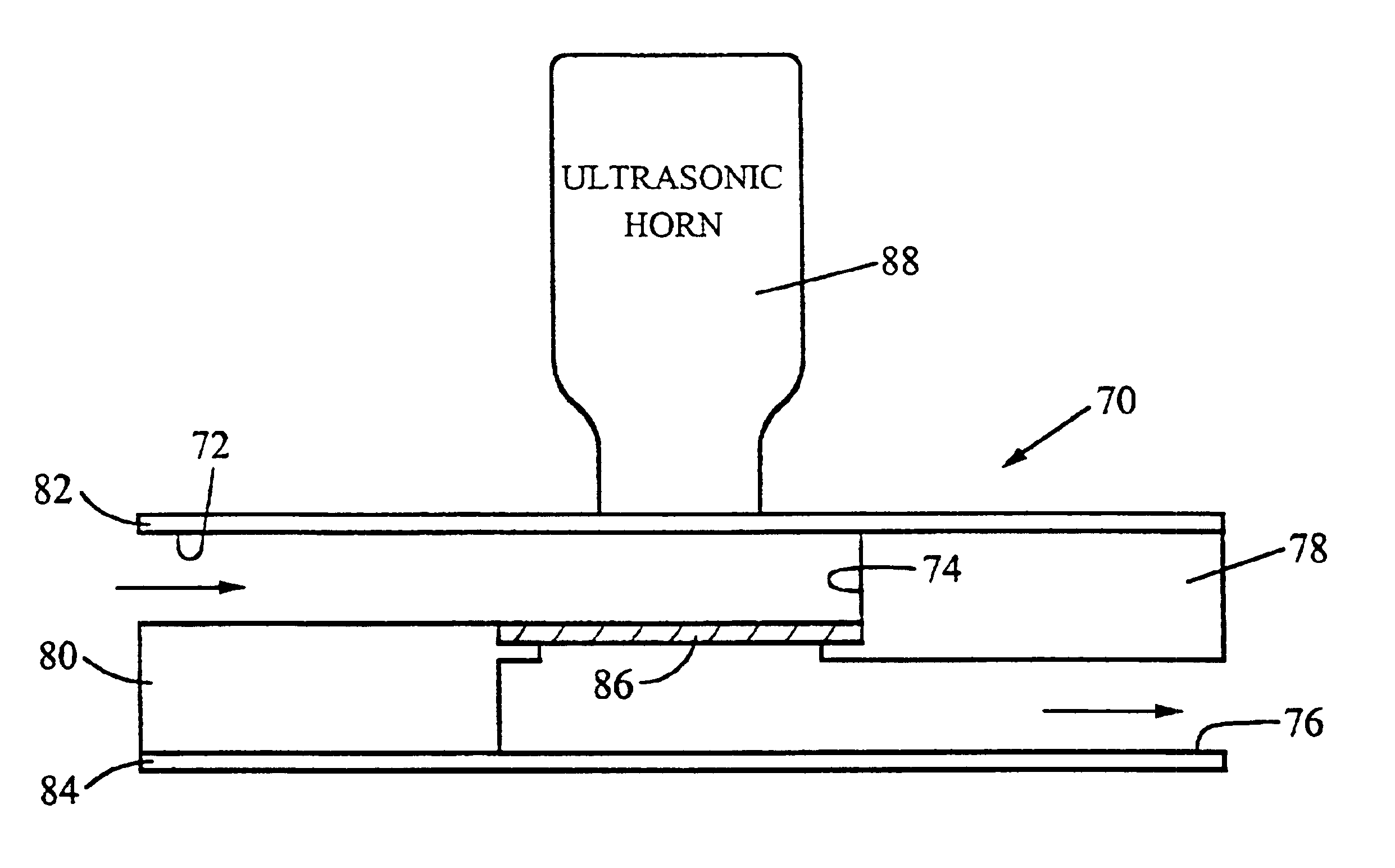
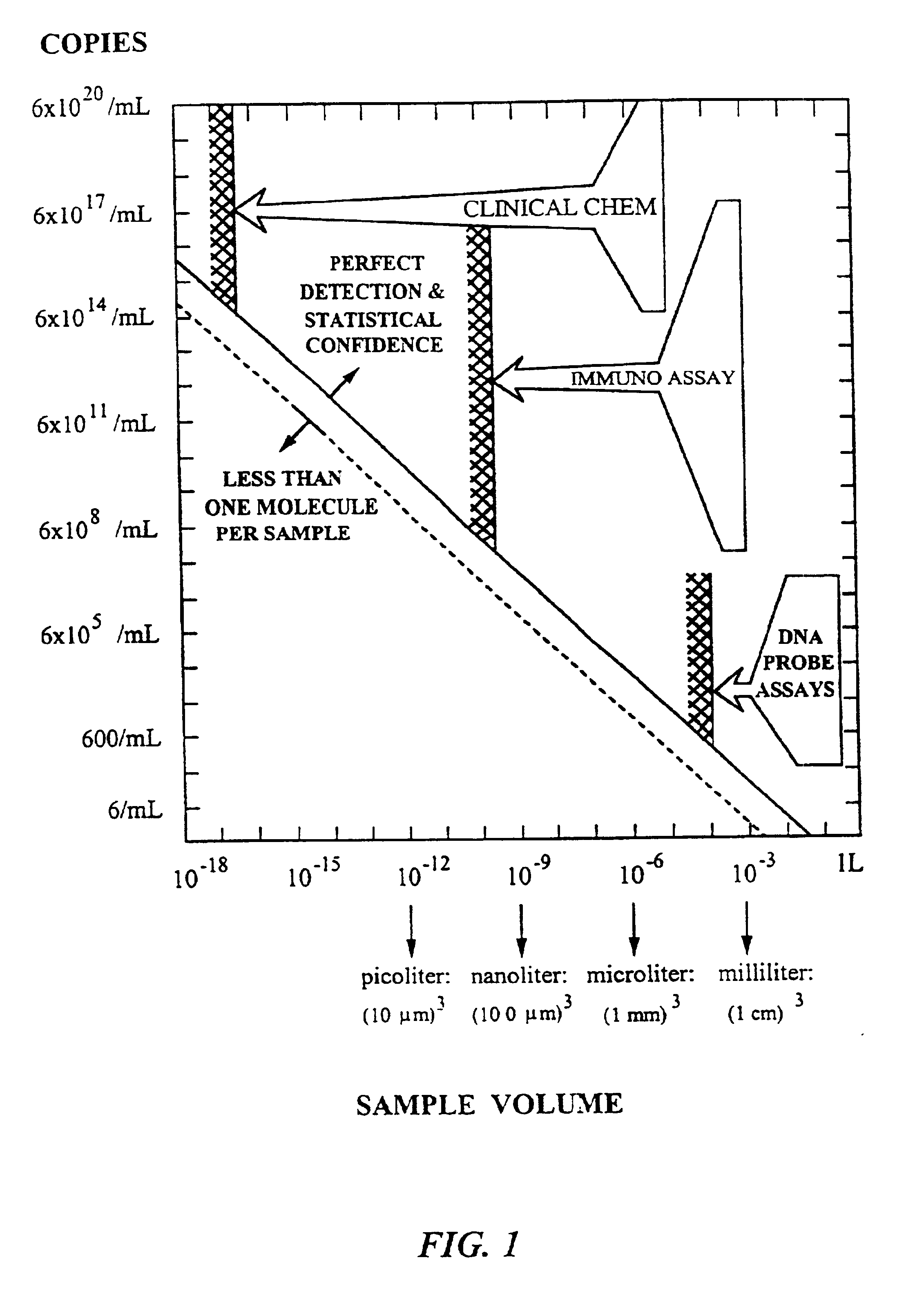
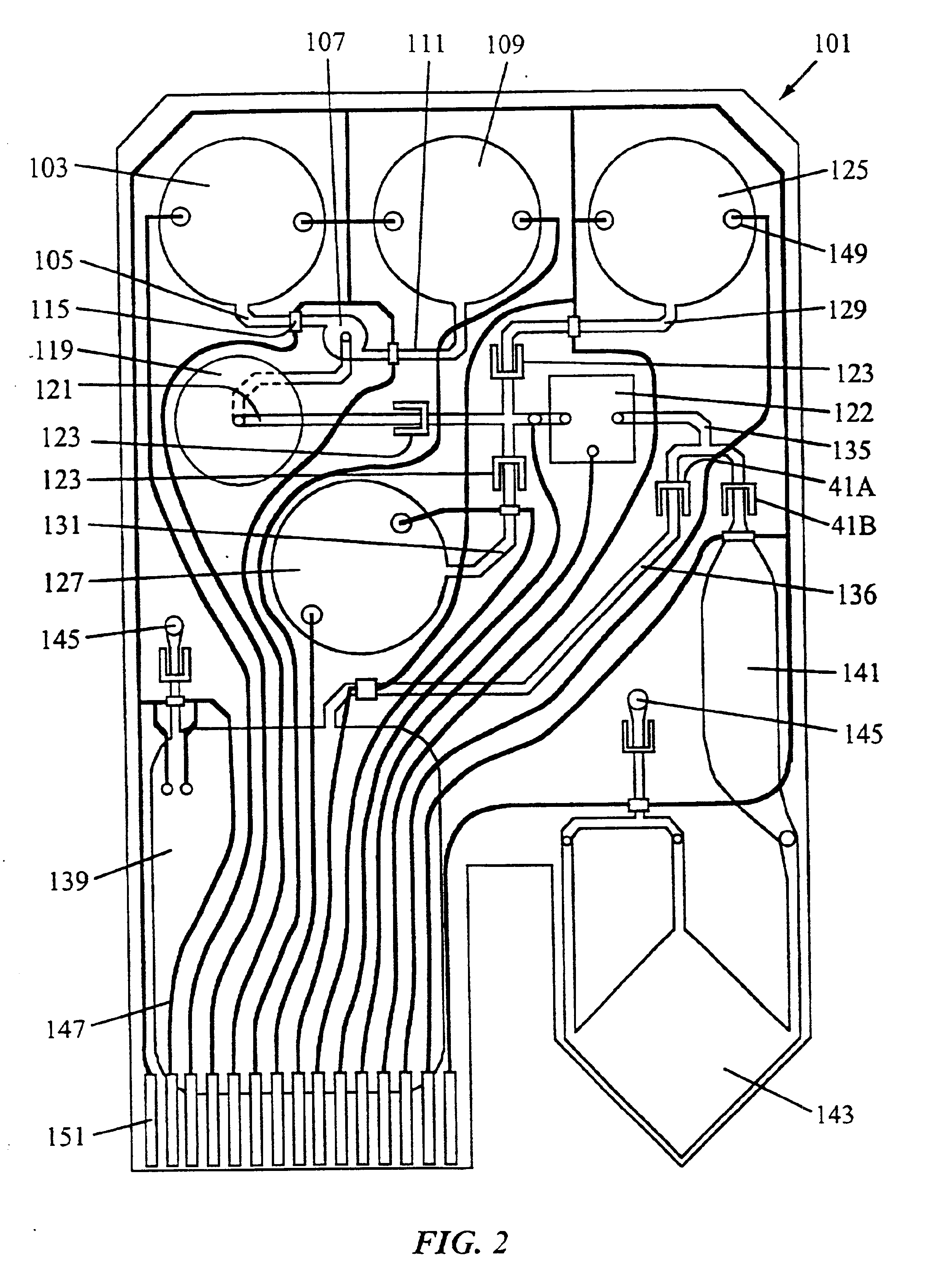
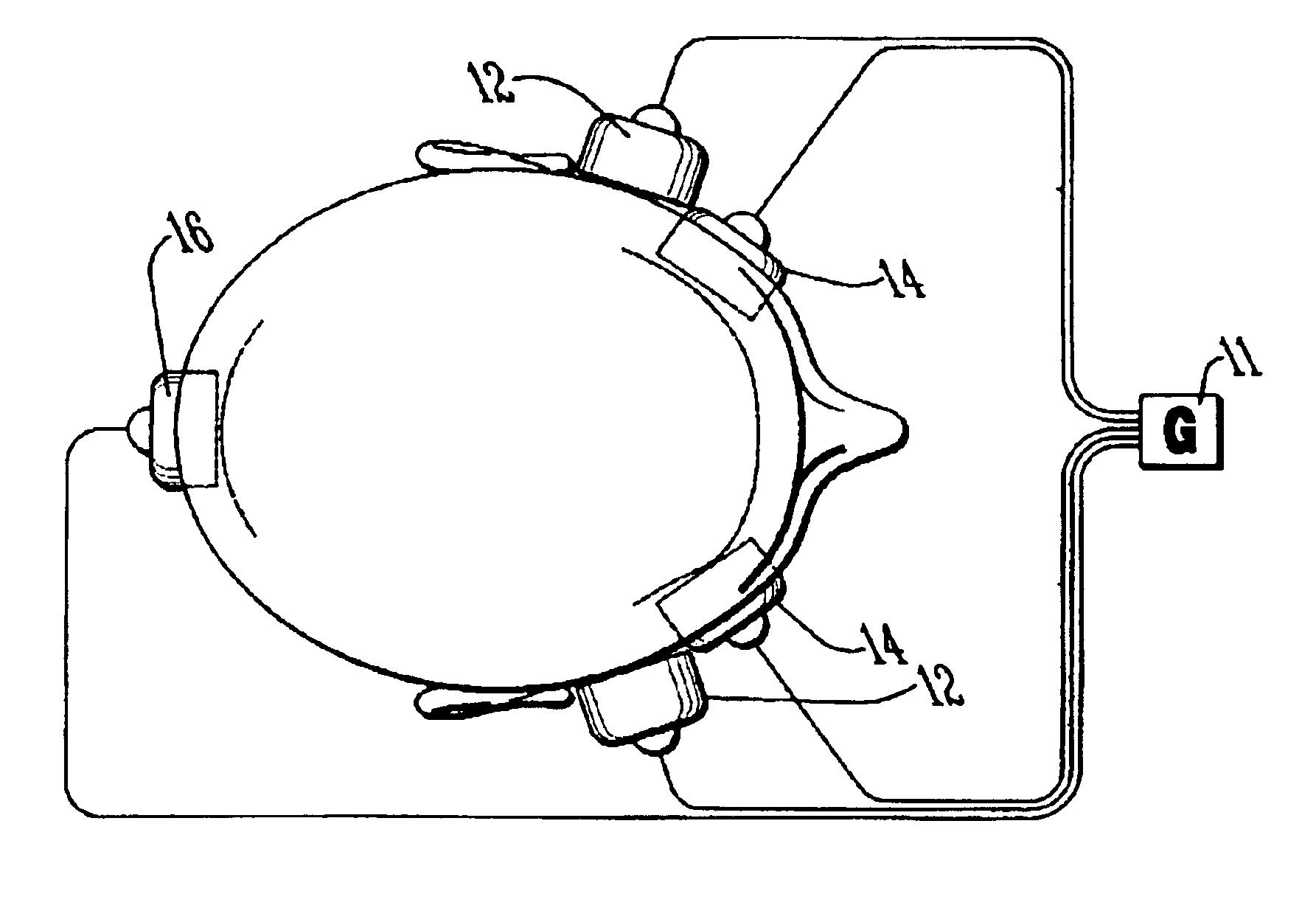
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2463 results about "Sonication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sonication is the act of applying sound energy to agitate particles in a sample, for various purposes such as the extraction of multiple compounds from plants, microalgae and seaweeds. Ultrasonic frequencies (>20 kHz) are usually used, leading to the process also being known as ultrasonication or ultra-sonication.
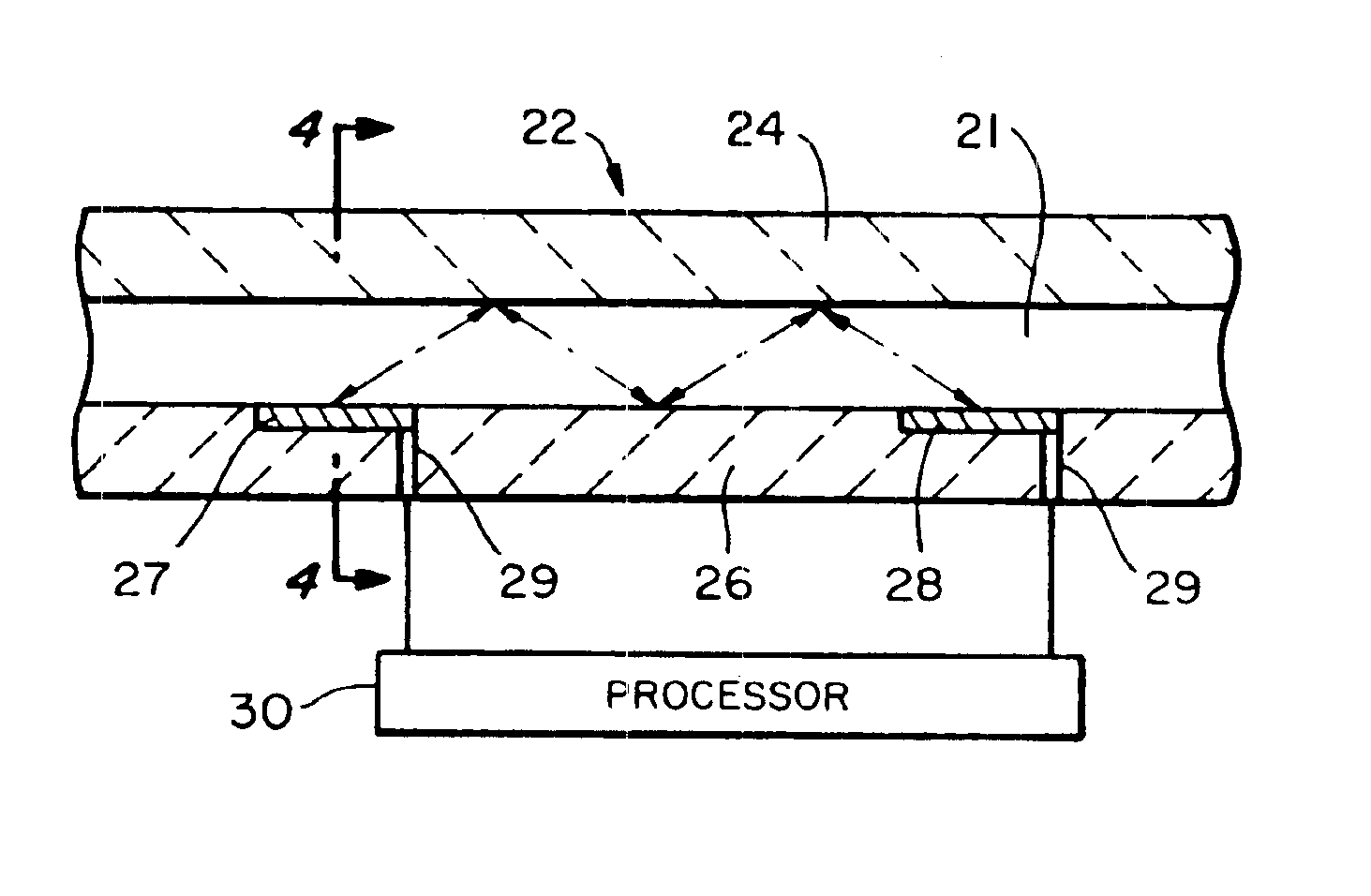
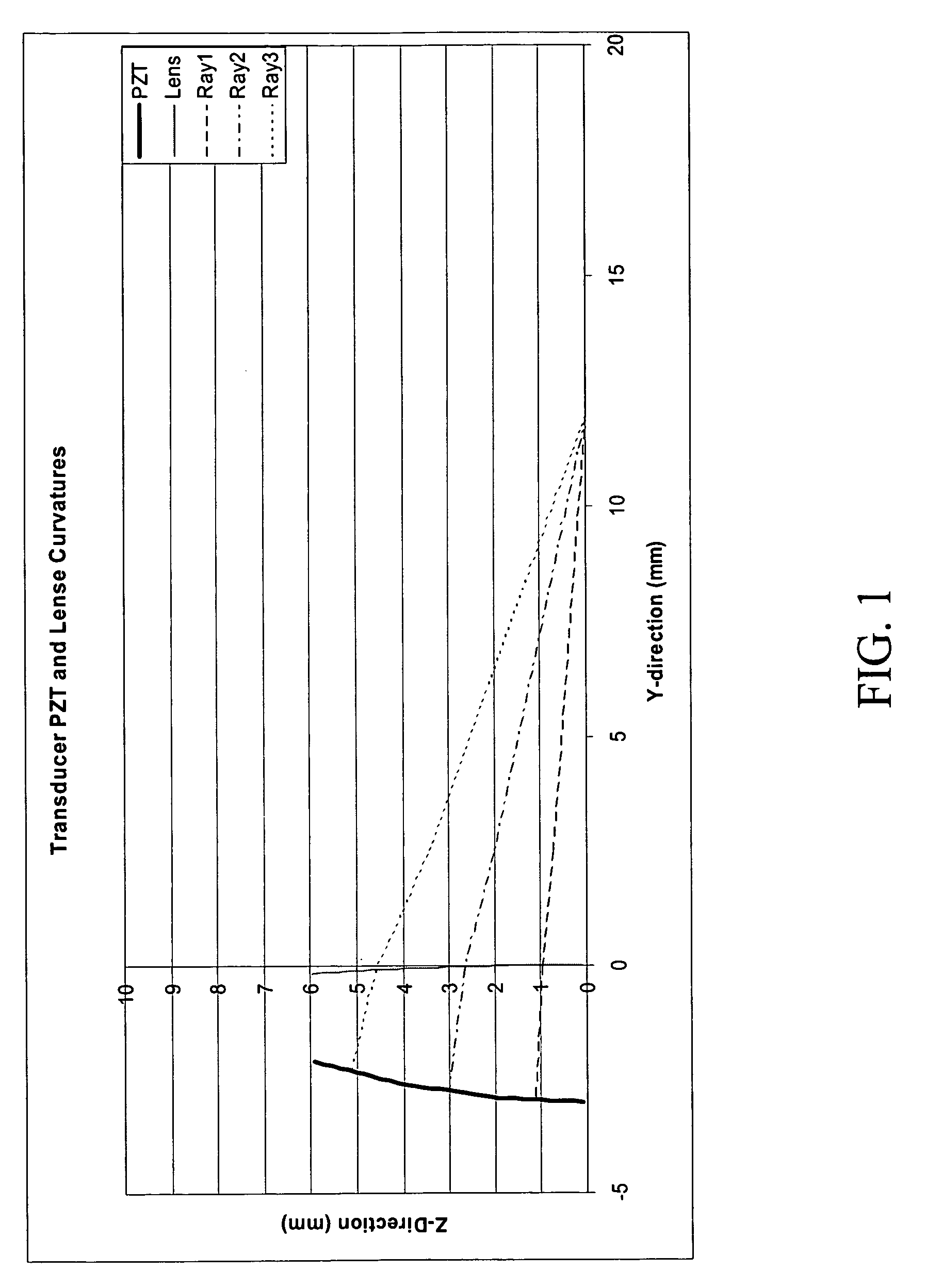
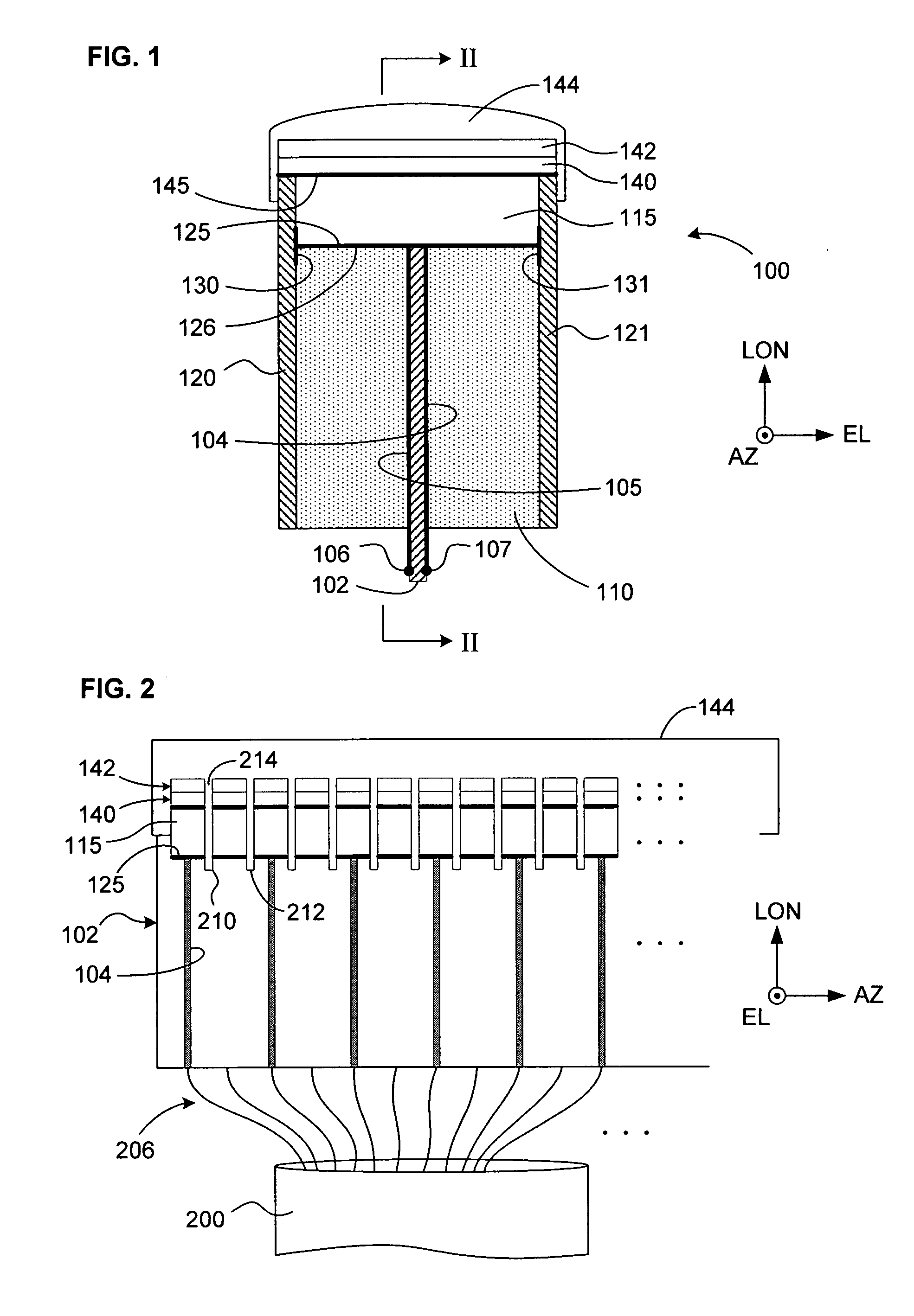
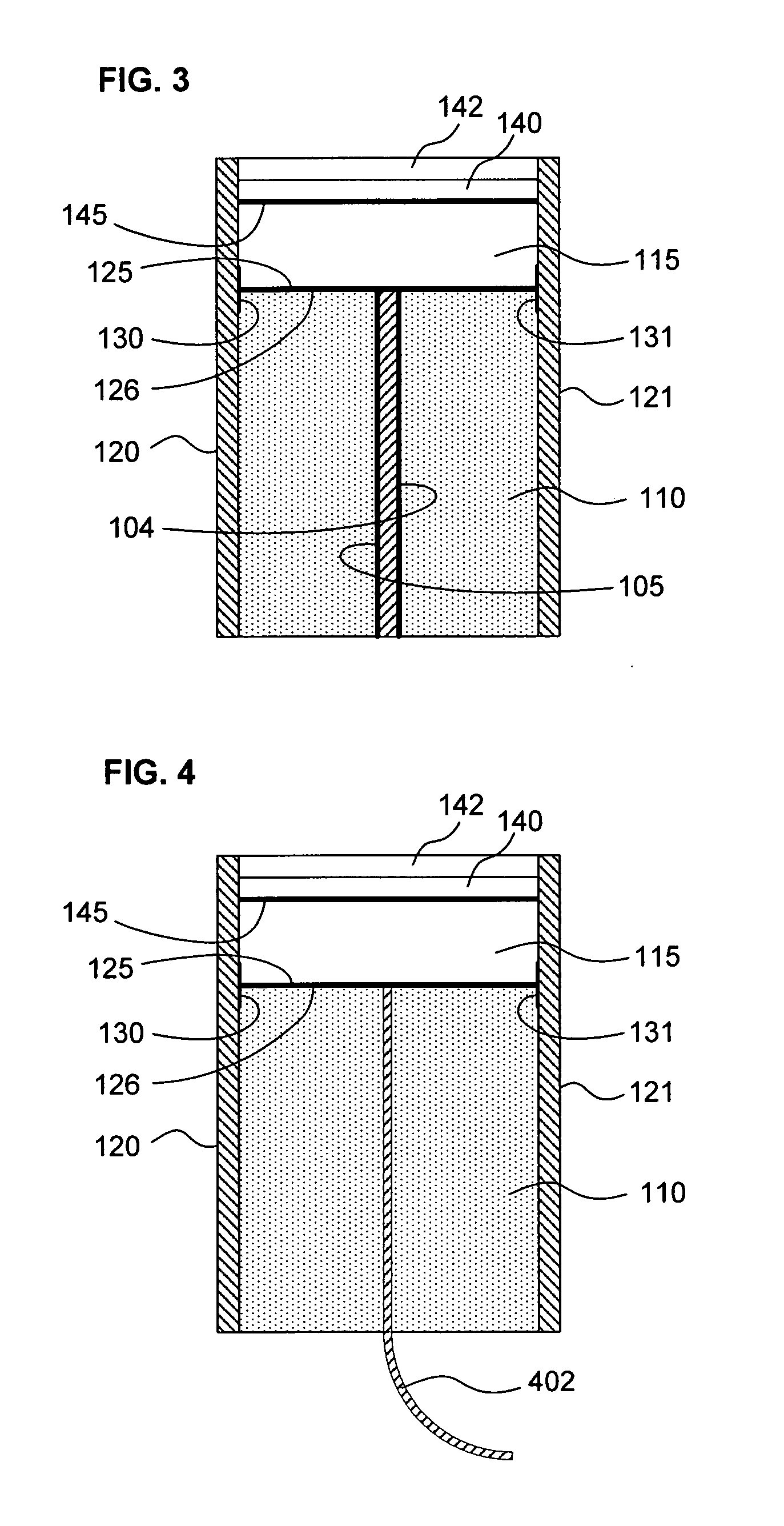
Magnetostrictive actuator of a medical ultrasound transducer assembly, and a medical ultrasound handpiece and a medical ultrasound system having such actuator
ActiveUS8487487B2Efficiently sculpt teeth or remove boneLow powerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Apparatus and method for using augmented reality vision system in surgical procedures
ActiveUS9123155B2Improve eyesightAvoid enteringMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgerySurgical siteX-ray
A system and method for improving a surgeon's vision by overlaying augmented reality information onto a video image of the surgical site. A high definition video camera sends a video image in real time. Prior to the surgery, a pre-operative image is created from MRI, x-ray, ultrasound, or other method of diagnosis using imaging technology. The pre-operative image is stored within the computer. The computer processes the pre-operative image to decipher organs, anatomical geometries, vessels, tissue planes, orientation, and other structures. As the surgeon performs the surgery, the AR controller augments the real time video image with the processed pre-operative image and displays the augmented image on an interface to provide further guidance to the surgeon during the surgical procedure.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
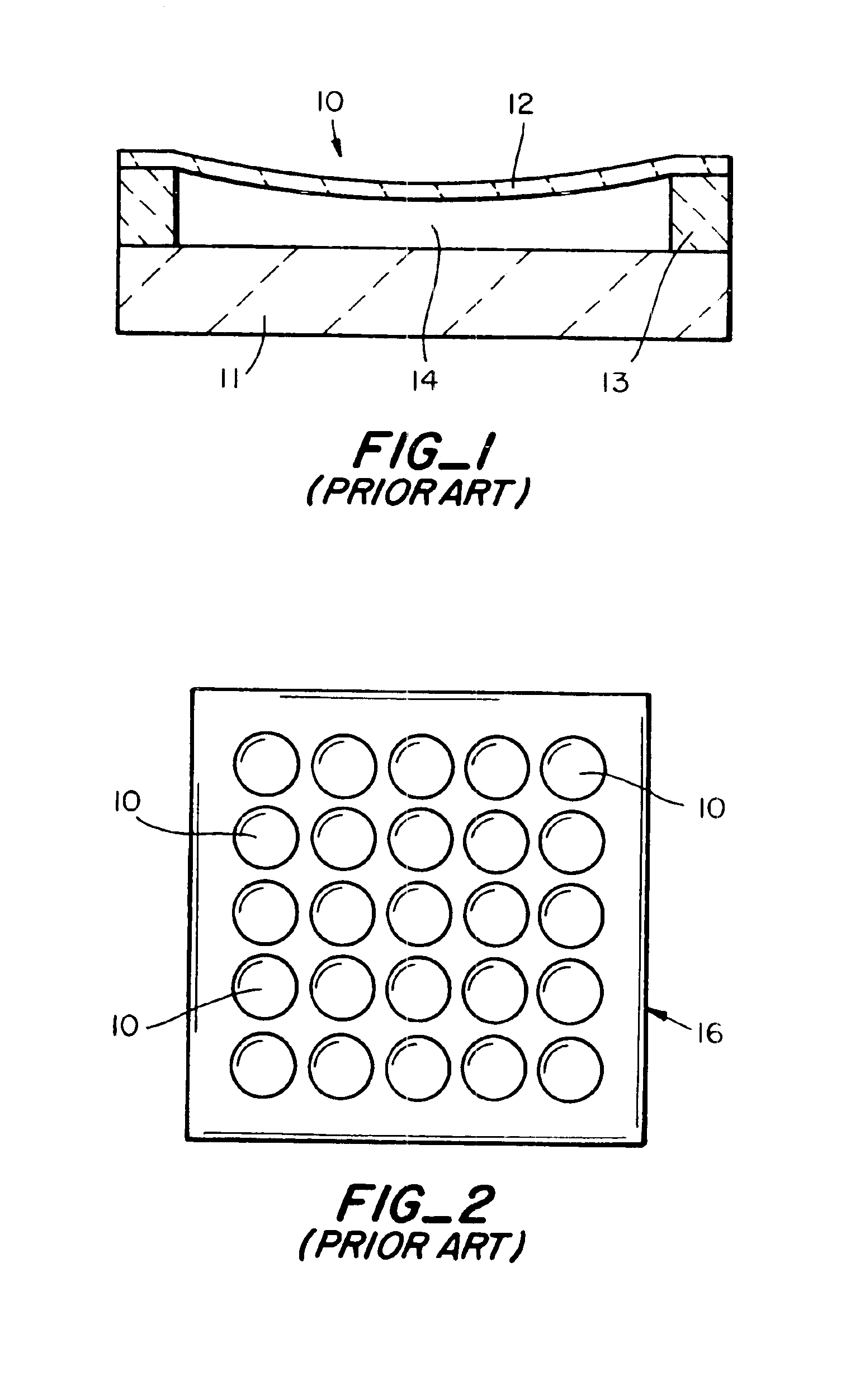
Device for lysing cells, spores, or microorganisms
InactiveUS6878540B2Improve convenienceImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismSpore
A device for use with an ultrasonic transducer to lyse components of a fluid sample comprises a cartridge having a lysing chamber, an inlet port in fluid communication with the lysing chamber, and an outlet port for exit of the sample from the lysing chamber. The inlet and outlet ports are positioned to permit flow of the sample through the lysing chamber, and the chamber contains at least one solid phase for capturing the sample components to be lysed as the sample flows through the chamber. The lysing chamber is defined by at least one wall having an external surface for contacting the transducer to effect the transfer of ultrasonic energy to the chamber.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Systems and methods for characterization of materials and combinatorial libraries with mechanical oscillators
InactiveUS6182499B1Optical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologySonificationVisual perception
Methods and apparatus for screening diverse arrays of materials are provided. In one aspect, systems and methods are provided for imaging a library of materials using ultrasonic imaging techniques. The system includes one or more devices for exciting an element of the library such that acoustic waves are propagated through, and from, the element. The acoustic waves propagated from the element are detected and processed to yield a visual image of the library element. The acoustic wave data can also be processed to obtain information about the elastic properties of the library element. In another aspect, systems and methods are provided for generating acoustic waves in a tank filled with a coupling liquid. The library of materials is then placed in the tank and the surface of the coupling liquid is scanned with a laser beam. The structure of the liquid surface disturbed by the acoustic wave is recorded, the recorded disturbance being representative of the physical structure of the library. In another aspect of the invention, a mechanical resonator is used to evaluate various properties (e.g., molecular weight, viscosity, specific weight, elasticity, dielectric constant, conductivity, etc.) of the individual liquid elements of a library of materials. The resonator is designed to ineffectively excite acoustic waves. The frequency response of the resonator is measured for the liquid element under test, preferably as a function of time. By calibrating the resonator to a set of standard liquids with known properties, the properties of the unknown liquid can be determined. An array of library elements can be characterized by a single scanning transducer or by using an array of transducers corresponding to the array of library elements. Alternatively, multiple resonators of differing design may be used to evaluate each element of a library of elements, thus providing improved dynamic range and sensitivity.
Owner:FREESLATE
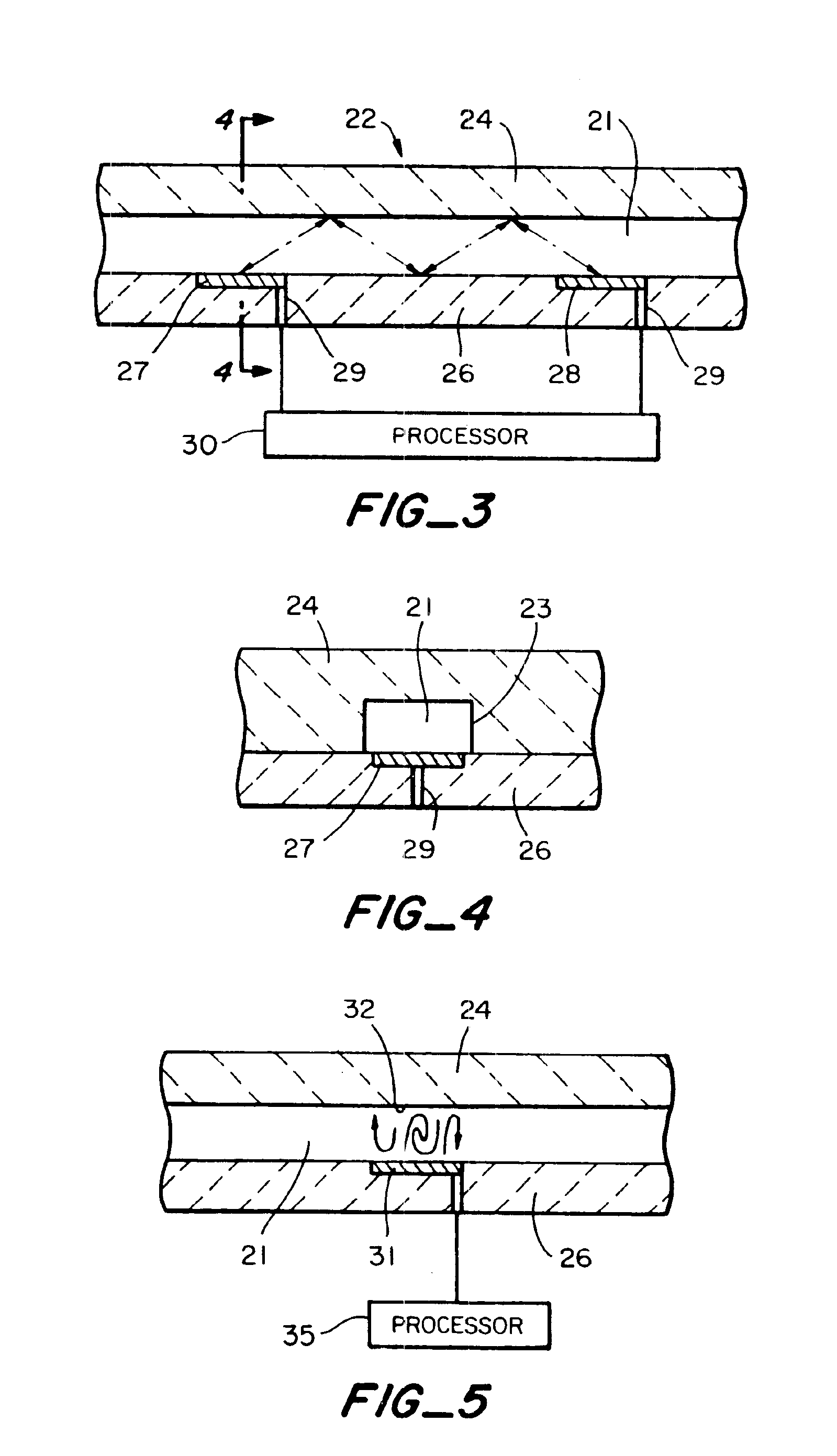
Device and method for lysing cells, spores, or microorganisms
InactiveUS6887693B2Simple designImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSporeMicroorganism
A device for lysing components (e.g., cells, spores, or microorganisms) of a fluid sample comprises a cartridge having a lysing chamber for receiving the sample and having at least one solid phase in the lysing chamber for capturing the sample components to be lysed. An ultrasonic transducer is coupled to a wall of the lysing chamber to transfer ultrasonic energy to the captured sample components.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Surface-functionalized mesoporous carbon materials
ActiveUS9249241B2Effectively and efficiently functionalizedPractical and cost-effective for large scale productionProcess efficiency improvementPolyvinyl polymerSolvent
A functionalized mesoporous carbon composition comprising a mesoporous carbon scaffold having mesopores in which polyvinyl polymer grafts are covalently attached, wherein said mesopores have a size of at least 2 nm and up to 50 nm. Also described is a method for producing the functionalized mesoporous composition, wherein a reaction medium comprising a precursor mesoporous carbon, vinyl monomer, initiator, and solvent is subjected to sonication of sufficient power to result in grafting and polymerization of the vinyl monomer into mesopores of the precursor mesoporous carbon. Also described are methods for using the functionalized mesoporous carbon, particularly in extracting metal ions from metal-containing solutions.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Ultrasound apparatus and method for augmented clot lysis
ActiveUS6945937B2Overcome problemsReduce thermal effectsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationUltrasonic sensor
An apparatus and method for using ultrasound augmented with microbubbles, thrombolytic drugs or other agents for clot lysis wherein at least one ultrasound transducer generates a plurality of acoustic signals and time, amplitude, phase and frequency modulation of the signals provide more uniform power delivery with fewer gaps in the ultrasound field. Interference patterns from one or multiple transducers are constantly shifted in position. A phased array of transducers may generate a beam that is swept over the area to be treated. In another embodiment, an array of transducers may generate ultrasound at a number of slightly varying frequencies to produce an interference pattern that sweeps in and out through the targeted tissue. A single array may be used to produce both effects simultaneously or separately.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Mosaic arrays using micromachined ultrasound transducers
InactiveUS6865140B2Optimal acoustic image qualityImprove image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBurglar prevention lockingSonificationUltrasonic sensor
An ultrasound transducer array includes a multiplicity of subelements interconnected by a multiplicity of microelectronic switches, each subelement comprising a respective multiplicity of micromachined ultrasound transducer (MUT) cells. The MUT cells within a particular subelement are hard-wired together. The switches are used to configure the subelements to form multiple concentric annular elements. This design dramatically reduces complexity while enabling focusing in the elevation direction during ultrasonic image data acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Defect free composite membranes, method for producing said membranes and use of the same
InactiveUS7172075B1Good water permeabilityStrong physical adhesionSemi-permeable membranesSynthetic resin layered productsFruit juiceChemical composition
Owner:ACCORD PARTNER
Fluidic device with integrated capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
InactiveUS6854338B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducersSonification
The present invention provides fluidic devices and systems which have micromachined ultrasonic transducers integrated into microchannels. The ultrasonic transducers generate and receive ultrasonic waves. The transducers can be disposed and operated to measure fluid characteristics such as pressure, density, viscosity, flow rate and can also be used to mix and pump fluids.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
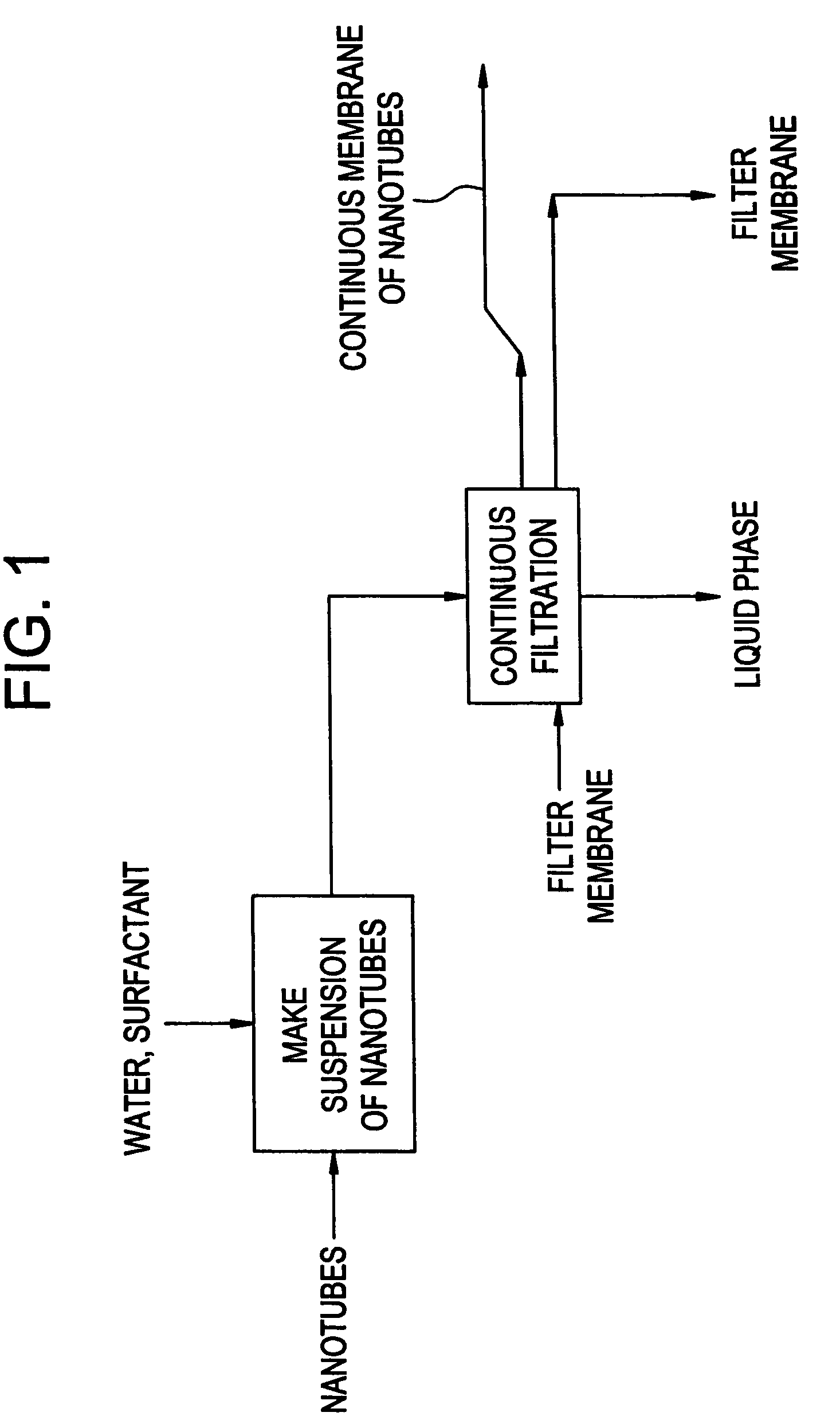
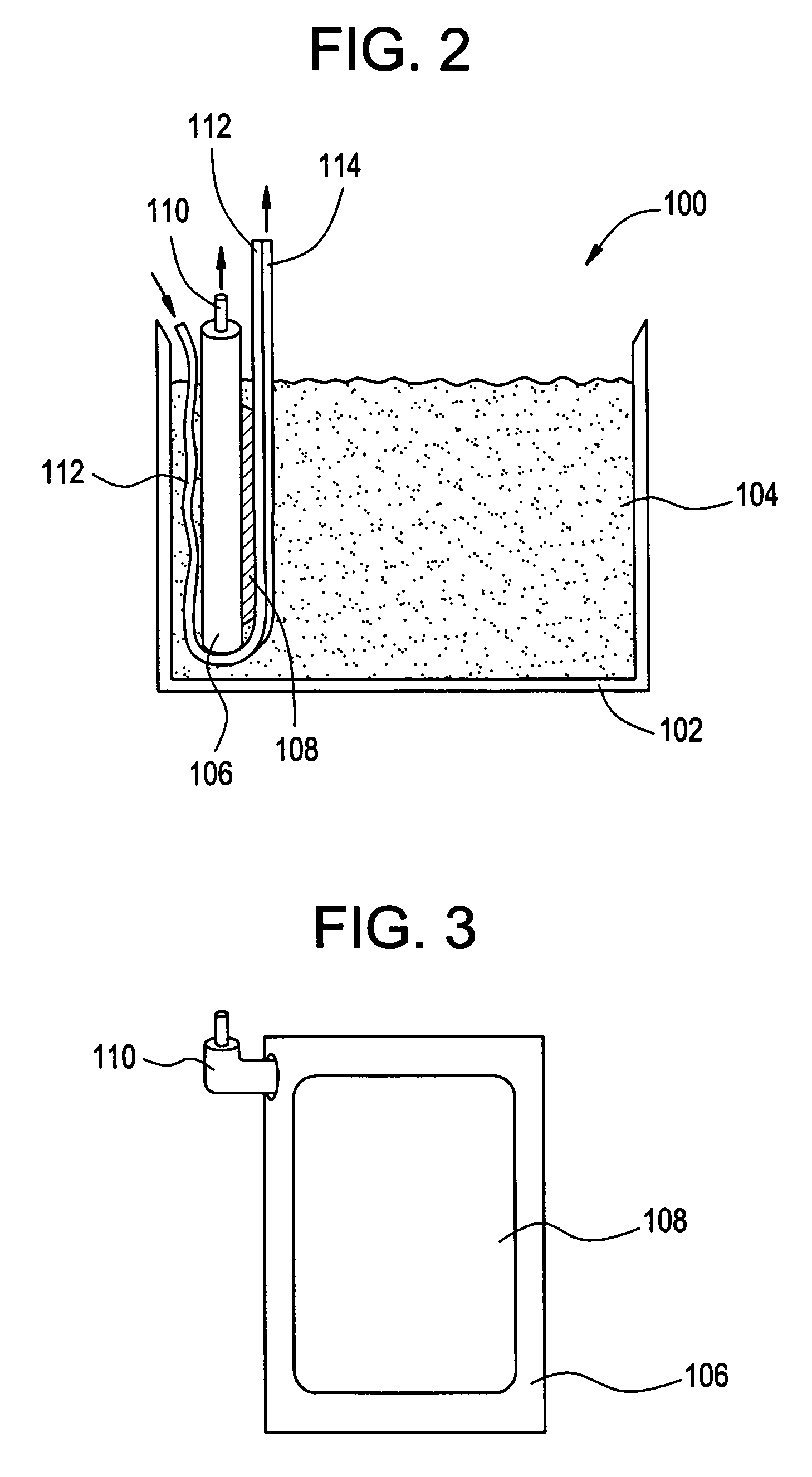
Method for continuous fabrication of carbon nanotube networks or membrane materials
Methods and devices are provided for the continuous production of a network of nanotubes or other nanoscale fibers. The method includes making a suspension of nanoscale fibers dispersed in a liquid medium, optionally with surfactant and / or sonication, and filtering the suspension by moving a filter membrane through the suspension, such that the nanoscale fibers are deposited directly on the filter membrane as the fluid medium flows through the filter membrane, thereby forming a continuous membrane of the nanoscale fibers. The deposition of the nanoscale fibers can occur when and where the filter membrane moves into contact with a static, porous filter element or a dynamic, porous filter element. The filtering can be conducted within a magnetic field effective to align the nanoscale fibers, and / or with the aid of vacuum to pull water through the filter membrane, applied pressure to press water though the filter membrane, or a combination thereof.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Micromachined ultrasonic transducer cells having compliant support structure
ActiveUS7030536B2Increase the effective areaReduce couplingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitorUltrasonic transducer array
A micromachined ultrasonic transducer array comprising a multiplicity of cMUT cells built on a substrate. Each cMUT cell comprises a compliant support structure built on the substrate, a membrane supported over a cavity by the compliant support structure, a first electrode supported by the membrane, and a second electrode that forms a capacitor with the first electrode, the cavity being disposed between the first and second electrodes. The compliant support structure uncouples the non-membrane outer surface of each cMUT cell from the supporting substrate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
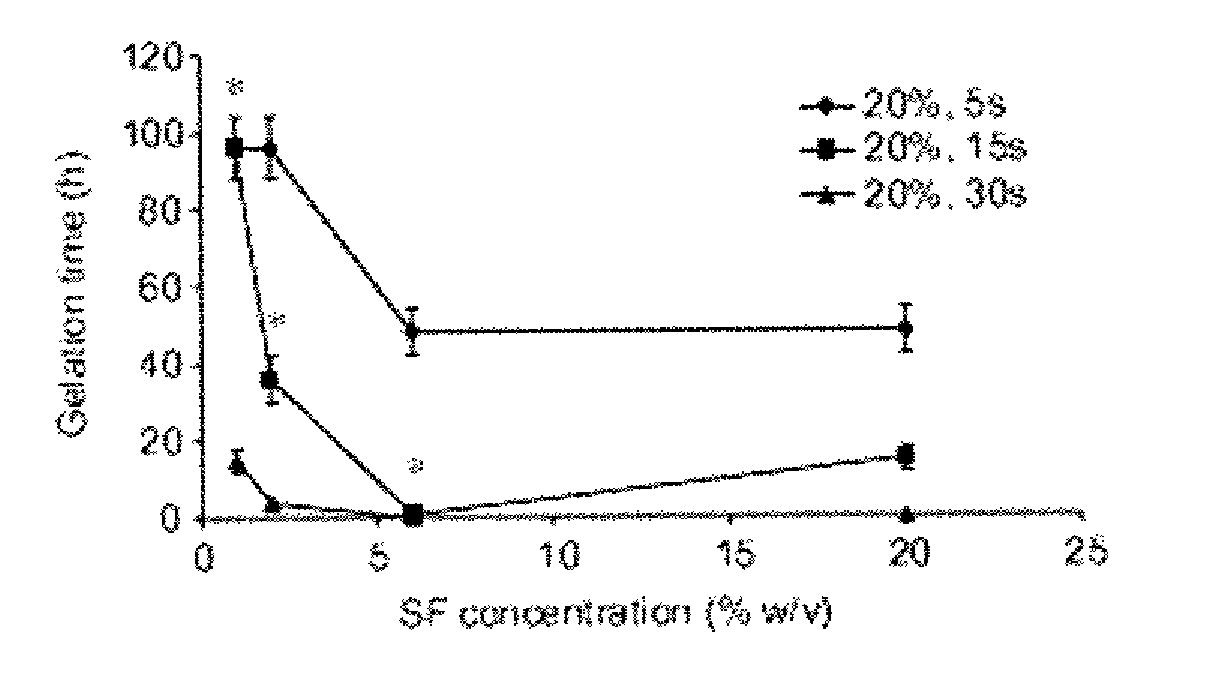
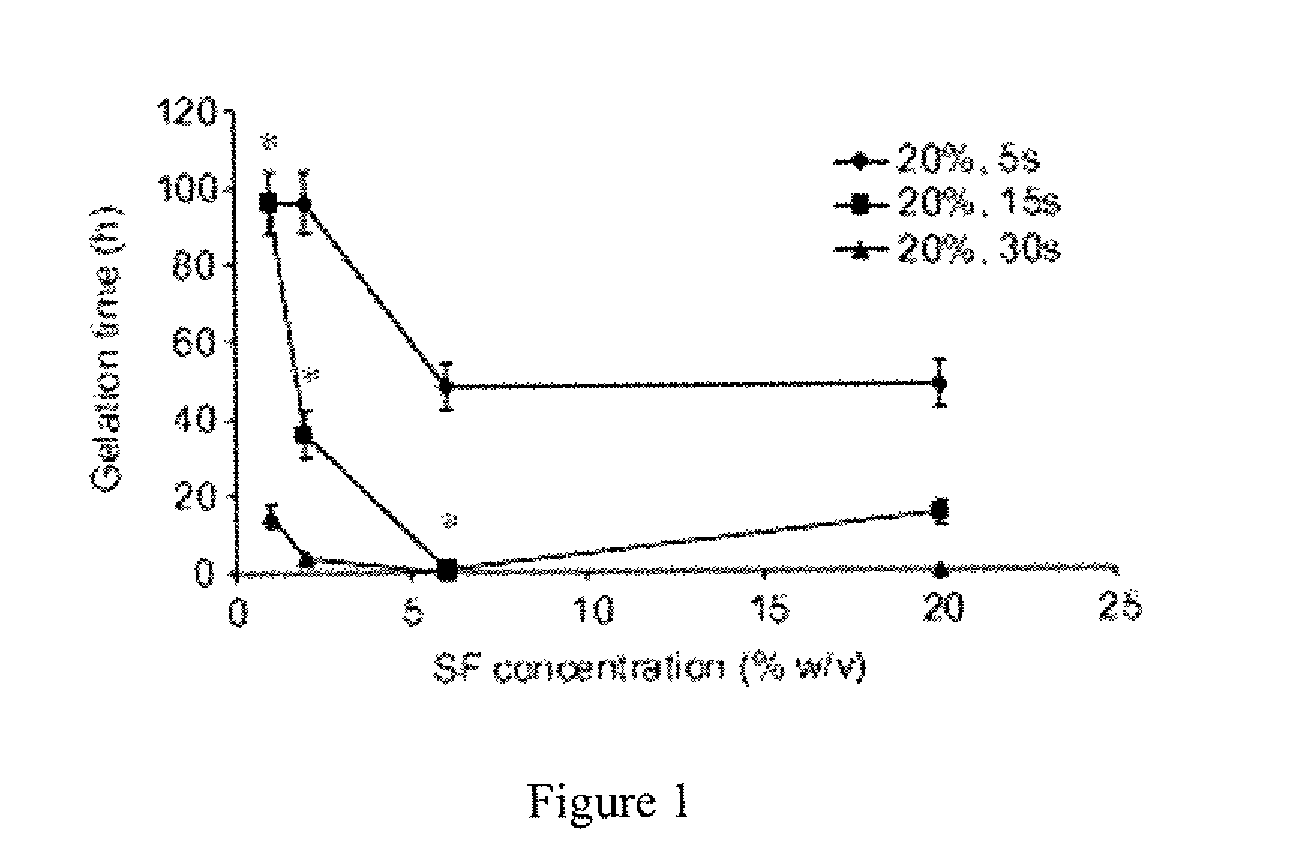
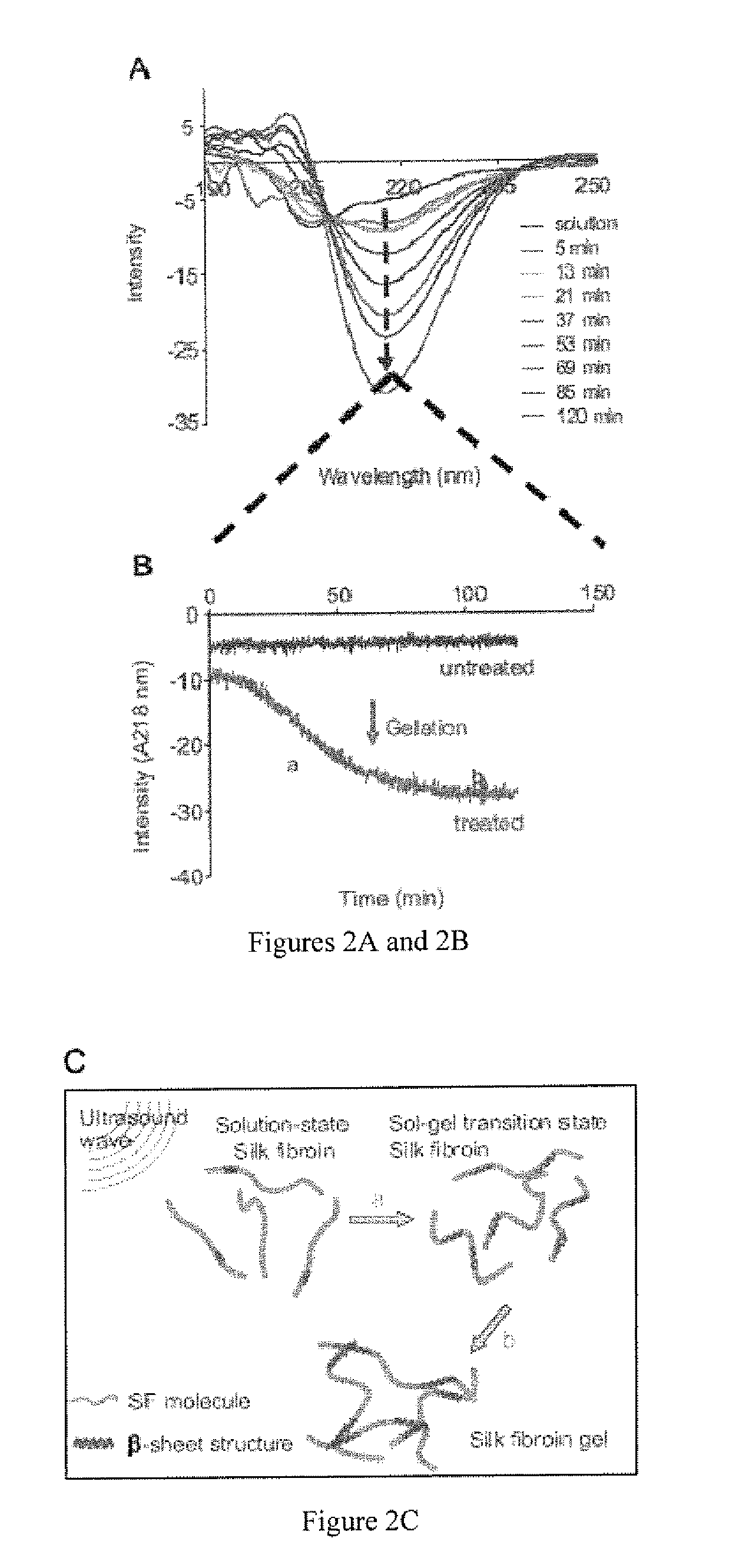
Method for silk fibroin gelation using sonication
ActiveUS20100178304A1Fast gelationCell from functioningBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDelivery vehicleViable cell
This invention provides for a process of rapidly forming silk fibroin gelation through ultrasonication. Under the appropriate conditions, gelation can be controlled to occur within two hours after the ultrasonication treatment. Biological materials, including viable cells, or therapeutic agents can be encapsulated in the hydrogels formed from the process and be used as delivery vehicles.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
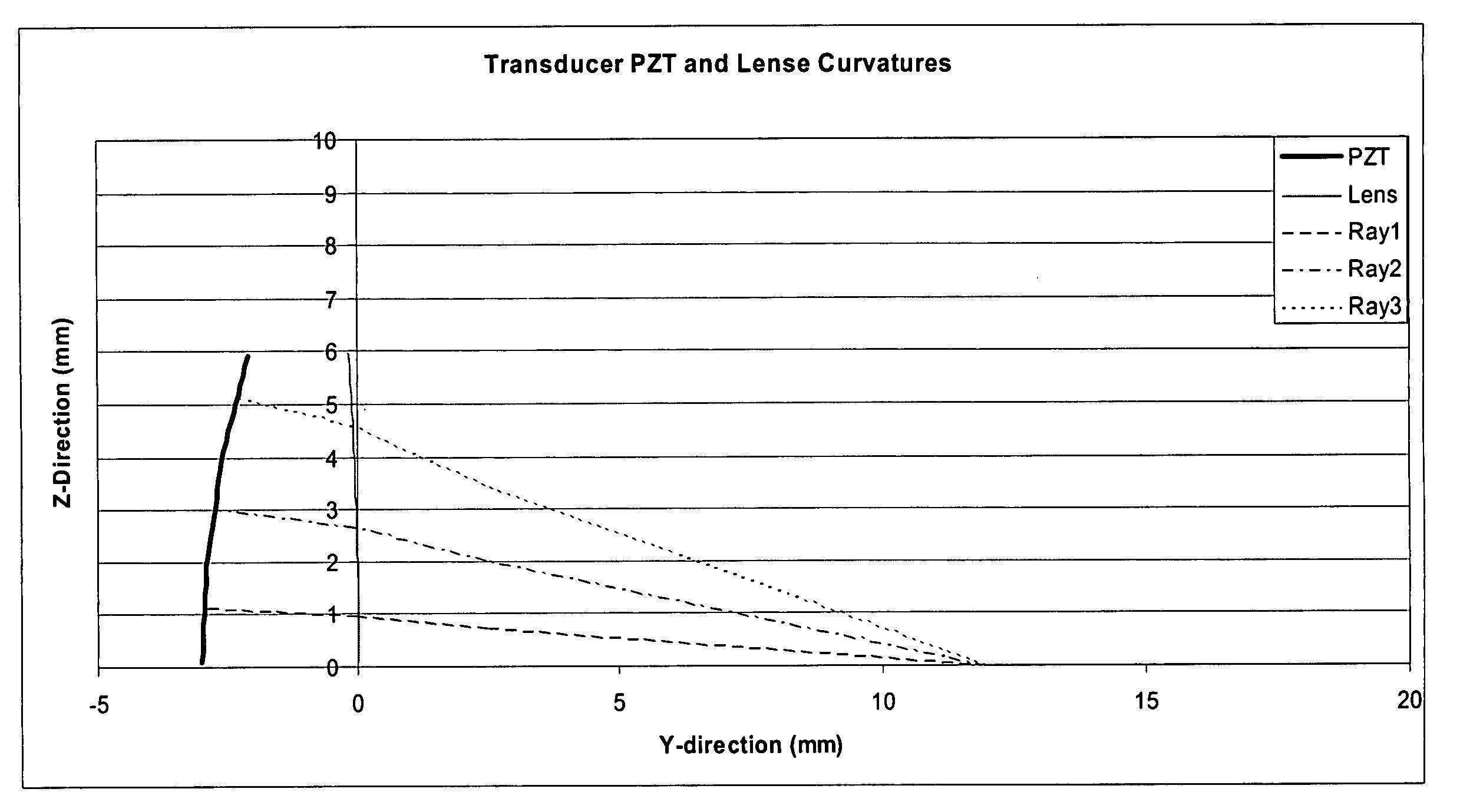
Ultrasound interfacing device for tissue imaging
InactiveUS7931596B2Minimal effect on the ultrasound signalsAvoid pollutionSurgeryCatheterTissue imagingMinimal effect
Owner:ISCI SURGICAL
External ultrasound lipoplasty
InactiveUS7955281B2Safer procedureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationSonification
This invention relates to a non-invasive, safer alternative to current lipoplasty procedures. The preferred embodiment of the invention is a multi-channel system that focuses the low mega Hertz ultrasound at user selectable depths, where fat cells are to be emulsified. The system has independent user control of the main emulsifying property, cavitation, and thermal heating, which can independently be used for skin tightening. One part of the system is a handheld transducer, in shape similar to a typical small diagnostic ultrasound transducer. The other part of the system includes a transmitter with internal tracking of procedure time and with a disabling feature.
Owner:NIVASONIX
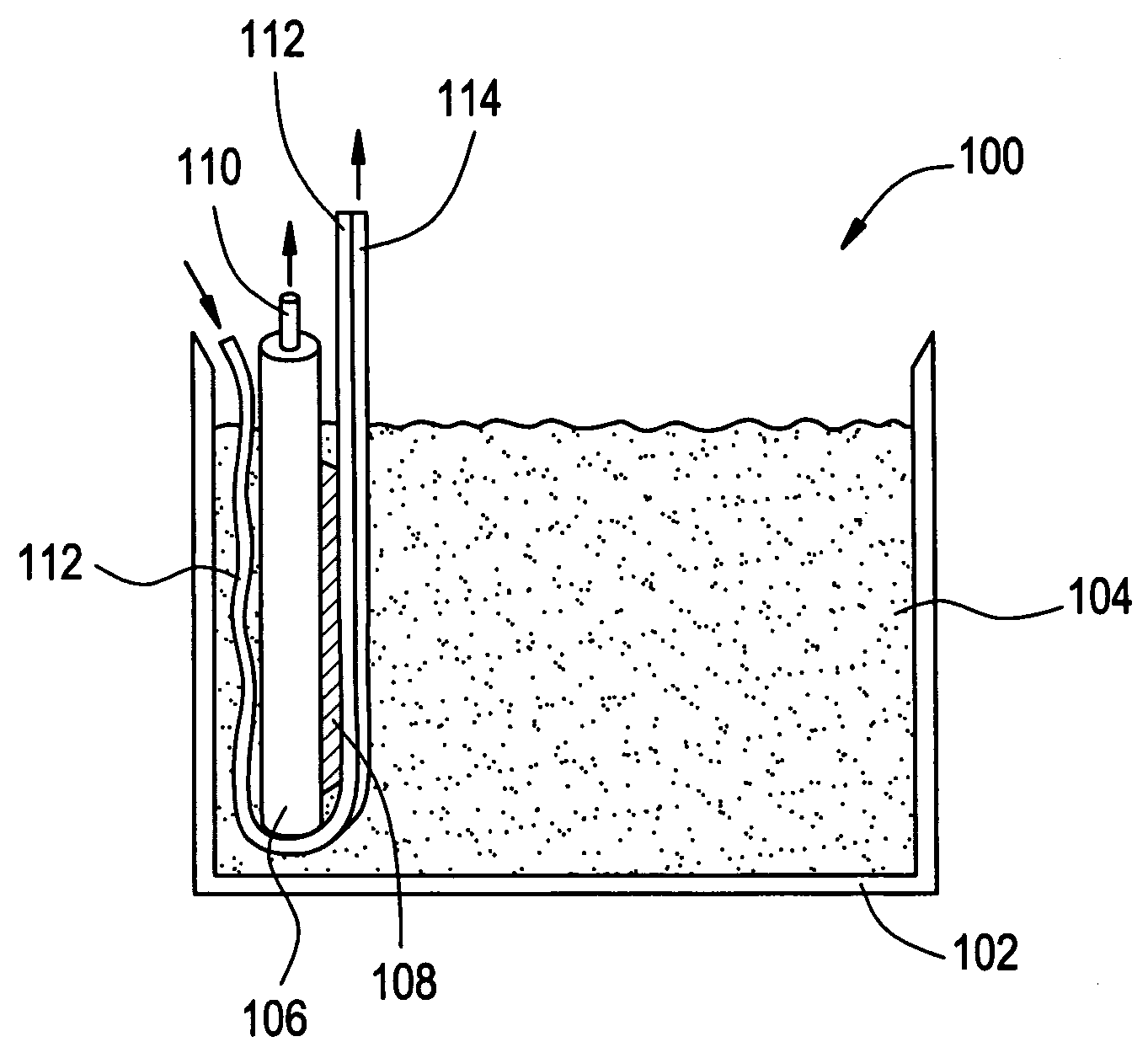
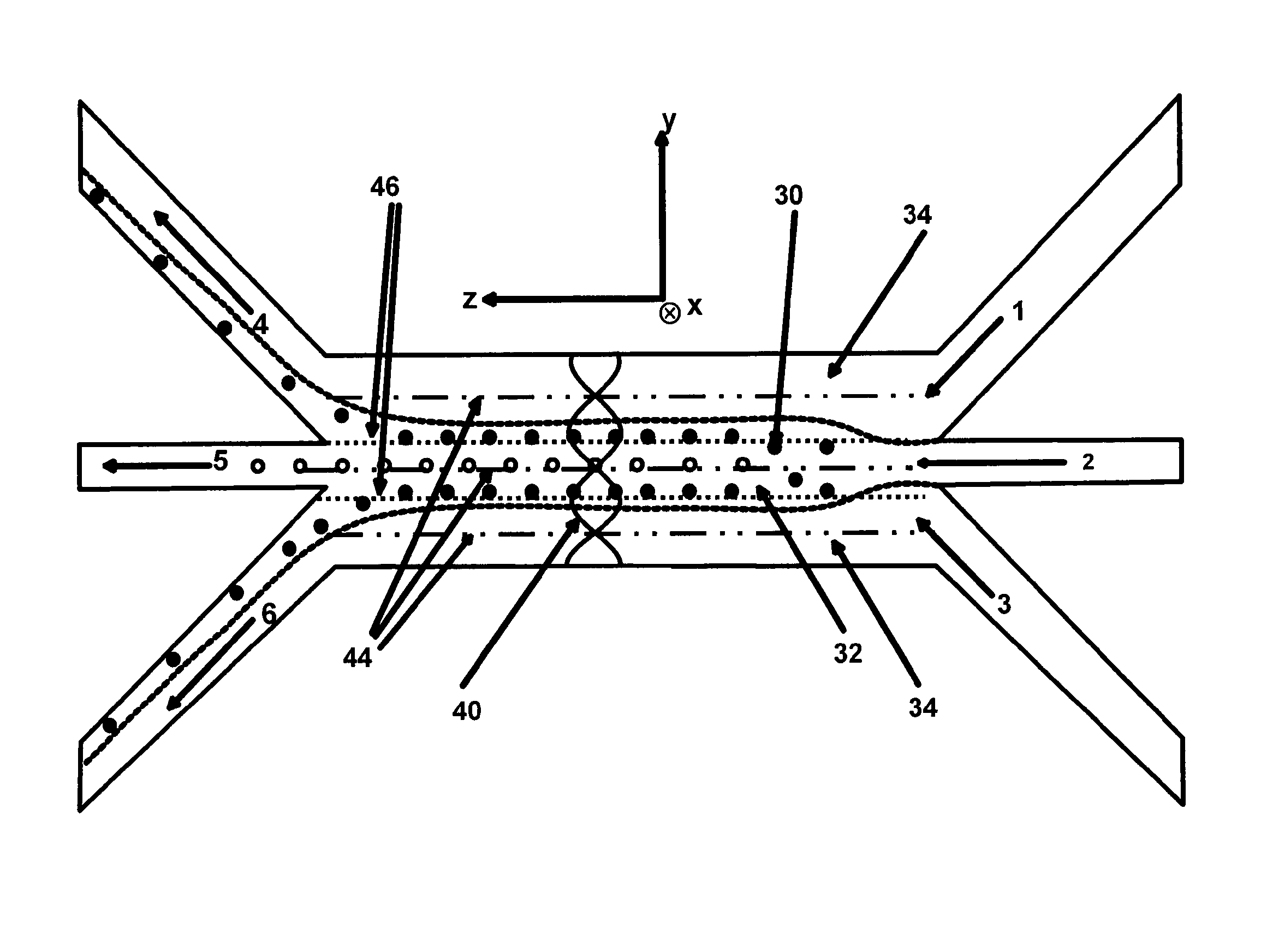
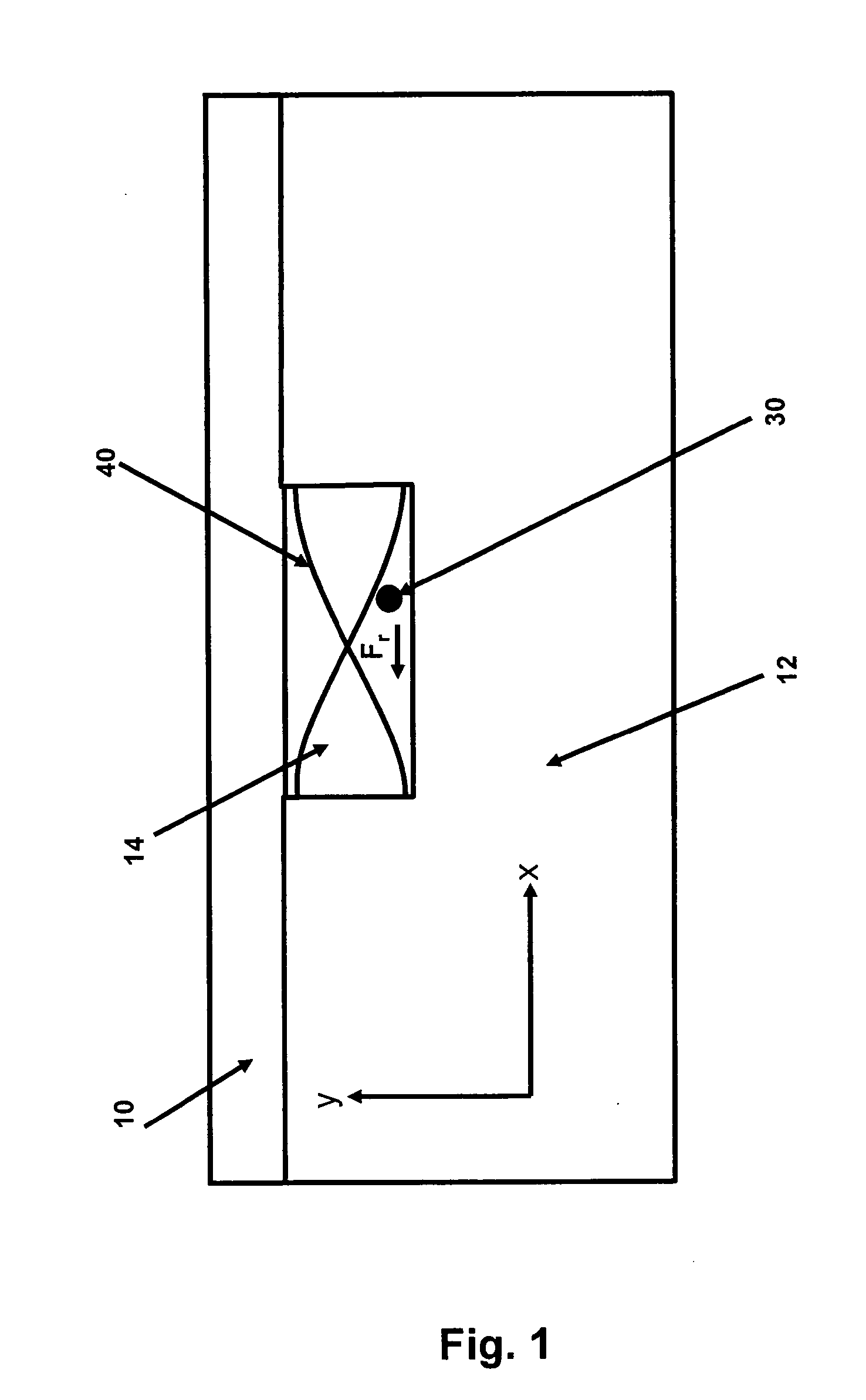
Separation of particles in liquids by use of a standing ultrasonic wave
InactiveUS20110154890A1Reduce sensitivityReduce the amount requiredAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesLaboratory glasswaresSonificationLength wave
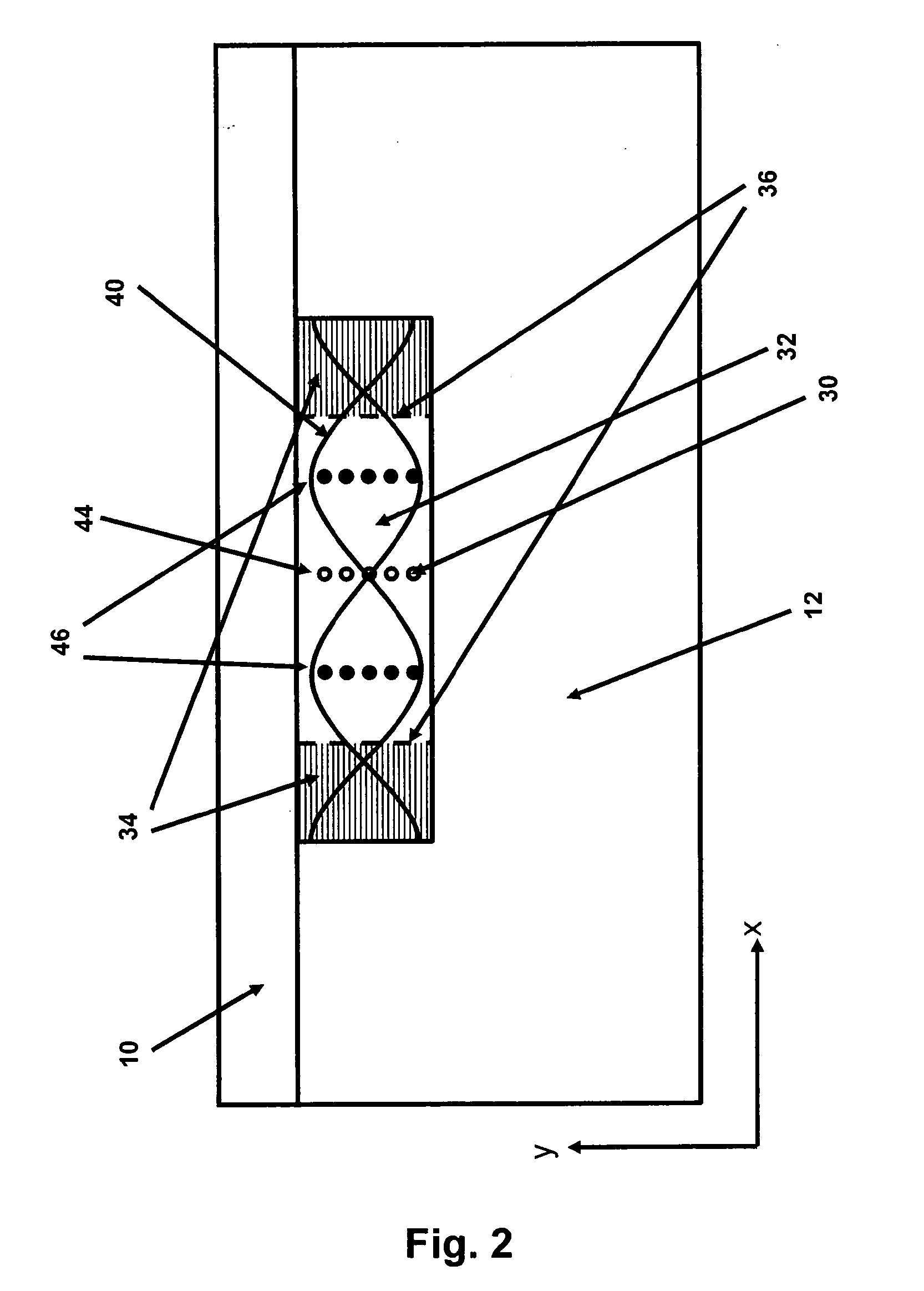
The invention relates to a device for manipulation of particles (30) in a sample liquid (32) said device comprising a source of ultrasound (16) capable of emitting ultrasound with a given wavelength, an inlet for a sample liquid (2), one or more outlets (4, 5, 6) and a compartment (14), being dimensioned to support a standing ultrasonic wave (40) of said wavelength, characterised in that the device further comprises an inlet for sheath liquid (1, 3) configured to direct a sheath liquid (34) to extend substantially in parallel to an anti-node plane (46) of the ultrasonic standing wave (40) proximate to a sheathed compartment wall. Specifically the device may be used in combination with a particle enumeration device for enumeration of somatic cells in milk.
Owner:FOSS ANALYTICAL AS
Device and method for separation
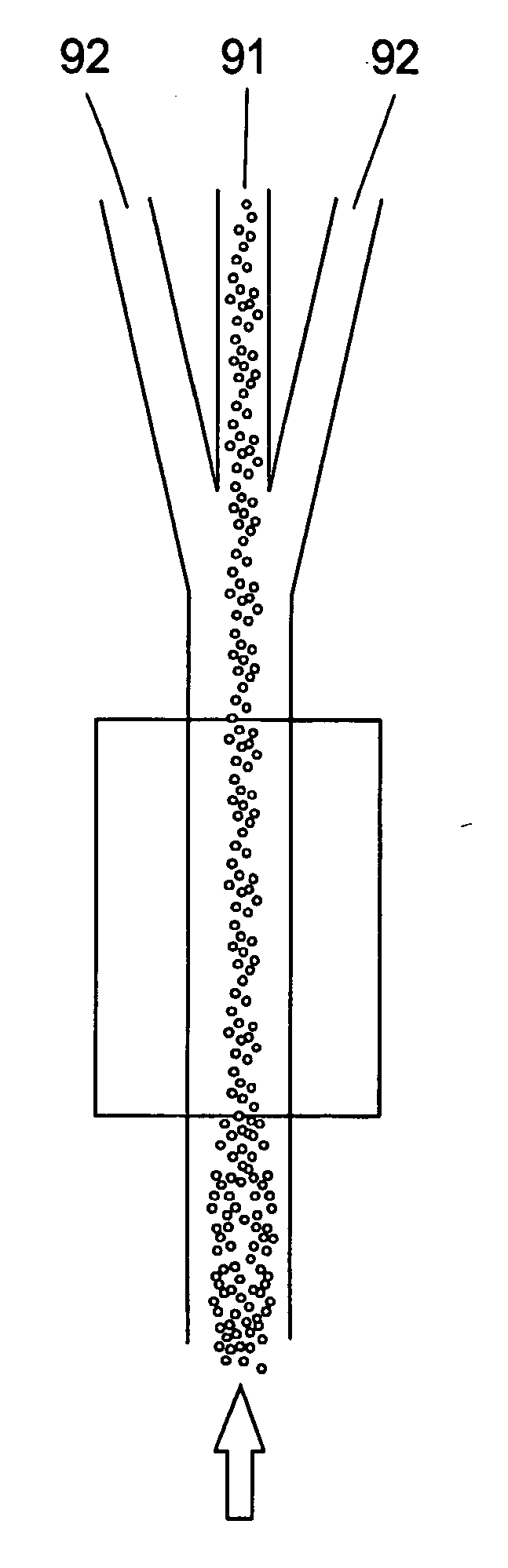
InactiveUS20040069717A1Raise the possibilityHigh particle separationOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationElectricityEngineering
The present invention provides a device and a method for separating particles from fluids using ultrasound, laminar flow, and stationary wave effects comprisinga micro-technology channel system with an integrated branching point or branching fork, and a single ultrasound source. One of the characteristics of the invention is that the single ultrasound source, which generates the standing waves, excites the complete structure including the channel system. No special reflectors or the like are needed. Extremely thin dividers can separate the flow, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the device. The device could be manufactured in silicon and the ultrasound energy could preferably be delivered by a piezoelectric element.
Owner:ERYSAVE
Apparatus and program for estimating viscoelasticity of soft tissue using ultrasound
InactiveUS20050085728A1Reduce harmAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic probe attachmentSonificationViscoelasticity
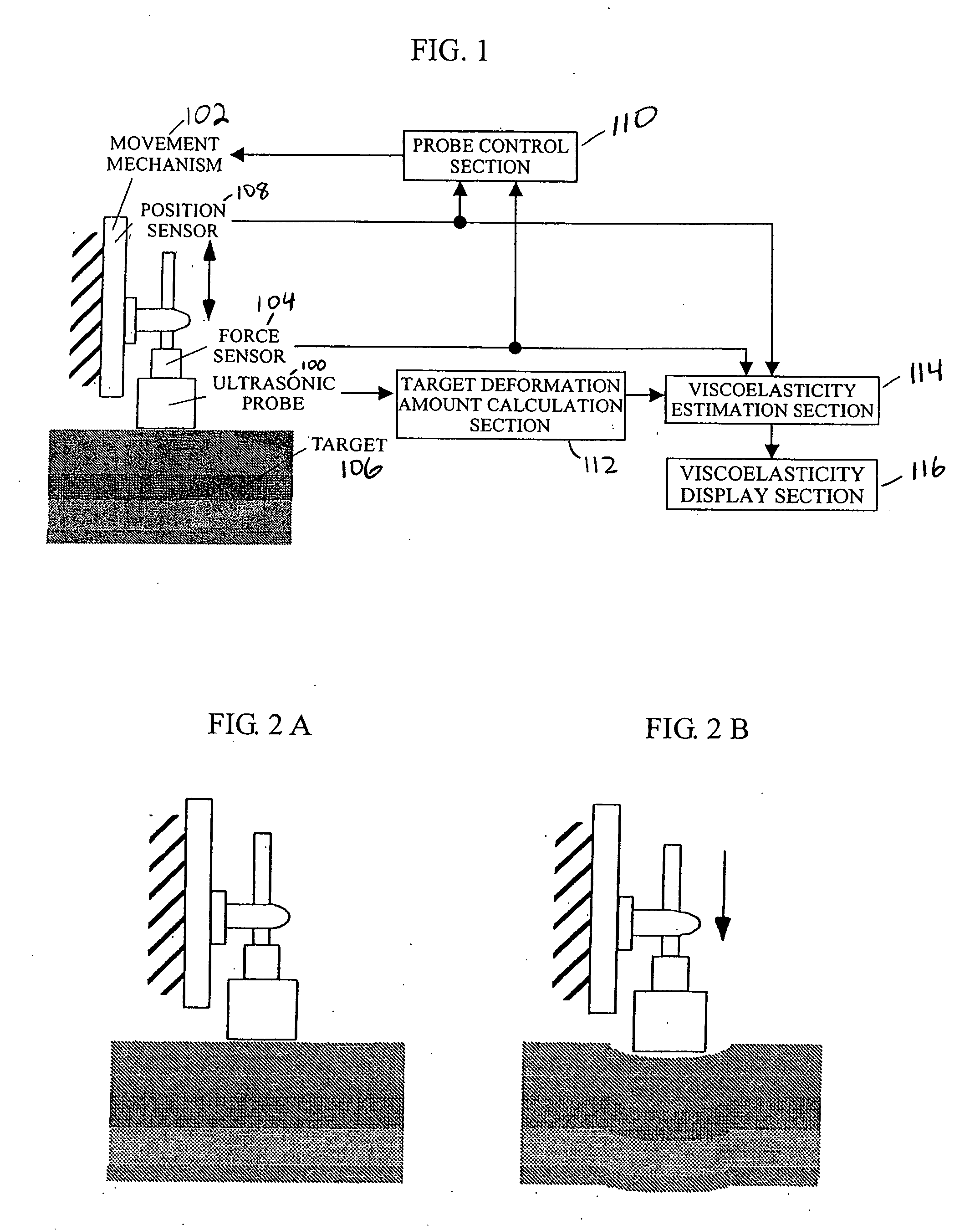
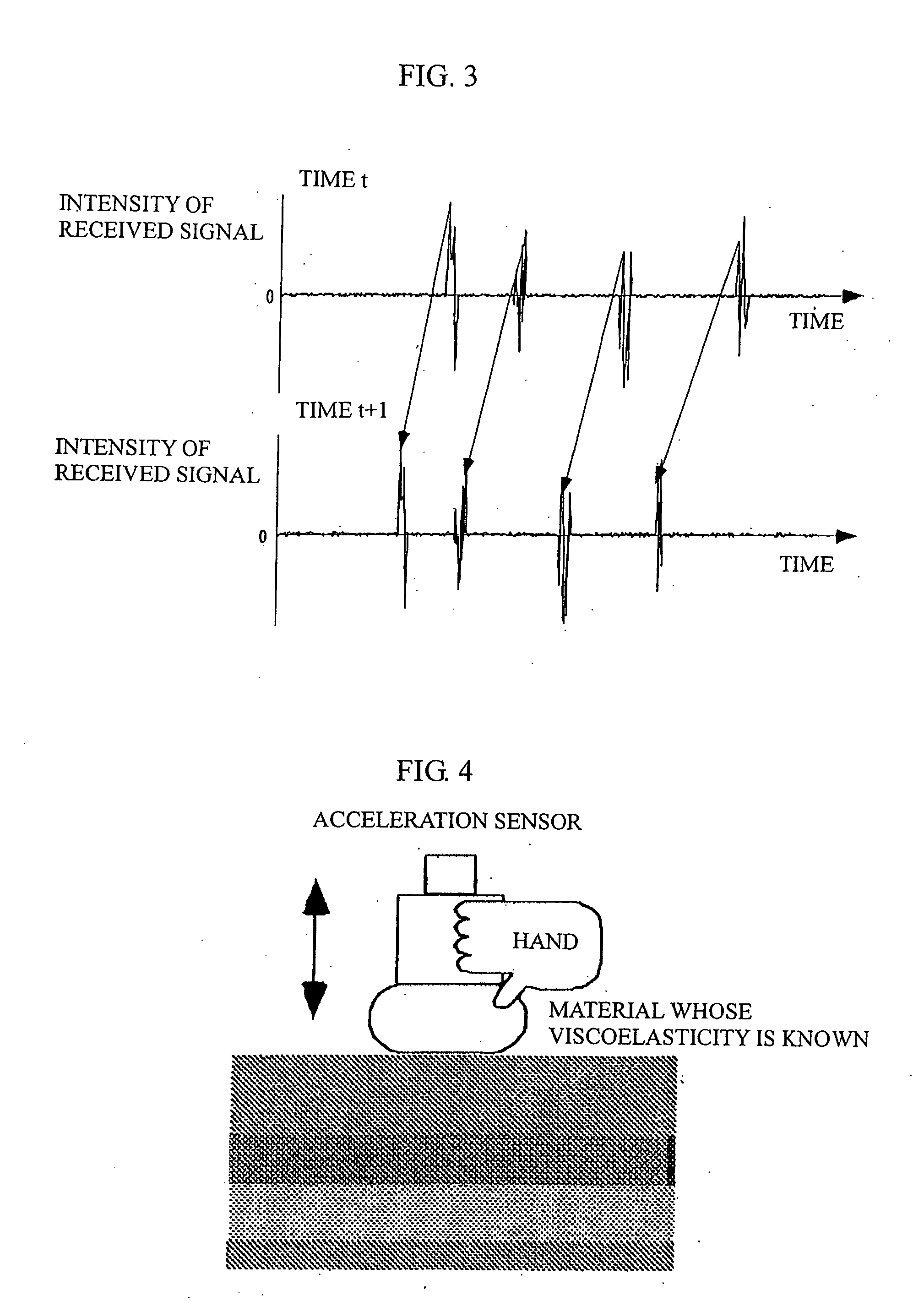
The present invention allows even soft tissue such as body tissue having a hierarchic structure of skin, fat, muscle and bone, etc., to be estimated and allows estimation only through a short-time pressing operation to thereby reduce damages to the soft tissue. The present invention is constructed of an ultrasonic probe for transmitting / receiving an ultrasonic signal, a target deformation amount calculation section for calculating an amount of deformation of a target shape from a time variation of data received from the ultrasonic probe, a movement mechanism for moving the ultrasonic probe, a probe control section for controlling the probe, a position sensor for measuring the position of the probe, a force sensor for measuring a force applied to the probe section, a viscoelasticity estimation section for estimating viscoelasticity of the target based on values obtained from the position sensor, force sensor, target deformation amount calculation section and a viscoelasticity display section for presenting the estimated viscoelasticity to the user.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Method of forming nanoparticles and microparticles of controllable size using supercritical fluids and ultrasound
The current invention, Supercritical Antisolvent Precipitation with Enhanced Mass Transfer (SAS-EM) provides a significantly improved method for the production of nano and micro-particles with a narrow size distribution. The processes of the invention utilize the properties of supercritical fluids and also the principles of virbrational atomization to provide an efficient technique for the effective nanonization or micronization of particles. Like the SAS technique, SAS-EM, also uses a supercritical fluid as the antisolvent, but in the present invention the dispersion jet is deflected by a vibrating surface that atomizes the jet into fine droplets. The vibrating surface also generates a vibrational flow field within the supercritical phase that enhances mass transfer through increased mixing. Sizes of the particles obtained by this technique are easily controlled by changing the vibration intensity of the deflecting surface, which in turn is controlled by adjusting the power input to the vibration source. A major advantage of the SAS-EM technique is that it can be successfully used to obtain nanoparticles of materials that usually yield fibers or large crystals in SAS method. Microencapsulation via coprecipitation of two or more materials can also be achieved using the SAS-EM technique.
Owner:UNIV AUBURN
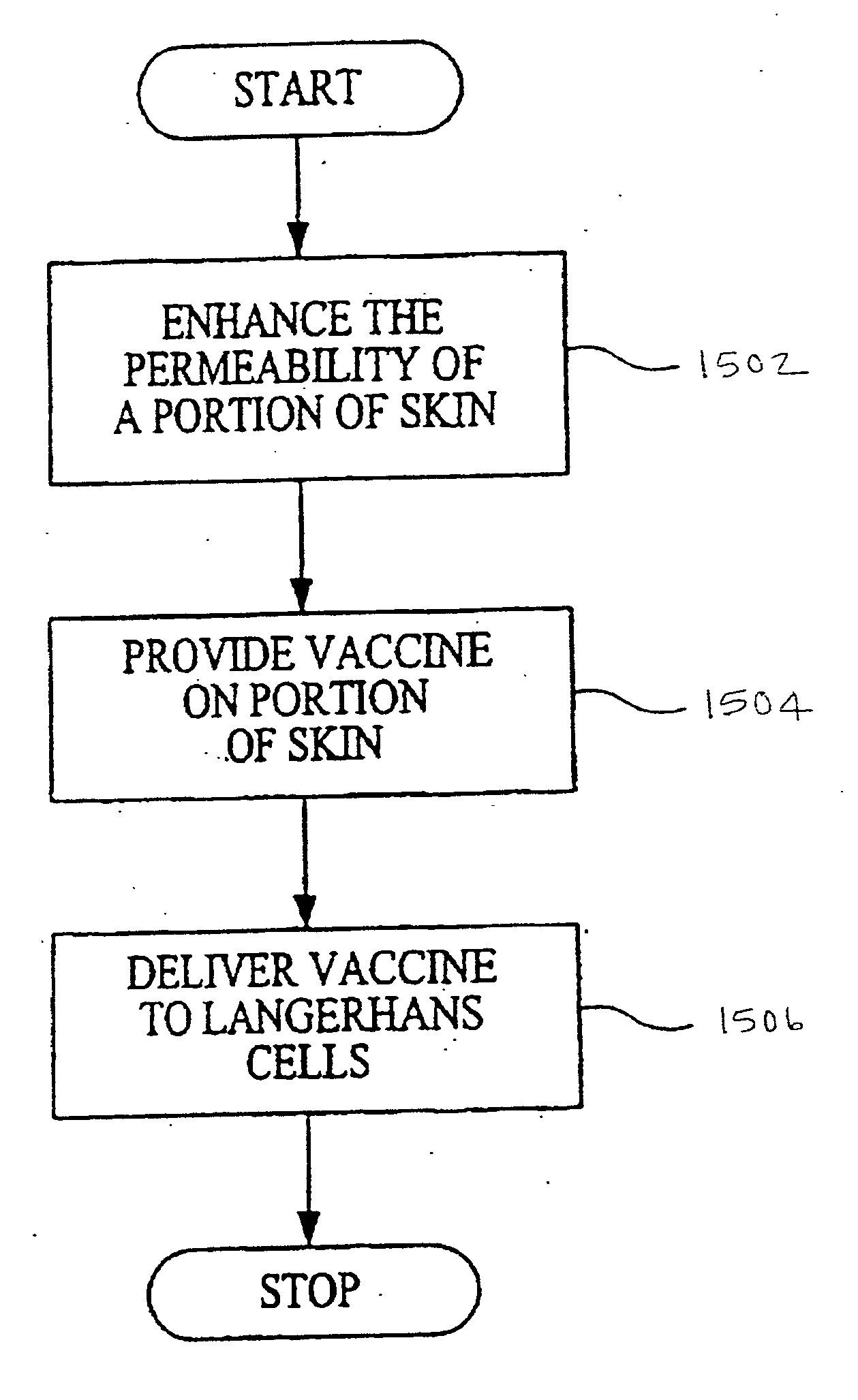
Agents and methods for enhancement of transdermal transport
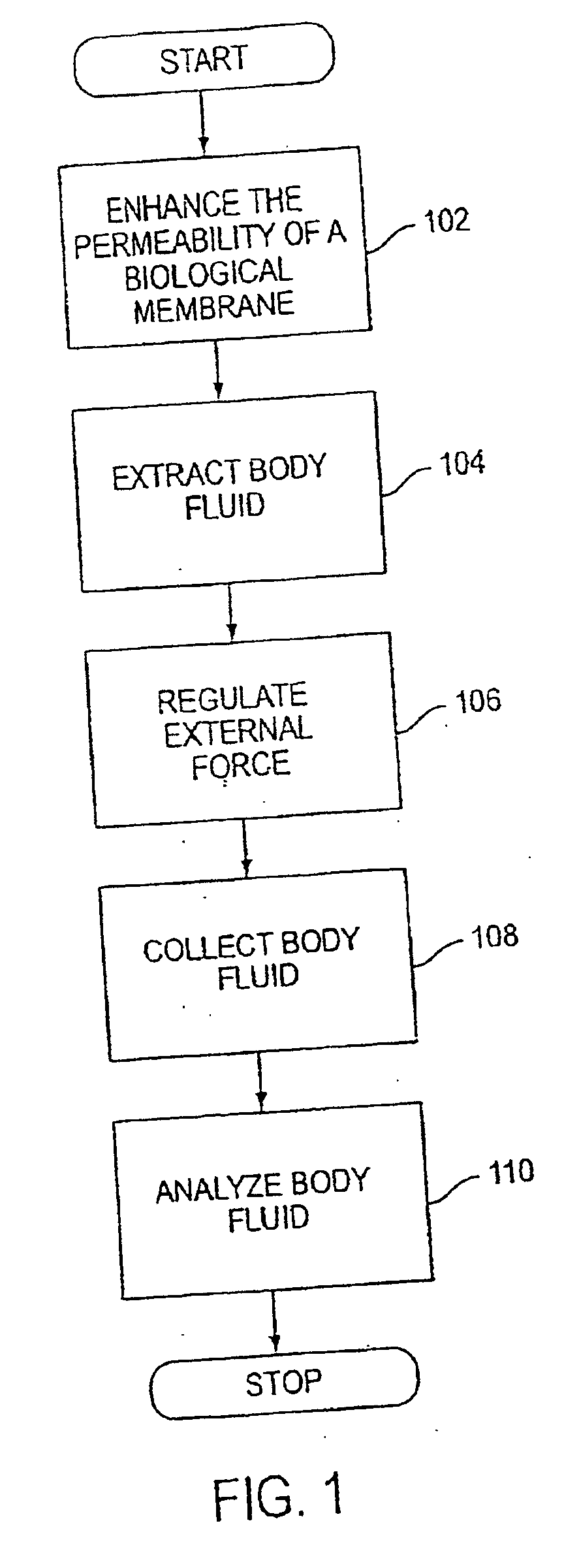
InactiveUS20060015058A1Enhance transdermal transportImproved transdermal transportElectrotherapySurgeryAnalyteBiological membrane
The invention according to an exemplary embodiment relates to a method for transporting a substance across a biological membrane comprising the steps of applying a delipidation agent to a portion of the biological membrane, applying a hydration agent to the portion of the biological membrane, sonicating the portion of the biological membrane, and transporting the substance across the biological membrane. The step of applying the delipidation agent may be carried out prior to or simultaneously with the step of applying the hydration agent. The hydration agent may be applied before, during, or after the sonication step. The methods according to exemplary embodiments of the invention can provide improved transdermal transport in applications such as continuous analyte extraction and analysis and transdermal delivery of drugs and vaccines.
Owner:KELLOGG SCOTT C +7
Rotational intravascular ultrasound probe and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100160788A1Electrical transducersOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorDrive shaft
A rotational intravascular ultrasound probe for insertion into a vasculature and a method of manufacturing the same. The rotational intravascular ultrasound probe comprises an elongate catheter having a flexible body and an elongate transducer shaft disposed within the flexible body. The transducer shaft comprises a proximal end portion, a distal end portion, a drive shaft extending from the proximal end portion to the distal end portion, an ultrasonic transducer disposed near the distal end portion for obtaining a circumferential image through rotation, and a transducer housing molded to the drive shaft and the ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Device and Method For Particle Manipulation in Fluid
InactiveUS20100193407A1Water/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsLaboratory glasswaresPlanar substrateEngineering
A device for manipulating particles present in a fluid medium is disclosed. The device comprises a planar substrate, formed with at least one primary microchannel to allow passage of the fluid medium therethrough. The primary microchannel(s) has walls and a base and being in fluid communication with a plurality of secondary microchannels via at least one branching point. The device further comprises one or more ultrasound transmission pairs, positioned at opposite sides of the walls to generate ultrasound waves propagating through the fluid medium, substantially parallel to the planar substrate, such as to form a standing wave within the primary microchannel.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Ultrasonic wave irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS6450979B1Increase body temperatureImprove heat generationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyBiological bodyLiving body
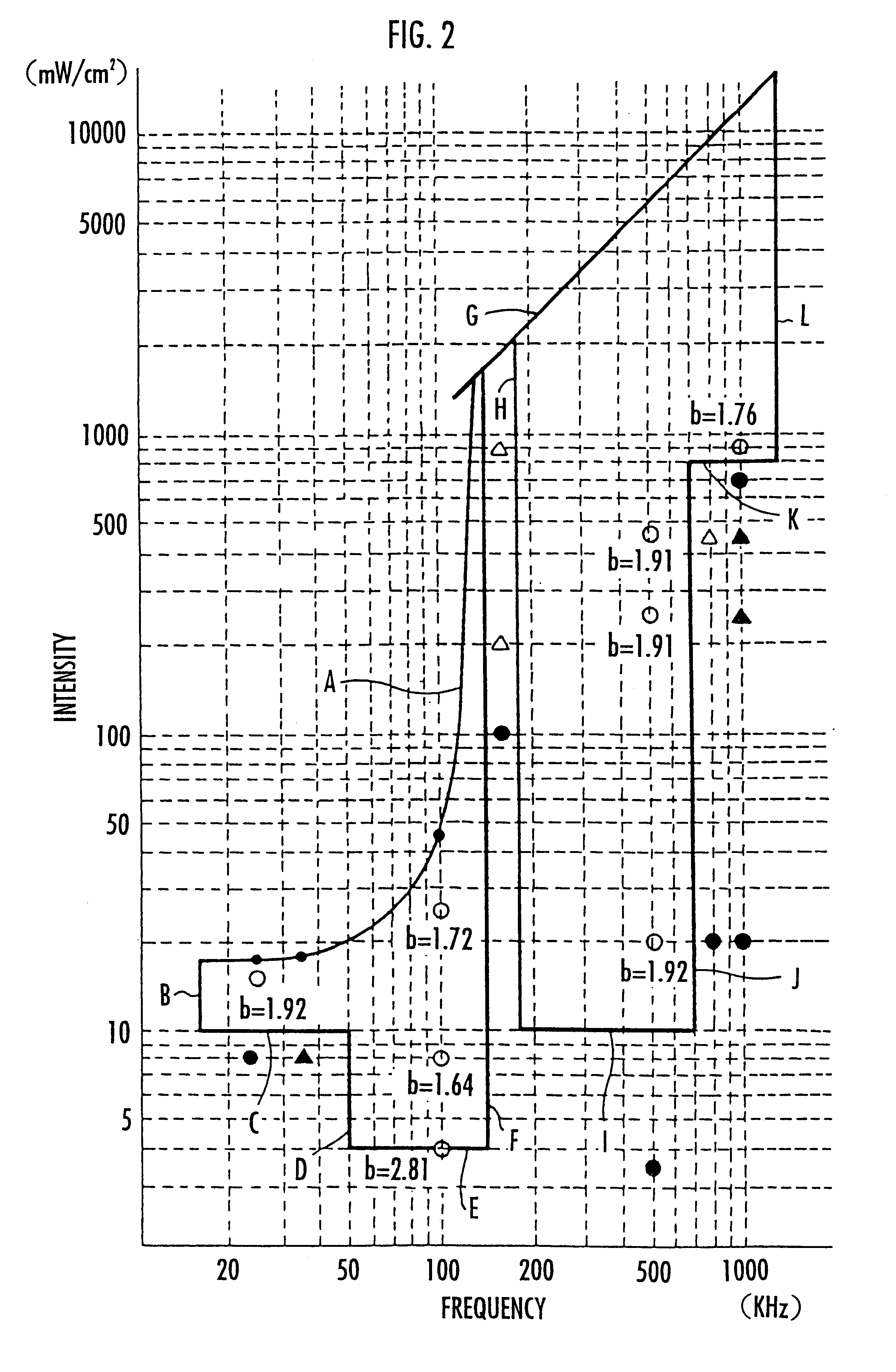
This invention discloses an equipment for lipolysis of fat of a living body by ultrasound sonication. An effective ultrasound is characterized in low frequency 15-140 kHz region, by an intensity when in a range of 15-50 kHz, which is greater than 10 mw / cm2and below a hemolysis limit, and an intensity when in a range of 50-140 kHz, which is greater than 4 mW / cm2 and below the hemolysis limit or the safety level defined by MI. The invention is further characterized in a high frequency 180-1.3 MHz region, by an intensity when in a range of 180-700 kHz, which is greater than 10 mw / cm2 and below the safety level defined by M.I, and the intensity when in a range of 700 kHz-1.3 MHz, which is greater than 800 mw / cm2and below the safety level defined by MI.
Owner:MIWA SCI LAB
Ultrasound apparatus and method for augmented clot lysis
ActiveUS20050085748A1Limited rangeOvercome problemsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationUltrasonic sensor
An apparatus and method for using ultrasound augmented with microbubbles, thrombolytic drugs or other agents for clot lysis wherein at least one ultrasound transducer generates a plurality of acoustic signals and time, amplitude, phase and frequency modulation of the signals provide more uniform power delivery with fewer gaps in the ultrasound field. Interference patterns from one or multiple transducers are constantly shifted in position. A phased array of transducers may generate a beam that is swept over the area to be treated. In another embodiment, an array of transducers may generate ultrasound at a number of slightly varying frequencies to produce an interference pattern that sweeps in and out through the targeted tissue. A single array may be used to produce both effects simultaneously or separately.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Method and system for high resolution ultrasonic imaging of small defects or anomalies.
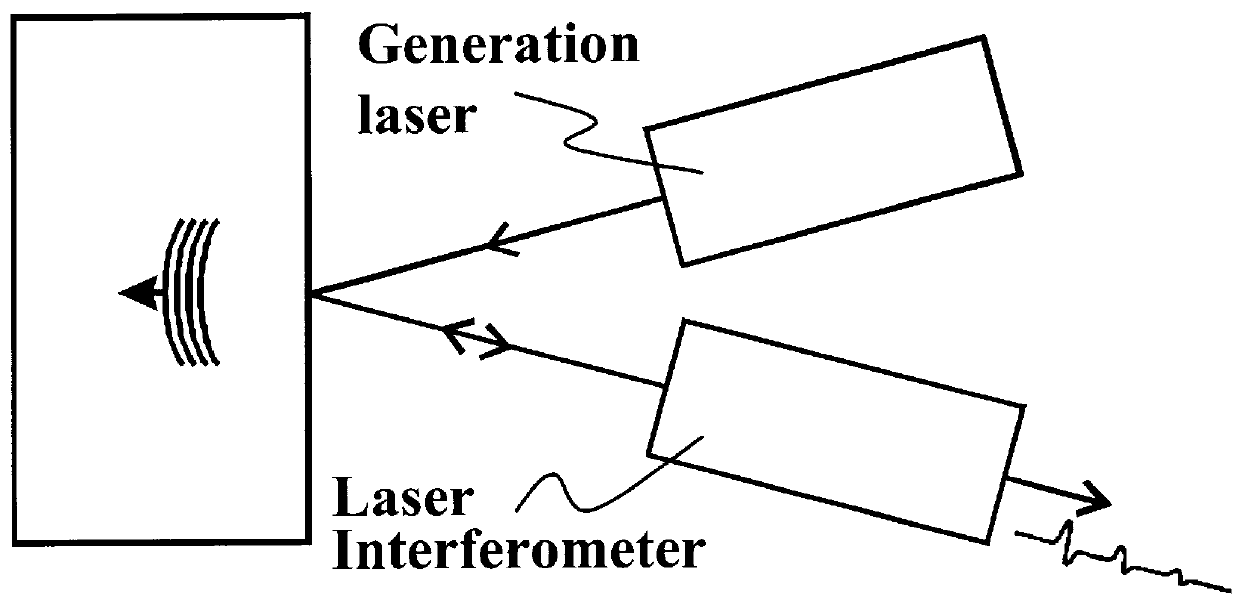
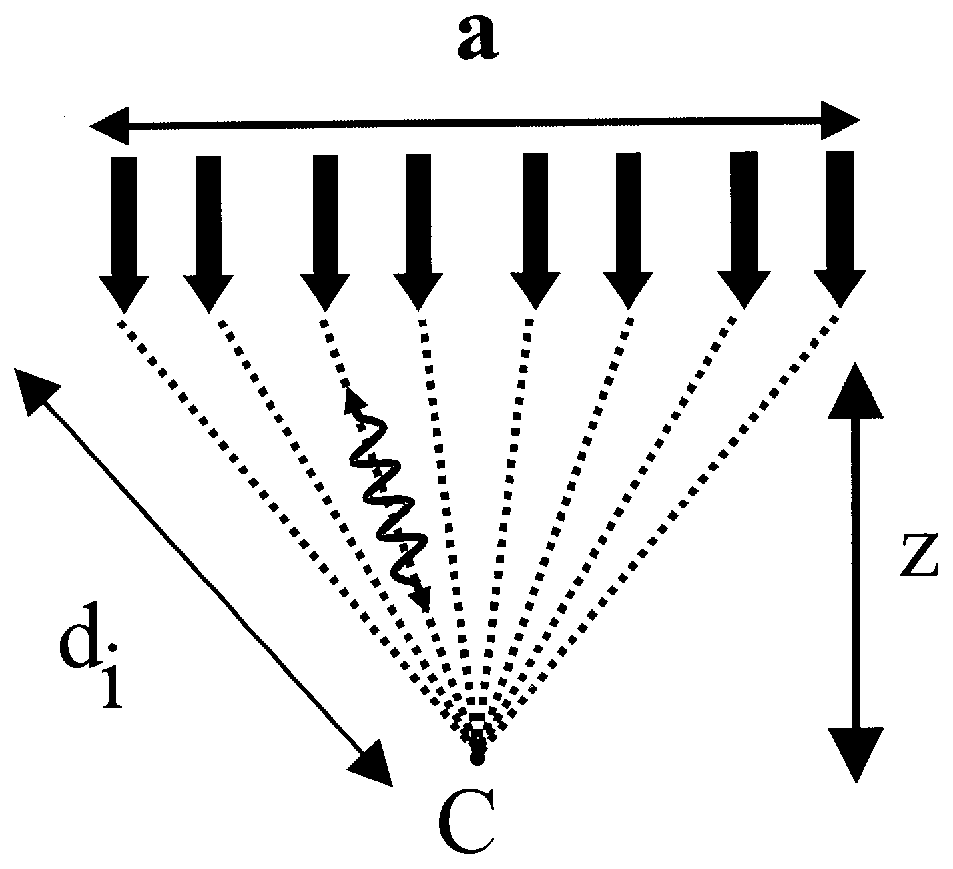
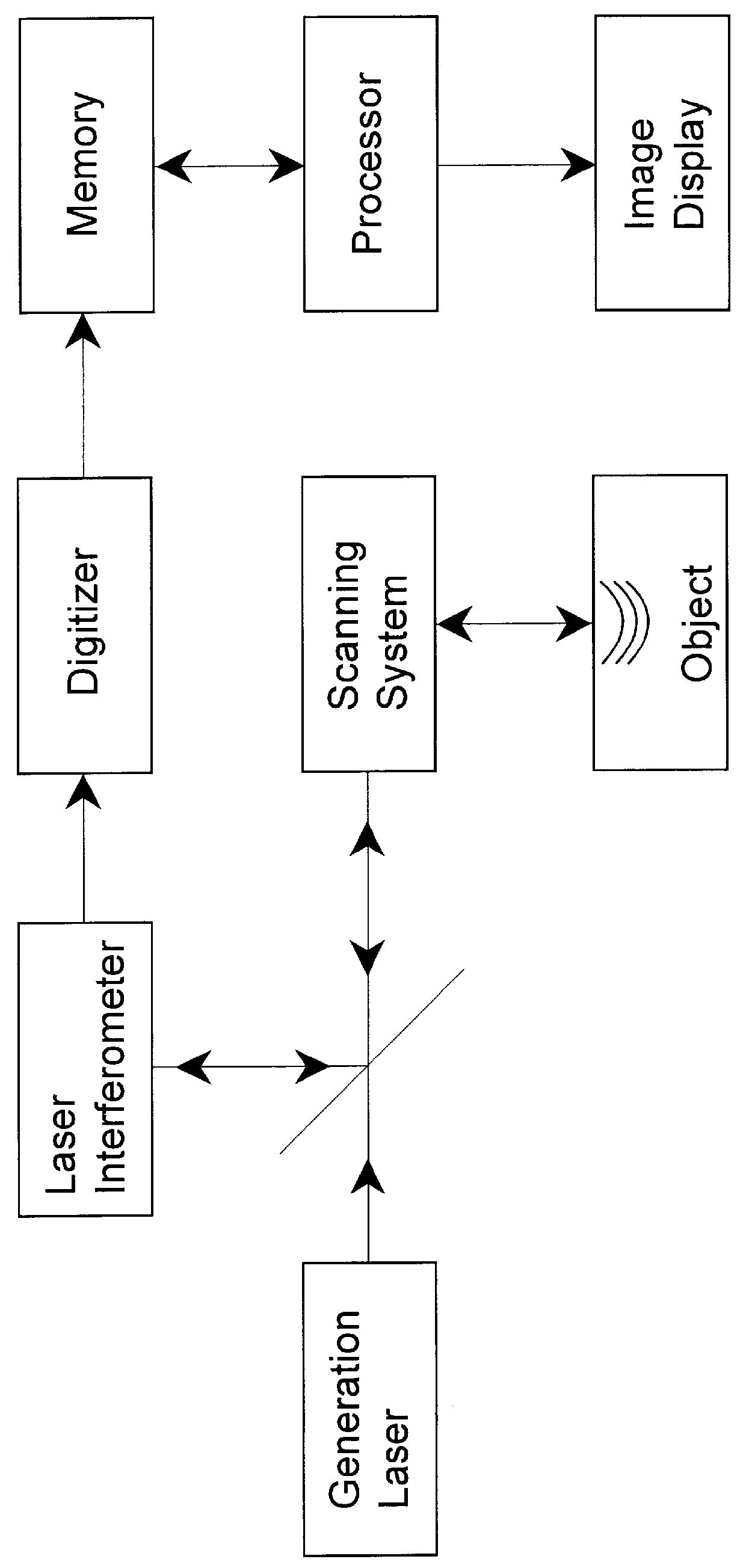
InactiveUS6128092ARadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySonificationSynthetic aperture focusing
A method and system is provided for enhanced ultrasonic detection and imaging of small defects inside or at the surface of an object. The Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique (SAFT) has been used to improve the detectability and to enhance images in conventional ultrasonics and this method has recently been adapted to laser-ultrasonics. In the present invention, an improved version of the frequency-domain SAFT (F-SAFT) based on the angular spectrum approach is described. The method proposed includes temporal deconvolution of the waveform data to enhance both axial and lateral resolutions, control of the aperture and of the frequency bandwidth to improve signal-to-noise ratio, as well as spatial interpolation of the subsurface images. All the above operations are well adapted to the frequency domain calculations and embedded in the F-SAFT data processing. The aperture control and the spatial interpolation allow also a reduction of sampling requirements to further decrease both inspection and processing times. This method is of particular interest when ultrasound is generated by a laser and detected by either a contact ultrasonic transducer or a laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Diagnostic ultrasound transducer
ActiveUS20090034370A1Easy to guaranteeGood electrical contactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic sensorEngineering
An ultrasound transducer includes an array of PZT elements mounted on a non-recessed distal surface of a backing block. Between each element and the backing block is a conductive region formed as a portion of a metallic layer sputtered onto the distal surface. Traces on a longitudinally extending circuit board—preferably, a substantially rigid printed circuit board, which may be embedded within the block—connect the conductive region, and thus the PZT element, with any conventional external ultrasound imaging system. A substantially “T” or “inverted-L” shaped electrode is thereby formed for each element, with no need for soldering. At least one longitudinally extending metallic member mounted on a respective lateral surface of the backing block forms a heat sink and a common electrical ground. A thermally and electrically conductive layer, such as of foil, transfers heat from at least one matching layer mounted on the elements to the metallic member.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY SCIENTIFIC CO LTD
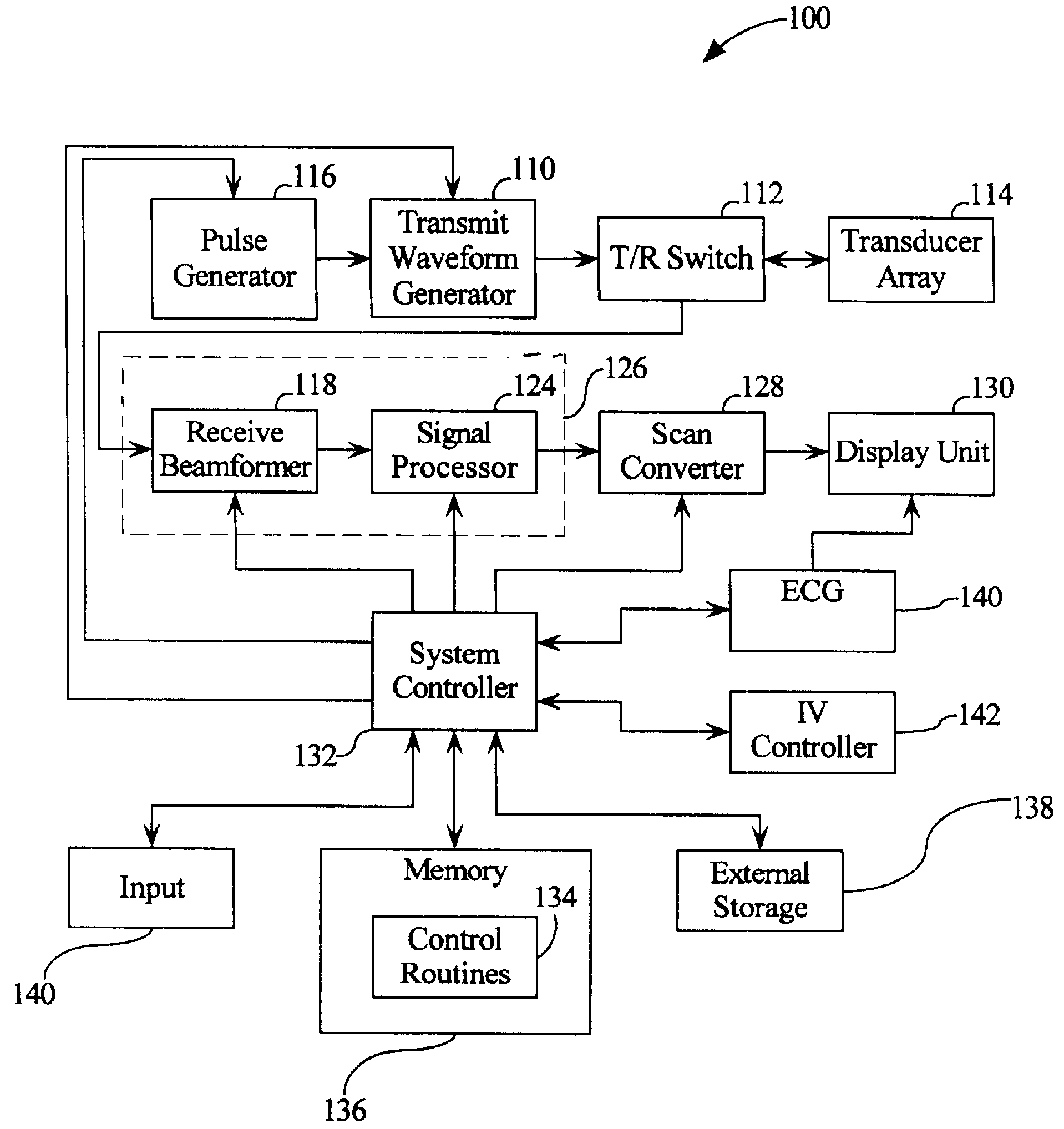
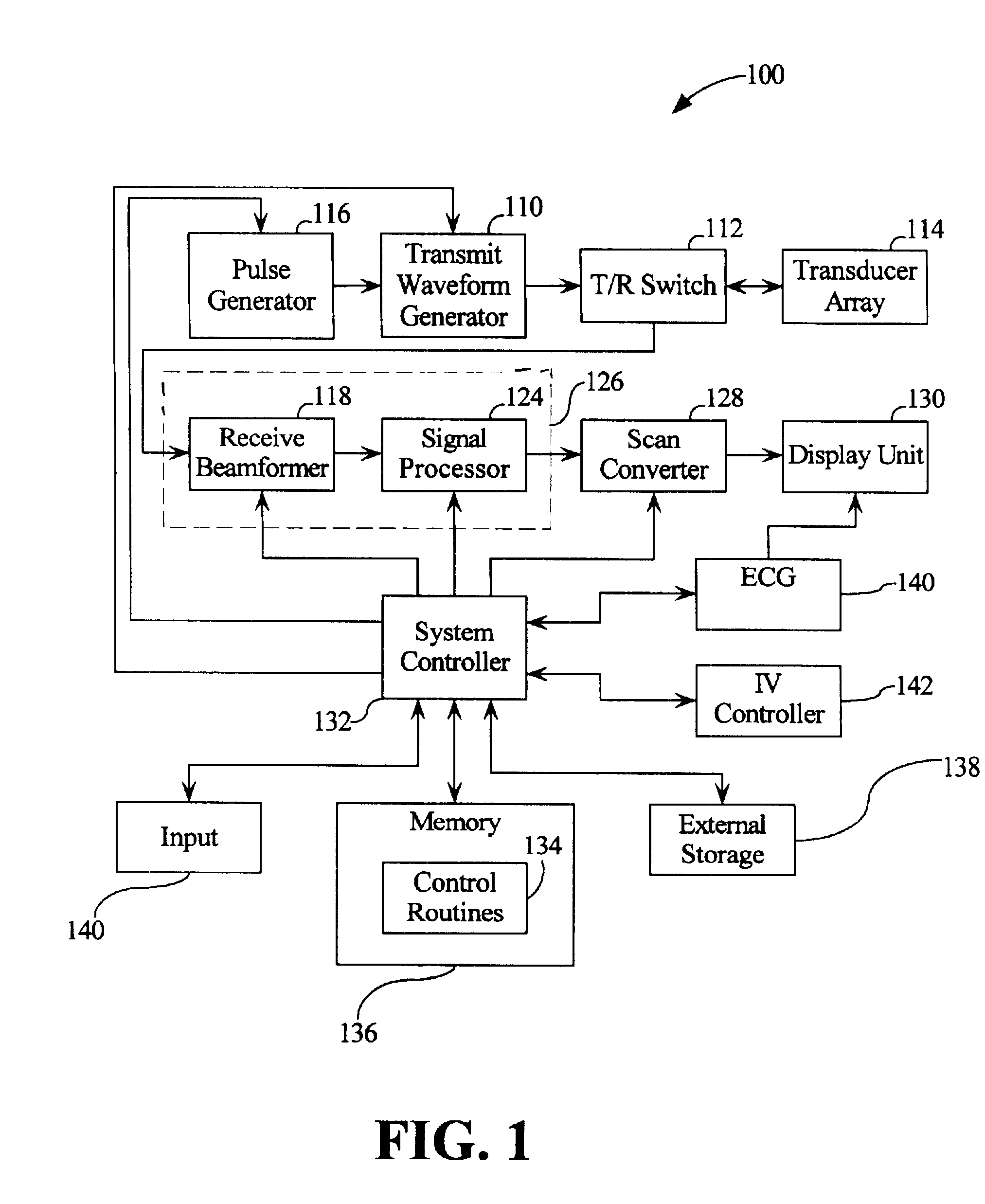
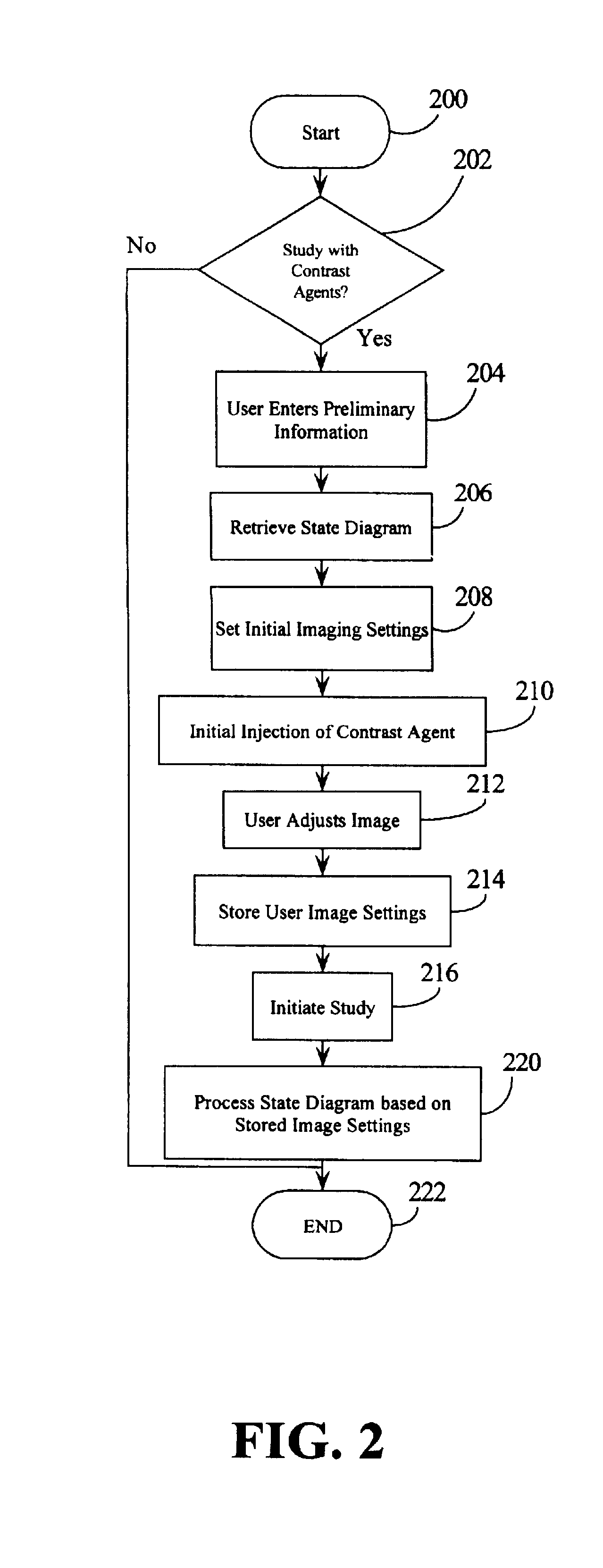
Automated ultrasound system for performing imaging studies utilizing ultrasound contrast agents
InactiveUS6503203B1Simplify such studyFast informationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound system that has transmit and receive circuitry that, pursuant to a plurality of image settings, transmits ultrasound signals into a patient, receives echoes from a patient and outputs a signal representative of the echo. Control circuitry is provided that sequentially adjusts the image settings so as to cause the transmit and receive circuitry to have a sequence of imaging configurations during an ultrasound imaging study. A memory may be provided that stores a plurality of state diagrams, each defining a sequence of imaging configurations for a particular imaging study, which are accessible by the control circuitry, wherein the control circuitry accesses a selected state diagram to conduct an imaging study. Such a system is particularly useful for imaging studies that utilize contrast agents.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for the ultrasonic actuation of the cantilever of a probe-based instrument
The cantilever of a probe-based metrology instrument such as an AFM is deflected by directing a beam of ultrasonic energy at the cantilever to apply ultrasonically generated acoustic radiation pressure to the cantilever. The energy is generated by an ultrasonic actuator such as a ZnO transducer driven by a power source such an RF signal generator. The transmitted beam preferably is shaped by focusing, collimation, or the like so that it impinges at least primarily on a region of interest of the cantilever such as the free end. The ultrasonic actuator produces a much better controlled force on the cantilever than can be achieved through the use of a traditional piezoelectric actuator and, accordingly, produces a response free of spurious effects (at least when the cantilever is operating in liquid). It also has a frequency bandwidth in the MHz range.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Carbon naoparticle-containing hydrophilic nanofluid
InactiveUS20070158610A1Stabilize nanoparticle dispersionImprove thermal conductivityHeat-exchange elementsCarbon nanotubeHydrophile
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a stable suspension of carbon nanoparticles in a hydrophilic thermal transfer fluid to enhance thermal conductive properties and other characteristics such as freezing point of an antifreeze coolant. The process involves the step of dispersing carbon nanoparticles directly into a mixture of a thermal transfer fluid and other additives in the present of surfactants with intermittent ultrasonication. The present invention also relates to the composition of a hydrophilic nanofluid, which comprises carbon nanoparticles, particularly carbon nanotubes, a hydrophilic thermal transfer fluid, and at least one surfactant. Addition of surfactants significantly increases the stability of nanoparticle dispersion.
Owner:SOUTH DAKOTA SCHOOL OF MINES AND TECHNOLOGY
Acoustic inspection device
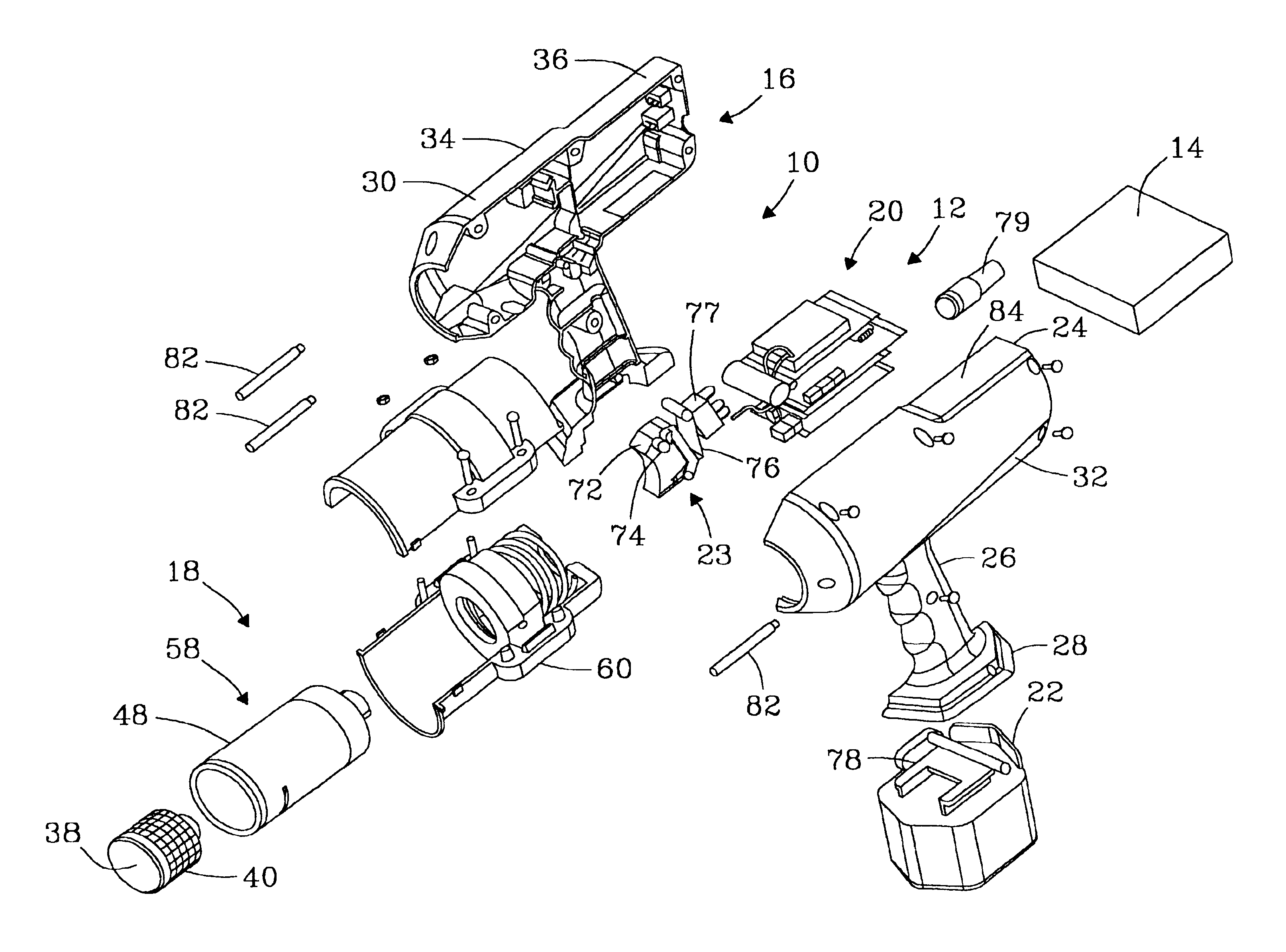
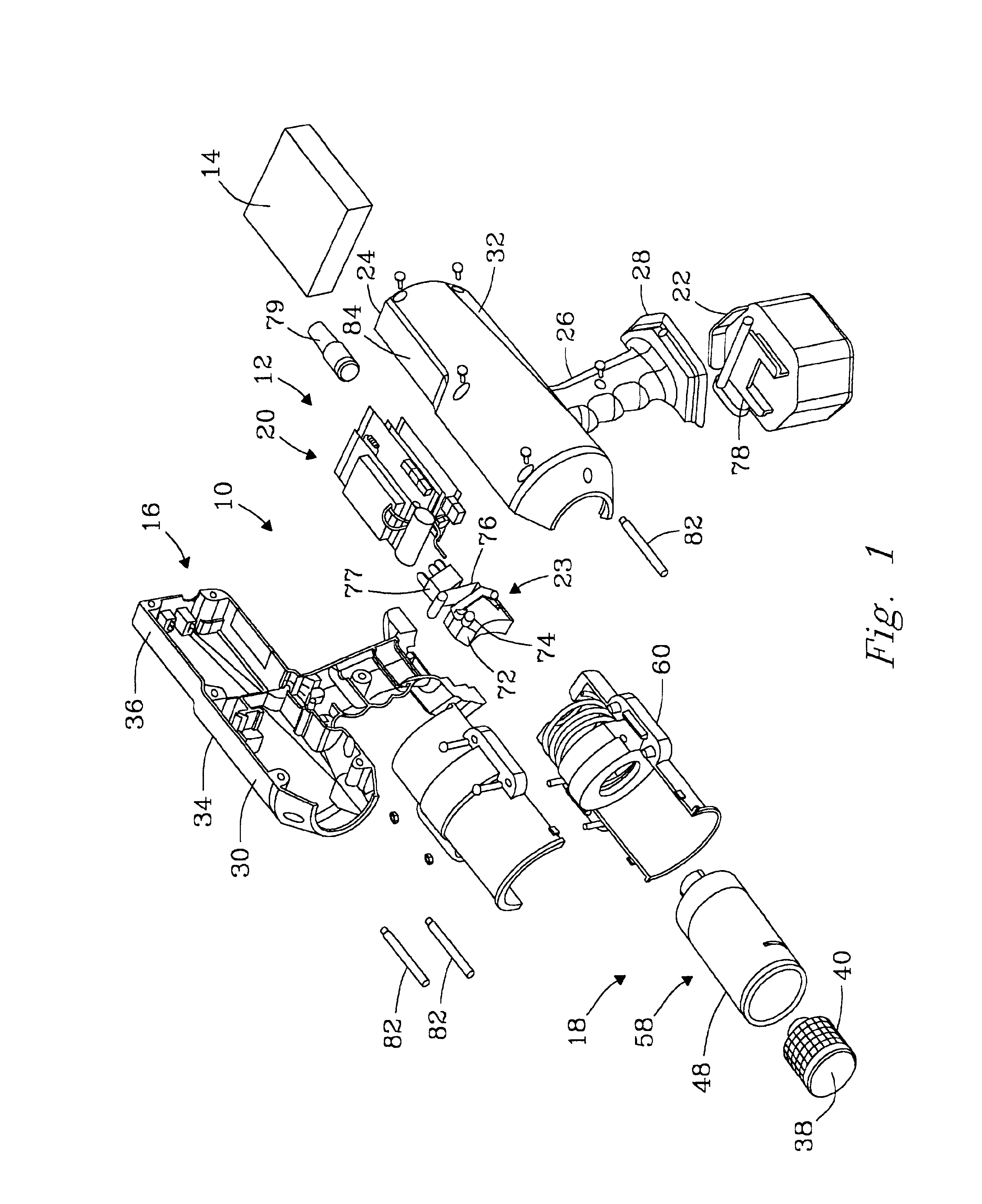
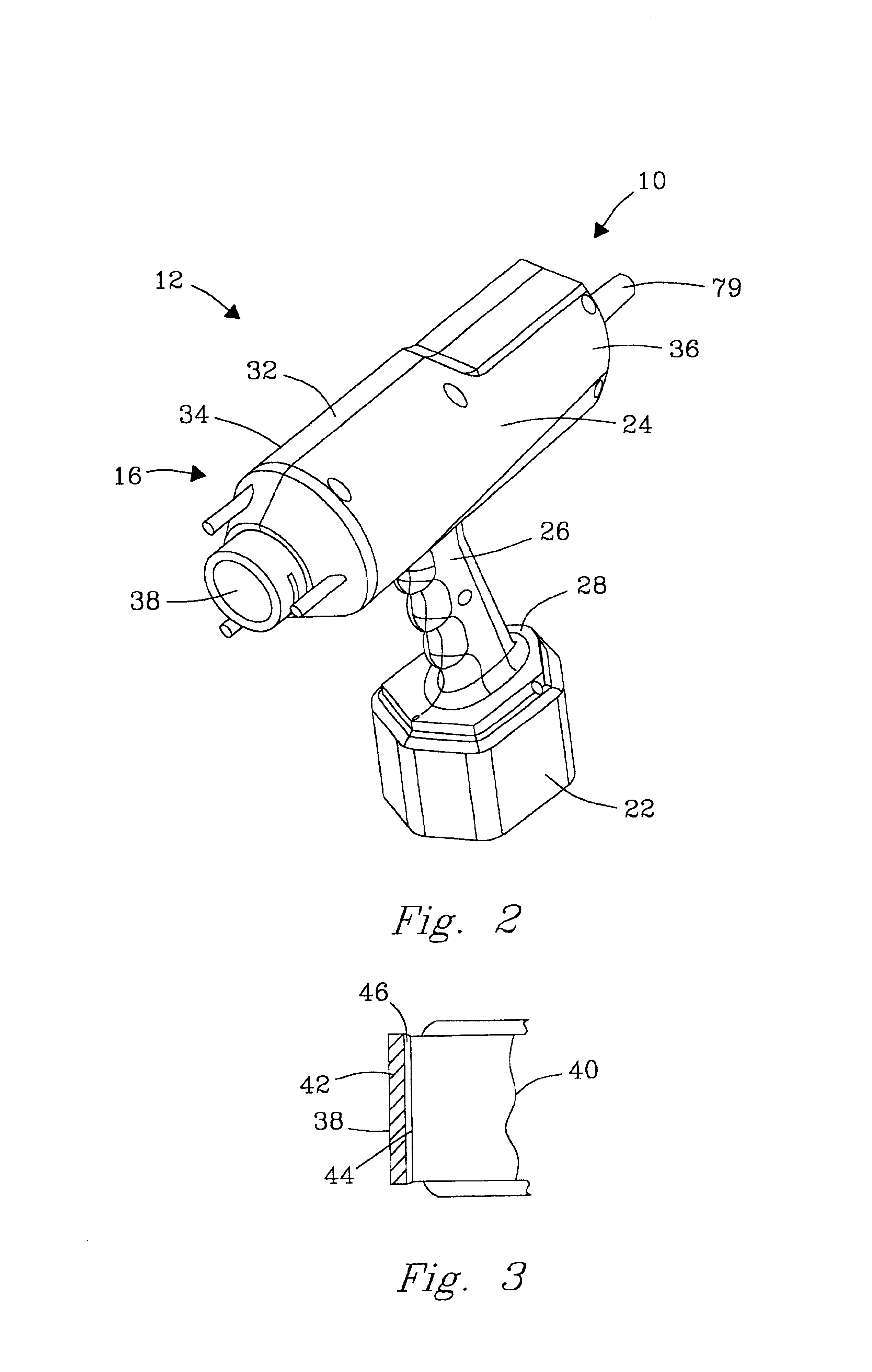
InactiveUS6938488B2Minimal noise figureRapid determinationUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansMagnetic property measurementsUltrasound sonographyTransducer
An ultrasound inspection apparatus particularly adapted to examine containers (sealed or unsealed) containing a liquid or solid bulk material. The apparatus has an overall configuration of a hand held pistol with a front transducer contact surface that is positioned against a front wall of the container. An ultrasound pulse is transmitted from the apparatus to be reflected from a back wall of a container being investigated. The received echo pulse is converted to a digital waveform. The waveform is analyzed relative to temperature, travel distance of the pulse(s), and time of travel to ascertain characteristics of the liquid or other materials and to provide identification of the same.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com