Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
902 results about "Ultrasound energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultrasound energy, simply known as ultrasound, is a type of mechanical energy called sound characterized by vibrating or moving particles within a medium. Ultrasound is distinguished by vibrations with a frequency greater than 20,000 Hz, compared to audible sounds that humans typically hear with frequencies between 20 and 20,000 Hz. Ultrasound energy requires matter or a medium with particles to vibrate to conduct or propagate its energy. The energy generally travels through most mediums in the form of a wave in which particles are deformed or displaced by the energy then reestablished after the energy passes. Types of waves include shear, surface, and longitudinal waves with the latter being one of the most common used in biological applications. The characteristics of the traveling ultrasound energy greatly depend on the medium that it is traveling through. While ultrasound waves propagate through a medium, the amplitude of the wave is continually reduced or weakened with the distance it travels. This is known as attenuation and is due to the scattering or deflecting of energy signals as the wave propagates and the conversion of some of the energy to heat energy within the medium. A medium that changes the mechanical energy from the vibrations of the ultrasound energy into thermal or heat energy is called viscoelastic. The properties of ultrasound waves traveling through the medium of biological tissues has been extensively studied in recent years and implemented into many important medical tools.
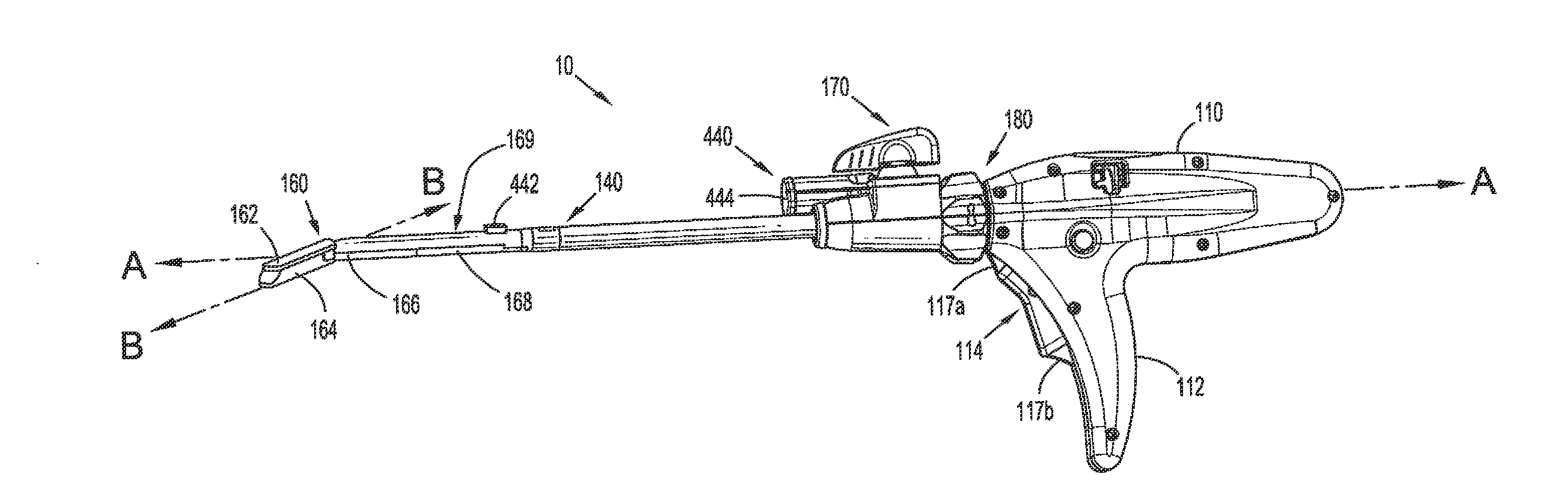
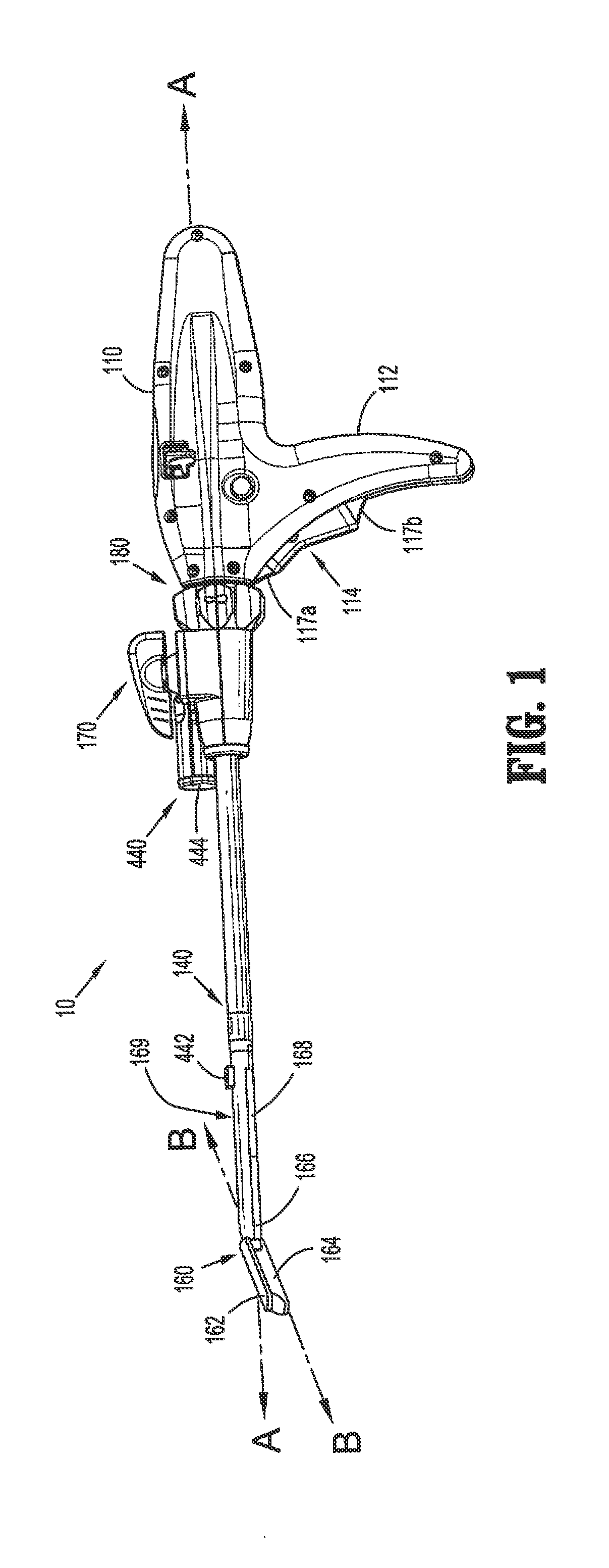
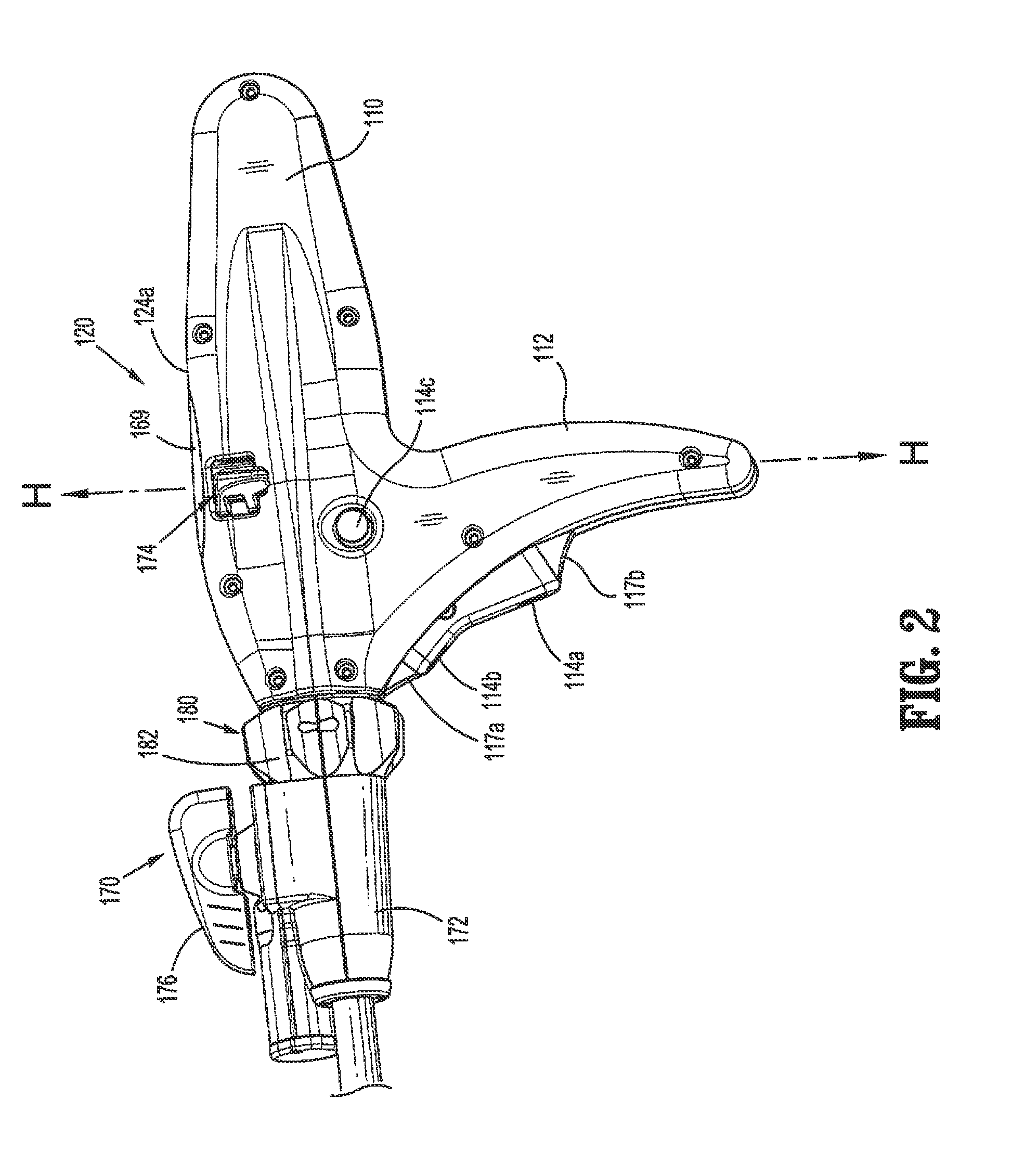
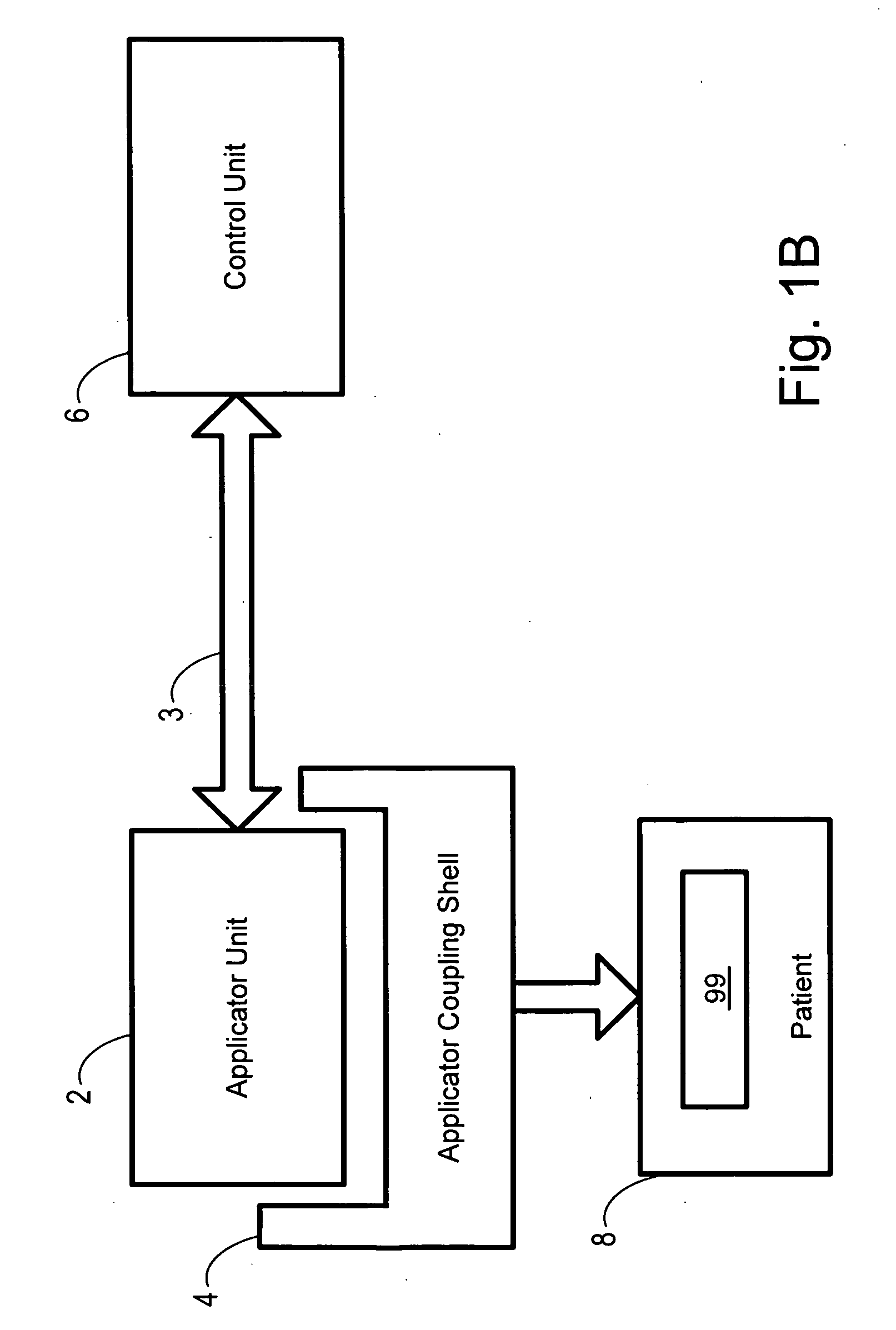
Powered surgical stapling device
An end effector includes first and second jaw members moveable relative to one another. Each of the first and second jaw members including a tissue contacting surface opposing the tissue contacting surface of the other jaw member. The end effector includes a detection assembly that is disposed within the first or second jaw member that is configured to detect an attribute of tissue between the first and second jaw members. The detection assembly may include a light source configured to emit light towards tissue between the first and second jaw members or may include an ultrasound transducer configured to emit ultrasound energy towards tissue between the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
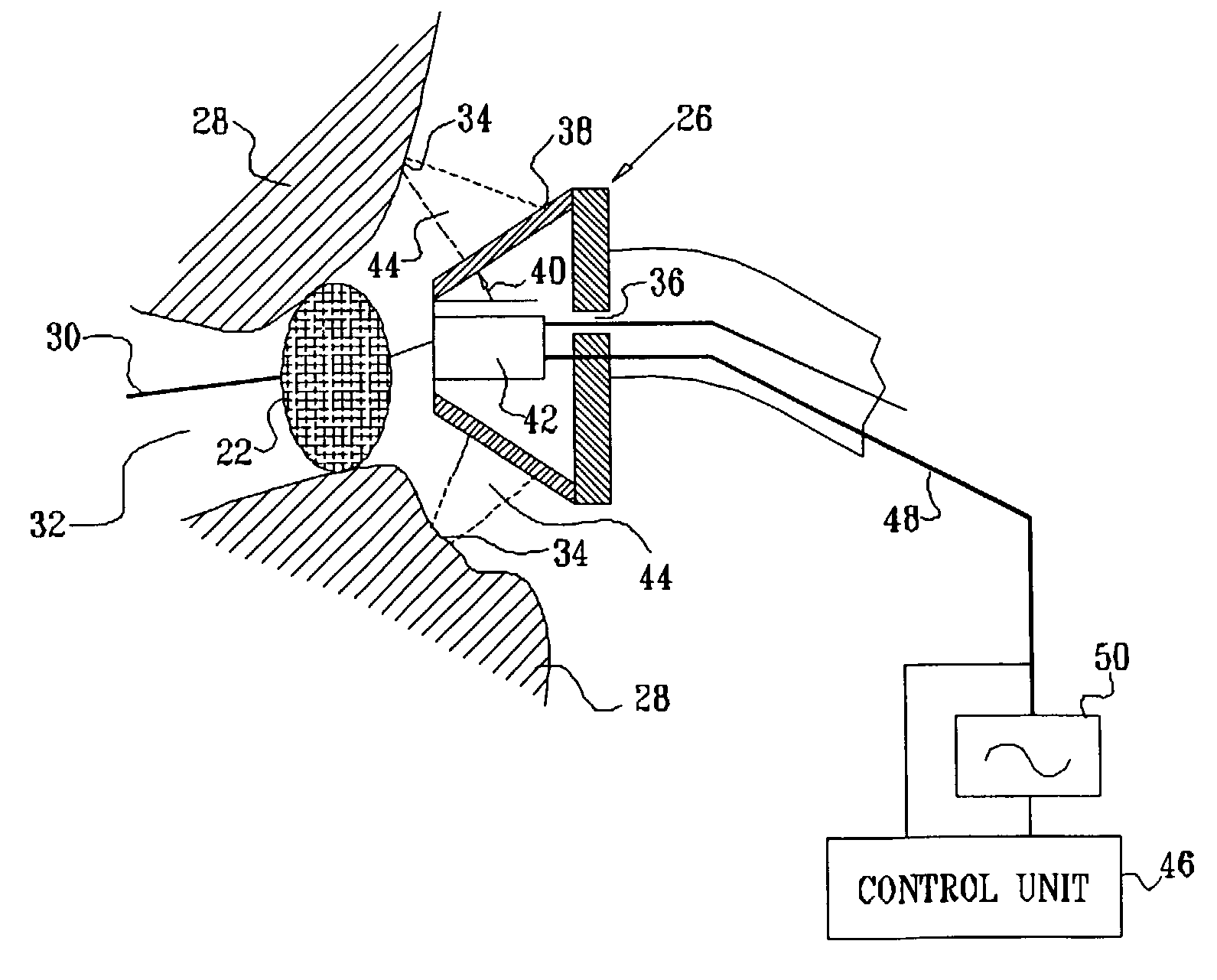
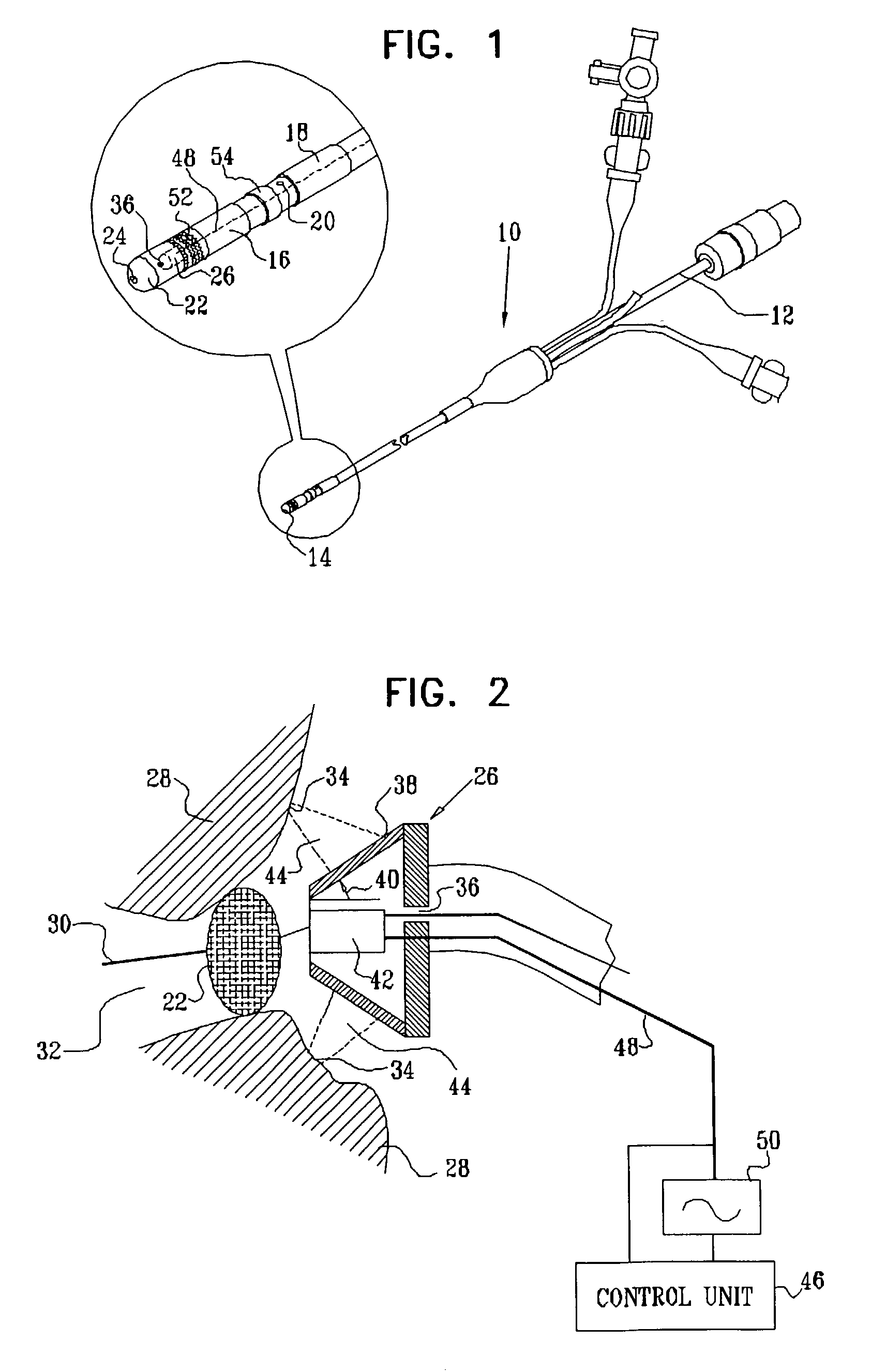
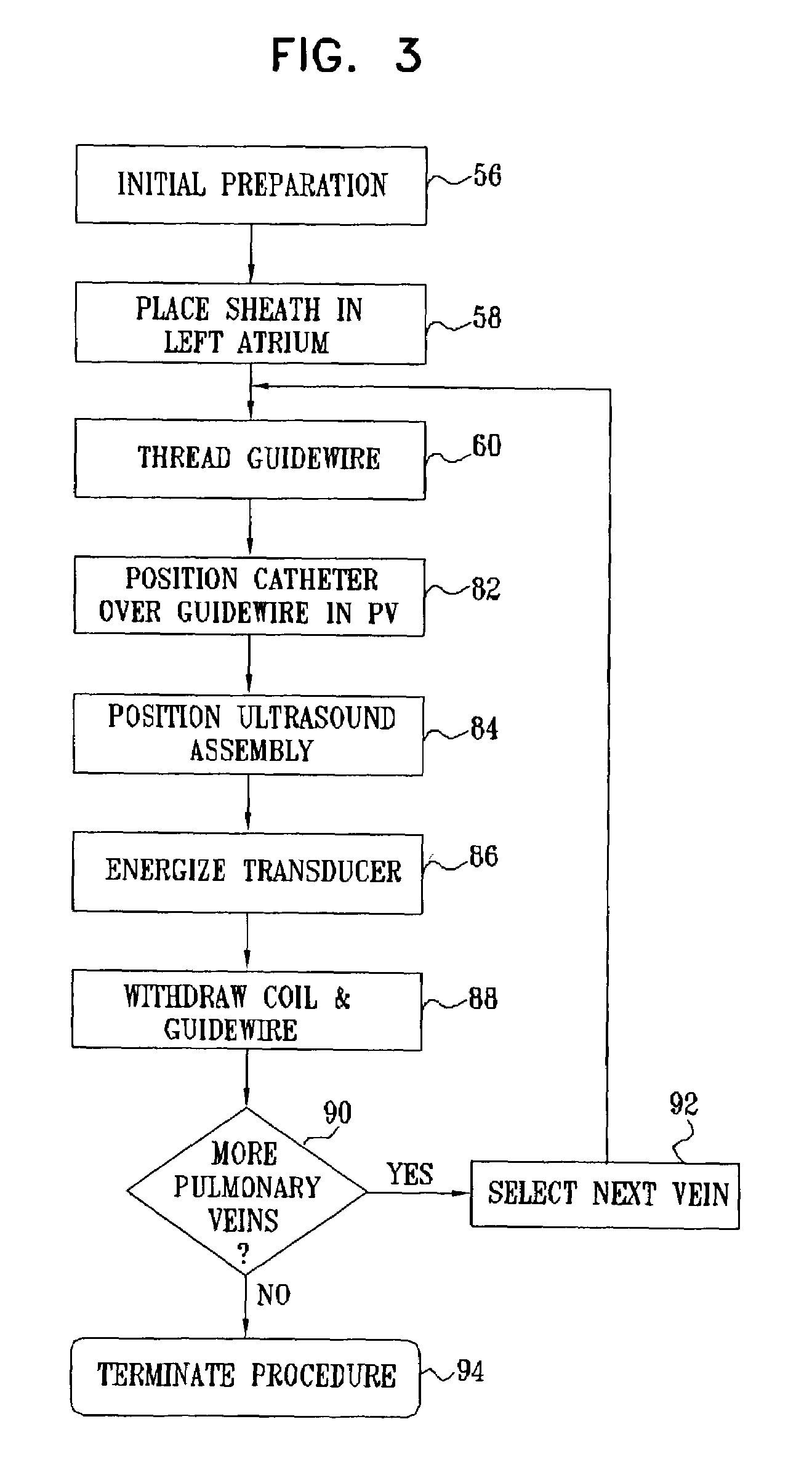
Ultrasound pulmonary vein isolation
A catheter introduction apparatus provides an ultrasound assembly for emission of ultrasound energy. In one application the catheter and the ultrasound assembly are introduced percutaneously, and transseptally advanced to the ostium of a pulmonary vein. An anchoring balloon is expanded to center an acoustic lens in the lumen of the pulmonary vein, such that energy is converged circumferentially onto the wall of the pulmonary vein when a transducer is energized. A circumferential ablation lesion is produced in the myocardial sleeve of the pulmonary vein, which effectively blocks electrical propagation between the pulmonary vein and the left atrium.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Powered surgical stapling device
ActiveUS10779818B2Function increaseDiagnosticsBattery isolationMechanical engineeringBiomedical engineering
An end effector includes first and second jaw members moveable relative to one another. Each of the first and second jaw members including a tissue contacting surface opposing the tissue contacting surface of the other jaw member. The end effector includes a detection assembly that is disposed within the first or second jaw member that is configured to detect an attribute of tissue between the first and second jaw members. The detection assembly may include a light source configured to emit light towards tissue between the first and second jaw members or may include an ultrasound transducer configured to emit ultrasound energy towards tissue between the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Multi-modality ablation device
ActiveUS7074218B2Minimum activation timeEffects damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyRadio frequencyUltrasound energy
An instrument for ablation of tissue. The instrument including: a body having at least one surface for contacting a tissue surface, the at least one surface being substantially planar; an ultrasonic transducer disposed in the body for generating ultrasonic energy and directing at least a portion of the ultrasonic energy to the tissue surface, the ultrasonic transducer being operatively connected to an ultrasonic generator; at least one radio-frequency electrode disposed on the at least one surface for directing radio frequency energy to the tissue surface, the at least one radio-frequency electrode being operatively connected to a power source; and one or more switches for selectively coupling at least one of the ultrasonic transducer to the ultrasonic generator and the at least one radio-frequency electrode to the power source.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Method and system for wireless battery charging utilizing ultrasonic transducer array based beamforming
InactiveUS20130241468A1Near-field transmissionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSonificationBattery charge
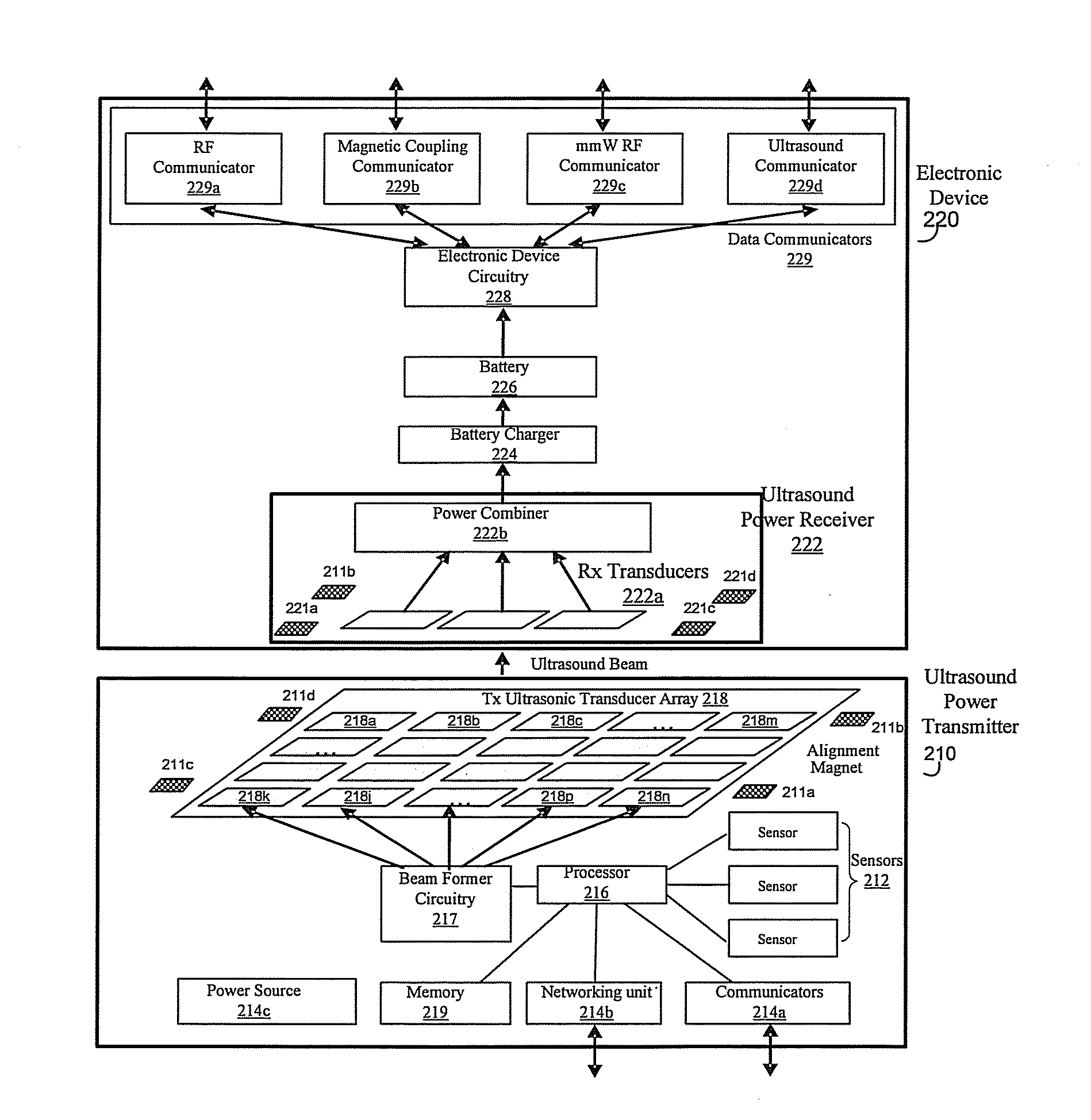
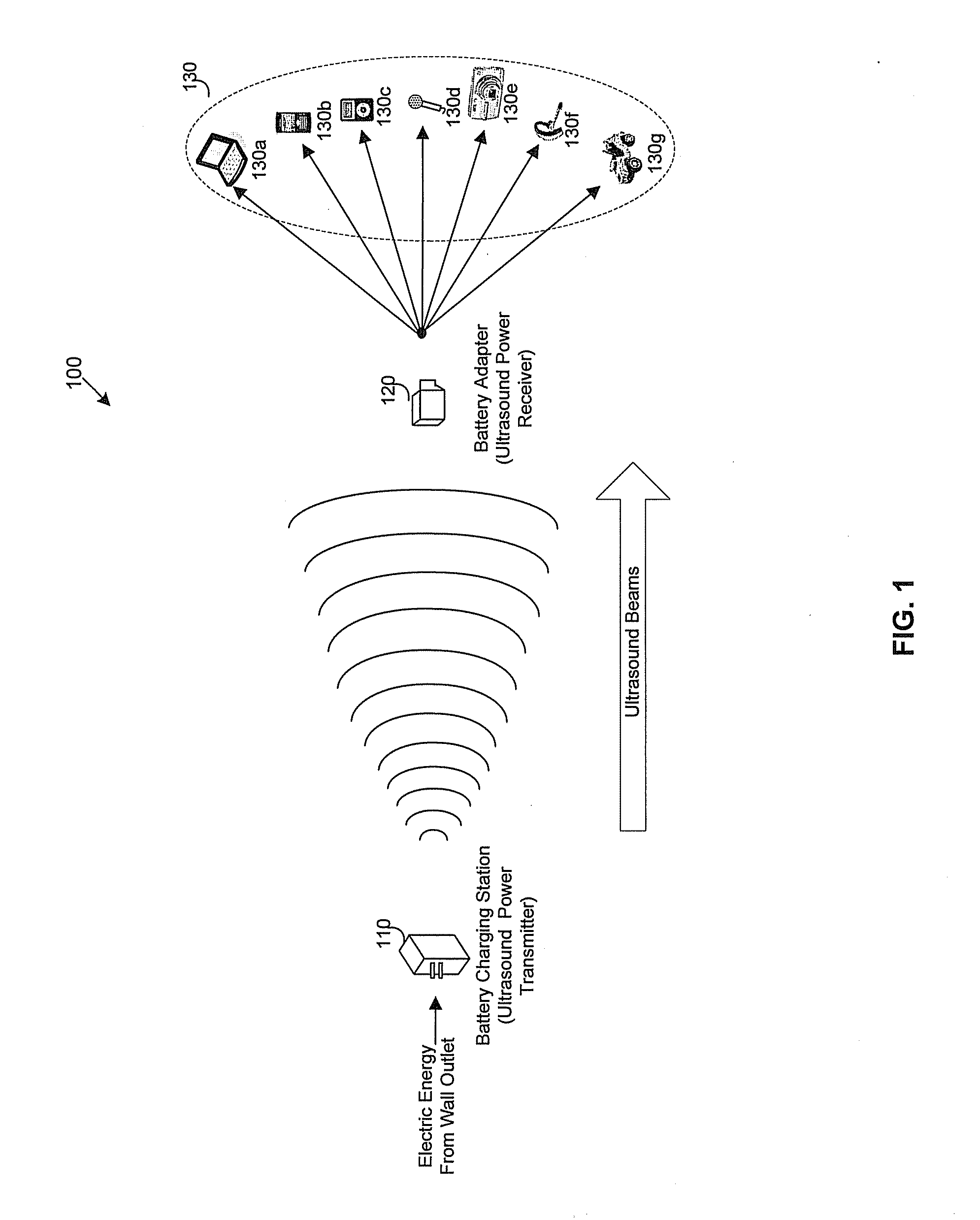
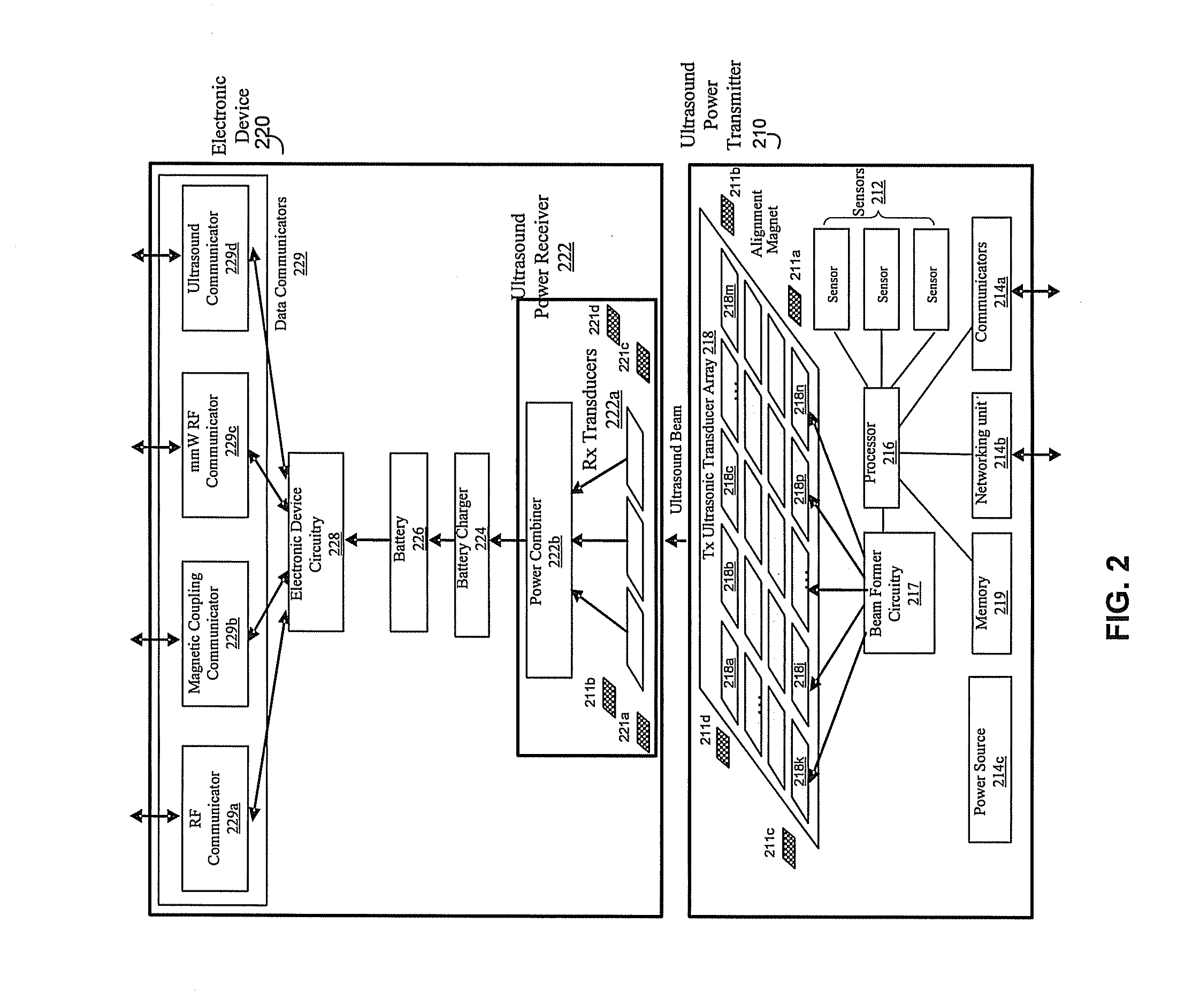
An ultrasound power transmitter comprising a transmit ultrasonic transducer array has a plurality of transmit ultrasonic transducers. The ultrasound power transmitter activates a set of transmit ultrasonic transducers in close proximity of an electronic device to be arranged to beam ultrasound energy to the electronic device. Alignment magnets of the ultrasound power transmitter are aligned with corresponding alignment magnets of the electronic device to manage the ultrasound beaming. The ultrasound energy may be converted into electric power to charge the battery of the electronic device. Feedbacks may be provided by the electronic device to the ultrasound power transmitter to increase power transmission efficiency. The ultrasound power transmitter may pair the electronic device with other different electronic devices utilizing ultrasonic signals. A spacer with good ultrasound power transmission properties may be located between the ultrasound power transmitter and an ultrasound power receiver of an intended electronic device to enhance power transmission.
Owner:ARRAY IP LLC
Ultrasonic radial focused transducer for pulmonary vein ablation
ActiveUS7066895B2Overcome disadvantagesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyVeinPulmonary vein ablation
A method for ablating tissue with ultrasonic energy is provided. The method including: generating ultrasonic energy from one or more ultrasonic transducers; and focusing the ultrasonic energy in the radial direction by one of: shaping the one or more ultrasonic transducers to focus ultrasonic energy in the radial direction; and arranging one or more lenses proximate the one or more ultrasonic transducers for focusing the ultrasonic energy from the one or more ultrasonic transducers in a radial direction.
Owner:ETHICON INC
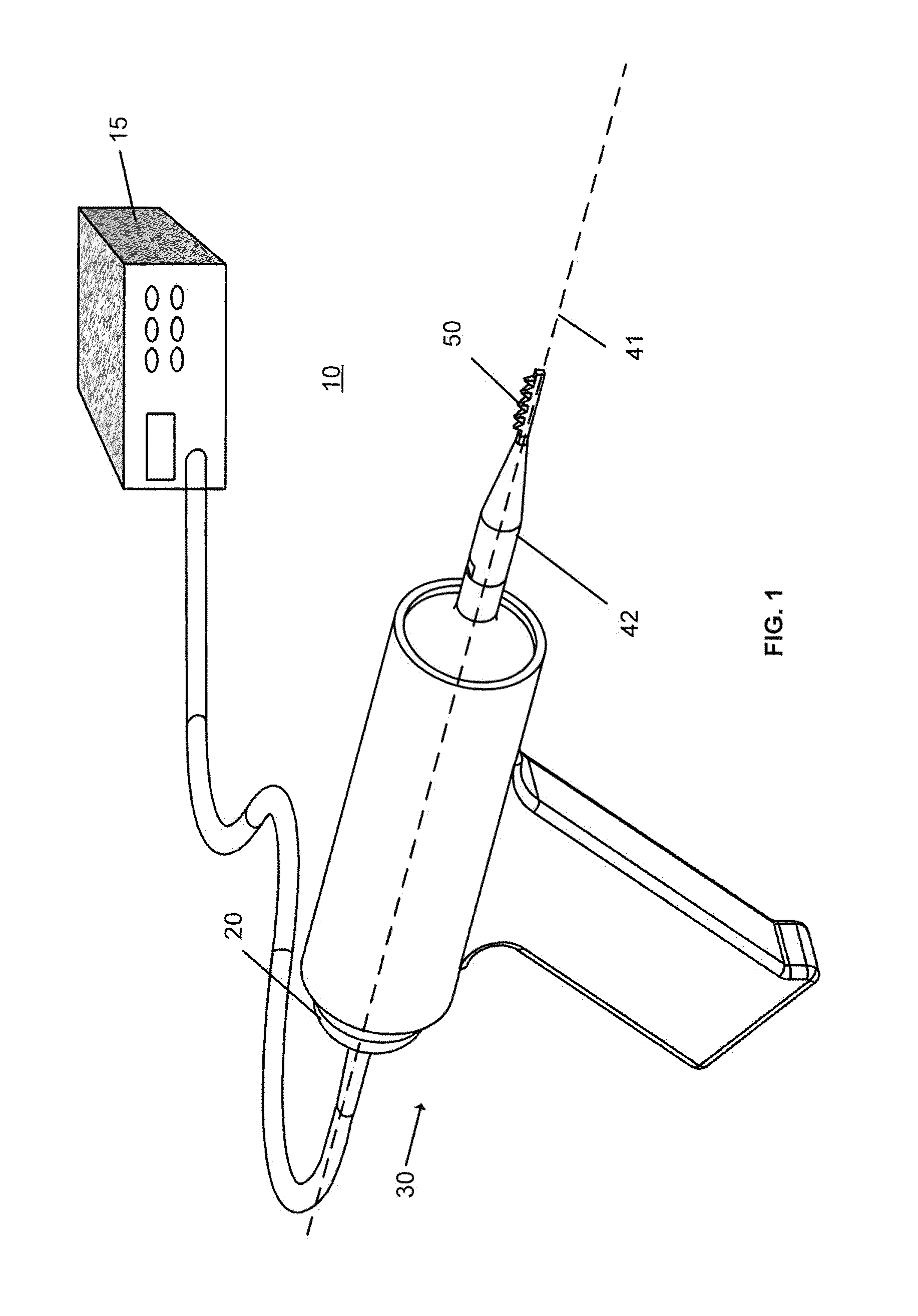
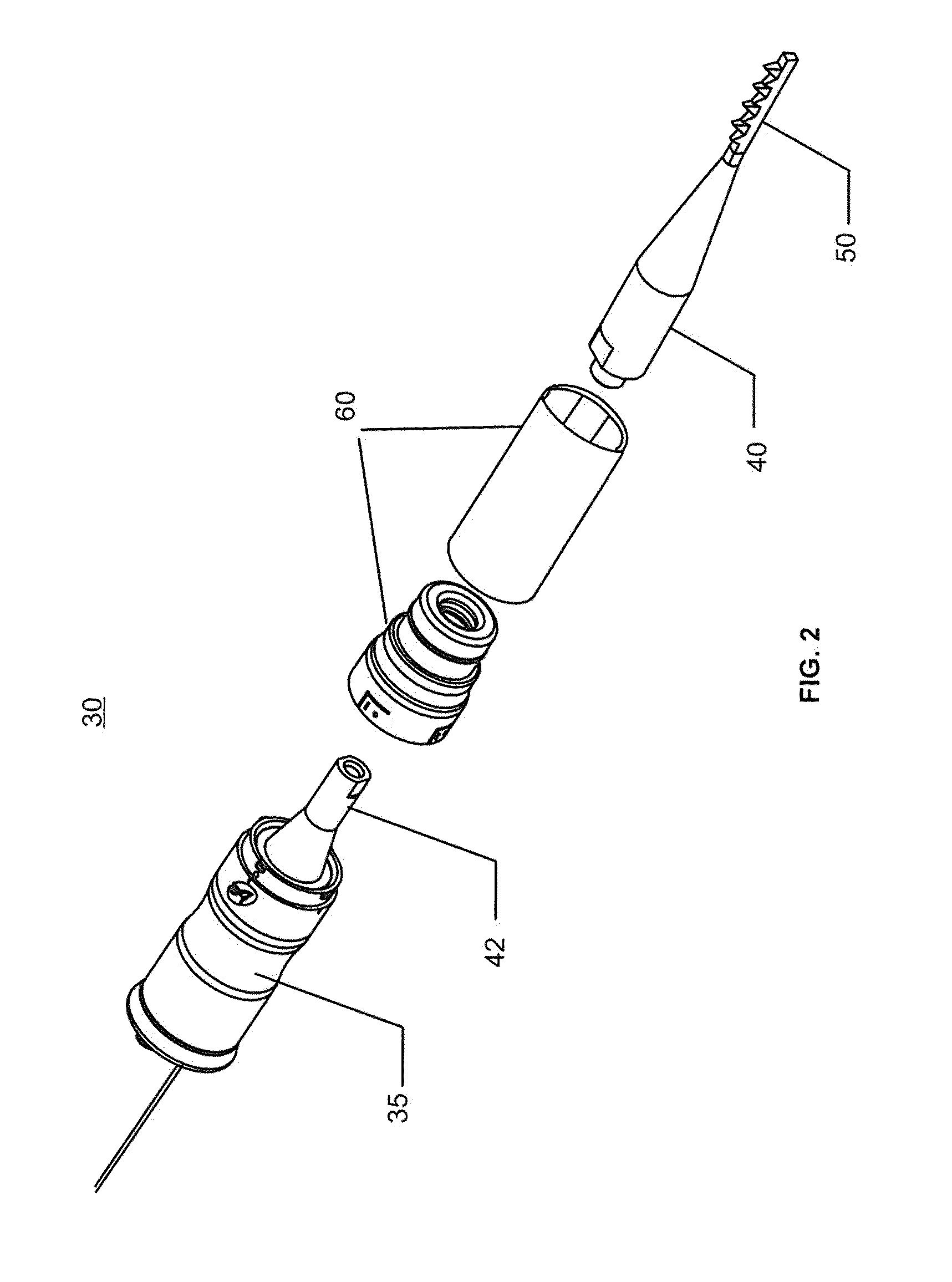
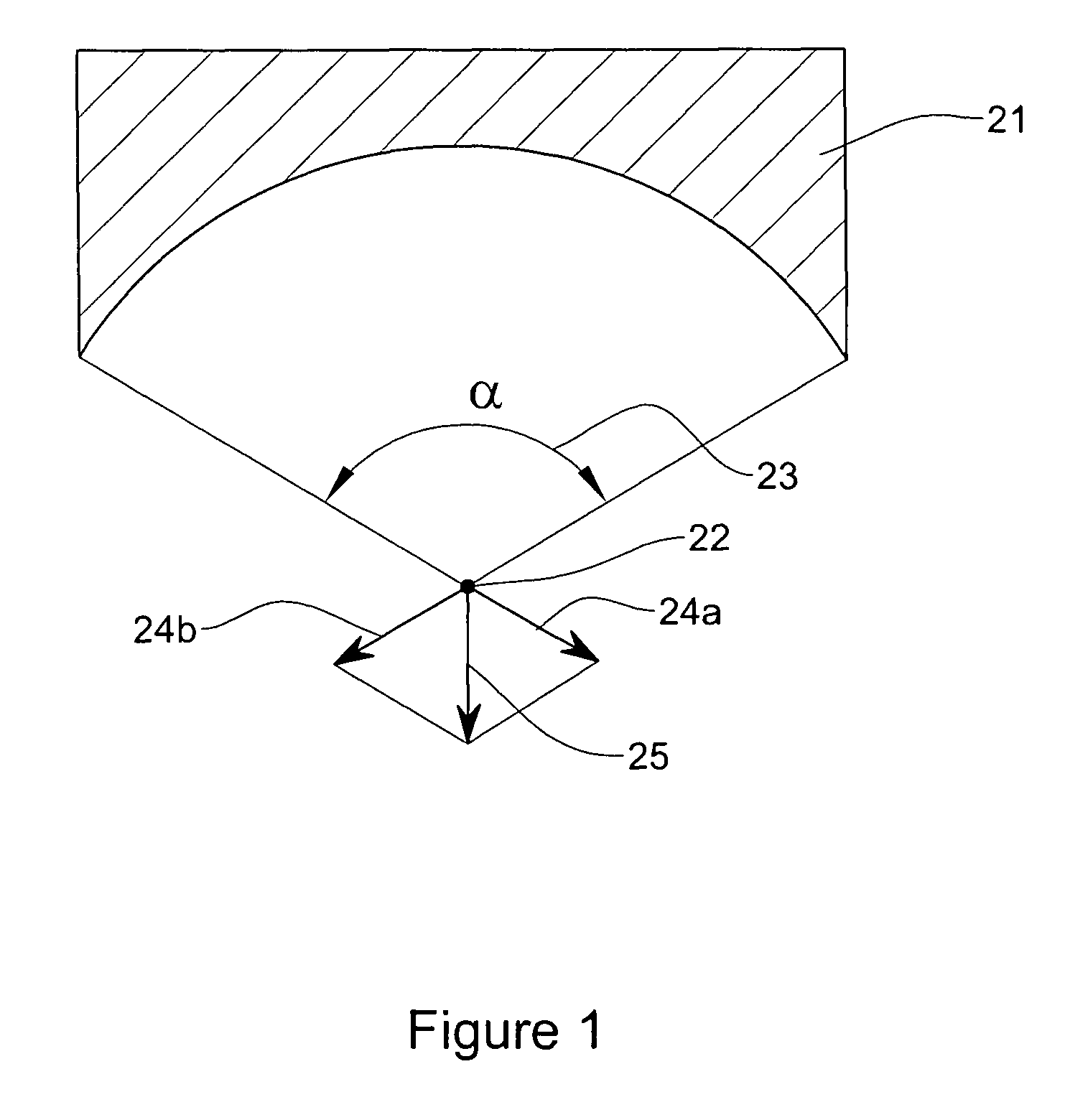
Apparatus and method for the treatment of tissue with ultrasound energy by direct contact
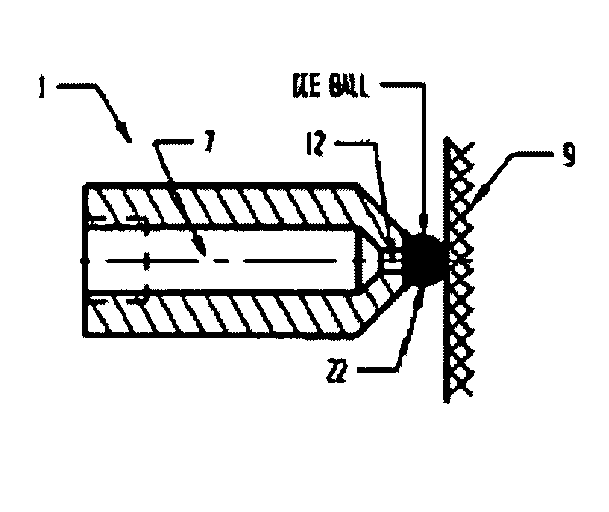
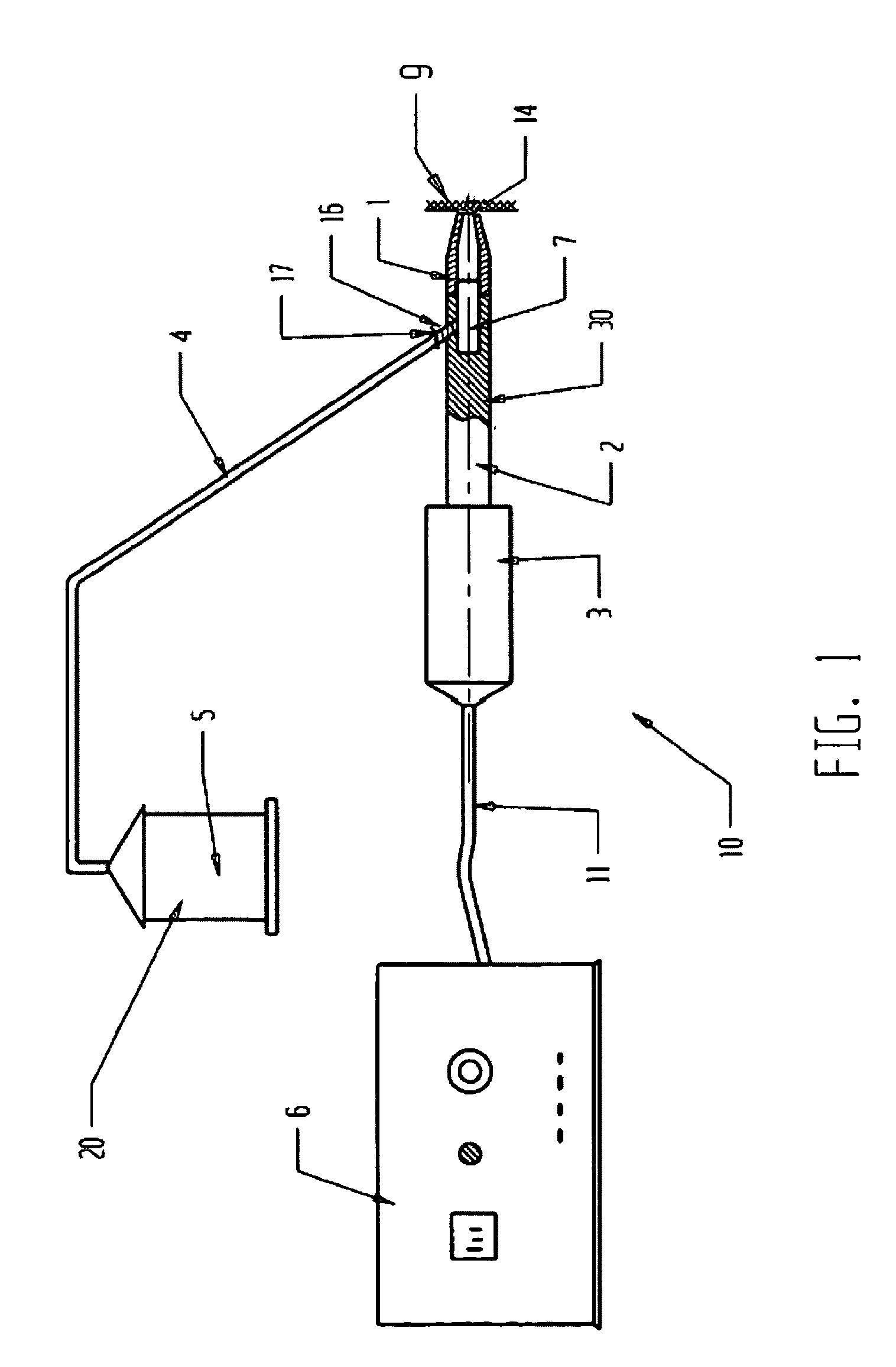
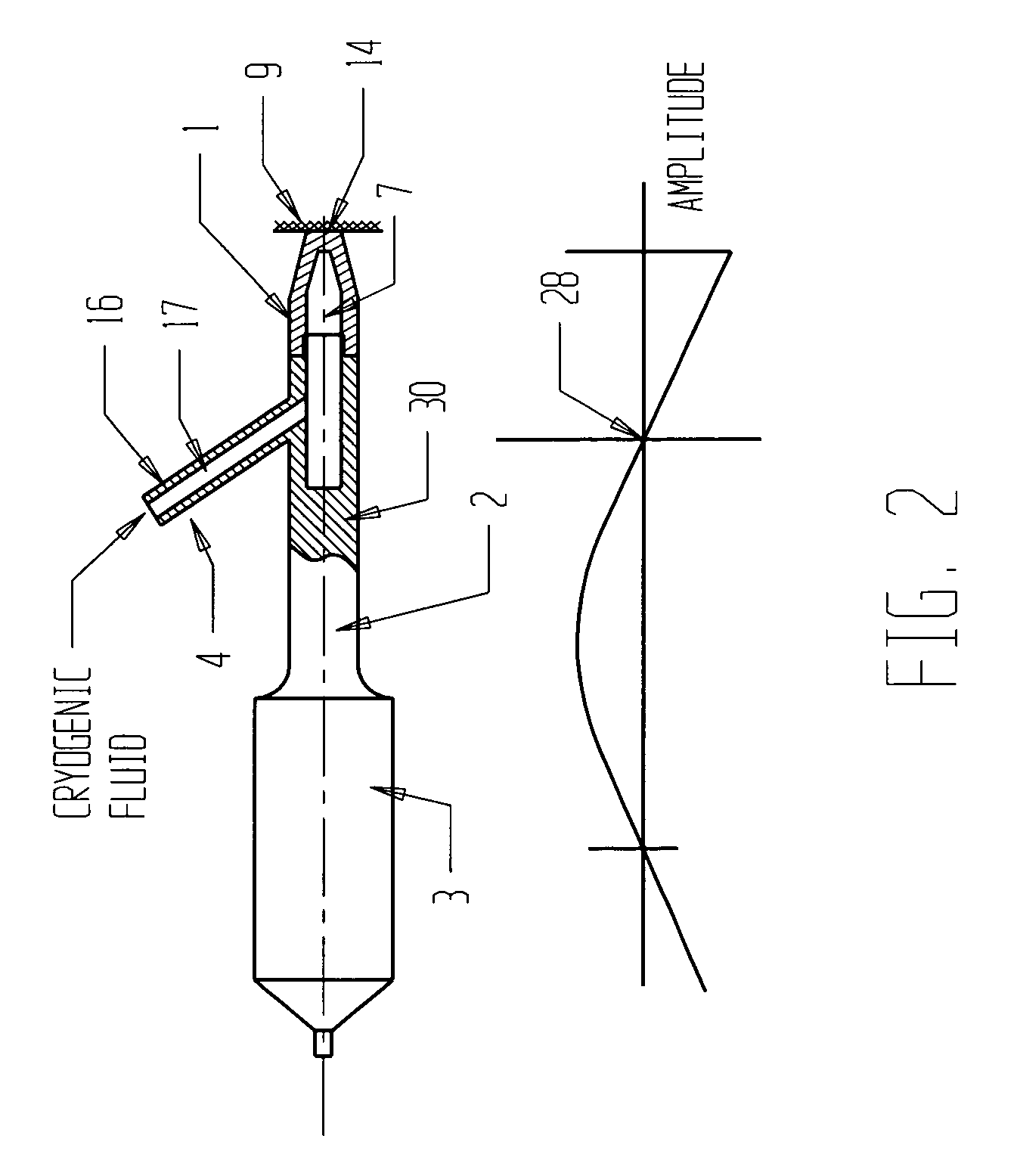
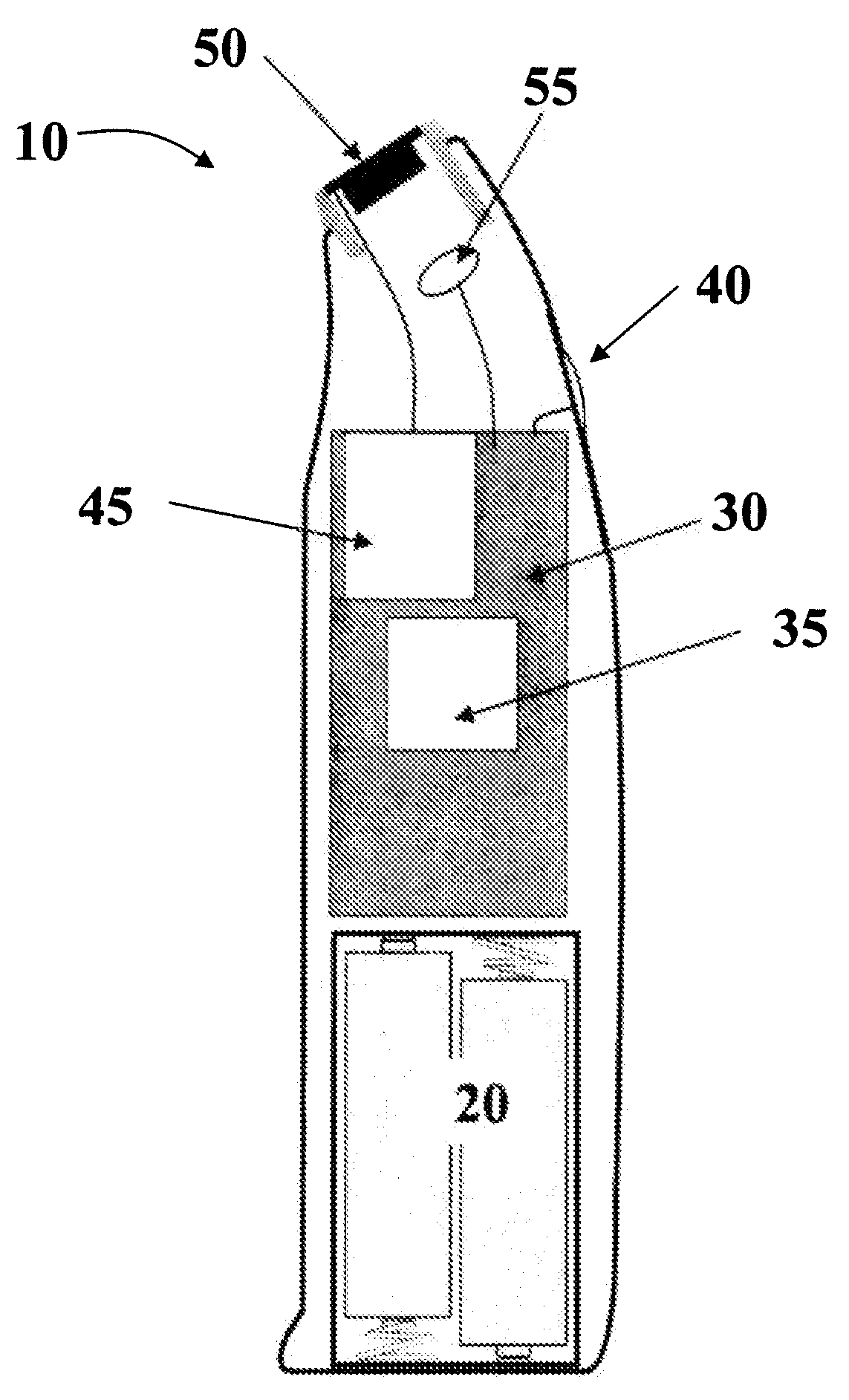
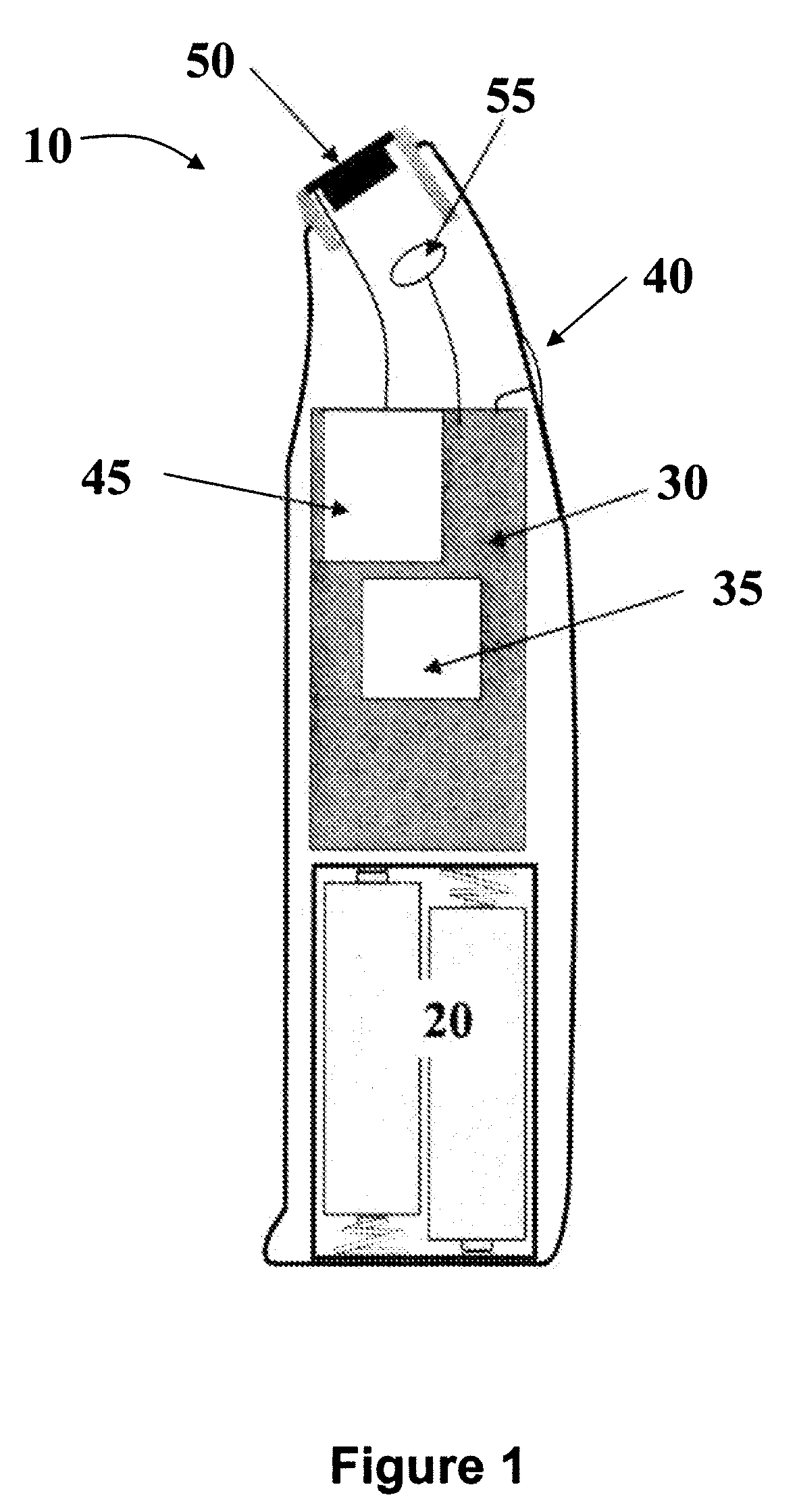
Apparatus and method for the treatment of tissue, such as hard and soft tissues, wounds, tumors, muscles, and cartilage, through the direct contact of ultrasound energy is disclosed. Ultrasound energy is delivered to a target area through direct contact with an ultrasound tip. Ultrasound energy is also delivered through direct contact with a coupling medium. The ultrasound tip is specially designed to comprise of a cavity area for controlled fragmentation and the simultaneous sonication of a target area. The specially designed ultrasound tip allows for ultrasound energy to focus on a target area. The ultrasound apparatus may be moved in a variety of different directions during the treatment of tissue.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
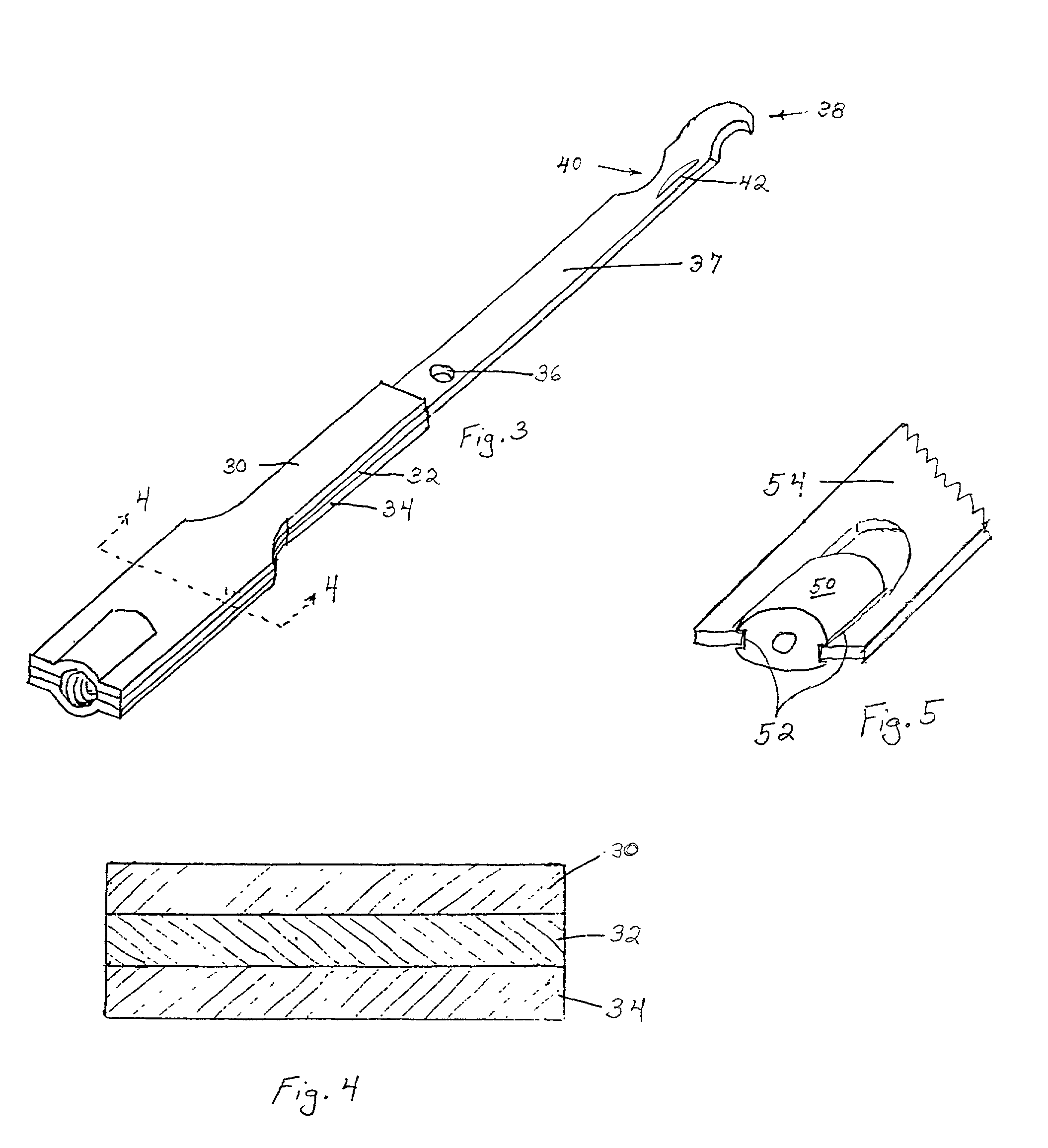
Balanced ultrasonic curved blade
InactiveUS20070016236A1Reduce lateral movementAdd additional massSurgeryEngineeringUltrasound energy
Methods and devices that provide reduced transverse motion in a curved ultrasonic blade and / or ultrasonic surgical instrument with functional asymmetries. An ultrasonic blade in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes a curved functional portion of an ultrasonic blade, wherein the center of mass of the curved functional portion lies on the mid-line of a waveguide delivering ultrasonic energy to the blade. Balancing in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, using placement of the center of mass of the curved portion of the blade appropriately, provides blade balance in a proximal portion of the blade, without reduction of mass and inherent stress increase proximal to the end-effector.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area containing a plurality of lesions
InactiveUS20050267454A1Improve the level ofWithout impairingUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesHigh intensityHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
A method of thermal ablation using high intensity focused ultrasound energy includes the steps of positioning an ultrasound emitting member, emitting ultrasound energy from the ultrasound emitting member, focusing the ultrasound energy, ablating with the focused ultrasound energy to form an ablated tissue area and removing the ultrasound emitting member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area
InactiveUS20060025756A1Easy positioningEasily manipulateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyHigh intensityHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
A method of thermal ablation using high intensity focused ultrasound energy includes the steps of positioning one or more ultrasound emitting members within a patient, emitting ultrasound energy from the one or more ultrasound emitting members, focusing the ultrasound energy, ablating with the focused ultrasound energy to form an ablated tissue area and removing the ultrasound emitting member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Focused ultrasound for pain reduction
InactiveUS20060184069A1Relieve painUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationTransducer
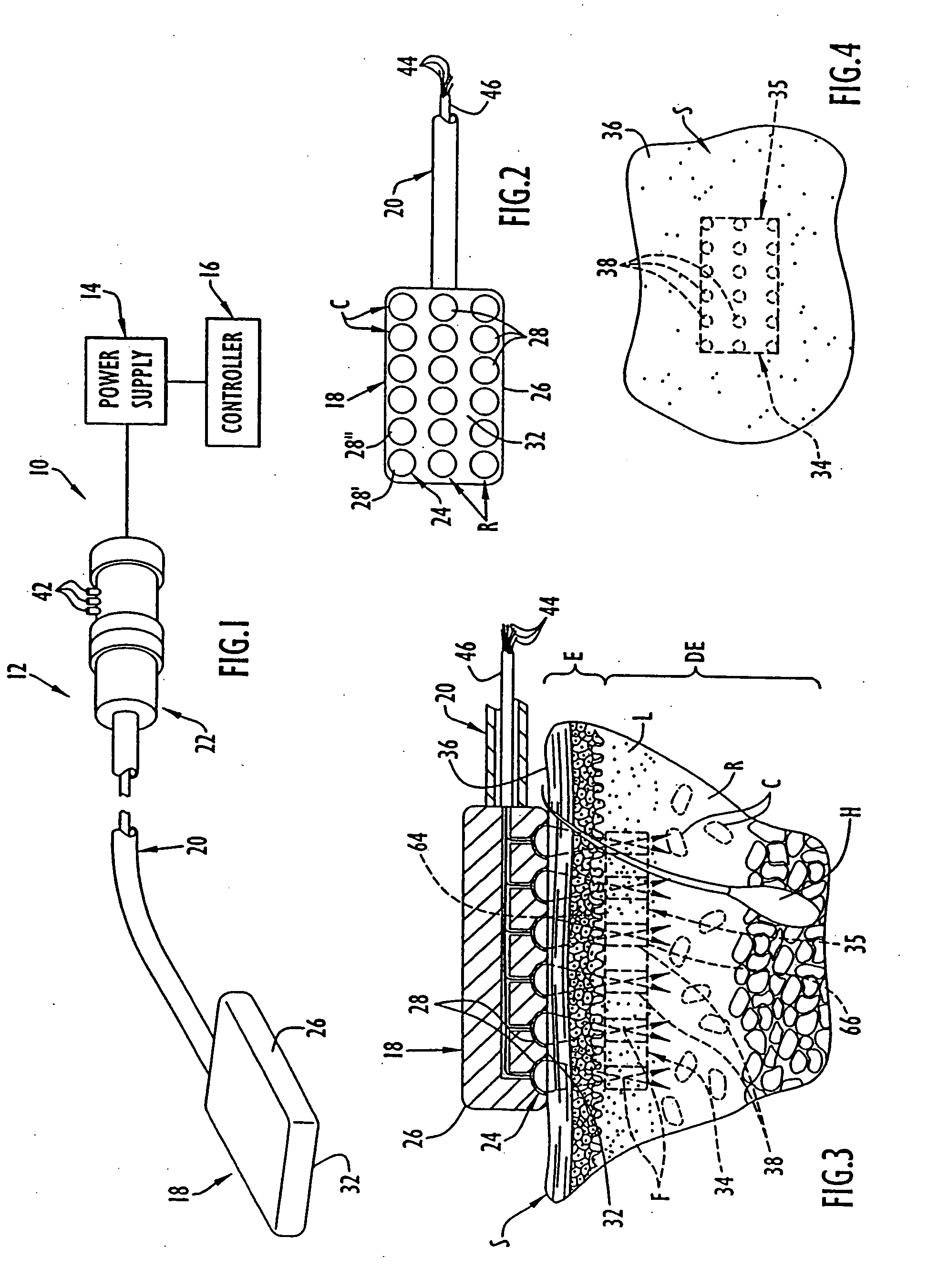
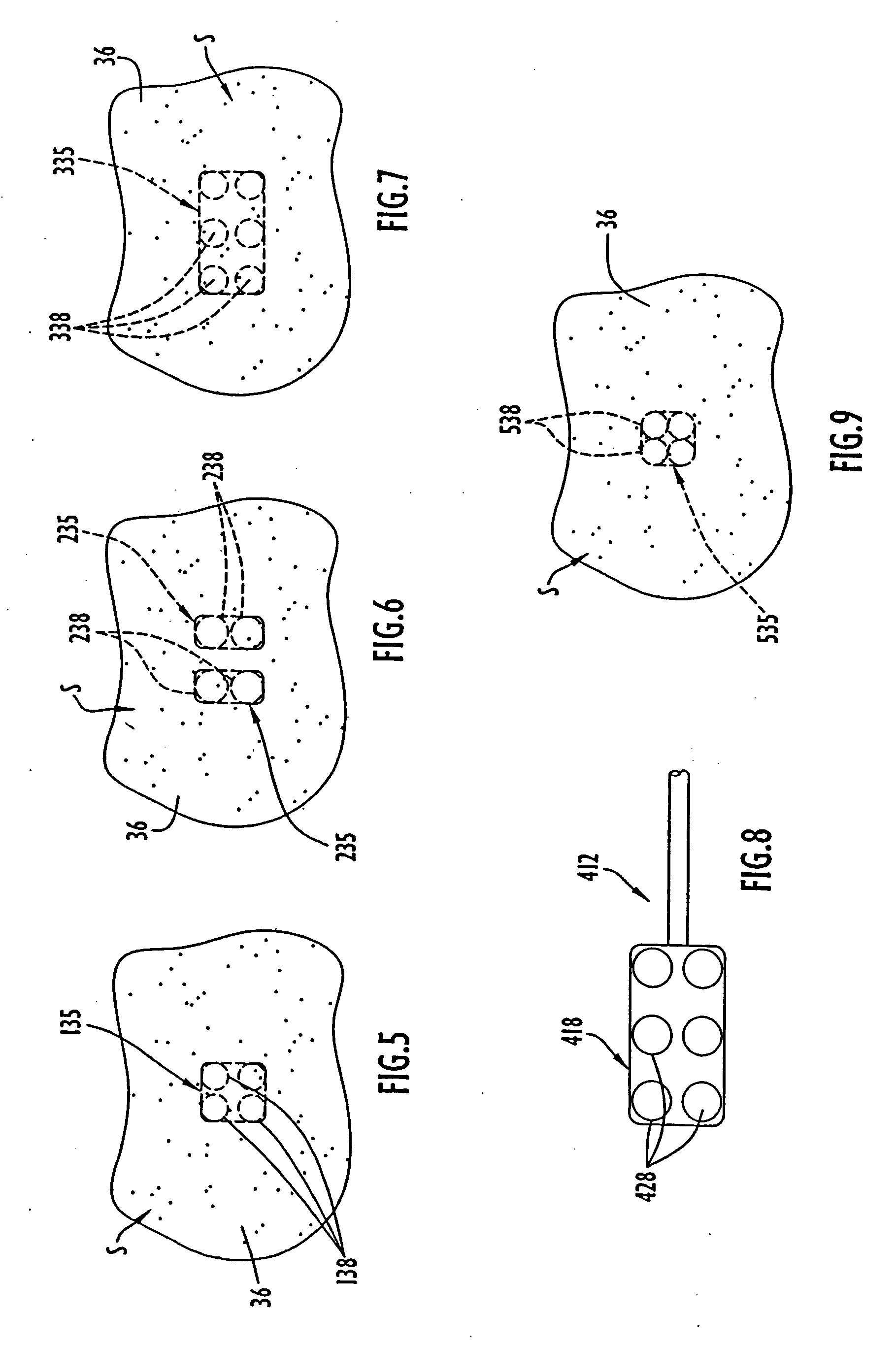
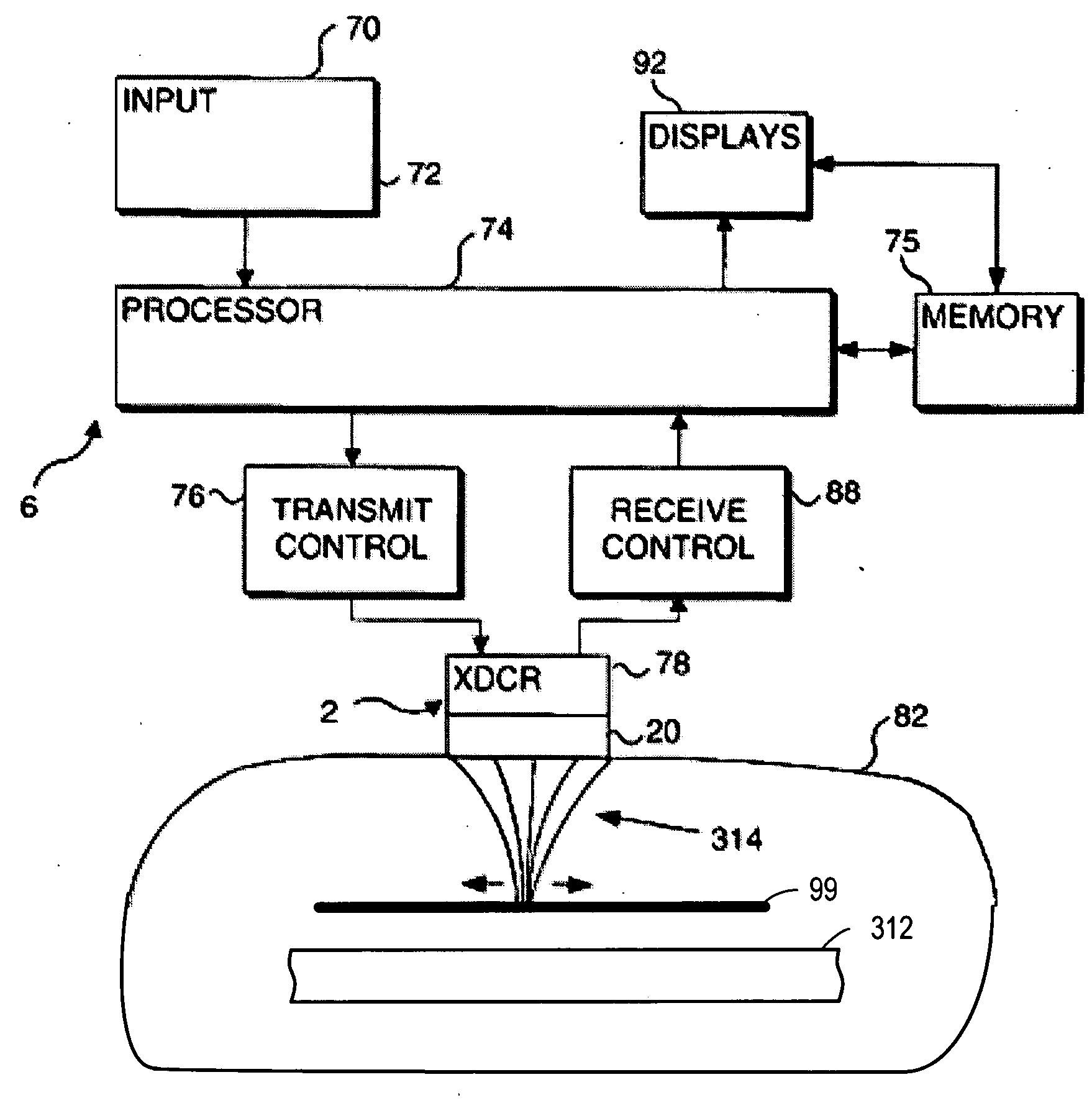
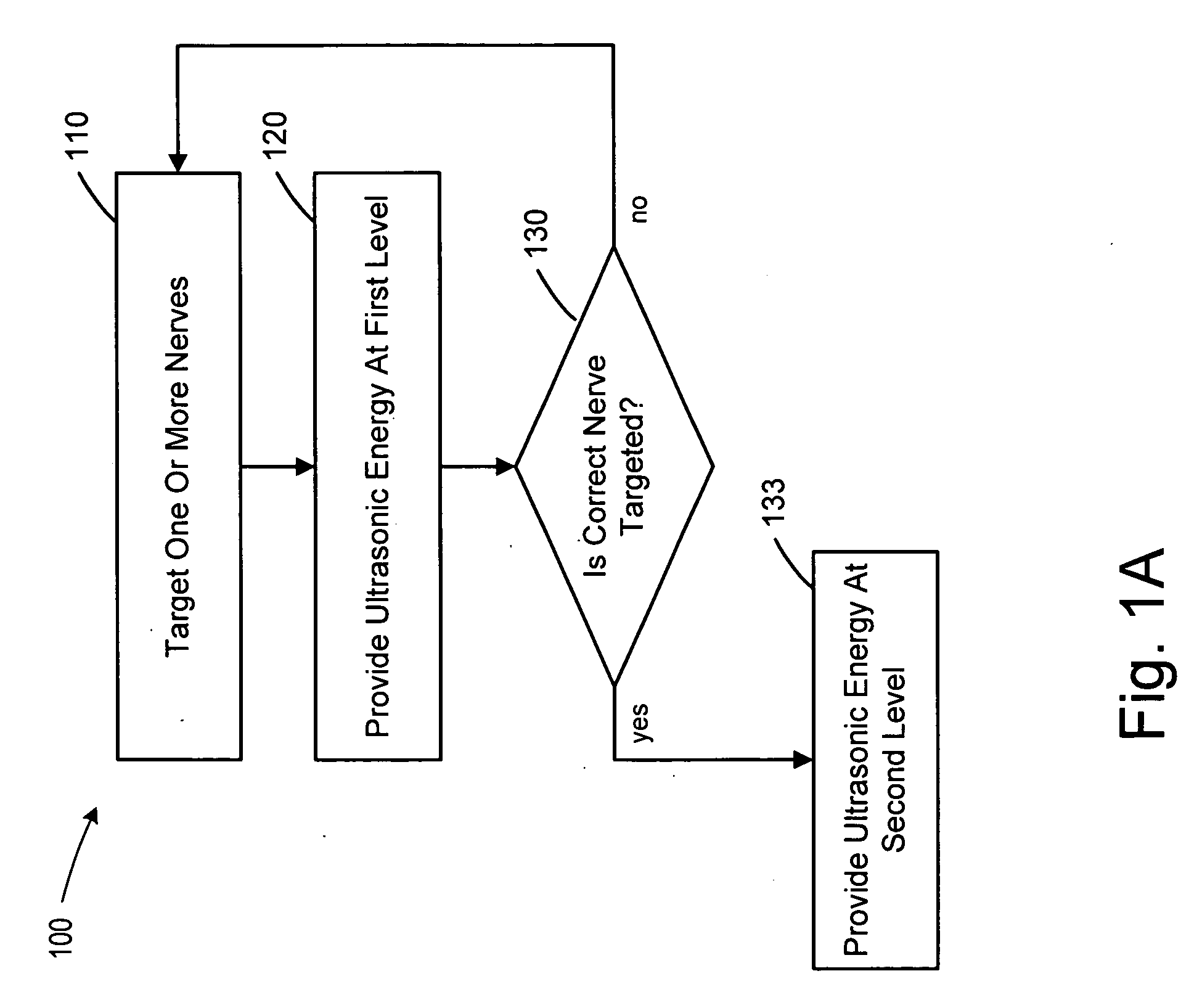
Methods and devices that provide ultrasonic energy used to cause one or more nerves to become dysfunctional. A nerve to be treated is placed in the focal zone of ultrasonic energy emitted by ultrasound transducer. A first level of ultrasonic energy is provided to the nerve using the ultrasound transducer, the first level sufficient to stimulate the nerve. A verification is made that the desired nerve is being stimulated by the first level of ultrasonic energy. For example, the patient may be asked to confirm that the ultrasonically stimulated nerve corresponds to the pain that is affecting the patient. Subsequent to verifying the stimulated nerve is the nerve desired for the reduction of pain, a second level of ultrasonic energy is delivered to the nerve using the ultrasound transducer, the second level of ultrasonic energy sufficient to cause nerve dysfunction.
Owner:VAITEKUNAS JEFFREY J
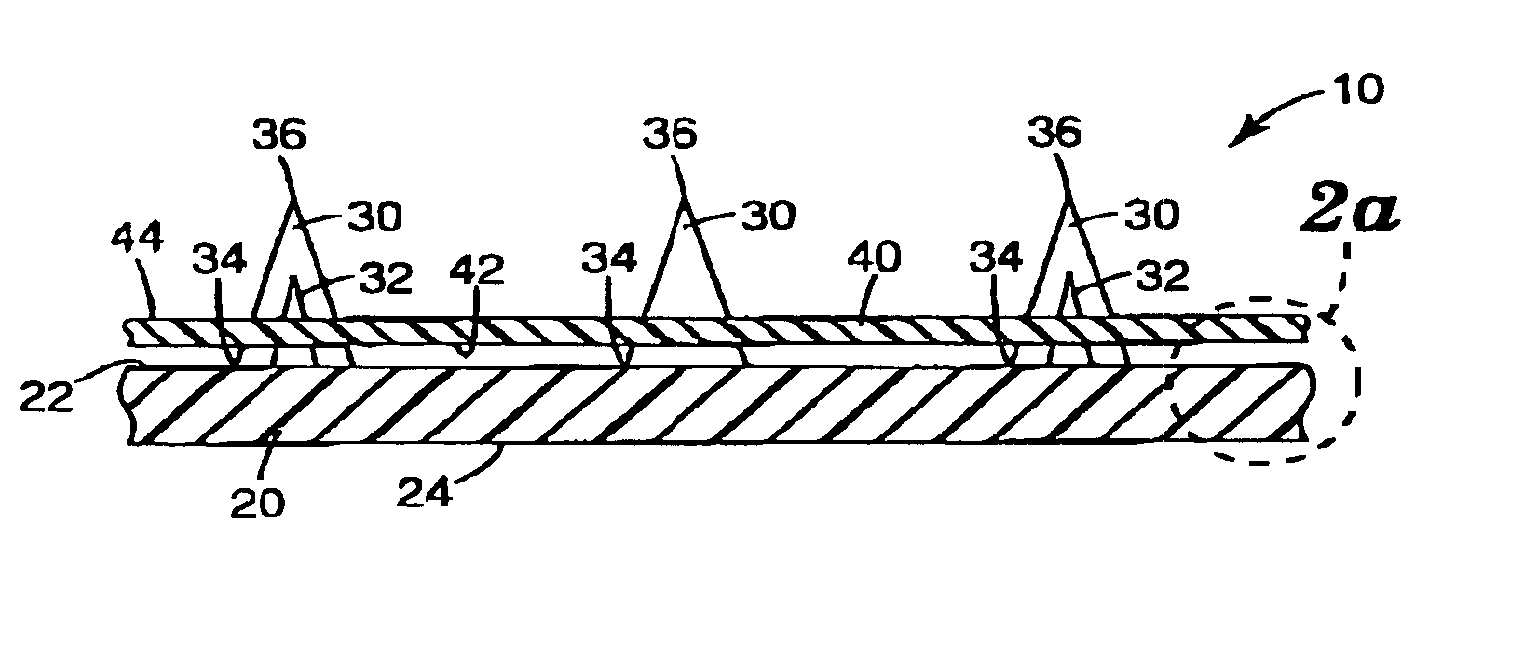
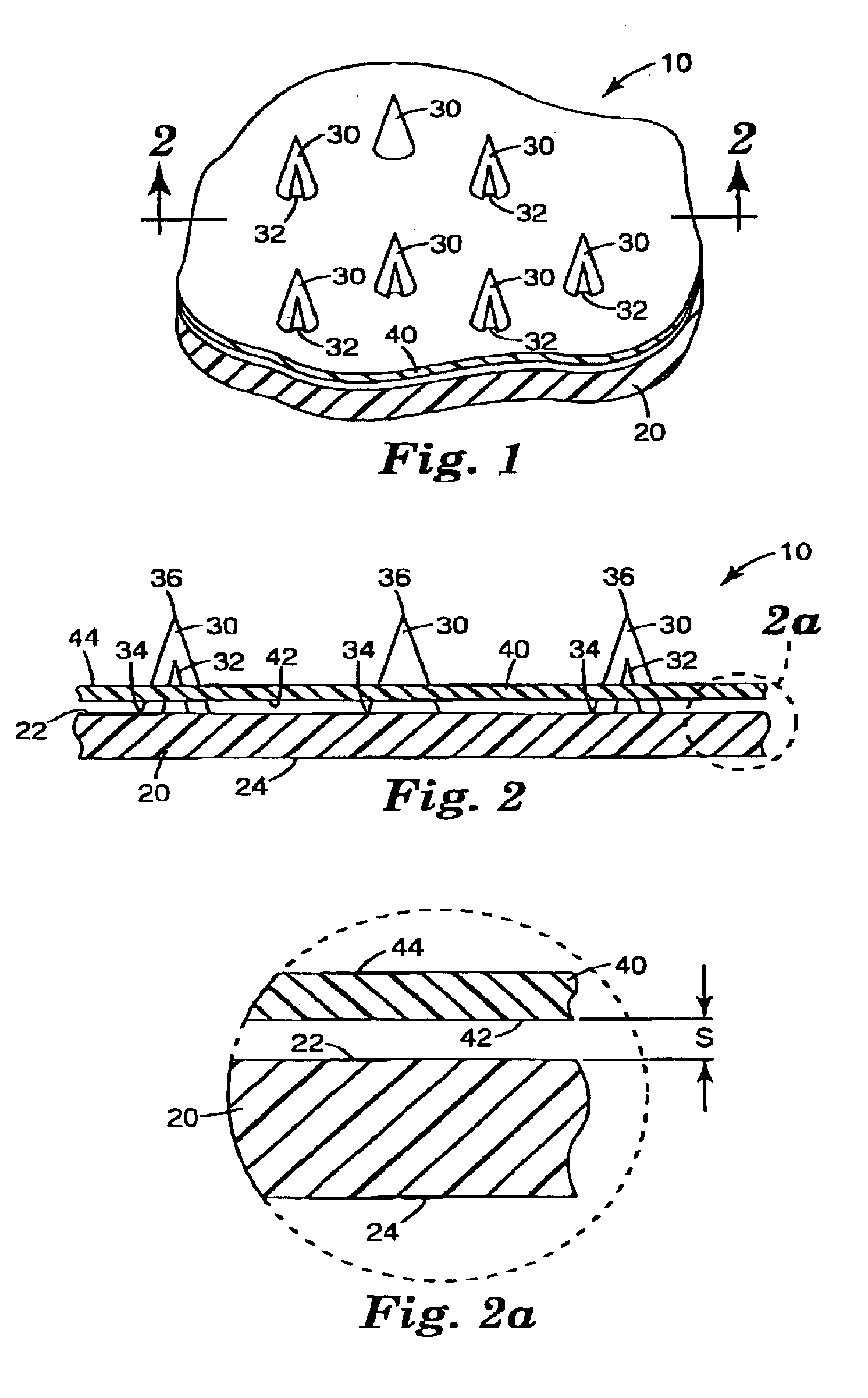
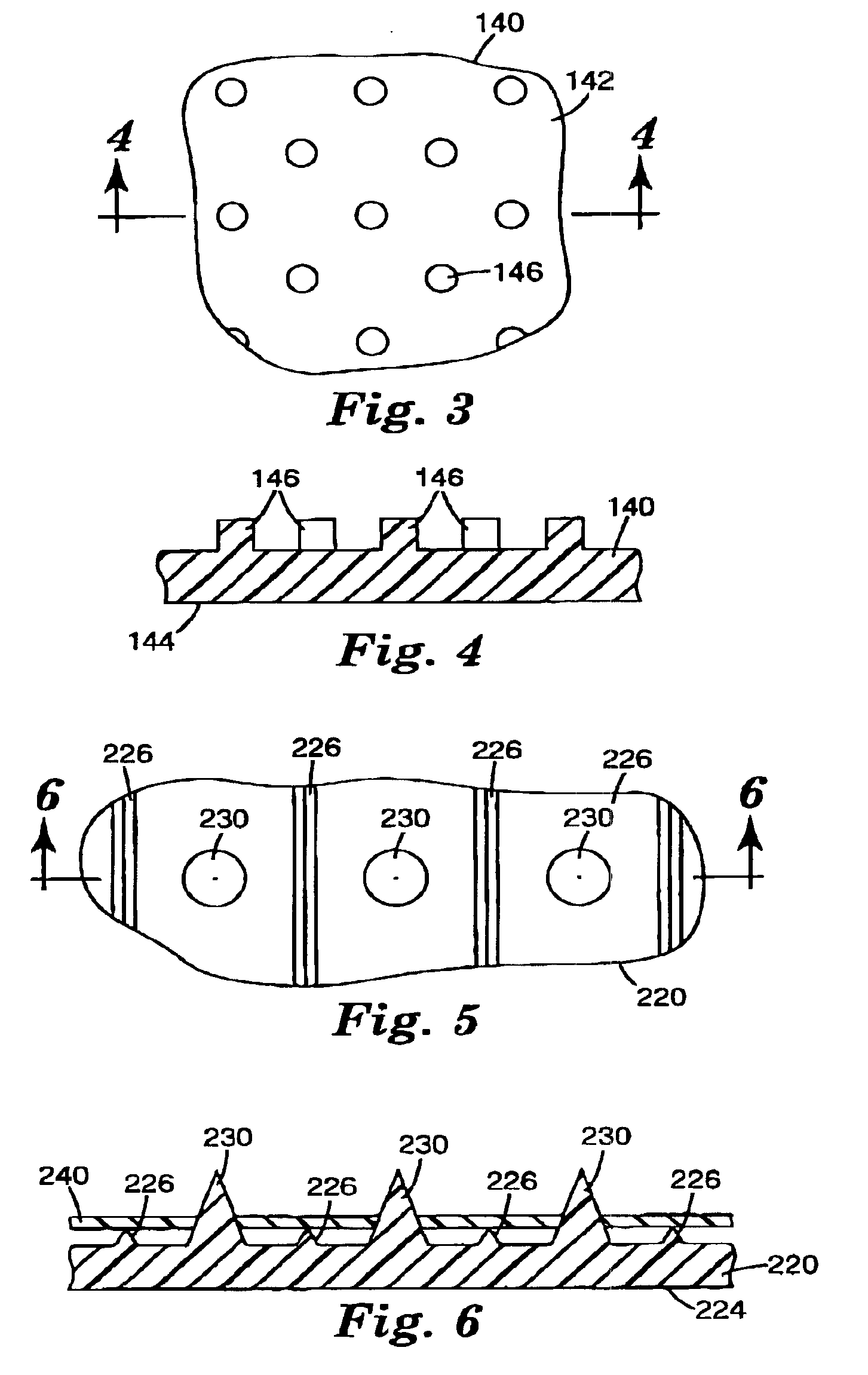
Microneedle devices and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS6908453B2Enhanced fluid movementImprove actionSurgical needlesMicroneedlesCapillary volumeSubstrate surface
Microneedle devices and methods of manufacturing the microneedle devices. The microneedle devices include microneedles protruding from a substrate, with the microneedles piercing a cover placed over the substrate surface from which the microneedles protrude. The cover and the microneedle substrate together define a capillary volume in fluid communication with the base of each microneedle. One manner of using microneedle arrays of the present invention is in methods involving the penetration of skin to deliver medicaments or other substances and / or extract blood or tissue. Manufacturing methods may include simultaneous application of pressure and ultrasonic energy when piercing the cover with the microneedles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
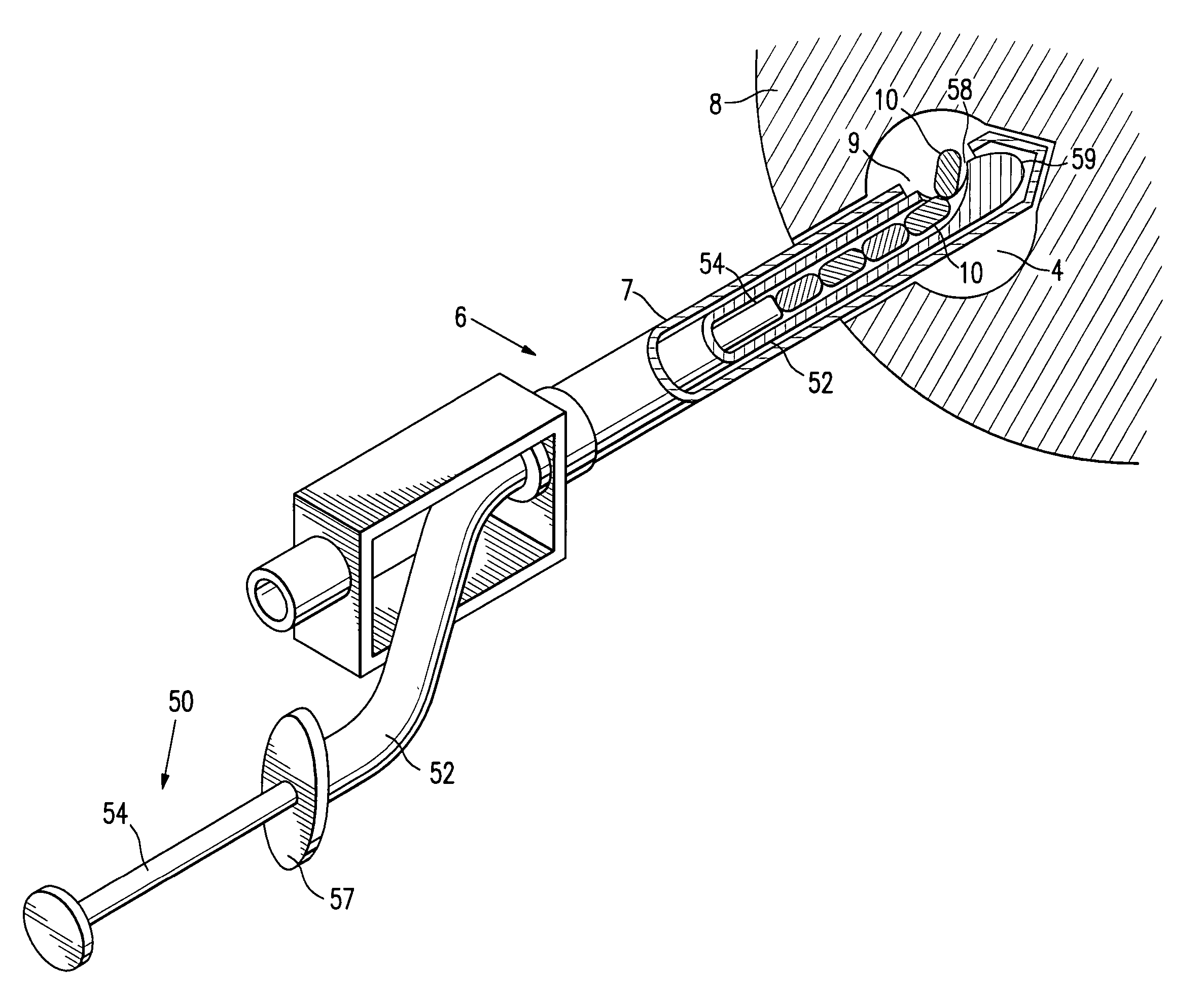
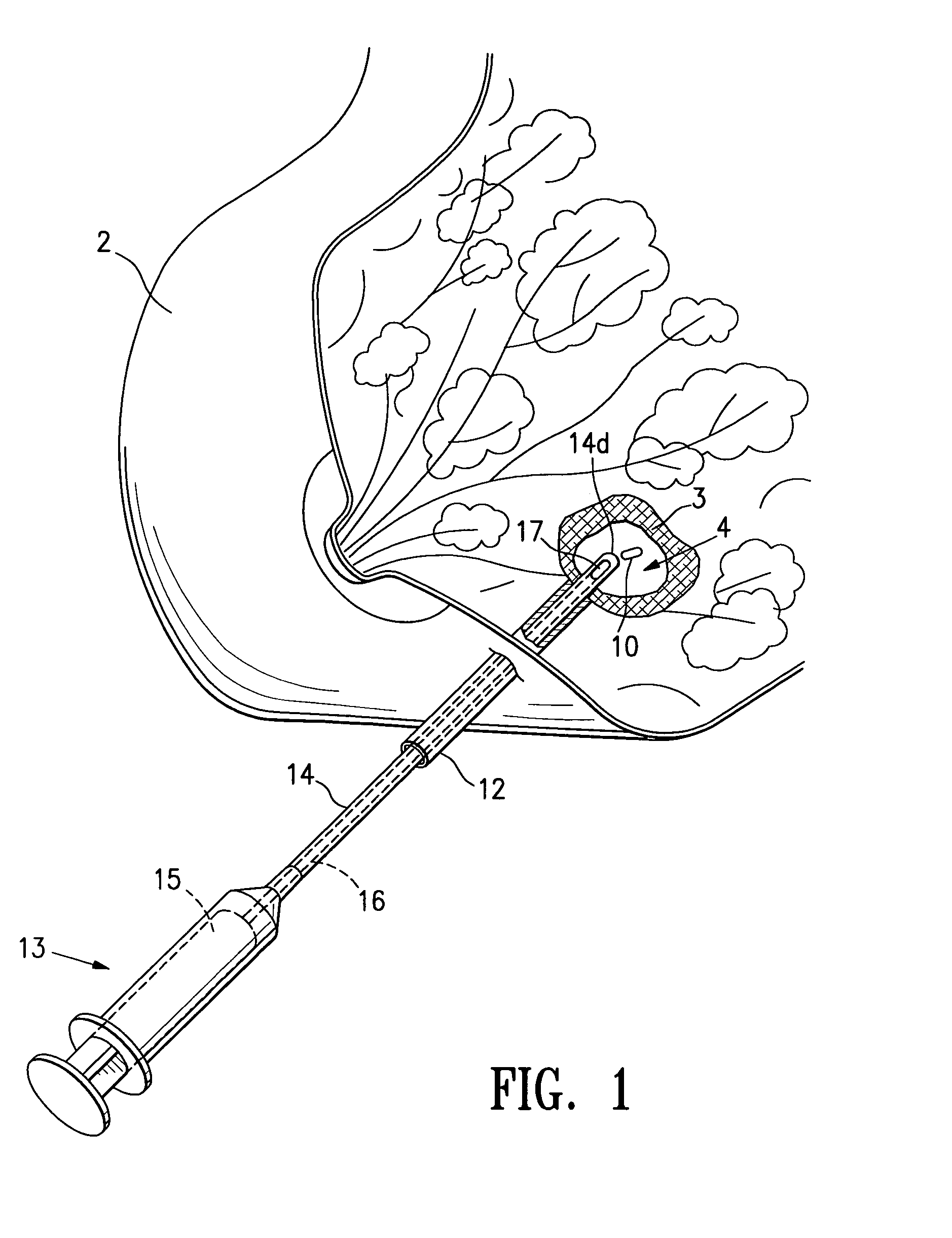
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS6993375B2Enhance acoustical reflective signature and signalEasy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
Owner:SENORX
Ultrasound surgical saw
This invention discloses methods and devices using ultrasound energy for resecting bone tissue during surgical procedures. The disclosure describes the use of ultrasound surgical saw consisting of an ultrasound generator, ultrasound transducer and ultrasound horn including a cutting blade to resect bone tissue without excessive temperature rise during typical surgical procedures. The cutting blade provides a self-clearing design that includes at least two teeth disposed to prevent accumulation of bone chips within the proximity of the teeth. The design of the cutting blade allows the mechanical motion of the blade and the emission of the ultrasound energy to remove accumulated bone chips and prevent excessive temperature rise.
Owner:BABAEV ELIAZ
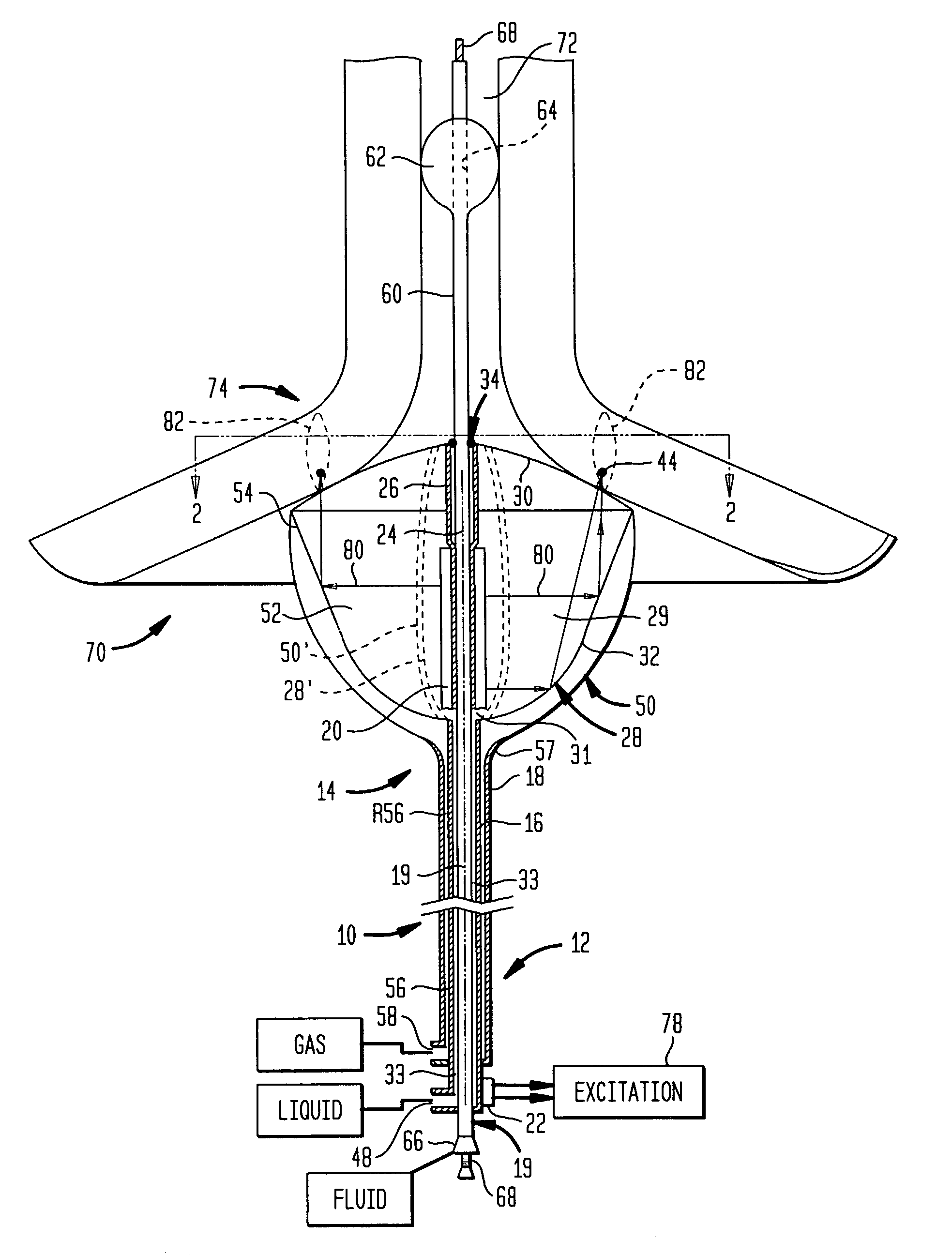
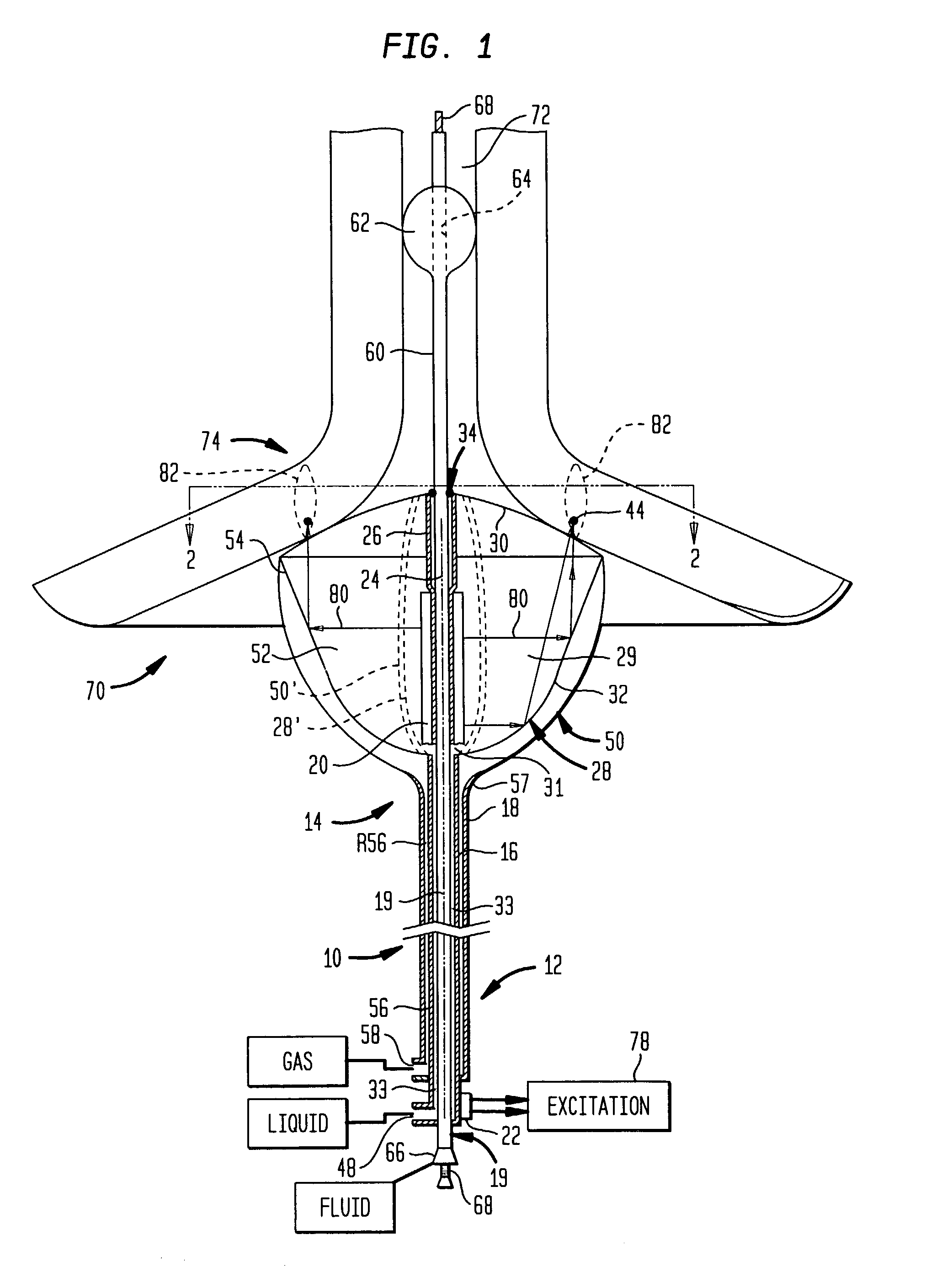
Thermal treatment methods and apparatus with focused energy application
InactiveUS7083614B2Minimize reflectionCollapse of structureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMedicineAcoustic energy
A collapsible ultrasonic reflector incorporates a gas-filled reflector balloon, a liquid-filled structural balloon an ultrasonic transducer disposed within the structural balloon. Acoustic energy emitted by the transducer is reflected by a highly reflective interface between the balloons. In a cardiac ablation procedure, the ultrasonic energy is focused into an annular focal region to ablate cardiac tissue extending in an annular path along the wall. Devices for stabilizing the balloon structure and for facilitating collapse and withdrawal of the balloon structure are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +1
Focused ultrasound system with adaptive anatomical aperture shaping
ActiveUS20060058671A1Reducing ultrasound energyUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesSonificationTransducer
A method of treating tissue within a body includes directing an ultrasound transducer having a plurality of transducer elements towards target body tissue, and delivering ultrasound energy towards the target tissue from the transducer elements such that an energy intensity at the target tissue is at or above a prescribed treatment level, while an energy intensity at tissue to be protected in the ultrasound energy path of the transducer elements is at or below a prescribed safety level.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
Method and apparatus for treatment of adipose tissue
ActiveUS20070239075A1Small sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySubcutaneous adipose tissueRadiology
The invention provides methods and apparatuses for the treatment of adipose tissue. The methods comprise application of ultrasound energy to a region of adipose tissue, and the apparatuses comprise at least one source of ultrasound energy configured to direct ultrasound energy through a skin surface into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. In one embodiment, a pressure gradient is created in the region generating relative movement between fat cell constituents having different densities. In another embodiment, a protrusion of skin and underlying adipose tissue containing is formed and ultrasound energy is radiated into the adipose tissue in the protrusion. In another embodiment, an RF electric field is generated inside a region of adipose tissue together with the ultrasound energy.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Method and apparatus for treatment of adipose tissue
ActiveUS8133191B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySubcutaneous adipose tissueSkin surface
The invention provides methods and apparatuses for the treatment of adipose tissue. The methods comprise application of ultrasound energy to a region of adipose tissue, and the apparatuses comprise at least one source of ultrasound energy configured to direct ultrasound energy through a skin surface into the subcutaneous adipose tissue. In one embodiment, a pressure gradient is created in the region generating relative movement between fat cell constituents having different densities. In another embodiment, a protrusion of skin and underlying adipose tissue containing is formed and ultrasound energy is radiated into the adipose tissue in the protrusion. In another embodiment, an RF electric field is generated inside a region of adipose tissue together with the ultrasound energy.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
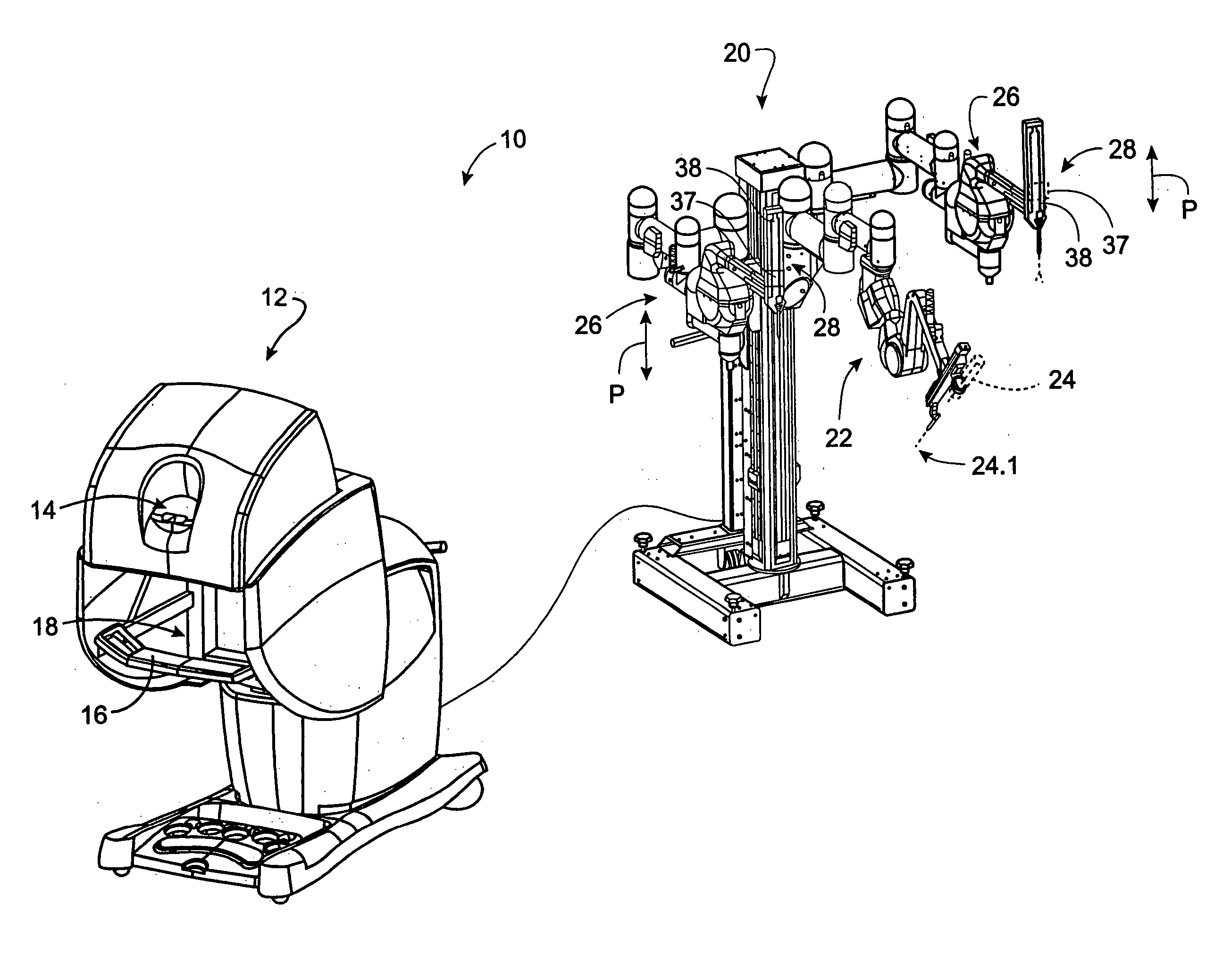
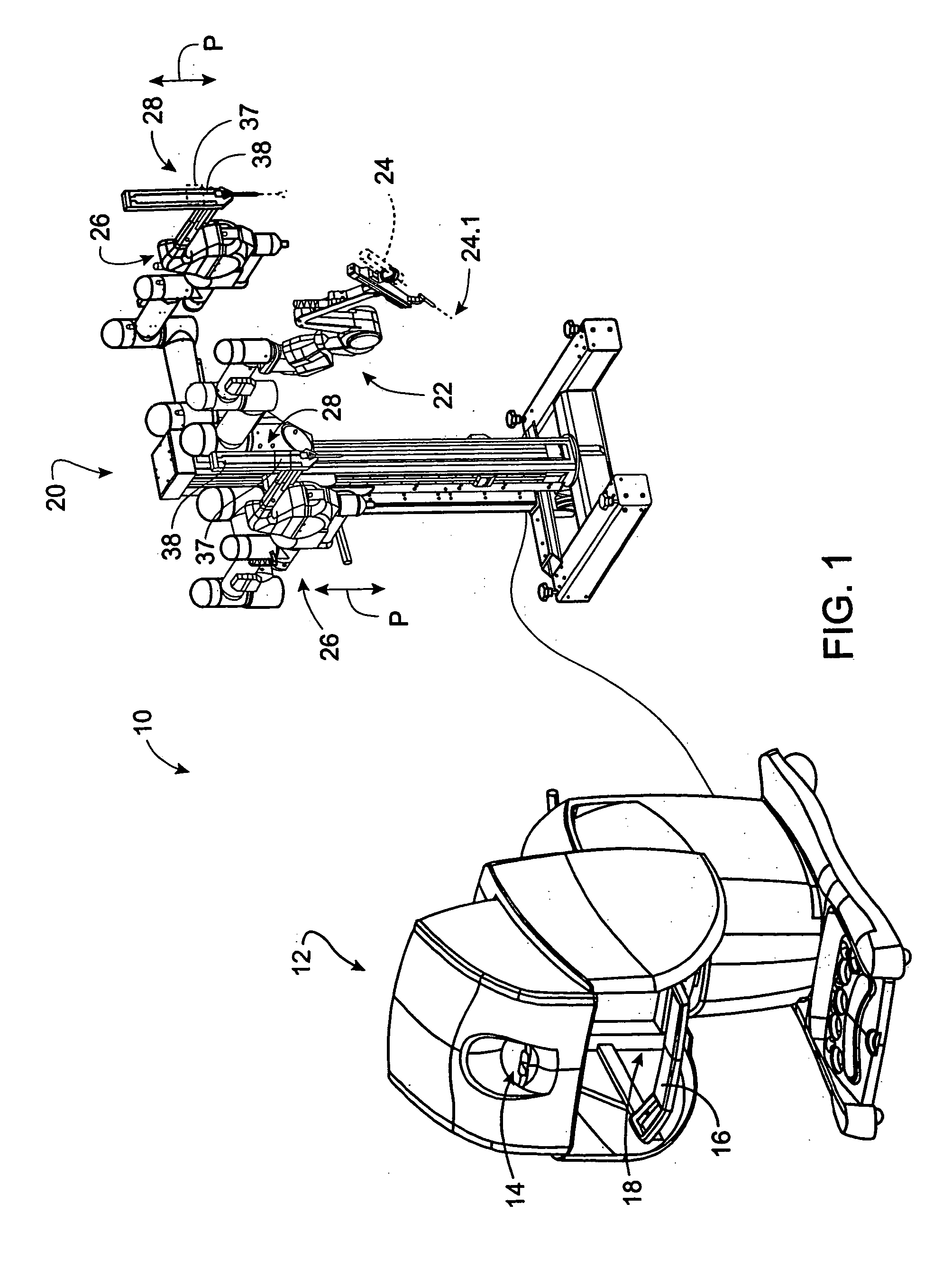
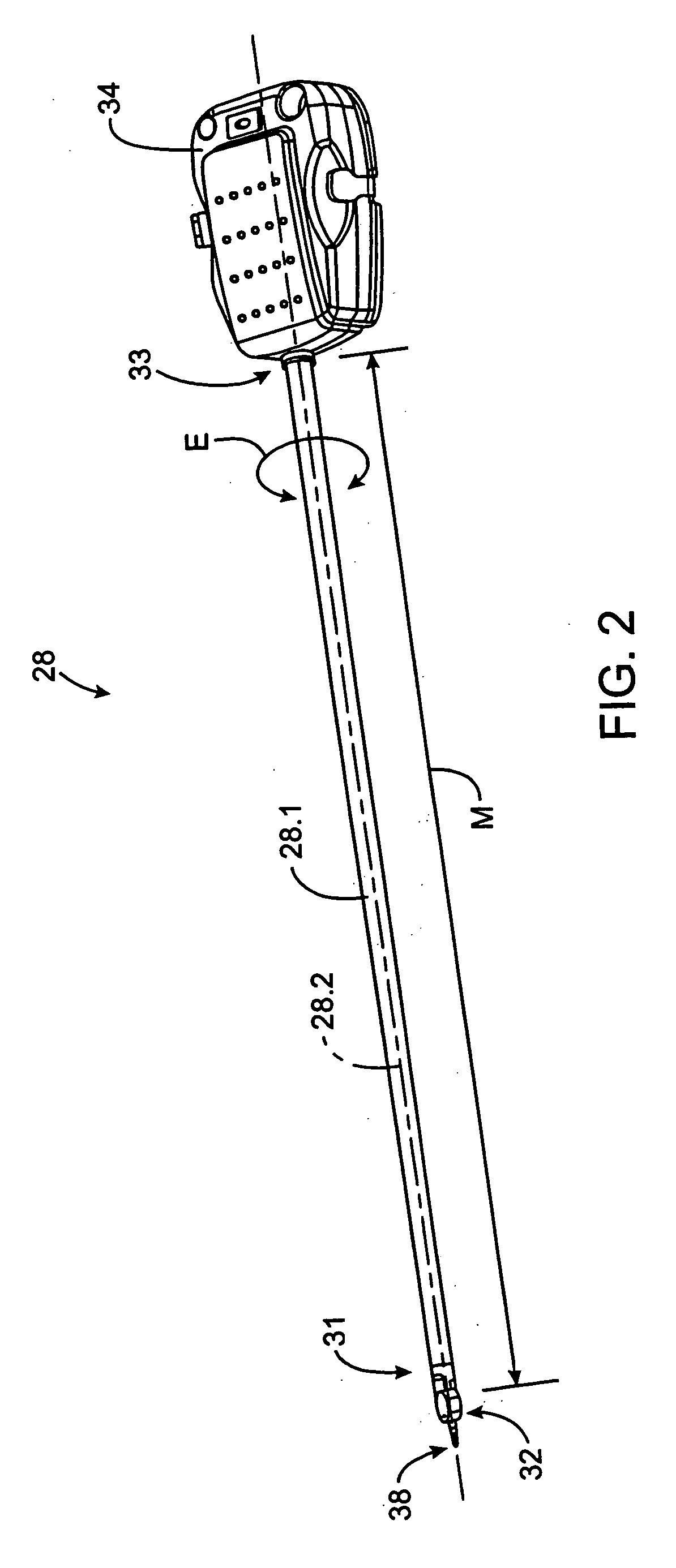
Robotic surgical tool with ultrasound cauterizing and cutting instrument
InactiveUS20050021018A1Enhancing robotic surgeryPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical siteActuator
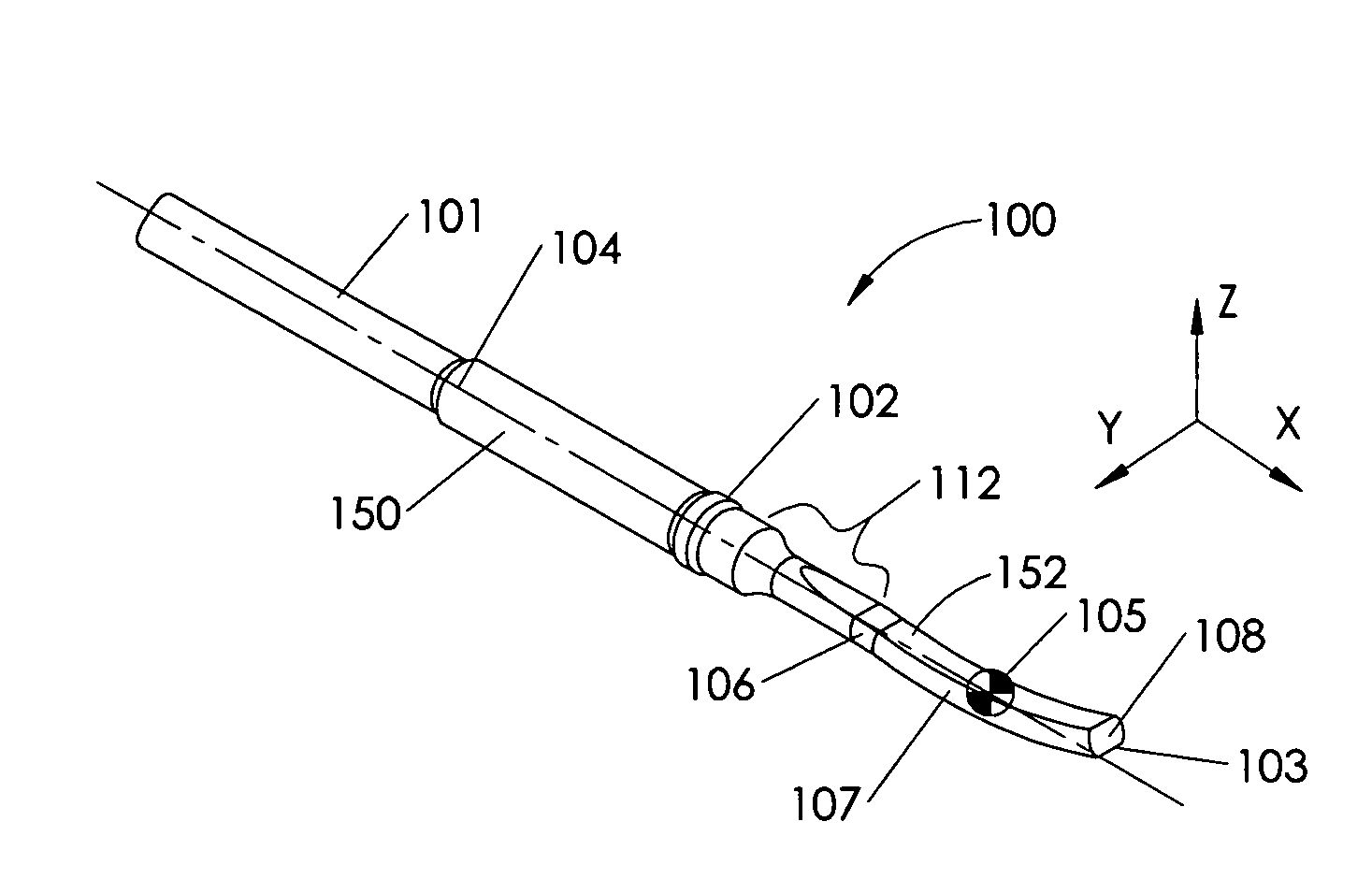
A surgical instrument for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes an elongate shaft with an ultrasound probe, an end effector at the distal end of the shaft, and a base at the proximal end of the shaft. The end effector includes an ultrasound probe tip and the surgical instrument is generally configured for convenient positioning of the probe tip within a surgical site by a robotic surgical system. Ultrasound energy delivered by the probe tip may be used to cut, cauterize, or achieve various other desired effects on tissue at a surgical site. In various embodiments, the end effector also includes a gripper, for gripping tissue in cooperation with the ultrasound probe tip. The base is generally configured to removably couple the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system and to transmit forces from the surgical system to the end effector, through the elongate shaft. A method for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes coupling the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system, positioning the probe tip in contact with tissue at a surgical site, and delivering ultrasound energy to the tissue.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
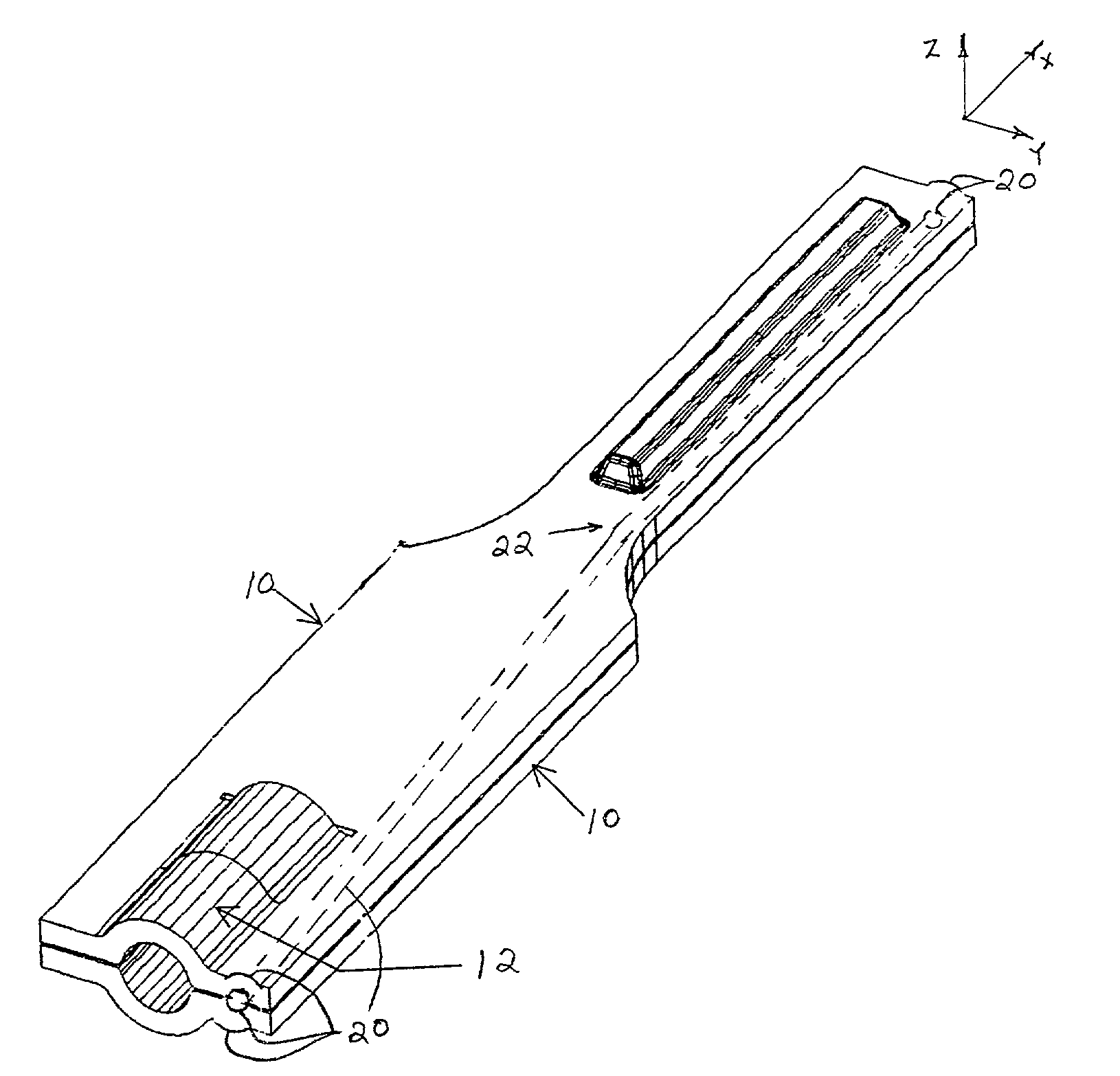
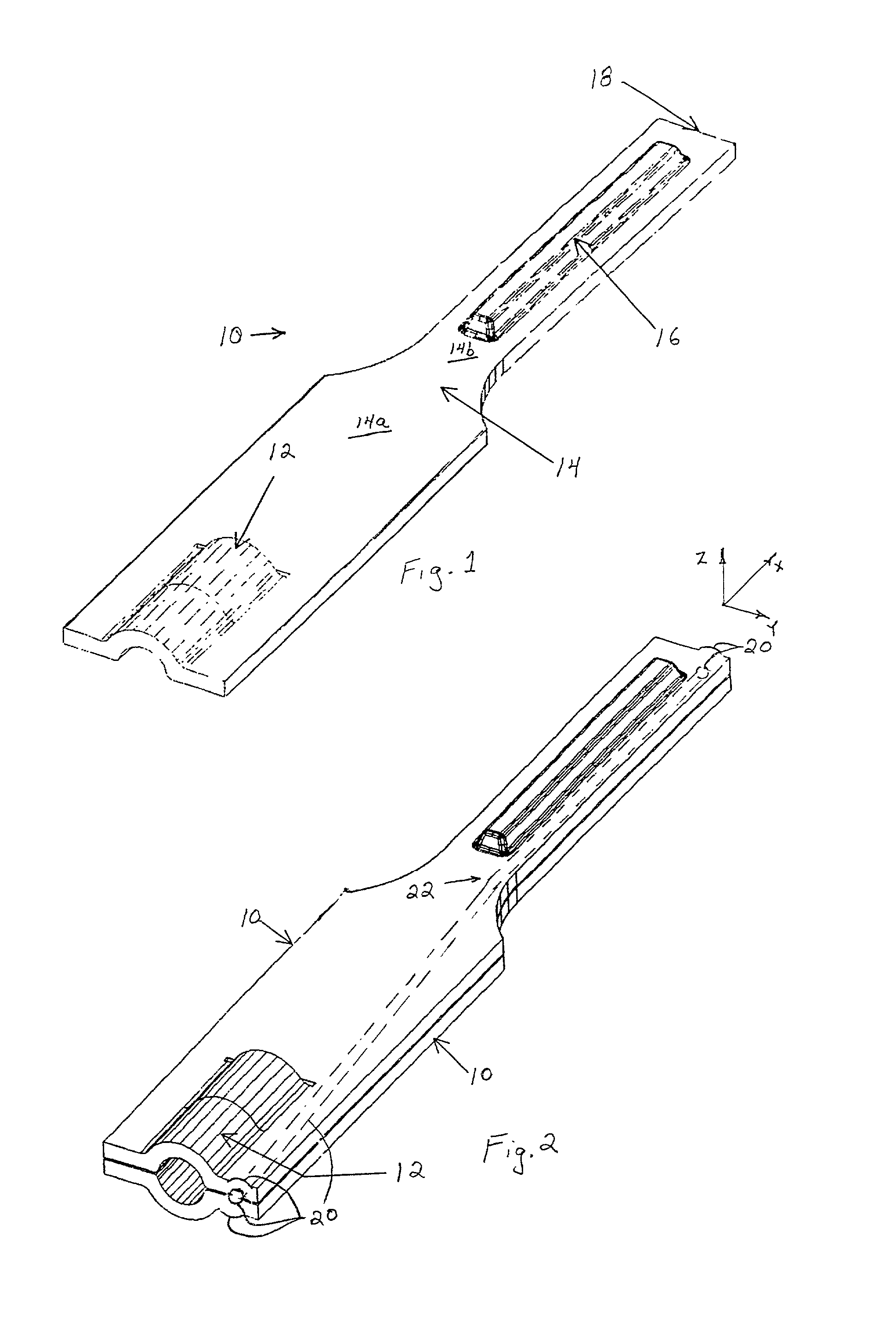
Laminated ultrasonic end effector
InactiveUS7530986B2Reduce manufacturing costReduce material wasteSurgical needlesTrocarEnergy transferAcoustic energy
A laminated ultrasonic waveguide and a method of fabrication thereof including stamping at least two pieces of sheet stock to form stamped parts of the laminated ultrasonic waveguide. The stamped parts are then laminated together to form a laminated ultrasonic waveguide for transferring ultrasonic acoustic energy along a longitudinal axis of the laminated ultrasonic waveguide. The laminated ultrasonic waveguide may be part of an ultrasonic surgical instrument having an active tip end-effector, which is placed in contact with tissue of a patient to couple ultrasonic energy transferred along the laminated ultrasonic waveguide to the tissue. The stamped pieces of sheet stock can also be stamped to form one or more channels extending along the length of the laminated ultrasonic waveguide. The laminated ultrasonic waveguide can also define a connector at a proximal end thereof to transfer ultrasonic energy into the laminated ultrasonic waveguide. In different embodiments, the laminated ultrasonic waveguide comprises first and second (and third or more) stamped pieces of sheet stock that are laminated together.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Apparatus and methods for the selective removal of tissue using combinations of ultrasonic energy and cryogenic energy
InactiveUS7572268B2Improve cooling effectAvoid stickingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound deviceUltrasound energy
An ultrasonic apparatus and method is provided for the selective and targeted removal of unwanted tissues. The apparatus and methods may utilize combinations of ultrasonic and cryogenic energy for the selective removal tissue. The apparatus generates and delivers to the tissue cryogenic and ultrasonic energy either in combination or in sequence, provides resize ablation of unwanted tissue parts, and may be used on various body tissues including internal organs.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
Method and apparatus for treating vascular obstructions
InactiveUS20080097251A1Avoid damageImprove efficiencyUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesVascular obstructionTransducer
Method and device for treating vascular obstruction using ultrasonic energy in combination with cryogenic energy and / or an expandable member is disclosed. Ultrasound energy is delivered from a specially designed ultrasound transducer that is inserted in a blood vessel. Ultrasound energy can be delivered in conjunction with cryogenic energy. Ultrasound energy can also be delivered in conjunction with an expandable member such as expandable tubing, a hinged transducer, or a balloon. Ultrasound energy can also be delivered in conjunction with both cryogenic energy and an expandable member. The use of ultrasound energy in combination with cryogenic energy and / or an expandable member can treat a vascular obstruction.
Owner:BABAEV EILAZ
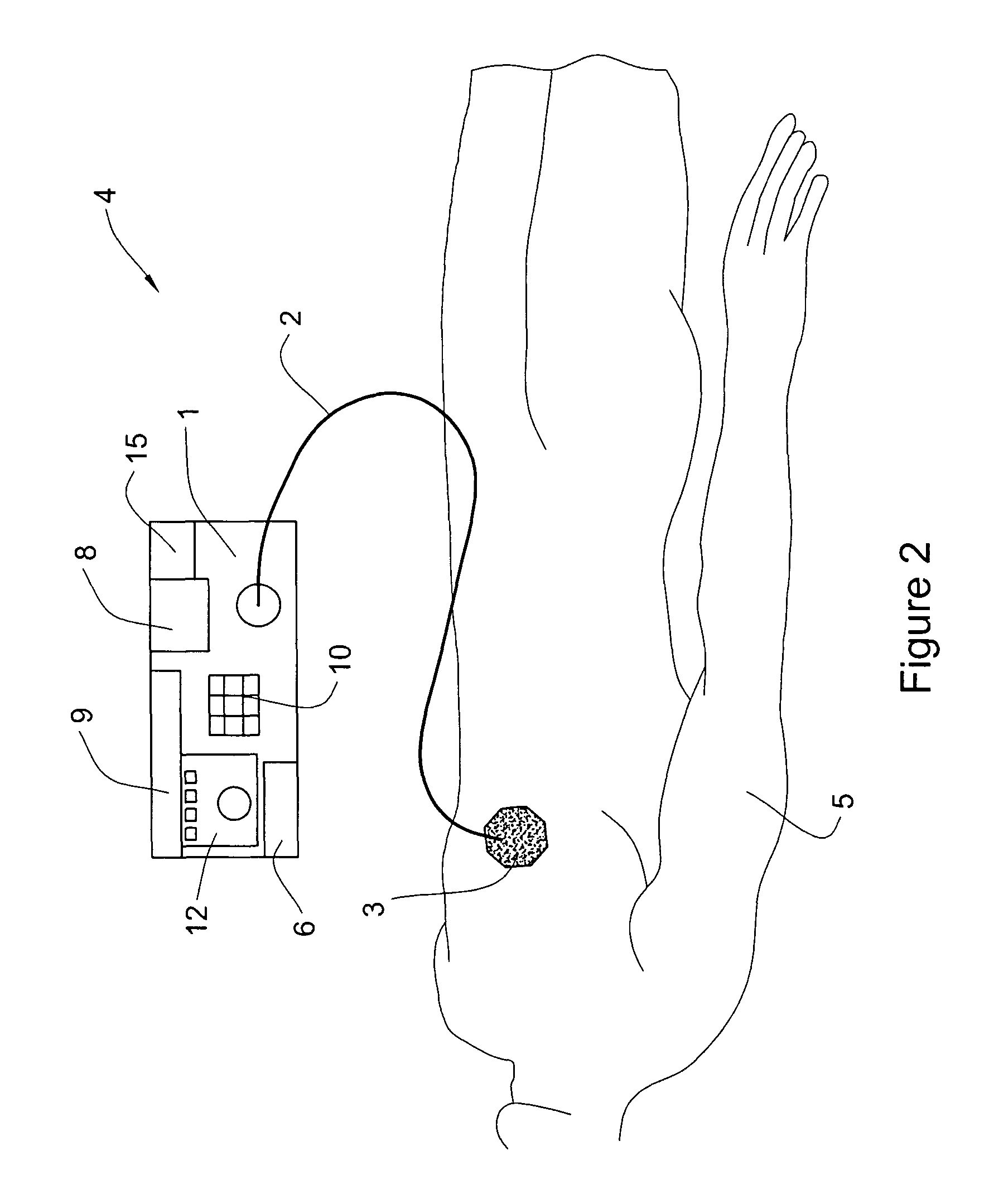
Portable ultrasound device for the treatment of wounds
InactiveUS7878991B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocus ultrasoundMedicine
Device and methods for the treatment of wounds using ultrasound energy are disclosed. The portable wound treatment device may deliver ultrasound energy to a wound through direct contact with the ultrasound tip and / or through a liquid coupling medium. Several ultrasound tips specially designed to concentrate and focus ultrasound energy onto a wound are also disclosed. The ultrasound tip may also possess an abrasive peripheral boundary to aid in debriding the wound and / or removing necrotic tissue. The disclosed invention may have multiple beneficial effects in treating a wound such as sterilizing a wound, reducing external bleeding, and / or providing pain relief.
Owner:BACOUSTICS LLC
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS20020193784A1Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentApoptosisGene product
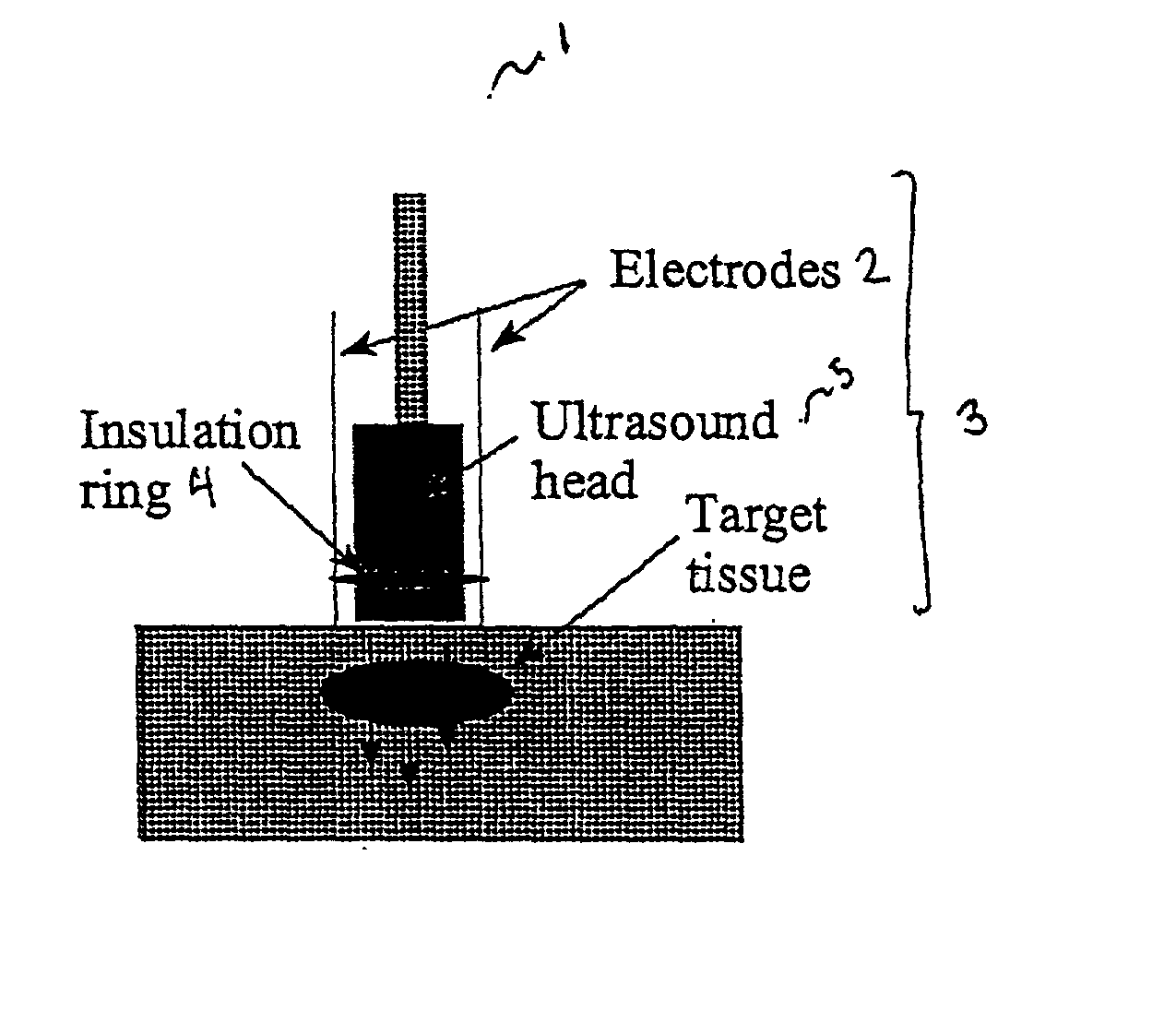
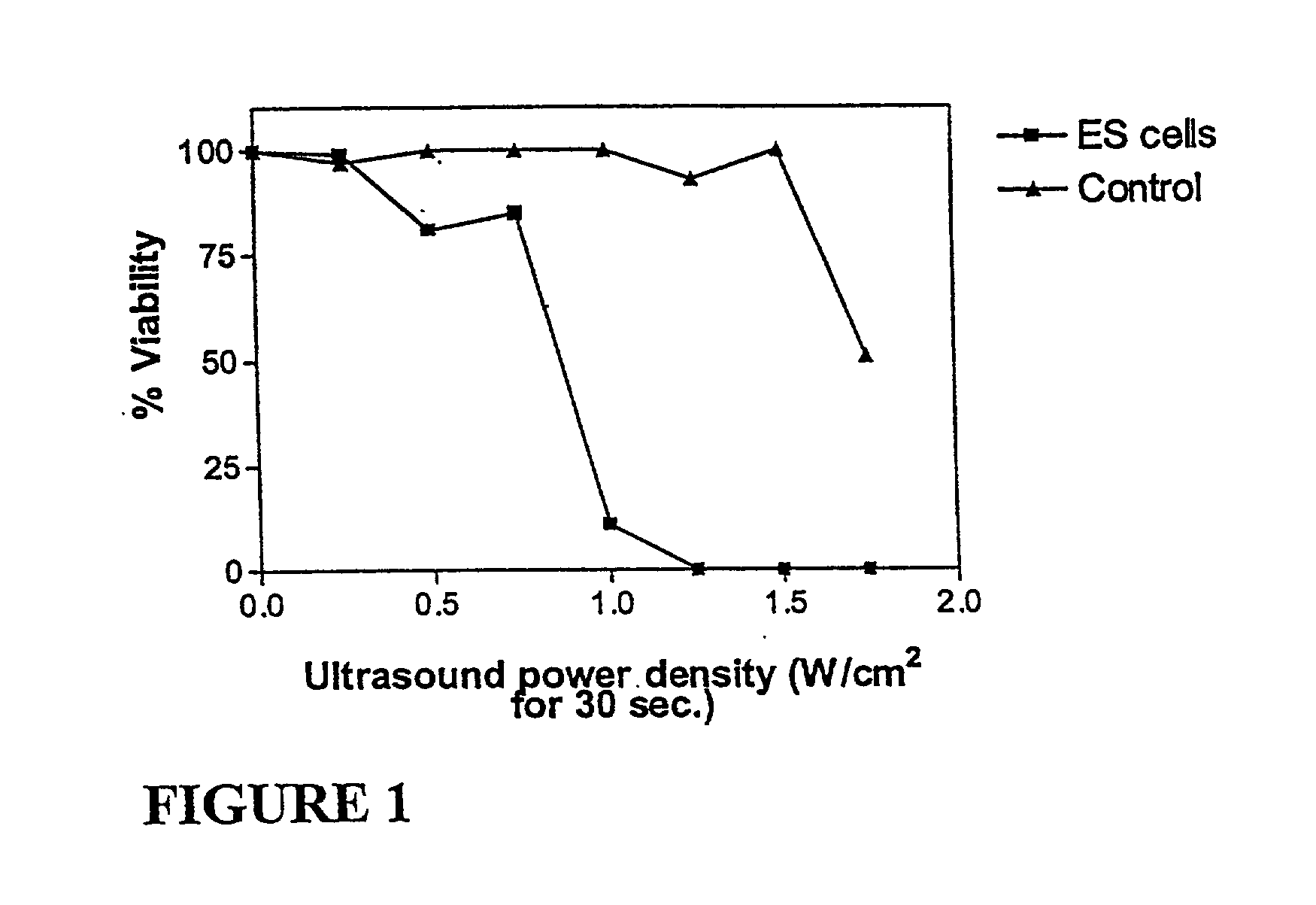
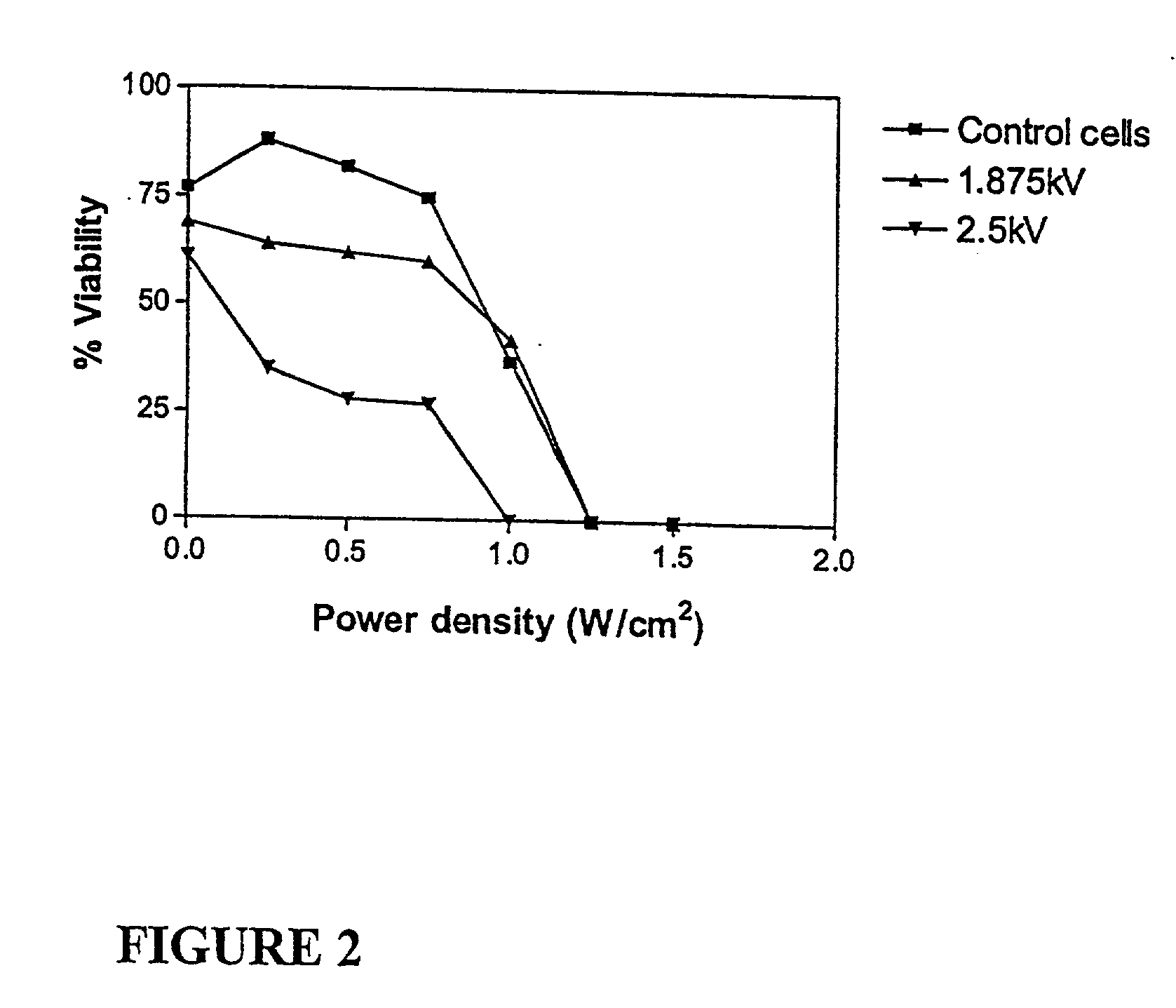
The invention provides a method of sensitising target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitised (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimising harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitise cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
Devices and Methods for Treatment of Skin Conditions
InactiveUS20080139974A1Removing fine wrinkleClean skinUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyWrinkle skinHand held
Devices and methods for the treatment of skin conditions and lesions are disclosed herein. A compact hand held device that can be safely used by those suffering from skin conditions, such as acne, warts, cold blisters, blemished skin, or fine wrinkles. The devices employ the application of ultrasound energy and heat for the treatment of skin conditions and lesions. Typically, the peak temperatures employed are about 40° C. to about 70° C. by the devices, are achieved in less than about 20 second, and maintained for less than about 40 second. Ultrasound absorption and thermal conduction transfers heat from the device to the skin and causes a biological response that accelerates acne clearing, treats blemished skin, itching, or fine wrinkles. The total heat transferred is low enough to prevent burns.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Balanced ultrasonic curved blade
InactiveUS20090270891A1Reduce axial torsionReduce lateral movementSurgeryEngineeringUltrasound energy
Methods and devices that provide reduced transverse motion in a curved ultrasonic blade and / or ultrasonic surgical instrument with functional asymmetries. An ultrasonic blade in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes a curved functional portion of an ultrasonic blade, wherein the center of mass of the curved functional portion lies on the mid-line of a waveguide delivering ultrasonic energy to the blade. Balancing in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, using placement of the center of mass of the curved portion of the blade appropriately, provides blade balance in a proximal portion of the blade, without reduction of mass and inherent stress increase proximal to the end-effector.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Methods and devices for providing acoustic hemostasis
InactiveUS6083159AEasy to aimReduce releaseChiropractic devicesEye exercisersInternal bleedingRadiology
Methods and apparatus for the remote coagulation of blood using high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) are provided. A remote hemostasis method comprises identifying a site of internal bleeding and focusing therapeutic ultrasound energy on the site, the energy being focused through an intervening tissue. An apparatus for producing remote hemostasis comprises a focused therapeutic ultrasound radiating surface and a sensor for identifying a site of internal bleeding, with a registration means coupled to the radiating surface and the sensor to bring a focal target and the bleeding site into alignment. The sensor generally comprises a Doppler imaging display. Hemostasis enhancing agents may be introduced to the site for actuation by the ultrasound energy.
Owner:THS INT
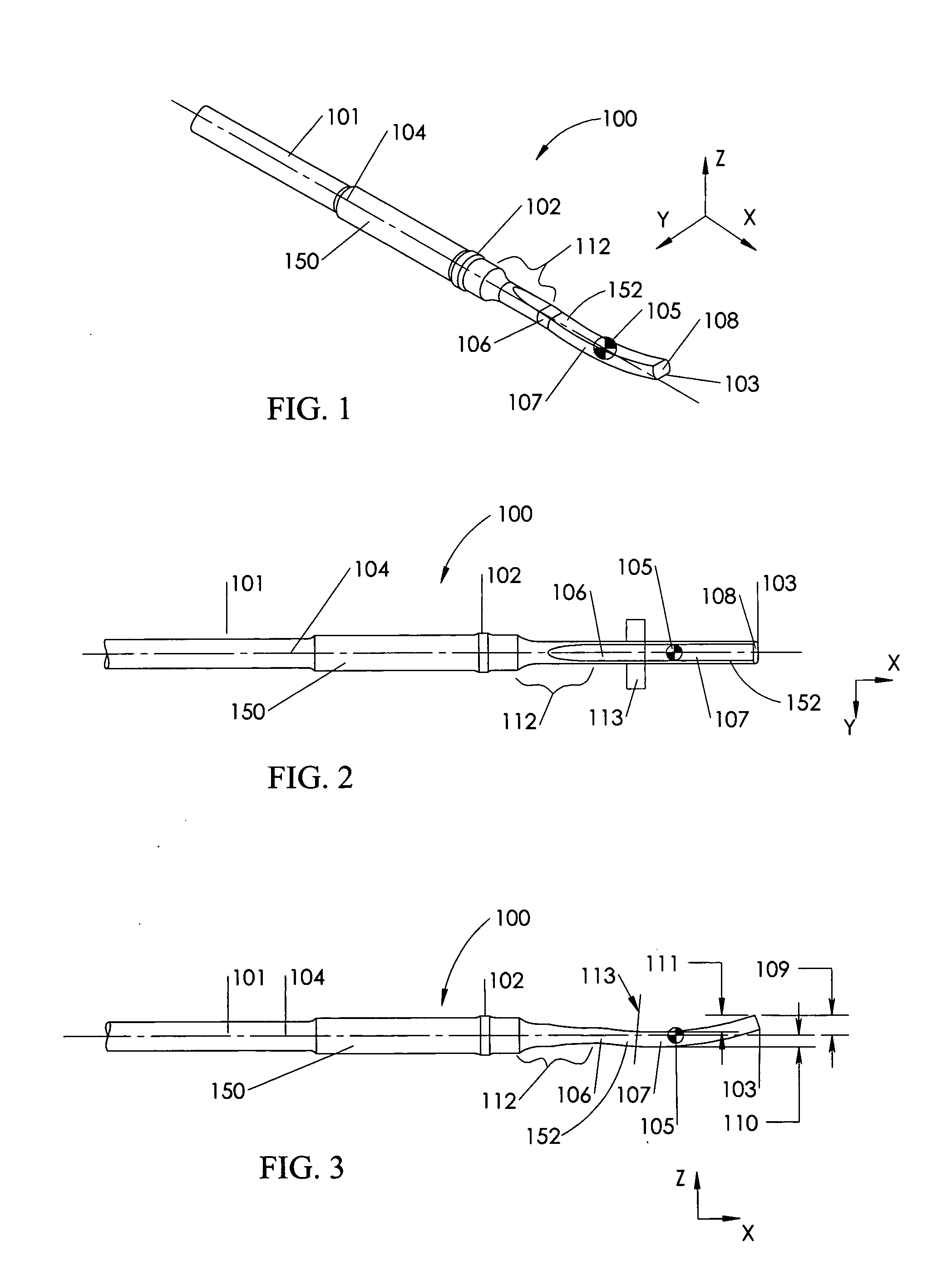
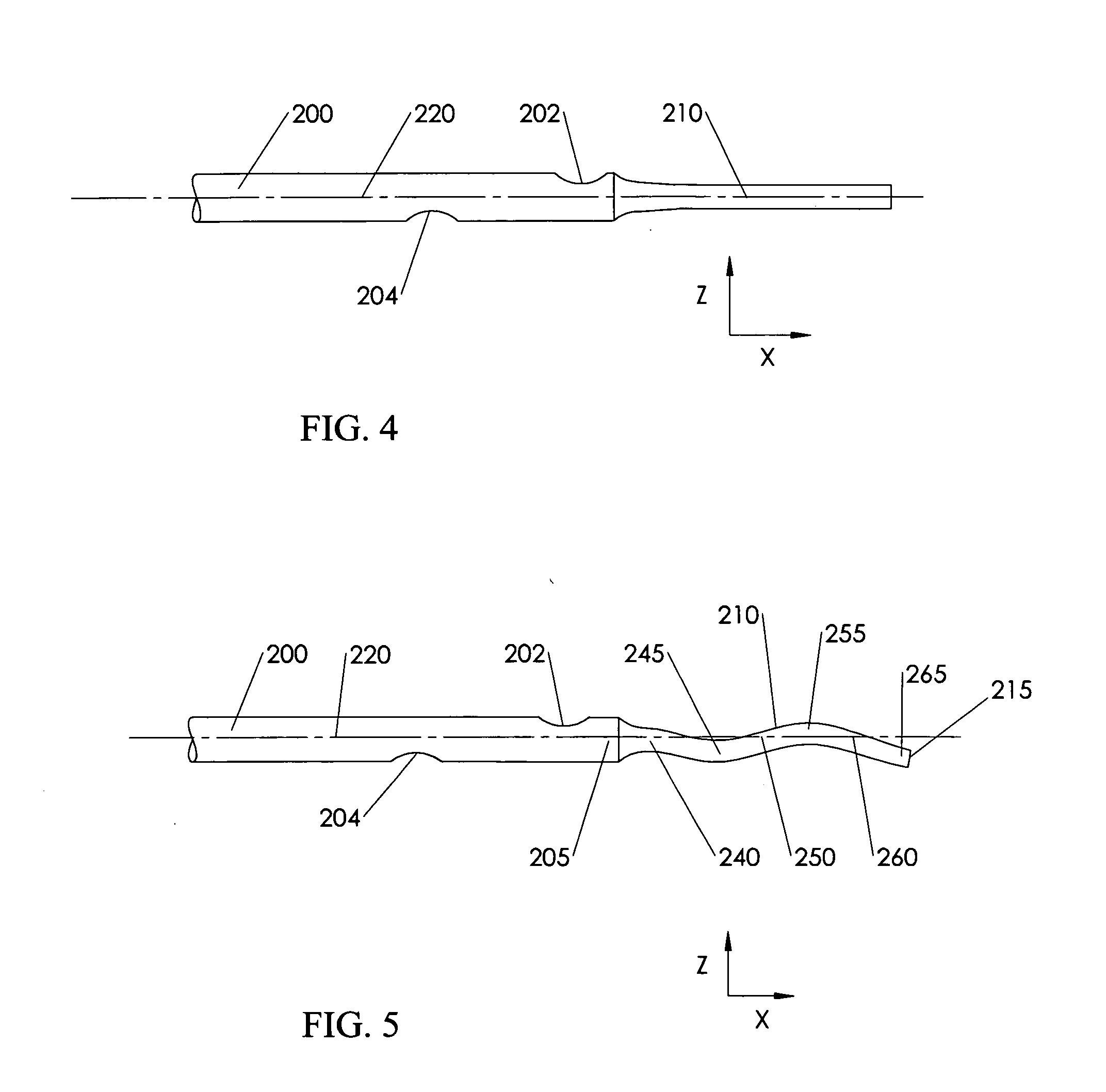
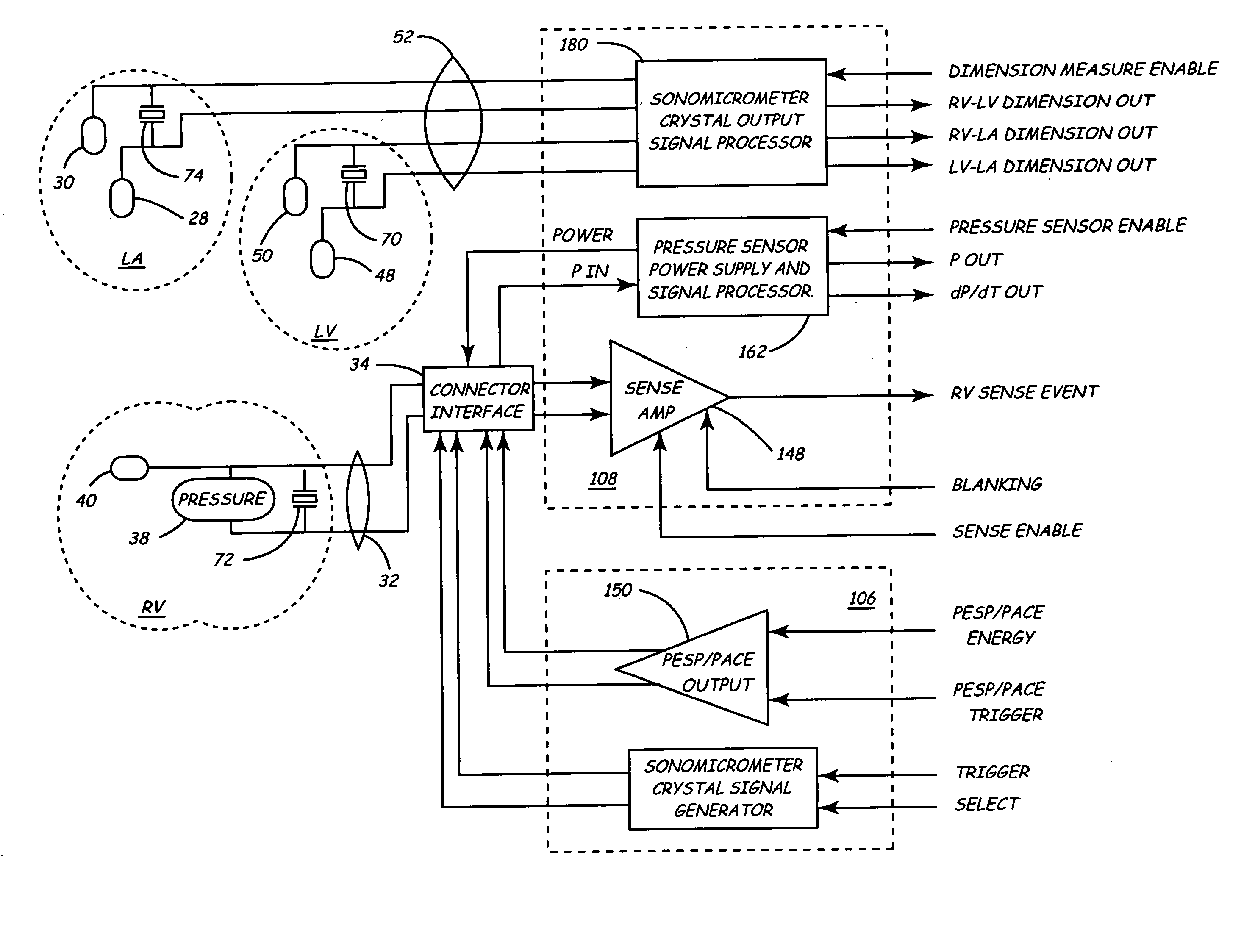
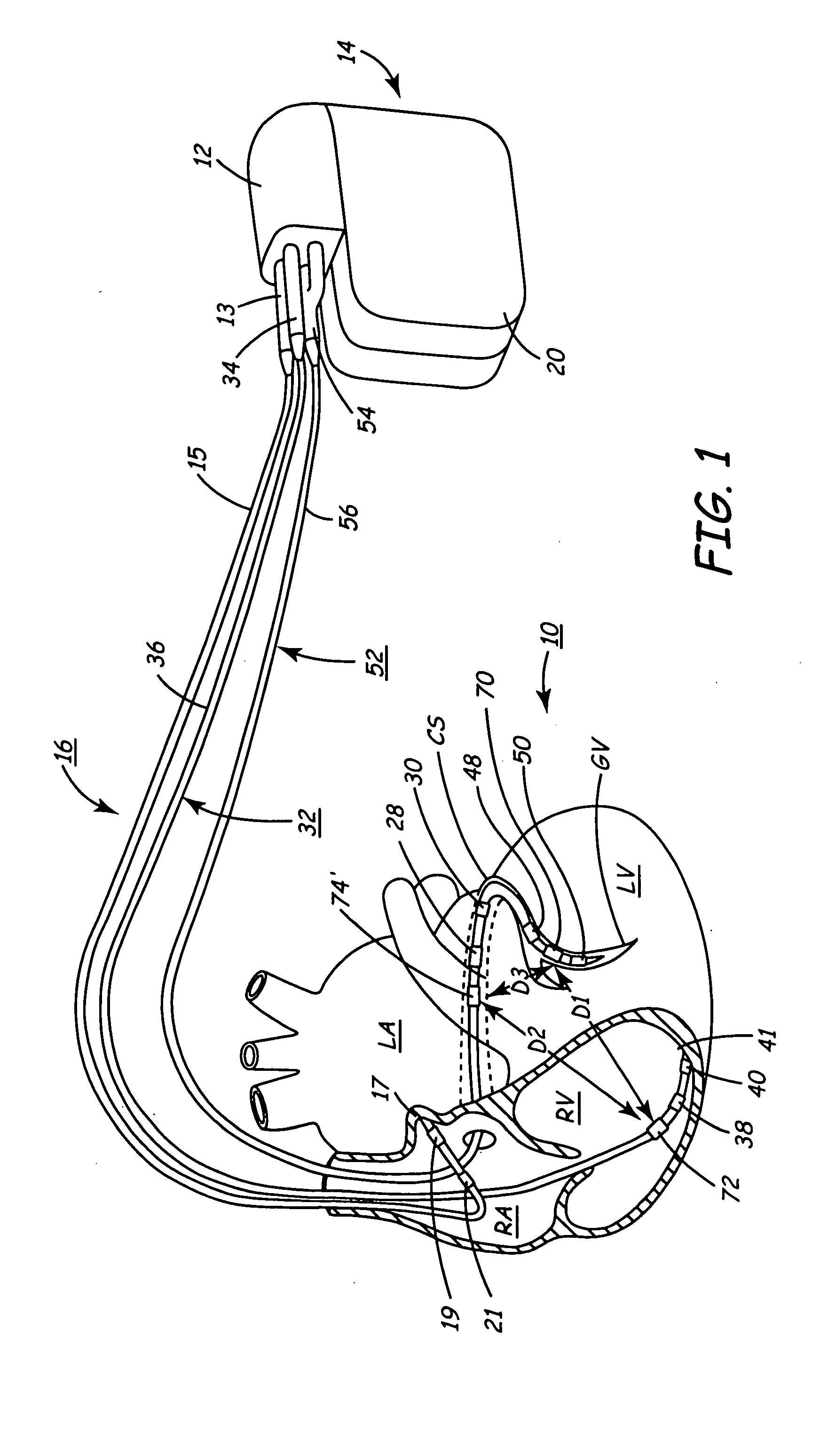
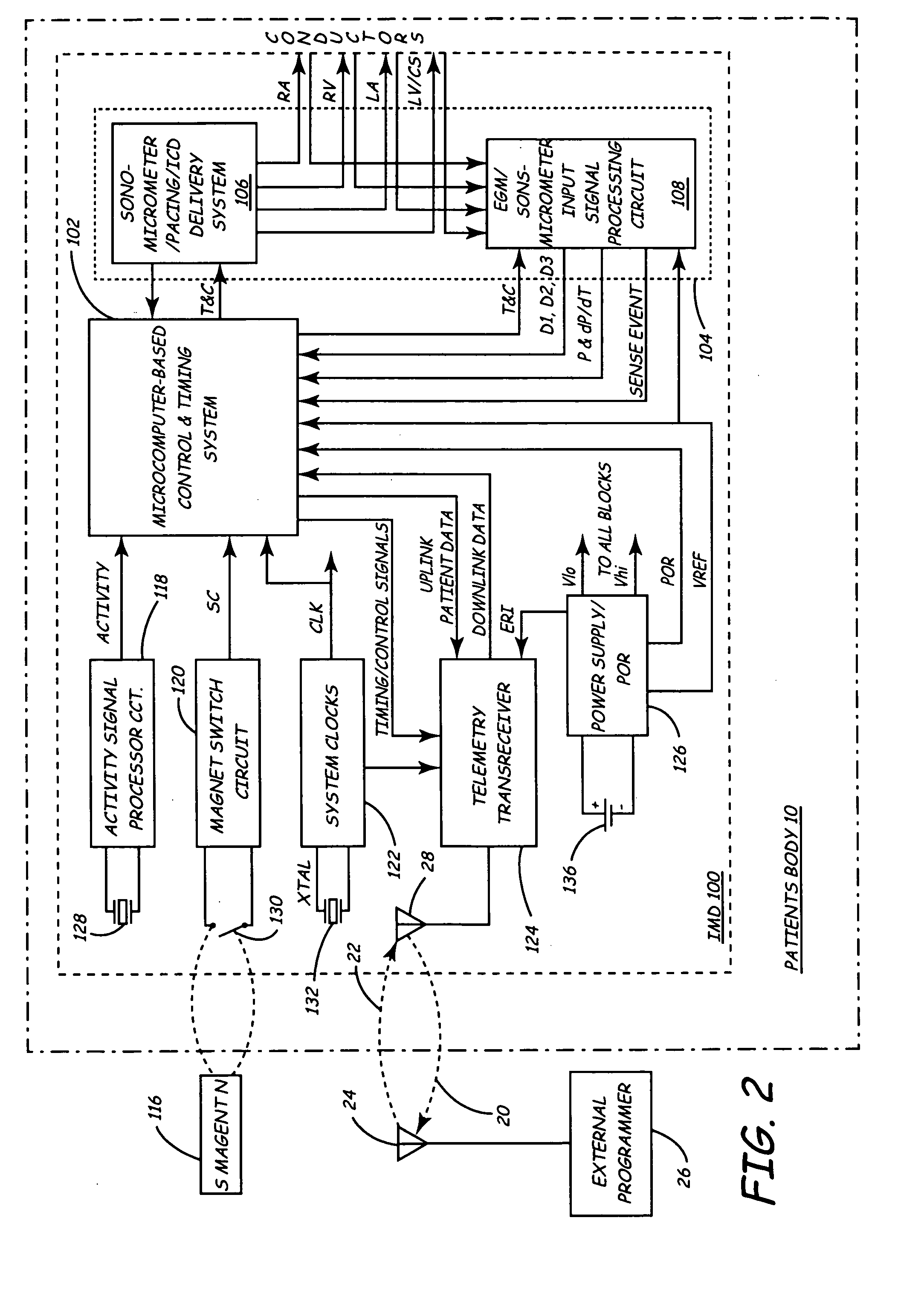
Implantable medical device for monitoring cardiac blood pressure and chamber dimension
InactiveUS20050027323A1Maximize cardiac outputConvenient timeCatheterHeart stimulatorsSonificationHeart chamber
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) for monitoring signs of acute or chronic cardiac heart failure by measuring cardiac blood pressure and mechanical dimensions of the heart and providing multi-chamber pacing optimized as a function of measured blood pressure and dimensions are disclosed. The dimension sensor or sensors comprise at least a first sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal mounted to a first lead body implanted into or in relation to one heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound transmitter when a drive signal is applied to it and at least one second sonomicrometer crystal mounted to a second lead body implanted into or in relation to a second heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound receiver. The ultrasound receiver converts impinging ultrasound energy transmitted from the ultrasound transmitter through blood and heart tissue into an electrical signal. The time delay between the generation of the transmitted ultrasound signal and the reception of the ultrasound wave varies as a function of distance between the ultrasound transmitter and receiver which in turn varies with contraction and expansion of a heart chamber between the first and second sonomicrometer crystals. One or more additional sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal can be mounted to additional lead bodies such that the distances between the three or more sonomicrometer crystals can be determined. In each case, the sonomicrometer crystals are distributed about a heart chamber such that the distance between the separated ultrasound transmitter and receiver crystal pairs changes with contraction and relaxation of the heart chamber walls.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Acoustic-optical therapeutical devices and methods
InactiveUS20050137656A1Effective and specific body therapyUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyMicrometerMedicine
Acoustic-optical therapy devices and methods for therapeutical purposes are disclosed in this invention. The devices provide a combination of ultrasound energy and optical pulsed energy exposed to human and animal body at frequencies of ultrasound and optical pulses within the range of 1 Hz to 1 GHz and at wavelengths from 0.2 micrometer to 20 micrometers. Both ultrasound energy and pulsed light radiation are delivered in effective combinations to maximize the therapy. Because of different interaction nature of ultrasound and light with body, the new invented devices will provide much more effective and specific body treatment.
Owner:UNITED LAB & MFG
Method and system for noninvasive mastopexy
ActiveUS20060074314A1Avoid cavitationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound imagingMastopexy
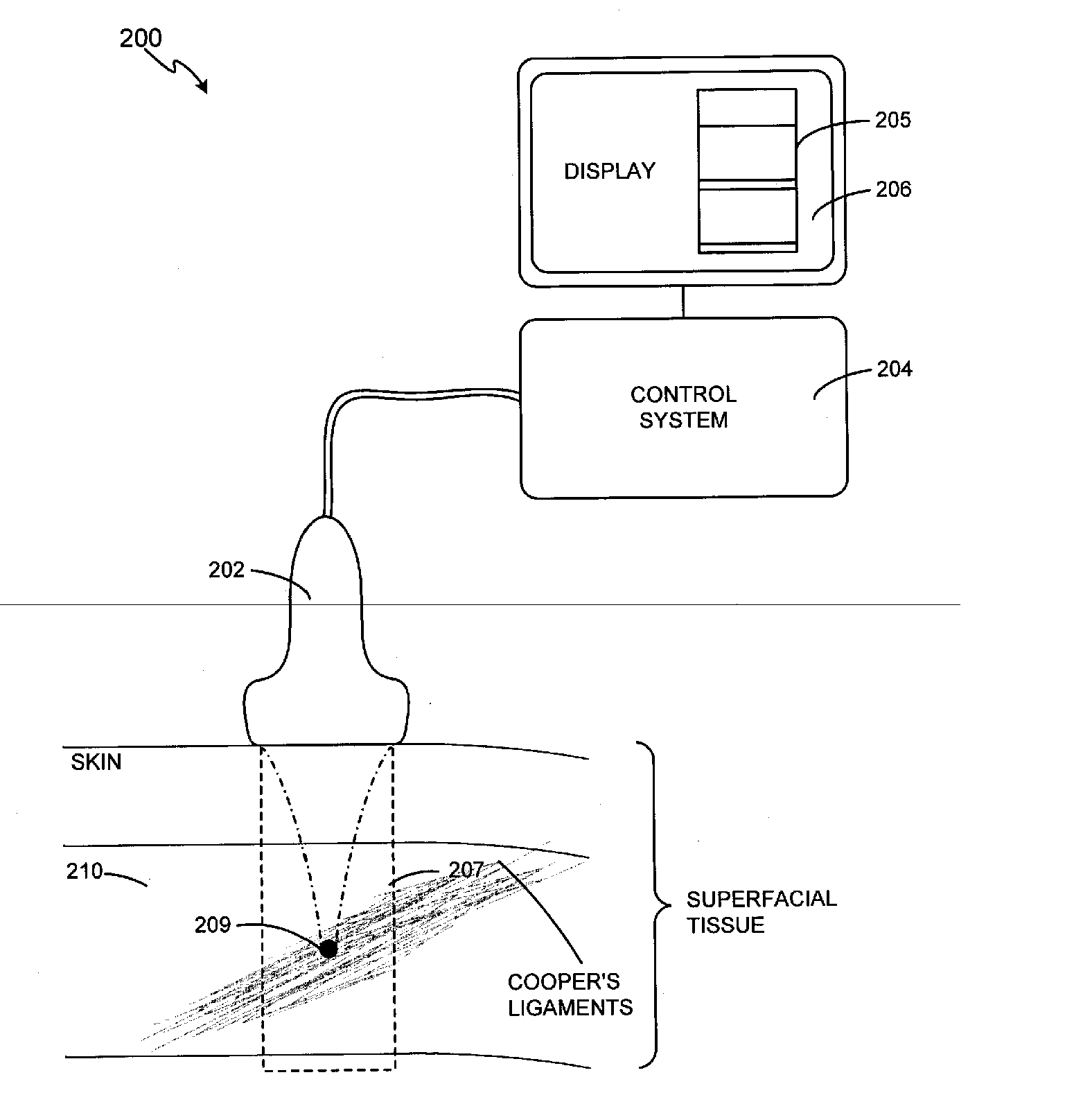
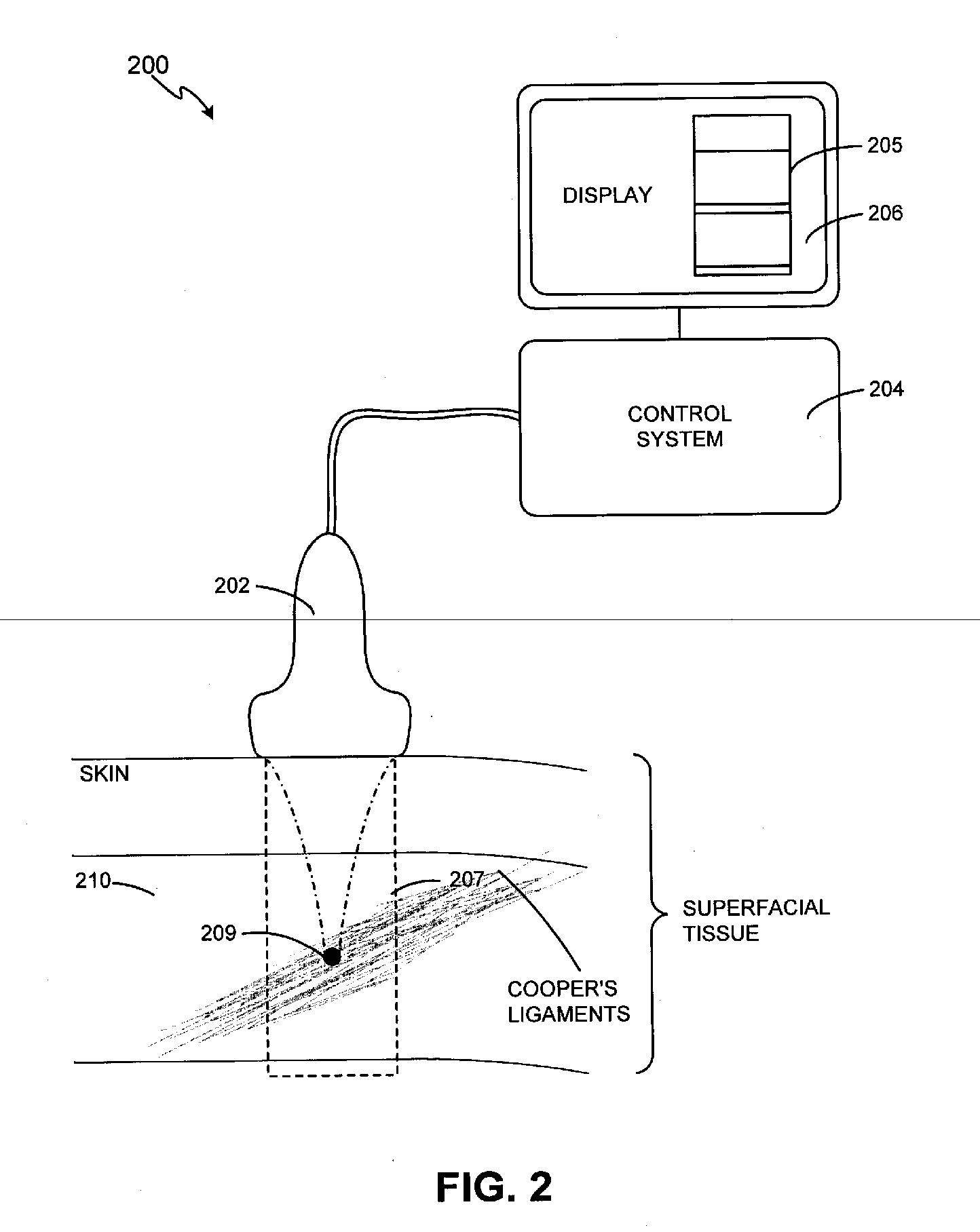
Methods and systems for noninvasive mastopexy through deep tissue tightening with ultrasound are provided. An exemplary method and system comprise a therapeutic ultrasound system configured for providing ultrasound treatment to a deep tissue region, such as a region comprising muscular fascia and ligaments. In accordance with various exemplary embodiments, a therapeutic ultrasound system can be configured to achieve depth from 1 mm to 4 cm with a conformal selective deposition of ultrasound energy without damaging an intervening tissue in the range of frequencies from 1 to 15 MHz. In addition, a therapeutic ultrasound can also be configured in combination with ultrasound imaging or imaging / monitoring capabilities, either separately configured with imaging, therapy and monitoring systems or any level of integration thereof.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com