Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Correlogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the analysis of data, a correlogram is an image of correlation statistics. For example, in time series analysis, a correlogram, also known as an autocorrelation plot, is a plot of the sample autocorrelations rₕ versus h (the time lags). If cross-correlation is used, the result is called a cross-correlogram. The correlogram is a commonly used tool for checking randomness in a data set. This randomness is ascertained by computing autocorrelations for data values at varying time lags.
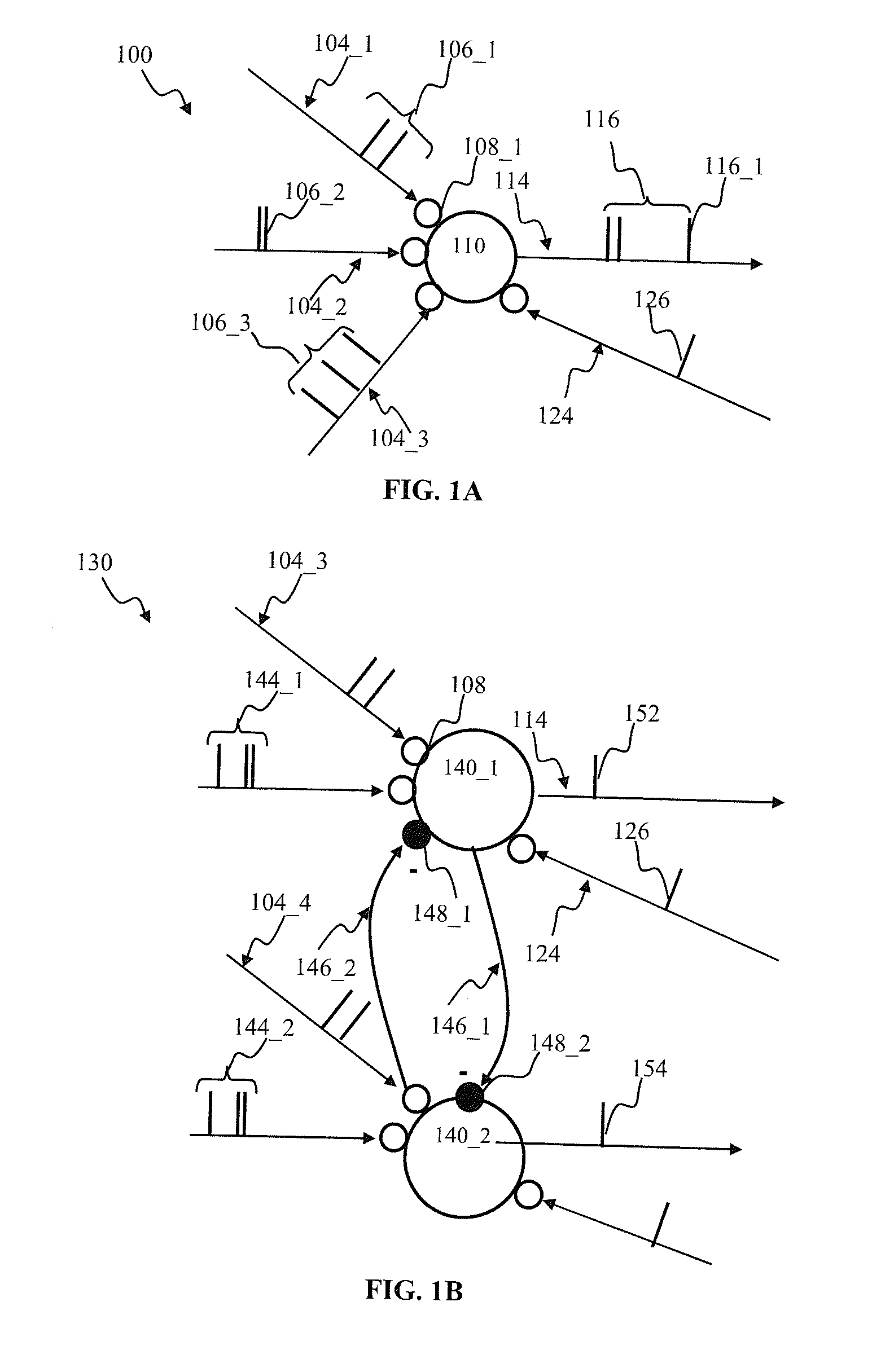
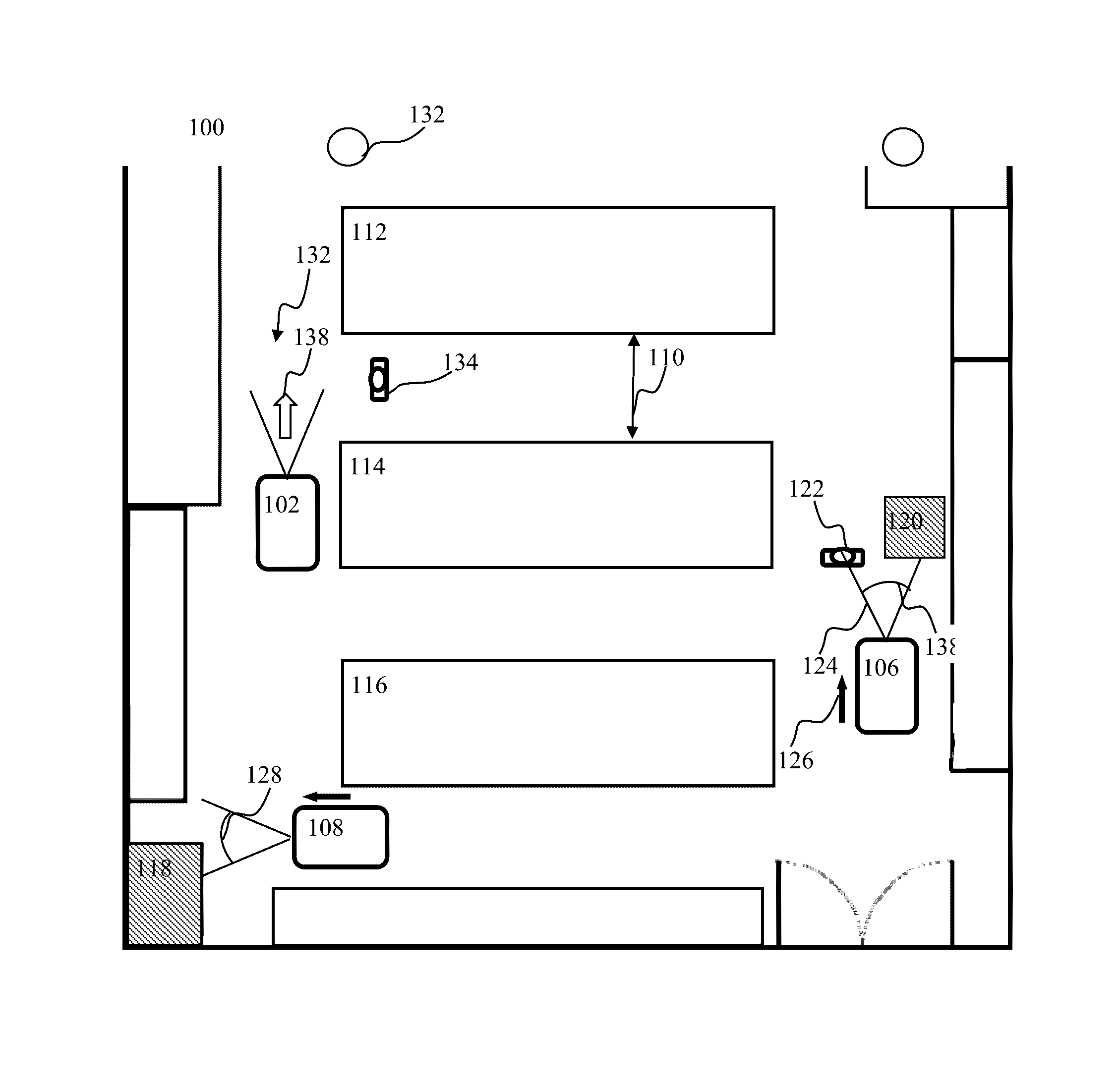
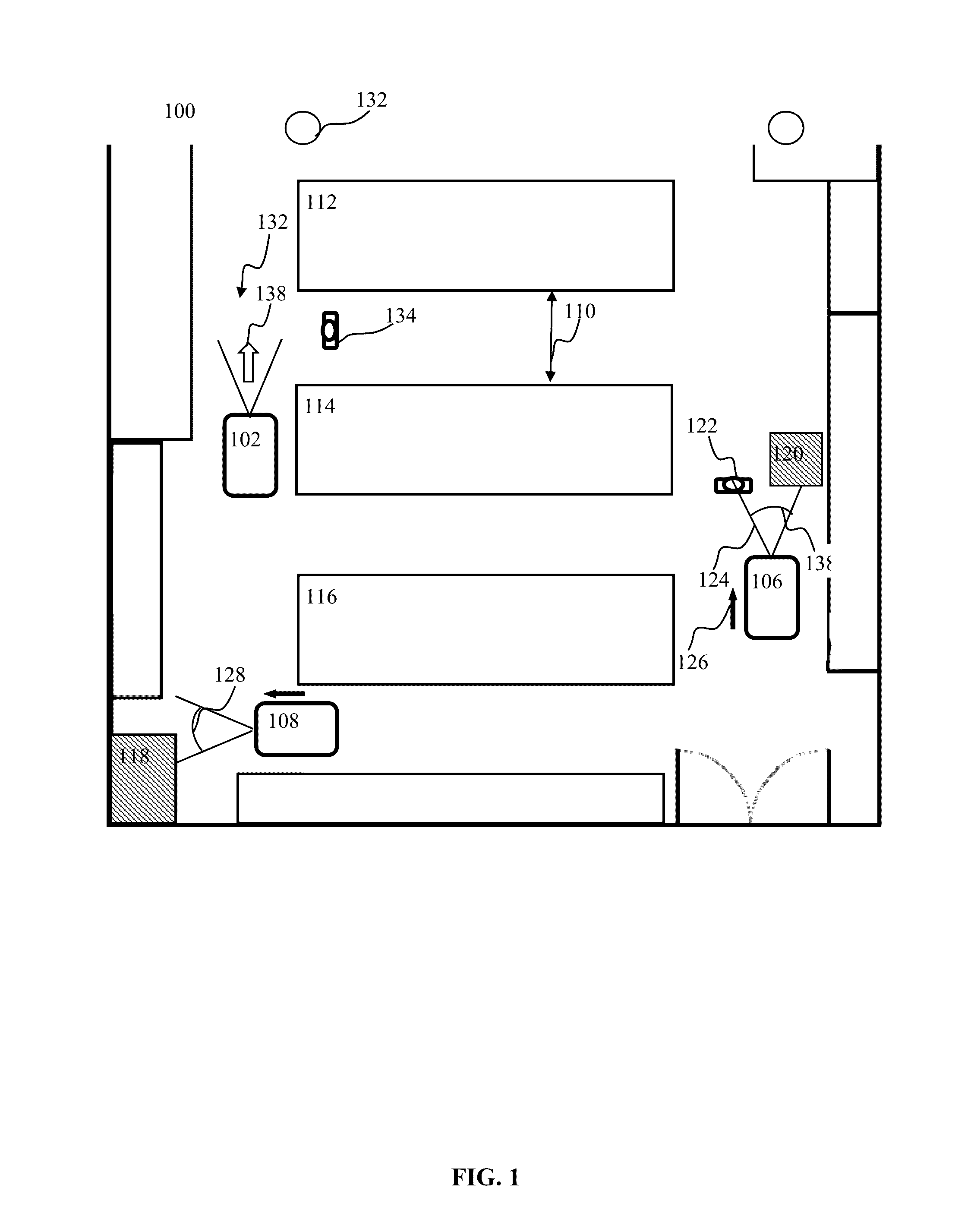
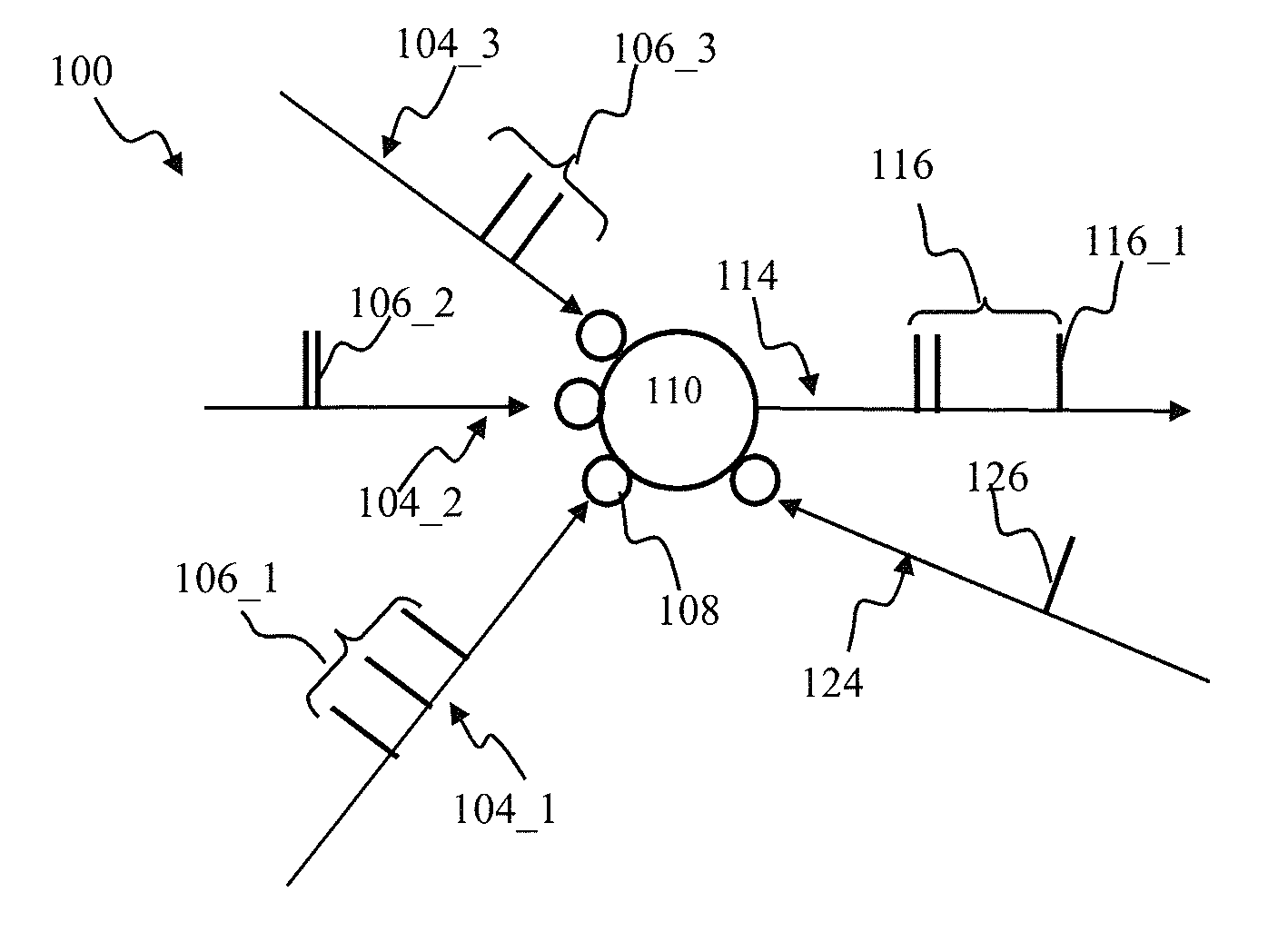
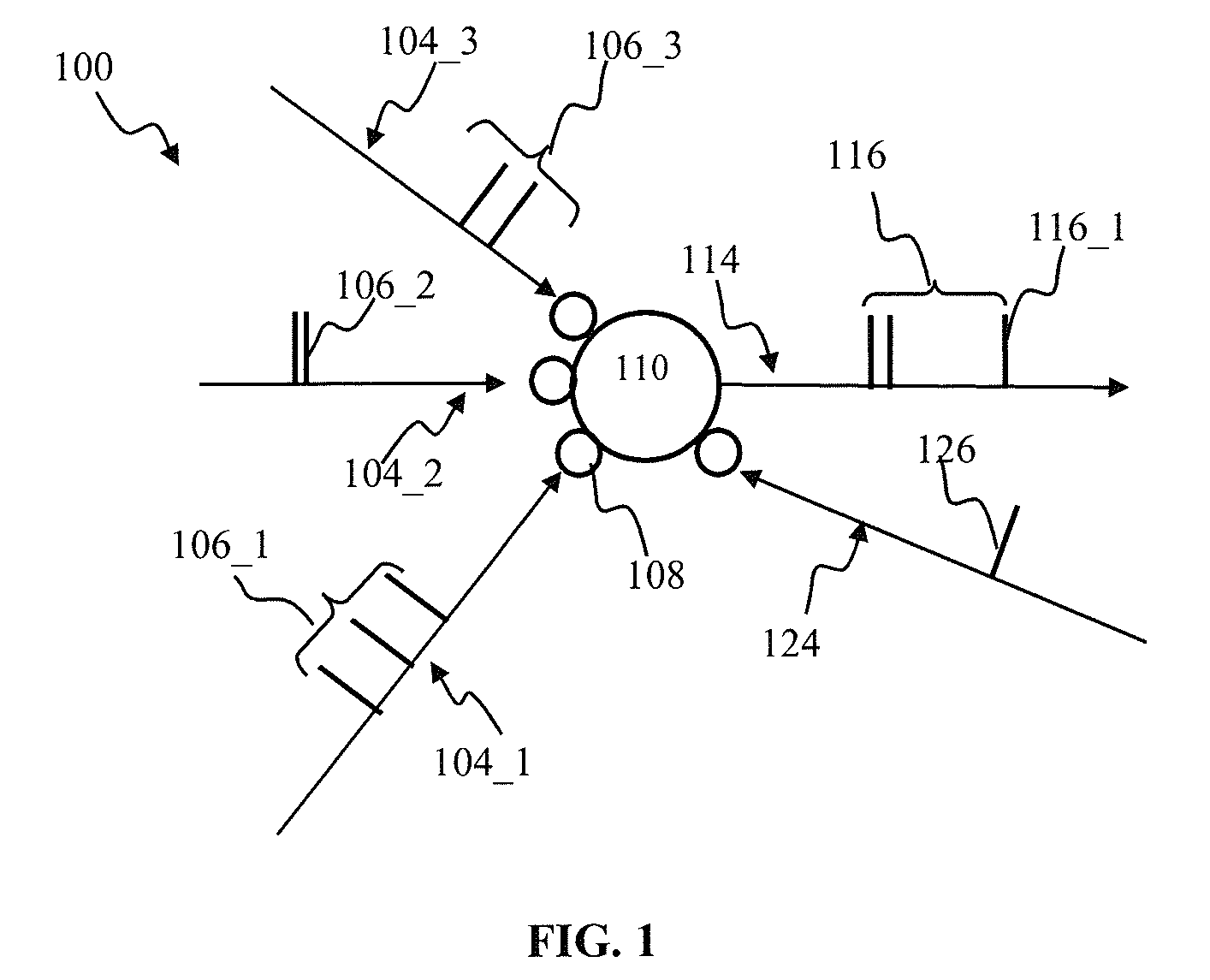
Modulated plasticity apparatus and methods for spiking neuron network
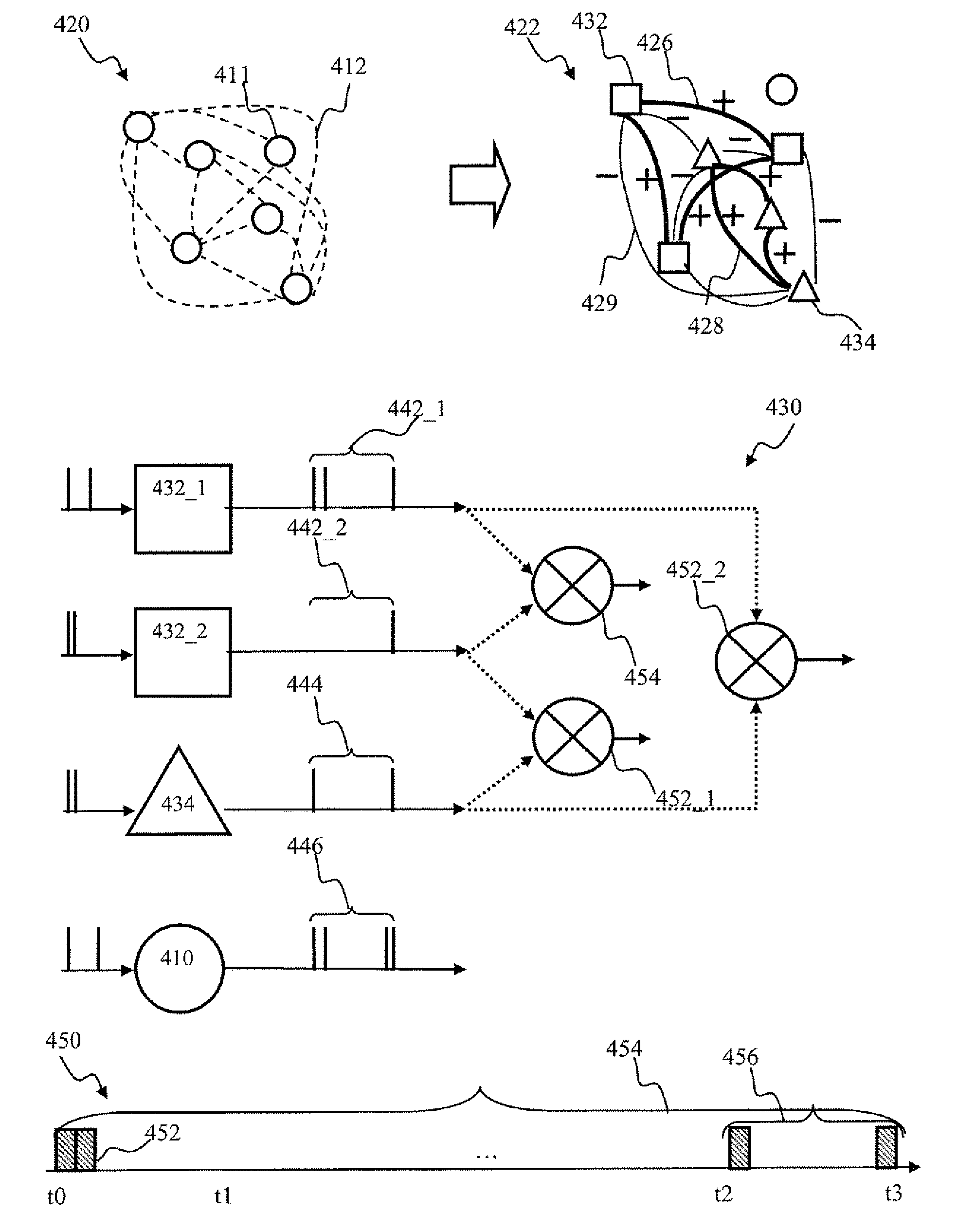
Apparatus and methods for modulated plasticity in a spiking neuron network. A plasticity mechanism may be configured for example based on a similarity measure between post-synaptic activities of two or more neurons that may be receiving the same feed-forward input. The similarity measure may comprise a dynamically determined cross-correlogram between the output spike trains of two neurons. An a priori configured similarity measure may be used during network operation in order to update efficacy of inhibitory connections between neighboring neurons. Correlated output activity may cause one neuron to inhibit output generation by another neuron thereby hindering responses by multiple neurons to the same input stimuli. The inhibition may be based on an increased efficacy of inhibitory lateral connection. The inhibition may comprise modulation of the pre synaptic portion the plasticity rule based on efficacies of feed-forward connection and inhibitory connections and a statistical parameter associated with the post-synaptic rule.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Apparatus and methods for activity-based plasticity in a spiking neuron network
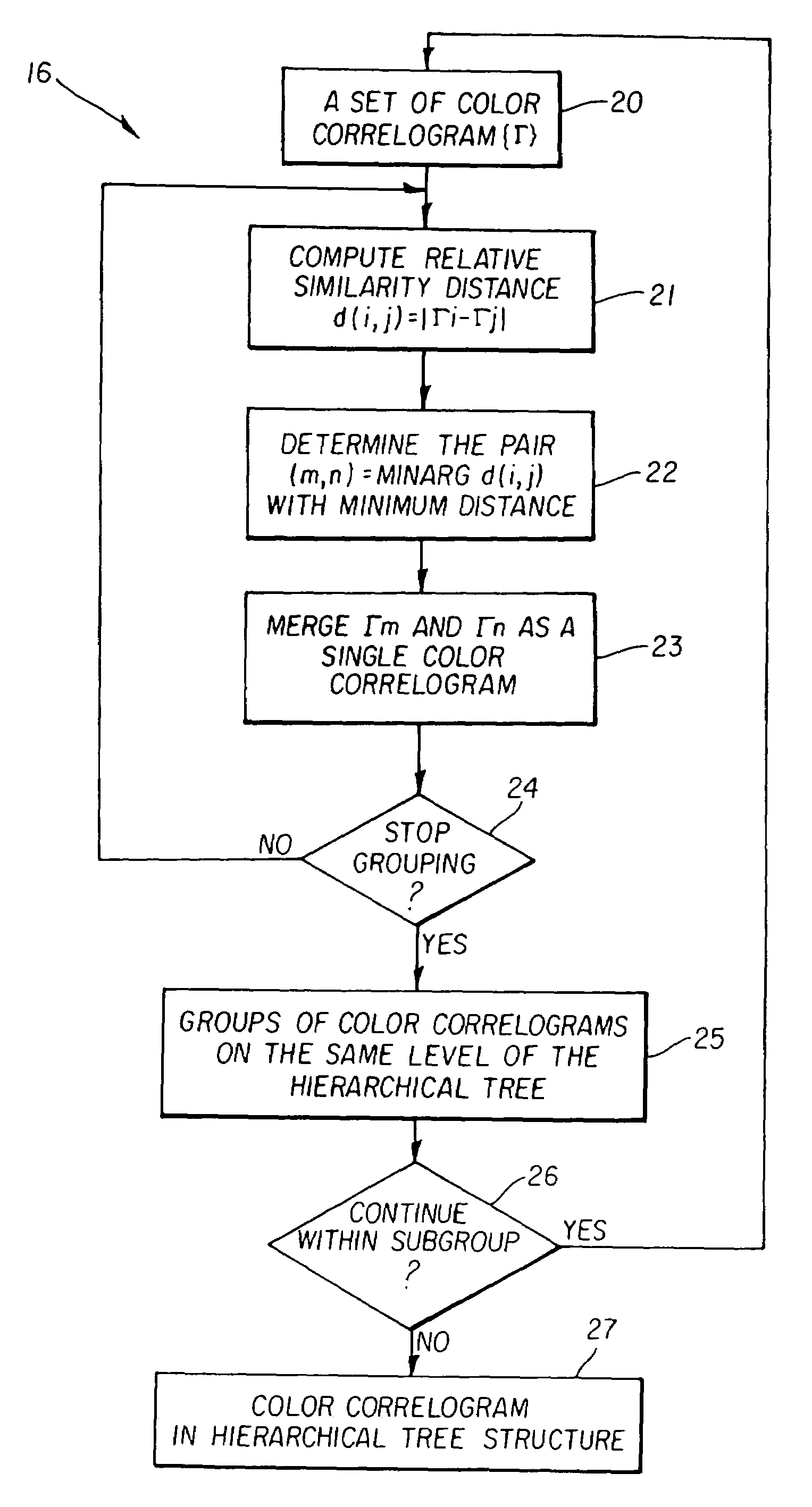
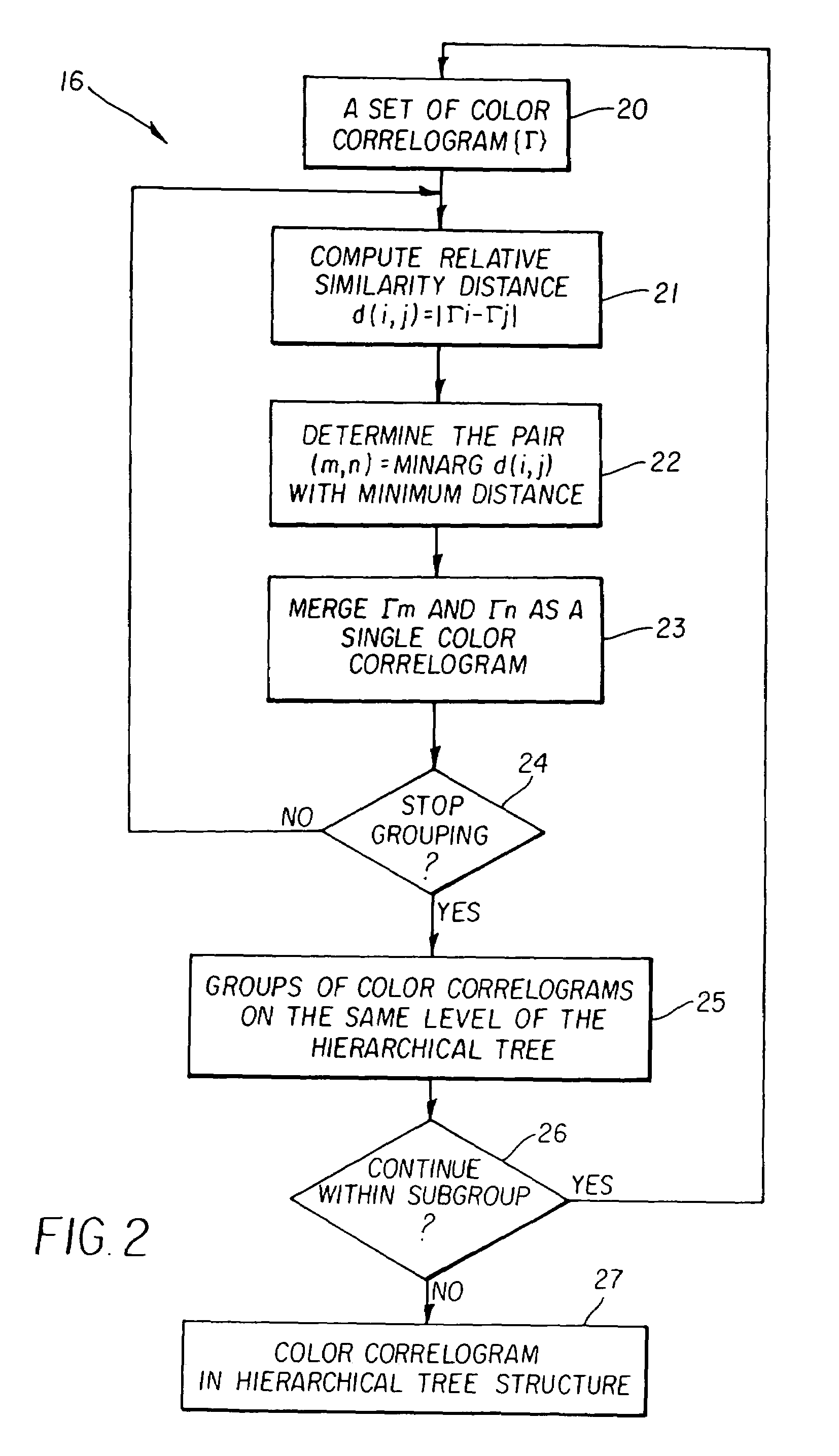
ActiveUS8972315B2Improve performanceGood curative effectDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in spiking neuron network. The network may comprise feature-specific units capable of responding to different objects (red and green color). Plasticity mechanism may be configured based on difference between two similarity measures related to activity of different unit types obtained during network training. One similarity measure may be based on activity of units of the same type (red). Another similarity measure may be based on activity of units of one type (red) and another type (green). Similarity measures may comprise a cross-correlogram and / or mutual information determined over an activity window. Several similarity estimates, corresponding to different unit-to-unit pairs may be combined. The combination may comprise a weighted average. During network operation, the activity based plasticity mechanism may be used to potentiate connections between units of the same type (red-red). The plasticity mechanism may be used to depress connections between units of different types (red-green).
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Apparatus and methods for activity-based plasticity in a spiking neuron network
ActiveUS20140122399A1Improve performanceGood curative effectDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in spiking neuron network. The network may comprise feature-specific units capable of responding to different objects (red and green color). Plasticity mechanism may be configured based on difference between two similarity measures related to activity of different unit types obtained during network training. One similarity measure may be based on activity of units of the same type (red). Another similarity measure may be based on activity of units of one type (red) and another type (green). Similarity measures may comprise a cross-correlogram and / or mutual information determined over an activity window. Several similarity estimates, corresponding to different unit-to-unit pairs may be combined. The combination may comprise a weighted average. During network operation, the activity based plasticity mechanism may be used to potentiate connections between units of the same type (red-red). The plasticity mechanism may be used to depress connections between units of different types (red-green).
Owner:BRAIN CORP
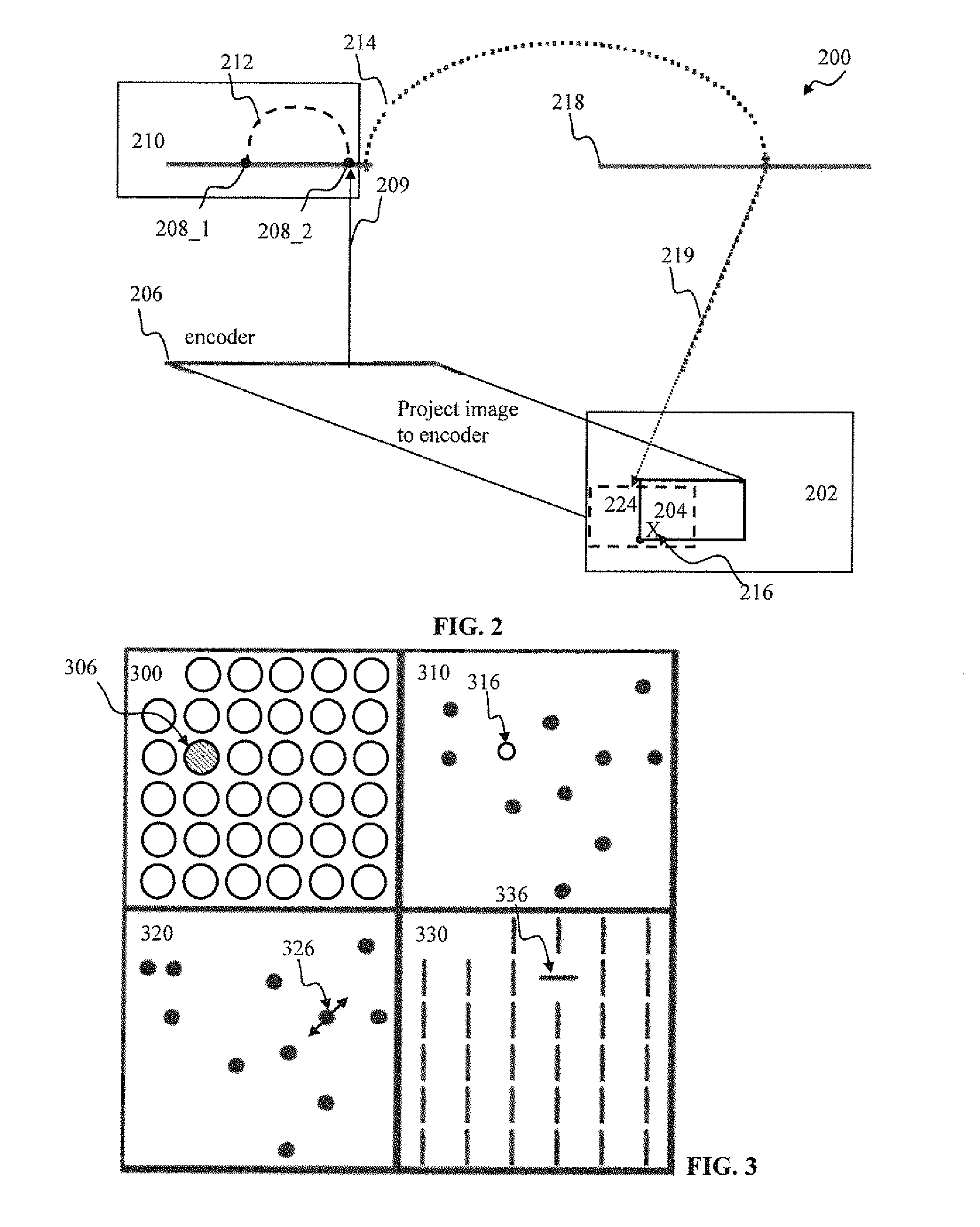
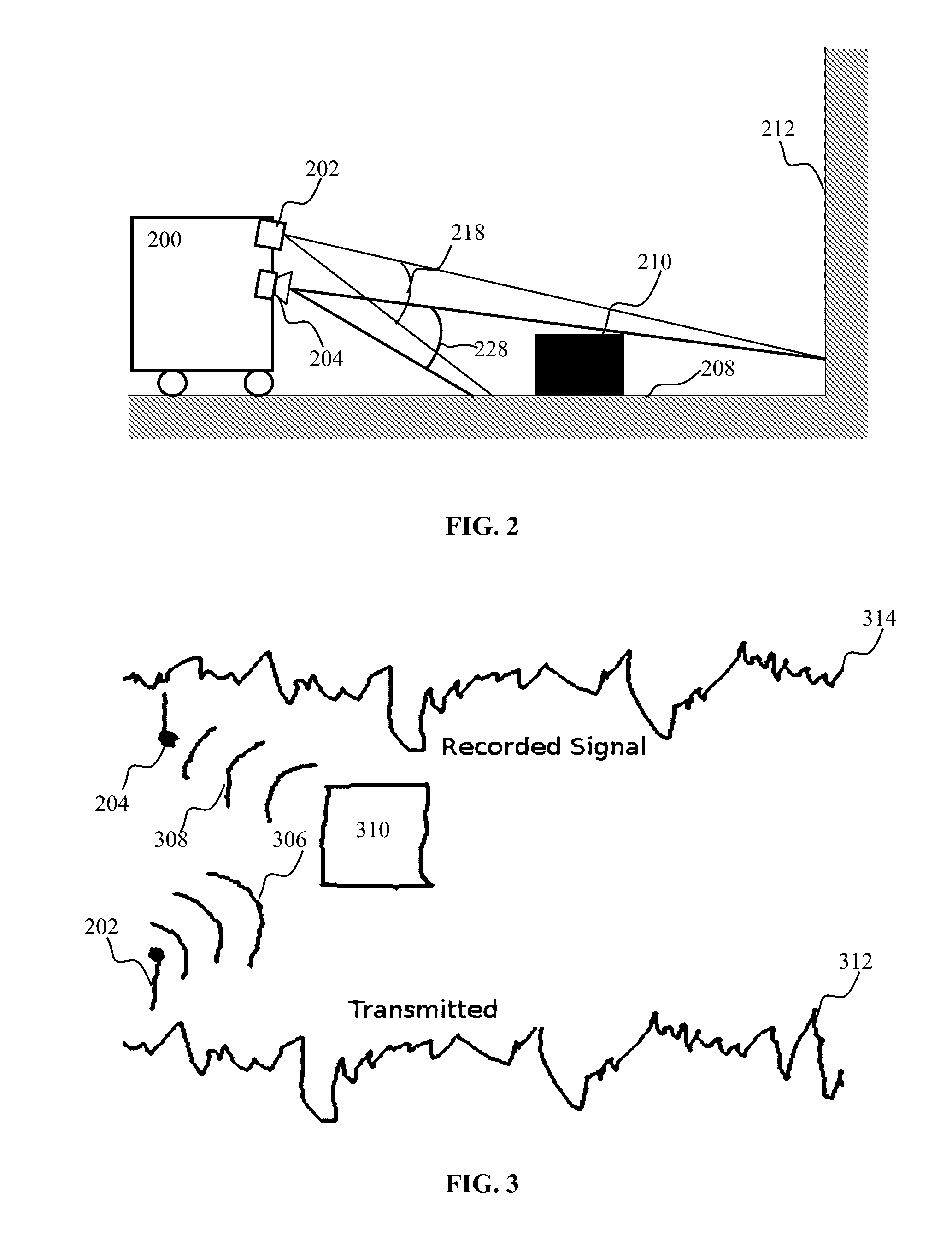
Apparatus and methods for detection of objects using broadband signals
ActiveUS20170023661A1Electromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime lagBroadband transmission
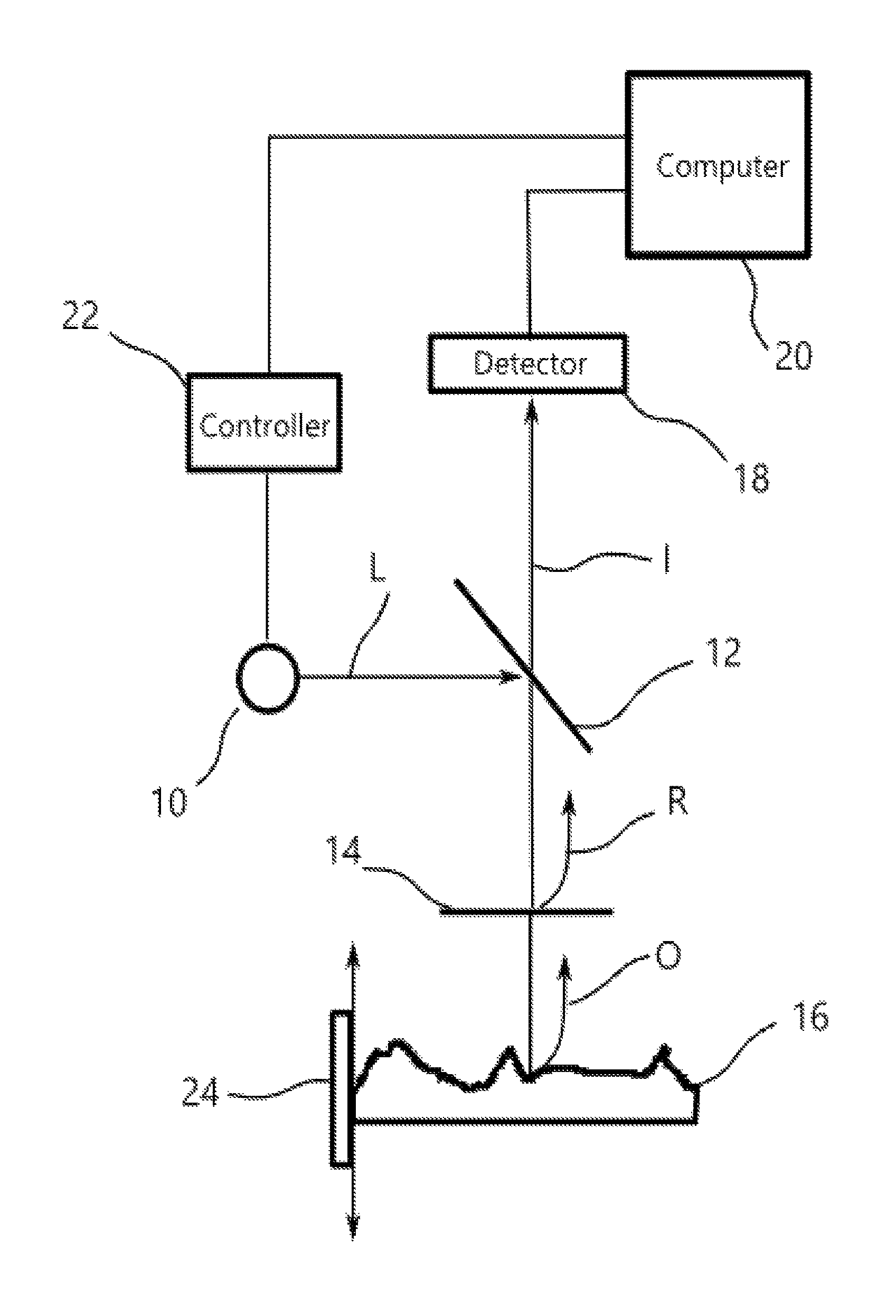
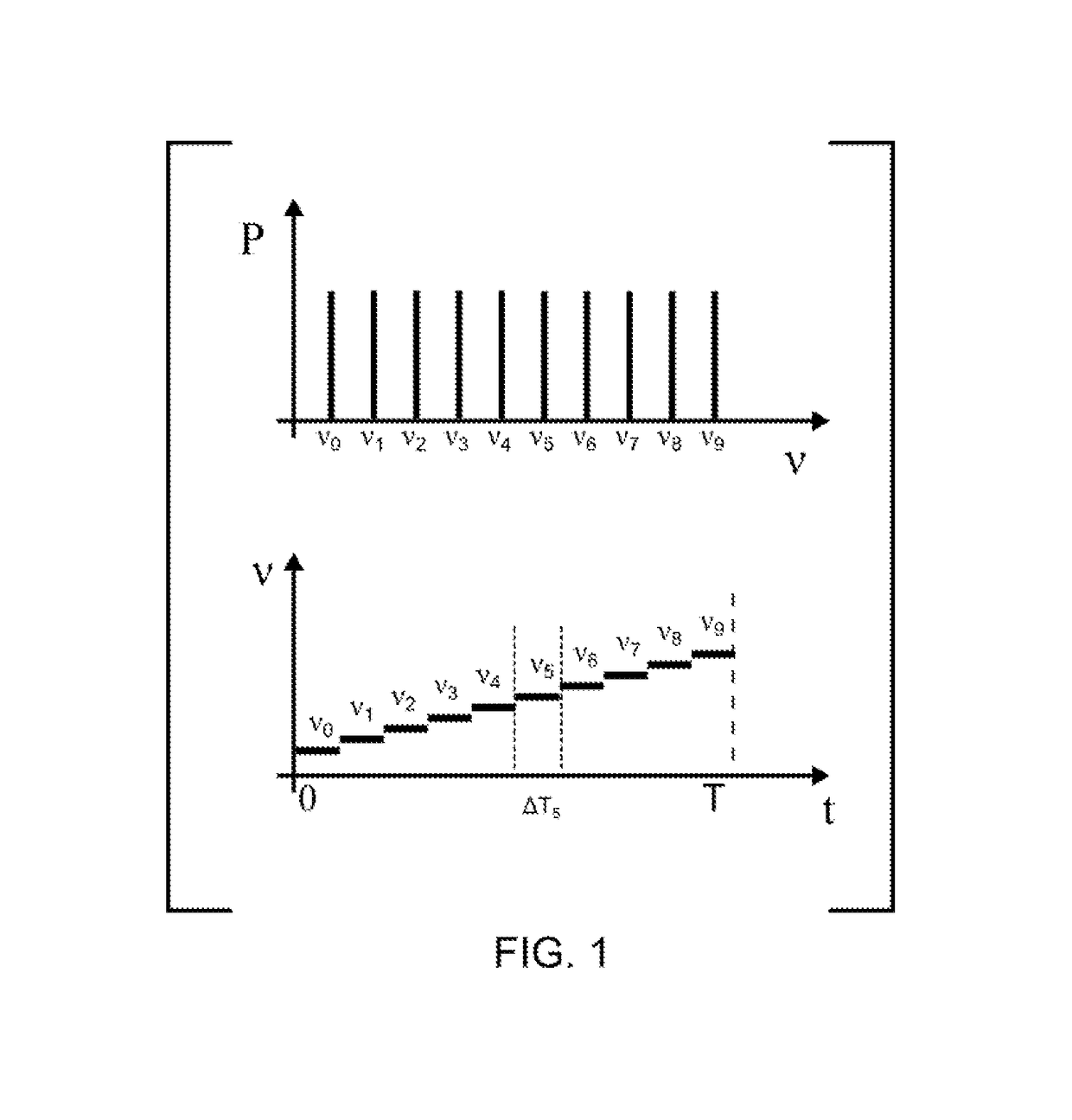
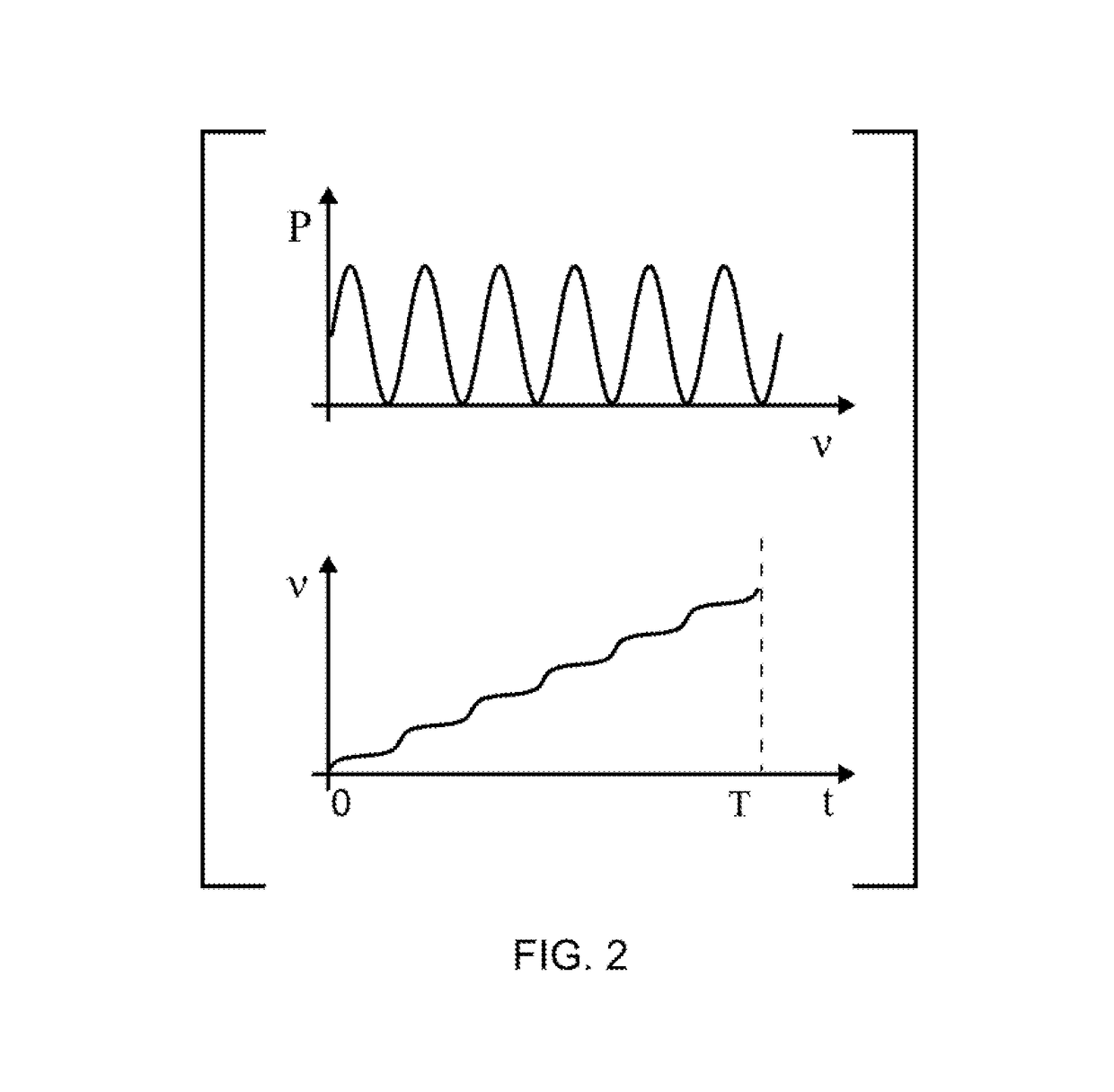
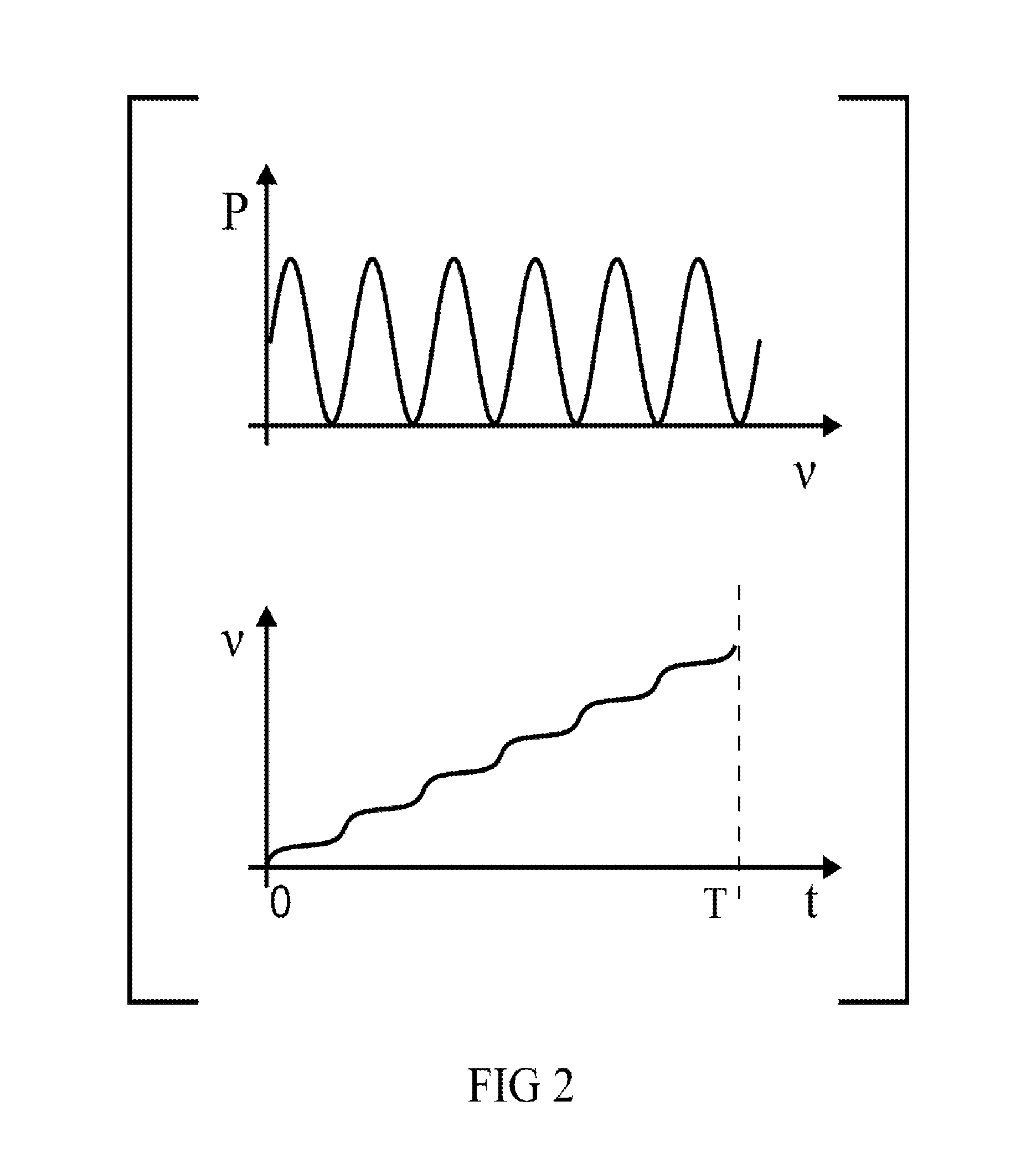
Broadband signal transmissions may be used for object detection and / or ranging. Broadband transmissions may comprise a pseudo-random bit sequence or a bit sequence produced using, a random process. The sequence may be used to modulate transmissions of a given wave type. Various types of waves may be utilized, pressure, light, and radio waves. Waves reflected by objects within the sensing volume may be sampled. The received signal may be convolved with a time-reversed copy of the transmitted random sequence to produce a correlogram. The correlogram may be analyzed to determine range to objects. The analysis may comprise determination of one or more peaks / troughs in the correlogram. Range to an object may be determines based on a time lag of a respective peak.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
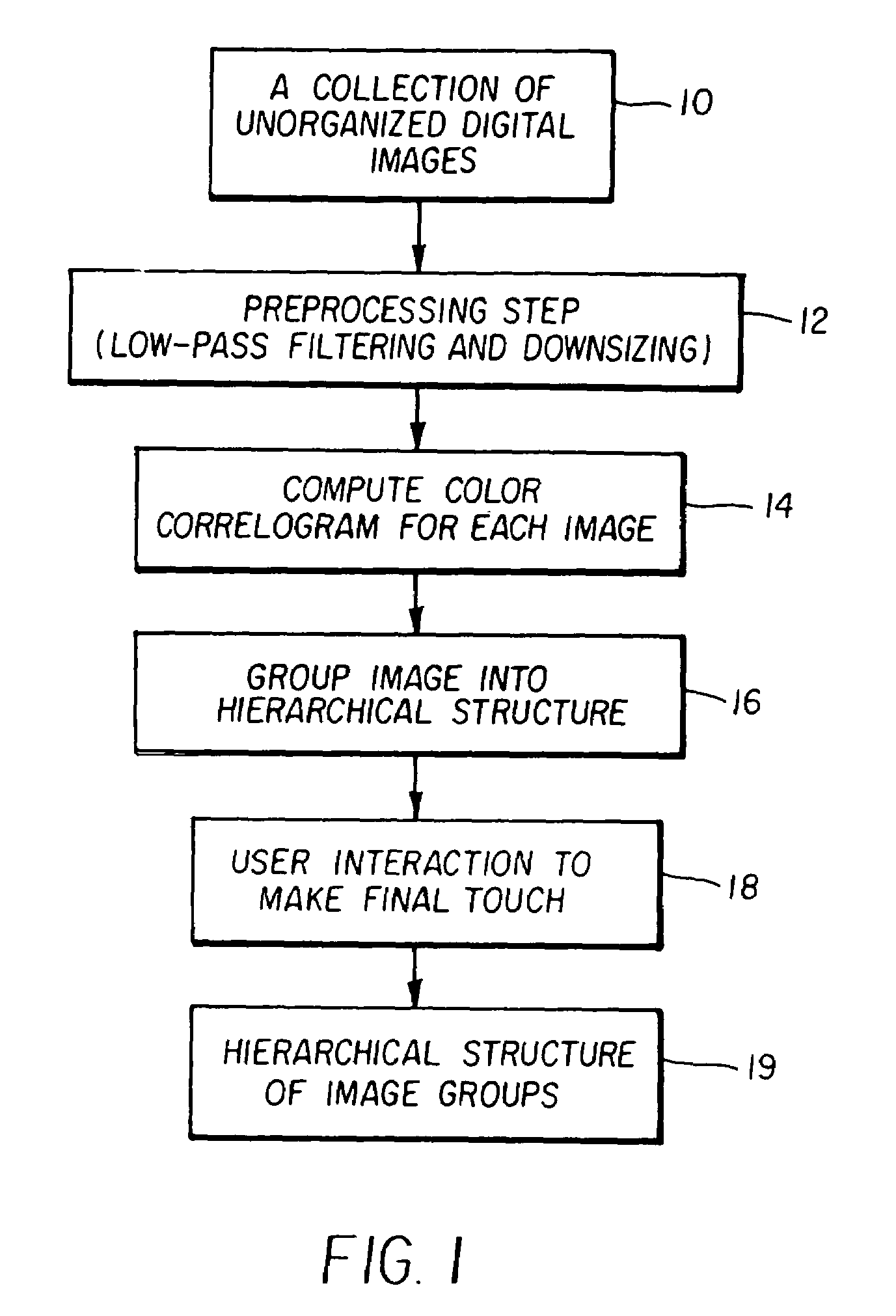
Method and system for automated grouping of images
InactiveUS6993180B2Efficient and effective implementationData processing applicationsImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
A method of automated content-based grouping of digital images without using auxiliary metadata and training data set, comprises the steps of computing a color correlogram from image pixel values for each of the digital images, grouping the color correlograms into groups within a hierarchical structure based on relative similarities of the color correlograms, and assigning the images to the groups based on the hierarchical structure of the color correlograms.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Nonlinear overlap method for time scaling
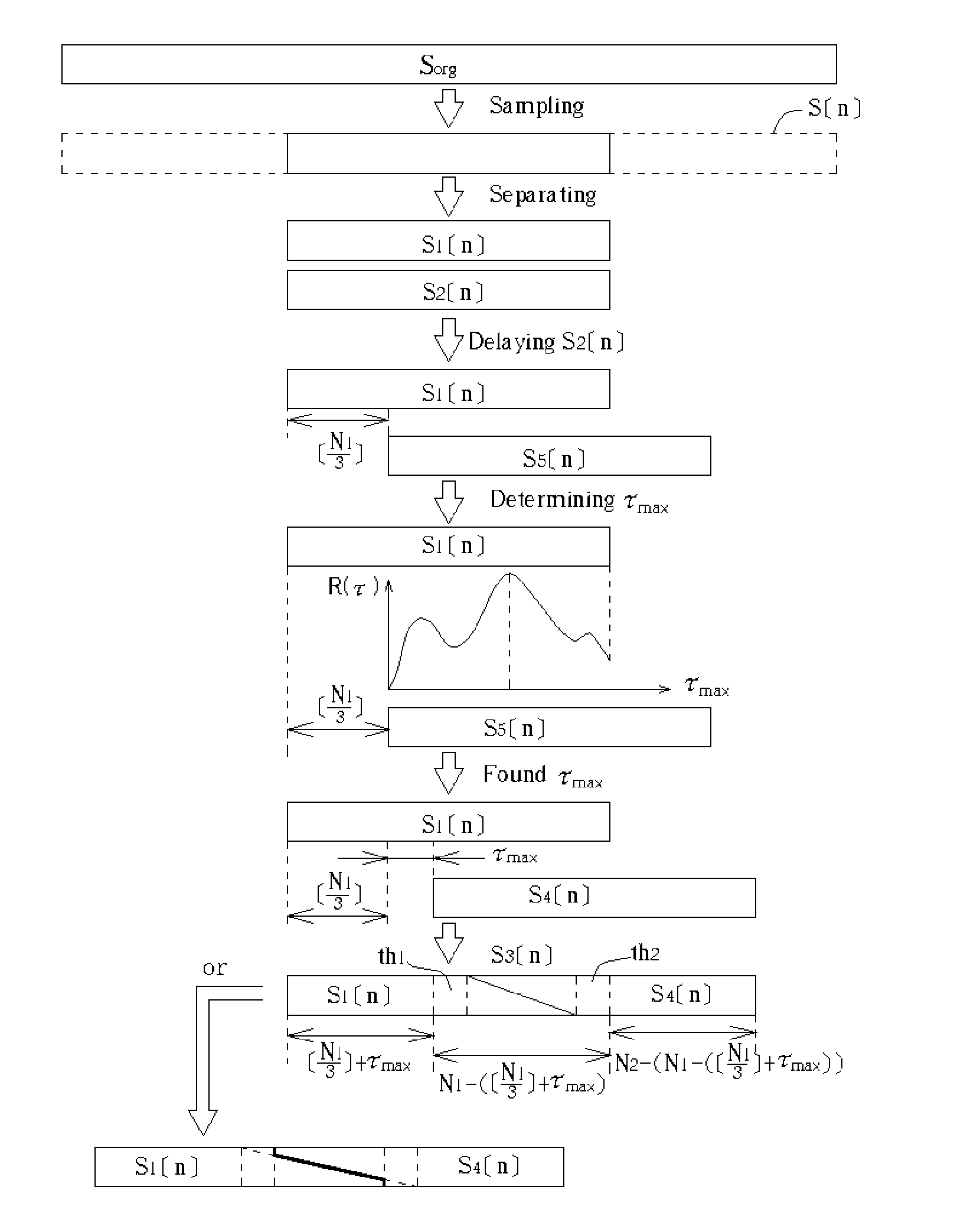
InactiveUS20050025263A1Efficient synthesisQuality improvementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCorrelation functionCorrelogram
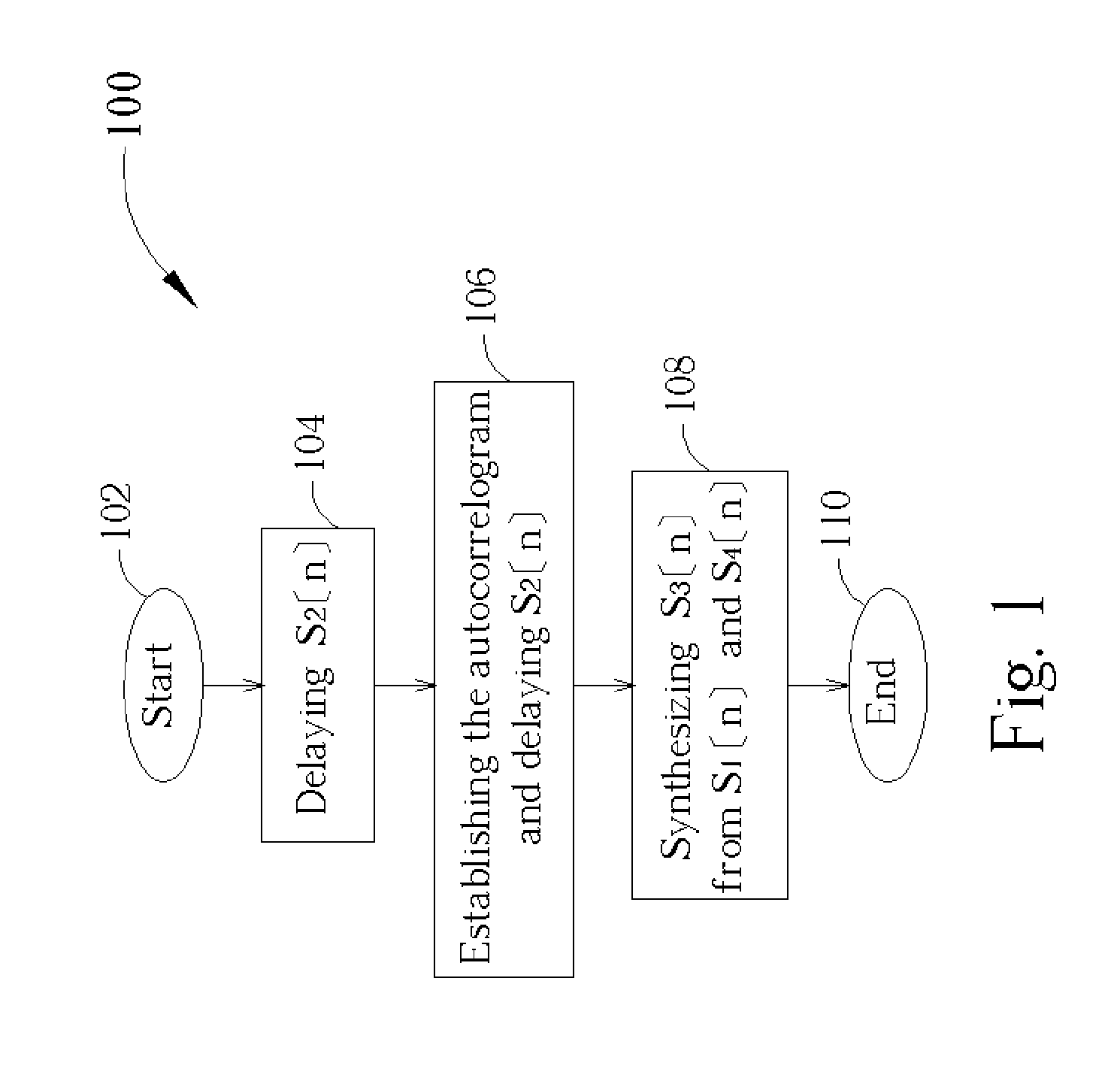
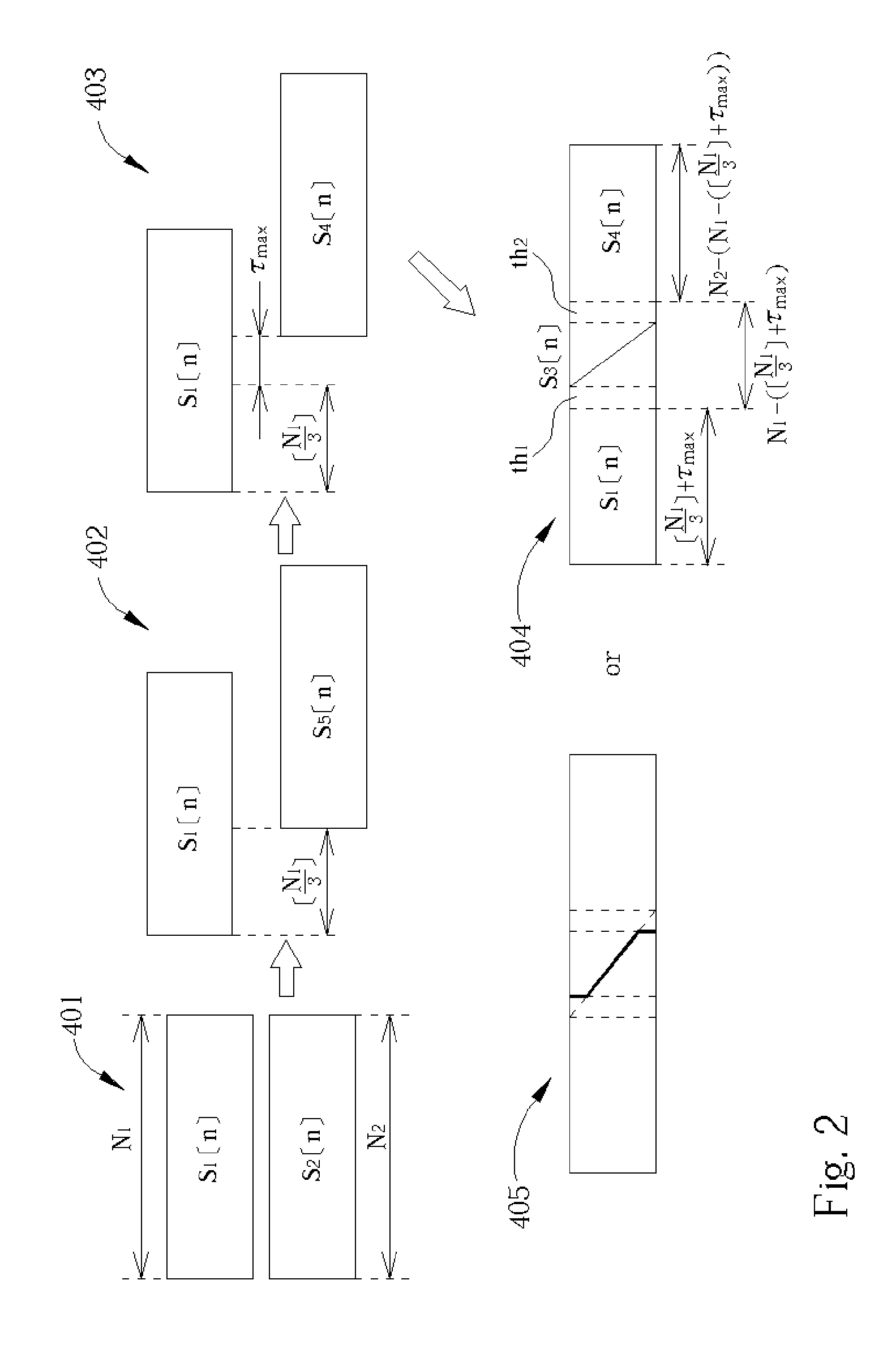
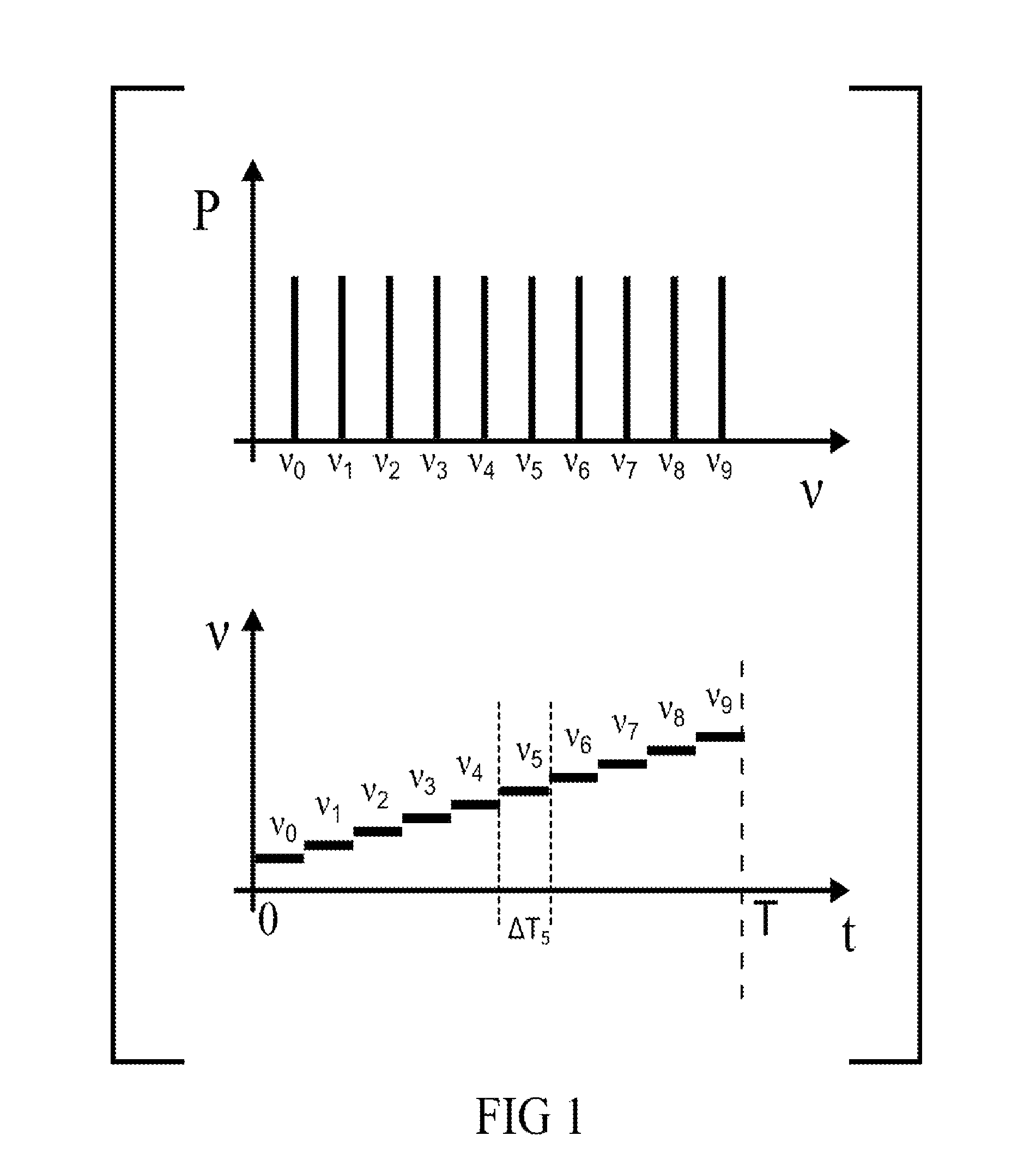
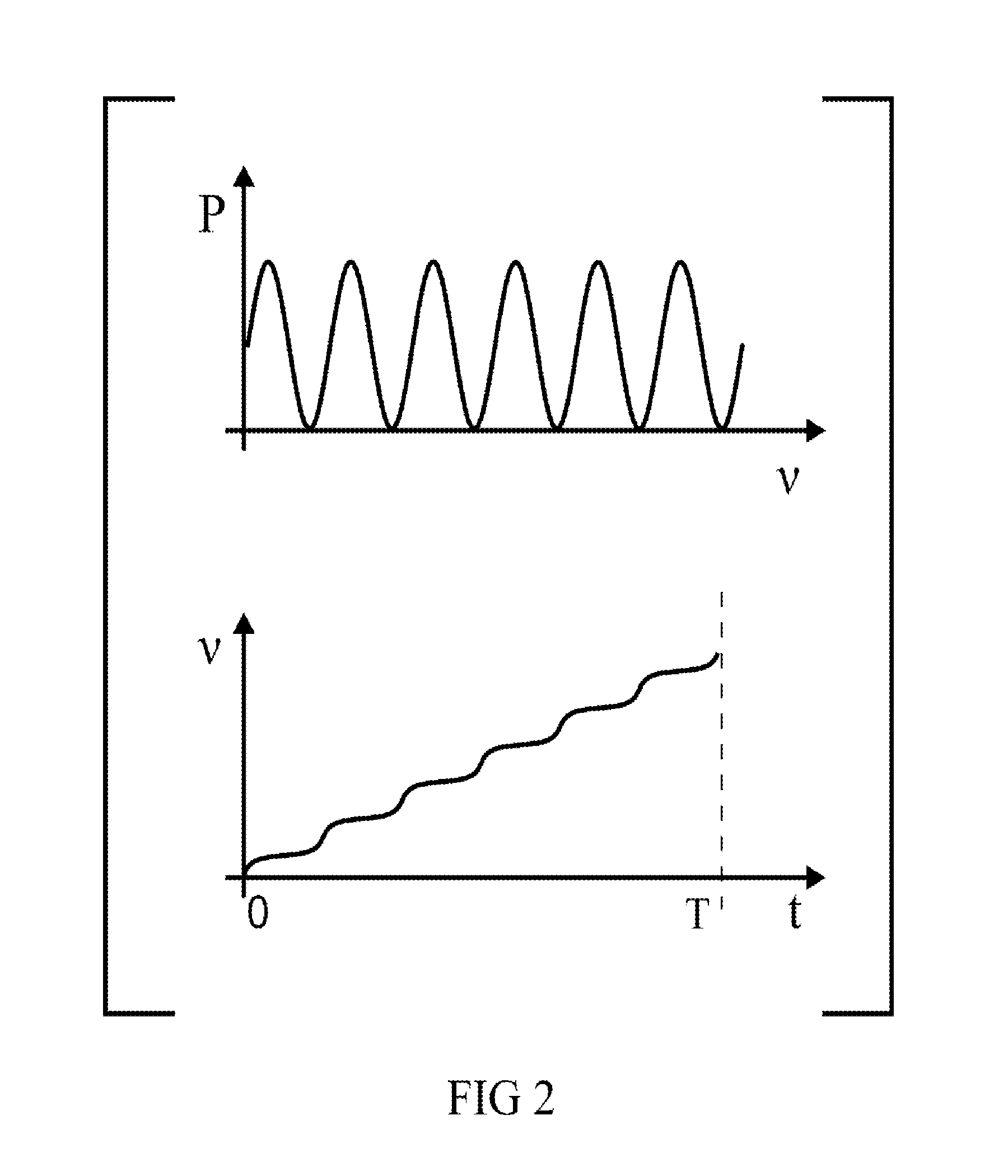
A nonlinear overlap method for time scaling to synthesize an S1[n] and an S2[n] into an S3[n] is disclosed. The S1[n] and the S2[n] having N1 and N2 signals respectively. The nonlinear overlap method includes the following steps: (a) delaying the S2[n] by a predetermined number and forming an S5[n], (b) establishing a correlogram of a cross-correlation function of the S1[n] and S5[n], and (c) setting S3[n] as a number of S1[n] when 0<=n<; as a number formed by overlap-adding the S1[n] and an S4[n] in a weighting manner when (the predetermined number+the maximum index+the first threshold)<=n<(N1−a second threshold); and as a number of S4 wherein the first and second thresholds are not equal to zero at the same time, and the S4[n] is formed by delaying the S5[n] by the maximum index.
Owner:ALICORP
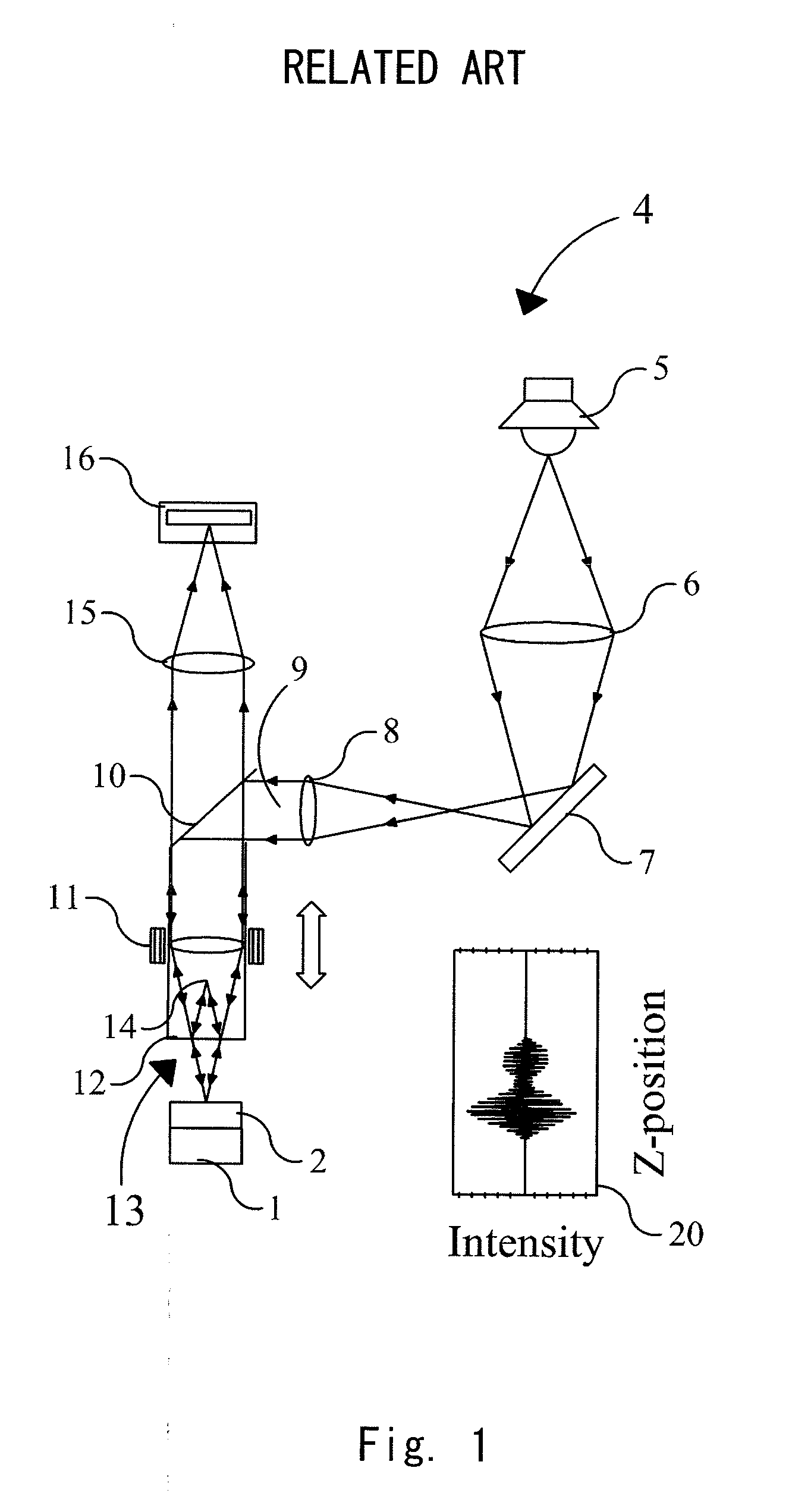
Correction of scanning errors in interferometric profiling
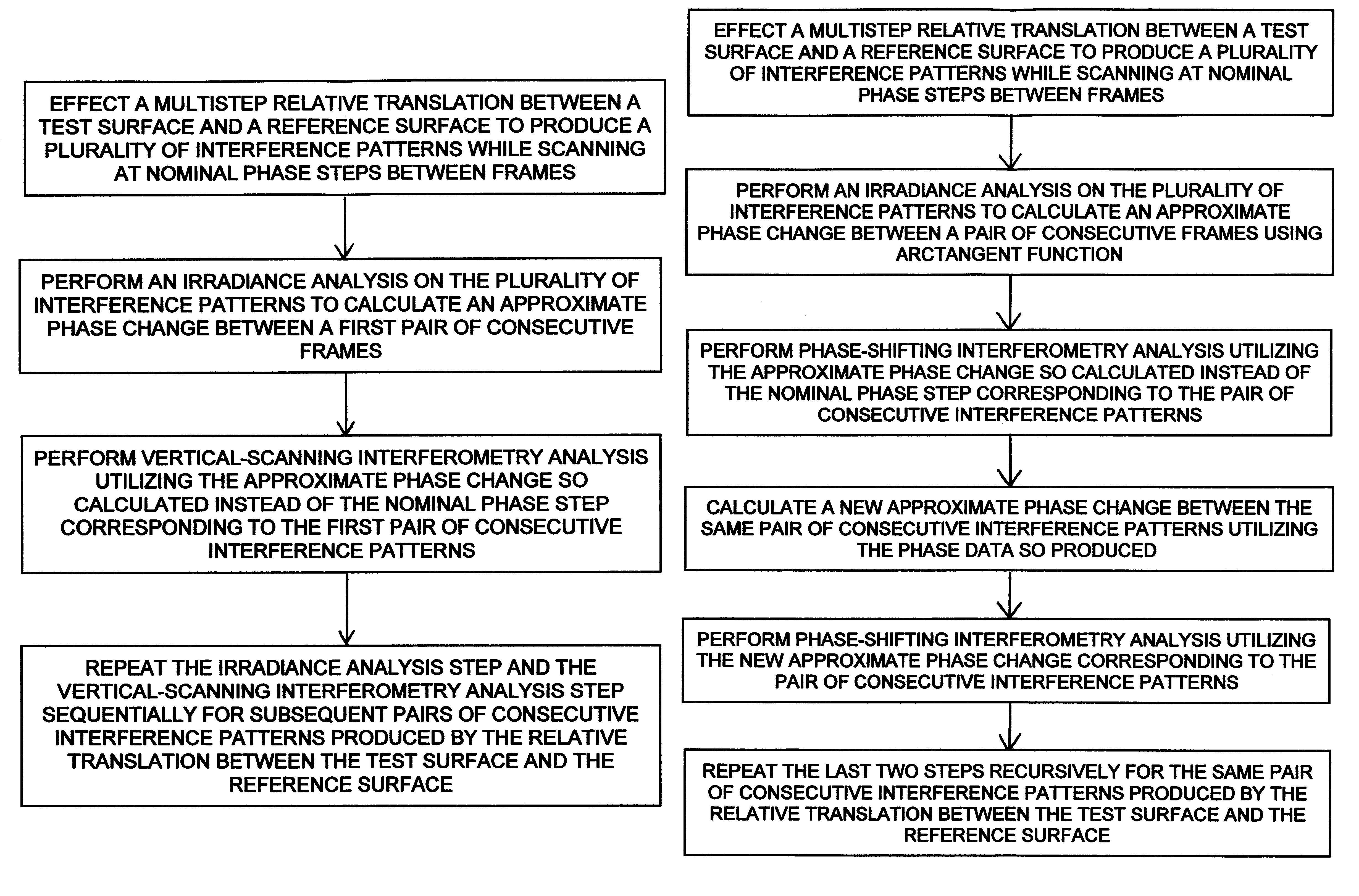
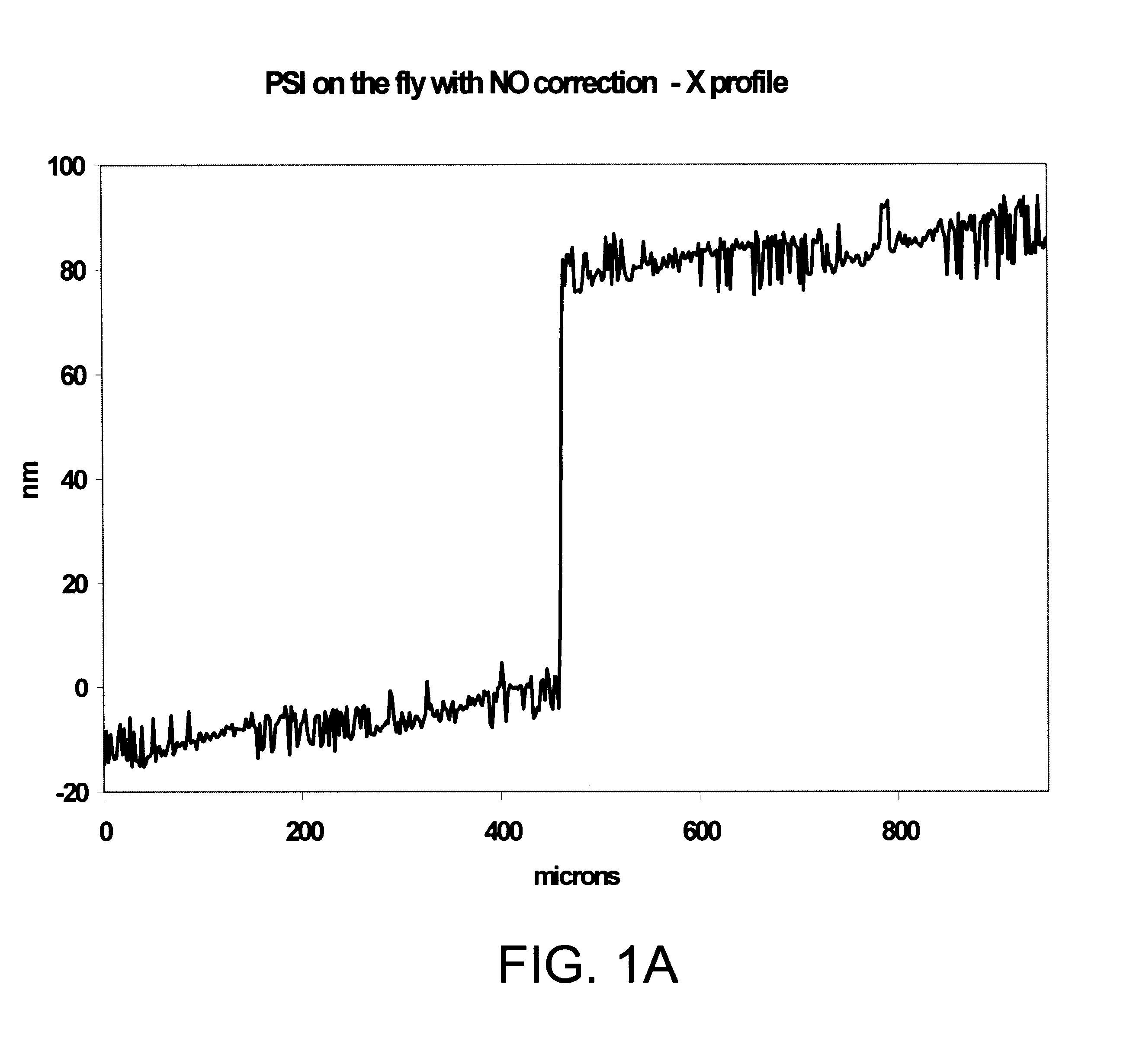
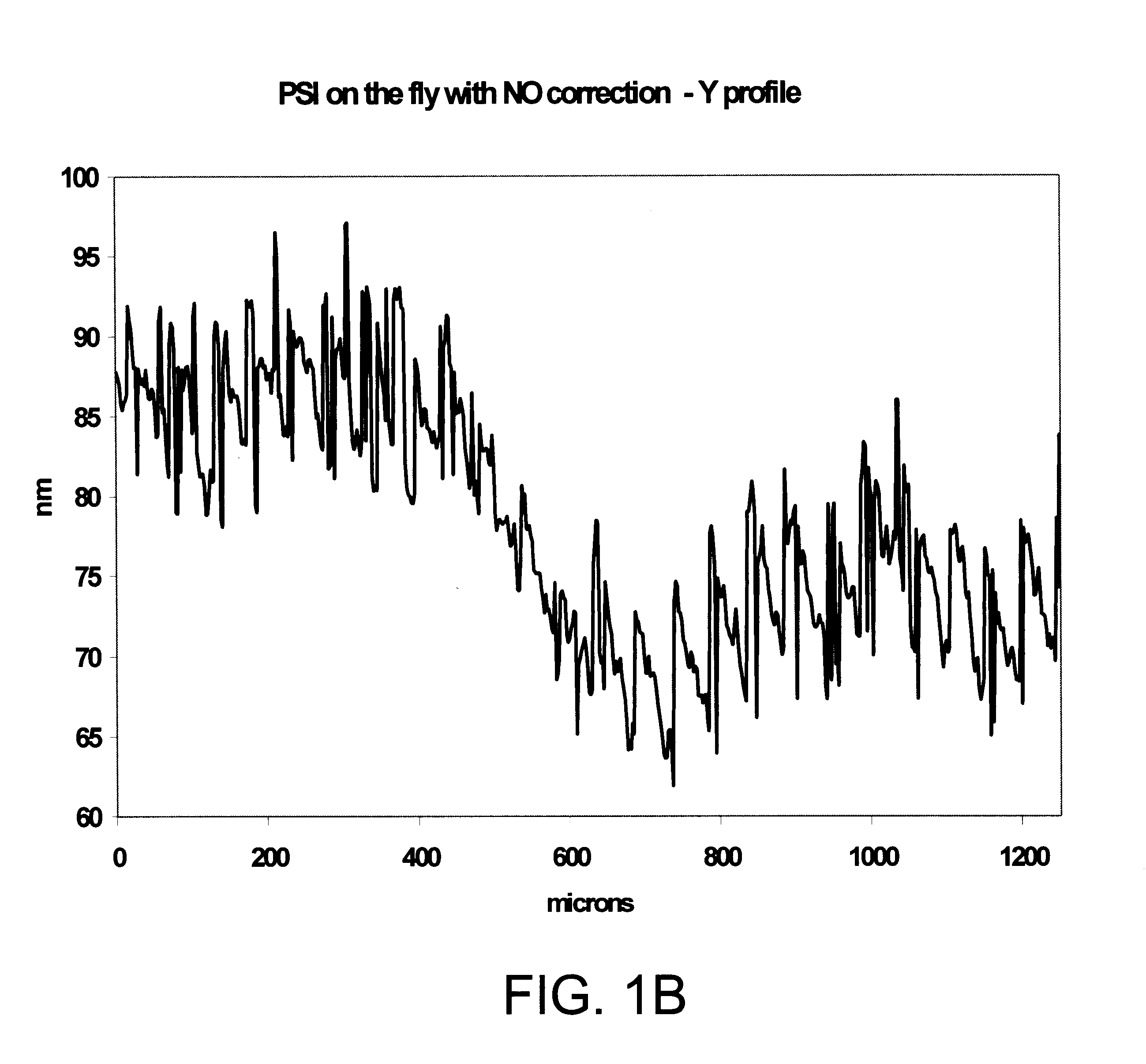
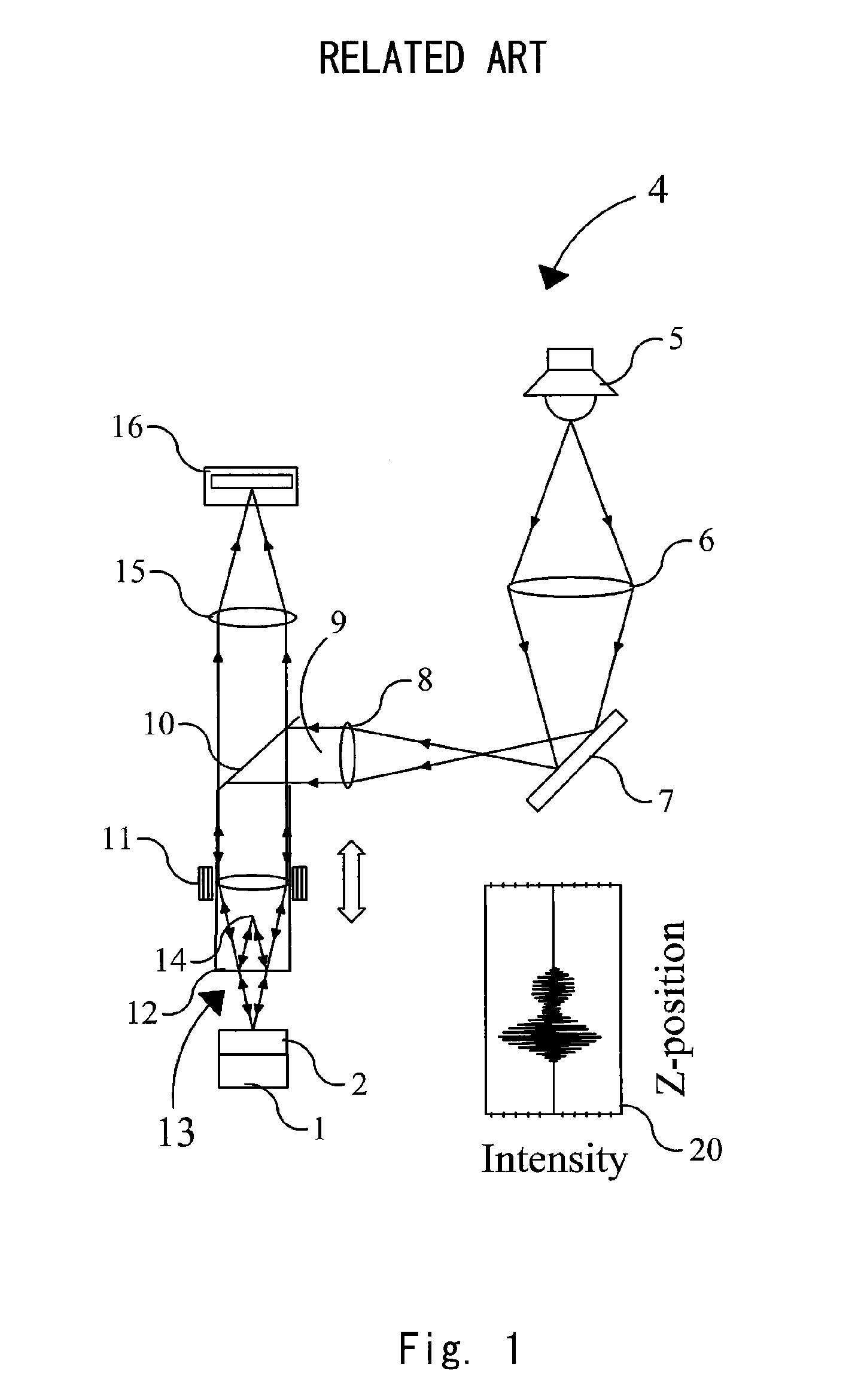
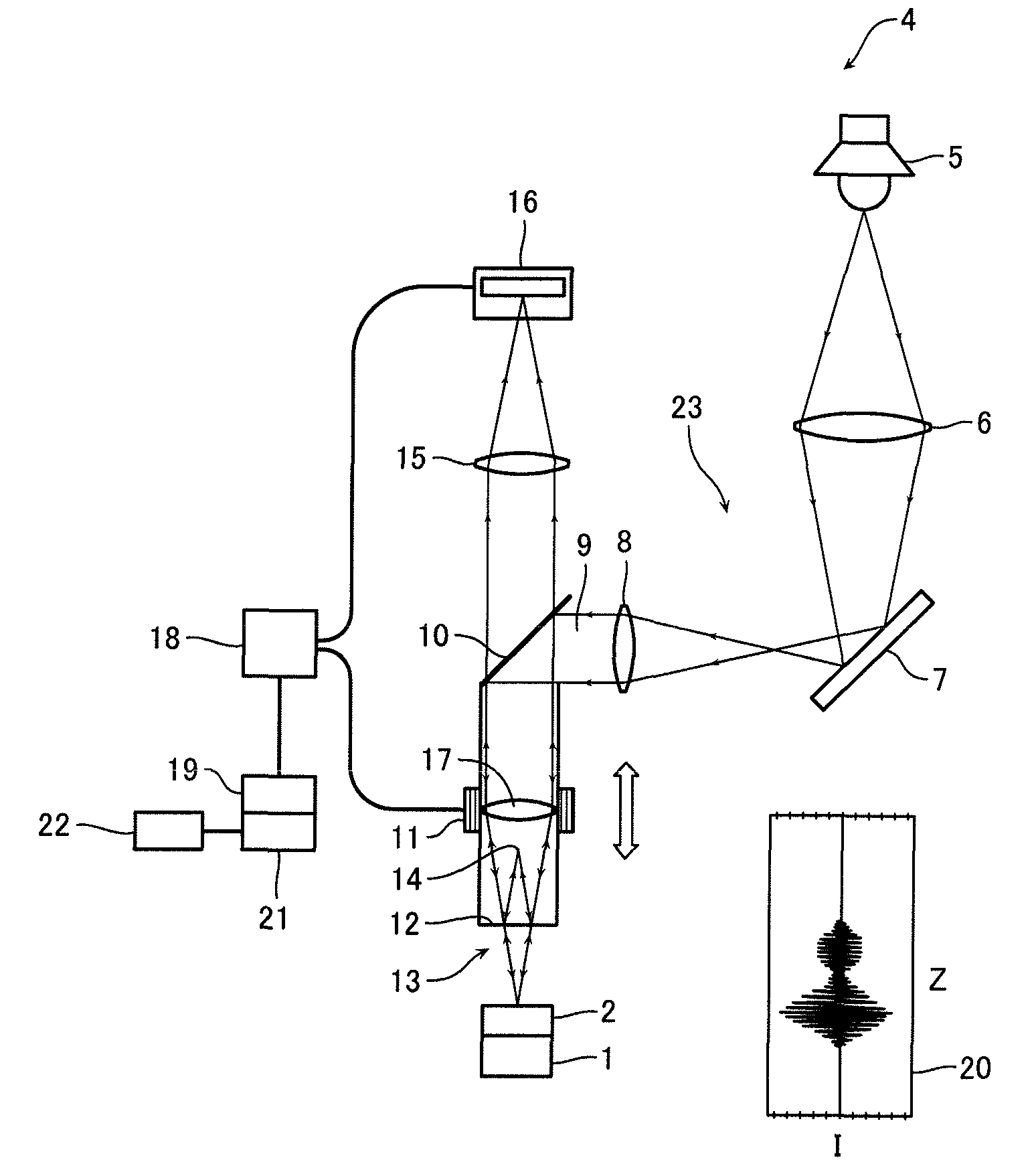
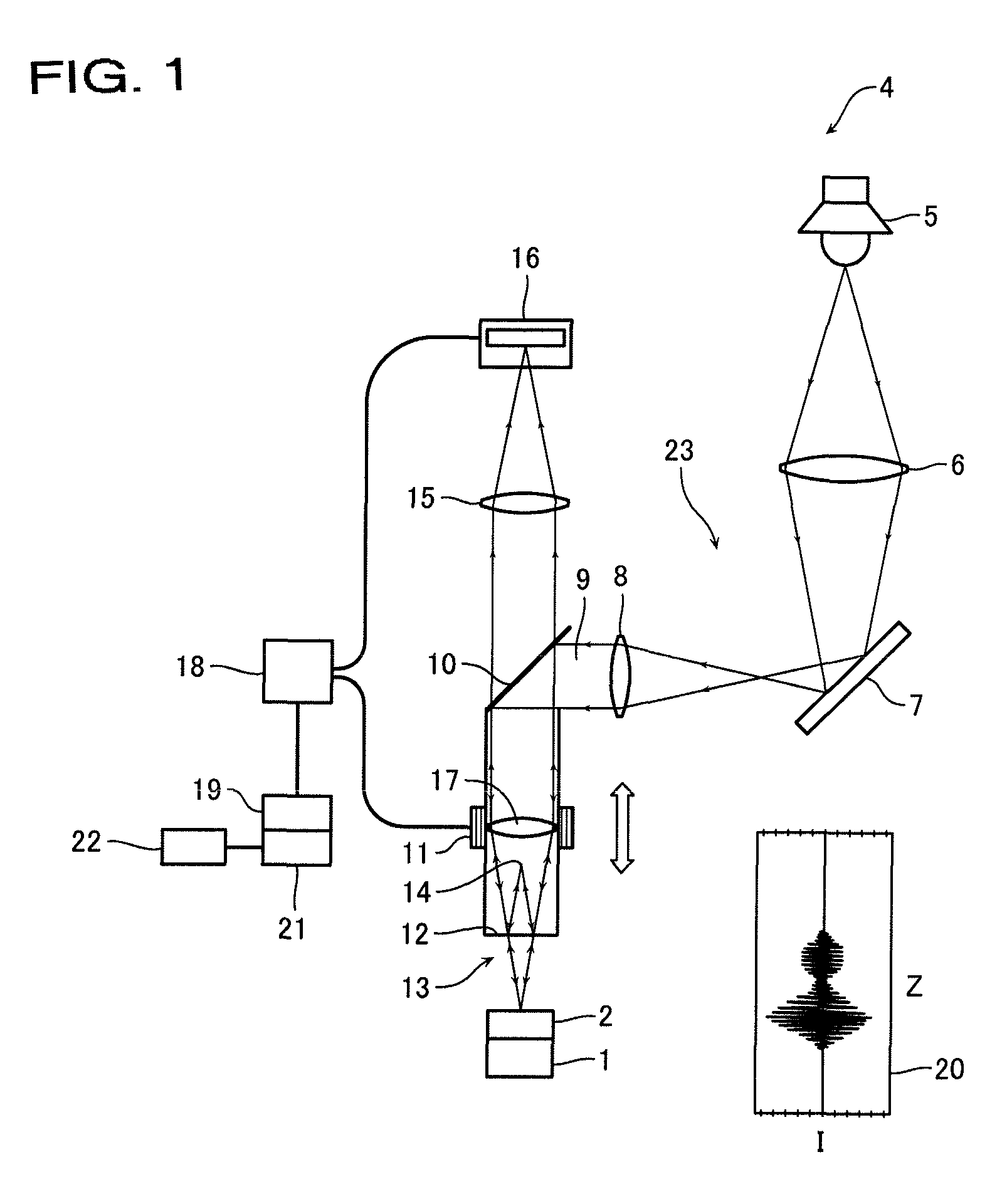
Interferometric measurements are carried out in conventional manner to produce a correlogram corresponding to successive scanner steps. An approximation of the actual scan-step size between frames is calculated from multiple-frame intensity data collected around the frame of interest using common irradiance algorithms. The scan-step size so measured is then used in standard PSI, VSI or PSIOTF algorithms, instead of the scanner's nominal phase step. According to one embodiment, the invention utilizes a five-frame PSI algorithm to produce an average scan-step size of four scan steps. According to another embodiment, the phase step between frames is calculated directly utilizing a novel five-frame algorithm that produces an approximation of actual phase step for a given frame, rather than an average value of four steps around the frame. The method requires reduced data processing and can advantageously be applied "on-the fly" as intensity data are acquired during scanning.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Spiking neuron sensory processing apparatus and methods for saliency detection
ActiveUS9218563B2Improve performanceDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkSpiking neural network
Apparatus and methods for salient feature detection by a spiking neuron network. The network may comprise feature-specific units capable of responding to different objects (red and green color). The plasticity mechanism of the network may be configured based on difference between two similarity measures related to activity of different unit types obtained during network training. One similarity measure may be based on activity of units of the same type (red). Another similarity measure may be based on activity of units of one type (red) and another type (green). Similarity measures may comprise a cross-correlogram and / or mutual information determined over an activity window. During network operation, the activity based plasticity mechanism may be used to potentiate connections between units of the same type (red-red). The plasticity mechanism may be used to depress connections between units of different types (red-green). The plasticity mechanism may effectuate detection of salient features in the input.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Bat-wing attenuation in white-light interferometry
Bat wings are removed at step discontinuities within the coherence length of the light source of a vertical-scanning interferometer. A first height profile is obtained from a correlogram using a coherence-sensing technique. A second height profile is obtained from phase measurements at the best-focus frame position of the scanner. The two profiles are compared, and phase ambiguities are removed in conventional manner. In addition, during unwrapping the differences in height between two adjacent pixels obtained both by coherence sensing and by phase measurements are compared to flambd / 4. Where the inter-pixel height difference calculated by coherence sensing is smaller and the inter-pixel height difference calculated by phase is larger than flambd / 4, the phase measurement is corrected by 2pi increments until both coherence and phase inter-pixel height differences are within flambd / 4. This additional step removes bat-wing effects from profiles obtained by phase measurement.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
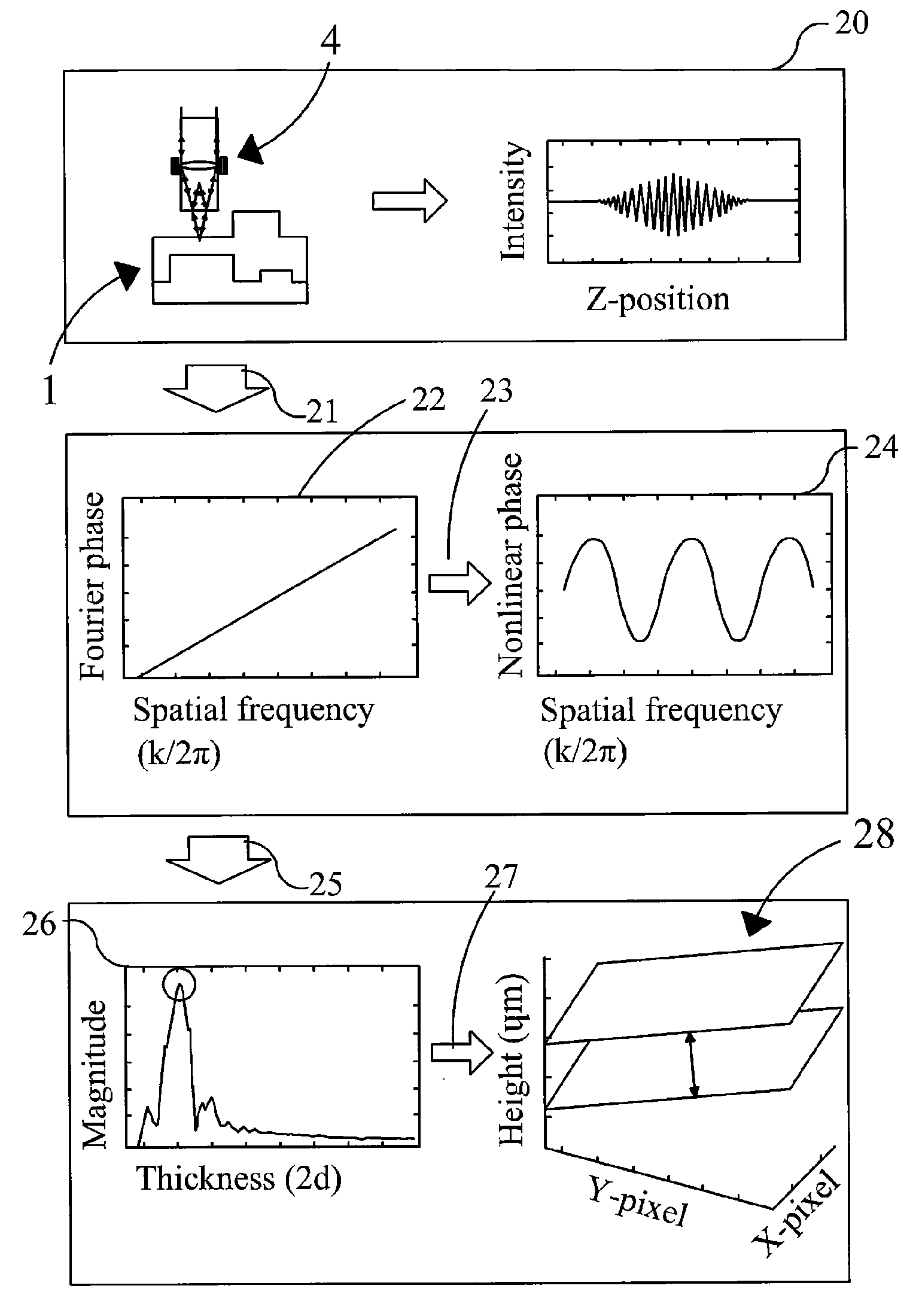
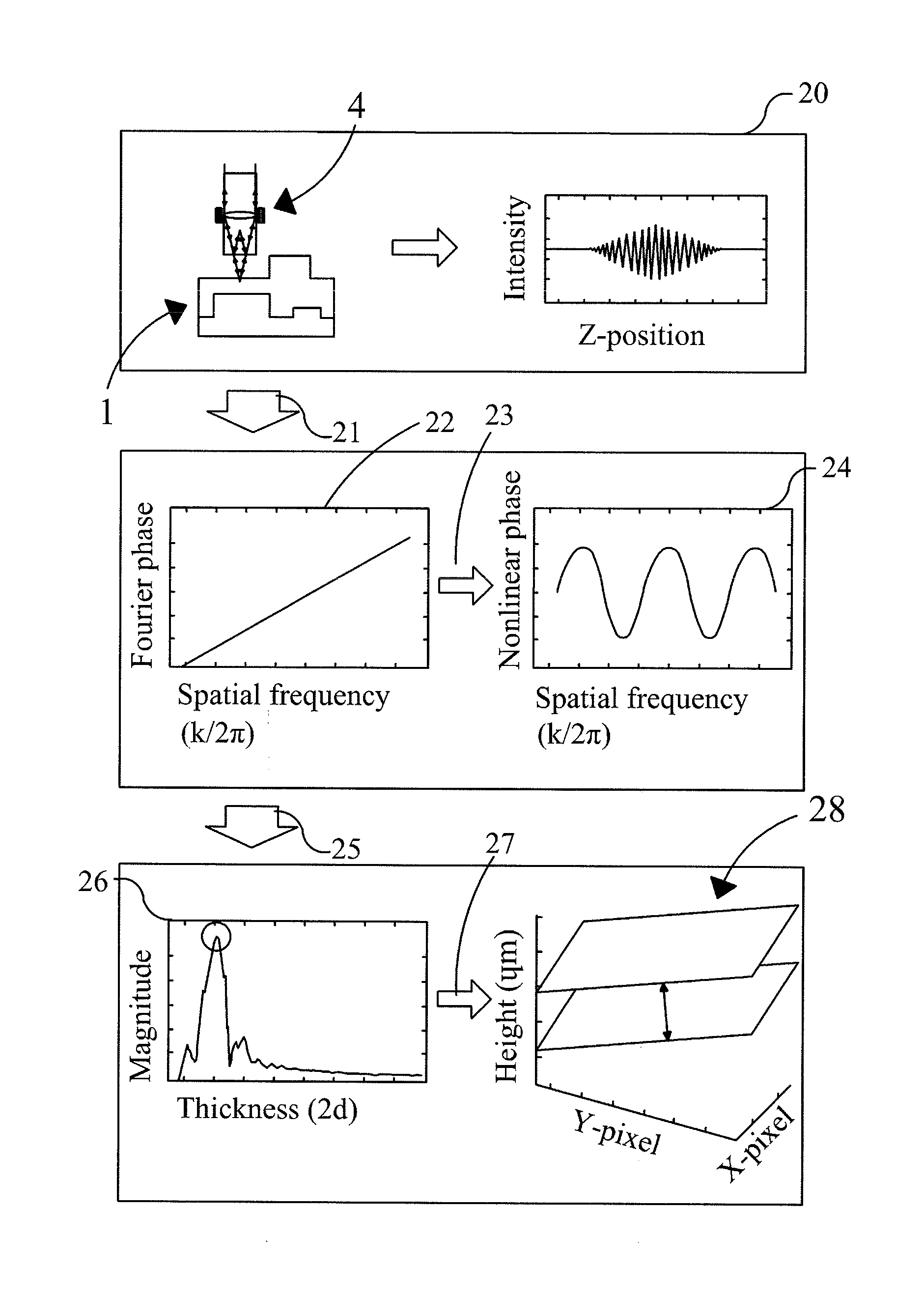
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
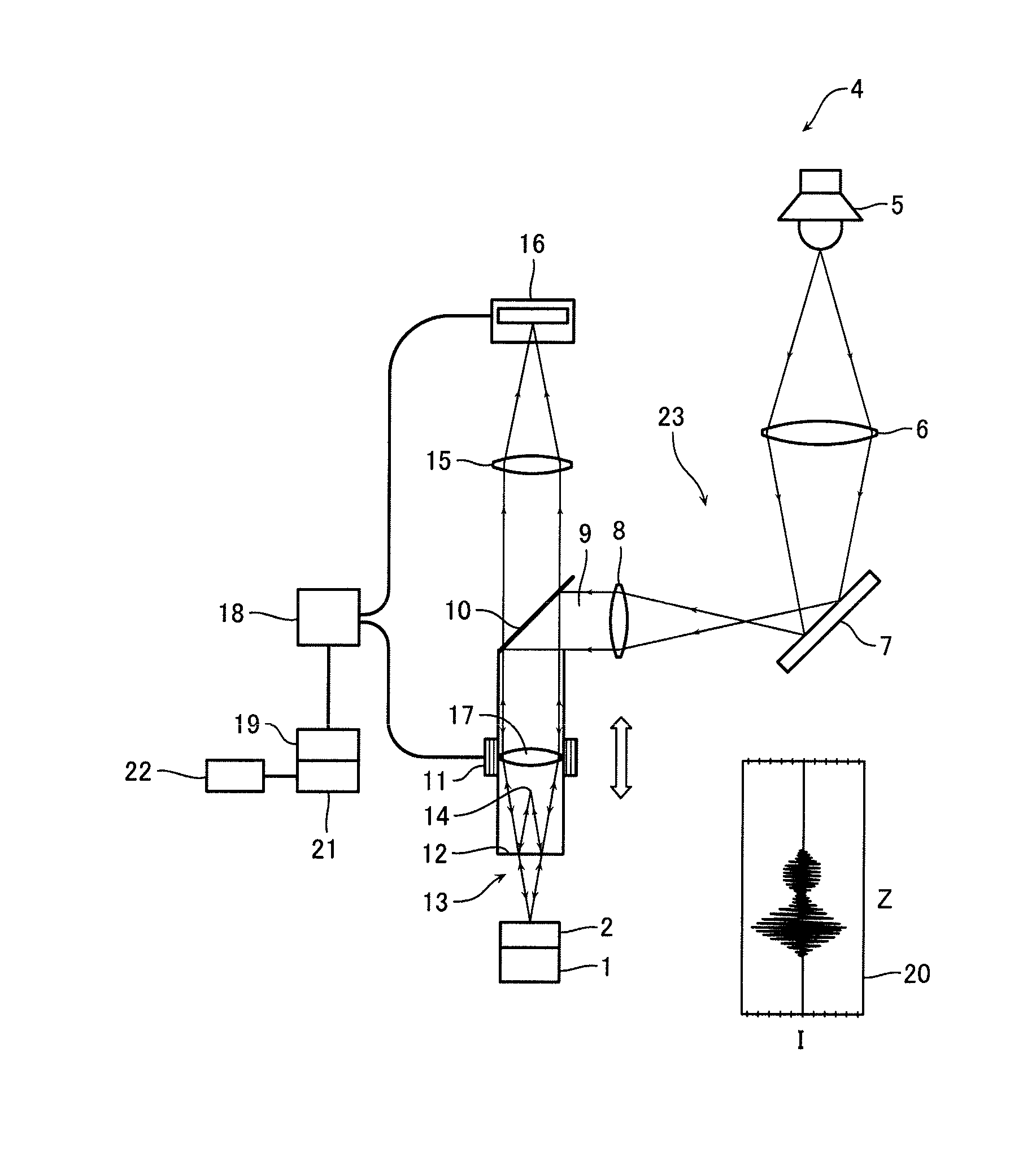
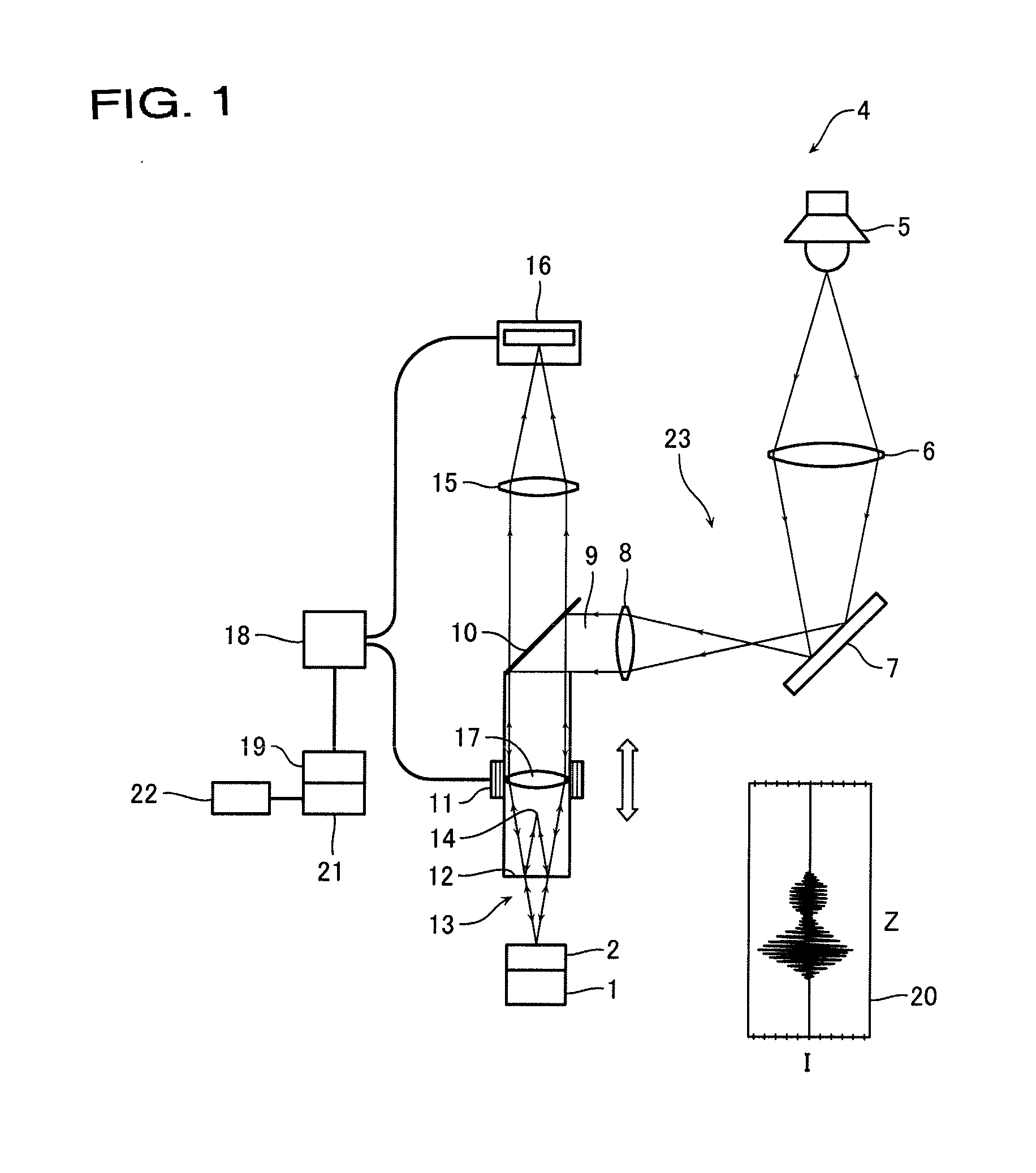
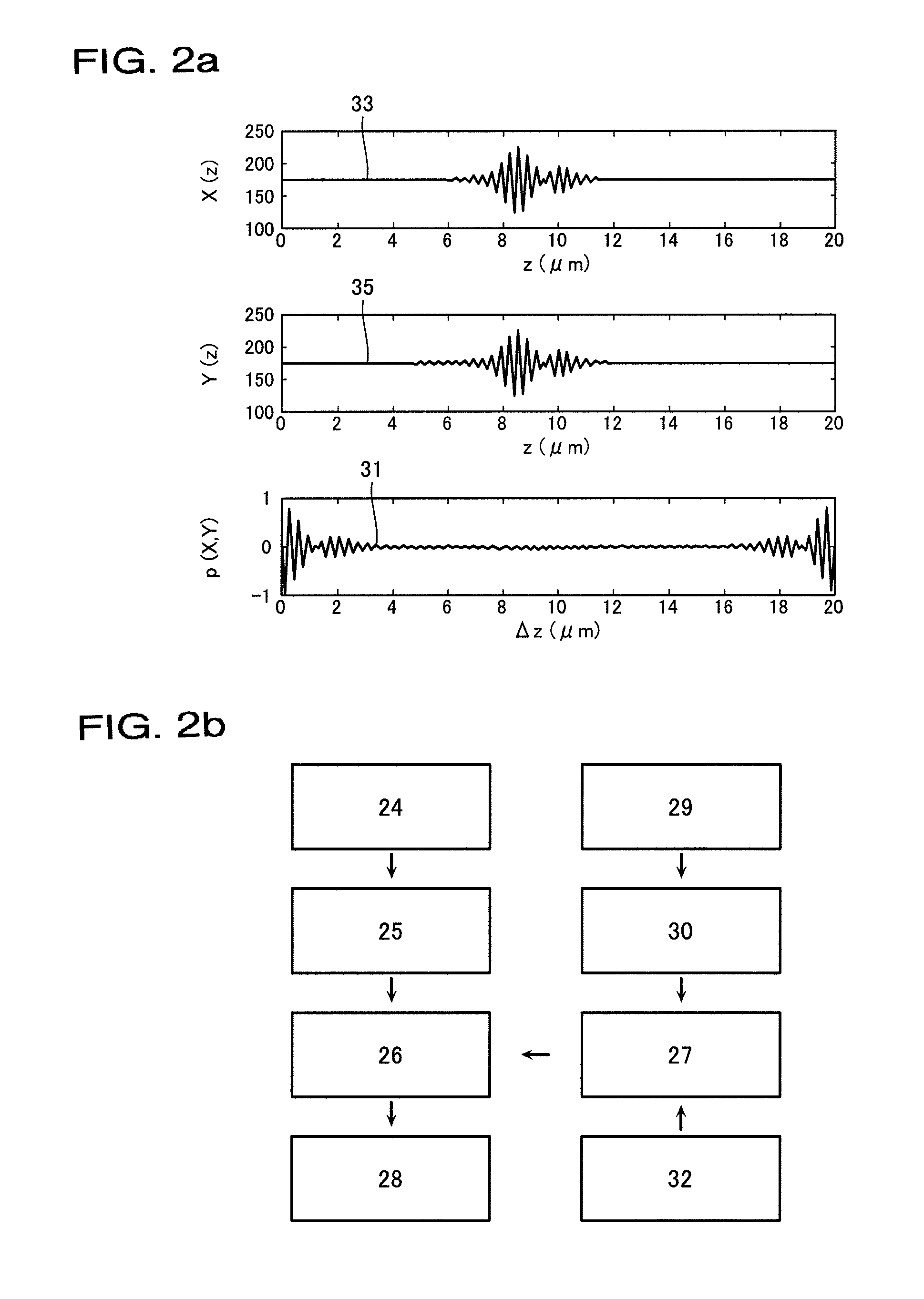
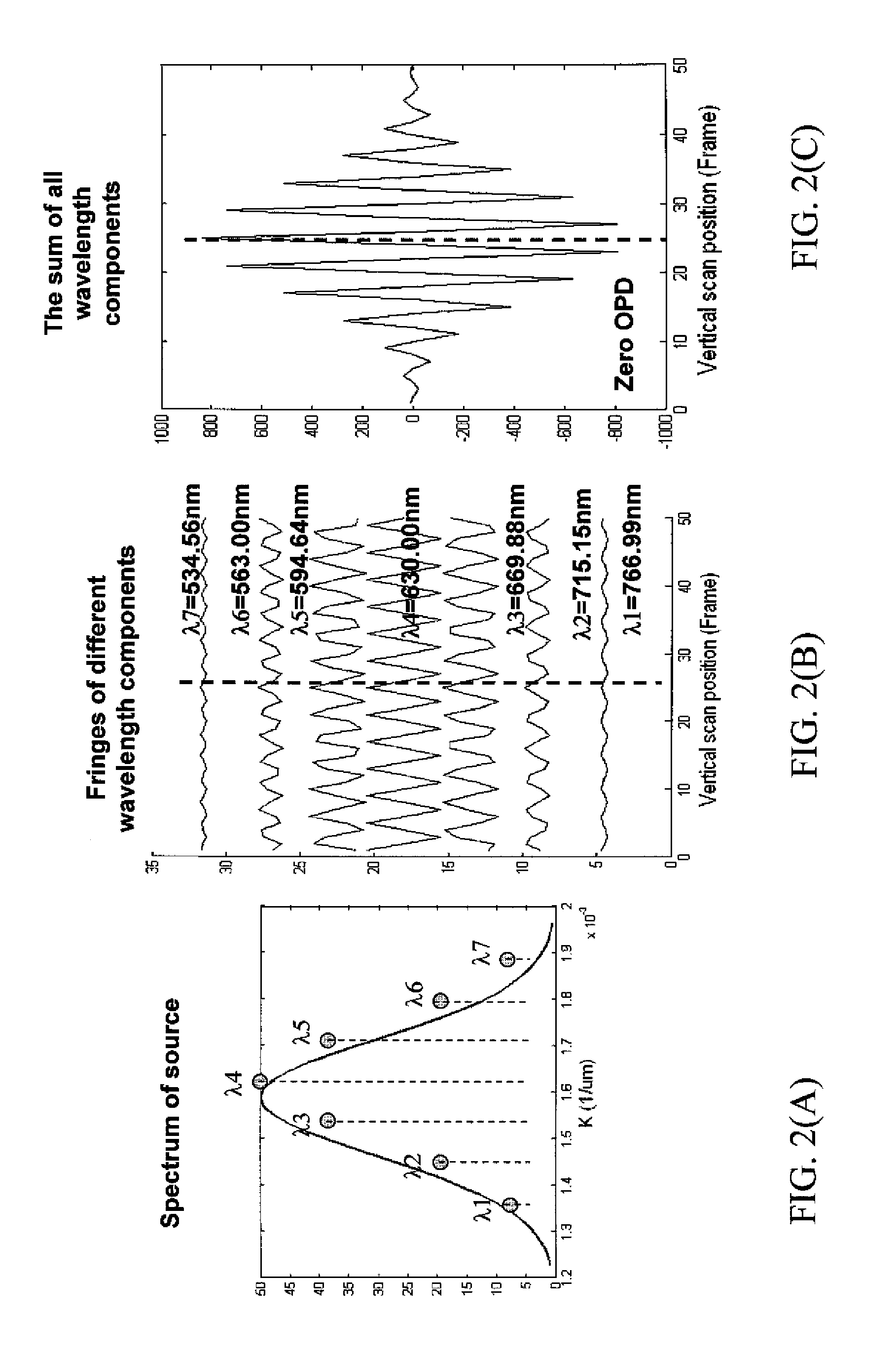
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
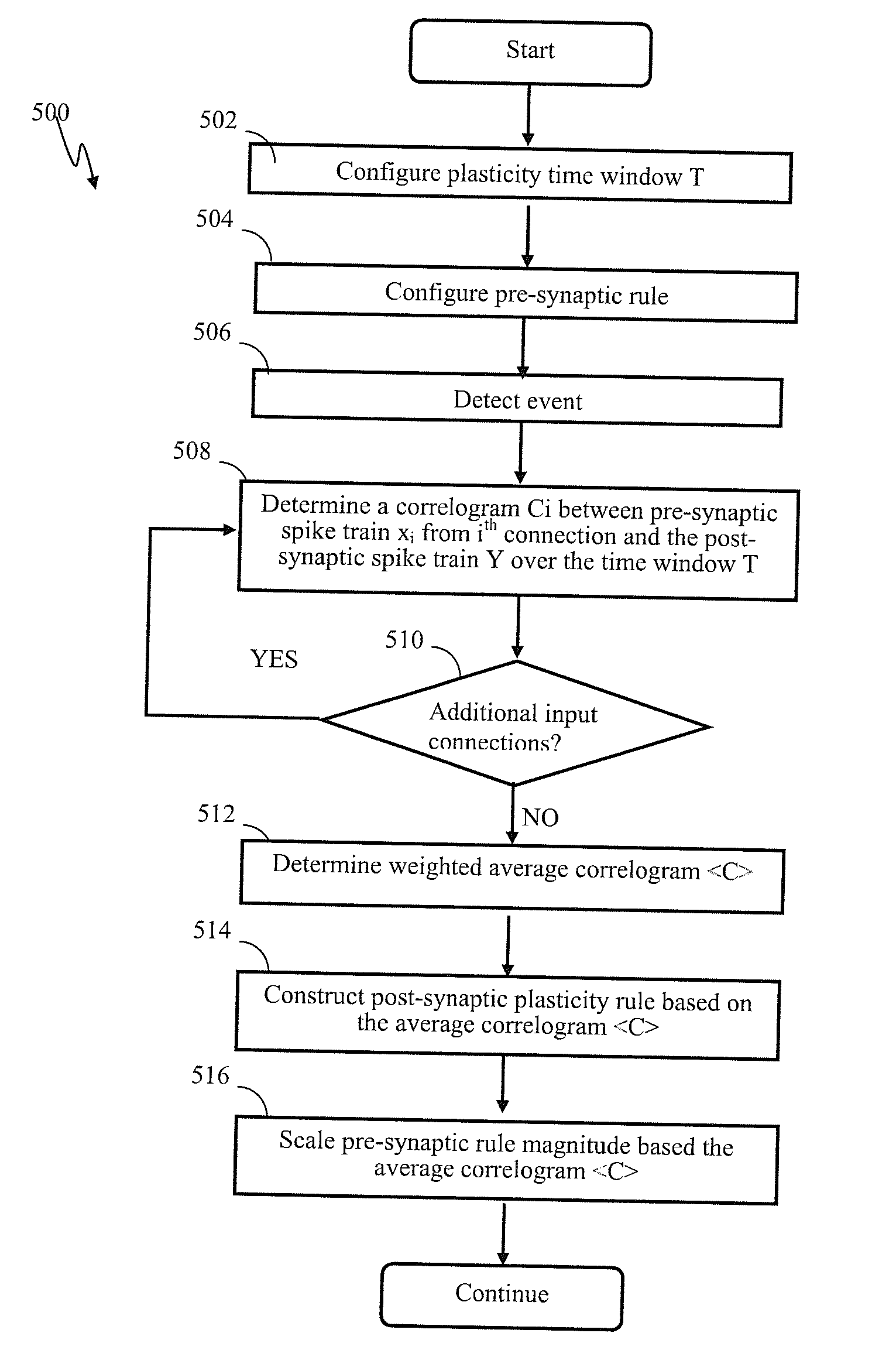
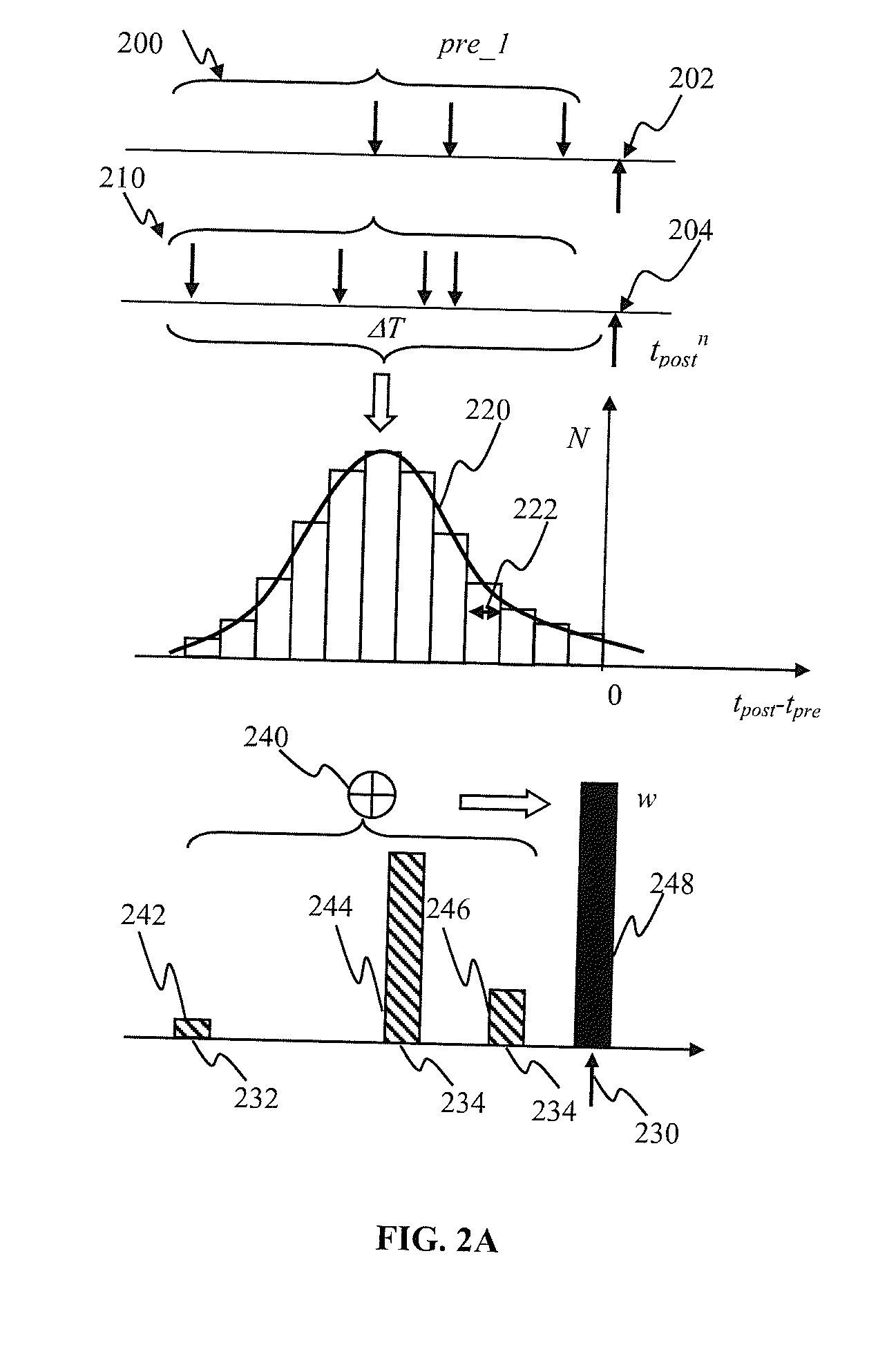
Adaptive plasticity apparatus and methods for spiking neuron network
ActiveUS9183493B2Improve academic performanceDigital data processing detailsNeural architecturesSynapseSpike train
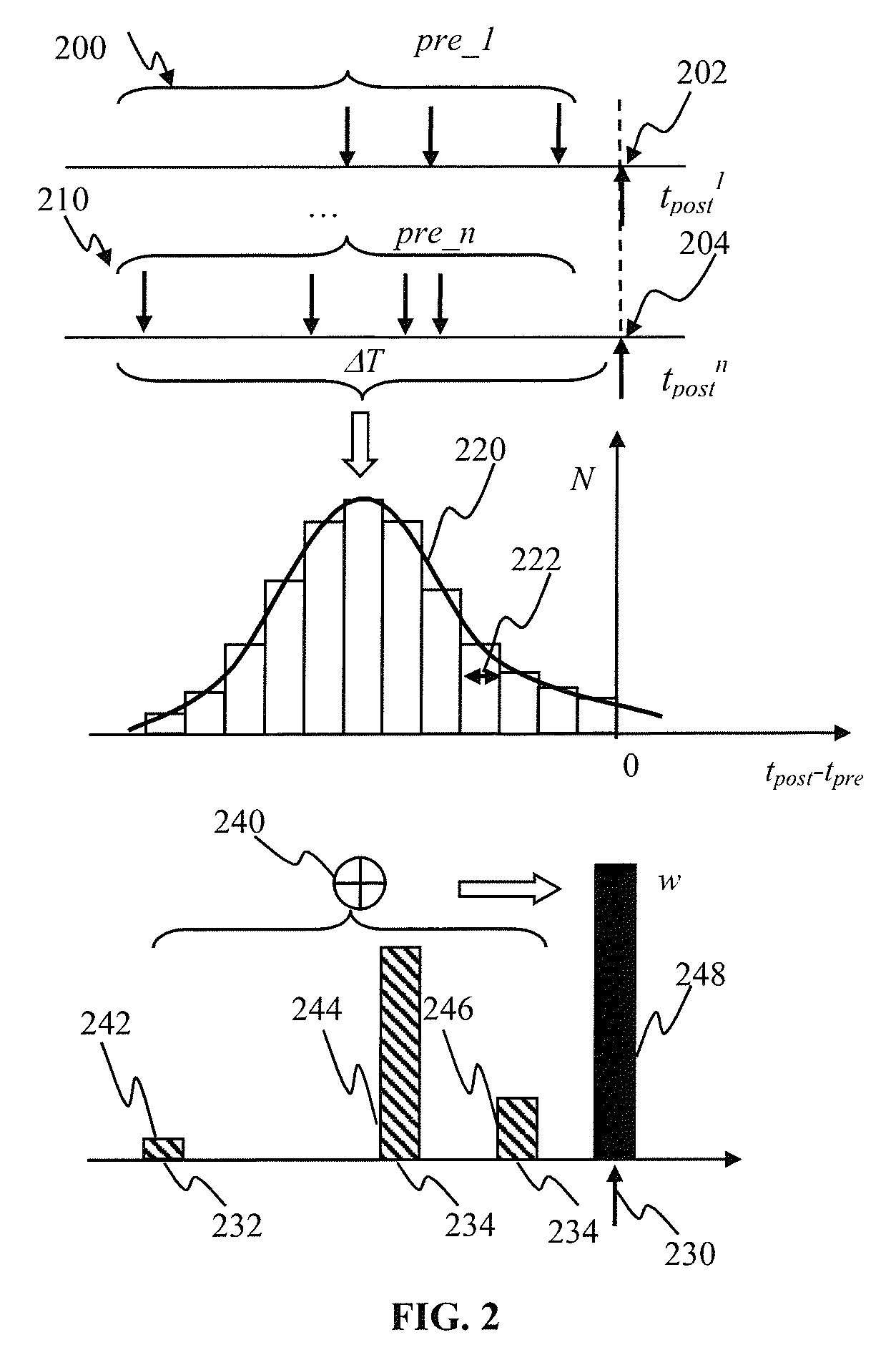
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in a spiking neuron network. In one implementation, a plasticity mechanism is configured based on a similarity measure between neuron post-synaptic and pre-synaptic activity. The similarity measure may comprise a cross-correlogram between the output spike train and input spike train, determined over a plasticity window. Several correlograms, corresponding to individual input connections delivering pre-synaptic input, may be combined. The combination may comprise for example a weighted average. The averaged correlograms may be used to construct the long term potentiation component of the plasticity. The long term depression component of the plasticity may comprise e.g., a monotonic function based on a statistical parameter associated with the adaptively determined long term potentiation component.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
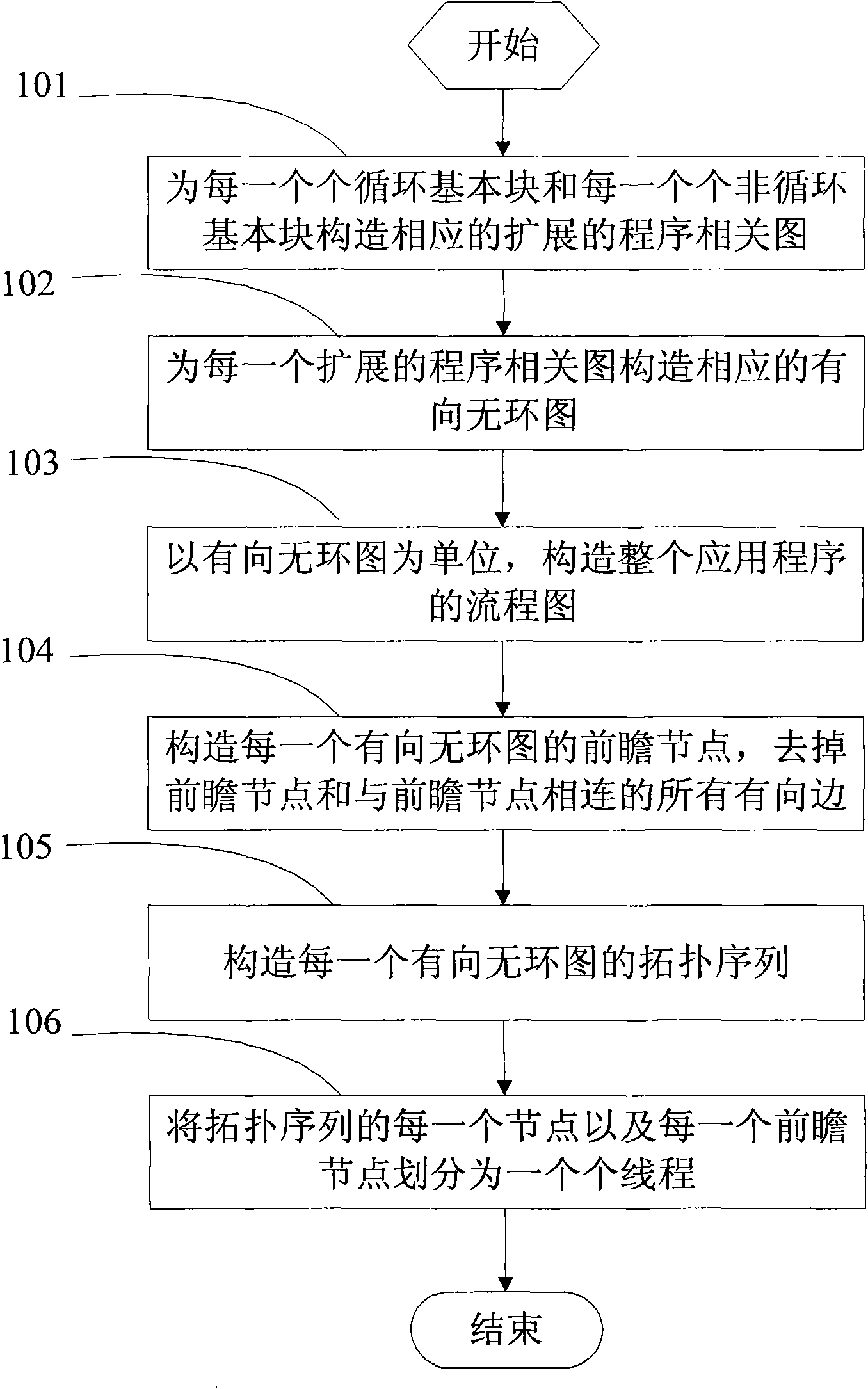
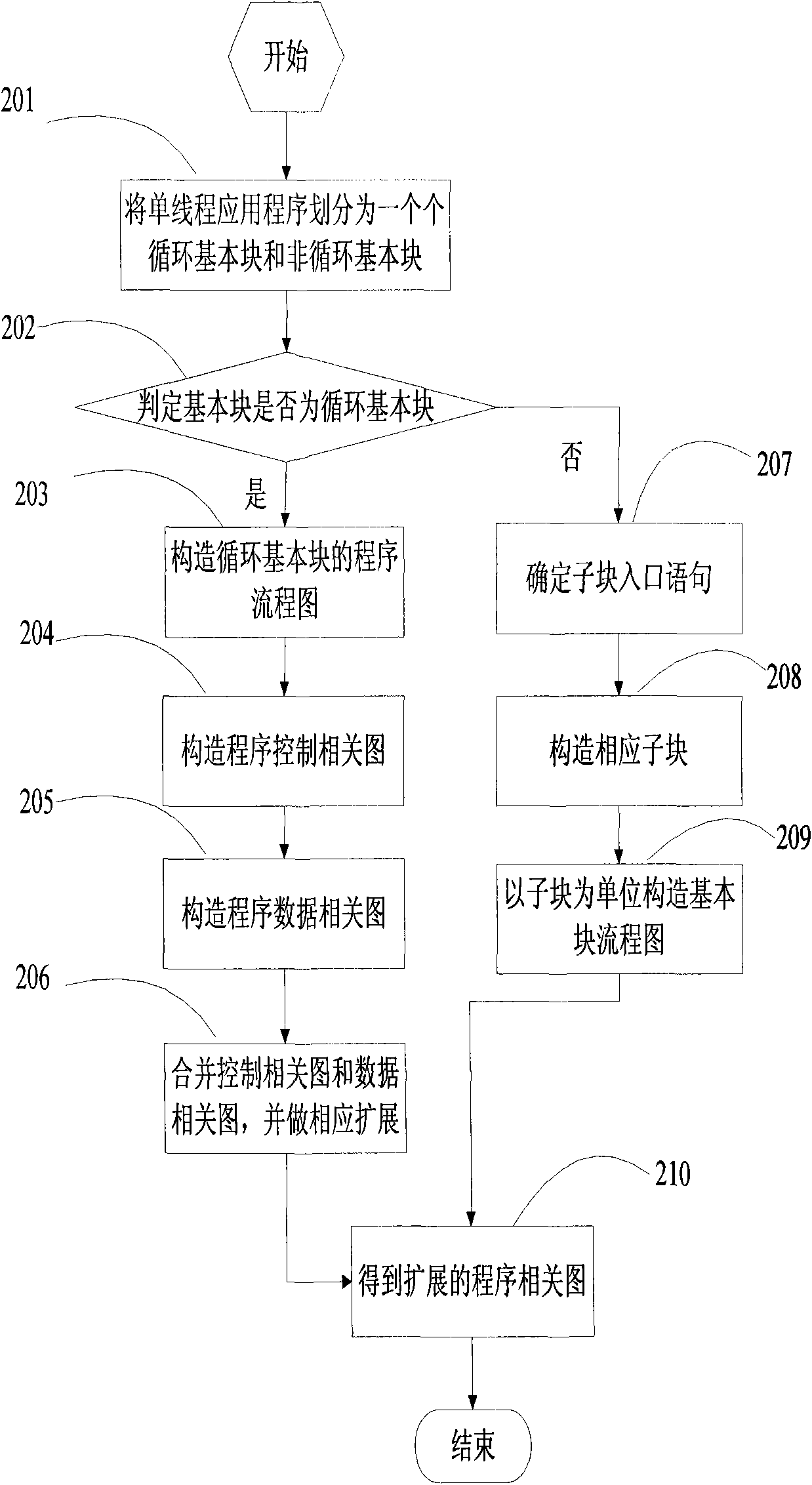
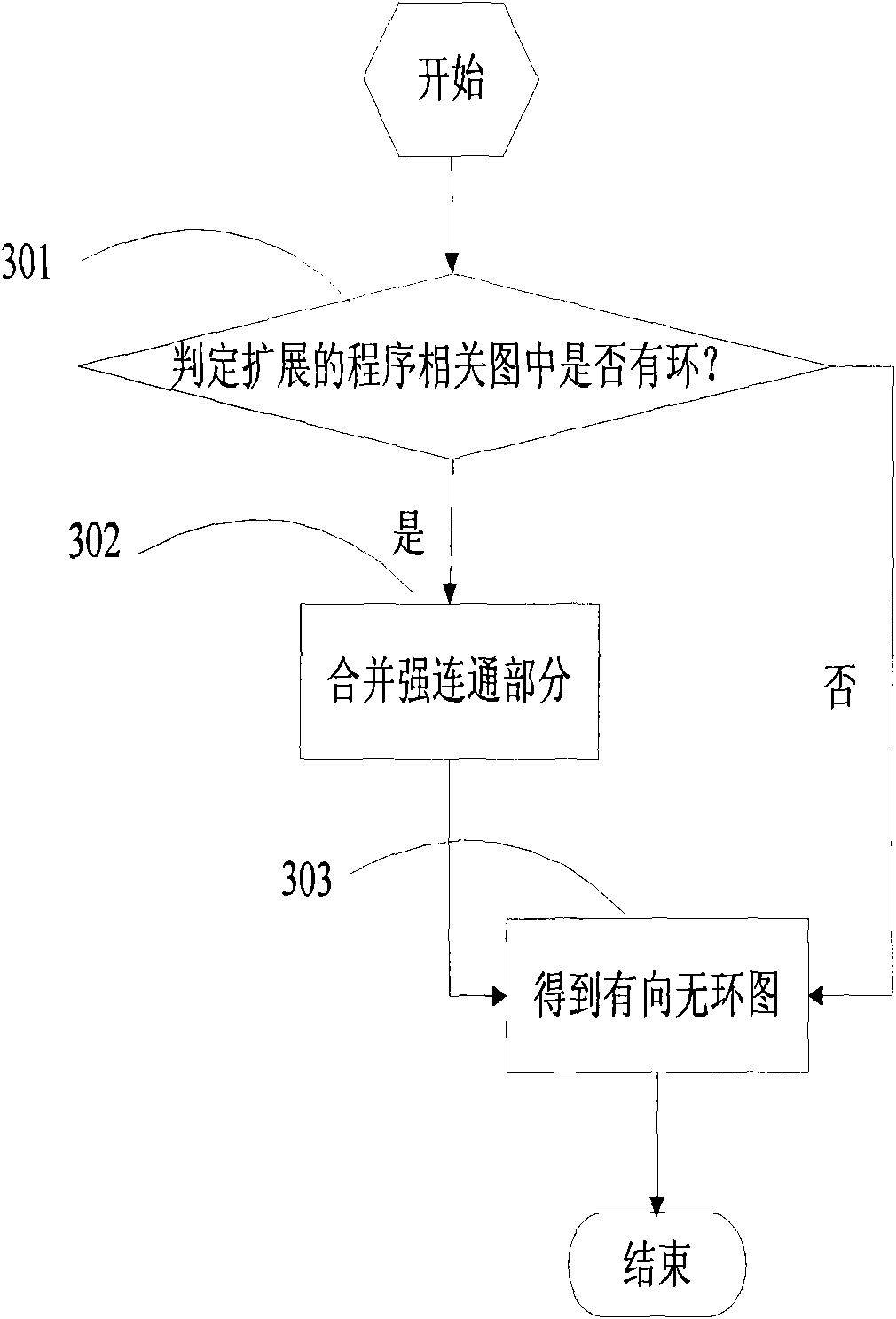
Forward-looking multithreading partitioning method
InactiveCN101655783AFast executionIncrease profitConcurrent instruction executionTopological orderTopological sorting
The invention discloses a forward-looking multithreading partitioning method, comprising the following steps: constructing a corresponding expanding program correlogram for each loop statement basic block and each non loop statement basic block in a single threading application program; designing a corresponding directed acyclic graph for each expanding program correlogram; designing a forward-looking node for each directed acyclic graph, and removing the node from the directed acyclic graph; performing topological sorting for each directed acyclic graph; at last, partitioning forward-lookingmultithreading for a single-chip multi-core processor according to the sequence semantics in the single threading application program and the obtained topological order. The method performs forward-looking multithreading partitioning by the loop statement and the non loop statement, can fully dig control dependency and data dependency in the program, fully utilizes thread-level parallelism, reduces unnecessary delay waiting by forward-looking performing, increases the performing speed of the program on the multi-core processor and improves the utilization ratio of the processor.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Signal sectioning for profiling printed-circuit-bord vias with vertical scanning interferometry
ActiveUS20150103357A1Sufficient lightingMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansSurface roughnessSurface level
The rough bottom surface of a recessed feature partially obscured by an overlying structure is profiled interferometrically with acceptable precision using an objective with sufficiently large numerical aperture to illuminate the bottom under the obscuring structure. The light scattering produced by the roughness of the surface causes diffused light to return to the objective and yield reliable data fringes. Under such appropriate numerical-aperture and surface roughness conditions, the bottom surface of such recessed features can be profiled correctly simply by segmenting the correlograms produced by the scan and processing all fringes that correspond to the bottom surface elevation.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Heterodyne spectrally controlled interferometry
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
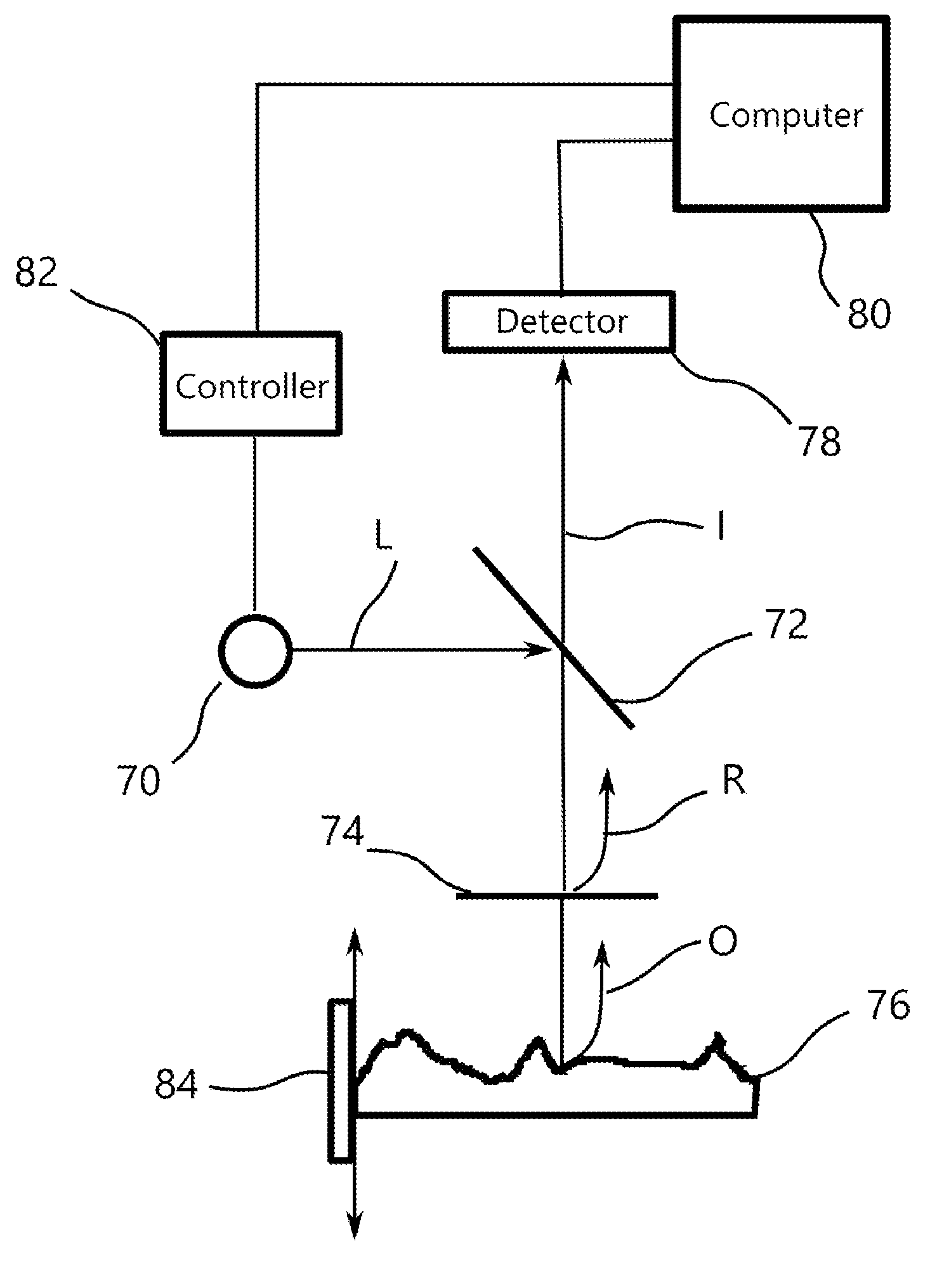
Correlation based adaptive system monitoring
ActiveUS10599545B2Improve monitoring accuracyReduce measurementHardware monitoringMultiple digital computer combinationsData miningSystem monitoring
A method, system and computer program product for adaptive system monitoring. In one embodiment, the method comprises generating time-varying correlation graphs indicating correlations between a multitude of parameters of the system, and using the correlation graphs to identify monitoring logic for monitoring the system. In an embodiment, the correlation graphs are used to select a group of the parameters as monitoring parameters, and these monitoring parameters are dynamically changed. In one embodiment, the monitoring parameters form sets of monitoring parameters, and each set of monitoring parameters is used to monitor the system for an associated period of time. The lengths of these monitoring periods are changed based on the rate of change of the correlation graphs. In an embodiment, the rate at which the monitoring parameters are changed is itself changed based on the rate of change of the correlation graphs.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Time-multiplexed spectrally controlled interferometry
A tunable light source having a temporal coherence length such that interference fringes are detected within the optical path difference of the interferometer is spectrally controlled to produce multiple wavelengths during sequential fractions of the integration time of the detector of the interferometer. The wavelengths are selected so as to produce a visible correlogram at each integration time according to spectrally controlled interferometry (SCI) principles. Such different wavelengths may be produced by stepwise or continuous modulation. The modulation step is repeated sequentially while changing the period of modulation to produce a succession of predetermined spatial patterns of interference fringes, as required for interferometric measurements. The approach enables the practice of SCI with common-path apparatus used for conventional phase shifting, thereby combining the advantages of high-coherence and white-light interferometry.
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
ActiveUS20120218560A1Accurate measurementImprove accuracyUsing optical meansLinear componentAmplitude function
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Heterodyne spectrally controlled interferometry
Heterodyne interferometry is combined with spectrally-controlled interferometry (SCI) to achieve the advantages of both. Phase shifts produced by SCI produce phase-shifted correlograms suitable for heterodyne interferometric analysis, thereby enabling interferometric measurements with conventional common-path apparatus free of coherence noise and scanning-related errors, and with the precision of conventional heterodyne interferometry. A spectrum-modulating light source suitable for the invention is obtained by combining a rotating spiral grating with a multi-slit grating placed in the front focal plane of a collimating lens that propagates the light toward a blazed diffraction grating. Another exemplary spectrum-modulating light source is obtained by combining a slit spectrometer with an acousto-optic modulator.
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
Method and apparatus for determining a property of a surface
ActiveUS20130335747A1Method is fastSure easyPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansUltimate tensile strengthInterferometry
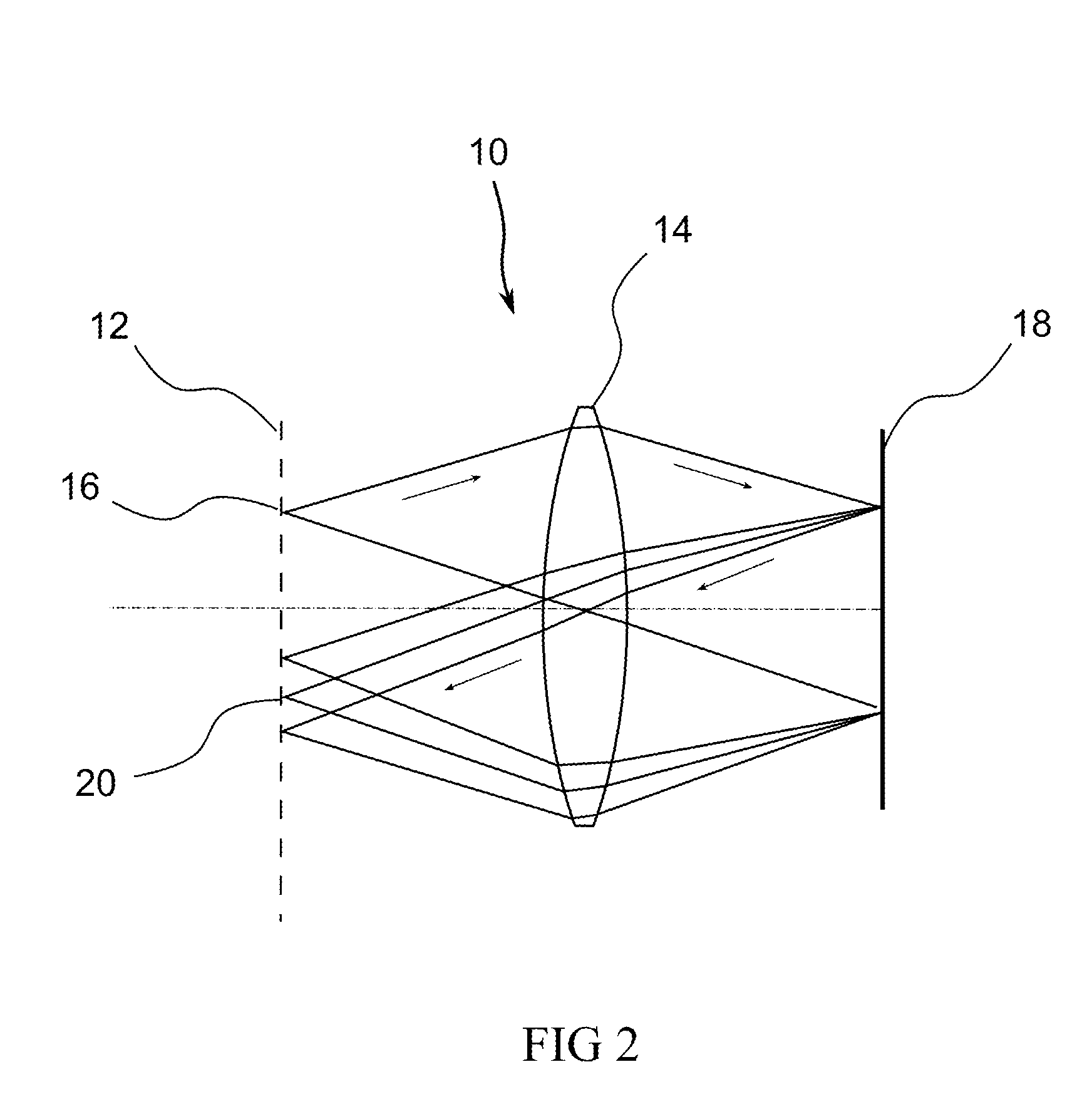
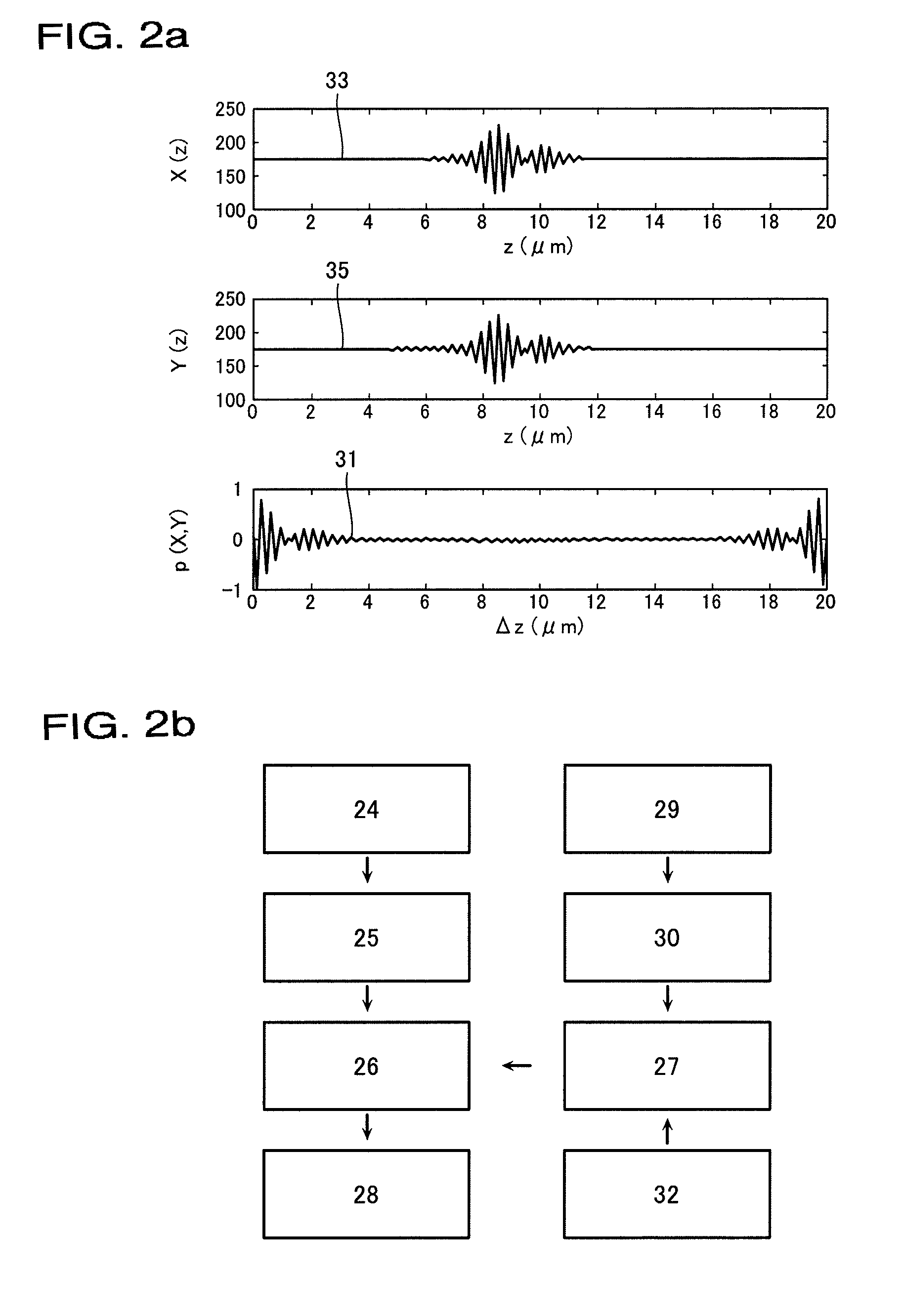
Method of determining a property of a sample from a correlogram obtainable by scanning of a surface of the sample through a focal plane of an objective using broad-band interferometry is provided. The correlogram may be displaying interference radiation intensity as a function of the scanning distance from the surface. The correlogram may be correlated with a secondary correlogram to obtain a cross correlogram or with the same correlogram to obtain an autocorrelogram. A property of the sample may be determined from the auto or cross correlogram.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
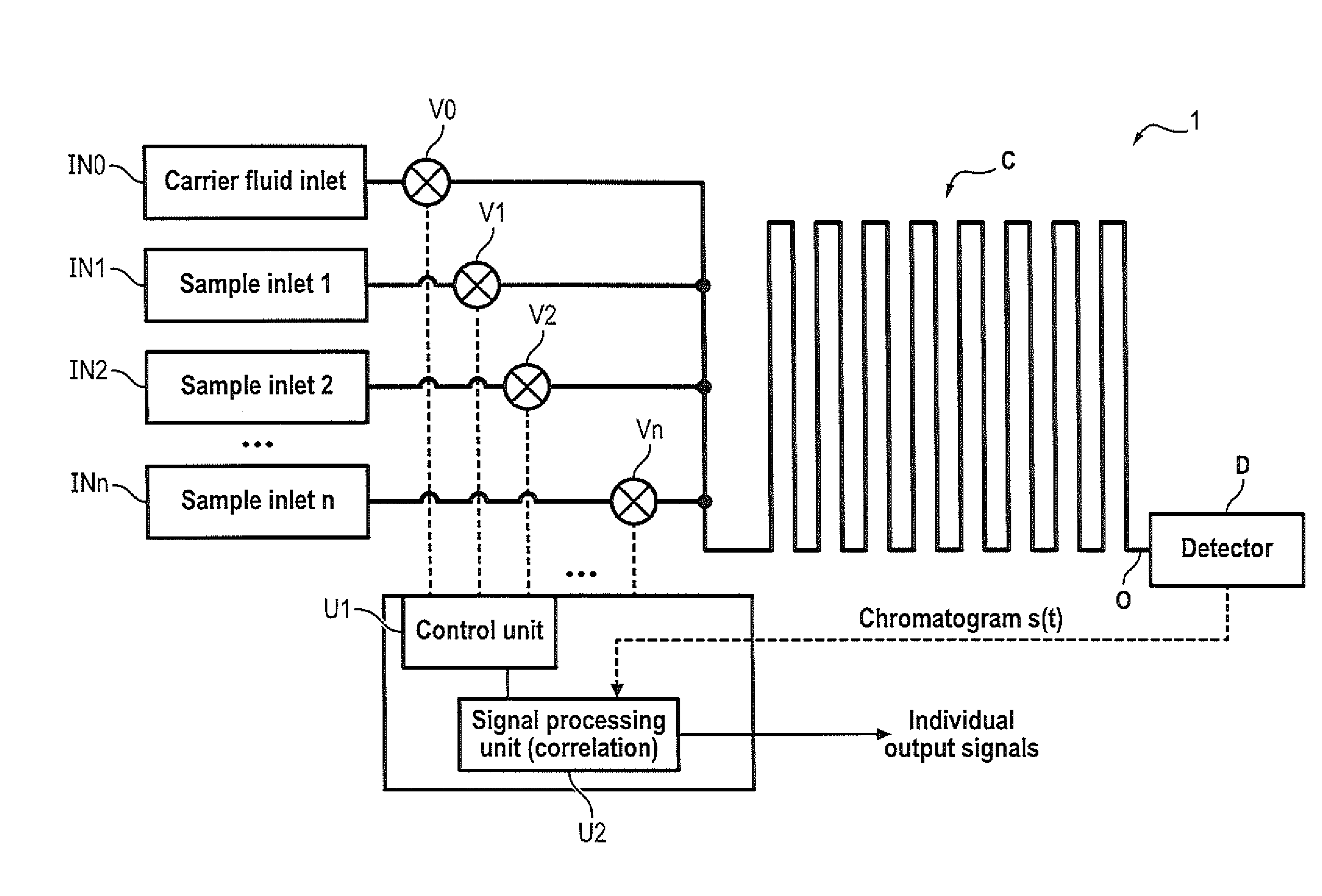
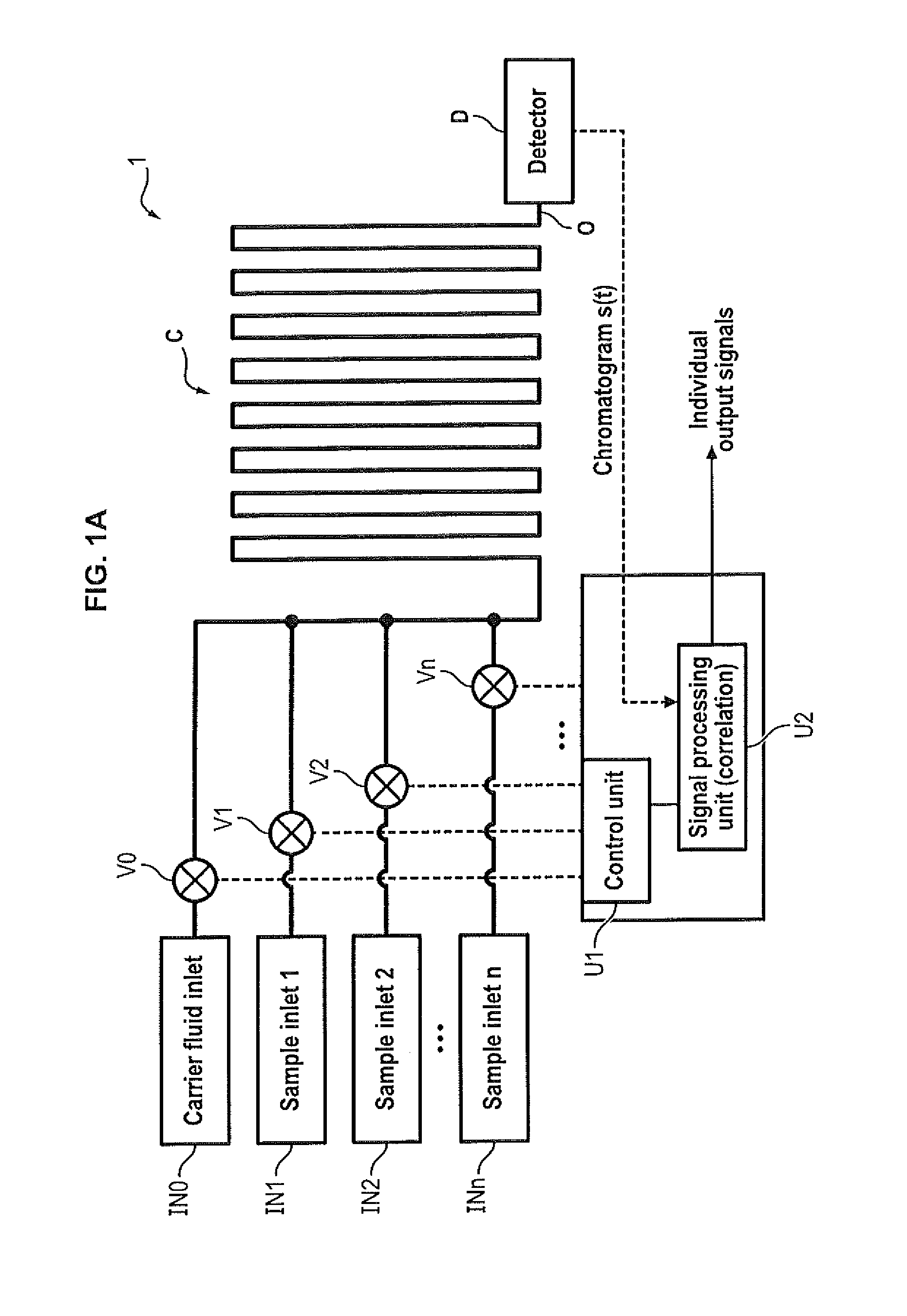
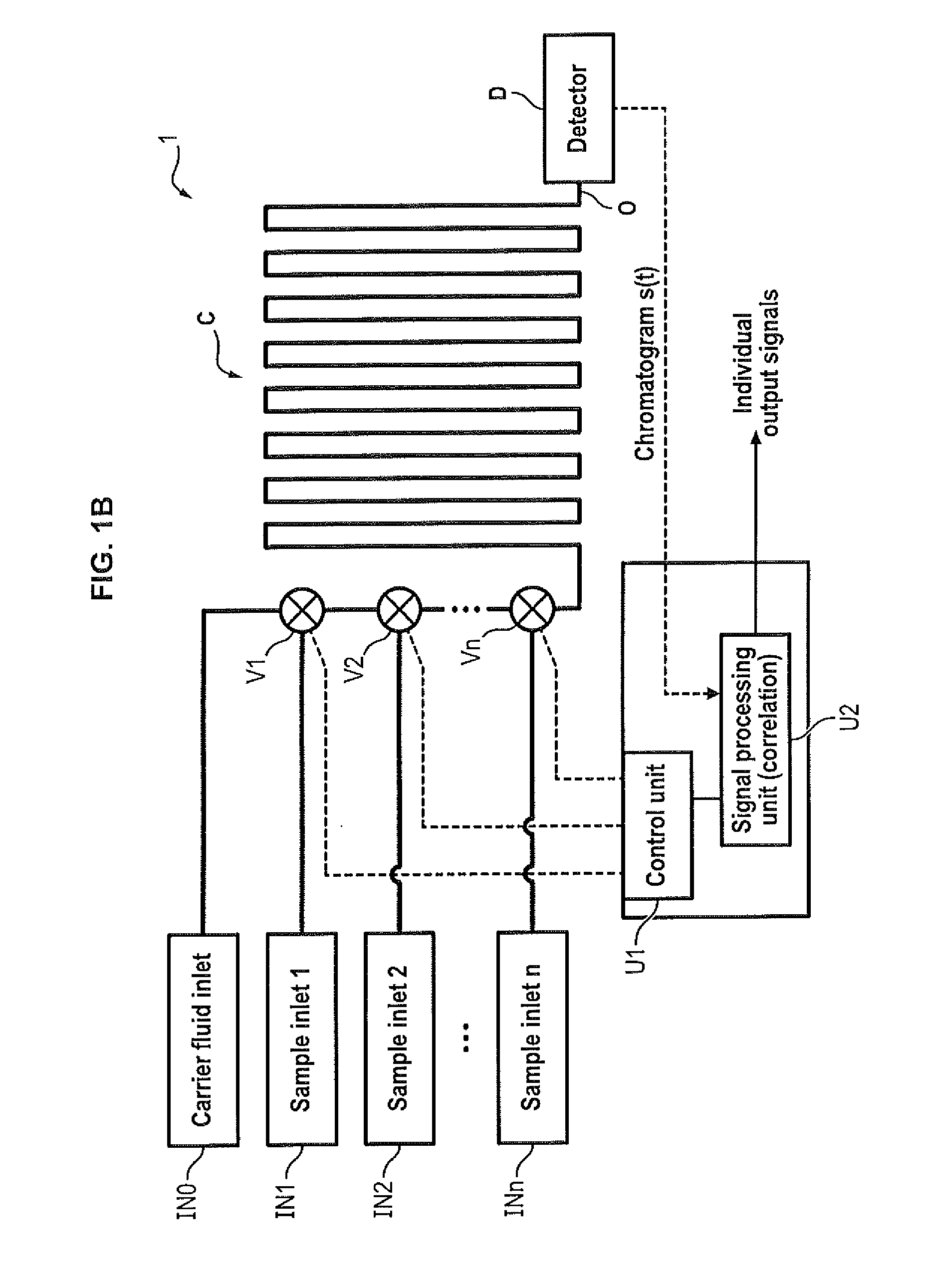
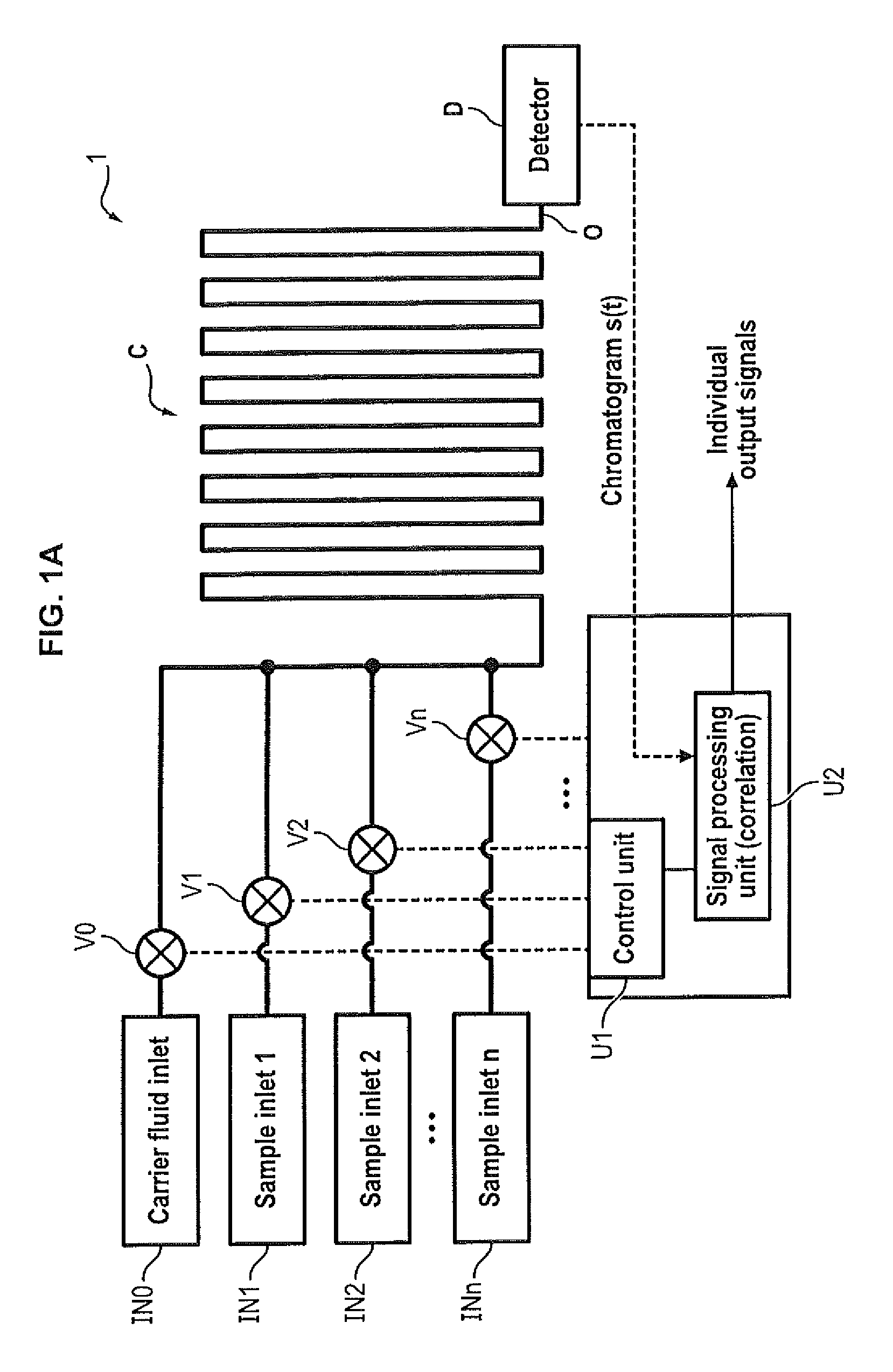
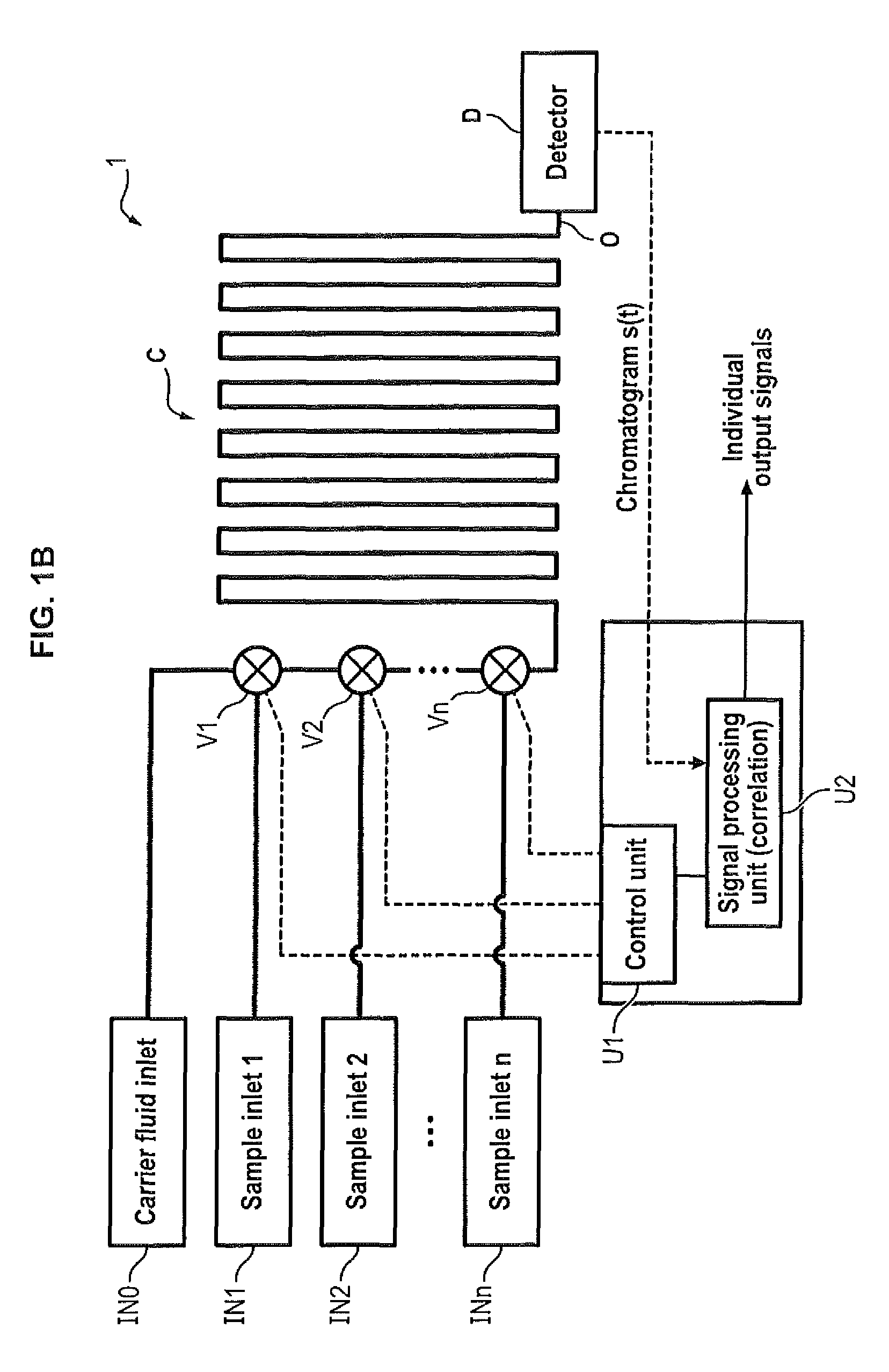
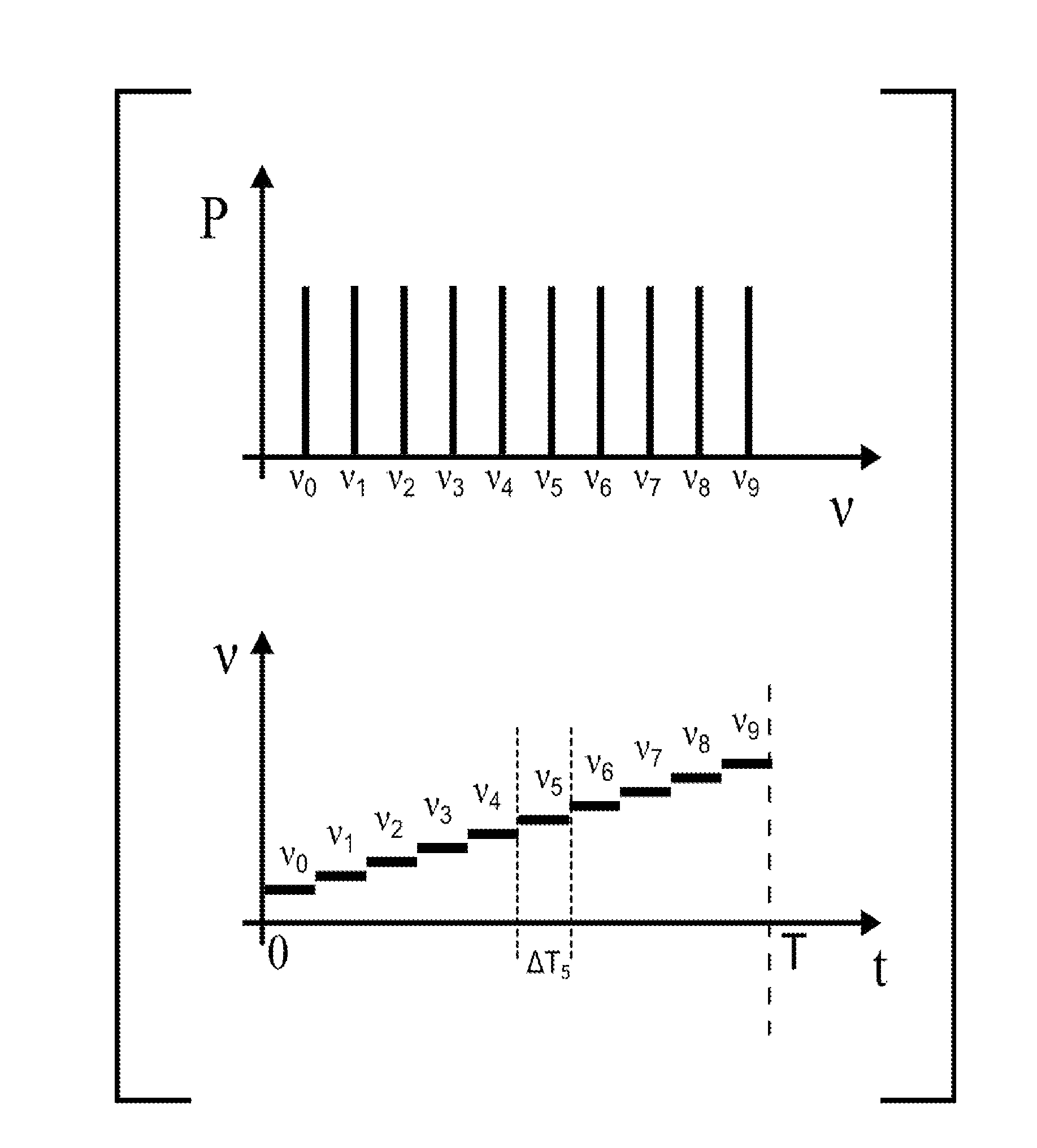
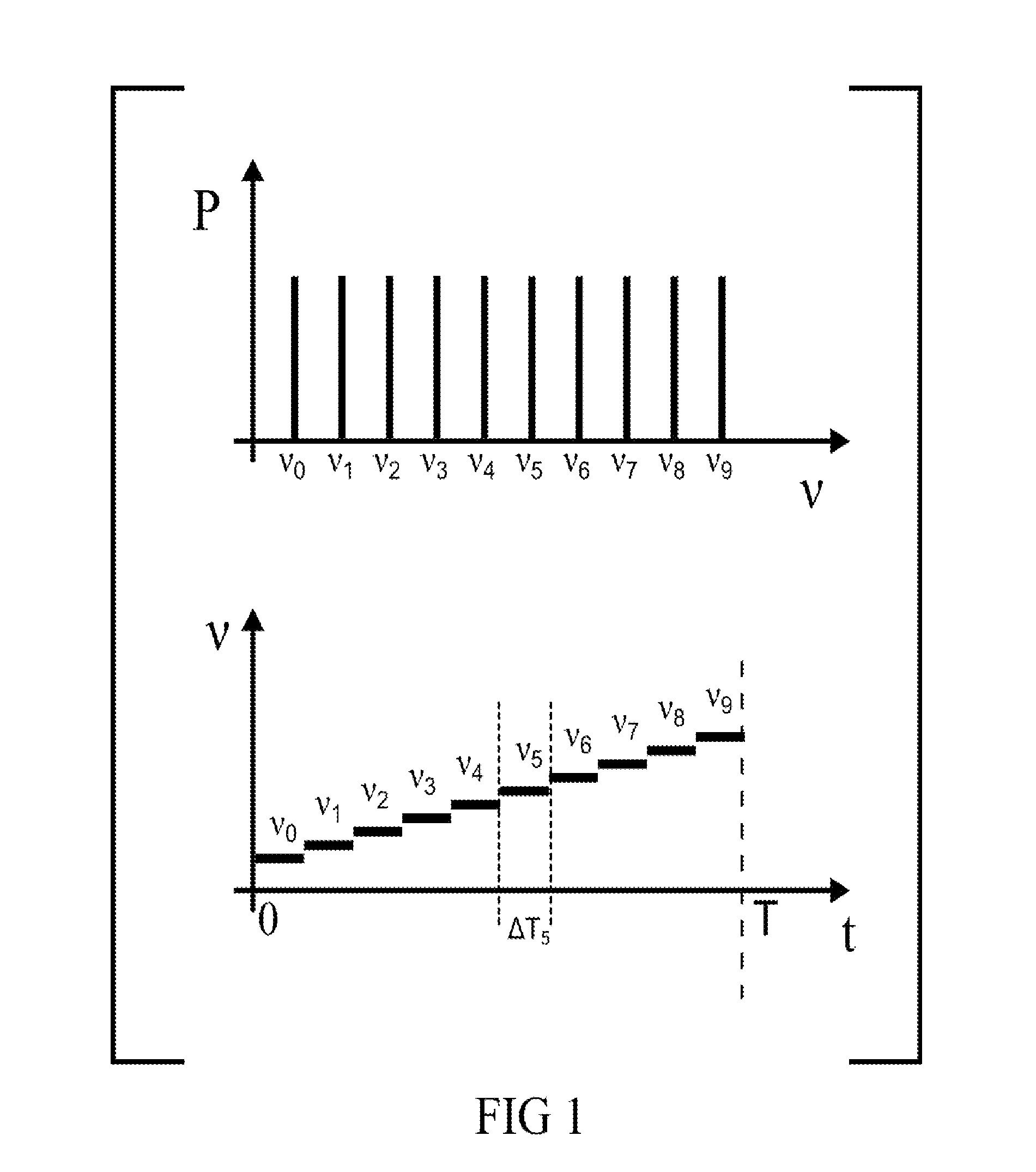
Multiple sample chromatography using a stochastic injection technique
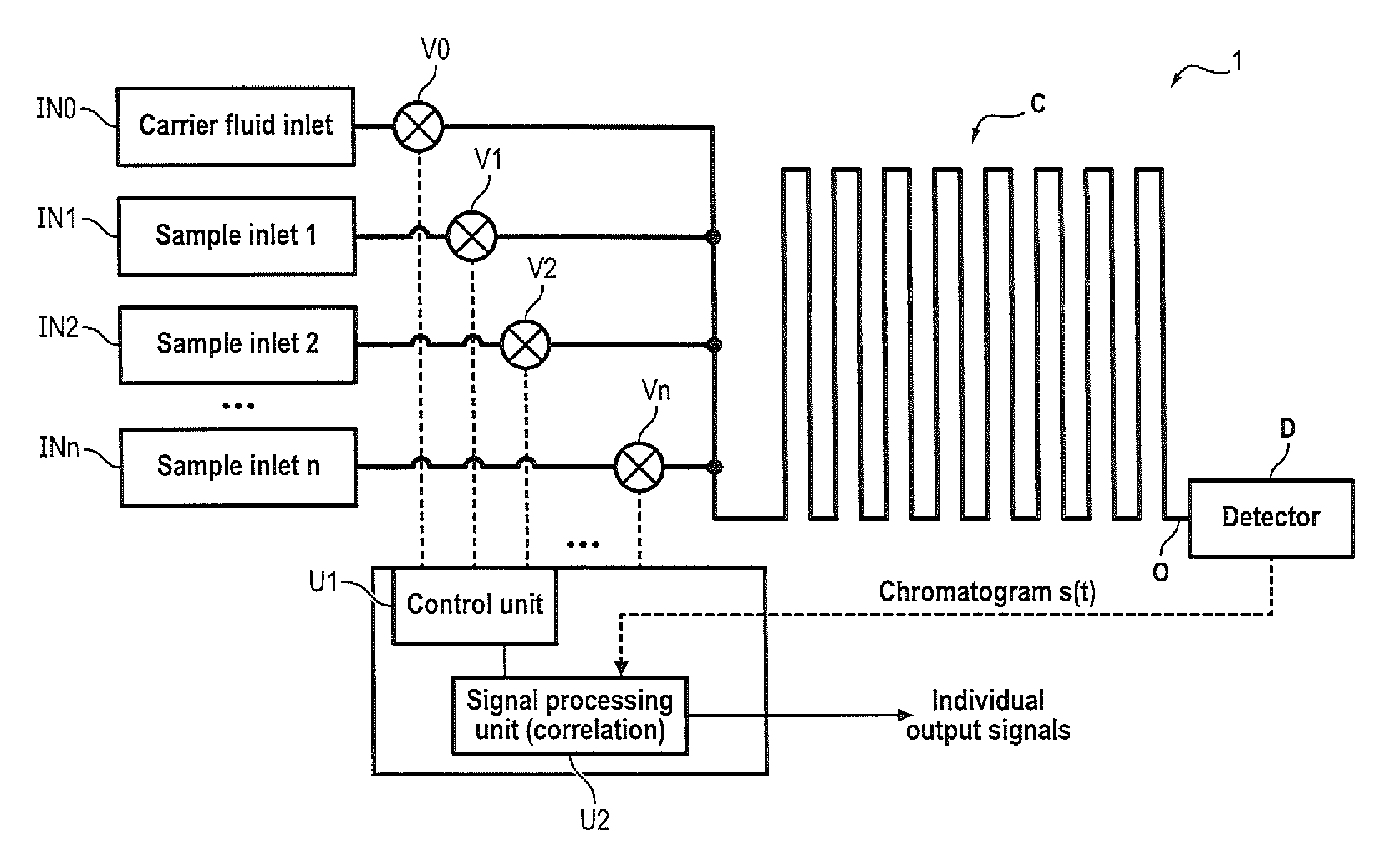
ActiveUS20150204825A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove accuracySamplingComponent separationCorrelation functionChromatography column
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously analyzing at least two samples using a chromatography device comprising a chromatography column having an inlet and an outlet, and at least one detector placed at the outlet of the chromatography column, the method comprising steps of: injecting fractions of each independent sample at the inlet of the chromatography column, the fractions of each independent sample being injected according to a specific injection timing sequence derived from a pseudo-random binary sequence associated with said independent sample; recording a signal generated by said detector for a period of time at least equal to a duration of the longest of the specific injection timing sequences; cross-correlating the recorded signal and a derived correlation function, said derived correlation function being derived from the pseudo-random binary sequence associated with one of the independent samples, so as to obtain an individual correlogram signal specific to said independent sample; and analyzing data of interest of the individual correlogram signal so as to obtain an output signal indicative of a composition of the sample.
Owner:INSTITUT FR DES SCI & TECH DES TRANSPORTS DE LAMENAGEMENT & DES RESEAUX +1
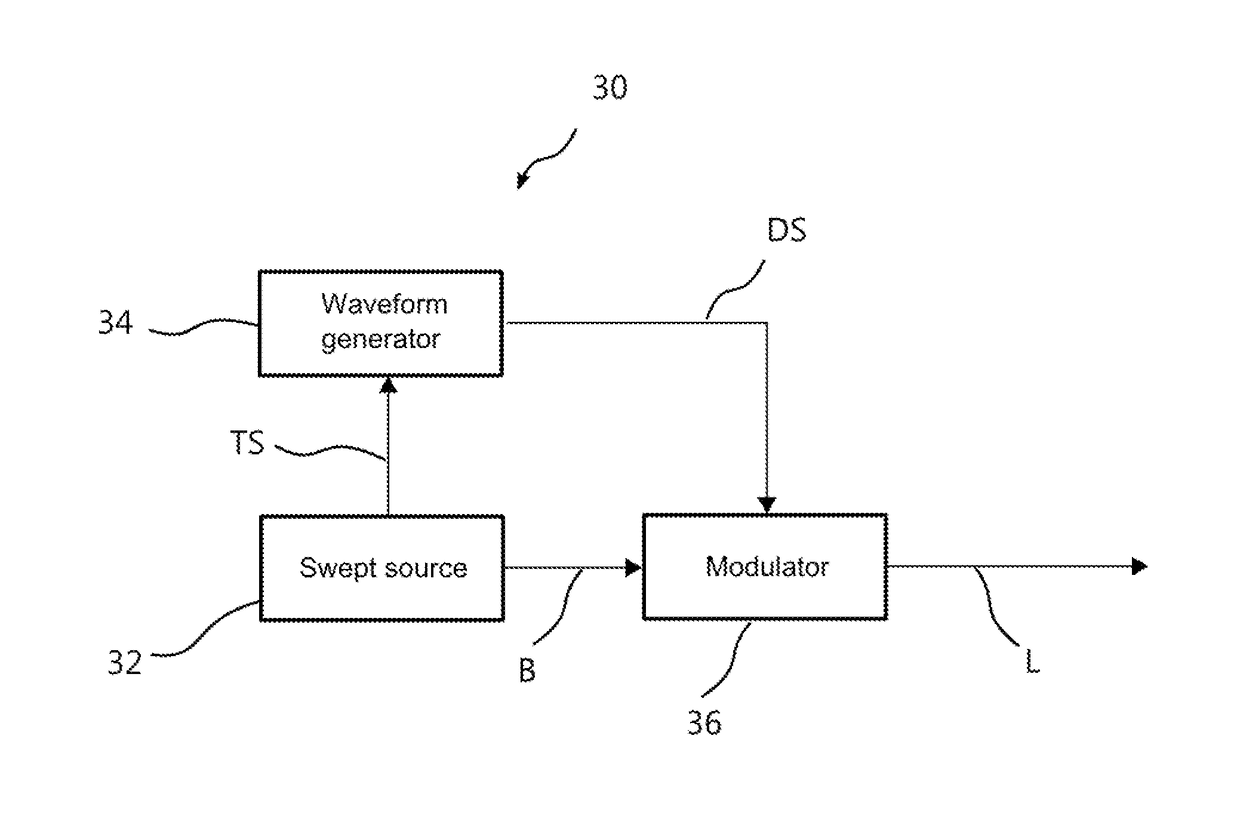
Time-multiplexed spectrally controlled interferometry
ActiveUS9696211B2Optical measurementsUsing optical meansWhite light interferometryOptical pathlength
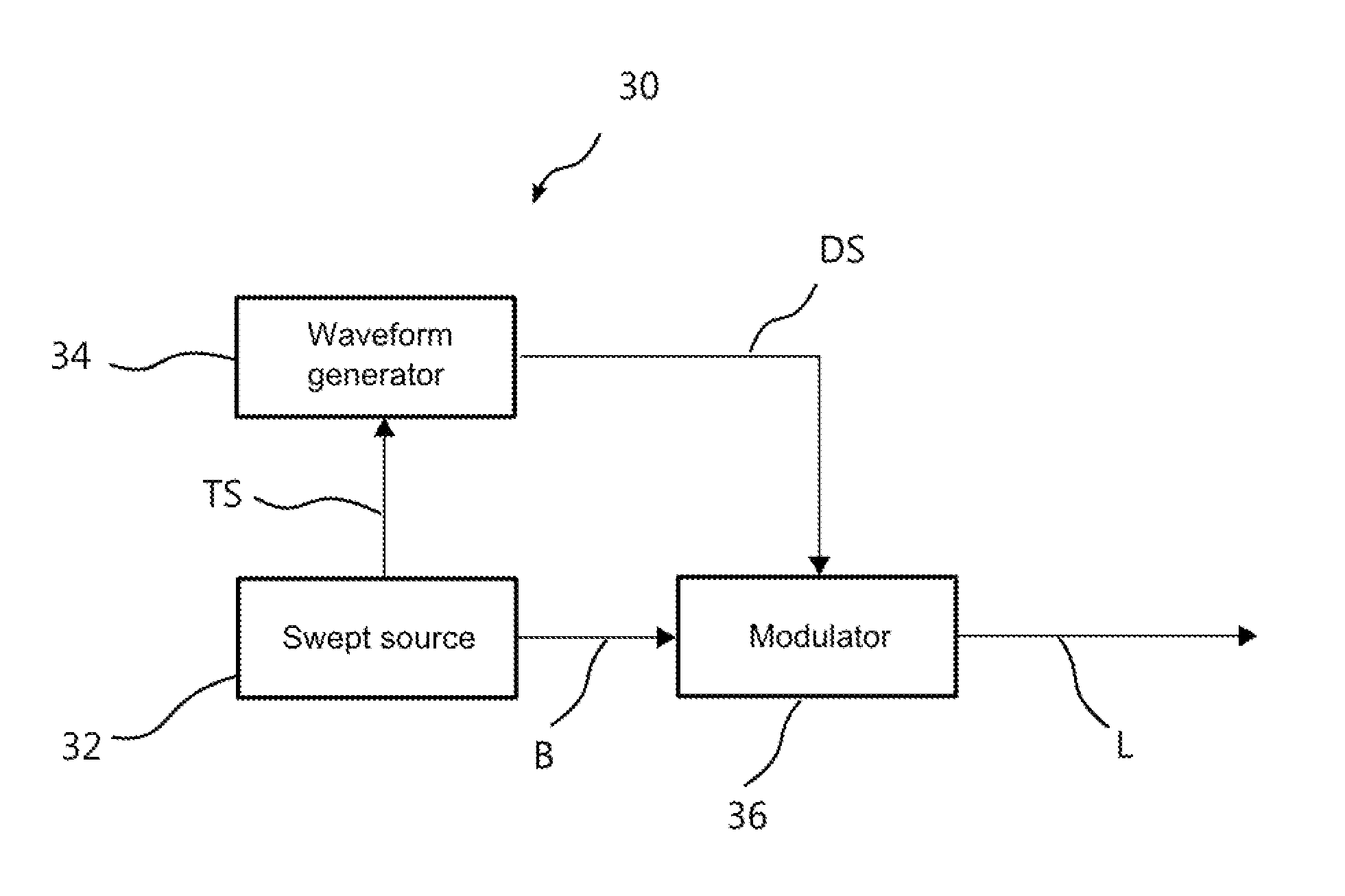
A tunable light source having a temporal coherence length such that interference fringes are detected within the optical path difference of the interferometer is spectrally controlled to produce multiple wavelengths during sequential fractions of the integration time of the detector of the interferometer. The wavelengths are selected so as to produce a visible correlogram at each integration time according to spectrally controlled interferometry (SCI) principles. Such different wavelengths may be produced by stepwise or continuous modulation. The modulation step is repeated sequentially while changing the period of modulation to produce a succession of predetermined spatial patterns of interference fringes, as required for interferometric measurements. The approach enables the practice of SCI with common-path apparatus used for conventional phase shifting, thereby combining the advantages of high-coherence and white-light interferometry. A suitable time-modulated source combines a coherent source with an optical modulator and a waveform generator synchronized with the source.
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
Method and apparatus for determining a property of a surface
ActiveUS9103651B2Method is fastSure easyPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansInterferometryBroad band
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Time-multiplexed spectrally controlled interferometry
A tunable light source having a temporal coherence length such that interference fringes are detected within the optical path difference of the interferometer is spectrally controlled to produce multiple wavelengths during sequential fractions of the integration time of the detector of the interferometer. The wavelengths are selected so as to produce a visible correlogram at each integration time according to spectrally controlled interferometry (SCI) principles. Such different wavelengths may be produced by stepwise or continuous modulation. The modulation step is repeated sequentially while changing the period of modulation to produce a succession of predetermined spatial patterns of interference fringes, as required for interferometric measurements. The approach enables the practice of SCI with common-path apparatus used for conventional phase shifting, thereby combining the advantages of high-coherence and white-light interferometry. A suitable time-modulated source combines a coherent source with an optical modulator and a waveform generator synchronized with the source.
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
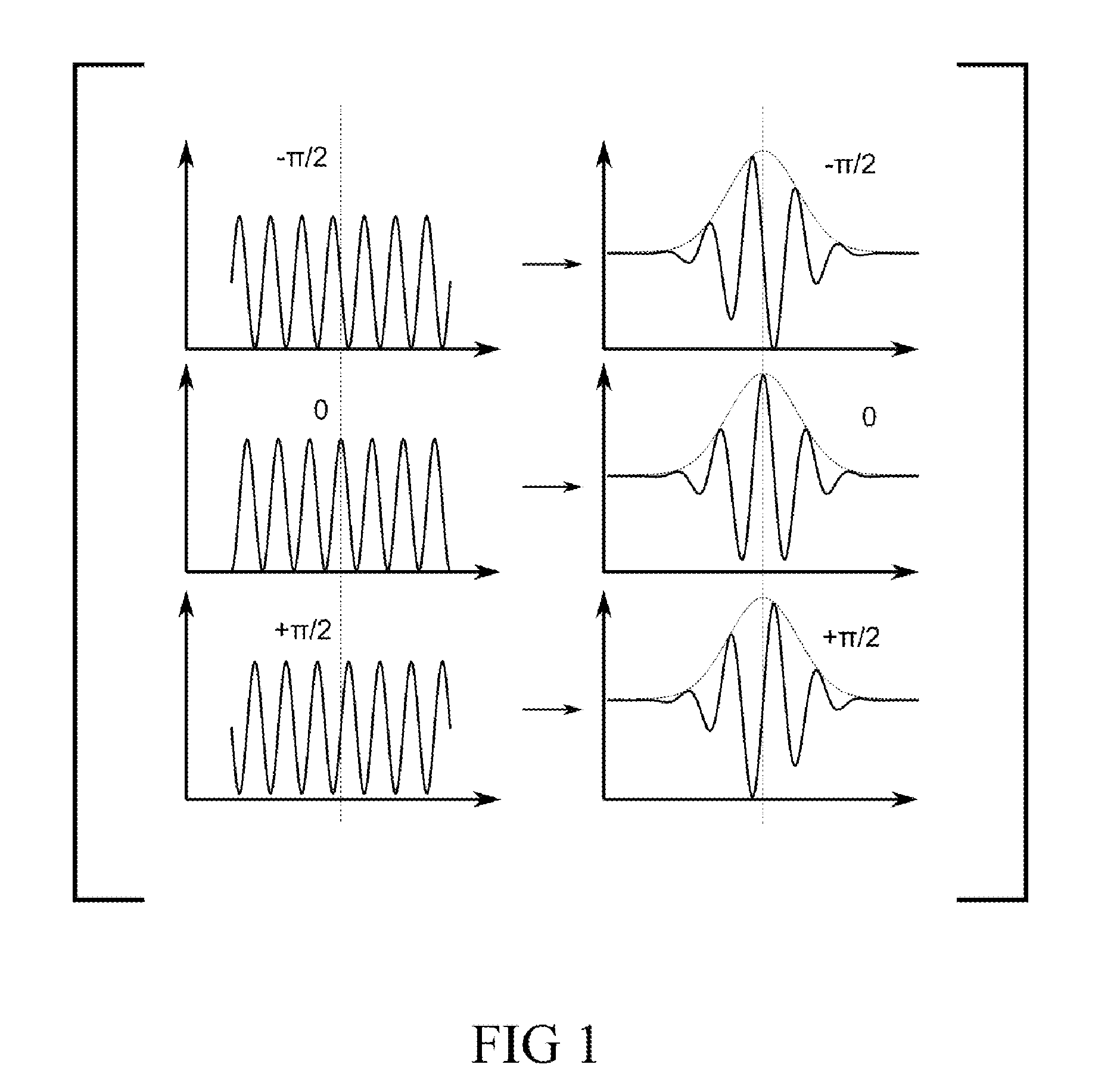
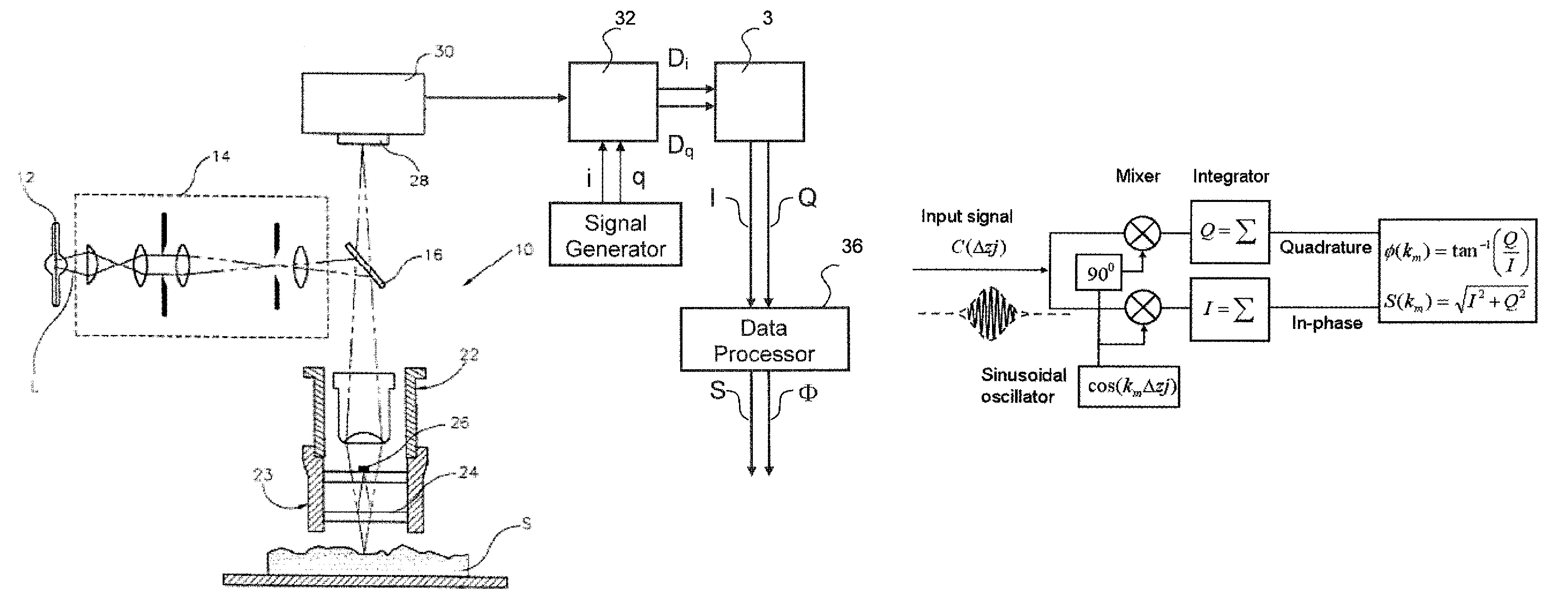
In-phase/in-quadrature demodulator for spectral information of interference signal
ActiveUS7864327B1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumQuadrature modulation
Sinusoidal in-phase and in-quadrature signals at a given spatial frequency are combined with the irradiance signals generating a correlogram of interest and integrated over the length of the correlogram data-acquisition scan. The integration outputs are then used to calculate the amplitude and the phase of the correlogram signal at the selected spatial frequency, thereby producing targeted spectral information. The signal generator used to generate the in-phase and in-quadrature sinusoidal signals may be scanned advantageously through any desired range of spatial frequencies, thereby producing corresponding amplitude and phase spectral information for the correlogram. Because the procedure produces spectral information independently of the number of data frames acquired during the interferometric scan, it is materially more rapid than conventional FFT analysis.
Owner:VEECO METROLOGY
Multiple sample chromatography using a stochastic injection technique
ActiveUS9322812B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove accuracyComponent separationCorrelation functionChromatography column
Owner:INSTITUT FR DES SCI & TECH DES TRANSPORTS DE LAMENAGEMENT & DES RESEAUX +1
Time-multiplexed spectrally controlled interferometry
A tunable light source having a temporal coherence length such that interference fringes are detected within the optical path difference of the interferometer is spectrally controlled to produce multiple wavelengths during sequential fractions of the integration time of the detector of the interferometer. The wavelengths are selected so as to produce a visible correlogram at each integration time according to spectrally controlled interferometry (SCI) principles. Such different wavelengths may be produced by stepwise or continuous modulation. The modulation step is repeated sequentially while changing the period of modulation to produce a succession of predetermined spatial patterns of interference fringes, as required for interferometric measurements. The approach enables the practice of SCI with common-path apparatus used for conventional phase shifting, thereby combining the advantages of high-coherence and white-light interferometry.
Owner:OLSZAK ARTUR
Signal sectioning for profiling printed-circuit-board vias with vertical scanning interferometry
The bottom surface of a via drilled in a fiber-reinforced PCB is profiled interferometrically with acceptable precision using an objective with sufficiently large numerical aperture to illuminate the bottom under the fibers. The light scattering produced by the inherent roughness of the surface of the via bottom causes diffused light to return to the objective and yield reliable data fringes. Under such appropriate numerical-aperture and surface roughness conditions, the bottom surface of vias can be profiled correctly simply by segmenting the correlograms produced by the scan and processing all fringes that correspond to the bottom surface elevation.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
ActiveUS8804129B2Increase speedFast processingSpectral/fourier analysisPhase-affecting property measurementsAmplitude functionLinear component
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
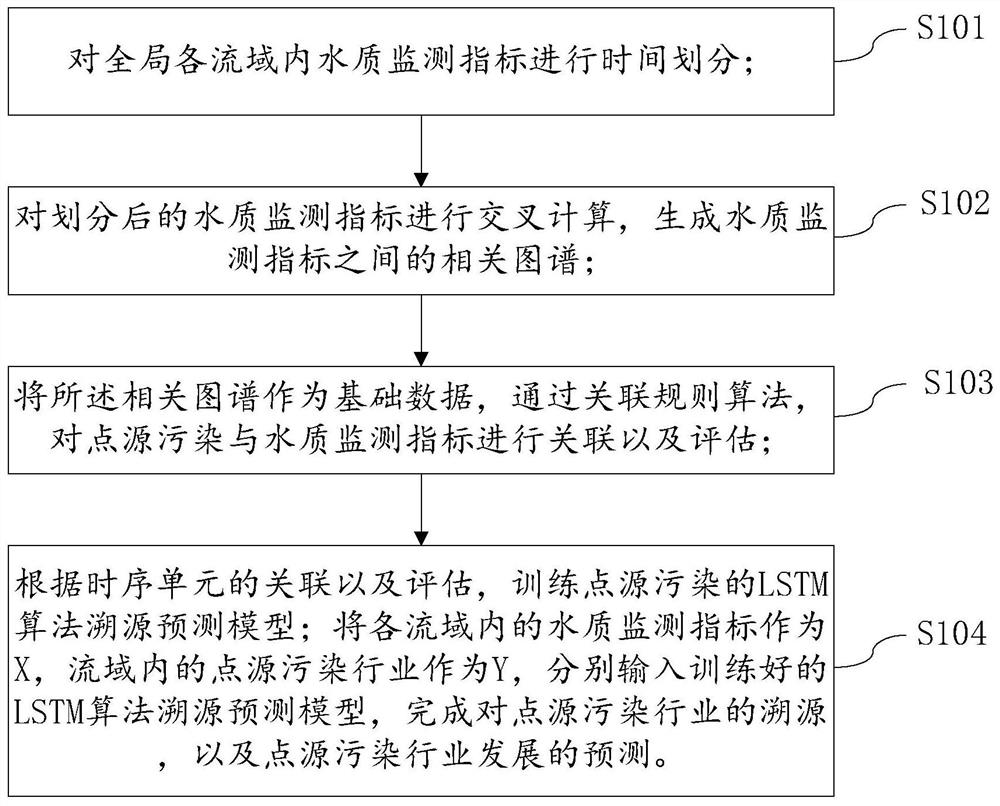
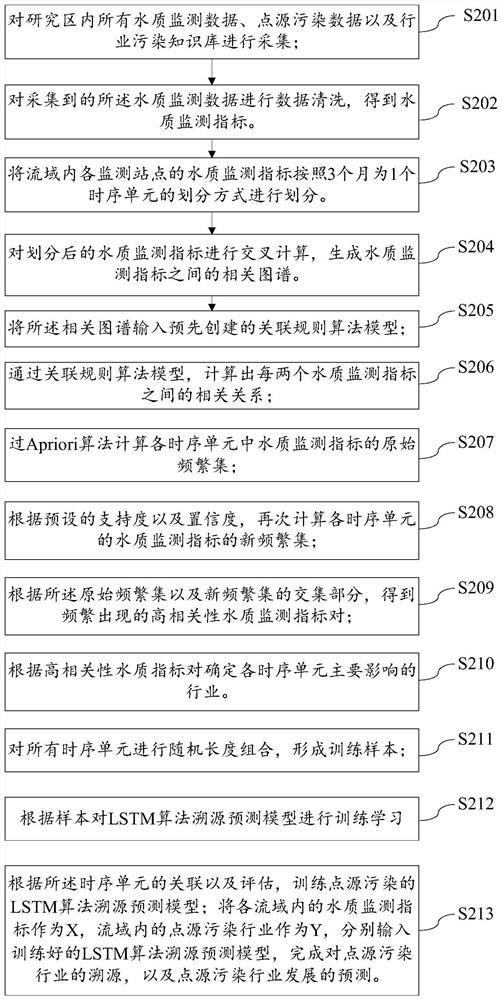
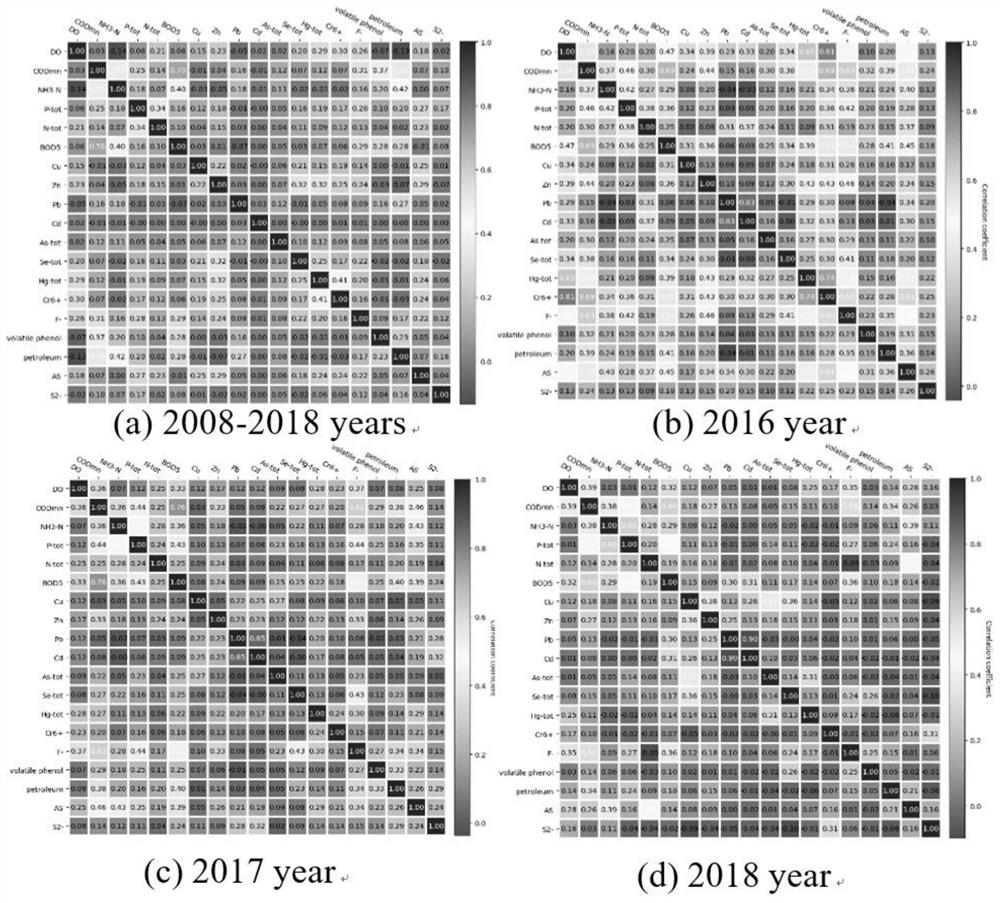
Watershed pollution traceability prediction method and device based on artificial intelligence
The invention provides a watershed pollution traceability prediction method and device based on artificial intelligence, and relates to the technical field of water environment information processing. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out cross correlation calculation on water quality monitoring indexes, taking a correlation map between the water quality indexes as input basic data, and delaying the correlation between the indexes to the correlation between point source pollution through an association rule algorithm; finally, mining potential laws of the water quality related atlas in time by using an LSTM algorithm, and realizing accurate prediction of point source pollution. The method aims to predict a main control industry point source causing water quality change, point source pollution, water quality monitoring data and an industry pollution knowledge base are used as data sets, a core algorithm in an intelligent voice technology is innovatively introduced into the environment field, algorithms such as cross correlation, association rules and a long-short term memory network are adopted, the artificial intelligence technology is used for identifying main point source pollution influencing future water quality changes.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for performing film thickness measurements using white light scanning interferometry
InactiveUS20120191412A1Accurate measurementImprove accuracyDigital computer detailsUsing electrical meansAmplitude functionLinear component
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for measuring the thickness of a transparent film by broad band interferometry, comprising the steps of preparing a correlogram of the film by an interferometer, applying a Fourier transformation to said correlogram to obtain a Fourier phase function, removing a linear component thereof, applying a second integral transformation to the remaining non-linear component to obtain an integral amplitude function of said non-linear component, identifying the peak location of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the film as the double value of the abscissa at said peak location considering a refractive index of a film which is dependent on wavelength. The last two steps may be replaced by identifying the peak locations of said integral amplitude function and determining the thickness of the films as the double values of the abscissas at the peak locations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com