Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3023 results about "Frequency selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frequency-dependent selection occurs when the fitness of a genotype depends on its frequency. It is possible for the fitness of a genotype to increase (positively frequency-dependent) or decrease (negatively frequency-dependent) as the genotype frequency in the population increases. Examples of frequency dependence can arise in systems of mimicry:
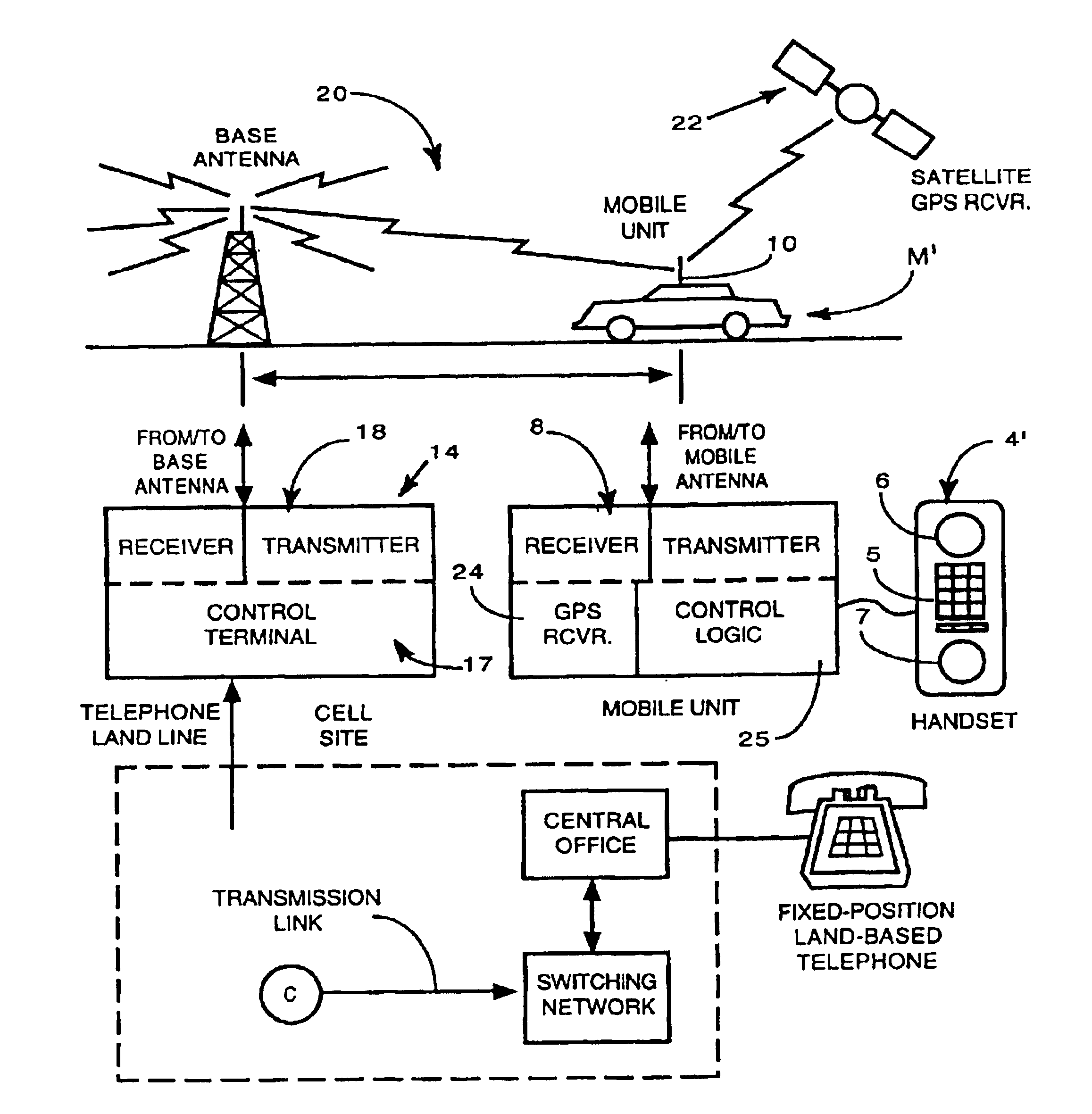
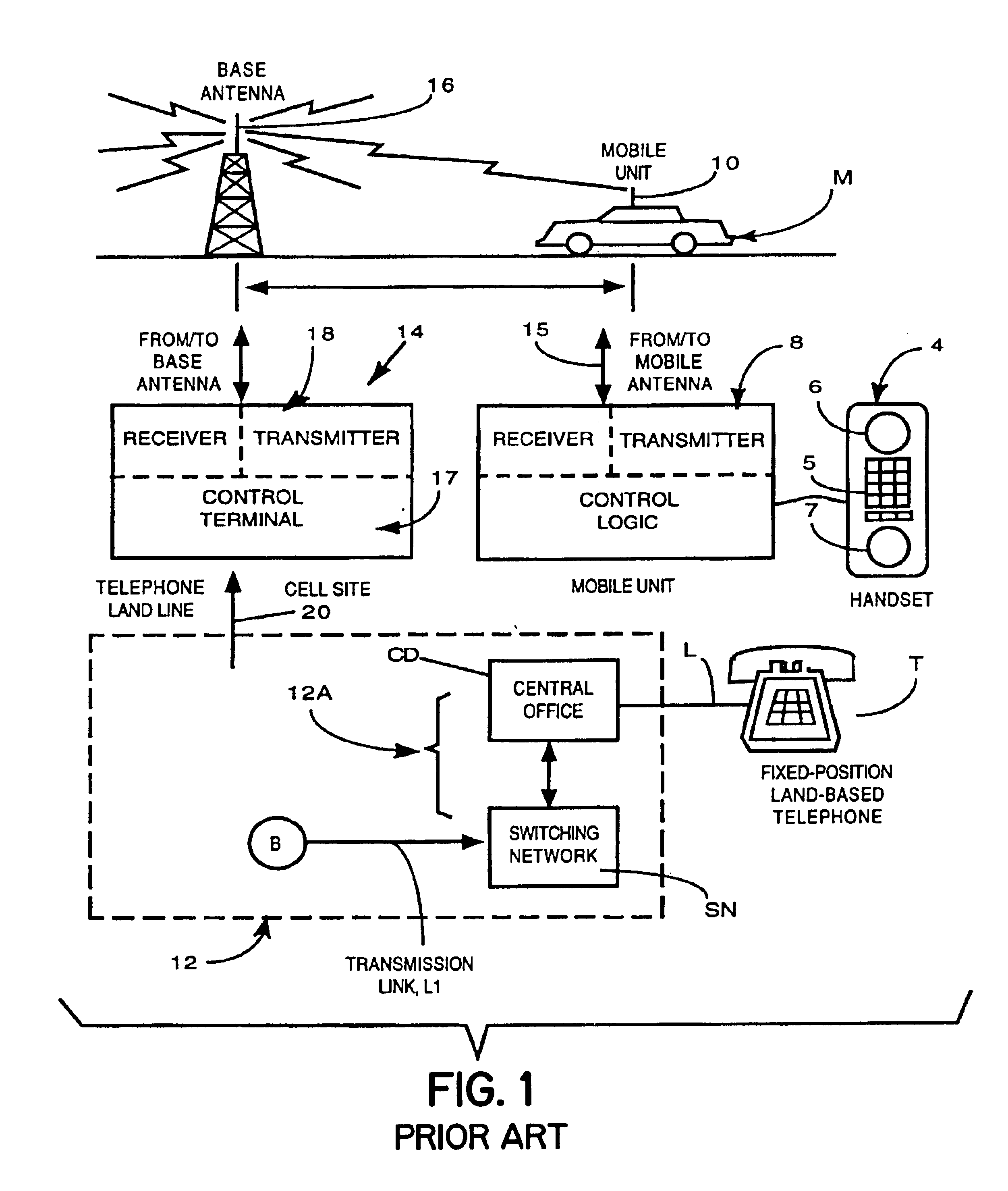
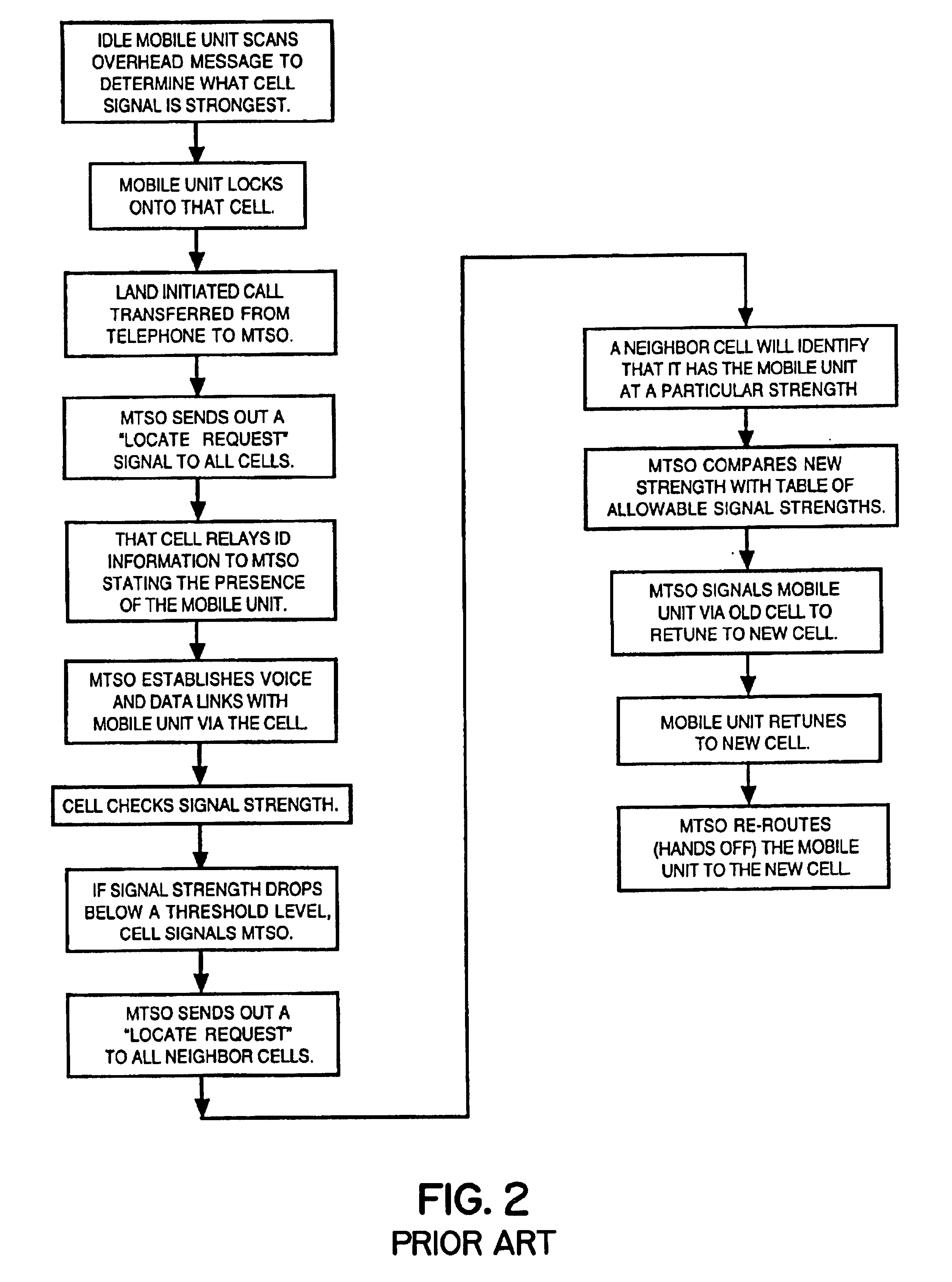
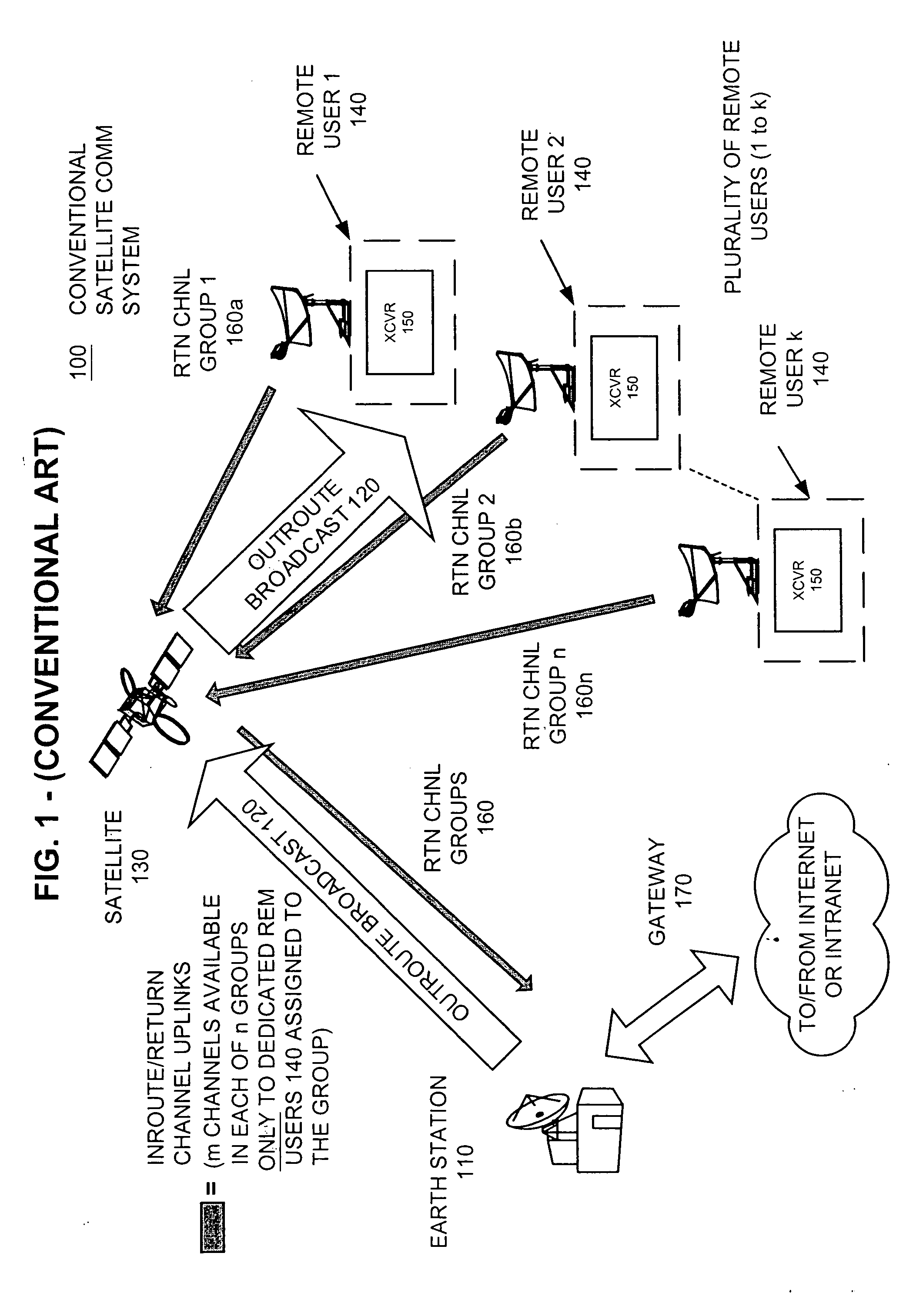
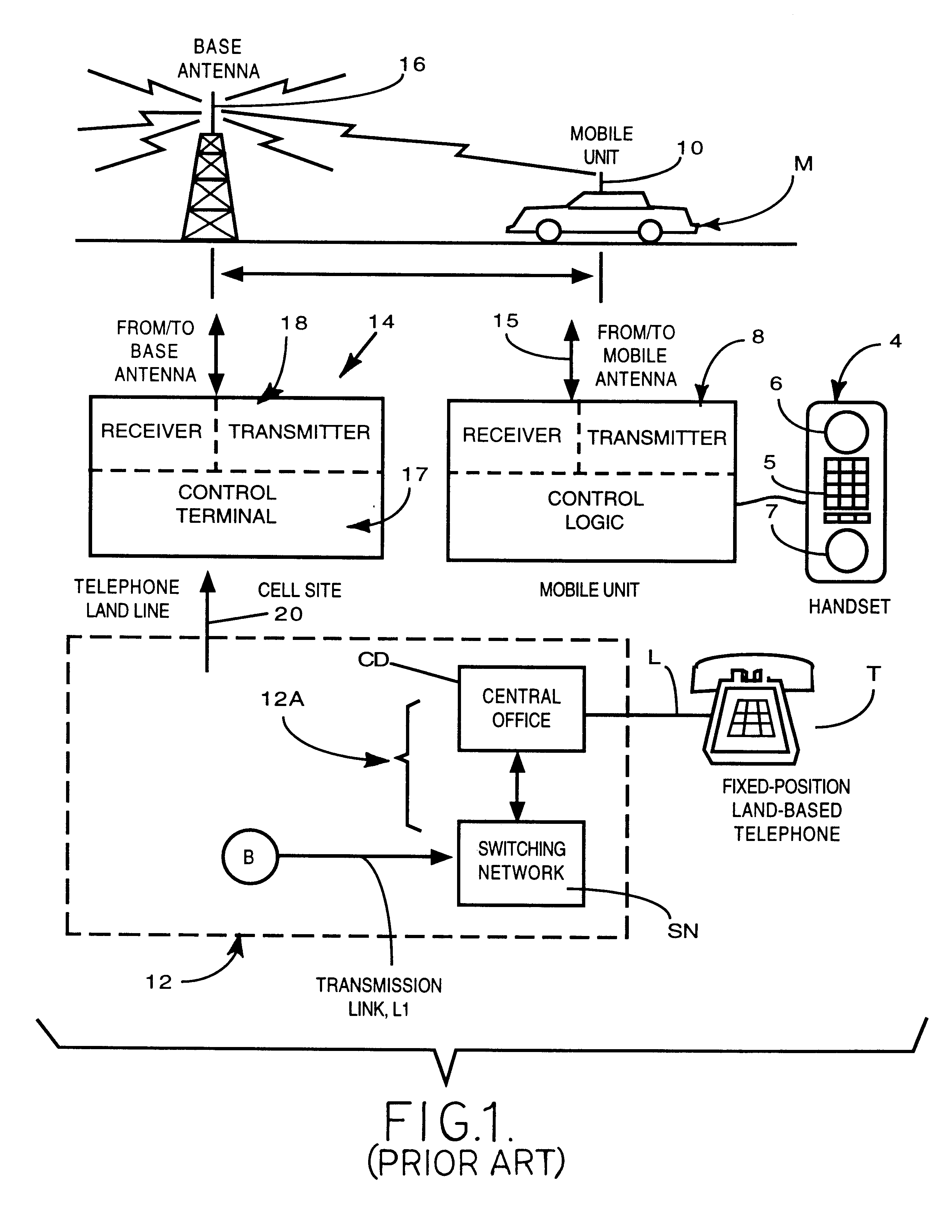
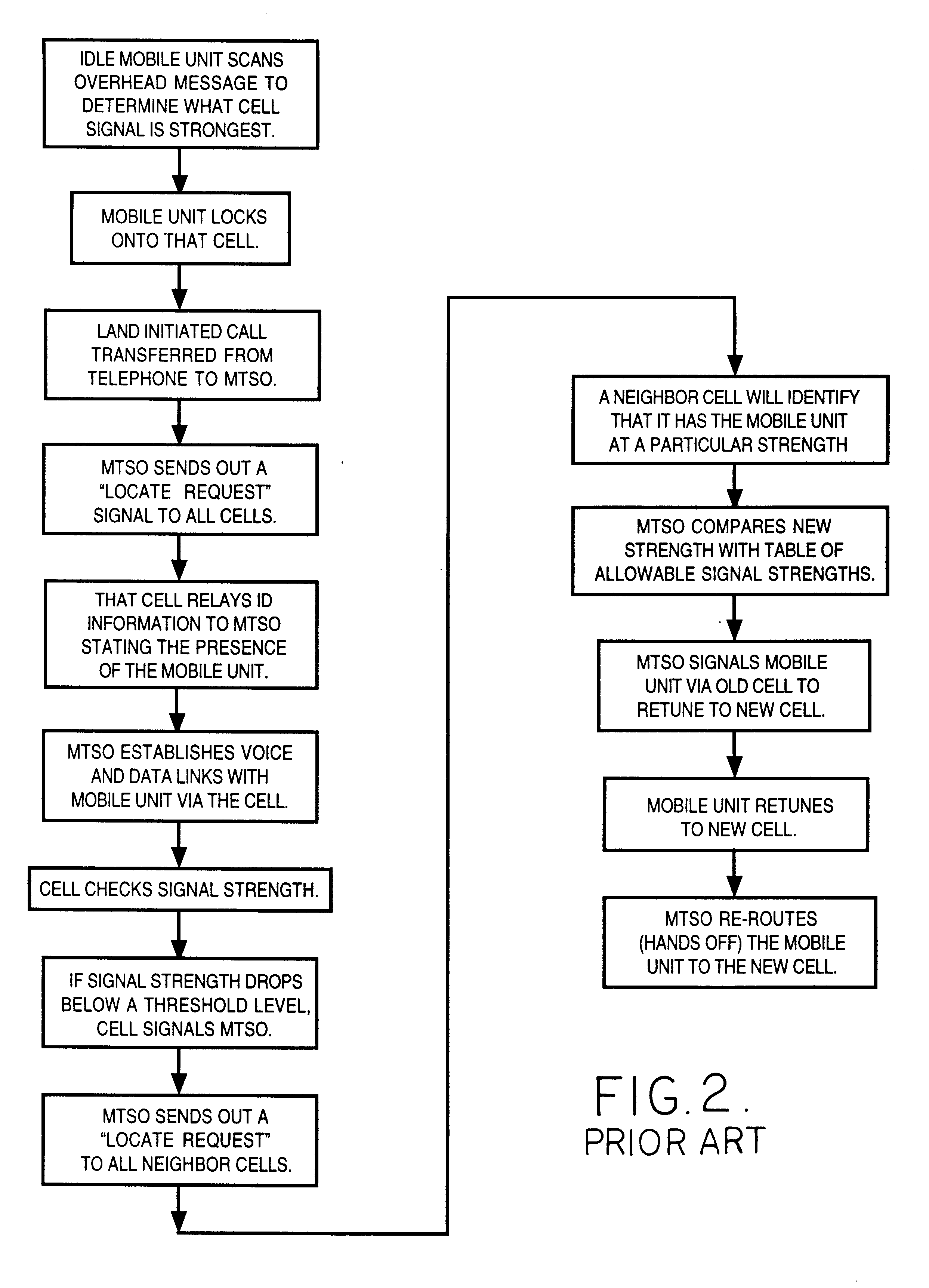
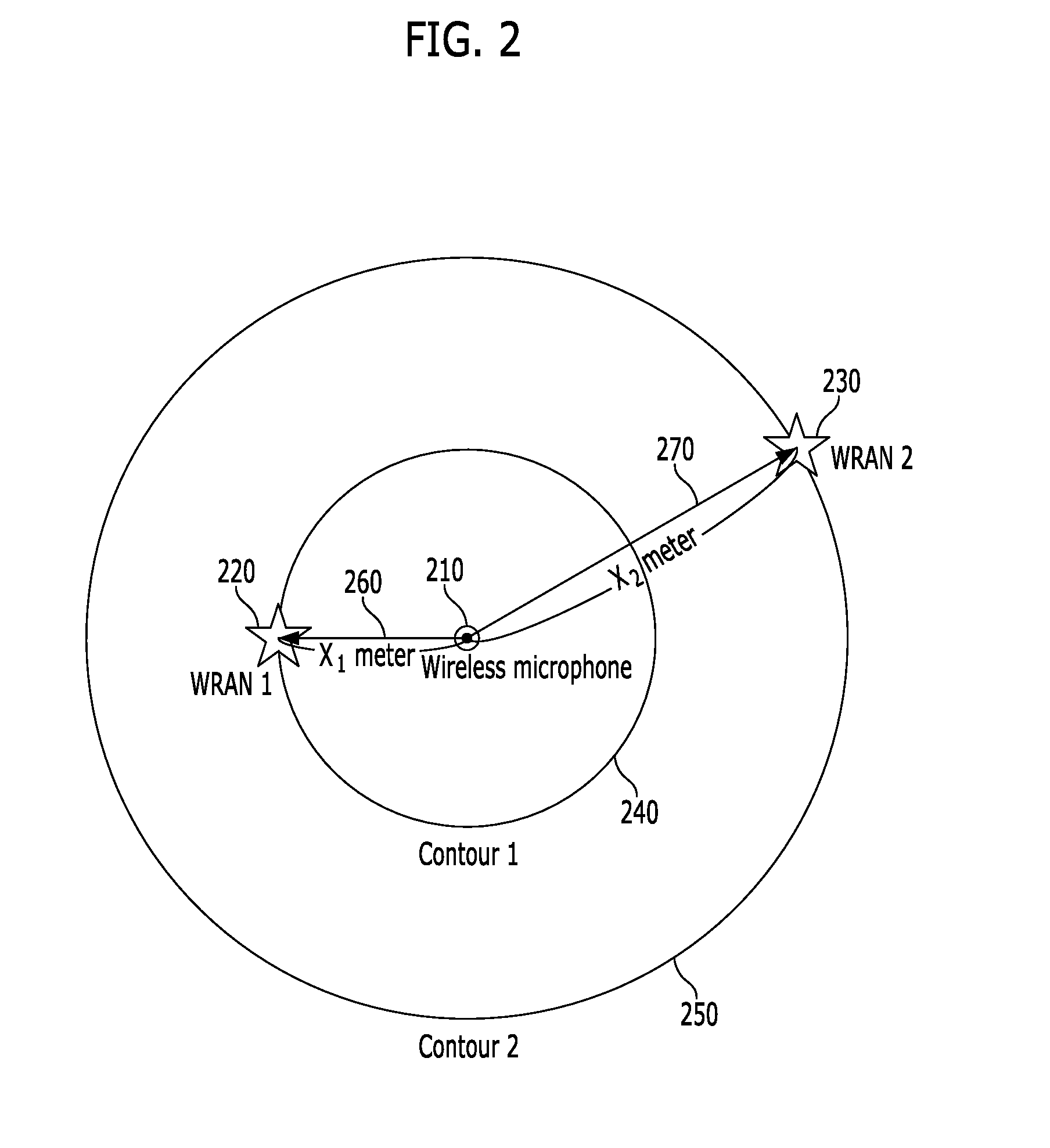
Cellular telephone system that uses position of a mobile unit to make call management decisions
InactiveUS6847822B1Efficient and accurate servicePrecise processingEmergency connection handlingTelephonic communicationCell siteGeolocation
A cellular telephone system has call management decisions made based on the exact geographic location of the mobile unit. These call management decisions include billing and taxing decisions, cell site selection, frequency selection and even cellular system selection. The decisions are continuously updated during a call whereby decisions can be made and changed regardless of where a call originated. Cell site location, and even cellular system selection, can be made in a specific manner to best serve the needs of the mobile user, the cellular system as well as the public. It is even possible for a cellular system to locate one or more of its cell sites in the geographic area served by another cellular system. In some cases, cellular systems might even share cell sites.
Owner:EMSAT ADVANCED GEO LOCATION TECH
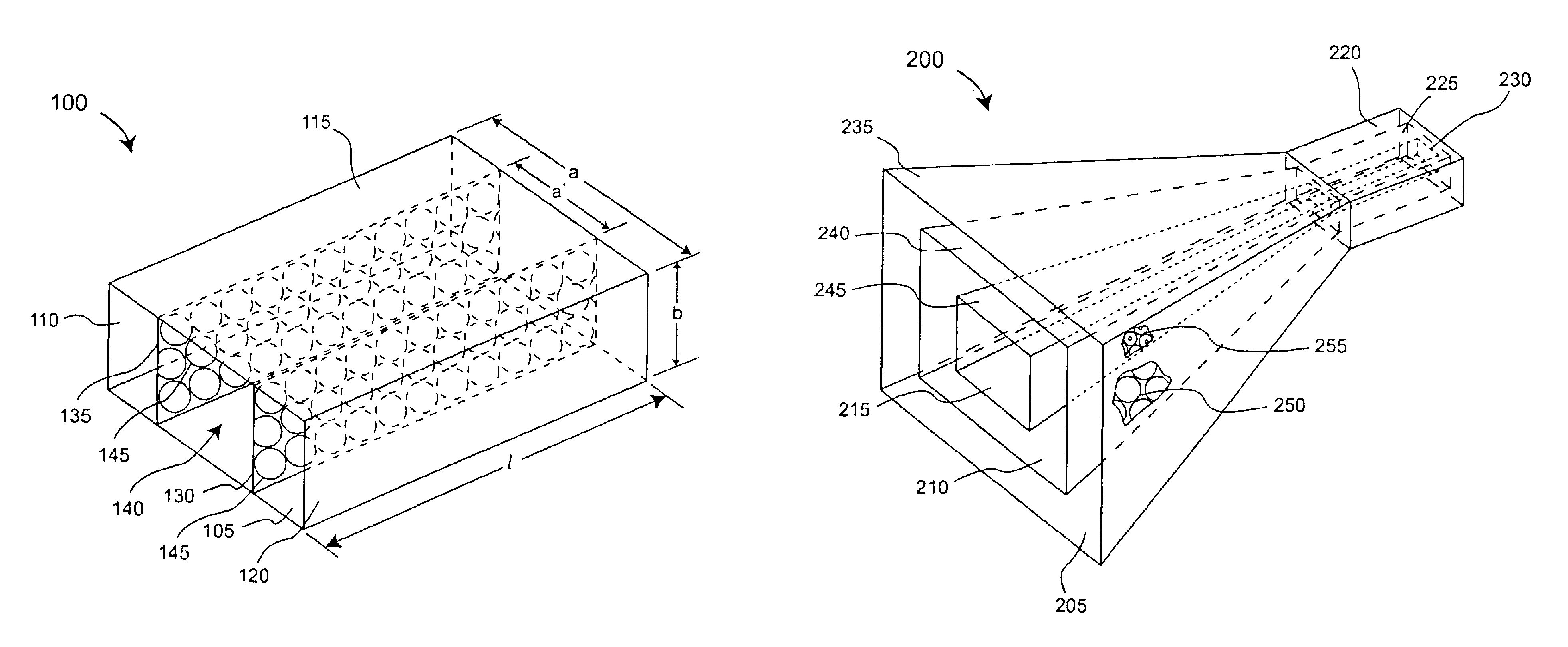
Multi-band horn antenna using frequency selective surfaces
InactiveUS6985118B2Grating lobe of the antenna is reducedImprove permeabilityWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandHorn antenna
A waveguide (100) including at least one outer surface (105, 110, 115, 120) defining a waveguide cavity (140) and at least one inner surface (130, 135) positioned within the waveguide cavity (140). The inner surface (130, 135) includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) having a plurality of FSS elements (145) coupled to at least one substrate. The substrate defines a first propagation medium such that an RF signal having a first wavelength in the first propagation medium can pass through the FSS (130, 135). The FSS (130, 135) is coupled to a second propagation medium such that in the second propagation medium the RF signal has a second wavelength which is at least twice as long as a physical distance between centers of adjacent FSS elements (145). The second wavelength can be different than the first wavelength.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
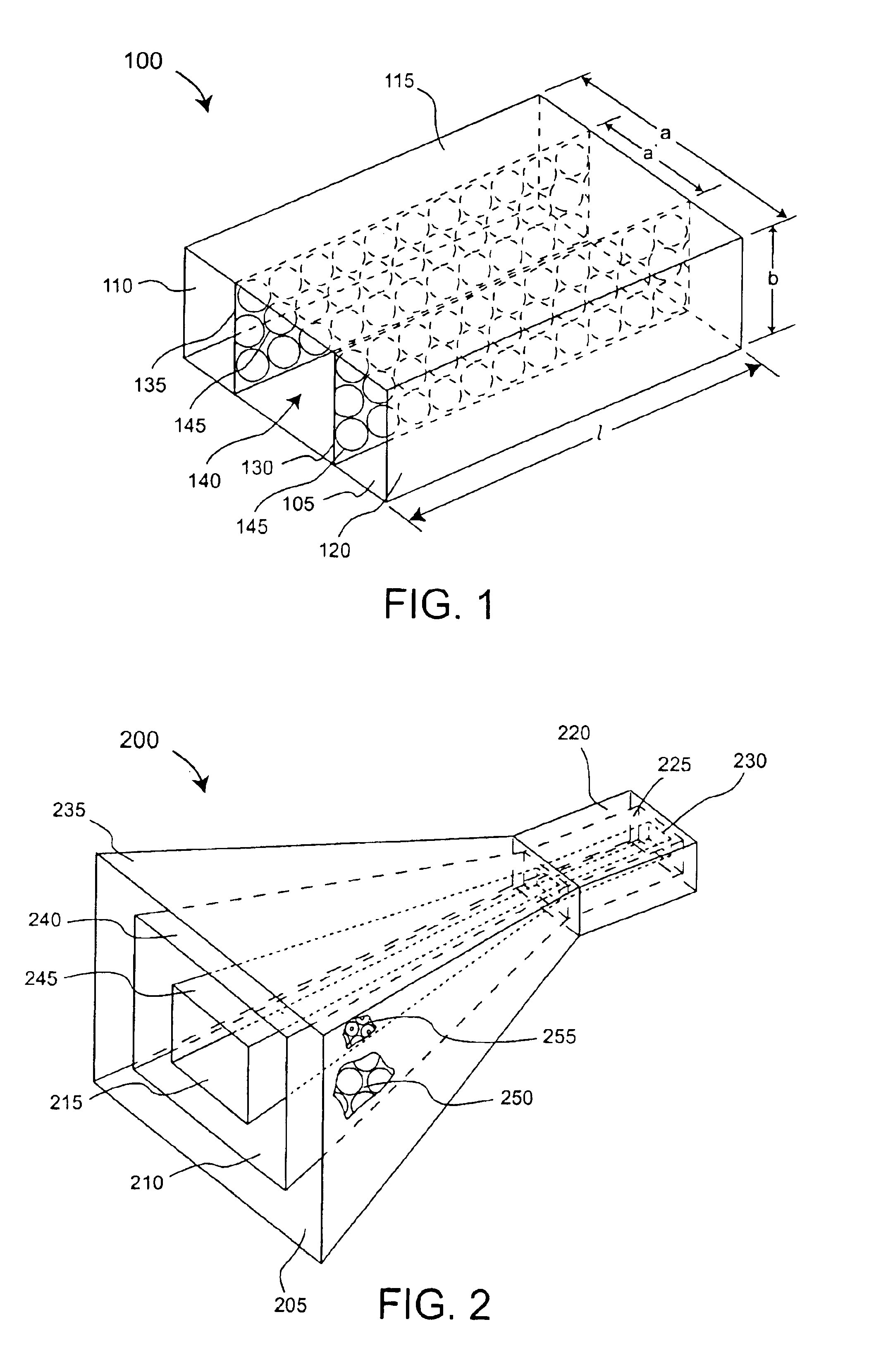
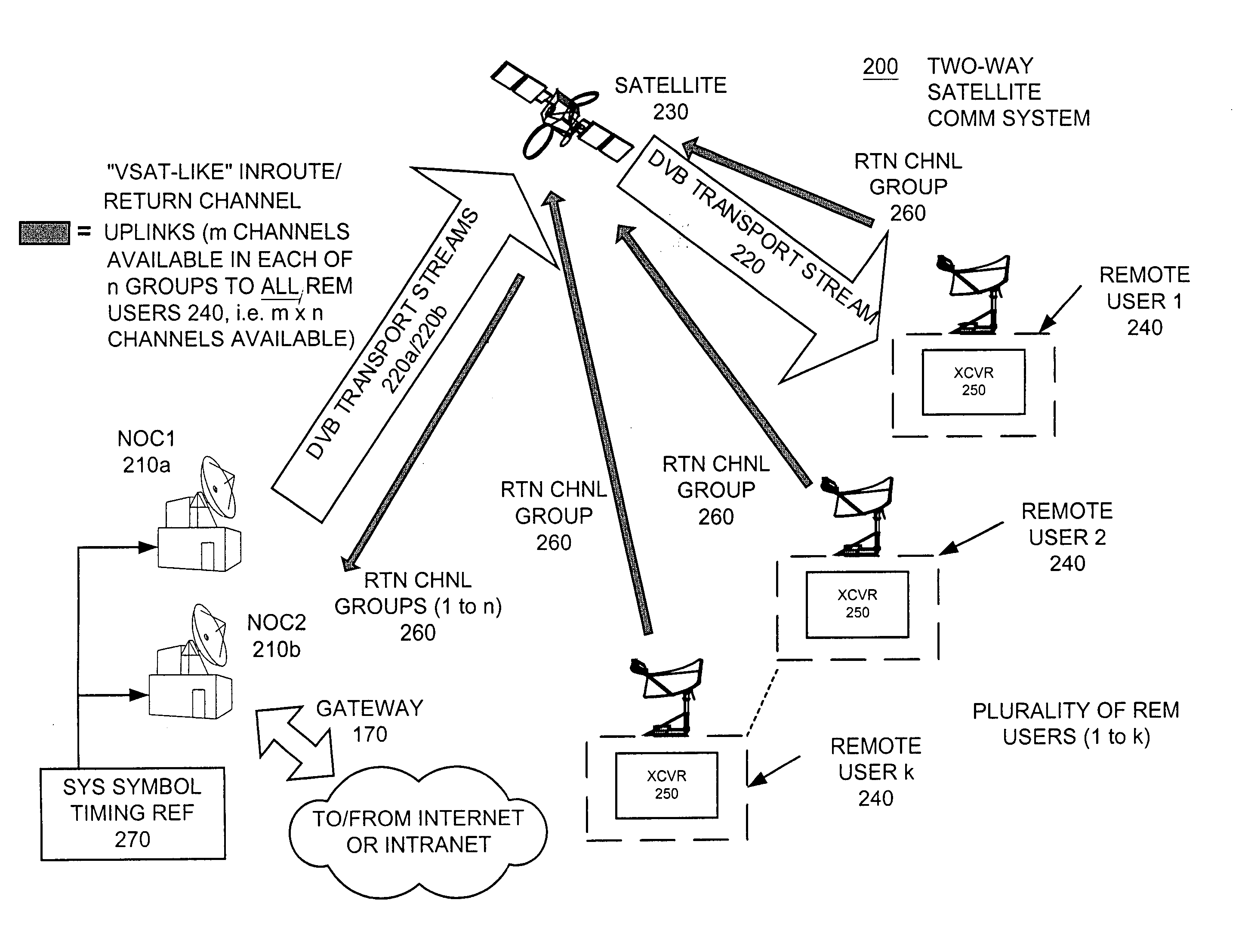
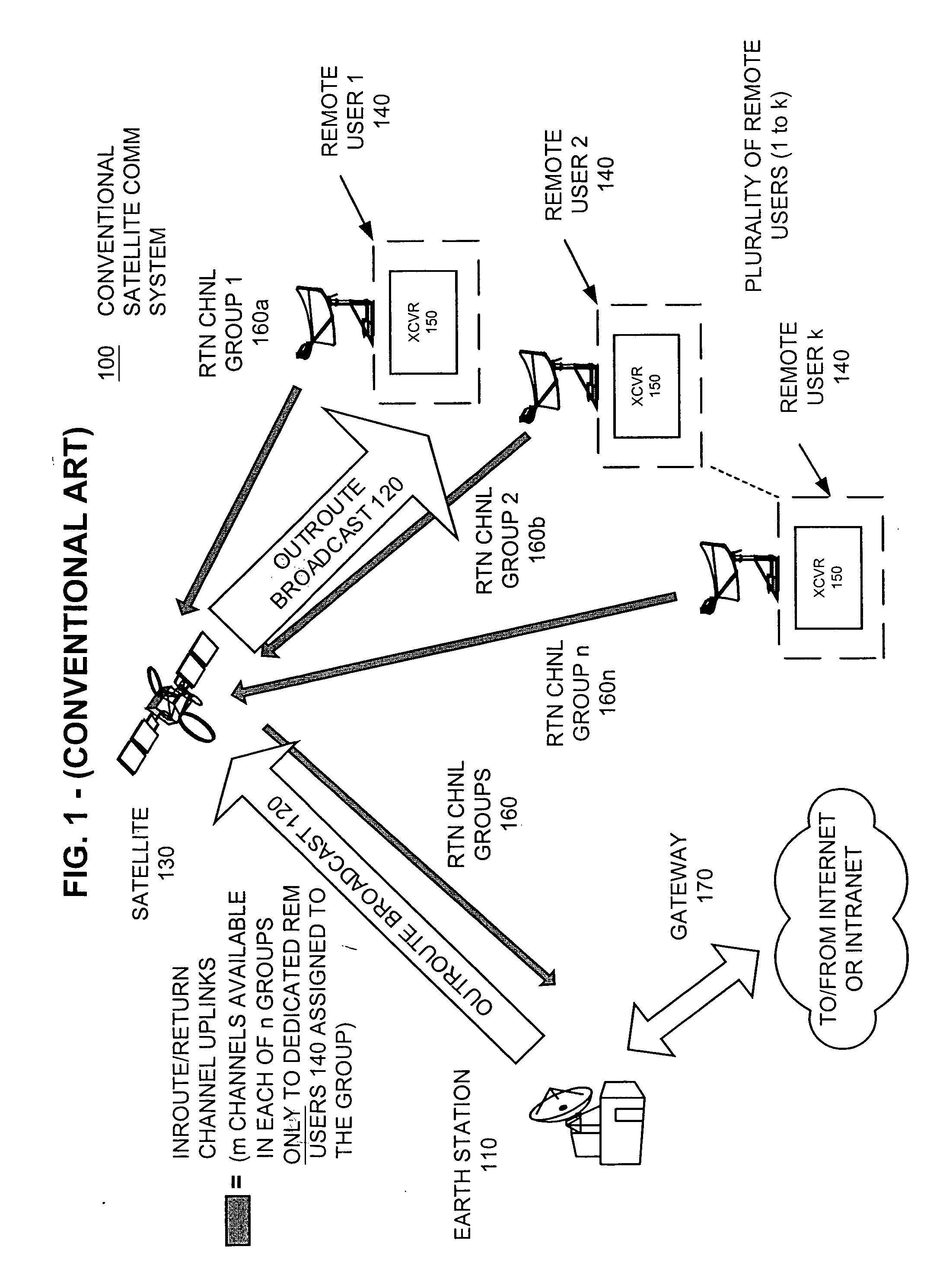
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
InactiveUS20050053033A1Balance traffic loadOptimize bandwidth allocationFrequency-division multiplex detailsAntenna supports/mountingsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Cellular telephone system that uses position of a mobile unit to make call management decisions
InactiveUS6324404B1Efficient and accurate servicePrecise processingEmergency connection handlingTelephonic communicationCell siteGeolocation
A cellular telephone system has call management decisions made based on the exact geographic location of the mobile unit. These call management decisions include billing and taxing decisions, cell site selection, frequency selection and even cellular system selection. The decisions are continuously updated during a call whereby decisions can be made and changed regardless of where a call originated. Cell site location, and even cellular system selection, can be made in a specific manner to best serve the needs of the mobile user, the cellular system as well as the public. It is even possible for a cellular system to locate one or more of its cell sites in the geographic area served by another cellular system. In some cases, cellular systems might even share cell sites.
Owner:SYGNET COMM +1
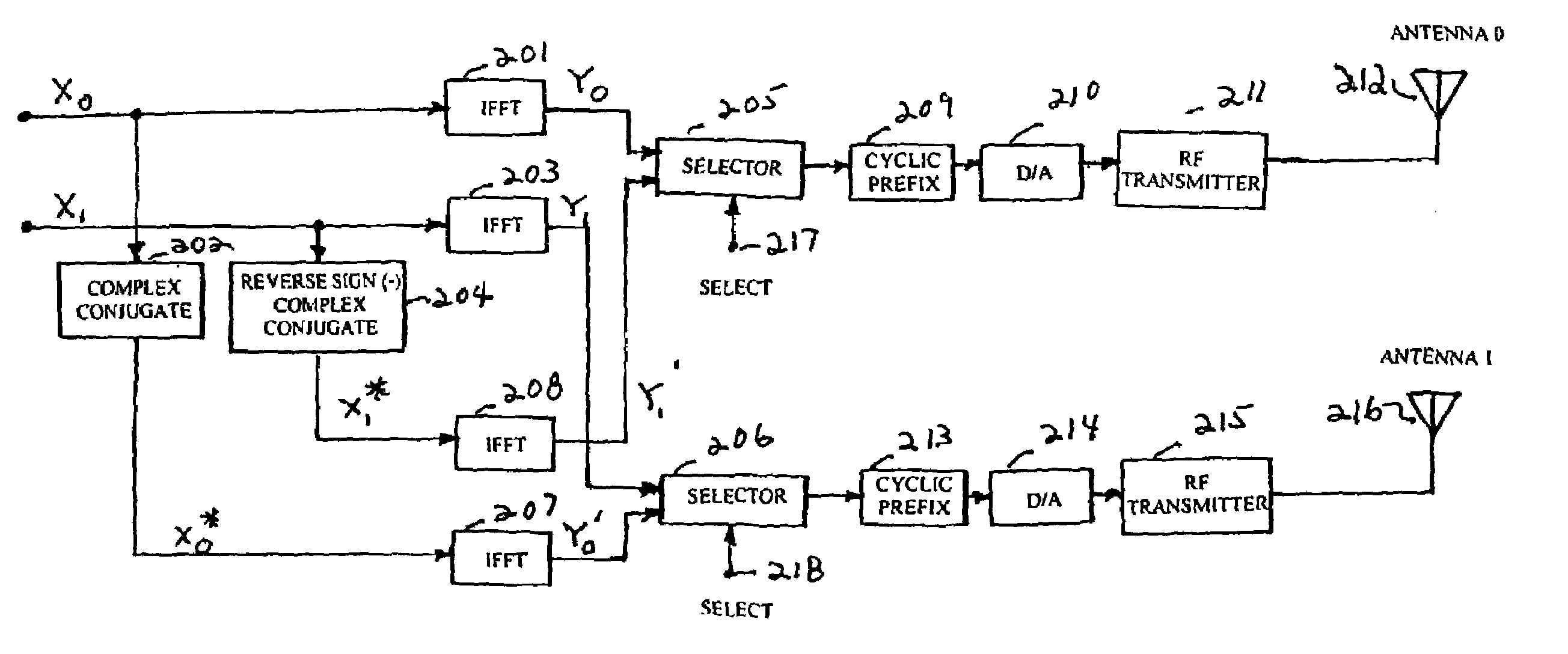
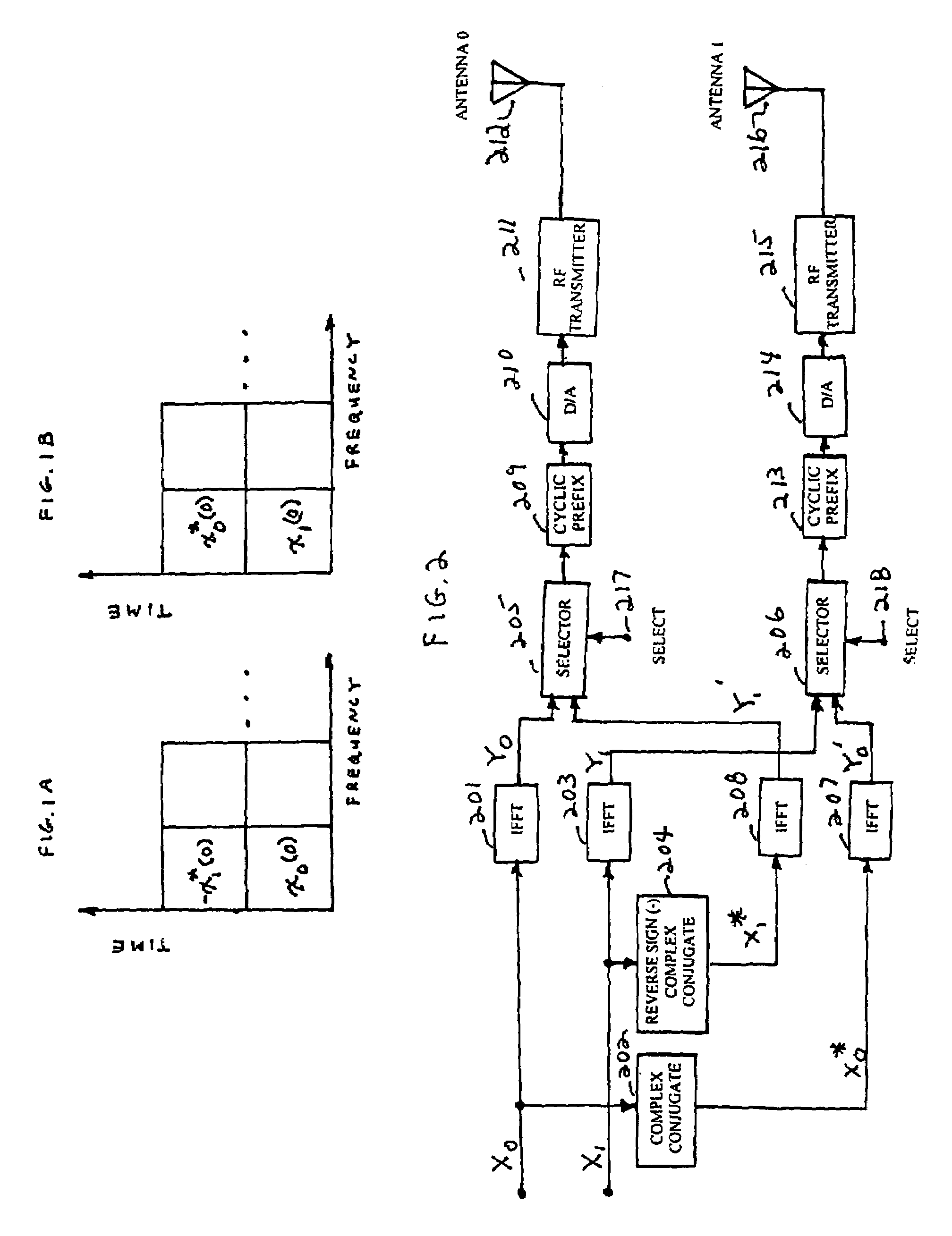
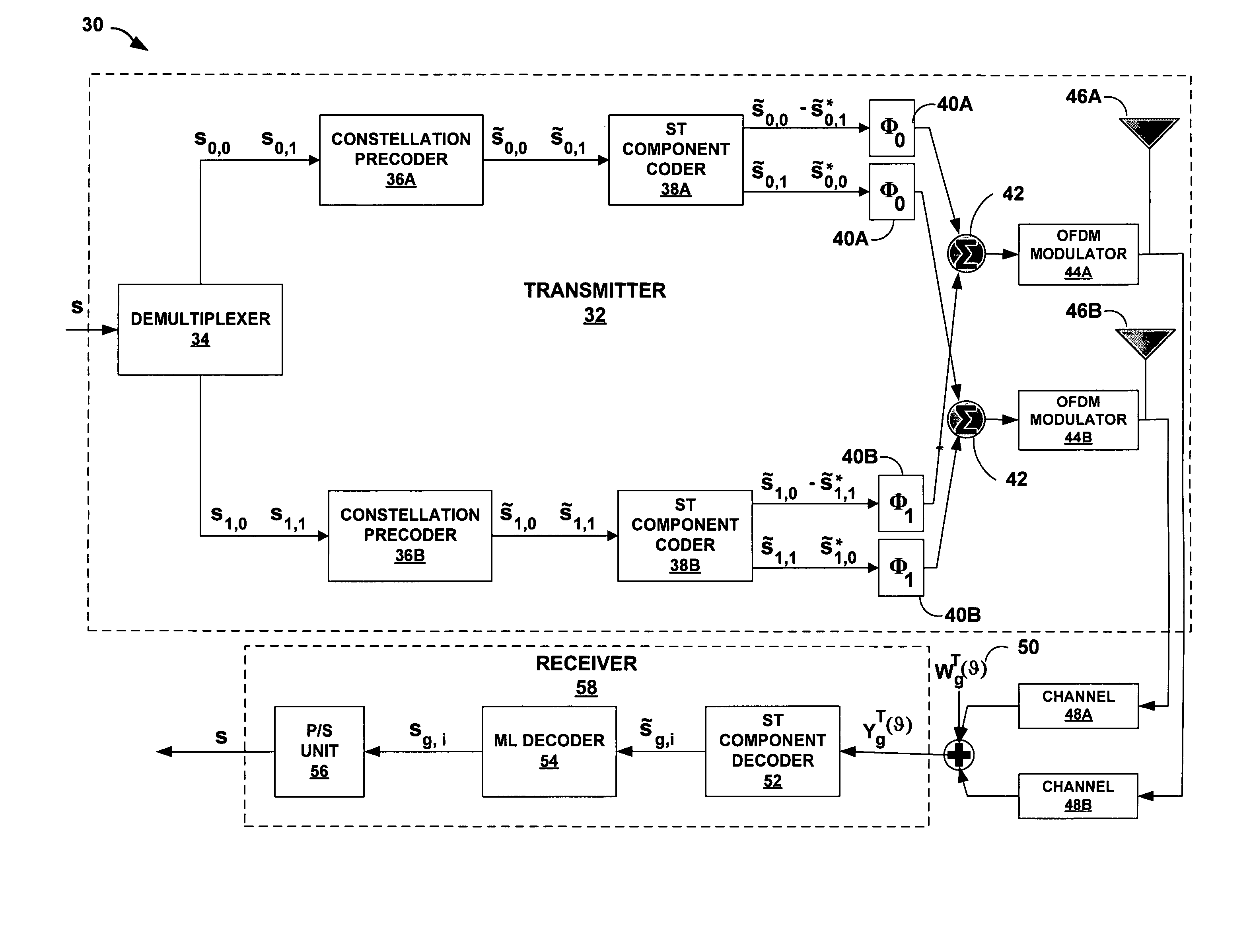
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing transmit diversity system for frequency-selective fading channels
InactiveUS7020072B1Reduce complexityIncrease transmission diversitySpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplexReverse orderSignal on
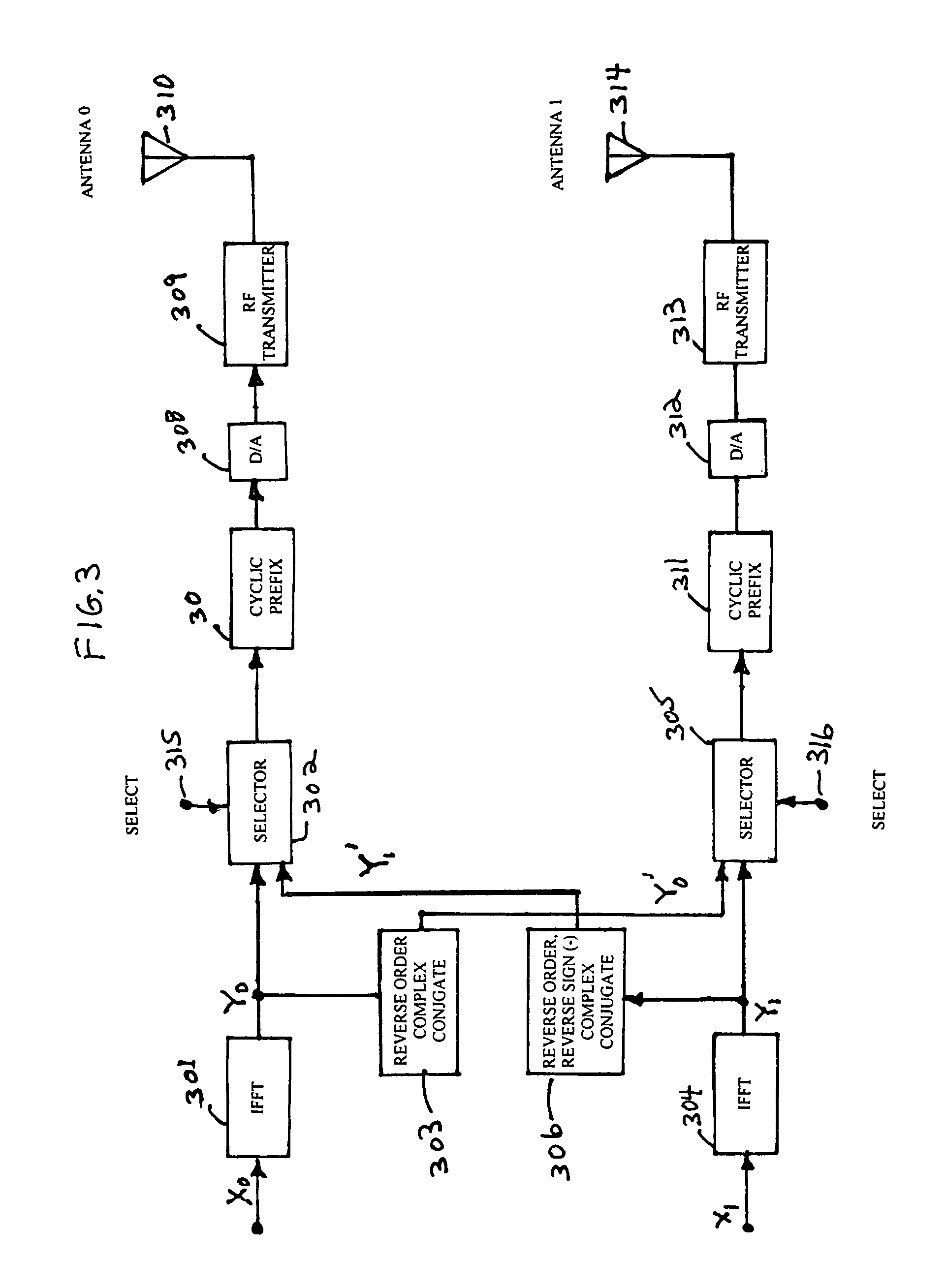
Wireless communications for frequency-selective fading channels is realized by employing a system including orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) in combination with an at least two antenna transmit diversity arrangement. Specifically, OFDM converts a multipath channel into a plurality of narrowband subchannels each having flat fading. Then, the signals on the same frequency subchannels of the at least two antennas are grouped together. Considering a first frequency subchannel, during a first OFDM time interval, a first signal and a second signal are transmitted on the first frequency subchannel from a first antenna (0) and from a second antenna (1), respectively. During a second OFDM time interval, a reverse sign (−) complex conjugate of the second signal and a complex conjugate of the first signal are transmitted from the first antenna and the second antenna, respectively. In a specific embodiment of the invention, reduced complexity in the implementation is realized by a reverse order complex conjugate and a reverse order, reverse sign (−) complex conjugate and judicious selection of the processed data signals in order to transmit the appropriate ones of the signals during the first and second OFDM intervals. Again, if the channel remains constant over the two OFDM intervals, diversity combination is realized for each frequency subchannel. In another embodiment of the invention, antenna-group hopping is employed in conjunction with pairing in time of the OFDM frequency subchannel signals to realize increased transmit diversity without rate loss.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
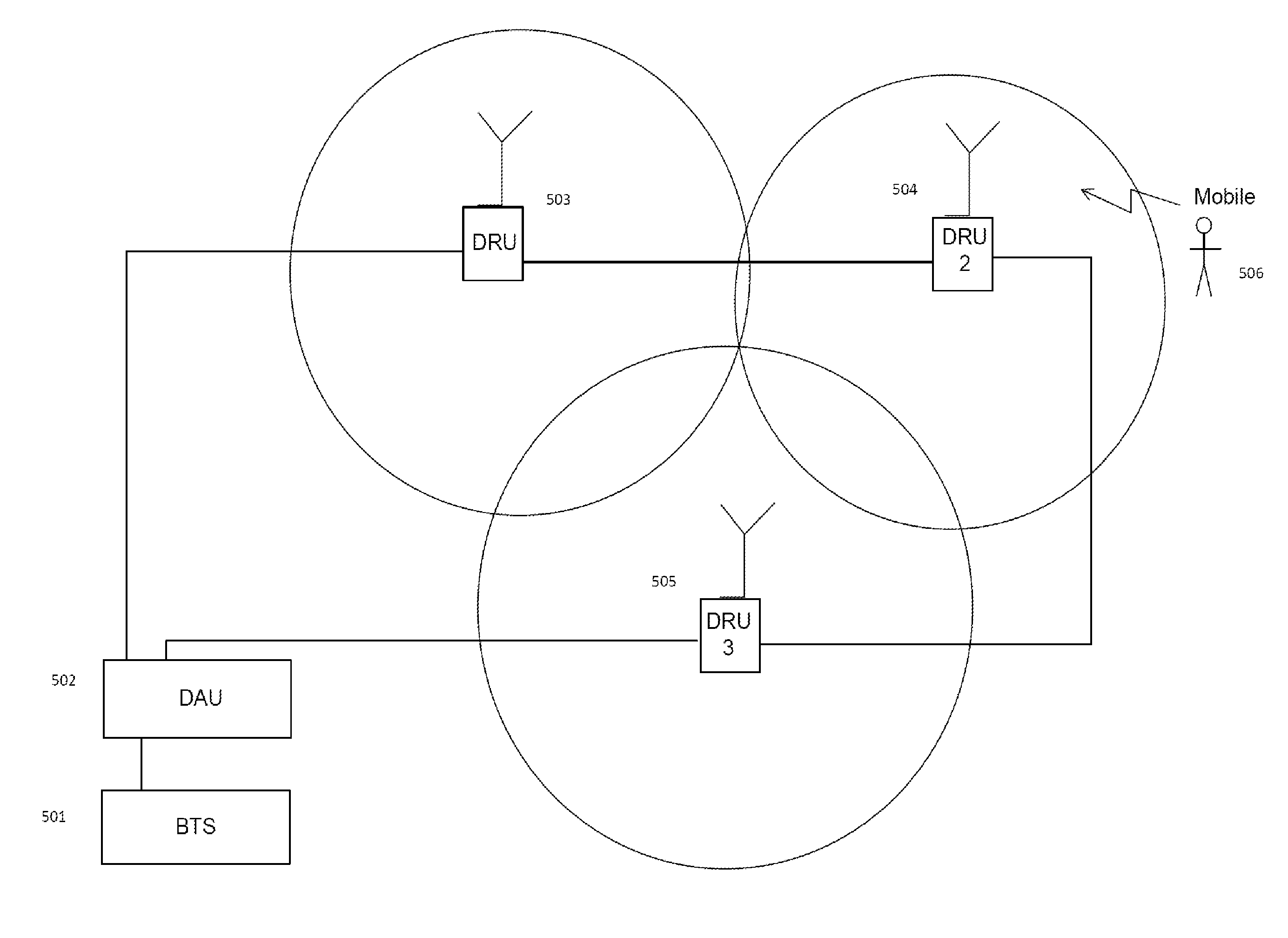
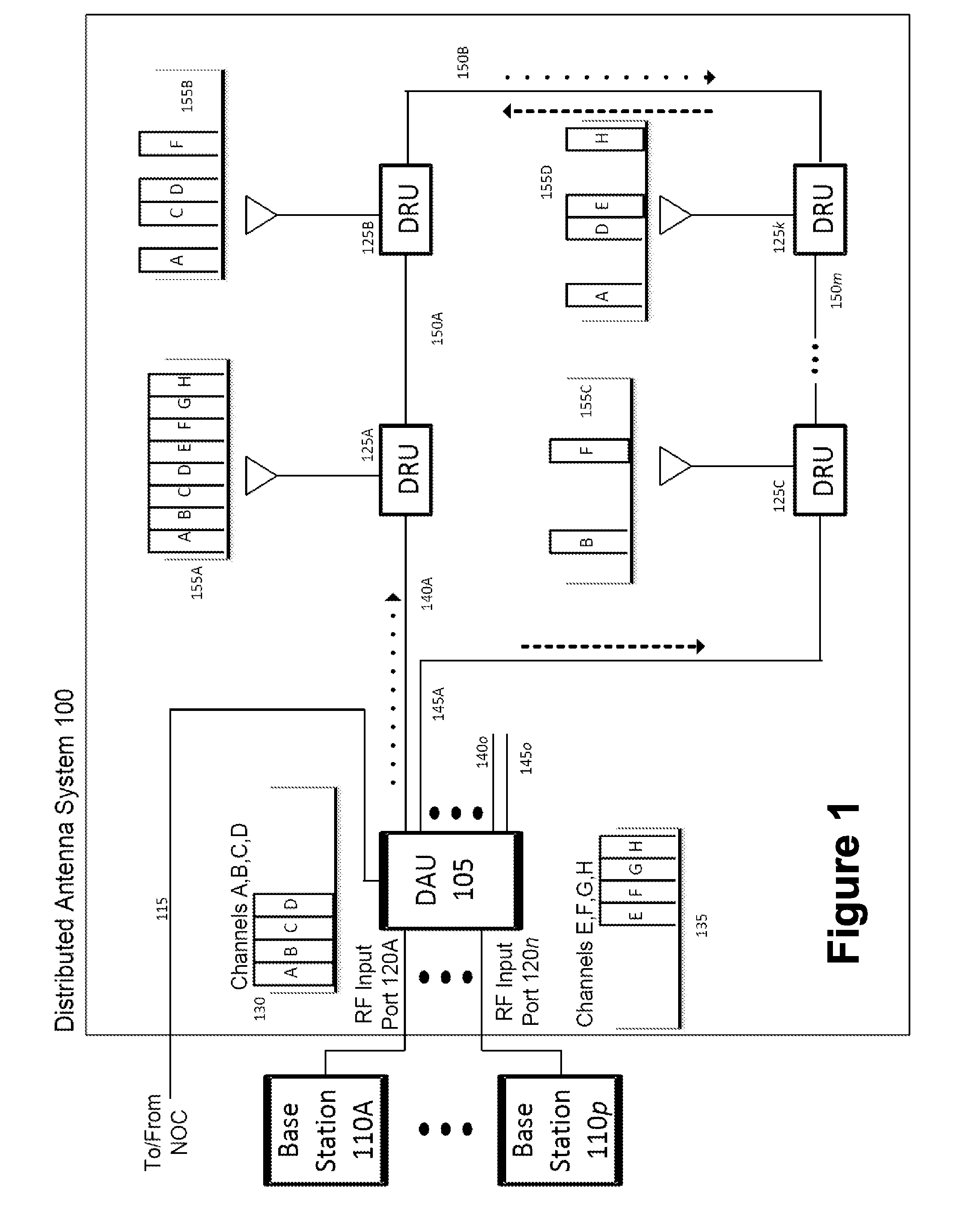
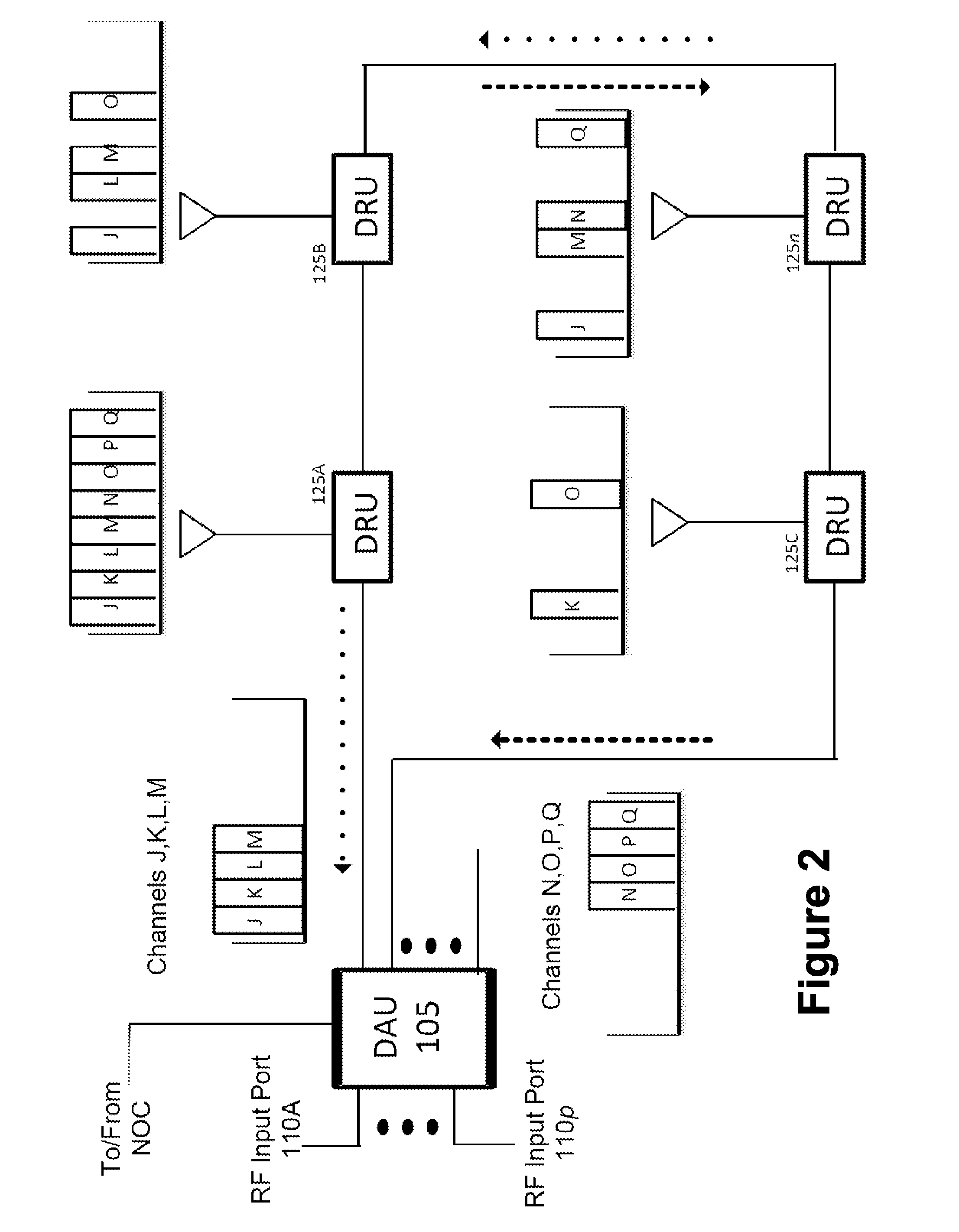
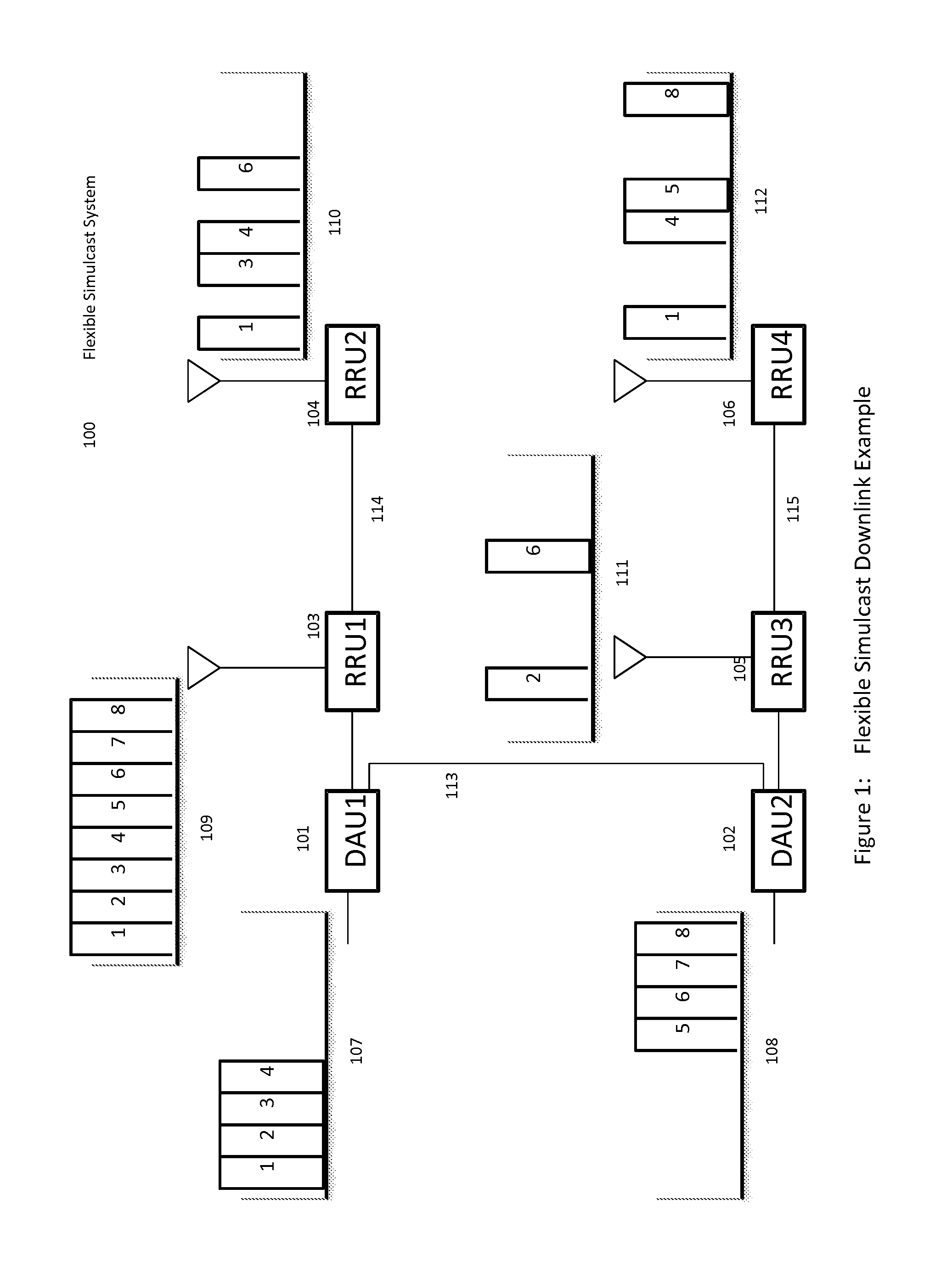
Remotely Reconfigurable Distributed Antenna System and Methods
ActiveUS20120039320A1Improve efficiencyImprove traffic capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower amplifiersDistributed antenna systemCarrier signal
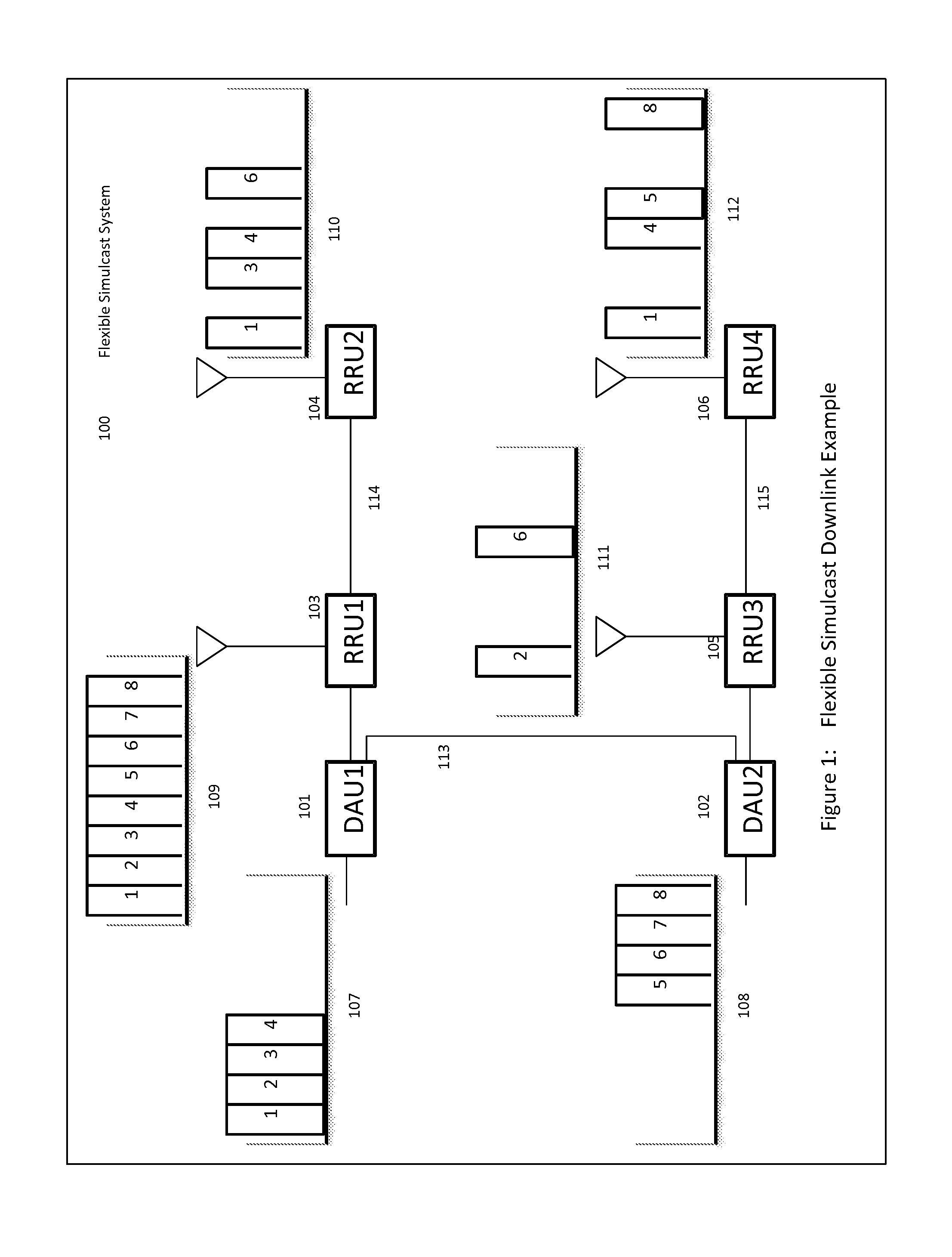
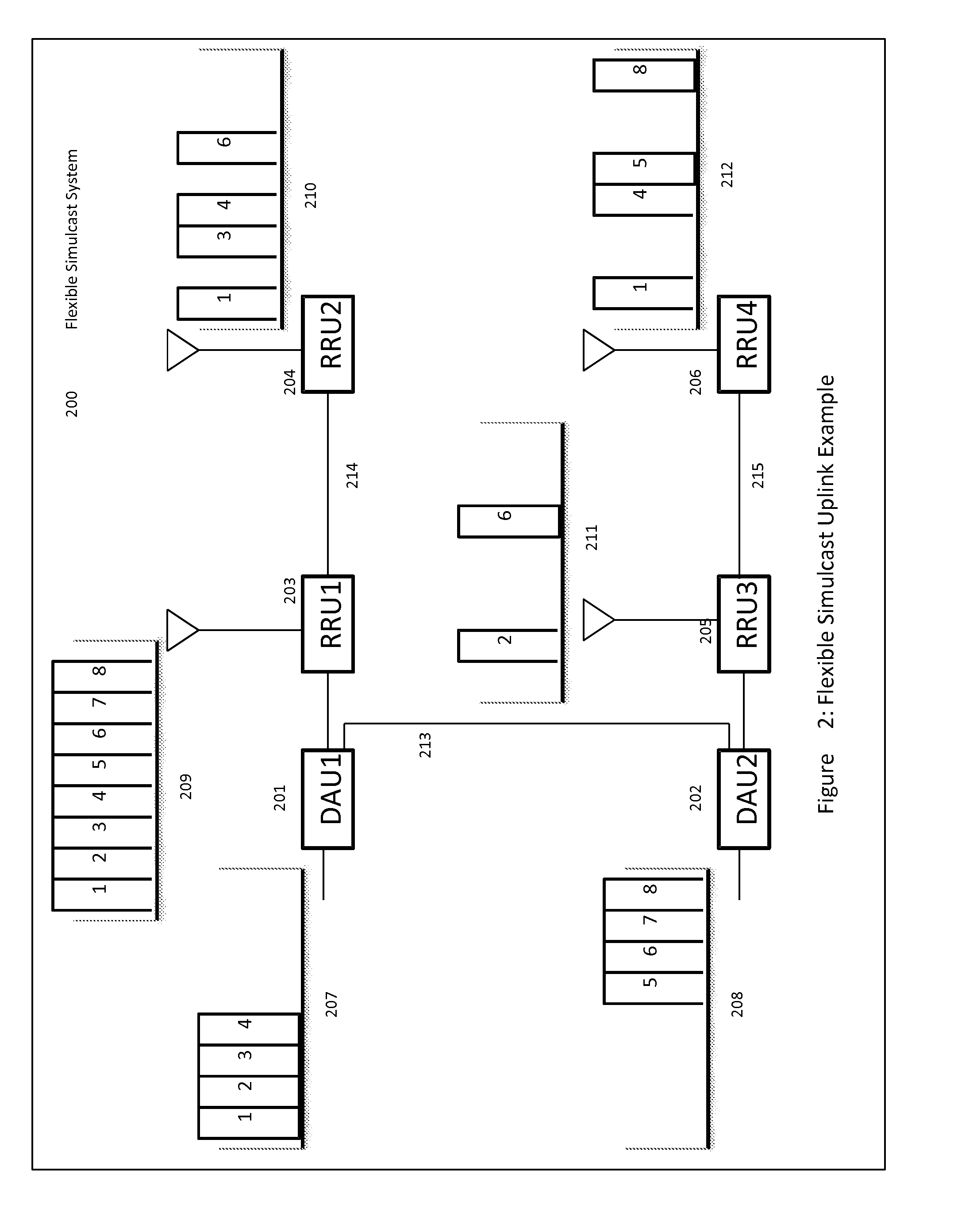
The present disclosure is a novel utility of a software defined radio (SDR) based Distributed Antenna System (DAS) that is field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation-independent), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. The present disclosure enables a high degree of flexibility to manage, control, enhance, facilitate the usage and performance of a distributed wireless network such as flexible simulcast, automatic traffic load-balancing, network and radio resource optimization, network calibration, autonomous / assisted commissioning, carrier pooling, automatic frequency selection, frequency carrier placement, traffic monitoring, traffic tagging, pilot beacon, etc. As a result, the SDR DAS can increase the efficiency and traffic capacity of the operators' wireless network.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Daisy-Chained Ring of Remote Units For A Distributed Antenna System
ActiveUS20120039254A1High degree of flexibility to manage, controlIncrease capacitySite diversityModulated-carrier systemsDistributed antenna systemCarrier signal
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
InactiveUS20050030932A1Optimized bandwidth allocation schemeBalance traffic loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
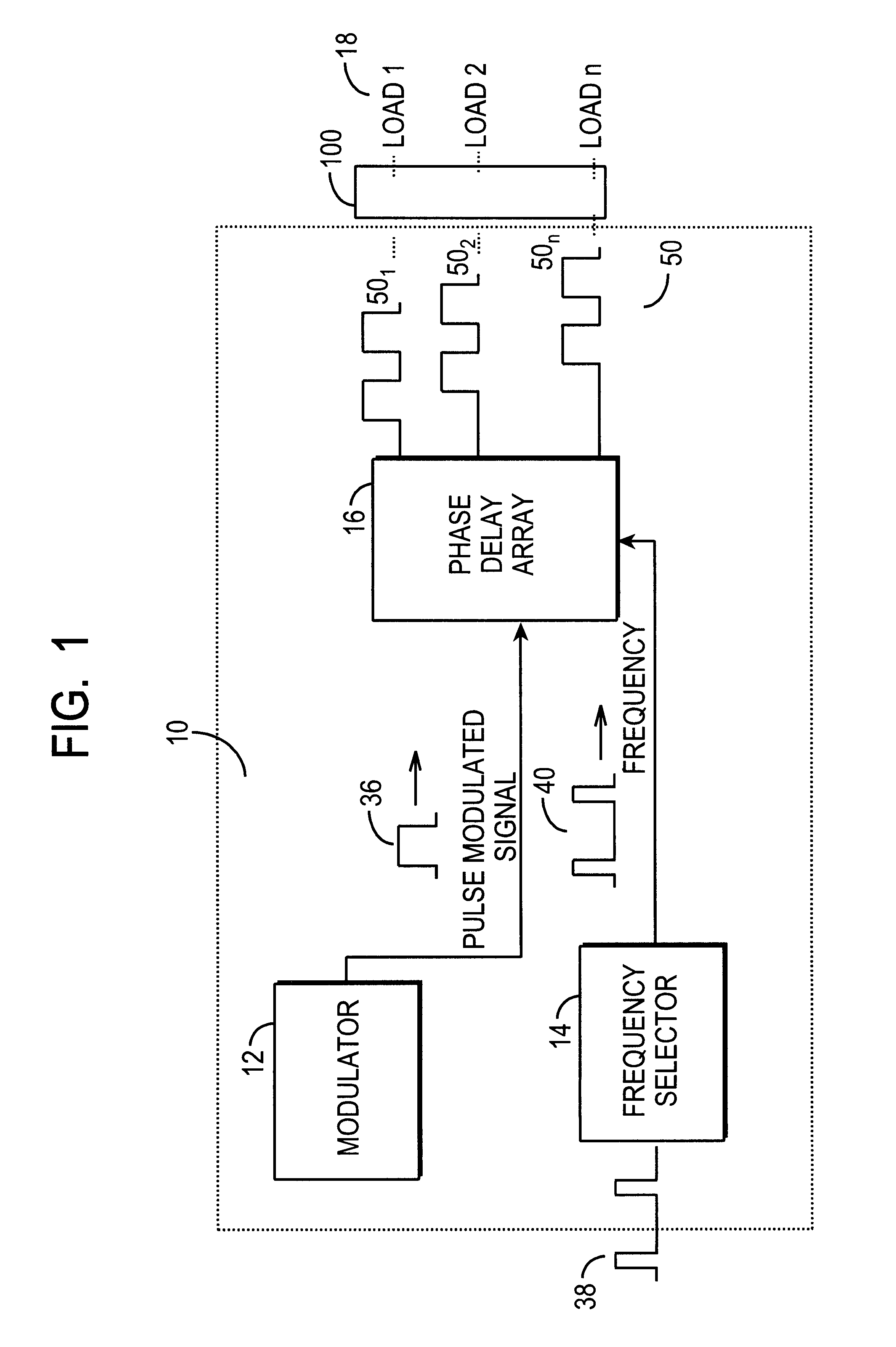
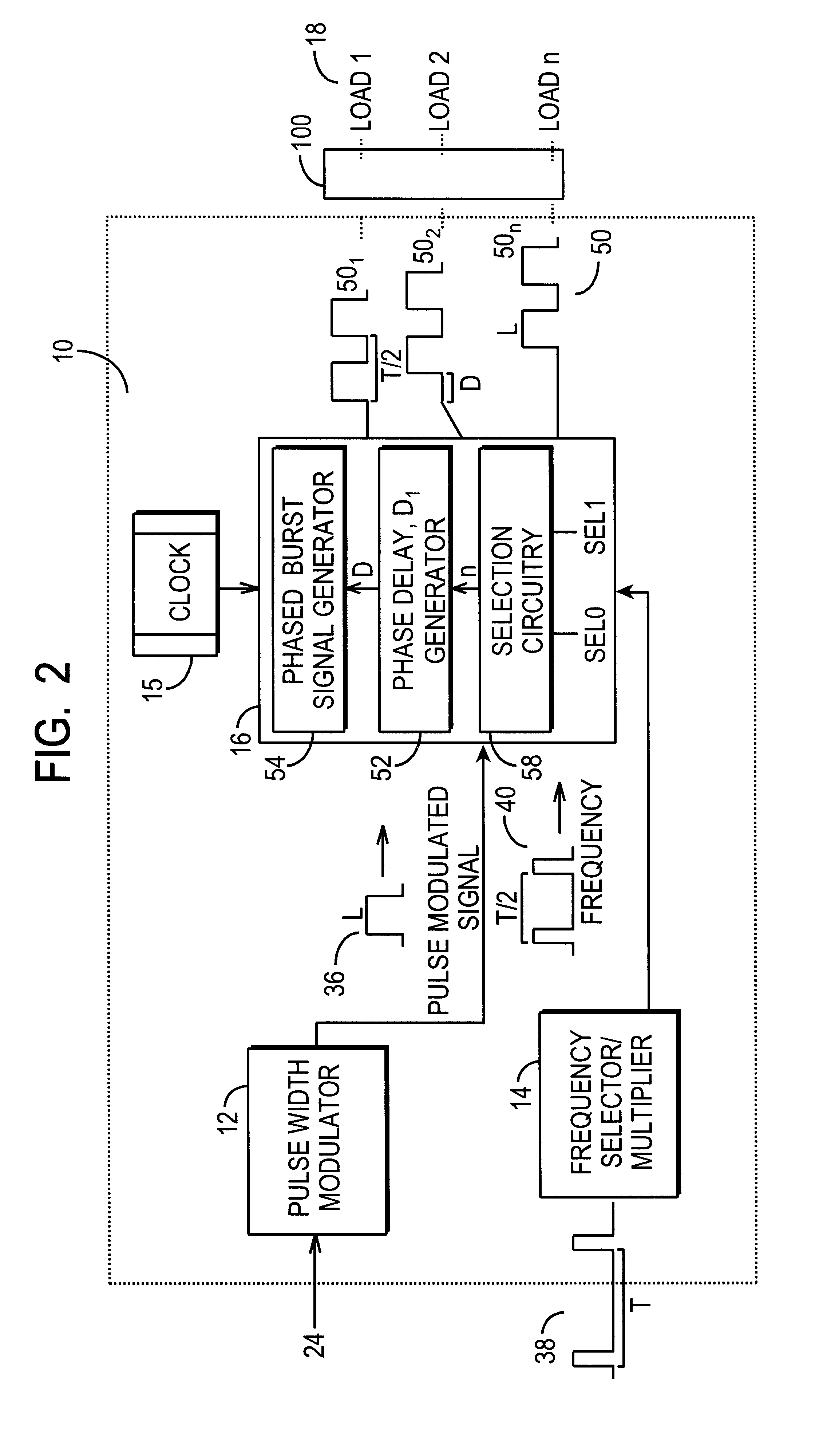
Sequential burst mode activation circuit
A sequential burst mode regulation system to deliver power to a plurality of loads. In the exemplary embodiments, the system of the present invention generates a plurality of phased pulse width modulated signals from a single pulse width modulated signal, where each of the phased signals regulates power to a respective load. Exemplary circuitry includes a PWM signal generator, and a phase delay array that receives a PWM signal and generates a plurality of phased PWM signals which are used to regulate power to respective loads. A frequency selector circuit can be provided that sets the frequency of the PWM signal using a fixed or variable frequency reference signal.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
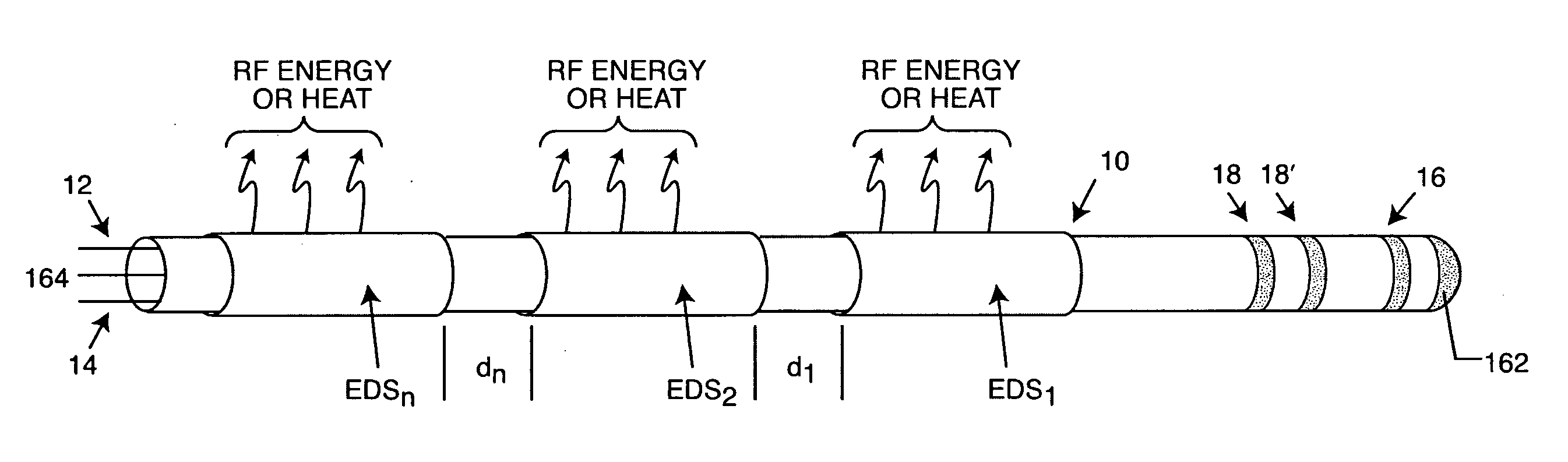
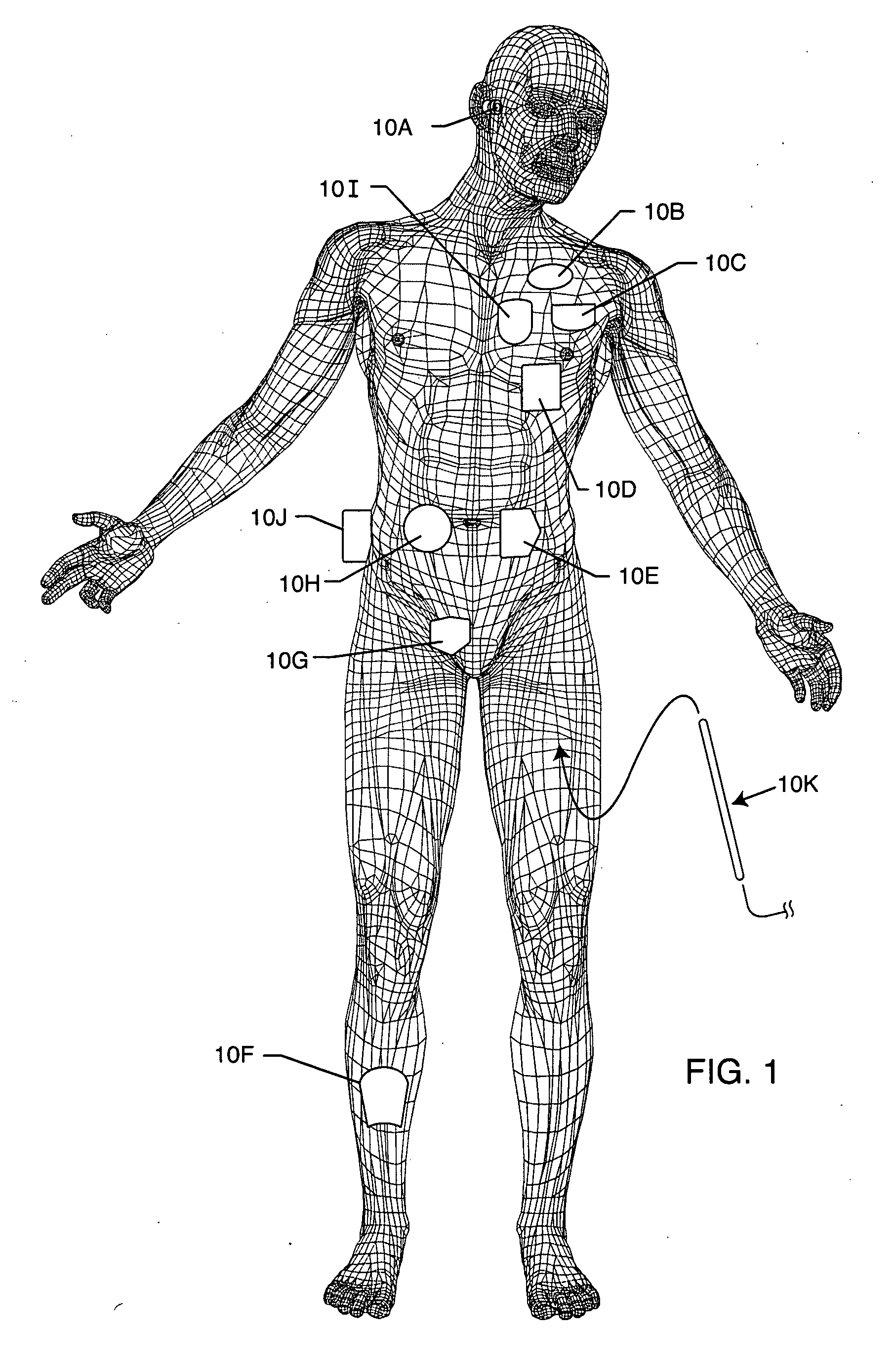
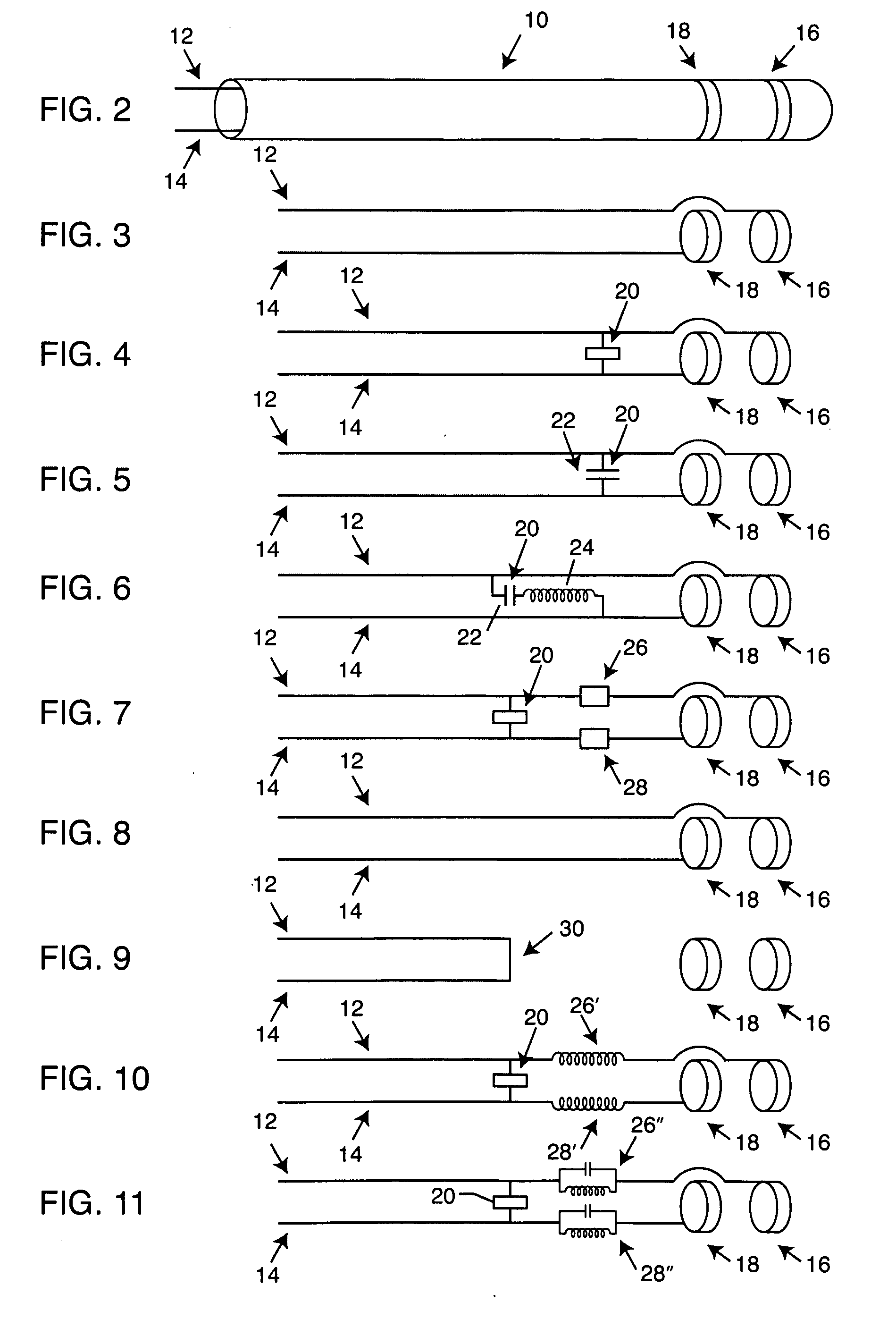
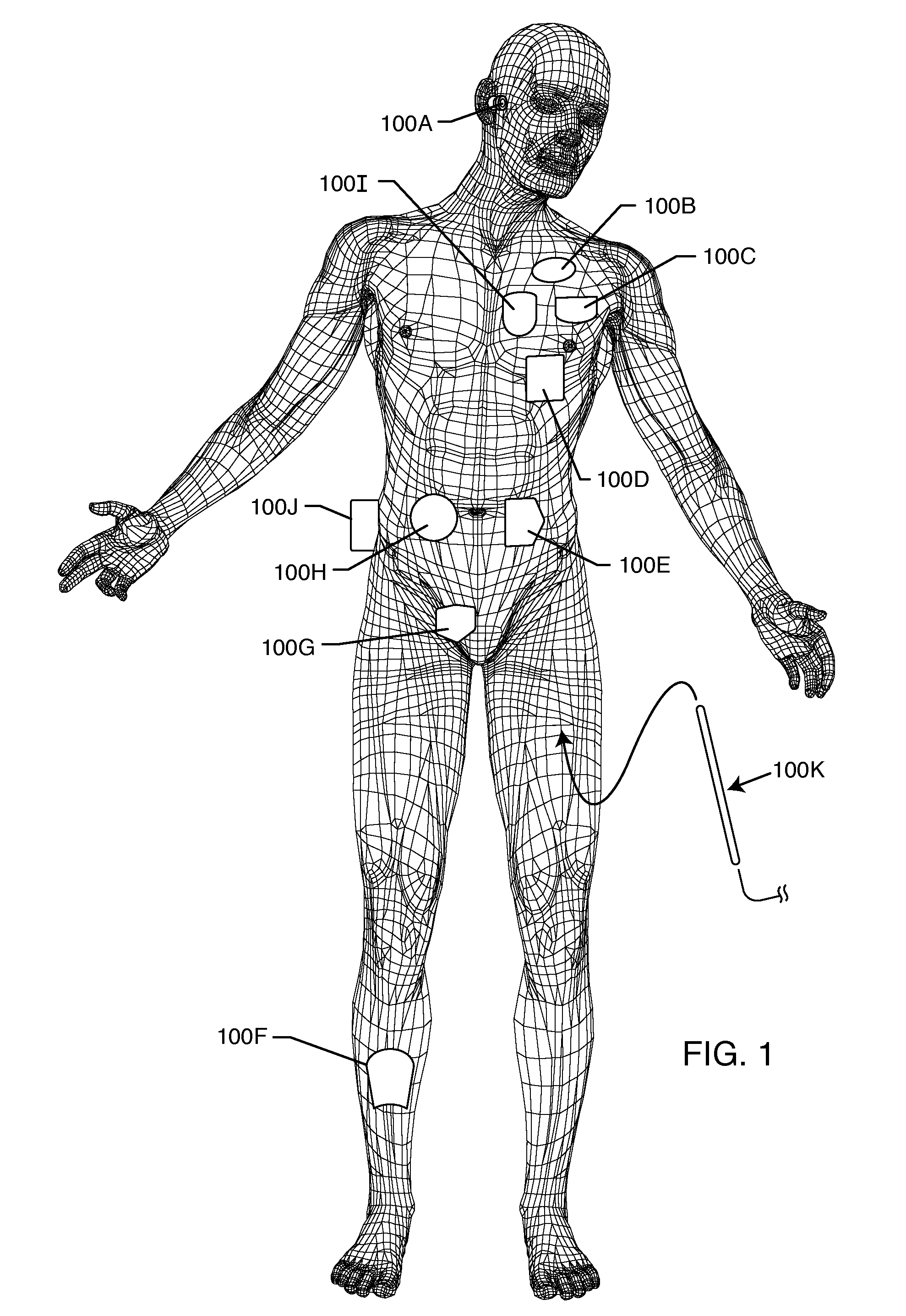
Frequency selective passive component networks for implantable leads of active implantable medical devices utilizing an energy dissipating surface
InactiveUS20100023000A1Increase temperatureAbility to in properMultiple-port networksElectrocardiographyEnergy transferRf field
Decoupling circuits are provided which transfer energy induced from an MRI pulsed RF field to an energy dissipating surface. This is accomplished through broadband filtering or by resonant filtering. In a passive component network for an implantable leadwire of an active implantable medical device, a frequency selective energy diversion circuit is provided for diverting high-frequency energy away from a leadwire electrode to a point or an area spaced from the electrode, for dissipation of high-frequency energy.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
CDMA transceiver techniques for wireless communications
InactiveUS20040120274A1Spatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityWireless transmissionCommunications system
The present invention is related to a method for multi-user wireless transmission of data signals in a communication system having at least one base station and at least one terminal. It comprises, for a plurality of users, the following steps: adding robustness to frequency-selective fading to the data to be transmitted. performing spreading and scrambling of at least a portion of a block of data, obtainable by grouping data symbols by demultiplexing using a serial-to-parallel operation, combining (summing) spread and scrambled portions of the blocks of at least two users, adding transmit redundancy to the combined spread and scrambled portions, and transmitting the combined spread and scrambled portions with transmit redundancy.
Owner:RPX CORP
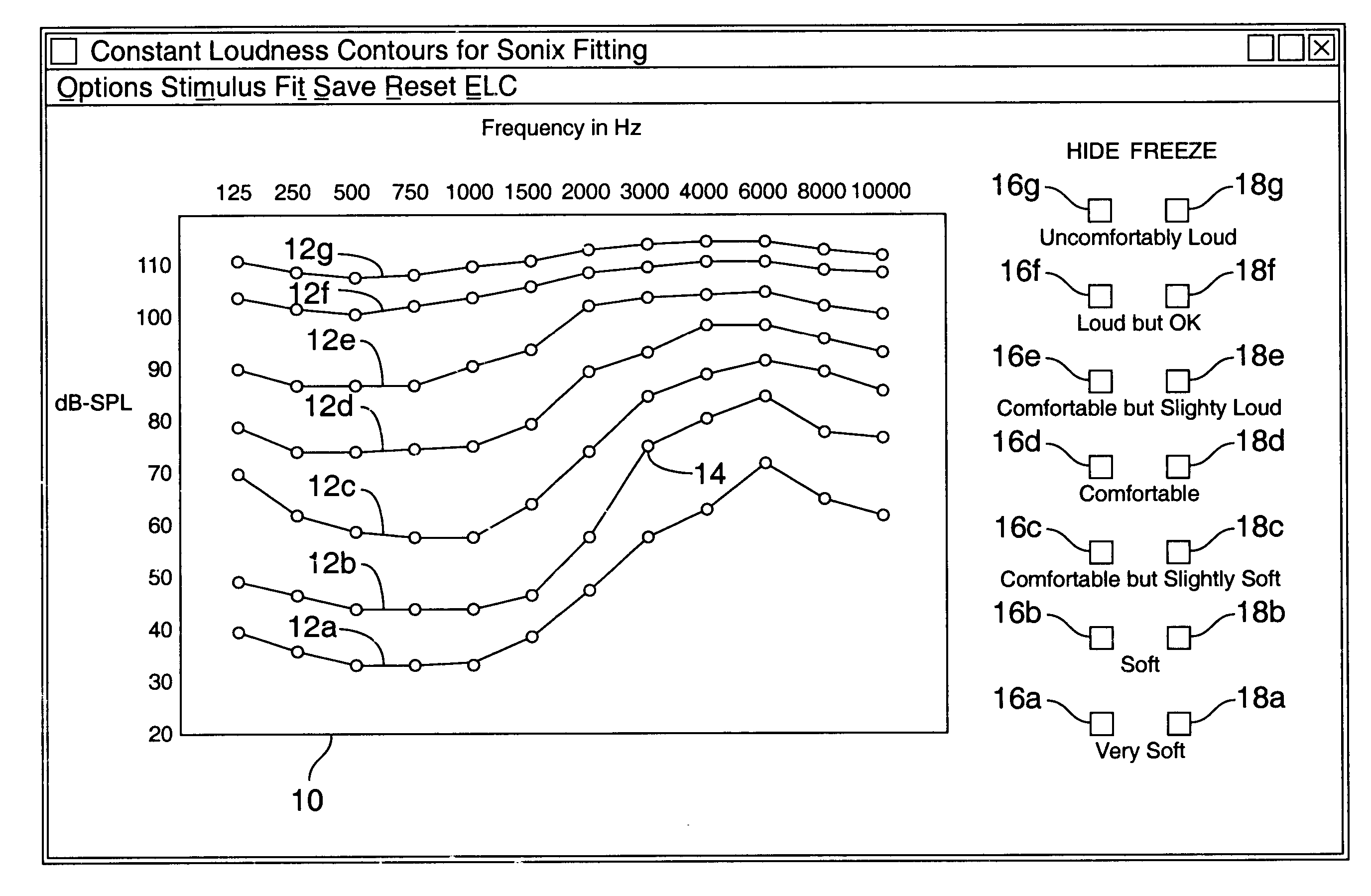
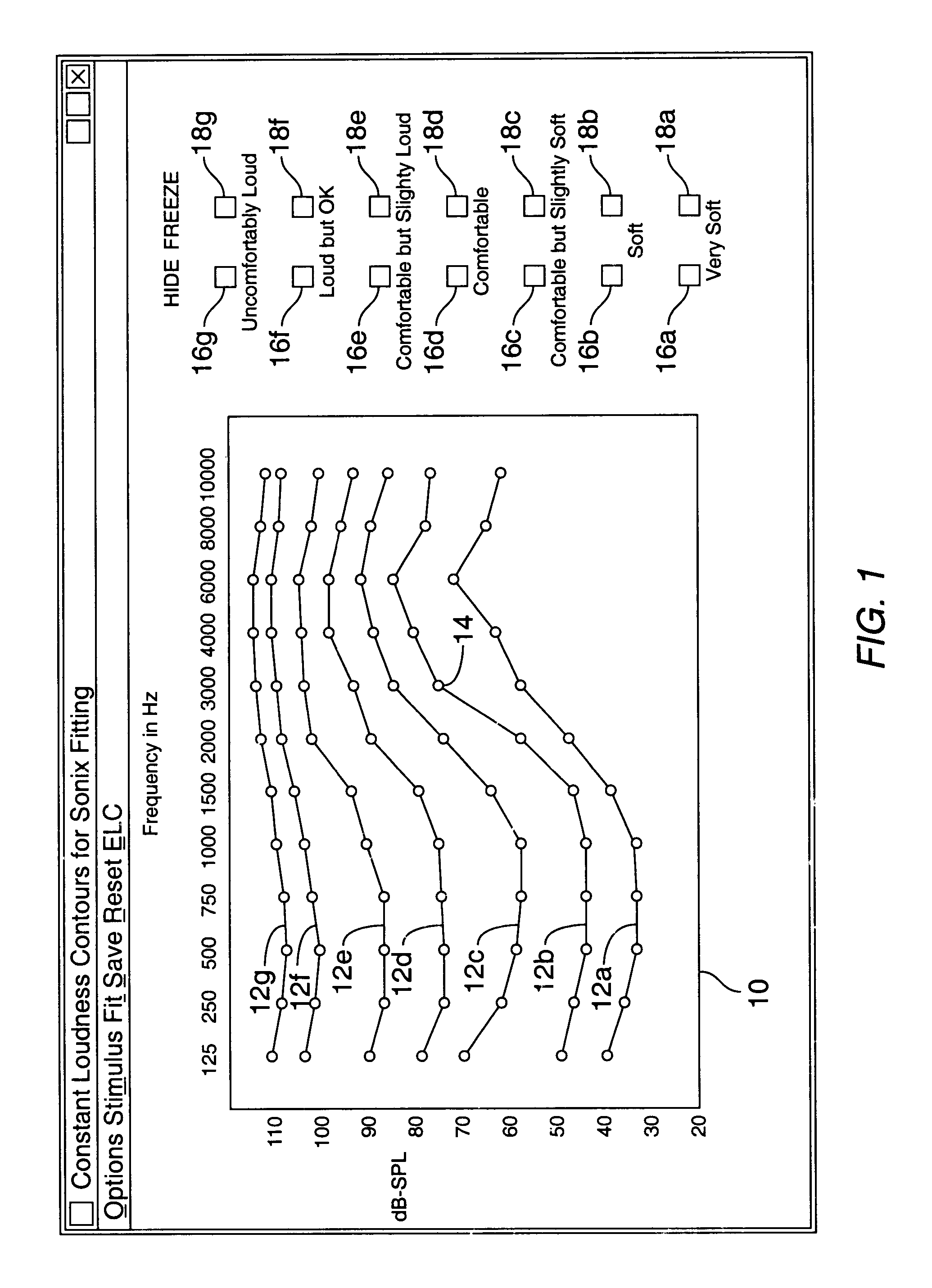
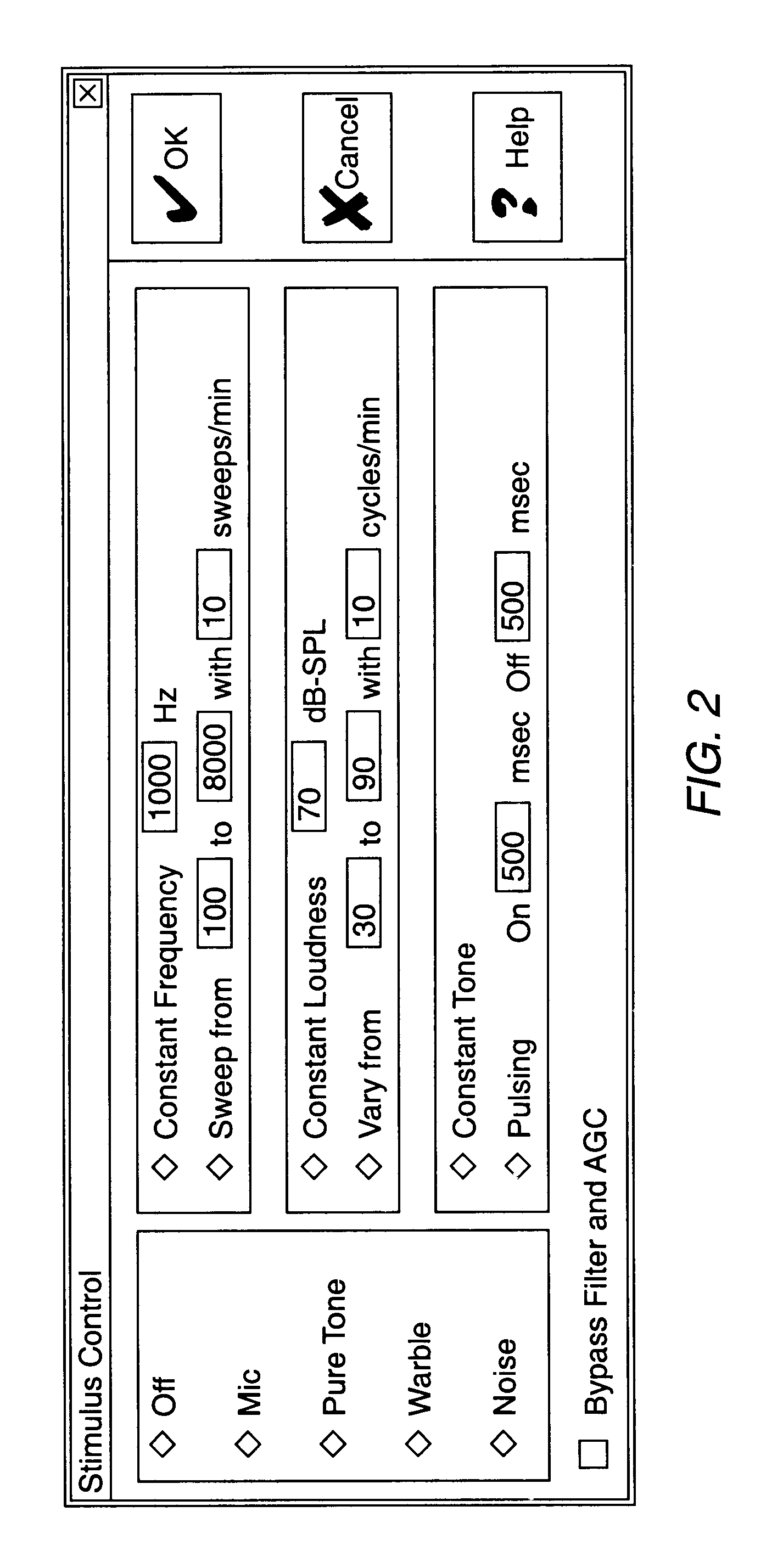
Hearing aid fitting system
A method for fitting a hearing compensation device comprises selecting a plurality of loudness levels for a plurality of frequencies and comparing each loudness level for each frequency for perceived sameness. The loudness levels may then be adjusted as needed to achieve perceived sameness across the frequency spectrum. A gain curve for each frequency is calculated from the selected plurality of loudness levels.
Owner:SONIC INNOVATIONS +1
Frequency hopping in 5GHz WLAN via dynamic frequency selection
ActiveUS20040037247A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsReceived signal strength indication
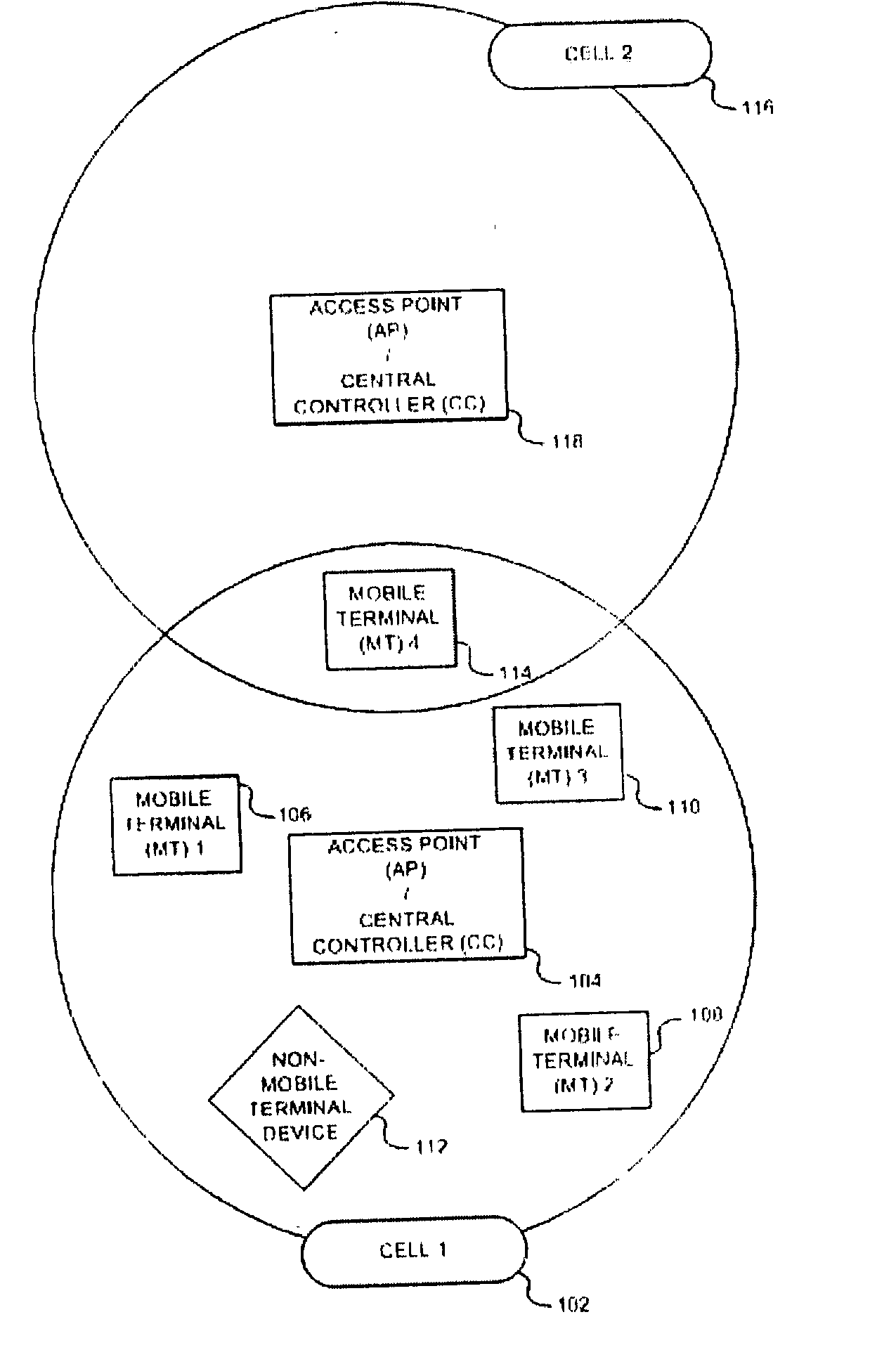
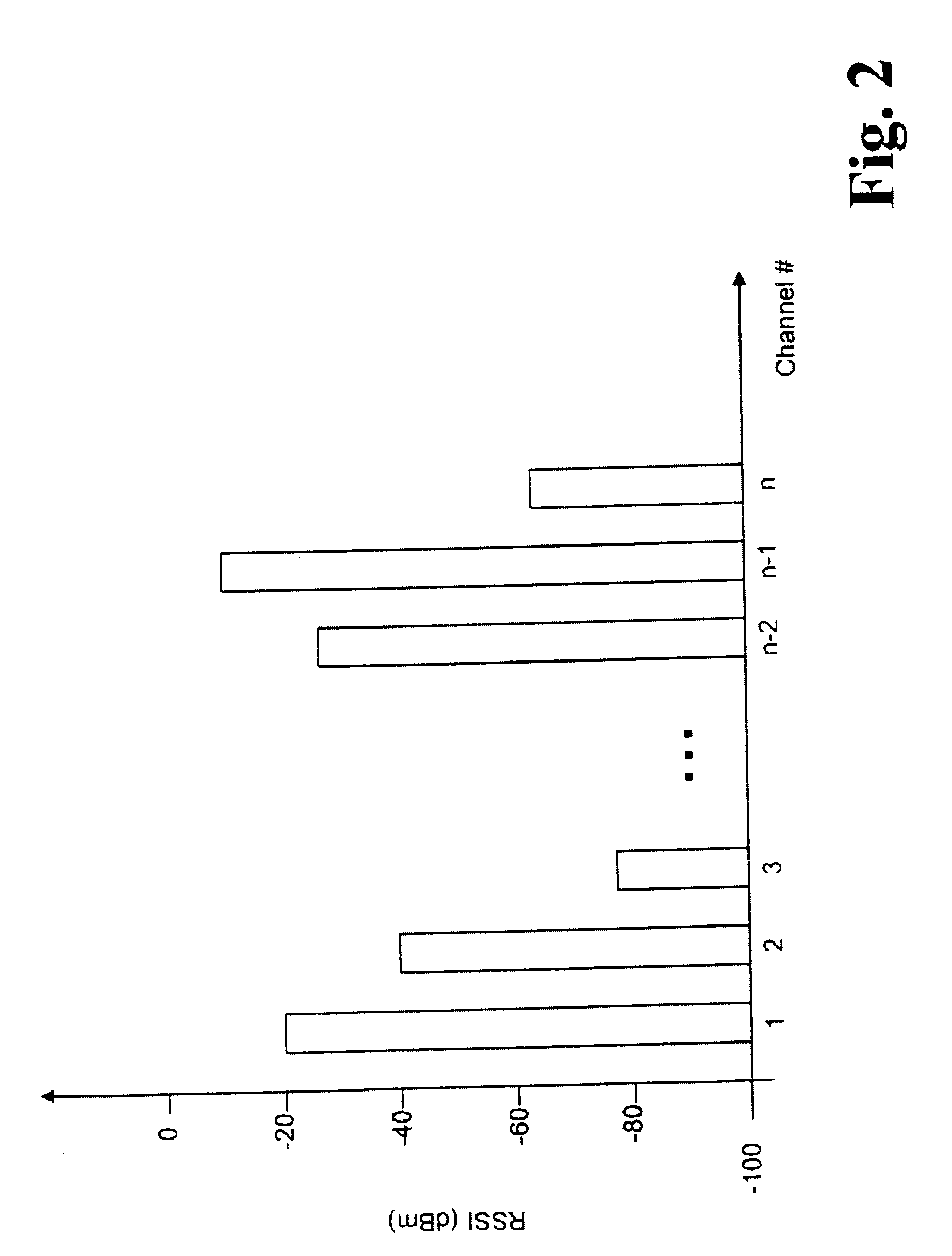
Disclosed is a method and system for dynamically selecting a communication channel between an access point (AP) and a plurality of mobile terminals (MTs) in a wireless local area network (WLAN), the method having the steps of: (a) measuring a channel quality of a plurality of frequency channels; (b) reporting to said AP from said plurality of MTs of said candidate channels including a received signal strength indication (RSSI) of all channels measured; and, (c) selecting one of said channels based on said channel quality report for use in communication between said AP and said plurality of MTs.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Broadband carrier frequency selection
InactiveUS20070054682A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionUltra-widebandBroadband
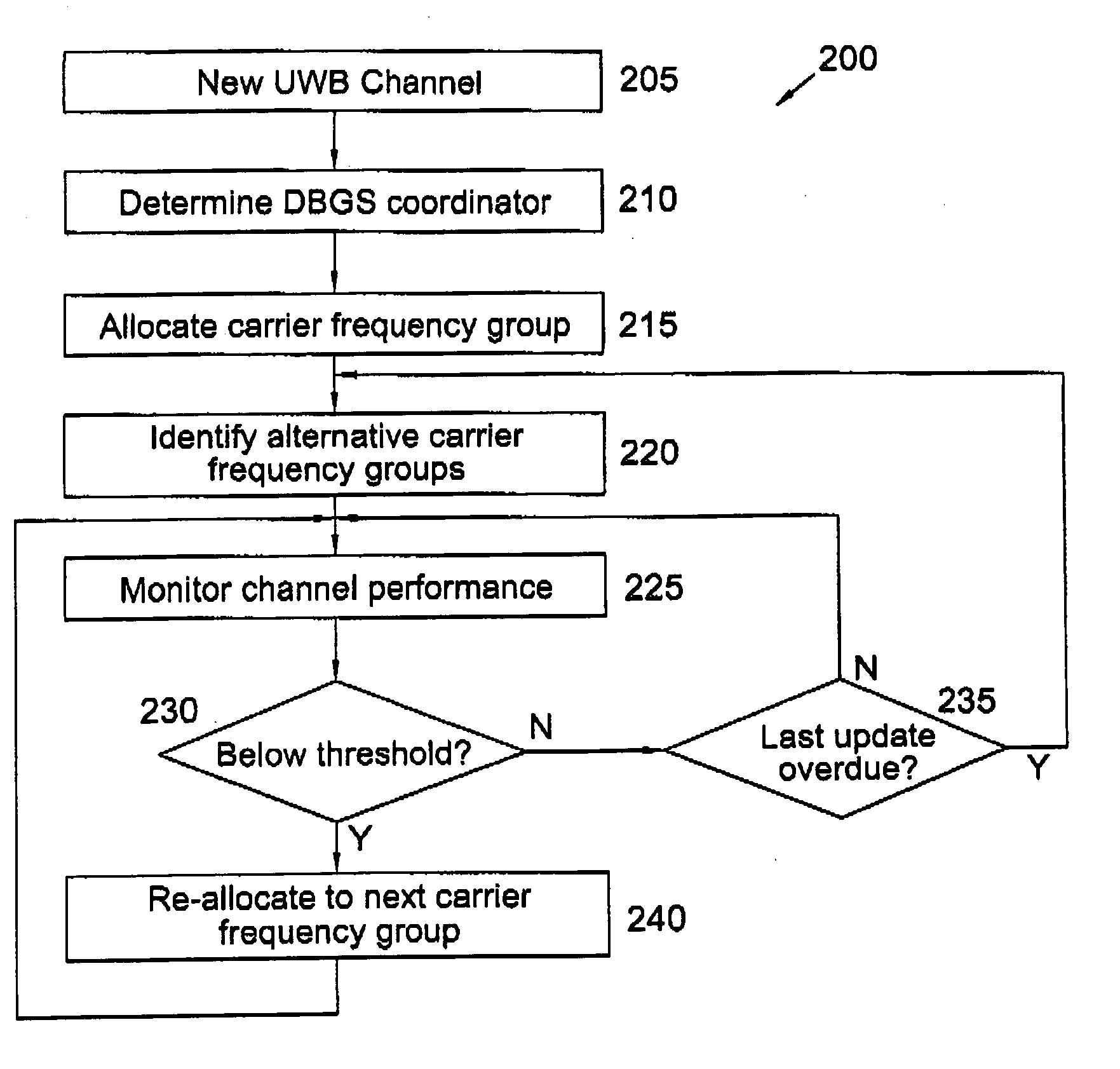
The present invention relates to broadband wireless communication using multiple carrier frequencies, and the selection or allocation of those frequencies. The invention is particularly but not exclusively related to ultra wideband (UWB) technologies. The present invention provides a method of dynamically selecting carrier frequencies for carrying a broadband channel, the method comprising: allocate a group of carrier frequencies for carrying the broadband channel; identify a number of alterative groups of carrier frequencies; monitor channel performance of the broadband channel for the allocated group of carrier frequencies; re-allocate the broadband channel to be carried by one of the alternative groups of carrier frequencies in response to the monitored channel performance degrading below a threshold.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
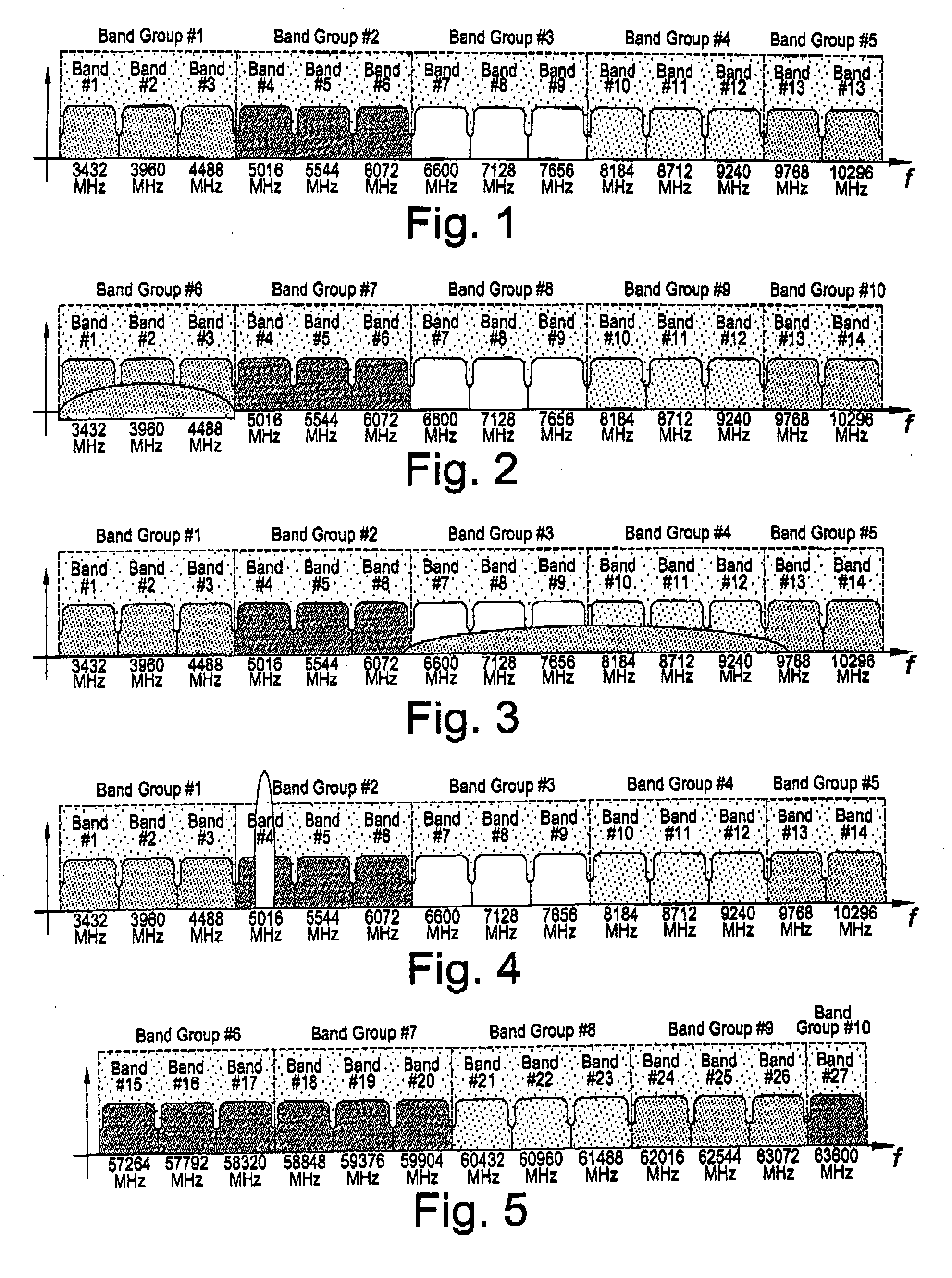
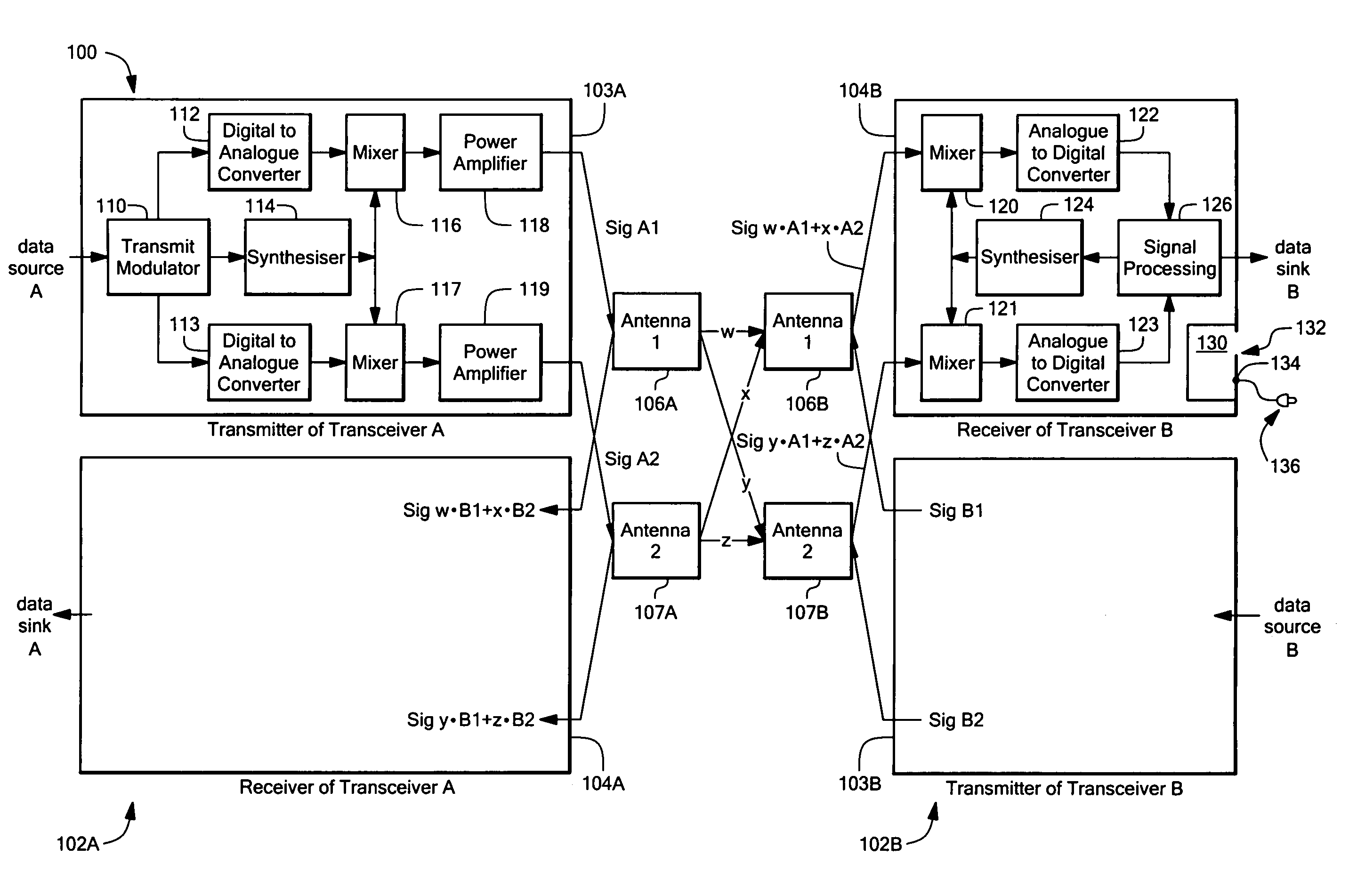
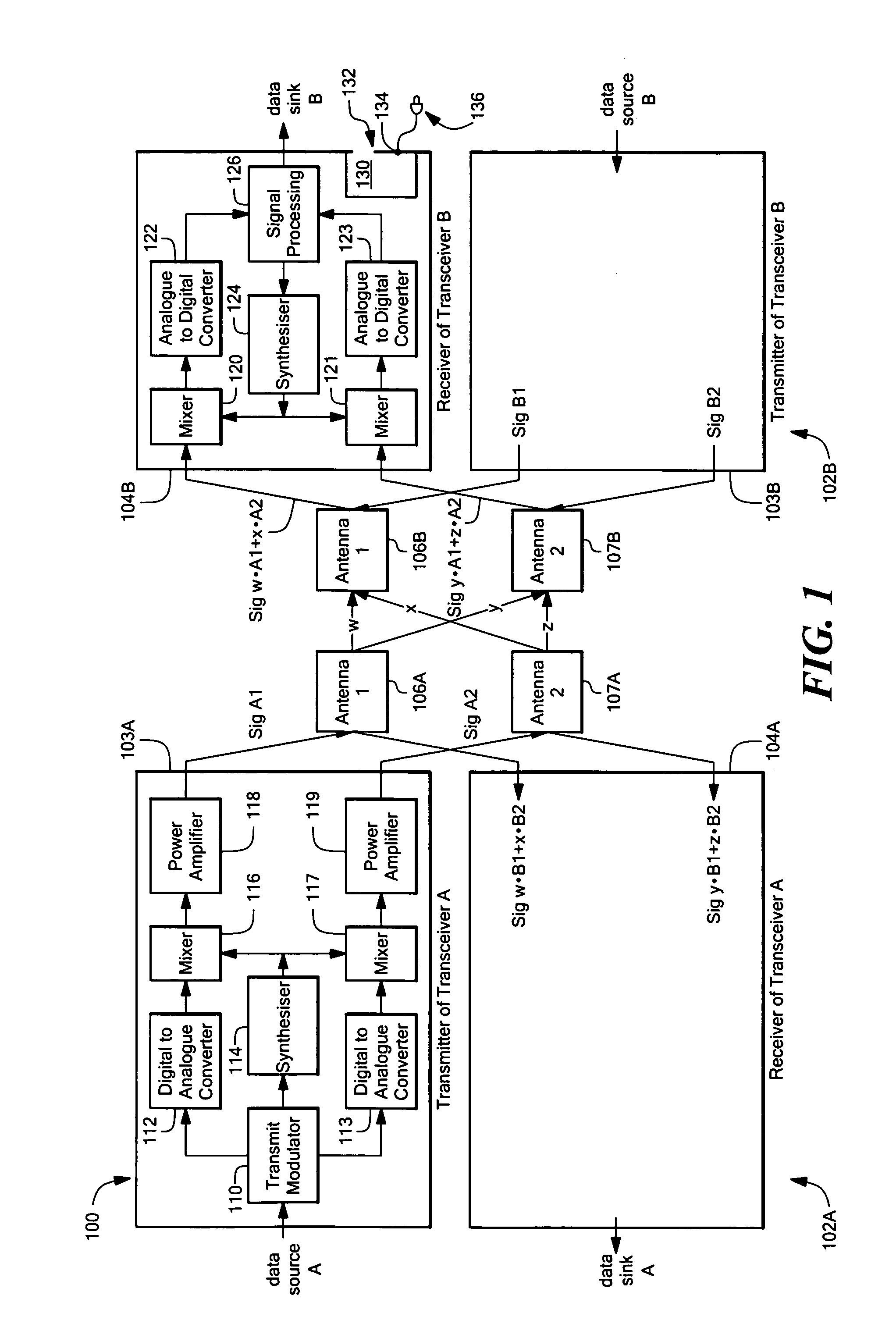
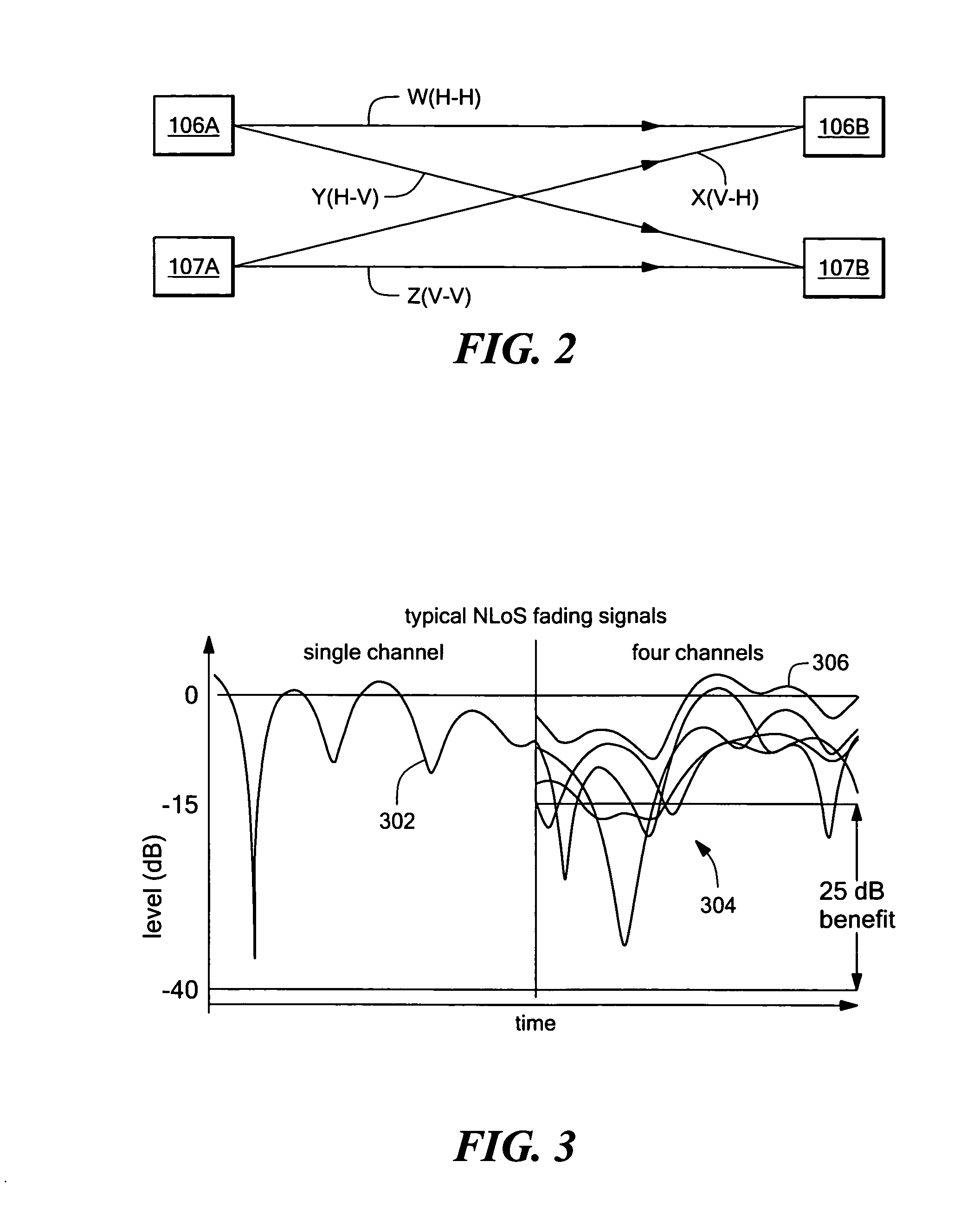
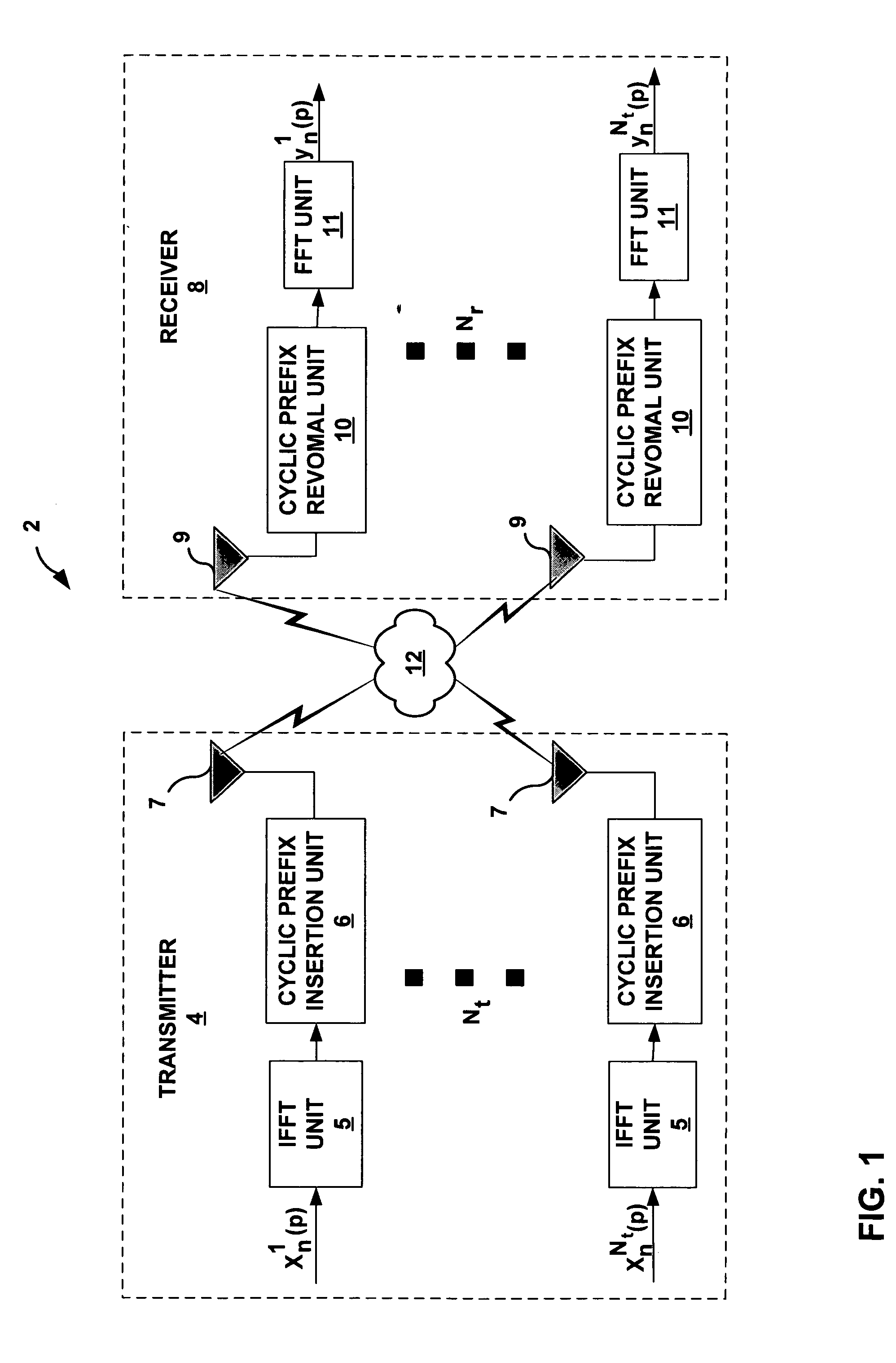
Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communications system
ActiveUS7333455B1Minimize waterMinimize ground bounce nullPower managementModulated-carrier systemsPolarization diversityFrequency spectrum
A wireless broadband communications system that can transmit signals over communications links with multiple modes of diversity, thereby allowing signals having very low correlation to propagate over the link along multiple orthogonal paths. The system can be implemented as a non-line-of-sight (NLOS) system or a line-of-sight (LOS) system. The NLOS system employs orthogonal frequency division modulation (OFDM) waveforms to reduce multi-path interference and frequency selective fading, adaptive modulation to assure high data rates in the presence of channel variability, and spectrum management to achieve increased data throughput and link availability. The LOS system employs space-time coding and spatial and polarization diversity to minimize ground bounce nulls. The system achieves levels of link availability, data throughput, and system performance that have heretofore been unattainable in wireless broadband communications systems.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
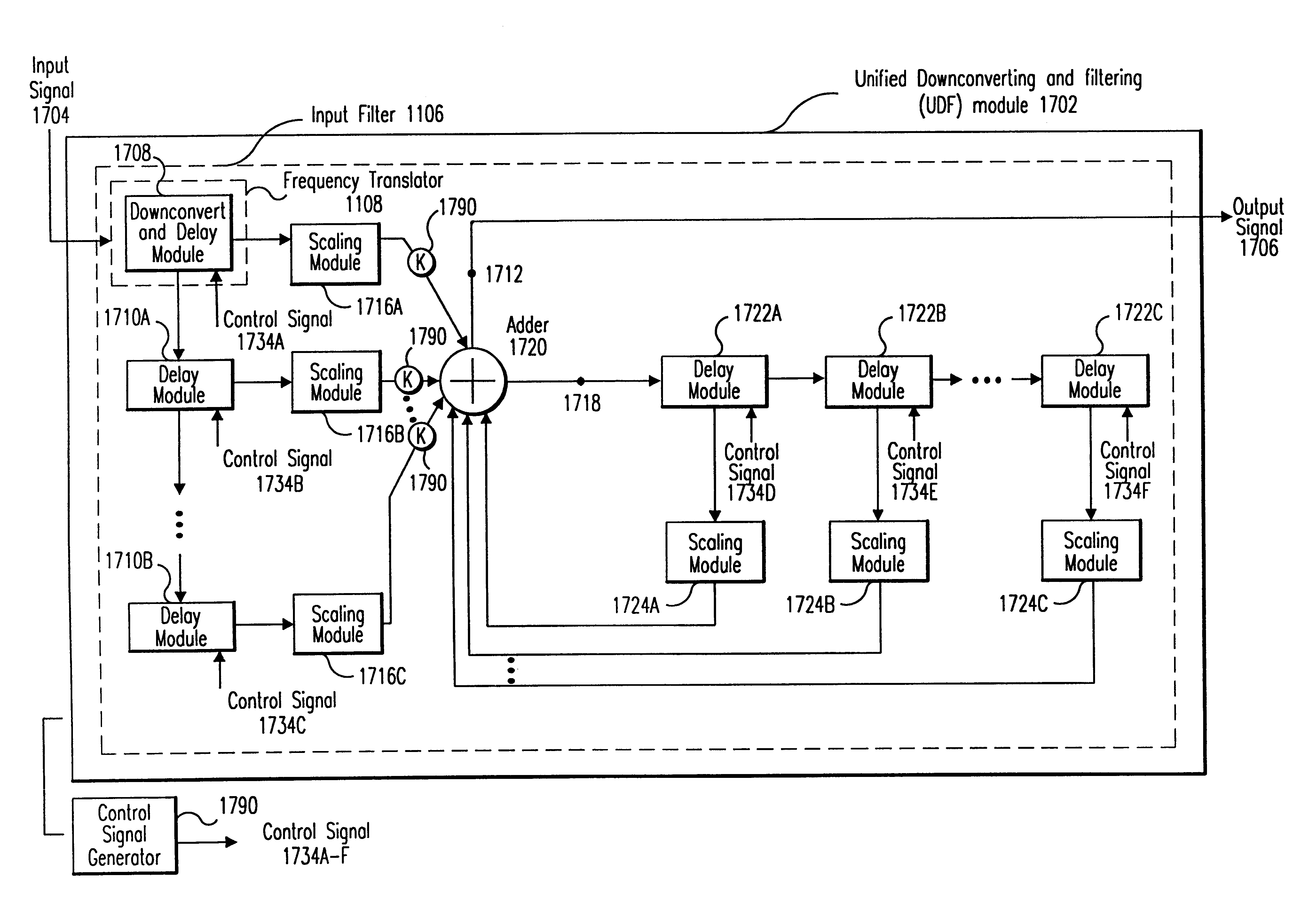
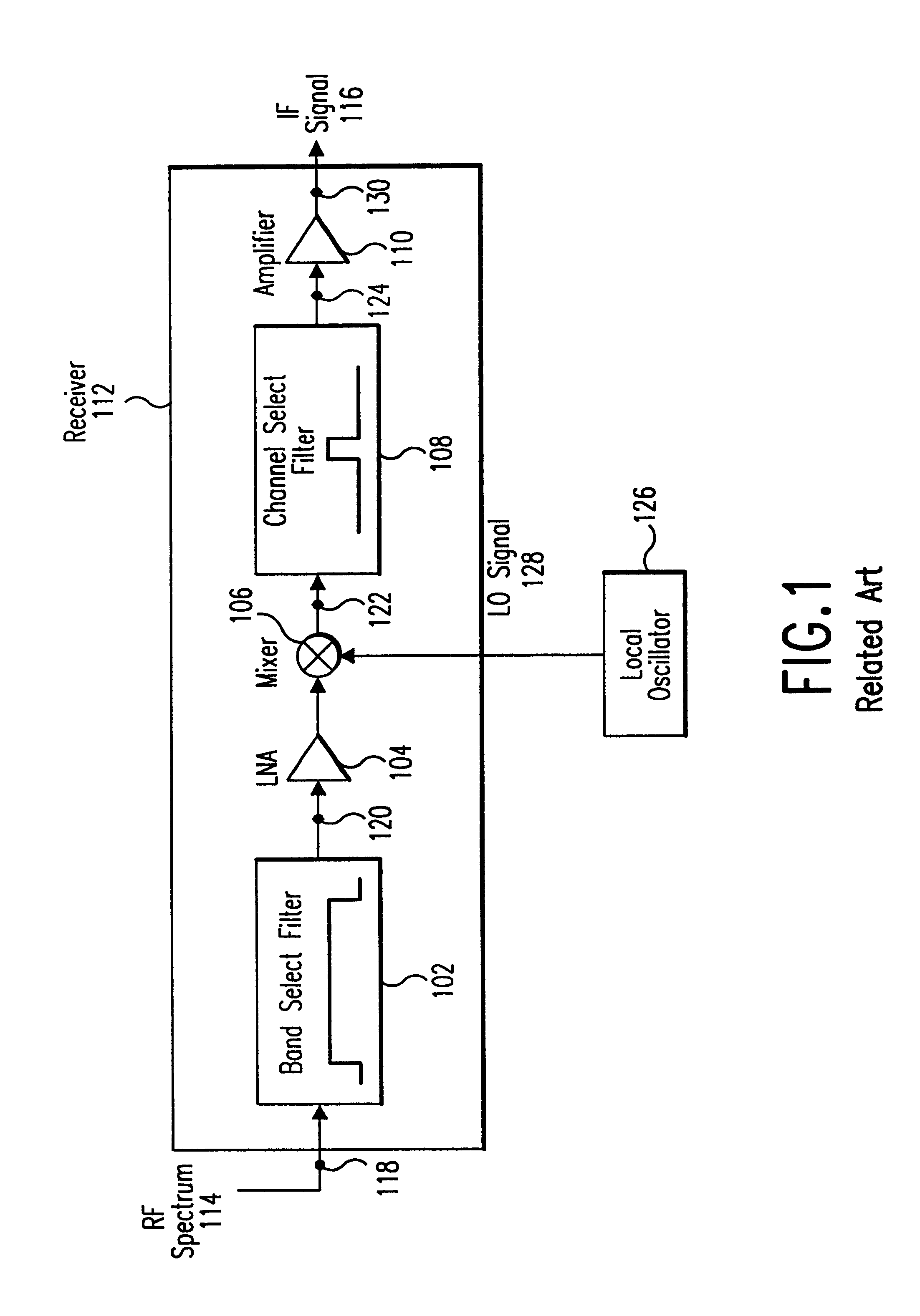
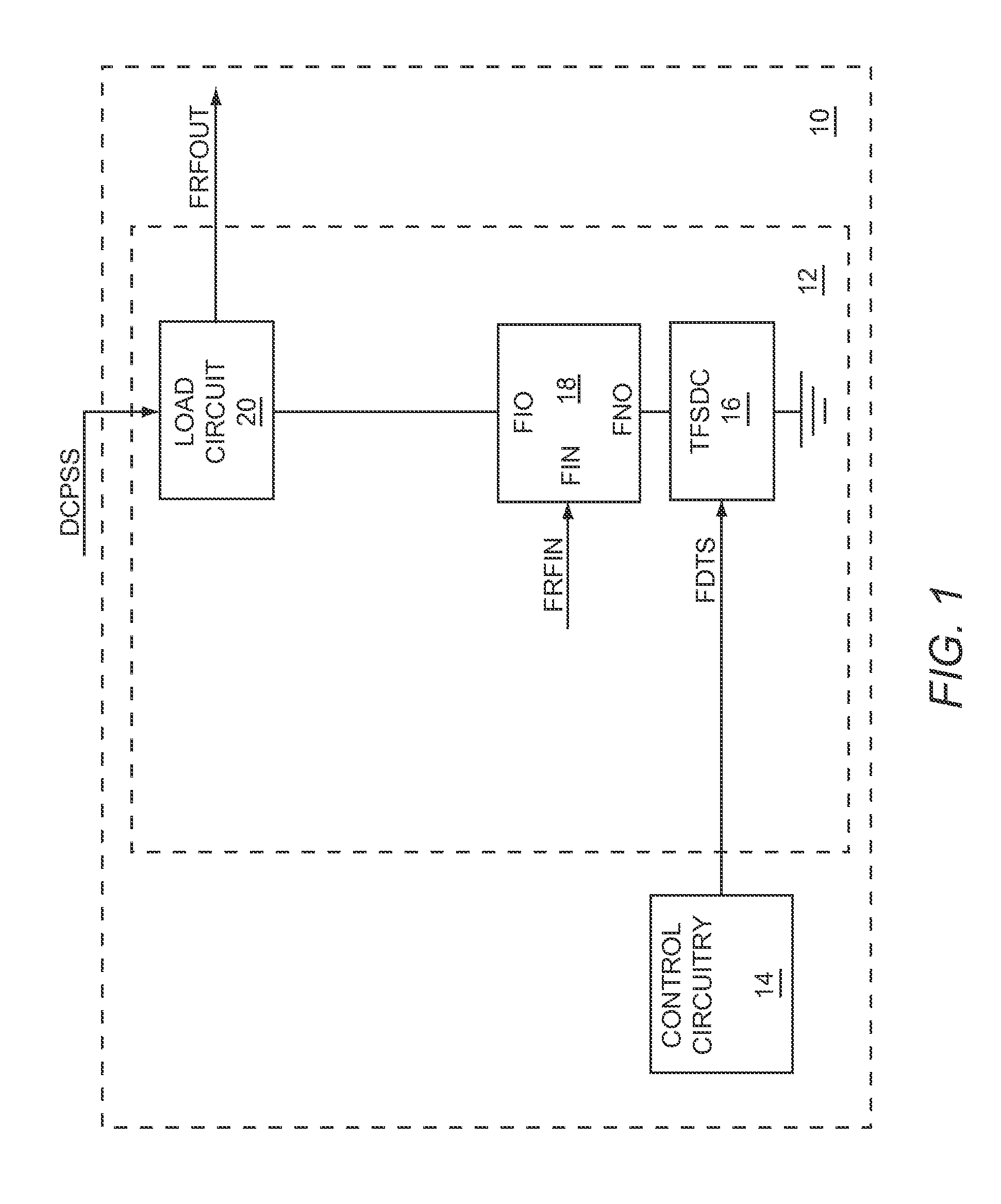
Integrated frequency translation and selectivity
Methods and apparatuses for frequency selectivity and frequency translation, and applications for such methods and apparatuses, are described herein. The method includes steps of filtering an input signal, and down-converting the filtered input signal. The filtering and the down-conversion operations are performed in an integrated, unified manner. The apparatus described herein can be implemented as an integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
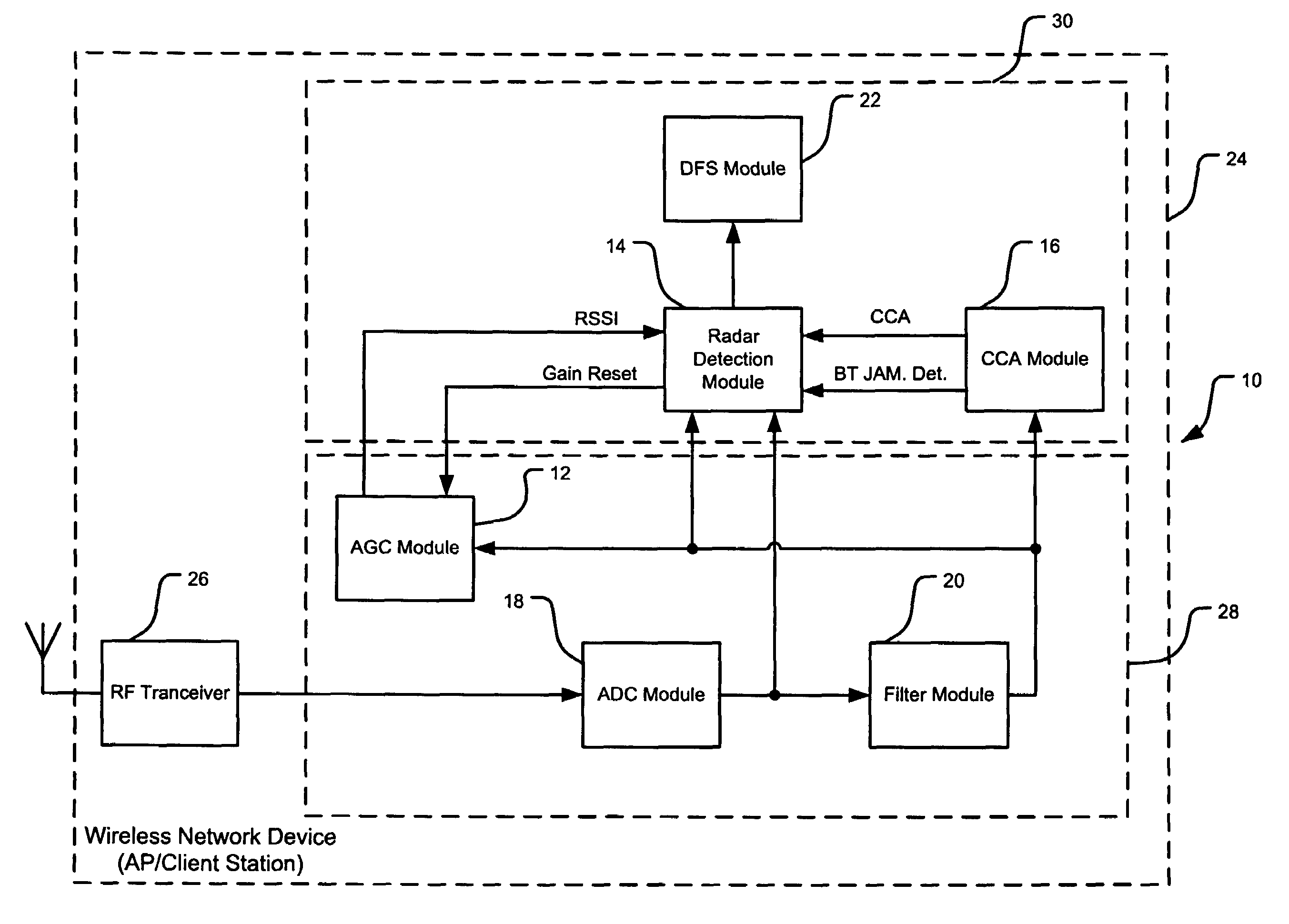
Radar detection and dynamic frequency selection
ActiveUS7702044B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunication jammingAutomatic controlControl signal
A wireless network device includes a correlation module, an automatic gain control module, and a control module. The correlation module correlates a predetermined portion of a radio frequency (RF) signal and generates a correlation signal based thereon. The automatic gain control (AGC) module generates a gain control signal based on said RF signal. The control module selectively determines whether said RF signal is a radar signal based on said correlation signal and said gain control signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
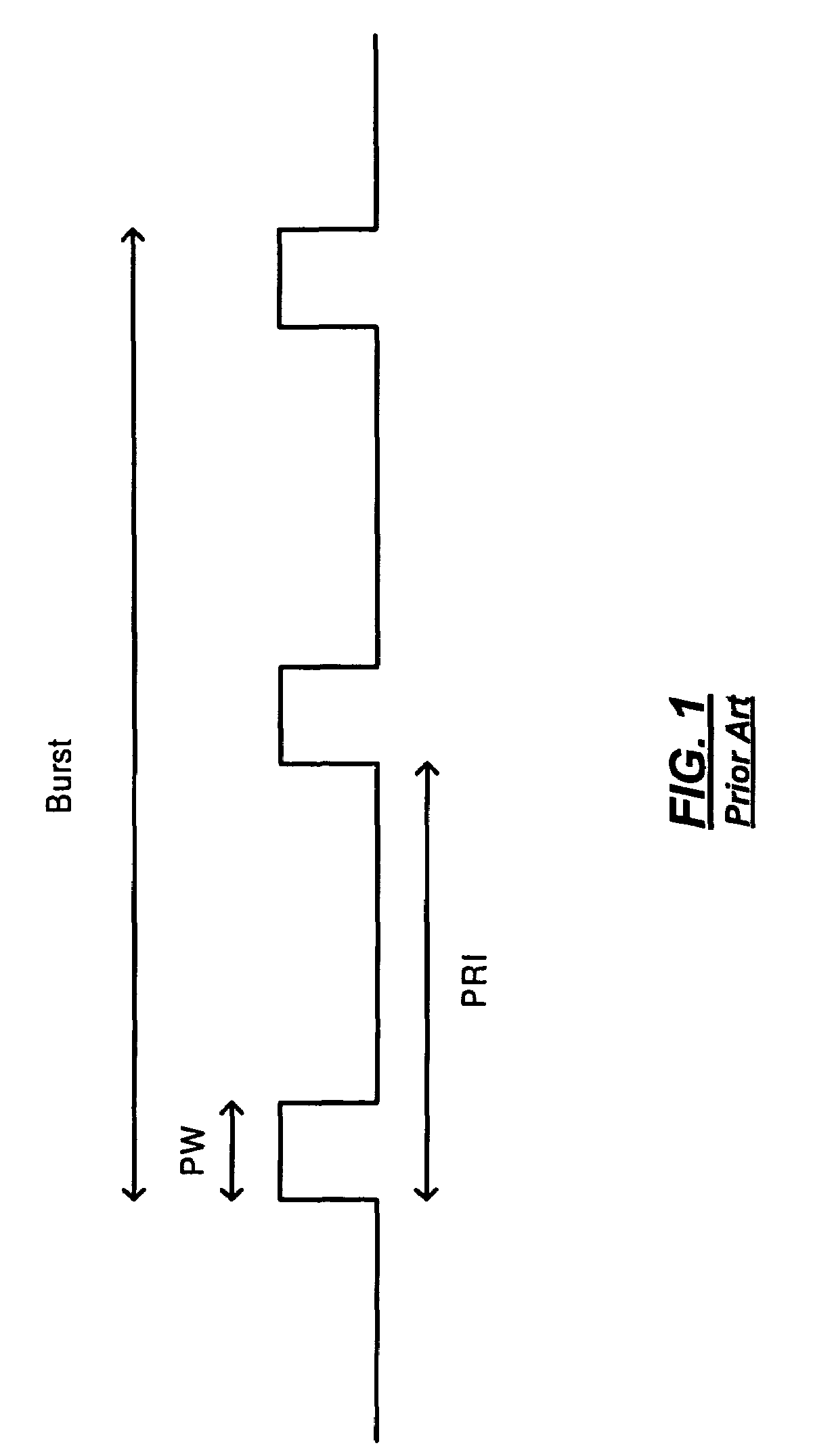
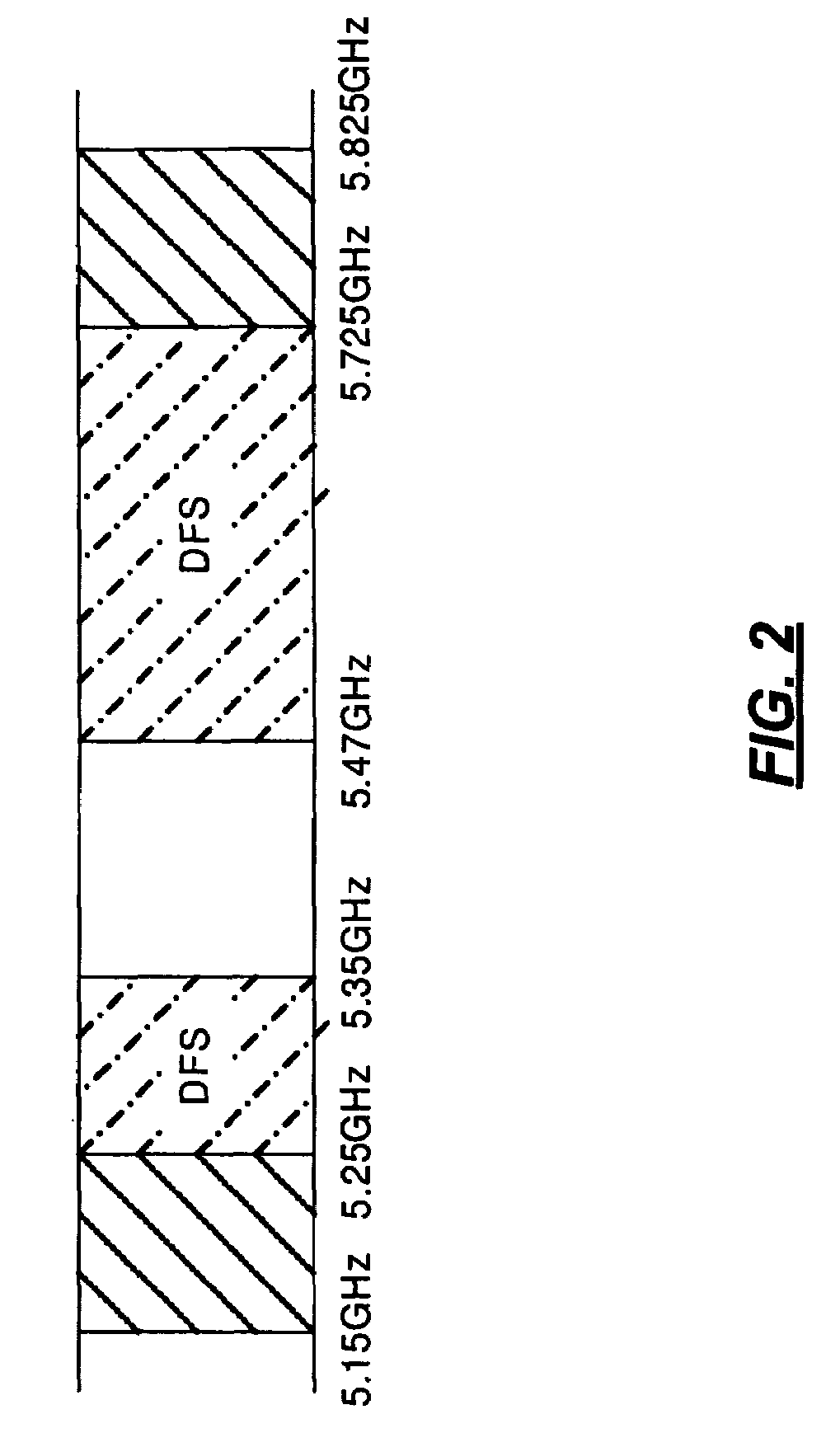
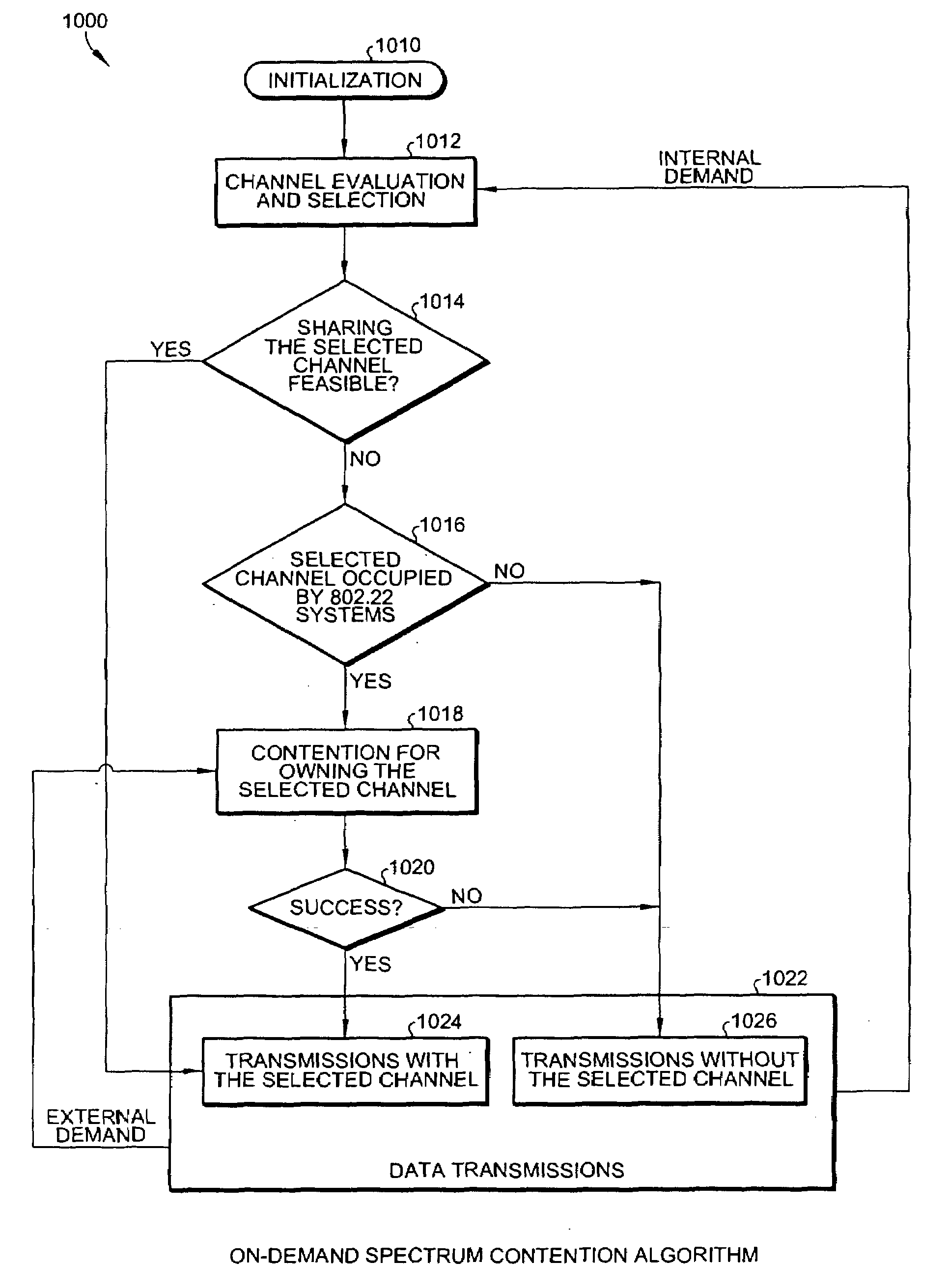
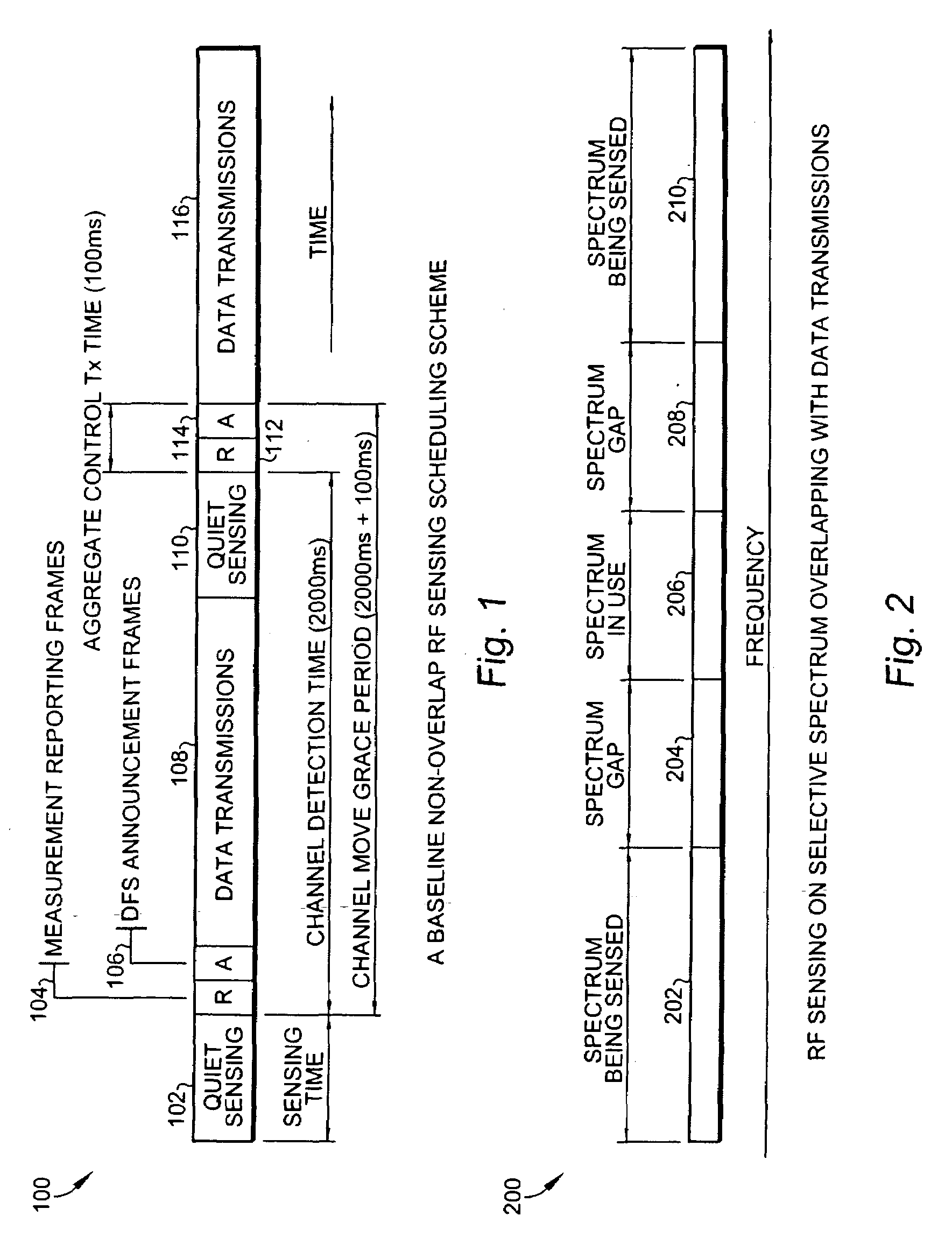
Methods of RF sensing control and dynamic frequency selection control for cognitive radio based dynamic spectrum access network systems-cognitive dynamic frequency hopping
ActiveUS20080090581A1Improve protectionError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkFrequency spectrum
This invention relates to cognitive radio based wireless communications of dynamic spectrum access networks, and more particularly to a method of addressing radio frequency sensing control and dynamic frequency selection control. A method called Cognitive Dynamic Frequency Hopping that is based on the selective Simultaneous Sensing and Data Transmissions is described. The Cognitive Dynamic Frequency Hopping method is further facilitated by a collision avoidance technique. The described method satisfies both reliable and timely RF sensing for guaranteeing licensed user protection, and QoS satisfaction for services of the dynamic spectrum access systems.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
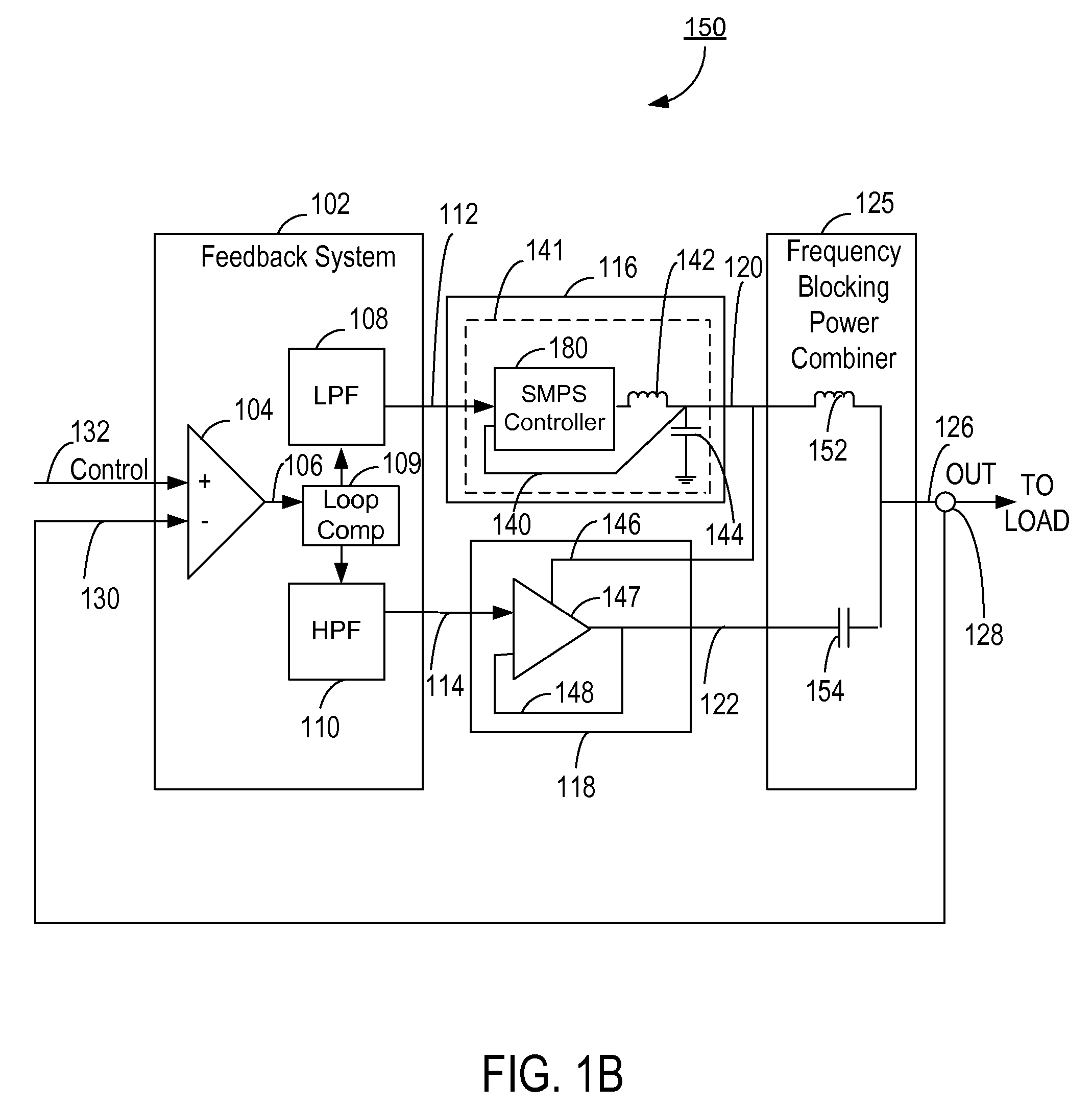
Power combining power supply system
ActiveUS20080104432A1Reduce the impactHigh bandwidthVolume/mass flow measurementDc-dc conversionLow speedPower combiner
A power supply system comprises a low-speed power supply and a high-speed power supply configured to operate in first and second frequency ranges, respectively, and generate first and second outputs, respectively. The lower end of the second frequency range is at least higher than a lower end of the first frequency range. A frequency blocking power combiner circuit combines the power from the first output with the power from the second output to generate a combined, third output for driving a load, while providing frequency-selective isolation between the first and second outputs. A feedback circuit is coupled to receive the combined, third output through a global feedback loop. The feedback circuit generates first and second power supply control signals for controlling the low-speed power supply and the high-speed power supply, respectively, based on a difference between the third output and the predetermined control signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Space-time-frequency coded OFDM communications over frequency-selective fading channels
ActiveUS20050002325A1Maximal diversityHigh coding gainsTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexComputer architectureCarrier signal
Techniques are described for space-time-frequency (STF) coding of multi-carrier transmissions over frequency-selective fading channels. In particular, techniques for STF coding of MIMO-OFDM systems are described that provide maximum diversity, high coding gains, and low decoding complexity are described. A set of generally correlated OFDM subcarriers are divided into groups of subcarriers creating a set of group STF (GSTF) subsystems, within which STF coding is applied to each GSTF subsystem. Subcarrier grouping preserves maximum diversity gains and simplifies both the code construction within each GSTF and decoding complexity. ST coding techniques are used in designing STF block (STFB) and STF trellis (STFT) codes which are applied within GSTF subsystems.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
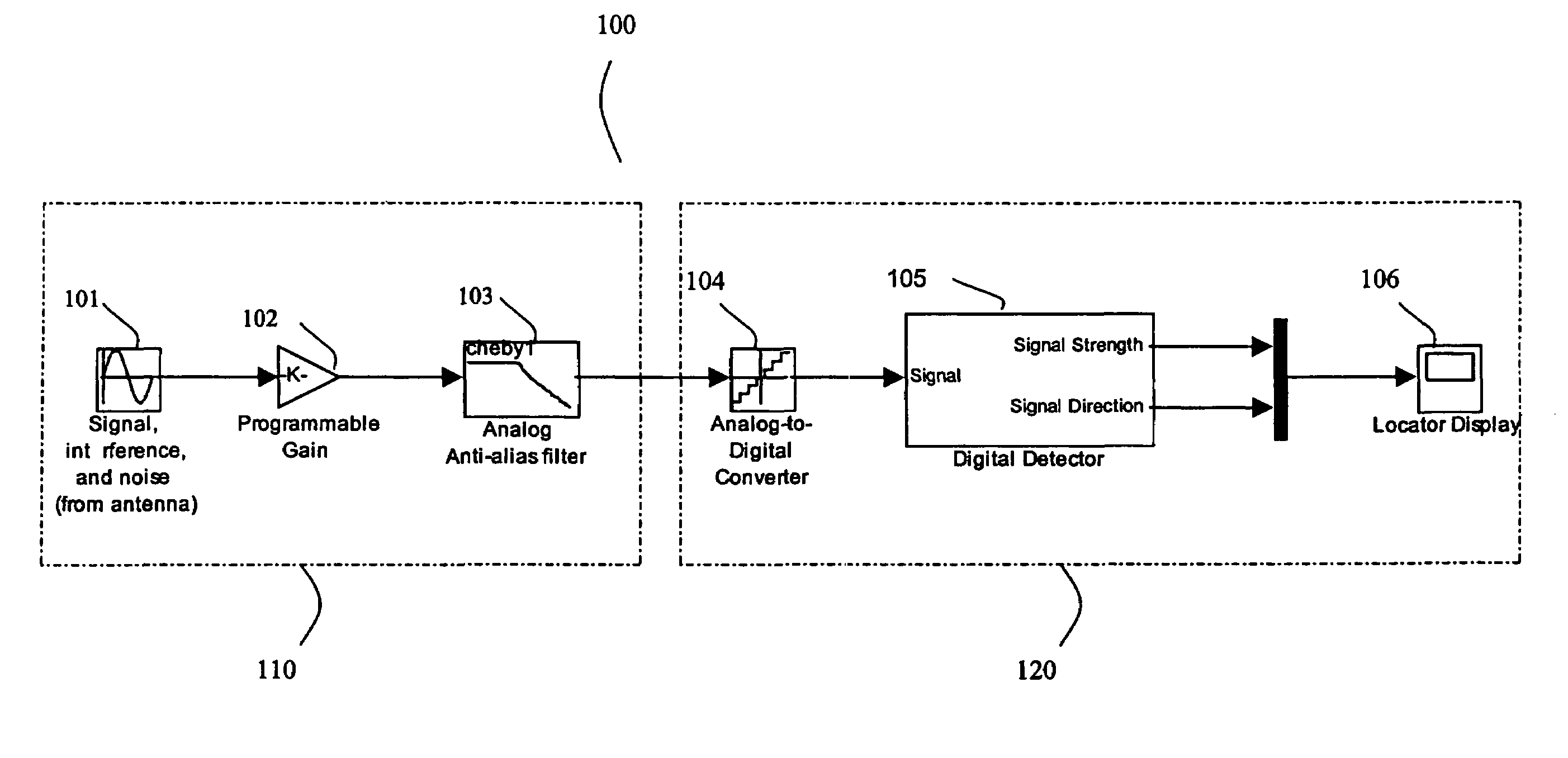
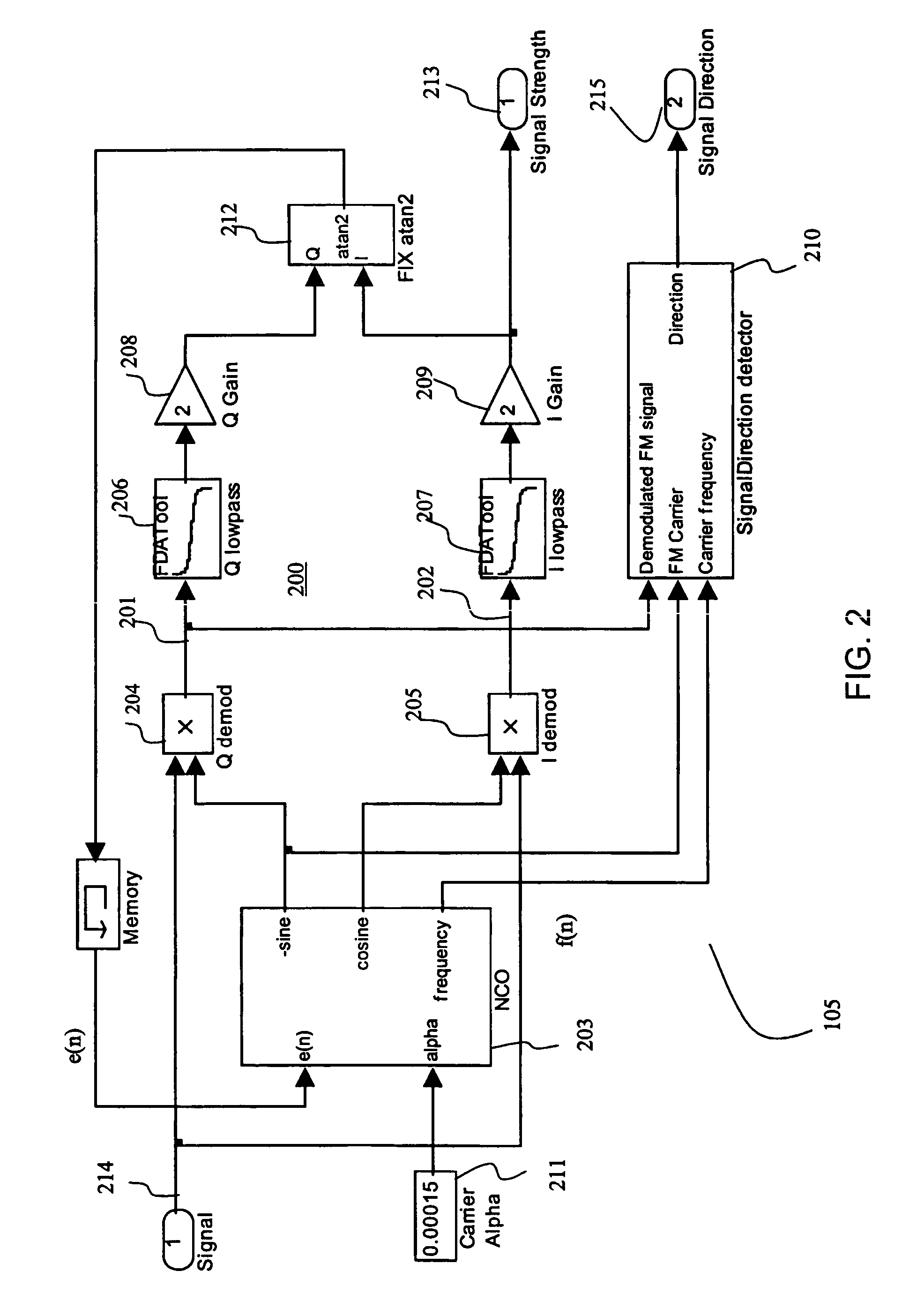
Method and apparatus for digital detection of electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction in metallic pipes and cables
InactiveUS7062414B2Low hardware requirementsWide resistance to component tolerancesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingCarrier signal
A new digital architecture for metallic pipe and cable locators, providing accurate estimation of the fundamental locate parameters, electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction, and utilizing a nested Digital Phase-Locked Loop (DPLL) structure is disclosed. The obstacles to signal direction measurement in low SINR environments using the signal select method are overcome and a more precise phase comparison between the carrier and the FM modulation signals is obtained. The architecture further significantly reduces analog front-end hardware requirements, offers wider resistance to component tolerances, lower calibration and test time, and provides flexible frequency selectivity. Locators according to the present invention provide accurate estimation of the fundamental physical parameters of line location (electromagnetic signal strength and signal direction) in extremely noisy environments, using Digital Signal Processing (DSP) methods.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
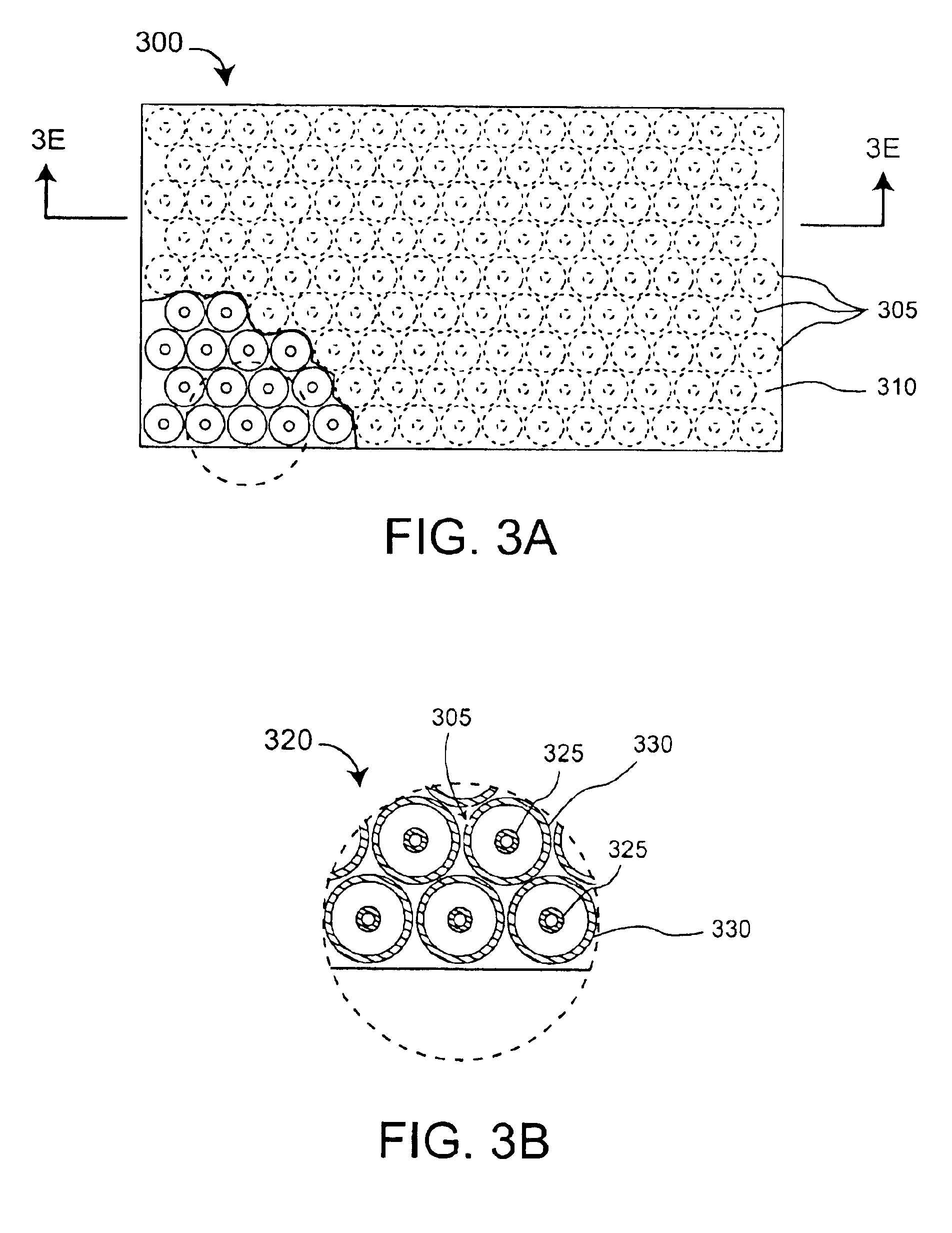
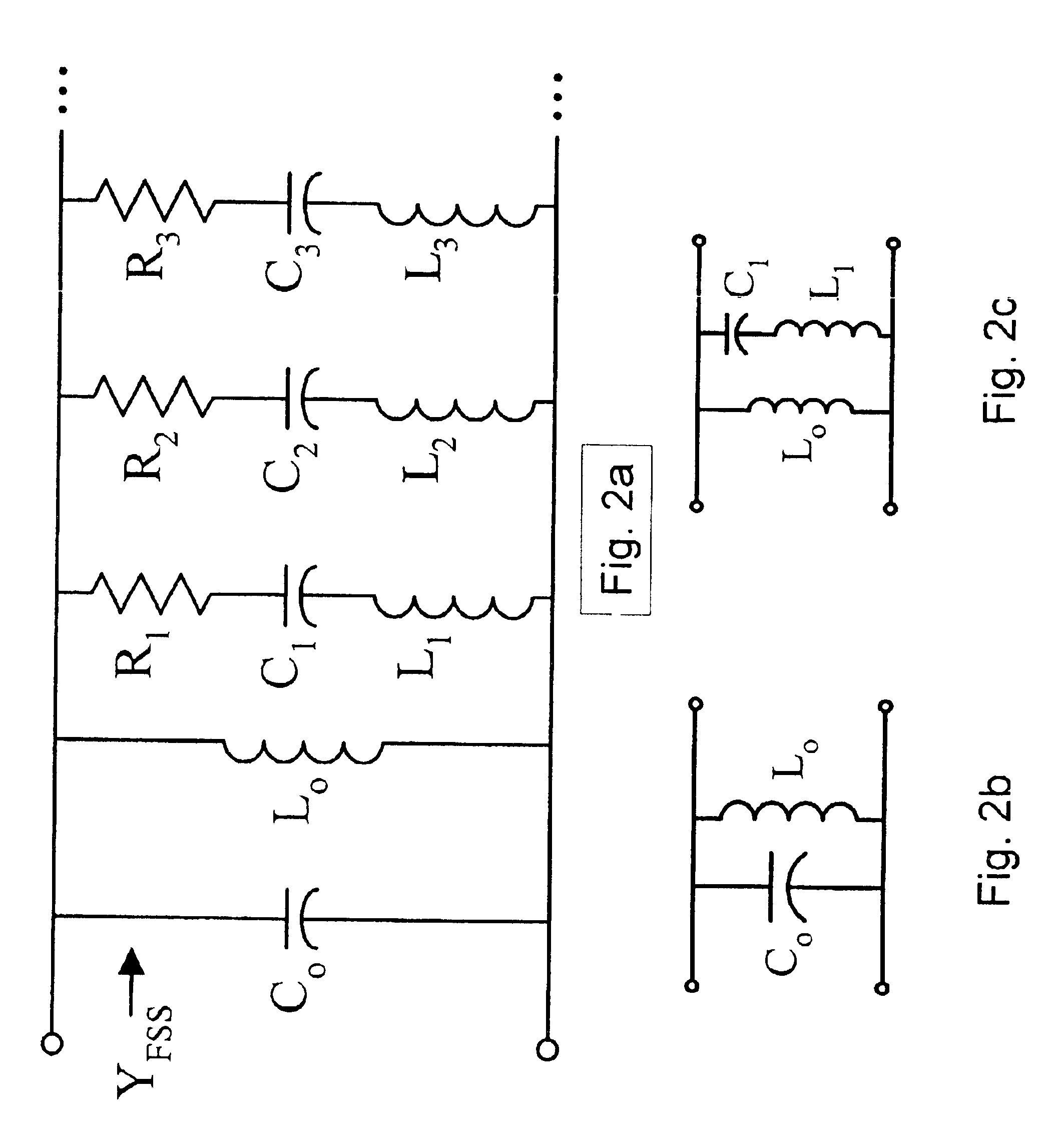
Low frequency enhanced frequency selective surface technology and applications
ActiveUS7071889B2Reduce physical sizeHigh surfaceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsWave structureCapacitance
DC inductive FSS technology is a printed slow wave structure usable for reduced size resonators in antenna and filter applications of wireless applications. It is a dispersive surface defined in terms of its parallel LC equivalent circuit that enhances the inductance and capacitance of the equivalent circuit to obtain a pole frequency as low as 300 MHz. The effective sheet impedance model has a resonant pole whose free-space wavelength can be greater than 10 times the FSS period. A conductor-backed DCL FSS can create a DC inductive artificial magnetic conductor (DCL AMC), high-impedance surface with resonant frequencies as low as 2 GHz. Lorentz poles introduced into the DCL FSS create multi-resonant DCL AMCs. Antennas fabricated from DCL FSS materials include single-band elements such as a bent-wire monopole on the DCL AMC and multi-band (dual and triple) shorted patches, similar to PIFAs with the patch / lid being a DCL FSS.
Owner:OAE TECH INC
Integrated frequency translation and selectivity with a variety of filter embodiments
Methods and apparatuses for frequency selectivity and frequency translation, and applications for such methods and apparatuses, are described herein. The method includes steps of filtering an input signal, and down-converting the filtered input signal. The filtering and the down-conversion operations are performed in an integrated, unified manner. The apparatus described herein can be implemented as an integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Using degeneration in an active tunable low-noise radio frequency bandpass filter
ActiveUS8314653B1Easy to FeedbackReduce gainSwitched capacitor networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesLow noiseBandpass filtering
The present disclosure relates to a first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter that includes at least a first transistor element and a tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit coupled to a first non-inverting output of the first transistor element. The first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter combines low noise amplifier (LNA) and tunable bandpass filter functionalities into a single active RF bandpass filter. The tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit uses degeneration at frequencies outside of a passband of the active RF bandpass filter to increase feedback, thereby decreasing gain of the active RF bandpass filter. By decreasing the gain, linearity of the active RF bandpass filter may be improved in the presence of strong interfering RF signals, thereby enabling elimination of passive bandpass filter elements, such as surface acoustic wave (SAW) and bulk acoustic wave (BAW) filters, without degrading reception of in-band RF signals.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Transmit diversity for acknowledgement and category 0 bits in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080267158A1Use minimizedSimple and efficient transmit diversitySignal allocationCode division multiplexCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method of transmitting acknowledgement / nonacknowledgement (ACK / NACK) signals including multiplexing ACK / NACK signals; and repeatedly transmitting for predetermined times the multiplexed signal with each of repetitions of transmitting the multiplexed signal being spread in a frequency domain and being mapped to a plurality of discrete resource units each having a pair of neighboring subcarriers and a predetermined number of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) control symbols.A method for transmitting Category 0 bits, including modulating the Category 0 bits; repeatedly transmitting the modulated Category 0 bits with each of repetitions of transmitting the modulated Category 0 bits being spread in a frequency domain and being mapped to a plurality of discrete resource units each having a pair of subcarriers and a predetermined number of OFDM control symbols; and mapping the modulated Category 0 bits by a frequency selective transmit diversity (FSTD).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Frequency selective passive component networks for active implantable medical devices utilizing an energy dissipating surface
InactiveUS20100217262A1Direct contact guaranteeMultiple-port networksElectrotherapyRf fieldEnergy transfer
Decoupling circuits are provided which transfer energy induced from an MRI pulsed RF field to the housing for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) which serves as an energy dissipating surface. This is accomplished through broadband filtering or by resonant filtering. In a passive component network for an AIMD, a frequency selective energy diversion circuit is provided for diverting high-frequency energy away from an AIMD lead to the AIMD housing for dissipation of said high-frequency energy.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
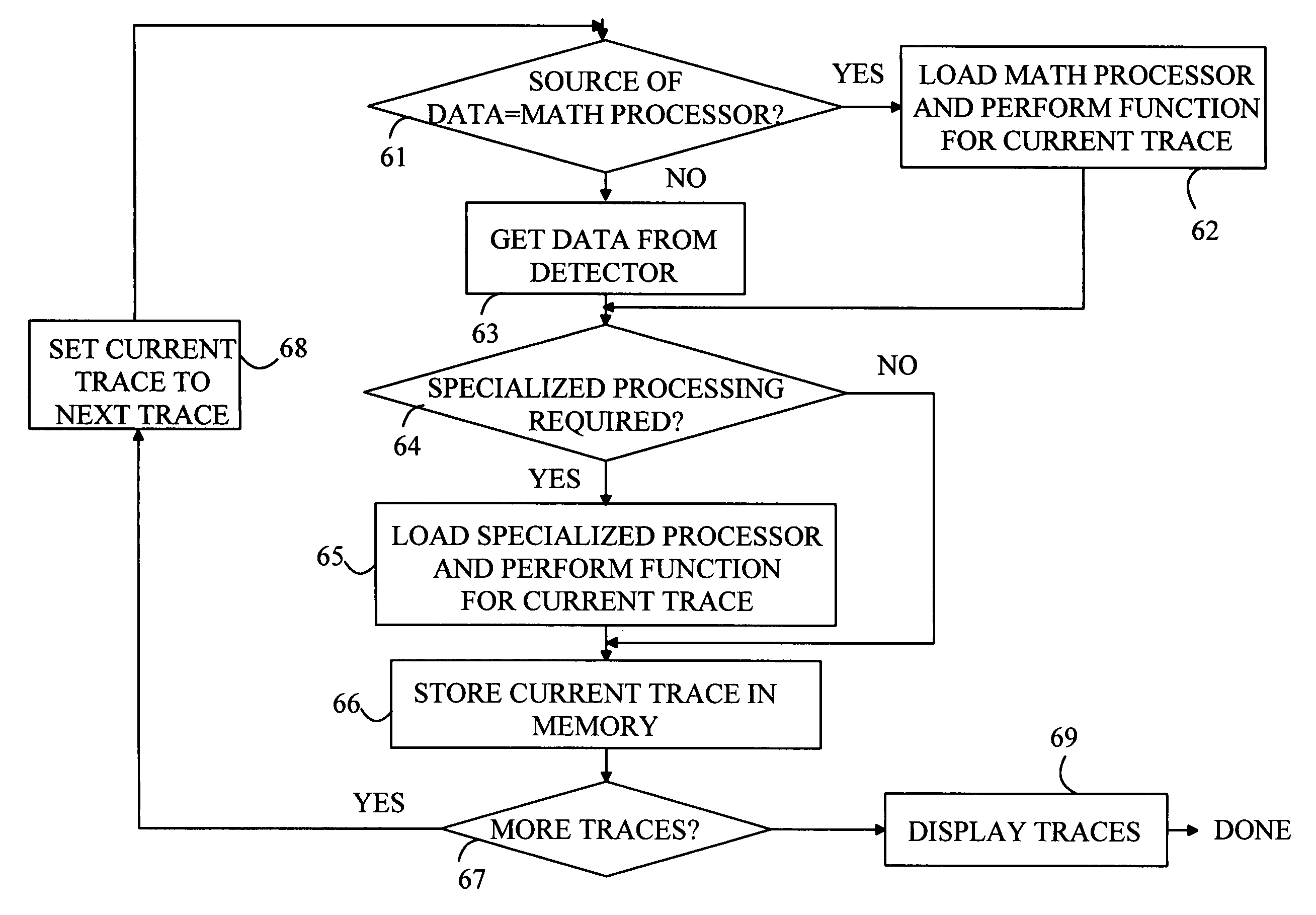
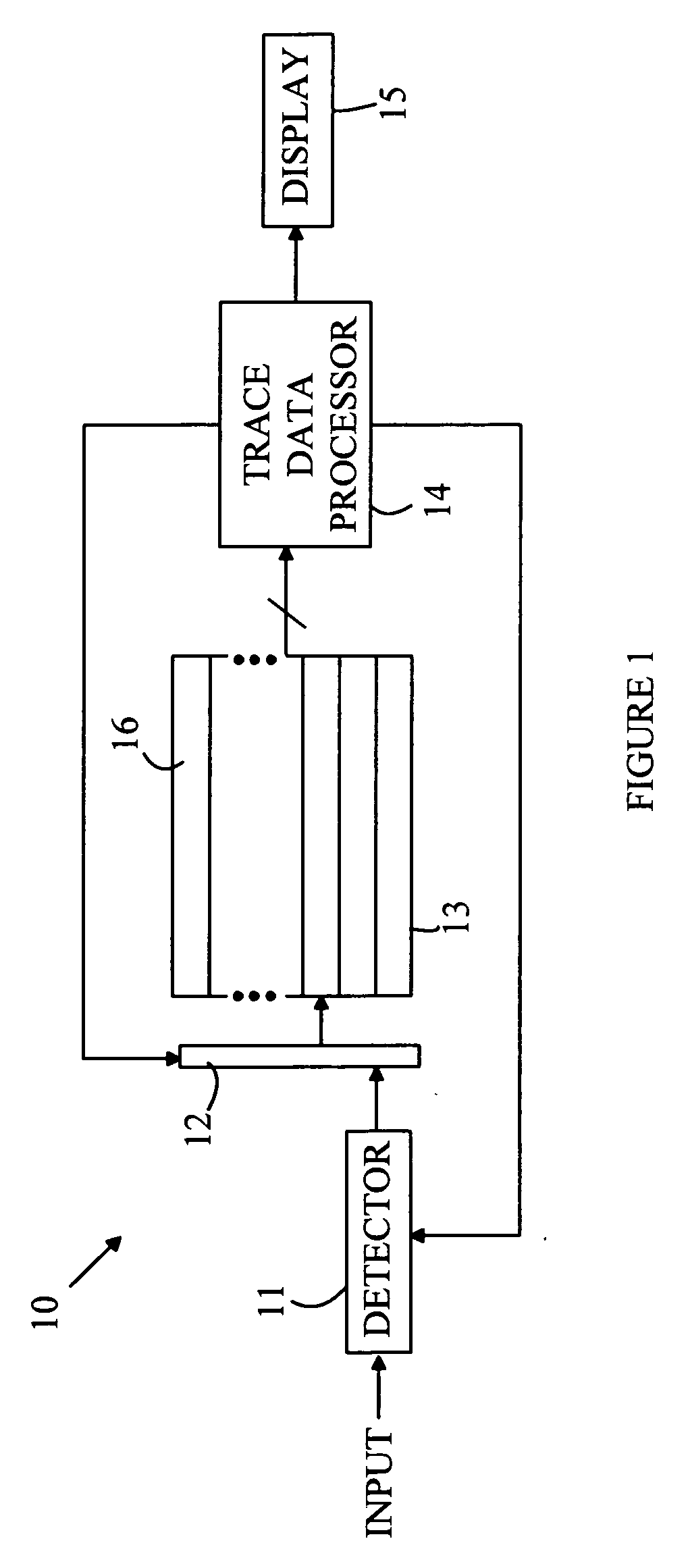
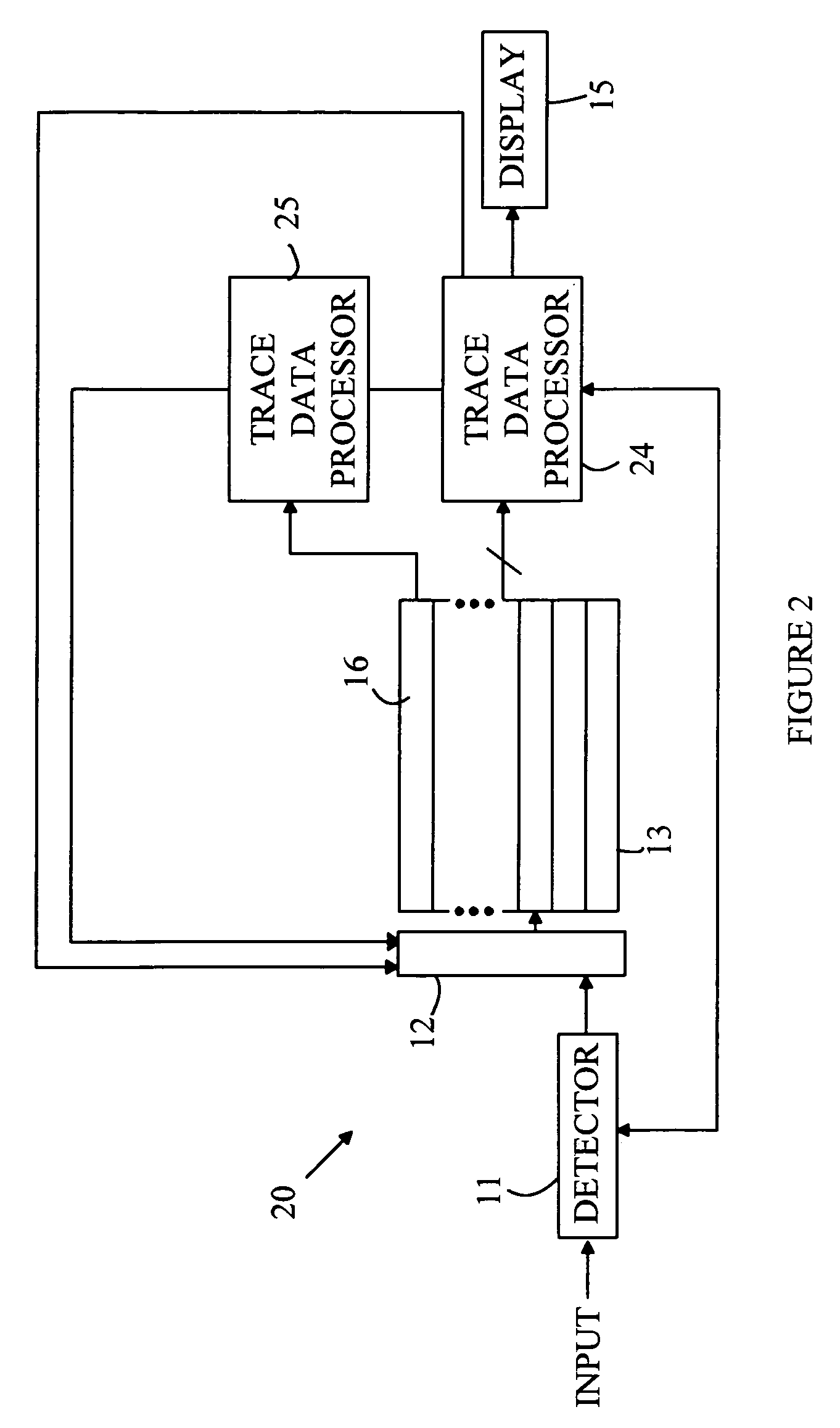
Spectrum analyzer with cascadable trace math functions
InactiveUS20070233409A1Spectral/fourier analysisAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
A spectrum analyzer is disclosed. The analyzer includes a detector, a trace memory, a controller, a trace math processor and a display. The controller generates a plurality of frequency selection signal values and records the measured amplitudes at each of the generated frequency selection values to form a measured trace that is stored in slots in the trace memory. The trace math processor performs trace mathematical operations on traces stored in the trace memory to generate a math trace that is stored in the trace memory. The controller stores a plurality of trace math programs, each program corresponding to one of the trace storage slots in the trace memory and specifies the trace mathematical operations that are to be performed to generate a new trace to be stored in that trace storage slot. The controller executes the stored trace math program for each trace slot in a predetermined order.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Remotely reconfigurable distributed antenna system and methods
ActiveUS8682338B2Increase capacityImprove efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower amplifiersDistributed antenna systemCarrier signal
The present disclosure is a novel utility of a software defined radio (SDR) based Distributed Antenna System (DAS) that is field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation-independent), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. The present disclosure enables a high degree of flexibility to manage, control, enhance, facilitate the usage and performance of a distributed wireless network such as flexible simulcast, automatic traffic load-balancing, network and radio resource optimization, network calibration, autonomous / assisted commissioning, carrier pooling, automatic frequency selection, frequency carrier placement, traffic monitoring, traffic tagging, pilot beacon, etc. As a result, the SDR DAS can increase the efficiency and traffic capacity of the operators' wireless network.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
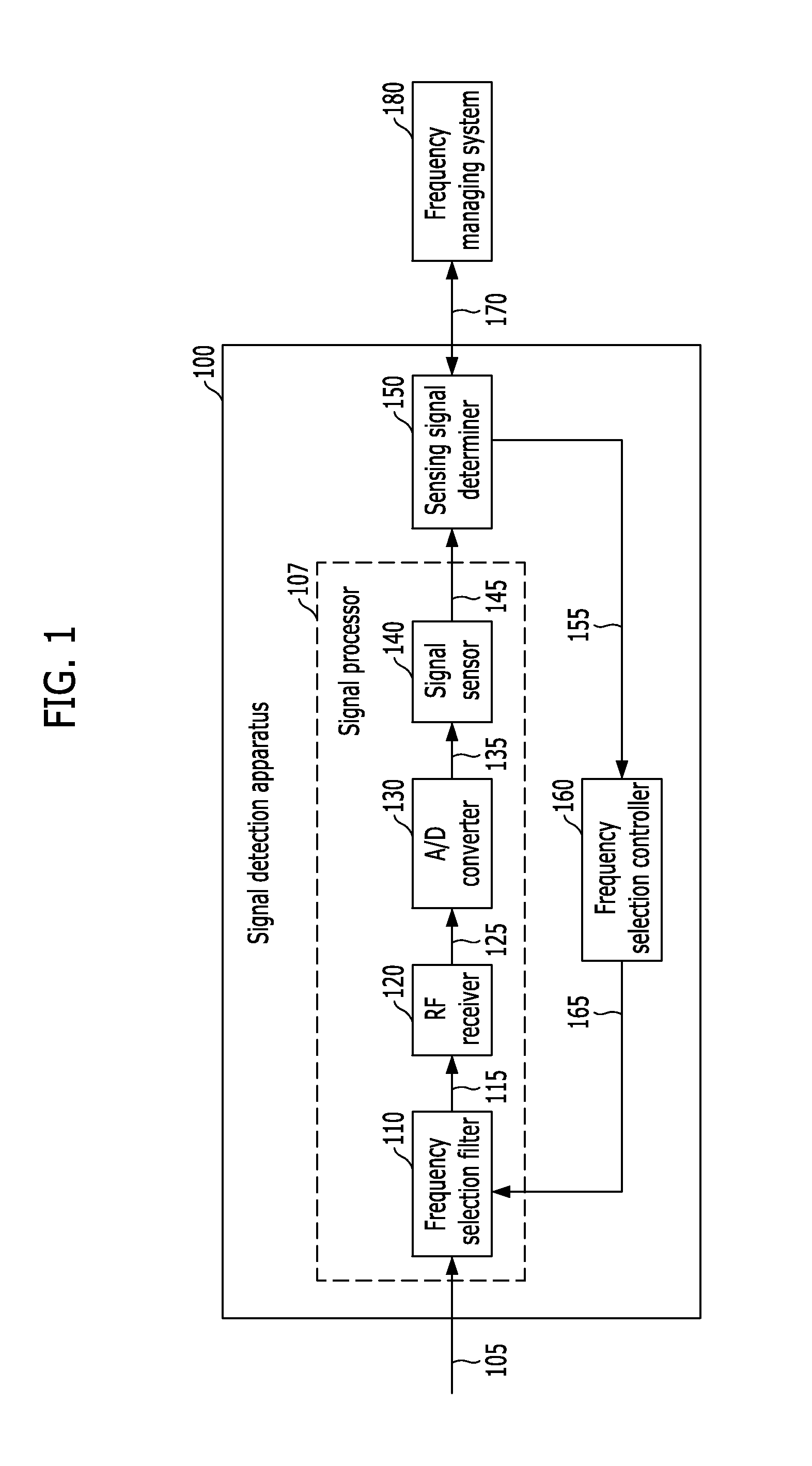
Apparatus and method for detecting signal in common frequency band
An apparatus for detecting a signal in a common frequency band includes: a signal processor configured to extract a selected band signal from received wireless signals by filtering the received wireless signal based on a frequency selection control signal, convert the extracted signal to a baseband signal, and detect a predetermined signal; a sensing signal determiner configured to determine existence of the signal, output a determination result, and outputs a frequency selection generating signal when the predetermined signal is absent; and a frequency selection controller configured to output the frequency selection control signal by selecting a target band among a plurality of previously decided bands.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and system for selectively reducing call-setup latency through management of paging frequency
InactiveUS20030148785A1Lower latencyReceive quicklyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMobile stationCall setup
A method and system for selectively reducing call-setup latency. The method and system provides for selectively increasing the paging frequency used for paging certain mobile stations, so as to decrease the time that it takes to establish radio-link connectivity with those mobile stations. The method and system is particularly useful when establishing real-time communication sessions, such as instant chat sessions, but may be useful in other scenarios as well.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com