Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
345 results about "Biological structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
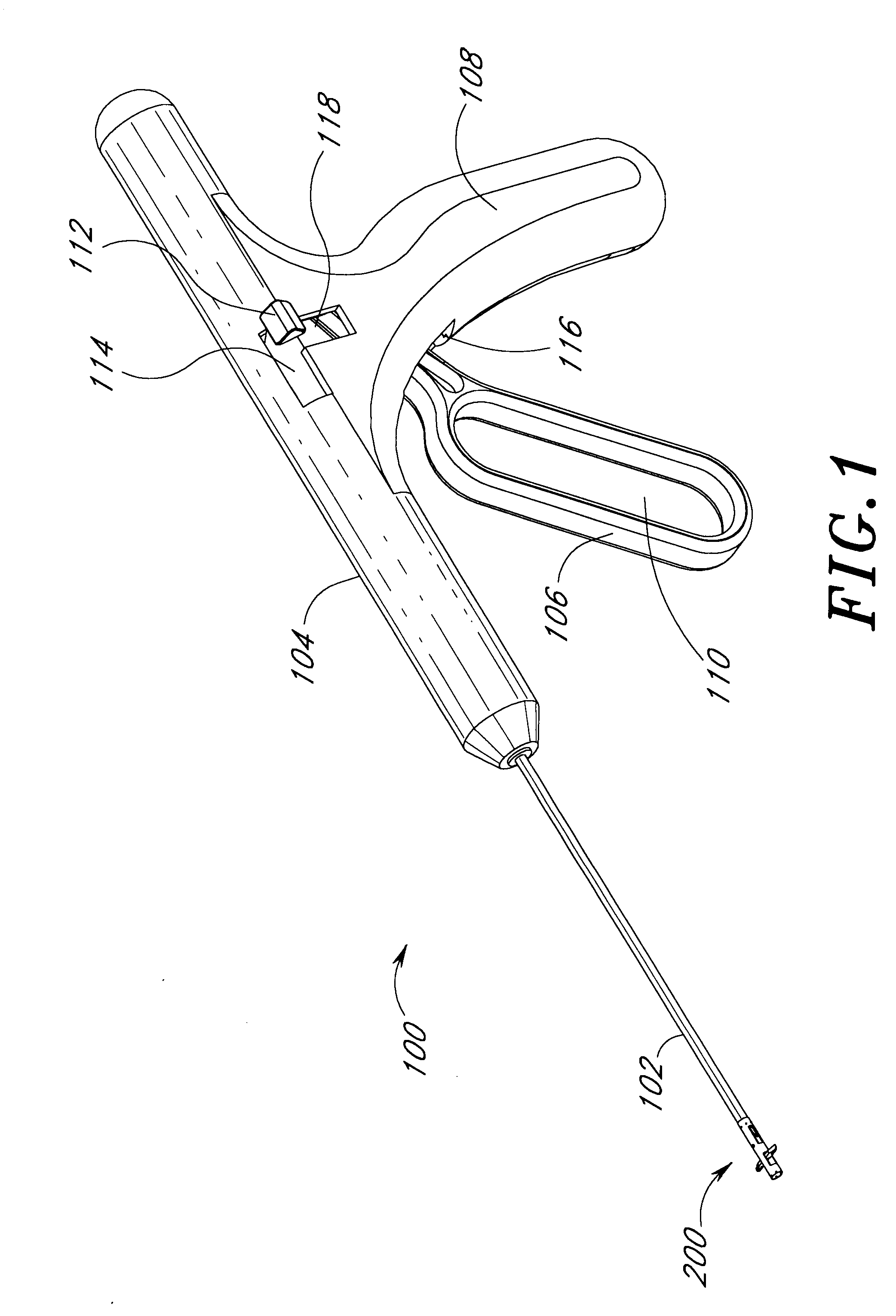
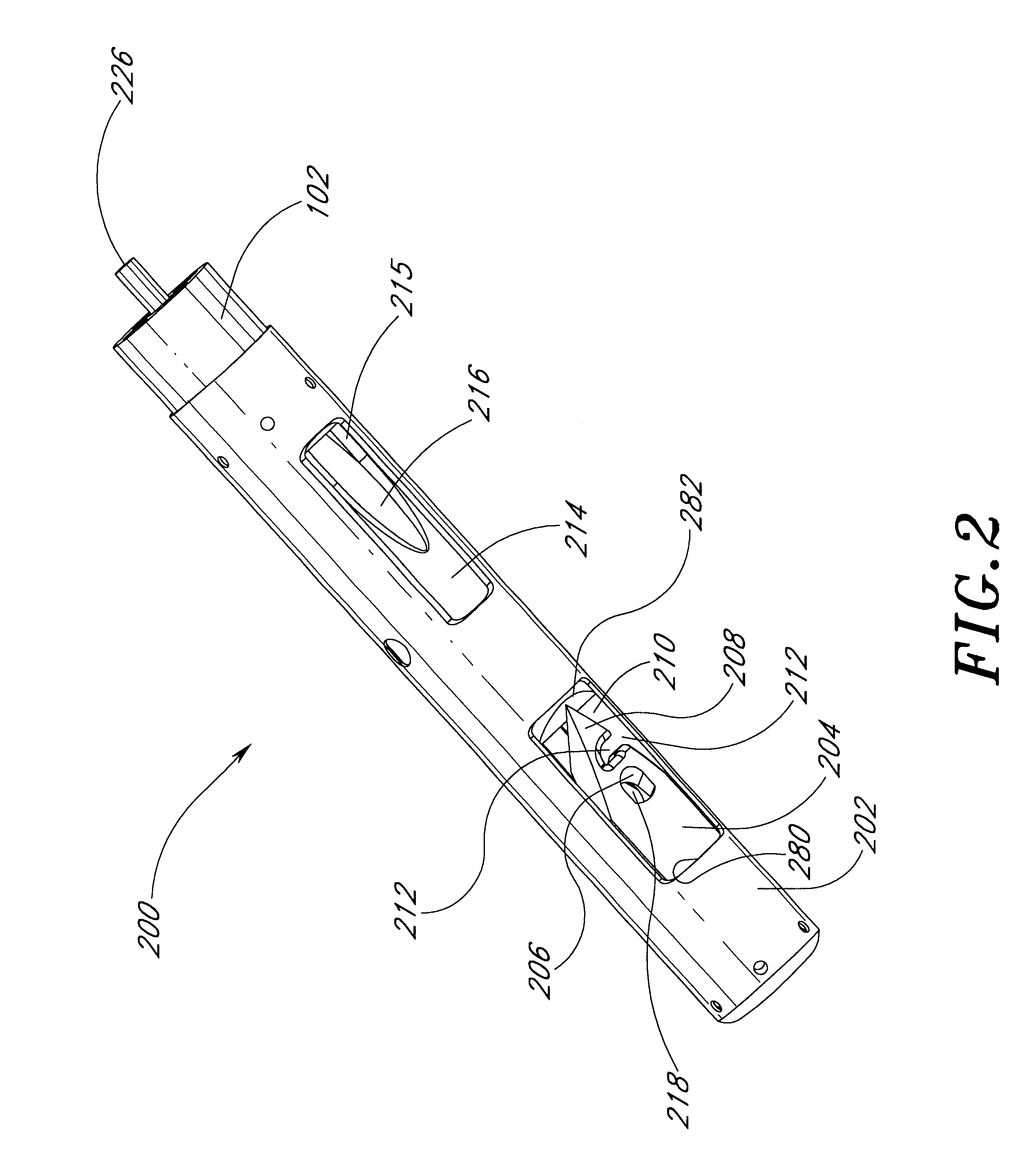
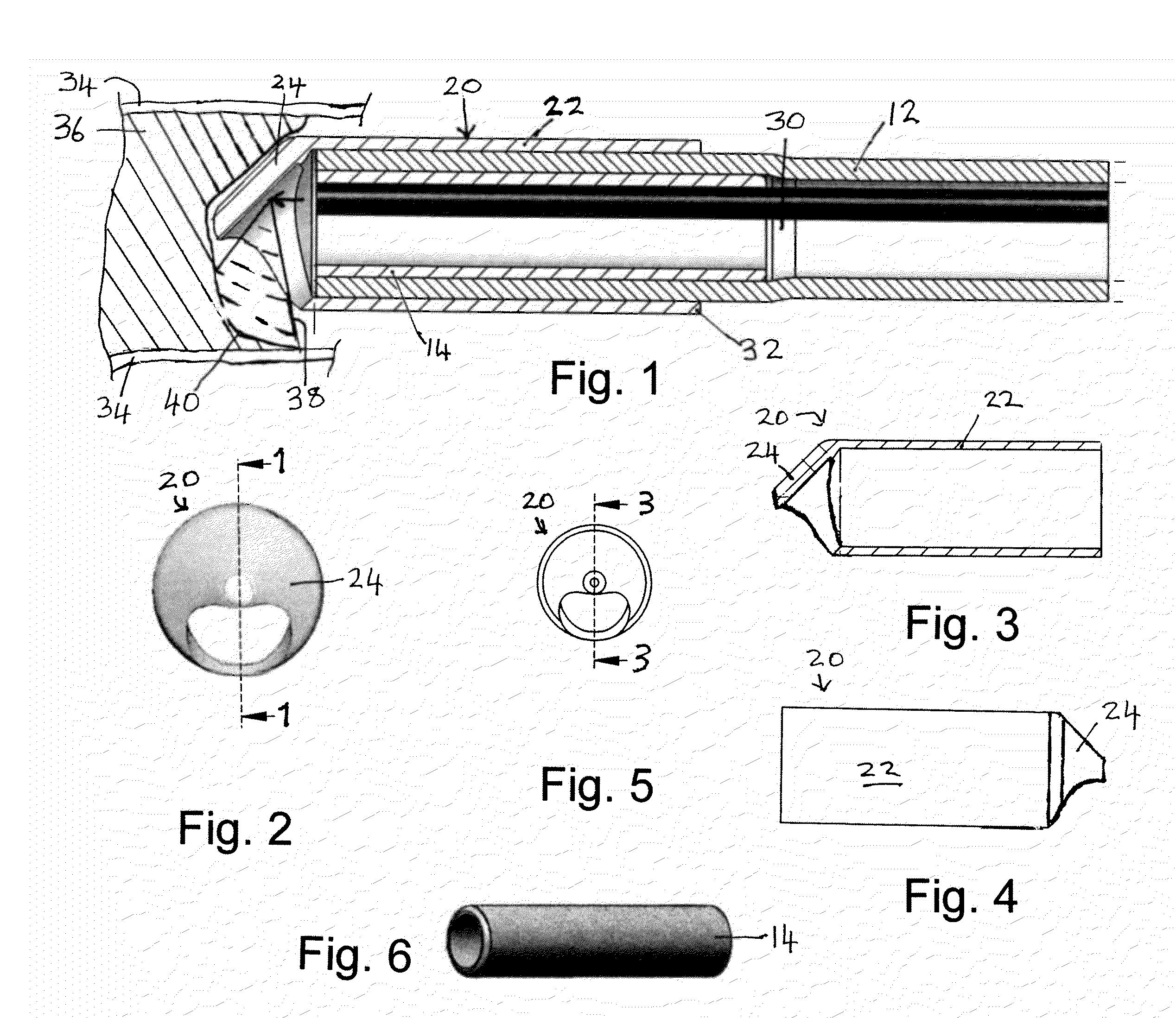
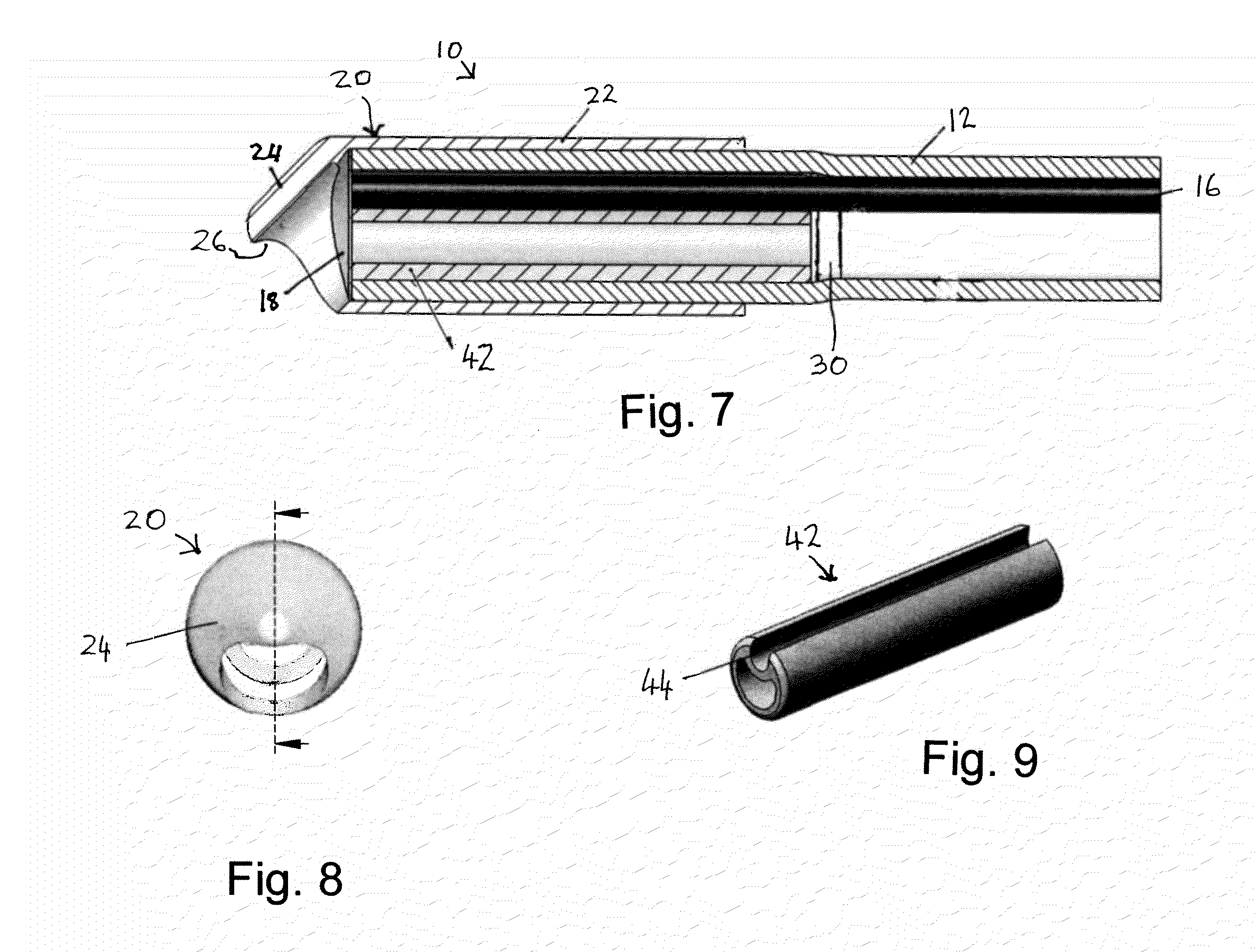
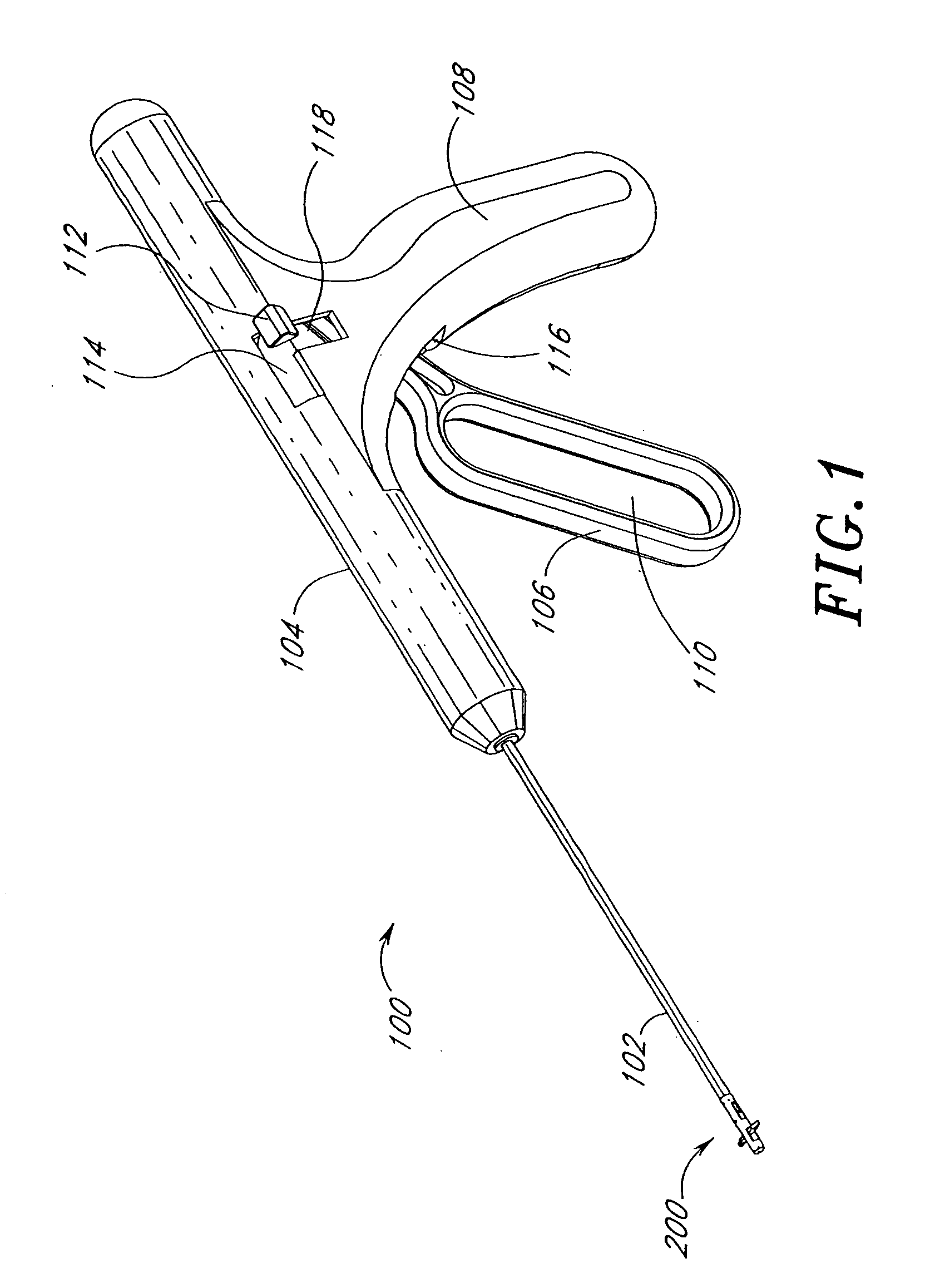
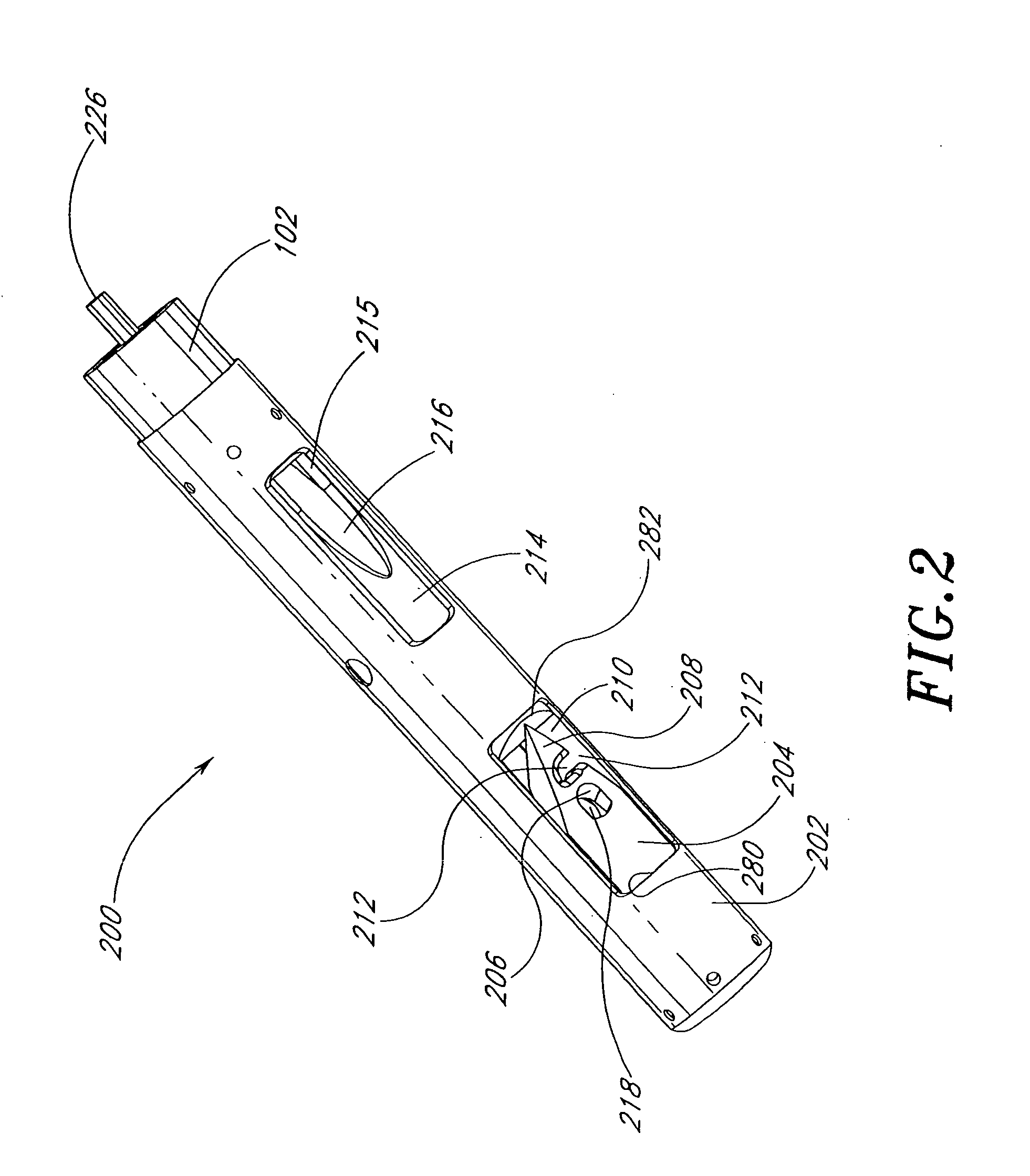
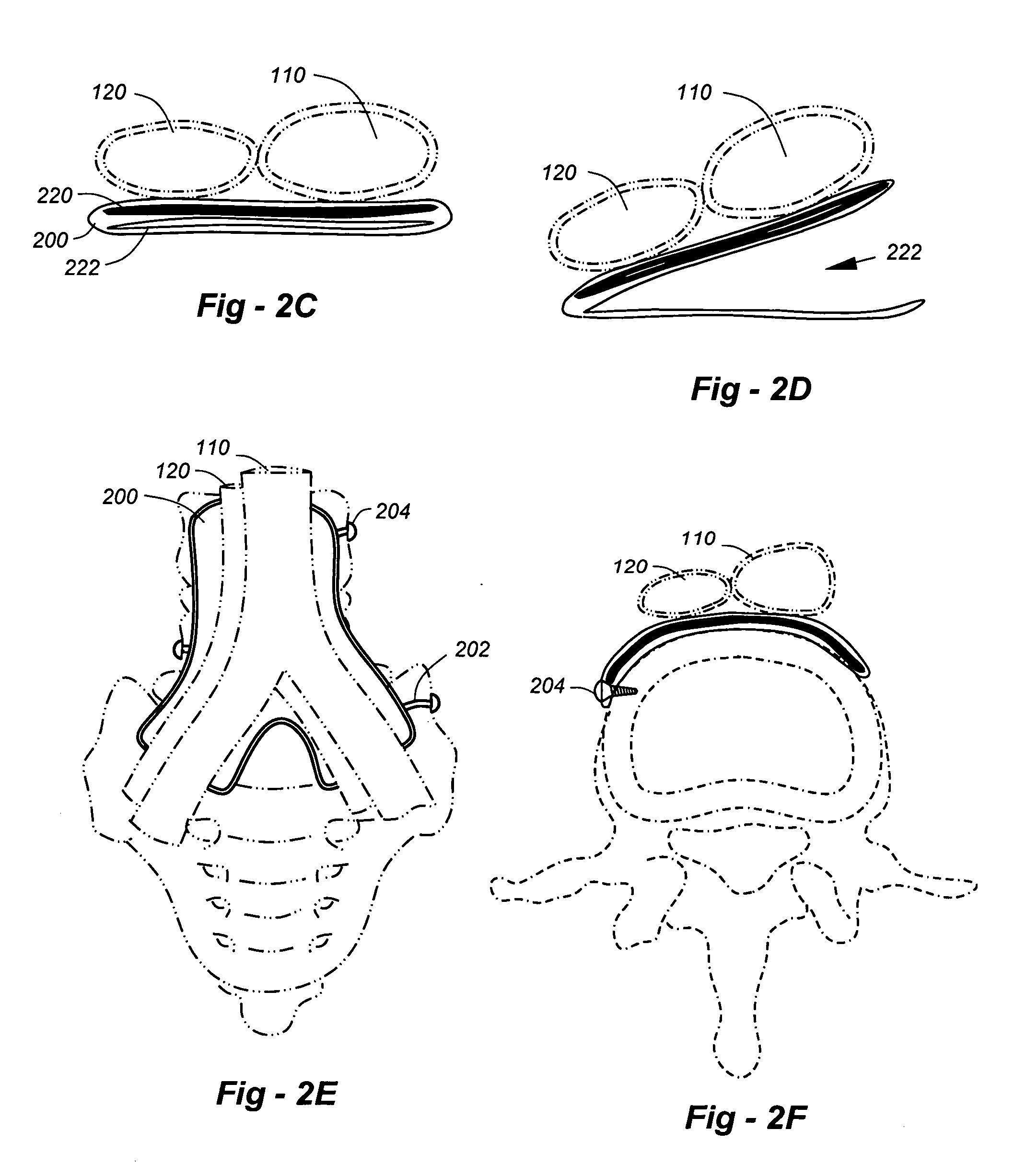
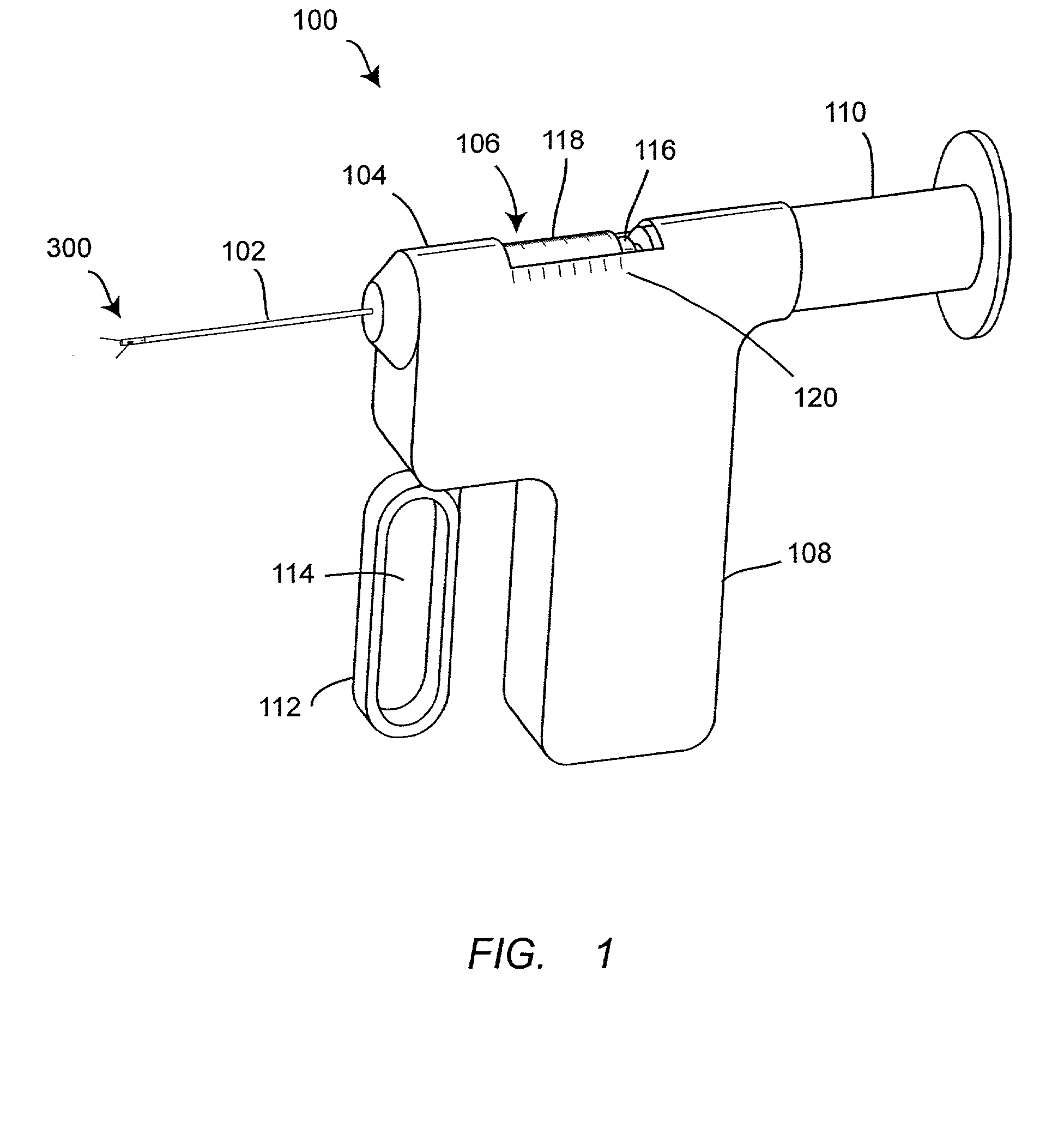
Suturing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6911034B2Quickly and easily applying sutureSeparate applicationSuture equipmentsWound clampsAnatomySurgery
A suturing apparatus comprises an elongated body, at least one arms movable relative to the elongated body and at least one needle movable relative to the elongated body. The arm releasably holds an end portion of a length of suture. The arm has a sharp end portion adapted to pierce an inner surface of a wall of a biological structure and pass an end portion of the suture through the inner surface. The needle is adapted to pierce the inner surface of such biological structure at a location proximal to the location where the end portion of the suture was inserted. The needle captures an end portion of the suture from the arm and draws the end portion of the suture back through the inner surface. The end of the suture is then drawn out of the biological structure by removing the elongated body.
Owner:STERILIS
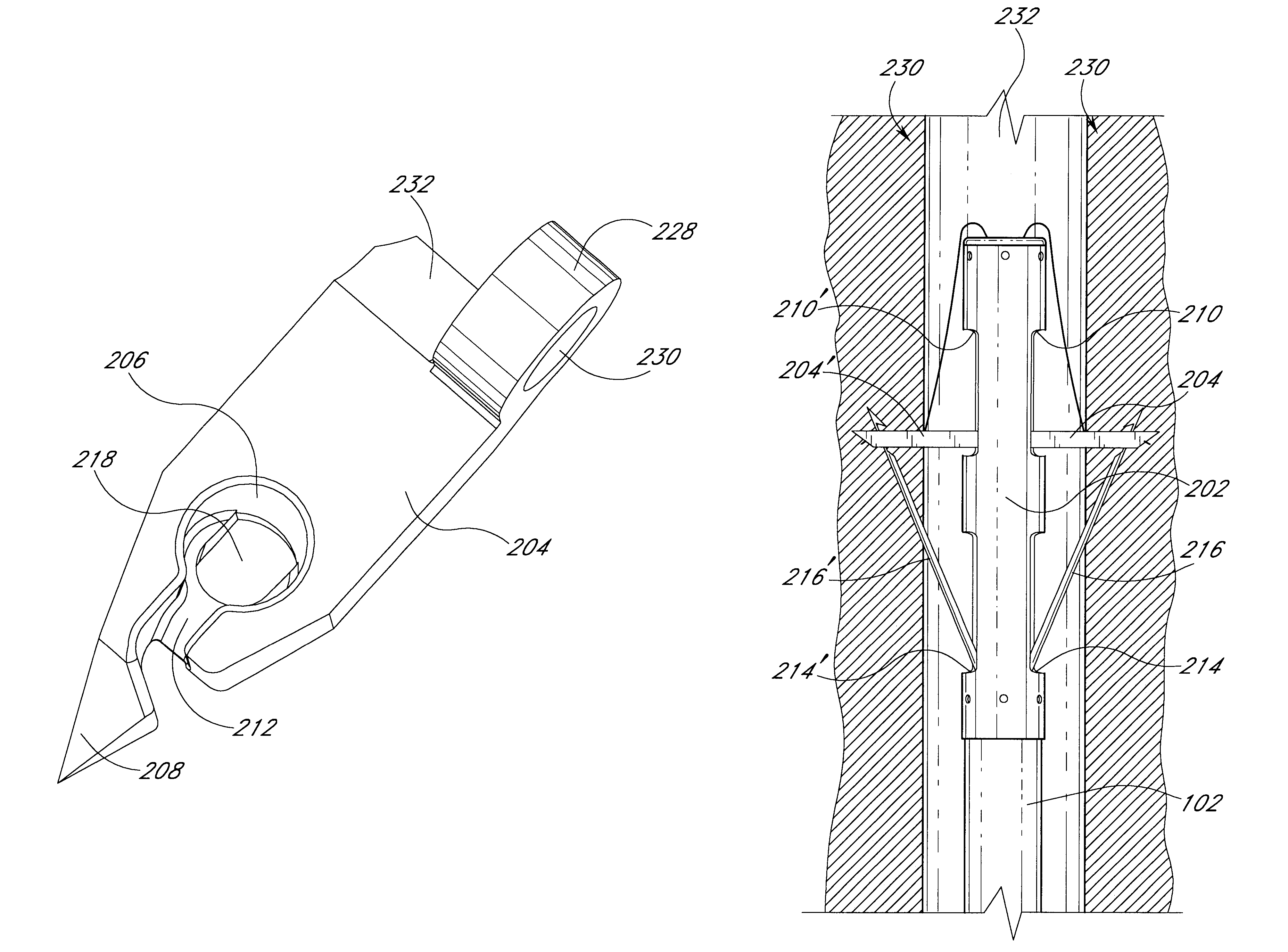
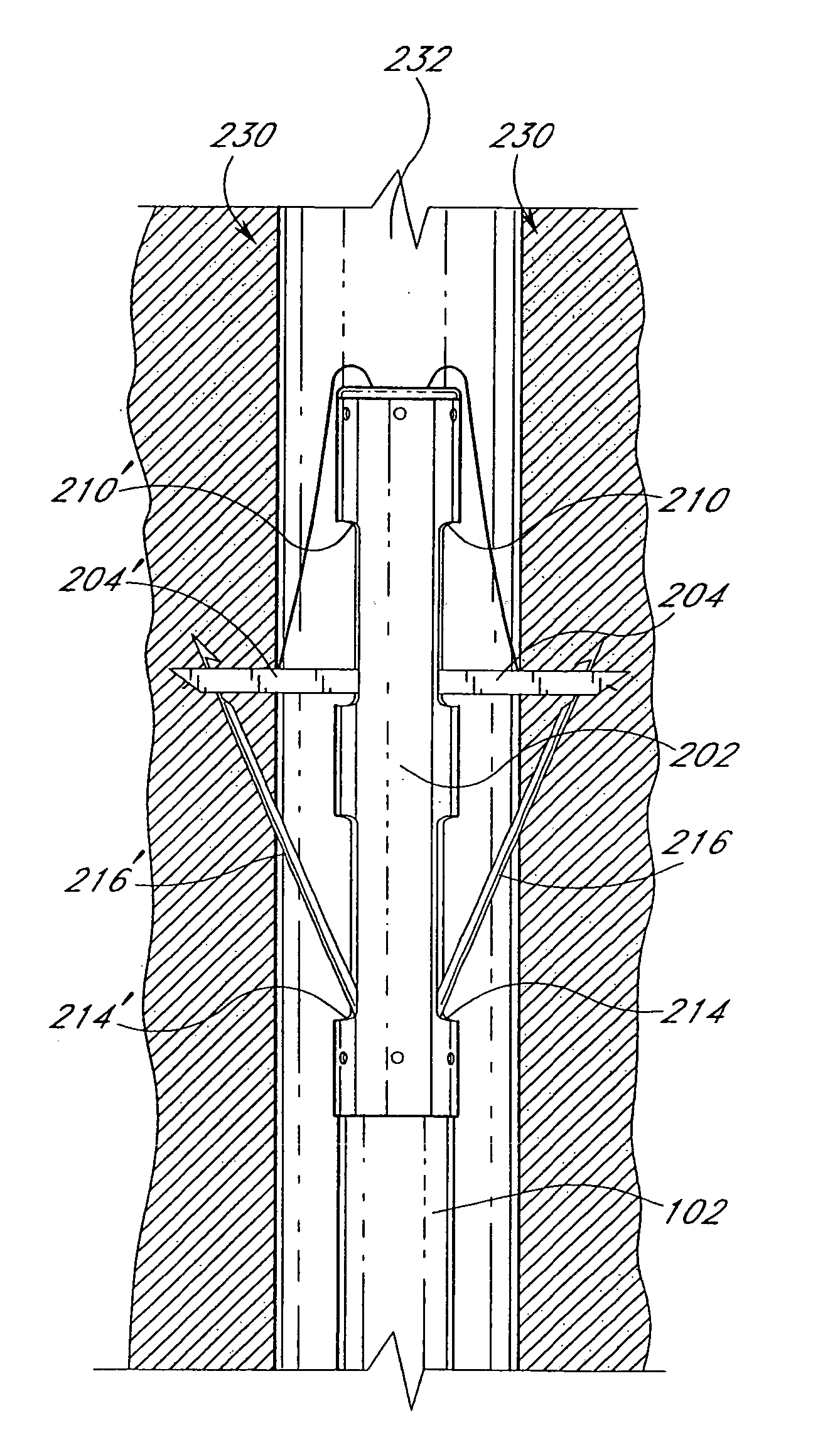
Suturing device and method for sealing an opening in a blood vessel for other biological structure
InactiveUS7004952B2Many of complicationMany of costSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesDistal portionVia incision
A suturing device allows a physician to remotely seal an incision in a blood vessel or other biological tissue. The device comprises an elongated tubular body having a distal portion which is adapted to be inserted percutaneously through the incision and into the blood vessel. The distal portion has first and second retractable arms which extend from the distal portion of the body and releasably hold a suture within the blood vessel. First and second retractable needles, each of which is configured to catch the suture from a respective arm, are provided along the body proximal to the retractable arms. The arms and the needles are remotely movable by the physician using a handle or other control mechanism provided at a distal portion of the device. In operation, the arms are initially deployed within the blood vessel to hold the ends of the suture beyond the circumference of the tubular body. The needles are then deployed from and then retracted into the body, during which time the needles pierce the vessel wall on opposite sides of the incision, release the suture ends from the retractable arms, and pull the suture through the vessel wall. The device is particularly useful for closing an incision in an artery following a catheterization procedure. In one embodiment, the catheter sheath introducer (CSI) used to perform the catheterization procedure is left in place during the suturing procedure.
Owner:WHITEBOX CAPITAL ARBITRAGE PARTNERS +1
Compositions, devices, systems, for using a Nanopore
ActiveUS20100035260A1Low costRapidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore in the absence of requiring a terminating nucleotide. The devices and methods are also used to determine rapidly (˜>50 Hz) the nucleotide base sequence of a polynucleotide under feedback control or using signals generated by the interactions between the polynucleotide and the nanopore. The invention is of particular use in the fields of drug discovery, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
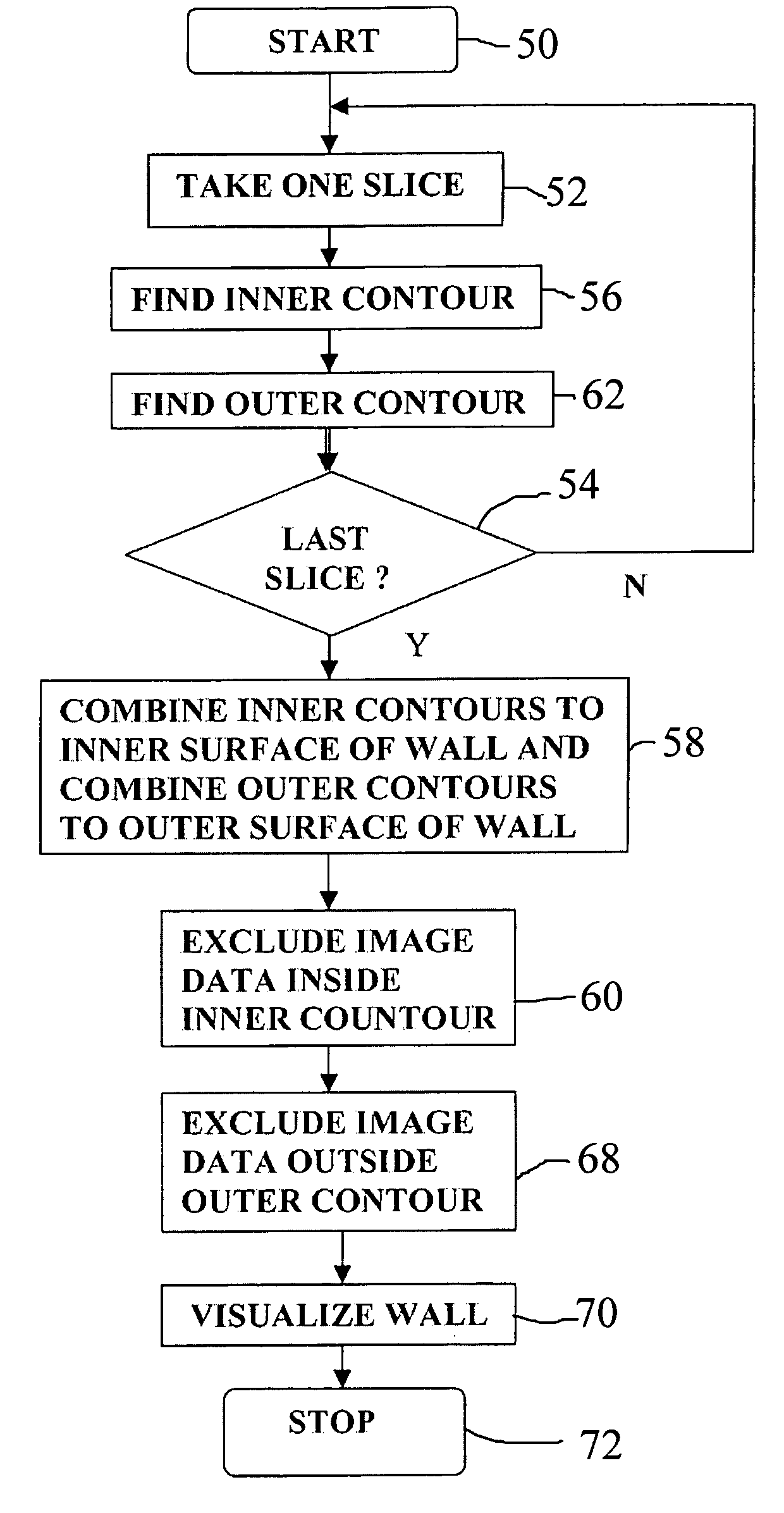
Method and apparatus for visualization of biological structures with use of 3D position information from segmentation results
A data processing methodology and corresponding apparatus for visualizing the characteristics of a particular object volume in an overall medical / biological environment receives a source image data set pertaining to the overall environment. First and second contour surfaces within the environment are established which collectively define a target object volume. By way of segmenting, all information pertaining to structures outside the target object volume are excluded from the image data. A visual representation of the target object based on nonexcluded information is displayed. In particular, the method establishes i) the second contour surface through combining both voxel intensities and relative positions among voxel subsets, and ii) a target volume by excluding all data outside the outer surface and inside the inner surface (which allows non-uniform spacing between the first and second contour surfaces). The second contour surface is used as a discriminative for the segmenting.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Virtual endoscopy
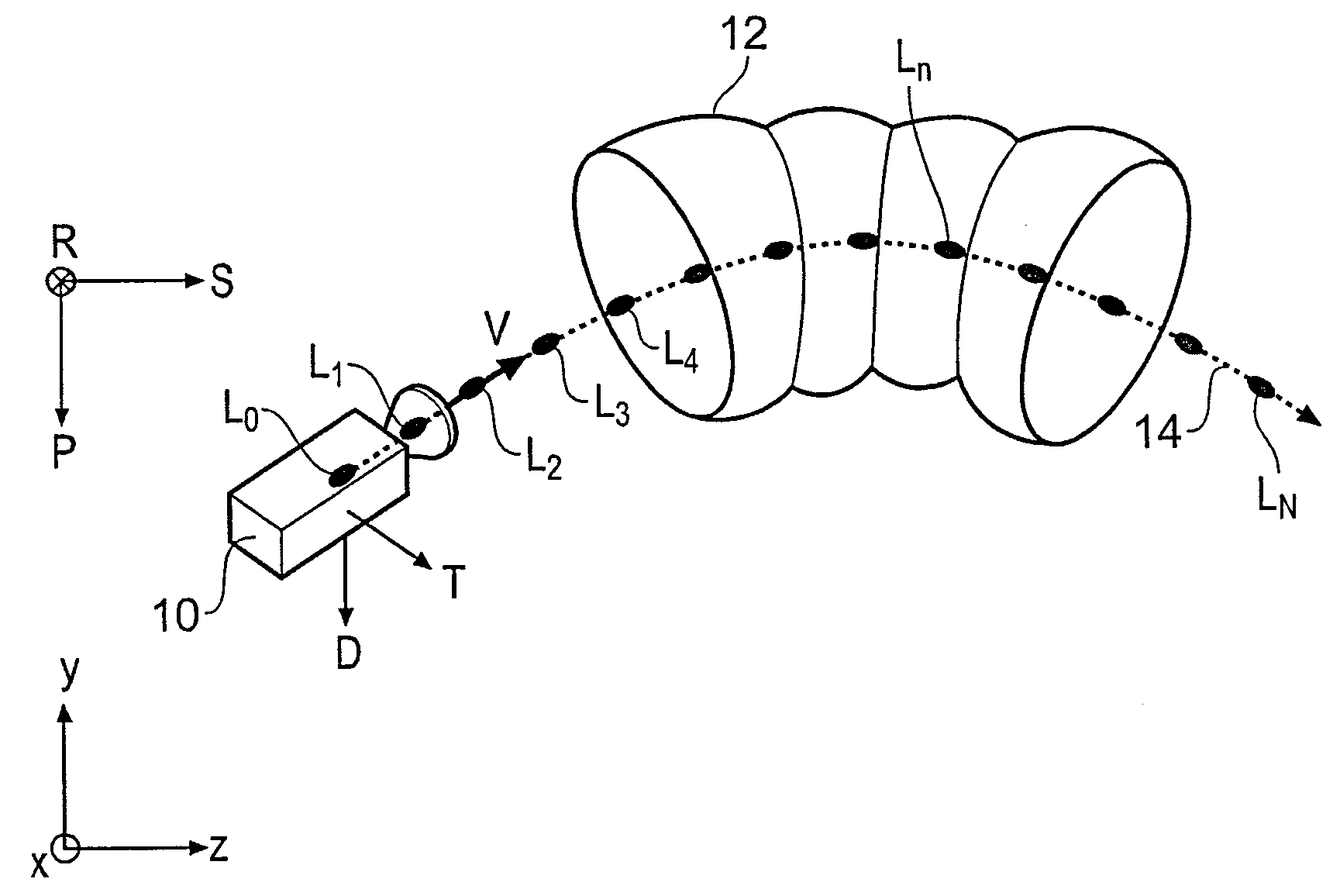
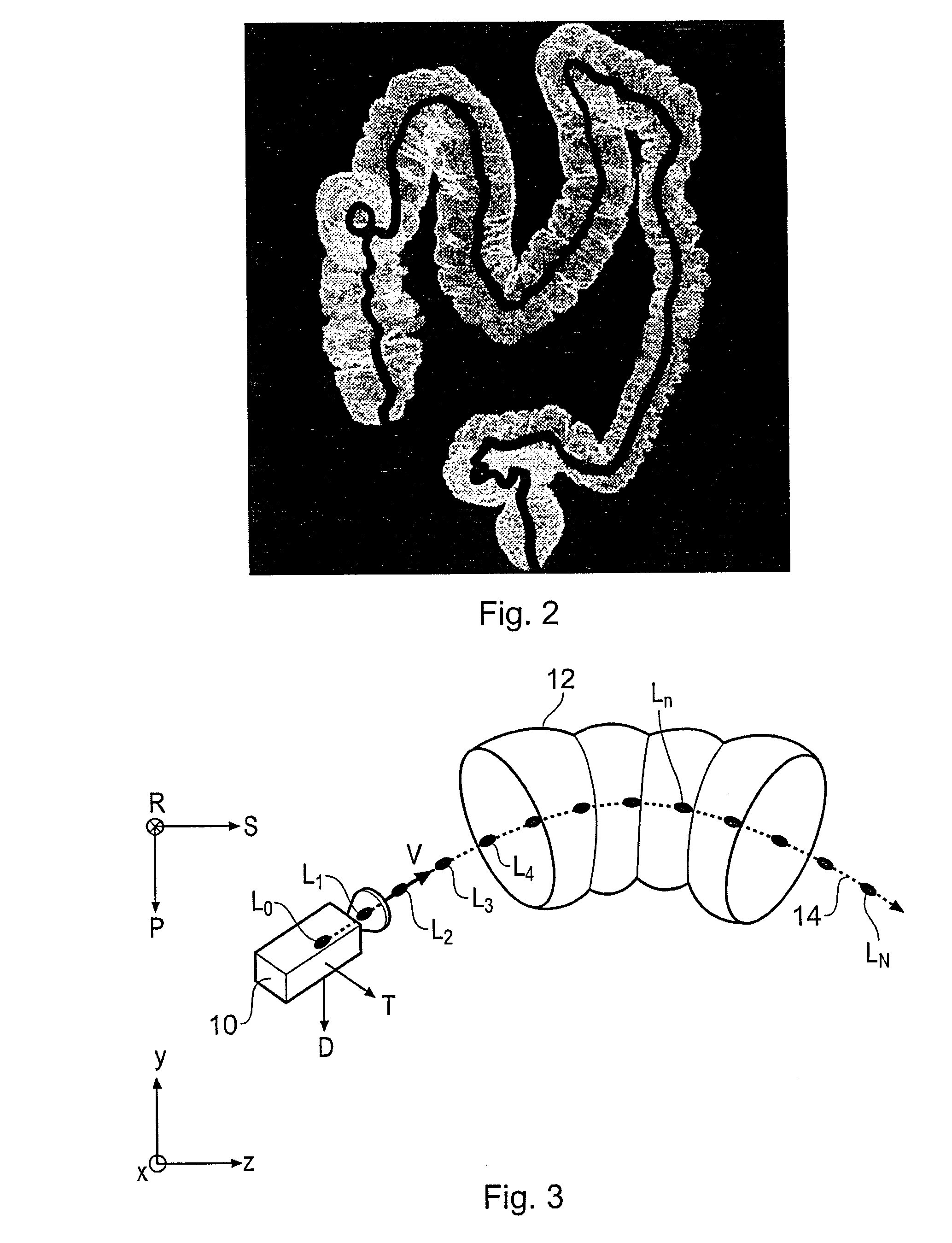
InactiveUS20080118117A1Full effectImproved angular separationSurgeryEndoscopesData setVirtual camera
A method of orienting a virtual camera for rendering a virtual endoscopy image of a lumen in a biological structure represented by a medical image data set, e.g., a colon. The method comprises selecting a location from which to render an image, determining an initial orientation for the virtual camera relative to the data set for the selected location based on the geometry of the lumen, determining an offset angle between the initial orientation and a bias direction; and orienting the virtual camera in accordance with a rotation from the initial orientation towards the bias direction by a fractional amount of the offset angle which varies according to the initial orientation. The fractional amount may vary according to the offset angle and / or a separation between a predetermined direction in the data set and a view direction of the virtual camera for the initial orientation. Thus the camera orientation can be configured to tend towards a preferred direction in the data set, while maintaining a good view of the lumen and avoiding barrel rolling effects.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL VISUALIZATION SYST EURO
Process and system for treating a vascular occlusion or other endoluminal structure
A process and instruments for diminishing an undesired endoluminal structure present at a treatment site in a mammalian treatment subject. The endoluminal can be or include a vascular occlusion, a biofilm or another undesired biological structure. The process can include applying mechanical shockwaves to the endoluminal structure and the endoluminal structure absorbing the applied mechanical shockwaves and becoming diminished, dispersed or weakened. The shockwaves can be generated by pulsed laser energy delivered to an ionizable target via an optical fiber.
Owner:KRESPI YOSEF
Method for multi-scale meshing of branching biological structures
InactiveUS20110093243A1Good specificationIncrease computing speedMedical simulationImage enhancementLocal pressureGrid partition
A structural and functional model for a lung or similar organ is virtually defined by encoding aspects of branching passageways. Larger passageways that are visible in medical images are surface mesh fitted to the anatomical surface geometry. Smaller distal passageways, beyond a given number of branch generations, are modeled by inference as linear passages with nominal diameters and branching characteristics, virtually filling the space within the outer envelope of the organ. The model encodes finite volumetric elements for elasticity and compliance in passageway walls, and for local pressure and flow conditions in passageway lumens during respiration. The modeling can assess organ performance, help to plan surgery or therapy, determine likely particle deposition, assess respiratory pharmaceutical dosing, and otherwise represent structural and functional organ parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Electrode array structures and methods of use for cardiovascular reflex control
A tissue stimulation device includes an electrode array having at least four independently switchable electrodes. In one embodiment, the electrode array comprises a flexible base to which the electrodes are fixed that flexes to encompass at least a portion of an artery or other elongate biological structure. The electrodes are electrically coupled to and energized by a signal generator coupled to a control system. In one embodiment, the array of electrodes are configured such that a suitable signal pattern for stimulation pulses between or among a set of the switchable electrodes may be determined without having to reposition the electrode assembly by using a series of signal patterns activating different combinations of switchable electrodes in response to sub-stimulation test signals to determine a signal pattern that provides suitable patient response. In another embodiment, the array of electrodes includes an array of selectively activatable multi-polar electrodes.
Owner:CVRX
Thermally reversible implant and filler
The invention relates to the use of a thermal reversible gel, such as a copolymer composition, as a biological filler or implant. The gel has a semi-solid form at body temperature, but upon cooling to a temperature below a threshold level, the gel is liquefied and can be re-shaped, re-sized, manipulated or removed from the body. The gel may be used as a subcutaneous implant, a biological filler, joint or tissue spacer, for wrinkle filling or other cosmetic implants, as a soft-tissue replacement for reconstructive surgery, or as a barrier within the lumen of a biological structure, such as a blood vessel. The implant may be used to provide reversible birth control by providing, for example, a reversible barrier to the cervix or a reversible blockage of the lumen of the vas deferens.
Owner:CHENG YU LING +3
Suturing device and method for sealing an opening in a blood vessel or other biological structure
InactiveUS20060195120A1Many of complicationMany of costSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesDistal portionVia incision
Owner:NOBLES ANTHONY A +2
Method and apparatus for visualization of biological structures with use of 3D position information from segmentation results
A data processing methodology (and corresponding data processing apparatus) for visualizing the characteristics of a particular object volume in an overall medical / biological environment comprises the following computer operated steps: receiving a source image data set as pertaining to the overall environment; establishing a first contour surface within the environment, and through using the first contour surface as seed data, establishing a second contour surface within the environment, which contour surfaces collectively defining a target object volume; by way of segmenting, excluding from the image data set all information pertaining to structures outside the target object volume; and visualizing the target object as being based on nonexcluded information. In particular, the method establishes the second contour surface through combining both voxel intensities and relative positions among voxel subsets, a target volume by excluding all data outside the outer surface and inside the inner surface, thereby allowing non-uniform spacing between the first and second contour surfaces, and uses the second contour surface as being discriminative for the segmenting.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
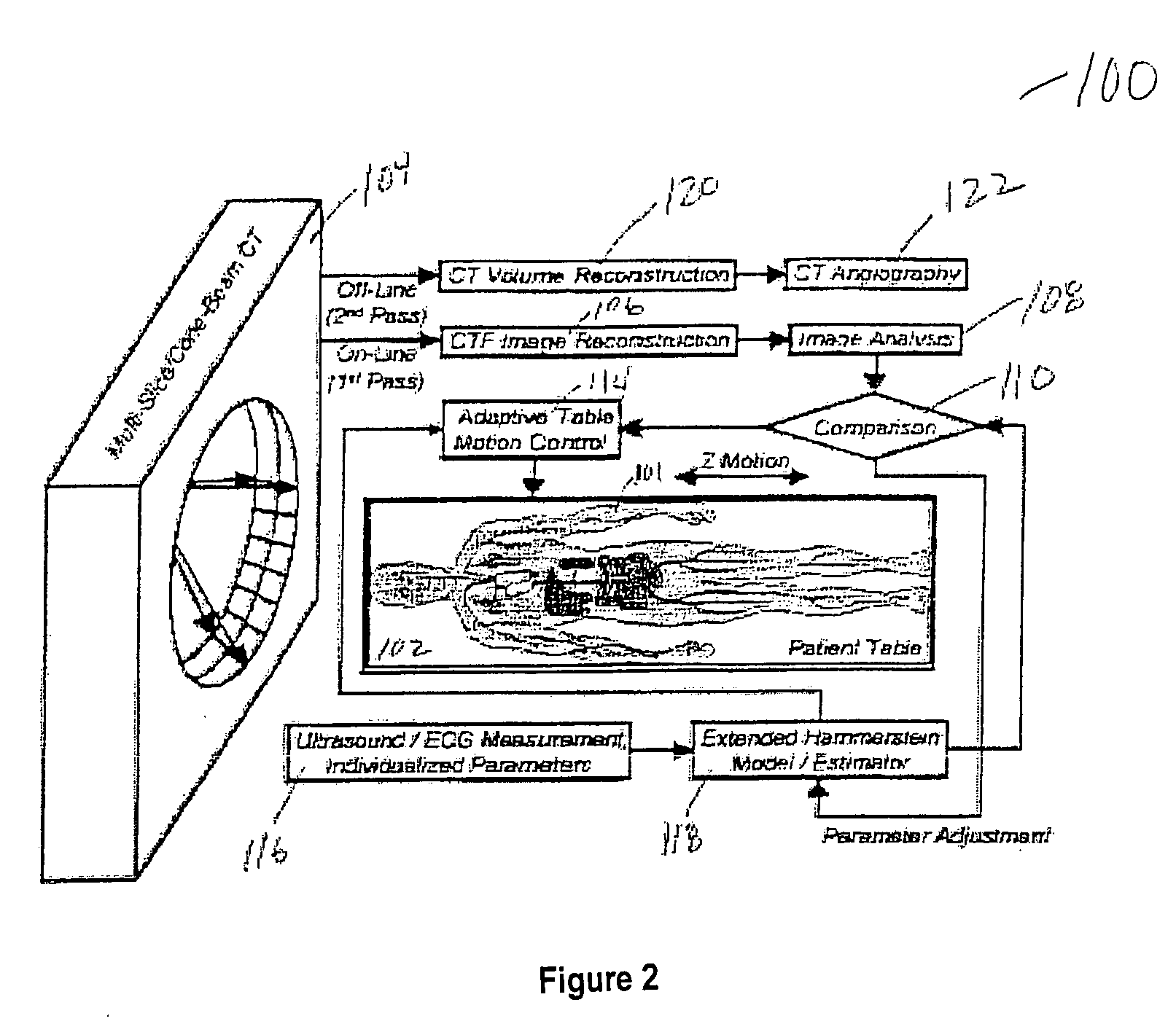
System and method for adaptive bolus chasing computed tomography (CT) angiography
A method of utilizing bolus propagation and control for contrast enhancement comprises measuring with an imaging device a position of a bolus moving along a path in a biological structure. The method further comprises predicting a future position of the bolus using a simplified target model and comparing the predicted future position of the bolus with the measured position of the bolus. A control action is determined to eliminate a discrepancy, if any, between the predicted position of the bolus and the measured position of the bolus and the relative position of the imaging device and the biological structure is adaptively adjusted according to the control action to chase the motion of the bolus.
Owner:IOWA RES FOUND UNIV OF
Suturing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050228407A1Quickly and easily applying sutureSeparate applicationSuture equipmentsSurgeryBiological structure
A suturing apparatus comprises an elongated body, at least one arms movable relative to the elongated body and at least one needle movable relative to the elongated body. The arm releasably holds an end portion of a length of suture. The arm has a sharp end portion adapted to pierce an inner surface of a wall of a biological structure and pass an end portion of the suture through the inner surface. The needle is adapted to pierce the inner surface of such biological structure at a location proximal to the location where the end portion of the suture was inserted. The needle captures an end portion of the suture from the arm and draws the end portion of the suture back through the inner surface. The end of the suture is then drawn out of the biological structure by removing the elongated body.
Owner:NOBLES ANTHONY A +3
Combination of magnetic and electromagnetic treatment method
InactiveUS20170106201A1Reduce the numberReduce volumeElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsSkin appearanceTherapeutic effect
Apparatus and methods for treatment of a biological structure using a combination of magnetic and optical treatment. The apparatus and method for treatment may be used for aesthetic applications such as cellulite treatment, body shaping or enhancing skin appearance. The combination of these methods provides faster and enhanced effects of the treatment.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Apparatus and method for treatment of biological structure
InactiveUS20180125416A1Improve efficiencyConvenient treatmentElectrotherapyOperating chairsMedicinePatient comfort
A magnetic stimulation device has components for positioning a patient into a correct treatment position, and for improving patient comfort. The methods may be used for improving the effectiveness of the stimulation by setting a magnetic field generating device in appropriate position by using feedback information.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Aesthetic method of biological structure treatment by magnetic field
ActiveUS20180001106A1Improve effectivenessReduce self-heatingElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMuscle contractionAdipose tissue
In methods for treating a patient, a time varying magnetic field is applied to a patient's body and causes a muscle contraction. The time-varying magnetic field may be monophasic, biphasic, polyphasic and / or static. The method may reduce adipose tissue, improve metabolism, blood and / or lymph circulation. The method may use combinations of treatments to enhance the visual appearance of the patient.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS +1
Aesthetic Method of Biological Structure Treatment by Magnetic Field
ActiveUS20180236254A1Improve the effectiveness of treatmentReduce self-heatingUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyVisual appearanceVisual perception
Methods for treating a patient using time varying magnetic field are described. The treatment methods combine various approaches for aesthetic treatment. The methods are focused on enhancing a visual appearance of the patient.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Methods and Apparatus for Magnetic Separation of Cells
ActiveUS20090220979A1Increase the magnetic field strengthStir wellBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSuperparamagnetic beadsTumor cells
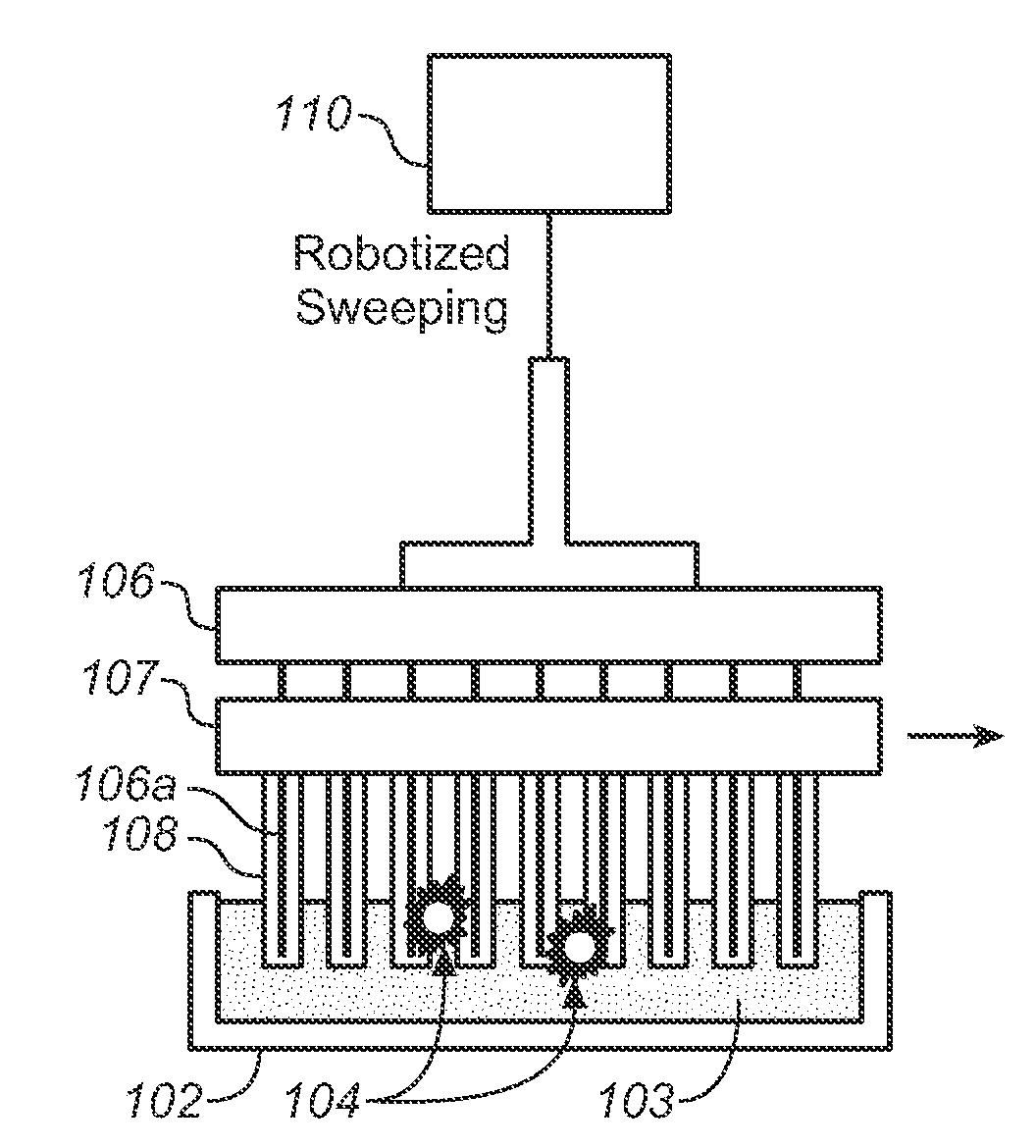
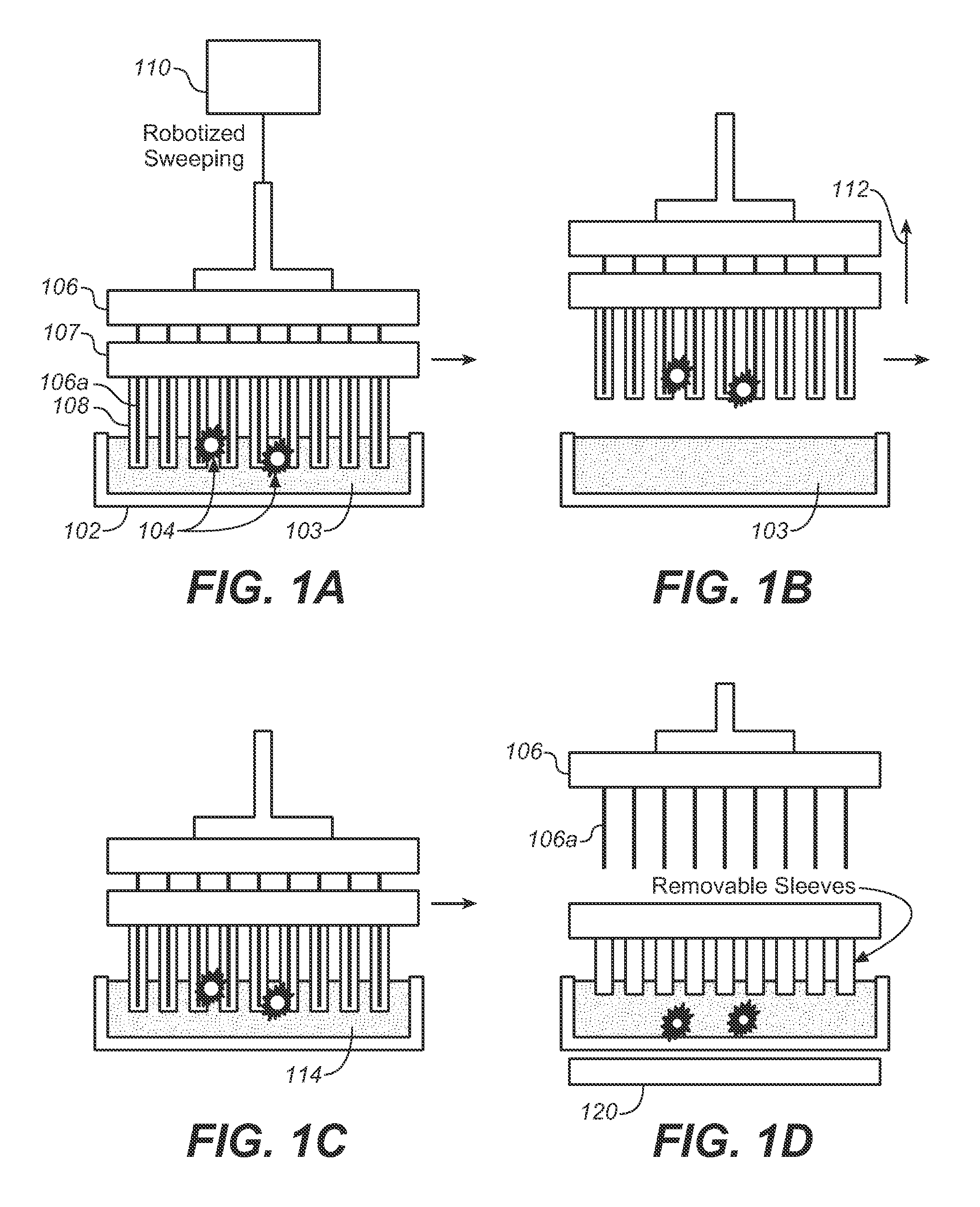
Described here is an automated robotic device that isolates circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or other biological structures with extremely high purity. The device uses powerful magnetic rods covered in removable plastic sleeves. These rods sweep through blood samples, capturing, e.g., cancer cells labeled with antibodies linked to magnetically responsive particles such as superparamagnetic beads. Upon completion of the capturing protocol, the magnetic rods undergo several rounds of washing, thereby removing all contaminating blood cells. The captured target cells are released into a final capture solution by removing the magnetic rods from the sleeves. Additionally, cells captured by this device show no reduced viability when cultured after capture. Cells are captured in a state suitable for genetic analysis. Also disclosed are methods for single cell analysis. Being robotic allows the device to be operated with high throughput.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Aesthetic method of biological structure treatment by magnetic field
ActiveUS10245439B1Improve the effectiveness of treatmentOptimize energy useElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsCancer researchLine of therapy
Methods for treating a patient using time varying magnetic field are described. The treatment methods combine various approaches for treatment.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Aesthetic methods of biological structure treatment by magnetic field
ActiveUS9937358B2Enhancing visual appearanceHigh repetition rateElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMuscle contractionMedicine
In a method for stimulation and treatment of a biological structure of a patient, the biological structure is treated by high power time-varying magnetic field. The treatment is followed by at least a partial muscle contraction. The method may be used in applications for non-invasive aesthetic medicine.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Energetically activated biomedical nanotheurapeutics integrating dental and medical treatments and procedures
A method that includes the following effects: the ability to expand, porositize, clean, decontaminate, debride, break-down and / or destroys, or aids and accentuates the dissolution or extraction of biological structures, nerves and tissues. The methodology uses nano-technology and / or other chemistries may or may not be excited by energy sources to expand and porositize the tissue, which enhances the penetration and effectiveness and acceleration of subsequent chemical, mechanical, and / or procedural steps in the protocol or process. Furthermore, the method includes the ability to associate with and / or initiate in the reconstructive growth and healing process associated with healthy tissue after surgery and / or the ability to destroy diseased or necrotic tissues or cells. The method also includes the ability to begin, construct or stage the activation of cells and / or tissues, including the area of transplantation and use in stem or primordial cell accentuation, their attachment and / or stimulation for growth and differentiation.
Owner:PIPSTEK LLC
Aesthetic method of biological structure stimulation by magnetic field
InactiveUS20170001025A1High repetition rateReduce the numberElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMuscle contractionMedicine
In a method for stimulation and treatment of a biological structure the biological structure is stimulated by high power time-varying magnetic field. The stimulation is followed by at least a partial muscle contraction. The method may be used e.g. in applications for non-invasive aesthetic medicine.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Self-assembling multicellular bodies and methods of producing a three-dimensional biological structure using the same
ActiveUS8143055B2Sufficient integrityEasy to handleSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTissue/virus culture apparatusCell bodiesLiving cell
Structures and methods for tissue engineering include a multicellular body including a plurality of living cells. A plurality of multicellular bodies can be arranged in a pattern and allowed to fuse to form an engineered tissue. The arrangement can include filler bodies including a biocompatible material that resists migration and ingrowth of cells from the multicellular bodies and that is resistant to adherence of cells to it. Three-dimensional constructs can be assembled by printing or otherwise stacking the multicellular bodies and filler bodies such that there is direct contact between adjoining multicellular bodies, suitably along a contact area that has a substantial length. The direct contact between the multicellular bodies promotes efficient and reliable fusion. The increased contact area between adjoining multicellular bodies also promotes efficient and reliable fusion. Methods of producing multicellular bodies having characteristics that facilitate assembly of the three-dimensional constructs are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Methods for controlling a magnetic stimulation device
InactiveUS20170001029A1Reduce noiseLocal control/monitoringSimulator controlMedicineAesthetic medicine
Methods of calculating and / or suggesting the maximal value of stimulation parameter are based on the safety concept of a magnetic stimulation device for treatment of a biological structure by a high power time-varying magnetic field. The safety concept protects the patient. The methods may be used e.g. in physiotherapy, psychotherapy, psychiatry or aesthetic medicine applications.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Method for generating anatomical M-mode displays
InactiveUSRE37088E1Improve anatomical information content in M-ModeImproving visual interpretabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationData set
A method for generating anatomical M-Mode displays for ultrasonic investigation of living biological structures during movement of the structure, for example a heart function, employing an ultrasonic transducer (21) comprises the acquisition of a time series of 2D or 3D ultrasonic images (22), arranging said time series so as to constitute data sets, providing at least one virtual M-Mode line (23) co-registered with said data sets, subjecting said data sets to computer processing on the basis of said at least one virtual M-Mode line, whereby interpolation along said at least one virtual M-Mode line is effected, and displaying the resulting computed anatomical M-Mode display (24) on a display unit.
Owner:VINGMED SOUND
High power time varying magnetic field therapy
ActiveUS20170120067A1High repetition rateIncrease muscle strengthElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsUrediniomycetidaeMuscle contraction
In a method for stimulation and treatment, a biological structure is stimulated by a high power time-varying magnetic field. The stimulation is followed by at least a partial muscle contraction. The methods can be used e.g. in physiotherapy, urology or urogynaecology.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
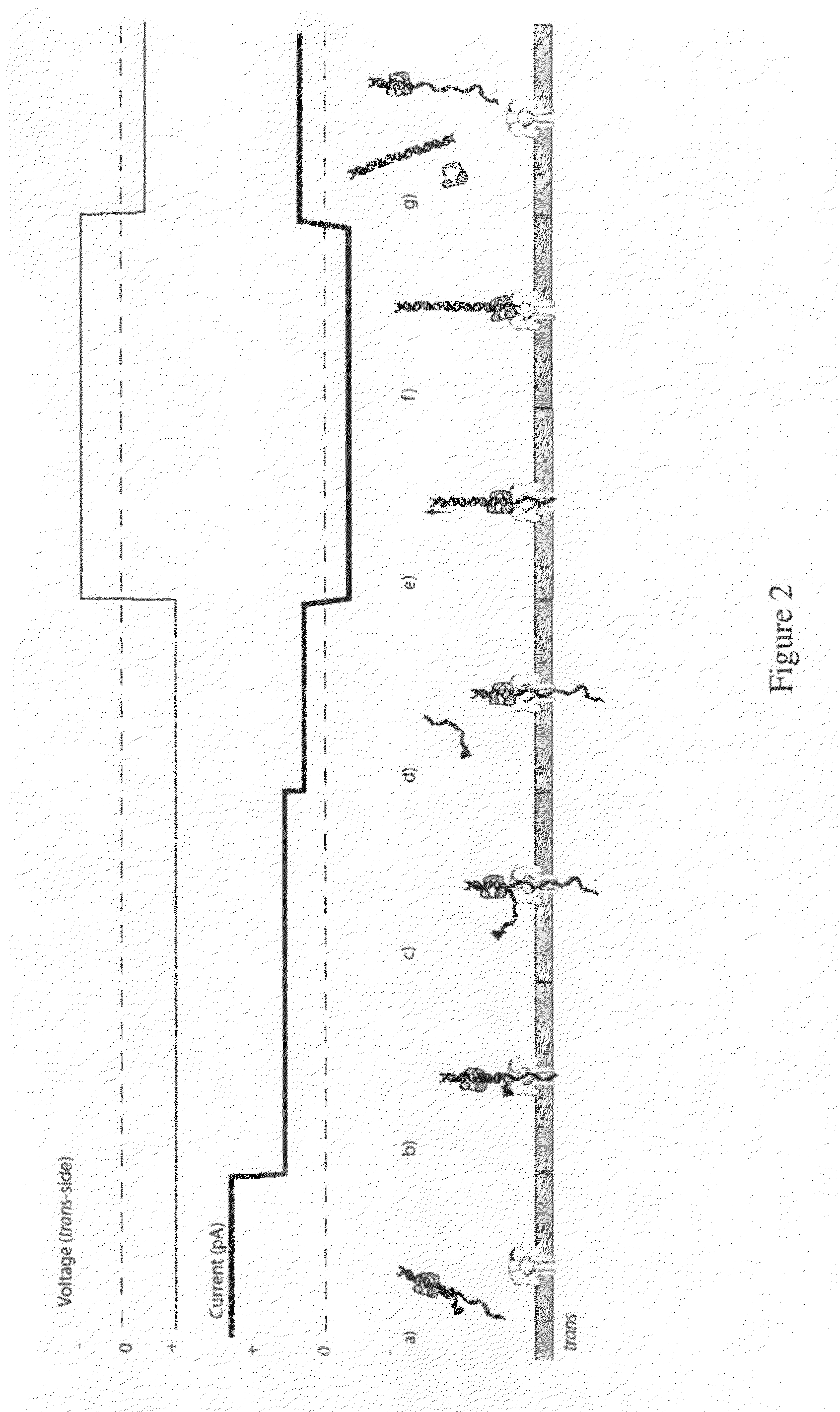
Control of DNA movement in a nanopore at one nucleotide precision by a processive enzyme
InactiveUS20140051068A1Improve the activity rateReduce decreaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore. Of particular note is the stability of the system in a saline medium and to detect individual nucleotide bases in a polynucleotide in real time and which may be used to sequence DNA for many hours without change of reagents. The invention is of particular use in the fields of forensic biology, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Protecting biological structures, including the great vessels, particularly during spinal surgery
InactiveUS20050126576A1Improve barrier propertiesAvoid formingRestraining devicesSurgeryIntracranial surgeryThoracic bone
Natural and / or synthetic materials to form a strong barrier between the skeletal system and the great vessels. In the preferred embodiments, a natural or synthetic material is used to prevent scar tissue from forming around the vessels and / or to act as barrier placed between the vessels and the skeletal system, including the spine. Devices according to the invention may also be used over the dura and nerves following laminectomy procedures, between the sternum and the pericardium or heart following cardiac procedures, in intra-abdominal procedures such as intestinal or vascular surgery, over the brain in intra-cranial surgery, over the ovaries or other organs or tissues in the female genitourinary system, over the prostate or other organ or tissues in the male genitourinary system, or in other surgeries on humans or animals.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
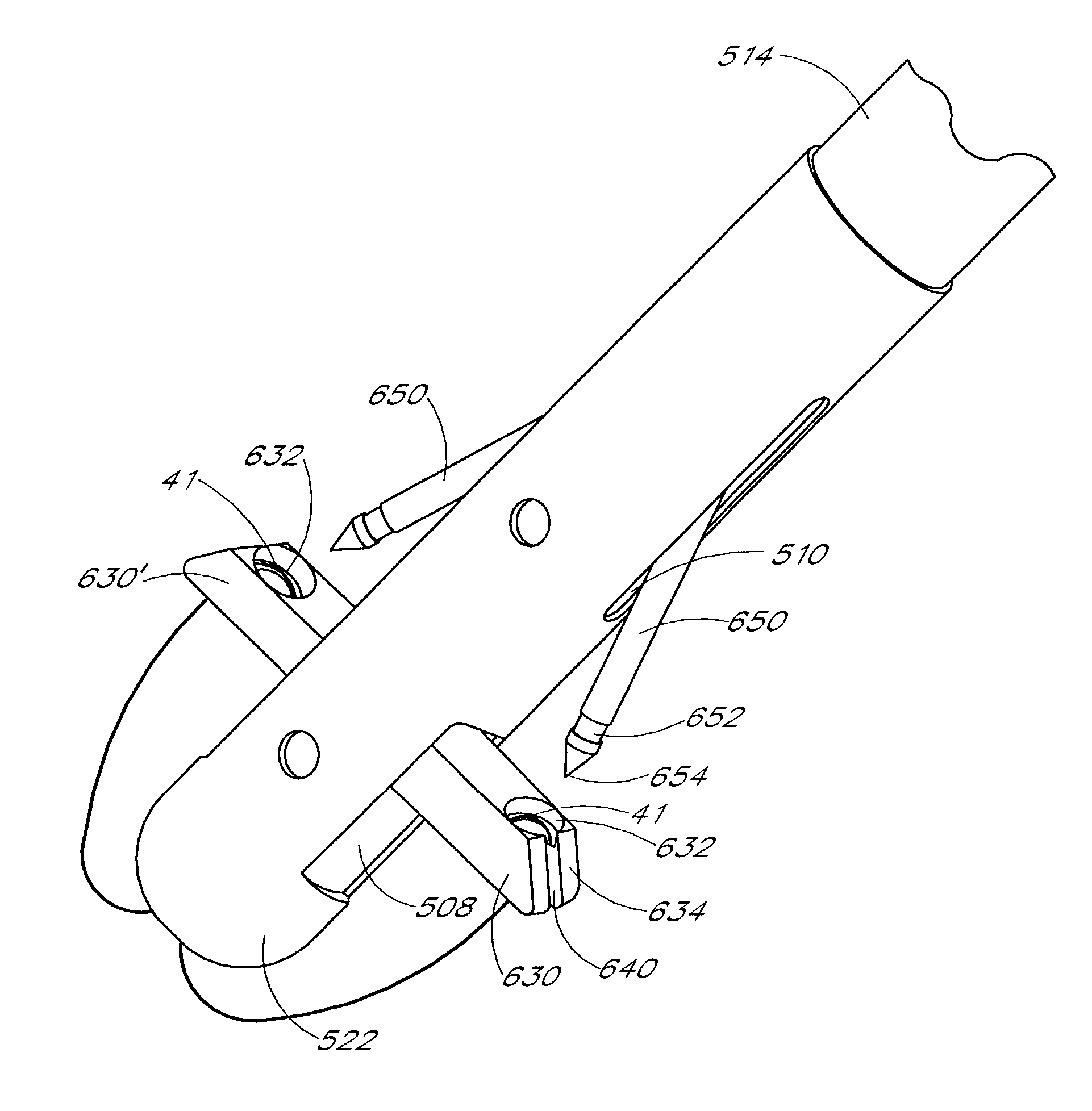
Fluid delivery and extraction device and method
A fluid delivery and extraction device enables the remote transfer of fluid to or from biological tissue. The device comprises an elongated member, a syringe movable relative to the elongated member and a pair of hypodermic needles movable relative to the elongated member. The elongated member has a distal portion which is adapted to be inserted into a biological structure. A steer wire or guide wire can be used to navigate the distal portion within cavernous biological structures, particularly body lumens. The distal portion has at least one retractable hypodermic needle that is configured to pierce the interior surface of a tubular biological structure and transfer fluid to or from the walls of the tubular biological structure. A physician can use a handle or other control mechanism provided at a proximal portion of the device to remotely move the hypodermic needles. A plunger can be used to transfer fluid through the hypodermic needles to or from the syringe. In operation, the hypodermic needles are deployed simultaneously or individually from the distal portion of the device. As the hypodermic needles move, they pierce the interior surface of the tubular biological structure. The hypodermic needles can also be configured to pass beyond the exterior surface of the tubular biological structure. The plunger is then used to transfer fluid either from the syringe to the patient or from the patient to the syringe. The hypodermic needles are then moved back to their retracted positions within the distal portion, and the device is withdrawn from the patient's body.
Owner:SUTURA
Low peak exotherm curable compositions
InactiveUS20050020696A1Surgical adhesivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesBiological structureDiluent
Compositions having a curable unsaturated compound, an adhesion promoter and curing agent which have a peak exotherm of less than 50° C. are disclosed. The compositions when cured are flexible bioadhesives which are also disclosed. Non-curable diluents can be included in the compositions. Flexible bioadhesives formed on biological structures and having low peak exotherms upon curing of curable compositions to form the flexible bioadhesives are disclosed. Compositions having a curable unsaturated compound and a curing agent and a peak exotherm of less than 50° C. are included in the invention.
Owner:MONTGOMERY ROBERT ERIC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com