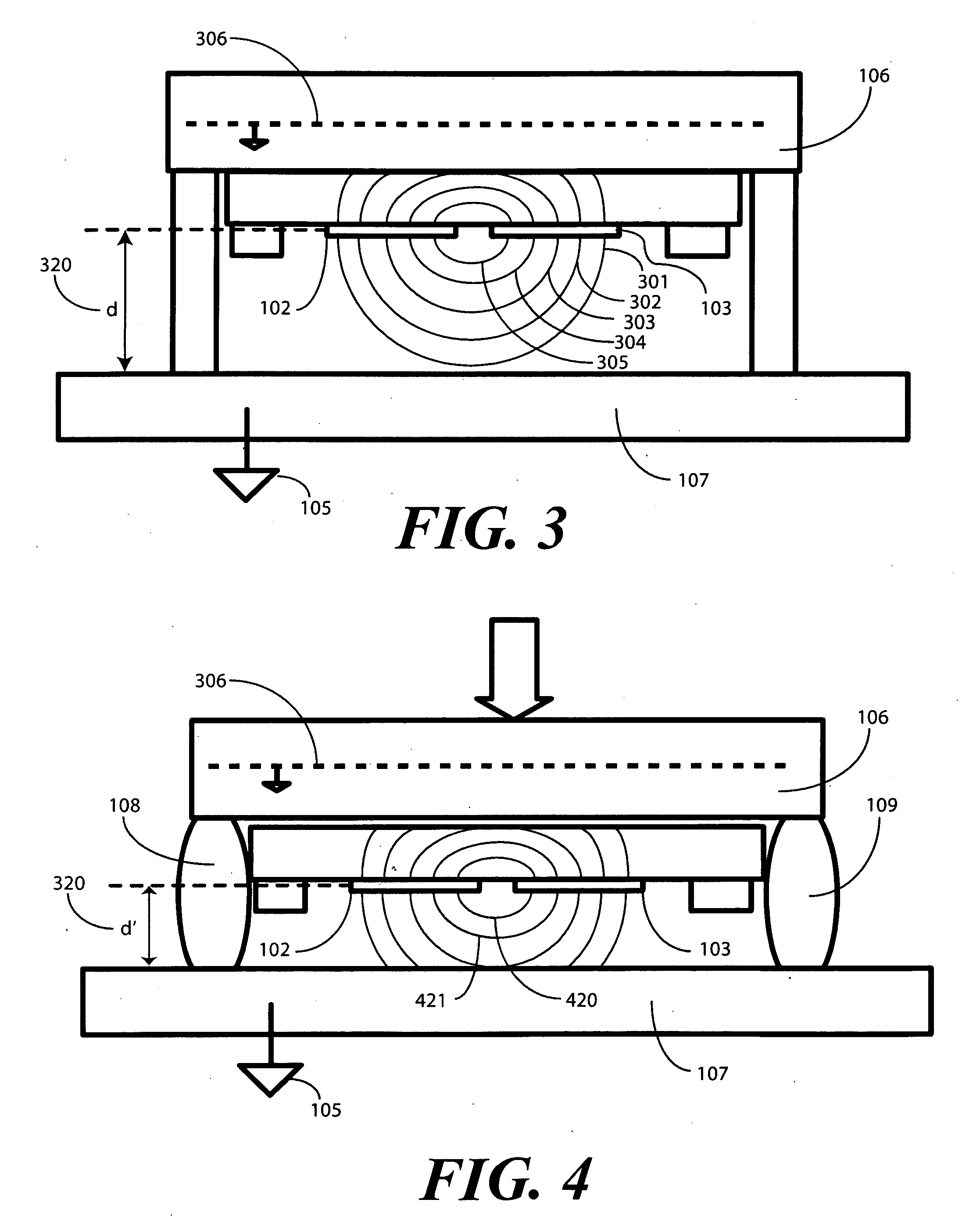
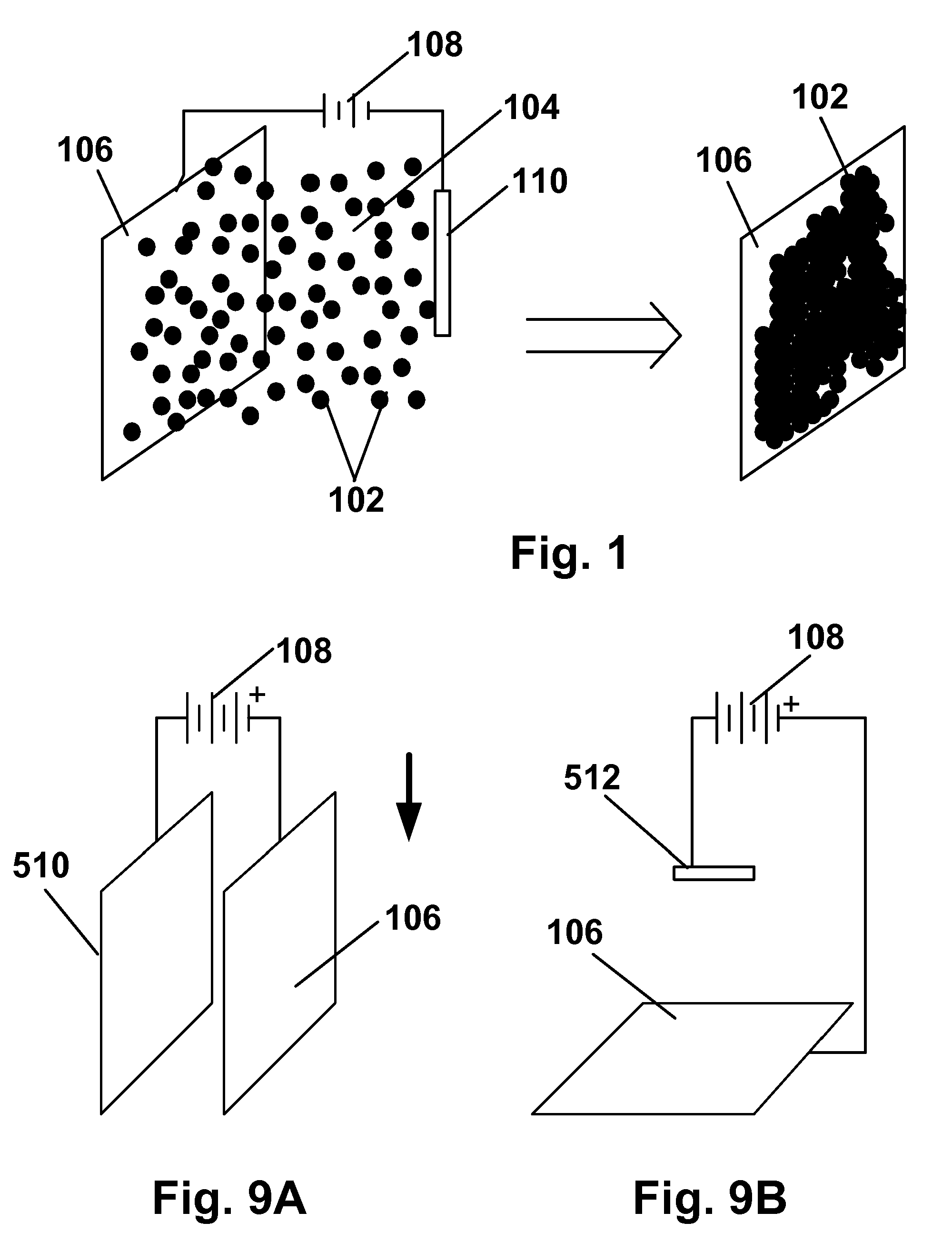
Single Sided Capacitive Force Sensor for Electronic Devices
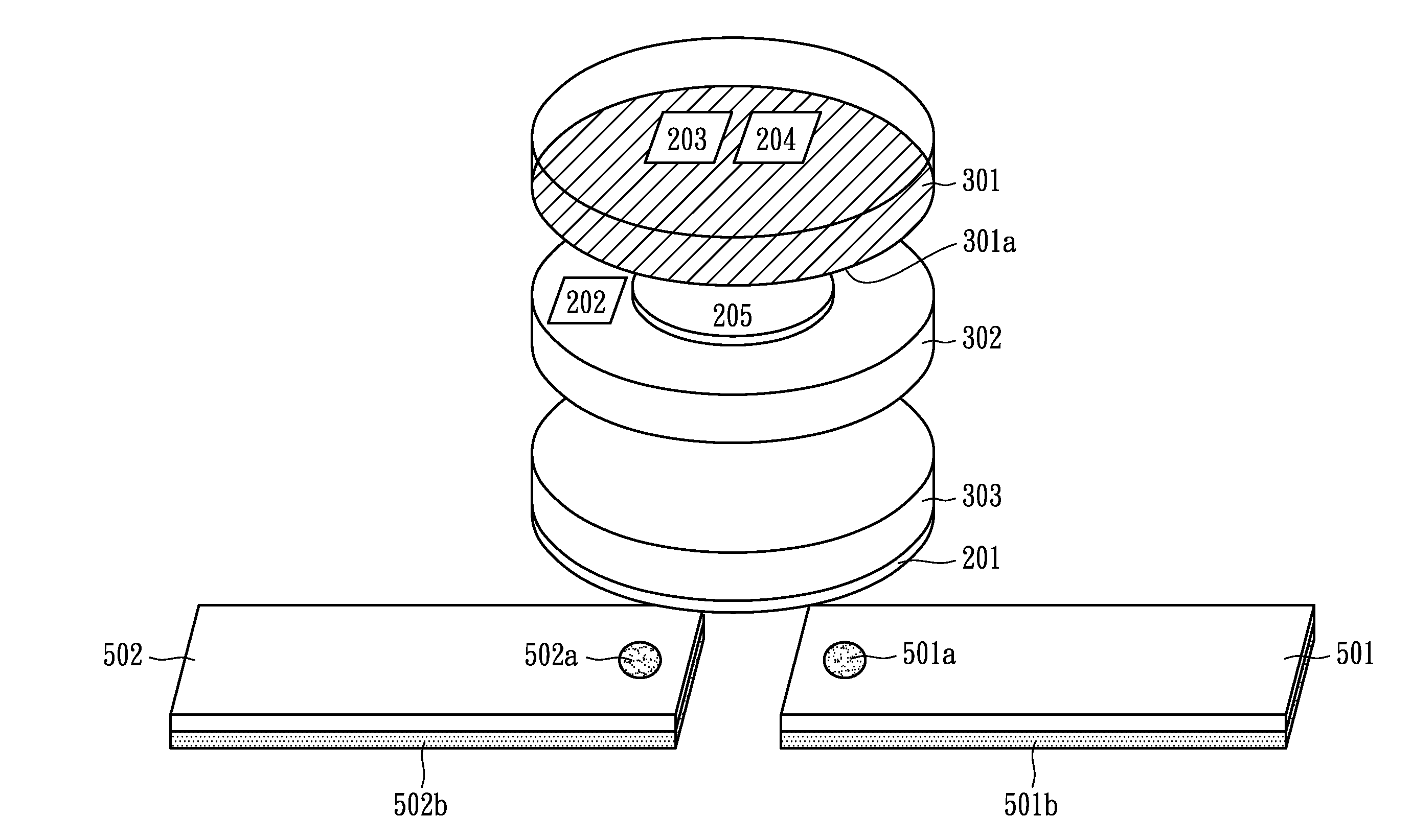
A capacitive force sensor (100) includes a substrate (101) having at least one electrode pair (102,103) defining a capacitance disposed thereon. The substrate (101) is fixed relative to a first plate (106). A drive circuit (104) is configured to apply a voltage relative to a circuit ground (105) to the electrode pair (102,103). The first plate (106) is separated from a second plate (107) that is coupled to circuit ground (105) by a compliance member (108,109). The compliance member (108,109) is configured to oppose a compression force (110) while allowing the first plate (106) to physically move relative to the second plate (107). A capacitive detection circuit (111) is then configured to detect a change the capacitance when the compliance member (108,109) is compressed. The compression force (110) is then determined from the change in capacitance and the spring constant of the compliance member (108,109).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Minimal device and method for effecting hyperthermia derived anesthesia
InactiveUS9031667B2Improve comfortLess chance of physical damageElectrotherapySurgical needlesFiberMammal
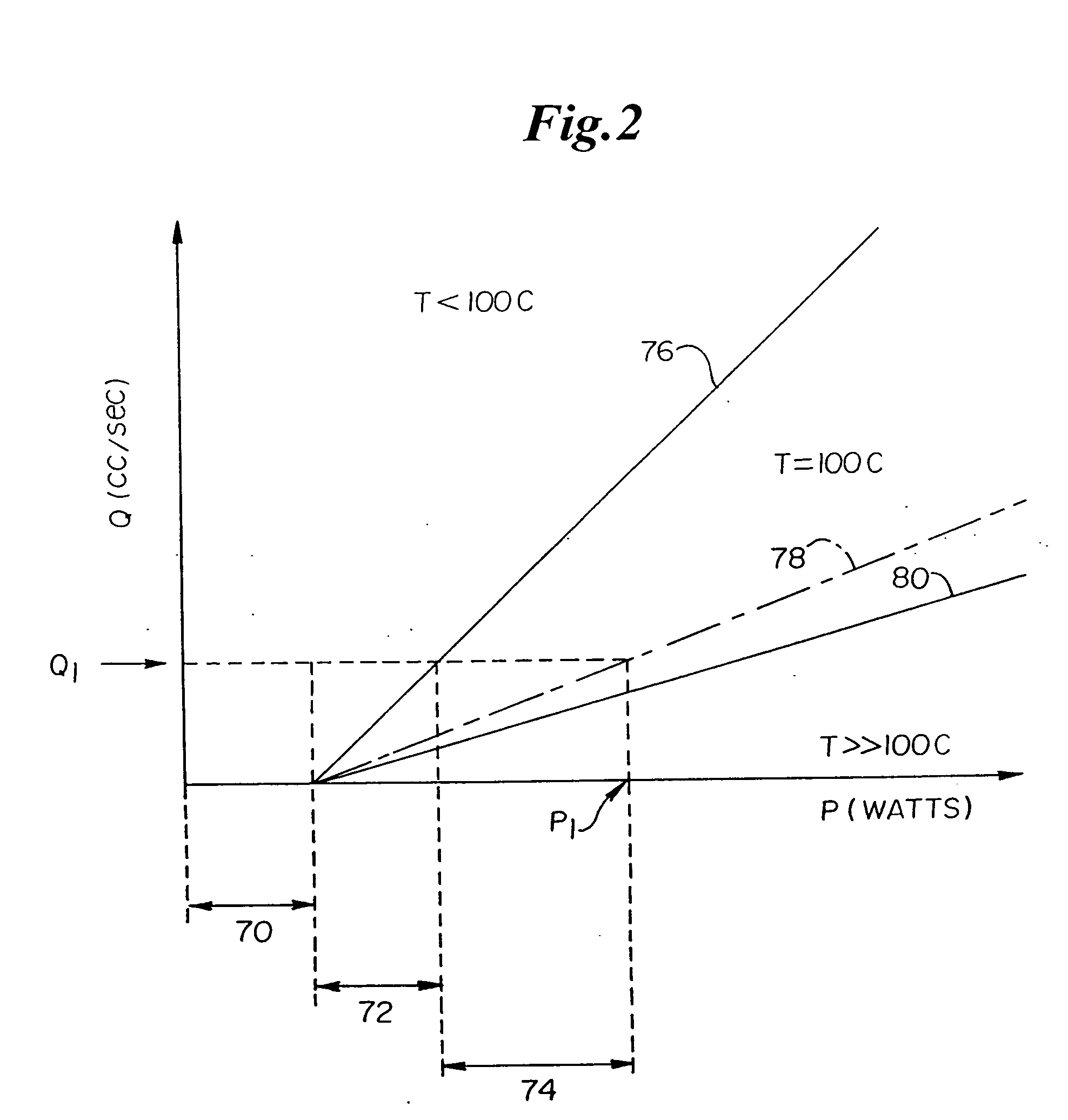
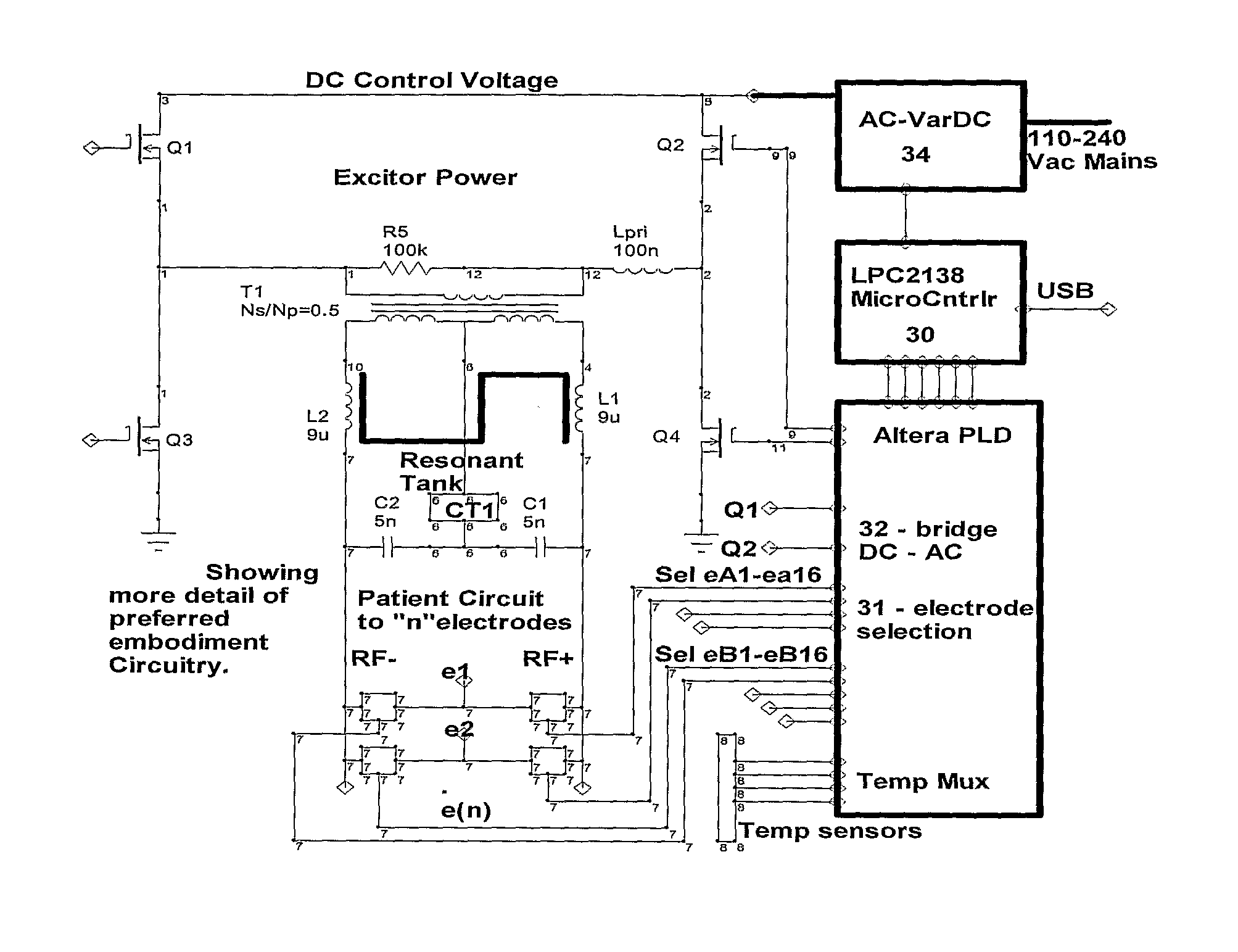
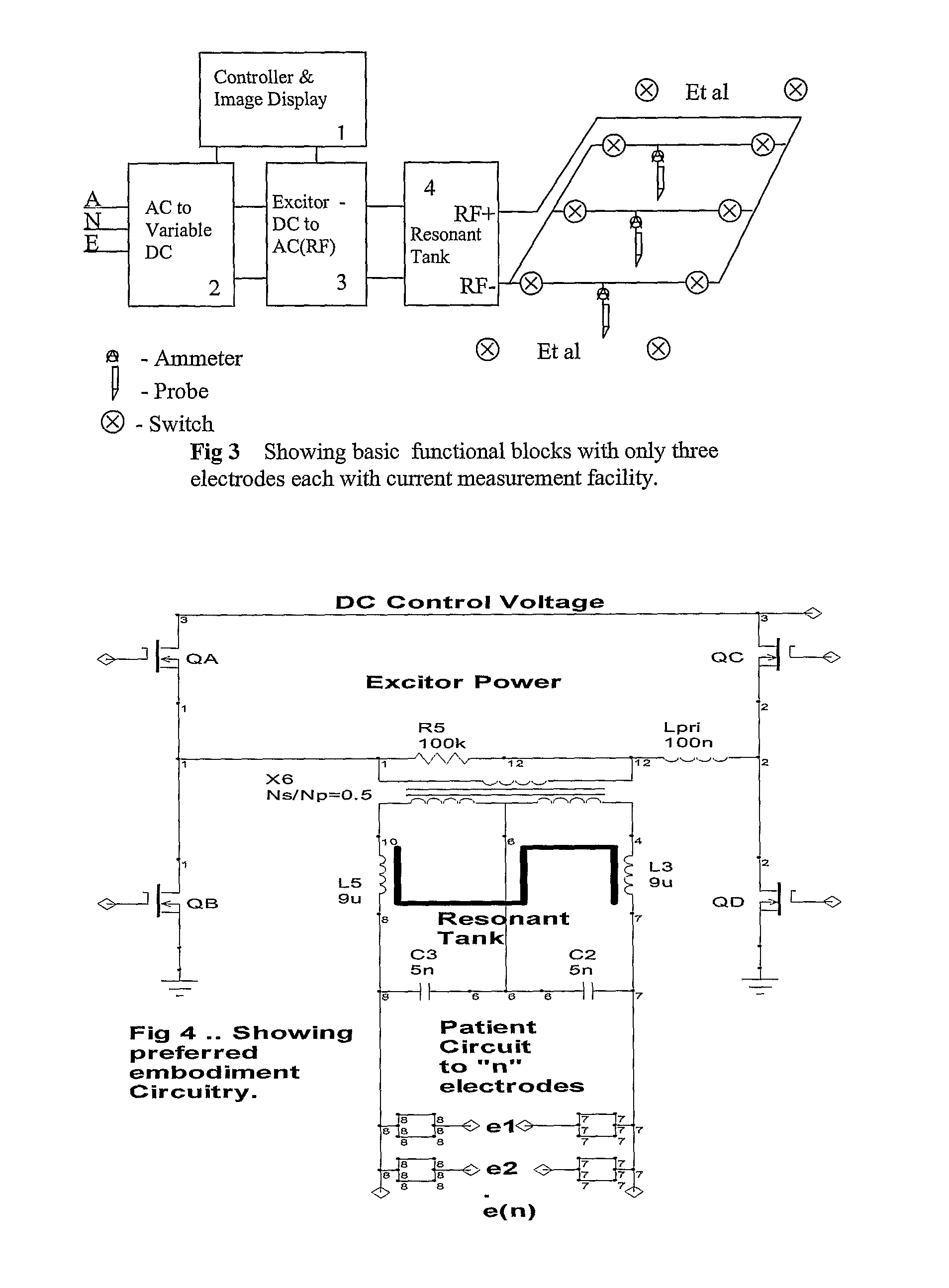
A method and device for inducing anaesthesia in mammals by the application of RF energy to create hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia. An RF generator drives a plurality of electrodes placed in tissue surrounding the target nerve fiber to desiccate the desired length of nerve fiber to be desiccated in a single deployment. The device allows high-speed selection / de-selection of bipolar electrode pairs or sets under continuous RF excitation. Activation of electrode pairs is adapted in response to sensed current density and temperature (by electrodes not in the current discharge activation phase) in order to create lesions of complex and well defined shape necessary for the production of hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia.
Owner:INTERVENTION TECH
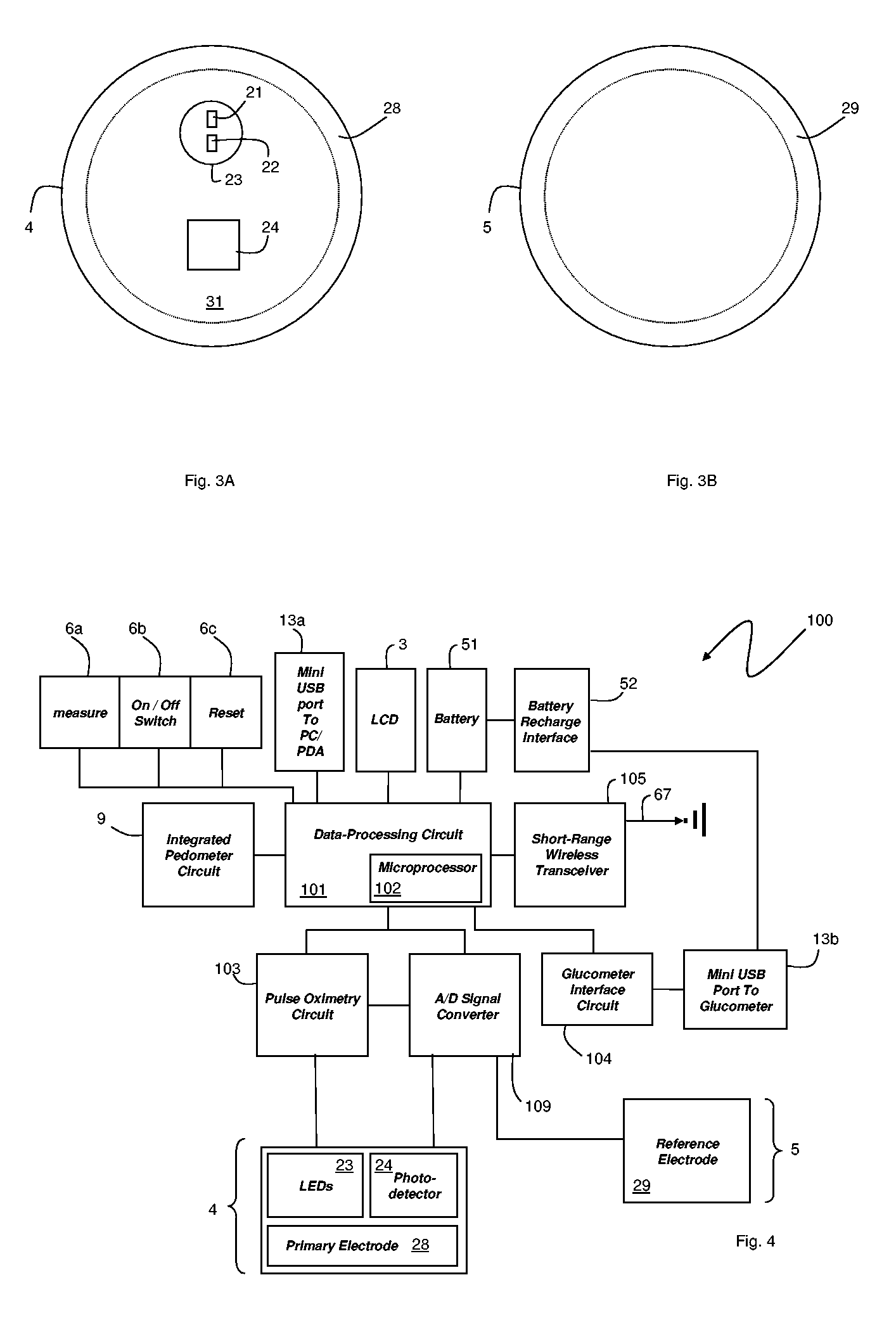
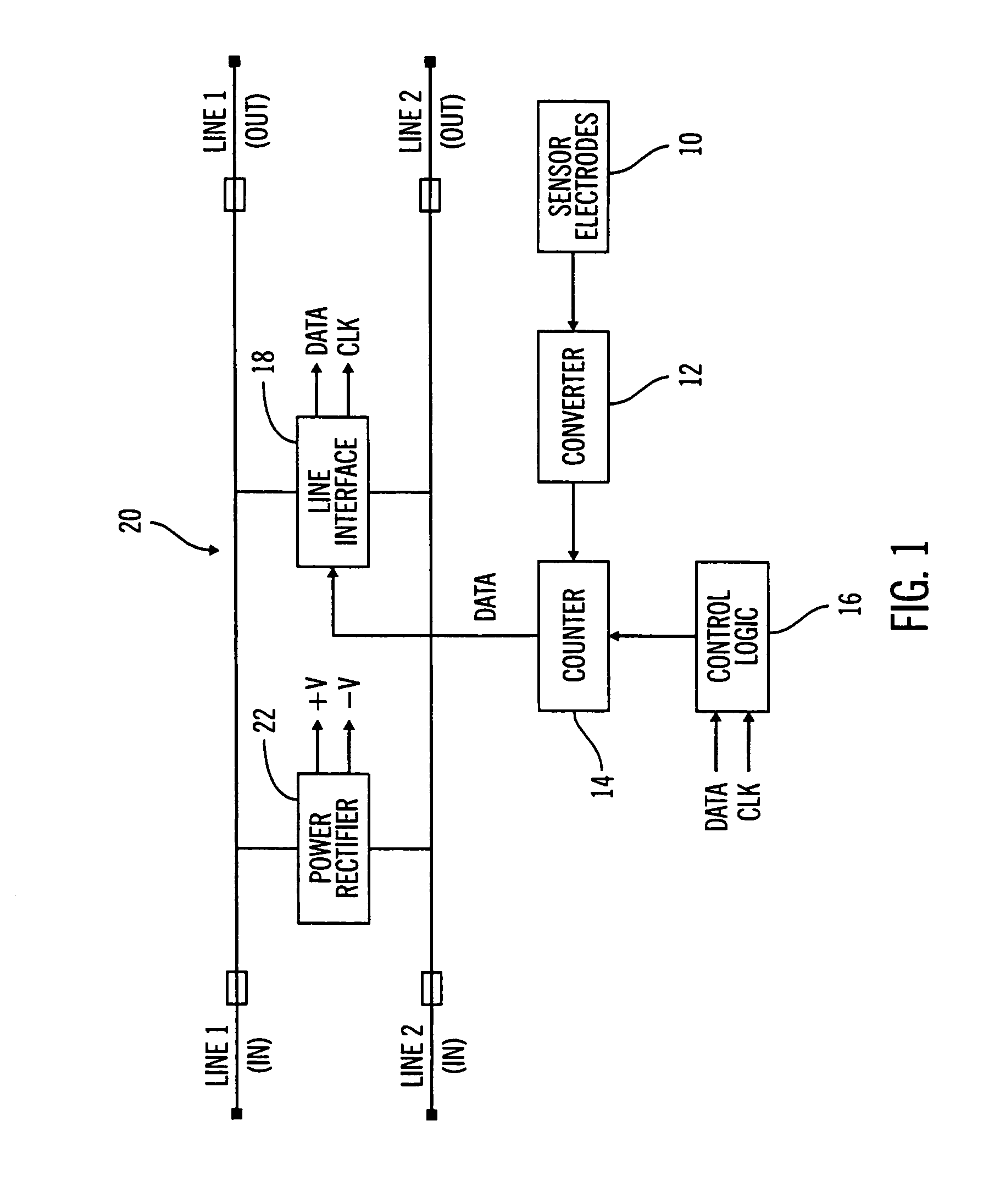
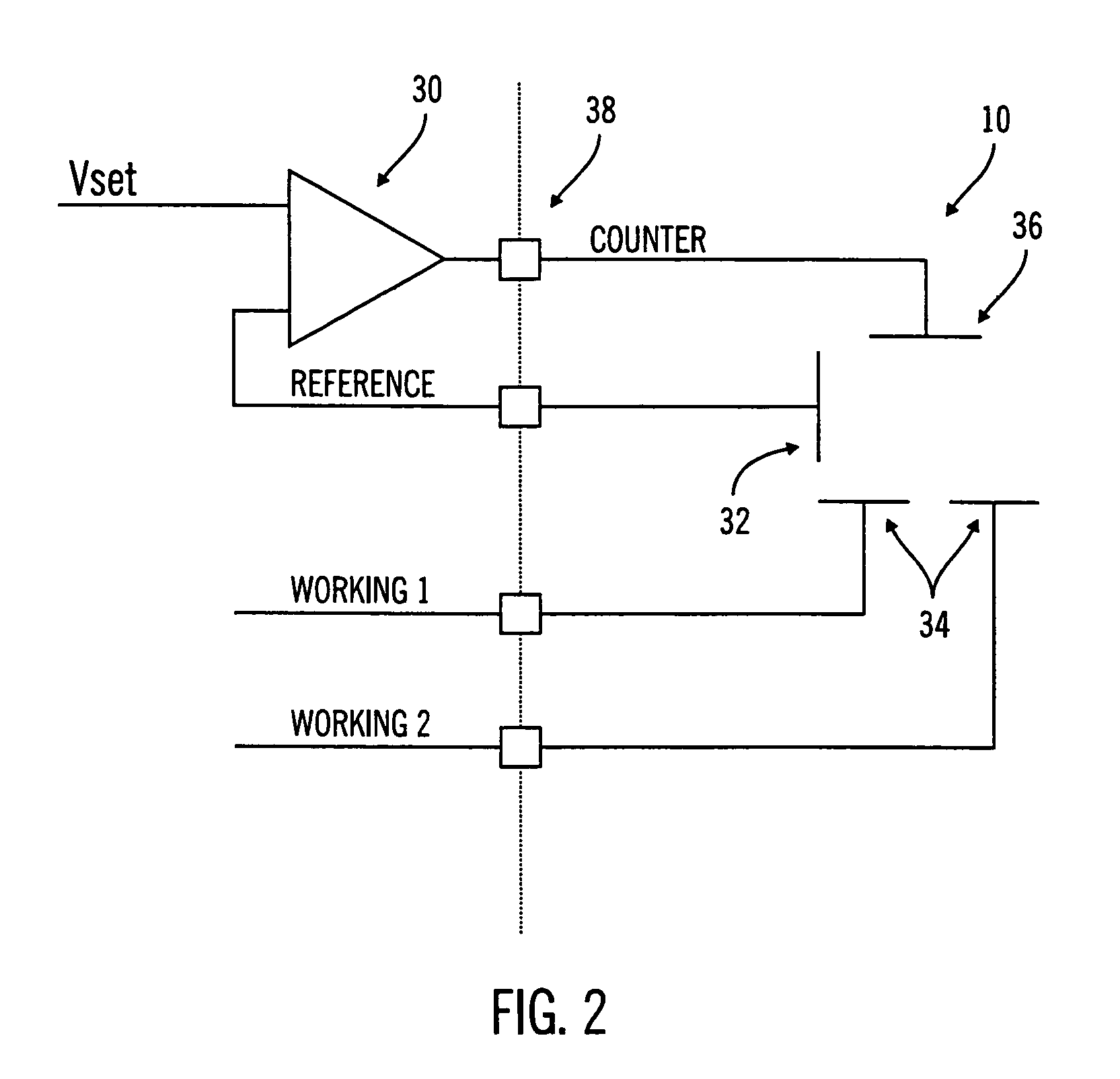
Implantable sensor electrodes and electronic circuitry
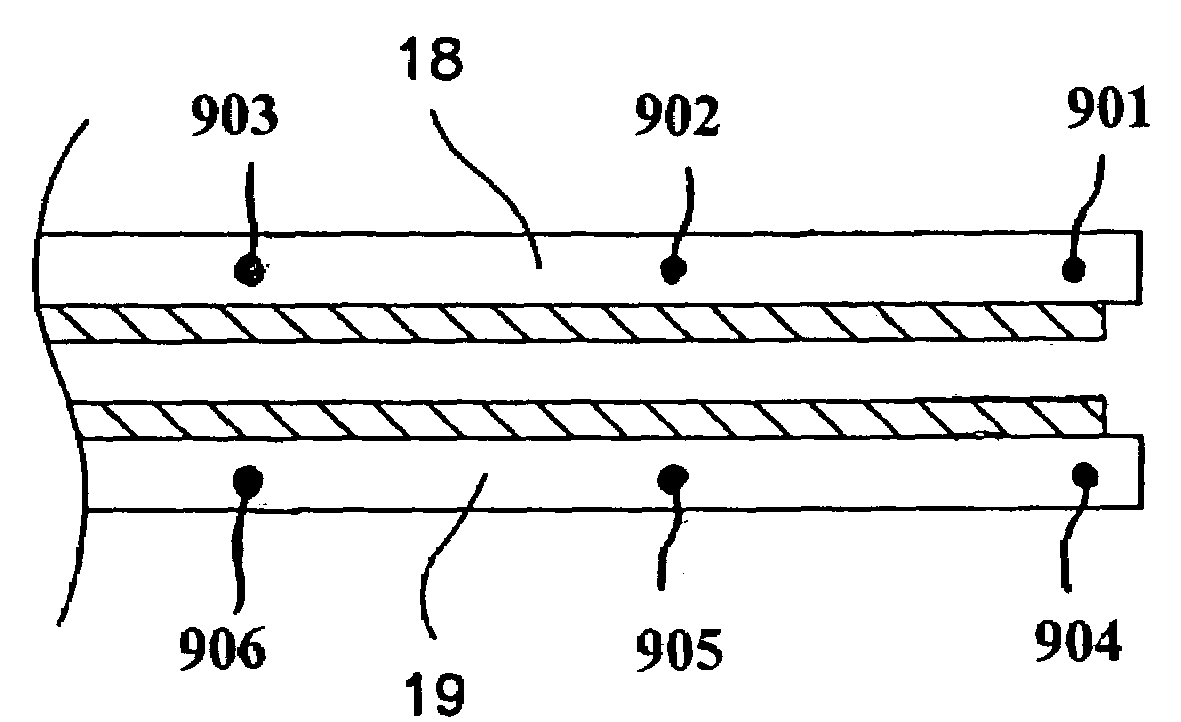
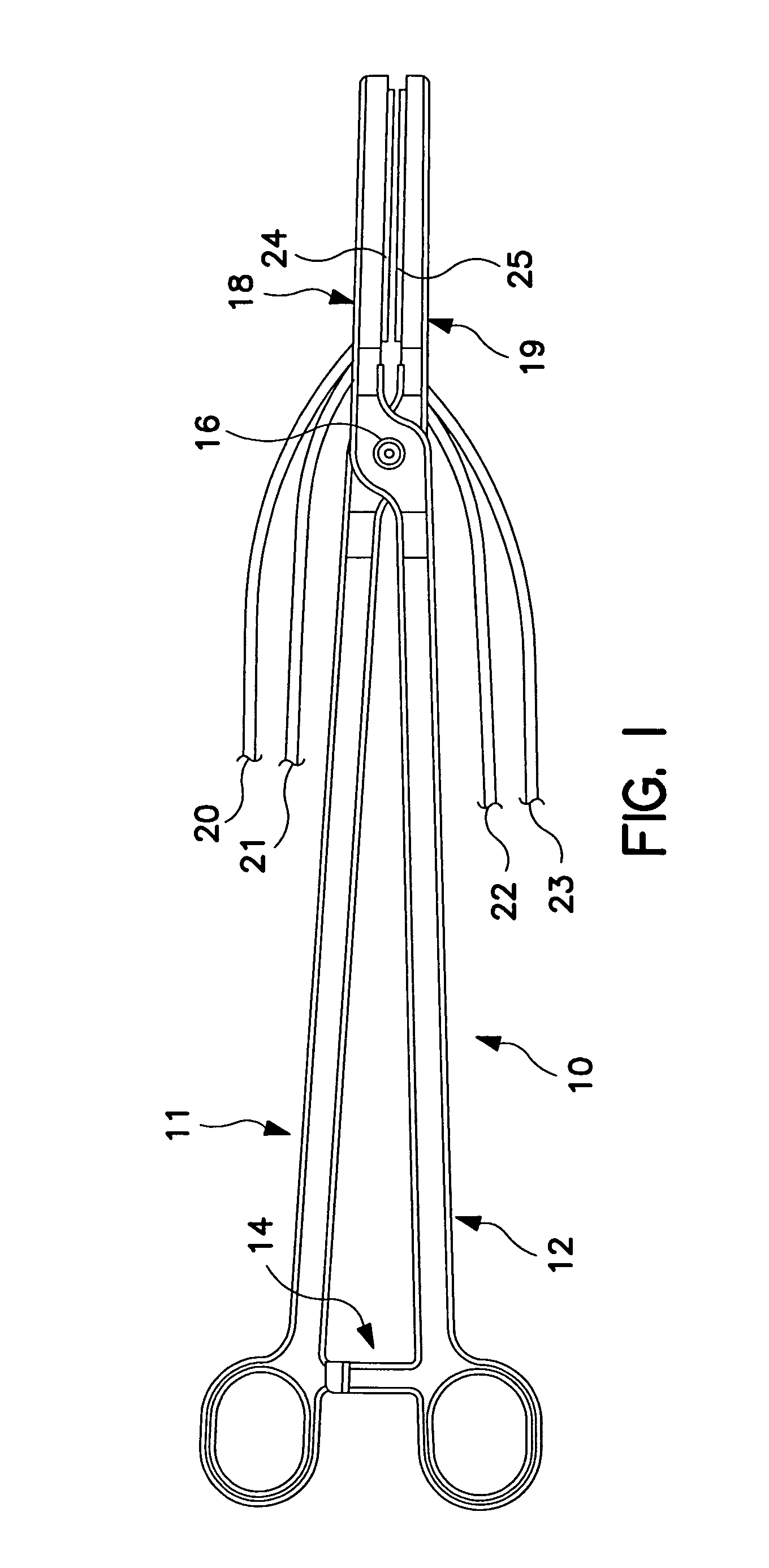
ActiveUS7525298B2Minimize cross-couplingImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringElectrode pair
An electronic circuit for sensing an output of a sensor having at least one electrode pair and circuitry for obtaining and processing the sensor output. The electrode pair may be laid out such that one electrode is wrapped around the other electrode in a U-shaped fashion. The electronic circuitry may include, among other things, a line interface for interfacing with input / output lines, a rectifier in parallel with the line interface, a counter connected to the line interface and a data converter connected to the counter and the electrode pair. The data converter may be a current-to-frequency converter. In addition, the rectifier may derive power for the electronic circuit from communication pulses received on the input / output lines.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
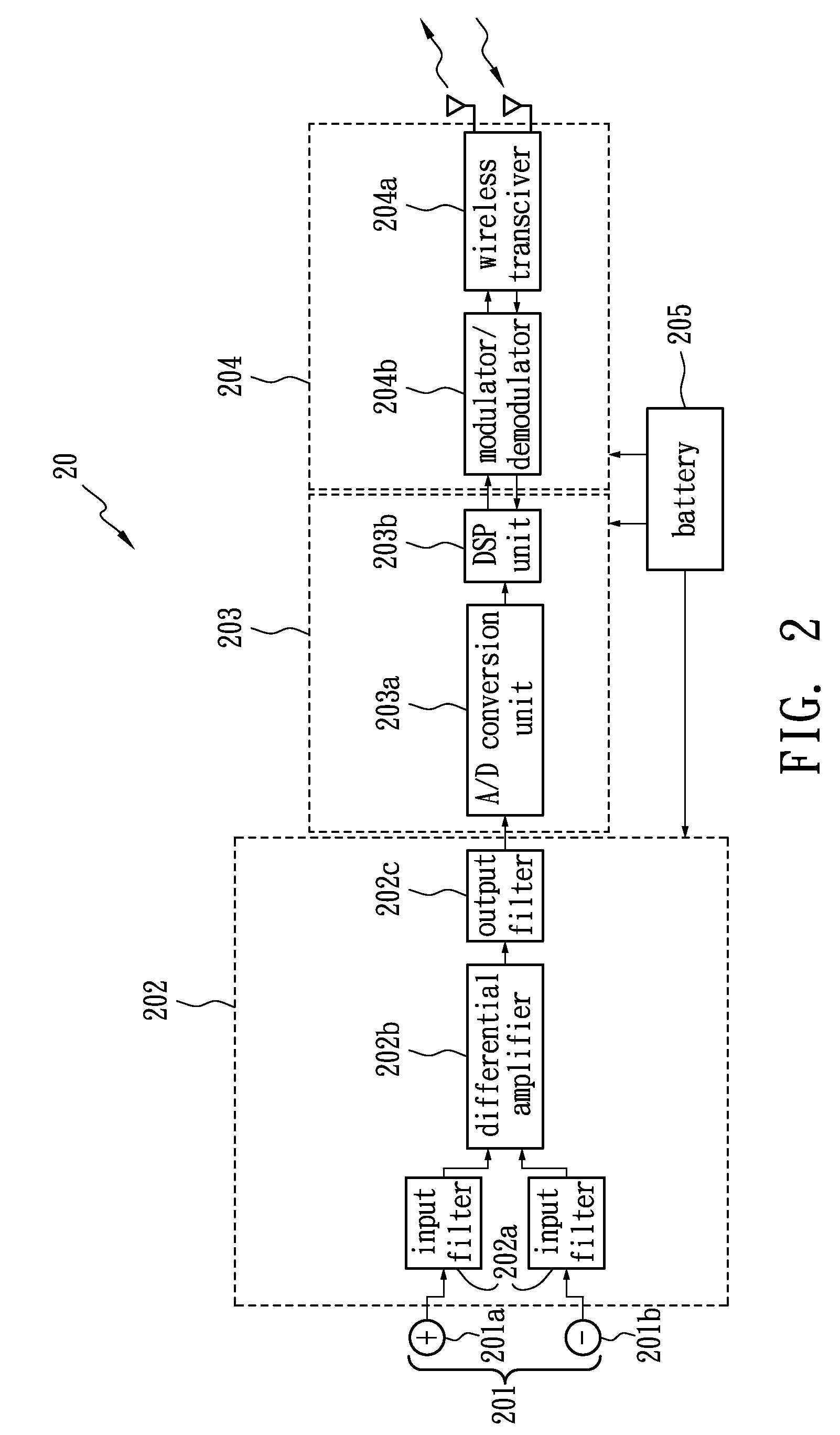
Miniature wireless apparatus for collecting physiological signals
InactiveUS7672714B2Simple materialLow costControlling membersElectrocardiographyMicrocontrollerData compression
Owner:KUO TERRY B J +2
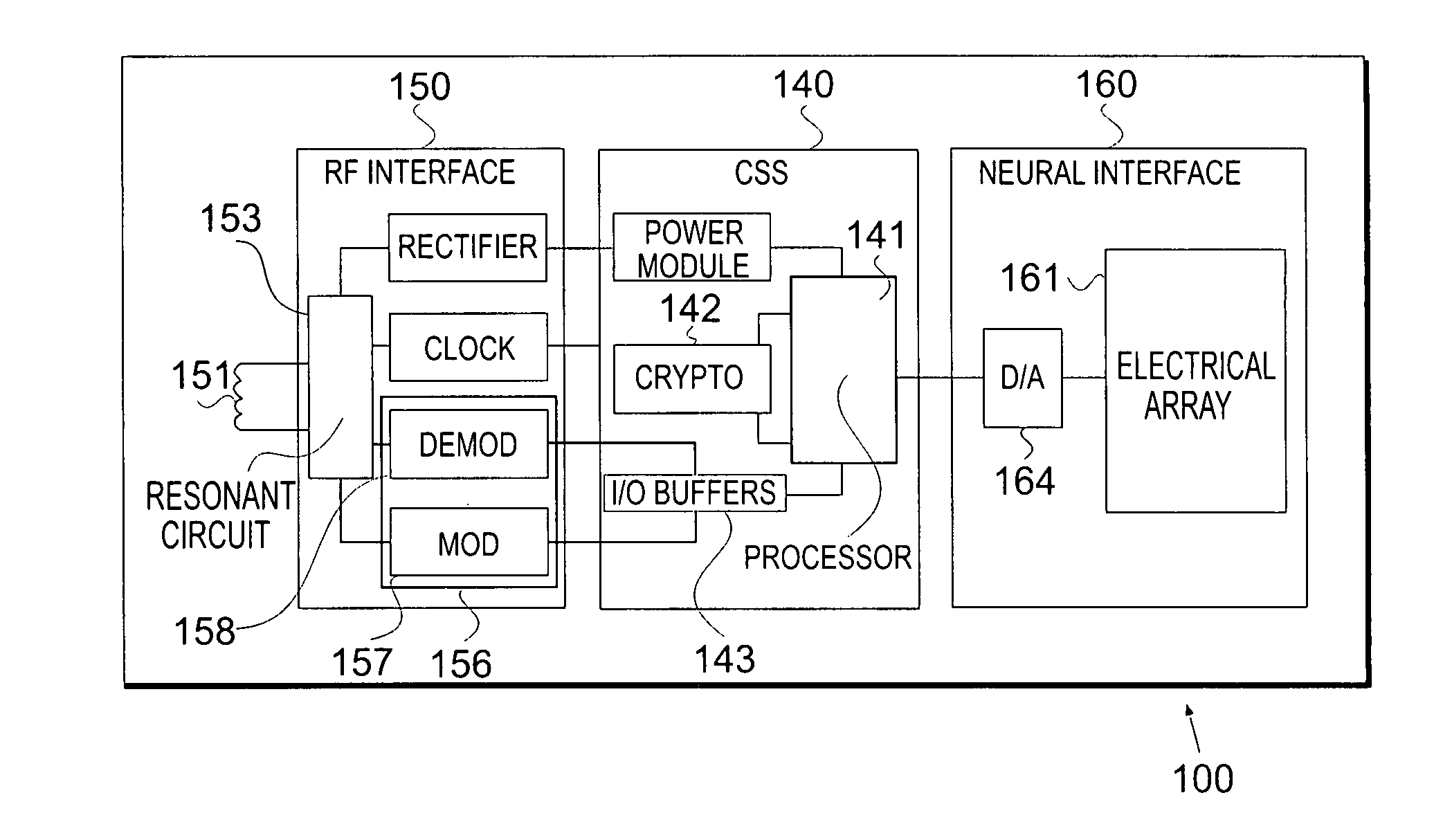
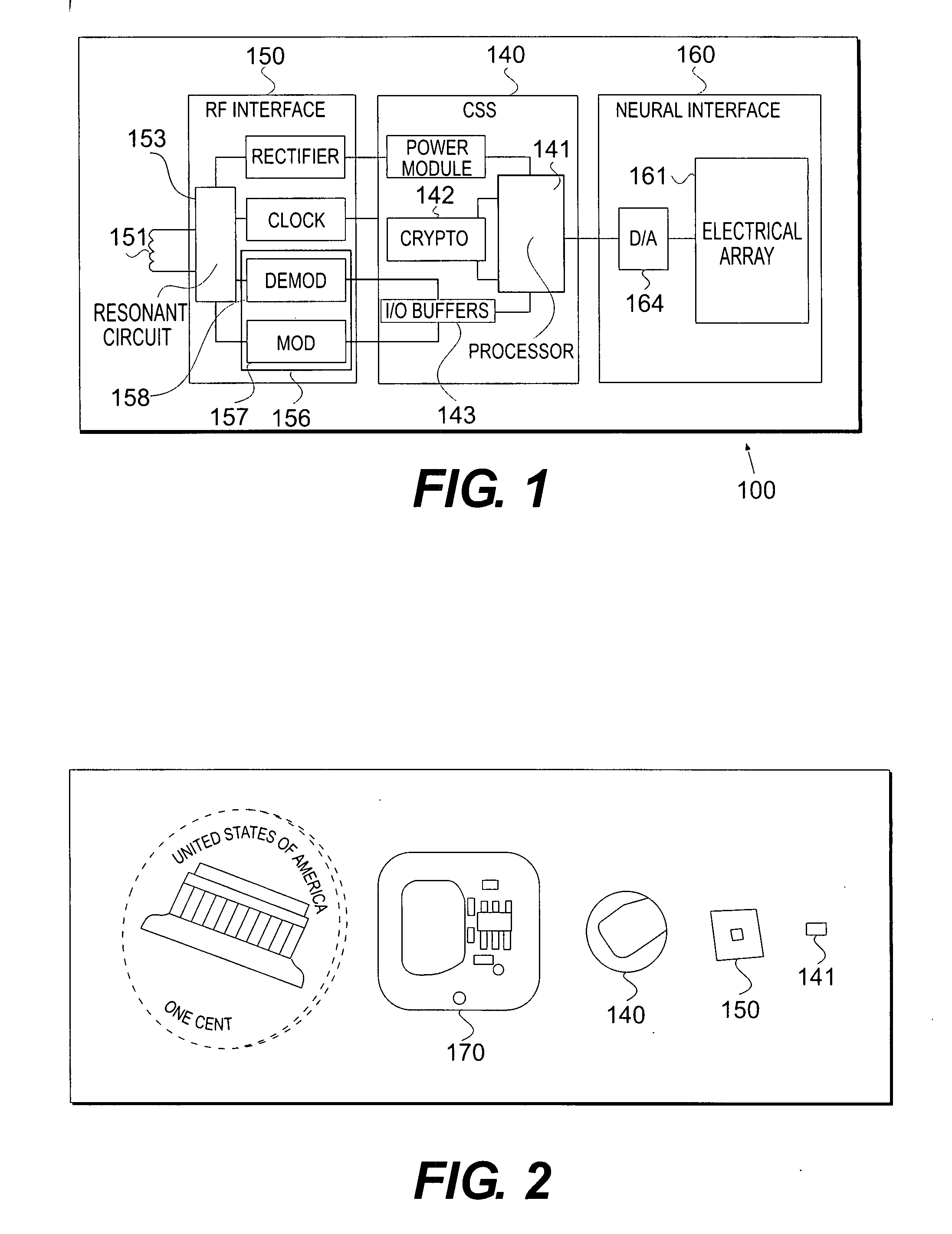
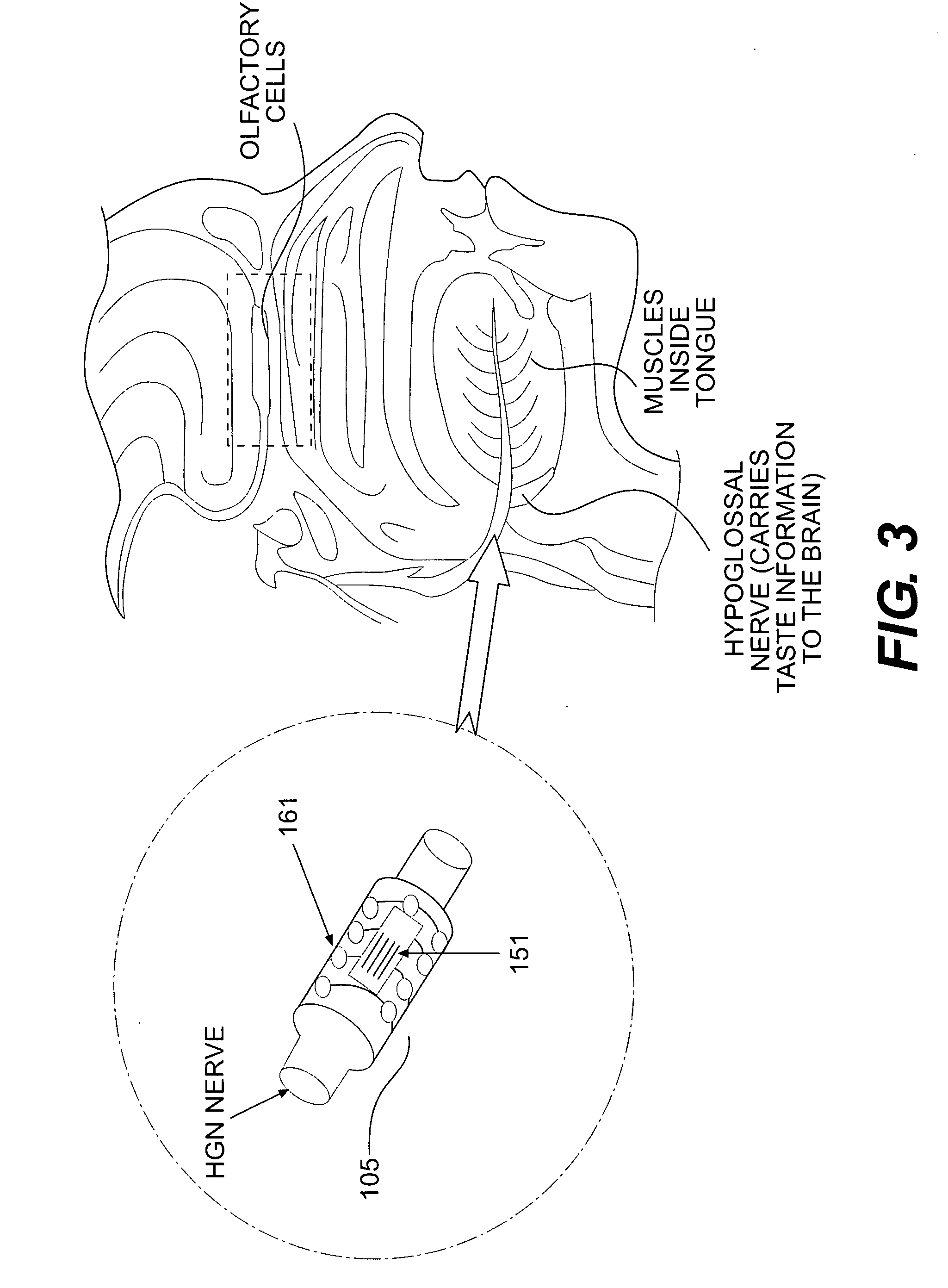
RFID-based apparatus, system, and method for therapeutic treatment of a patient
InactiveUS20070233204A1Ameliorate any conditionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesMultiplexerAnalog signal
Provided is an implantable RFID-enabled micro-electronic neurostimulator system comprising a) an internal subsystem having (i) an array of electrodes, where at least one electrode pair contacts a nerve; (ii) a multiplexer; (iii) digital to analog signal converter; and (iv) a RFID based control and stimulation chip; and (b) an external subsystem having (i) a controller; and (ii) an RF interface.
Owner:IMTHERA MEDICAL
Processes for the production of electrophoretic displays
ActiveUS7910175B2Electric shock equipmentsElectrophoretic coatingsPotential differenceElectrophoresis
A coating of an encapsulated electrophoretic medium is formed on a substrate (106) by dispersing in a fluid (104) a plurality of electrophoretic capsules (102), contacting at least a portion of a substrate (106) with the fluid (104); and applying a potential difference between at least a part of the portion of the substrate (106) contacting the fluid (104) and a counter-electrode (110) in electrical contact with the fluid (104), thereby causing capsules (102) to be deposited upon at least part of the portion of the substrate (106) contacting the fluid (102). Patterned coatings of capsules containing different colors may be deposited in registration with electrodes using multiple capsule deposition steps. Alternatively, patterned coatings of capsules may be formed by applying a fluid form of an electrophoretic medium to a substrate, and applying a temporally varying voltage between an electrode and the substrate. The process may be repeated to allow for deposition of full color displays.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
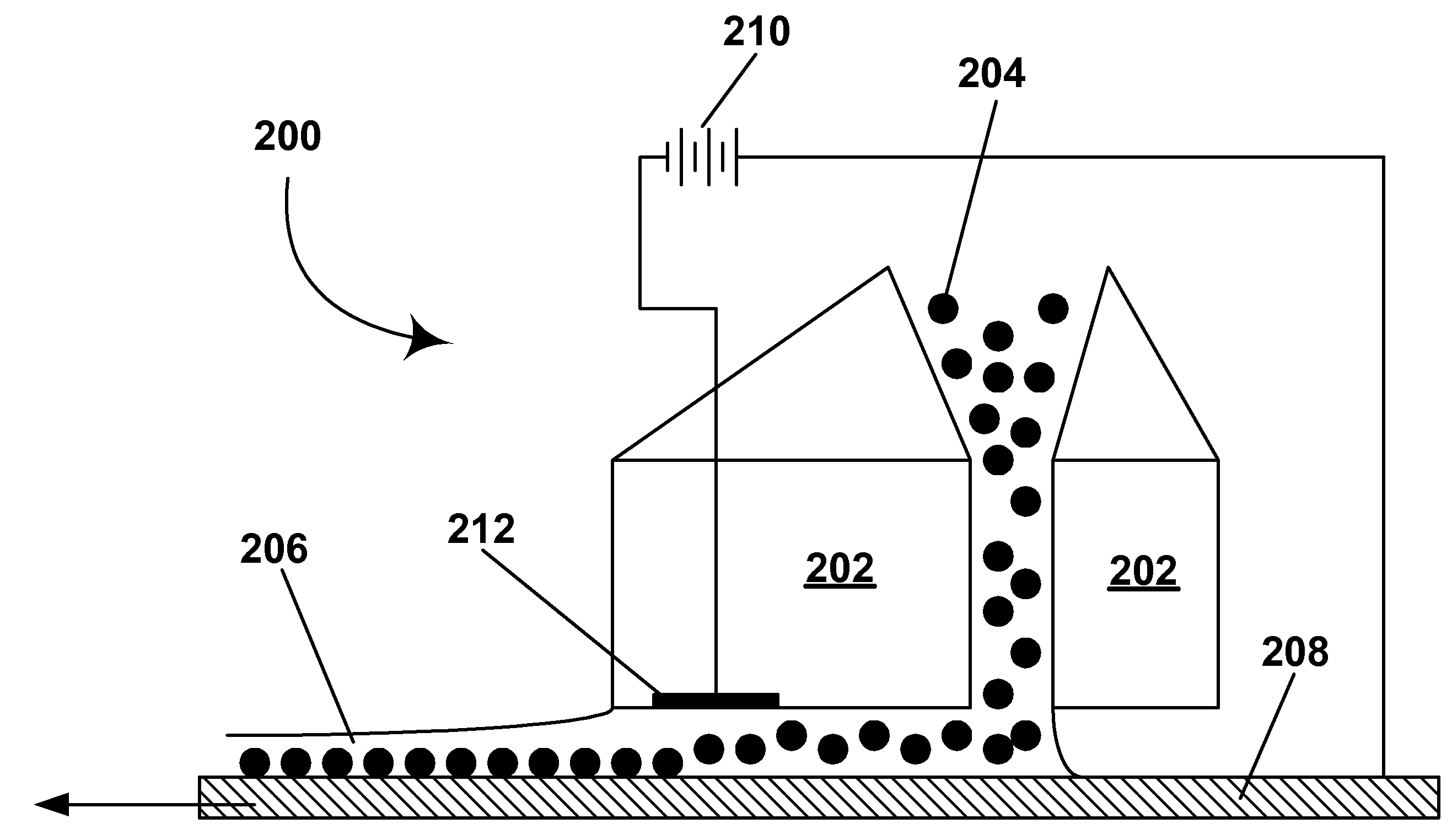
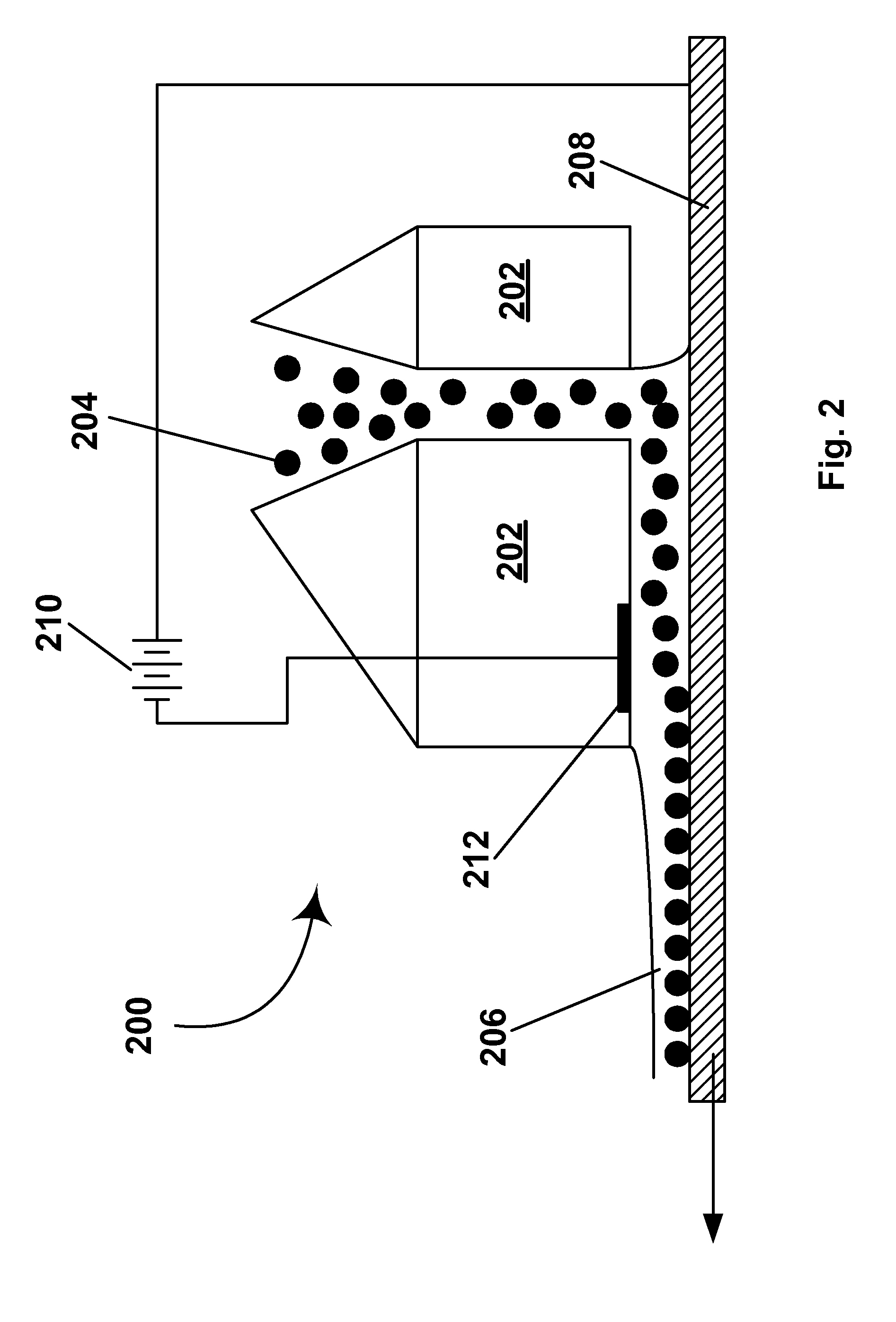
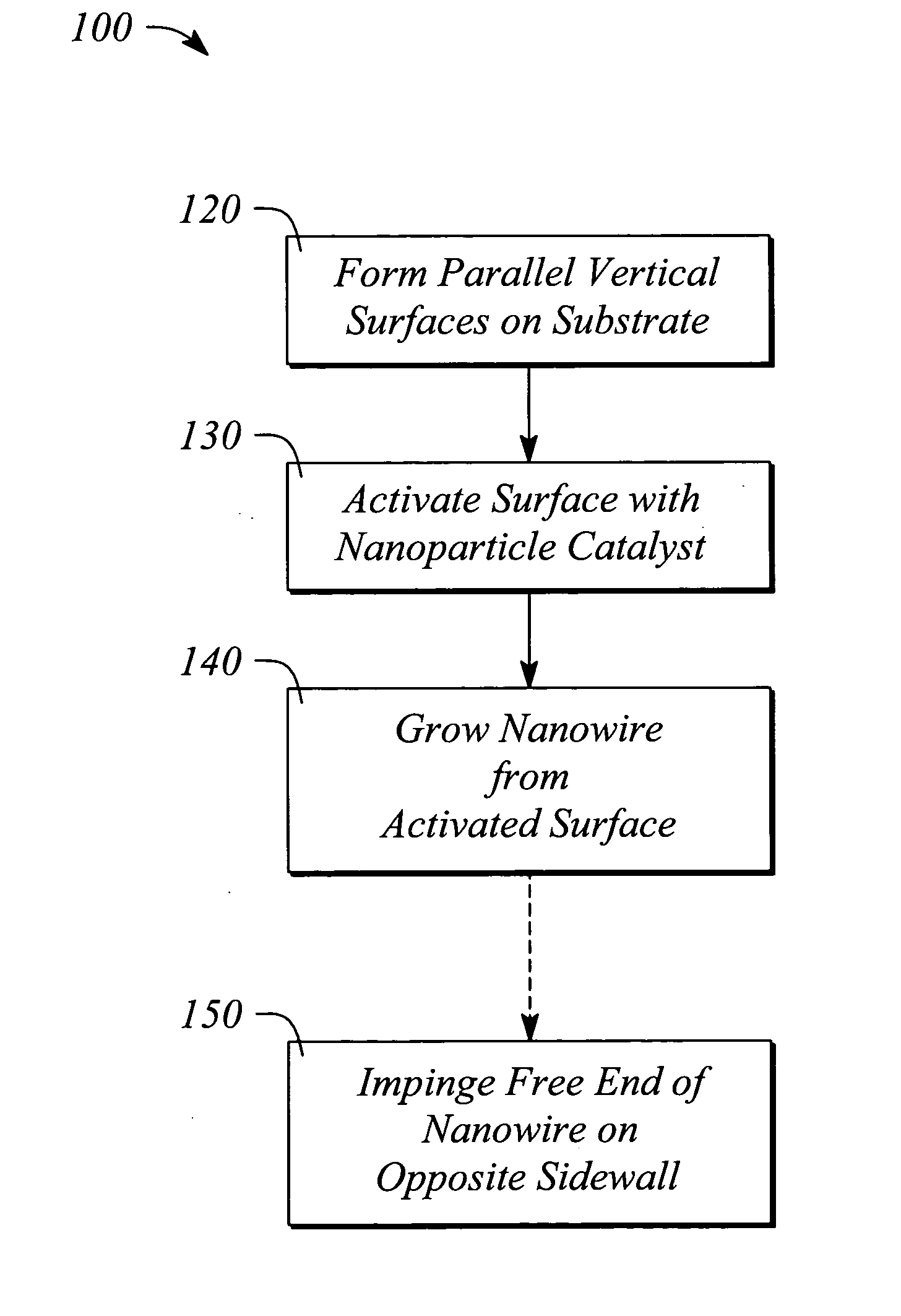
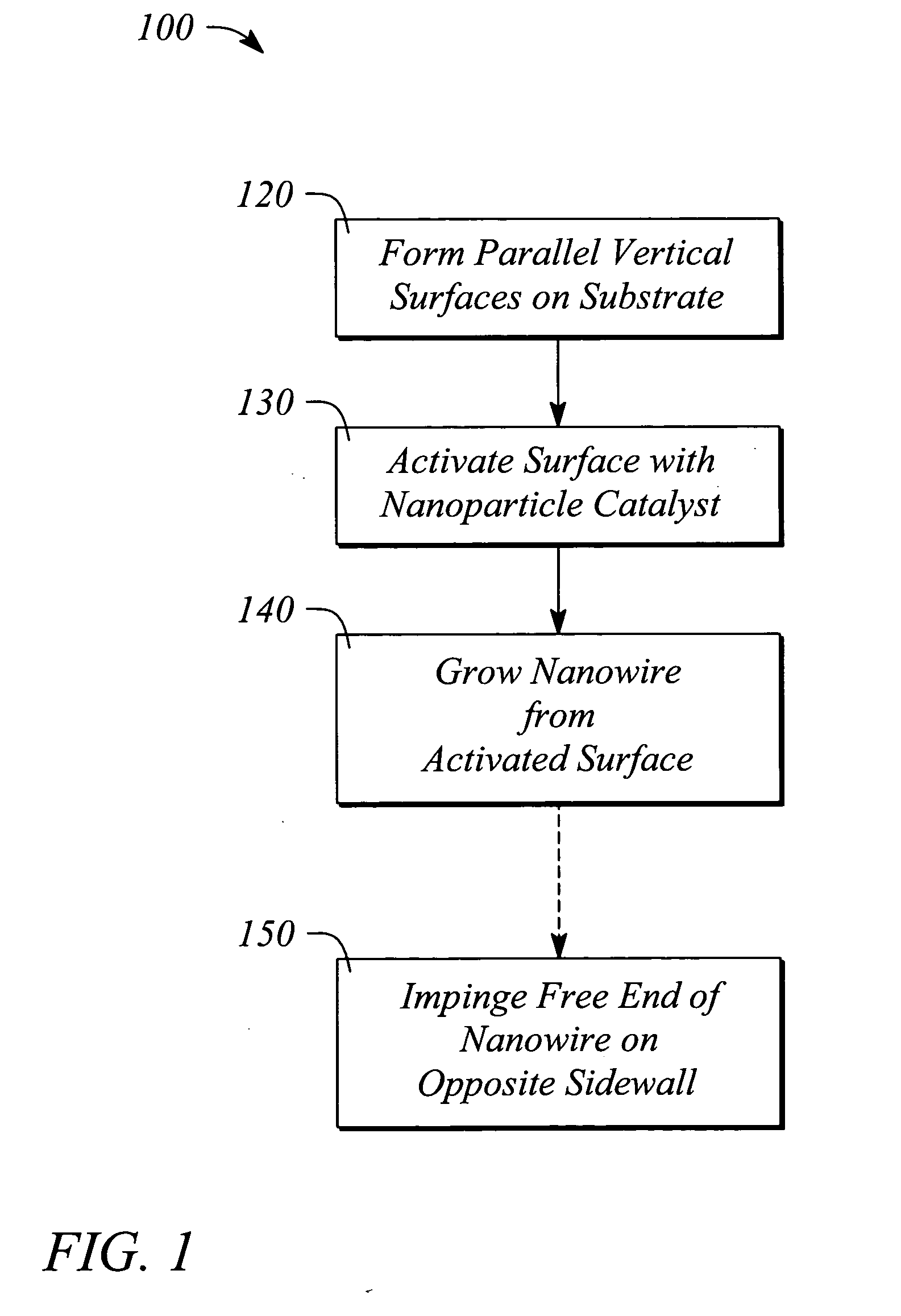
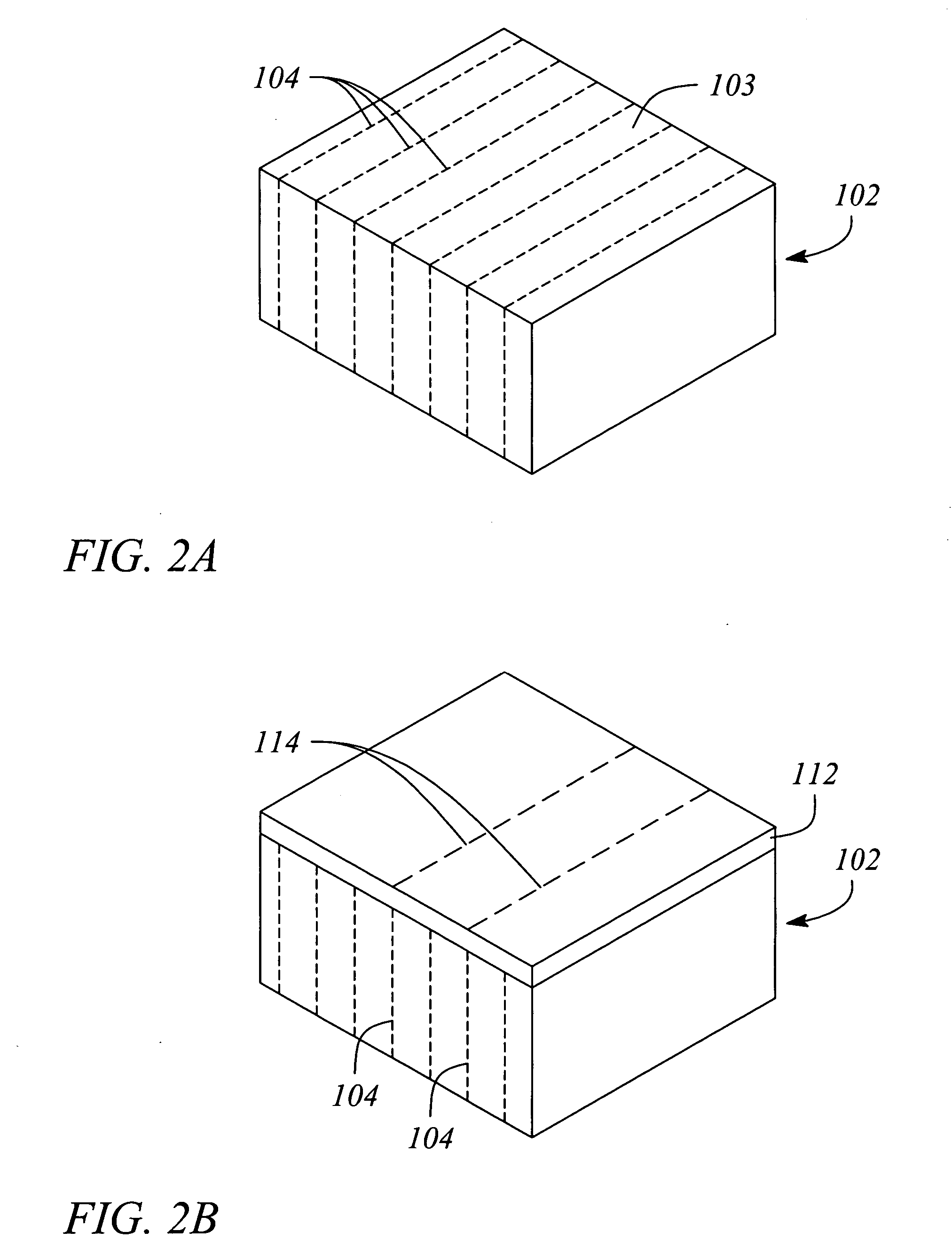
Methods of bridging lateral nanowires and device using same
InactiveUS20050133476A1Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanowireDevice material
A semiconductor nanowire is grown laterally. A method of growing the nanowire forms a vertical surface on a substrate, and activates the vertical surface with a nanoparticle catalyst. A method of laterally bridging the nanowire grows the nanowire from the activated vertical surface to connect to an opposite vertical surface on the substrate. A method of connecting electrodes of a semiconductor device grows the nanowire from an activated device electrode to an opposing device electrode. A method of bridging semiconductor nanowires grows nanowires between an electrode pair in opposing lateral directions. A method of self-assembling the nanowire bridges the nanowire between an activated electrode pair. A method of controlling nanowire growth forms a surface irregularity in the vertical surface. An electronic device includes a laterally grown nano-scale interconnection.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Fluid-assisted medical devices, systems and methods
A medical device (5) is provided which comprises a catheter tube having a distal end and a lumen, and configured to assist in applying tamponage to a bleeding source in a gastrointestinal tract when flexed. A catheter tip having a catheter tip outer surface is assembled with the tube adjacent the distal end of the tube. The catheter tip comprises a probe body comprising an electrically insulative material, at least one electrode pair located on the probe body which comprises a first electrode spaced from a second electrode, and a fluid distribution manifold to direct a fluid from inside the probe body towards the tip outer surface. The manifold comprises a central passage within the probe body and a plurality of lateral passages which extend from the central passage towards the tip outer surface. An extendable injection needle is housed within the central passage to provide treatment to tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
Symmetric touch screen system with carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive electrode pairs
InactiveUS20080238882A1Input/output processes for data processingElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A symmetric touch screen switch system in which both the touch side and panelside transparent electrodes are comprised of carbon nanotube thin films is provided. The fabrication of various carbon nanotube enabled components and the assembly of a working prototype touch switch using those components is described. Various embodiments provide for a larger range of resistance and optical transparency for the both the electrodes, higher flexibility due to the excellent mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Certain embodiments of the symmetric, CNT-CNT touch switch achieve excellent optical transparency (<3% absorption loss due to CNT films) and a robust touch switching characteristics in an electrical test.
Owner:NANTERO
Ablation system and method of use
A system and method for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the impedance of the tissue to be ablated. Rather than attempting to detect a desired drop or a desired increase impedance, completeness of a lesion is detected in response to the measured impedance remaining at a stable level for a desired period of time, referred to as an impedance plateau. The mechanism for determining transmurality of lesions adjacent individual electrodes or pairs may be used to deactivate individual electrodes or electrode pairs, when the lesions in tissue adjacent these individual electrodes or electrode pairs are complete, to create an essentially uniform lesion along the line of electrodes or electrode pairs, regardless of differences in tissue thickness adjacent the individual electrodes or electrode pairs. Complete or partial submersion in a fluid of the ablating portion of the ablation device may be detected prior to, during or following an ablation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Automated impedance measurement of an implantable medical device
The present invention automates impedance measurements between pairs of electrodes that are associated with a lead of an implanted device. Apparatus comprises a communications module and a processor, in which the processor communicates with the implanted device over a communications channel. The processor instructs the implanted device to perform a voltage measurement that is associated with a stimulation pulse between the pair of electrodes. The implanted device sends the voltage measurement to the apparatus over the communications channel from which the apparatus determines the impedance between the pair of electrodes. The apparatus initiates an impedance measurement for each pair of electrodes along the lead. With a plurality of leads, the apparatus repeats the impedance measurements for electrode pairs of the other leads. The embodiment also supports measuring a current between pairs of electrodes. The impedance measurements and current measurements are displayed to a clinician on a user interface.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Minimal Device and Method for Effecting Hyperthermia Derived Anesthesia
InactiveUS20080262490A1Improve comfortLess chance of physical damageElectrotherapySurgical needlesFiberMedicine
A method and device for inducing anaesthesia in mammals by the application of RF energy to create hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia. An RF generator drives a plurality of electrodes placed in tissue surrounding the target nerve fibre to desiccate the desired length of nerve fibre to be desiccated in a single deployment. The device allows high-speed selection / de-selection of bipolar electrode pairs or sets under continuous RF excitation. Activation of electrode pairs is adapted in response to sensed current density and temperature (by electrodes not in the current discharge activation phase) in order to create lesions of complex and well defined shape necessary for the production of hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia.
Owner:INTERVENTION TECH
Thin film plate phase change ram circuit and manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070224726A1Simple structureSmall reset currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit linePhase-change memory
A memory device comprising a access circuits, an electrode layer over the access circuits, an array of phase change memory bridges over the electrode layer, and a plurality of bit lines over the array of phase change memory bridges. The electrode layer includes electrode pairs. Electrode pairs include a first electrode having a top side, a second electrode having a top side and an insulating member between the first electrode and the second electrode. A bridge of memory material crosses the insulating member, and defines an inter-electrode path between the first and second electrodes across the insulating member.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Plasma display panel having high brightness and high contrast using light absorption reflection film
InactiveUS7323819B2Effective reflectionAlternating current plasma display panelsCold-cathode tubesElectrode pairDielectric layer
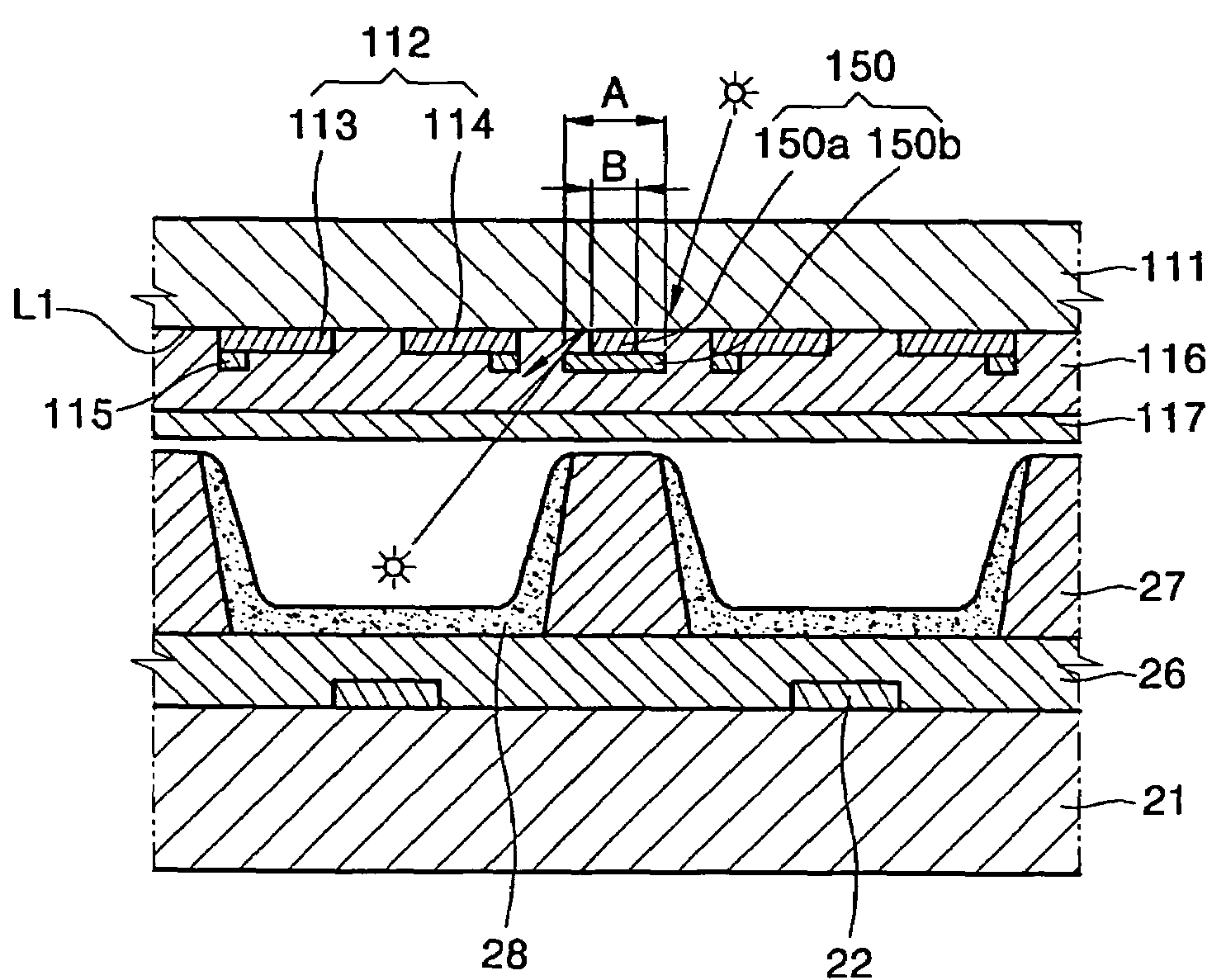
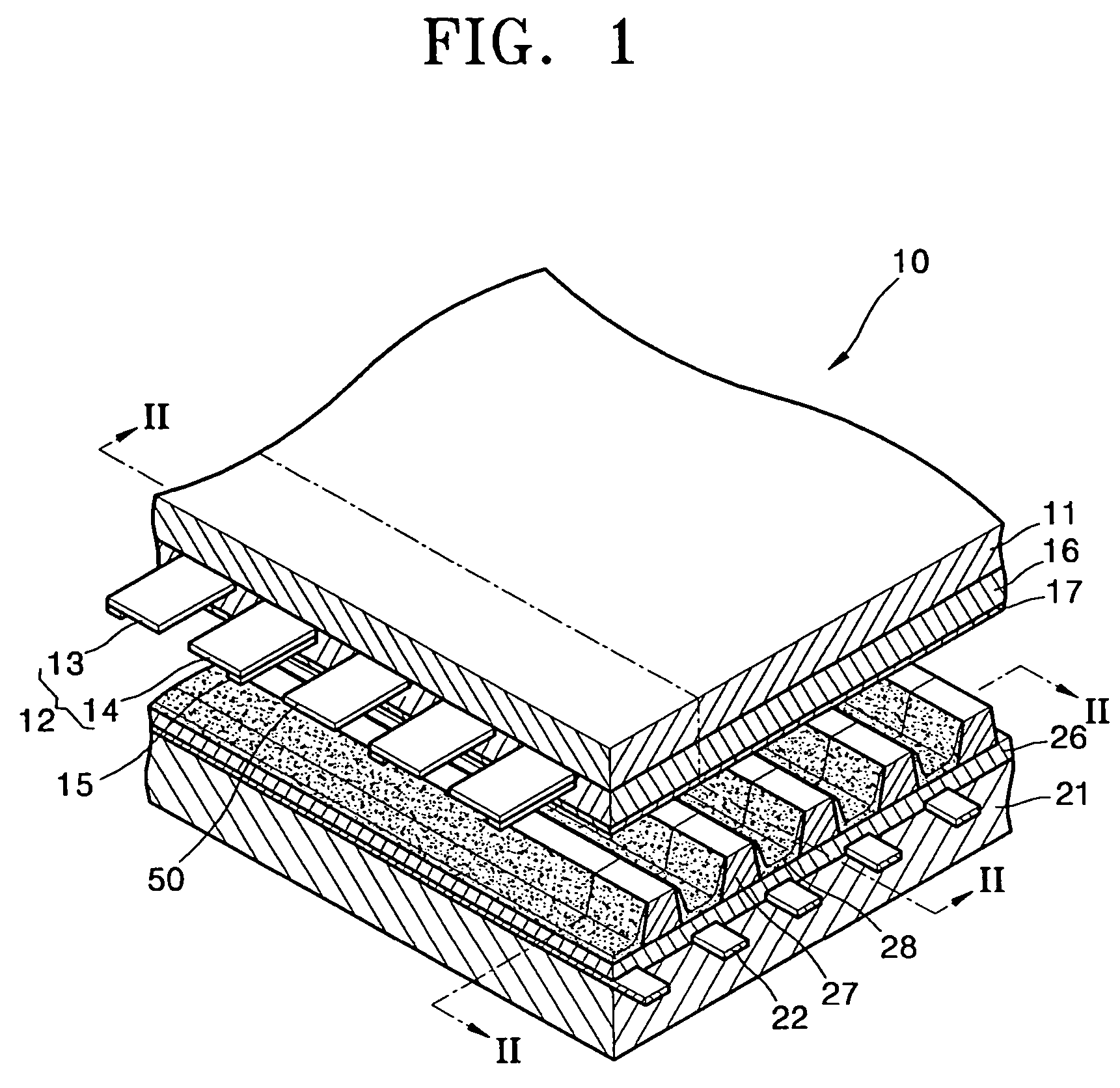
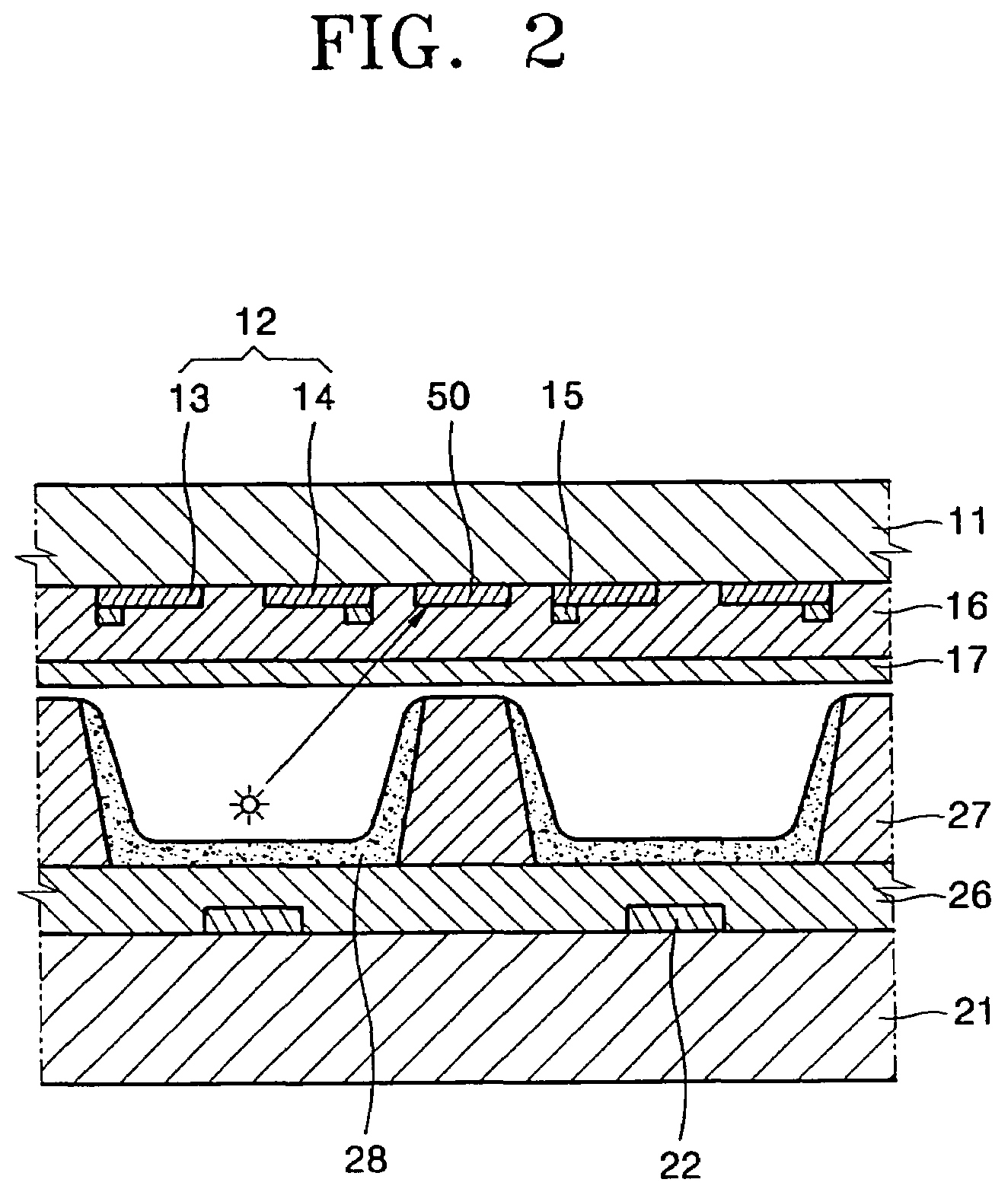
A plasma display panel having a light absorption reflection film that does not reflect light emitted from a discharge space in a non-discharge region includes: a rear substrate; a plurality of address electrodes arranged on a surface of the rear substrate; a rear dielectric layer arranged on the rear substrate to cover the address electrodes; a plurality of barrier ribs arranged on the rear dielectric layer to define discharge cells; a front substrate facing the rear substrate; a plurality of sustaining electrode pairs composed of X and Y electrodes; a light absorption reflection film including a first light absorption reflection film arranged between the adjacent sustaining electrode pairs and a second light absorption reflection film having a different width than that of the first light absorption reflection film, the second light absorption reflection film arranged on a lower surface of the first light absorption reflection film; and a front dielectric layer arranged on a lower surface of the front substrate to cover the X and Y electrodes and the light absorption reflection film.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Miniature wireless apparatus for collecting physiological signals
InactiveUS20070167848A1Simple materialLow costControlling membersElectrocardiographyMicrocontrollerData compression
Owner:KUO TERRY B J +2
Multi-zone bipolar ablation probe assembly
ActiveUS7416549B2Efficient ablationAdd dimensionSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingElectrode pairRadio frequency
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com