Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
198 results about "Learning rule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
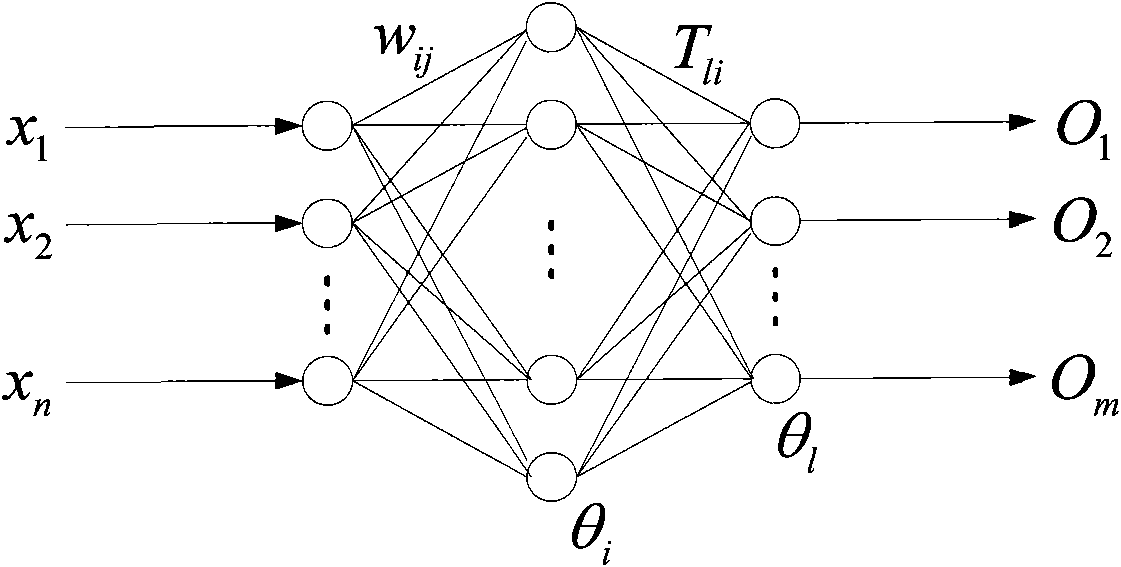
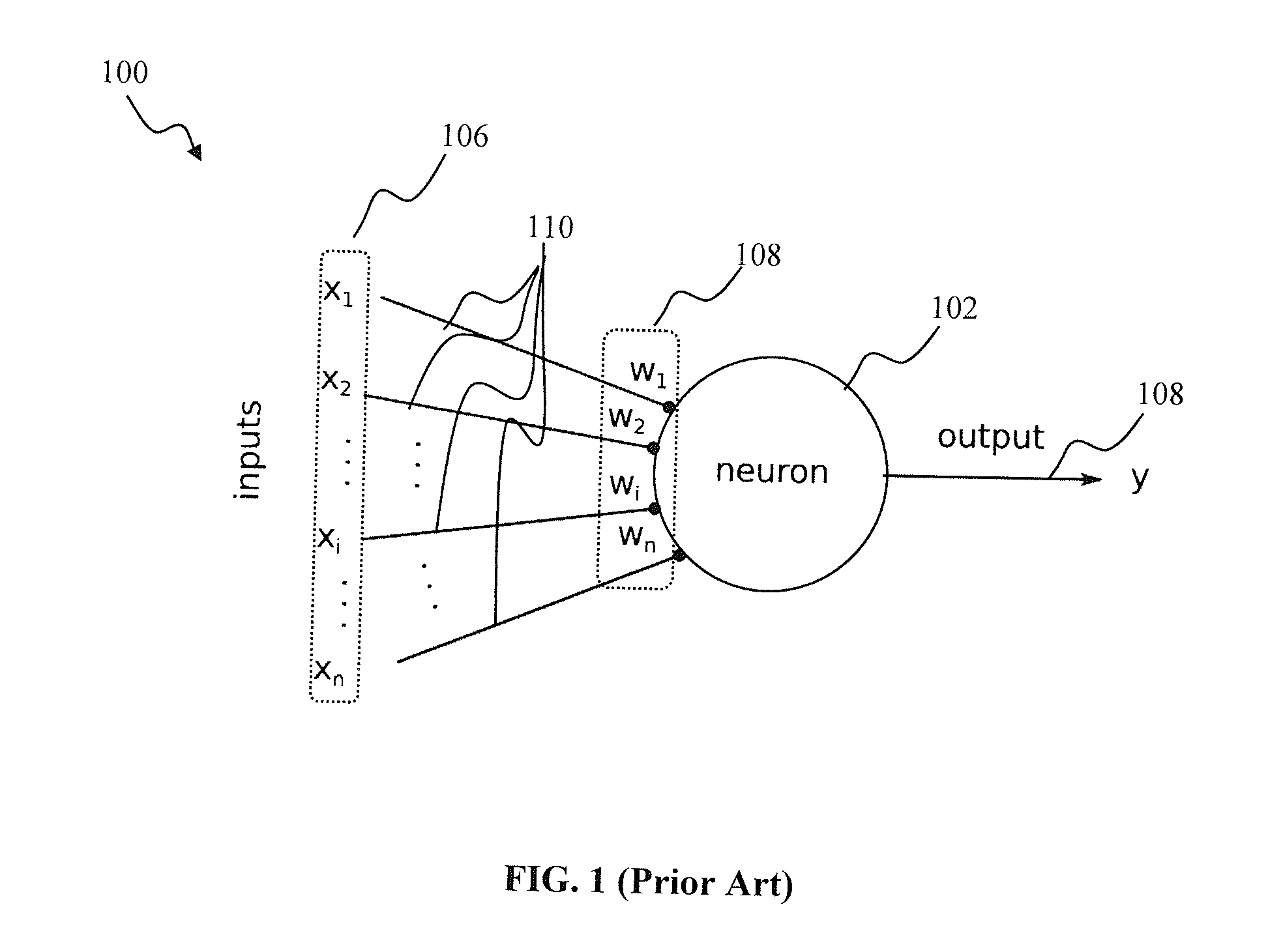
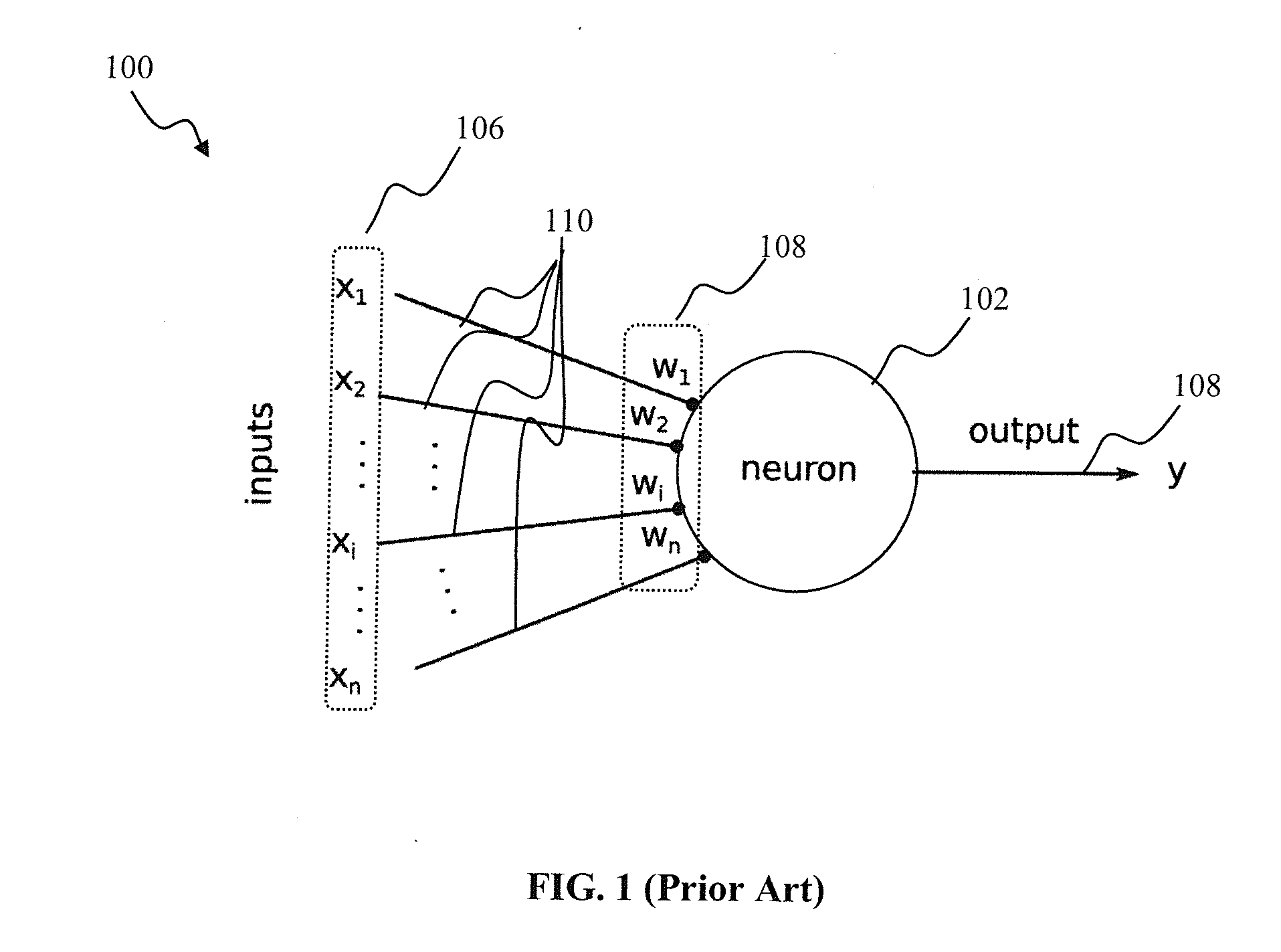
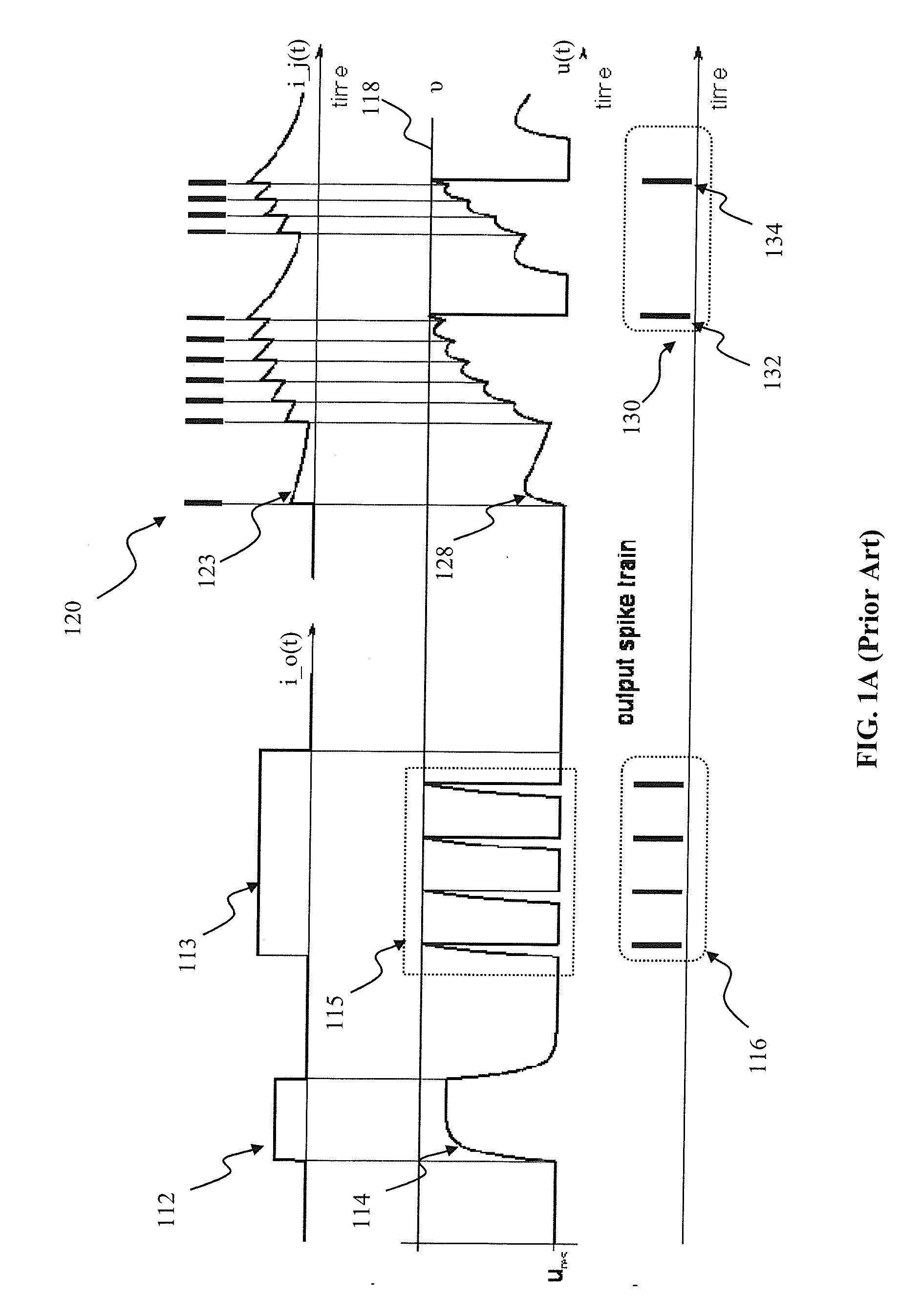
An artificial neural network's learning rule or learning process is a method, mathematical logic or algorithm which improves the network's performance and/or training time. Usually, this rule is applied repeatedly over the network. It is done by updating the weights and bias levels of a network when a network is simulated in a specific data environment. A learning rule may accept existing conditions (weights and biases) of the network and will compare the expected result and actual result of the network to give new and improved values for weights and bias. Depending on the complexity of actual model being simulated, the learning rule of the network can be as simple as an XOR gate or mean squared error, or as complex as the result of a system of differential equations.
TV content segmentation, categorization and identification and time-aligned applications
ActiveUS9510044B1Receiver side switchingCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti languageDisplay device
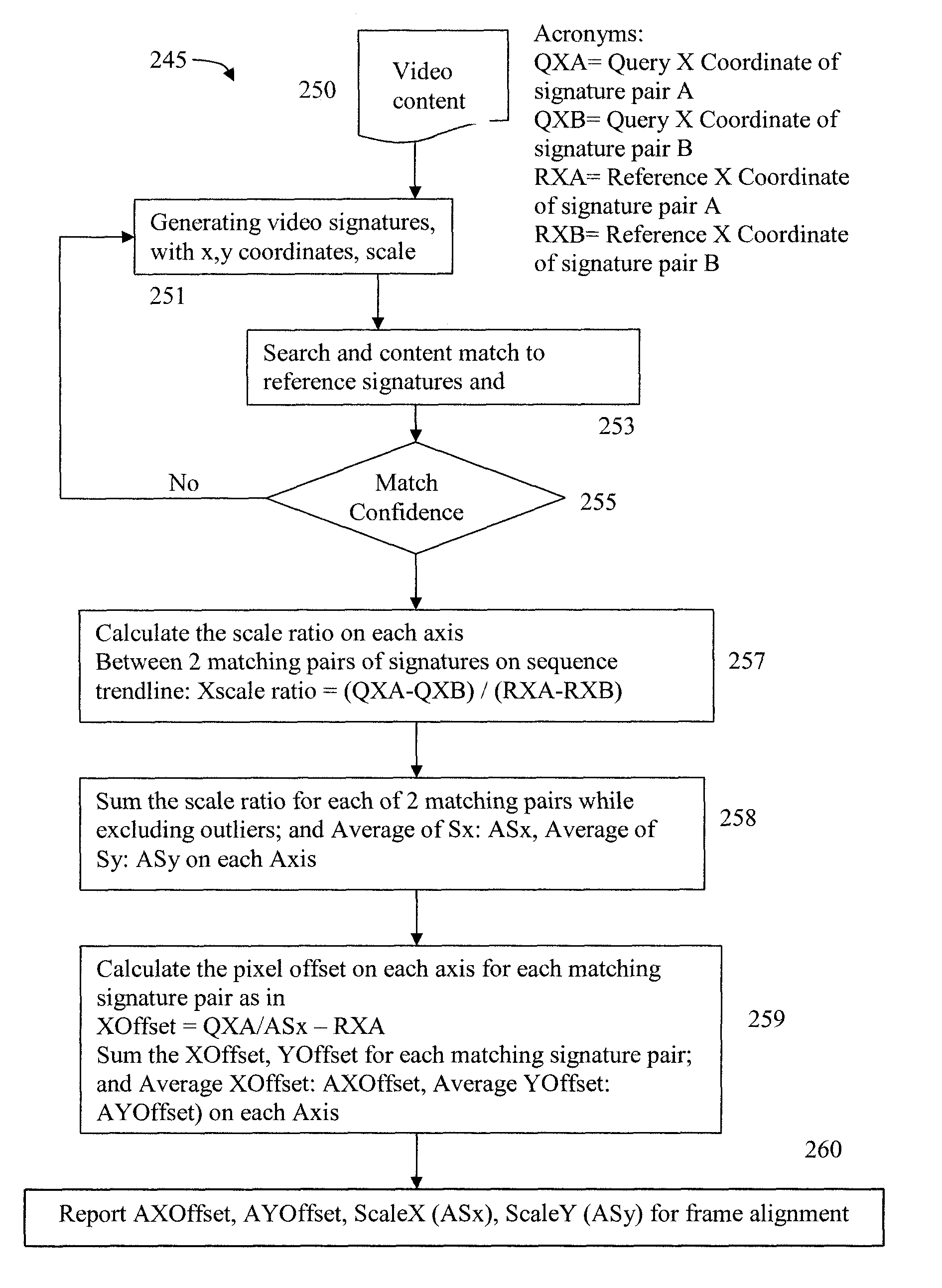
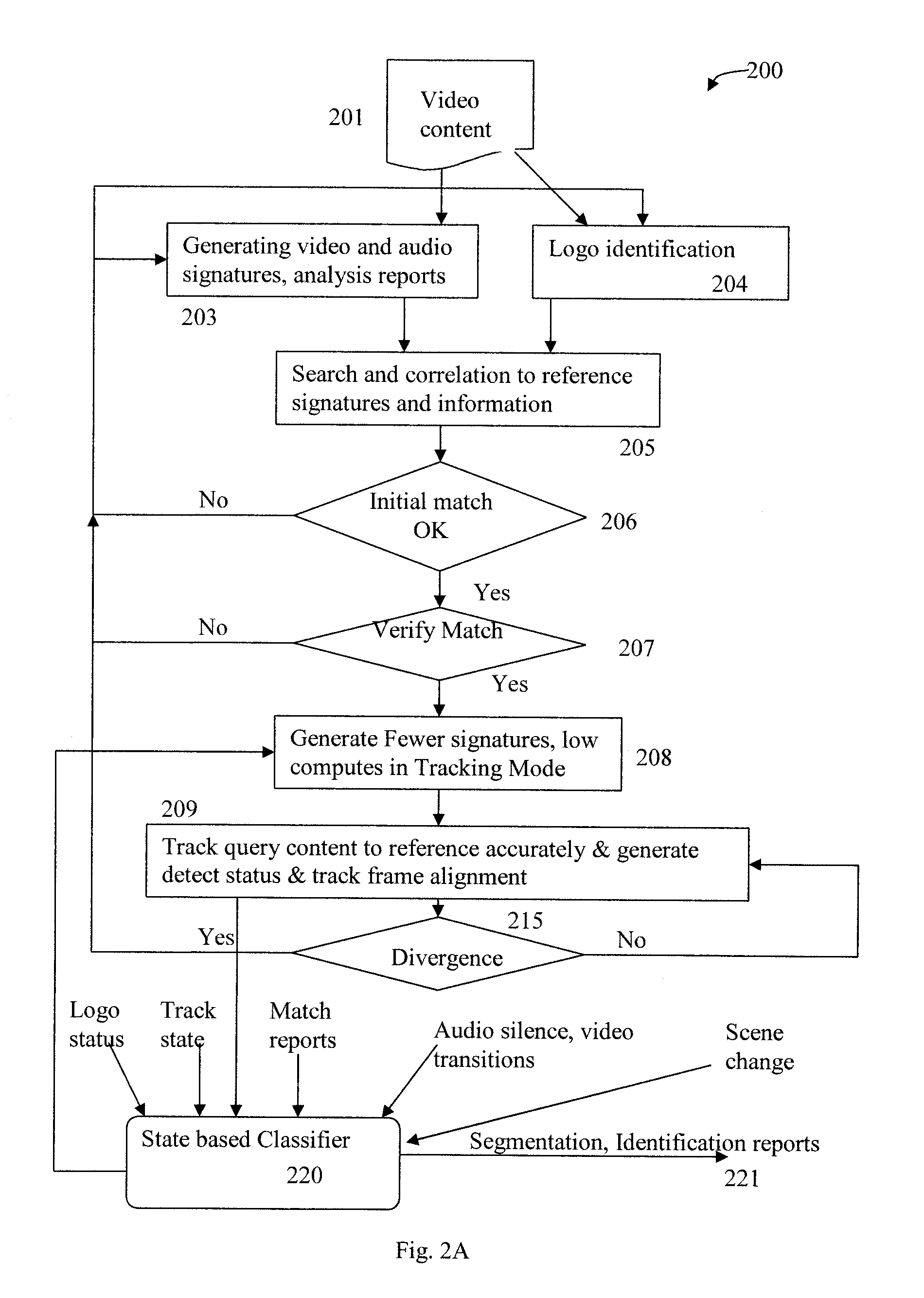
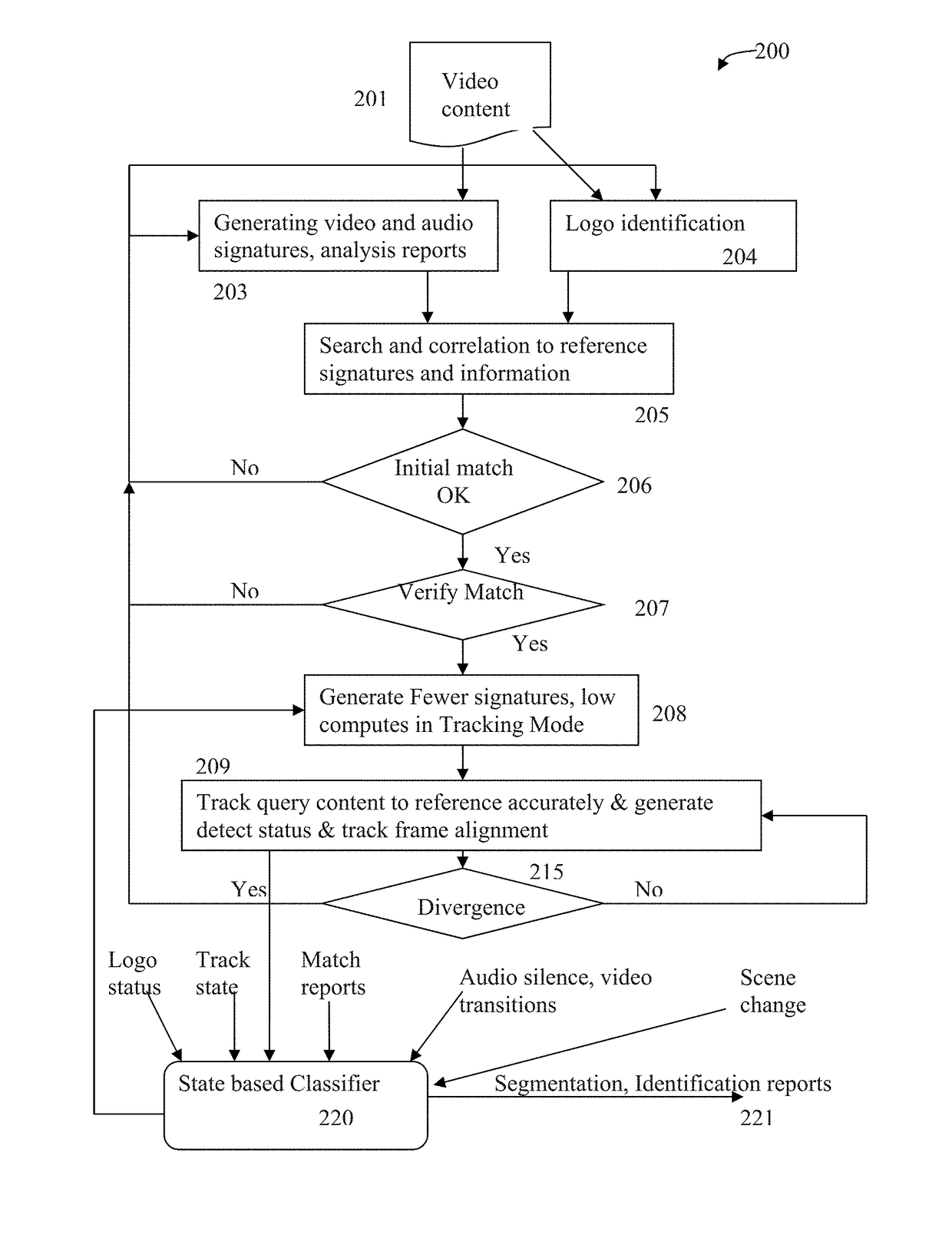
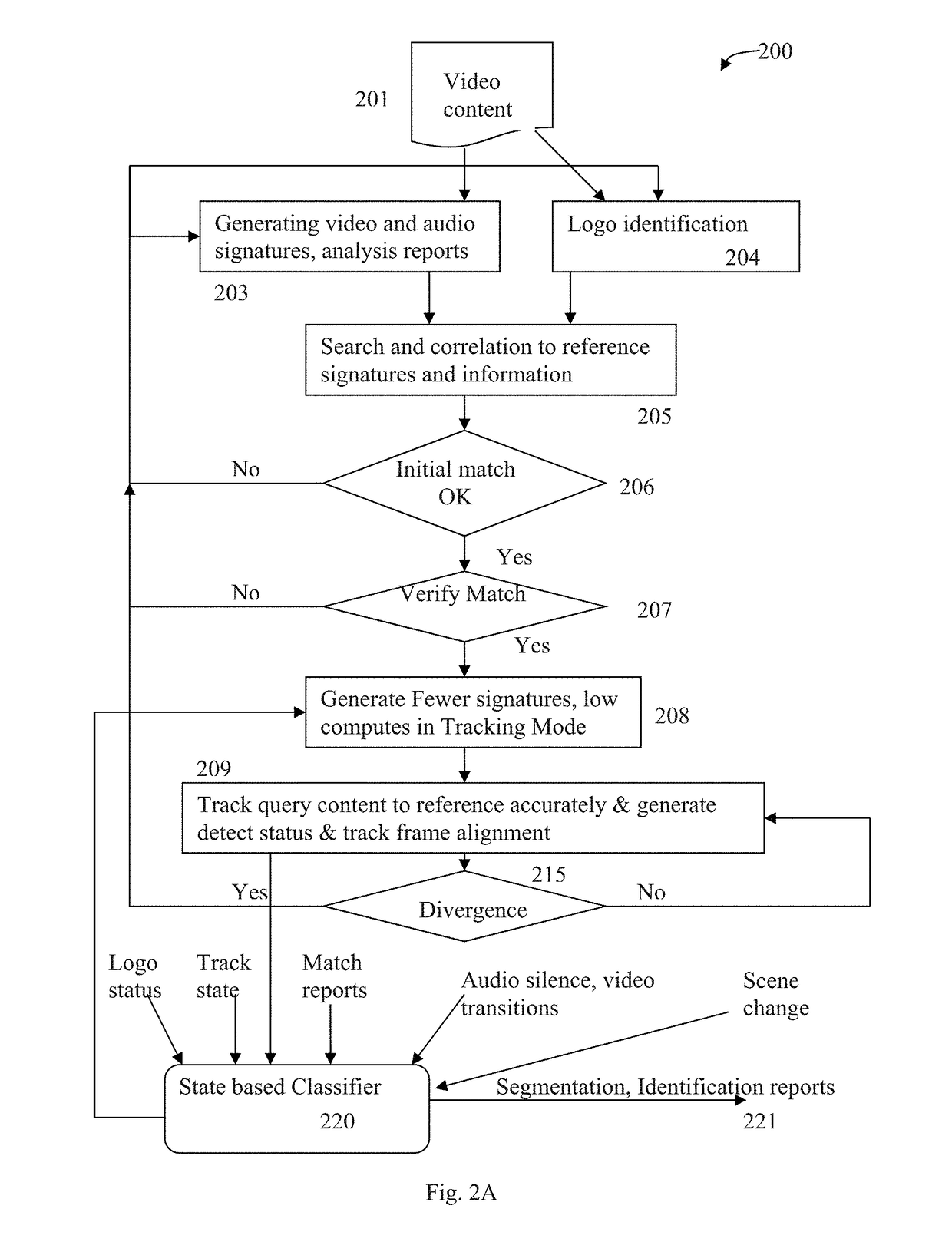
Content segmentation, categorization and identification methods are described. Content tracking approaches are illustrated that are suitable for large scale deployment. Time-aligned applications such as multi-language selection, customized advertisements, second screen services and content monitoring applications can be economically deployed at large scales. A client performs fingerprinting, scene change detection, audio turn detection, and logo detection on incoming video and gathers database search results, logos and text to identify and segment video streams into content, promos, and commercials. A learning engine is configured to learn rules for optimal identification and segmentation at each client for each channel and program. Content sensed at the client site is tracked with reduced computation and applications are executed with timing precision. A user interface for time-aligned publishing of content and subsequent usage and interaction on one or more displays is also described.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
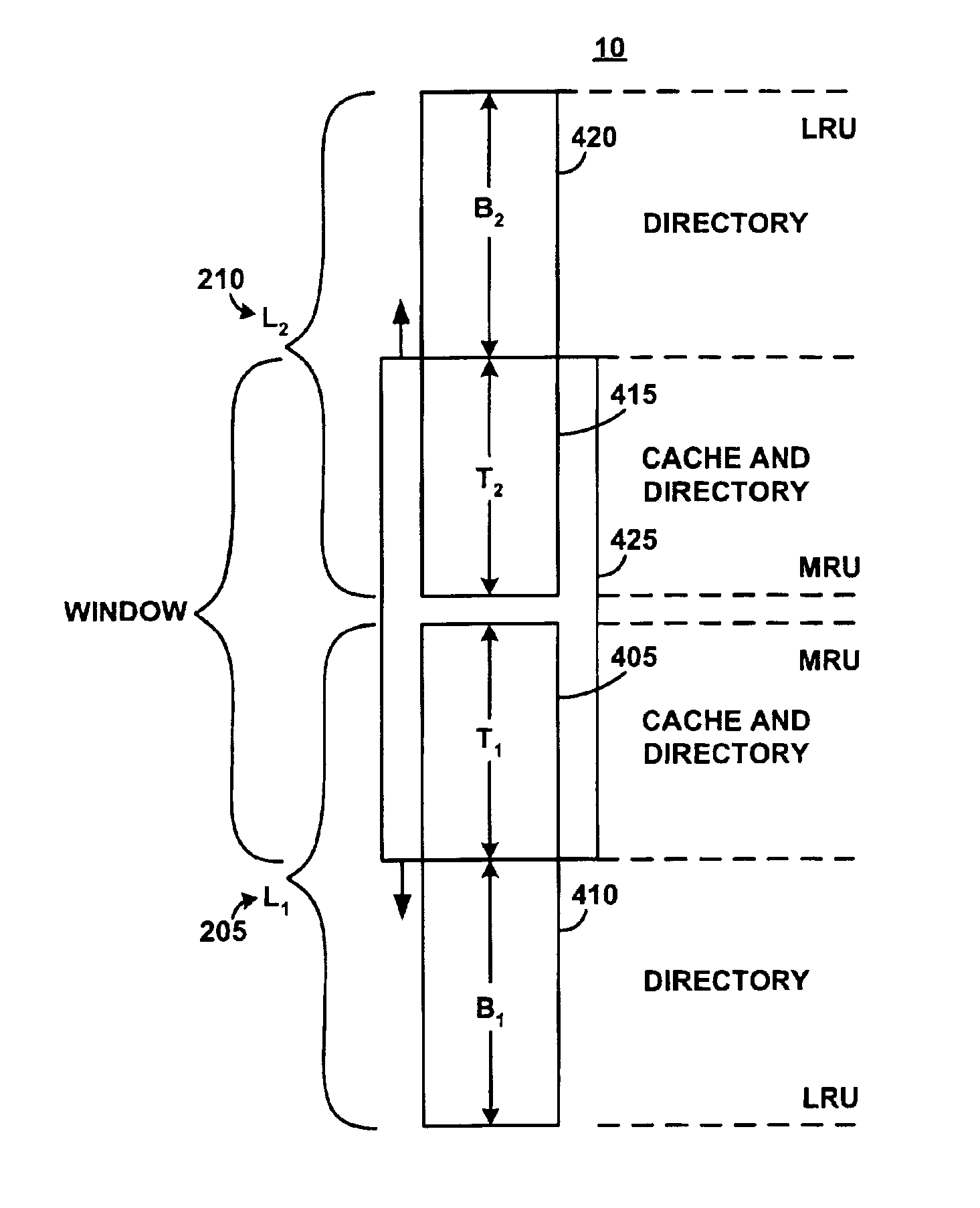
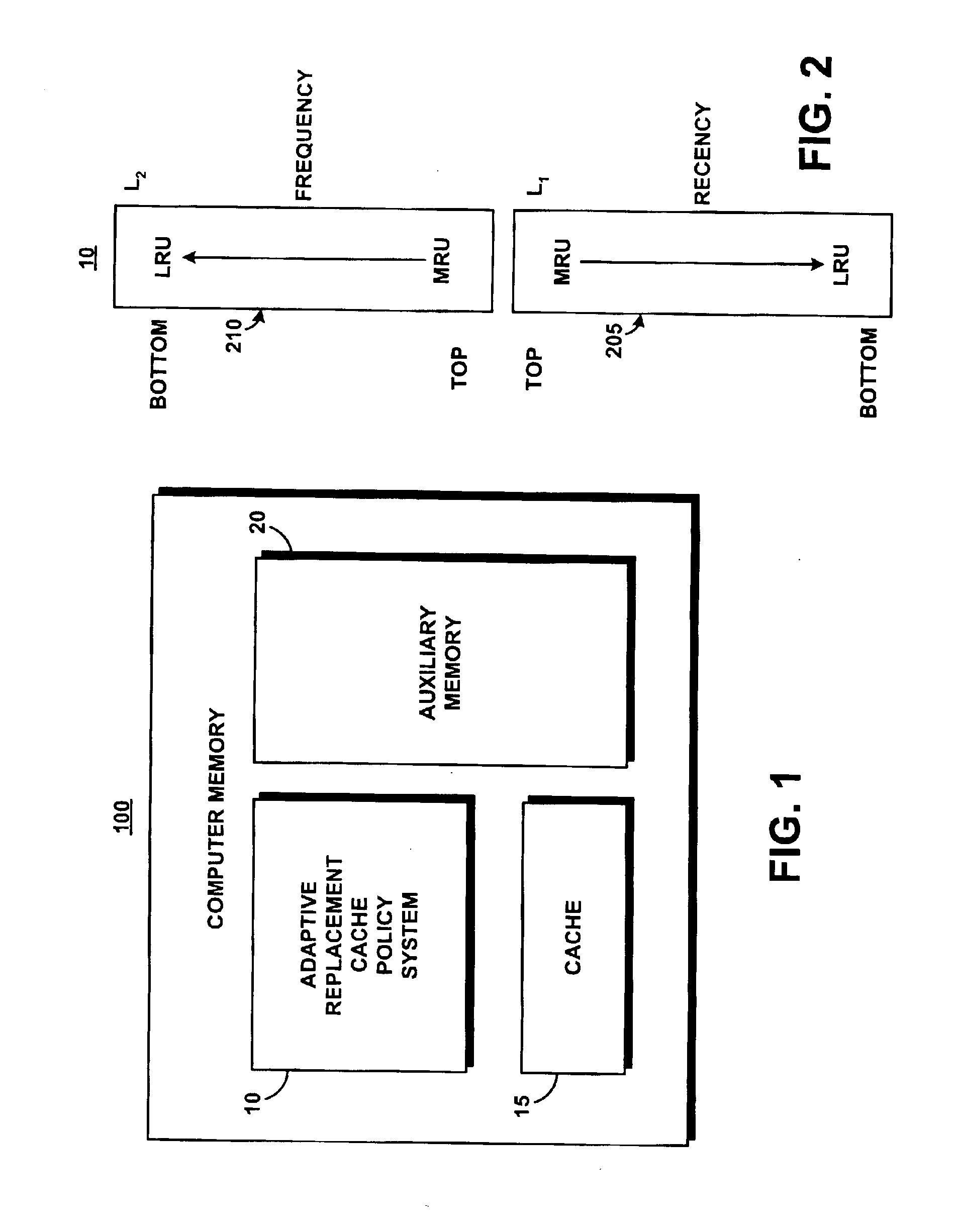
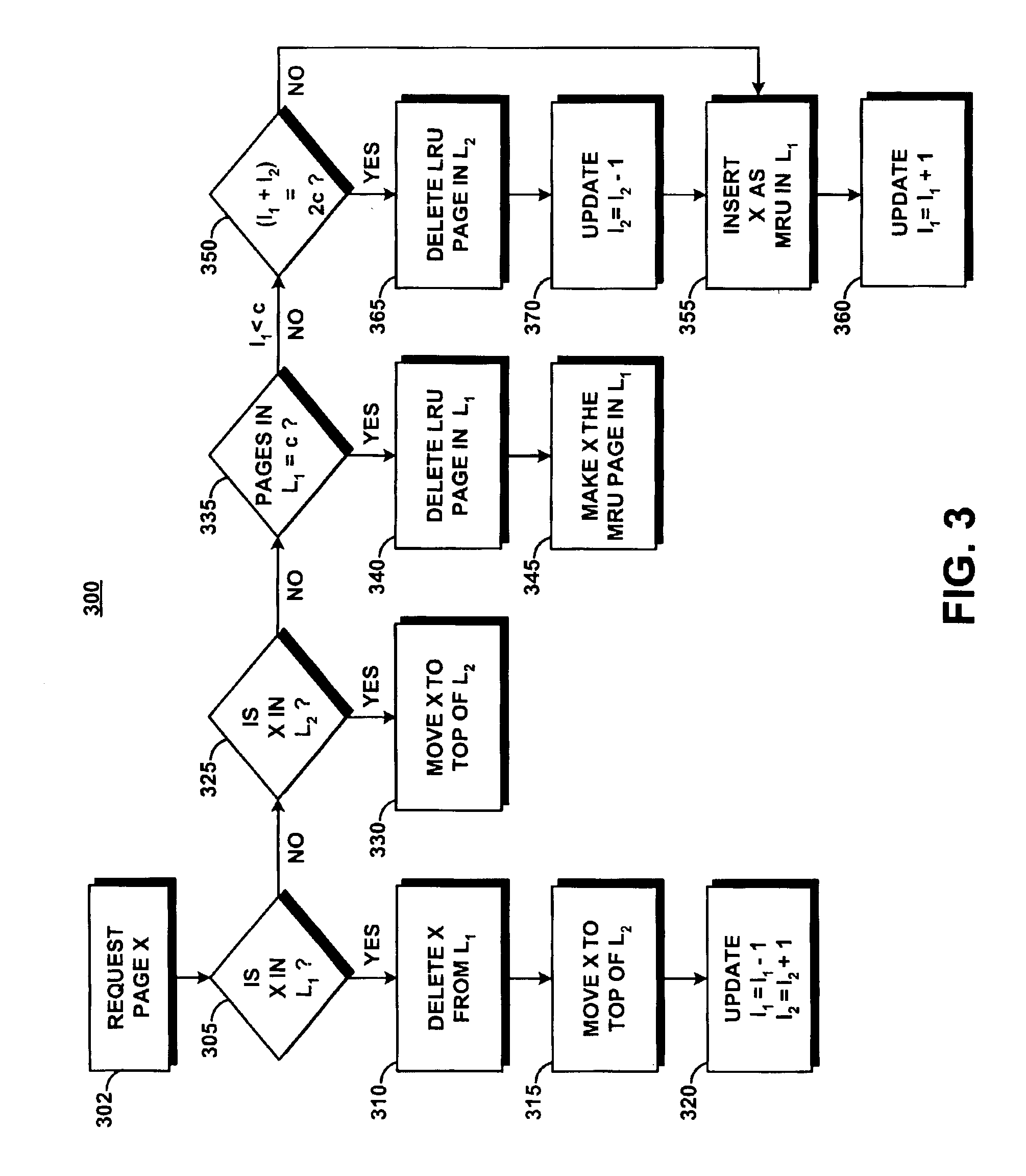
System and method for implementing an adaptive replacement cache policy
ActiveUS6996676B2Fast trackReduce overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSelf-tuningHome page
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Stochastic spiking network learning apparatus and methods
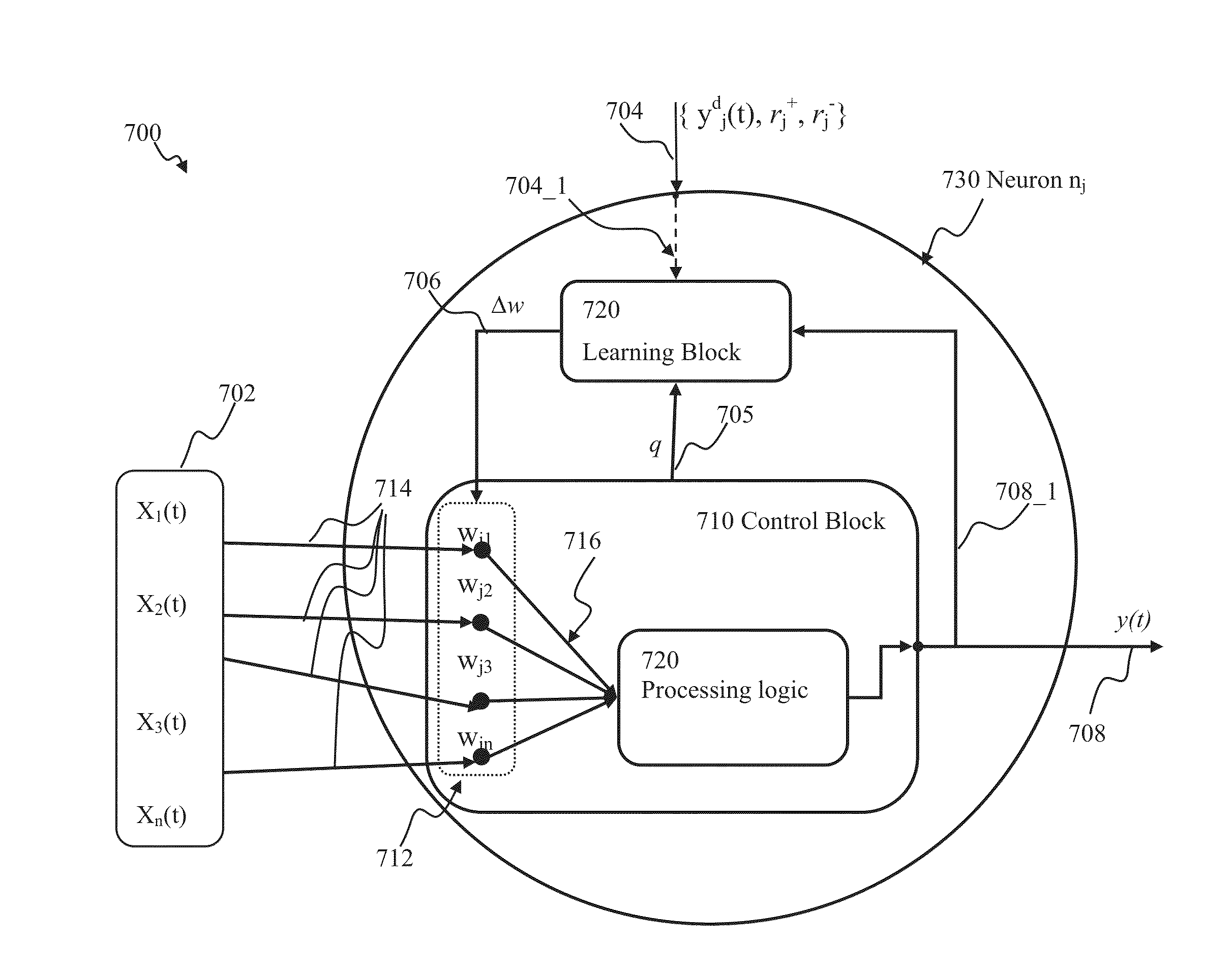
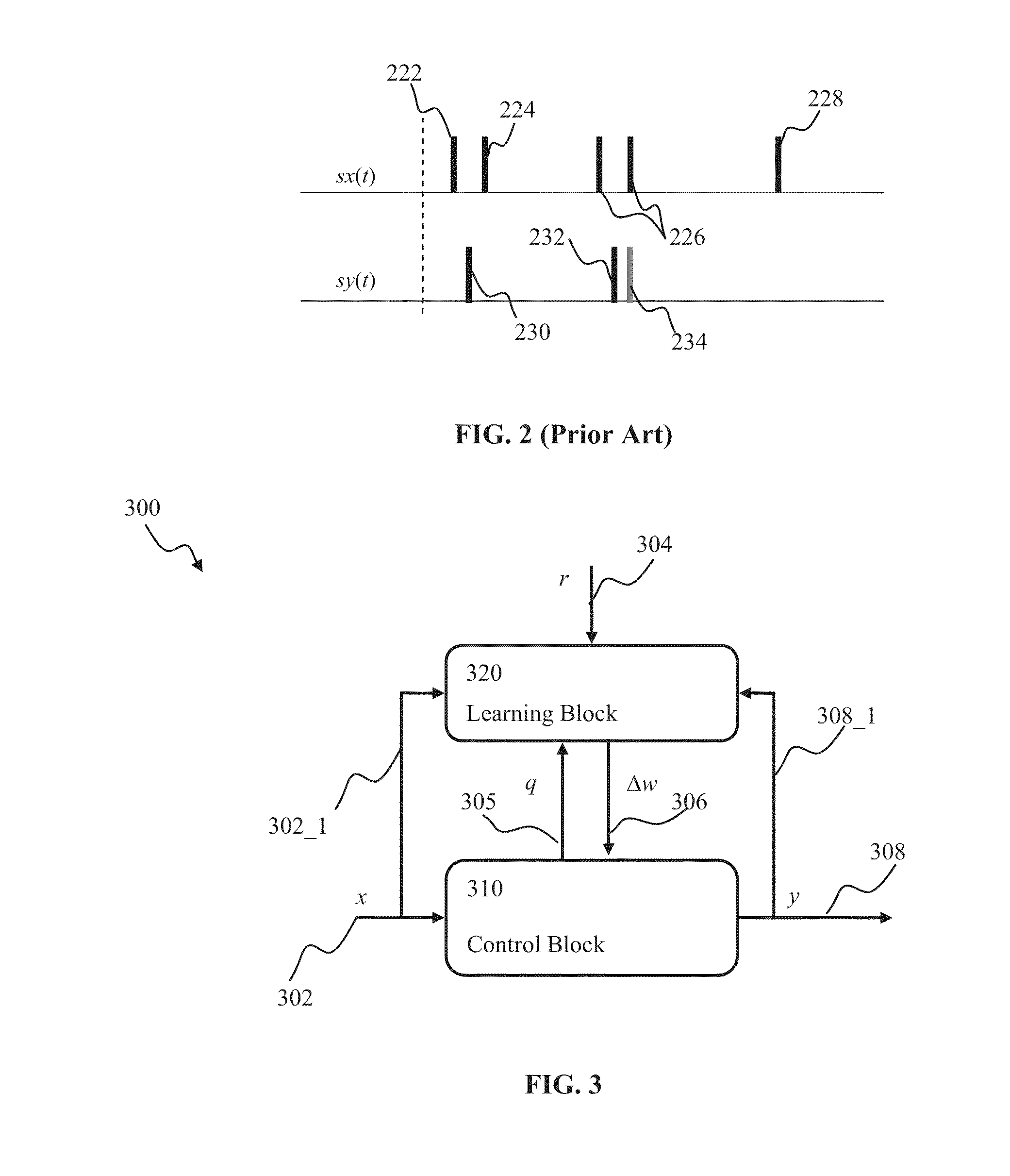
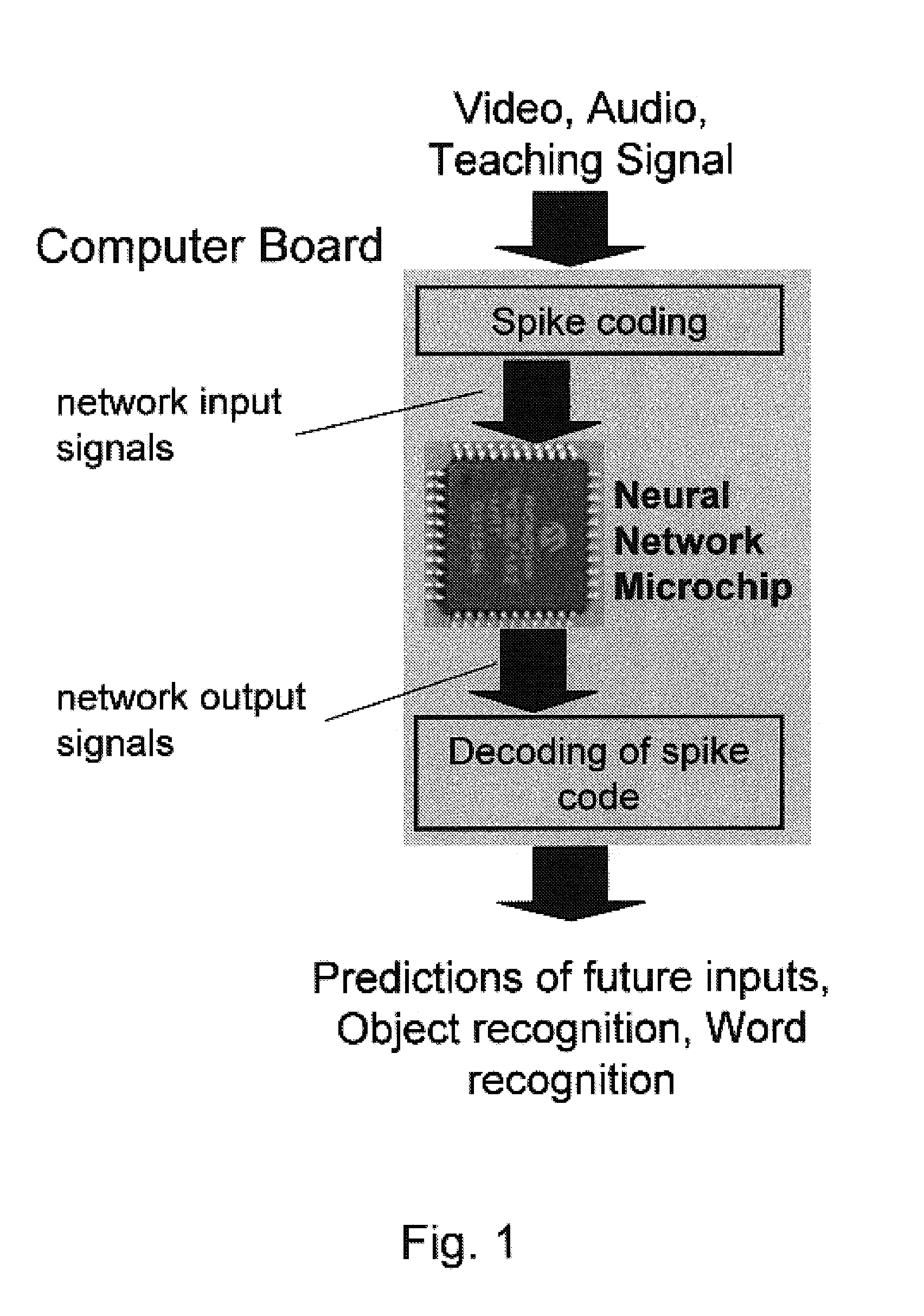
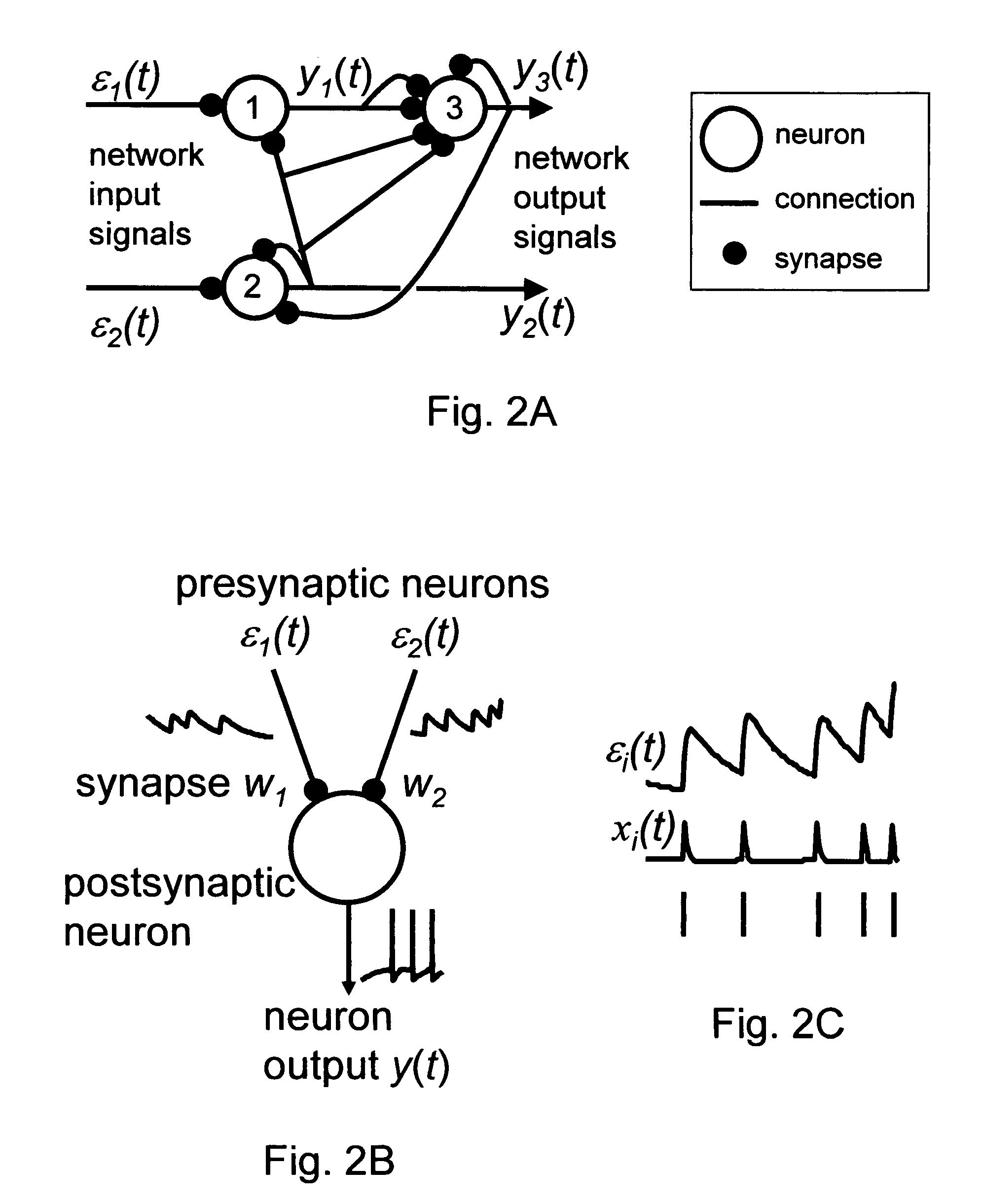
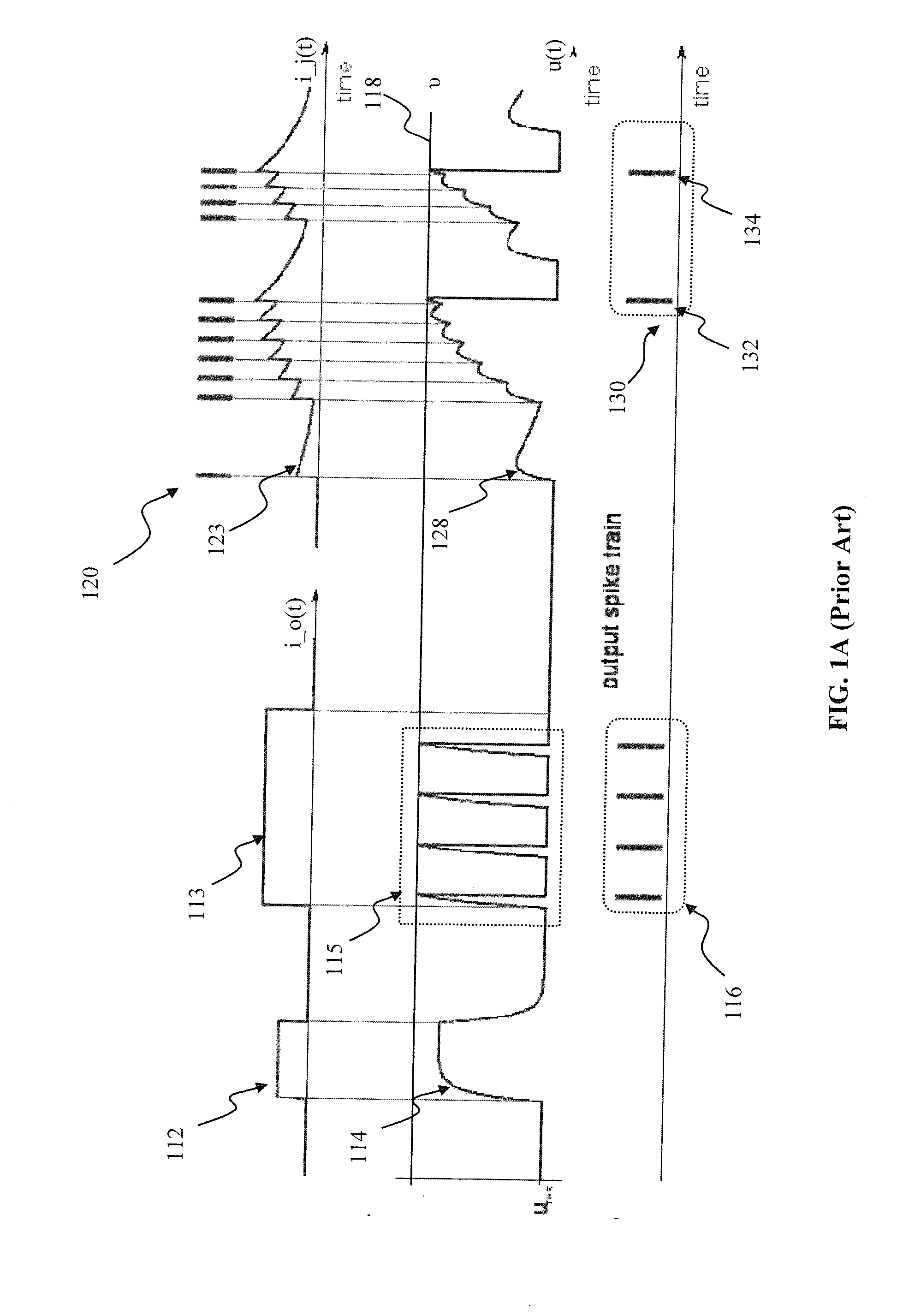
Generalized learning rules may be implemented. A framework may be used to enable adaptive spiking neuron signal processing system to flexibly combine different learning rules (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning) with different methods (online or batch learning). The generalized learning framework may employ time-averaged performance function as the learning measure thereby enabling modular architecture where learning tasks are separated from control tasks, so that changes in one of the modules do not necessitate changes within the other. Separation of learning tasks from the control tasks implementations may allow dynamic reconfiguration of the learning block in response to a task change or learning method change in real time. The generalized spiking neuron learning apparatus may be capable of implementing several learning rules concurrently based on the desired control application and without requiring users to explicitly identify the required learning rule composition for that task.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
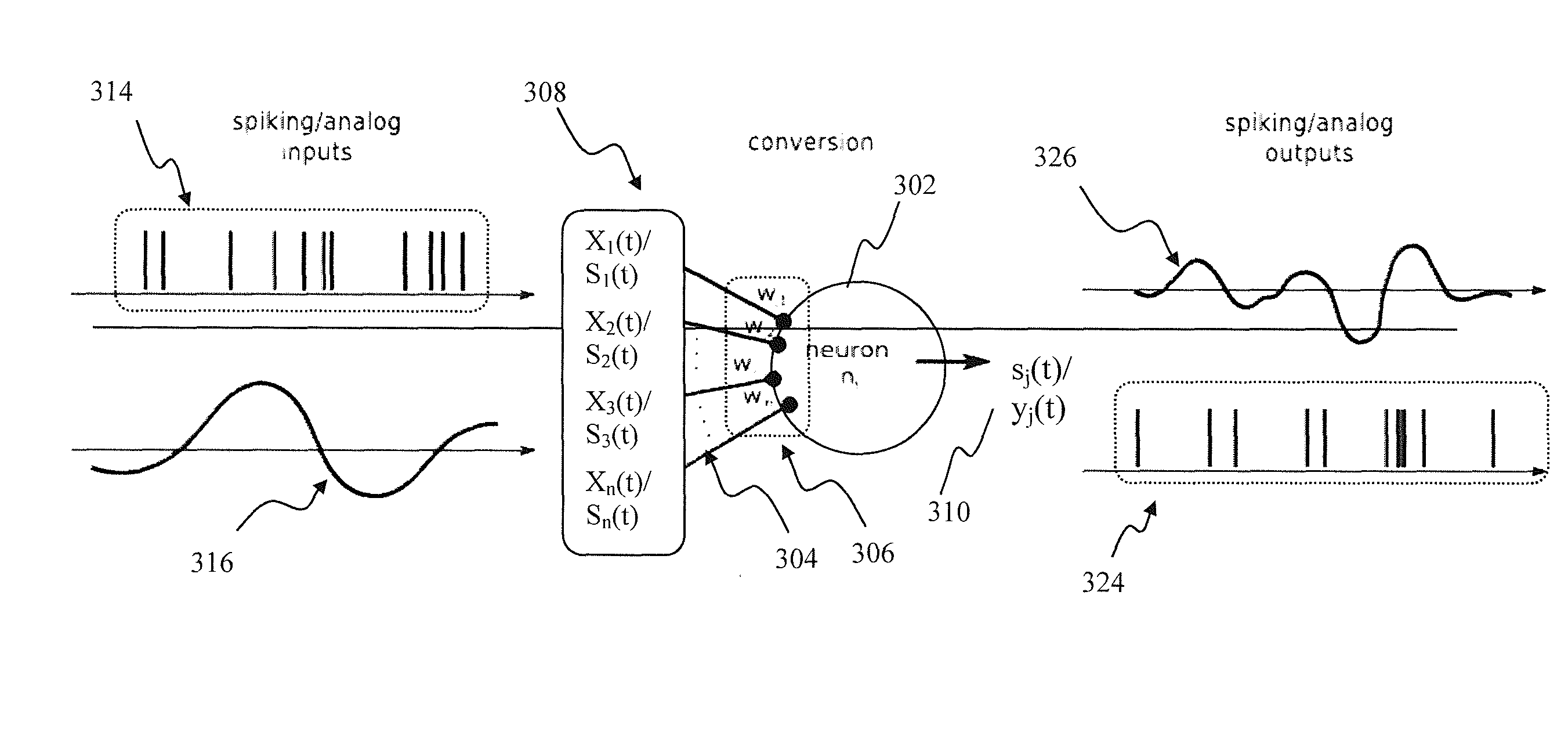
Neural network apparatus and methods for signal conversion
InactiveUS20130151450A1Digital computer detailsNeural architecturesNerve networkSpiking neural network
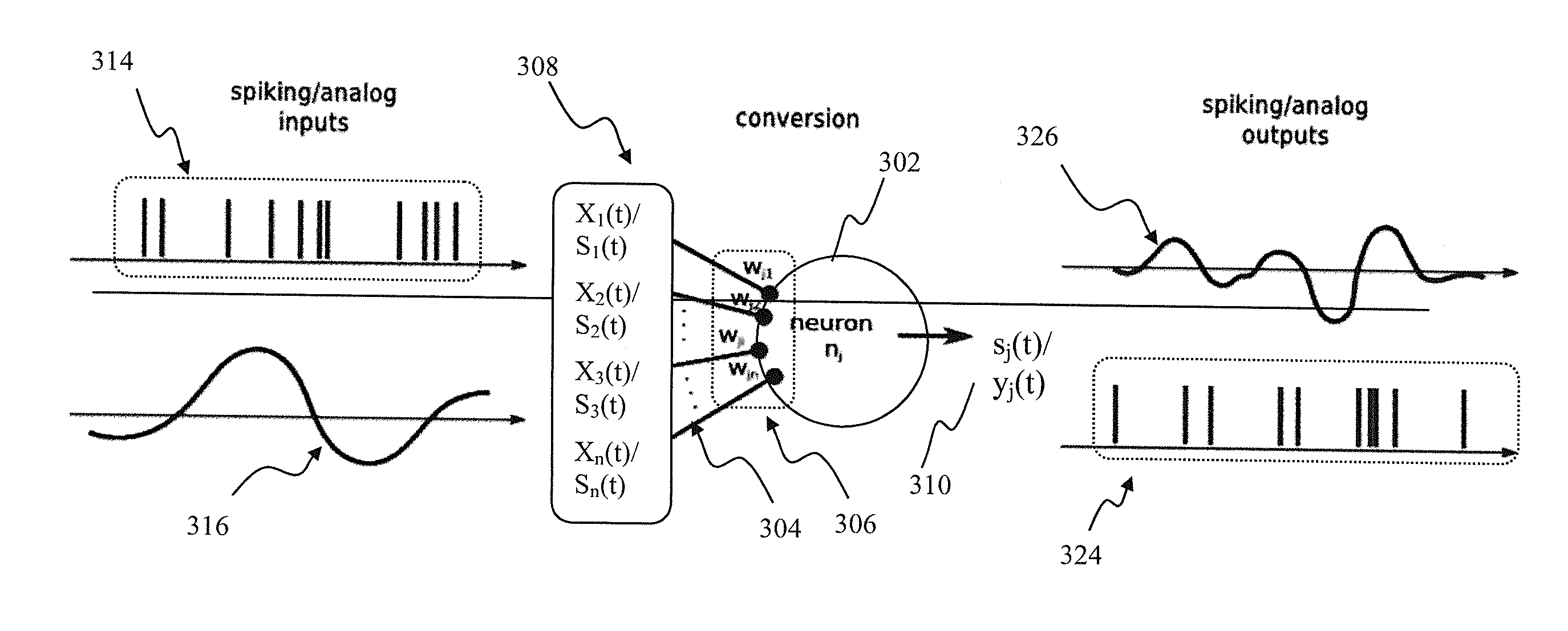
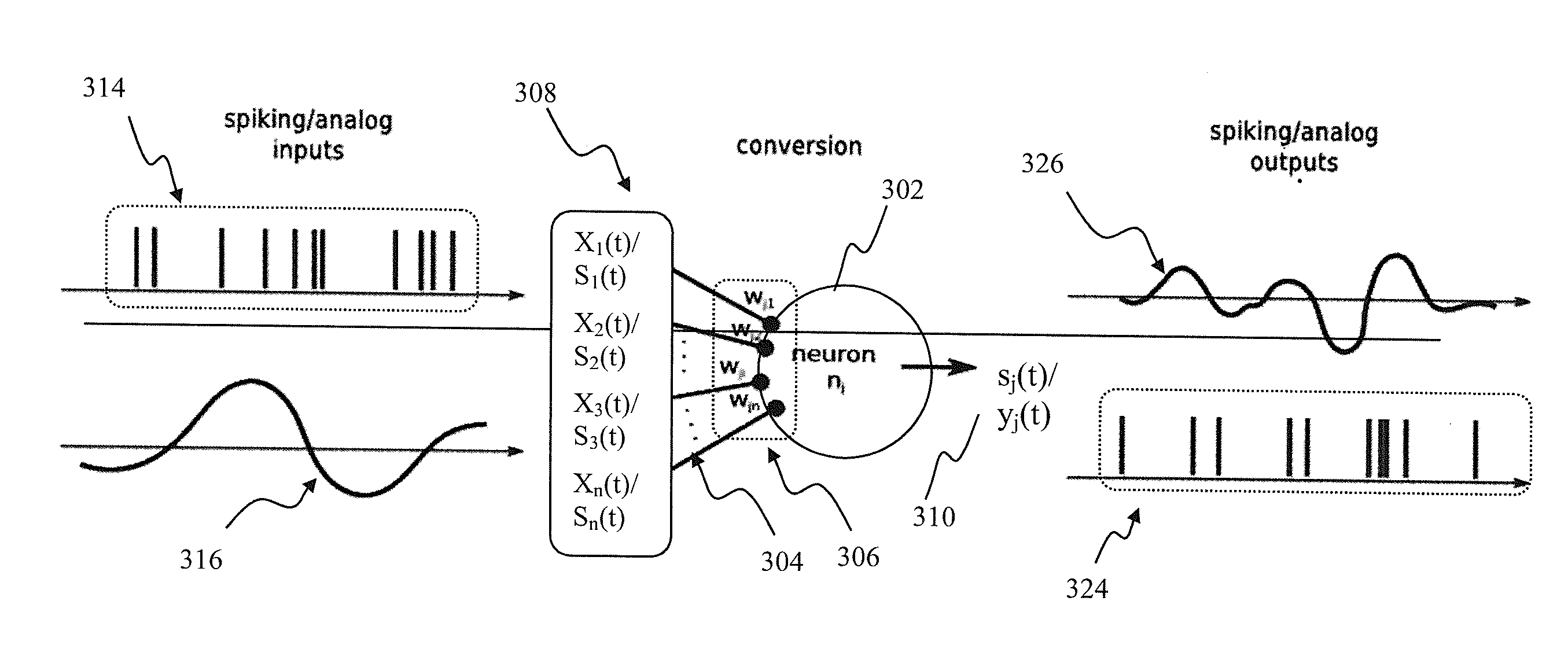
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:PONULAK FILIP
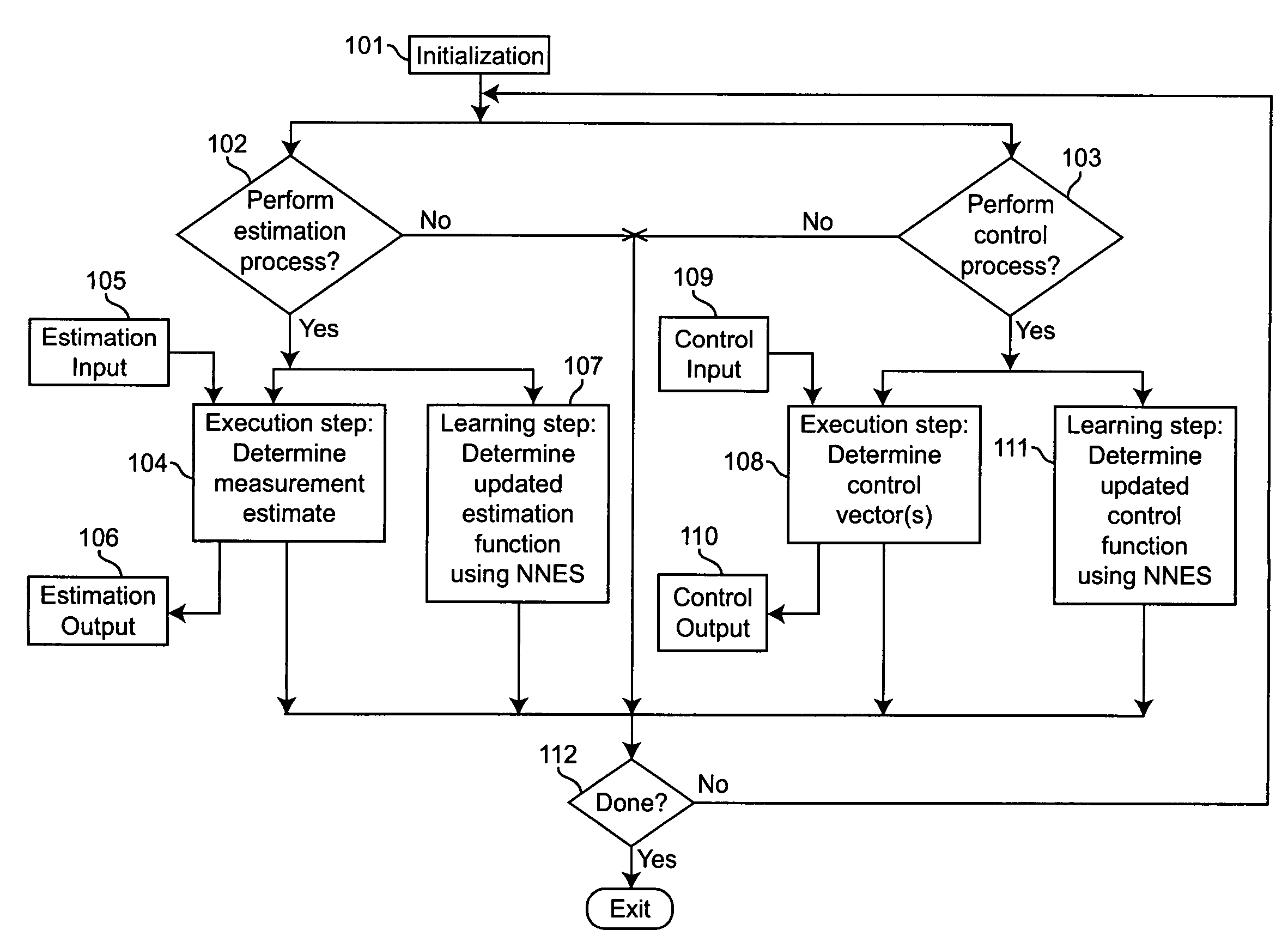
Neural networks for prediction and control
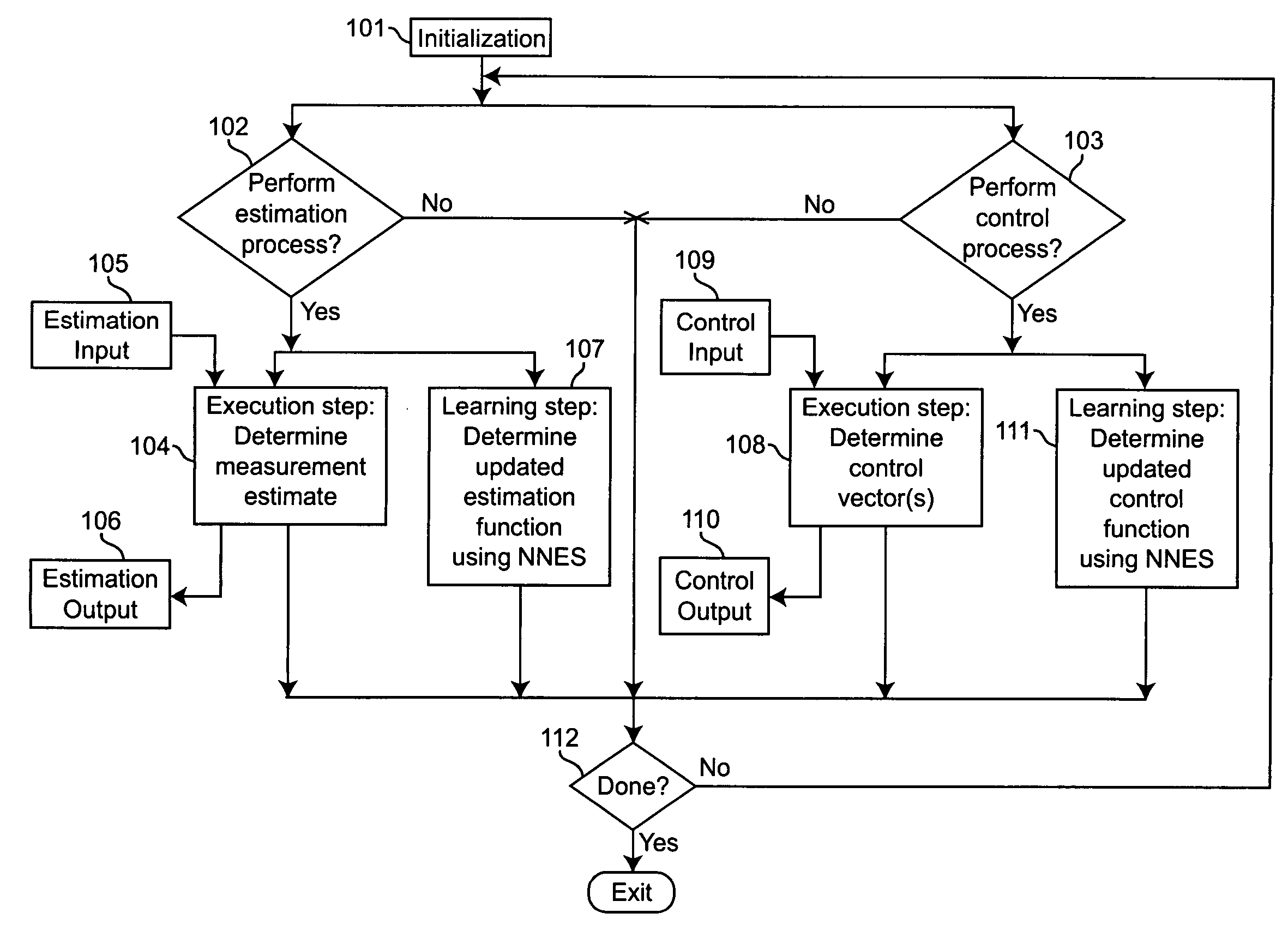
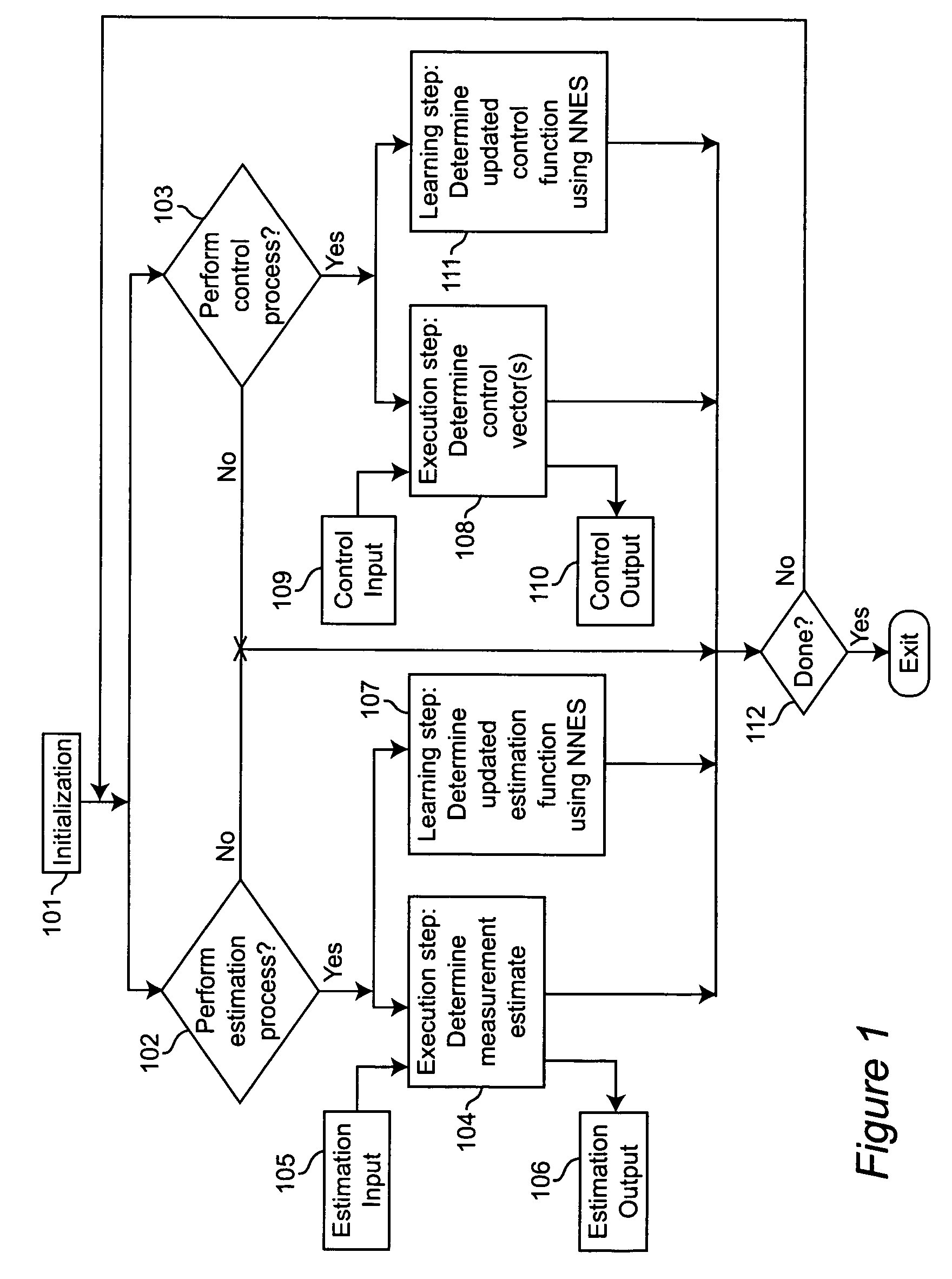
Neural networks for optimal estimation (including prediction) and / or control involve an execution step and a learning step, and are characterized by the learning step being performed by neural computations. The set of learning rules cause the circuit's connection strengths to learn to approximate the optimal estimation and / or control function that minimizes estimation error and / or a measure of control cost. The classical Kalman filter and the classical Kalman optimal controller are important examples of such an optimal estimation and / or control function. The circuit uses only a stream of noisy measurements to infer relevant properties of the external dynamical system, learn the optimal estimation and / or control function, and apply its learning of this optimal function to input data streams in an online manner. In this way, the circuit simultaneously learns and generates estimates and / or control output signals that are optimal, given the network's current state of learning.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Stochastic apparatus and methods for implementing generalized learning rules
ActiveUS20130325773A1Shorten the timeDigital computer detailsDigital dataPerformance functionModularity
Generalized learning rules may be implemented. A framework may be used to enable adaptive signal processing system to flexibly, combine different learning rules (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning) with different methods (online or batch learning). The generalized learning framework may employ time-averaged performance function as the learning measure thereby enabling modular architecture where learning tasks are separated from control tasks, so that changes in one of the modules do not necessitate changes within the other. The generalized learning apparatus may be capable of implementing several learning rules concurrently based on the desired control application and without requiring users to explicitly identify the required learning rule composition for that application.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
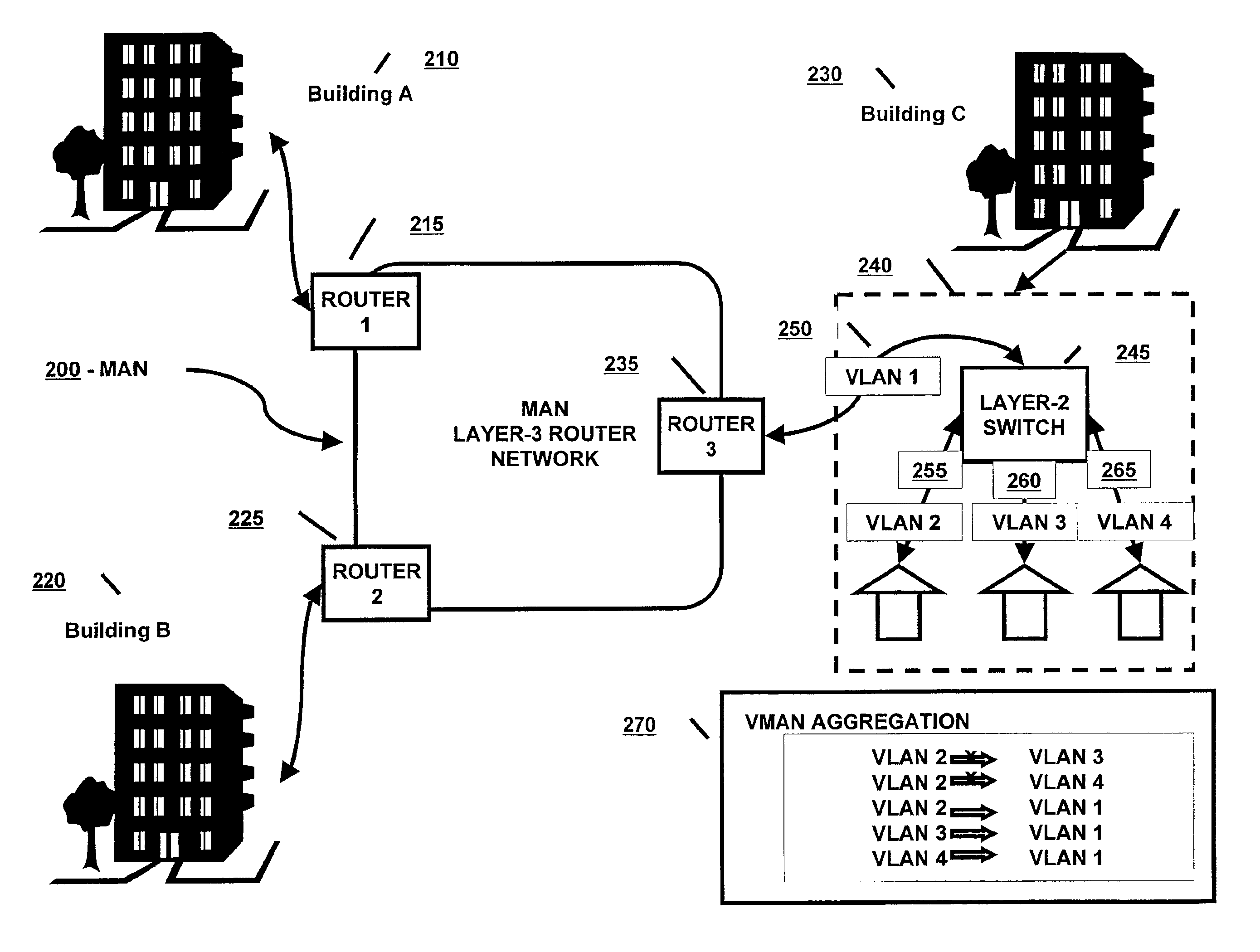
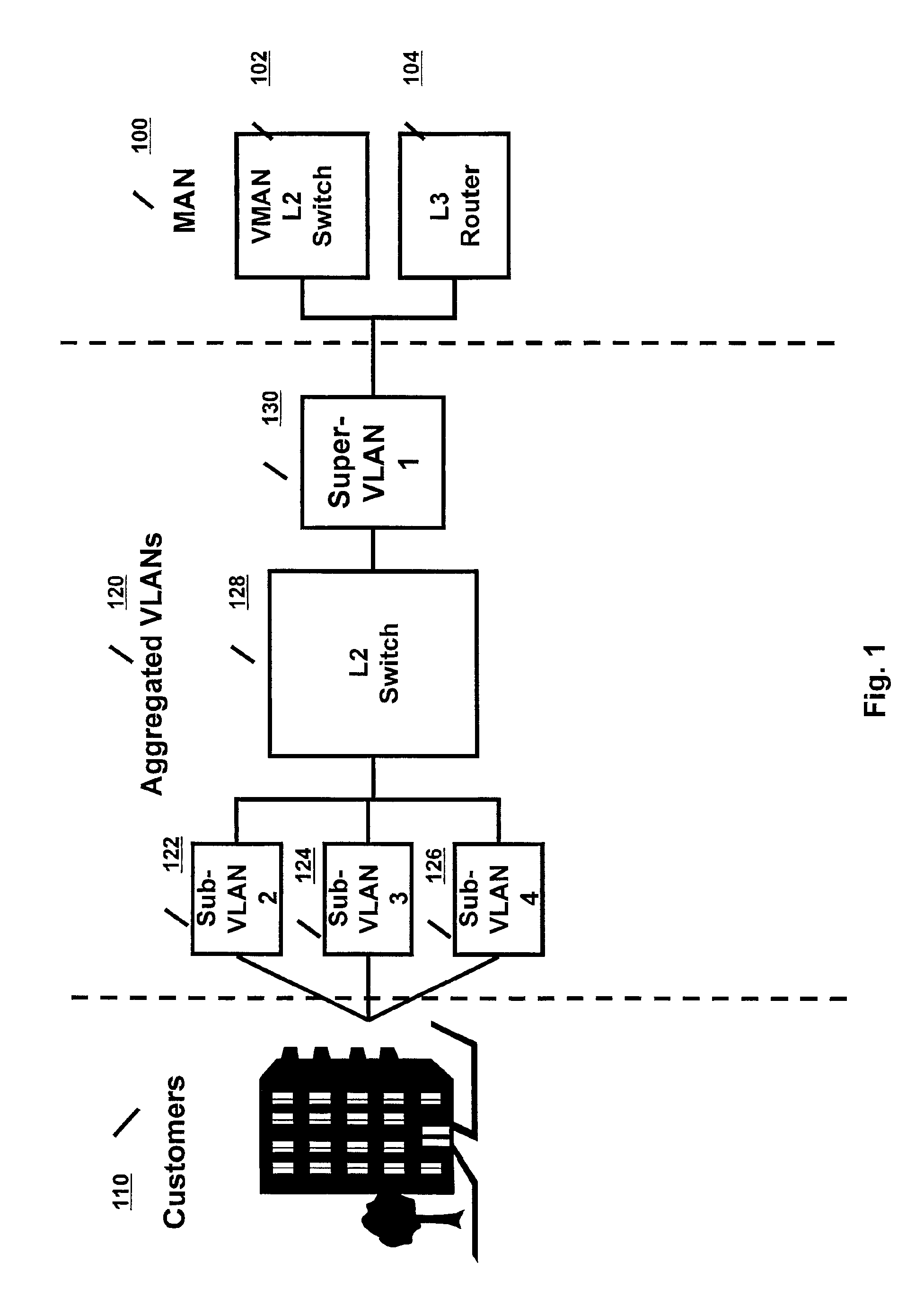
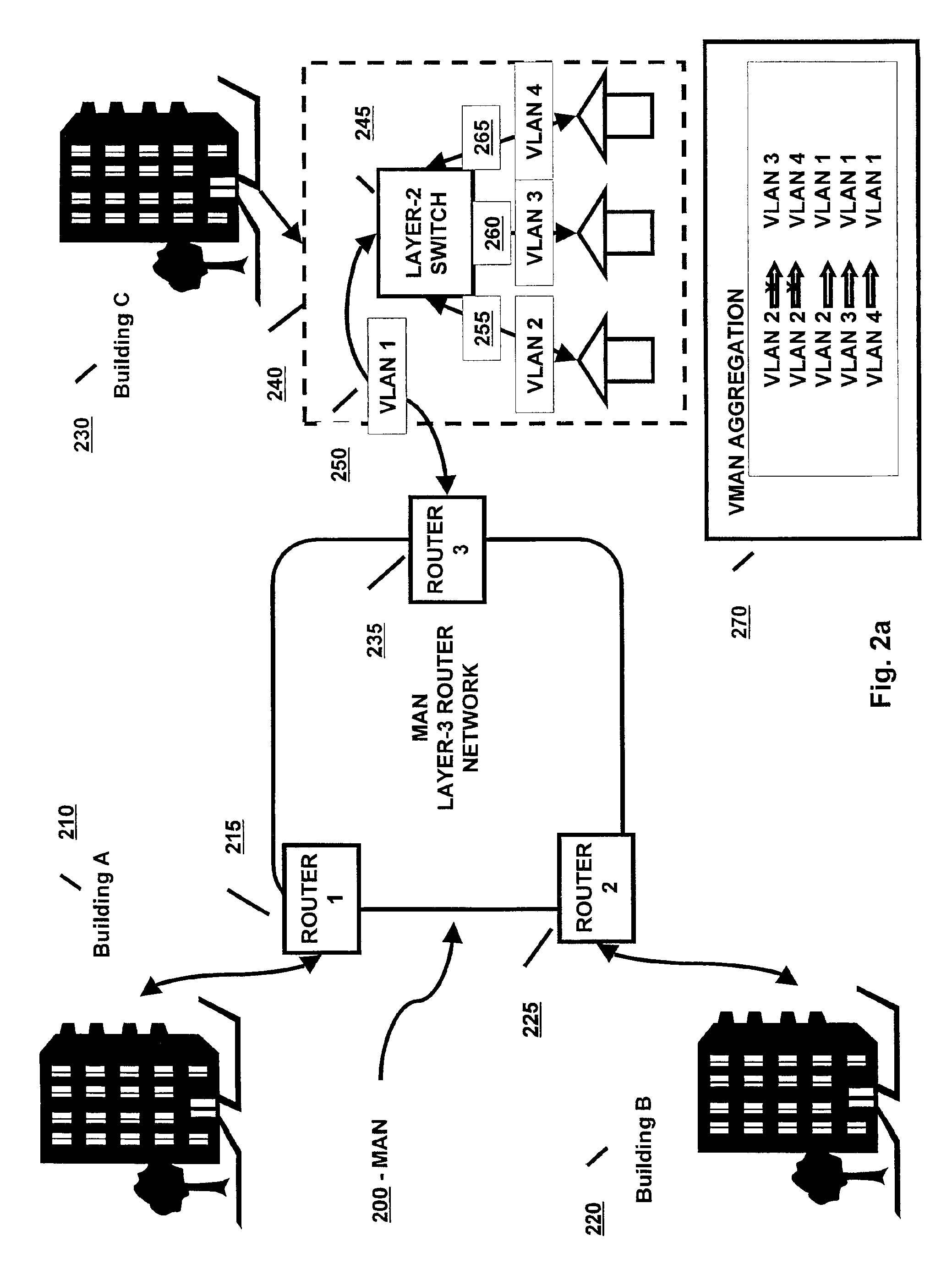
Method and system of aggregate multiple VLANs in a metropolitan area network
InactiveUS6912592B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsTraffic capacityNetwork packet
A method and system is provided in which data packets from multiple customer VLANs are forwarded over a MAN using VLAN aggregation. A layer-2 switch located at the edge of the MAN connects the customer VLANs to the MAN. The edge switch aggregates multiple customer VLANs (the “sub-VLANs”) into one provider VLAN (the “super-VLAN”). When a packet is forwarded from the sub-VLAN to the super-VLAN and vice versa, the edge switch uses modified bridge forwarding rules to exchange the customer-configured VLAN-IDs with the provider-configured VLAN-IDs before transporting the packet over the MAN. The edge switch further uses modified bridge media access control (MAC) address learning rules to isolate one customer's traffic from another's (i.e. isolate one sub-VLAN's traffic from another sub-VLAN's traffic).
Owner:ARISTA NETWORKS
Applications of an algorithm that mimics cortical processing
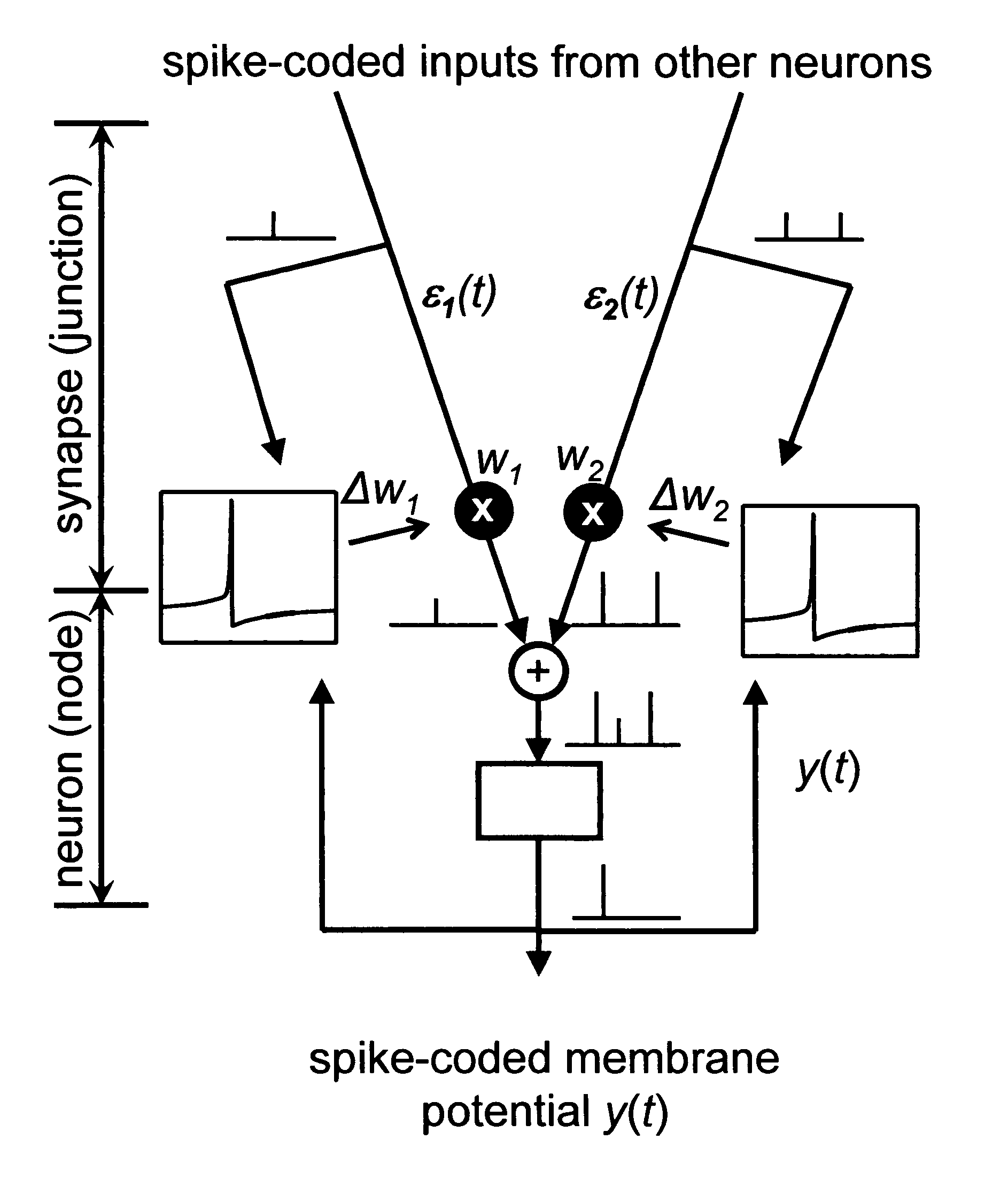
An information processing system having neuron-like signal processors that are interconnected by synapse-like processing junctions that simulates and extends capabilities of biological neural networks. The information processing systems uses integrate-and-fire neurons and Temporally Asymmetric Hebbian learning (spike timing-dependent learning) to adapt the synaptic strengths. The synaptic strengths of each neuron are guaranteed to become optimal during the course of learning either for estimating the parameters of a dynamic system (system identification) or for computing the first principal component. This neural network is well-suited for hardware implementations, since the learning rule for the synaptic strengths only requires computing either spike-time differences or correlations. Such hardware implementation may be used for predicting and recognizing audiovisual information or for improving cortical processing by a prosthetic device.
Owner:SURI ROLAND ERWIN
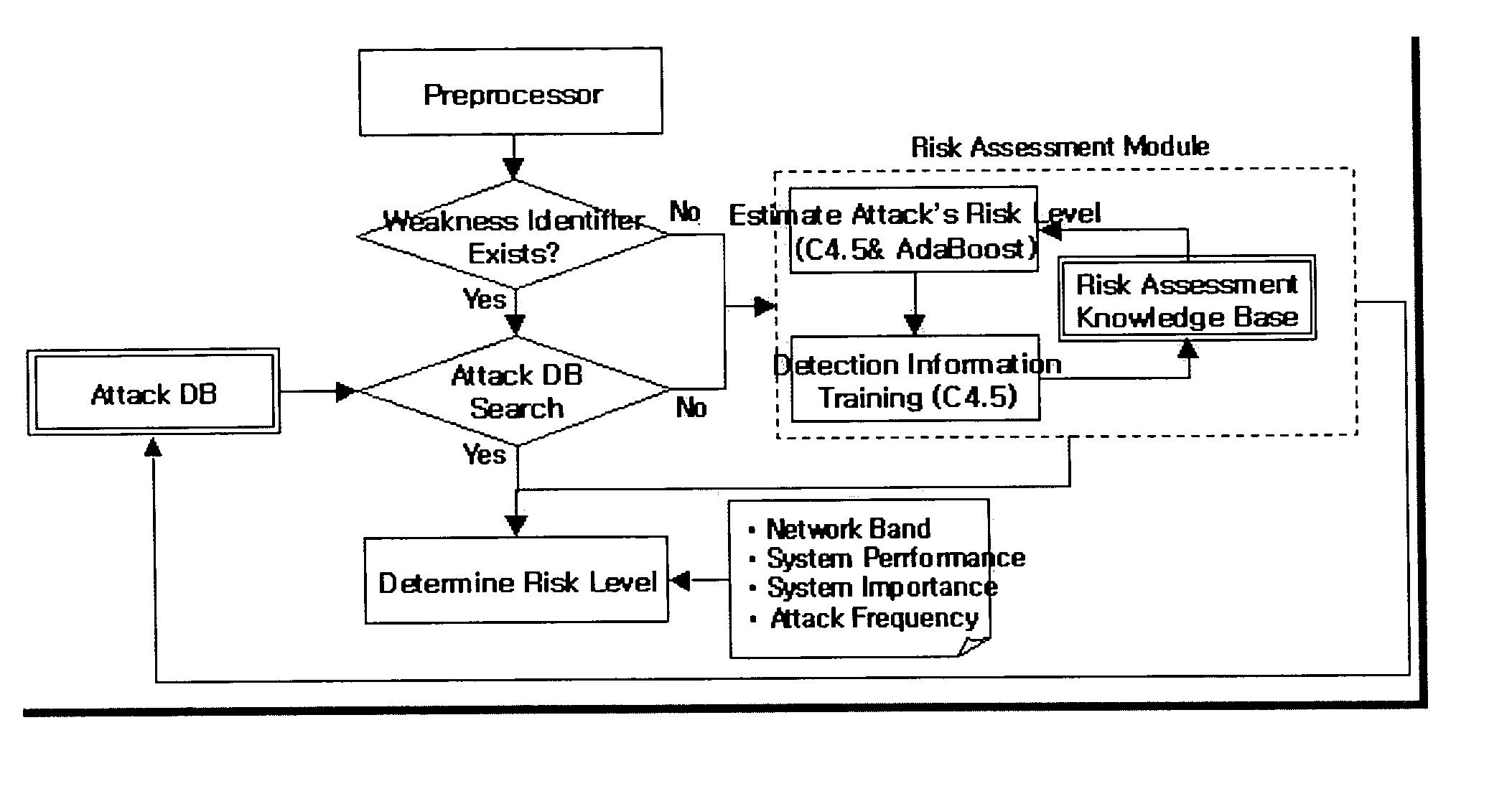
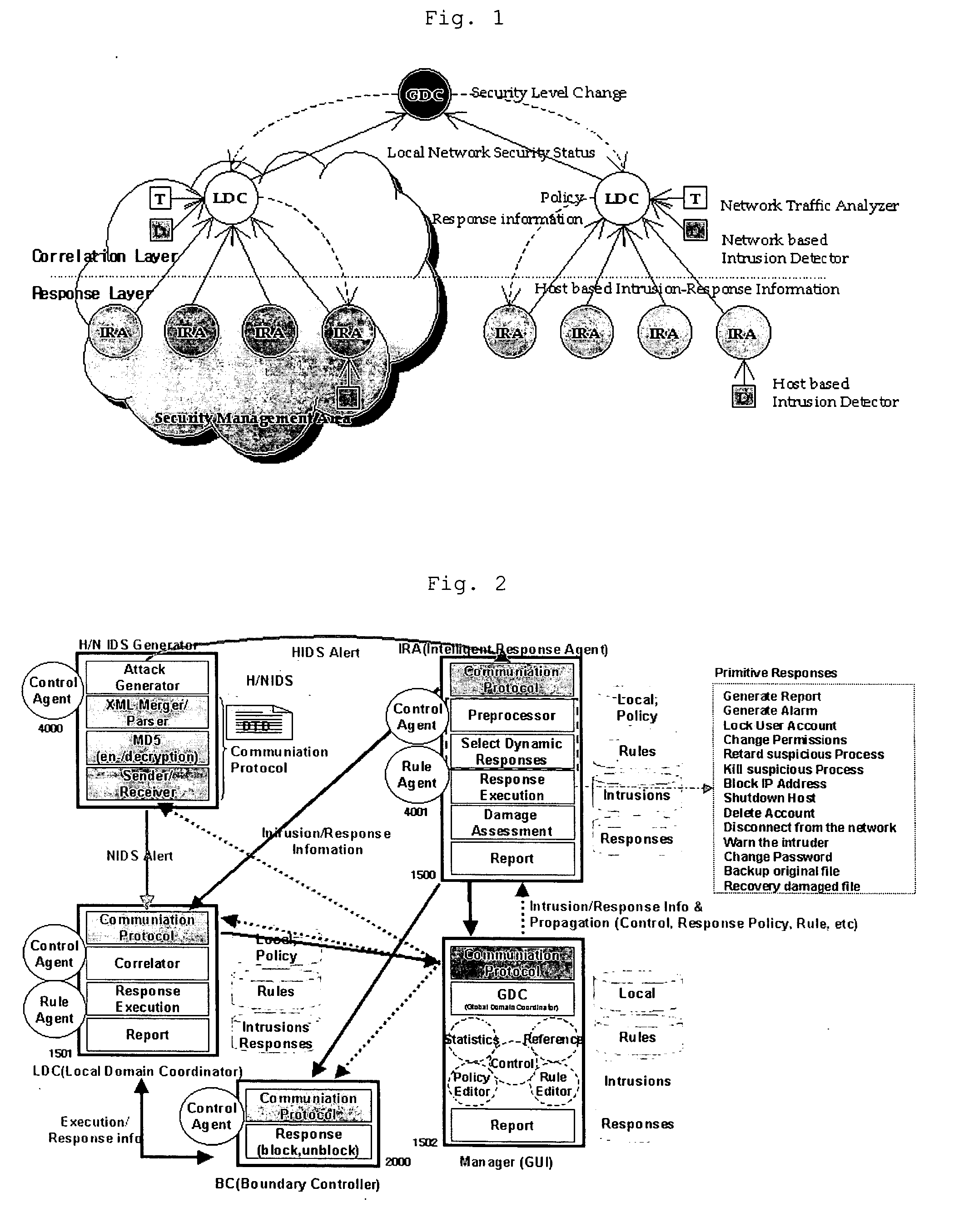
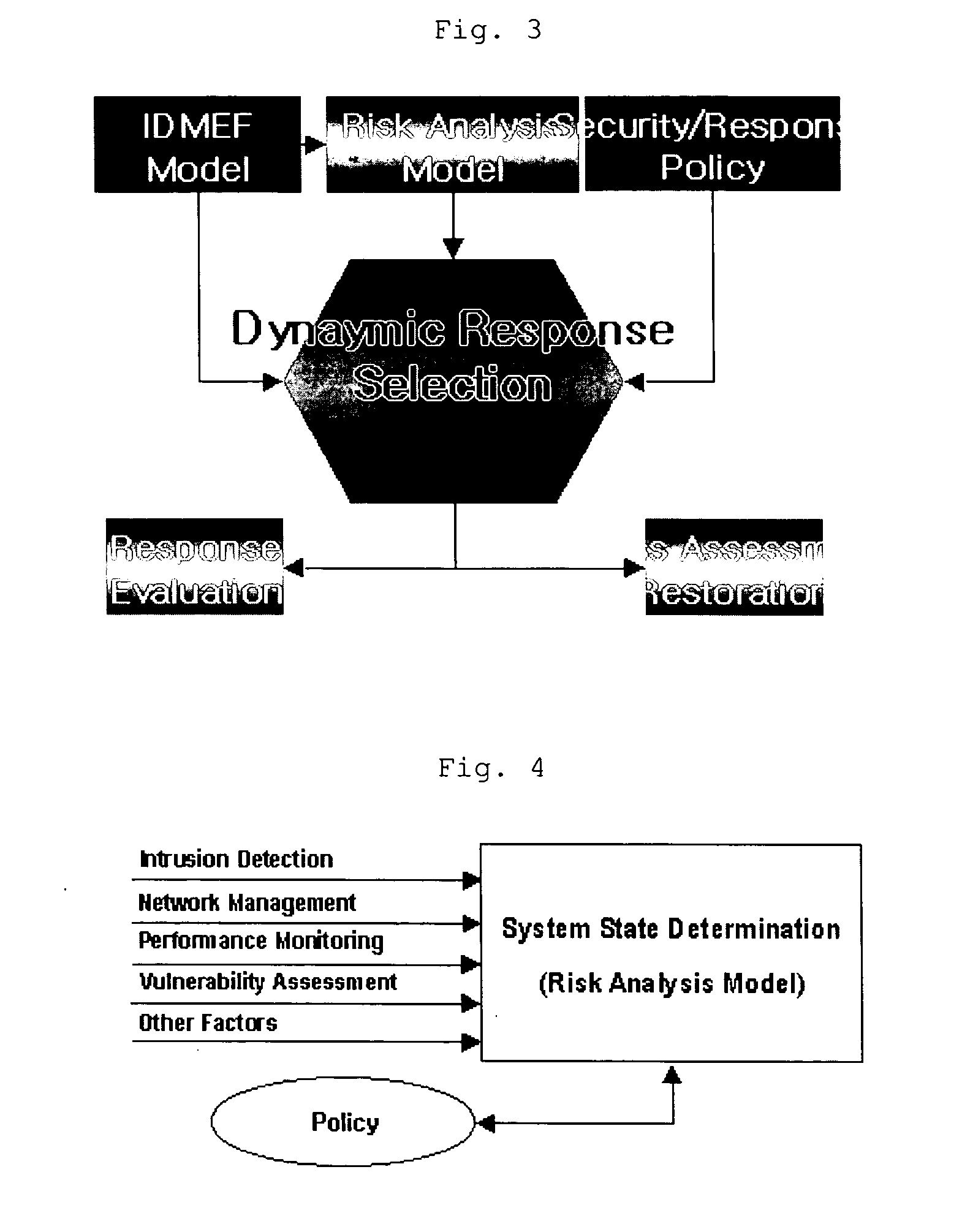
Method of risk analysis in an automatic intrusion response system
InactiveUS20050144480A1Guaranteed accuracyGuarantee efficiencyDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRisk levelIntrusion response systems
The present invention relates to a method of risk analysis in an automatic intrusion response system that provides computer-related security in a large scale dynamic network environment, comprising: (a) classifying intrusion detection information by using IDMEF data model; (b) establishing a risk assessment knowledge base; (c) learning rules of said knowledge base; and (d) assessing the risk level of an external attack based upon said knowledge base. Said risk level is determined by parameters such as intrusion detection information, weakness information, network bandwidth, system performance and importance, and frequency of attacks, etc.
Owner:KOREA INTERNET & SECURITY AGENCY
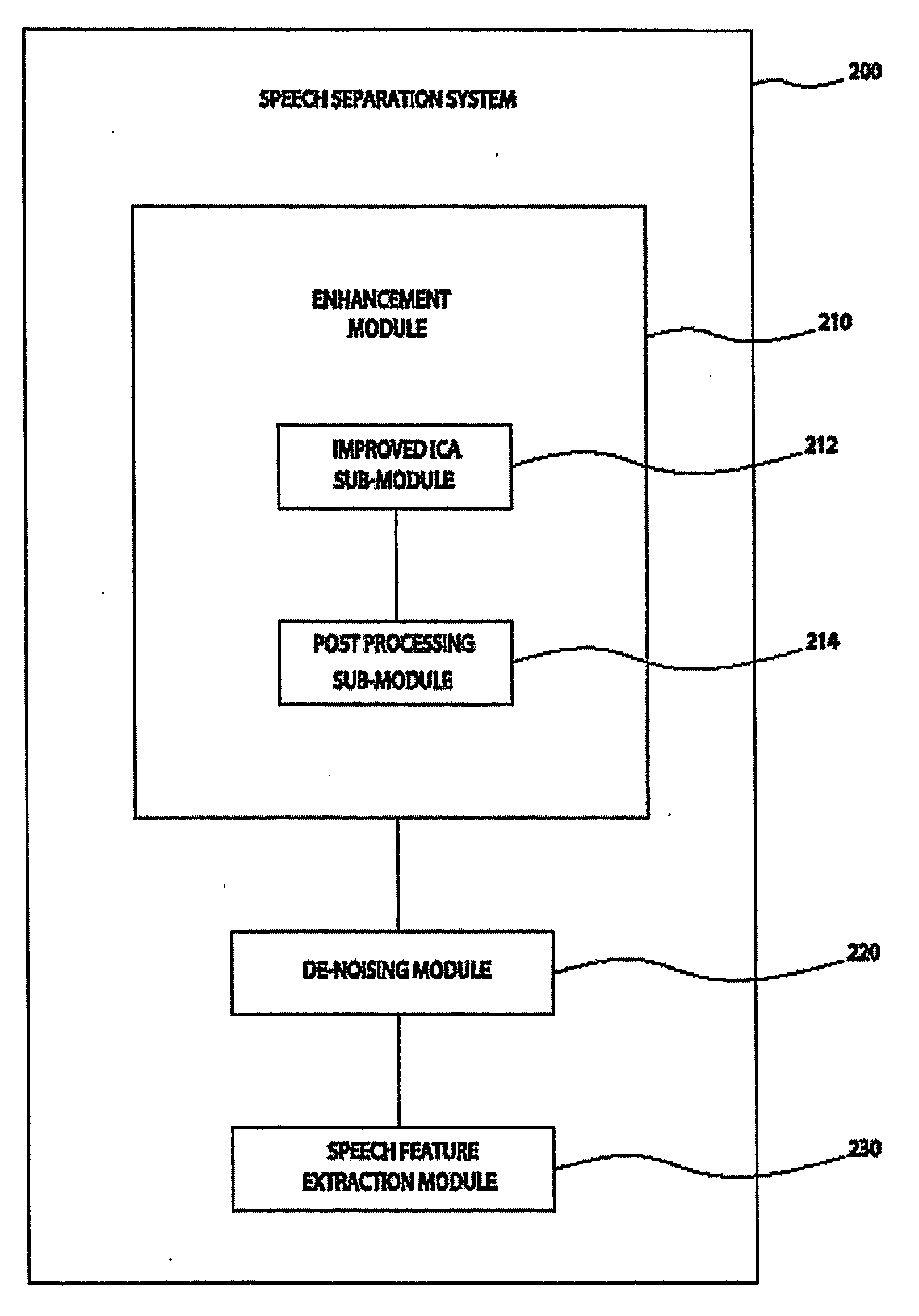
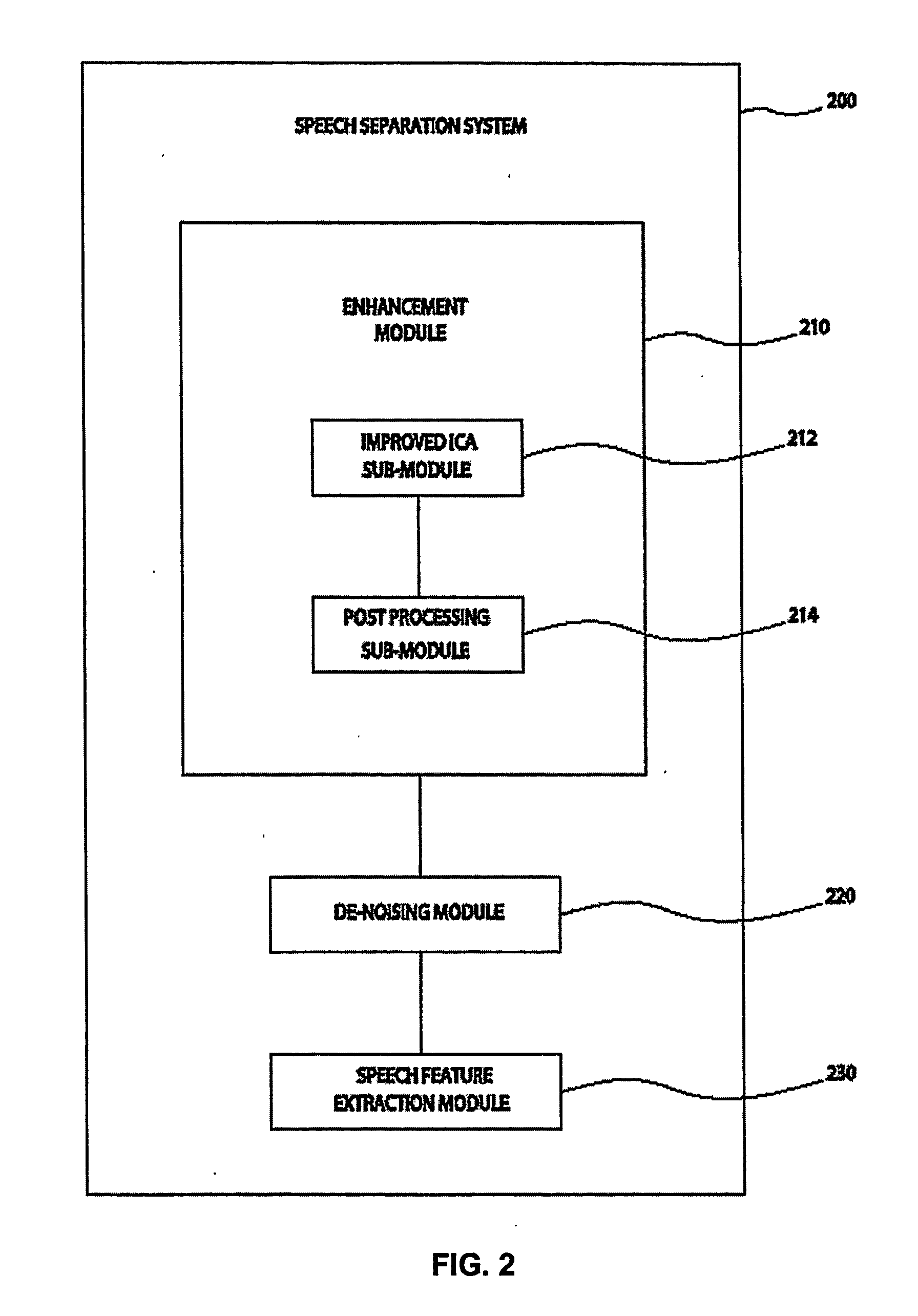
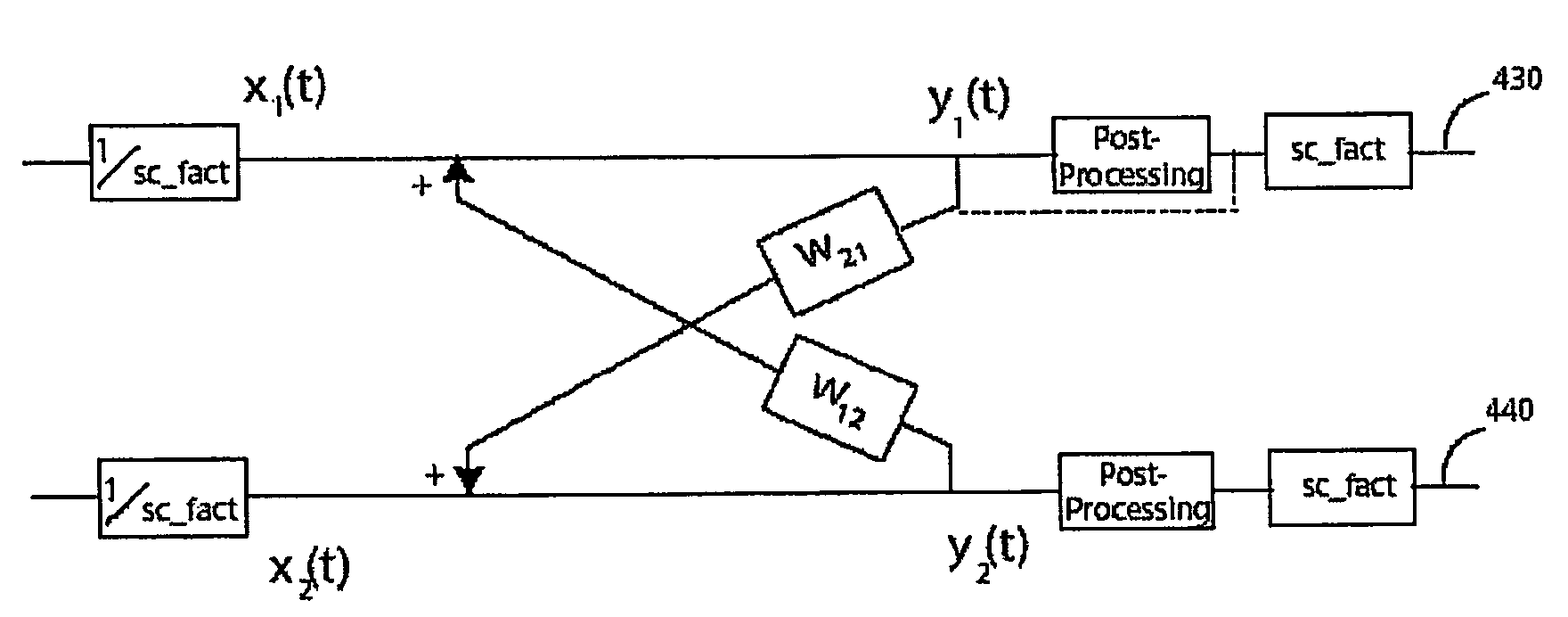
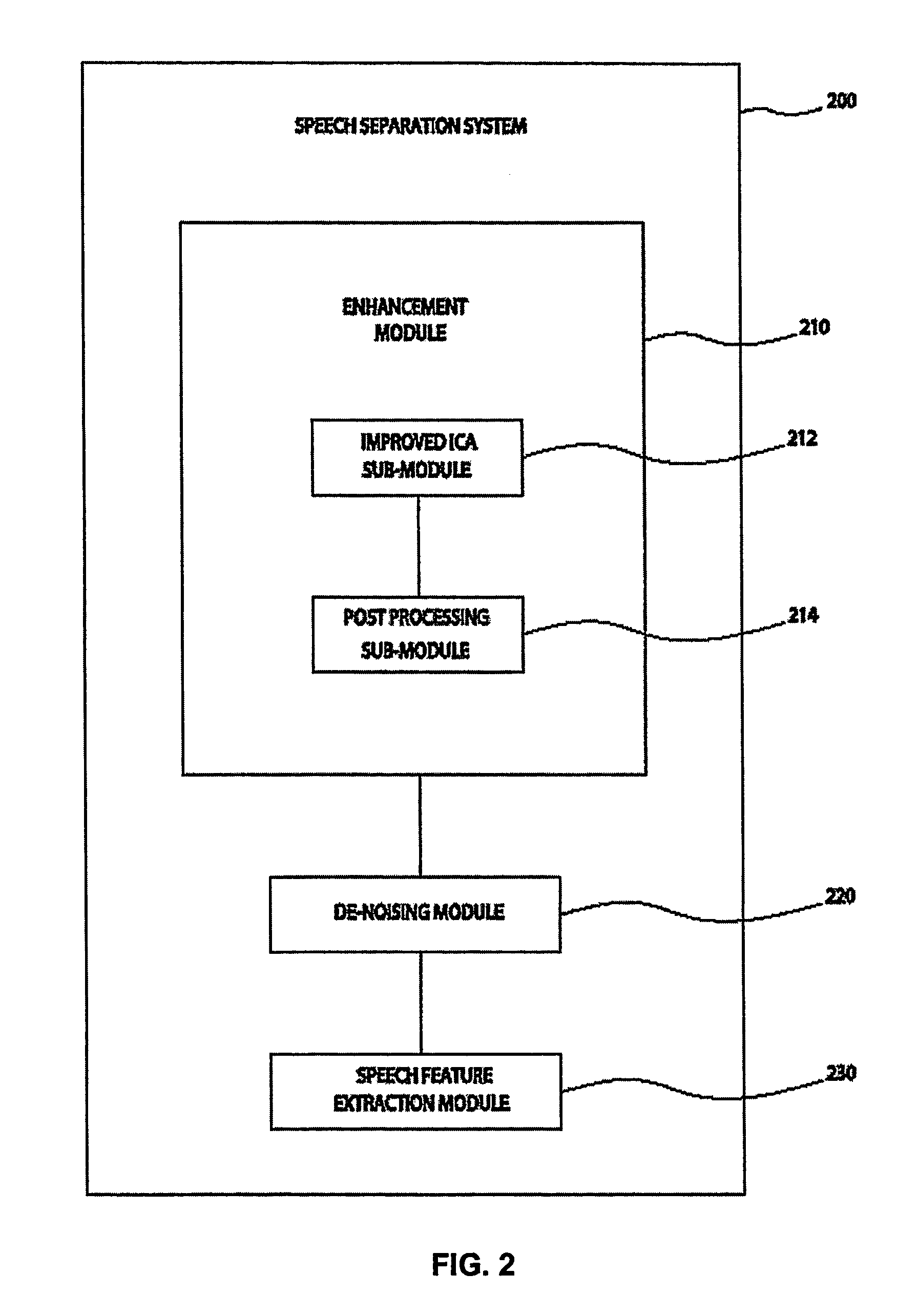
System and method for speech processing using independent component analysis under stability restraints
ActiveUS20060053002A1Constrain filter weight adaptation speedAvoid reverberation effectAdaptive networkSpeech analysisLearning ruleIndependent component analysis
A system and method for separating a mixture of audio signal into desired audio signals (430) (e.g., speech) and a noise sign (440) is disclosed. Microphones (310, 320) are positioned to receive the mixed audio signals, and an independent component analysis (ICA) processes (212) the sound mixture using stability constraints. The ICA process (508) uses predefined characteristics of the desired speech signal to identify and isolate a target sound signal (430). Filter coefficients are adapted with a learning rule and filter weight update dynamics are stabilized to assist convergence to a stable separated ICA signal result. The separated signals may be peripherally-processed to further reduce noise effects using post-processing (214) and pre-processing (220, 230) techniques and information. The proposed system is designed and easily adaptable for implementation on DSP units or CPUs in audio communication hardware environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
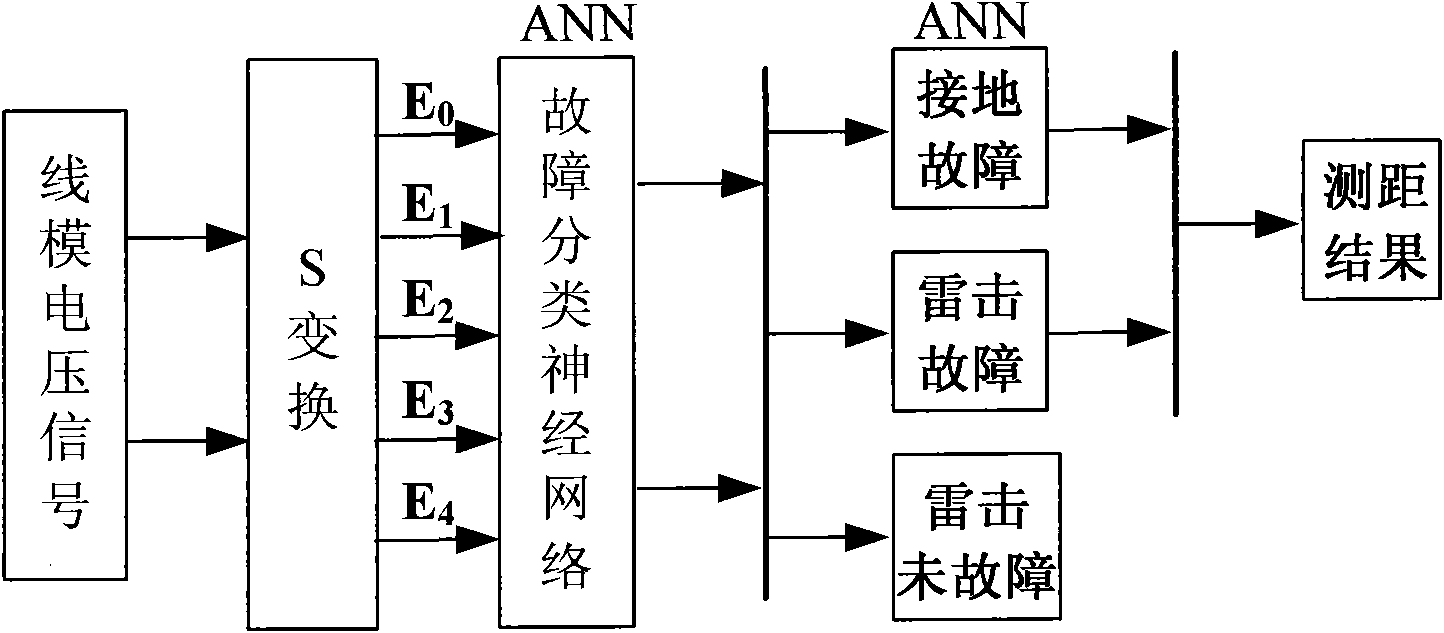
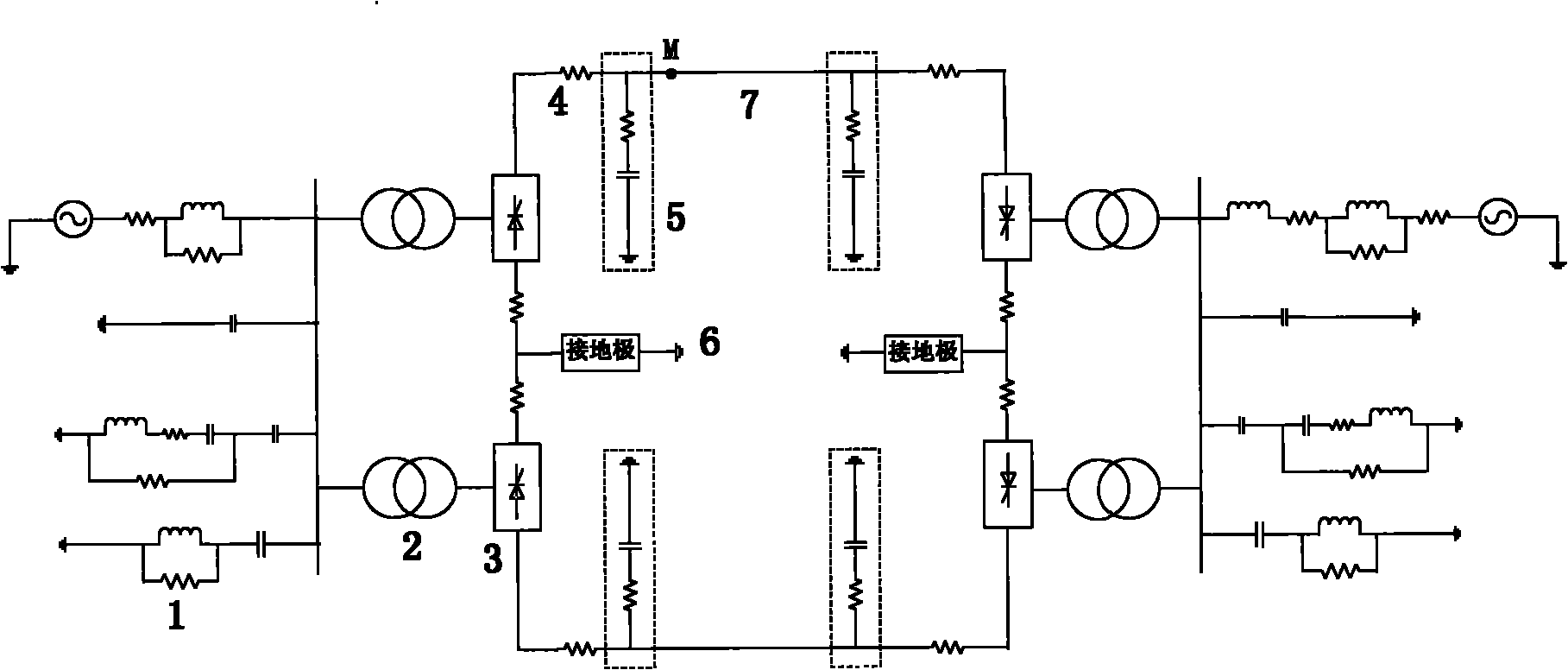
Intelligent fault classification and location method for ultra-high voltage direct current transmission line
ActiveCN101975910ALower requirementPracticalFault locationNeural learning methodsUltra high voltageElectric power system
The invention discloses an intelligent fault classification and location method for an ultra-high voltage direct current transmission line, and belongs to the technical field of relay protection of power systems. The method comprises the following steps of: classifying fault data by using a neural network by adopting a layered and distributed neural network model; distinguishing fault types; sending the classified data into different neural networks respectively for performing fault location; when the direct current transmission line has a fault and a sampling frequency is 10 kHz, selecting a discrete line mode voltage signal which has the sampling sequence length of 100 after the fault and performing S-transform, wherein a transform result is a complex time-frequency matrix of 51*100; solving the modulus of each element in the complex matrix to obtain transient energy distribution of the line mode voltage at all frequencies; selecting first five energy spectrums as sample properties; selecting a transfer function and a learning rule; setting proper neural network parameters for constructing a BP network model; and performing fault classification and fault location. A large number of simulation results show that the method has a good effect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus and methods for implementing learning for analog and spiking signals in artificial neural networks
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
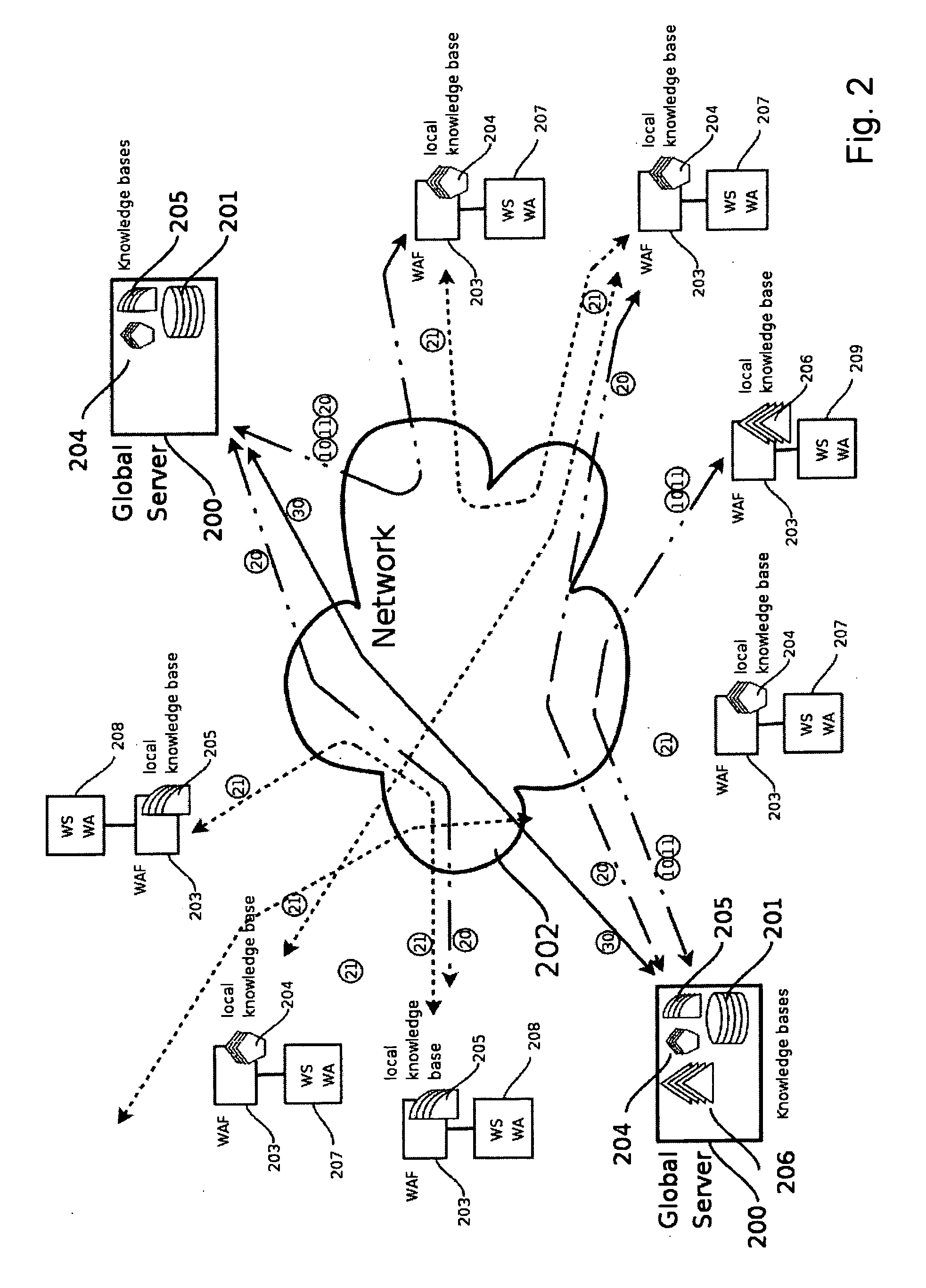
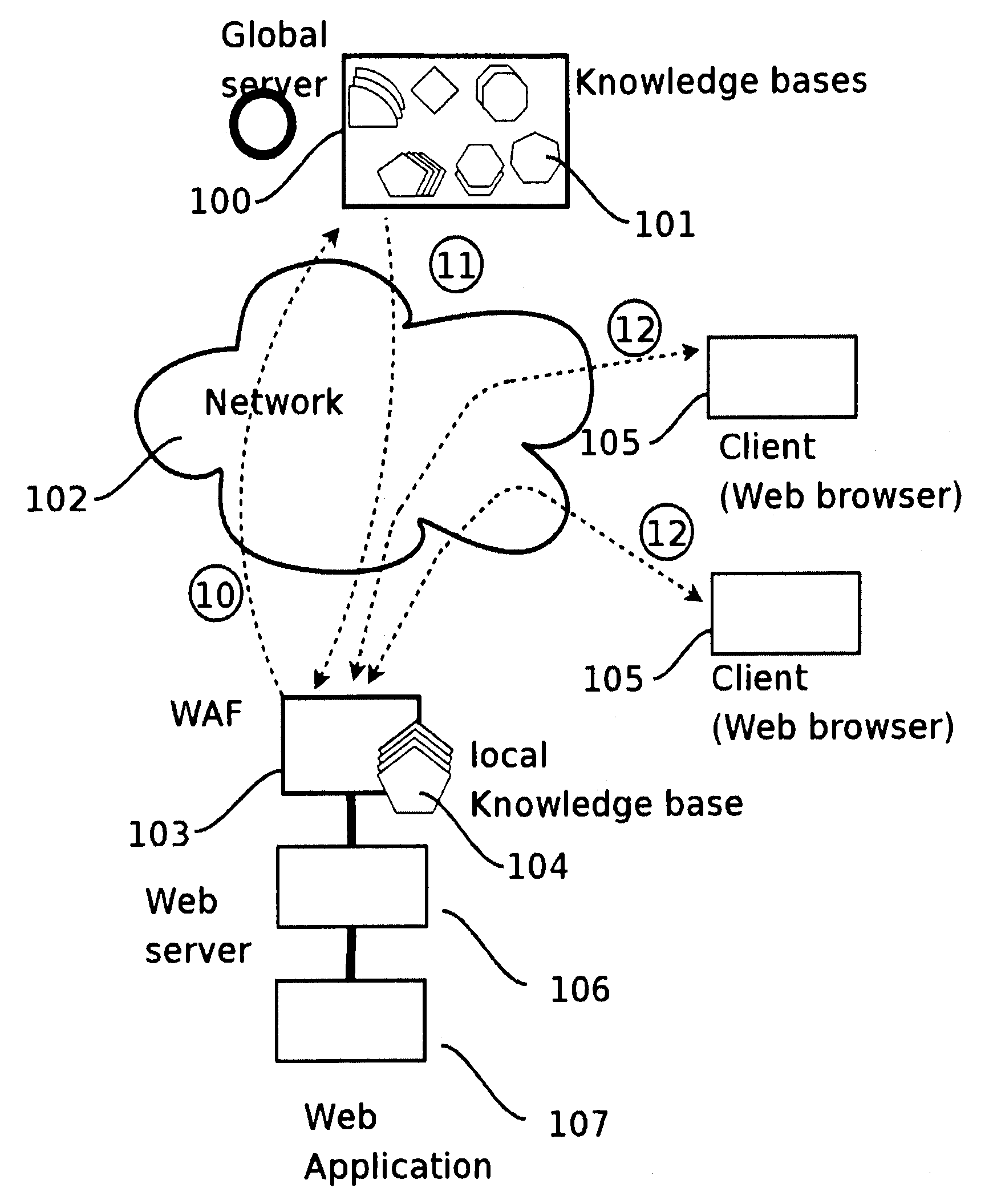
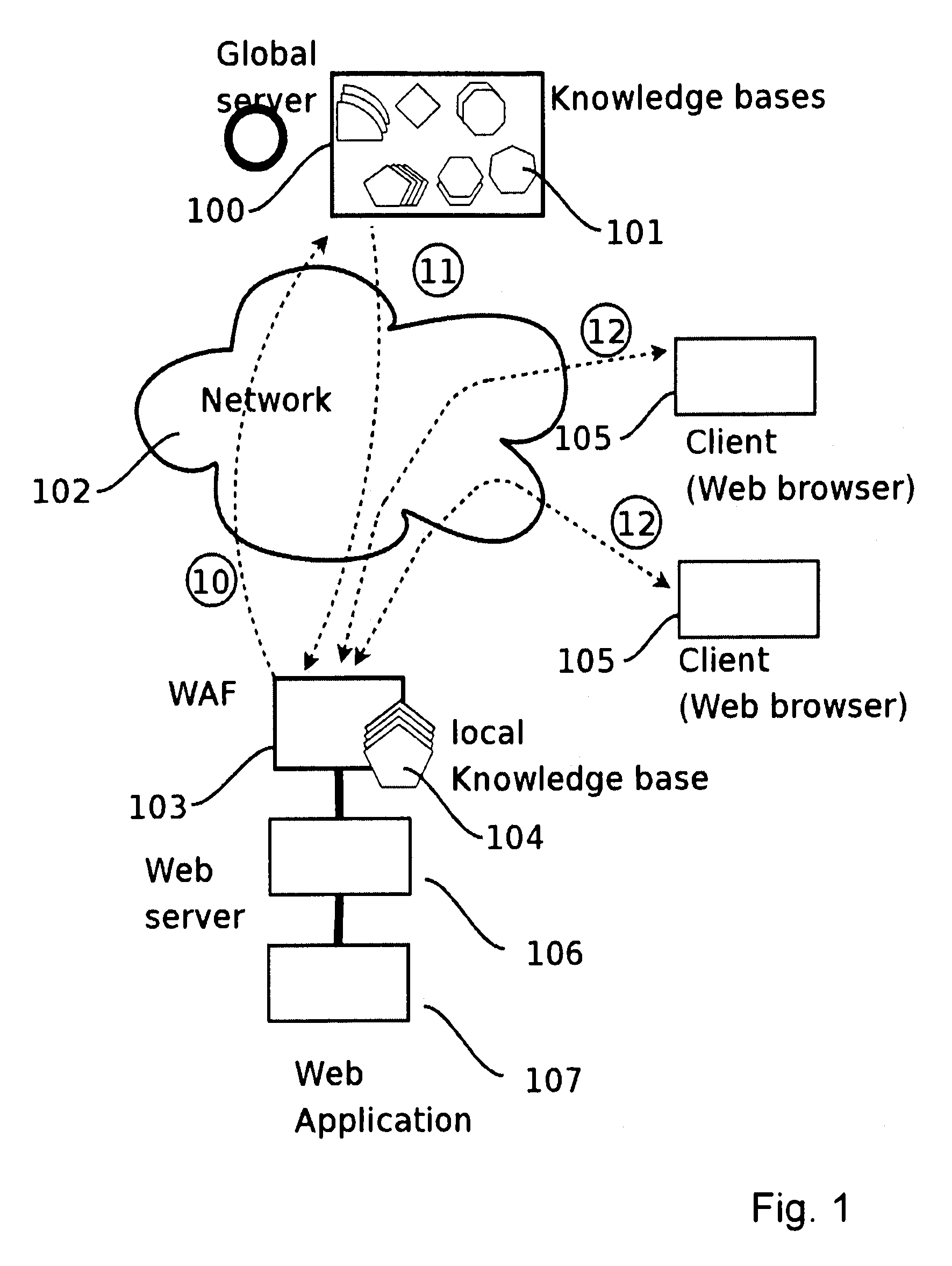
Distributed web application firewall
ActiveUS20090328187A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb applicationWeb service
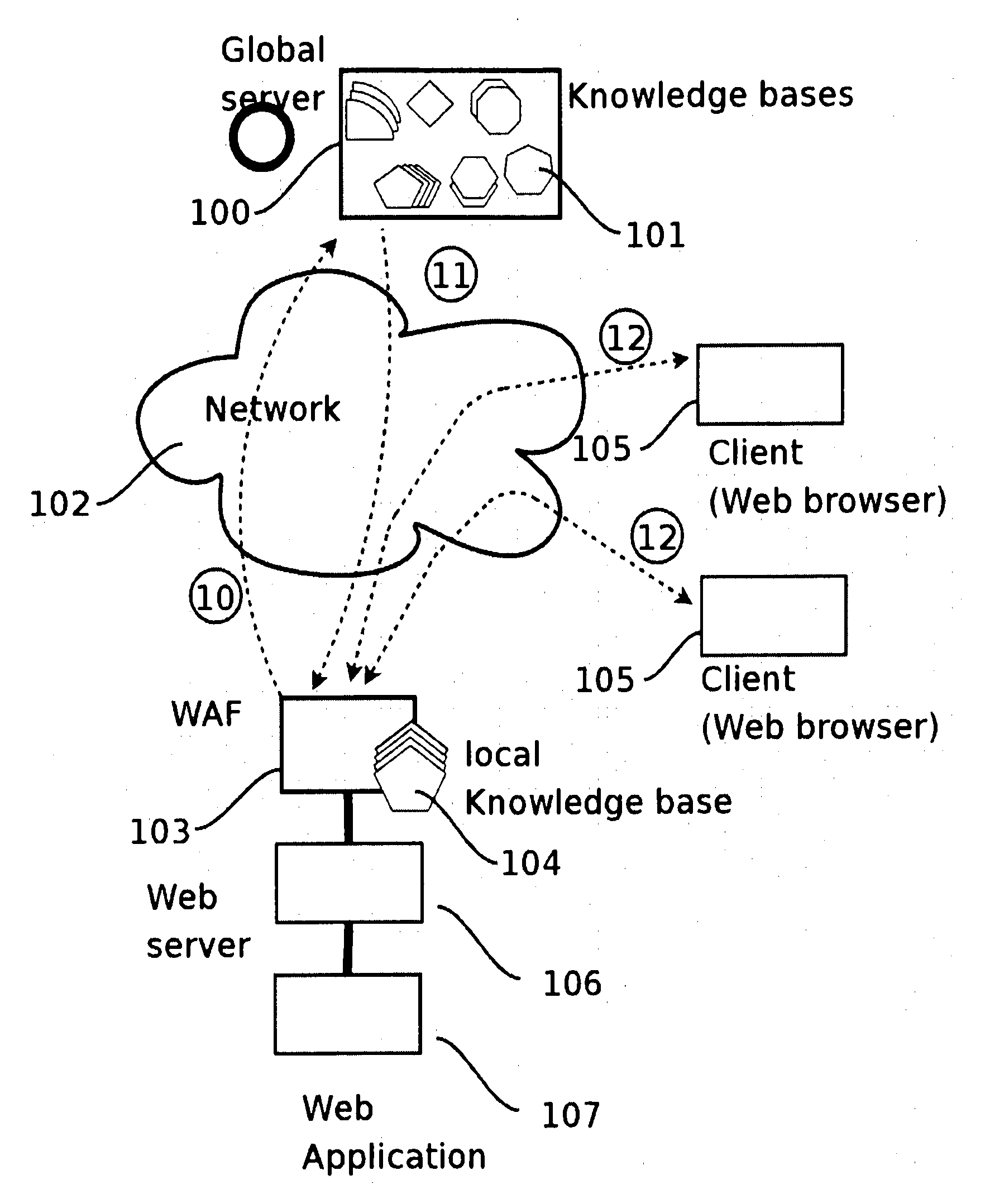
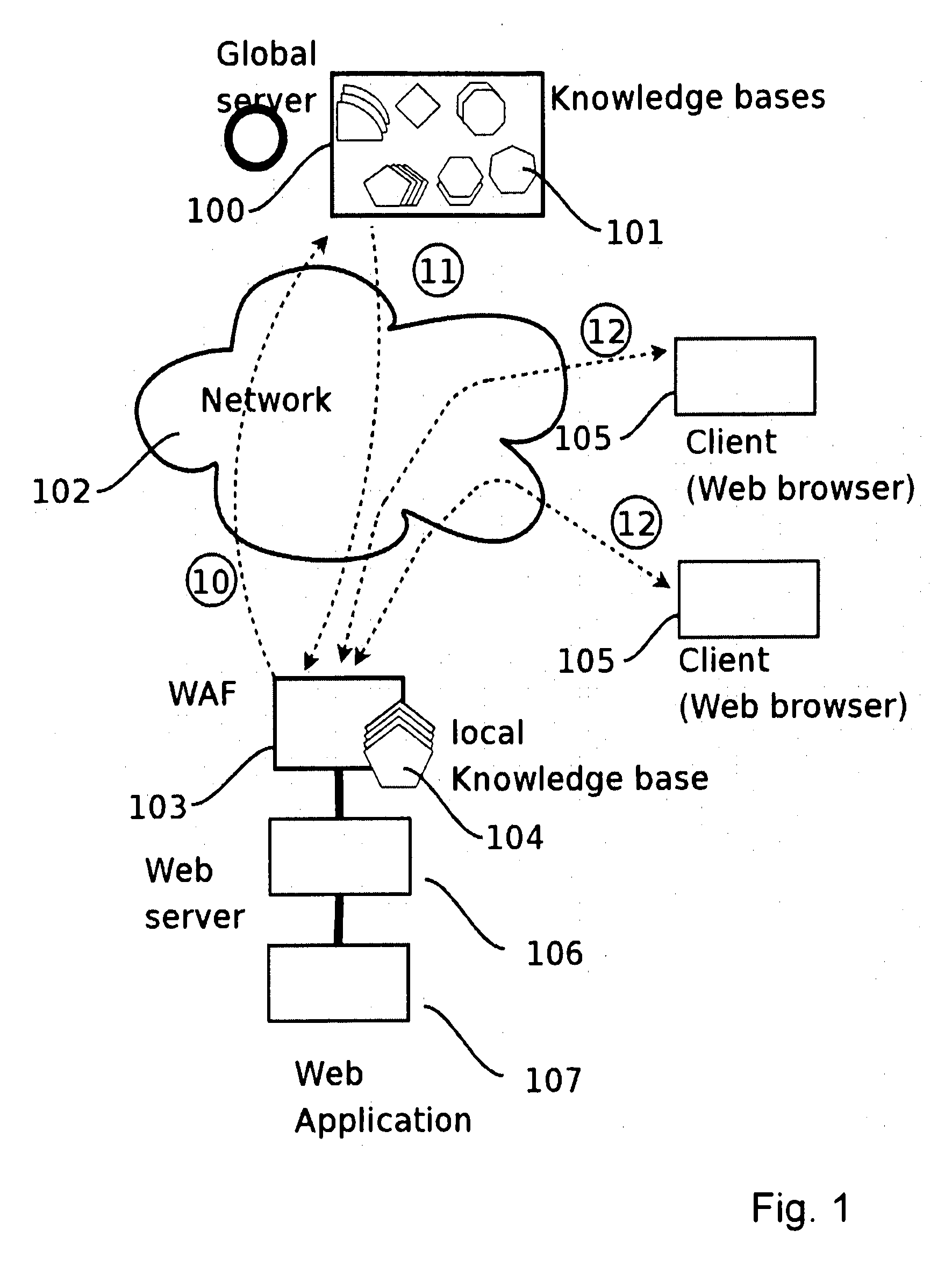
A method for protecting a Web application running on a first local Web Server bases from hacker attacks, said Web Server being connectable to at least one client, the method comprising the following steps: —providing a plurality of preset rules on said Server, which correspond to specific characteristics of HTTP requests; —receiving an HTTP request on said server from the client, said HTTP request comprising a plurality of characteristics; —analyzing said characteristics of said received HTTP request in accordance with said rules provided on said server; —rejecting said HTTP request, if said rules identify said HTTP request as harmful request; —accepting said HTTP request, if said rules identify said HTTP request as trustable request; —classifying said HTTP request as doubtful request, if said rules identify said request neither as harmful request nor as trustable request; —evaluating the characteristics of said doubtful local request; —generating a learned rule on basis of the edge base evaluation.
Owner:PULSE SECURE +1
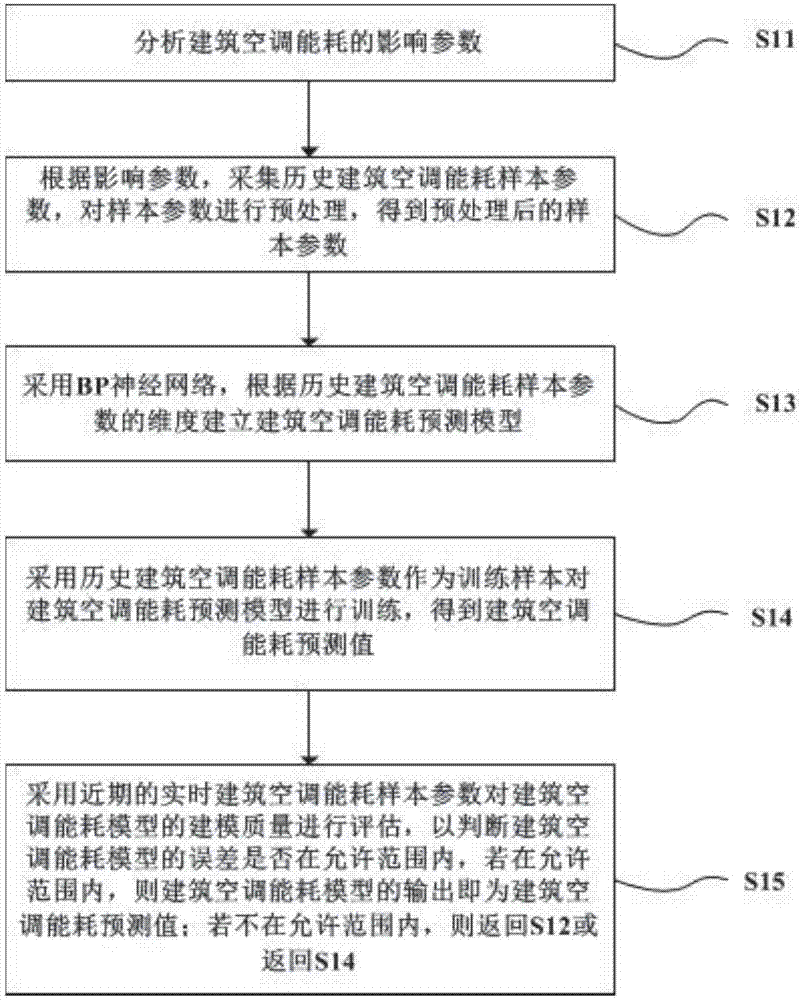
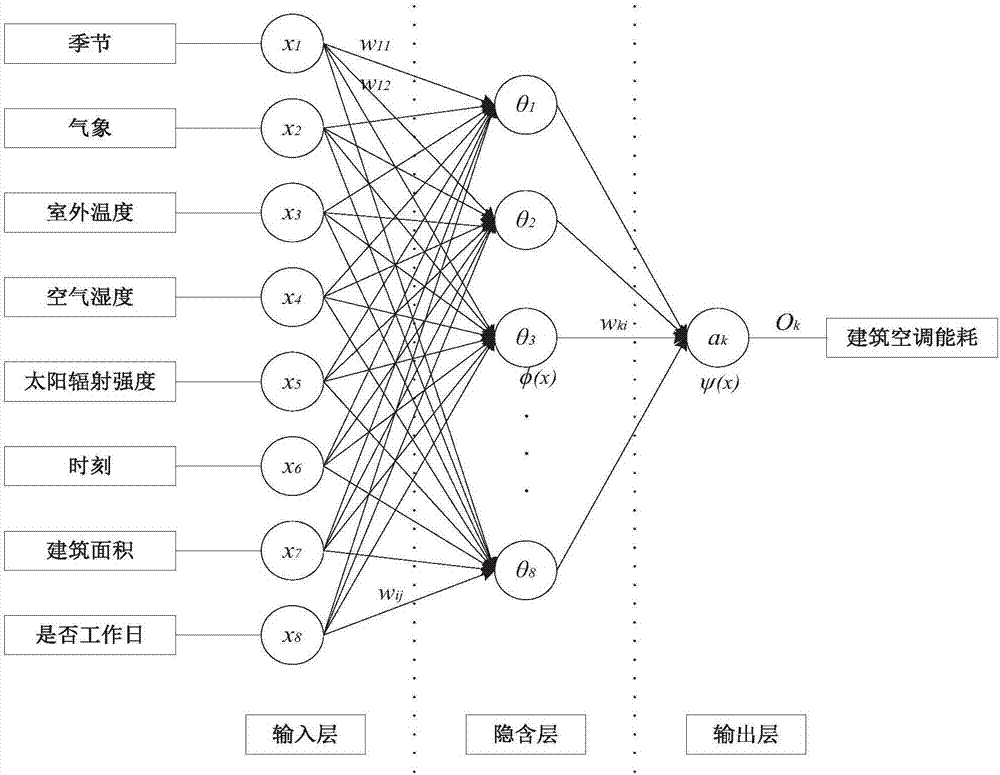
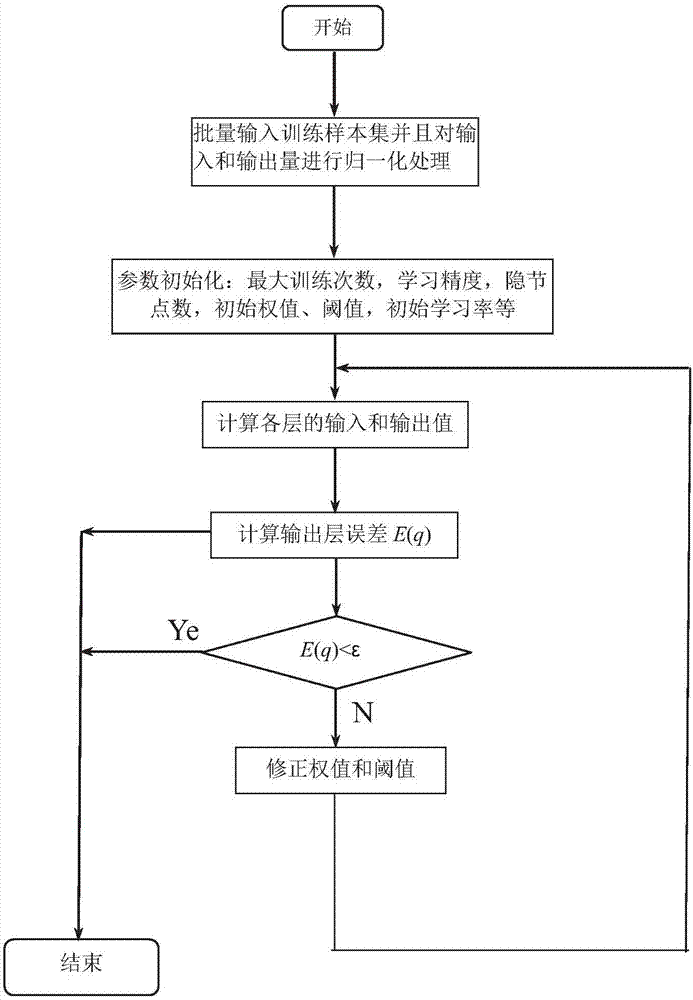
Building air-conditioning energy consumption prediction method based on BP neural network model
ActiveCN106874581AEasy to implementStrong nonlinear fitting abilityDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesLearning ruleNetwork model
The invention discloses a building air-conditioning energy consumption prediction method based on a BP neural network model. The method comprises: analyzing influence factors of building air-conditioning energy consumption; according to influence parameters, collecting historical building air-conditioning energy consumption sample parameters, and preprocessing the parameters; using a BP neural network, according to dimensionality of the sample parameters, establishing a building air-conditioning energy consumption prediction model; using the preprocessed sample parameters as a training sample, training the building air-conditioning energy consumption prediction model; collecting near-term real-time building air-conditioning energy consumption sample parameters to evaluate the building air-conditioning energy consumption prediction model; if errors are in an allowed range, output of the model being a building air-conditioning energy consumption predicted value; if not, training the model again. The building air-conditioning energy consumption prediction method based on a BP neural network model is advantaged in that learning rules are simple, a computer can easily implement, and the method has excellent robustness, memory capability, nonlinear mapping capability, and powerful self-learning capability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
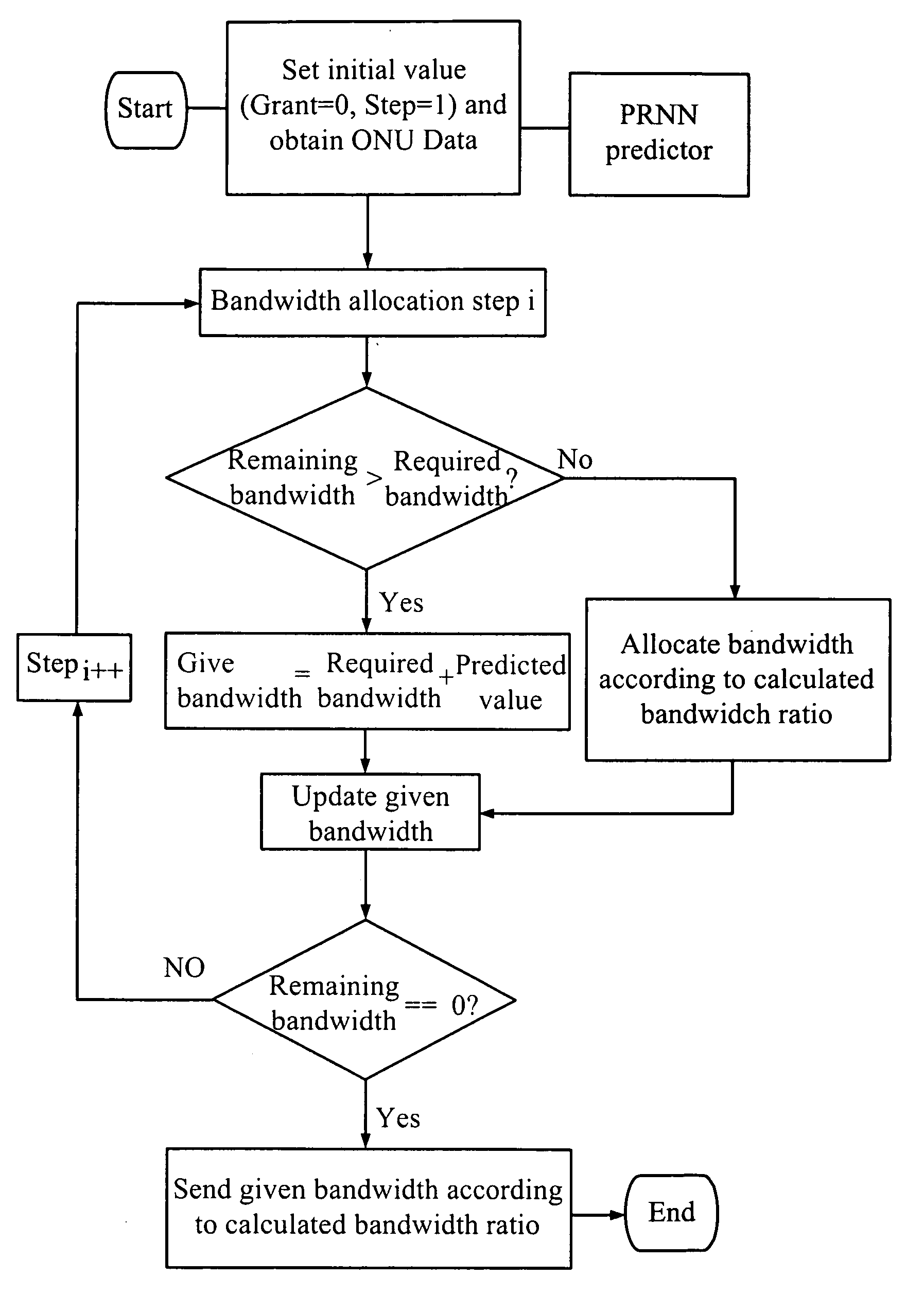
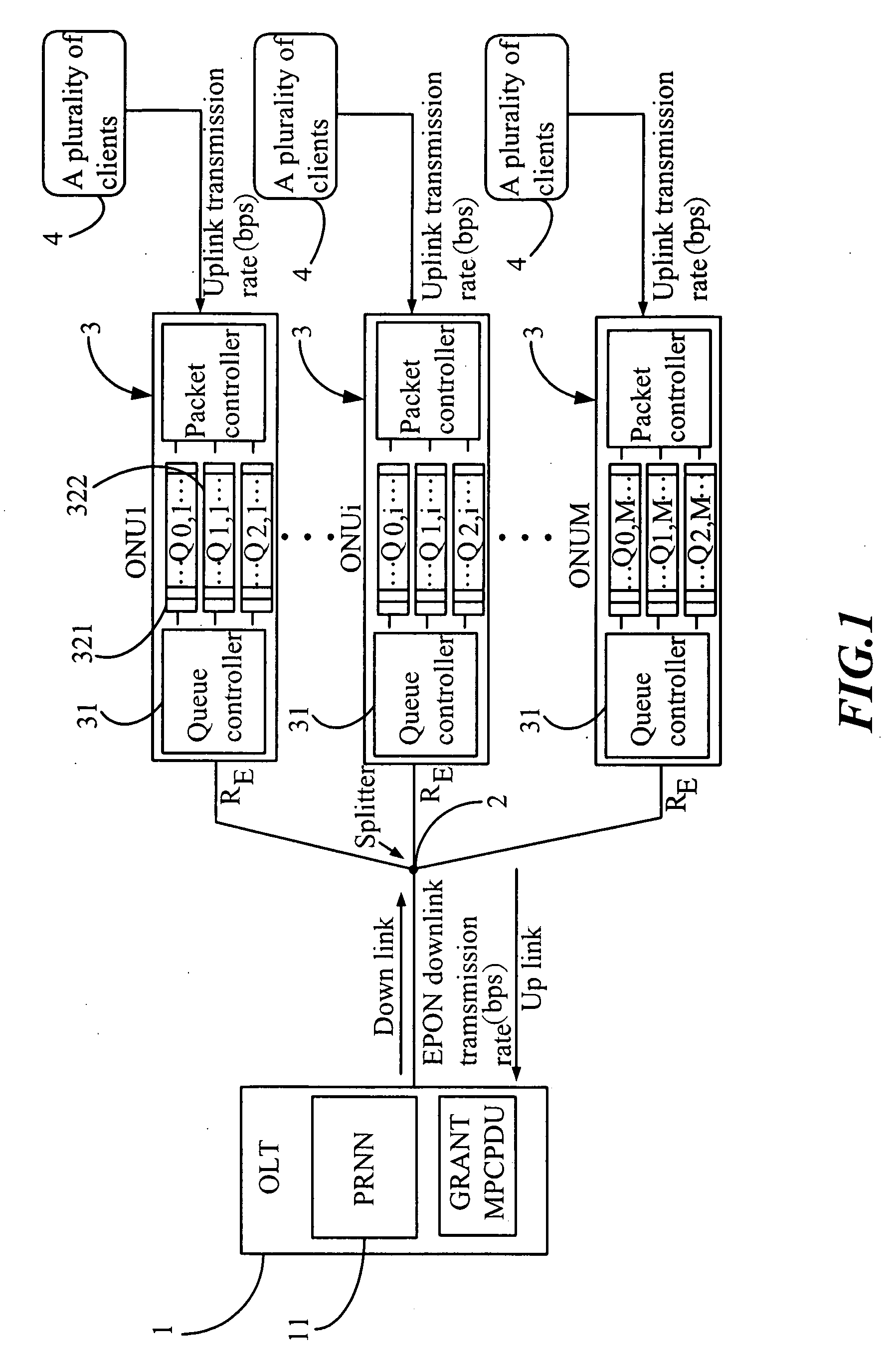
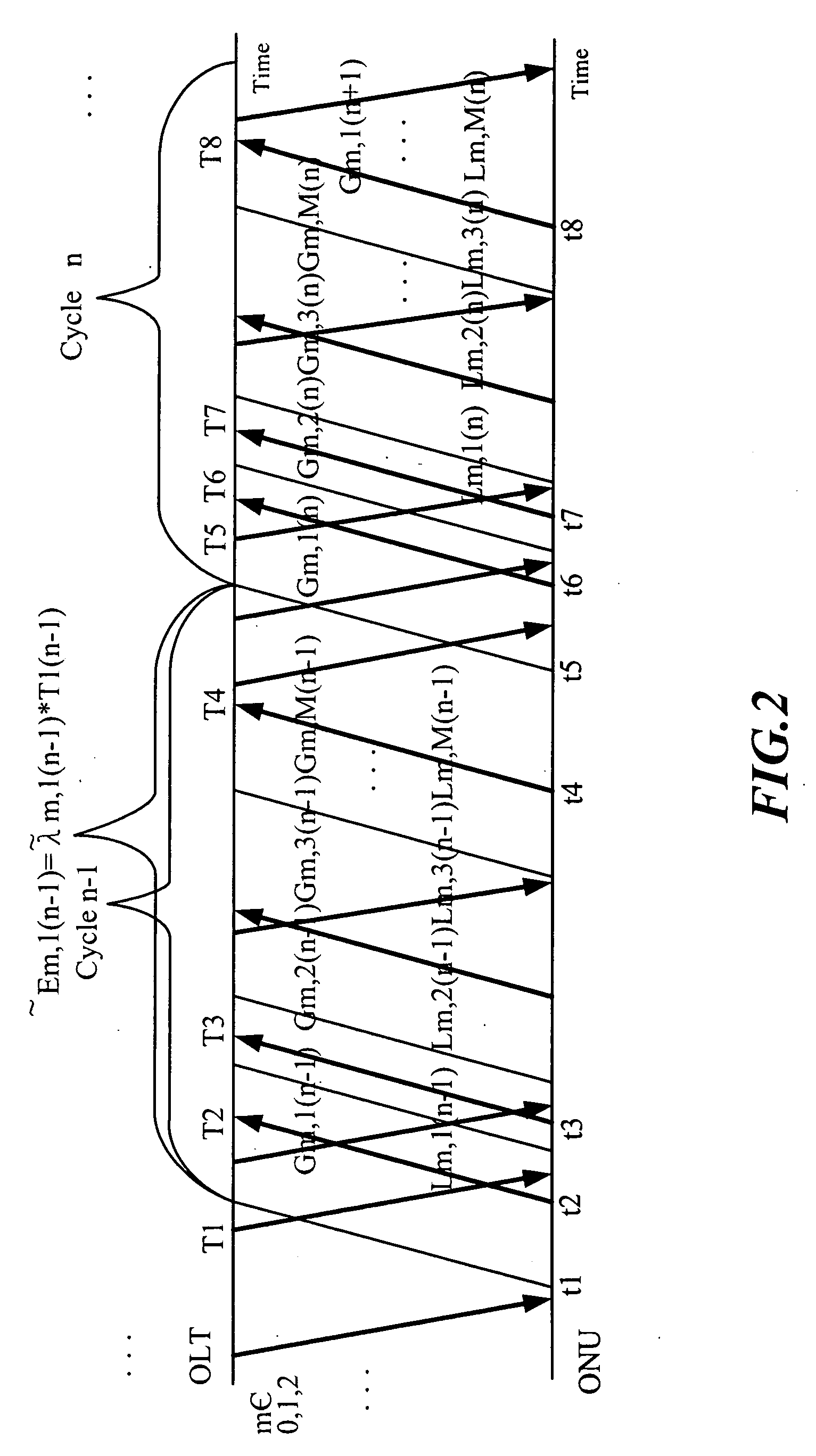
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation Method of Ethernet Passive Optical Network
InactiveUS20100254707A1Fast convergenceAccurate predictionMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsRecurrent neural netsPipeline scheduling
A dynamic bandwidth allocation method of an Ethernet passive optical network, comprises a predictor and a rule of QoS-promoted dynamic bandwidth allocation (PQ-DBA); the predictor predicts a client behavior and numbers of various kinds of packets by using a pipeline scheduling predictor consisted of a pipelined recurrent neural network (PRNN), and a learning rule of the extended recursive least squares (ERLS); the present invention establishes a better QoS traffic management for the OLT-allocated ONU bandwidth and client packets sent by priority.
Owner:CHUNGHWA TELECOM CO LTD
Neural networks for prediction and control
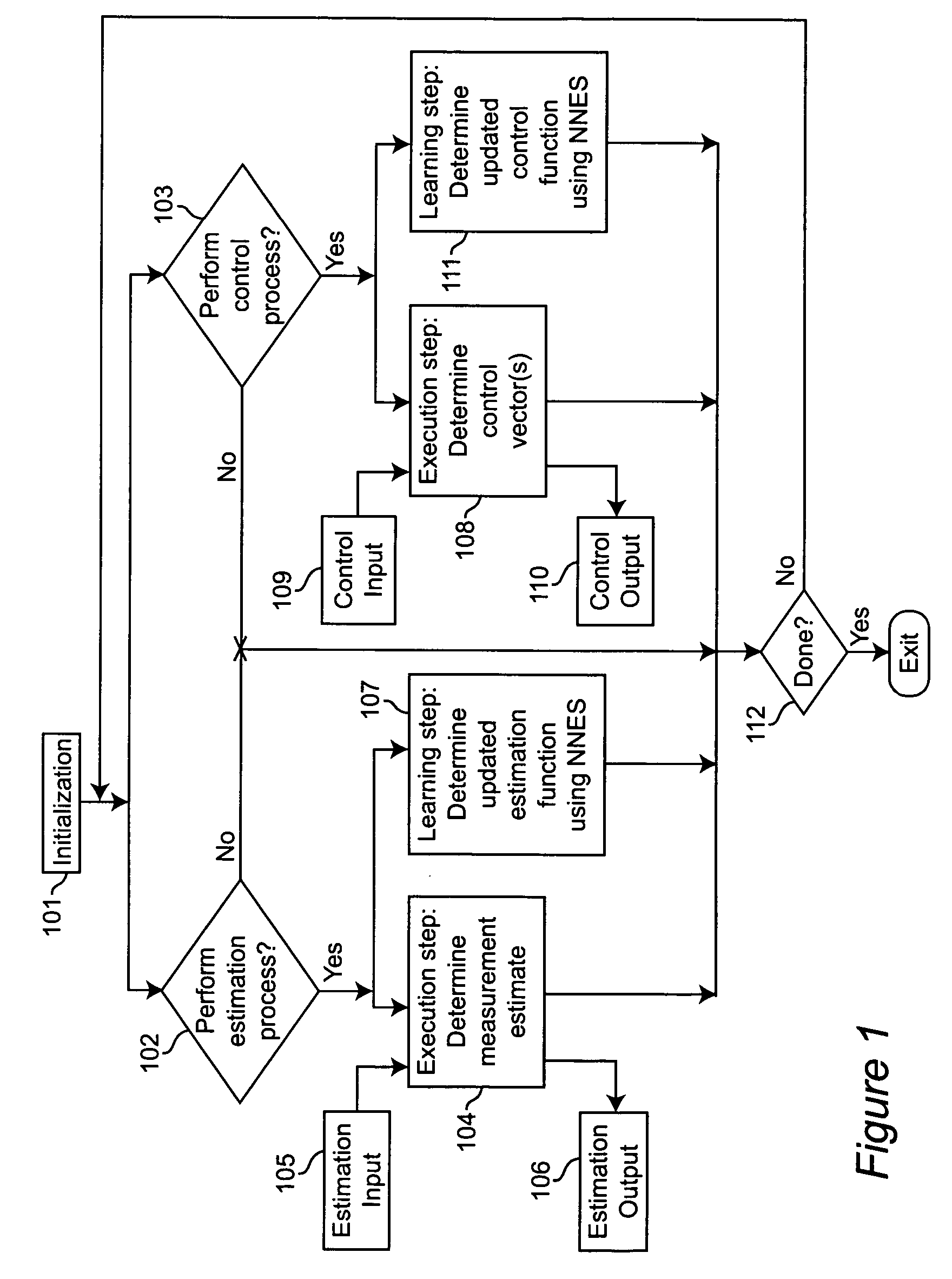
Neural networks for optimal estimation (including prediction) and / or control involve an execution step and a learning step, and are characterized by the learning step being performed by neural computations. The set of learning rules cause the circuit's connection strengths to learn to approximate the optimal estimation and / or control function that minimizes estimation error and / or a measure of control cost. The classical Kalman filter and the classical Kalman optimal controller are important examples of such an optimal estimation and / or control function. The circuit uses only a stream of noisy measurements to infer relevant properties of the external dynamical system, learn the optimal estimation and / or control function, and apply its learning of this optimal function to input data streams in an online manner. In this way, the circuit simultaneously learns and generates estimates and / or control output signals that are optimal, given the network's current state of learning.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
TV Content Segmentation, Categorization and Identification and Time-Aligned Applications
InactiveUS20170201793A1Receiver side switchingBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionMulti languageDisplay device
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
Apparatus and methods for implementing learning for analog and spiking signals in artificial neural networks
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:PONULAK FILIP
Dynamically reconfigurable stochastic learning apparatus and methods
Generalized learning rules may be implemented. A framework may be used to enable adaptive signal processing system to flexibly combine different learning rules (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning) with different methods (online or batch learning). The generalized learning framework may employ average performance function as the learning measure thereby enabling modular architecture where learning tasks are separated from control tasks, so that changes in one of the modules do not necessitate changes within the other. Separation of learning tasks from the control tasks implementations may allow dynamic reconfiguration of the learning block in response to a task change or learning method change in real time. The generalized learning apparatus may be capable of implementing several learning rules concurrently based on the desired control application and without requiring users to explicitly identify the required learning rule composition for that application.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
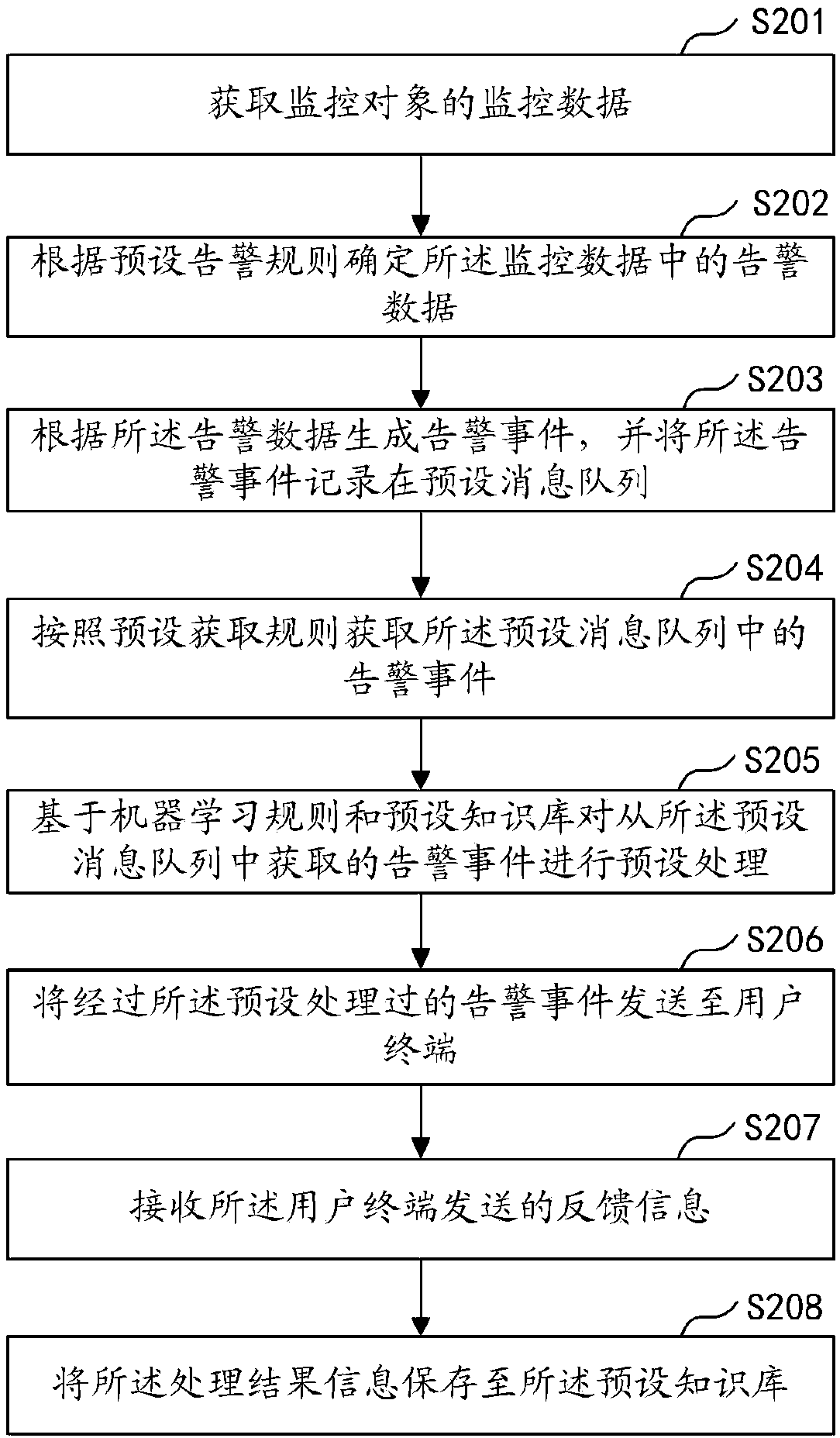
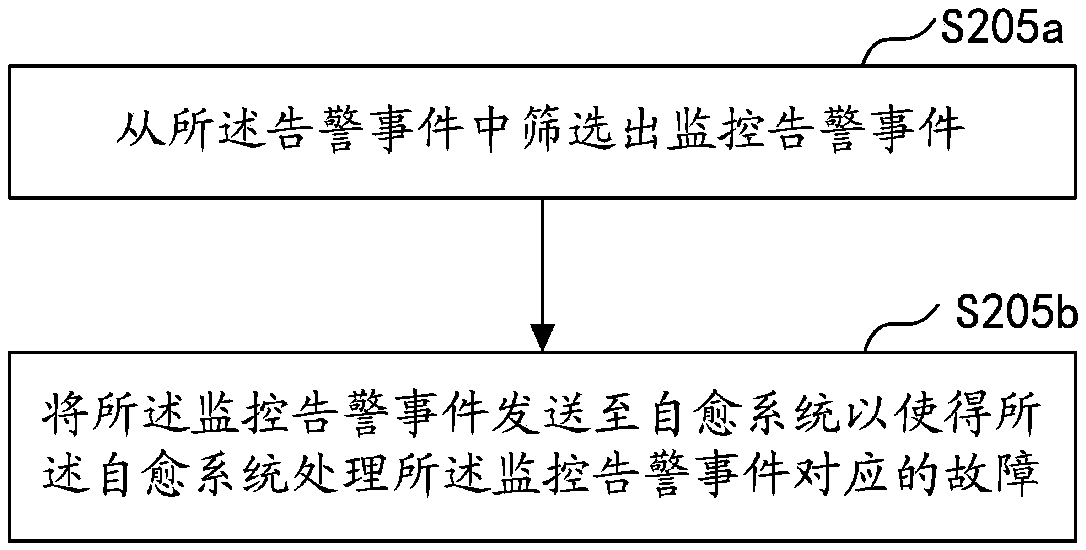
Alarm processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
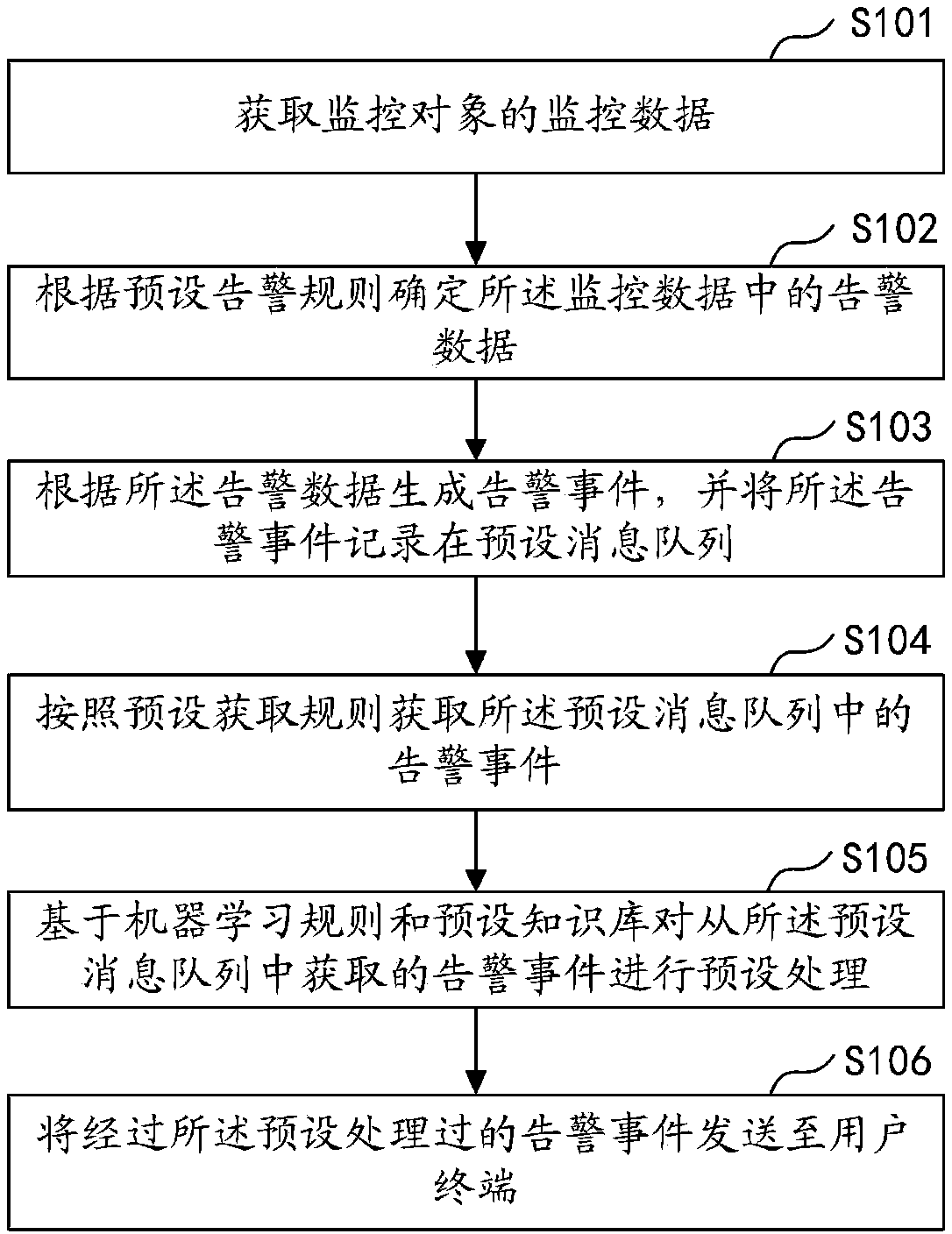
InactiveCN107832200AEliminate Alarm StormsHigh alarm accuracyHardware monitoringMachine learningMessage queueLearning rule
The embodiment of the invention discloses an alarm processing method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of monitoring monitor data of a monitor object;according to preset alarm rules, determining alarm data in the monitor data, wherein the alarm data is the monitor data triggering the preset alarm rules; according to the alarm data, generating an alarm event, and recording the alarm event into a preset message queue; according to the preset obtained rules, obtaining the alarm event in the preset message queue; on the basis of machine learning rules and a preset knowledge base, preprocessing the alarm event; sending the preprocessed alarm event to a user terminal. According to the alarm processing method, alarm storm can be eliminated, meanwhile, the alarm accuracy can be improved, and the number of invalid alarms is decreased.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Dynamic spectrum access method based on policy planning constrain Q study
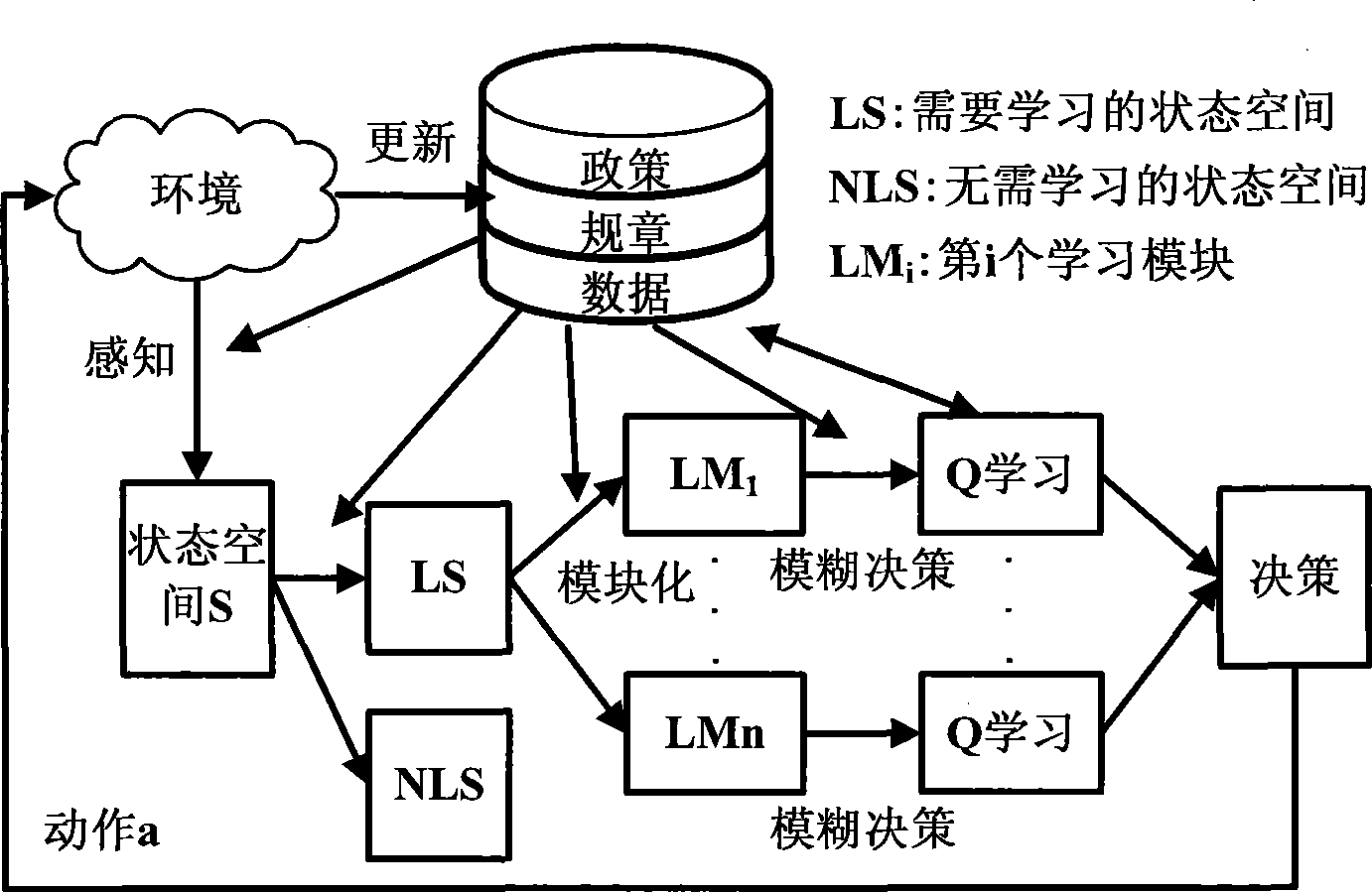
InactiveCN101466111AAvoid blindnessImprove learning efficiencyWireless communicationPropogation channels monitoringCognitive userFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a dynamic spectrum access method on the basis that the policy planning restricts Q learning, which comprises the following steps: cognitive users can divide the frequency spectrum state space, and select out the reasonable and legal state space; the state space can be ranked and modularized; each ranked module can finish the Q form initialization operation before finishing the Q learning; each module can individually execute the Q learning algorithm; the algorithm can be selected according to the learning rule and actions; the actions finally adopted by the cognitive users can be obtained by making the strategic decisions by comprehensively considering all the learning modules; whether the selected access frequency spectrum is in conflict with the authorized users is determined; if so, the collision probability is worked out; otherwise, the next step is executed; whether an environmental policy planning knowledge base is changed is determined; if so, the environmental policy planning knowledge base is updated, and the learning Q value is adjusted; the above part steps are repeatedly executed till the learning convergence. The method can improve the whole system performance, and overcome the learning blindness of the intelligent body, enhance the learning efficiency, and speed up the convergence speed.
Owner:COMM ENG COLLEGE SCI & ENGINEEIRNG UNIV PLA
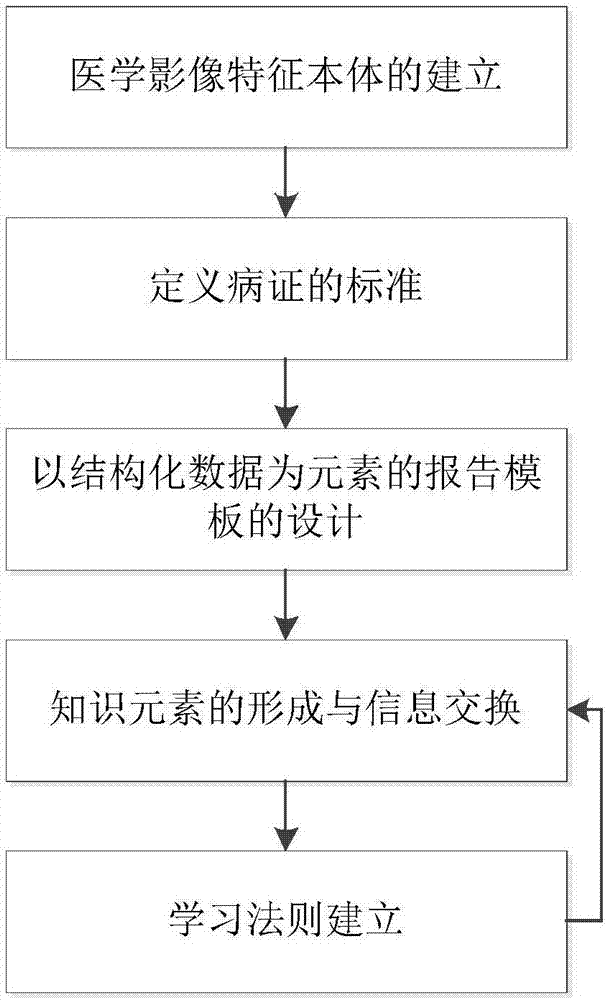
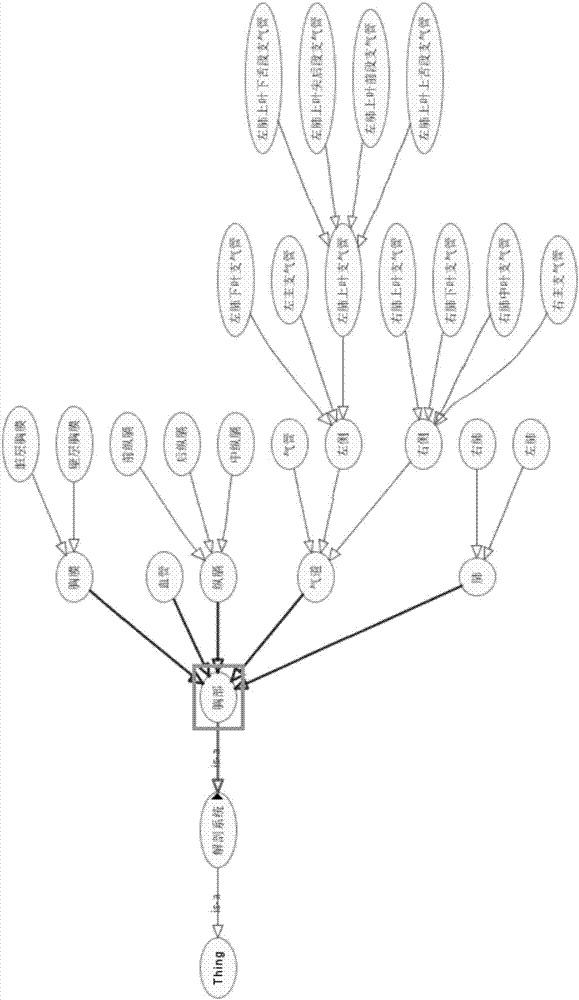
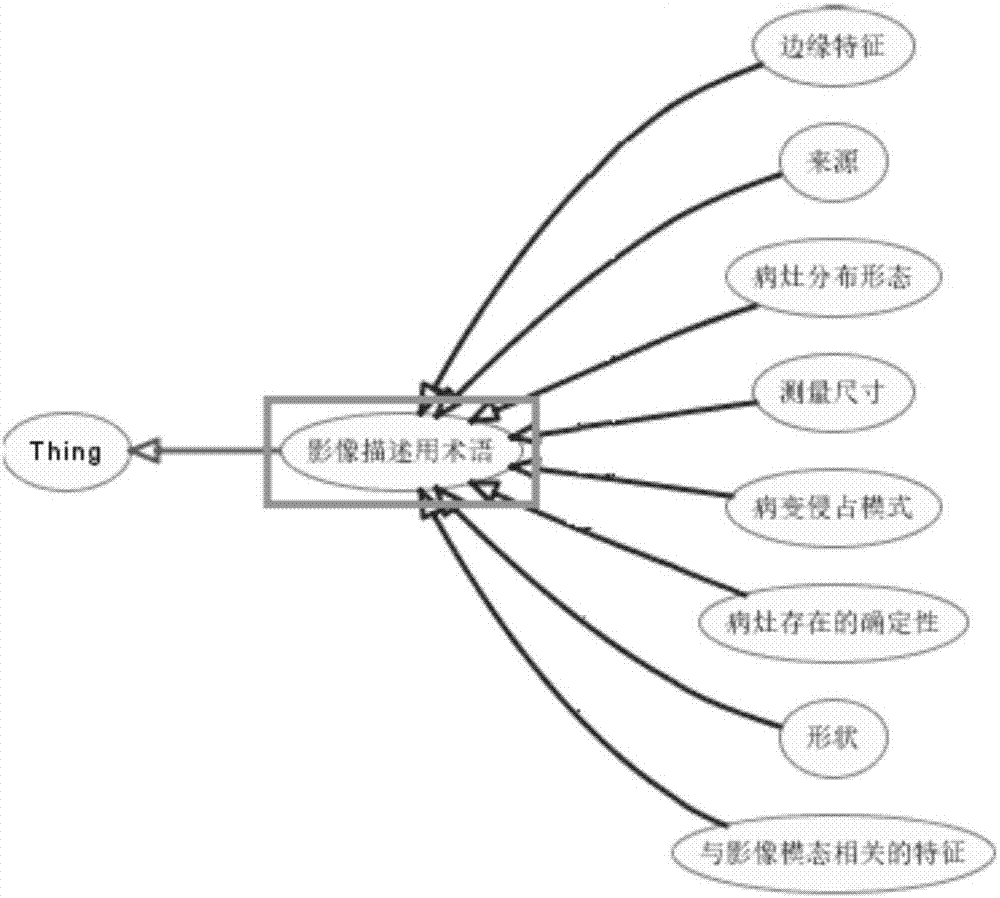
Structured report template-based medical image knowledge base establishment method
InactiveCN107463786AImprove the level ofAccurate image data supportSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseInformation processing
The invention relates to a structured report template-based medical image knowledge base establishment method and belongs to the field of medical information processing and application. For improving data availability, a multi-modal stored medical image is converted into structured big data, so that data innovation and value addition are realized and accurate data support is provided for medical research. The method comprises the steps of establishing characteristic noumena of the medical image; defining standards of disease syndromes; designing report templates by taking structured data as elements; forming knowledge elements and exchanging information; and establishing learning rules. Through noumenon library establishment, disease syndrome definition, a text report template, an image-text report template and a CDA document, a relationship between a diagnosis conclusion and image presentation is established, so that the retrieval efficiency is high and the accuracy is greatly enhanced; by establishing the learning rules, the knowledge elements are continuously perfected, so that the medical research is assisted and the medical image level of the whole industry is improved; and the method has extremely wide application values.
Owner:王卫鹏 +2
Weight adjustment circuit for variable-resistance synapses
InactiveCN102610274AImplement STDP weight adjustment functionSimple structureDigital storageSynapseNerve network
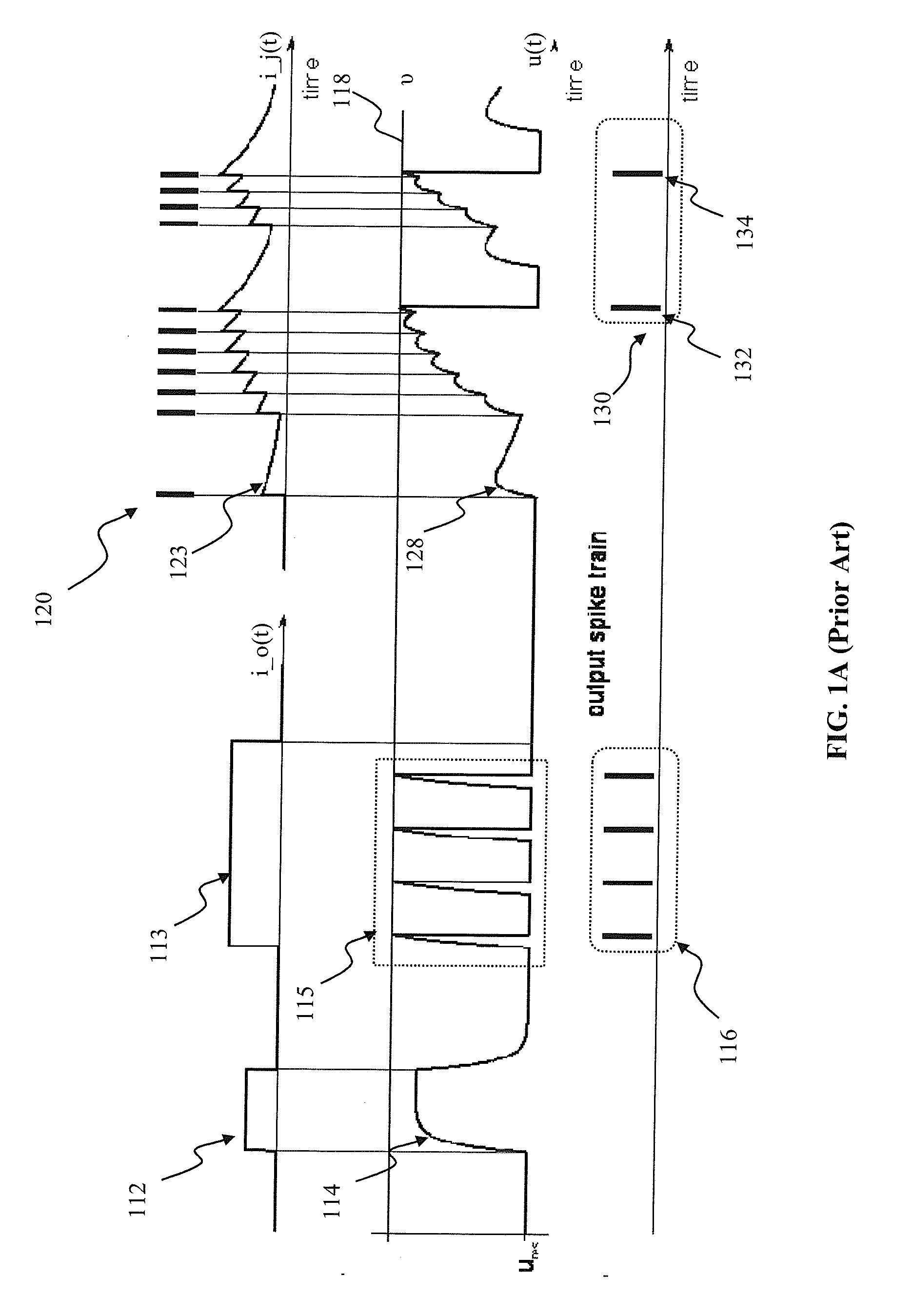
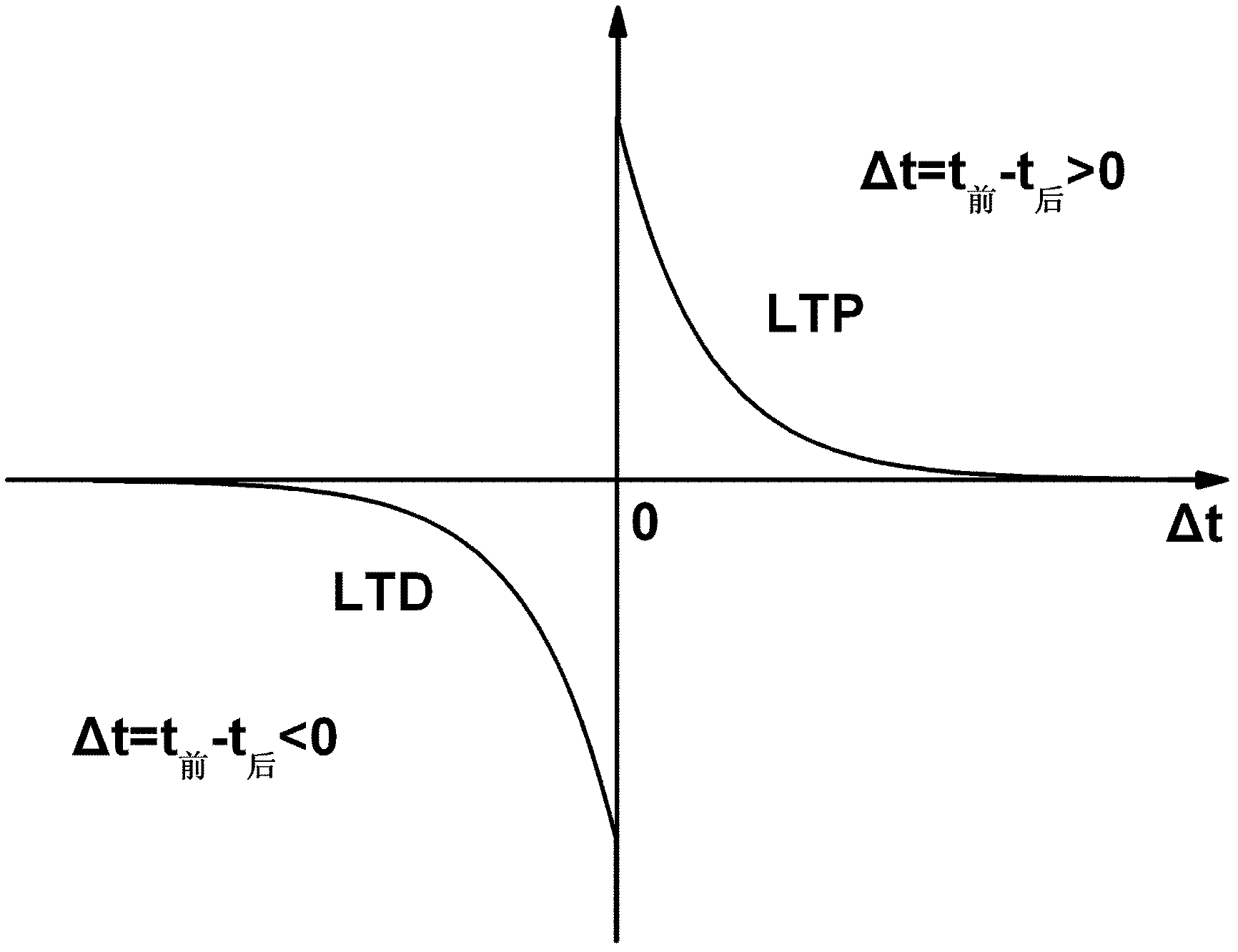
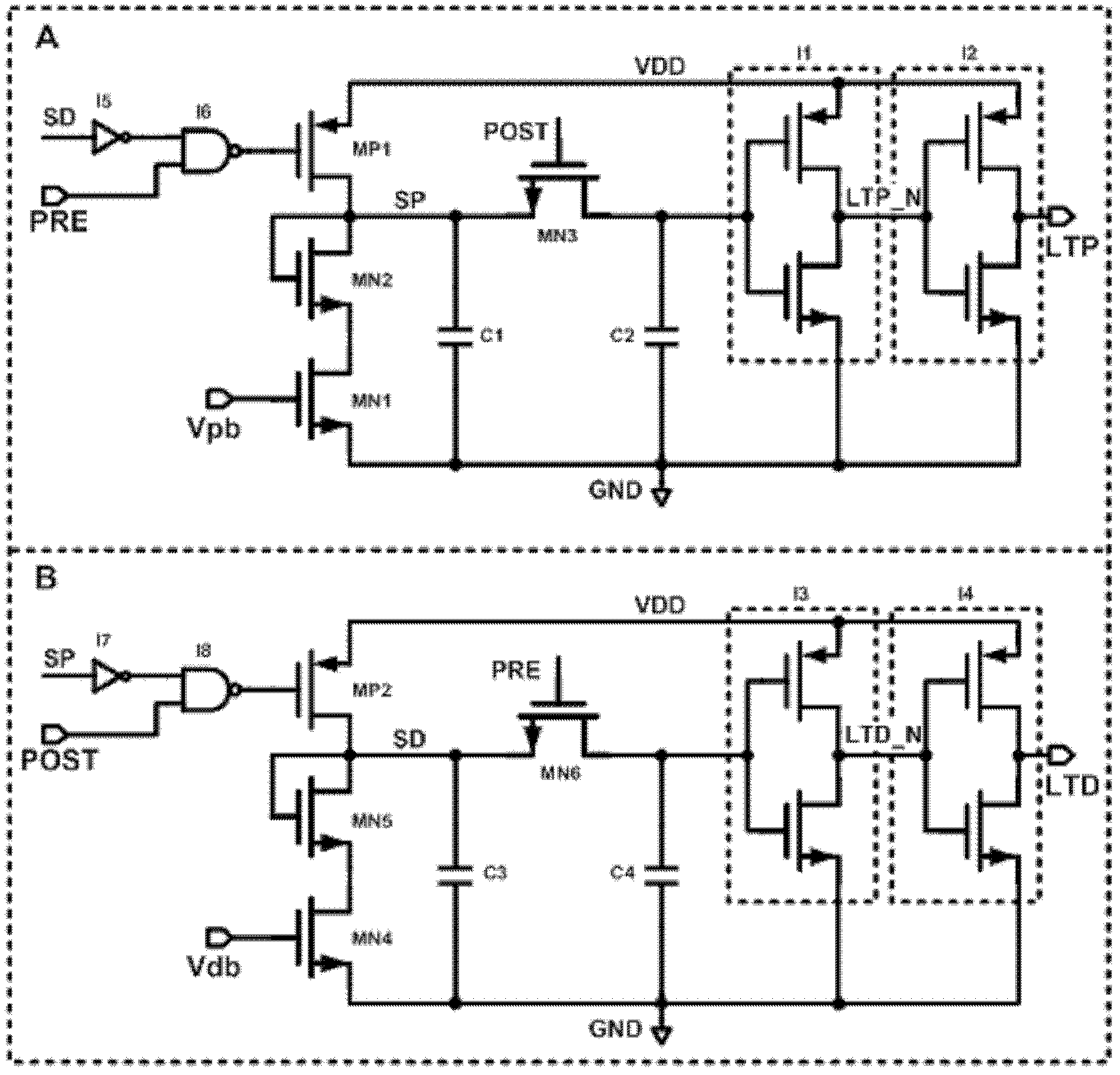
The invention discloses a weight adjustment circuit for variable-resistance synapses, which relates to the fields of integrated circuits and neural networks, and is used for carrying out weight adjustment on variable-resistance synapses. The circuit is composed of a weight enhancement adjustment subcircuit A (LTP (long term potentiation) adjustment) and a weight inhibition adjustment subcircuit B (LTD (long term depression) adjustment), wherein the two subcircuits respectively contain a charging pole, a discharging pole, a charge storage pole and an output pole. The core of the circuit is implemented by using an analog circuit mode, therefore, the number of transistors required by the circuit is greatly reduced; and meanwhile, through the setting of the bias voltage on a discharge tube in the discharge pole, the size of a weight adjustment time window can be adjusted conveniently. The circuit disclosed by the invention follows an STDP (spike timing dependent plasticity) learning rule, and LTP and LTD pulse outputs are generated according to the activities of nerve units at the two ends of the variable-resistance synapses so as to carry out corresponding weight adjustment on the variable-resistance synapses. The circuit disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, convenient in parameter adjustment, and suitable for applications, such as weight adjustment on electronic synapses of a large-scale neural network, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
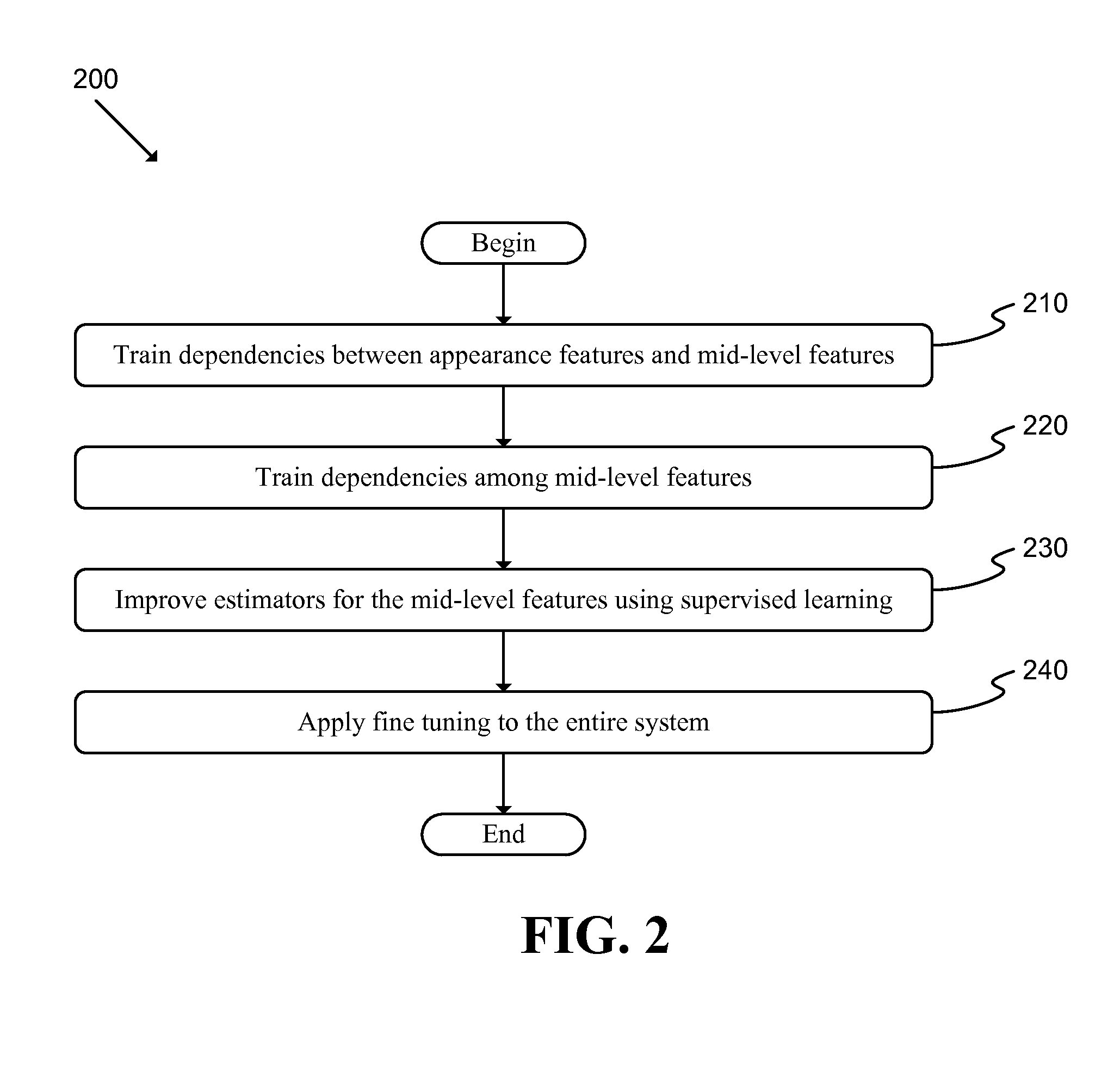
Evaluation of Three-Dimensional Scenes Using Two-Dimensional Representations
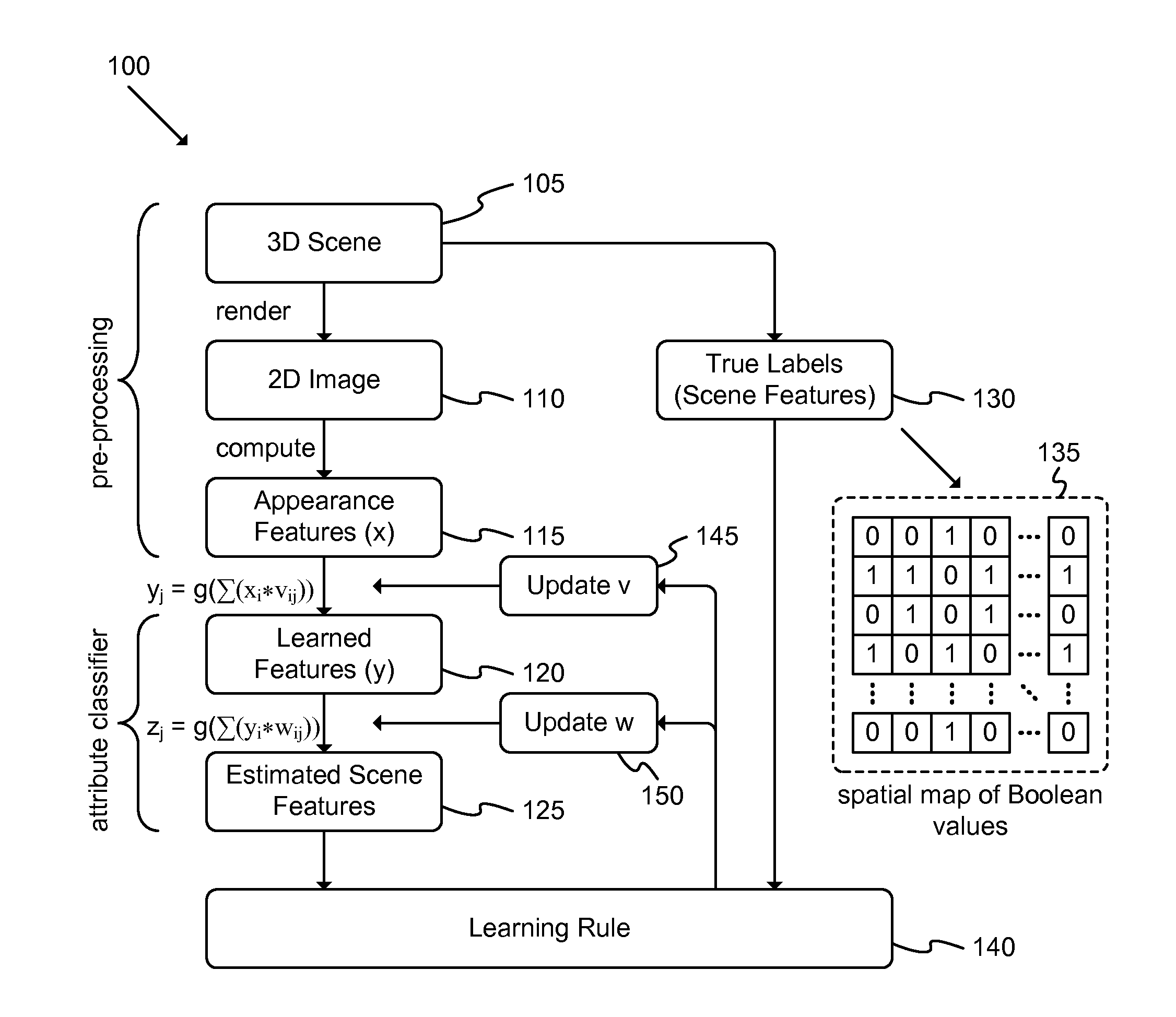
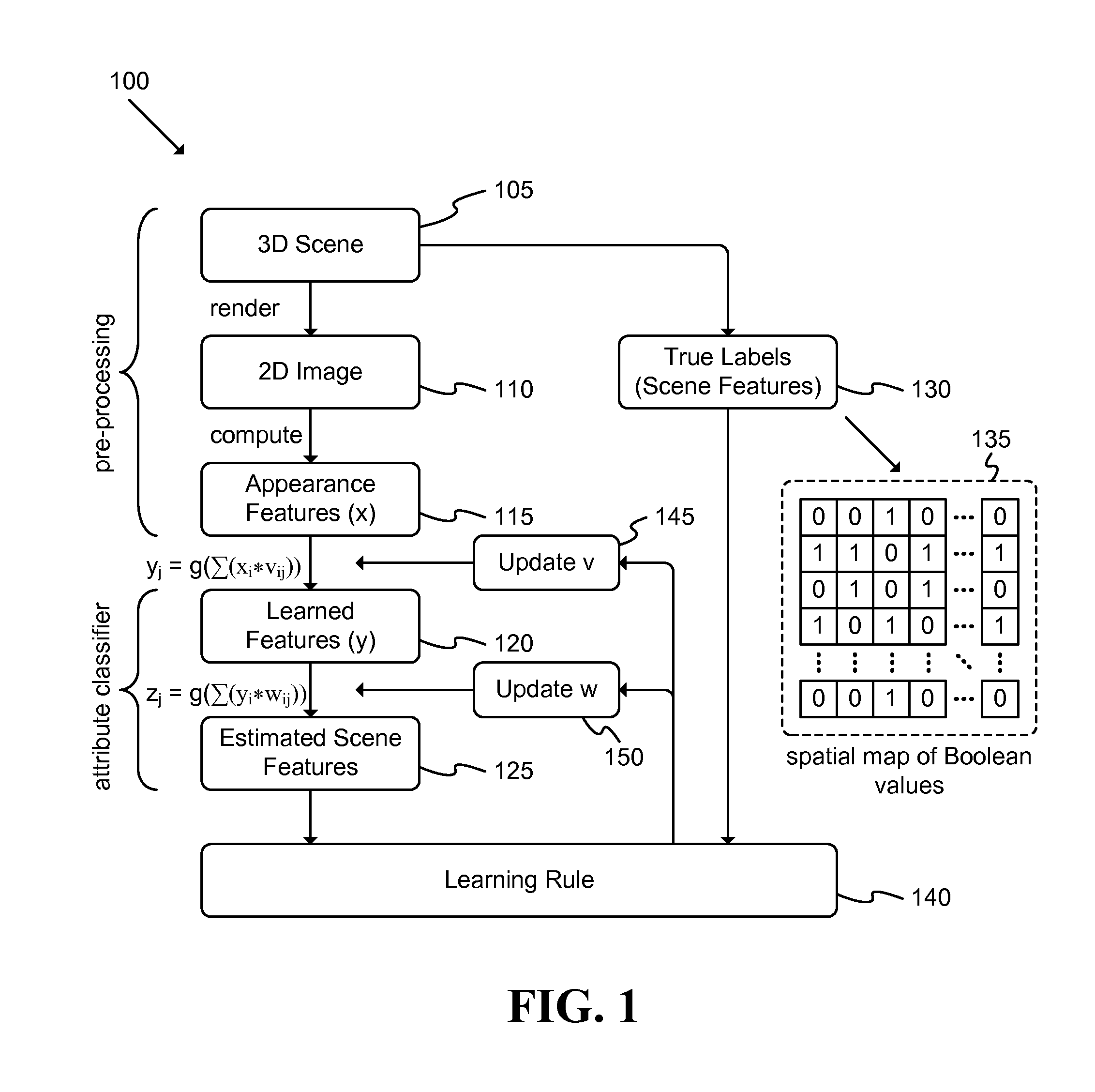
ActiveUS20130177235A1Impoverish taskImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingLearning ruleComputer science
A system adapted to implement a learning rule in a three-dimensional (3D) environment is described. The system includes: a renderer adapted to generate a two-dimensional (2D) image based at least partly on a 3D scene; a computational element adapted to generate a set of appearance features based at least partly on the 2D image; and an attribute classifier adapted to generate at least one set of learned features based at least partly on the set of appearance features and to generate a set of estimated scene features based at least partly on the set of learned features. A method labels each image from among the set of 2D images with scene information regarding the 3D scene; selects a set of learning modifiers based at least partly on the labeling of at least two images; and updates a set of weights based at least partly on the set of learning modifiers.
Owner:MEIER PHILIP
System and method for speech processing using independent component analysis under stability constraints
ActiveUS7383178B2Reduce information redundancyImprove voice qualityAdaptive networkSpeech analysisLearning ruleDependent component analysis
A system and method for separating a mixture of audio signal into desired audio signals (430) (e.g., speech) and a noise sign (440) is disclosed. Microphones (310, 320) are positioned to receive the mixed audio signals, and an independent component analysis (ICA) processes (212) the sound mixture using stability constraints. The ICA process (508) uses predefined characteristics of the desired speech signal to identify and isolate a target sound signal (430). Filter coefficients are adapted with a learning rule and filter weight update dynamics are stabilized to assist convergence to a stable separated ICA signal result. The separated signals may be peripherally-processed to further reduce noise effects using post-processing (214) and pre-processing (220, 230) techniques and information. The proposed system is designed and easily adaptable for implementation on DSP units or CPUs in audio communication hardware environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
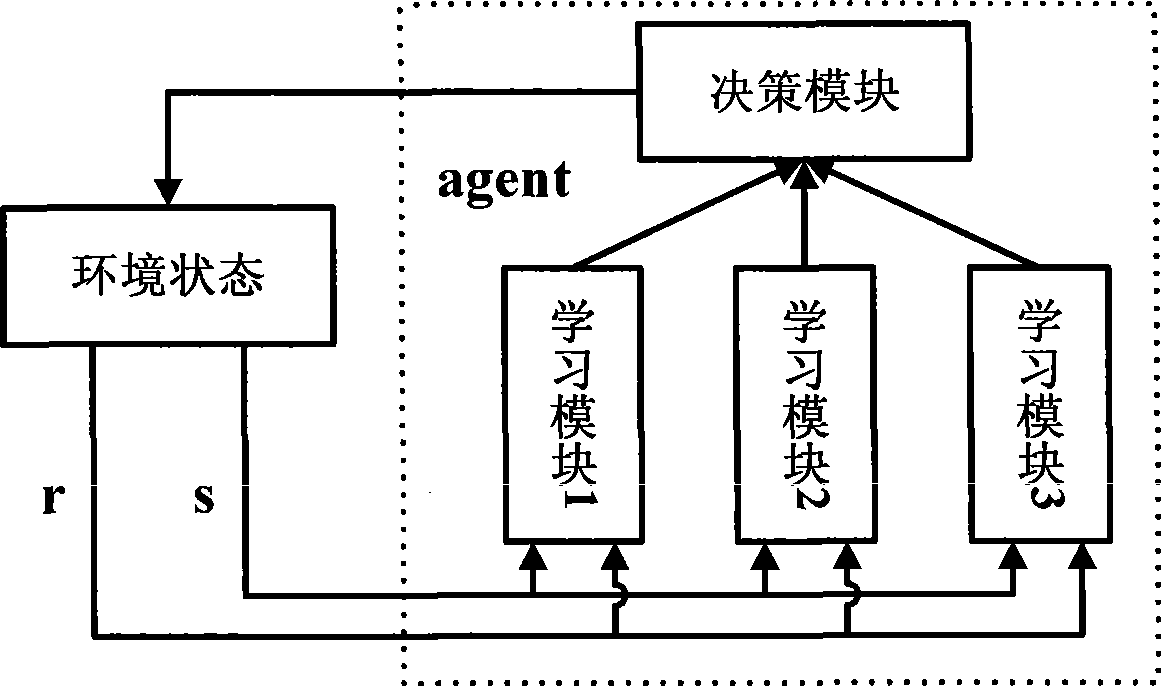
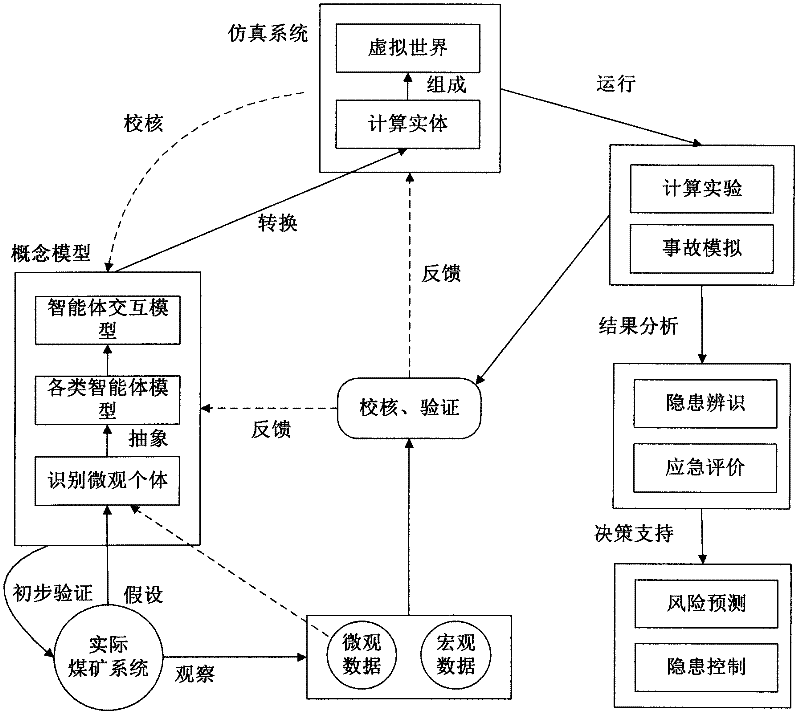
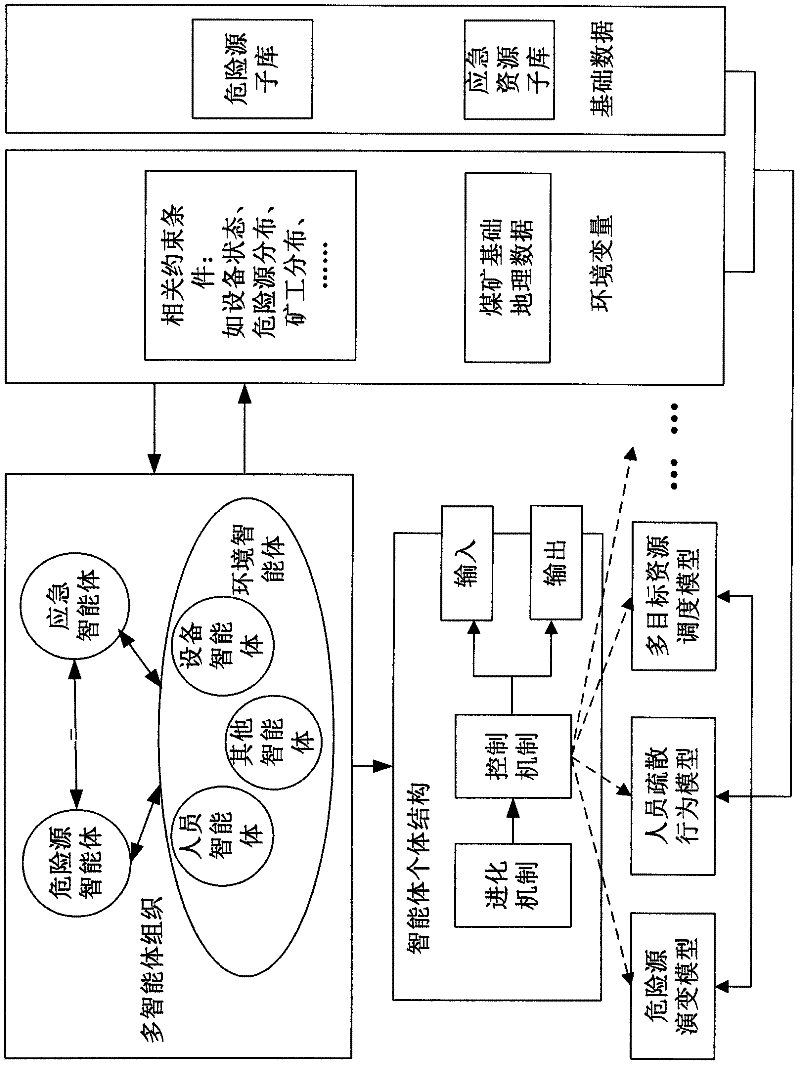
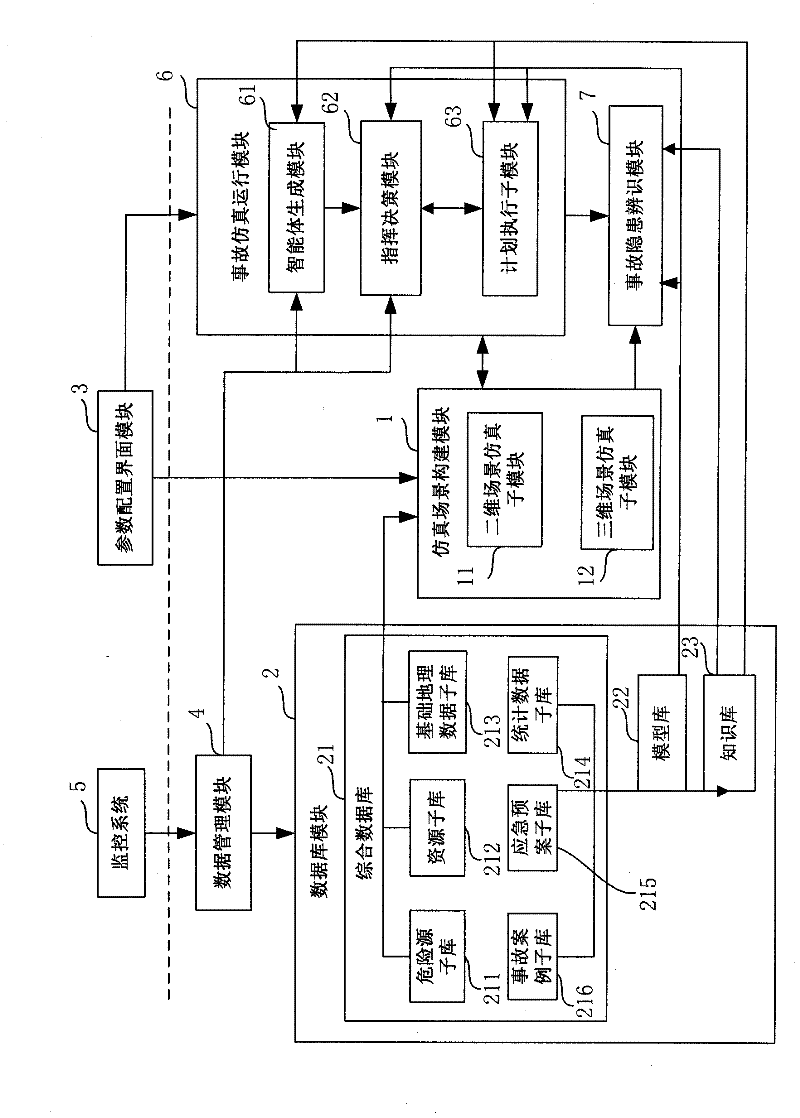
Coal mine accident simulating method and system based on multi-intelligent agent
InactiveCN102508995ARealize simulationReflect the state of evolutionSpecial data processing applicationsLearning ruleData mining
The invention discloses a coal mine accident simulating method and system based on a multi-intelligent agent. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an intelligent agent entity and a virtual simulating environment; selecting a preset model and preset knowledge to perform intelligent agent model computation to form a model computation result; performing the intelligent agent entity action computation and selecting the intelligent agent entity behavior; using the intelligent agent action experience learning rule to perform the intelligent agent entity behavior configuration, executing the intelligent agent entity behavior, updating the environment variable of the virtual simulating environment, and updating the current virtual simulating environment by a simulating scene constructing module based on the intelligent agent behavior state information and the updated environment variable; and updating a behavior selection parameter, and using the updated behavior selection parameter to perform the intelligent agent entity behavior computation at the next moment. The method and system provided by the invention can be used for imitating coal mine accidents in various environments so as to provide abundant information for immediately discovering the coal mine accident potential.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
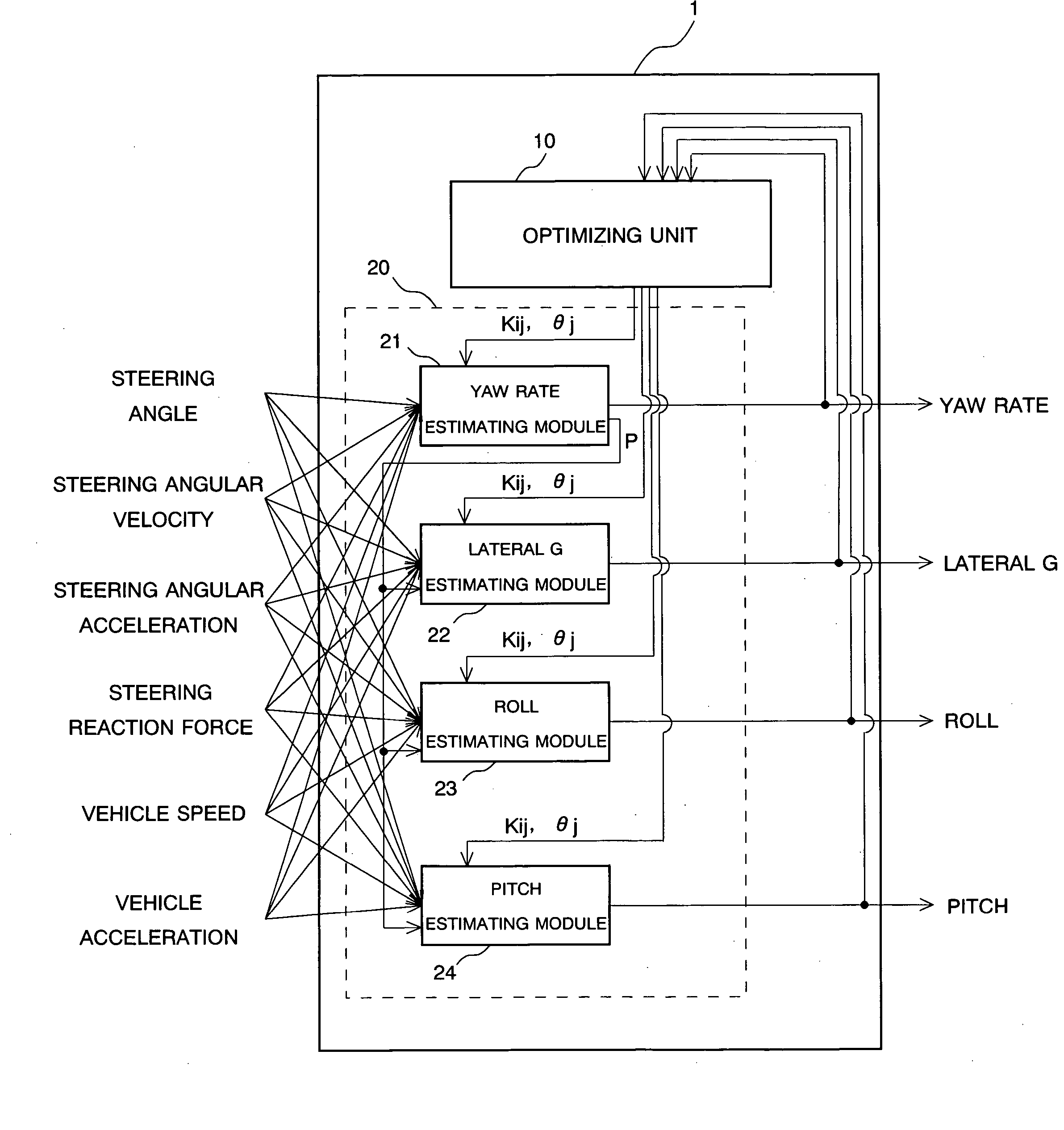
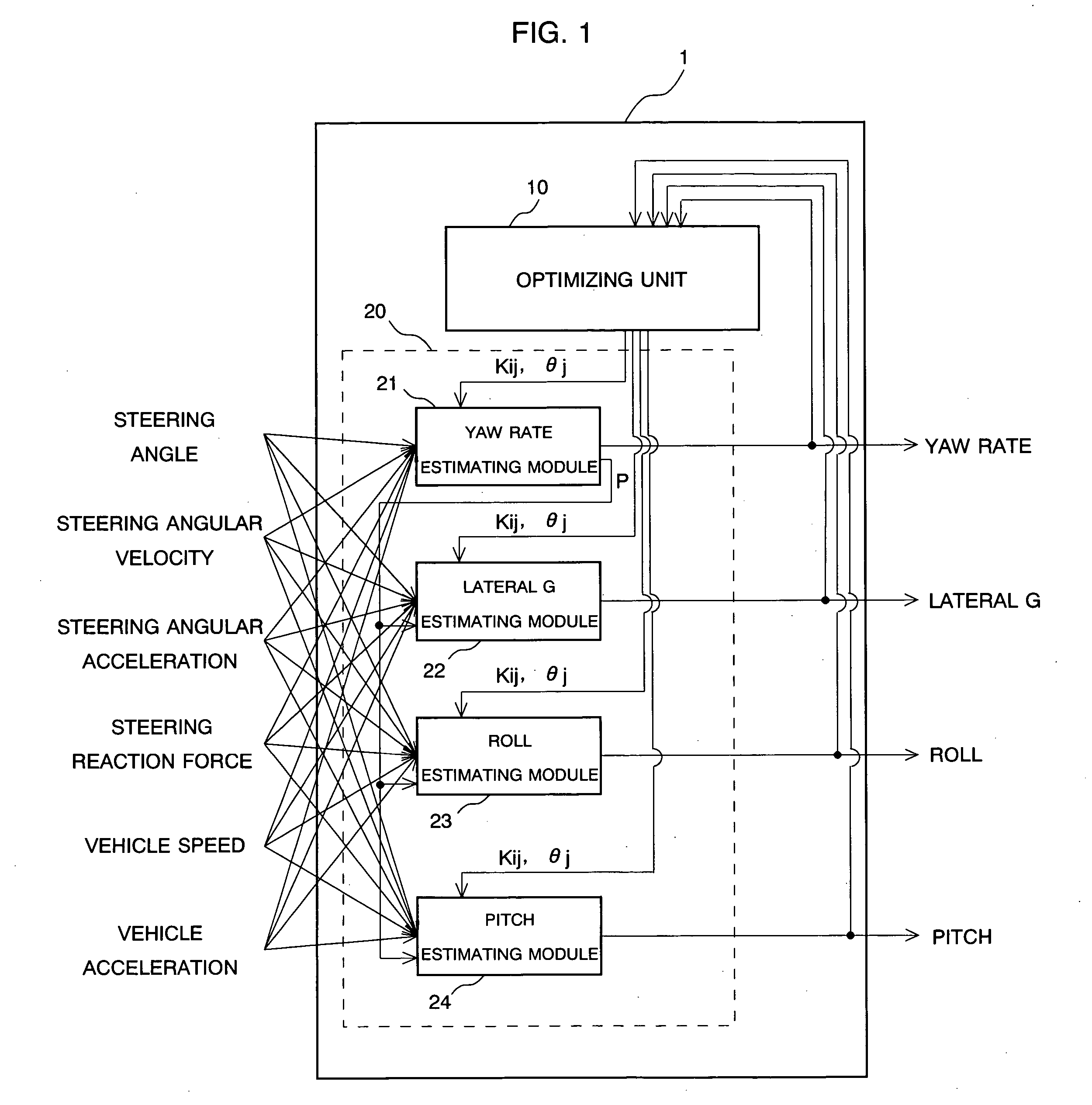
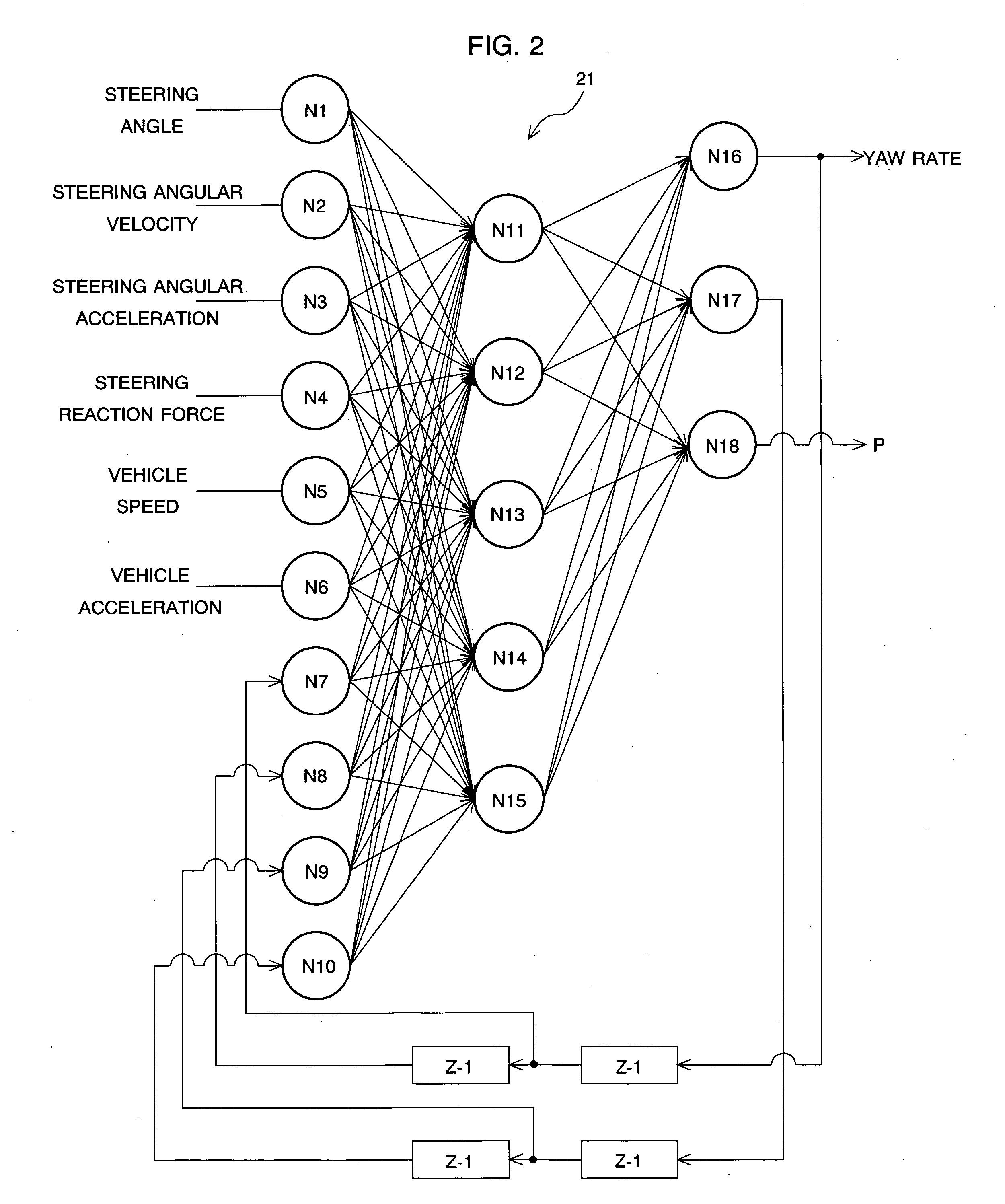
Vehicle motion model generating device and method for generating vehicle motion model
InactiveUS20040162644A1Digital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlWeight coefficientSimulation
There are equipped a first recurrent neural network formed by connecting plural nodes so as to have a loop in which the output from one node is input to another node in accordance with a predetermined coupling weight coefficient. Meanwhile, the output of at least one node is fed back to the node concerned or another node, and an optimizing unit for determining the optimum solution of the coupling weight coefficient in the first recurrent neural network based on a learning rule using a hereditary algorithm. In this case, the first recurrent neural network outputs a first parameter indicating a motion state of a vehicle based on predetermined input information, thereby functioning as a vehicle motion model.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Distributed web application firewall
ActiveUS8566919B2Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlWeb applicationComputer network
A method for protecting a Web application running on a first local Web Server bases from hacker attacks, said Web Server being connectable to at least one client, the method comprising the following steps: —providing a plurality of preset rules on said Server, which correspond to specific characteristics of HTTP requests; —receiving an HTTP request on said server from the client, said HTTP request comprising a plurality of characteristics; —analyzing said characteristics of said received HTTP request in accordance with said rules provided on said server; —rejecting said HTTP request, if said rules identify said HTTP request as harmful request; —accepting said HTTP request, if said rules identify said HTTP request as trustable request; —classifying said HTTP request as doubtful request, if said rules identify said request neither as harmful request nor as trustable request; —evaluating the characteristics of said doubtful local request; —generating a learned rule on basis of the edge base evaluation.
Owner:PULSE SECURE +1
Apparatus and methods for gating analog and spiking signals in artificial neural networks
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
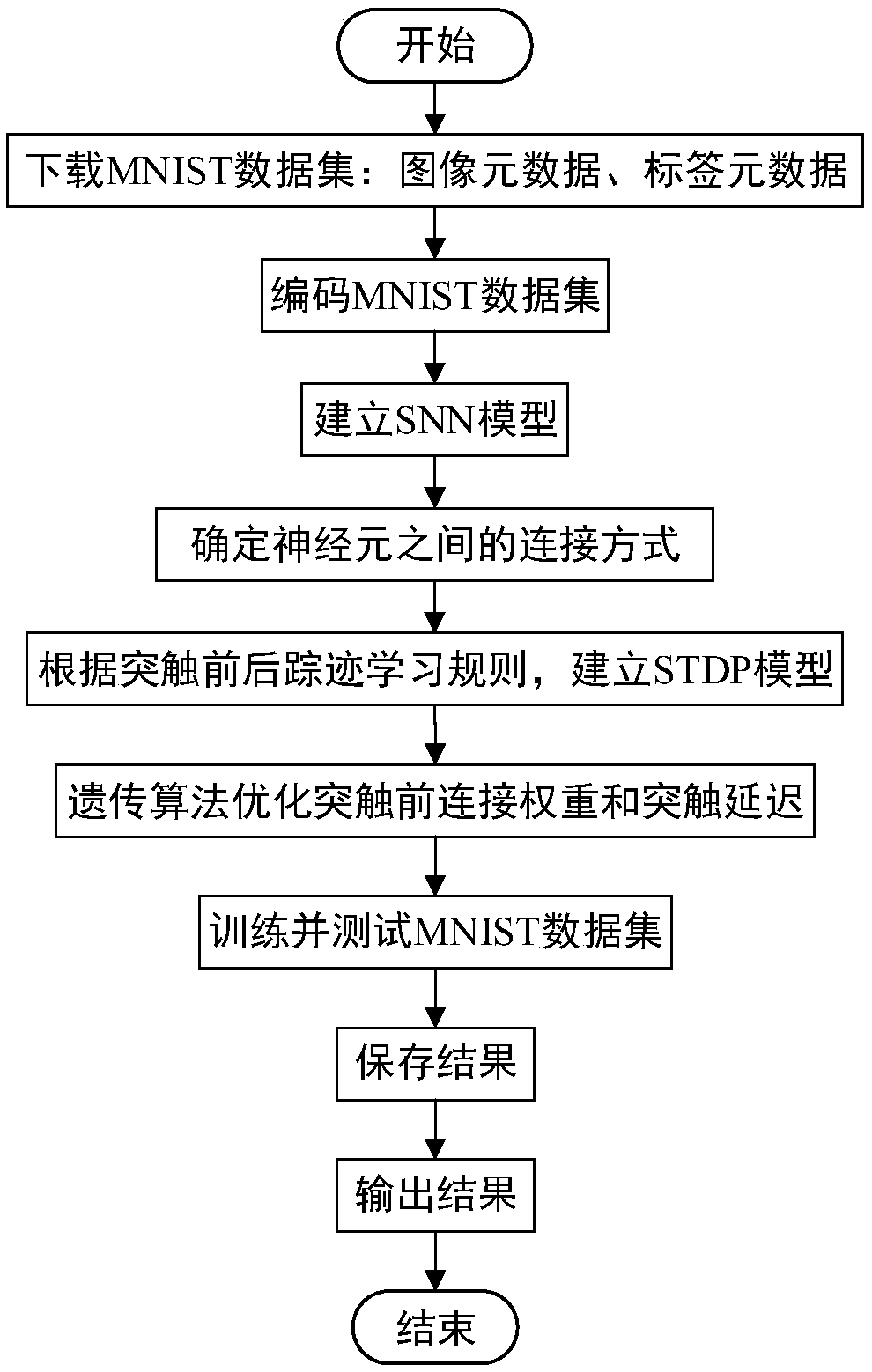
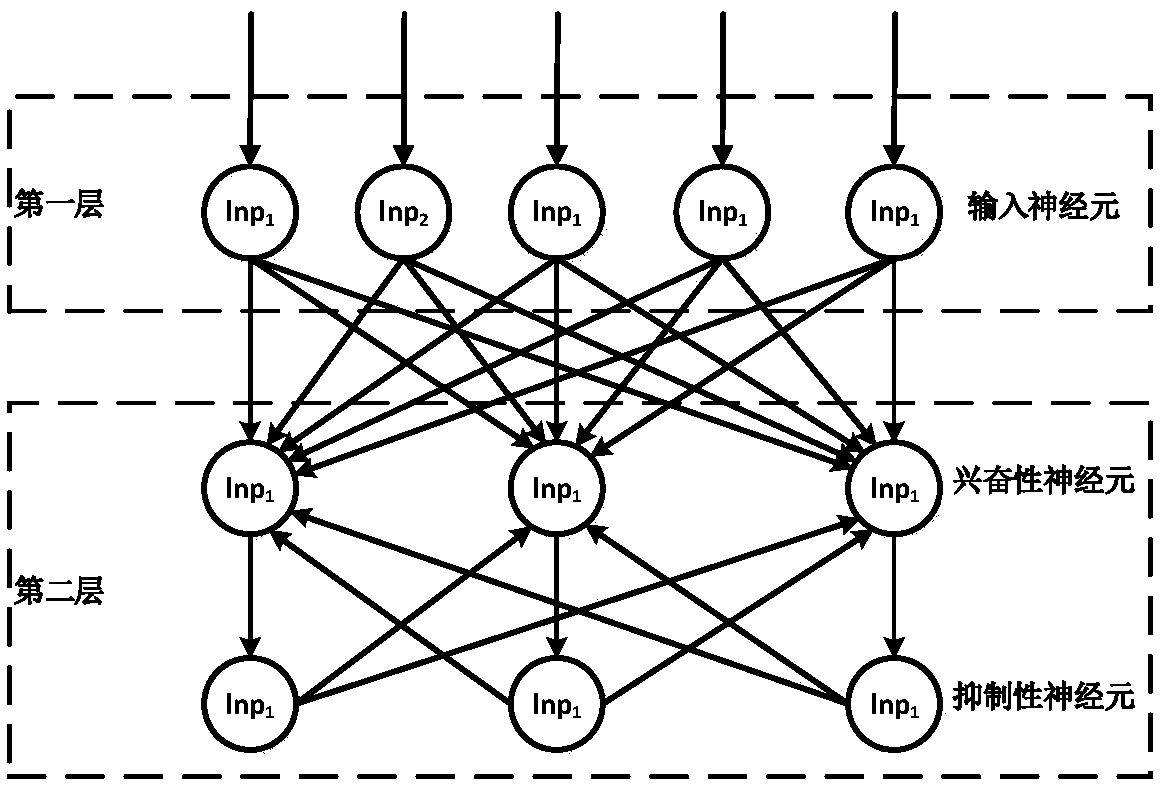
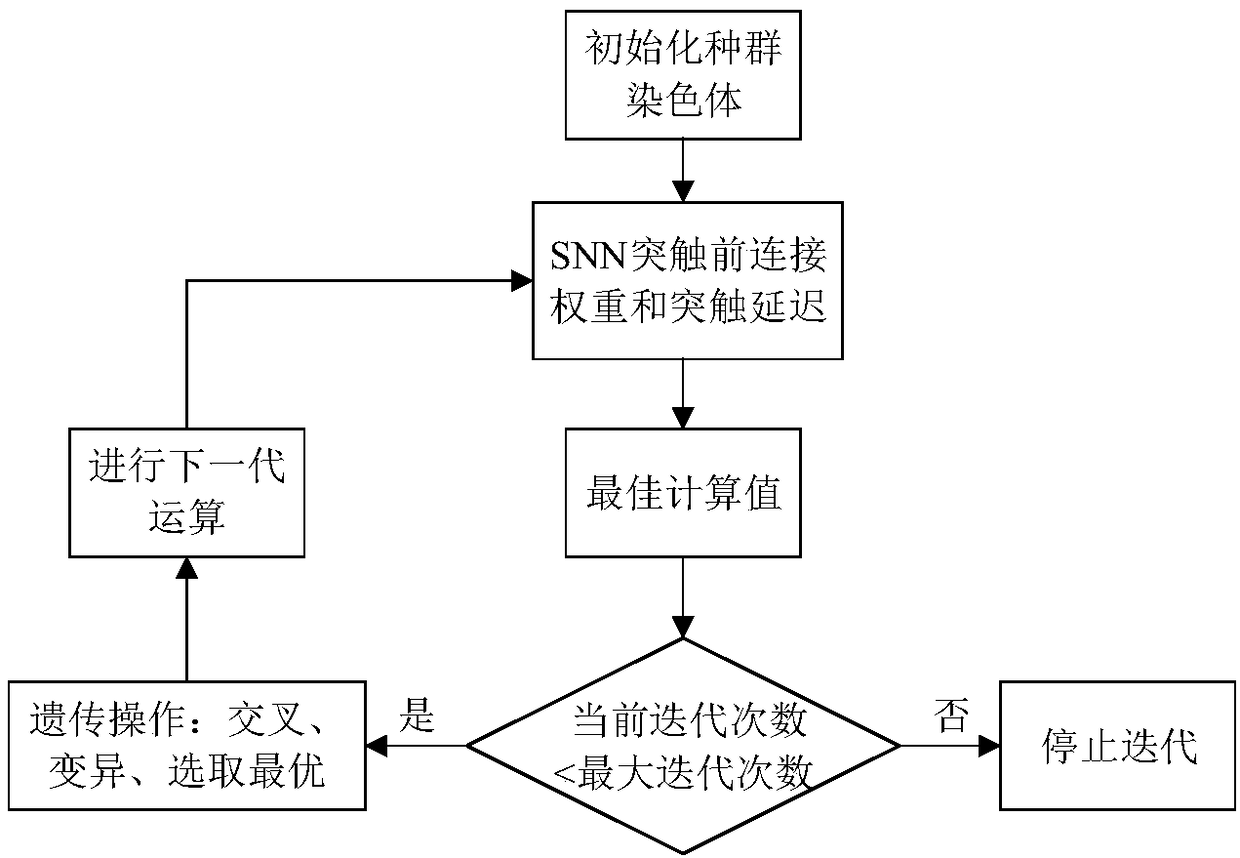
Handwritten digit identification method based on improved spiking neuron networks
ActiveCN108875846AUnsupervised Learning ImplementationIncrease training speedCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsNeuron networkData set
The invention discloses an unsupervised learning method of handwritten digit identification. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a spiking neural network model, and determining the connection mode between neurons according to an analog biological information processing mechanism; secondly, establishing a spiking time dependent plasticity model according to the synaptictrace learning rules; and finally, optimizing the pre-synaptic initial weight and the synaptic delay in the spiking neural networks by using a genetic algorithm, training and testing the MNIST (MixedNational Institute of Standards and Technology database) data set, thus achieving the unsupervised learning of handwritten digit identification. According to the unsupervised learning method of handwritten digit identification, experiments show that the training speed is effectively improved and the recognition accuracy is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com