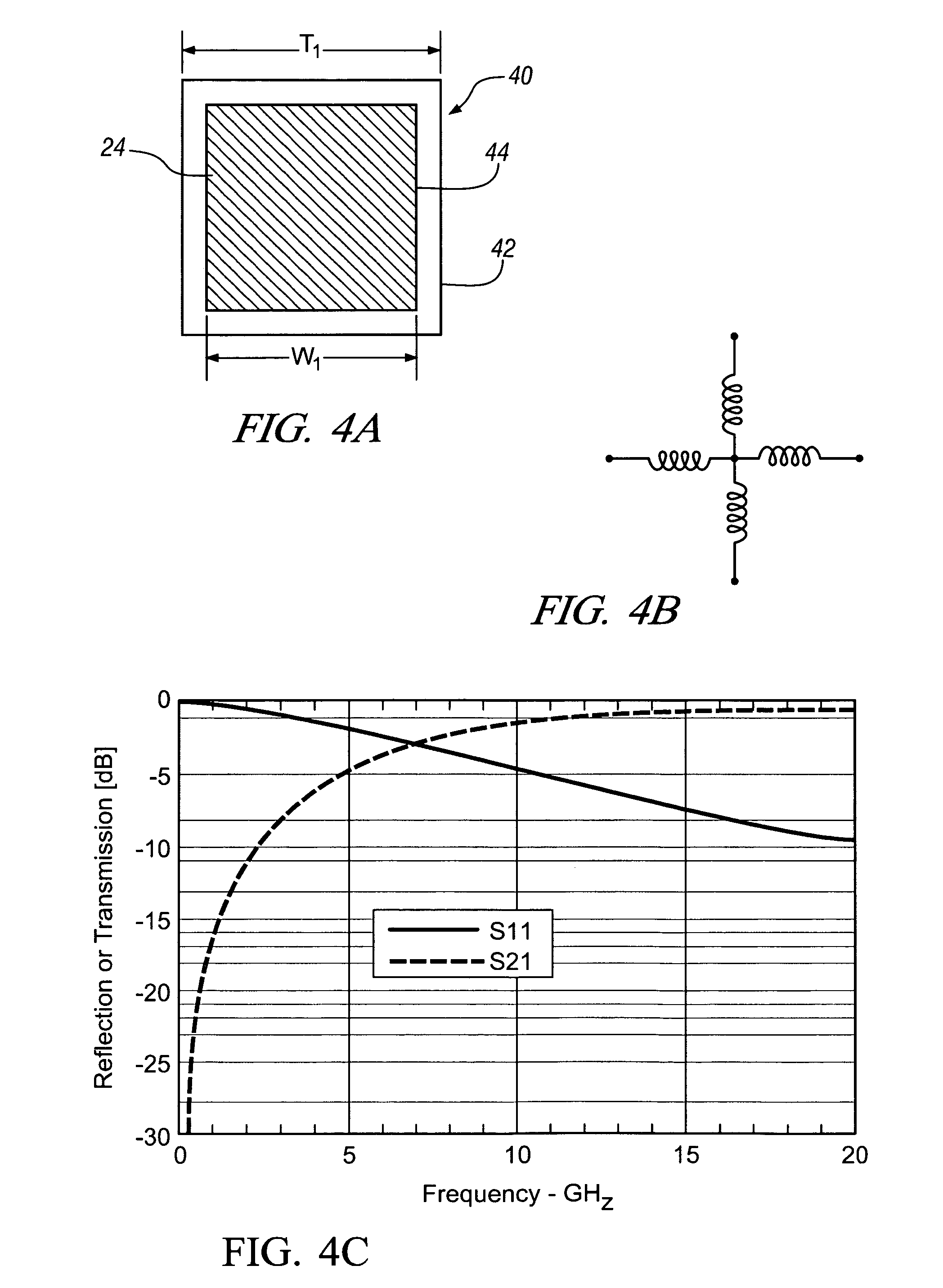
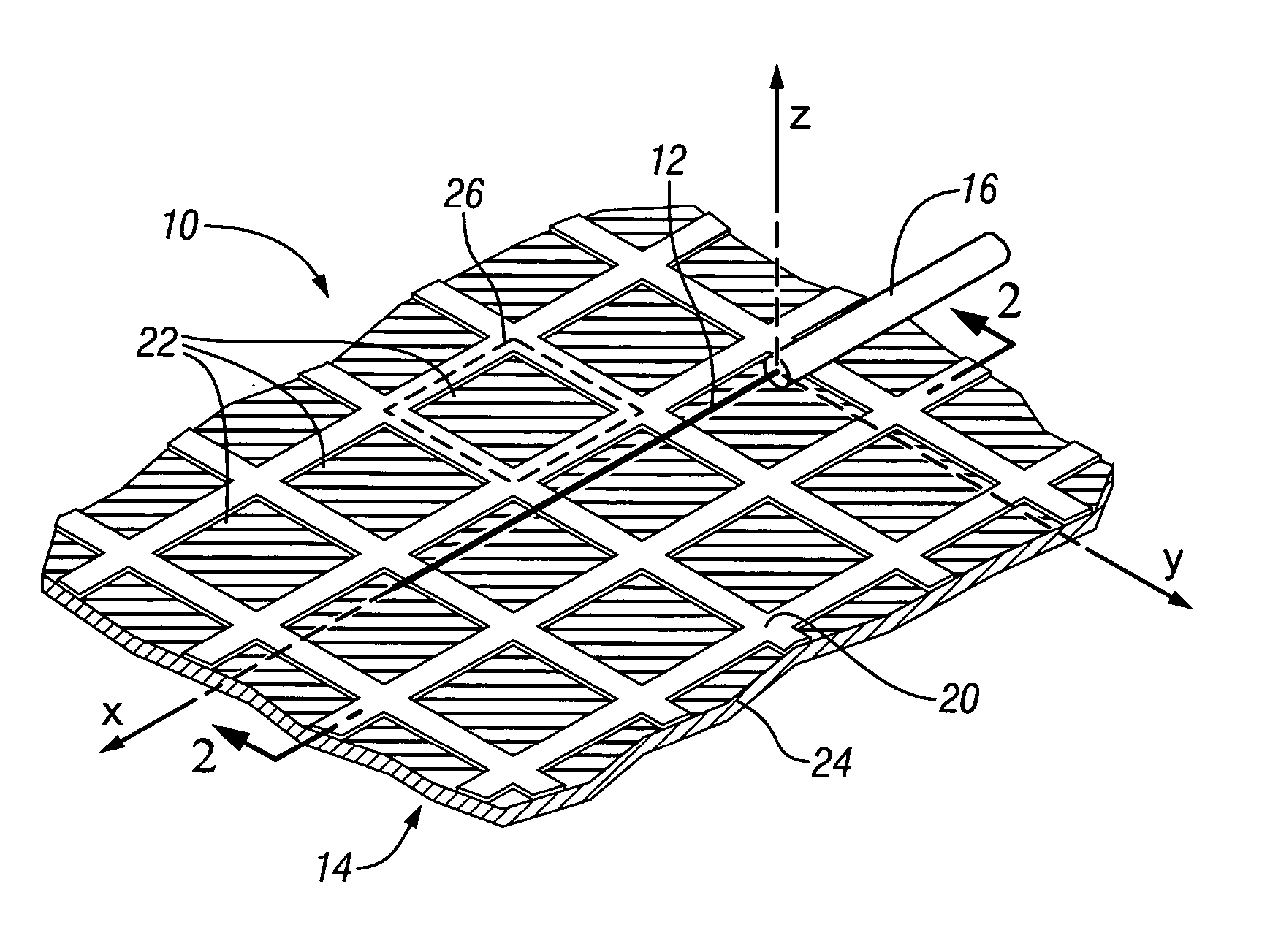
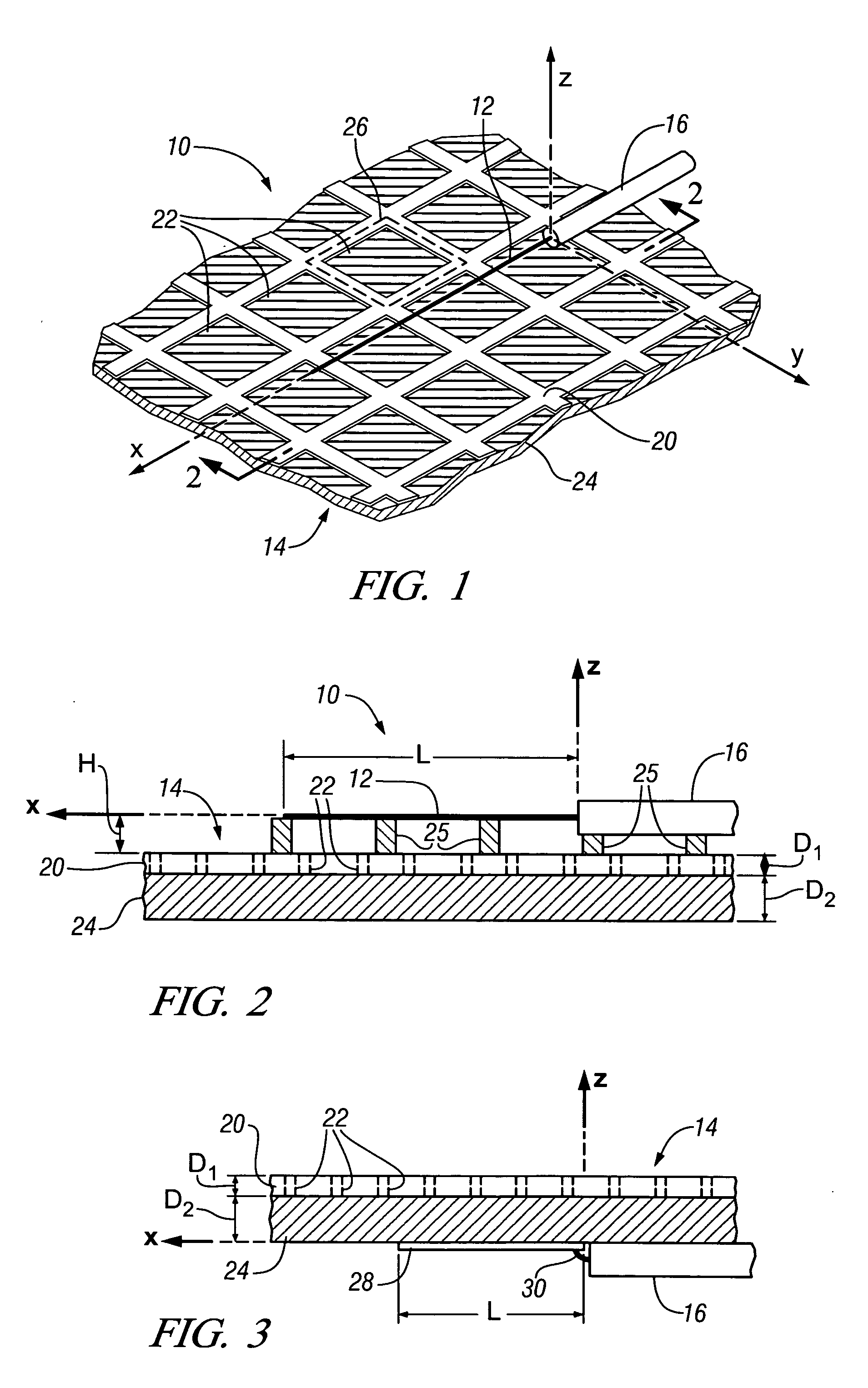
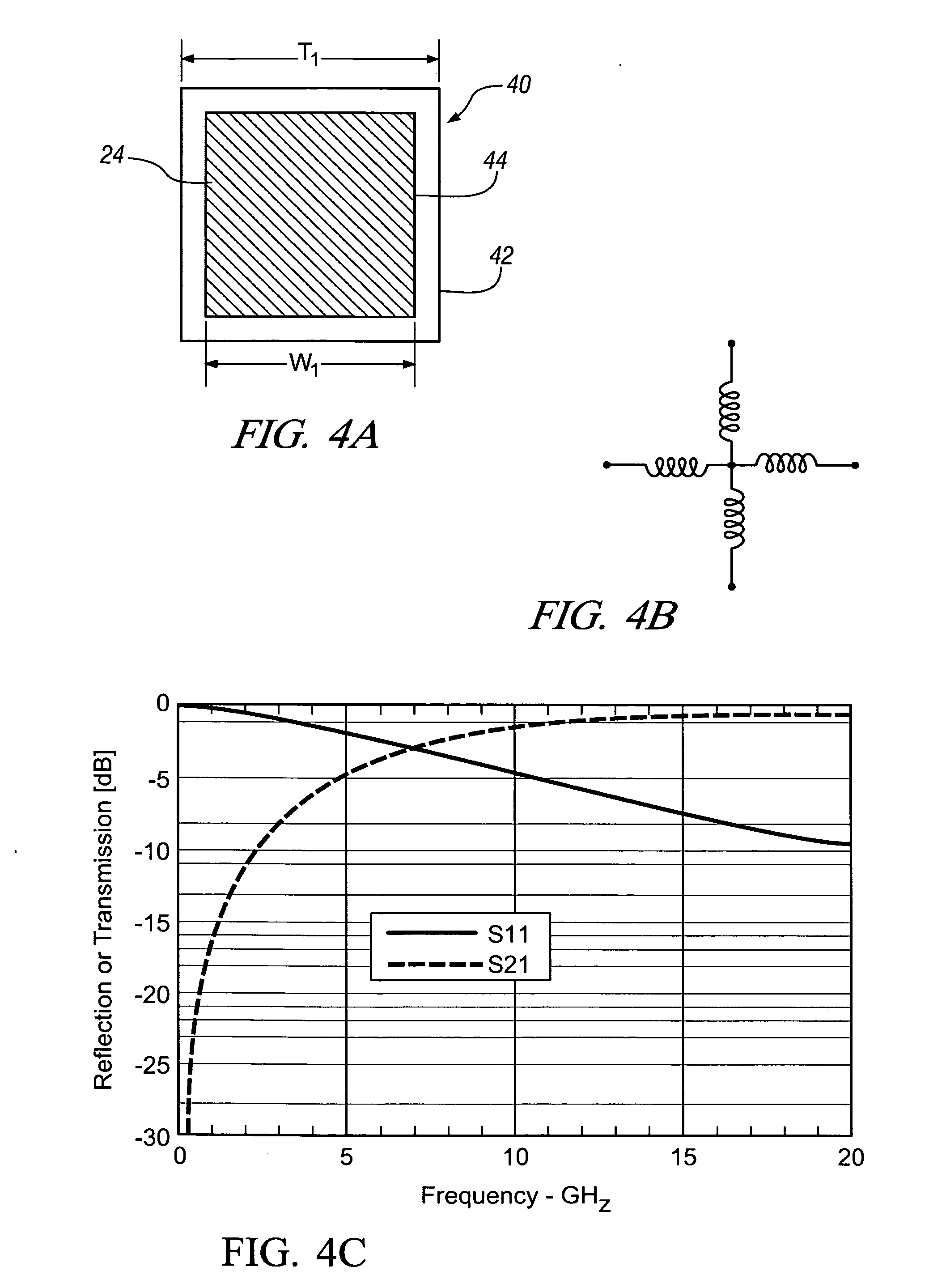
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
771 results about "Selective surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
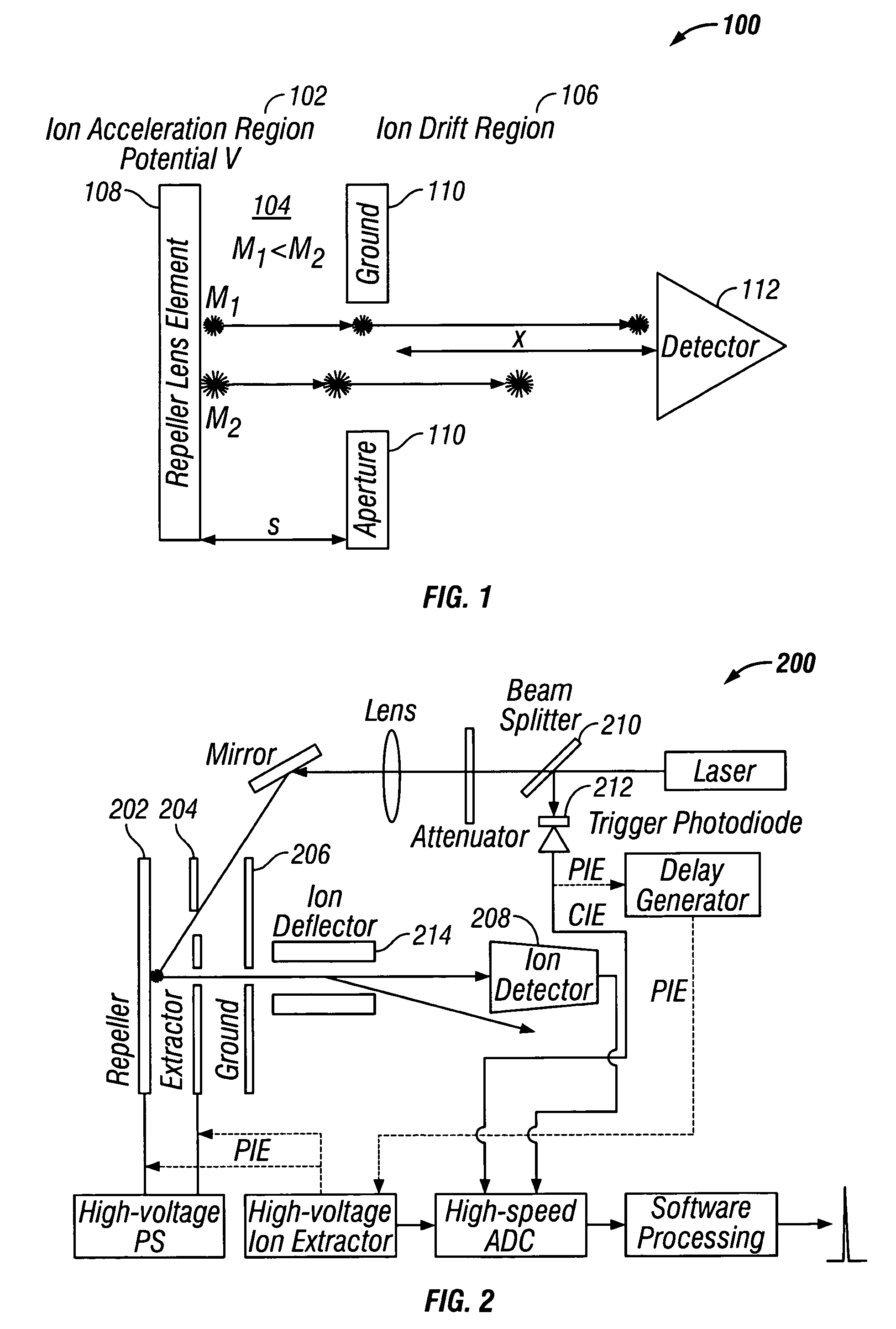
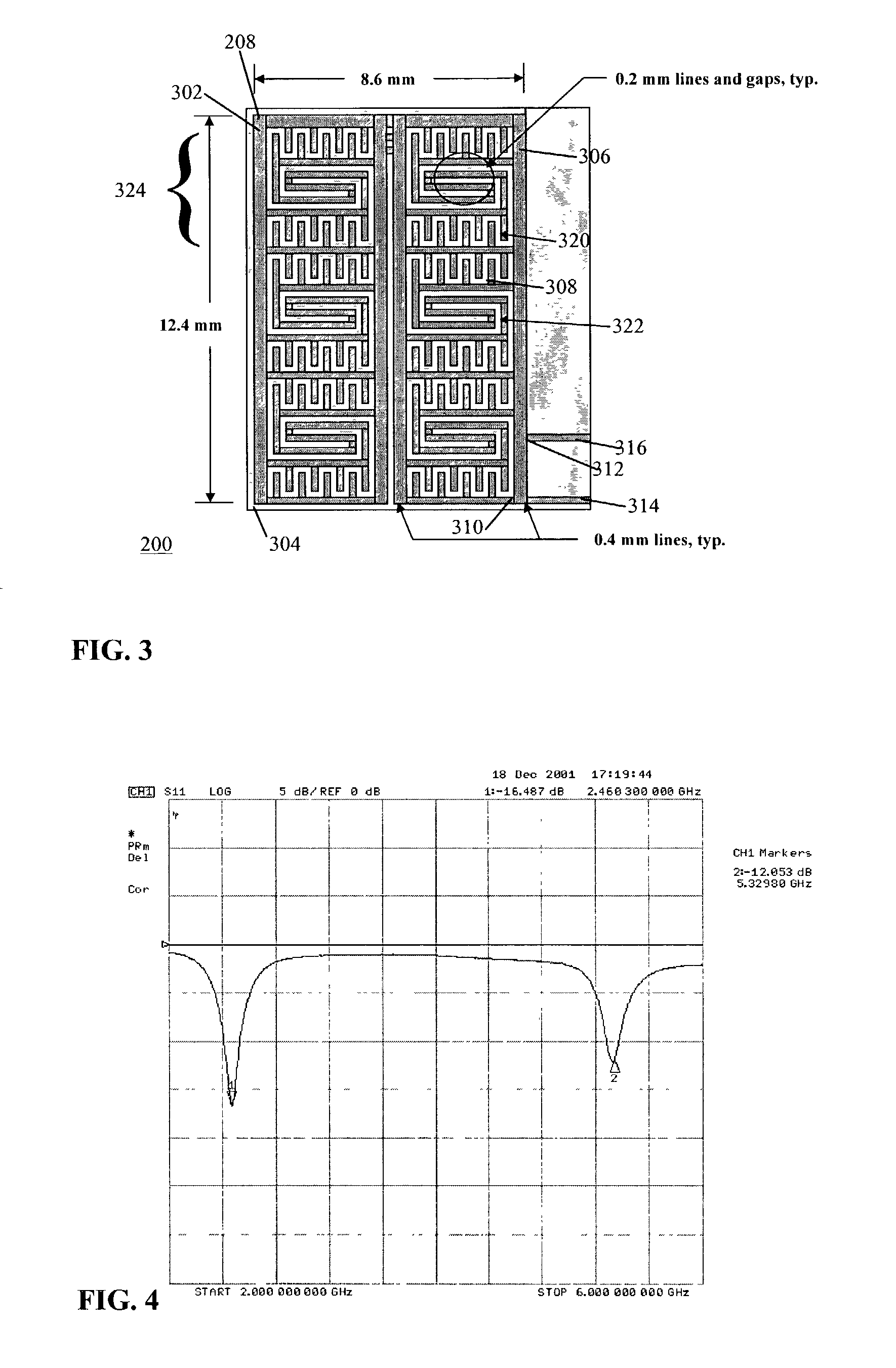
In solar thermal collectors, a selective surface or selective absorber is a means of increasing its operation temperature and/or efficiency. The selectivity is defined as the ratio of solar radiation absorption (αₛₒₗ) to thermal infrared radiation emission (εₜₕₑᵣₘ).
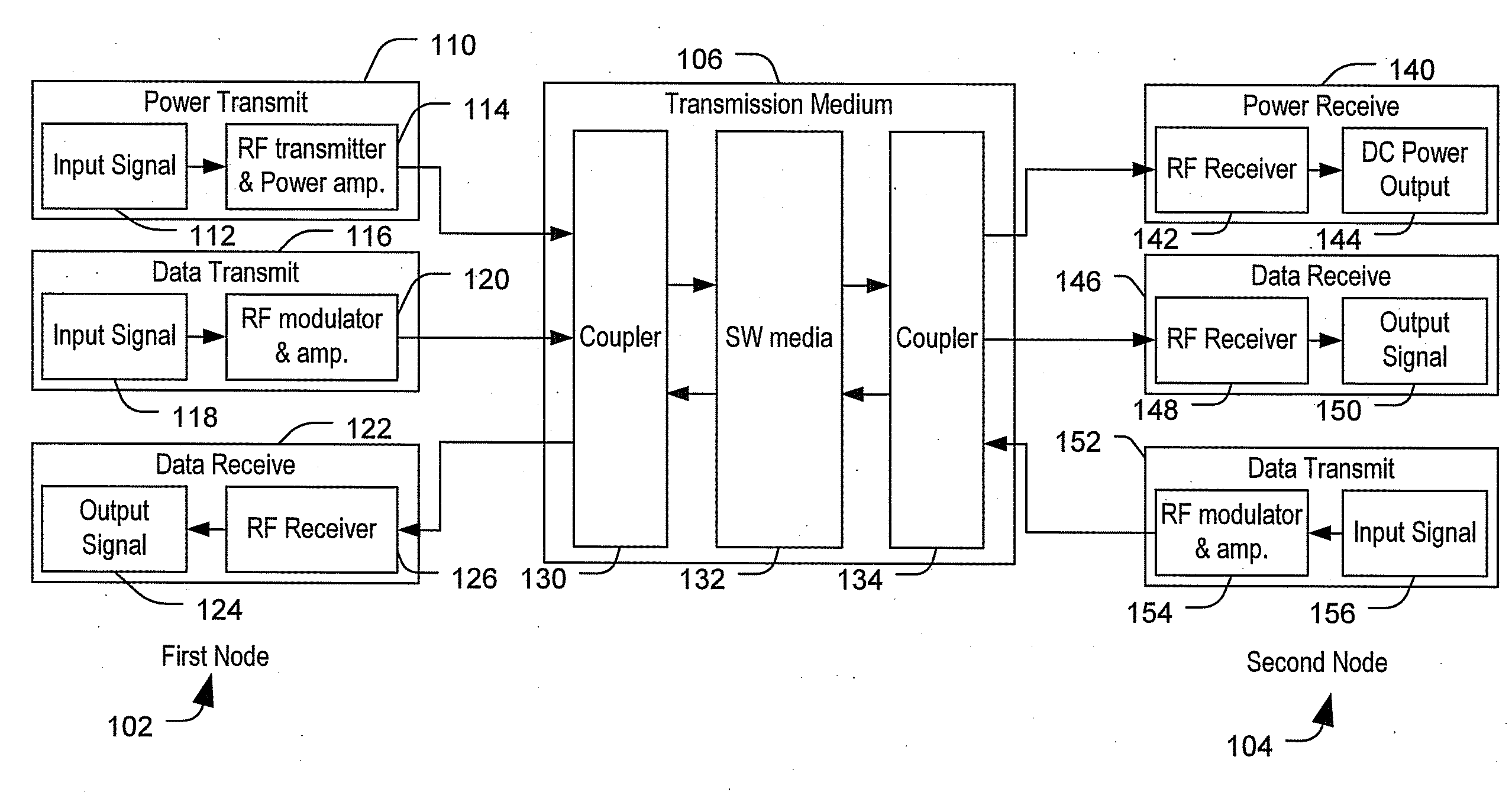
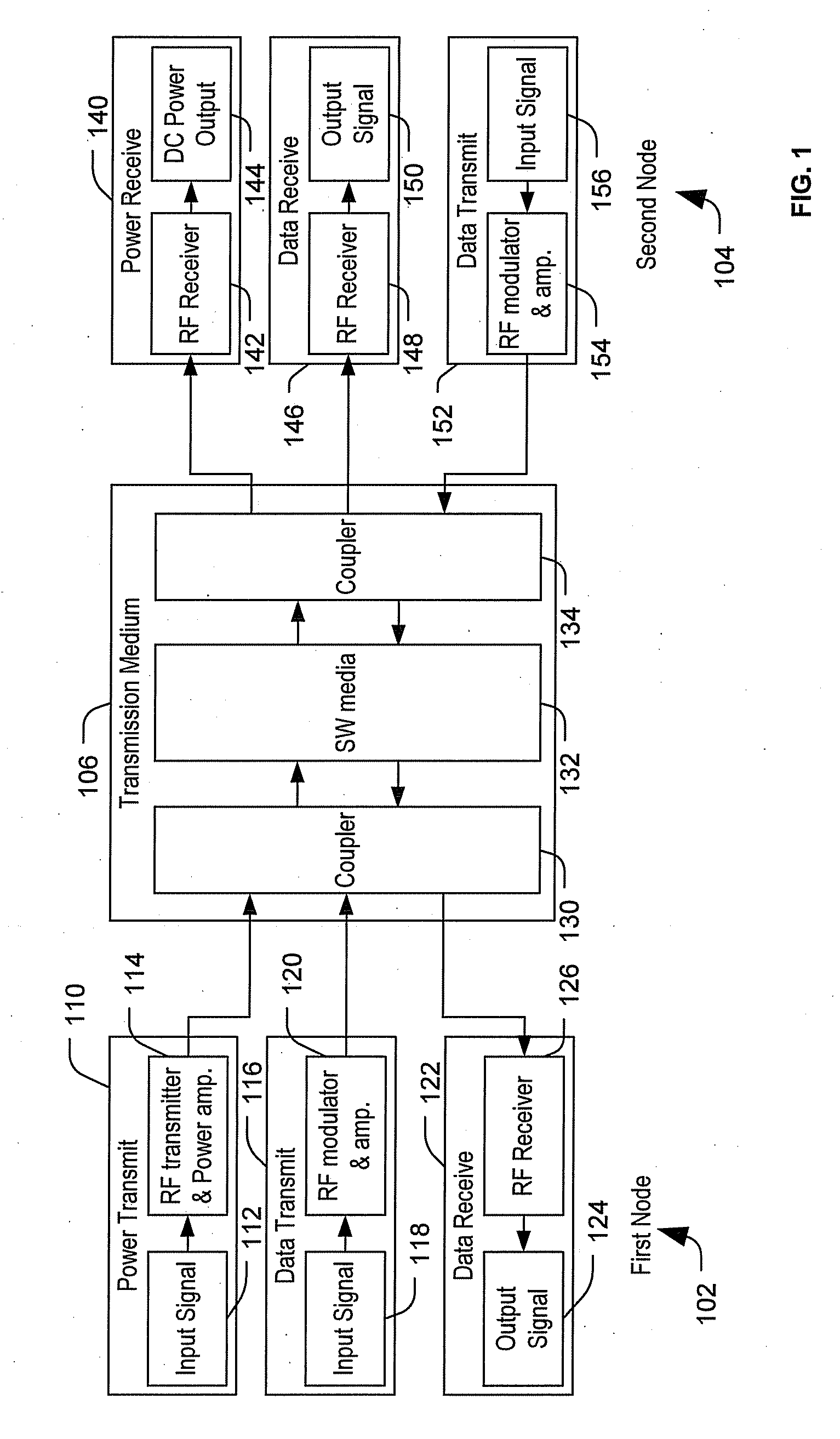
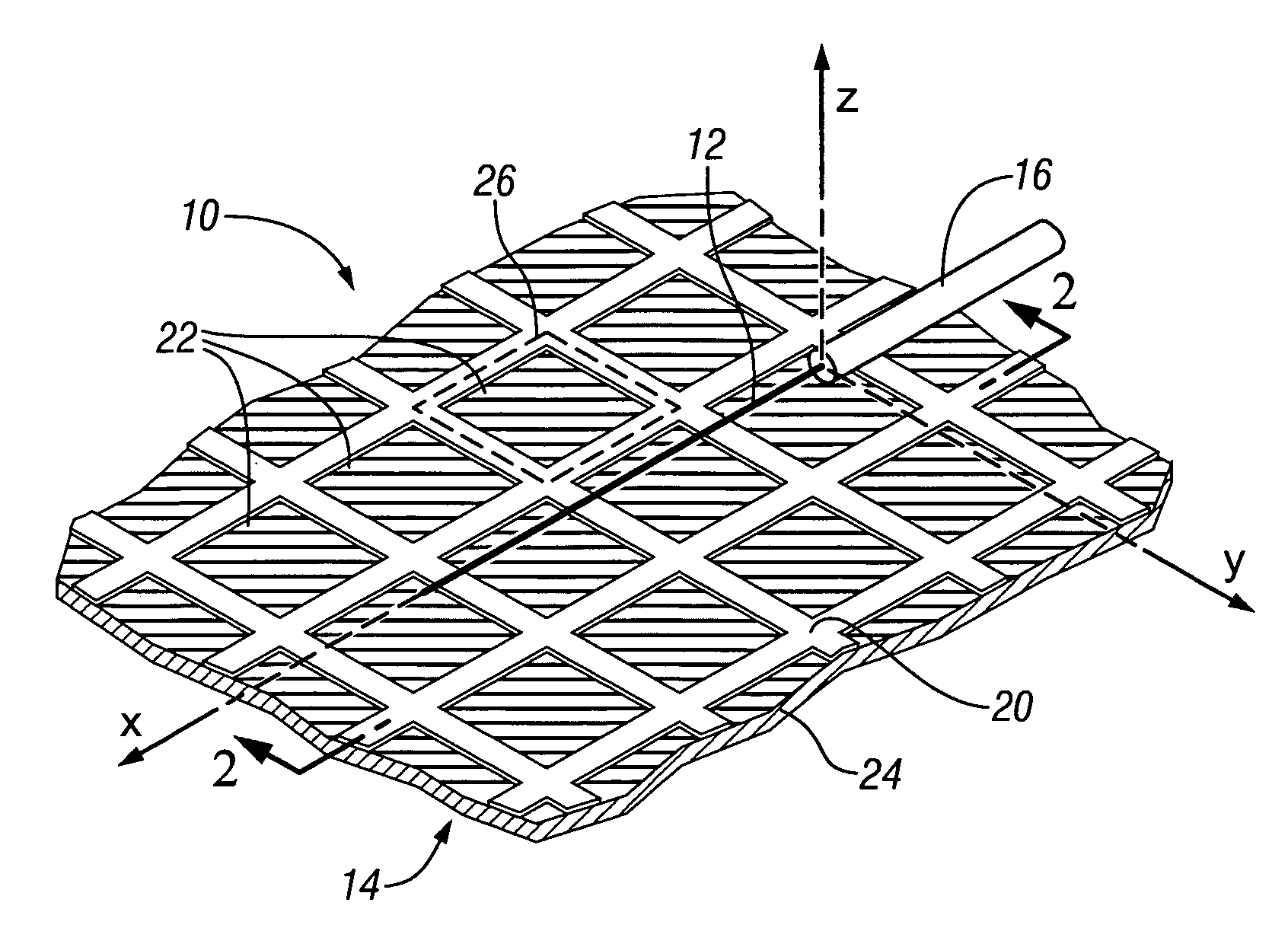
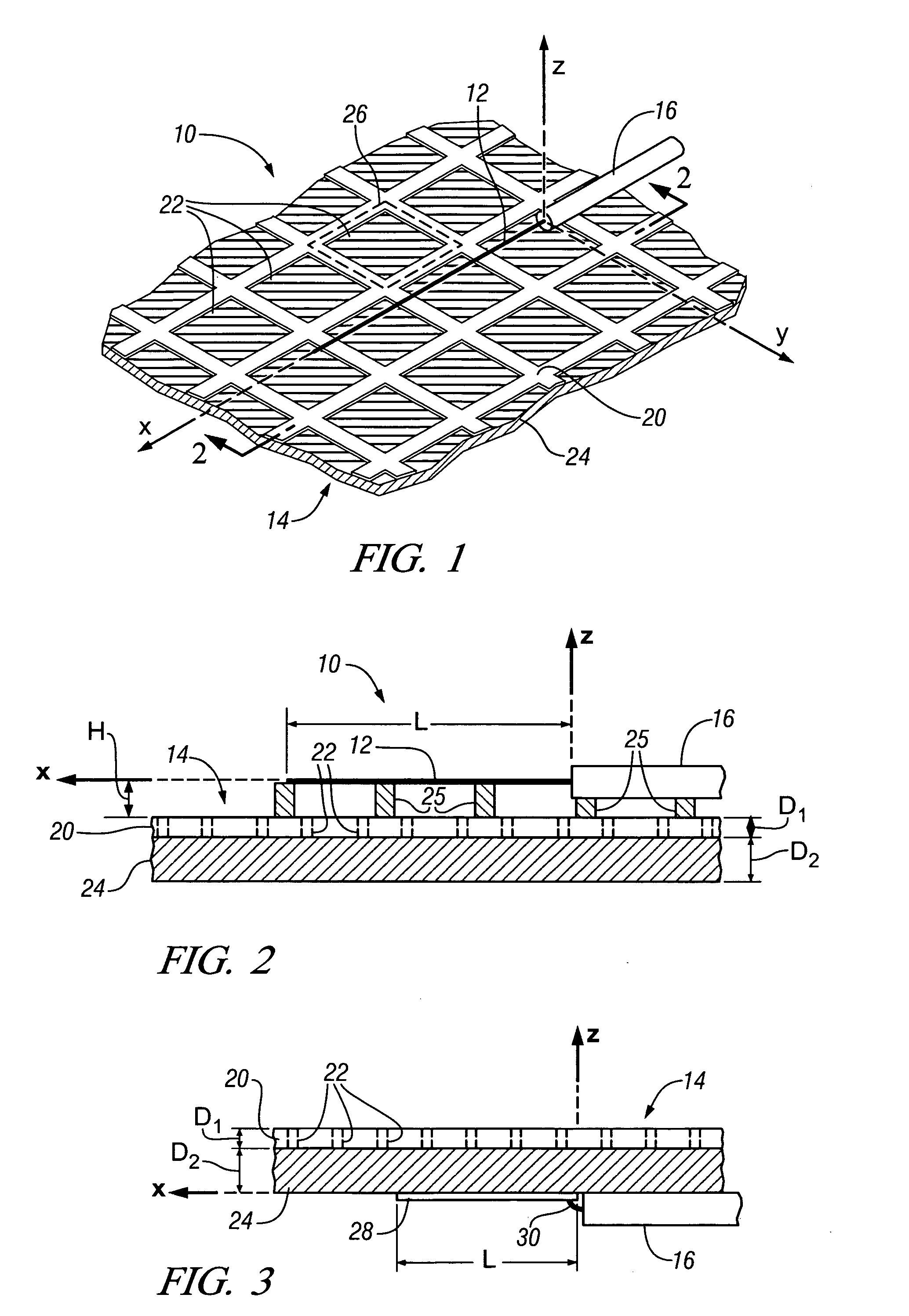
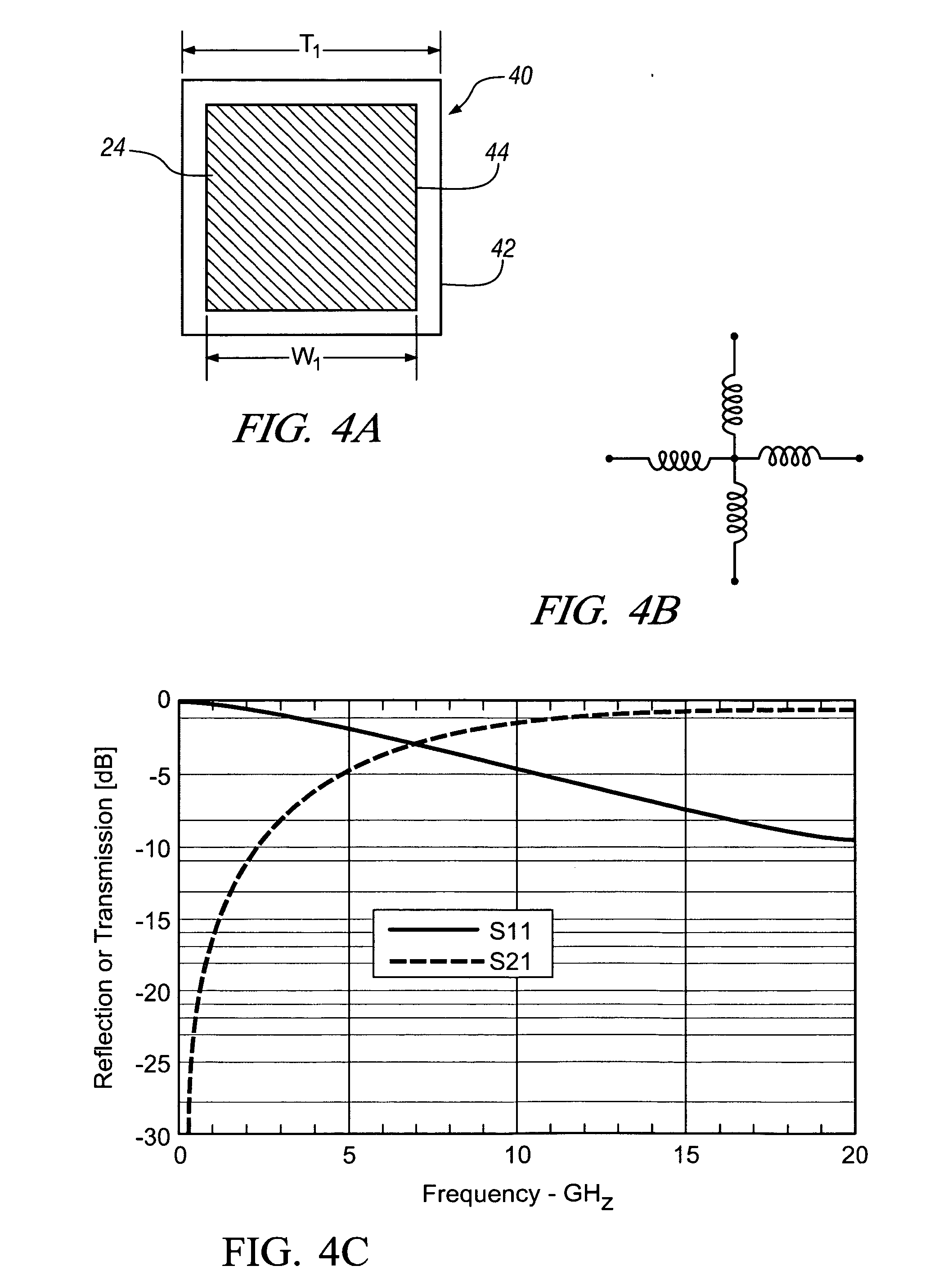
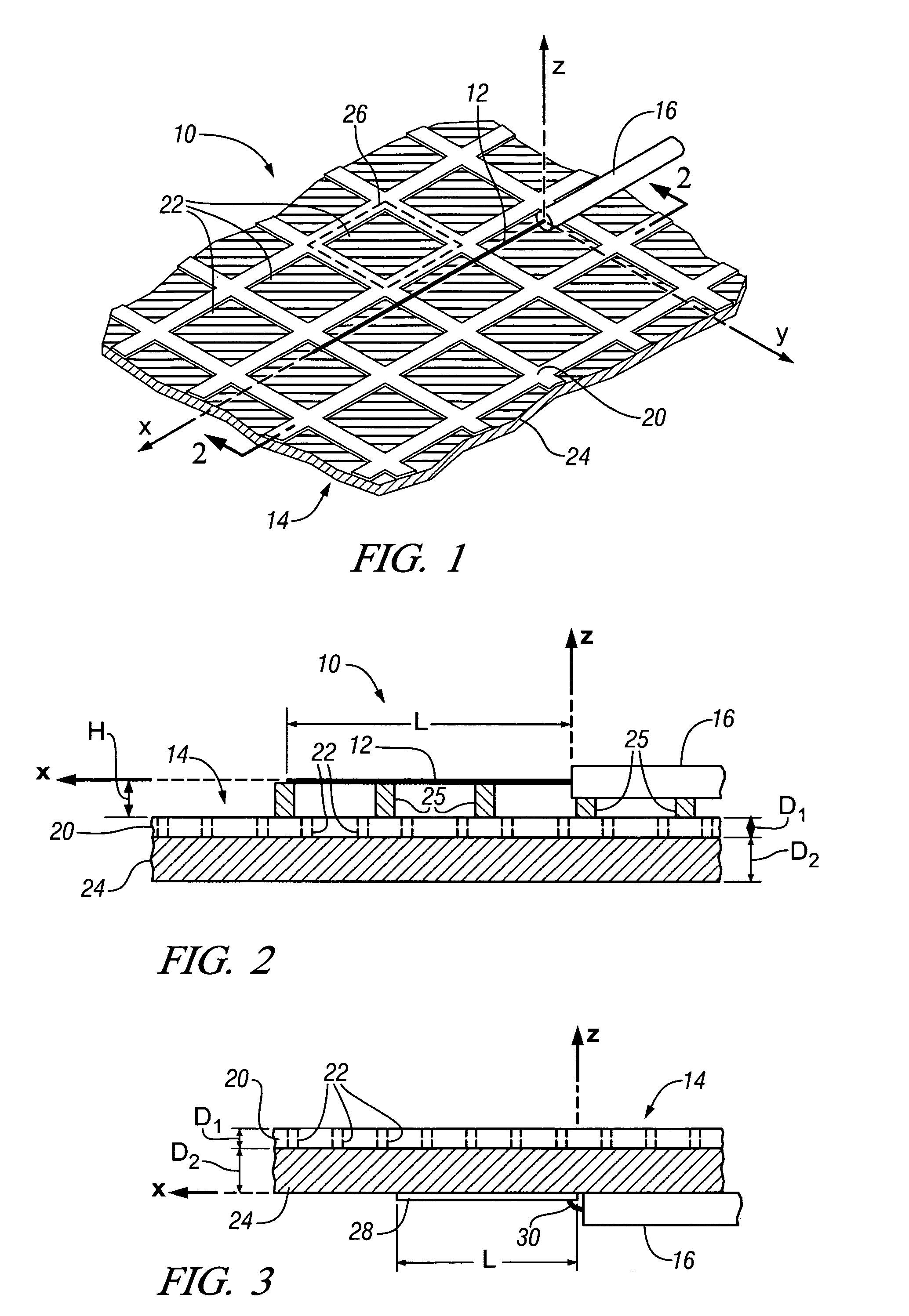
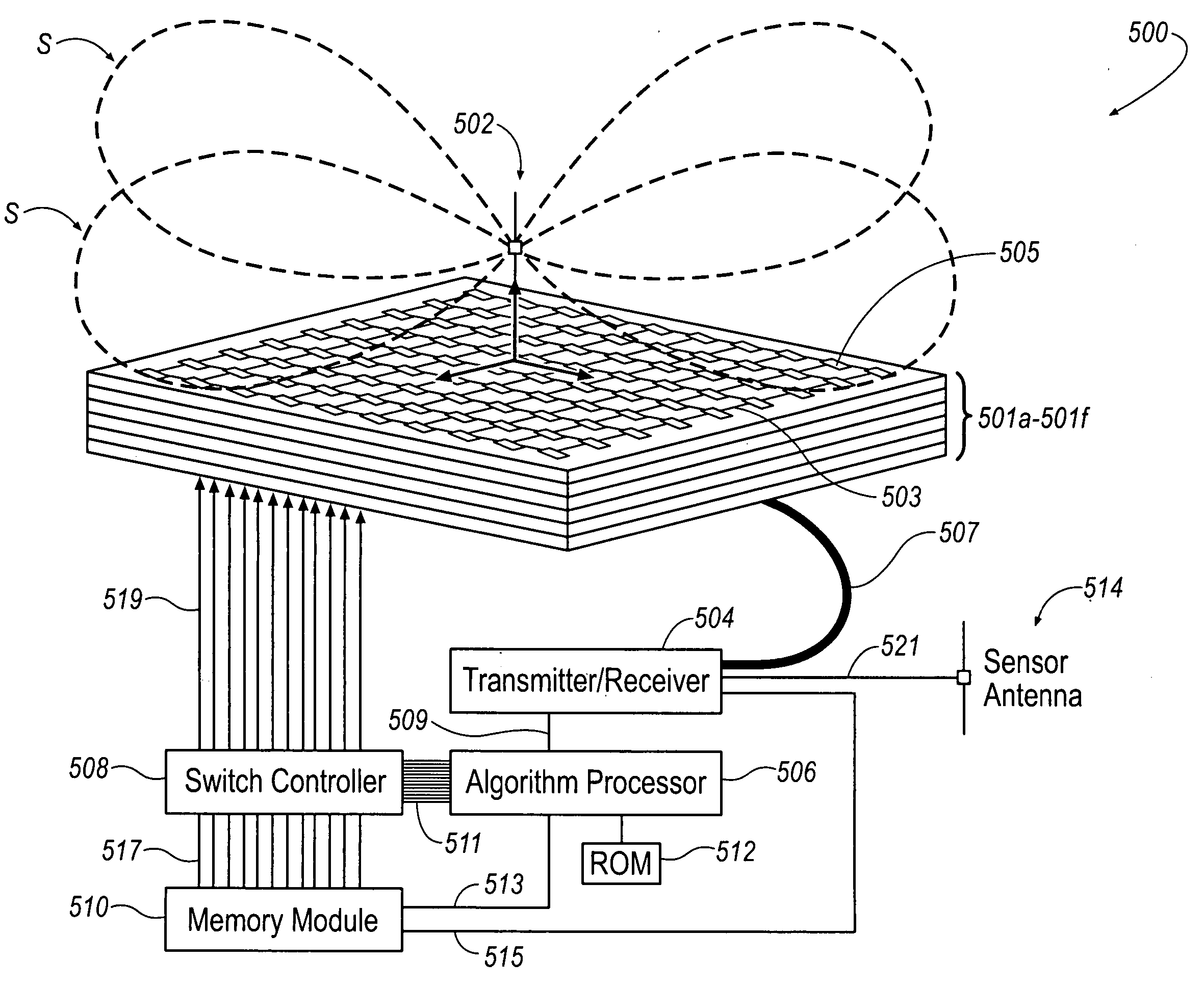
Transmitting power and data
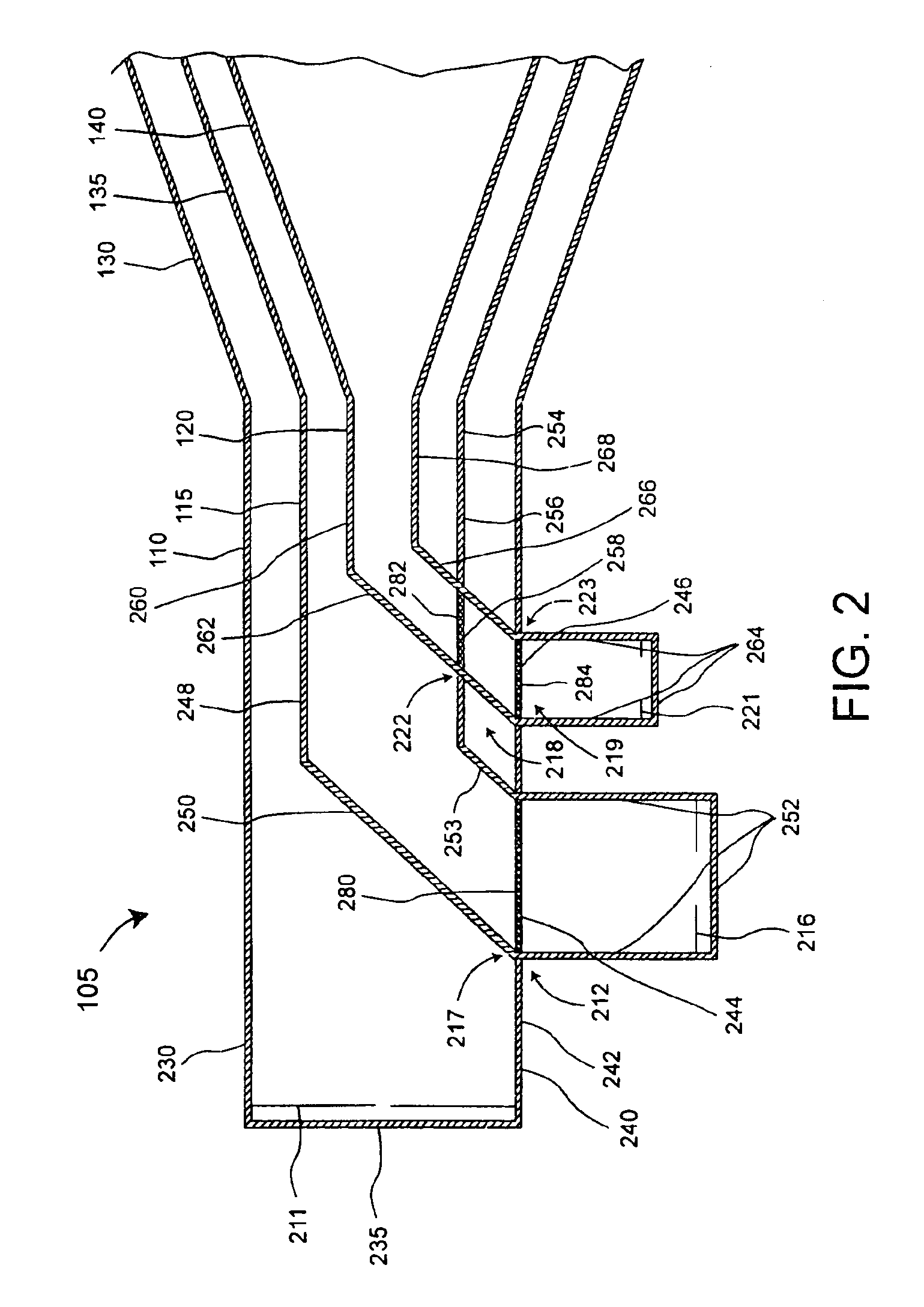
ActiveUS20100214183A1Waveguide mouthsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesTransmitted powerDielectric layer
Apparatus, systems and methods to transmit power and data are provided. A particular apparatus to transmit power and data includes a transmission medium. The transmission medium includes at least one first frequency selective surface (FSS) layer, at least one second FSS layer, and a dielectric layer separating the at least one first FSS layer and the at least one second FSS layer. In a particular embodiment, the apparatus also includes a first coupler coupled to the transmission medium to send a signal along the transmission medium and a second coupler coupled to the transmission medium. The second coupler may receive signals via the transmission medium, receive power via the transmission medium to power devices coupled to the second coupler, process and send data via the transmission medium, or any combination thereof.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
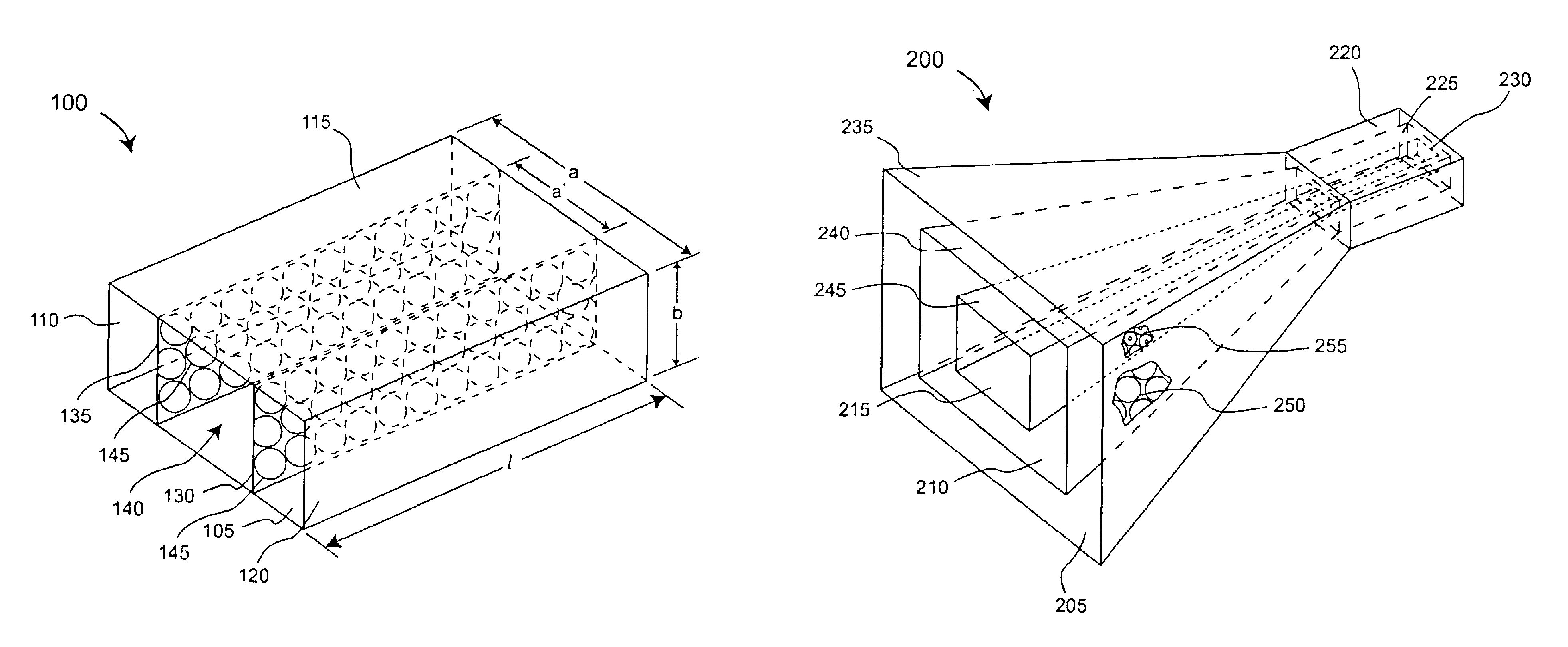
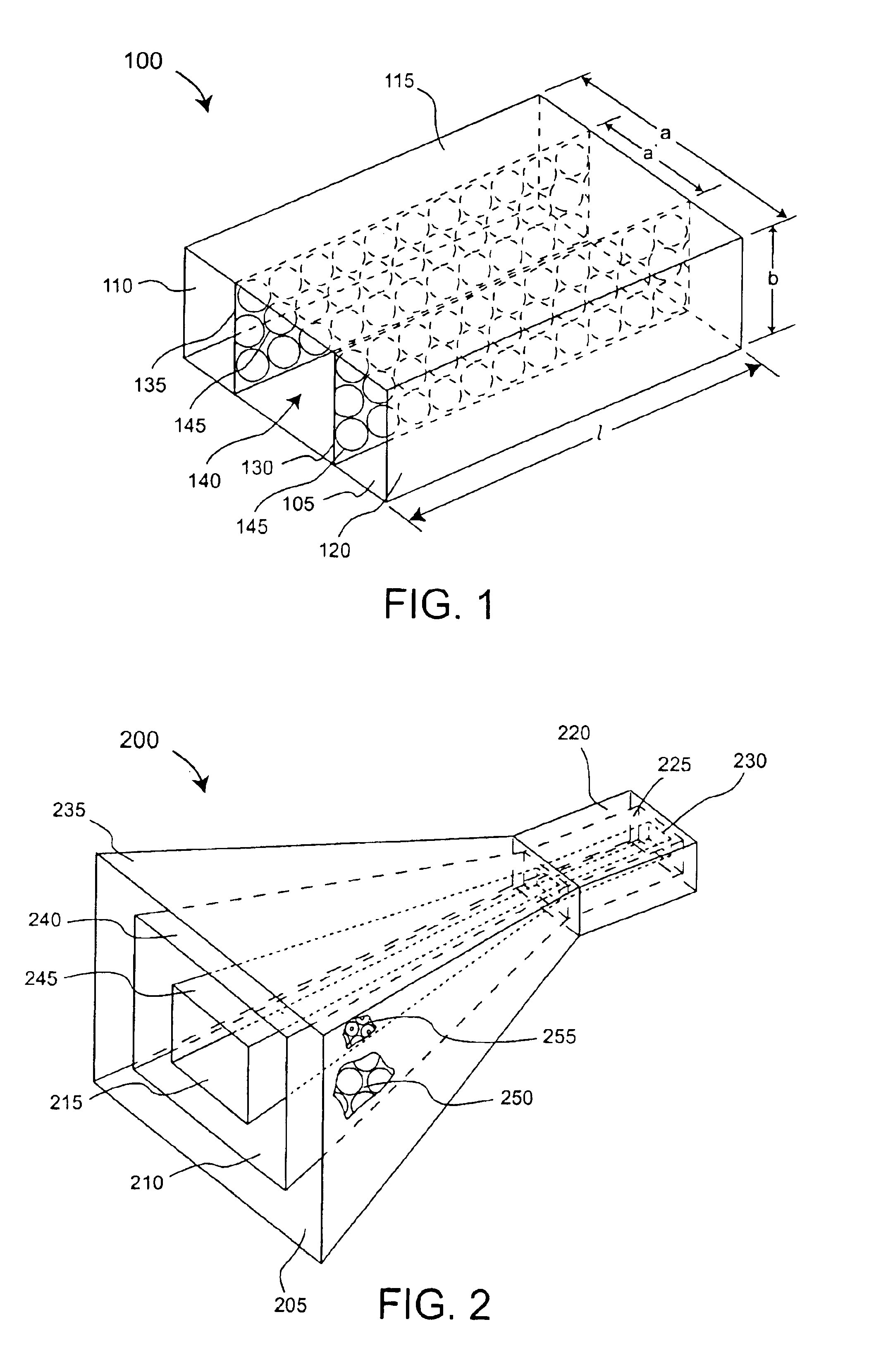
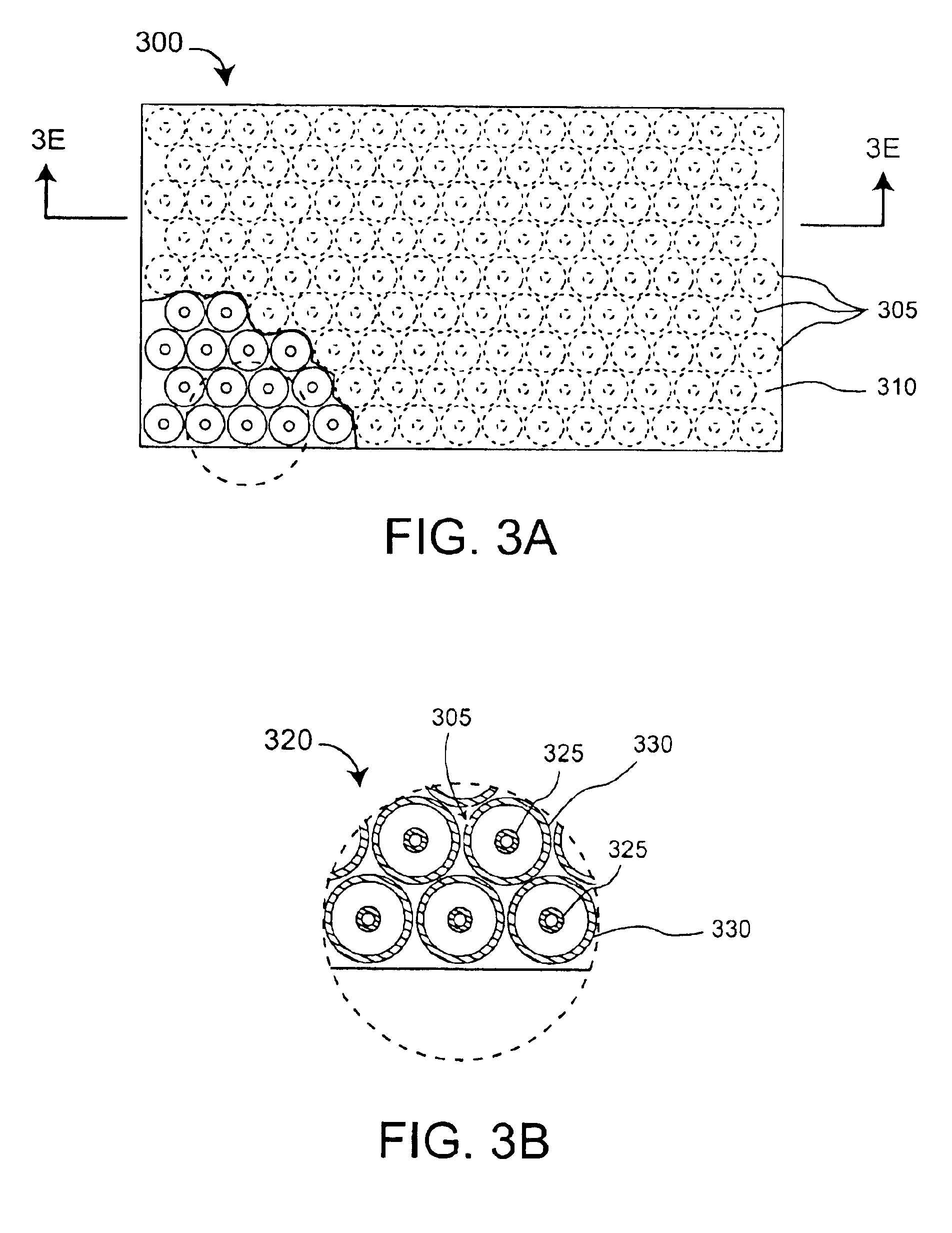
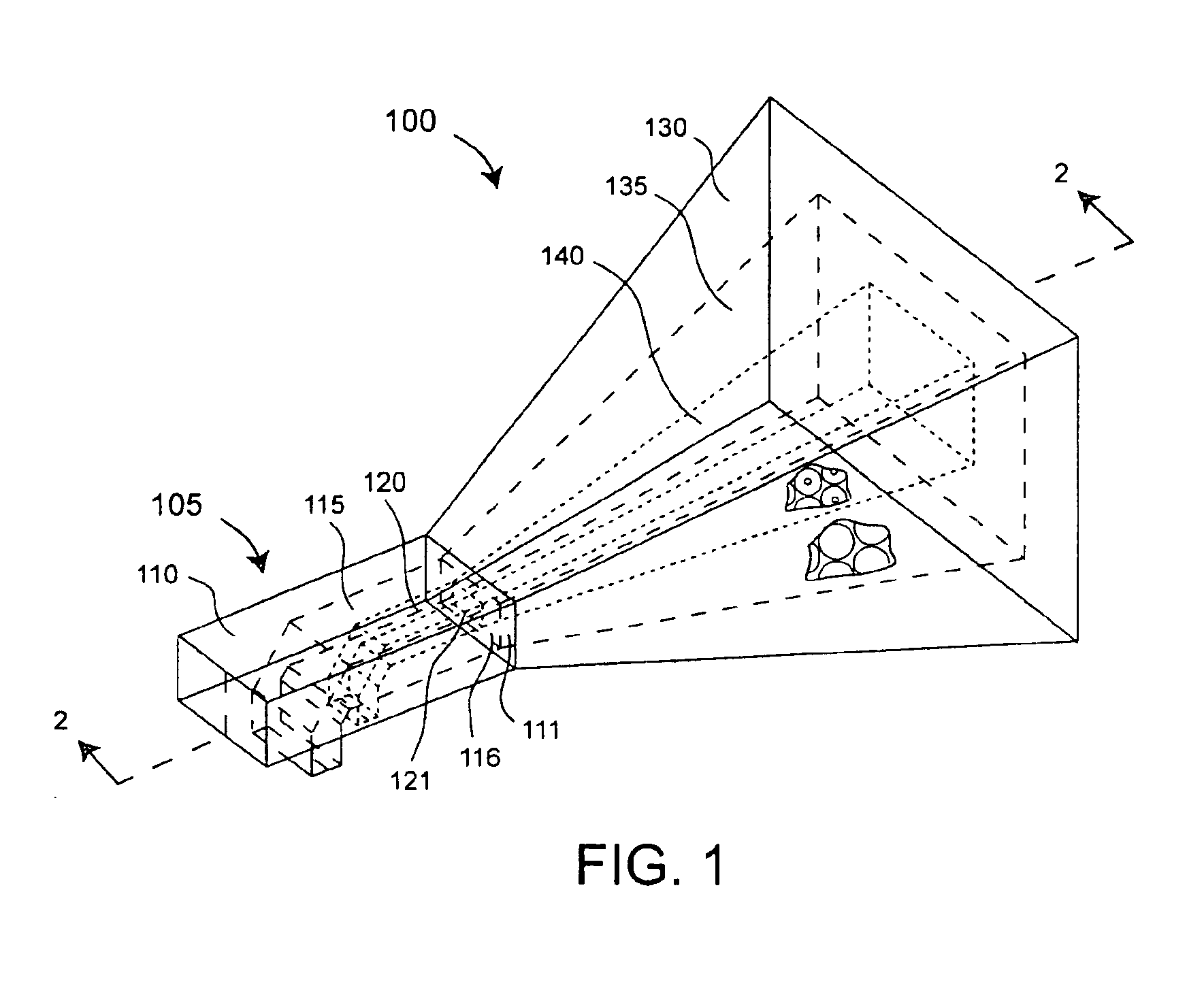
Multi-band horn antenna using frequency selective surfaces
InactiveUS6985118B2Grating lobe of the antenna is reducedImprove permeabilityWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandHorn antenna
A waveguide (100) including at least one outer surface (105, 110, 115, 120) defining a waveguide cavity (140) and at least one inner surface (130, 135) positioned within the waveguide cavity (140). The inner surface (130, 135) includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) having a plurality of FSS elements (145) coupled to at least one substrate. The substrate defines a first propagation medium such that an RF signal having a first wavelength in the first propagation medium can pass through the FSS (130, 135). The FSS (130, 135) is coupled to a second propagation medium such that in the second propagation medium the RF signal has a second wavelength which is at least twice as long as a physical distance between centers of adjacent FSS elements (145). The second wavelength can be different than the first wavelength.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
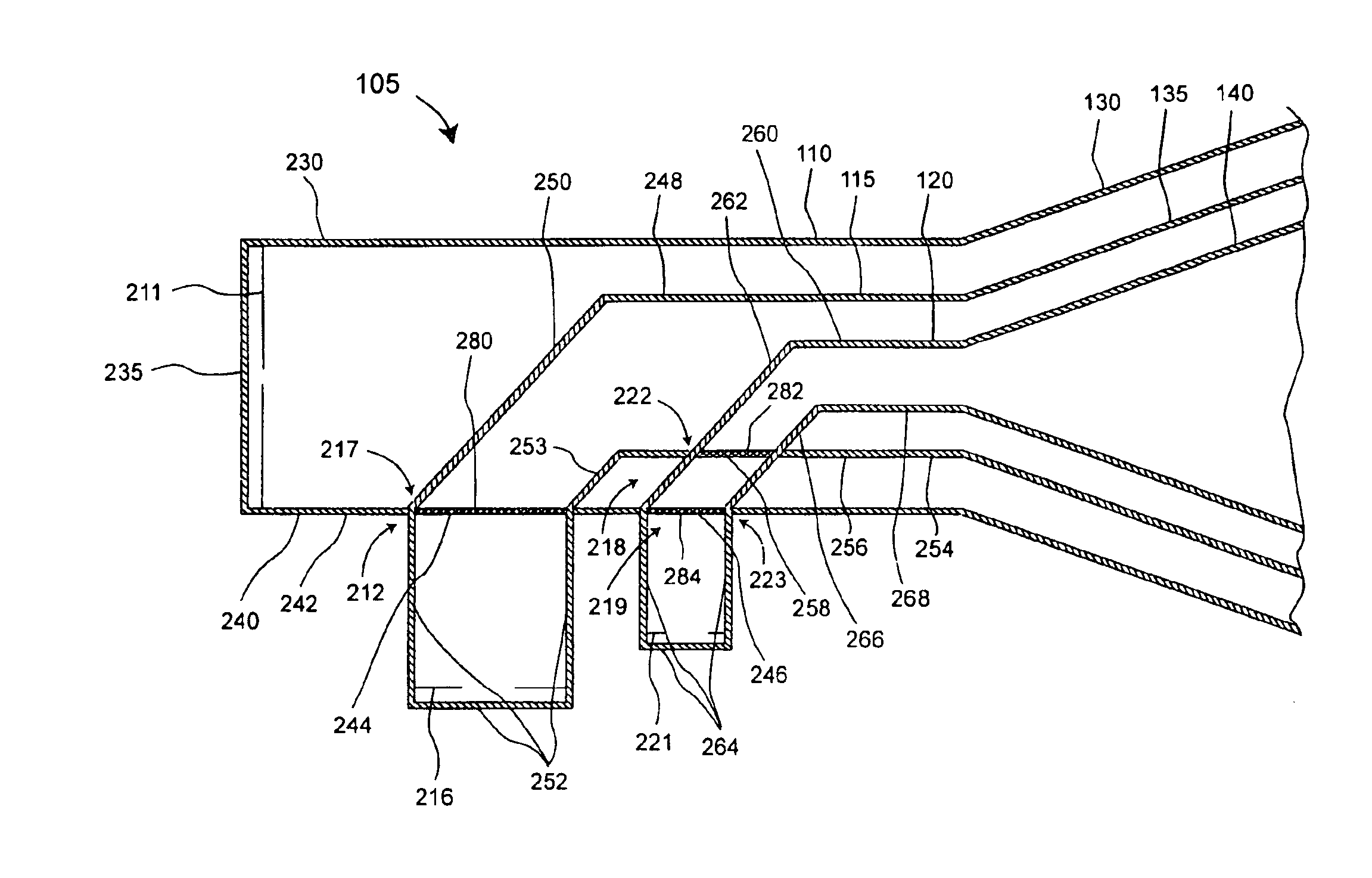
FSS feeding network for a multi-band compact horn
A feed structure (105) for a horn antenna (100). The feed structure can include a first waveguide (110) and a second waveguide (115) having a first portion at least partially disposed within the first waveguide. The second waveguide also can include a second portion intersecting a first wall (240) of the first waveguide. The first wall can include a first frequency selective surface (244) at an intersection (280) of the first wall and the second portion of the second waveguide. The first waveguide can be operatively coupled to a first horn section (130) and the second portion can be operatively coupled to a second horn section (135).
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Antennas
Owner:MBDA UK
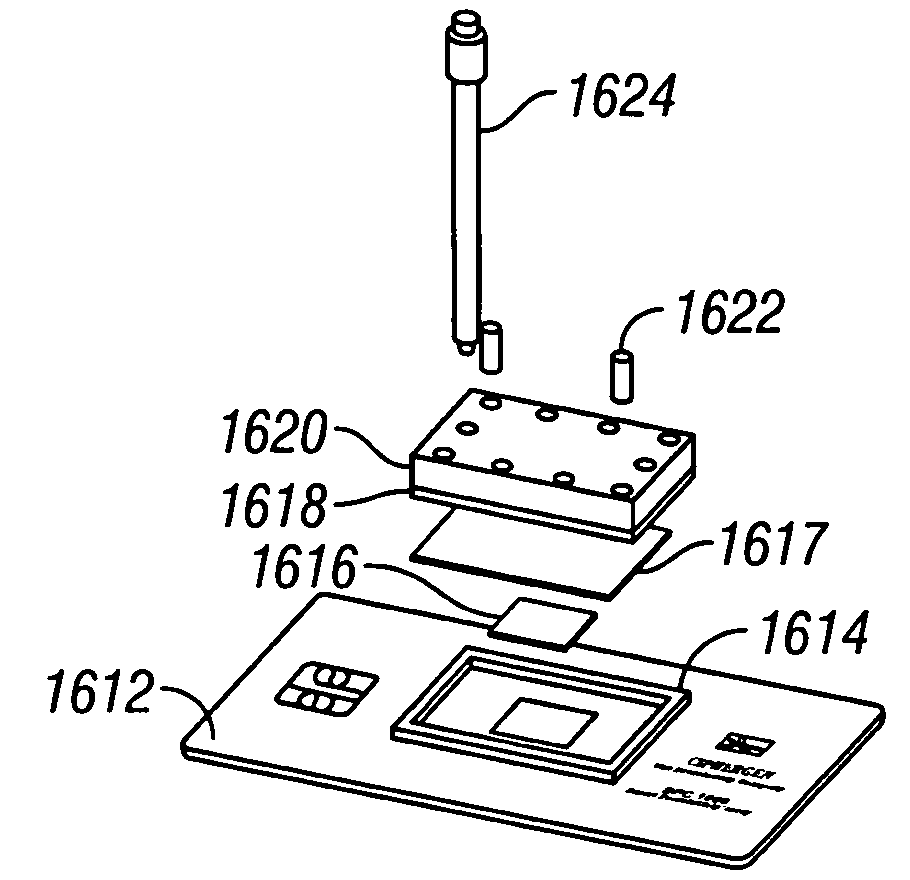
Apparatus for microfluidic processing and reading of biochip arrays
InactiveUS7046357B2Improve performanceParticle separator tubesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAnalyteAnalysis tools
A method and a device for detecting an analyte, including a substrate having a chemically selective surface; and a fluidic system disposed on the substrate, the manifold having at least one fluid path in communication with at least a discrete region of the surface, wherein the one fluid path and the discrete region together define a contained sample region on the surface. The fluidic system has a removable portion, wherein the removal of the removable portion of the fluidic system renders the discrete region directly interrogatable by a surface-based analytical tool.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
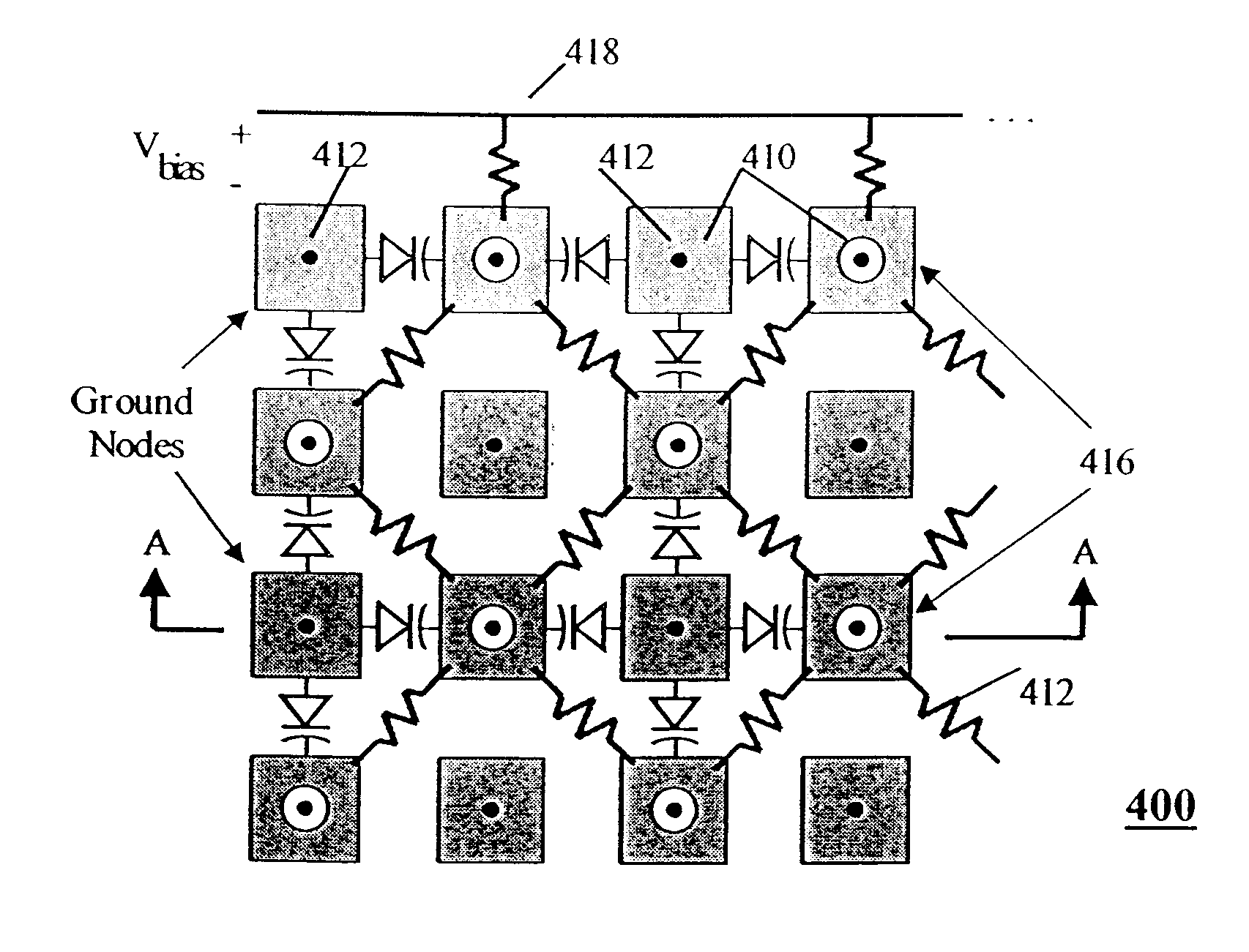
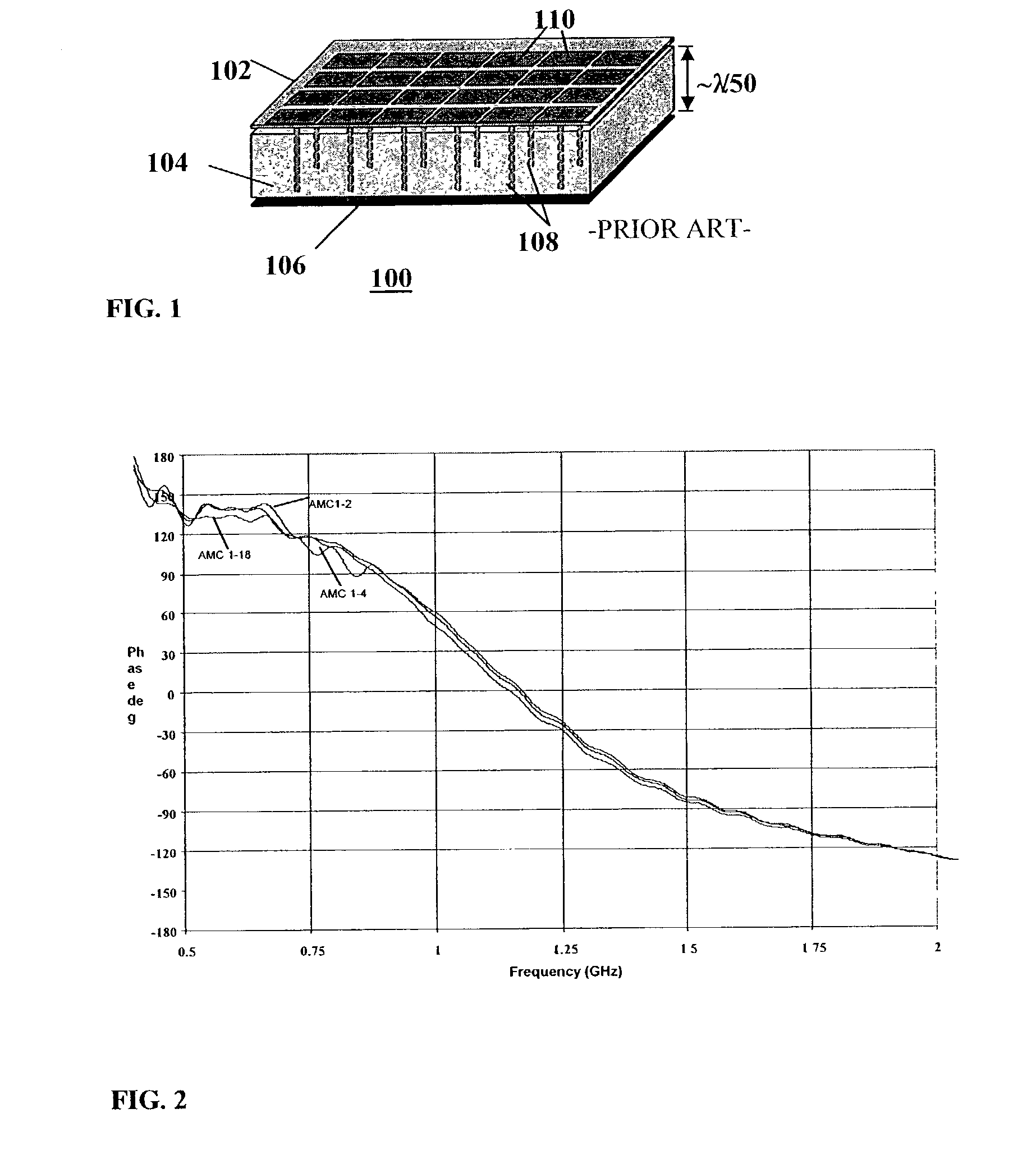
Reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor using voltage controlled capacitors with coplanar resistive biasing network
InactiveUS6525695B2Antenna feed intermediatesSlot antennasElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
Owner:TITAN AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS DIV
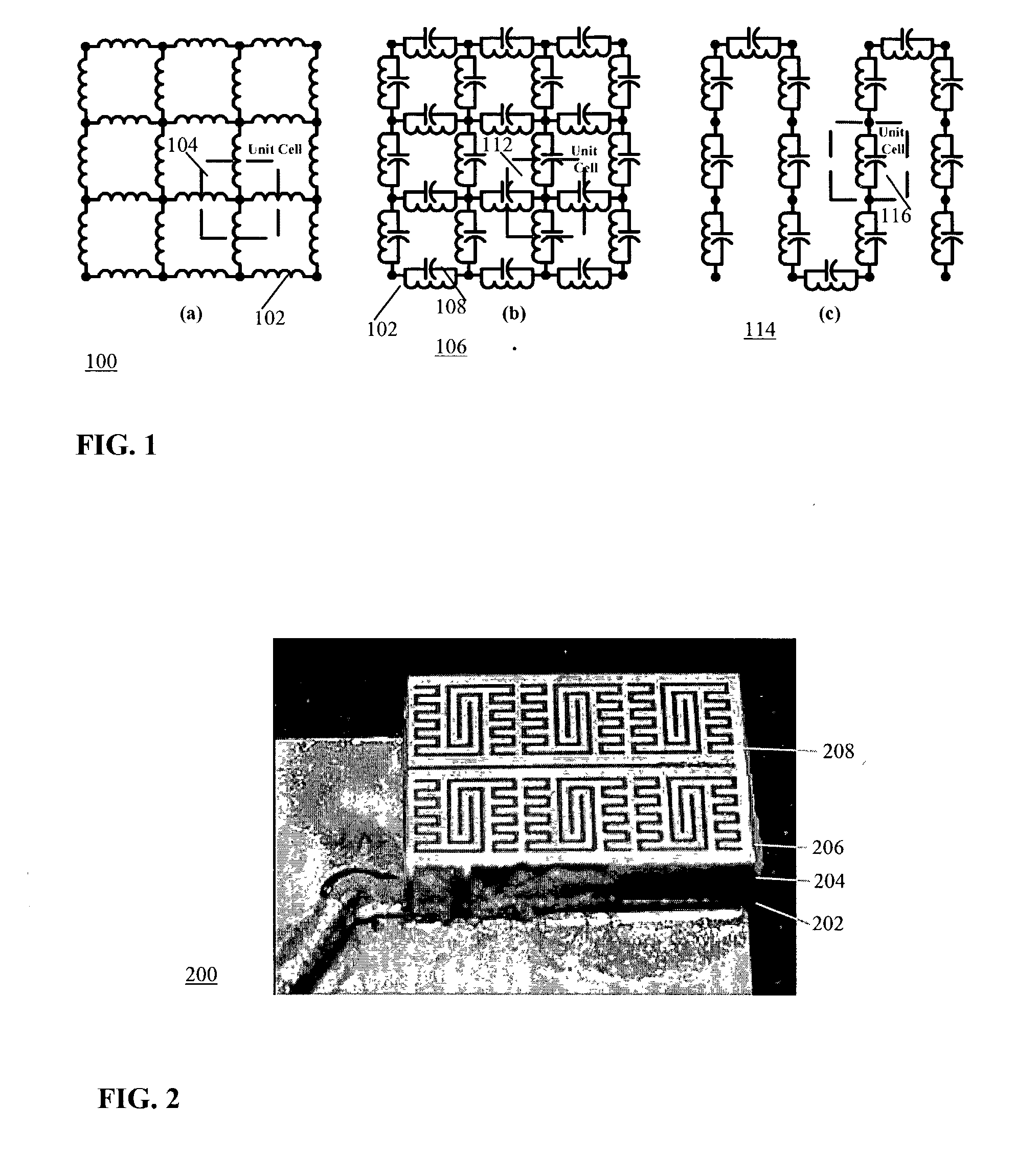
Low frequency enhanced frequency selective surface technology and applications
ActiveUS7071889B2Reduce physical sizeHigh surfaceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsWave structureCapacitance
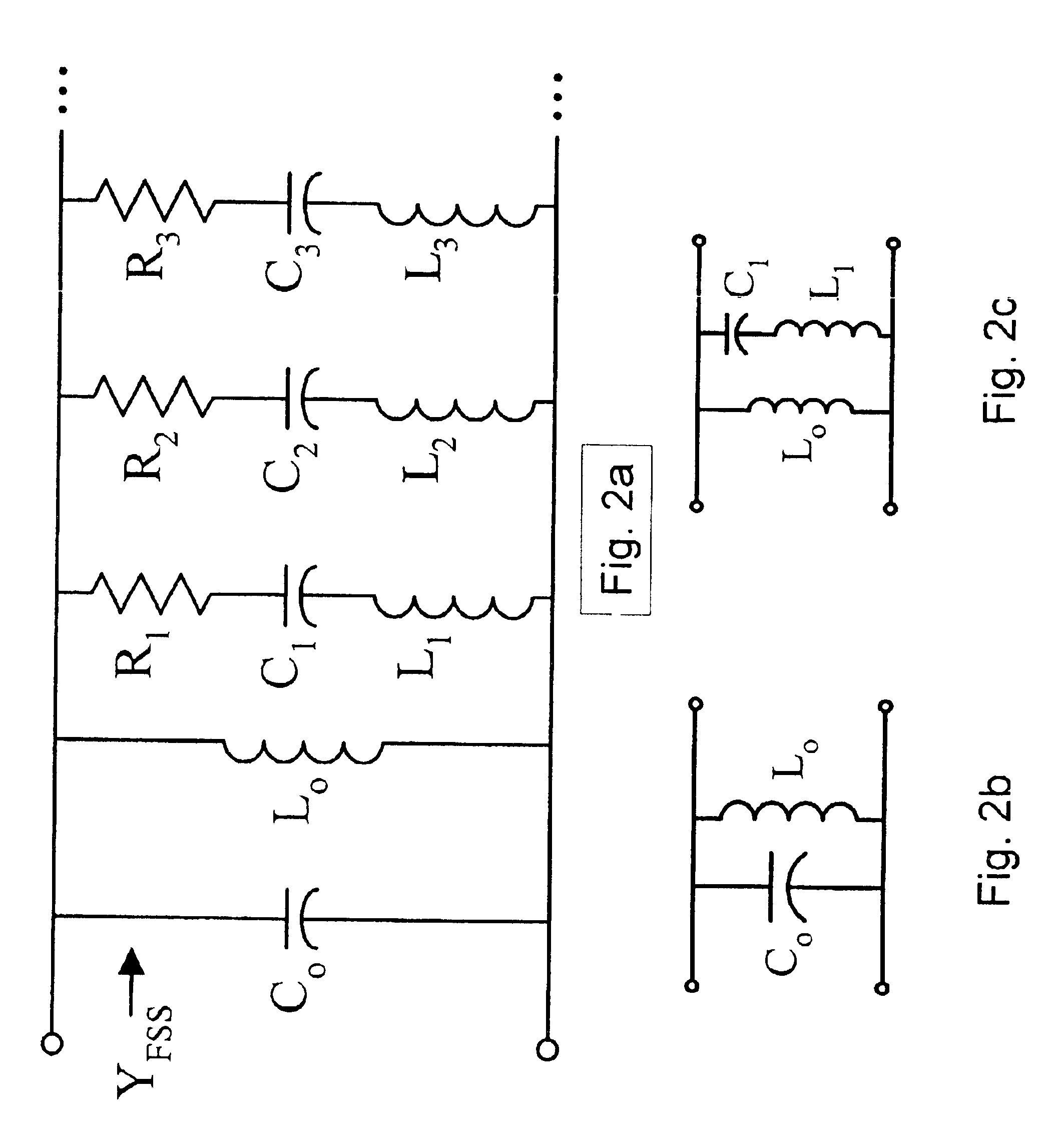
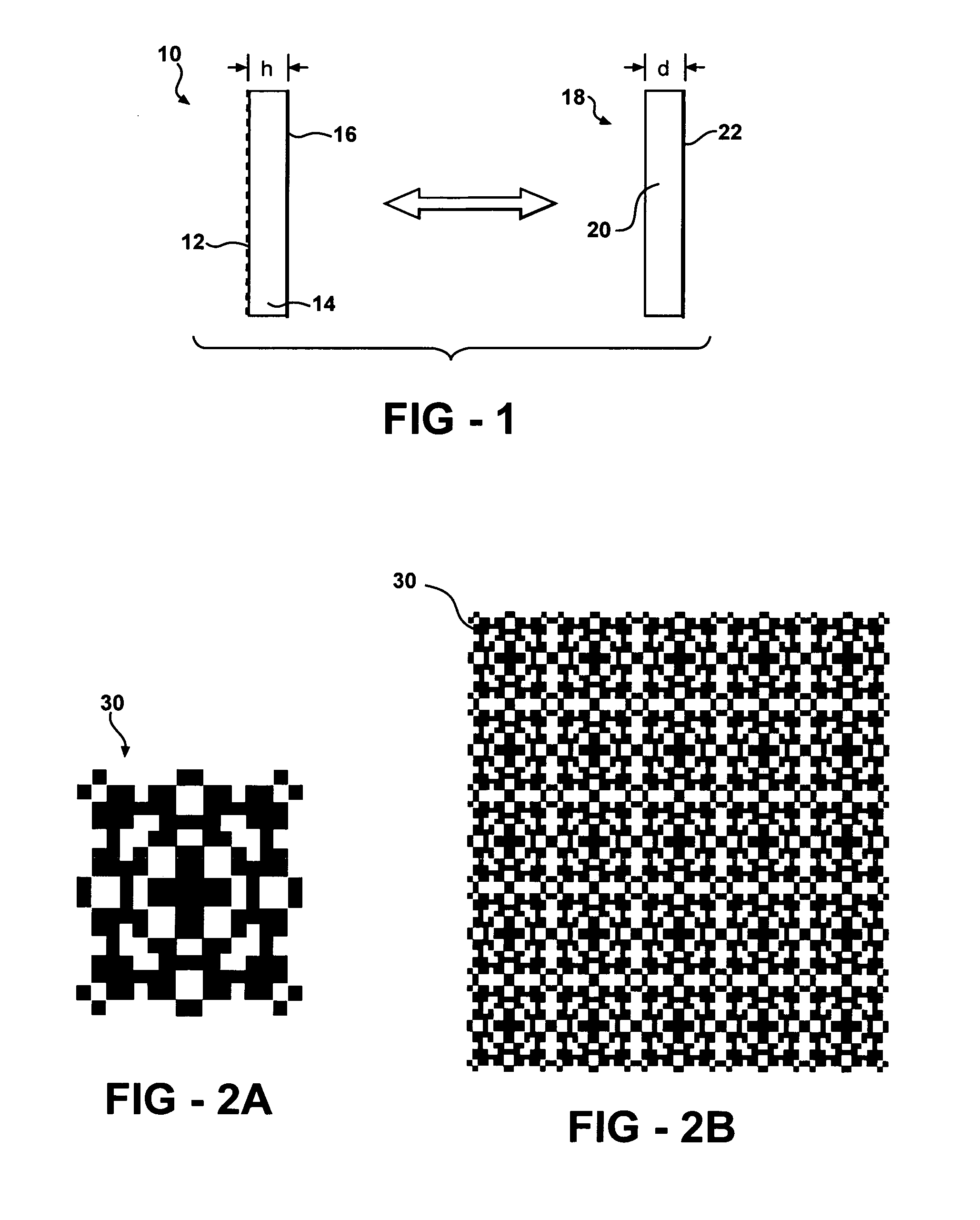
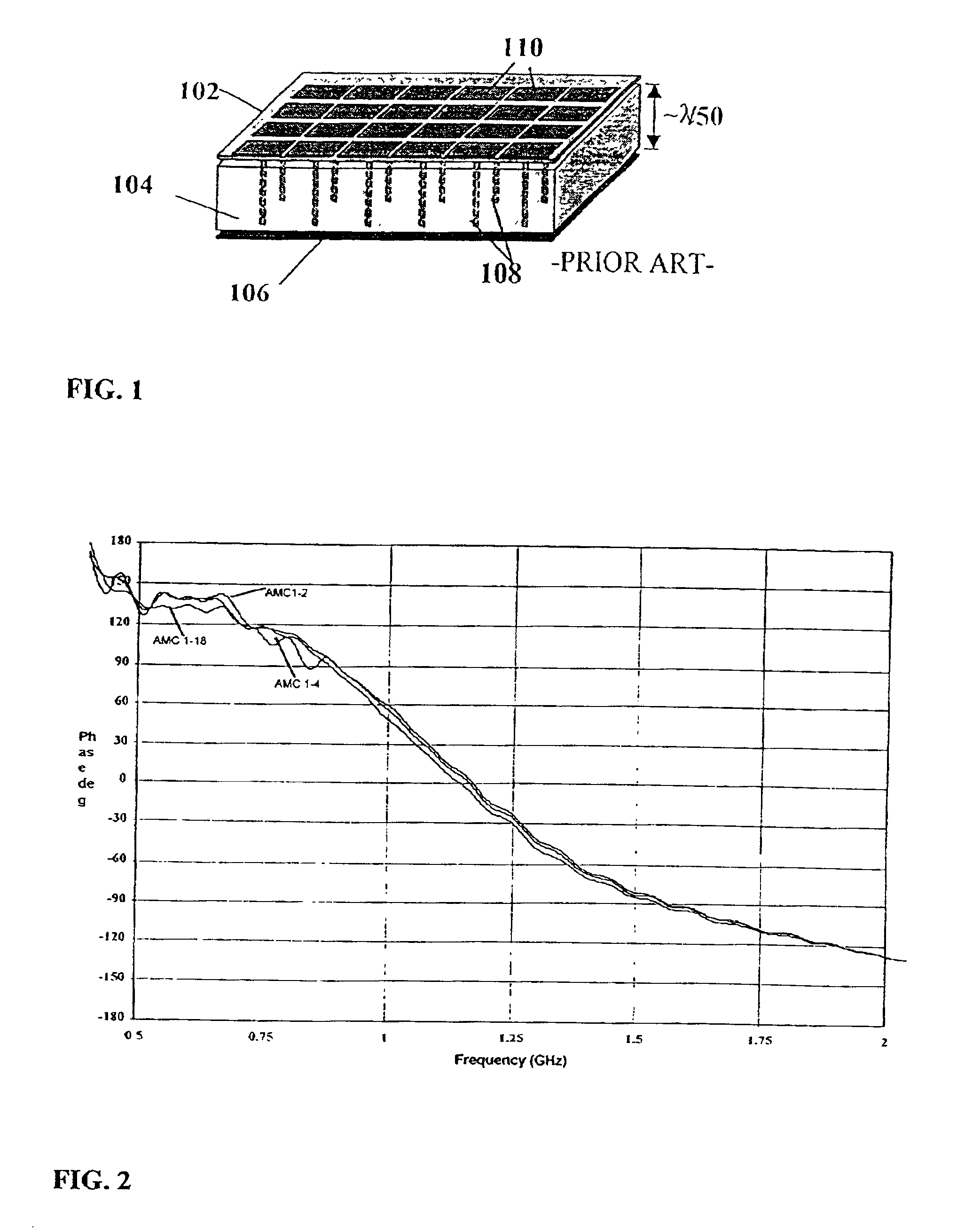
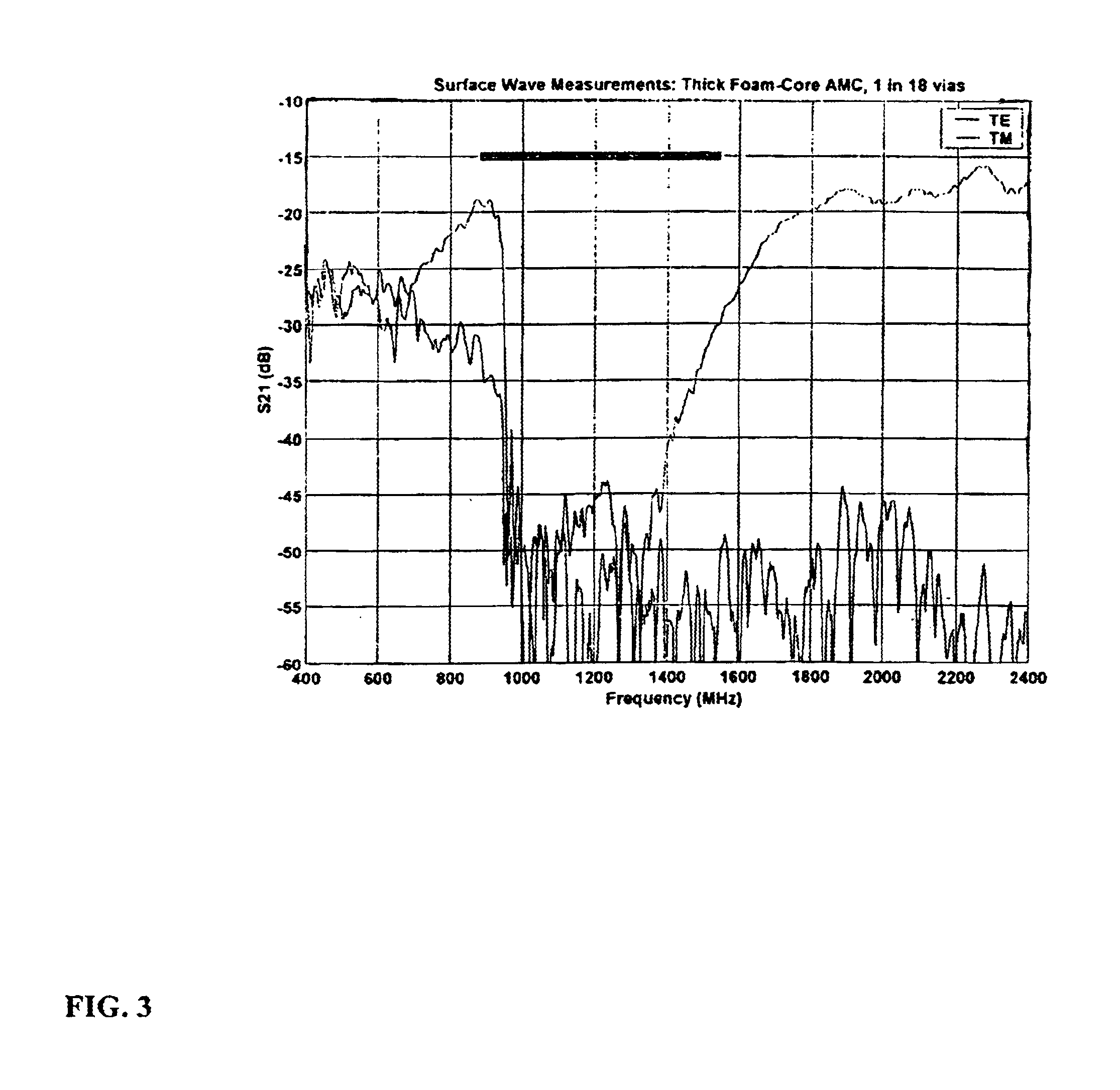
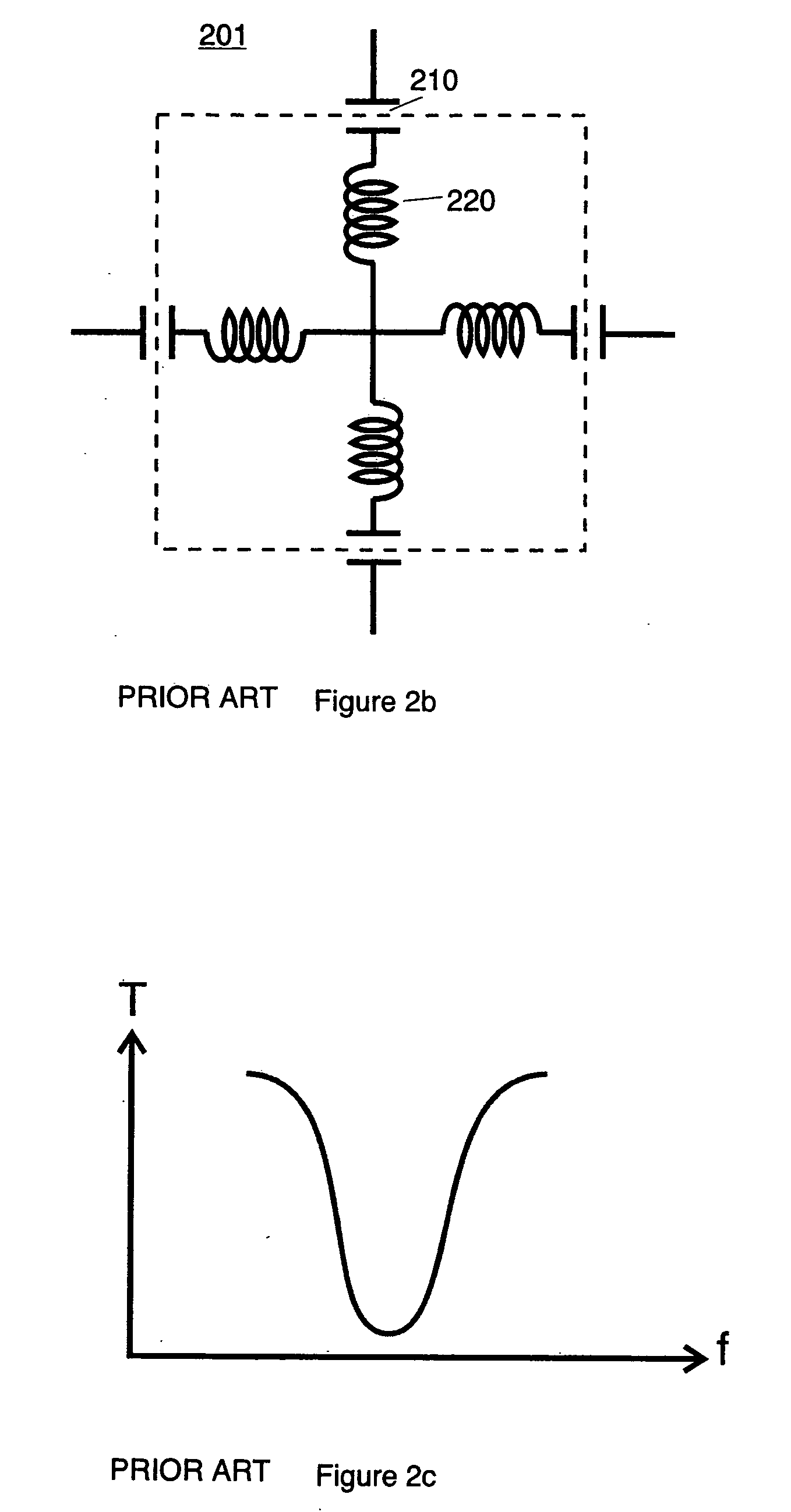
DC inductive FSS technology is a printed slow wave structure usable for reduced size resonators in antenna and filter applications of wireless applications. It is a dispersive surface defined in terms of its parallel LC equivalent circuit that enhances the inductance and capacitance of the equivalent circuit to obtain a pole frequency as low as 300 MHz. The effective sheet impedance model has a resonant pole whose free-space wavelength can be greater than 10 times the FSS period. A conductor-backed DCL FSS can create a DC inductive artificial magnetic conductor (DCL AMC), high-impedance surface with resonant frequencies as low as 2 GHz. Lorentz poles introduced into the DCL FSS create multi-resonant DCL AMCs. Antennas fabricated from DCL FSS materials include single-band elements such as a bent-wire monopole on the DCL AMC and multi-band (dual and triple) shorted patches, similar to PIFAs with the patch / lid being a DCL FSS.
Owner:OAE TECH INC
Broadband antennas over electronically reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor surfaces
InactiveUS6917343B2Improve antenna efficiencyRadiating elements structural formsAntenna feed intermediatesCapacitanceEngineering
A low profile antenna system includes an artificial magnetic conductor comprising a frequency selective surface (FSS) having an effective sheet capacitance which is electronically variable to control resonant frequency of the AMC and the resonant frequency of an antenna element positioned adjacent to the FSS.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP +1
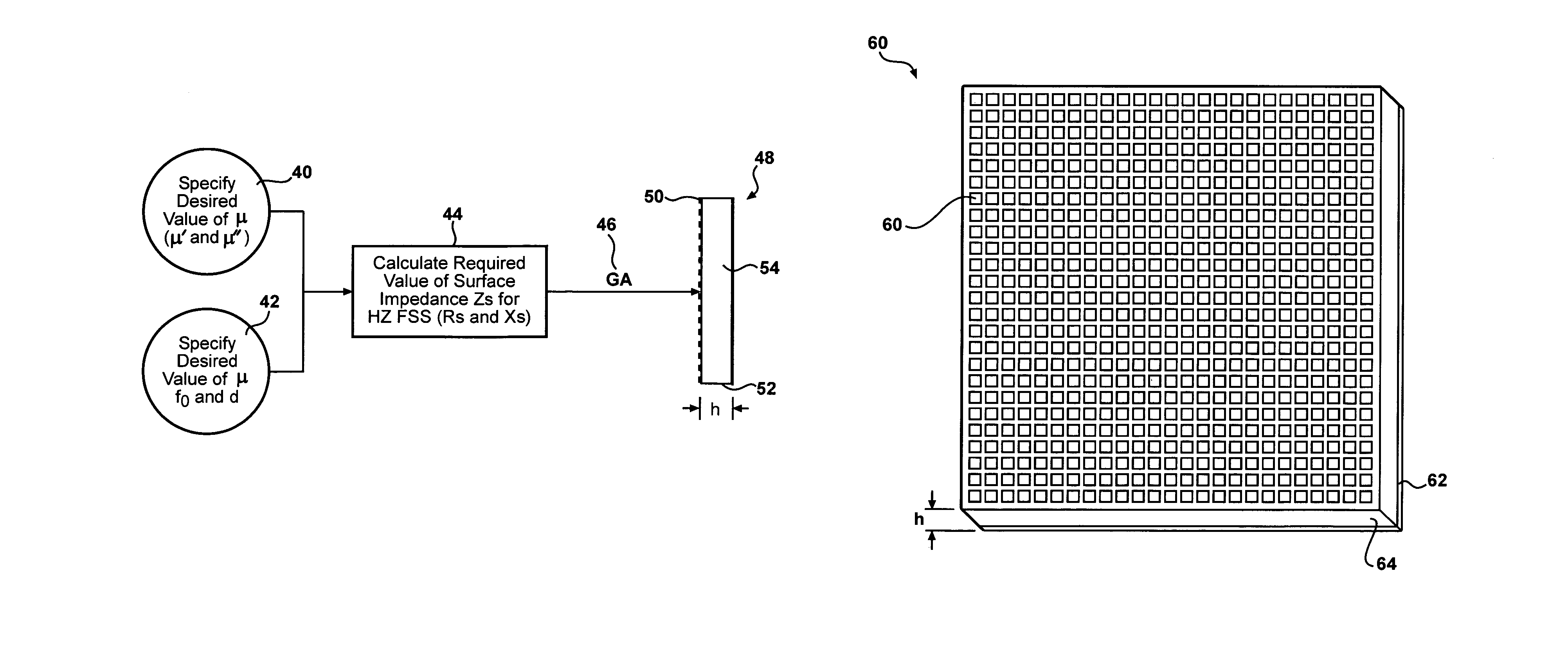
Synthesis of metamaterial ferrites for RF applications using electromagnetic bandgap structures
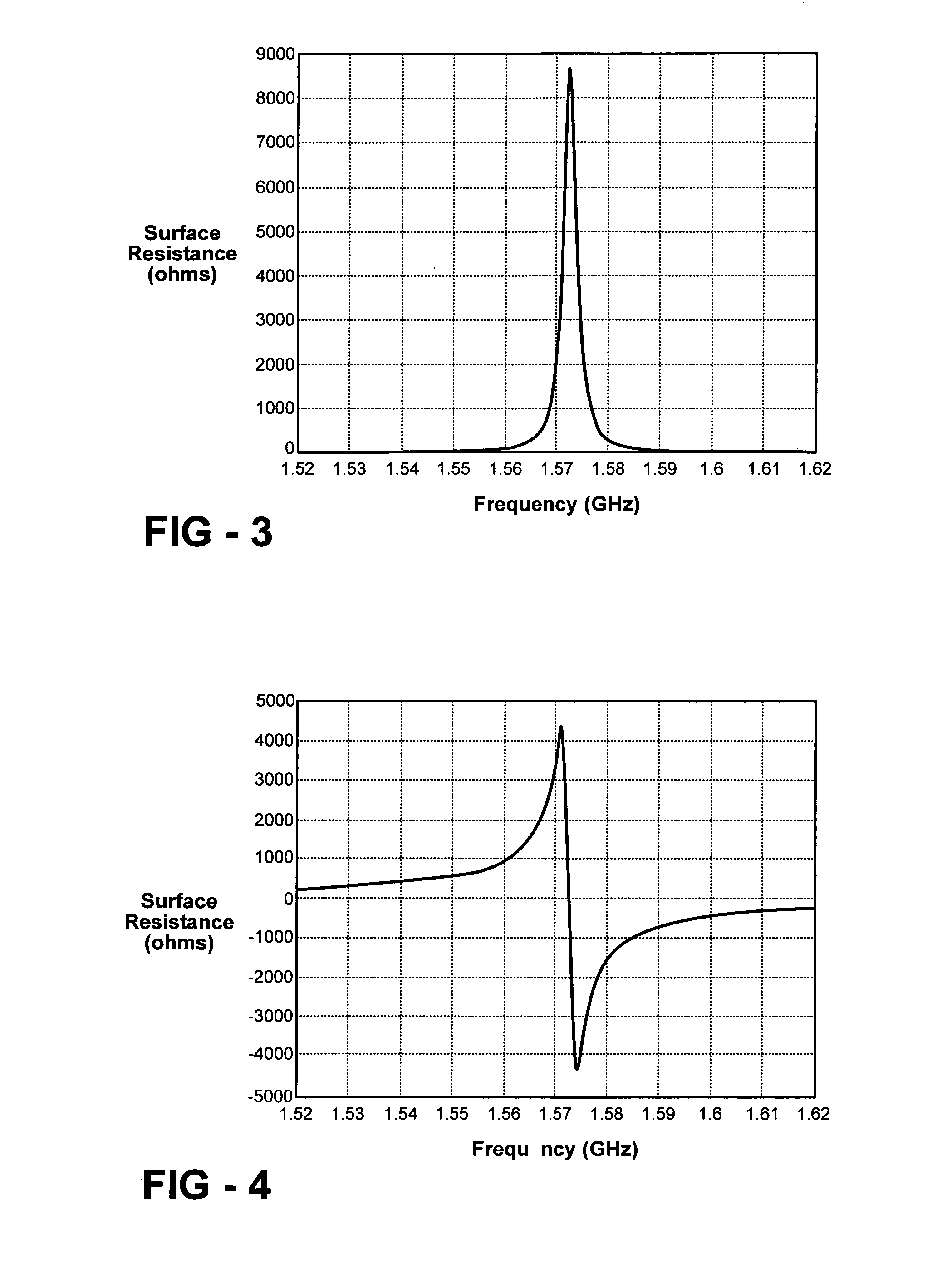
By configuring a high impedance frequency selective surface (HZ-FSS) structure for the appropriate values of surface impedance (surface resistance and surface reactance), a high frequency artificial ferrite metamaterial can be synthesized with almost any desired value of real and imaginary permeability. Materials with these properties have not previously been physically realizable at frequencies above 1 GHz.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor using voltage controlled capacitors with coplanar resistive biasing network
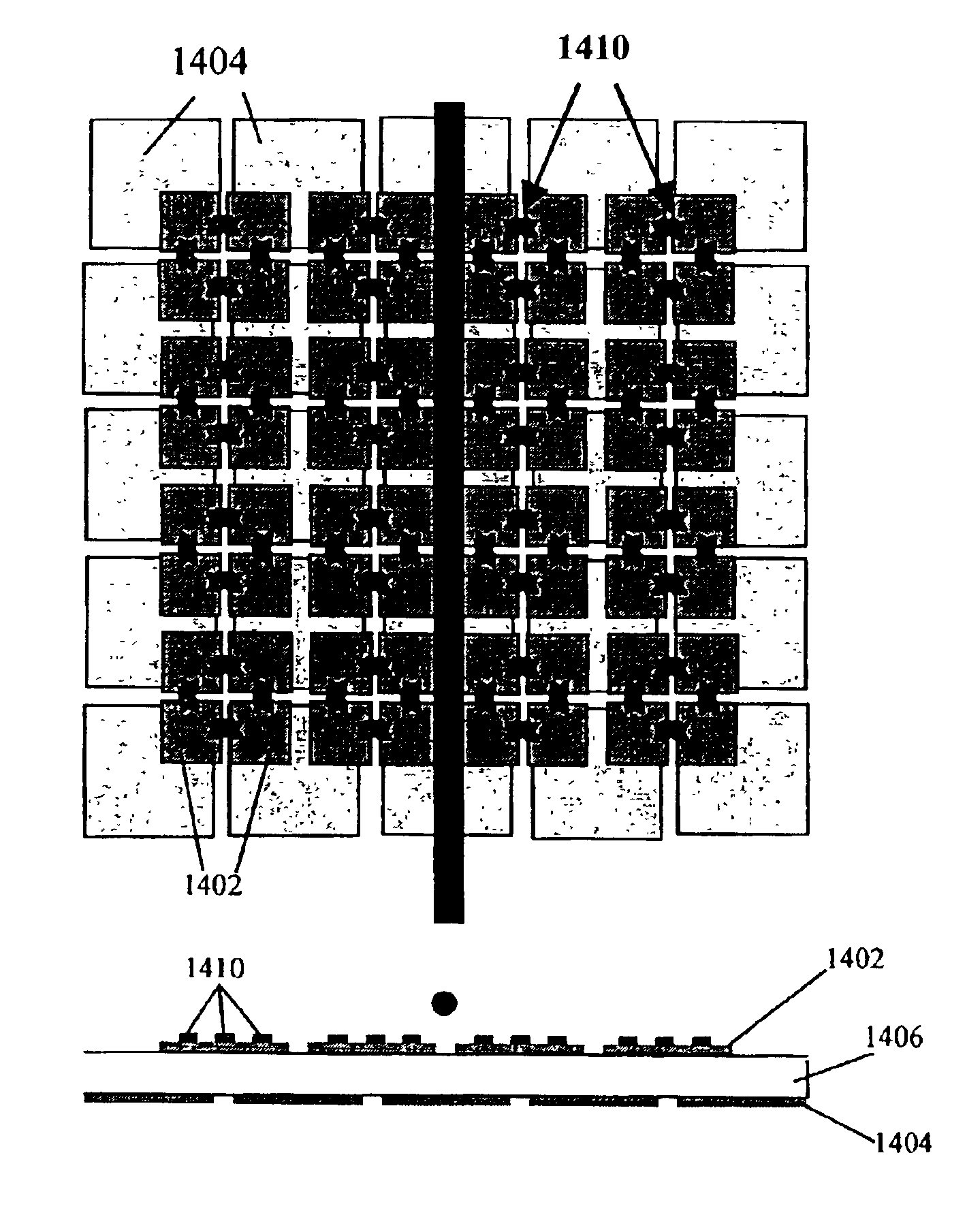
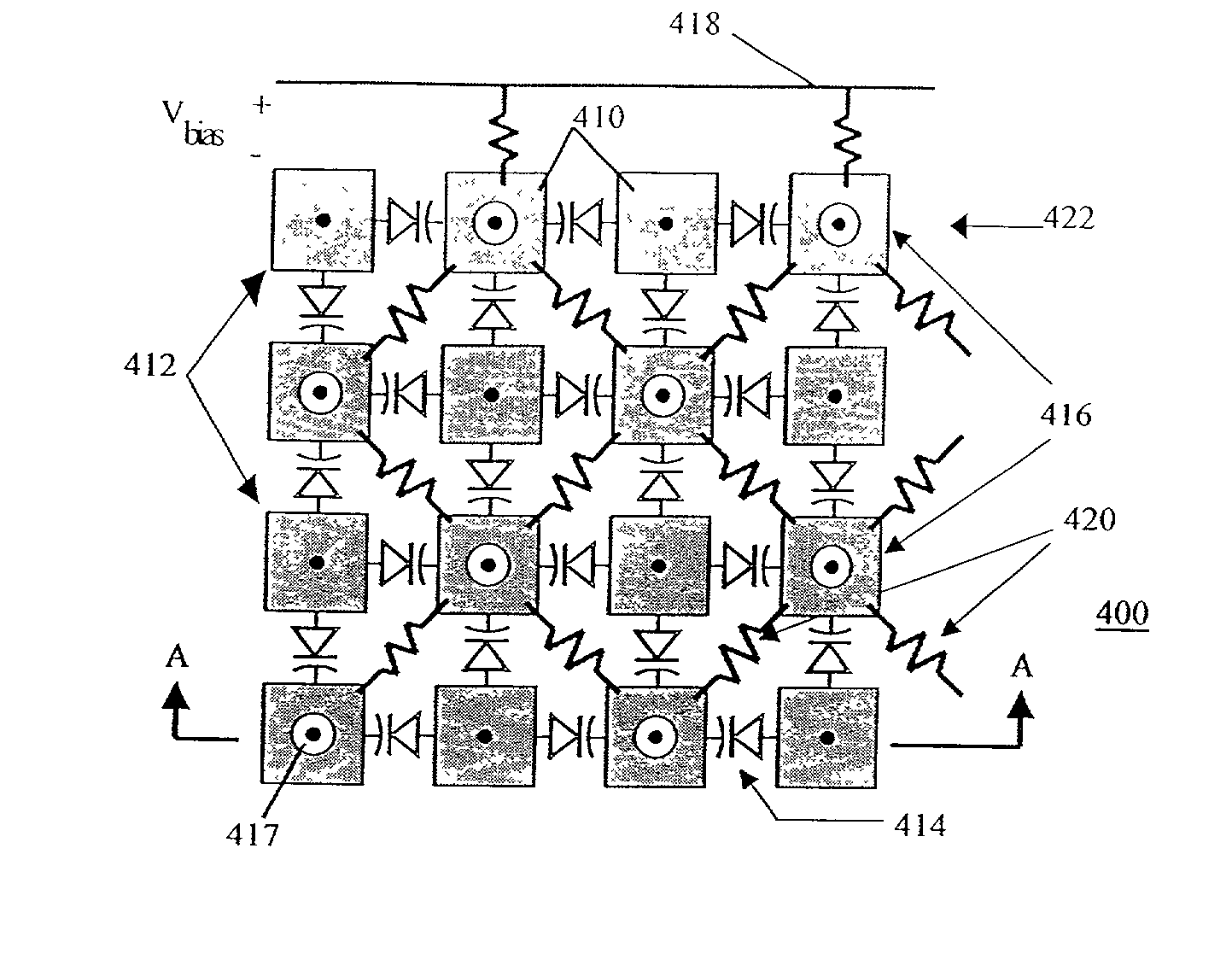
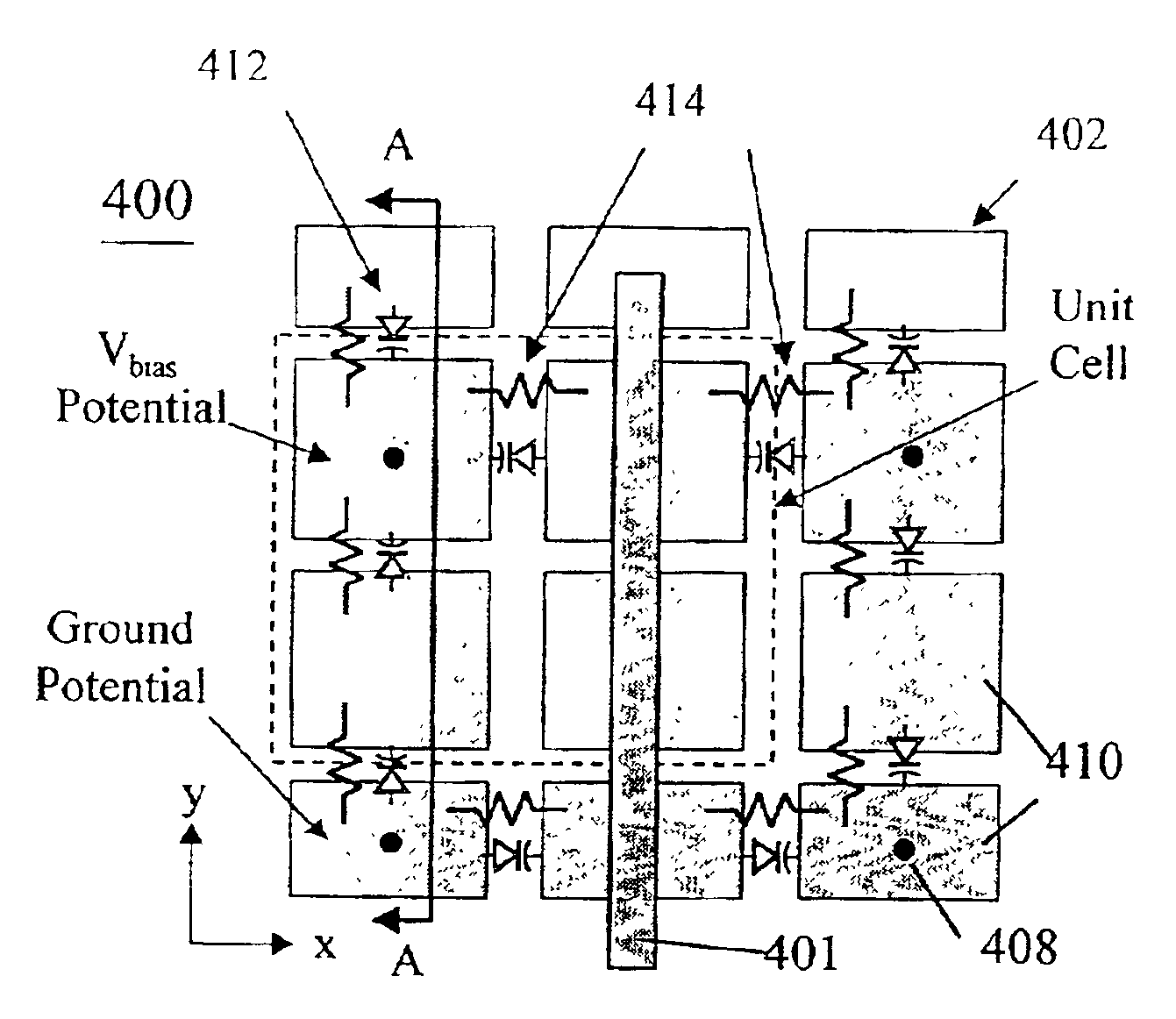
A frequency reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor (AMC) includes a ground plane, a spacer layer disposed adjacent the ground plane and a plurality of vias in electrical contact with the ground plane and extending from a surface of the ground plane in direction of the spacer layer. The AMC further includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) disposed on the spacer layer and including a periodic pattern of bias node patches alternating with ground node patches, the ground node patches being in electrical contact with respective vias of the plurality of vias, and components between selected bias node patches and ground node patches, the components having a capacitance which is variable in response to a bias voltage. A network of bias resistors between adjacent bias node patches provides the tuning voltage.
Owner:TITAN AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS DIV
Reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor
InactiveUS6897831B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceEngineering
An electronically reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor (RAMC) includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) having an effective sheet capacitance which is variable to control resonant frequency of the RAMC. In one embodiment, the RAMC further includes a conductive backplane structure and a spacer layer separating the conductive backplane structure and the FSS. The spacer layer includes conductive vias extending between the conductive backplane structure and the FSS, and voltage variable capacitive circuit elements coupled with the FSS and responsive to bias voltages applied on one or more bias signal lines routed through the conductive backplane structure and the conductive vias.
Owner:TITAN AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS DIV +1
Tunable frequency selective surface
An apparatus and methods for operating a frequency selective surface are disclosed. The apparatus can be tuned to an on / off state or transmit / reflect electromagnetic energy in any frequency. The methods disclosed teach how to tune the frequency selective surface to an on / off state or transmit / reflect electromagnetic energy in any frequency.
Owner:HRL LAB
Reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor
InactiveUS20020167457A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceEngineering
An electronically reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor (RAMC) includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) having an effective sheet capacitance which is variable to control resonant frequency of the RAMC. In one embodiment, the RAMC further includes a conductive backplane structure and a spacer layer separating the conductive backplane structure and the FSS. The spacer layer includes conductive vias extending between the conductive backplane structure and the FSS, and voltage variable capacitive circuit elements coupled with the FSS and responsive to bias voltages applied on one or more bias signal lines routed through the conductive backplane structure and the conductive vias.
Owner:TITAN AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS DIV +1
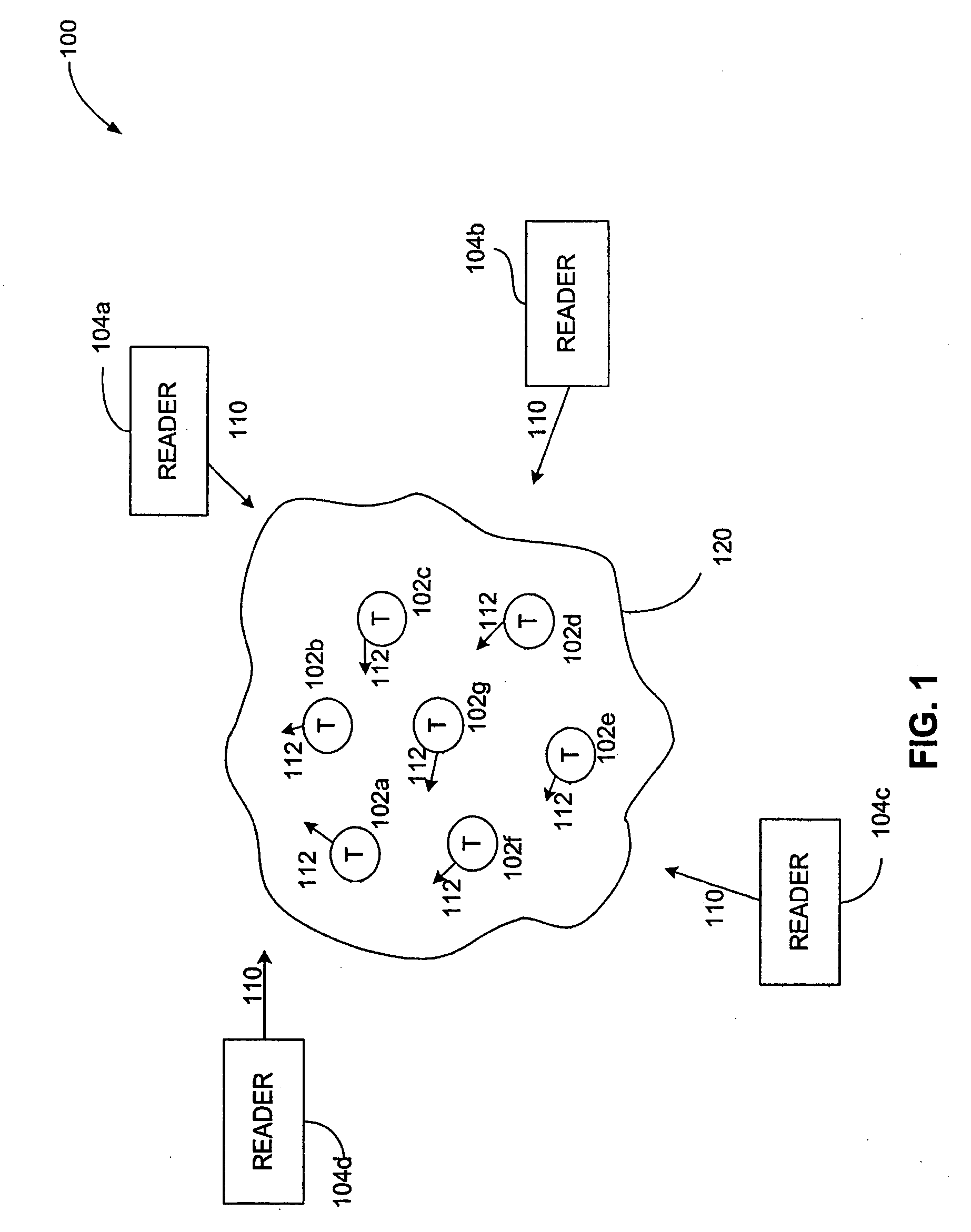
Frequency selective surface aids to the operation of RFID products
ActiveUS20080150691A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringSlide plate
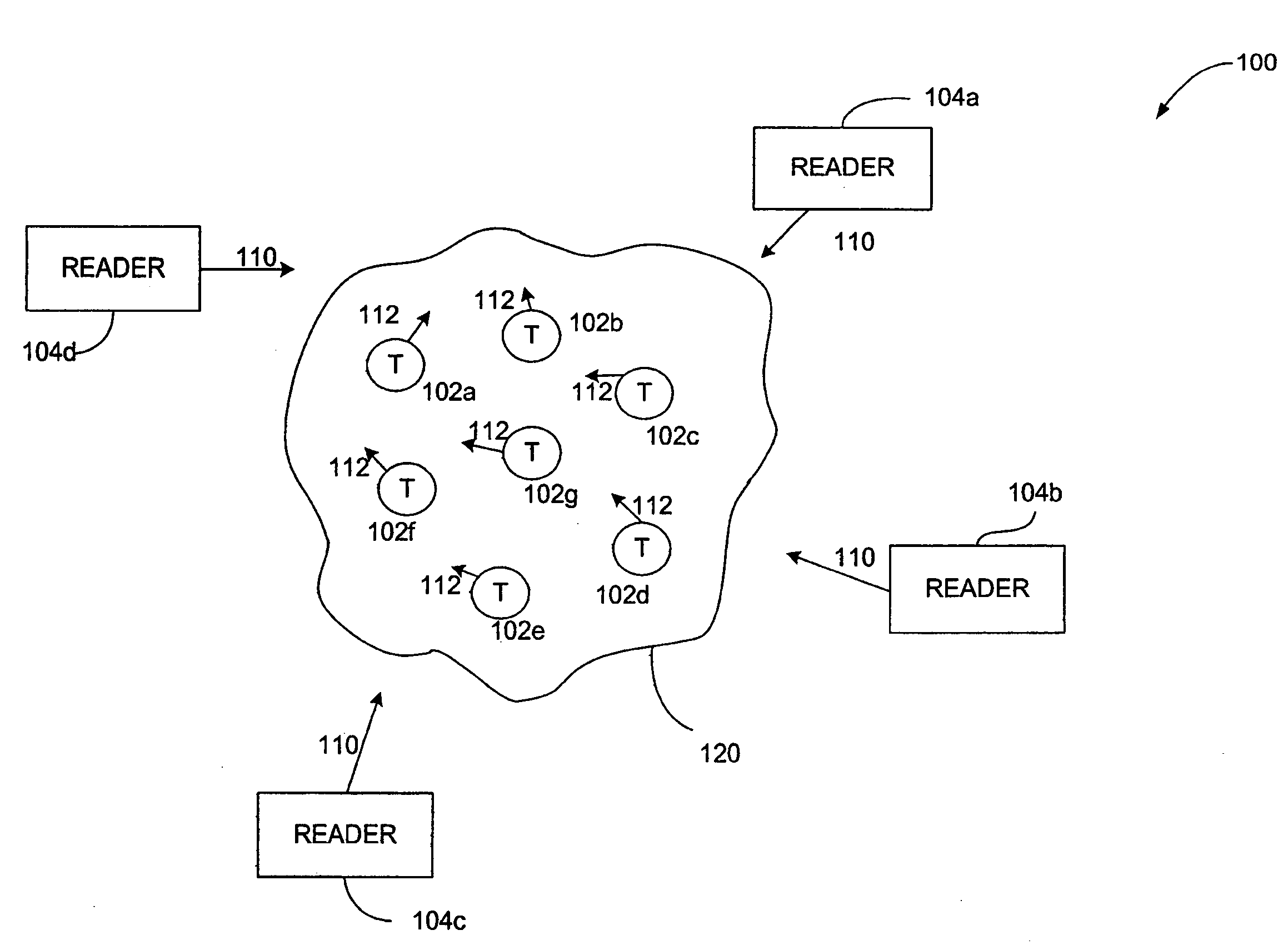
The present invention is directed to systems that use frequency selective surfaces (FSS) to aid in the operation of radio frequency identification (RFID) devices and products. In one embodiment, a system for interrogating radio frequency identification (RFID) tags includes a conveyor belt and an RFID reader. The conveyor belt has a first surface and a second surface. The first surface is configured to receive an item to which an RFID tag is affixed and the second surface is configured to slide on a metal slide plate. The RFID reader is configured to transmit instructions embodied in a radio frequency (RF) signal to the RFID tag, wherein the metal slide plate is positioned between the RFID reader and the RFID tag and comprises a frequency selective surface that is substantially transparent to the RF signal.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
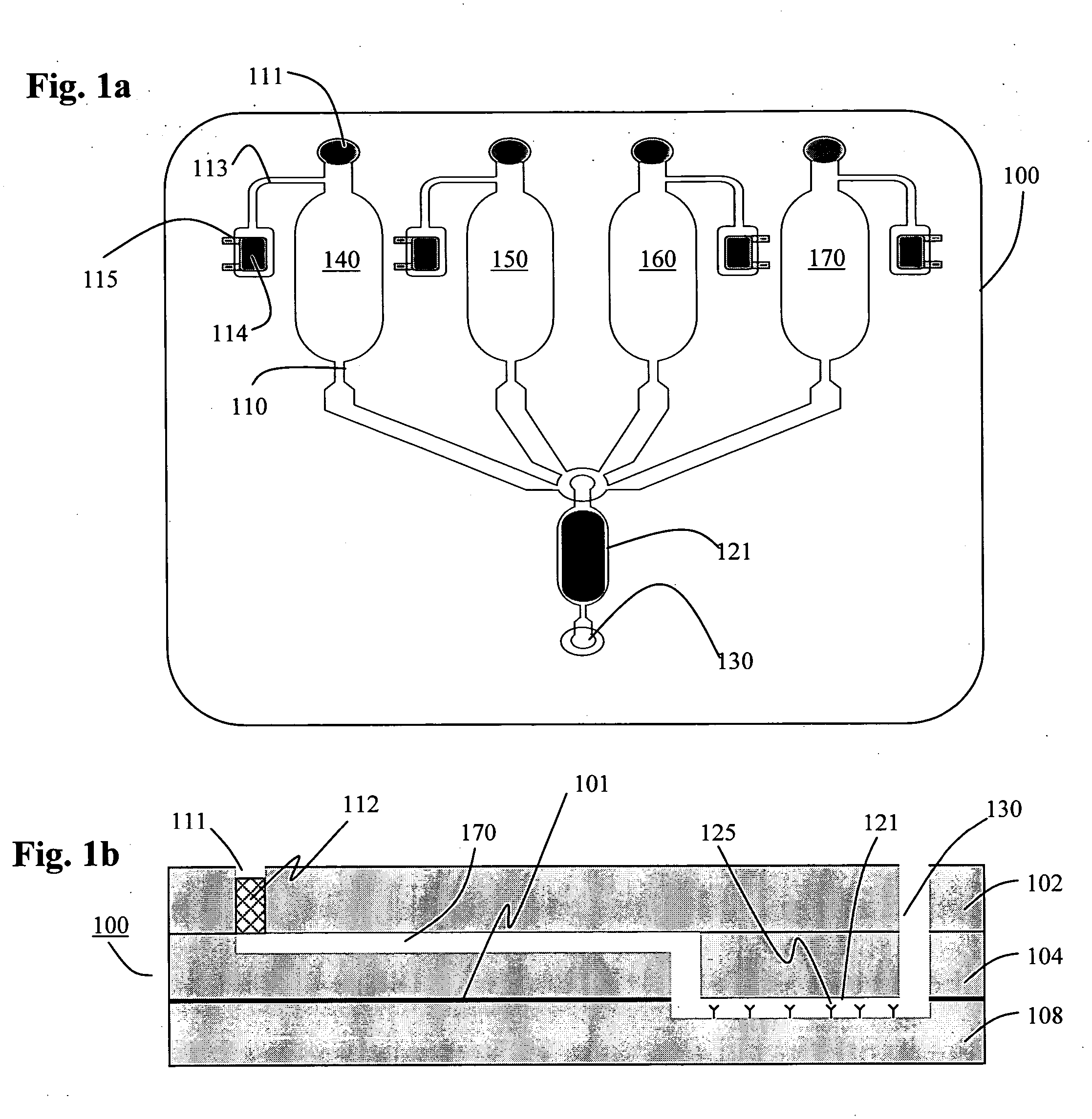
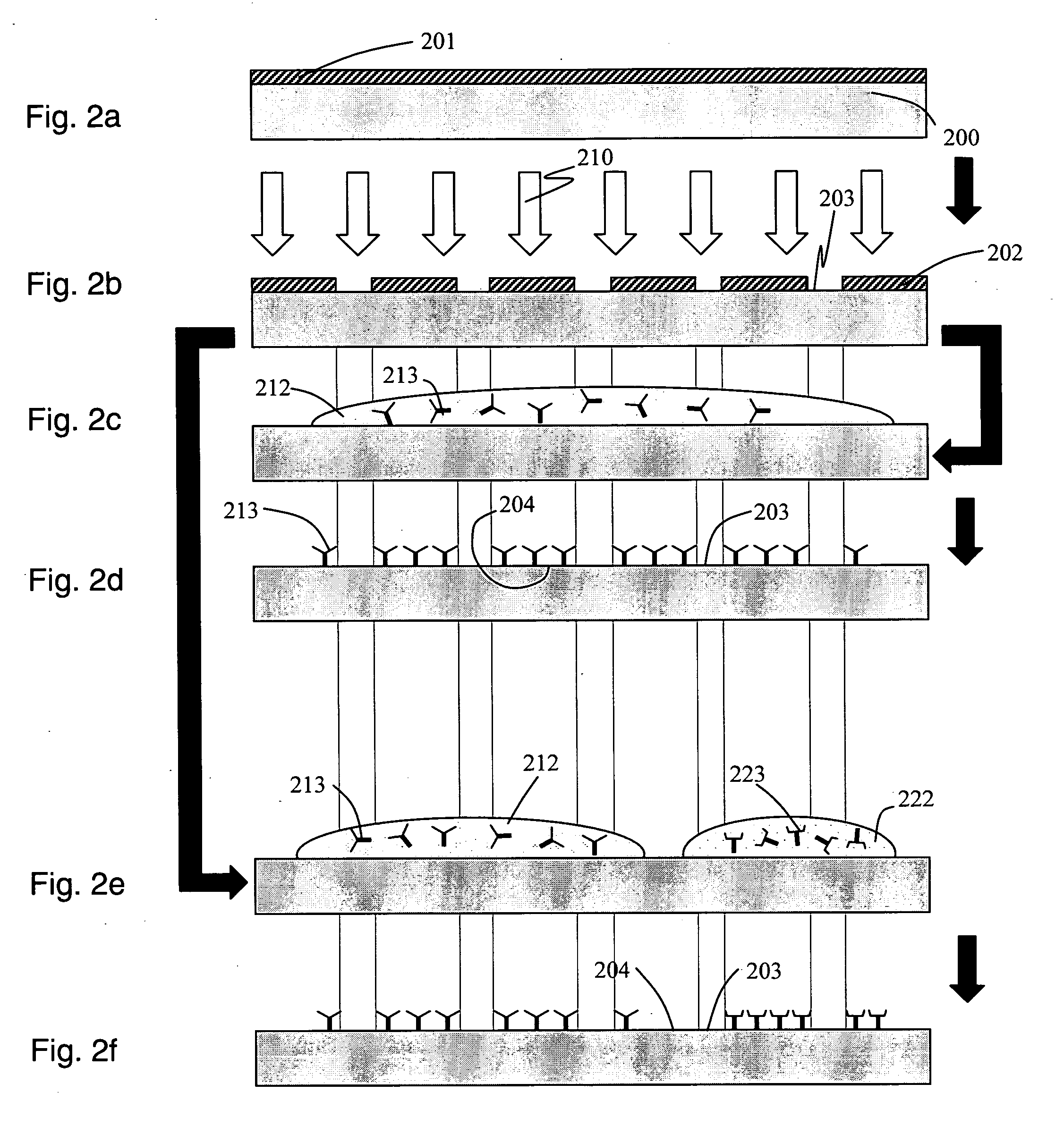
Fully integrated protein lab-on-a-chip with smart microfluidics for spot array generation
InactiveUS20050130226A1High detection sensitivityLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careDot matrix
Techniques for the fabrication of fully-integrated lab-on-a-chips (or biochips) specifically oriented towards point-of-care detection of biomolecules using immunoassay based detection techniques are disclosed. A primary task for the development of such biochips is the development of techniques to precisely deposit and localize the capture antibody on pre-determined locations over the biochip. The use of selective surface modification, specifically control over the surface energy, to achieve localized adsorption of the capture antibody is disclosed. Another approach, also disclosed, describes the use of smart passive microfluidics to confine the flow of the capture antibody along certain paths of the biochip and thereby control the locations over which the capture antibody is adsorbed. Furthermore, the use of an integrated microlens array as means of enhancing the detection sensitivity of the biochip is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
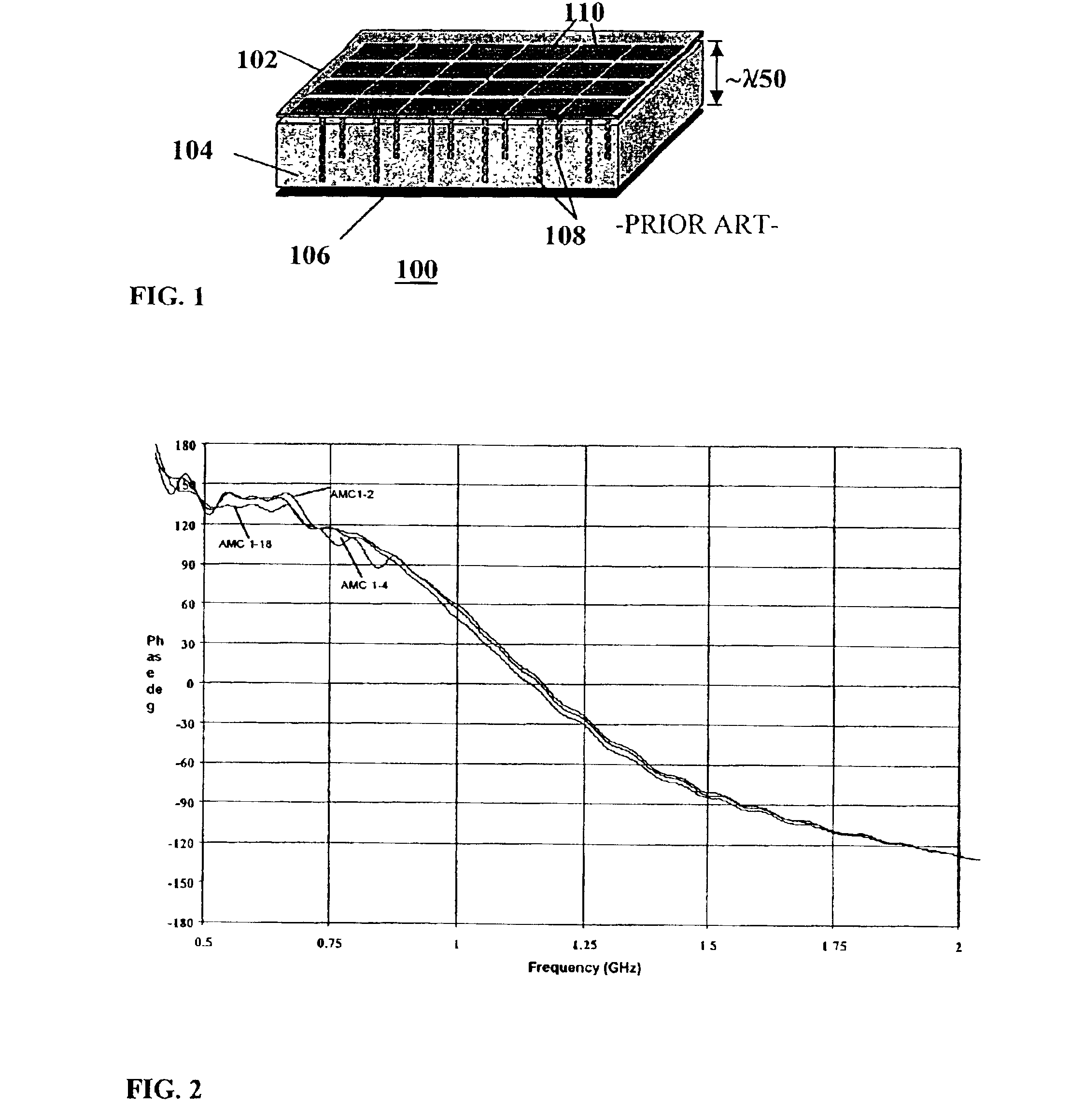
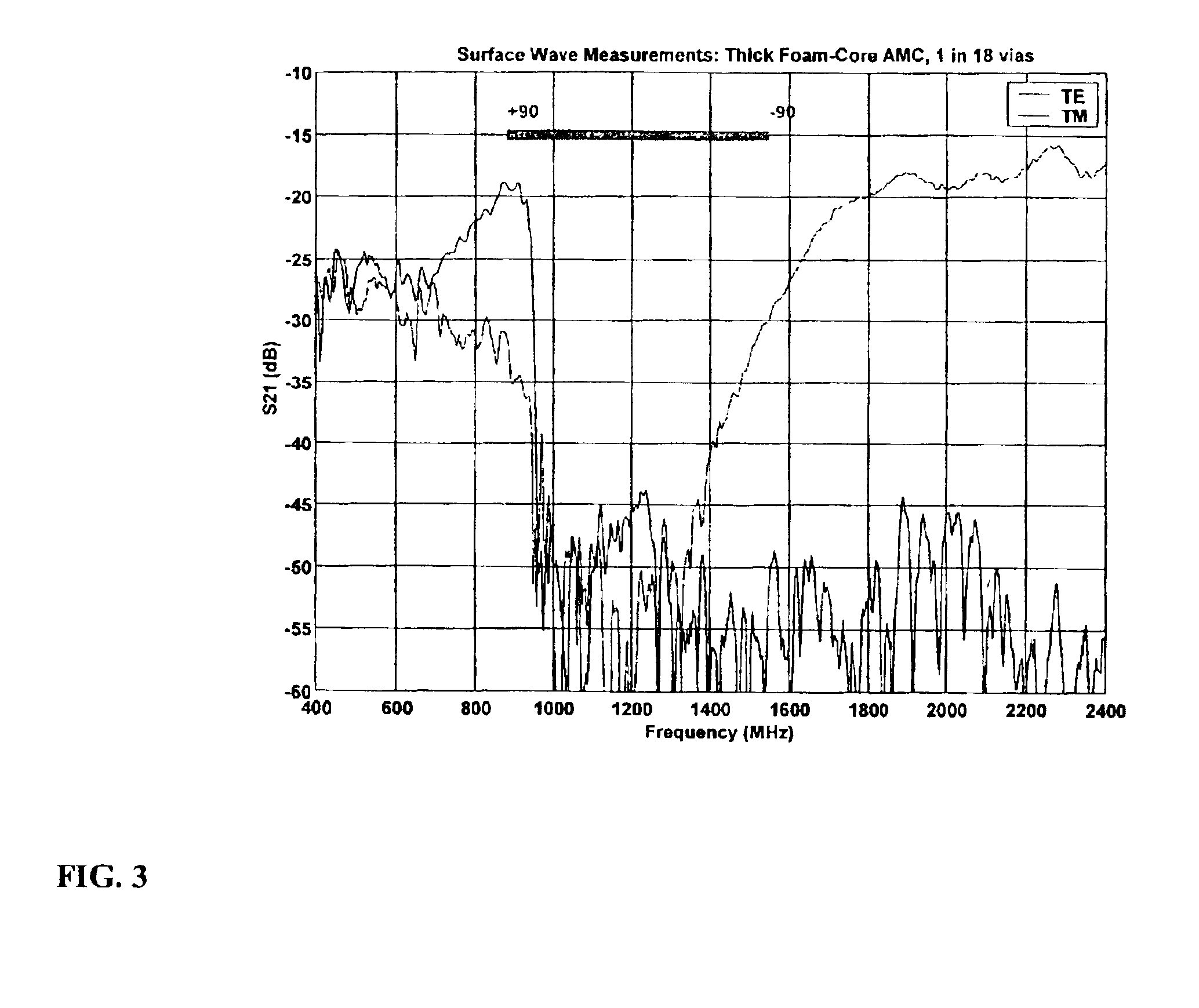
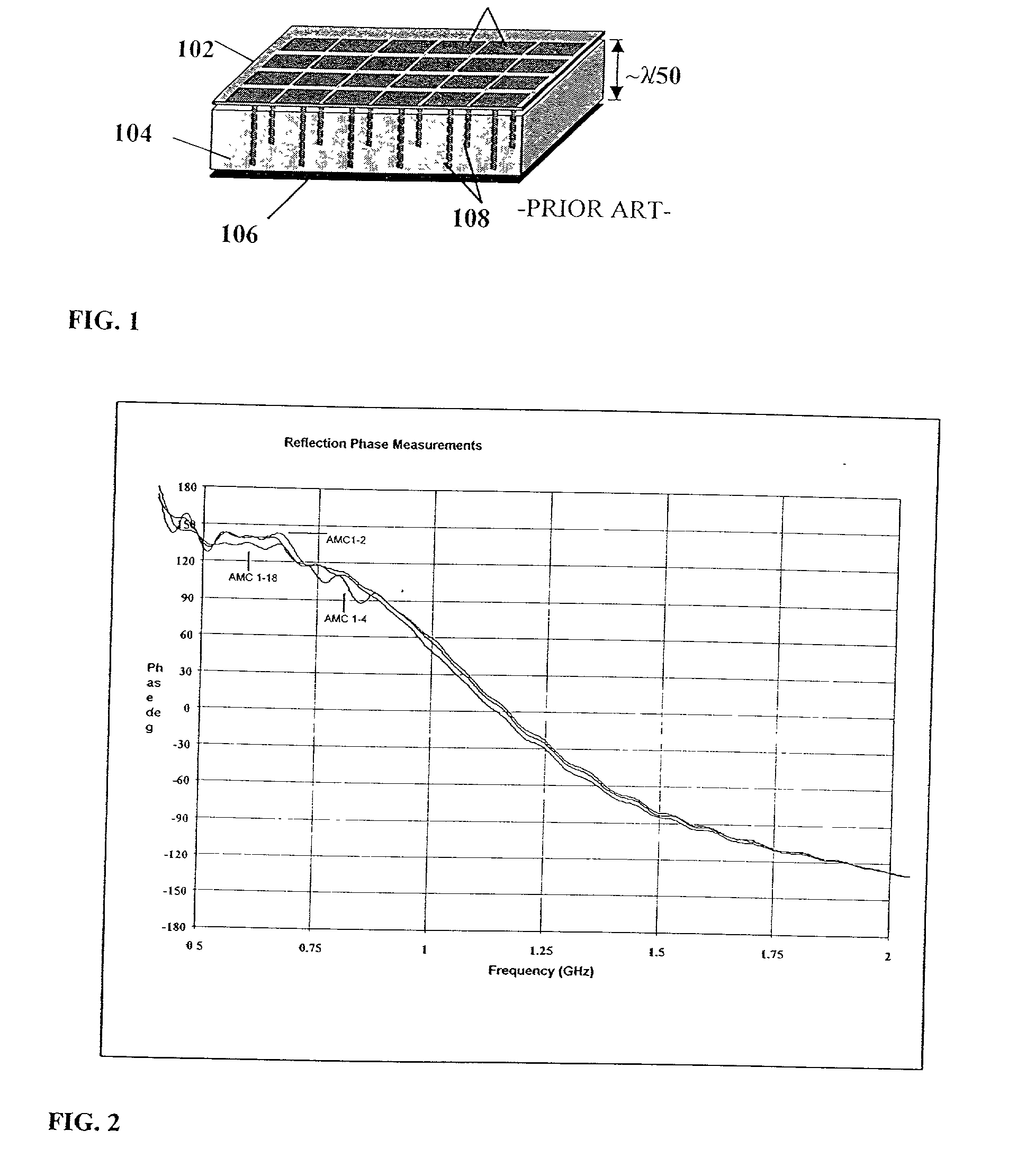
Multi-resonant, high-impedance surfaces containing loaded-loop frequency selective surfaces
InactiveUS6670932B1High surfaceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsGround planeSelective surface
An artificial magnetic conductor includes a frequency selective surface having a frequency dependent permeability mu1z in a direction normal to the frequency dependent surface, a conductive ground plane, and a rodded media disposed between the frequency selective surface and the conductive ground plane.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
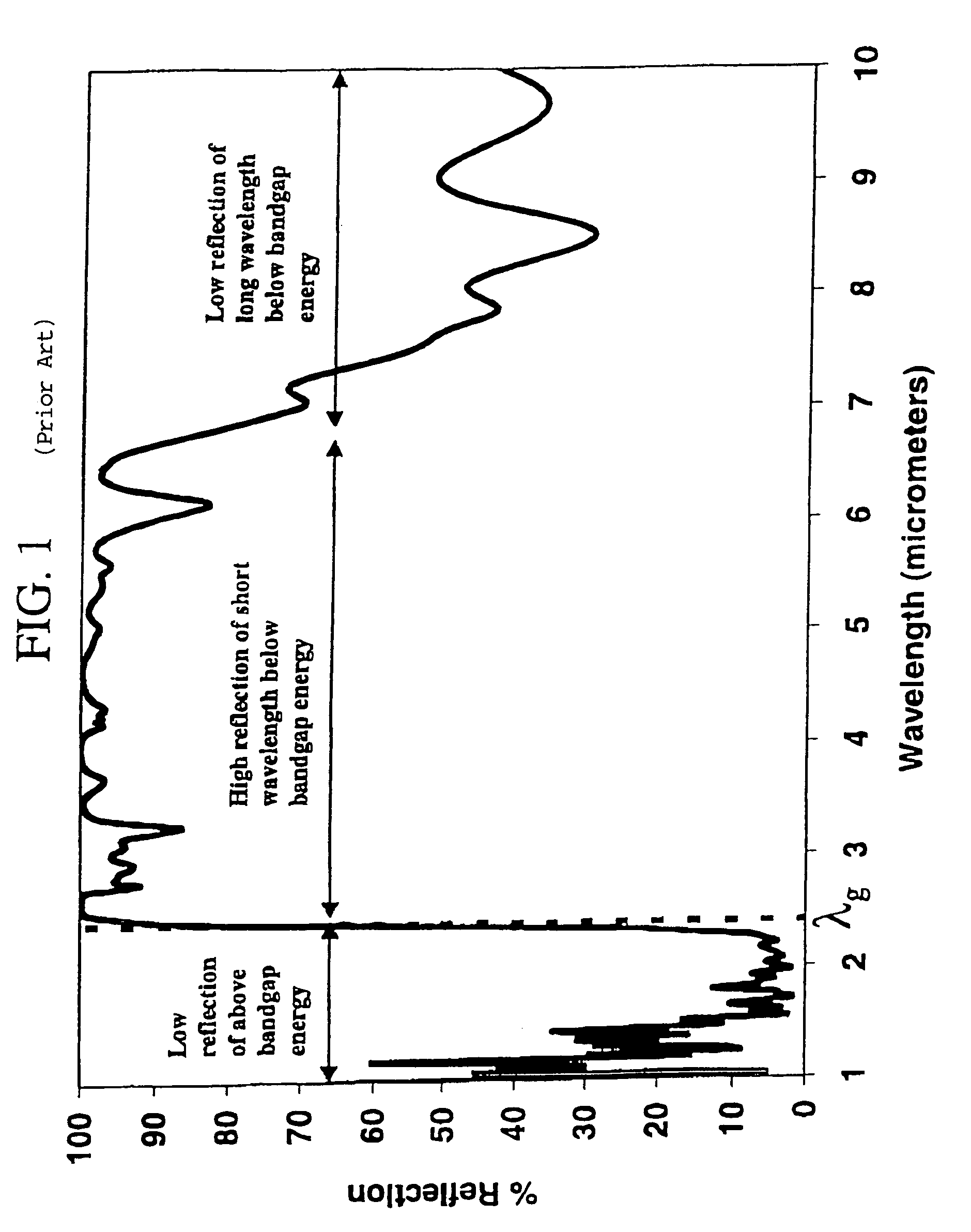
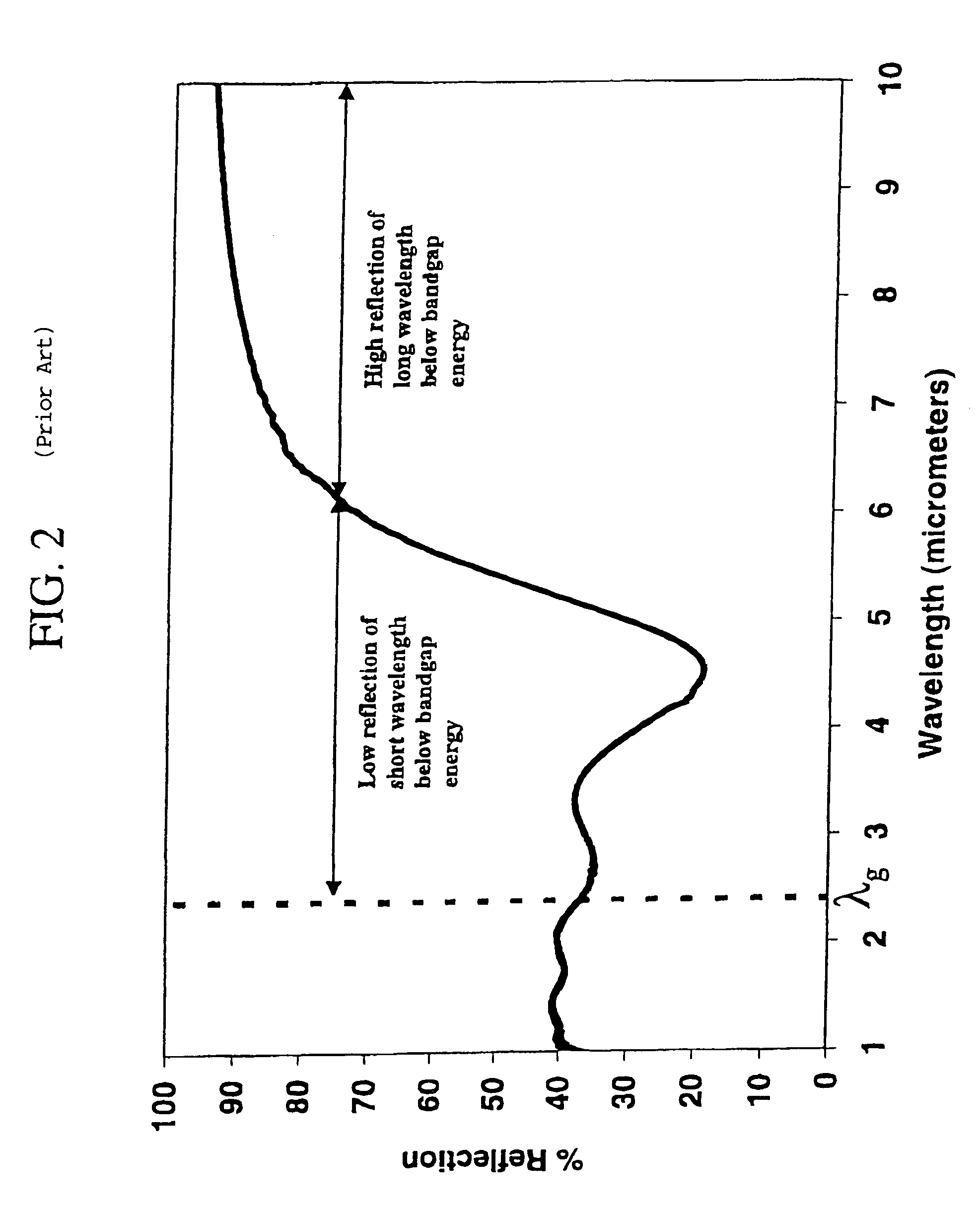
Tandem filters using frequency selective surfaces for enhanced conversion efficiency in a thermophotovoltaic energy conversion system
InactiveUS7166797B1High bandgap energyImprove reflectivityMirrorsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTransmittanceLength wave
This invention relates to the field of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) direct energy conversion. In particular, TPV systems use filters to minimize parasitic absorption of below bandgap energy. This invention constitutes a novel combination of front surface filters to increase TPV conversion efficiency by reflecting useless below bandgap energy while transmitting a very high percentage of the useful above bandgap energy. In particular, a frequency selective surface is used in combination with an interference filter. The frequency selective surface provides high transmission of above bandgap energy and high reflection of long wavelength below bandgap energy. The interference filter maintains high transmission of above bandgap energy and provides high reflection of short wavelength below bandgap energy and a sharp transition from high transmission to high reflection.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Broadband antennas over electronically reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductor surfaces
InactiveUS20030112186A1Improve antenna efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceWide band
A low profile antenna system includes an artificial magnetic conductor comprising a frequency selective surface (FSS) having an effective sheet capacitance which is electronically variable to control resonant frequency of the AMC and the resonant frequency of an antenna element positioned adjacent to the FSS.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP +1
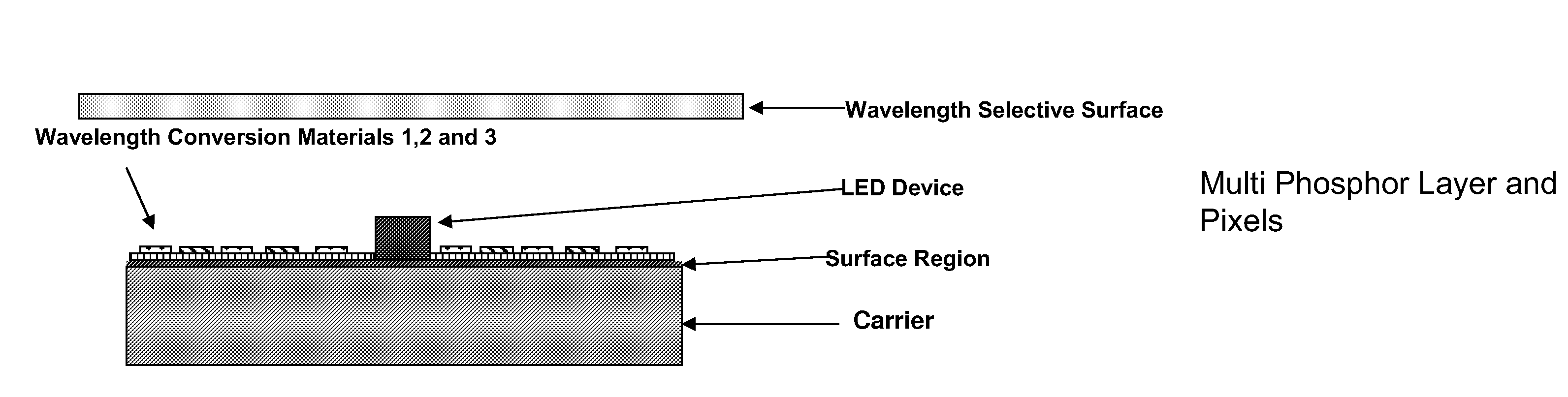
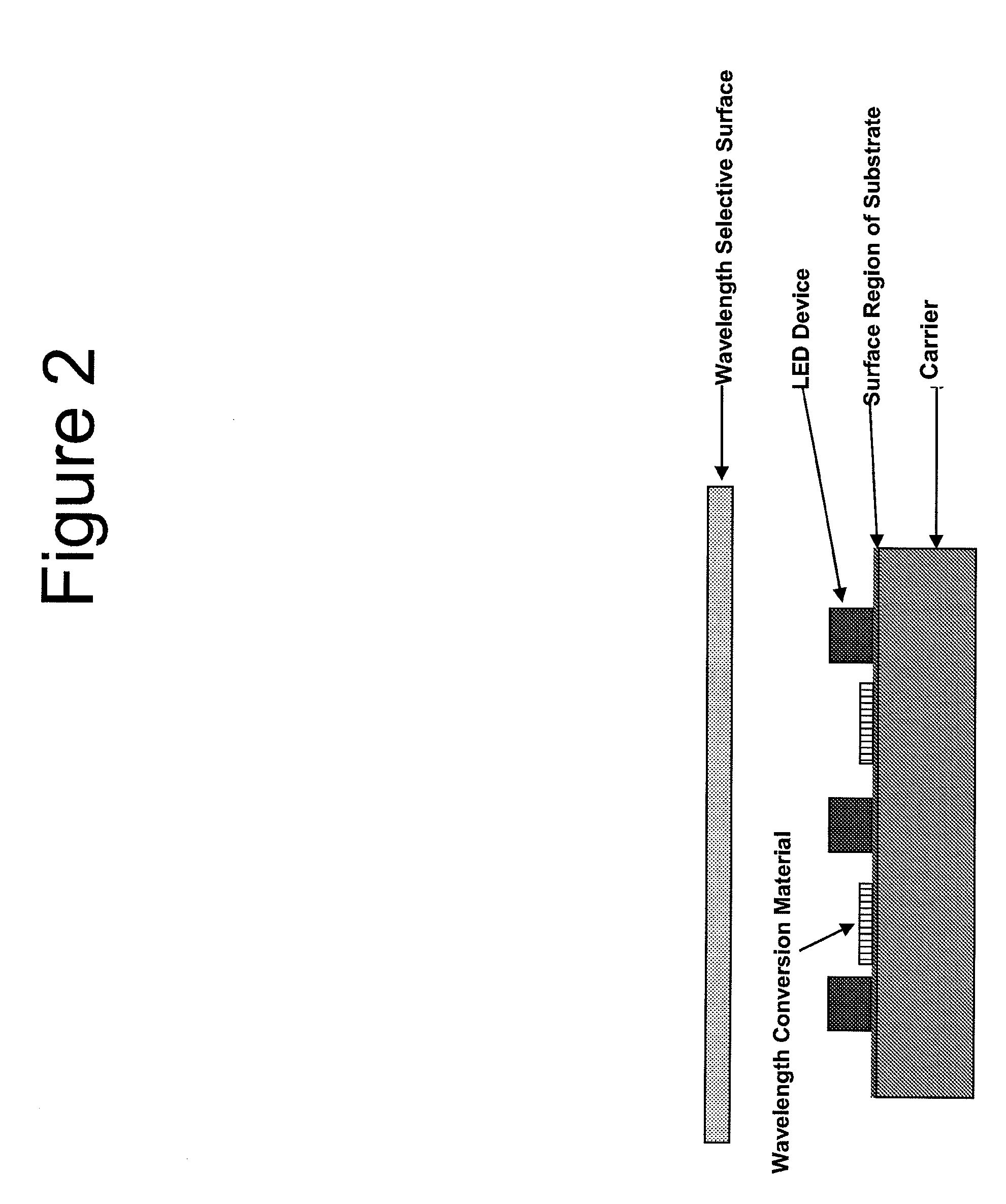
Reflection Mode Package for Optical Devices Using Gallium and Nitrogen Containing Materials
InactiveUS20110215348A1Easy to implementConvenient lightingPoint-like light sourceSolid-state devicesNitrogenLength wave
An optical device includes an LED formed on a substrate and a wavelength conversion material, which may be stacked or pixilated, within vicinity of the LED. A wavelength selective surface blocks direct emission of the LED device and transmits selected wavelengths of emission caused by an interaction with the wavelength conversion material.
Owner:SORAA
Isolation assembly for coiled tubing
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
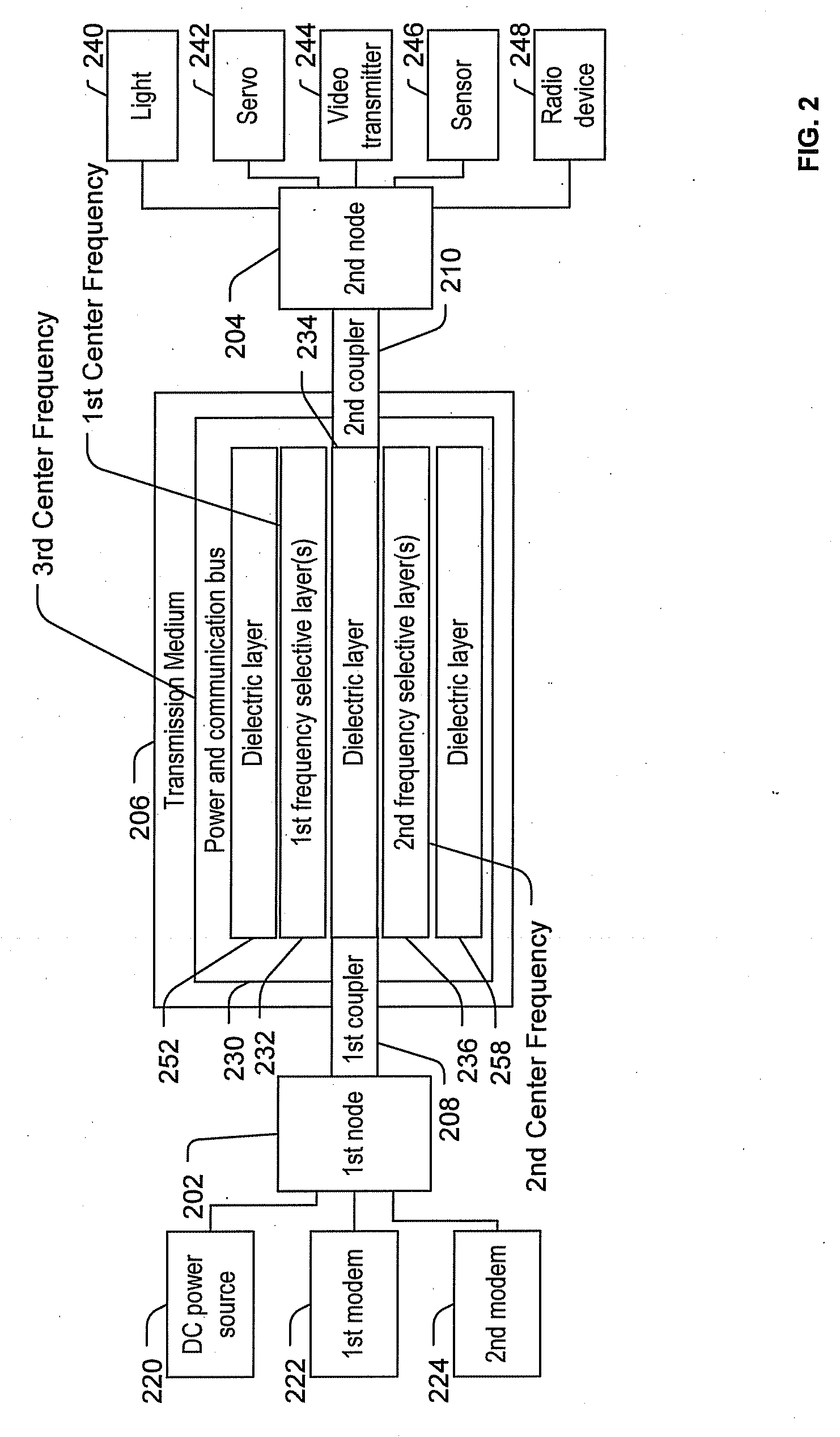
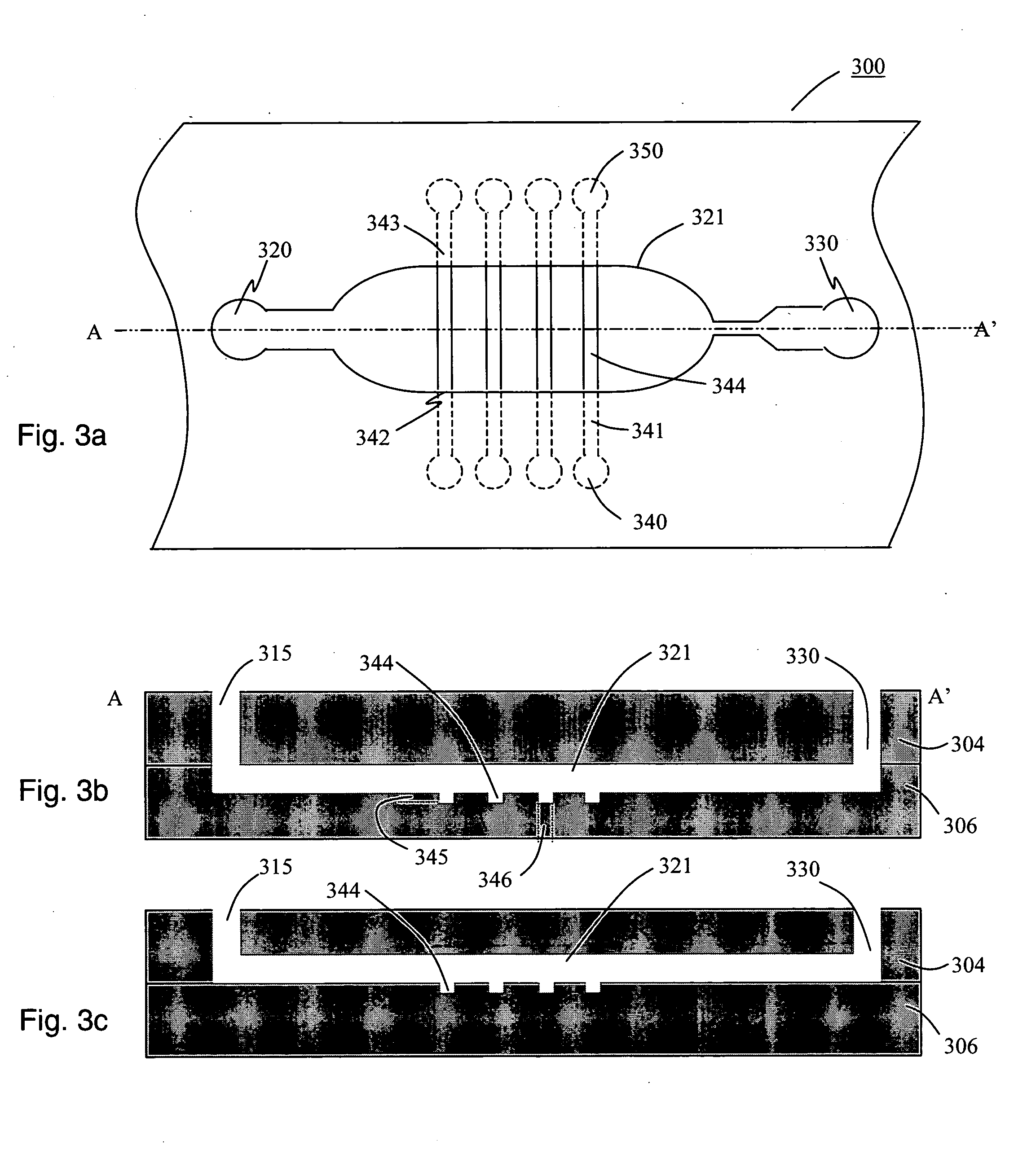
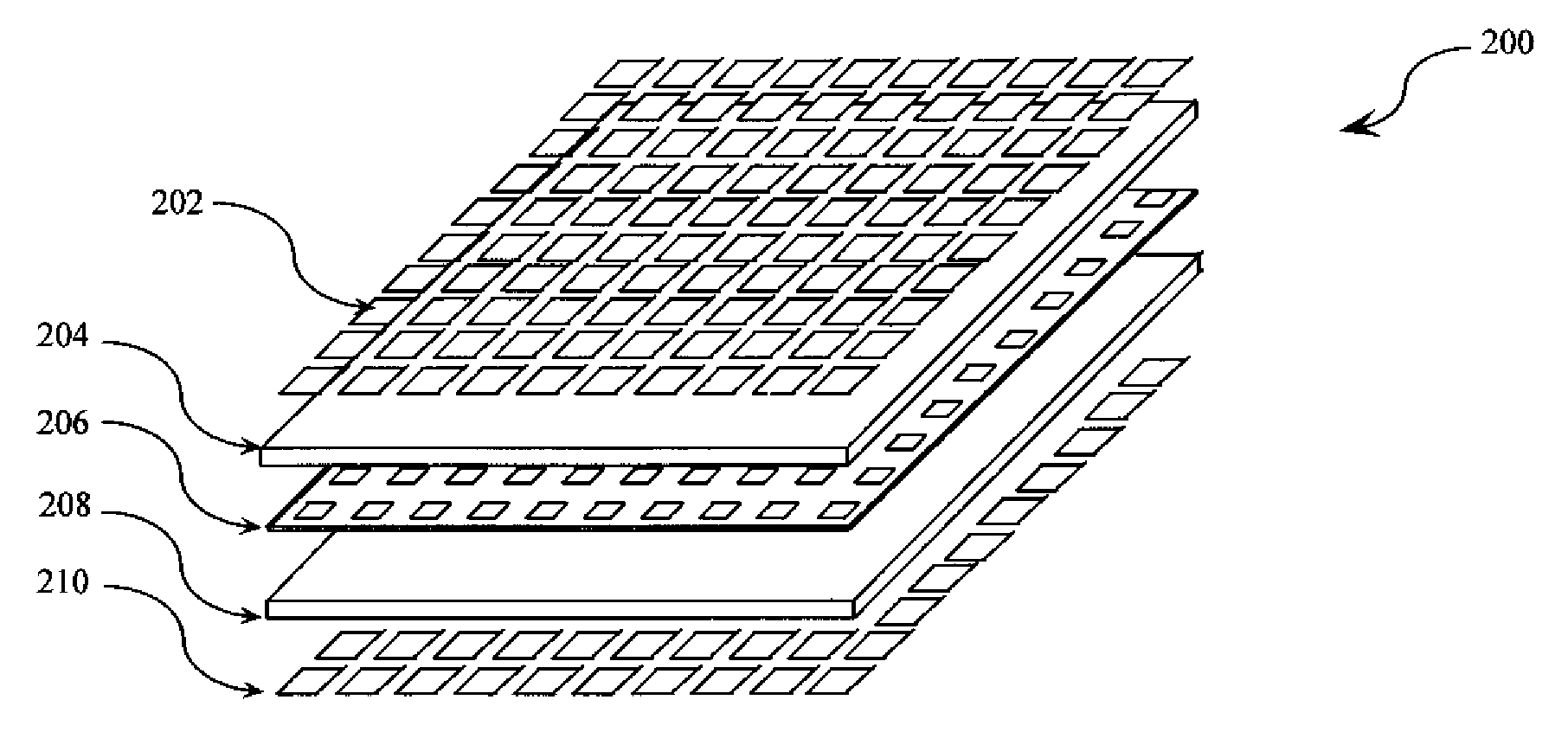
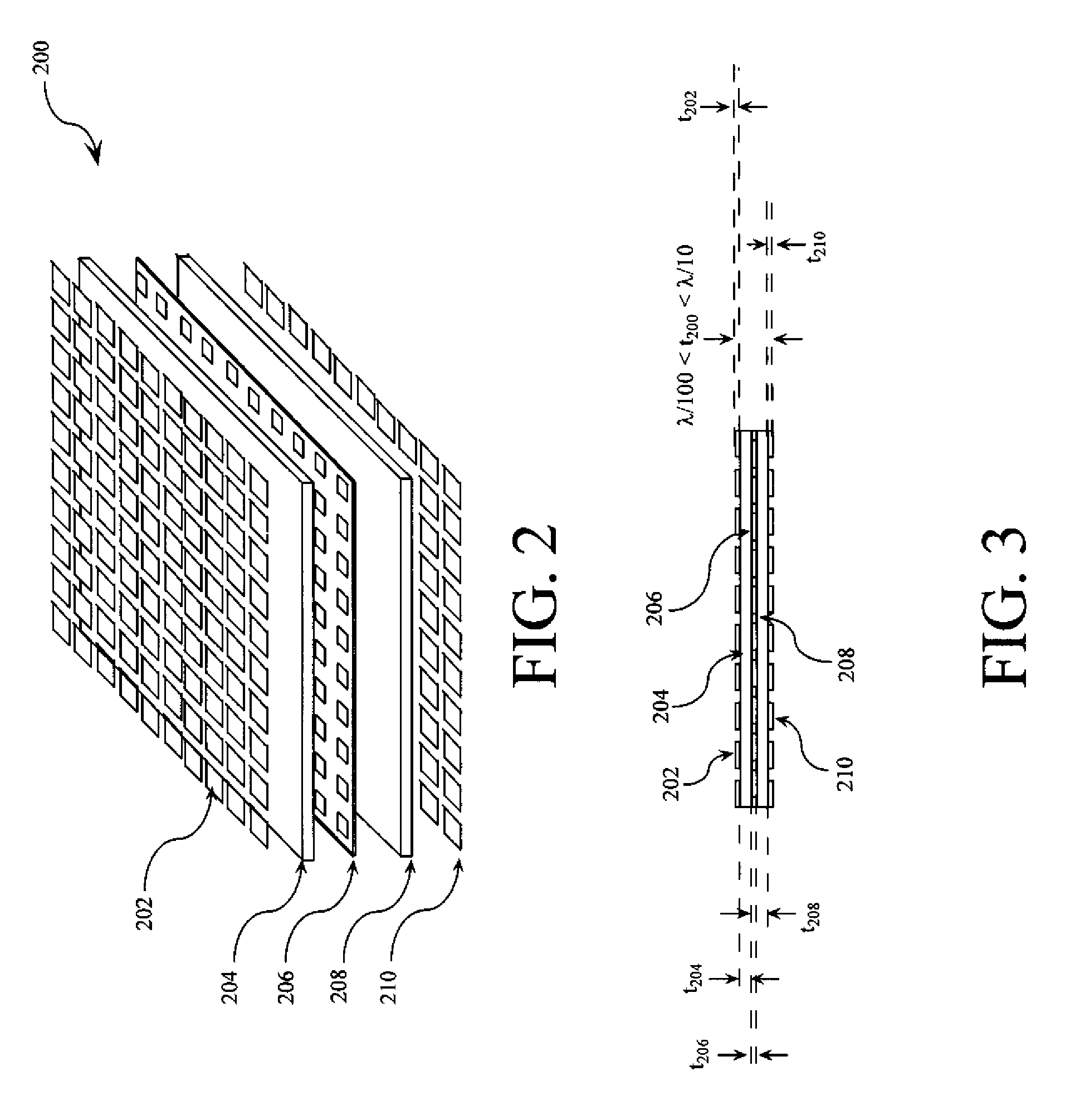
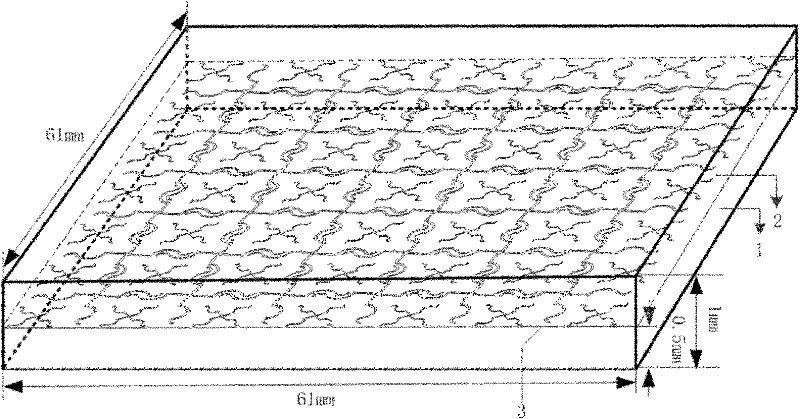
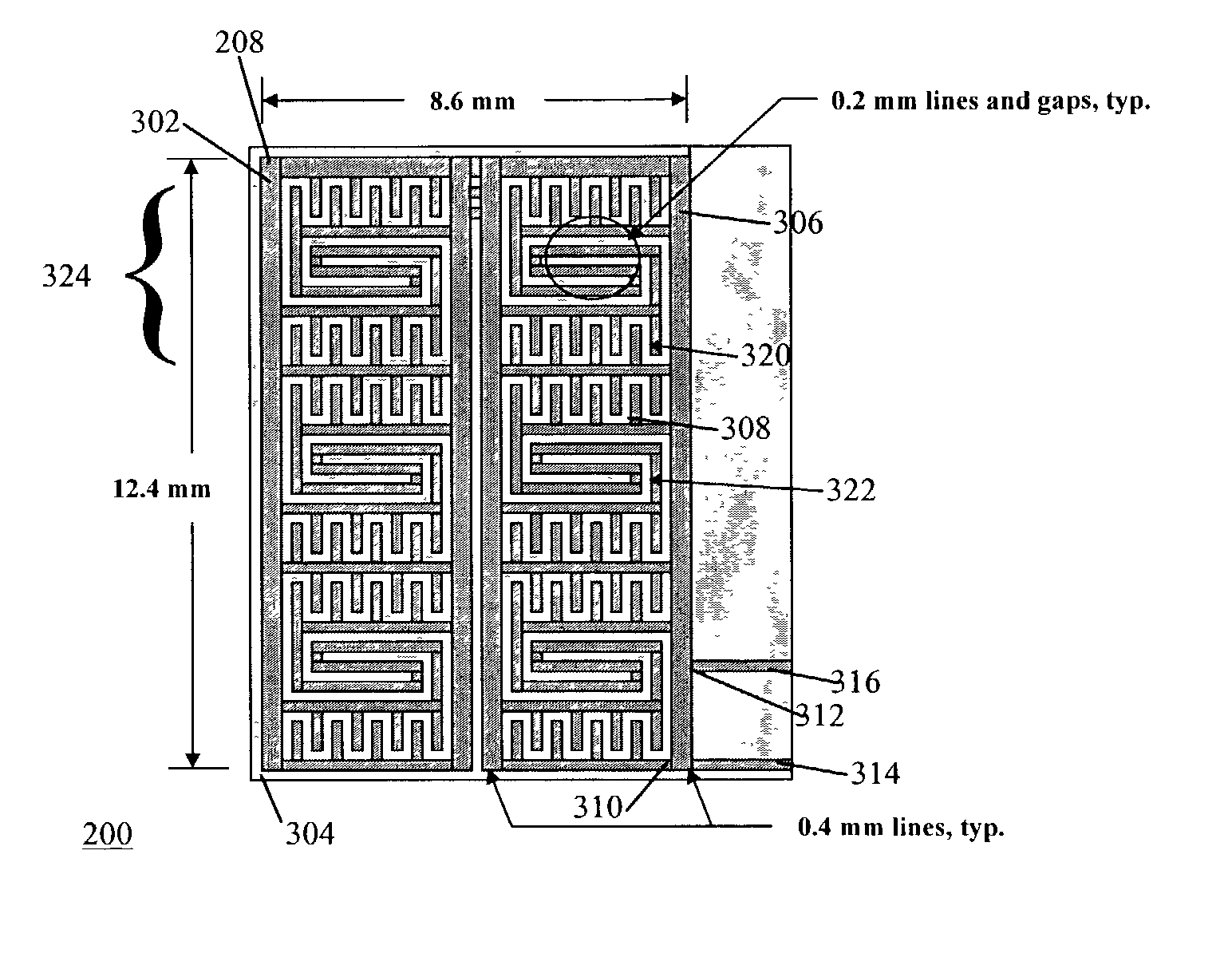
Low-profile frequency selective surface based device and methods of making the same
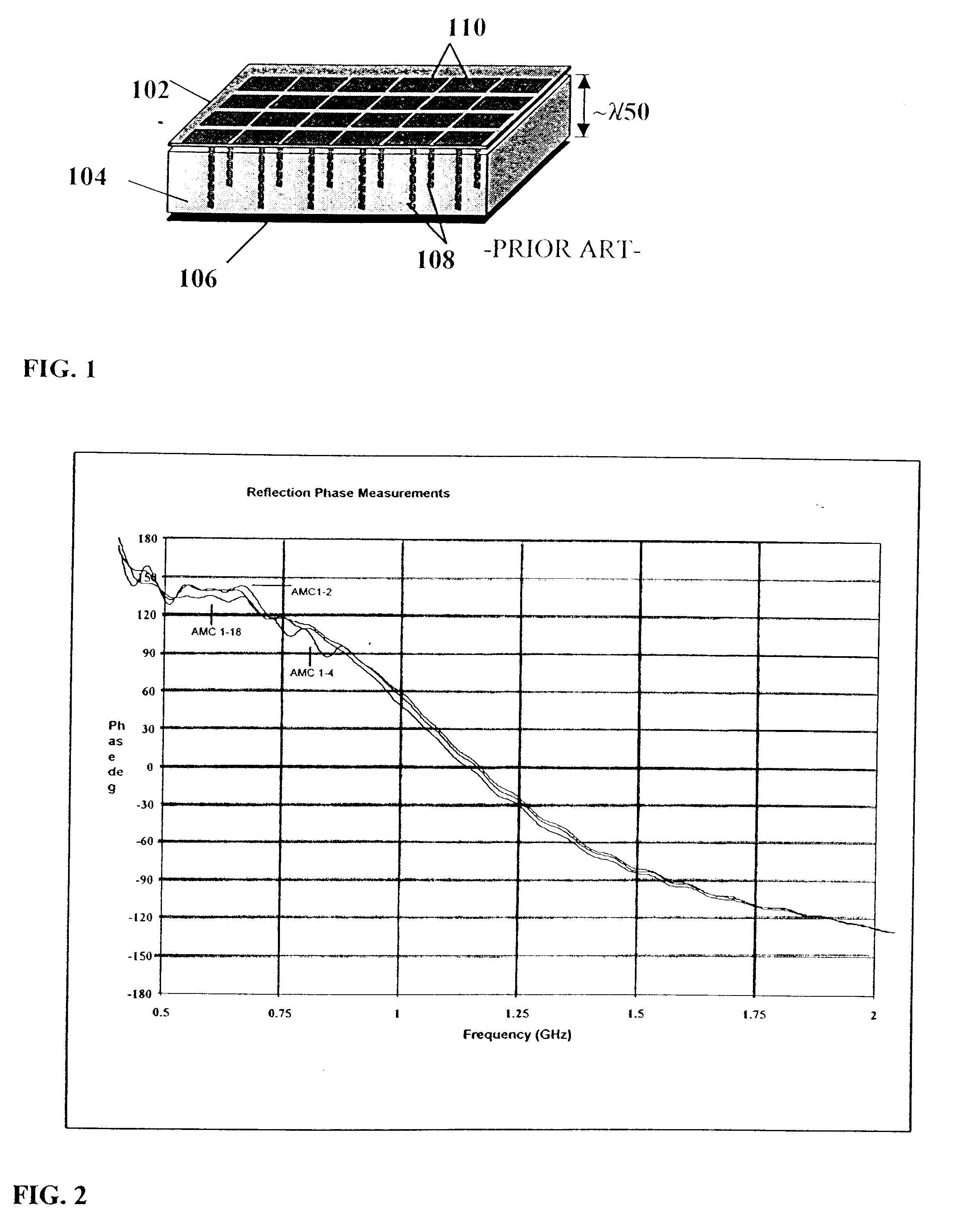
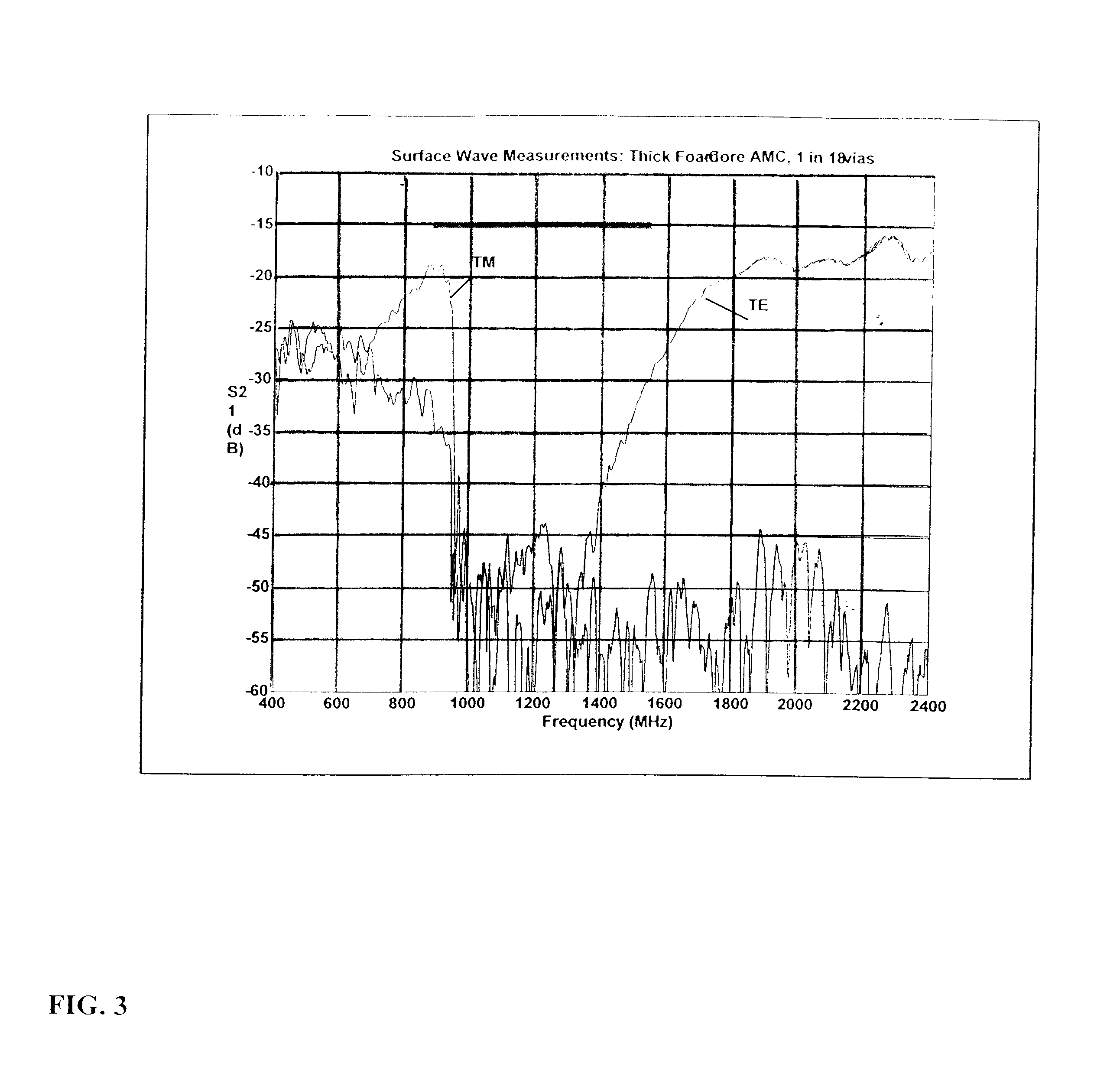
InactiveUS20090273527A1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesPolarised antenna unit combinationsSelective surfaceQ factor
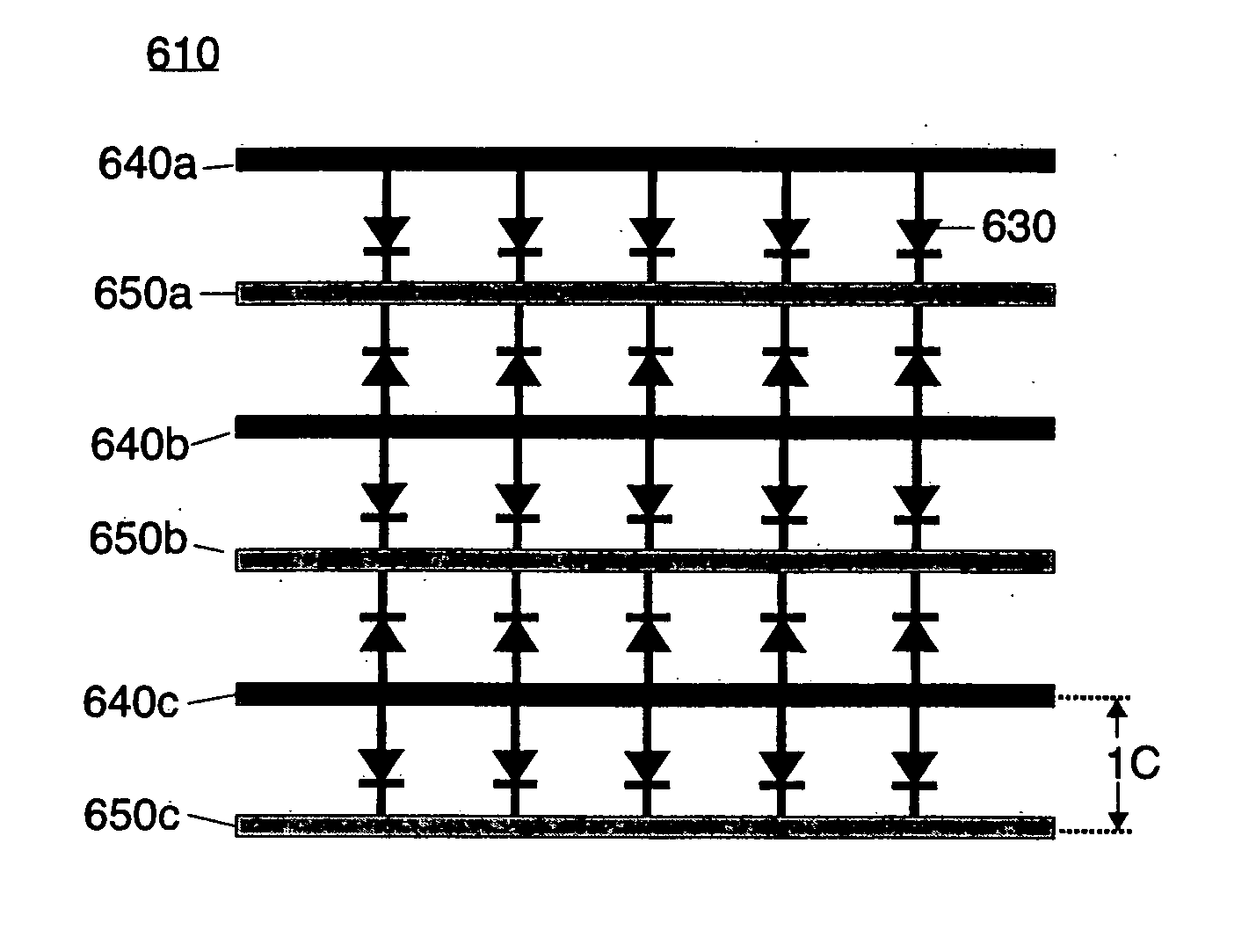
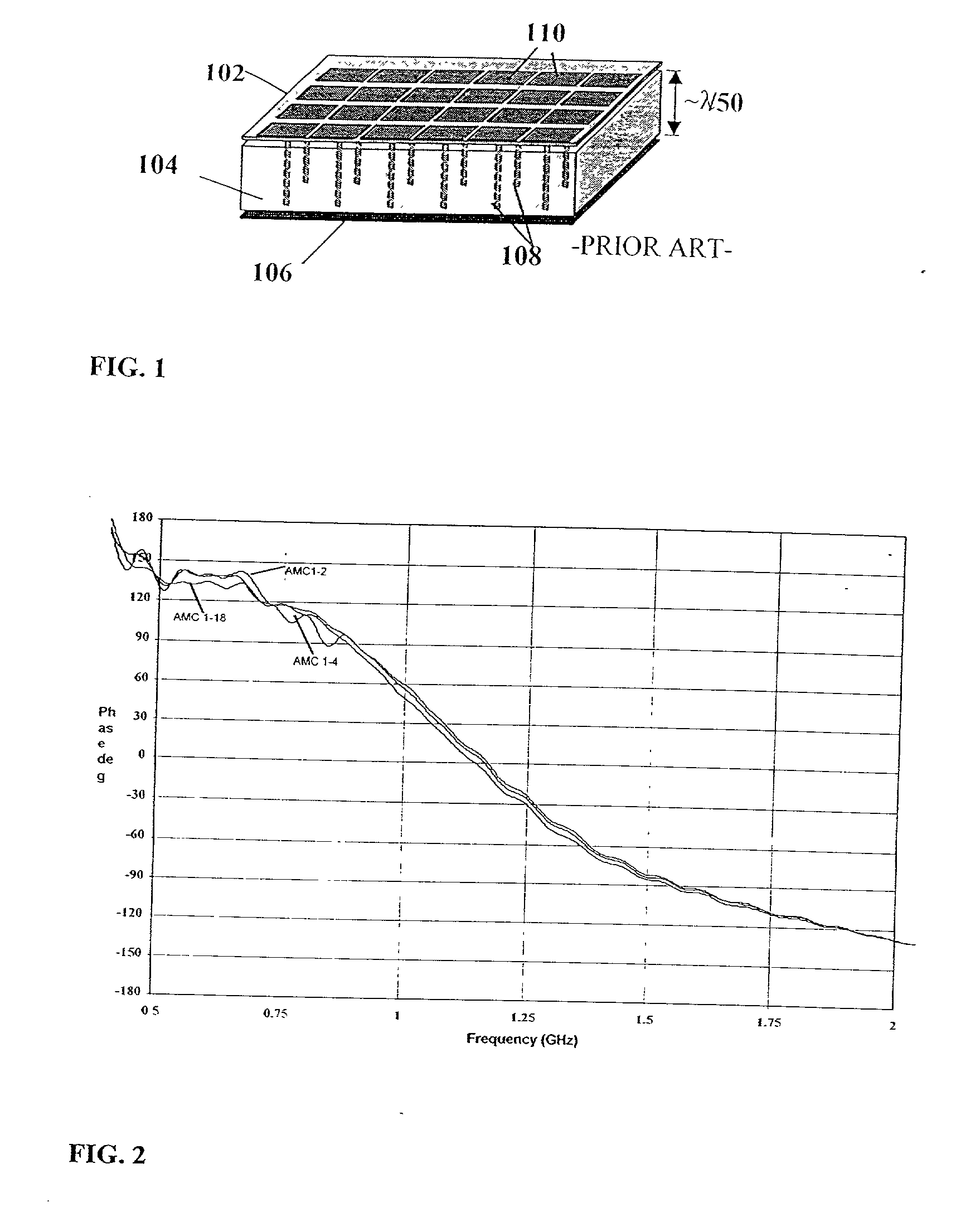
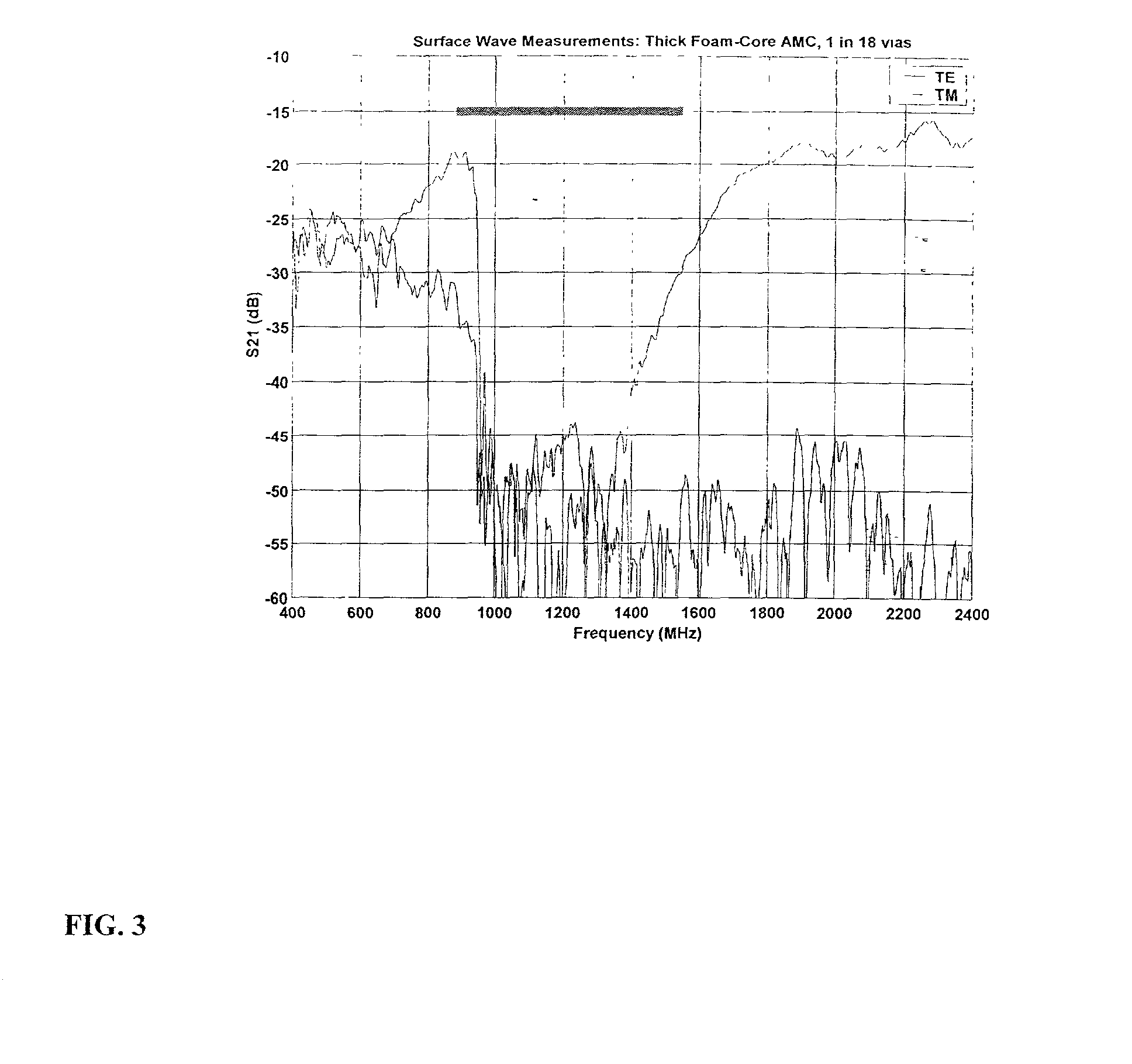
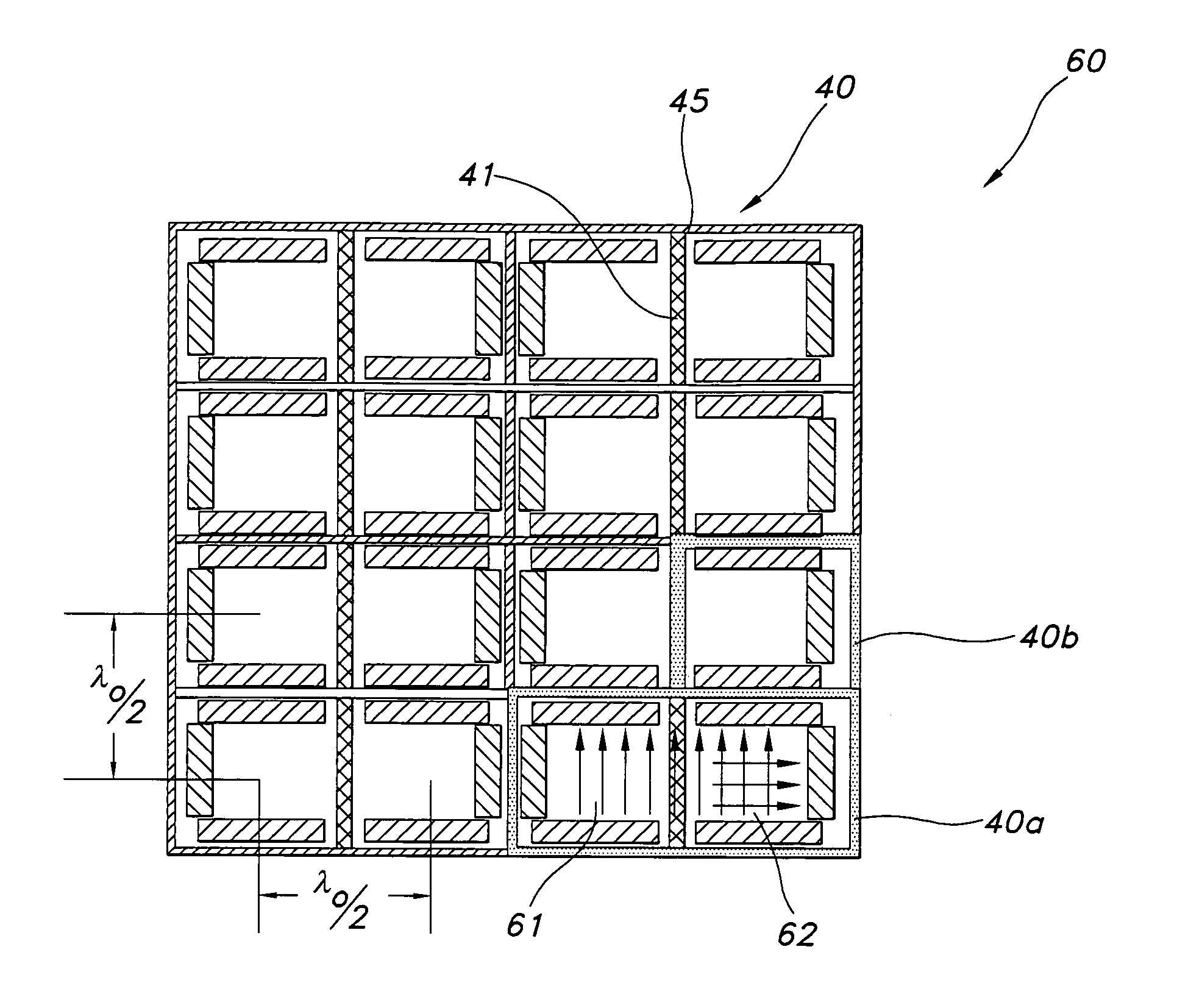
A frequency selective surface-based (FSS-based) device (200) for processing electromagnetic waves providing at least a third-order response. The FSS-based device includes a first FSS (202), a second FSS (210), and a high quality factor (Q) FSS (206) interposed between the first and second FSSs. A first dielectric layer (204) and a second dielectric layer (208) separate the respective FSS layers. The first and second FSSs have first and second primary resonant frequencies, respectively. The high Q FSS has a lower primary resonant frequency relative to the first and second primary resonant frequencies. The overall electrical thickness of the PSS device can be <λ / 10. The high Q FSS has a loaded quality factor of at least thirty at the lower primary resonant frequency.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Radar and infrared compatible stealthy material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102179968AAchieve broadband absorbing performanceReduce IR emissivityLaminationLamination apparatusGlass fiberScreen printing
The invention discloses a radar and infrared compatible stealthy material and a preparation method thereof. The compatible stealthy material is mainly formed by compounding a radar wave absorbing structural layer and an infrared stealthy functional layer, wherein the radar wave absorbing structural layer is made of a glass fiber reinforced glass steel composite material; and the infrared stealthy functional layer is a capacitive frequency selective surface. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing the capacitive frequency selective surface by a printed circuit board (PCB) process; preparing a layer of resistance sheet on glass fiber plain cloth by using conductive carbon slurry through a screen printing process; preparing the glass fiber reinforced glass steel composite material by using epoxy resin as a base material and the glass fiber plain cloth as a reinforcing material through a resin forming process; and curing to make the capacitive frequency selective surface compounded and superposed so as to obtain the radar and infrared compatible stealthy material. The compatible stealthy material has a simple structure and low cost, is convenient to prepare, and has the duplex characteristics of high reflection of an infrared wave band and high permeation of a radar wave band.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Low-loss, dual-band electromagnetic band gap electronically scanned antenna utilizing frequency selective surfaces
A dual-band electromagnetic band gap (EBG) electronically scanned antenna utilizing frequency selective surfaces (FSS) uses FSS waveguide phase shifters. Each FSS waveguide phase shifter has a low-frequency phase shifter with low-frequency EBG devices on vertical waveguide walls, horizontal waveguide broadwalls that are substantially twice the width of the vertical waveguide walls and an FSS located at the center of the horizontal waveguide broadwalls. Two high-frequency phase shifters are formed within the low-frequency phase shifter. Each high-frequency phase shifter comprises a vertical waveguide wall, the FSS, half of the horizontal waveguide broadwalls, and high-frequency EBG devices located on each half of the horizontal waveguide broadwalls, The FSS is transparent at a low frequency and opaque at a high frequency.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
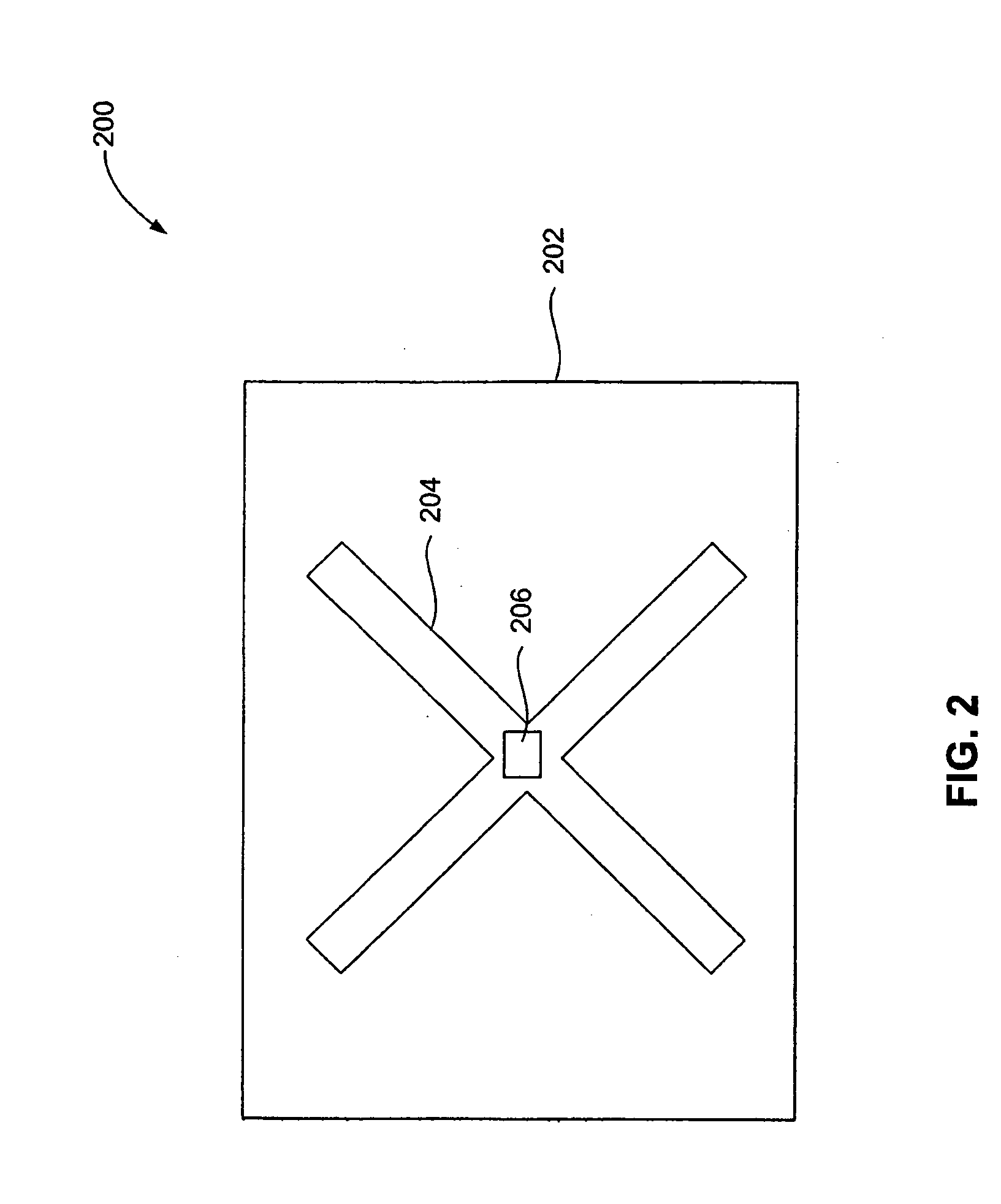
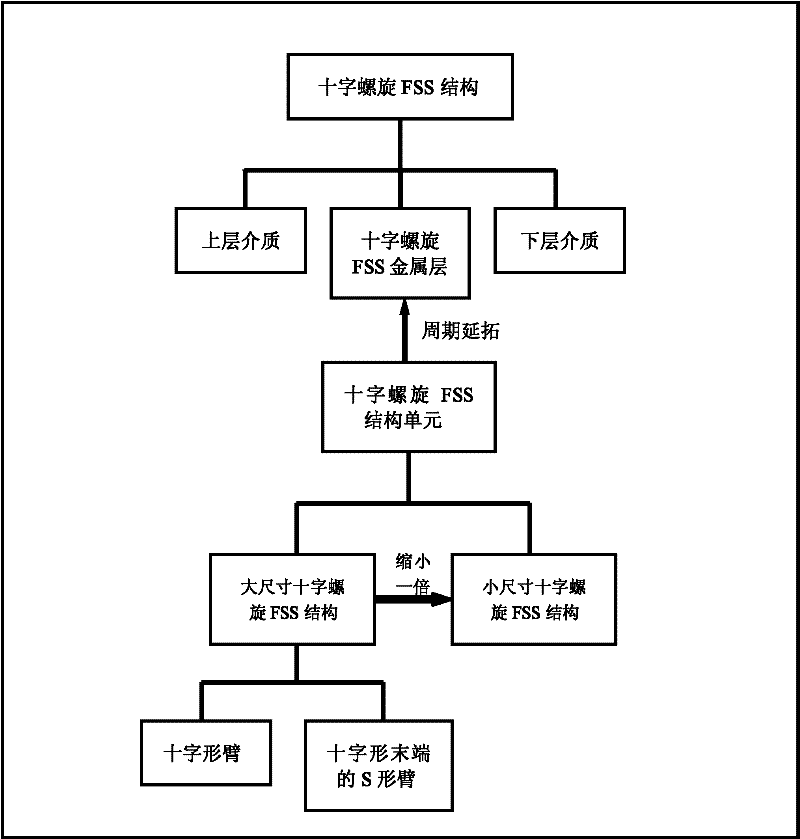
Cross spiral frequency selective surface (FSS) structure with dual band characteristics and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a cross spiral frequency selective surface (FSS) structure with dual band characteristics and a construction method thereof. The structure consists of an upper dielectric layer, a lower dielectric layer and an intermediate cross spiral FSS structure layer. The construction method comprises the following six steps of: 1, establishing structure units of the cross spiral FSS structure layer with the thickness of zero by using computer simulation technology (CST) software; 2, periodically extending the structure units towards directions X and Y to obtain the integrated 6*6 cross spiral FSS structure layer; 3, establishing the dielectric layers of the cross spiral FSS structure, and embedding the cross spiral FSS structure layer into a dielectric substrate by using the CST software; 4, capturing the cross spiral FSS structure unit from the CST software for incident wave transmittance analysis, regulating parameters of the structure unit, changing the resonance frequency of a stop band, and replacing an original structure by using the regulated structure unit; 5, setting the parameters such as boundaries and the like of the constructed cross spiral FSS structure, and testing the bandwidth stability and frequency selectivity of the structure; and 6, machining and manufacturing the cross spiral FSS structure by adopting a double-sided copper-clad plate according to an optimal size determined by the step 4.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
DC inductive shorted patch antenna
InactiveUS20030137457A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectricityGround plane
A direct current (DC) inductive shorted patch antenna includes a direct current inductive (DCL) frequency selective surface (FSS) forming the radiating element, a ground plane, a feed, and a radio frequency (RF) short to the ground plane positioned between the feed and the radiating element.
Owner:OAE TECH INC
Method for forming borderless gate structures and apparatus formed thereby
InactiveUS6207514B1Low powerAdd dimensionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
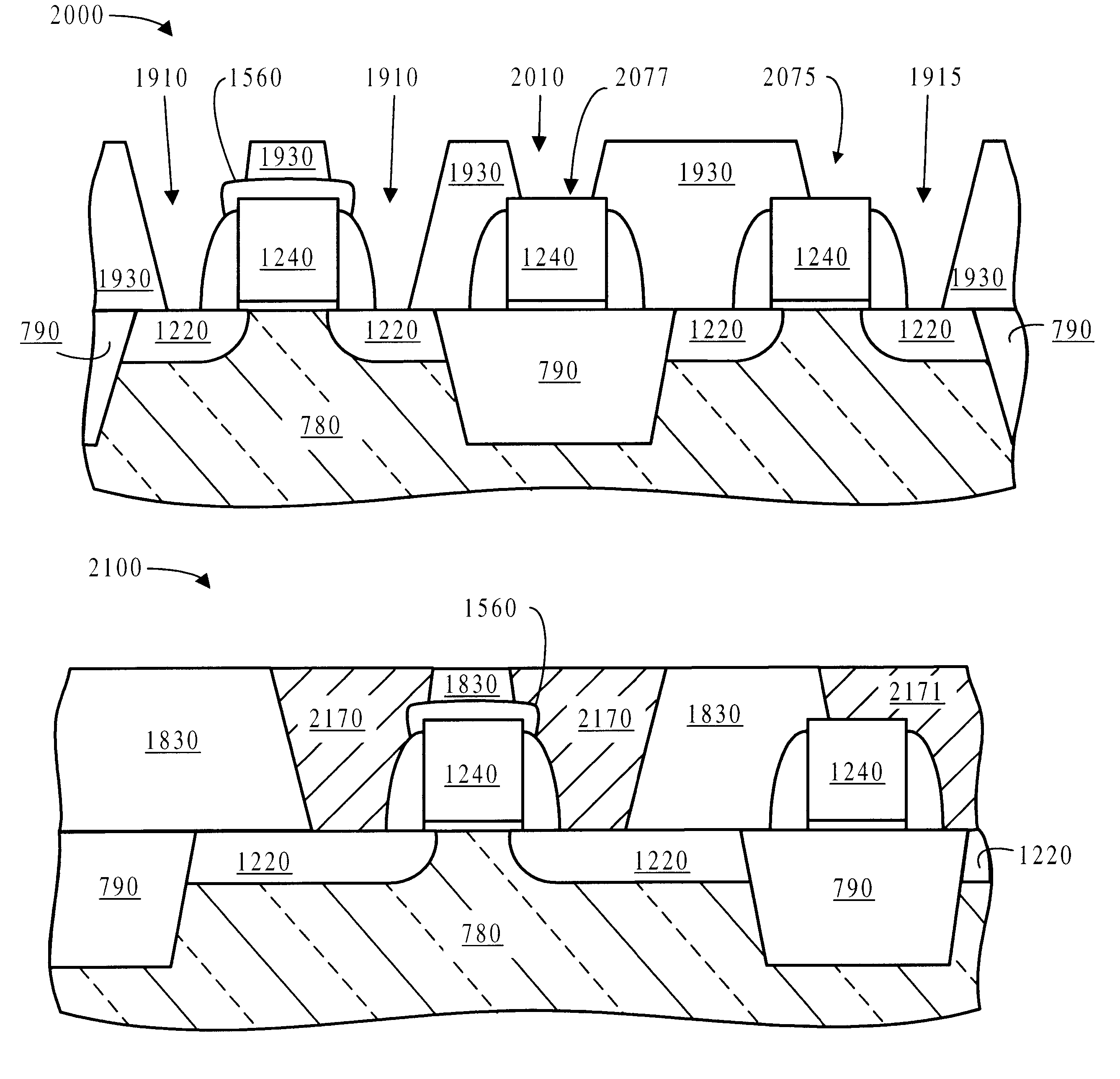
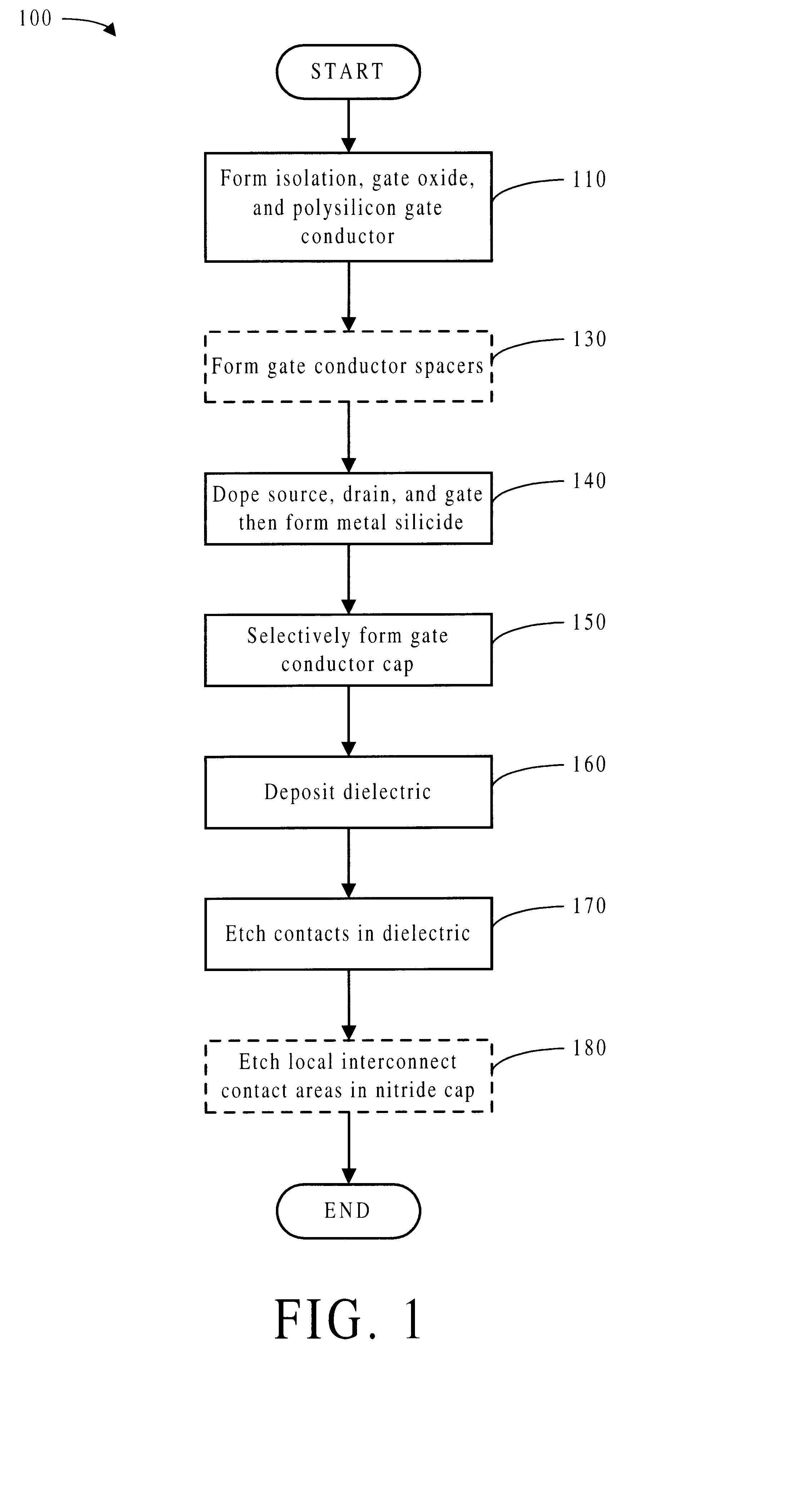
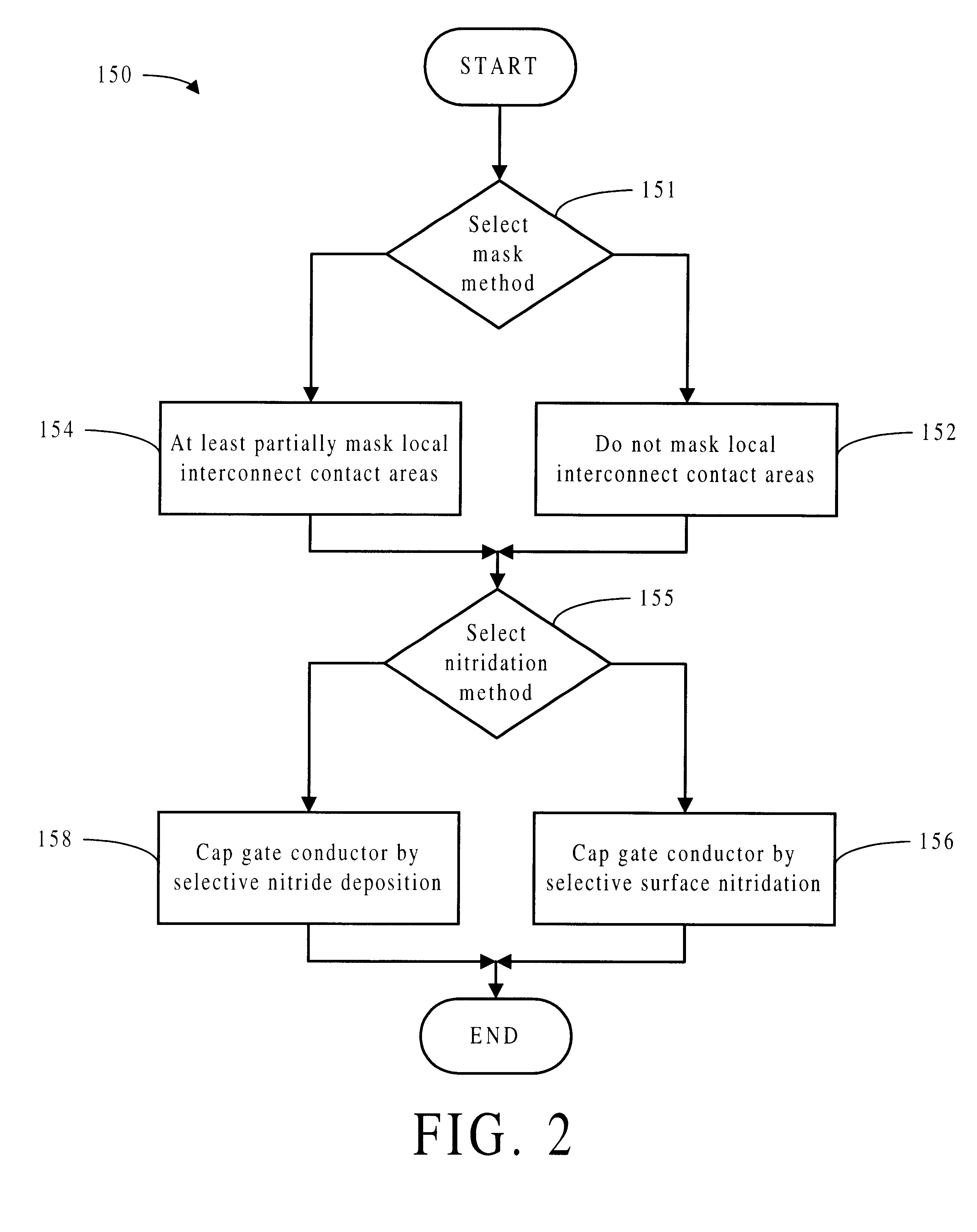
A method for forming a gate conductor cap in a transistor comprises the steps of: a) forming a polysilicon gate conductor; b) doping the polysilicon gate; c) doping diffusion areas; and d) capping the gate conductor by a nitridation method chosen from among selective nitride deposition and selective surface nitridation. The resulting transistor may comprise a capped gate conductor and borderless diffusion contacts, wherein the capping occurred by a nitridation method chosen from among selective nitride deposition and selective surface nitridation and wherein a portion of the gate conductor is masked during the nitridation method to leave open a contact area for a local interconnect or a gate contact.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for fabricating antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics
InactiveUS20070159395A1Promote near field coupling of electromagnetic energyGreat fabricationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsCombined useConductive materials
The radiation properties and wave guiding properties of frequency selective surfaces are used in conjunction with closely spaced antenna elements to fabricate antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics. The direction, magnitude, and polarization of radiation patterns for such antenna structures can be adjusted by varying the texture or patterning of layers of conducting material forming the frequency selective surfaces. The invention enables the fabrication of low profile antenna structures that can easily be conformed or integrated into complex surfaces without sacrificing antenna performance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for fabricating antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics
InactiveUS7429961B2Promote near field coupling of electromagnetic energyGreat fabricationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsConductive materialsAntenna element
The radiation properties and wave guiding properties of frequency selective surfaces are used in conjunction with closely spaced antenna elements to fabricate antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics. The direction, magnitude, and polarization of radiation patterns for such antenna structures can be adjusted by varying the texture or patterning of layers of conducting material forming the frequency selective surfaces. The invention enables the fabrication of low profile antenna structures that can easily be conformed or integrated into complex surfaces without sacrificing antenna performance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics
InactiveUS20070159396A1Promote near field coupling of electromagnetic energyGreat fabricationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRadiation patternSelective surface
The radiation properties and wave guiding properties of frequency selective surfaces are used in conjunction with closely spaced antenna elements to fabricate antenna structures having adjustable radiation characteristics. The direction, magnitude, and polarization of radiation patterns for such antenna structures can be adjusted by varying the texture or patterning of layers of conducting material forming the frequency selective surfaces. The invention enables the fabrication of low profile antenna structures that can easily be conformed or integrated into complex surfaces without sacrificing antenna performance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Dynamic frequency selective surfaces
An antenna system is disclosed. The antenna system includes at least one antenna element and an adaptable frequency-selective-surface responsive to operating characteristics of the at least one antenna element and / or surrounding environmental conditions
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com