Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
739results about "Frequency diversity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
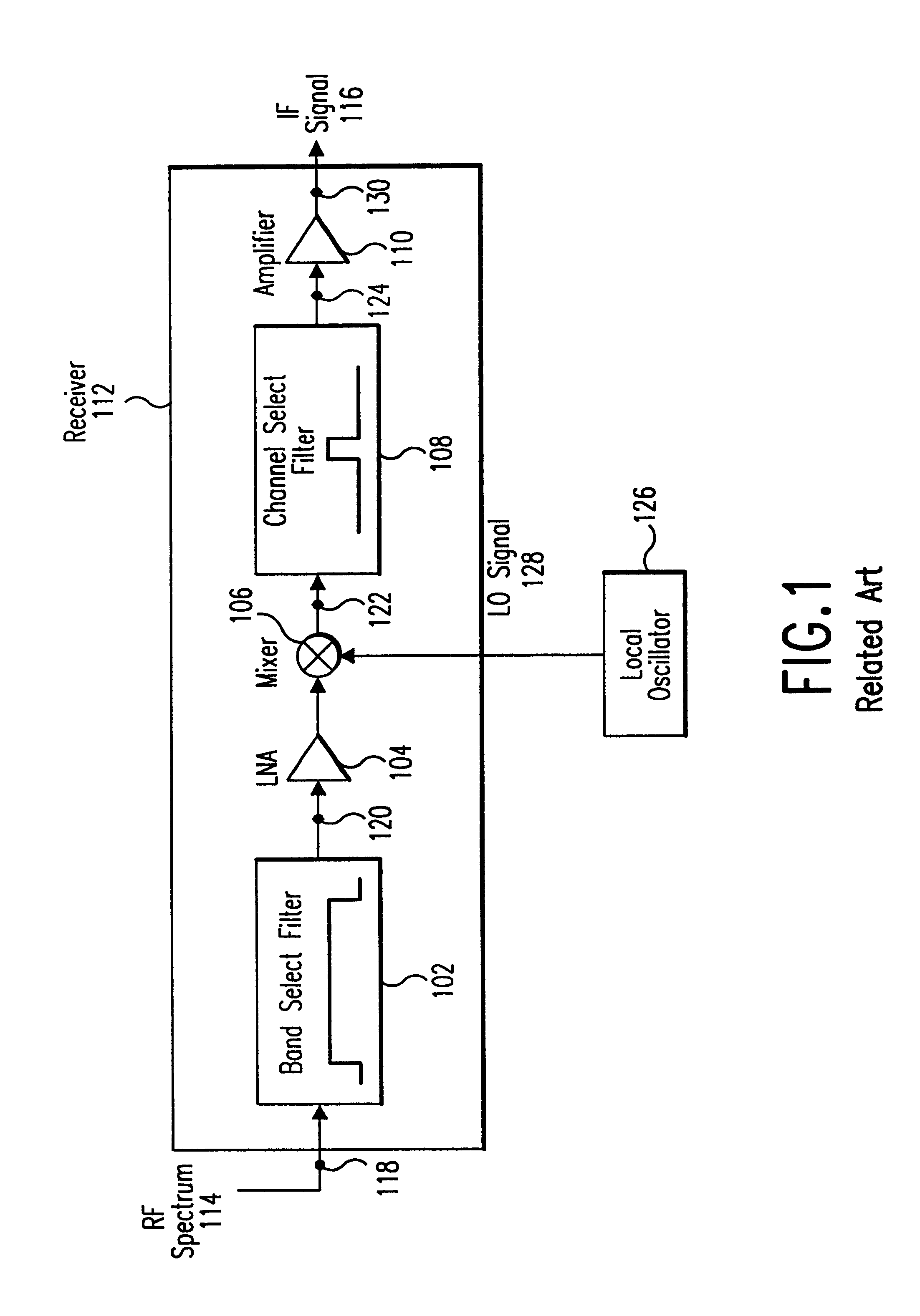
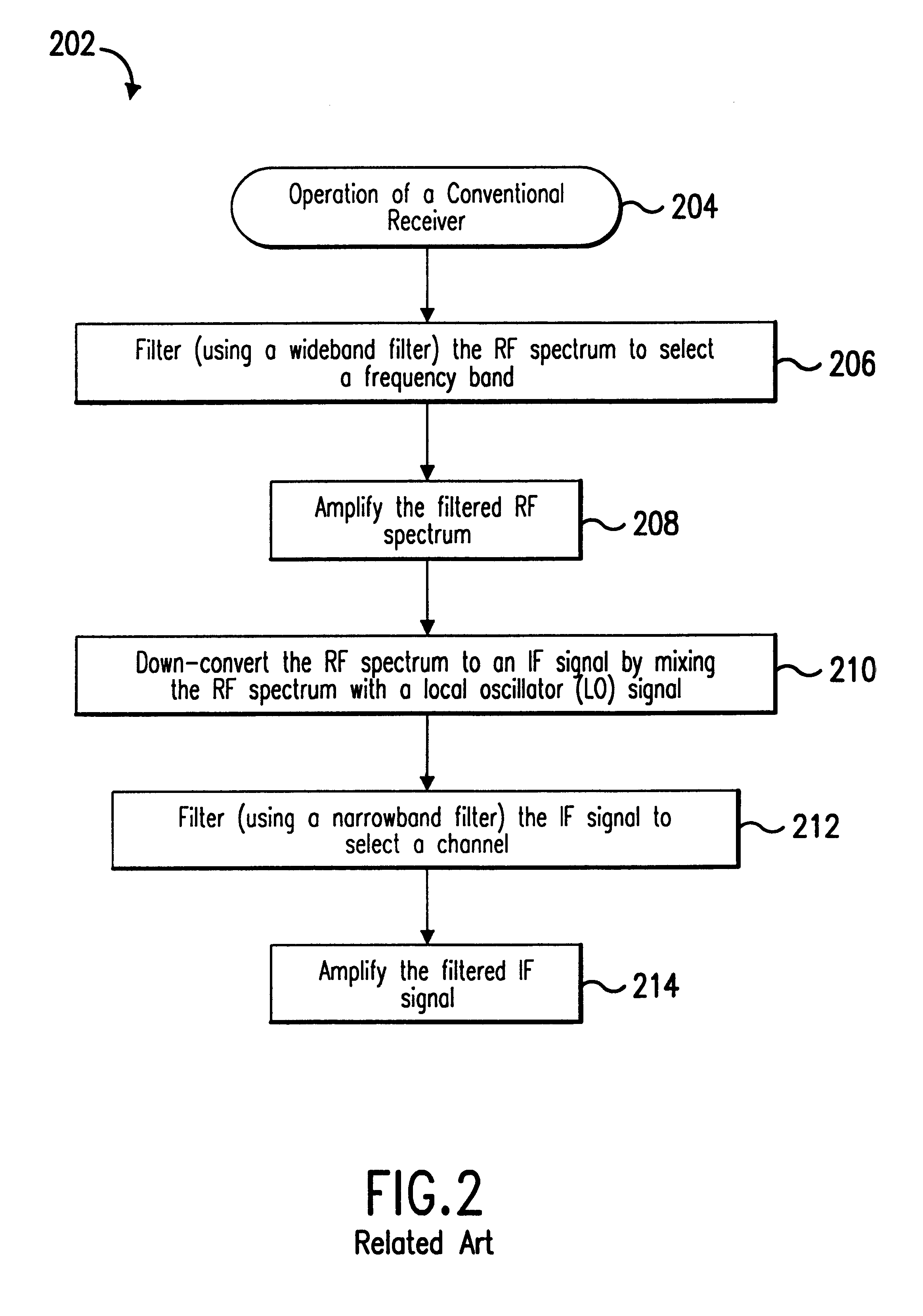
Method and apparatus for measuring reporting channel state information in a high efficiency, high performance communications system
InactiveUS6473467B1Efficient sharingInterference minimizationSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityChannel state informationCommunications system
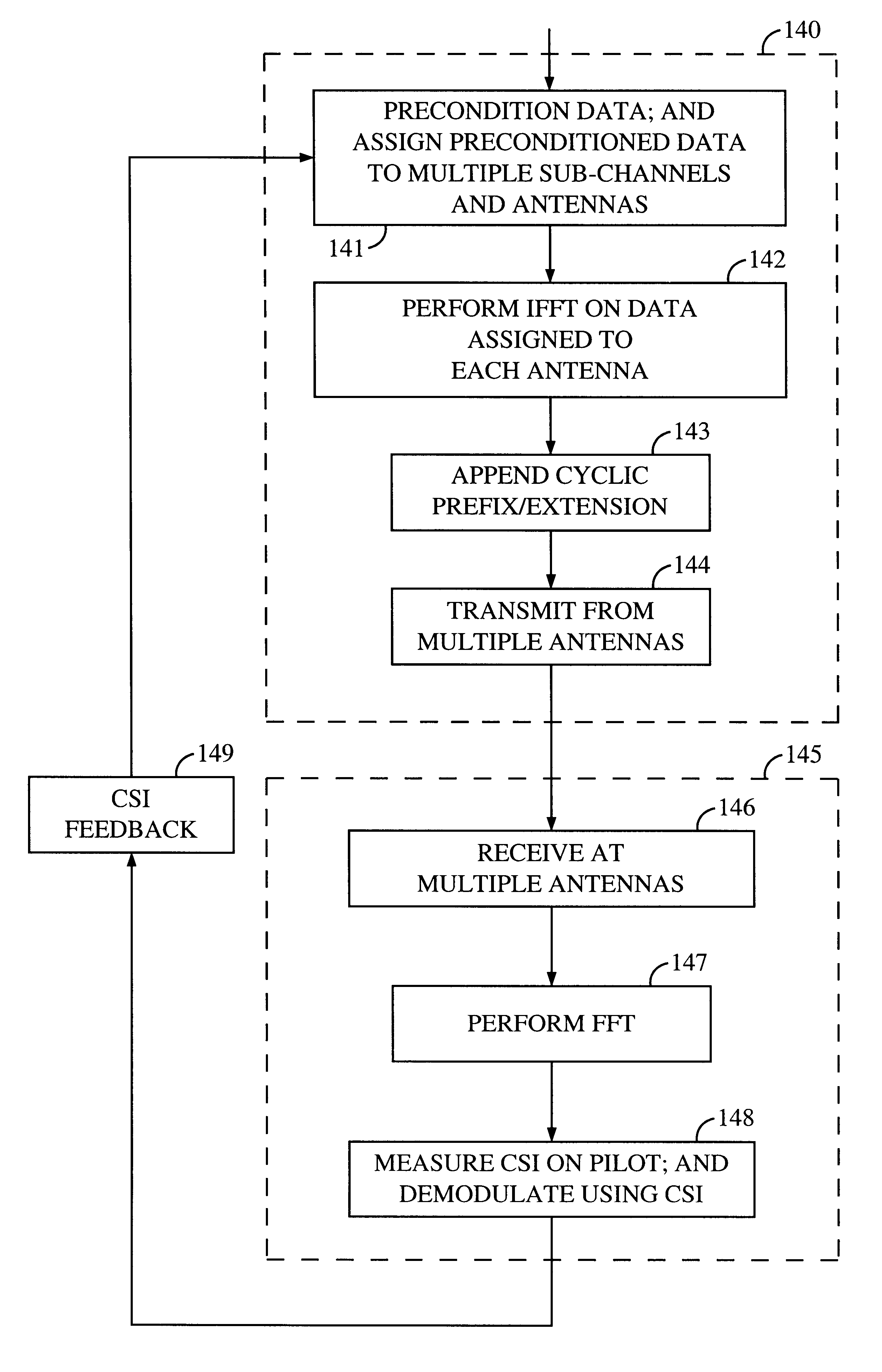
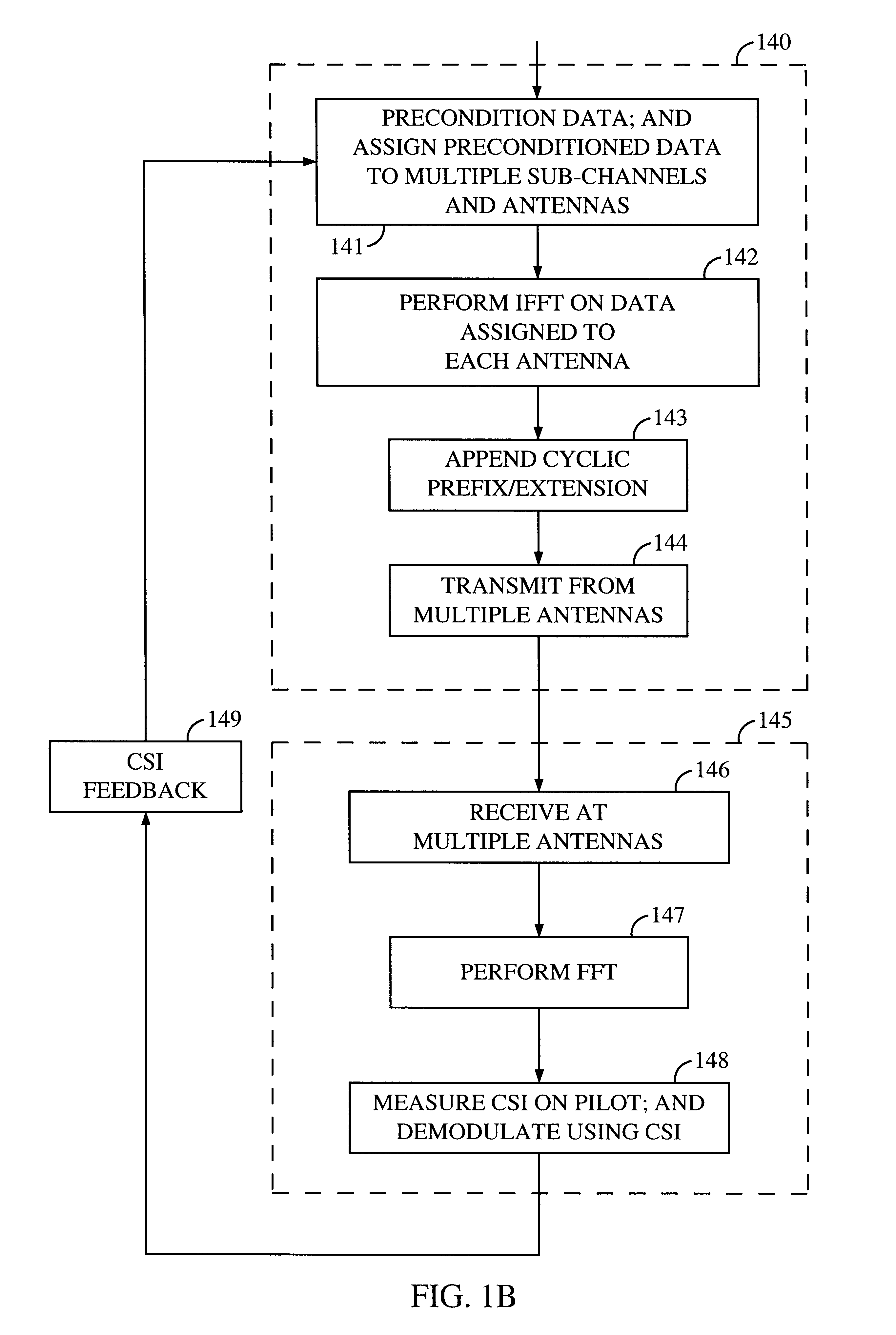
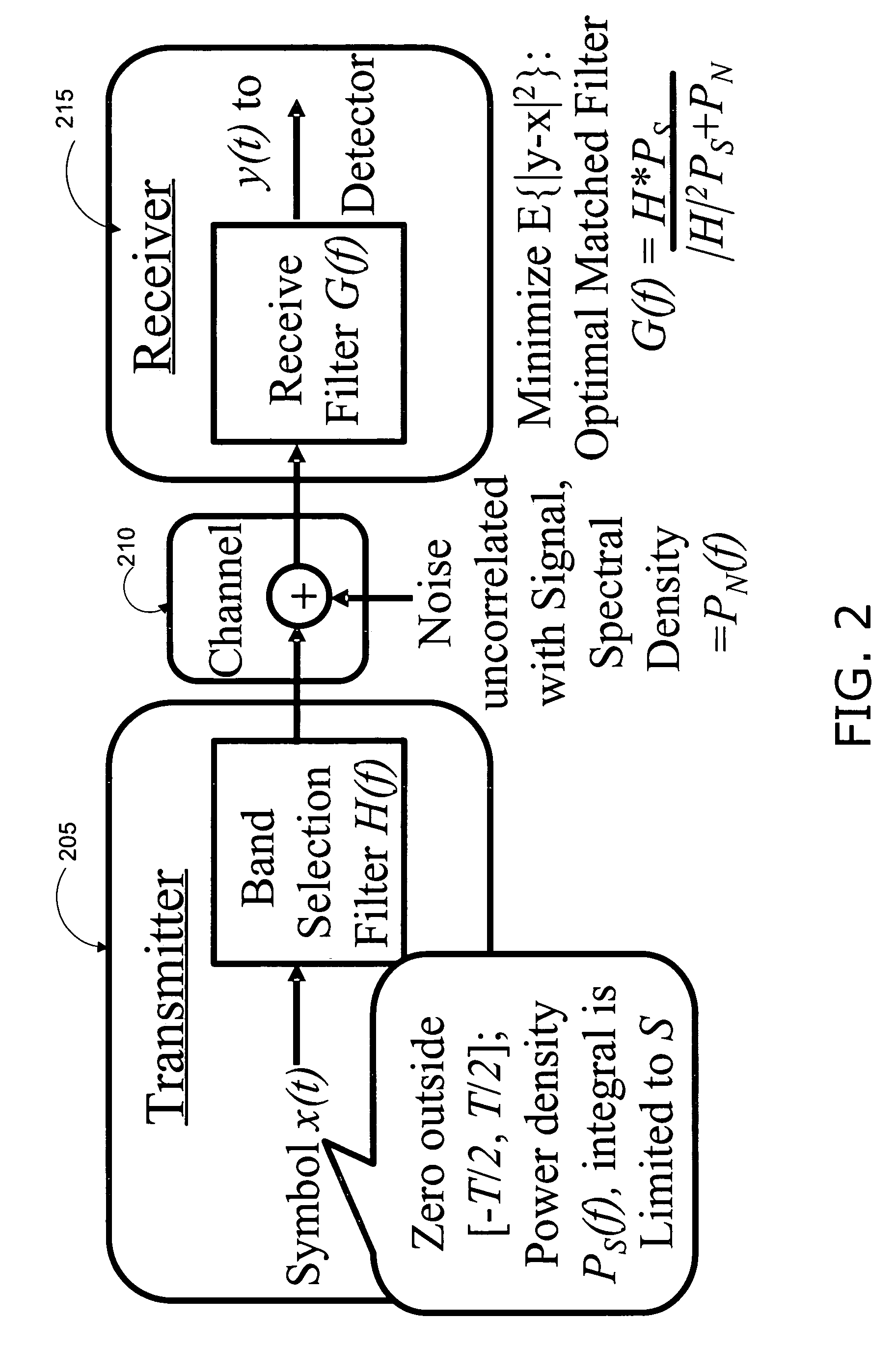
Channel state information (CSI) can be used by a communications system to precondition transmissions between transmitter units and receiver units. In one aspect of the invention, disjoint sub-channel sets are assigned to transmit antennas located at a transmitter unit. Pilot symbols are generated and transmitted on a subset of the disjoint sub-channels. Upon receipt of the transmitted pilot symbols, the receiver units determine the CSI for the disjoint sub-channels that carried pilot symbols. These CSI values are reported to the transmitter unit, which will use these CSI values to generate CSI estimates for the disjoint sub-channels that did not carry pilot symbols. The amount of information necessary to report CSI on the reverse link can be further minimized through compression techniques and resource allocation techniques.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
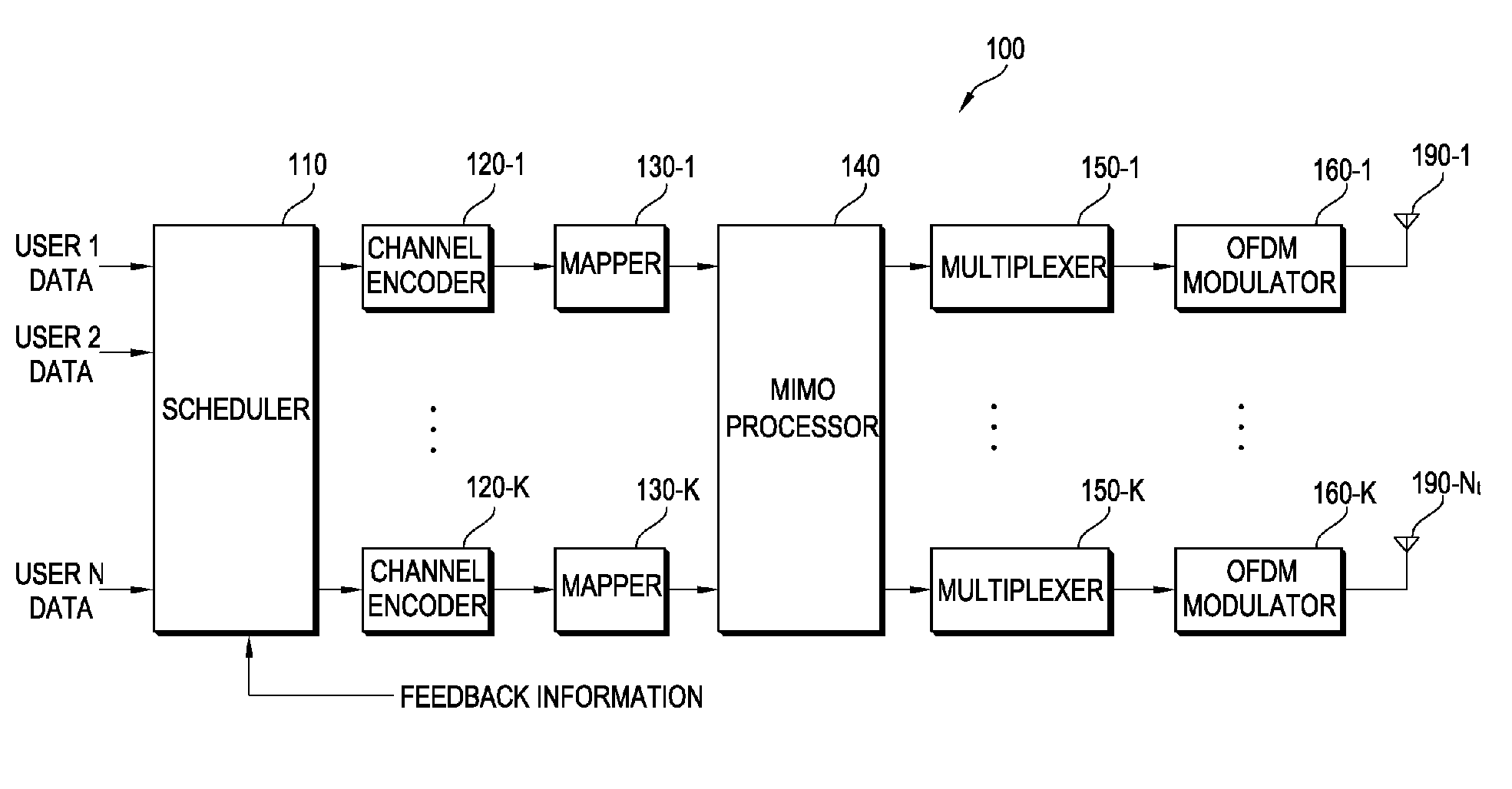
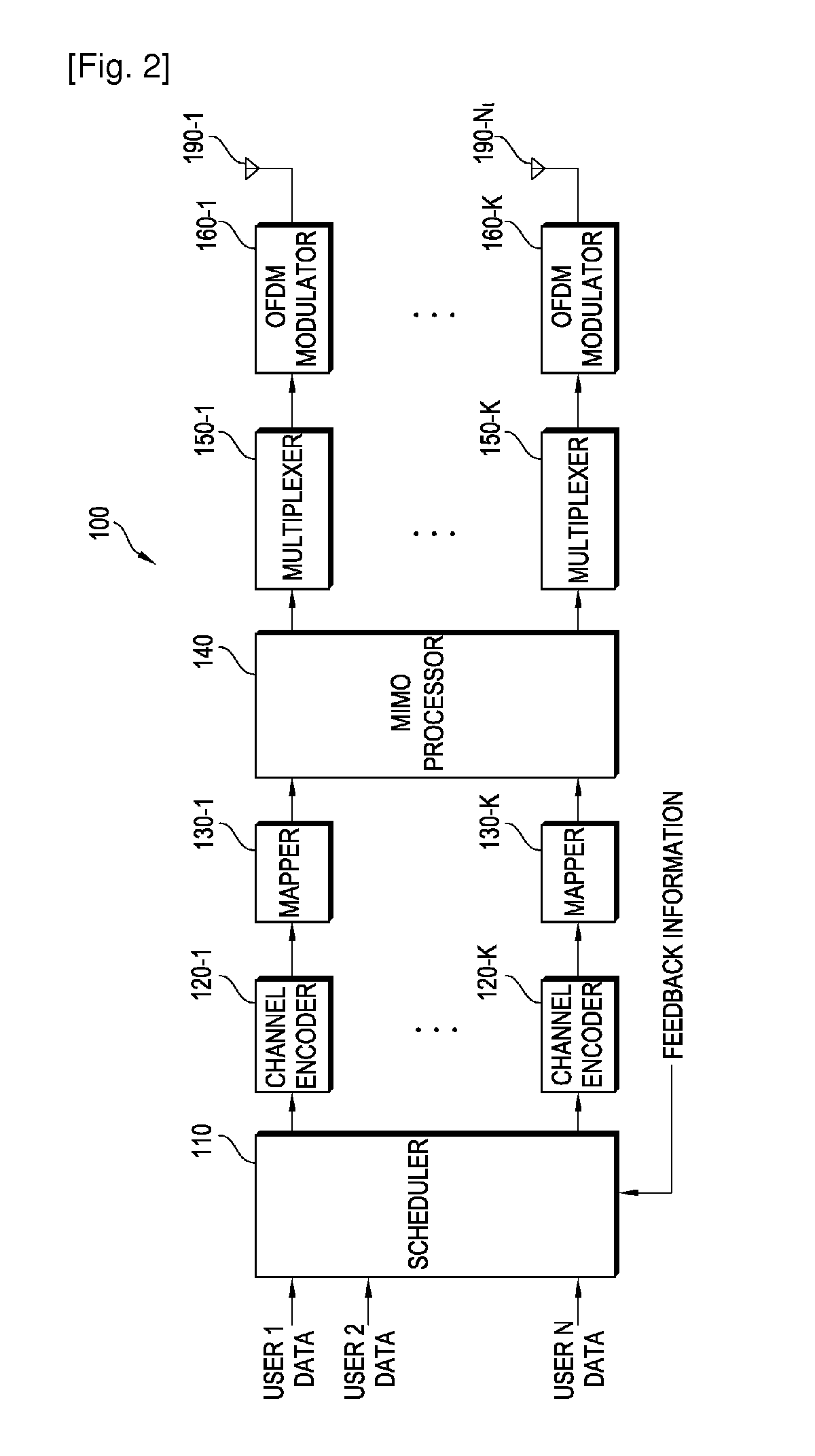
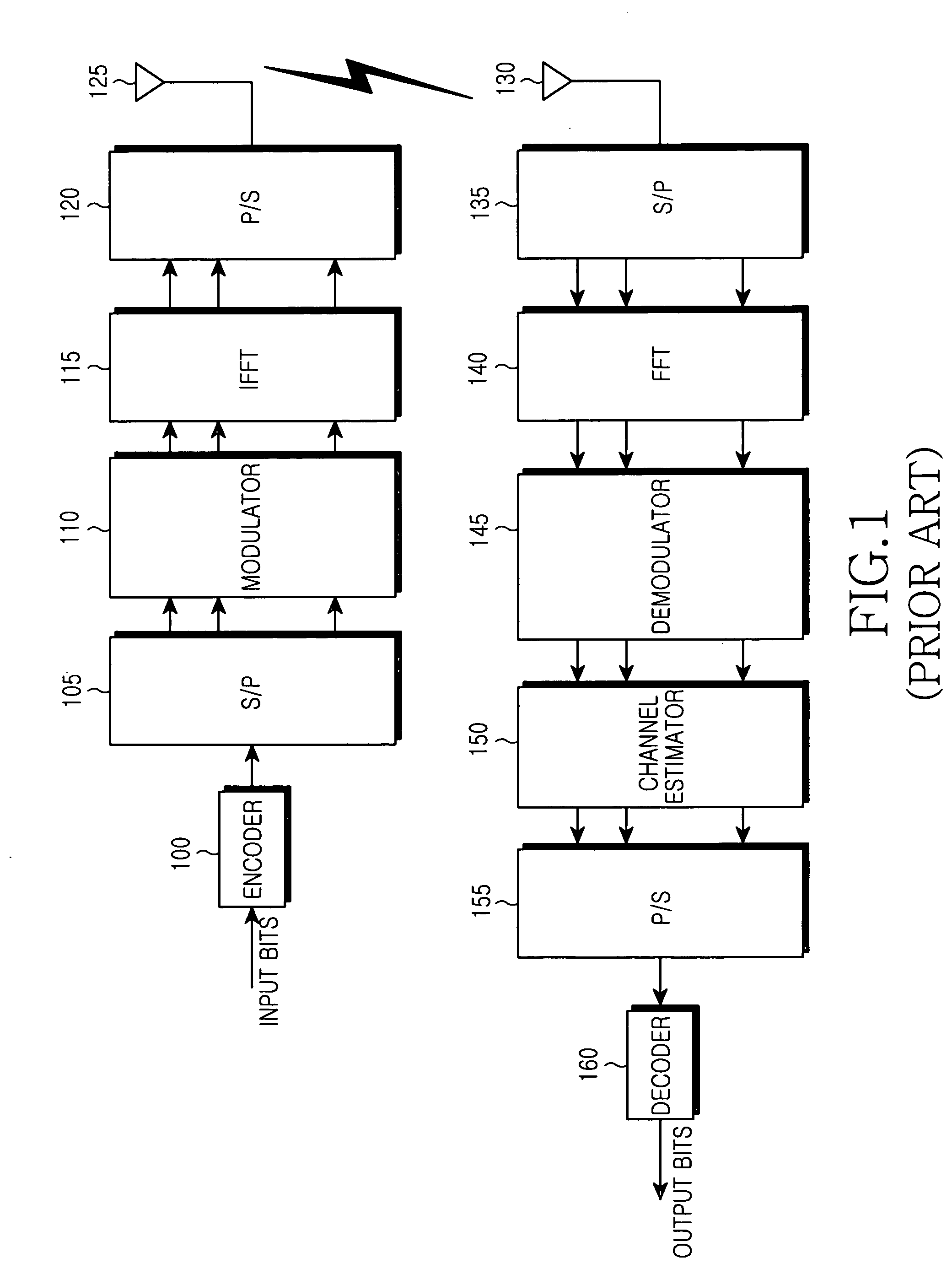
High efficiency high performance communications system employing multi-carrier modulation
InactiveUS20020154705A1Increase diversityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityData streamHigh performance communication
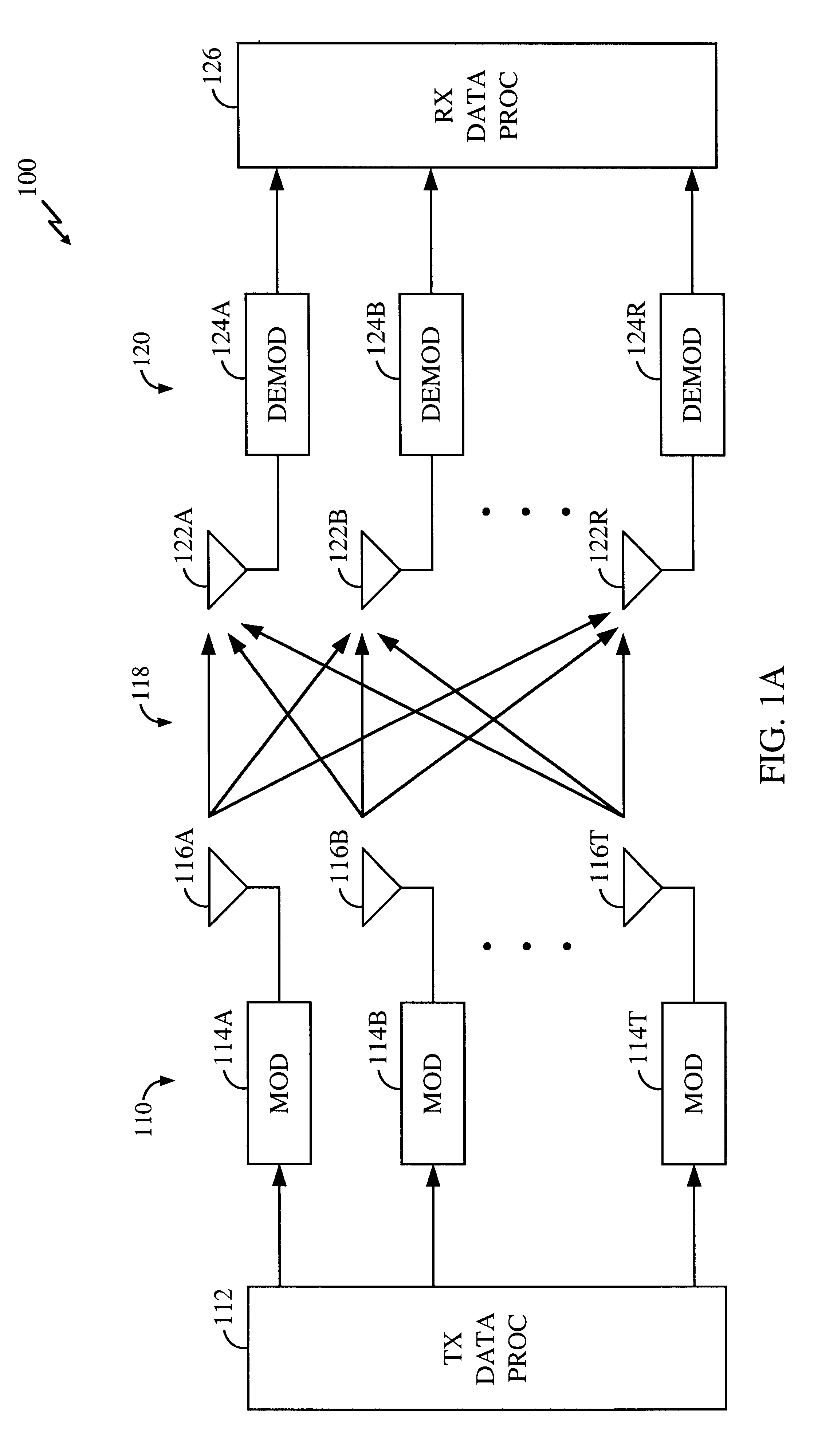
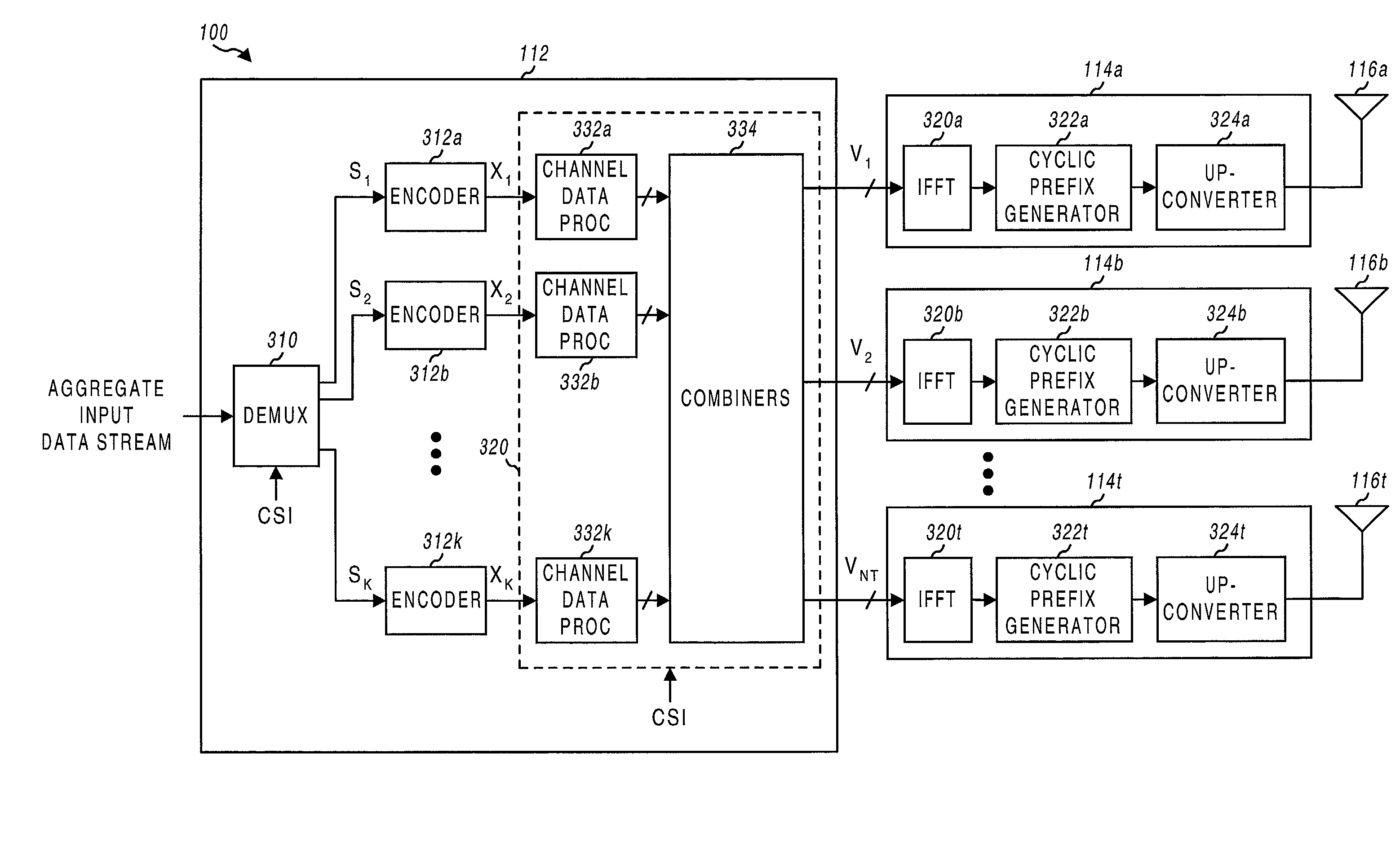
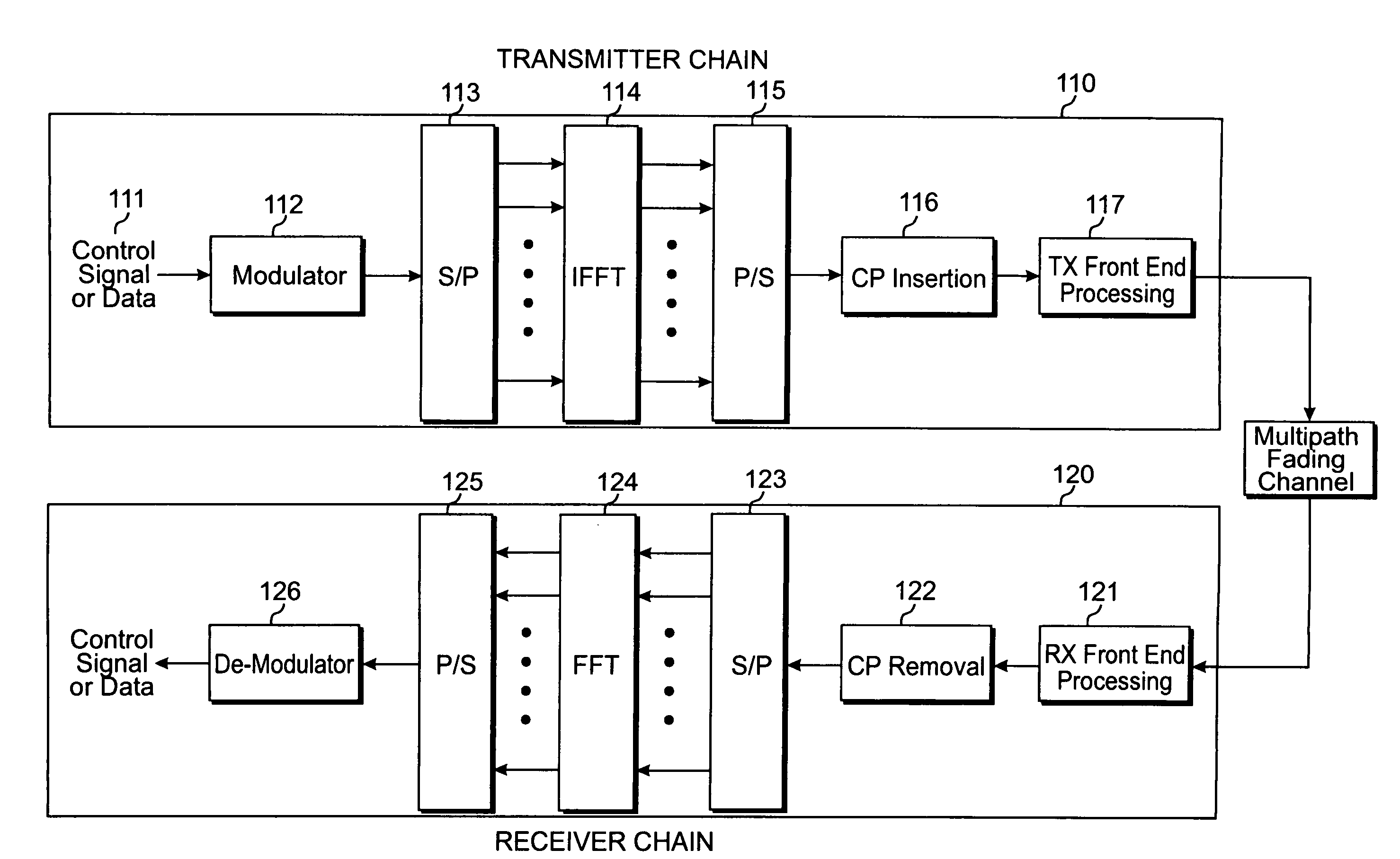
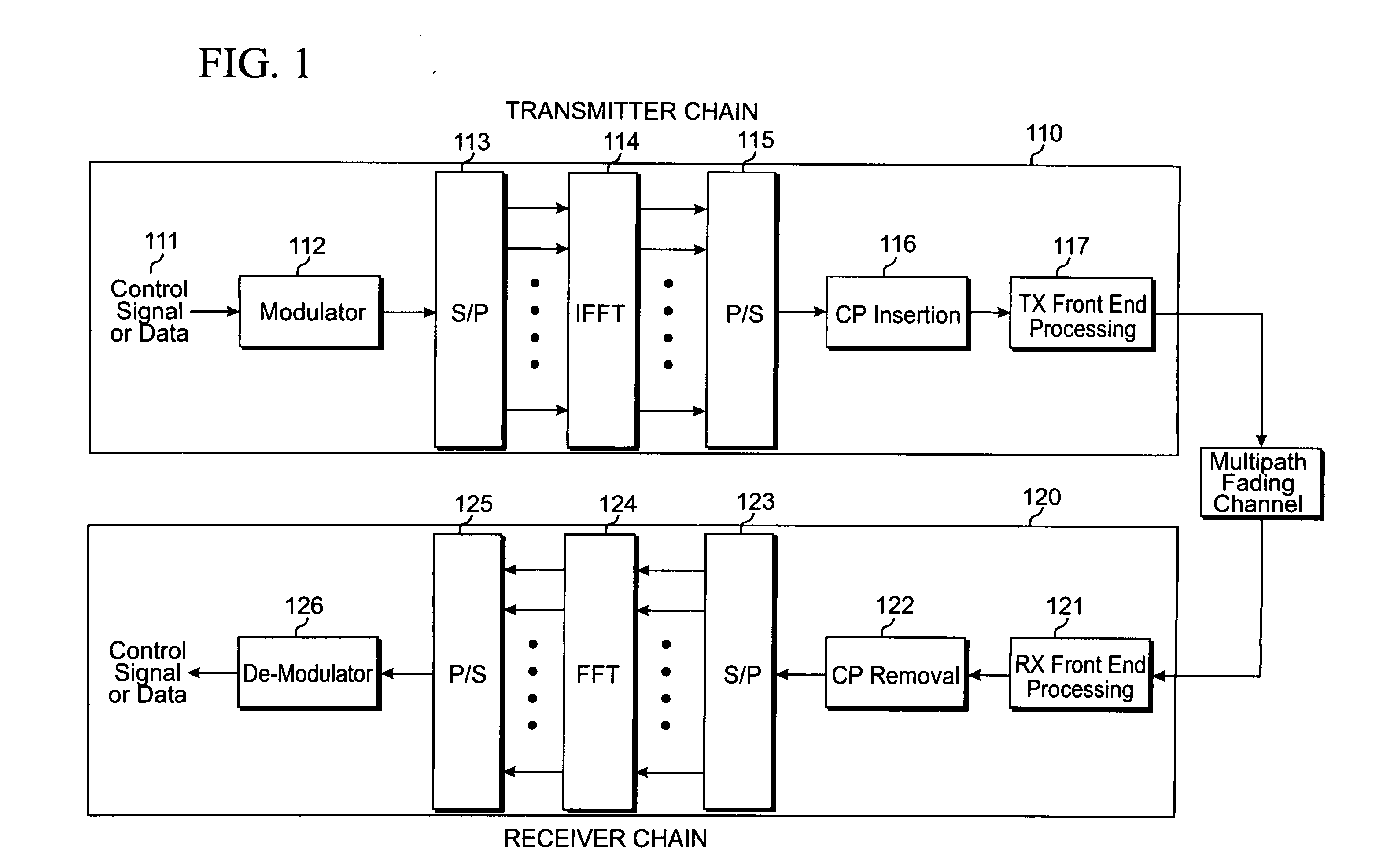
Transmitter and receiver units for use in a communications system and configurable to provide antenna, frequency, or temporal diversity, or a combination thereof, for transmitted signals. The transmitter unit includes a system data processor, one or more modulators, and one or more antennas. The system data processor receives and partitions an input data stream into a number of channel data streams and further processes the channel data streams to generate one or more modulation symbol vector streams. Each modulation symbol vector stream includes a sequence of modulation symbol vectors representative of data in one or more channel data streams. Each modulator receives and modulates a respective modulation symbol vector stream to provide an RF modulated signal, and each antenna receives and transmits a respective RF modulated signal. Each modulator may include an inverse (fast) Fourier transform (IFFT) and a cyclic prefix generator. The IFFT generates time-domain representations of the modulation symbol vectors, and the cyclic prefix generator repeats a portion of the time-domain representation of each modulation symbol vector. The channel data streams are modulated using multi-carrier modulation, e.g., OFDM modulation. Time division multiplexing (TDM) may also be used to increase flexibility.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multiple access method and system
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Multiplexing and transmission of multiple data streams in a wireless multi-carrier communication system
ActiveUS20050058089A1Facilitate power-efficientFacilitate robust receptionEnergy efficient ICTTransmission path divisionMultiplexingCoding block
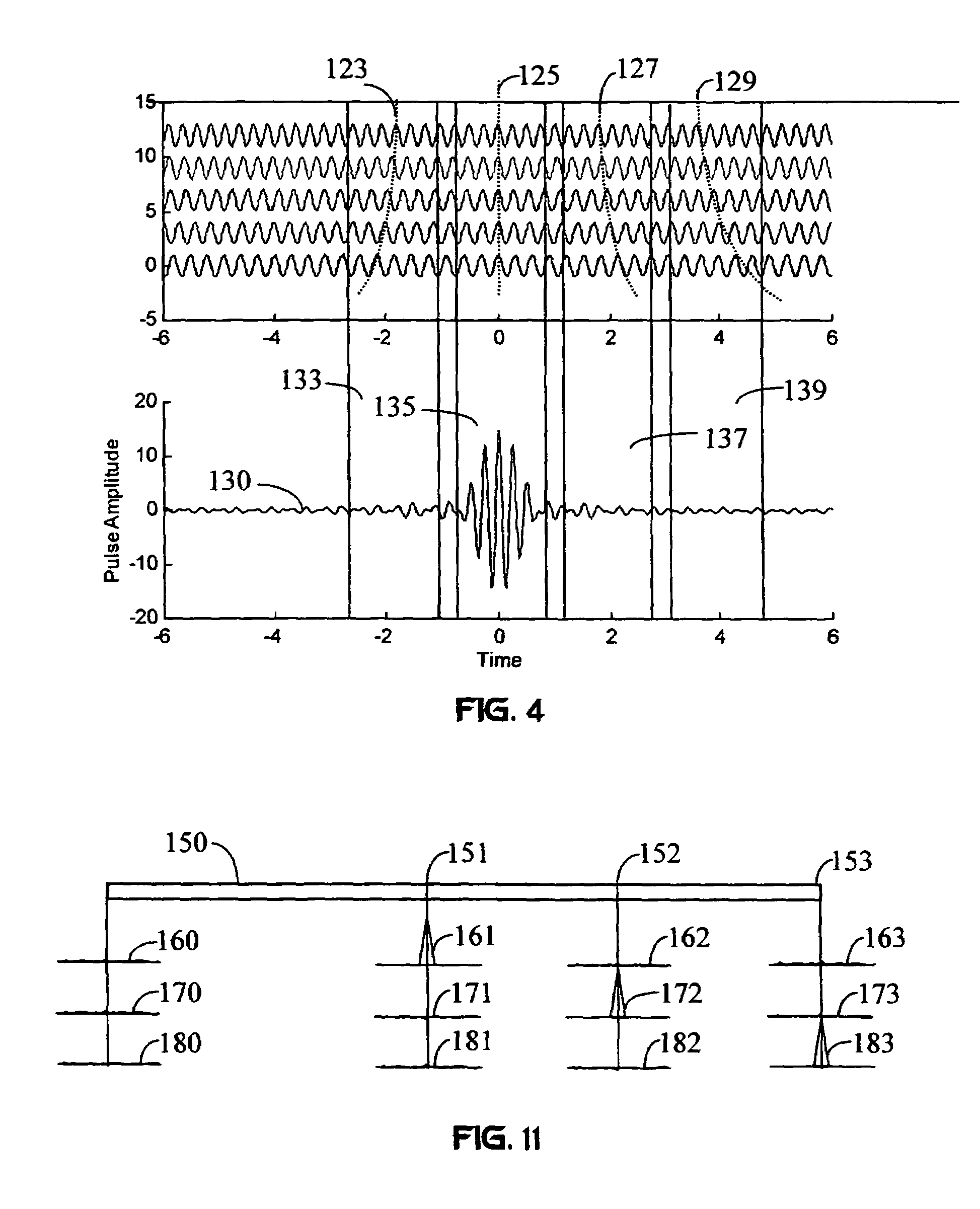
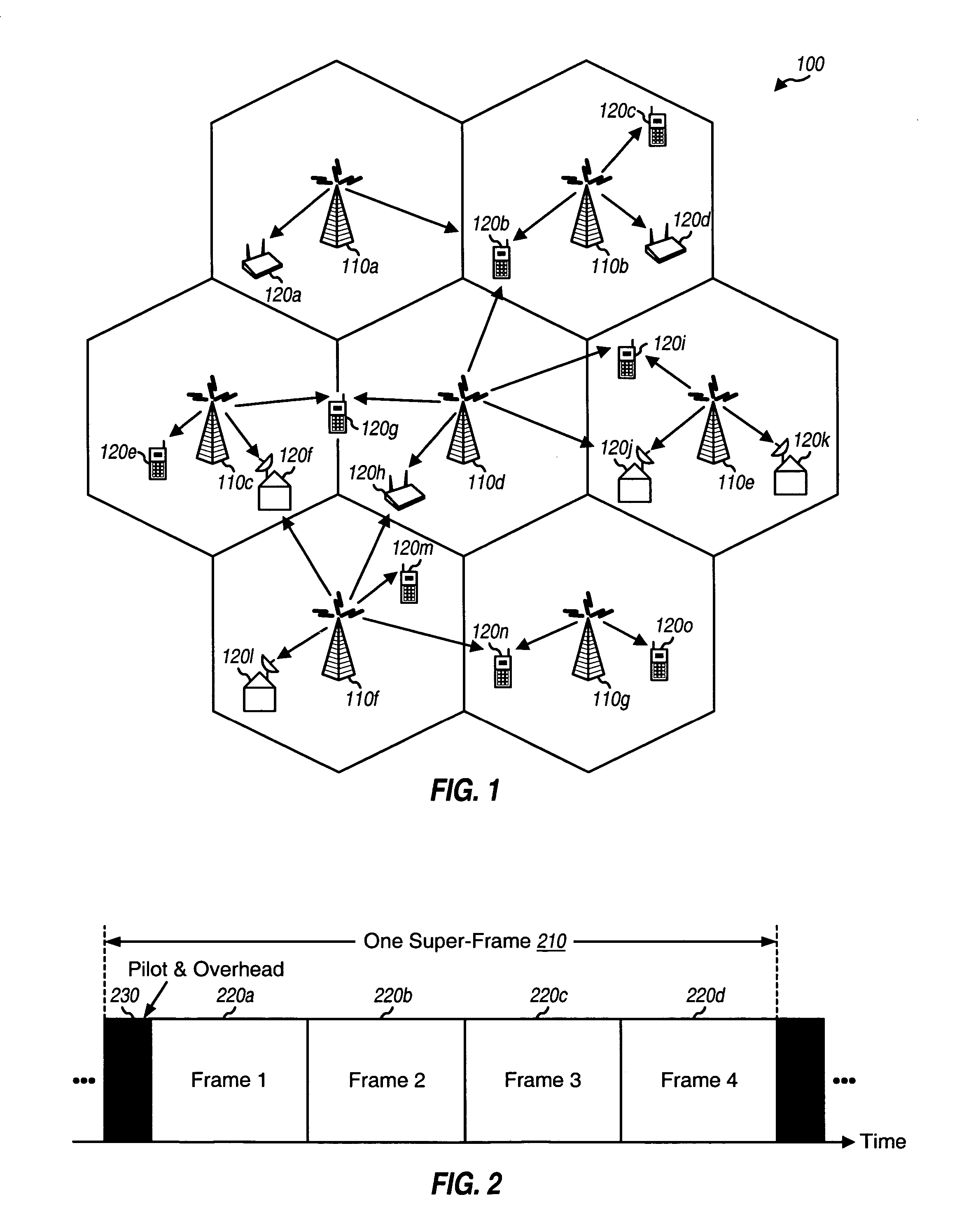
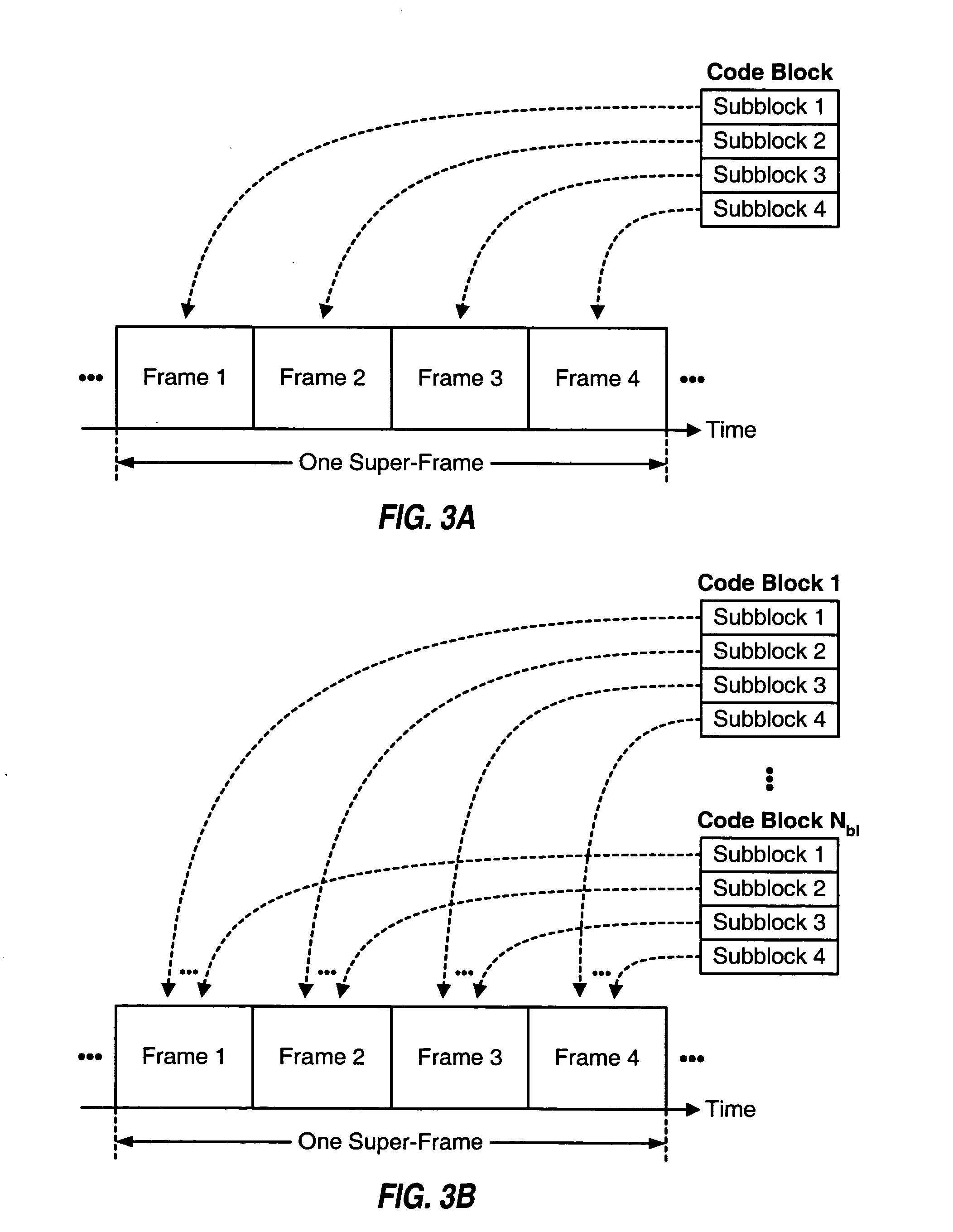
Techniques for multiplexing and transmitting multiple data streams are described. Transmission of the multiple data streams occurs in “super-frames”. Each super-frame has a predetermined time duration and is further divided into multiple (e.g., four) frames. Each data block for each data stream is outer encoded to generate a corresponding code block. Each code block is partitioned into multiple subblocks, and each data packet in each code block is inner encoded and modulated to generate modulation symbols for the packet. The multiple subblocks for each code block are transmitted in the multiple frames of the same super-frame, one subblock per frame. Each data stream is allocated a number of transmission units in each super-frame and is assigned specific transmission units to achieve efficient packing. A wireless device can select and receive individual data streams.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
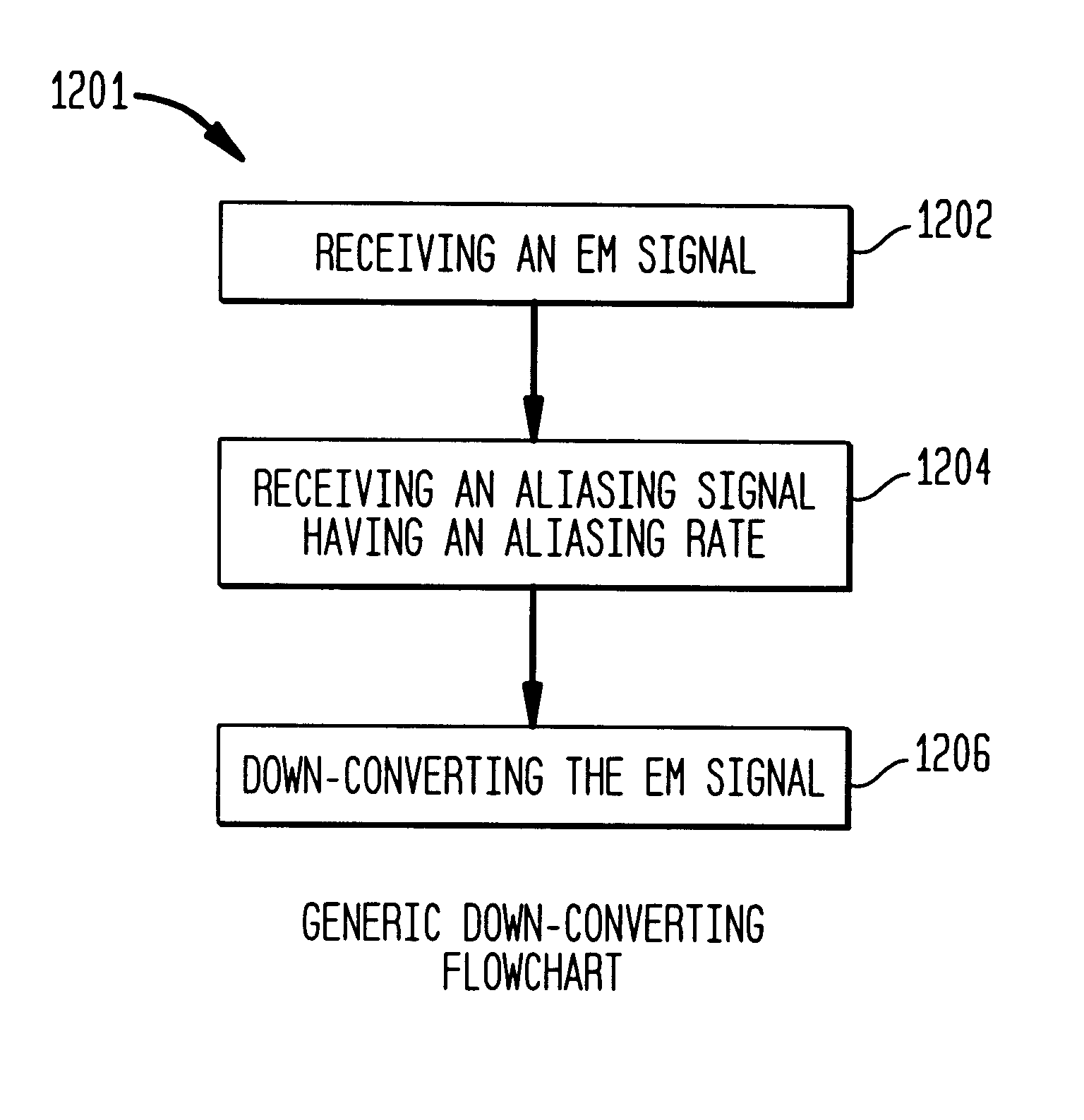
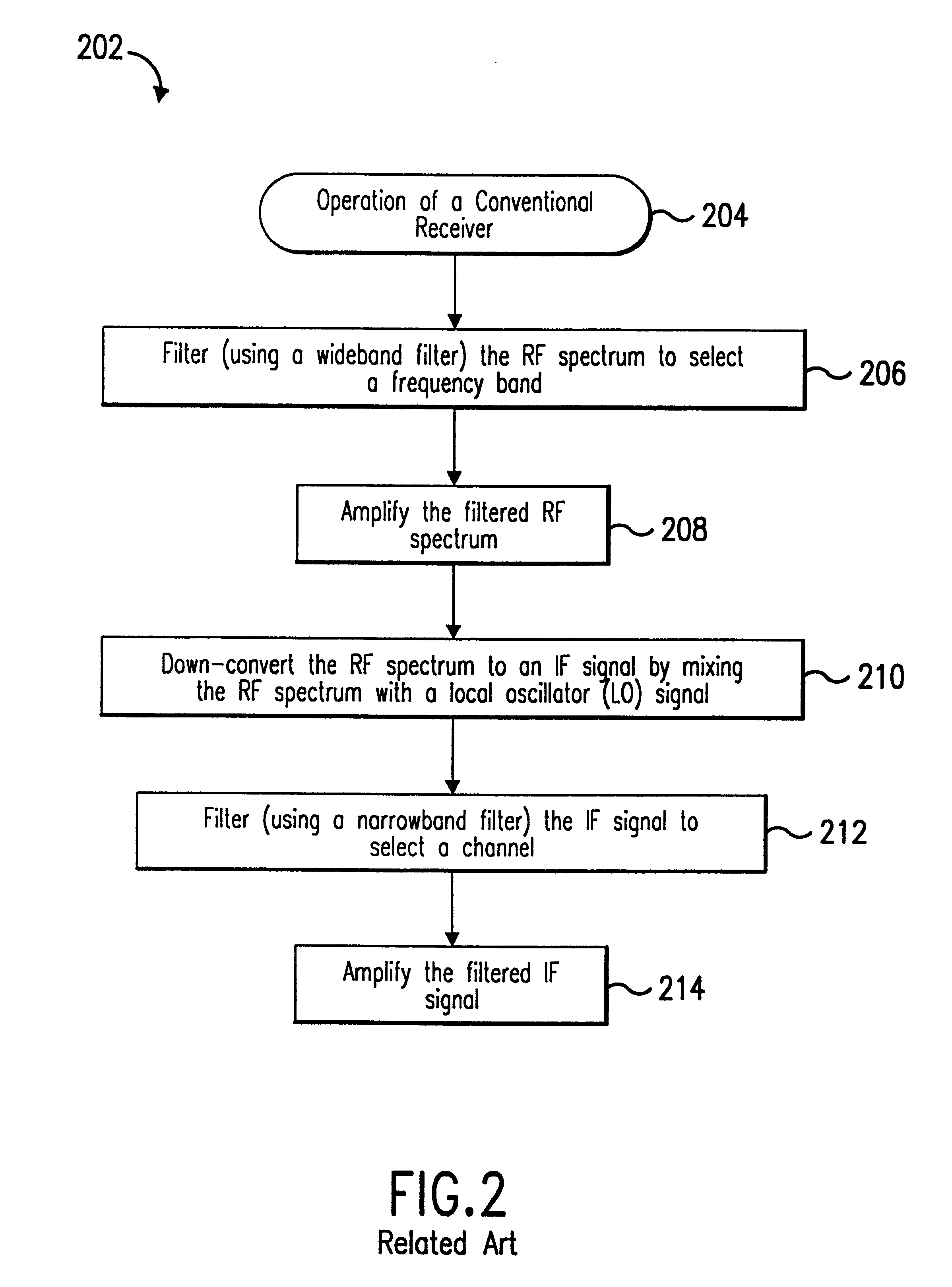
Method and system for down-converting electromagnetic signals
InactiveUS6061551AResonant long antennasModulation transferenceIntermediate frequencyElectromagnetic shielding
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal are described herein. Briefly stated, such methods, systems, and apparatuses operate by receiving an EM signal and an aliasing signal having an aliasing rate. The EM signal is aliased according to the aliasing signal to down-convert the EM signal. The term aliasing, as used herein, refers to both down-converting an EM signal by under-sampling the EM signal at an aliasing rate, and down-converting an EM signal by transferring energy from the EM signal at the aliasing rate. In an embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to a demodulated baseband information signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is a frequency modulated (FM) signal, which is down-converted to a non-FM signal, such as a phase modulated (PM) signal or an amplitude modulated (AM) signal.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Methods and apparatus of enhancing performance in wireless communication systems
ActiveUS7142864B2Constrain performance of systemExtension of timeSpatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringCommunications systemMobile device
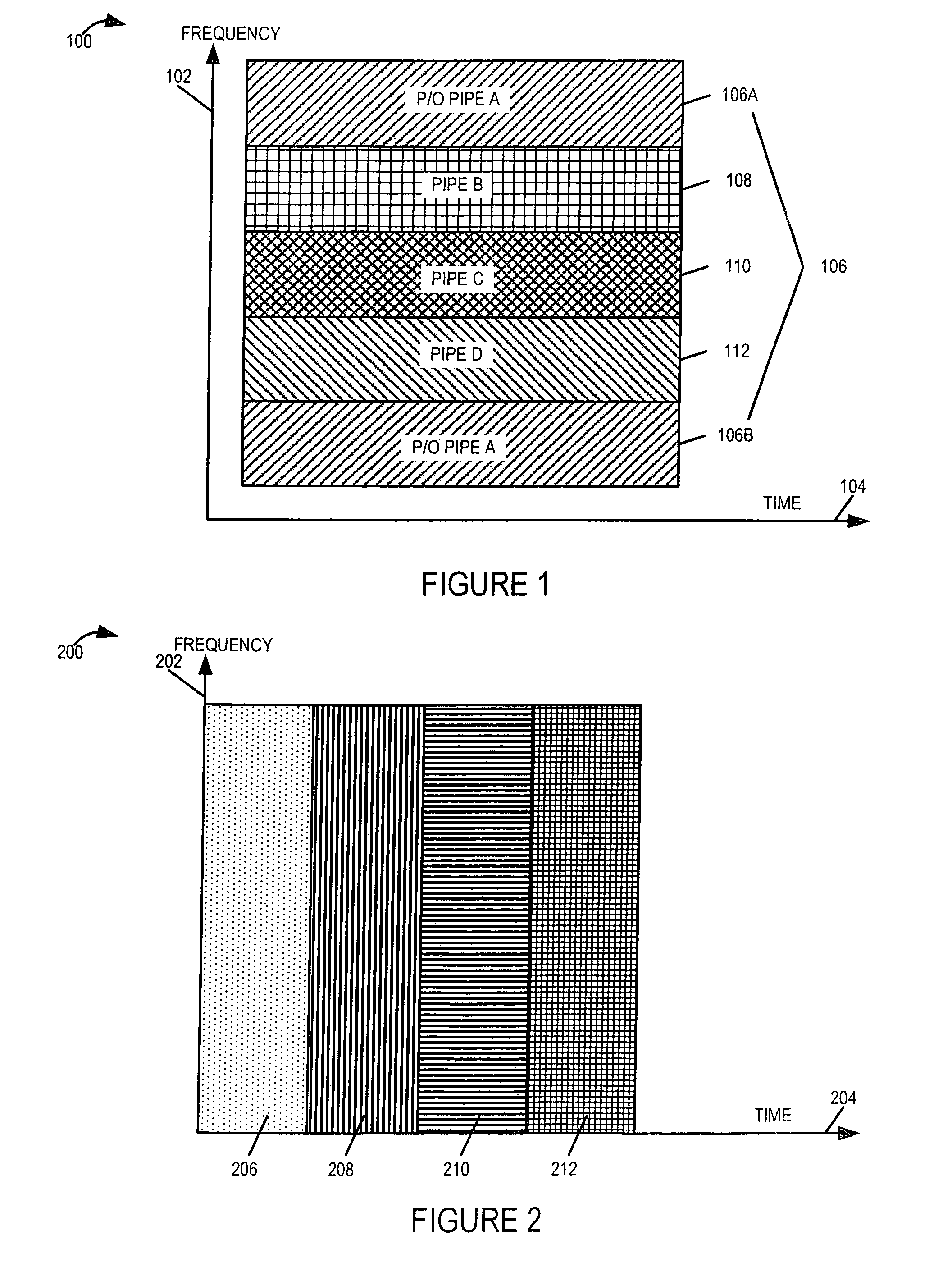
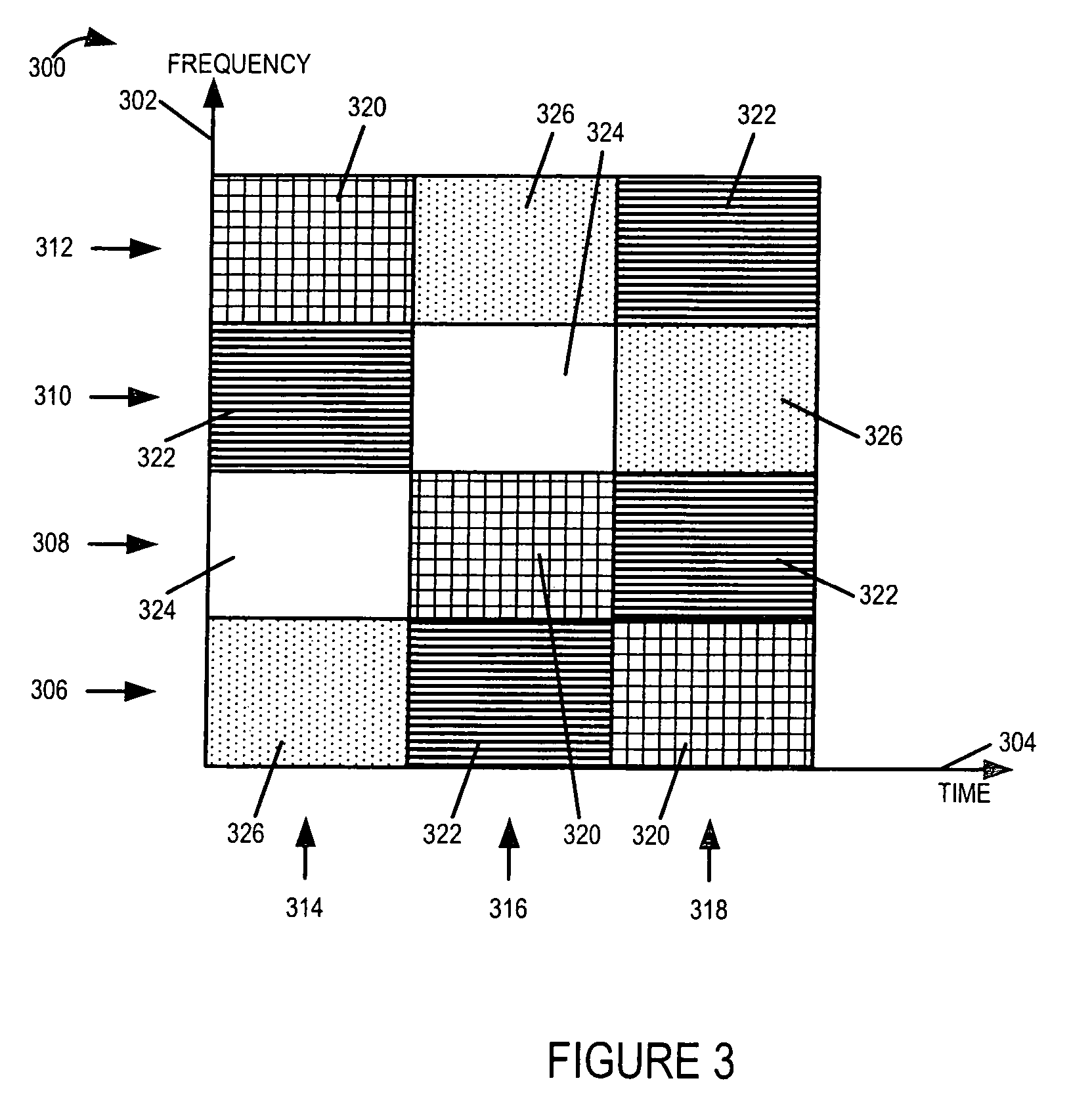
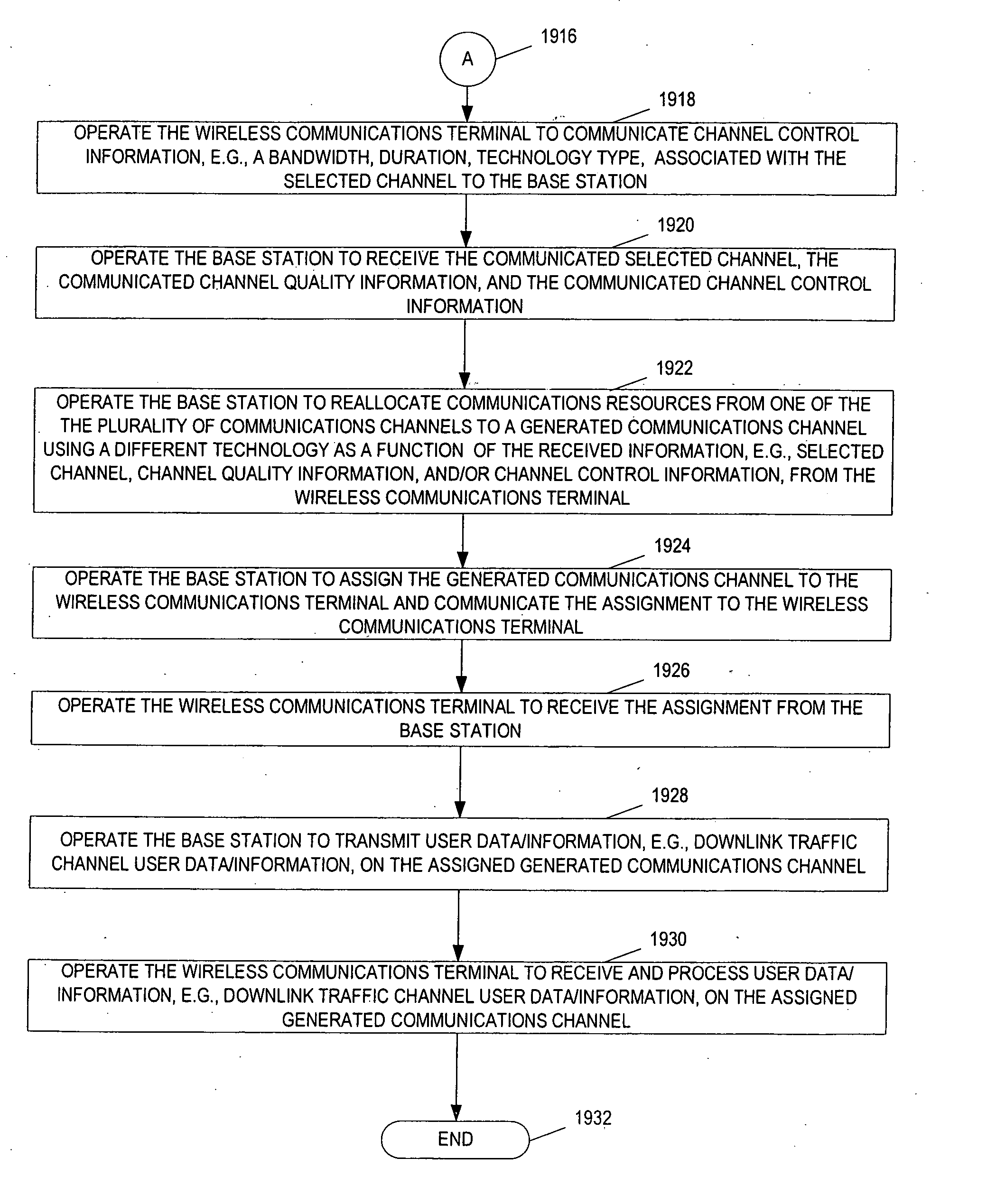
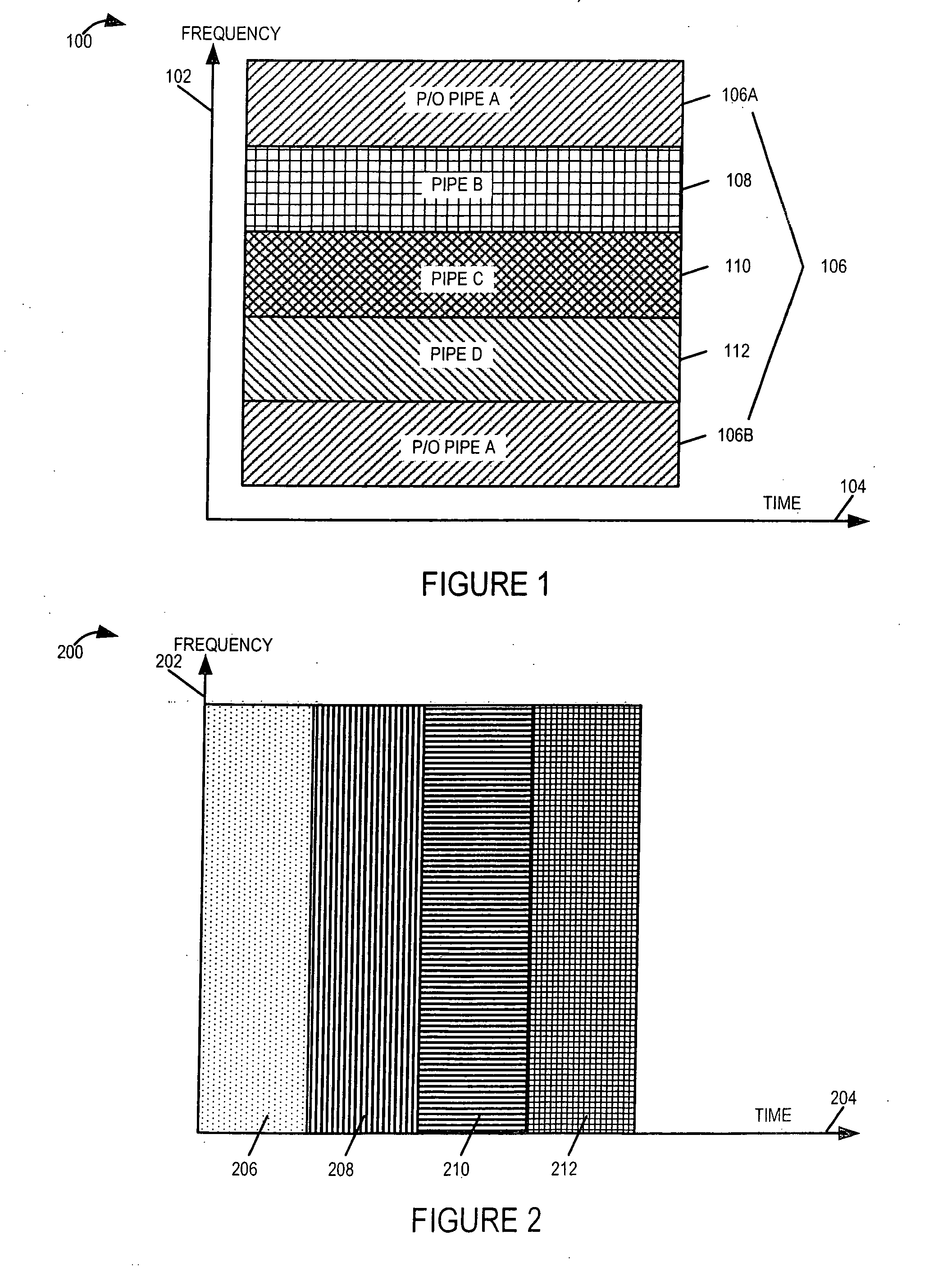
Methods and apparatus for supporting and using multiple communications channels corresponding to different transmit technologies and / or access technologies in parallel within a cell of a wireless communications system are described. Mobile nodes support multiple technologies and can switch between the technology being used at a particular point in time, e.g., from a first channel corresponding to a first technology to a second channel corresponding to a different technology which provides better transmission characteristics, e.g., a better perceived channel quality. Mobiles maintain at least two sets of channel quality information at any one point in time. Mobiles select the better channel and communicate the channel selection to the base station or communicate channel quality information for multiple channels to the basestation and allow the base station to select the channel corresponding to the technology providing the better conditions for the mobile. Different mobiles in the same cell may support different technologies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Methods and apparatus of enhancing performance in wireless communication systems
ActiveUS20050181799A1Constrain performance of systemExtension of timeSpatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringCommunications systemMobile device
Methods and apparatus for supporting and using multiple communications channels corresponding to different transmit technologies and / or access technologies in parallel within a cell of a wireless communications system are described. Mobile nodes support multiple technologies and can switch between the technology being used at a particular point in time, e.g., from a first channel corresponding to a first technology to a second channel corresponding to a different technology which provides better transmission characteristics, e.g., a better perceived channel quality. Mobiles maintain at least two sets of channel quality information at any one point in time. Mobiles select the better channel and communicate the channel selection to the base station or communicate channel quality information for multiple channels to the basestation and allow the base station to select the channel corresponding to the technology providing the better conditions for the mobile. Different mobiles in the same cell may support different technologies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
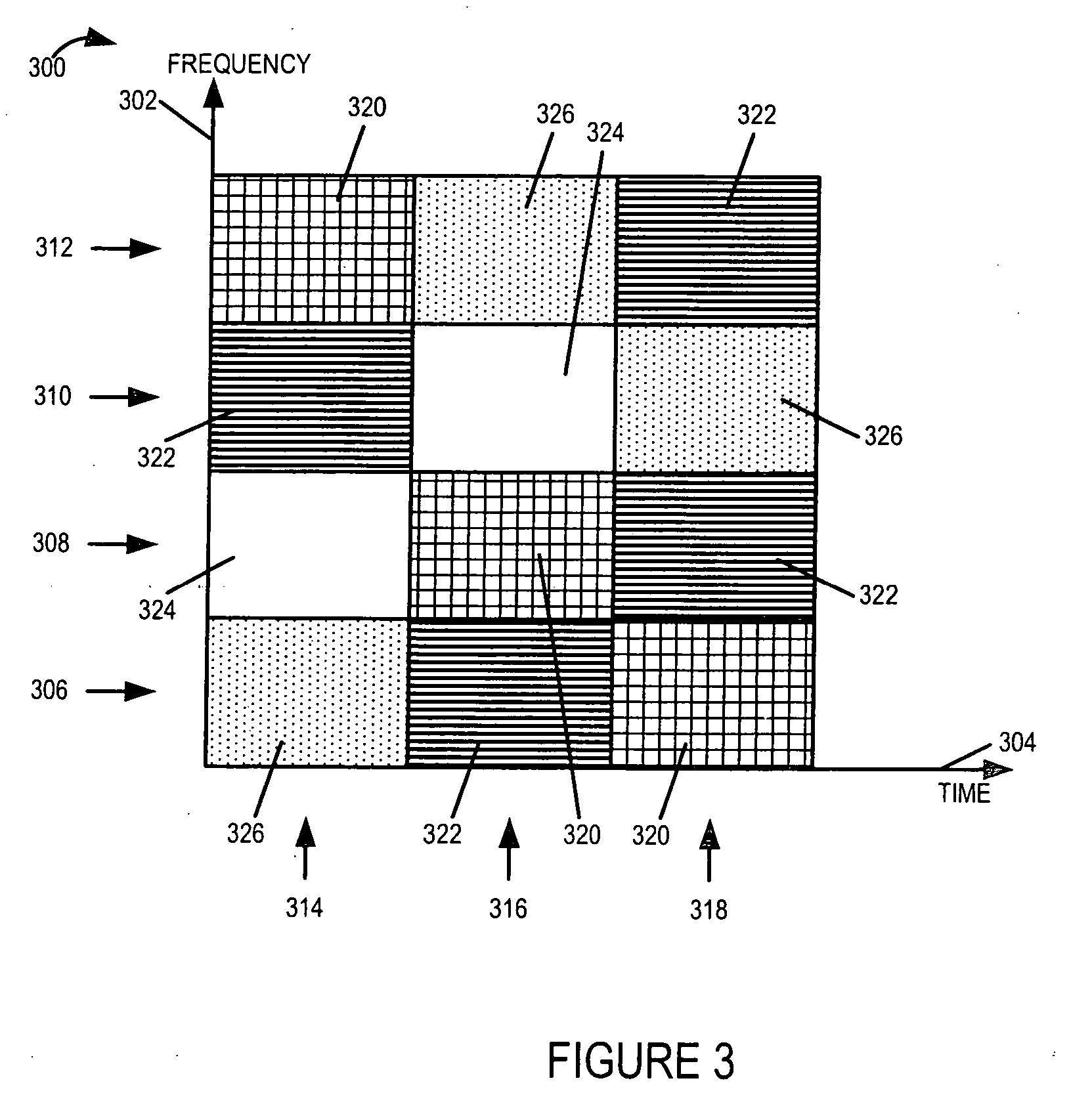
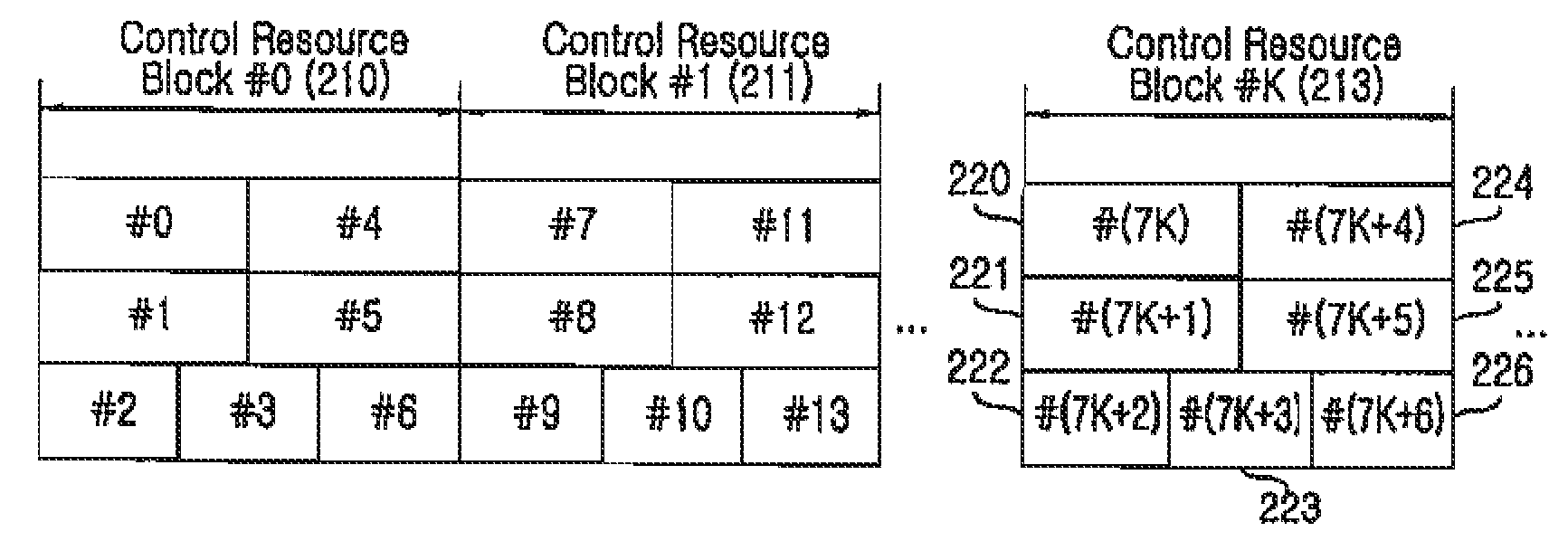
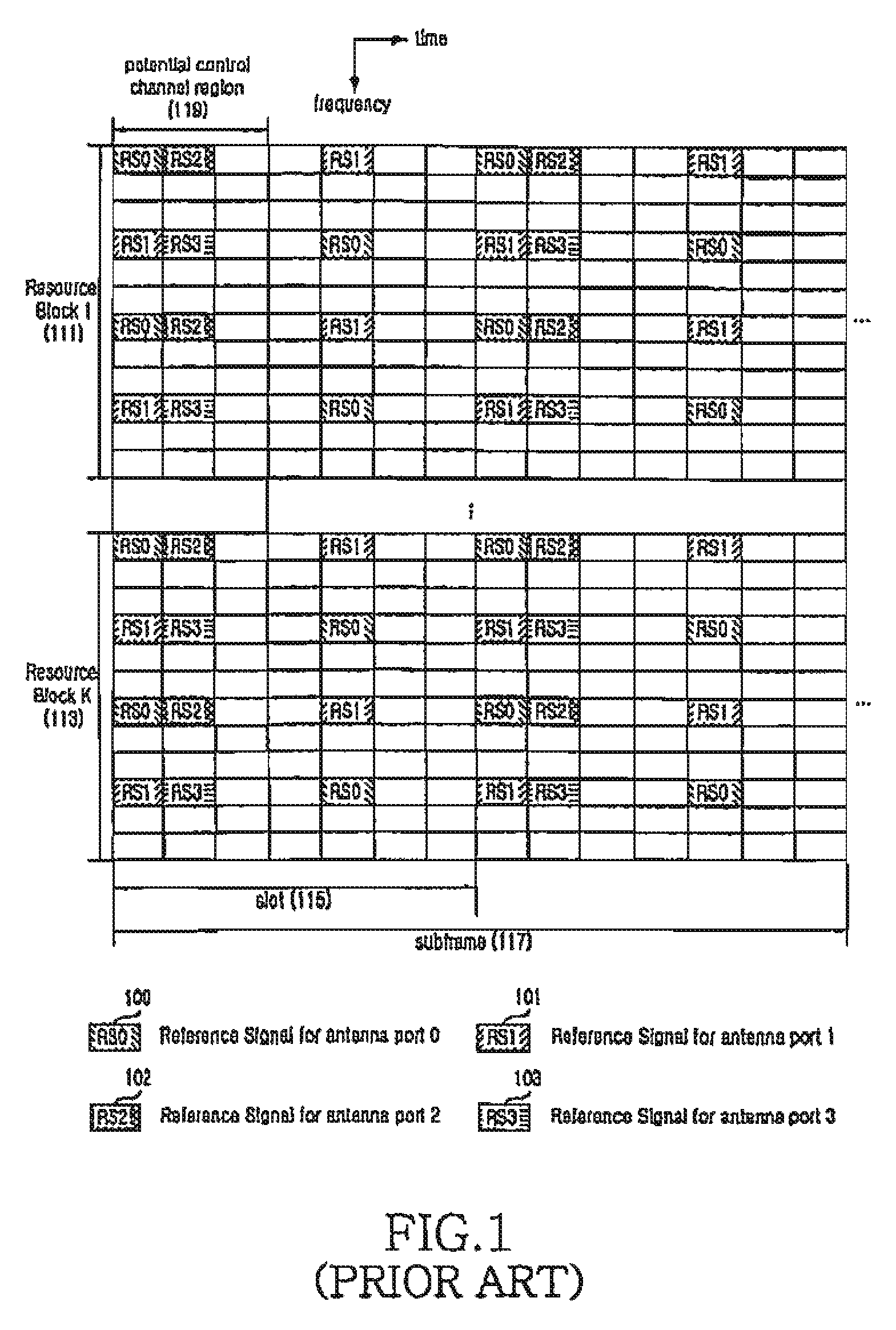
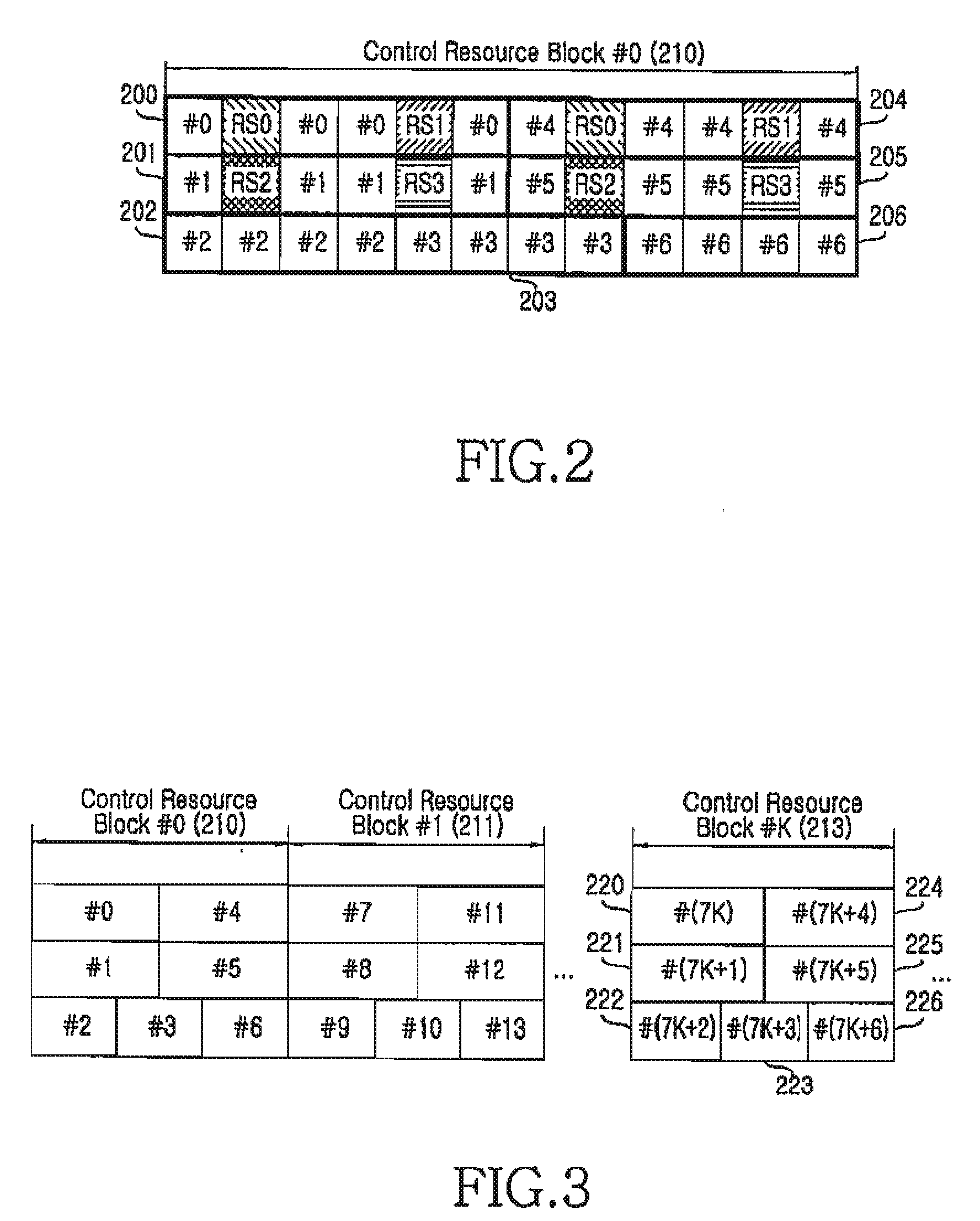
Method and apparatus for allocating resources of a control channel in a mobile communication system using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
ActiveUS20090097447A1Increase diversity gainModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionTelecommunicationsDistribution control
A method is provided for allocating resources of a control channel in a mobile communication system using Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). The method includes, when a time index and a frequency index of available Resource Elements (REs) are defined as l and k, respectively, dividing the available REs in a two-dimensional structure of (k, l); and time-first-allocating each RE to a plurality of RE groups while increasing the time index l for each frequency index k from an initial value up to a predetermined range.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Spectrum-adaptive networking
ActiveUS7483711B2Improve spectral efficiencyImprove throughputPower managementResonant long antennasTransceiverFrequency spectrum
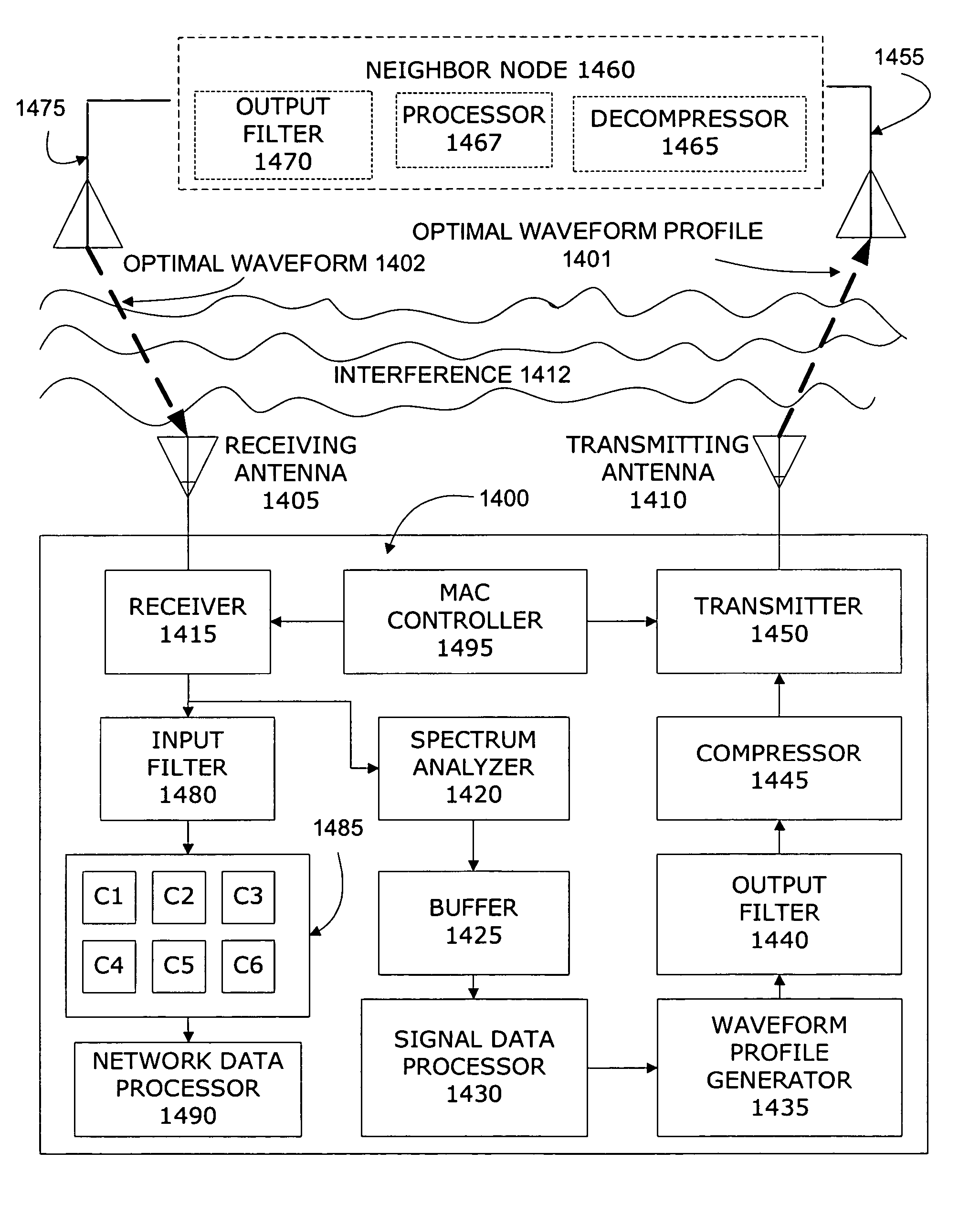
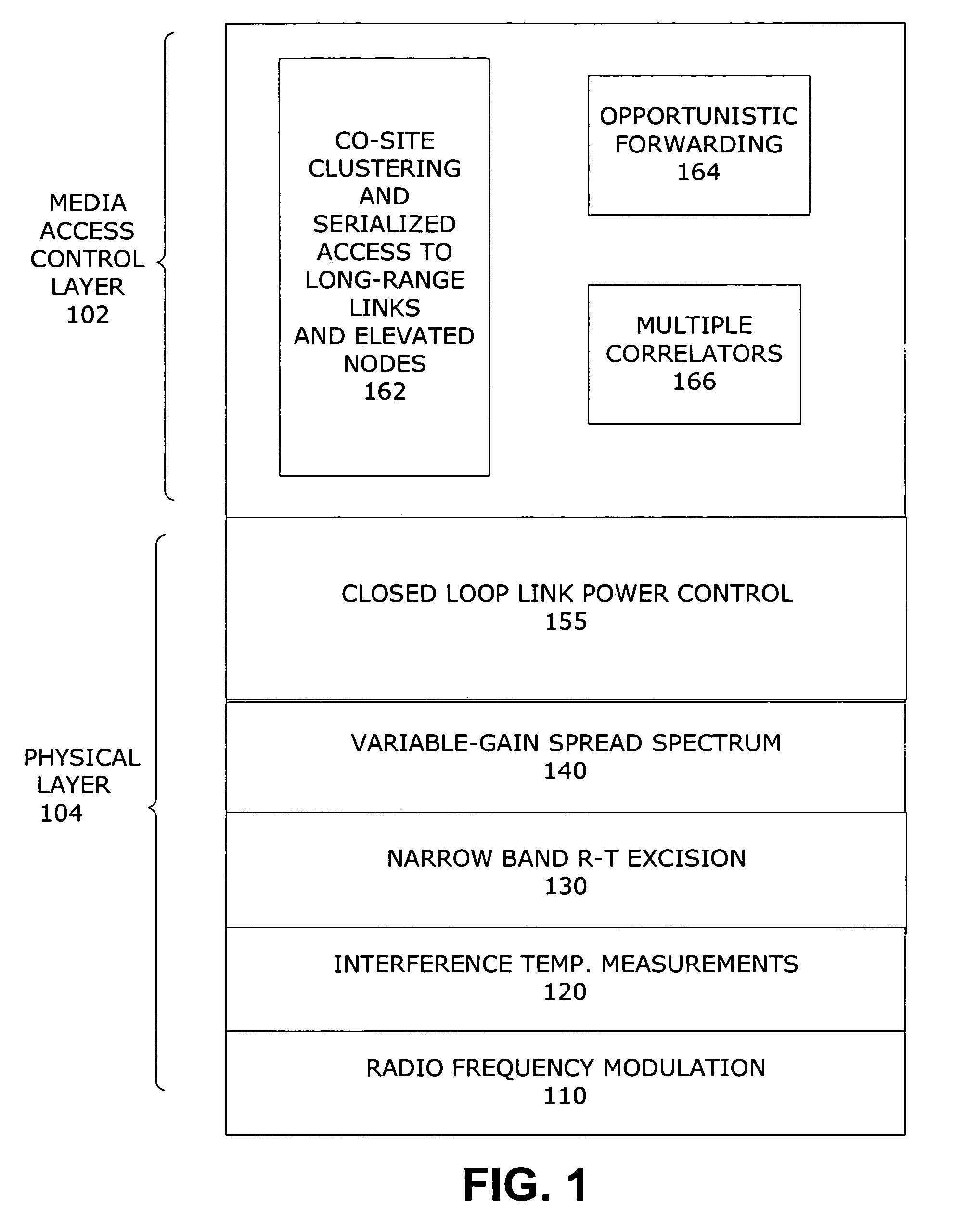
The present invention increases the available spectrum in a wireless network by sharing existing allocated (and in-use) portions of the RF spectrum in a manner that will minimize the probability of interfering with existing legacy users. The invention provides interference temperature-adaptive waveforms, and a variety of physical and media access control protocols for generating waveforms based on measurement and characterization of the local spectrum. The invention measures the local spectrum at a receiving node, generates an optimal waveform profile specifying transmission parameters that will water-fill unused spectrum up to an interference limit without causing harmful interference to primary and legacy transmitters using the same frequency bands, and enables simultaneous transmit and receive modes at a multiplicity of transceivers in a wireless network. The invention also provides closed loop feedback control between nodes, co-site interference management, intersymbol interference mitigation, wide sense stationary baseband signaling and modulation, and power limited signaling for avoiding detection and interception.
Owner:USTA TECH LLC
Beacon signaling in a wireless system
InactiveUS6985498B2Improve and optimize system performanceImprove throughputPower managementFrequency diversityEngineeringData transmission
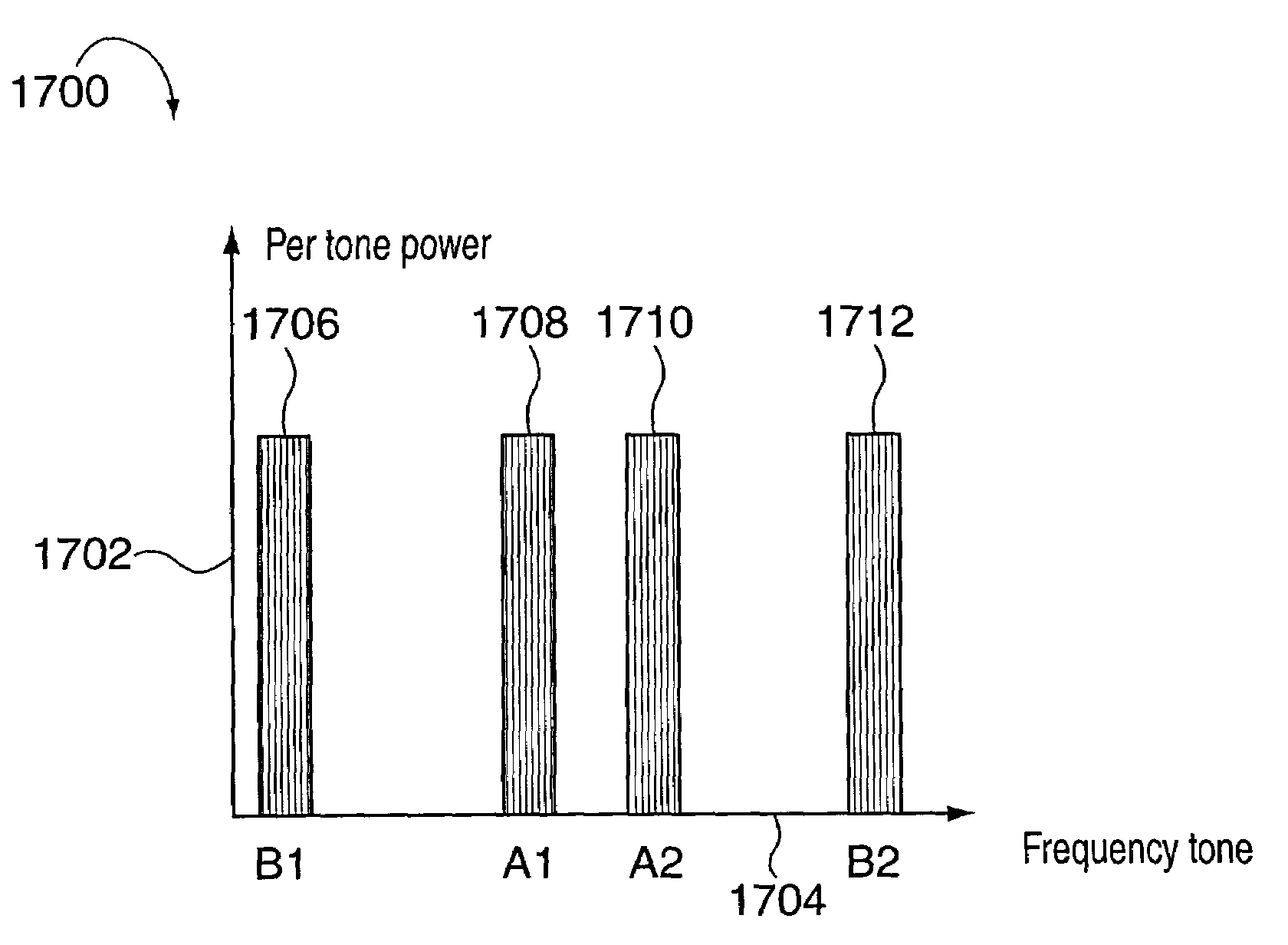
A few high power tones used for synchronization and / or other purposes are transmitted in a FDM system during a period of time, e.g., a symbol transmission time period. During normal data transmission symbol periods signals are transmitted using at least 10 tones, e.g., per symbol time. Less than 5 high power signals are transmitted in a symbol time with at least 80% the maximum total transmitter power transmitted being allocated to the high power signals where the maximum total transmitter power is determined from a period of time which may includes one or more data and / or high power tone transmission periods. When the high power tones are transmitted at most 20% of transmitter power is available for transmitting other tones with the power normally being distributed among multiple tones. Normally some tones which would be transmitted in a symbol time go unused during transmission of the high power signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
CDMA transceiver techniques for wireless communications
InactiveUS20040120274A1Spatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityWireless transmissionCommunications system
The present invention is related to a method for multi-user wireless transmission of data signals in a communication system having at least one base station and at least one terminal. It comprises, for a plurality of users, the following steps: adding robustness to frequency-selective fading to the data to be transmitted. performing spreading and scrambling of at least a portion of a block of data, obtainable by grouping data symbols by demultiplexing using a serial-to-parallel operation, combining (summing) spread and scrambled portions of the blocks of at least two users, adding transmit redundancy to the combined spread and scrambled portions, and transmitting the combined spread and scrambled portions with transmit redundancy.
Owner:RPX CORP
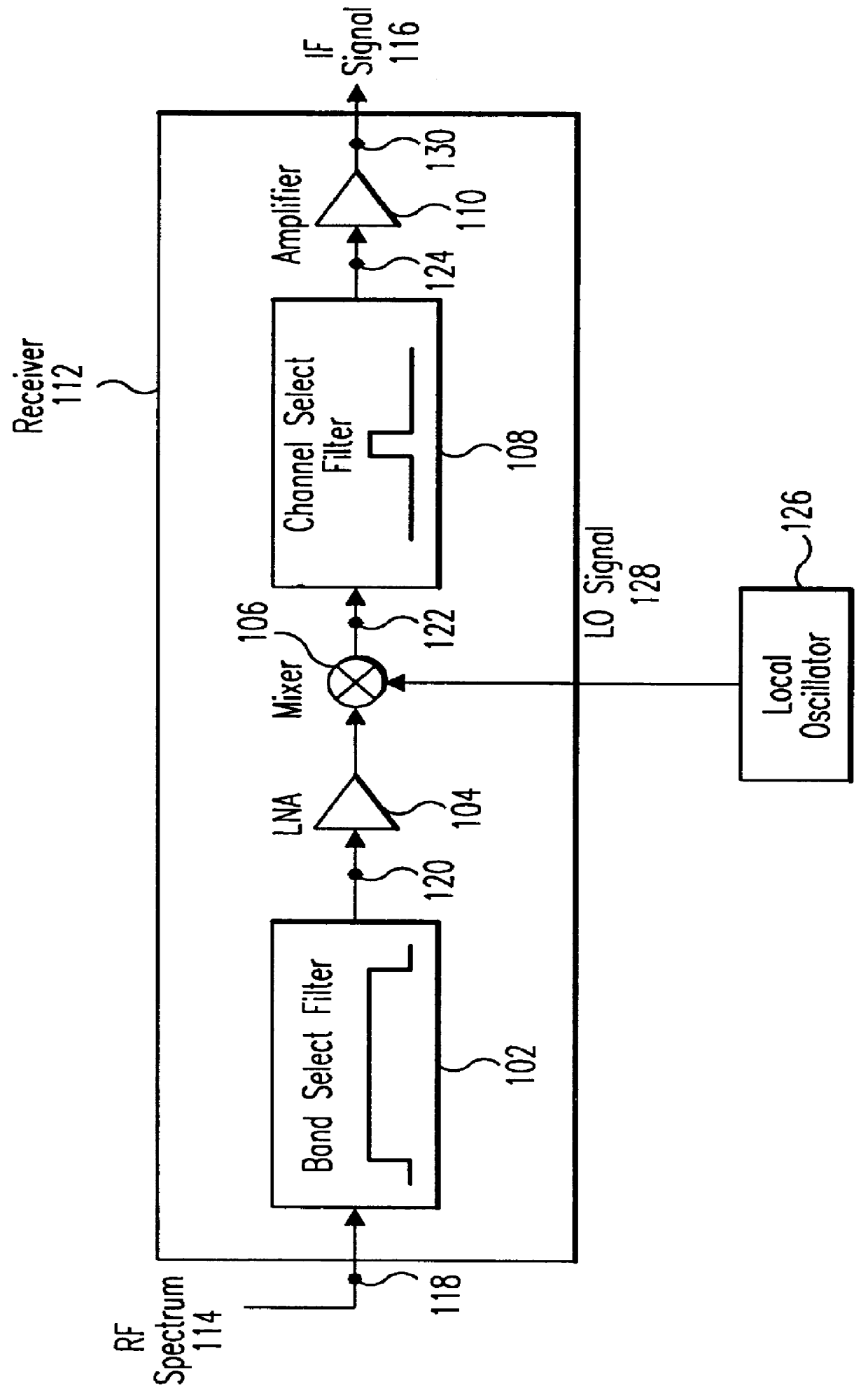
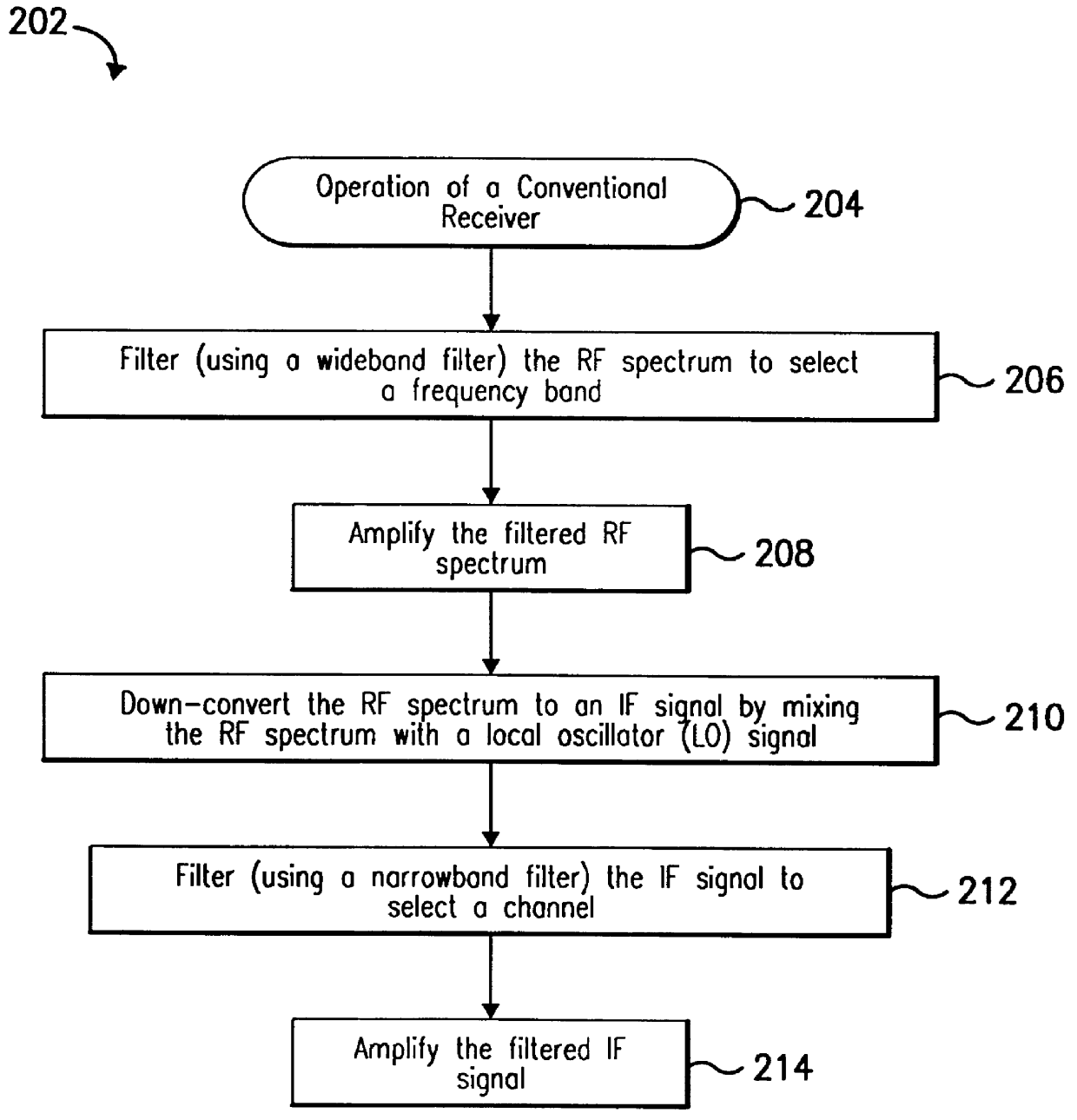
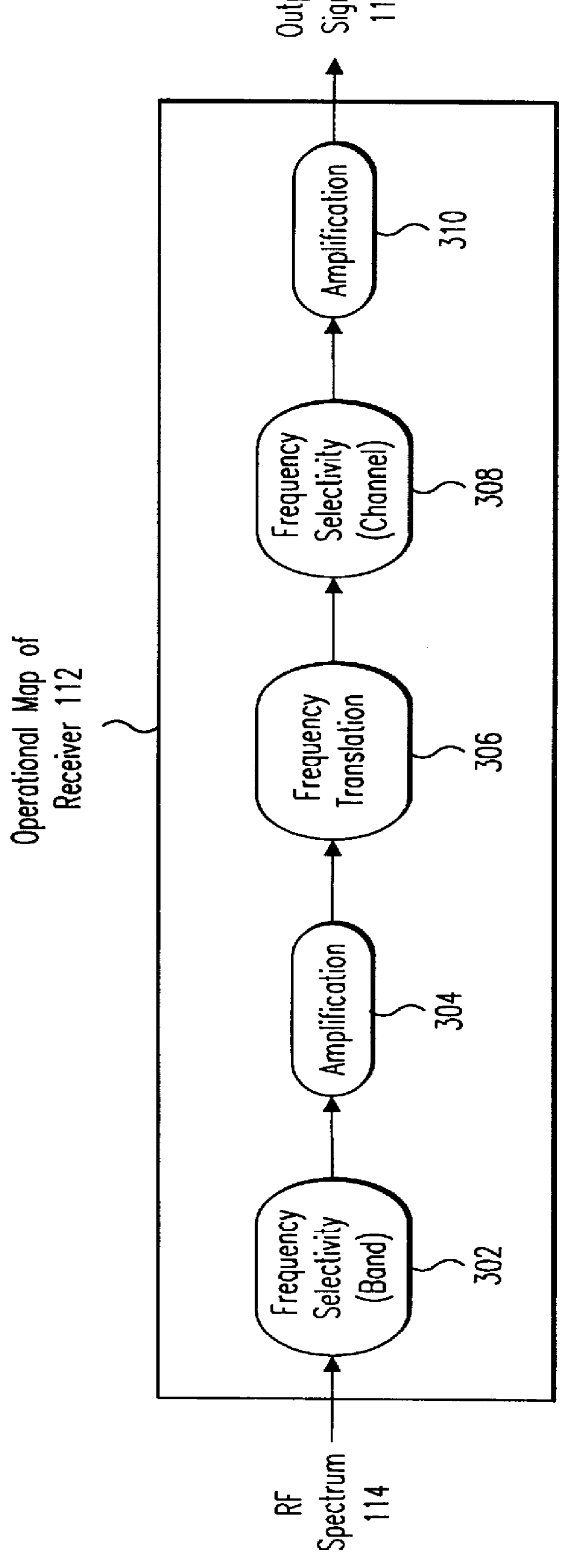
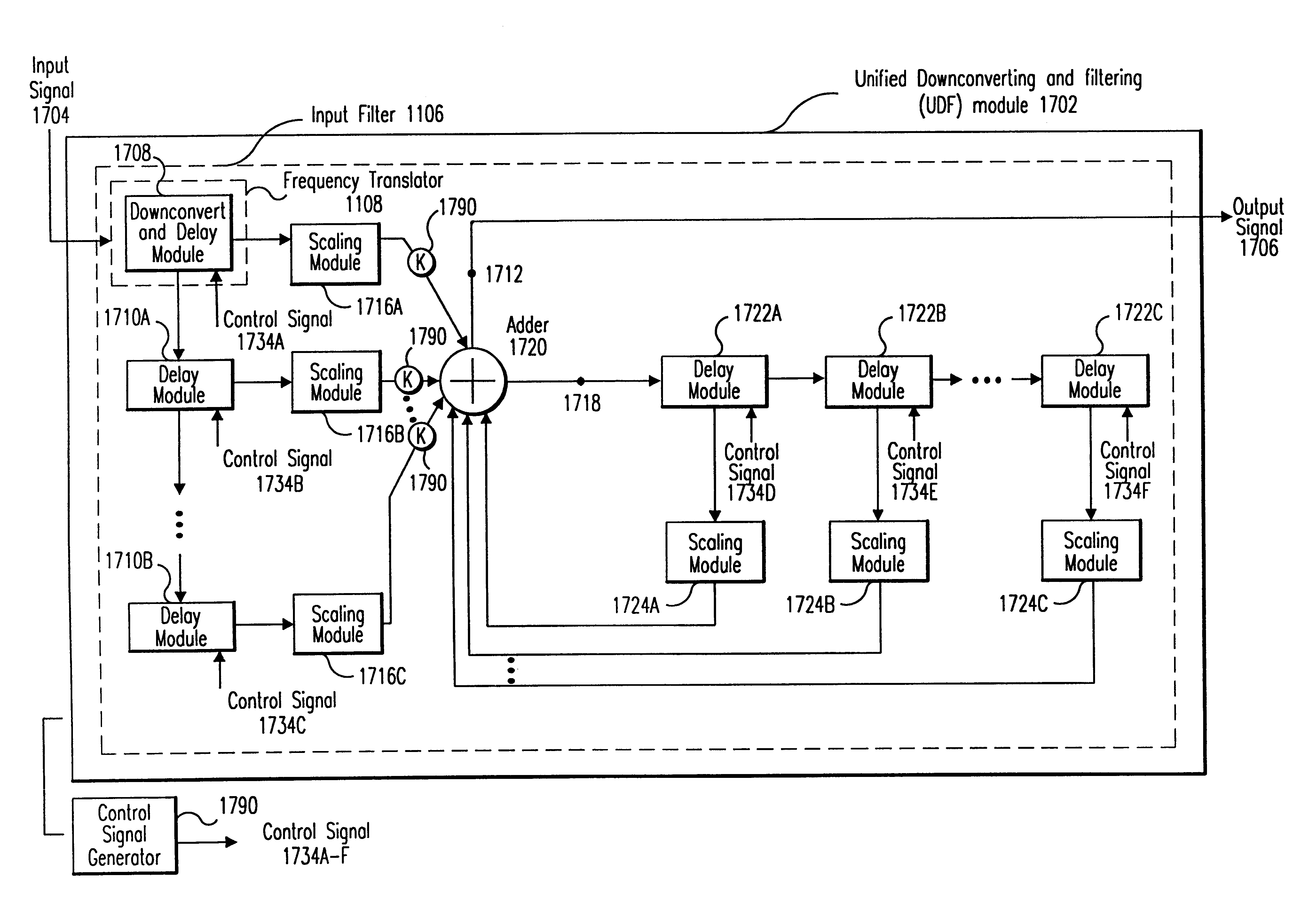
Integrated frequency translation and selectivity
InactiveUS6049706AModulation transferenceFrequency diversitySoftware engineeringFrequency selectivity
Methods and apparatuses for frequency selectivity and frequency translation, and applications for such methods and apparatuses, are described herein. The method includes steps of filtering an input signal, and down-converting the filtered input signal. The filtering and the down-conversion operations are performed in an integrated, unified manner. The apparatus described herein can be implemented as an integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Method for transmitting control information in multiple antenna system
ActiveUS20100111226A1Improve data transfer efficiencyReduce radio resourceModulated-carrier systemsElectric discharge tubesData transmissionPrecoding matrix
A method of transmitting control information includes dividing frequency bandwidth into ranges to which the same PMI (precoding matrix index) is applied, obtaining multiple antenna information by the range to which the same PMI is applied and transmitting the multiple antenna information. Since multiple antenna information is transmitted by the unit of a range to which the same PMI is applied, radio resources allocated for transmitting the multiple antenna information may be reduced, thereby enhancing data transmission efficiency.
Owner:AEGIS 11 SA
Method and system for down-converting electromagnetic signals by sampling and integrating over apertures
InactiveUS6266518B1Reduce frequencySufficiently reproducedResonant long antennasModulation transferenceIntermediate frequencyEngineering
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal are described herein. Briefly stated, such methods, systems, and apparatuses operate by receiving an EM signal and an aliasing signal having an aliasing rate. The EM signal is aliased according to the aliasing signal to down-convert the EM signal. The term aliasing, as used herein, refers to both down-converting an EM signal by under-sampling the EM signal at an aliasing rate, and down-converting an EM signal by transferring energy from the EM signal at the aliasing rate. In an embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to a demodulated baseband information signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is a frequency modulated (FM) signal, which is down-converted to a non-FM signal, such as a phase modulated (PM) signal or an amplitude modulated (AM) signal.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
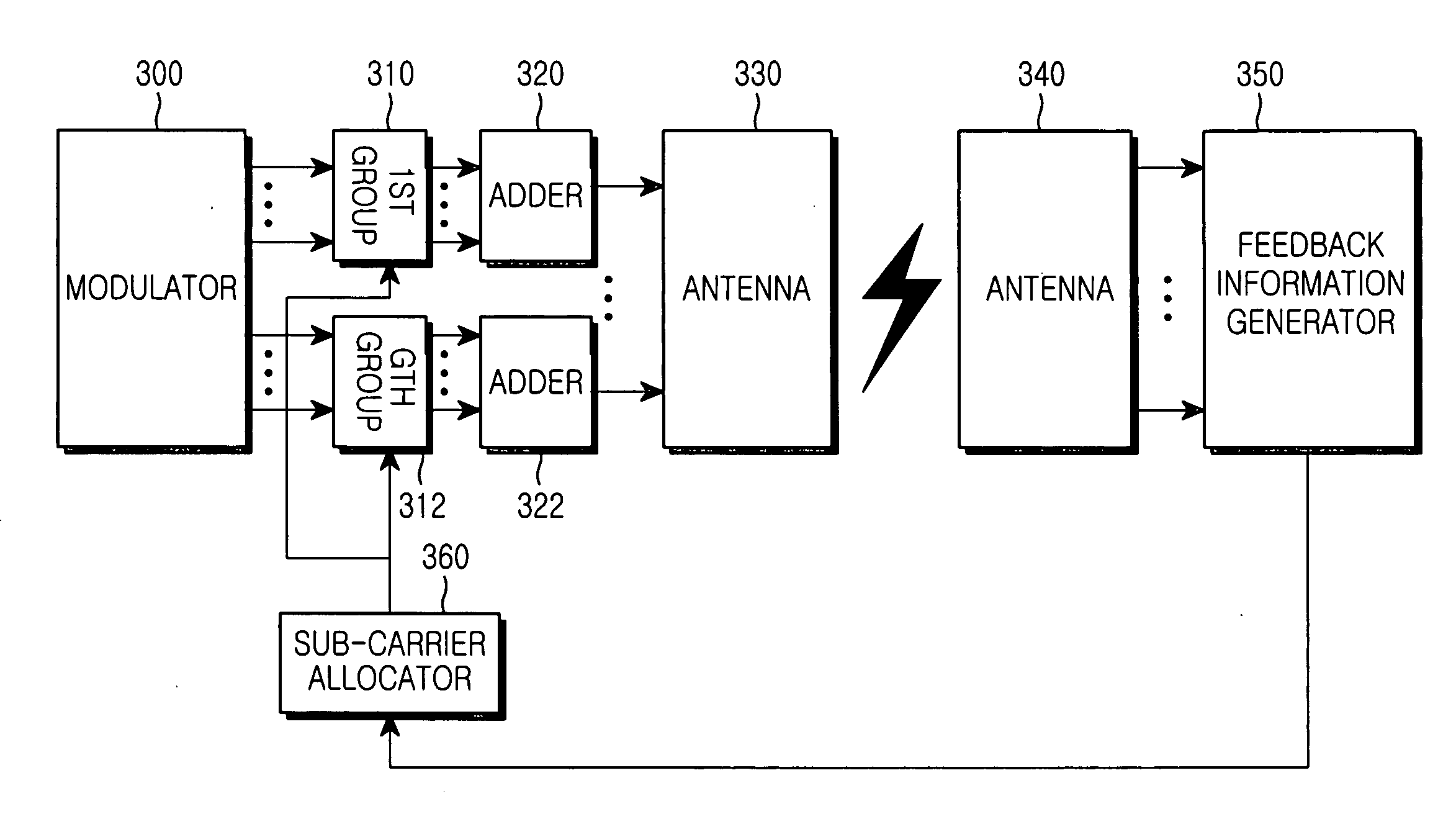
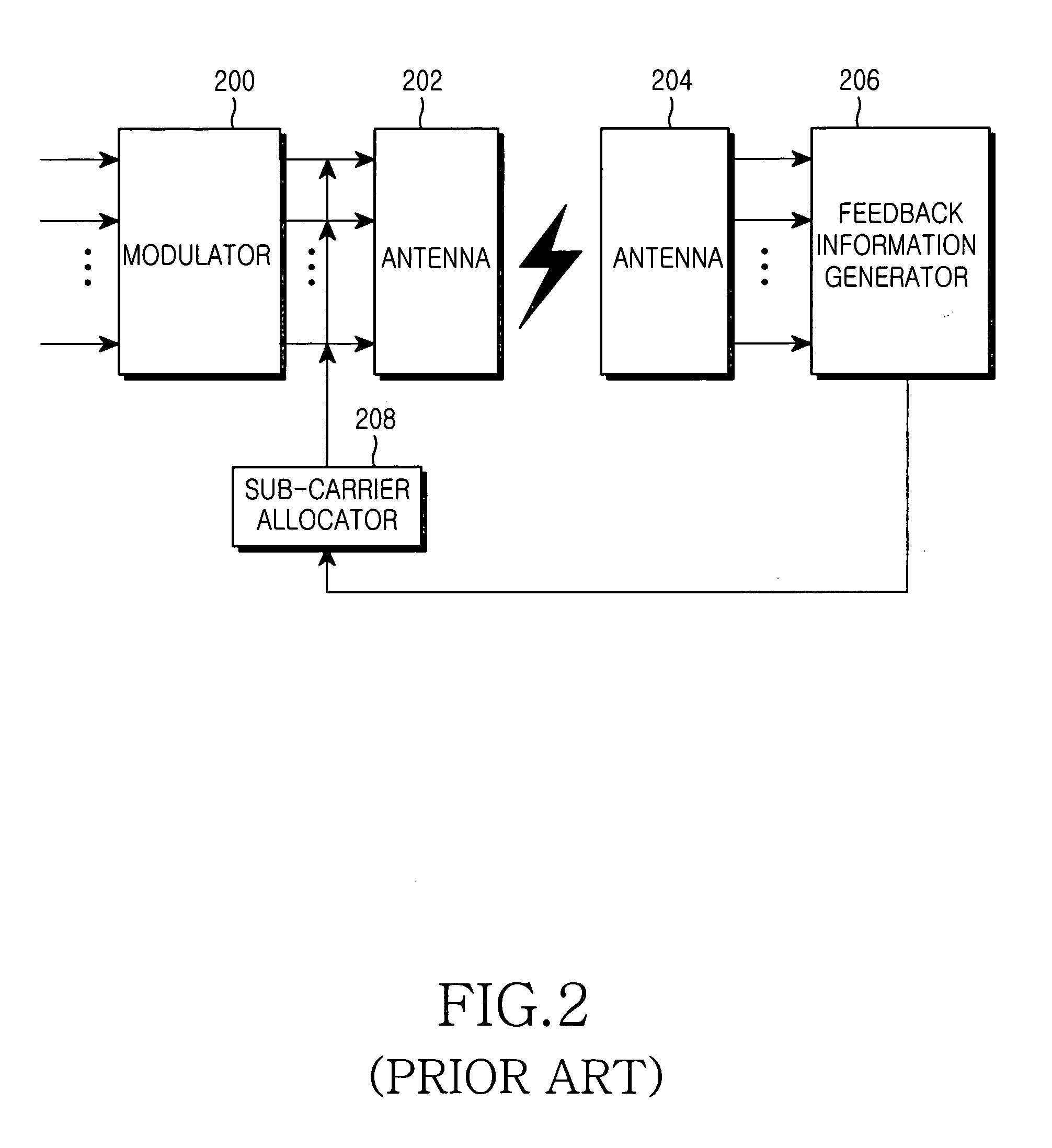
Apparatus and method for assigning sub-carriers in an orthogonal frequency division multiplex system
ActiveUS20070140102A1Reduce feedbackSpatial transmit diversityTransmission path divisionCarrier signalData transmission
An apparatus and method for assigning sub-carriers in an orthogonal frequency division multiplex (OFDM) system are disclosed. In the apparatus and method, data is transmitted through at least one transmit antenna. At least two sub-carriers in a predetermined frequency band are assigned to a user equipment (UE), for data transmission. A Node B groups sub-carriers available to the OFDM system into sub-carrier groups, each having at least two sub-carriers, transmits data to the UE on sub-carriers in the sub-carrier groups, selects at least one sub-carrier group for the UE based on channel condition information about each of the sub-carrier groups received from the UE, and assigns the selected sub-carrier group to the UE.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
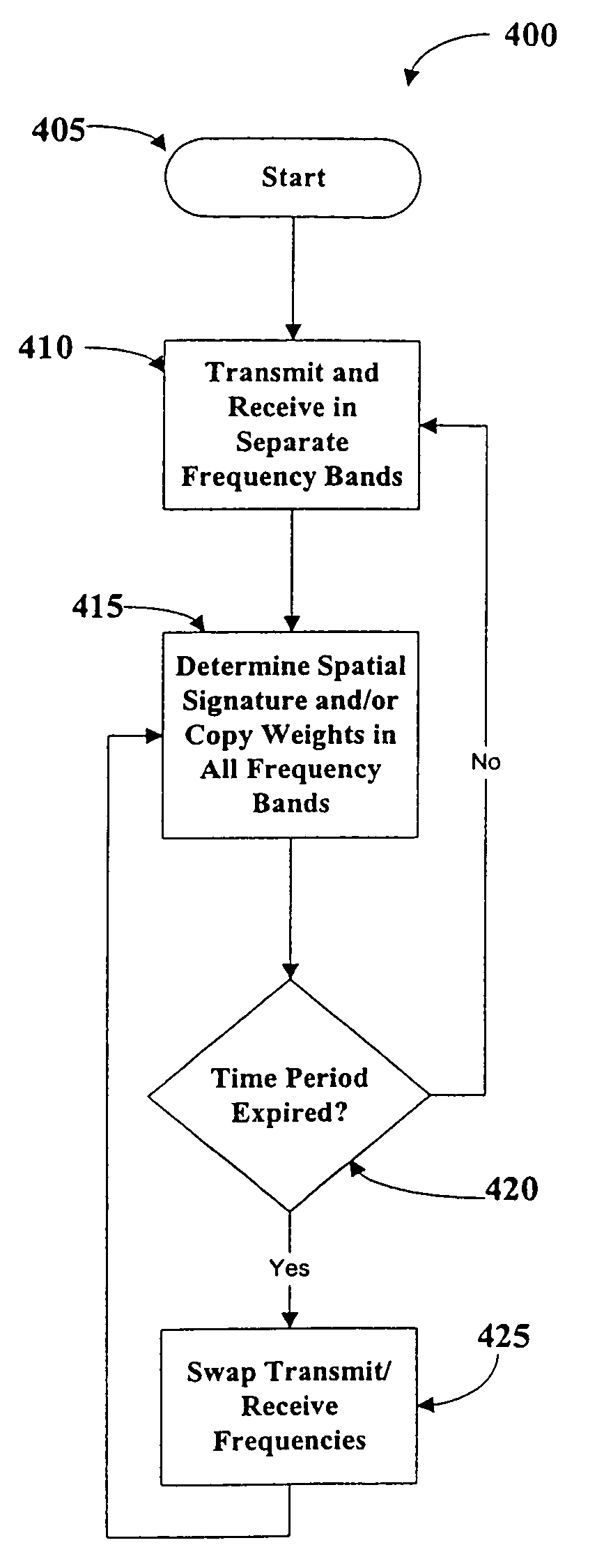
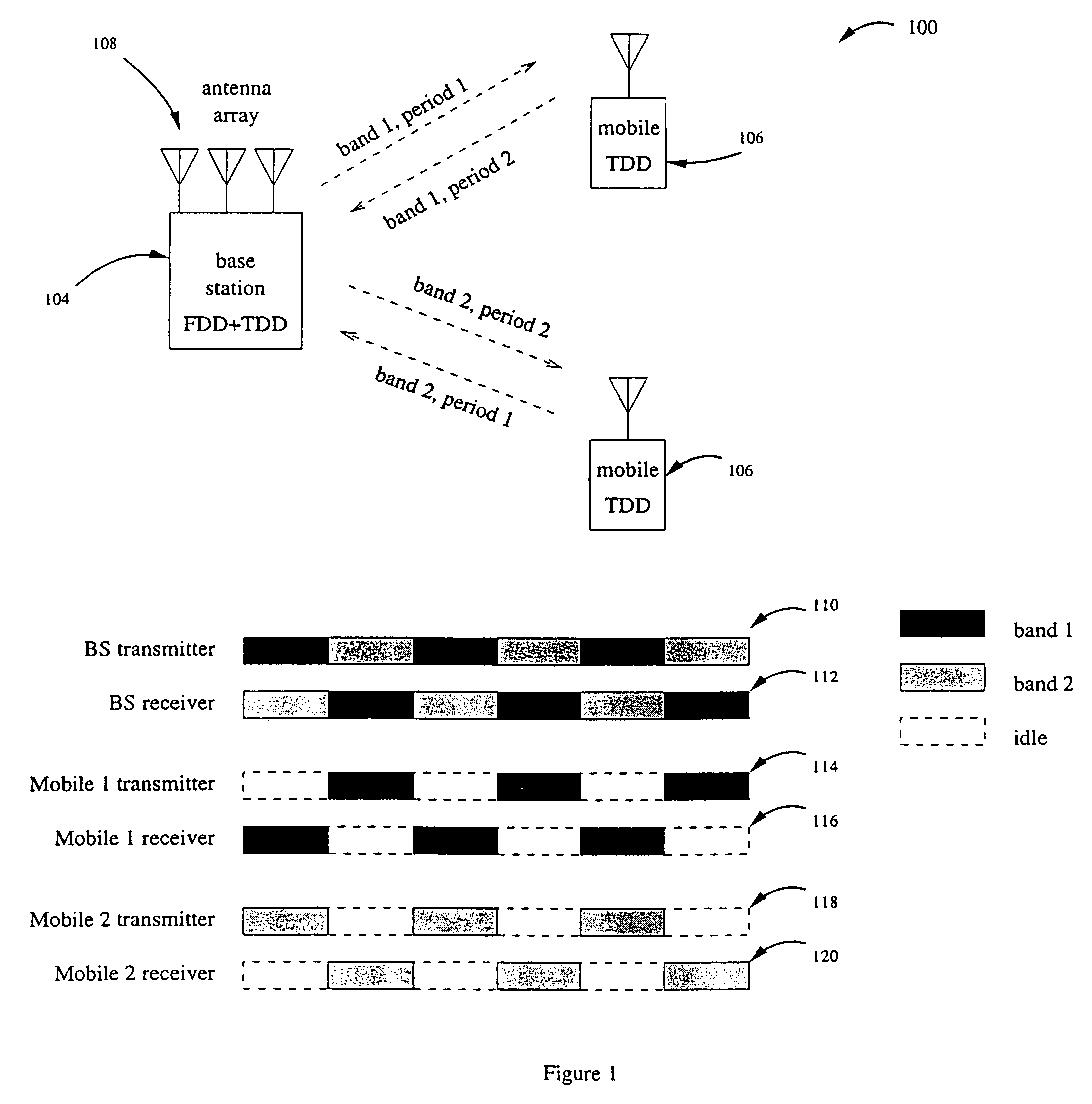
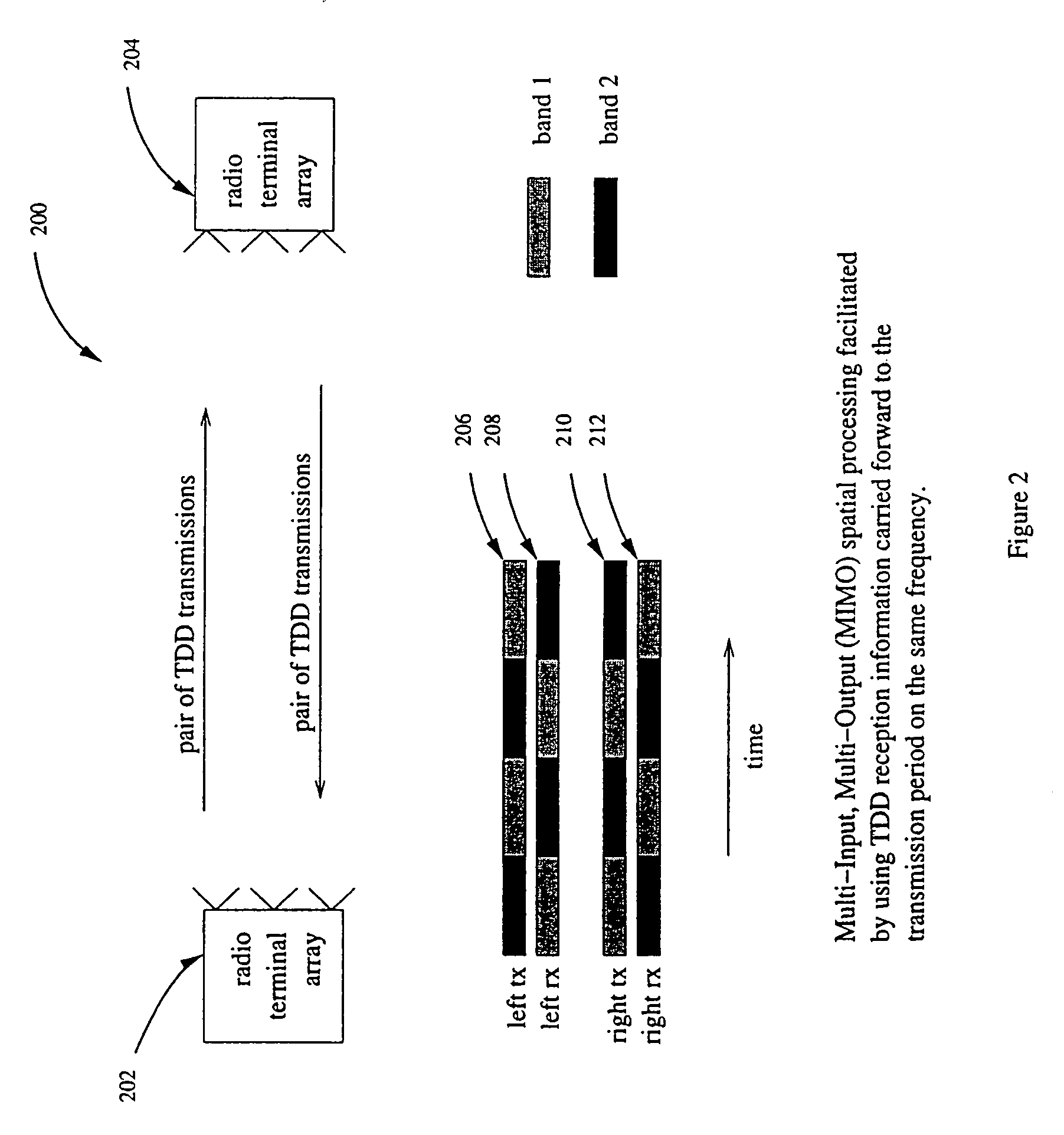
Operating time division duplex (TDD) wireless systems in paired spectrum (FDD) allocations
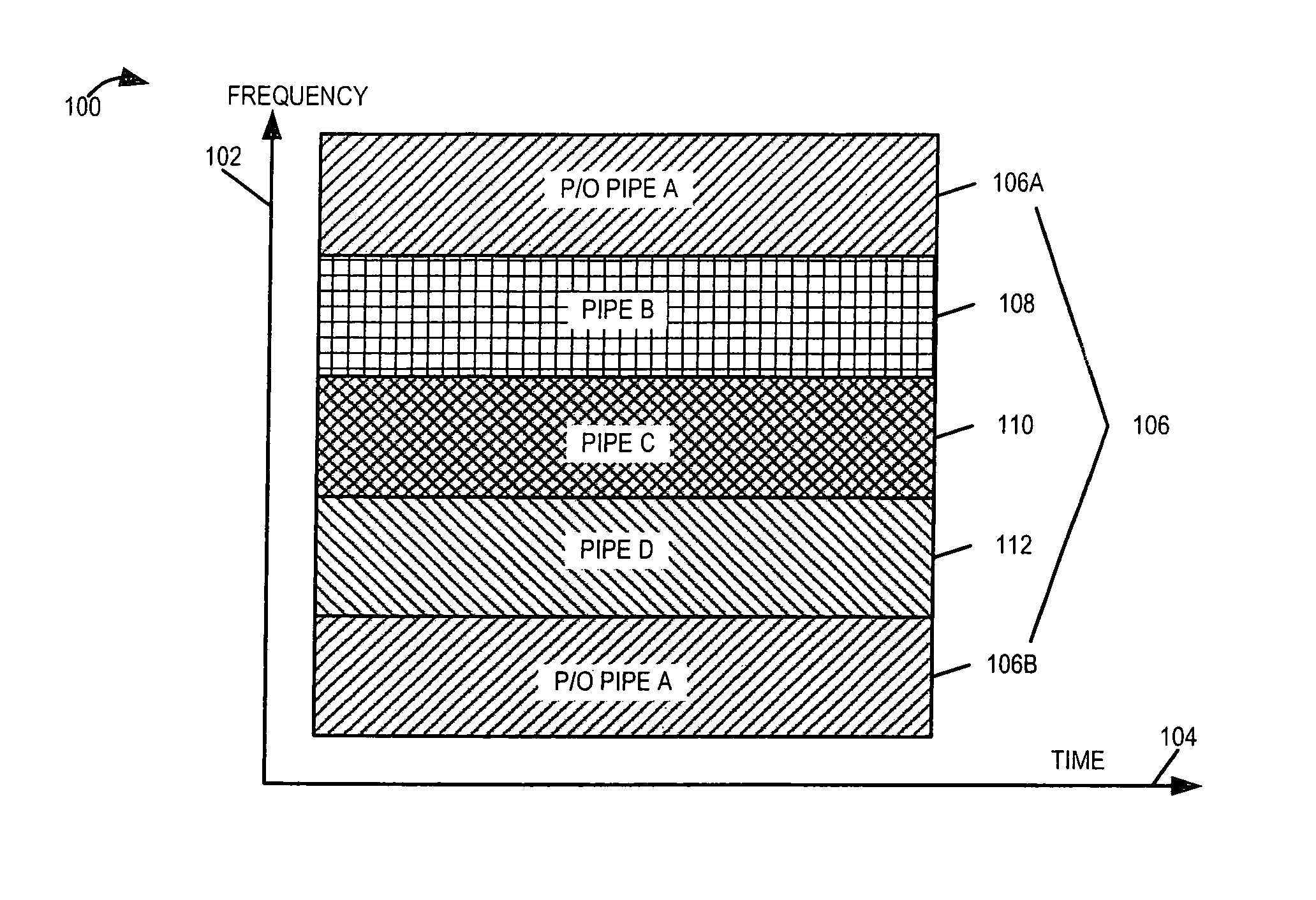
ActiveUS7336626B1Easy to copyIncrease profitFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency diversityCommunications systemTime segment
A wireless communication system operates in a combined FDD and TDD mode. During a first time period, data may be transmitted at a first frequency band and received at a second frequency band. During a second time period, data is transmitted at the second frequency band and received at the first frequency band. The first and second time periods may be of identical durations, thereby creating a 50% duty cycle. When the base station operates with multiple frequency bands, spatial processing parameters such as the spatial signature or copy weights of the mobile stations may be collected in all frequency bands, thereby allowing the full processing advantage of adaptive antenna.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
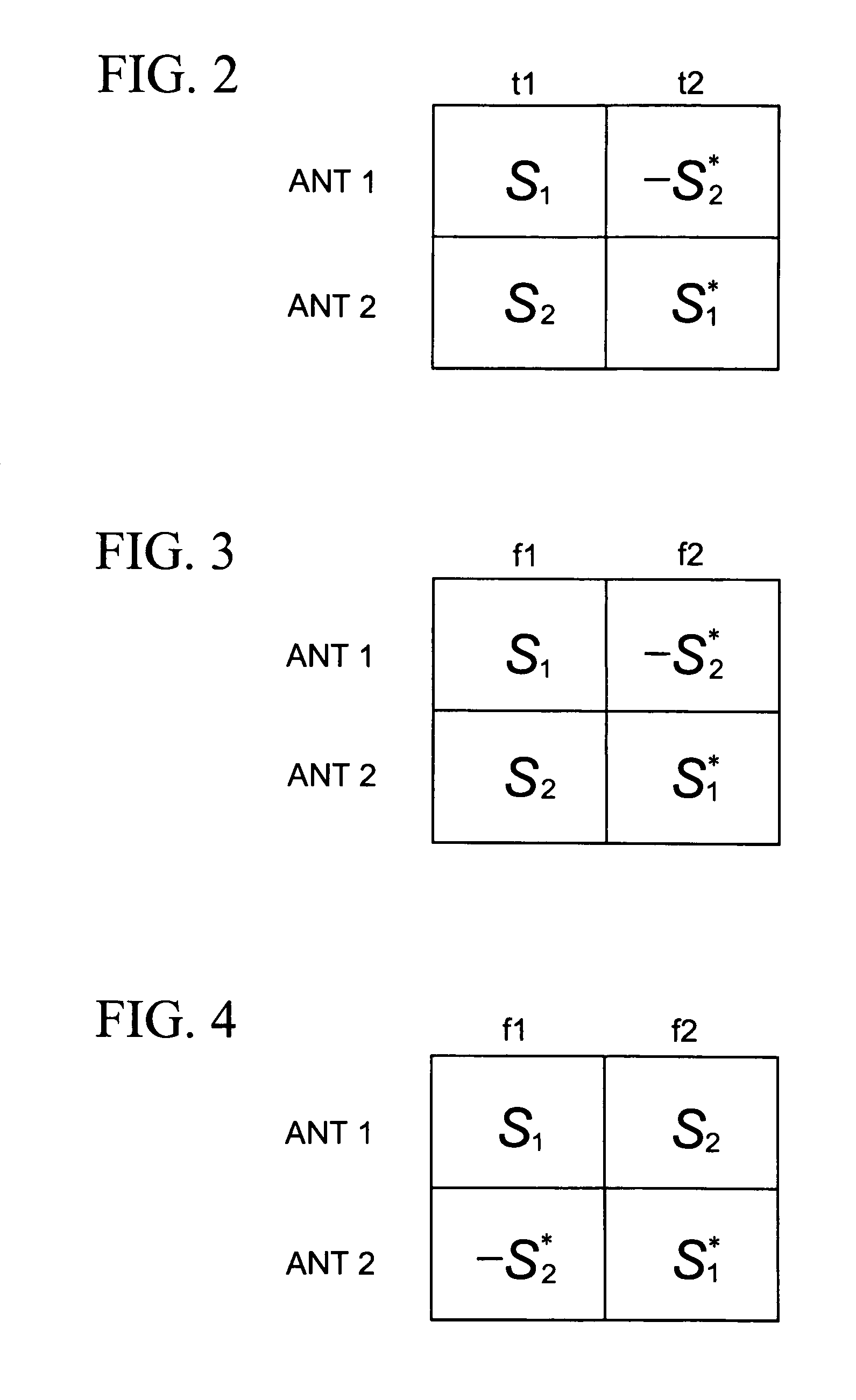
Transmission symbols mapping for antenna diversity
InactiveUS20080304593A1Polarisation/directional diversityError detection/correctionTime domainBurst transmission
Methods and apparatus for transmitting data via multiple antennas by using antenna diversity. A transmission diversity scheme is established such that two transmission matrices that are in accordance with the space frequency block code combined with Frequency switched transmit diversity (SFBC+FSTD) scheme, are alternatively applied in either the frequency domain, or the time domain, or both of the frequency domain or then time domain. The symbols in the transmission matrices may be transmitted either as one burst in a primary broadcast channel (PBCH), or as discrete bursts in the primary broadcast channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
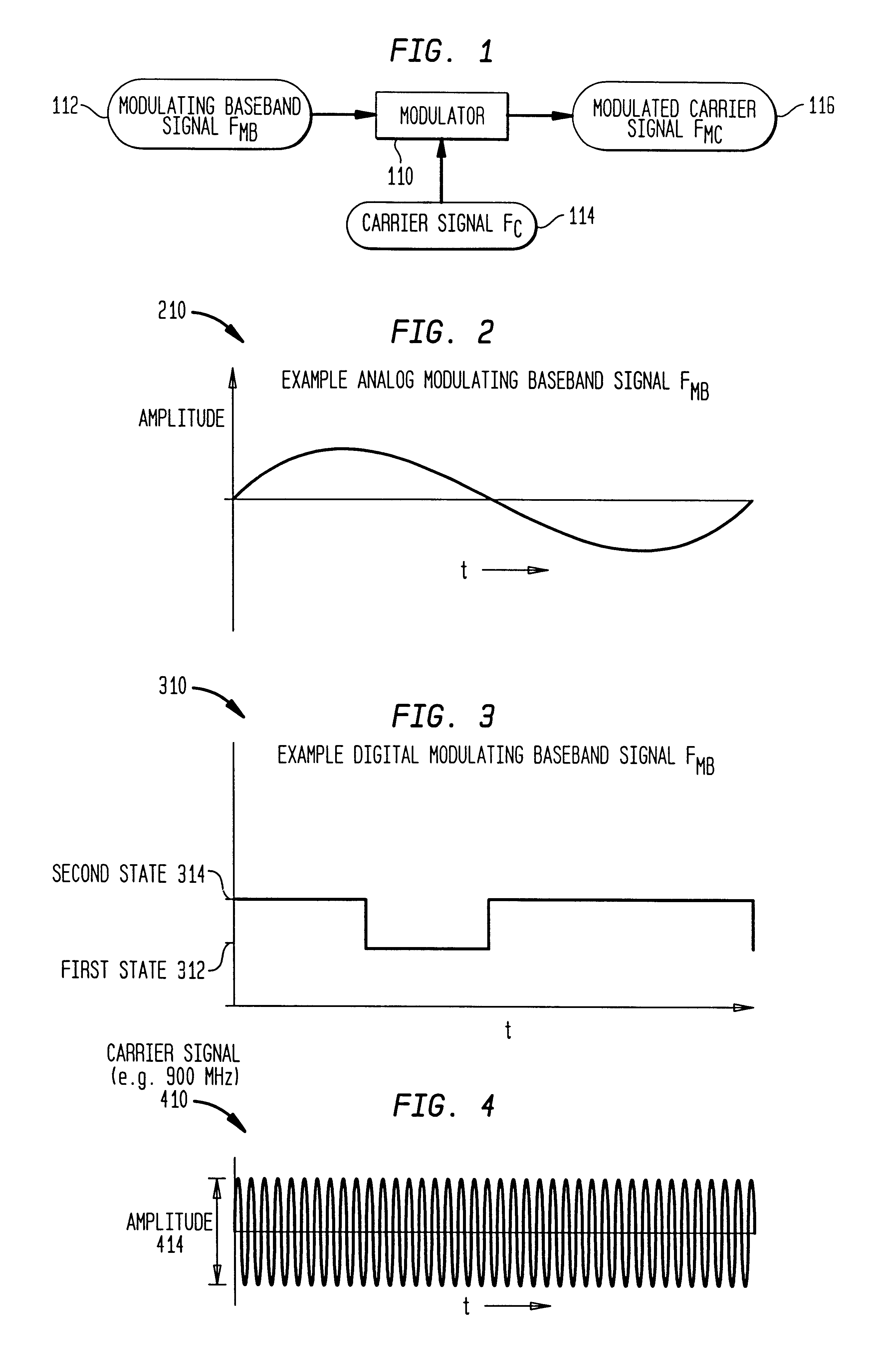
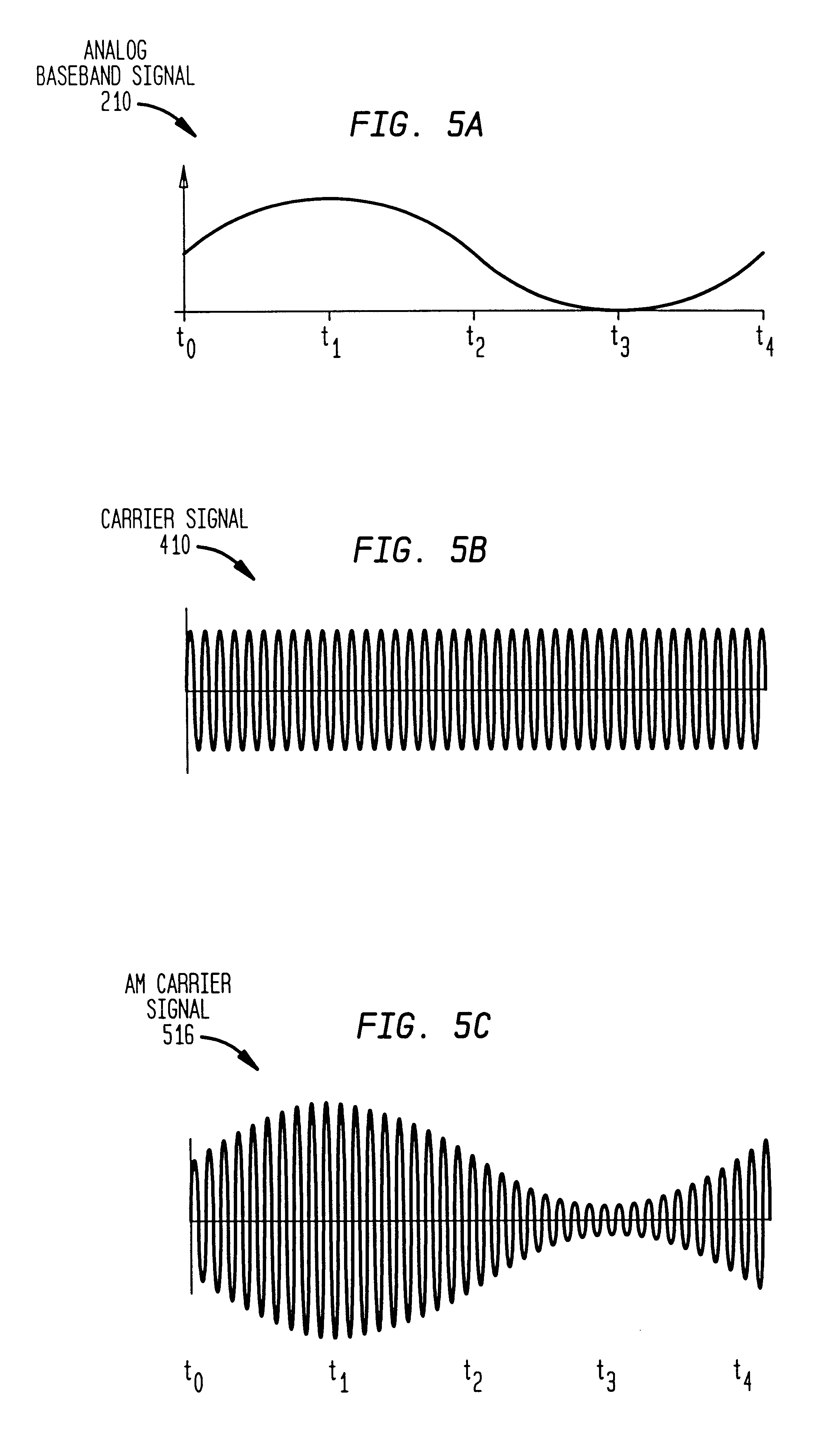
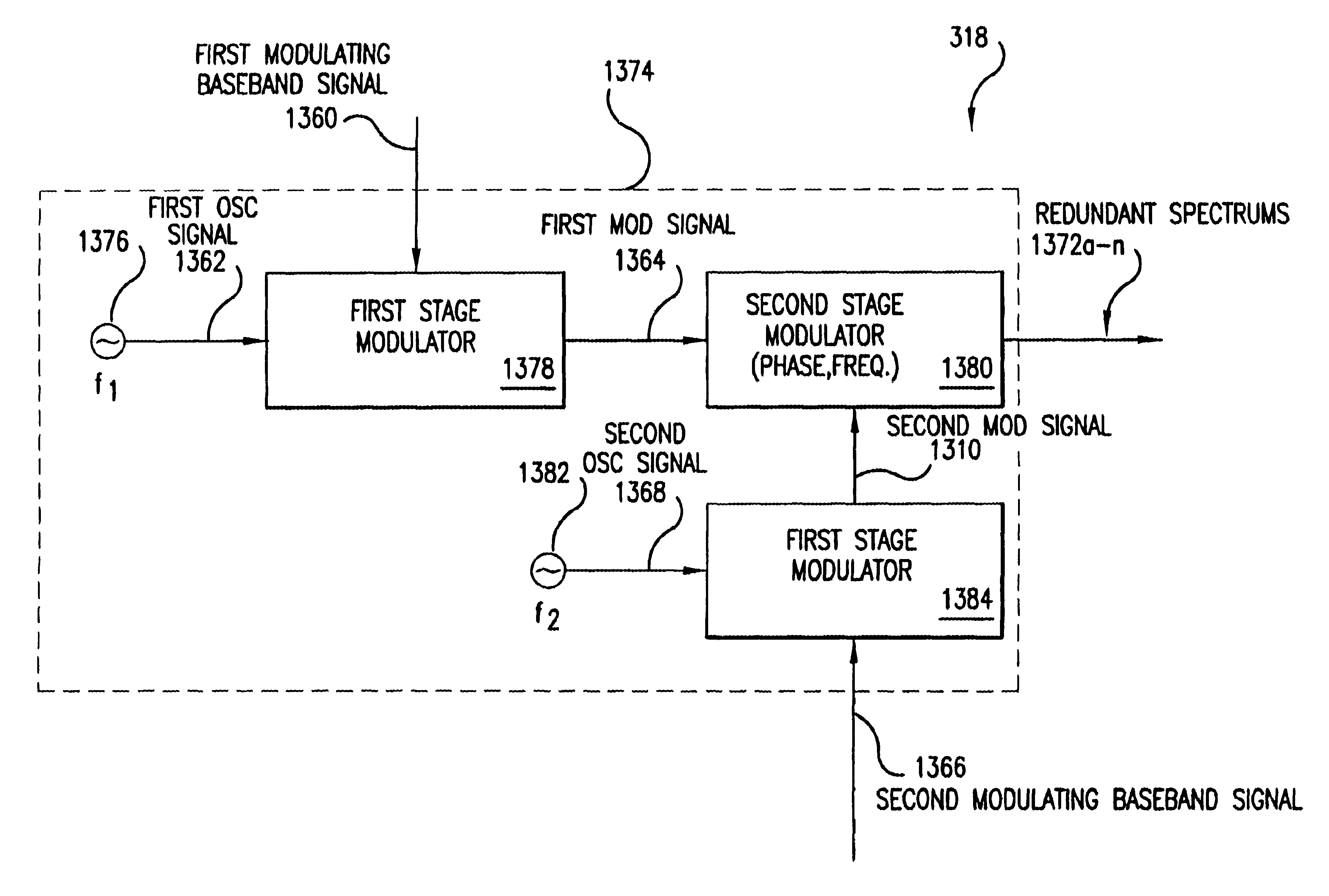
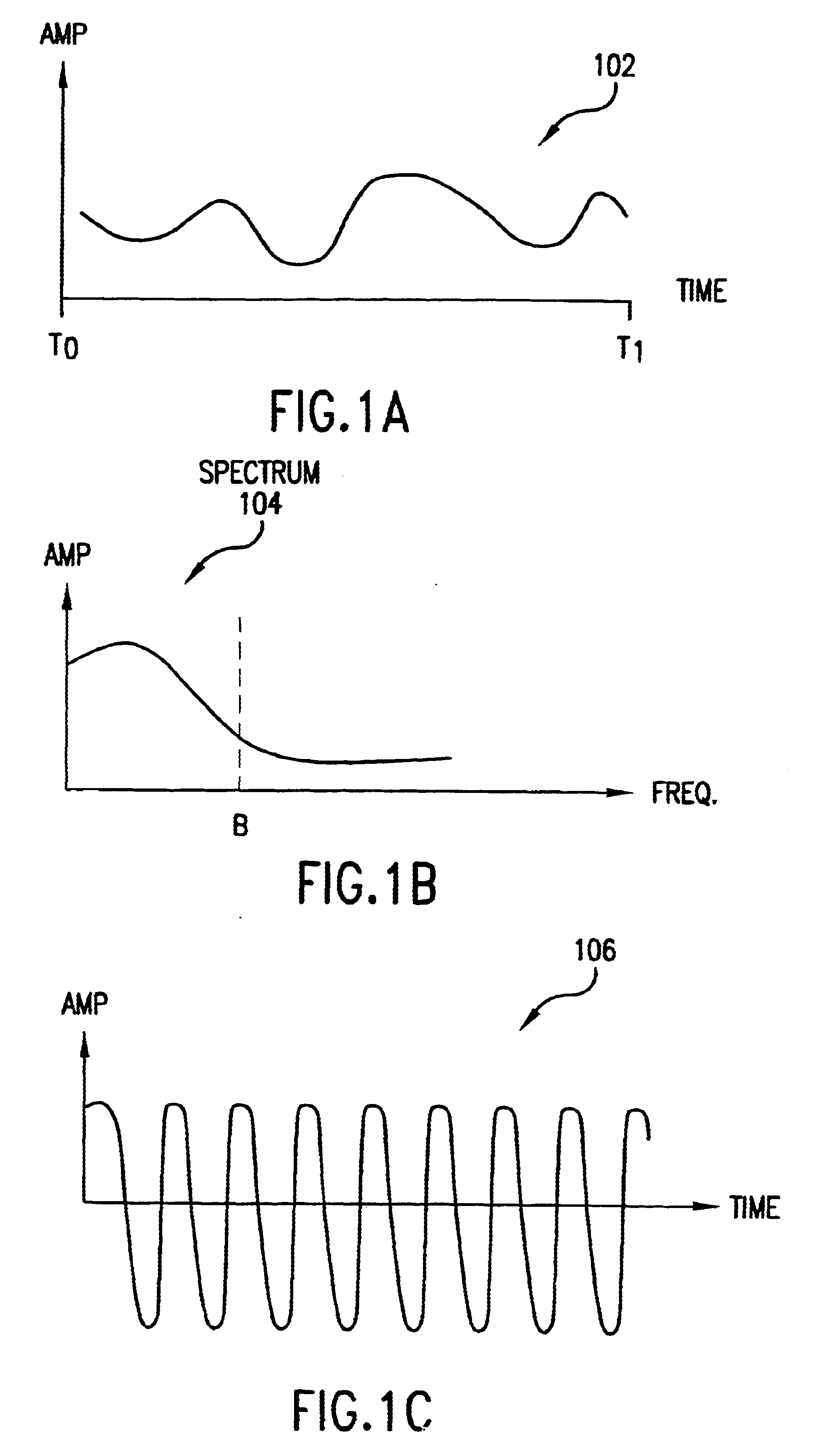
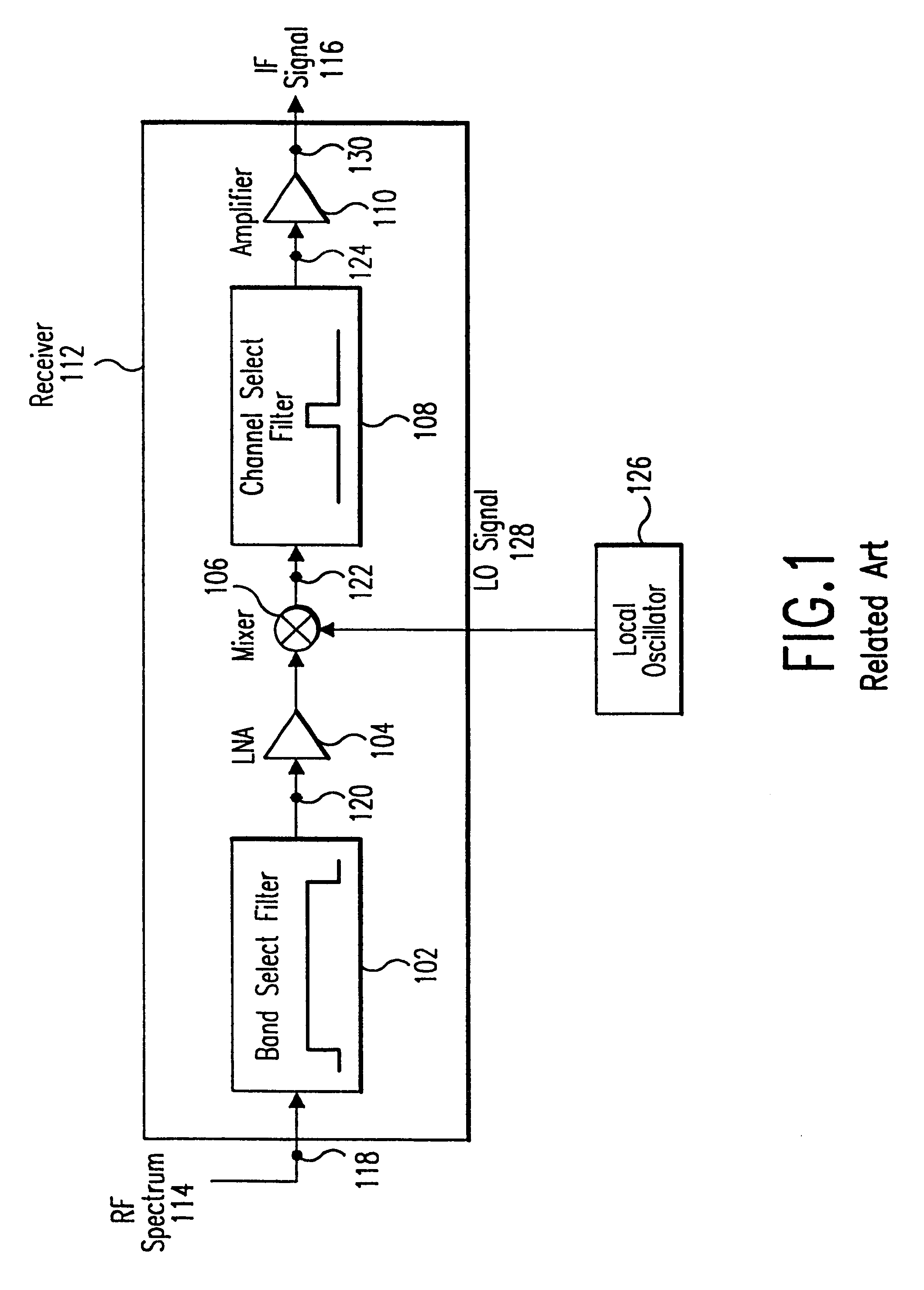
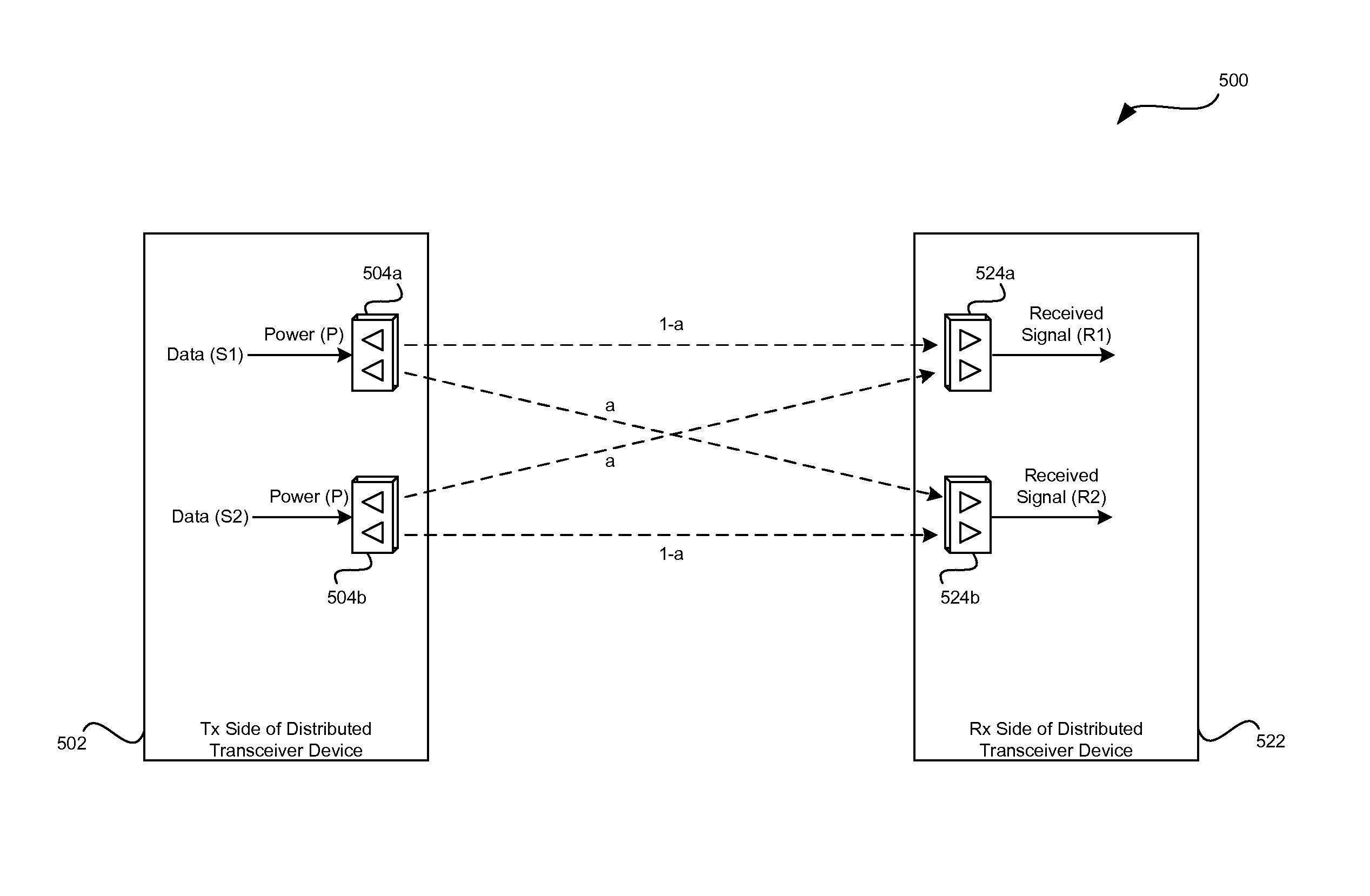
Method and system for ensuring reception of a communications signal
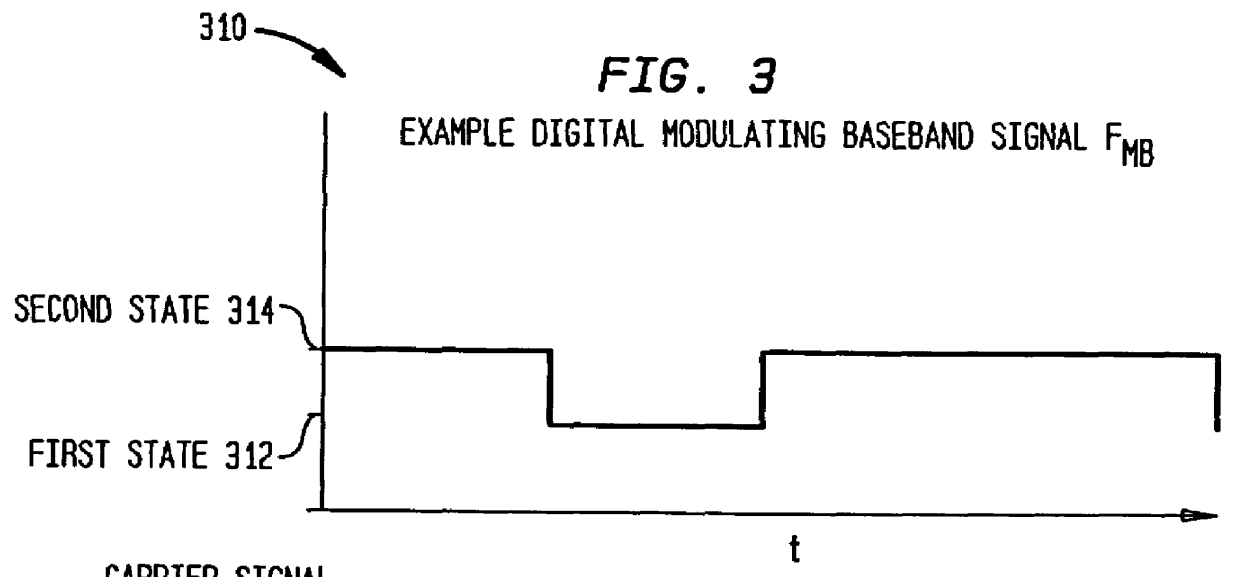
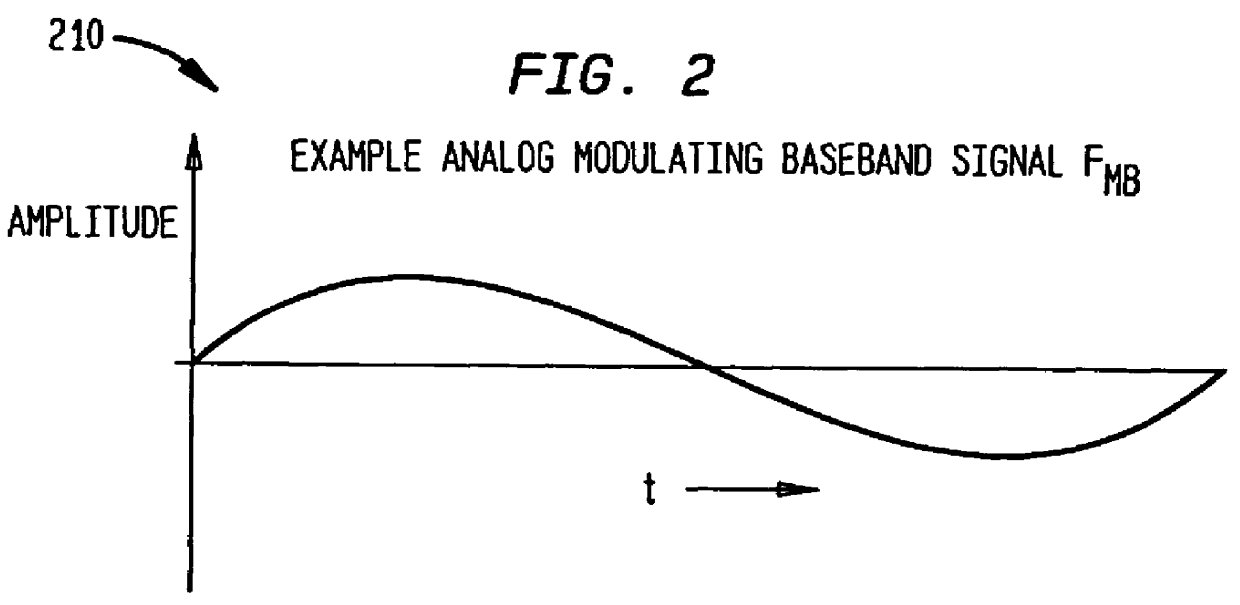
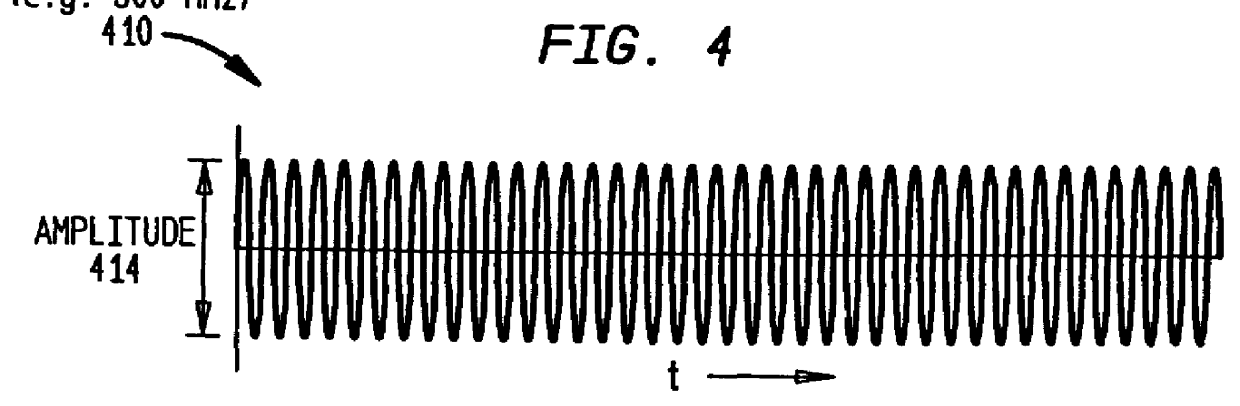
The present invention includes a system and method for ensuring reception of a communications signal. A modulating baseband signal with desired information is accepted, and a plurality of redundant spectrums is generated. Each redundant spectrum comprises the necessary amplitude, phase, and frequency information to substantially reconstruct the modulating baseband signal. It is expected but not required that the redundant spectrums will be generated at a first location and sent to a second location over a communications medium. At the second location, the redundant spectrums are independently processed to recover a demodulating baseband signal for each of the redundant spectrums. In one embodiment, an error detection process is employed at the second location to detect and eliminate those demodulated baseband signals that have been corrupted during transmission. An error-free demodulated baseband signal is selected from the remaining demodulated baseband signals. The error-free demodulated baseband signal is representative of the modulating baseband signal sent over the communications medium.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Integrated frequency translation and selectivity
Methods and apparatuses for frequency selectivity and frequency translation, and applications for such methods and apparatuses, are described herein. The method includes steps of filtering an input signal, and down-converting the filtered input signal. The filtering and the down-conversion operations are performed in an integrated, unified manner. The apparatus described herein can be implemented as an integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
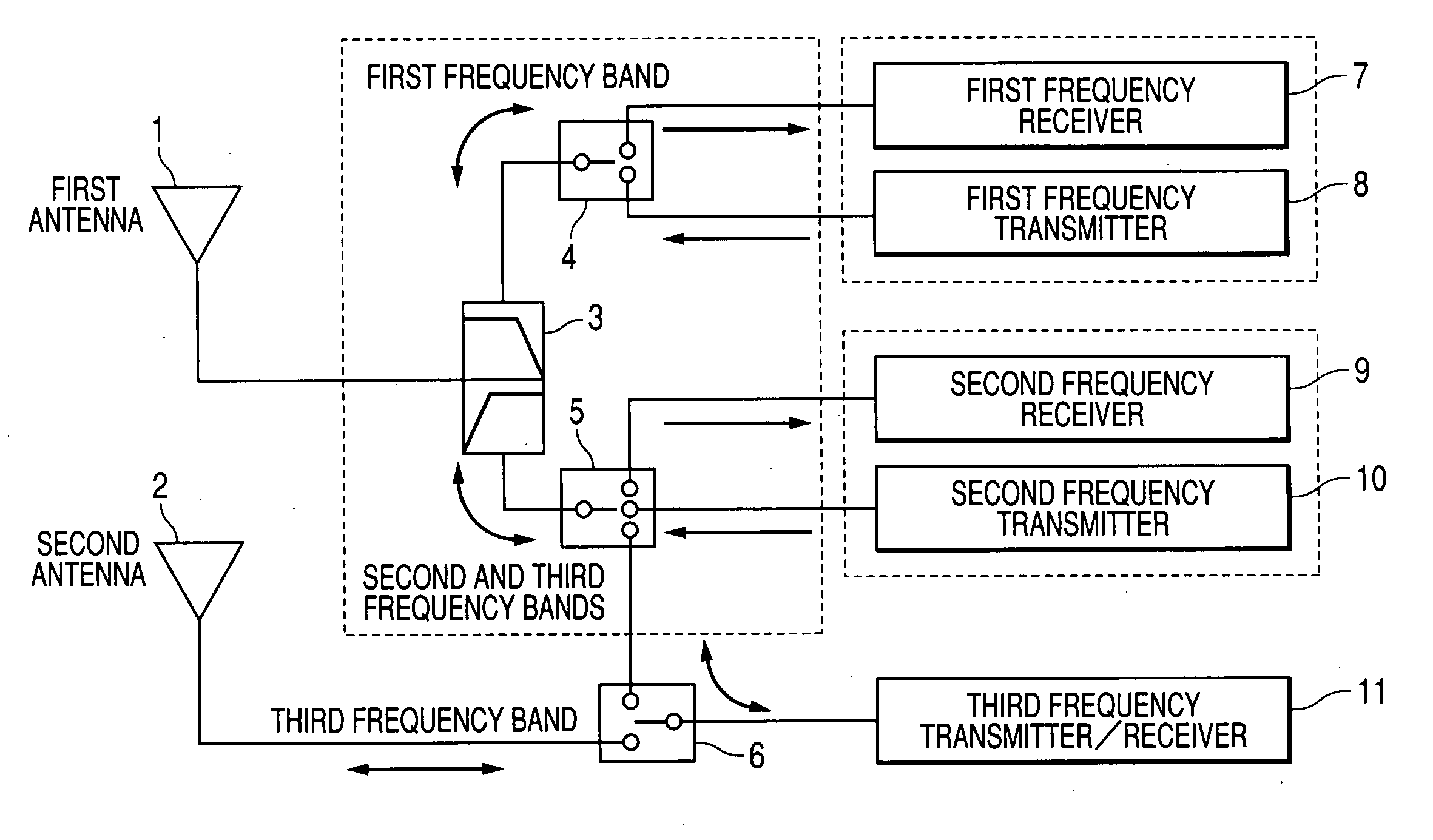
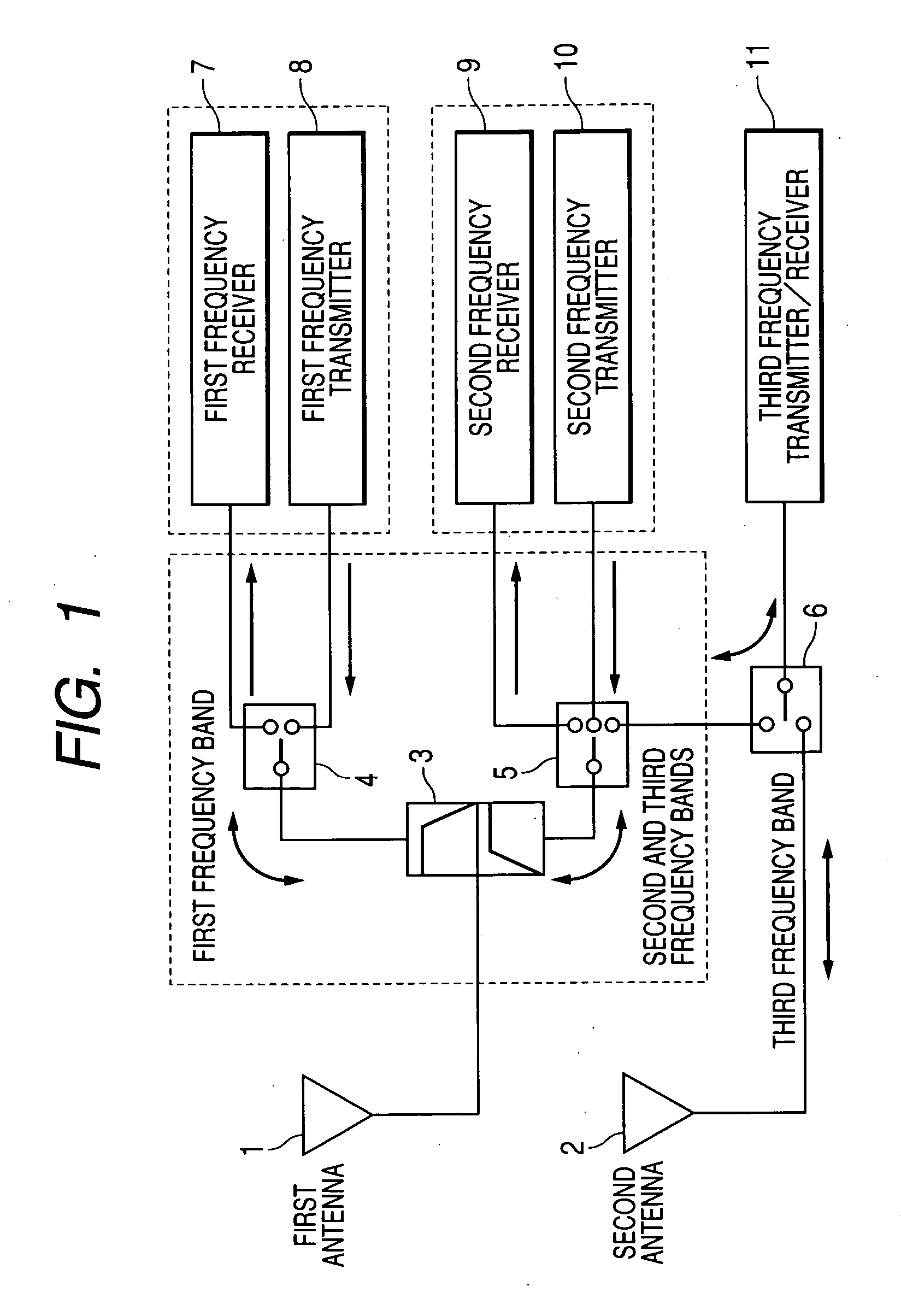
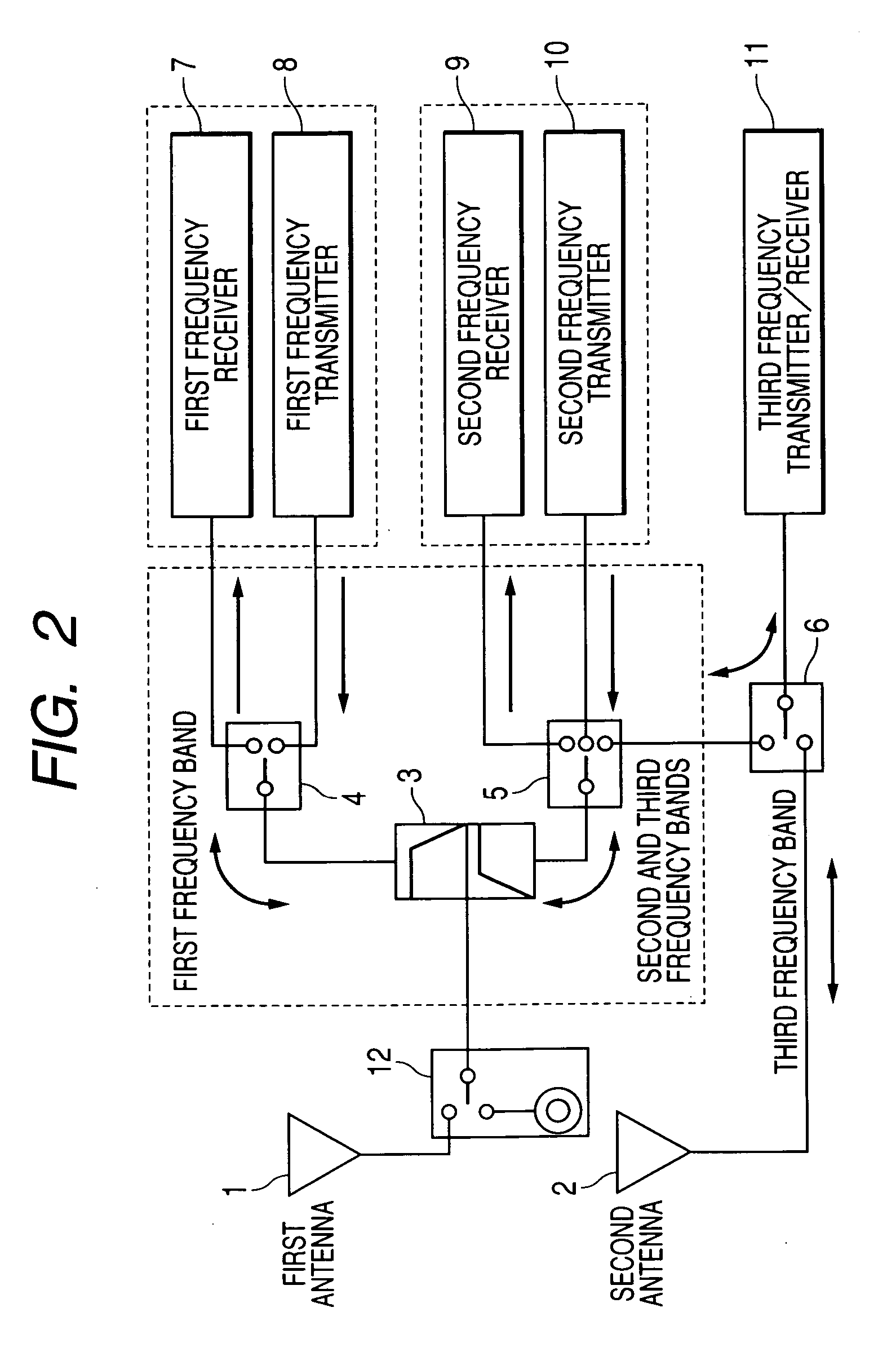
Antenna device
InactiveUS20050277387A1Easy constructionSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityCommunications systemEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide an antenna device which corresponds to a plurality of radio communications systems and frequency bands, which can simultaneously carry out a reception and a transmission of different radio communications systems, and which is capable of using antenna diversity by a simple construction. An antenna device comprises a first antenna (1) matching with first, second, and third frequency bands, a second antenna (2) matching with the third frequency band, a diplexer (3) and the like. For signals of the first frequency band, a high-frequency switch circuit (4) connects a transmitter (8) or a receiver (7) to the diplexer (3) by switching. For signals of the second frequency band, the high-frequency switch (5) connects a receiver (9) or a transmitter (10) to the diplexer (3) by switching. For signals of the third frequency band, the high-frequency switch circuit (5) and a high-frequency switch circuit (6) connect the second antenna (2) or diplexer (3) to a transmitter / receiver (11) by switching.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
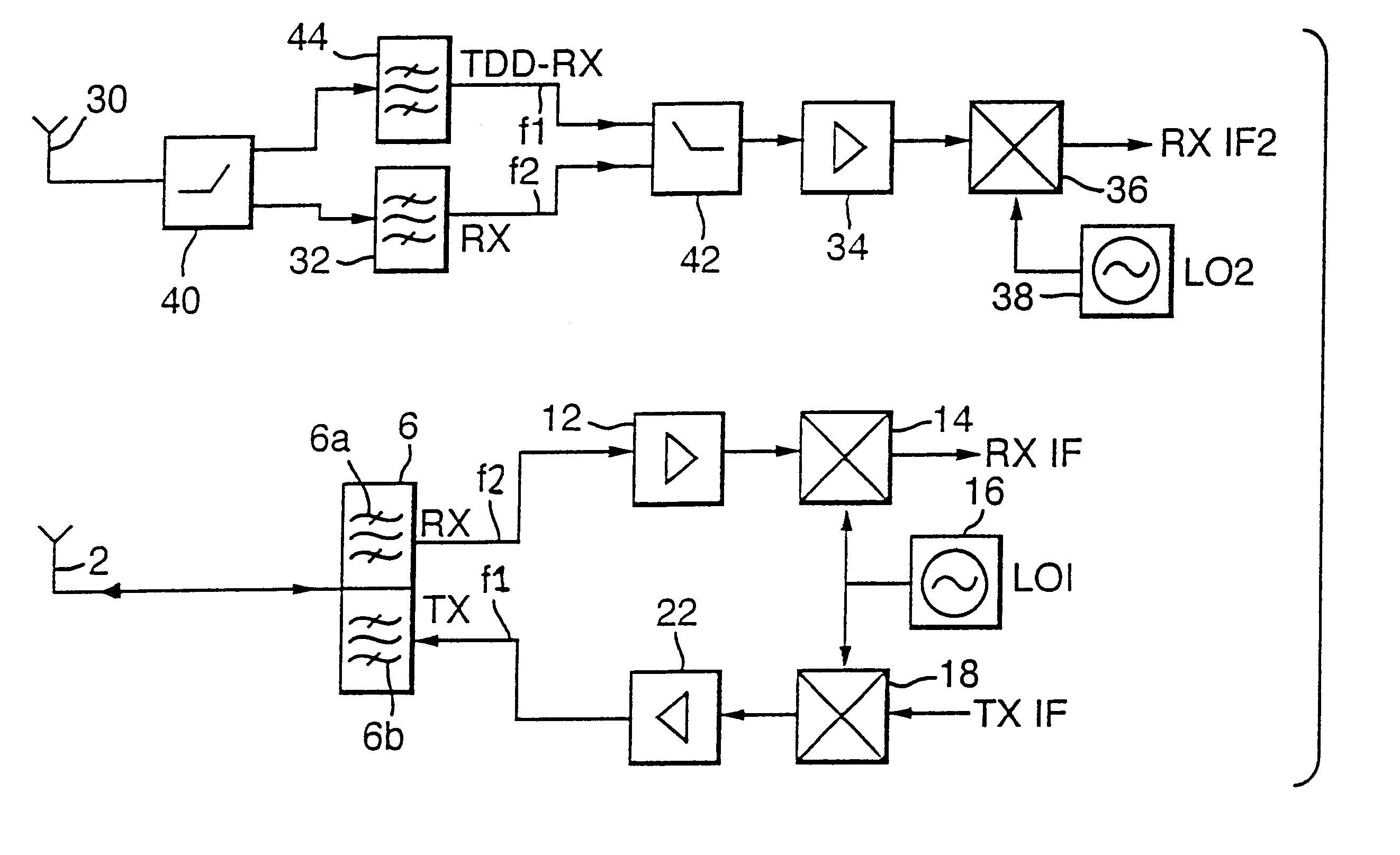
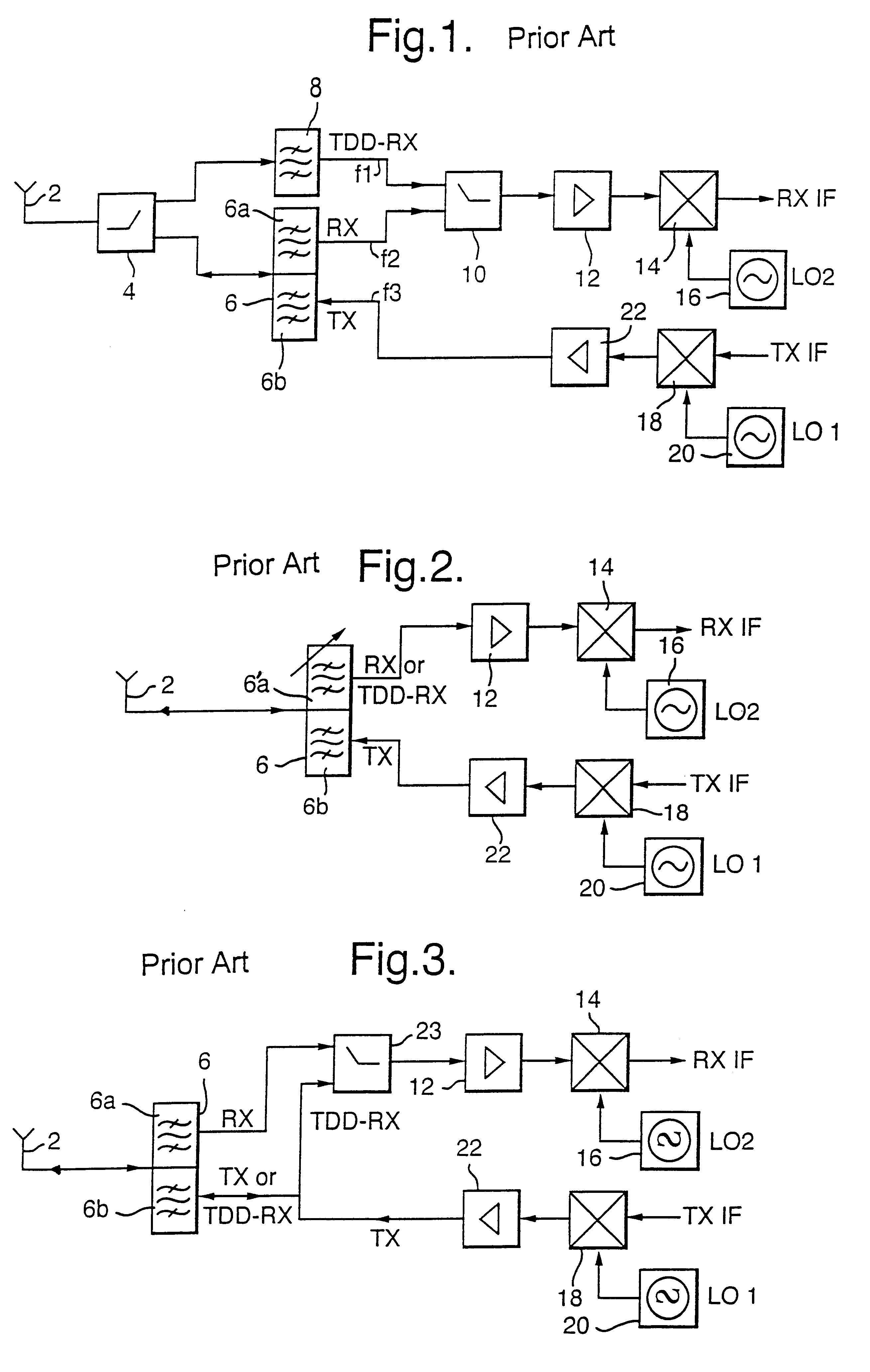
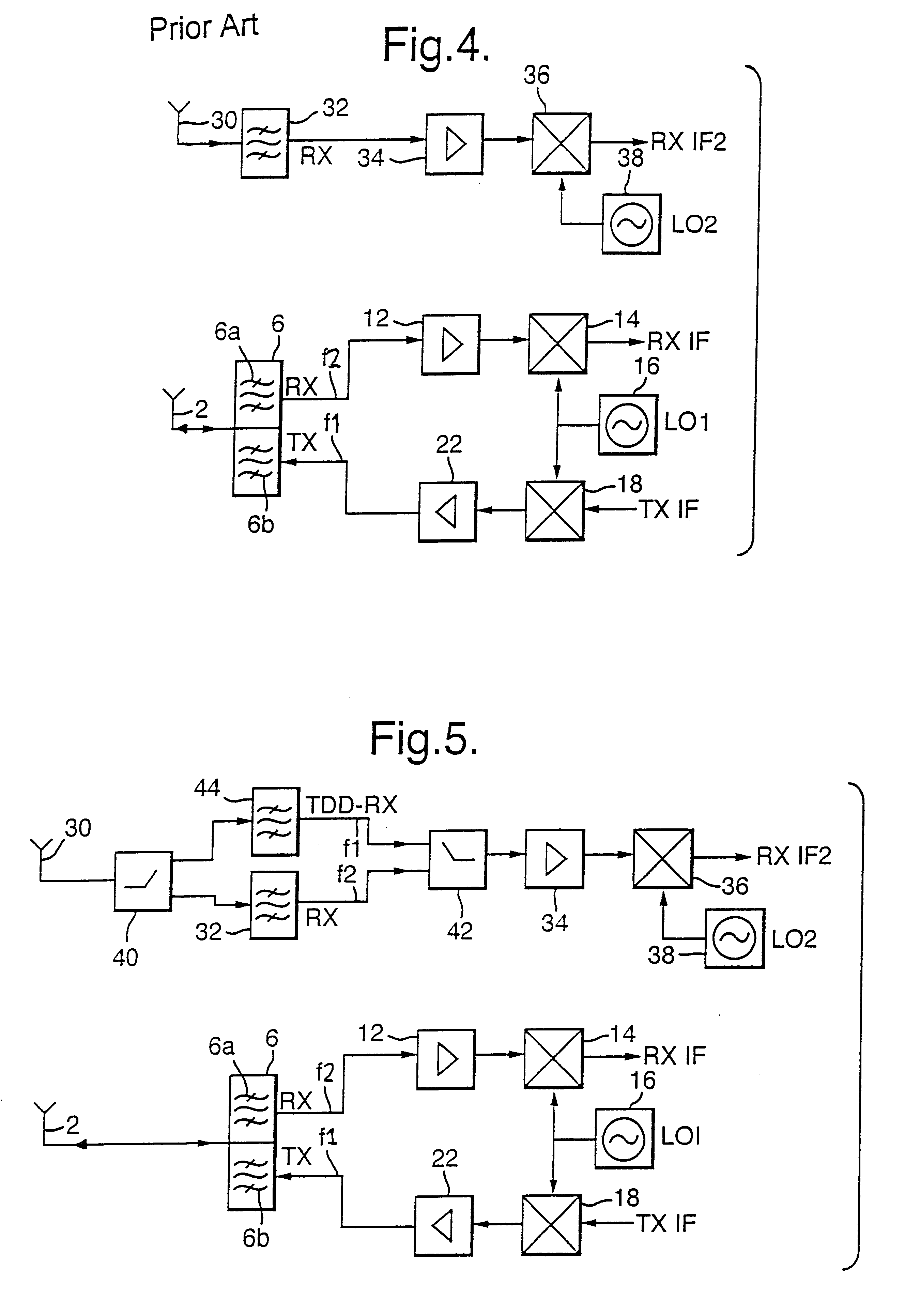
Wireless communication transceiver having a dual mode of operation
A transceiver for use in wireless communications including a first antenna and first filter coupled thereto to transmit signals in a first frequency range and a second antenna and second filter means coupled thereto to receive signals in the first frequency range or a second different frequency, in dependence on a mode of operation of the transceiver. In a first mode of operation the transceiver is arranged to transmit signals in the first frequency range via the first antenna and to receive signals in the second frequency range via the second antenna, and in a second mode of operation, the transceiver is arranged to receive signals in the first frequency range via the second antenna. Alternatively, the second antenna and second filter may receive signals in a third frequency range and in the second mode of operation, the transceiver is arranged to receive signals in the third frequency range via the second antenna.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Integrated frequency translation and selectivity with a variety of filter embodiments
Methods and apparatuses for frequency selectivity and frequency translation, and applications for such methods and apparatuses, are described herein. The method includes steps of filtering an input signal, and down-converting the filtered input signal. The filtering and the down-conversion operations are performed in an integrated, unified manner. The apparatus described herein can be implemented as an integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
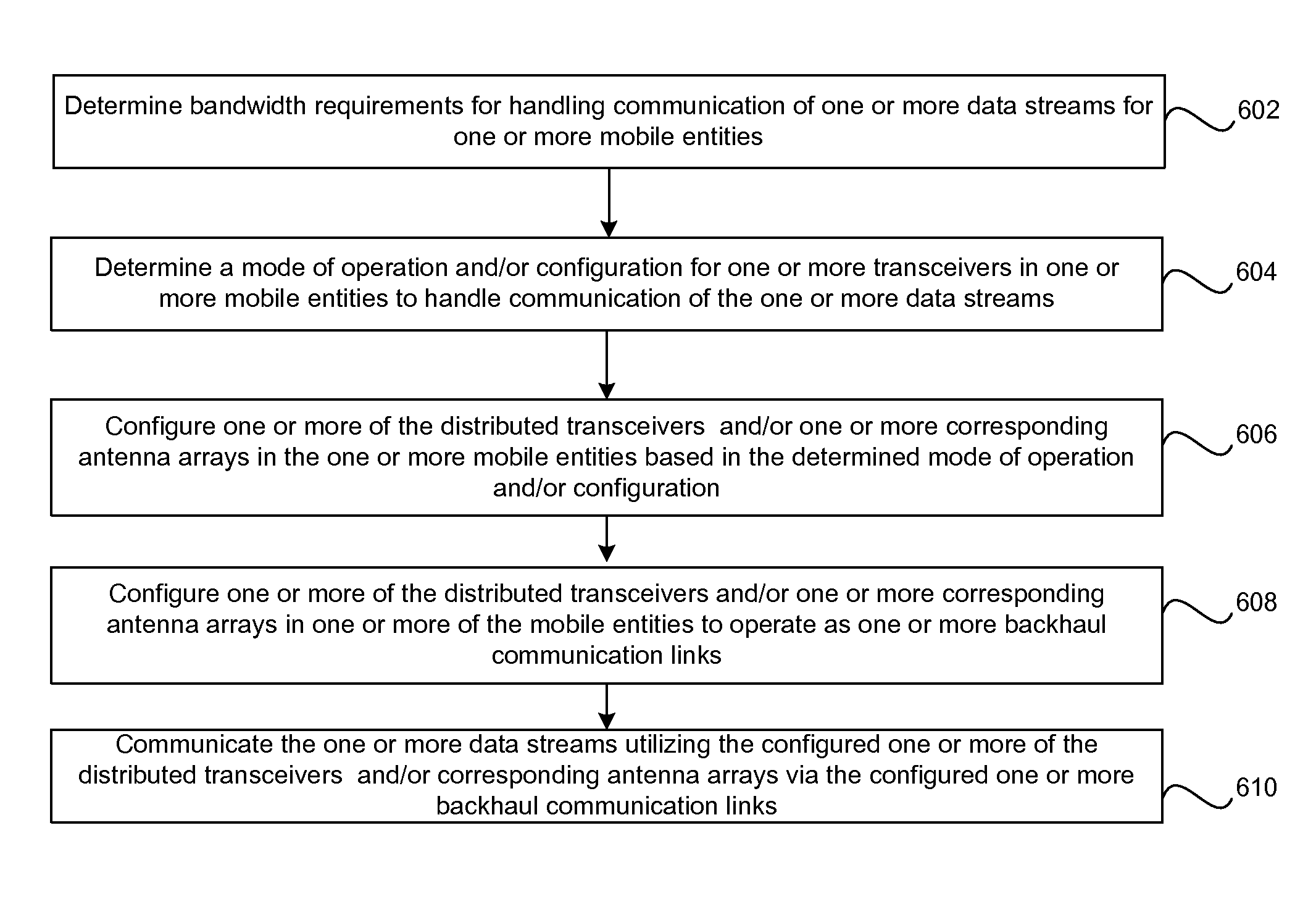
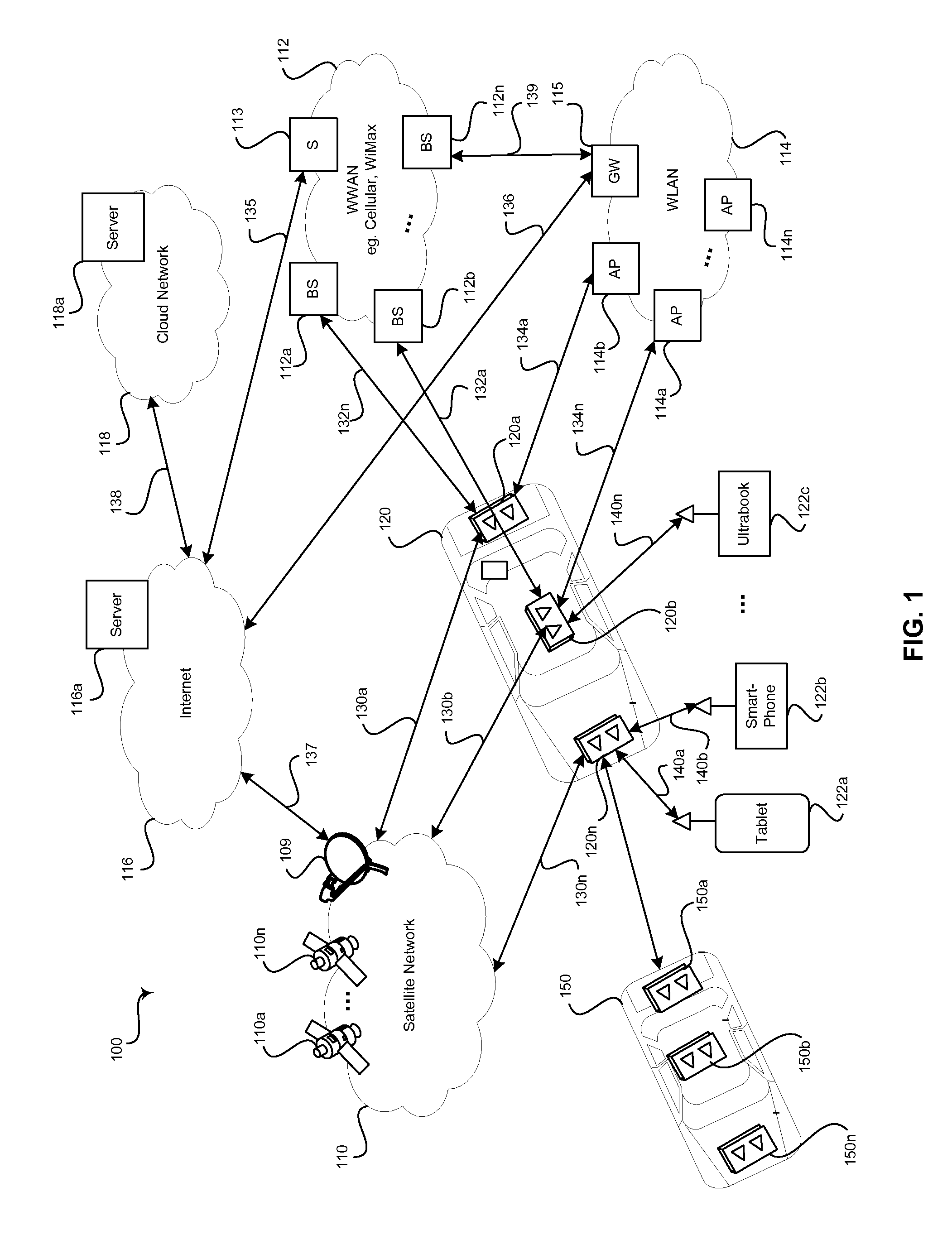
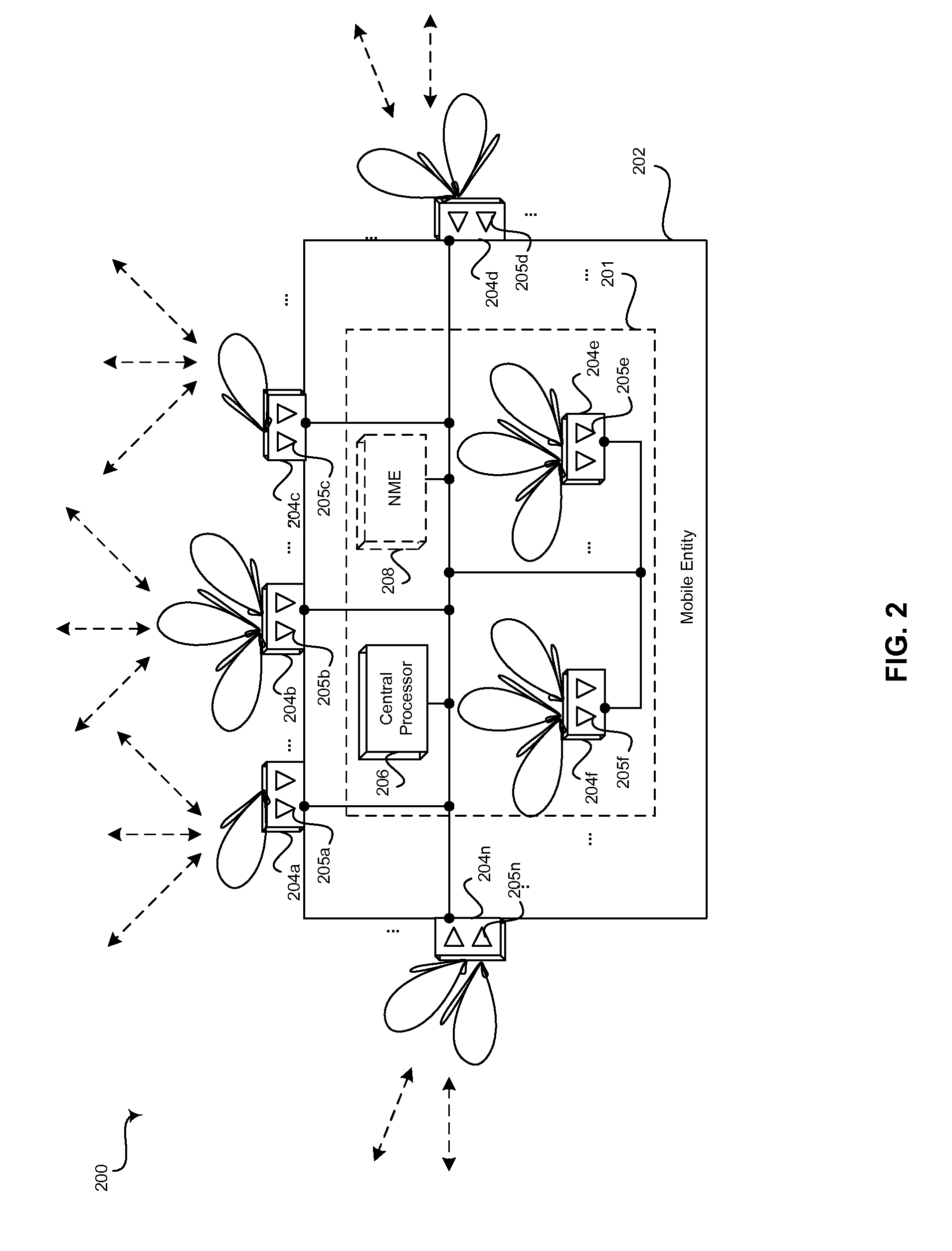
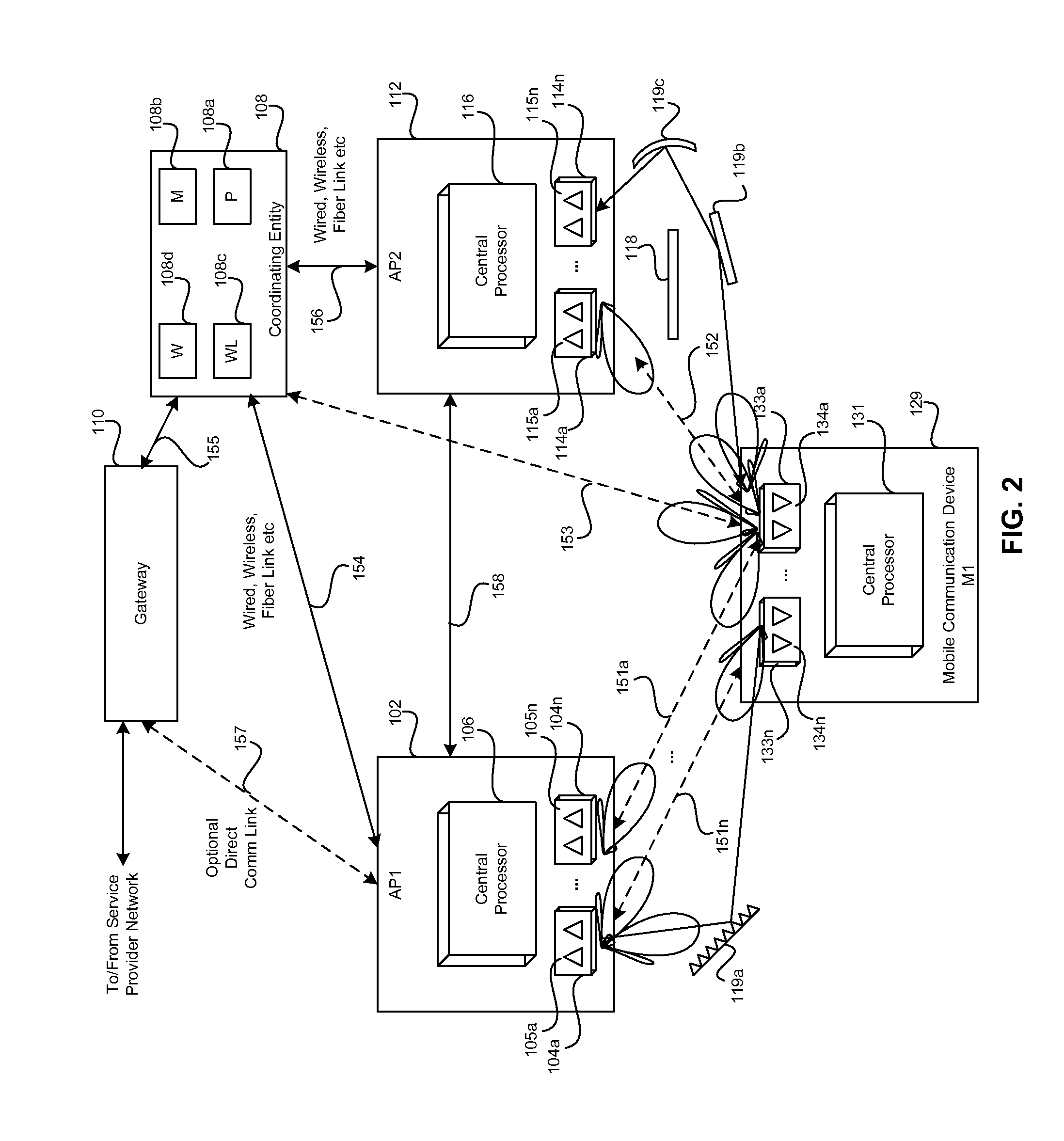
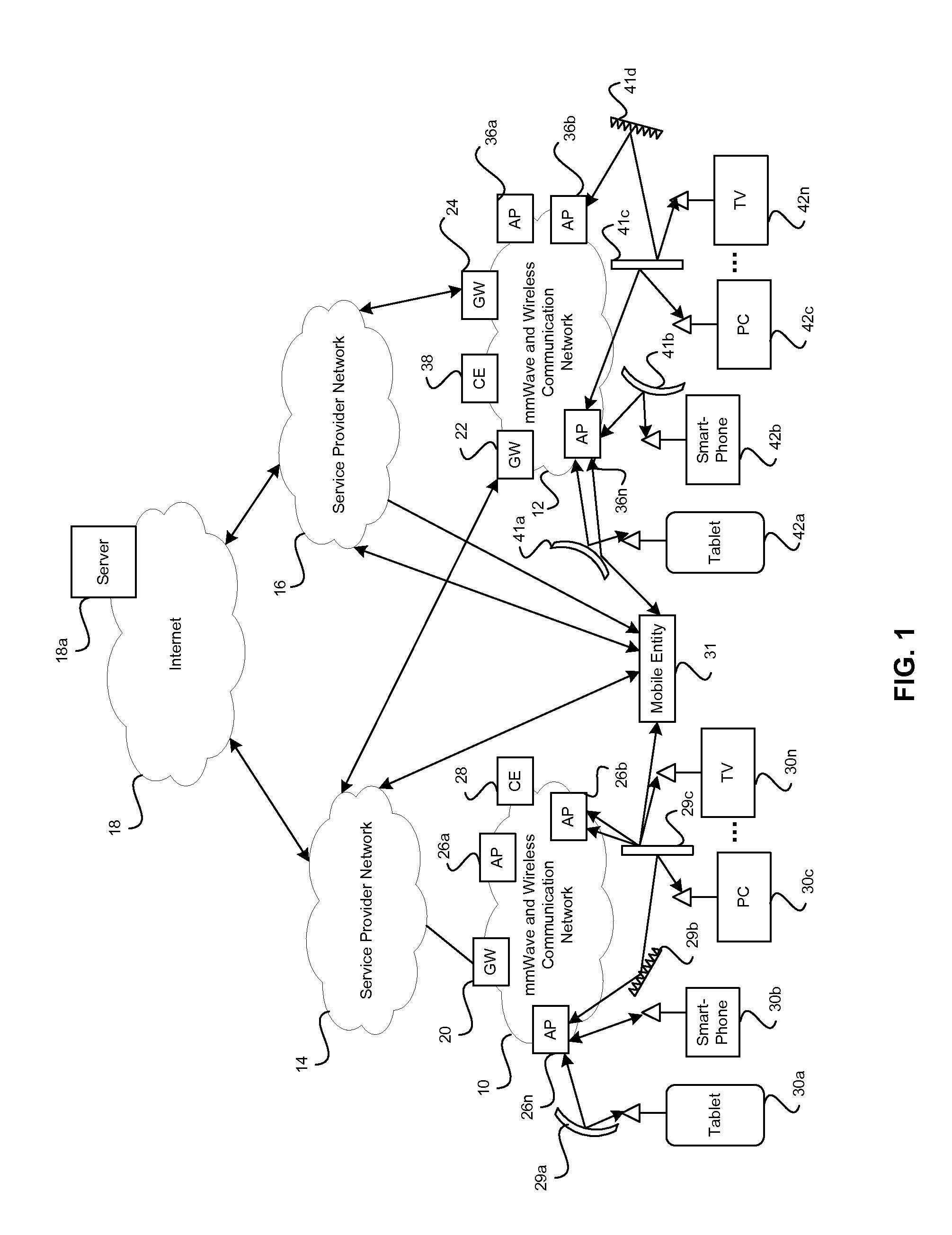
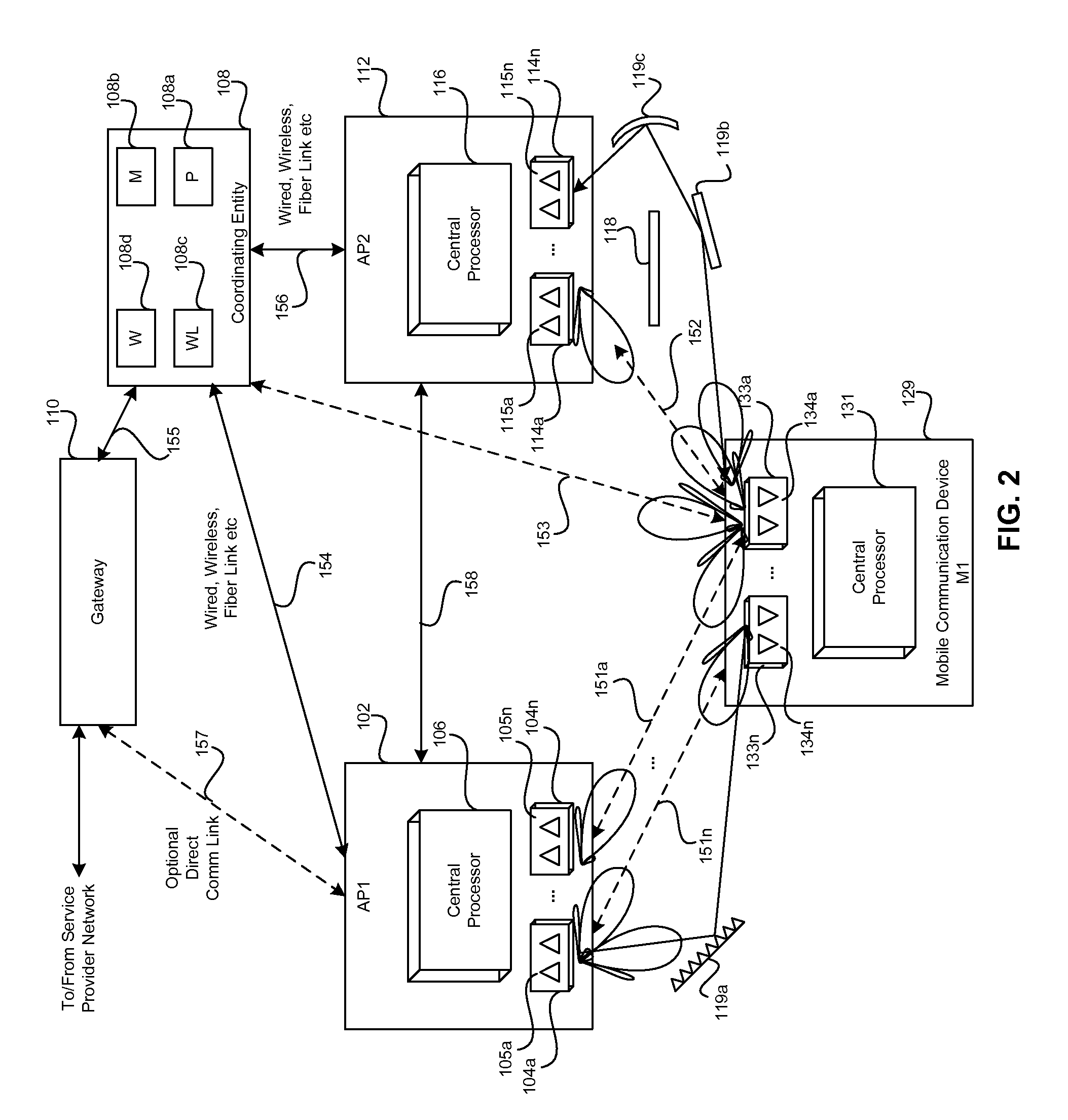
Method and system for distributed transceivers and mobile device connectivity
A plurality of distributed transceivers in a mobile entity such as a car, a truck, an omnibus (bus), a trailer, a mobile home, train, bus, a forklift, construction equipment, a boat, a ship, and / or an aircraft, and / or one or more corresponding antenna arrays that are communicatively coupled to the distributed transceivers are configured to handle communication of one or more data streams among one or more of a plurality of wireless communication networks, one or more other mobile entities and / or one or more mobile communication devices. The data streams may be communicated utilizing the configured one or more of the plurality of distributed transceivers and / or the one or more corresponding antenna arrays. The wireless communication networks includes a satellite network, a wireless wide area network, a wireless medium area network, a wireless local area network, a wireless personal area network, a network cloud and / or the Internet.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
Method and system for optimizing communication in leaky wave distributed transceiver environments
ActiveUS20140044043A1Facilitate communicationSite diversityReceivers monitoringData streamTransceiver
A communication device may comprise a plurality of distributed transceivers and one or more corresponding antenna arrays. A processor may configure a first distributed transceiver to receive signals comprising one or more first data streams via one or more first communication links. The processor may configure a second distributed transceiver to receive signals comprising one or more second data streams via one or more second communication links. The processor may determine a channel response matrix associated with communication of the one or more first data streams via the one or more first communication links and / or the one or more second data streams via the one or more second communication links. The processor may optimize one or both of link capacity and / or link reliability of the one or more first communication links and / or the one or more second communication links based on the determined channel response matrix.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
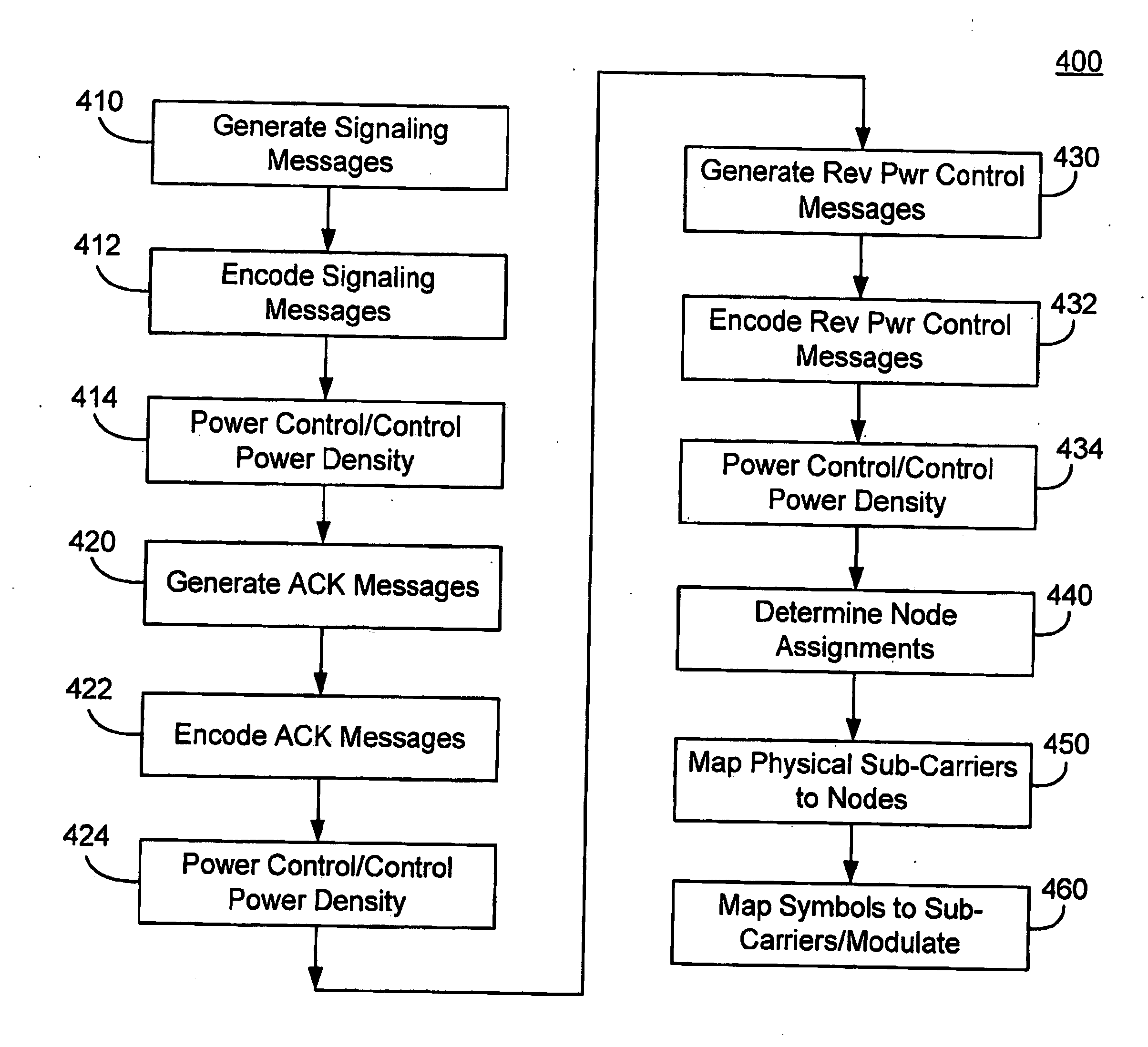
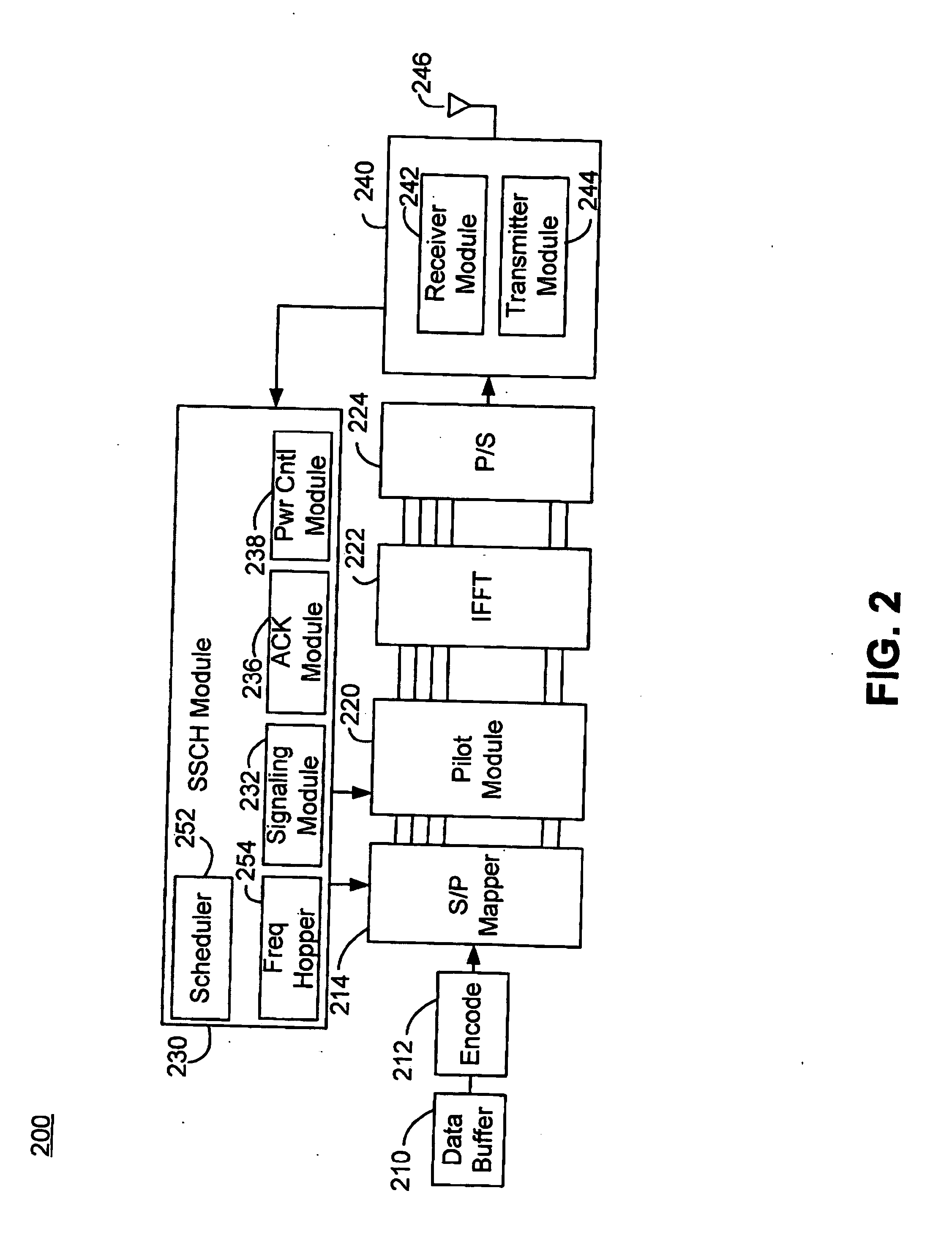
Resource allocation for shared signaling channels
ActiveUS20070211616A1Fixed bandwidth overhead for the channelPower managementModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemResource allocation
A shared signaling channel can be used in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) communication system to provide signaling, acknowledgement, and power control messages to access terminals within the system. The shared signaling channel may comprise reserved logical resources that can be assigned to subcarriers, OFDM symbols, or combinations thereof.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for intelligently controlling propagation environments in distributed transceiver communications
A communication device comprising a plurality of distributed transceivers and one or more corresponding antenna arrays is operable to determine characteristics of one or more objects that are sensed within a surrounding communication environment of the communication device. The communication device may configure one or more of the plurality of distributed transceivers and / or one or more of the corresponding antenna arrays to handle communication of one or more data streams based on the determined characteristics. Exemplary characteristics may comprise reflective property and / or refractive property of the sensed one or more objects within the surrounding communication environment of the communication device. The communication device may be operable to store the determined characteristics, corresponding temporal information and / or spatial information for the sensed one or more objects, and / or signal propagation characteristics within a surrounding communication environment of the communication device.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
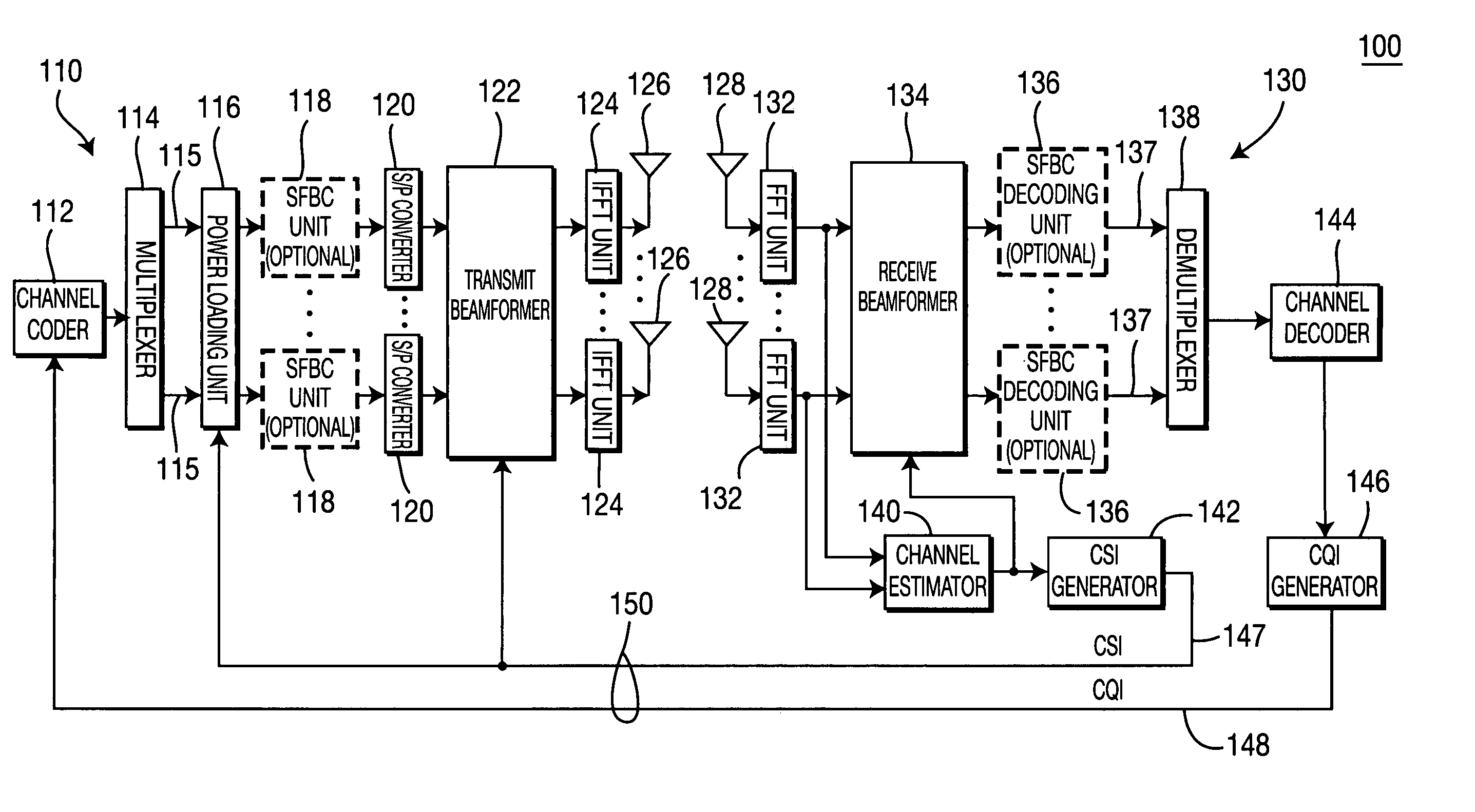
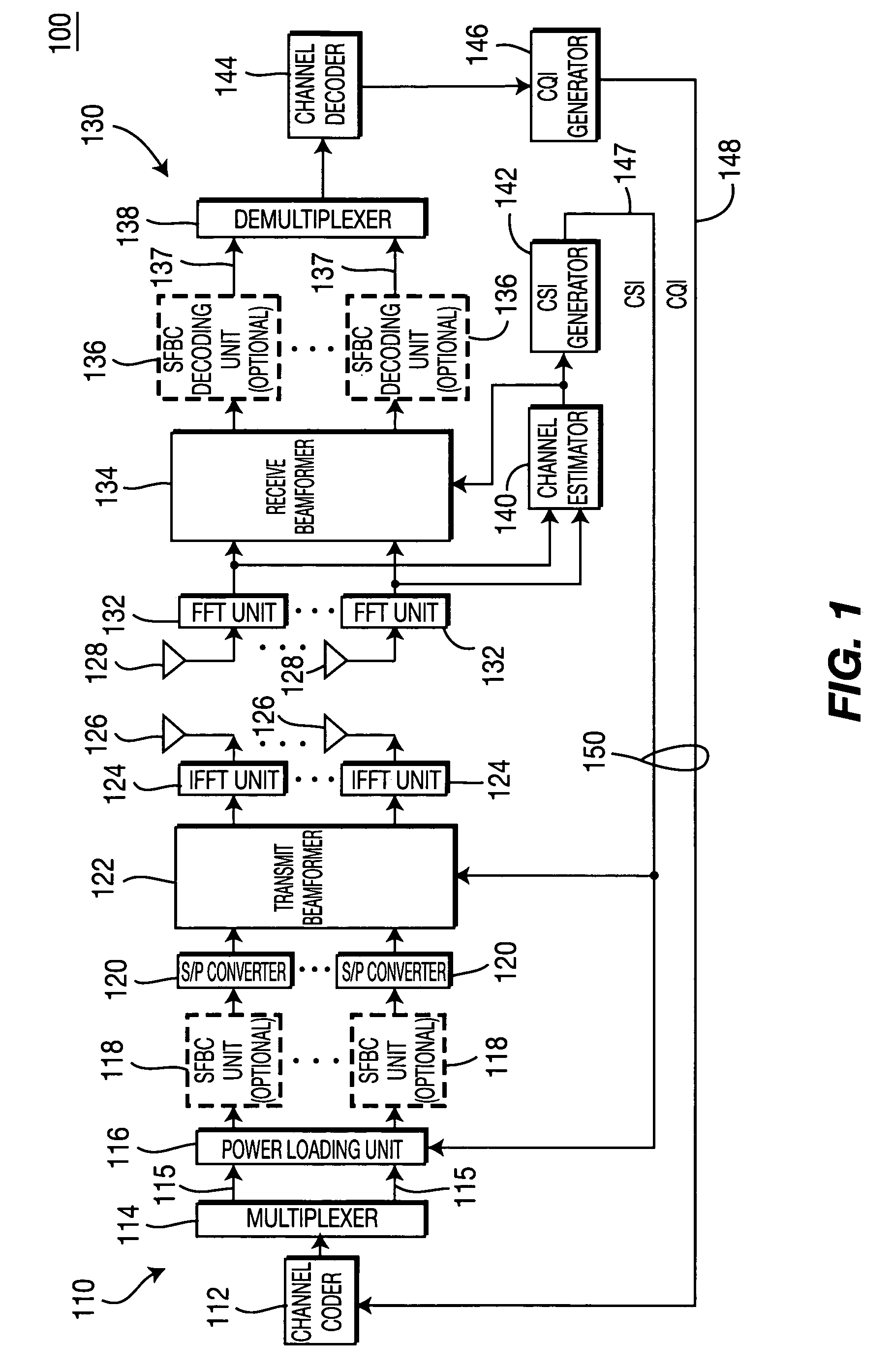
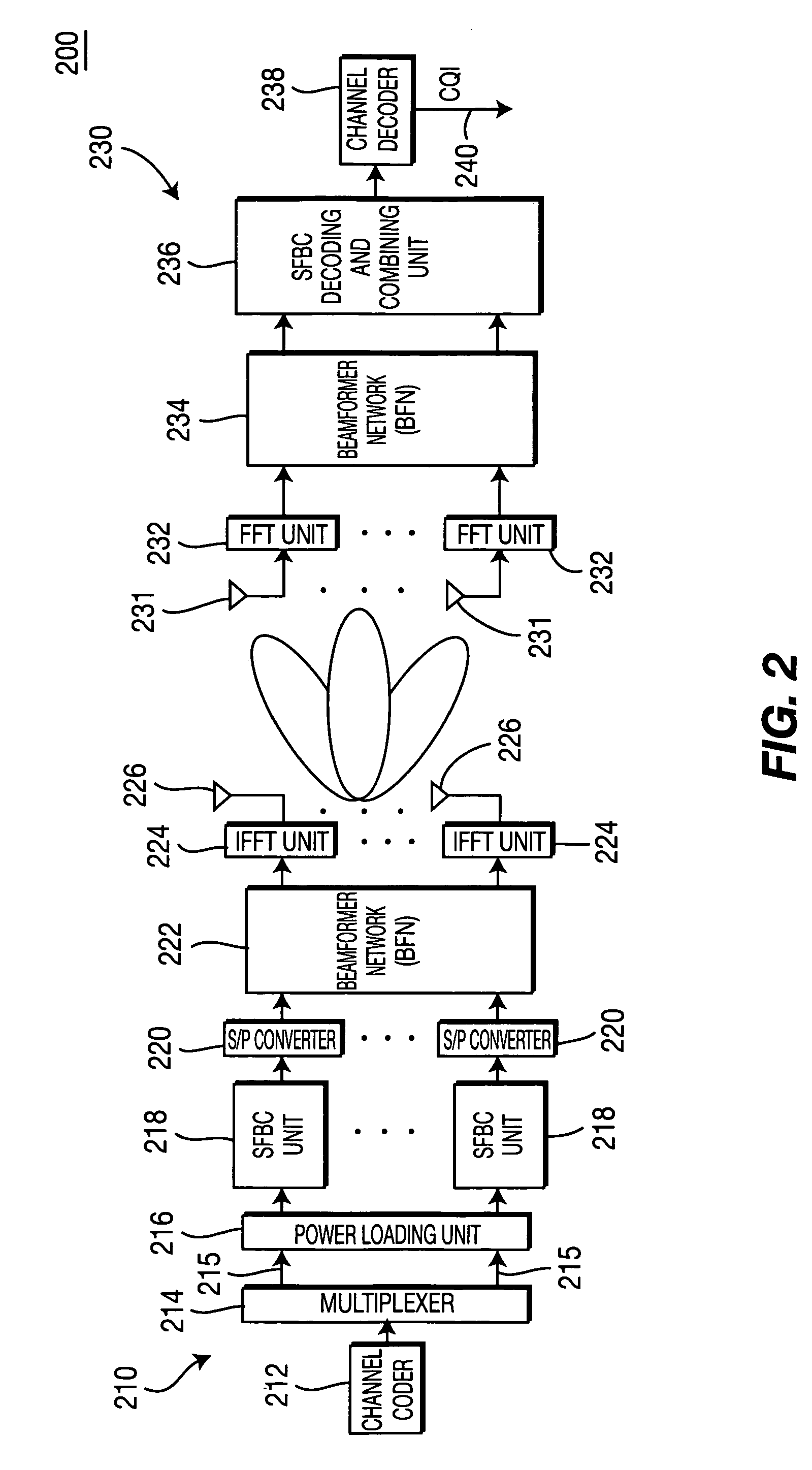
Method and apparatus for combining space-frequency block coding, spatial multiplexing and beamforming in a MIMO-OFDM system
ActiveUS20060133530A1Modulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionData streamFrequency-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for combining space-frequency block coding (SFBC), spatial multiplexing (SM) and beamforming in a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system. The system includes a transmitter with a plurality of transmit antennas and a receiver with a plurality of receive antennas. The transmitter generates at least one data stream and a plurality of spatial streams. The number of generated spatial streams is based on the number of the transmit antennas and the number of the receive antennas. The transmitter determines a transmission scheme in accordance with at least one of SFBC, SM and beam forming. The transmitter transmits data in the data stream to the receiver based on the selected transmission scheme.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
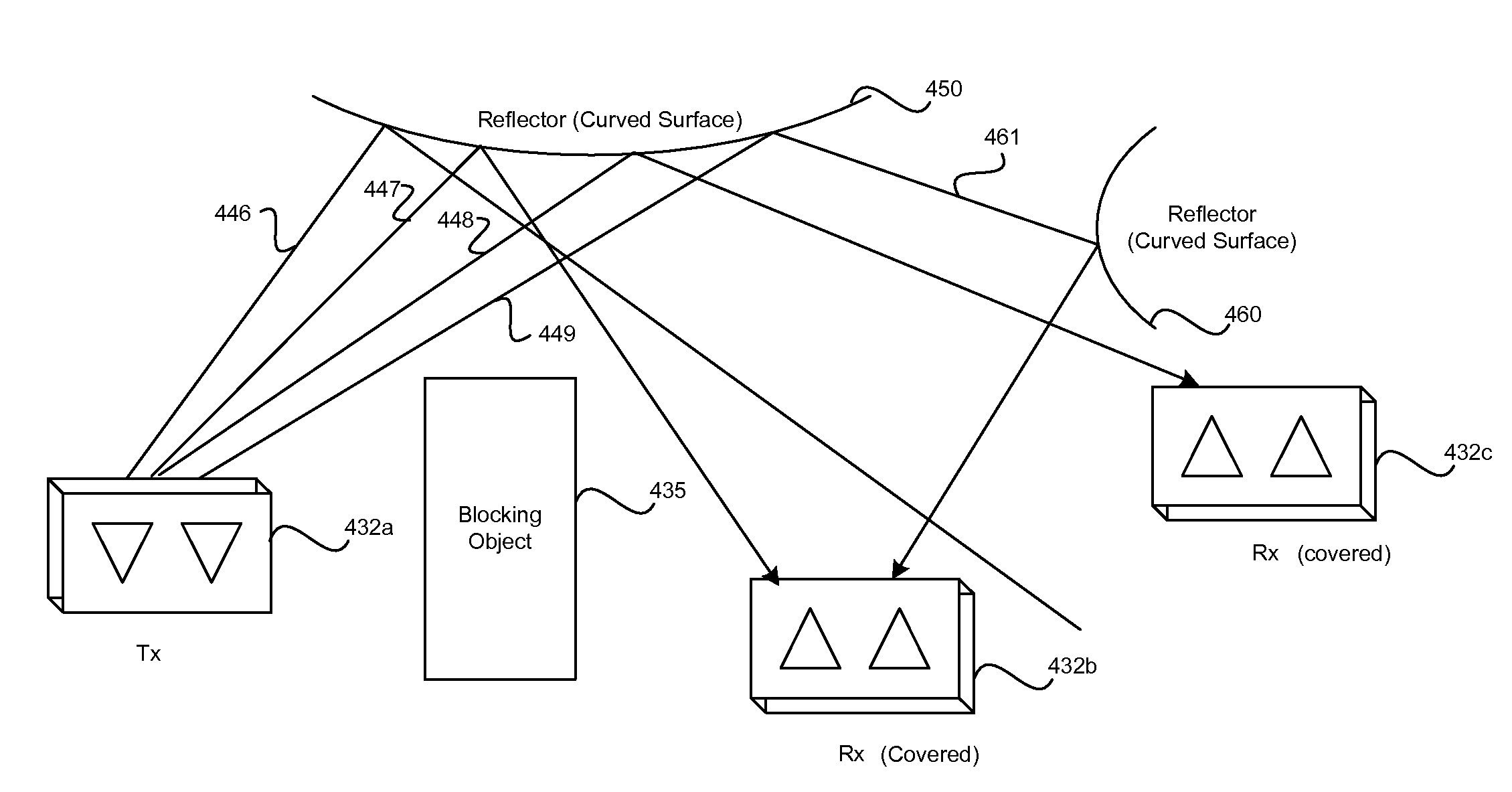
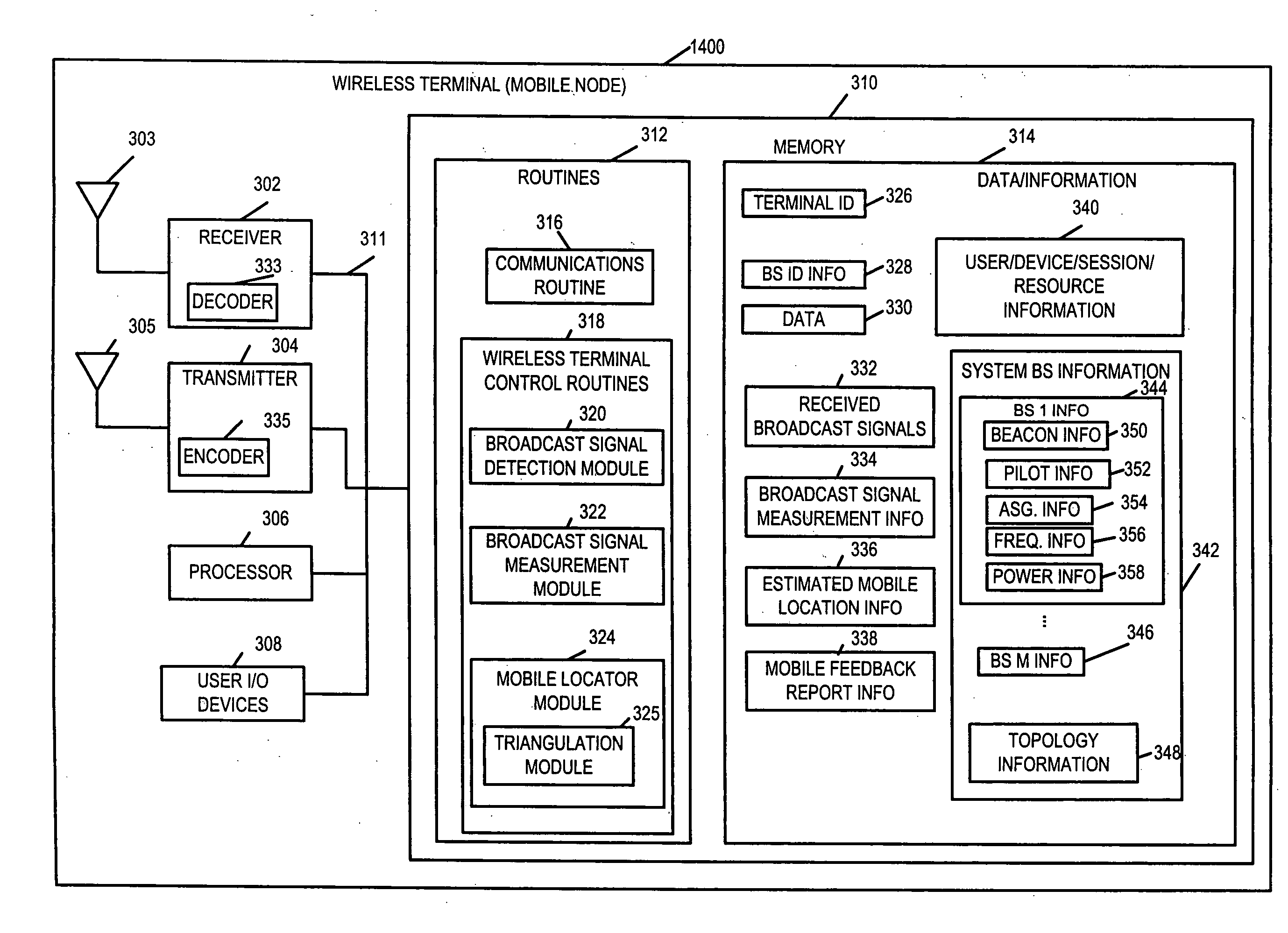
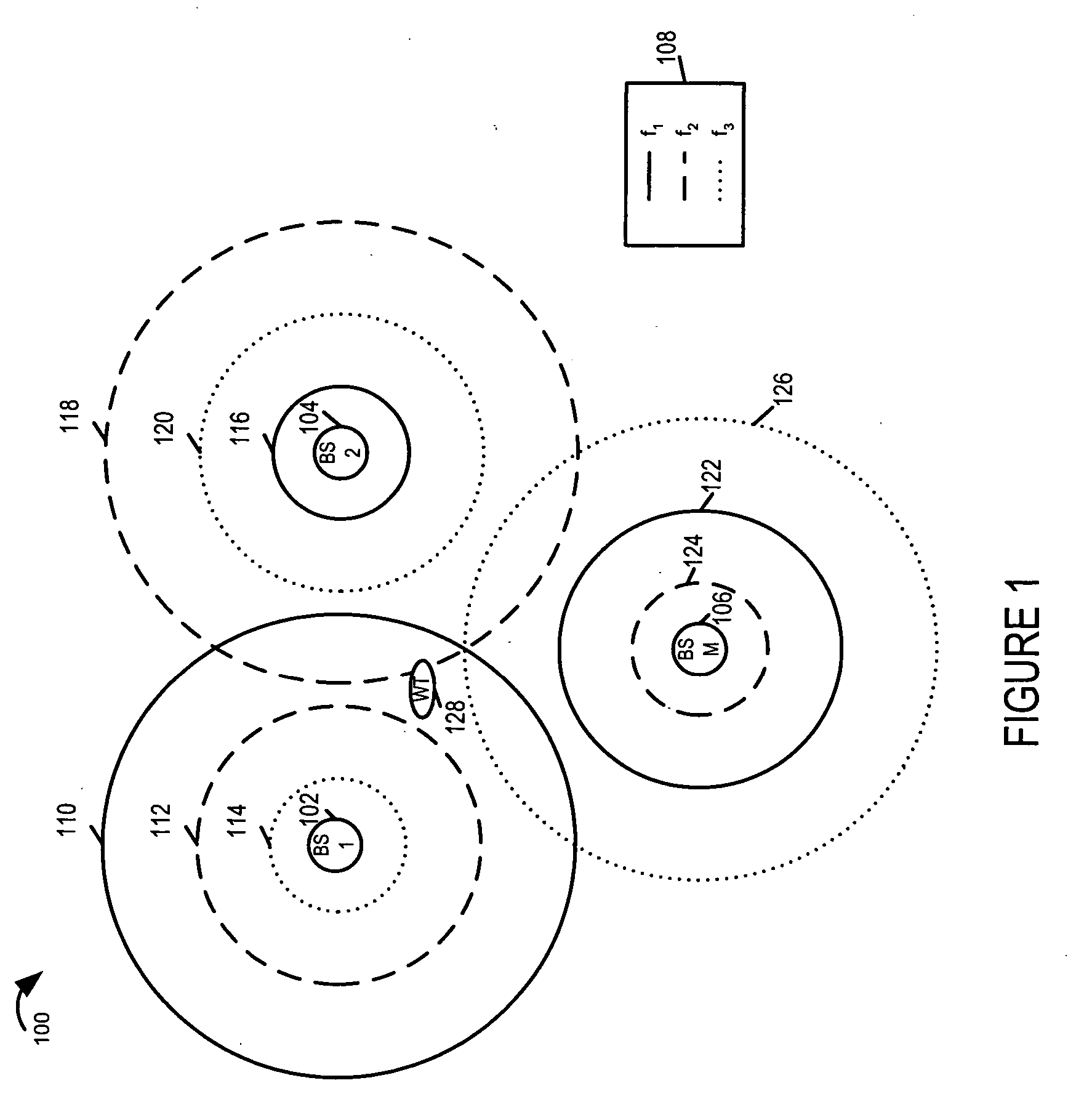
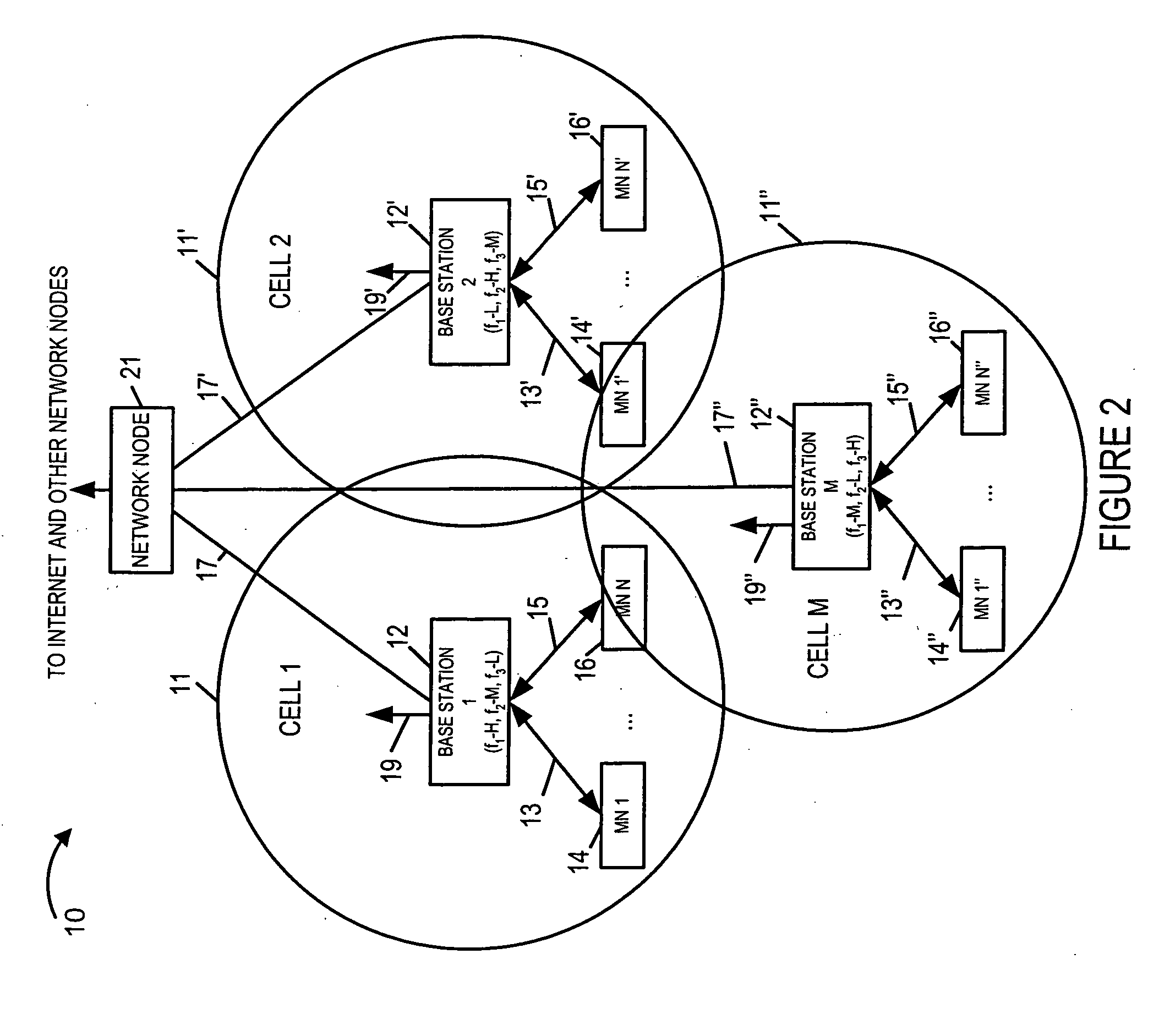
Wireless terminal location using apparatus and methods employing carrier diversity
Wireless terminals, e.g., mobile nodes, receive, identify, and measure broadcast signals from a plurality of cells. They determine relative transmission power relationships corresponding to the received measured signals and determine at least two channel gain ratios. A geographic area is determined corresponding to the obtained at least two channel gain ratios and information indicating the geographic region in which such gain ratios may be detected. Each cell's base station transmits broadcast signals, e.g., beacon signals, pilot signals, and / or assignment signals for one more carriers. Some base stations use multiple carriers at different power levels. Some adjacent cells use different power levels for the same carrier. This carrier diversity approach tends to reduce overall interference in the system, yet provides mobiles with a variety of different strength signals which may be monitored and which vary as a function of distance from the source transmitter.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
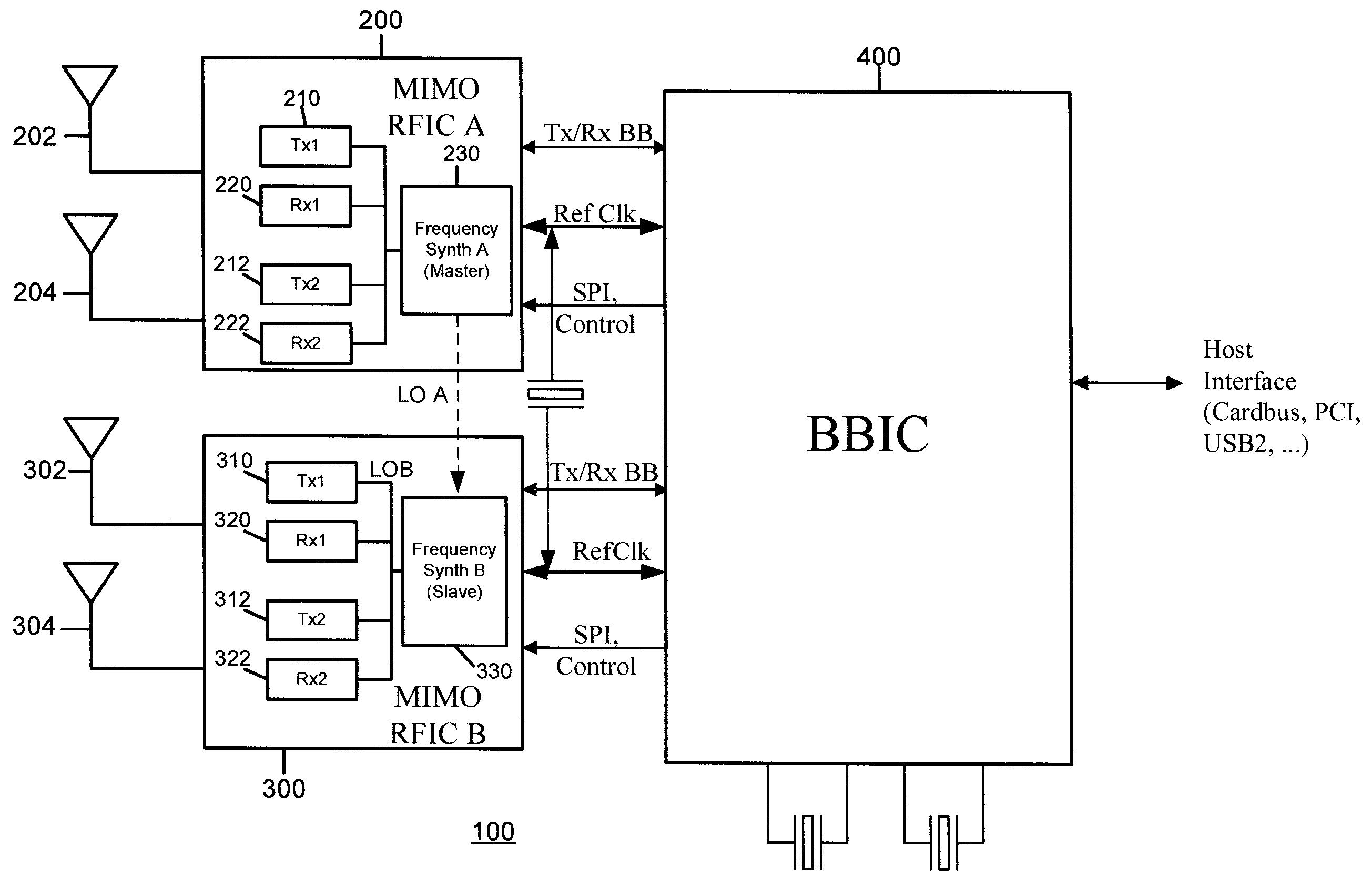
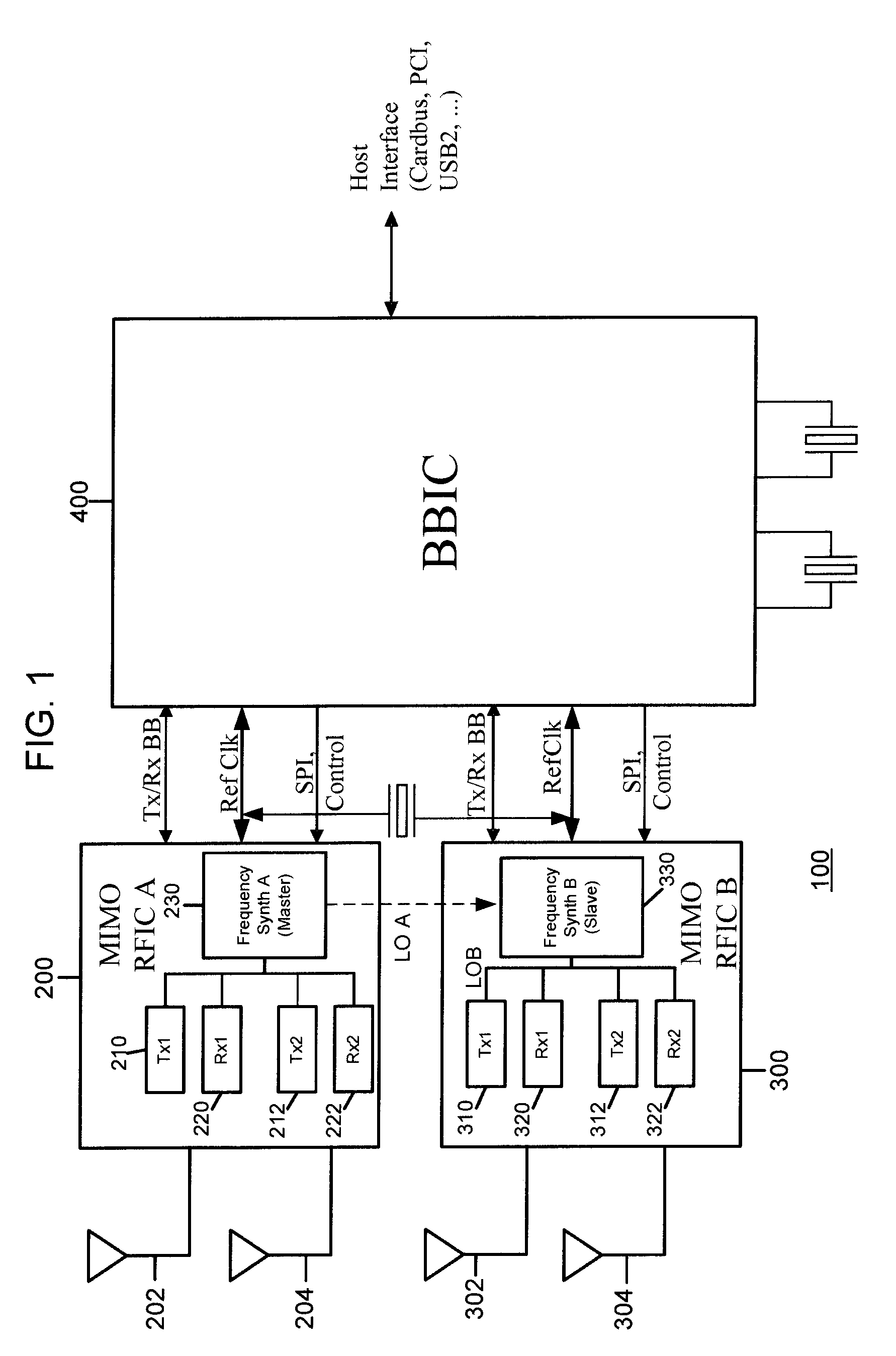
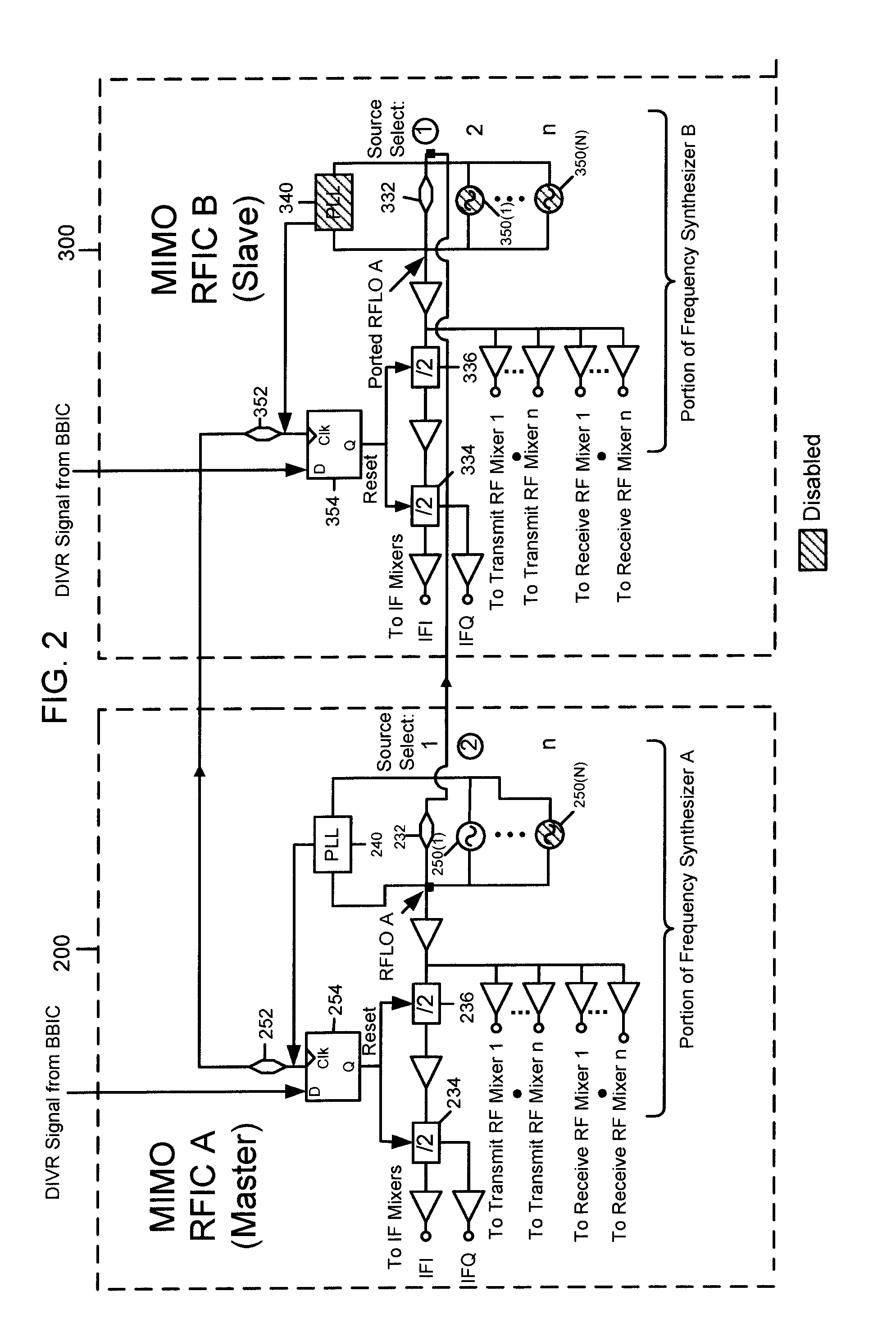
Master-Slave Local Oscillator Porting Between Radio Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20050064892A1Improve performanceAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayPulse automatic controlLocal oscillator signalRFIC
A technique to share a local oscillator signal between two radio frequency integrated circuits (RFICs). The local oscillator signal generated internally by one RFIC is ported to the other RFIC for use in transmit and / or receive operation. The local oscillator signal that is ported may be an RF local oscillator signal. Each RFIC may include a bi-directional port circuit that can be operated to make the RFIC a master, slave or may be totally disabled to disable the porting feature. This is particularly useful in RFICs that are used to communicate using MIMO radio algorithms which rely for optimum performance on phase and frequency coherency among a plurality of transmitters and a plurality of receivers.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
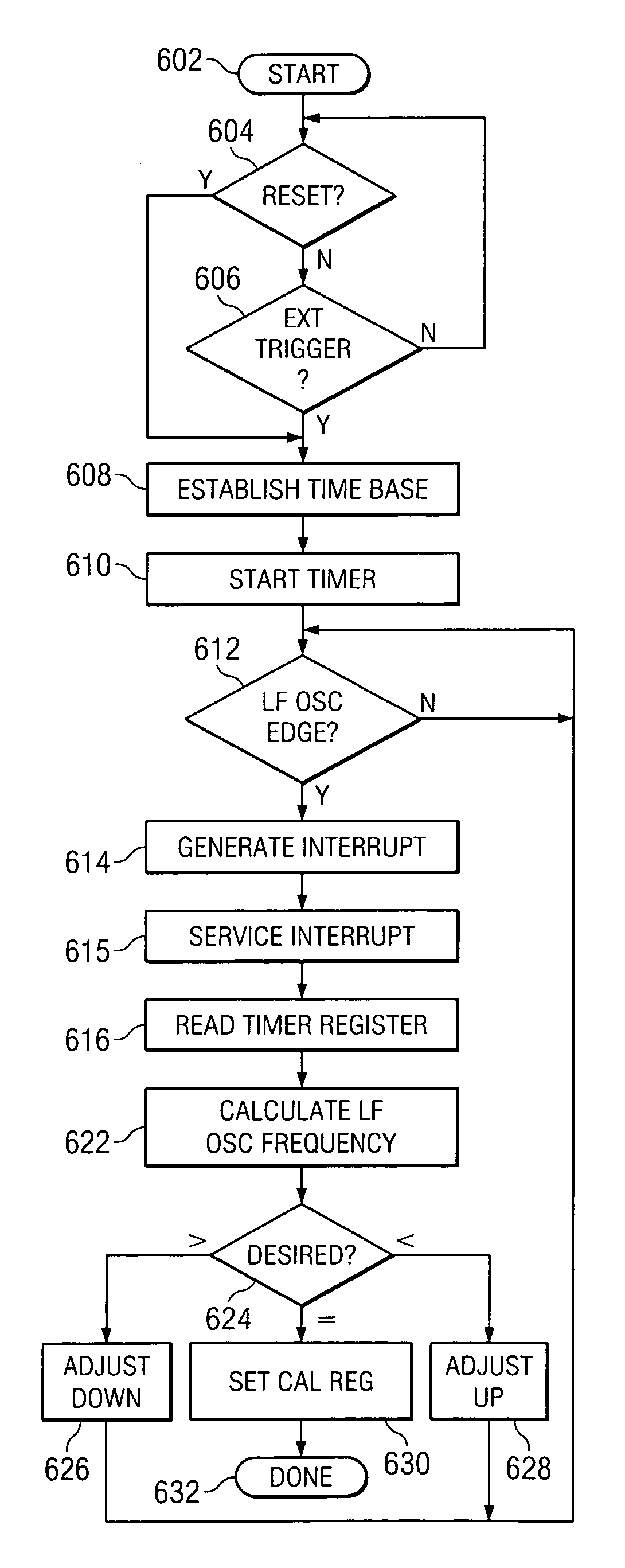
Precise frequency generation for low duty cycle transceivers using a single crystal oscillator
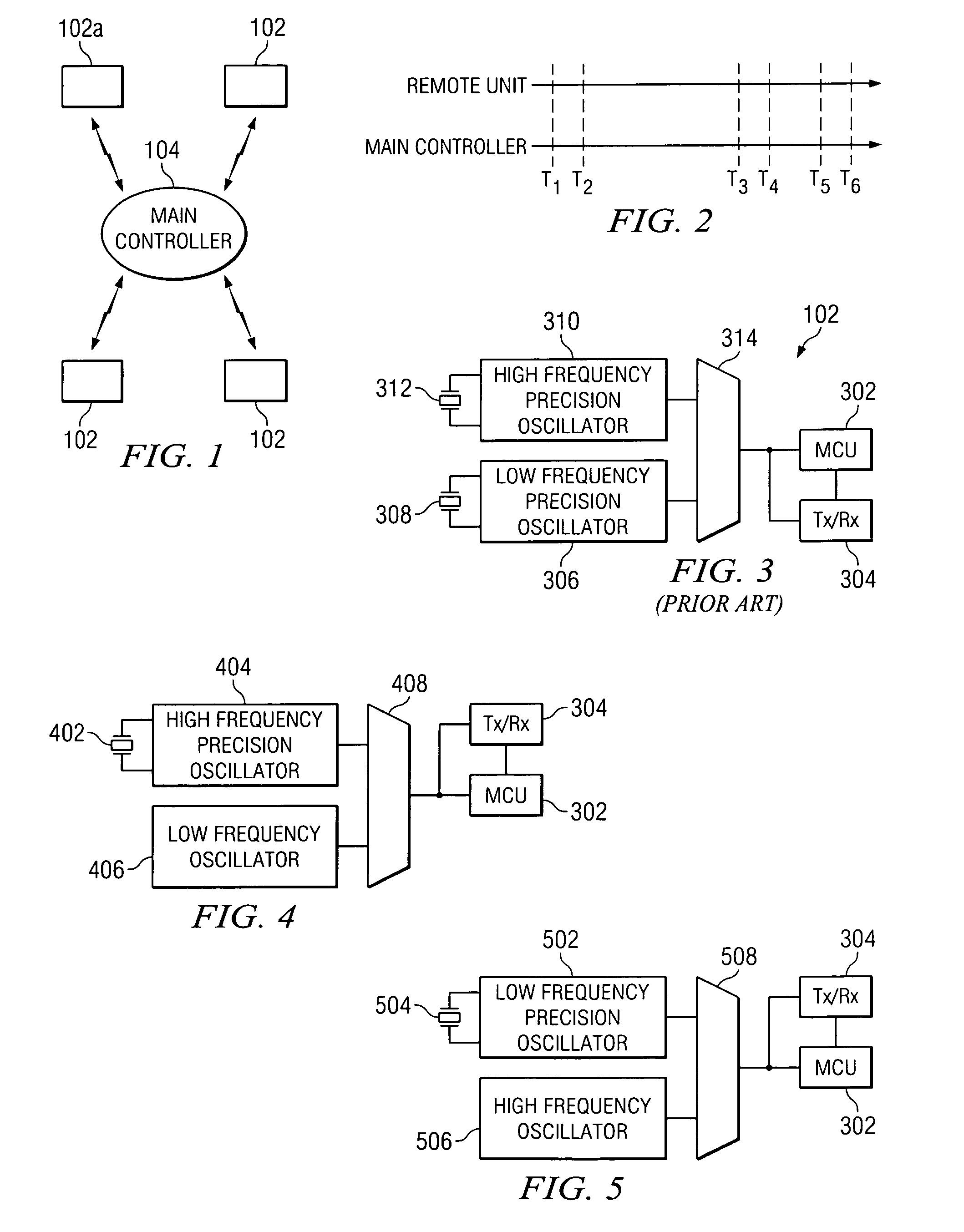
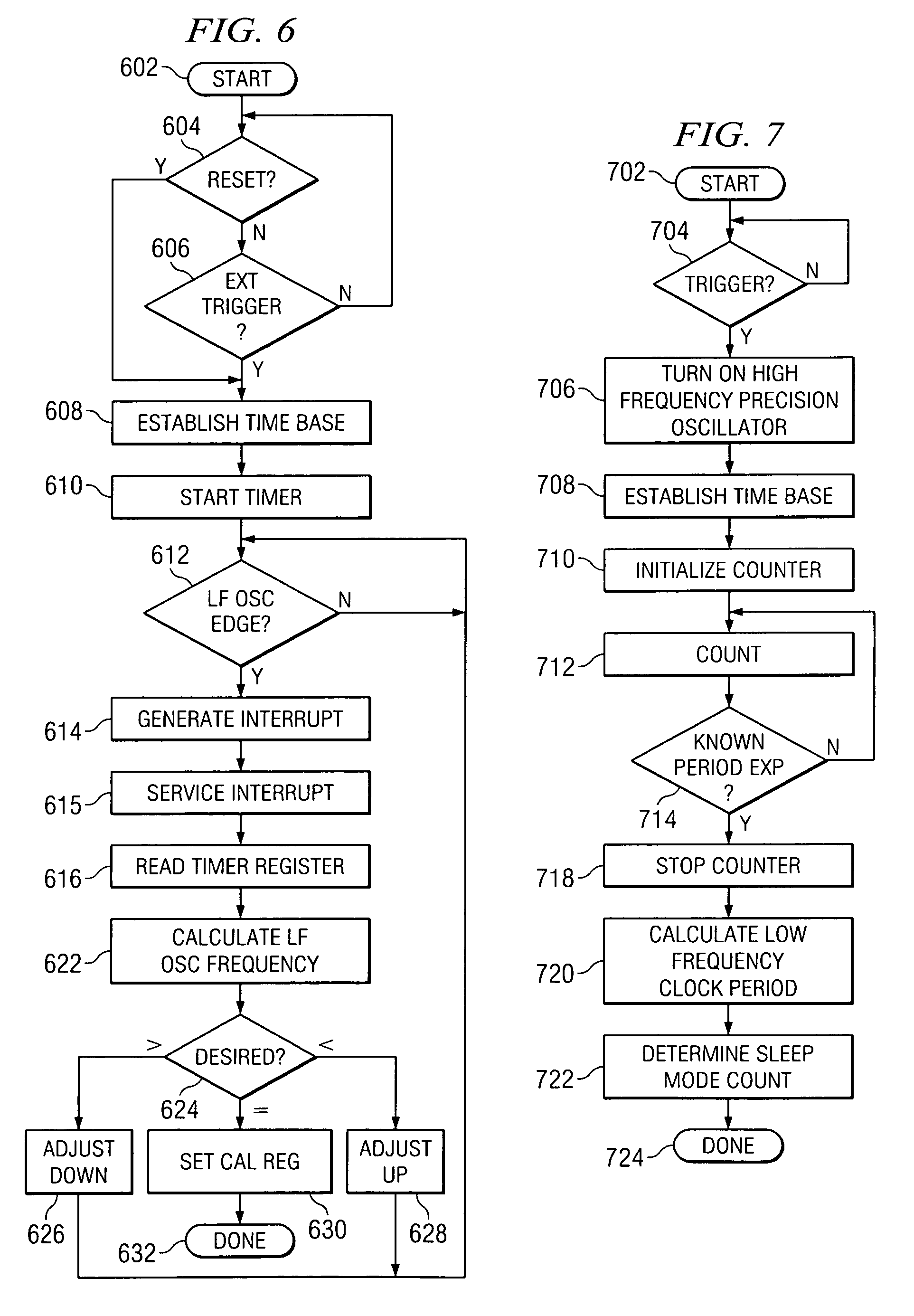
An apparatus and method for calibrating a non-crystal oscillator in a transceiver unit using a crystal-oscillator includes the step of establishing a time base based upon oscillations of the crystal oscillator. A comparison of the number of oscillations for the non-crystal oscillator and the crystal oscillator is made during a known time period is made. An adjustment is determined based upon the established time base and the compared number of oscillations. The transceiving of the transceiver unit is then controlled based upon this adjustment.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com