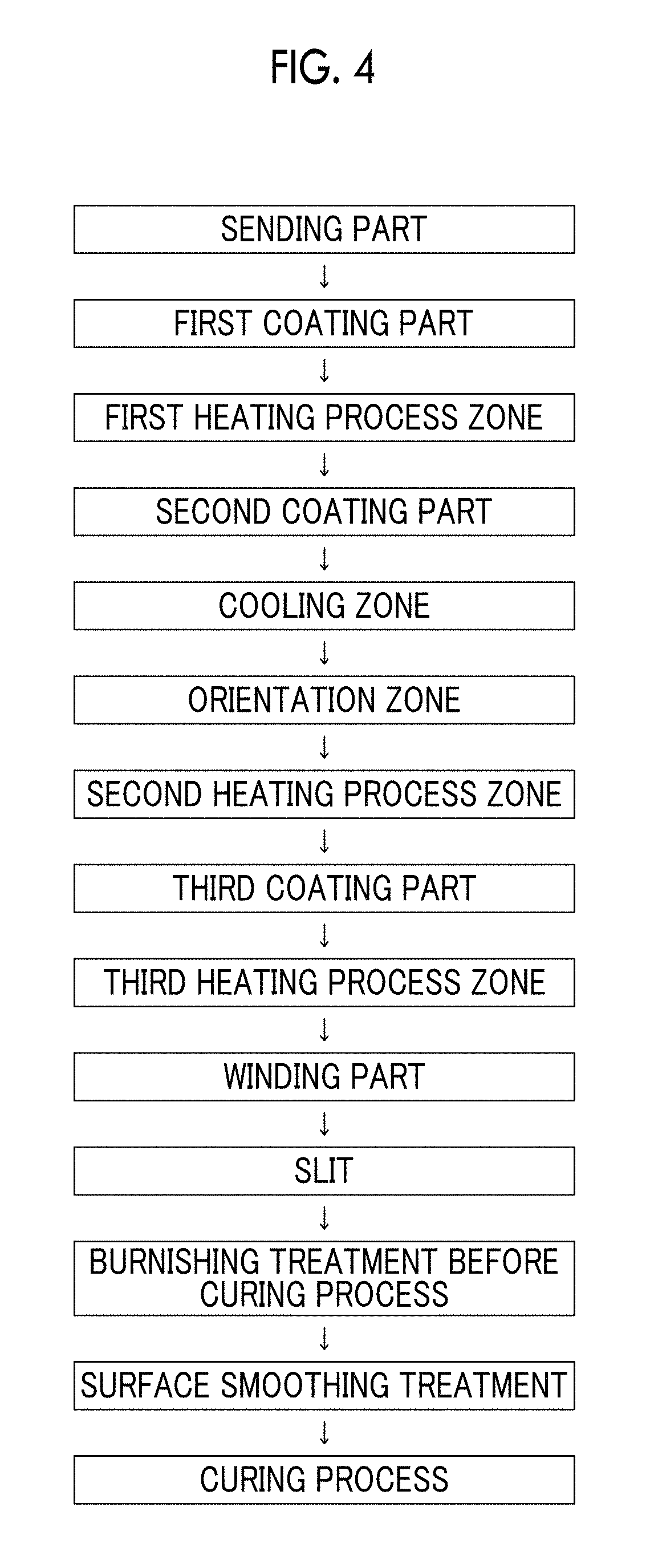
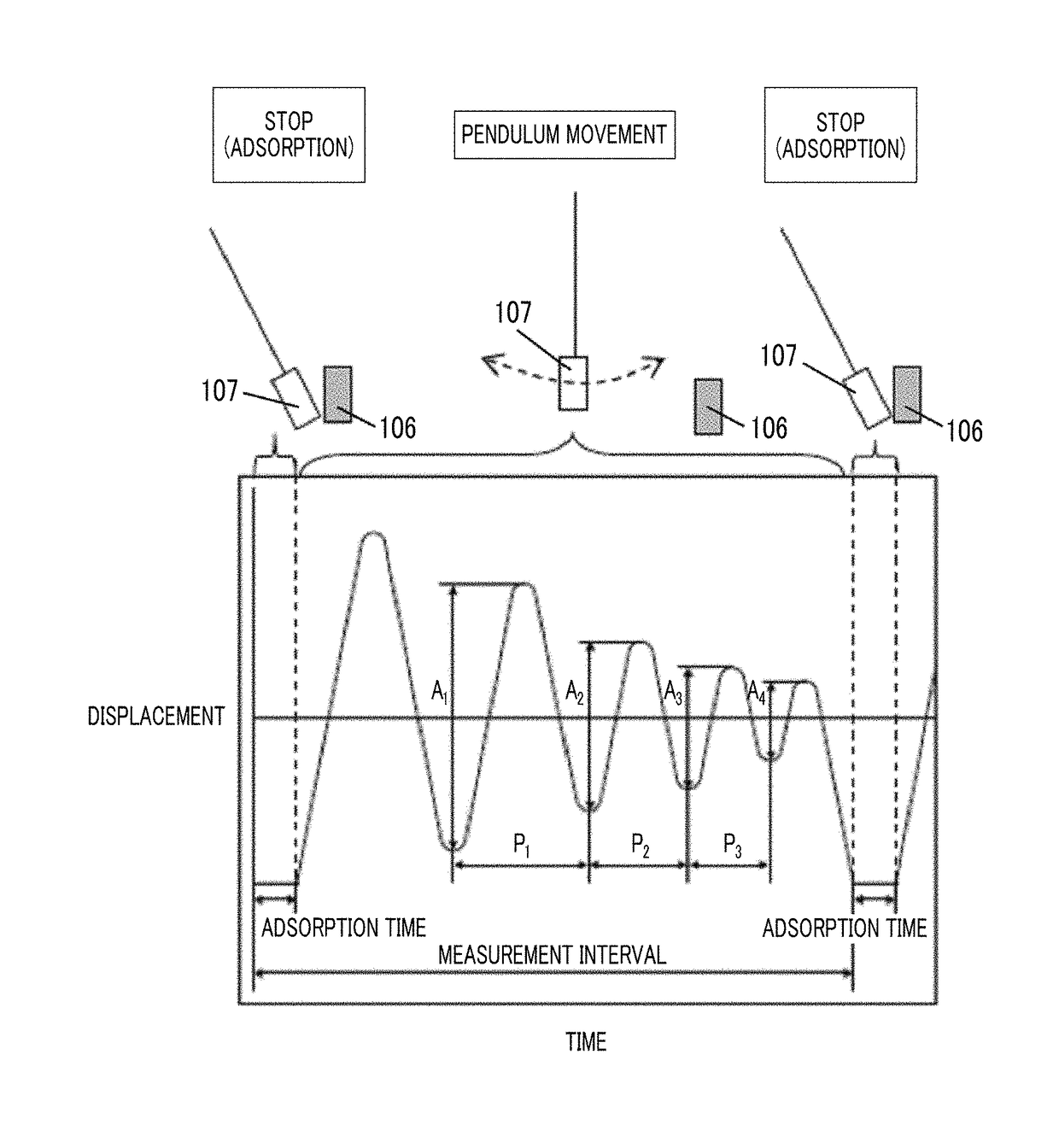
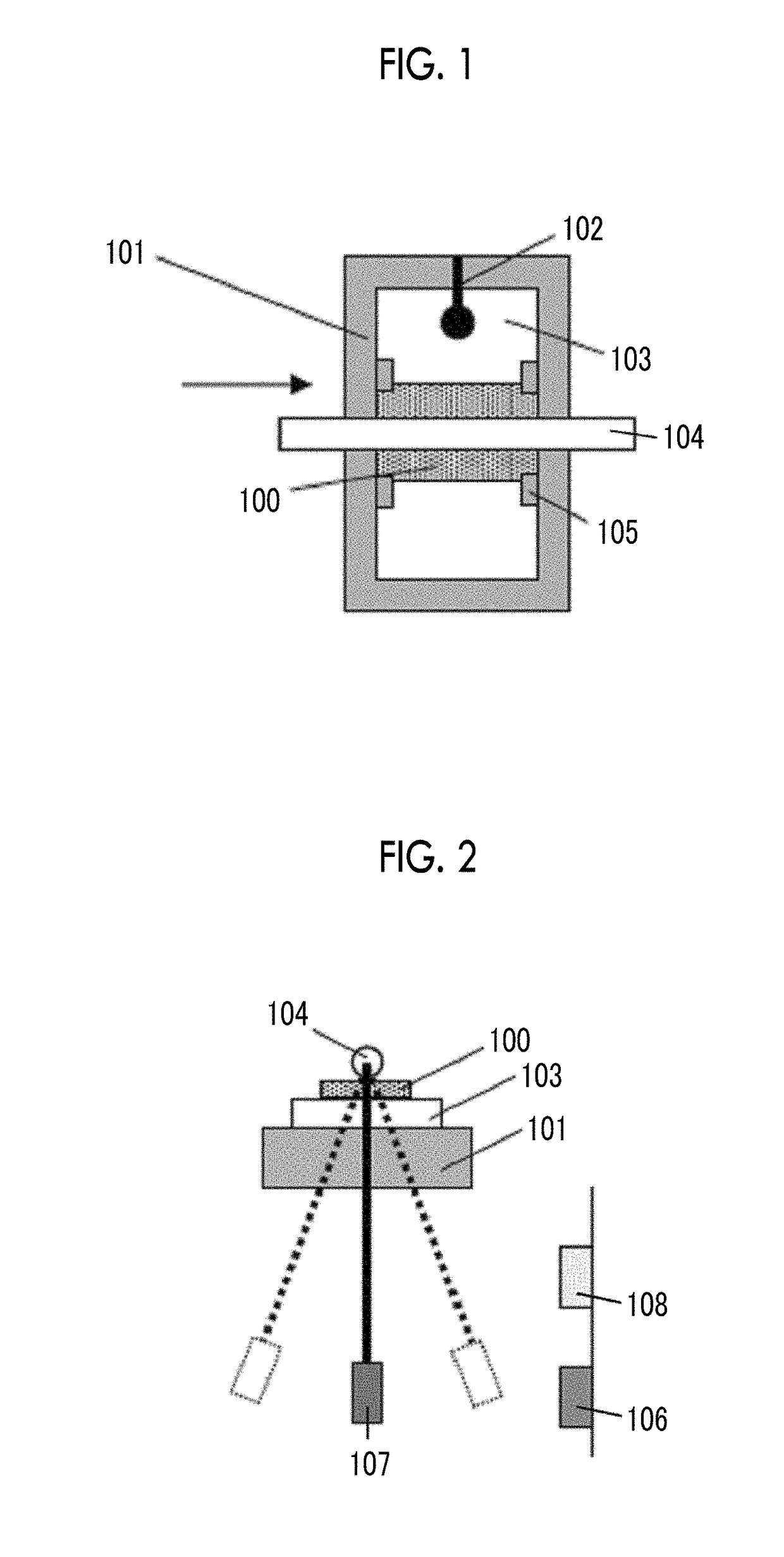
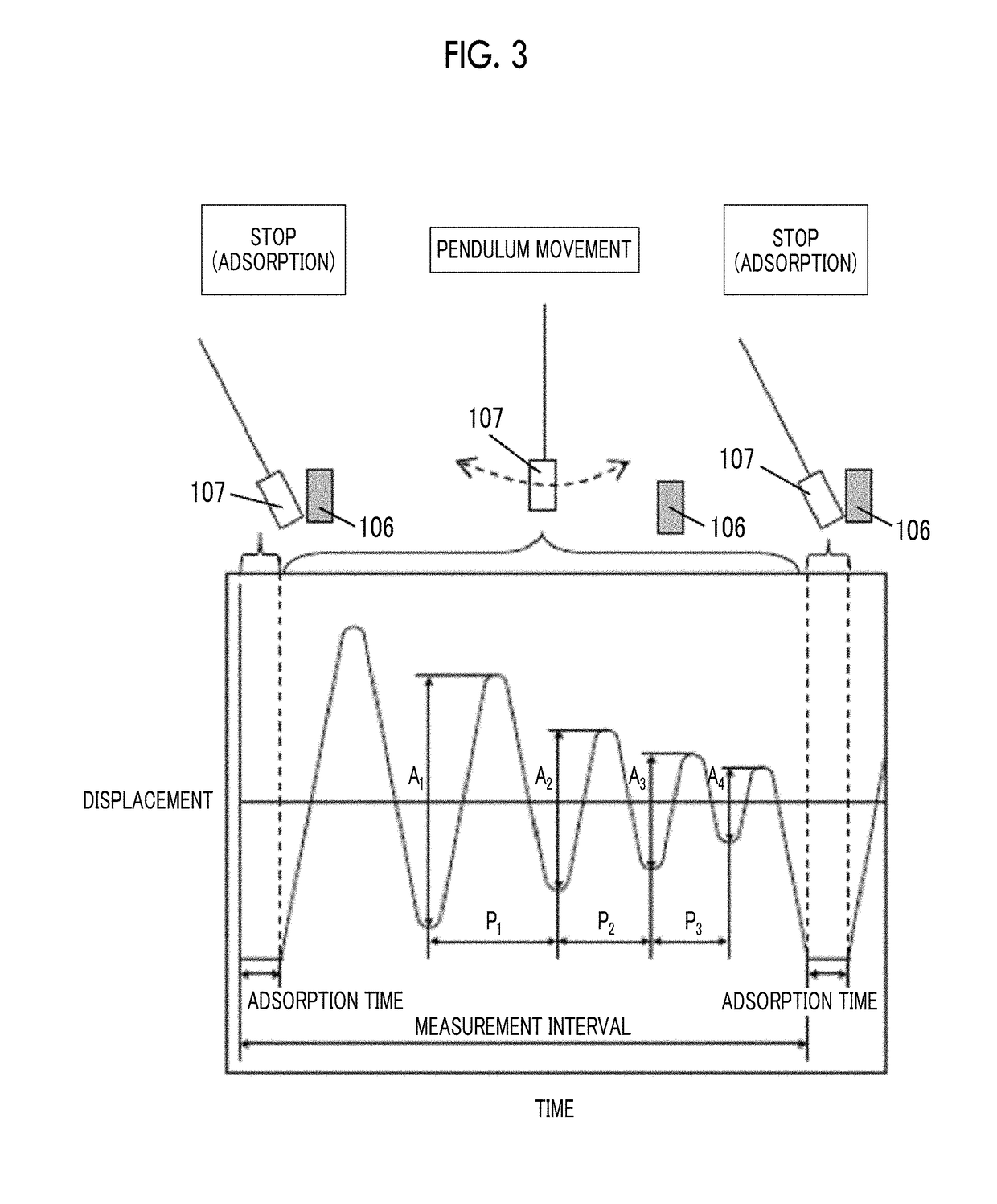
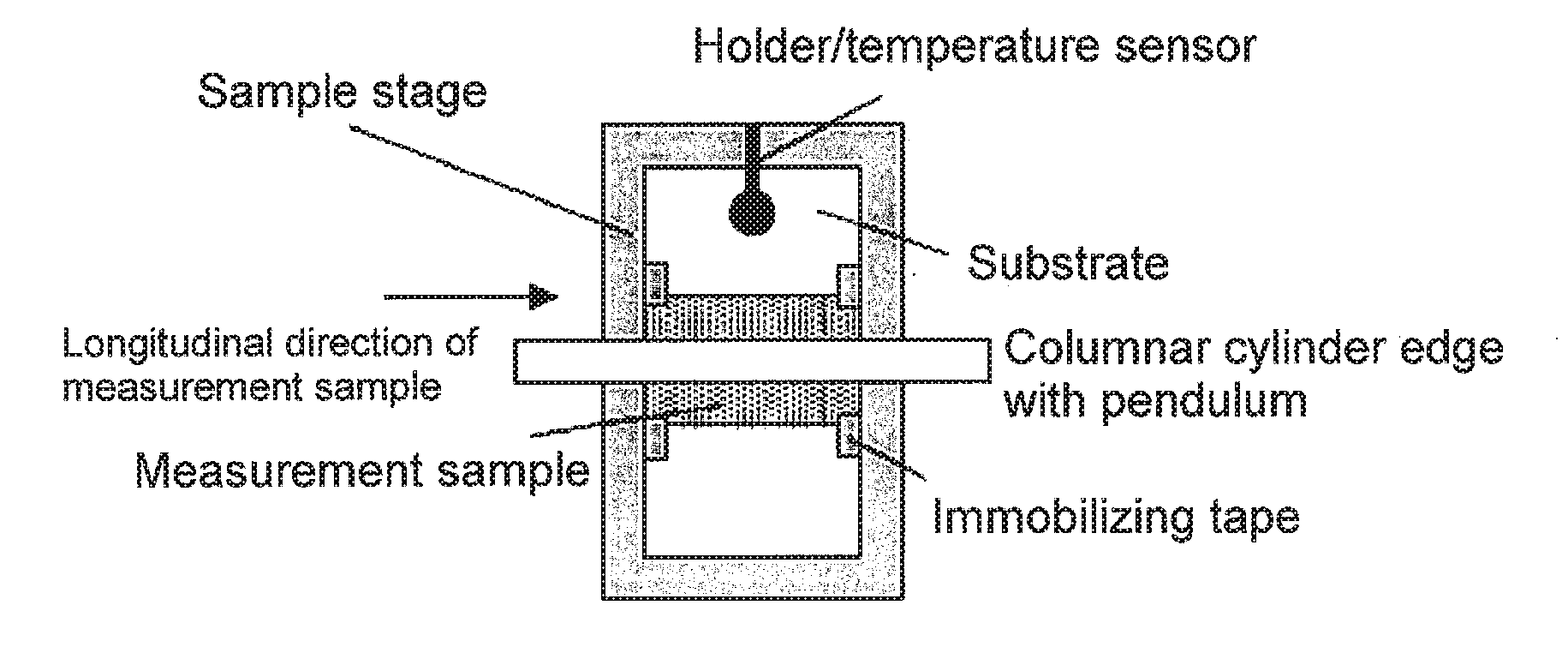
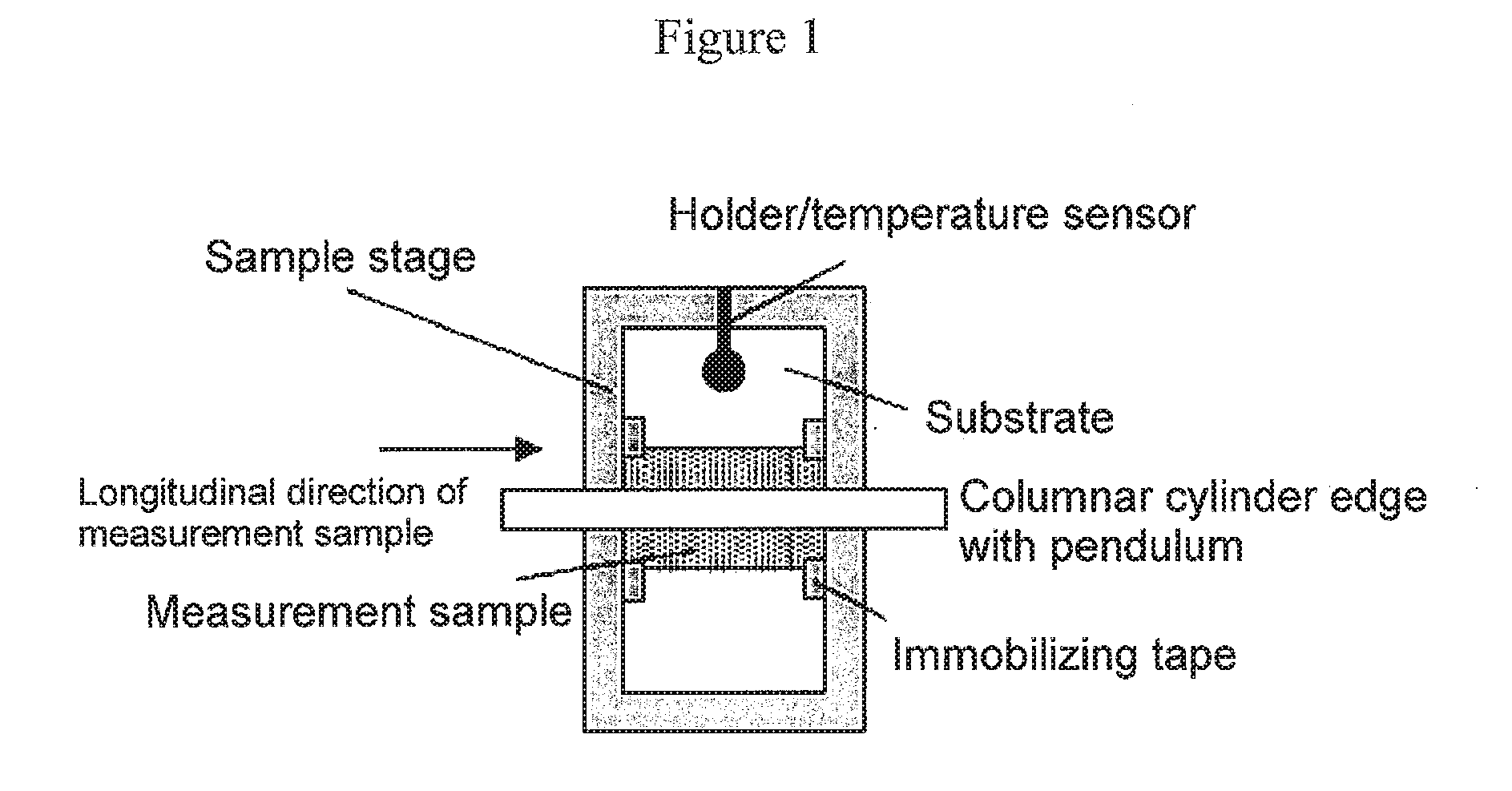
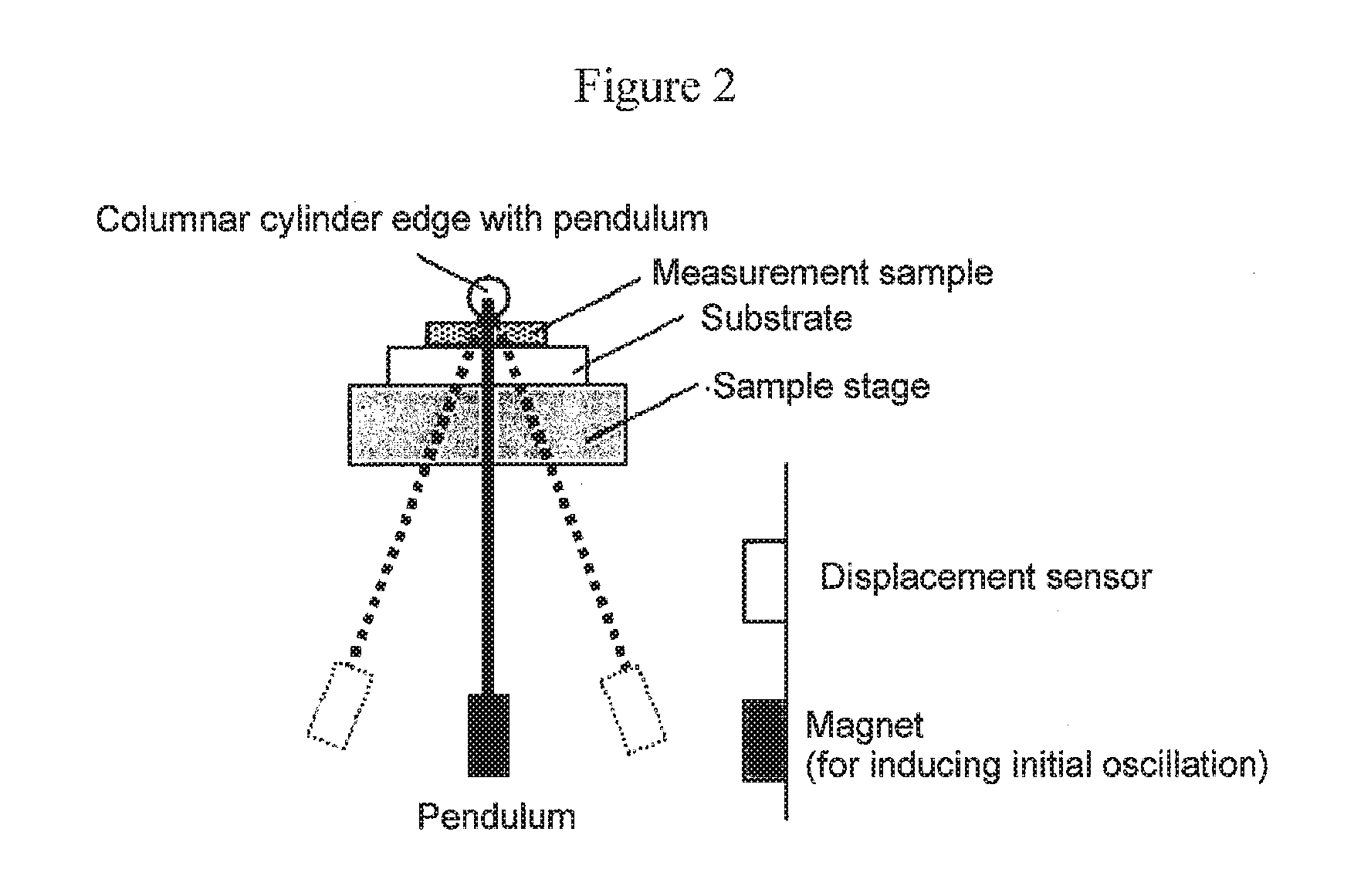
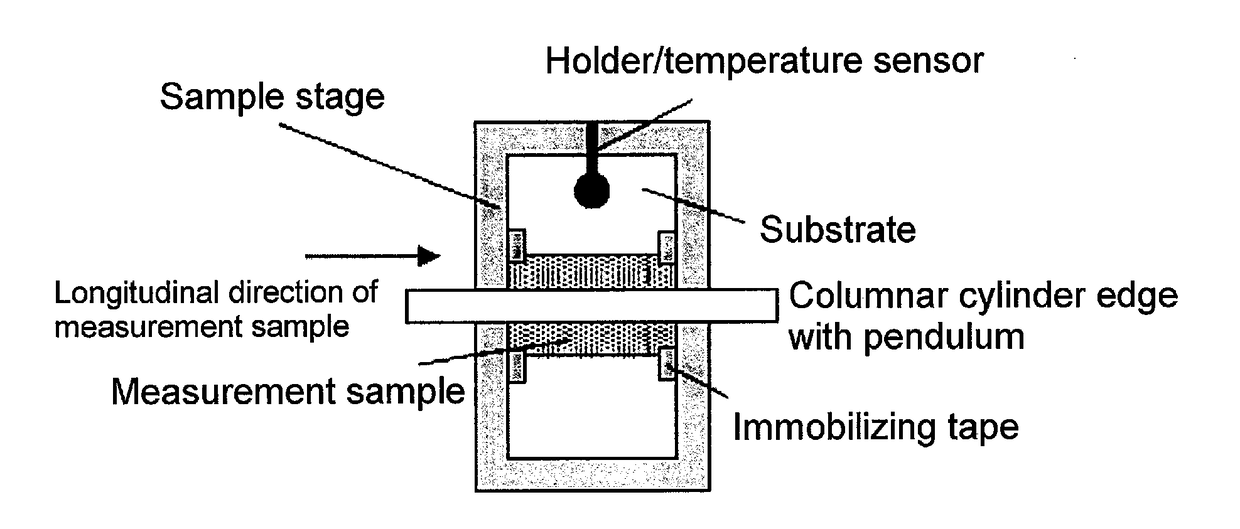
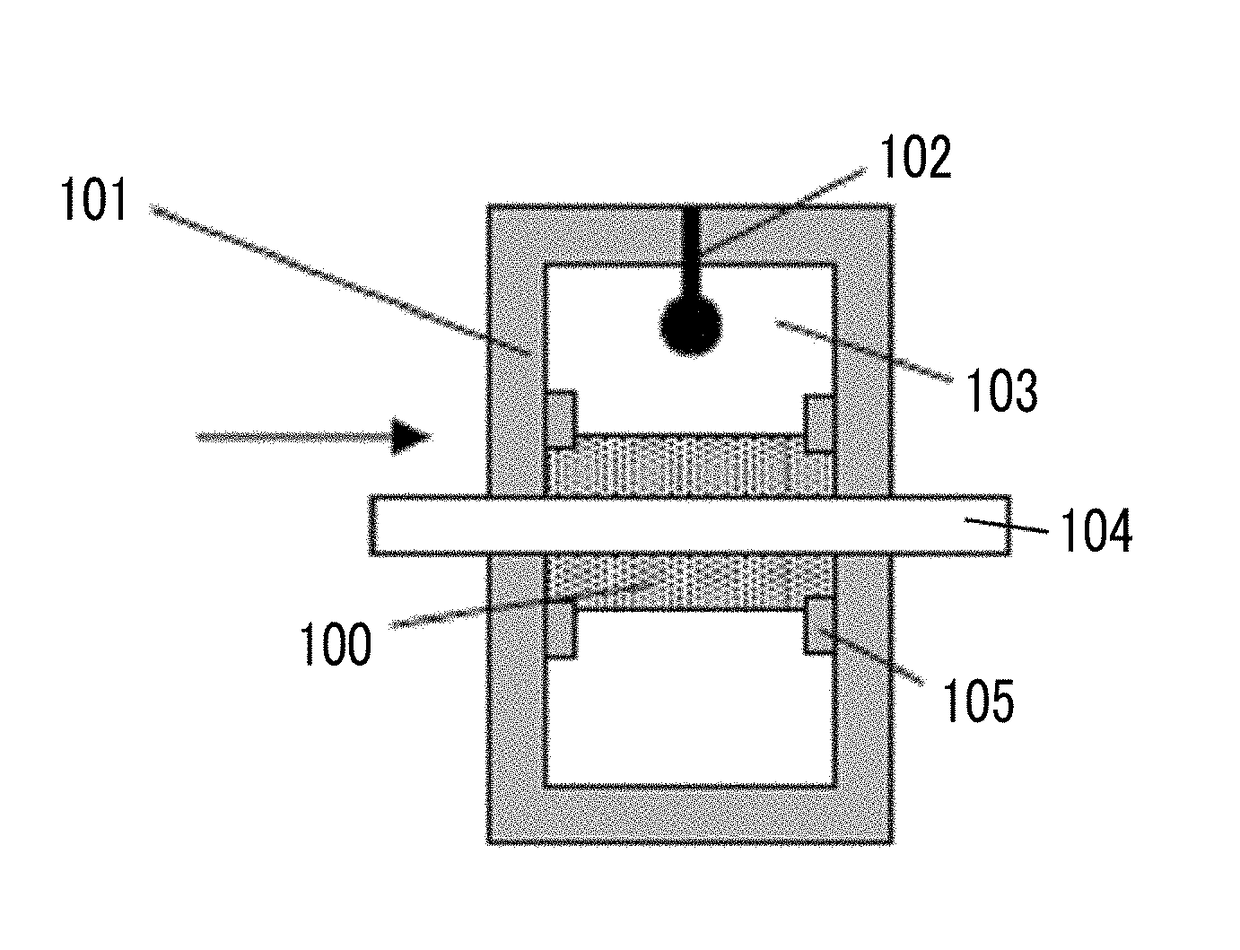
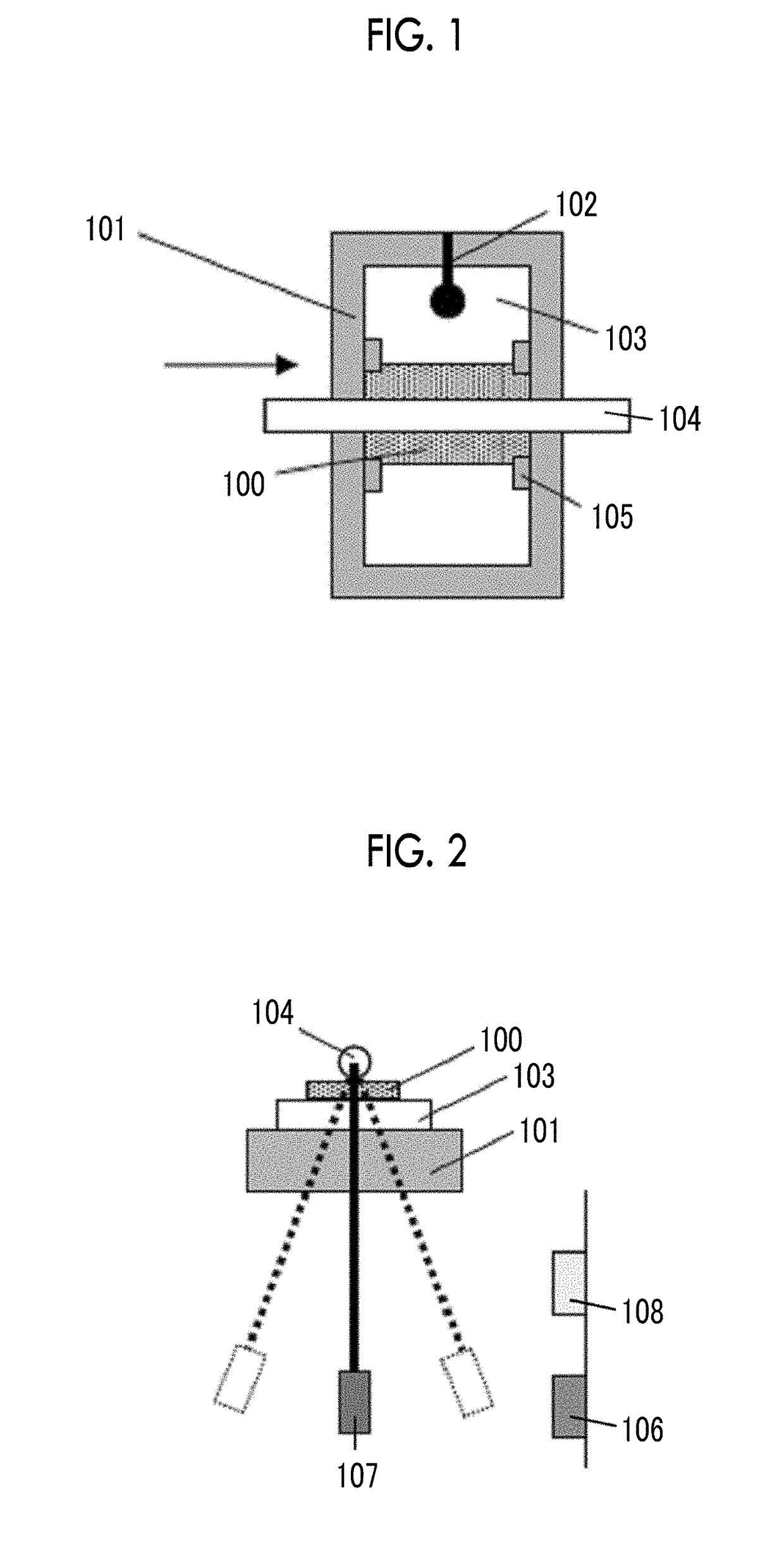
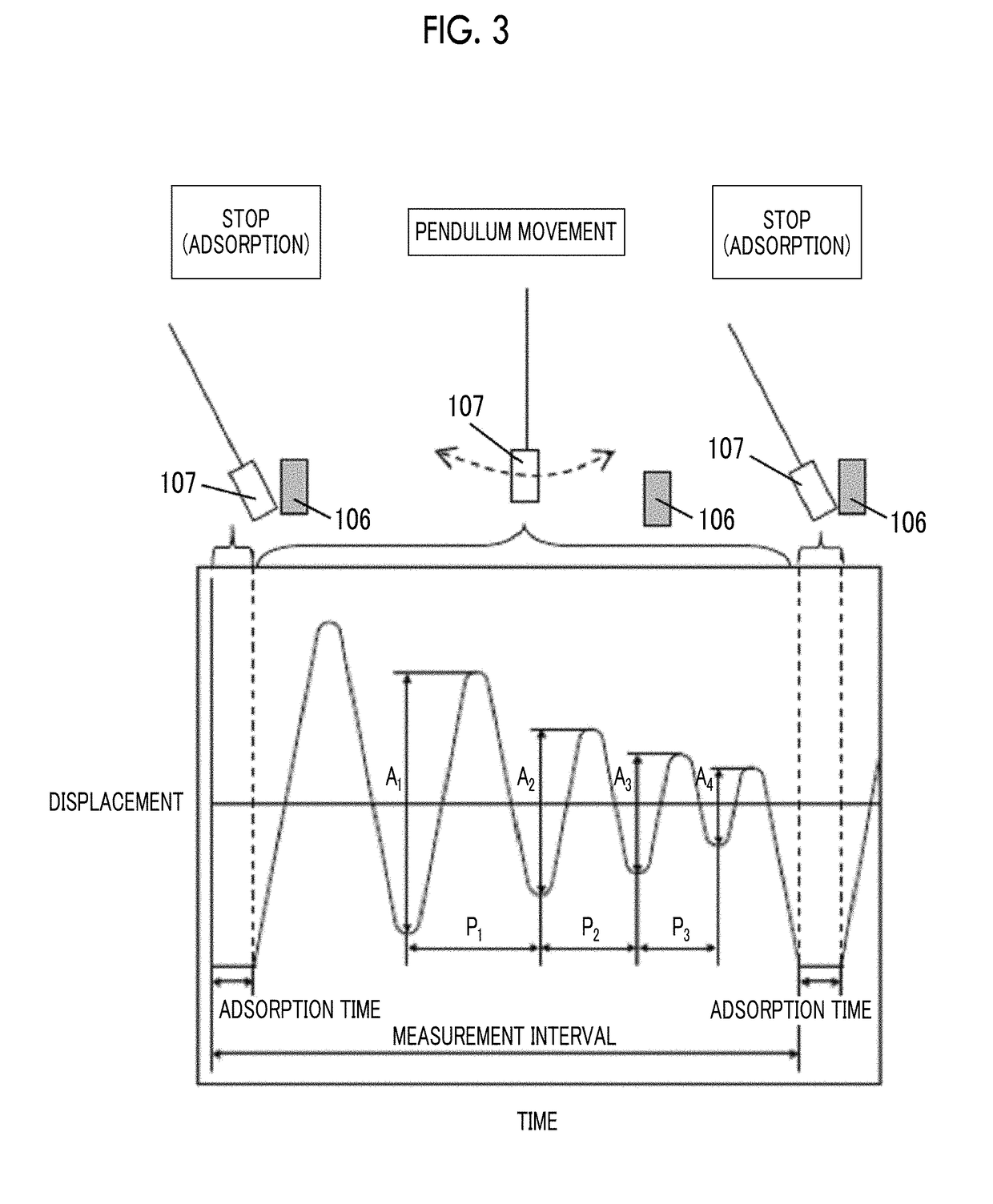
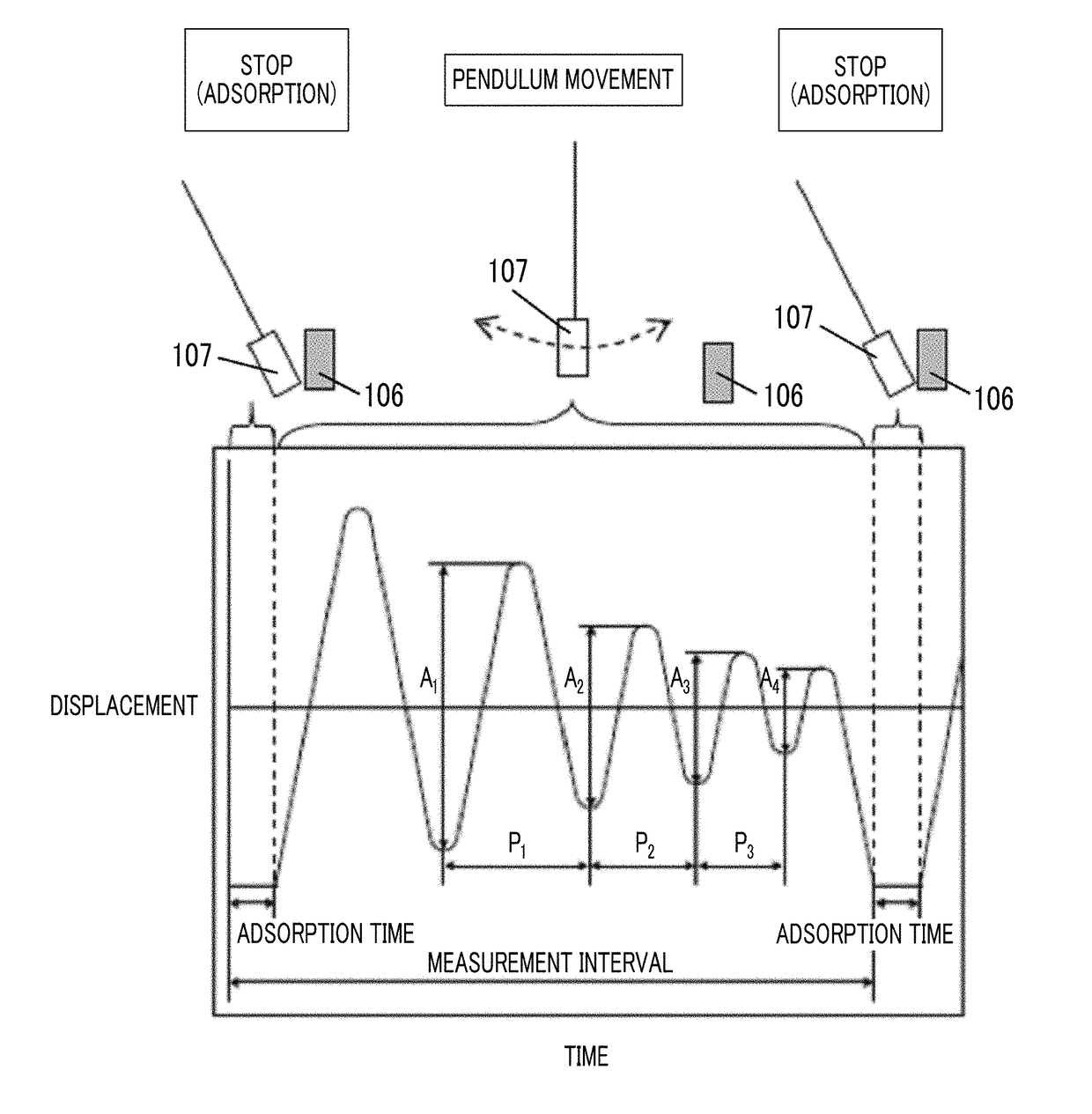
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1163 results about "Viscoelasticity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain when stretched and immediately return to their original state once the stress is removed.
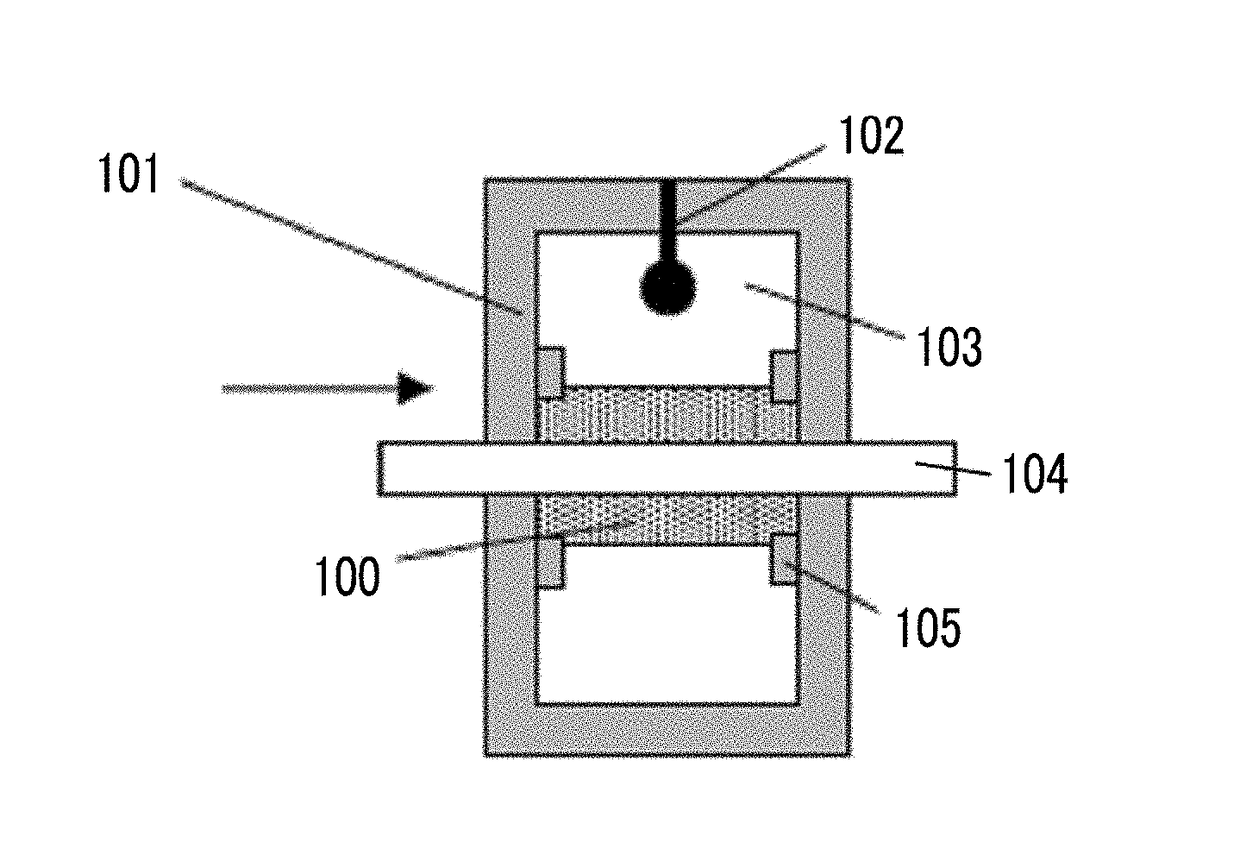
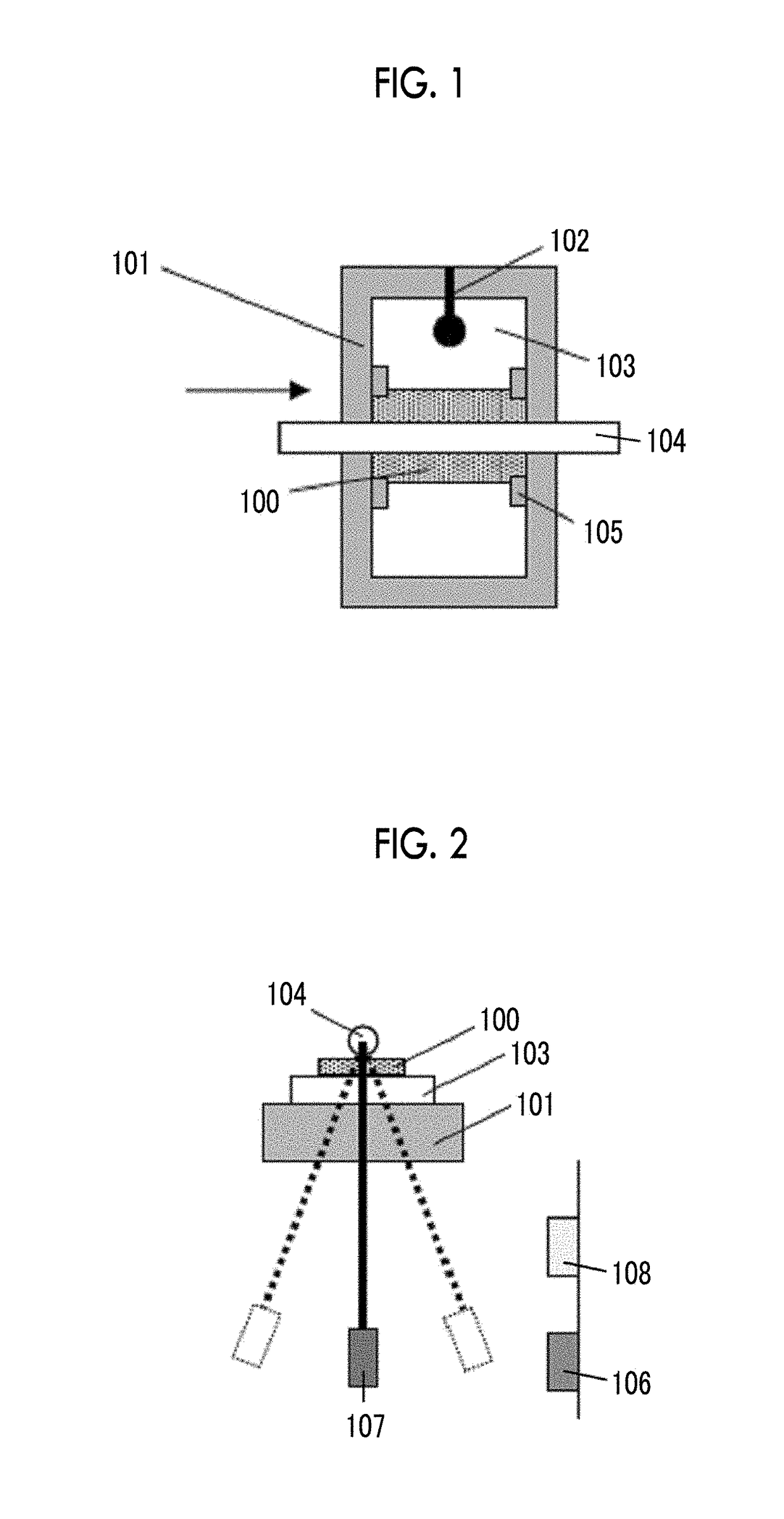
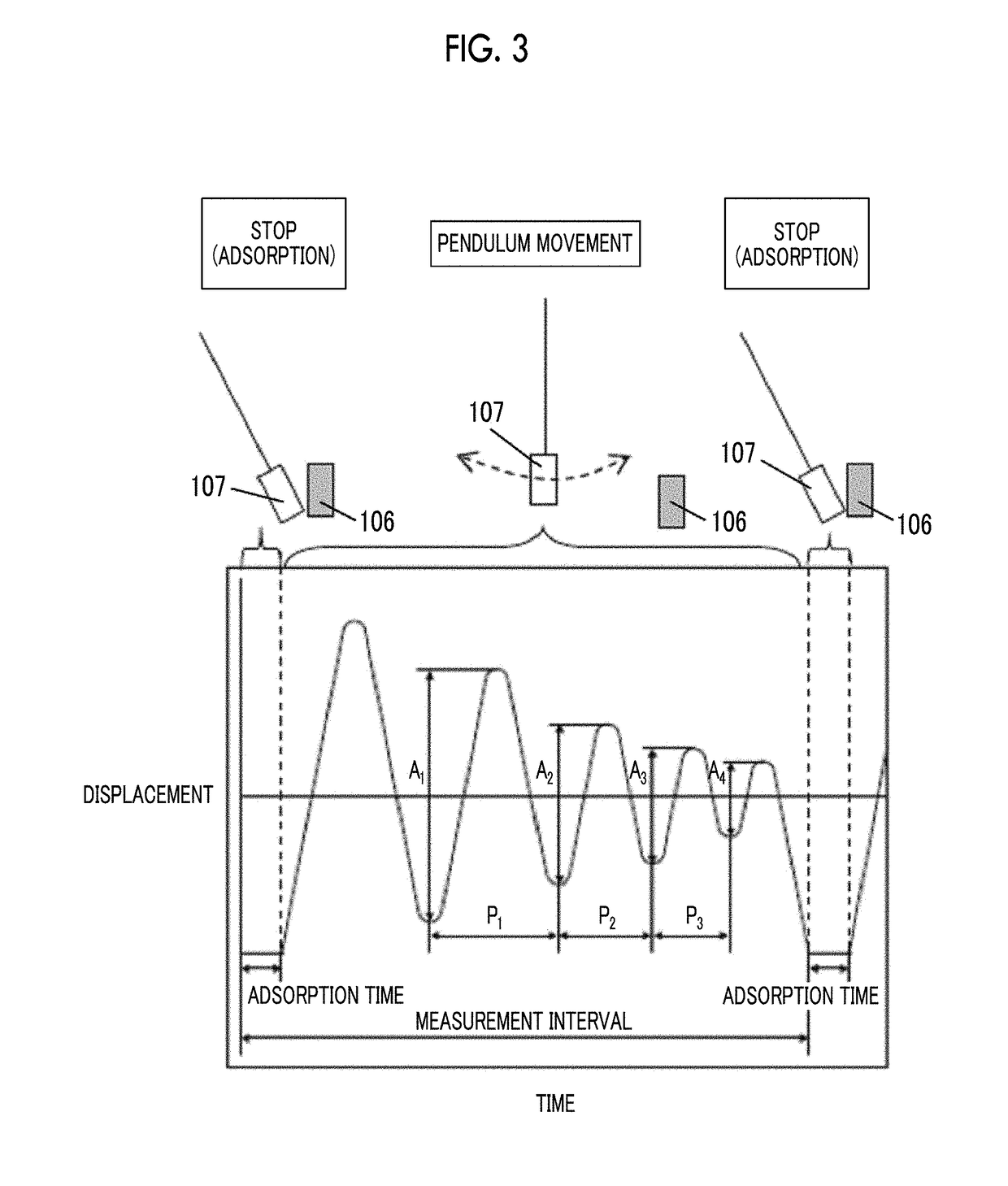
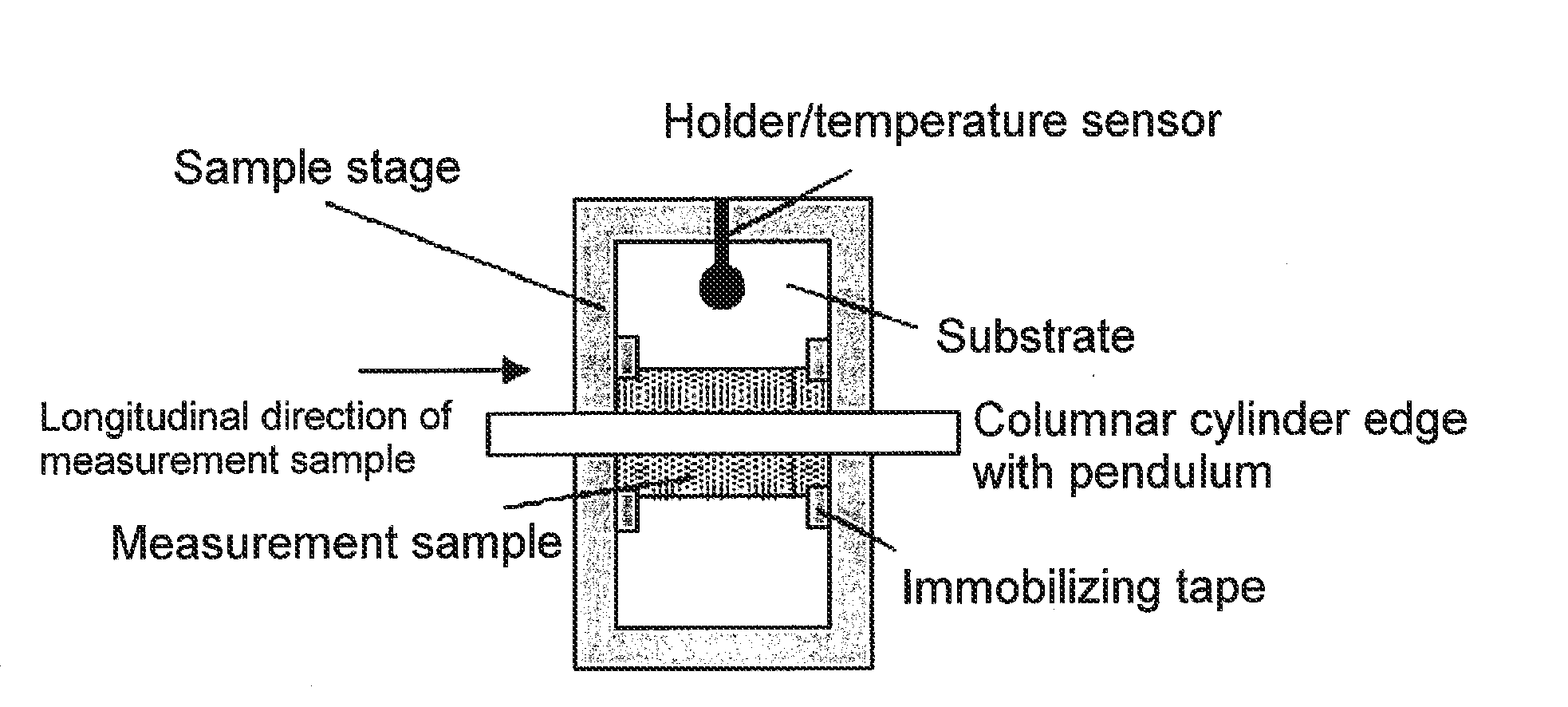
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103131A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againDisposition/mounting of recording headsMagnetic materials for record carriersIn planeX-ray
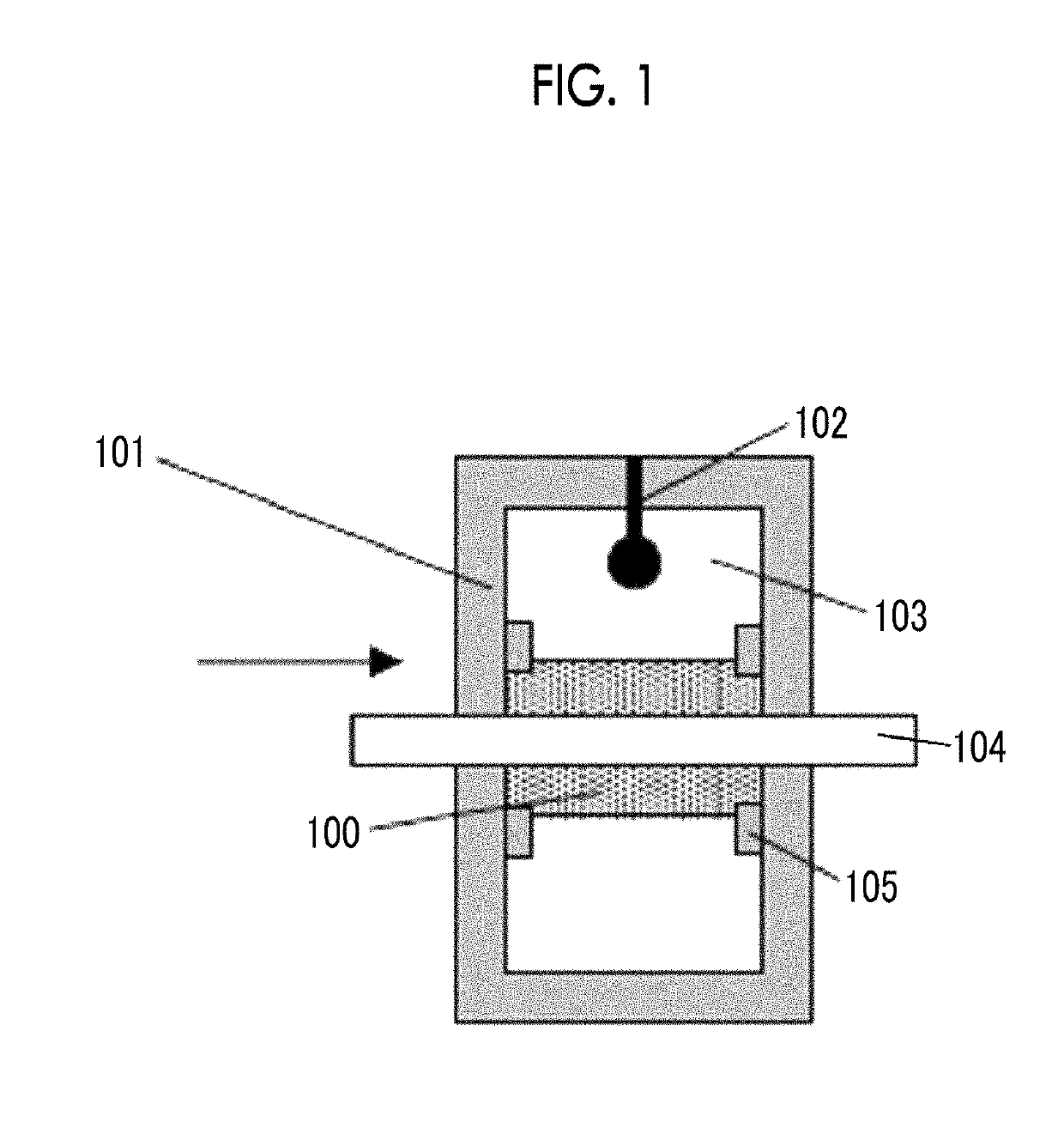
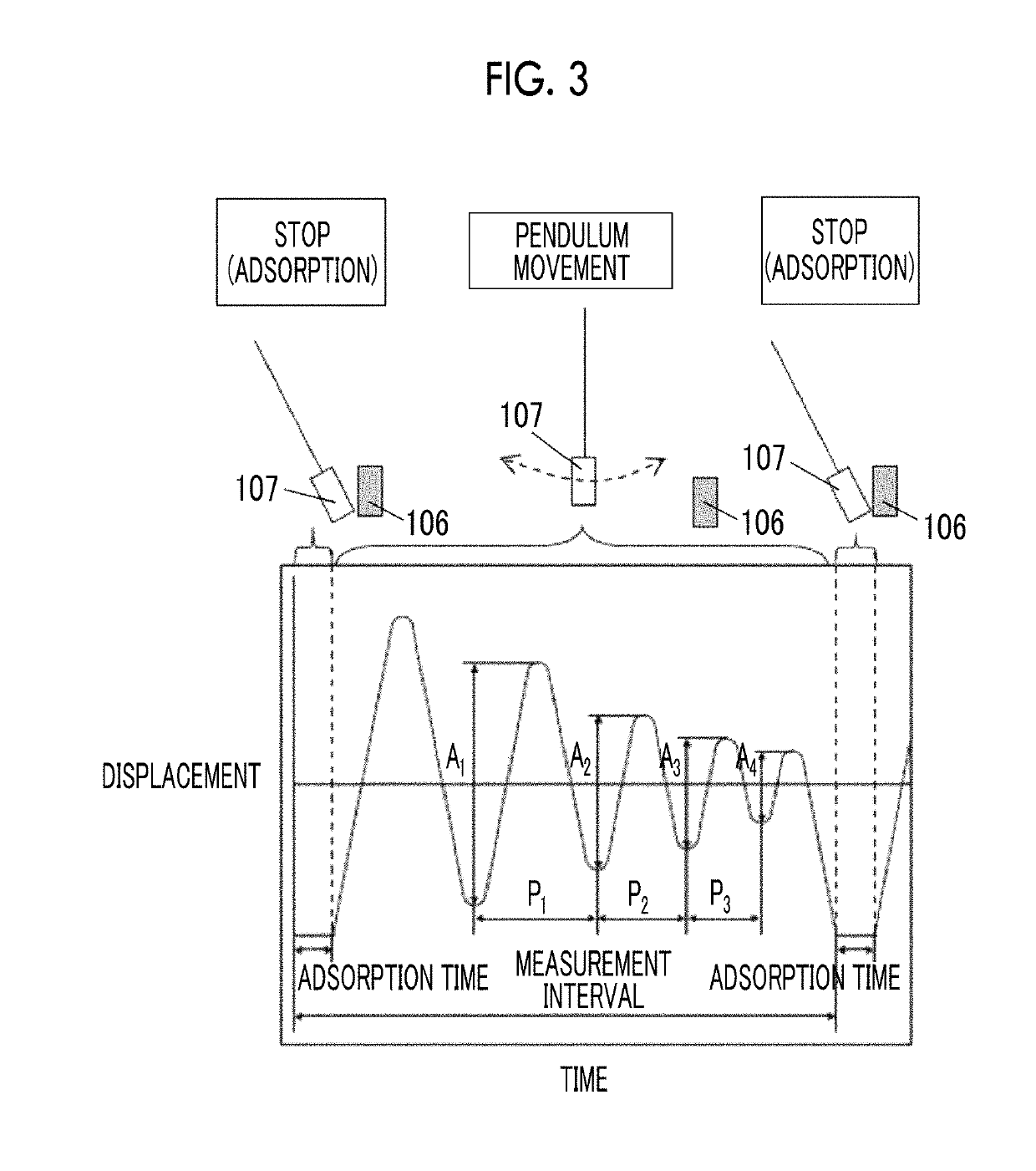
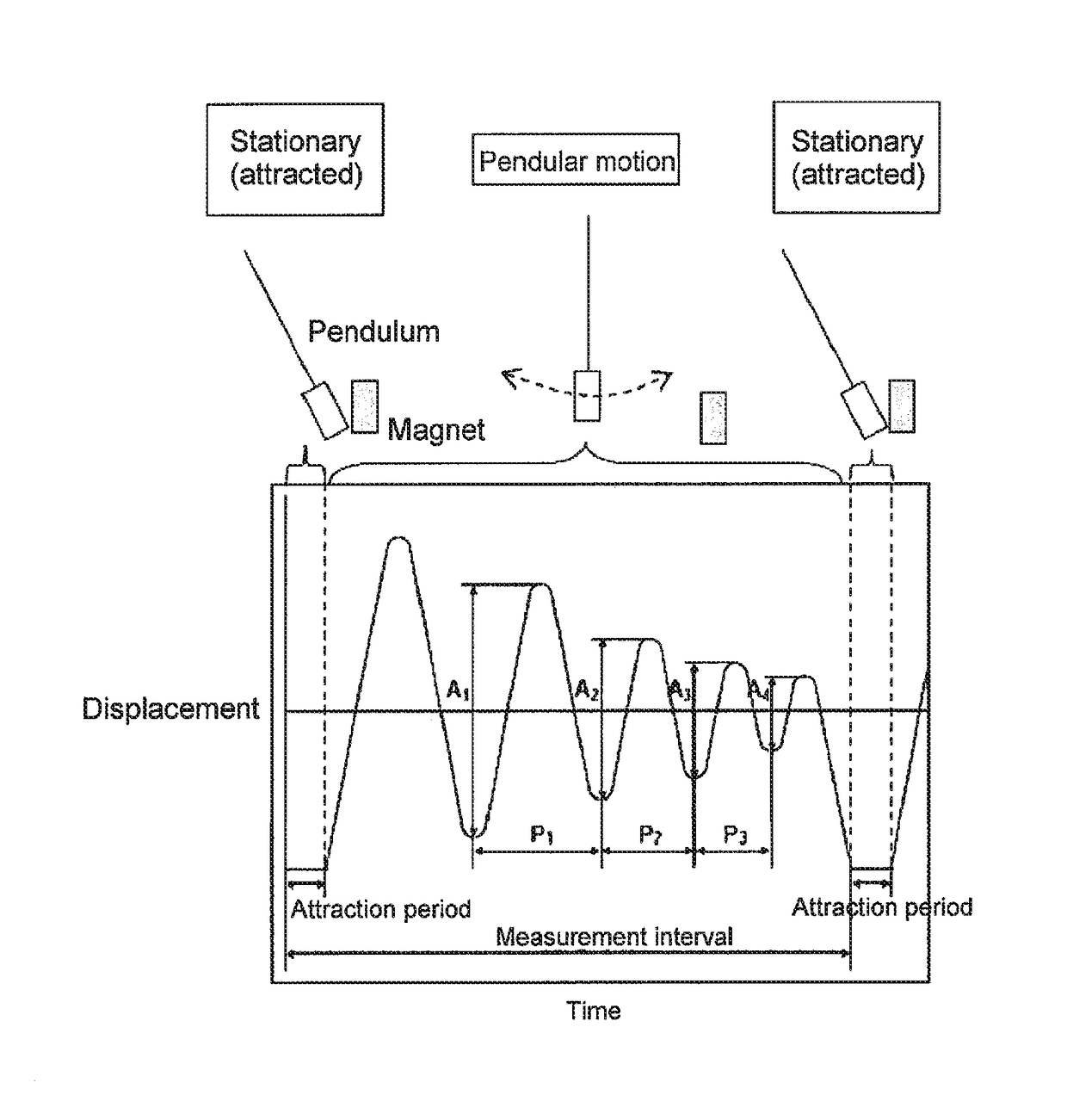
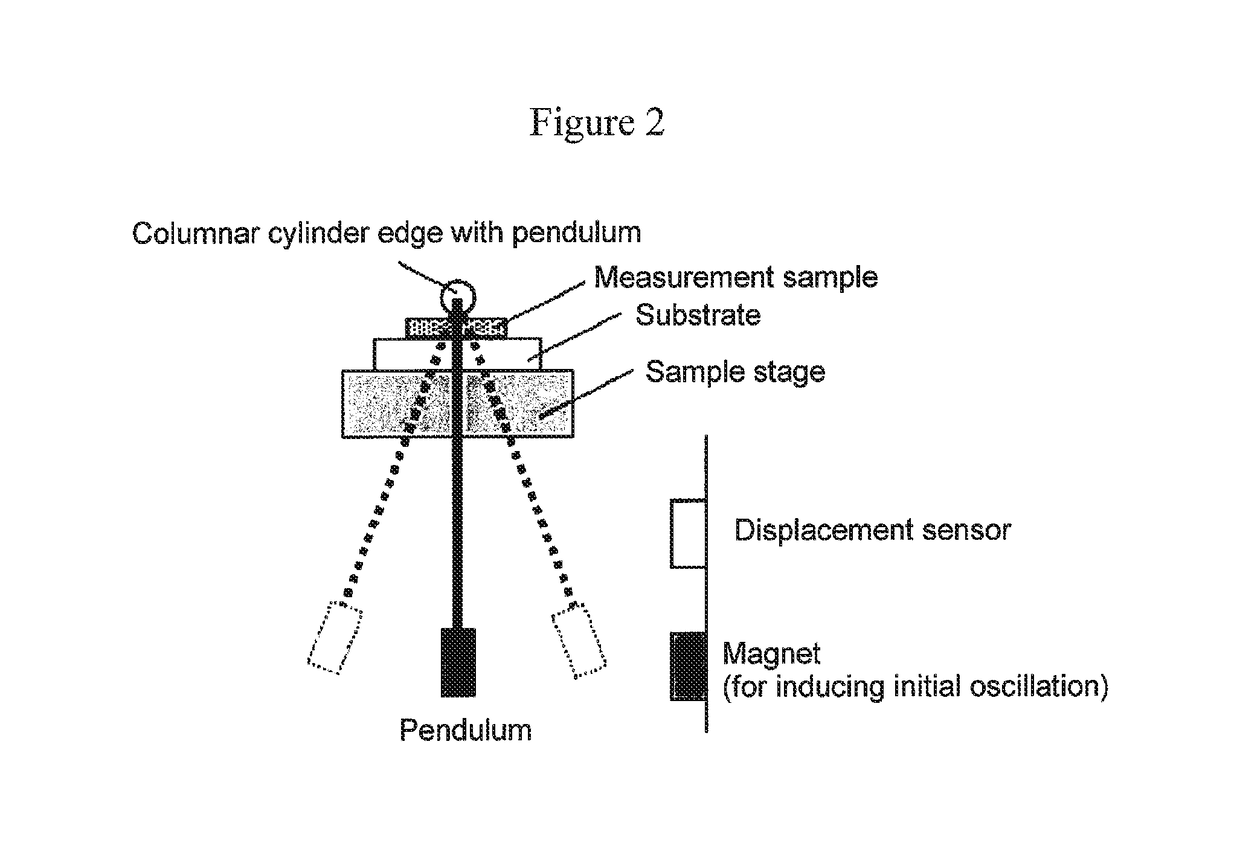
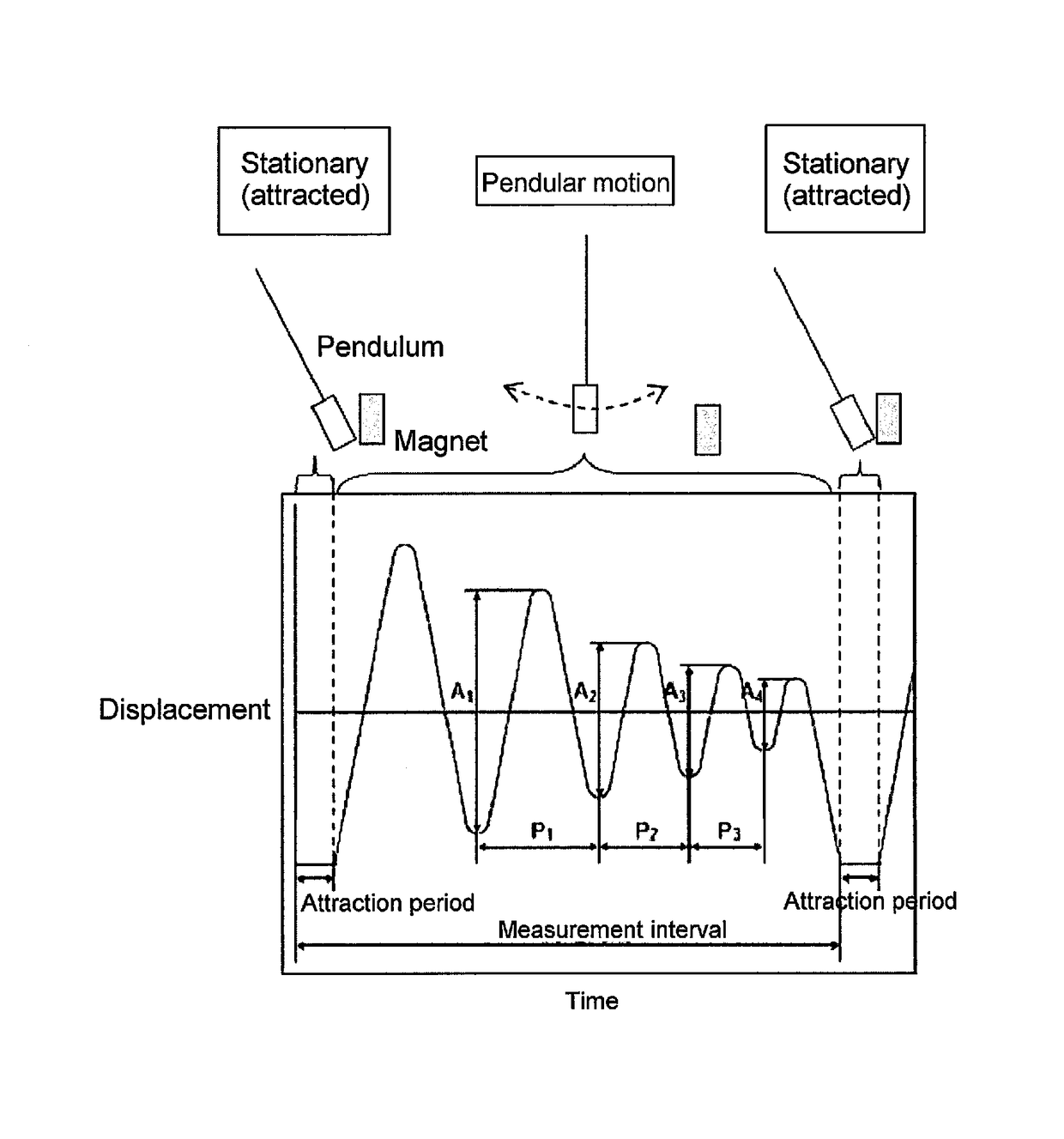
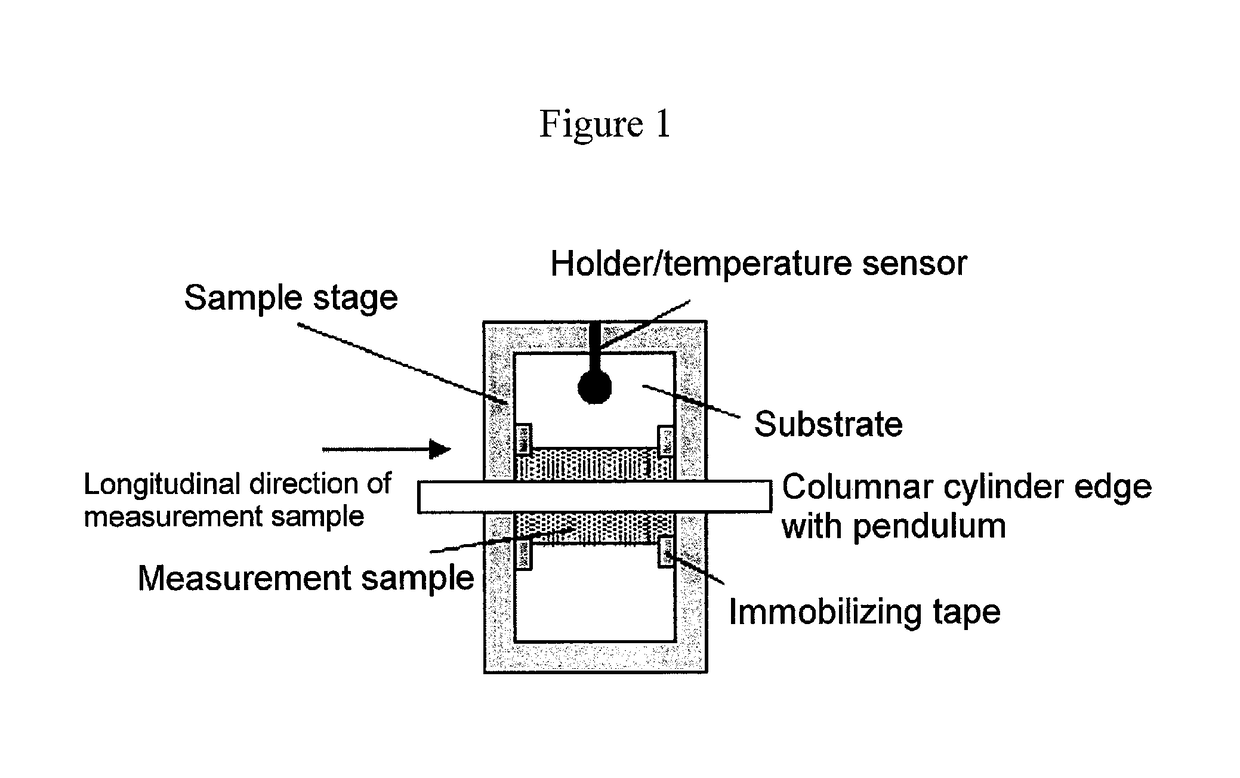
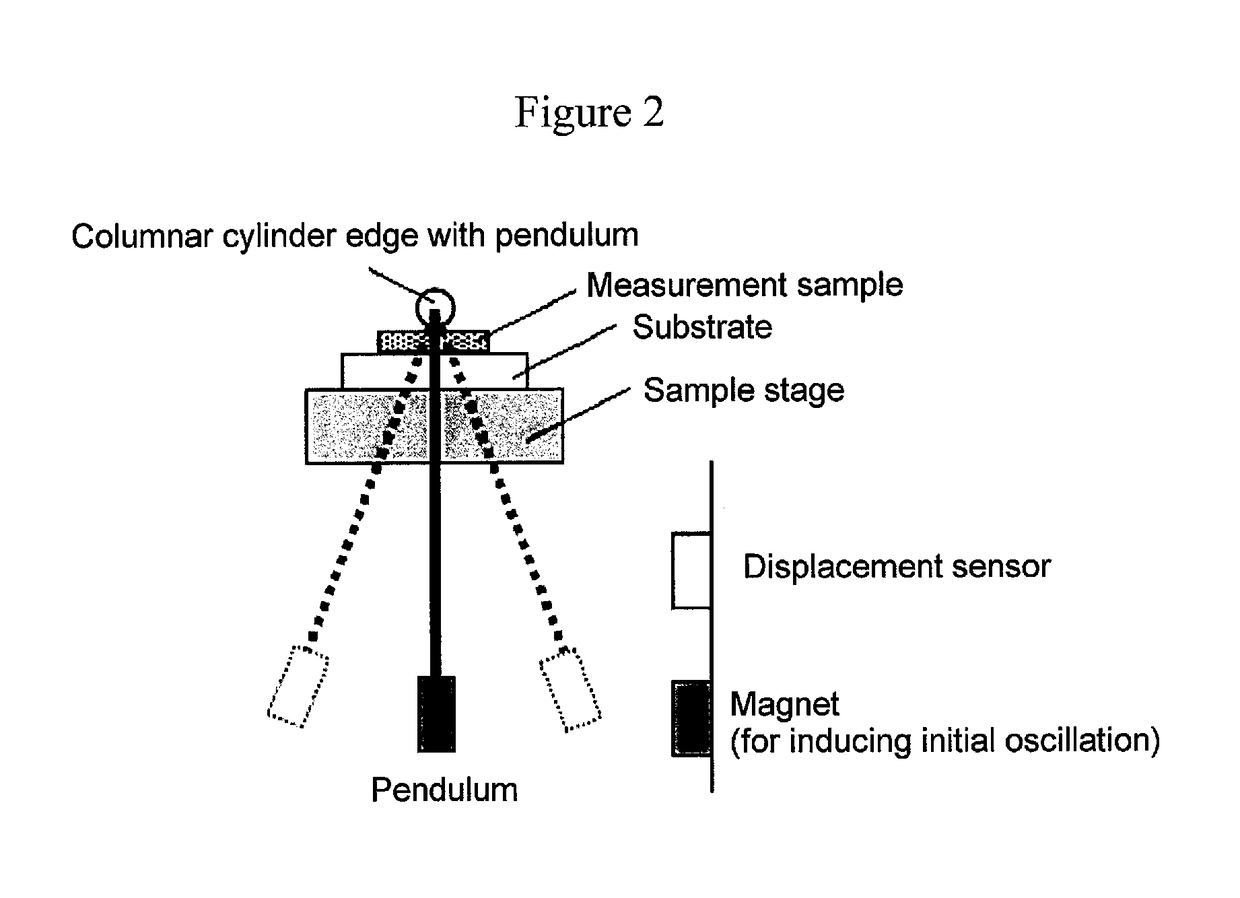
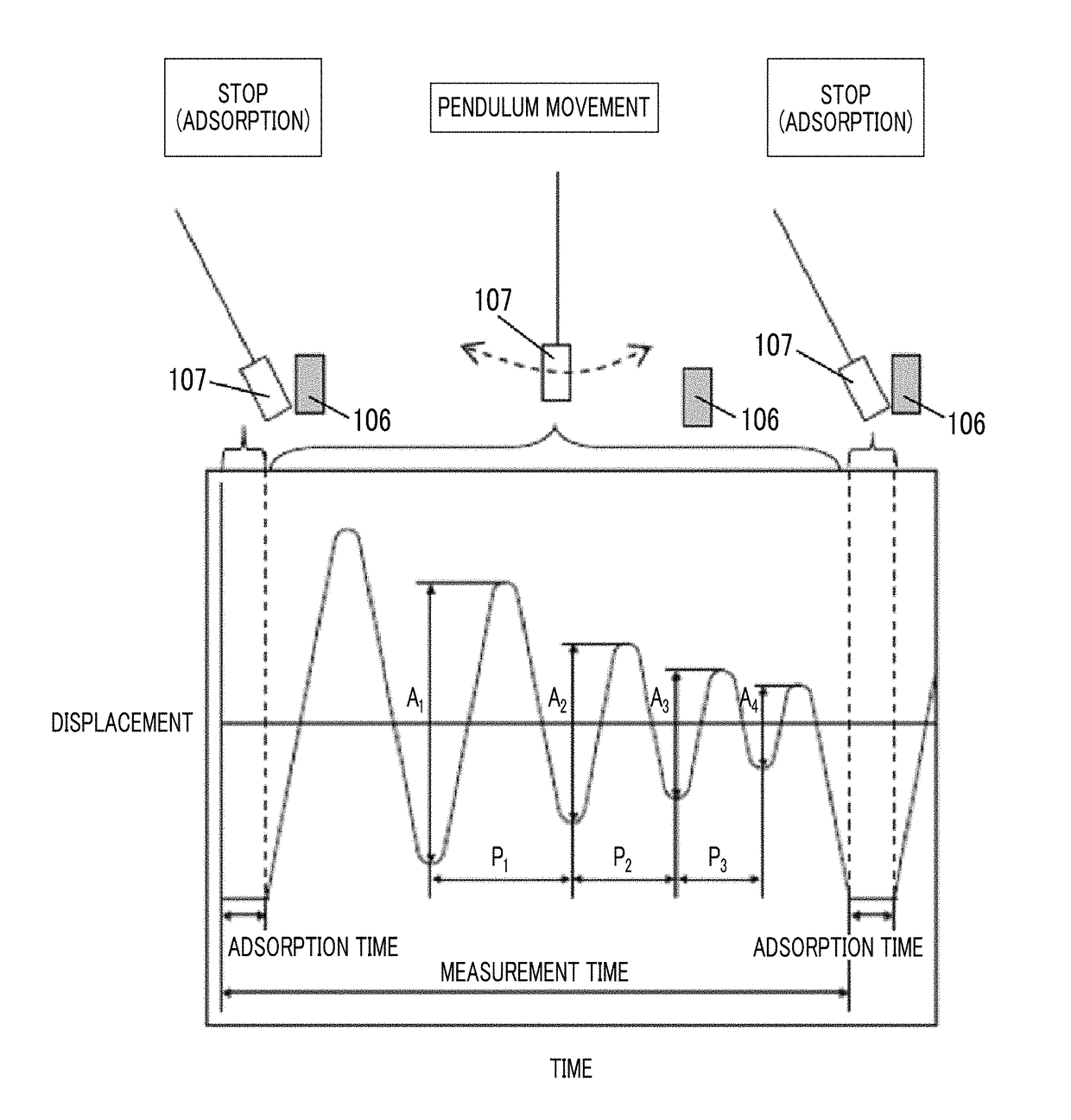
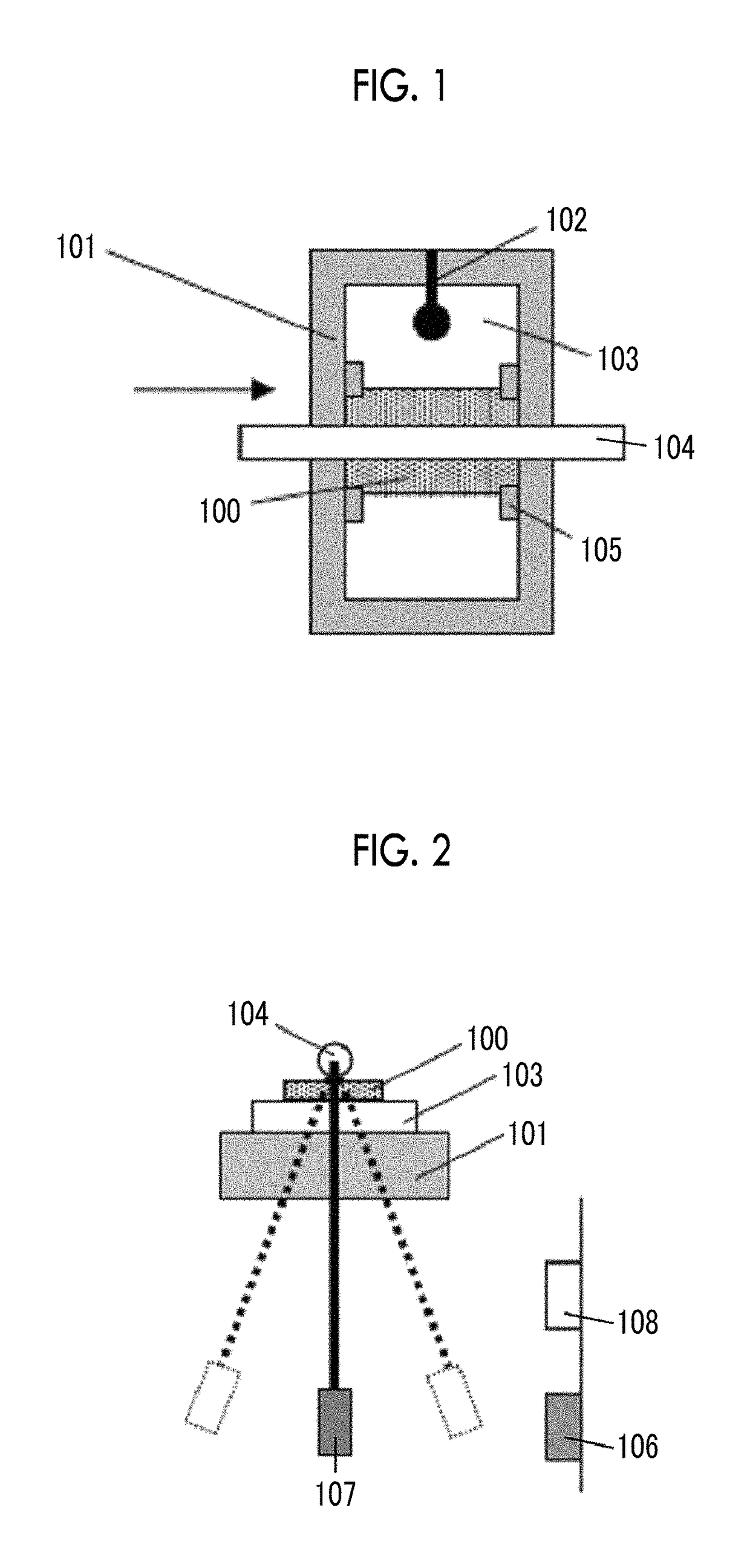
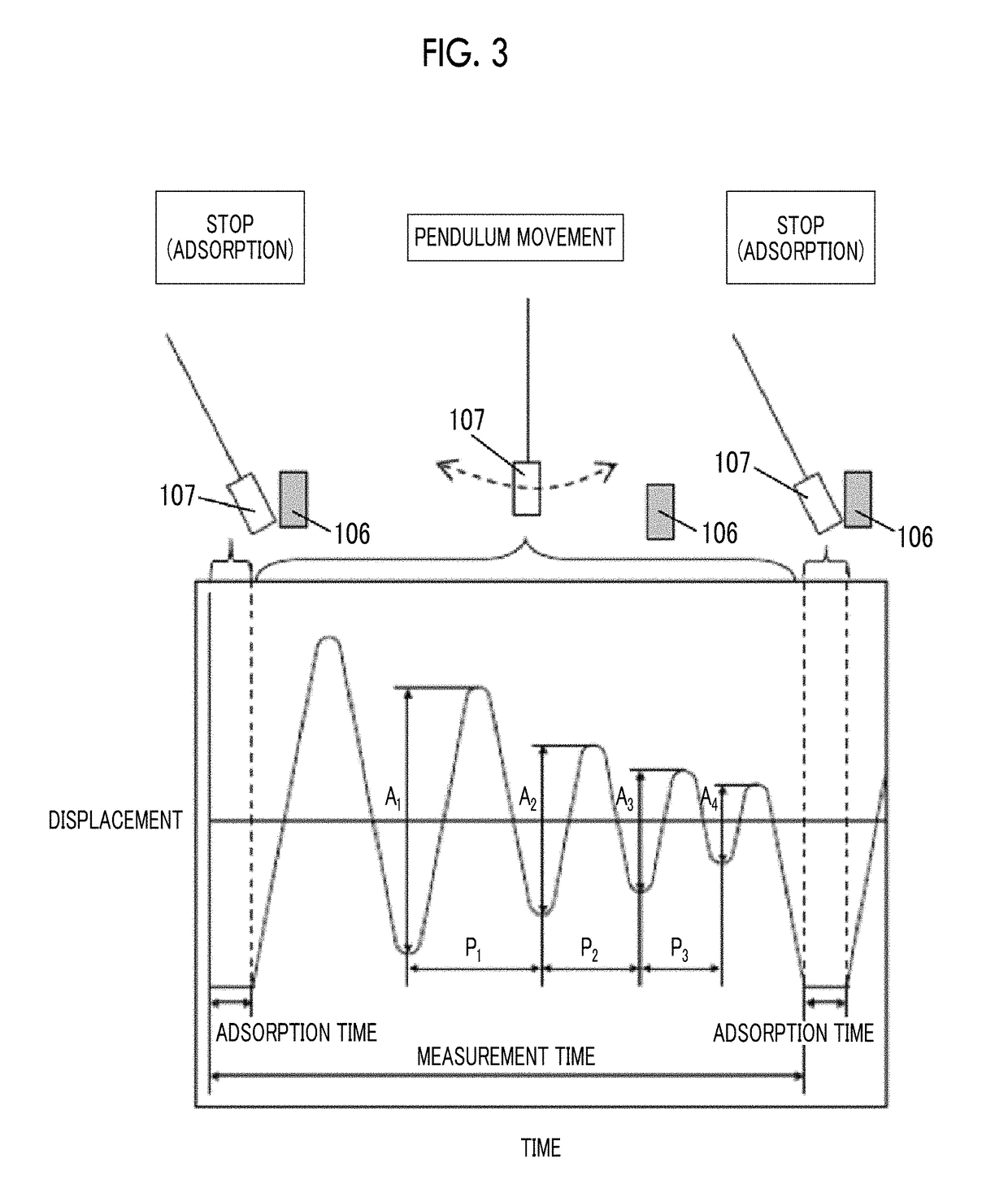
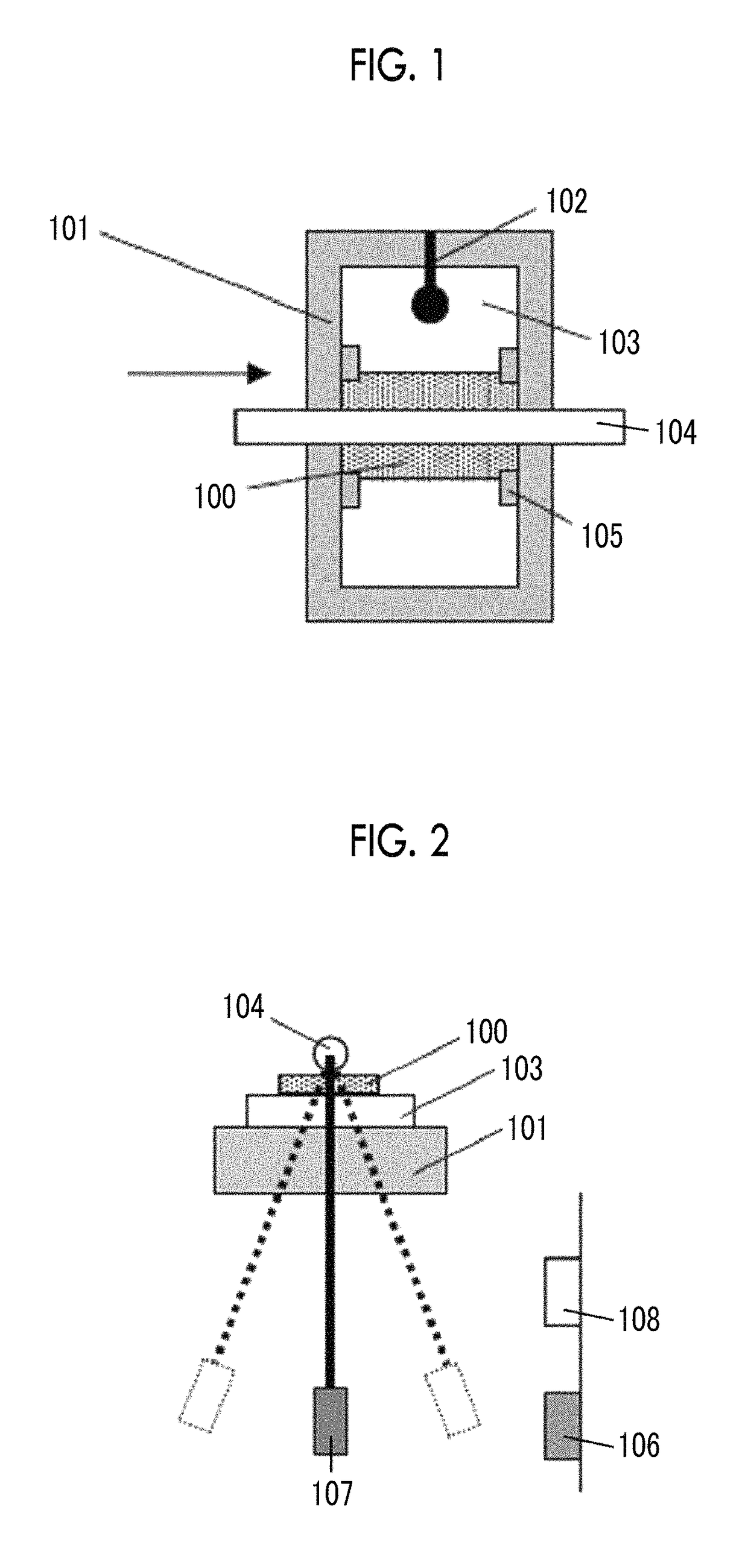
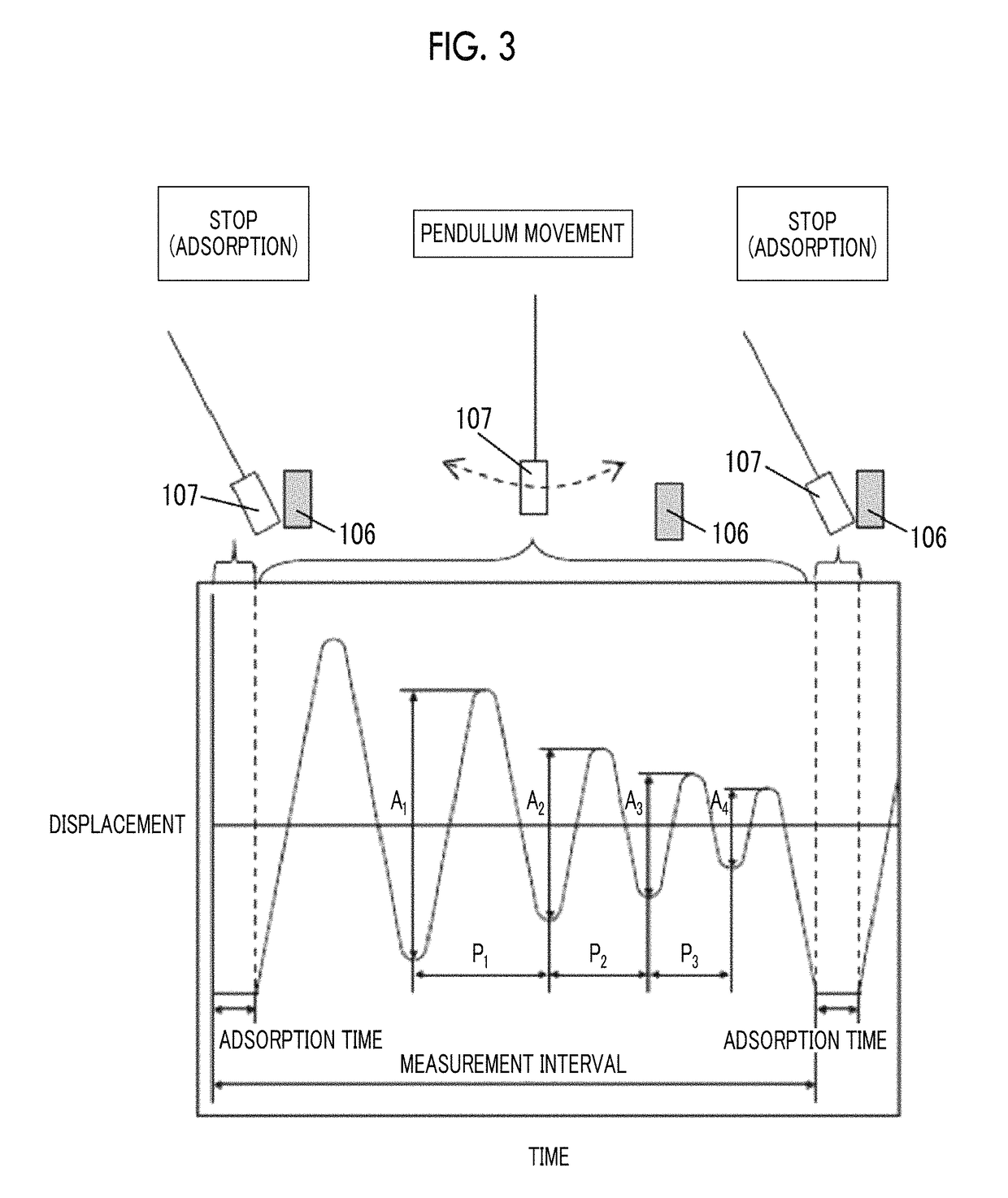
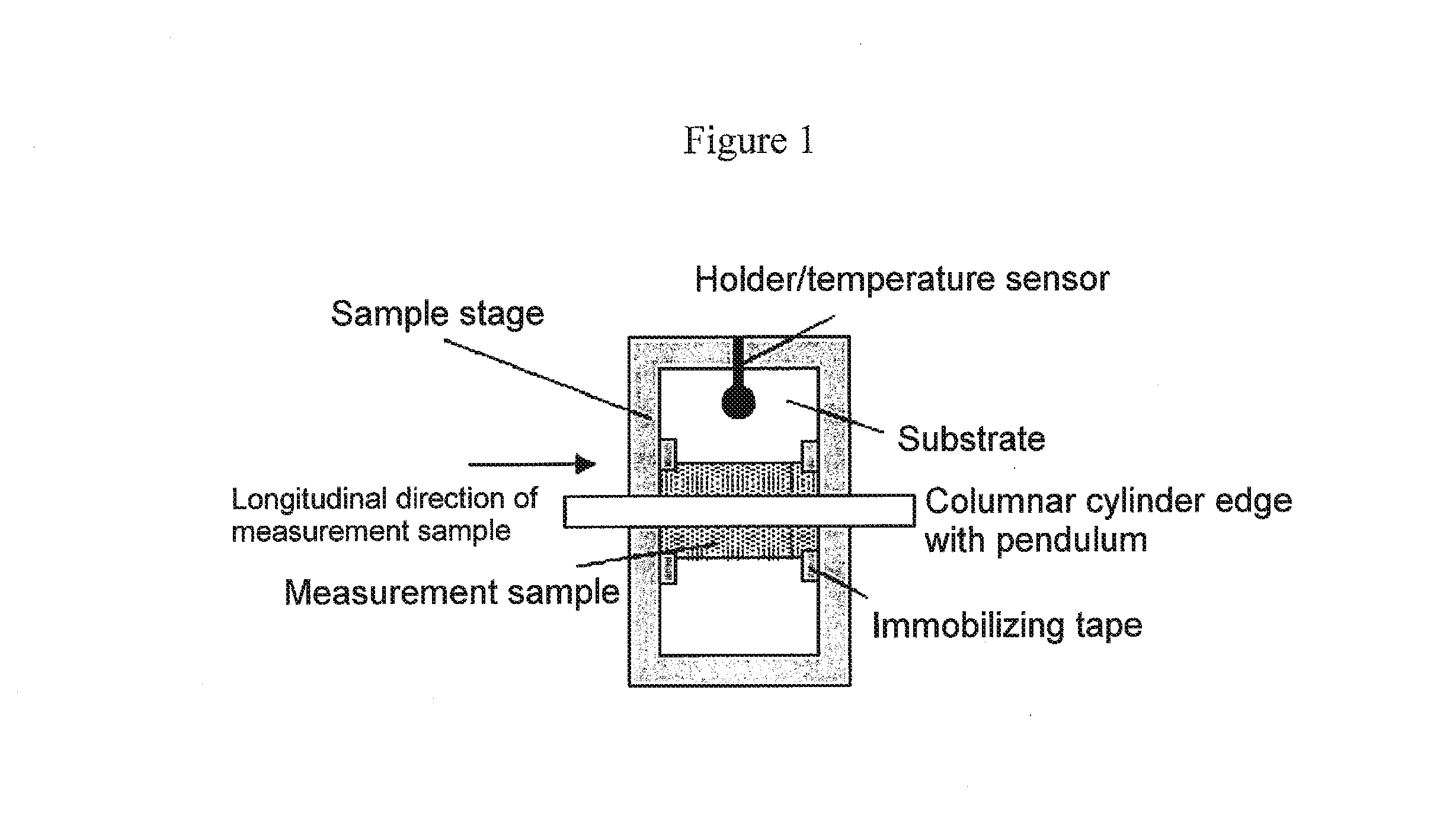
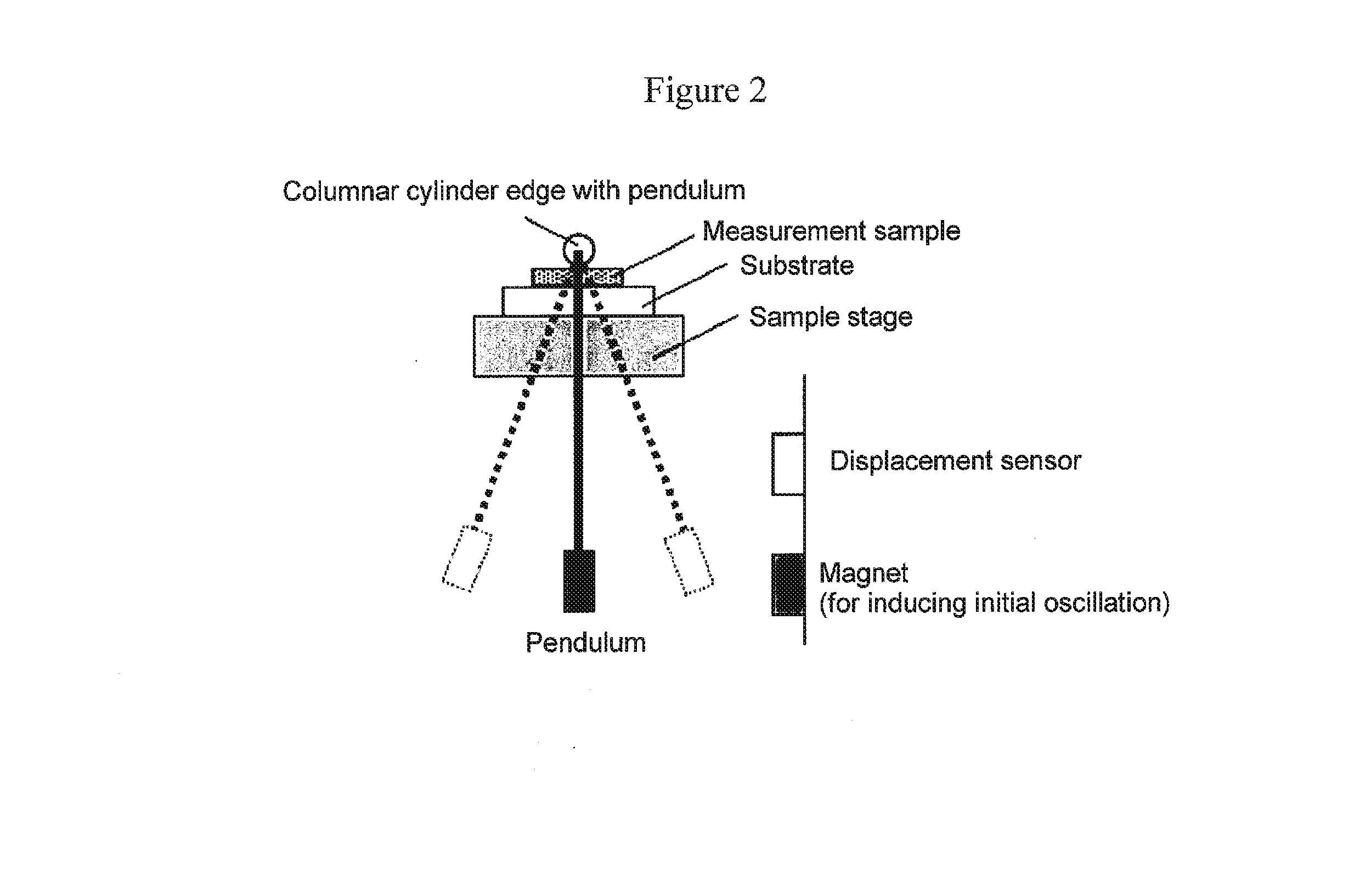
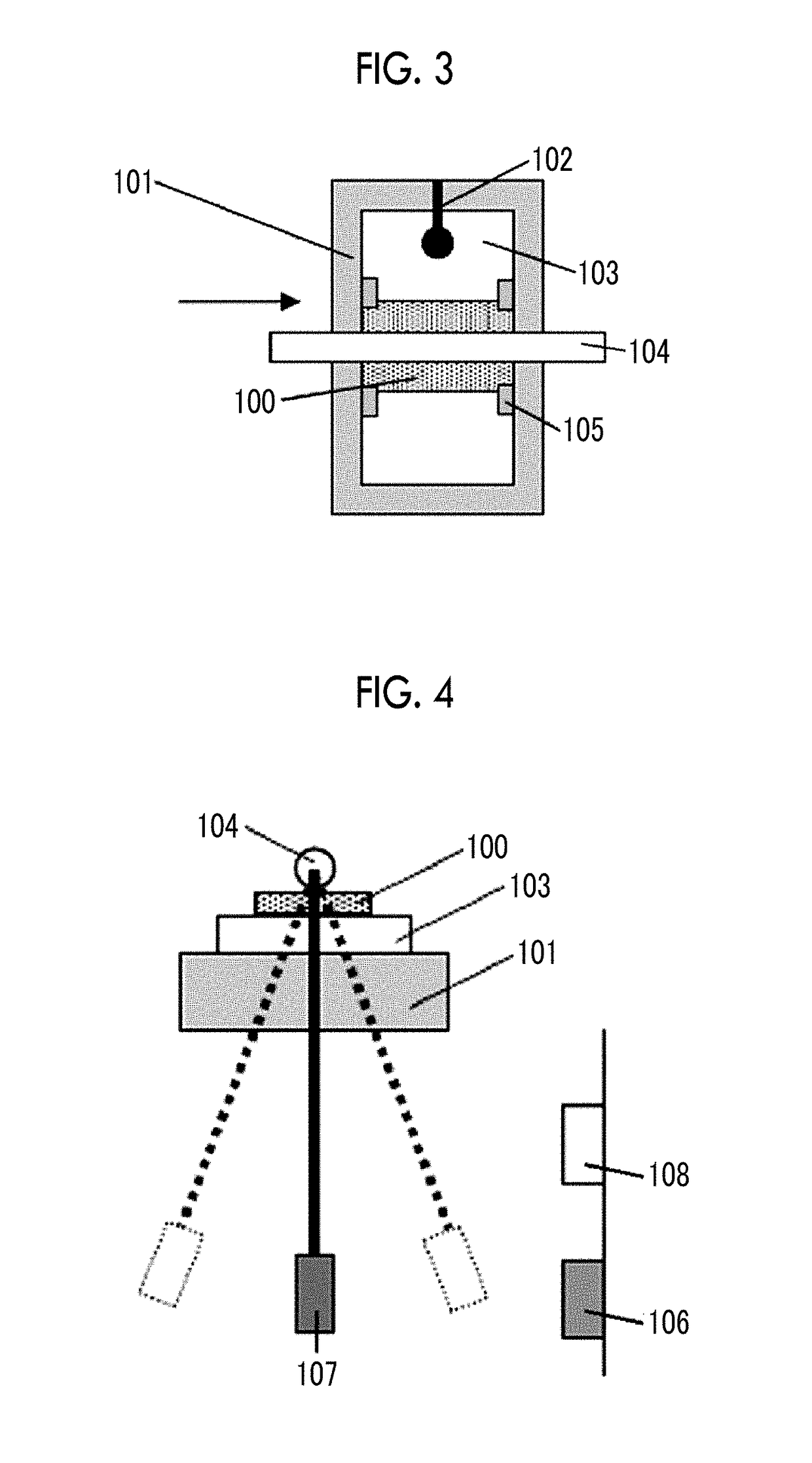
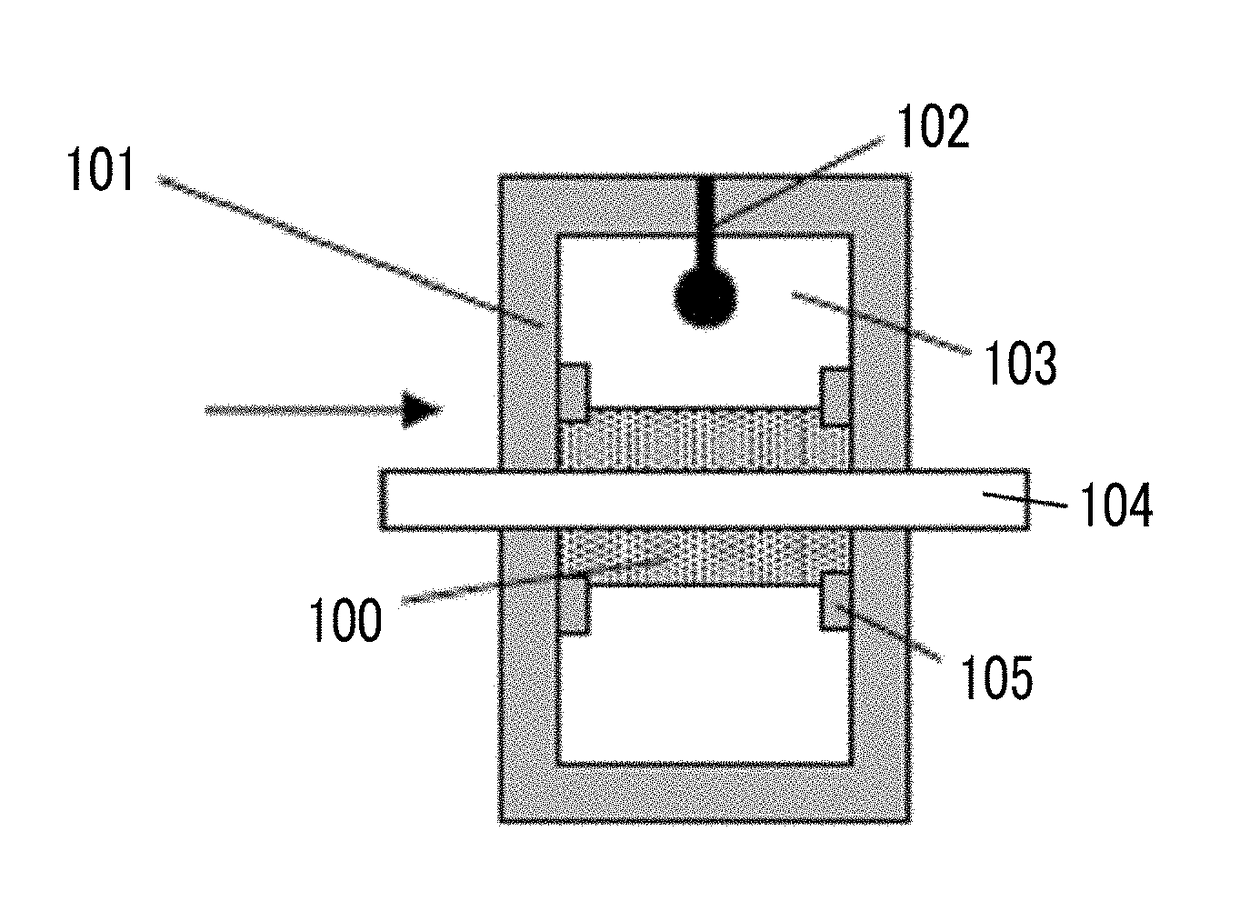
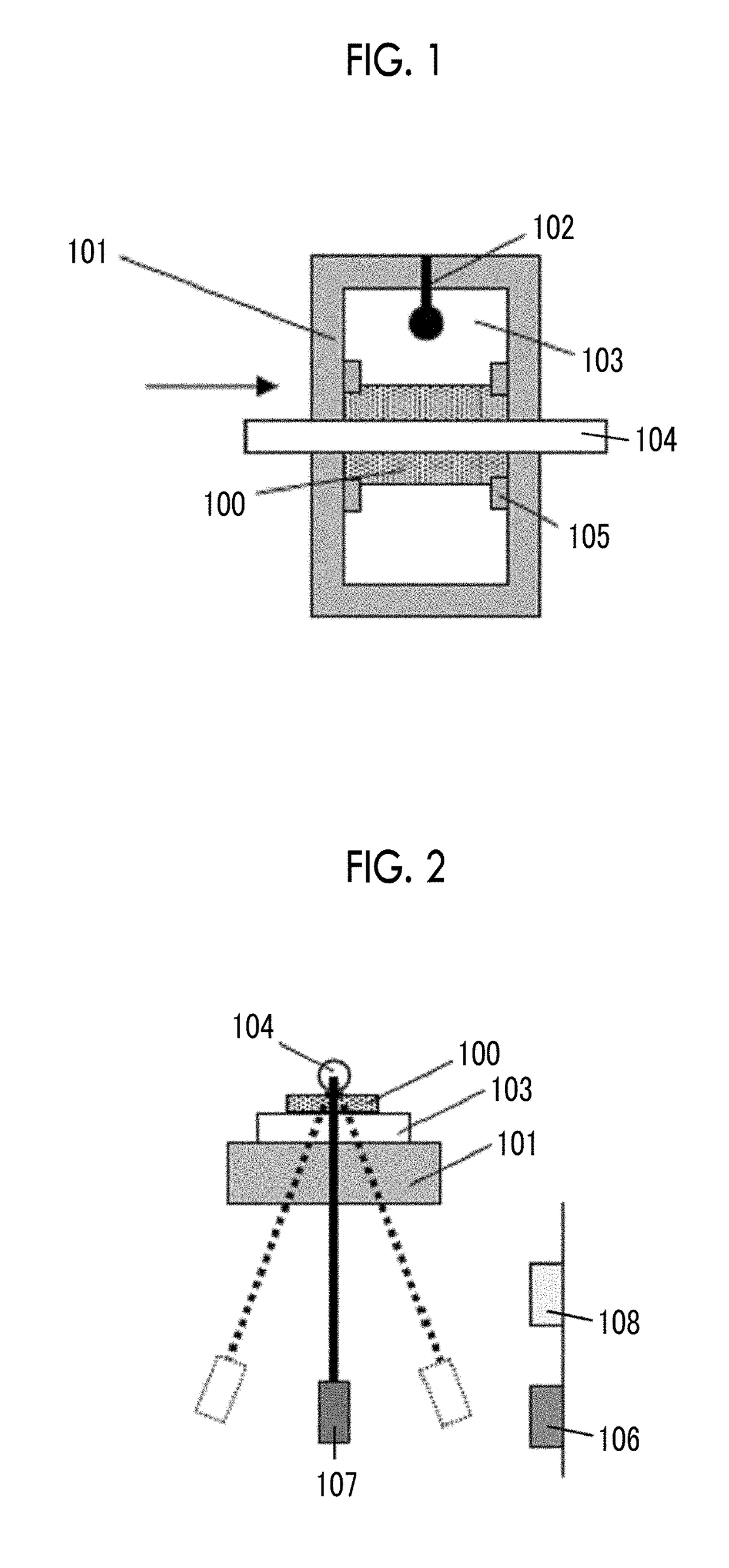
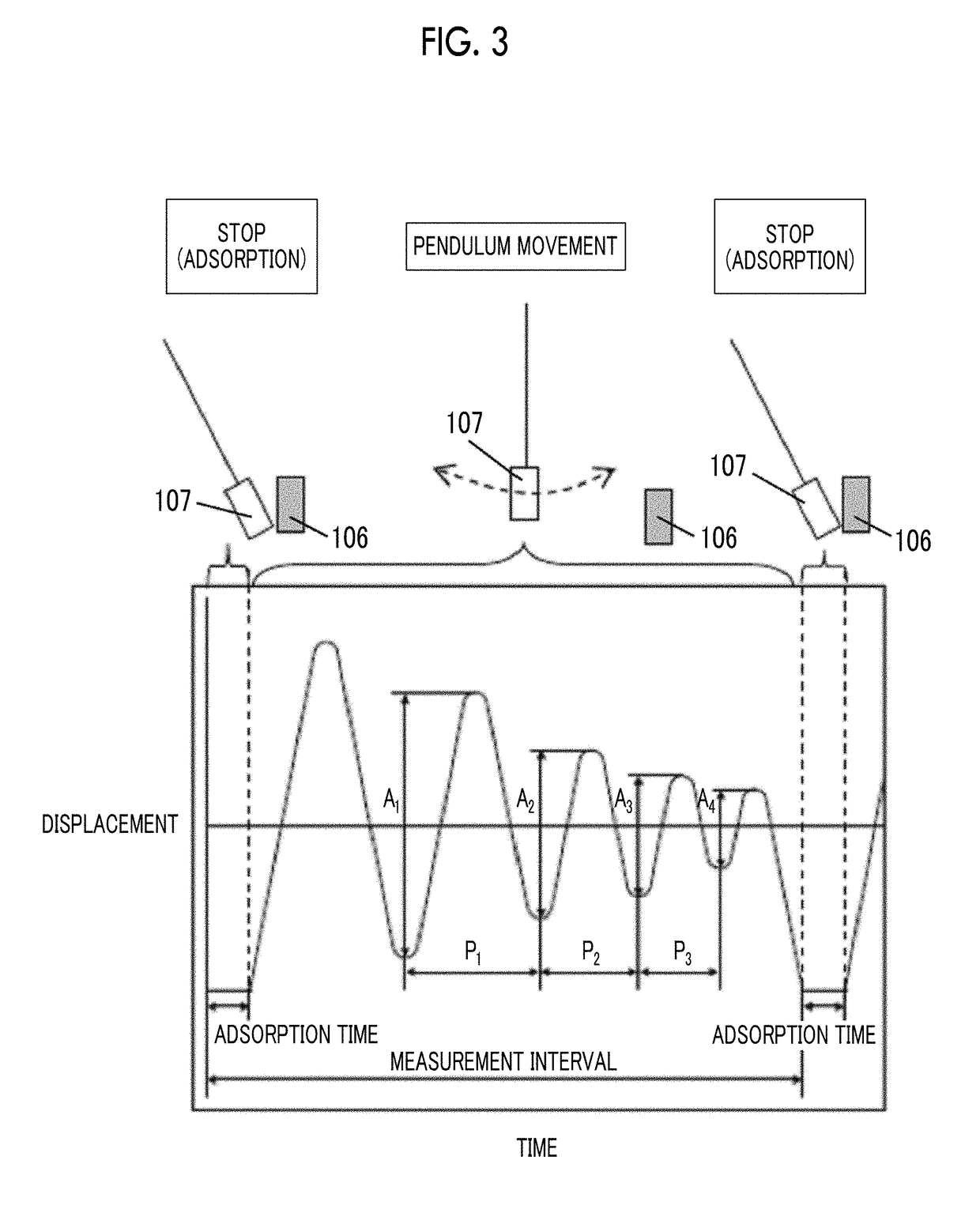
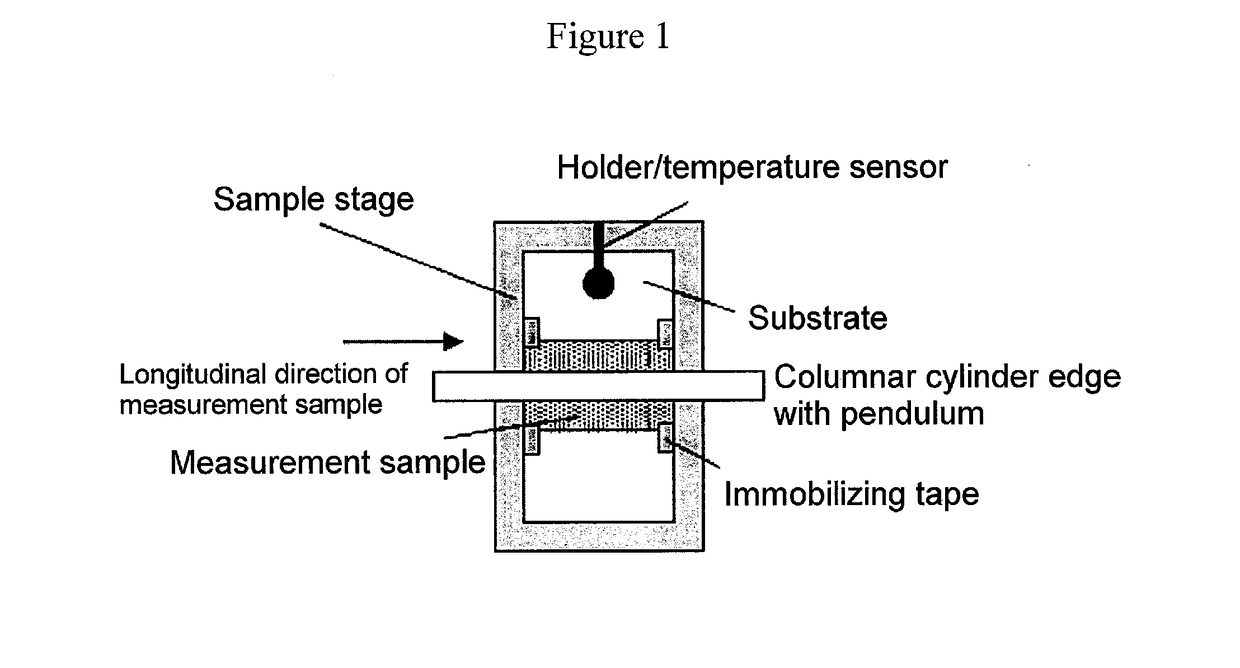
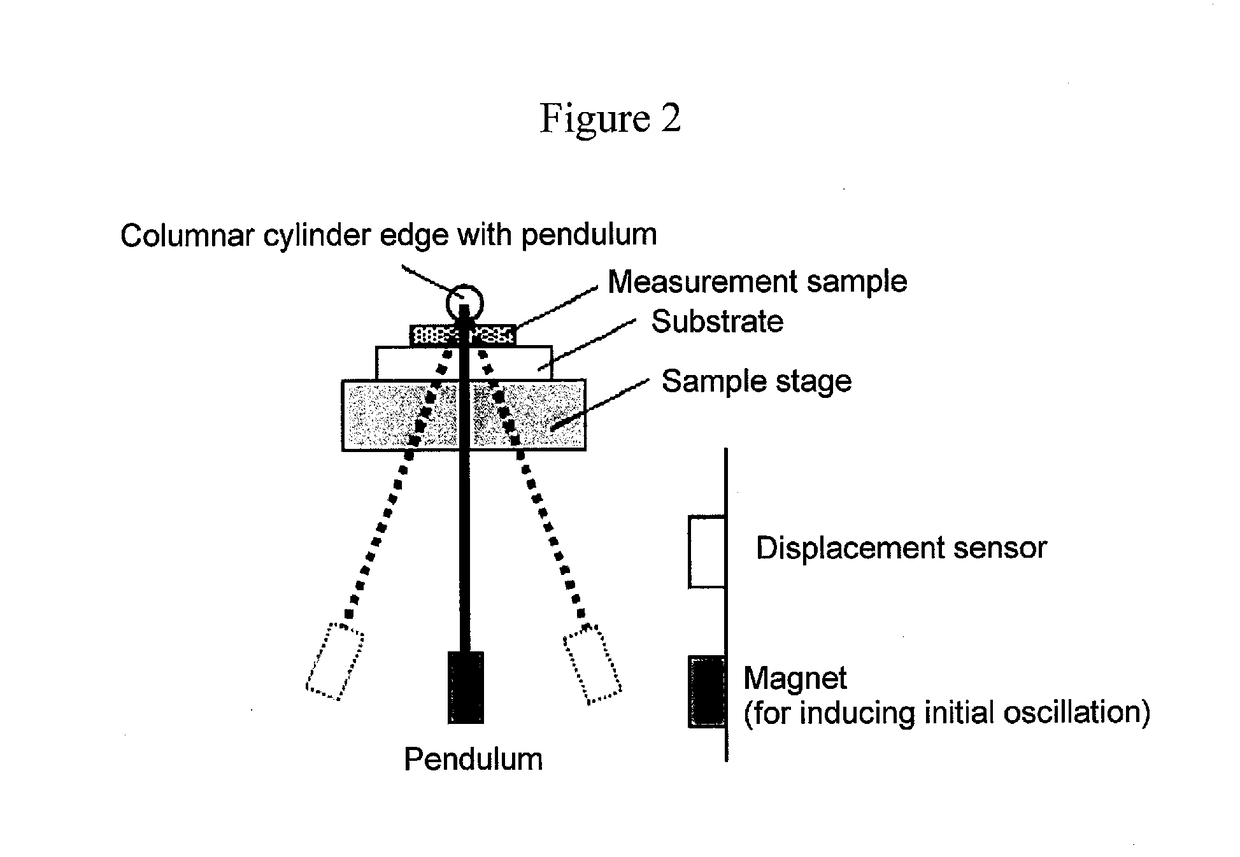
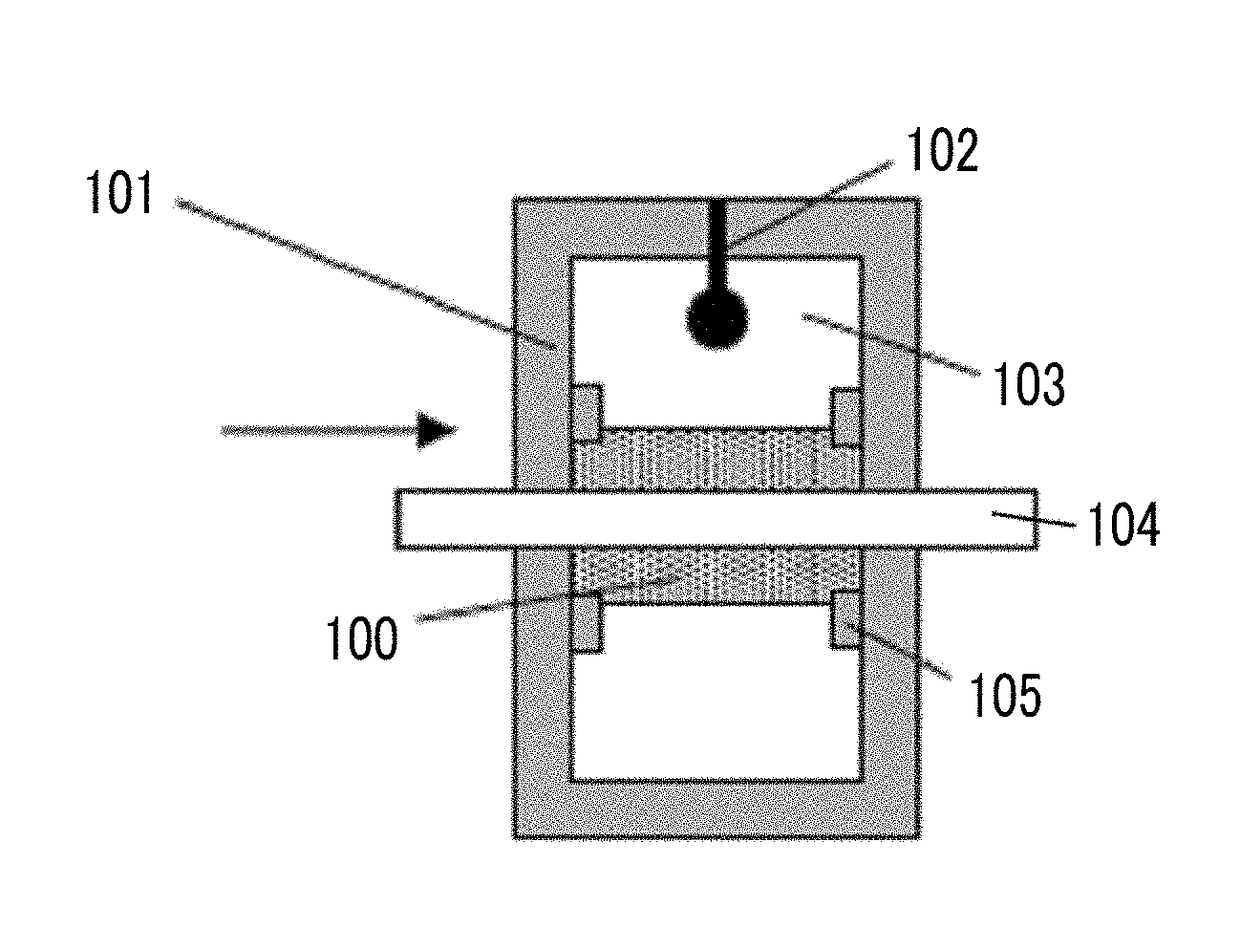
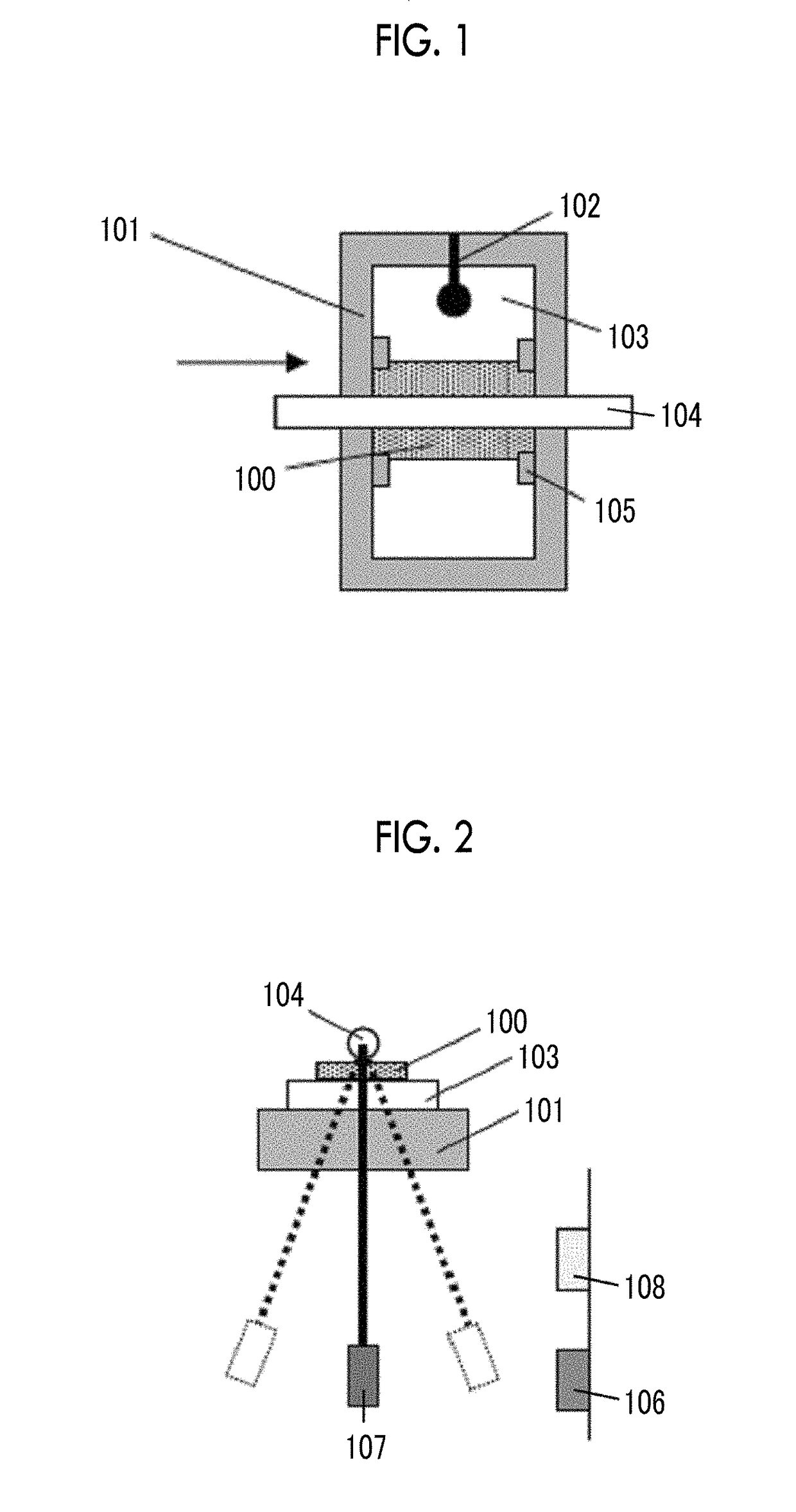
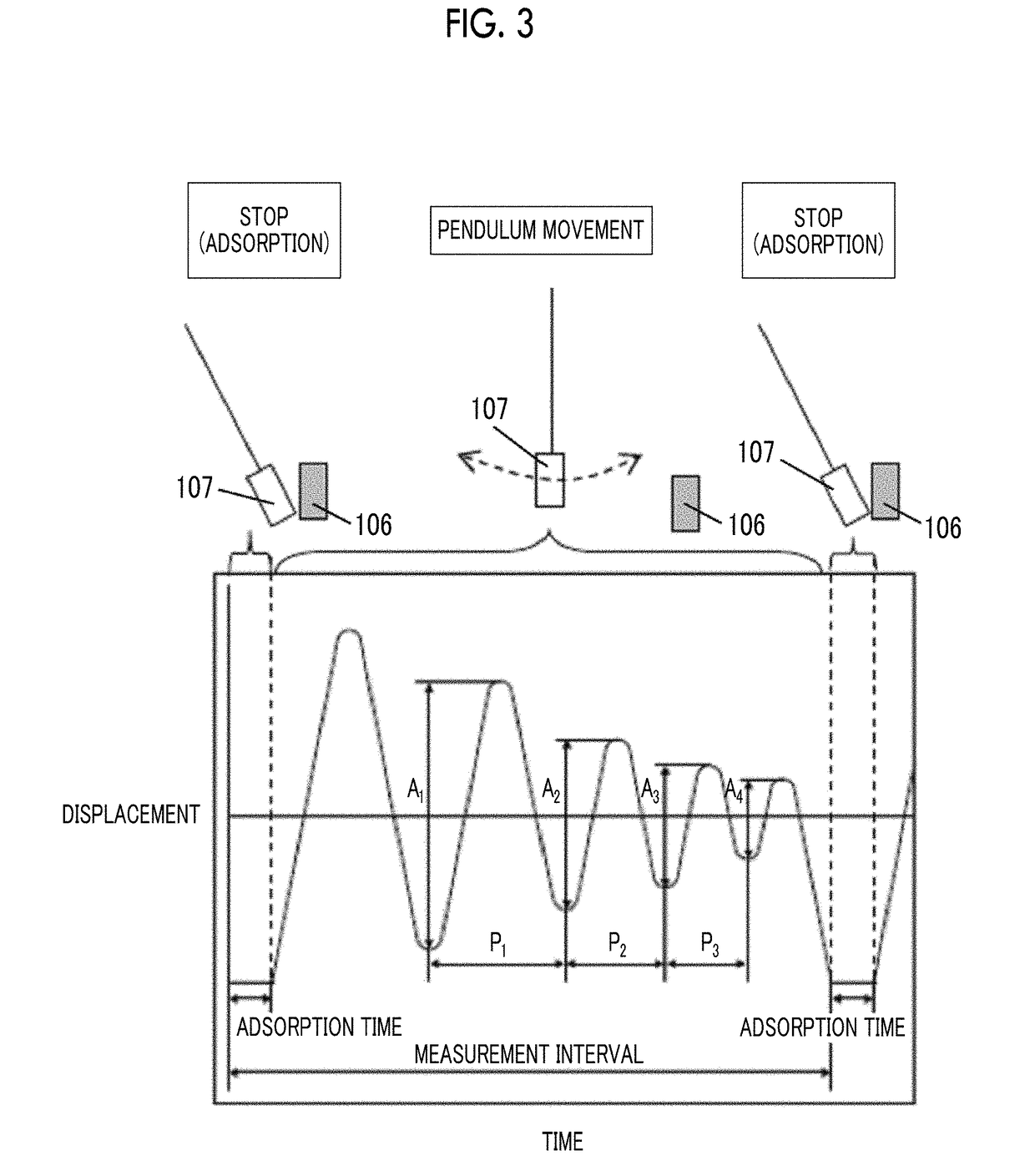
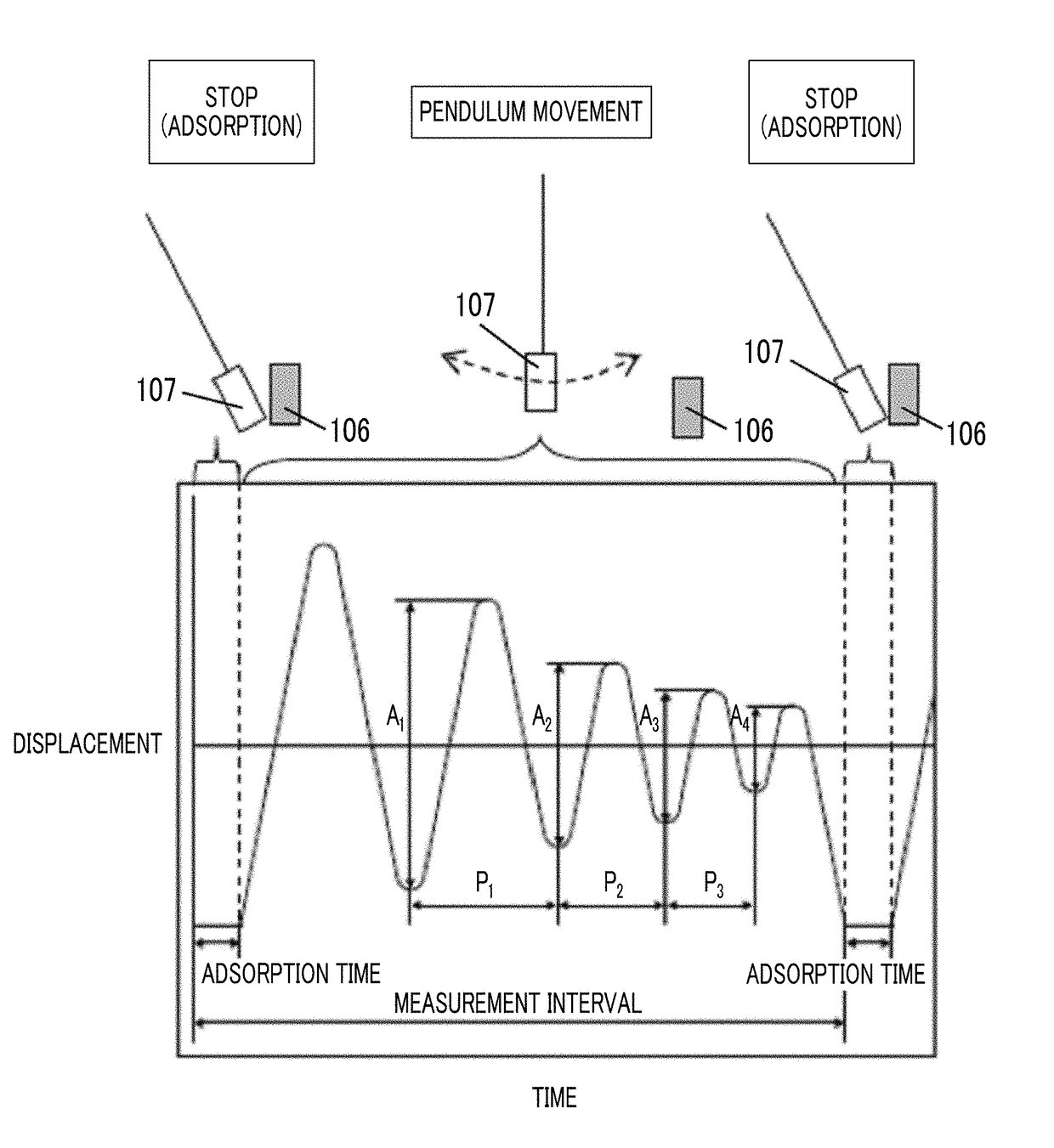
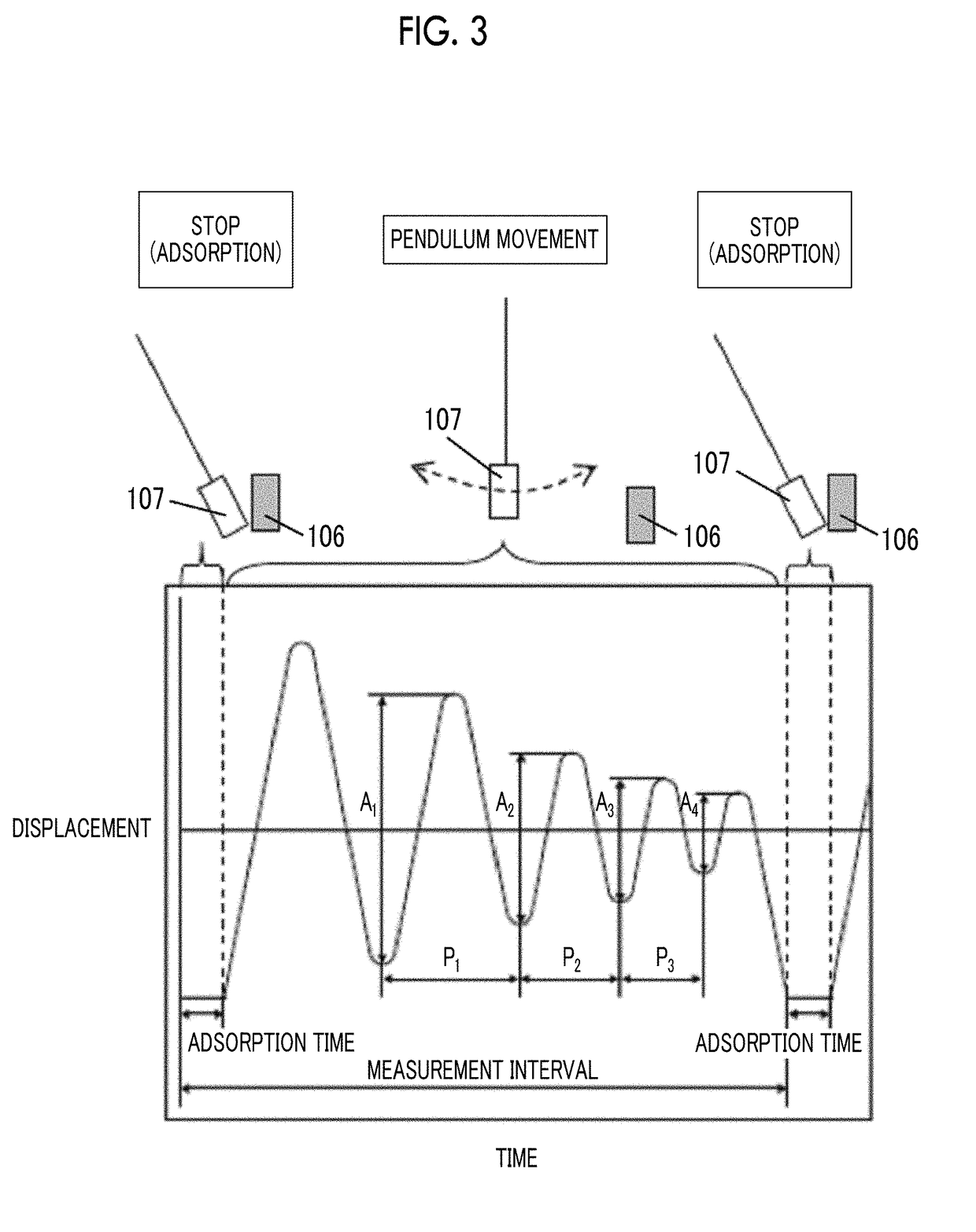
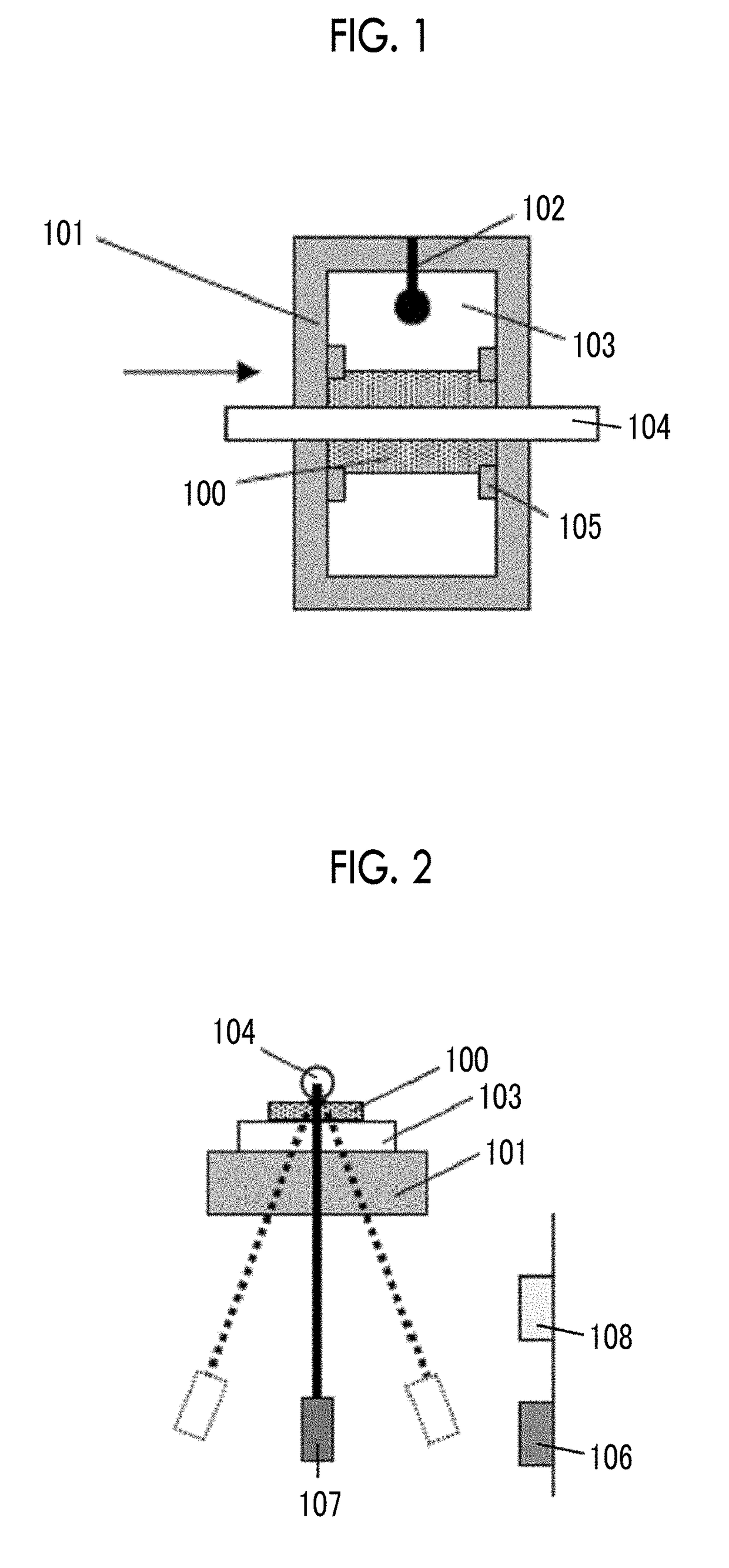
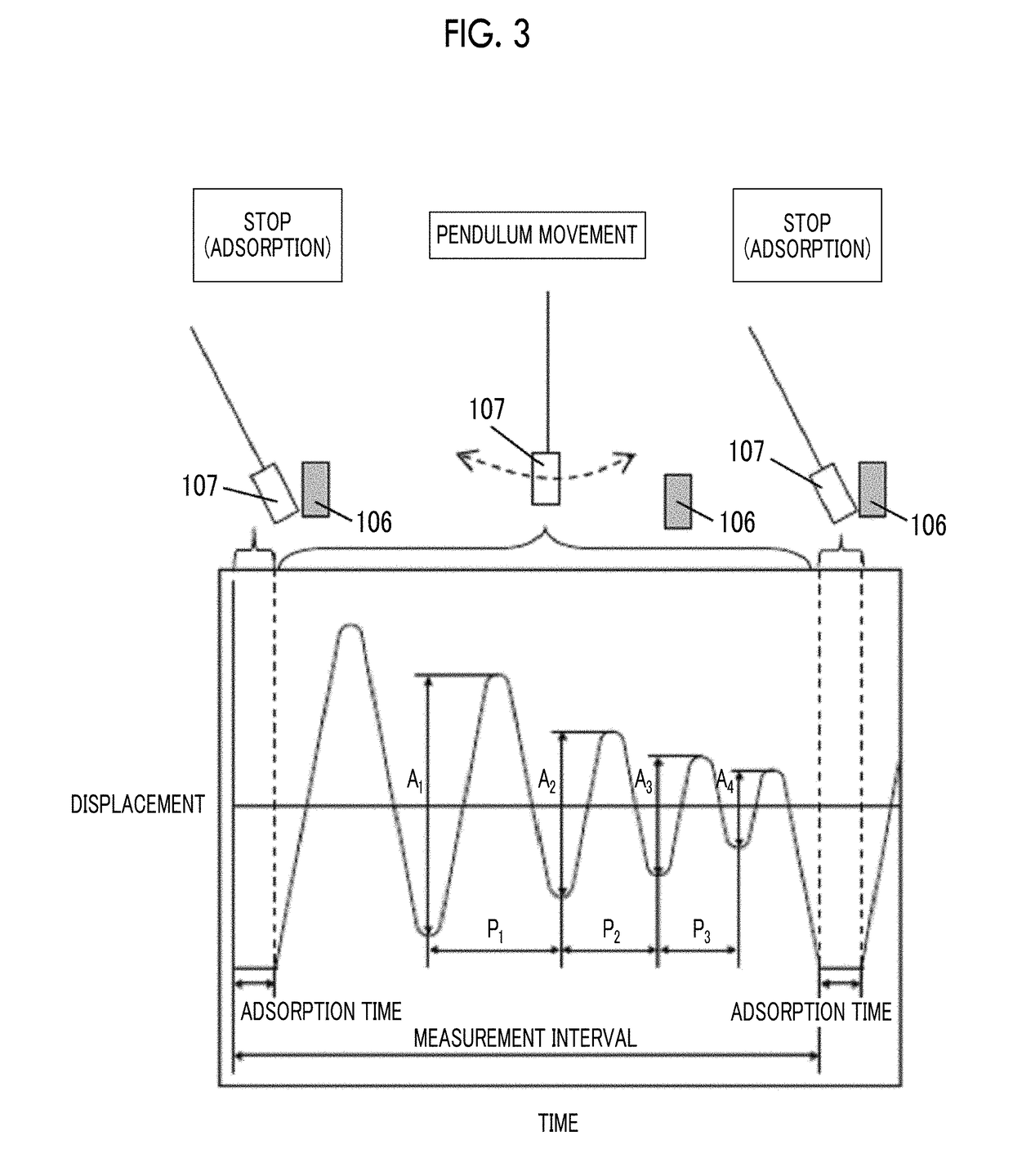
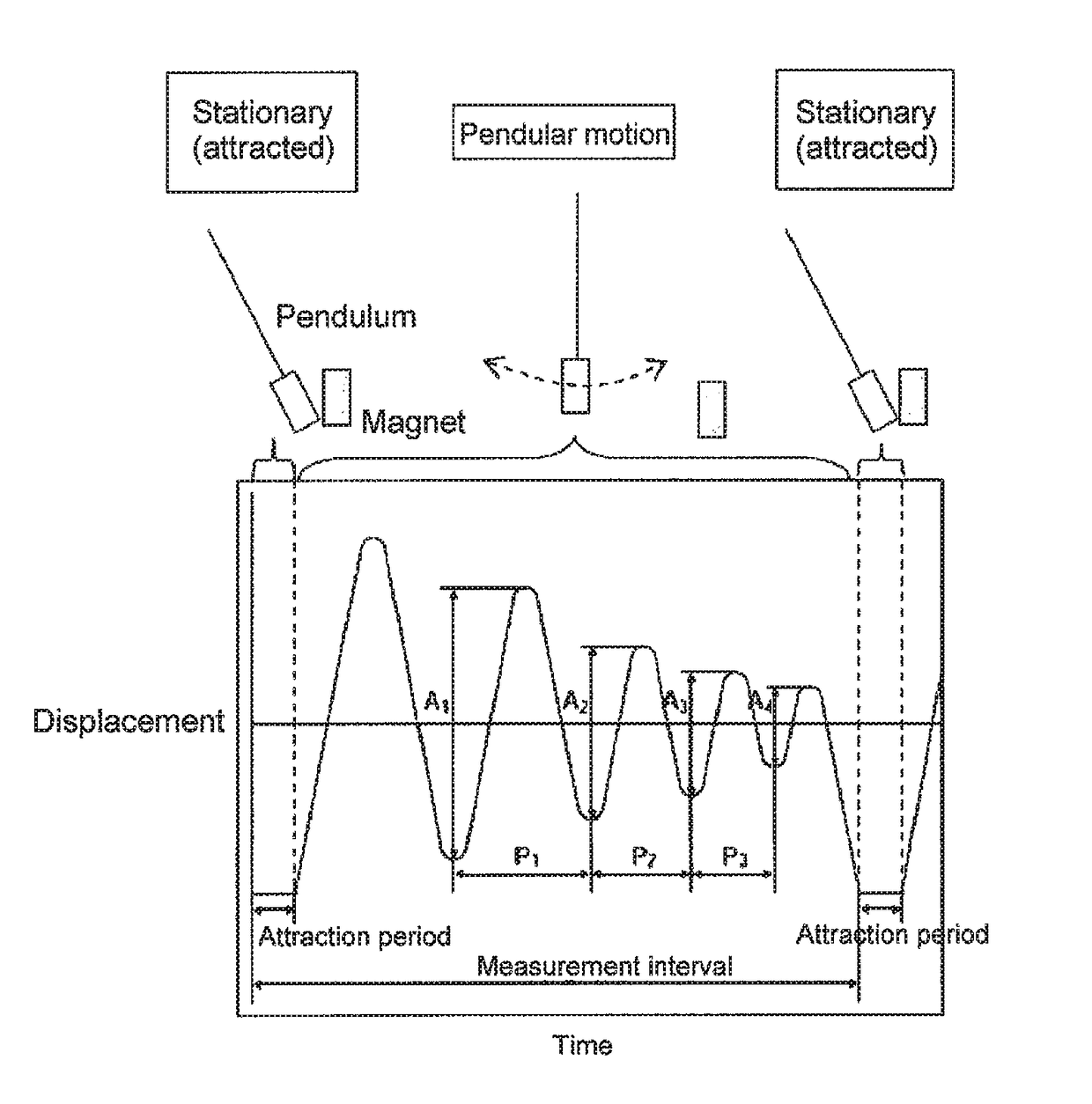
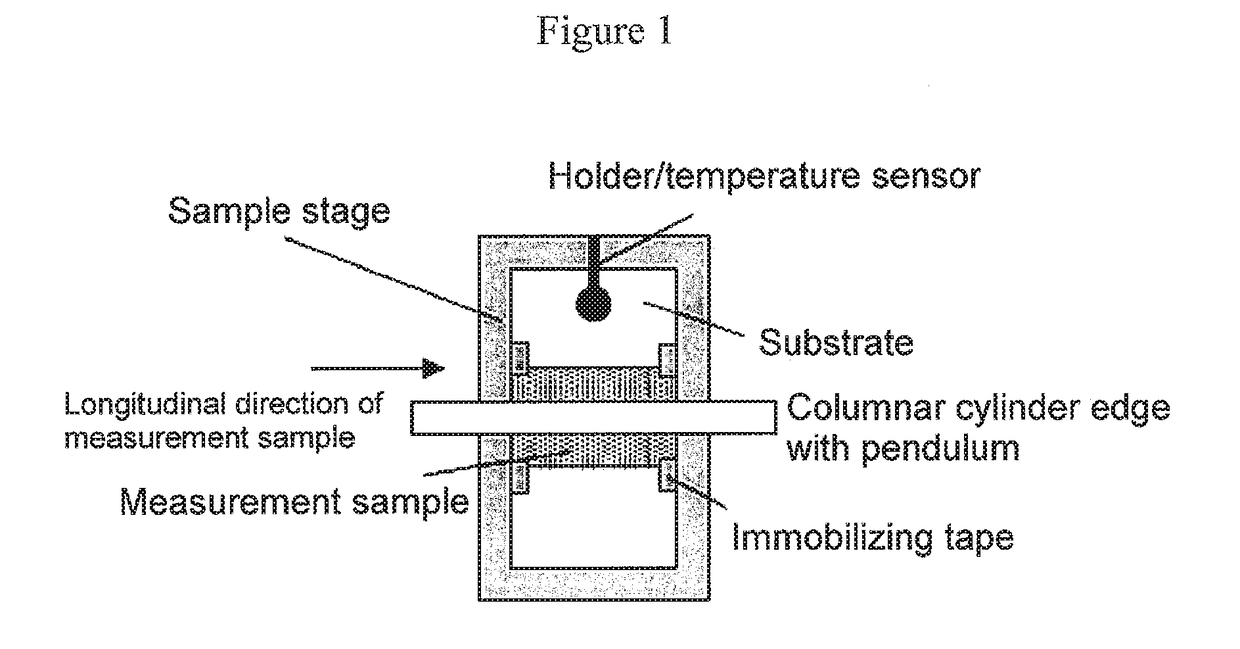
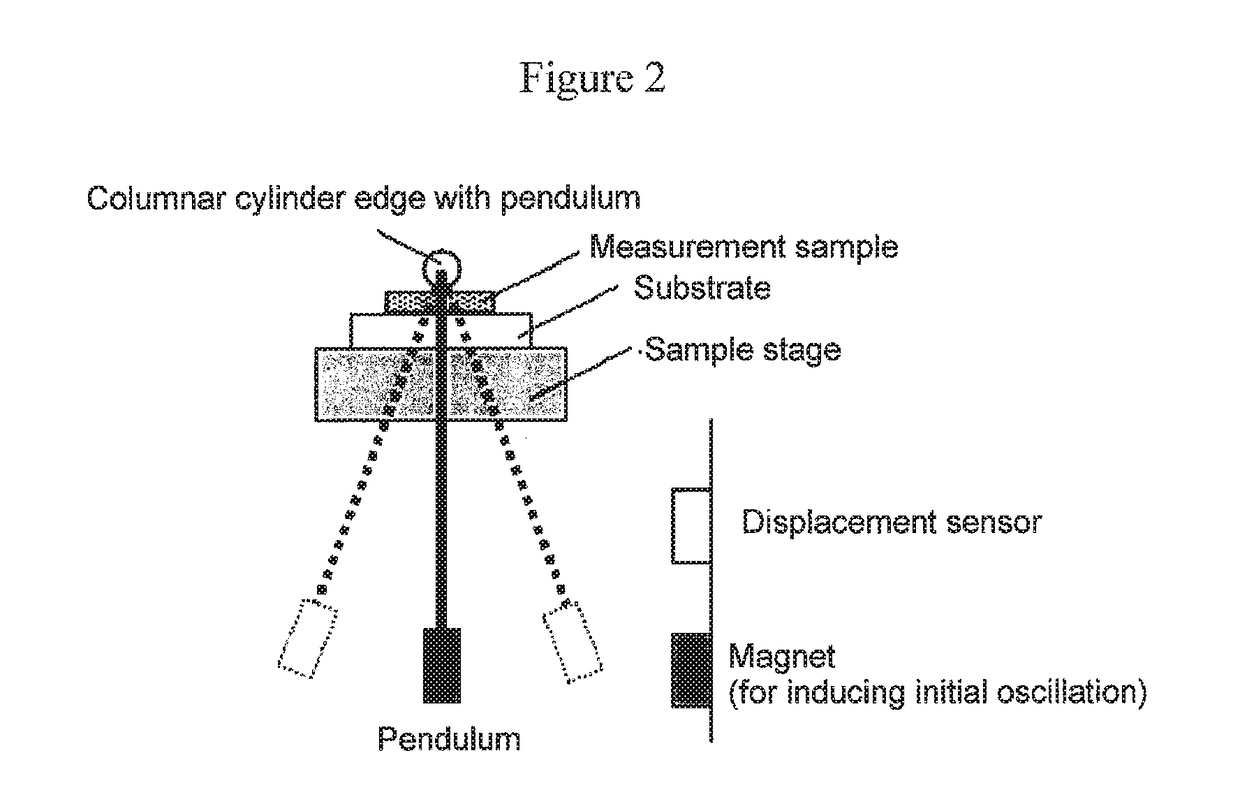
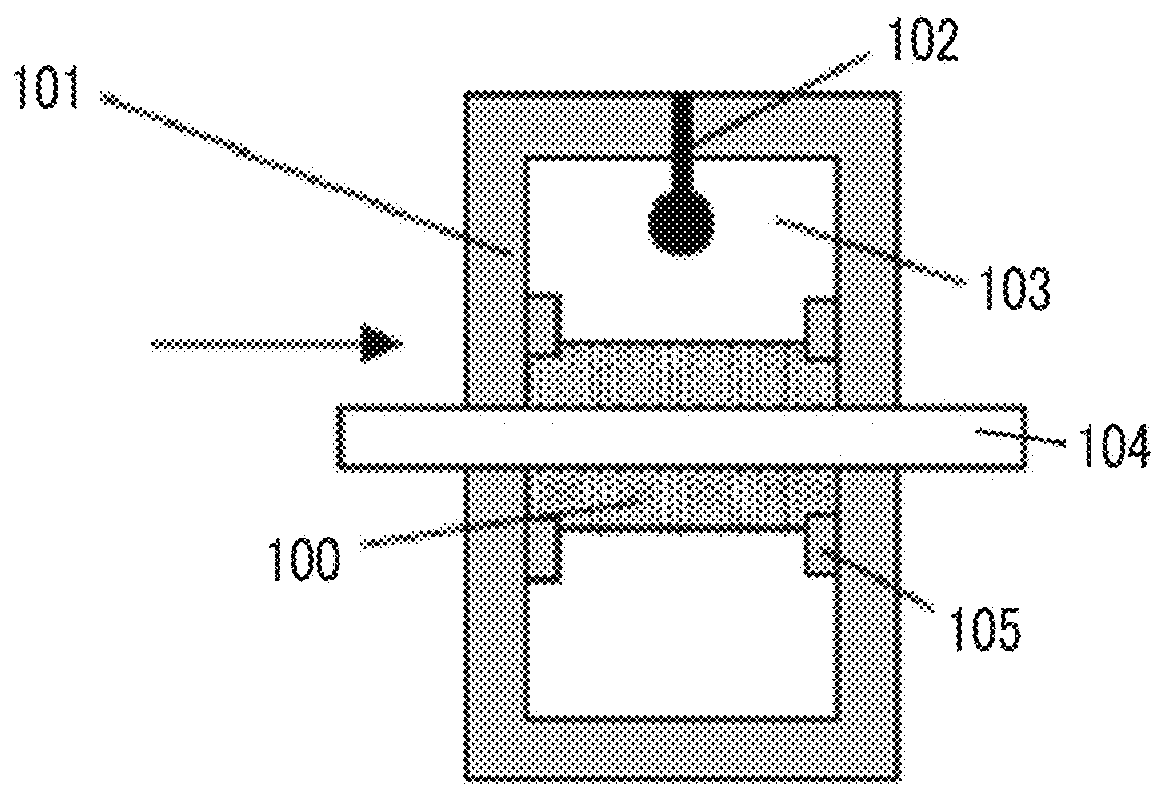
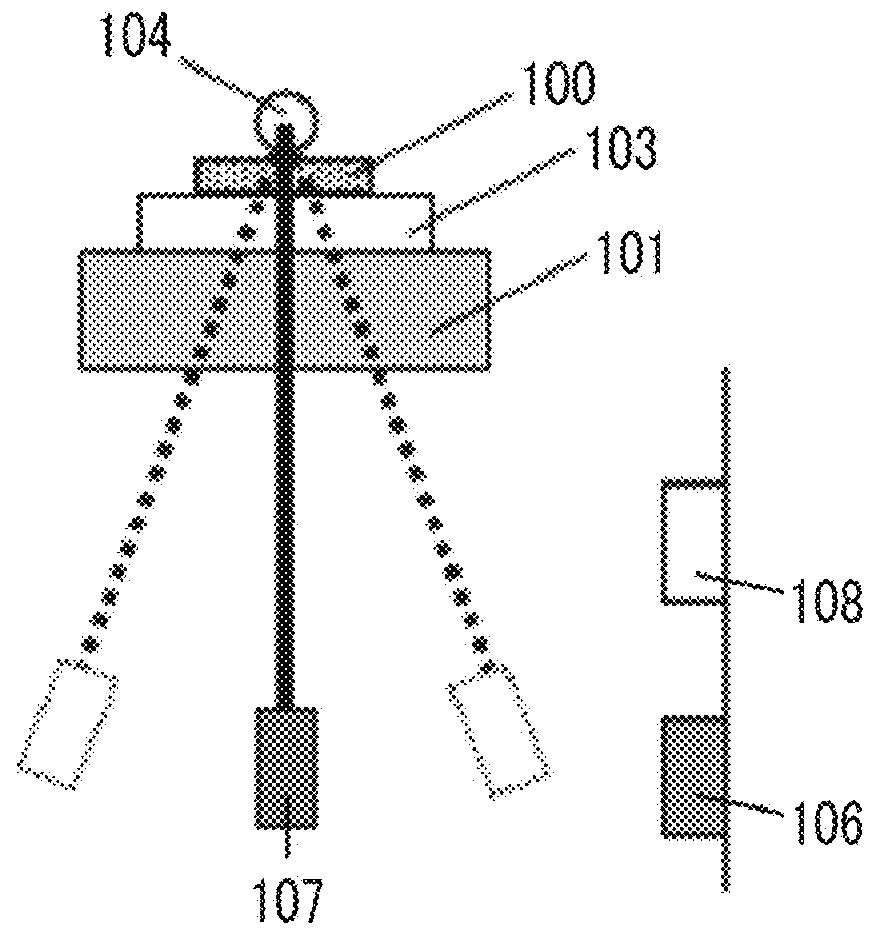
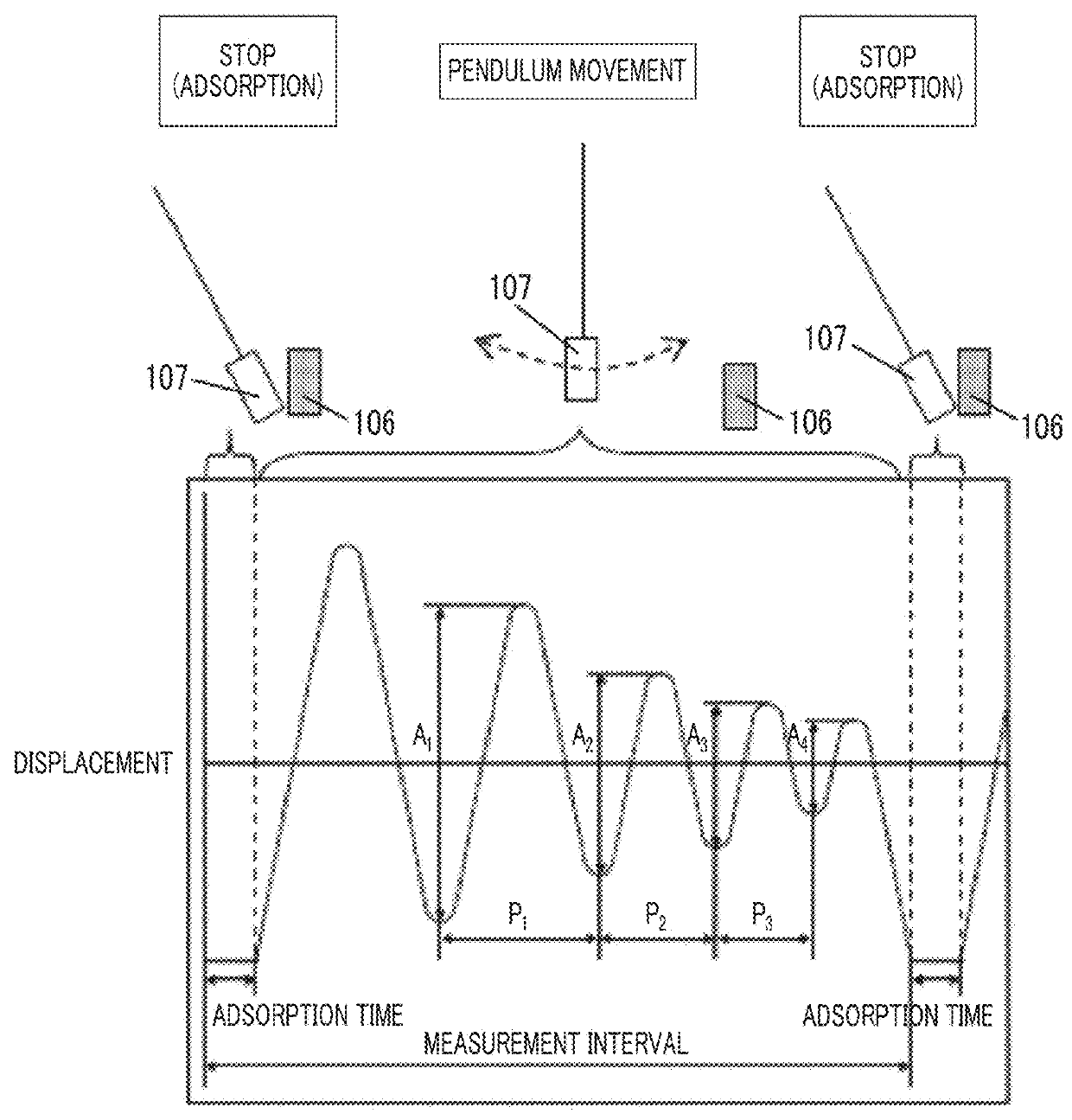
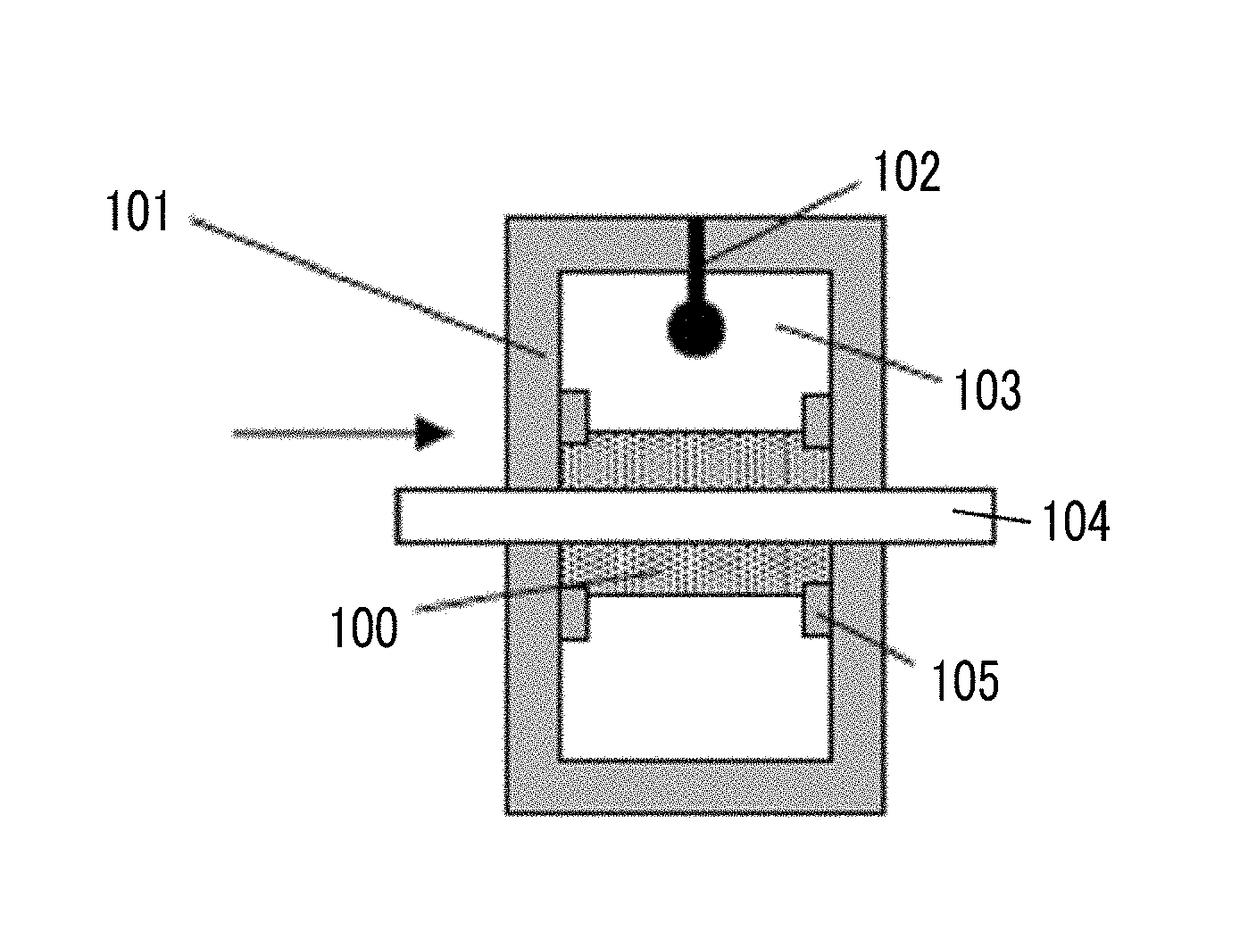
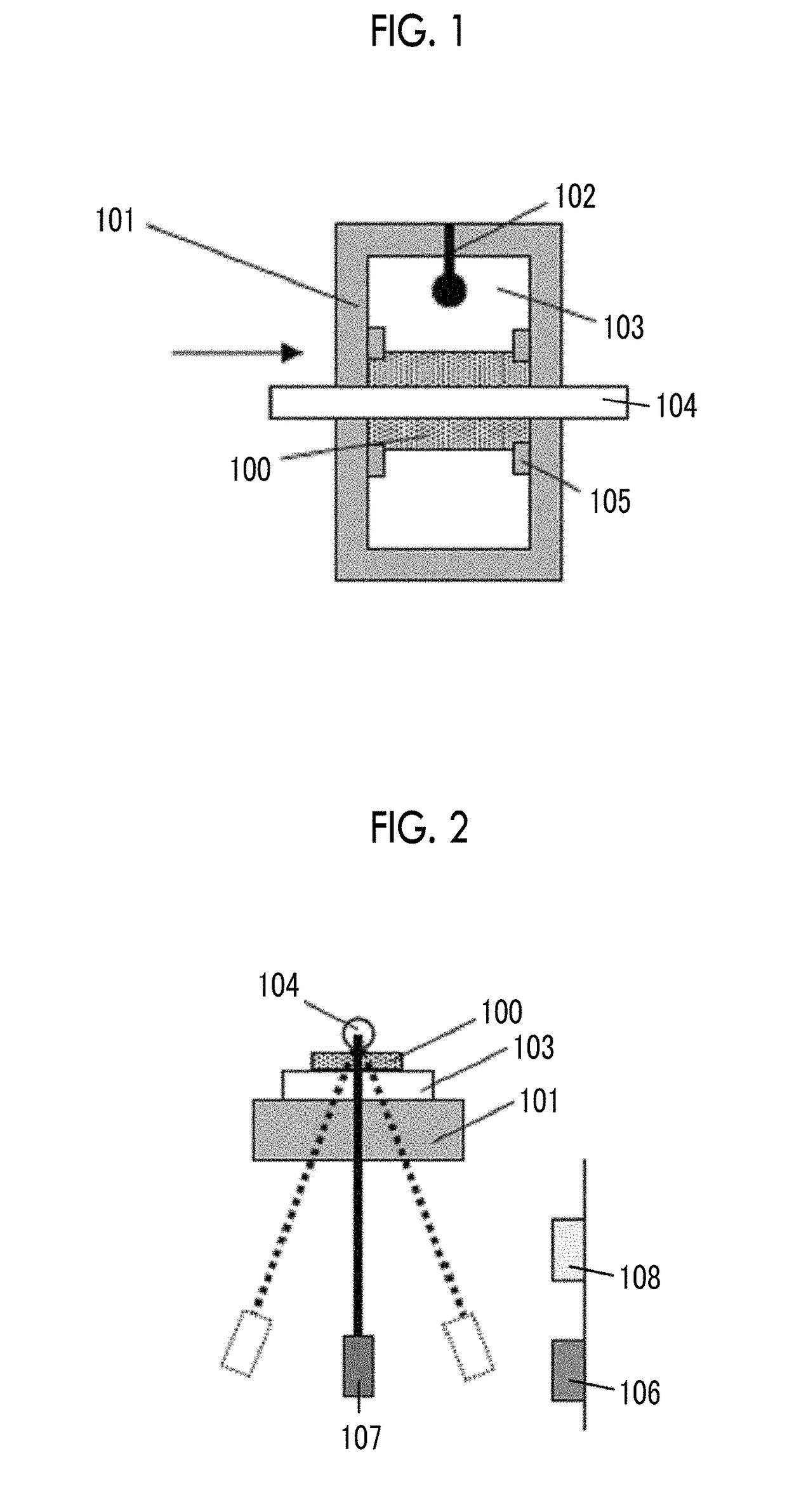
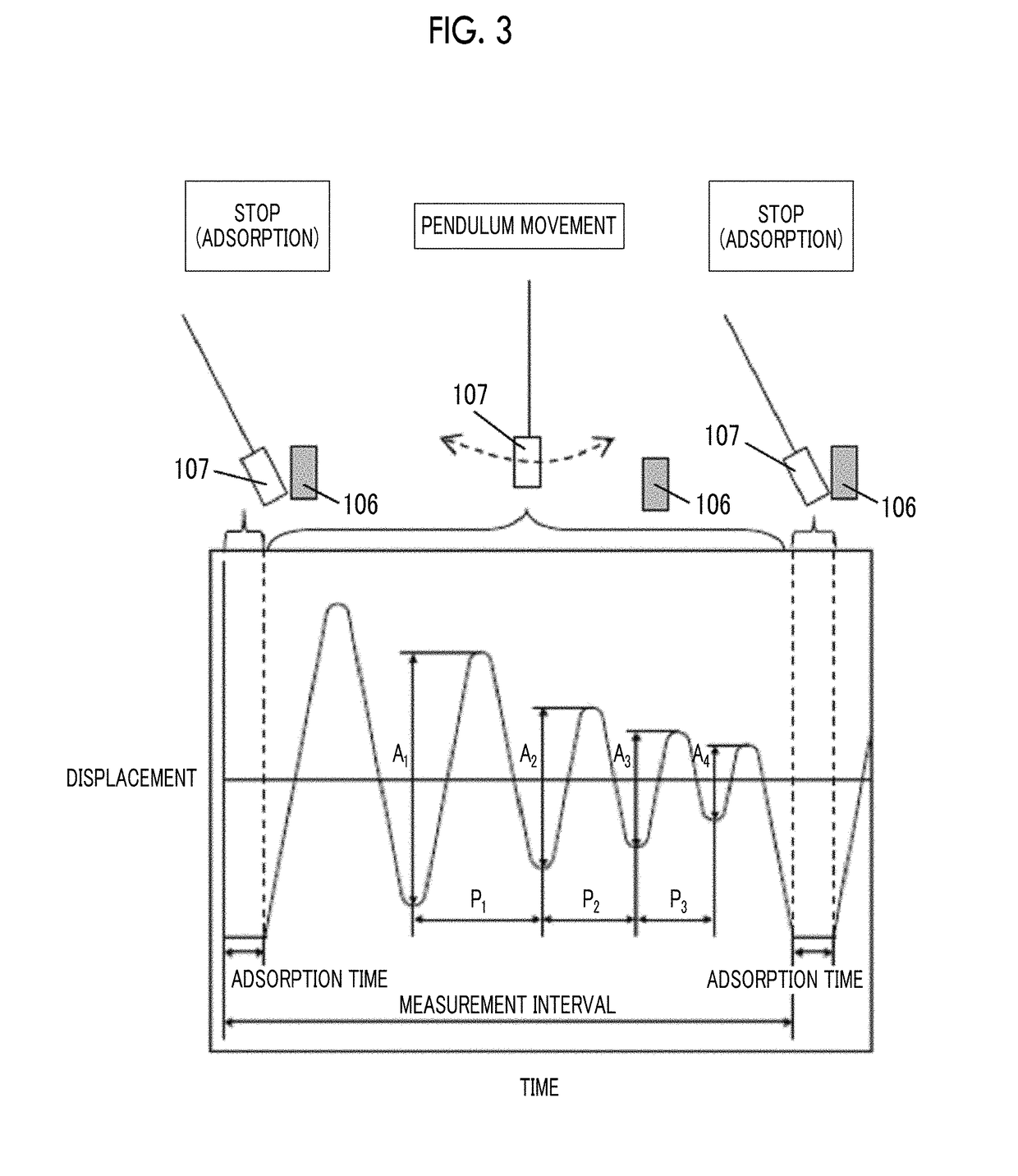
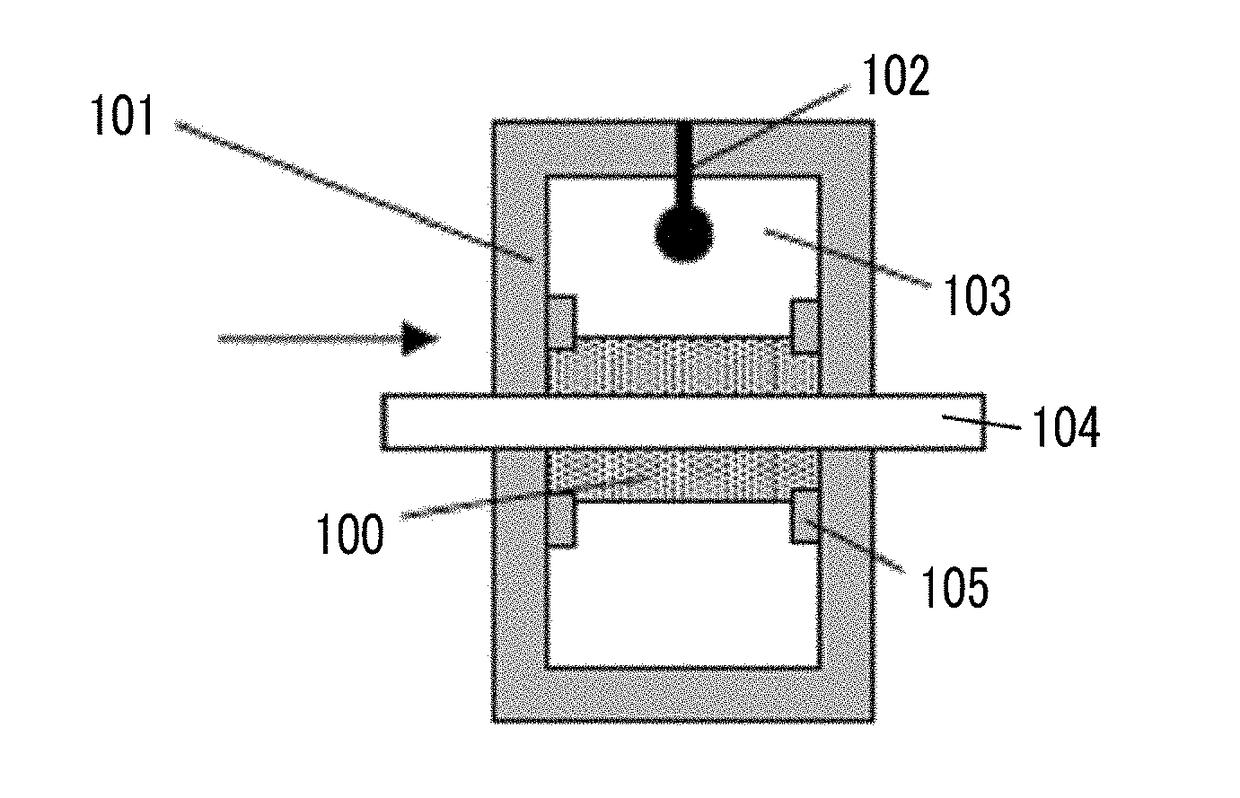
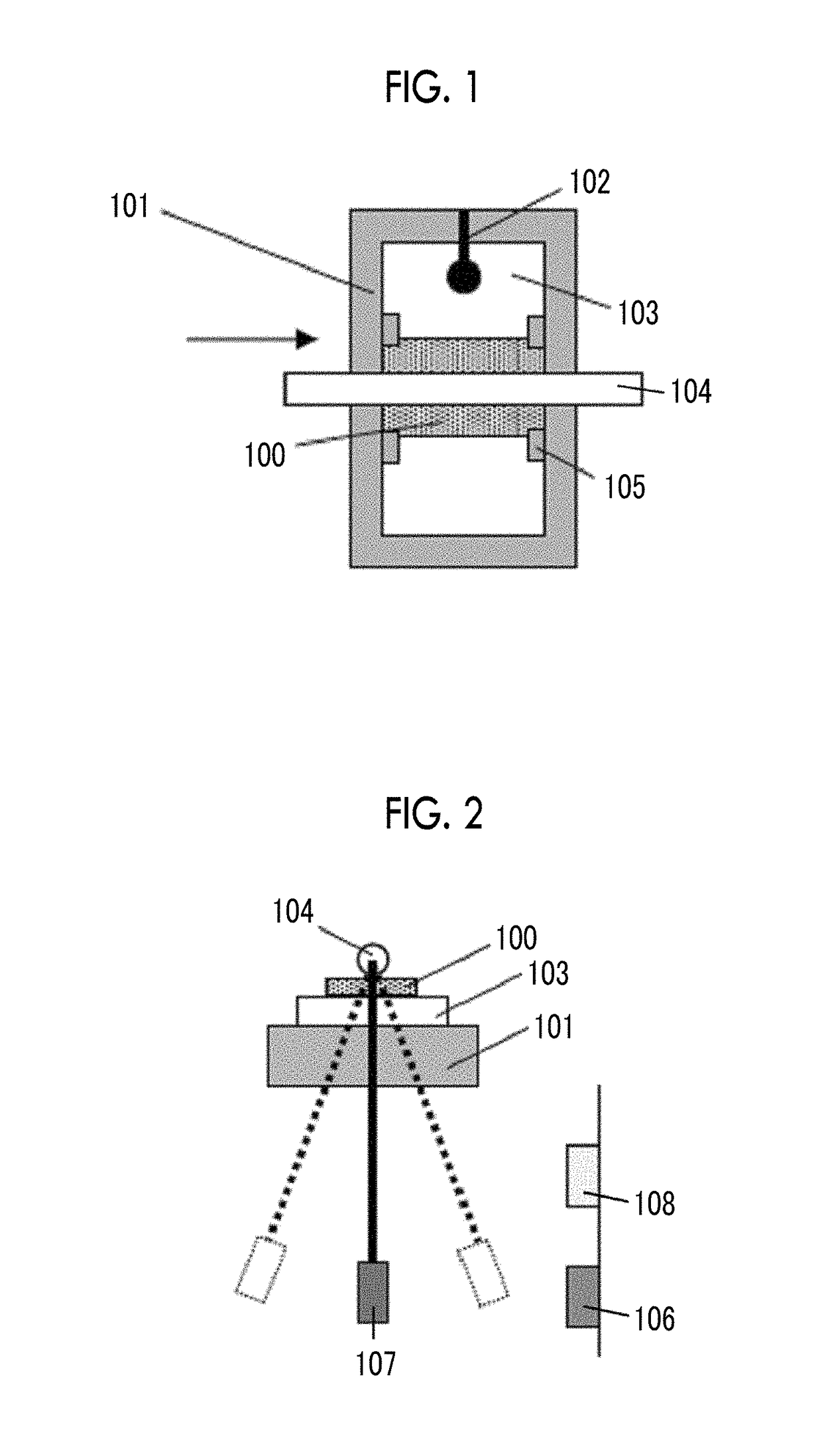
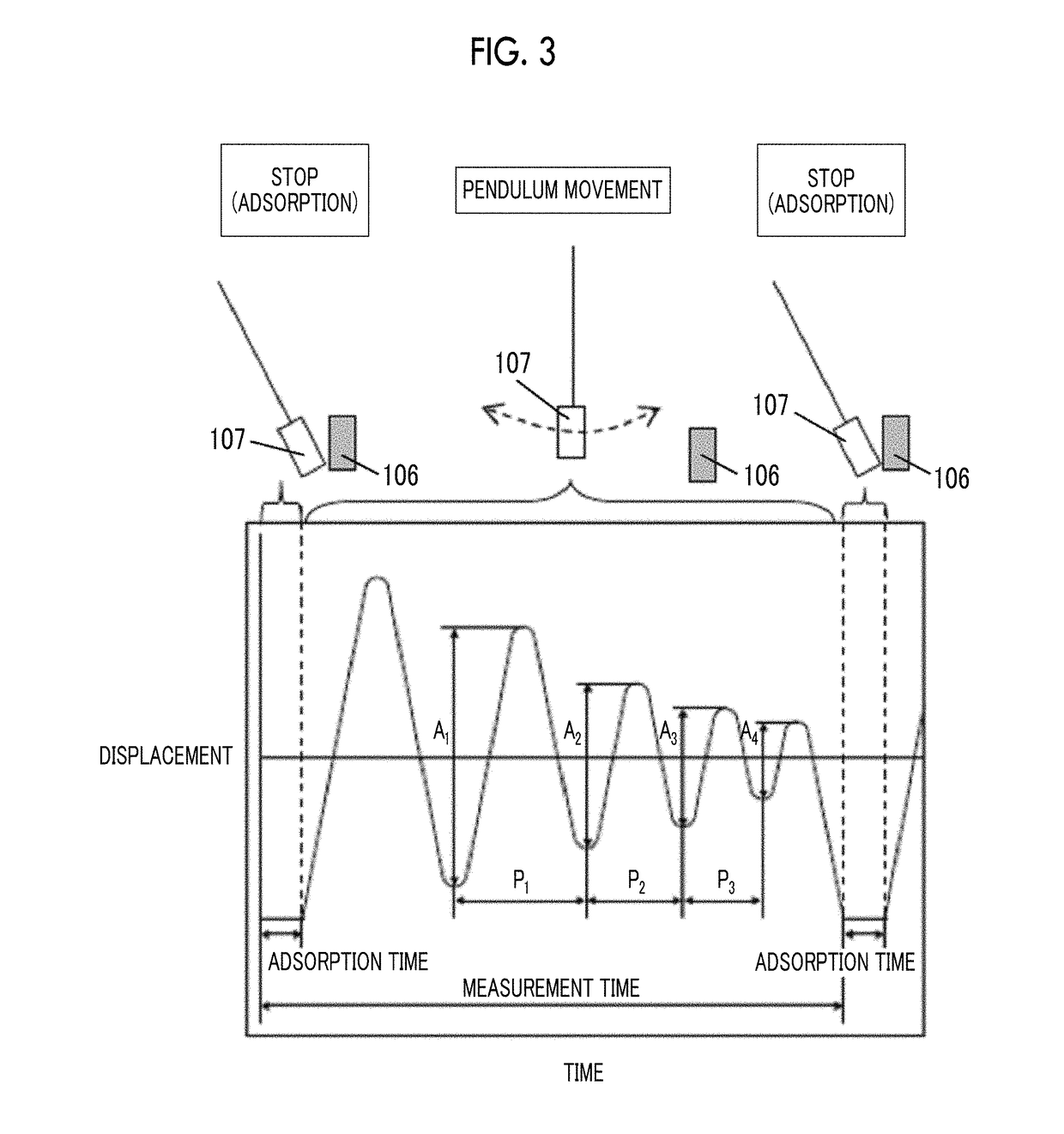
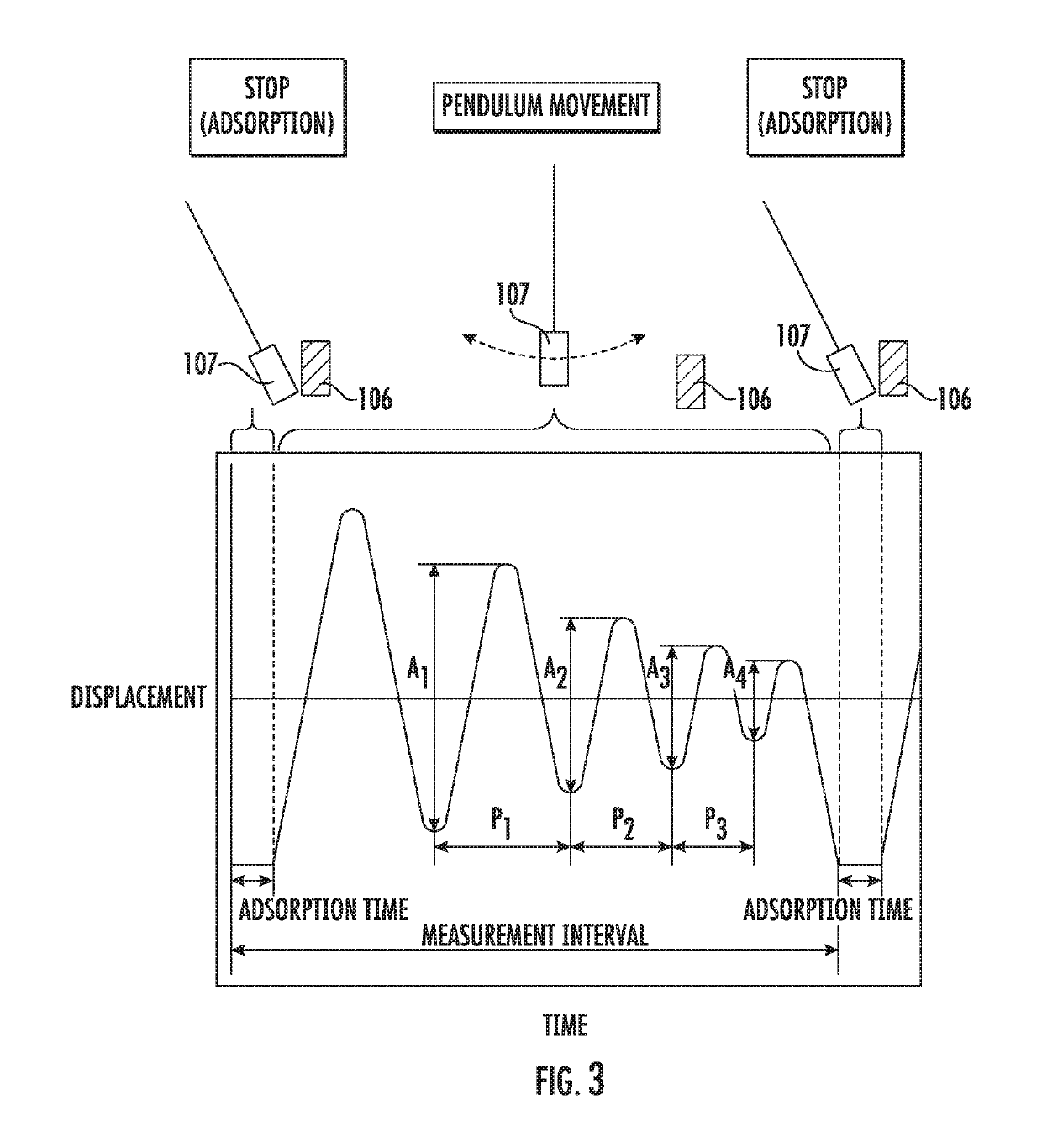
Provided are a magnetic recording medium, in which a magnetic layer includes ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, and an oxide abrasive, an intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic recording medium is 0.65 to 1.00, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape having controlled surface properties of the magnetic layer and method of manufacturing the same
The magnetic tape has a nonmagnetic layer containing nonmagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, and has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on the nonmagnetic layer, wherein the combined thickness of the magnetic layer and the nonmagnetic layer is less than or equal to 0.80 μm; and the logarithmic decrement as determined by a pendulum viscoelasticity test on the surface on the magnetic layer side of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 0.050 and the coefficient of friction as measured on a base portion of the surface on the magnetic layer side is less than or equal to 0.35.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape having controlled surface properties of the magnetic layer and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS10026434B2Improve surface smoothnessImprove featuresRecord information storageTape carriersMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS9972351B1Avoid it happening againImprove accuracyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeEngineering
The magnetic tape device including: a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a magnetic head including a tunnel magnetoresistance effect type element as a servo pattern reading element, the magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, the magnetic layer includes a servo pattern, and logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10062403B1Improve accuracyExact reproductionTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a TMR head, the magnetic tape includes a servo pattern in the magnetic layer, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and a ratio (Sdc / Sac) of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster thereof in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180240481A1Lower the resistance valueAvoid it happening againAlignment for track following on tapesTape carriersX-rayEngineering
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head as a servo head; and a magnetic tape which includes a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder and a binding agent, and including a servo pattern, an XRD intensity ratio (Int(110) / Int(114)) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180240478A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head as a reproducing head; and a magnetic tape which includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, an XRD intensity ratio (Int(110) / Int(114)) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
The magnetic tape has a nonmagnetic layer containing nonmagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, and has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on the nonmagnetic layer, wherein the combined thickness of the magnetic layer and the nonmagnetic layer is less than or equal to 0.80 μm; and the logarithmic decrement as determined by a pendulum viscoelasticity test on the surface on the magnetic layer side of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 0.050 and the coefficient of friction as measured on a base portion of the surface on the magnetic layer side is less than or equal to 0.35.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372727A1Restrain output decreaseImprove accuracyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a non-magnetic layer including non-magnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic layer, in which the total thickness of the non-magnetic layer and the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, and logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180240489A1Lower the resistance valueAvoid it happening againMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape device including: a magnetic tape including a servo pattern on a magnetic layer; and a TMR head as a servo head, in which a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape calculated by Expression 1: ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C. is equal to or smaller than 0.50, wherein the SFD25° C. is SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. is SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20170053671A1Increase recording capacityReduce thicknessTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on the surface on one side of a nonmagnetic support and has a backcoat layer containing nonmagnetic powder and binder on the surface on the other side of the nonmagnetic support, wherein the backcoat layer is less than or equal to 0.30 μm in thickness; and the logarithmic decrement as determined by a pendulum viscoelasticity test on the surface on the backcoat layer side of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 0.060.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20180301165A1Improve surface smoothnessImprove featuresTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the centerline average surface roughness Ra as measured on the surface on the magnetic layer side of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 1.8 nm, and the logarithmic decrement as determined by a pendulum viscoelasticity test on the surface on the magnetic layer side of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180240479A1Lower the resistance valueImprove smoothnessManufacture head surfaceTape carriersMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a TMR head as a reproducing head, in which a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape calculated by Expression 1: ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C. is equal to or smaller than 0.50, wherein, in Expression 1, the SFD25° C. is a switching field distribution SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. is a switching field distribution SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20180240493A1Improve surface smoothnessPrevent decrease in reproduction outputMaterials with ironRecord information storageMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape calculated by Expression 1: ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C. is equal to or greater than 0.35. In Expression 1, the SFD25° C. is a switching field distribution SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. is a switching field distribution SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducting method
ActiveUS20180240476A1Lower the resistance valueImprove smoothnessMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a reproducing head, in which the reproducing head is a TMR head, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and a ratio (Sdc / Sac) of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20180240495A1Deterioration of characteristicMaterials with ironRecord information storageScanning tunneling microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a non-magnetic layer including non-magnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic layer, in which the total thickness of the non-magnetic layer and the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, the magnetic layer includes an abrasive, a percentage of a plan view maximum area of the abrasive confirmed in a region having a size of 4.3 μm×6.3 μm of the surface of the magnetic layer with respect to the total area of the region, obtained by plane observation performed by using a scanning electron microscope is equal to or greater than 0.02% and less than 0.06%, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape having controlled surface properties of the backcoat layer and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS10026435B2Increase recording capacityReduce thicknessTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on the surface on one side of a nonmagnetic support and has a backcoat layer containing nonmagnetic powder and binder on the surface on the other side of the nonmagnetic support, wherein the backcoat layer is less than or equal to 0.30 μm in thickness; and the logarithmic decrement as determined by a pendulum viscoelasticity test on the surface on the backcoat layer side of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 0.060.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180182425A1Avoid it happening againReduce resistanceMaterials with ironRecord information storageMagnetic tapeEngineering
The magnetic tape device includes: a magnetic tape; and a reproducing head, in which the reproducing head is a magnetic head including a tunnel magnetoresistance effect type element as a reproducing element, the magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, and logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20180240492A1Avoid it happening againRecord information storageTape carriersCoated surfaceMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape includes a back coating layer having a thickness equal to or smaller than 0.30 μm and including fatty acid ester, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the back coating layer is equal to or smaller than 0.060, a full width at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the back coating layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape is respectively greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 10.0 nm, and a difference between a spacing measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the back coating layer after performing the vacuum heating and a spacing measured before performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20180240488A1Avoid it happening againAvoid edge damageProtective coatings for layersTape carriersMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on one surface side of the non-magnetic support; and a back coating layer including non-magnetic powder and a binding agent on the other surface side of the non-magnetic support, in which a thickness of the back coating layer is equal to or smaller than 0.30 μm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the back coating layer is equal to or smaller than 0.060, and a contact angle with respect to 1-bromonaphthalene measured regarding a surface of the back coating layer is 15.0° to 30.0°.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103130A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againDisposition/mounting of recording headsMagnetic materials for record carriersMagnetic tapeViscoelasticity
Provided are a magnetic tape, in which a magnetic layer includes a ferromagnetic powder, a binding agent, and an oxide abrasive, ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape calculated by Expression 1, ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C., is equal to or smaller than 0.50, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
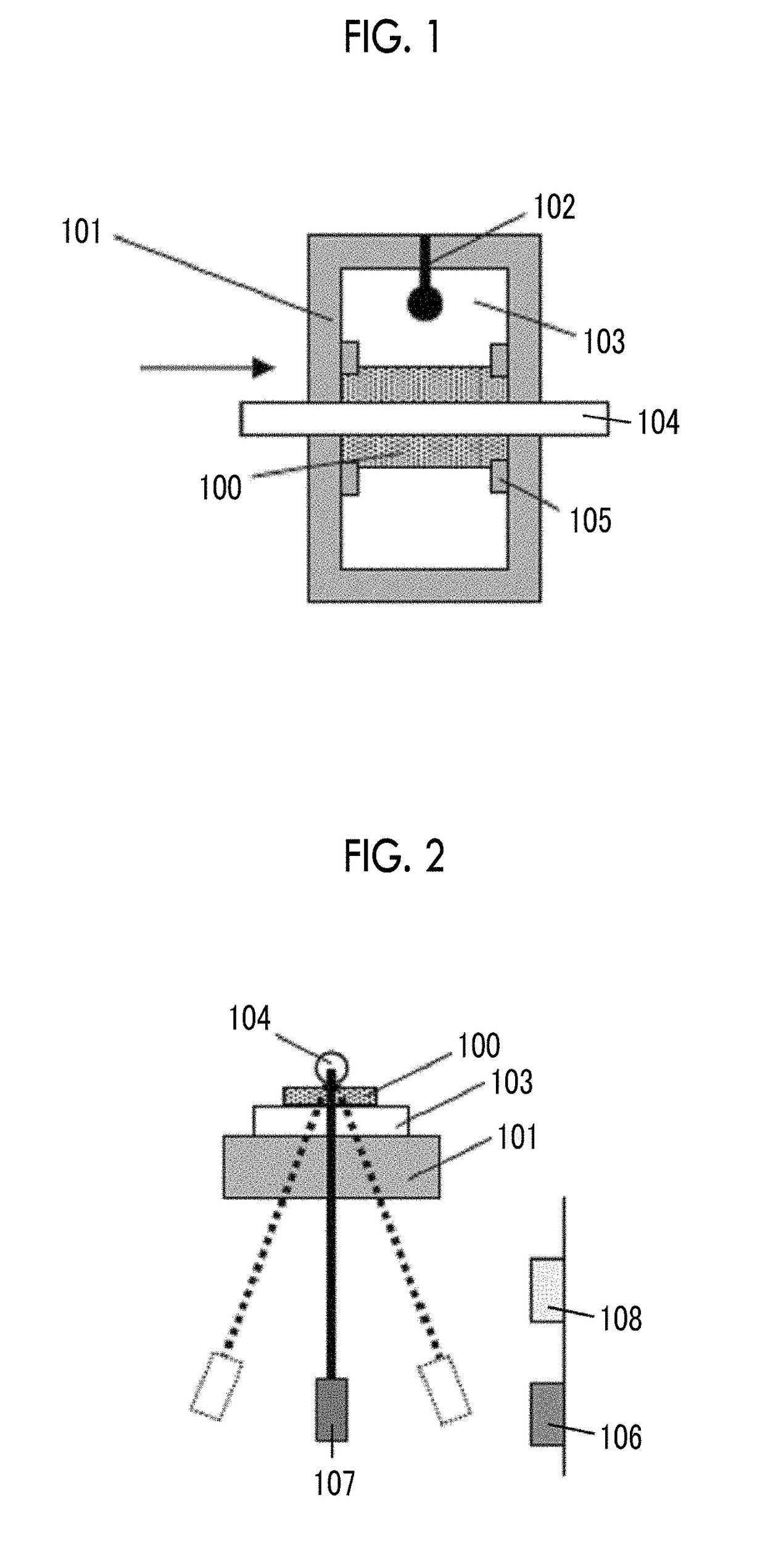
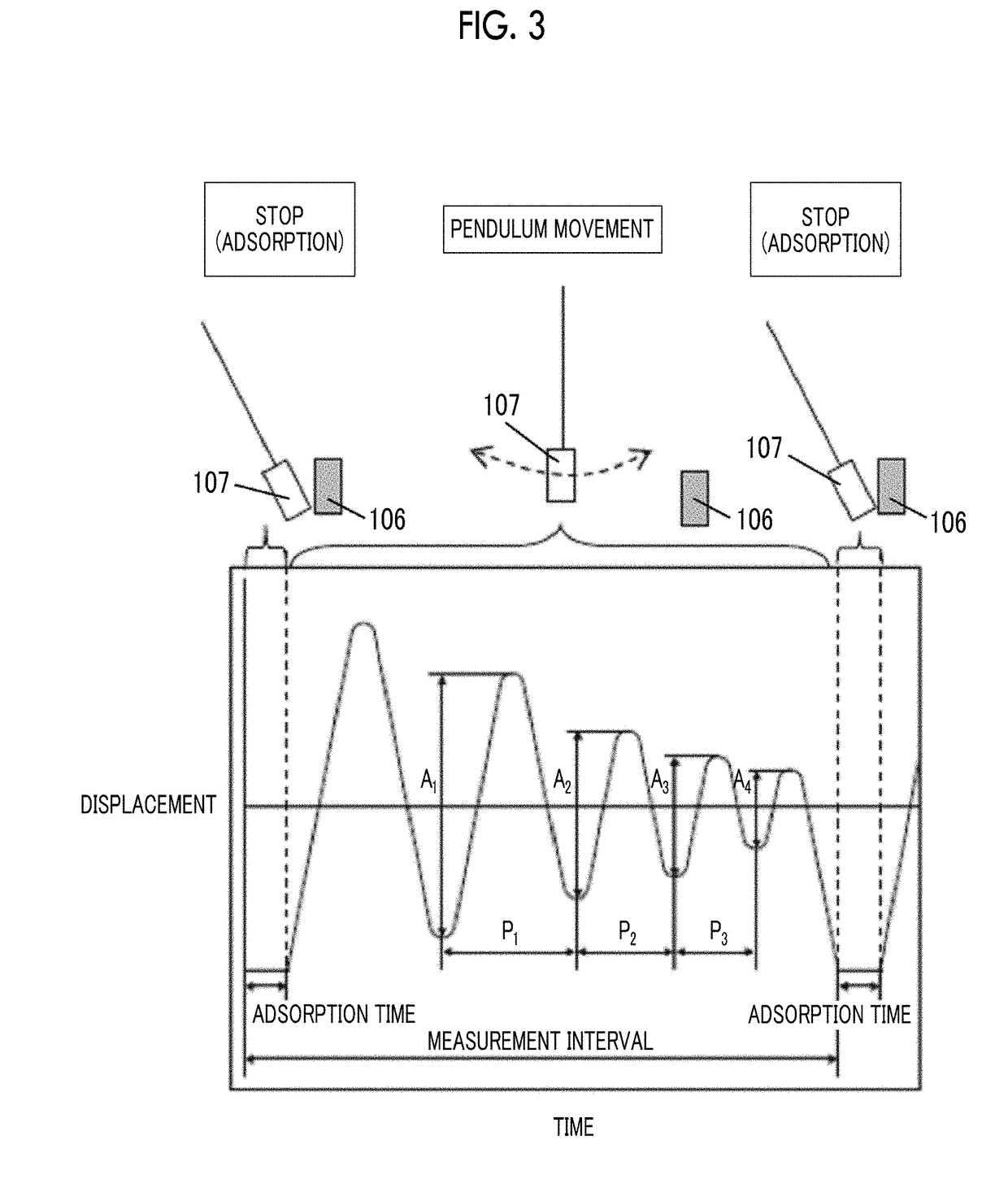
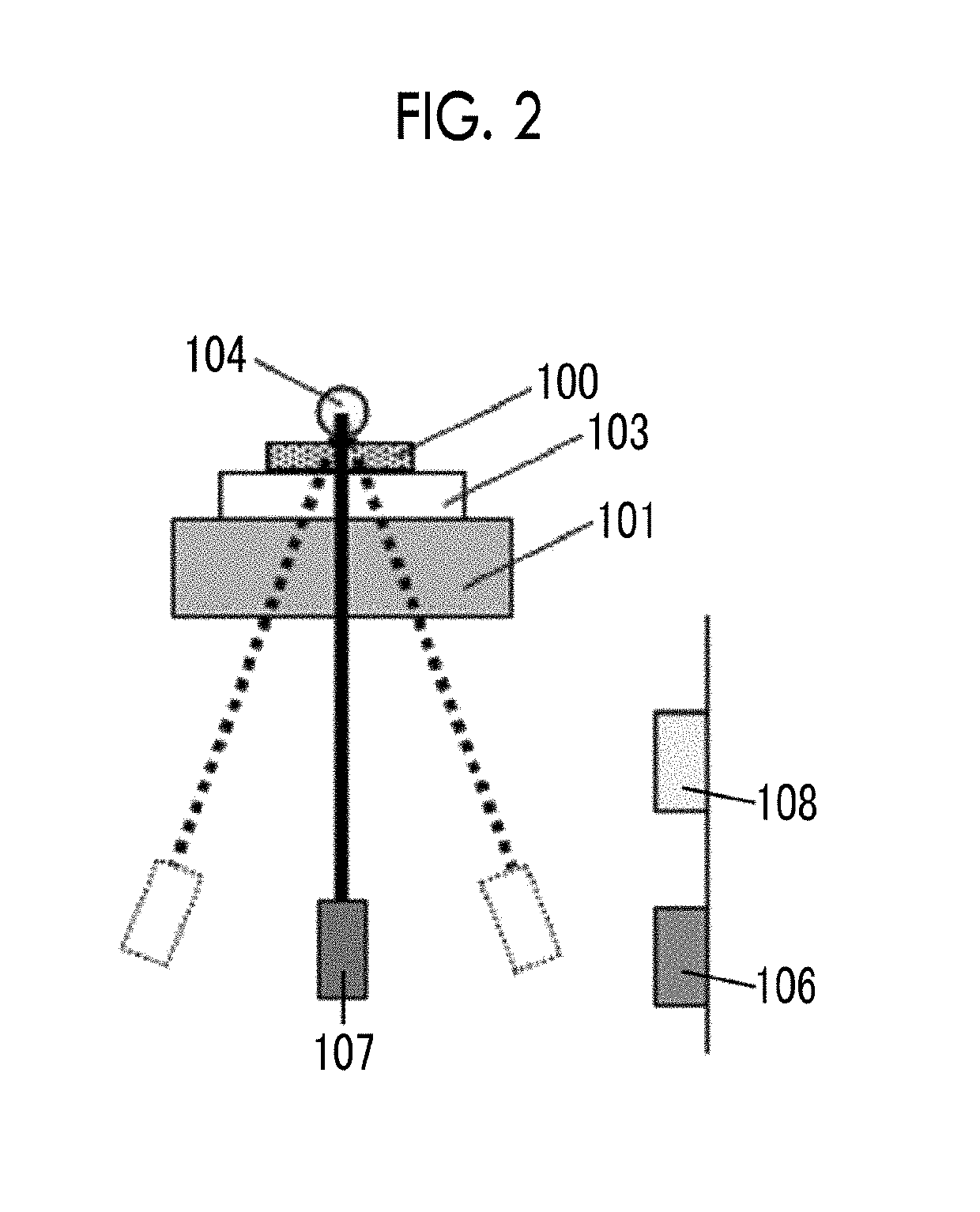
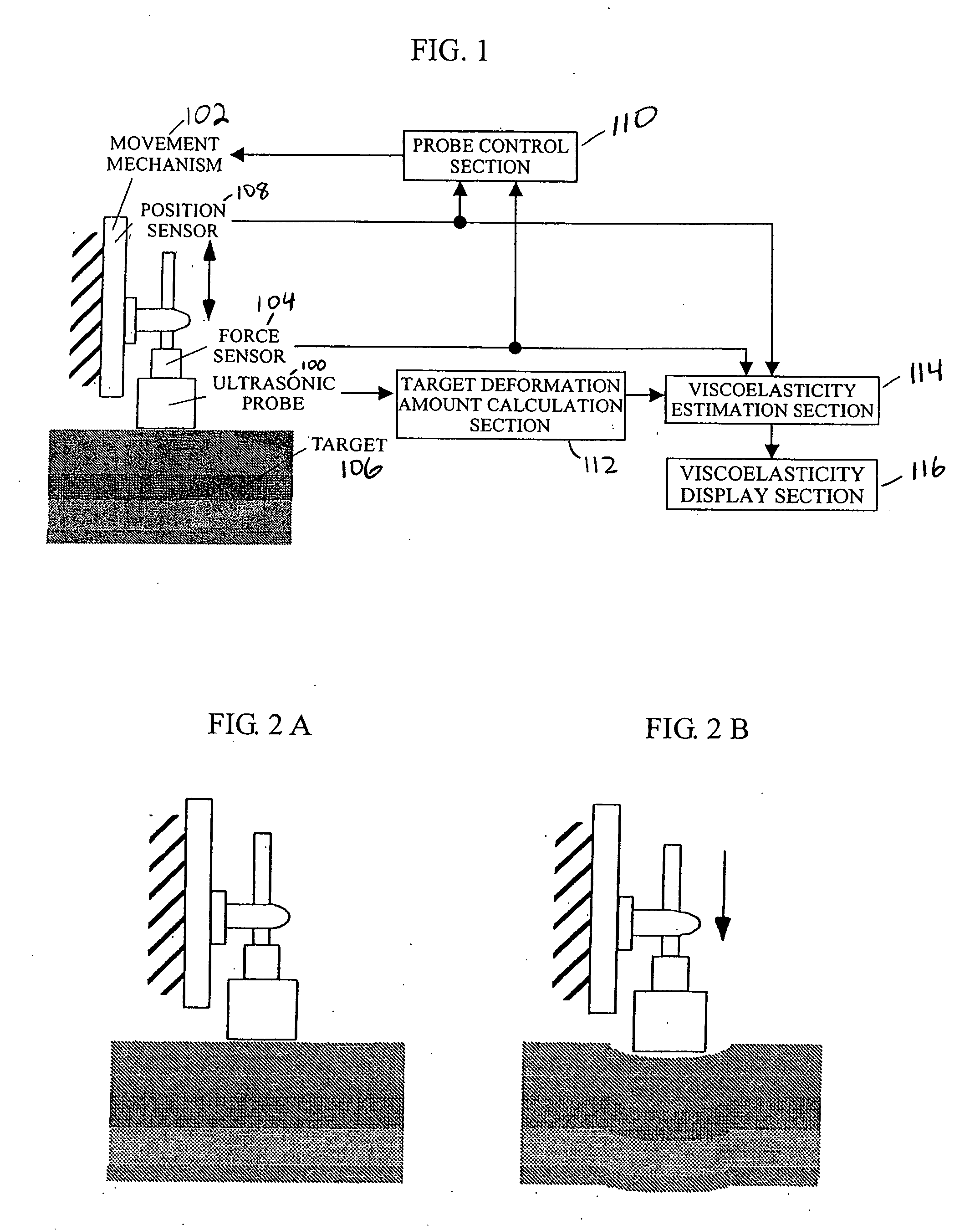
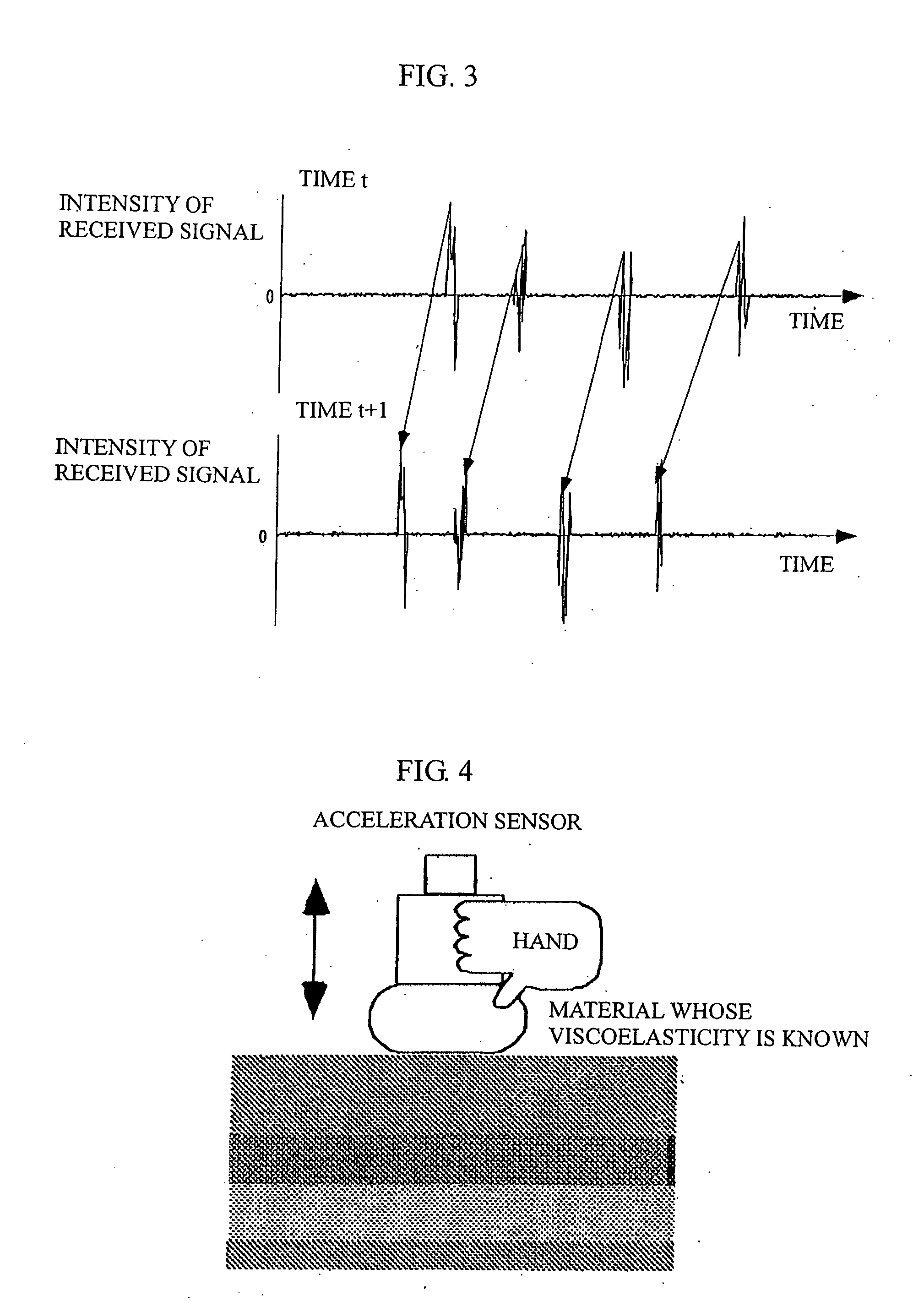
Apparatus and program for estimating viscoelasticity of soft tissue using ultrasound
InactiveUS20050085728A1Reduce harmAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostic probe attachmentSonificationViscoelasticity
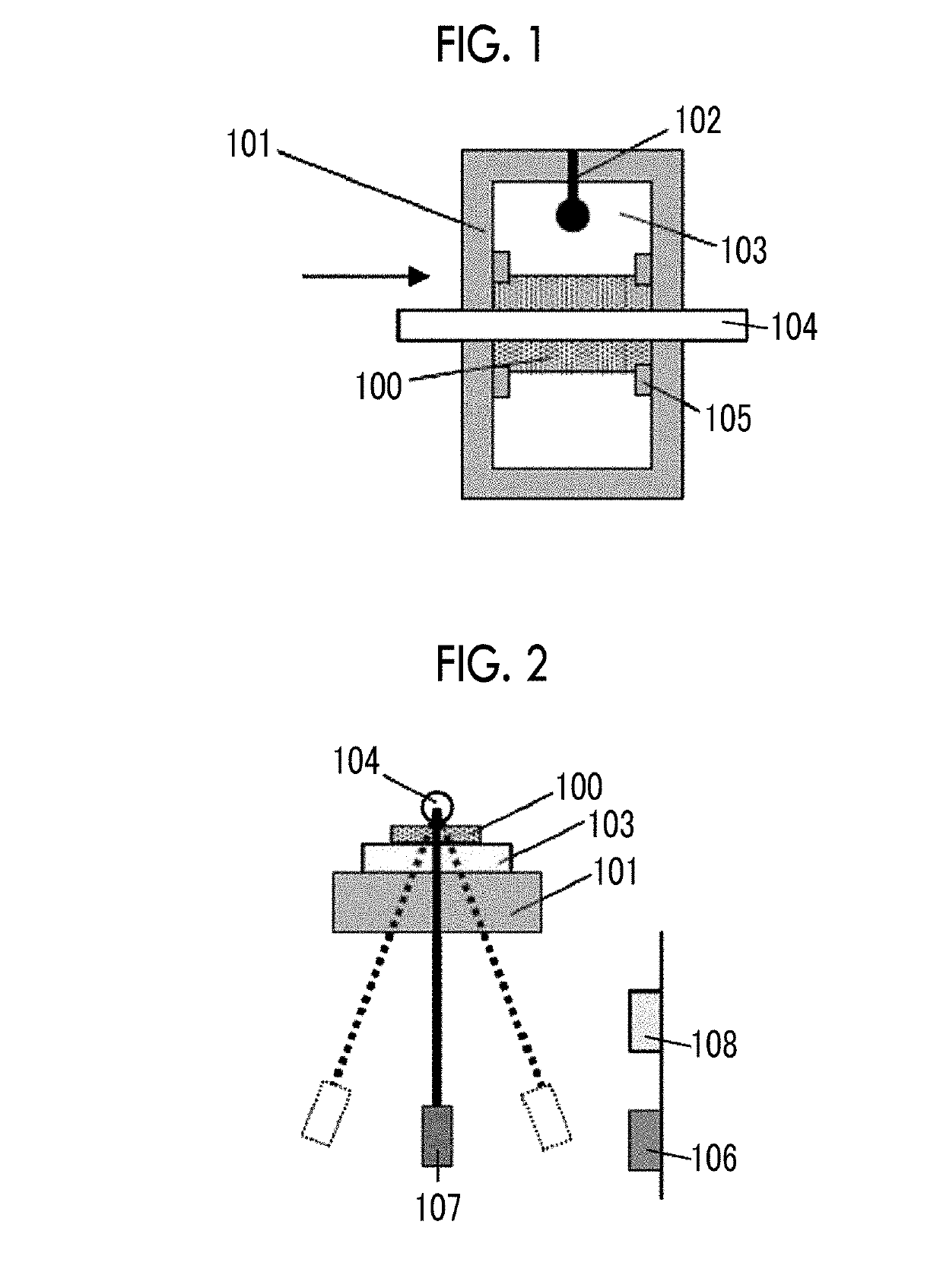
The present invention allows even soft tissue such as body tissue having a hierarchic structure of skin, fat, muscle and bone, etc., to be estimated and allows estimation only through a short-time pressing operation to thereby reduce damages to the soft tissue. The present invention is constructed of an ultrasonic probe for transmitting / receiving an ultrasonic signal, a target deformation amount calculation section for calculating an amount of deformation of a target shape from a time variation of data received from the ultrasonic probe, a movement mechanism for moving the ultrasonic probe, a probe control section for controlling the probe, a position sensor for measuring the position of the probe, a force sensor for measuring a force applied to the probe section, a viscoelasticity estimation section for estimating viscoelasticity of the target based on values obtained from the position sensor, force sensor, target deformation amount calculation section and a viscoelasticity display section for presenting the estimated viscoelasticity to the user.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20190027180A1Improve surface smoothnessAvoid it happening againMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder, non-magnetic powder, and a binding agent and a back coating layer including non-magnetic powder and a binding agent, in which the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, an Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the hack coating layer is equal to or smaller than 0.060.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
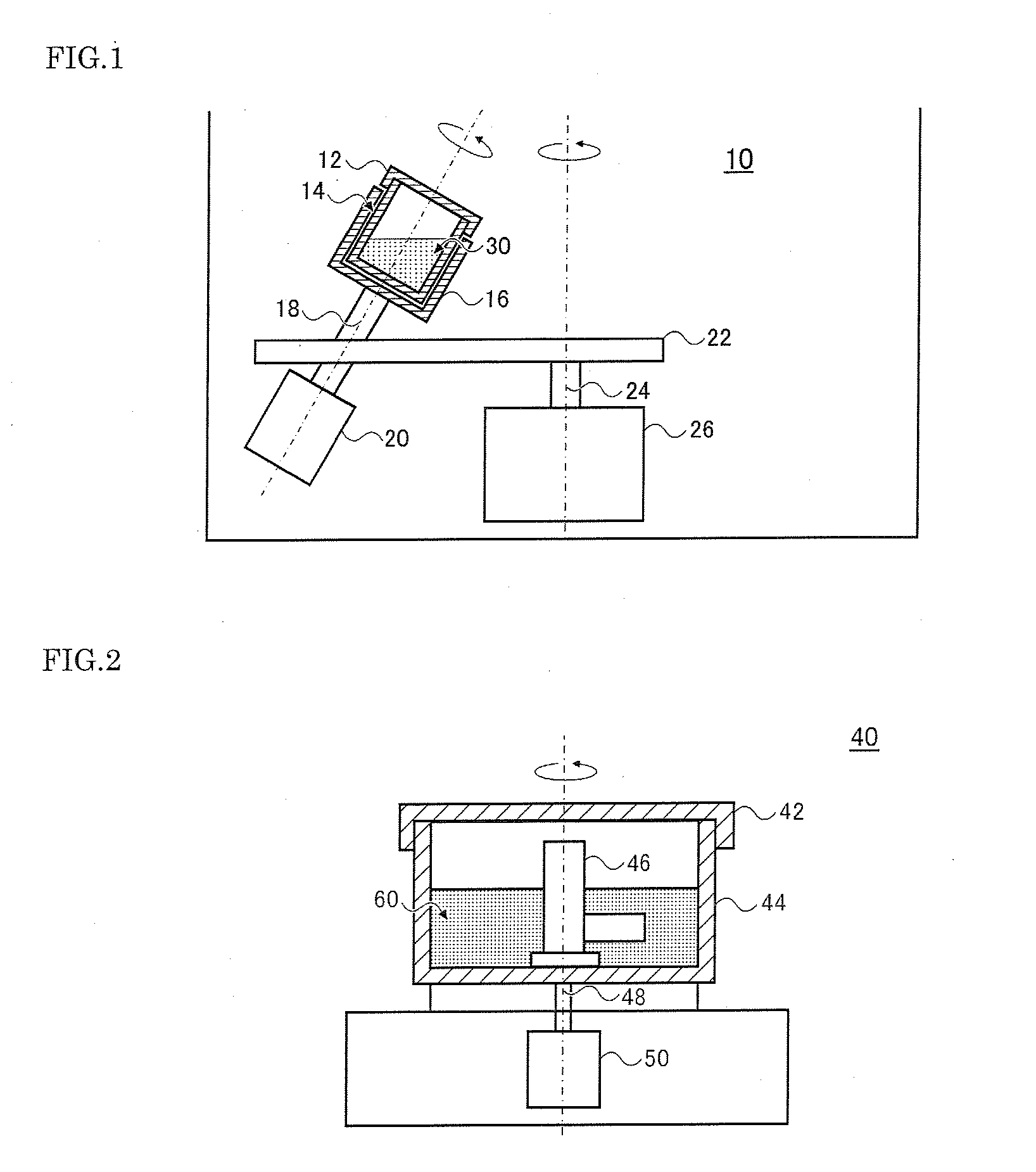
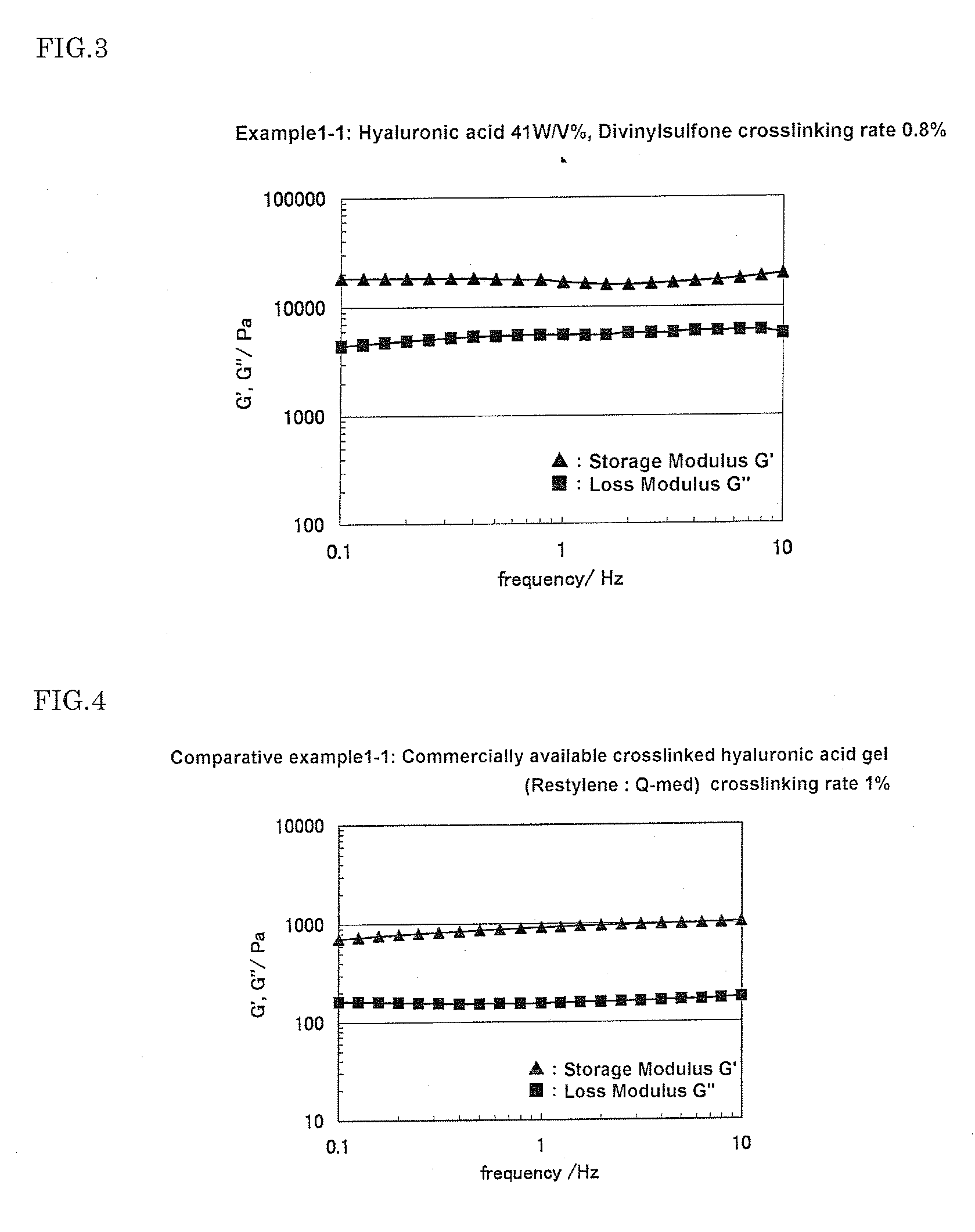
Process For Preparing Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Gel
InactiveUS20110034684A1Cross-linking rate were lowHigh viscoelasticityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronic acidViscoelasticity
A novel process which can simply prepare a crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel having a small crosslinking agent content and exhibiting excellent viscoelasticity is provided.A process for preparing a crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel, comprising stirring and mixing a mixture containing 10 W / V % or more of hyaluronic acid, a crosslinking agent and water under acidic or alkaline condition.
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
Toner and full-color image forming method
InactiveUS6586147B2High transparencyExcellent low temperature fixabilityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternWaxImage formation
A toner, particularly a color toner suitable for full-color image formation through a substantially oil-less heat-pressure fixing device, is formed from at least a binder resin, a colorant and a wax. The toner has viscoelasticity including: a storage modulus at 80° C. (G'80) in a range of 1x106-1x1010 dN / m2, storage moduli at temperatures of 120-180° C. (G'120-180) in a range of 5x103-1x106 dN / m2, and loss tangents (tan delta=G'' / G' as a ratio between G'' (loss modulus) and G' (storage molecules)) including a loss tangent at 180° C. (tan delta180) and a minimum of loss tangents over a temperature range of 120-180 ° C. (tan deltamin) satisfying 1<=tan delta180 / tan deltamin. The toner further exhibits a thermal behavior providing a heat-absorption curve according to differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showing a maximum heat-absorption peak temperature in a range of 50-110° C. in a temperature range of 30-200° C.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic tape device employing TMR head and magnetic tape with characterized magnetic layer, and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10403314B2Improve accuracyAccurate informationMagnetic materials for record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesIn planeX-ray
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Fixing device, and image forming apparatus using the fixing device
InactiveUS7702271B2High imagingHigh quality tonerElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
Owner:RICOH KK
Electroacoustic converter film, flexible display, vocal cord microphone, and musical instrument sensor
ActiveUS20140210309A1Increase flexibilityExcellent acoustic characteristicsElectrophonic musical instrumentsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin film electrodeDisplay device
Provided is an electroacoustic converter film including: a polymeric composite piezoelectric body having piezoelectric particles dispersed in a viscoelastic matrix which is formed of a polymer material exhibiting viscoelasticity at ordinary temperatures; thin film electrodes formed on both sides of the polymeric composite piezoelectric body; and protective layers formed on surfaces of the thin film electrodes. The electroacoustic converter film serves as a speaker capable of being integrated with a flexible display without impairing lightweightness or flexibility, and has considerable frequency dispersion in the storage modulus and also has a local maximum of the loss tangent around ordinary temperatures. A flexible display, a vocal cord microphone and a musical instrument sensor, in each of which the electroacoustic converter film is used, are also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for measuring viscosity and/or elasticity of liquid
InactiveUS20100005865A1Accurate measurementHigh viscosityFlow propertiesElectrical measurementsResonanceViscosity
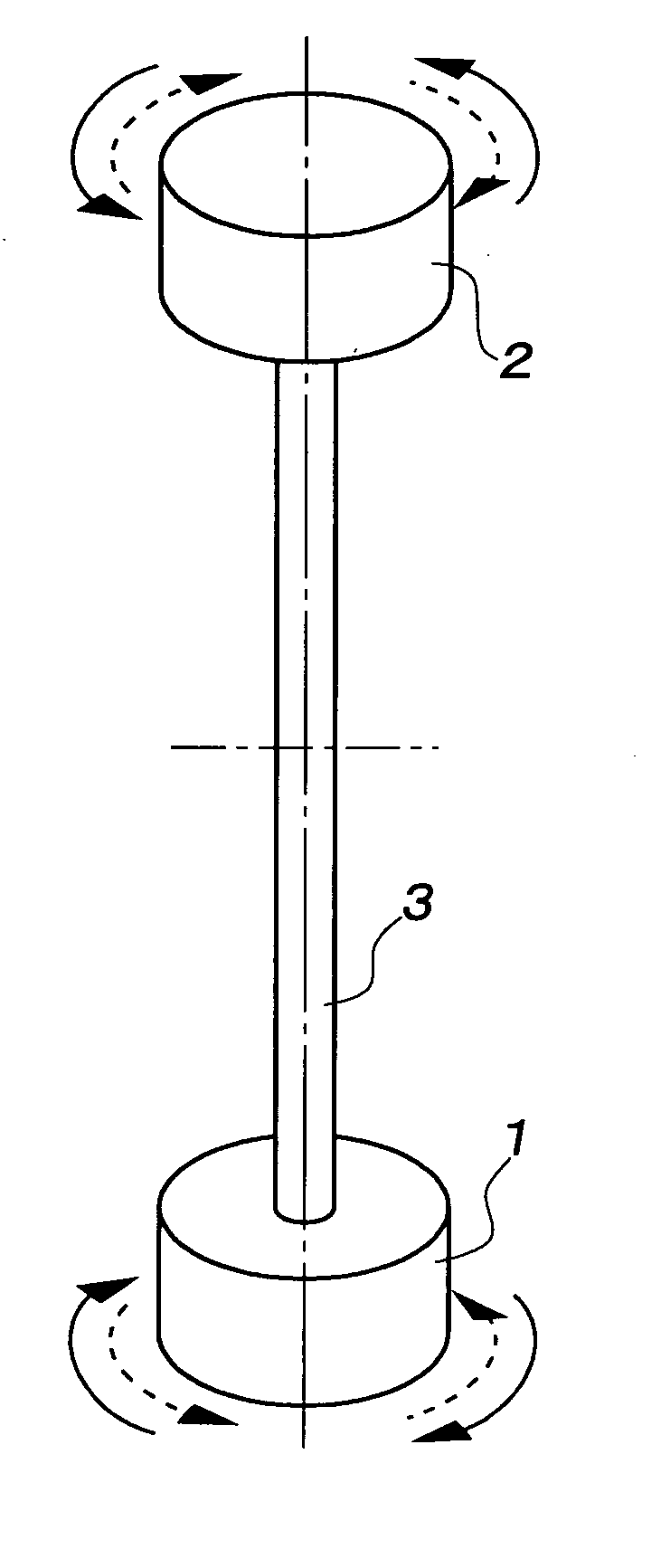
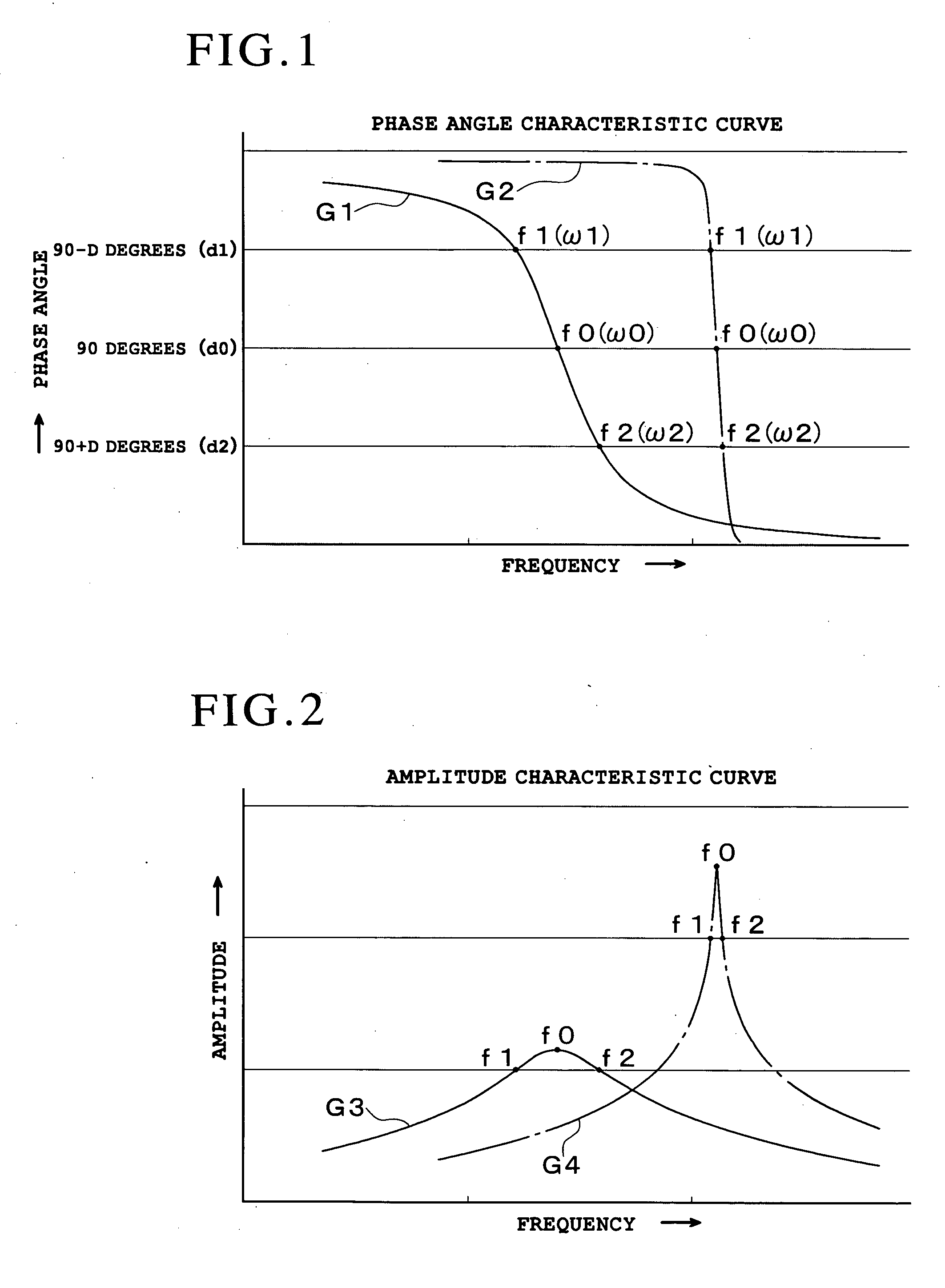
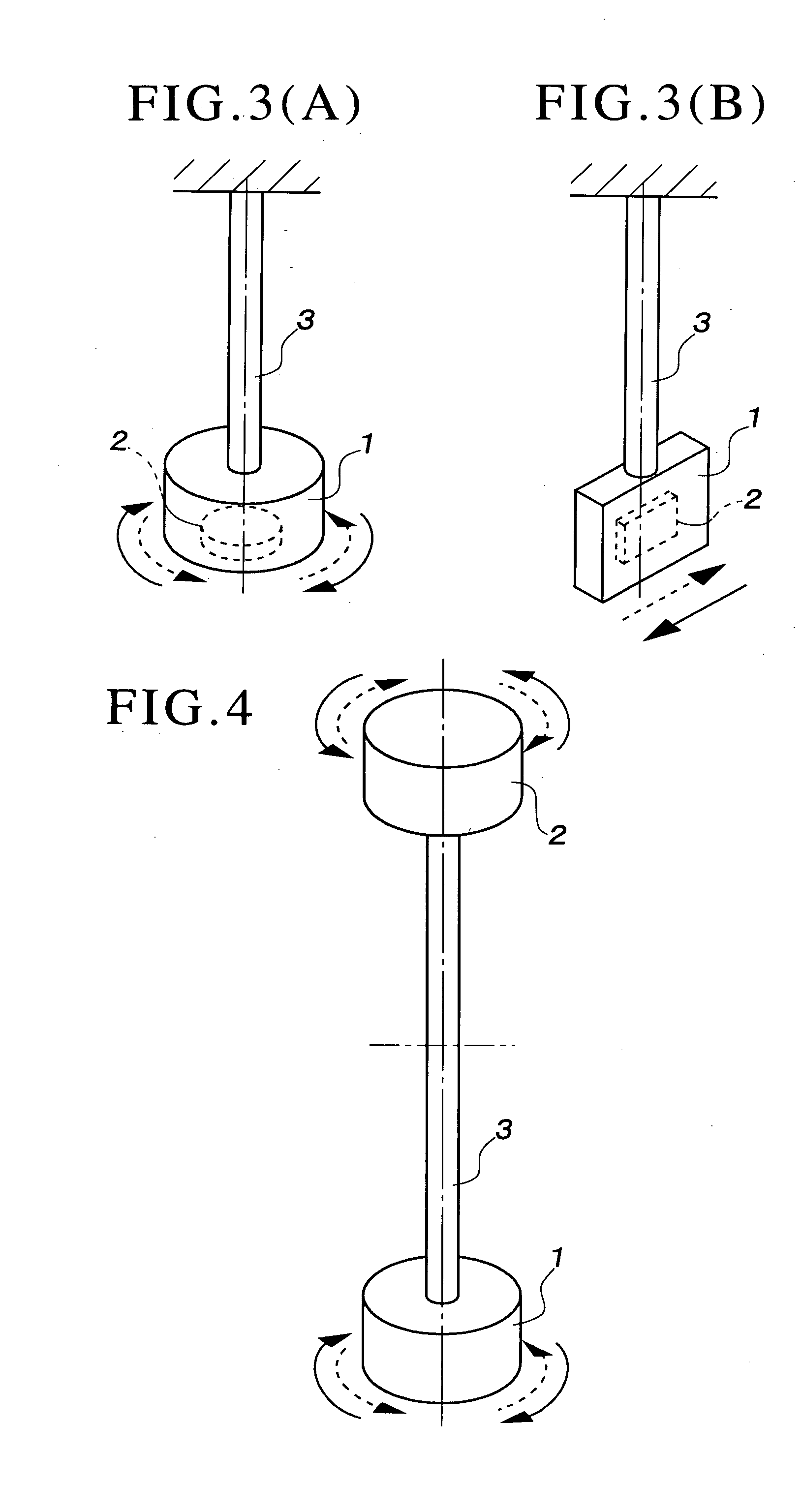
The present invention provides a method for measuring the viscosity and / or elasticity of a liquid by which accurate viscoelasticity measurement can be performed on a wide variety of liquids to be tested ranging from low viscosity liquids to high viscosity liquids, and viscosity and / or elasticity can be precisely determined from the viscoelasticity. This method includes: measuring three frequency values that are the resonance frequency value (f0) on the amplitude characteristic curve obtained through the vibration of the liquid tester 1 in the liquid being tested, a low frequency value lower (f1) than the resonance frequency value (f0) on the amplitude characteristic curve, and a high frequency value (f2) higher than the resonance frequency value (f0) on the amplitude characteristic curve; calculating the real part of the impedance of the liquid being tested, using the high frequency value (f2) and the low frequency value (f1); calculating the imaginary part of the impedance of the liquid being tested, using the resonance frequency value (f0); and calculating the viscosity value and / or the elasticity value of the liquid being tested from the real part and the imaginary part of the impedance.
Owner:SEKONIC CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190295587A1High humidity environmentLower temperature riseRecord information storageTape carriersMagnetic tapeRefractive index
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy measured regarding an in-plane direction of the magnetic layer and a refractive index Nz measured regarding a thickness direction of the magnetic layer is 0.25 to 0.40, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com