Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Structural biology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Structural biology is a branch of molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics concerned with the molecular structure of biological macromolecules (especially proteins, made up of amino acids, RNA or DNA, made up of nucleotides, membranes, made up of lipids) how they acquire the structures they have, and how alterations in their structures affect their function. This subject is of great interest to biologists because macromolecules carry out most of the functions of cells, and it is only by coiling into specific three-dimensional shapes that they are able to perform these functions. This architecture, the "tertiary structure" of molecules, depends in a complicated way on each molecule's basic composition, or "primary structure."
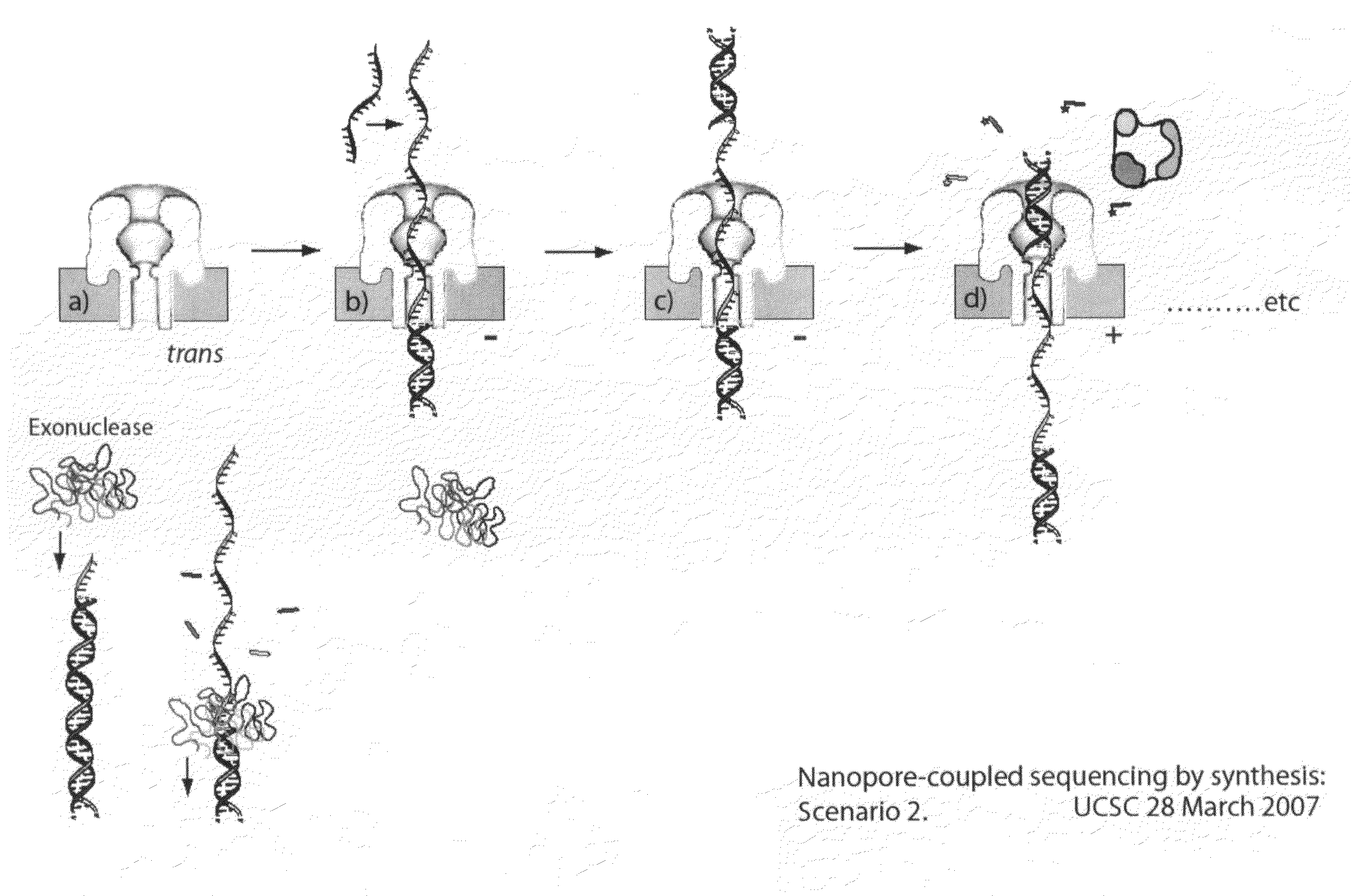
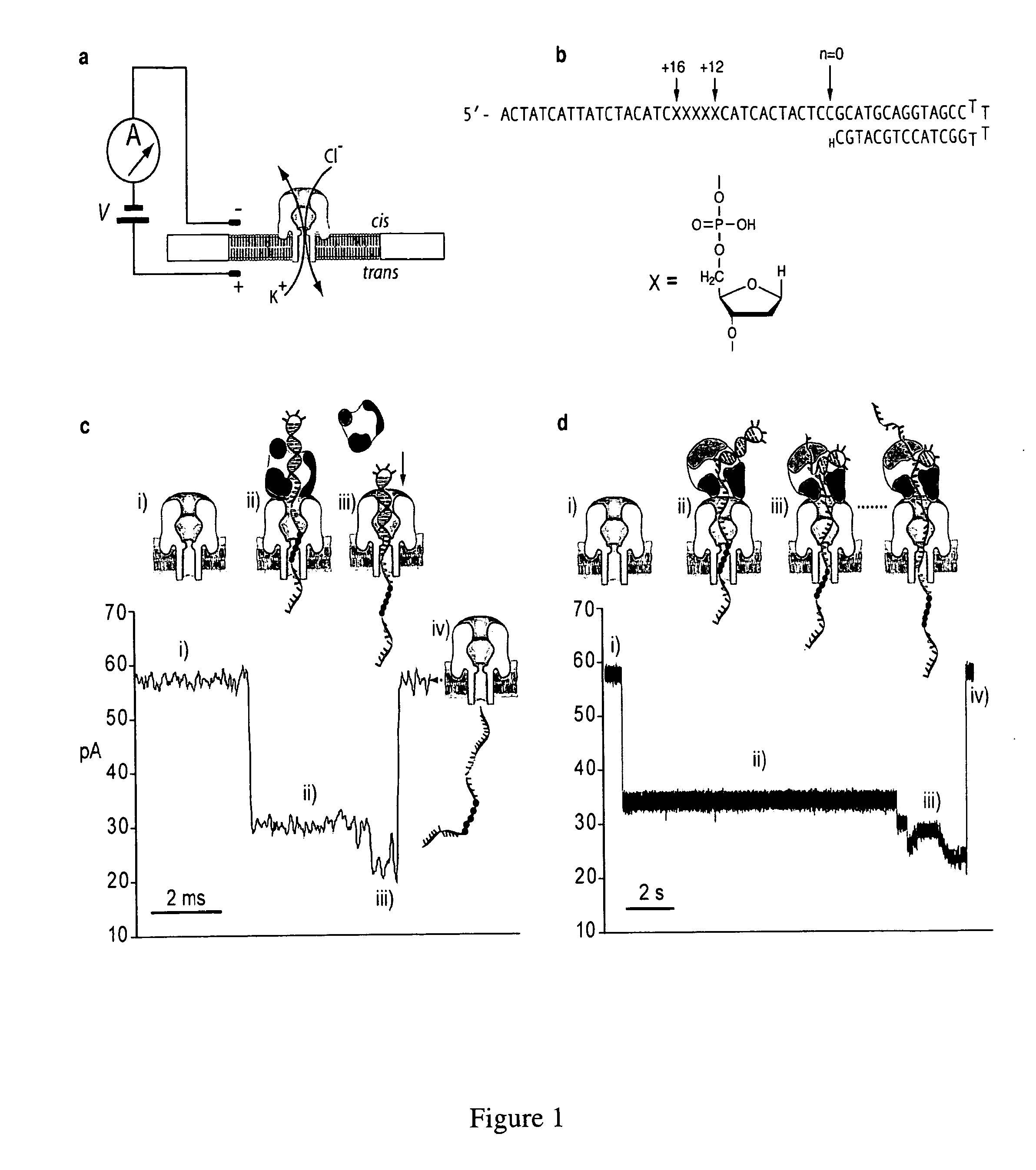
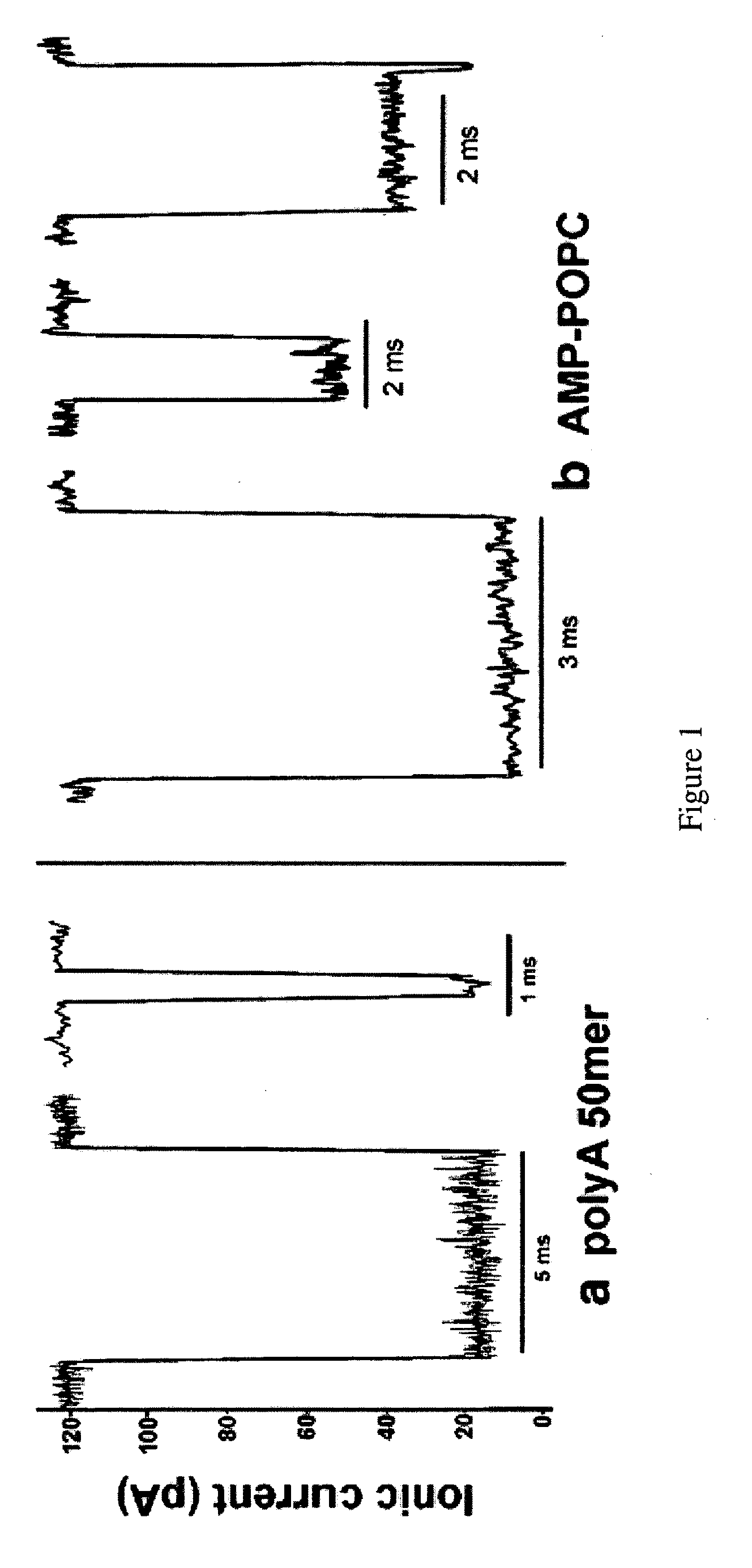
Compositions, devices, systems, for using a Nanopore
ActiveUS20100035260A1Low costRapidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
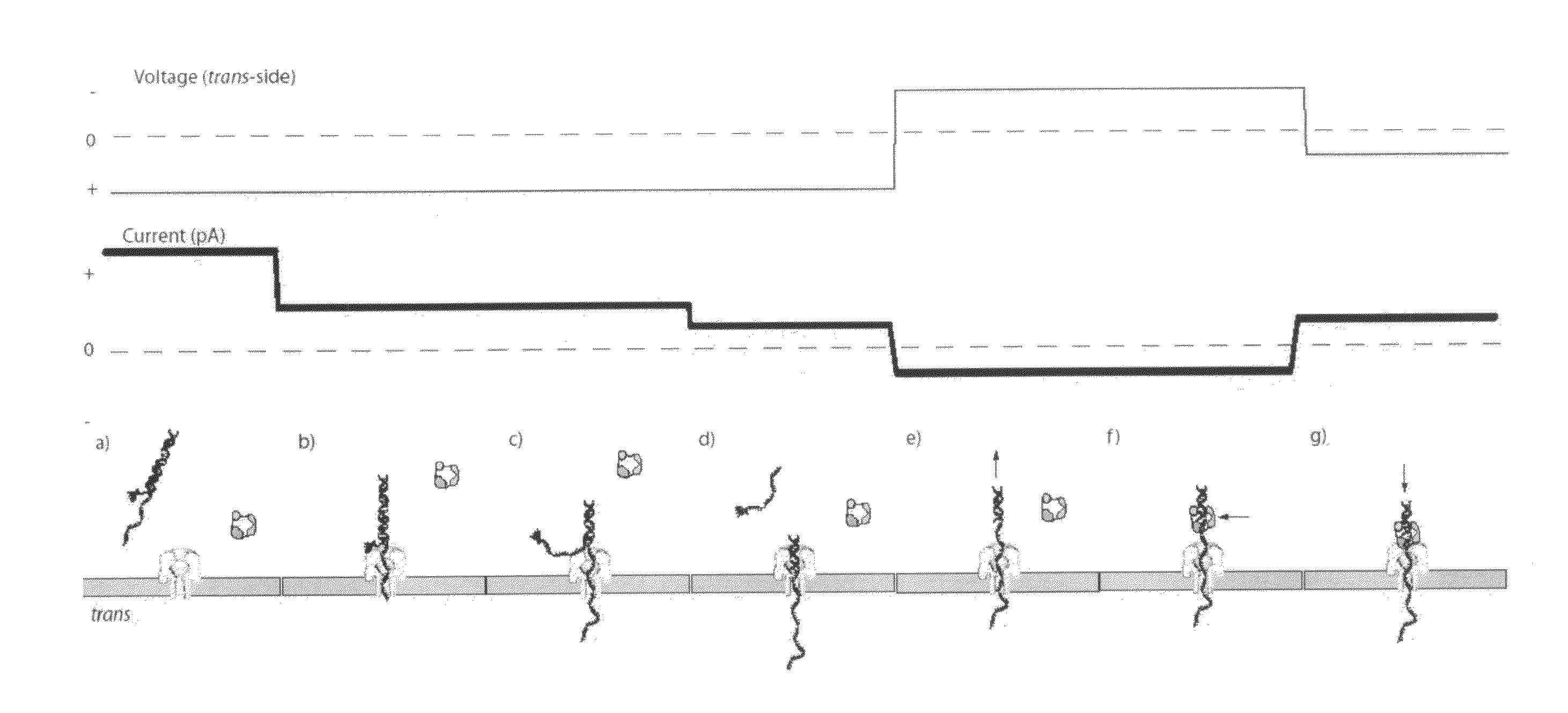
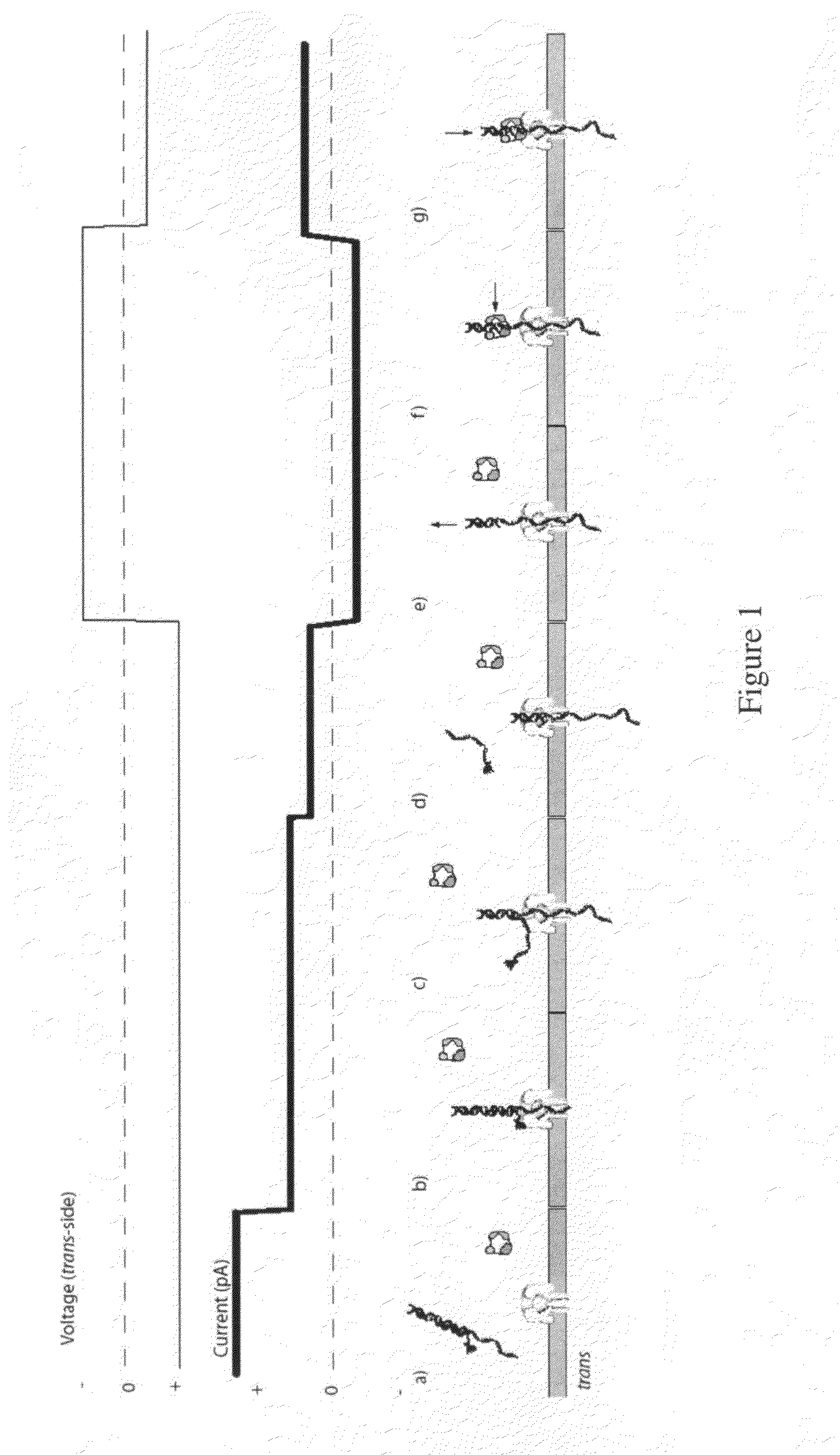
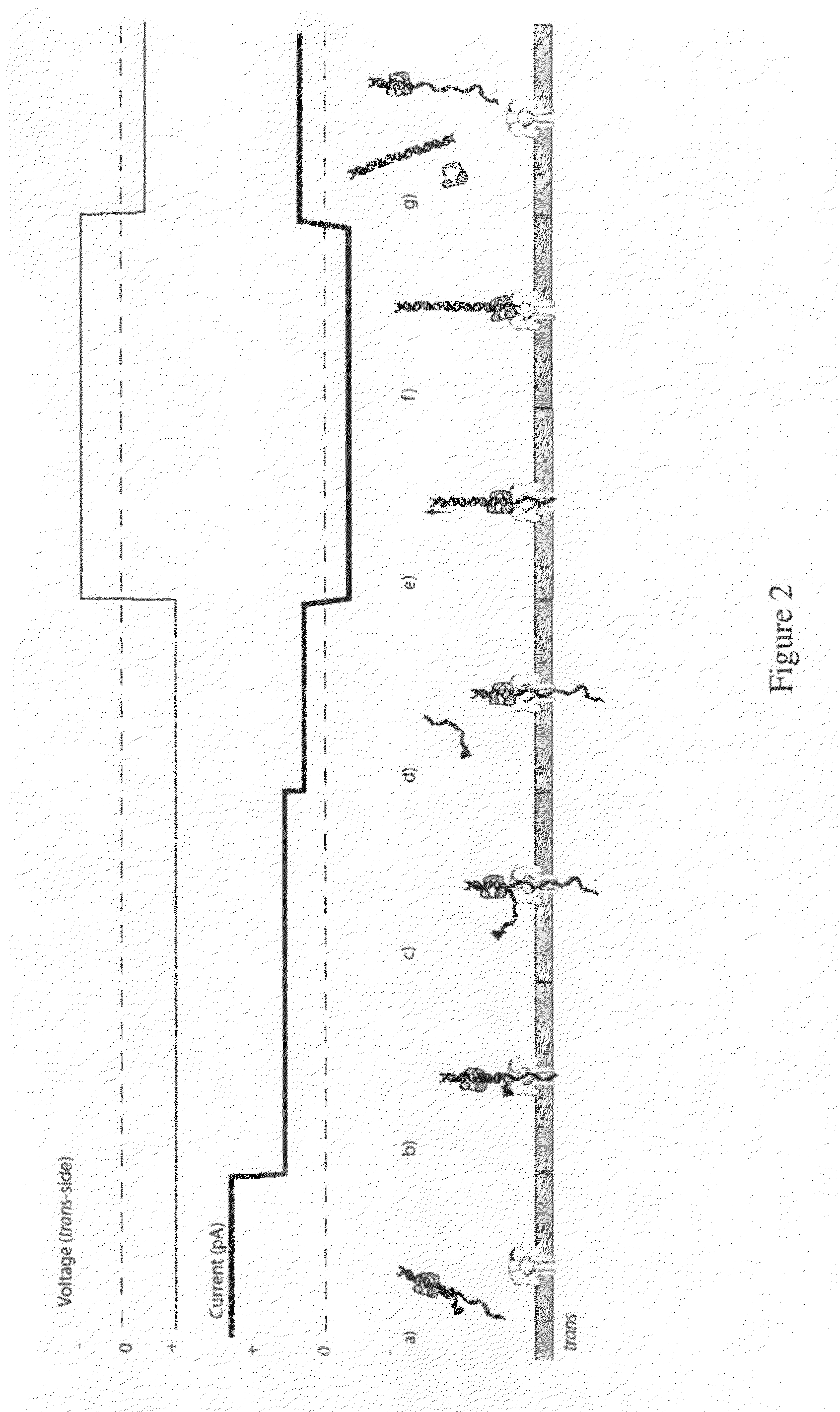
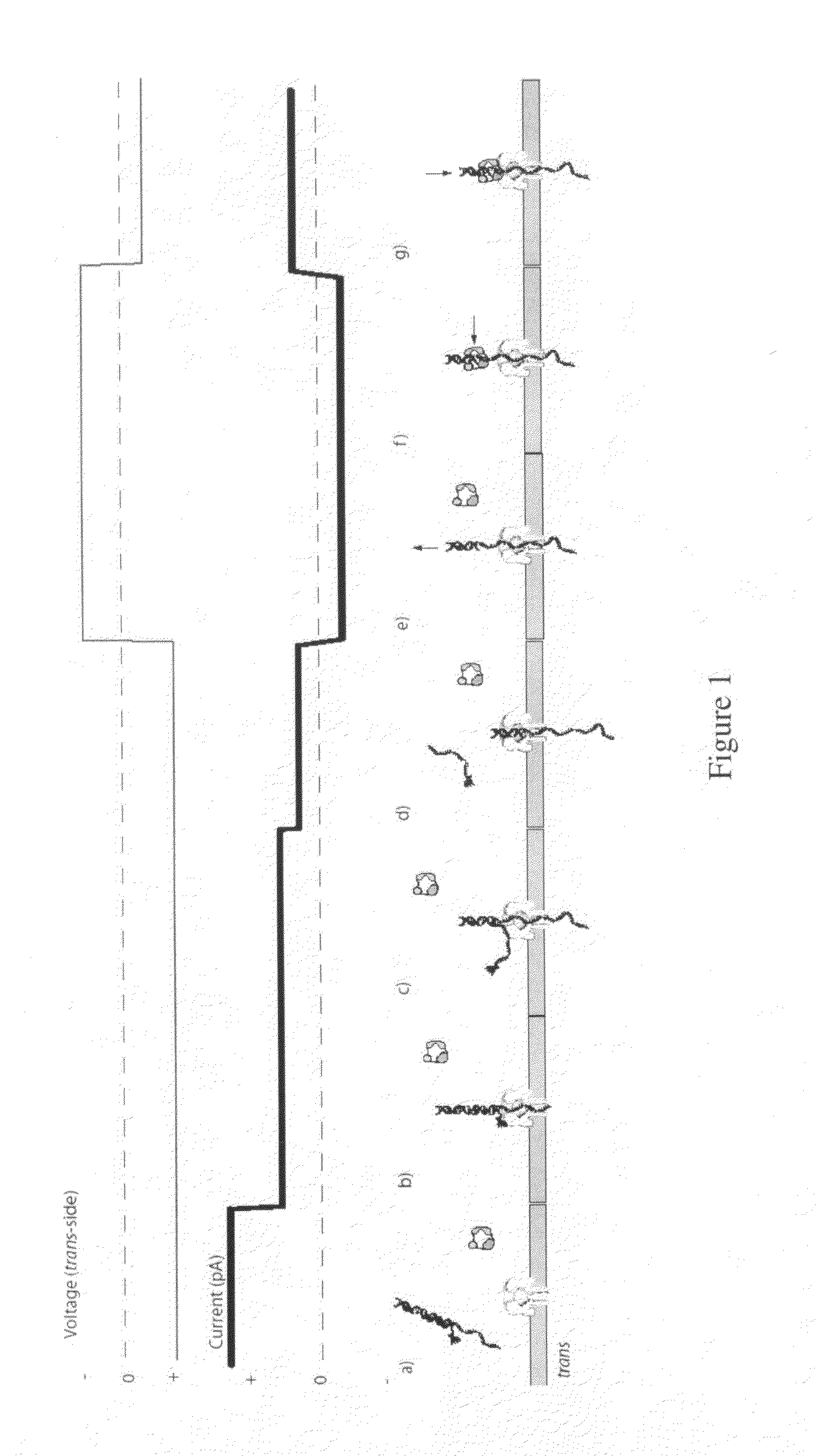
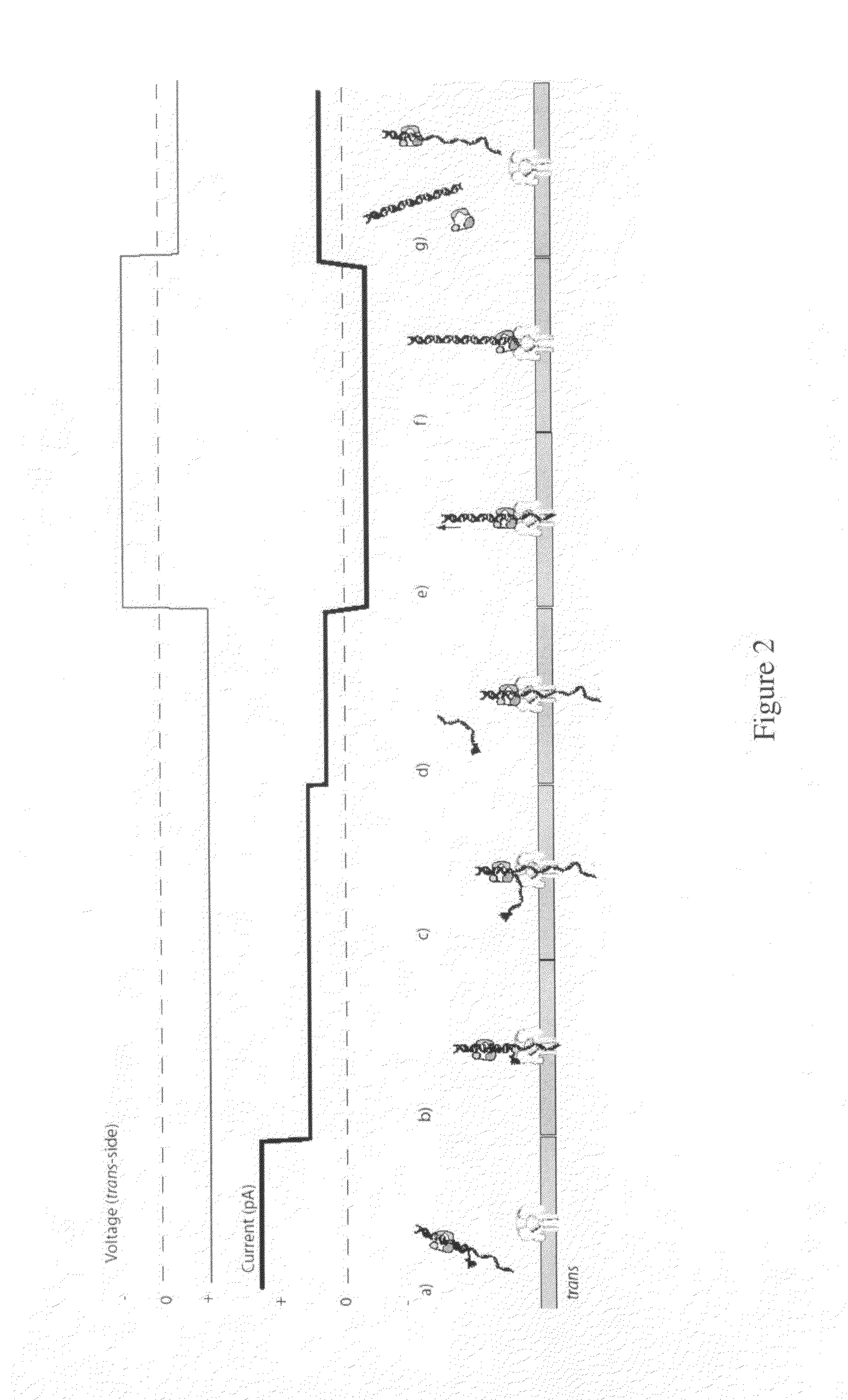
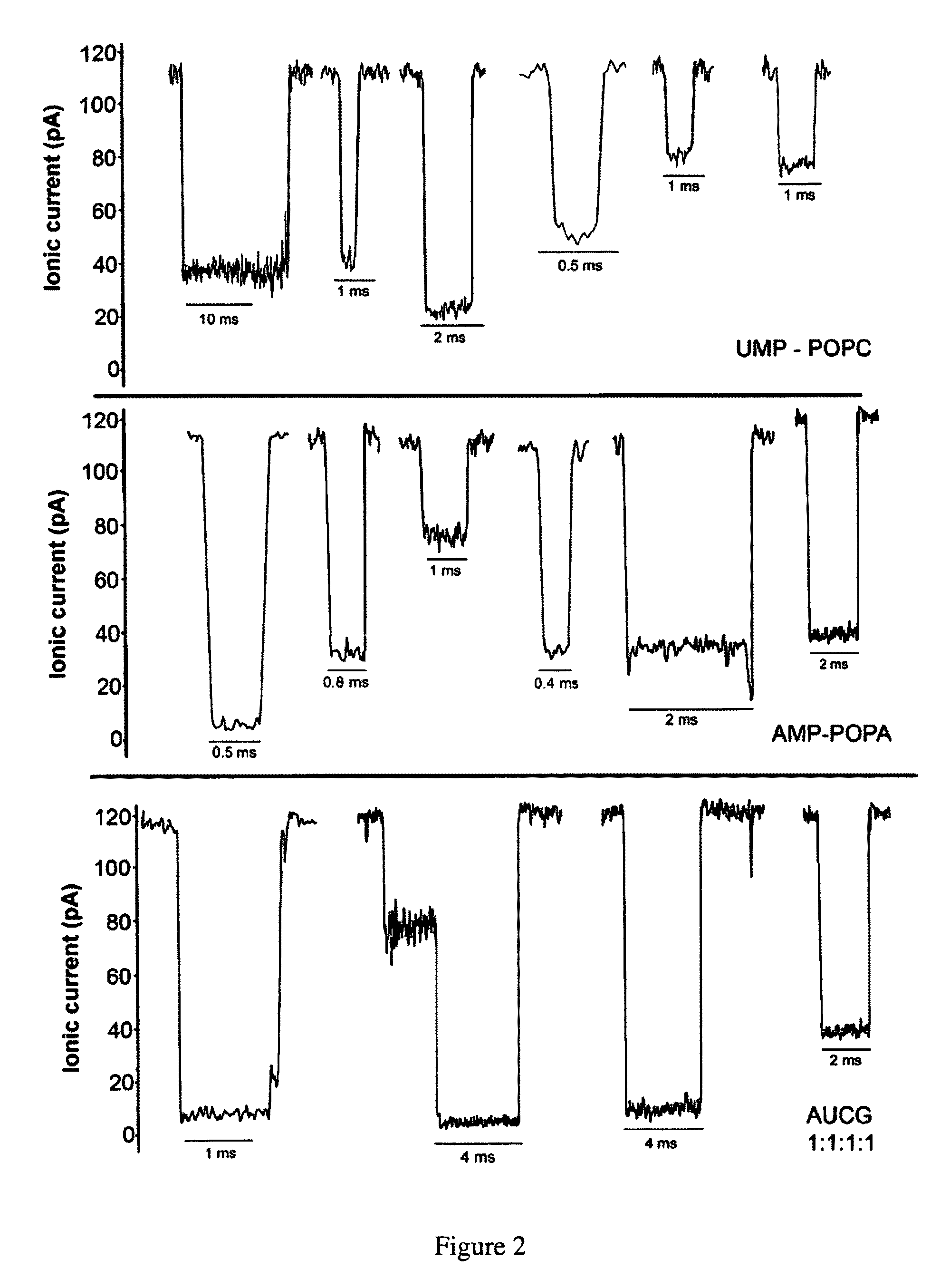
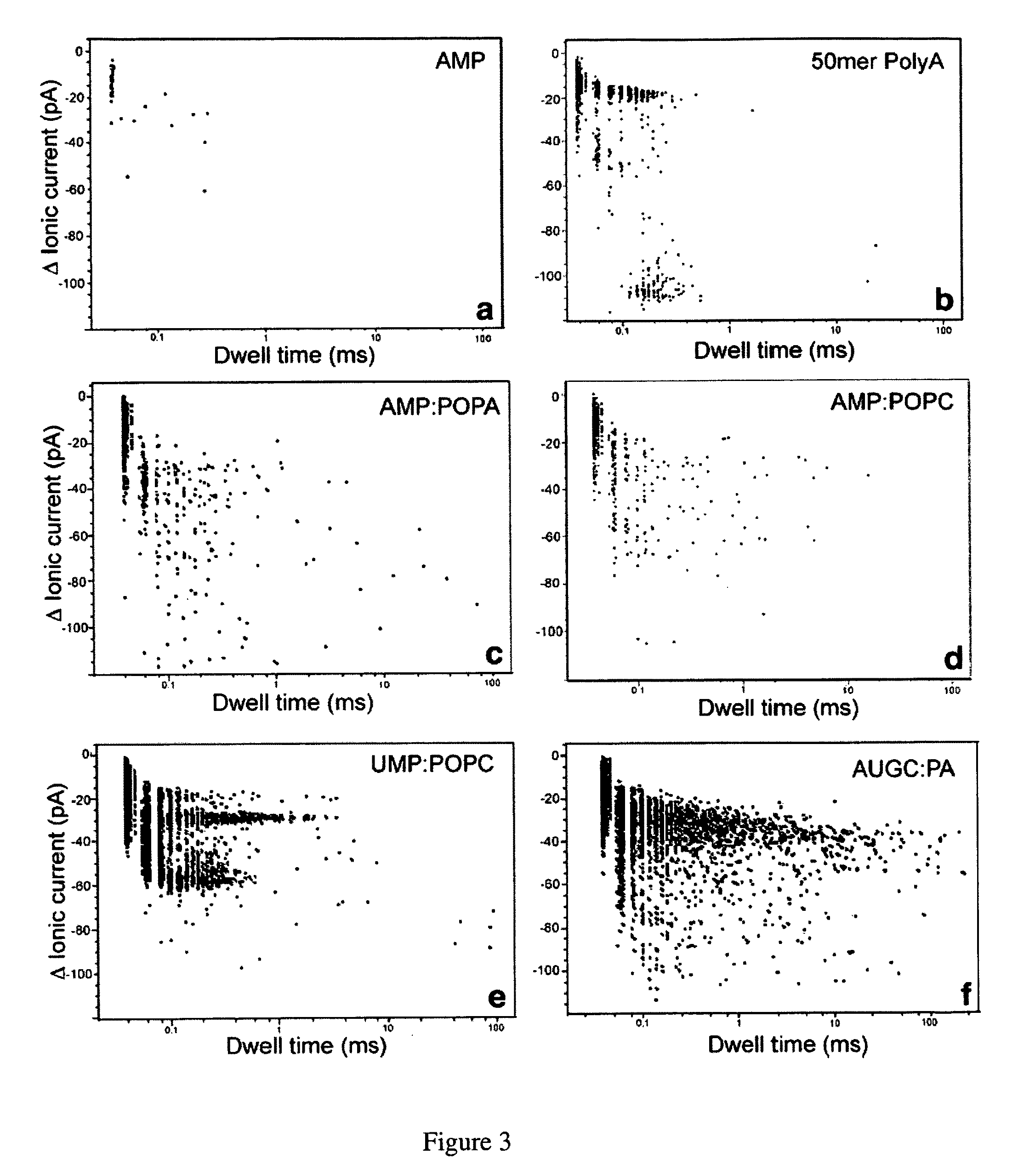
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore in the absence of requiring a terminating nucleotide. The devices and methods are also used to determine rapidly (˜>50 Hz) the nucleotide base sequence of a polynucleotide under feedback control or using signals generated by the interactions between the polynucleotide and the nanopore. The invention is of particular use in the fields of drug discovery, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions, devices, systems, and methods for using a nanopore
InactiveUS20110005918A1Low costRapidityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore. The devices and methods are also used to determine rapidly (˜>50 Hz) the nucleotide base sequence of a polynucleotide under feedback control or using signals generated by the interactions between the polynucleotide and the nanopore. The invention is of particular use in the fields of molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
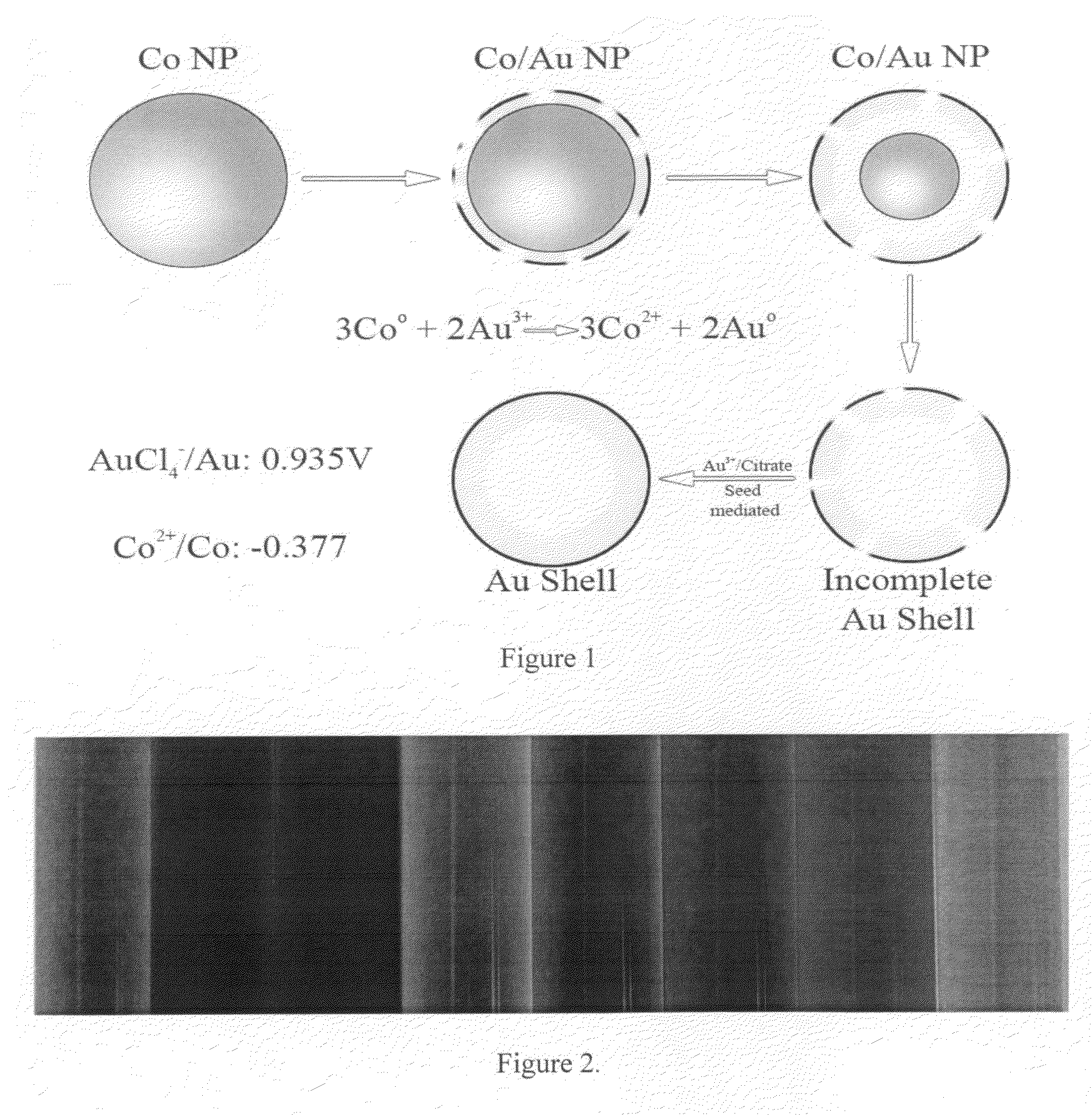
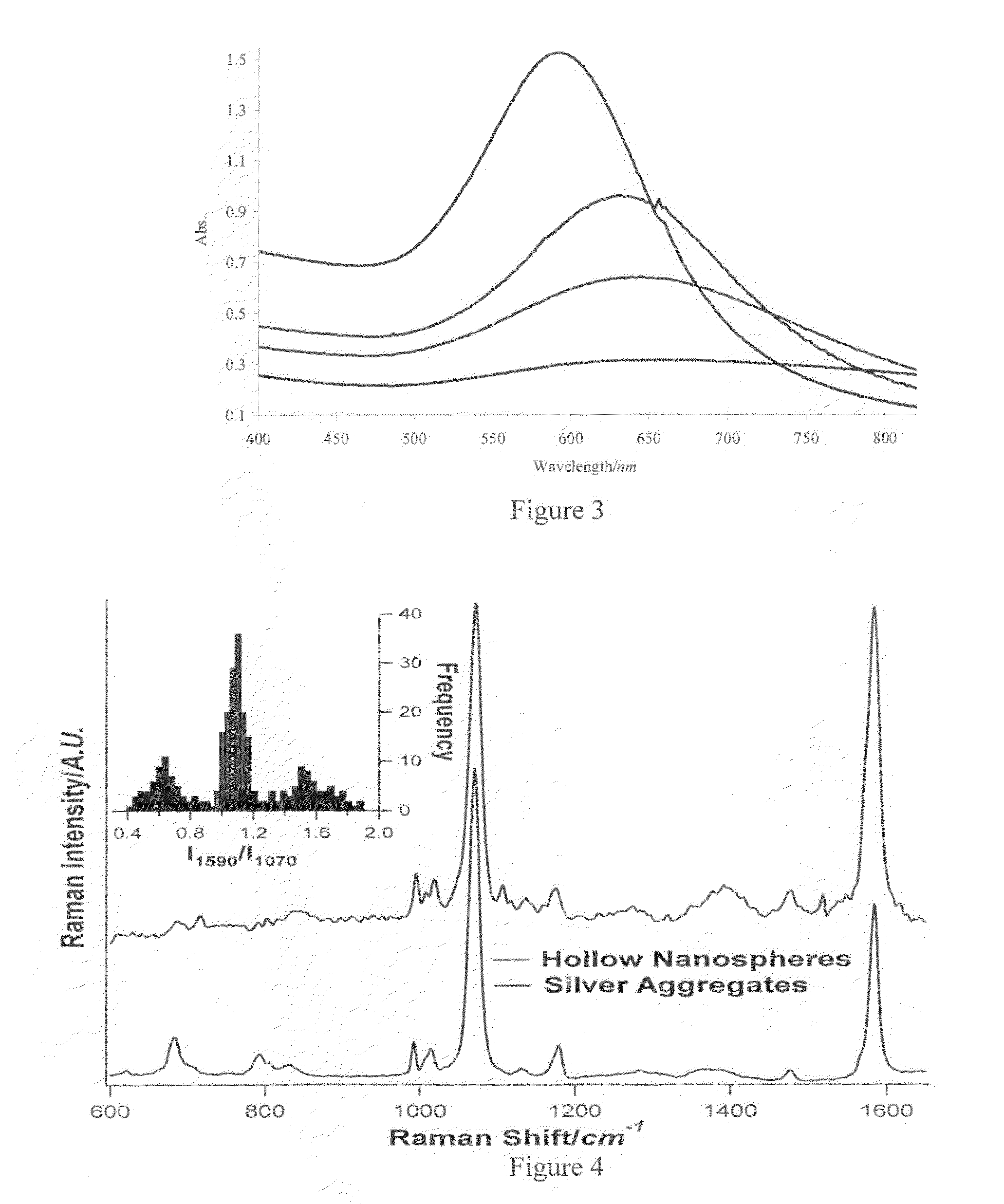
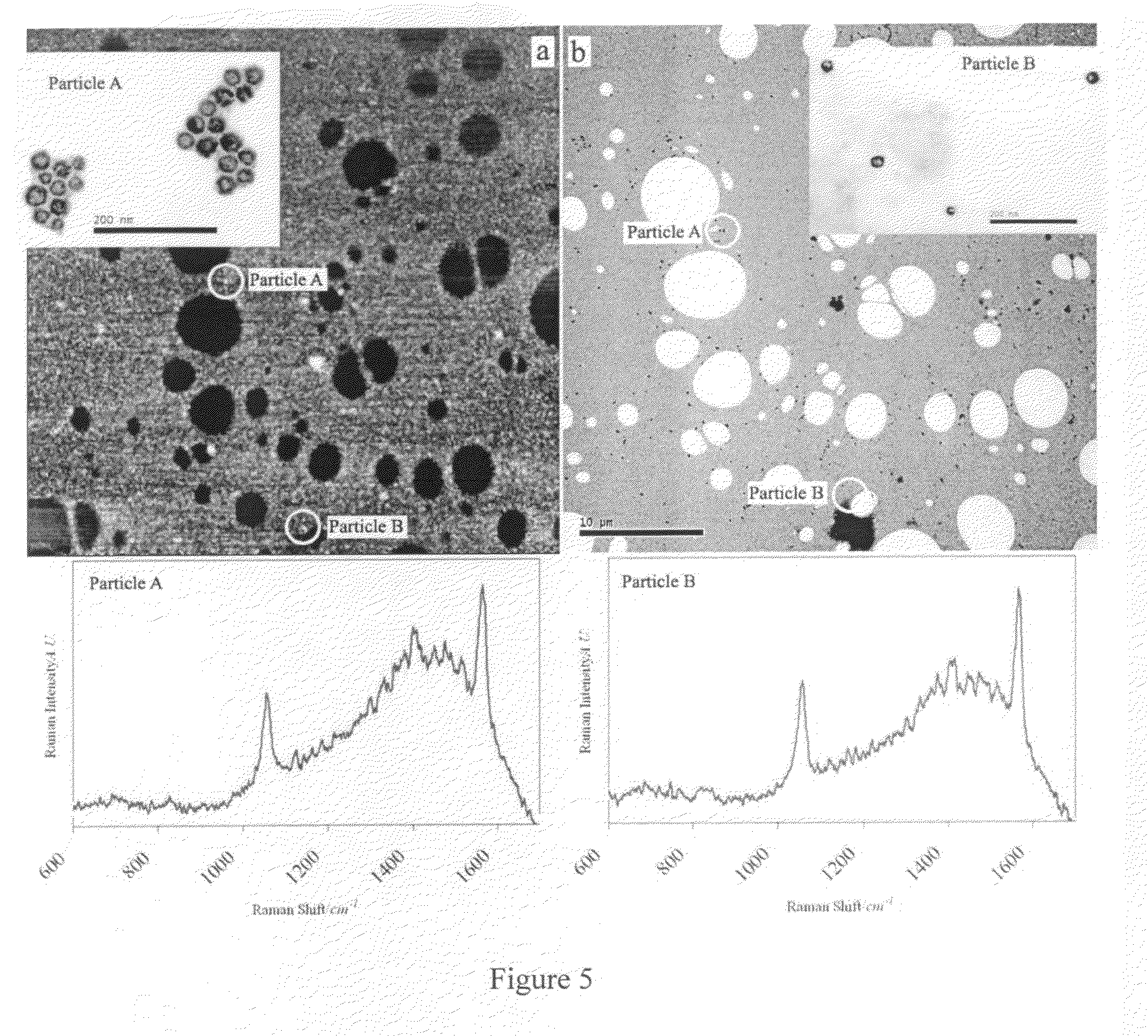
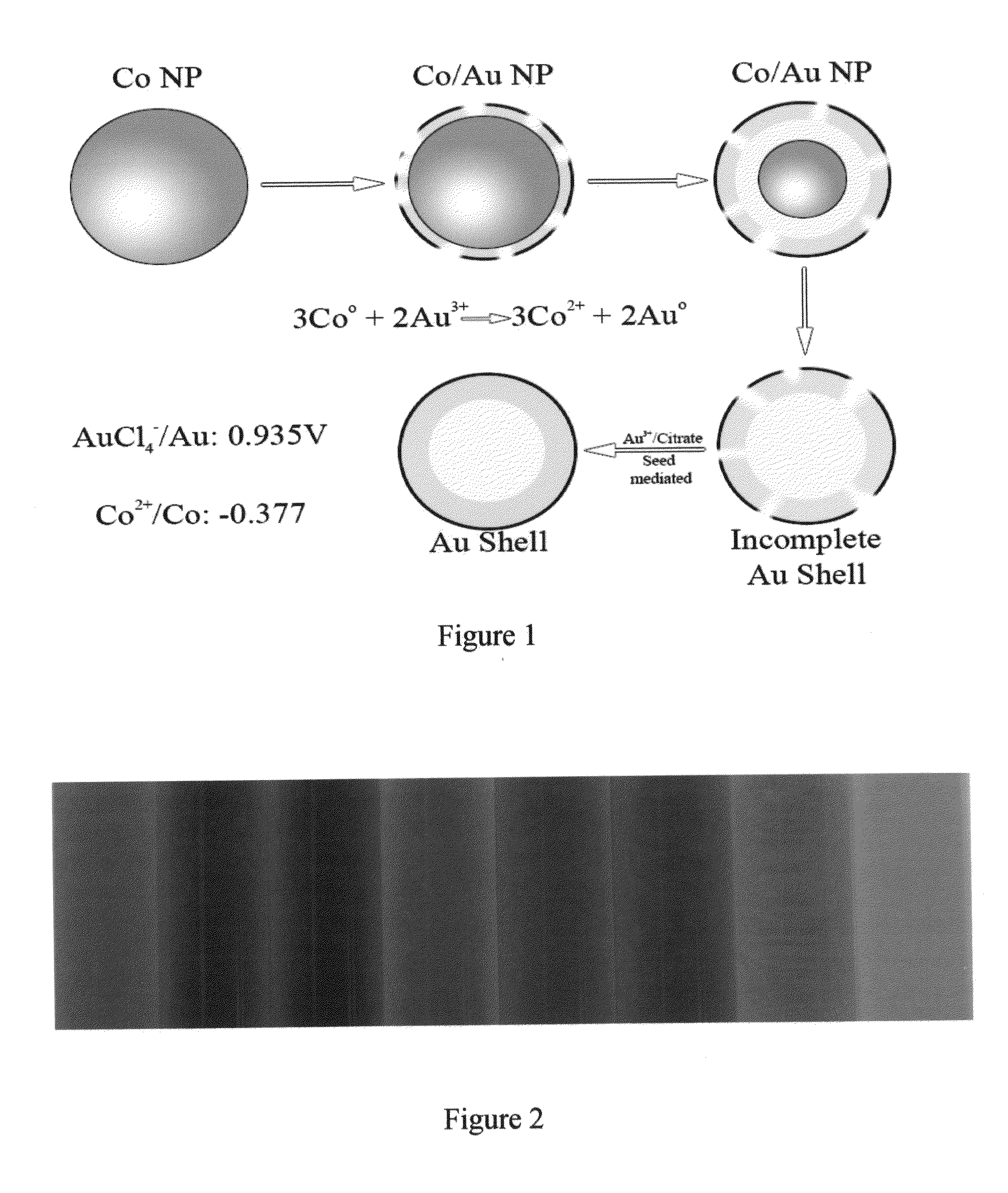
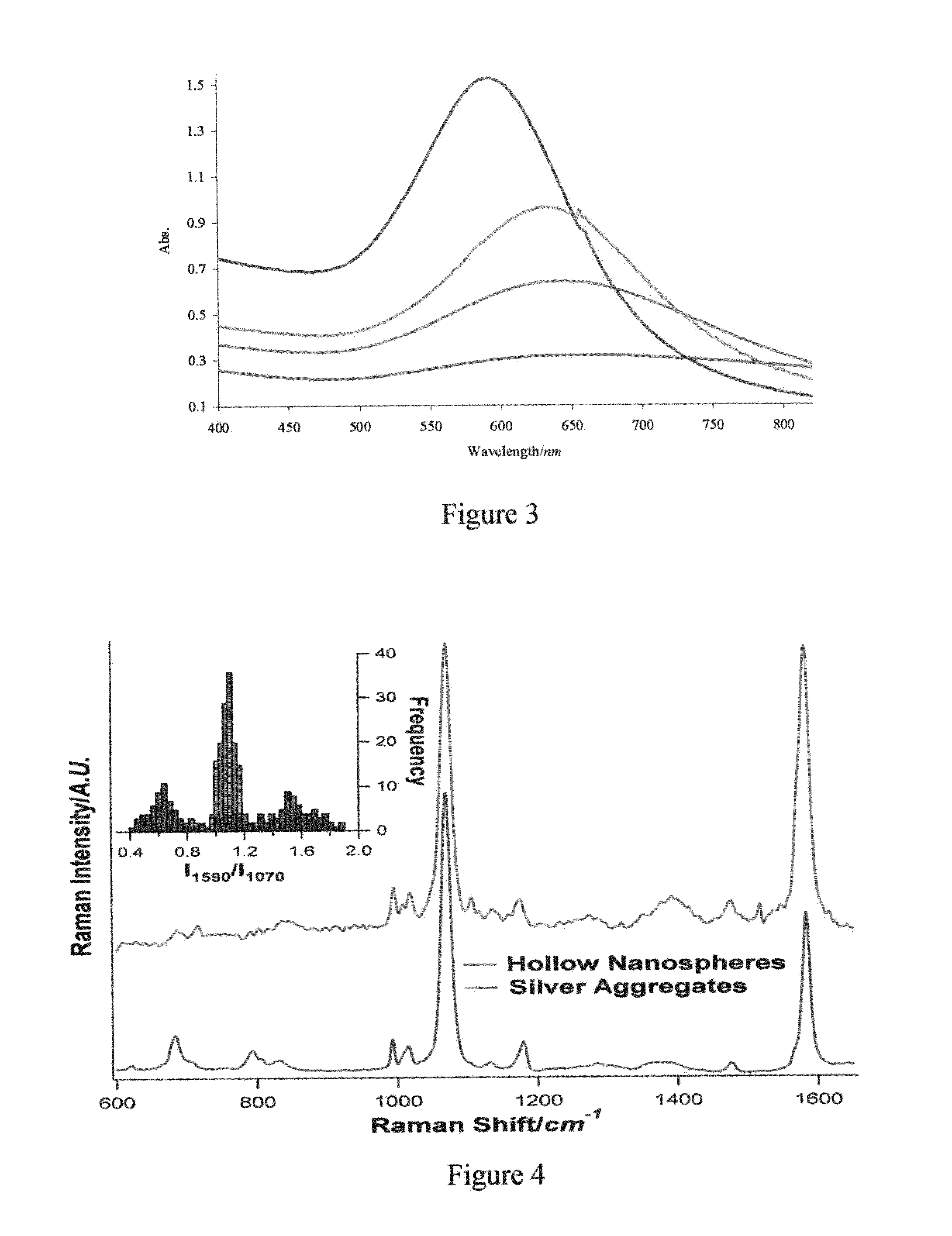
Targeted hollow gold nanostructures and methods of use
InactiveUS20090263485A1Easy to use detectionPowder deliverySynthetic resin layered productsSpherical shapedMolecular switch
Provided are novel nanostructures comprising hollow nanospheres and nanotubes for use as chemical sensors and molecular specific photothermal coupling agents. The nanostructures can be used in laser-induced phototherapy for treatment of cancer and other disorders. The nanostructures can also be used as a sensor that detects molecules. The nanostructures are of particular use in the fields of clinical diagnosis, clinical therapy, clinical treatment, and clinical evaluation of various diseases and disorders, manufacture of compositions for use in the treatment of various diseases and disorders, for use in molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof. The hollow gold nanospheres have a unique combination of spherical shape, small size, and strong, tunable, and narrow surface plasmon resonance absorption covering the entire visible to near IR region.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Control of DNA movement in a nanopore at one nucleotide precision by a processive enzyme
InactiveUS20140051068A1Improve the activity rateReduce decreaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural biologyMolecular switch
The invention herein disclosed provides for devices and methods that can detect and control an individual polymer in a mixture is acted upon by another compound, for example, an enzyme, in a nanopore. Of particular note is the stability of the system in a saline medium and to detect individual nucleotide bases in a polynucleotide in real time and which may be used to sequence DNA for many hours without change of reagents. The invention is of particular use in the fields of forensic biology, molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
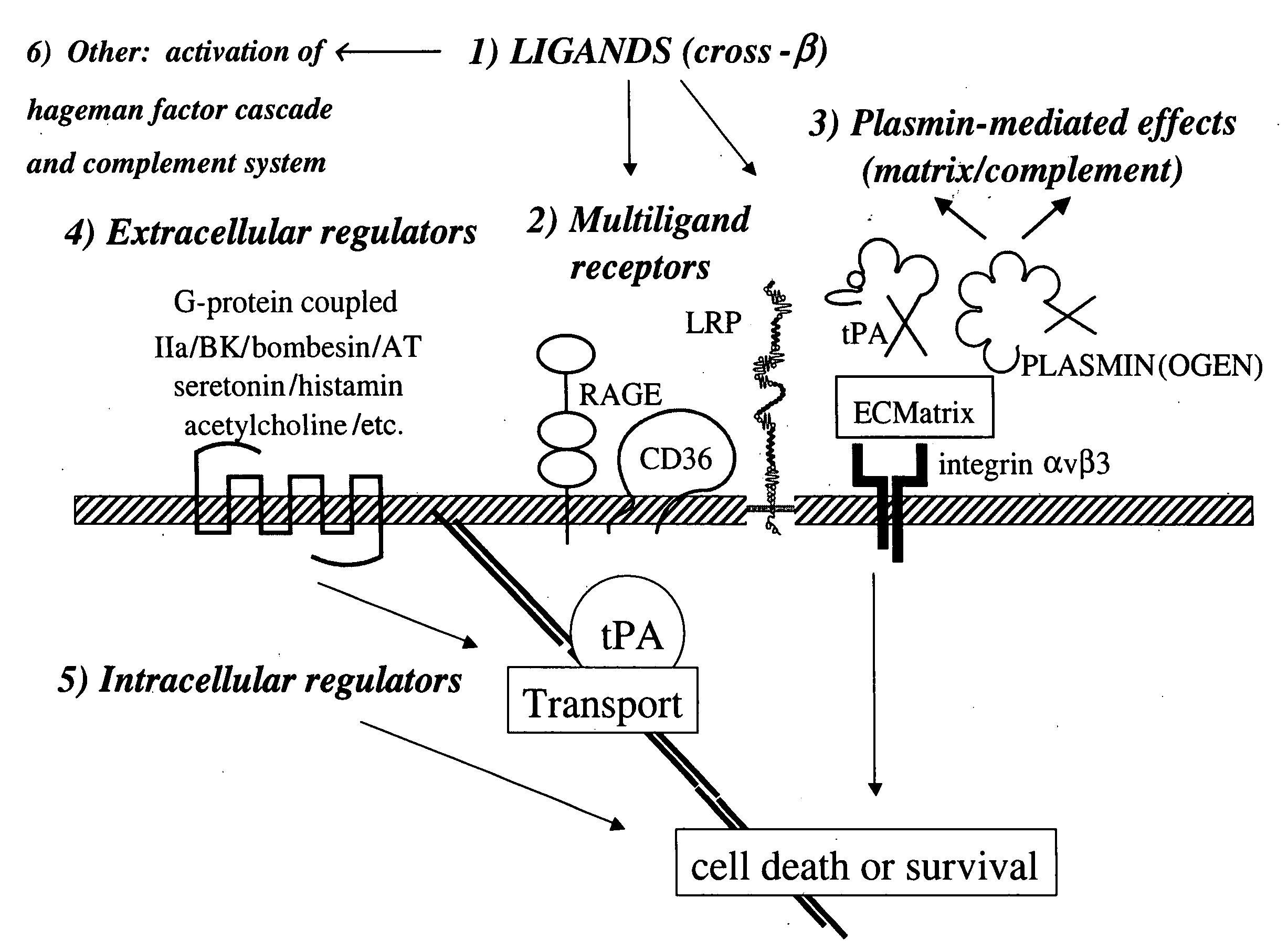
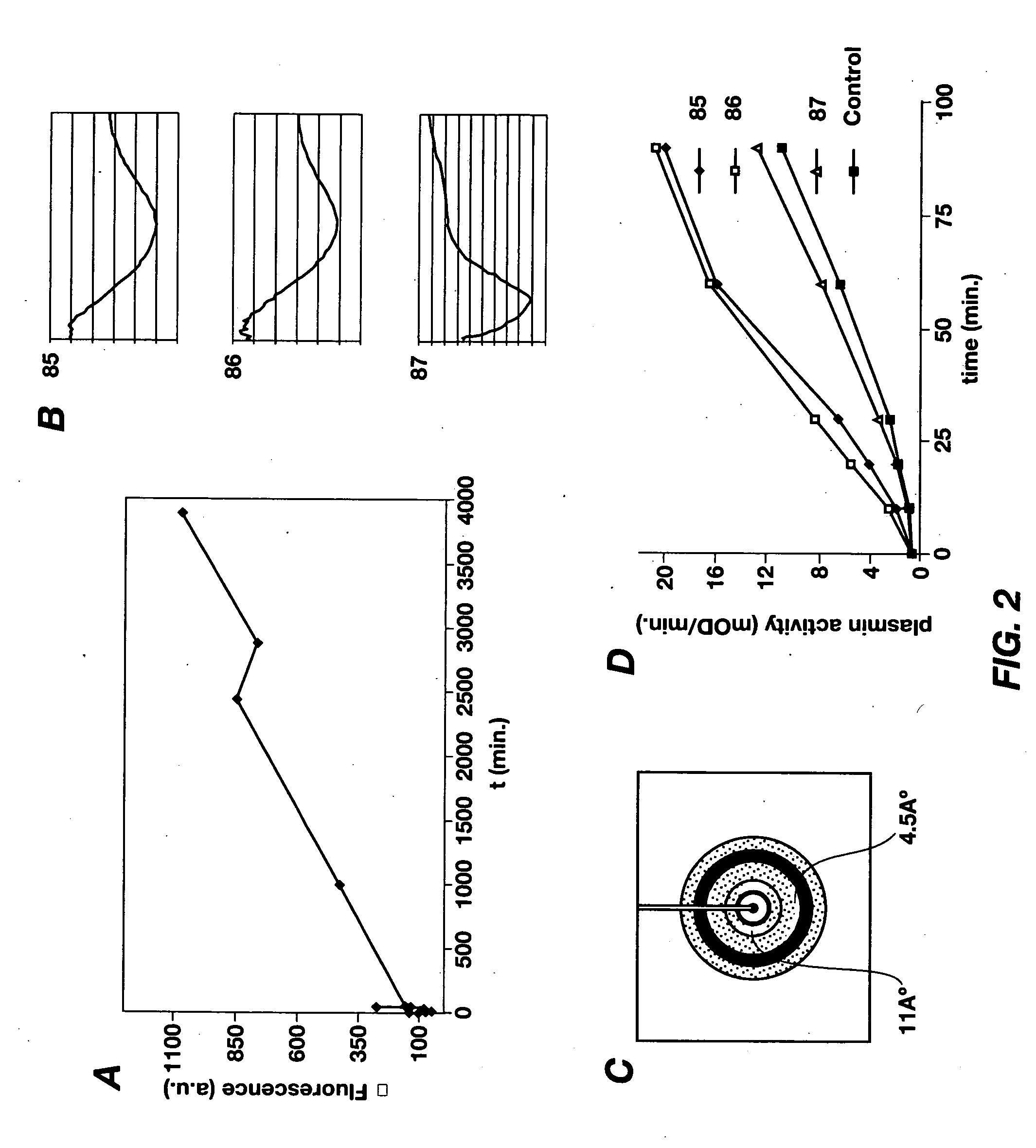
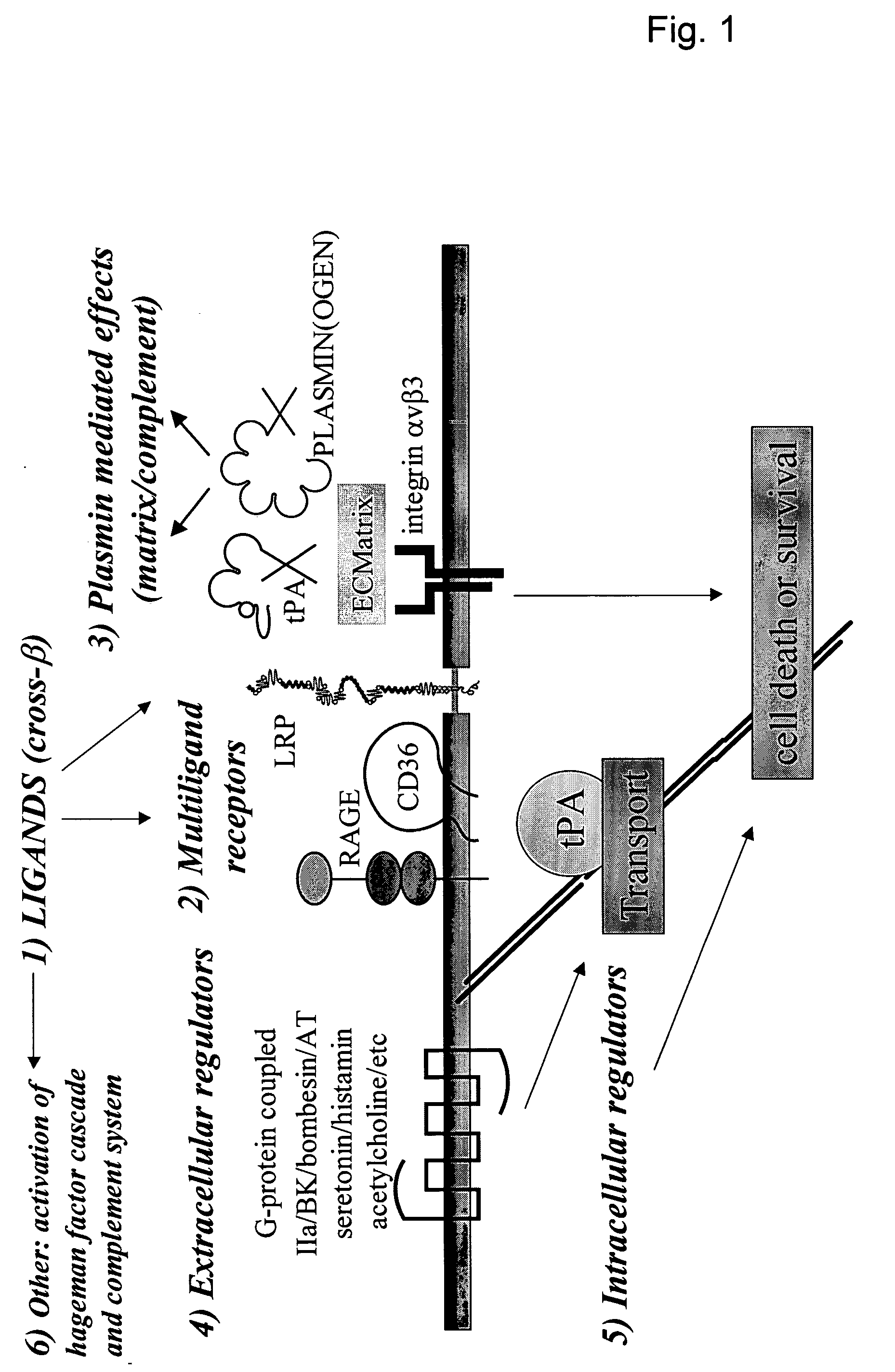
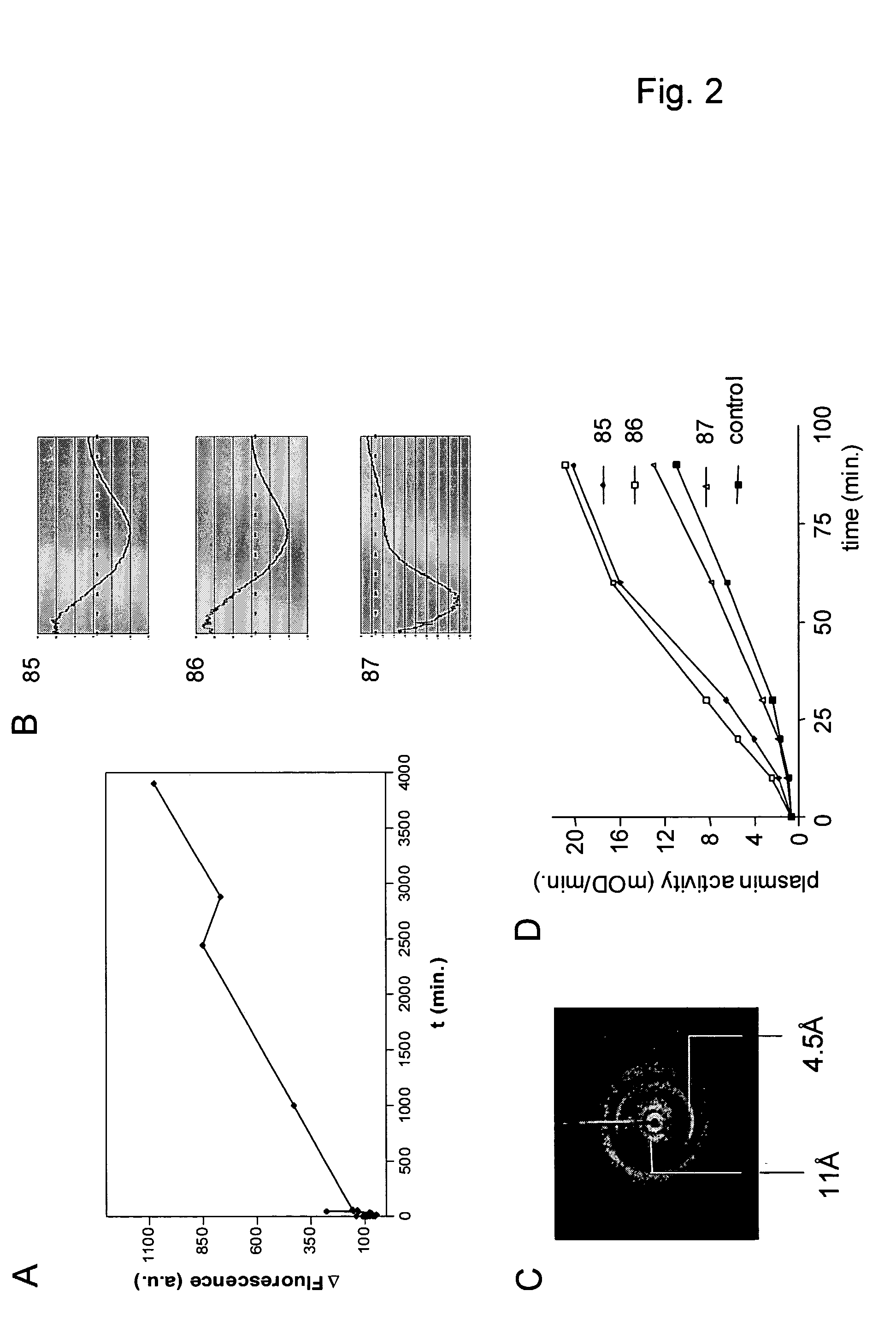
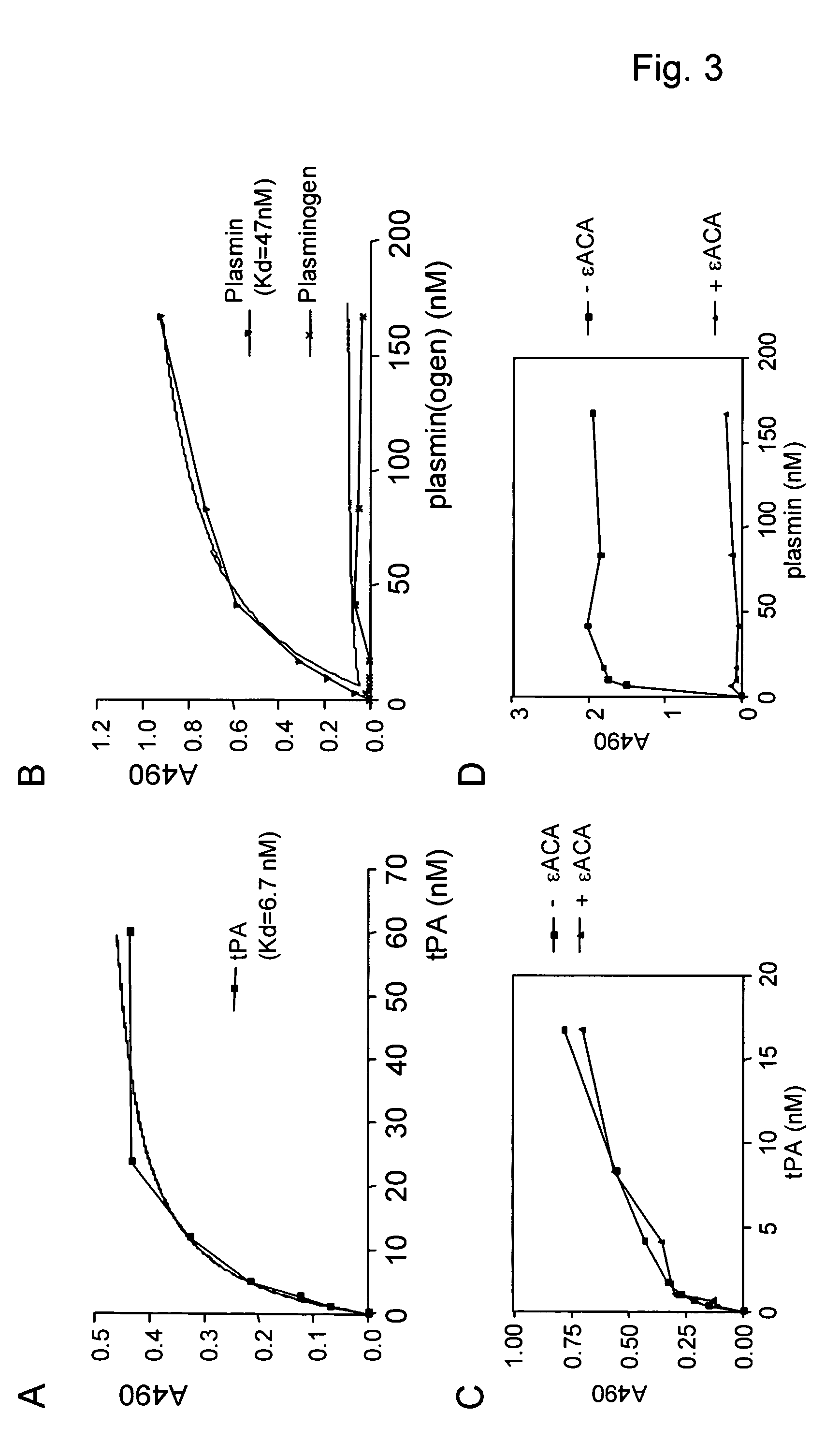
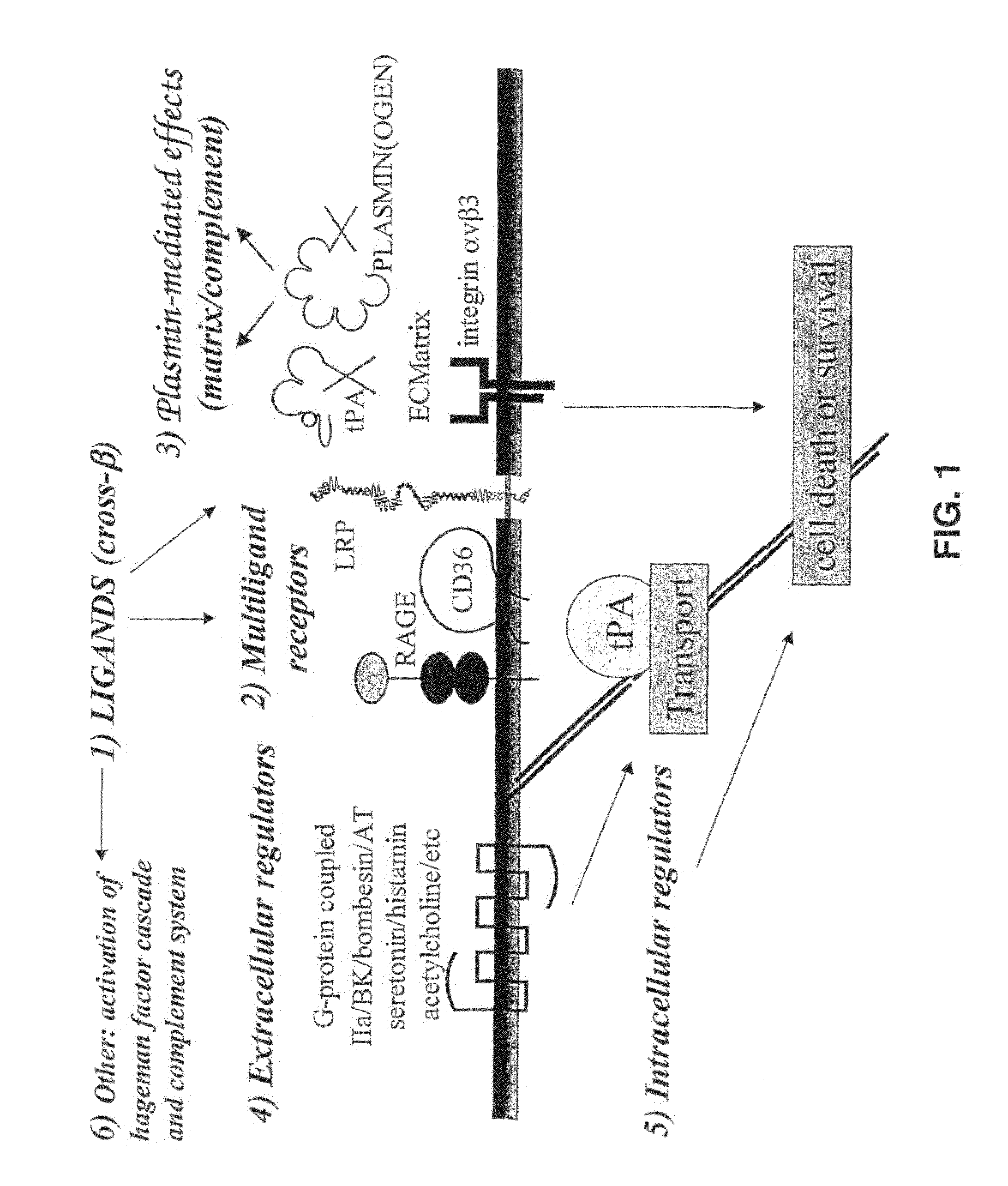
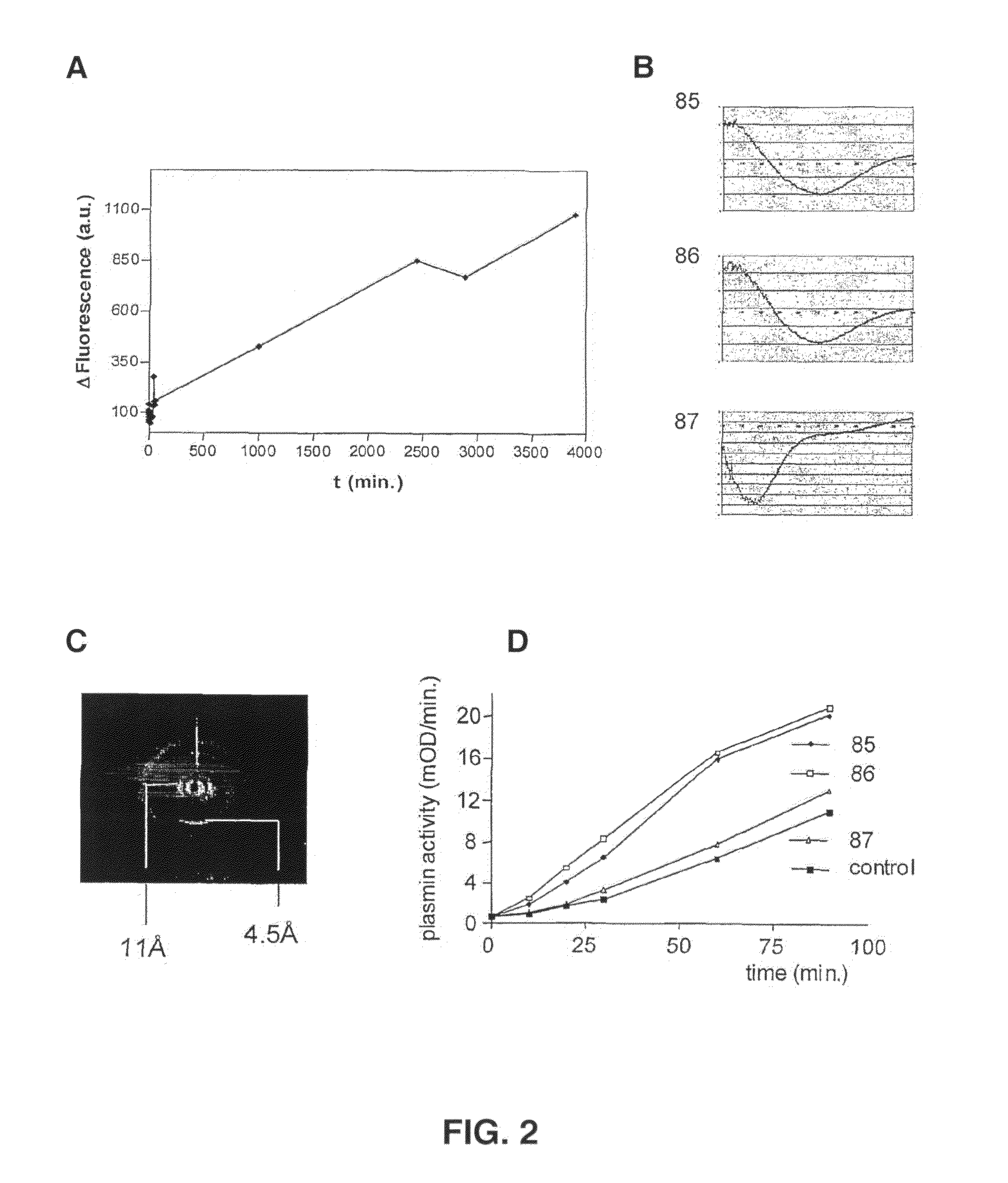
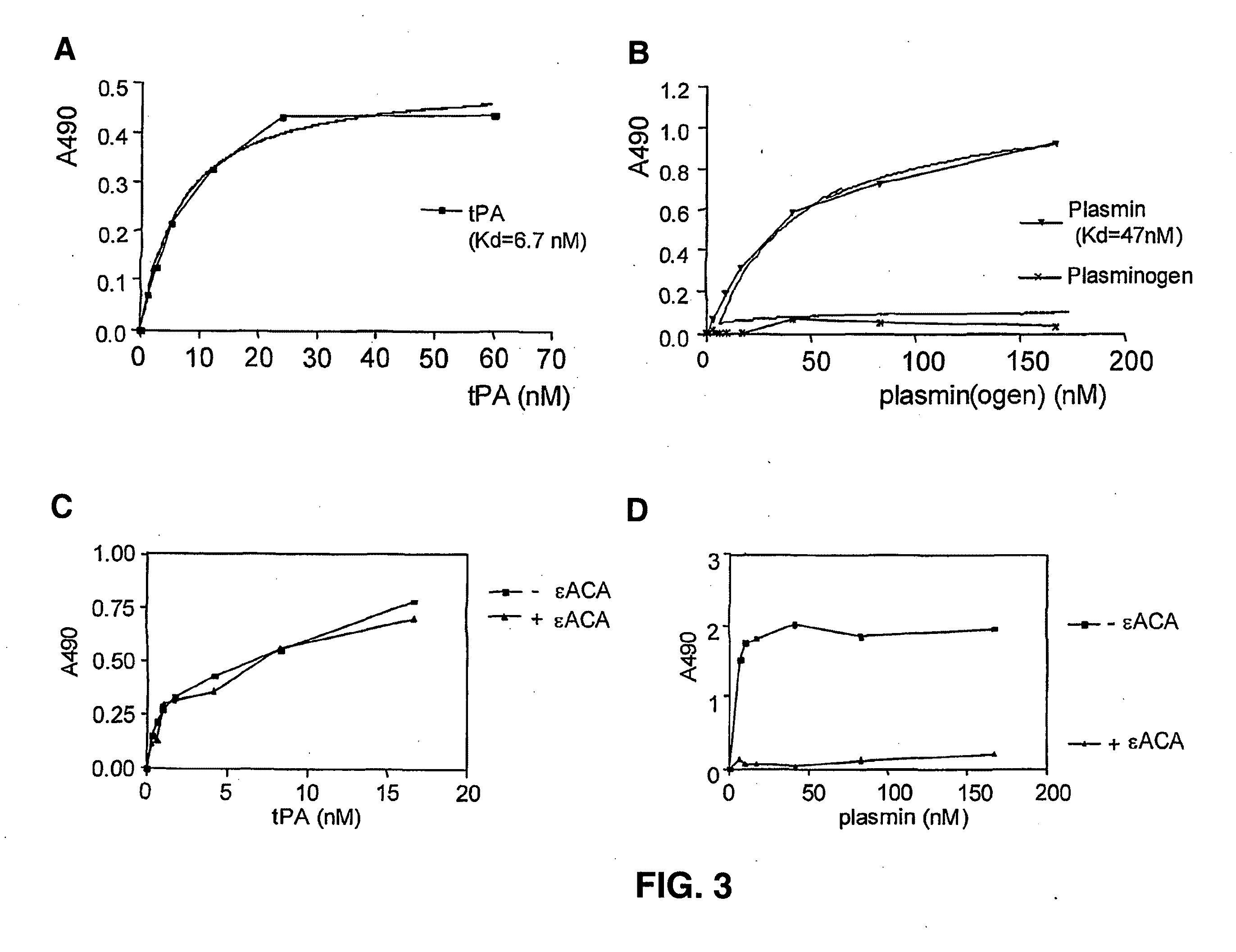
Cross-beta structure comprising amyloid binding proteins and methods for detection of the cross-beta structure, for modulating cross-beta structures fibril formation and for modulating cross-beta structure-mediated toxicity and method for interfering with blood coagulation
InactiveUS20070003552A1Increase local cytotoxicityIncrease fibrinolysisImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPeptide/protein ingredientsGreek letter betaStructural biology
The invention relates to the field of biochemistry, molecular biology, structural biology and medicine. More in particular, the invention relates to cross-β structures and the biological role of these cross-β structures.
Owner:CROSSBETA BIOSCIENCES BV
Targeted hollow gold nanostructures and methods of use
InactiveUS20140012224A1Easy to use detectionMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismDiseasePhotothermal ablation
Provided are novel nanostructures comprising hollow nanospheres (HGNs) and nanotubes for use as chemical sensors, molecular specific photothermal coupling agents, and photothermal ablation compounds. The nanostructures can be used in electromagnetic radiation-induced phototherapy for treatment of cancer and other disorders. The nanostructures can also be used as a sensor that detects molecules. The nanostructures are of particular use in the fields of clinical diagnosis, clinical therapy, clinical treatment, and clinical evaluation of various diseases and disorders, manufacture of compositions for use in the treatment of various diseases and disorders, for use in molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof. The hollow gold nanospheres have a unique combination of spherical shape, small size, and strong, tunable, and narrow surface plasmon resonance absorption covering the entire visible to near IR region.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for identifying similar 3D substructures onto 3D atomic structures and its applications
InactiveUS20050182570A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingStructural biologyCompound (substance)
The invention pertains to the field of structural biology and relates to a process to compare various three-dimensional (3D) structures and to identify functional similarities among them. The process of comparison of 3D atomic structures of the invention is based on the comparisons of defined chemical groups onto the 3D atomic structures and allows the detection of local similarities even when neither the fold nor sequence for example aminoacid sequences for polypeptides sequences or nucleotide sequences for nucleic acid sequences are conserved. This process requires the attribution of selected physico-chemical parameters to each atom of a 3D atomic structure, then the representation of each 3D atomic structure by a graph of chemical groups.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Cross-beta structure comprising amyloid-binding proteins and methods for detection of the cross-beta structure, for modulating cross-beta structures fiber formation and modulating cross-beta structure-mediated toxicity
The invention relates to the field of biochemistry, molecular biology, structural biology and medicine. More in particular, the invention relates to cross-β structures and the biological role of these cross-β structures. In one embodiment, the invention discloses a method for modulating extracellular protein degradation and / or protein clearance comprising modulating cross-β(beta) structure formation (and / or cross-β structure-mediated activity) of the protein present in the circulation.
Owner:CROSSBETA BIOSCIENCES BV
Cross-beta structure comprising amyloid-binding proteins and methods for detection of the cross-beta structure, for modulating cross-beta structures fibril formation and for modulating cross-beta structure-mediated toxicity
The invention relates to the field of biochemistry, molecular biology, structural biology and medicine. More in particular, the invention relates to cross-β structures and the biological role of these cross-β structures. In one embodiment, the invention discloses a method for modulating extracellular protein degradation and / or protein clearance comprising modulating cross-β(beta) structure formation (and / or cross-β structure-mediated activity) of the protein present in the circulation.
Owner:CROSSBETA BIOSCIENCES BV
Cross-Beta Structure Comprising Amyloid Binding Proteins and Methods for Detection of the Cross-Beta Structure, for Modulating Cross-Beta Structures Fibril Formation and for Modulating Cross-Beta Structure-Mediated Toxicity and Method for Interfering With Blood Coagulation
InactiveUS20090202980A1Increase local cytotoxicityIncrease fibrinolysisImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsDead animal preservationFiberStructural biology
The invention relates to the field of biochemistry, molecular biology, structural biology and medicine. More in particular, the invention relates to cross-β structures and the biological role of these cross-β structures.
Owner:CROSSBETA BIOSCIENCES BV
Antibody humanization by framework assembly
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
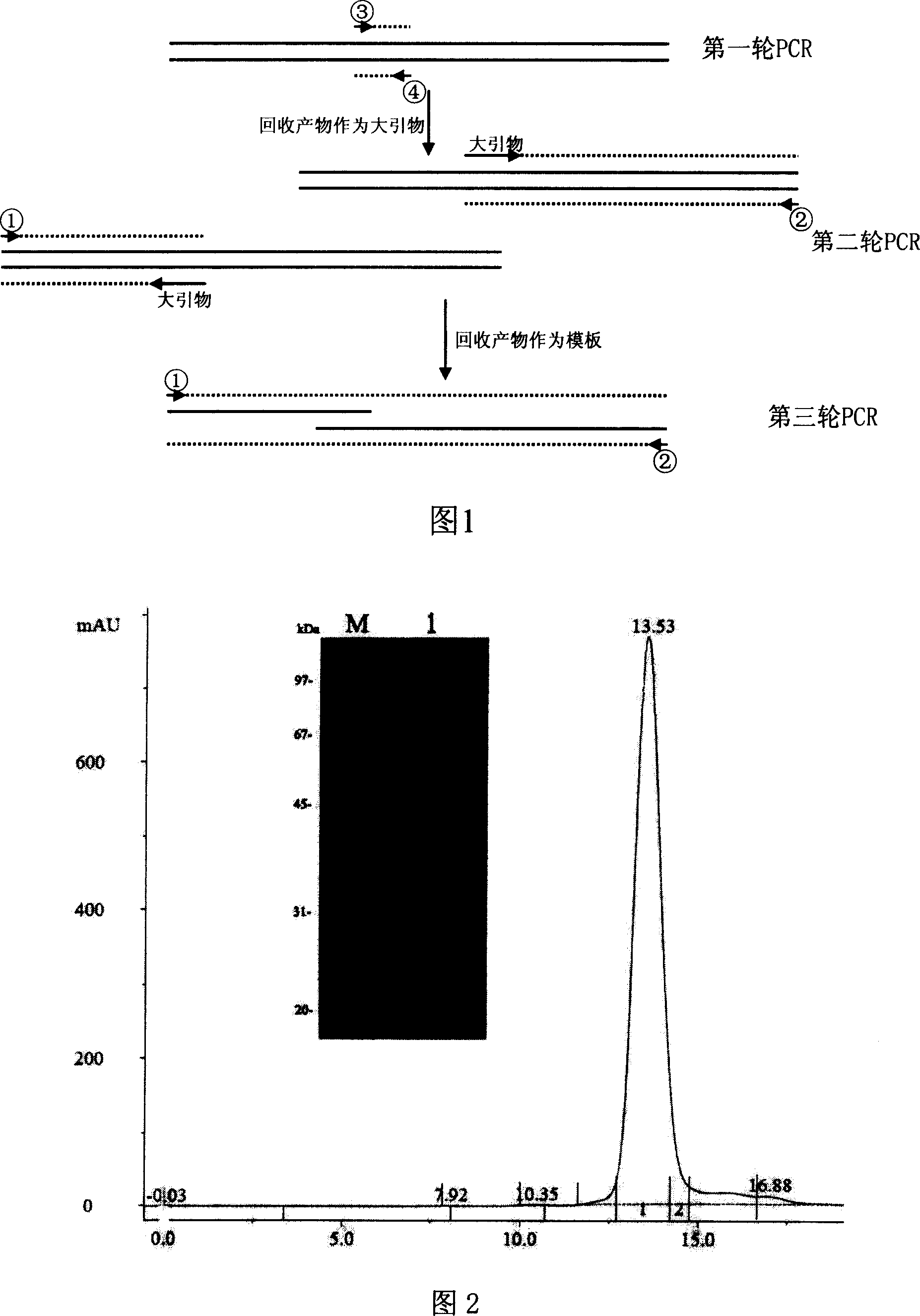
Expression, purification and crystallization of urokinase catalyst structure domain mutant
InactiveCN101024827ALow costImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySerine proteinasesPichia pastoris
The invneiton relates to expression, purification and crystallization of urokinase catalytic domain mutant, relating to the field of medicine, biotechnique, and structural biology. And the invention provides a techical method of expression, purification and crystallization of urokinase catalytic domain mutant in Pichia pastoris. And the cultured urokinase catalytic domain mutant has crystallographic space group R3, and unit cell parameters: a=b=120.48, c=42.45, alpha=beta=90.0deg, and gama=120.0 deg. And this protein has serine proteinase activity, appliable to high flux screening of urokinase inhibitor; and its high resolution crystal provides a research and development platform for design and development of urokinase inhibitor.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
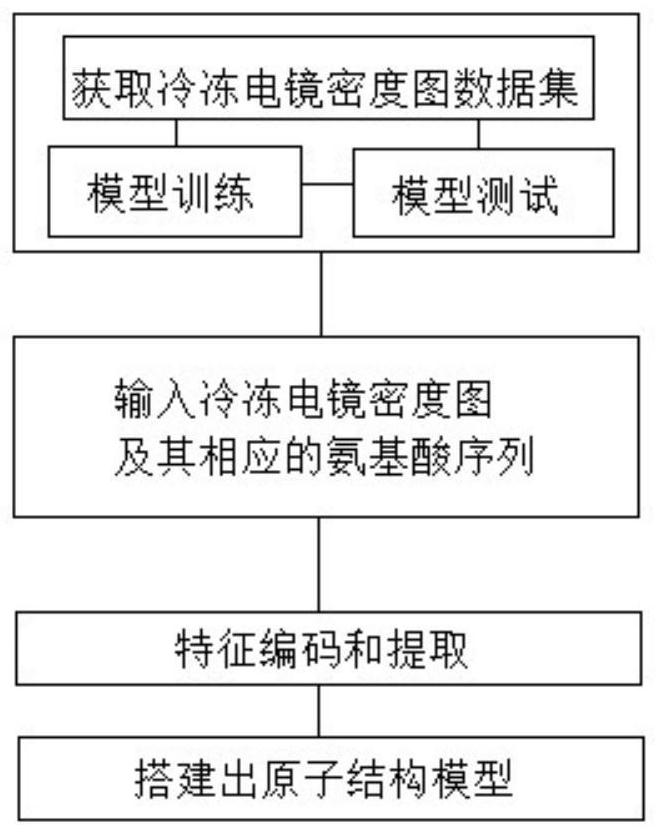
Cryoelectron microscope atomic model structure building method and system based on deep learning and application
PendingCN113990384AFully matchedNo lossGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionStructural biologyChemical physics
The invention discloses a cryoelectron microscope atomic model structure building method and system based on deep learning and application. The method comprises the steps of: 1, obtaining a cryoelectron microscope density map data set, and carrying out model training and model testing; 2, inputting a cryoelectron microscope density map and a corresponding amino acid sequence; and 3, carrying out feature coding and extraction on the cryoelectron microscope density map and the corresponding amino acid sequence, and building an atomic structure model. According to the measurement method provided by the invention, the generated amino acid atom model has structural biological characteristics, the structural biological rationality of the predicted amino acid atom model is ensured, accurate prediction of the end-to-end all-differentiable amino acid internal atom structure is finally realized, certain superiority is achieved, and the atomic model effect predicted by a plurality of tests is verified. In addition, the improvement effect in model building in middle and low resolution is also very obvious.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
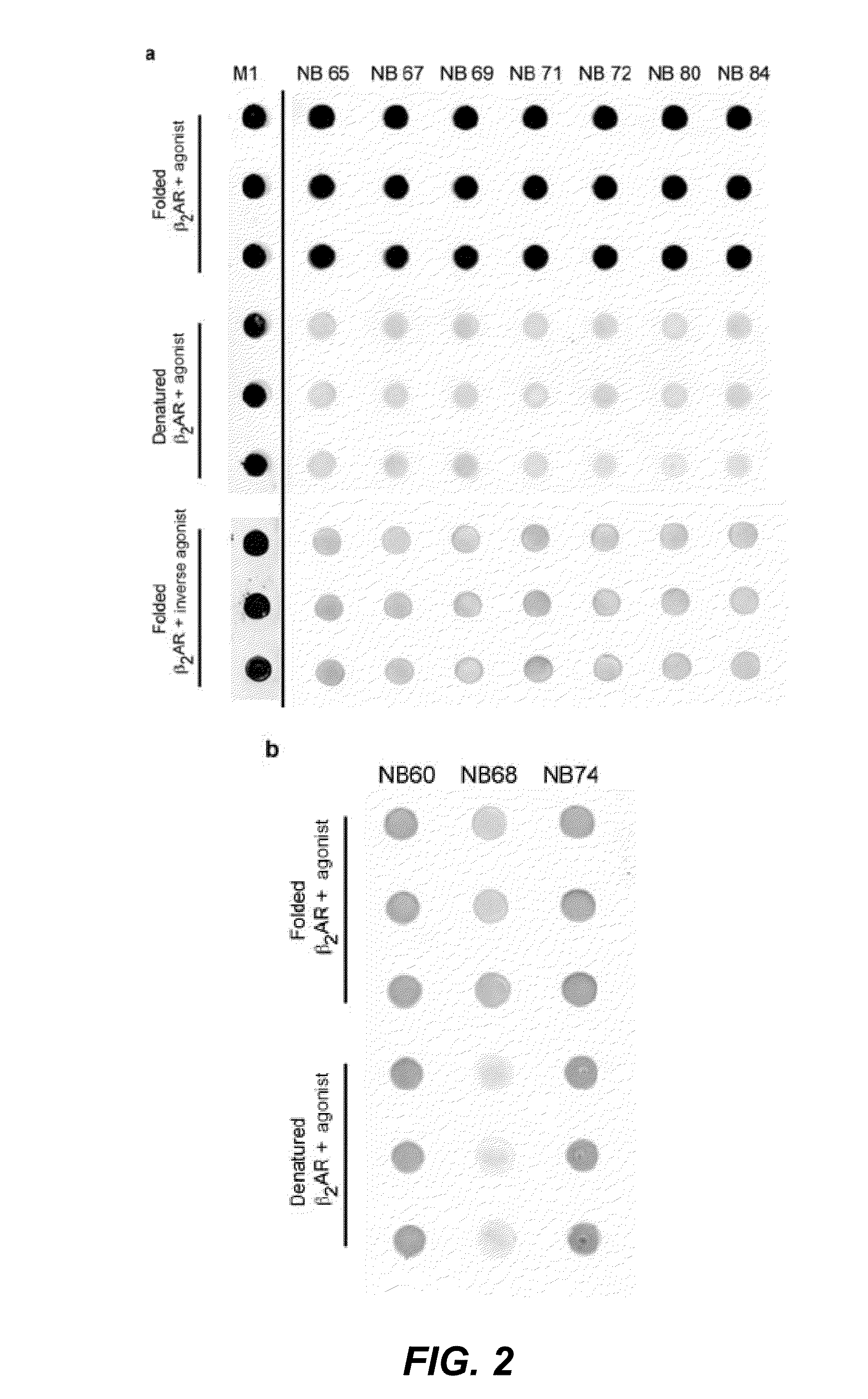
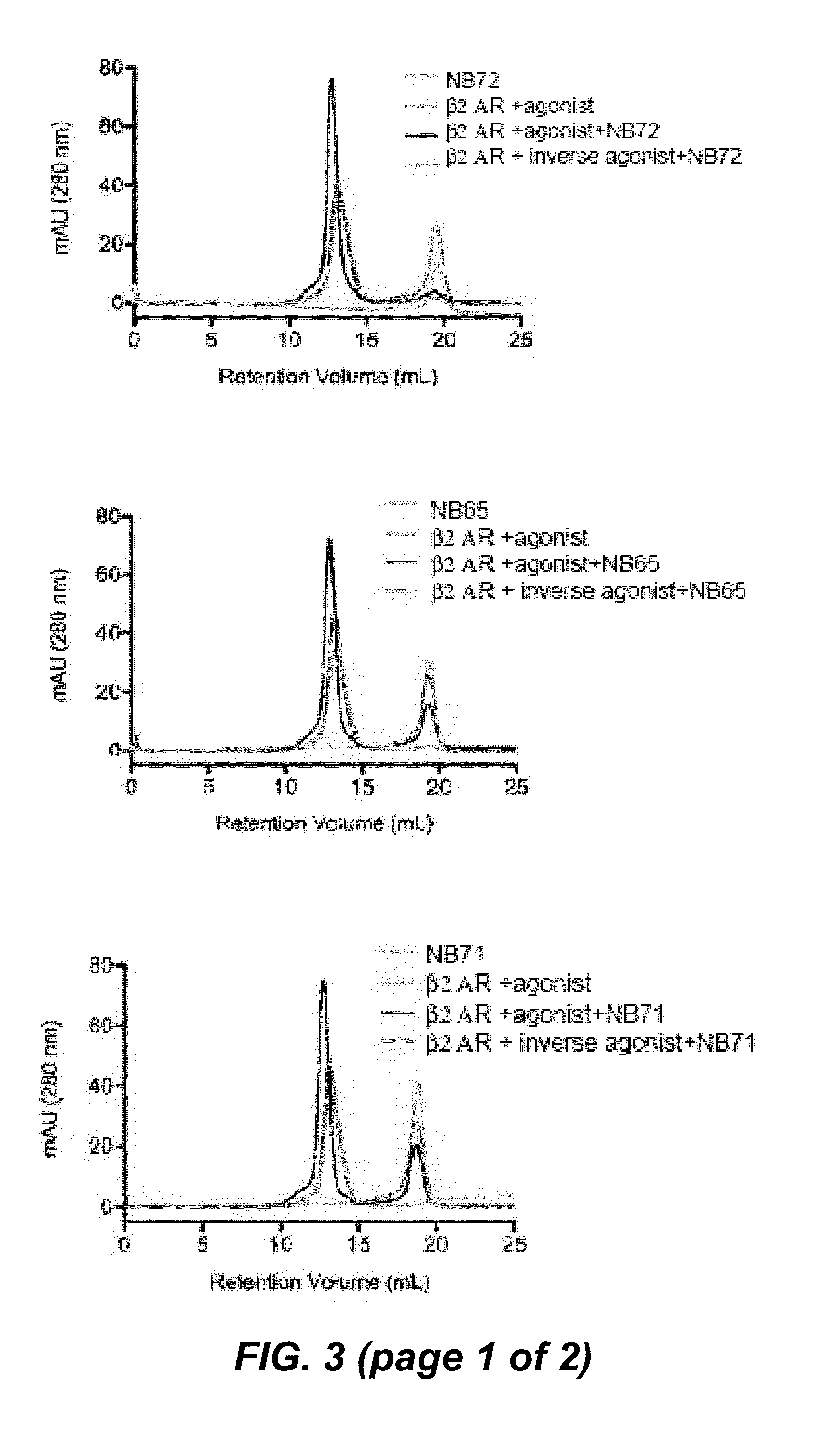
Protein binding domains stabilizing functional conformational states of gpcrs and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130137856A1Improve thermal stabilityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderStructural biologyDisease
The present invention relates to the field of GPCR structure biology and signaling. In particular, the present invention relates to protein binding domains directed against or capable of specifically binding to a functional conformational state of a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). More specifically, the present invention provides protein binding domains that are capable of increasing the stability of a functional conformational state of a GPCR, in particular, increasing the stability of a GPCR in its active conformational state. The protein binding domains of the present invention can be used as a tool for the structural and functional characterization of G-protein-coupled receptors bound to various natural and synthetic ligands, as well as for screening and drug discovery efforts targeting GPCRs. Moreover, the invention also encompasses the diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic usefulness of these protein binding domains for GPCR-related diseases.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Binding domains directed against gpcr:g protein complexes and uses derived thereof
ActiveUS20140275487A1Easy to identifyStable captureVirusesUnicellular algaeHeterologousStructural biology
The present invention relates to the field of G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) structural biology and signaling. In particular, the present invention relates to binding domains directed against and / or specifically binding to GPCR:G protein complexes. Also provided are nucleic acid sequences encoding such binding domains and cells expressing or capable of expressing such binding domains. The binding domains of the present invention can be used as universal tools for the structural and functional characterization of G-protein coupled receptors in complex with downstream heterotrimeric G proteins and bound to various natural or synthetic ligands, for investigating the dynamic features of G protein activation, as well as for screening and drug discovery efforts that make use of GPCR:G protein complexes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +3
Establishment of method for preparing recombinant protein vaccine of type A H1N1 influenza virus
InactiveCN101716340AEngineering antibody technology is simpleLow costAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsEscherichia coliAntigenic analysis
The invention belongs to the field of zoonosis researches, and relates to a method for preparing a vaccine of zoonosis. In the method, an HA gene in a cDNA sequence of a type A H1N1 California virus strain (A / California / 08 / 2009(H1N1)) is selected as a research content; the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, analyzing a sequence of the part of an HA protein leaked outside an envelope according to structural biology software; secondly, selecting a part with high immunogenicity according to an antigenic analysis, and constructing a prokaryotic expression vector pGEX-6P-1-HA by using a genetic fragment obtained through a gene synthesis method; and thirdly, converting a masculine recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli to obtain a recombinant strain (Escherichia coli BL21 rosseta / pGEX-6P-1-HA truncated protein). Through a plurality of chromatography methods, a purified HA truncated protein of the H1N1 is obtained; and by utilizing the expression vector and an adjuvant together to immune organisms, the protective effect on the H1N1 virus is achieved.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
Novel three-dimensional reconstruction system
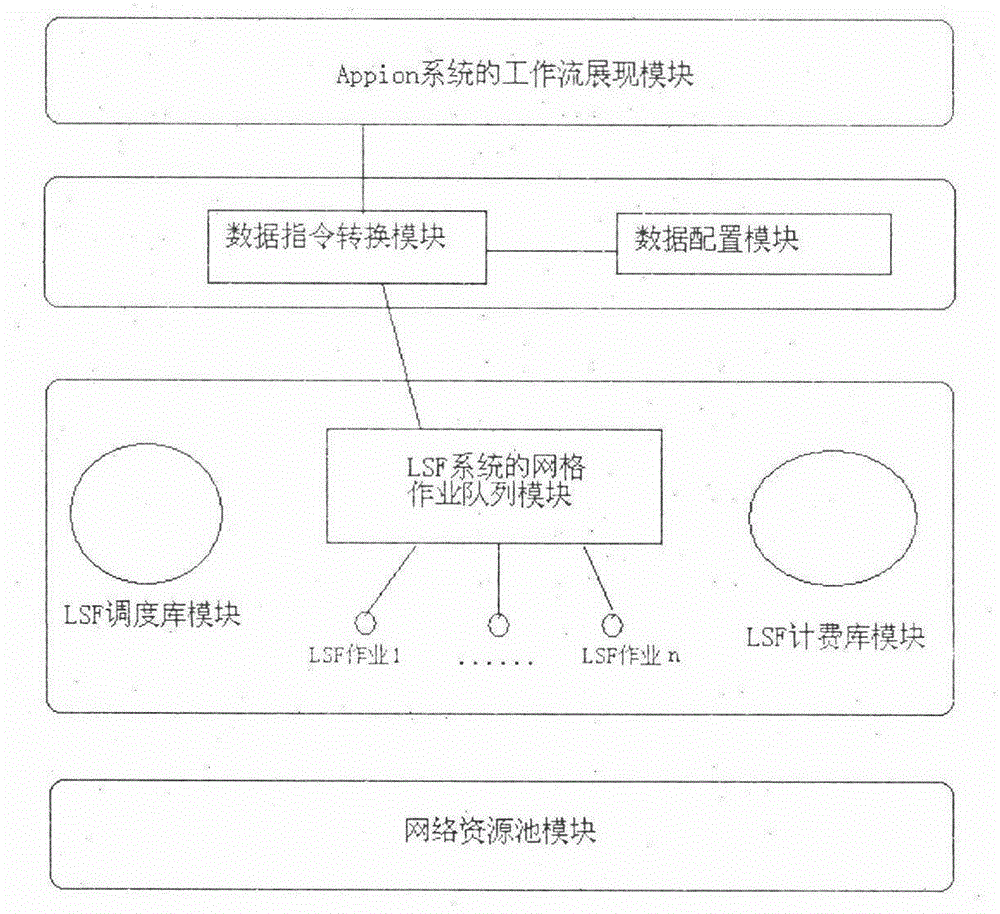
InactiveCN104537713AReduce work intensityImprove research efficiency3D modellingResource poolResearch efficiency
A novel three-dimensional reconstruction system comprises a workflow presenting module of an Appion system, a data instruction conversion module, a data configuration module, a grid job queue module of an LSF system, an LSF scheduling library module, an LSF billing library module and a network resource pool module. The novel system based on the LSF system, the Appion system and a cryo-electron microscopy technology achieves three-dimensional reconstruction. The system ingeniously and organically combines the Appion system, a cryo-electron microscopy biological structure research technology and a grid calculation technology based on an LSF, and forms a novel cryo-electron microscopy three-dimensional reconstruction technology. The technology is mainly characterized by achieving a three-dimensional reconstruction assembly line technology, and the assembly line technology can effectively reduce work intensity of electron microscopic image analysis of biologic samples and effectively improve research efficiency of an electron microscopy three-dimensional reconstruction method in structural biology.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
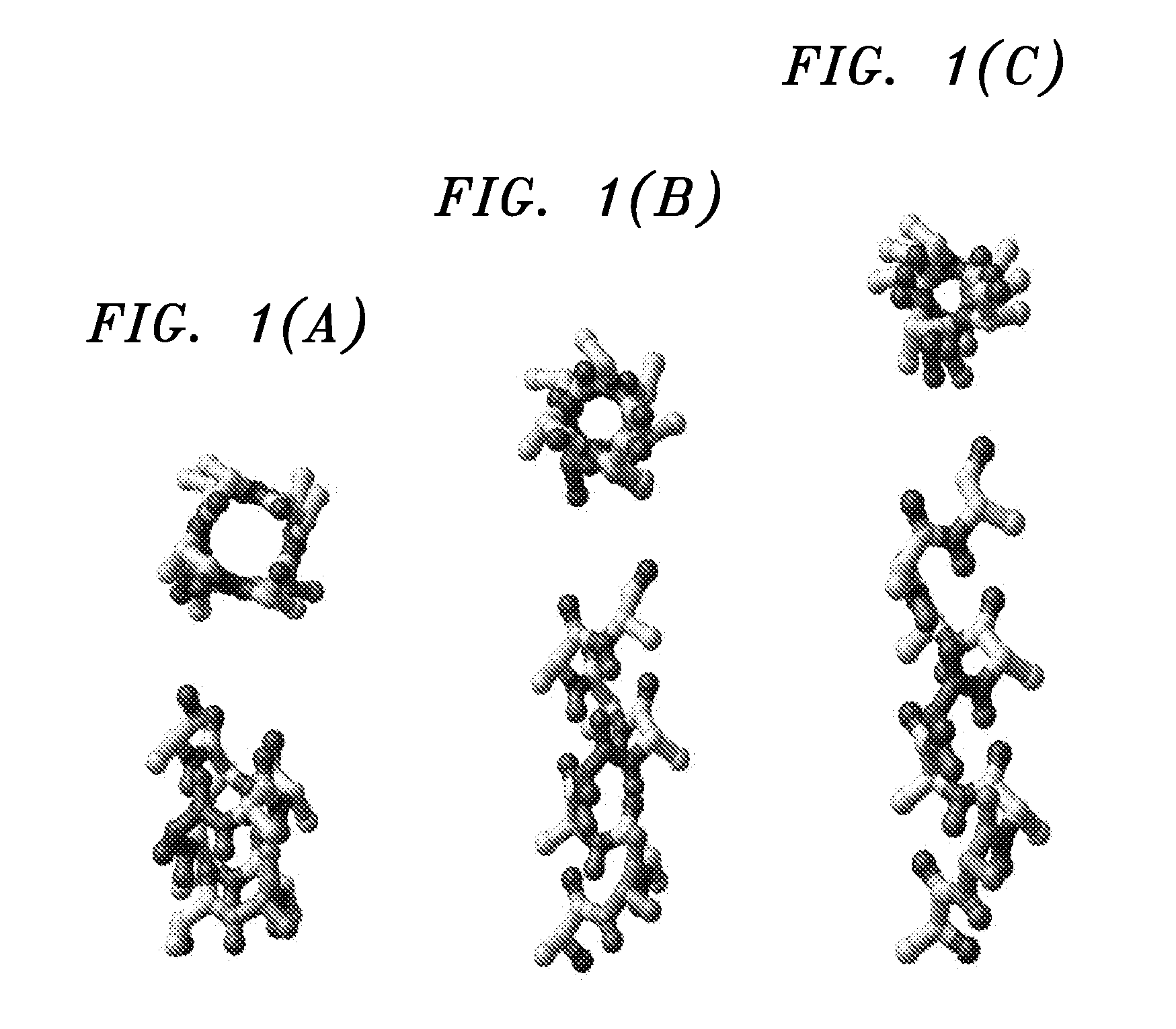
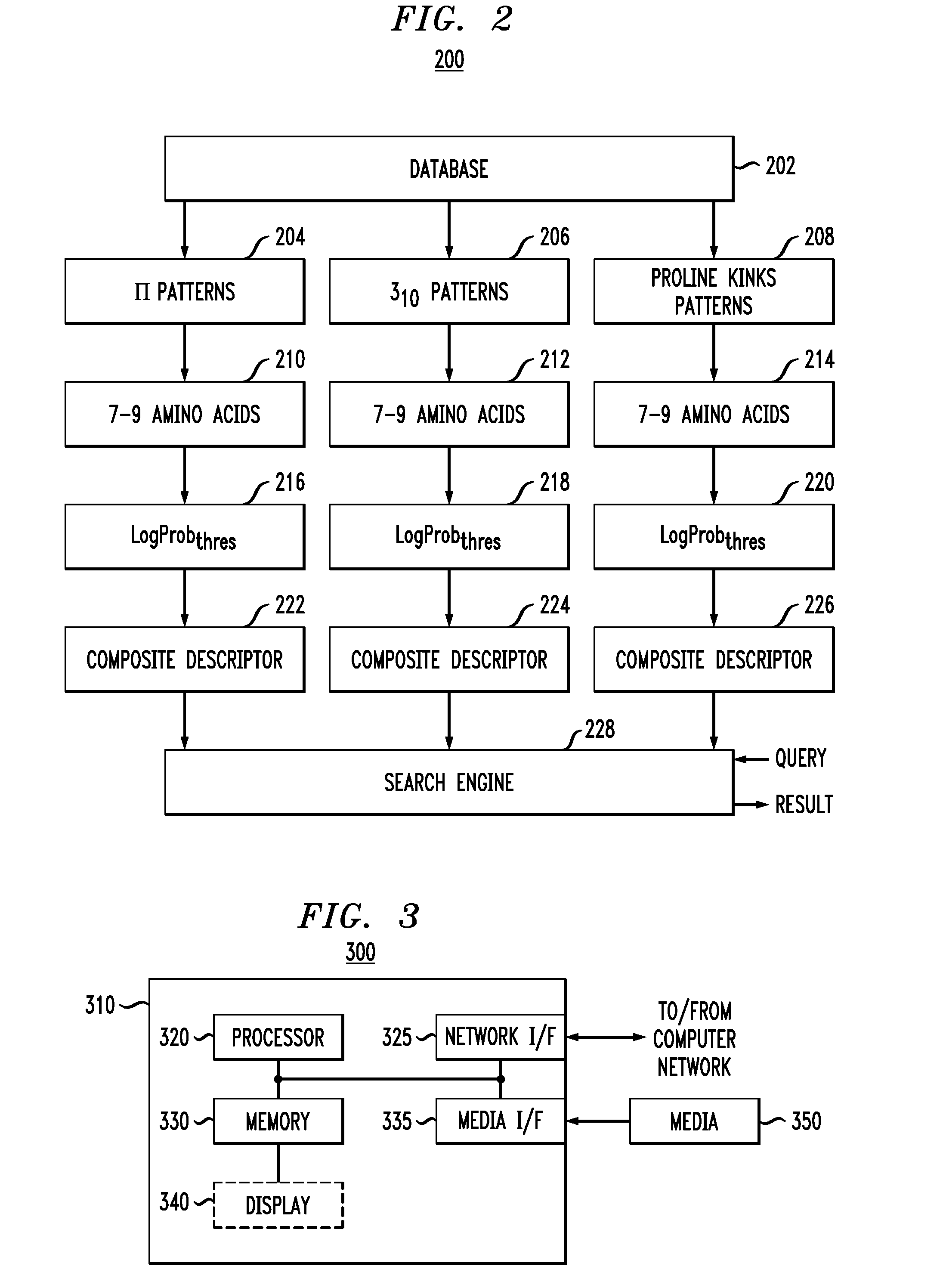
Sequence pattern descriptors for transmembrane structural details
InactiveUS20080133142A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsStructural biologyTrue positive rate
The relationship between an amino acid sequence of a protein and its three-dimensional structure is at the very core of structural biology and bioinformatics. The occurrence and conservation of non-canonical conformations is a “local” phenomenon, i.e., non-canonical conformations are encoded intra-helically by short peptide sequences (heptapeptides at most). Effective descriptors can be formed for these short sequences employing training sets. Multiple, distinct patterns are created representing these sequences. A composite descriptor is formed by selecting from among the patterns discovered. The composite descriptor has a high level of sensitivity and specificity while, at the same time, a boosted signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:IBM CORP
cDNA overall length nucleotide sequence of human EBLN-1 gene and cloning method thereof
The invention discloses a cDNA overall length nucleotide sequence of a human EBLN-1 gene and a cloning method thereof. According to the invention, the cloning method comprises the following steps of: respectively amplifying a 5' end fragment and a 3' end fragment of human EBLN-1 gene according to 5'RACE and 3'RACE technologies and sequencing; then, splicing to obtain the cDNA overall length nucleotide sequence of the human EBLN-1 gene according to the 3' end sequence, the 5' end sequence and a known cDNA part sequence; performing analysis of an opened reading frame and an untranslated region; and deducing to obtain an amino acid sequence which codes the EBLN-1 protein according to the opened reading frame. The cDNA overall length nucleotide sequence of the human EBLN-1 gene can be used for subsequently expressing a recombinant protein for preparing corresponding antibodies or performing structural biological study, for studying EBLN-1 gene function through RNA interference and overexpression or further studying the effect of the untranslated region in regulation of gene expression, and finally laying a foundation for illustrating the physiological action of EBLN-1 gene in human body and the relation with diseases, in particular mental diseases.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Epitope polypeptide combination capable of inducing immunity and application thereof
PendingCN113372417AVerify immune response propertiesHighly conservativeSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigen epitopeCtl epitope
The invention discloses an epitope polypeptide combination capable of inducing immunity and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of biology, and aims to carry out molecular design of related vaccines by utilizing immunoinformatics on the basis of epitope analysis optimization. Based on a structural antigen epitope vaccine design strategy, a B cell epitope, a Th epitope and a CTL epitope on a new coronavirus S protein are determined through immunoinformatics to induce a main neutralizing antibody, activate cellular immune response and induce body fluid and cellular immune balance. The epitope vaccine is designed through connection of a molecular adjuvant and candidate antigen epitopes, antigenicity, physicochemical properties, protein secondary structure and tertiary structure modeling of the epitope vaccine are analyzed, vaccine conformation B cell epitopes are analyzed by means of a structural biological tool, and immune response characteristics of the vaccine are verified through molecular docking with TLR4 and immune response simulation stimulation. Information analysis results show that the designed candidate epitope combination has well balanced humoral immune and cellular immune response capabilities.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Antibody humanization by framework assembly
ActiveUS20120316085A1Generate efficientlyPeptide librariesLibrary screeningAntigenStructural biology
An improved method for producing humanized antibody or an antigen binding fragment thereof is described. The method, designated framework-assembly, bypasses the reliance on structural biology and the construction of large libraries. It is easier to implement and more efficient than the rational design and empirical methods. Also described are humanized antibodies produced by the method and related framework-assembly library.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
Lipid-assisted synthesis of polymer compounds and methods for their use
The invention herein disclosed provides for methods for the synthesis of polymers from monomers. In particular the method provides for the synthesis of polynucleotides from mononucleotides in the absence of catalytic enzymes. The method comprises providing an aqueous solution having a plurality of phospholipid molecules and monomer molecules; subjecting the aqueous solution to fluctuating temperature conditions; subjecting the aqueous solution to fluctuating cycles of drying and hydrating conditions; subjecting the aqueous solution to fluctuating [H+] conditions; the fluctuating conditions thereby allowing formation of a chemical bond between at least two monomers to create a polymer. The invention is of particular use in the fields of molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
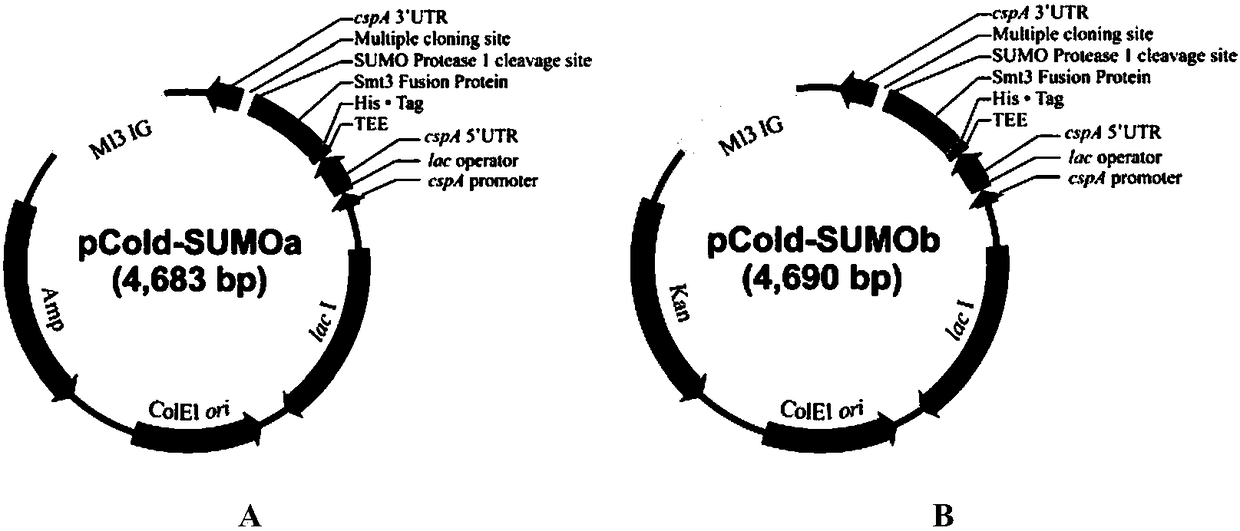
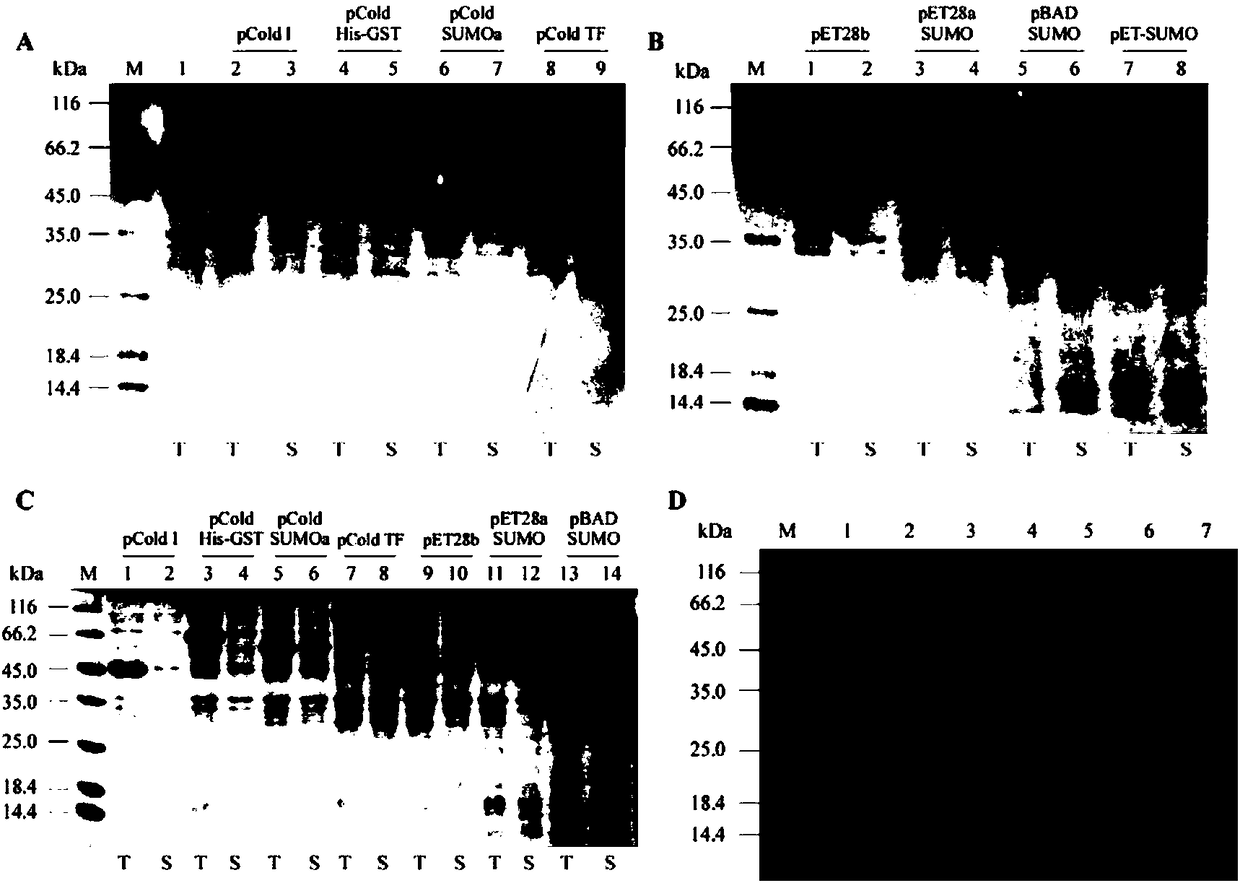
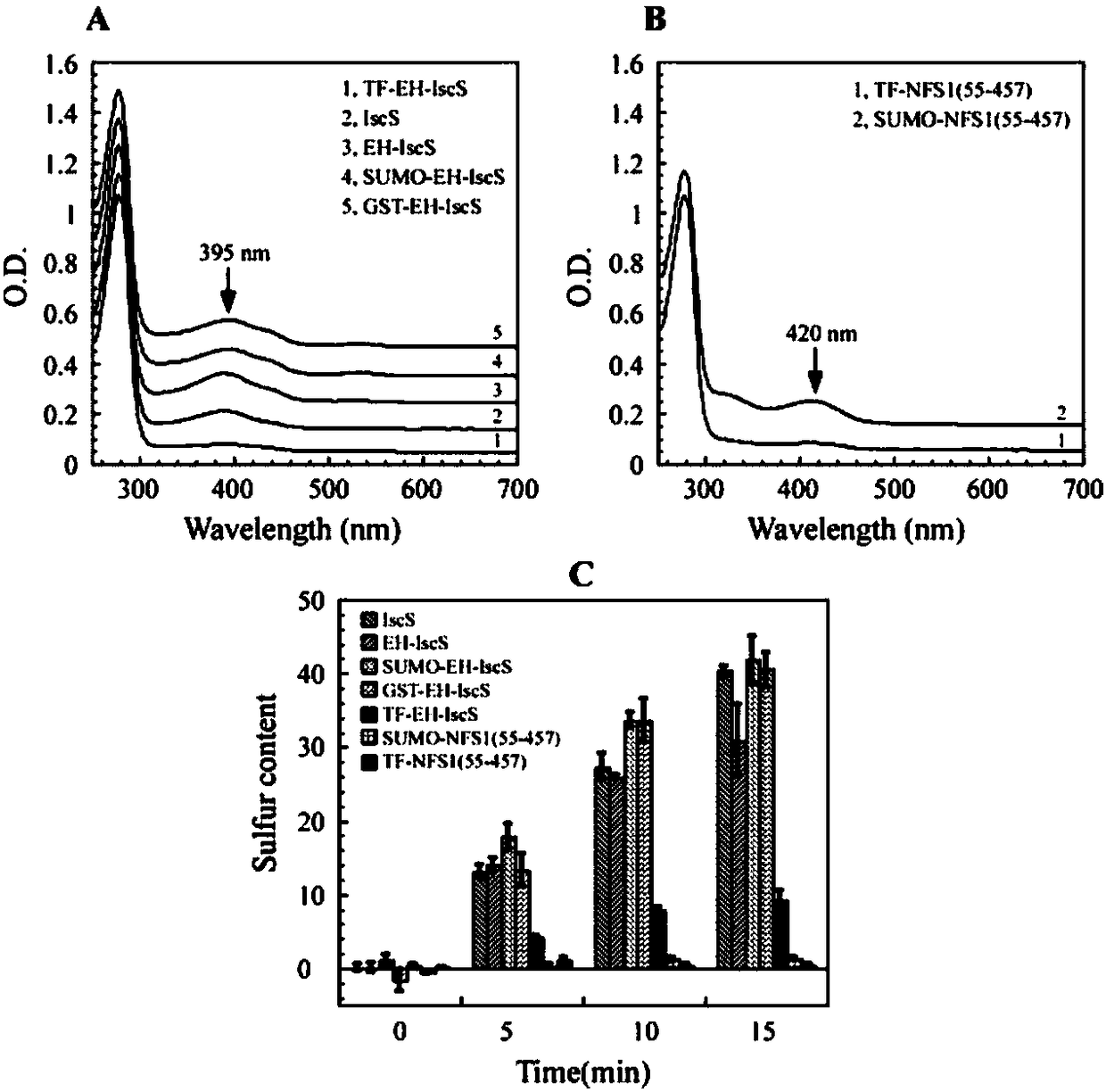
Construction method and application of Escherichia coli cold shock assistant dissolving type expression plasmids
The invention relates to a construction method of Escherichia coli cold shock assistant dissolving type expression plasmids, and a method for preparing a water-soluble heterogenous polypeptide by applying the Escherichia coli cold shock assistant dissolving type expression plasmid. The cold shock assistant dissolving type expression plasmids for realizing small ubiquitin modified protein (SUMO) and exogenous gene fusion expression under the control of a promoter of a cold shock gene is constructed by using a seamless cloning technology. A chimeric cysteine desulfurase is cloned into the plasmids, such as widely-known pCold I and PET28 series plasmids, to obviously improve the water solubility, the stability and the enzyme activity of recombinant proteins. The SUMO has no influences on thetarget protein space conformation of widely-known pCold TF plasmids. The cutting efficiency of an SUMO label is more than 95% when enzyme digestion is performed at 25 DEG C for 1 h according to a ratio of Ulp1 protease to the recombinant protein of 1 U : (0.5-1) mg, so the Escherichia coli cold shock assistant dissolving type expression plasmids are very suitable for preparing proteins having natural N ends in the fields of bioengineering pharmacy and structural biology.
Owner:HUNAN DANWEI BILOGICALTECH
Lipid-assisted synthesis of polymer compounds and methods for their use
The invention herein disclosed provides for methods for the synthesis of polymers from monomers. In particular the method provides for the synthesis of polynucleotides from mononucleotides in the absence of catalytic enzymes. The invention is of particular use in the fields of molecular biology, structural biology, cell biology, molecular switches, molecular circuits, and molecular computational devices, and the manufacture thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Recombinant avian influenza subunit vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113150083ASsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifProtective antigenAntigen
The invention relates to the technical field of vaccine preparation, and especially relates to a recombinant avian influenza subunit vaccine and a preparation method thereof. A head structure in a main protective antigen HA skeleton of H5 subtype avian influenza is reserved, and a neck area of a vaccine H5 is replaced with an influenza HA neck area having broad-spectrum immune protection after structural biology design and transformation, so that the neck area can be proved to protect mutant strains of different H5 and provide broad-spectrum protection on H7 in a mouse experiment.
Owner:SHANXI ACAD OF ADVANCED RES & INNOVATION
Gas phase sample preparation for cryo-electron microscopy
ActiveUS11092523B2Improve imaging resolutionShorten Image Acquisition TimeNanoparticle analysisPreparing sample for investigationAmorphous iceResolution (mass spectrometry)
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Application of multifunctional graphene grid in three-dimensional reconstruction of cryoelectron microscope
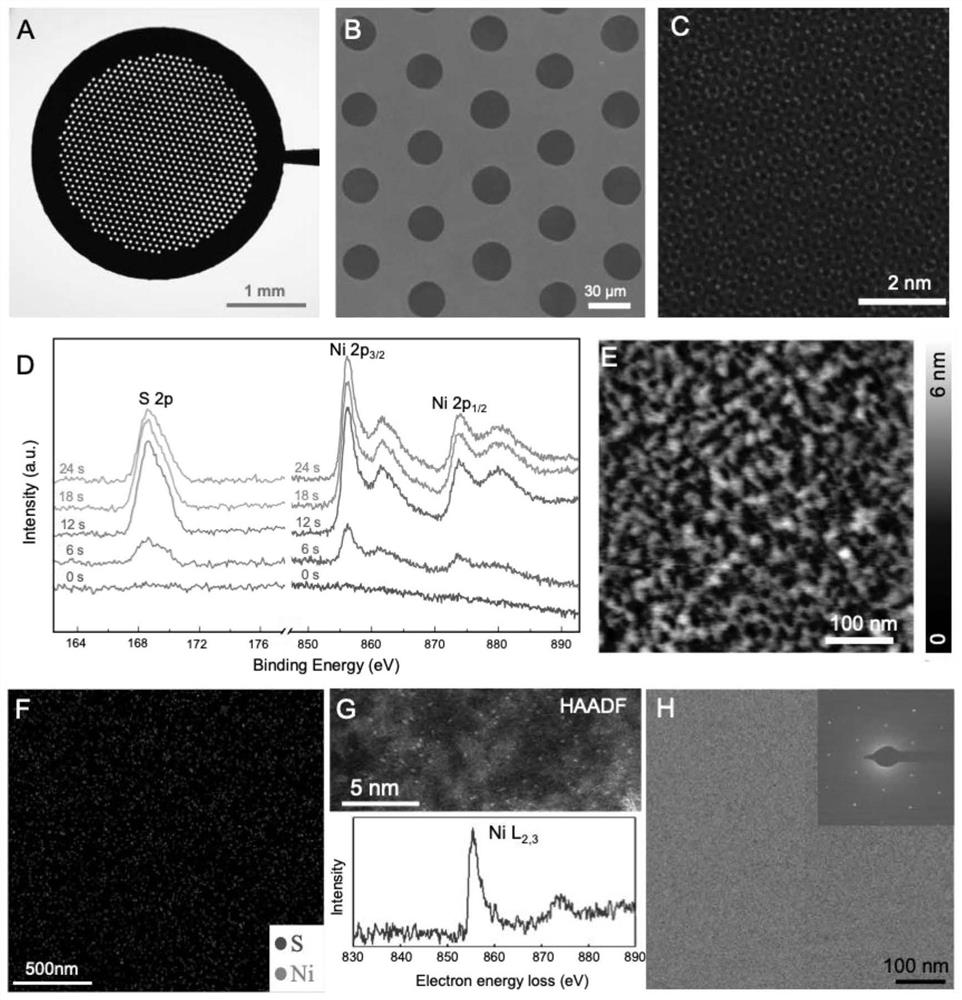
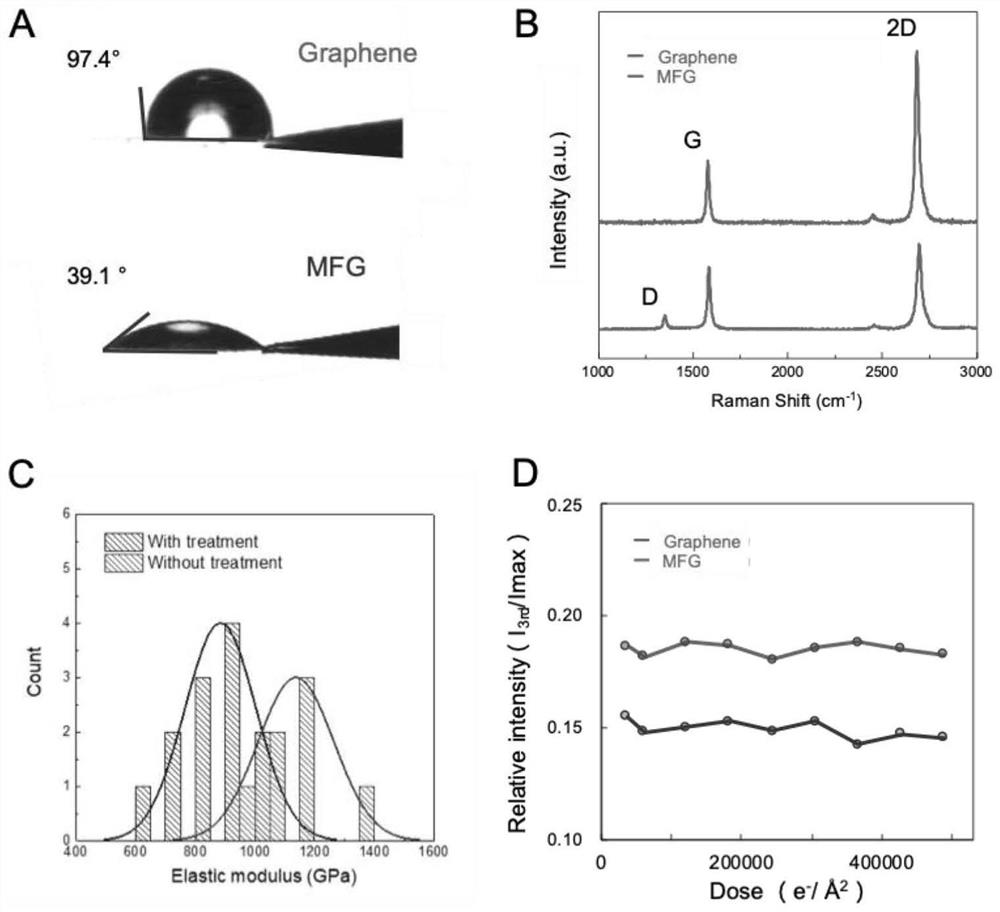
ActiveCN113960078ALimiting Structure Solution EfficiencyFix interface issuesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNickel saltCopper foil
The invention discloses an application of a multifunctional graphene grid in three-dimensional reconstruction of a cryoelectron microscope. The preparation method of the multifunctional graphene grid comprises the following steps: etching a copper foil covered with a graphene film grown by CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) to obtain the graphene grid; performing oxygen plasma treatment on the graphene grid; then, adopting an MES buffer solution containing EDC and NHS treat the graphene grid; activating the graphene grid by adopting nitrilotriacetic acid and biotin; and finally reacting with nickel salt. The multifunctional graphene grid can specifically anchor a target biomolecule on the surface of the multifunctional graphene grid, so that the interface problem of air and water is avoided, the orientation distribution of particles can be controlled, and by constructing related protein purification tags to different directions of each biomacromolecule, abundant Euler angles are provided, and the structural analysis of biomacromolecules is more reliable and more efficient, so that the multifunctional graphene grid can promote the universality and repeatability of application of a cryoelectron microscope in structural biological analysis.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
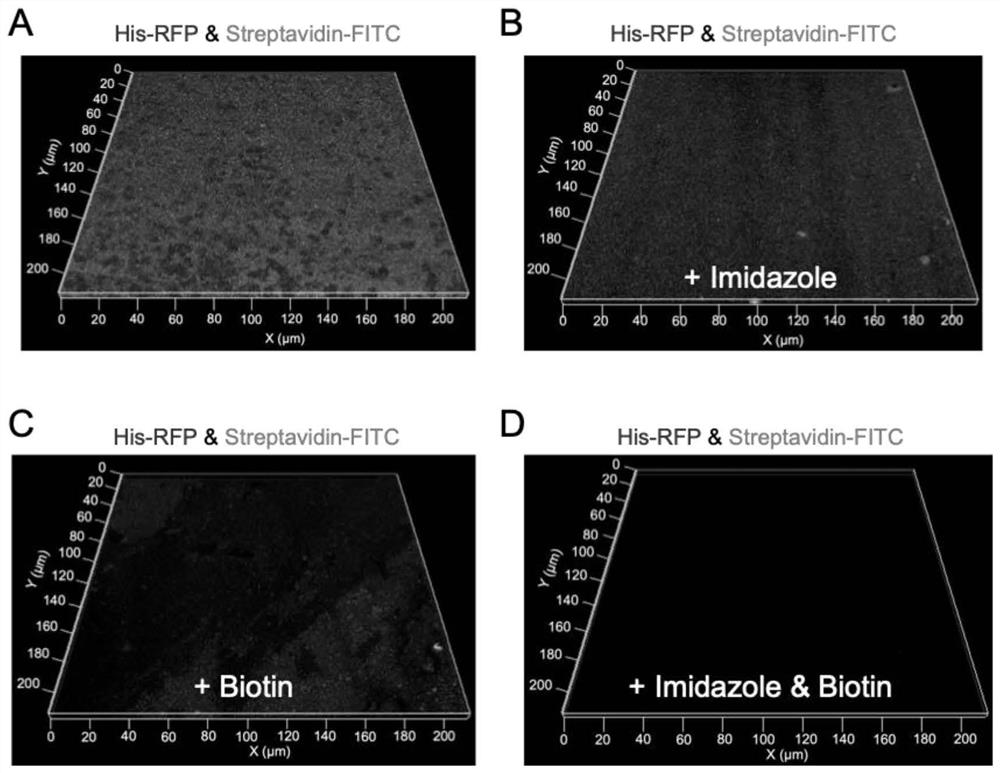
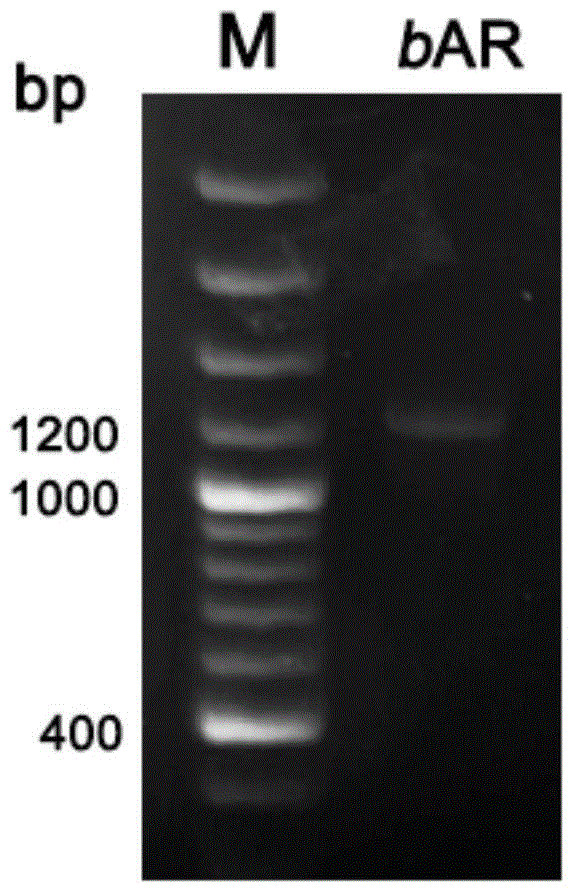
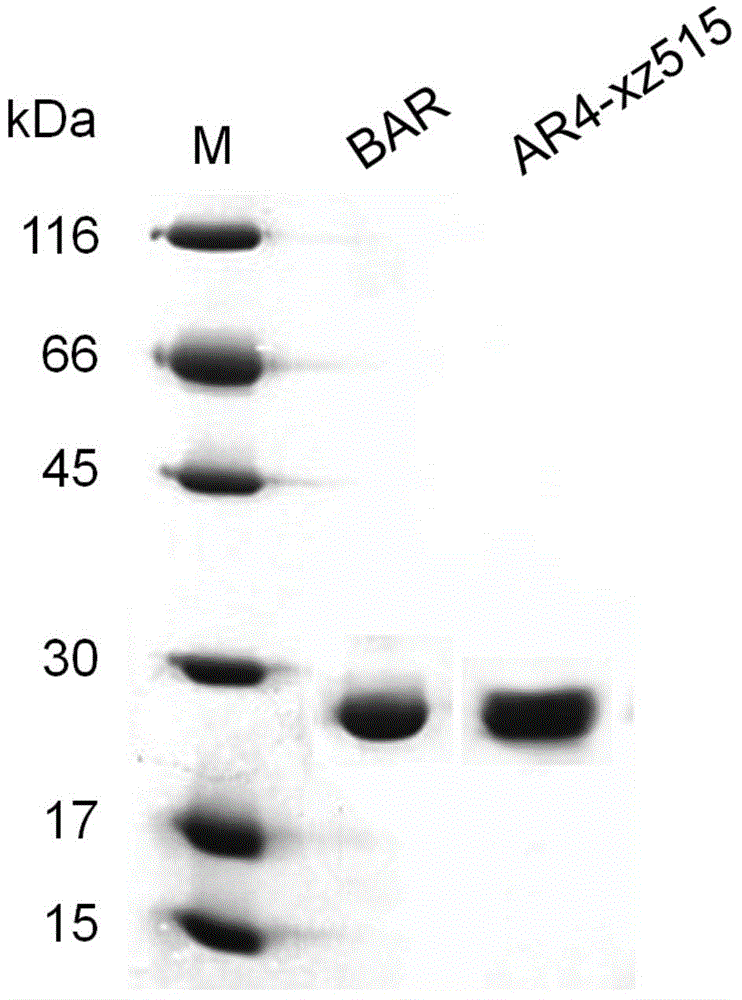
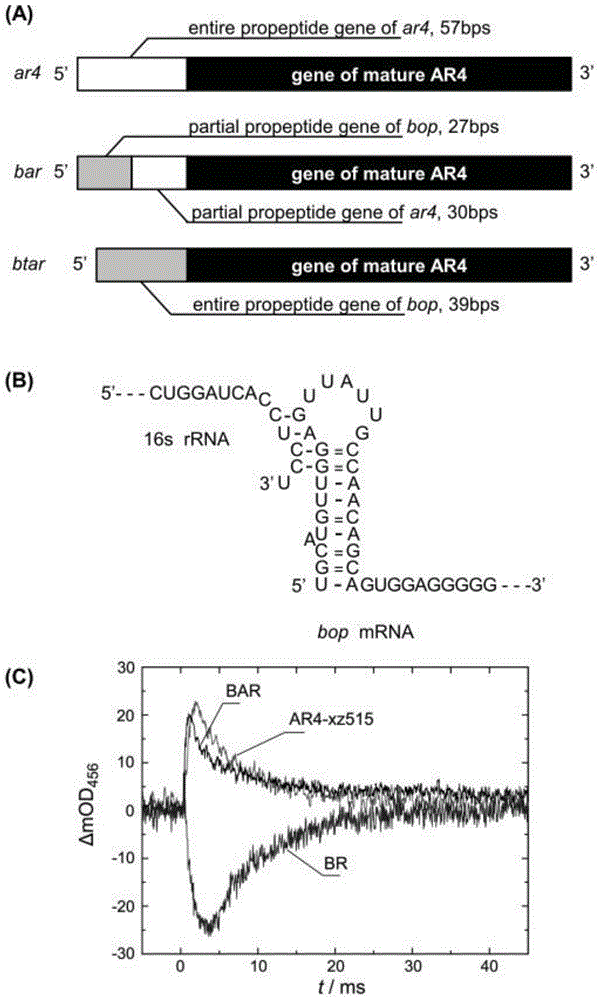
Recombinant archaerhodopsin 4 protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104672314AIntermediate life extensionGood space foldMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesStructural biologyNucleotide
The invention provides a recombinant archaerhodopsin 4 protein. An encoding nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and an amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a preparation method of the recombinant archaerhodopsin 4 protein. By utilizing a gene engineering method, an AR4 gene is appropriately modified, and converted into halobacterium L33 for performing protein expression. The invention also provides application of the recombinant archaerhodopsin 4 protein in structural biology research.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol
ActiveCN103622938AGrowth inhibitionPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseStructural biology
The invention discloses an anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol. The 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol low molecular weight compound is screened out through a candidate medicine screening platform combining structural biology, bioinformatics and biology activity testing and can be applied to the anti-tumor field, or is combined with other medicines or means so as to be applied to the anti-tumor field. The 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol can be used for the targeted inhibition of HAb18G / CD147 protein and can be applied in the preparation of medicines for treating diseases related to HAb18G / CD147 protein high expression (such as tumors, especially liver cancer).
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
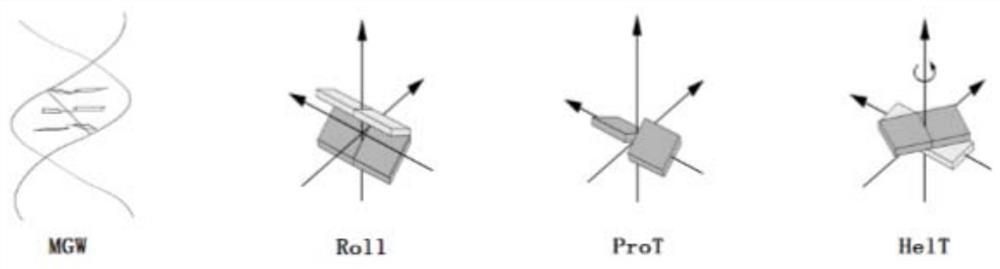
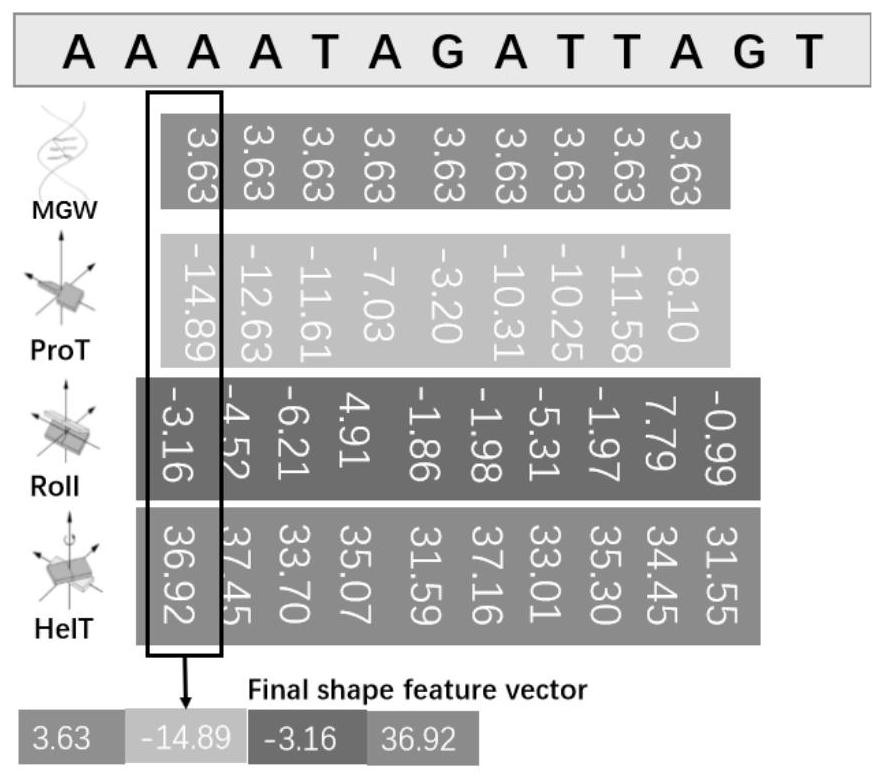
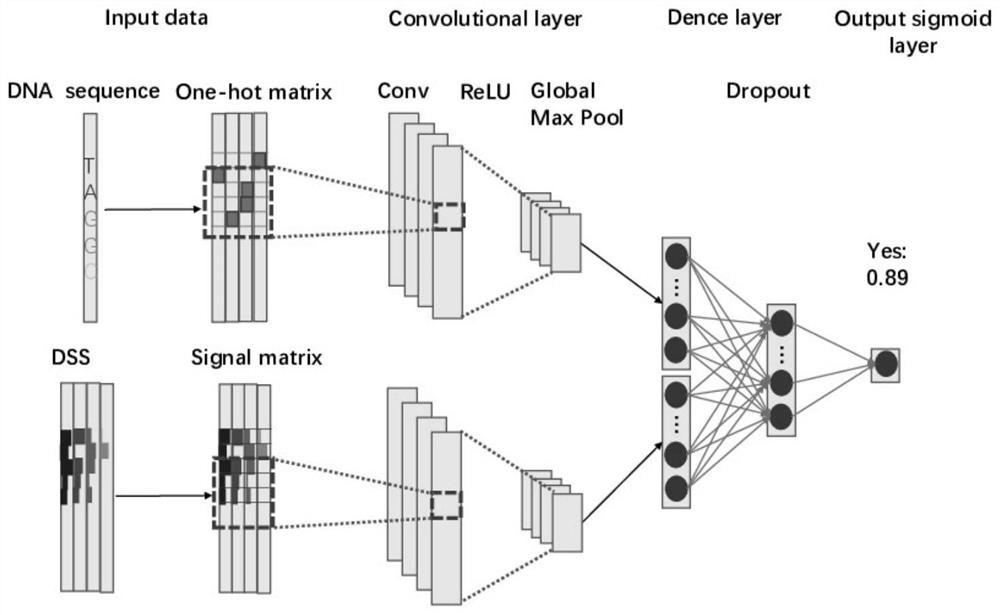
Transcription factor binding site prediction method fusing with DNA shape features
The invention relates to a transcription factor binding site prediction method fusing DNA shape features, belongs to the field of bioinformatics, and provides a new model for predicting transcription factor binding sites by using CNN in combination with DNA sequence and shape feature information by combining knowledge of structural biology, genomics and a deep learning neural network. Meanwhile, a special data set containing DNA shape features and DNA sequence information is constructed, and corresponding DNA shape information is added on the basis of a traditional transcription factor prediction data set. Therefore, the prediction accuracy of the DNA transcription factor binding site is improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


























![Anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol Anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/33b4f5f6-81ef-4dbf-b158-19eeb50b909f/HDA0000413713830000011.png)
![Anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol Anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/33b4f5f6-81ef-4dbf-b158-19eeb50b909f/HDA0000413713830000012.png)
![Anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol Anti-tumor application of 3-{2-[([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-methyl)amino]-1-ethoxy}phenol](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/33b4f5f6-81ef-4dbf-b158-19eeb50b909f/HDA0000413713830000021.png)