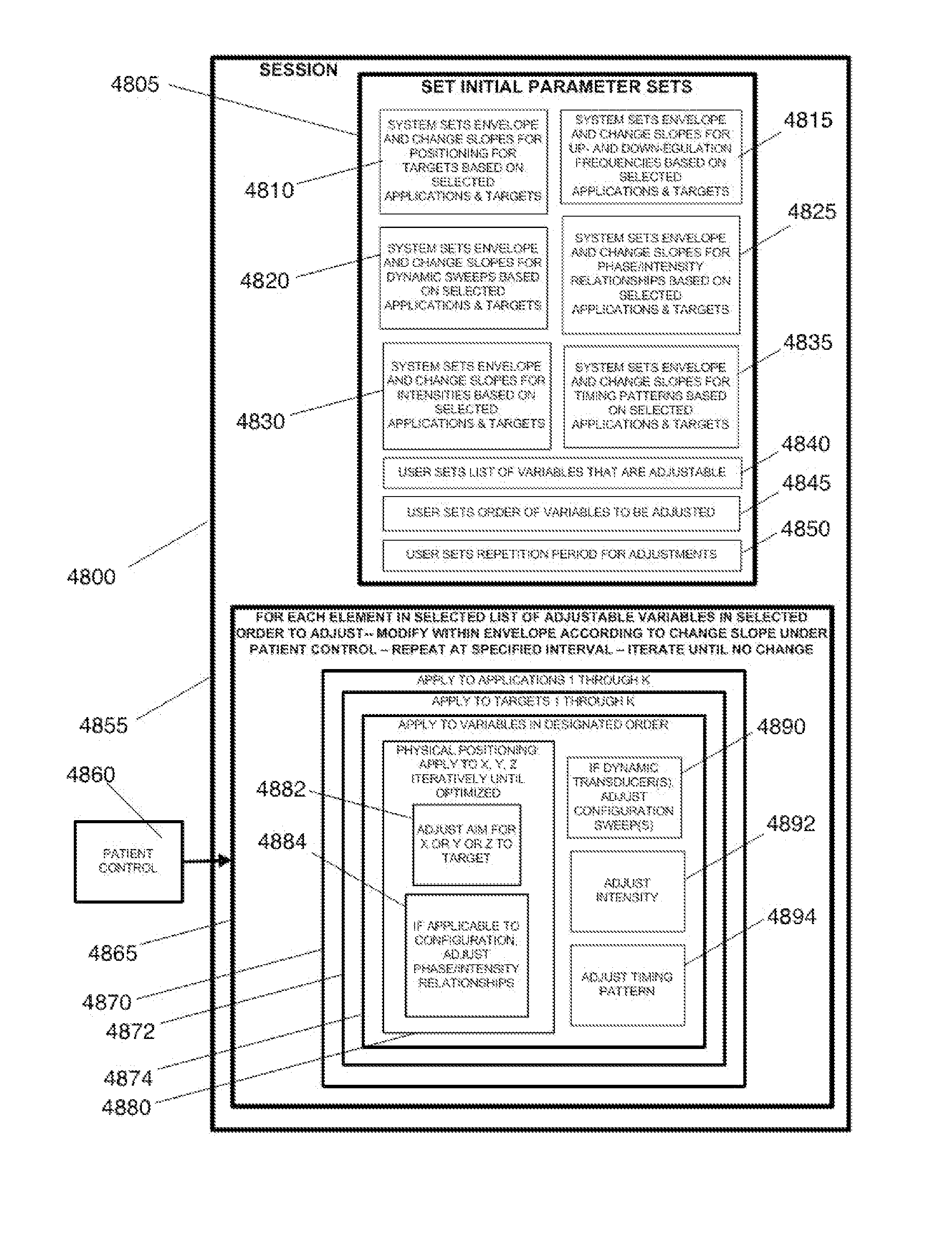
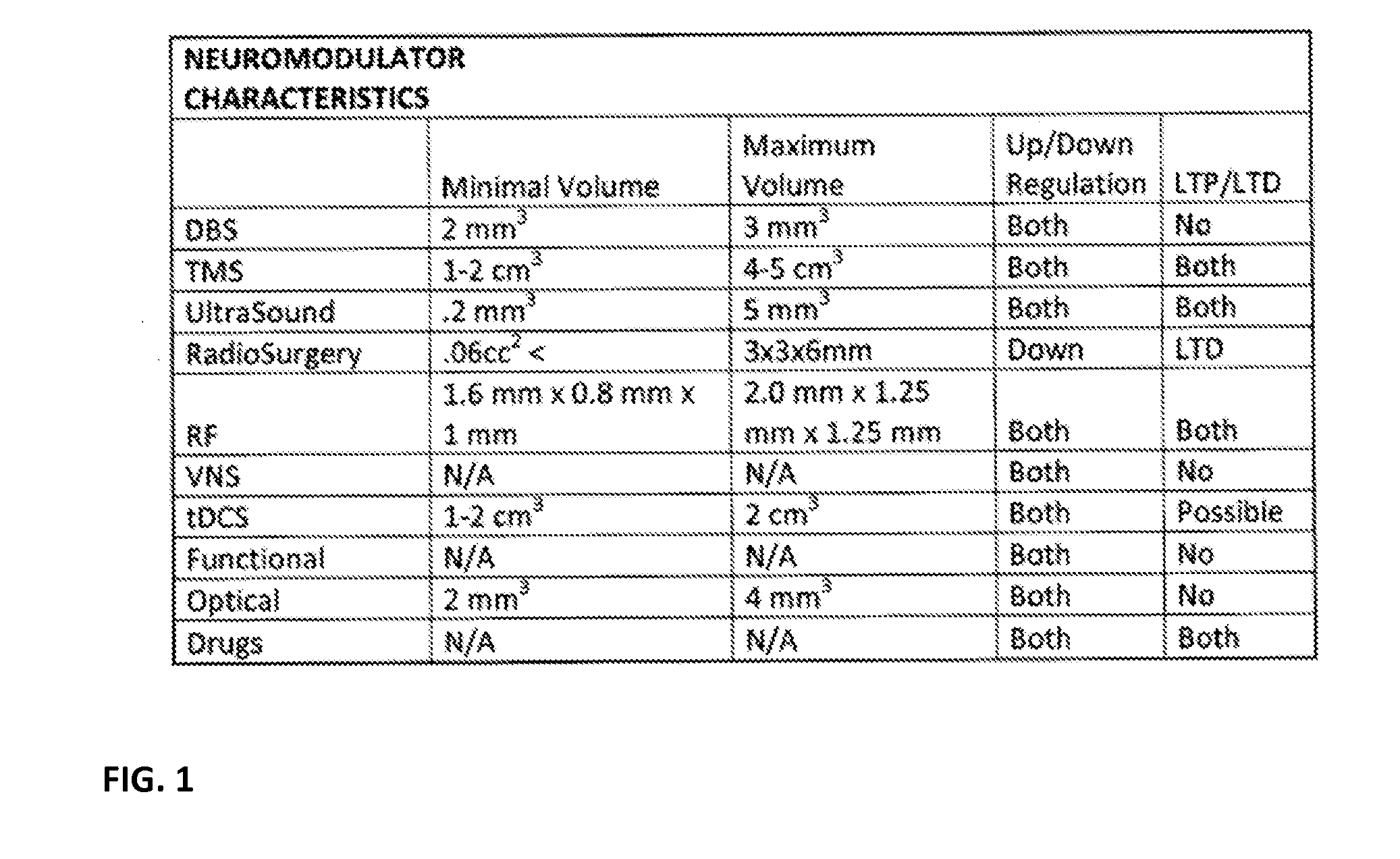
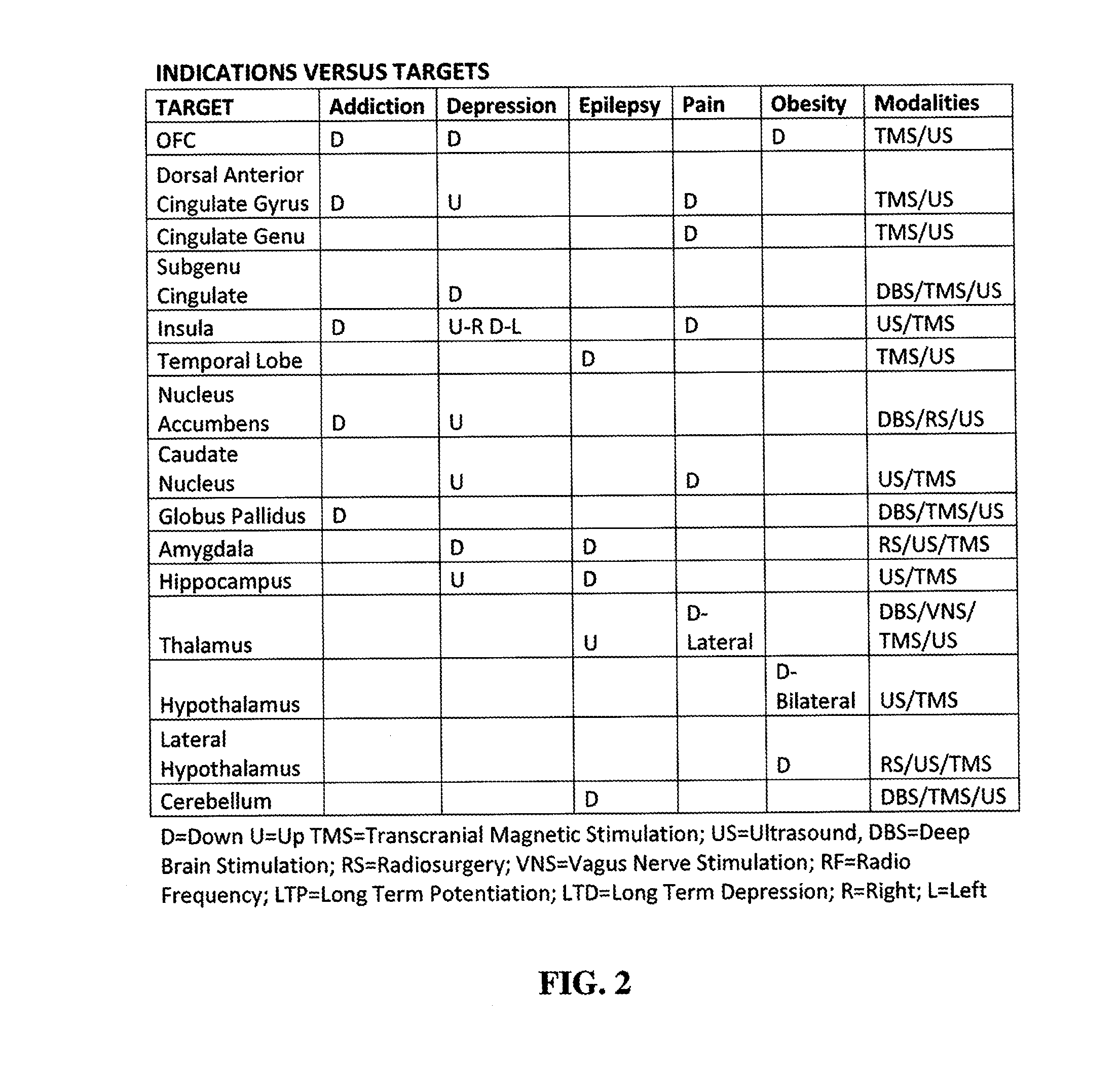
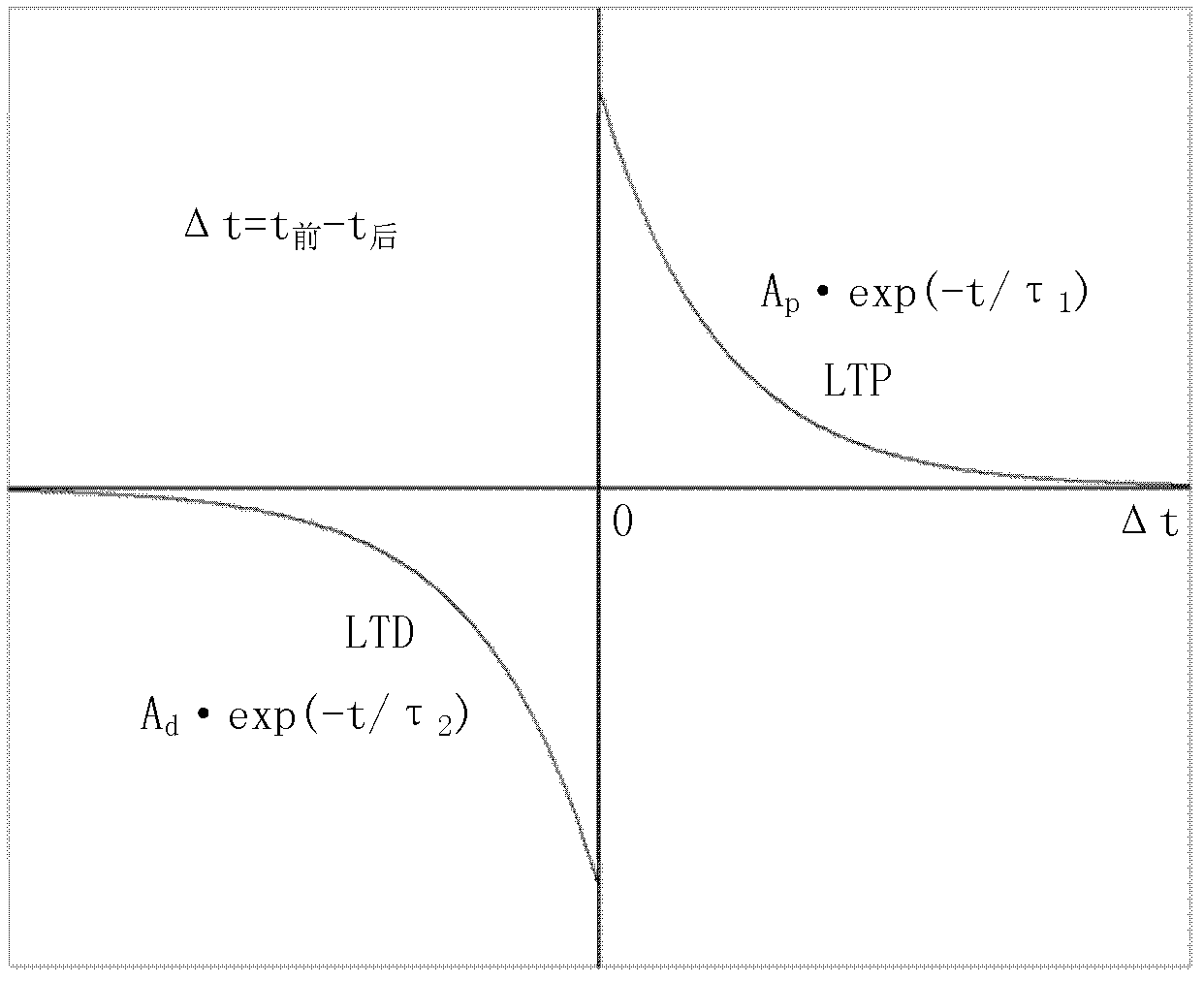Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Long-term potentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
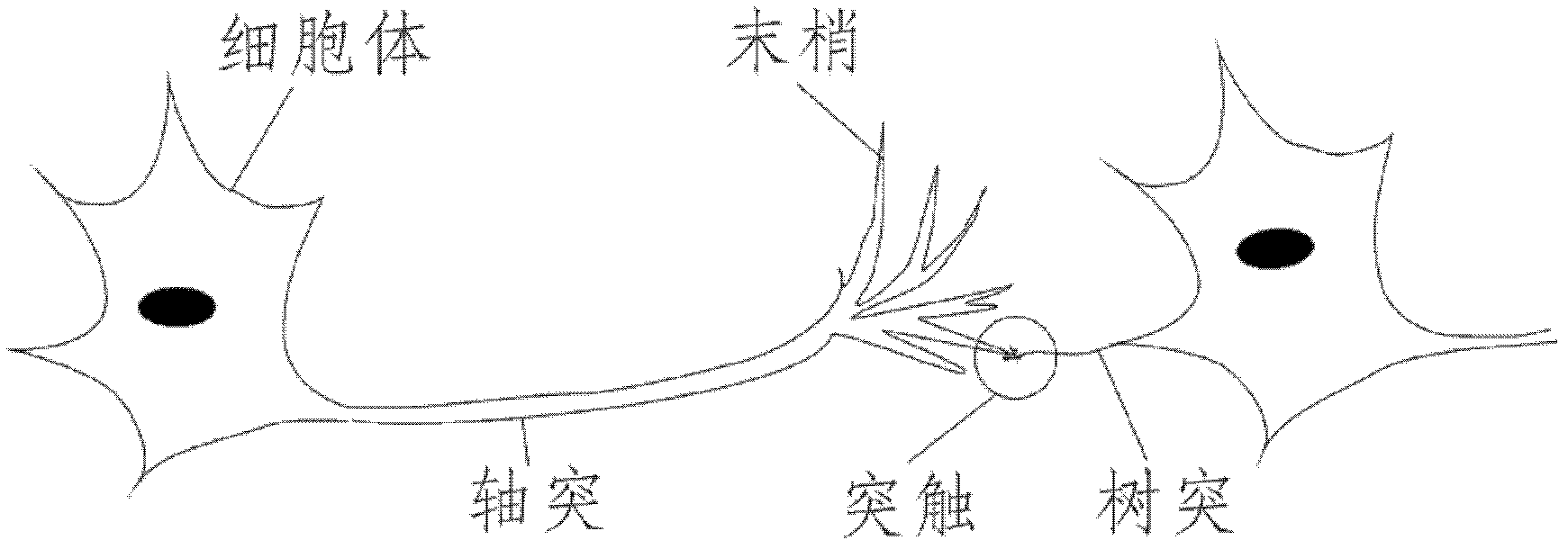
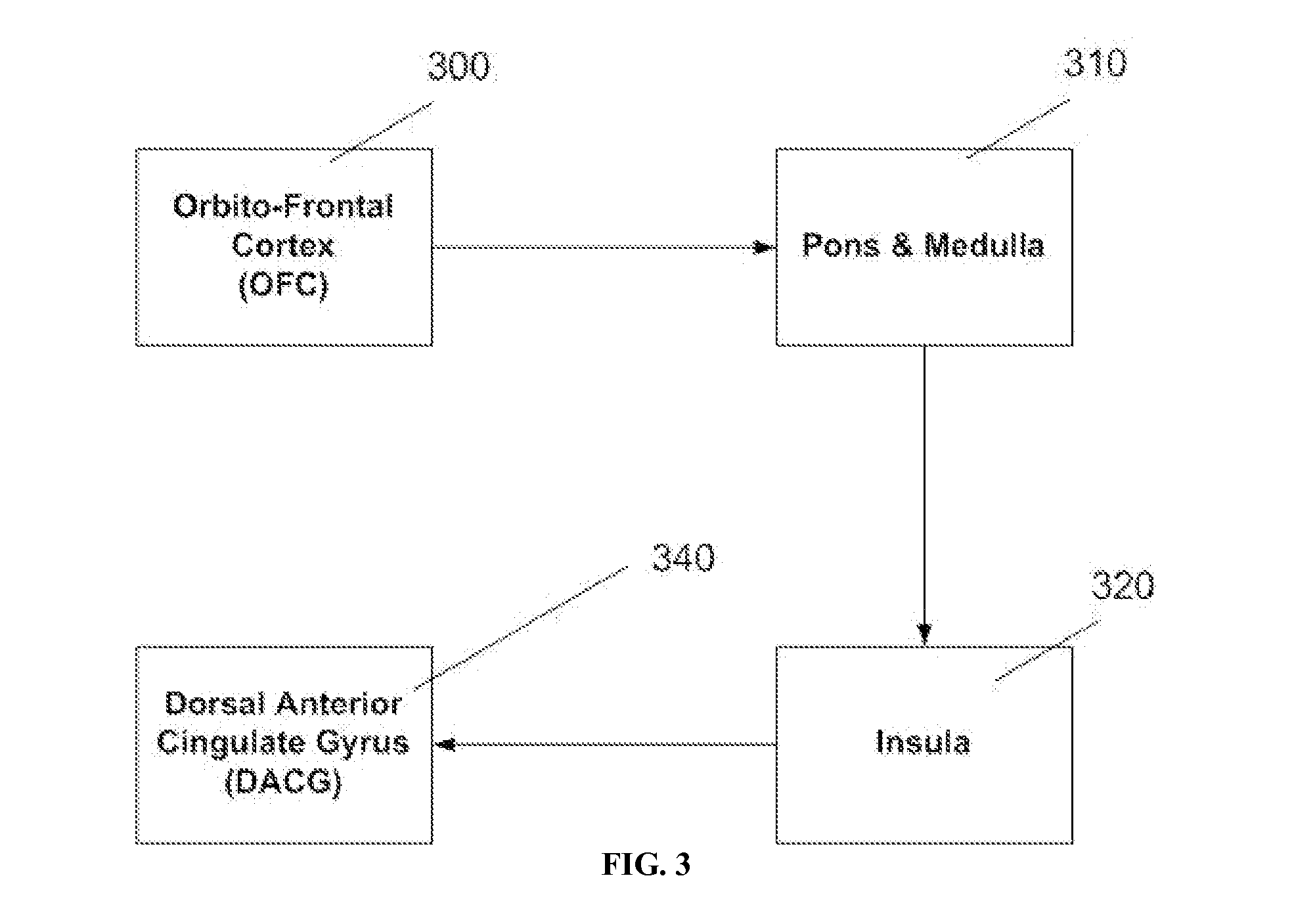
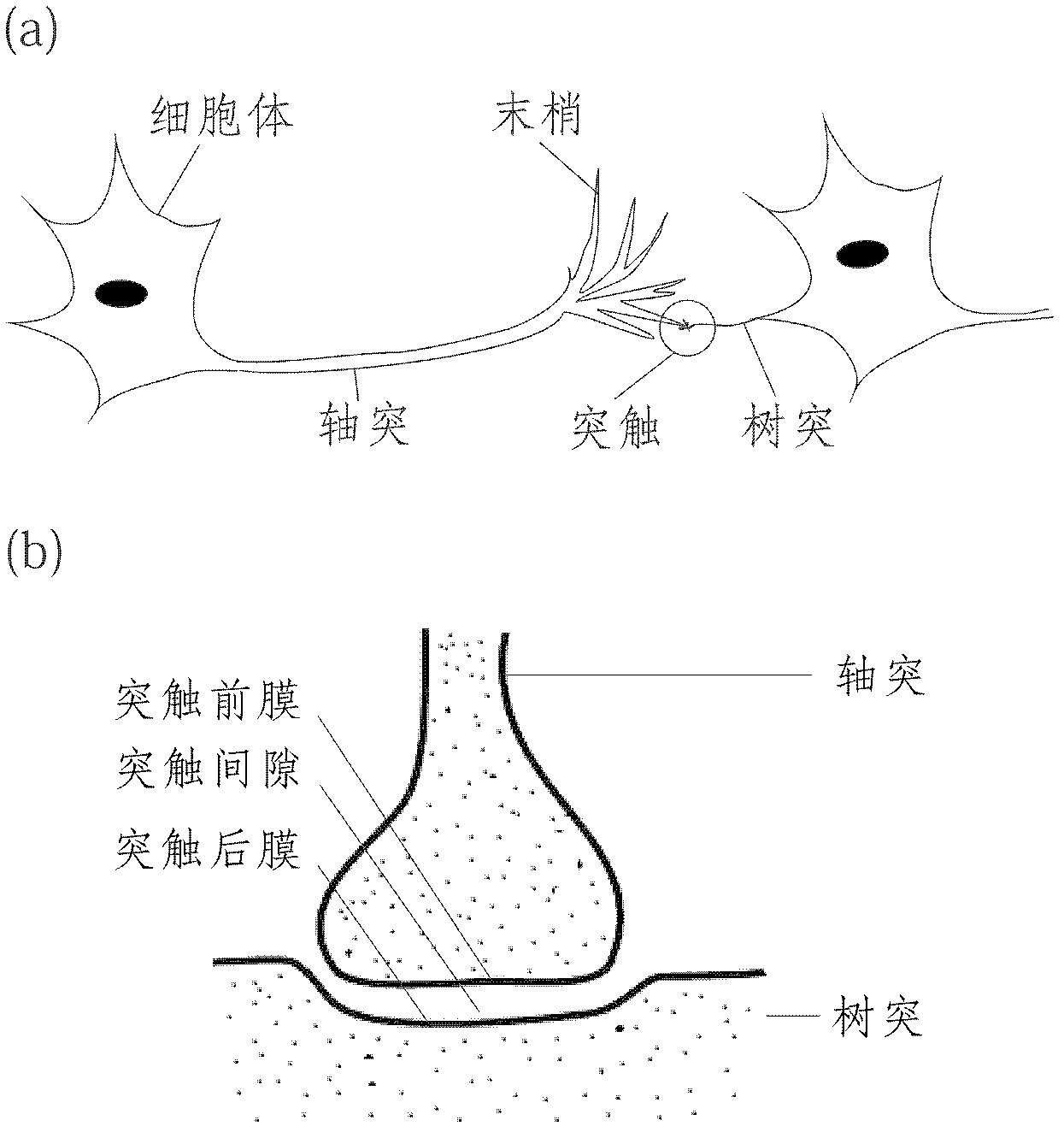
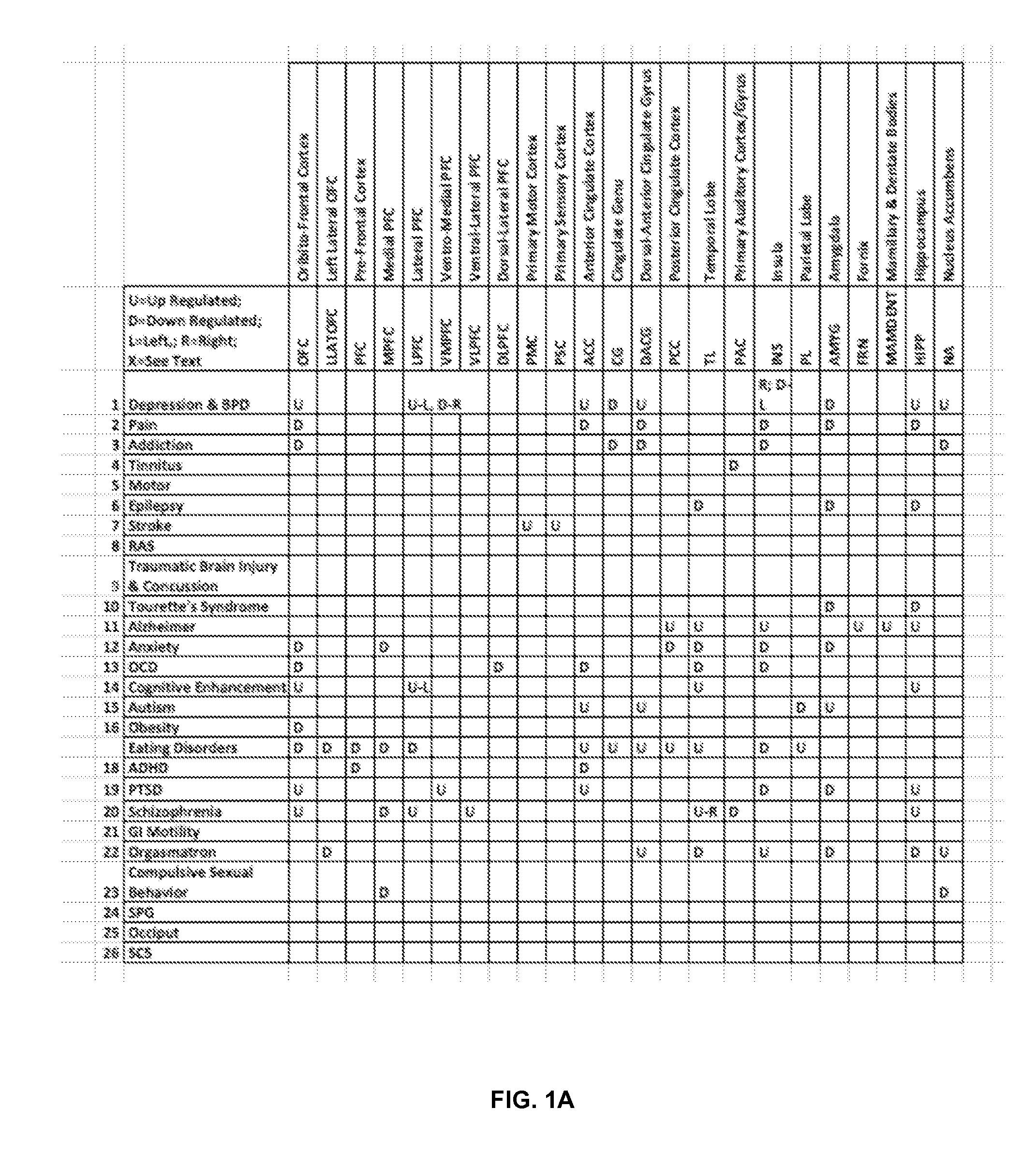
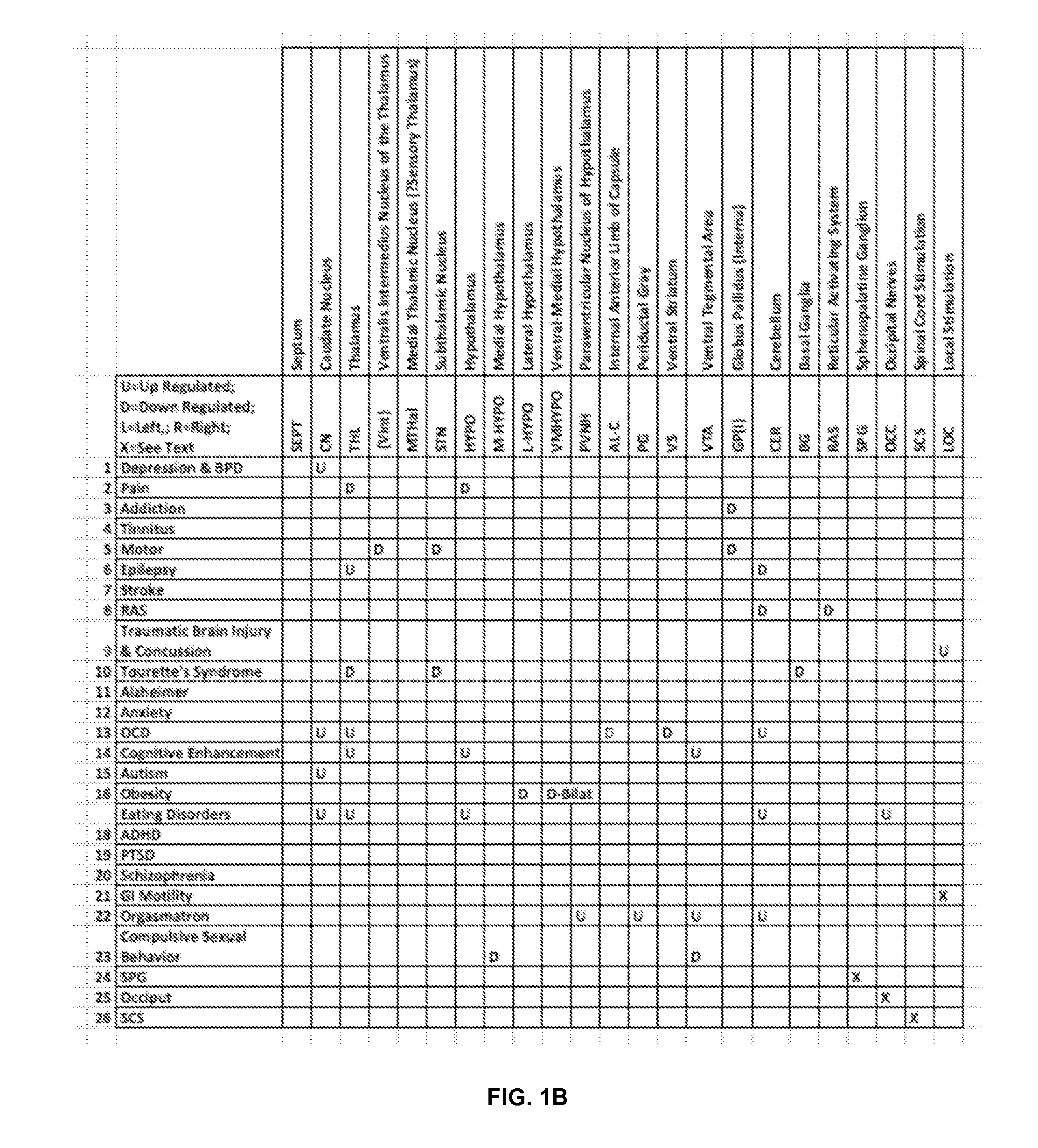
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons. The opposite of LTP is long-term depression, which produces a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength.
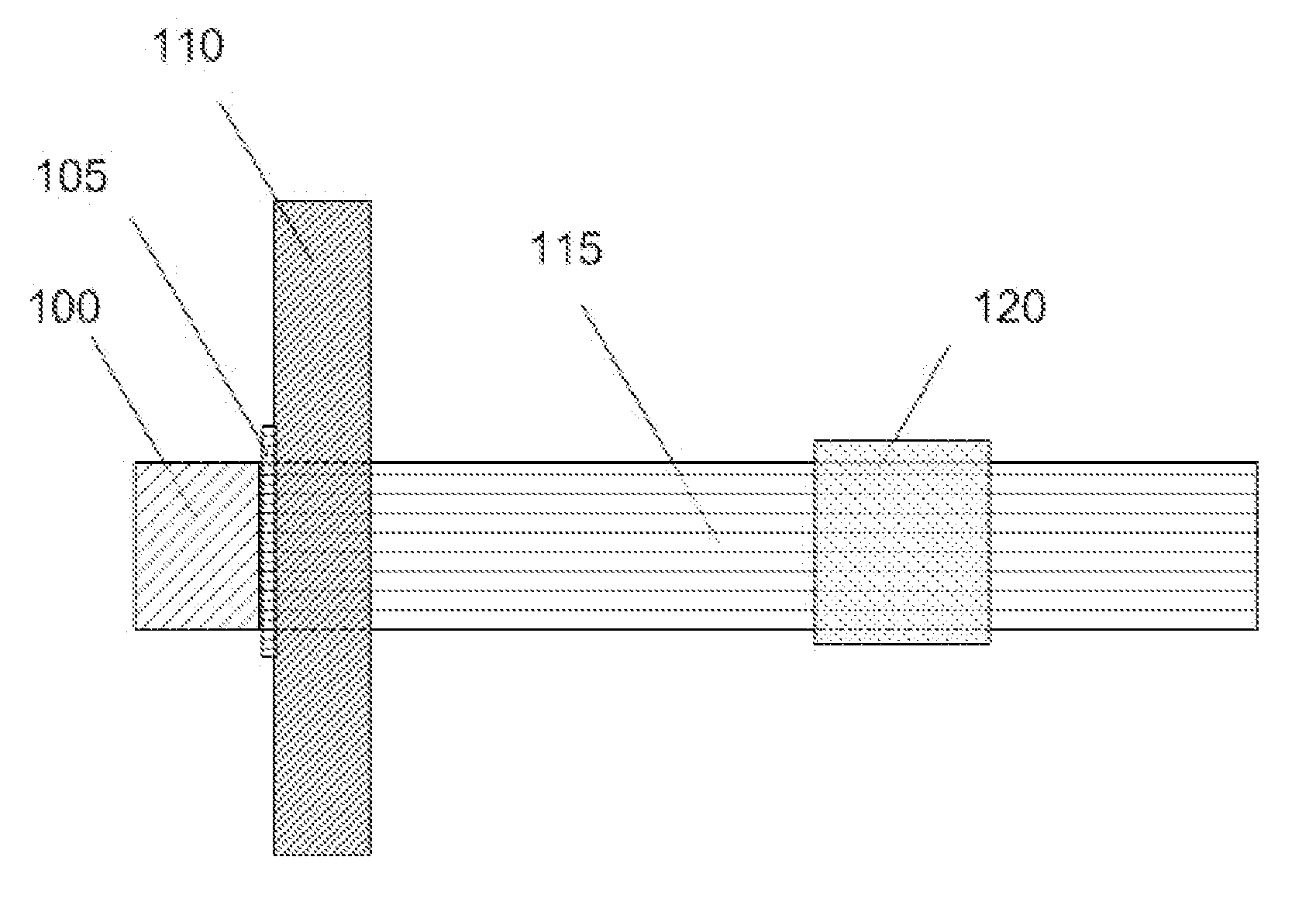
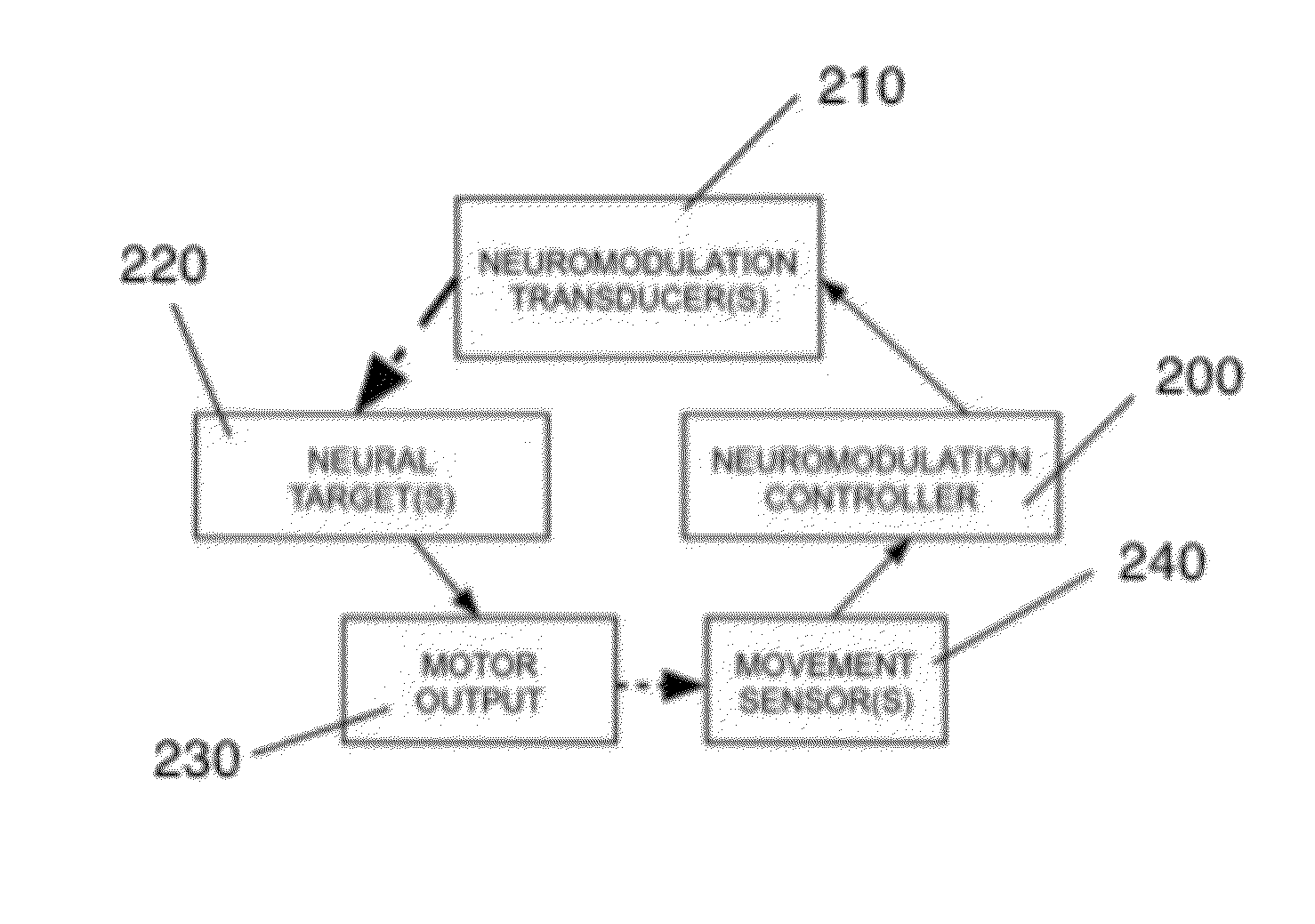
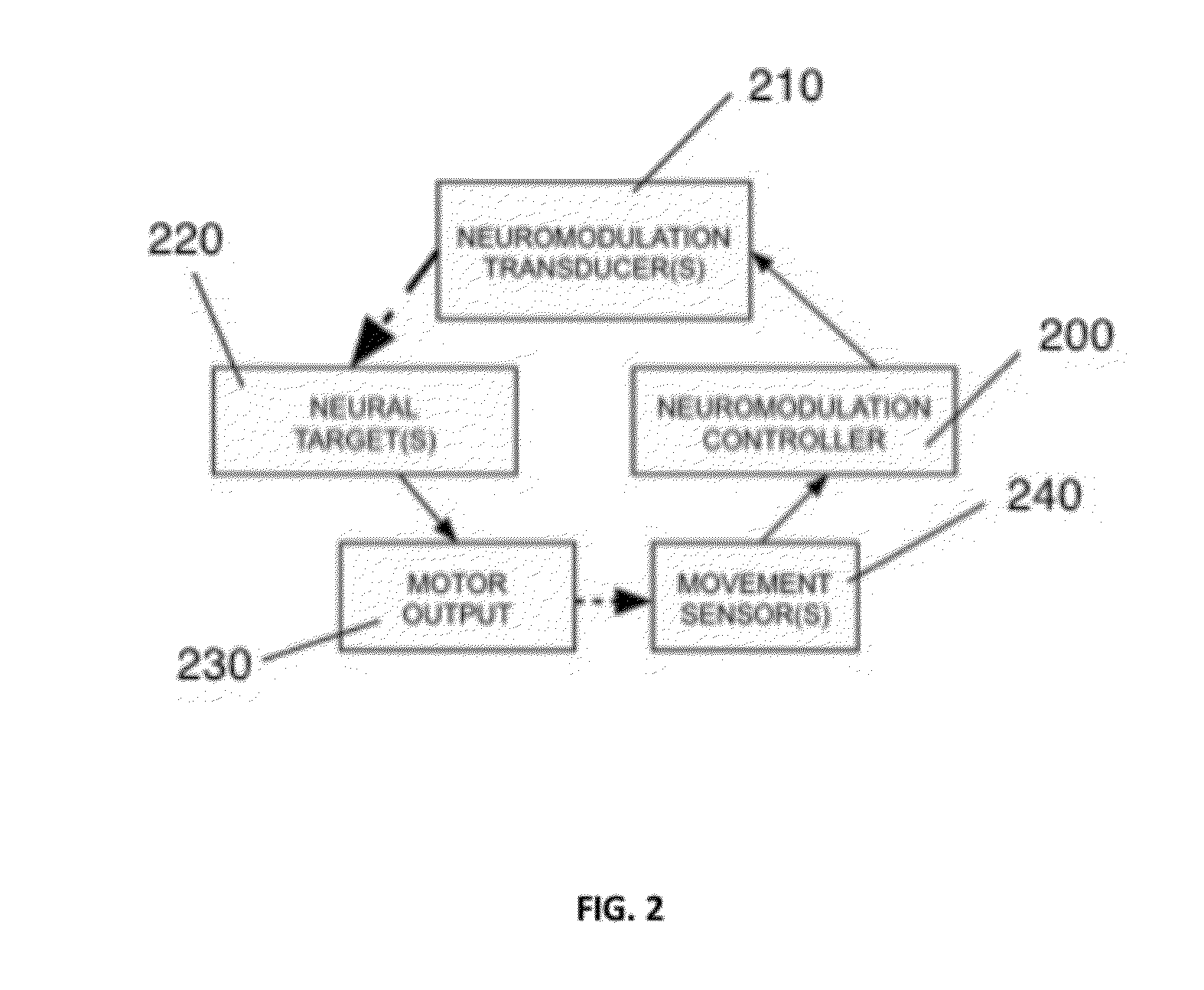
Devices and methods for optimized neuromodulation and their application
InactiveUS20160001096A1Reduce image distortionLow costUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySpinal cord
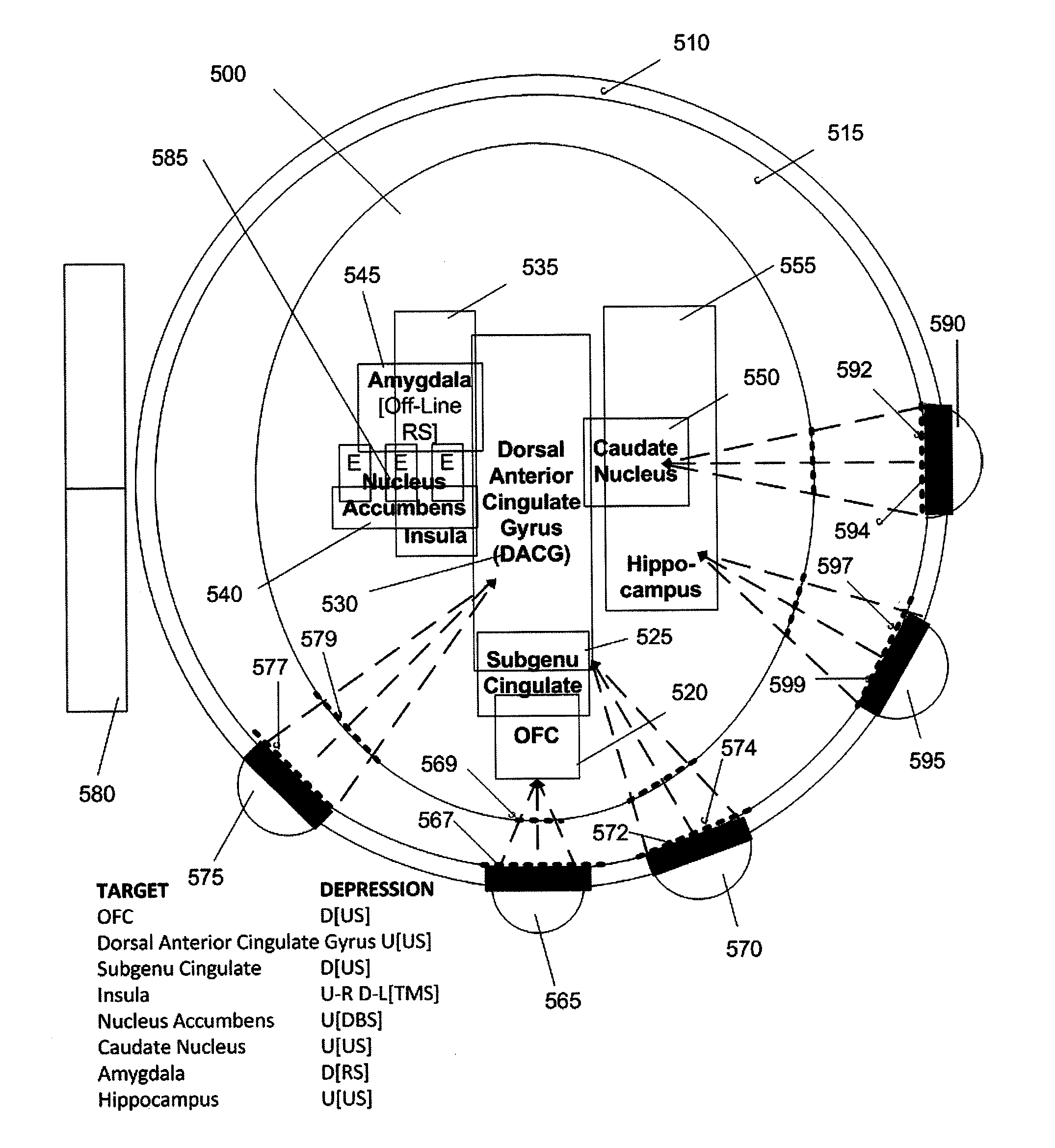
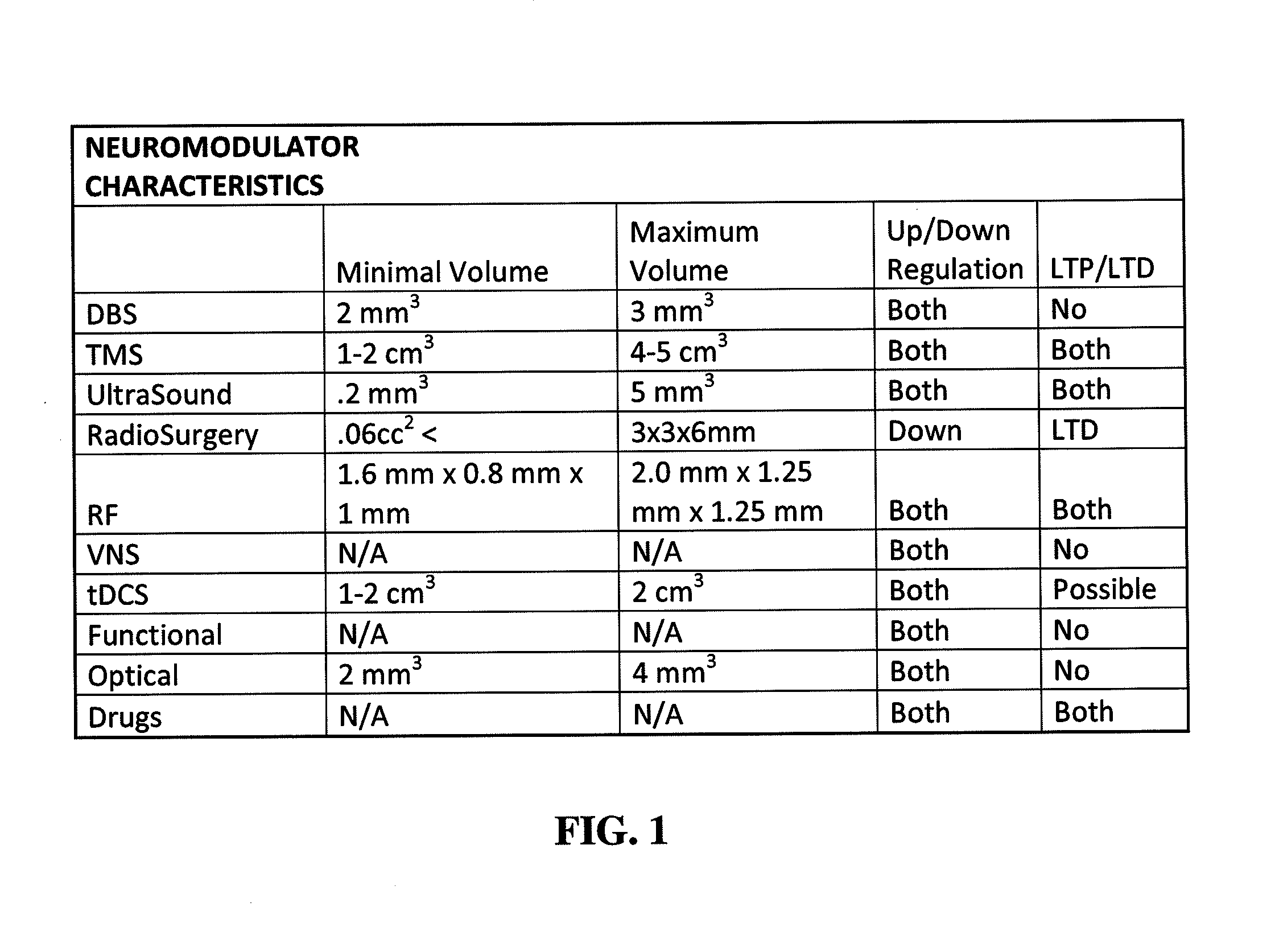
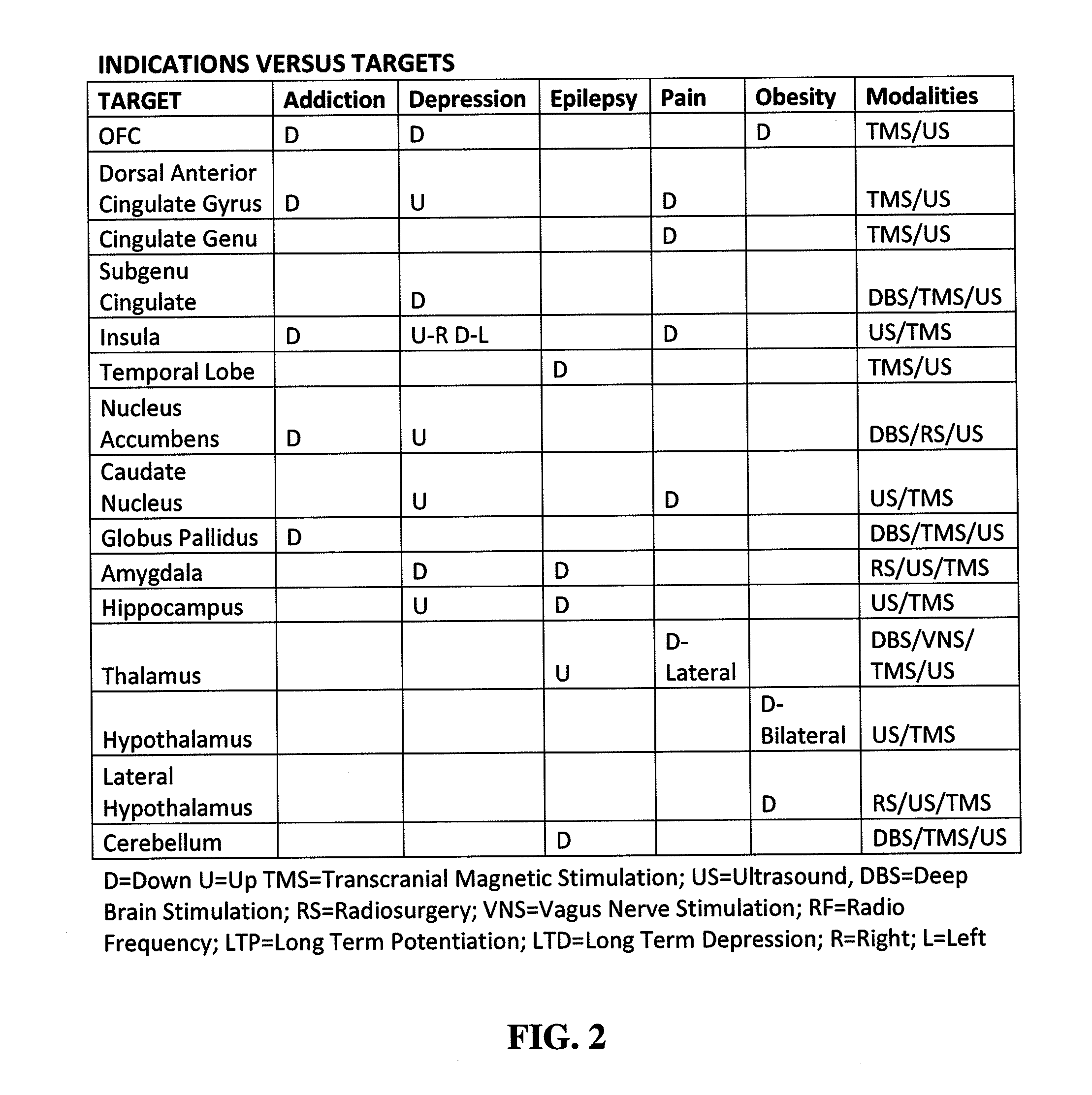
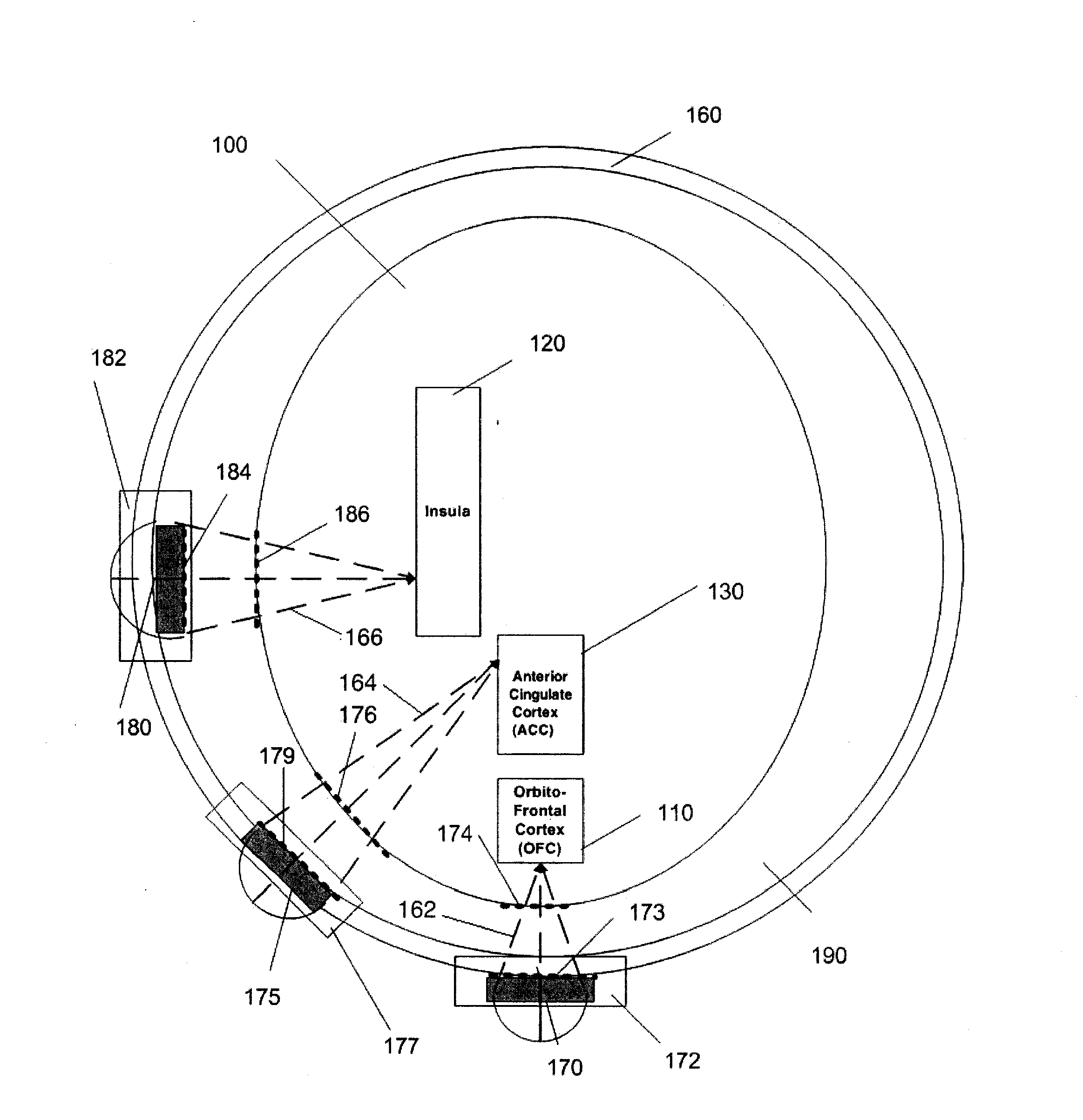
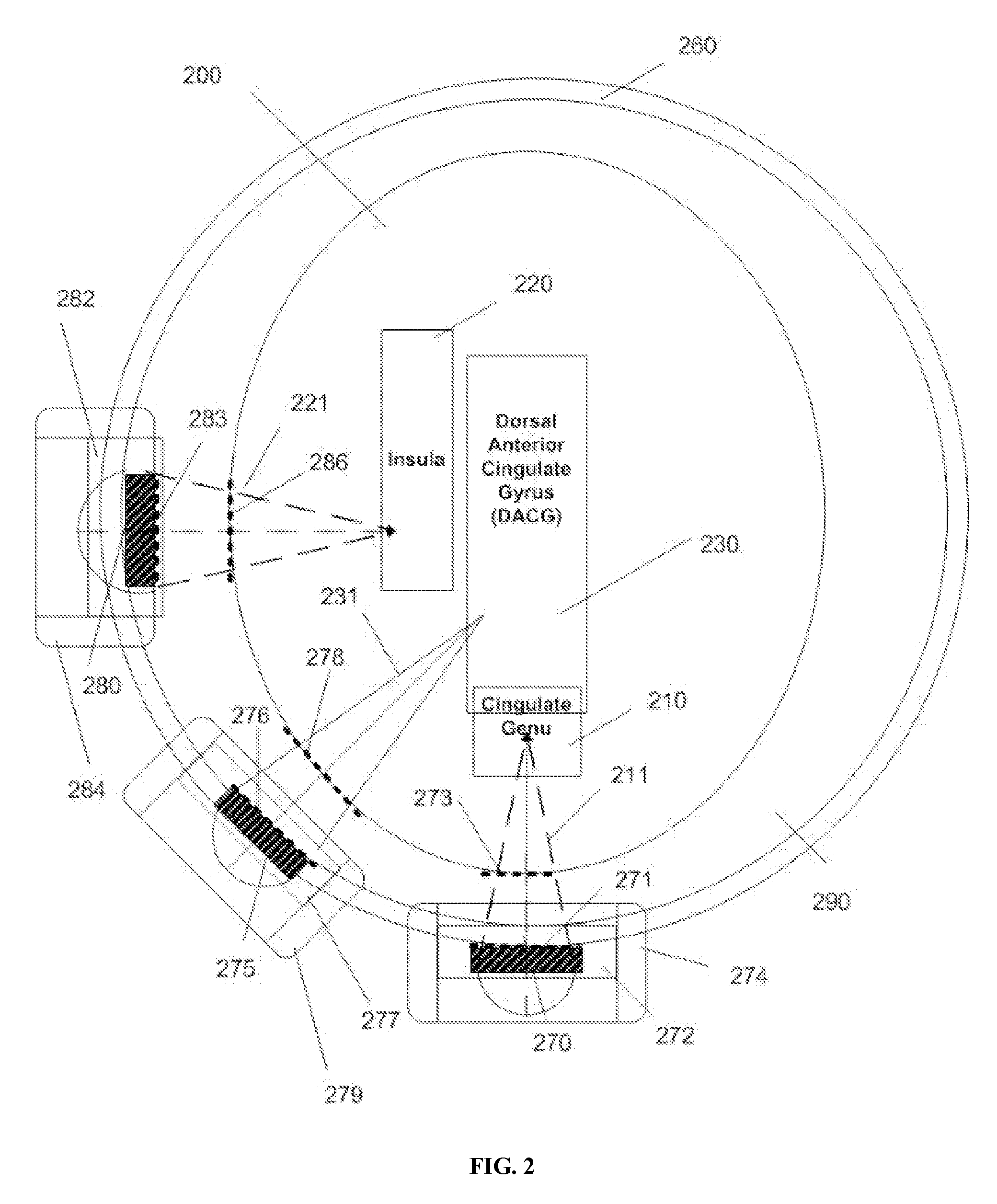
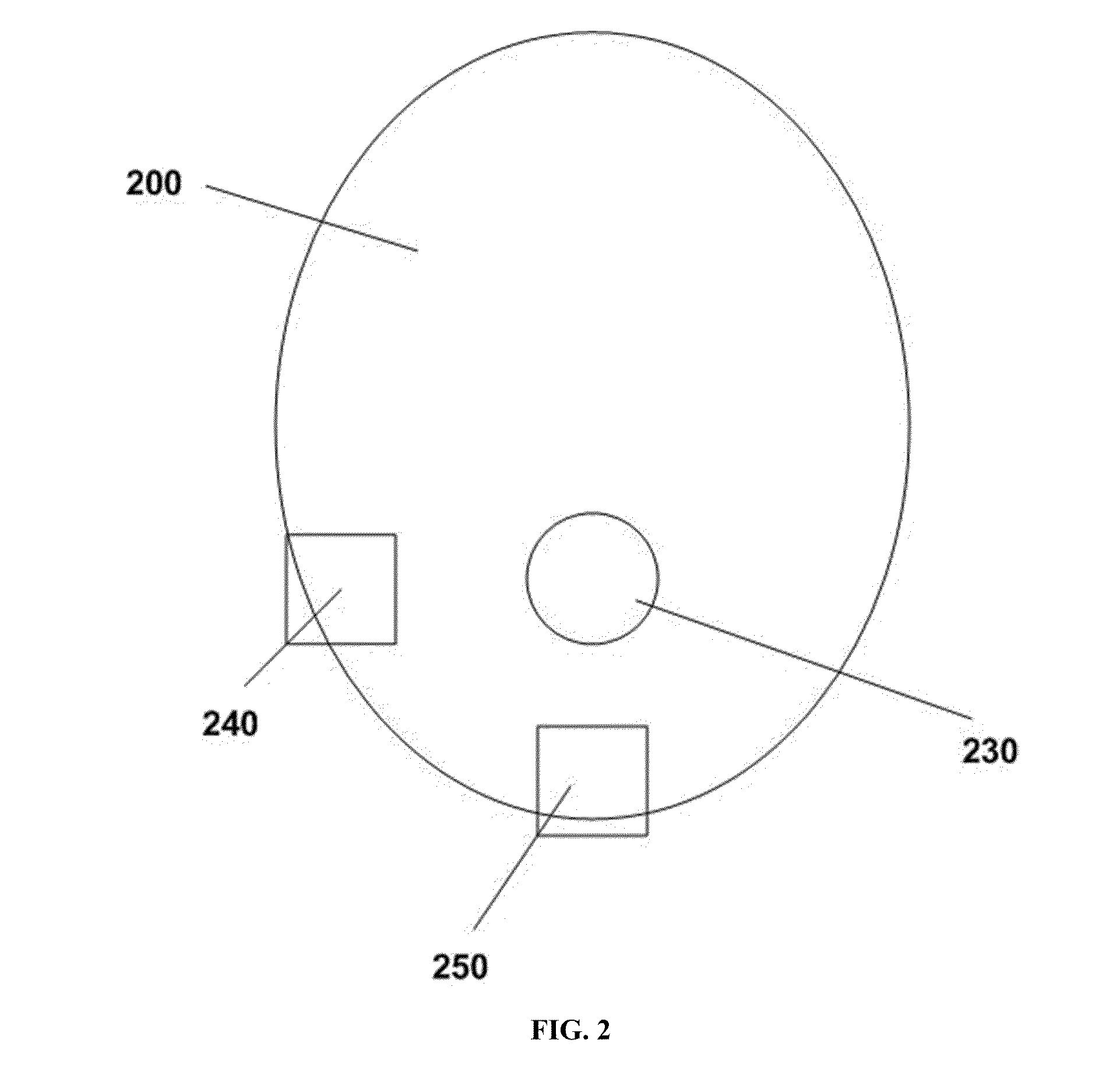
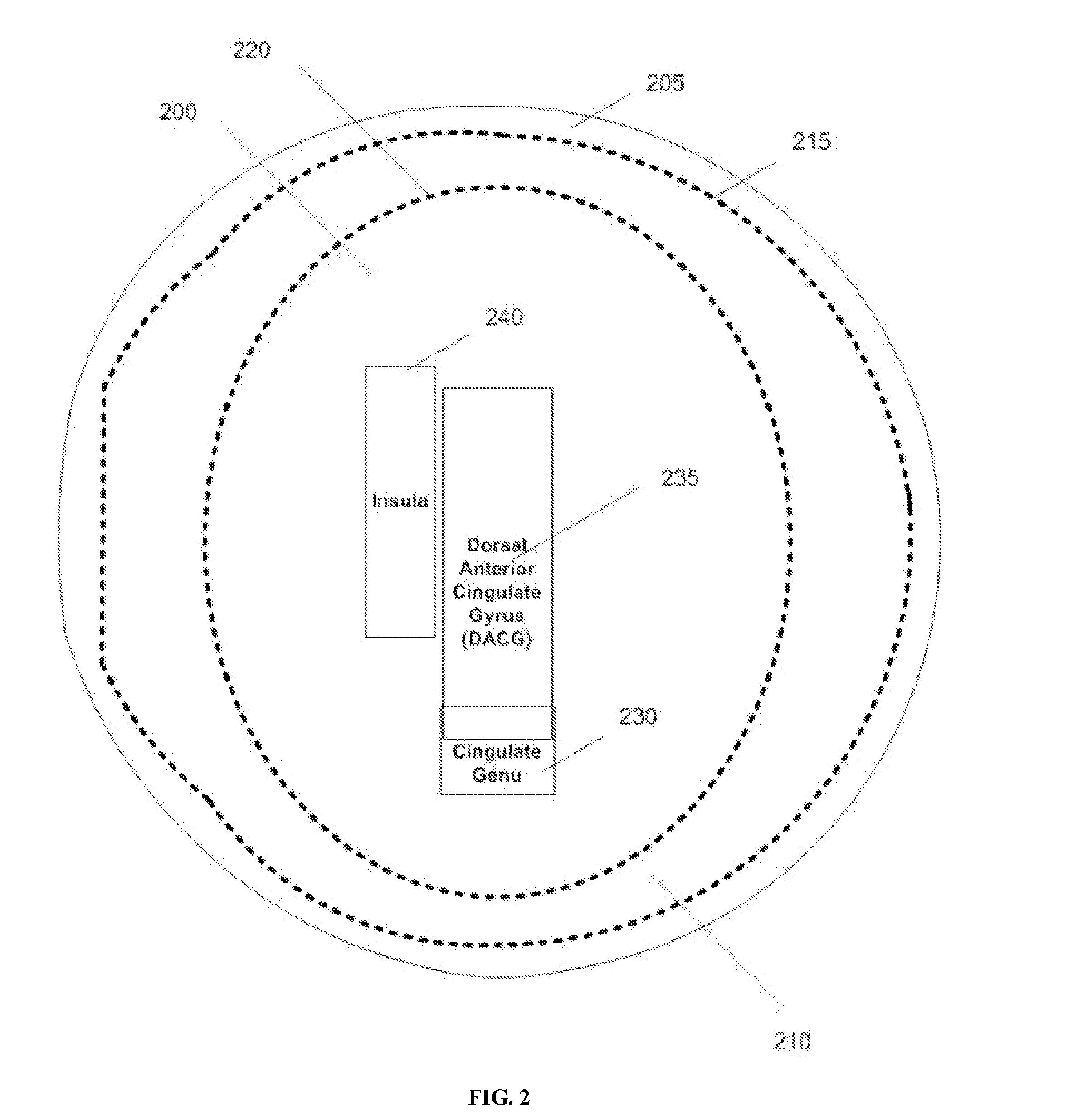
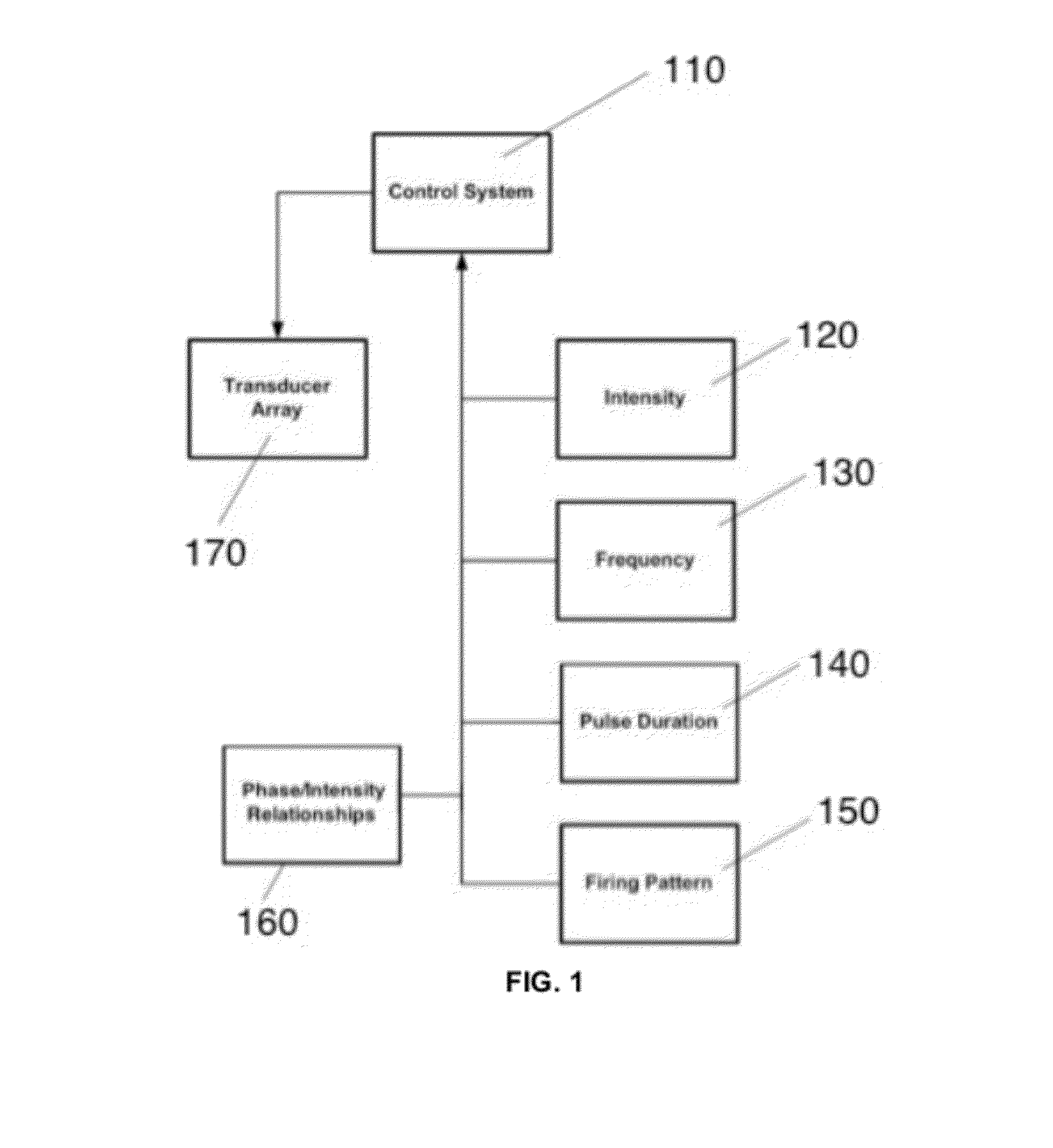
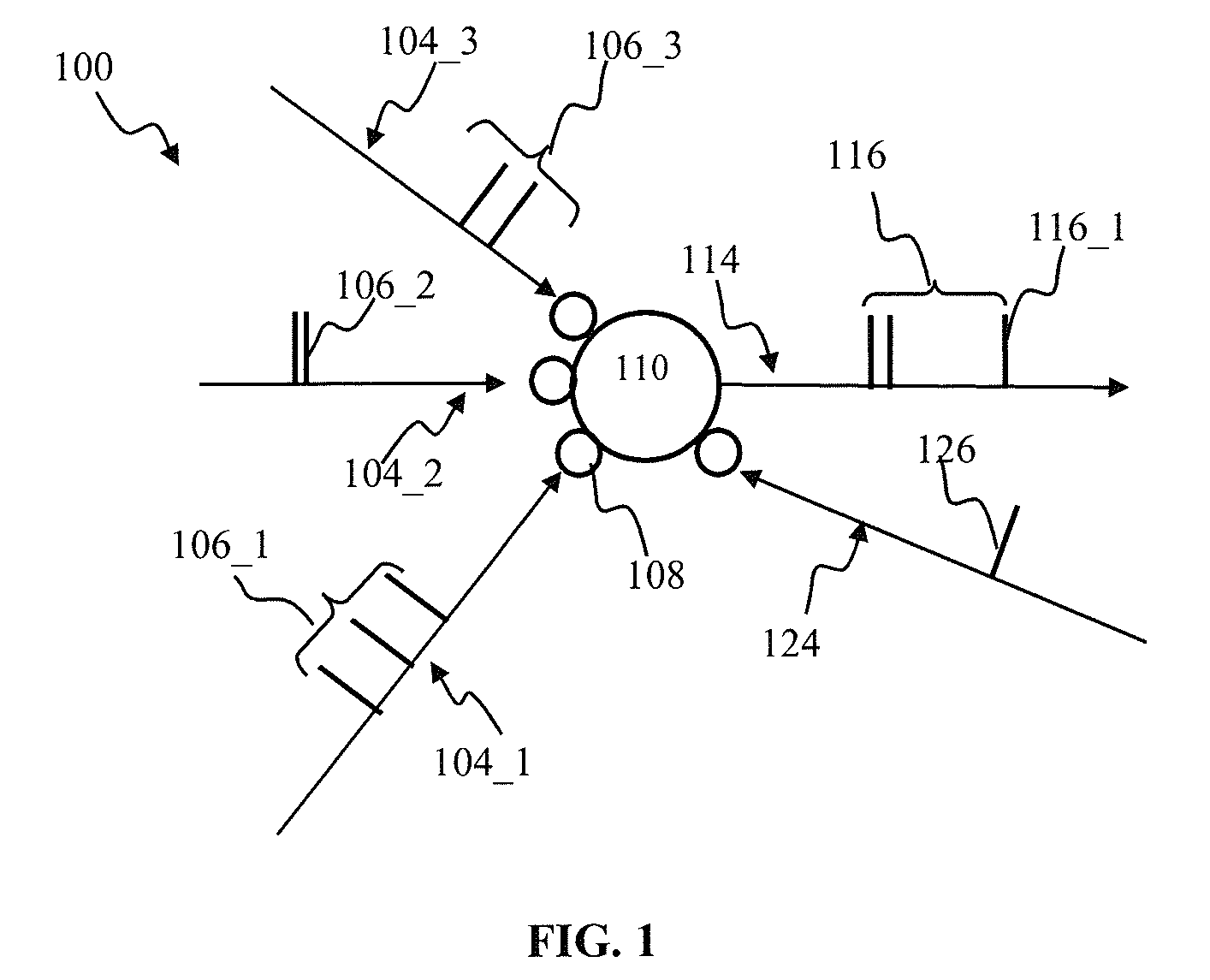
Disclosed are methods and systems for optimized deep or superficial deep-brain stimulation using multiple therapeutic modalities impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). Also disclosed are methods for treatment of clinical conditions and obtaining physiological impacts. Also disclosed are: methods and systems for Guided Feedback control of non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation; patterned neuromodulation, ancillary stimulation, treatment planning, focused shaped or steered ultrasound; methods and systems using intersecting ultrasound beams; non-invasive ultrasound-neuromodulation techniques to control the permeability of the blood-brain barrier; non-invasive neuromodulation of the spinal cord by ultrasound energy; methods and systems for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound for evaluating the feasibility of neuromodulation treatment using non-ultrasound / ultrasound modalities; neuromodulation of the whole head, treatment of multiple conditions, and method and systems for neuromodulation using ultrasound delivered in sessions.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Conditional plasticity spiking neuron network apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140012788A1Improve performanceDigital computer detailsDigital dataNeuron networkNerve network
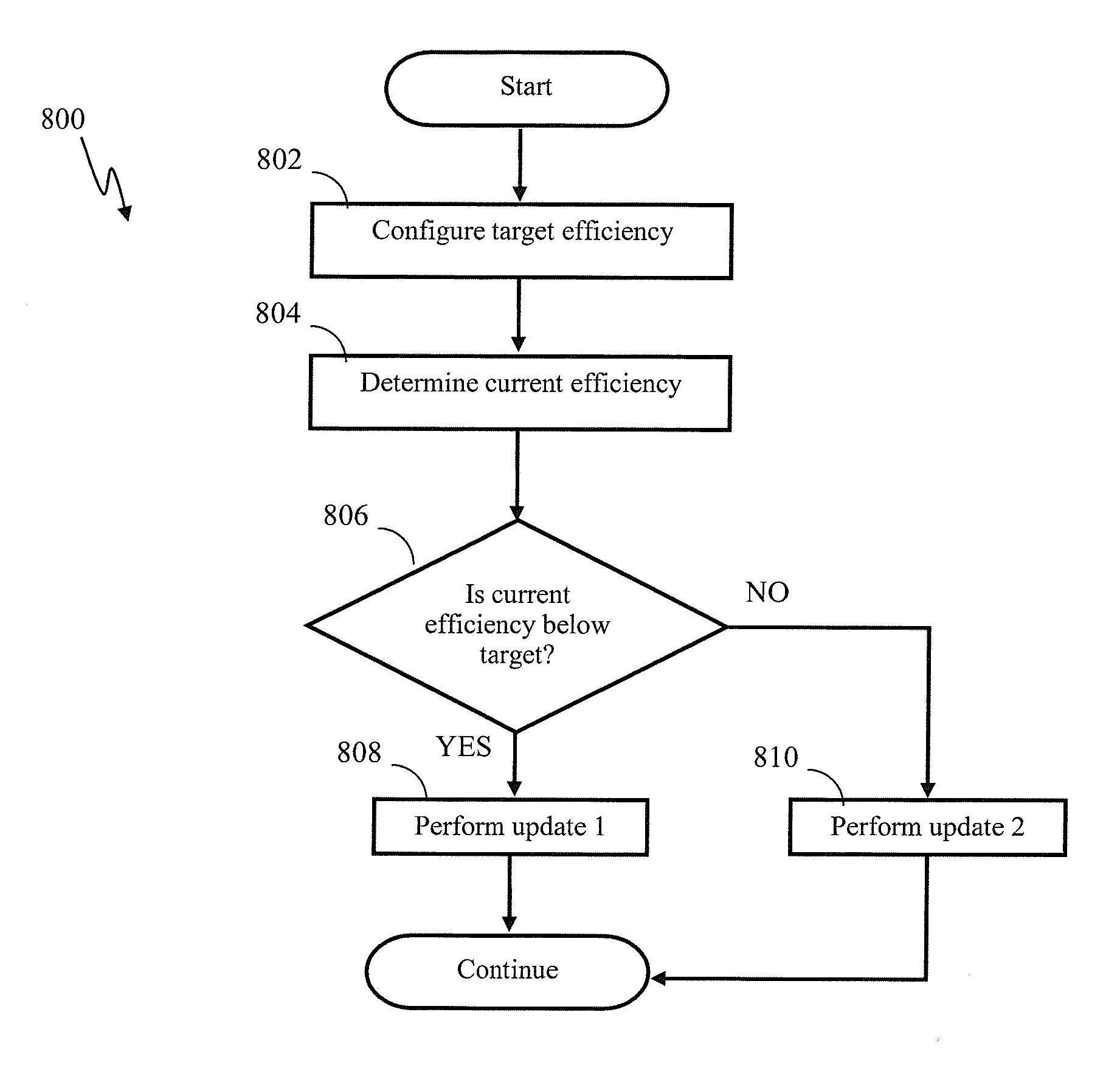
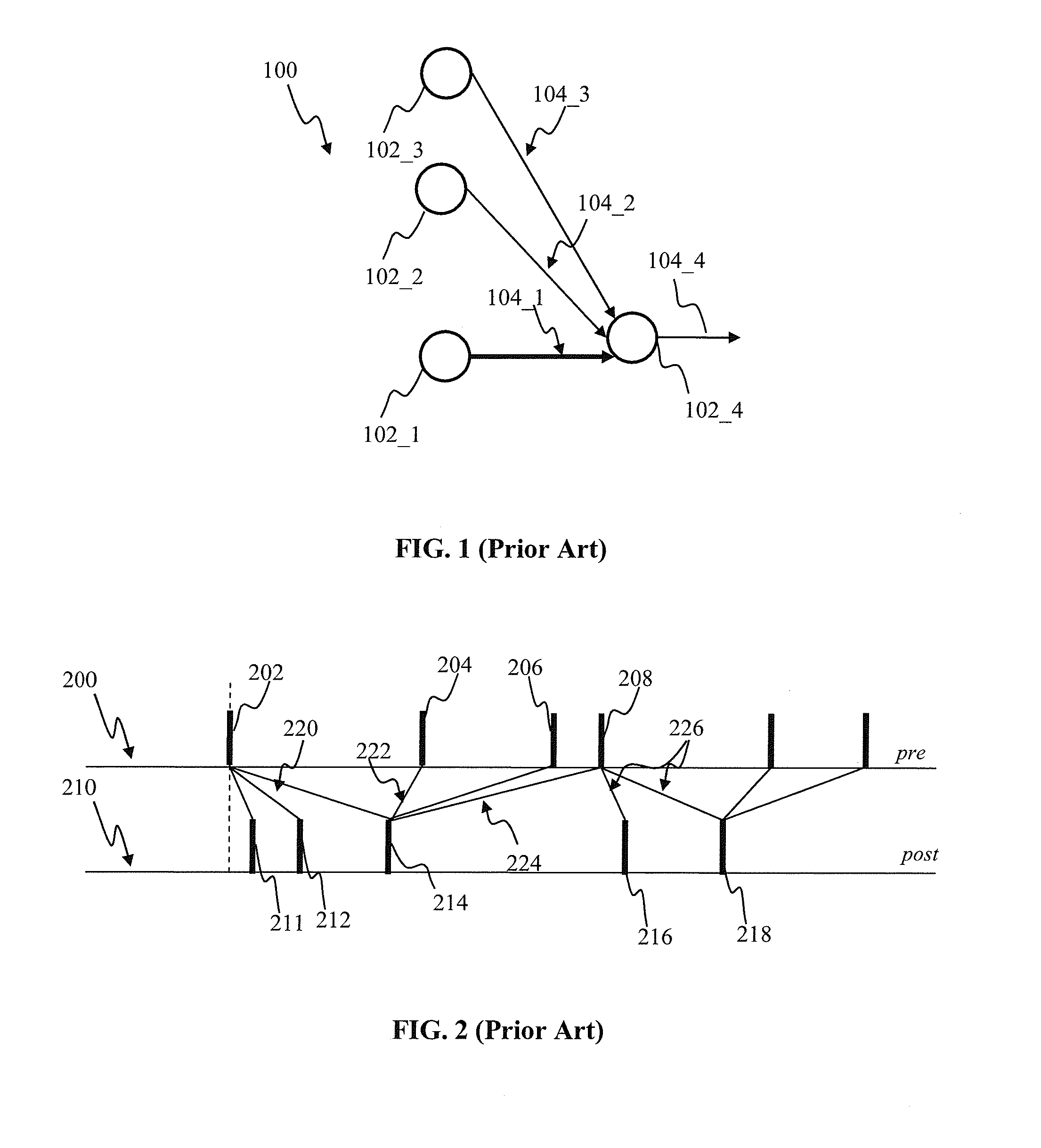
Apparatus and methods for conditional plasticity in a neural network. In one approach, conditional plasticity mechanism is configured to select alternate plasticity rules when performing connection updates. The selection mechanism is adapted based on a comparison of actual connection efficiency and target efficiency. For instance, when actual efficiency is below the target value, the STDP rule may be modulated to increase long term potentiation. Similarly, when actual efficiency is above the target value, the STDP rule may be modulated to increase long term connection depression. The conditional plasticity mechanism dynamically adjusts connection efficacy, and prevents uncontrolled increase of connection weights, thereby improving network operation when processing information of a varying nature.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
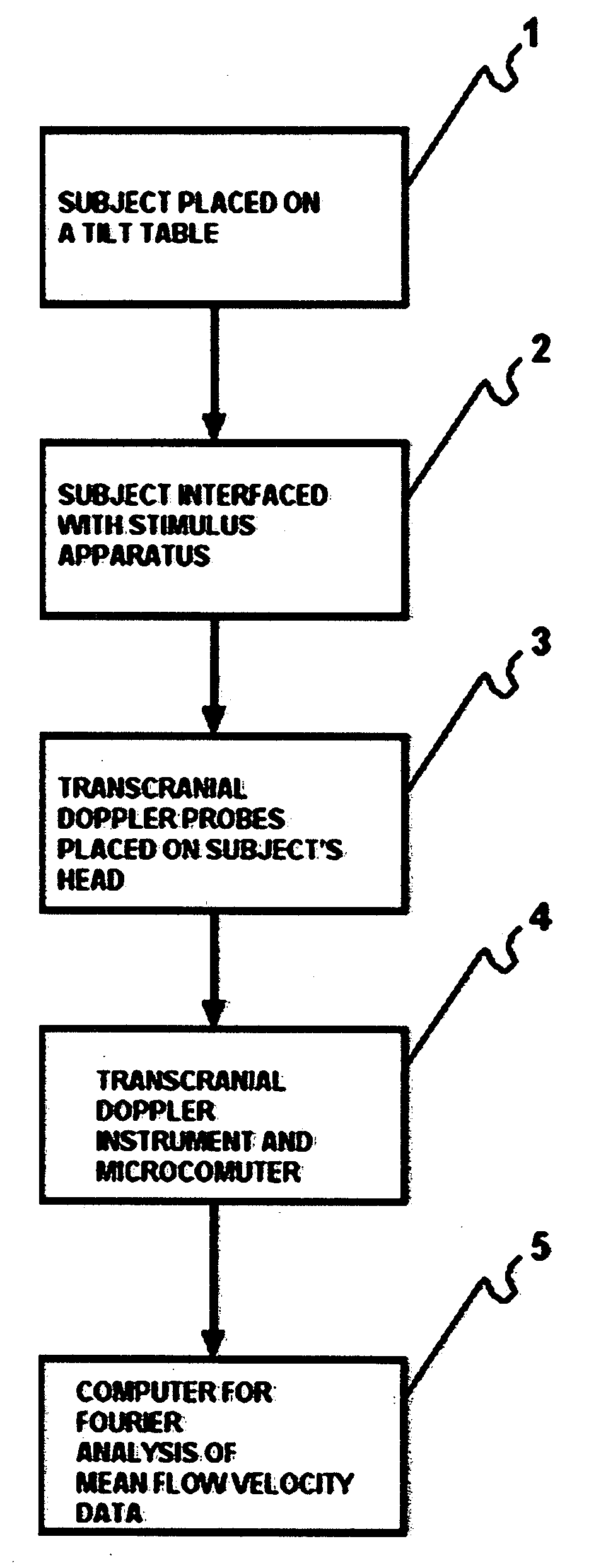
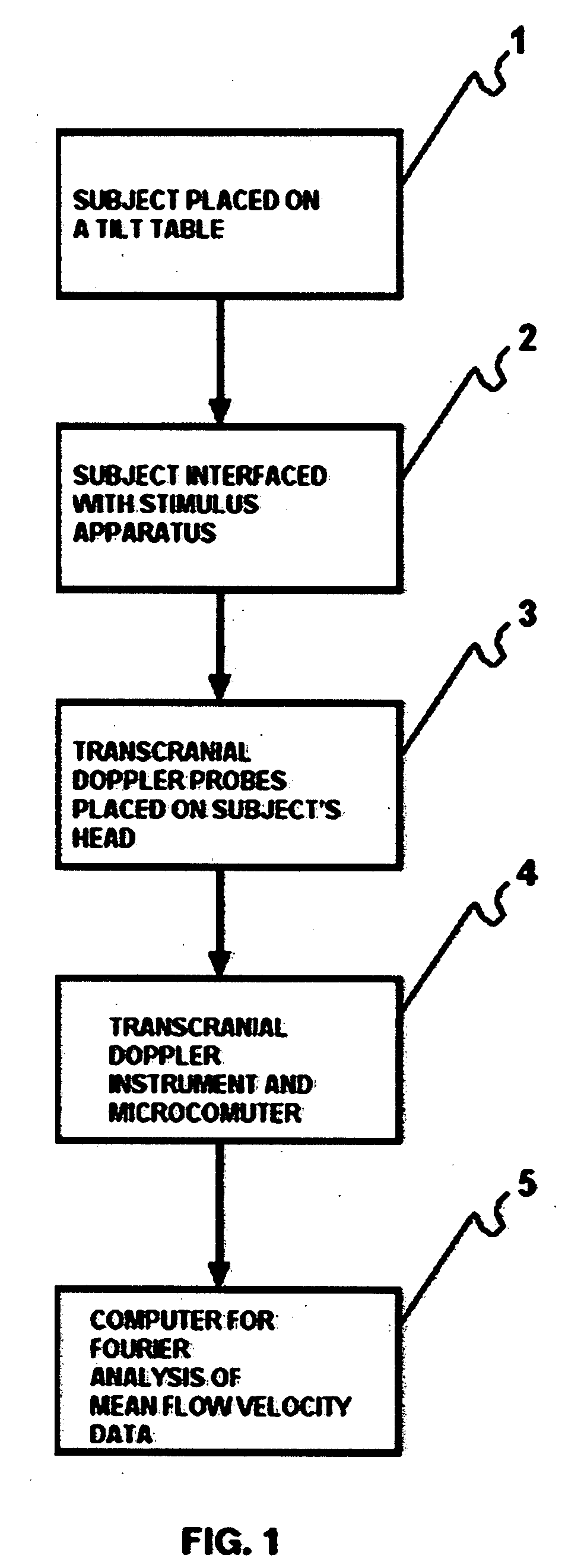
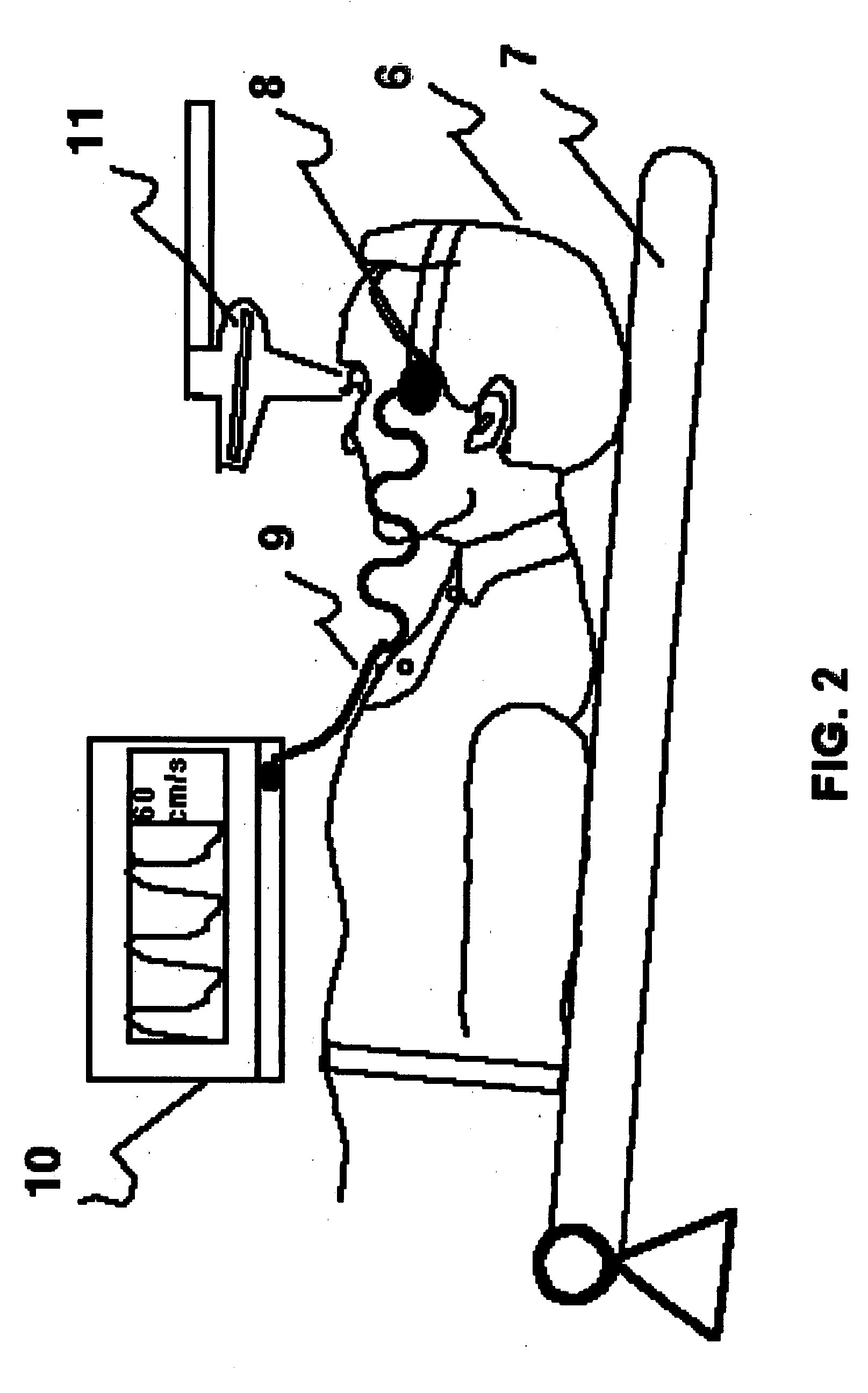
Method for inducing and monitoring long-term potentiation and long-term depression using transcranial doppler ultrasound device in head-down bed rest
InactiveUS20080221452A1Blood flow measurement devicesCatheterUltrasound deviceUltrasound attenuation
The present invention provides a method for monitoring long-term potentiation and long-term depression, comprising placing a subject in head down rest position and monitoring in real-time cerebral mean blood flow velocity using a transcranial Doppler device during psychophysiologic tasks. The method involves using Fourier analysis of mean blood flow velocity data to derive spectral density peaks of cortical and subcortical processes. The effect of head-down rest at different time intervals is seen as accentuation of the cortical peaks in long-term potentiation and attenuation of subcortical peaks in long-term depression. The effect of different interventions could be evaluated for research, diagnosis, rehabilitation and therapeutic use.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
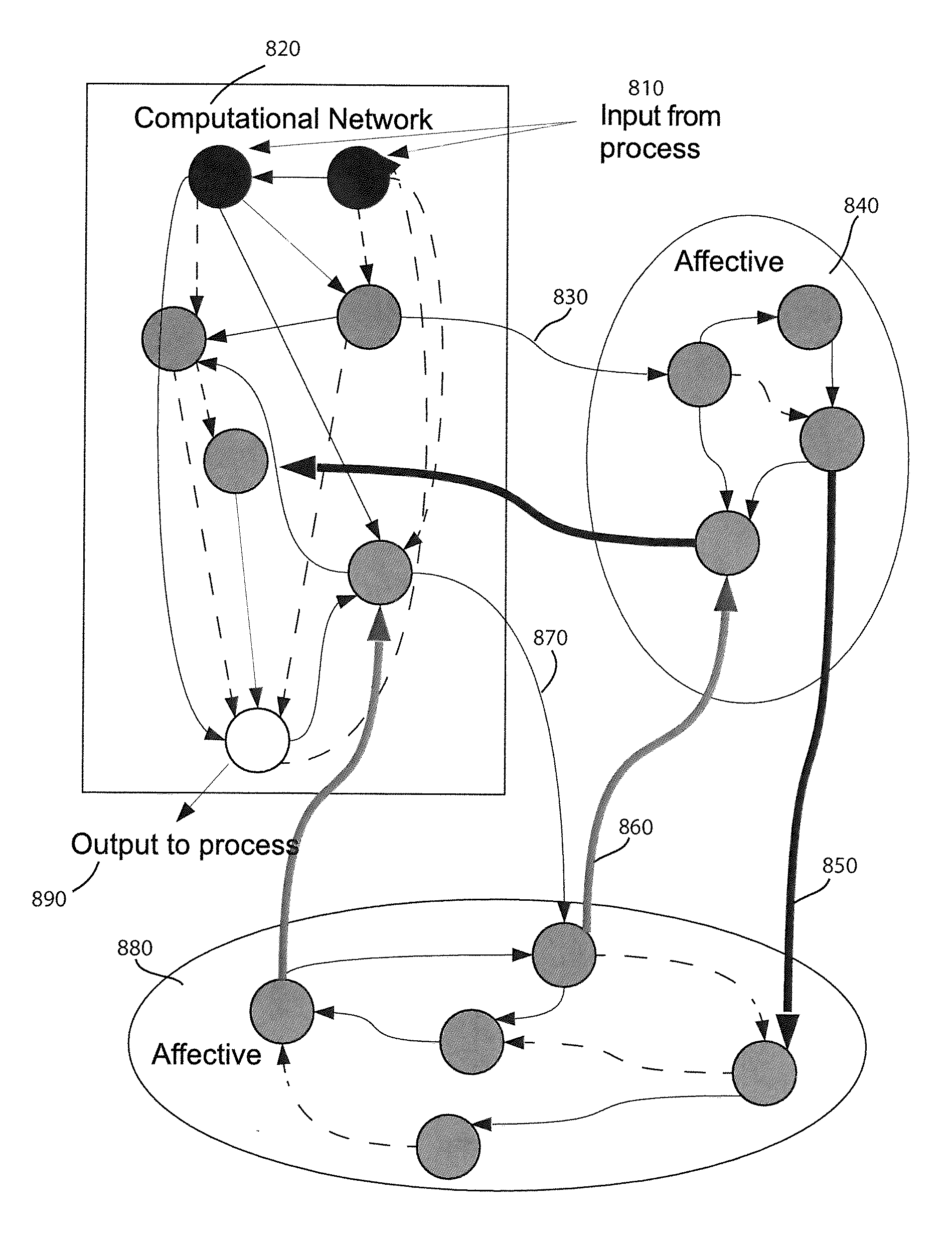
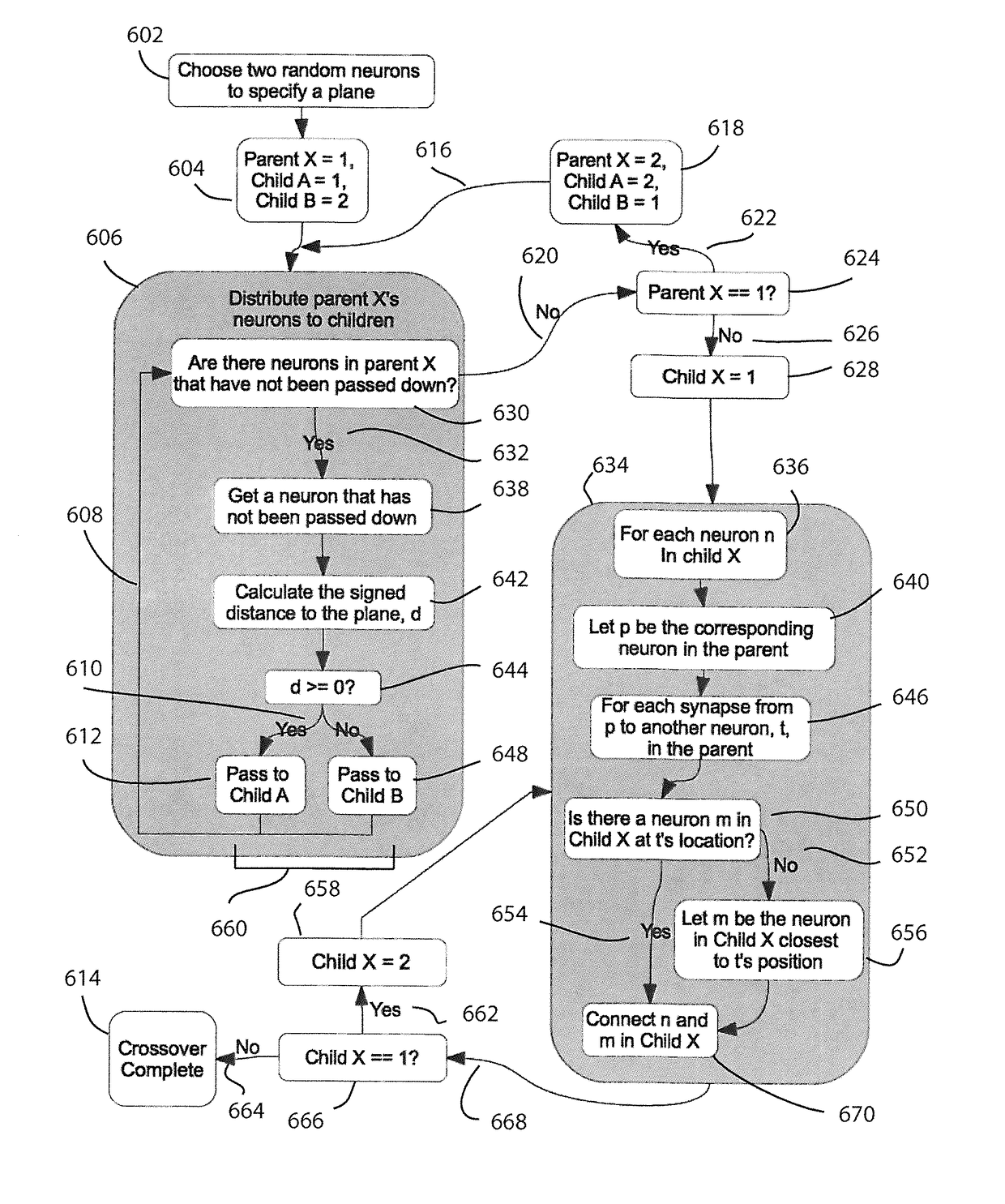
Method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network
ActiveUS20150106310A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsDigital dataComputational neuroscienceAnomaly detection
A method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired dynamic architecture (NIDA) for an artificial neural network is disclosed. The method comprises constructing, in one embodiment, an artificial neural network embodiment in a multi-dimensional space in memory such that a neuron is connected by a synapse to another neuron. The neuron and the synapse each have parameters and have features of long-term potentiation and long-term depression. Furthermore, crossover and mutation are employed to select children of parents. Through learning, an initial network may evolve into a different network when NIDA is applied to solve different problems of control, anomaly detection and classification over selected time units. The apparatus comprises in one embodiment a computational neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network with at least one affective network coupled to receive input data from an environment and to output data to the environment.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Neuromodulation devices and methods
InactiveUS20130281890A1Increase probabilityIncreased riskUltrasound therapyHead electrodesLong-term potentiationNon invasive
Disclosed are methods and systems for deep or superficial deep-brain stimulation using multiple therapeutic modalities, including up-regulation or down-regulation using ultrasound impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). Also disclosed are: methods and systems for patient-feedback control of non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation; devices for producing shaped or steered ultrasound for non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation; methods and systems using intersecting ultrasound beams; non-invasive ultrasound-neuromodulation techniques to control the permeability of the blood-brain barrier; non-invasive neuromodulation of the spinal cord by ultrasound energy; methods and systems for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound for evaluating the feasibility of neuromodulation treatment using non-ultrasound / ultrasound modalities; and method and systems for neuromodulation using ultrasound delivered in sessions.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Ultrasound neuromodulation treatment of depression and bipolar disorder
InactiveUS20120283502A1Treatment for depressionAffect stateUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsBipolar mood disorderBipolar I disorder
Owner:NEUROTREK
Orgasmatron via deep-brain neuromodulation
InactiveUS20110213200A1Effective serviceUltrasound therapyHead electrodesUltrasonic sensorMultiple point
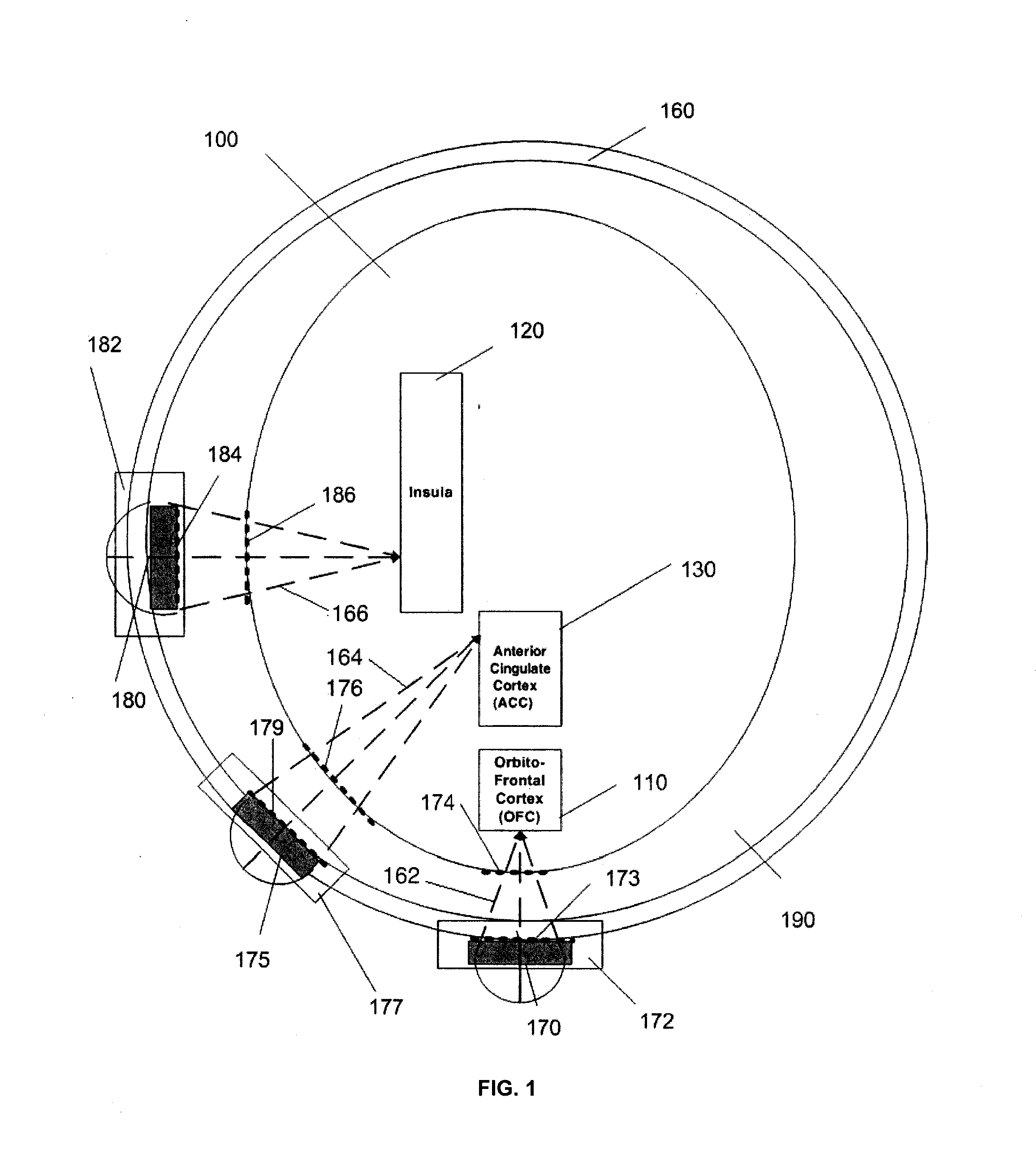
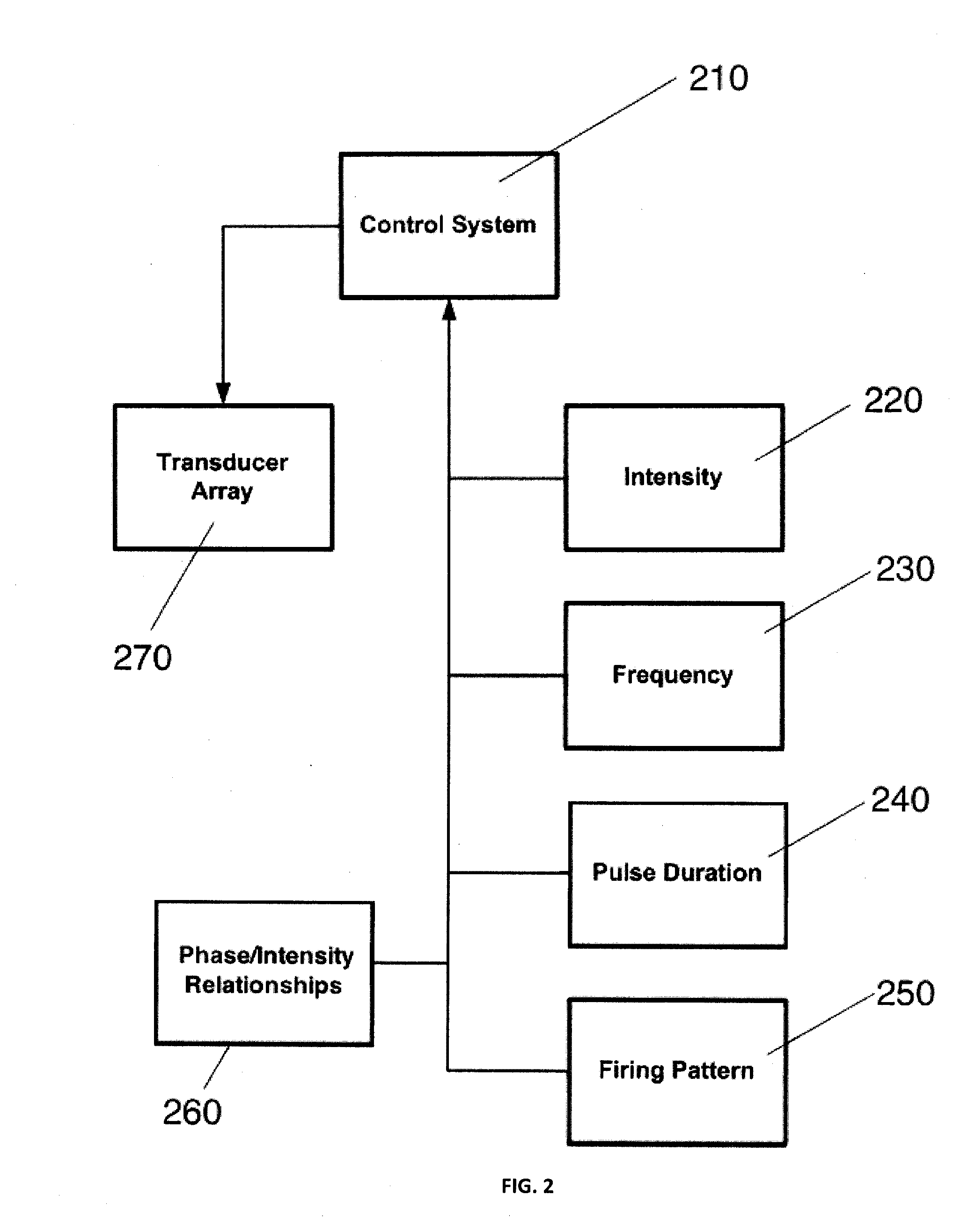
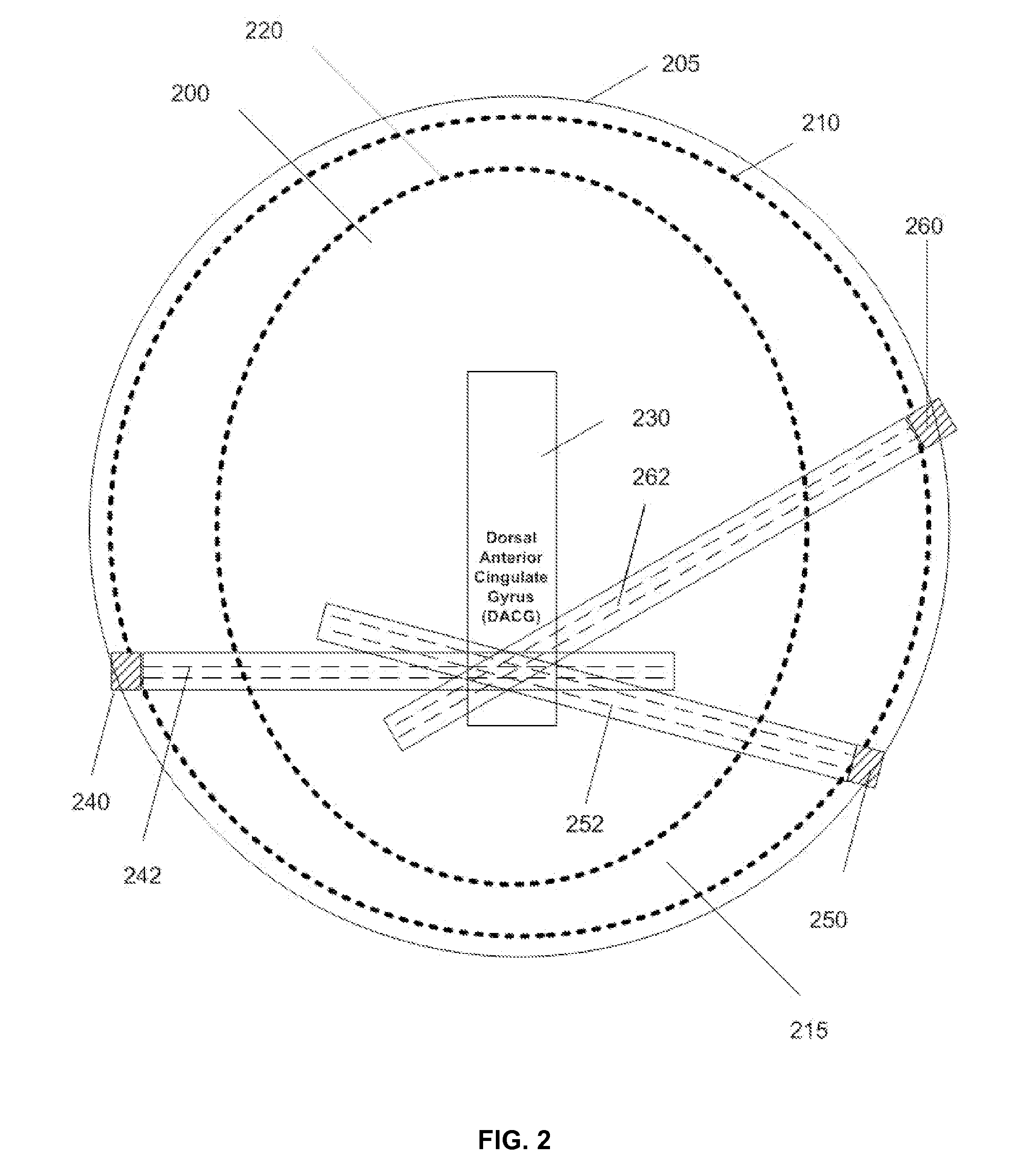
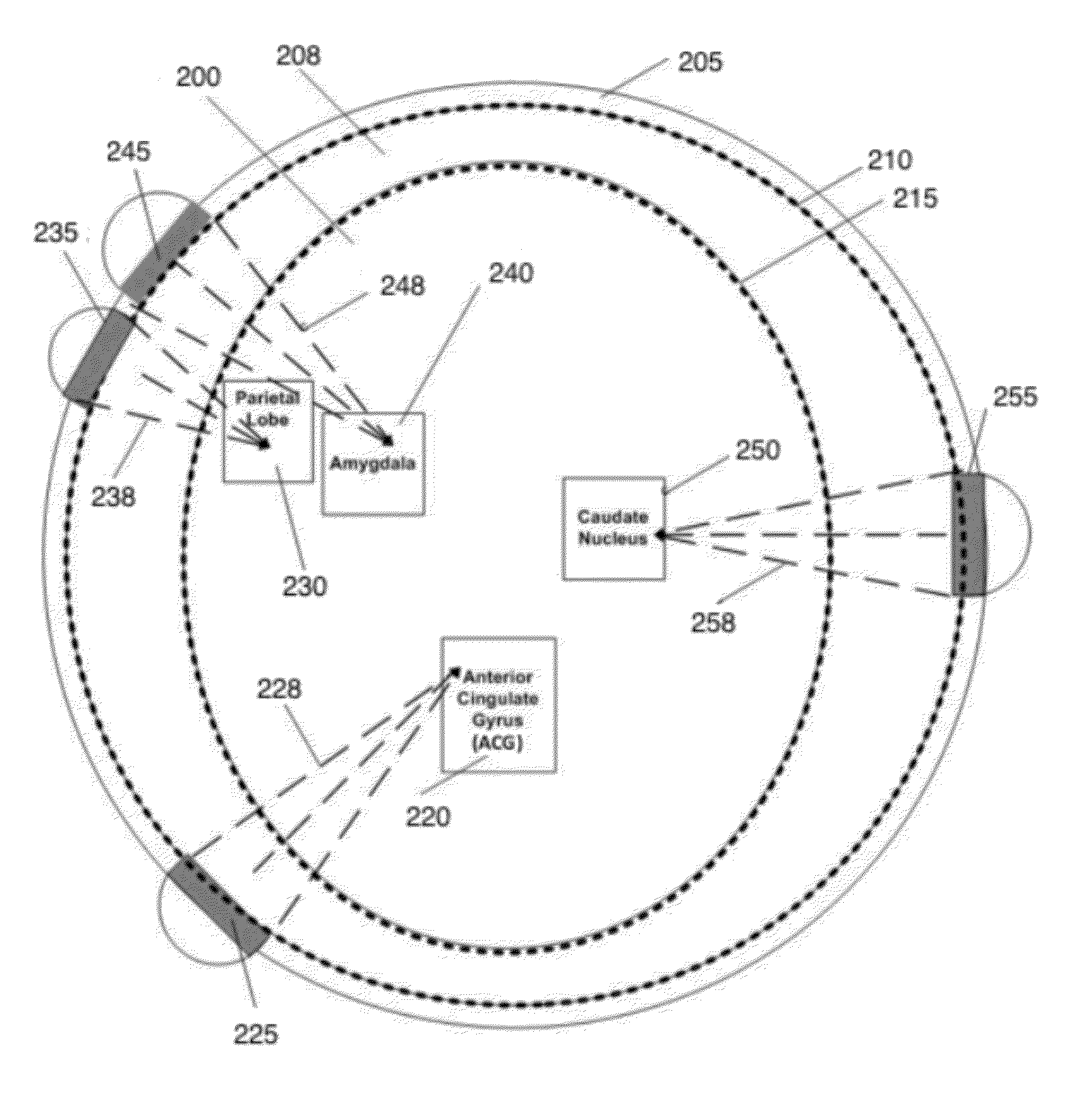
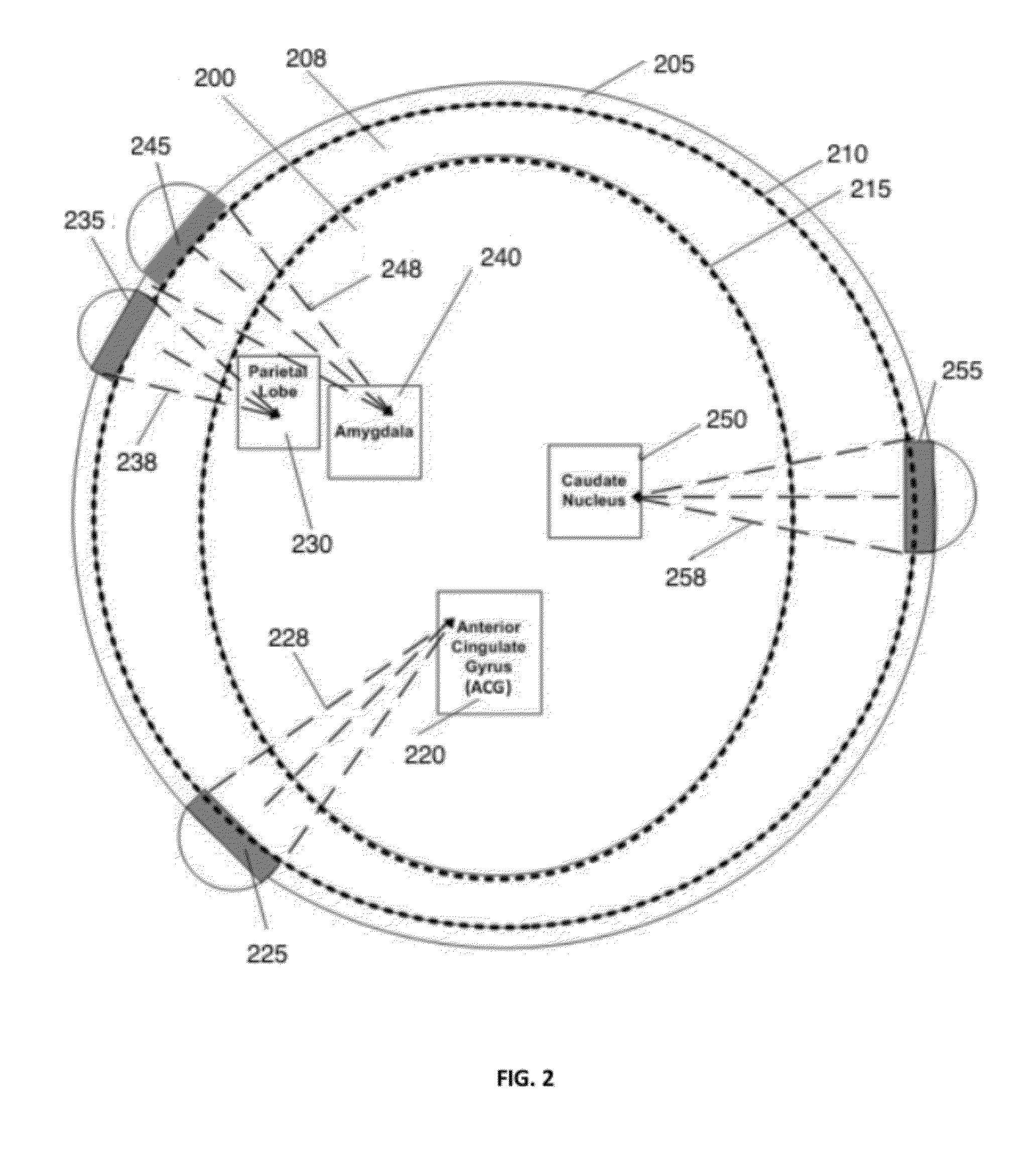
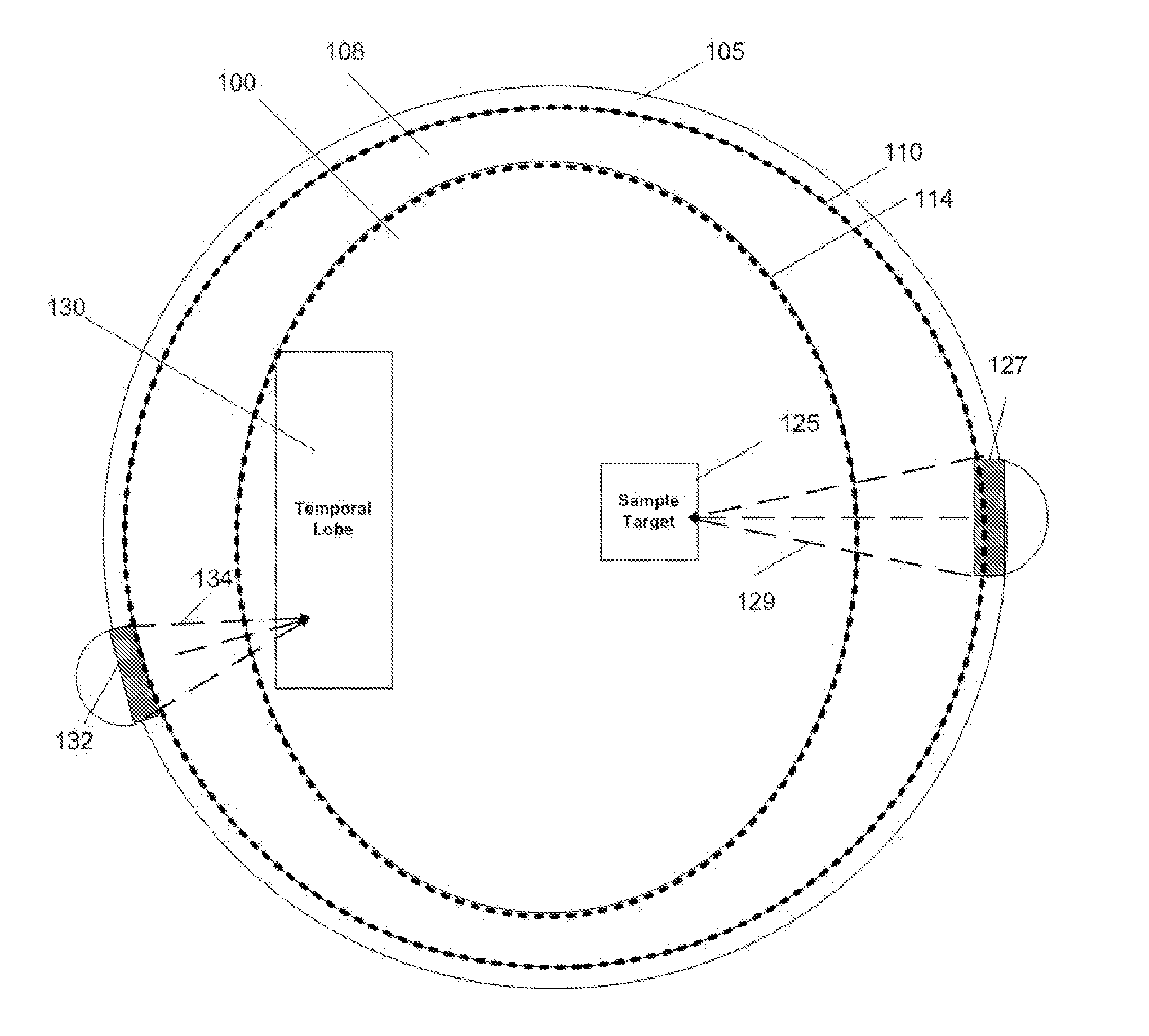
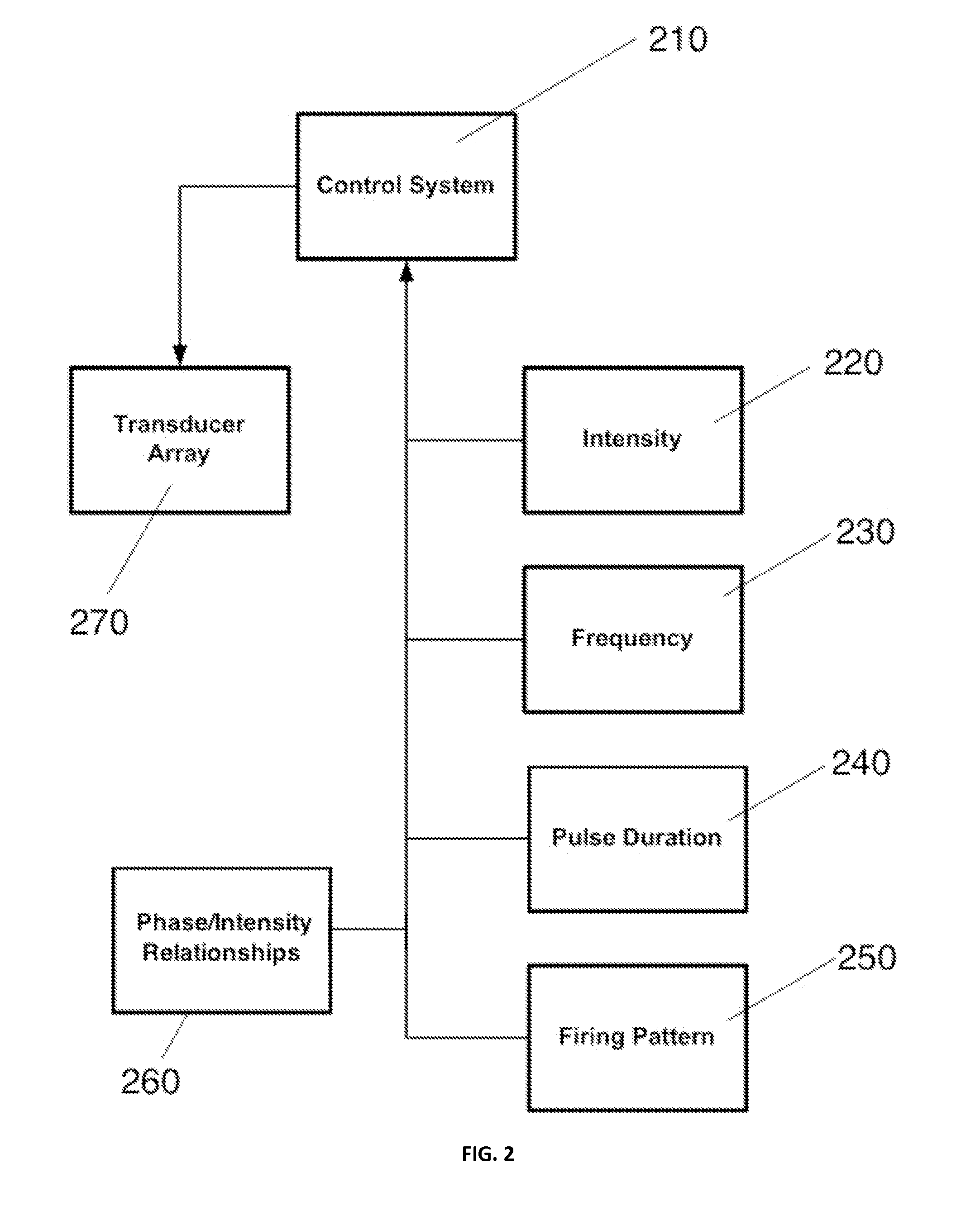
It is the purpose of this invention to provide methods and systems for non-invasive deep brain neuromodulation using ultrasound for the treatment of anorgasmia, hypo-orgasmia, and for the production of orgasms (Orgasmatron). This can include impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). The ultrasound transducers are attached at fixed positions on a holder. Use of ancillary monitoring or imaging to provide feedback is optional. Control of the ultrasonic transducers includes control of direction of the energy emission, intensity, frequency, and phase / intensity relationships to targeting and accomplishing up-regulation and / or down-regulation.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
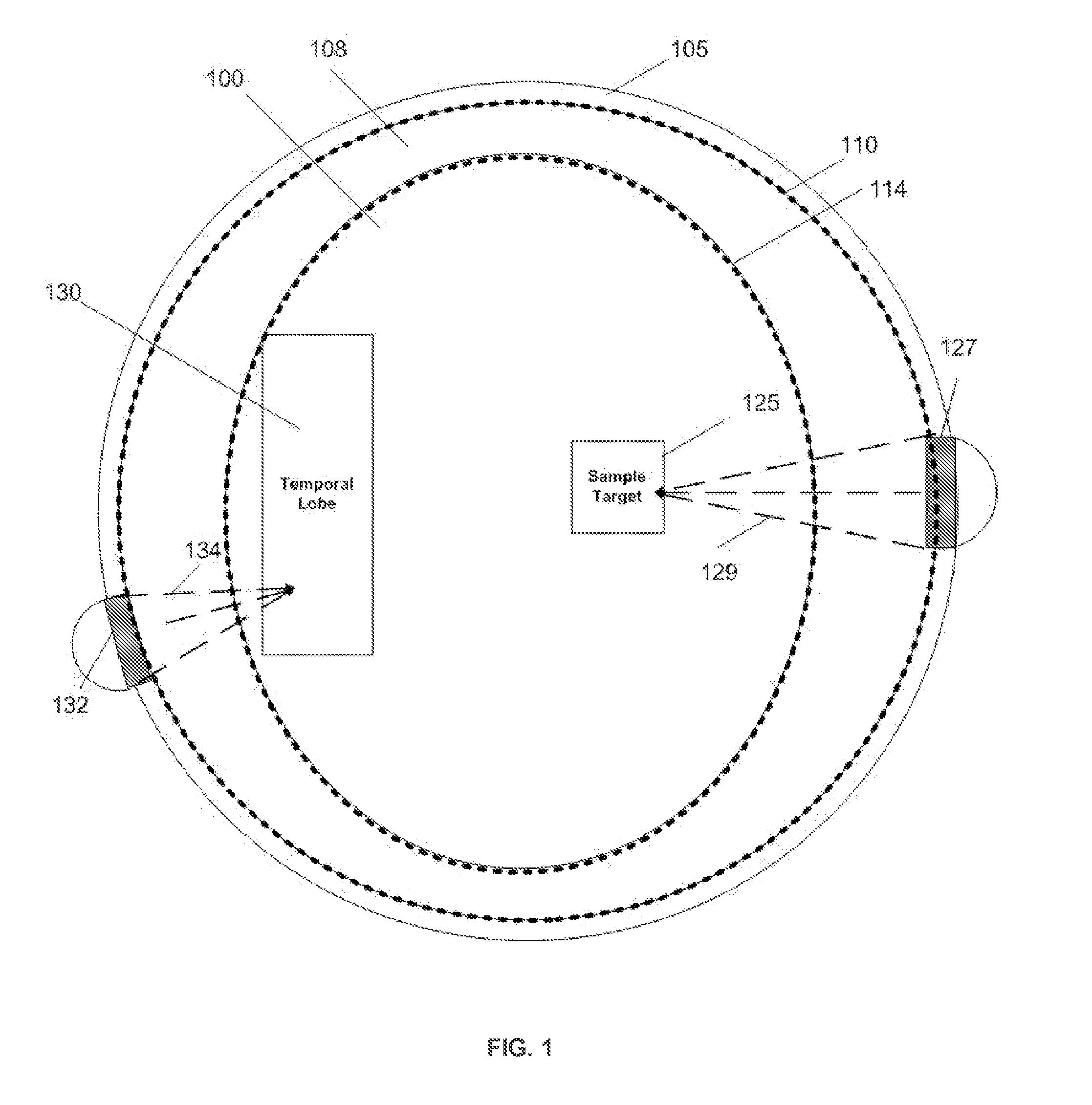
Ultrasound-intersecting beams for deep-brain neuromodulation
Disclosed are methods and devices for ultrasound-mediated non-invasive deep brain neuromodulation impacting one or a plurality of points in a neural circuit using intersecting ultrasound beams. Depending on the application, this can produce short-term effects (as in the treatment of post-surgical pain) or long-term effects in terms of Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD) to treat indications such as neurologic and psychiatric conditions. Multiple beams intersect and summate at one or a plurality of targets. The ultrasound transducers are used with control of direction of the energy emission, intensity, frequency (carrier frequency and / or neuromodulation frequency), pulse duration, pulse pattern, and phase / intensity relationships to targeting and accomplishing up-regulation and / or down-regulation.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Method and apparatus for providing random selection and long-term potentiation and depression in an artificial network
ActiveUS20150106315A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesNeuronSynapse structure
A digital circuit element of a two dimensional dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a neuron / synapse select input functional to select the digital circuit element to function as one of a neuron and a synapse. In one embodiment of a DANNA array of such digital circuit elements, a destination neuron may be connected to a first neuron by a first synapse in one dimension, a second destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a second synapse in a second dimension and, optionally, a third destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a third synapse thus forming multiple levels of neuron and synapse digital circuit elements. In one embodiment, multiples of eight inputs may be selectively received by the digital circuit element selectively functioning as one of a neuron and a synapse. The dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may implement long-term potentiation or depression to facilitate learning through the use of an affective system and random selection of input events.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
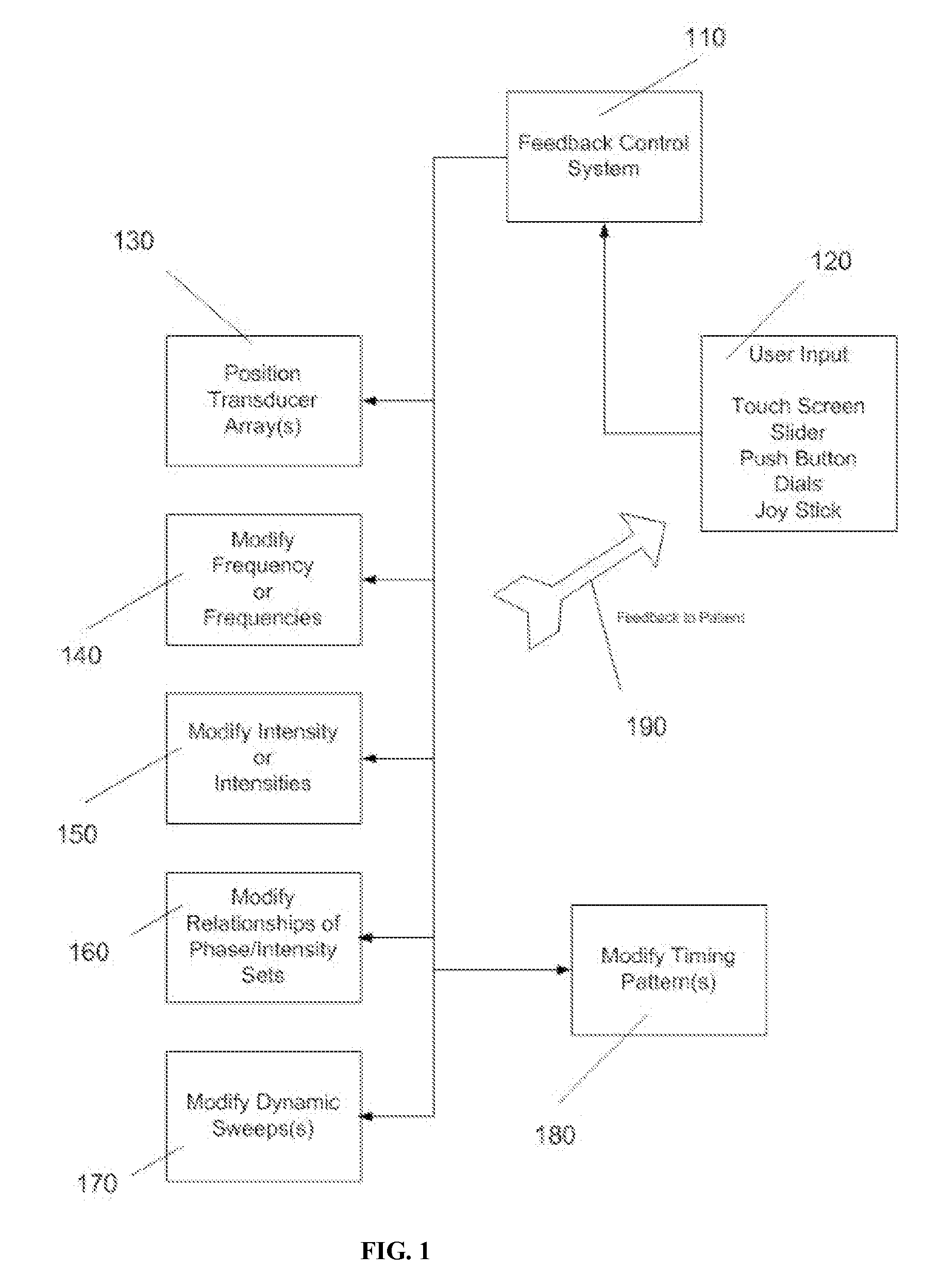
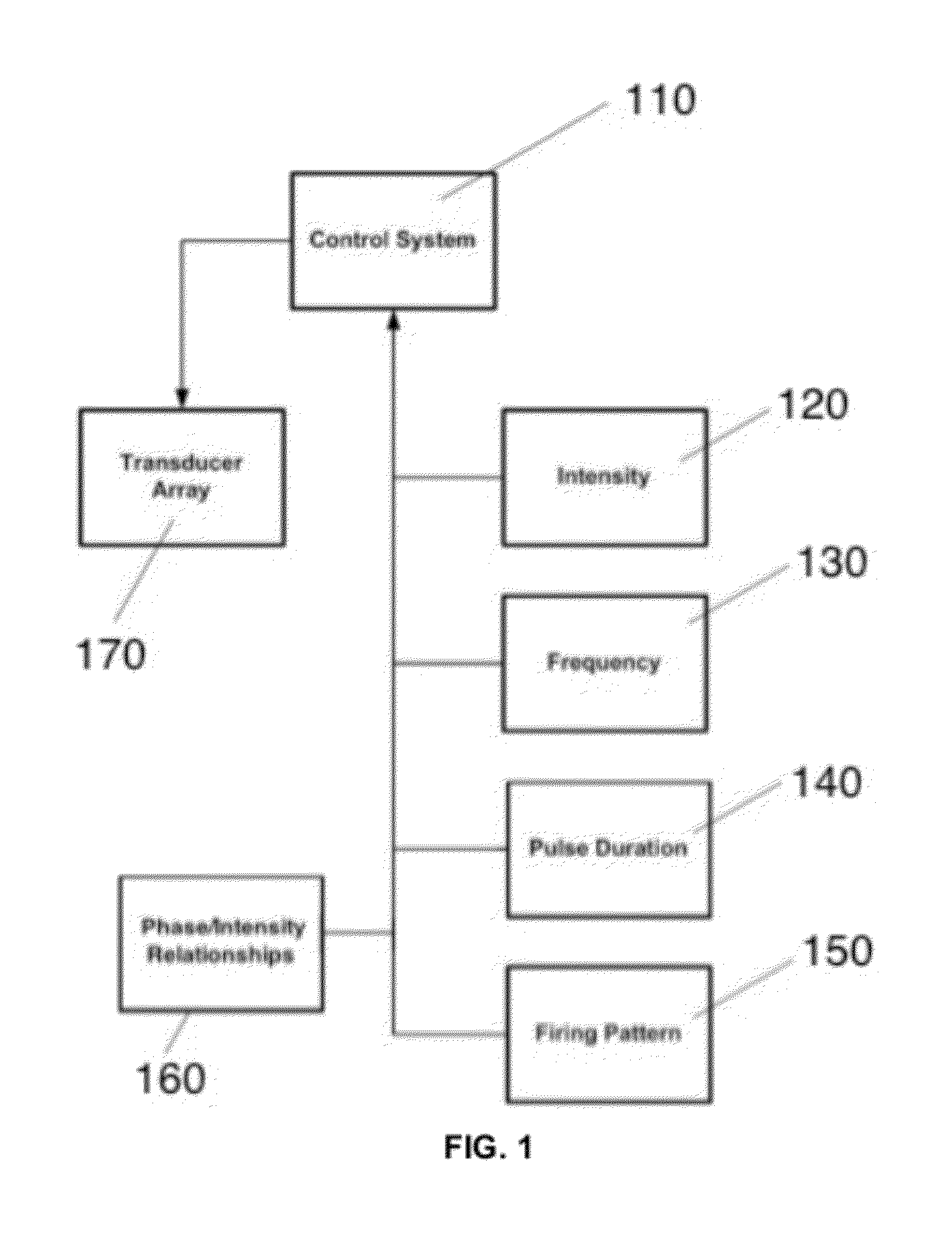
Patient feedback for control of ultrasound deep-brain neuromodulation
InactiveUS20110178442A1Optimize patient experienceDecrease in acute painUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesDiseaseSonification
Disclosed are methods and systems and methods for patient-feedback control of non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation using sound impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce acute effects and, with application in multiple sessions, Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD) to treat indications such as neurologic and psychiatric conditions. One or more of sonic transducer positioning, intensity, frequency, dynamic sweeps, phase / intensity relationships, and firing patterns are changed through feedback from the patient to optimize patient experience through up-regulation or down regulation. Examples are decreases in acute pain or tremor due to more effective impact on the neural targets.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Devices and methods for optimized neuromodulation and their application
InactiveUS20170246481A1Less riskPromote resultsUltrasound therapyHead electrodesDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySpinal cord
Disclosed are methods and systems for optimized deep or superficial deep-brain stimulation using multiple therapeutic modalities impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). Also disclosed are methods for treatment of clinical conditions and obtaining physiological impacts. Also disclosed are: methods and systems for Guided Feedback control of non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation; patterned neuromodulation, ancillary stimulation, treatment planning, focused shaped or steered ultrasound; methods and systems using intersecting ultrasound beams; non-invasive ultrasound-neuromodulation techniques to control the permeability of the blood-brain barrier; non-invasive neuromodulation of the spinal cord by ultrasound energy; methods and systems for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound for evaluating the feasibility of neuromodulation treatment using non-ultrasound / ultrasound modalities; neuromodulation of the whole head, treatment of multiple conditions, and method and systems for neuromodulation using ultrasound delivered in sessions.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Weight adjustment circuit for variable-resistance synapses
InactiveCN102610274AImplement STDP weight adjustment functionSimple structureDigital storageSynapseNerve network
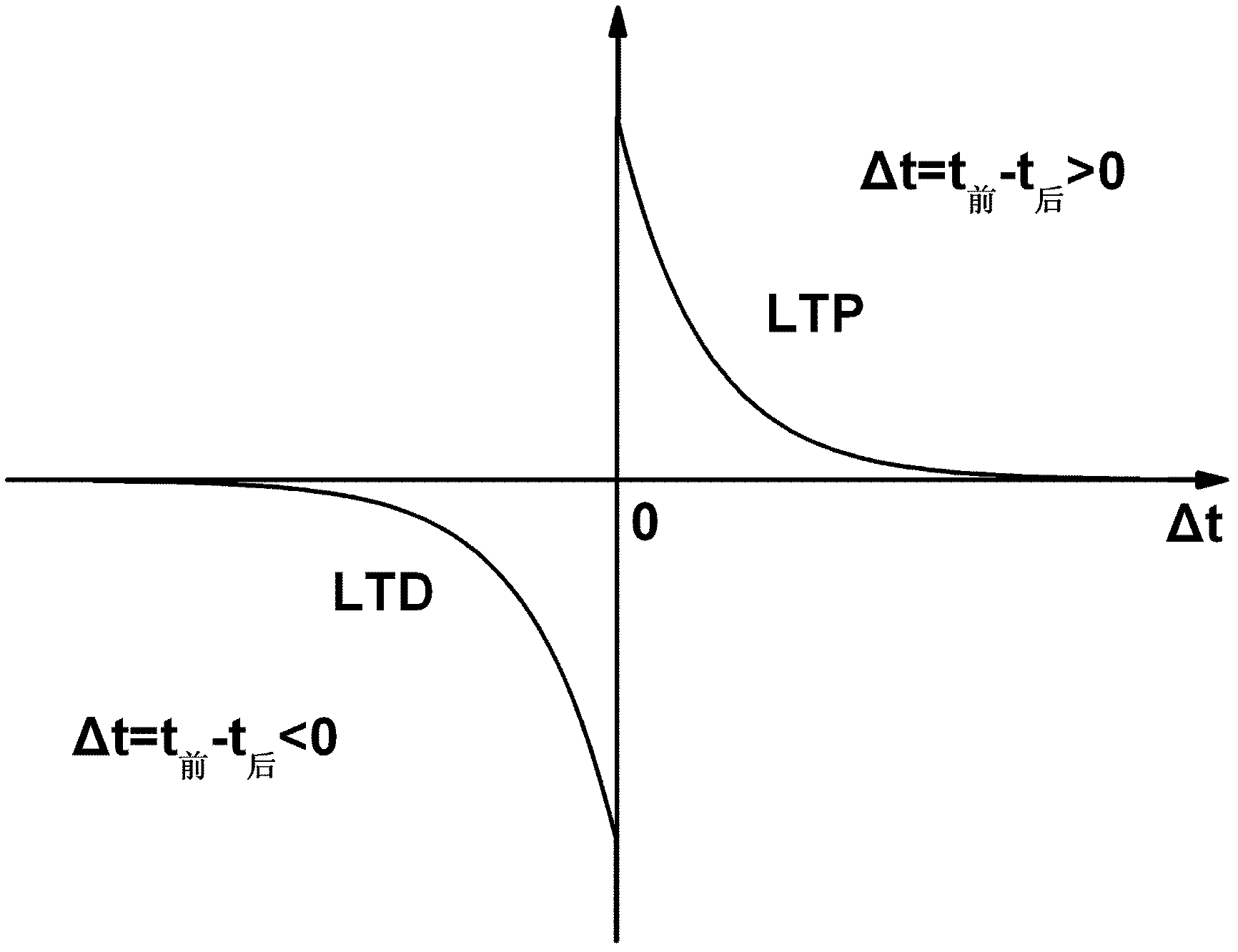
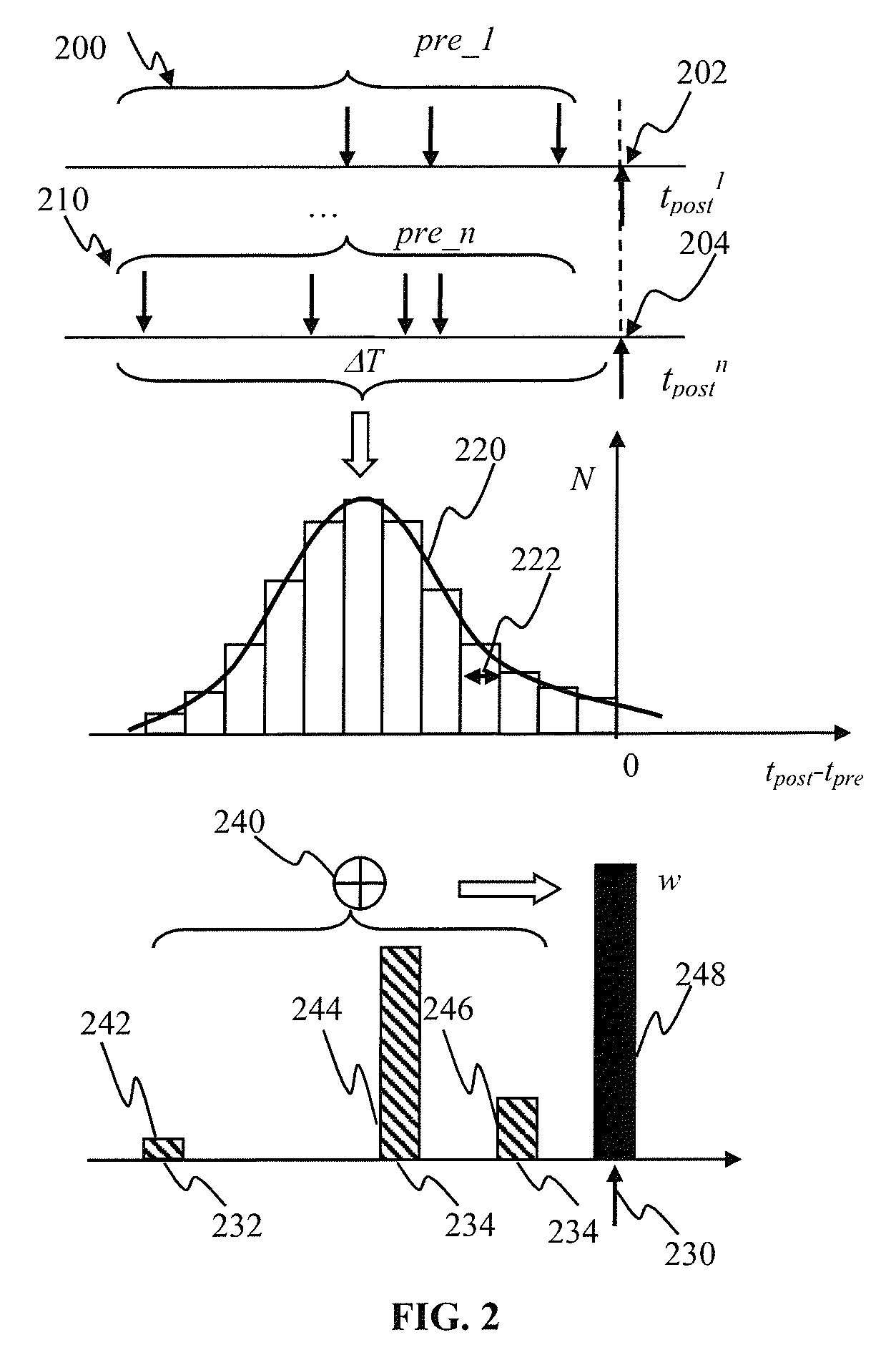
The invention discloses a weight adjustment circuit for variable-resistance synapses, which relates to the fields of integrated circuits and neural networks, and is used for carrying out weight adjustment on variable-resistance synapses. The circuit is composed of a weight enhancement adjustment subcircuit A (LTP (long term potentiation) adjustment) and a weight inhibition adjustment subcircuit B (LTD (long term depression) adjustment), wherein the two subcircuits respectively contain a charging pole, a discharging pole, a charge storage pole and an output pole. The core of the circuit is implemented by using an analog circuit mode, therefore, the number of transistors required by the circuit is greatly reduced; and meanwhile, through the setting of the bias voltage on a discharge tube in the discharge pole, the size of a weight adjustment time window can be adjusted conveniently. The circuit disclosed by the invention follows an STDP (spike timing dependent plasticity) learning rule, and LTP and LTD pulse outputs are generated according to the activities of nerve units at the two ends of the variable-resistance synapses so as to carry out corresponding weight adjustment on the variable-resistance synapses. The circuit disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, convenient in parameter adjustment, and suitable for applications, such as weight adjustment on electronic synapses of a large-scale neural network, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Human face recognition method based on local feature learning
InactiveCN102156887AEasy to identifyImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionPositive sampleFeature learning
The invention discloses a human face recognition method based on local feature learning, which comprises the following steps of: (a) partitioning a known classified human face sample into blocks, and calculating data of the human face sample of each block through an LBP (Length Between Perpendiculars) operator and an LTP (Long-Term Potentiation) operator to obtain a local histogram vector a of data of the human face sample of each block; (b) performing chi-square histogram distance calculation on local histogram vectors of the same positions on any two different human face samples of the same person in all human face samples to obtain a positive sample feature library; and (c) performing chi-square histogram distance calculation on local histogram vectors of the same positions on any two human face samples of different persons in all human face samples to obtain a negative sample feature library. The human face recognition method based on the local feature learning, provided by the invention, has the advantages of quick response, high accuracy and good recognition effect.
Owner:MYDIGITHAT TECH
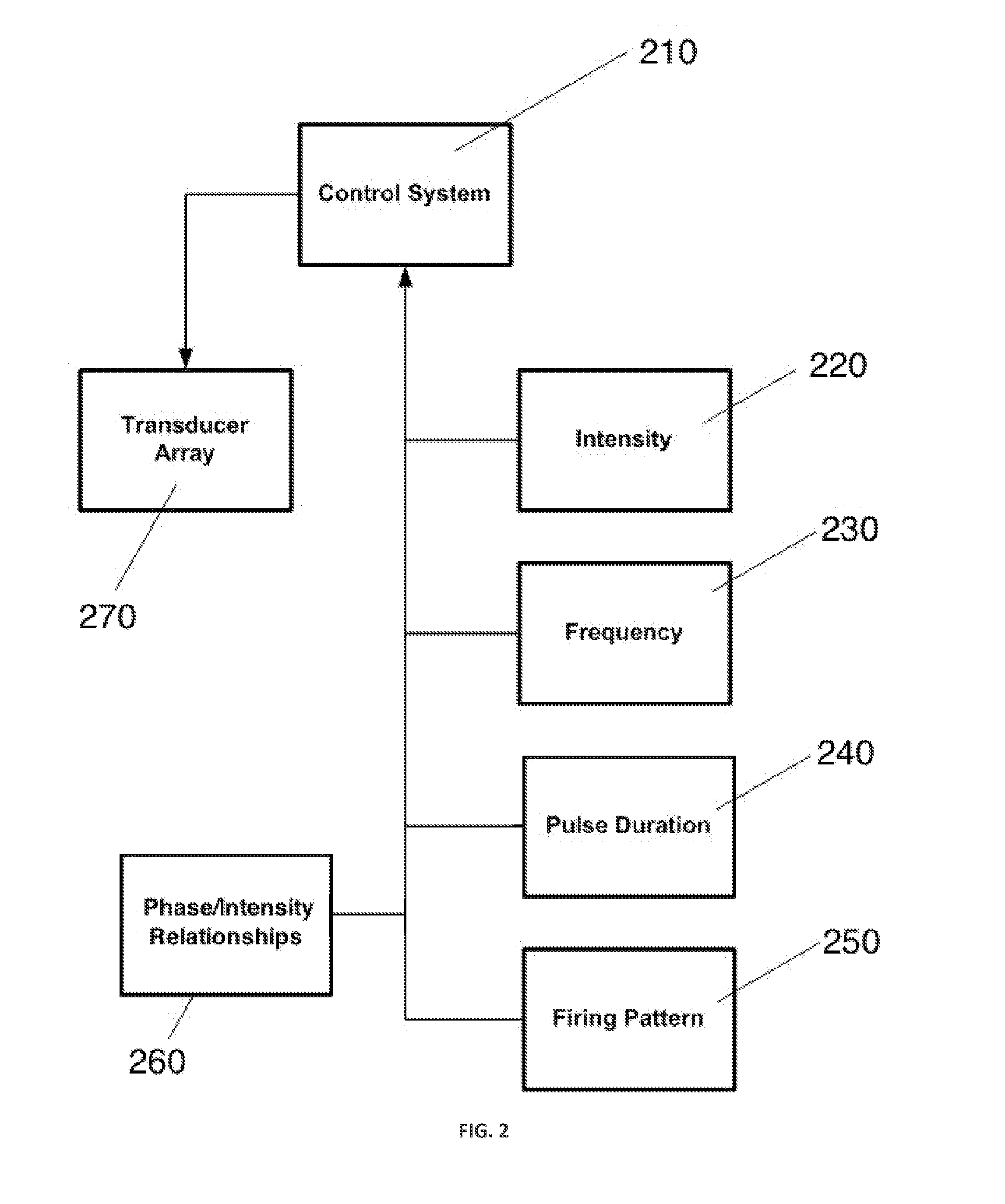
Patterned control of ultrasound for neuromodulation
InactiveUS20120197163A1Enhanced non-invasive superficialUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsDiseaseSonification
Disclosed are methods and devices for ultrasound-mediated non-invasive deep brain neuromodulation impacting one or a plurality of points in a neural circuit using patterned inputs. These are applicable whether the ultrasound beams intersect at the targets or not. Depending on the application, this can produce short-term effects (as in the treatment of post-surgical pain) or long-term effects in terms of Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD) to treat indications such as neurologic and psychiatric conditions. The ultrasound transducers are used with control of frequency, firing pattern, and intensity to produce up-regulation or down-regulation.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Ultrasound neuromodulation of the reticular activating system
Disclosed are methods and systems and methods for neuromodulation of the Reticular Activating System using ultrasound to produce acute effects or Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). Included is control of direction of the energy emission, intensity, pulse duration, frequency, and phase / intensity relationships to targeting and accomplishing up-regulation and / or down-regulation. The invention can be applied for a variety of clinical purposes such as reversibly putting a patient to sleep or waking them up (for example, for the purpose of anesthesia) or reversibly putting a patient into a coma (for example for the purpose of protecting or rehabilitating the brain of the patient after a stroke or head injury).
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
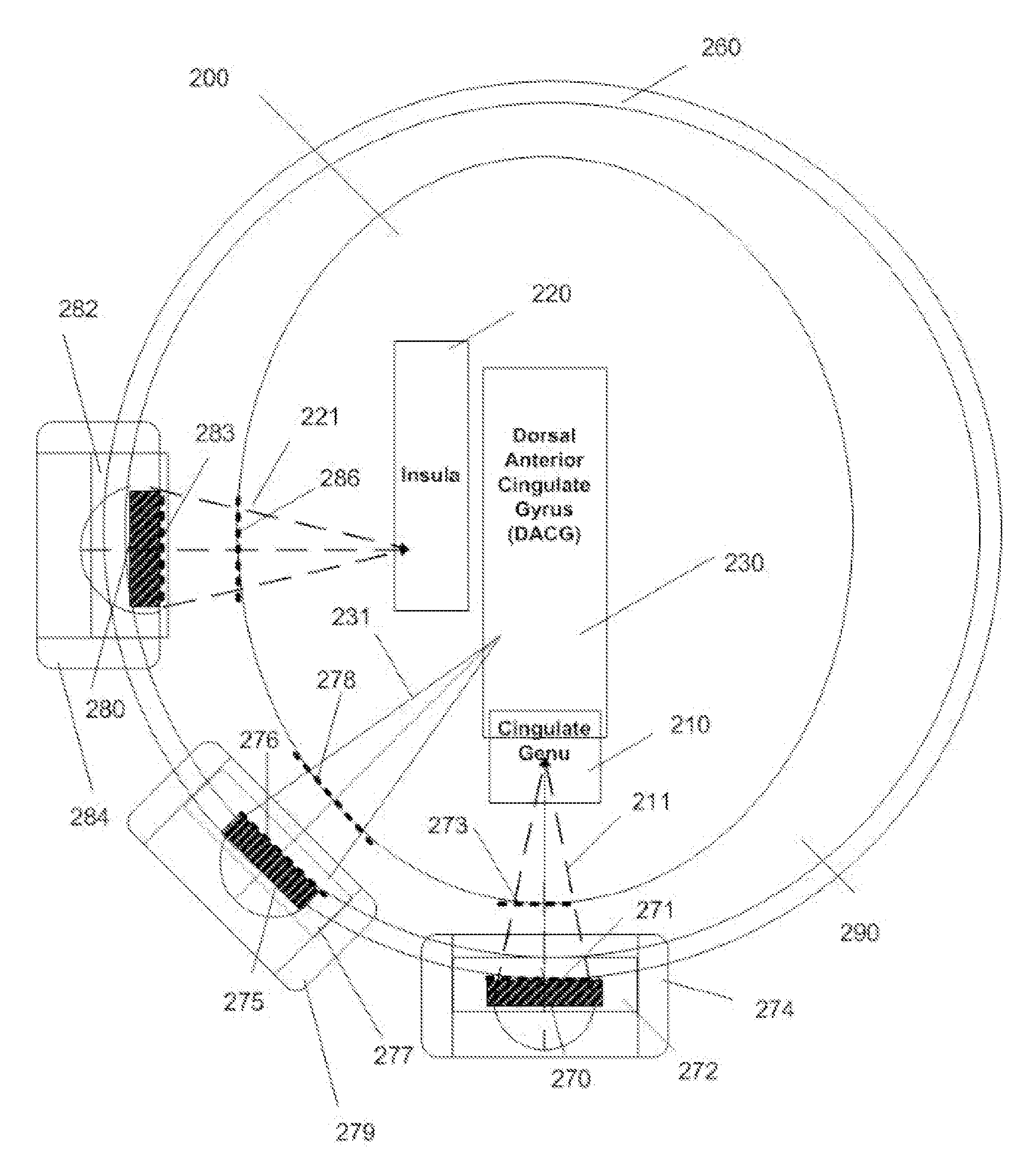
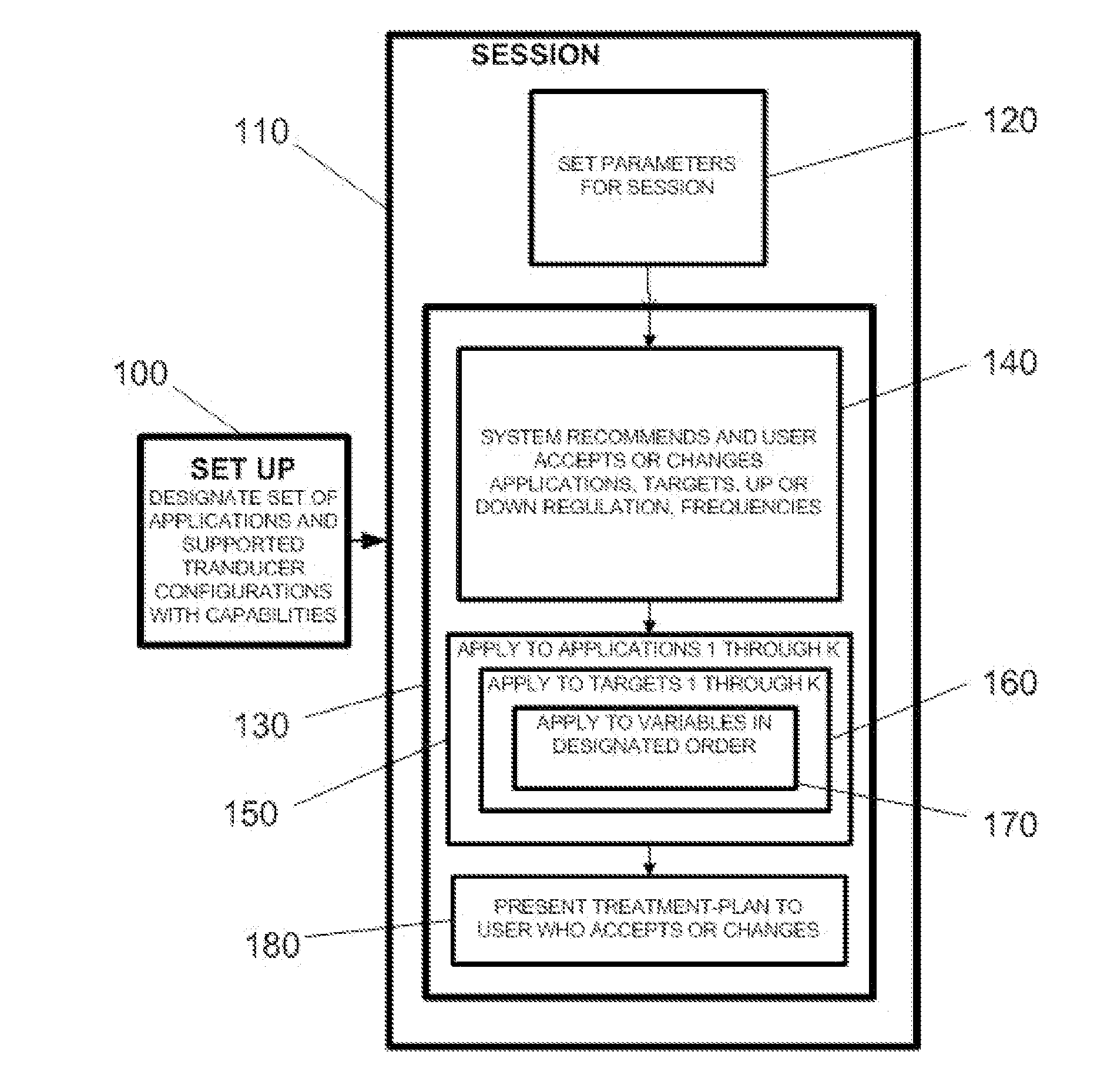
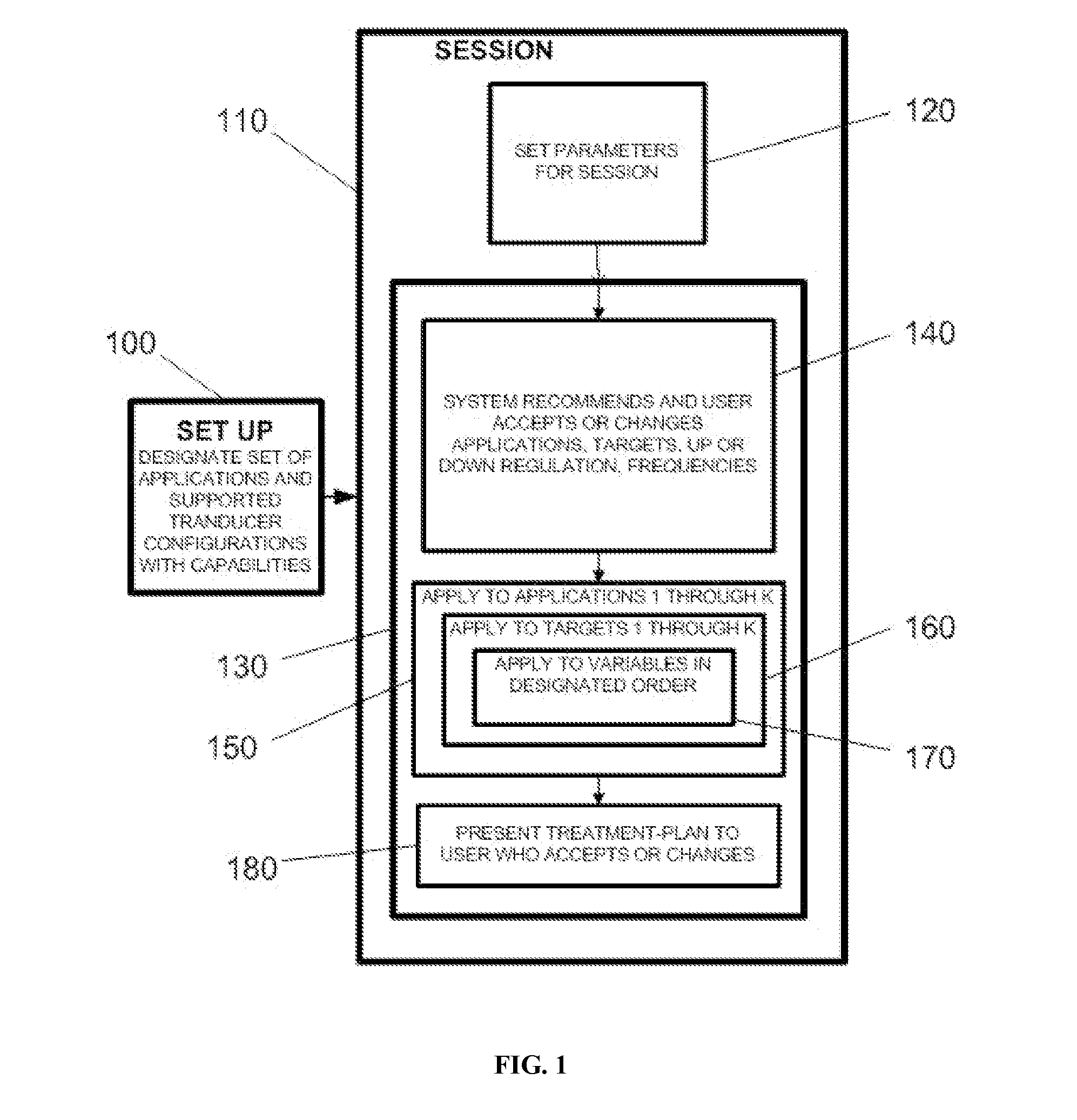
Treatment planning for deep-brain neuromodulation
InactiveUS20130066350A1Good benefitUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDiseaseUltrasonic sensor
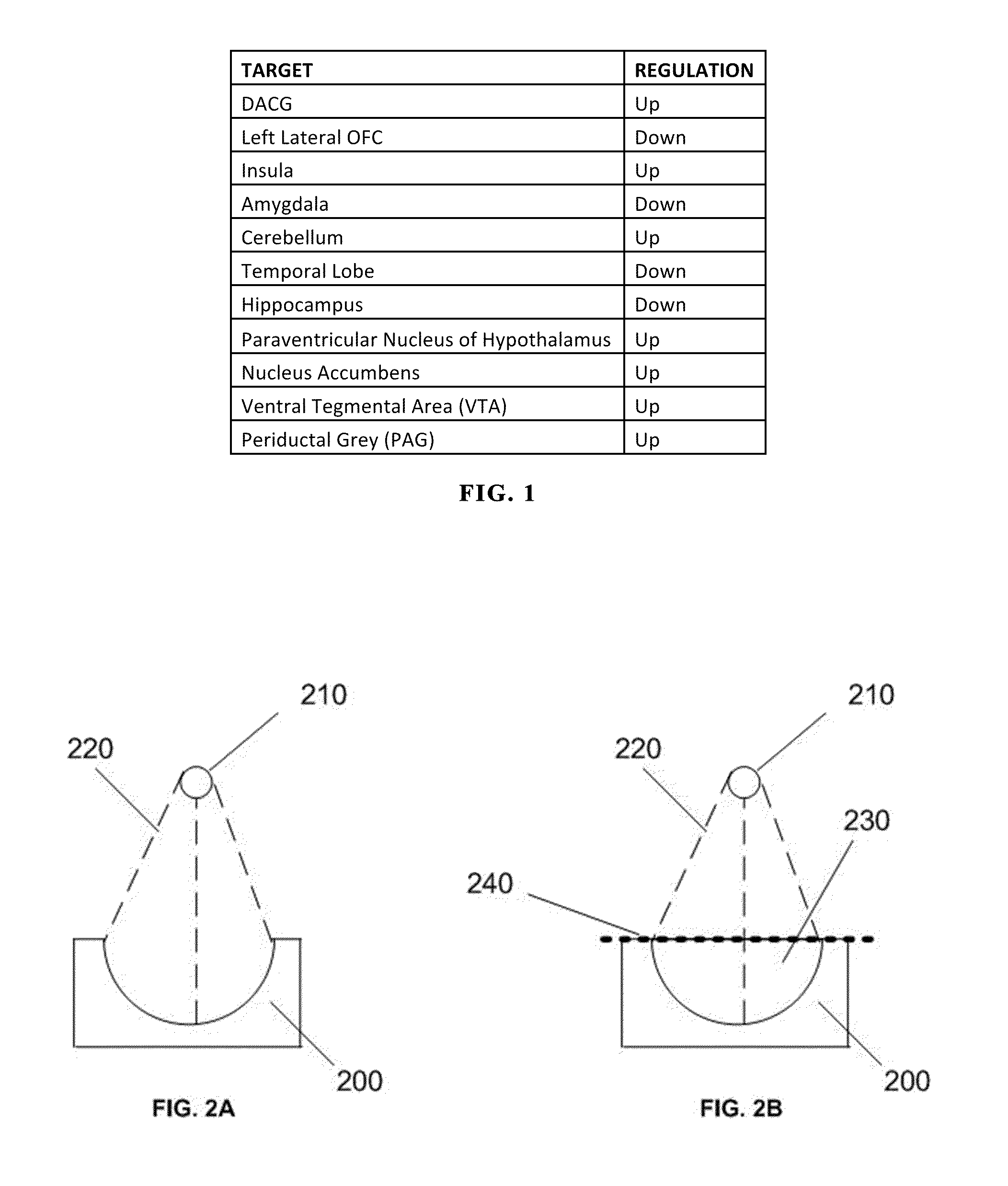
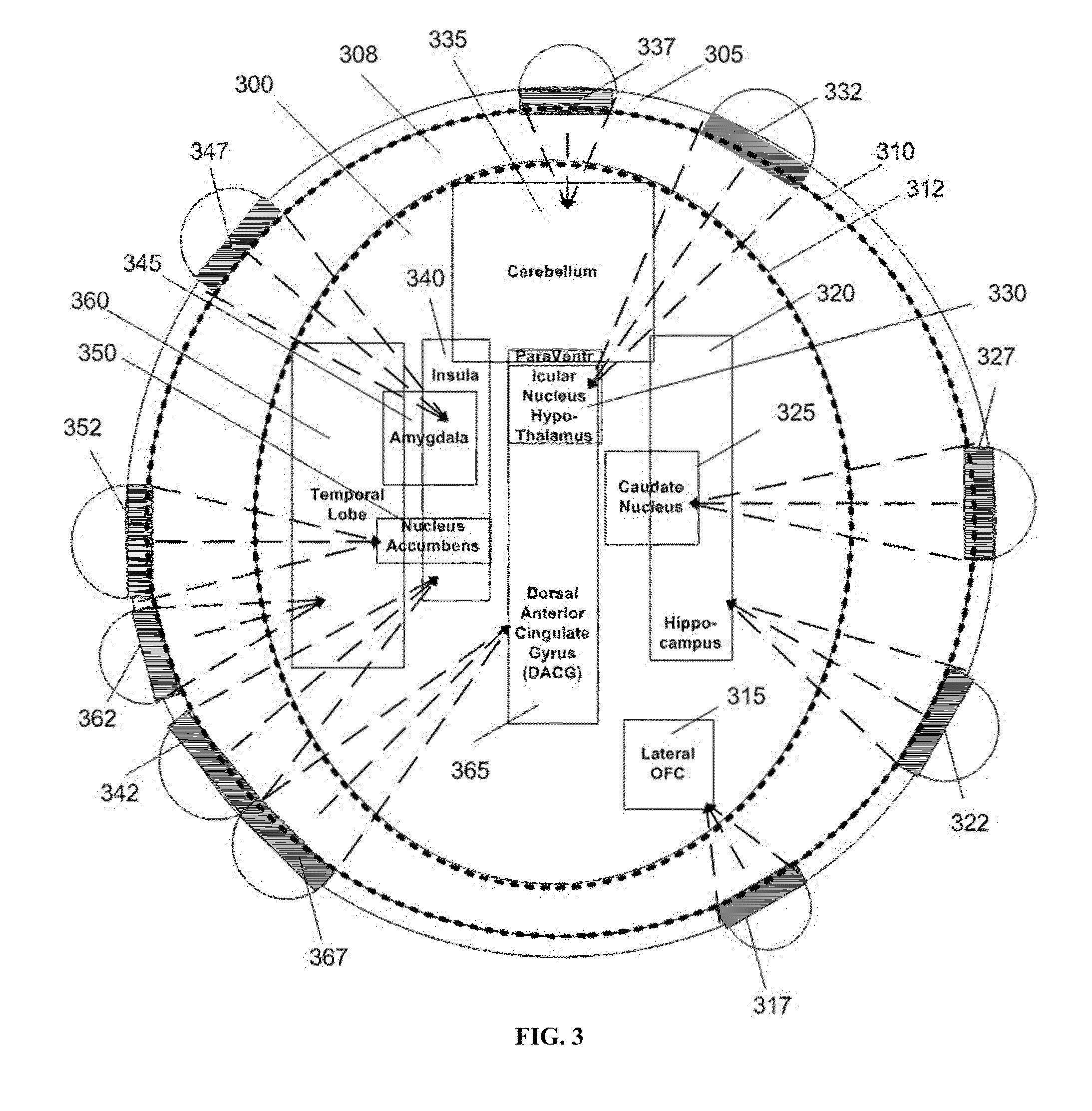
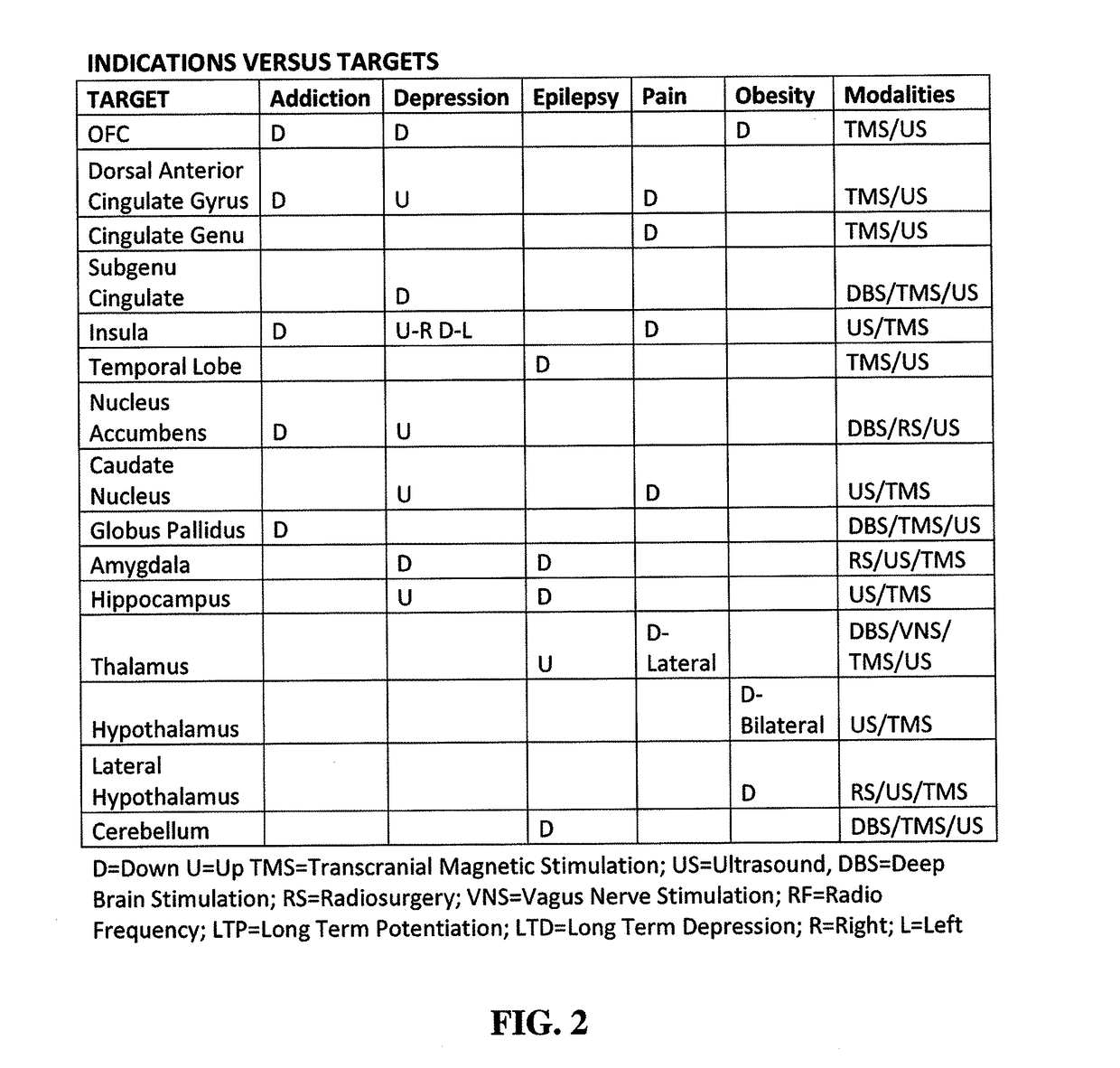
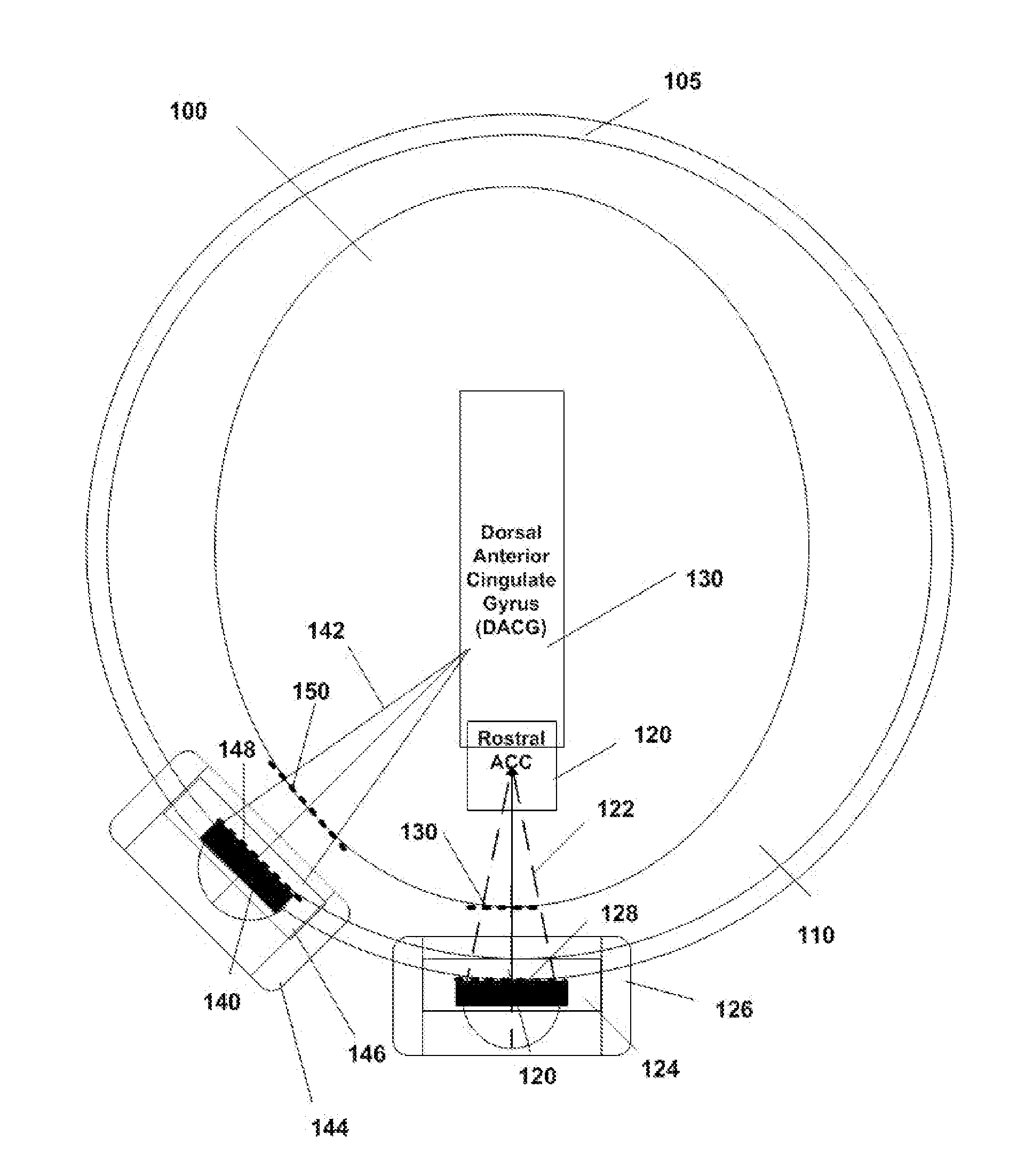
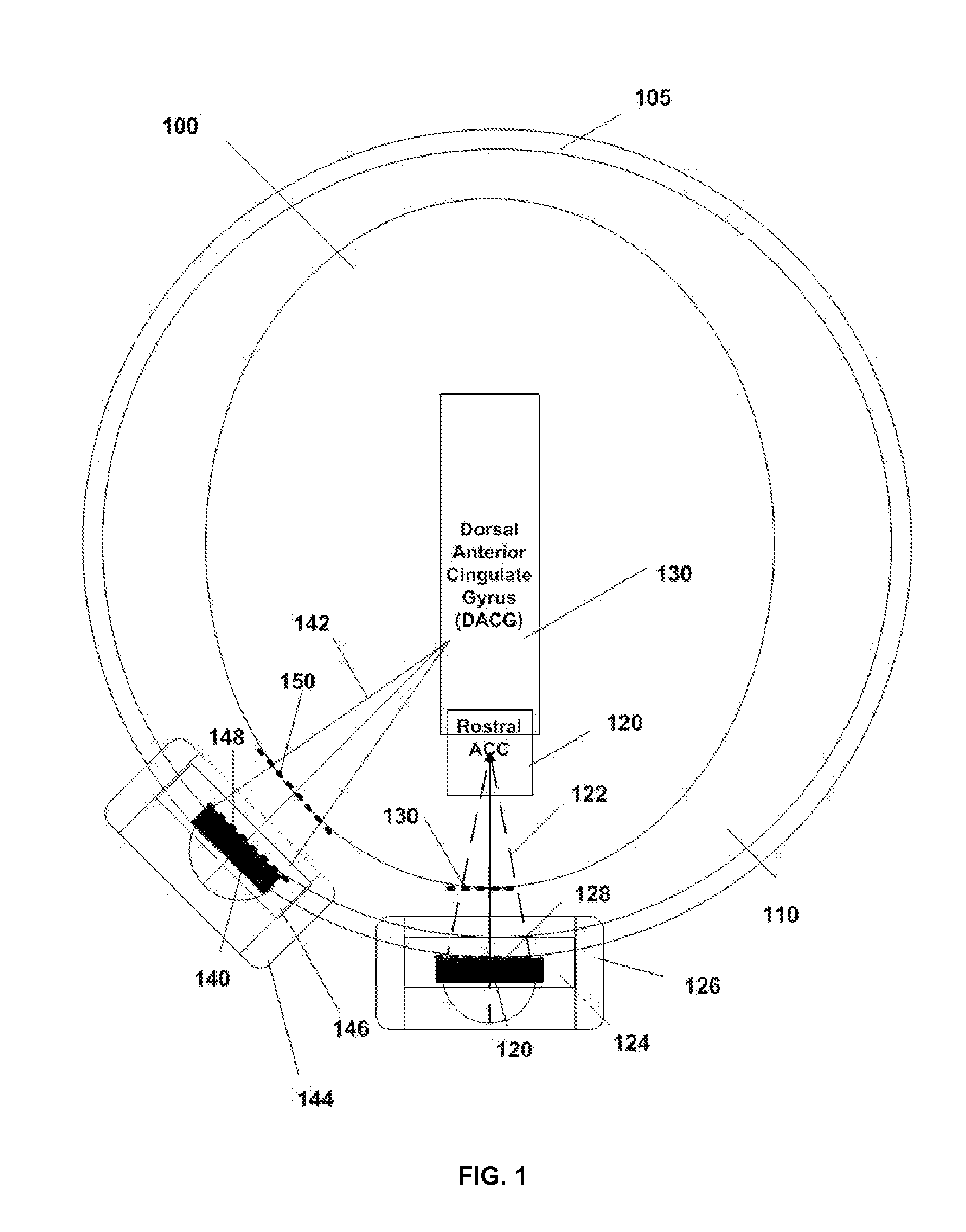
Disclosed are methods and systems for treatment planning for deep brain or superficial neuromodulation using ultrasound and other treatment modalities impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce acute effects or Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD) to treat indications such as neurologic and psychiatric conditions. Ultrasound transducers or other energy sources are positioned and the anticipated effects on up-regulation and / or down-regulation of their direction of energy emission, intensity, frequency, firing / timing pattern, and phase / intensity relationships mapped onto the recommended treatment-planning targets. The maps of treatment-planning targets onto which the mapping occurs can be atlas (e.g., Tailarach Atlas) based or image (e.g., fMRI or PET) based. Atlas and imaged-based maps may be representative and applied directly or scaled for the patient or may be specific to the patient.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Shaped and steered ultrasound for deep-brain neuromodulation
Disclosed are devices for producing shaped or steered ultrasound for non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation impacting one or a plurality of points in a neural circuit. Depending on the application this can produce short-term effects (as in the treatment of post-surgical pain) or long-term effects in terms of Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD) to treat indications such as neurologic and psychiatric conditions. The ultrasound transducers are used with control of direction of the energy emission, control of intensity, control of frequency for up-regulation or down-regulation, and control of phase / intensity relationships for focusing on neural targets.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
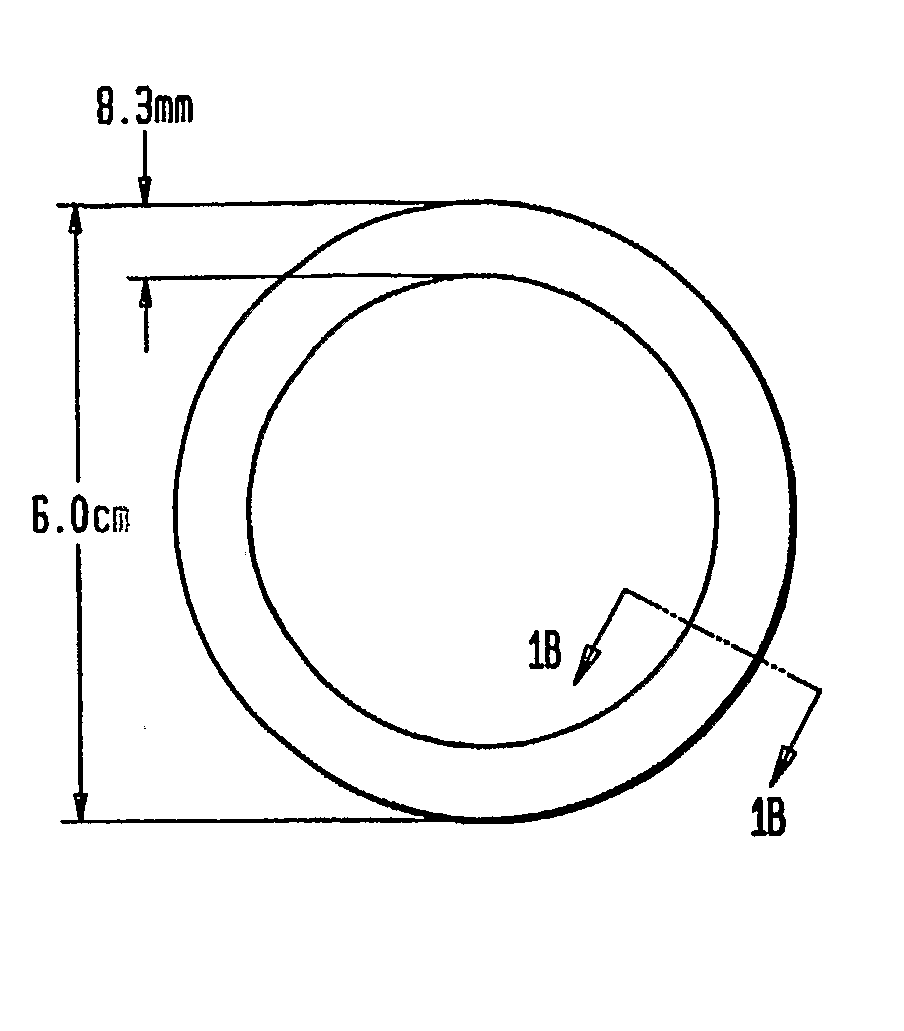
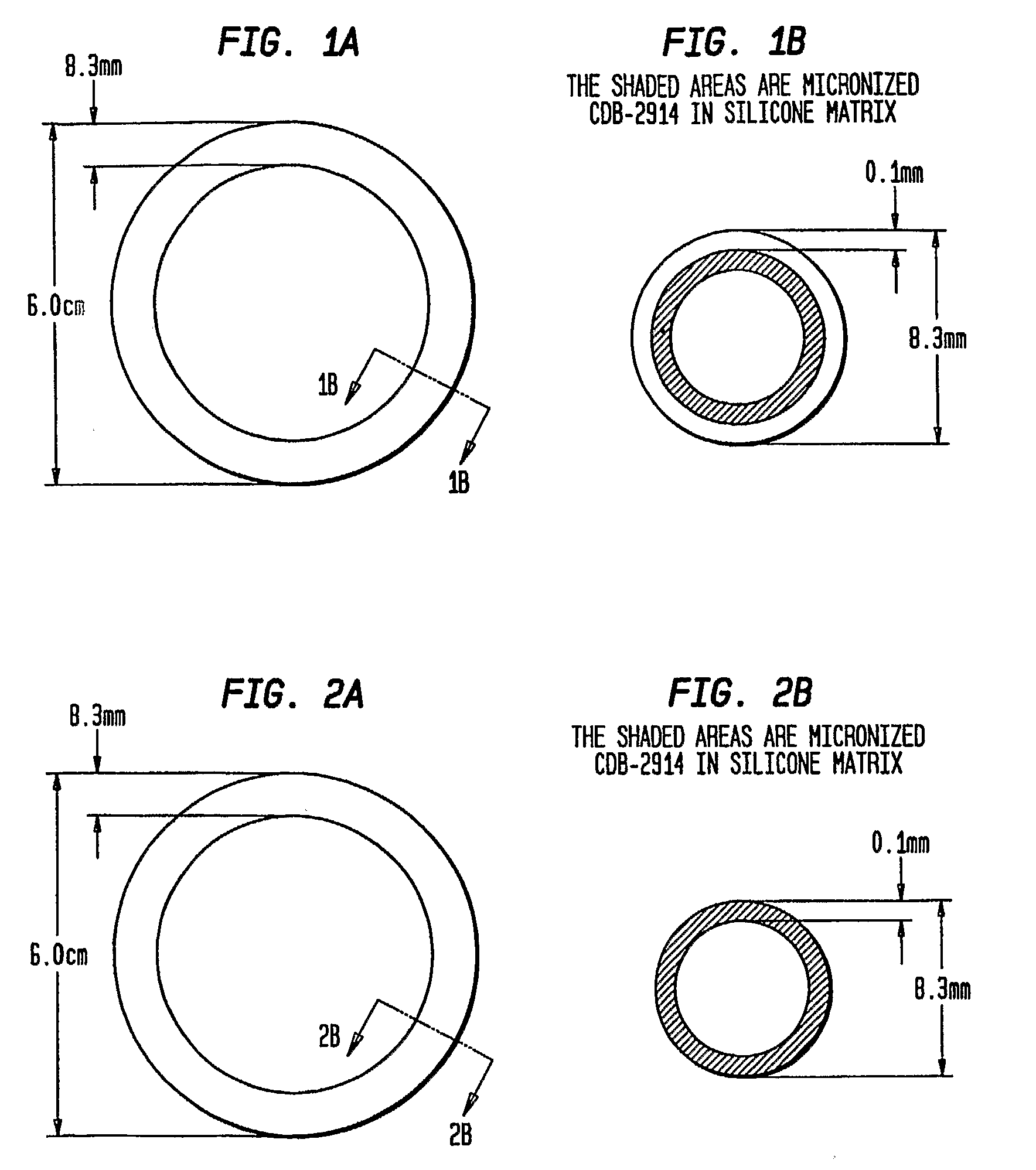
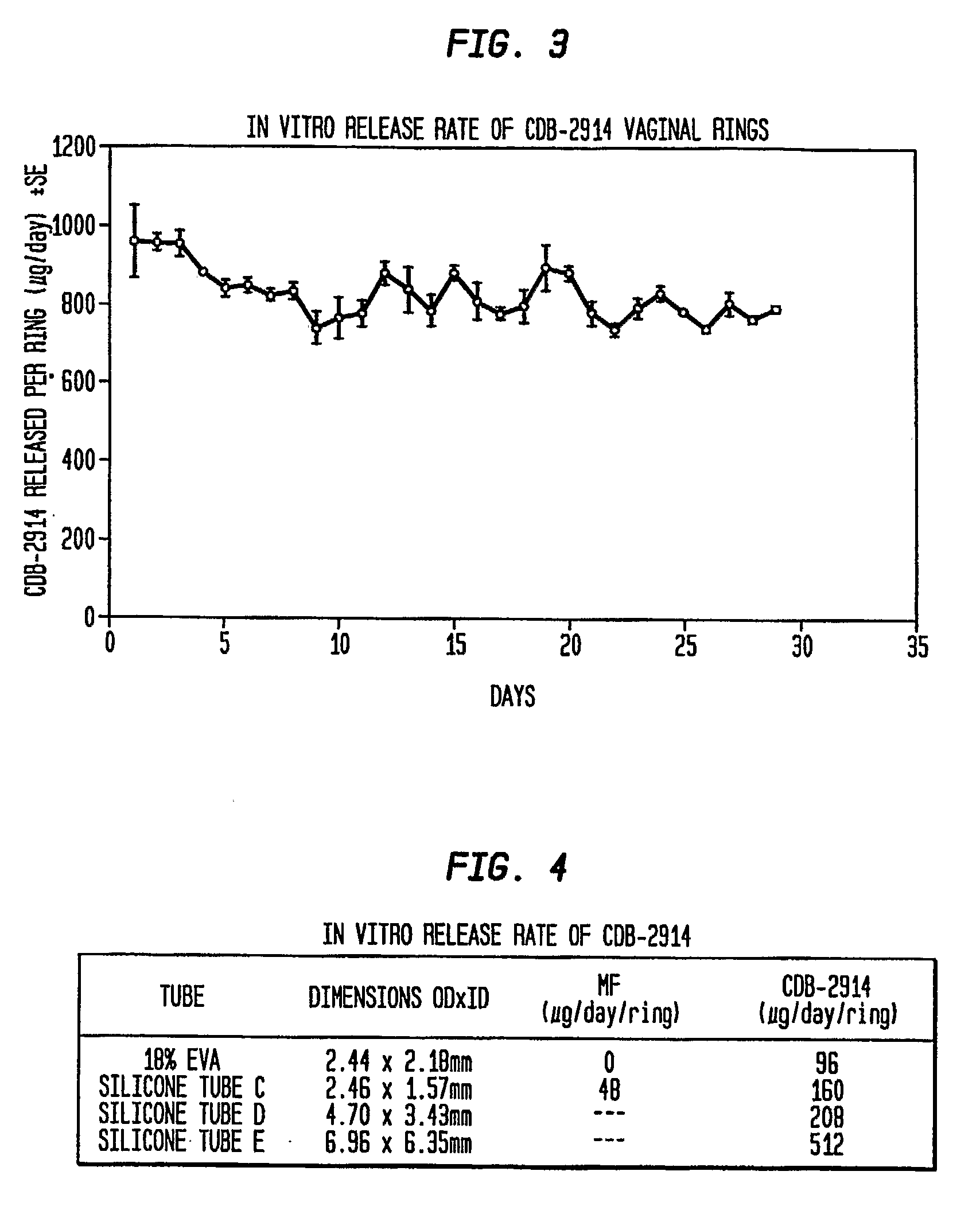
Sustained Release Compositions Containing Progesterone Receptor Modulators
ActiveUS20080199511A1Easily terminatedDevoid of side effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProgesterone receptor modulatorsPR - Progesterone receptor
Disclosed are sustained release compositions for vaginal or transdermal administration that contain a progesterone receptor modulator such as CDB-2914 (also referred to as VA-2914), and methods of using them for long term contraception or therapeutic purposes. Also disclosed are methods for making the compositions.
Owner:LAB HRA PHARMA SA
Method for extracting face characteristic based on local three-value mode
ActiveCN102163283AAccurate extractionEnhanced inhibitory effectCharacter and pattern recognitionLong-term potentiationPyramid
The invention relates to a method for extracting a face characteristic based on a local three-value mode, belonging to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly carrying out down sampling on an original face image to construct a face image pyramid, then calculating LTP (long-term potentiation) characteristics of all the pixel points in an image at each layer, and then dividing the LTP characteristics of all the pixel points into positive LTP sub characteristics and negative LTP sub characteristics, respectively carrying out statistics to obtain a positive LTP sub characteristic value histogram and a negative LTP sub characteristic value histogram of the image at each layer in the face image pyramid, and finally connecting vectors H+ and H- corresponding to the positive LTP sub characteristic value histogram and the negative LTP sub characteristic value histogram as the final characteristic of the original face image I (x, y). In the invention, the local characteristic of the LTP characteristic and the statistics characteristics of all the local LTP characteristic histograms are utilized to realize uniformity of the local characteristic and global characteristic, and the LTP characteristic has a better inhibition effect on noise compared with the LBP (local binary pattern) characteristic which is frequently adopted. The extracted characteristic has the characteristics of constant rotation and constant grey scale, and face characteristic can be accurately extracted under the influences that illumination condition is changed, face expression is changed and a gesture is changed.
Owner:厚普清洁能源(集团)股份有限公司
New use of ginsenoside Rg1
InactiveCN101084909AReduce stress damageReduce inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderLong-term potentiationNeurotoxic effect
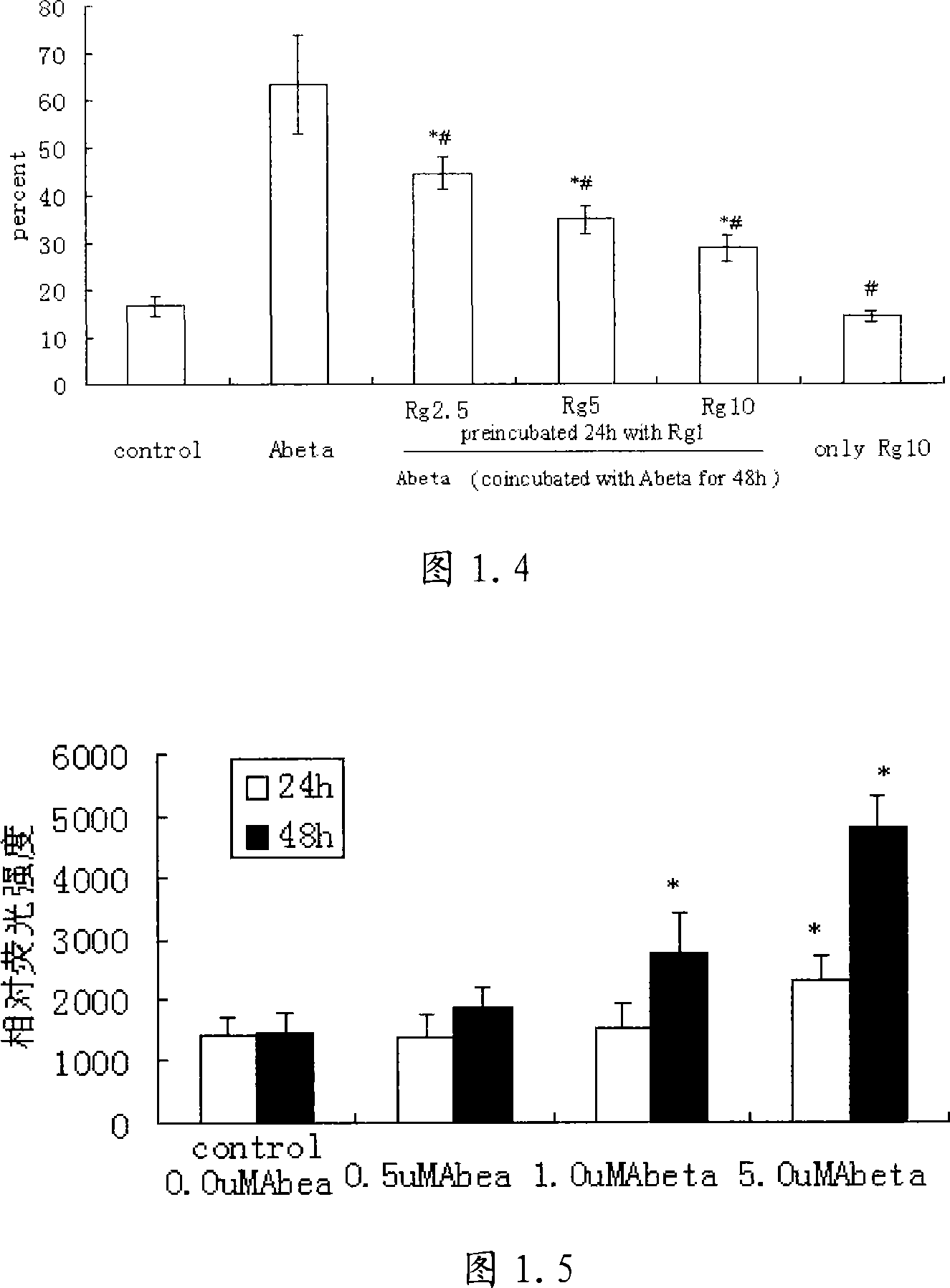
The invention relates to an application of ginsenoside Rg 1 for treating / preventing Alzheimer disease, and provides new use of ginsenoside Rg 1 in treating / preventing Alzheimer disease caused by A beta 1-42 induced neurotoxic effect. This provided Chinese medicinal monomer of ginsenoside Rg 1 has the following functions: protecting cytochondriome and reducing neuron apoptosis through relieving oligo-A beta 1-42 induced neuron stress injury, relieving inhibiting effect of A beta 1-42 on PKA-CREB signal passage, contributing to form long-term potentiation, and improving memory, thereby providing direct powerful experimental foundation and theoretical basis for ginsenoside Rg 1 in treating Alzheimer disease, and has high scientific and originality, and application value.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV UNION HOSPITAL
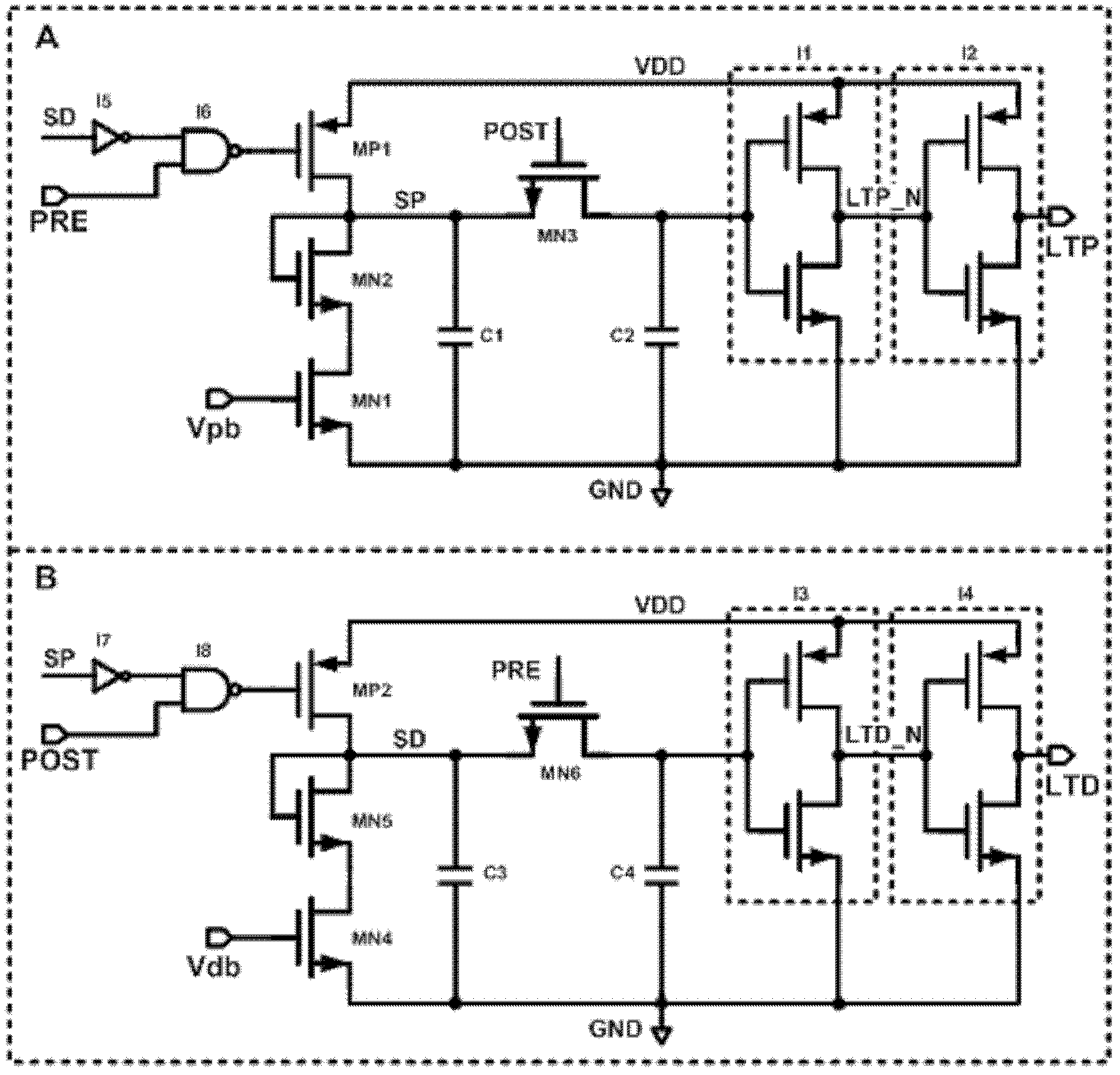
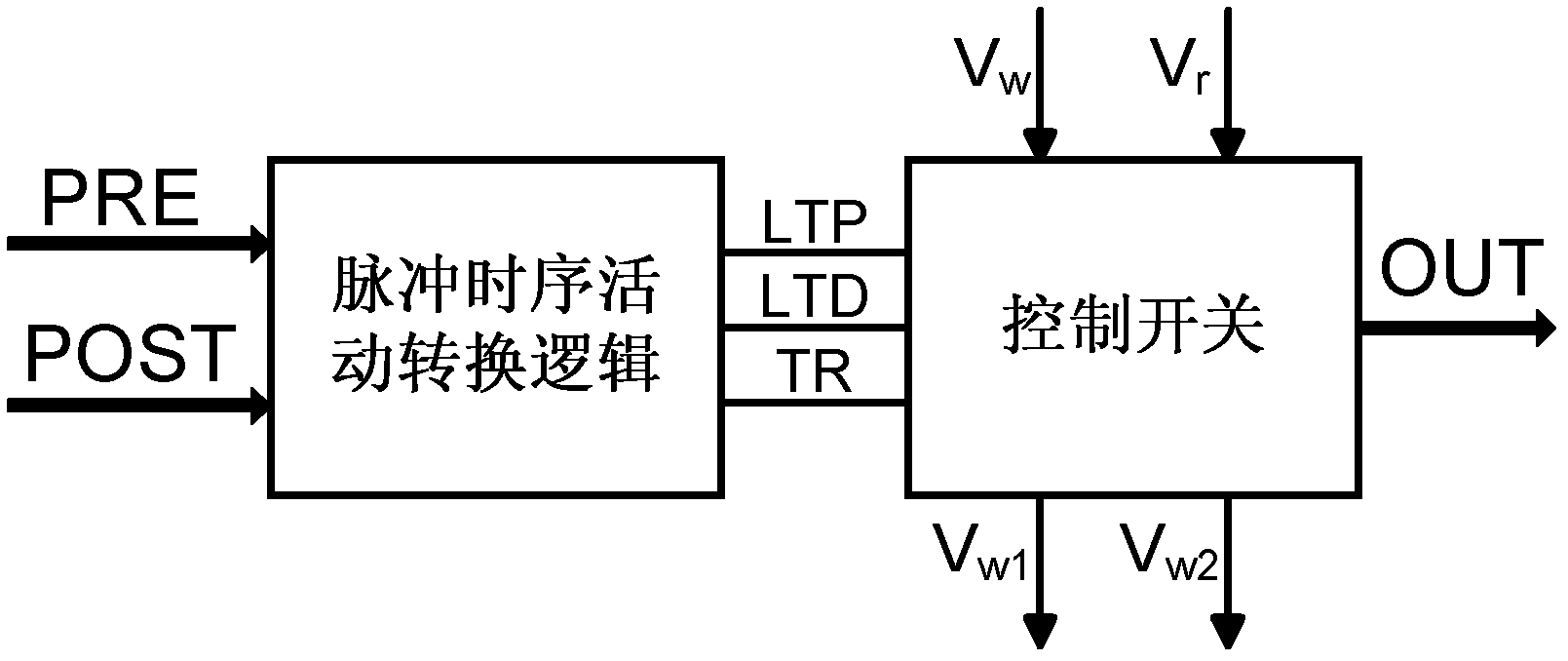
Spike timing activity conversion circuit
The invention relates to a principle about the connection among neurons in neural networks in integrated circuits and biology. A spike timing activity conversion circuit is composed of spike timing activity conversion logic and a control switch. The spike timing activity conversion logic receives a signal (PRE) and a signal (POST) which are treated to generate a long term potentiation (LTP) signal, a long term depression (LTD) signal or a transmission control (TR) signal. The three signals are output to the control switch, which is in connection with write operation voltage (Vw) and read operation voltage (Vr) of a resistive synapse. Under the control of the TR, LTP and LTD signals, output (OUT) of transinformation can be generated, or proper voltage can be output to Vw1 and Vw2 which are voltages respectively added to the two ends of the resistive synapse. The invention provides a conversion circuit, which can convert a spike timing activity relation into corresponding LTP and LTD spikes for output according to an STDP (spike timing dependent plasticity) rule, thus realizing the function of an STDP model. Therefore, the conversion circuit can be conveniently applied in neural networks, electronic synaptic weight adjustment and other circuits.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ultrasound neuromodulation for treatment of autism spectrum disorder and alzheimers disease and other dementias
Disclosed are methods and systems and methods for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound for the Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorders and Alzheimer's Disease and other dementias. The neuromodulation can produce acute or long-term effects. The latter occur through Long-Term Depression (LTD) and Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) via training. Included is control of direction of the energy emission, intensity, frequency, pulse duration, firing pattern, and phase / intensity relationships to targeting and accomplishing up regulation and / or down regulation.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Ultrasound-neuromodulation techniques for control of permeability of the blood-brain barrier
InactiveUS20130079682A1Change in permeabilityAlter permeability of blood-brain barrierUltrasound therapySurgeryMedicineBeam steering
Disclosed are methods and systems and methods employing non-invasive ultrasound-neuromodulation techniques to control the permeability of the blood-brain barrier. For example, such an alteration can permit increased penetration of a medication to increase its therapeutic effect. The neuromodulation can produce acute or long-term effects. The latter occur through Long-Term Depression (LTD) and Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) via training. Included is control of direction of the energy emission, intensity, frequency (carrier and / or neuromodulation frequency), pulse duration, firing pattern, and phase / intensity relationships for beam steering and focusing on targets and accomplishing up-regulation and / or down-regulation.
Owner:MISCHELEVICH DAVID J
Methods and compositions for treating plasticity in a subject
InactiveUS20060069012A1Stay plasticLowering long-term potentiationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPhysiologySubject matter
Methods and compositions for at least maintaining plasticity in a system of a subject are provided. Embodiments of the subject methods include lowering long term potentiation in said subject in a manner effective to at least maintain plasticity of a system in said subject.
Owner:PALO ALTO INVESTORS
Ultrasound neuromodulation treatment of movement disorders, including motor tremor, tourette's syndrome, and epilepsy
Disclosed are methods and systems and methods for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound to treat movement disorders (e.g., tremor disorders such as Parkinson's Disease and essential tremor, Tourette's Syndrome, and epilepsy). Also included are the Tourette's vocalizations. The neuromodulation can produce acute or long-term effects. The latter occur through Long-Term Depression (LTD) and Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) via training Included is control of direction of the energy emission, intensity, frequency, pulse duration, firing pattern, and phase / intensity relationships to targeting and accomplishing up regulation and / or down regulation.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network
A method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired dynamic architecture (NIDA) for an artificial neural network is disclosed. The method comprises constructing, in one embodiment, an artificial neural network embodiment in a multi-dimensional space in memory such that a neuron is connected by a synapse to another neuron. The neuron and the synapse each have parameters and have features of long-term potentiation and long-term depression. Furthermore, crossover and mutation are employed to select children of parents. Through learning, an initial network may evolve into a different network when NIDA is applied to solve different problems of control, anomaly detection and classification over selected time units. The apparatus comprises in one embodiment a computational neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network with at least one affective network coupled to receive input data from an environment and to output data to the environment.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Conditional plasticity spiking neuron network apparatus and methods
Apparatus and methods for conditional plasticity in a neural network. In one approach, conditional plasticity mechanism is configured to select alternate plasticity rules when performing connection updates. The selection mechanism is adapted based on a comparison of actual connection efficiency and target efficiency. For instance, when actual efficiency is below the target value, the STDP rule may be modulated to increase long term potentiation. Similarly, when actual efficiency is above the target value, the STDP rule may be modulated to increase long term connection depression. The conditional plasticity mechanism dynamically adjusts connection efficacy, and prevents uncontrolled increase of connection weights, thereby improving network operation when processing information of a varying nature.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
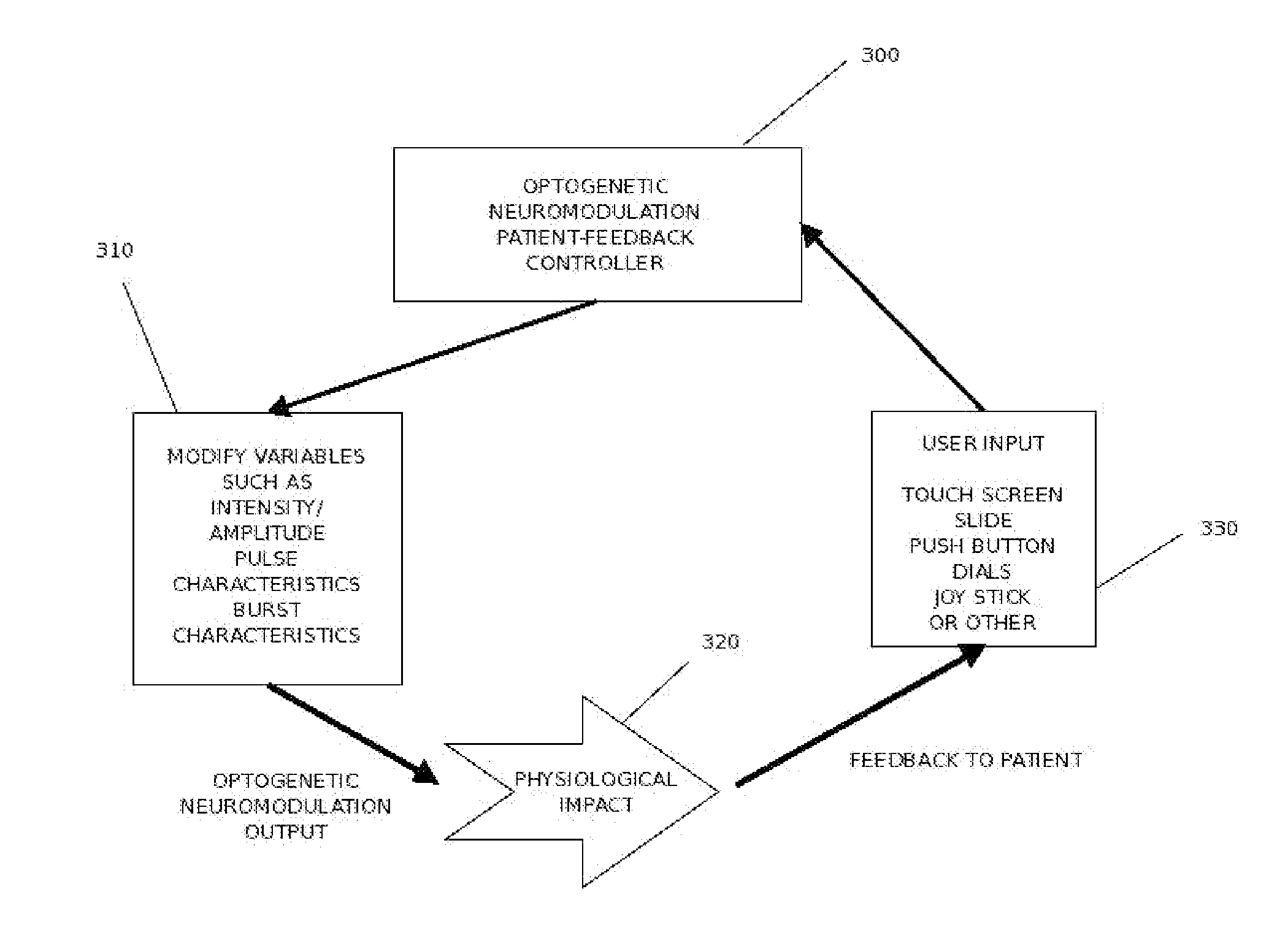
Targeted optogenetic neuromodulation for treatment of clinical conditions
Disclosed are methods and systems and methods for methods for neuromodulation of deep-brain and other neural targets in mammals using optogenetics to treat clinical conditions or achievement of a physiological state. The neuromodulation can produce acute or long-term effects. The latter occur through Long-Term Depression (LTD) and Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) via training. Included is control of optical intensity / amplitude, pulse width, pulse shape, pulse rate, burst frequency, pulse pattern, burst rate, burst width, and optical-fiber configuration including through the stimulation of incorporated opsins in the target neural membranes accomplishing up-regulation and / or down-regulation.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Adaptive plasticity apparatus and methods for spiking neuron network
ActiveUS9183493B2Improve academic performanceDigital data processing detailsNeural architecturesSynapseSpike train
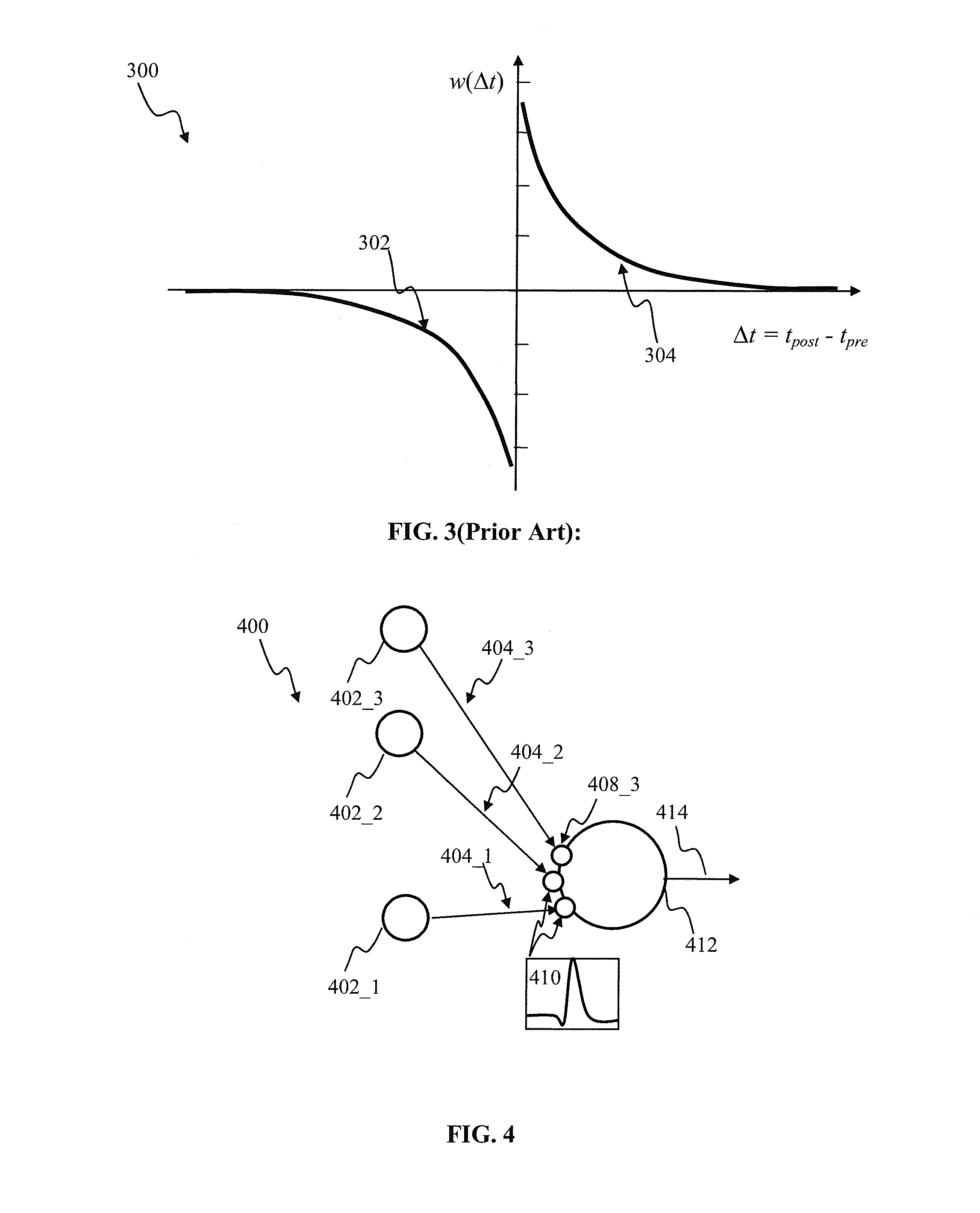
Apparatus and methods for plasticity in a spiking neuron network. In one implementation, a plasticity mechanism is configured based on a similarity measure between neuron post-synaptic and pre-synaptic activity. The similarity measure may comprise a cross-correlogram between the output spike train and input spike train, determined over a plasticity window. Several correlograms, corresponding to individual input connections delivering pre-synaptic input, may be combined. The combination may comprise for example a weighted average. The averaged correlograms may be used to construct the long term potentiation component of the plasticity. The long term depression component of the plasticity may comprise e.g., a monotonic function based on a statistical parameter associated with the adaptively determined long term potentiation component.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Ultrasound neuromodulation treatment of pain
Disclosed are methods and systems and methods for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound to treat acute or chronic pain. The neuromodulation can produce acute effects or Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). Included is control of direction of the energy emission, intensity, frequency, pulse duration, and phase / intensity relationships to targeting and accomplishing up regulation and / or down regulation.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com