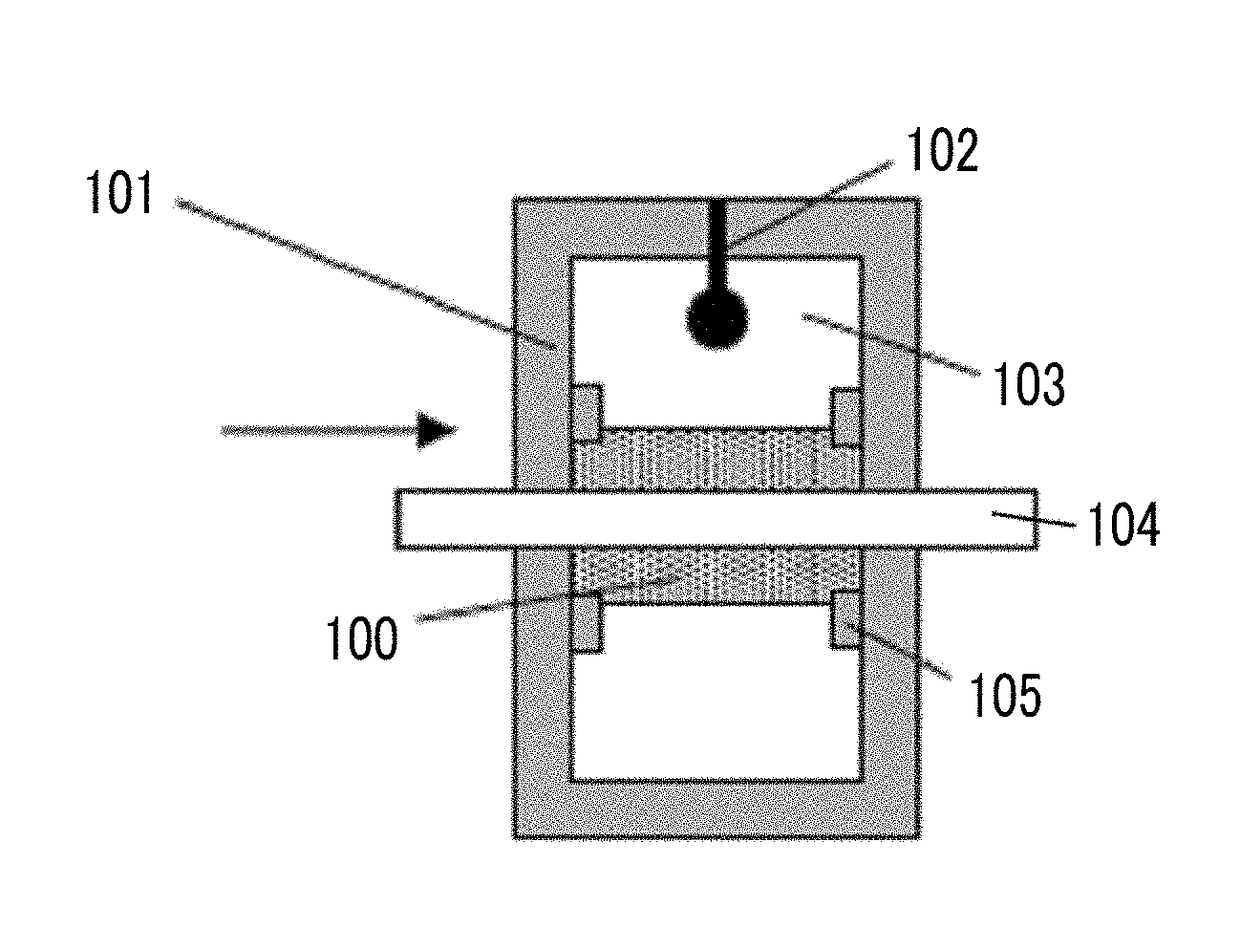
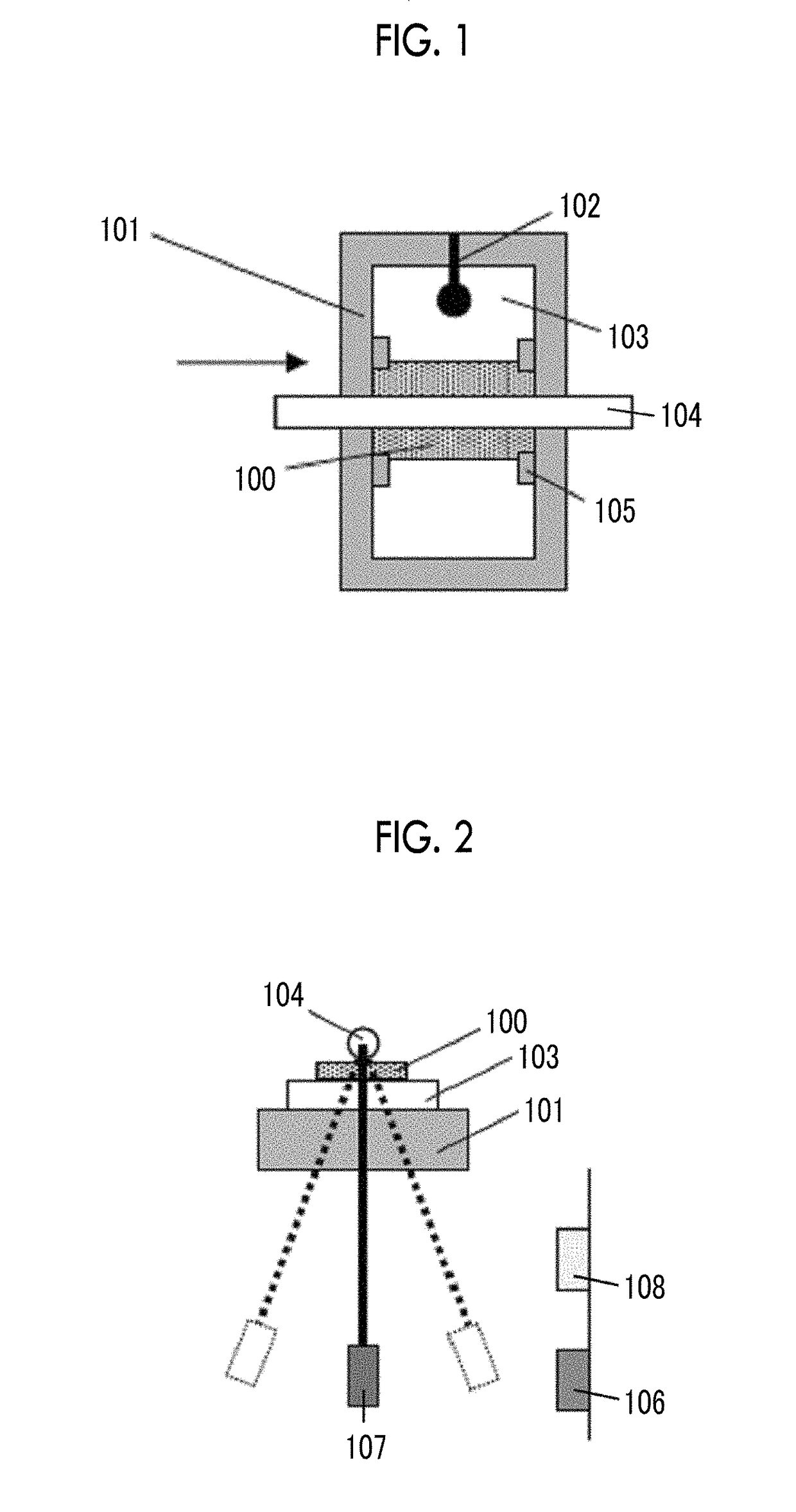
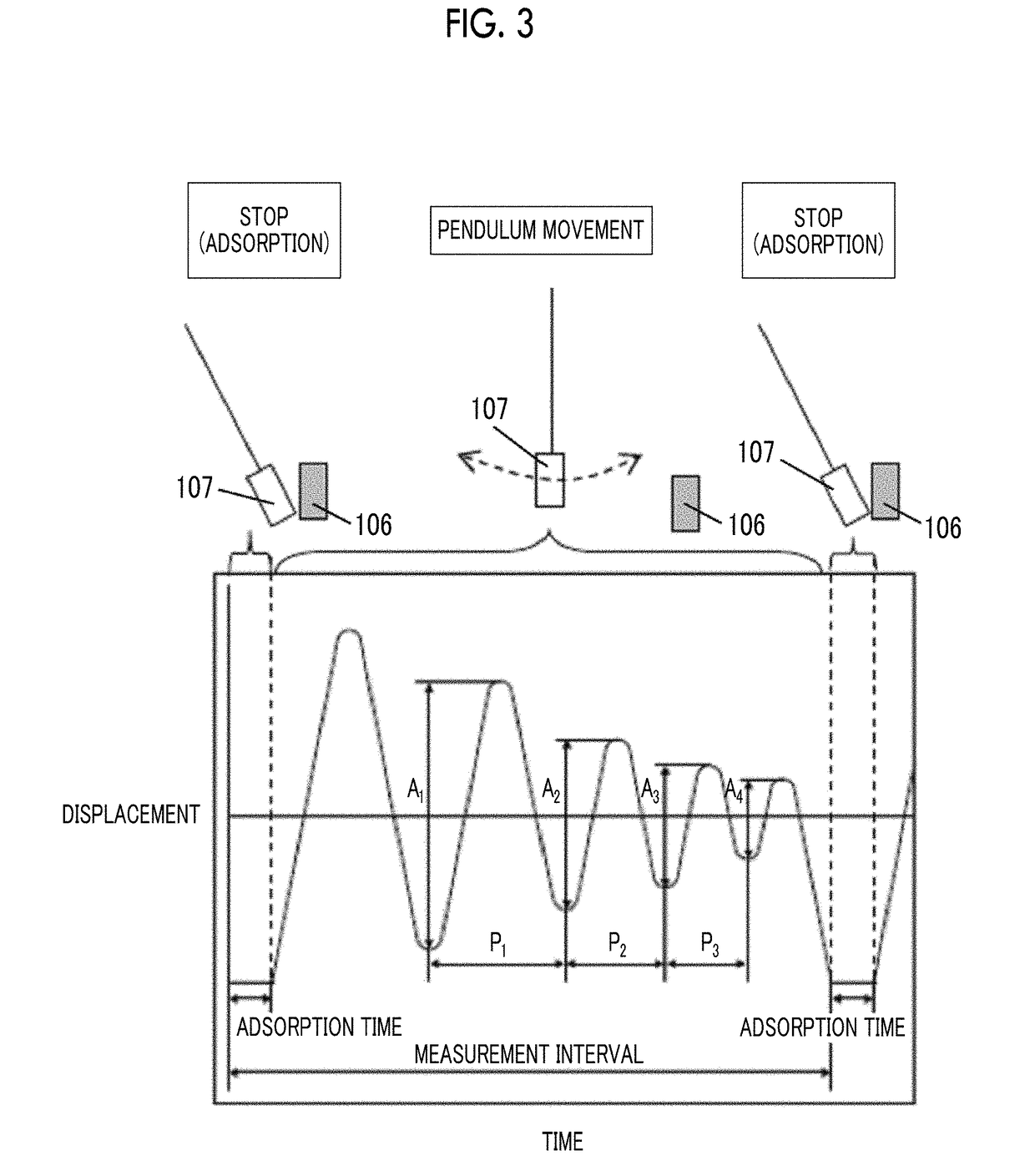
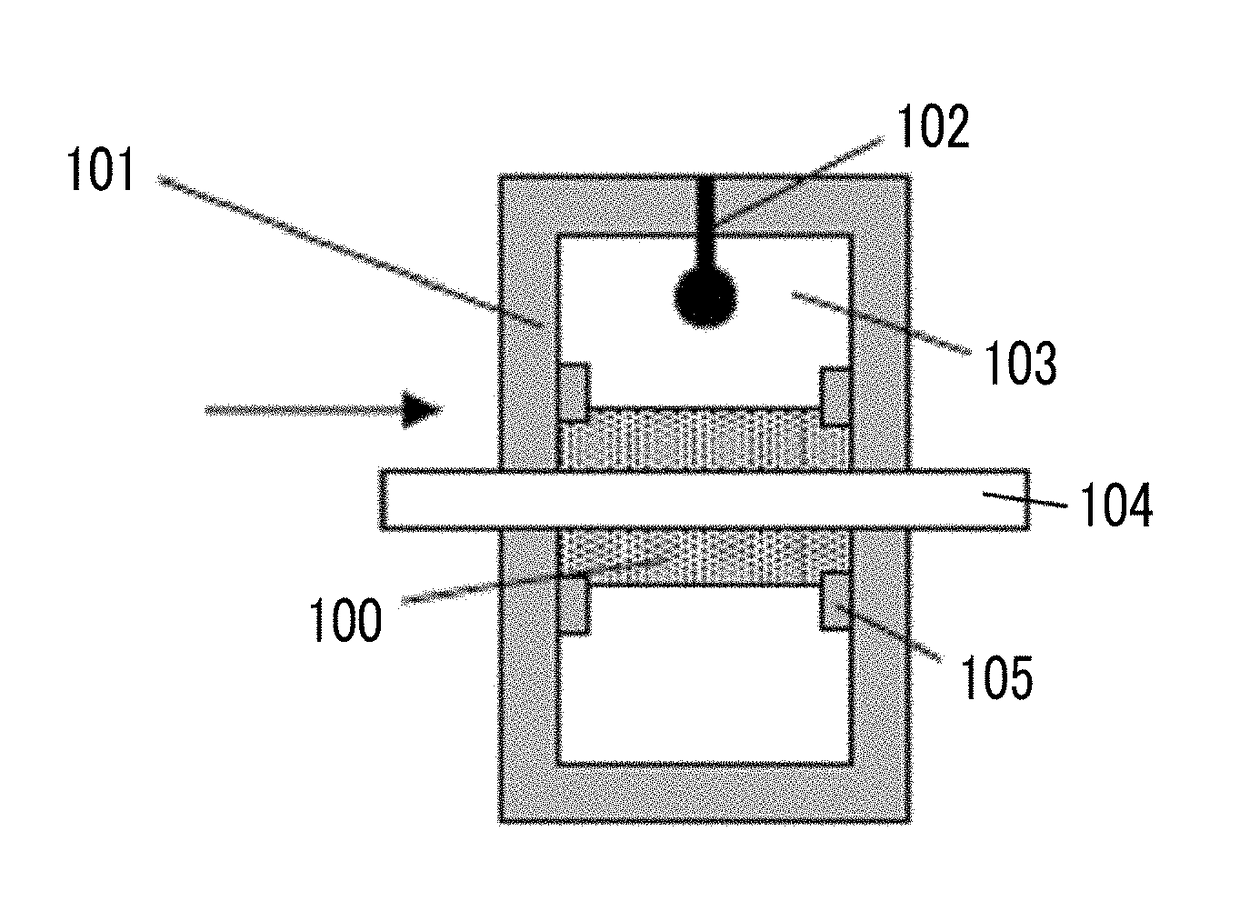
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9097results about How to "Improve smoothness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semiconductor device in which zinc oxide is used as a semiconductor material and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
ActiveUS7501293B2Improve surface smoothnessHigh crystallinityTransistorLaser detailsSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A semiconductor device having excellent crystallinity and excellent electric characteristics includes a ZnO thin film having excellent surface smoothness. ZnO-based thin films (an n-type contact layer, an n-type clad layer, an active layer, a p-type clad layer, and a p-type contact layer) primarily including ZnO are formed sequentially by an ECR sputtering method or other suitable method on a zinc-polar surface of a ZnO substrate. A transparent electrode and a p-side electrode are formed by an evaporation method or other suitable method on a surface of the p-type contact layer, and an n-side electrode is formed on an oxygen-polar surface of the ZnO substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Cyclic azine derivatives, processes for producing these, and organic electroluminescent element containing these as component
ActiveUS20120214993A1Improve drivabilityAccelerate emissionsOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceOrganic compound
A cyclic azine compound represented by general formula (1):wherein each Ar1 represents an aromatic group, which is unsubstituted or substituted by a C1-4 alkyl group, a phenyl group or a pyridyl group; and A represents a group selected from those which are represented by general formulae (2) to (5), described in the description. The cyclic azine compound is useful for an organic compound layer of fluorescent or phosphorescent EL device.
Owner:TOSOH CORP +1
Low zirconium, hafnium-containing compositions, processes for the preparation thereof and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060062910A1Improve propertyDesire morphologyGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorMetal
This invention relates to hafnium-containing compositions having a zirconium concentration of less than about 500 parts per million, a process for producing the hafnium-containing compositions, organometallic precursor compositions containing a hafnium-containing compound and having a zirconium concentration of less than about 500 parts per million, a process for producing the organometallic precursor compositions, and a method for producing a film or coating from the organometallic precursor compositions. The organometallic precursor compositions are useful in semiconductor applications as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or atomic layer deposition (ALD) precursors for film depositions.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Low zirconium, hafnium-containing compositions, processes for the preparation thereof and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060193979A1Improve propertiesDesired morphologyGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesPretreated surfacesHafniumChemical vapor deposition
This invention relates to hafnium-containing compositions having a zirconium concentration of less than about 500 parts per million, a process for producing the hafnium-containing compositions, organometallic precursor compositions containing a hafnium-containing compound and having a zirconium concentration of less than about 500 parts per million, a process for producing the organometallic precursor compositions, and a method for producing a film or coating from the organometallic precursor compositions. The organometallic precursor compositions are useful in semiconductor applications as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or atomic layer deposition (ALD) precursors for film depositions.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
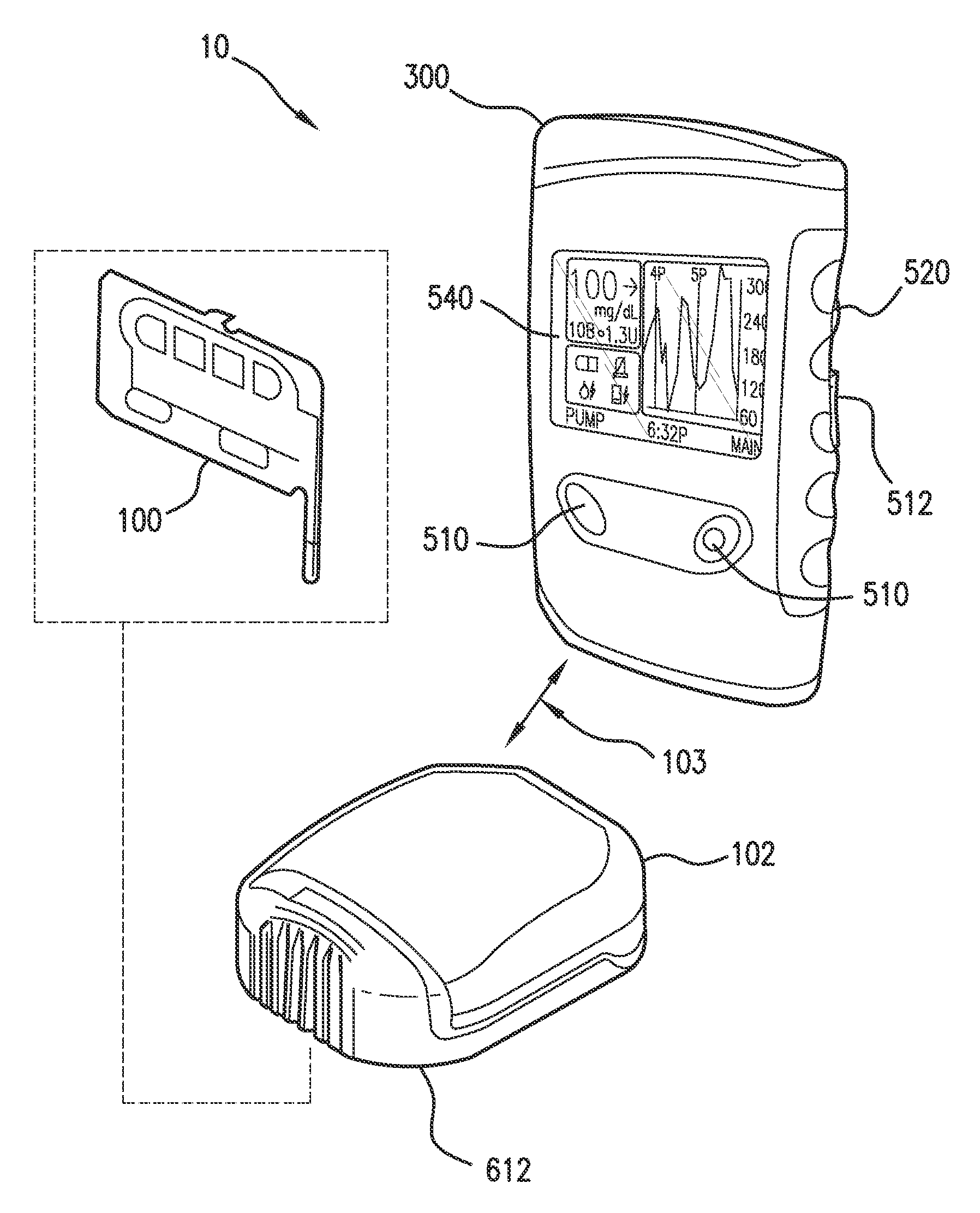
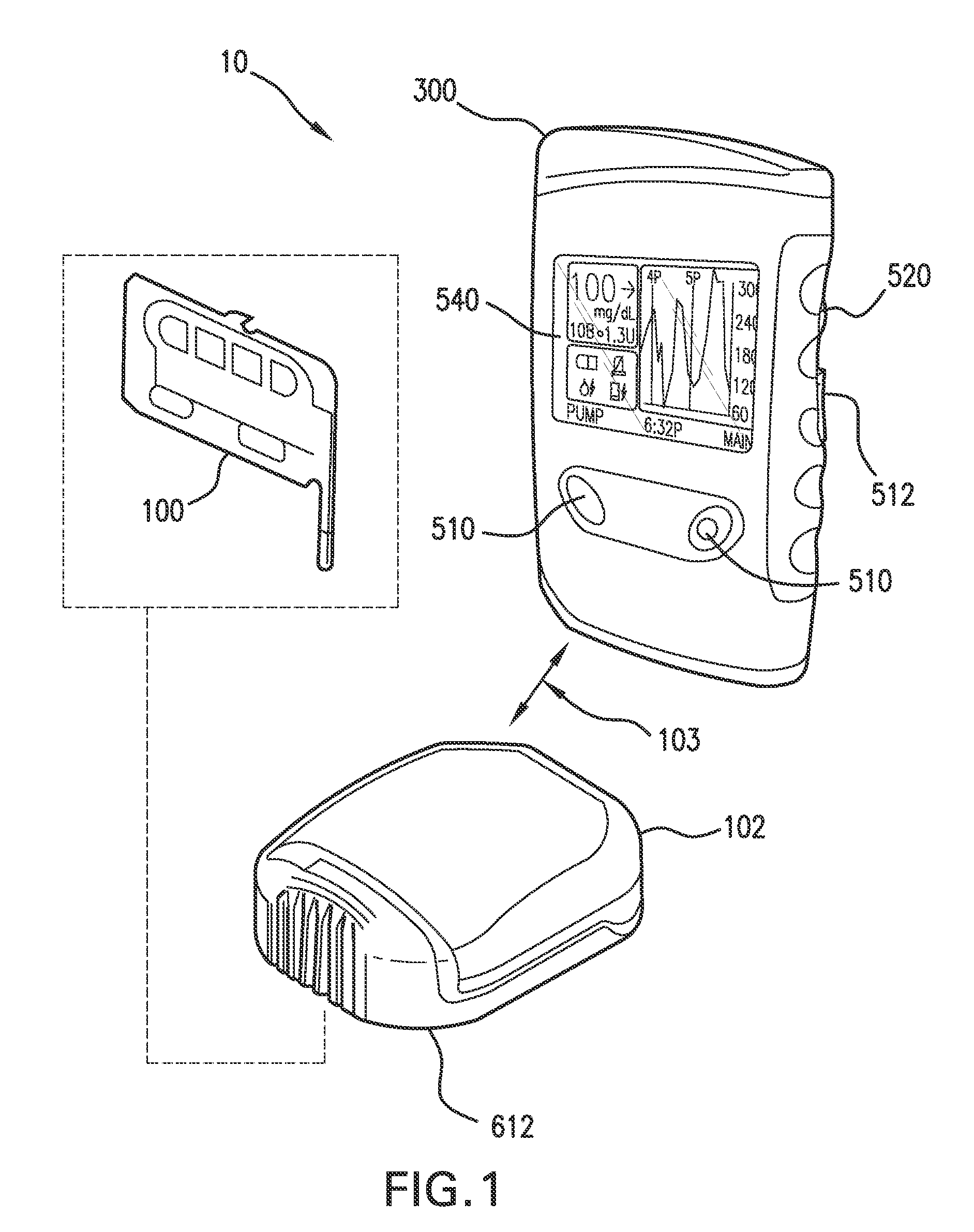
Inserter device including rotor subassembly
InactiveUS20110106126A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove reliabilityCatheterSensorsLinear motionEngineering
An inserter subassembly including a rotor and drive member such that rotation of the rotor is translated to a linear motion including insertion and refraction paths.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
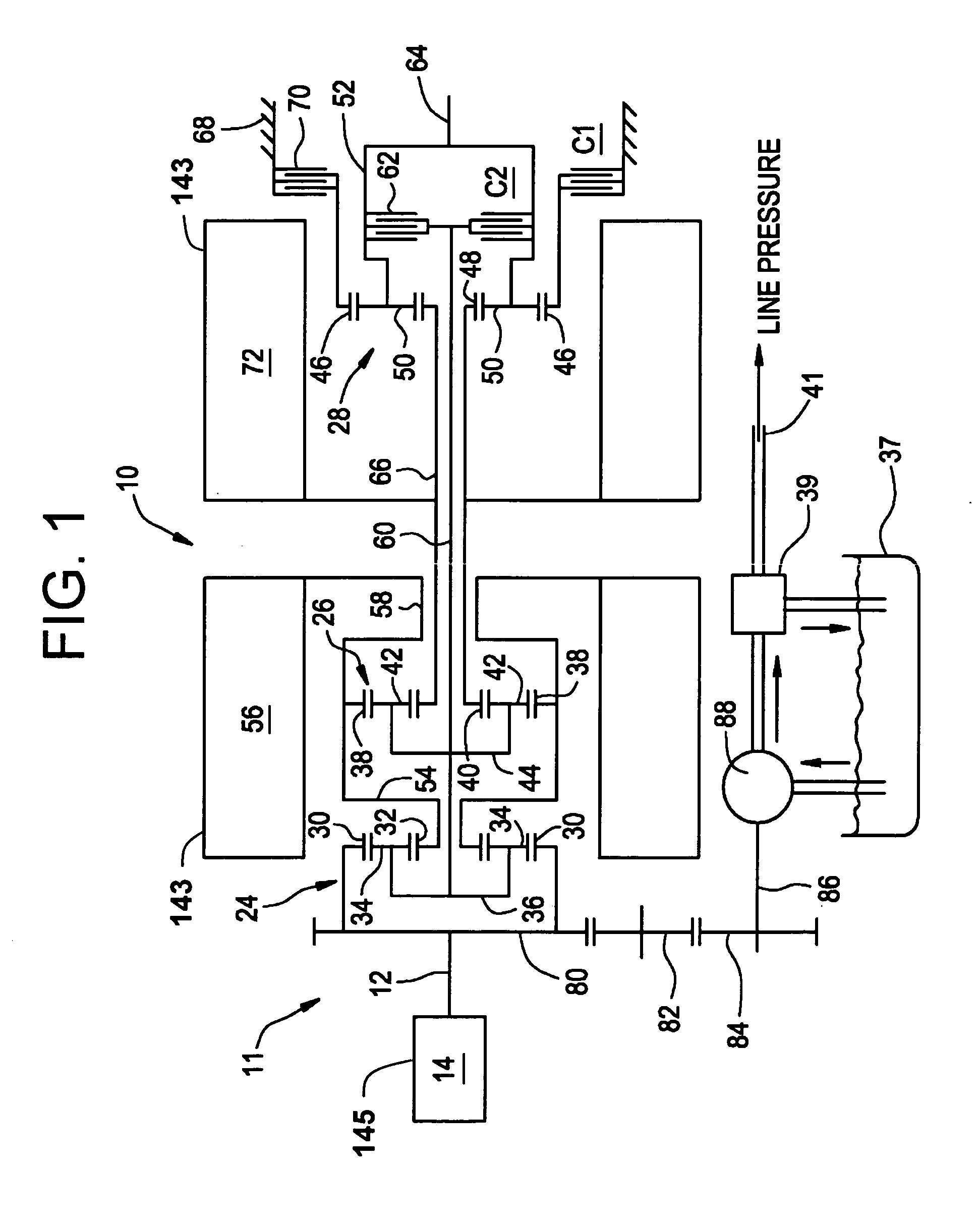
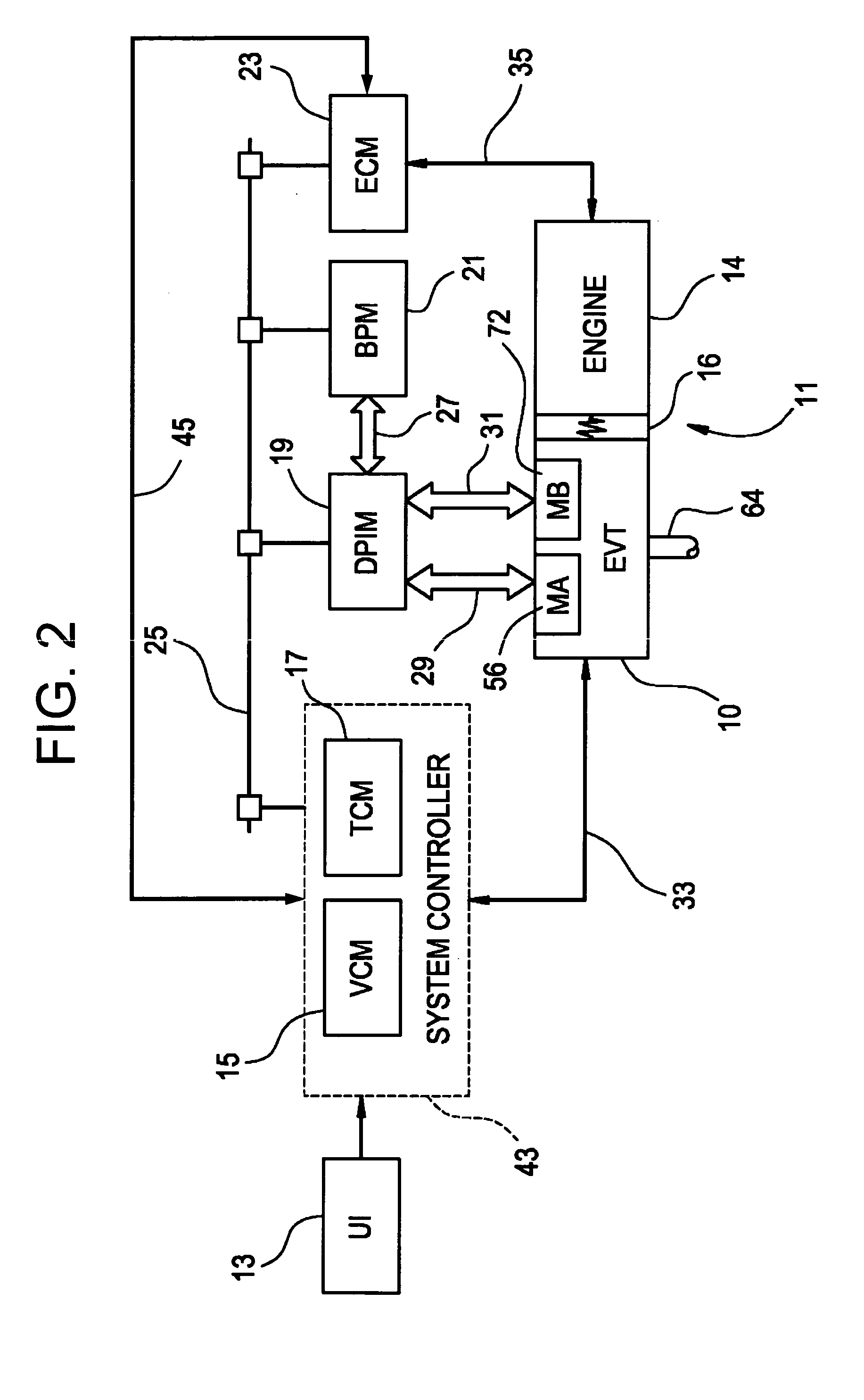
Method for active engine stop of a hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20050255968A1Increased durabilityImprove smoothnessHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlElectric machineResonance
A method for providing an active engine stop of the engine of a hybrid electric vehicle. The method utilizes the electric machine to oppose the and rapidly stop the rotation of the engine at a controlled rate. The method includes the calculation of an input speed reduction trajectory using the engine speed when the active engine stop request is made and a predetermined speed reduction interval. The predetermined speed reduction interval is preferably less than a time from the active stop request to the shutoff command to the electric machine. The method provides rapid deceleration of the engine, particularly through the powertrain resonance speed, thereby reducing the amount of vibration energy dissipated through the powertrain and vehicle chassis. The method also removes the electric machine torques from the engine prior to achieving zero engine speed in order to avoid imparting a negative engine speed or counter-rotation of the engine. The method preferably comprises a complementary series of software control functions that allow the vehicle to actively stop the engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Treated filler or pigment containing natural carbonate
InactiveUS6666953B1Reduce weightReduce wearNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPhysical chemistryKaolin clay
The invention concerns a pigment, filler or mineral containing a natural calcium carbonate, treated with one of more providers of H3O<+> ions and gaseous CO2, allowing a reduction in the weight of paper for a constant surface area without loss of physical properties when it is used as a pigment or coating filler for the said paper. In particular, the invention concerns a pigment, filler or mineral containing a natural calcium carbonate or dolomite or mixtures of talc and calcium carbonate, of kaolin and carbonate or carbonate alone or in combination with natural and / or synthetic fibers or similar, treated with one or more medium-strong or strong providers of H3O<+> ions in the presence of gaseous CO2. Applications are particularly in the paper industry, obtaining in particular good sheet properties i.e. a reduction its weight for a given surface area.
Owner:OMYA DEV AG
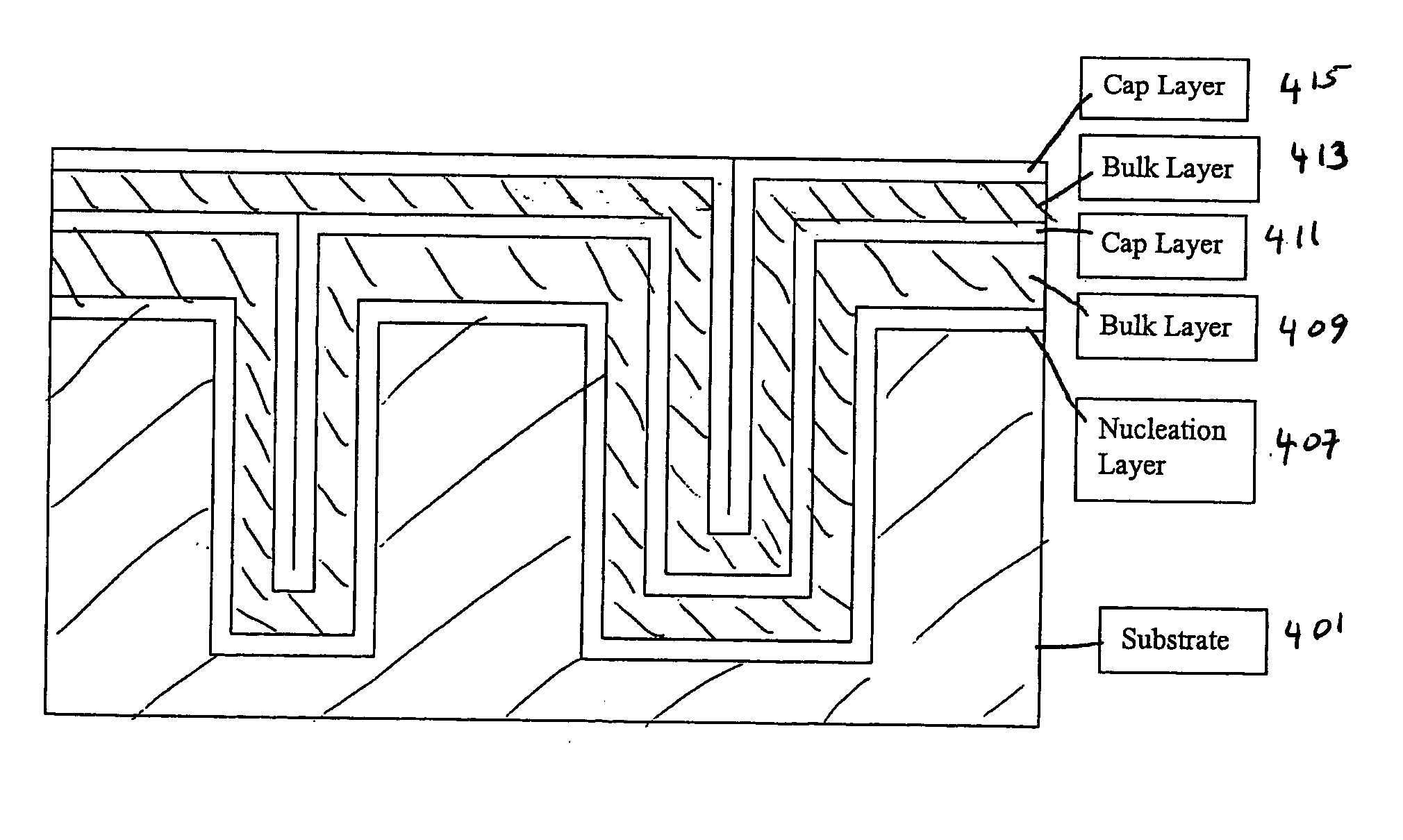
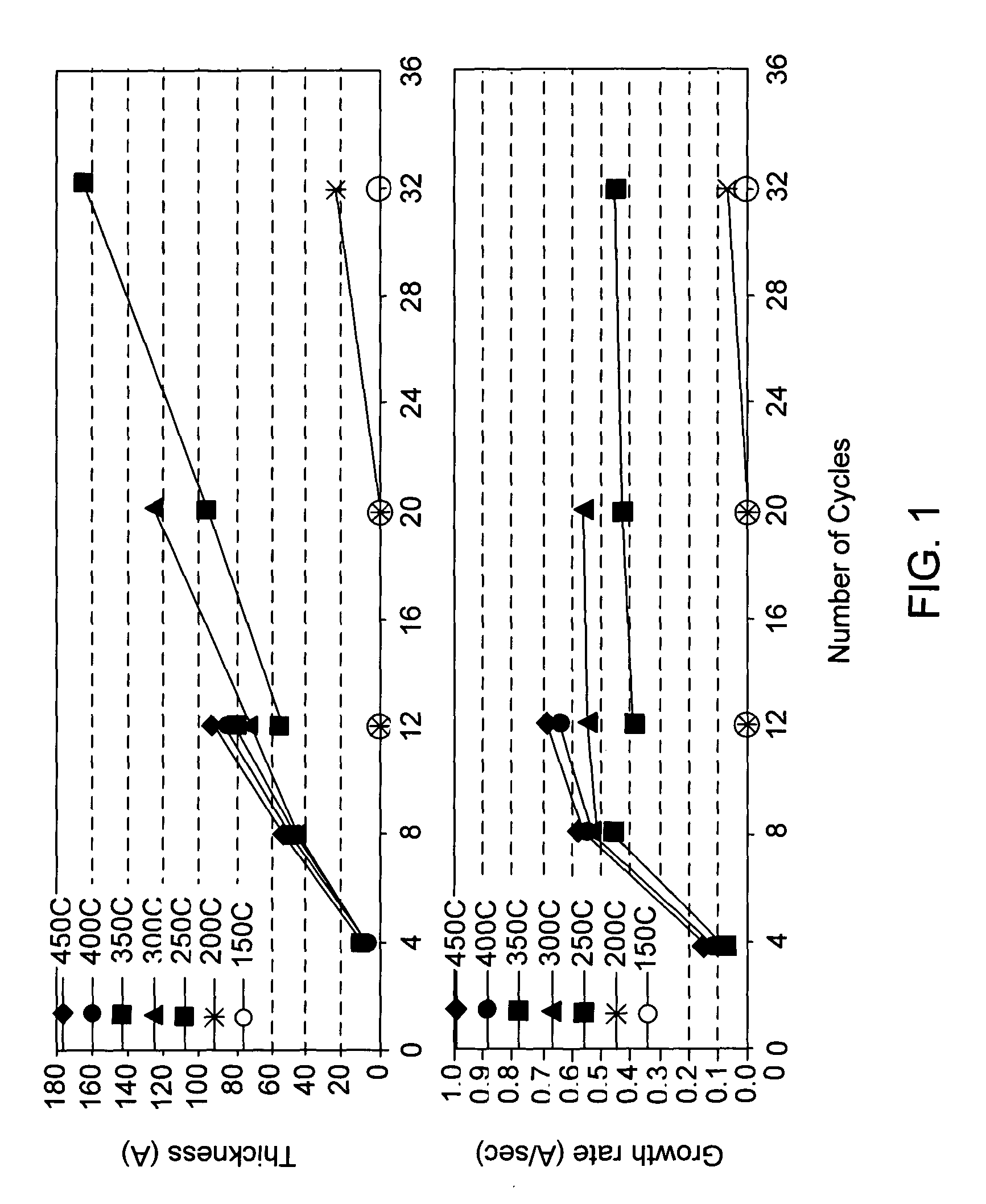
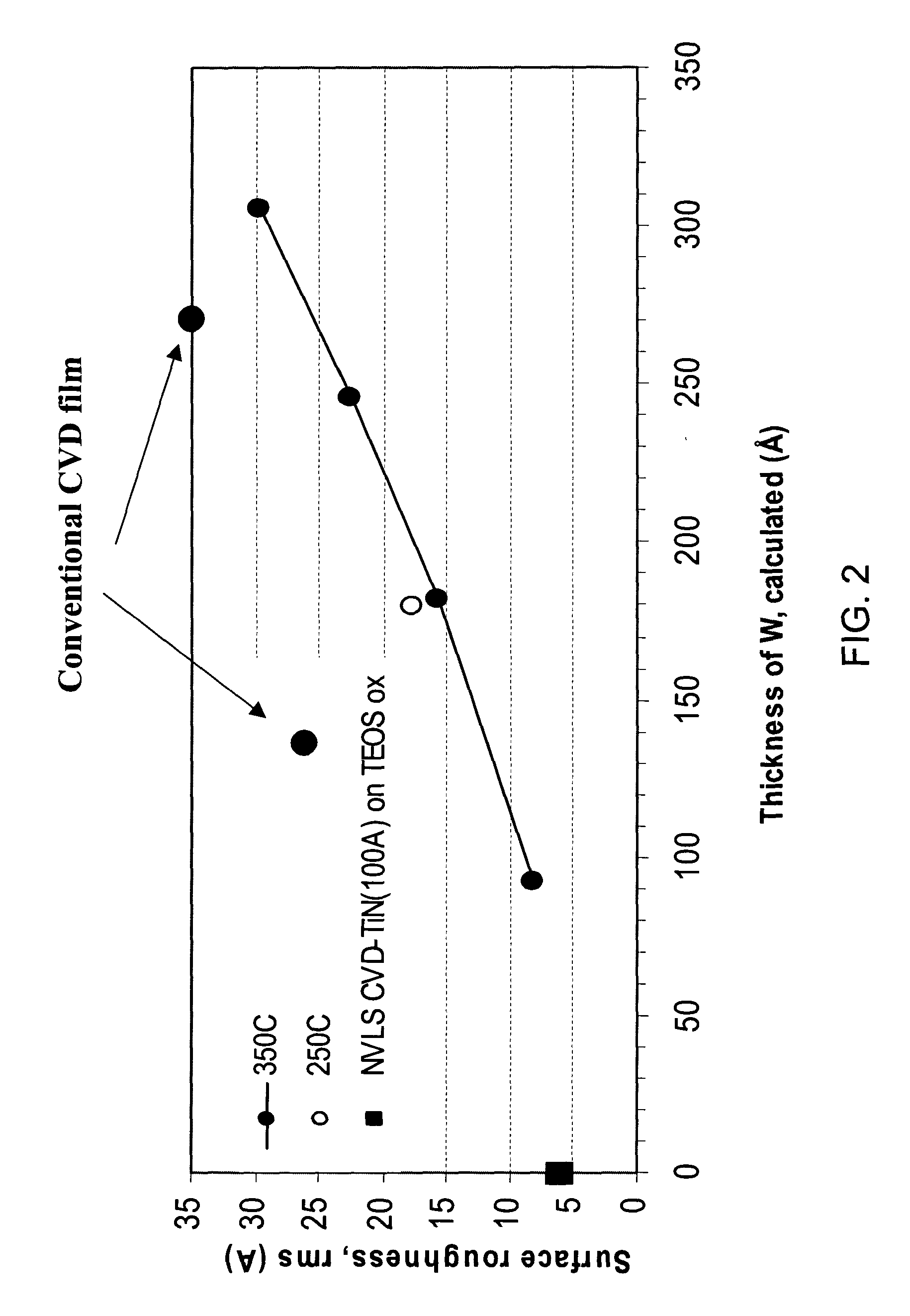
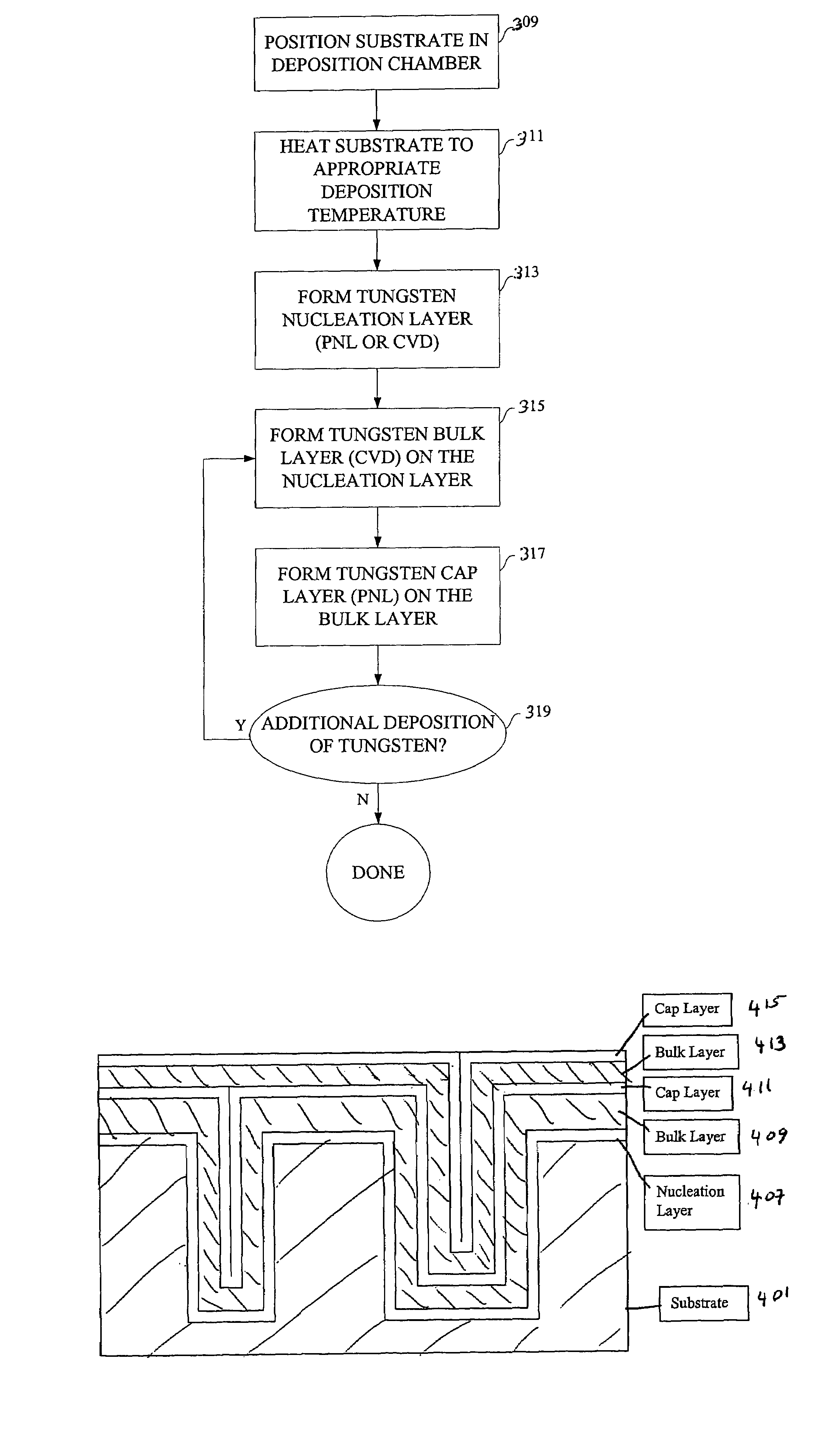
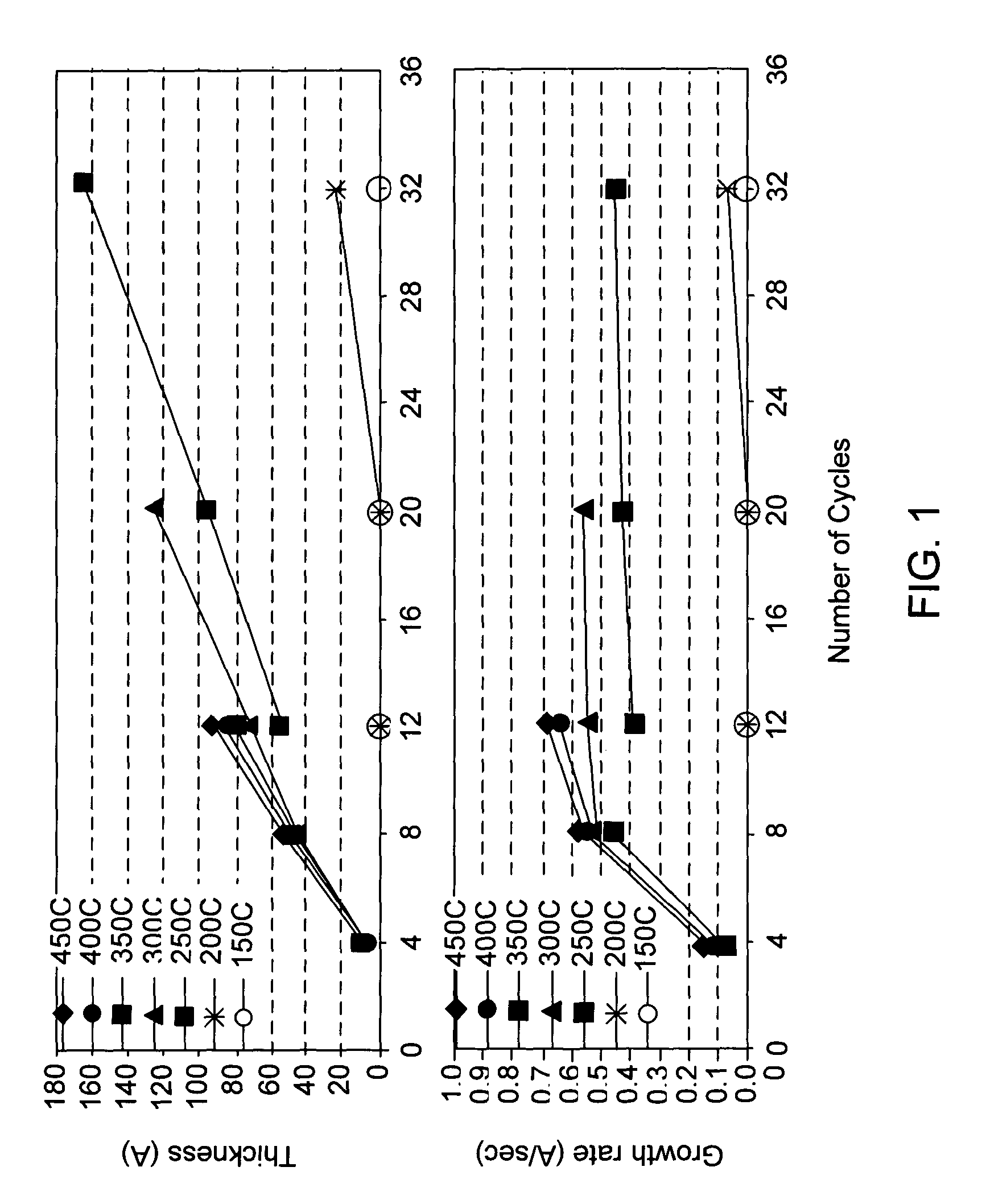
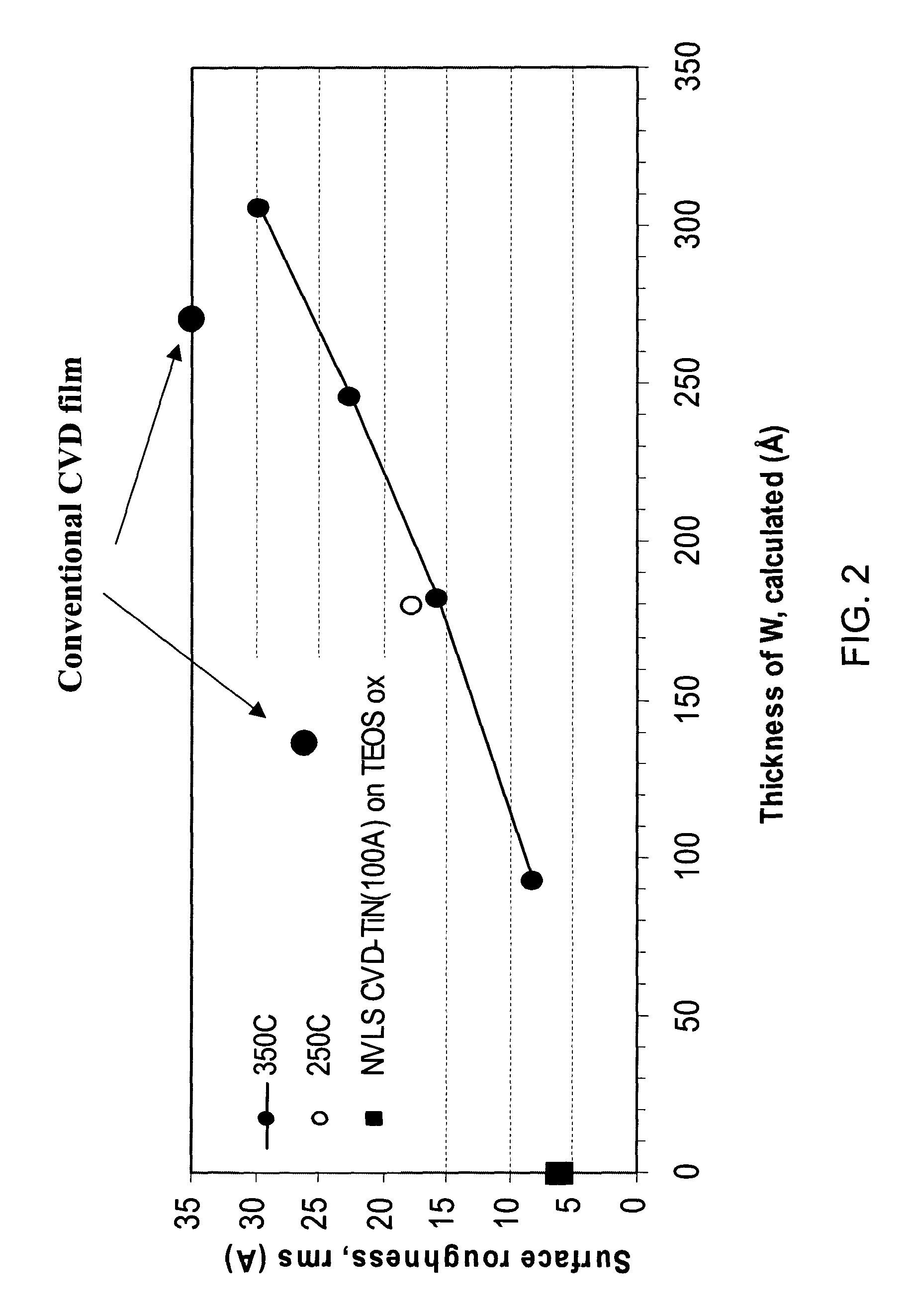
Method for reducing tungsten film roughness and improving step coverage
InactiveUS20050031786A1Increase probabilityLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefuse receptaclesNucleationSemiconductor
A tungsten nucleation film is formed on a surface of a semiconductor substrate by alternatively providing to that surface, reducing gases and tungsten-containing gases. Each cycle of the method provides for one or more monolayers of the tungsten film. The film is conformal and has improved step coverage, even for a high aspect ratio contact hole.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for reducing tungsten film roughness and improving step coverage
InactiveUS7141494B2Increase probabilityLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefuse receptaclesNucleationTungsten film
A tungsten nucleation film is formed on a surface of a semiconductor substrate by alternatively providing to that surface, reducing gases and tungsten-containing gases. Each cycle of the method provides for one or more monolayers of the tungsten film. The film is conformal and has improved step coverage, even for a high aspect ratio contact hole.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Multilayer structure with high perpendicular anisotropy for device applications
ActiveUS20110293967A1Improve performanceLow costMagnetic measurementsPretreated surfacesPerpendicular anisotropyMagnetic media
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and Hc are enhanced in magnetic devices with a Ta / M1 / M2 seed layer where M1 is preferably Ti, and M2 is preferably Cu, and including an overlying (Co / Ni)X multilayer (x is 5 to 50) that is deposited with ultra high Ar pressure of >100 sccm to minimize impinging energy that could damage (Co / Ni)X interfaces. In one'embodiment, the seed layer is subjected to one or both of a low power plasma treatment and natural oxidation process to form a more uniform interface with the (Co / Ni)X multilayer. Furthermore, an oxygen surfactant layer may be formed at one or more interfaces between adjoining (Co / Ni)X layers in the multilayer stack. Annealing at temperatures between 180° C. and 400° C. also increases Hc but the upper limit depends on whether the magnetic device is MAMR, MRAM, a hard bias structure, or a perpendicular magnetic medium.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Holographic human-machine interfaces
ActiveUS7054045B2Reduced weight and size and power consumptionImprove smoothnessInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingHuman–machine interfaceSignal generator
Owner:HOLOTOUCH
Method and apparatus for improved processing with a gas-cluster ion beam
ActiveUS7060989B2Smoothing capabilityImprove etching effectMaterial analysis by optical meansIon beam tubesGas cluster ion beamLight beam
Apparatus and methods for improving processing of workpieces with gas-cluster ion beams and modifying the gas-cluster ion energy distribution in the GCIB. In a reduced-pressure environment, generating an energetic gas-cluster ion beam and subjecting the beam to increased pressure region.
Owner:TEL EPION
Integrated circuit support structures and their fabrication
ActiveUS7635641B2Suitable for mass productionHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineering physicsProtection layer
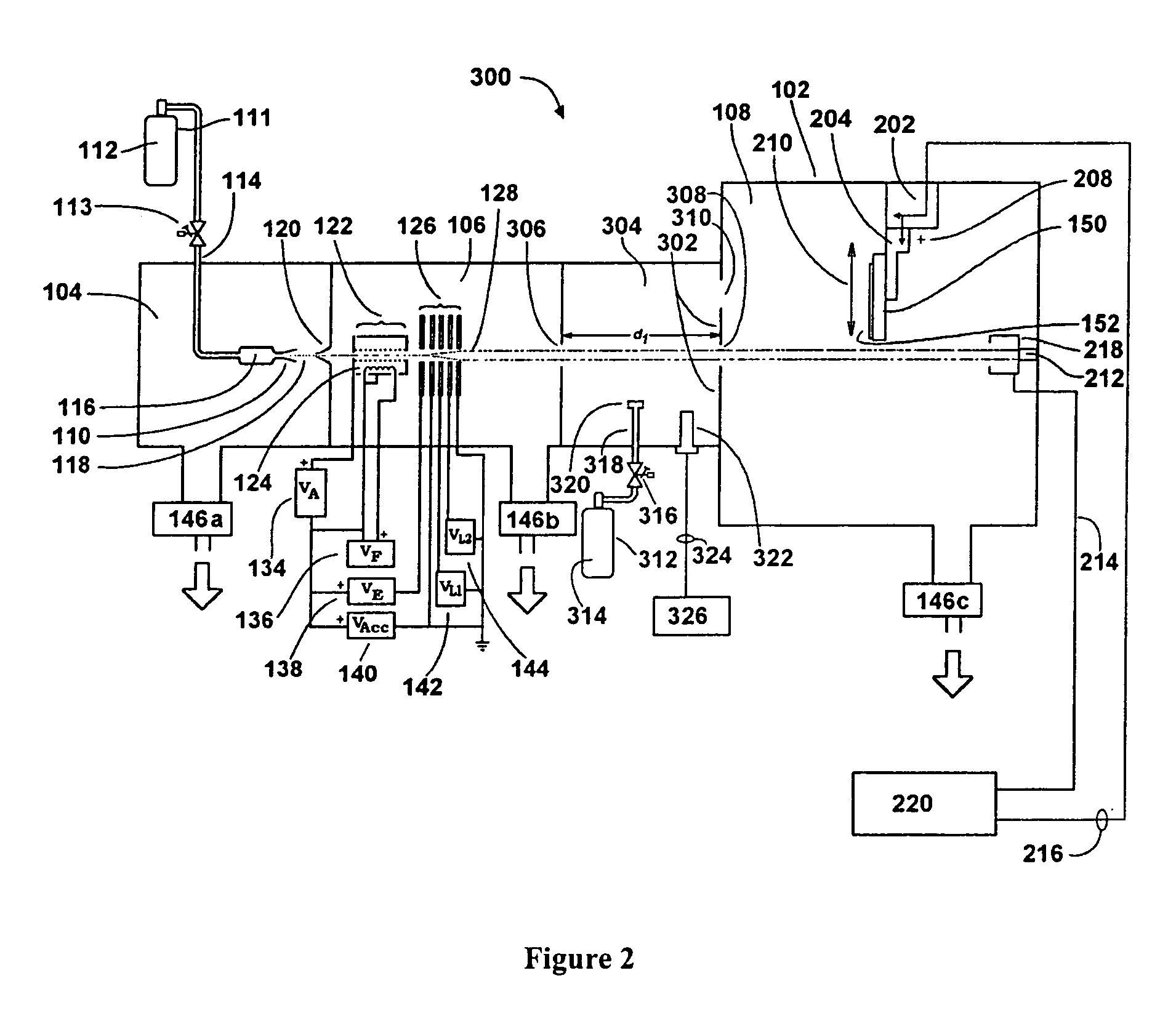
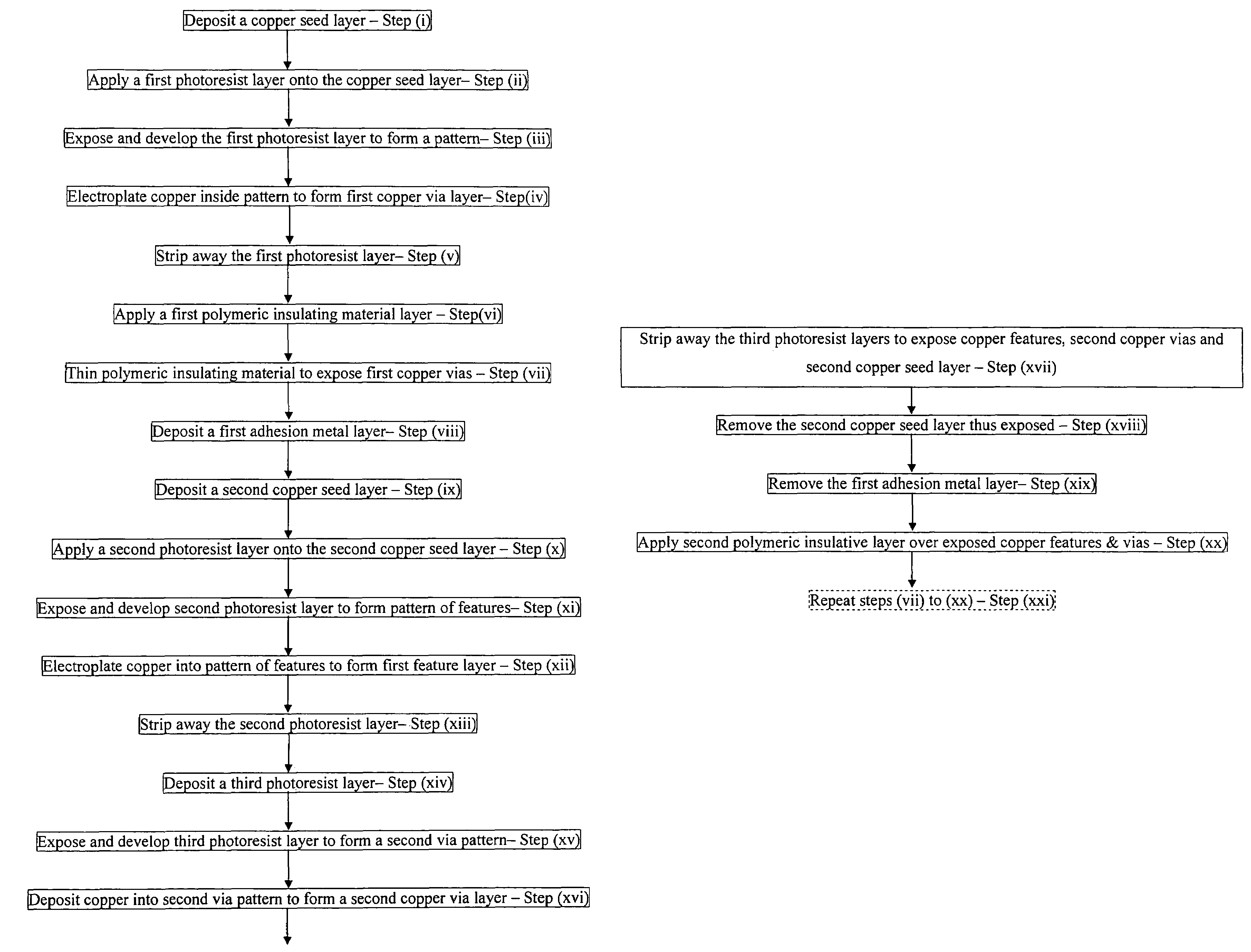
A method of fabricating an electronic substrate comprising the steps of; (A) selecting a first base layer; (B) depositing a first etchant resistant barrier layer onto the first base layer; (C) building up a first half stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, the conductive layers being interconnected by vias through the insulating layers; (D) applying a second base layer onto the first half stack; (F) applying a protective coating of photoresist to the second base layer; (F) etching away the first base layer; (G) removing the protective coating of photoresist; (H) removing the first etchant resistant barrier layer; (I) building up a second half stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, the conductive layers being interconnected by vias through the insulating layers, wherein the second half stack has a substantially symmetrical lay up to the first half stack; (J) applying an insulating layer onto the second hall stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, (K) removing the second base layer, and (L) terminating the substrate by exposing ends of vias on outer surfaces of the stack and applying terminations thereto.
Owner:ZHUHAI ADVANCED CHIP CARRIERS & ELECTRONICS SUBSTRATE SOLUTIONS TECH
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180286448A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMaterials with ironTape carriersMagnetic tapeFull width at half maximum
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head (reproducing head); and a magnetic tape including a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder, a binding agent, and fatty acid ester, in which Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the magnetic layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, a difference between spacings before and after the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm, and ΔSFD (=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C.) in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 0.50.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180286451A1Prevent occurrenceDecrease in resistance valueMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesSurface measurementMagnetic layer
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head (servo head); and a magnetic tape, in which a magnetic layer of the magnetic tape includes fatty acid ester, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding a surface of the magnetic layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, a difference between spacings before and after the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm, and ΔSFD (=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C.) in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 0.50.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
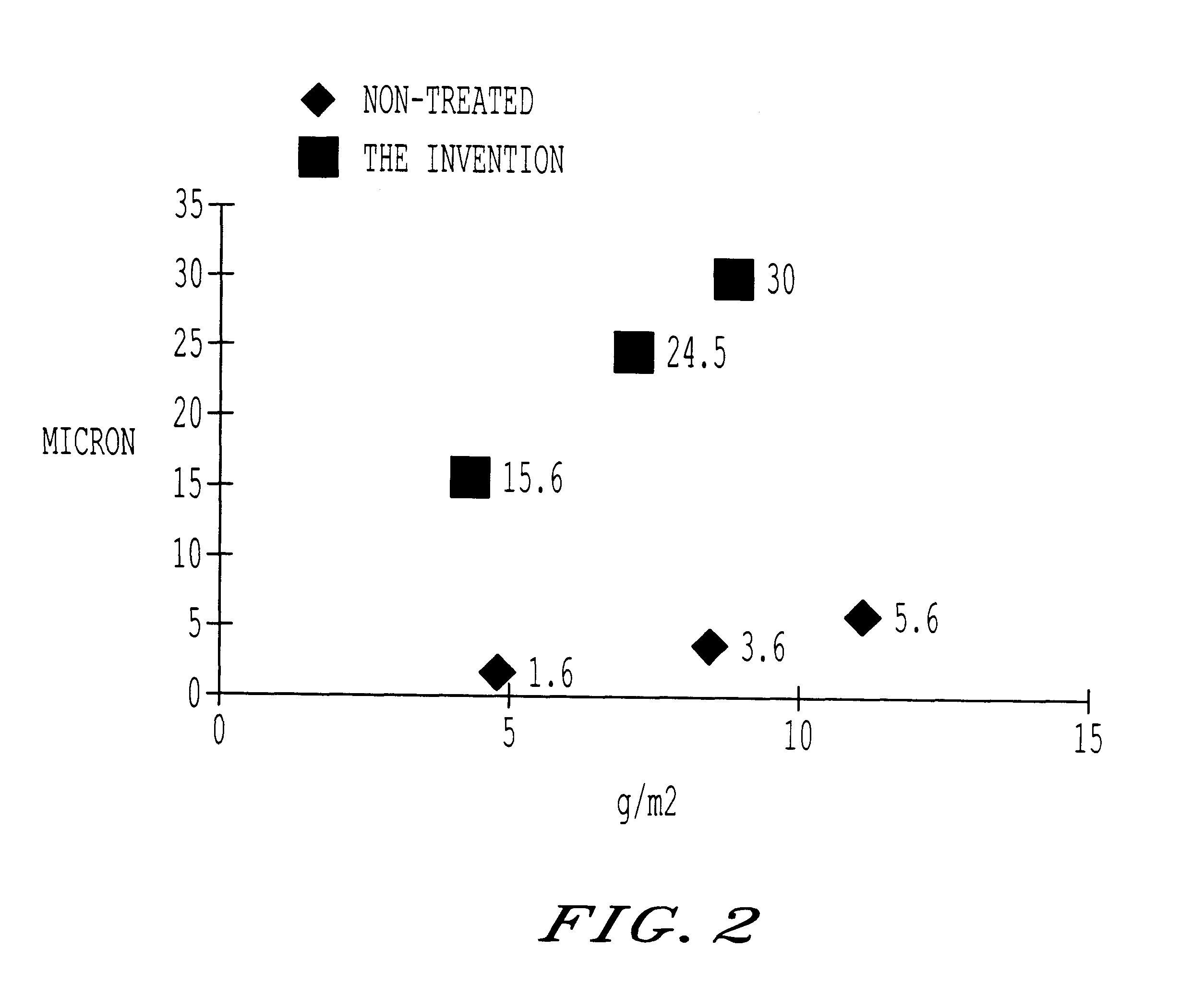
Smooth finish UV ink system and method
InactiveUS20060075917A1Improve surface smoothnessReduced drop spreadDuplicating/marking methodsOther printing apparatusEngineeringPrinting ink
A printing method includes steps of applying an ink-receptive coating to a substrate; printing an actinic radiation-curable ink jet ink over the coating; and curing the printed ink jet ink. An article printed by the method has a ink-receptive coating layer with a cured print. An apparatus for carrying out the method includes a coating station at which the ink-receptive coating is applied to a substrate, an ink jet printhead at which the energy-curable ink jet ink is applied, and a source of actinic radiation for curing the applied ink. The ink may be applied in sufficient amount to achieve a color density comparable to that obtained using other printing processes such as flexographic or gravure printing processes. The ink-receptive coating layer may be of a thickness sufficient to provide improve surface smoothness and / or reduced drop spread relative to an uncoated substrate.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180286442A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMaterials with ironRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head (reproducing head); and a magnetic tape including a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, and fatty acid ester, in which an XRD intensity ratio obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio is 0.65 to 1.00, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the magnetic layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, and a difference between spacings before and after the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
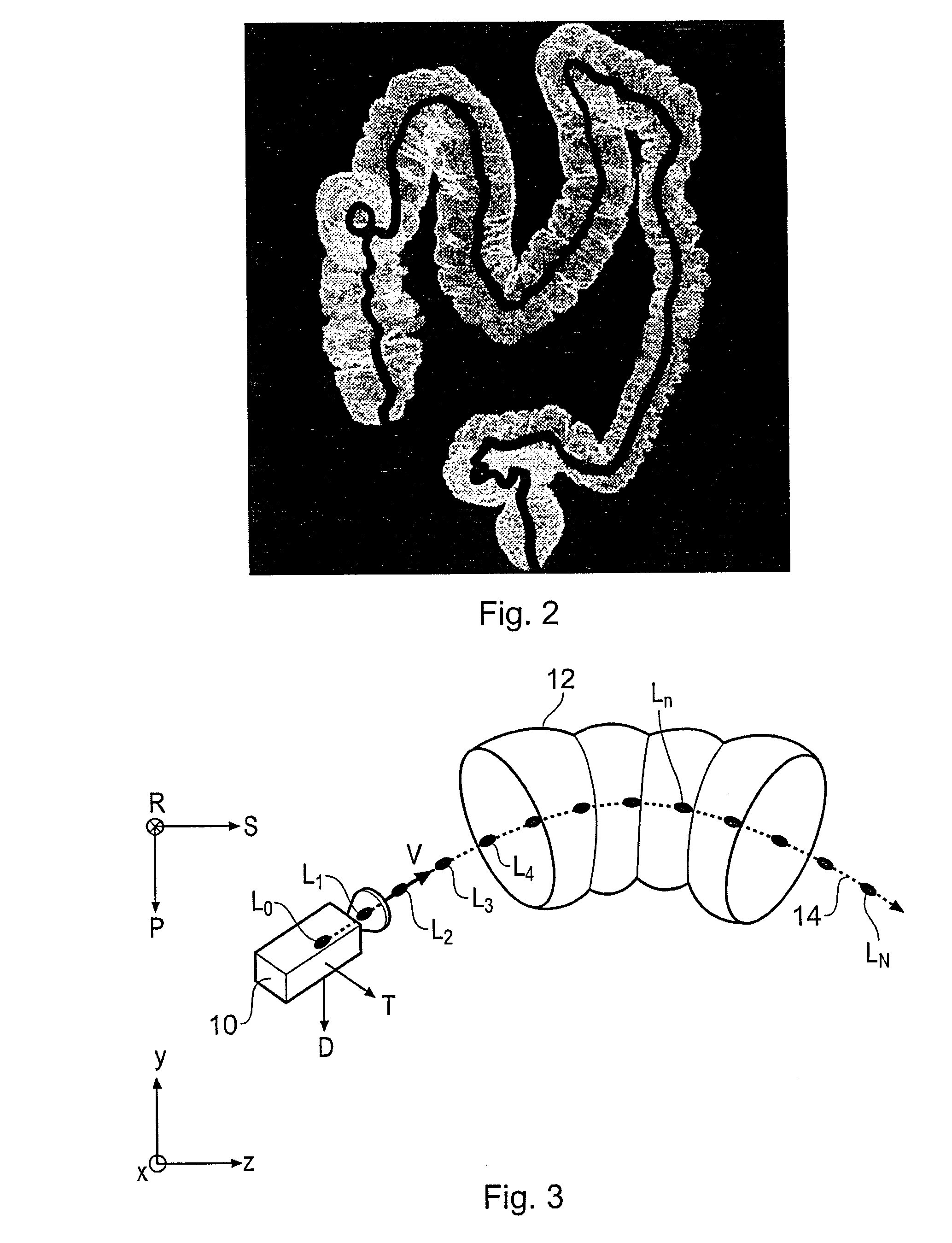
Virtual endoscopy
InactiveUS20080118117A1Full effectImproved angular separationSurgeryEndoscopesData setVirtual camera
A method of orienting a virtual camera for rendering a virtual endoscopy image of a lumen in a biological structure represented by a medical image data set, e.g., a colon. The method comprises selecting a location from which to render an image, determining an initial orientation for the virtual camera relative to the data set for the selected location based on the geometry of the lumen, determining an offset angle between the initial orientation and a bias direction; and orienting the virtual camera in accordance with a rotation from the initial orientation towards the bias direction by a fractional amount of the offset angle which varies according to the initial orientation. The fractional amount may vary according to the offset angle and / or a separation between a predetermined direction in the data set and a view direction of the virtual camera for the initial orientation. Thus the camera orientation can be configured to tend towards a preferred direction in the data set, while maintaining a good view of the lumen and avoiding barrel rolling effects.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS6939606B2Excellent characteristicsImprove smoothnessMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersNon magneticFerromagnetism
A magnetic recording medium is provided that includes, in order, (1) a non-magnetic support, a radiation-cured layer formed by applying a layer containing a radiation curing compound and curing by exposure to radiation, and a magnetic layer having a ferromagnetic powder dispersed in a binder, or (2) a non-magnetic support, a radiation-cured layer formed by applying a layer containing a radiation curing compound and curing by exposure to radiation, a non-magnetic layer having a non-magnetic powder dispersed in a binder, and a magnetic layer having a ferromagnetic powder dispersed in a binder; the radiation-cured layer including 0.3 to 30 parts by weight of an inorganic powder relative to 100 parts by weight the radiation curing compound.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10062403B1Improve accuracyExact reproductionTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
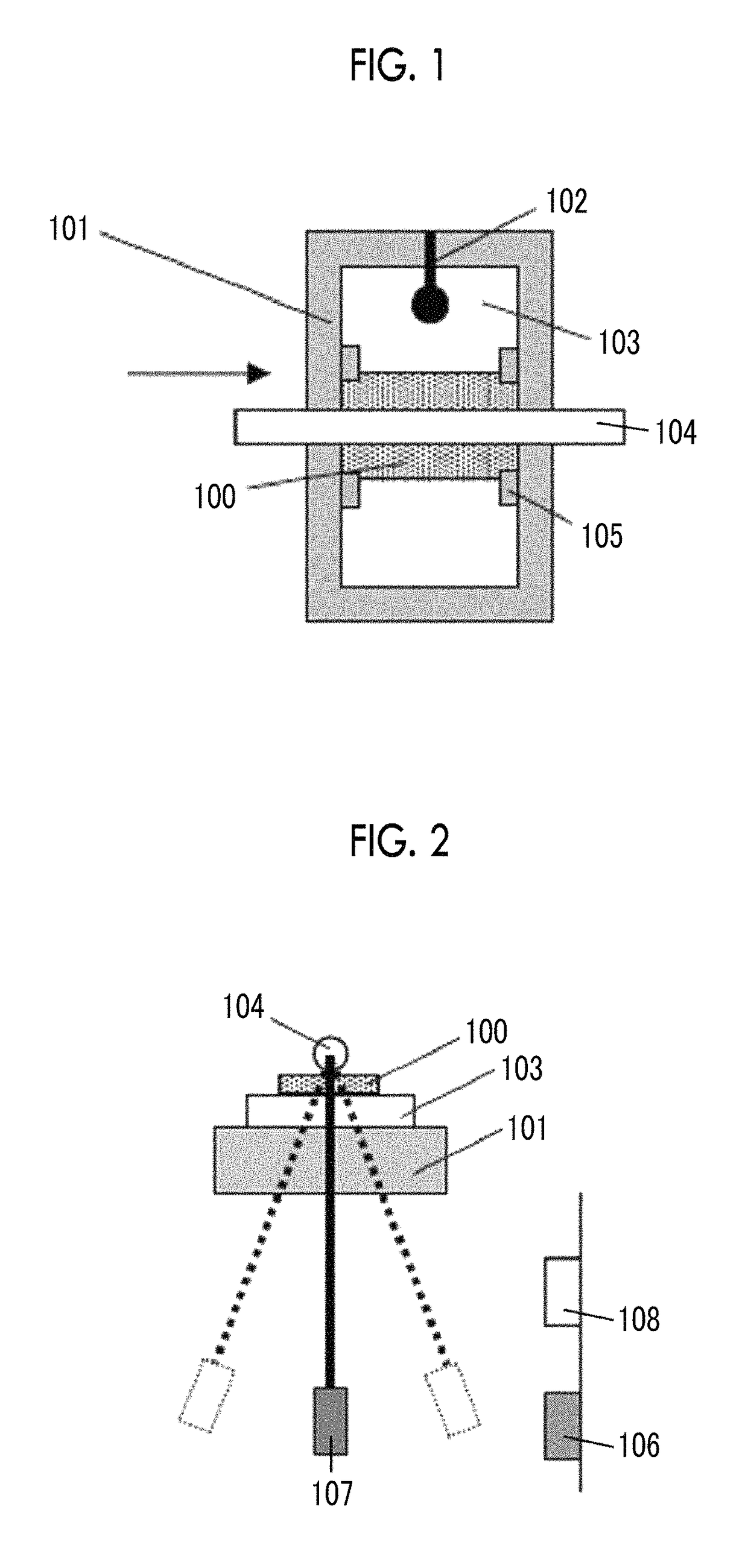
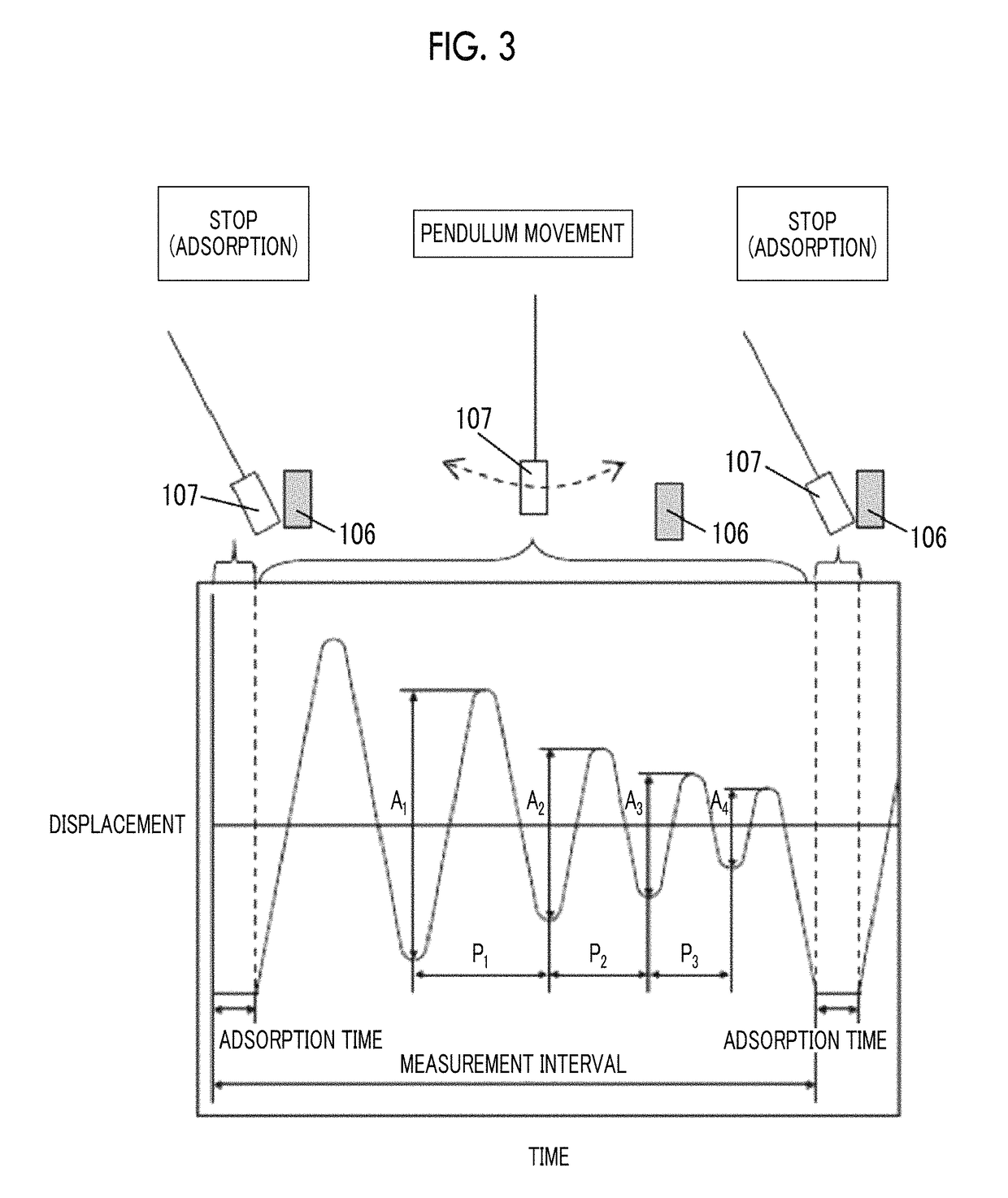
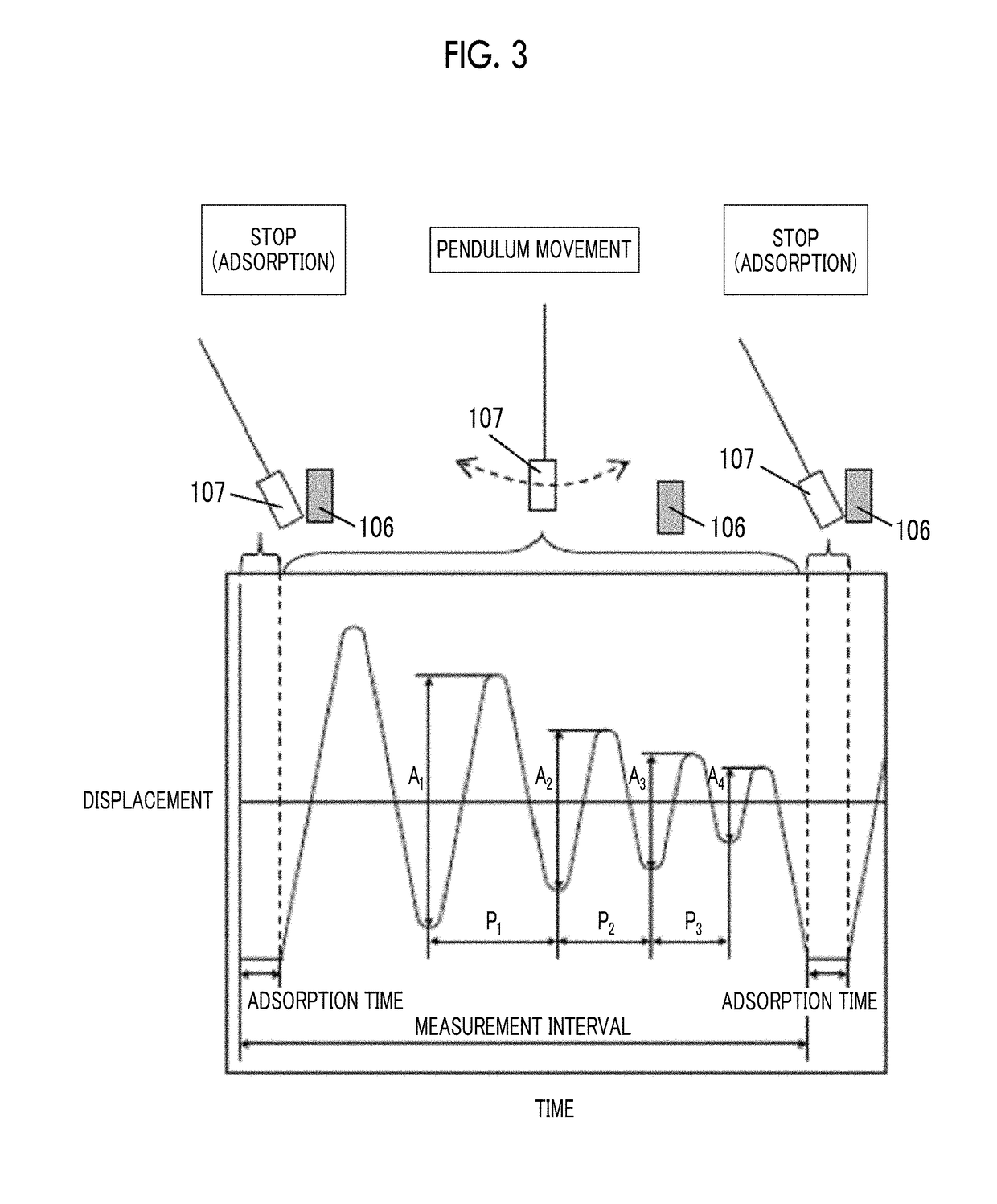
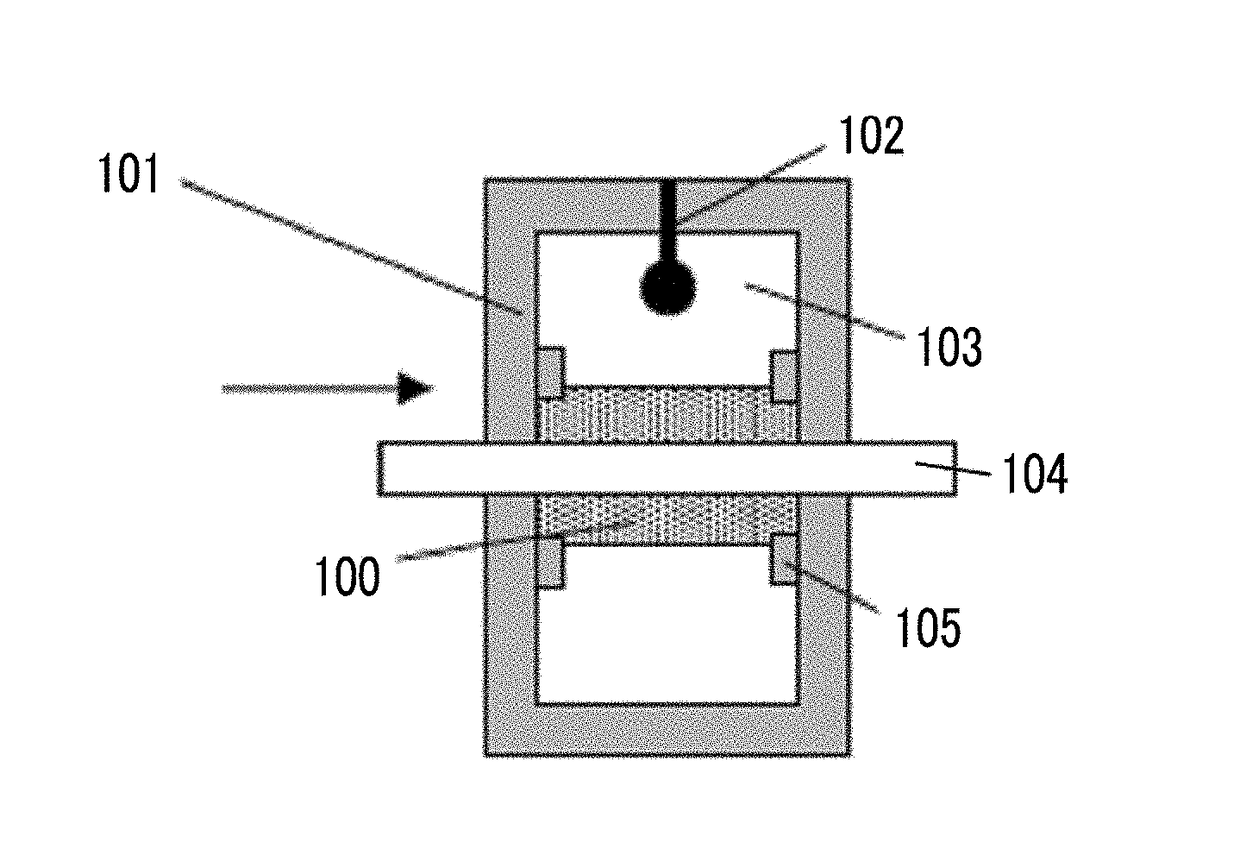
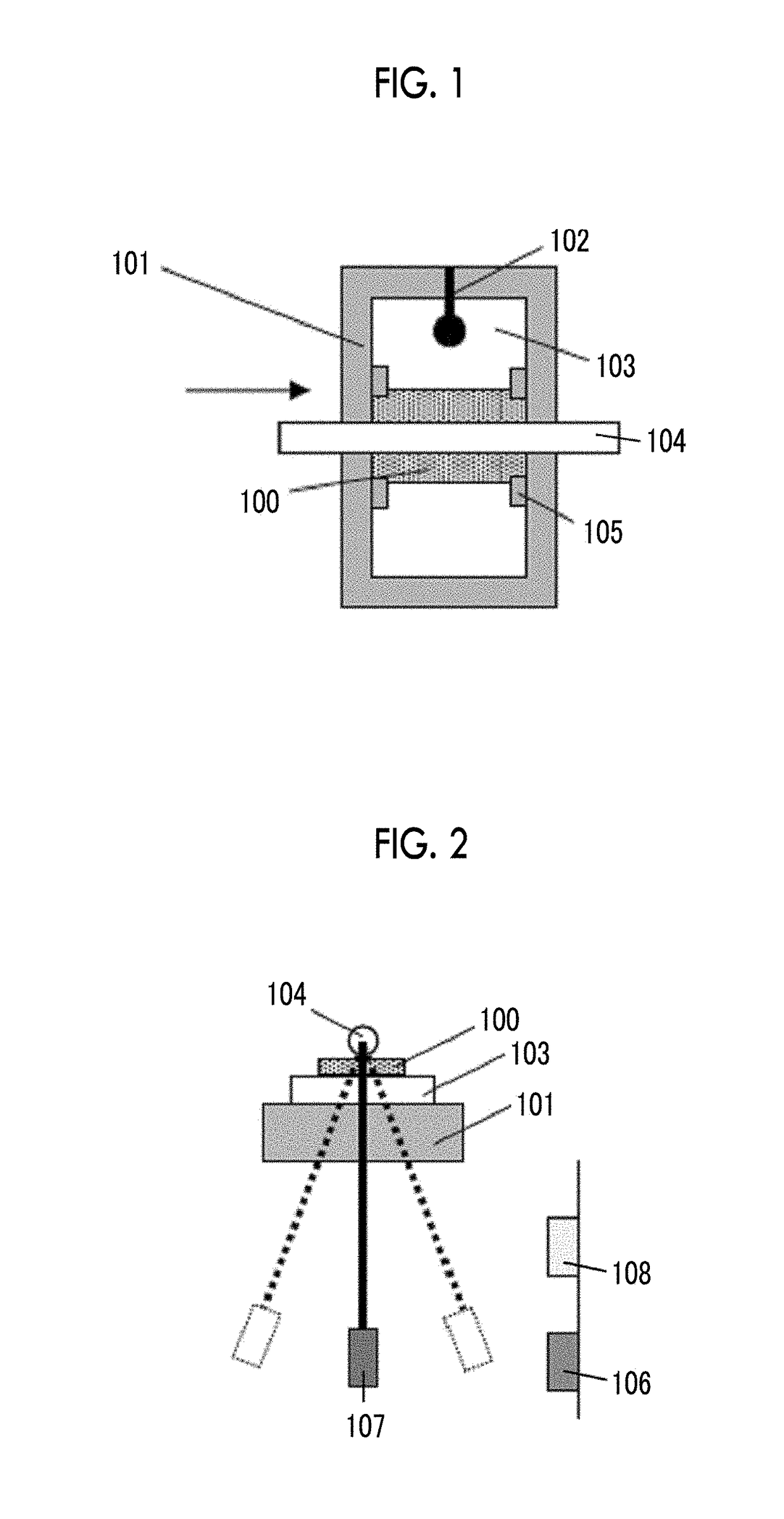
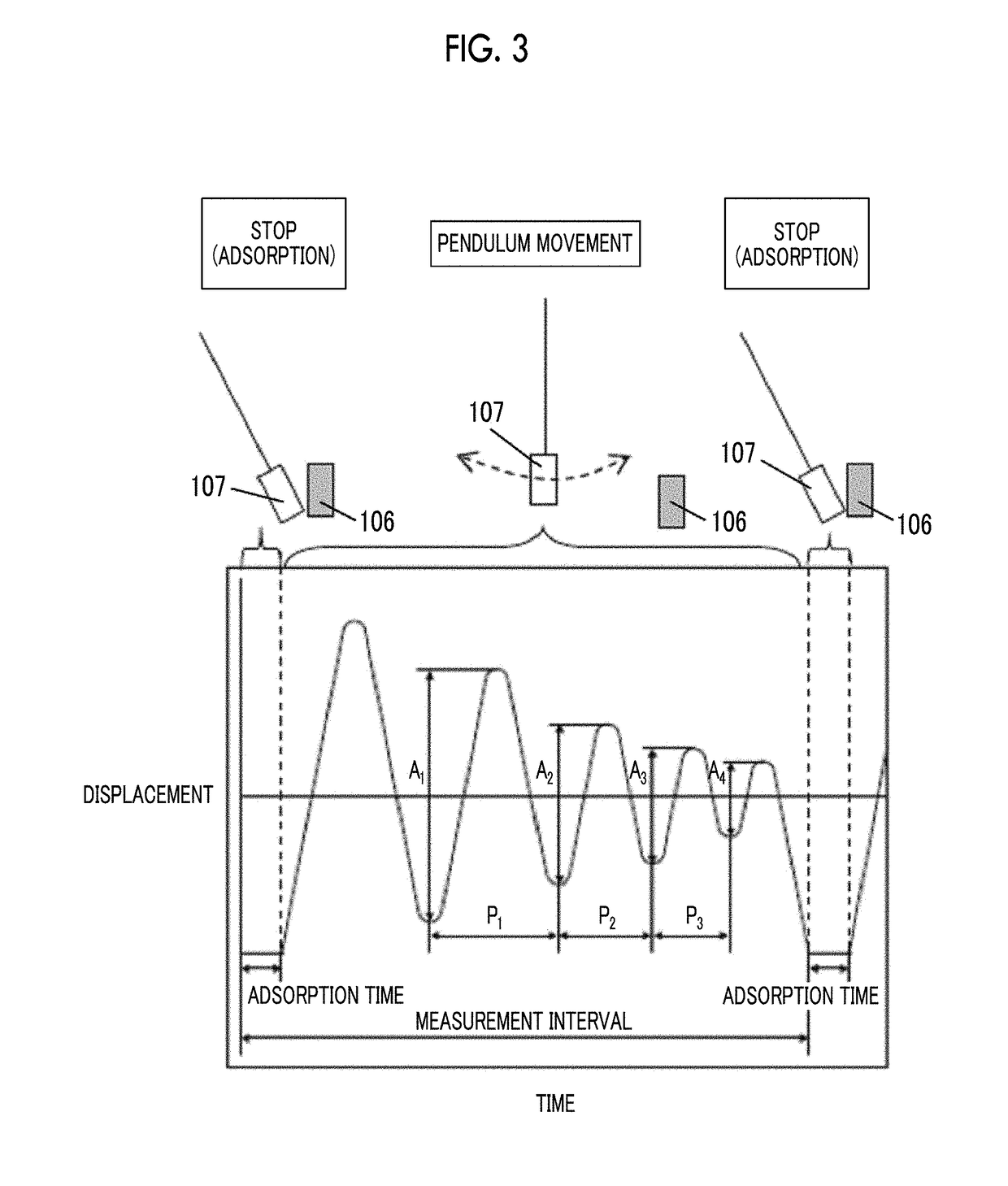
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which the servo head is a TMR head, the magnetic tape includes a servo pattern in the magnetic layer, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and a ratio (Sdc / Sac) of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster thereof in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Multifunctional blending and liquid supplying vehicle
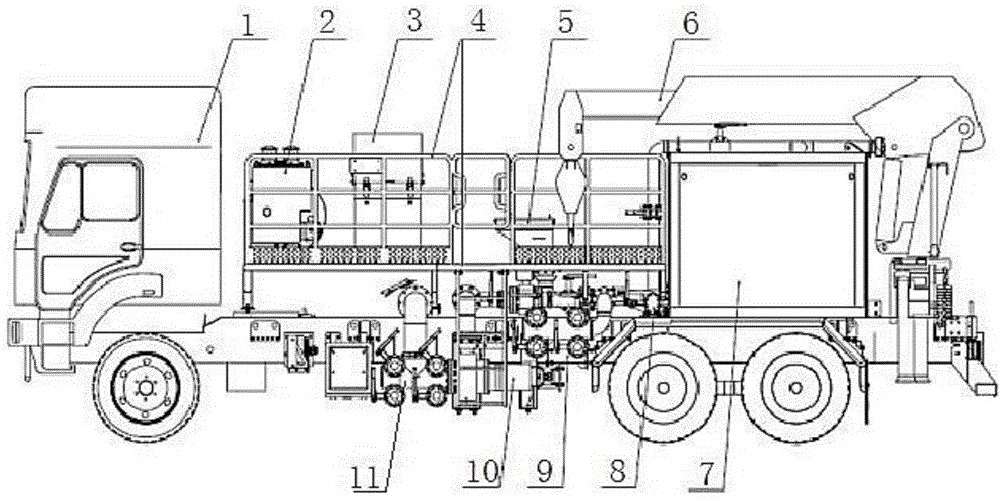
InactiveCN104057864AReduce labor costsAchieve mixingFluid removalItem transportation vehiclesControl systemElectrical control
The invention relates to a multifunctional blending and liquid supplying vehicle, which comprises a chassis, wherein an operation platform, a hydraulic oil tank, a dry powder feeder, an operation box for an electrical control system, a lorry-mounted crane and a liquid adding tank are fixedly arranged above the main beam of the chassis, wherein a centrifugal pump, an exhaust manifold and a suction manifold are arranged on each of two sides of the middle part of the main beam of the chassis, the exhaust manifold is communicated with the water outlet of the centrifugal pump, and the suction manifold is communicated with the water inlet of the centrifugal pump; the liquid adding pump is fixedly arranged on the side wall of the liquid adding tank, the water inlet of the liquid adding pump is communicated with the liquid adding tank, and the water outlet of the liquid adding tank is communicated with the exhaust manifold; a discharge opening in the lower end of the dry powder feeder is communicated with the exhaust manifold; the engine of the chassis is connected with a hydraulic pump, and the hydraulic pump is connected with the centrifugal pump, the lorry-mounted crane, the liquid adding tank and the liquid adding pump through a hydraulic multiway valve; the electrical control system is connected with the engine of the chassis, the hydraulic pump and the hydraulic multiway valve. The multifunctional blending and liquid supplying vehicle provided by the invention is low in cost, high in working efficiency, and can achieve various oil field operation functions.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH CO LTD
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180286450A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMaterials with ironRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape including a magnetic layer; and a TMR head (reproducing head), in which an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Speed control method used for numerical control machine
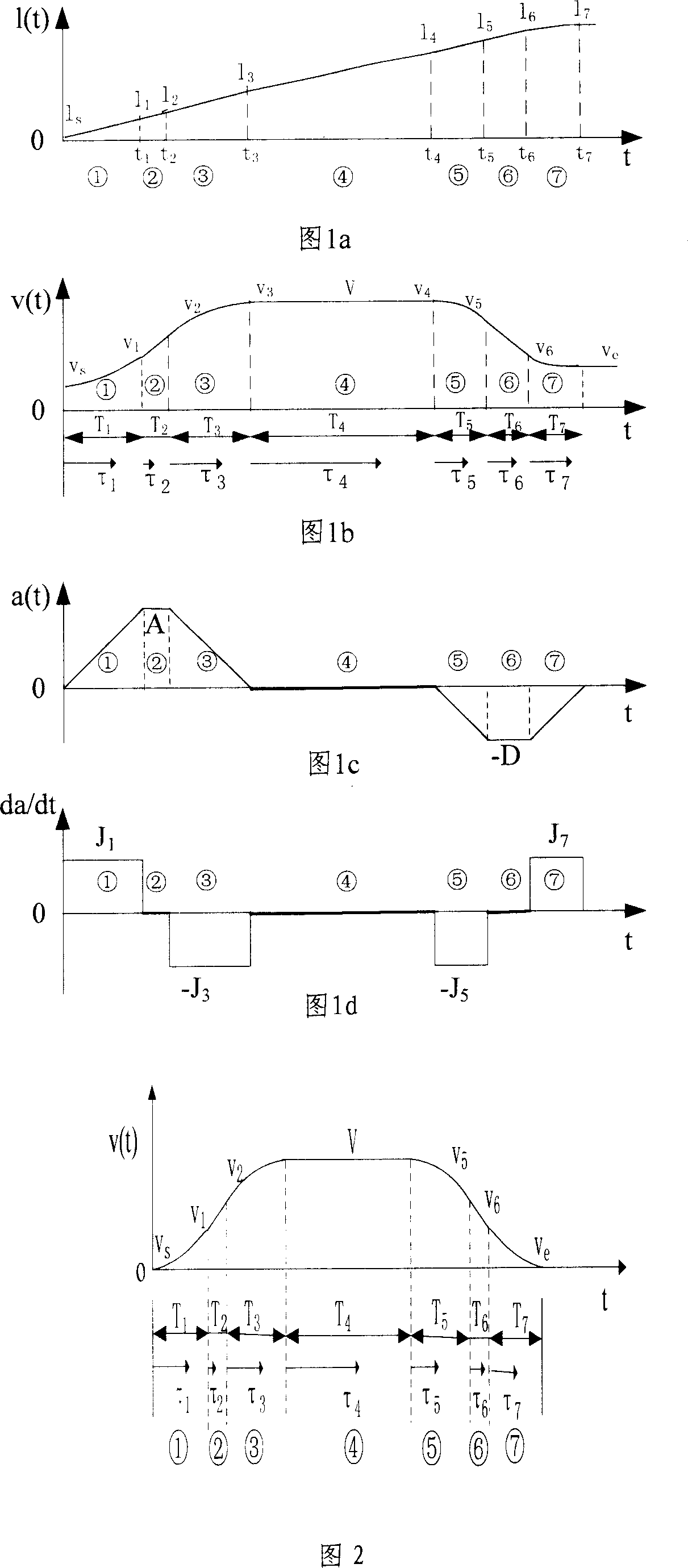
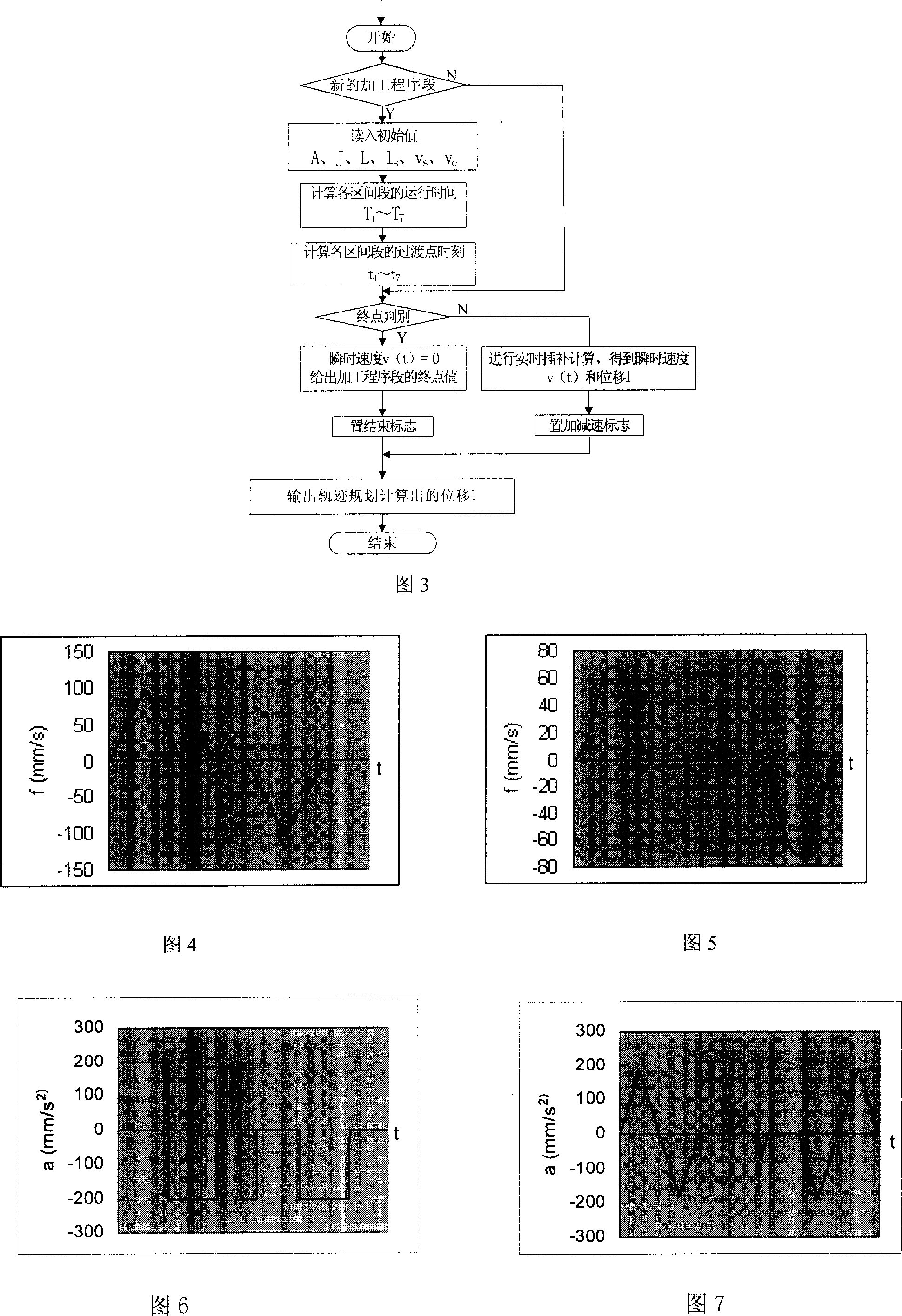
InactiveCN1971457AReduce shockImprove smoothnessComputer controlSimulator controlNumerical controlControl theory
The invention discloses acceleration and deceleration controlling means used in numerical control machine, the concept of 'add-acceleration' is introduced against the dynamic property of the controlled member, the add-acceleration is constant in stage of acceleration and deceleration, the two physical quantities of acceleration and add-acceleration are setting; the segmented handling method of add-accelerating sections, uniform accelerating sections, decelerated accelerating sections, uniform speed sections, add-decelerating sections, uniformly-retarded sections and decelerated deceleration sections is adopted, after the interval discrimination, the real-time interpolating calculation in every interval is exceeded based on the integral relation between the add-acceleration, acceleration, speed and displacement, the S type velocity curve is formed to realize the flexible acceleration and deceleration control; the destination discrimination process is proceeded before the interpolating calculation can increase the machining precision of the acceleration and deceleration control. The method is simple, the impact is small, the speed is smooth, the machining precision is high and the flexible control can be realized.
Owner:中国科学院沈阳计算技术研究所有限公司 +1
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180240481A1Lower the resistance valueAvoid it happening againAlignment for track following on tapesTape carriersX-rayEngineering
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head as a servo head; and a magnetic tape which includes a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder and a binding agent, and including a servo pattern, an XRD intensity ratio (Int(110) / Int(114)) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180240478A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head as a reproducing head; and a magnetic tape which includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, an XRD intensity ratio (Int(110) / Int(114)) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic signal reproduction system and magnetic signal reproduction method
ActiveUS20100246073A1Excellent electromagnetic characteristicExcellent running durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersTape carriersMohs scale of mineral hardnessHardness
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a nonmagnetic support. A height of protrusions with a protrusion density of 0.002 protrusion / μm2 or lower on a surface of the magnetic layer as measured by AFM is 40 nm or lower; a density of protrusions that are 15 nm or higher in height on the surface of the magnetic layer as measured by AFM ranges from 0.01 to 0.18 protrusion / μm2; and the protrusions that are 15 nm or higher in height include protrusions formed of carbon black and protrusions formed of a substance with a Mohs' hardness exceeding 7, and an average height of the protrusions formed of carbon black is greater than an average height of the protrusions formed of the substance with a Mohs' hardness exceeding 7.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180286439A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessTape carriersRecord information storageMagnetic force microscopeMagnetic tape
The magnetic tape device includes a TMR head and a magnetic tape, in which the magnetic tape includes fatty acid ester in a magnetic layer, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is 2.0 nm or smaller, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding a surface of the magnetic layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are greater than 0 nm and 7.0 nm or smaller, a difference between spacings before and after the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and 8.0 nm or smaller, and a ratio of an average area Sdc of a magnetic cluster of the magnetic tape in a DC demagnetization state and an average area Sac of a magnetic cluster thereof in an AC demagnetization state measured with a magnetic force microscope is 0.80 to 1.30.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180240479A1Lower the resistance valueImprove smoothnessManufacture head surfaceTape carriersMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape; and a TMR head as a reproducing head, in which a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape calculated by Expression 1: ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C. is equal to or smaller than 0.50, wherein, in Expression 1, the SFD25° C. is a switching field distribution SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. is a switching field distribution SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180240489A1Lower the resistance valueAvoid it happening againMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeSurface roughness
The magnetic tape device including: a magnetic tape including a servo pattern on a magnetic layer; and a TMR head as a servo head, in which a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding the surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape calculated by Expression 1: ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C. is equal to or smaller than 0.50, wherein the SFD25° C. is SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. is SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180286453A1Prevent occurrenceDecrease in resistance valueMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesPhysicsPeak area
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape including a magnetic layer, in which an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com