Method for generating anatomical M-mode displays
a technology of anatomical mmode and display screen, which is applied in the field of generating anatomical mmode displays, can solve the problems of difficult manual compensation, difficult to find, and scarce windows, and achieve the effect of improving the visual interpretability of relative motion/thickening phenomena and improving the analysis of wall thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
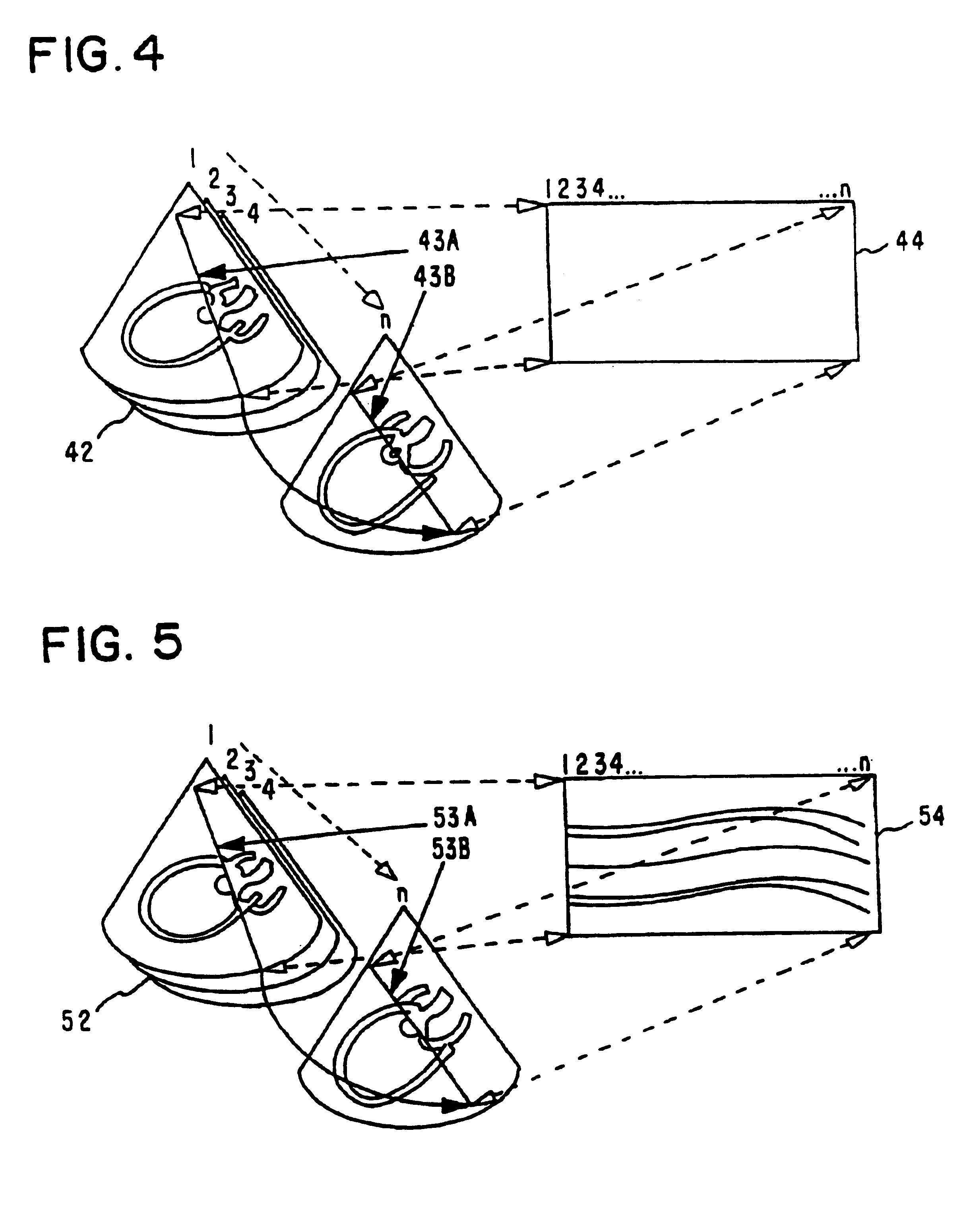
FIG. 1 illustrates conventional M-Mode imaging. An ultrasound transducer 11 is schematically indicated in relation to an ultrasonic image 12 obtained by angular scanning of the acoustical beam of the transducer. In this conventional method by the M-Mode line or corresponding acoustical beam 13 is fixed at a given position and the ultrasonic signal along the beam is mapped as a function of time in the M-Mode display 14. Extreme temporal resolution can be achieved with this prior art because a new time sample can be generated as soon as the data for one beam has been gathered. This prior art for M-Mode imaging will on the other hand limit the positioning of the M-Mode line 13 according to the acoustic windows and scanning geometry.
TILTED M-MODE LINES
This invention relates to how M-Mode images can be generated by extraction of interpolated displays from time series of 2D or 3D images. The concept of a "tilted" M-Mode display 24 is illustrated in FIG. 2. The "virtual" M-Mode line 23 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com