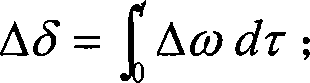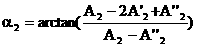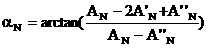Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
235 results about "Phase step" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
As nouns the difference between step and phase. is that step is an advance or movement made from one foot to the other; a pace while phase is a distinguishable part of a sequence or cycle occurring over time.
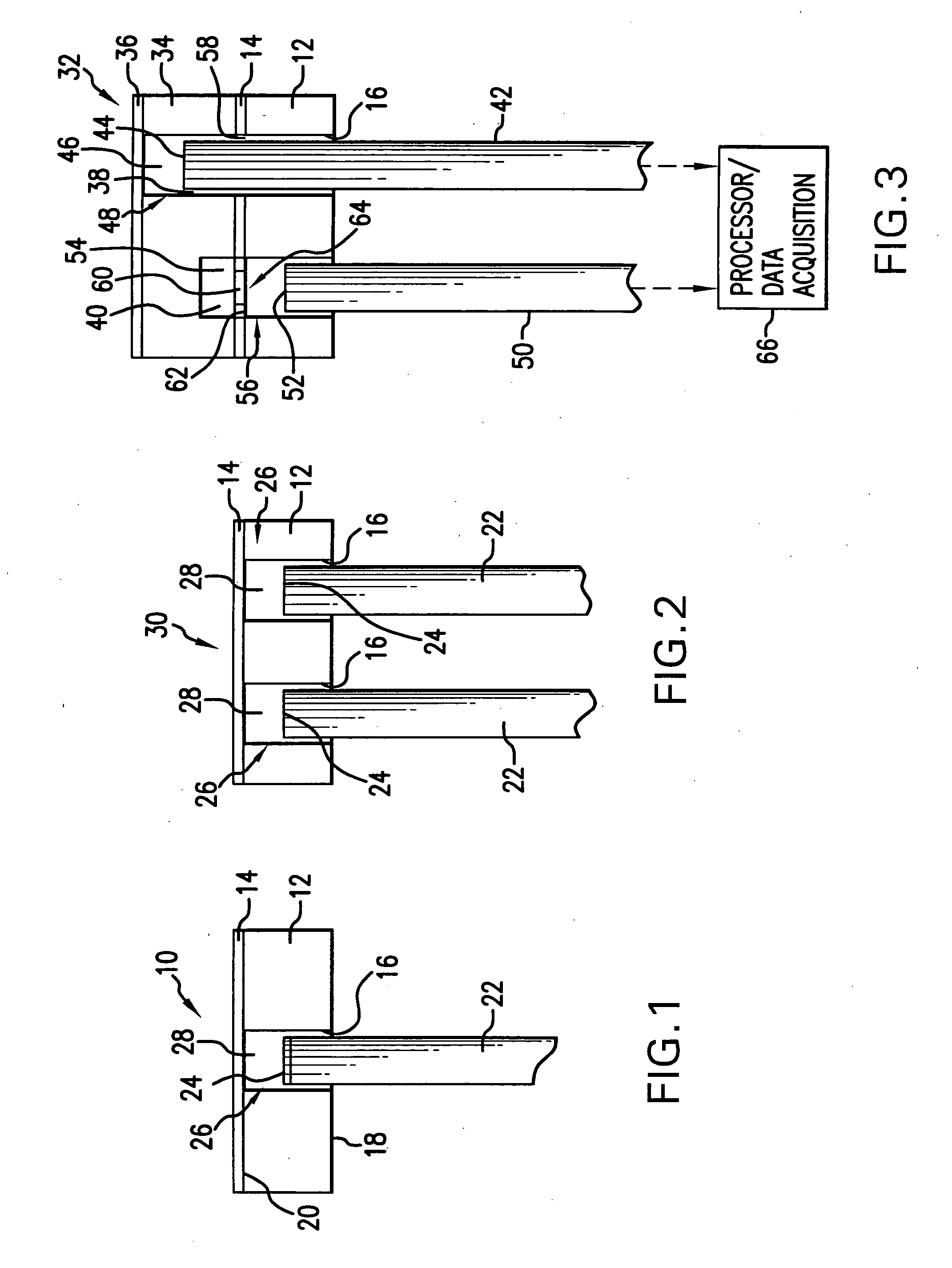
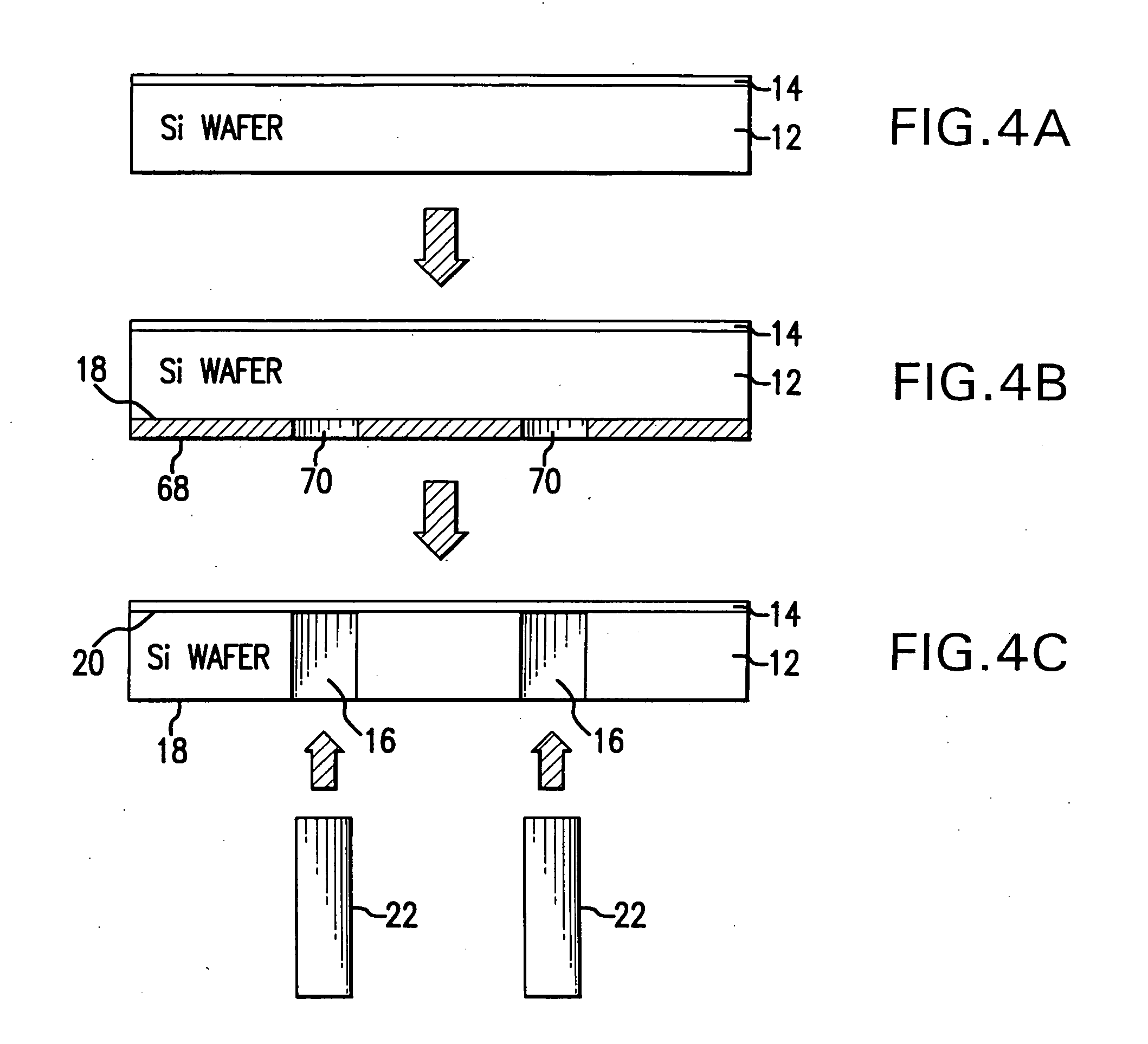
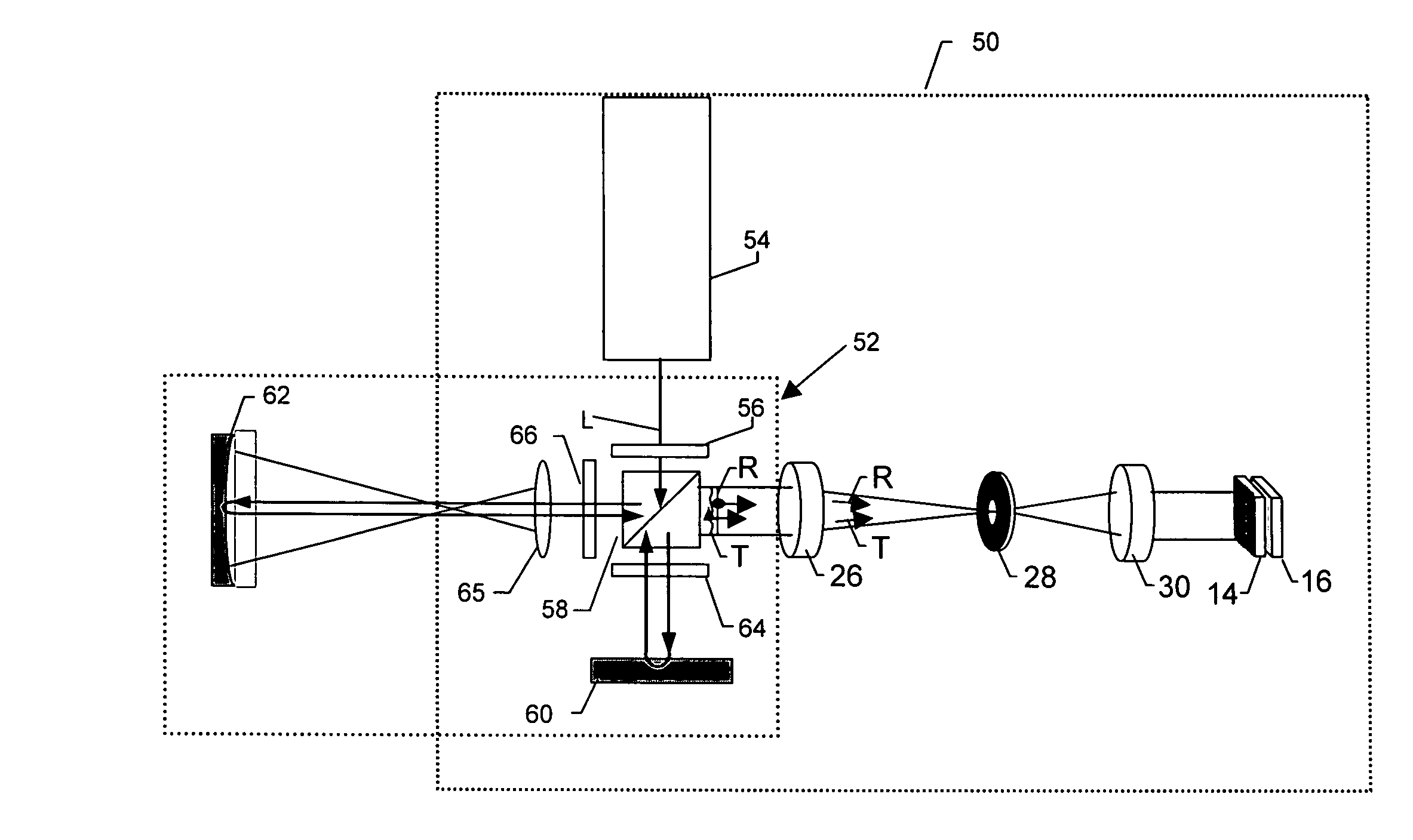
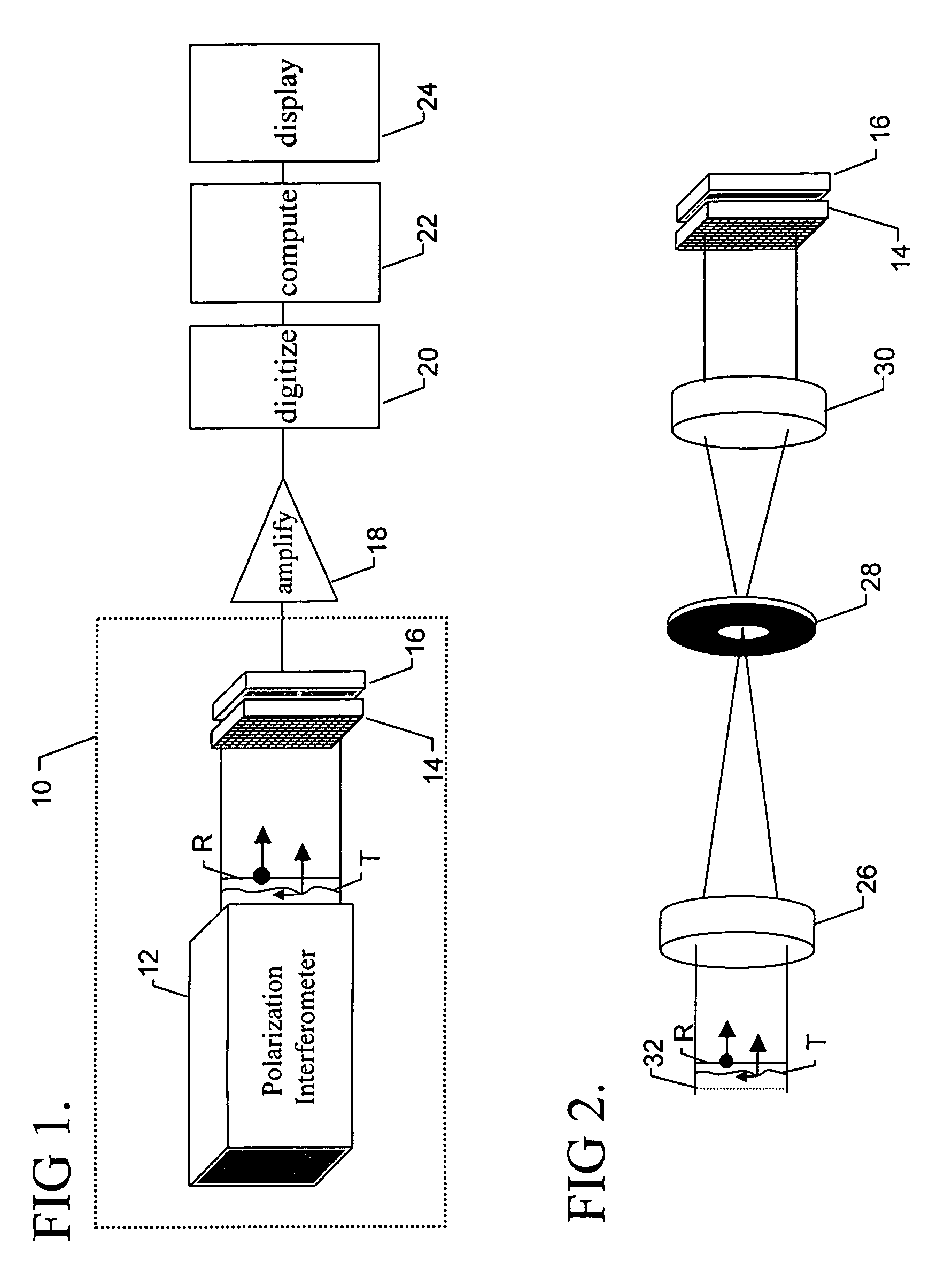
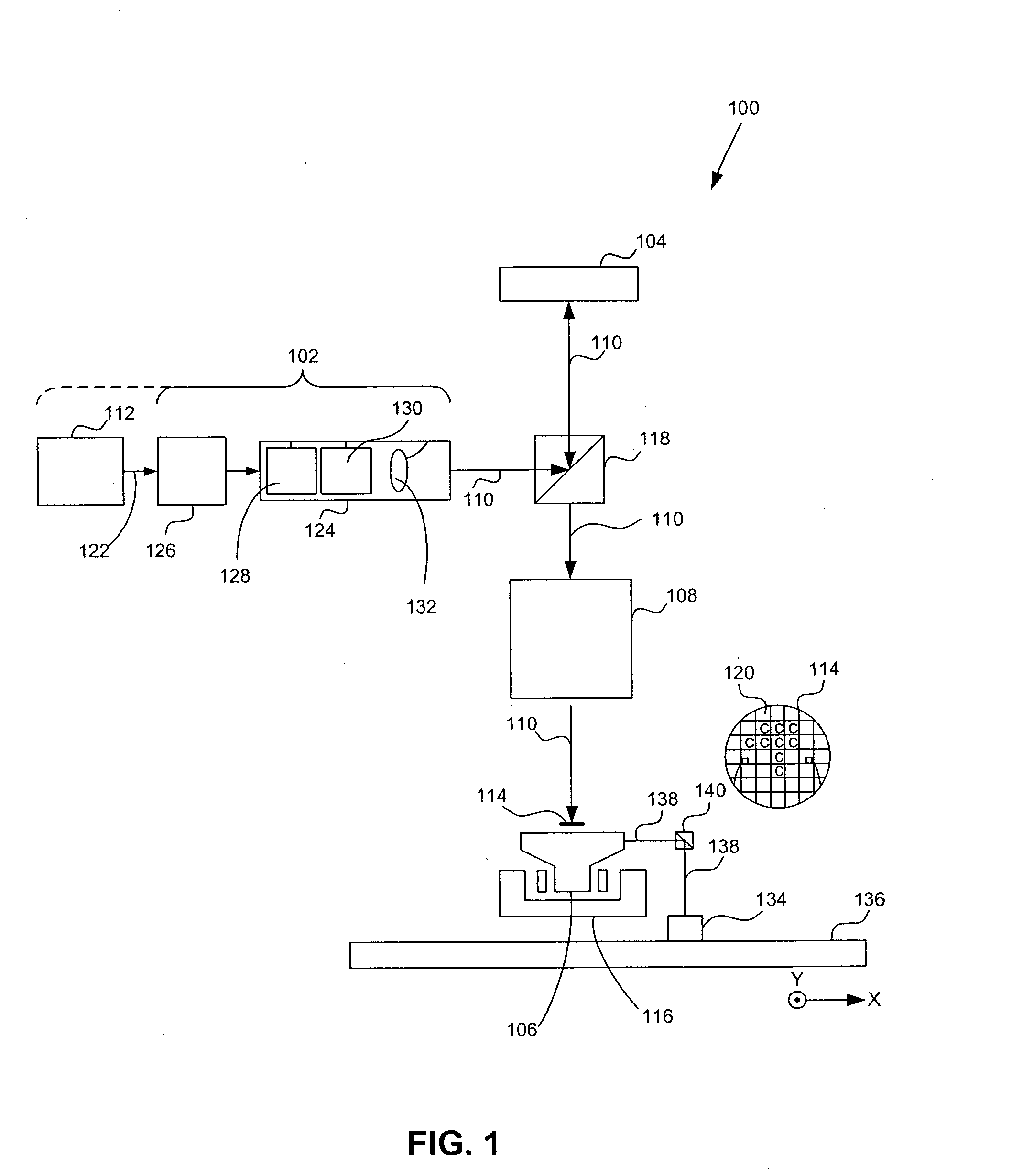
Pixelated phase-mask interferometer
ActiveUS20050046865A1Avoiding chromatic dispersionAvoid complexityInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase differenceDetector array
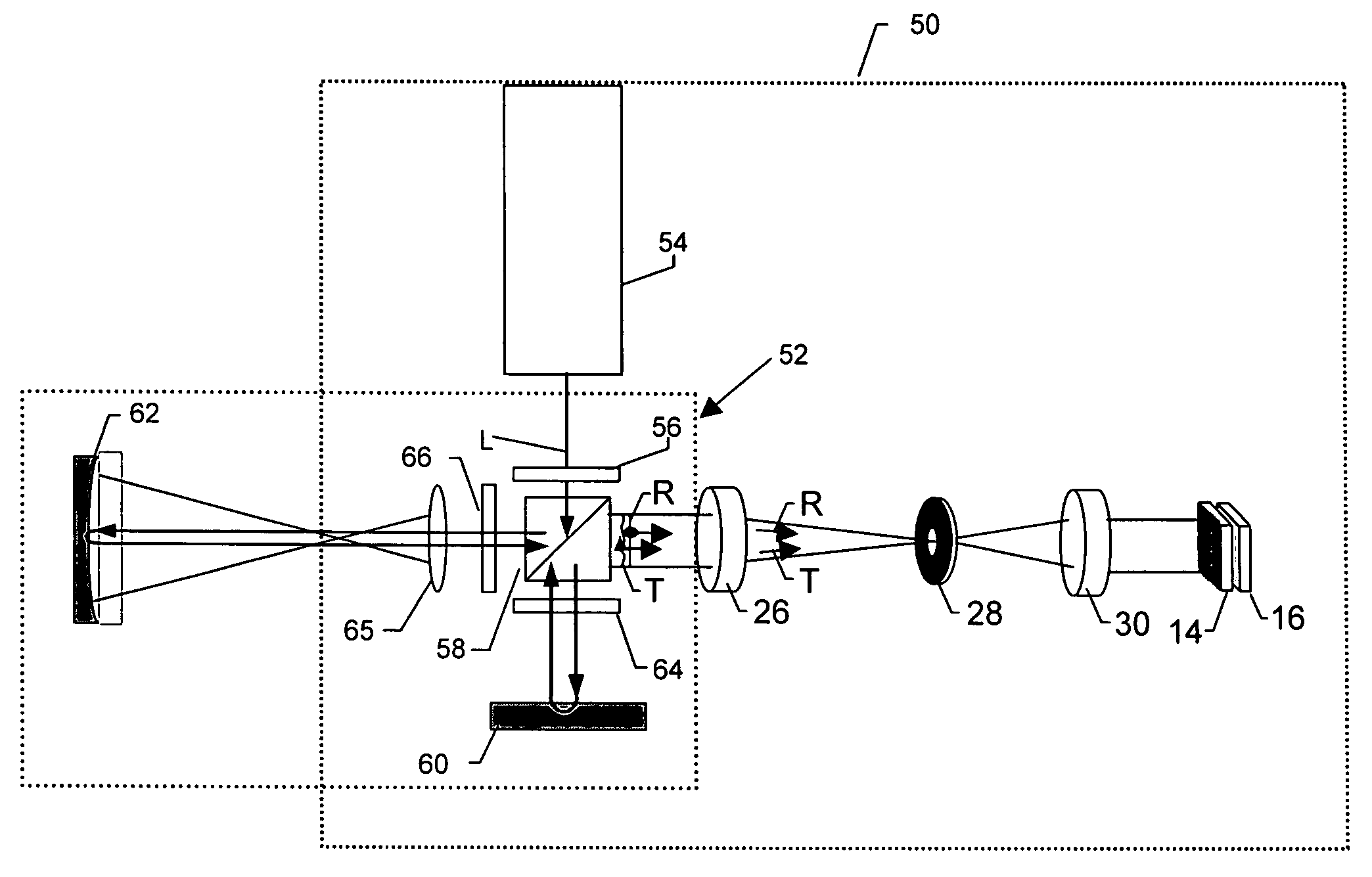
A phase-difference sensor measures the spatially resolved difference in phase between orthogonally polarized reference and test wavefronts. The sensor is constructed as a pixelated phase-mask aligned to and imaged on a pixelated detector array. Each adjacent pixel of the phase-mask measures a predetermined relative phase shift between the orthogonally polarized reference and test beams. Thus, multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be synthesized at the same time by combining pixels with identical phase-shifts. The multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be combined to calculate standard parameters such as modulation index or average phase step. Any configuration of interferometer that produces orthogonally polarized reference and object beams may be combined with the phase-difference sensor of the invention to provide, single-shot, simultaneous phase-shifting measurements.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
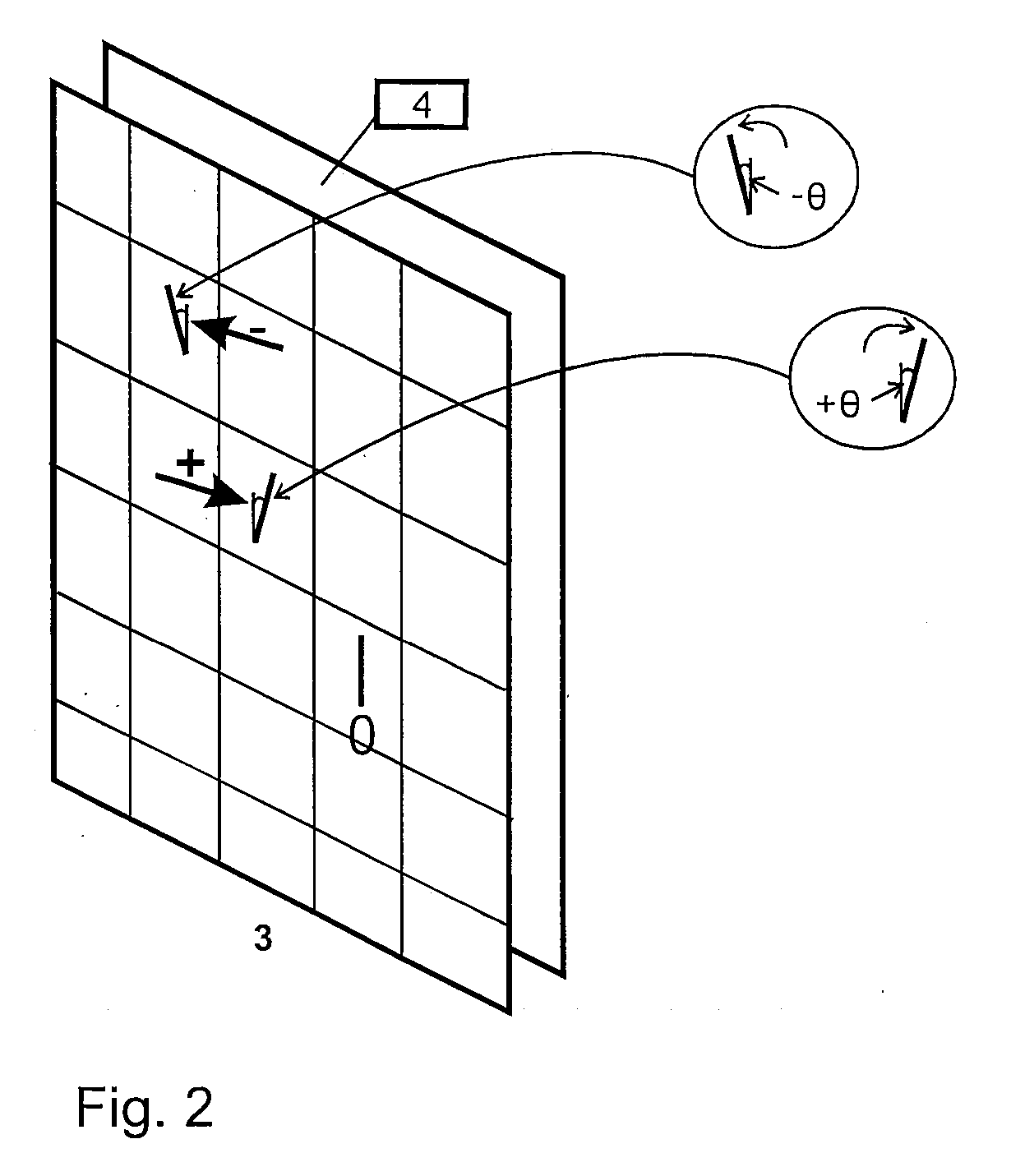
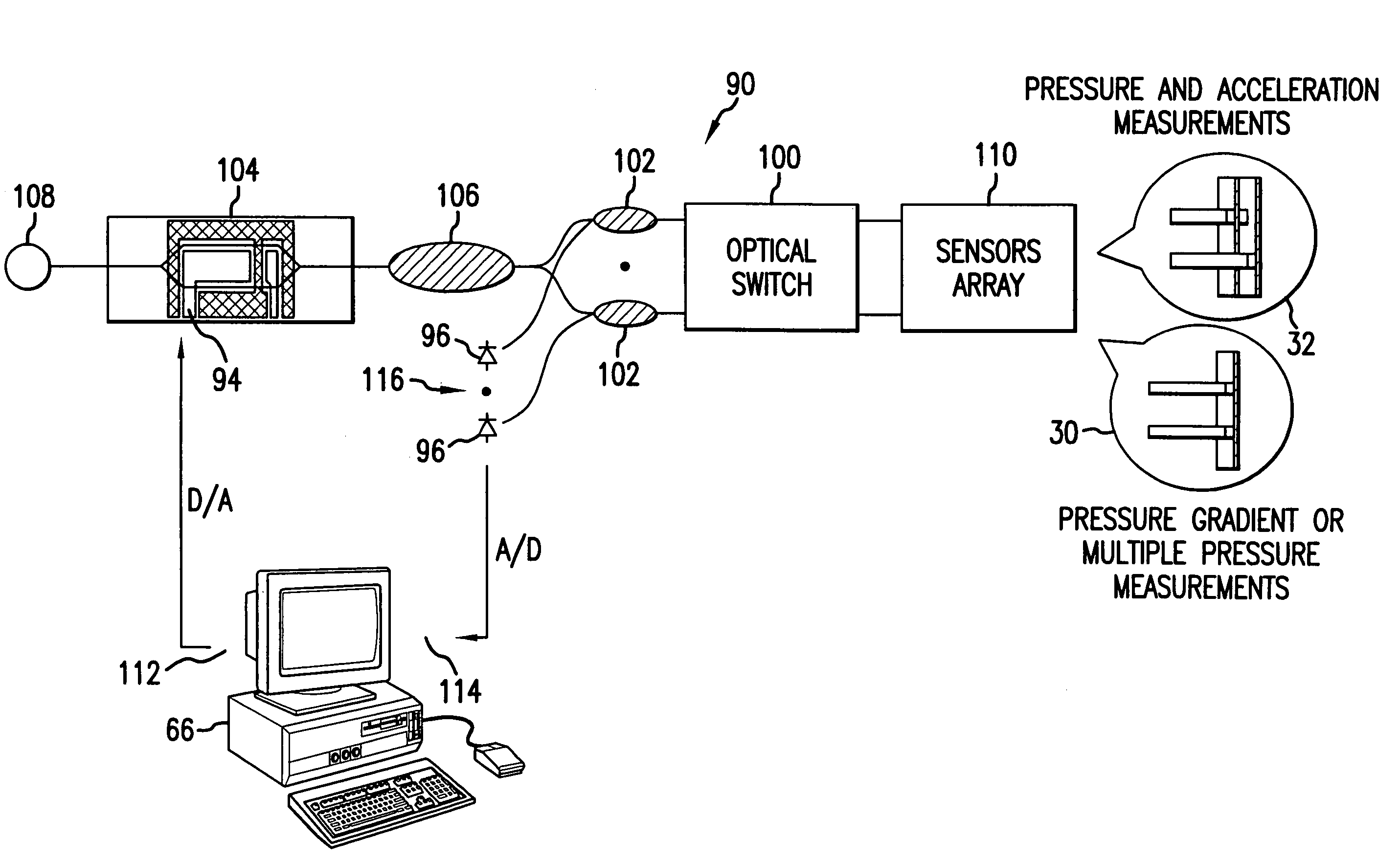
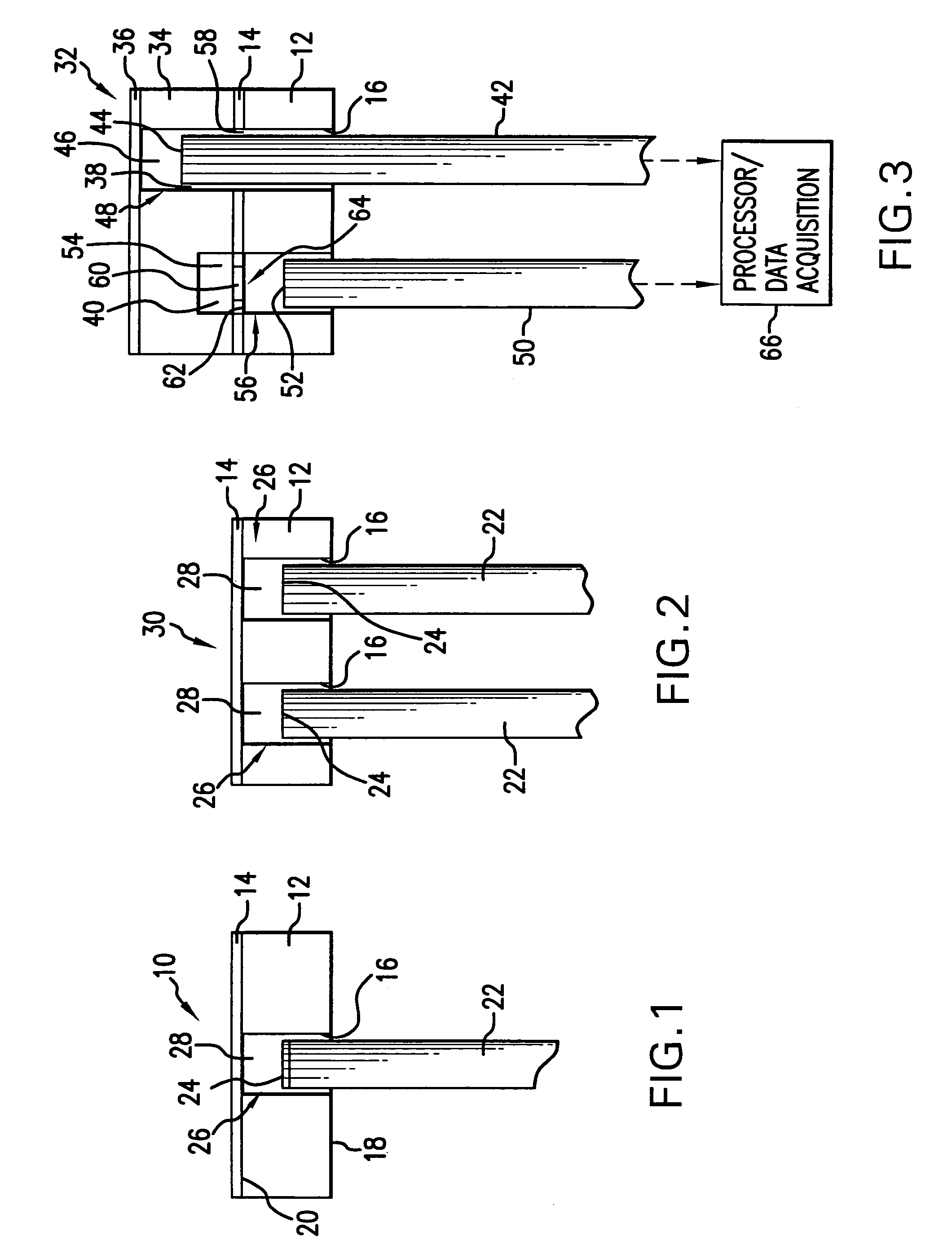
Micro-optical sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements
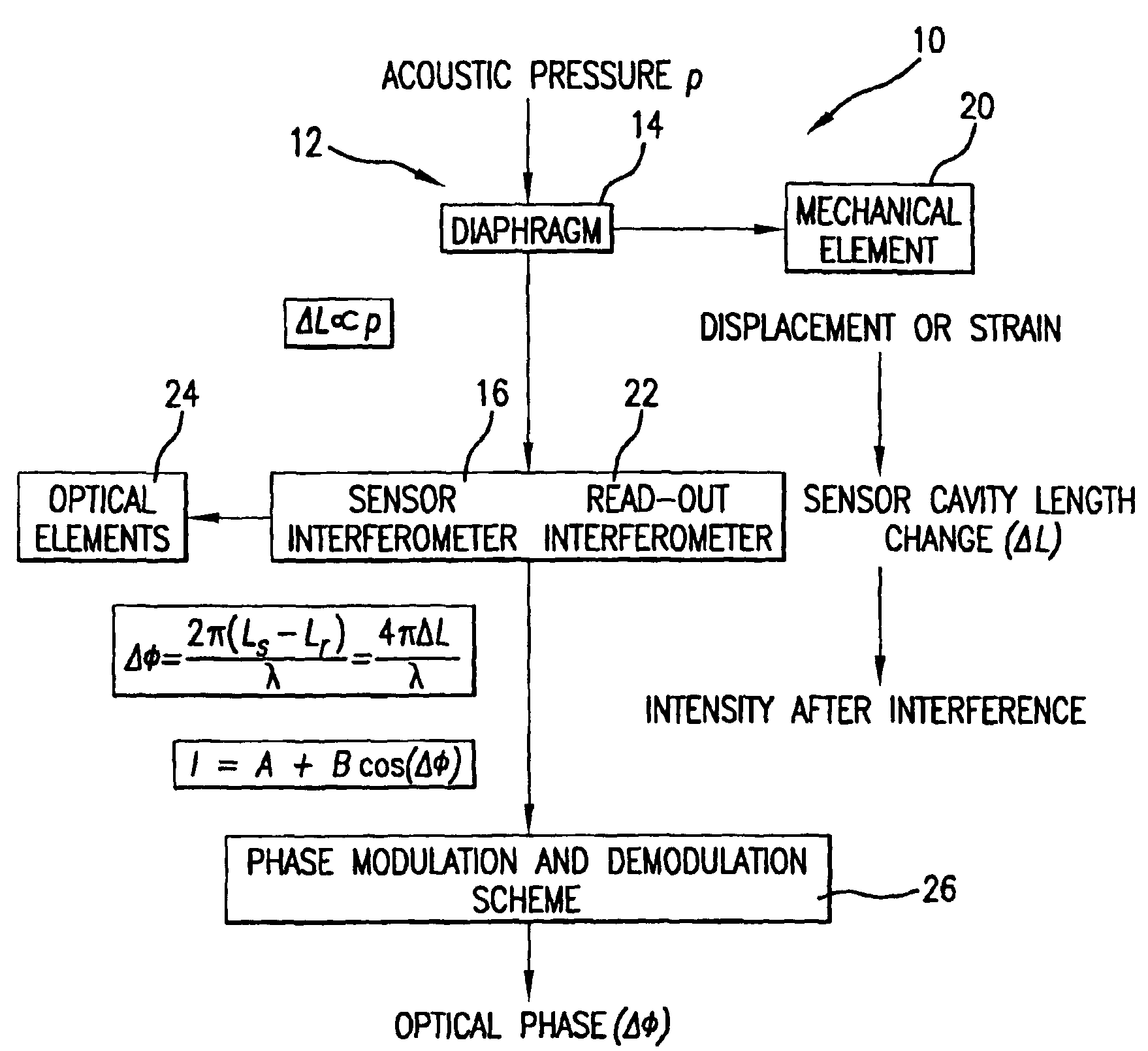
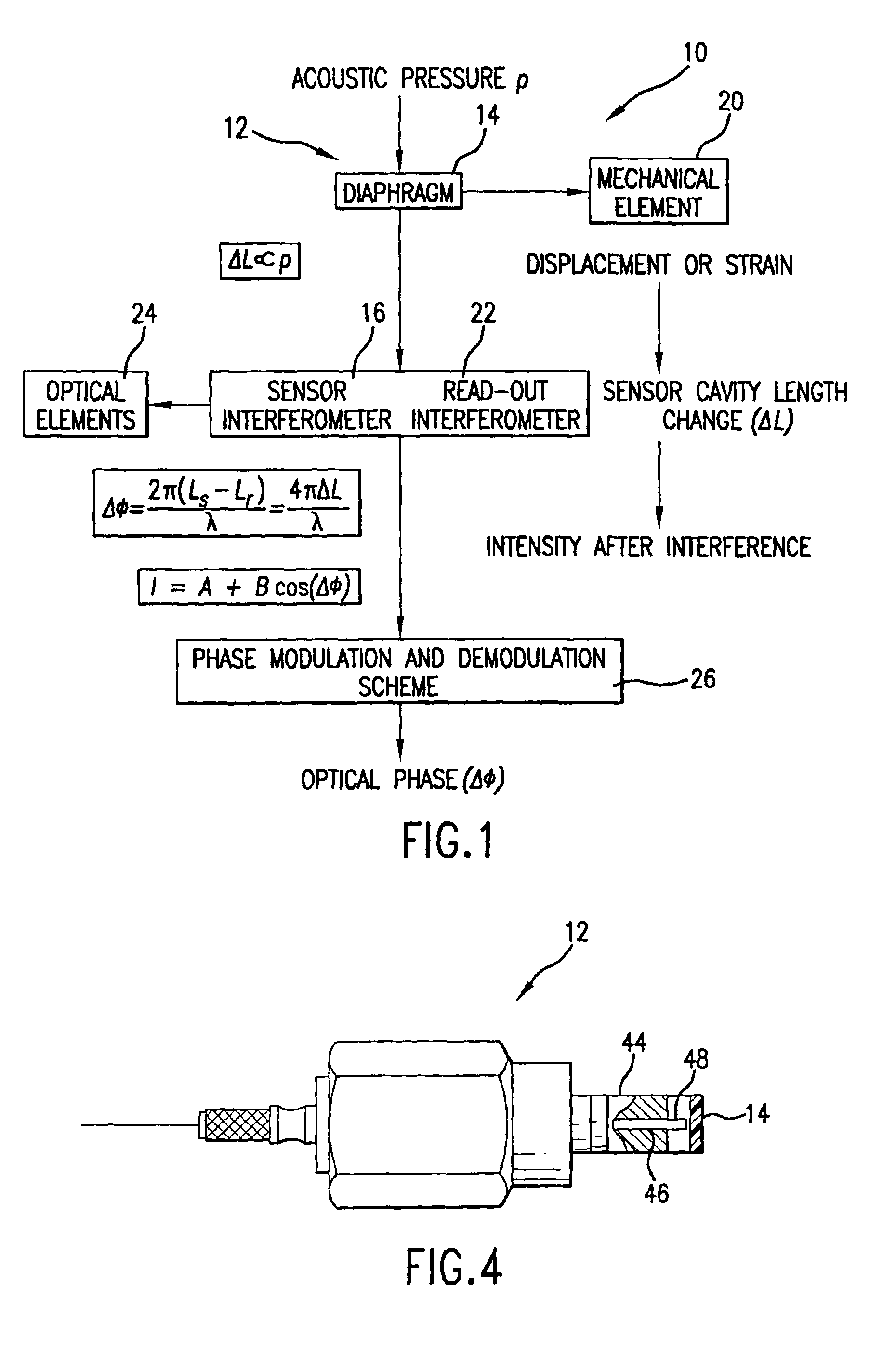
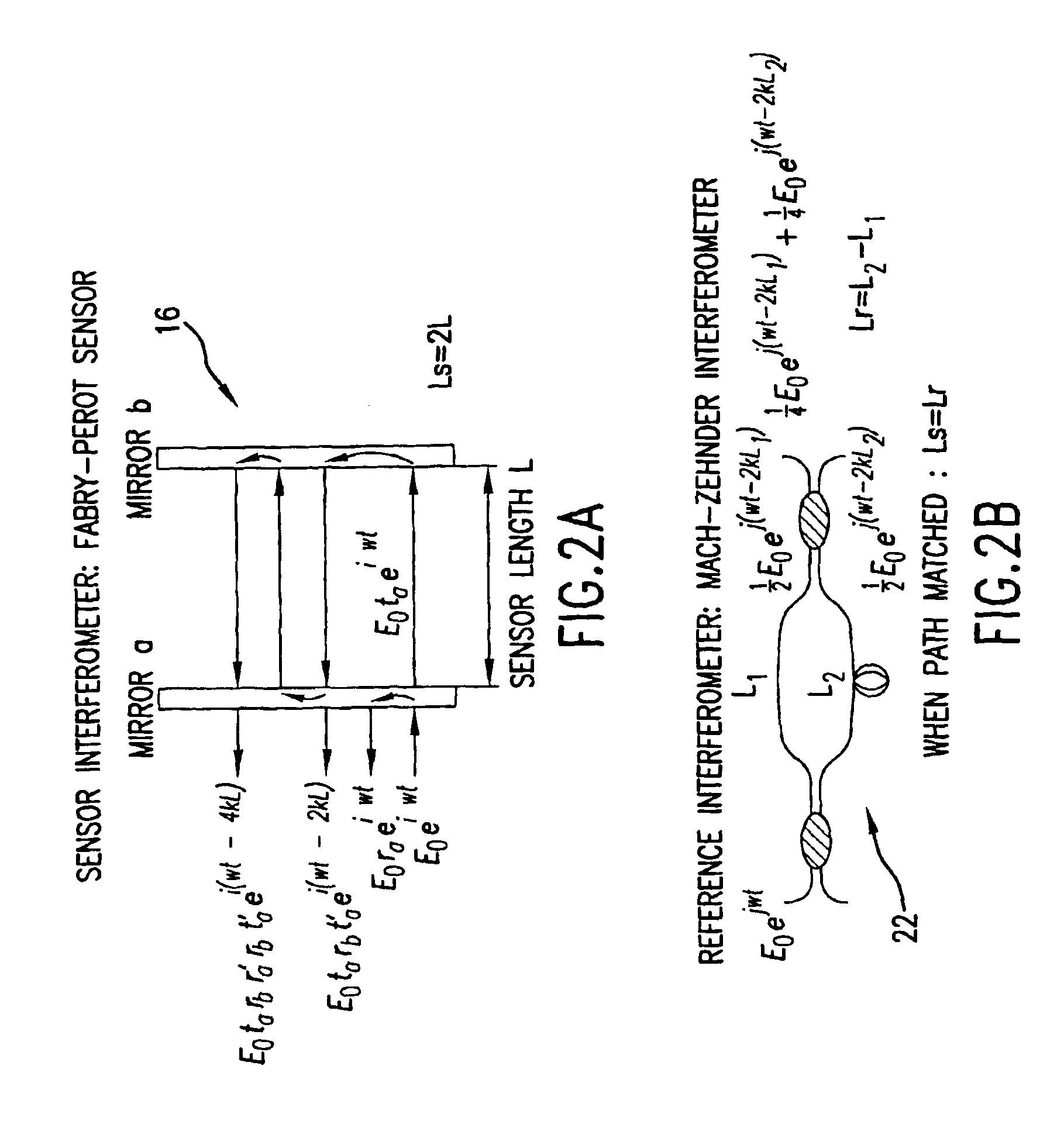
InactiveUS20050157305A1Good flexibilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansFiberPhase step
A micro-optical fiber tip based sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements in a wide bandwidth, the design of which allows for multiplexity of the input side of the system is based on micro-electromechanical fabrication techniques. The optical portion of the system is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer combination that allows a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source. A phase modulation and demodulation scheme takes advantage of the Integrated Optical Circuit phase modulator and multi-step phase-stepping algorithm for providing high frequency and real time phase signal demodulation. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors each of which has a diaphragm that is used as a transducer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Pixelated phase-mask interferometer
ActiveUS7230717B2Increase rangeReduce complexityInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase differenceDetector array
A phase-difference sensor measures the spatially resolved difference in phase between orthogonally polarized reference and test wavefronts. The sensor is constructed as a pixelated phase-mask aligned to and imaged on a pixelated detector array. Each adjacent pixel of the phase-mask measures a predetermined relative phase shift between the orthogonally polarized reference and test beams. Thus, multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be synthesized at the same time by combining pixels with identical phase-shifts. The multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be combined to calculate standard parameters such as modulation index or average phase step. Any configuration of interferometer that produces orthogonally polarized reference and object beams may be combined with the phase-difference sensor of the invention to provide, single-shot, simultaneous phase-shifting measurements.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
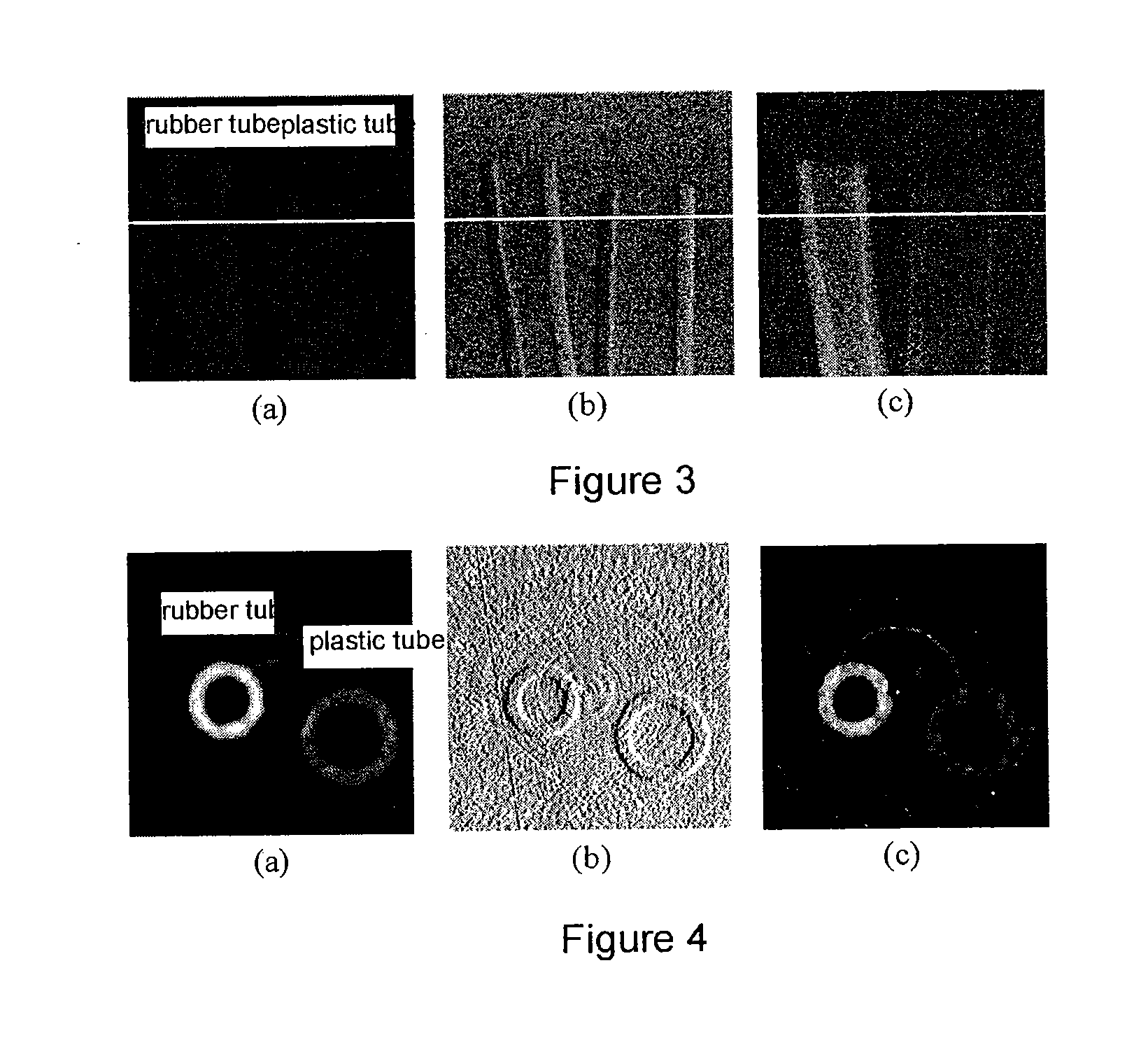
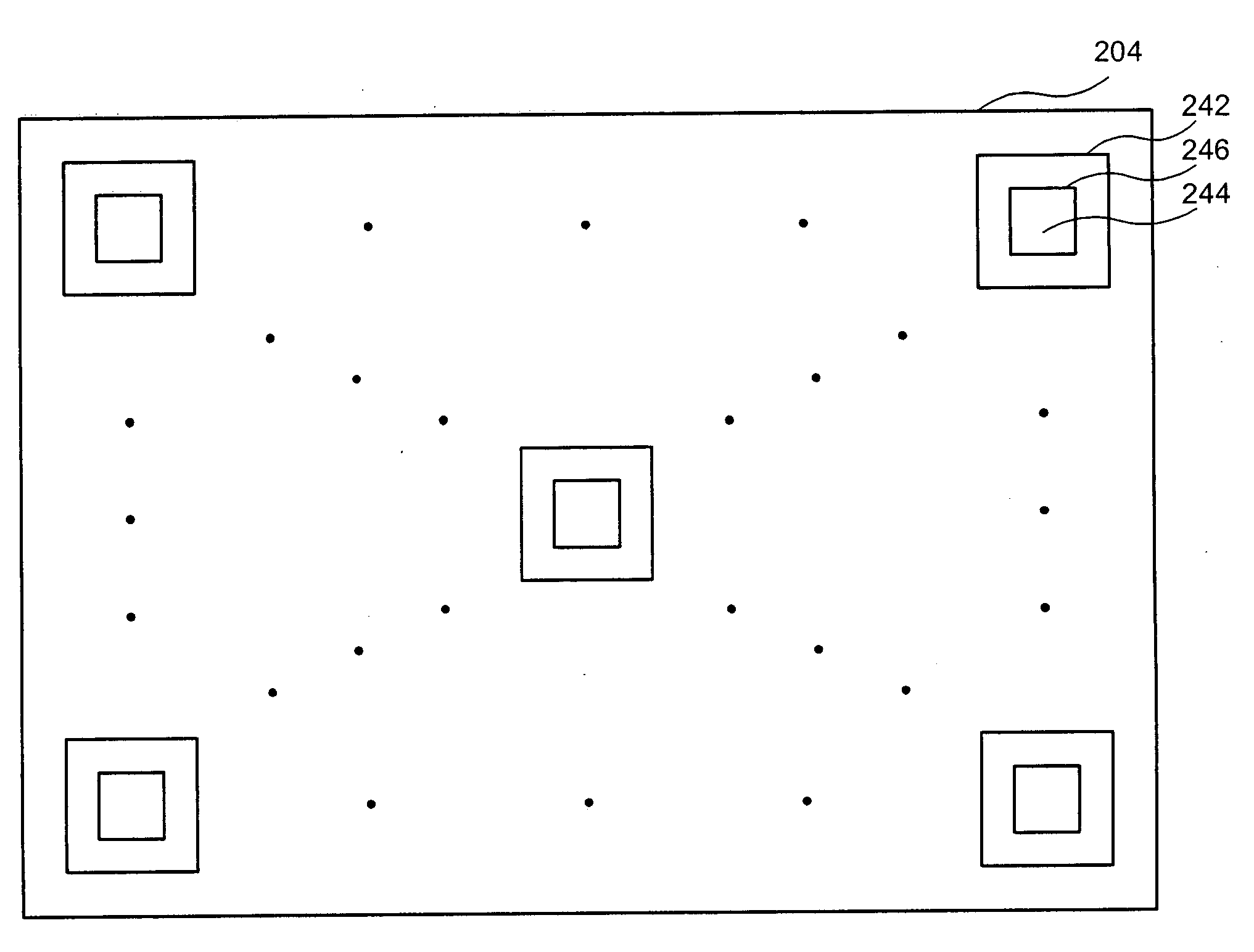
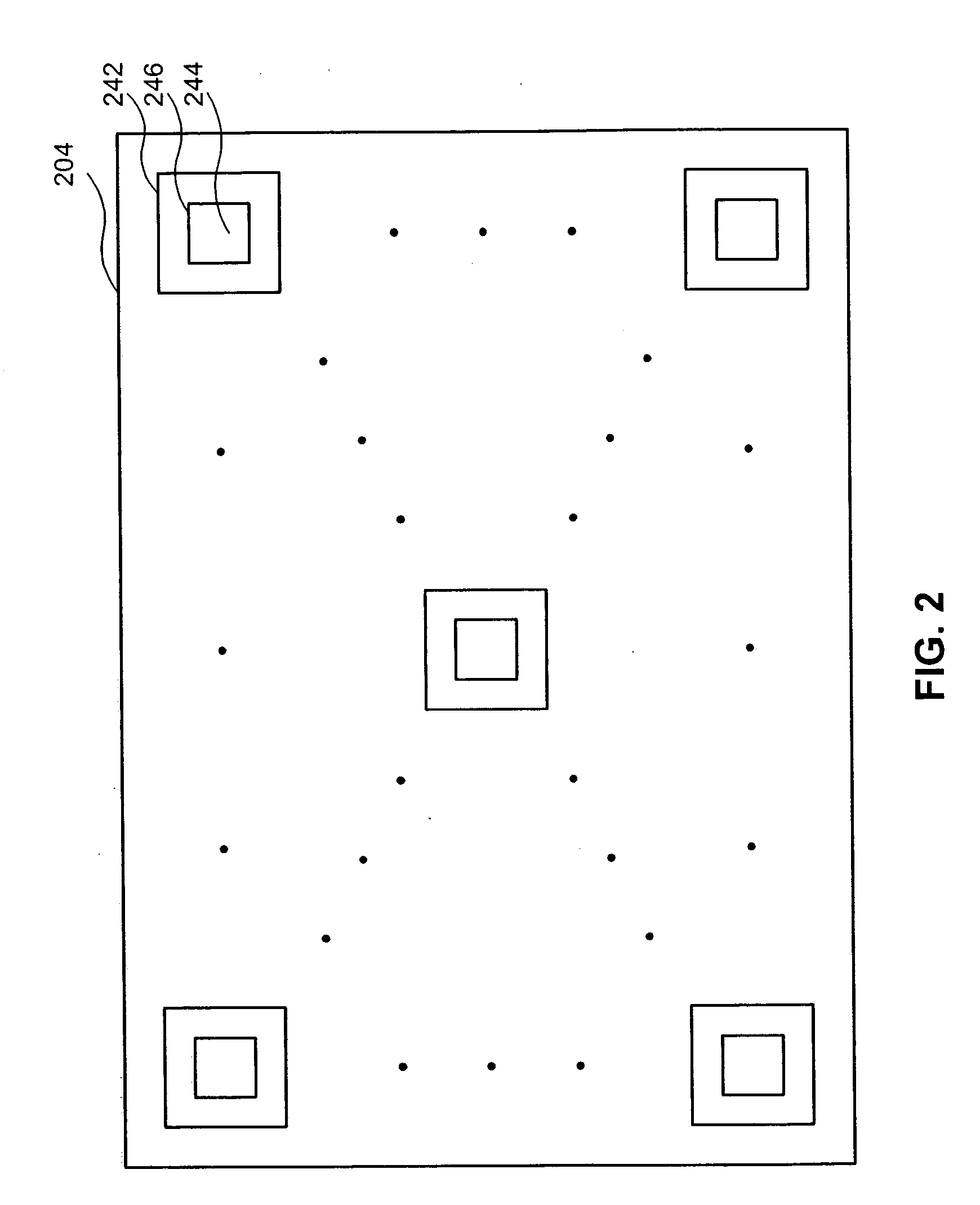
Low dose single step grating based X-ray phase contrast imaging
InactiveCN102325498ASmall doseImage quality is not degradedMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsHard X-raysGrating
Phase sensitive X-ray imaging methods can provide substantially increased contrast over conventional absorption based imaging, and therefore new and otherwise inaccessible information. The use of gratings as optical elements in hard X-ray phase imaging overcomes some of the problems that have impaired the wider use of phase contrast in X-ray radiography and tomography. So far, to separate the phase information from other contributions detected with a grating interferometer, a phase-stepping approach has been considered, which implies the acquisition of multiple radiographic projections. Here,an innovative, highly sensitive X-ray tomographic phase contrast imaging approach is presented based on grating interferometry, which extracts the phase contrast signal without the need of phase stepping. Compared to the existing phase step approach, the main advantage of this new method dubbed 'reverse projection' is the significantly reduced delivered dose, without degradation of the image quality. The new technique sets the pre-requisites for future fast and low dose phase contrast imaging methods, fundamental for imaging biological specimens and in-vivo studies.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Fiber tip based sensor system for acoustic measurements
InactiveUS6901176B2Easy to measureSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansAccelerometerPhase step
A fiber optic sensor system for acoustic measurements over a 6 kHz bandwidth, the design of which allows for multiplexity of the input side of the system, and where the optical part of the system is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer as well, that allows a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source, as well as the optical intensity fluctuations. A phase modulation and demodulation scheme takes advantage of the Integrated Optical Circuit phase modulator and multi-step phase-stepping algorithm for providing for high frequency and real time phase signal demodulation. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors which have a diaphragm, which is used as the transducer. Pressure microphone, velocity sensor, as well as accelerometer, are built based on the fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
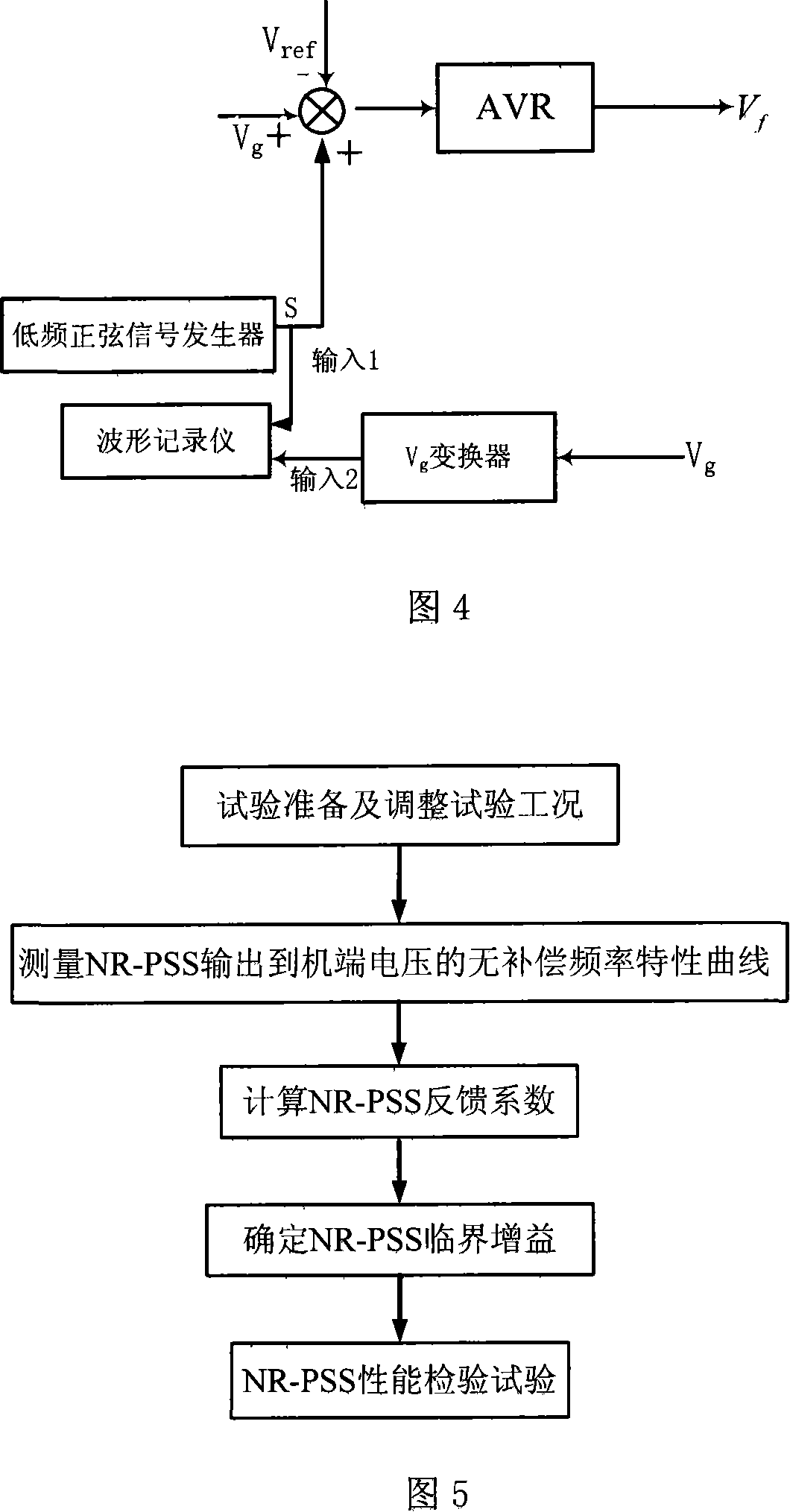
Method for regulating frequency domain based nonlinear power system stabilizer parameter
ActiveCN101119094AClear thinkingSimple stepsFrequency analysisDynamo-electric machine testingGain coefficientEngineering
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Controllable device for phase modulation
ActiveUS20090284671A1Shorter switching delayShort delayLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesSpatial light modulatorPhase modulation
A controllable device for phase modulation of coherent light with modulator cells comprising liquid crystal molecules is provided which realises a large number of phase steps per modulator cell and whose switching delay is shorter than 1 ms. The device can include a spatial light modulator with a modulator matrix having regularly arranged controllable LC modulator cells, a light source which illuminates the modulator matrix, and control means for controlling the phase modulation in the LC modulator cells. The modulator matrix can be configured to comprise a controllable λ / 2 plate disposed between two non-controllable λ / 4 plates; the controllable LC modulator cells can be PSS liquid crystal; each LC modulator cell is controllable locally with a positive or negative voltage value, depending on the actual phase values to be written; and the control means generate a globally constant phase offset for the phase values to be written in every other frame.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Micro-optical sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements
InactiveUS7428054B2Good flexibilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansFiberPhase step
A micro-optical fiber tip based sensor system for pressure, acceleration, and pressure gradient measurements in a wide bandwidth, the design of which allows for multiplexity of the input side of the system is based on micro-electromechanical fabrication techniques. The optical portion of the system is based on low coherence fiber-optic interferometry techniques which has a sensor Fabry-Perot interferometer and a read-out interferometer combination that allows a high dynamic range and low sensitivity to the wavelength fluctuation of the light source. A phase modulation and demodulation scheme takes advantage of the Integrated Optical Circuit phase modulator and multi-step phase-stepping algorithm for providing high frequency and real time phase signal demodulation. The system includes fiber tip based Fabry-Perot sensors each of which has a diaphragm that is used as a transducer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
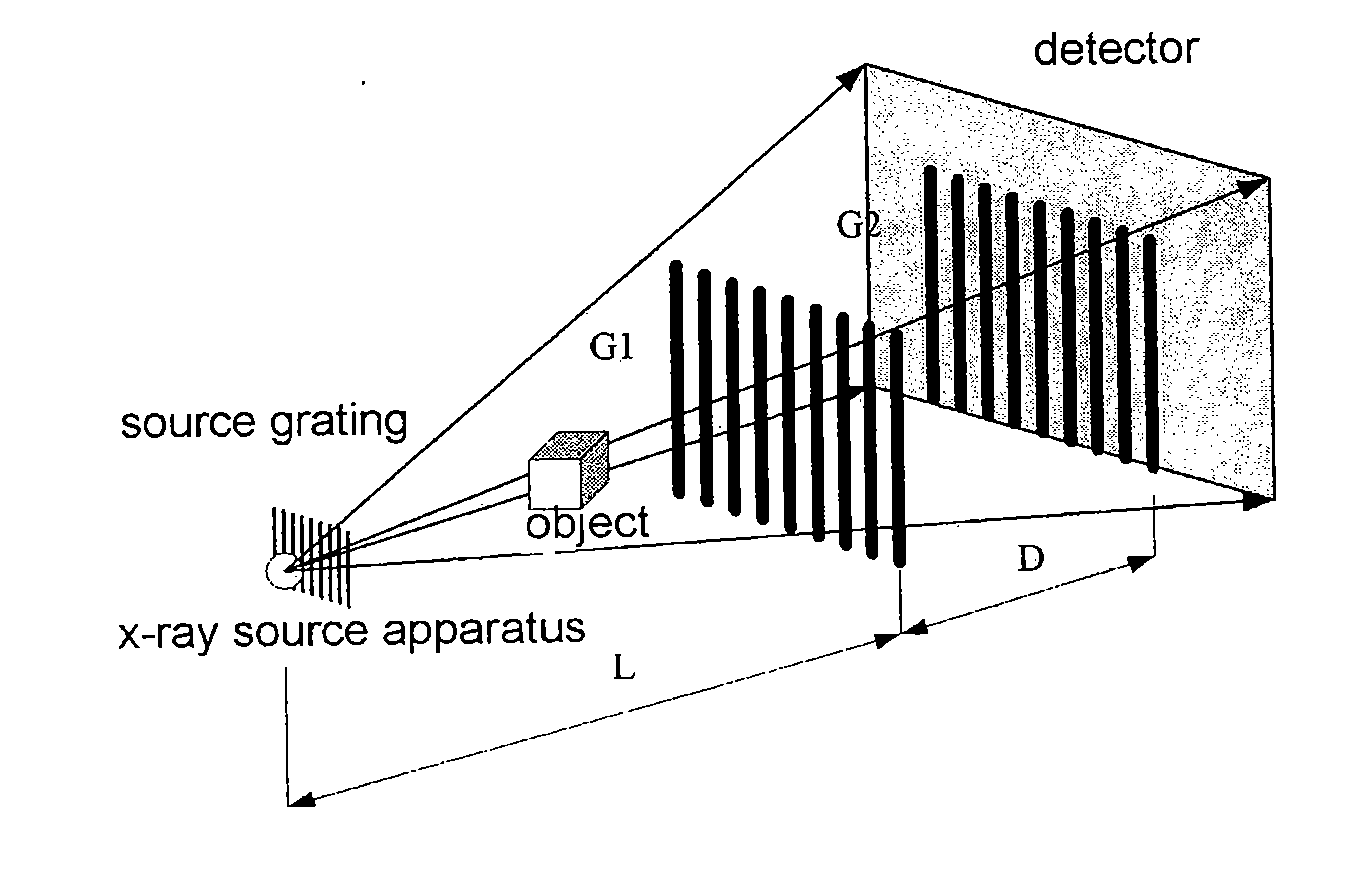
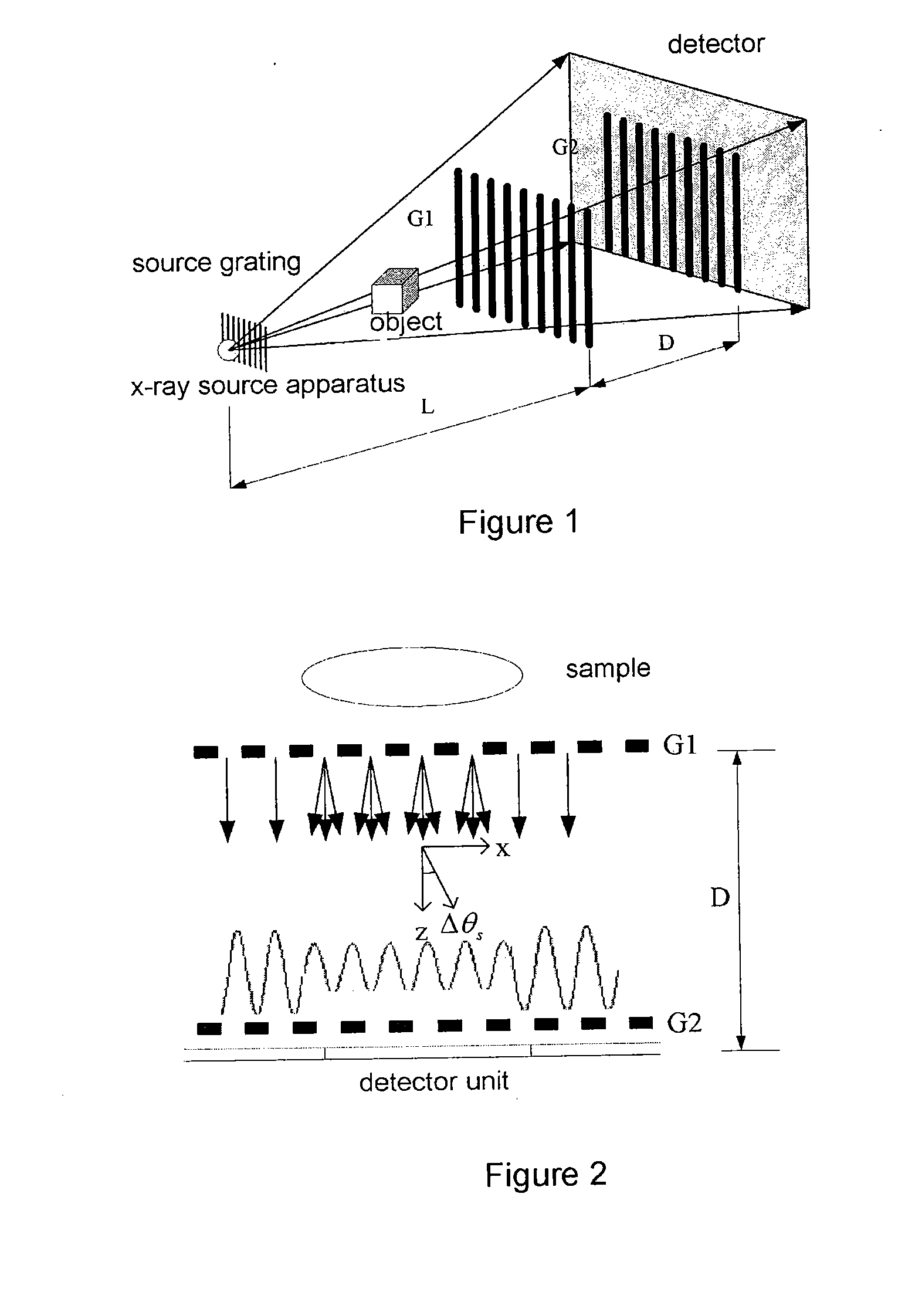
X-ray dark-field imaging system and method
ActiveUS20110293064A1Contrast ratio is reducedReduce the ratioImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingGratingX-ray
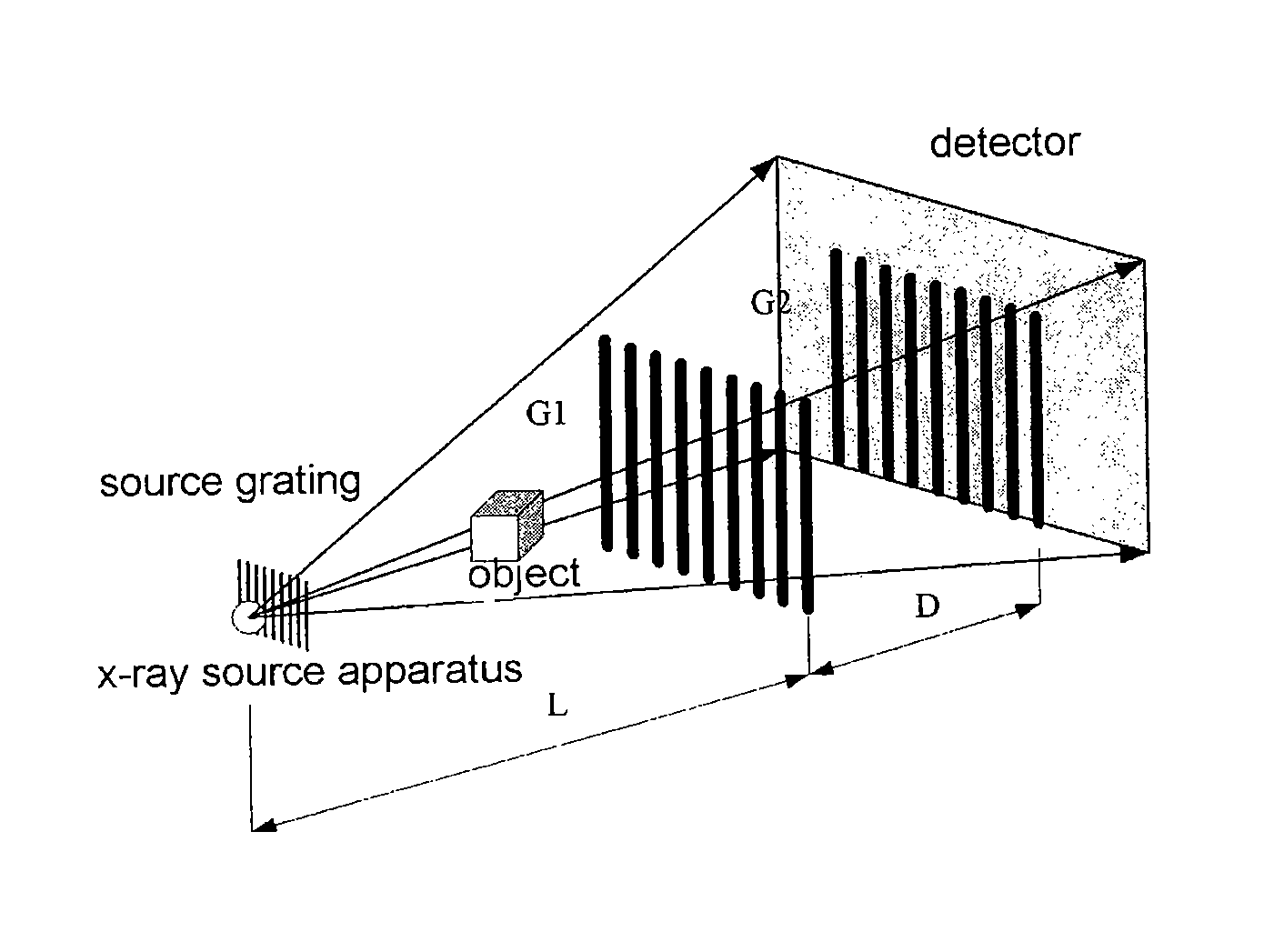
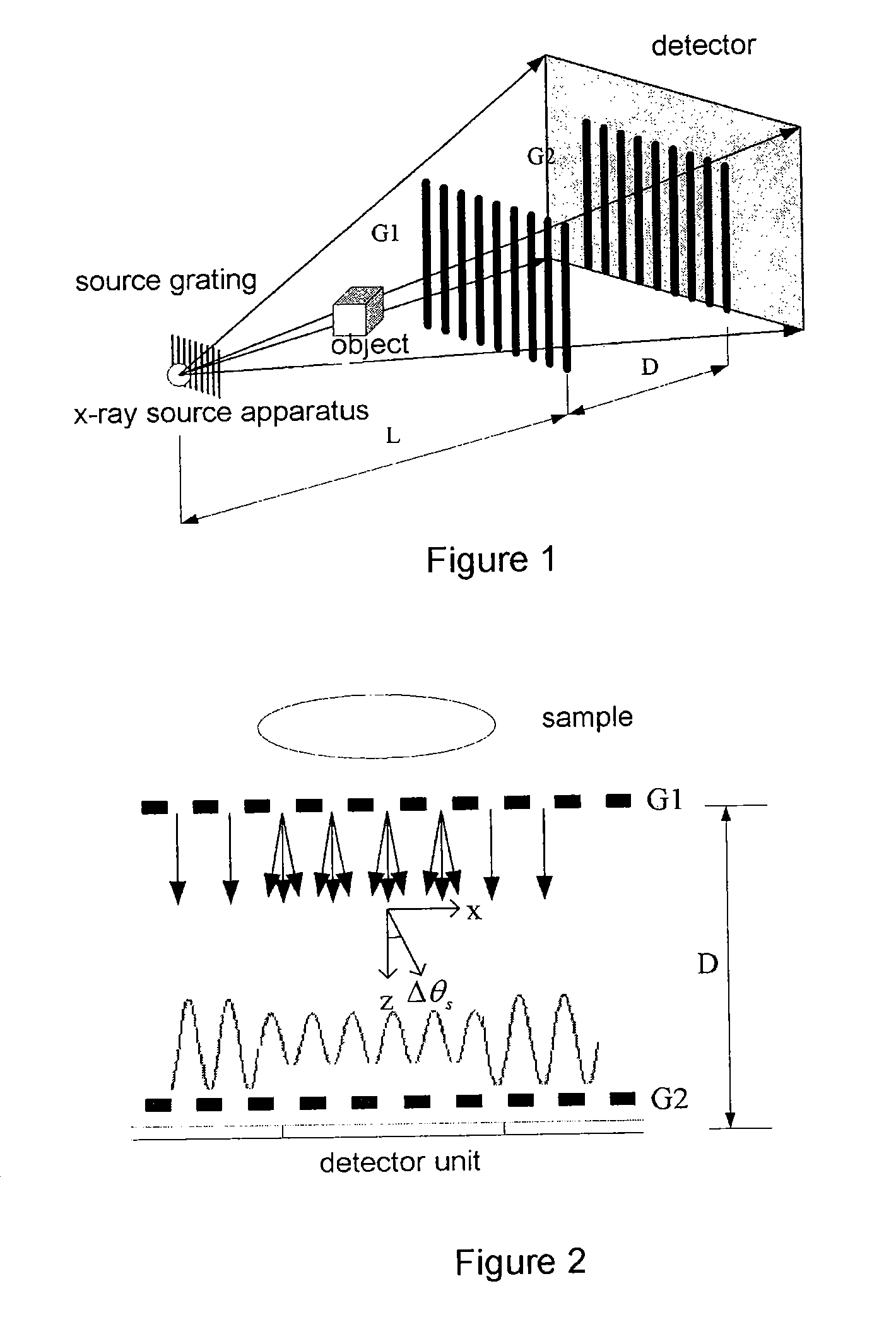
An x-ray imaging technology, performing an x-ray dark-field CT imaging of an examined object using an imaging system which comprises an x-ray source, two absorbing gratings G1 and G2, an x-ray detector, a controller and a data processing unit, comprising the steps of: emitting x-rays to the examined object; enabling one of the two absorbing gratings G1 and G2 to perform phase stepping motion within at least one period range thereof; where in each phase stepping step, the detector receives the x-ray and converts it into an electric signal; wherein through the phase stepping of at least one period, the x-ray intensity at each pixel point on the detector is represented as an intensity curve; calculating a second moment of scattering angle distribution for each pixel, based on a contrast of the intensity curve at each pixel point on the detector and an intensity curve without presence of the examined object; taking images of the object at various angles, then obtaining an image with scattering information of the object in accordance with a CT reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
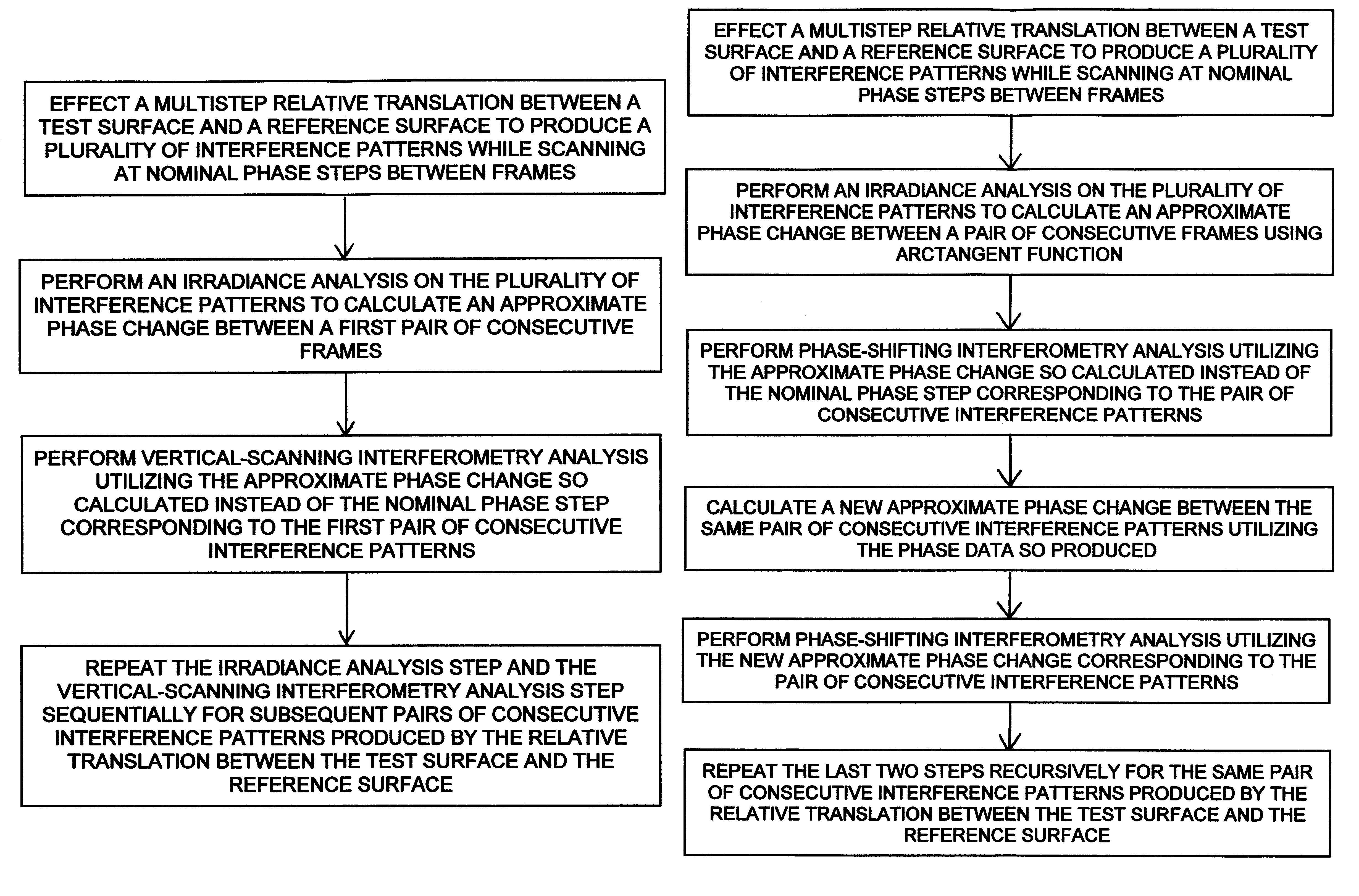
Correction of scanning errors in interferometric profiling
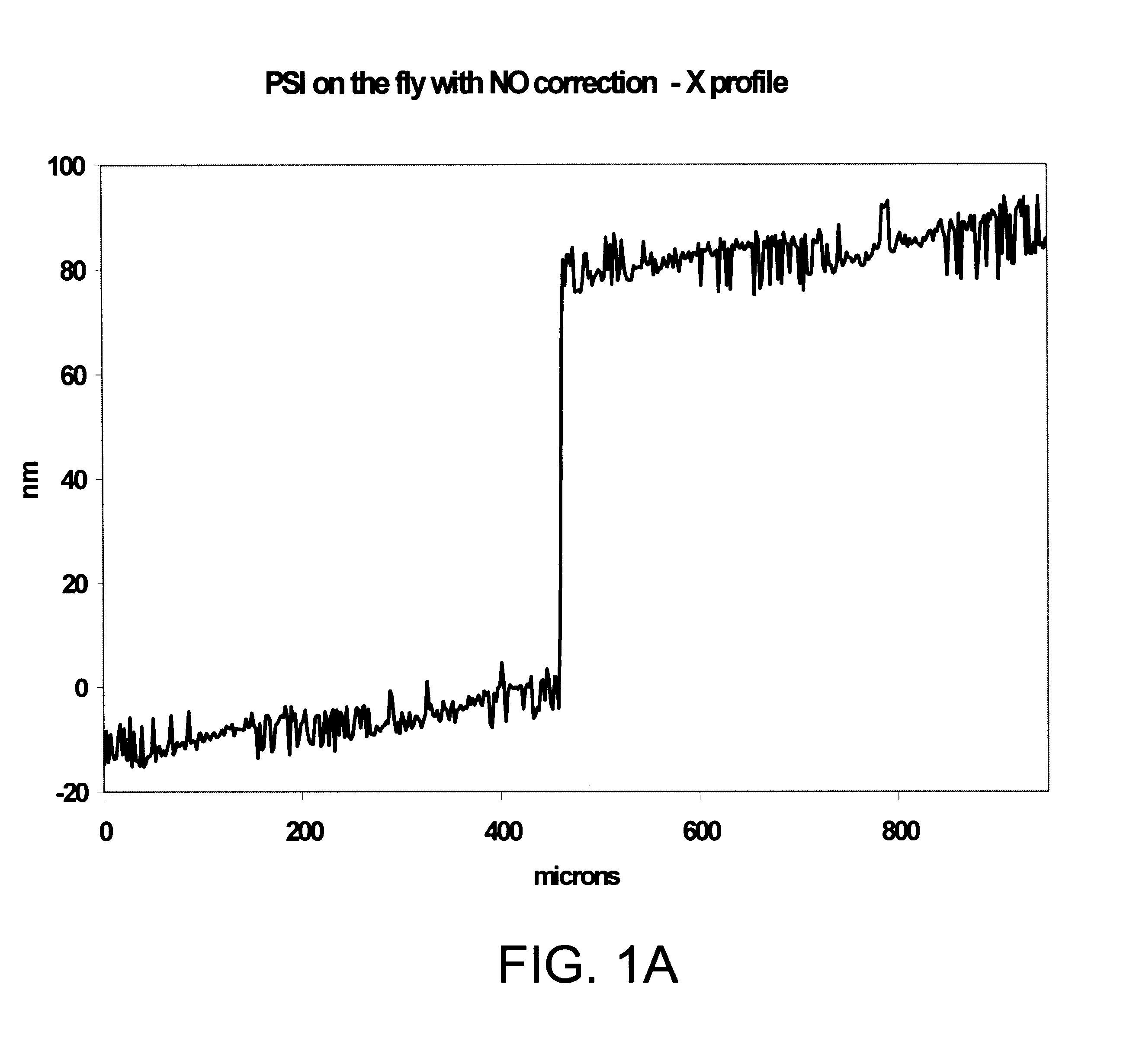
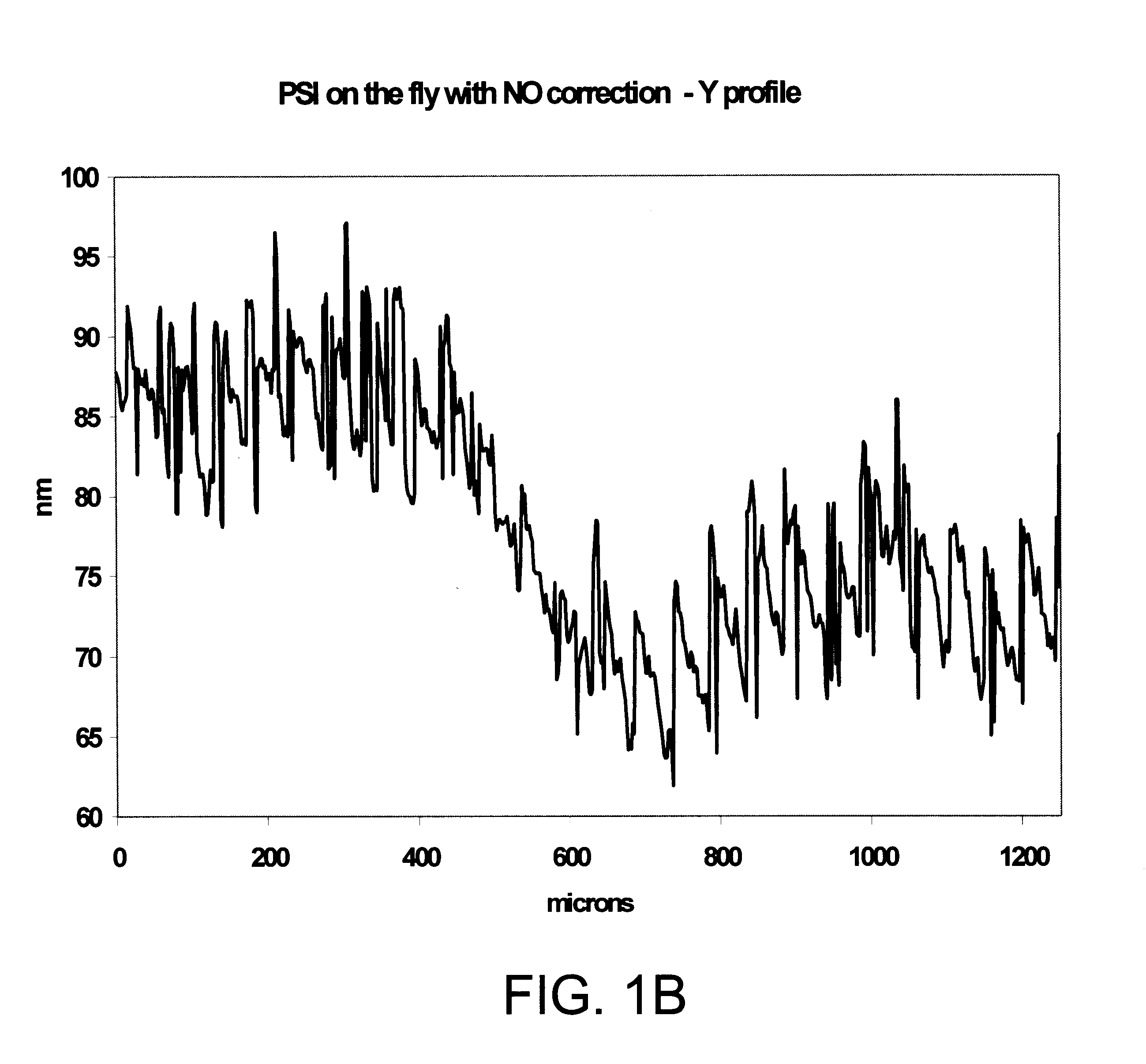
Interferometric measurements are carried out in conventional manner to produce a correlogram corresponding to successive scanner steps. An approximation of the actual scan-step size between frames is calculated from multiple-frame intensity data collected around the frame of interest using common irradiance algorithms. The scan-step size so measured is then used in standard PSI, VSI or PSIOTF algorithms, instead of the scanner's nominal phase step. According to one embodiment, the invention utilizes a five-frame PSI algorithm to produce an average scan-step size of four scan steps. According to another embodiment, the phase step between frames is calculated directly utilizing a novel five-frame algorithm that produces an approximation of actual phase step for a given frame, rather than an average value of four steps around the frame. The method requires reduced data processing and can advantageously be applied "on-the fly" as intensity data are acquired during scanning.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
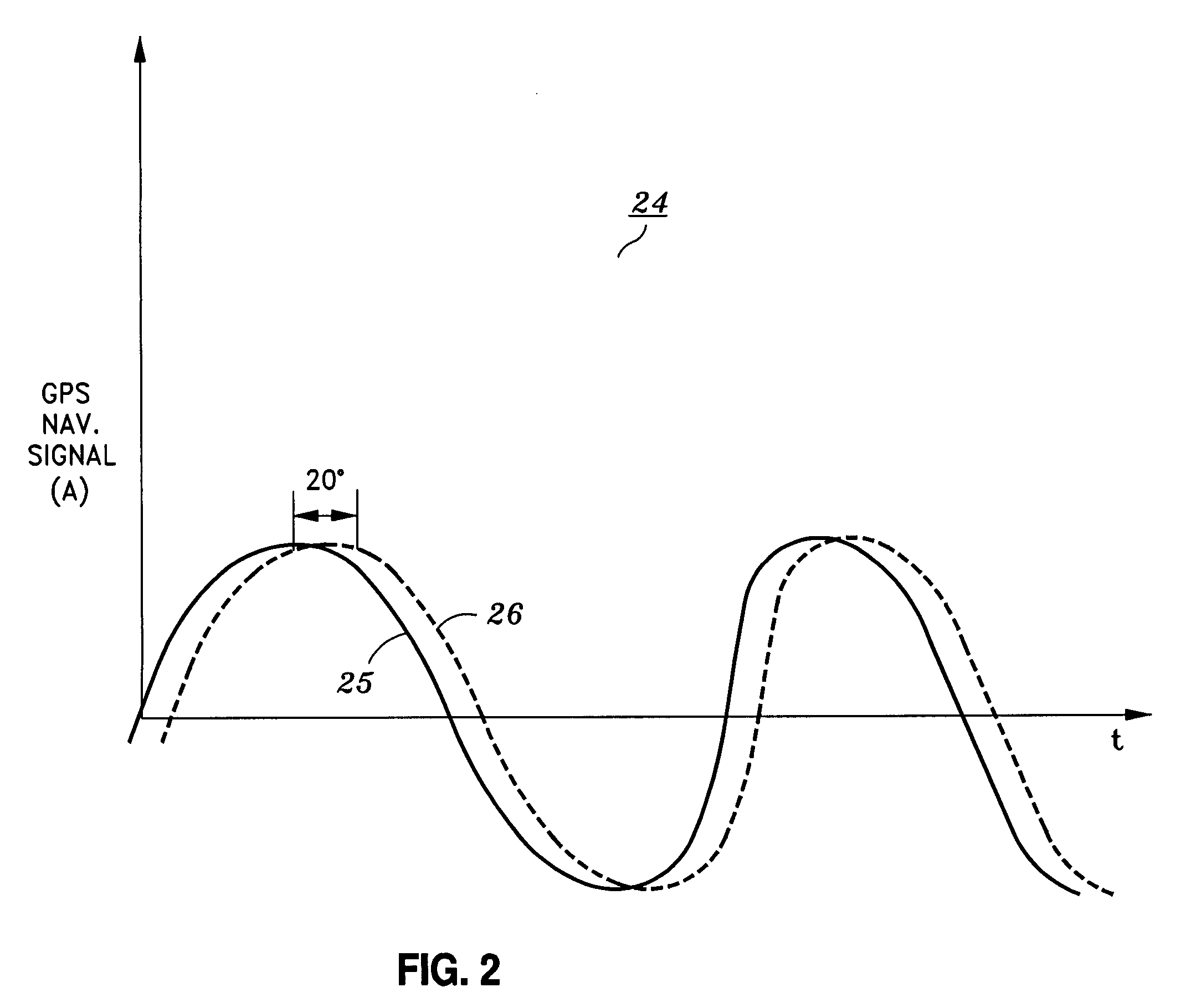
Phase step alert signal for GPS integrity monitoring
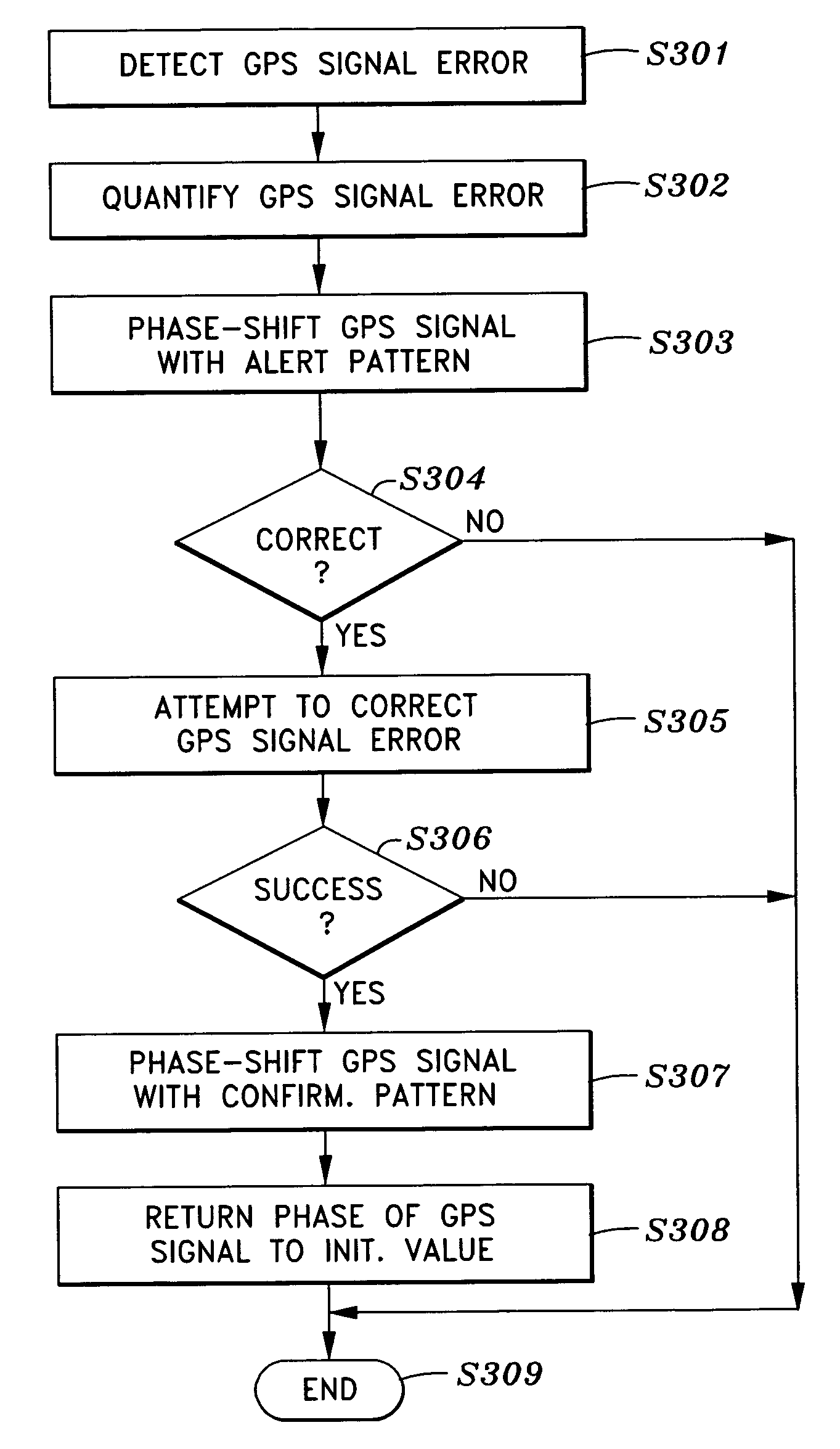
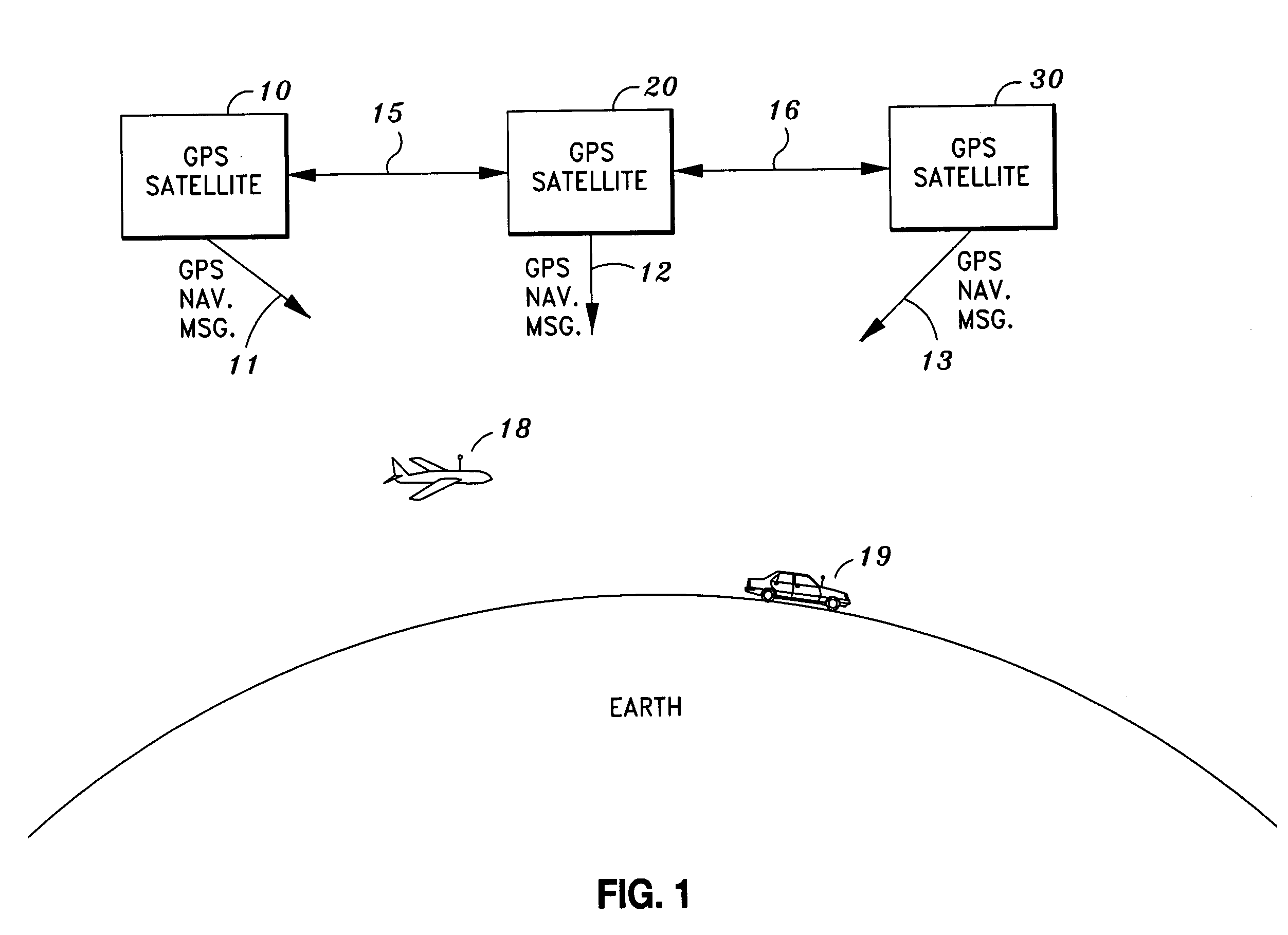
InactiveUS7095369B1Confidence in the integrity of the GPS signalPosition fixationRadio transmissionPhase shiftedEngineering
Alerting a user of an integrity error in a global positioning system (GPS) signal transmitted from a transmitter in a global positioning system (GPS) satellite, by detecting an error in the global positioning system (GPS) signal, alerting the user of the error by shifting a phase of the global positioning system (GPS) signal from an initial value by a predetermined phase-shift amount, and returning, in the case that the detected error is corrected, the phase of the global positioning system (GPS) signal to the initial value. Preferably, the GPS signal is phase-shifted by the predetermined phase-shift amount using an alert timing pattern which indicates the level of detected error.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
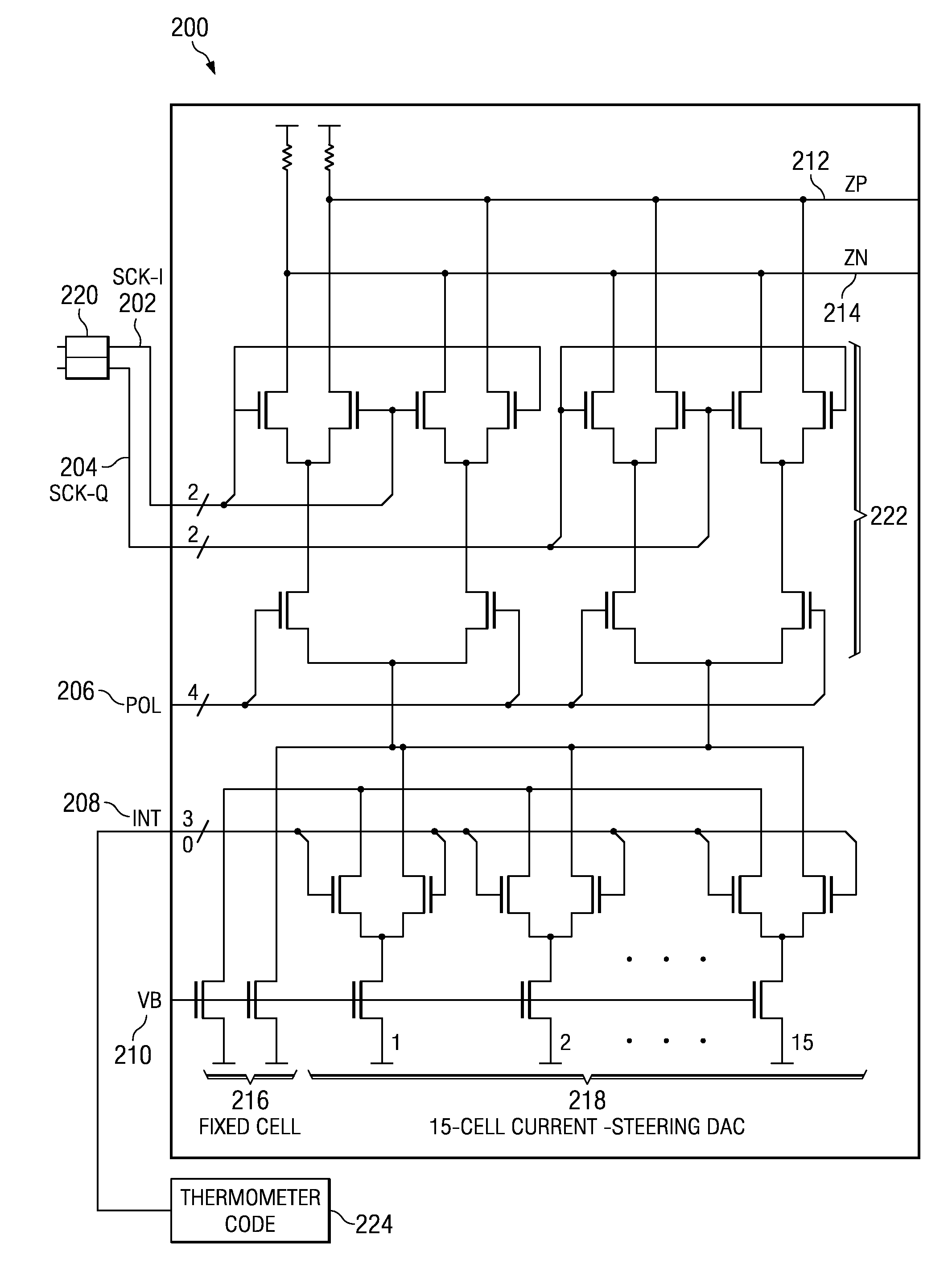
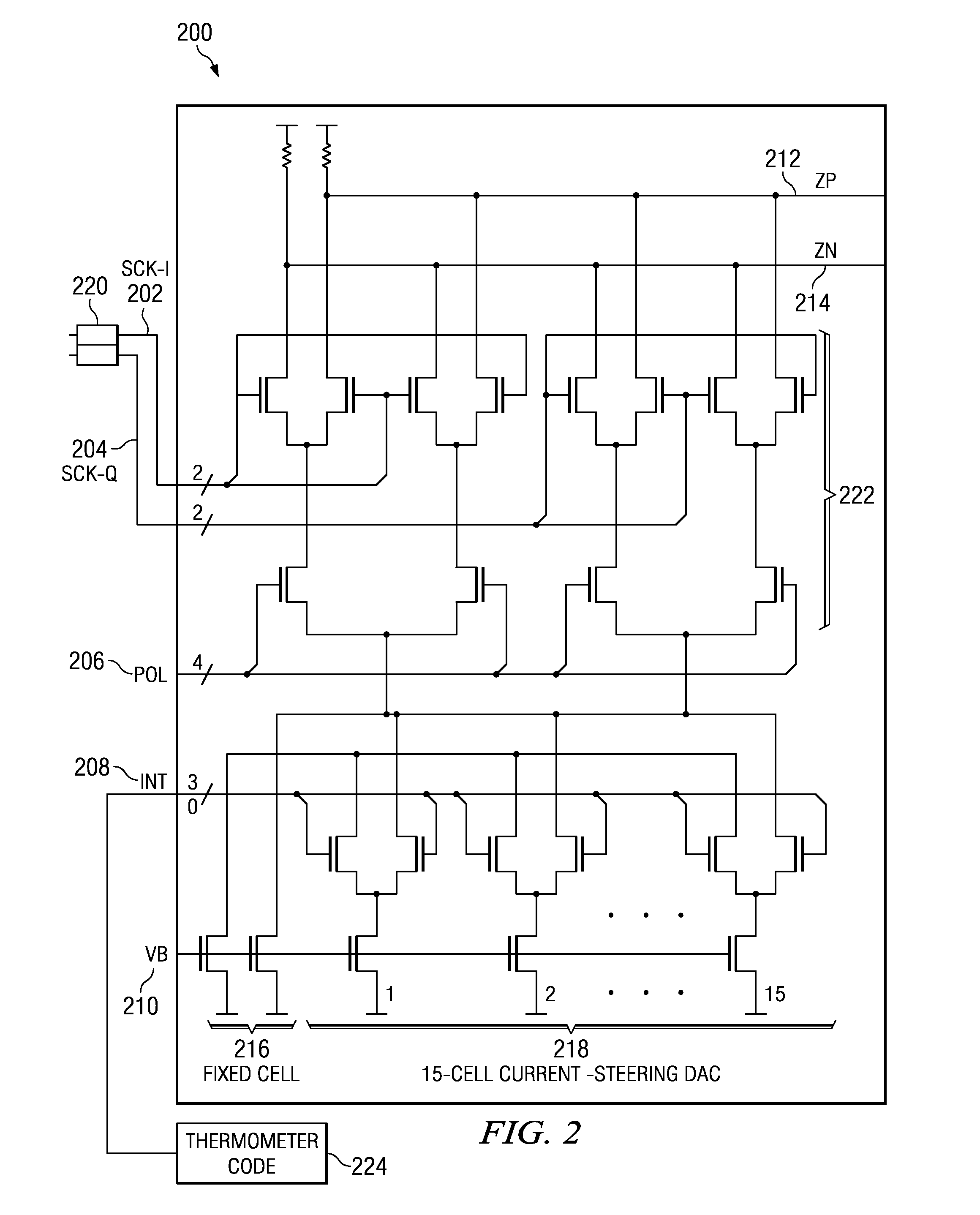
Phase shifting using asymmetric interpolator weights
Illustrative embodiments provide an apparatus for phase shifting to produce uniform phase steps in a predictable manner to improve the linearity of conversion. The apparatus comprises a phase selector for selecting two or more phases to create selected phases and a phase interpolator capable of receiving the selected phases. The apparatus further comprises a set of digital to analog converter cells connected to the phase interpolator, wherein interpolator weight distribution among the set of digital to analog converter cells is non-linear, and a thermometer code in communication with the set of digital to analog converter cells, wherein the thermometer code adjusts output of the set of digital to analog converter cells to phase shift the selected phases.
Owner:IBM CORP
Coherent combining device of self-adaption high-order transverse mode lasers
The invention relates to a coherent combining device of self-adaption high-order transverse mode lasers, which comprises a solid laser, a deformable mirror, a beam matching system, a CCD camera, a beam splitting reflector, a high-pressure amplifier, a focusing lens, an attenuation system and a computer. High-order transverse mode lasers output by the solid laser are irradiated to the deformable mirror after being expanded by the beam matching system; laser beams reflected by the deformable mirror are gathered on the CCD camera at a focal position after passing through the beam splitting reflector, the attenuation system and the focusing lens in sequence; an optimization algorithm placed in the computer iterates along the direction enabling the strength of the peak value of a focal spot on the CCD camera to work out a voltage signal; the voltage signal is loaded to each driver of the deformable mirror after being amplified by the high-pressure amplifier to drive the deformable mirror to generate corresponding deformation so as to compensate the distortion in the whole wavefront phases of the high-order transverse mode lasers, compensate the pi-phase step of sidelobes of both sides of each nodel line of the high-order transverse mode lasers and improve the coherent feature and the focusable capability of the high-order transverse mode lasers. The invention can improve the coherent performance and the focusable capability among high-order transverse mode beams.
Owner:MINGDEZHIXING BEIJING TECH CO LTD
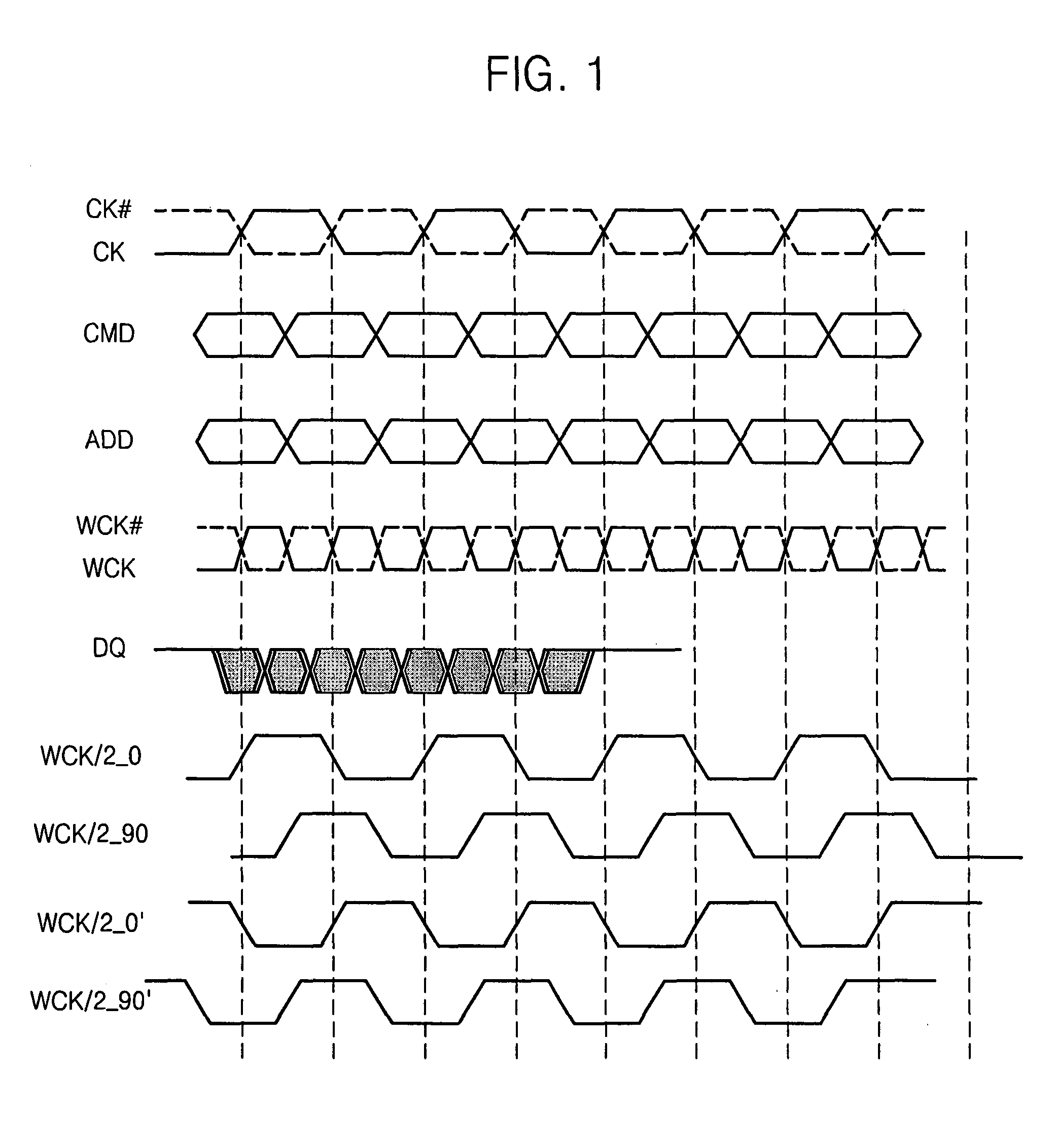
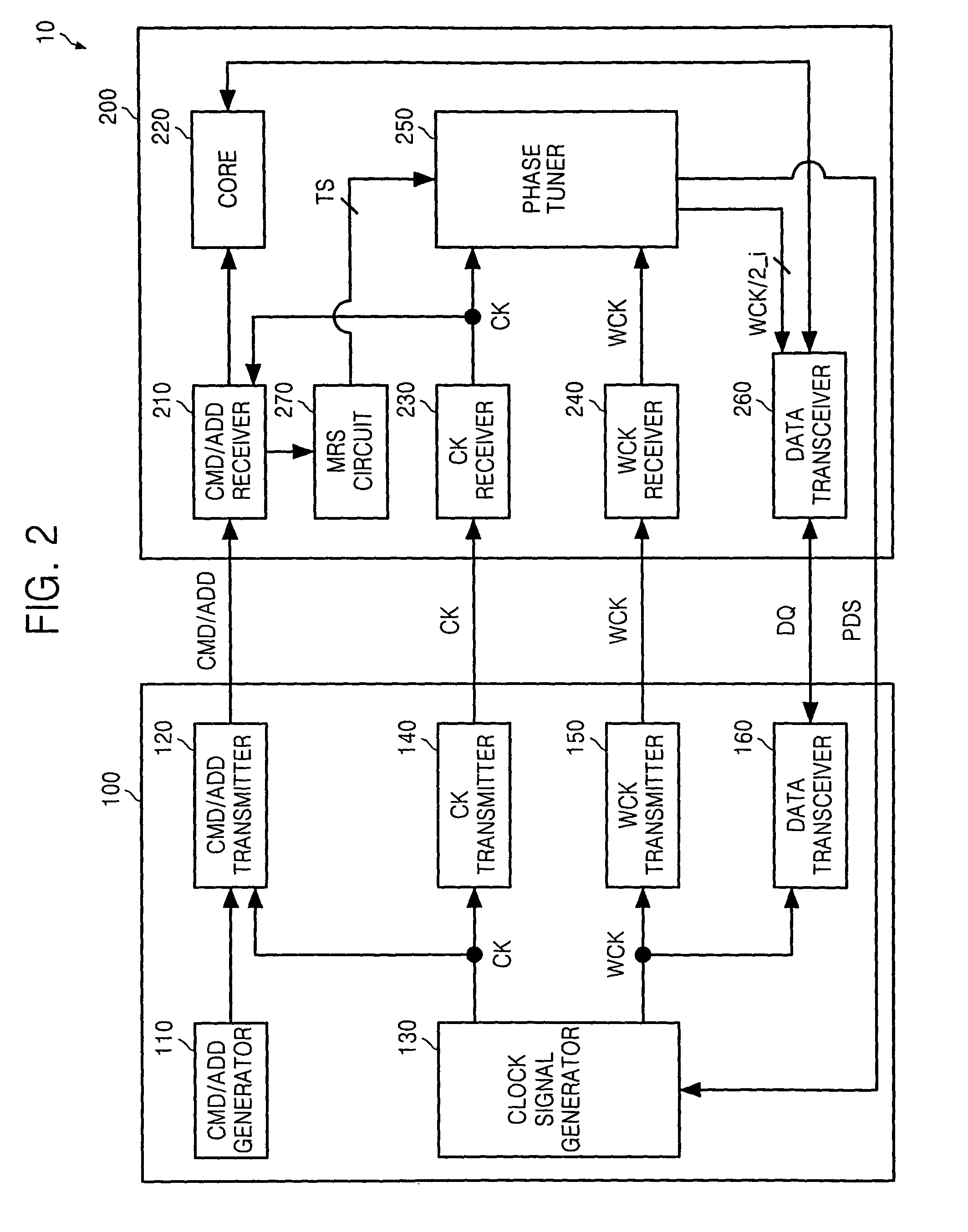
Method and apparatus for tuning phase of clock signal
A method and apparatus for tuning a phase of a data clock signal having a different frequency than a main clock signal. The method of tuning includes coarse tuning by receiving the data clock signal, dividing the data clock signal to generate a frequency-divided clock signal having a same frequency as the main clock signal, repeatedly shifting the frequency-divided clock signal to generate multiphase frequency-divided clock signals at a predetermined phase interval, comparing a phase of each of the multiphase frequency-divided clock signals with a phase of the main clock signal, and determining a phase shift amount based on a comparison result, and fine tuning by comparing a phase of a multiphase frequency-divided clock signal corresponding to the phase shift amount with the phase of the main clock signal and adjusting the phase of the data clock signal by a predetermined phase step based on the comparison result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
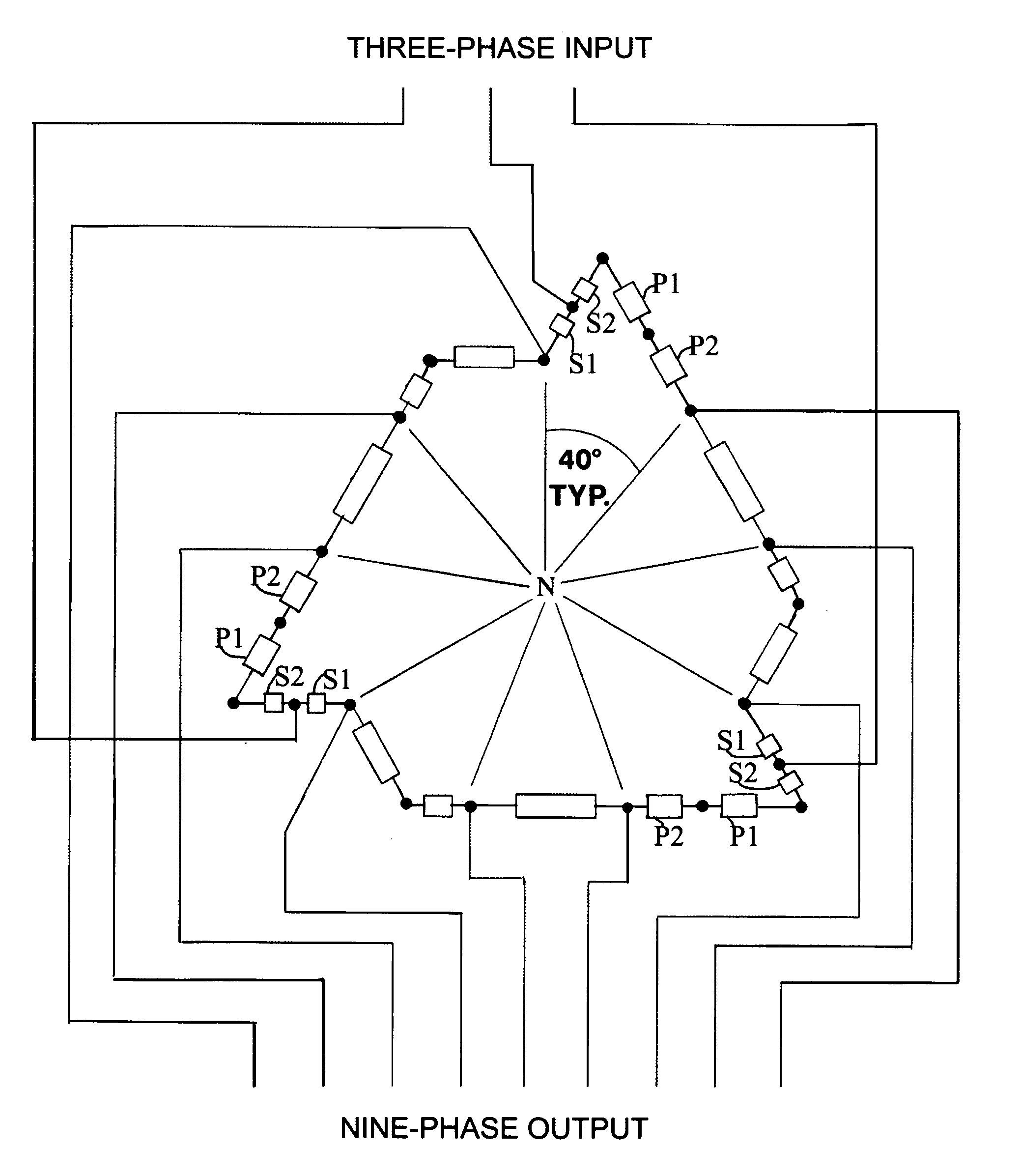
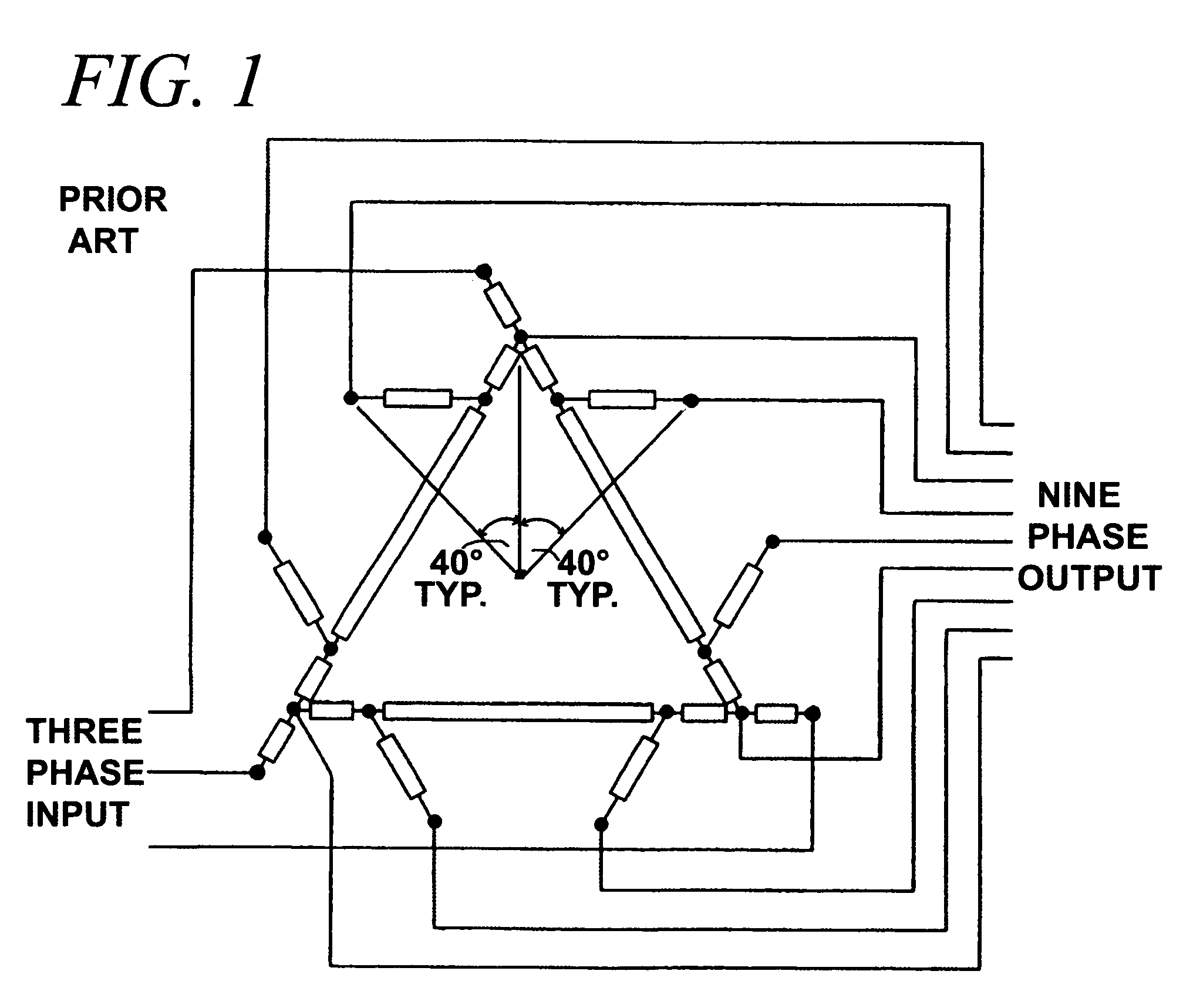
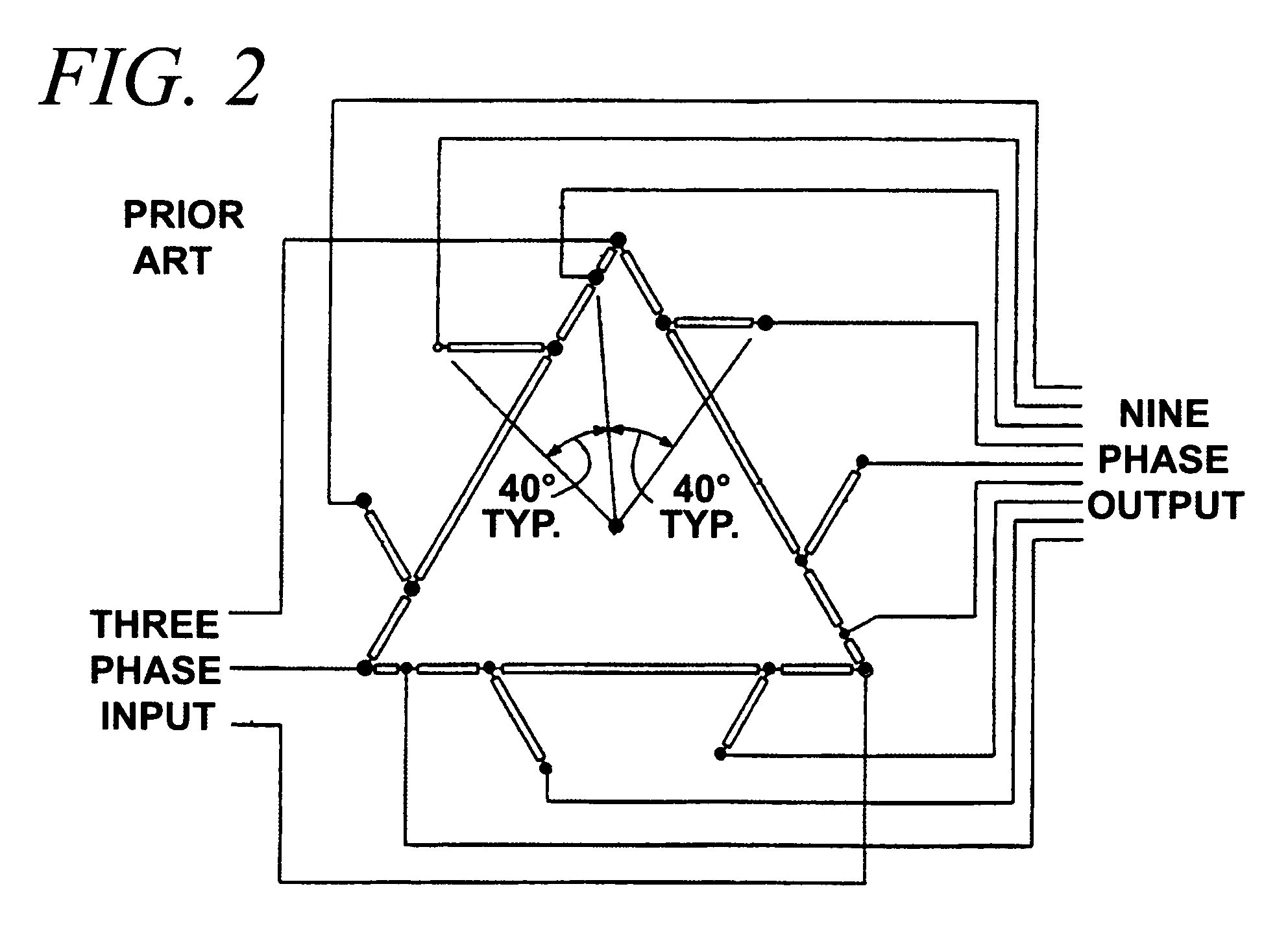
Nine-phase step-up/step-down autotransformer
InactiveUS7274280B1Easy to manufacturePractical and convenientConversion without intermediate conversion to dcFixed transformersAutotransformerTransformer
An irregular polygon connection of a three-phase autotransformer using only five windings per phase provides a source of nine-phase power suitable for an 18-pulse AC to DC power converter. The windings are connected in a manner to limit the amount of third harmonic current circulating in them. When the autotransformer is used to power a nine-phase AC to DC converter its kVA rating is typically less than 50% of the DC load kW. An additional tap on one of the five windings allows a wide range of AC output voltages to be obtained. Voltages greater than, less than, or equal to the AC input voltage can be obtained. Other multi-phase outputs are feasible. Additional isolated windings can provide means for the invention to operate as an efficient double-wound transformer.
Owner:SCHAFFNER MTC LLC
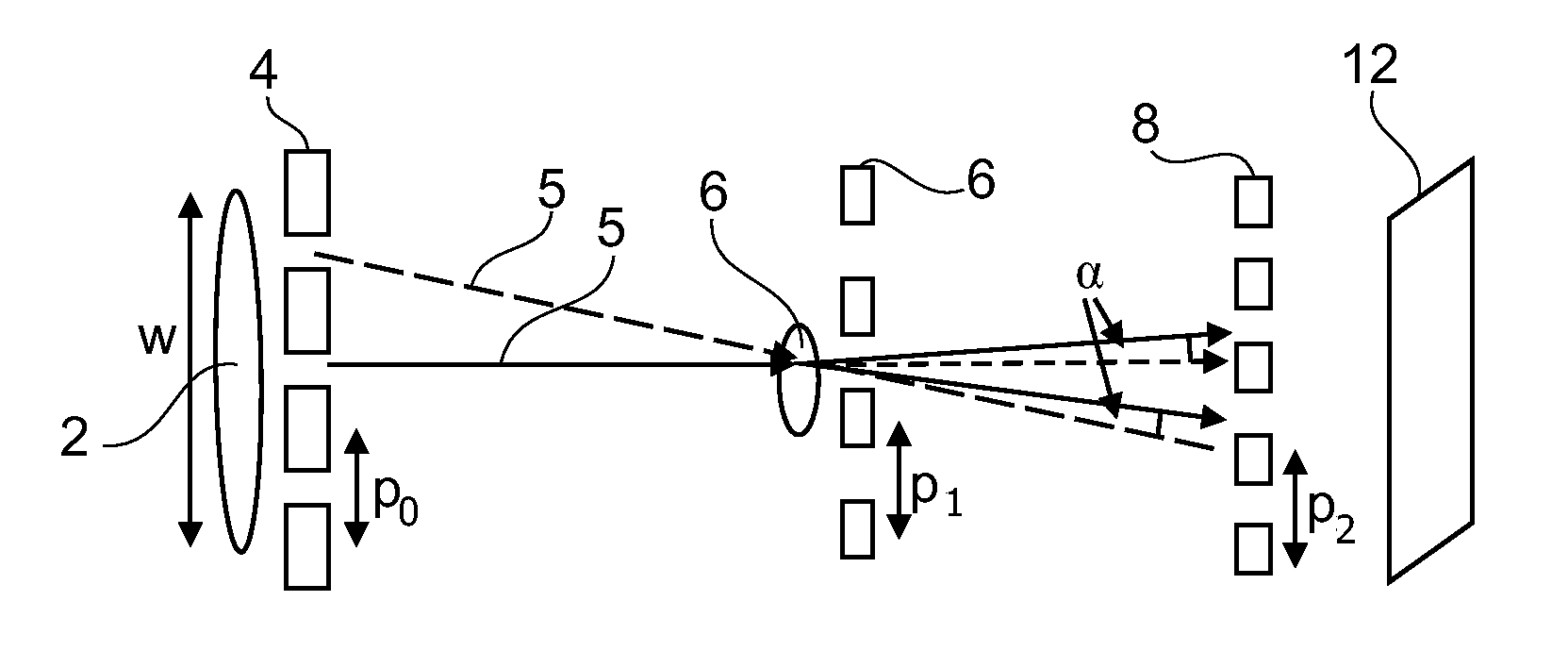
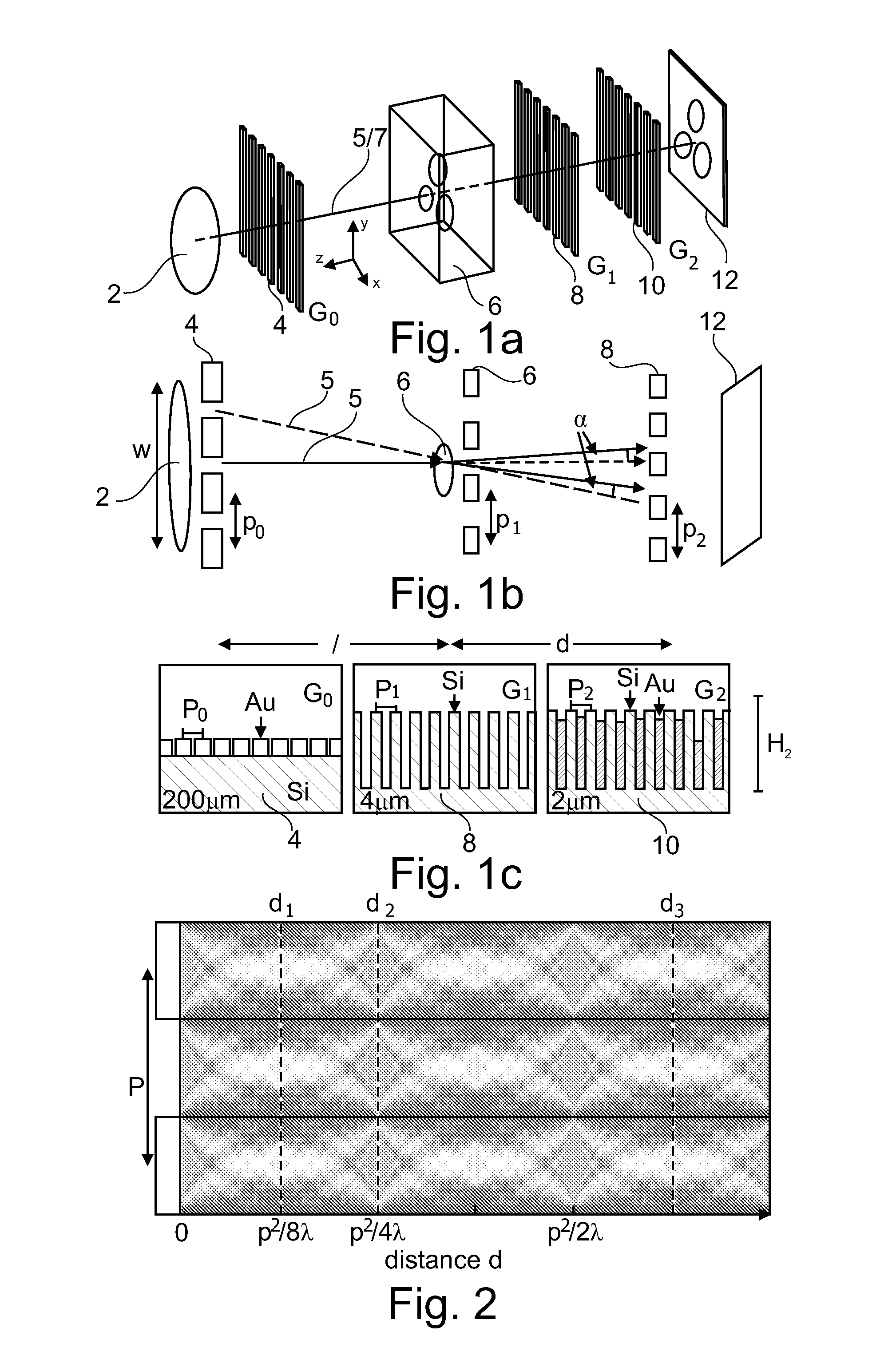
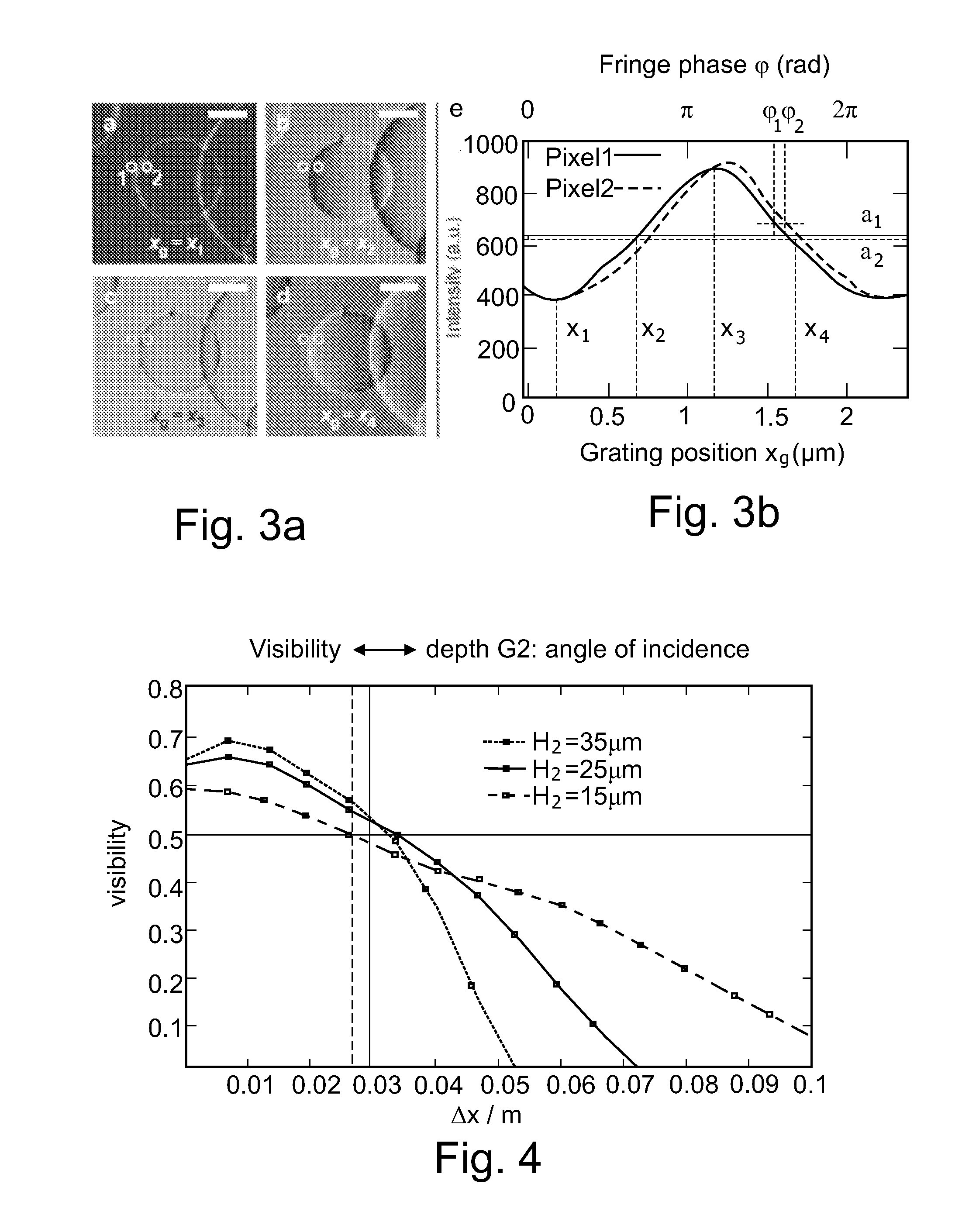
Non-parallel grating arrangement with on-the-fly phase stepping, x-ray system
ActiveUS20120236985A1Diminished readabilityRestricted degrees of freedomImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionVisibilitySoft x ray
The present invention relates to X-rayimage acquisition technology in general. Employing phase-contrast imaging for X-rayimage acquisition may significantly enhance the visibility of structures in images acquired. However, phase-contrast information may only be obtainable in a small detector region with subsequent image acquisitions requiring individual phase stepping states to allow reconstruction of an X-ray image. Accordingly, a grating arrangement for phase-contrast imaging is provided which may allow on the fly phase stepping during a field of view scan. According to the present invention a grating arrangement (1) for phase-contrast imaging is provided, comprising a first grating element (8) and a second grating element (10). Each of the first grating element (8) and the second grating element (10) comprises a trench structure. The trench structure comprises at least one trench region (9) and at least one barrier region (3). The at least one trench region (9) and the at least one barrier region (3) are at least locally arranged in parallel. The first grating element (8) and the second grating element (10) are arranged such that the trench structure of the first grating element (8) and the trench structure of the second grating element (10) are non-parallel comprising an angle α.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
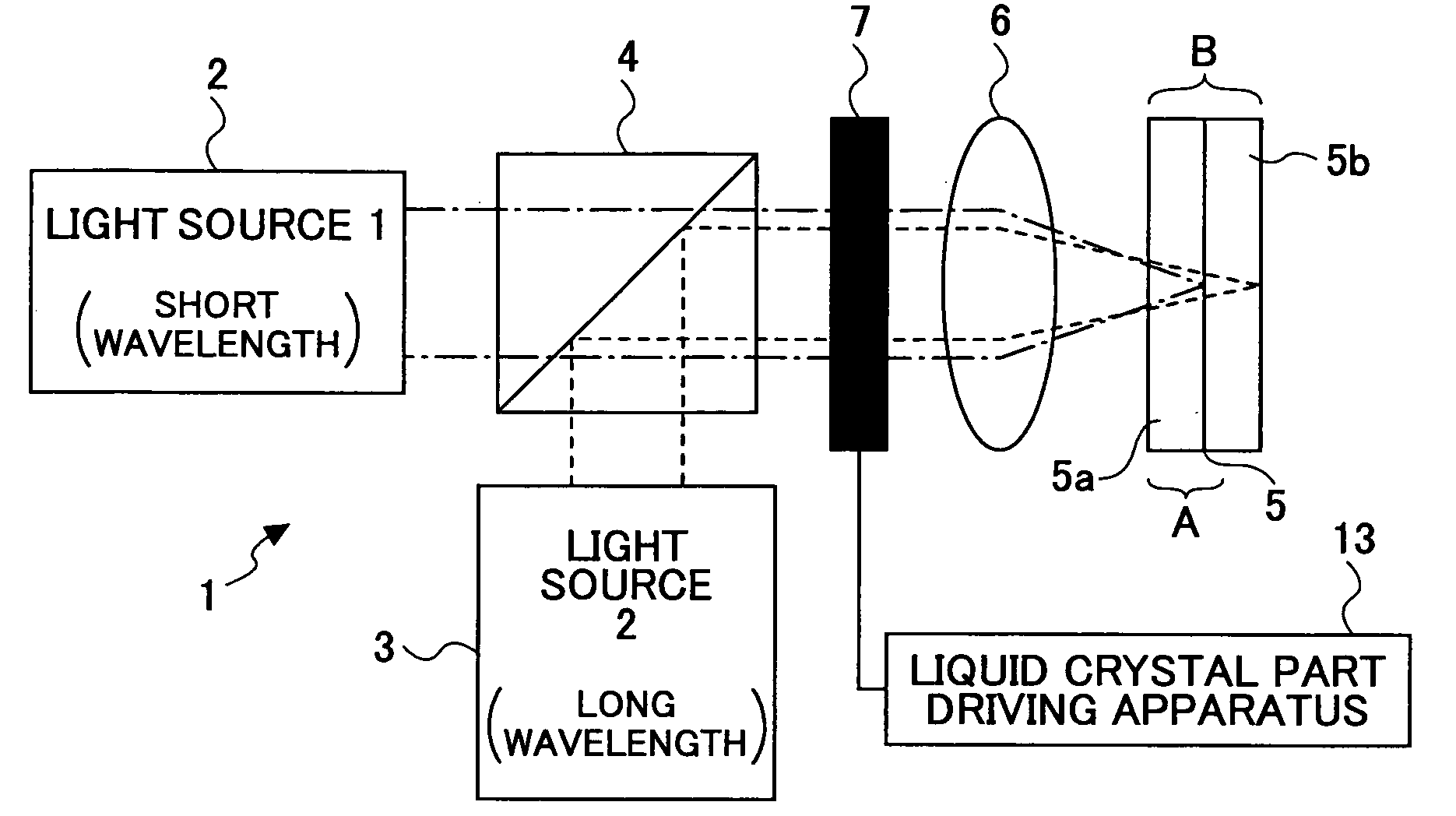
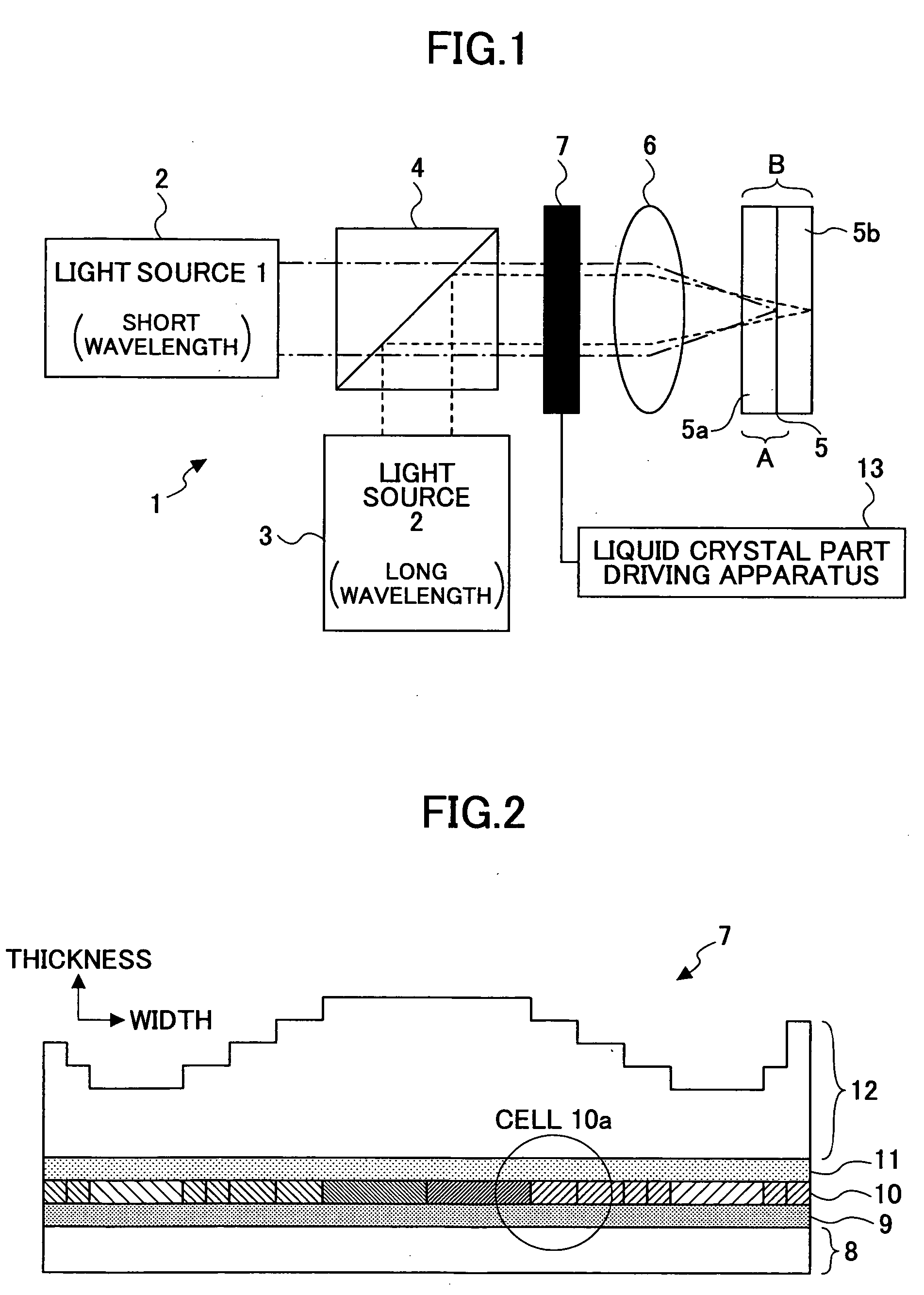
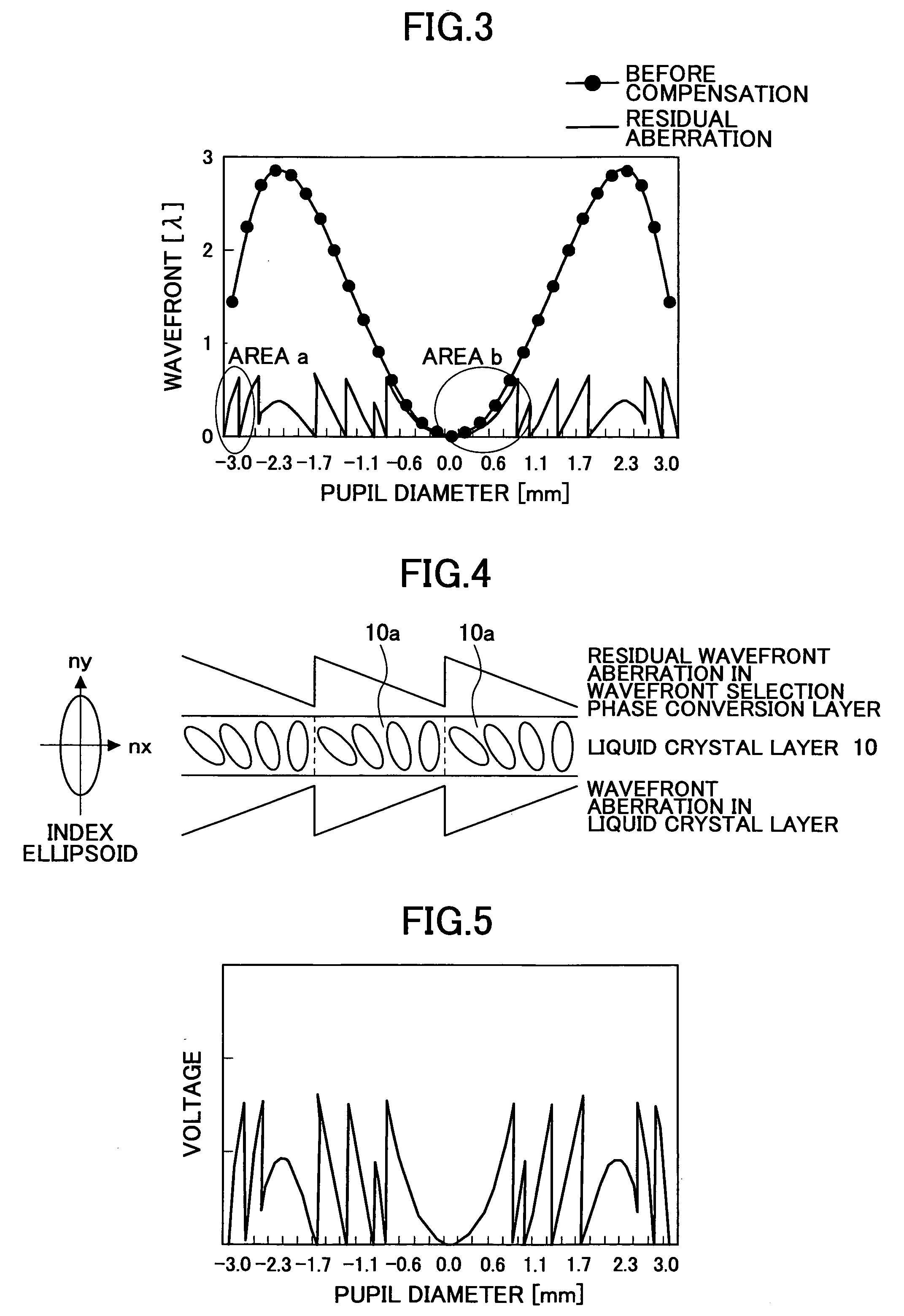
Wavefront aberration compensation element, optical pickup, and optical disk apparatus
InactiveUS20050174918A1Record information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupLength wave
A wavefront aberration compensation element includes a wavelength selection phase plate having a plurality of phase steps having various thicknesses at various areas, a liquid crystal layer for obtaining a prescribed wavefront aberration, and a pair of first and second electrode layers having the liquid crystal layer disposed therebetween, wherein either one of the wavelength selection phase plate and the pair of first and second electrode layers having the liquid crystal layer disposed therebetween is stacked on the other.
Owner:RICOH KK
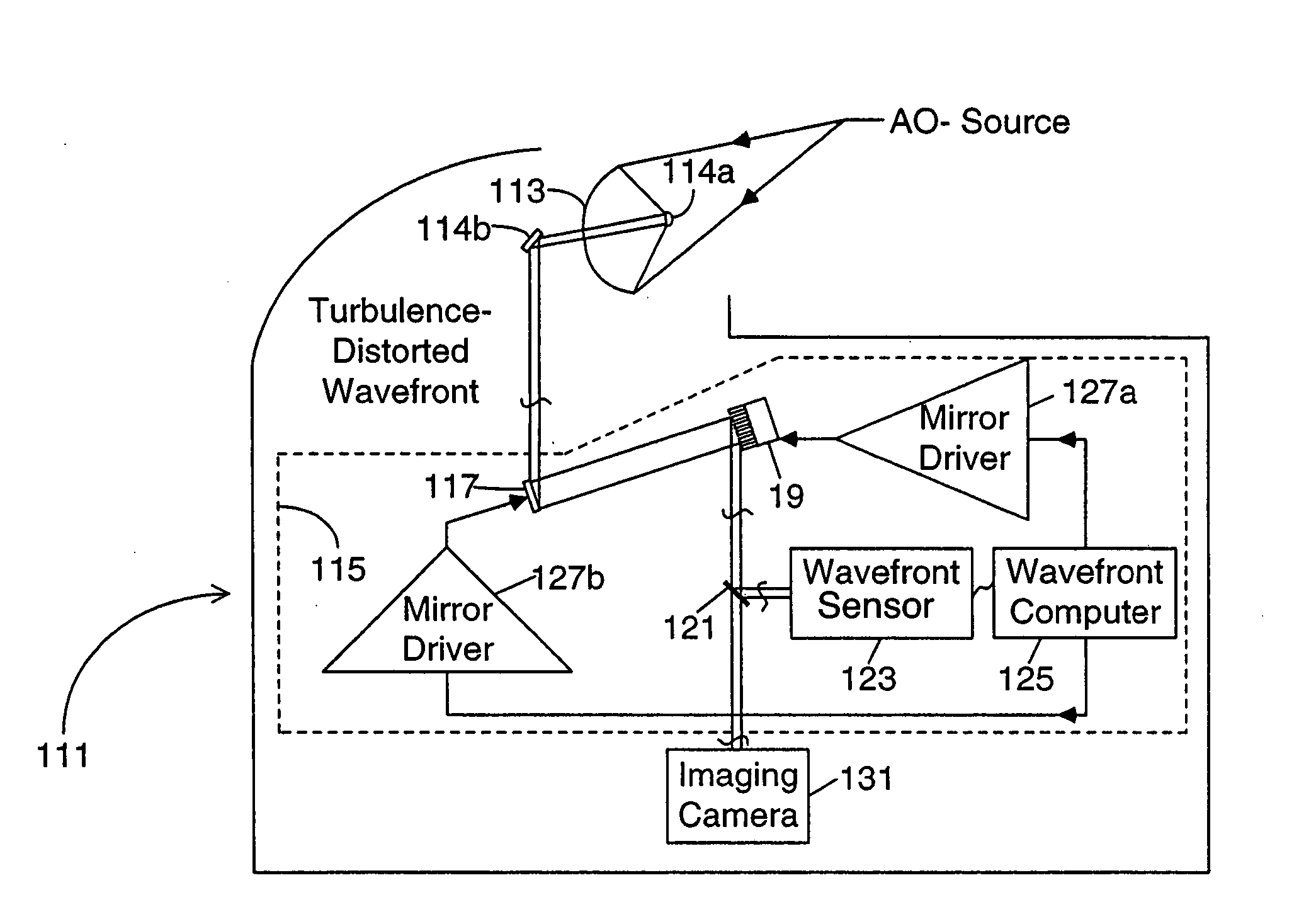
Method and apparatus for wavefront measurement that resolves the 2-pi ambiguity in such measurement and adaptive optics systems utilizing same
InactiveUS20050098707A1Step of become largeImprove tolerancePhotometry using reference valueOptical measurementsWavefront sensorAmbiguity
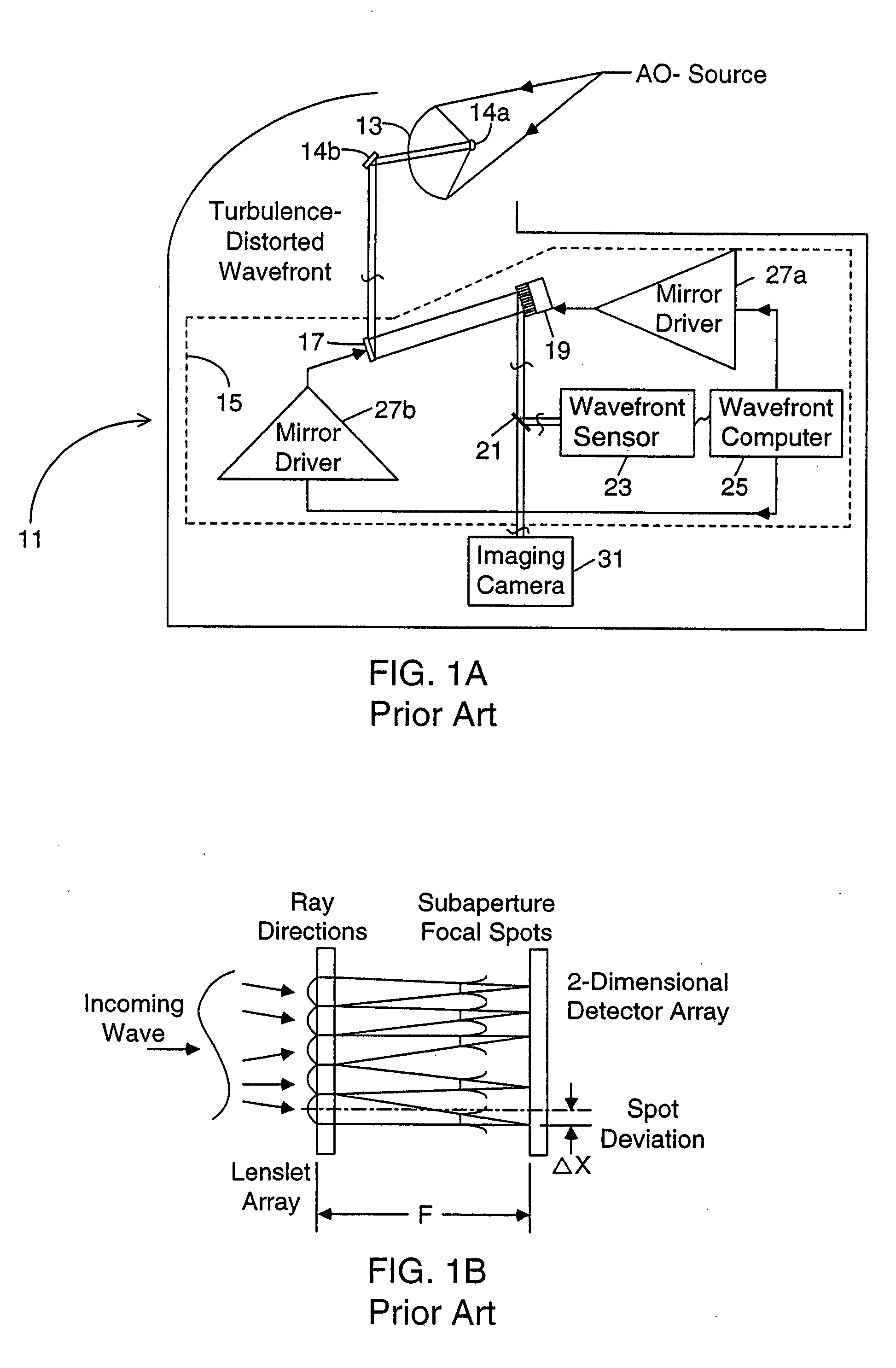
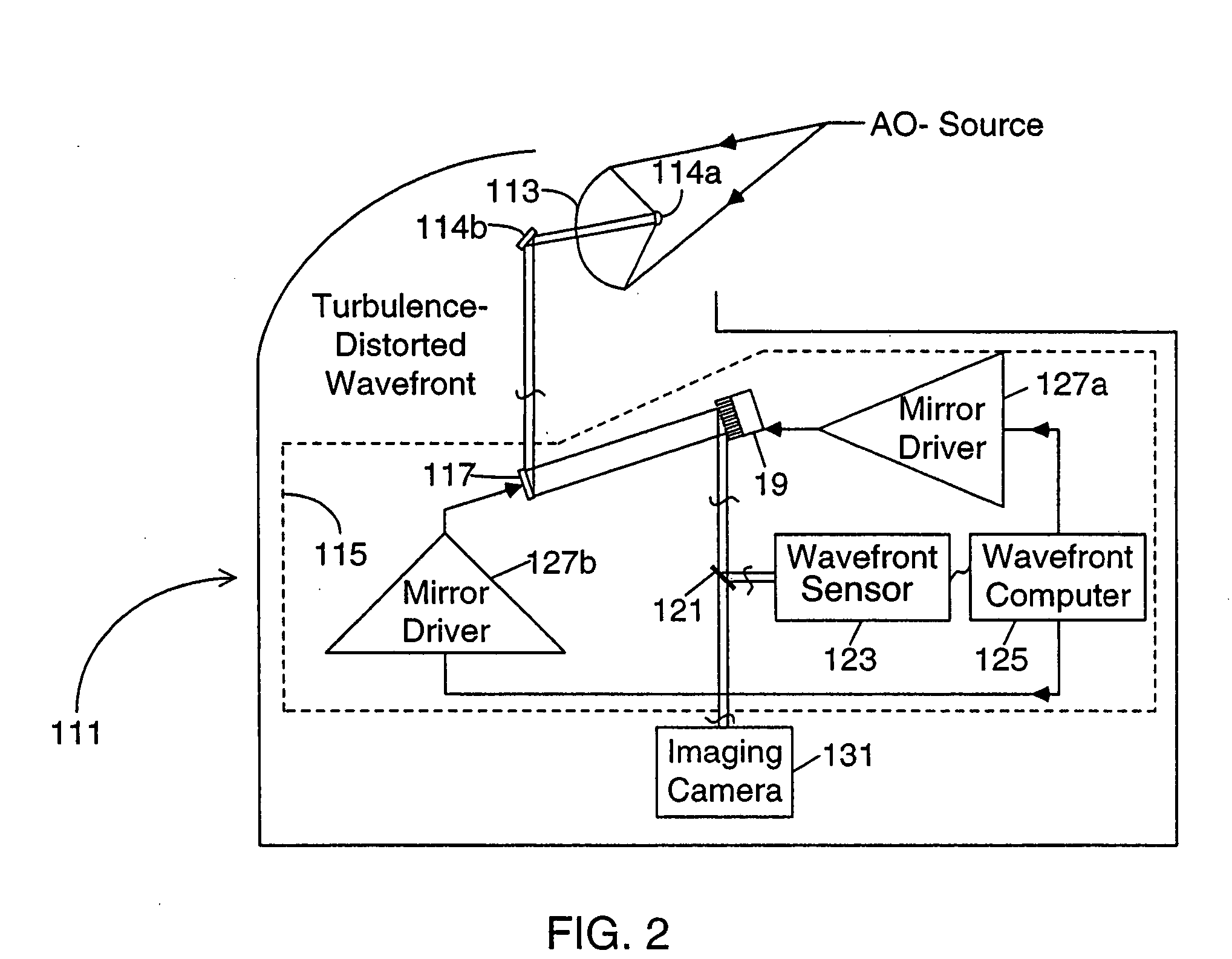
An improved wavefront sensor for characterizing phase distortions in incident light including optical elements that spatially sample the incident light and form a dispersed spot with a fringe pattern corresponding to samples of the incident light. An imaging device captures an image of the dispersed spot with said fringe pattern formed by said optical elements. And an image processor that analyzes the spectral components of the fringe pattern of a given dispersed spot to derive a measure of the local phase distortion without ambiguity in the corresponding sample of incident light. The optical elements may comprise refractive elements, diffractive elements or a combination thereof (such as a grism). The wavefront sensor may be part of an adaptive optic system (such as a large-aperture space telescope) to enable the measurement and correction of large phase steps across adjacent mirror segments of a deformable mirror.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
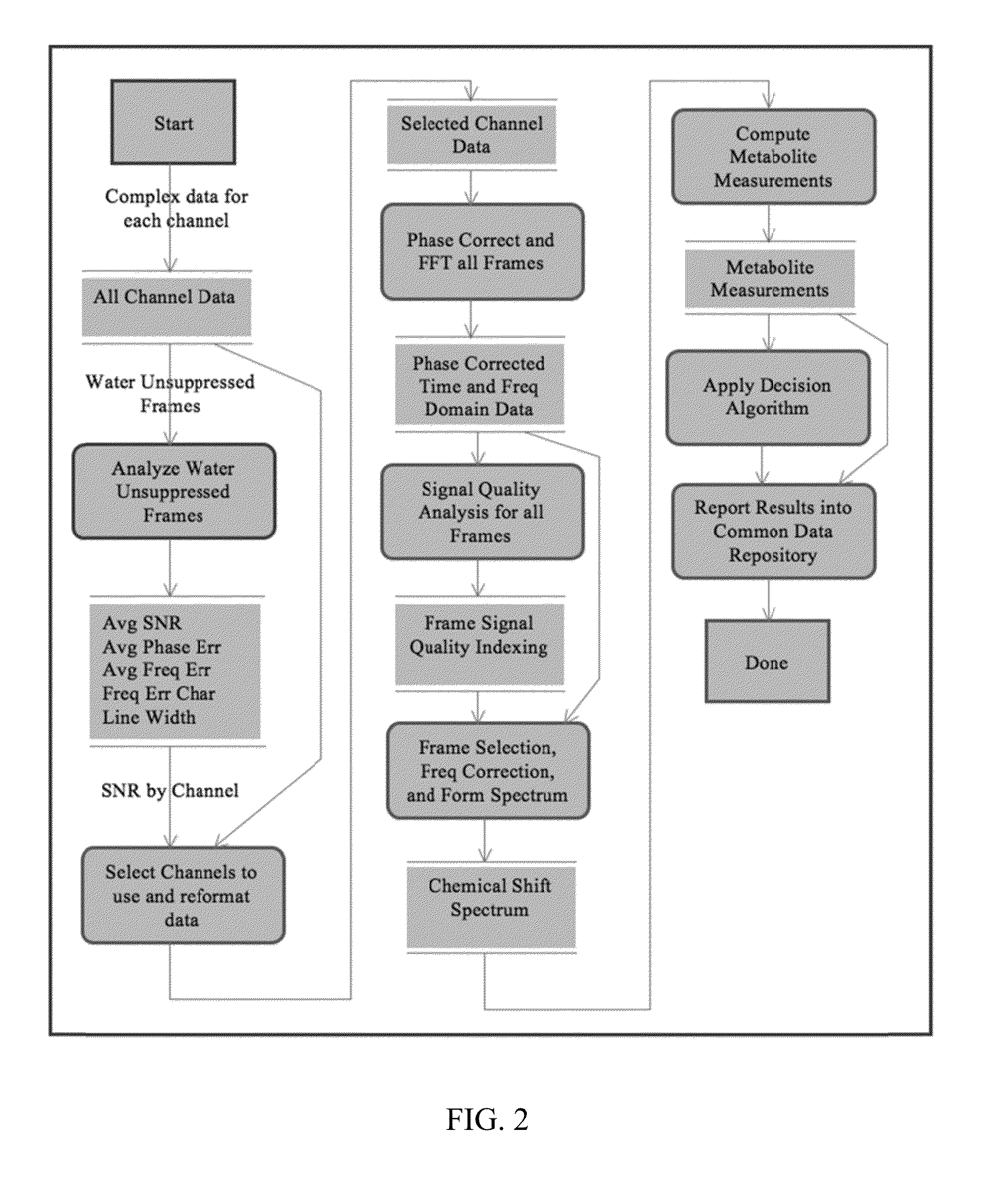
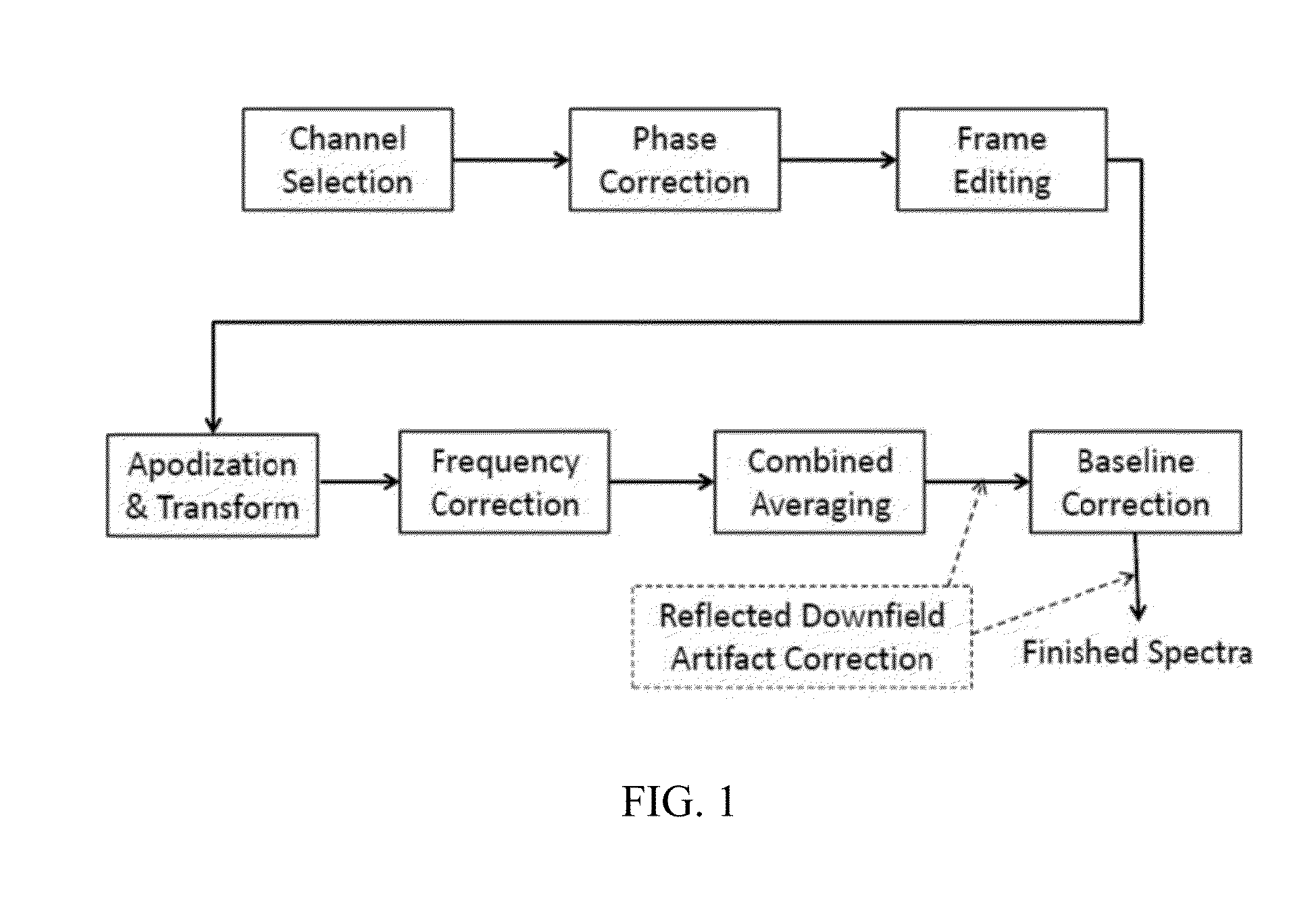
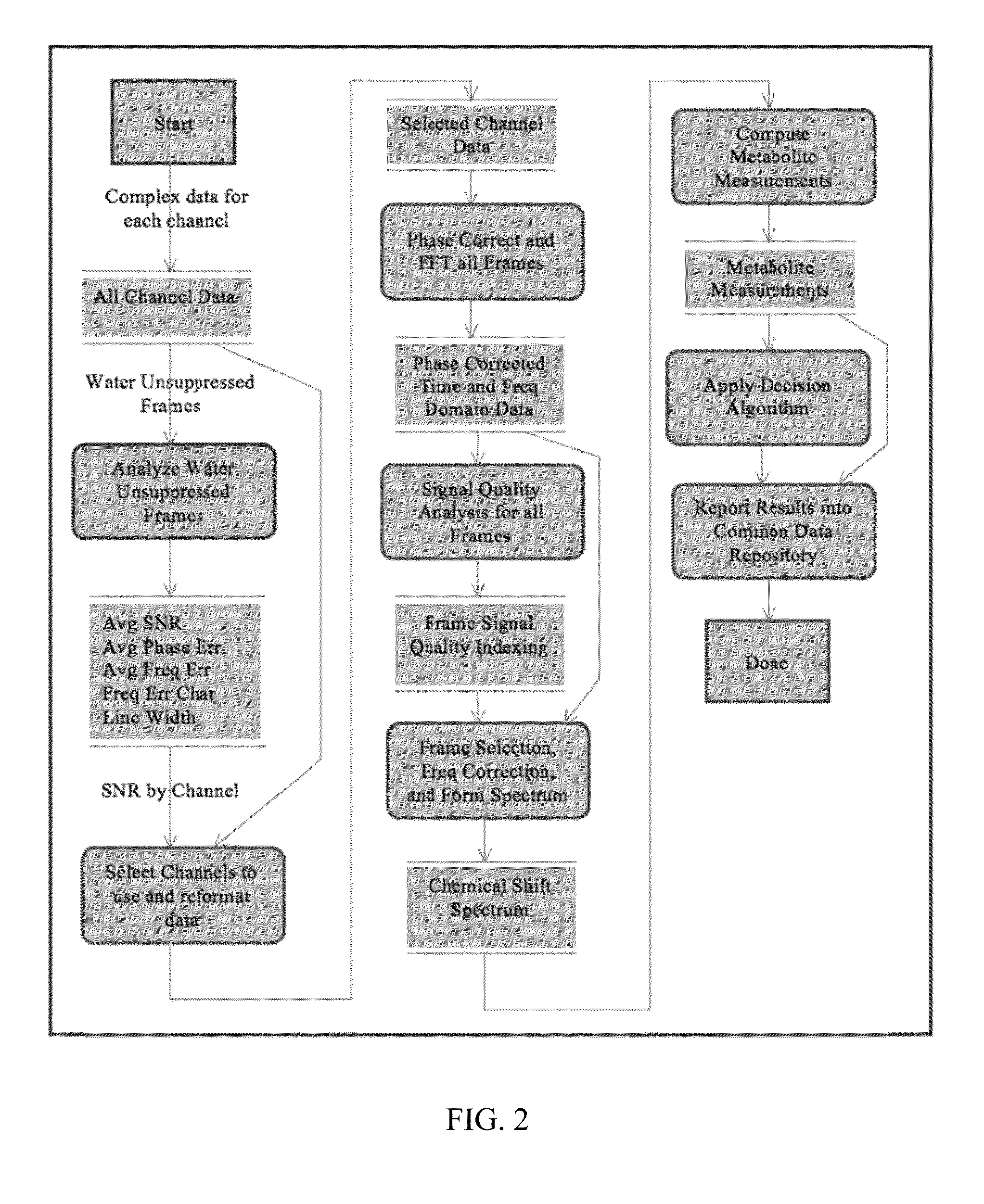
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy pulse sequence, acquisition, and processing system and method
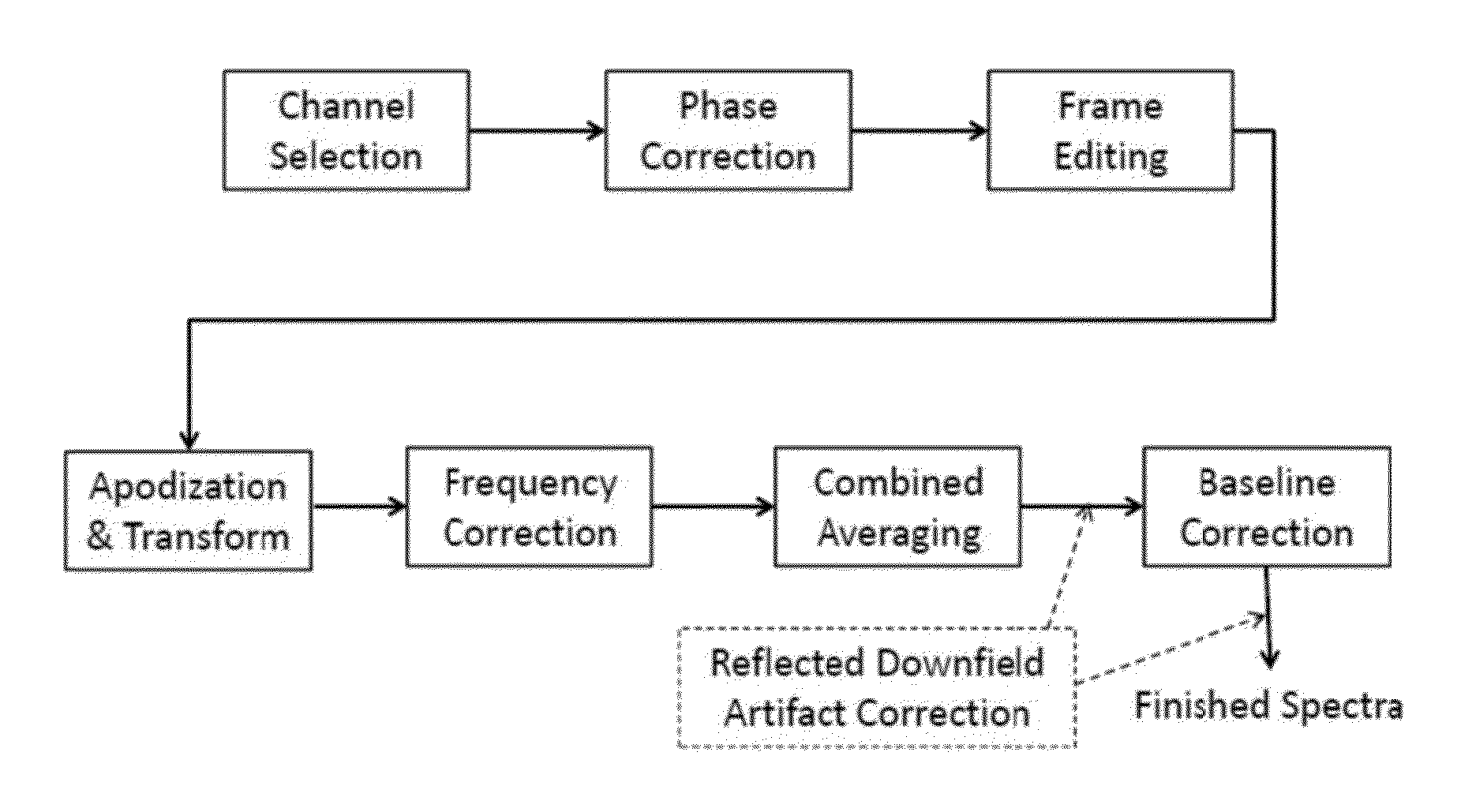
ActiveUS8965094B2Enhanced frequency shift artifact correctionEliminate the effects ofImage analysisDiagnostics using spectroscopyMagnetic resonance spectroscopicMultiple frame
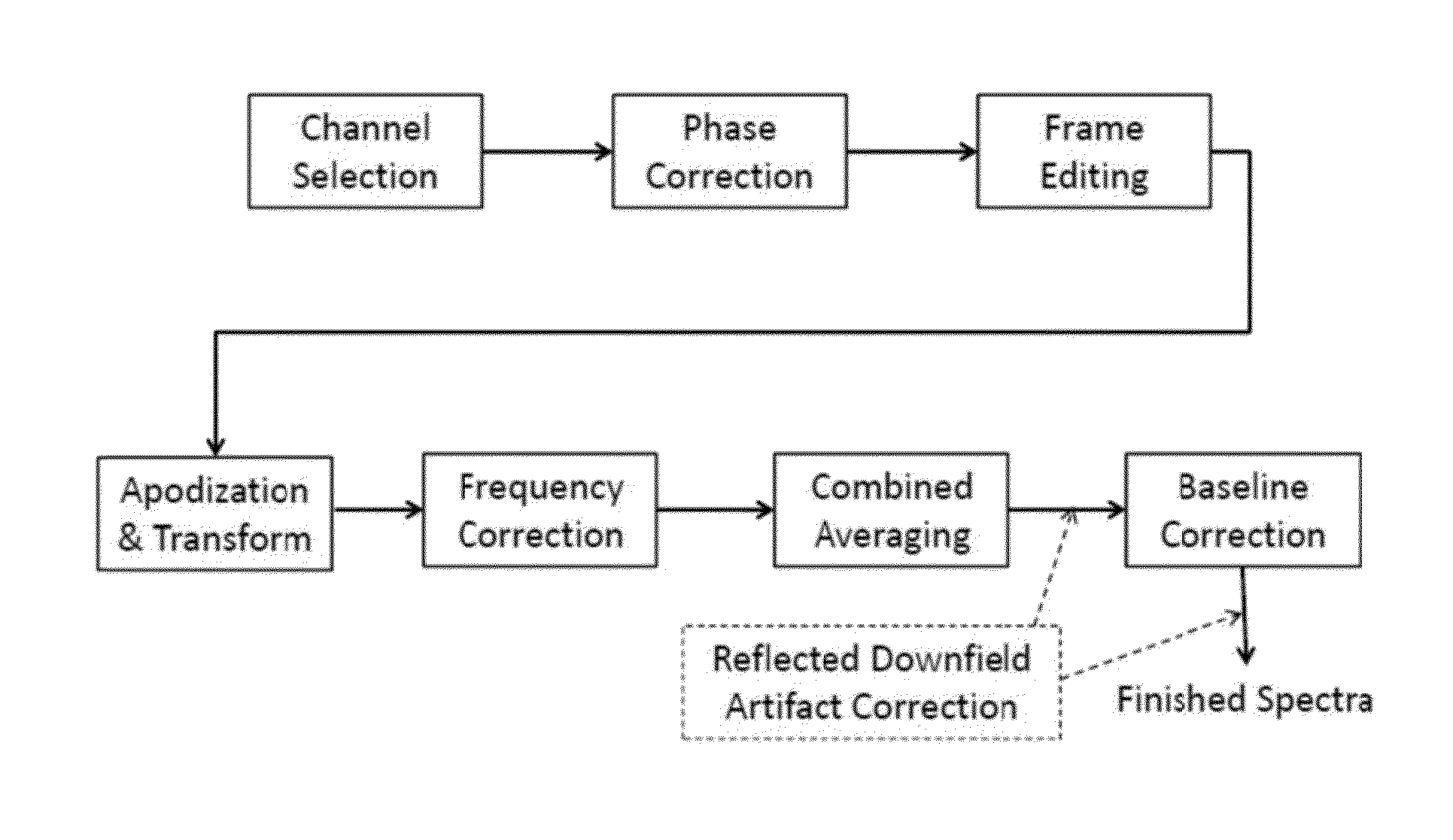
Systems and methods are provided for processing a set of multiple serially acquired magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) free induction decay (FID) frames from a multi-frame MRS acquisition series from a region of interest (ROI) in a subject, and for providing a post-processed MRS spectrum. Processing parameters are dynamically varied while measuring results to determine the optimal post-processed results. Spectral regions opposite water from chemical regions of interest are evaluated and used in at least one processing operation. Frequency shift error is estimated via spectral correlation between free induction decay (FID) frames and a reference spectrum. Multiple groups of FID frames within the acquired set are identified to different phases corresponding with a phase step cycle of the acquisition. Baseline correction is also performed via rank order filter (ROF) estimate and a polynomial fit. Sections of the ROF may be excluded from the polynomial fit, such as for example sections determined to be associated with relevant spectral peaks.
Owner:ACLARION INC
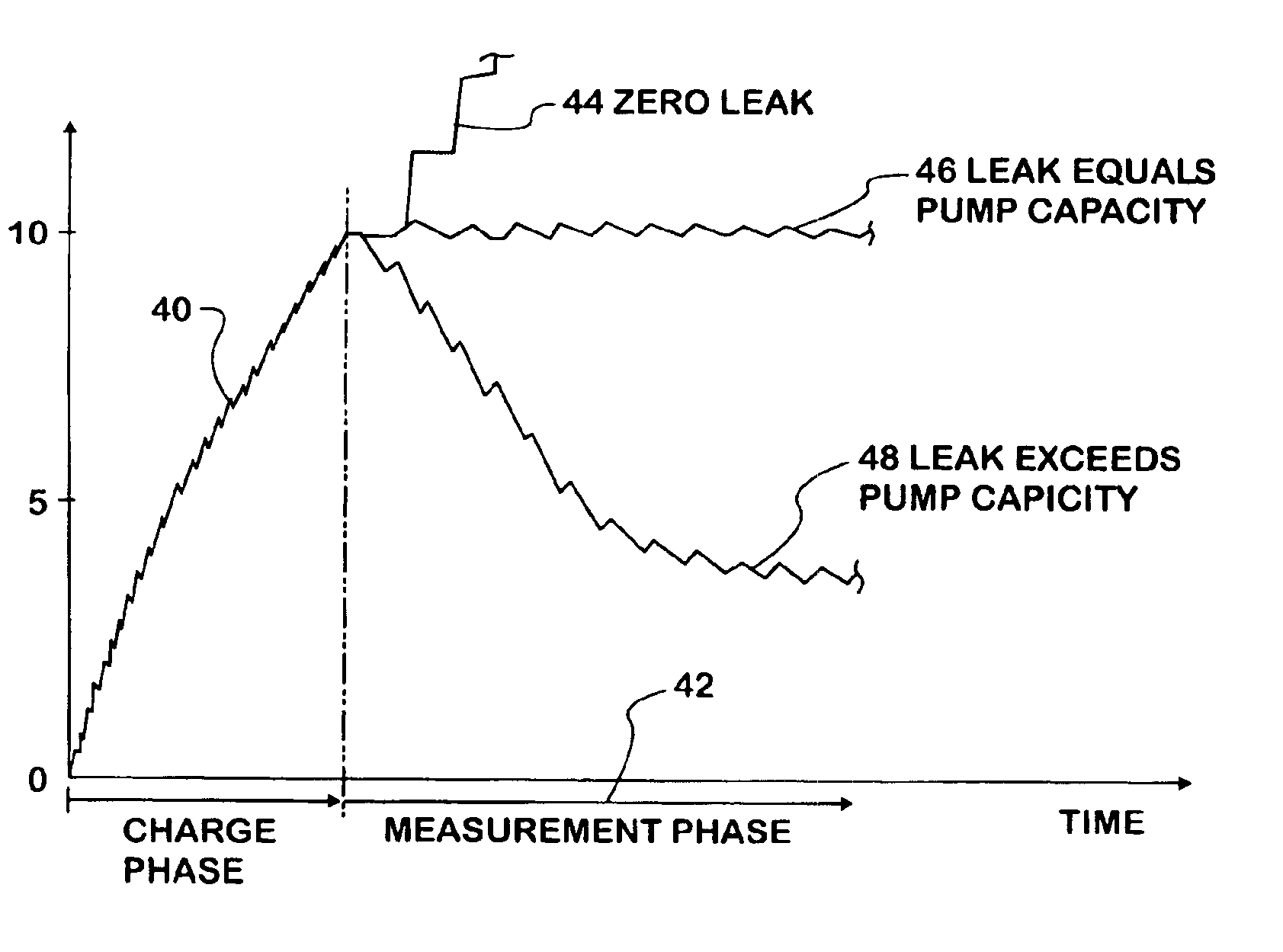
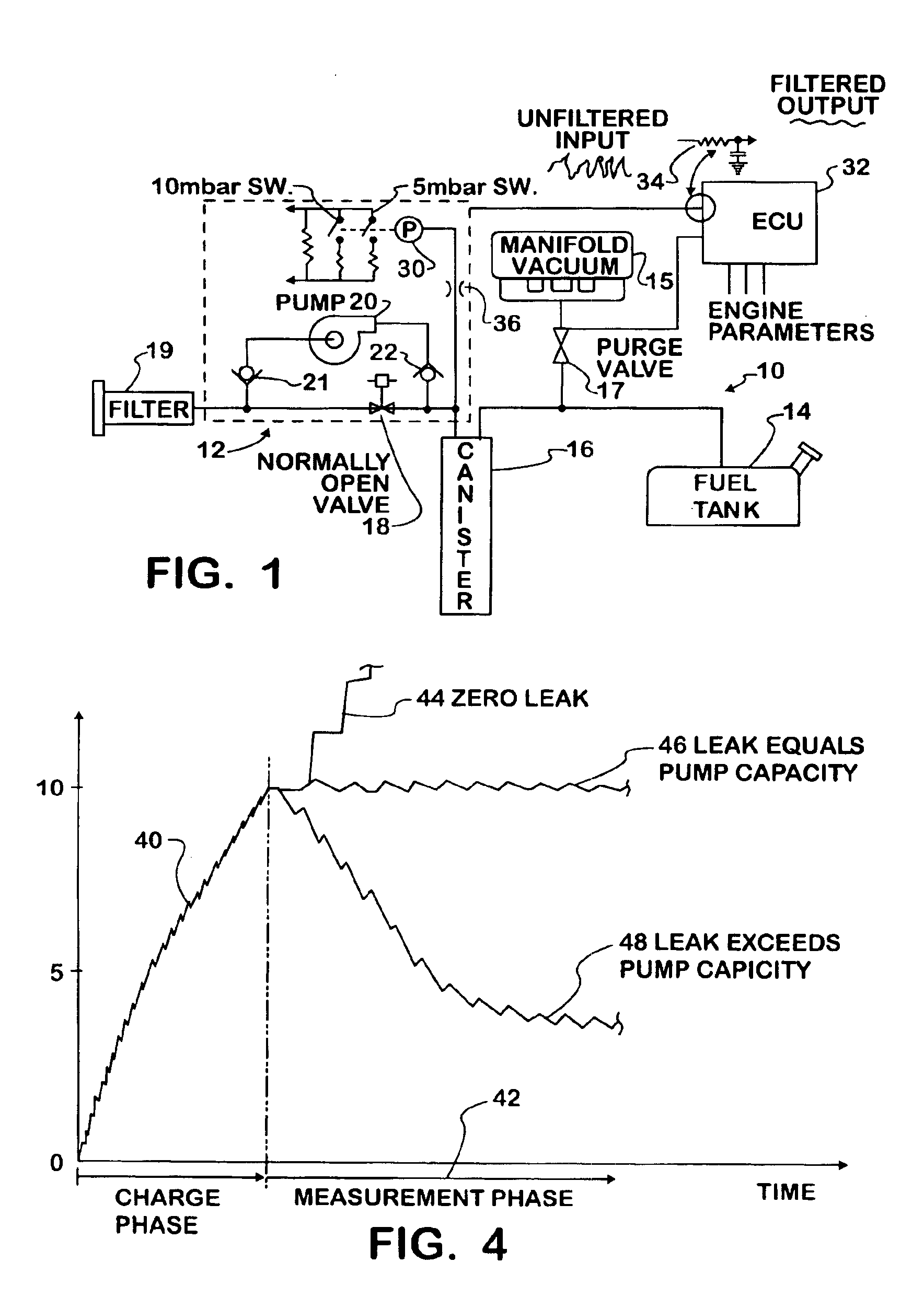
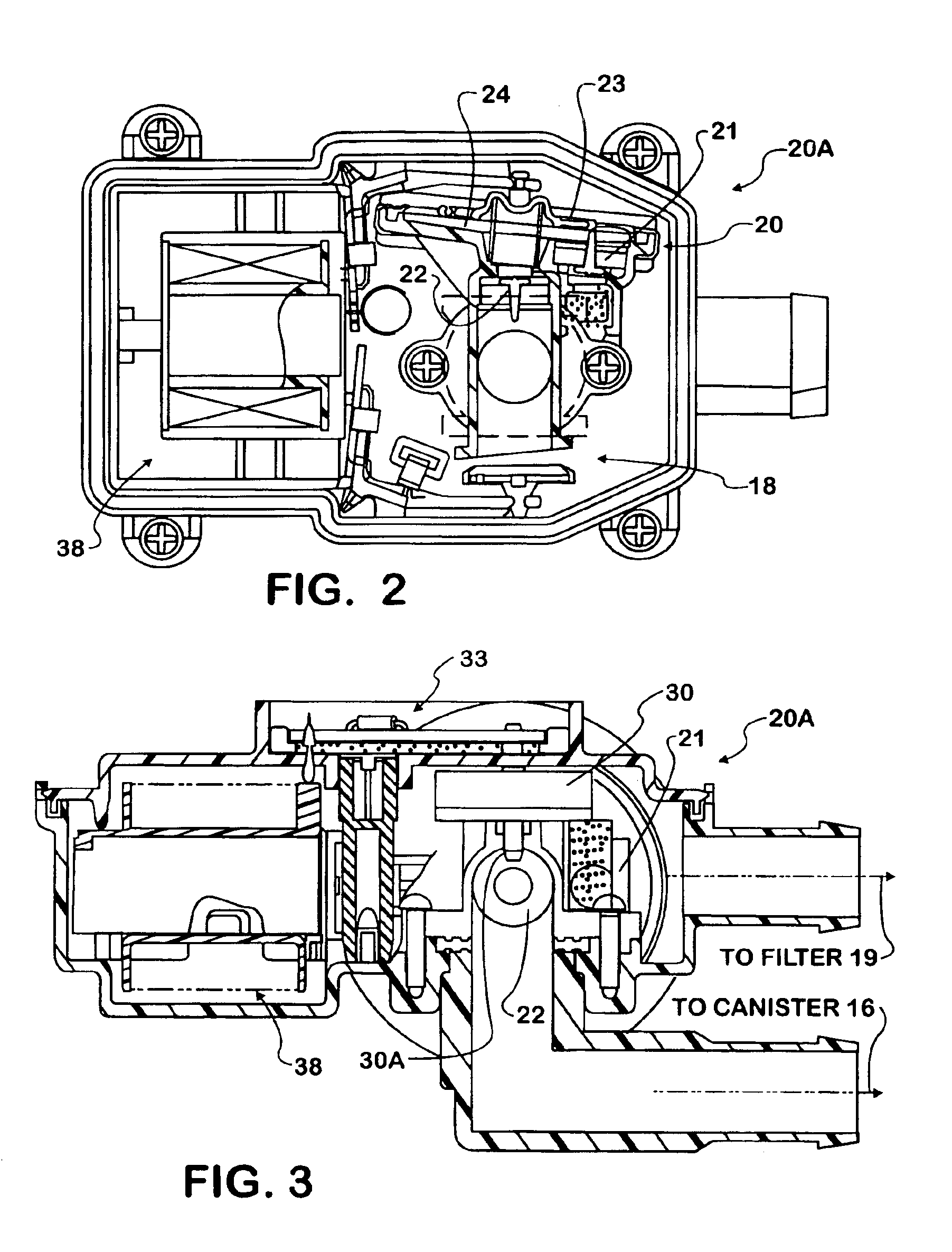
Fuel vapor leak test system and method comprising successive series of pulse bursts and pressure measurements between bursts
InactiveUS6951126B2Suitable performanceDetection of fluid at leakage pointNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringForced-air
A leak test system and method for a motor vehicle fuel system. A pump forces air under pressure into vapor containment space. The pump operates in accordance with steps established by a processor. The pump creates superatmospheric pressure in the space during an initial charging phase step, and after completion of that step, the pump performs a measurement phase step that forces pulses of air into the space in a succession of pulse bursts. Each burst contains a succession of individual pulses, preferably in equal numbers, and each successive burst is delayed from an immediately prior burst by a time interval substantially longer than the time intervals between individual pulses in each burst, preferably by constant time intervals. The processor processes data corresponding to a measurement of pressure in the space after the occurrence of at least one of such bursts and as a result indicates leakage from the space.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE INC
MEMS capacitive switch
InactiveCN104037027AIncrease the areaReduce up state capacitanceElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysInsulation layerRadio frequency
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic science, and relates to an MEMS capacitive switch. The MEMS capacitive switch comprises a substrate with an insulation layer, a signal transmission line and ground electrodes on the two sides, a dielectric layer is arranged on the surface of the signal transmission line, three metal coverage areas are arranged on the surface of the dielectric layer, the two ground electrodes are respectively provided with a fixed anchor point, and the two fixed anchor points support a drive electrode structure. The drive electrode structure is of a two-wing type phase step structure, and comprises a first drive electrode in the middle, a second drive electrode and a third electrode, the second drive electrode and the third electrode are arranged on the two wings, the two sides of the first drive electrode are connected with the fixed anchor points through clamped beams, the second drive electrode and the third drive electrode are connected with the first drive electrode through cantilever beams, and the distance between the second drive electrode and the third drive electrode and the signal transmission line is larger than the distance between the first drive electrode and the signal transmission line. The areas of the three drive electrodes are increased in sequence. Three work frequency bands can be achieved, and the MEMS capacitive switch has the advantages of being low in insertion loss, high in isolation degree and low in drop-down voltage and can be applied to a radio-frequency or microwave communication system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy pulse sequence, acquisition, and processing system and method
ActiveUS20140064586A1Enhanced frequency shift artifact correctionEliminate the effects ofImage analysisDiagnostics using spectroscopyPulse sequenceHandling system
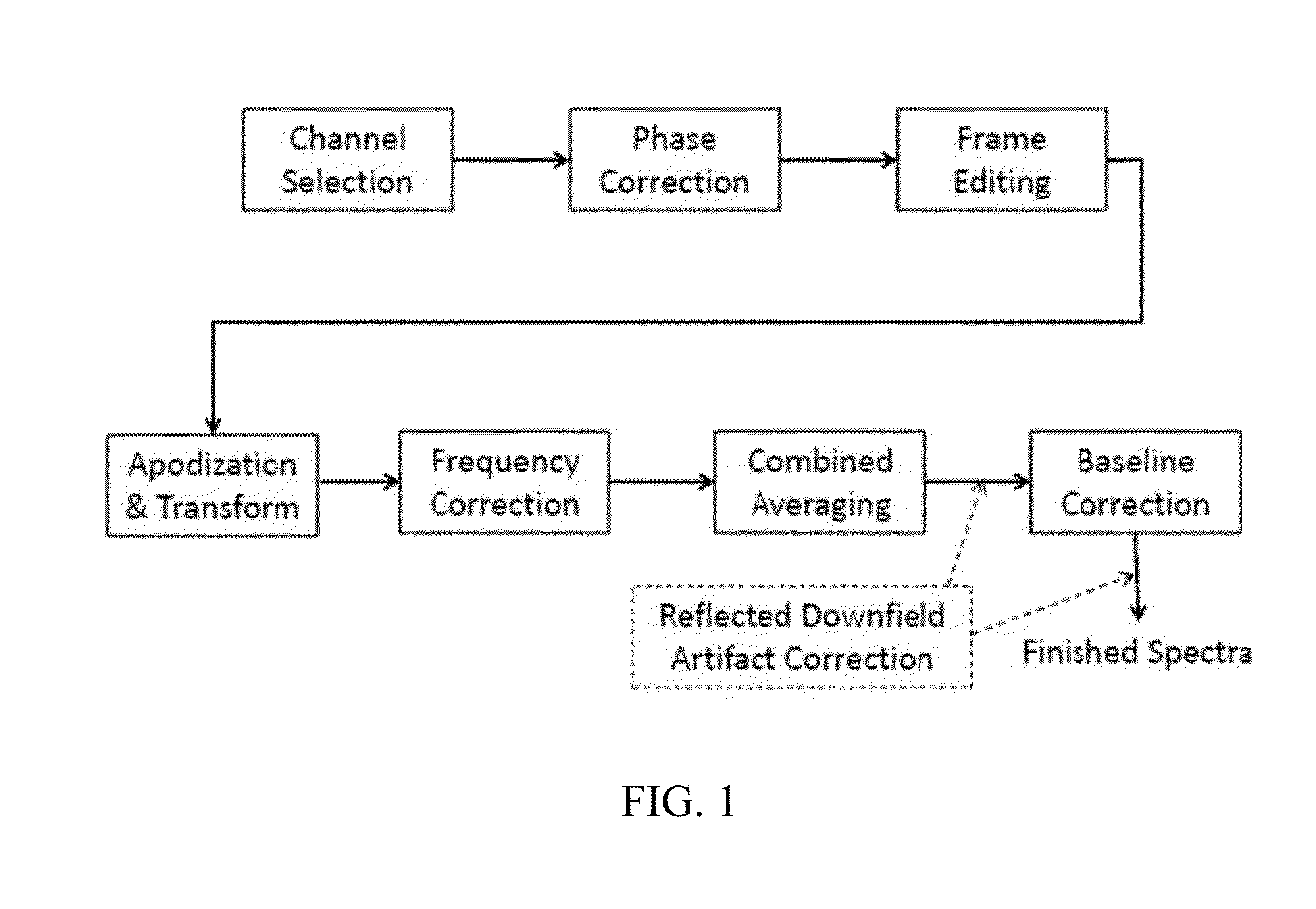
Systems and methods are provided for processing a set of multiple serially acquired magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) free induction decay (FID) frames from a multi-frame MRS acquisition series from a region of interest (ROI) in a subject, and for providing a post-processed MRS spectrum. Processing parameters are dynamically varied while measuring results to determine the optimal post-processed results. Spectral regions opposite water from chemical regions of interest are evaluated and used in at least one processing operation. Frequency shift error is estimated via spectral correlation between free induction decay (FID) frames and a reference spectrum. Multiple groups of FID frames within the acquired set are identified to different phases corresponding with a phase step cycle of the acquisition. Baseline correction is also performed via rank order filter (ROF) estimate and a polynomial fit. Sections of the ROF may be excluded from the polynomial fit, such as for example sections determined to be associated with relevant spectral peaks.
Owner:ACLARION INC
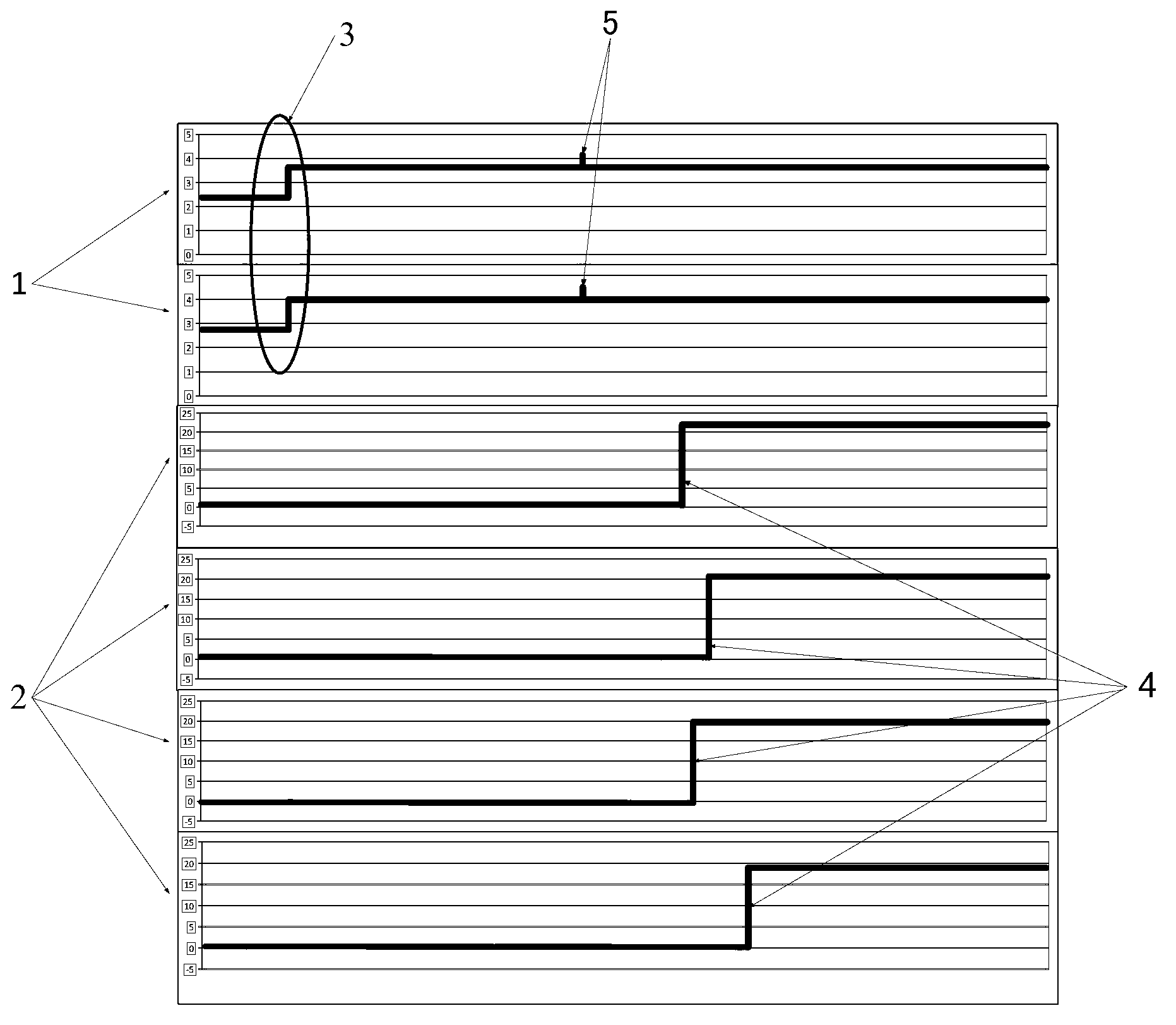
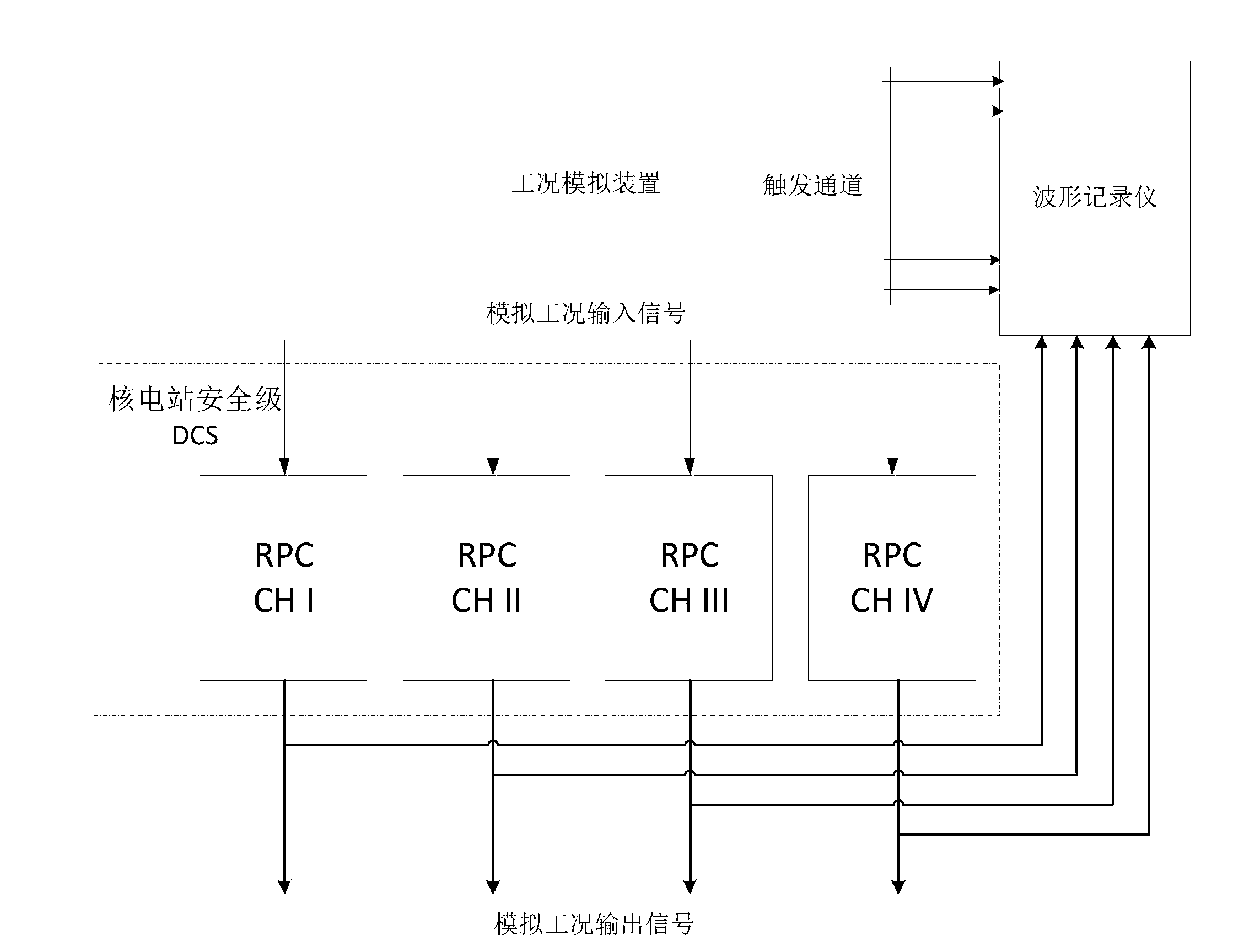
Method for automatically processing safety level DCS response time testing data in nuclear power station
ActiveCN103019223AImprove processing efficiencyQuality improvementElectric testing/monitoringProcess safetyStep response
The invention discloses a method for automatically processing safety level DCS response time testing data in a nuclear power station. A simulated condition signal waveform file *.CSV recorded by a waveform recorder is automatically analyzed, and a corresponding phase step response point of each channel in each oscillogram can be determined, so that the response time of each output channel is determined. After multiple *.CSV files recorded under the same working condition are repeatedly analyzed, the files are summarized and screened, and the response time of the current equipment to be detected under the working condition is obtained. Due to computer automation and batch data analysis, a high-efficiency and reliable method is provided for analyzing the response time testing data of a reactor protection system.
Owner:CHINA TECHENERGY +1
X-ray dark-field imaging system and method
An x-ray imaging technology, performing an x-ray dark-field CT imaging of an examined object using an imaging system which comprises an x-ray source, two absorbing gratings G1 and G2, an x-ray detector, a controller and a data processing unit, comprising the steps of: emitting x-rays to the examined object; enabling one of the two absorbing gratings G1 and G2 to perform phase stepping motion within at least one period range thereof; where in each phase stepping step, the detector receives the x-ray and converts it into an electric signal; wherein through the phase stepping of at least one period, the x-ray intensity at each pixel point on the detector is represented as an intensity curve; calculating a second moment of scattering angle distribution for each pixel, based on a contrast of the intensity curve at each pixel point on the detector and an intensity curve without presence of the examined object; taking images of the object at various angles, then obtaining an image with scattering information of the object in accordance with a CT reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Damping injection control method for improving power angle oscillation of water turbine generator set
InactiveCN101915203AMake full use of the essential characteristics of dynamicsImprove oscillation characteristicsClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPid control algorithmEquivalent control
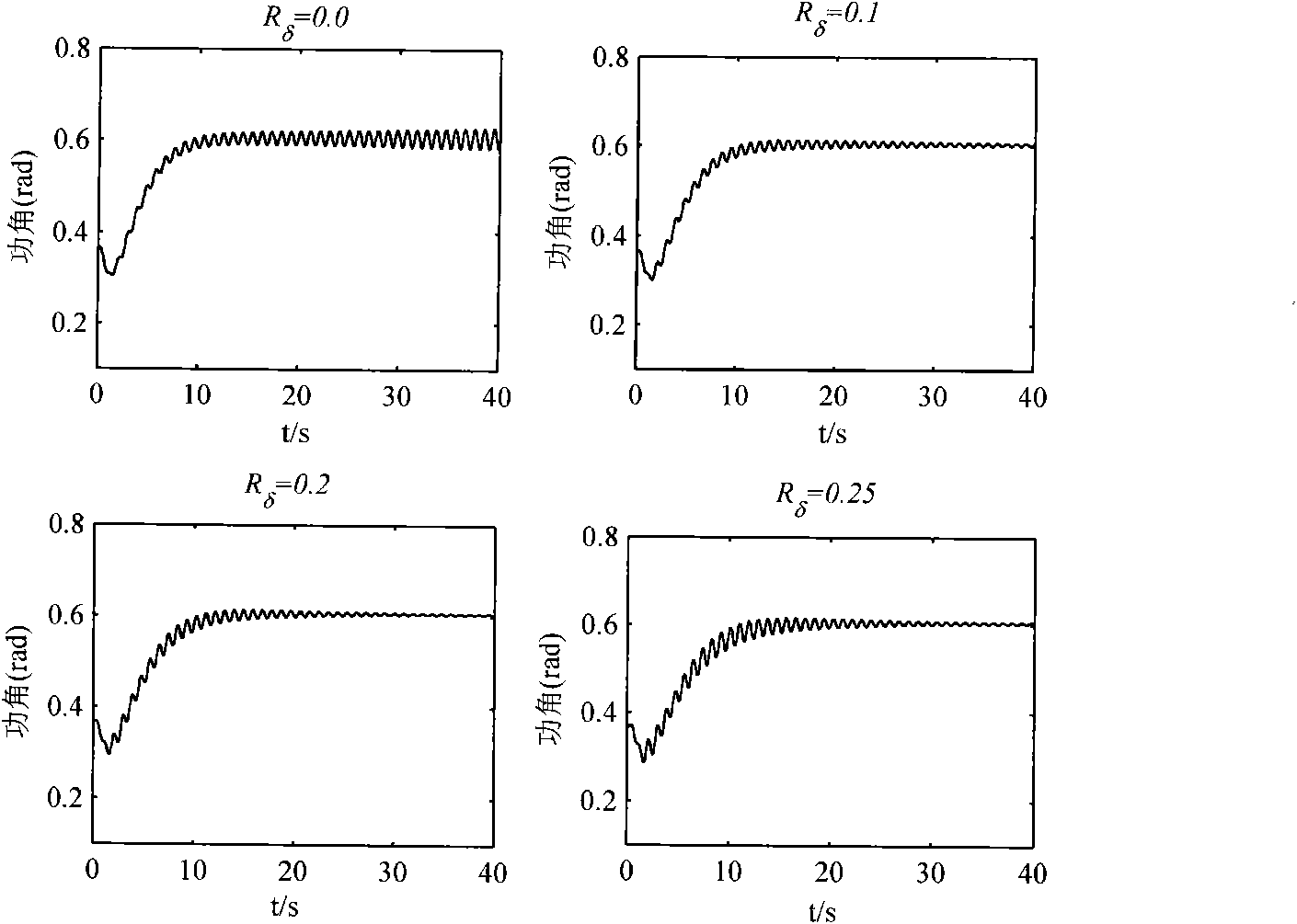
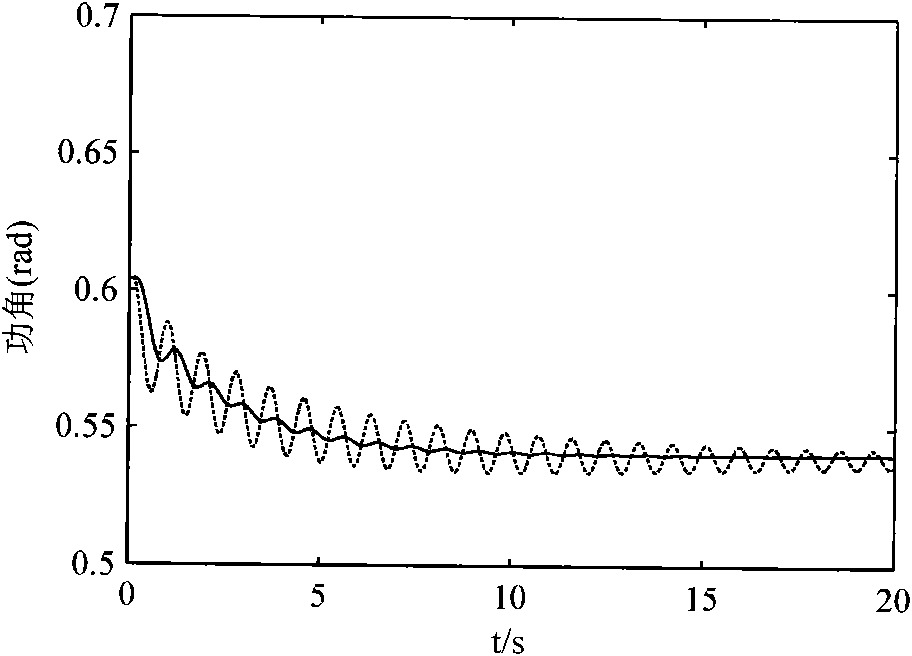
The invention relates to a damping injection control method for improving power angle oscillation of a water turbine generator set. An autocorrelation factor of the unit power angle is increased based on the structural analysis of a Hamilton model damping matrix of the water turbine generator set, namely the power angle damping is injected based on a dynamical mechanism associated inside the system, and the structural change is equivalent by designing a corresponding control law. Due to the applicability analysis of the equivalent control law, a variable structure control strategy by combining the algorithm and a traditional PID control algorithm is provided so as to control the machine set, and corresponding solutions are provided for the control of output phase step and other problems. The simulation proves that: the provided control algorithm can effectively improve the oscillating characteristics of the power angle of the machine set, even can keep the stability of the machine set under lower damping.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cavity bubble system of rubidium atom frequency standard
ActiveCN102769464AReduce the volume of the microwave cavityResonant frequency adjustment is simple and effectivePulse automatic controlPerformance indexFrequency standard
The invention discloses a cavity bubble system of the rubidium atom frequency standard. Integrated filtering absorption bubbles are fixed in a medium tube through heat conduction silicone grease and are arranged on one side of a microwave cavity, the direction of a microwave magnetic field is perpendicular to a coupling ring, one end of a heating tube is a full closed end, a heating power tube is fixed on the heating tube through a screw, a C field coil is wound around the medium tube, and two ends of the C field tube are fixed through insulation clamping rings. the integrated filtering absorption bubbles, the C field coil, the insulation clamping rings are placed in the microwave cavity, a microwave circuit plate covers one open end of the microwave cavity and is placed in the heating tube with the microwave cavity, one end of the coupling ring is connected with a phase step diode, and the other end of the coupling ring is connected with an external radio frequency signal wire. The phase step diode is welded on a microwave circuit board, a photoelectric cell is bonded to the microwave circuit board, and the heating power tube is fixed on the microwave cavity through a screw. The cavity bubble system is simple in structure, small in size, simple in cavity frequency micro-adjustment, high in performance index and easy to process.
Owner:武汉中科坤德科技有限公司
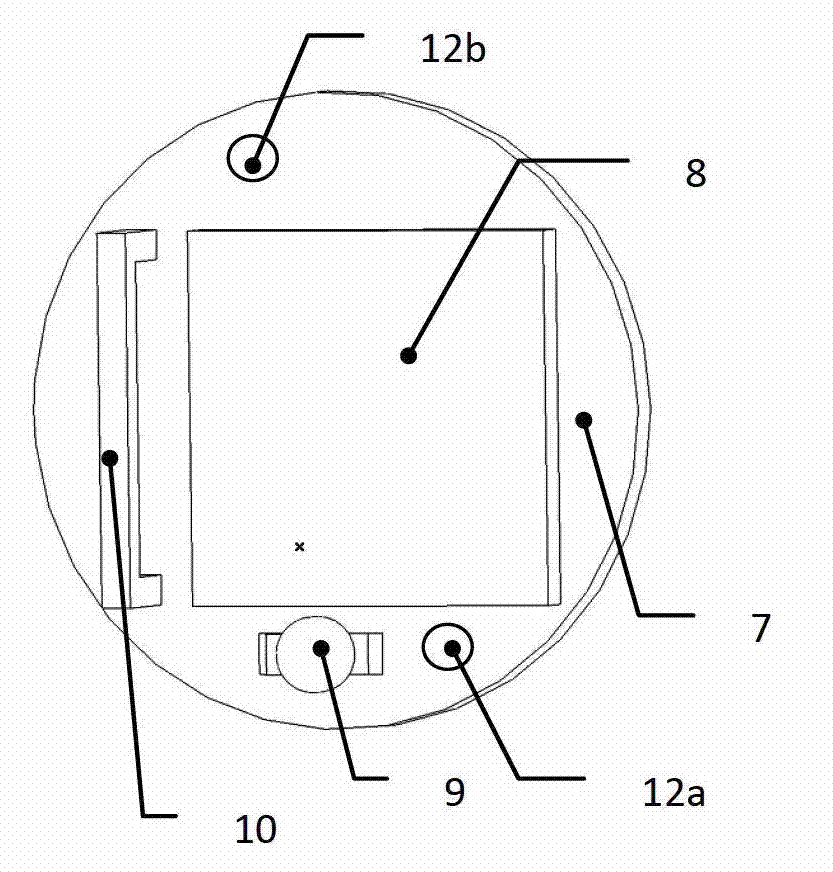
Pattern generator using a dual phase step element and method of using same
A system and method are used to pattern light using an illumination system, an array of individually controllable components, and a projection system. The illumination system supplies a beam of radiation. The array of individually controllable elements patterns the beam. The array of individually controllable elements comprises mirrors having first and second steps on opposite edges. The projection system projects the patterned beam onto a target portion of an object. In various examples, the object can be a display, a semiconductor substrate or wafer, a flat panel display glass substrate, or the like, as is discussed in more detail below.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Step-control mechanical sampling device
InactiveCN102944443AFully automatedImprove the sampling operation environmentWithdrawing sample devicesPulse controlMotor drive
The invention relates to a step-control mechanical sampling device. The device is characterized in that a structure portion comprises a sampler component, an air cylinder component and a sample delivery component. The sampler component is composed of a transition support, a spring seat, a step motor, a coupling, a transmission screw nut, a transmission screw, a sampling arm, a spring and a sampling head. A switching power supply supplies DC24V power for a plane diaphragm pressure sensor at the lower end of the connection disc, the plane diaphragm pressure sensor outputs current signals in a range of 4mA to 20mA according to pressure imposed by a sample, and the current signals in a range of 4mA to 20mA acquired through the plane diaphragm pressure sensor are subjected to analog-to-digital (AD) conversion and sent to a single chip microcomputer to be processed to output pulse control signals. The pulse control signals are output to a FD5-3 five-phase step motor driving controller which controls the action of the step motor, and accordingly, the step-control mechanical sampling is achieved.
Owner:TECHN CENT FOR SAFETY OF INDAL PRODS TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for optimizing radio frequency impulse phases in fast spin echo impulse sequence
ActiveCN103278785AReduce dependencyImprove optimization efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoStimulated echo
The invention provides a method for optimizing radio frequency impulse phases in a fast spin echo impulse sequence. According to the method, a spin echo and an excited echo are separated through the difference of effects of the spin echo and the excited echo according to spoiled gradients so as to ensure that the spin echo coincide with the excited spin echo more accurately; an optimized inversion impulse phase can be acquired through simple calculation according to the phase relation of the spin echo and an inversion impulse and the relation of the excited echo and the inversion impulse. The method for optimizing the radio frequency impulse phases in the fast spin echo impulse sequence can reduce the affect of unsatisfactory factors of instrument hardware on an FSE sequence parameter optimization process and the degree of dependence of the optimal parameter searching process on the phase step precisions, and therefore optimizing efficiency is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
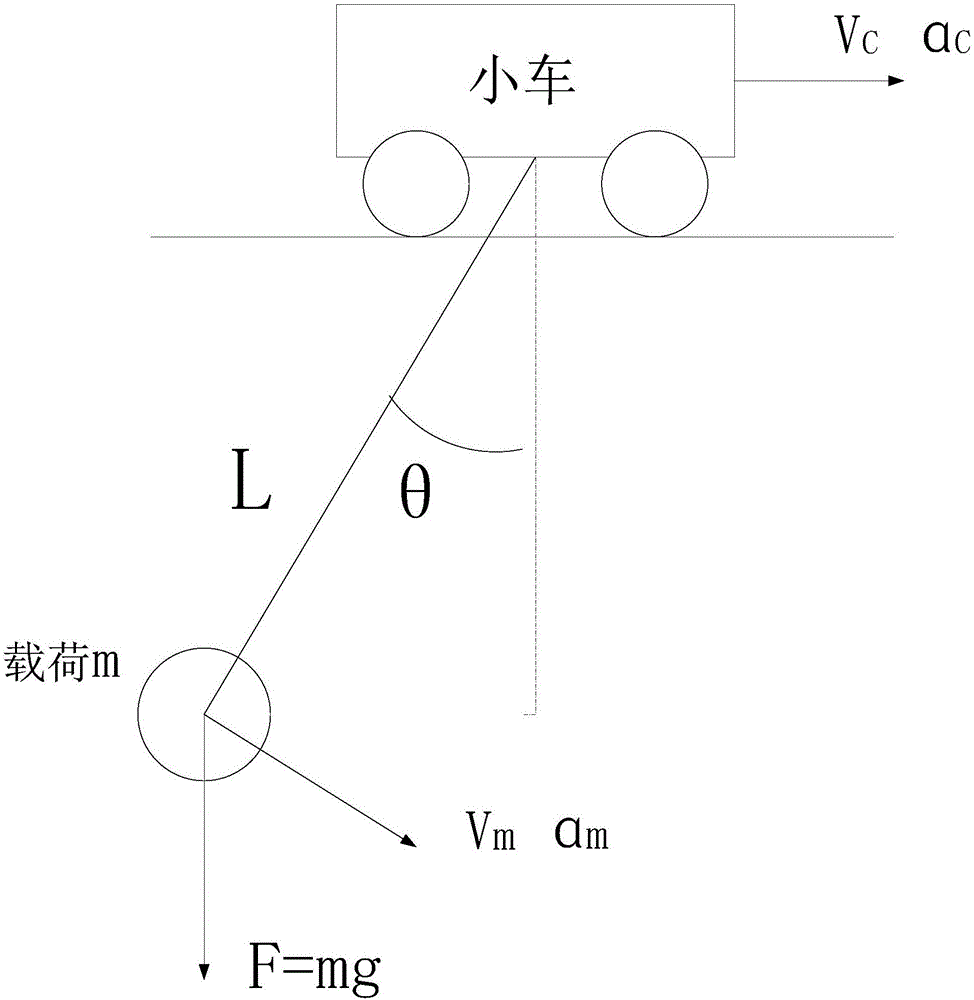
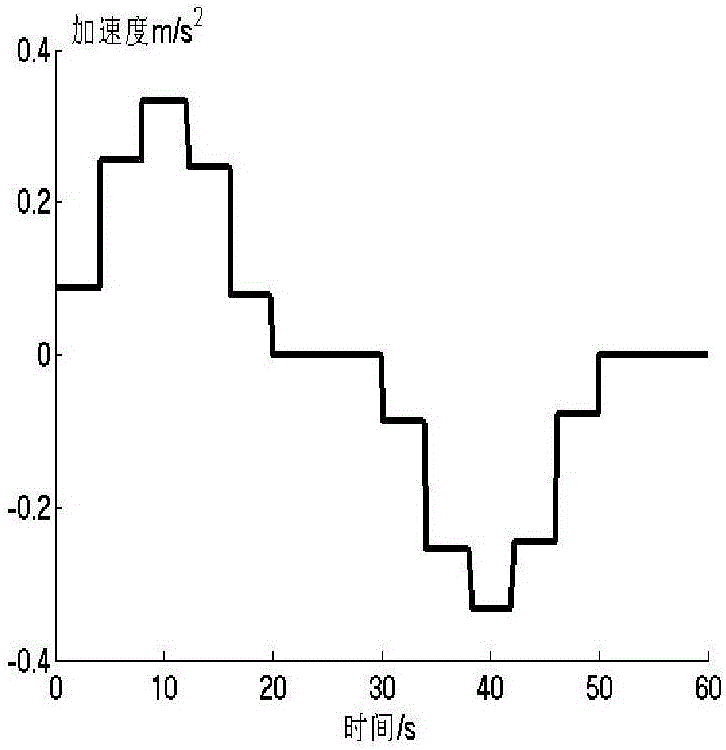
Crane anti-swinging control method based on positive and negative POSICAST input reshaping method
The invention relates to a crane anti-swinging control method based on a positive and negative POSICAST input reshaping method, which is applicable to any n time lag conditions. When the time lag of a designed reshaping device is shorter, the maximum value of a swinging angle is larger; when the time lag is longer, the maximum value of the swinging angle is smaller; meanwhile, when the jumping of an accelerated velocity is smaller, and the speed is gentler. A user can select freely according to actual conditions. The crane anti-swinging control method disclosed by the invention is applicable to a damping system and is also applicable to a non-damping second-order system. The method is an open loop control method, so that the method has the advantages that a measurement sensor for closed loop feedback is not needed. The crane anti-swinging control method utilizes phase step accelerated velocity input and aims at reshaping of phase step accelerated velocity output; compared with a pulse accelerated velocity input method, the speed is continuously changed, and a project is easy to realize. The crane anti-swinging control method is suitable for taking any phase step signal as input, and a damping second-order system is used for an anti-swinging system or a system for enabling certain output to finally return back to an original position.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com