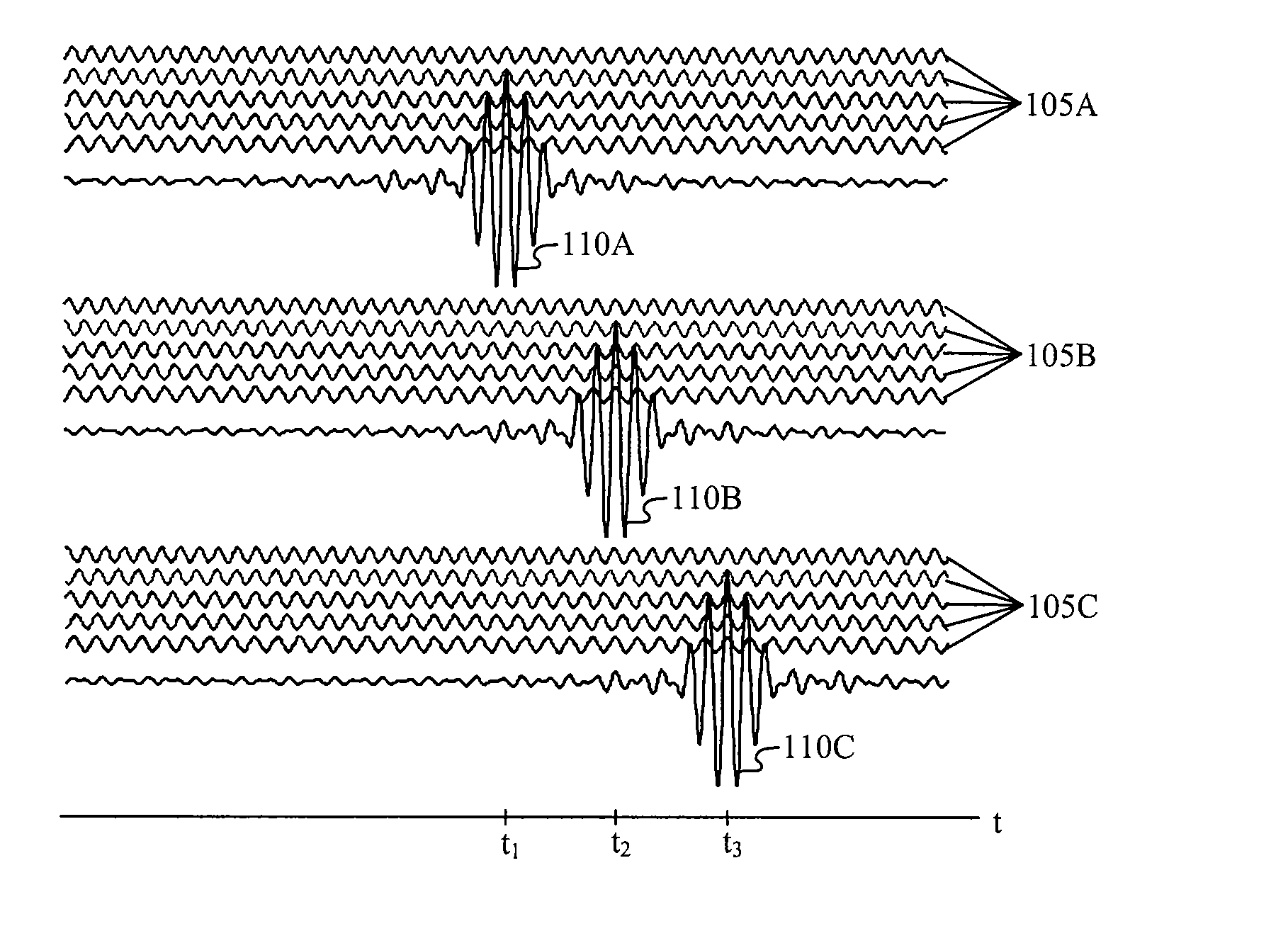
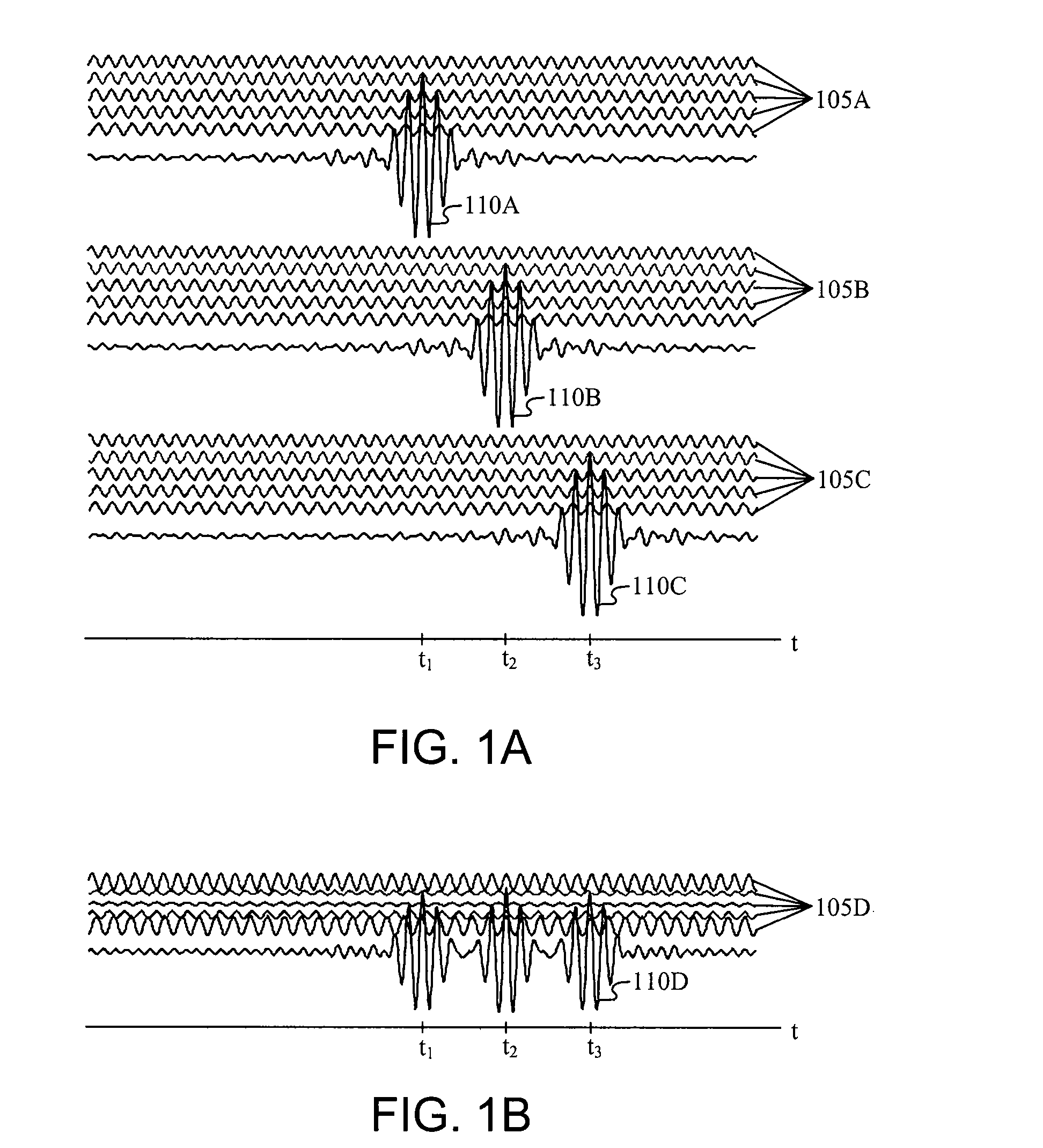
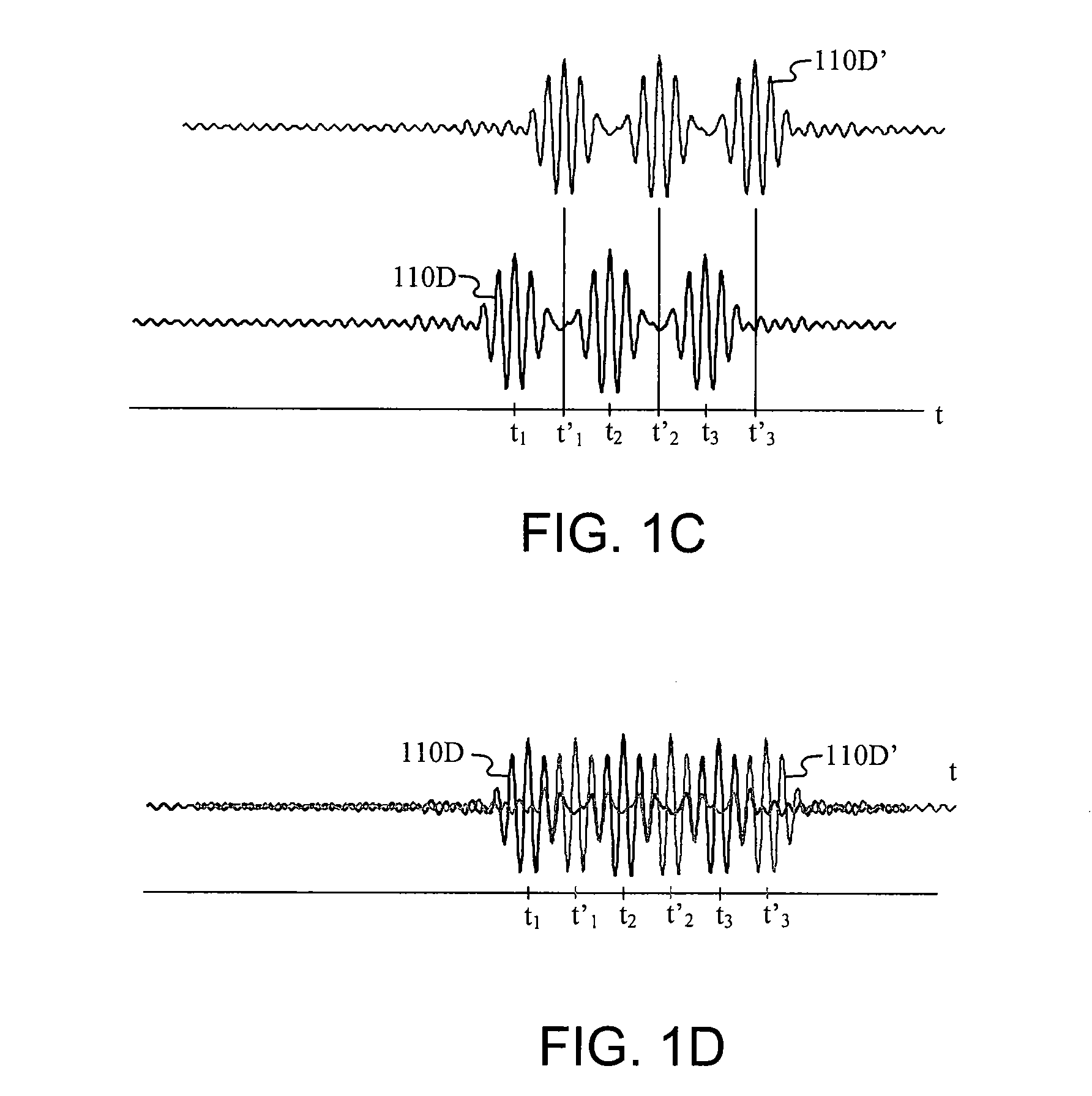
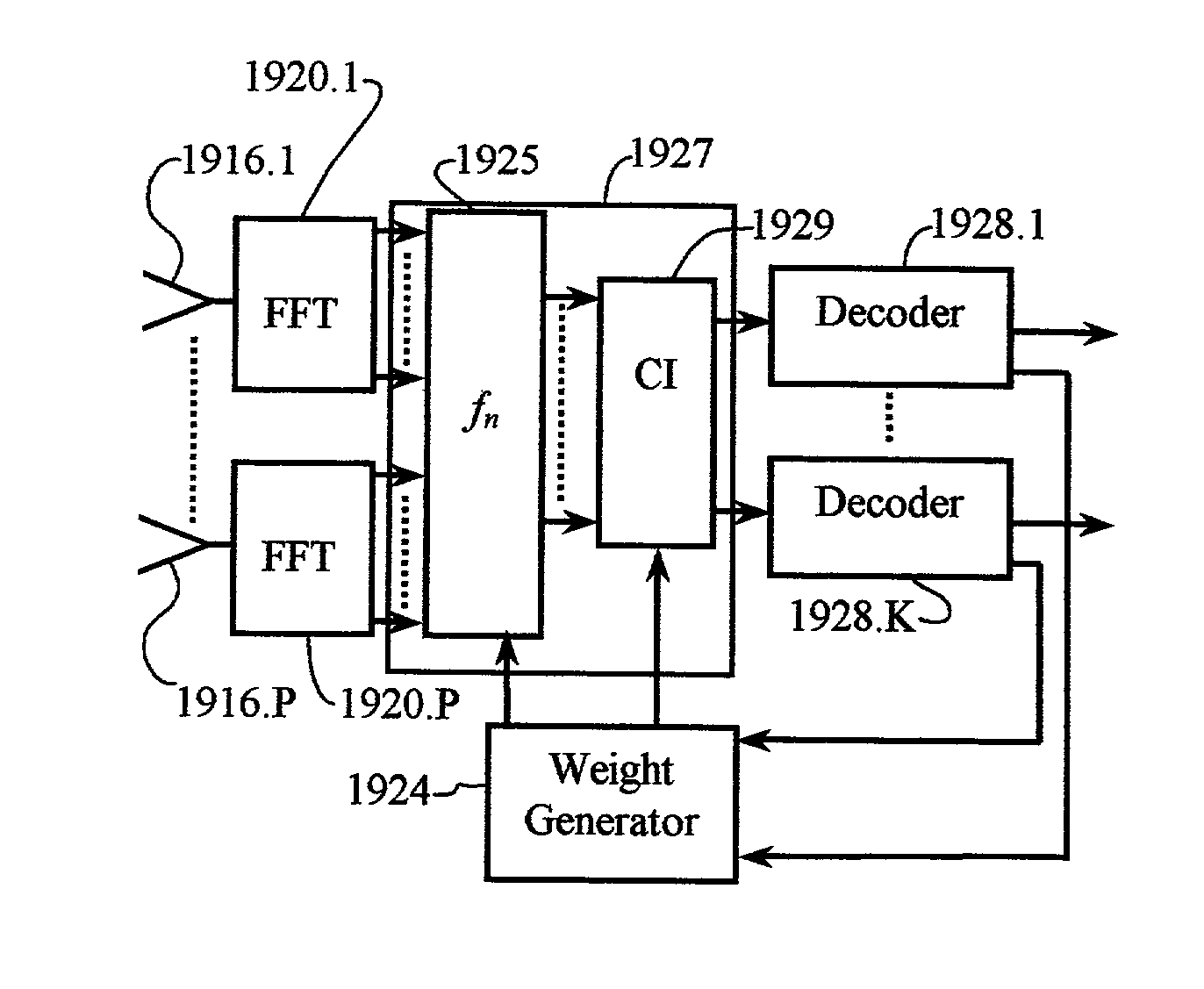
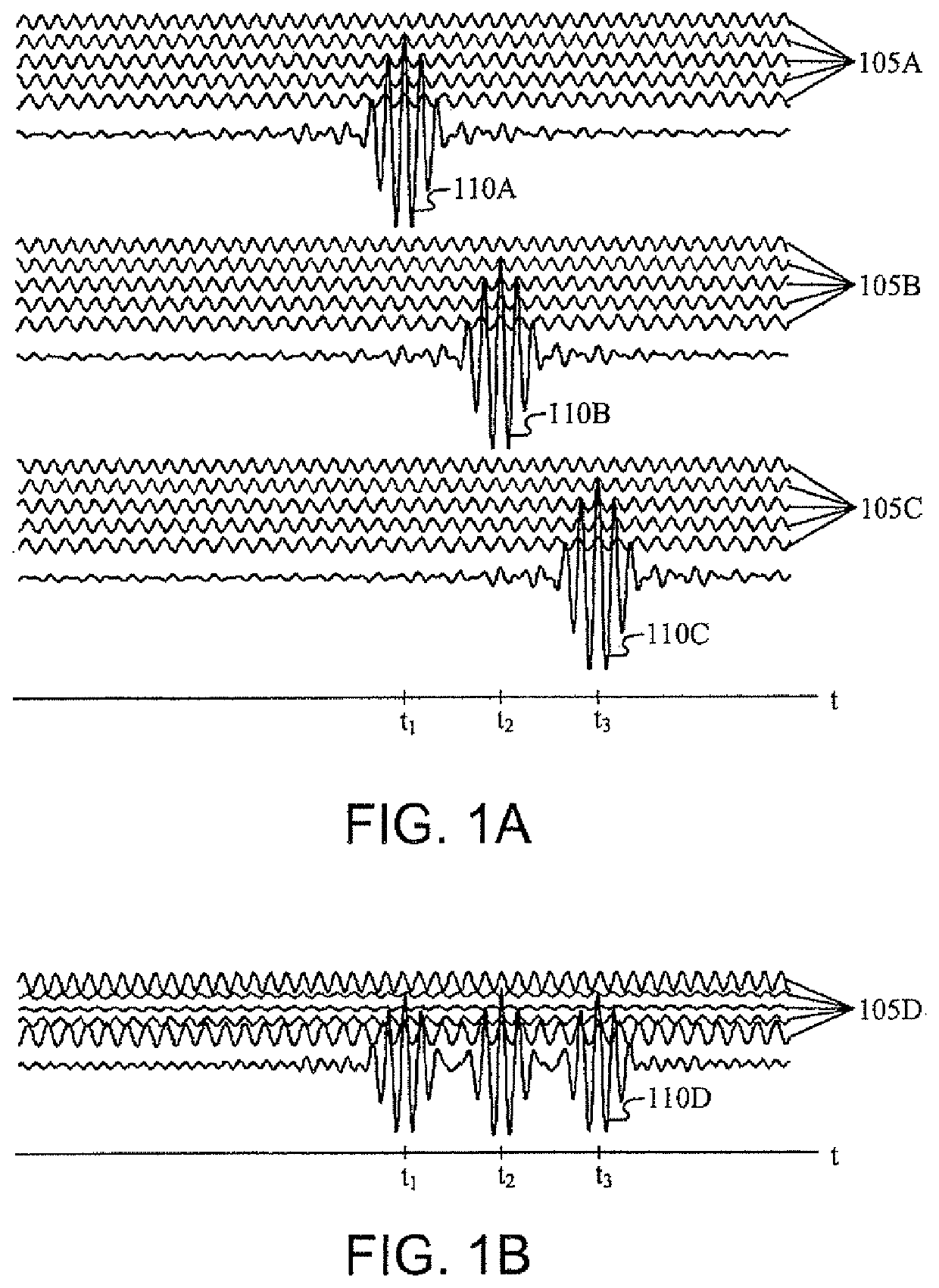
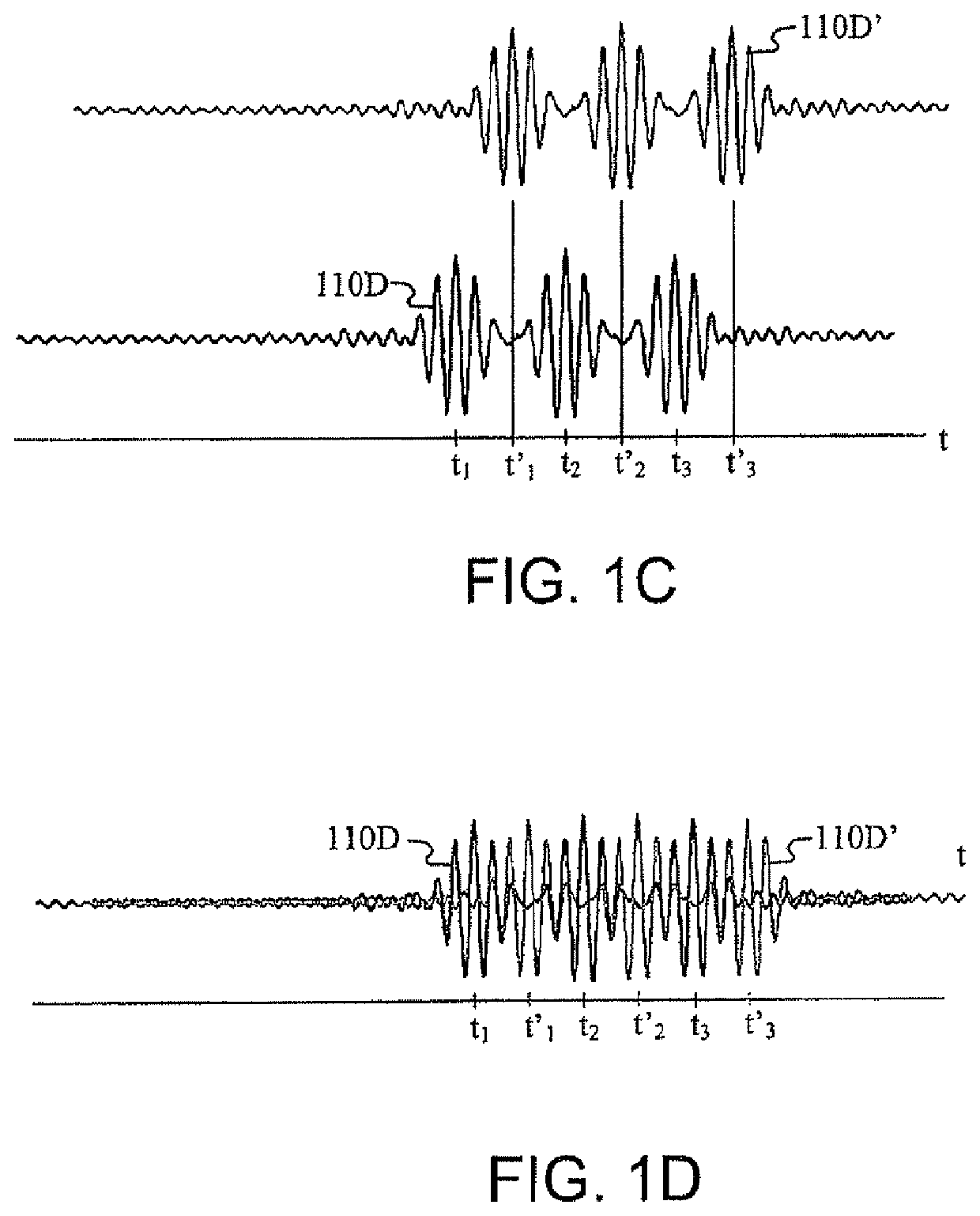
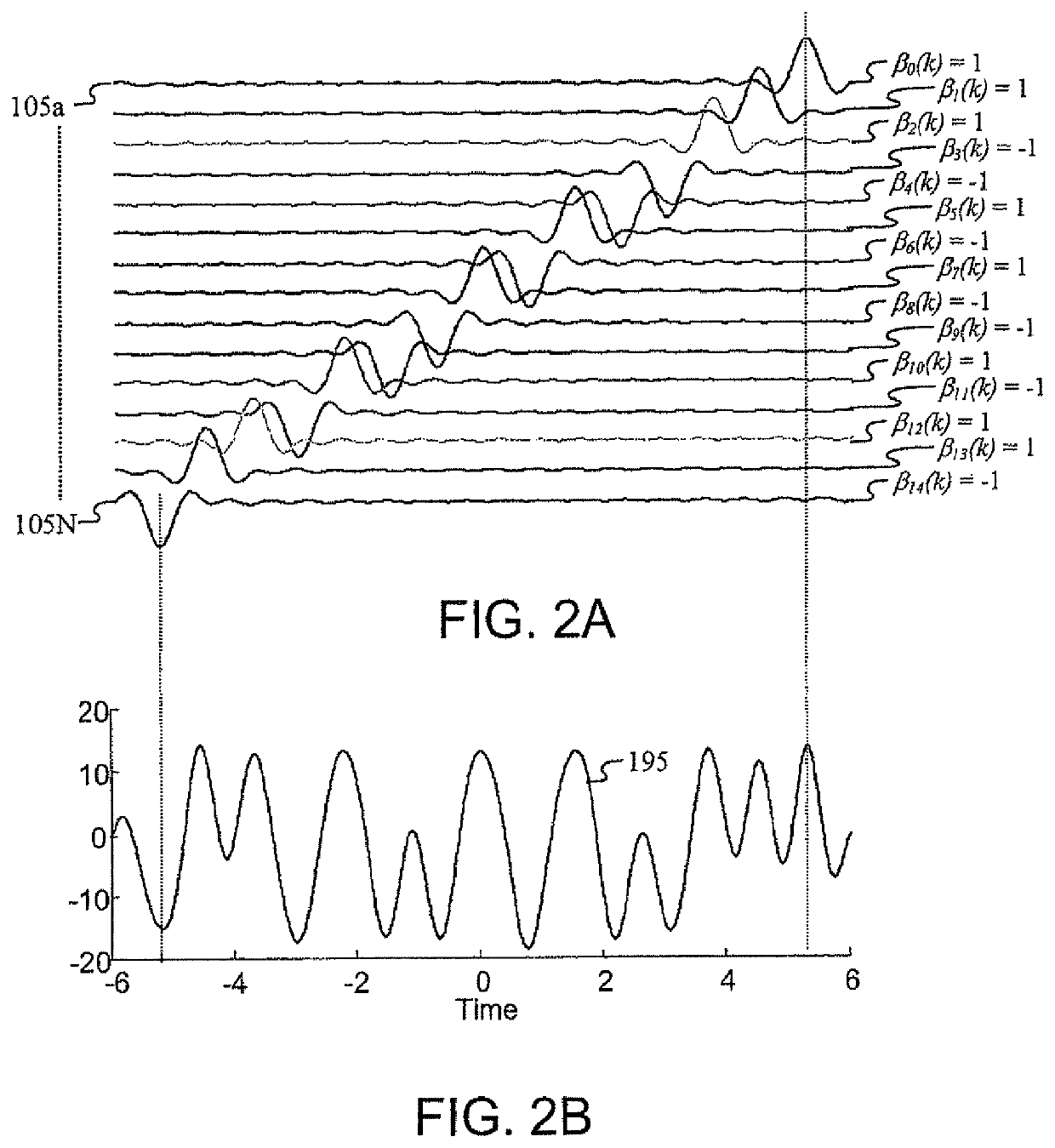
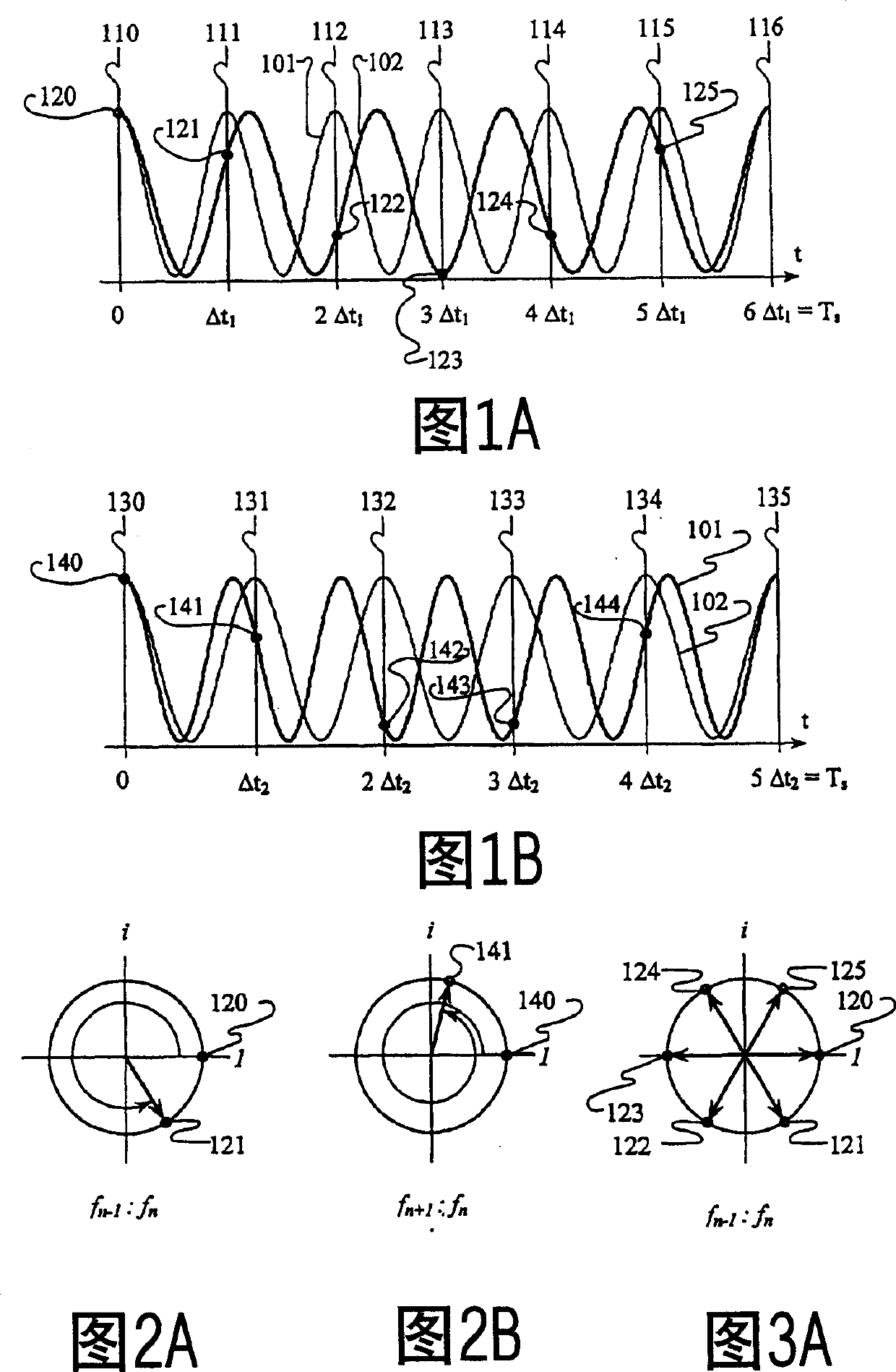
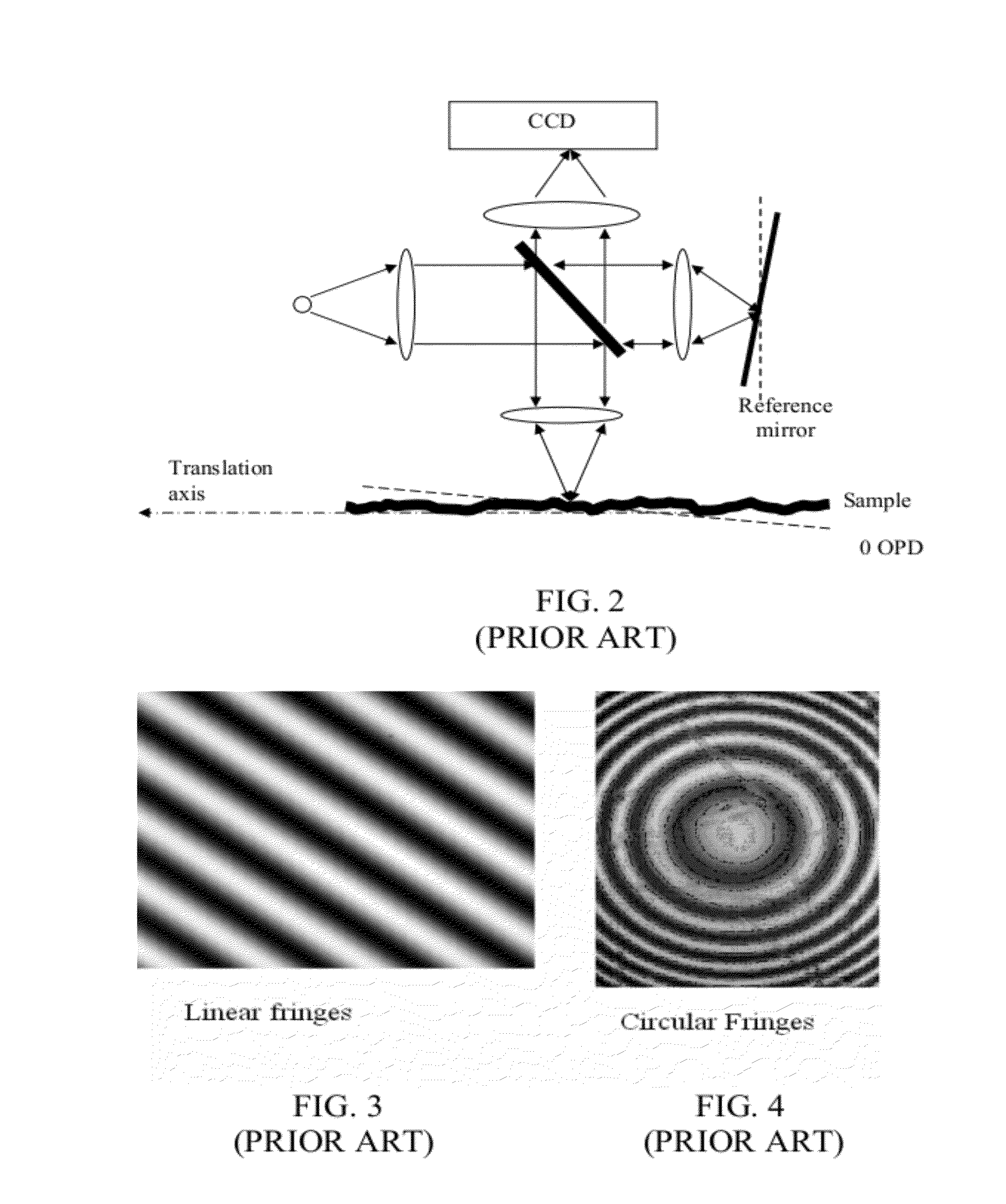
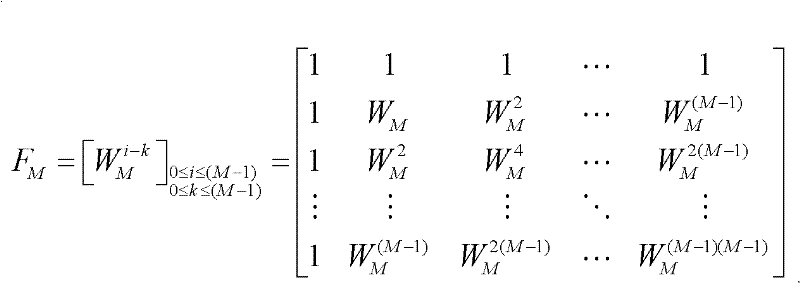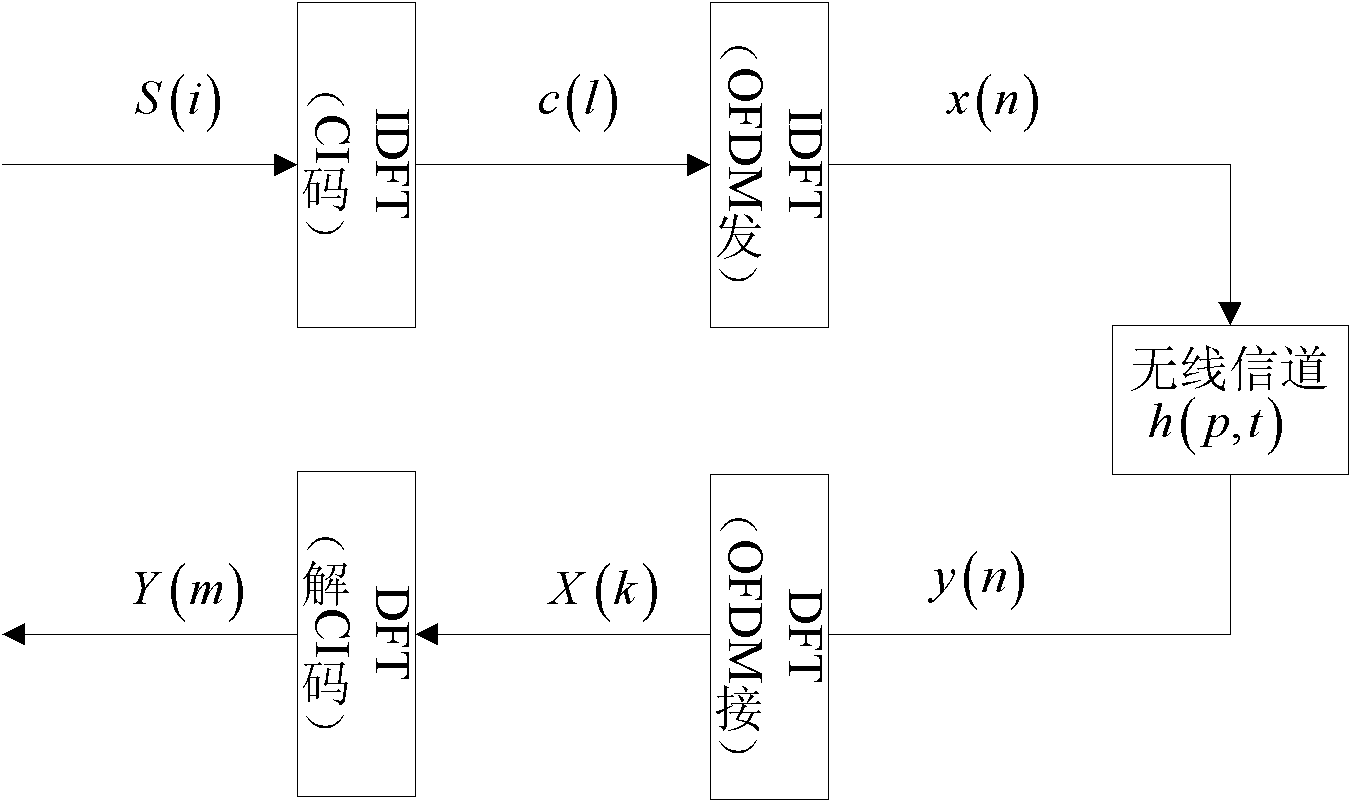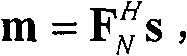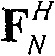Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Carrier interferometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
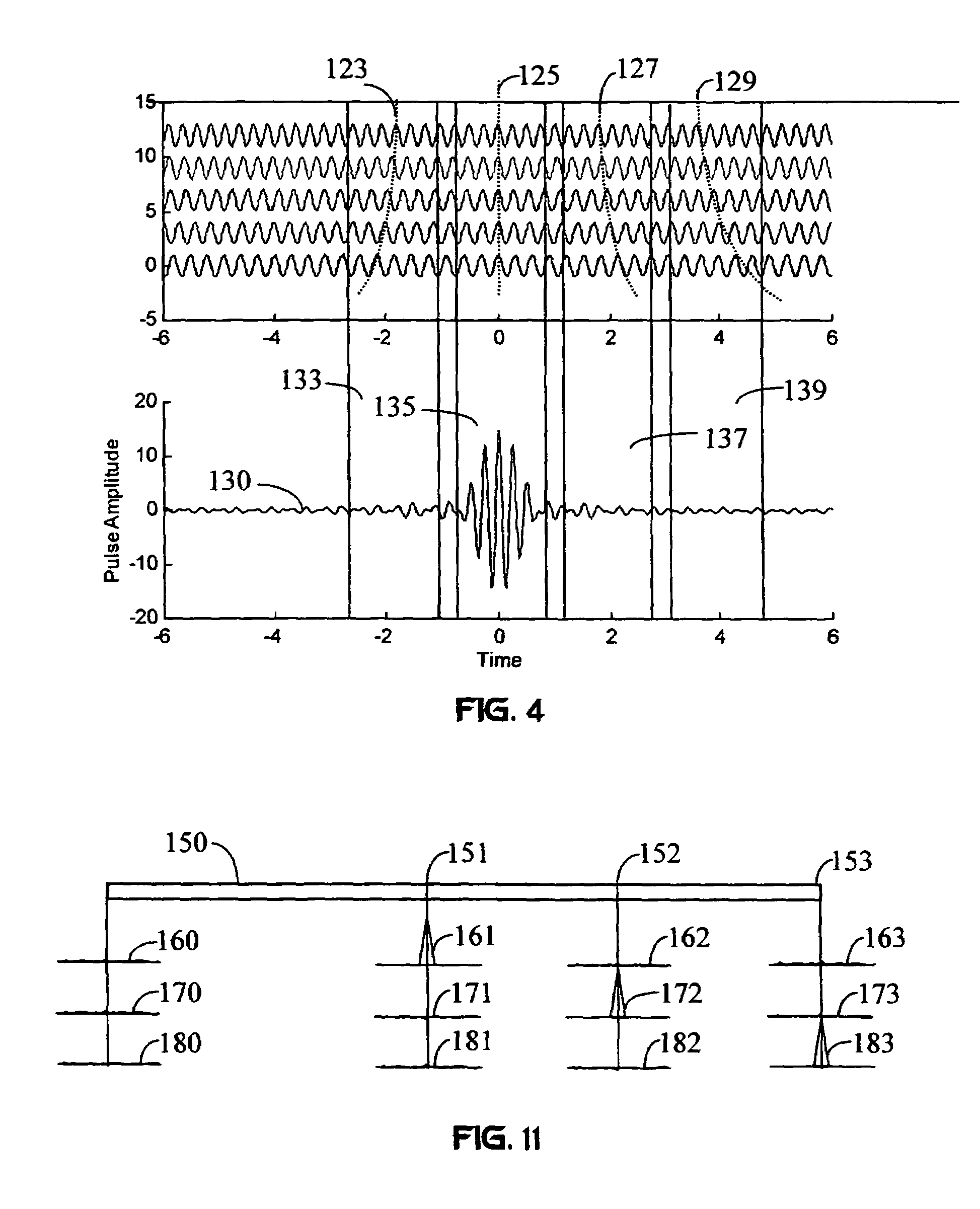
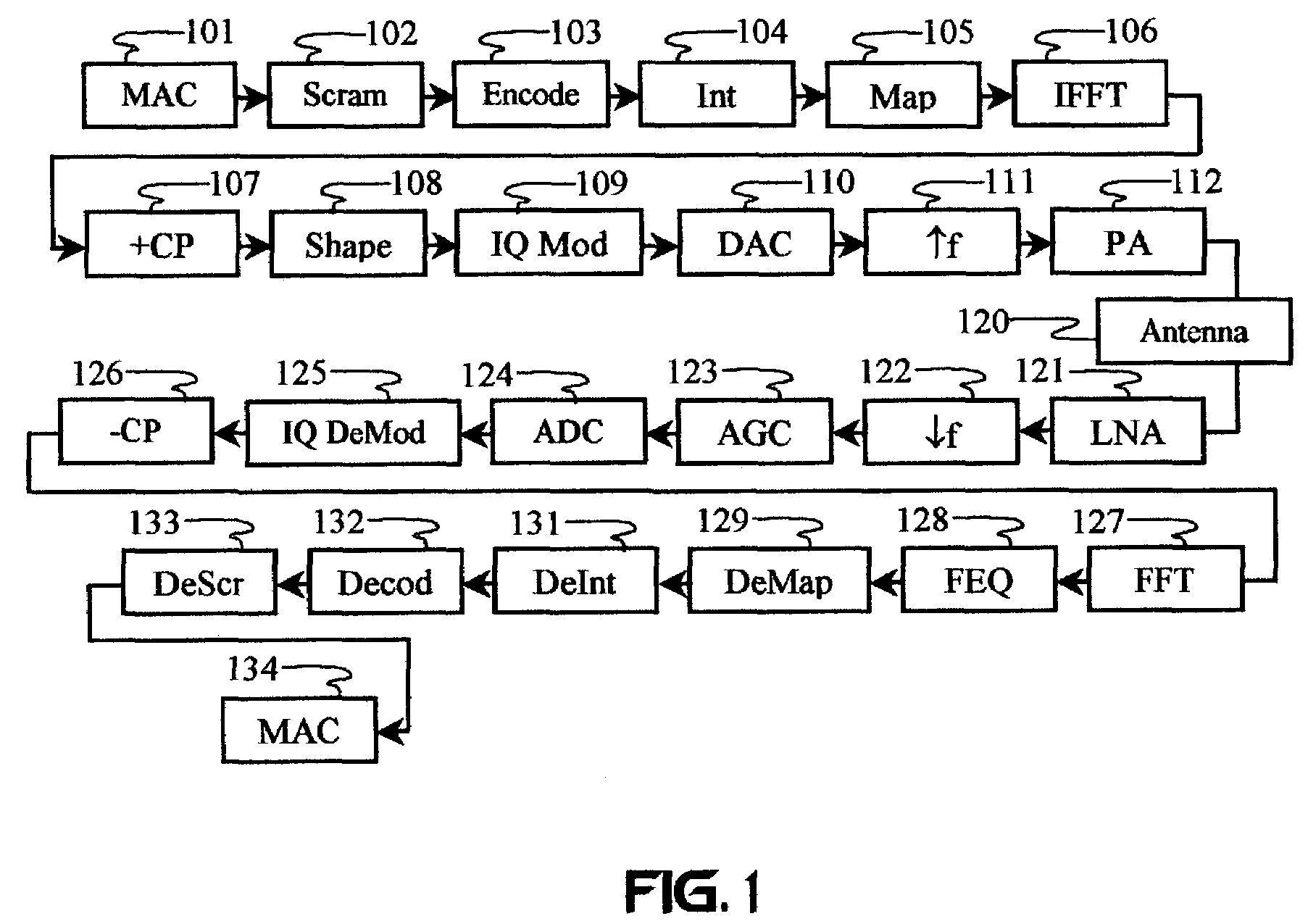
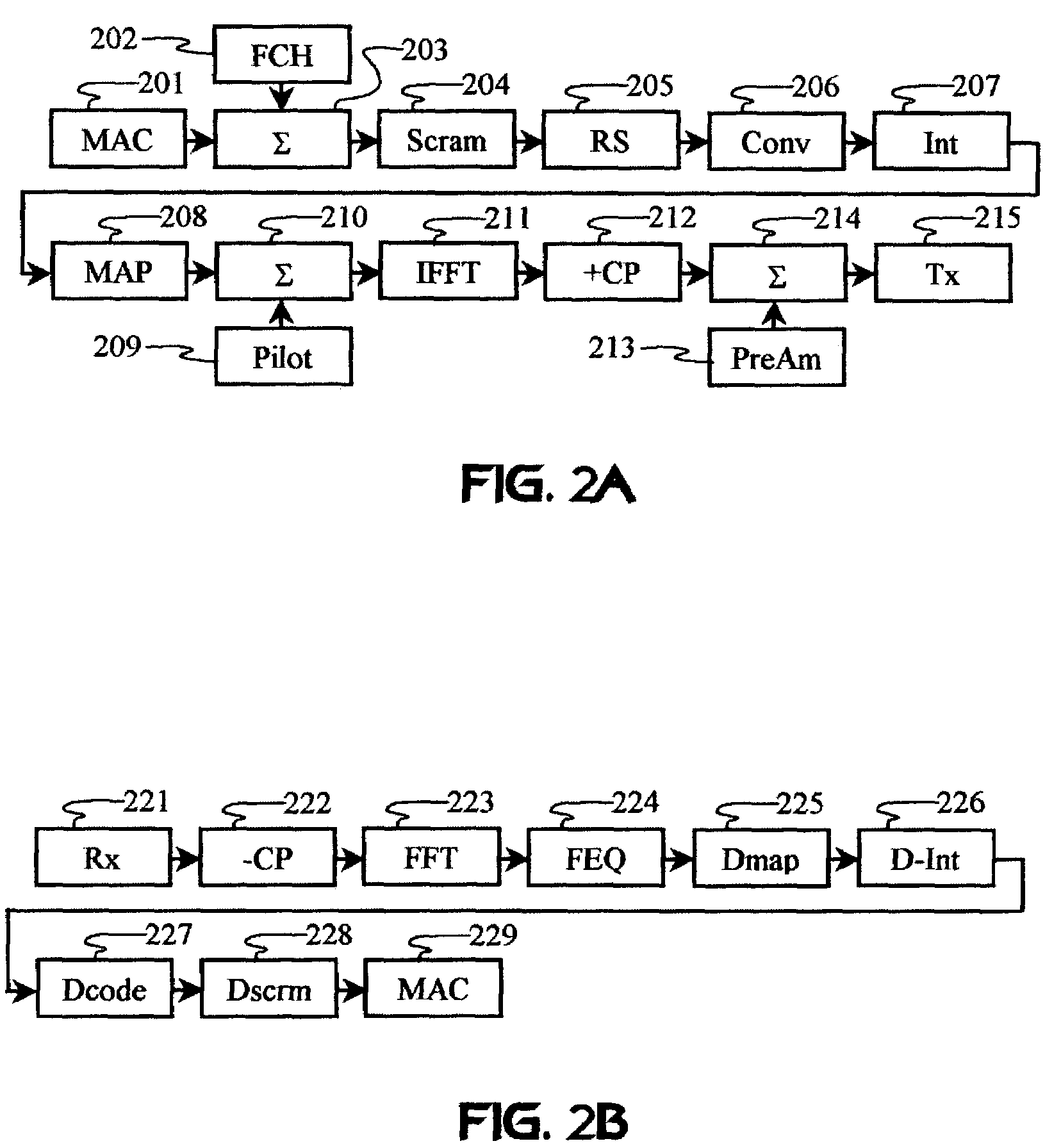
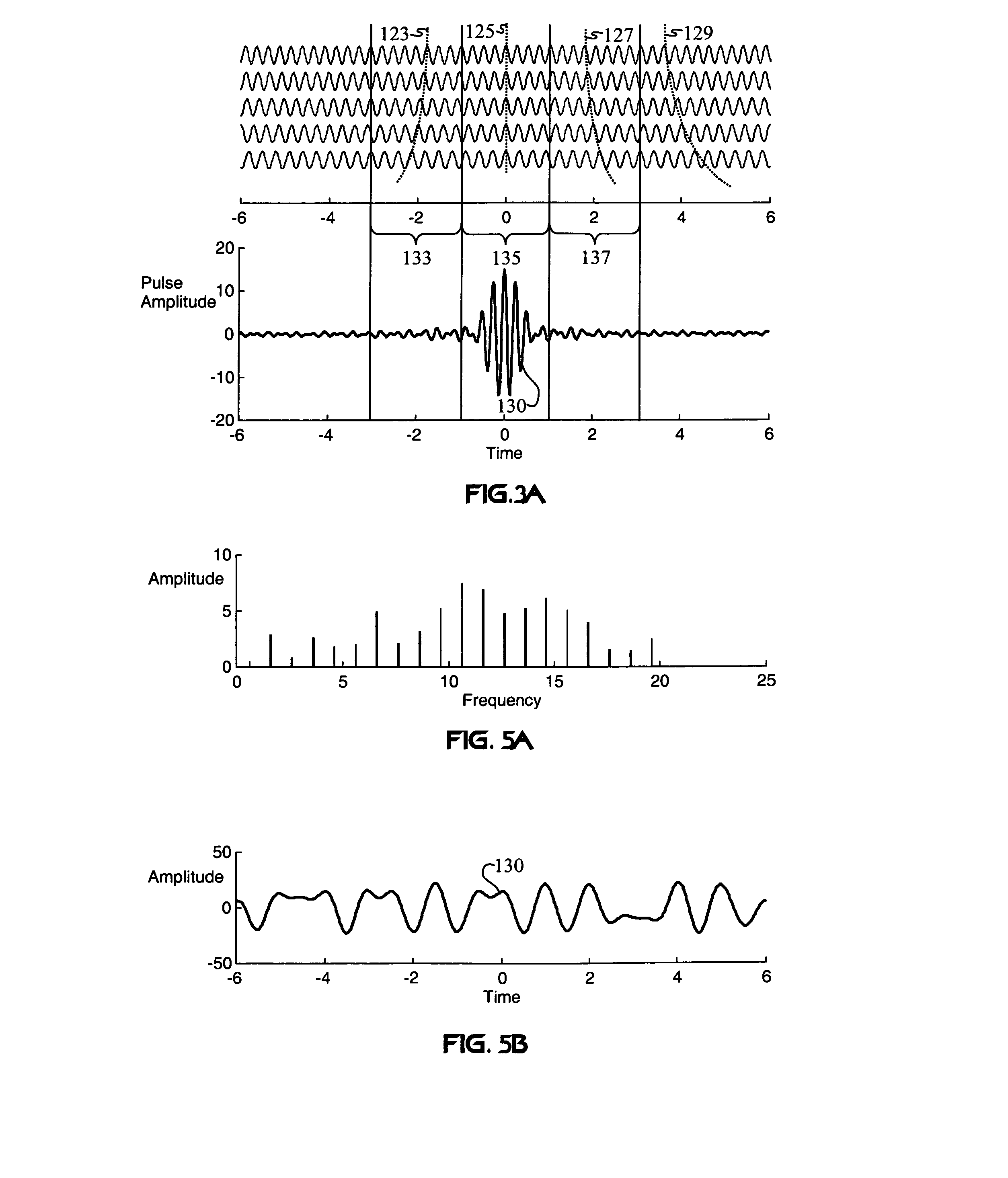
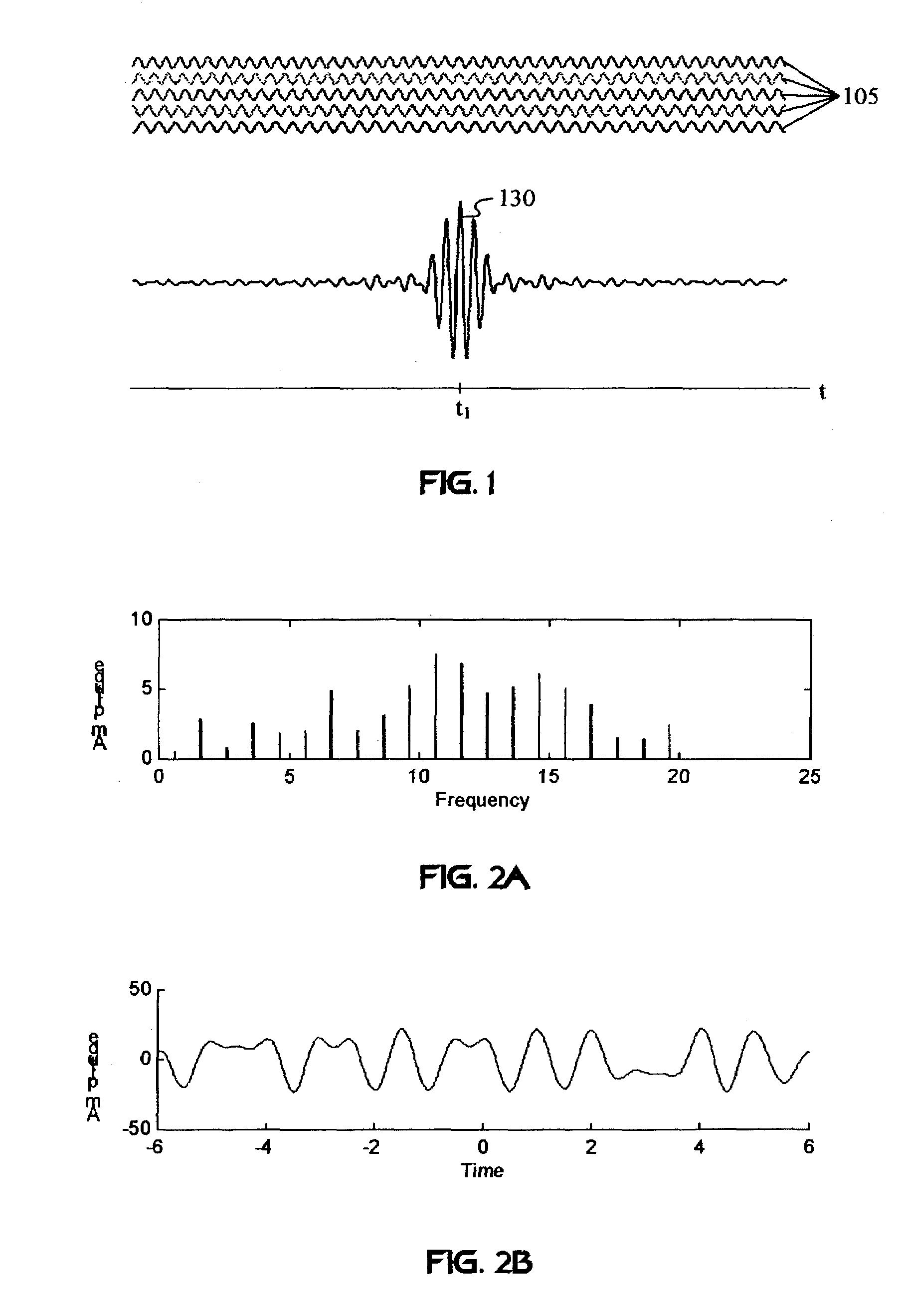
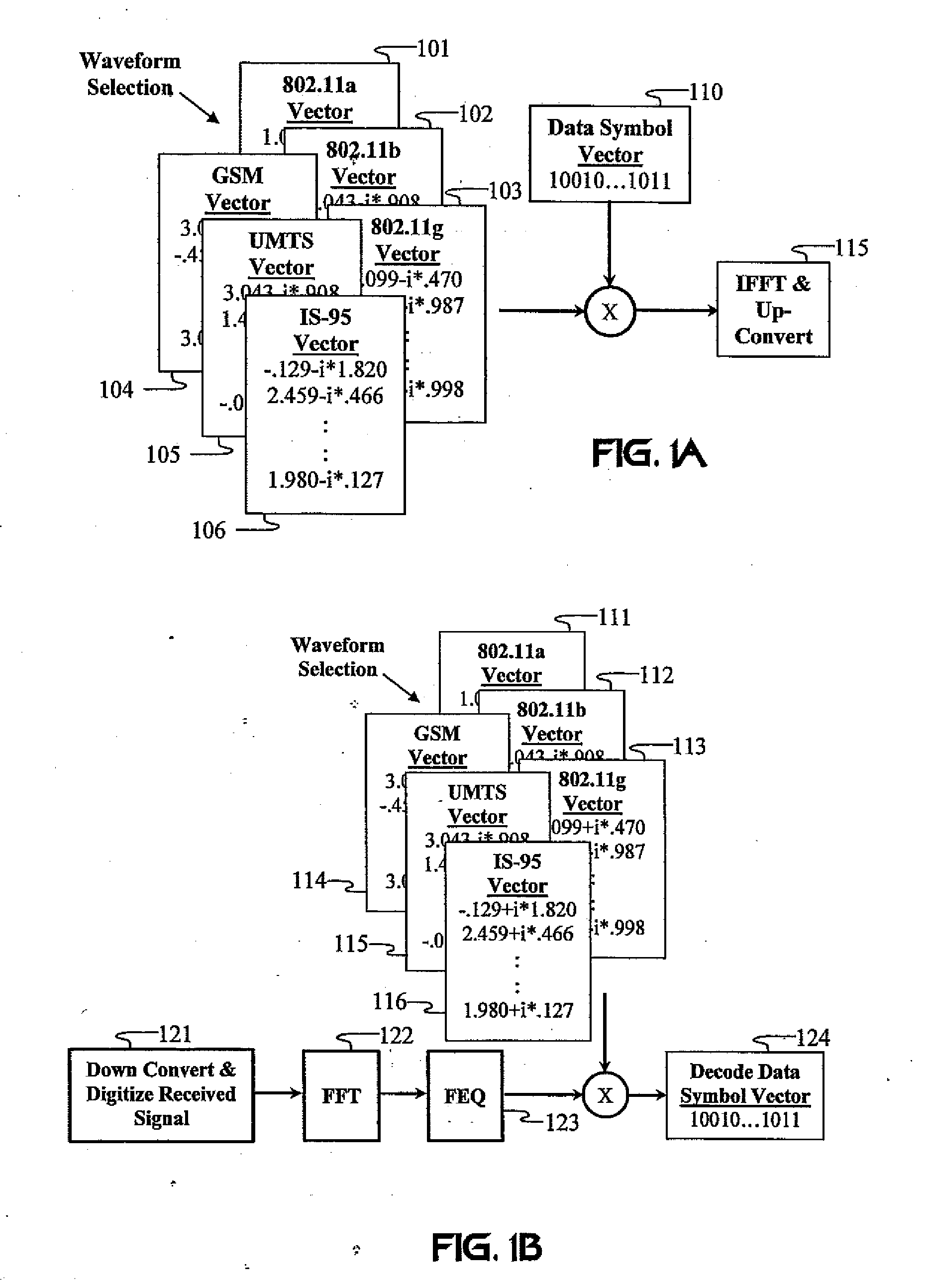
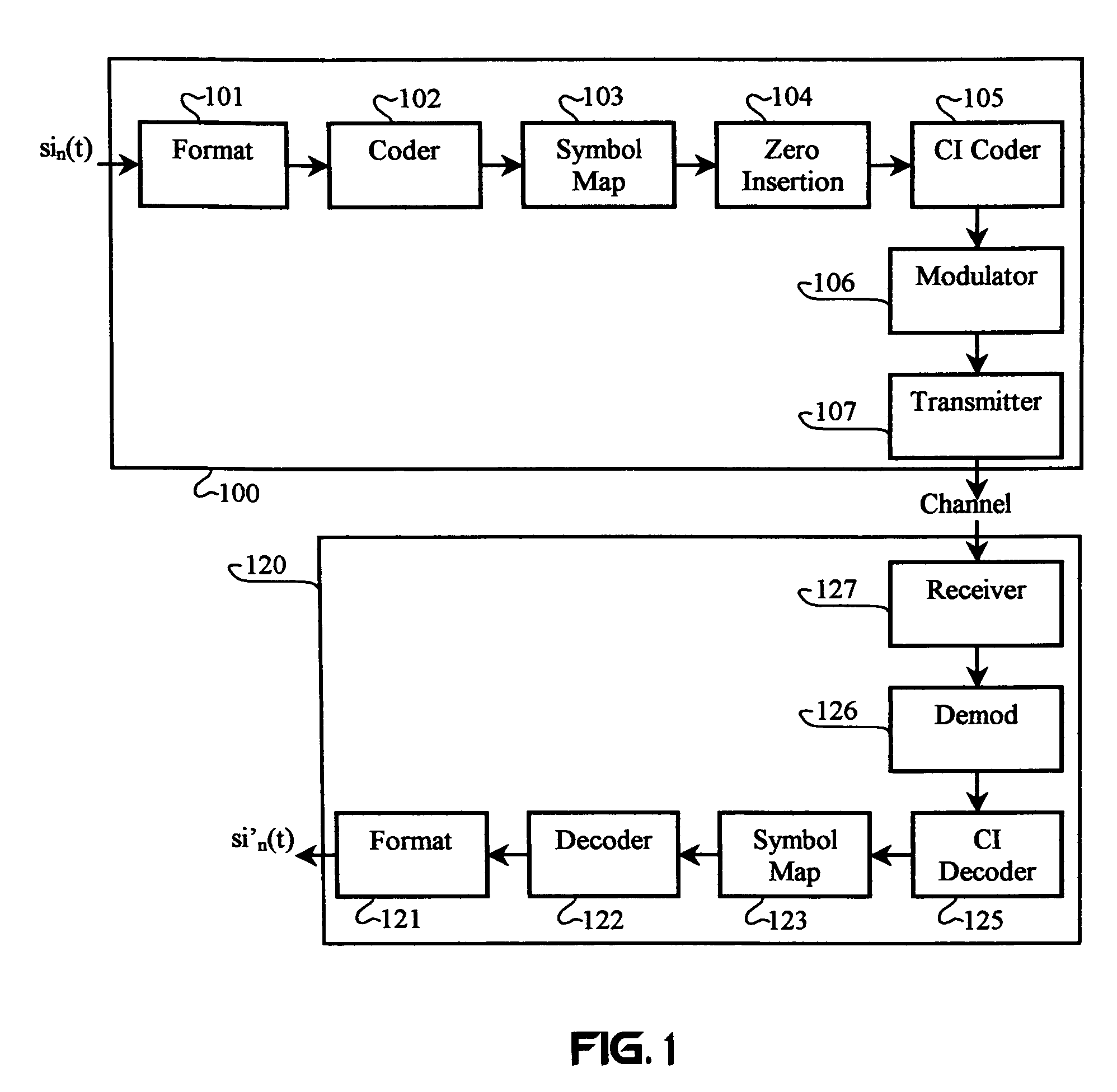
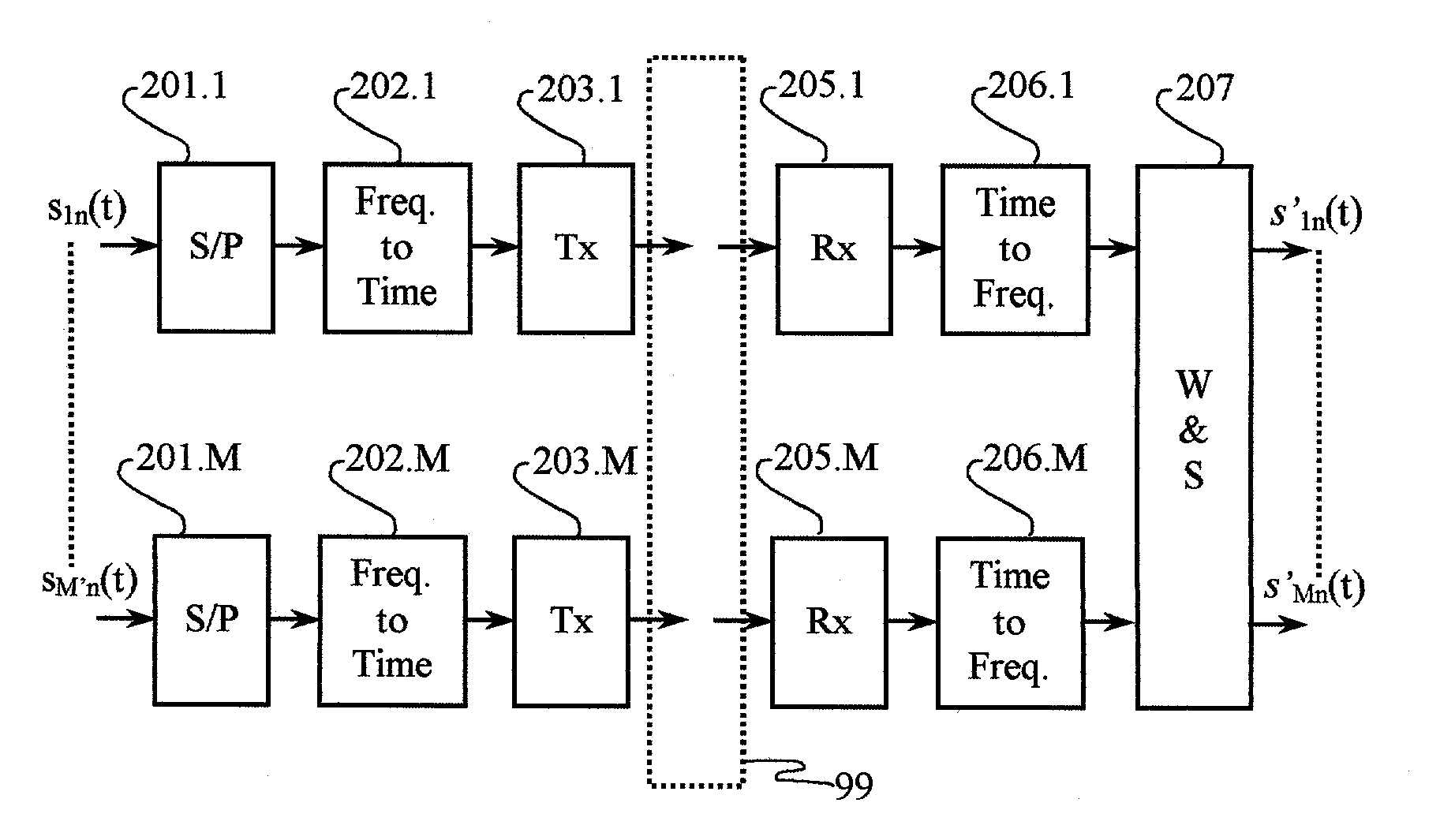
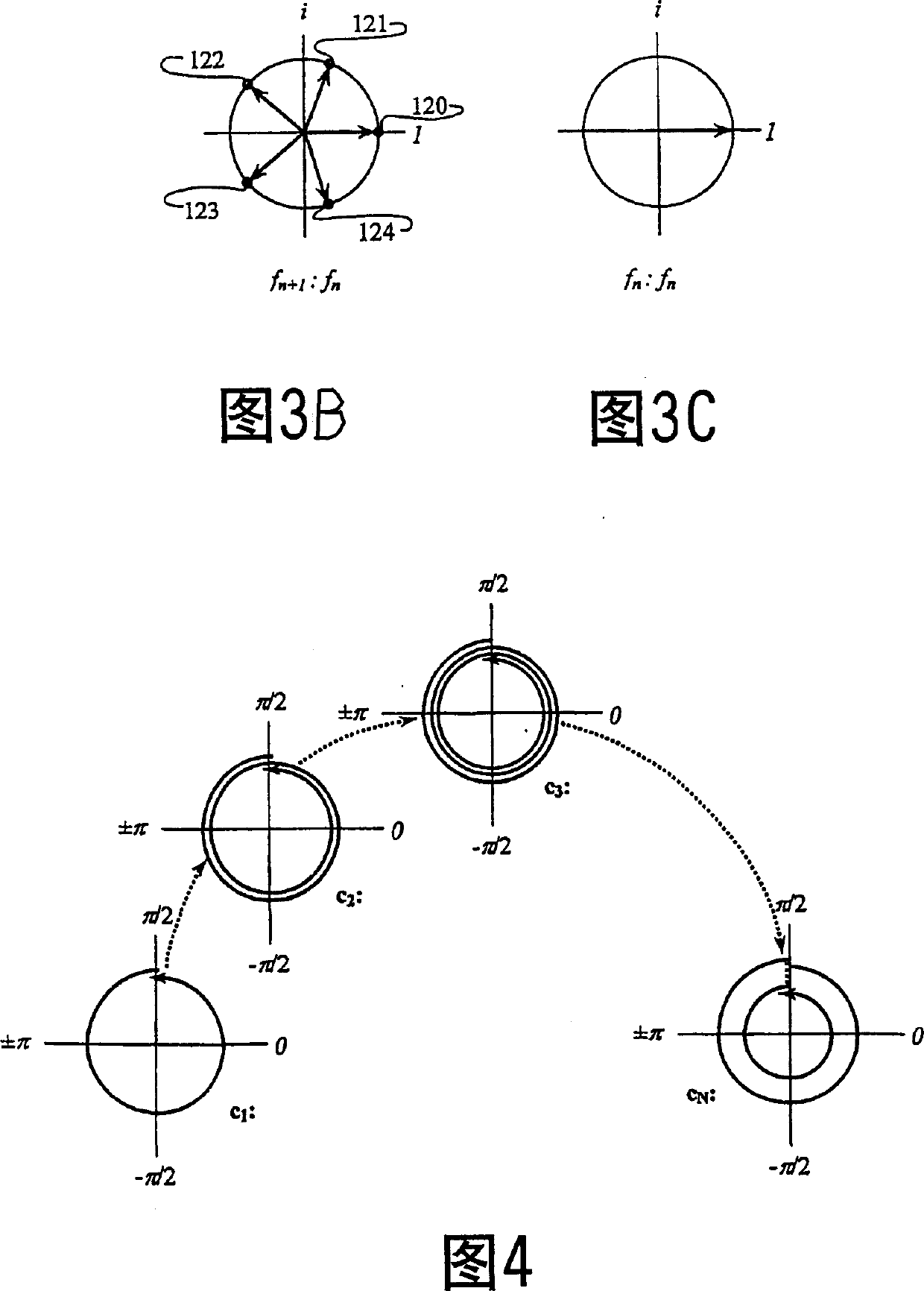
Carrier Interferometry (CI) is a spread spectrum scheme designed to be used in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) communication system for multiplexing and multiple access, enabling the system to support multiple users at the same time over the same frequency band.
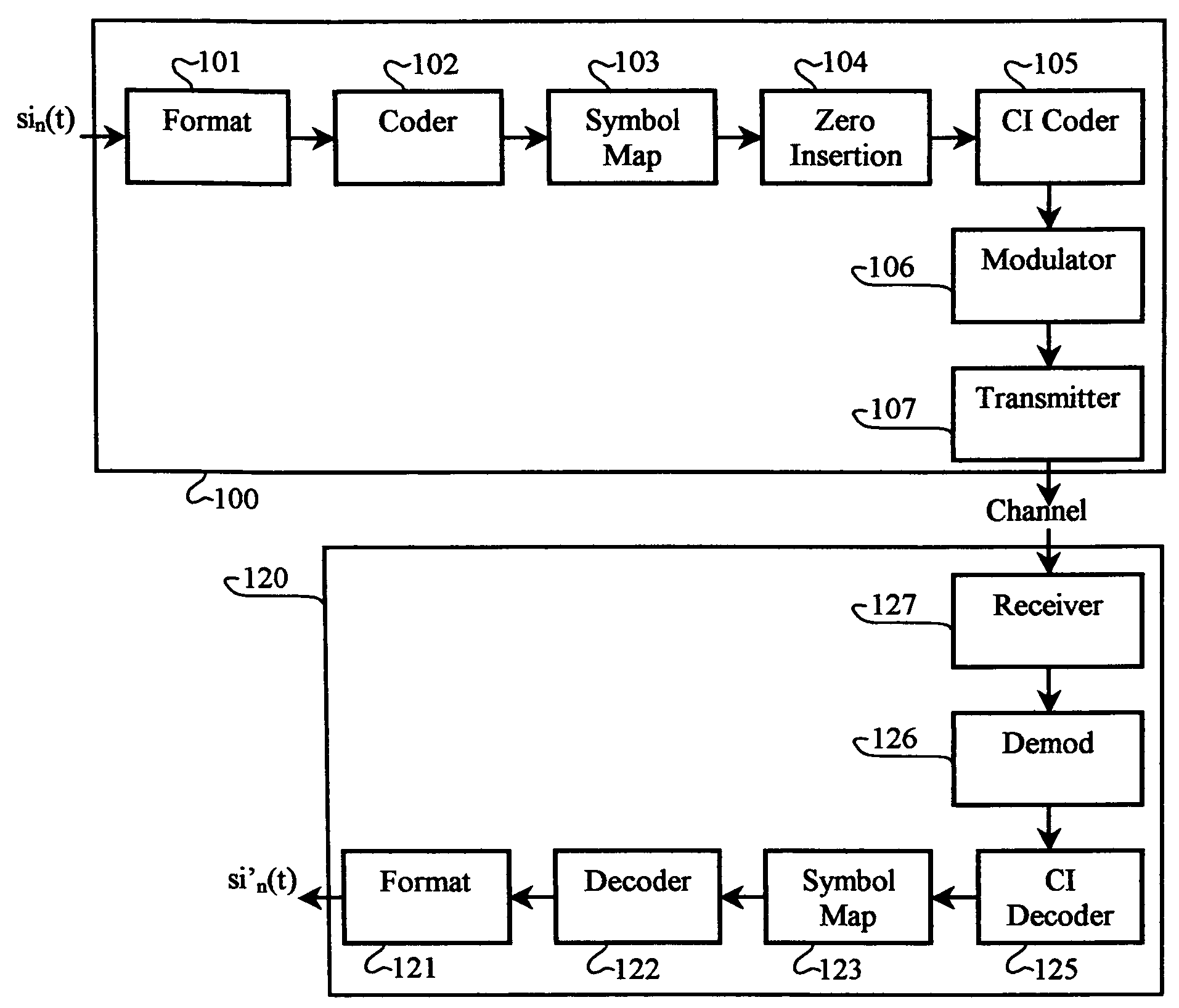
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
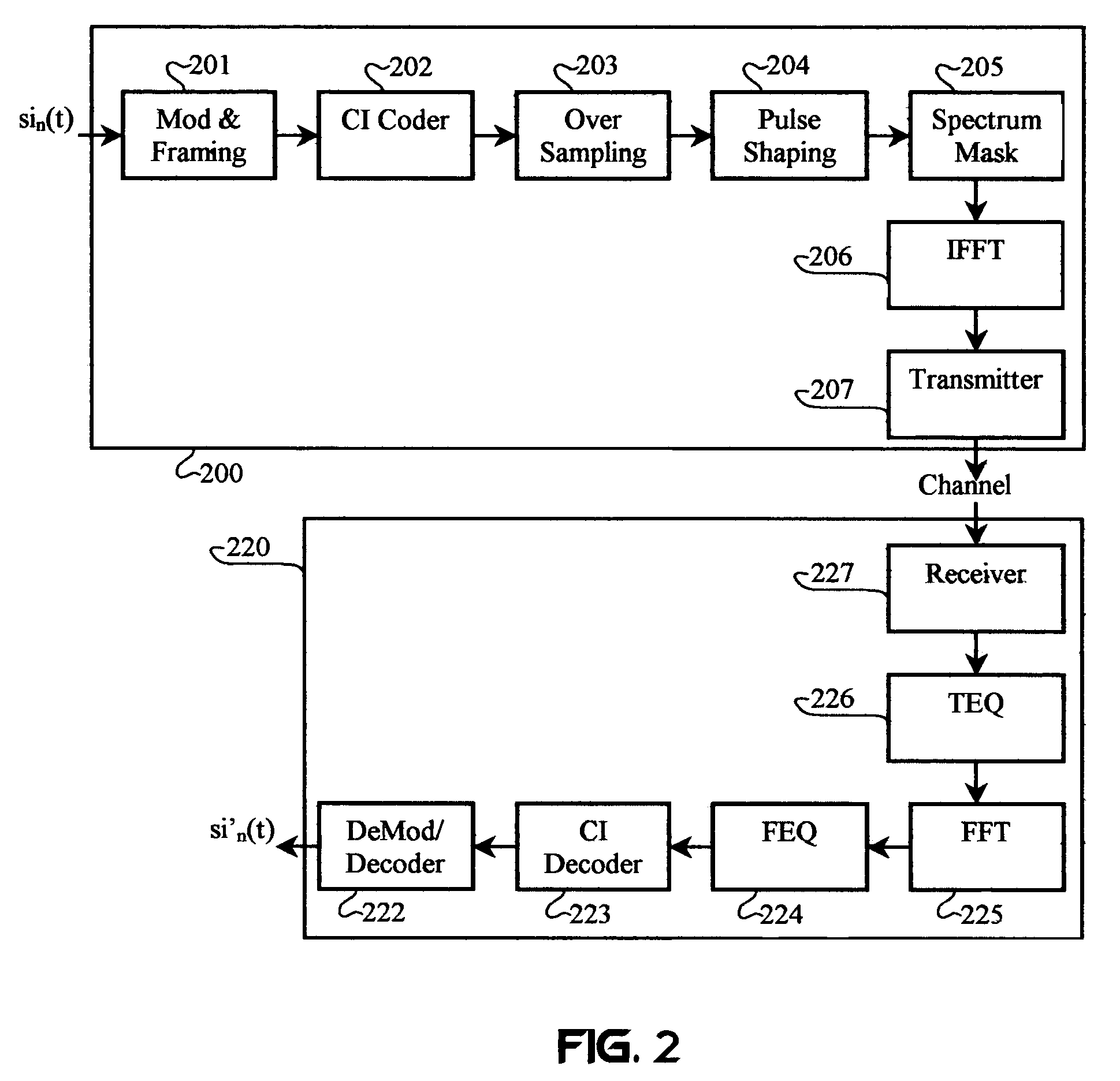
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Multiple access method and system
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
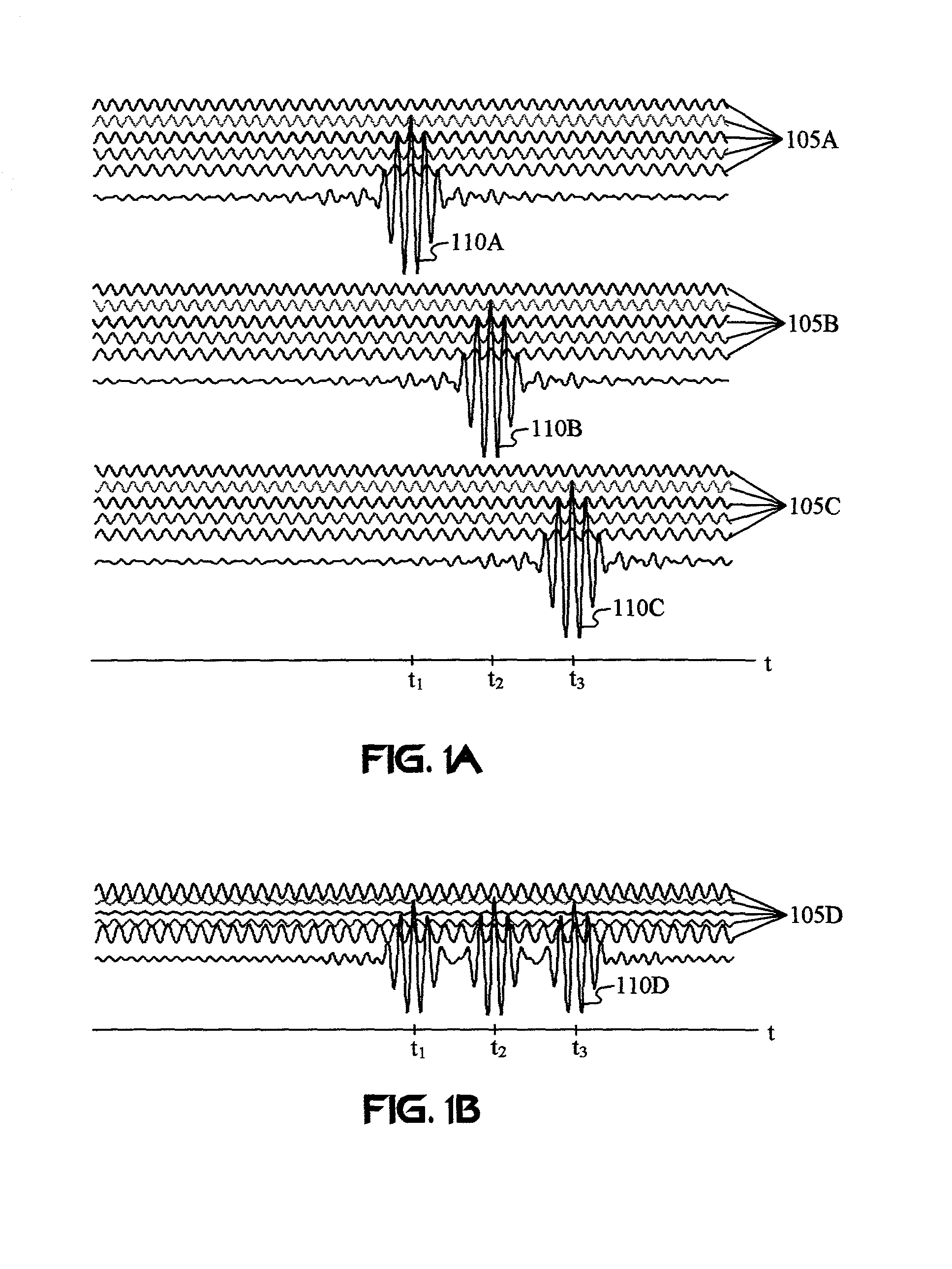
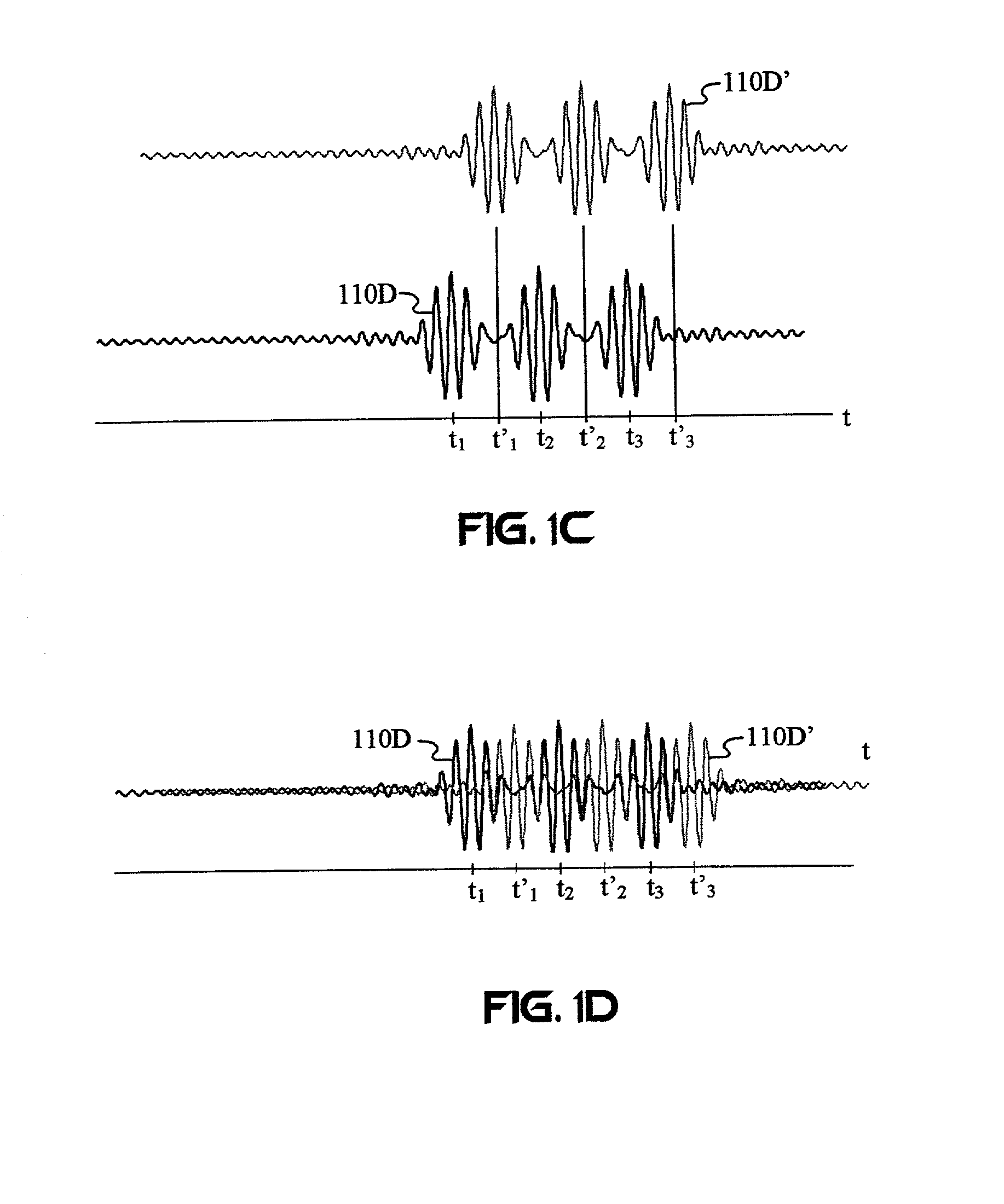
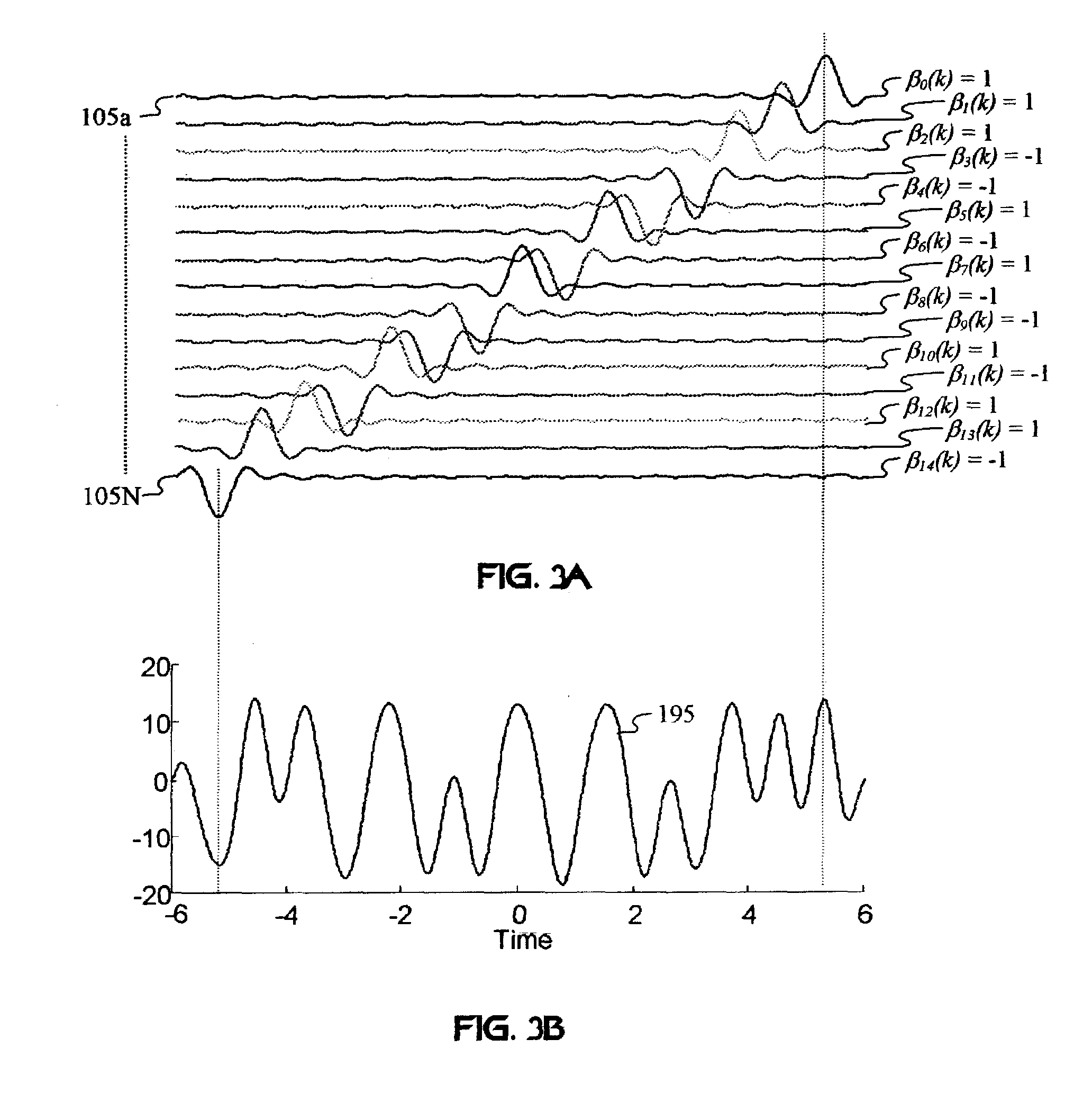
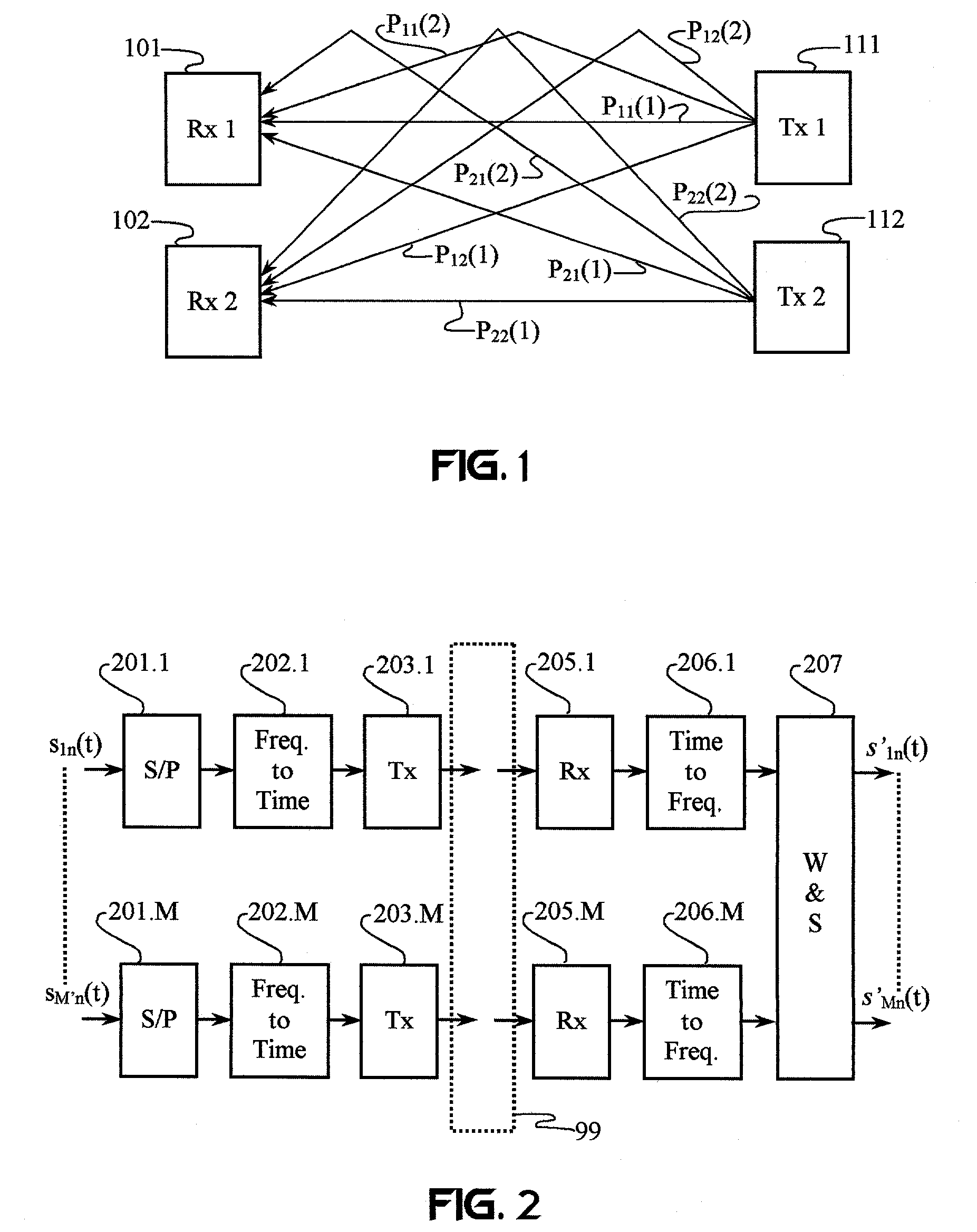
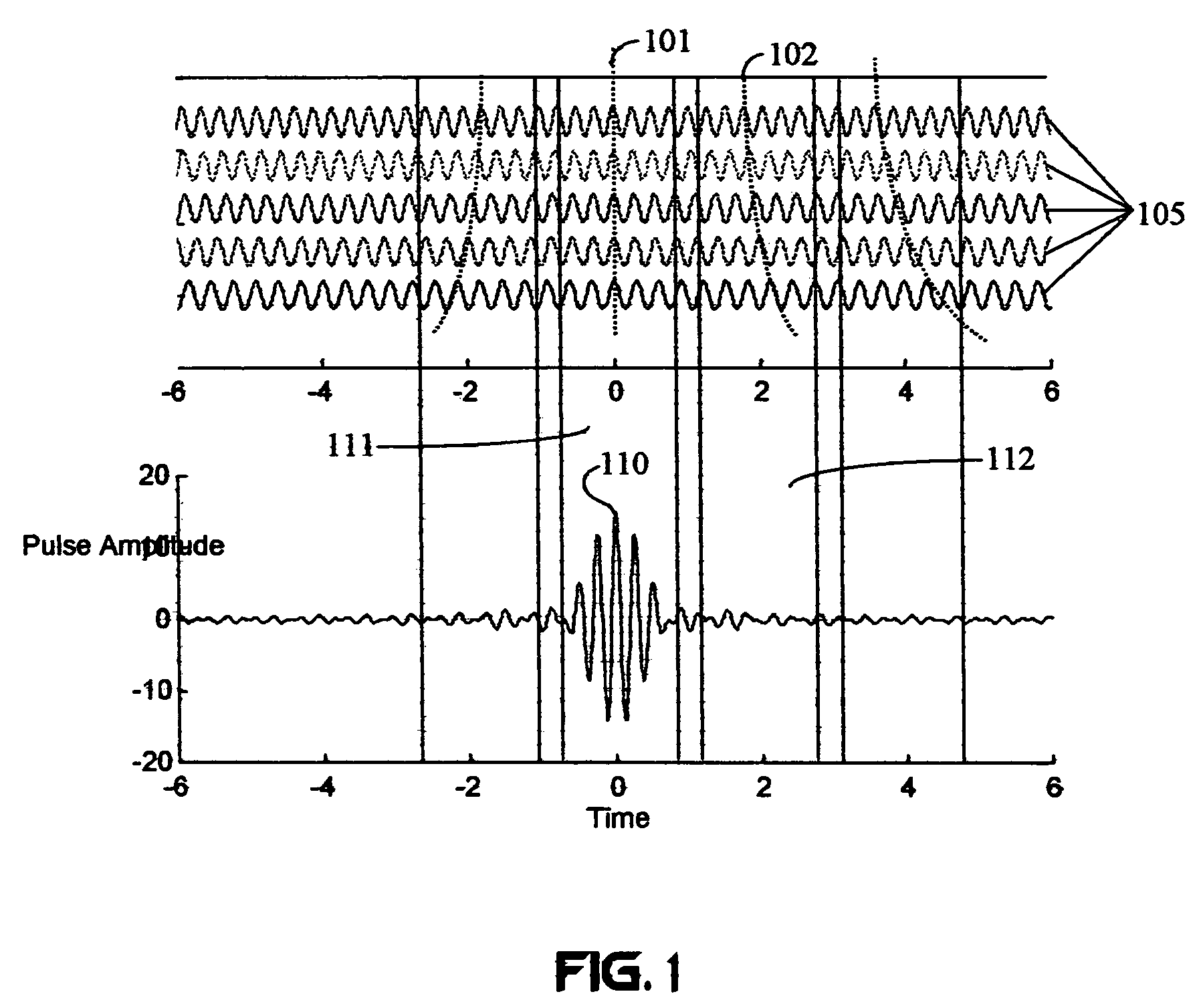
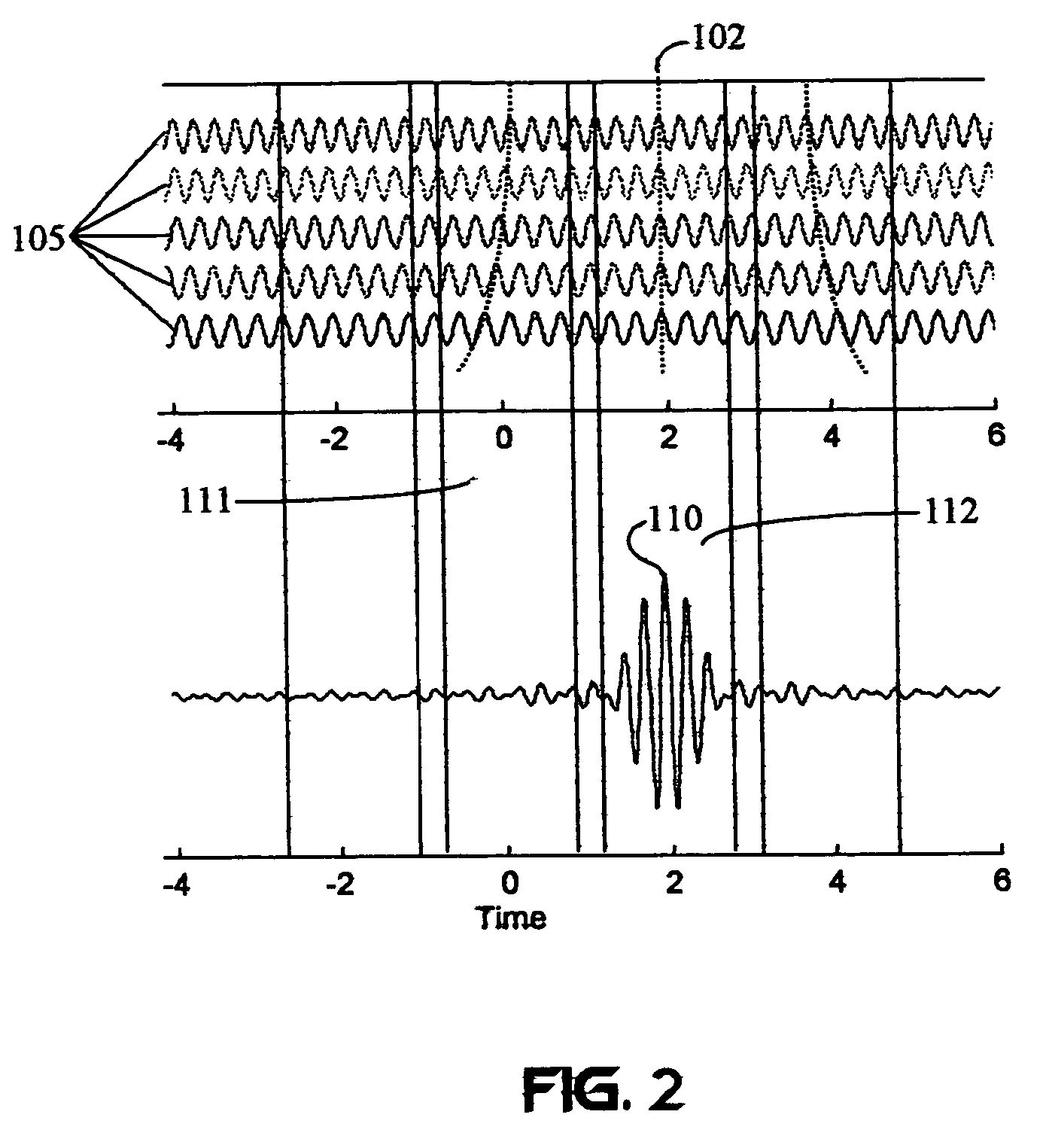
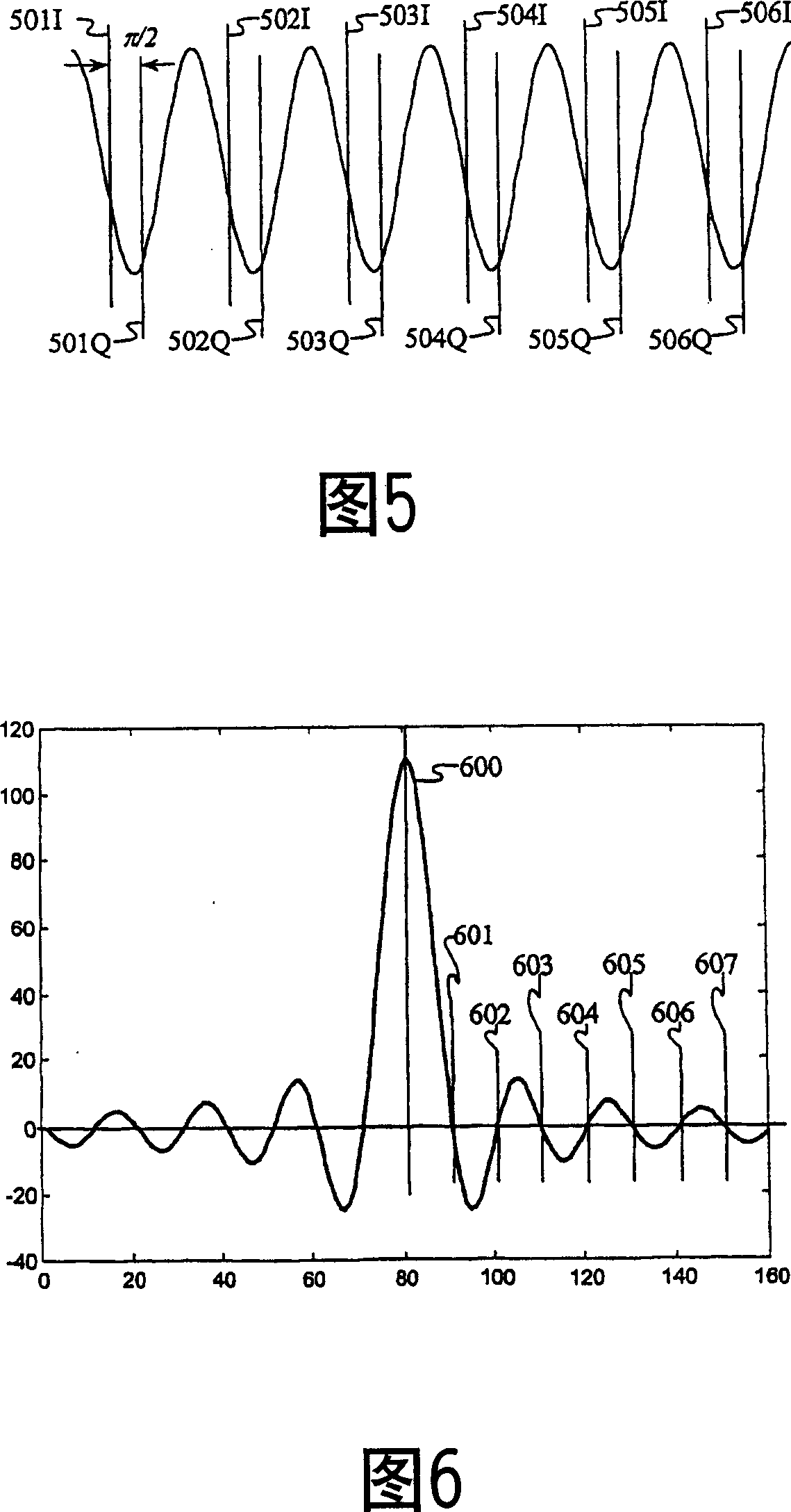
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Orthogonal superposition coding for direct-sequence communications
ActiveUS7317750B2Efficient processingImprove signal to noise ratioTransmission path divisionInter user/terminal allocationFrequency spectrumSuperposition coding
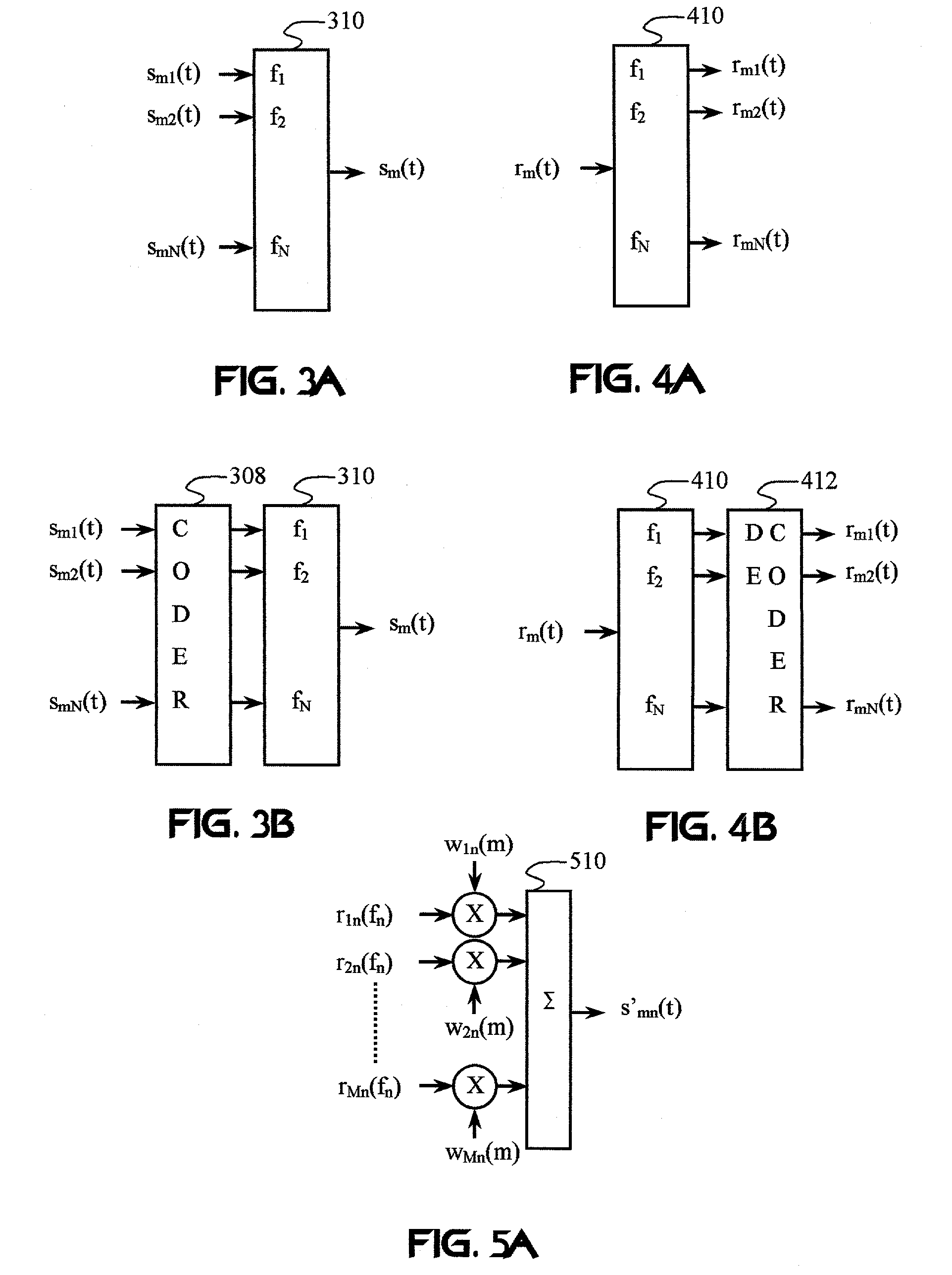
An adaptation to Carrier Interferometry synthesis and analysis provides for complex coding and decoding in a sliding window transform. Coding and decoding functionality can be extended to spatial processing in systems employing multiple transceiver elements. Poly-amplitude codes permit successive interference cancellation in spatial and frequency-domain processing. Handoffs in cellular systems are facilitated by selecting spectral / base station combinations that optimize link performance.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Carrier interferometry networks
ActiveUS20080095121A1Improve throughputImprove bit error rateEnergy efficient ICTModulated-carrier systemsWireless mesh networkTelecommunications link
Applications of CI processing to ad-hoc and peer-to-peer networking significantly improve throughput, network capacity, range, power efficiency, and spectral efficiency. CI-based subscriber units perform network-control functions to optimize network performance relative to channel conditions, network loads, and subscriber services. CI codes are used to identify and address network transmissions. Channel characteristics of communication links are employed to encode, address, and authenticate network transmissions. CI transceivers used as relays and routers employ unique characteristics of transmission paths to code and decode network transmissions. A central processor is adapted to perform array processing with signals received from, and transmitted by, a plurality of subscriber units in a wireless network.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Software adaptable high performance multicarrier transmission protocol
InactiveUS7418043B2Reduce PAPREnhance other technique used for PAPR mitigationModulated carrier system with waveletsSecret communicationTransmission protocolTime domain
Techniques for reducing peak-to-average power in multicarrier transmitters employ peak cancellation with subcarriers that are impaired by existing channel conditions. The use of Carrier Interferometry (CI) coding further improves the effectiveness of peak reduction. CI coding can also be impressed onto pulse sequences in the time domain, which enhances spectral selection and facilitates peak-power control.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Method and apparatus for using multicarrier interferometry to enhance optical fiber communications
InactiveUS7076168B1Increase diversityImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTModulated-carrier systemsSignal qualityFrequency reuse
A redundently modulated multicarrier protocol known as Carrier Interference Multiple Access (CIMA) is used in an optical-fiber network having wireless links at network nodes. CIMA is a protocol that can be used to create wireless protocols (such as TDMA and CDMA) having enhanced capacity and reduced system complexity. A CIMA optical-fiber network uses dispersion to enhance signal quality and facilitate switching. CIMA achieves both diversity benefits and capacity enhancements by providing redundancy in at least one diversity parameter while providing orthogonality in another diversity parameter. This basic operating principle of CIMA may be combined with multi-user detection to achieve frequency reuse and improved power efficiency. In the wireless link, diversity may be used to reduce the effects of small-scale fading on interferometry multiplexing.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Unified multi-carrier framework for multiple-access technologies
InactiveUS7406261B2Reduce the impactReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsOptical multiplexTransmission protocolCarrier signal
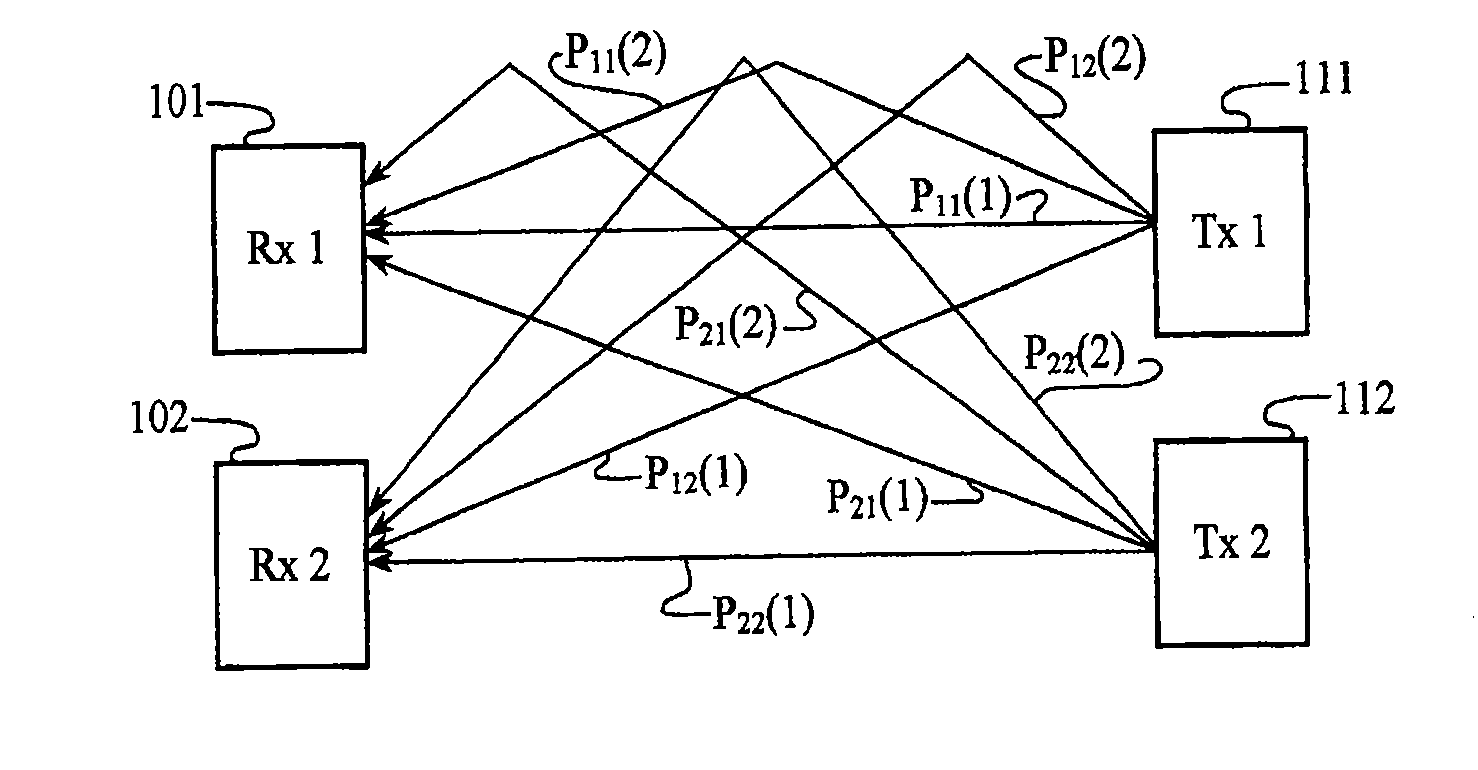
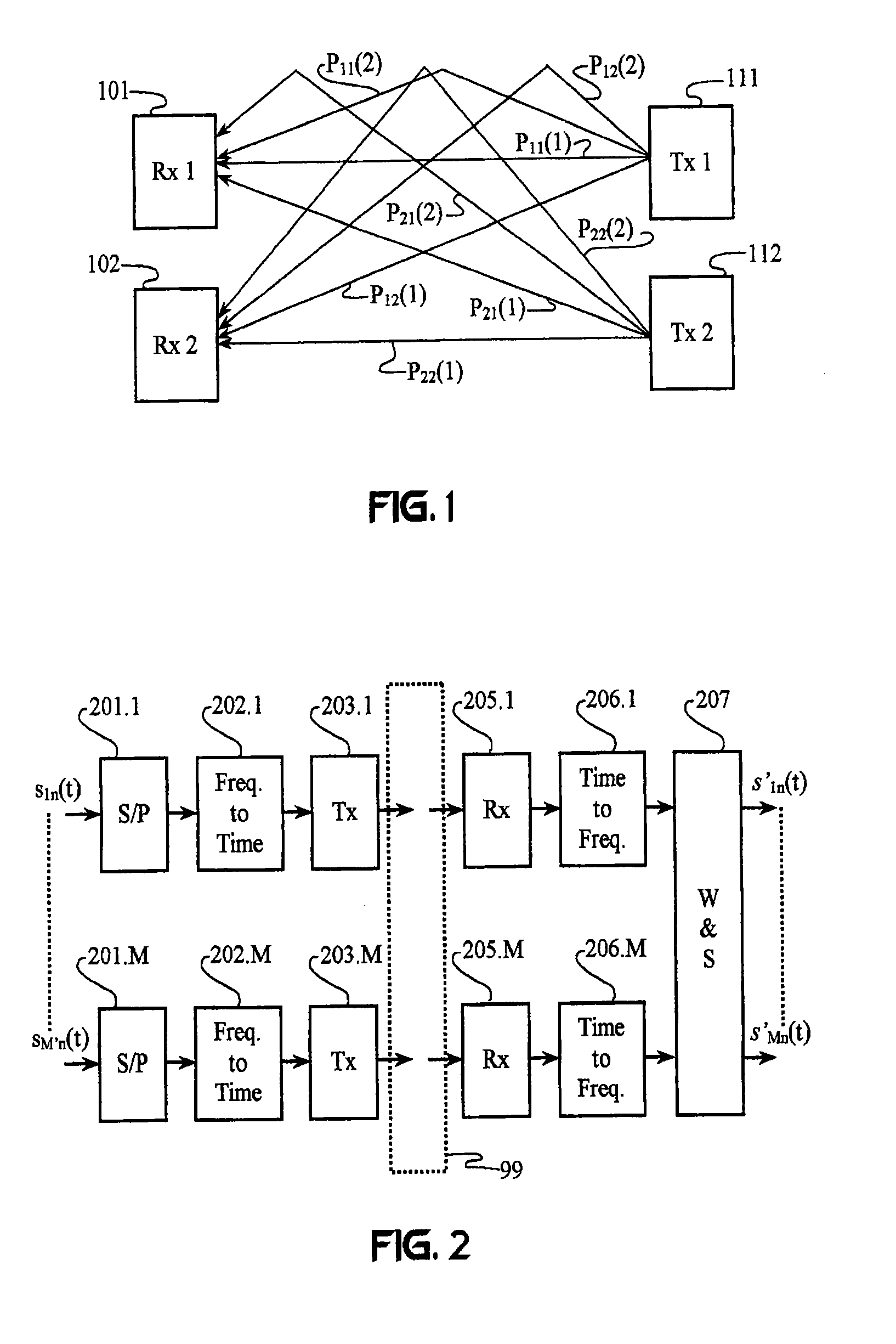
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Orthogonality is provided by carrier interference, which causes a narrow pulse in the time domain corresponding to each transmitted data symbol. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Equivalently, pulse waveforms may be generated from an appropriate selection of polyphase sub-carrier codes. Time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers may be employed for multiple access. Received signals are processed by combining frequency-domain components corresponding to a desired user's allocated carriers. Individual data symbols are processed by providing polyphase decoding, matched filtering, or time-domain shifting the received carriers. Carrier Interferometry components may be used to build various signals corresponding to other transmission protocols.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Software Adaptable High Performance Multicarrier Transmission Protocol
InactiveUS20080310484A1Reduce PAPRReduce complexityModulated carrier system with waveletsSecret communicationTransmission protocolFrequency spectrum
Techniques for reducing peak-to-average power in multicarrier transmitters employ peak cancellation with subcarriers that are impaired by existing channel conditions. The use of Carrier Interferometry (CI) coding further improves the effectiveness of peak reduction. CI coding can also be impressed onto pulse sequences in the time domain, which enhances spectral selection and facilitates peak-power control.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Carrier interferometry coding with applications to cellular and local area networks
InactiveUS7787514B2Reduce transmissionEasy to spreadSecret communicationChannel estimationTelecommunicationsArea network
An adaptation to Carrier Interferometry synthesis and analysis provides for frequency-varying subcarriers. Coding and decoding functionality can be extended to orthogonal chirped and frequency-hopped waveforms. Poly-amplitude codes permit successive interference cancellation in spatial and frequency-domain processing. Dynamic re-sectorization and bandwidth exchange are facilitated by subcarrier allocation.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
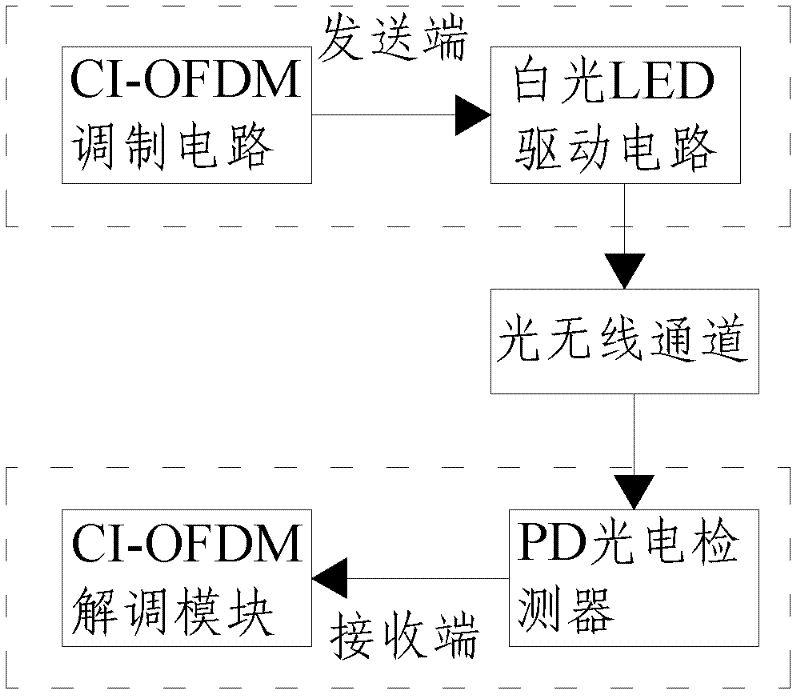
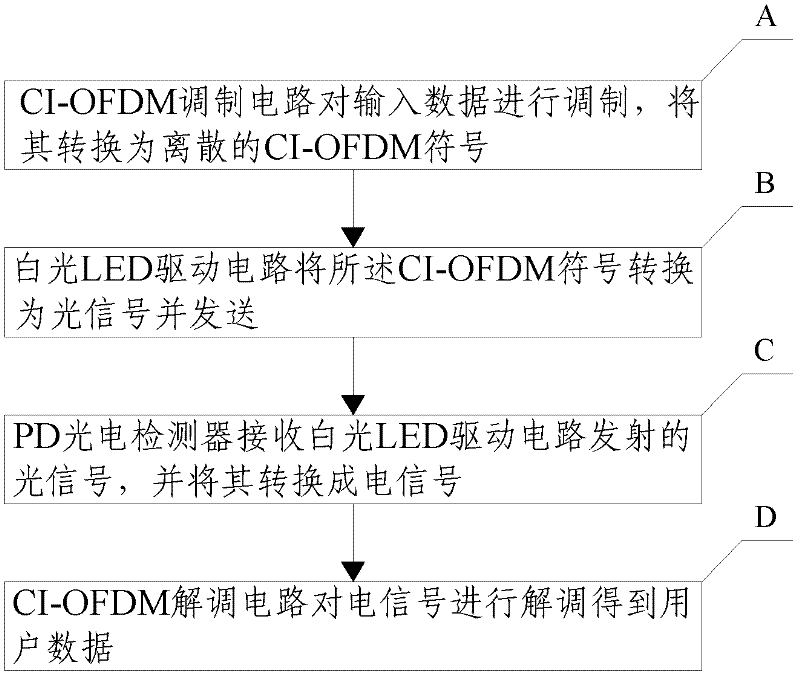
Visible light communication system and method thereof
InactiveCN102244635AImprove transmission qualityImprove performanceClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsEngineeringOptical communication
The invention discloses a visible light communication system and a visible light communication method thereof, which relate to the technical field of wireless optical communication. The system comprises a transmitter and a receiver. An input signal is converted into an optical signal by the transmitter, the optical signal is transmitted to the receiver by a wireless optical channel, and the receiver converts the optical signal into an electrical signal and outputs the electrical signal. The transmitter comprises a carrier interferometry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CI-OFDM) modulation circuit and a white light-emitting diode (LED) drive circuit which are connected, wherein the CI-OFDM modulation circuit is used for performing CI-OFDM modulation on data input by a user; and the white LED drive circuit is used for converting the electrical signal generated by the CI-OFDM modulation circuit into the optical signal. The receiver comprises a PD photoelectric detector and a CI-OFDM demodulation circuit which are connected, wherein the PD photoelectric detector is used for performing P / D conversion on the received optical signal to convert the optical signal into the electrical signal; and the CI-OFDM demodulation circuit is used for performing CI-OFDM demodulation on the received data. By the system and the method, the transmission quality of the visible light communication system can be effectively improved, and the peak-to-average power ratio of an OFDM transmitted signal can be reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cancellation systems for multicarrier transceiver arrays
InactiveUS7092352B2Improve bindingImprove bandwidth efficiencyMagnetic measurementsError preventionTransceiverTime division multiple access
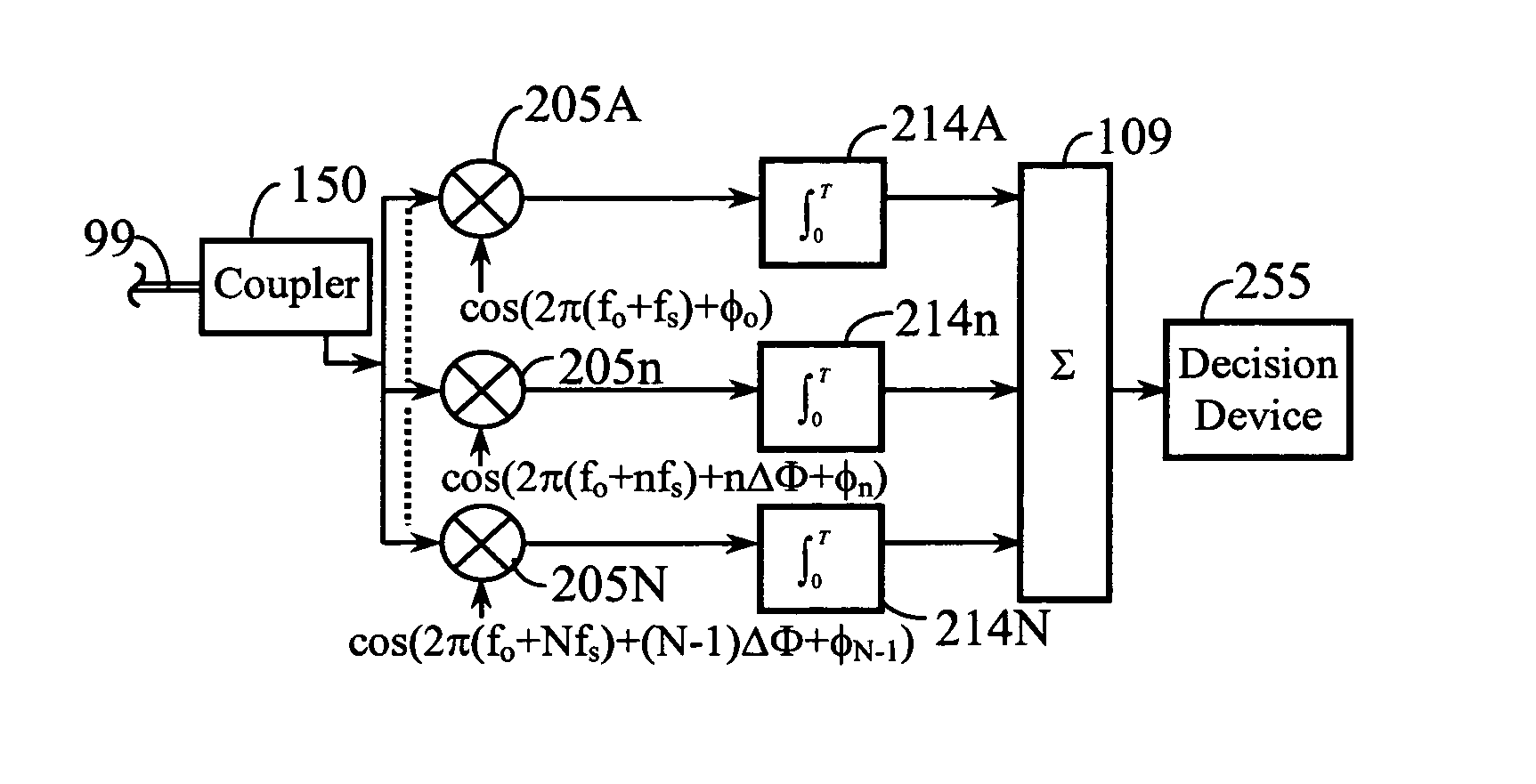
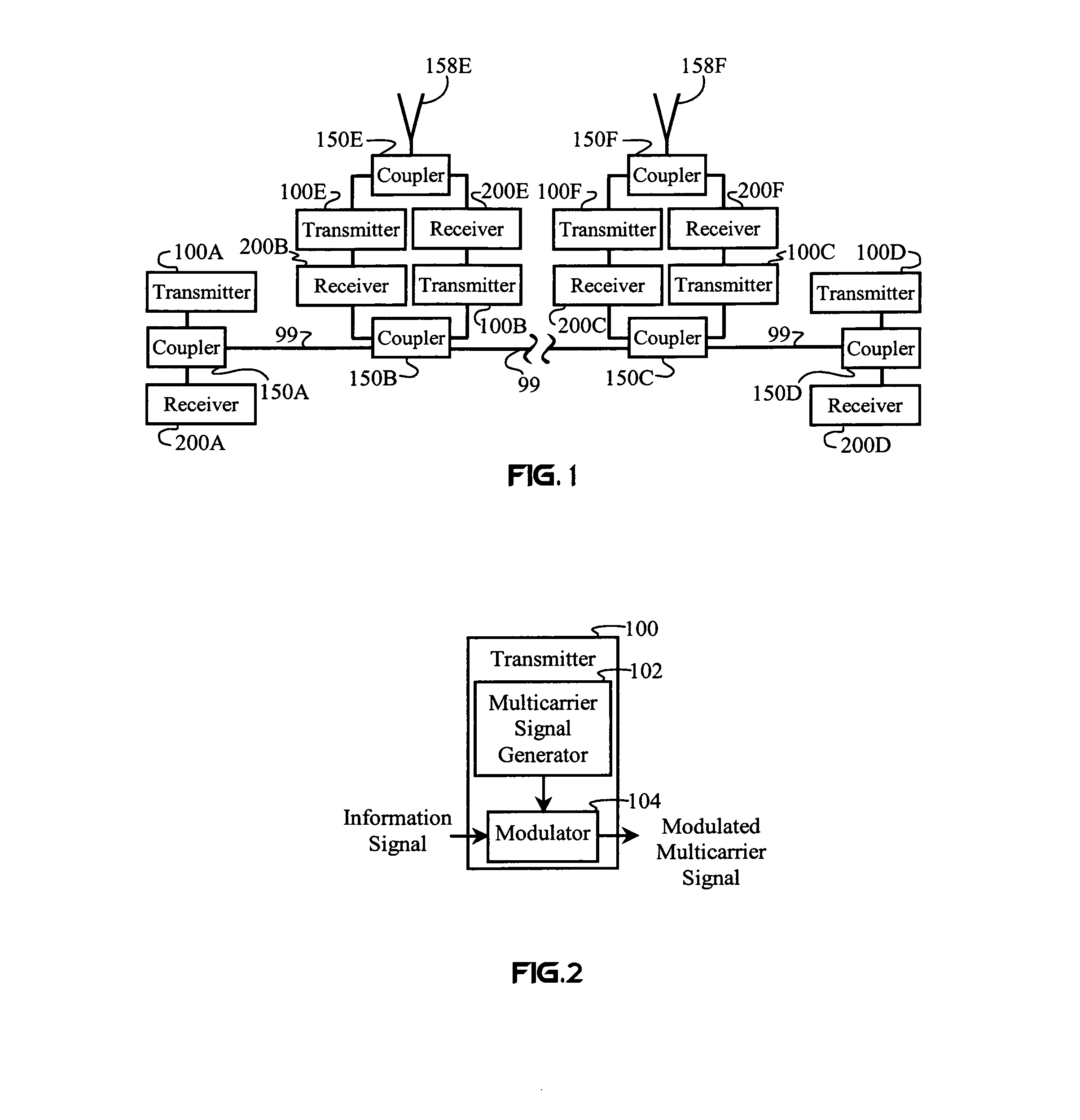
Frequency-dependent cancellation separates a plurality of interfering signals received by a plurality of receivers. Received wideband single-carrier signals or multicarrier signals are separated into a plurality of narrowband subcarriers. Sub-carrier frequencies and frequency-band characteristics may be selected with respect to channel characteristics (e.g., coherence bandwidth, interference, etc.). A cancellation circuit provides complex weights to the sub-carrier components. Weighted components associated with each sub-carrier frequency are combined to separate a plurality of interfering signals. Optionally, a plurality of the separated subcarriers may be combined to reconstruct at least one transmitted single-carrier signal from a plurality of frequency components. Combining may include decoding, such as to reconstruct a coded sequence of data symbols transmitted via direct-sequence coding, code division multiple access (CDMA), multicarrier CDMA, carrier interferometry (CI), CI coding, or coded orthogonal frequency division multiplexing.
Owner:S AQUA SEMICONDUCTOR LLC
Method and apparatus for transmitting signals having a carrier-interferometry architecture
InactiveUS7639597B2Quality improvementIncrease wireless capacitySecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTransmission protocolCarrier signal
Transmission waveforms are synthesized from orthogonal subcarriers using appropriate combinations of complex sub-carrier codes. This allows conventional single-carrier signaling (such as GSM and CDMA transmission protocols) to be generated and received using a multicarrier platform that is similar to OFDM. Carrier interferometry provides unprecedented bandwidth efficiency and enables substantial improvements in interference rejection, power efficiency, and system versatility.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Cancellation Systems for Multicarrier Transceiver Arrays
InactiveUS20070060058A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyImprove performanceMagnetic/electric field screeningRadio transmissionTransceiverCarrier signal
Frequency-dependent cancellation separates a plurality of interfering signals received by a plurality of receivers. Received wideband single-carrier signals or multicarrier signals are separated into a plurality of narrowband subcarriers. Sub-carrier frequencies and frequency-band characteristics may be selected with respect to channel characteristics (e.g., coherence bandwidth, interference, etc.). A cancellation circuit provides complex weights to the sub-carrier components. Weighted components associated with each sub-carrier frequency are combined to separate a plurality of interfering signals. Optionally, a plurality of the separated subcarriers may be combined to reconstruct at least one transmitted single-carrier signal from a plurality of frequency components. Combining may include decoding, such as to reconstruct a coded sequence of data symbols transmitted via direct-sequence coding, code division multiple access (CDMA), multicarrier CDMA, carrier interferometry (CI), CI coding, or coded orthogonal frequency division multiplexing.
Owner:LOT 41 ACQUISITION FOUND
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
ActiveUS11075786B1Low costImprove system performanceSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Carrier interferometry coding and multicarrier processing
InactiveCN1484877AFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiplex code generationPhysical layerCarrier signal
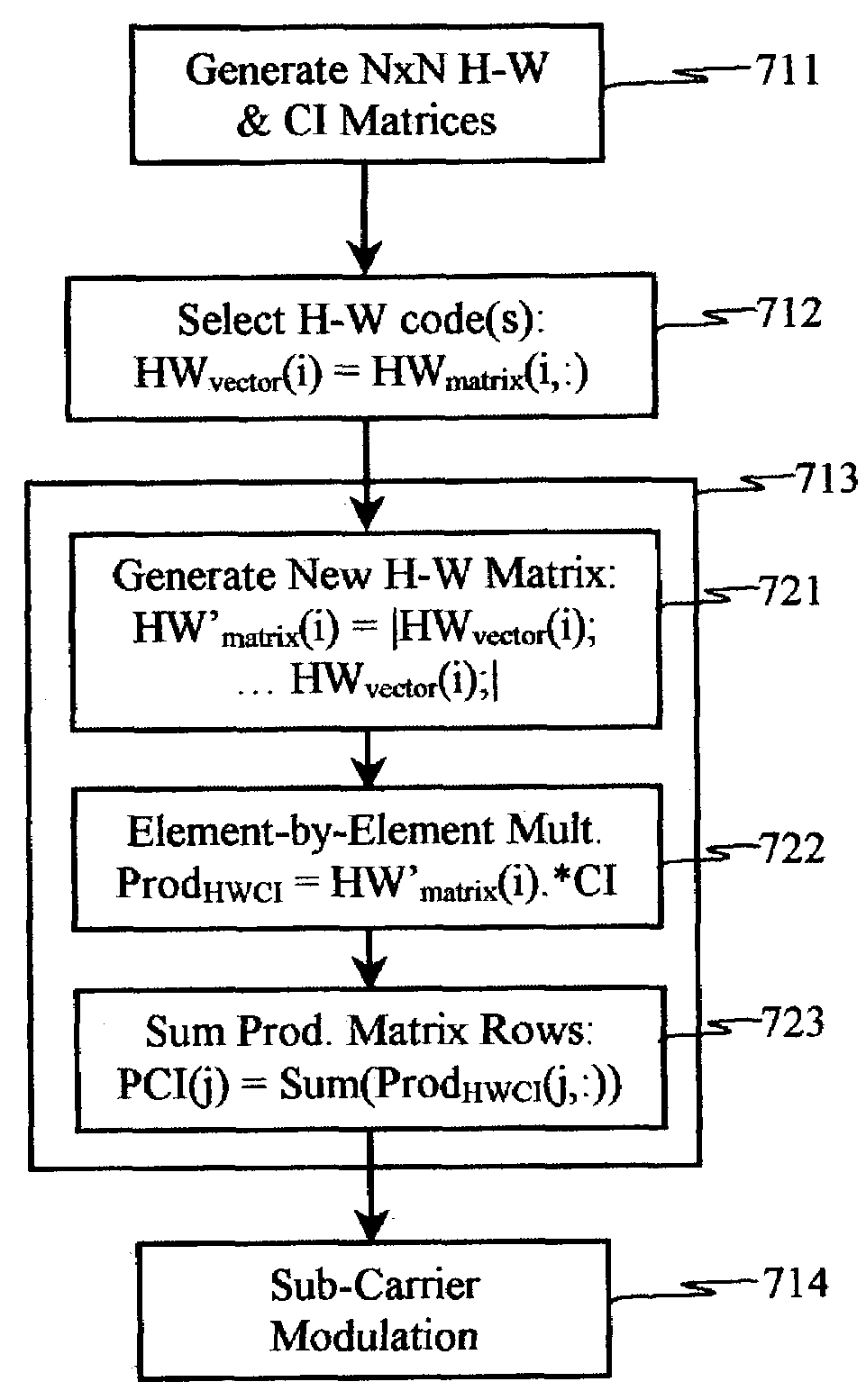
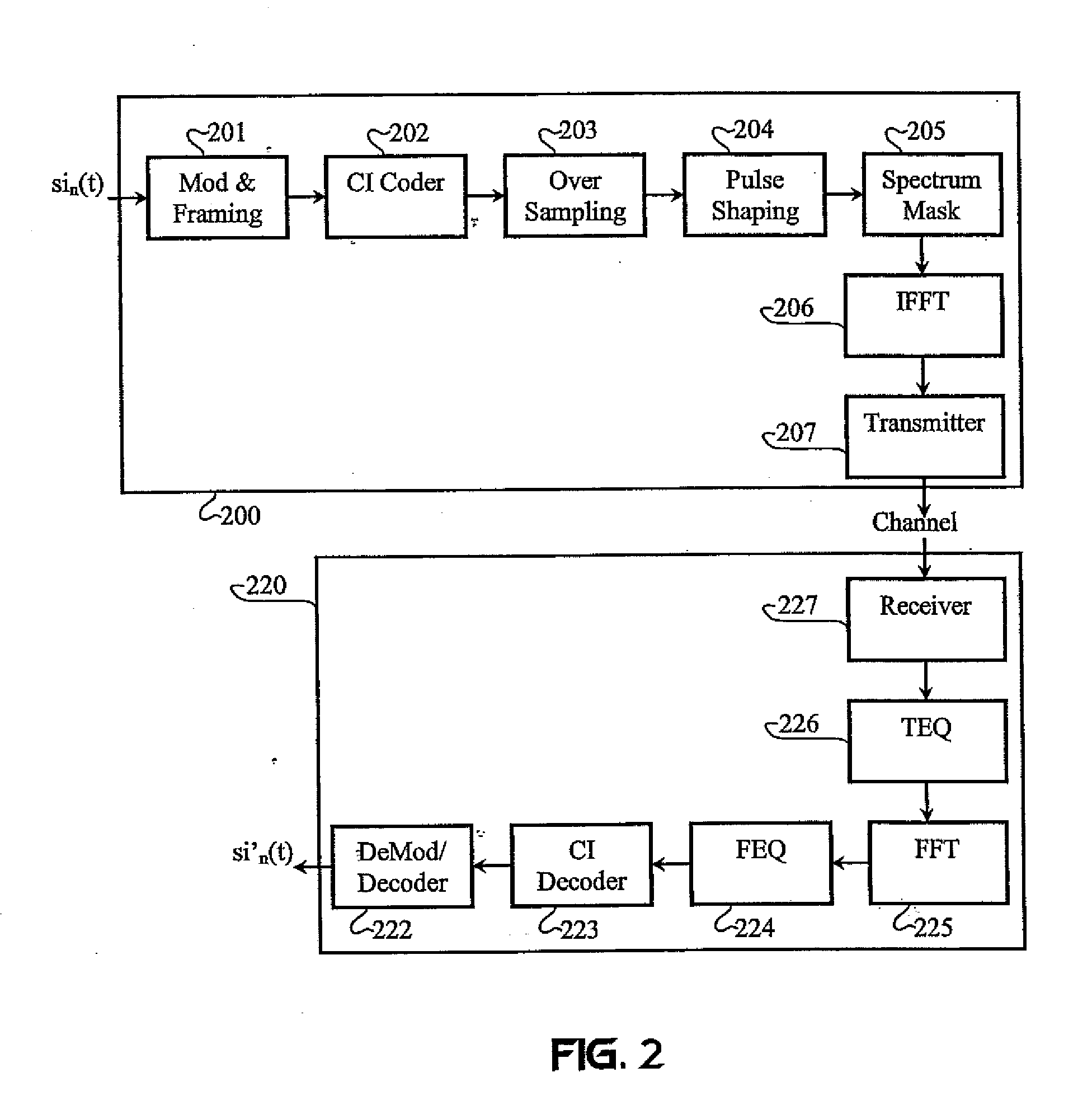
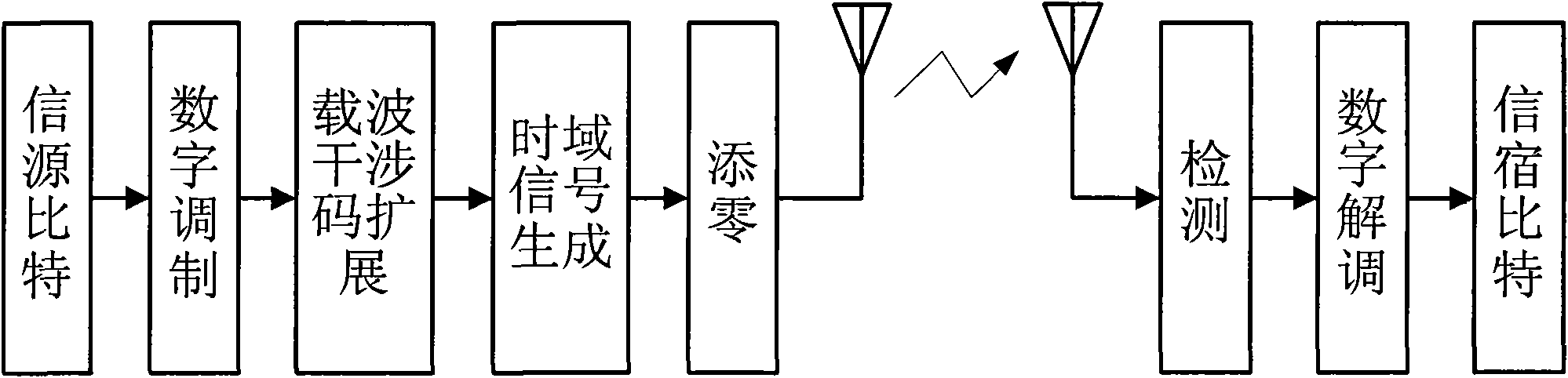
Carrier Interferometry (CI) codes include families of orthogonal polyphase codes that have no length restrictions and can be used for direct-sequence and multicarrier coding. Quasi-orthogonal CI channel codes simultaneously improve probability-of-error performance and increase throughput. CI filtering (701, 702), which is based on CI codes, enables filtering and correlation operations via sampling and adding. CI codes simplify transform operations, such as Fourier transforms, by reducing or eliminating complex multiplications. CI filtering may be used to simplify synthesis and analysis functions and allow all physical-layer processing operations to be consolidated into simple sub-carrier selection and weighting operations. Thus, CI processing enables a software-defined baseband processor.
Owner:罗特41采购基金会有限公司
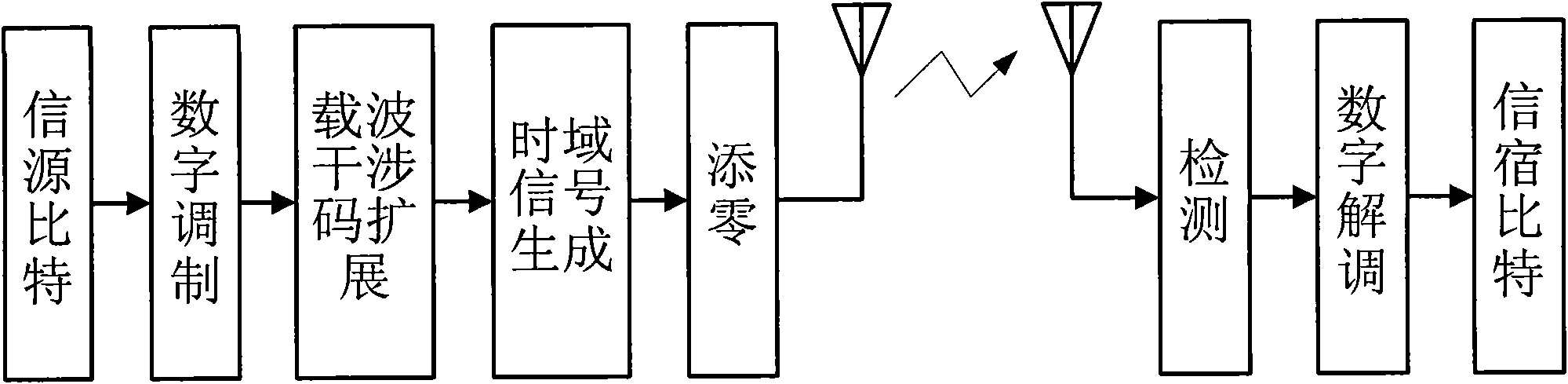
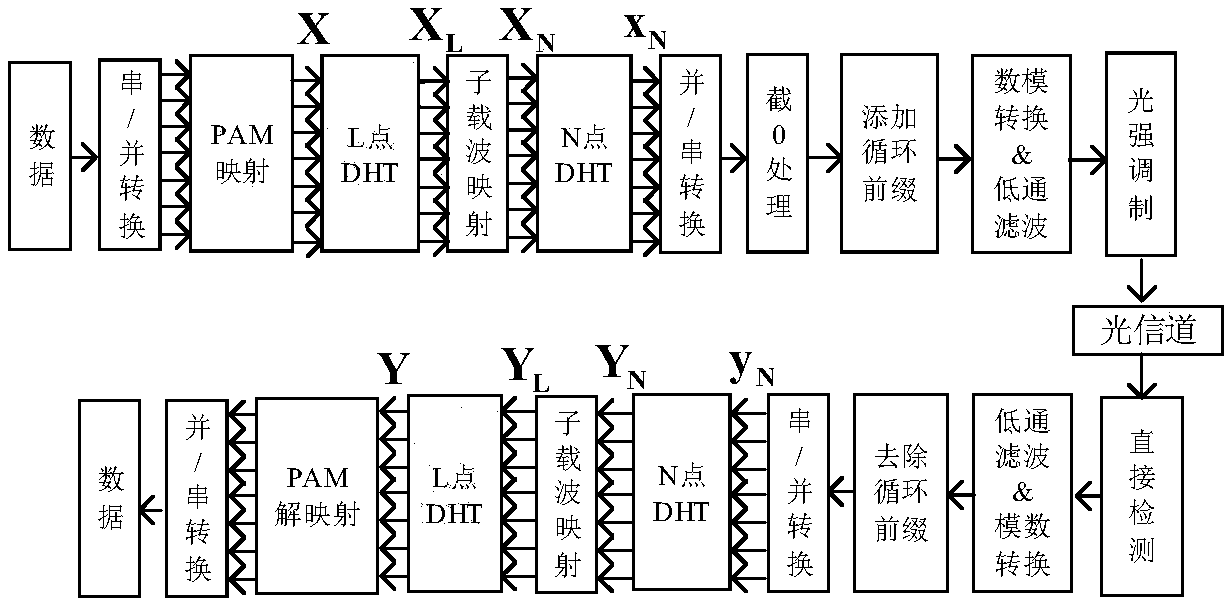
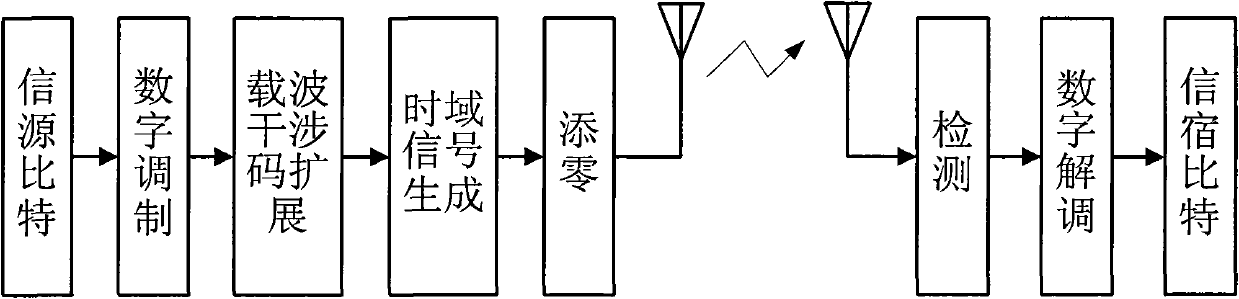
Zero padding mode-based CI-OFDM communication method
InactiveCN101917252AImprove bit error rate performanceError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsZero paddingCyclic prefix
The invention discloses a zero padding mode-based carrier interferometry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CI-OFDM) communication method, and belongs to the field of communication technology. The conventional CI-OFDM system eliminates intersymbol interference by using a cyclic prefix (CP) mode when adding a guard interval so as to remove the data of the cyclic prefix at a receiving end; but the processing method causes loss of part of received information so as to reduce the bit error rate of the system. The zero padding mode is adopted as the guard interval during the data transmission and detection is performed by combining the data symbol of the guard interval in the data receiving process, so the frequency diversity gain is fully utilized and the bit error rate of the system is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
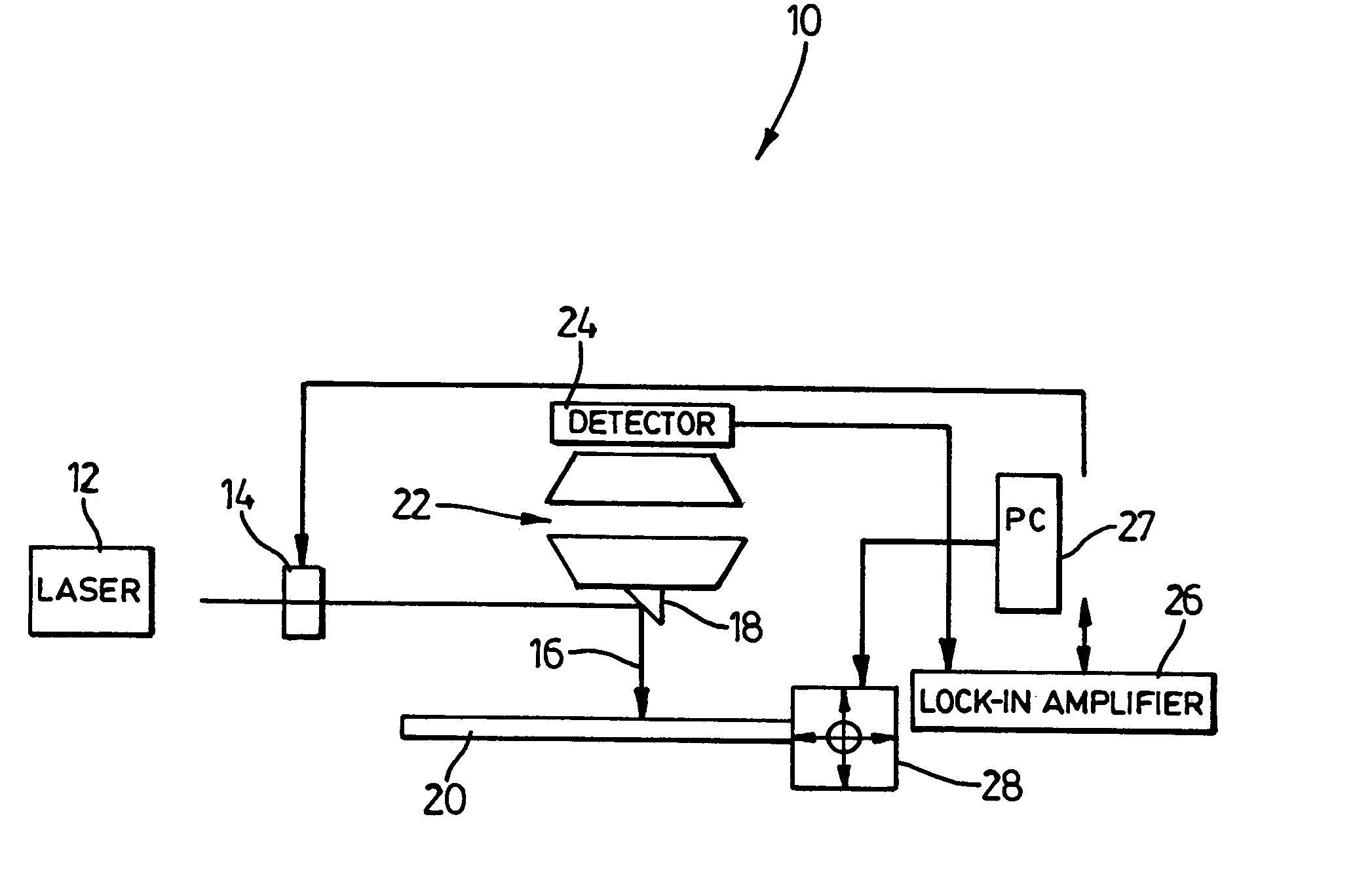
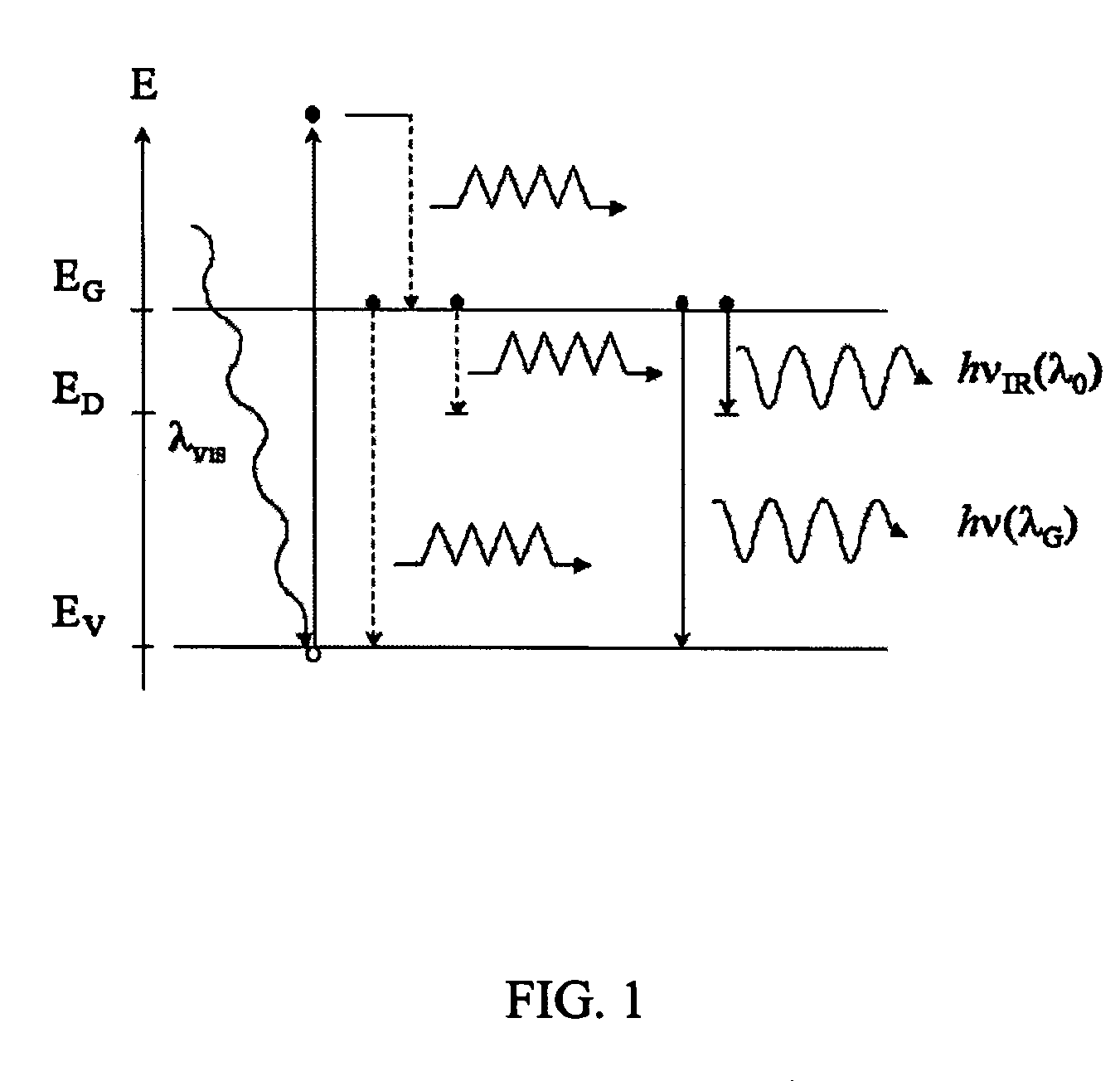
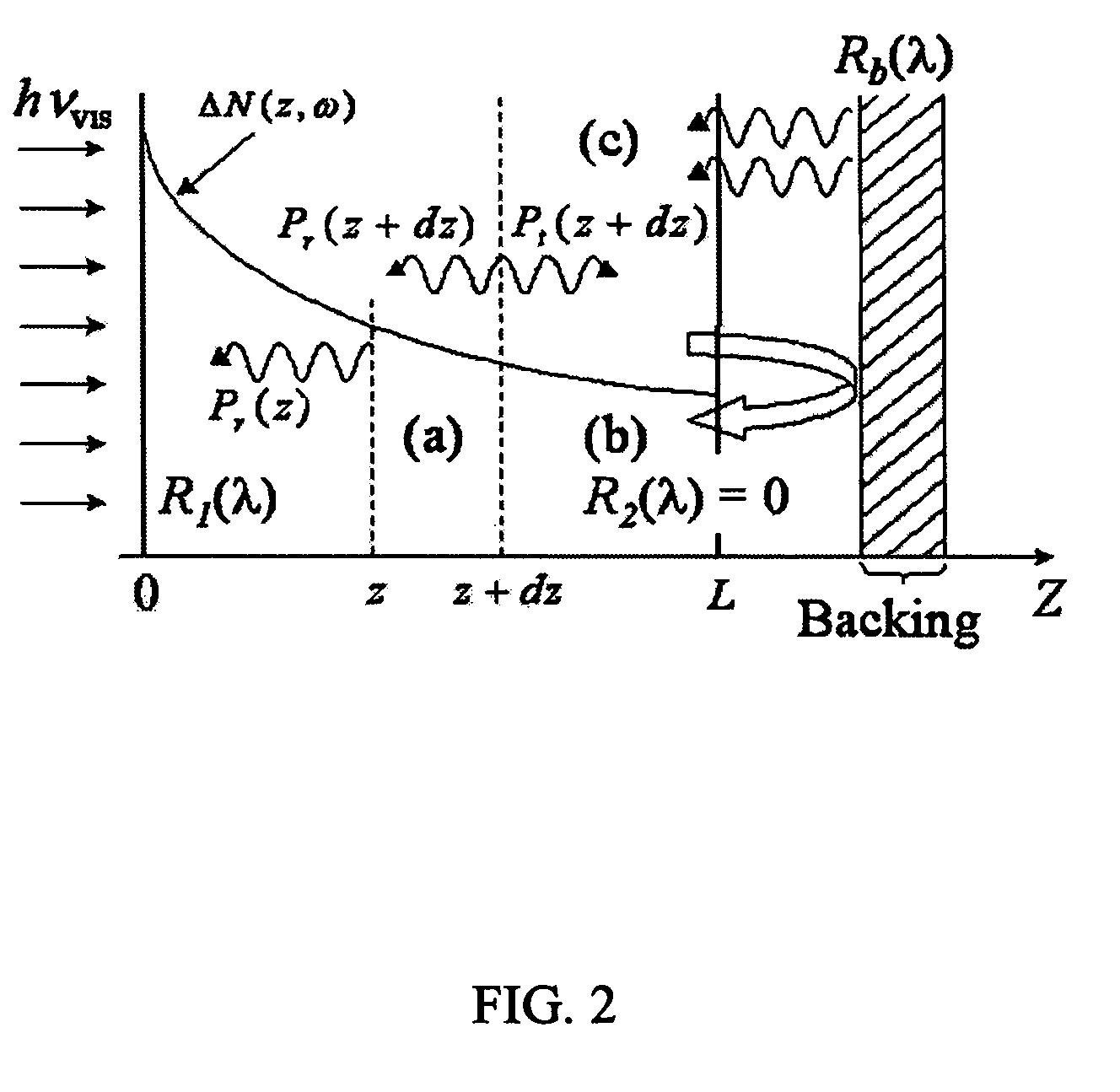
Method of photocarrier radiometry of semiconductors
ActiveUS7045786B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSemiconductor materialsCarrier signal
The present invention relates to metrologic methodologies and instrumentation, in particular laser-frequency domain infrared photocarrier radiometry (PCR), for contamination and defect mapping and measuring electronic properties in industrial Si wafers, devices and other semiconducting materials. In particular the invention relates to the measurement of carrier recombination lifetime, τ, carrier diffusivity, D, surface recombination velocities, S, carrier diffusion lengths, L, and carrier mobility, μ, as well as heavy metal contamination mapping, ion implantation mapping over a wide range of dose and energy, and determination of the concentration of mobile impurities in SiO2 layers on semiconductor substrates. The present invention provides a method and complete photocarrier radiometric apparatus comprising novel signal generation and analysis techniques (carrier-wave interferometry) as well as novel instrumental hardware configurations based on the physical principle of photocarrier radiometry. The method comprises (a) optical excitation of the sample with a modulated optical excitation source and (b) detection of the recombination-induced infrared emission while filtering any Planck-mediated emissions. The present invention provides an instrumental method for detecting weak inhomogeneities among semiconducting materials that are not possible to detect with conventional single-ended photocarrier radiometry. The method comprises (a) irradiating both sides of the sample with modulated optical excitation sources that are 180 degrees out of phase with respect to one another and (b) monitoring the diffusion of the interfering, separately generated carrier waves through the corresponding recombination-induced IR emissions for PCR detection, or the use of an alternative detection scheme that monitors a sample property dependent on the carrier wave transport in the sample.
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +1
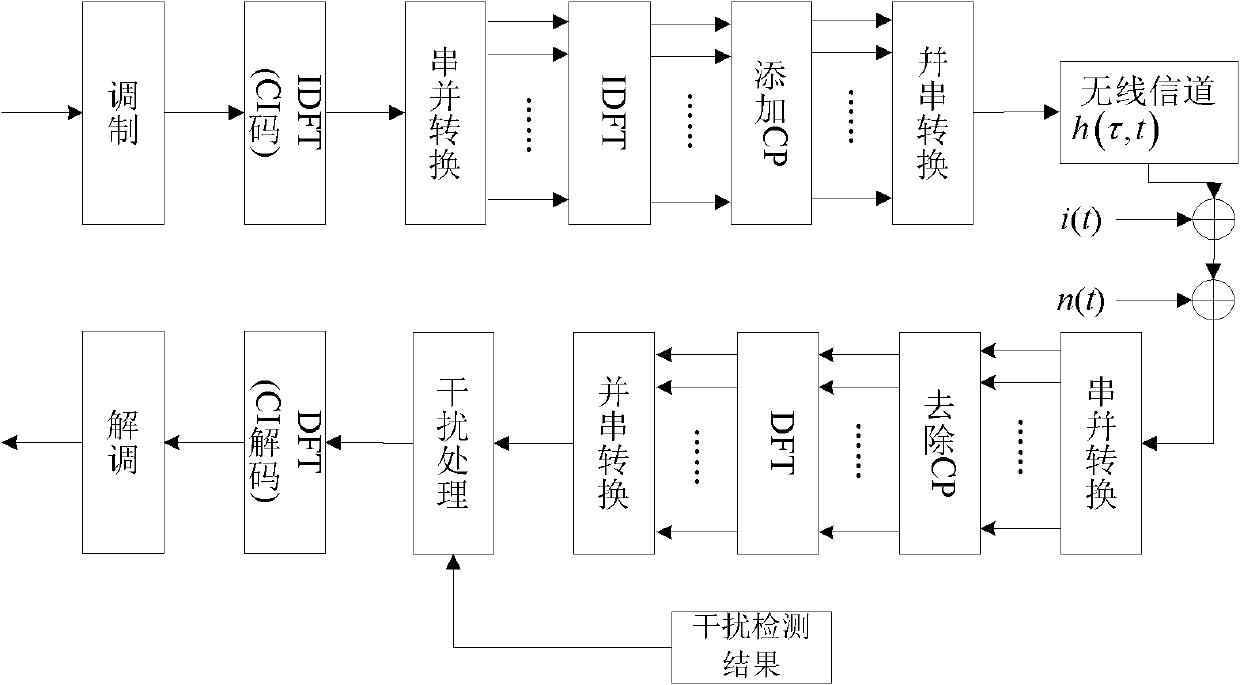
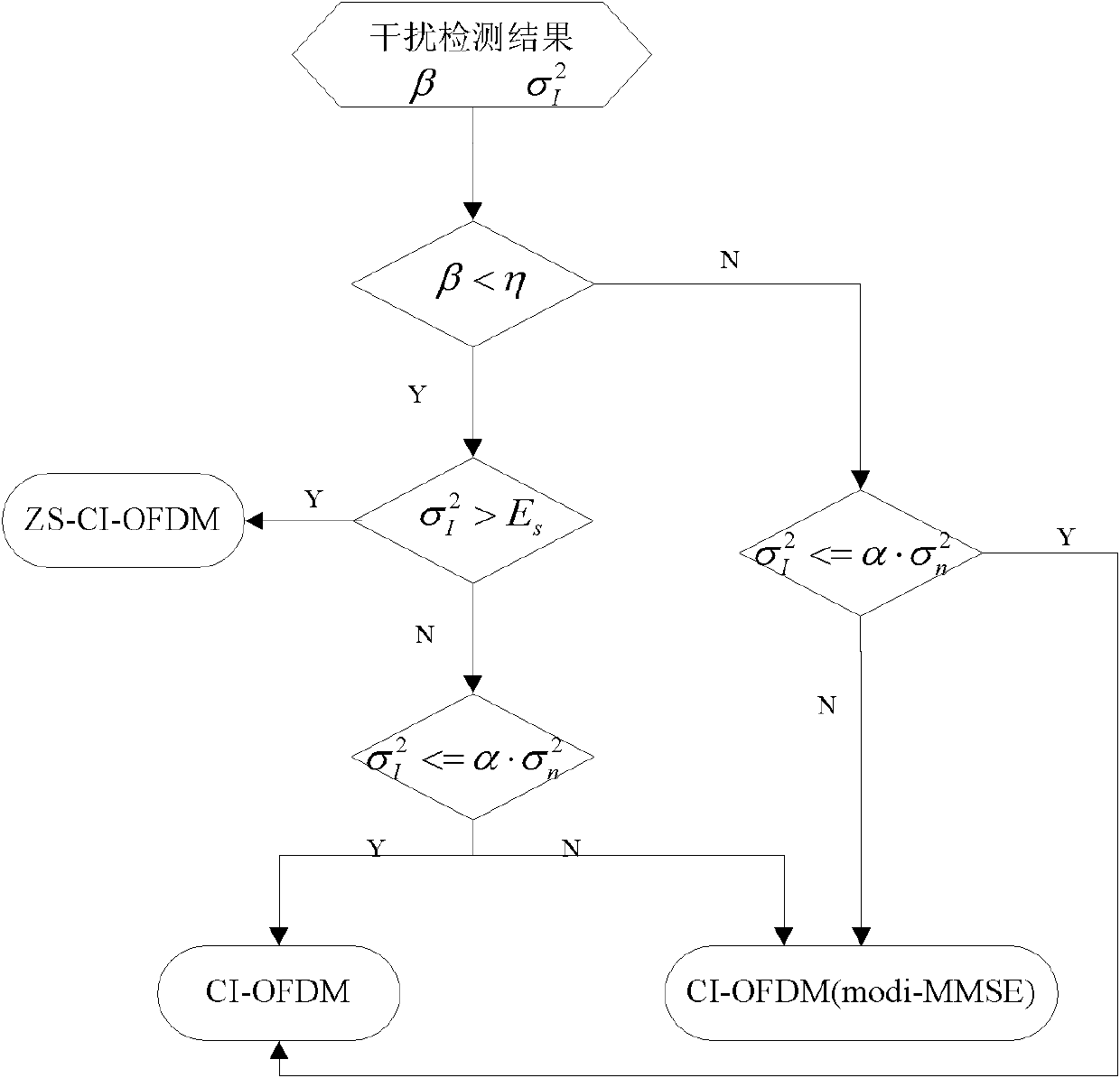
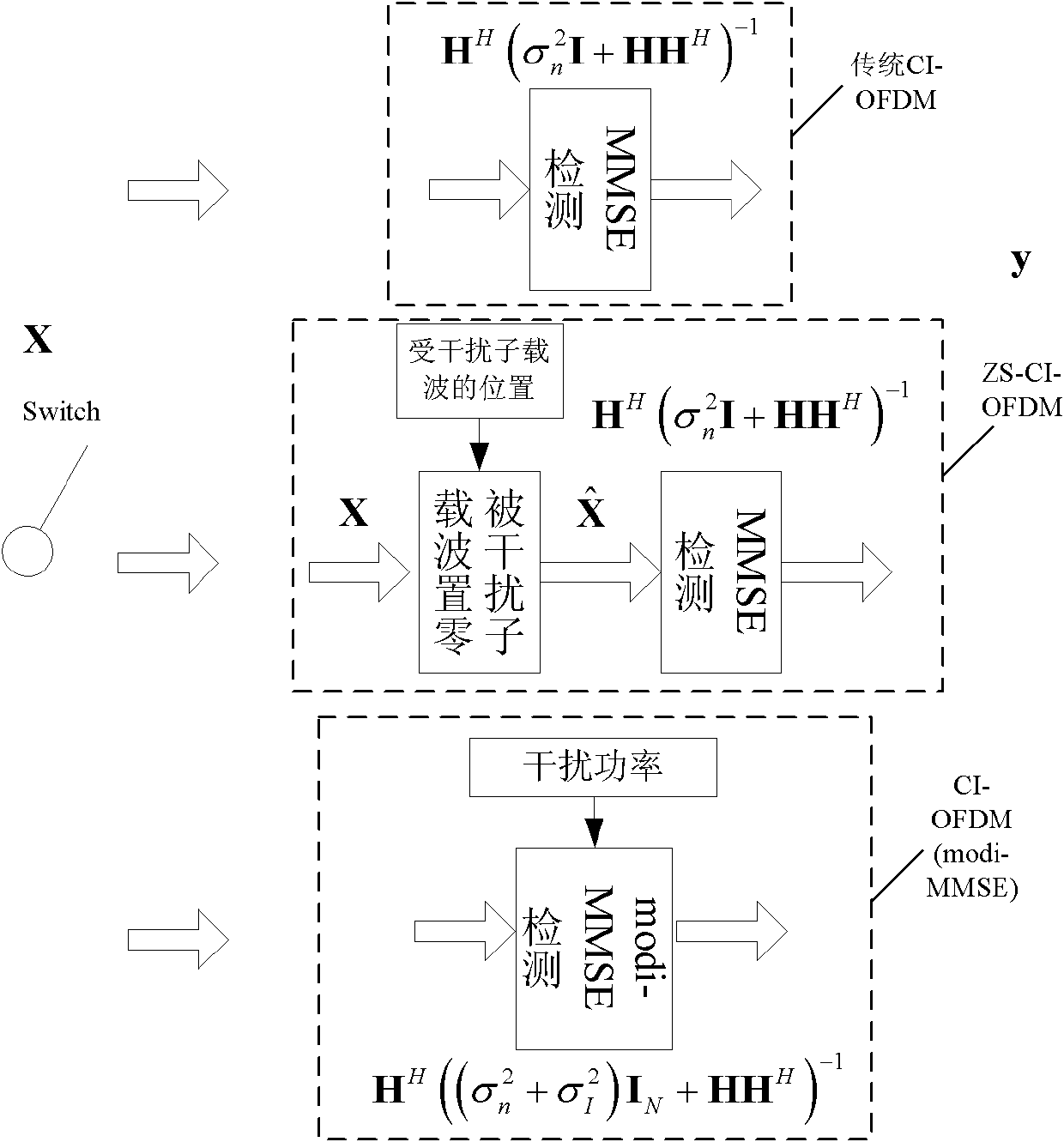
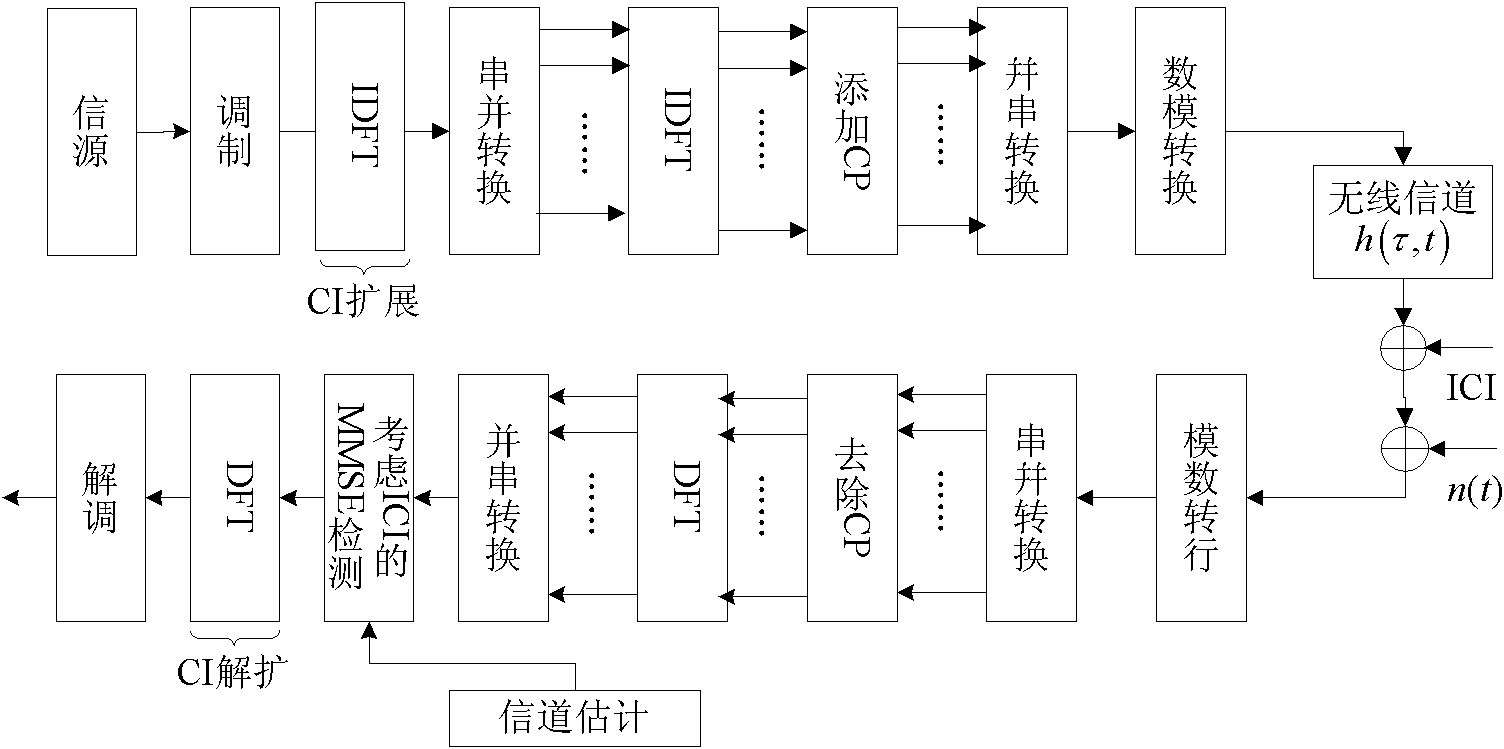
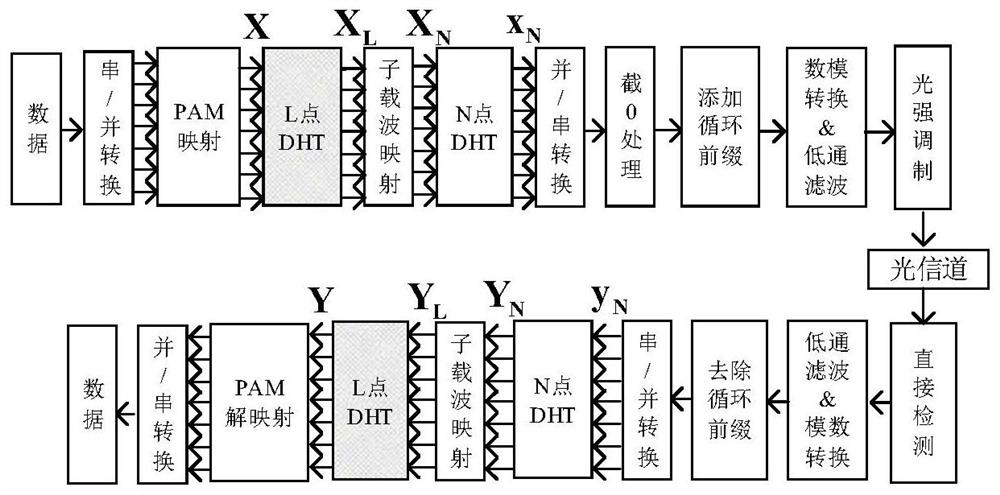
Interference processing method based on carrier interferometry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CI-OFDM) system
InactiveCN102148780AEliminate effectiveEasy to operateMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLow speedTransceiver
The invention discloses an interference processing method based on a carrier interferometry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CI-OFDM) system. The method is characterized in that a transceiver structure of the CI-OFDM system carries out OFDM receipt after a transceiver receives data so as to obtain frequency domain data after the OFDM receipt; and an interference detection result, the ratio that interference bandwidth accounts for total communication channel bandwidth as well as interference power are utilized to process the frequency domain data. By adopting the characteristic thatthe CI-OFDM is utilized to expand each path of low-speed parallel data to all sub-carries via using orthogonal CI codes, according to performance differences exerted by resisting different interferences via using the CI-OFDM under minimum mean squared error (MMSE) equilibrium, a traditional CI-OFDM is introduced under the MMSE equilibrium; the CI-OFDM performing zero setting on interfered sub-carriers at a receiving end and the CI-OFDM with consideration of the interference power of the MMSE equalizer carry out self-adaptive processing on power and bandwidth of different interference signals,thus effectively eliminating the interferences.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Large-surface defect detection by single-frame spatial-carrier interferometry
ActiveUS8275573B1Quick identificationRapidly identifying unexpected irregularityFeeler-pin gaugesMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsFourier transform on finite groupsAdaptive algorithm
An adaptive algorithm is tailored to fit the local fringe frequency of single-frame spatial-carrier data under analysis. Each set of data points used sequentially by the algorithm is first processed with a Fourier Transform to find the local frequency of the fringes being analyzed. That information is then used to adapt the algorithm to the correct phase step thus calculated, thereby optimizing the efficiency and precision with which the algorithm profiles the local surface area. As a result, defects are identified and measured with precision even when the slope of the surface varies locally to the point where the algorithm without adaptive modification would not be effective to measure them. Once so identified, the defects may be measured again locally with greater accuracy by conventional temporal PSI.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
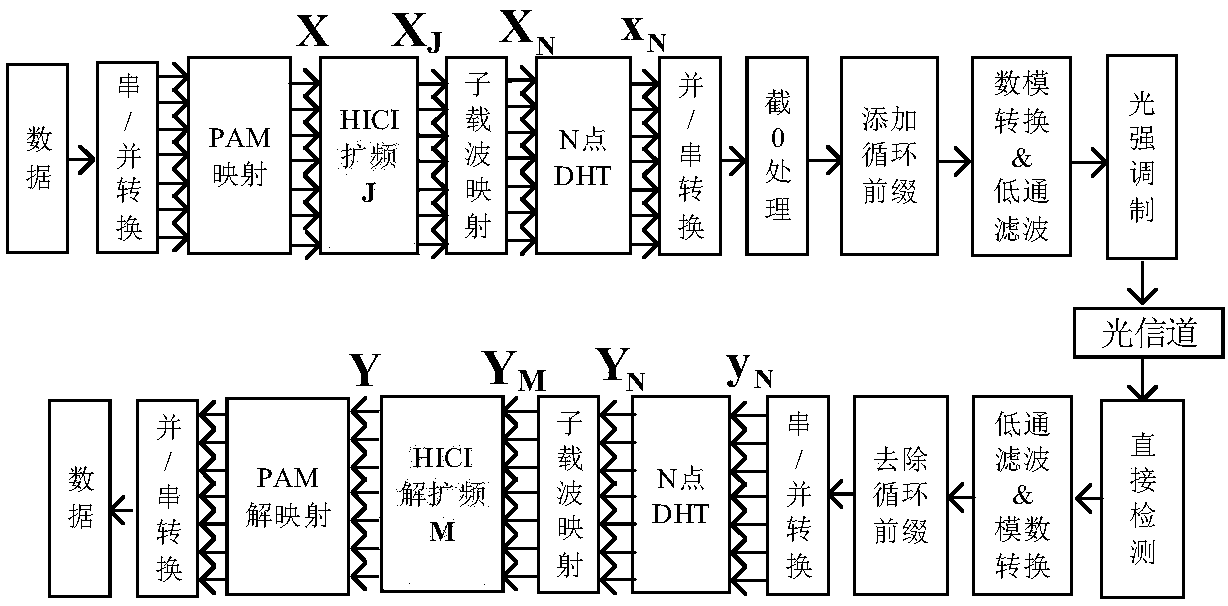
VLC system OOFDM modulation method based on hadamard matrix amplification
ActiveCN108040027AReduce intervalReduced ability to fight PSNMulti-frequency code systemsElectromagnetic transmissionCommunications systemParallel computing
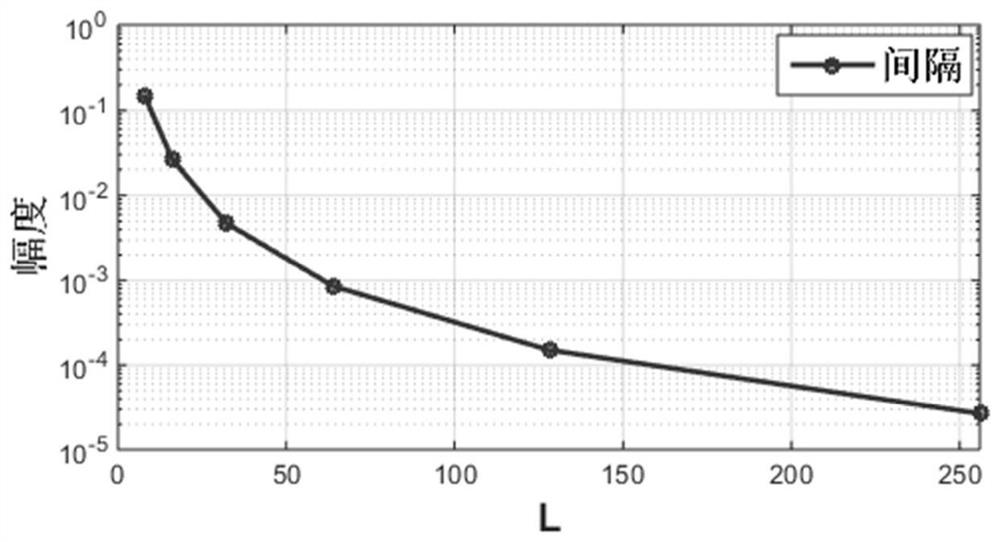
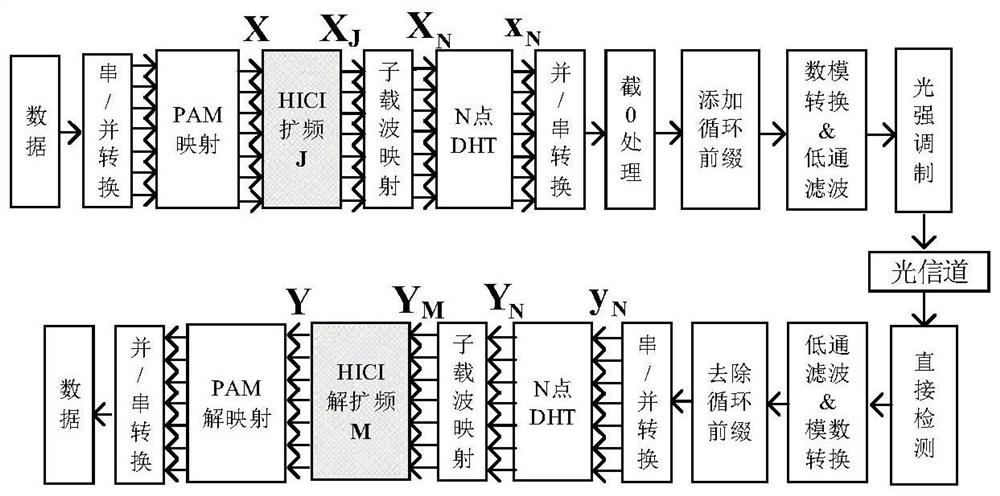
The invention provides a visible light communication (VLC) system optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OOFDM) modulation method based on hadamard matrix amplification, which keeps the orthogonality characteristics of a matrix by utilizing hadamard matrix amplification, and forms an HICI code by performing the hadamard matrix amplification on a carrier interferometry (CI) spread code, so that code element interval of the HICI code and the CI spread code keeps consistent. Compared with the traditional CI spread code, the HICI code does not cause reduction of the code element interval along with the increasing of the number of subcarriers, and simultaneously has the capability of reducing OOFDM-based VLC system signal PAPR and the capability of withstanding PSN. Based on theoretical analysis and simulation results, the HICI code provided by the VLC system OOFDM modulation method based on hadamard matrix amplification, which is provided by the invention, improves the capability of the original CI spread code to withstand the PSN and simultaneously has the capability of reducing the OOFDM communication system PAPR.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
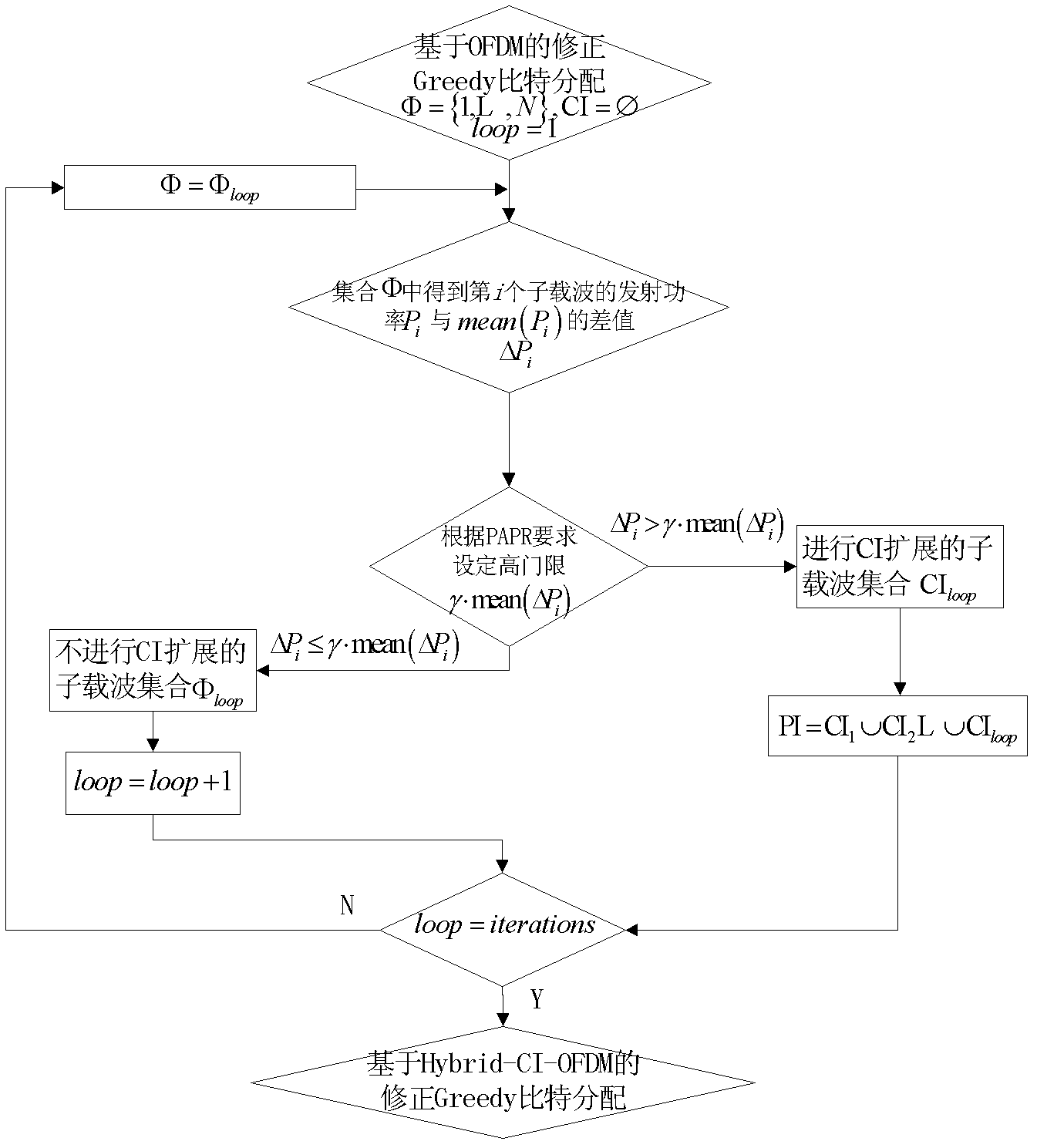
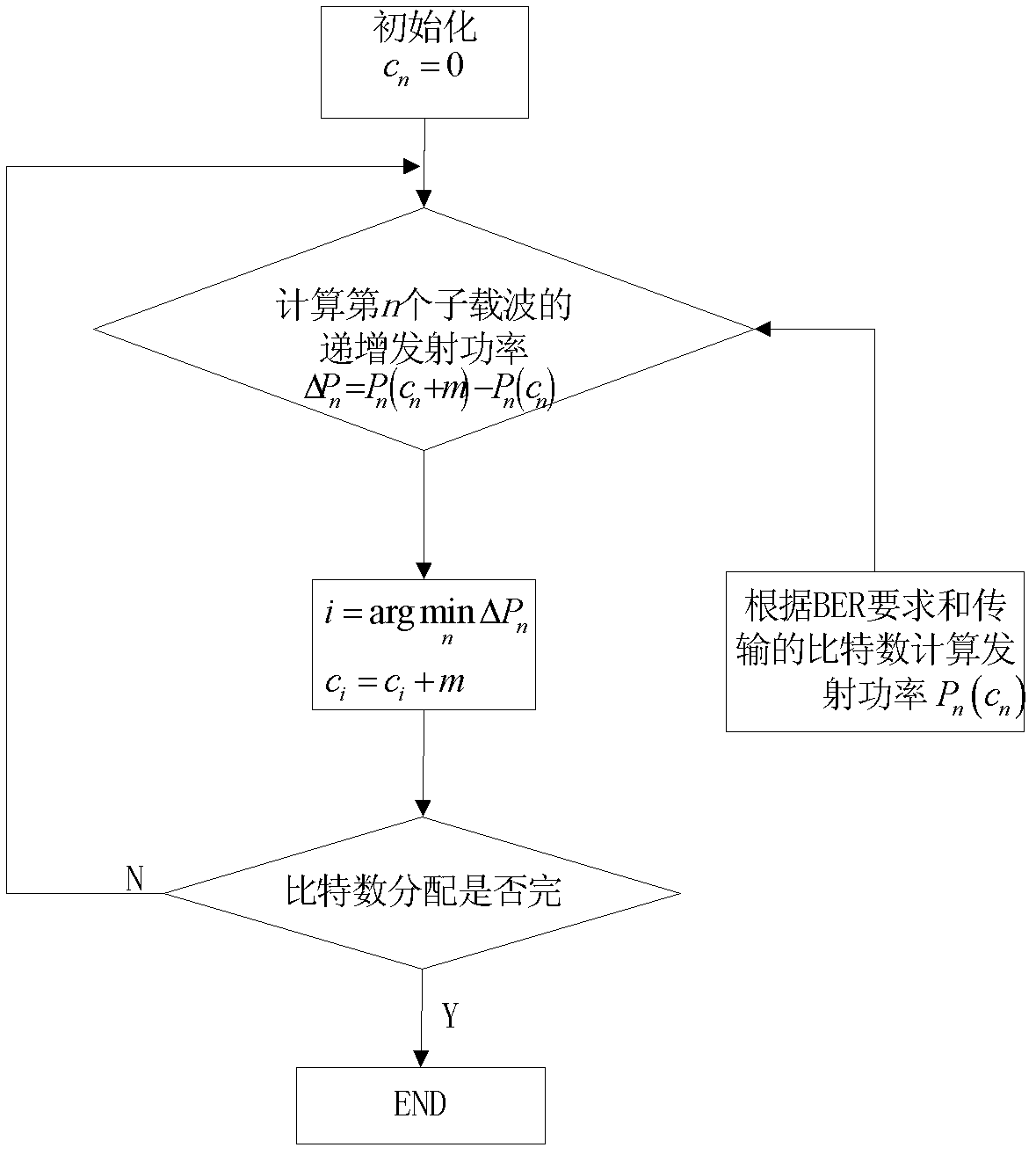
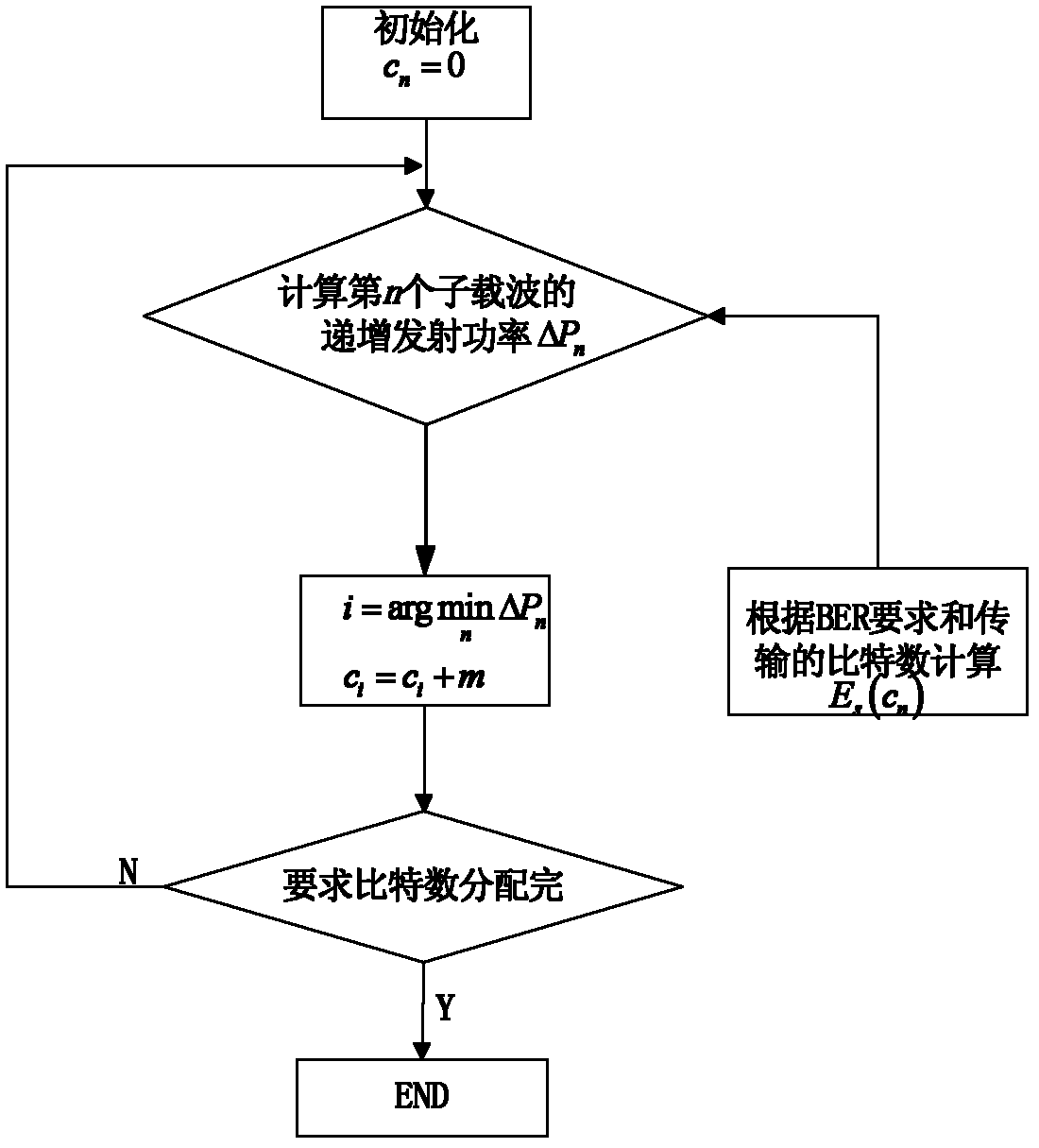
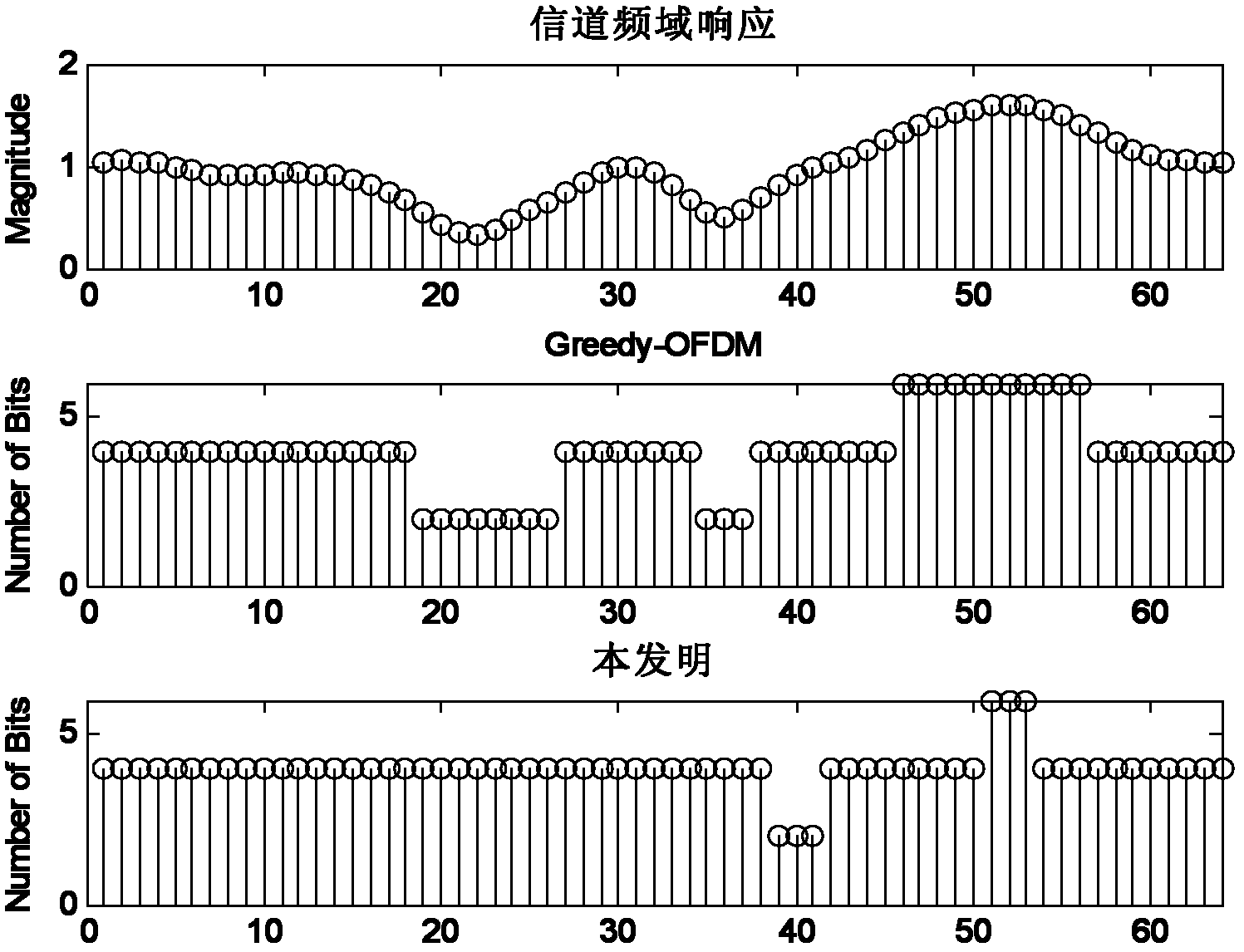
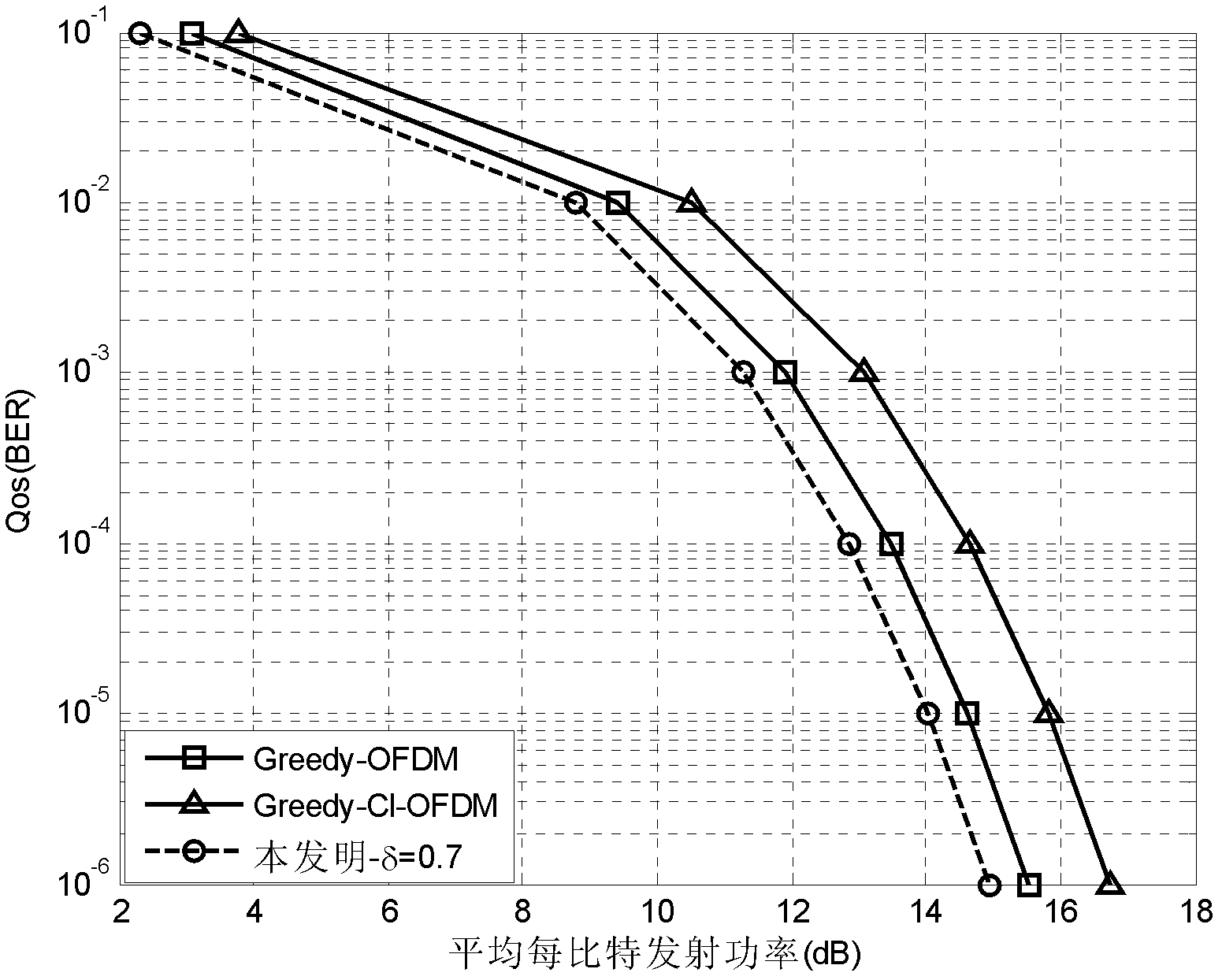
Adaptive modulation method for optimizing peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR)
InactiveCN102325115AReduce complexityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsQuality of serviceTransmitted power
The invention discloses an adaptive modulation method for optimizing a peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). The method provided by the invention is improved on the basis of a traditional Greedy adaptive bit allocation method, and m bits are allocated to a subcarrier every time, thus, the complexity in computing is reduced; meanwhile, the modulation ways of the m number of bits can also be flexibly matched; next, CI-OFDM (Carrier Interferometry-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) is regarded as a power linear amplitude limiting way, N subcarriers are divided into subcarriers subjected to CI expansion and subcarriers not subjected to CI expansion through a single-threshold step or a double-threshold step, the PAPR is limited by a power threshold, and respective advantages of OFDM and the CI-OFDM are combined, so that the optimization of transmitting power and the PAPR is realized under the condition that the service quality and the transmission rate are fixed.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Carrier interferometry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CI-OFDM) communication method based on consideration of inter-carrier interference (ICI) influences under time-varying fading channels
InactiveCN102148788AImprove estimation accuracyImprove detection accuracyBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainInverse discrete fourier transform
The invention provides a carrier interferometry orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CI-OFDM) communication method based on consideration of inter-carrier interference (ICI) influences under time-varying fading channels, belonging to the technical field of communications. The method comprises the steps as follows: a sender sequentially carries out digital modulation and carrier interference code extension on information source data, then transforms symbols of the extended data to time domains by inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) at an N point, and finally performs OFDM transmission after cyclic prefixes are added; after a receiver receives the data, the receiver gets rid of the cyclic prefixes, and transforms symbols of the received data to frequency domains by discrete Fourier transform (DFT) at the N point; the received OFDM signals are detected, and the influences caused by the ICI are considered in the detection so as to obtain estimated values of data symbols whichare subjected to the digital modulation; and carrier interference code de-extension and the digital modulation are sequentially carried out on the modulated data symbols by the DFT at the N point so as to obtain information sink bit data. In the method, because the ICI influences are considered in the signal detection, and combined noises and the data symbols are taken as receiving signals, thus the minimum mean square error (MMSE) equilibrium can be performed more accurately. Compared with a traditional OFDM communication method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of thegrains produced by frequency multipath diversity and the improvement of error rate performance gains and channel estimation accuracy due to reduction of the ICI.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Carrier interferometry networks
InactiveUS10673758B2Improve throughputImprove bit error rateModulated-carrier systemsMultiplex code generationTransceiverCarrier signal
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
A device for measuring soil moisture by GNSS direct reflection signal carrier interferometry
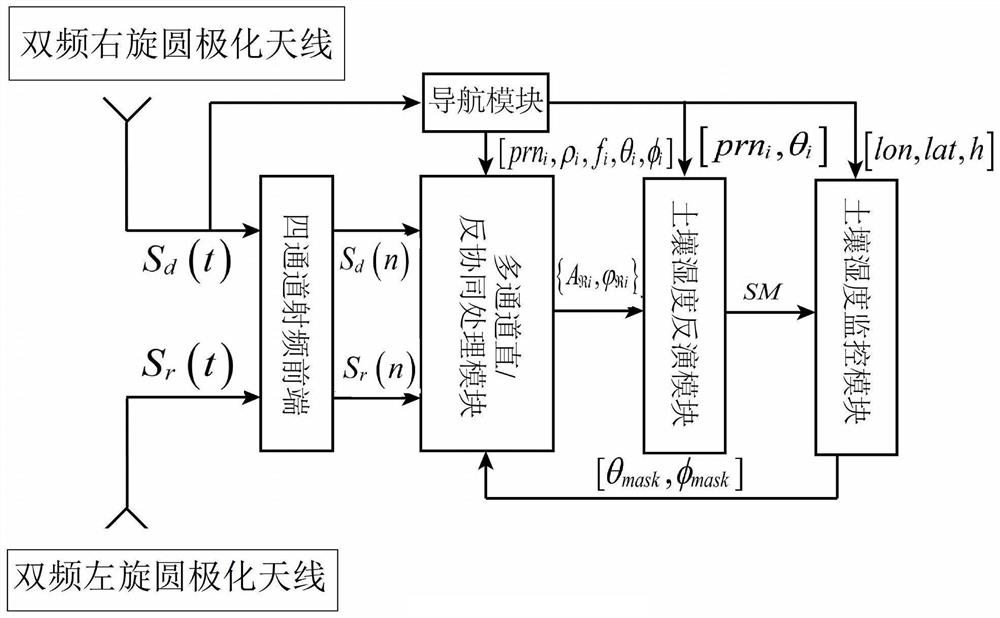
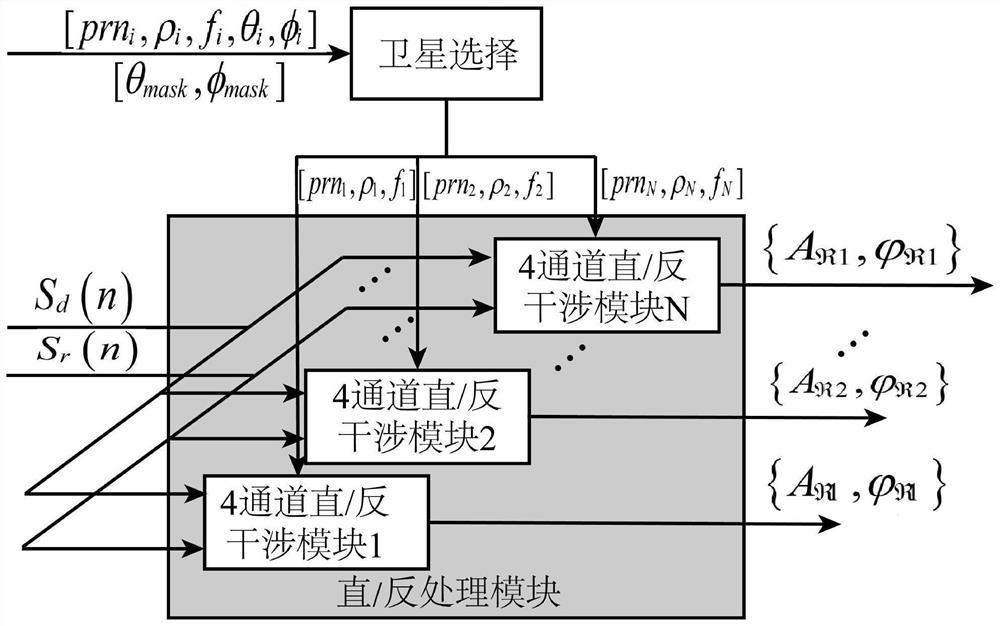
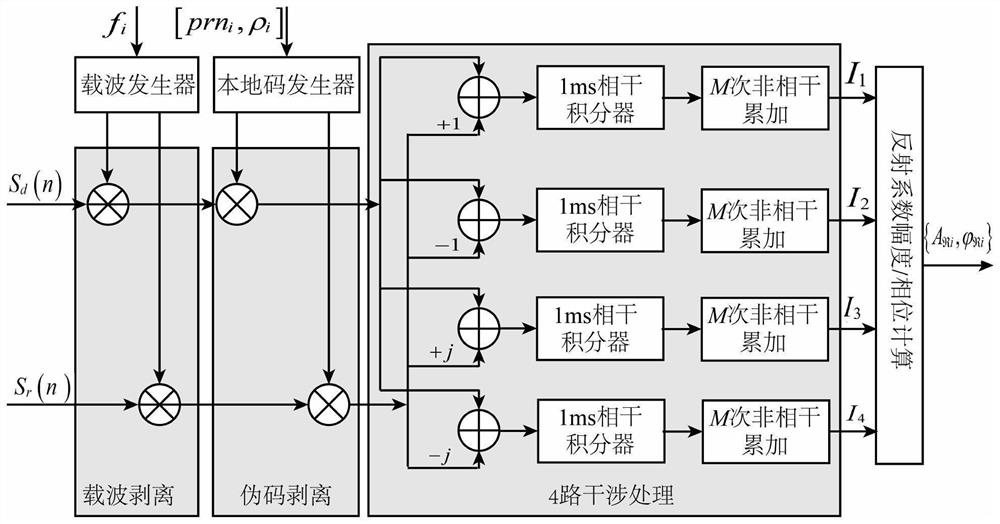
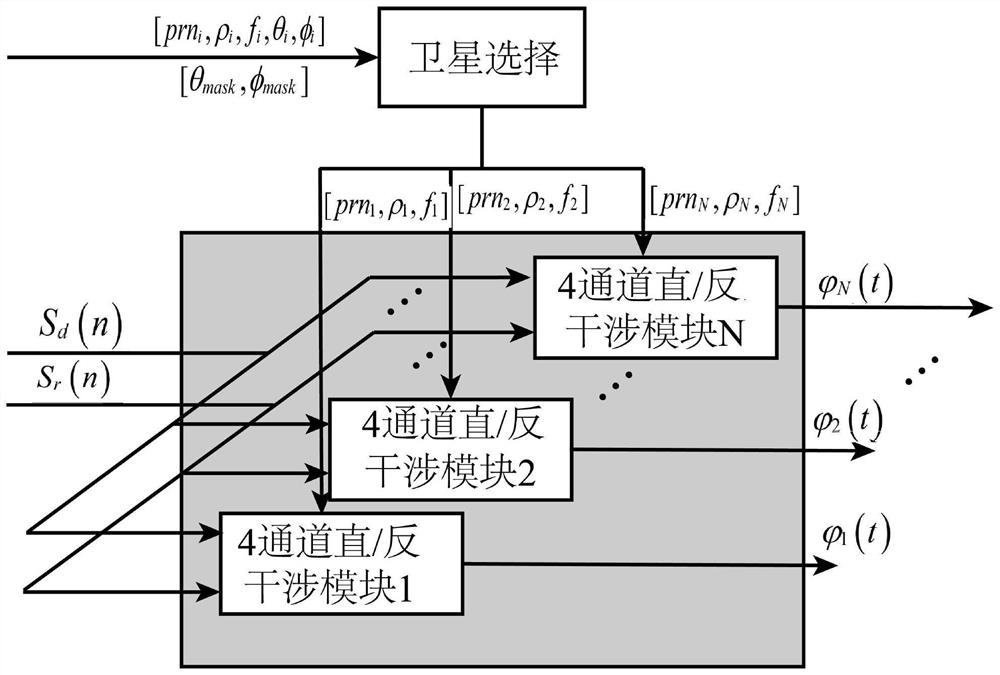
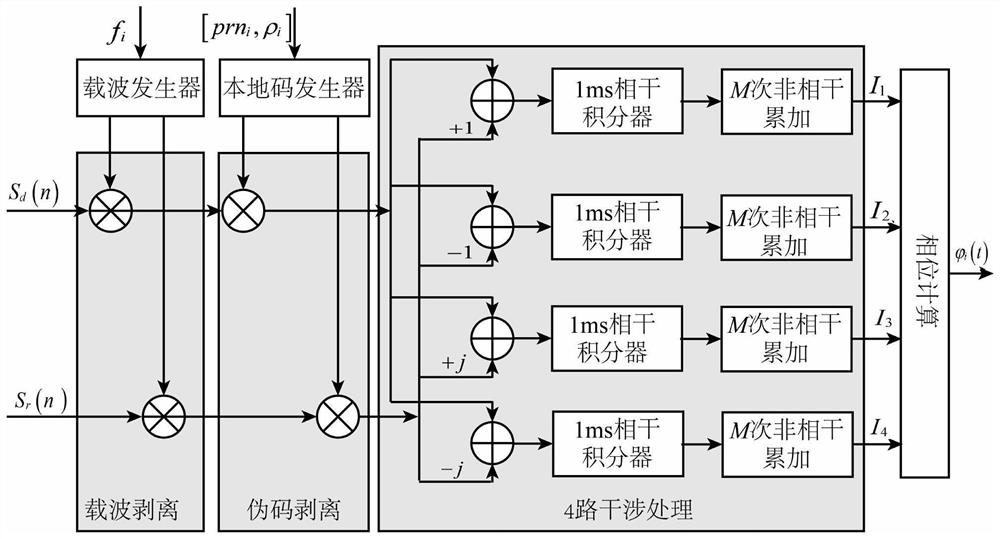
ActiveCN113049777BLow costReduce power consumptionEarth material testingSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalEdaphic
The invention discloses a device for measuring soil moisture by GNSS direct reflection signal carrier interference. In this device, the dual-frequency right-handed circularly polarized antenna receives direct signals from N satellites in the navigation system; the navigation system includes GPS satellite navigation system and Beidou satellite navigation system; the dual-frequency left-handed circularly polarized antenna receives The reflected signal of the navigation system; the dual-mode navigation module generates positioning information; the four-channel RF front-end converts the direct signal and the reflected signal to obtain four digital intermediate frequency signals; the multi-channel direct / reverse collaborative processing module converts the four digital intermediate frequency signals according to the positioning information Perform interference processing to obtain the reflectivity amplitude and reflectivity phase; the soil moisture inversion module is used to perform inversion according to the reflectivity amplitude, reflectivity phase and location information to obtain the moisture of the soil to be measured. The invention is applied to a plurality of satellite signals with different elevation angles to obtain soil moisture, has high measurement accuracy and wide application range.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A device for gnss direct reflection signal carrier interferometry to measure lake water level
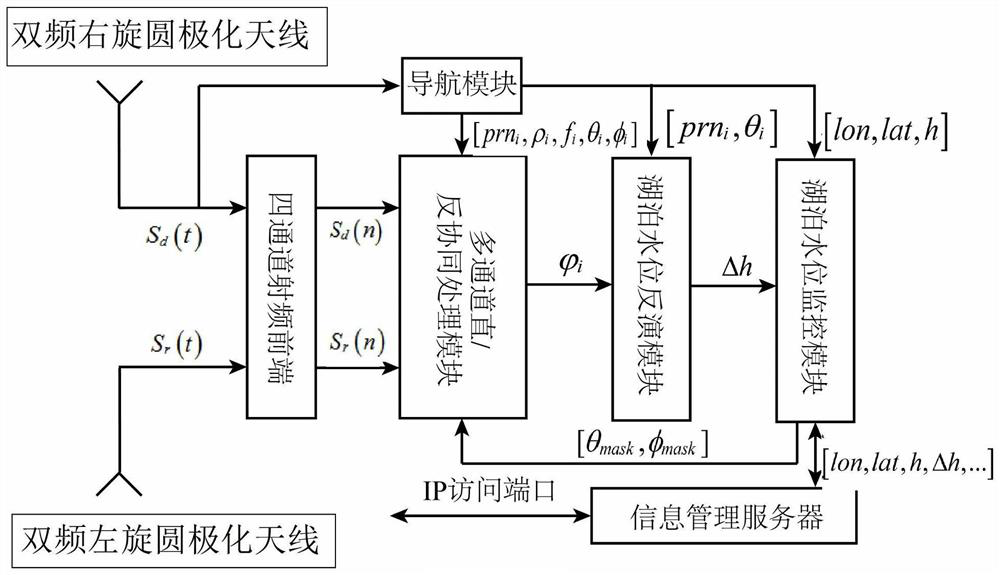
ActiveCN113049062BReduced measurement accuracyLow costMachines/enginesSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalNavigation system
The invention discloses a device for measuring lake water level by GNSS direct reflection signal carrier interference. In this device, the dual-frequency right-handed circularly polarized antenna receives direct signals from N satellites in the navigation system; the navigation system includes the GPS satellite navigation system and the Beidou satellite navigation system; the dual-frequency left-handed circularly polarized antenna receives The reflection signal of the reflected navigation system; the dual-mode navigation module generates positioning information; the four-channel RF front-end converts the direct signal and the reflected signal to obtain four digital intermediate frequency signals; The intermediate frequency signal is subjected to interference processing to obtain the carrier phase delay of the reflected signal relative to the direct signal; the lake water level inversion module is used to perform inversion according to the carrier phase delay and positioning information to obtain the water level of the lake to be measured. The invention is applied to a plurality of satellite signals with different elevation angles to obtain the lake water level, has high measurement accuracy and wide application range.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
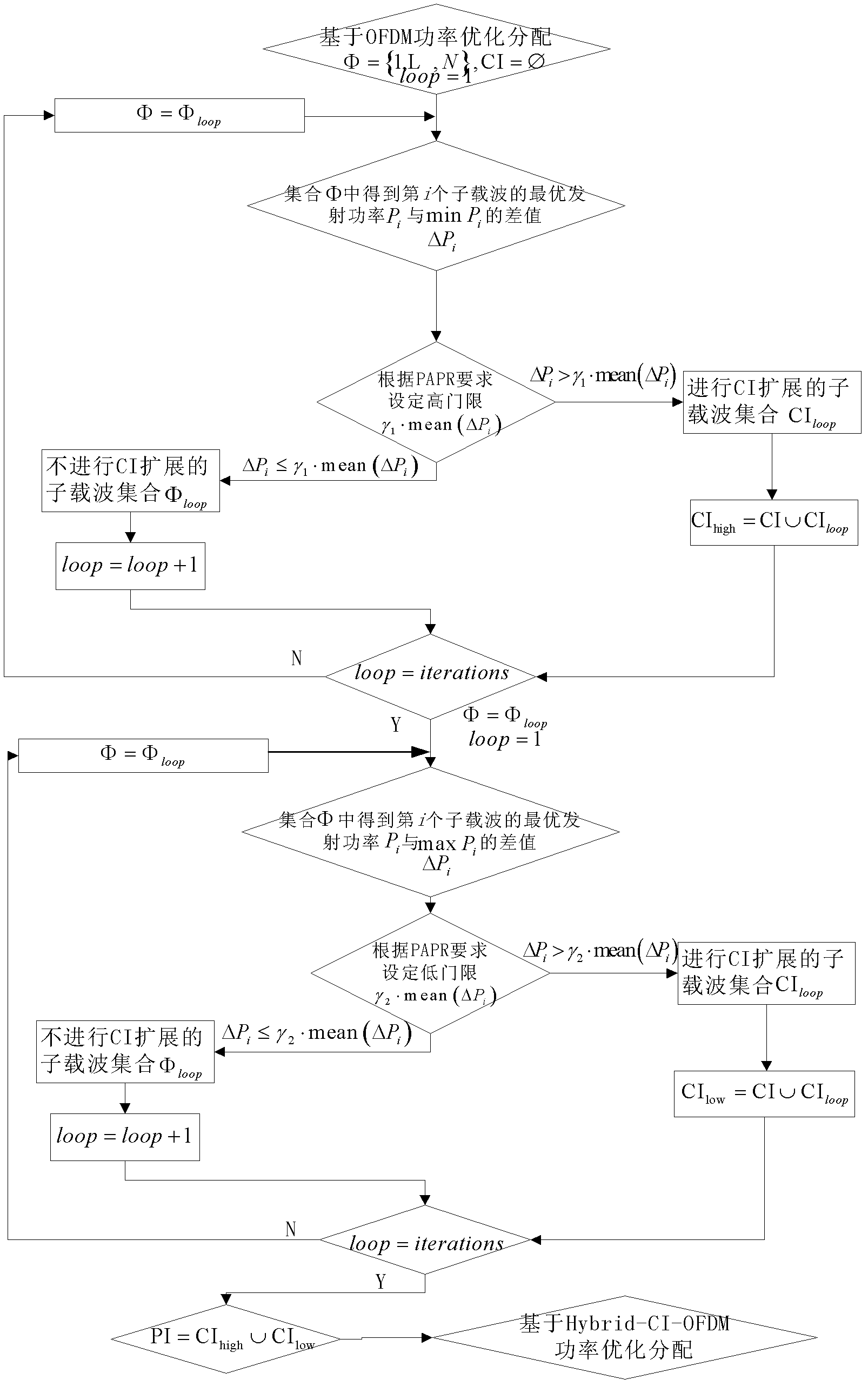
Multicarrier-based adaptive modulation method
InactiveCN102325114BReduce complexityTransmit power optimizationError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsQuality of serviceRound complexity
The invention discloses a multicarrier-based adaptive modulation method belonging to the technical field of communication. The method is improved on the basis of a traditional Greedy adaptive bit allocation method, and m bits are allocated to a subcarrier every time, thus, the complexity in computing is reduced; meanwhile, whether to carry out CI (Carrier Interferometry) expansion or OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) transmission is determined according to the frequency domain response of each subchannel, and furthermore, respective advantages of OFDM and CI-OFDM are combined so that the optimization of transmitting power is realized under the condition that the service quality and the transmission rate are fixed.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
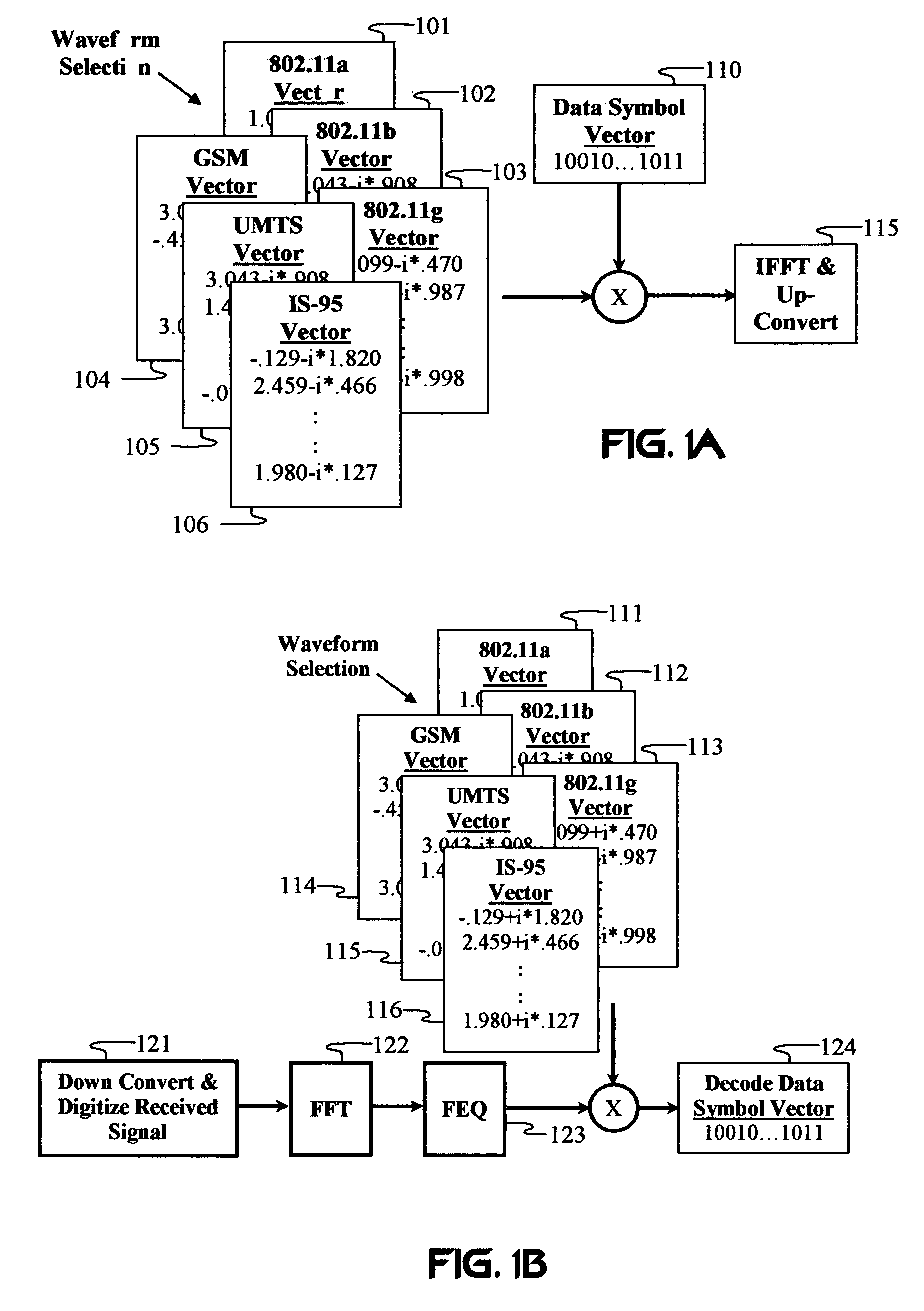
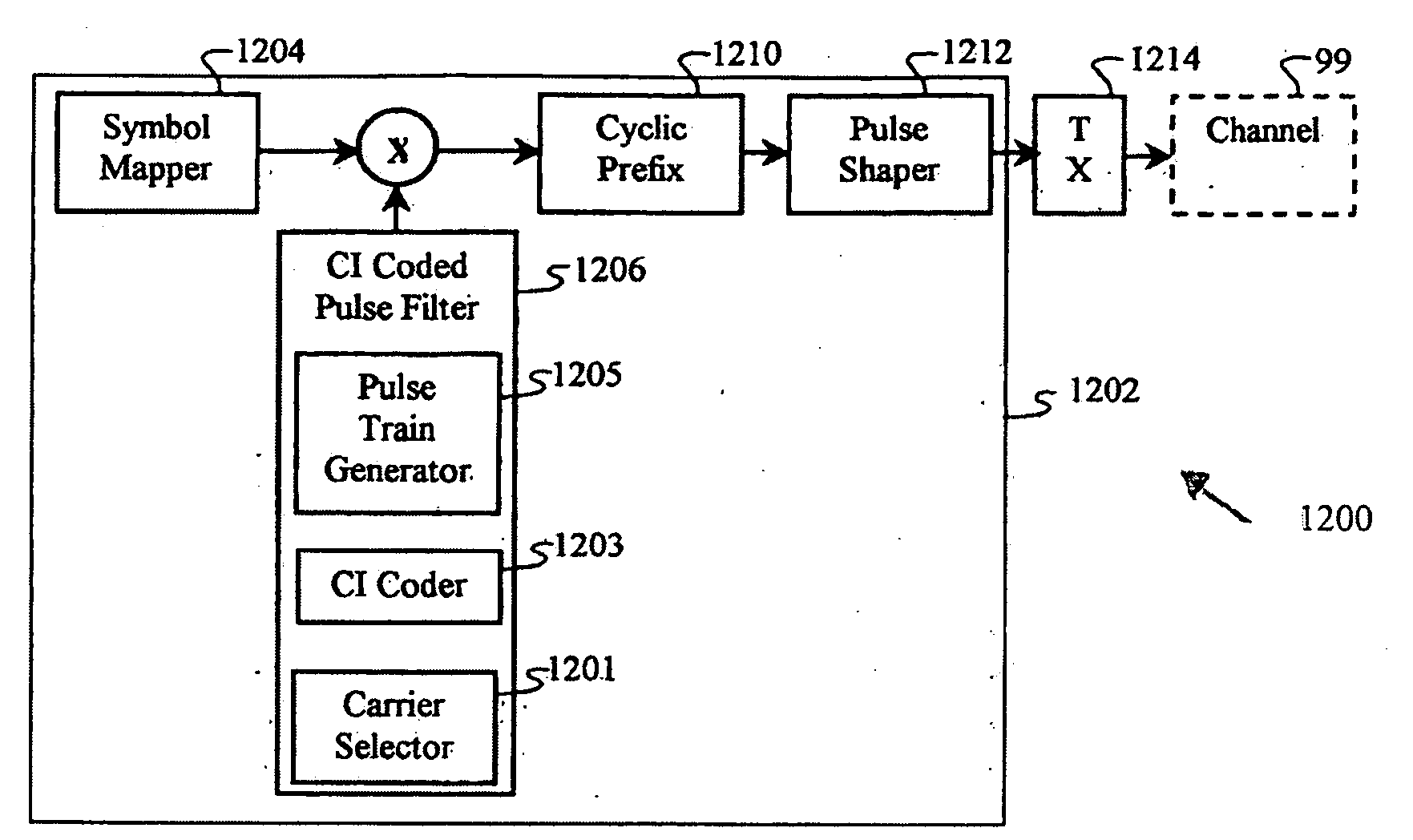
Carrier Interferometry Transmitter
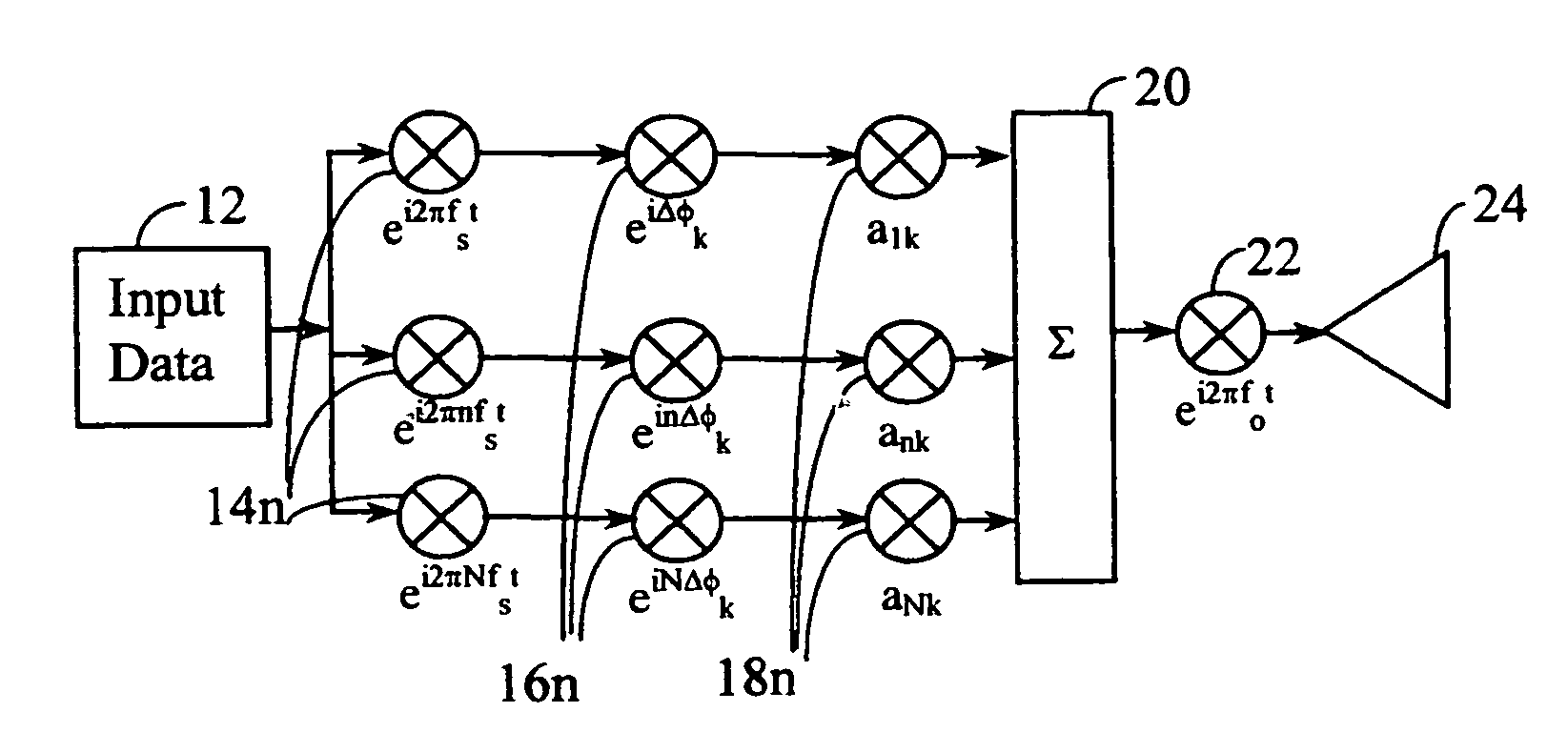
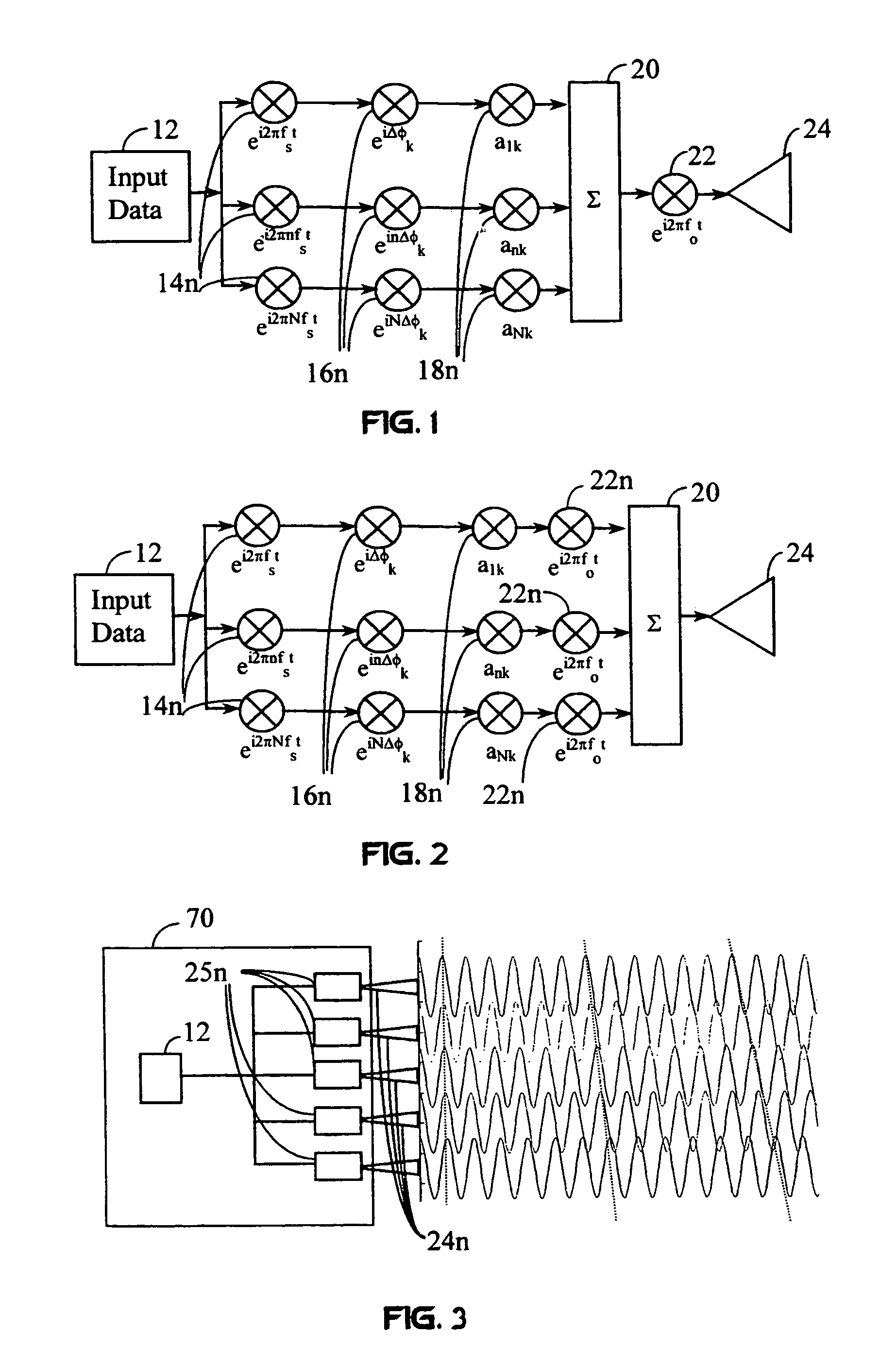
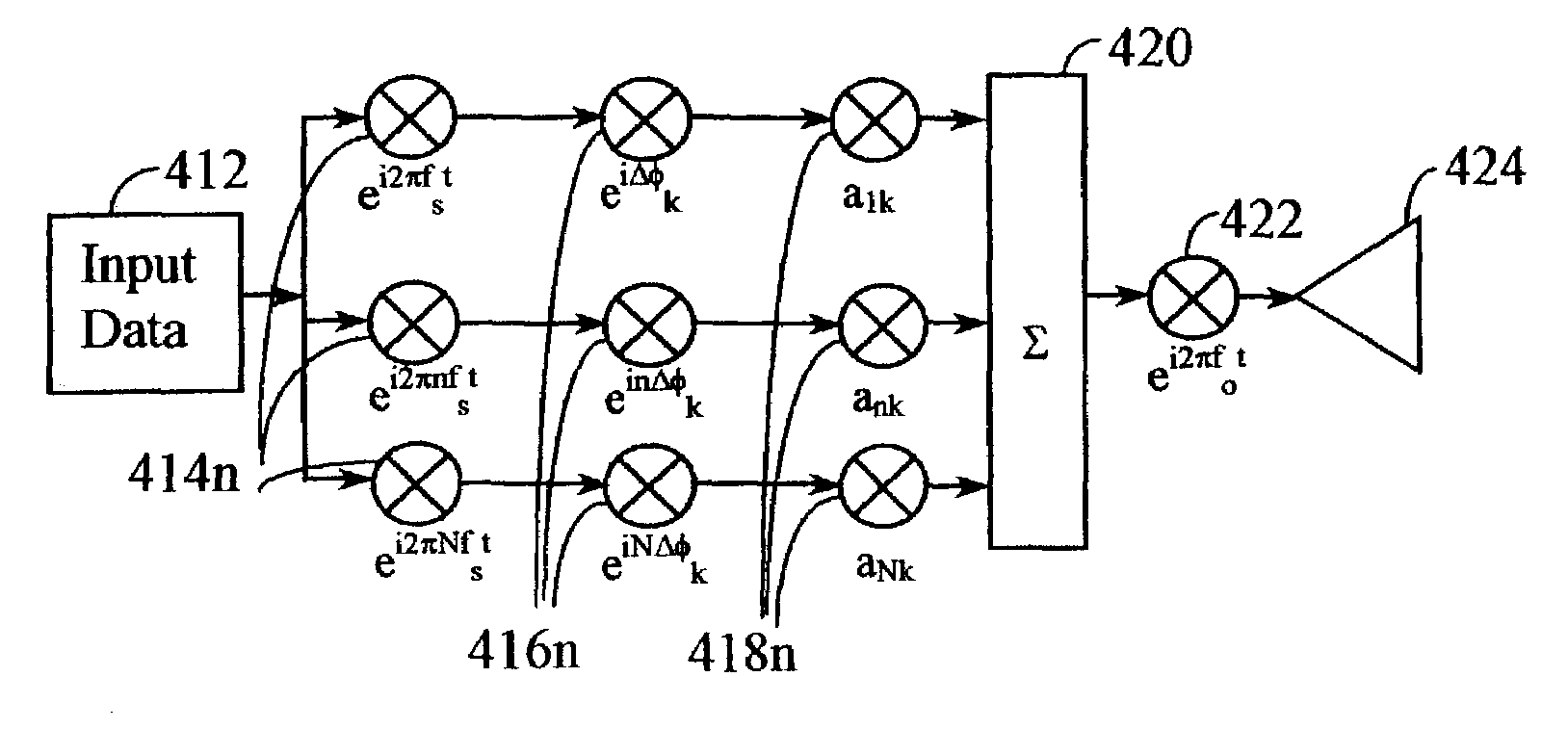
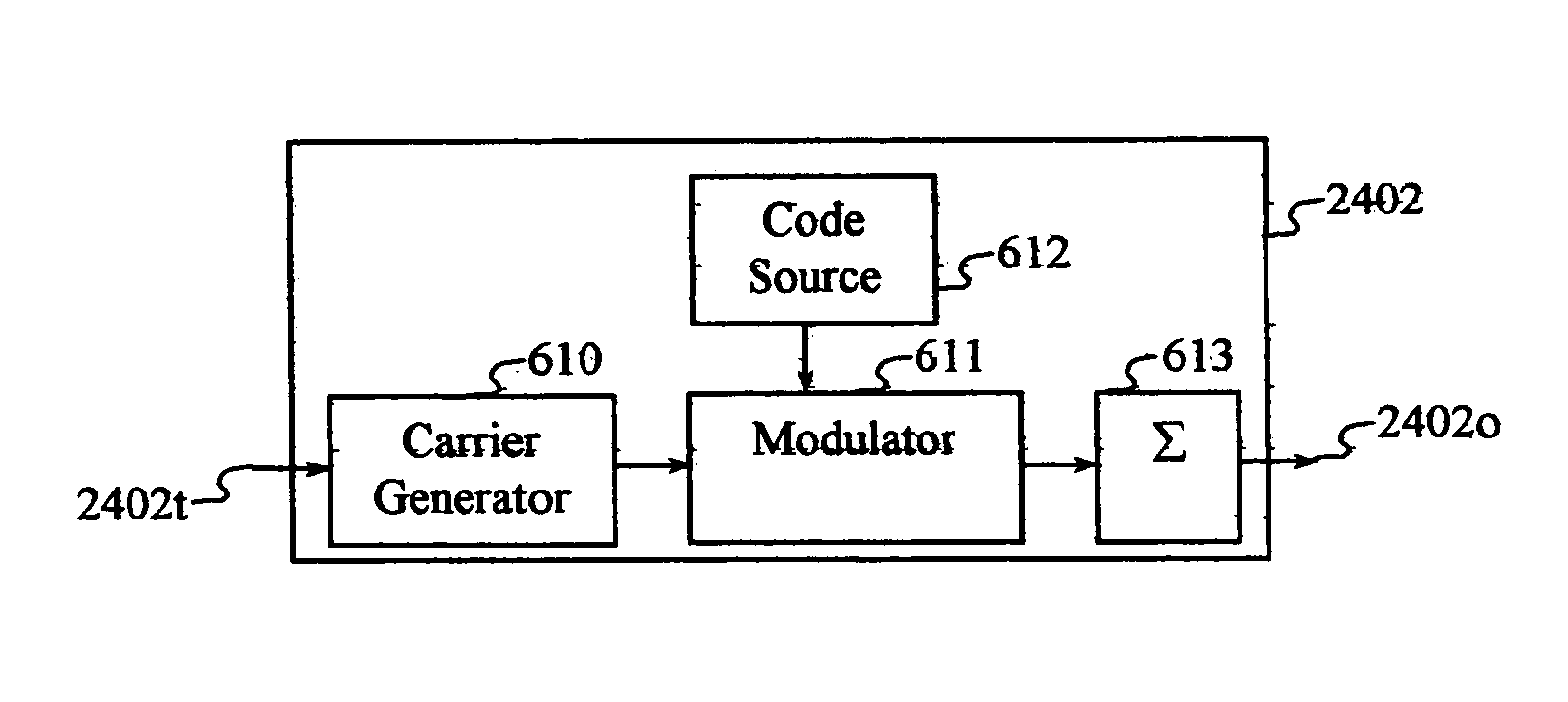
A transmitter in a wireless communication network comprises a Carrier Interferometry (CI) coder and a multicarrier modulator communicatively coupled to the CI coder. The CI coder encodes a plurality of data symbols with a plurality of CI codes to produce a plurality of CI symbol values, wherein each of the plurality of CI symbol values equals a sum of information-modulated CI code chips. Each information-modulated CI code chip equals a CI code chip multiplied by one of the plurality of data symbols. The modulator modulates each CI symbol value onto a different subcarrier frequency to produce a multicarrier signal.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Zero padding mode-based CI-OFDM communication method
InactiveCN101917252BImprove bit error rate performanceError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsZero paddingCyclic prefix
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
OofDM Modulation Method of VLC System Based on Hadamard Matrix Amplification
ActiveCN108040027BReduce intervalReduced ability to fight PSNMulti-frequency code systemsElectromagnetic transmissionCommunications systemAlgorithm
The invention provides a visible light communication (VLC) system optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OOFDM) modulation method based on hadamard matrix amplification, which keeps the orthogonality characteristics of a matrix by utilizing hadamard matrix amplification, and forms an HICI code by performing the hadamard matrix amplification on a carrier interferometry (CI) spread code, so that code element interval of the HICI code and the CI spread code keeps consistent. Compared with the traditional CI spread code, the HICI code does not cause reduction of the code element interval along with the increasing of the number of subcarriers, and simultaneously has the capability of reducing OOFDM-based VLC system signal PAPR and the capability of withstanding PSN. Based on theoretical analysis and simulation results, the HICI code provided by the VLC system OOFDM modulation method based on hadamard matrix amplification, which is provided by the invention, improves the capability of the original CI spread code to withstand the PSN and simultaneously has the capability of reducing the OOFDM communication system PAPR.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com