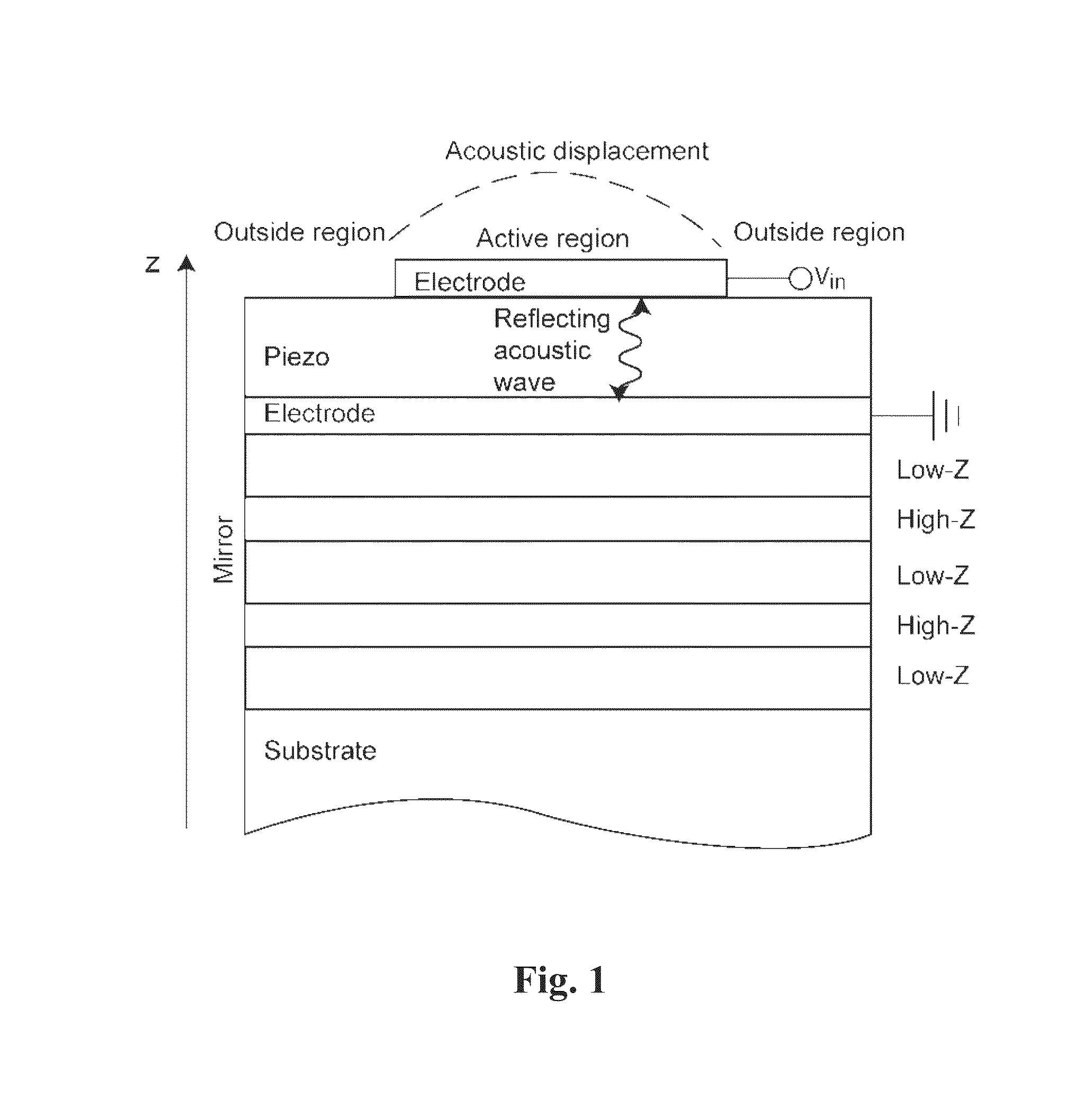
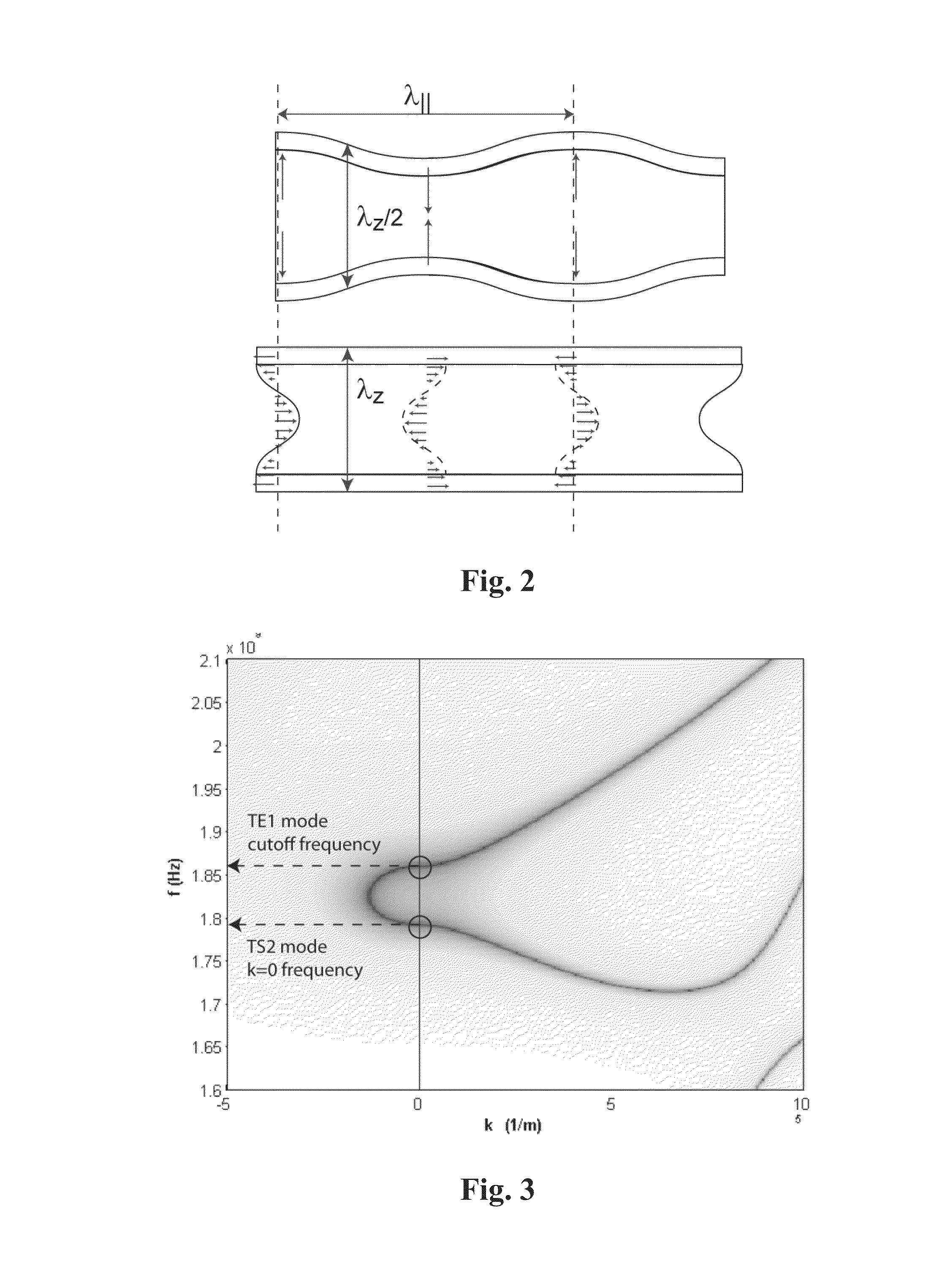
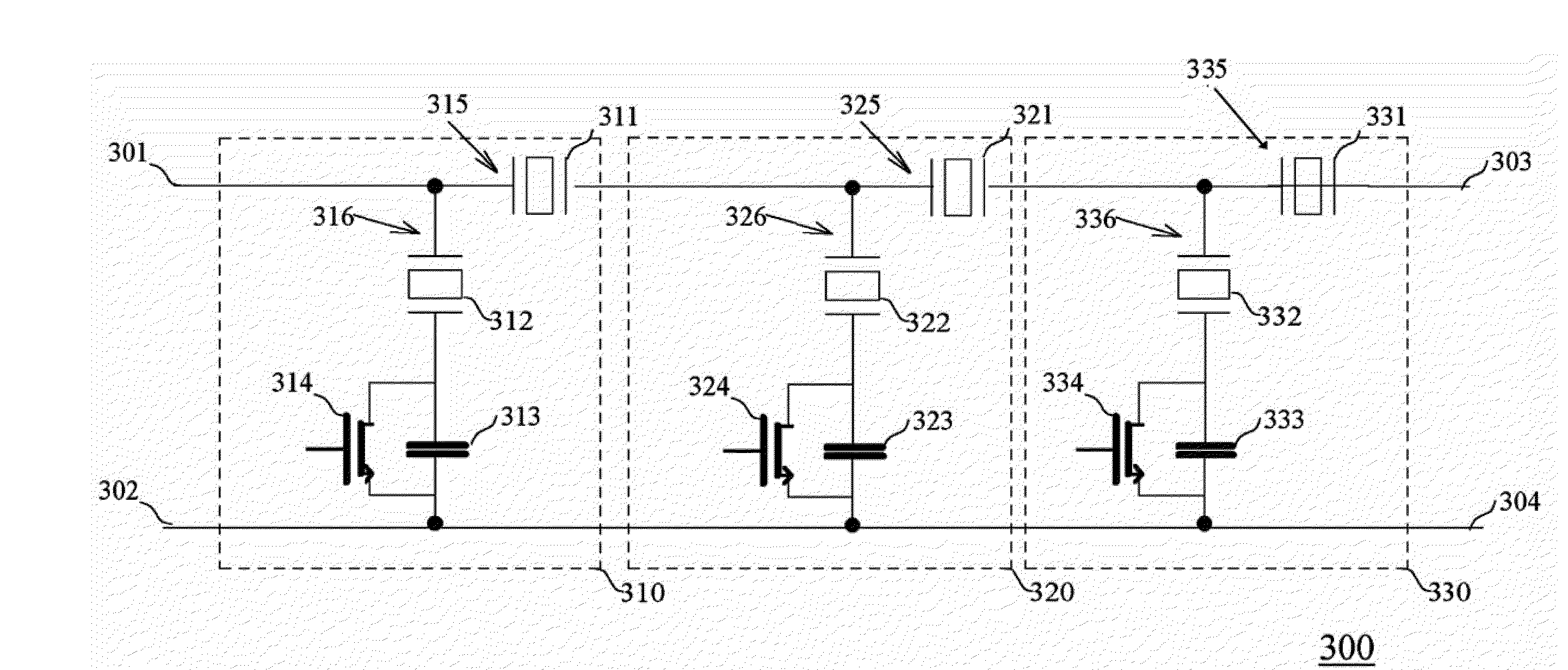
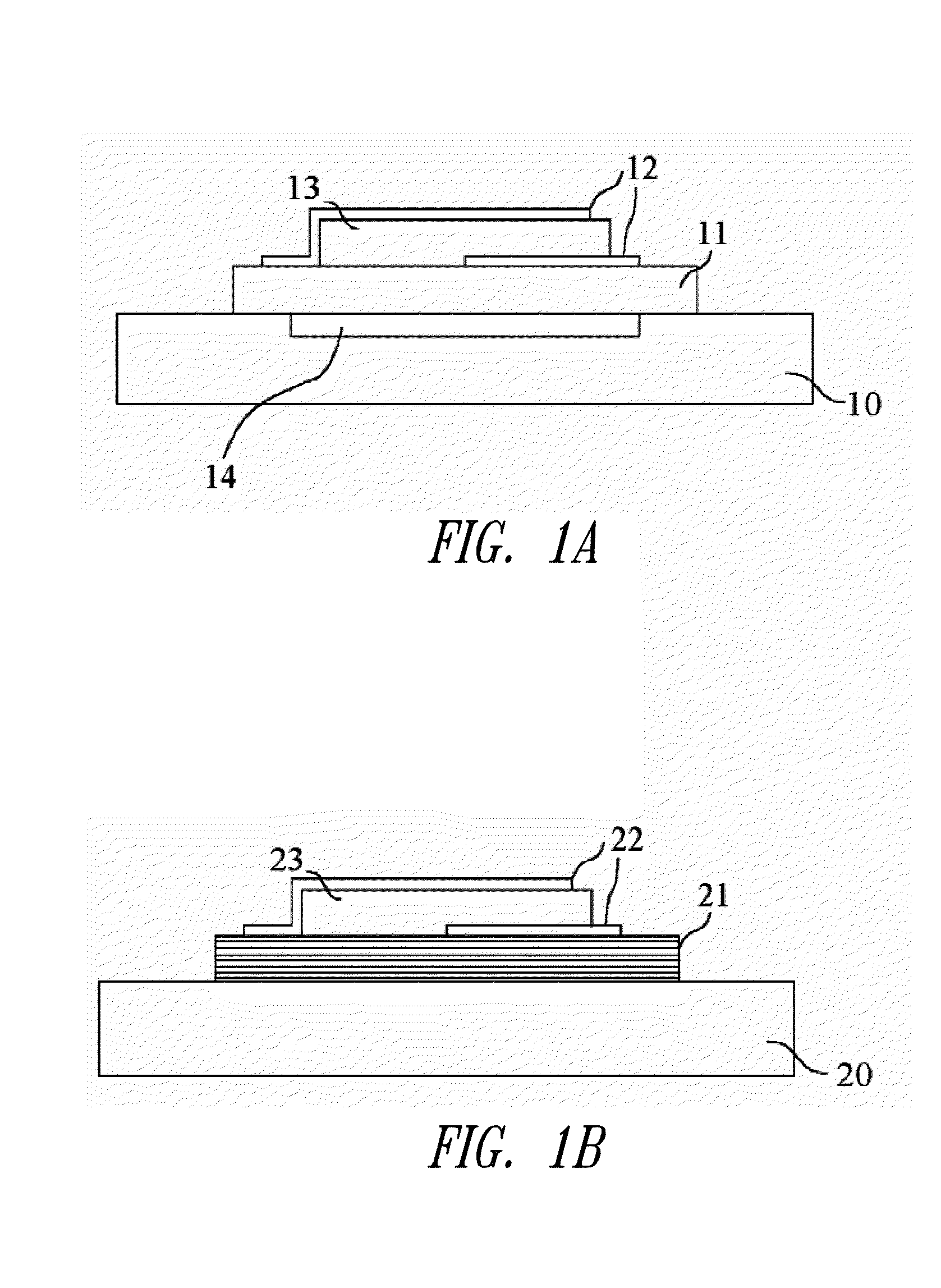
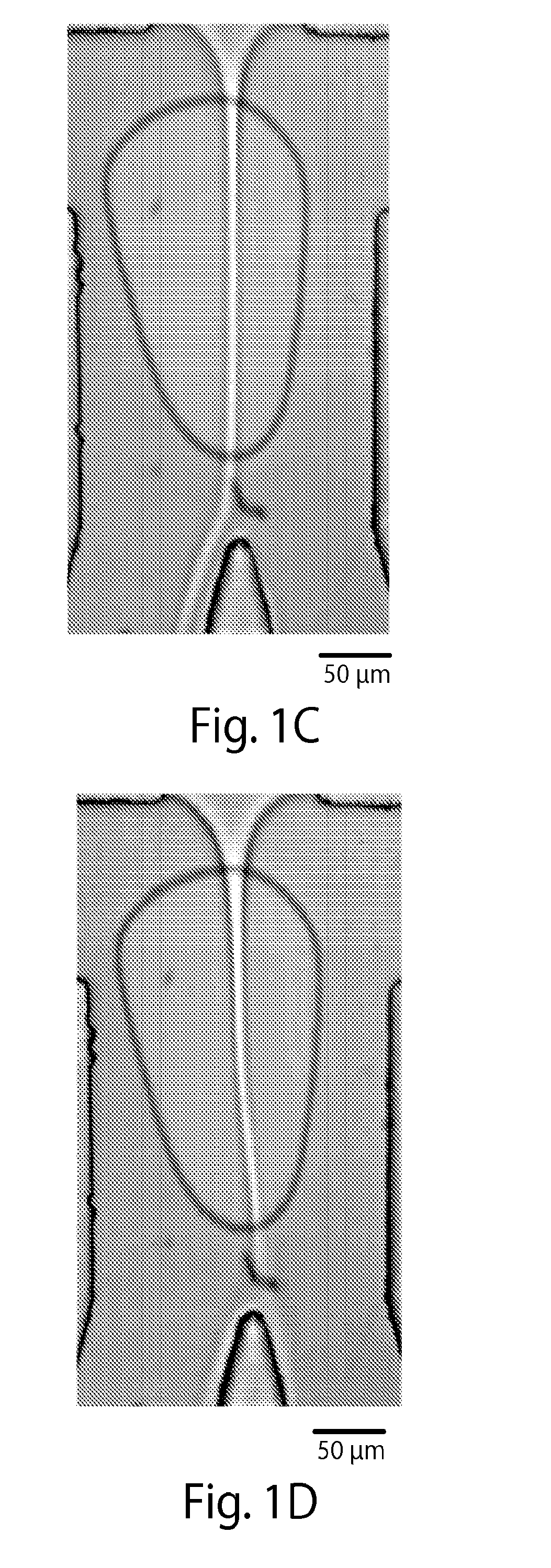
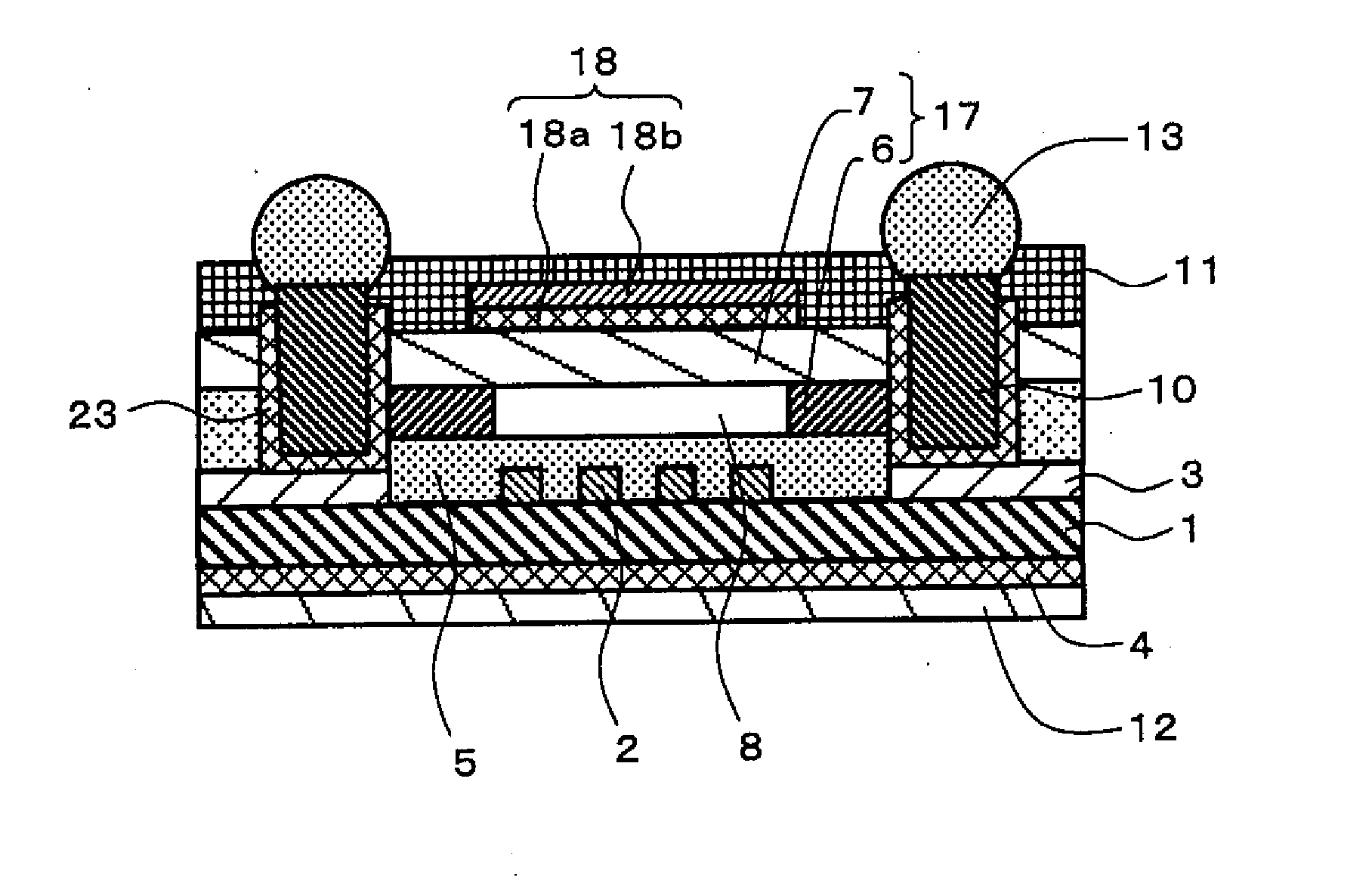
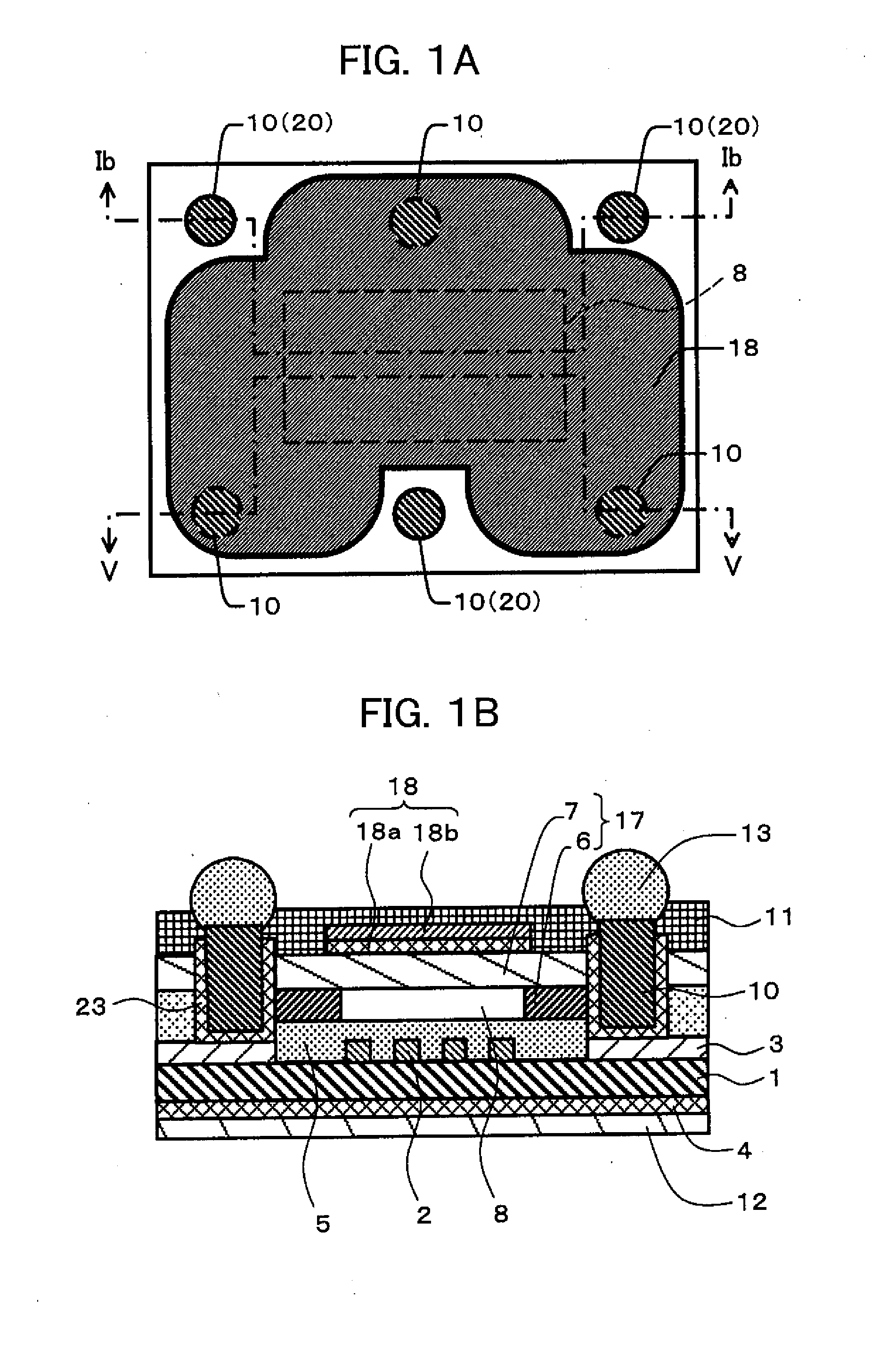
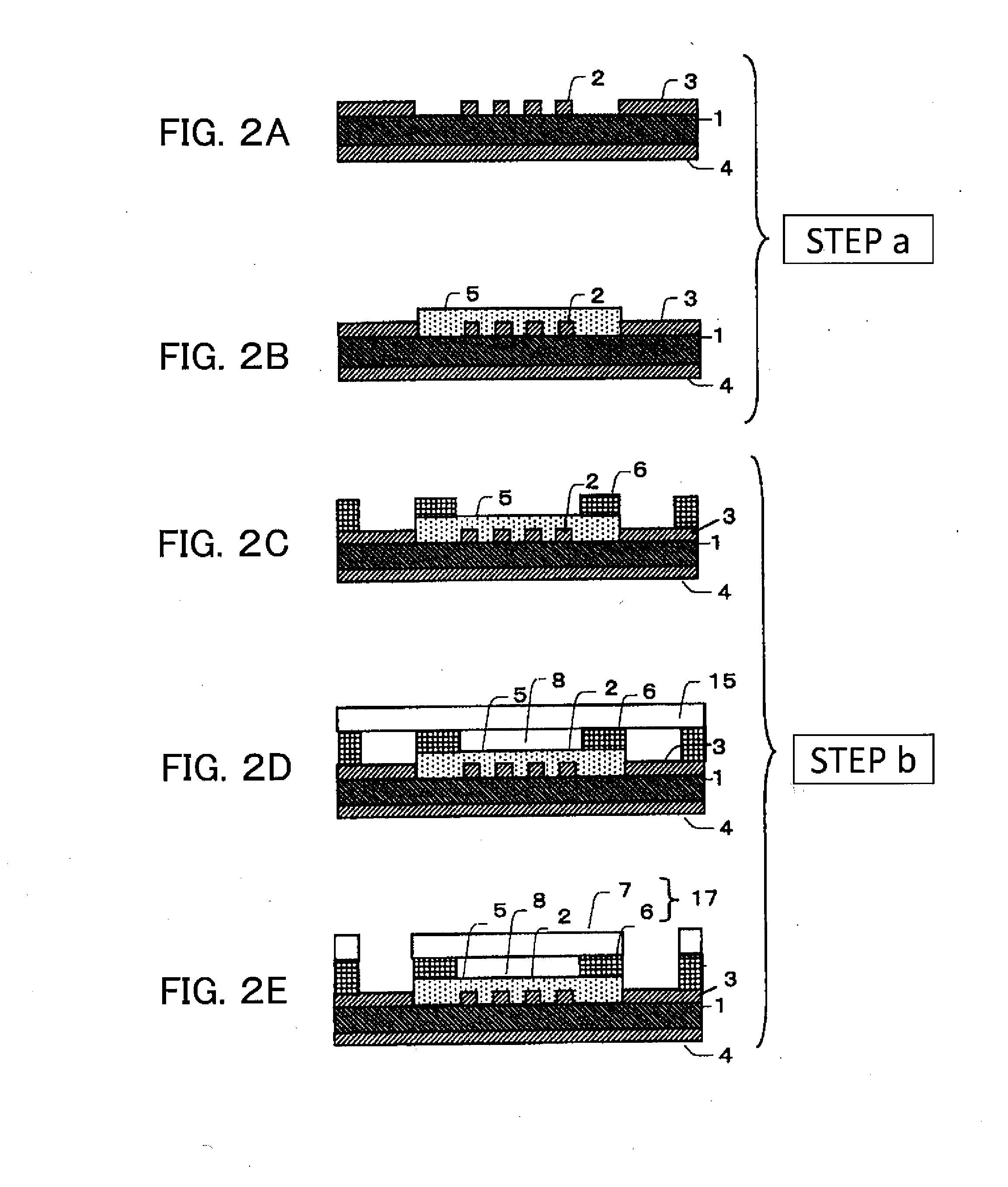
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1144 results about "Bulk acoustic wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
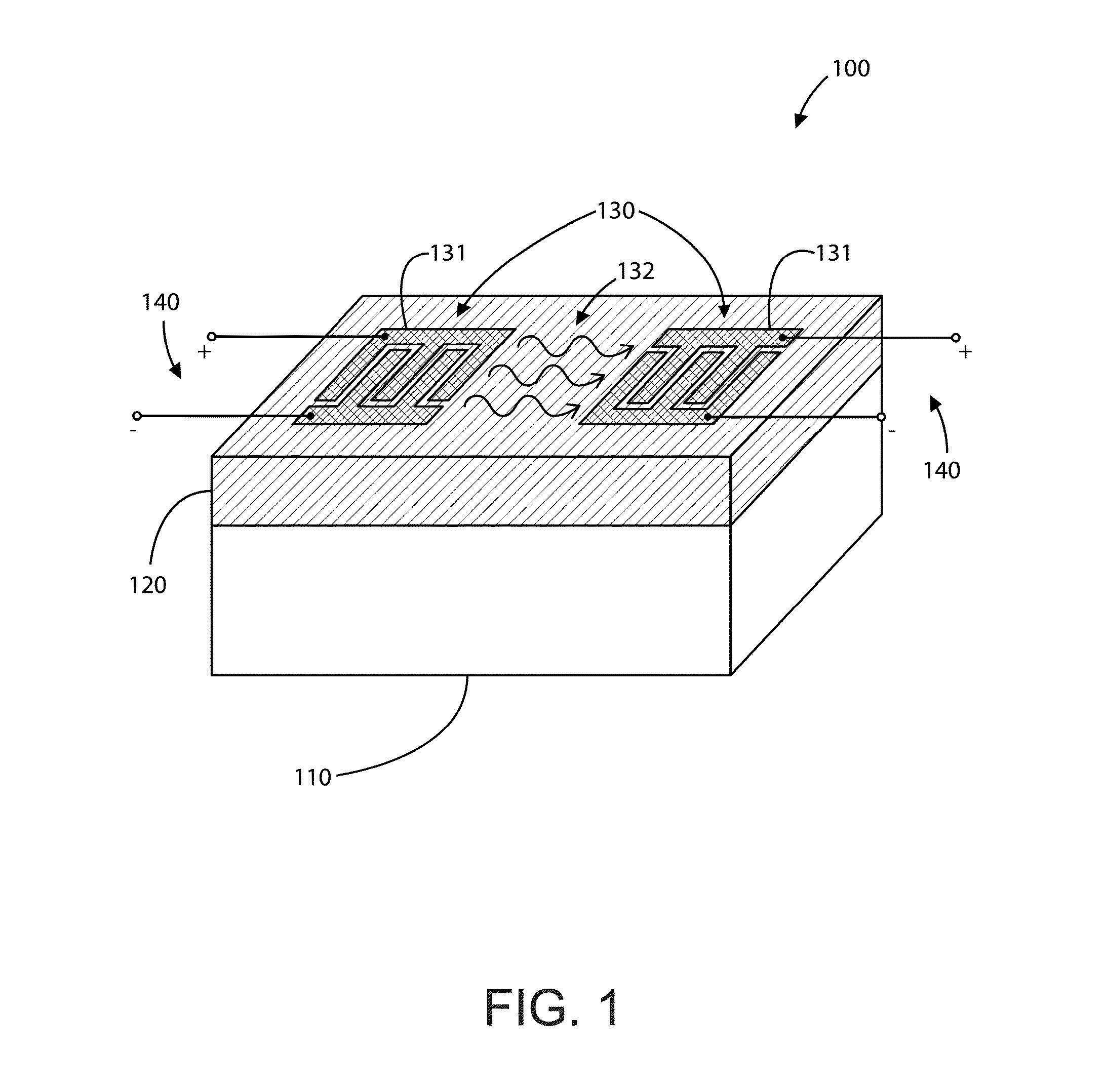
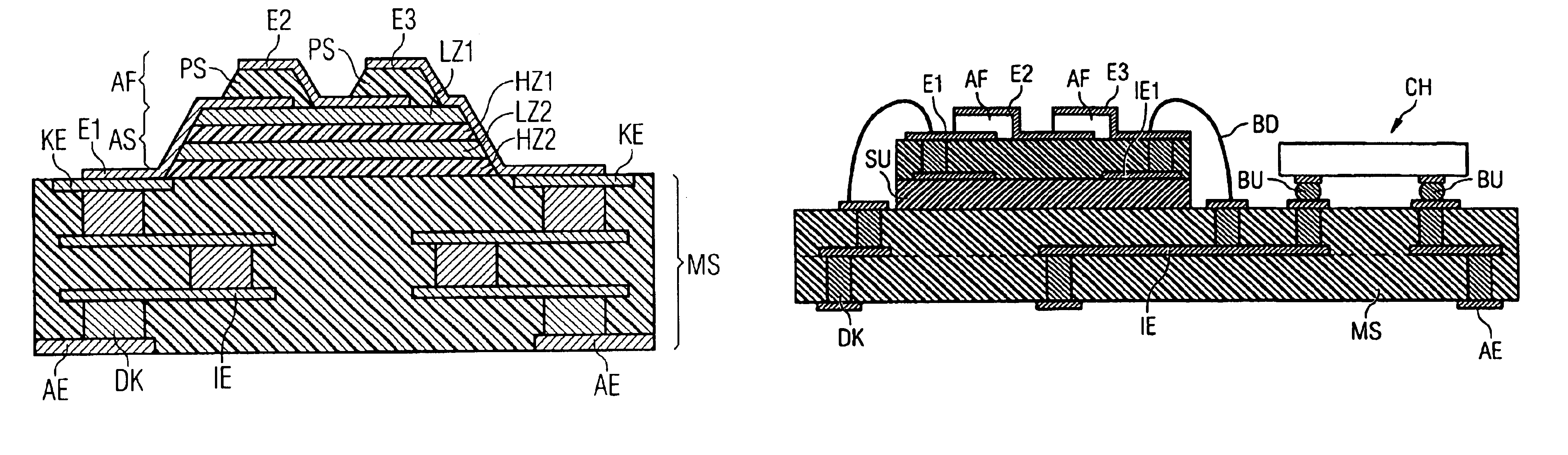
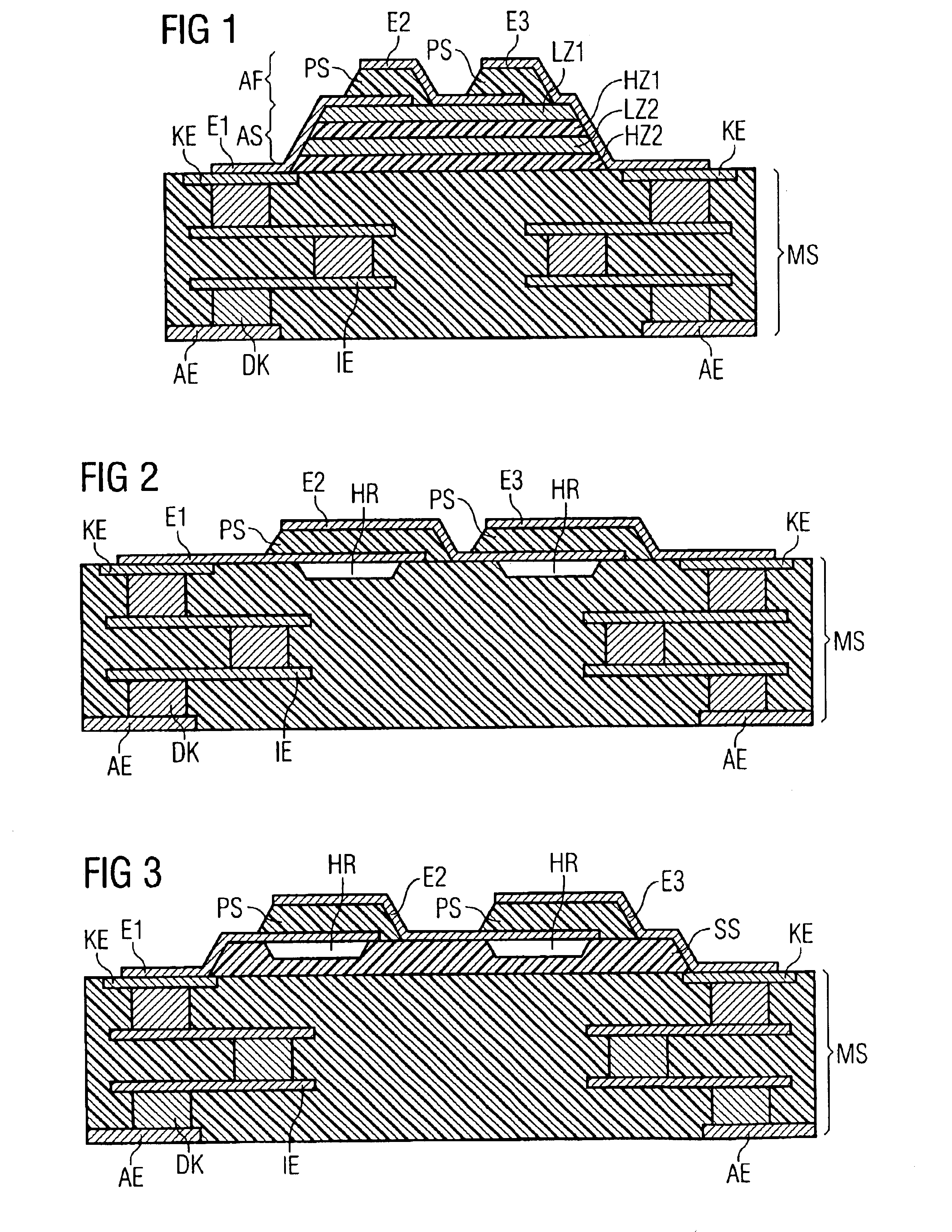
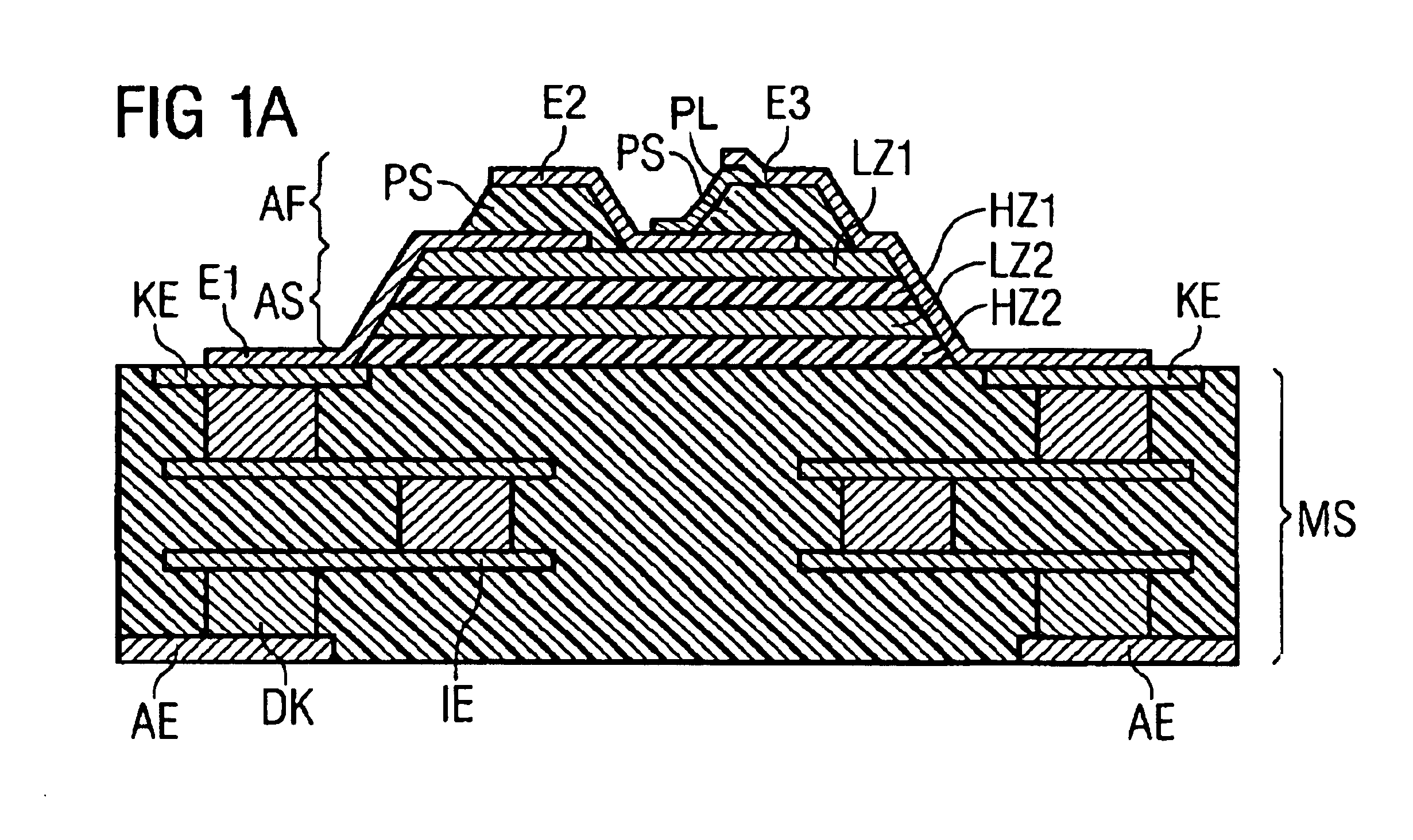
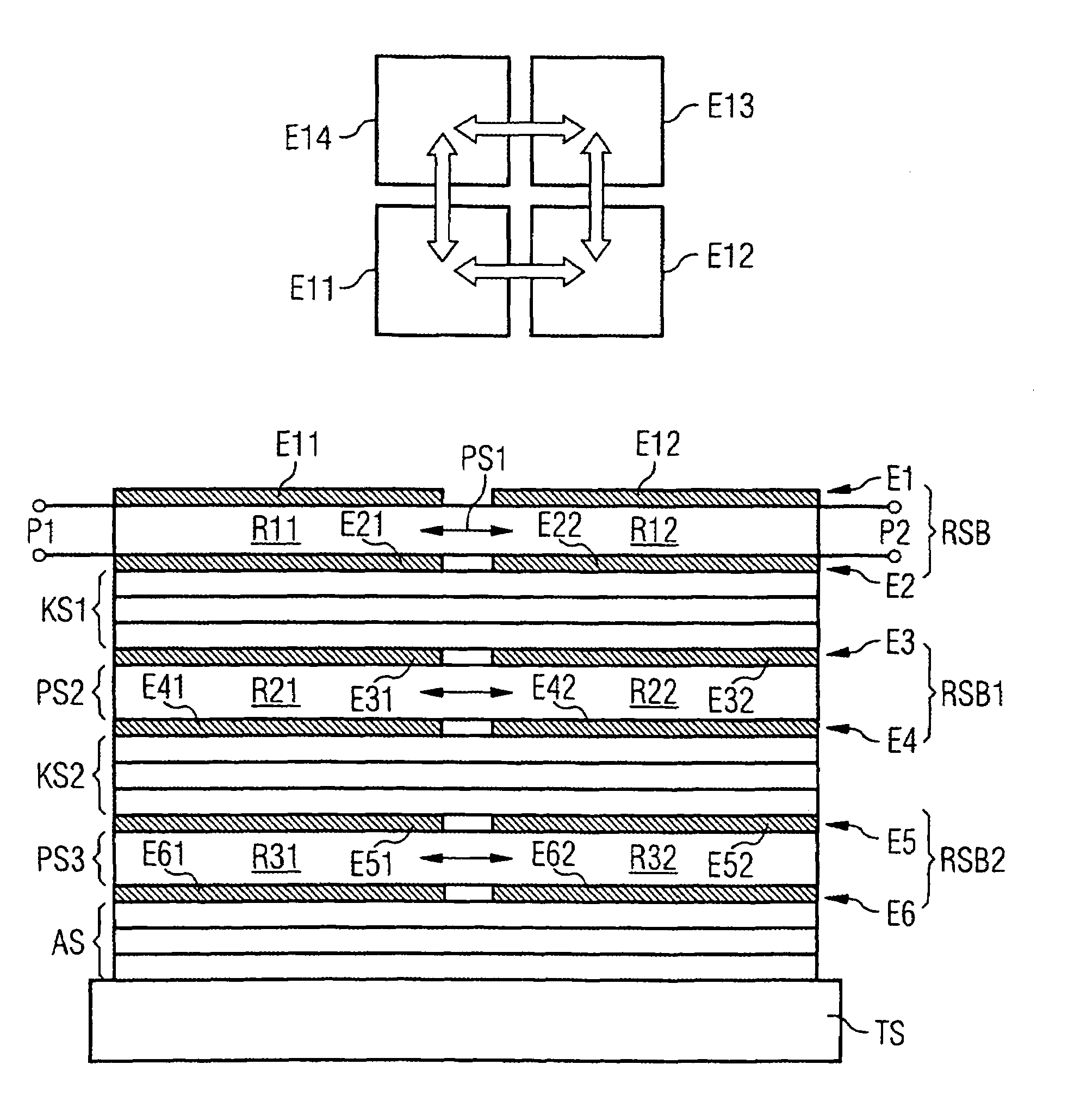
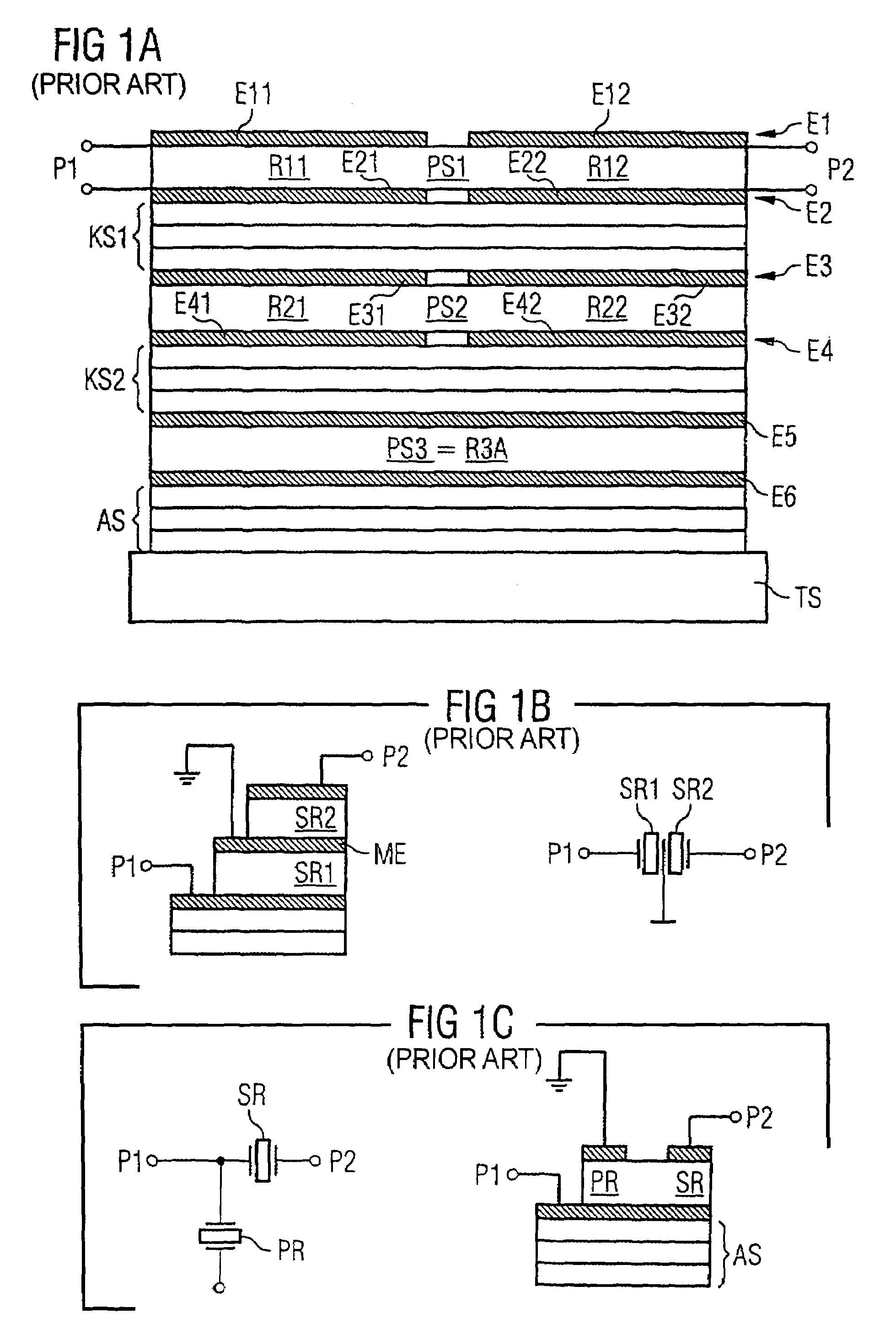
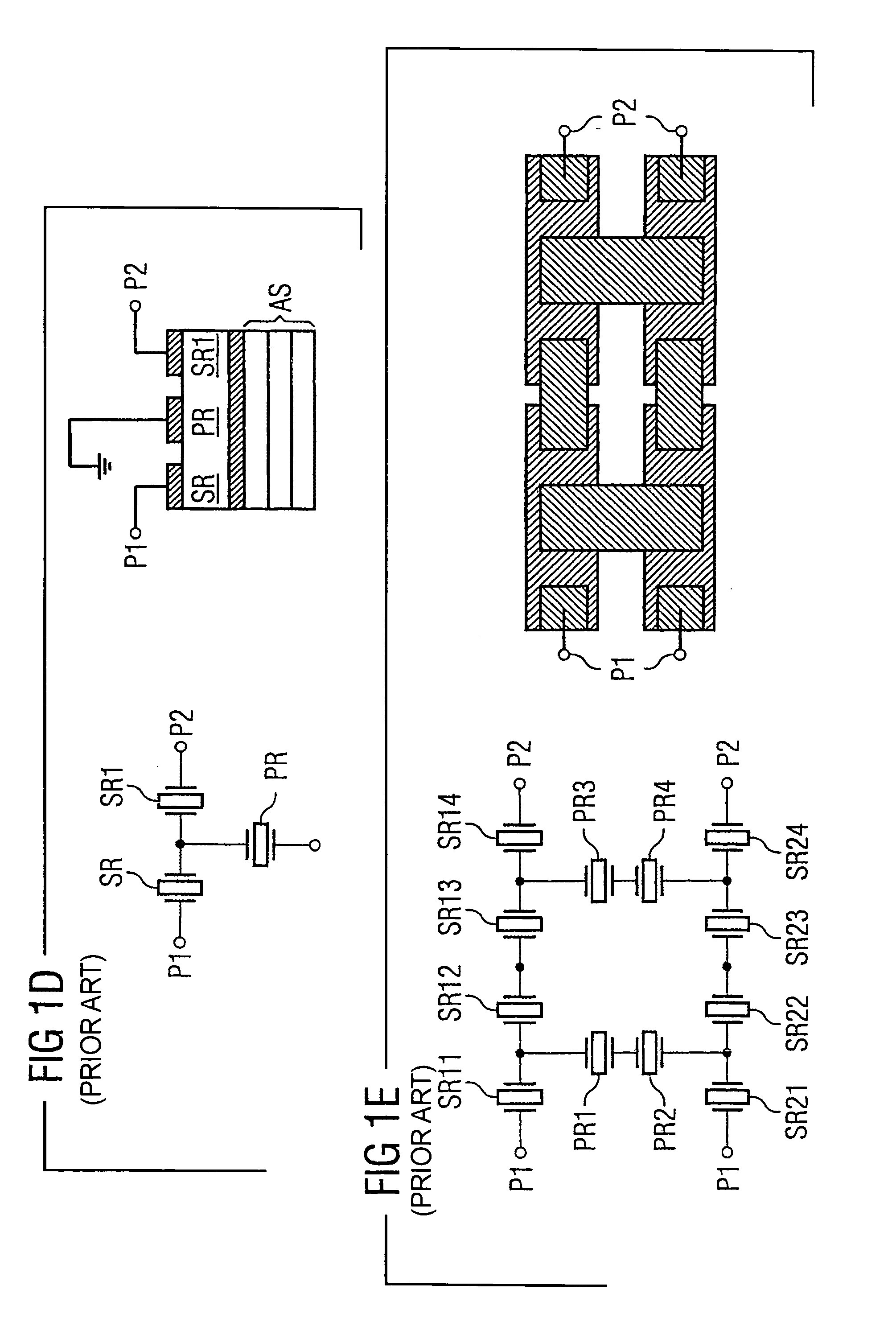
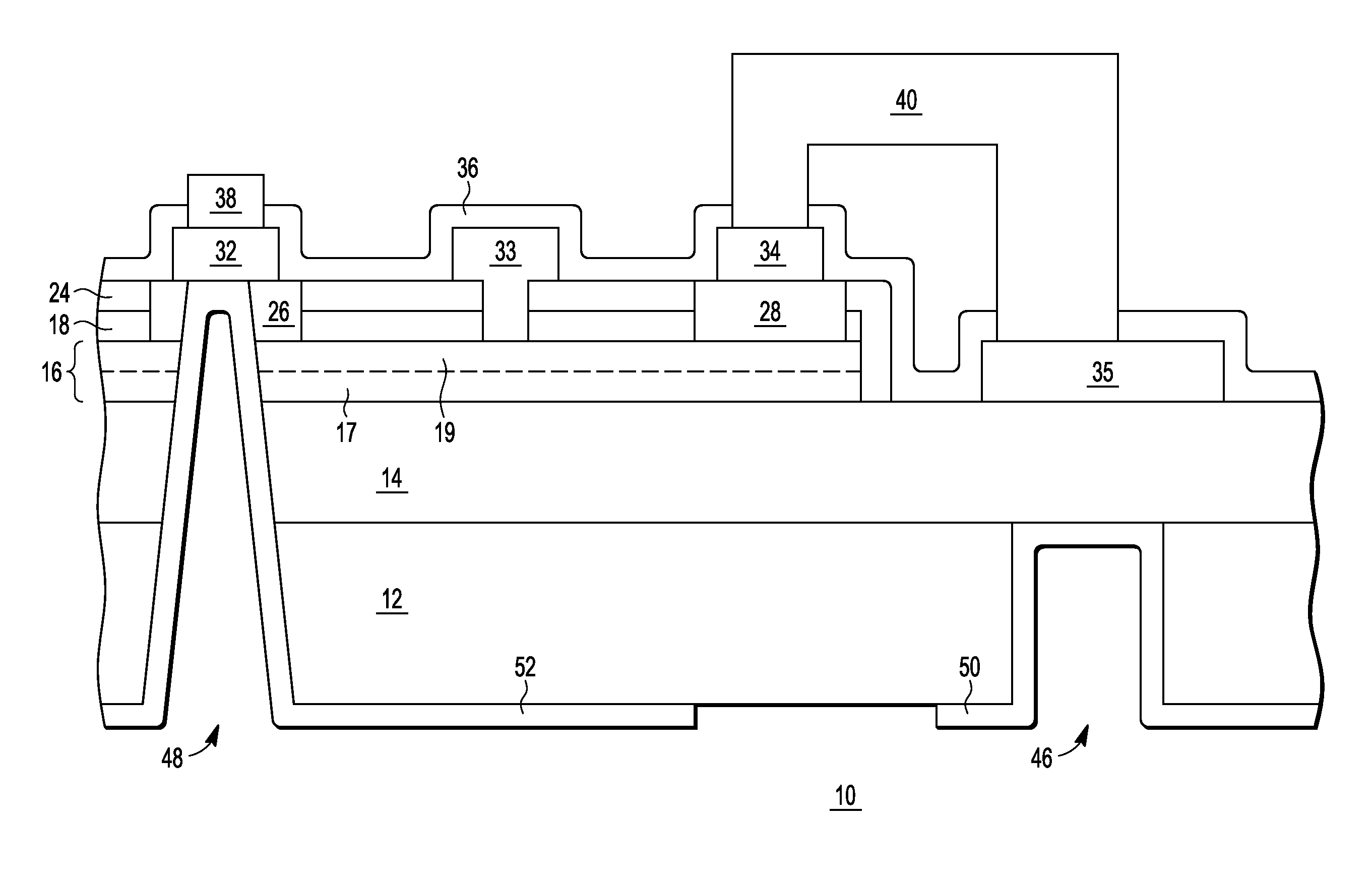
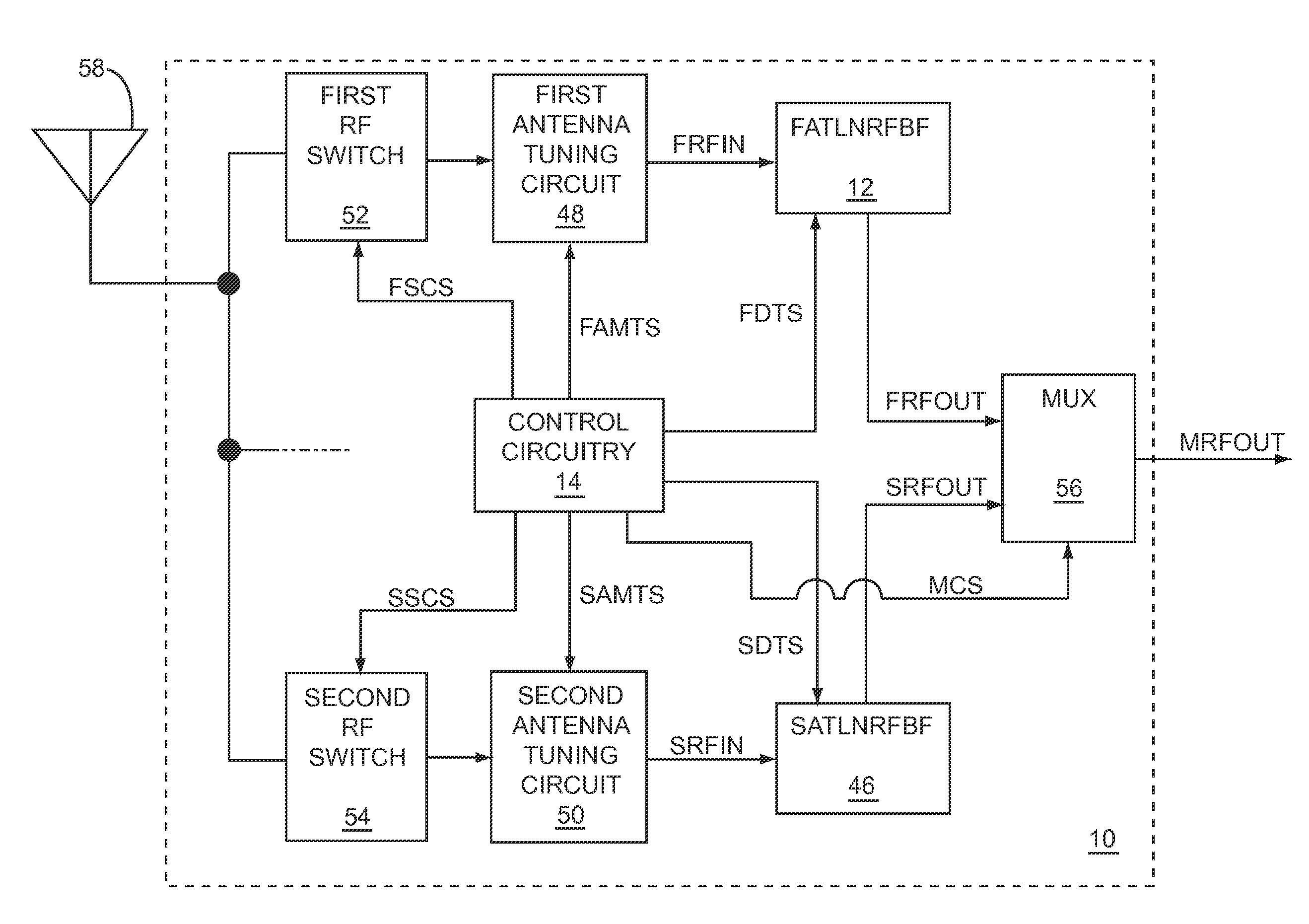
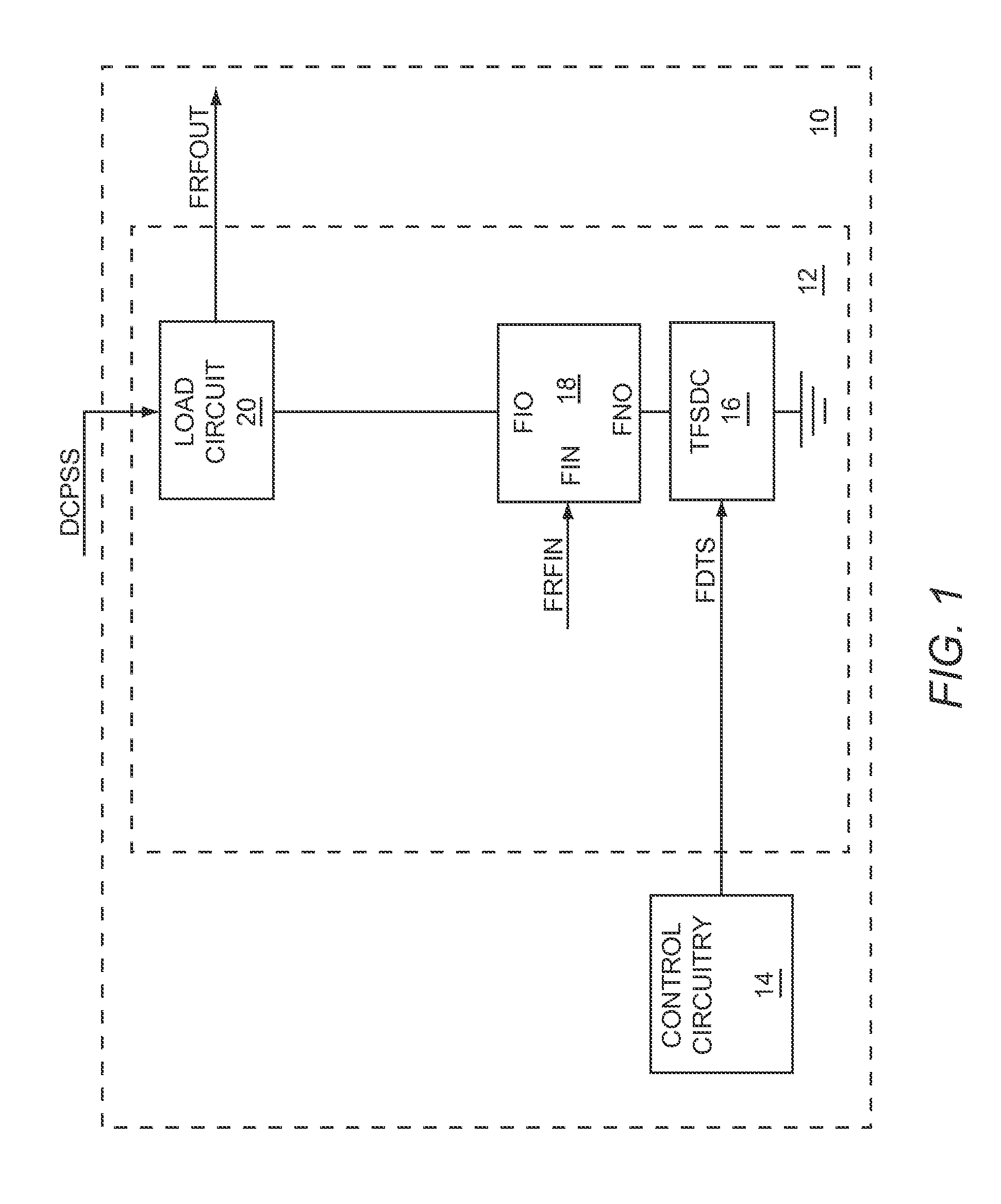
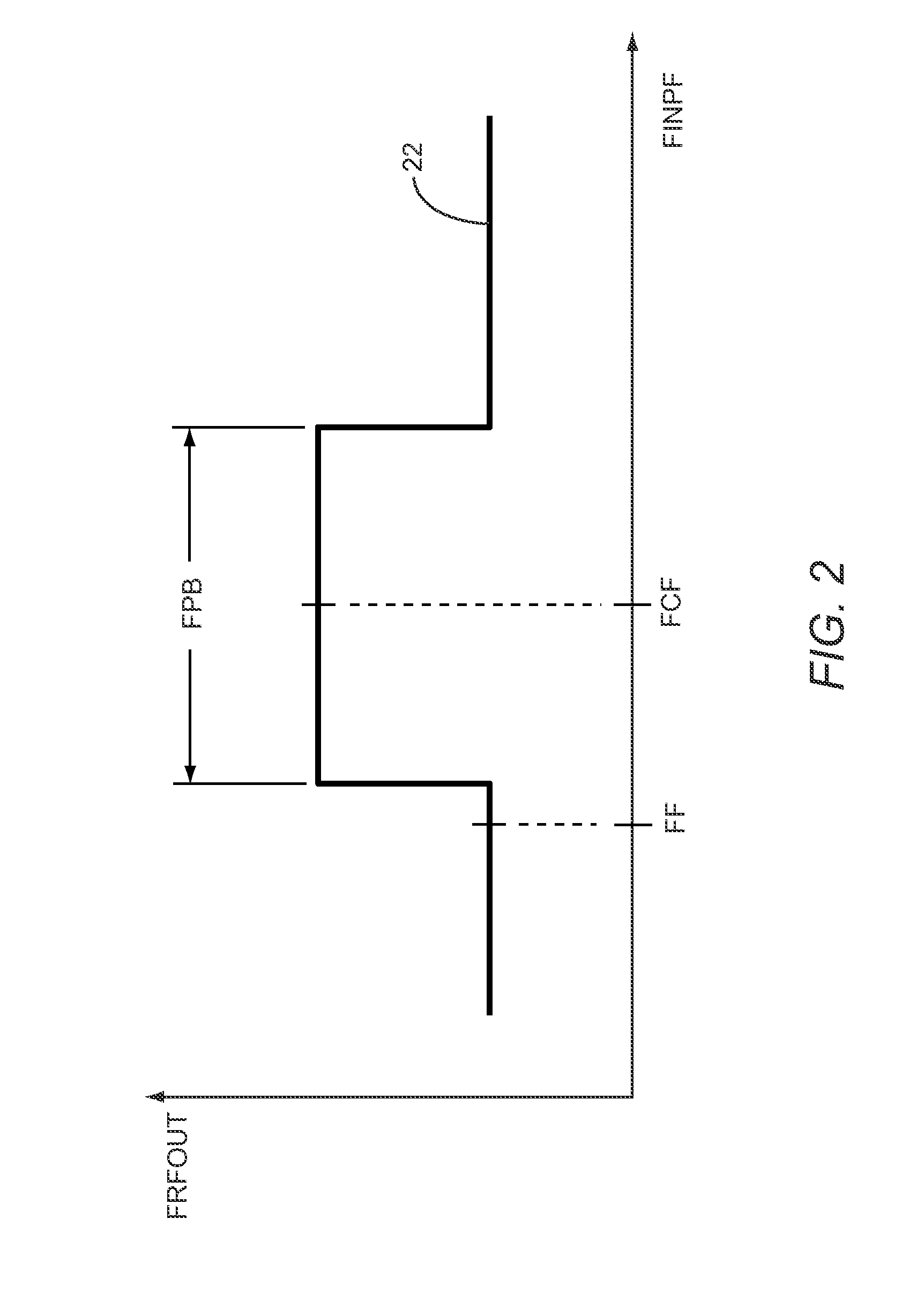
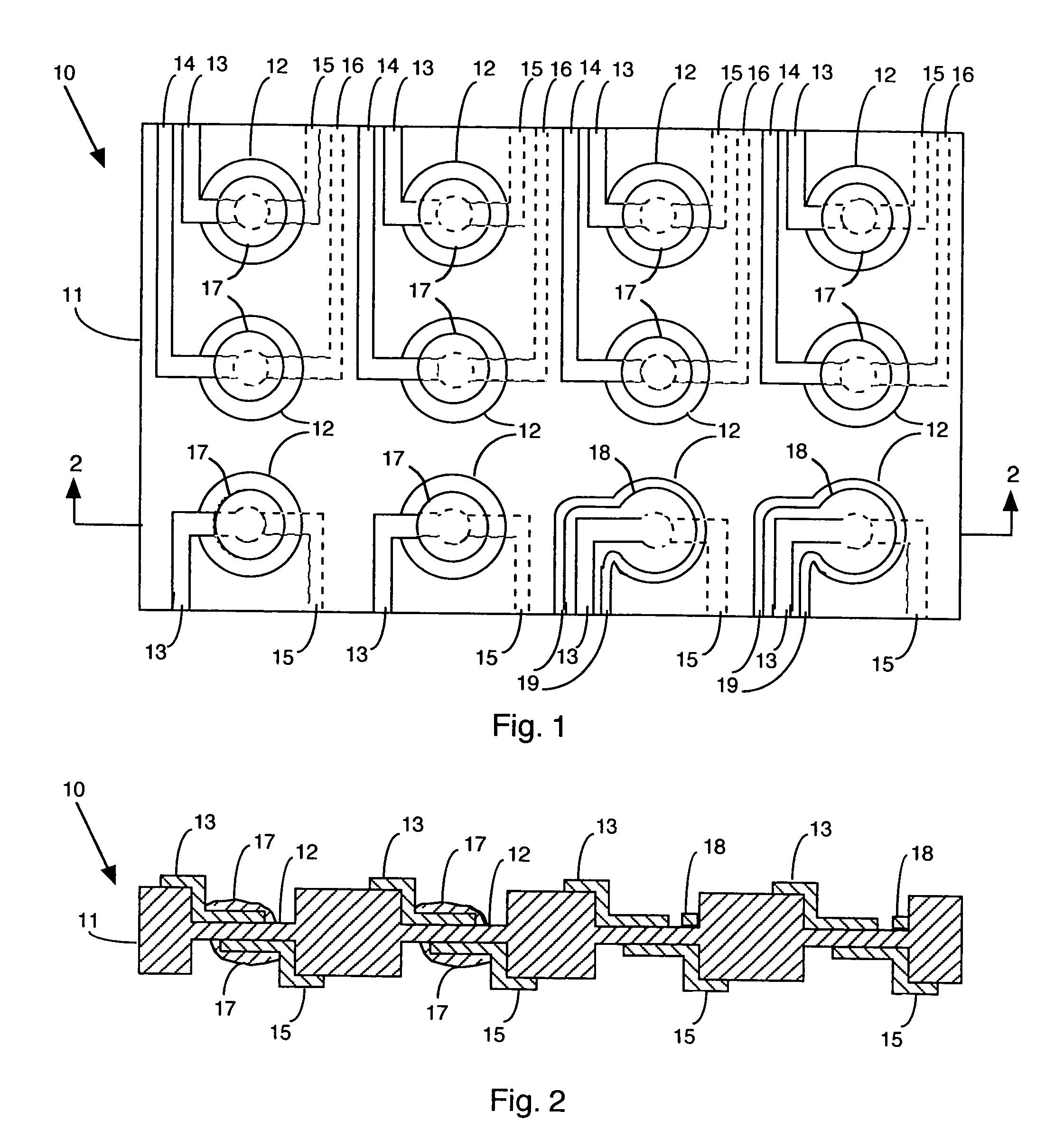
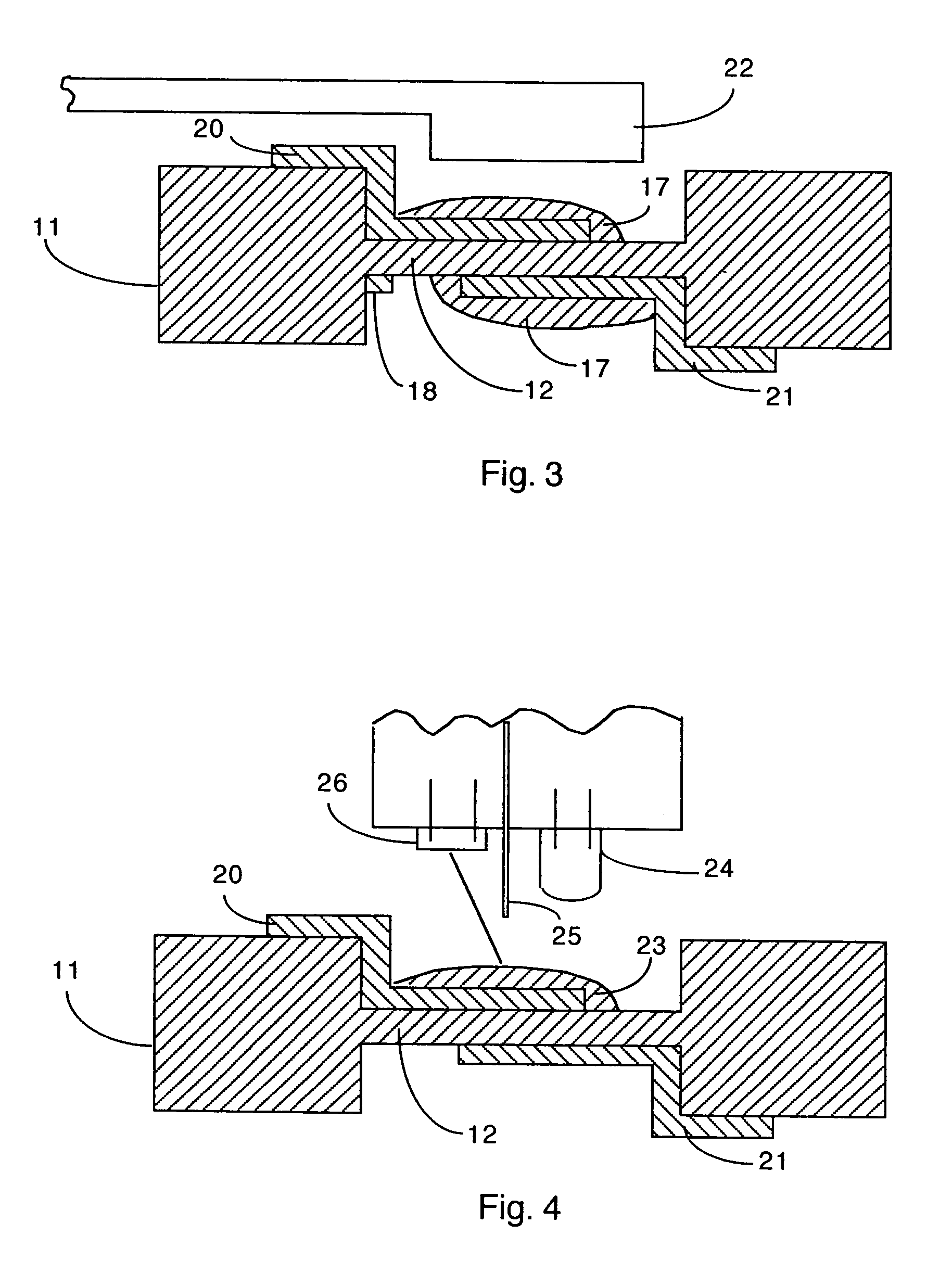
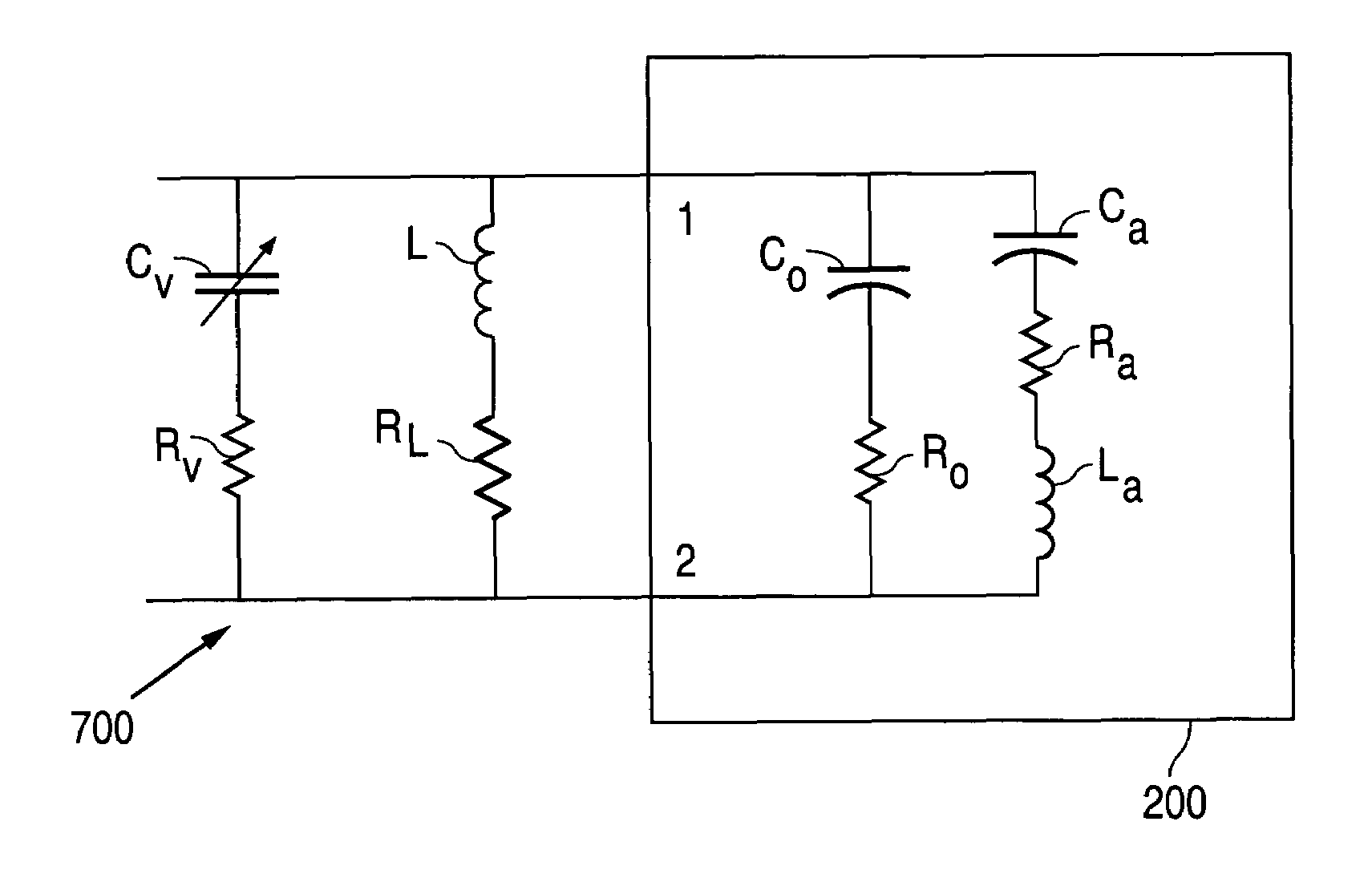
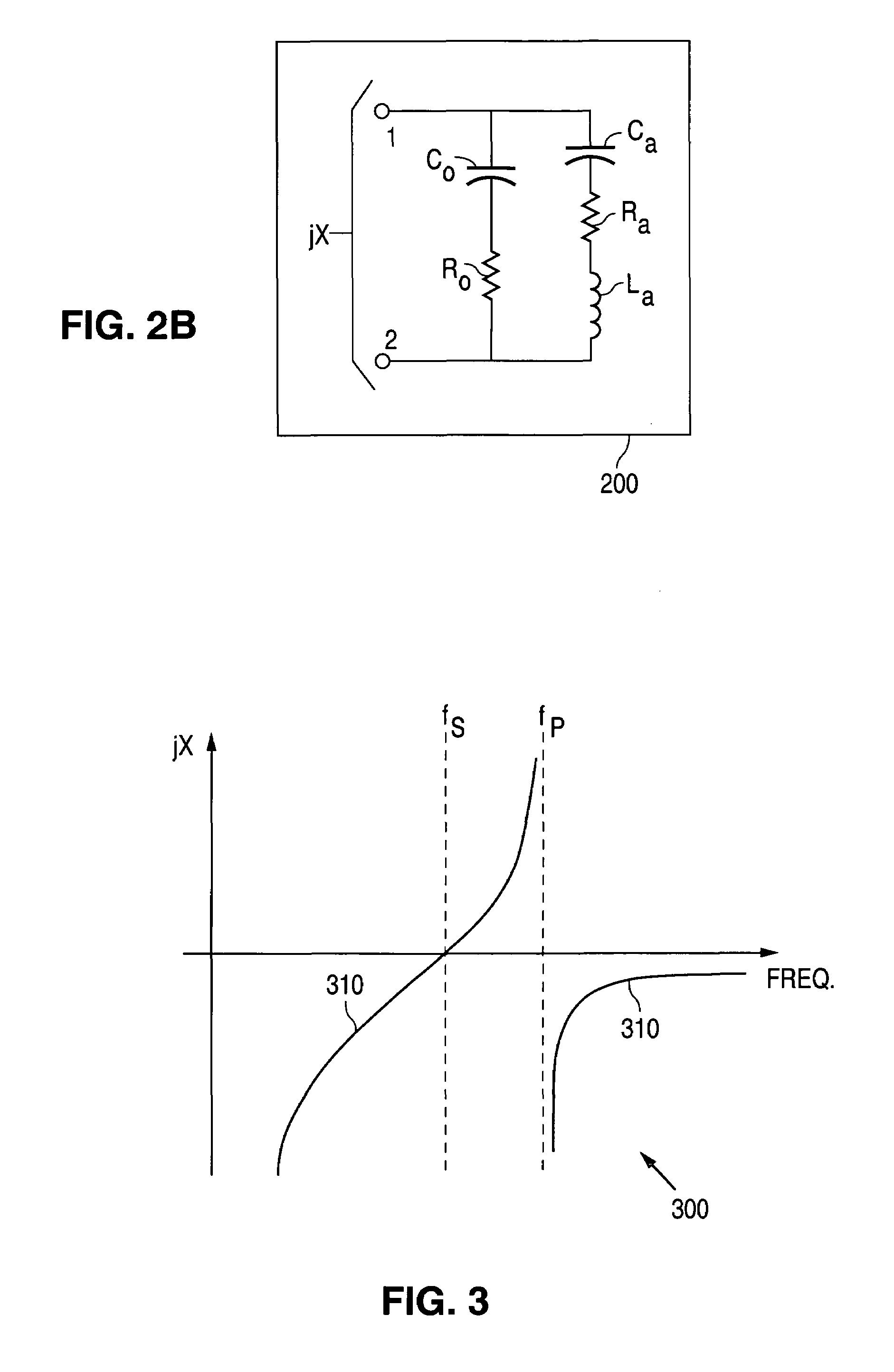
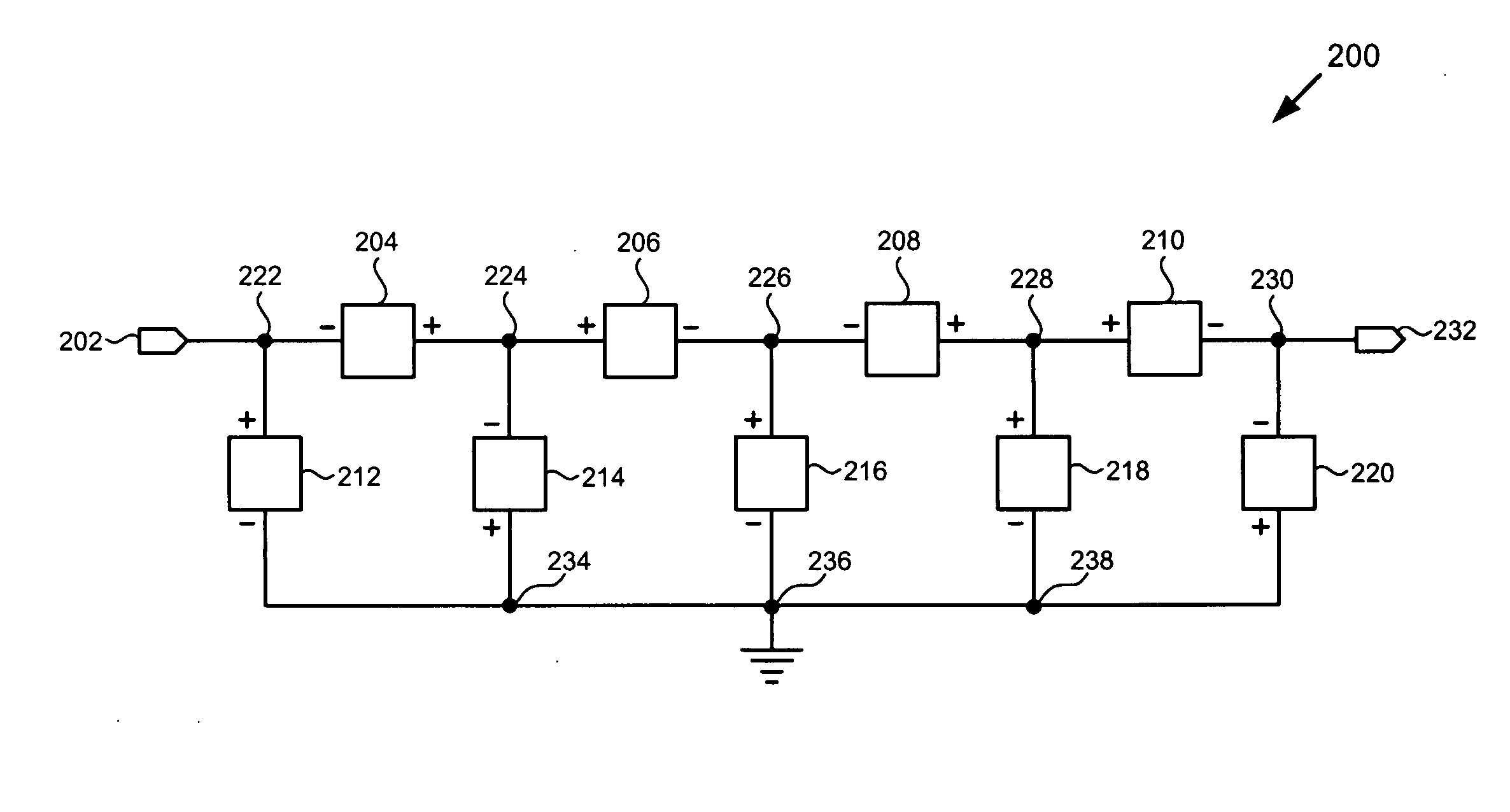
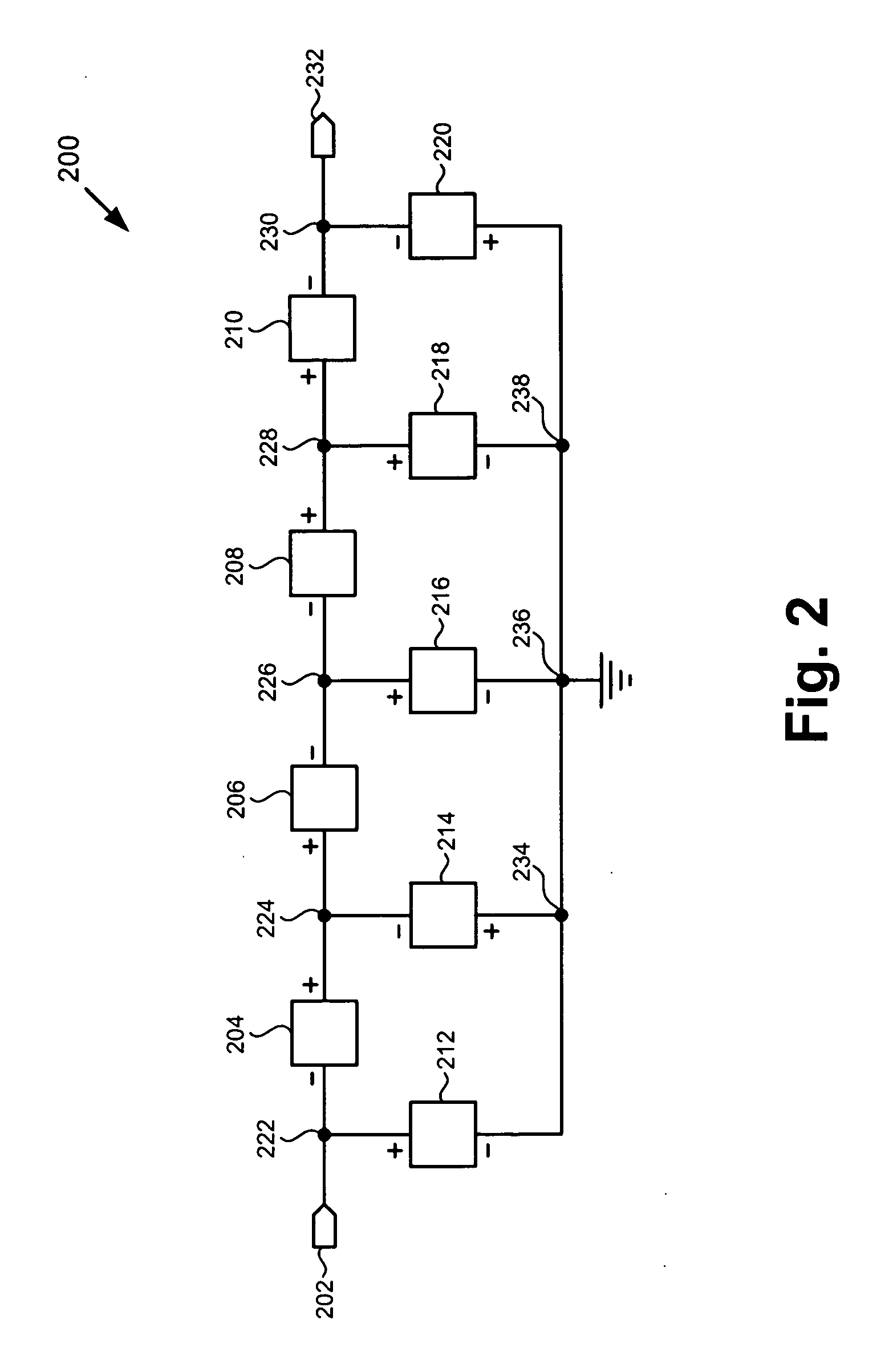
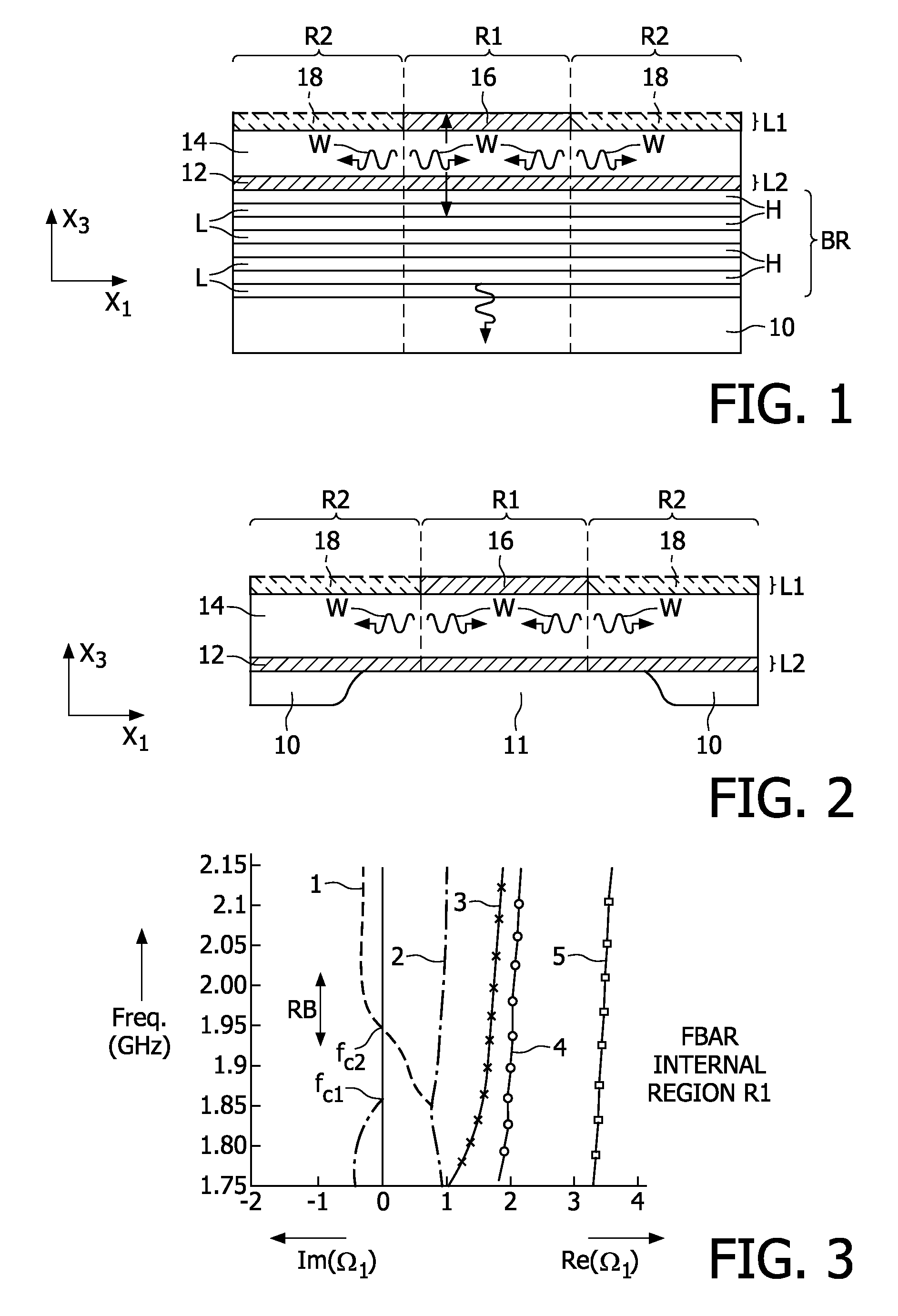
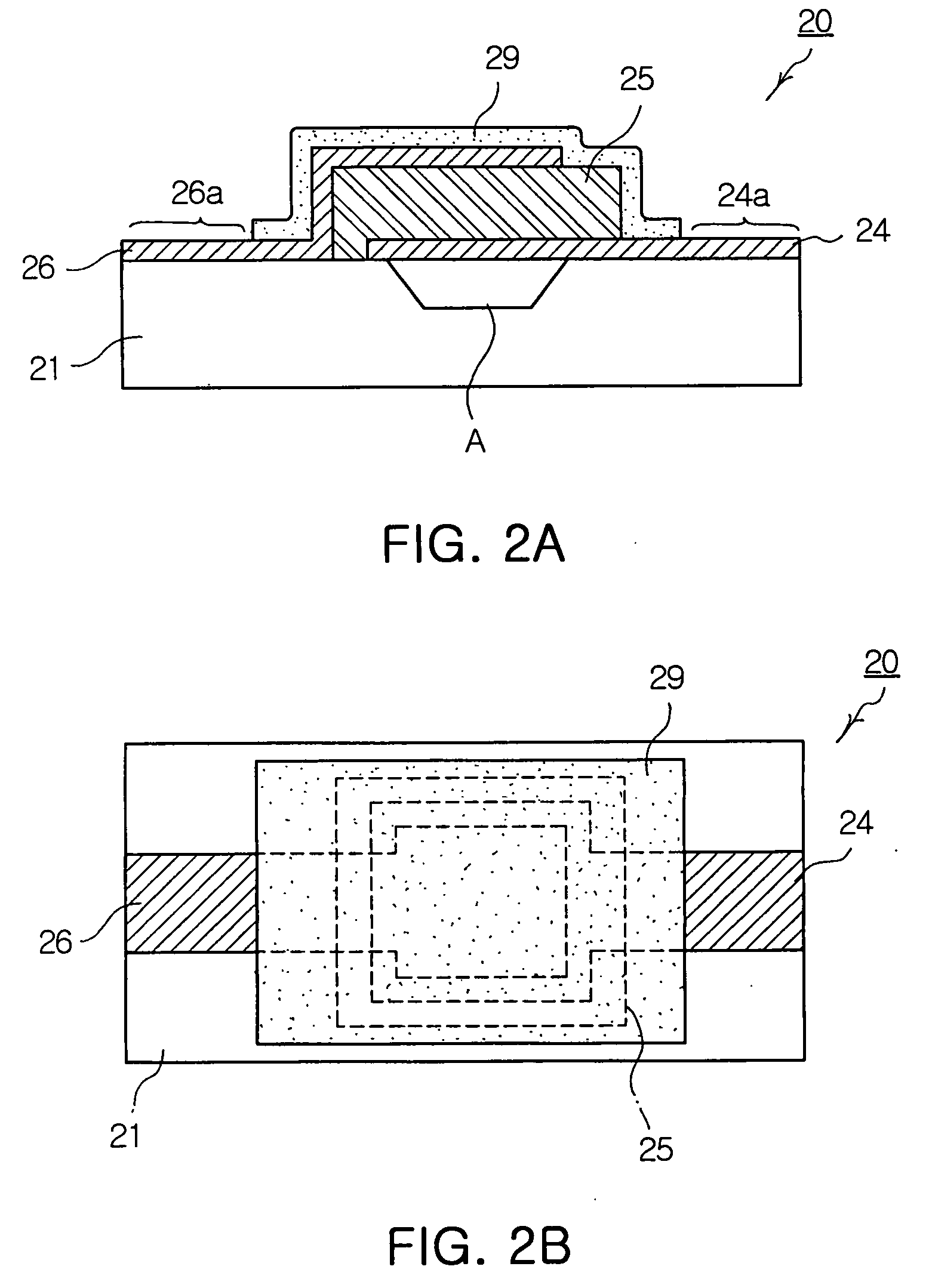
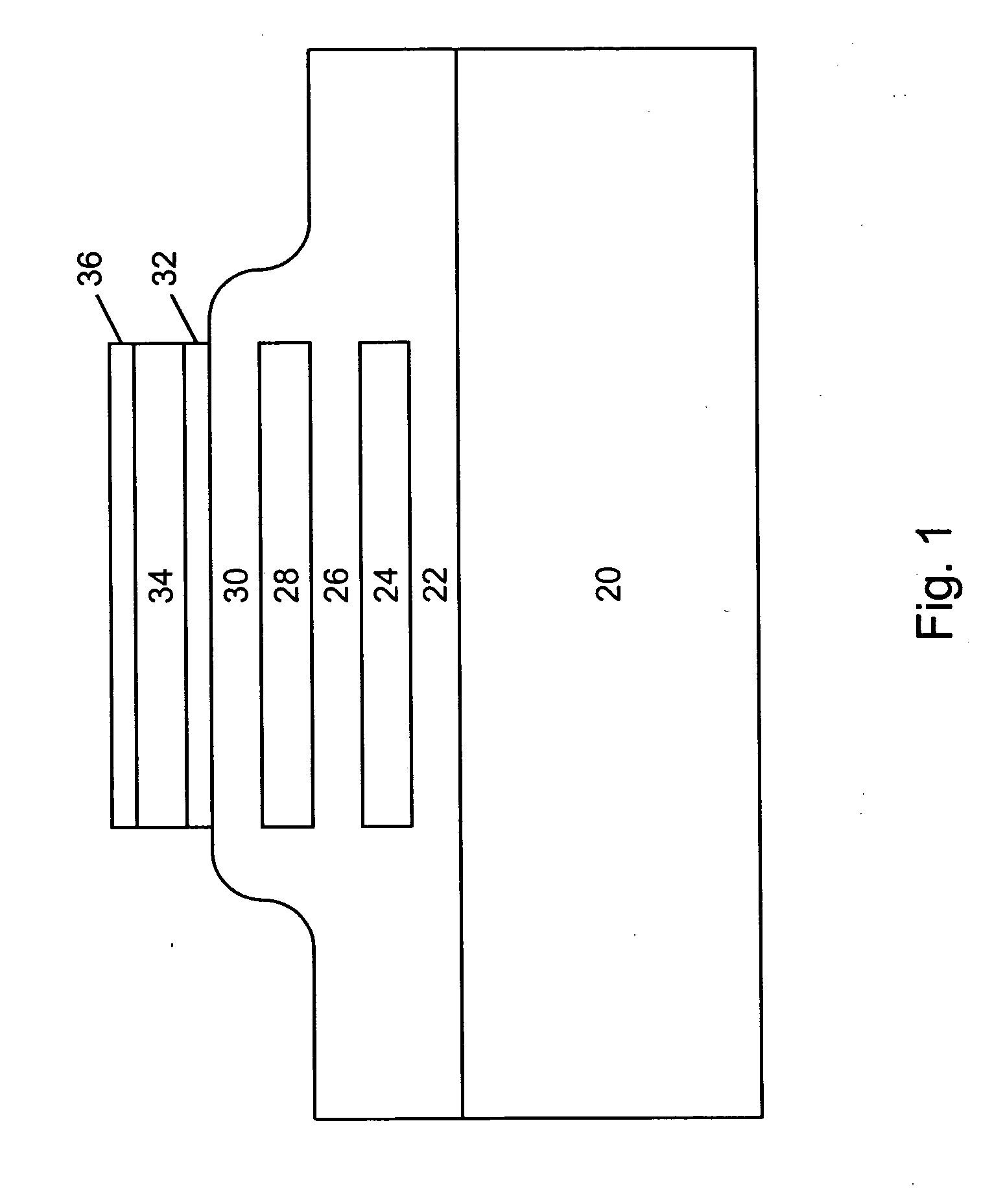
Component functioning with bulk acoustic waves having coupled resonators
ActiveUS20050012570A1Improve transmission characteristicsImprove featuresImpedence networksBandpass filteringCoupling
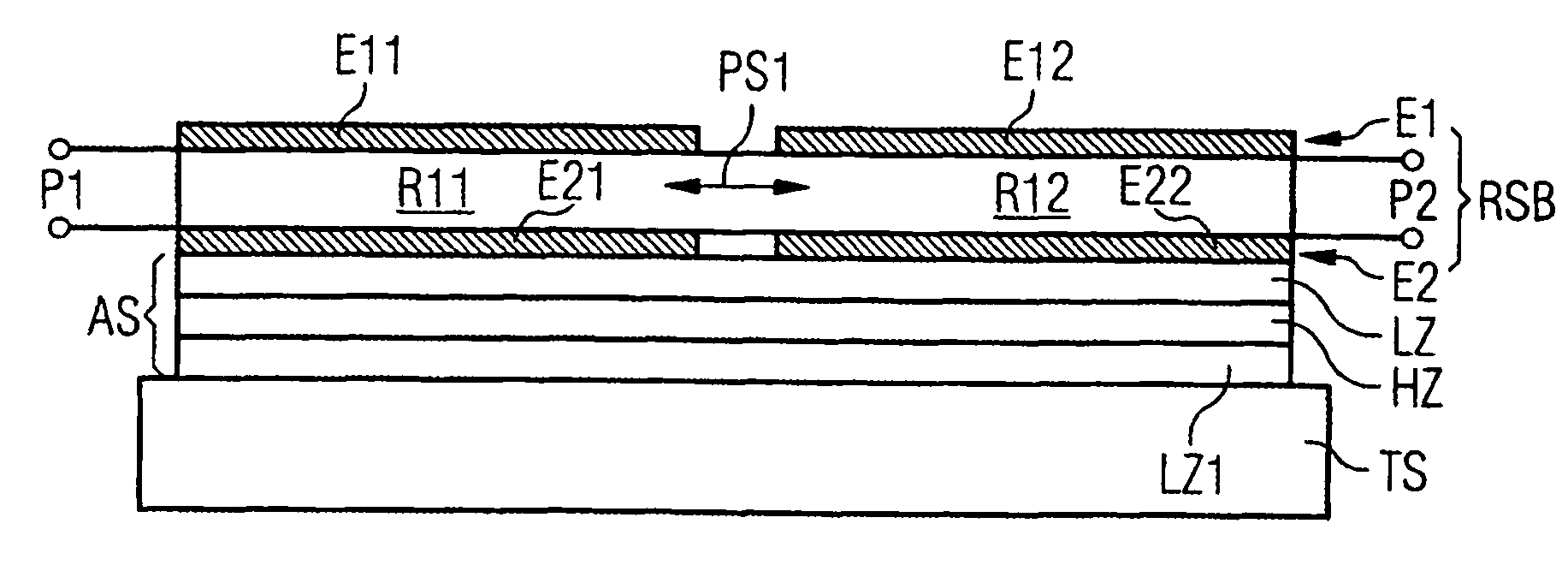
A component that functions with bulk acoustic waves, particularly a bandpass filter, has an increased number of degrees of design freedom in order to improve the transmission characteristics of the component. The component has BAW resonators coupled acoustically in the vertical and / or lateral direction through common electrodes, coupling layer systems and through the excitation of lateral acoustic modes. Through the acoustic coupling of the resonators, it is possible to create additional pole points in the transfer function so that in this manner, the rejection band characteristics of a bandpass filter can be improved. Through acoustic paths which are added in addition to the electrical connection, the insertion loss can be reduced. Through an acoustic coupling instead of an electrical connection, decoupling between input and output loops of a circuit can be achieved.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Single crystal acoustic resonator and bulk acoustic wave filter
ActiveUS20160028367A1AdvantageSimple and cost-effectivePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMetallic materialsCarbide
A method of wafer scale packaging acoustic resonator devices and an apparatus therefor. The method including providing a partially completed semiconductor substrate comprising a plurality of single crystal acoustic resonator devices provided on a silicon and carbide bearing material, each having a first electrode member, a second electrode member, and an overlying passivation material. At least one of the devices to be configured with an external connection, a repassivation material overlying the passivation material, an under metal material overlying the repassivation material. Copper pillar interconnect structures are then configured overlying the electrode members, and solder bump structures are form overlying the copper pillar interconnect structures.
Owner:AKOUSTIS INC
Tunable bulk acoustic wave mems microresonator
InactiveUS20050162040A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcousticsBulk acoustic wave
A suspended film bulk acoustic micro-resonator that includes a beam made of a piezoelectric material fixed to a support and sandwiched between excitation electrodes. The resonator also includes a mechanism modifying limiting conditions of the resonator composed of the excited beam to modify the micro-resonator resonant frequency.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Component working with acoustic waves and having a matching network
InactiveUS6927649B2High power compatibilityDependabilityImpedence networksSolid-state devicesAcoustic waveEngineering
A component working with acoustic bulk waves is provided that has a multi-layer substrate, where the multi-layer substrate comprises an integrated matching network and further circuit elements for adapting the electrical filter properties and can serve as carrier substrate for thin-film resonators.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Component functioning with bulk acoustic waves having coupled resonators
A component that functions with bulk acoustic waves, particularly a bandpass filter, has an increased number of degrees of design freedom in order to improve the transmission characteristics of the component. The component has BAW resonators coupled acoustically in the vertical and / or lateral direction through common electrodes, coupling layer systems and through the excitation of lateral acoustic modes. Through the acoustic coupling of the resonators, it is possible to create additional pole points in the transfer function so that in this manner, the rejection band characteristics of a bandpass filter can be improved. Through acoustic paths which are added in addition to the electrical connection, the insertion loss can be reduced. Through an acoustic coupling instead of an electrical connection, decoupling between input and output loops of a circuit can be achieved.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Component operating with bulk acoustic waves, and having asymmetric/symmetrical circuitry
ActiveUS6917261B2Reduce phase differenceBalance-unbalance networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCouplingPhase difference
A component operating with bulk acoustic waves has two Bulk Acoustic Wave (BAW) resonators that are stacked and are acoustically coupled to one another, with a first resonator being connected to an asymmetric port, and a second resonator being connected to a symmetrical port. The acoustic coupling is provided by a partially permeable coupling layer system, which has an alternating sequence of at least two λ / 4 mirror layers with different acoustic impedance. The coupling layer system furthermore has a compensation layer, which has an approximate thickness of λ / 8. The compensation layer according to the invention makes it possible to match any discrepancy in the phase difference (which is caused by reflections on the mirror layers) from the predetermined 180° between the connections of the symmetrical port to approximately 180°.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Resonator, frequency filter, duplexer, electronic device, and method of manufacturing resonator
InactiveUS20130234805A1Low mechanical strengthImprove productivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFrequency filteringAcoustic wave
A resonator according to the present invention includes a supporting substrate, a piezoelectric layer, a pair of excitation electrodes, and a bonding layer. The piezoelectric layer is made of a piezoelectric material. The pair of excitation electrodes is formed on the upper surface of the piezoelectric layer so as to excite bulk acoustic waves. The bonding layer has a cavity formed therein so as to face the excitation electrode pair through the piezoelectric layer, and the bonding layer bonds the supporting substrate to the lower surface of the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
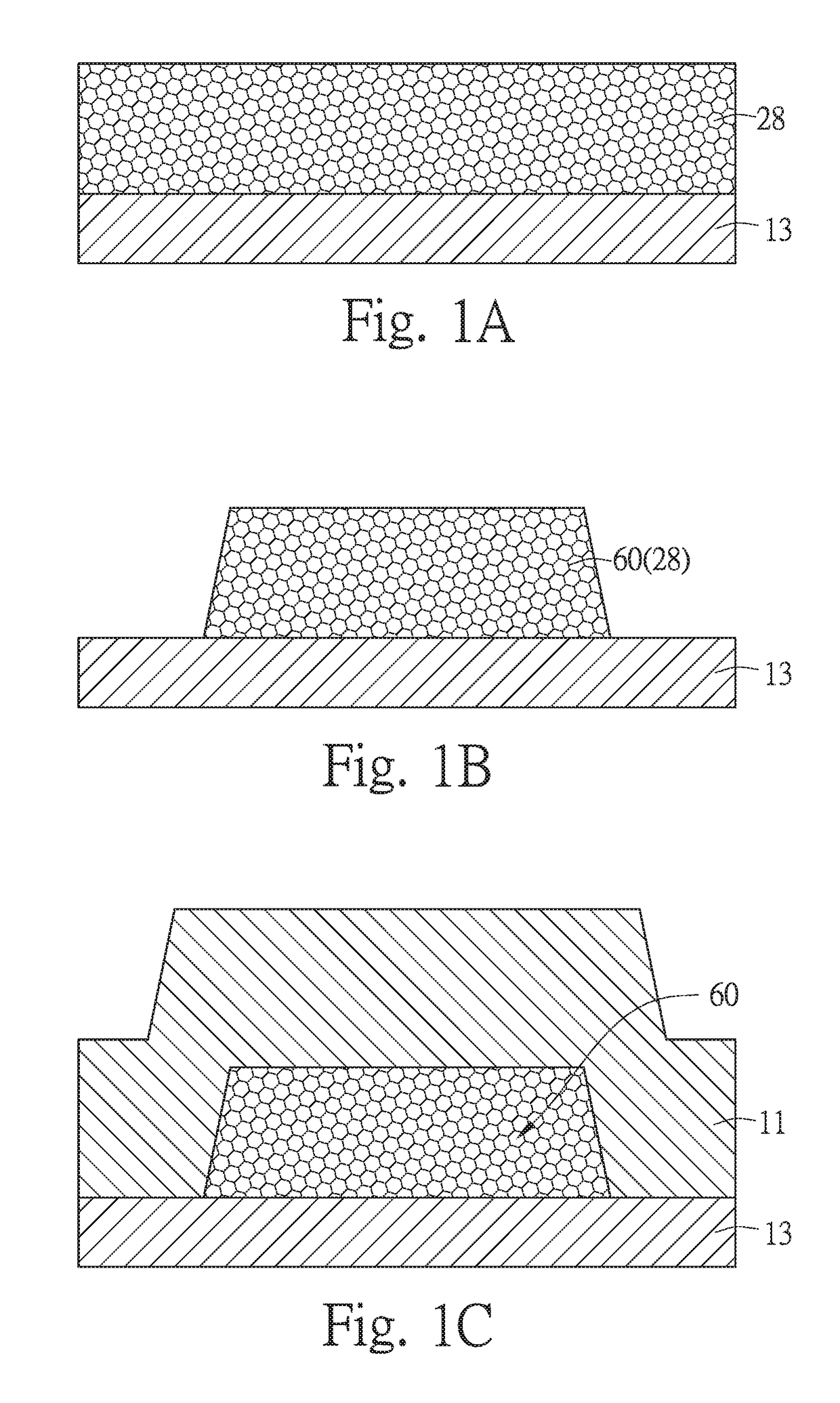
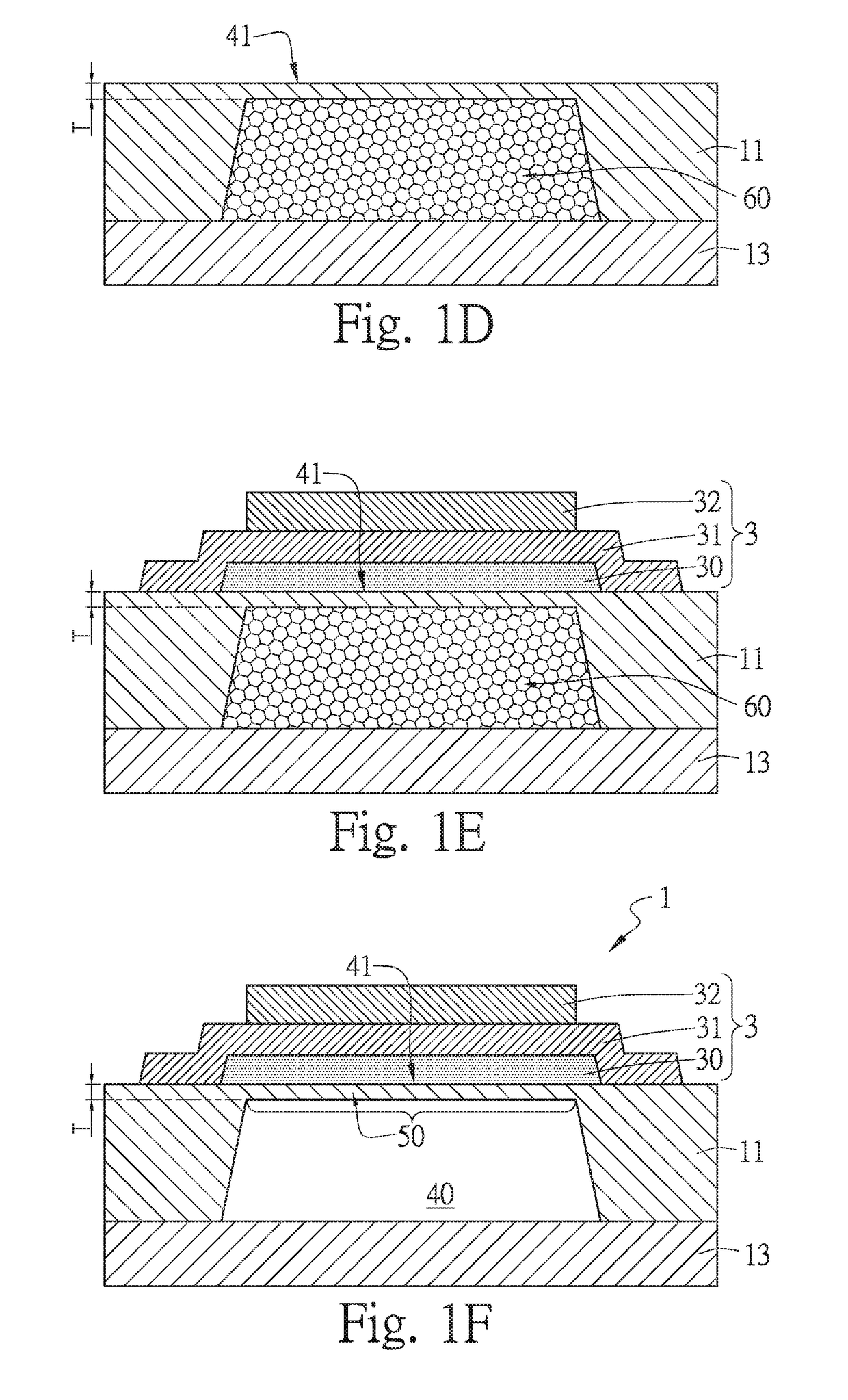
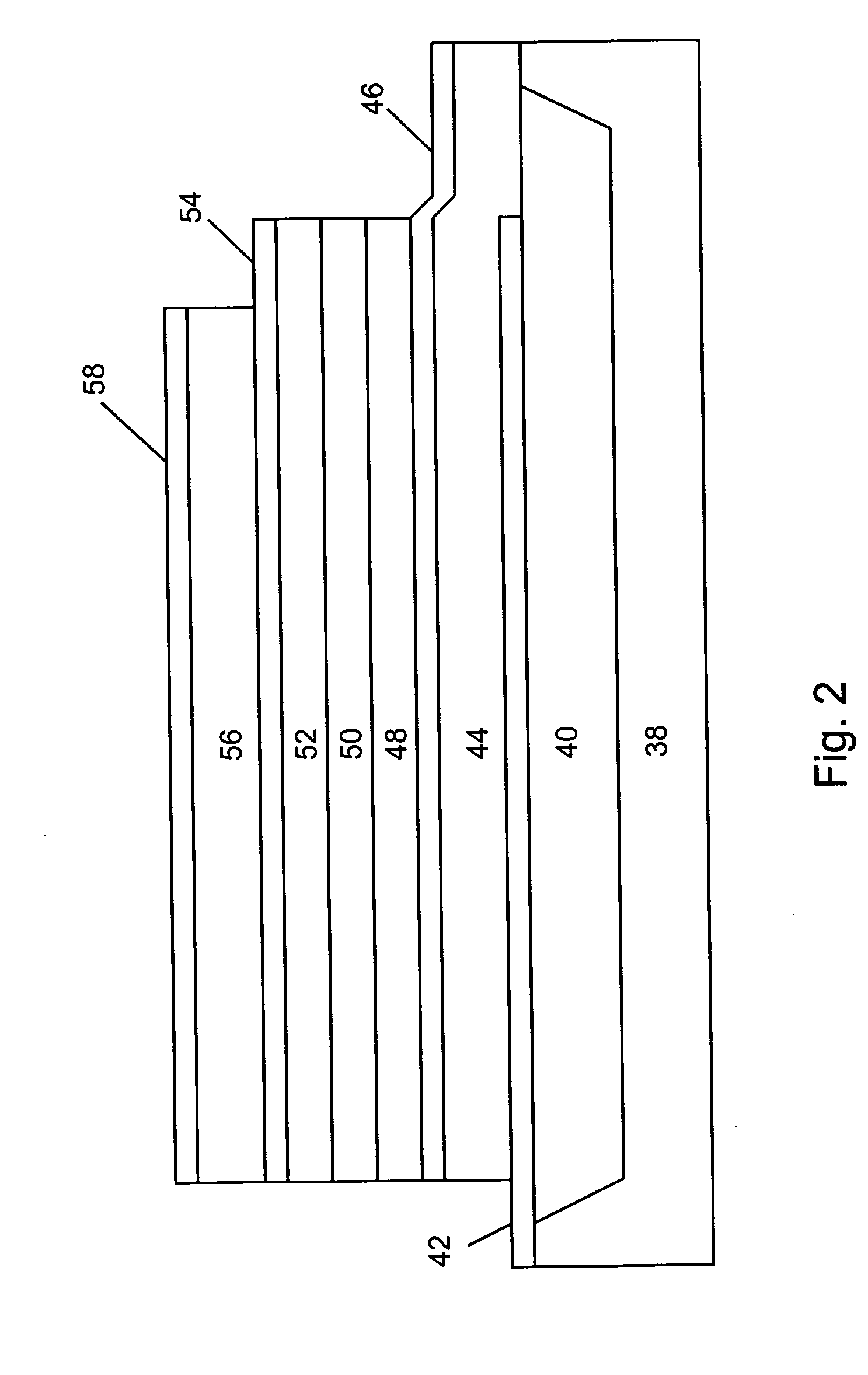
Film bulk acoustic wave resonator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101465628AHigh application frequencyReduce the requirements of the manufacturing process for equipmentImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorBulk acoustic wave
The invention discloses a thin film bulk acoustic wave resonator which comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, a piezoelectric layer and electrodes, and is characterized in that 1. A smooth concave groove and the buffer layer are arranged on the upper end surface of the substrate; the buffer layer crosses the concave groove and forms an air gap provided with a smooth upper convex edge with the substrate, and completely covers the air gap; the height of the lower top surface of the air gap is less than that of the substrate, and the air gap has flat surface and even change edge; 2. The edge of the buffer layer, which is contacted with the air gap and is close to the substrate is in smooth and outer-convex shape; the piezoelectric layer is arranged on the buffer layer; the electrodes include a bottom electrode and a top electrode; the bottom electrode is arranged in the piezoelectric layer on the buffer layer; the top electrode is arranged on the piezoelectric layer. The thin film bulk acoustic wave resonator has ingenious structure; a FBAR with stable structure and low loss can be fabricated on the substrate through the method, and the CMP process is avoided, so the thin film bulk acoustic wave resonator can be integrated into a CMOS chip conveniently.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Integrated circuit having a bulk acoustic wave device and a transistor
ActiveUS8304271B2Impedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAcousticsIntegrated circuit
A bulk GaN layer is on a first surface of a substrate, wherein the bulk GaN layer has a GaN transistor region and a bulk acoustic wave (BAW) device region. A source / drain layer is over a first surface of the bulk GaN layer in the GaN transistor region. A gate electrode is formed over the source / drain layer. A first BAW electrode is formed over the first surface of the bulk GaN layer in the BAW device region. An opening is formed in a second surface of the substrate, opposite the first surface of the substrate, which extends through the substrate and exposes a second surface of the bulk GaN layer, opposite the first surface of the bulk GaN layer. A second BAW electrode is formed within the opening over the second surface of the bulk GaN layer.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Using degeneration in an active tunable low-noise radio frequency bandpass filter
ActiveUS8314653B1Easy to FeedbackReduce gainSwitched capacitor networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesLow noiseBandpass filtering
The present disclosure relates to a first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter that includes at least a first transistor element and a tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit coupled to a first non-inverting output of the first transistor element. The first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter combines low noise amplifier (LNA) and tunable bandpass filter functionalities into a single active RF bandpass filter. The tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit uses degeneration at frequencies outside of a passband of the active RF bandpass filter to increase feedback, thereby decreasing gain of the active RF bandpass filter. By decreasing the gain, linearity of the active RF bandpass filter may be improved in the presence of strong interfering RF signals, thereby enabling elimination of passive bandpass filter elements, such as surface acoustic wave (SAW) and bulk acoustic wave (BAW) filters, without degrading reception of in-band RF signals.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Laterally coupled bulk acoustic wave filter with improved passband characteristics
ActiveUS9219466B2Quality improvementImprove responseImpedence networksLongitudinal waveAcoustic wave
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Bulk acoustic wave resonator filter being digitally reconfigurable, with process
ActiveUS20090251235A1Simple designLess-costly to implementImpedence networksCapacitanceResonator filter
A filtering circuit with BAW type acoustic resonators having at least a first quadripole and a second quadripole connected in cascade, each quadripole having a branch series with a first acoustic resonator of type BAW and a branch parallel with each branch having an acoustic resonator of type BAW, the first acoustic resonator having a frequency of resonance series approximately equal to the frequency of parallel resonance of the second acoustic resonator, the branch parallel of the first quadripole having a first capacitance connected in series with the second resonator and, in parallel with the capacitance, a first switching transistor to short circuit the capacitance.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
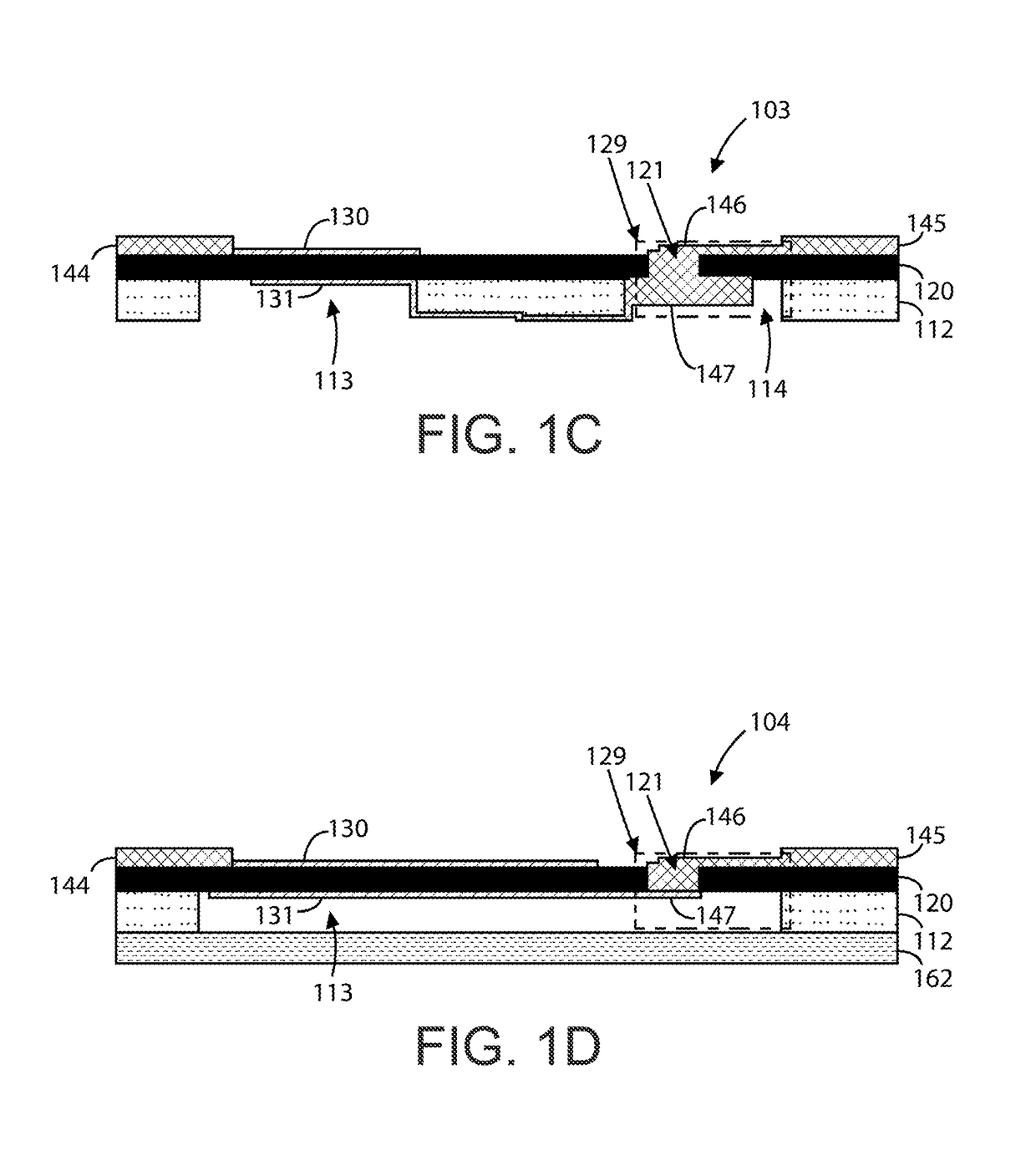
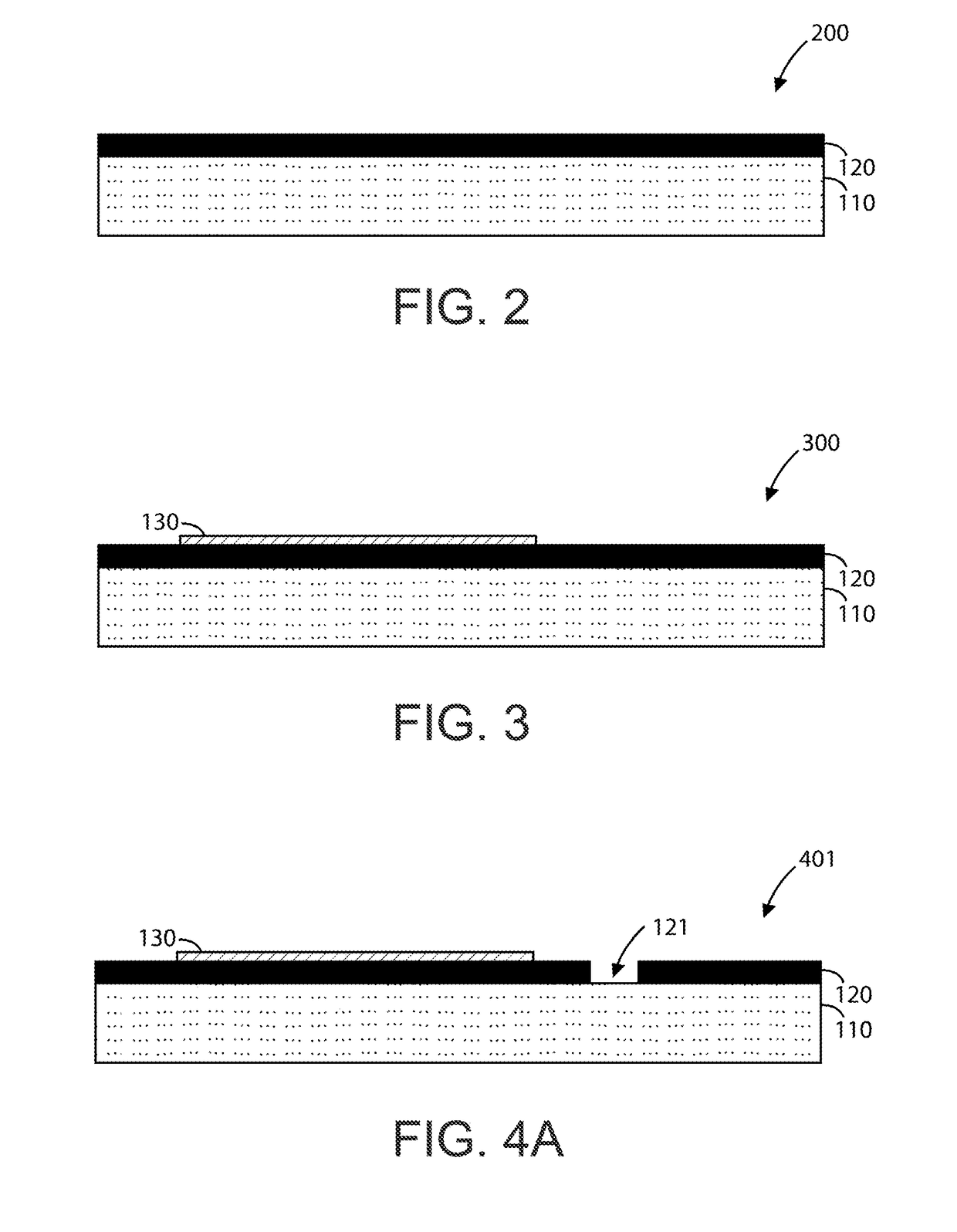
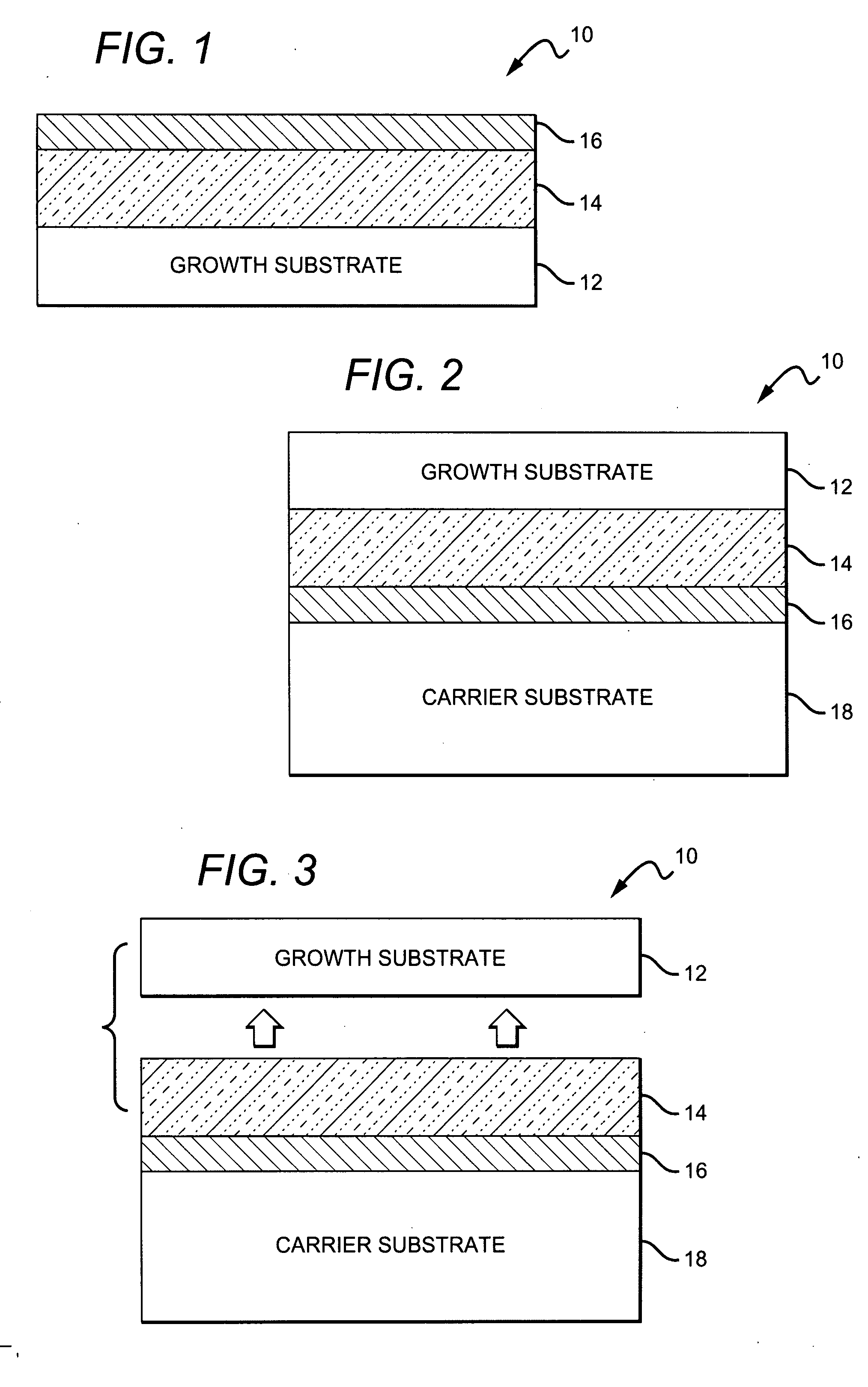
Bulk acoustic device and method for fabricating
ActiveUS7982363B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksAcoustic waveOptoelectronics
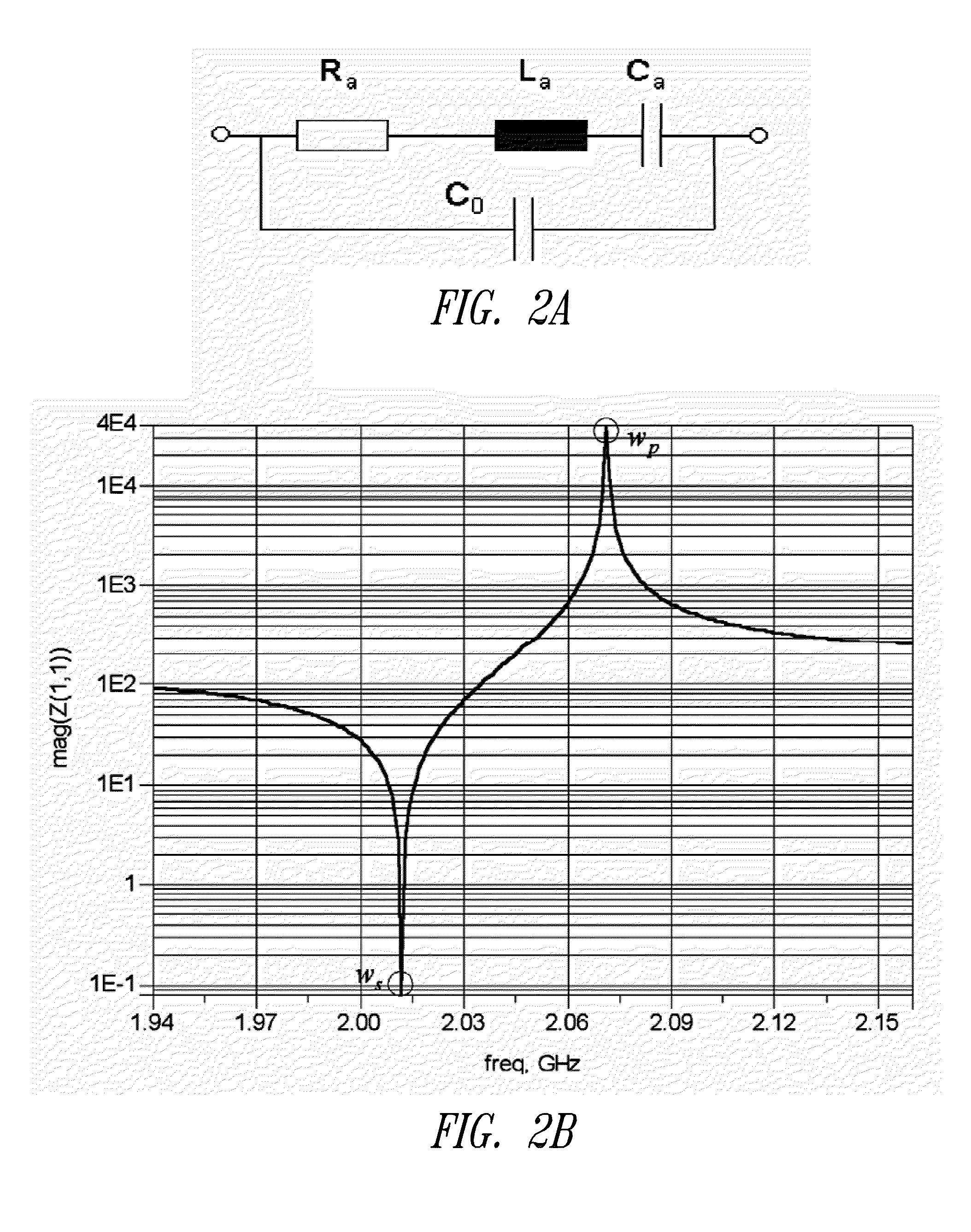
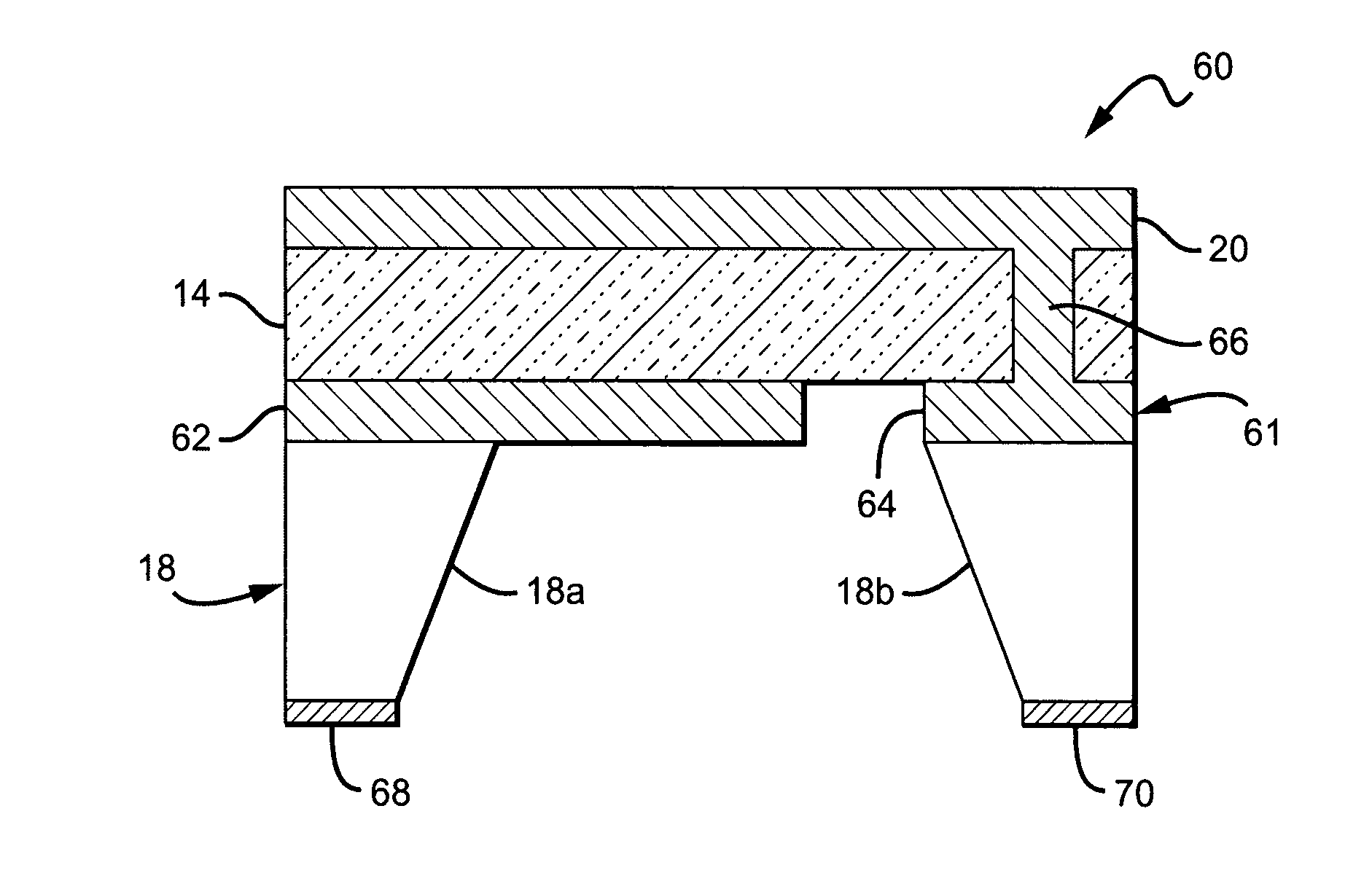
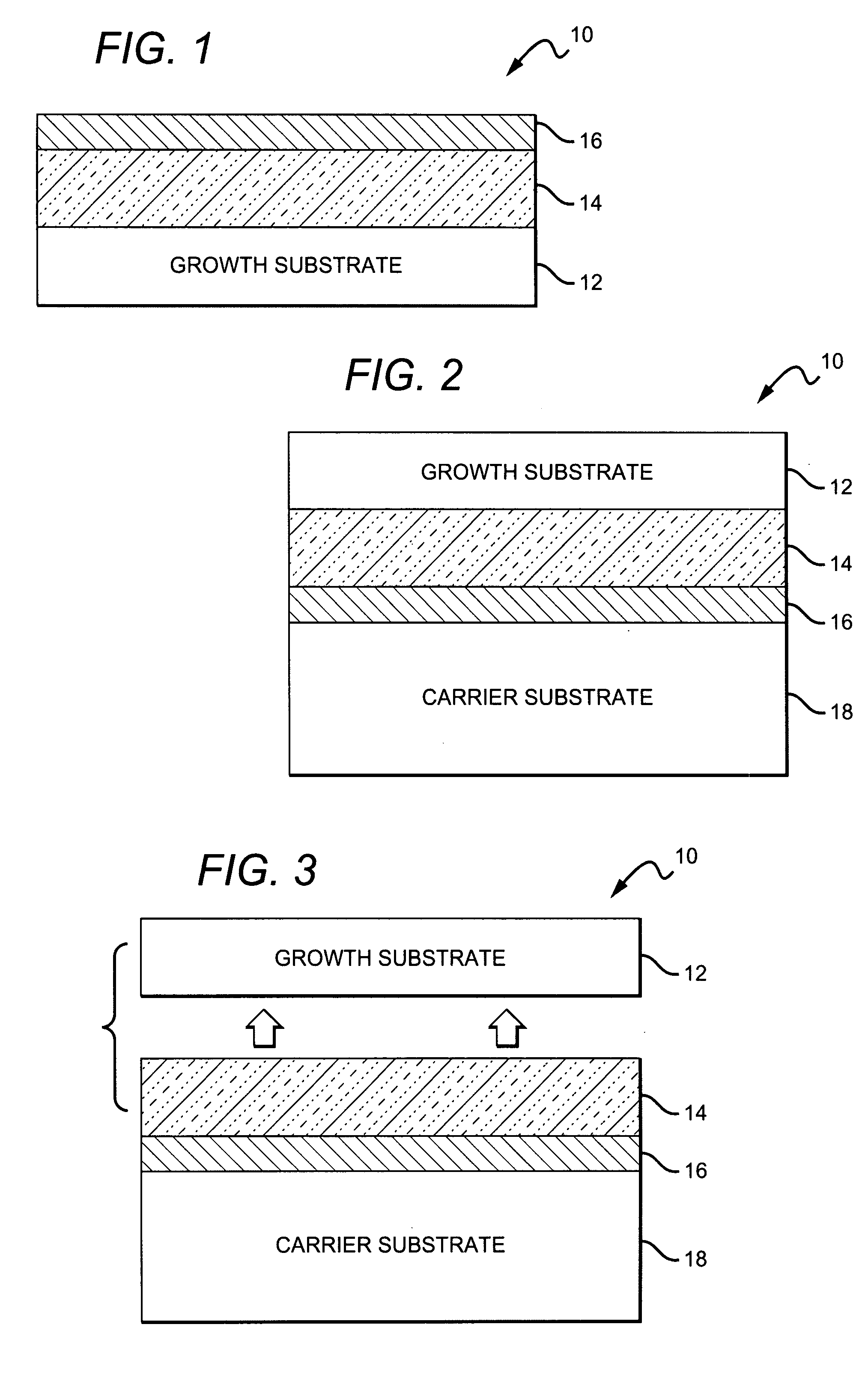
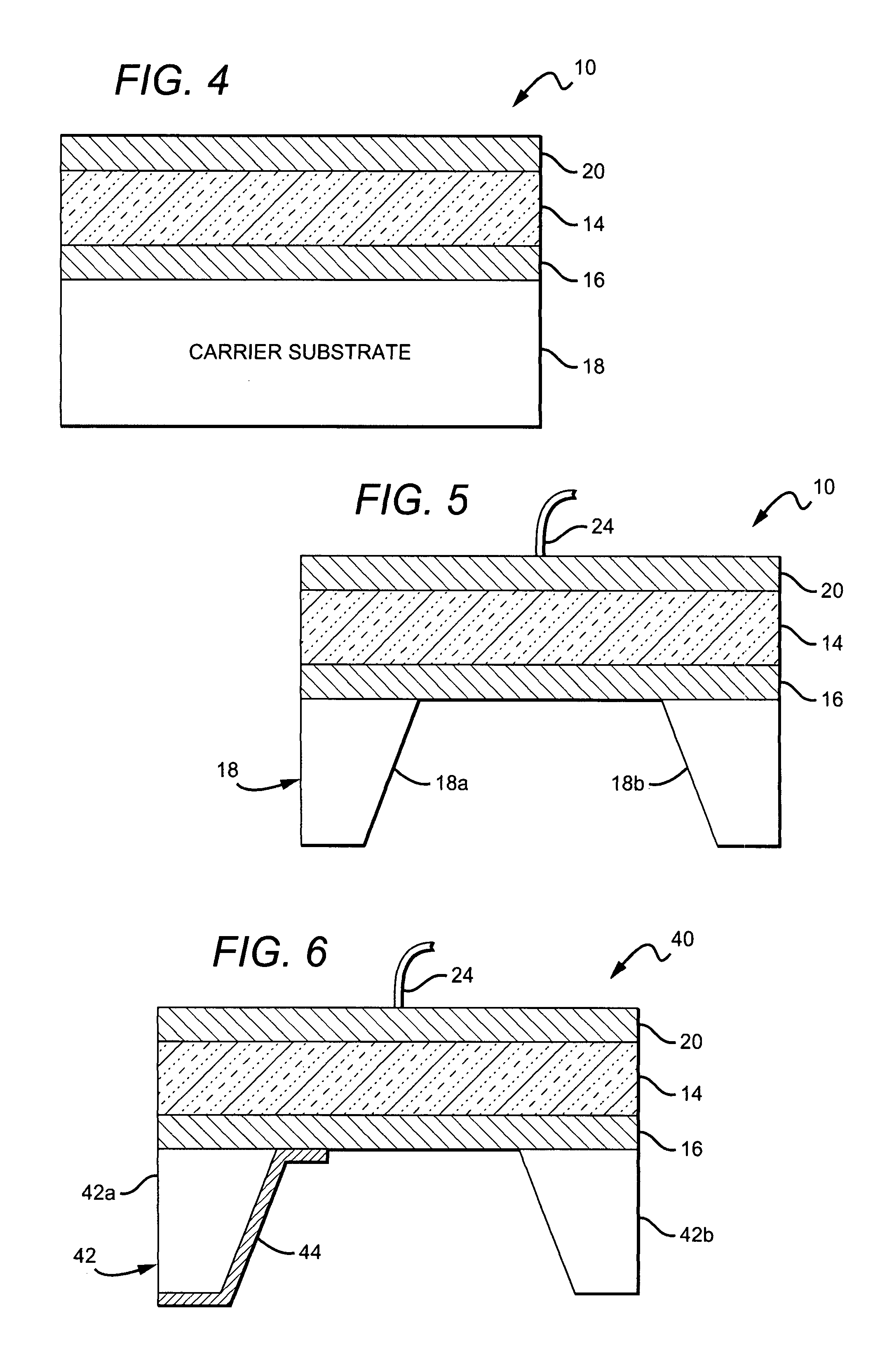
A method for fabricating a bulk acoustic wave (BAW) device comprising providing a growth substrate and growing an Group-III nitride epitaxial layer on the growth substrate. A first electrode is deposited on the epitaxial layer. A carrier substrate is provided and the growth substrate, epitaxial layer and first electrode combination is flip-chip mounted on the carrier substrate. The growth substrate is removed and a second electrode is deposited on the epitaxial layer with the epitaxial layer sandwiched between the first and second electrodes. A bulk acoustic wave (BAW) device comprises first and second metal electrodes and a Group-III nitride epitaxial layer sandwiched between the first and second electrodes. A carrier substrate is included, with the first and second electrodes and epitaxial layer on the carrier substrate.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Integrated biological and chemical sensors
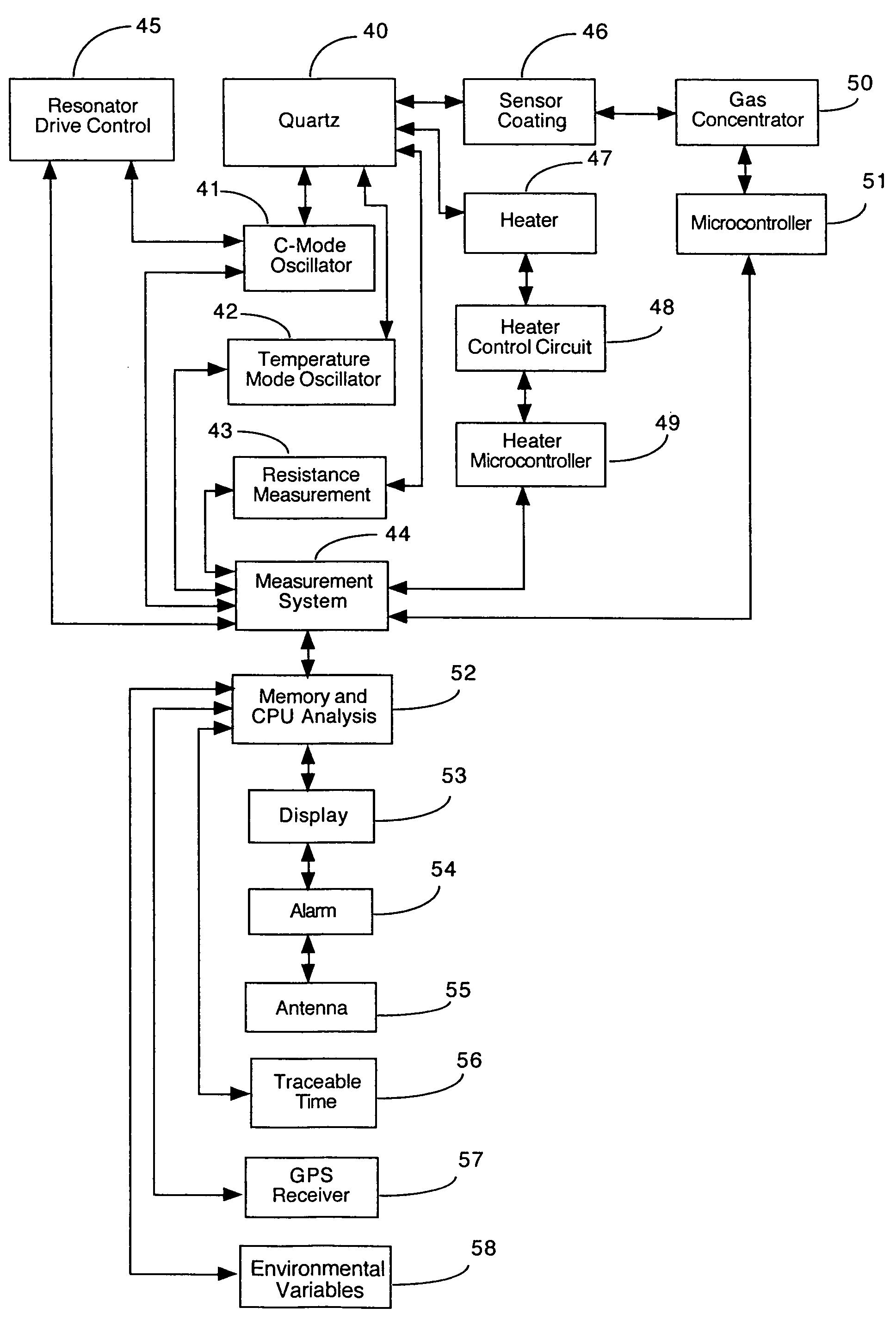
InactiveUS6955787B1The process is fast and accurateOptical signal enhancementVibration measurement in solidsWave amplification devicesDual modeSurface acoustic wave
An array of piezoelectric resonators used in a sensor device in order to identify chemical and biological agents. The resonators can operate as bulk acoustic wave (BAW), surface acoustic wave (SAW), or Love mode devices. The sensor device integrates gravimetric, calorimetric, thermal gravimetric, voltage gravimetric and optical detection methods into one sensor system, improving the accuracy of identifying hazardous agents. For gravimetric detection, dual-mode resonators provide simultaneous calorimetric and gravimetric data, one type from each mode. Resonators with heaters on the surfaces will provide thermal gravimetric data. An optical detector can be used to analyze the optical signal from the surface of a coated resonator. Additionally, voltage gravimetric measurements can be made with an electric field set up between the resonator and an external electrode. Thermal voltage gravimetric measurements can be made by adding an integrated heater on the resonator with an external electrode. An alarm can be activated upon the identification of a hazardous agent. The sensor device can utilize other valuable information, including traceable time, GPS location, and variables related to temperature, humidity, air speed, and air direction.
Owner:HANSON WILLIAM PAYNTER
5G BAND n79 ACOUSTIC WAVE RESONATOR RF FILTER CIRCUIT
ActiveUS20190068164A1High rejectionLow insertion lossImpedence networksSemiconductor devicesAcoustic waveInductor
An RF circuit device using modified lattice, lattice, and ladder circuit topologies. The devices can include four resonator devices and four shunt resonator devices. In the ladder topology, the resonator devices are connected in series from an input port to an output port while shunt resonator devices are coupled the nodes between the resonator devices. In the lattice topology, a top and a bottom serial configurations each includes a pair of resonator devices that are coupled to differential input and output ports. A pair of shunt resonators is cross-coupled between each pair of a top serial configuration resonator and a bottom serial configuration resonator. The modified lattice topology adds baluns or inductor devices between top and bottom nodes of the top and bottom serial configurations of the lattice configuration. These topologies may be applied using single crystal or polycrystalline bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonators.
Owner:AKOUSTIS INC
Bulk acoustic device and method for fabricating
ActiveUS20080284541A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesOptoelectronicsAcoustic wave
A method for fabricating a bulk acoustic wave (BAW) device comprising providing a growth substrate and growing an Group-III nitride epitaxial layer on the growth substrate. A first electrode is deposited on the epitaxial layer. A carrier substrate is provided and the growth substrate, epitaxial layer and first electrode combination is flip-chip mounted on the carrier substrate. The growth substrate is removed and a second electrode is deposited on the epitaxial layer with the epitaxial layer sandwiched between the first and second electrodes. A bulk acoustic wave (BAW) device comprises first and second metal electrodes and a Group-III nitride epitaxial layer sandwiched between the first and second electrodes. A carrier substrate is included, with the first and second electrodes and epitaxial layer on the carrier substrate.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
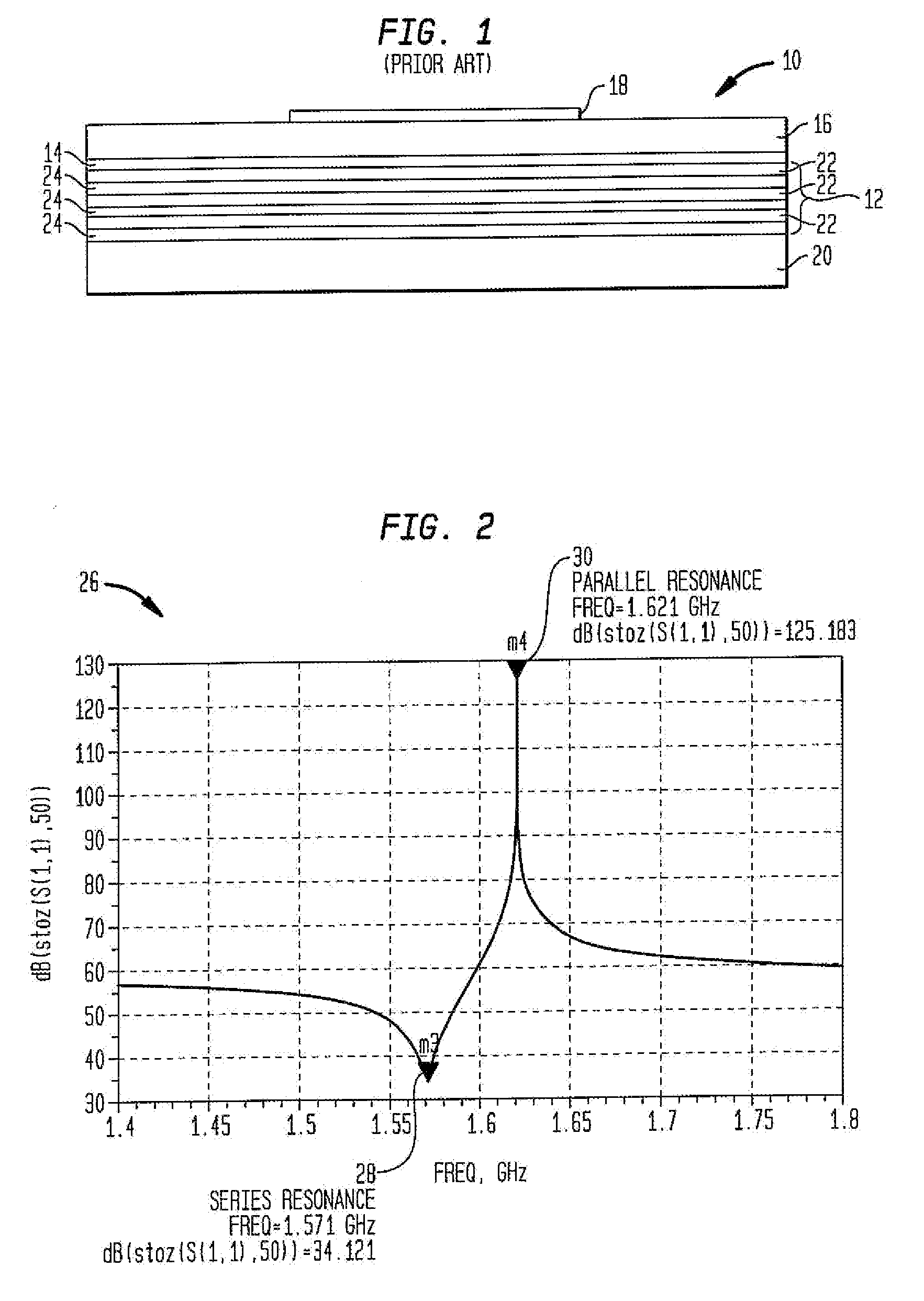
Apparatus and method for extending tuning range of electro-acoustic film resonators
InactiveUS7030718B1Increase spacingExceeding initial spacingImpedence networksElectric pulse generatorThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorAcoustic wave
A tuning circuit for adjusting an oscillation frequency of an oscillator circuit. The tuning circuit comprises a film bulk acoustic wave resonator (FBAR) having a series resonance frequency and a parallel resonance frequency, and an inductor coupled in series or parallel with the film bulk acoustic wave resonator. The series connection of the inductor and FBAR decreases the series resonance frequency. The parallel connection of the inductor and the FBAR increases the parallel resonance frequency. The tuning circuit further comprises a varactor coupled in series or parallel with the inductor and the FBAR combination. The varactor tunes the oscillation frequency over the increased tuning range.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Method for fabricating bulk acoustic wave resonator with mass adjustment structure
ActiveUS20180191322A1High mechanical strengthSuppress spurious modeImpedence networksResonanceAcoustic wave
A method for fabricating bulk acoustic wave resonator with mass adjustment structure, comprising following steps of: forming a sacrificial structure mesa on a substrate; etching the sacrificial structure mesa such that any two adjacent parts have different heights, a top surface of a highest part of the sacrificial structure mesa is coincident with a mesa top extending plane; forming an insulating layer on the sacrificial structure mesa and the substrate; polishing the insulating layer to form a polished surface; forming a bulk acoustic wave resonance structure including a top electrode, a piezoelectric layer and a bottom electrode on the polished surface; etching the sacrificial structure mesa to form a cavity; the insulating layer between the polished surface and the mesa top extending plane forms a frequency tuning structure, the insulating layer between the mesa top extending plane and the cavity forms a mass adjustment structure.
Owner:WIN SEMICON
Film bulk acoustic wave resonator, its fabrication method and film bulk acoustic wave resonator filter using the resonator
InactiveUS20090127978A1ConnectionGuaranteed StrengthPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorResonator filter
The film bulk acoustic wave resonator includes a laminate structure composed of a piezoelectric layer, and first and second electrode layers interposing at least part of the piezoelectric layer, in which the first metal electrode is dispersively formed on an electrode plane facing the second metal electrode, and a gap is formed in a substrate correspondingly to the laminate-structured resonance part. Except for an area of a wire electrode electrically connected to the first electrode layer and an area of a wire electrode electrically connected to the second electrode layer, the piezoelectric layer, first electrode layer and second electrode layer do not come in contact with the insulating substrate but are supported on a hollow. Also, a prop is formed in the gap to support the laminate structure.
Owner:HITACHI MEDIA ELECTORONICS CO LTD
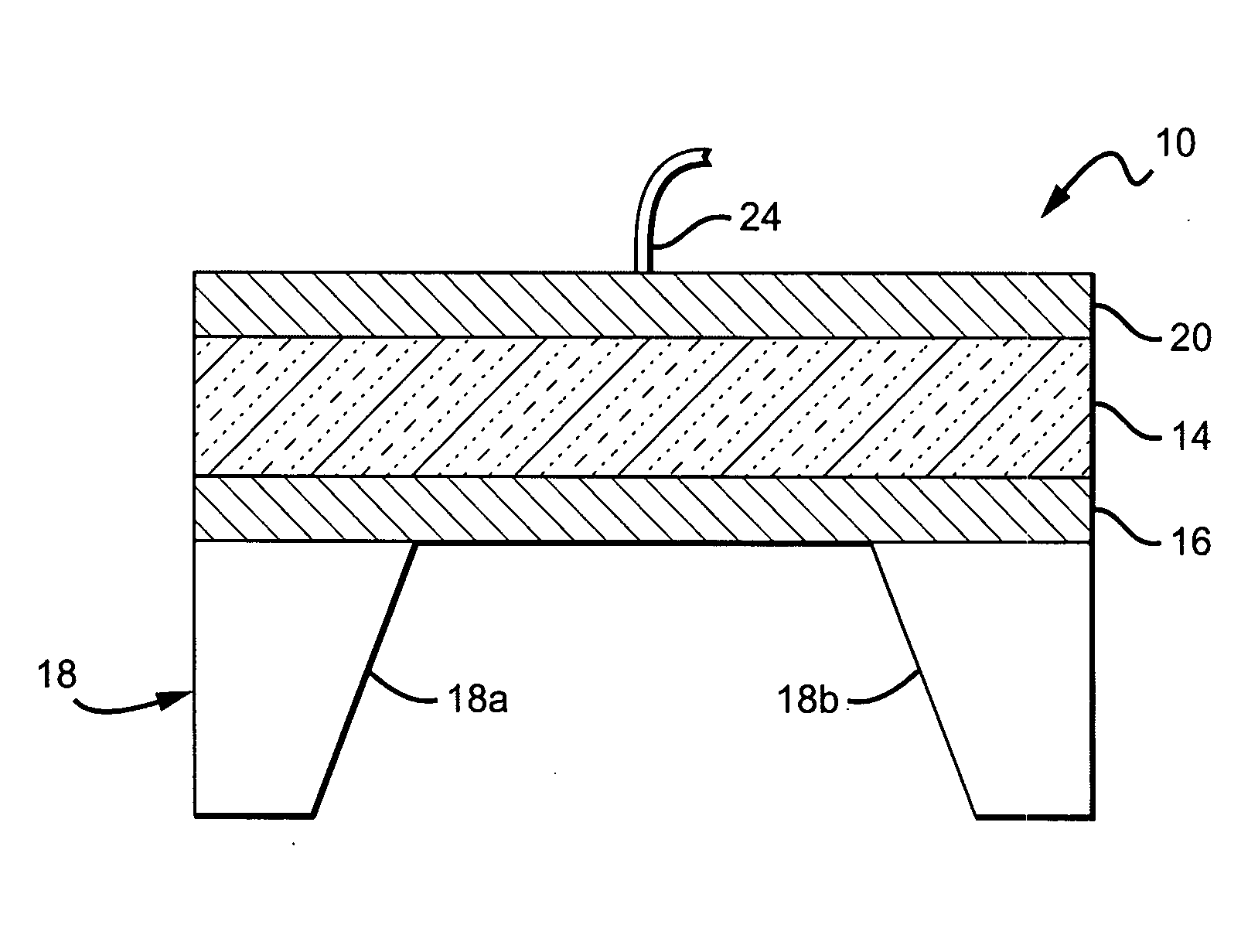
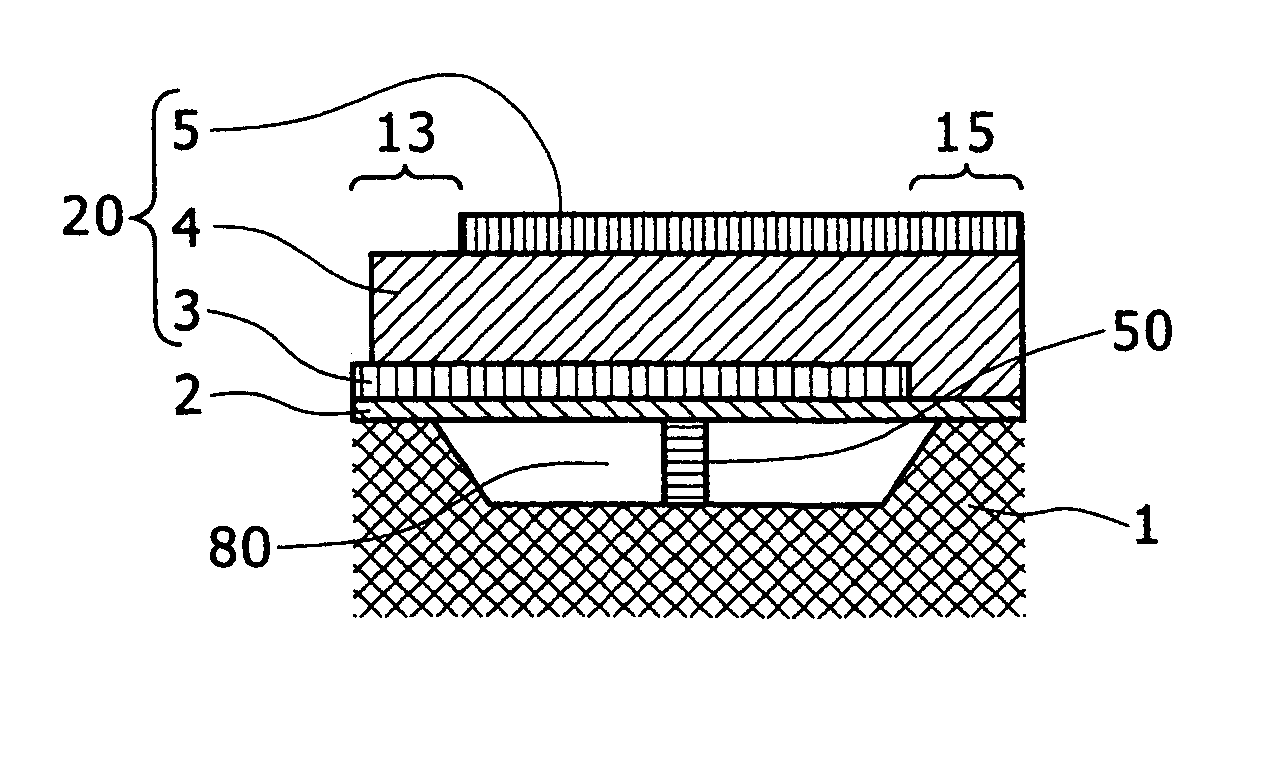
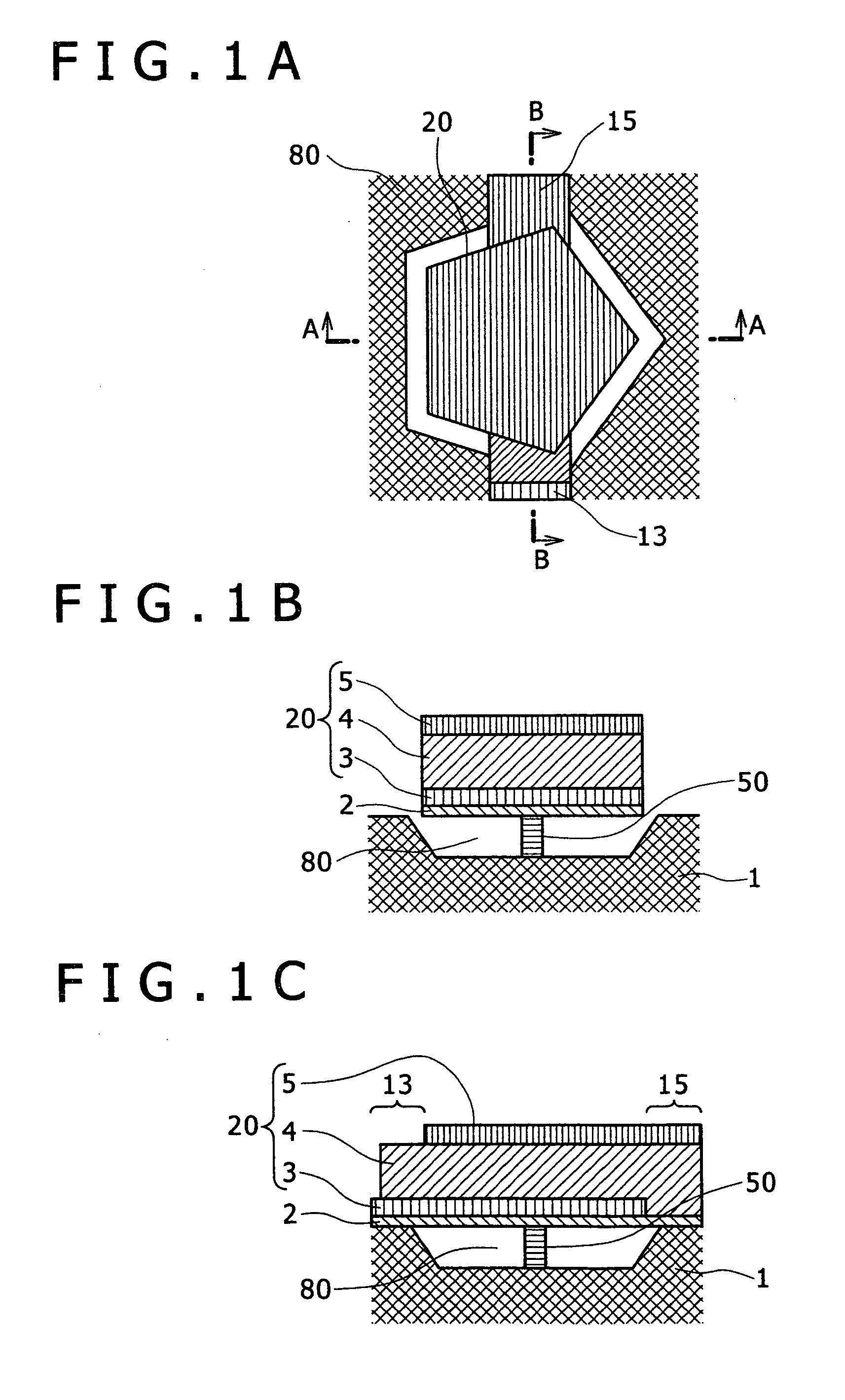
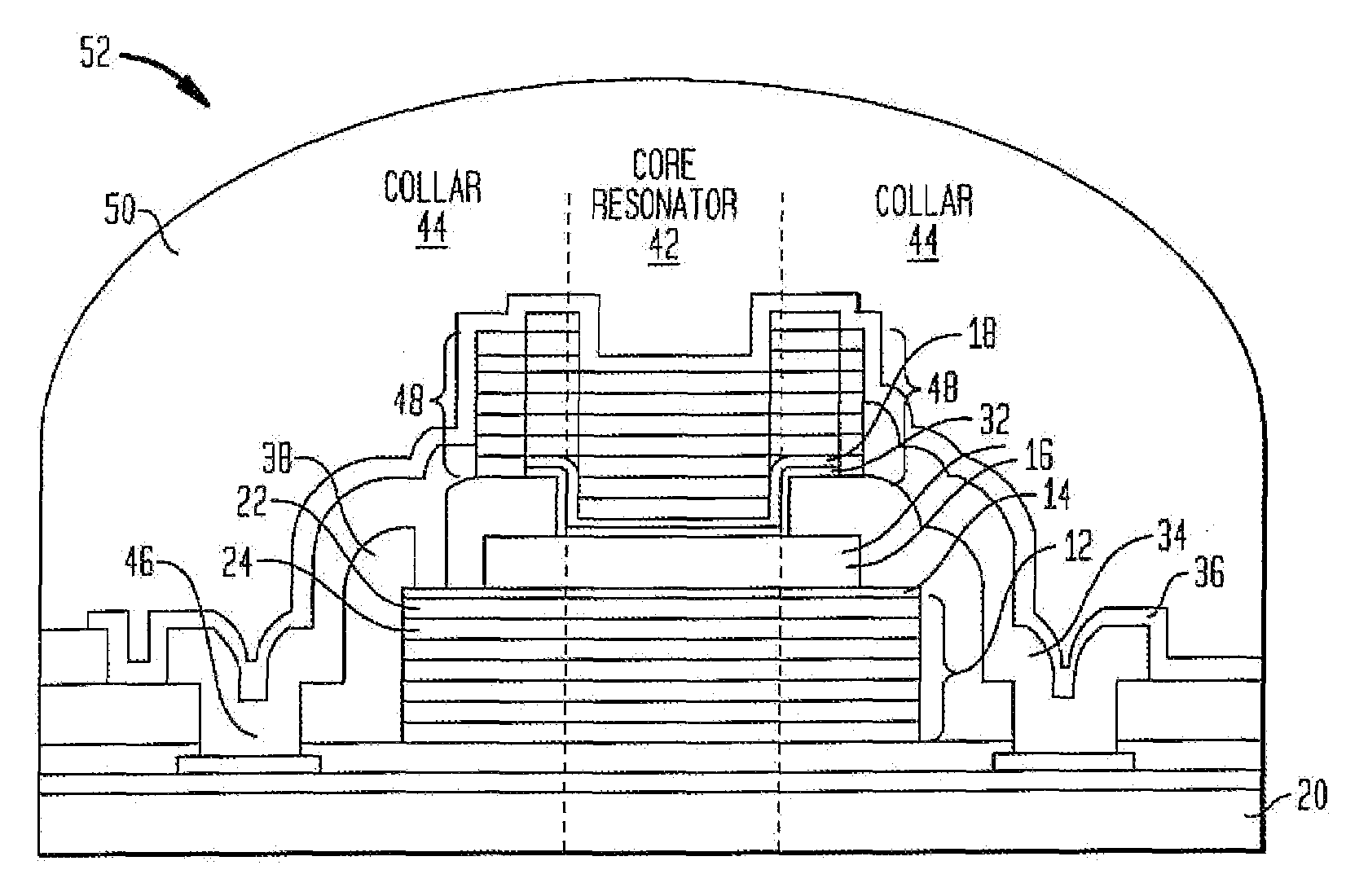
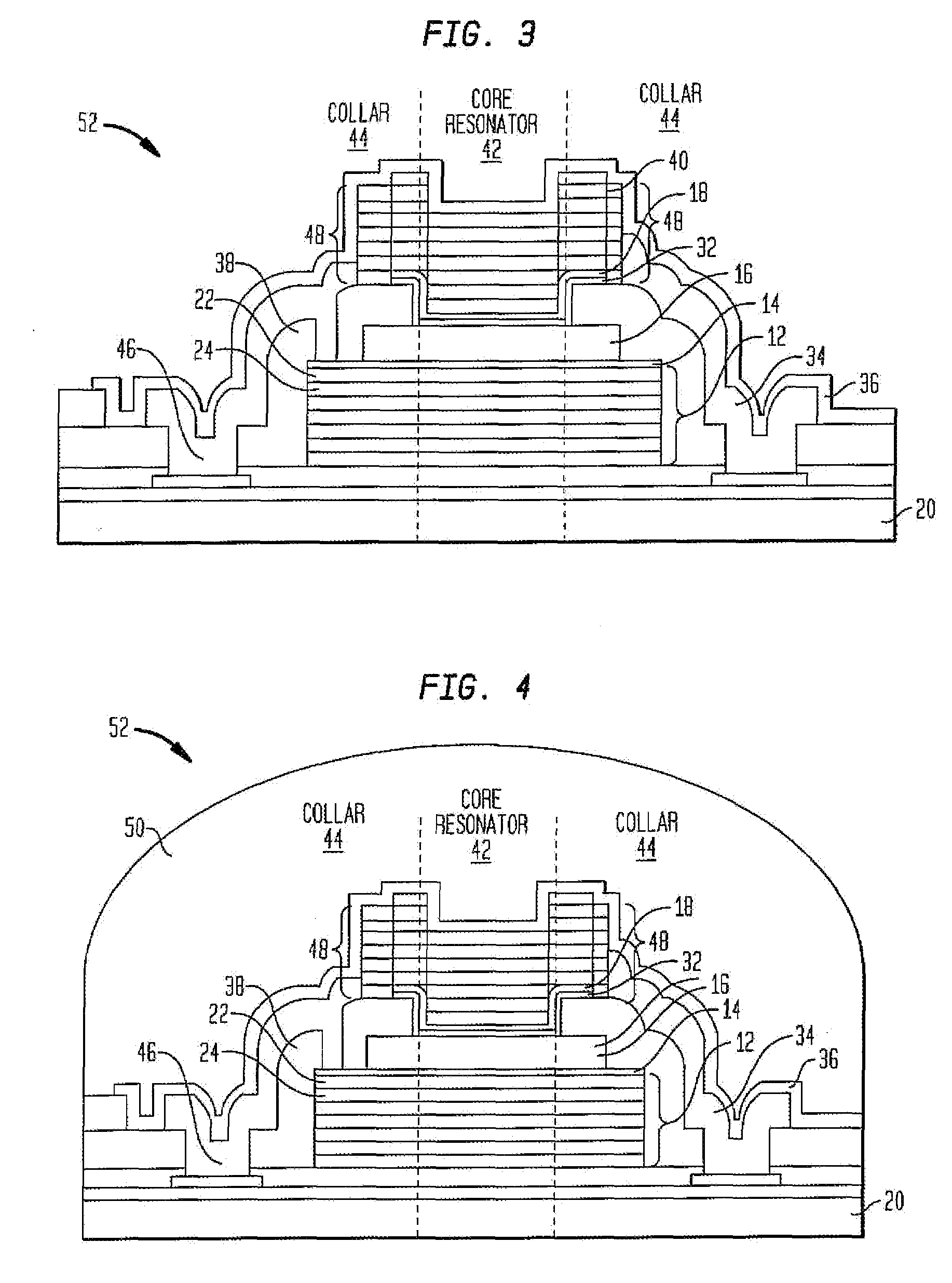
Protected resonator
ActiveUS20100187948A1Excellent inertial resistanceIncrease resistancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksEnvironmental effectResonance
A bulk acoustic wave resonator structure that isolates the core resonator from both environmental effects and aging effects. The structure has a piezoelectric layer at least partially disposed between two electrodes. The structure is protected against contamination, package leaks, and changes to the piezoelectric material due to external effects while still providing inertial resistance. The structure has one or more protective elements that limit aging effects to at or below a specified threshold. The resonator behavior is stabilized across the entire bandwidth of the resonance, not just at the series resonance. Examples of protective elements include a collar of material around the core resonator so that perimeter and edge-related environmental and aging phenomena are kept away from the core resonator, a Bragg reflector formed above or below the piezoelectric layer and a cap formed over the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
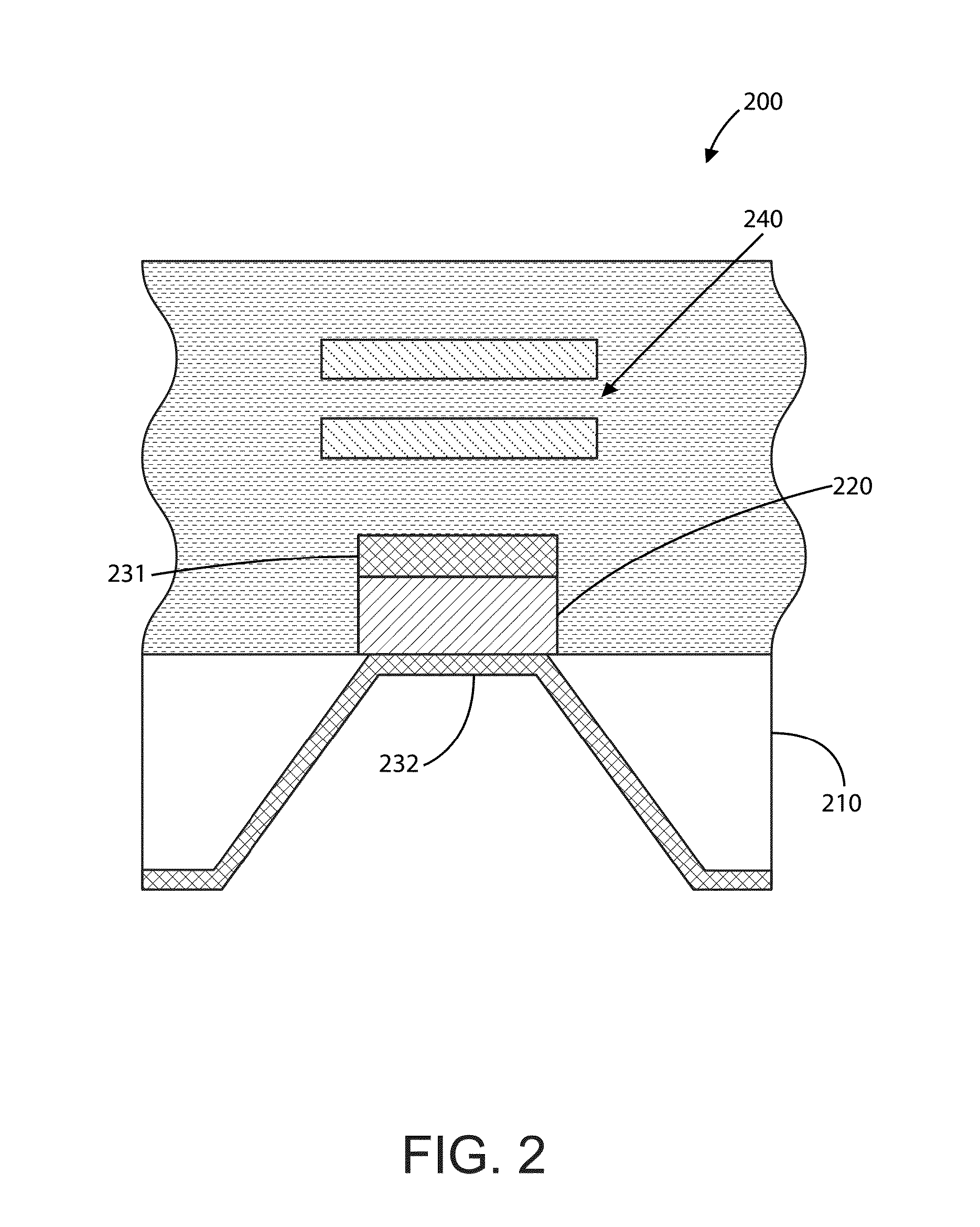
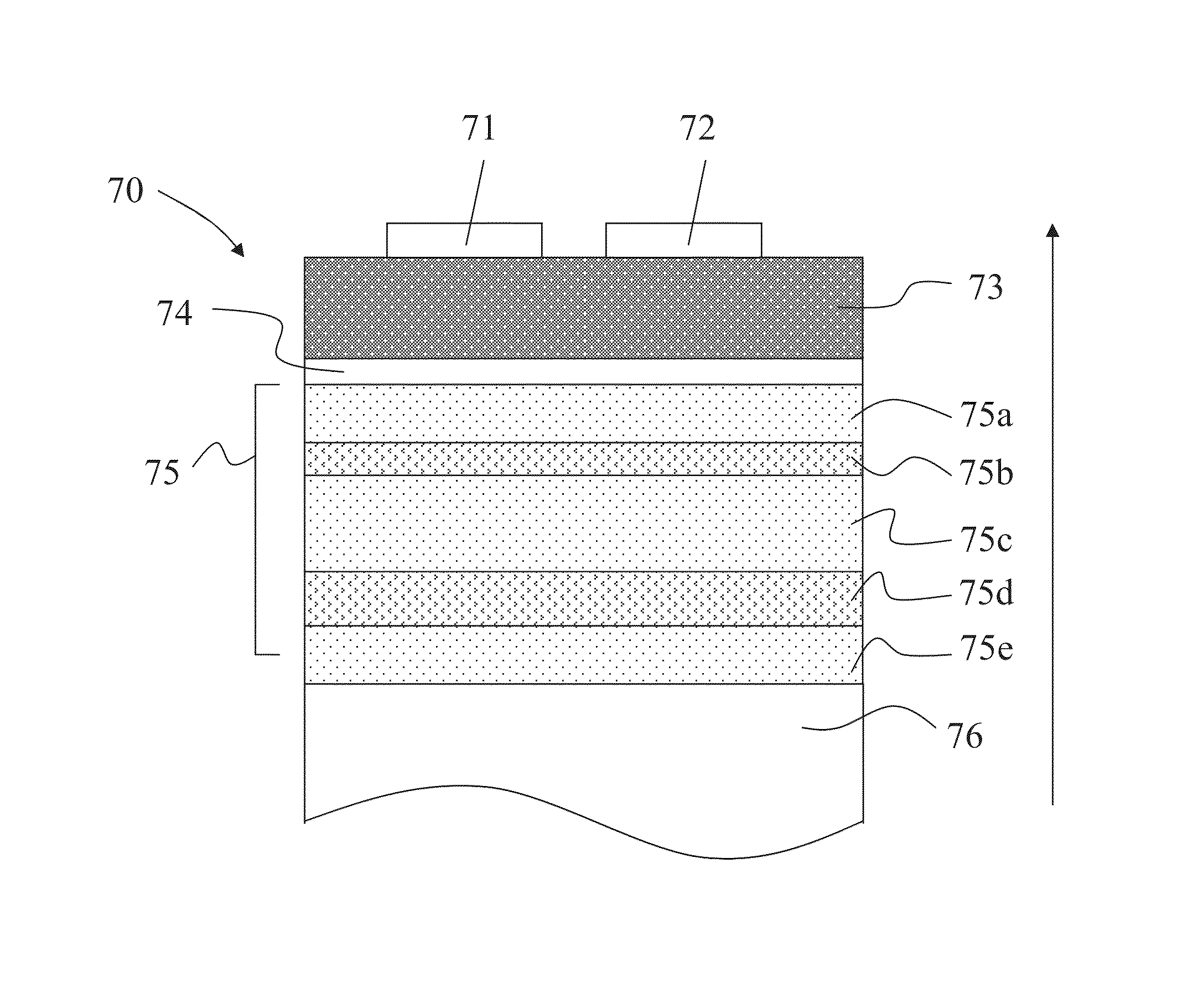
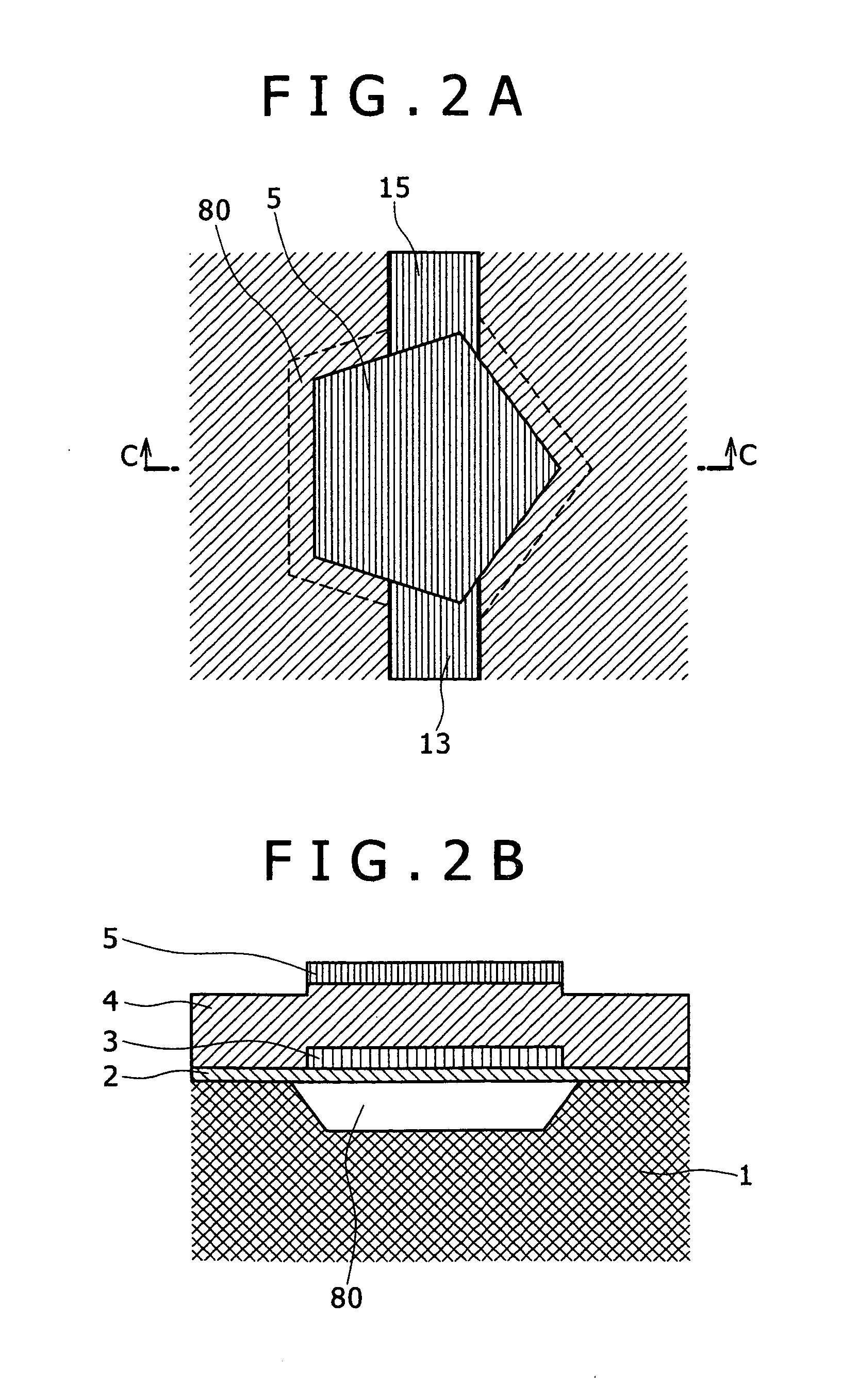
Acoustic resonator having collar structure
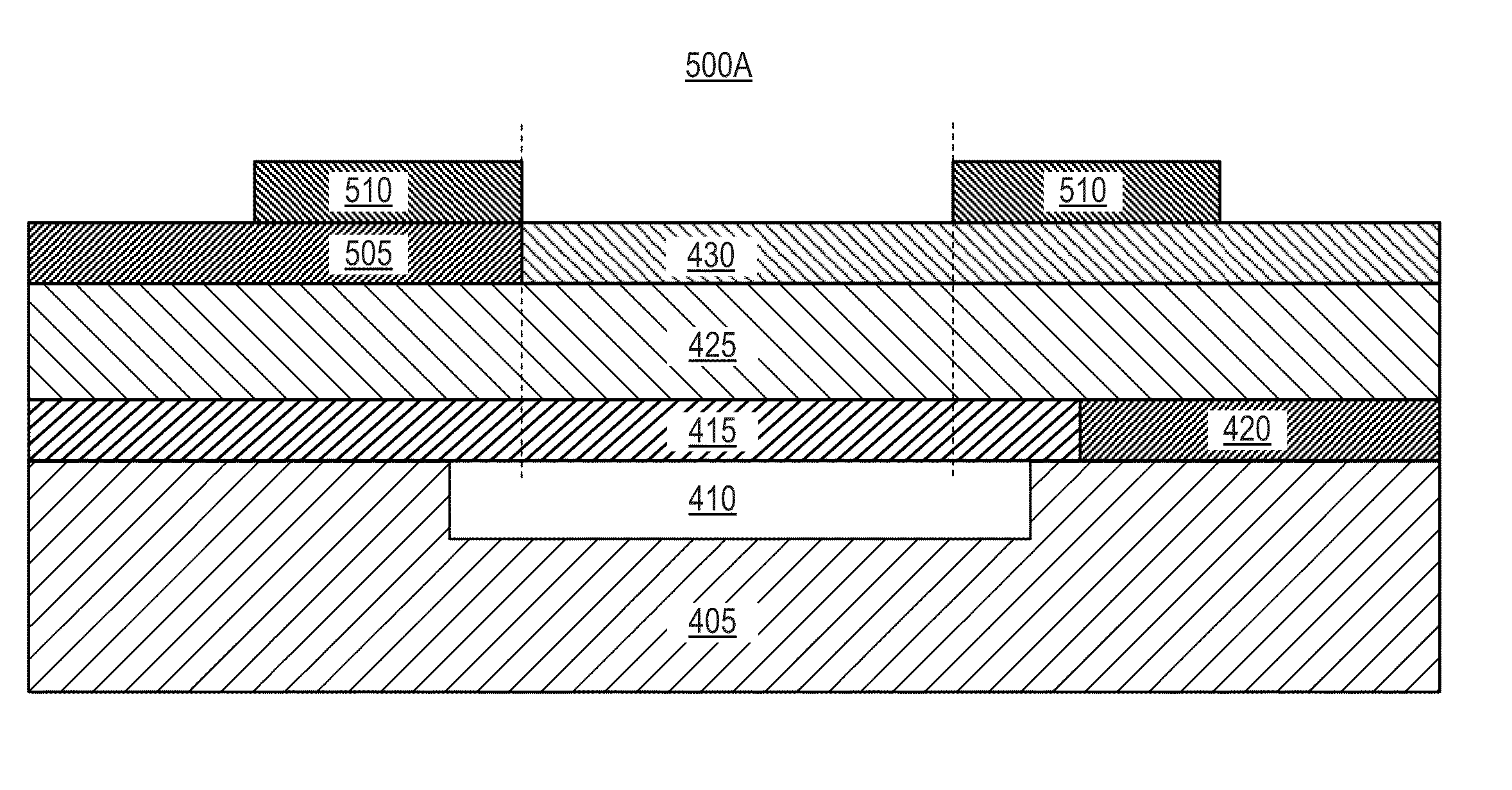
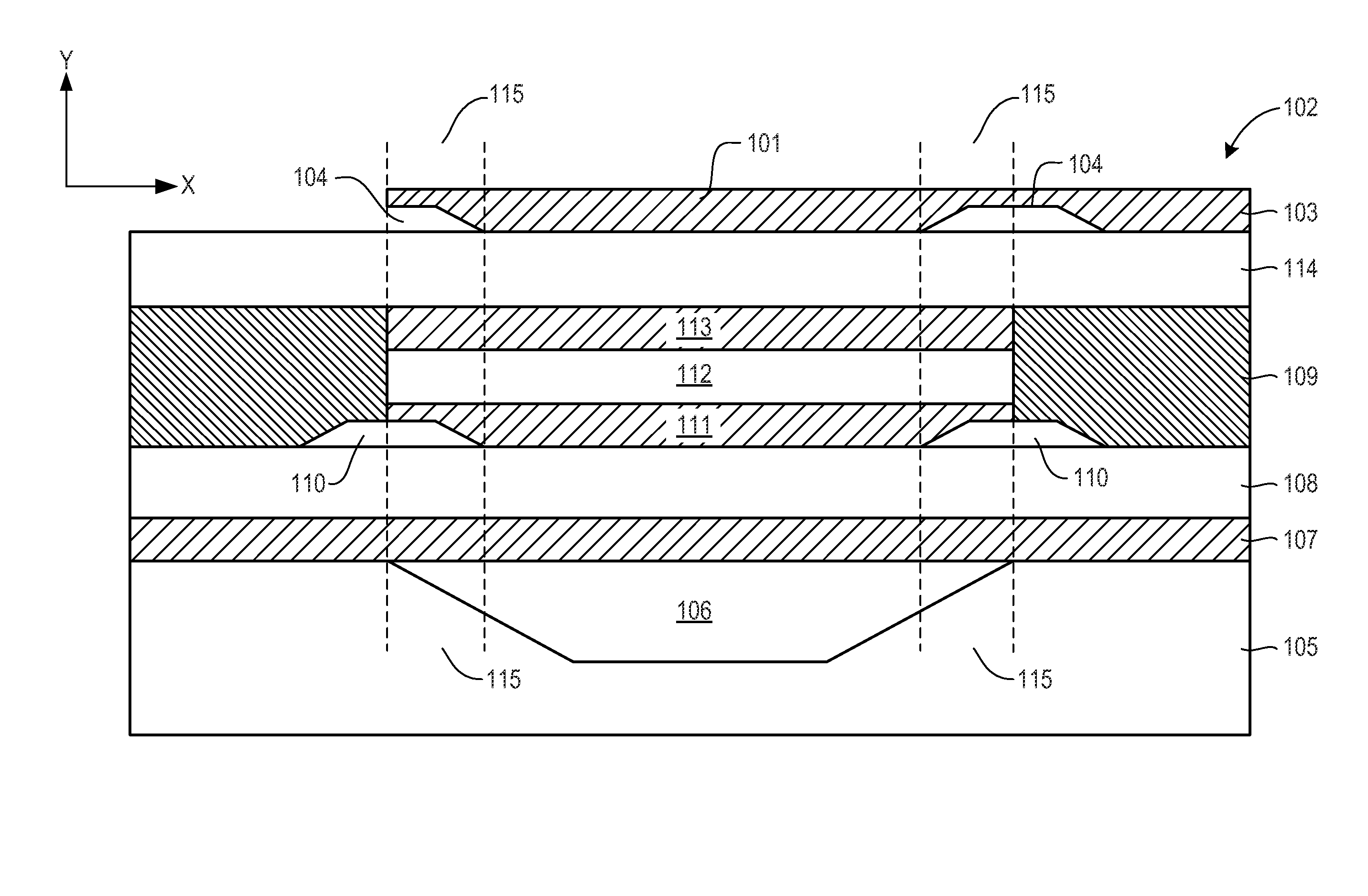
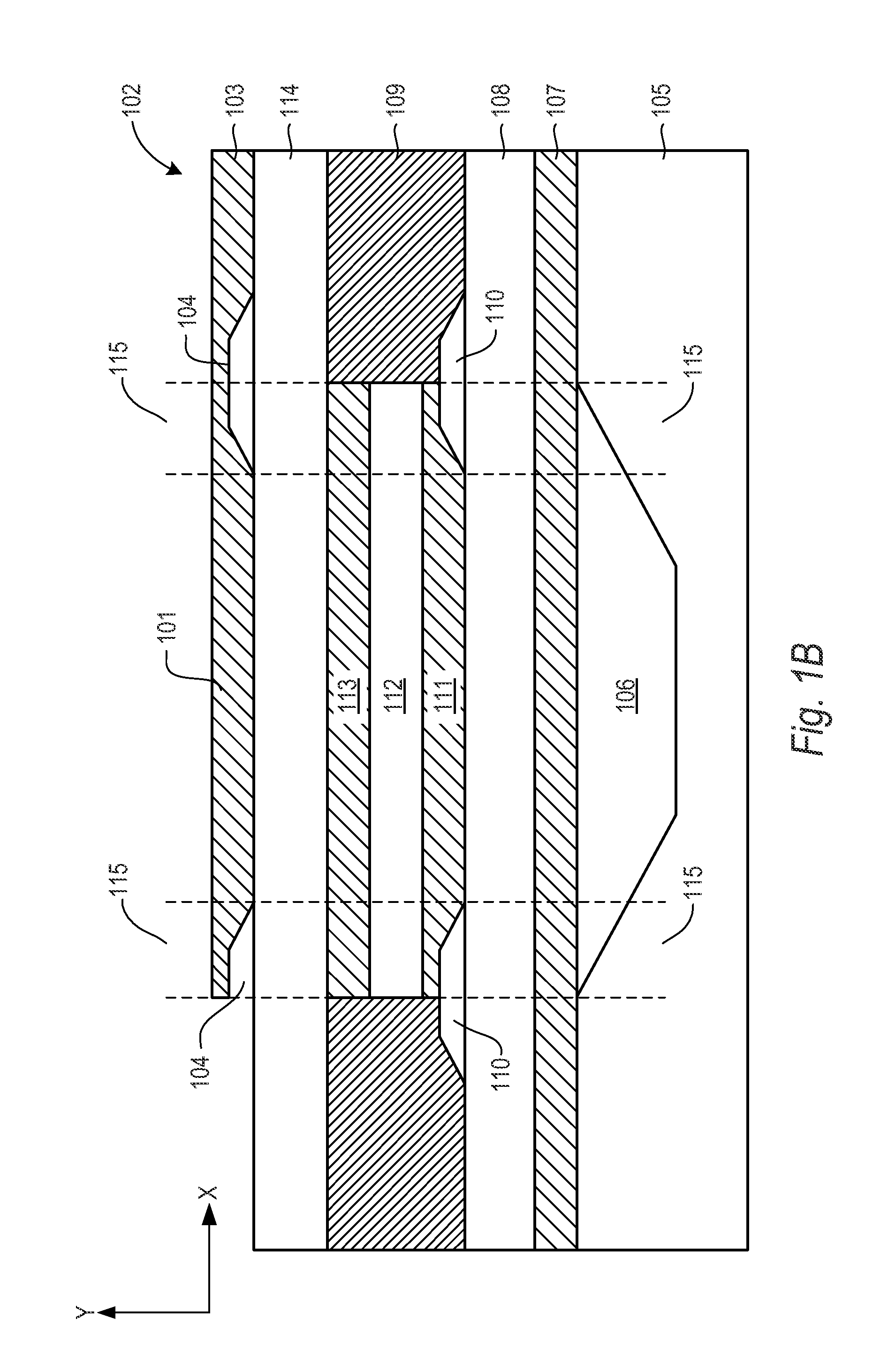
A bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonator structure comprises a first electrode disposed over a substrate, a first piezoelectric layer disposed over the first electrode, a second electrode disposed over the first piezoelectric layer, and a collar structure disposed around a perimeter of an active region defined by an overlap between the first electrode, the second electrode, and the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Acoustic waves in microfluidics
Various aspects of the present invention relate to the control and manipulation of fluidic species, for example, in microfluidic systems. In one set of embodiments, droplets may be sorted using surface acoustic waves. The droplets may contain cells or other species. In some cases, the surface acoustic waves may be created using a surface acoustic wave generator such as an interdigitated transducer, and / or a material such as a piezoelectric substrate. The piezoelectric substrate may be isolated from the microfluidic substrate except at or proximate the location where the droplets are sorted, e.g., into first or second microfluidic channels. At such locations, the microfluidic substrate may be coupled to the piezoelectric substrate (or other material) by one or more coupling regions. In some cases, relatively high sorting rates may be achieved, e.g., at rates of at least about 1,000 Hz, at least about 10,000 Hz, or at least about 100,000 Hz, and in some embodiments, with high cell viability after sorting.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
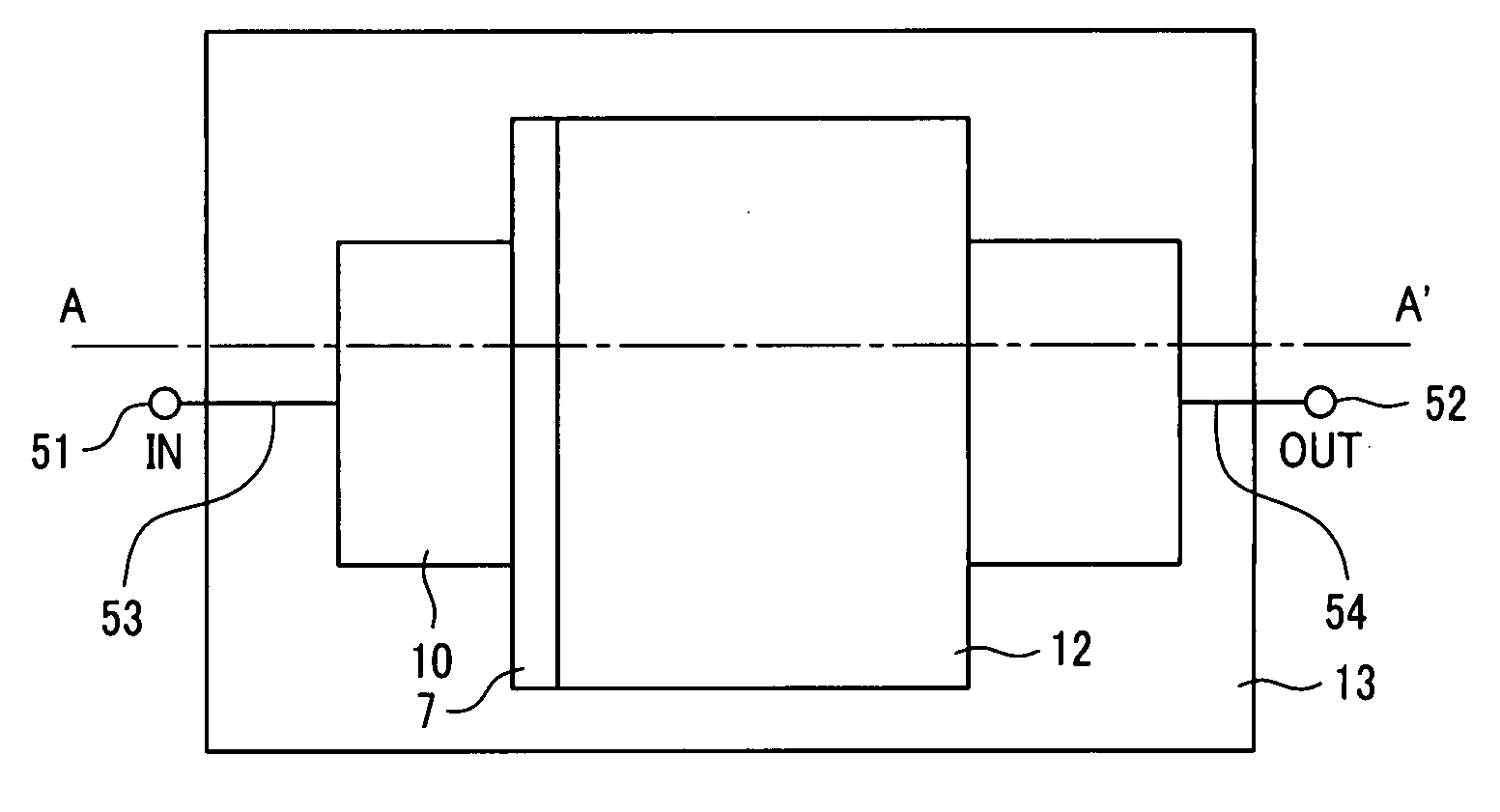
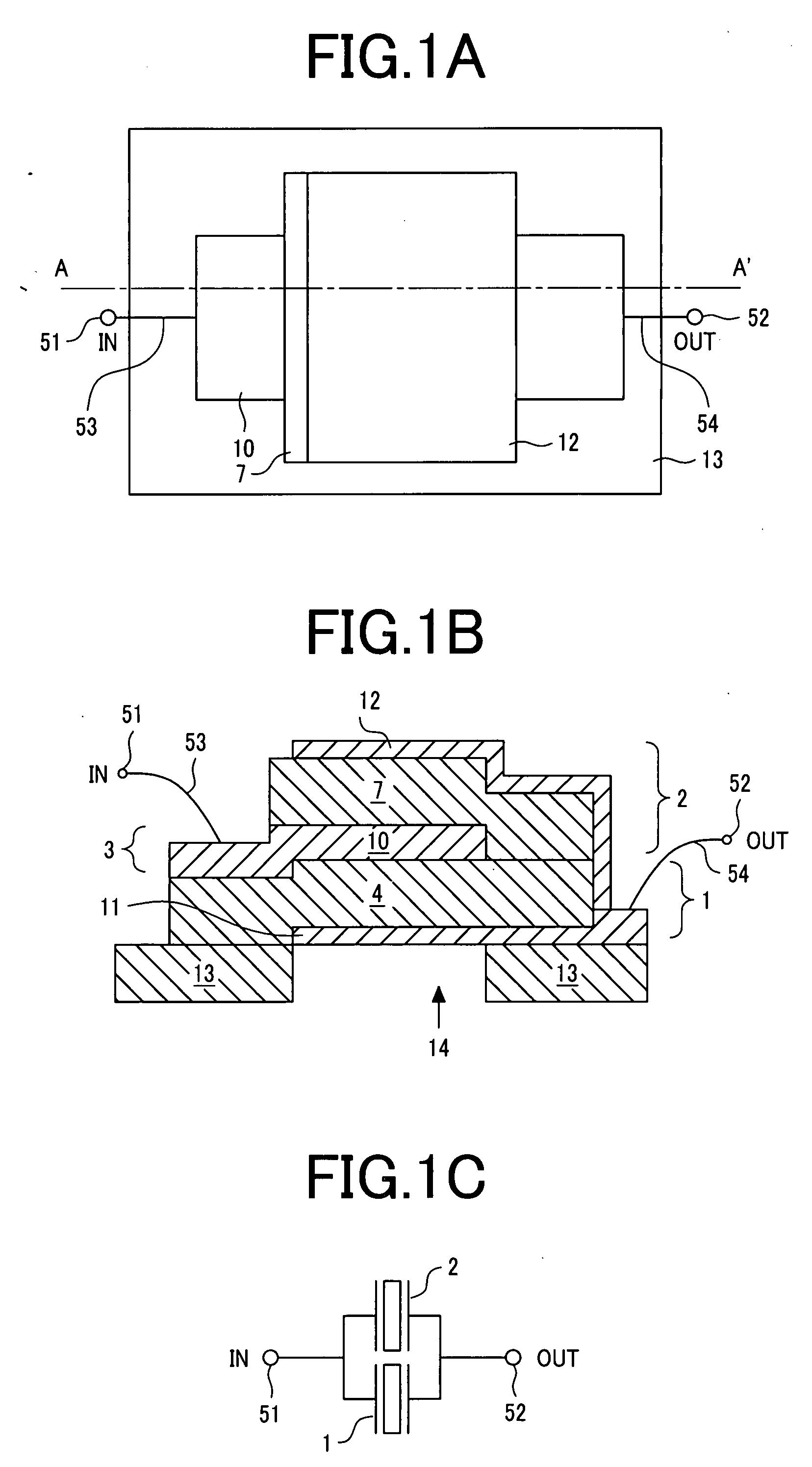
Acoustic Wave Device
ActiveUS20100225202A1Little changeImprove moisture resistanceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAcoustic waveBulk acoustic wave
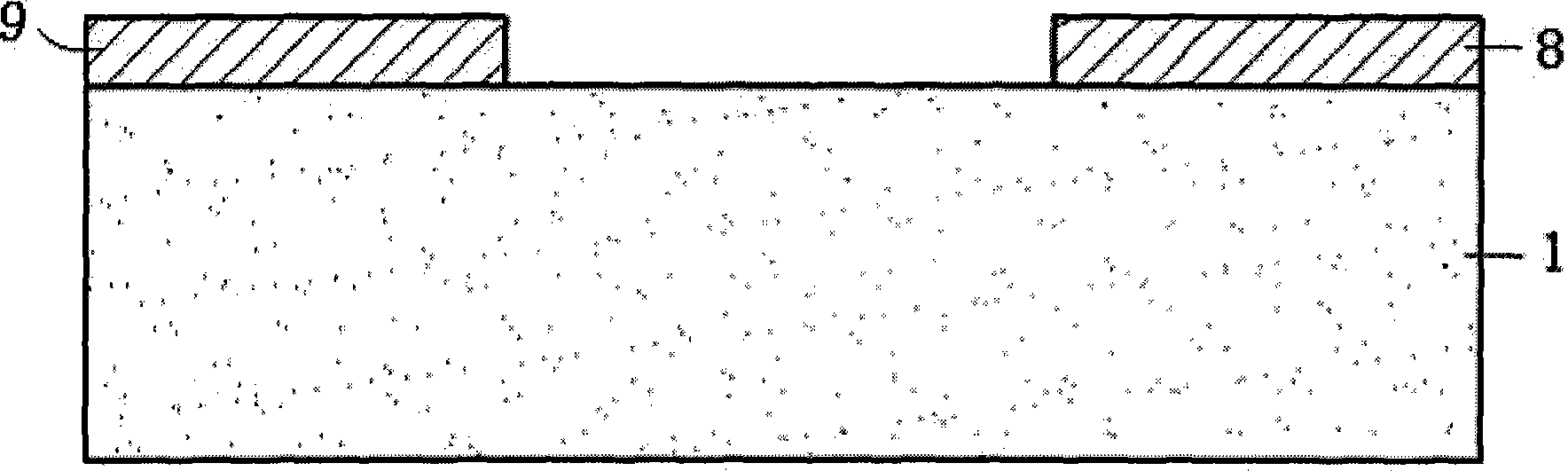
Provided is a highly reliable acoustic wave device wherein deterioration of electrical characteristics due to deformation of a protective cover is suppressed. A method for manufacturing such acoustic wave device is also provided. The acoustic wave device has a piezoelectric substrate 1 propagating an acoustic wave; an excitation electrode arranged on a first main surface of the piezoelectric substrate 1; a columnar outside connection-use electrode 10 electrically connected to the excitation electrode; a protective cover 17 having a hollow accommodating space 8 in which the excitation electrode is accommodated on the first main surface; and a conductive layer 18 connected to the electrode 10 on the protective cover 17.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Bulk acoustic wave filter with reduced nonlinear signal distortion
ActiveUS20080007369A1Reduced nonlinear signal distortionMinimizes undesirable nonlinear signal distortionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksHarmonicDistortion
A filter circuit includes at least one series resonator having a first terminal and a second terminal, where the first and second terminals of the at least one series resonator are coupled to an input and an output of the filter circuit, respectively. The filter circuit further includes at least one shunt resonator having a first terminal and a second terminal, where the first terminal of the at least one shunt resonator is coupled to the input of the filter circuit and the second terminal of the at least one shunt resonator is coupled to ground. A polarity of the first terminal of the at least one series resonator and a polarity of the first terminal of the at least one shunt resonator are selected so as to reduce harmonic signal generation and other types of distortion in the filter circuit.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
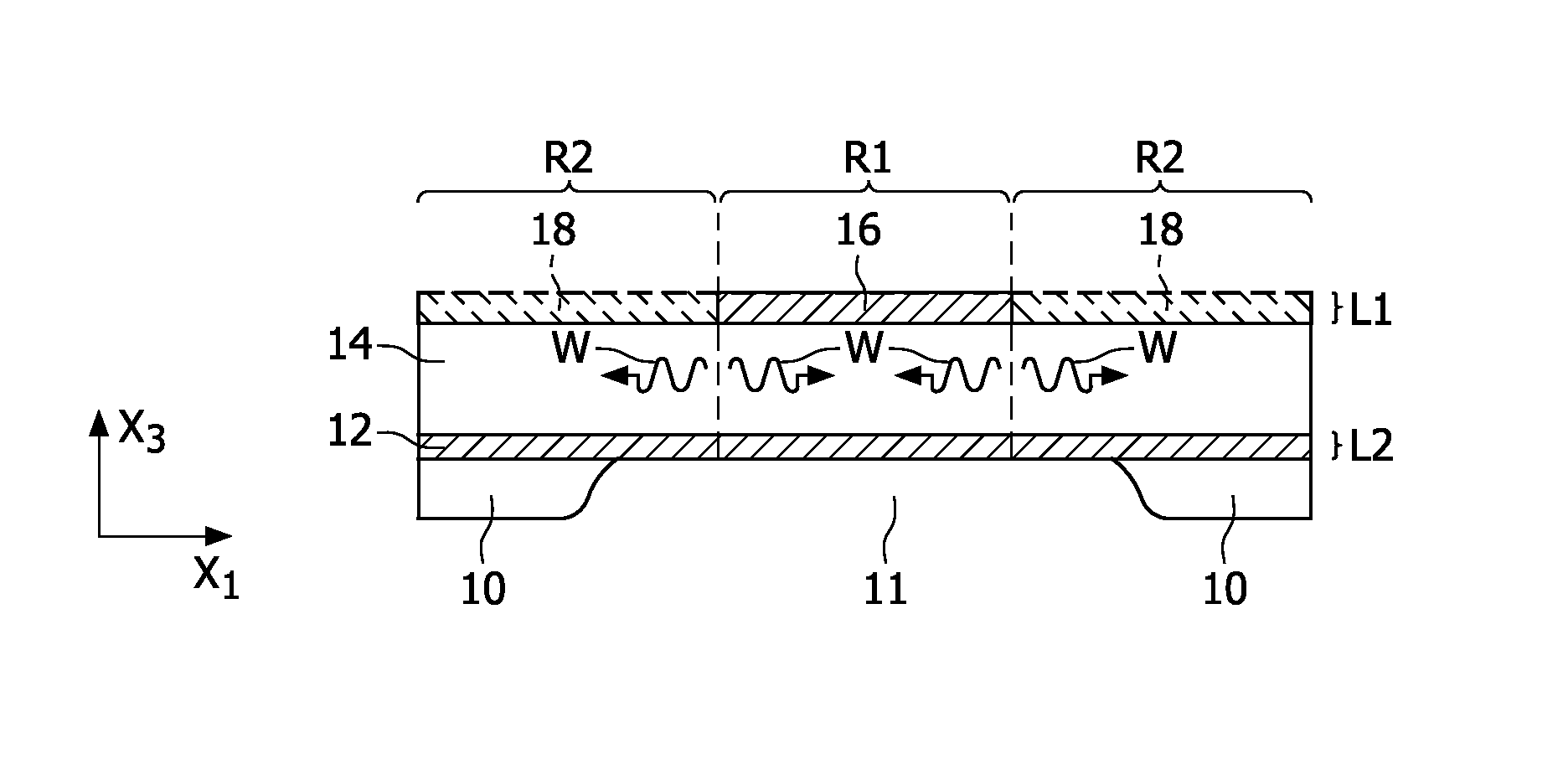
Thin-film bulk-acoustic wave (BAW) resonators
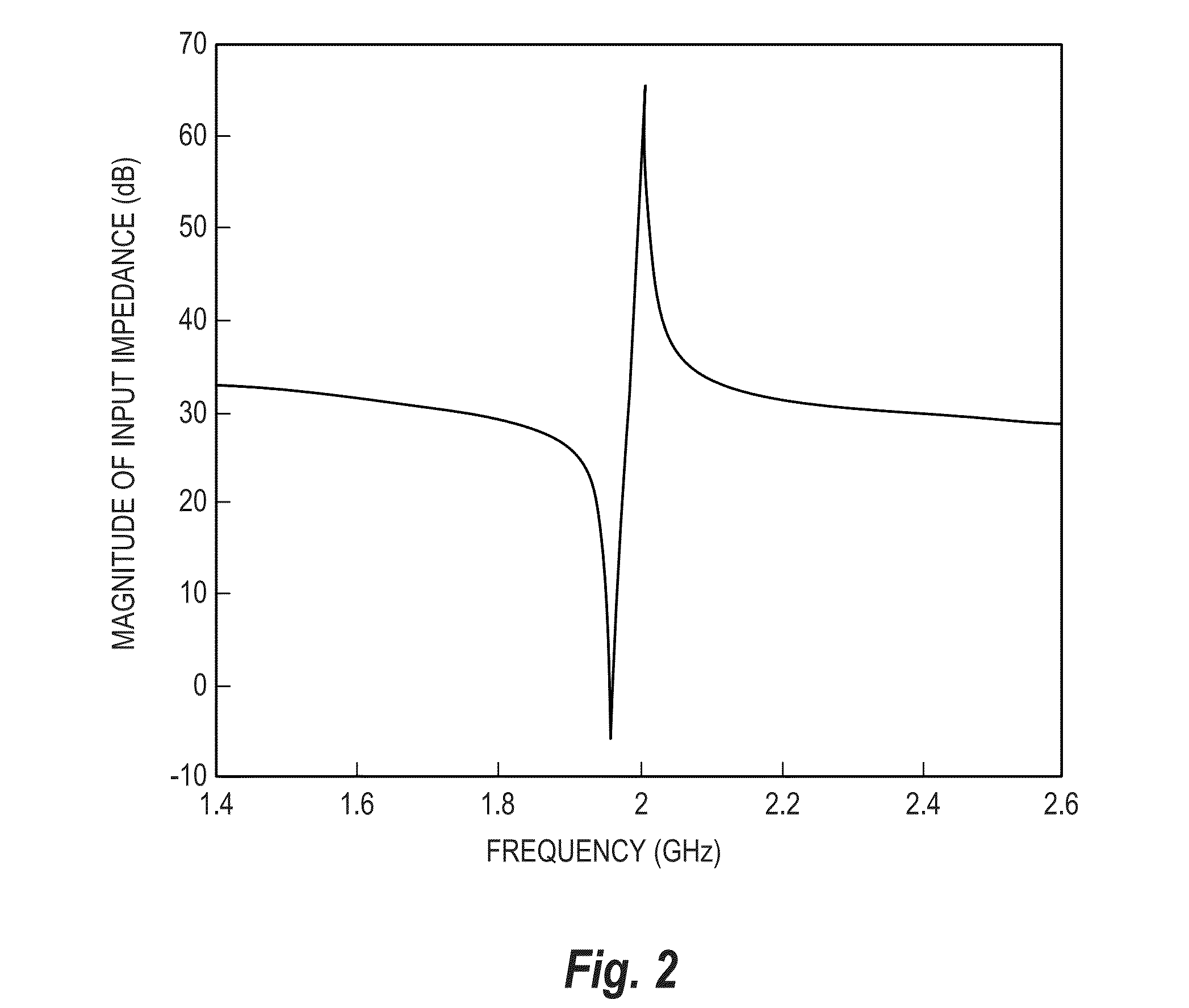
ActiveUS8008993B2Reduce lossesReduced insertion lossPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksSelectivity filterAcoustics
A thin-film bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonator, such as SBAR or FBAR, for use in RF selectivity filters operating at frequencies of the order of 1 GHz. The BAW resonator comprises a piezoelectric layer (14) having first and second surfaces on opposing sides, a first electrode (16) extending over the first surface, and a second electrode (12) extending over the second surface, the extent of the area of overlap (R1) of the first and second electrodes determining the region of excitation of the fundamental thickness extensional (TE) mode of the resonator. The insertion loss to the resonator is reduced by providing a dielectric material (18) in the same layer as the first electrode (16) and surrounding that electrode. The material constituting the dielectric material (18) has a different mass, typically between 5% and 15%, from the material comprising the first electrode (16) it surrounds. The mass of the dielectric material (18) can be lower or higher than the mass of the first electrode (16). Planarisation of the dielectric material (18) enhances the performance of the device.
Owner:QORVO US INC
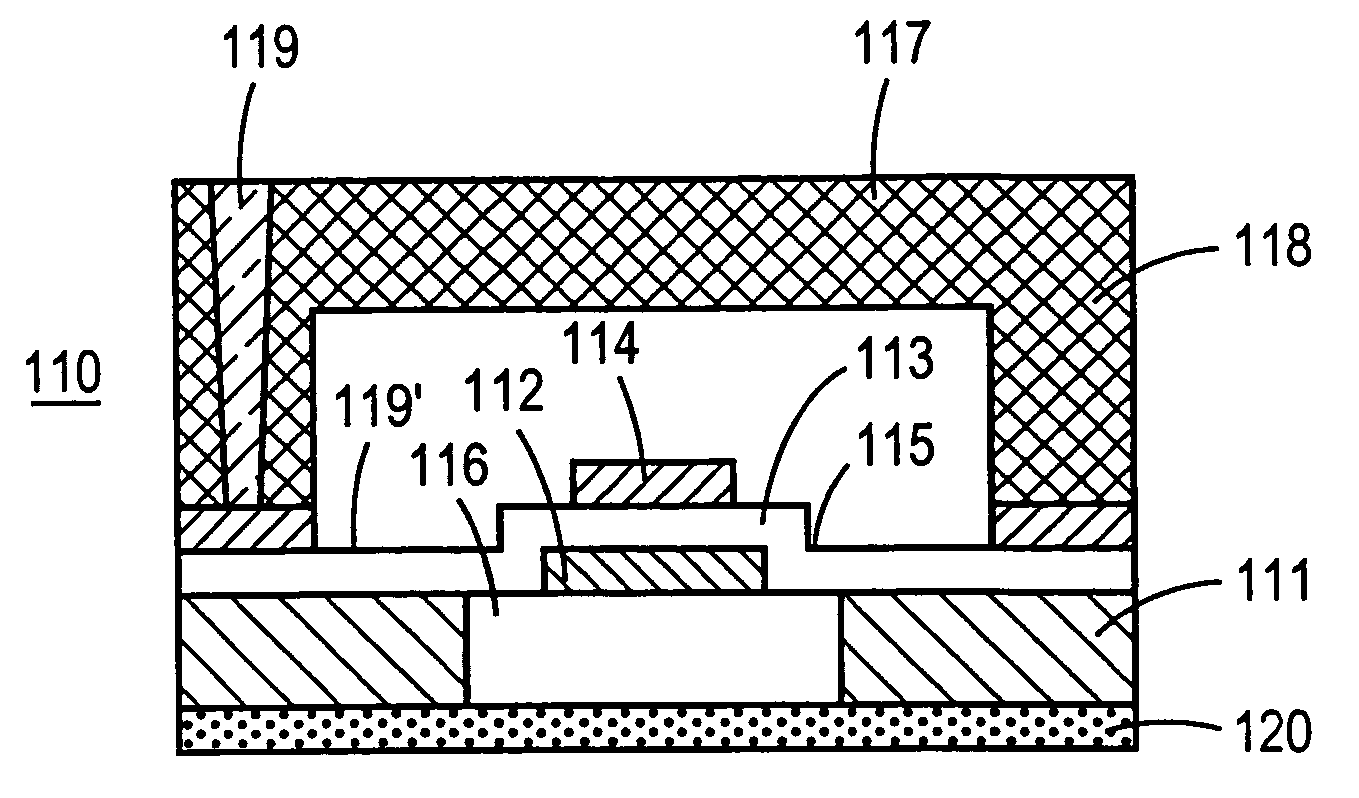
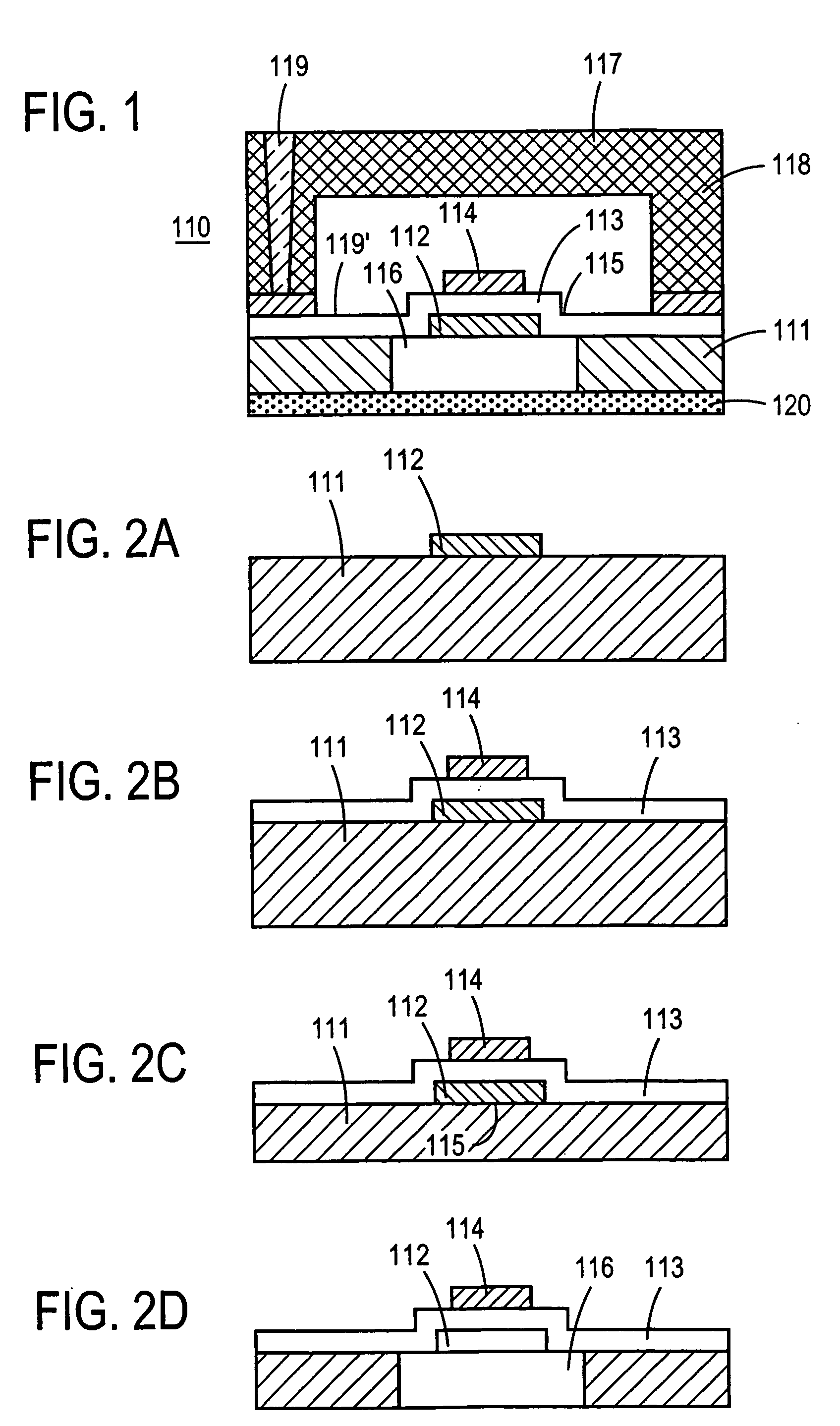
Film bulk acoustic wave resonator device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050140247A1Stability protectionEasy to adjustPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorAcoustics
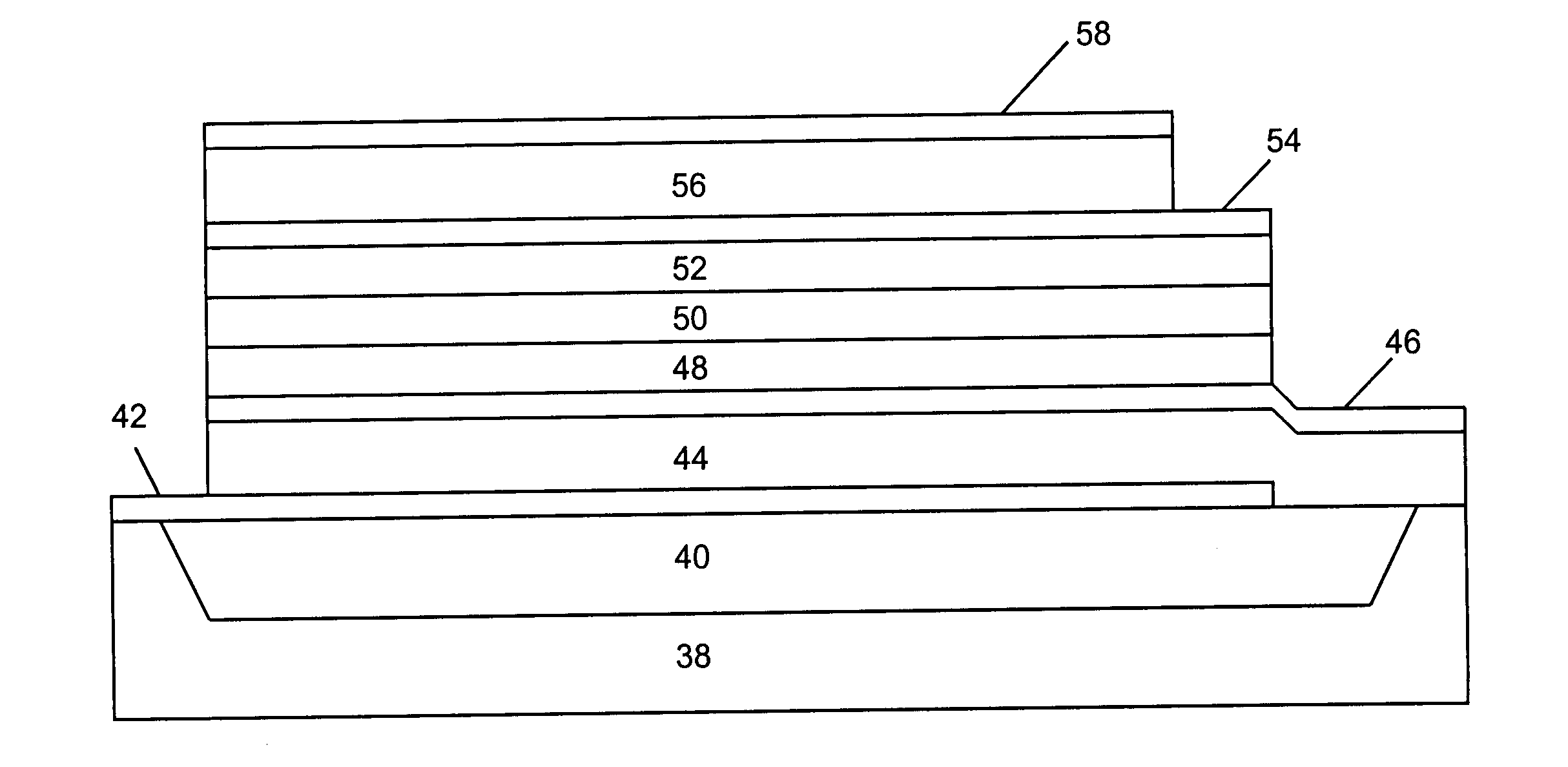
Disclosed herein is an FBAR (film bulk acoustic wave resonator) device and a manufacturing method thereof. The FBAR device comprises a substrate, a resonance unit including a lower electrode, a piezoelectric film, and an upper electrode, which are successively stacked on the substrate, and a passivation layer formed substantially throughout an upper surface and peripheral surface of the resonance unit in order to protect the resonance unit. A partial region of the passivation layer formed on at least the upper electrode has a thickness required to compensate for a difference between a resonant frequency of the resonance unit and a desired target resonant frequency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
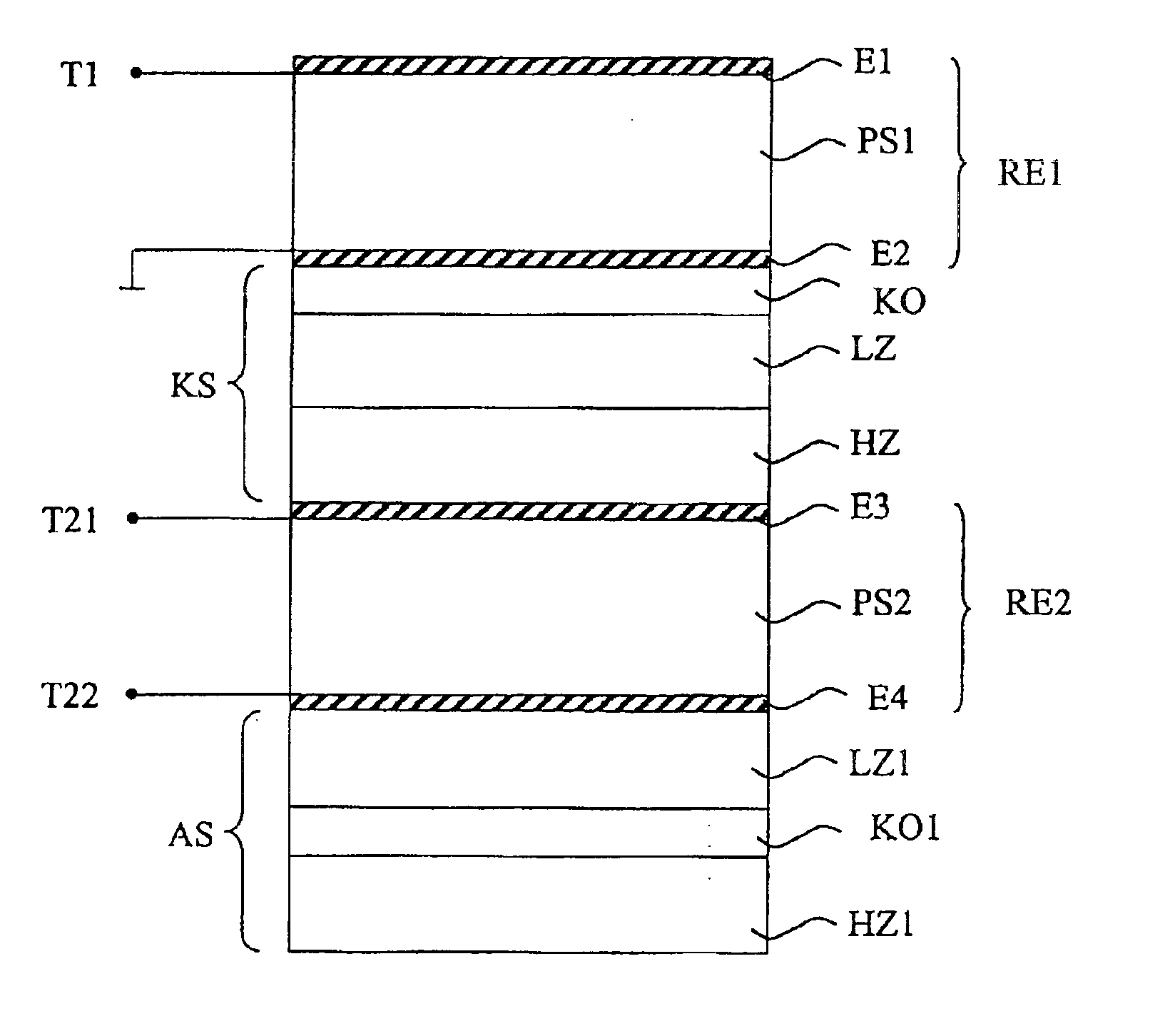
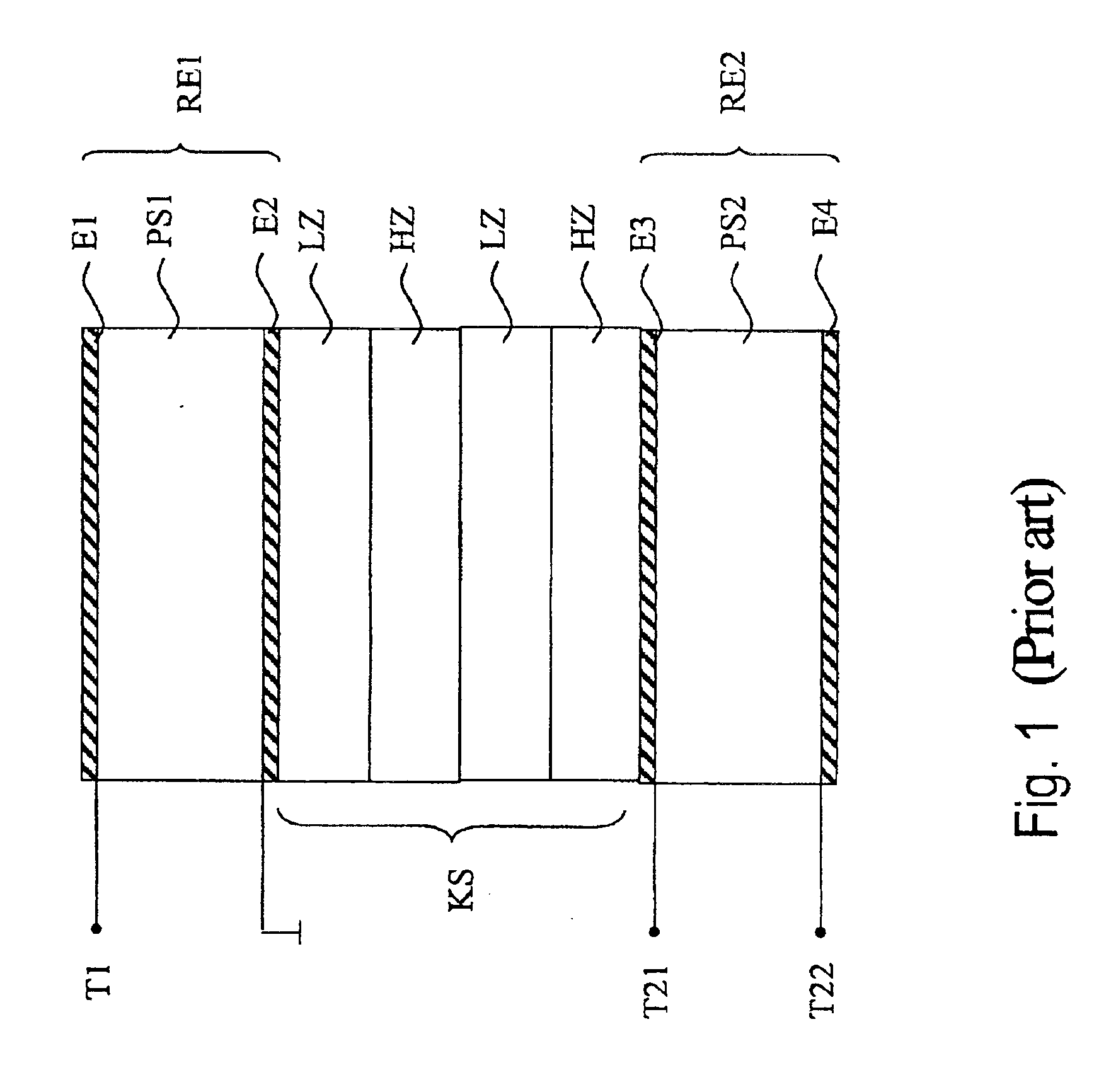
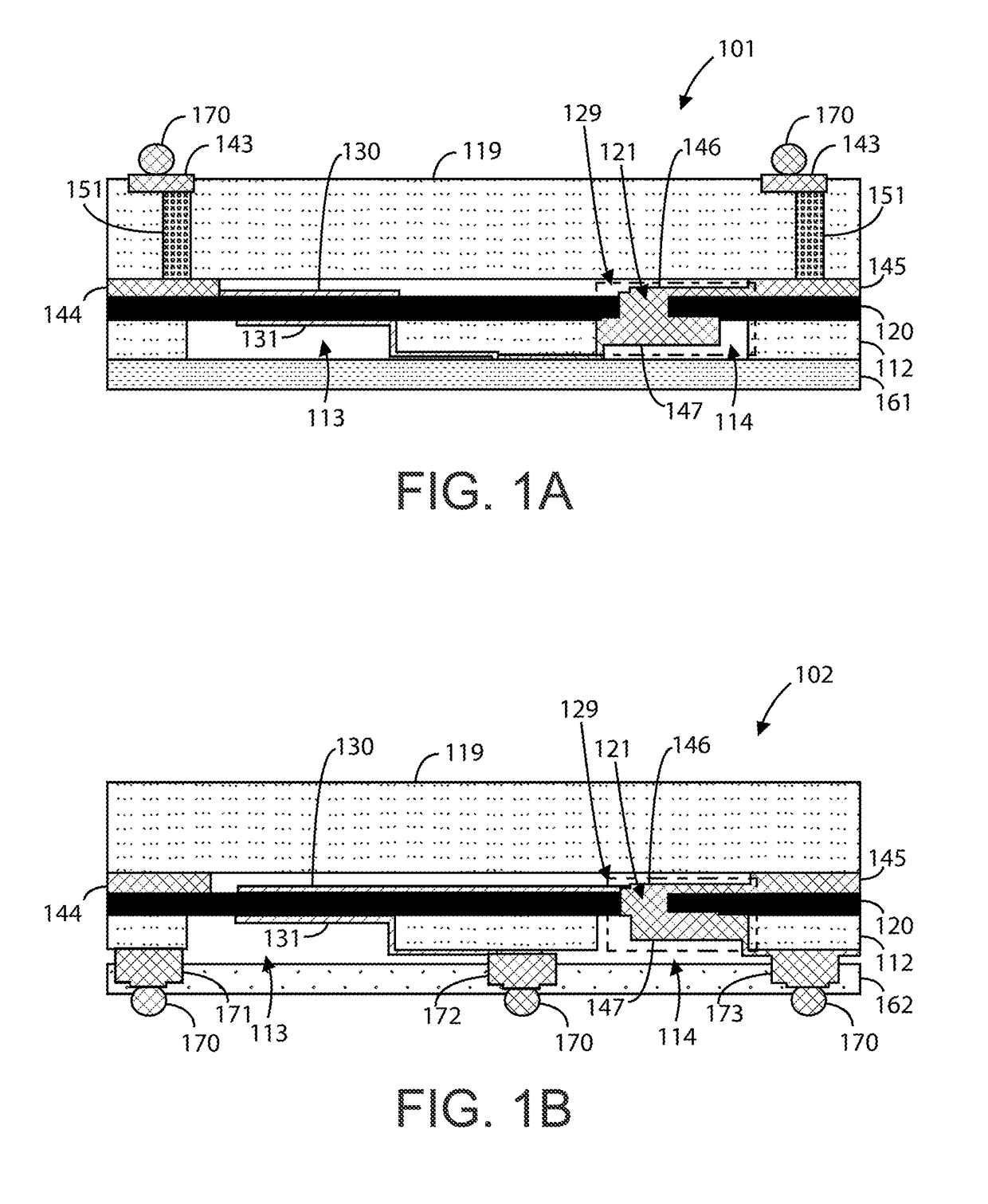
Bulk acoustic wave resonator, filter and duplexer and methods of making same
ActiveUS20050218755A1Maximize device densityBetter resonatorImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrical connectionAcoustic wave
A resonator having a membrane formed of a piezoelectric layer sandwiched between first and second electrode is suspended above a cavity formed from the back surface of the support structure. In one embodiment, the cavity walls are substantially perpendicular to the back surface. In another embodiment, the first electrode is formed in the cavity such that it is electrically connected to an electrode on the back surface of the support structure. In yet another embodiment, the cavity is formed via an etch through via holes in the back surface of the support structure, which leads to greater flexibility in designing a method of manufacture while reducing the need for alignment relative to other designs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coupled resonator filter comprising a bridge
ActiveUS20120218056A1Impedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesResonator filterCoupling
In accordance with a representative embodiment, a bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonator structure, comprises: a first BAW resonator comprising a first lower electrode, a first upper electrode and a first piezoelectric layer disposed between the first lower electrode and the first upper electrode; a second BAW resonator comprising a second lower electrode, a second upper electrode and a second piezoelectric layer disposed between the second lower electrode and the second upper electrode; an acoustic coupling layer disposed between the first BAW resonator and the second BAW resonator; and a bridge disposed between the first lower electrode of the first BAW resonator and the second upper electrode of the second BAW resonator.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Titanium-tungsten alloy based mirrors and electrodes in bulk acoustic wave devices
Titanium-tungsten alloy based mirrors and electrodes in bulk acoustic wave devices simplify processing by eliminating the need for adhesion, barrier and seed layers, and preserve the advantages of tungsten layers. Alternate layers of high and low acoustic impedance materials are use, wherein the high acoustic impedance layers are titanium-tungsten alloy layers, preferably deposited by physical vapor deposition, and isotropically patterned with a wet etch. SiO2 is preferably used for the low acoustic impedance layers, though other low acoustic impedance materials may be used if desired. Electrodes and loads may also be a Titanium-tungsten alloy. Titanium-tungsten alloys in the range of 3 to 15 percent of titanium by weight are preferred.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Thin film bulk acoustic wave resonator structure and filter, and radio-frequency module using them
InactiveUS20080169884A1Reducing area of elementWidePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorManufacturing technology
A thin film bulk acoustic wave (BAW) resonator structure and filter which can be fabricated by inexpensive manufacturing techniques and in smaller size than conventional such products are to be provided. The BAW resonator structure and filter have a substrate, a first BAW resonator placed over the substrate, an acoustic reflection layer placed over the first BAW resonator and a second BAW resonator placed over the acoustic reflection layer, and the acoustic reflection layer is electroconductive. Herein, the acoustic reflection layer constitutes a first electrode, and this first electrode electrically connects and acoustically separates the first BAW resonator and the second BAW resonator.
Owner:HITACHI MEDIA ELECTORONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com