Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
180 results about "Absorption loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
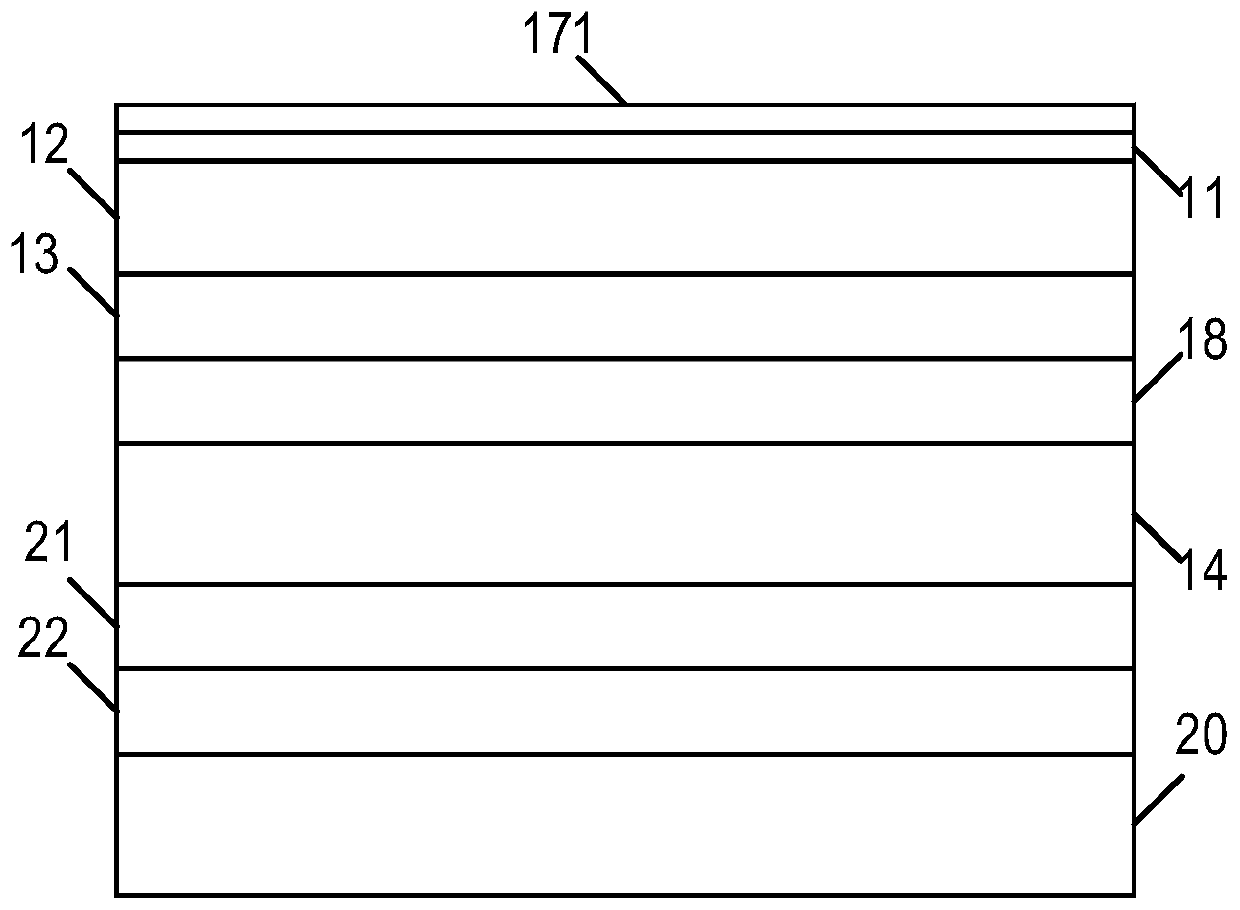
Liquid crystal display device having particular reflective polarizer
InactiveUS7006173B1Wide viewing angleReduce power consumptionNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
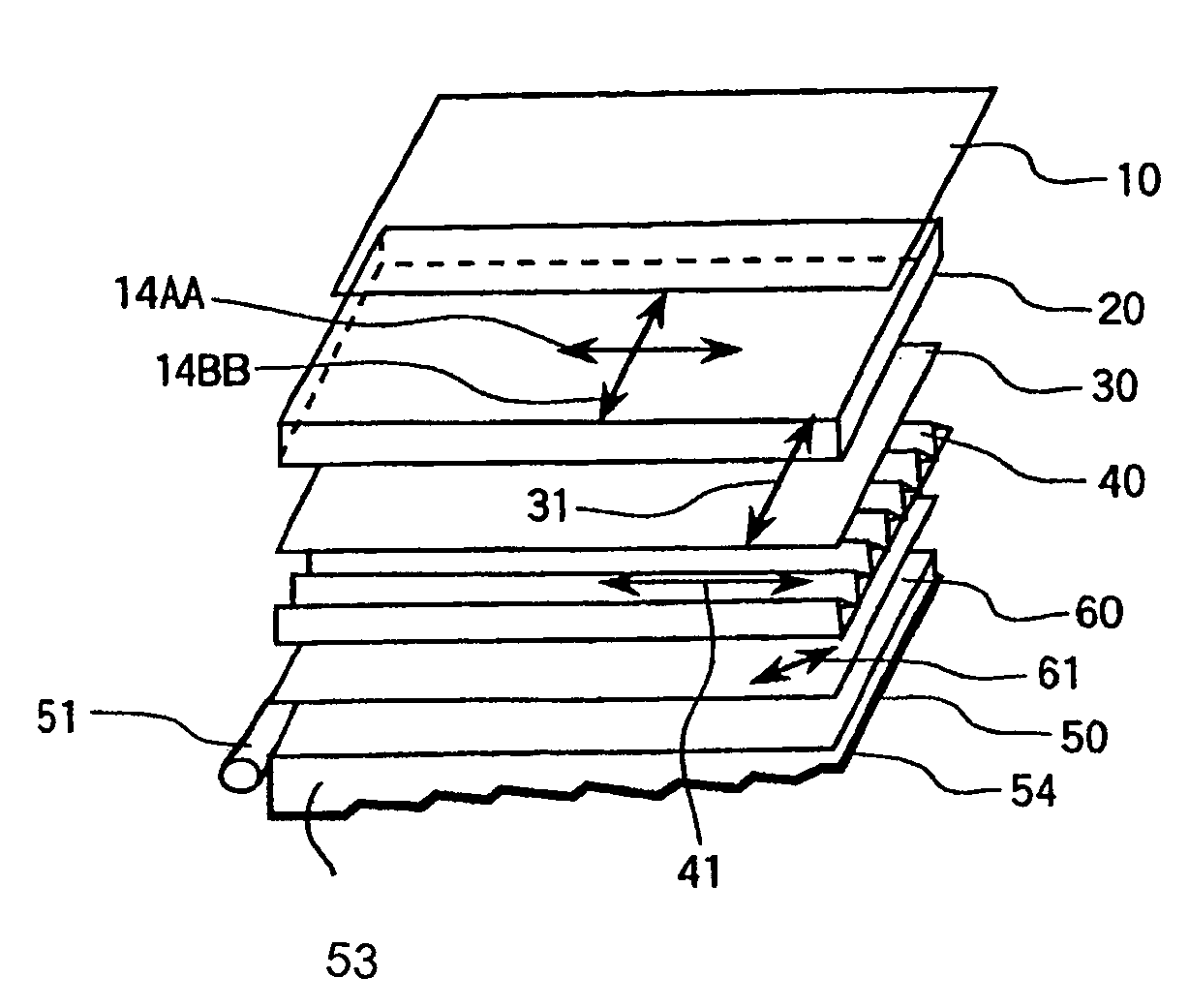
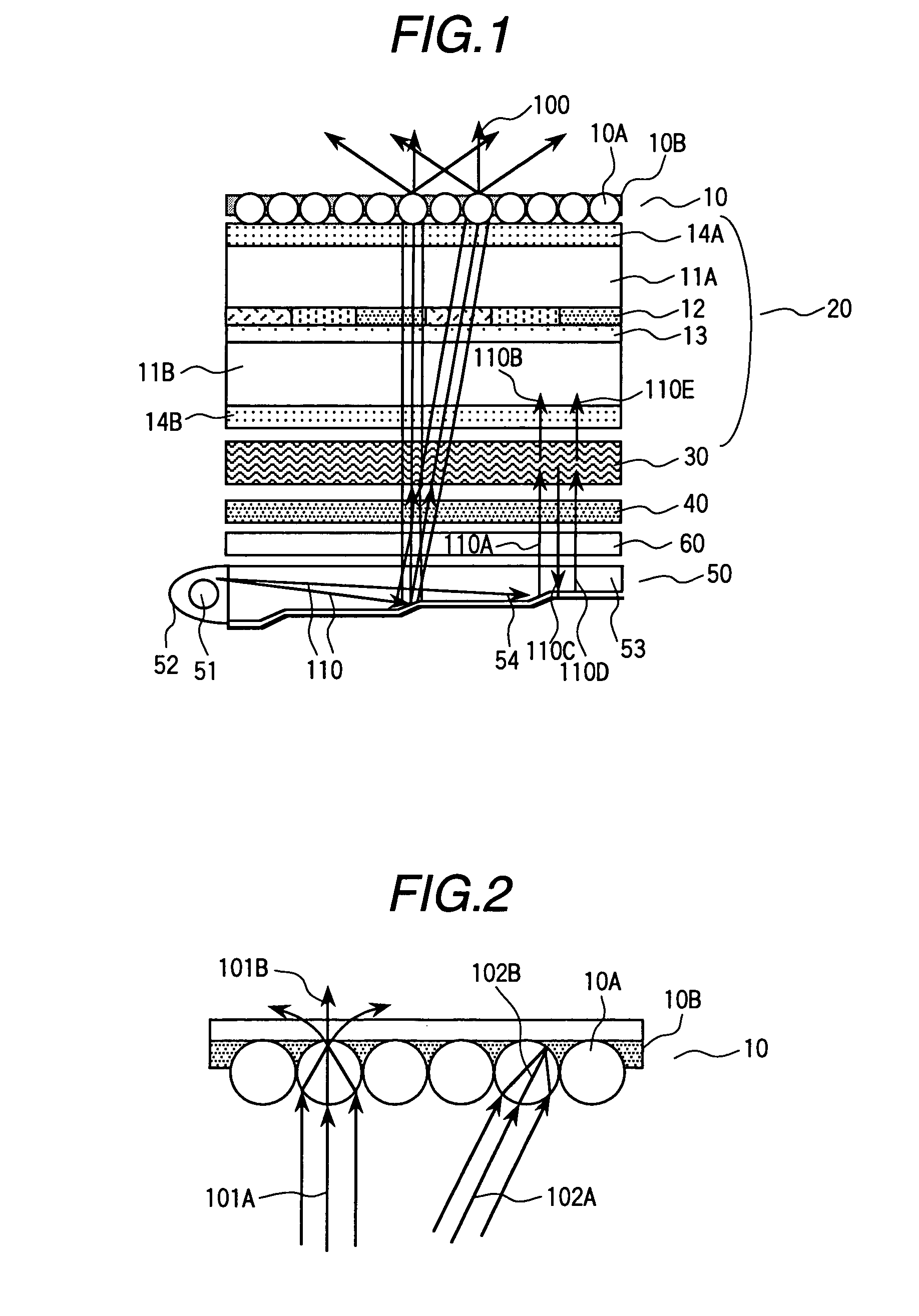
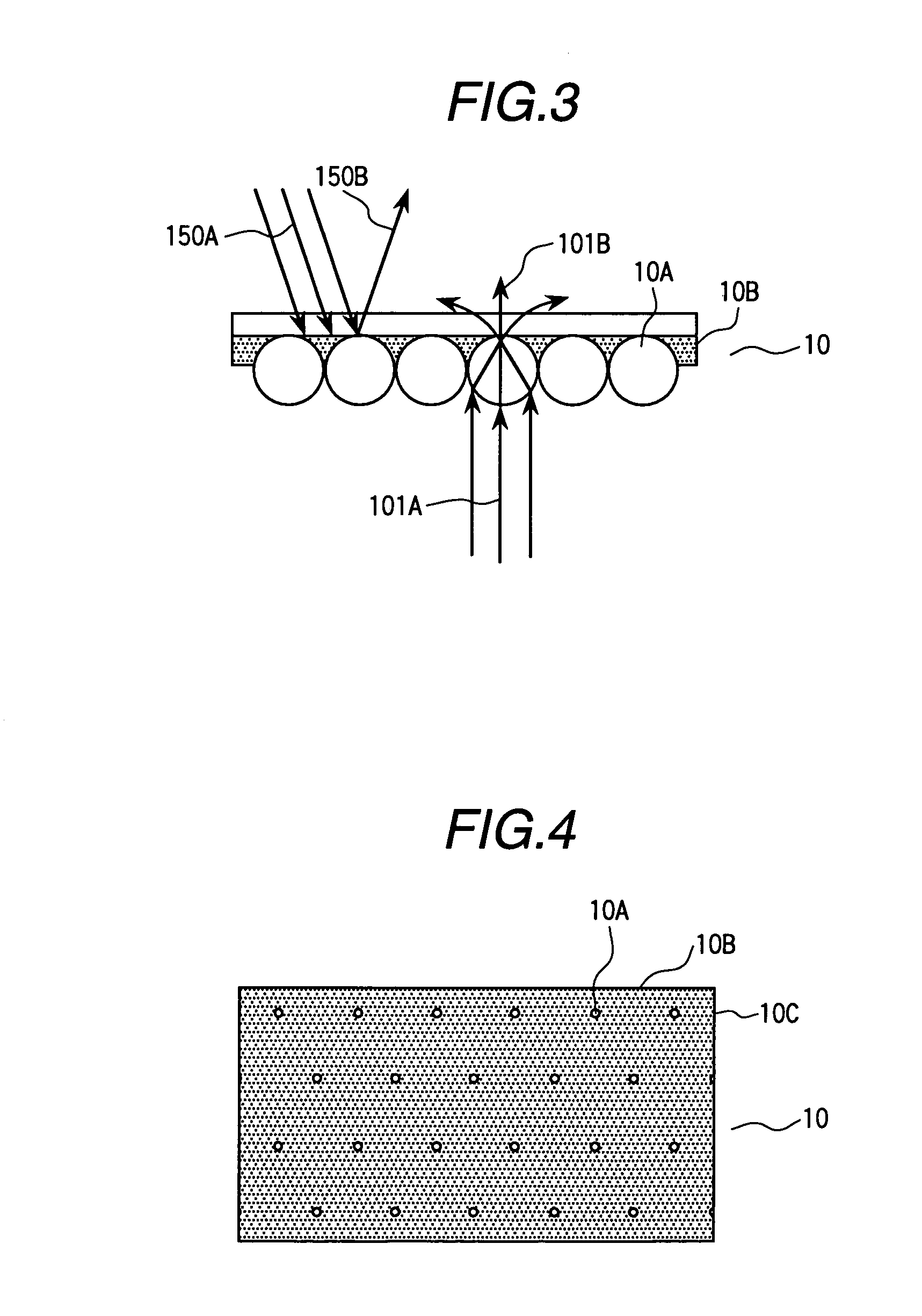
In order to realize liquid crystal display devices having a wide viewing angle and reduce the absorption loss by polarizers and color filters, and arrangement of reflective color selective means, reflective polarizing selective means, a light control element, and others are specified. The liquid crystal display device able to produce a display of high performance and improved brightness is formed of liquid crystal display elements 20 for controlling polarizing light so that the major axis direction of a pixel is arranged approximately in parallel with a direction wherein the linearly polarized light component of the projected light projected from said illumination device is high; an illumination device 50 arranged at a rear plane of the liquid crystal display element; a reflector 54 arranged at a rear plane of the illumination device; light control elements 40 and reflective polarizing selective means 30 arranged between the liquid crystal display element and the illumination device; and a screen arranged at an opposite side relative to the illumination device of the liquid crystal display element.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Symmetric touch screen system with carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive electrode pairs
InactiveUS20080238882A1Input/output processes for data processingElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A symmetric touch screen switch system in which both the touch side and panelside transparent electrodes are comprised of carbon nanotube thin films is provided. The fabrication of various carbon nanotube enabled components and the assembly of a working prototype touch switch using those components is described. Various embodiments provide for a larger range of resistance and optical transparency for the both the electrodes, higher flexibility due to the excellent mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Certain embodiments of the symmetric, CNT-CNT touch switch achieve excellent optical transparency (<3% absorption loss due to CNT films) and a robust touch switching characteristics in an electrical test.
Owner:NANTERO
Light source device and crystal display device
InactiveUS20070014127A1Improve efficiencyLow costMechanical apparatusElongate light sourcesTransmittanceLight reflection
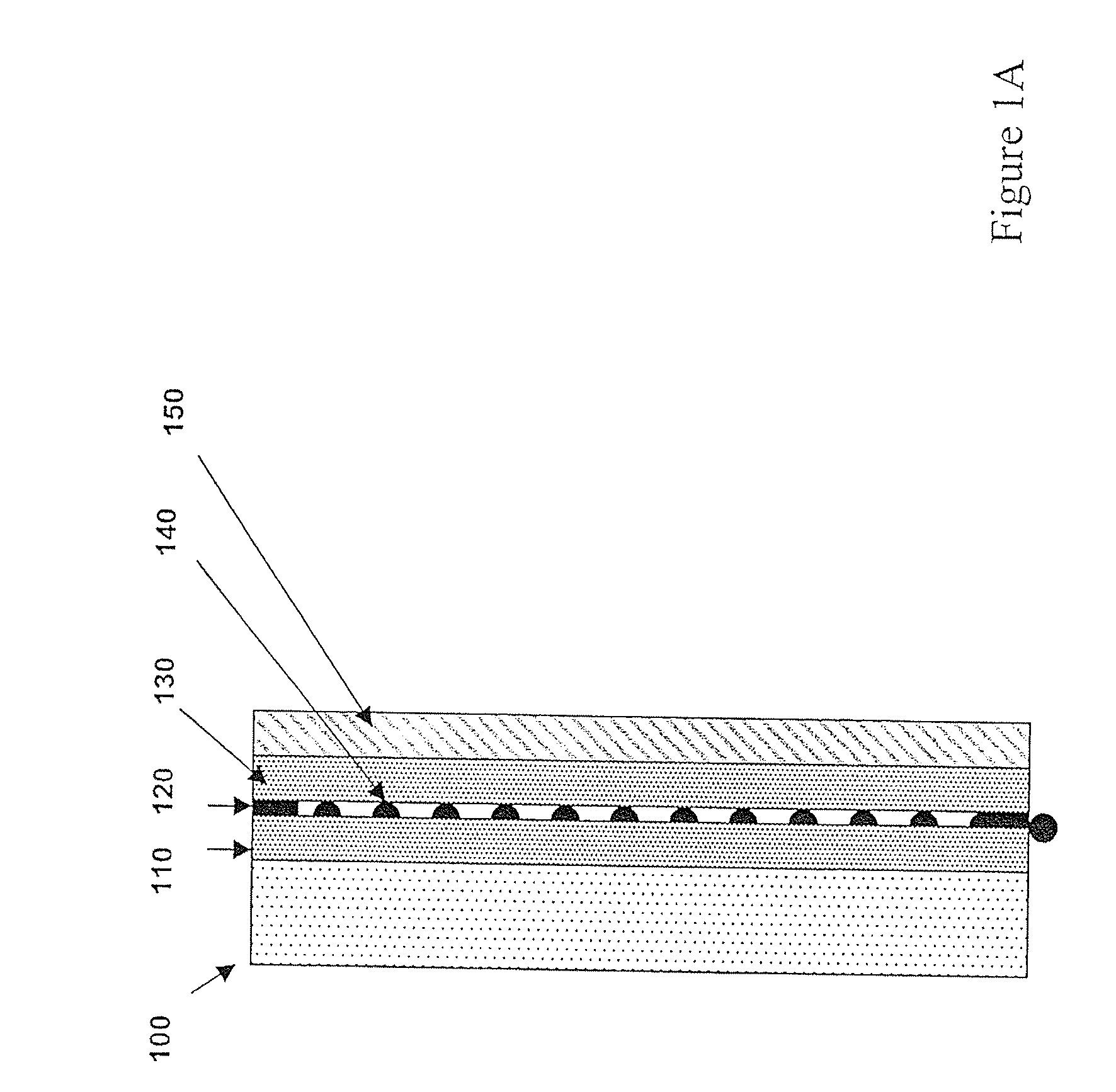
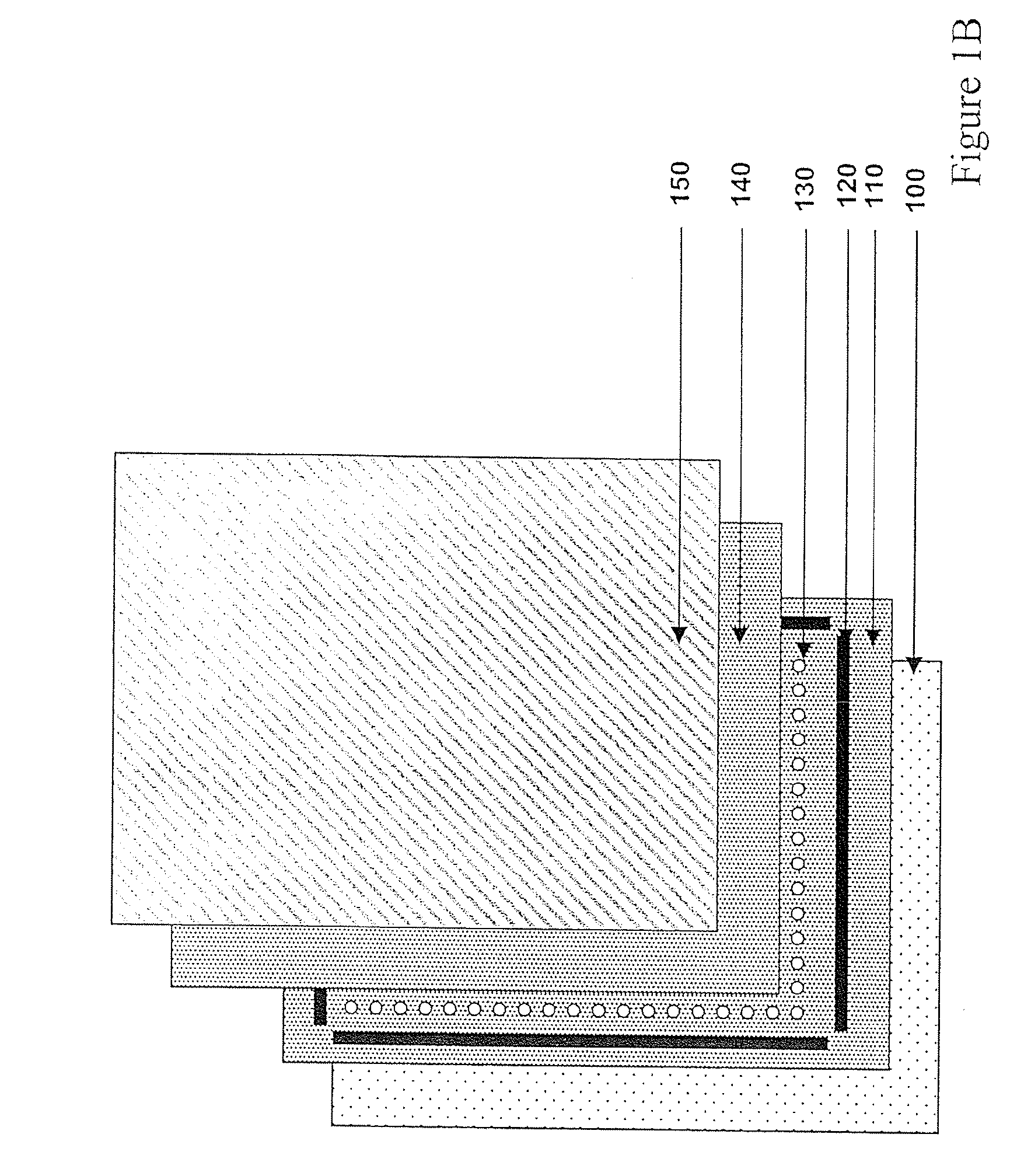
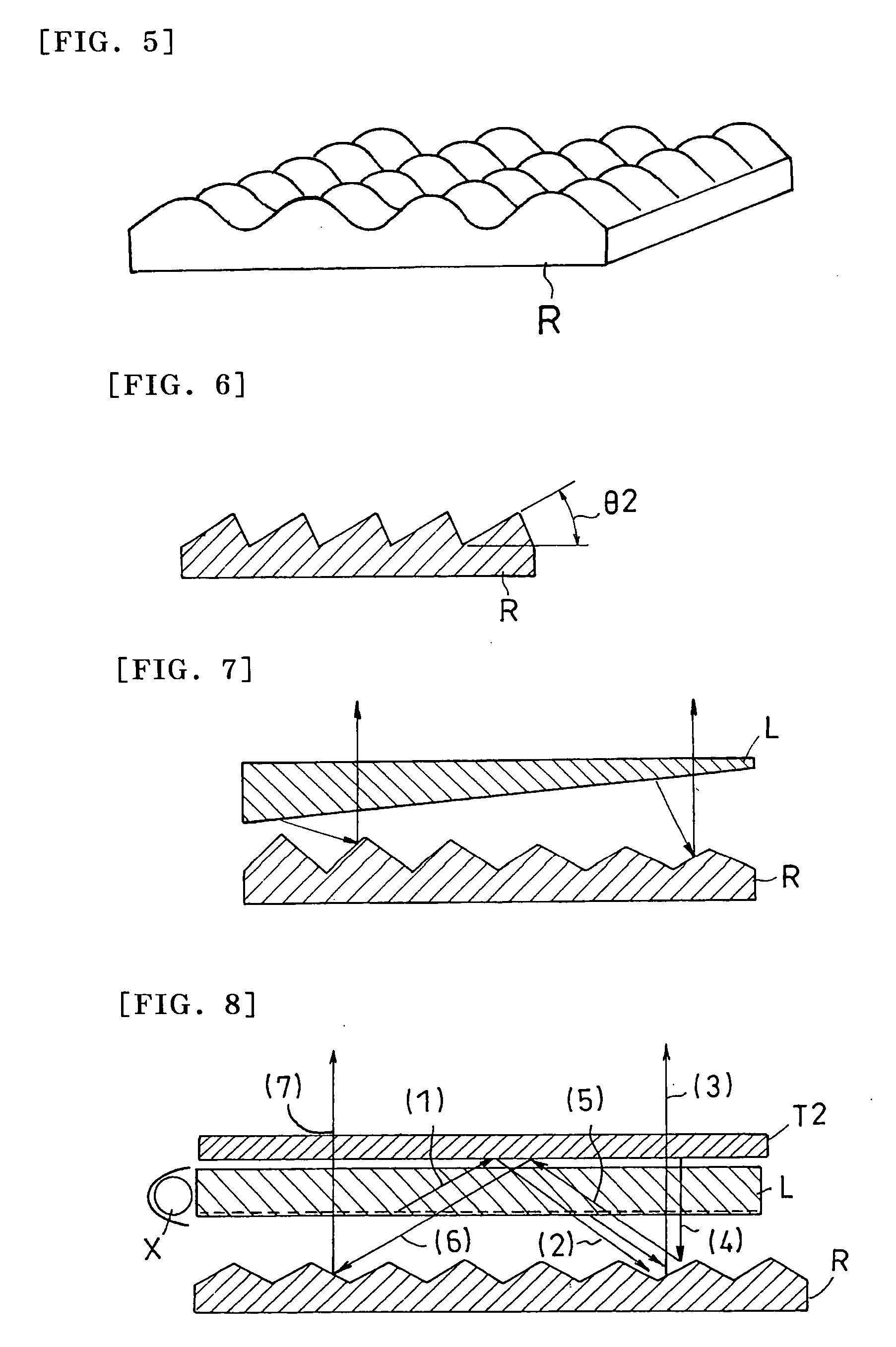
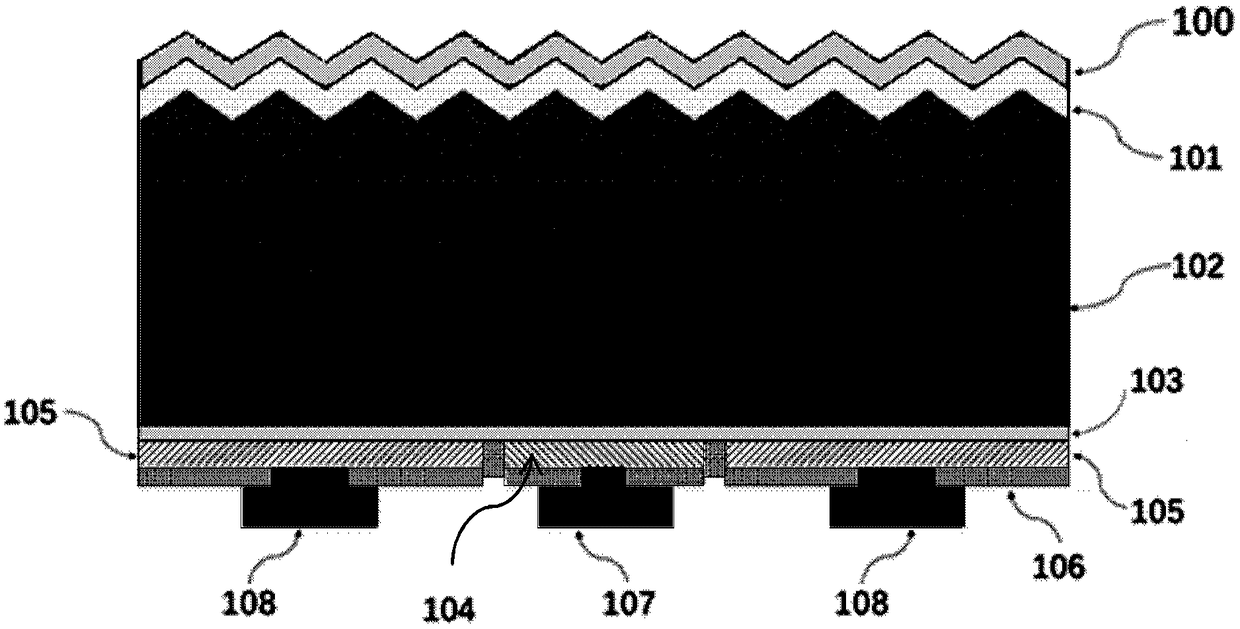
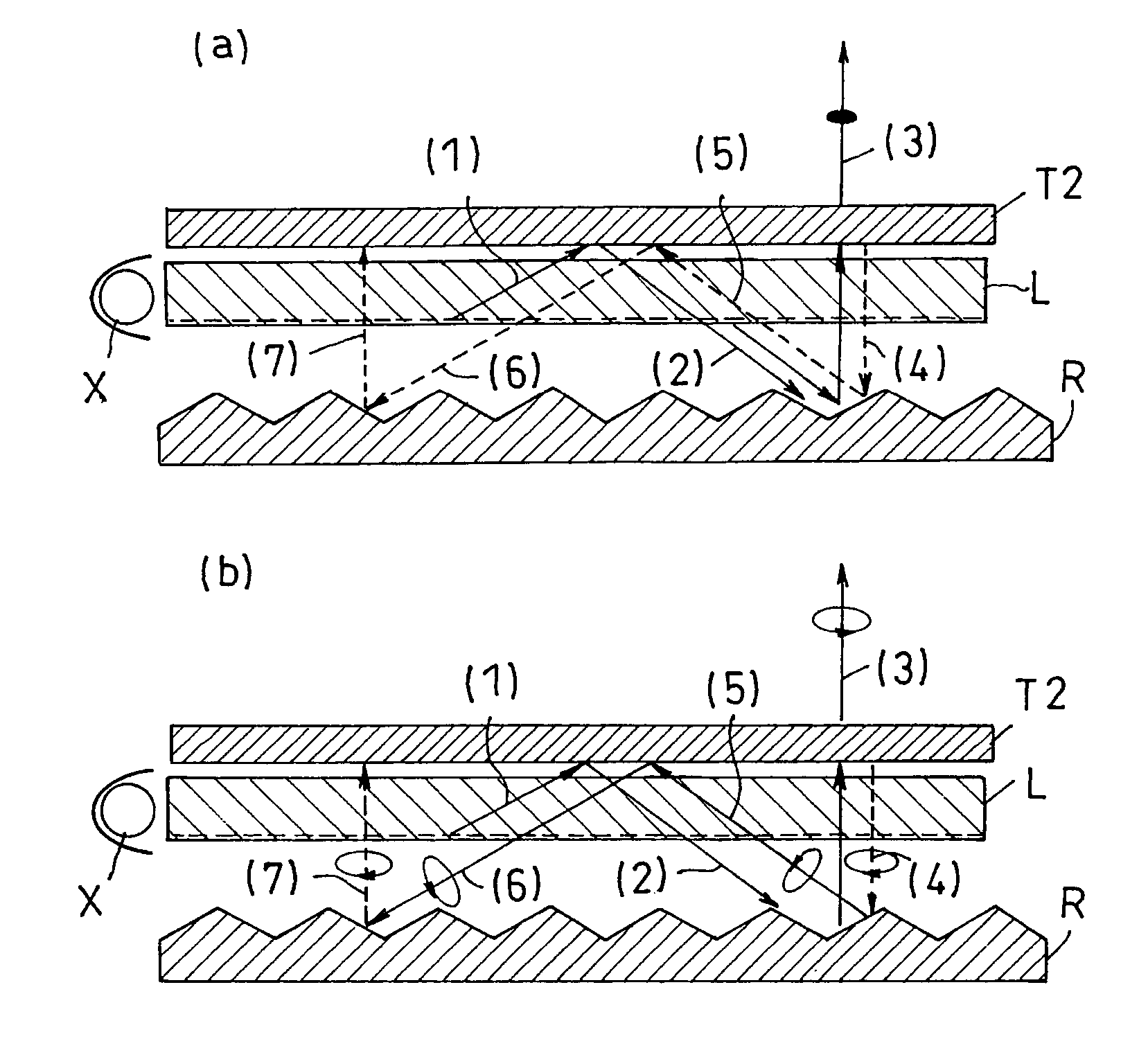
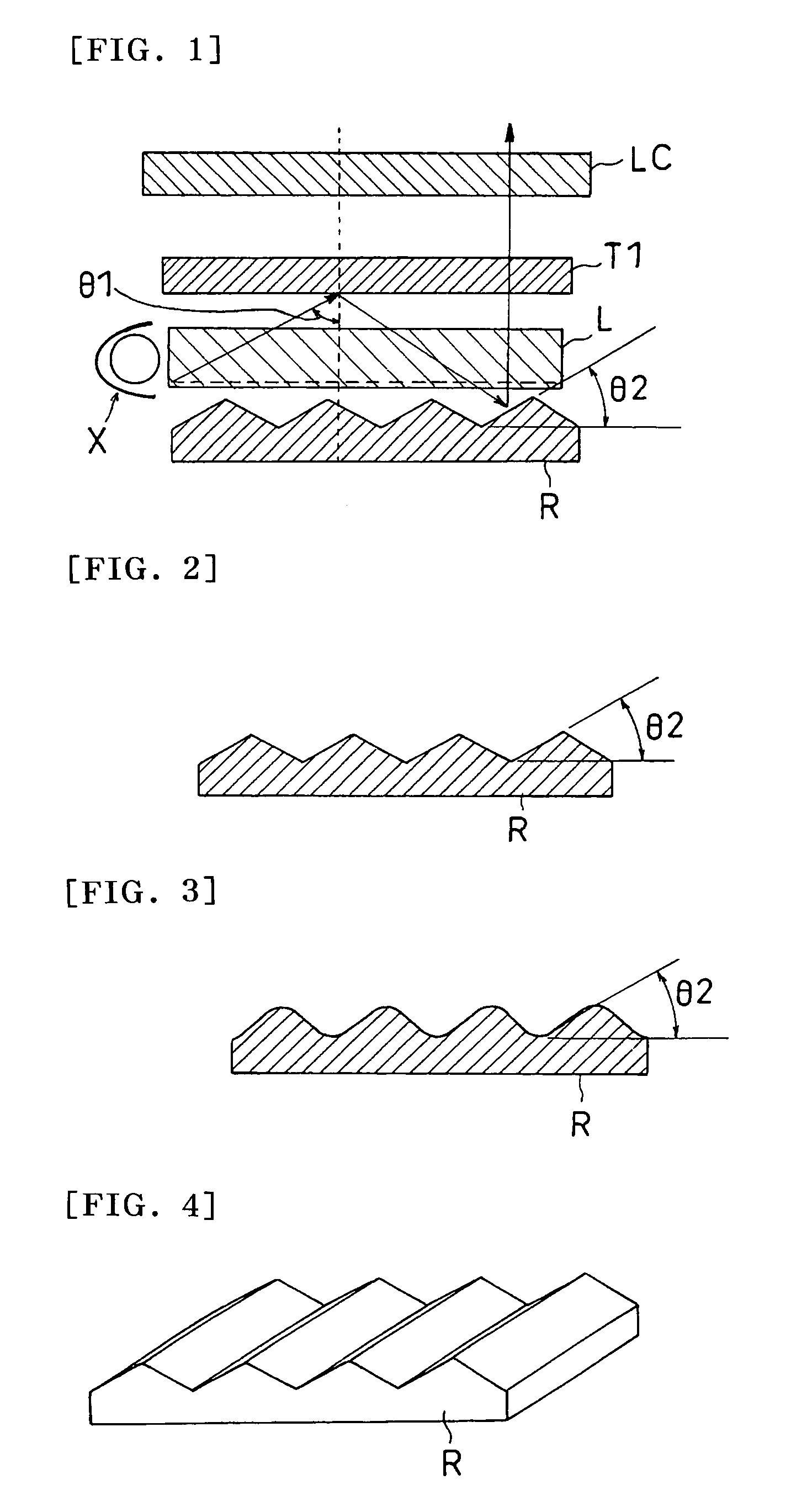
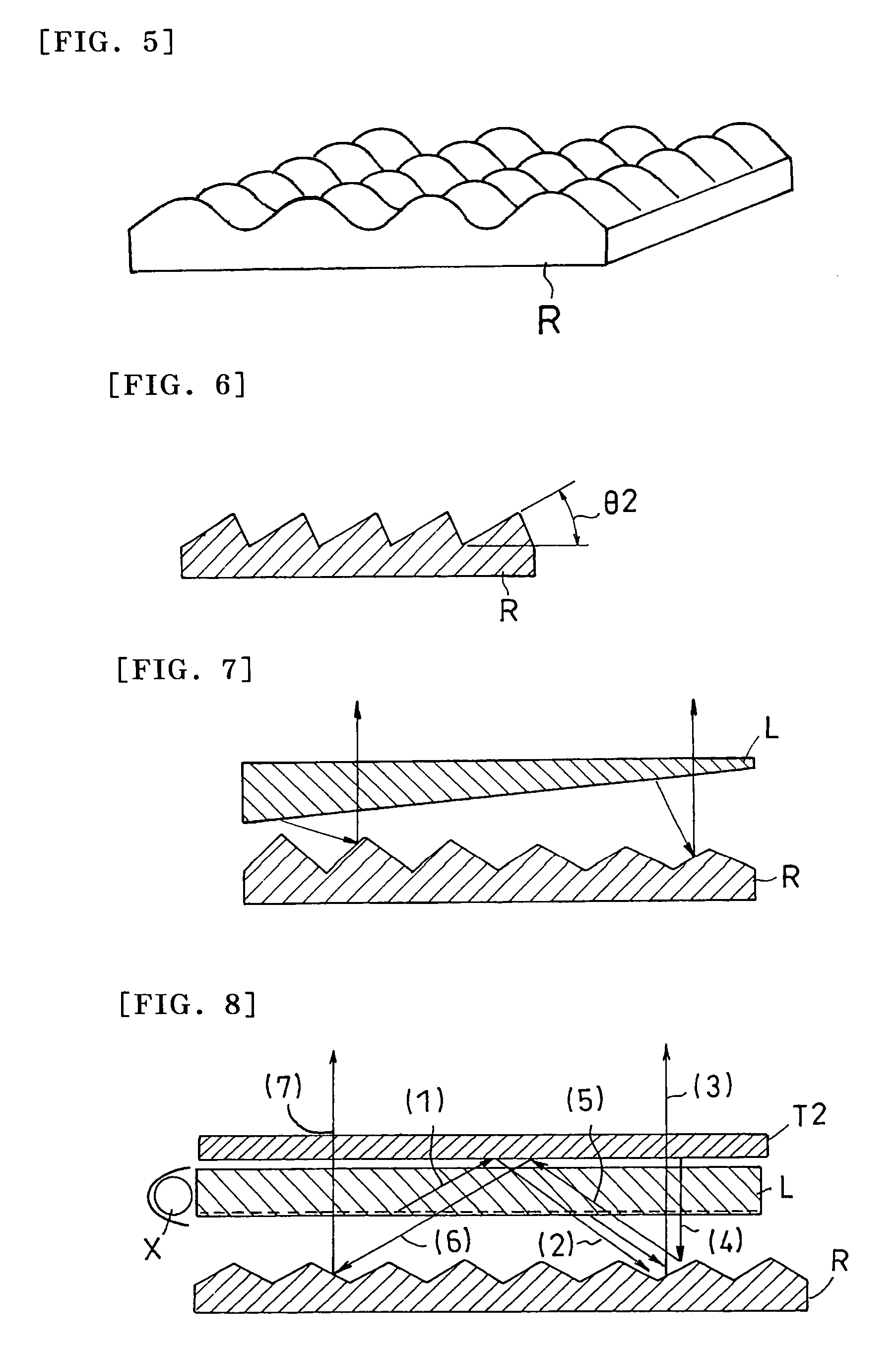
A light source comprising sidelight type backlight light guide plate (L), wherein a transmittance angle dependent layer (T1) which transmits normally incident light and reflects obliquely incident light is disposed on one surface of the sidelight type backlight light guide plate (L), and a reflection plate (R) having a repetitive slope structure is disposed on the other surface of the sidelight type backlight light guide plate (L). The invention light source is less in absorption loss due to repetition of light reflection and the like.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
High-Power Optoelectronic Device with Improved Beam Quality Incorporating A Lateral Mode Filtering Section
InactiveUS20070223549A1Simplified method of fabricatingLeakage losses is still relatively largeOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLight beamWaveguide
An optoelectronic device includes a planar active element, a vertical waveguide surrounding the active element in the vertical direction, and a lateral waveguide comprising at least one active section and at least one filter section following each other in the longitudinal direction. At least part of the active element within the active section generates optical gain in response to above-threshold pumping. The broad lateral waveguide in the active section can localize multiple lateral optical modes. In the filter section, no lateral confinement is provided for the lateral optical modes. The device further comprises means to ensure low absorption loss in the filter section and, therefore, ensure high efficiency. In one embodiment low absorption loss is achieved by pumping of at least part of the active element within the filter section. In another embodiment, the active element has small overlap with the vertical optical modes.
Owner:INNOLUME
Two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and production method thereof
InactiveCN104218443AWide wavelength rangeReduce absorption lossActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionMode-lockingWavelength
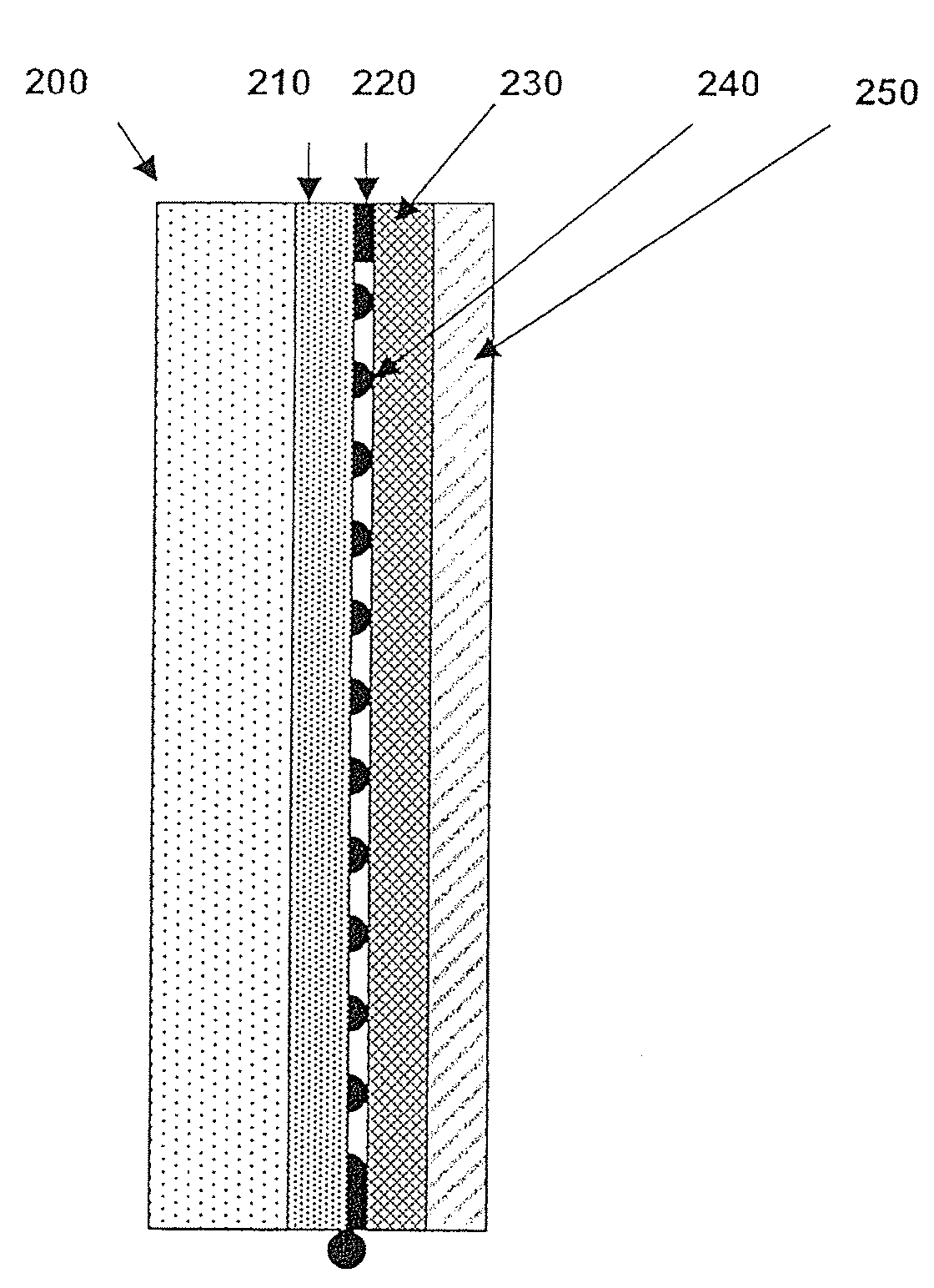
The invention relates to a two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and a production method thereof, and belongs to the field of saturable absorbers of lasers. The two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber comprises a substrate, a high-reflection layer, a saturable absorption layer and a functional layer. One end face of the functional layer is connected with the saturable absorption layer, one end face of the saturable absorption layer is connected with the high-reflection layer, and one end face of the high-reflection layer is connected with the substrate. By the two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and the production method thereof, application of the lasers, such as Q-switching, mode locking and optical signal processing, is realized. By the high-reflection layer formed by composite materials, absorption loss is reduced and reflection rate is increased, and optimal material combinations can be found in terms of different wave lengths.
Owner:鲍小志
Fluorination treatment apparatus, process for producing fluorination treated substance, and fluorination treated substance
InactiveUS20040006249A1Substance reductionHigh light transmittanceLavatory sanitorySolid state diffusion coatingReaction stepNuclear chemistry
According to the invention, a fluorination treated substance remarkably reduced in the light absorption loss of a substance to be treated, such as a fluoride thin film, a fluorination treatment apparatus capable of producing the fluorination treated substance, and a process for producing a fluorination treated substance can be provided. Disclosed is a process for producing a fluorination treated substance, comprising an enclosure step of enclosing a substance to be treated in a reactor and a fluorination reaction step of introducing a fluorine gas into the reactor to bring the substance to be treated into contact with the fluorine gas and thereby carry out fluorination reaction.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK +1
Single-layer planar chirality metal structure circular polarizer
InactiveCN104316988AReduce difficultyReduce processing costsPolarising elementsAntennasPlanar chiralityPolarizer
The invention relates to a single-layer planar chirality metal structure circular polarizer which belongs to electromagnetic wave devices, and belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic waves of optics, terahertz, microwaves and other frequency bands. The circular polarizer is formed by a single-layer metal structure with planar chirality, and the functions of the circular polarizer are achieved on the basis of a one-way mode switching principle. The circular polarizer is easy to machine and integrate, thin, small in size and compact in structure, has high efficiency of screening on left-hand and right-hand circular polarization electromagnetic waves, and is low in device absorption loss and high in transmittance. By changing the design of the size and the structural design of the circular polarizer, the circular polarization function can be achieved at different electromagnetic frequency bands such as optics, terahertz and microwaves. The circular polarizer can achieve low-cost and large-area manufacturing, and has important application in the fields of optical microscopy, three-dimensional display, laser technologies, communication, radar and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Electromagnetic shielding composite material
InactiveCN105555112AImprove shielding effectExtended propagation pathShielding materialsFiberReflection loss
The invention discloses an electromagnetic shielding composite material. Electromagnetic wave absorption layers and electromagnetic wave reflection layers are alternately overlapped to form electromagnetic shielding function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin, fiber carriers and electromagnetic absorption function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin and electromagnetic gradient reflection function bodies; in the overlapped electromagnetic wave reflection layers, the mass percentage compositions of short cut carbon fibers increase in gradient along the incident directions of the electromagnetic waves. According to the electromagnetic shielding composite material of the invention, the incident electromagnetic waves generate multi-reflection; the propagation paths of the electromagnetic waves in the material are increased; increase of the multi-reflection loss and absorption loss enables the shielding efficiency of the material to be increased; in adoption of the reflection layers of gradient structure, the electromagnetic waves will not escape away from the shielding material rapidly for reflection; more electromagnetic waves can enter the next shielding unit; therefore, the shielding efficiency of the material is further improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
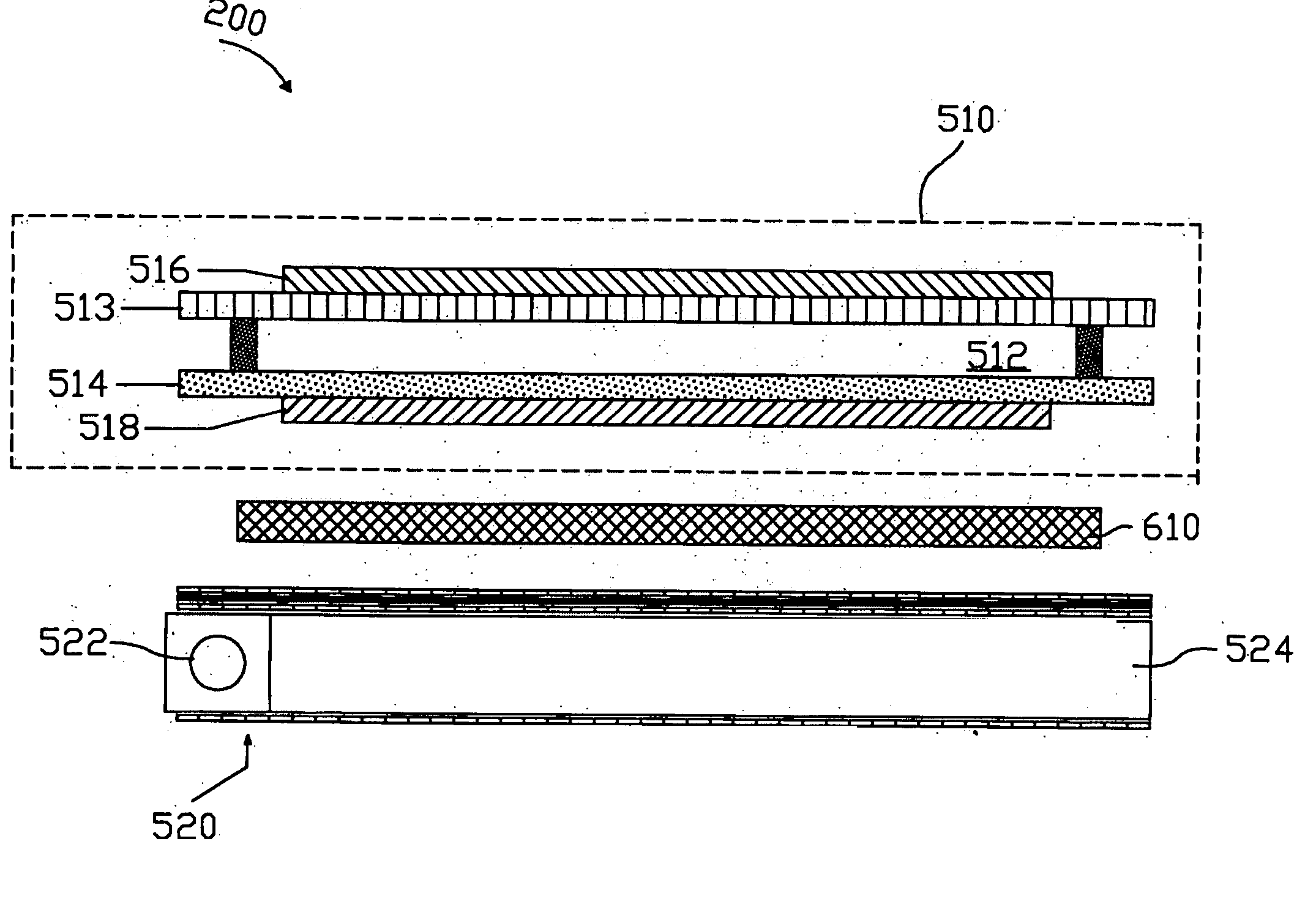
Quantum dot light-emitting component, backlight module and display device
InactiveCN105098039AImprove light extraction efficiencyAvoid absorption lossNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesQuantum dotDisplay device
The embodiment of the invention provides a quantum dot light-emitting component, a backlight module and a display device, relating to the field of photoelectric devices. On the premise of not increasing the volume of the component, the absorption loss in a light transmission process is reduced; and the light output efficiency of the quantum dot light-emitting component is increased. The quantum dot light-emitting component comprises a support frame, an excitation light source, a first reflecting layer and a quantum dot layer, wherein the support frame is shaped as a groove; the excitation light source is arranged at the bottom of the groove in the support frame and used for emitting excitation light; the first reflecting layer is arranged on the side wall of the support frame and used for reflecting the excitation light emitted on the side wall of the support frame by the excitation light source; the quantum dot layer is arranged at the opening of the groove of the support frame and emits light by being excited by the excitation light; and the excitation light source, the quantum dot layer and the support frame are packaged together so as to form an integral closed structure. The embodiment of the invention is used for manufacturing the quantum dot light-emitting component.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Ultraviolet light emitting diodes
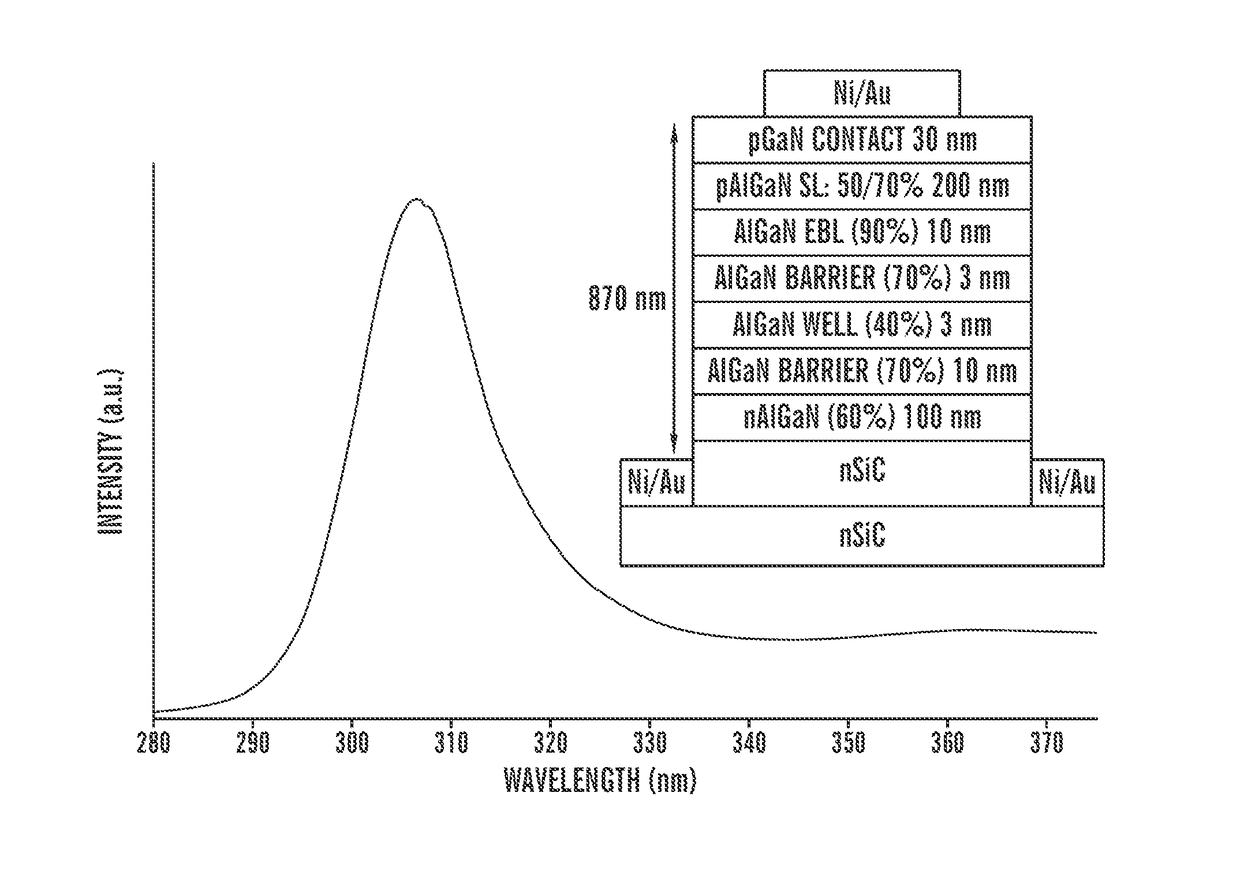
ActiveUS20170200865A1Increasing EEReduce absorption lossSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyDistributed Bragg reflector
The invention provides ultraviolet (UV) light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The UV LEDs can comprise abase layer including p-type SiC or p-type AlGaN, an active layer, and an n-AlGaN layer, wherein the active layer is disposed between the base layer and the n-AlGaN layer. In some embodiments, the absorption losses in p-SiC can be decreased or prevented by incorporating a conductive AlGaN Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR) between the p-type SiC layer and the active layer. In some embodiments, the n-AlGaN layer can be textured to increase the extraction efficiency (EE). In some embodiments, the external quantum efficiency of the LEDs can be 20-30% or more.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Method for measuring optical film absorption loss
InactiveCN101082537AHigh resolutionEasy to adjustTesting optical propertiesEntrance angleHigh resolution imaging
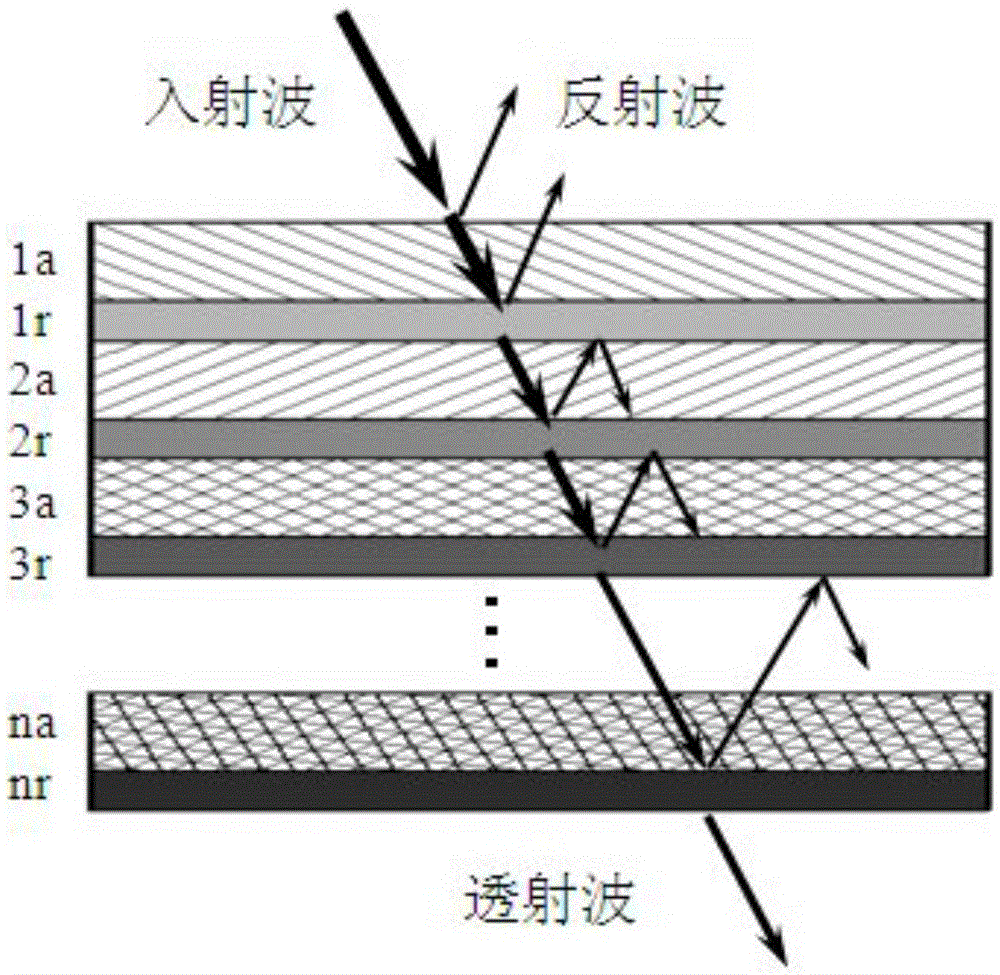
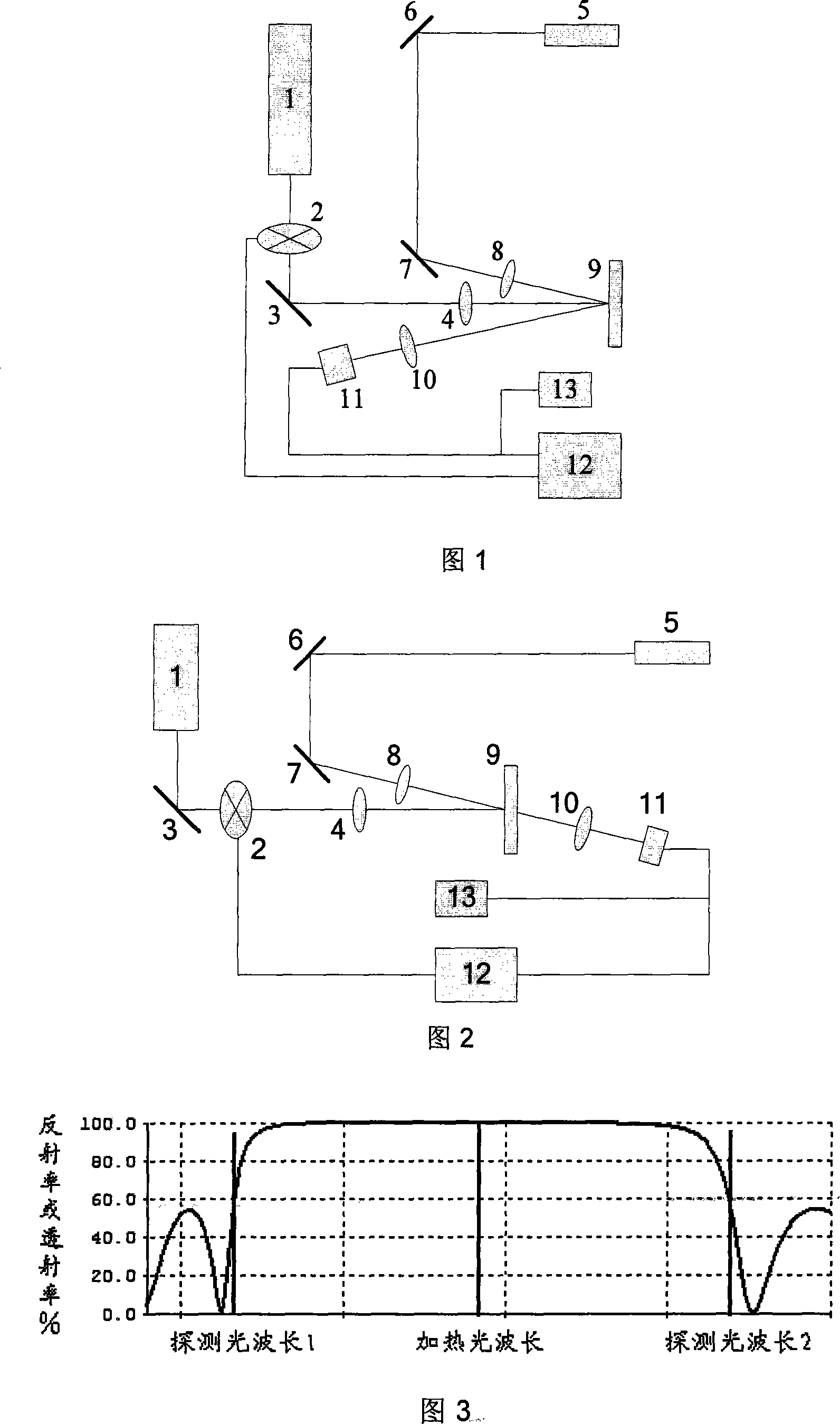
A kind of method of measuring the optics thin film absorption loss and it is characterized in that: utilizes the drift phenomenon generating by the optics thin film component reflection or the transmitted spectrum changing with the temperature and collects the proper detection optical wavelength and adjusts the entrance angle of the detection laser-beam (low power) relative to the sample surface and makes the detection optical wavelength located in the maximum location of the brim of reflection or transmitted spectrum. Makes the strength cyclic modulate (high power) continuous or impulse leaser-beam as the heating light-struck thin film component thin layer and detecting the same or adjacent location and makes the detection light beam from the sample surface reflection or transmitted light strength modulated or generated the transient variation. Use the photoelectric detection to monitor the real-time variation of the detection light strength of the thin film component reflection or transmission of the illuminating process of heating leaser-beam and monitor the absorption loss water of the thin film and the real-time variation of the optics performance and it can realize the absolute measurement of actual absorption deterioration by scaling the signal amplitude of vibration. In addition that it can realize the two-dimension high resolution imaging of the absorption deterioration by scanning the lateral attitude of the thin film component. The method can enhance the sensitivity of measurement the absorption deterioration at some conditions.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optoelectronic systems providing high-power high-brightness laser light based on field coupled arrays, bars and stacks of semicondutor diode lasers
ActiveUS20090116525A1Improve discriminationEfficient couplingLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayLow leakage
A semiconductor diode laser having a broad vertical waveguide and a broad lateral waveguide is disclosed emitting laser-light in a single vertical mode and a single lateral mode narrow beam. The vertical waveguide comprises a coupled cavity structure, wherein light, generated in the active medium placed in the first cavity leaks into the second cavity and returns back. Phase matching conditions govern the selection of a single vertical mode. A multi-stripe lateral waveguide comprises preferably a lateral photonic band crystal with a lateral optical defect created by selected pumping of multistripes. This approach allows the selection of a single lateral mode having a higher optical confinement factor and / or a lower absorption loss and / or a lower leakage loss compared to the rest lateral optical modes. This enables a single lateral mode lasing from a broad area field coupled laser array. A laser system comprised of multiple field coupled laser arrays on a single wafer and a set of external mirrors enables an ultra-broad field coupled laser bar emitting a coherent laser light in a single vertical optical mode and a single lateral optical mode. A laser system comprised of multiple ultra-broad field coupled laser bars on different wafers and a set of external mirrors enables an ultra-broad field coupled laser stack emitting coherent laser light in a single vertical optical mode and a single lateral optical mode. This allows realization of ultrahigh power ultrahigh brightness laser systems based on semiconductor diode lasers.
Owner:VI SYST GMBH
On-chip mode converter based silicon-germanium photoelectric detection apparatus
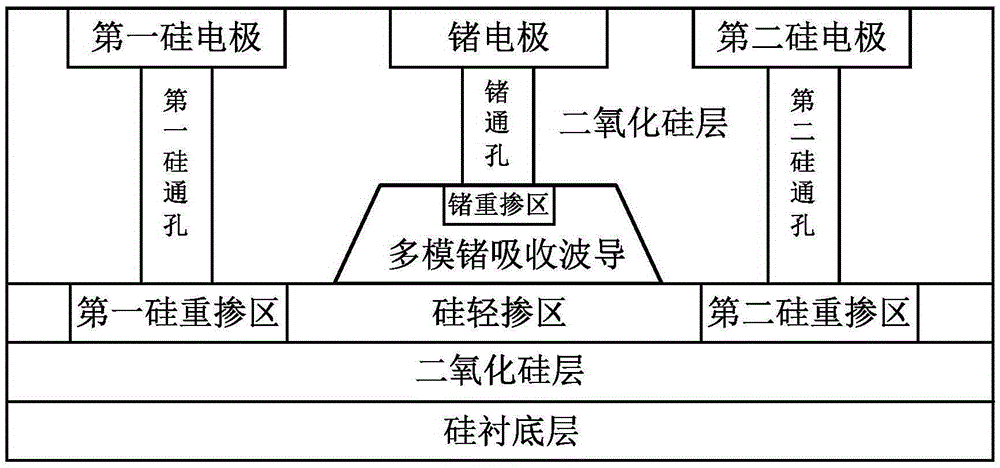
ActiveCN105405911AImprove responsivenessReduce absorption lossRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductor devicesCouplingResponsivity
The invention discloses an on-chip mode converter based silicon-germanium photoelectric detection apparatus, and relates to the field of an optical communication device. The silicon-germanium photoelectric detection apparatus comprises an insulating substrate, an optical coupler, an on-chip mode converter and a multi-mode silicon-germanium photoelectric detector; the optical coupler, the on-chip mode converter and the multi-mode silicon-germanium photoelectric detector are connected in sequence, and are all fixed on silicon wafers of the insulating substrate; the incident fundamental mode optical signal is transmitted to the optical coupler through single-mode fiber; the fundamental mode optical signal after being subjected to the coupling by the optical coupler enters the on-chip mode converter; the on-chip mode converter converts the fundamental mode optical signal into a multi-mode optical filed; the multi-mode optical field enters the multi-mode silicon-germanium photoelectric detector; and the multi-mode silicon-germanium photoelectric detector converts the multi-mode optical field into an electric signal. A germanium heavily-doped region in the silicon-germanium photoelectric detection apparatus is positioned in a region with relatively weak optical strength distribution in the multi-mode optical field; the absorption loss of the germanium heavily-doped region and germanium through holes on the optical field is obviously reduced, and the responsivity of the silicon-germanium photoelectric detection apparatus can be effectively improved.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Method for simultaneously measuring multi optical parameters of plane waveguide
InactiveCN1605848ASurface quality has no effectThe principle is simpleTesting optical propertiesMeasurement deviceRefractive index
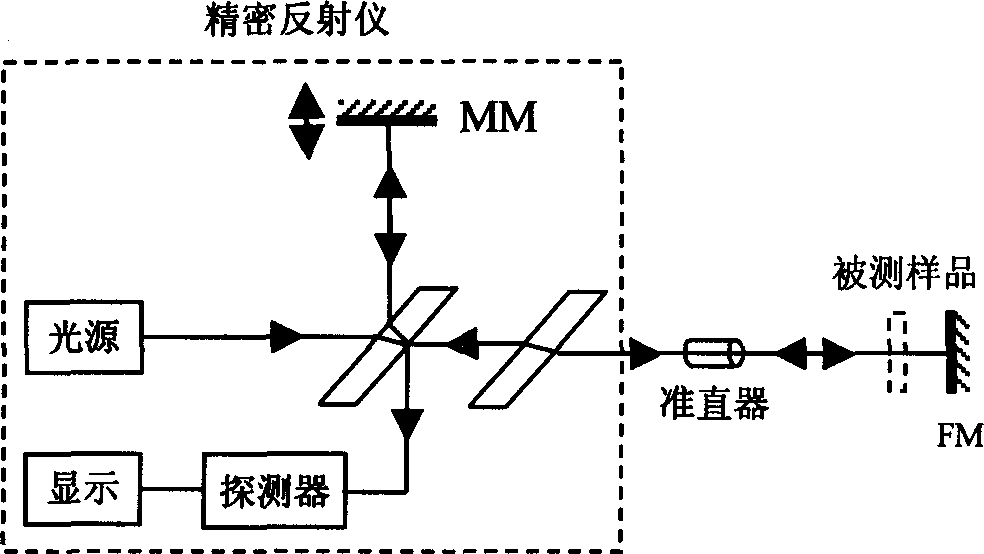
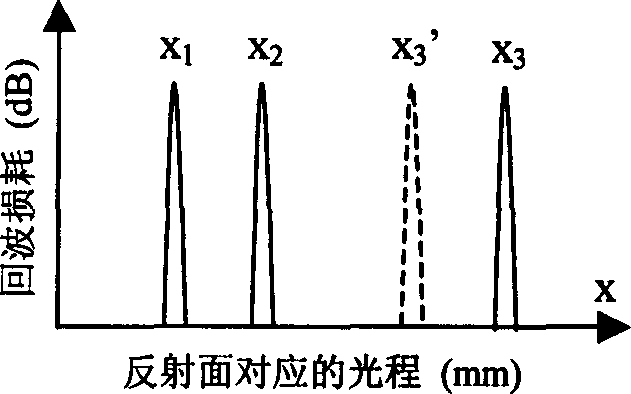
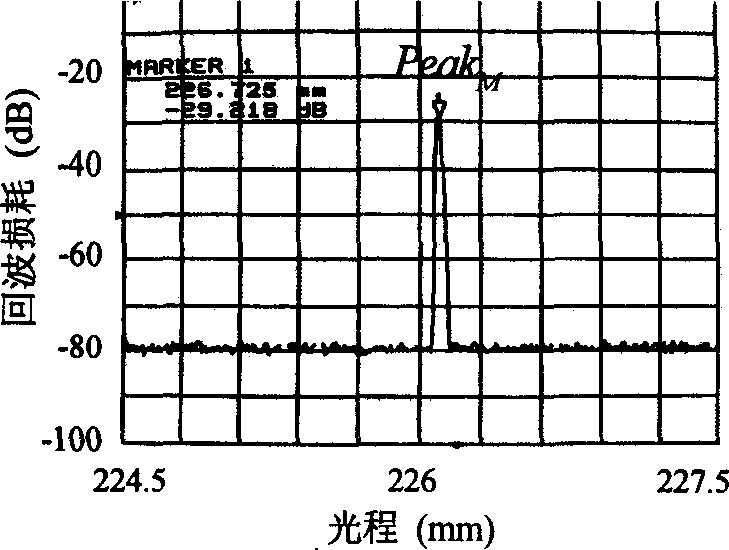
The simultaneous measuring process of several optical parameters of planar waveguide in planar waveguide technology field includes the following steps: constituting the measuring apparatus, measuring the optical path and echo loss corresponding to the fixed reflector before the measured waveguide insertion, installing the measured waveguide; measuring the optical path and echo loss corresponding to various interfaces after the measured waveguide insertion, calculating the refractive index and thickness of the measured sample, and calculating the insertion loss, absorption loss, reflectivity and diffuse reflection factor of the planar waveguide based on the measured optical path and echo loss of the direct interface reflections and multiple inner reflections between interfaces as well as the multiple reflection relation. The present invention has high measurement precision, simple calculation and other advantages.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Soluble fluorinated polyimide material and preparation method thereof
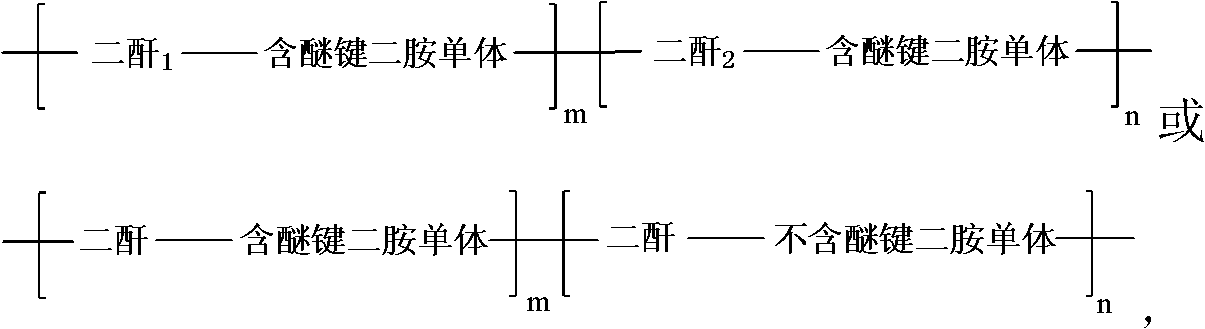
The invention discloses a soluble fluorinated polyimide material. The material is prepared by copolymerization of three monomers. The preparation method comprises: condensing and copolymerizing two dianhydride monomers and a diamine monomer having an ether bond according to the molar ratio of the two dianhydride monomers to the diamine monomer of 1:1, wherein the molar ratio of the two dianhydride monomers is 1:1 to 1:10; or condensing and copolymerizing a diamine monomer without an ether bond, a diamine monomer without ether bond and a dianhydride monomer according to a molar ratio of the diamine monomers to the dianhydride monomer of 1:1, wherein the molar ratio of the diamine with the ether bond to the diamine without the ether bond is 1:1 to 1:10. The general structural formula of the material is shown in description. The material has high solubility, low moisture rate, high thermal stability and low absorption loss.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Absorbing Solution, Method and Device for Absorbing CO2 or H2S or Both
ActiveUS20080078292A1Avoid performance degradationLow costCombination devicesGas treatmentOxygenDiamine
An absorbing solution according to the present invention is an absorbing solution that absorbs CO2 or H2S in gas or both of CO2 and H2S. The absorbing solution is formed by adding desirably 1 to 20 weight percent of tertiary monoamine to a secondary-amine composite absorbent such as a mixture of secondary monoamine and secondary diamine. Consequently, it is possible to control degradation in absorbing solution amine due to oxygen or the like in gas. As a result, it is possible to realize a reduction in an absorption loss, prevention of malfunction, and a reduction in cost. This absorbing solution is suitably used in an apparatus for removing CO2 or H2S or both of CO2 and H2S.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENG LTD +1
Anti-Reflection Film
ActiveUS20100171908A1Weaken colorWeaken unevennessPolarising elementsCoatingsTransmittanceLength wave
The present invention provides an anti-reflection film which weakens color in reflection light and prevents an occurrence of color unevenness. The anti-reflection film has a value in the range of 0.5-1.5% as an average luminous reflectance, a value in the range of 0.2-0.9% as a difference between the maximum and the minimum of spectral reflectance in the visible light region, a value in the range of 0.5-3.0% as an absorption loss in average luminous transmittance, a value in the range of 0.5-4.0% as a difference between the maximum and the minimum of absorption losses in light transmittance at all wavelengths within the visible light region, and a magnitude relation of Q450>Q550>Q650, where Q450, Q550 and Q650 is an absorption loss in light transmittance of said anti-reflection film at wavelengths of 450 nm, 550 nm 650 nm.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Method for pre-burying of negative electrode of hybrid super capacitor
InactiveCN104319115APull out in timeIncrease capacityHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for the pre-burying of the negative electrode of a hybrid super capacitor, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical energy. The hybrid super capacitor takes a multi-pore carbon material as a positive active material, an embeddable carbon material or an embeddable metallic oxide as a negative active material and an organolithium saline solution as an electrolyte. In a first formation process, the secondary addition of high concentration electrolyte is added to the hybrid super capacitor in a quiescent time of charging, so as to make up for the absorption loss of the reduction of ionic concentration of the electrolyte, which cannot be inversely buried, and the irreversibility of a positive electrode in the first charging process, thereby enabling the reduction amplitude of concentration of the electrolyte to be small.
Owner:惠州市鸣曦科技有限公司
Daylight illumination apparatus
InactiveUS20130155643A1Improve imitation abilityAdjustable intensityLighting applicationsPoint-like light sourcePhotoluminescenceLight guide
The invention relates to a daylight illumination apparatus. A daylight collector (3) collects daylight (4), which is guided to an illumination location to be illuminated along an optical path by a light guide (5), wherein the daylight is absorbed by the light guide. A photoluminescent material (6, 8) is arranged within the optical path and emits photoluminescent light that compensates for the absorption of the daylight by the light guide. Absorption losses of the daylight can therefore effectively be compensated, without necessarily needing, for example, an active compensation light source. This allows providing compensated day-light illumination in a technically relatively simple way.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method for Calibration-Free Scanned-Wavelength Modulation Spectroscopy for Gas Sensing
A method of calibration-free scanned-wavelength modulation spectroscopy (WMS) absorption sensing is provided by obtaining absorption lineshape measurements of a gas sample on a sensor using 1 / -normalized WMS-2 / j where an injection current to an injection current-tunable diode laser (TDL) is modulated at a frequency ̂ where a wavelength modulation and an intensity modulation of the TDL are simultaneously generated, extracting using a numerical lock-in program and a low-pass filter appropriate band-width WMS-<< / (n=1, 2, . . . ) signals, where the WMS-<< / signals are harmonics of the f, determining a physical property of the gas sample according to ratios of the WMS-<< / signals, determining the zero-absorption background using scanned-wavelength WMS, and determining non-absorption losses using at least two the harmonics, where a need for a non-absorption baseline measurement is removed from measurements in environments where collision broadening has blended transition linewidths, where calibration free WMS measurements without knowledge of the transition linewidth is enabled.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Crystalline silicon solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108336154AReduce compound rateImprove conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCrystalline siliconN type silicon
The present invention provides a crystalline silicon solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The crystalline silicon solar cell comprises: an N-type silicon substrate; a tunneling oxide layer formed on the back surface of the N-type silicon substrate; and a polysilicon layer formed on the tunneling oxide layer, wherein the polysilicon layer comprises alternatively distributed N+ polysilicon areas and P+ polysilicon areas, and a space is arranged between each neighboring N+ polysilicon area and P+ polysilicon area. The tunneling oxide layer, the N+ polysilicon areas and the P+ polysiliconareas form a passivation contact structure on the back surface of the N-type silicon substrate. According to the crystalline silicon solar cell and the preparation method thereof, the recombination rate of the back surface of a battery is effectively reduced, and the open circuit voltage of the battery is improved. Compared with the conventional back knot and back contact solar cells, the doping process of the front surface is saved, the battery preparation process is simplified, the absorption loss of light is reduced, and thus the solar cell can facilitate the improvement of battery performance and the reduction of cost.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Light source device and crystal display device
InactiveUS7841730B2Less in absorption lossLow costMechanical apparatusElongate light sourcesTransmittanceLight reflection
A light source comprising sidelight type backlight light guide plate (L), wherein a transmittance angle dependent layer (T1) which transmits normally incident light and reflects obliquely incident light is disposed on one surface of the sidelight type backlight light guide plate (L), and a reflection plate (R) having a repetitive slope structure is disposed on the other surface of the sidelight type backlight light guide plate (L). The invention light source is less in absorption loss due to repetition of light reflection and the like.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method for measuring transmission loss of optical element
ActiveCN101995328ASolve the measurement problem of weak absorption lossIncrease amplitudeTransmissivity measurementsTesting optical propertiesResonant cavityOptical axis
The invention relates to a method for measuring transmission loss of an optical element. The method comprises the following steps that: continuous laser is reshaped through a mode matching lens, and then enters an optical resonant cavity along an optical axis; two iris diaphragms of which the standoff distance is slightly larger than the thickness of the optical element to be measured are placed into the optical resonant cavity, wherein the clear aperture is less than the aperture of the optical element to be measured; after a shutoff laser beam is triggered, an output signal of the optical resonant cavity is recorded to fit fading time tau 0; the optical element to be measured is placed between the two iris diaphragms in the optical resonant cavity; the optical element to be measured is adjusted to make the surface of the optical element vertical to the optical axis; the output signal of the optical resonant cavity is recorded to fit fading time tau 1; the angle of the optical element to be measured is adjusted to make directly reflected light on the surface escape from the optical resonant cavity; the output signal of the optical resonant cavity is recorded to fit fading time tau 2; the absorption loss A of the optical element to be measured can be acquired by using the tau 0 and the tau 1; and the surface antireflective film residual reflectance R of the optical element to be measured is acquired by using the tau 1 and the tau 2. The method has the advantages of simple structure, high measurement precision, low system cost and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface-plasmon index guided (SPIG) waveguides and surface-plasmon effective index guided (SPEIG) waveguides
ActiveUS7184641B2Enhanced couplingNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guidePlasmonic waveguideCoupling
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
808nm large-power quantum well laser in non-aluminum active region of asymmetric structure
ActiveCN101340060AIncreased light confinement factorReduce leakageOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIndium arsenideWaveguide
The invention provides an aluminum-free active region 808nm high-power quantum-well laser with asymmetric structure. From the bottom to the top, the structure of the laser sequentially comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an N-type lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum-well layer, an upper waveguide layer, a potential barrier limiting layer, a P-type upper limiting layer, a transition layer and an ohmic contact layer, wherein, the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer are made of aluminum-free material Indium gallium phosphide, the quantum-well layer made of gallium indium arsenide phosphide material, the waveguide layer and the quantum-well layer form the aluminum-free active region, and one layer potential barrier limiting layer which is made of P-type aluminum gallium indium phosphide material and 50nm-150nm thick and has a band gap wider than that of the upper limiting layer is arranged between the upper limiting layer and the upper waveguide layer. The laser of the invention can increase the optical limiting factor of the P-type material region, reduce the optical leakage towards the P-type material region, reduce optical absorption loss of a current carrier at the highly doped area, and improve the work efficiency of the laser; the structure of the invention also improves the limiting effect of the active region on the carrier, reduce the leakage of the carrier and is favorable to the decrease of the threshold current.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Vertical-structure near ultraviolet light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109841714AImprove light extraction efficiencyEliminate transmissionSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellOptical communication
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
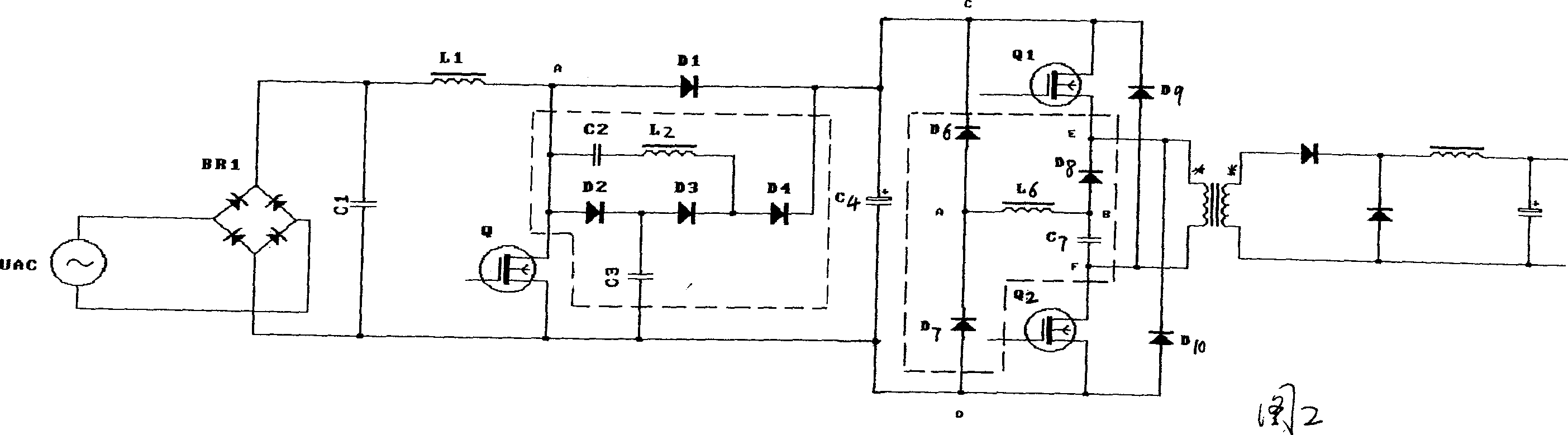
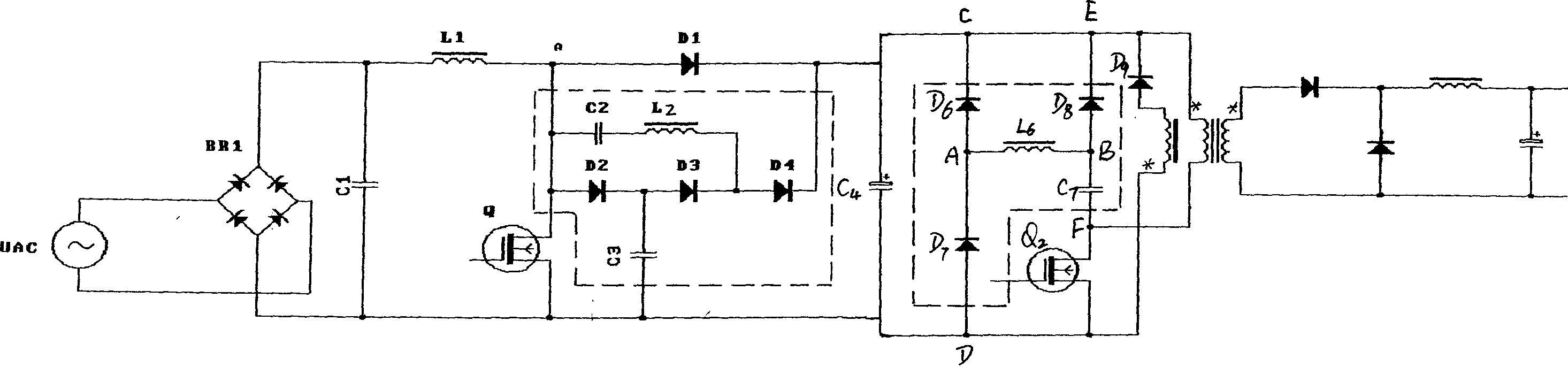
Soft switching circuit without absorption loss
InactiveCN1499703ASimple structureReasonable layoutEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceSoft switching
The invention modifies circuit structure with no absorption loss in existed soft switching as follows. In BOOST boosted circuit, a branch circuit composed of cascaded diode D2, D3 and D4 is connected to two ends of freewheeling diode D1 in BOOST circuit in parallel. One end of resonance branch circuit composed of capacitance C2 and inductance L2 is connected to positive end of diode D1, and the other end of the resonance branch circuit is connected to between diode D3 and D4. One end of capacitance C3 is connected between diode D2 and D3, and the other end is connected to end of cathode of switching tube. If needed, circuit with no absorption loss of positive / negative excited convertor can be added to modified circuit.
Owner:钱龙圣 +1
Optical converter module for display system
InactiveUS20050157233A1Increase brightnessPrismsPolarising elementsLiquid-crystal displayBrightness perception
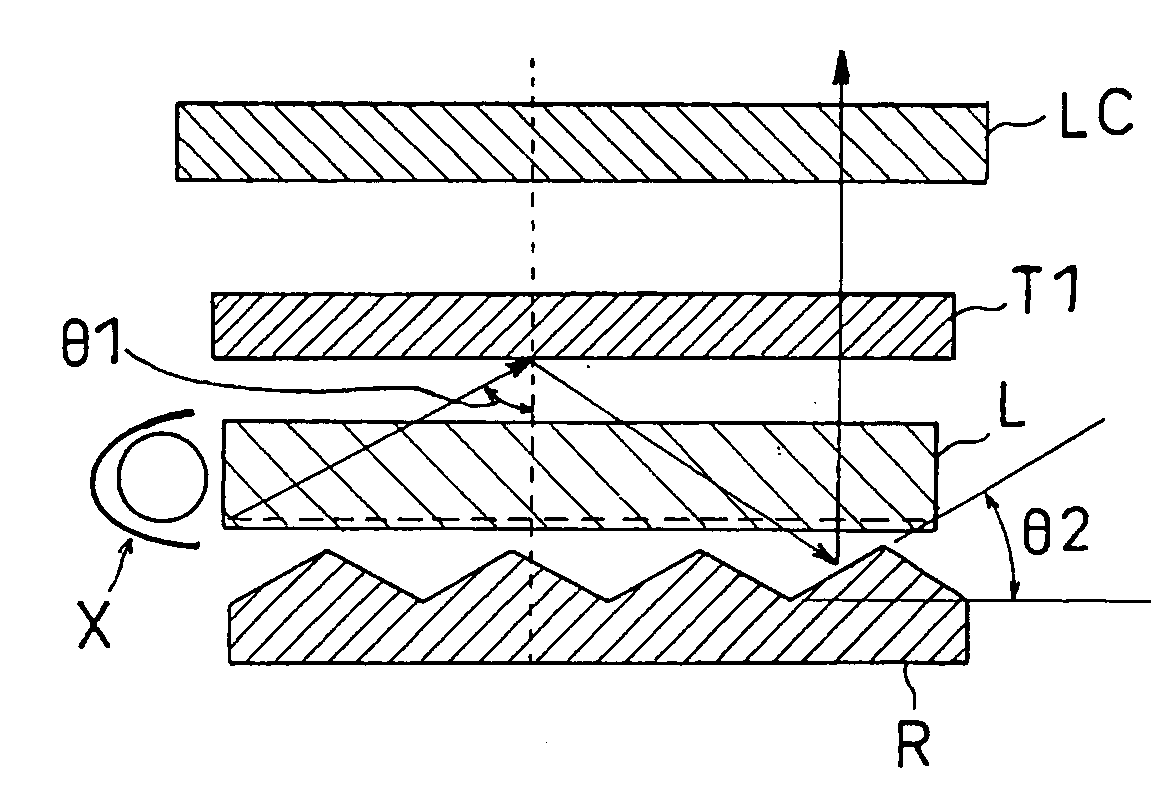
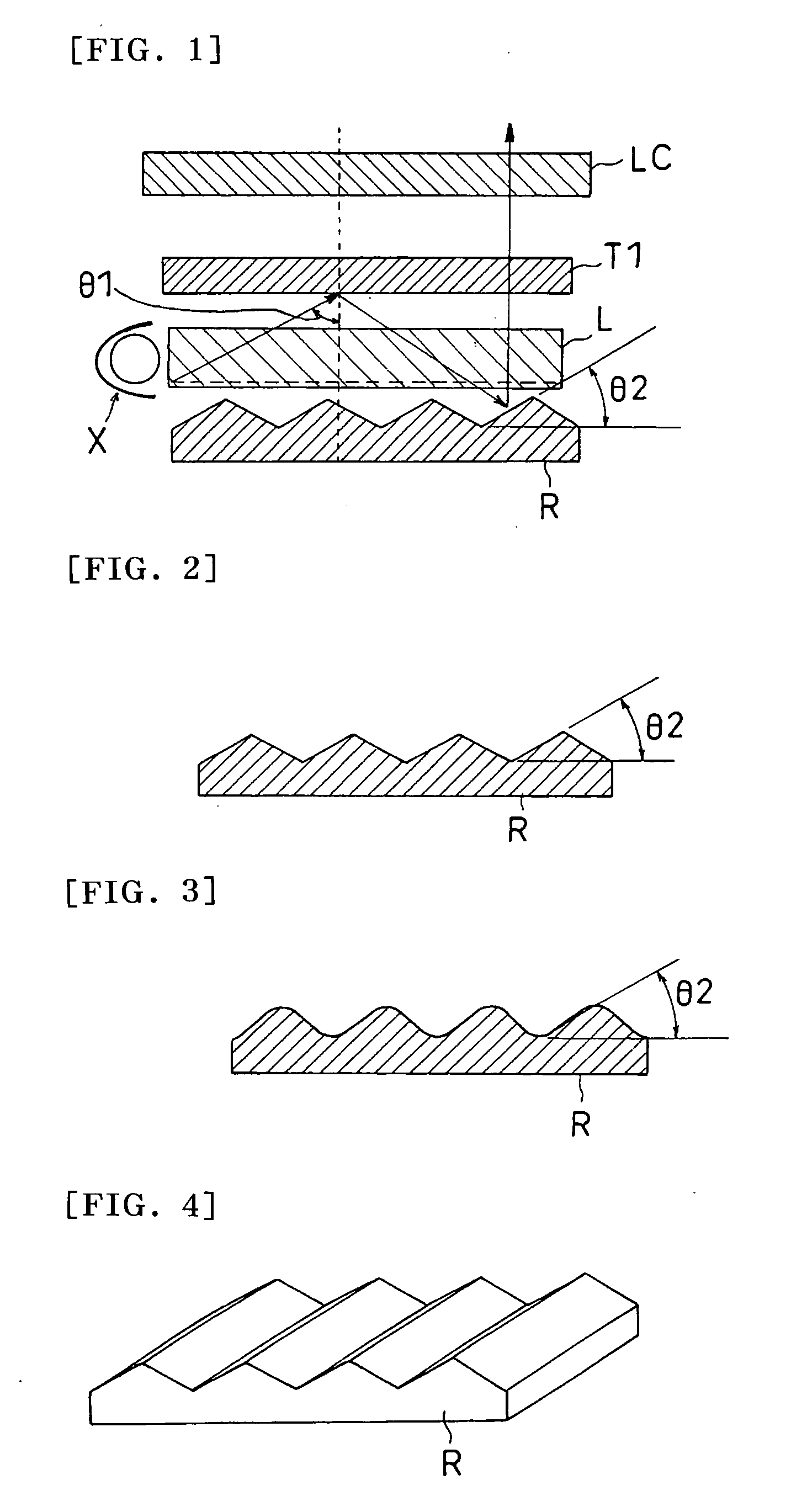
The present application describes a system and method for converting randomly polarized light into linearly polarized light without absorption loss to improve the brightness of a liquid crystal display system. According one embodiment, the liquid crystal display system includes an optical converter module configured to convert the randomly polarized light into linearly polarized light. The optical converter module is configured to convert the polarization of a first polarized component of the randomly polarized light to be substantially similar to a second polarized component. The optical converter module transmits the first and second polarized components having substantially similar polarization.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Comprehensive testing method of optical performance of deep ultraviolet optical element
InactiveCN103712782AReal-time monitoring of optical performance stabilityLow costTesting optical propertiesTime changesFluorescence spectrometry
The invention provides a comprehensive testing method of the optical performance of a deep ultraviolet optical element. According to the comprehensive testing method, the absorption loss absolute value of the deep ultraviolet optical element is measured based on the laser heat measurement technology; the fluorescence spectrum of the deep ultraviolet optical element is measured based on the laser-induced fluorescence spectrum technology when the deep ultraviolet optical element is irradiated by a deep ultraviolet laser; the defect level, the contents of doping components and the content of impurities of a material of the deep ultraviolet optical element are measured based on the Raman spectra technology. Through measurement of the absorption loss feature, the fluorescence spectrum feature and the Raman spectral feature of the deep ultraviolet optical element at the deep ultraviolet laser wavelength, the comprehensive optical performance of the deep ultraviolet optical element is estimated. By measuring the real-time change of the absorption loss, the fluorescence spectrum and the Raman spectrum of the deep ultraviolet optical element in the process of deep ultraviolet laser irradiation, the stability of the performance of the deep ultraviolet optical element is monitored. By the adoption of the same device, the optical feature parameters of the deep ultraviolet optical element are measured and the change of the optical feature of the deep ultraviolet optical element in the process of deep ultraviolet laser irradiation is monitored in real time.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Terahertz polarization maintaining optical fiber and manufacturing method thereof
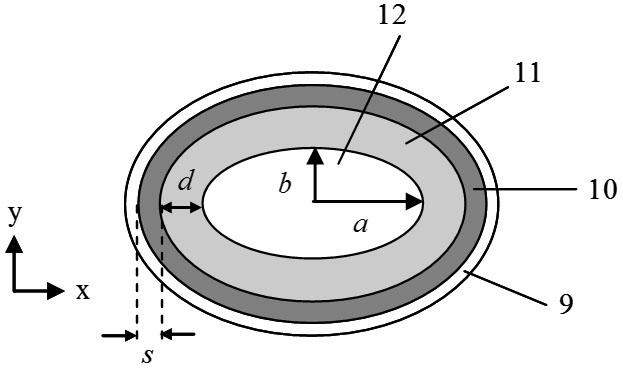
InactiveCN102608695AReduce lossHigh birefringenceOptical fibre with polarisationTerahertz radiationPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
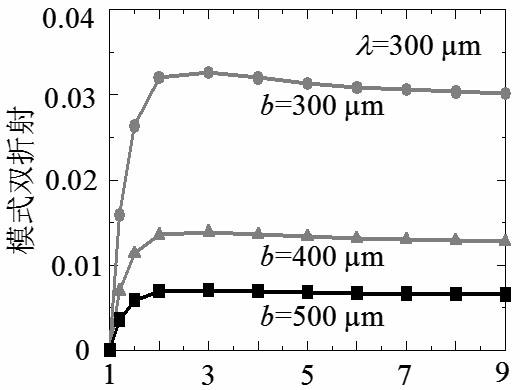
The invention belongs to the technical field of optoelectronic materials, and particularly relates to a terahertz polarization maintaining optical fiber and a manufacturing method of the terahertz polarization maintaining optical fiber. The terahertz polarization maintaining optical fiber is a medium / metal hollow optical fiber and is obtained by coating a metal film and a medium film on the inner wall of a base tube, the cross section of the terahertz polarization maintaining optical fiber is oval-shaped, and aperture size is determined according to the double refraction of a target and transmission loss, the ratio of an oval-shaped long shaft to an oval-shaped short shaft being 2:4, and the relationship between the double refraction and a normalization aperture. The optical fiber with the structure can obtain the double refraction in a 3*10<-2> mode and 2.4dB / m of absorption loss at 1THz (300mum).
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com