Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131 results about "Electromagnetic absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
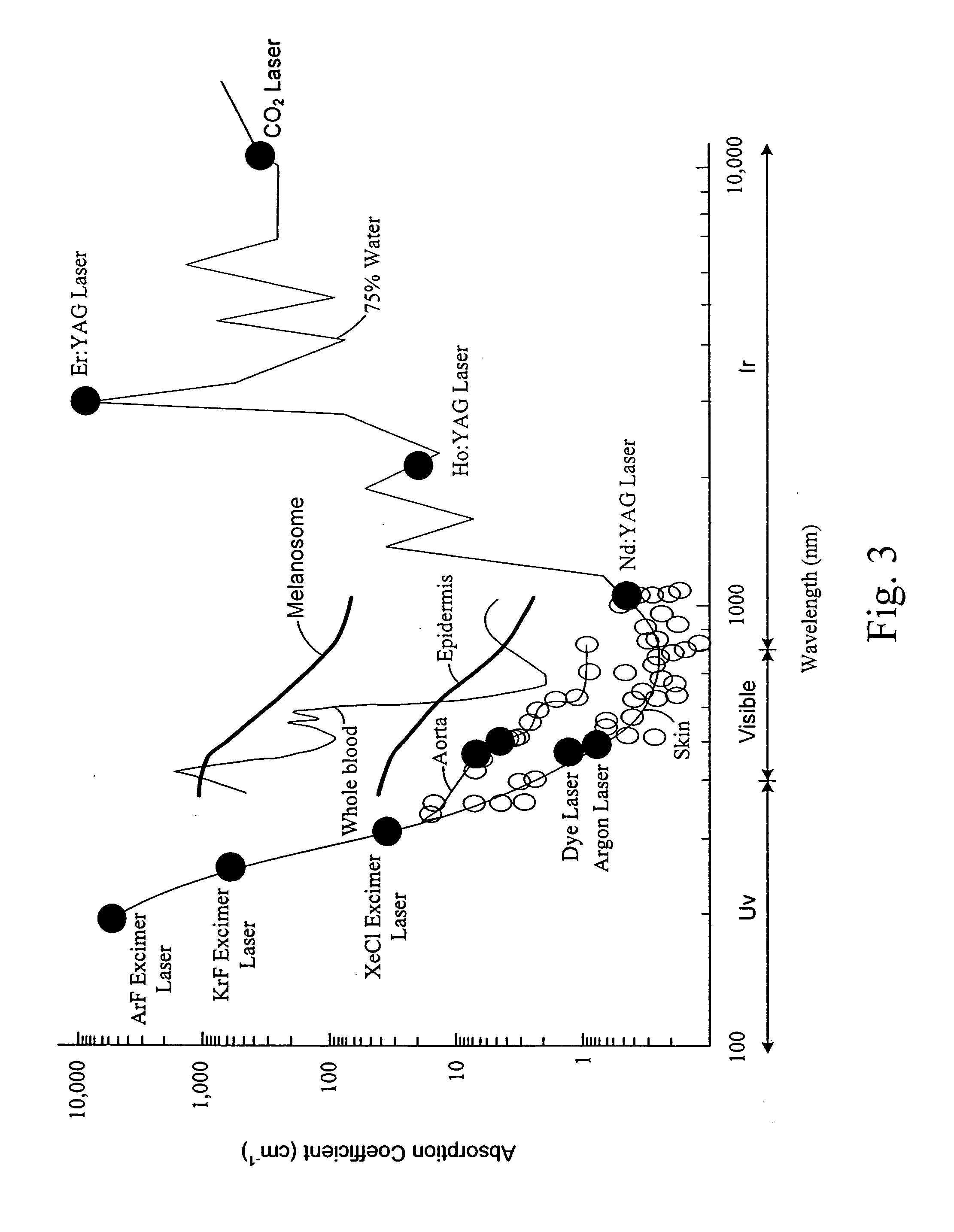
The absorption of electromagnetic radiation by water depends on the state of the water. The absorption in the gas phase occurs in three regions of the spectrum. Rotational transitions are responsible for absorption in the microwave and far-infrared, vibrational transitions in the mid-infrared and near-infrared.
Synthesis method of metallic oxide coated dissimilar metal 'core/shell'nano-particles
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a metal oxide-coated heterogeneous metal core-shell type nanometer particle, which belongs to the technical field of synthesizing nanometer composite material. The method is characterized in that metal and heterogeneous metal oxide micron powder is used as raw material and evenly mixed and pressed into block target material to be used as an anode. Hydrogen plasma is utilized as the heat source; the block target material is evaporated, and the core-shell type nanometer composite particle material is formed after the transformation of gaseous state-liquid state-solid state. The effect and advantage of the invention lies in that the root position-coating of the metal oxide pottery material to heterogeneous metal is realized in the process of evaporation and condensation; the invention is characterized by a simple method, low cost, little impurity, regular shape of the particle, and application to large scale production. The method can be used for preparing the core-shell type nanometer composite particles of a large variety of matters, and has wide application prospect in the fields of electromagnetic absorption / shielding, biomedicine, optoelectronic material, magnetic material, electrorheological fluid, and functional paint, etc.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Biomarkers sensing
InactiveUS20060270919A1Avoid large absorptionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorophoreElectromagnetic radiation
A method of, and system for, assaying for selected constituents in liquid mixtures confined by corresponding containing structures having relatively small electromagnetic absorption in at least one transmission wavelength range for transmissions of electromagnetic radiation therethrough, including in vivo assaying for a presence of selected constituents in bloodstreams in circulatory system passageways in mammalian bodies having relatively small electromagnetic radiation absorption in at least one transmission wavelength range for transmissions of electromagnetic radiation between such passageways and outer surfaces of corresponding bodily skin, based on, in the bloodstream example, introducing in a bloodstream a probe comprising a binding base capable of binding to at least one of the selected constituents and of also concurrently conjugating to two different fluorophores of which one has an emission spectra peak distribution in the transmission wavelength range that overlaps an absorption spectra peak distribution of that one remaining. Radiate at least some of the passageways from at least one location on the outer surfaces of the corresponding skin with electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths in the transmission wavelength range and also in an absorption spectra range of that fluorophore having an overlapping emission spectra peak distribution. Detect electromagnetic radiation at least at one location on the outer surfaces of the corresponding skin that has been transmitted from the evaluative radiated passageways of wavelengths in the transmission wavelength range and also in an emission spectra range of that fluorophore having an overlapping absorption spectra peak distribution wherein the emission spectra range differs from the overlapping emission spectra peak distribution.
Owner:MYTEK
Semiconductor device including electromagnetic absorption and shielding
ActiveUS20140231973A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionSolder maskDevice material
A semiconductor device is disclosed including material for absorbing EMI and / or RFI The device includes a substrate (202), one or more semiconductor die (224,225), and molding compound around the one or more semiconductor die (224,225). The material for absorbing EMI and / or RFI may be provided within or on a solder mask layer (210) on the substrate (202). The device may further include EMI / RFI-absorbing material around the molding compound and in contact with the EMI / RFI-absorbing material on the substrate to completely enclose the one or more semiconductor die in EMI / RFI-absorbing material.
Owner:SANDISK INFORMATION TECH SHANGHAI
Passive detection of analytes
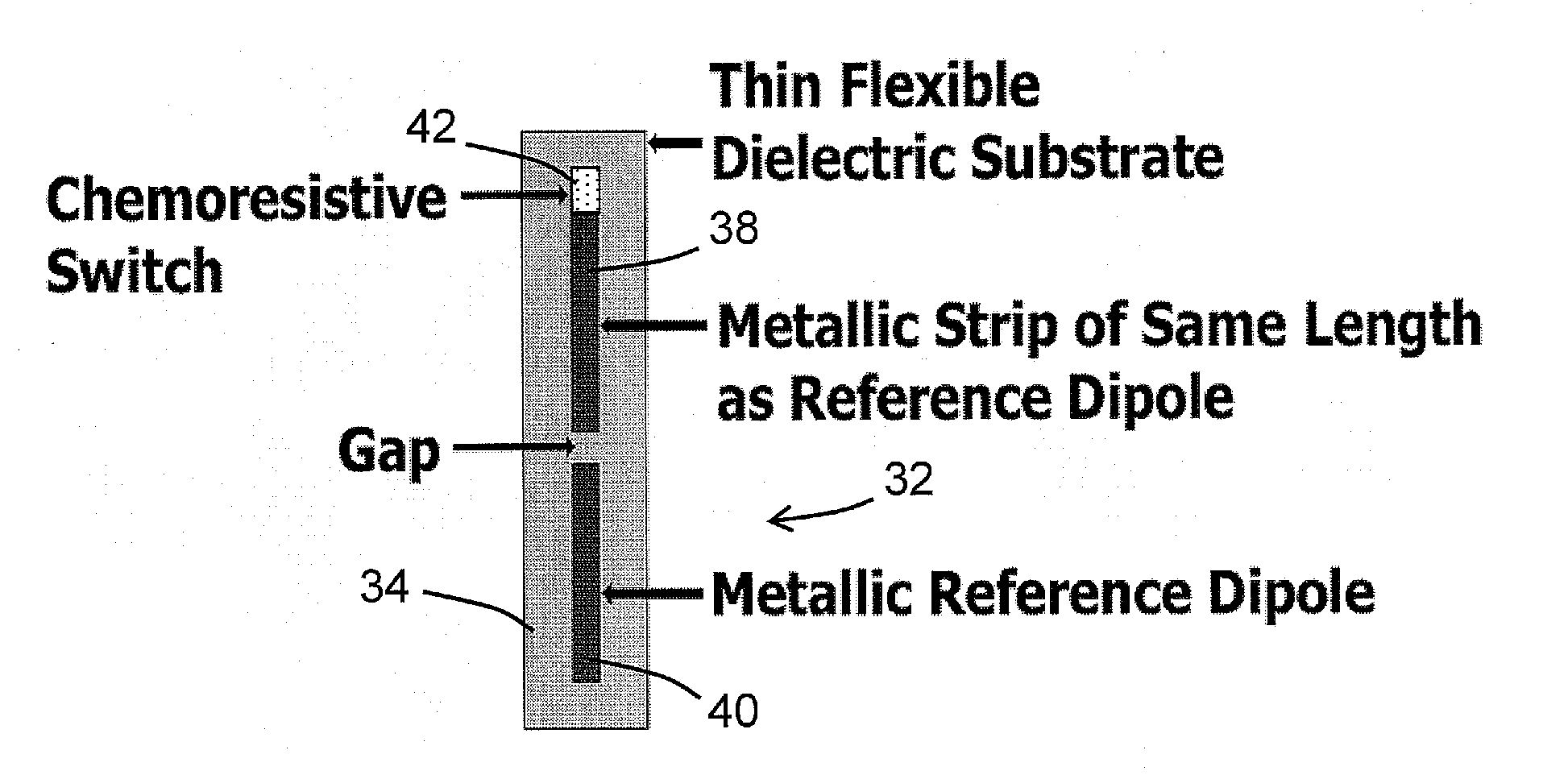
InactiveUS20100097048A1Increase electrical lengthReduced dimensionCurrent/voltage measurementRadiating elements structural formsAnalyteRadar
A passive element is provided to facilitate passive detection of analytes, such as analytes, using an electromagnetic probe beam. The probe beam may be provided by a radar and / or lidar system. In one example, a passive element comprises a reference dipole and a detection dipole, the detection dipole having an associated analyte-sensitive element, such as a chemoresistive or bioresistive element. When the analyte-sensitive element is in a modified conducting state due to the presence of an analyte, the detection cross section is modified whereas a reference cross section is substantially unchanged by the presence of the analyte. A passive element may comprise a frequency selective surface, for example including a frequency-selective surface (FSS) embedded in a dielectric layer and using an analyte-sensitive impedance layer to modify the electromagnetic absorption properties, allowing analyte detection.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
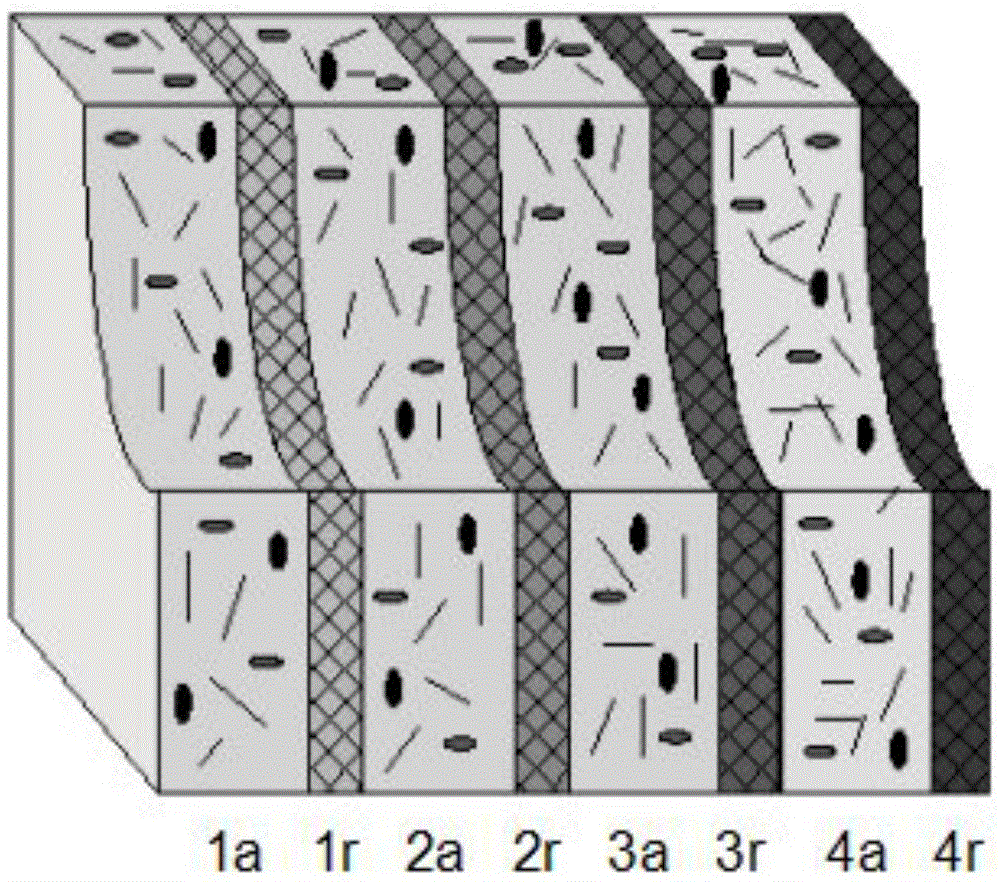
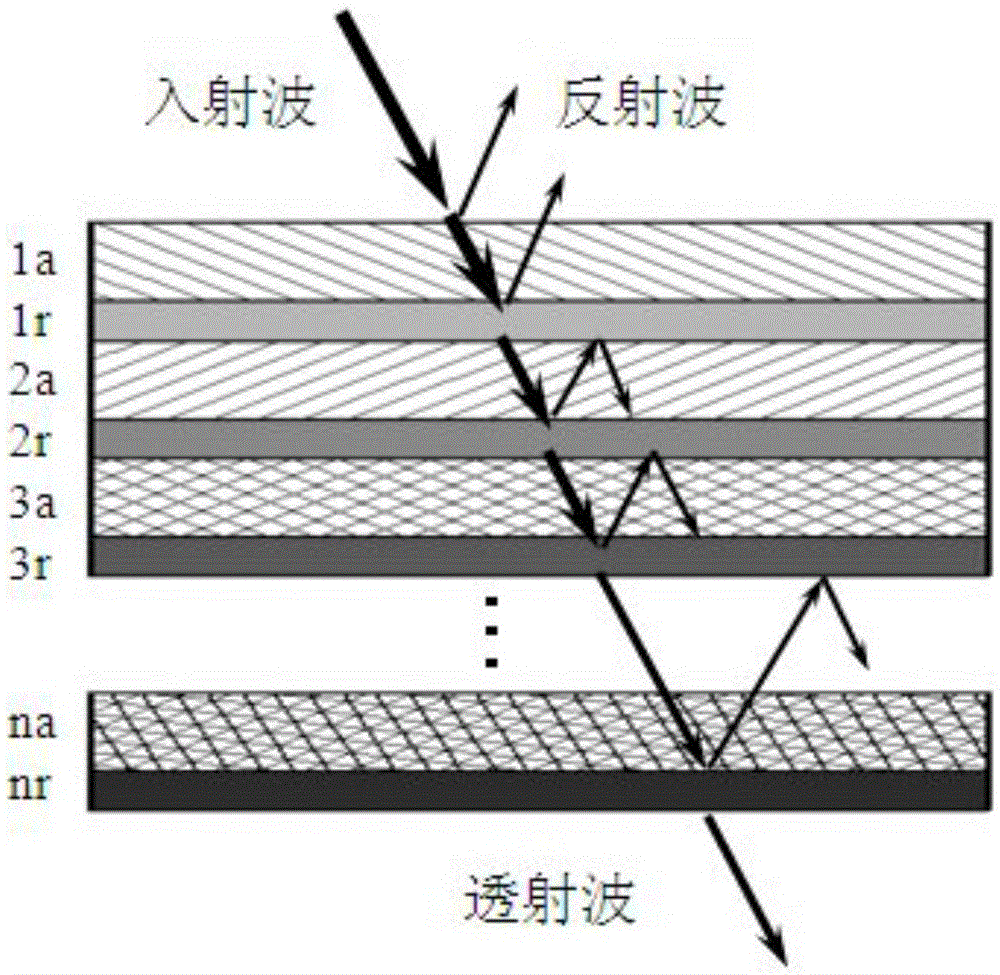
Electromagnetic shielding composite material
InactiveCN105555112AImprove shielding effectExtended propagation pathShielding materialsFiberReflection loss
The invention discloses an electromagnetic shielding composite material. Electromagnetic wave absorption layers and electromagnetic wave reflection layers are alternately overlapped to form electromagnetic shielding function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin, fiber carriers and electromagnetic absorption function bodies; the electromagnetic wave absorption layers are formed by compositing matrix resin and electromagnetic gradient reflection function bodies; in the overlapped electromagnetic wave reflection layers, the mass percentage compositions of short cut carbon fibers increase in gradient along the incident directions of the electromagnetic waves. According to the electromagnetic shielding composite material of the invention, the incident electromagnetic waves generate multi-reflection; the propagation paths of the electromagnetic waves in the material are increased; increase of the multi-reflection loss and absorption loss enables the shielding efficiency of the material to be increased; in adoption of the reflection layers of gradient structure, the electromagnetic waves will not escape away from the shielding material rapidly for reflection; more electromagnetic waves can enter the next shielding unit; therefore, the shielding efficiency of the material is further improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Hybrid polymer composites for electromagnetic wave shielding, and a method for fabricating the same
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
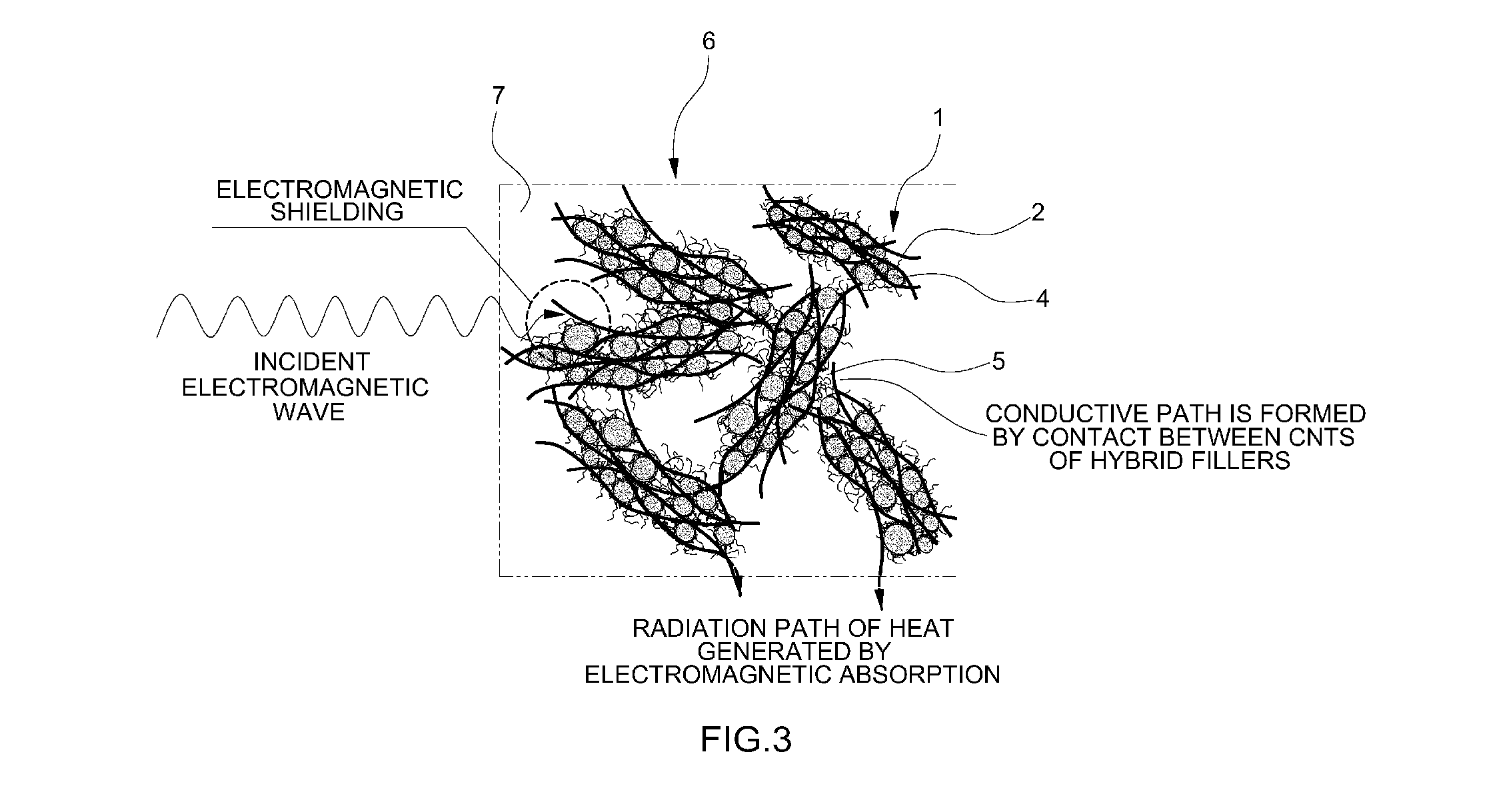
Hybrid filler for electromagnetic shielding composite material and method of manufacturing the hybrid filler
ActiveUS20130299732A1Improve shielding effectStrong absorption capacityMaterial nanotechnologyShielding materialsCarbon nanotubeGraphite
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Preparation method for electroconductive polyurethane complex with anion releasing function
The invention discloses a preparation method for an electroconductive polyurethane complex with an anion releasing function, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly vacuum-drying polytetrahydrofuran glycol, carbon nanotubes and tourmaline powder; separately mixing the dried carbon nanotubes and tourmaline powder with polytetrahydrofuran glycol, sealing in containers, standing at a certain temperature for several hours to obtain surface-modified carbon nanotubes and tourmaline powder, adding the surface-modified carbon nanotubes and the tourmaline powder into a solvent so as to be uniformly dispersed, adding polyurethane and reacting under a certain condition to obtain the polyurethane complex based on a complex system of the carbon nanotubes and the tourmaline powder. The obtained modified complex system of the carbon nanotubes and the tourmaline powder has the advantages of the carbon nanotubes and the tourmaline powder, so that the polyurethane complex has higher anionreleasing capability and electrical conductivity because of the synergistic effect of the carbon nanotubes and the tourmaline powder, and simultaneously has excellent ultraviolet and electromagnetic absorption properties and mechanical properties.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-directional resonant-type electromagnetic wave absorber, method for adjusting electromagnetic wave absorption performance using the same and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20110133978A1Easy to manufactureEasy to adjustMagnetic/electric field screeningCoatingsElectromagnetic wave absorberElectrical resistance and conductance
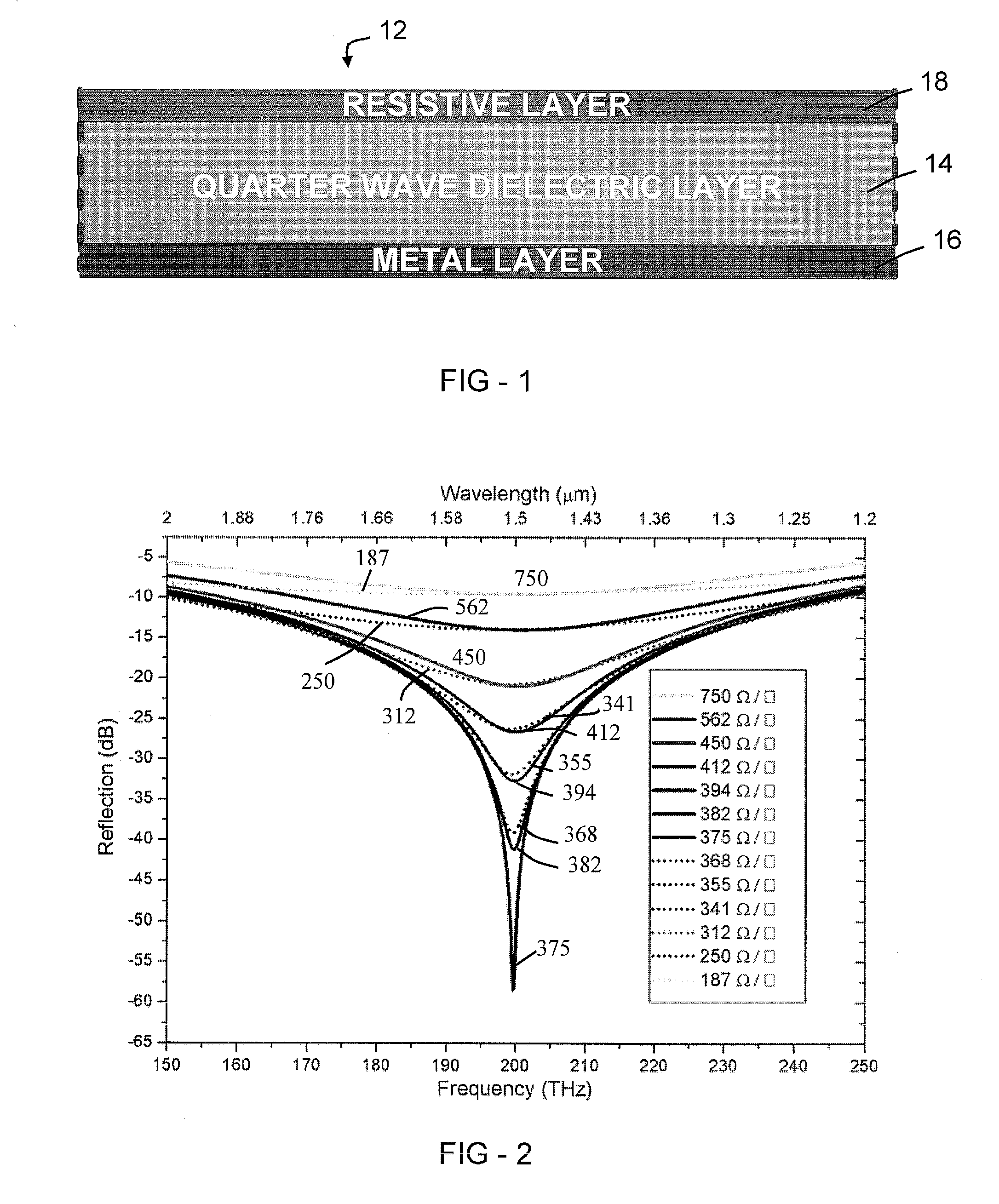
A multi-directional resonant-type electromagnetic wave absorber includes: at least one ground layer; a first dielectric layer and a second dielectric layer respectively formed on different outer surfaces of the ground layer; a first resistive pattern layer formed on an outer surface of the first dielectric layer; and a second resistive pattern layer formed on an outer surface of the second dielectric layer. Herein, the electromagnetic absorption performance is adjusted by changing one or more of thicknesses, permittivities, and permeabilities of the dielectric layers, thicknesses of the resistive pattern layers, and a reflection coefficient of the ground layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Low frequency electromagnetic absorption surface
A radiation absorber comprising a substrate having free charges capable of being driven to form resonance charge density oscillators and a dielectric layer coated onto said surface wherein the dielectric layer has a textured / patterned surface. The substrate is preferably metallic and the dielectric layer is waveform.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
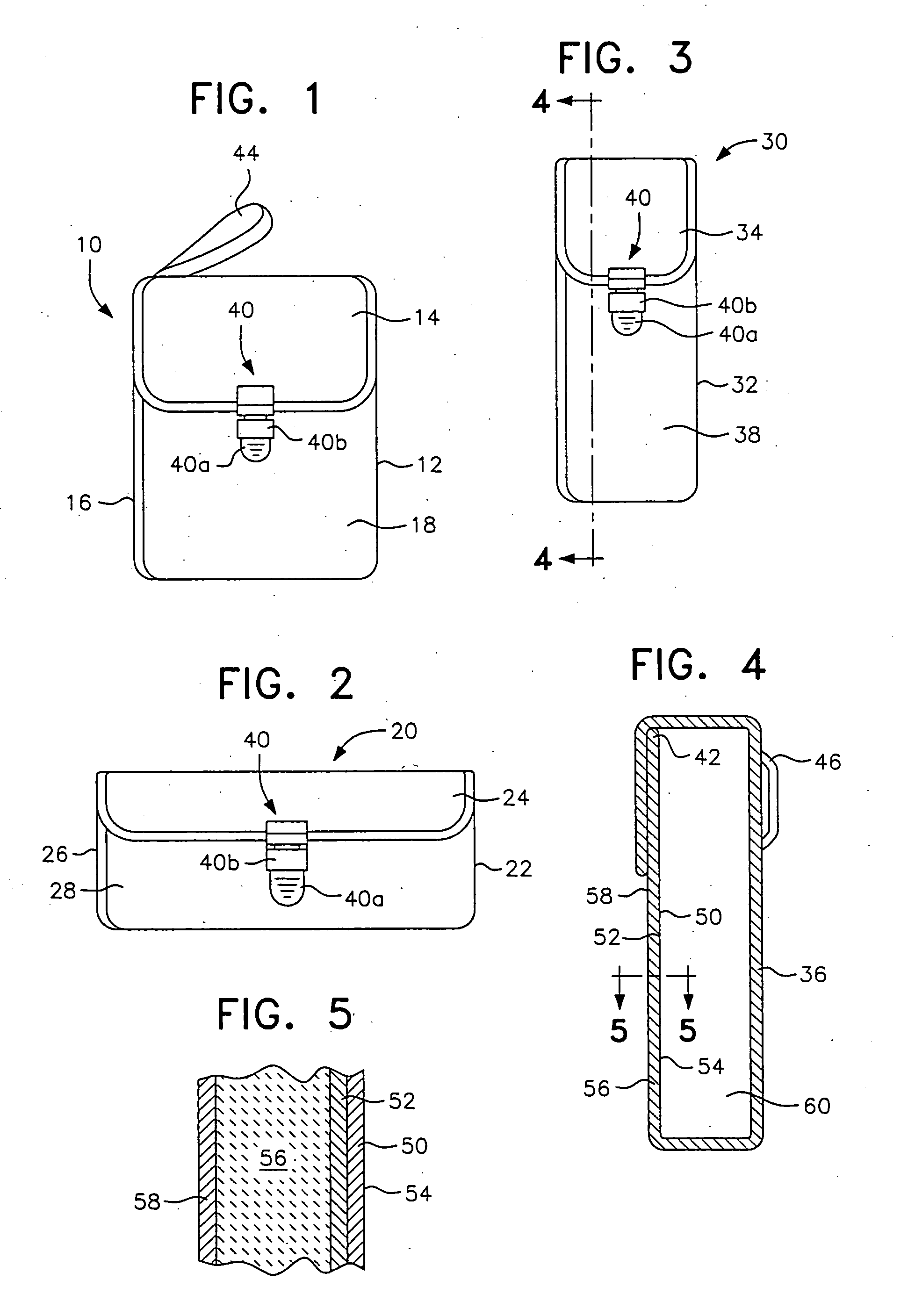
Personal electromagnetic security unit and method for electromagnetically shielding portable electronic communication and data devices and the like
InactiveUS20050092504A1Reliably obtain proper tensionComplete electromagnetic conductive sealMagnetic/electric field screeningHandbagsElectronic communicationEngineering
A personal electromagnetic security unit for shielding portable electronic communication and data devices such as cell phones and computers. The shielding unit includes a coated liner construction in which a high-attenuation metallized fabric is coated with a second attenuating material to enhance the electromagnetic absorption or reflection characteristics of the unit. This two-part conductive layer forms the inner liner of the shielding unit, with the coated side being protected by the unit's exterior material and preferably an intervening layer of padding.
Owner:UNITECH LLC
Nano iron oxide /graphite composite electromagnetic absorption material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101650977AImprove high temperature characteristicsLight weightScreening apparatusDielectric lossElectromagnetic absorption
The invention relates to a nano iron oxide / graphite composite electromagnetic absorption material and a preparation method thereof. The material is composite powder formed nano iron oxides and graphite oxides, and the nano iron oxides are uniformly distributed among the layers of the graphite oxides as well as the surface of the graphite oxides of the composite powder. The material of the invention enlarges the frequency range of wave absorption and meets practical use requirements through the composition of the nano iron oxides with strong dielectric loss and magnetic loss and the graphite oxides with high resistance loss.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for preparing nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide aerogel wave-absorbing material
InactiveCN108946711ANothing producedSimple and fast operationMagnetic/electric field screeningGrapheneEthylenediamineElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide aerogel (NGA) wave-absorbing material and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide hydrogel is formed through in-situ self-assembly of a one-step hydrothermal method by taking graphene oxide (GO) aqueous dispersion as a template and ethylenediamine (EDA) as a nitrogen doping agent and reducing agent, and the nitrogen doped NGA wave-absorbing material through dialysis and lyophilizing. The preparation method is environment-friendly, and has the advantages of no toxic or side product generation, simple preparation process, mild reaction condition and low cost. The aerogel wave-absorbing material has strong electromagnetic wave absorbing performance, wide absorptionfrequency band, low density and low packing ration, electromagnetic waves at different wavebands can be effectively absorbed by adjusting the nitrogen doping amount and thickness of a wave-absorbing coating, so that the NGA wave-absorbing material has an important application value in the field of electromagnetic absorption and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
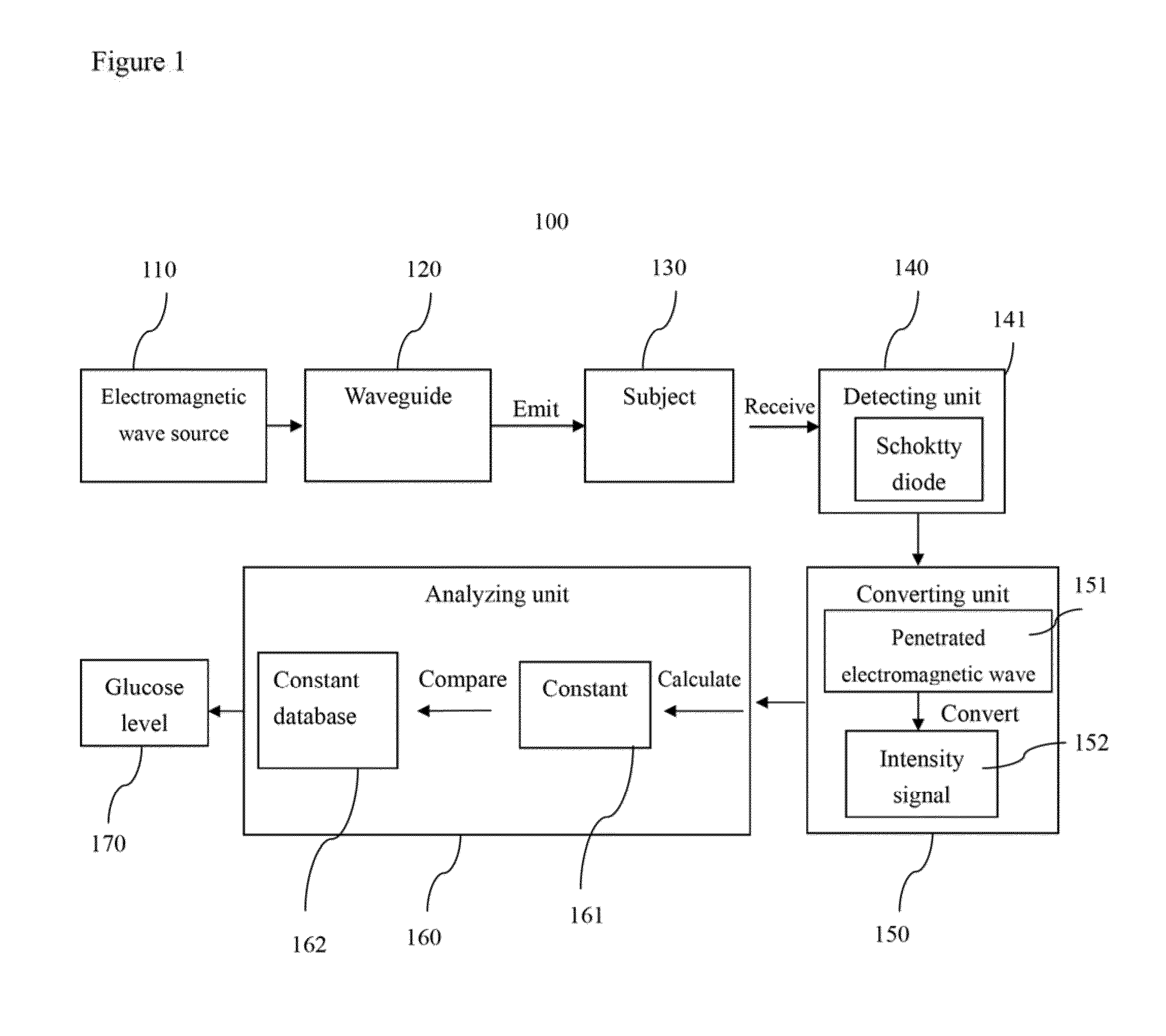
Method and device for detecting a blood glucose level using a electromagnetic wave
The present invention provides a method for detecting a blood glucose level of a subject using an electromagnetic wave. Because a different blood glucose level is accompanied by a different electromagnetic absorption constant, the present invention compares a detected blood glucose electromagnetic absorption constant of the subject with data in a blood glucose electromagnetic absorption constant database so as to obtain a blood glucose concentration of the subject. The present invention also provides a device for detecting a blood glucose level of the subject using the electromagnetic wave.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Preparation method of reduced graphene oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotube/nickel ferrite three-element nano composite wave-absorbing material
ActiveCN108690556ASimple and fast operationImprove conductivityOther chemical processesMagnetic/electric field screeningCarbon nanotubeElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a reduced graphene oxide / multi-walled carbon nanotube / nickel ferrite (RGO / MWCNTs / NiFe2O4) three-element nano composite wave-absorbing material and a preparation method thereof.The RGO / MWCNTs / NiFe2O4 three-element nano composite material with a local three-dimensional conducting network structure is prepared by adopting graphene oxide (GO), the multi-walled carbon nanotube,nickel nitrate hexahydrate and iron nitrate nonahydrate as precursors and carrying out one-step hydrothermal reaction. The preparation method is pollution-free and environmentally friendly, has no production of any toxic and harmful side products, and is simple in preparation process and low in cost; the prepared three-element nano composite wave-absorbing material is strong in capability of absorbing electromagnetic waves, wide in absorbing frequency band, small in thickness and low in density, can realize effective absorption of the electromagnetic waves with different wavebands by adjusting the content of MWCNTs in the composite material and the thickness of a coating layer, and has an important application value in the fields of electromagnetic absorption and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for uniformly cladding carbon nanotubes by nano ferroferric oxide magnetic particles
ActiveCN106047290ANo impuritiesOptimal Control StructureMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesIron saltsAlcohol
The invention discloses a method for uniformly cladding carbon nanotubes by nano ferroferric oxide magnetic particles. The method takes carbon nanotubes, iron salt and alcohol as reaction raw materials and sodium hydroxide or ammonia water provides an alkaline environment; ferroferric oxide cladded carbon nanotubes are obtained by adopting a polyol method; and finally, ethanol and de-ionized water are added to repeatedly wash the ferroferric oxide cladded carbon nanotubes. Frroferric oxide cladded on the surfaces of the carbon nanotubes, which is obtained by the method, is very uniform; the process is simple and the cost is low; and industrialized production is easy to realize. The carbon nanotubes cladded by the ferroferric oxide have conductivity and magnetic properties; and compared with pure carbon nanotubes, the electromagnetic absorption rate is greatly improved.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
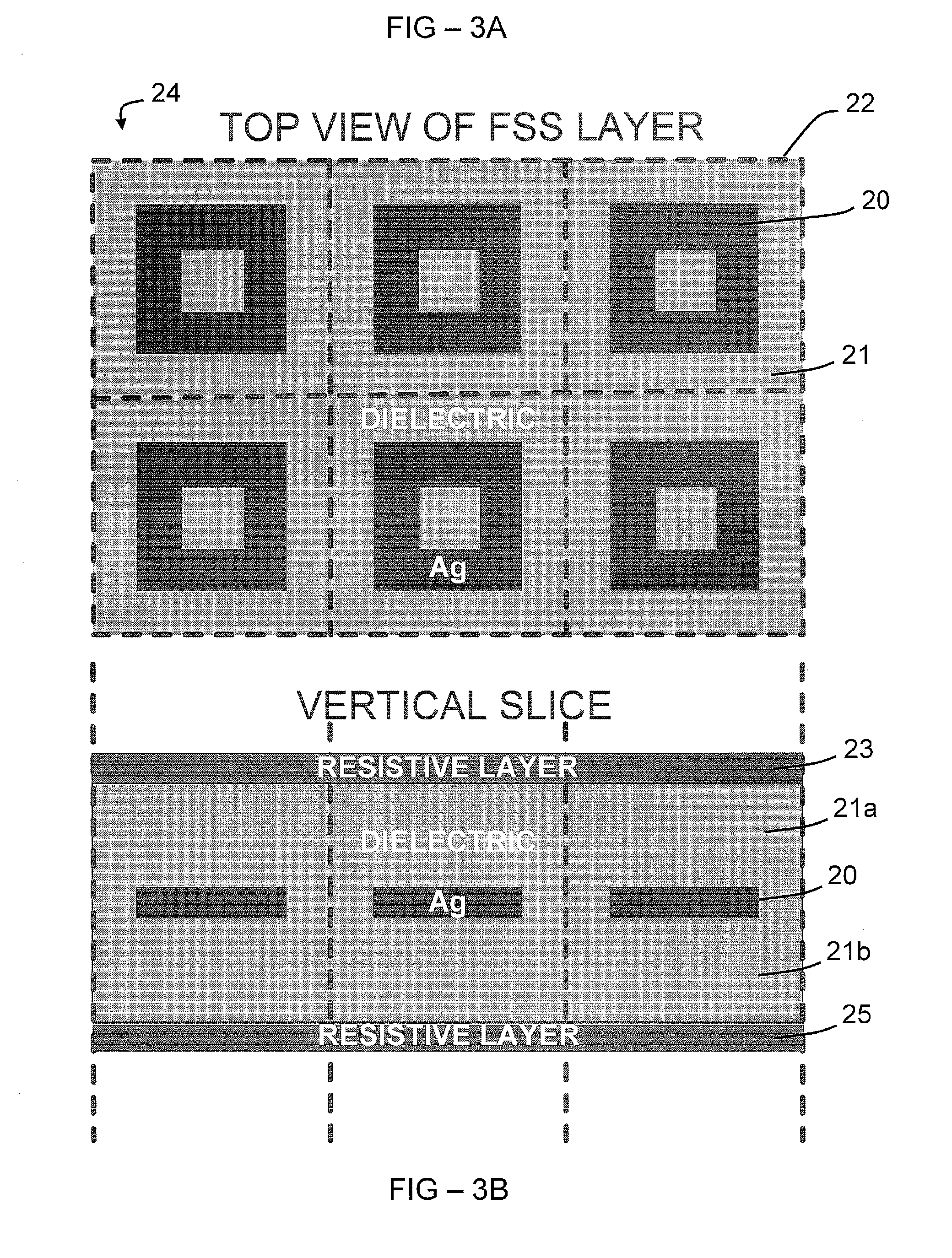
Electromagnetic absorption metamaterial
ActiveCN107453052AFlexible and controllable modulationEasy to depositAntennasOptical elementsComposite filmResonance
The invention provides an electromagnetic absorption metamaterial which has an upper surface that is in a working environment and includes a periodic resonance unit array. The upper surface of the electromagnetic absorption metamaterial is provided with a dielectric media composite film which is obtained by laminating solid dielectric media in different thickness proportions. The dielectric media composite film is made from at least two of the silicon oxide, silicon nitride, aluminium oxide, magnesium fluoride or silicon. According to the invention, since the electromagnetic absorption metamaterial is obtained by laminating media of different kinds in proportions, the dielectric film which has the refractive index between the maximum refractive index and the minimum refractive index of the selected media can be obtained, such that the surface lattice resonance can be modulated in a more flexible and controllable manner; since the dielectric media composite film is obtained by laminating solid dielectric layers in different thickness proportions, the dielectric media composite film can work in any working environment, even solid or moving environments.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for separating electron components in waste circuit board in electromagnetic induction
ActiveCN102327891ANo damageImprove separation efficiencySolid waste disposalElectronic waste recyclingElectromagnetic shieldingGas release
The invention discloses a method and system for separating electron components in a waste circuit board in electromagnetic induction. The system is characterized in that a heating electric wire with adjustable temperature, an air supply / air suction device, a transmitting device, an impact vibrating device, an electromagnetic absorption device, a component recycling net and a circuit board recycling baffle are arranged in a sealed box body with a feed port board; the waste circuit board is sent to a transmitting belt through the feed port, and slowly transmitted to a heating area, a part of electron components is separated under the high temperature and electromagnetic absorption effect, when the waste circuit board slowly passes through the impact vibrating device, the other electron components are separated under rapid impact effect; the electron components fall on the component recycling net to be recycled; a waste gas recycling processing device recycles and processes toxic and harmful gas released by the heated waste circuit board in the work process. The method and system in the invention is an efficient and harmless and has simple apparatus and high efficiency of separating the electron components, and is capable of processing the waste circuit board in batch in the earlier stage.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Heat-conducting and wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108276773AGood absorbencyImprove absorbing performanceHeat-exchange elementsHeat conductingSolvent
The invention provides a heat-conducting and wave-absorbing material and a preparation method thereof, wherein the heat-conducting and wave-absorbing material is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 200-400 parts of vinyl organosilicon, 150-550 parts of Si-H organosilicon, 0.1-5 parts of hydrogen-containing silicone oil, 50-400 parts of iron-silicon aluminum alloy magnetic powder,20-300 parts of SiO2 powder, 0.1-10 parts of a silane coupling agent, 0.005-0.5 part of a platinum catalyst, and 20-500 parts of a solvent. According to the present invention, the specific componentsare matched according to the specific ratio, such that the obtained heat-conducting and wave-absorbing material can excellent absorb K[alpha] electromagnetic waves so as to produce good electromagnetic absorption, and further has good thermal conductivity and good physical and mechanical property so as to easily achieve the normal operation of electronic equipment and improve the service life of the electromagnetic material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SAINTYEAR ELECTRONICS TECH
Preparation method of Fe-doped stannic oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanometer composite wave absorption material
ActiveCN109348696ANothing producedSimple and fast operationMaterial nanotechnologyMagnetic/electric field screeningTin dioxideHigh absorption
The invention discloses a Fe-doped stannic oxide / reduced graphene oxide (Fe-SnO2 / RGO) nanometer composite wave absorption material and a preparation method thereof. The Fe-SnO2 / RGO binary composite material is prepared by taking graphene oxide (GO), tin tetrachloride pentahydrate and iron nitrate nonahydrate as a precursor and by one-step hydrothermal reaction. The preparation method is green andenvironmental-friendly, no any harmful side product is generated, and the preparation process is simple and is low in cost. The prepared binary nanometer composite wave absorption material has the characteristics of high absorption strength, dual-band (C and Ku bands) absorption, low density and the like; and by adjusting the content of Fe<3+> doped in the composite material and the thickness of awave absorption coating layer, effective absorption of electromagnetic waves at different bands can be achieved, and the preparation method has important application value in the field of electromagnetic absorption and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
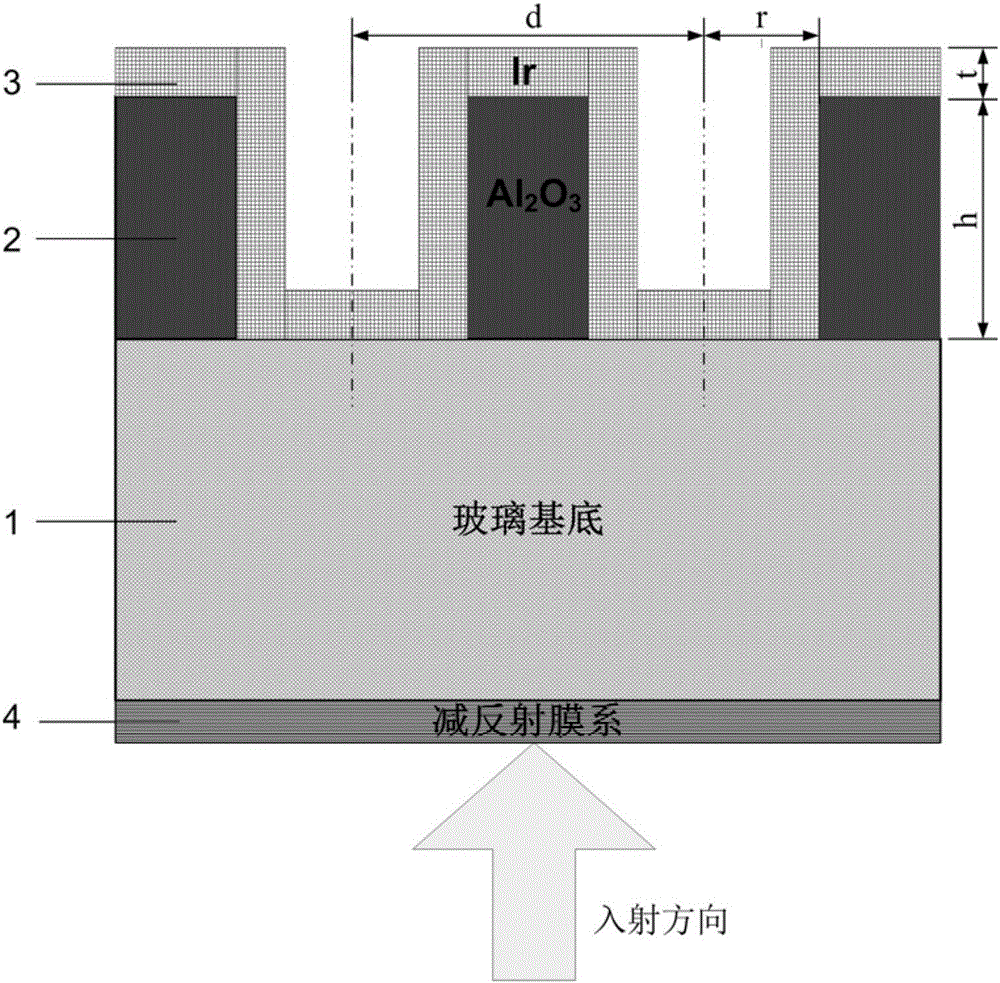
Porous-alumina-based visible near infrared broadband absorber and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a porous-alumina-based visible near infrared broadband absorber. The porous-alumina-based visible near infrared broadband absorber includes a substrate, wherein a high-low refractive index medium anti-reflection film system is arranged on the front side of the substrate; a bipass porous alumina template is arranged on the back side of the substrate; and the porous alumina template is covered by a metal thin film. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the above absorber. The porous-alumina-based visible near infrared broadband absorber and the preparation method thereof utilize the porous alumina template and use the layer of thin high absorbability metal structure covered on the porous alumina to realize strong resonance between the medium and the metal on the bottom surface and the side wall of the porous alumina holes so as to realize absorption of visible near infrared wave band broadband. The porous-alumina-based visible near infrared broadband absorber has the advantages of being simple in structure, being simple and convenient in preparation, being low in cost, being convenient for mass and batched production. Therefore, the porous-alumina-based visible near infrared broadband absorber is expected to be widely applied to the fields of elimination of stray light, space detection, imaging, photo-thermal conversion and electromagnetic absorption.
Owner:上海高能煜镀科技有限公司
Flexible polyimide-based composite dielectric film material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110330646ASmall coefficient of thermal expansionHigh electromagnetic absorption efficiencyDielectricReflection loss
The invention belongs to the field of dielectric materials and discloses a flexible polyimide-based composite dielectric film material and a preparation method thereof. The flexible polyimide-based composite dielectric film material is prepared by stirring MXene and polyamic acid formed by dianhydride and diamine at room temperature to obtain a mixed solution of MXene / PAA, coating a base materialwith the mixed solution of MXene / PAA, and amidating at 150-550 DEG C, wherein the MXene is Mn+1Xn, X is selected from C or N, M is selected from Sc, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo AND Mn transition metal elements. The preparation method of the flexible polyimide-based composite dielectric material is simple, the thickness is uniform and controllable, and the dielectric property is good; and as a supercapacitor device or an electromagnetic wave absorbing material, the flexible polyimide-based composite dielectric material has the characteristics of higher electromagnetic absorption efficiency, good cycle stability, small maximum reflection loss, wide absorption frequency range and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for preparing multi-walled carbon nano-tubes/cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material
InactiveCN109133038ASimple and fast operationNothing producedRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesOther chemical processesCarbon nanotubeCerium
The invention discloses a multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide (MWCNTs / CeO2) nano-composite wave absorbing material and a method for preparing the same. MWCNTs which are subjected to nitric acid reflux treatment are used as templates for the multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material, and cerium nitrate hexahydrate is used as a precursor for the multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material. The MWCNTs / CeO2 nano-composite wave absorbing material is prepared by the aid of one-step hydrothermal reaction. The multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material and the method have the advantages that the method is green and environmentally friendly, and is free of optionalhazardous byproducts and low in cost, optional surfactants can be omitted, and processes for preparing the multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material are simple; the multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material which is a binary nano-composite material prepared by the aid of the method is high in electromagnetic wave absorbing capacity, wide in absorption frequency band and low in density and is thin; the content of the MWCNTs in the multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material and the thicknesses of coatings can be adjusted, accordingly, electromagnetic waves with different wave bands can be effectively absorbed, and the multi-walled carbon nano-tubes / cerium dioxide nano-composite wave absorbing material and the method have important application values in the field of electromagnetic absorption and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Adduct of fluorescent dye and tumor avid tetrapyrrole
InactiveUS20090043090A1Facilitate entryReduce the possibilityBiocidePhotodynamic therapyLength waveWavelength shift
A compound having preferential localization in tumor tissue relative to normal tissue, a preferential electromagnetic absorption at a wavelength between about 660 and 900 nm, and a fluorescence at a wavelength shifted from the preferential absorption by at least +30 nm and preferably at least +50 nm. The compound further preferably destroys tumor tissue in which it is absorbed when exposed to light at its preferential absorption wavelength. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the compound is a conjugate of a tumor avid tetrapyrrole compound with a fluorescent dye, and more preferably the fluorescent dye is an indocyanine dye such as indocyanine green. The tumor avid tetrapyrrole compound is preferably a porphyrin derivative selected from the group consisting of chlorins, bacteriochlorins, purpurins and derivatives thereof.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Electromagnetic wave absorption board to be used in wireless LAN
In a double glazing where a pair of transparent glass sheets are arranged at an interval by having a spacer at the circumferential end portion and where a hollow layer sealed between the pair of glass sheets is formed, there is provided an electromagnetic absorption board used for wireless LAN, which is characterized in that the thickness of the glass sheet is in a range of 2.5-20 mm, that the thickness of the hollow layer is in a range of 2.5-15 mm, that at least one glass sheet of the pair of glass sheets is formed with a resistive film having a surface resistance (surface resistivity) in a range of 20Ω / □ to 2 kΩ / □, and that the resistive film is formed on a glass sheet side on the hollow layer side.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Electromagnetic wave absorption product and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101740142ARealize cleaner productionGood orientation distributionScreening apparatusCoatingsFiberShell molding
The invention aims at providing a method for manufacturing an electromagnetic wave absorption product and the electromagnetic wave absorption product prepared by adopting the method. The method comprises the following steps of: premixing a flat powder wave absorbing agent or a fiber wave absorbing agent with a high polymer material which can formed by a rotational molding way, then putting into a die and carrying out rotational molding. The flat powder wave absorbing agent or the fiber wave absorbing agent is in orientation distribution in a high polymer substrate by controlling the temperature and the rotation speed. In the invention, by matching with a laminated forming process, a two-dimensional electromagnetic absorption product with accurate thickness control can be manufactured; and by adopting the die design, a plurality of three-dimensional electromagnetic wave absorption products can be obtained.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method of three-dimensional reticular MWCNTs/NiFe2O4 (multi-wall carbon nanotube/nickel ferrite) composite wave absorbing material
ActiveCN108795379ANothing producedSimple and fast operationOther chemical processesMagnetic/electric field screeningCarbon nanotubeElectromagnetic shielding
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
External electromagnetic radiation absorption technique of electromagnetic furnace
PendingCN104676701ARadiation resistantDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusLED displayEngineering
The invention relates to an external electromagnetic radiation absorption technique of an electromagnetic furnace. A panel and a bottom cover are of anti-radiation structures with interlayers, the middle layer of the panel is a non-magnetic metal plate, the middle layer of the bottom cover is a magnetic metal plate, and the inner and outer faces of the interlayer of the bottom cover are insulating layers; a circular hole is formed on the metal plate in the middle layer of the panel, the circular hole and a heating coil in the furnace share the same center of the circle, and the diameter of the circular hole is greater than or equal to that of the heating coil; the panel is provided with a conductor contacted with a pot bottom and a connecting line, and the connecting line bypassing the rear edge or the left and right sides of the panel enters into the electromagnetic furnace to be connected with an electromagnetic absorption circuit; a shielding frame is arranged below an operation display part at the front end of the panel, the operation display circuit is mounted in the shielding frame and digital and LED display and touch buttons are exposed, and the shielding frame is connected with the electromagnetic absorption circuit; the other end of the electromagnetic absorption circuit is connected with the metal plate of the middle interlayer of the bottom cover and a protective grounded wire (E) of a single-phase three-core power supply line. Various external electromagnetic radiation absorption schemes are preferable.
Owner:CHENGDU YINDING TECH
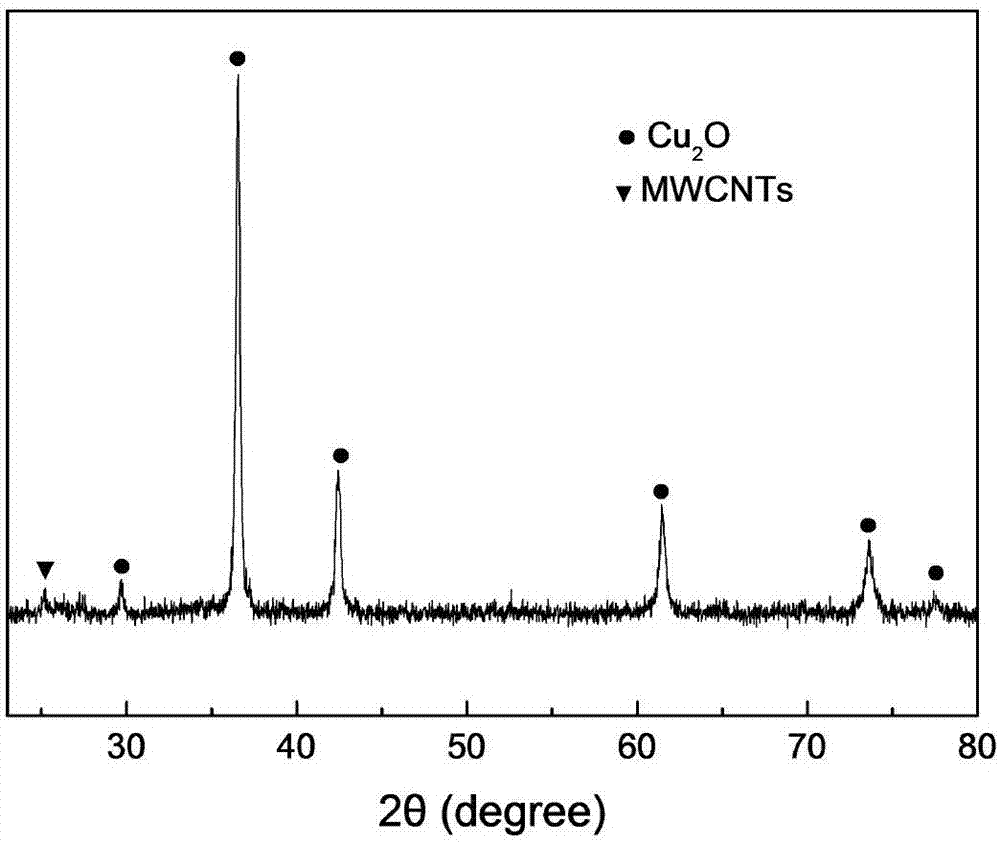
Cu2O/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) composite material, preparation method thereof and electromagnetic absorption application
ActiveCN107454815AIncrease the conductive pathPromote absorptionCarbon compoundsMagnetic/electric field screeningChemical platingNanoparticle
The invention discloses a Cu2O / multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) composite material, a preparation method thereof and electromagnetic absorption application. The Cu2O / MWCNTs composite material is synthesized by a simple chemical method, and Cu2O nanoparticles are disorderly grown on surfaces of the MWCNTs and in the MWCNTs. A hydrothermal method is employed, no any surfactant is added, a traditional electroplating or chemical plating method is prevented, pollution is relatively small, the preparation method is simple, green and environmental-friendly, reaction is easy to control, expensive equipment is not needed, and the preparation method can be used for industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Flaky porous nanometer zinc oxide and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105293567AAdjustable thicknessAperture size adjustableMaterial nanotechnologyZinc oxides/hydroxidesZno nanoparticlesCarbonate
The invention discloses flaky porous nanometer zinc oxide and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of nanometer zinc oxide preparation. The preparation method comprises the steps that zinc salt and urea serve as reaction raw materials, firstly, a hydrothermal reaction is conducted under the action of a template agent sodium citrate for generating a precursor zinc carbonate, zinc carbonate is calcinated for 4-6 hours at the temperature of 400-600 DEG C in a heat-preservation mode, nanometer zinc oxide particles which are good in dispersion and flacky and porous in morphology are obtained, the particle size of each particle is 2-10 micrometers, the thickness is 0.2-1 micrometer, the pore diameter is 50-300 micrometers, and the flaky porous nanometer zinc oxide can be widely applied to aspects such as gas-sensitiveness, catalysis, voltage dependent resistors and electromagnetic absorption. According to the flaky porous nanometer zinc oxide and the preparation method thereof, a hydrothermal method and a calcining method are combined for preparing the flaky porous nanometer zinc oxide particles, the process is simple, operation is easy and convenient to conduct, the flake thickness and pore diameter can be adjusted, and characteristics such as gas-sensitivity and electromagnetic absorption can be effectively controlled.
Owner:郑州丰元冶金材料有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com