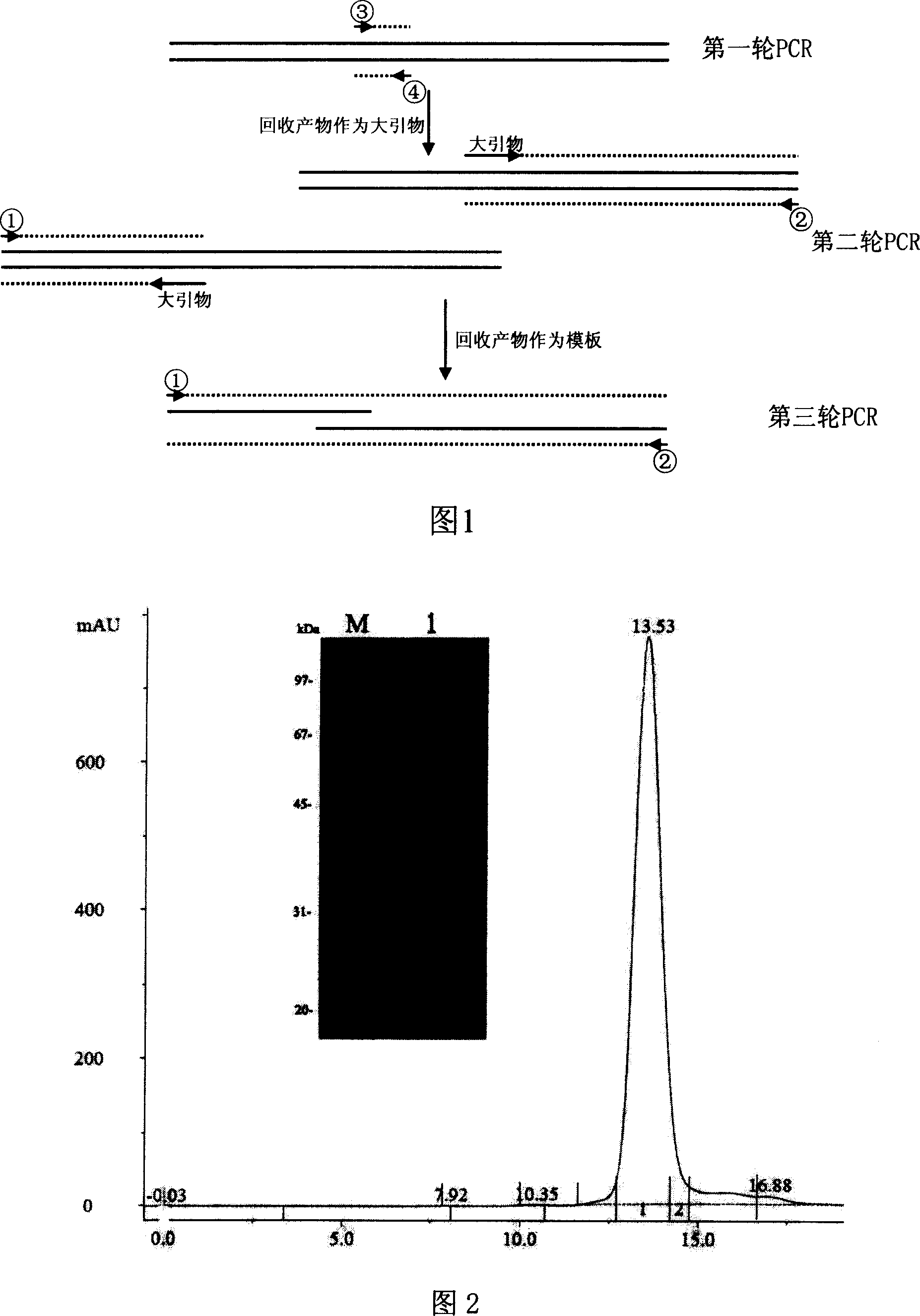
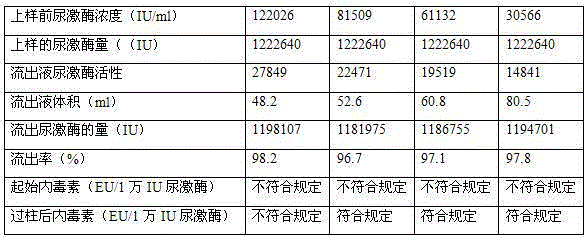
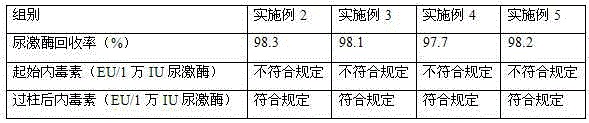
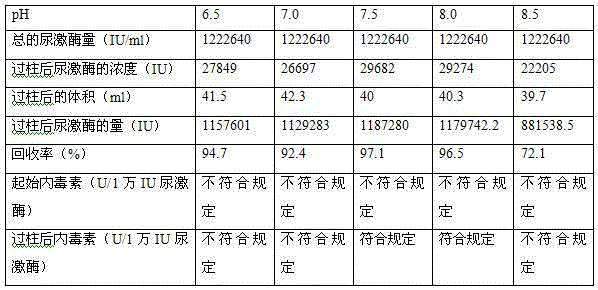
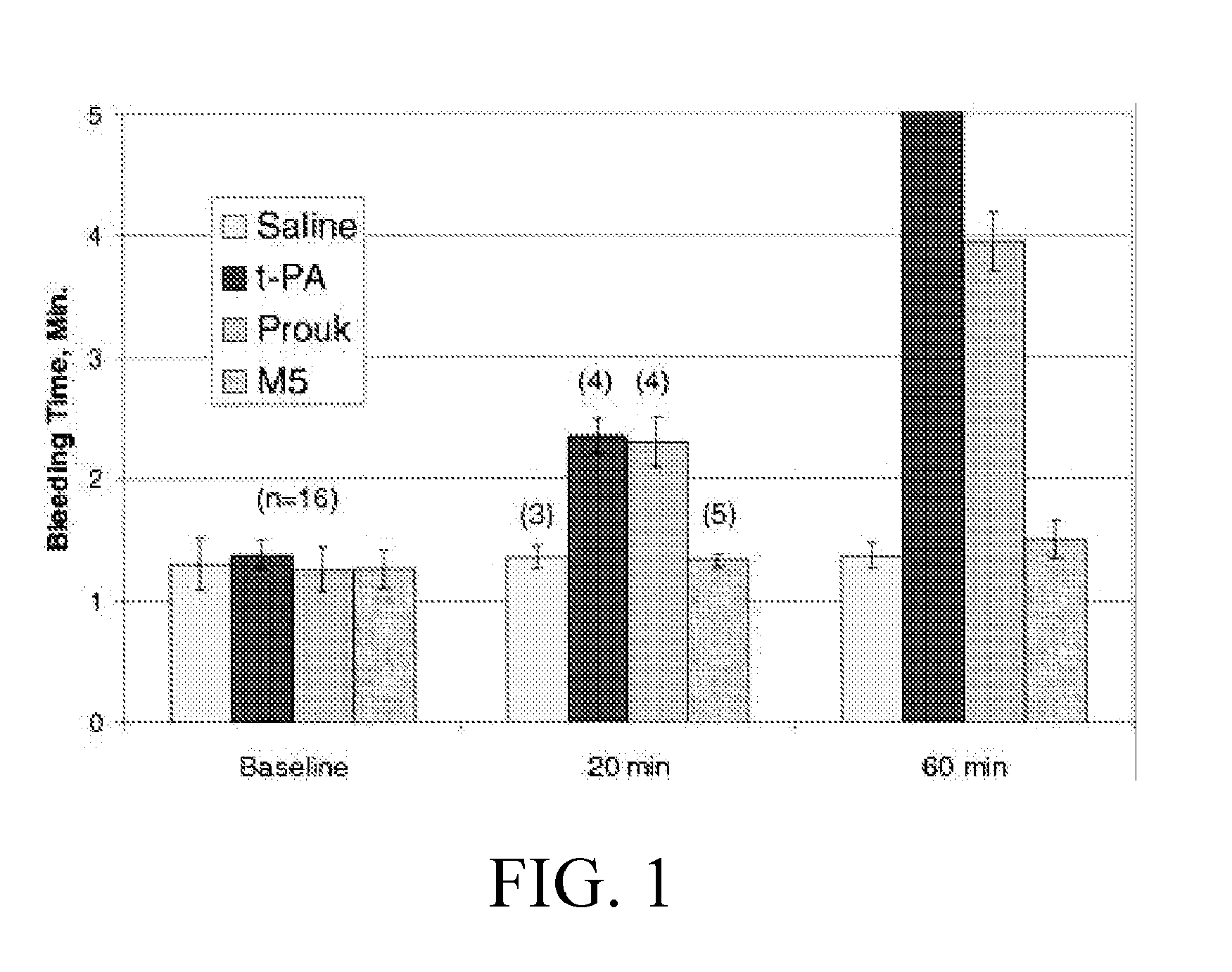
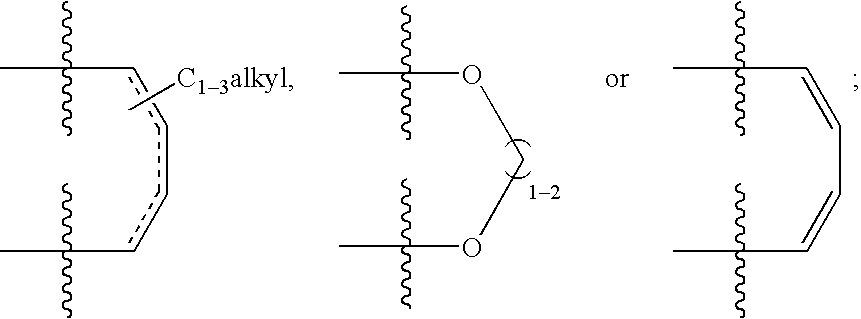Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
215 results about "Urokinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Urokinase, also known as urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), is a serine protease present in humans and other animals. The human urokinase protein was discovered, but not named, by McFarlane and Pilling in 1947. Urokinase was originally isolated from human urine, and it is also present in the blood and in the extracellular matrix of many tissues. The primary physiological substrate of this enzyme is plasminogen, which is an inactive form (zymogen) of the serine protease plasmin. Activation of plasmin triggers a proteolytic cascade that, depending on the physiological environment, participates in thrombolysis or extracellular matrix degradation. This cascade had been involved in vascular diseases and cancer progression.
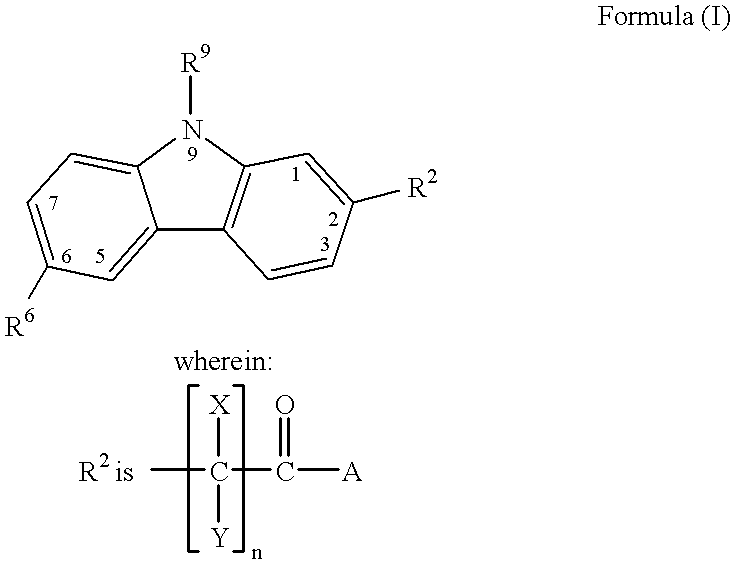
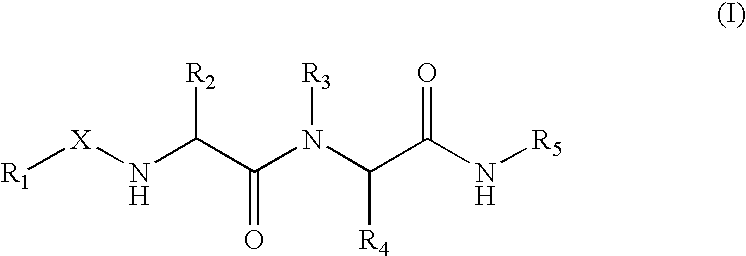
(Hetero)aryl-bicyclic heteroaryl derivatives, their preparation and their use as protease inhibitors
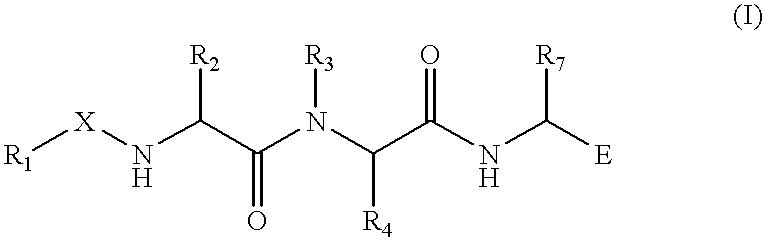
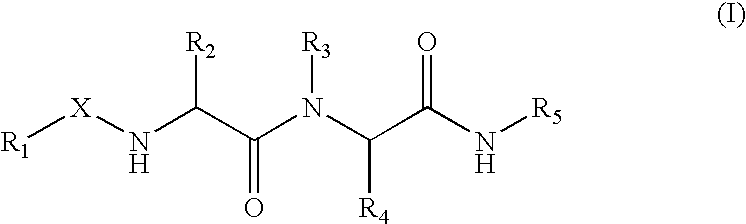
The present invention provides novel compounds of the Formula (I): A-B, its prodrug forms, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein A represents a saturated, unsaturated, or a partially unsaturated bicyclic heterocyclic ring structure, and B represents an aryl or a heteroaryl group. Preferred compounds of the present invention comprise a benzimidazole or indole nucleus. The compounds of this invention are inhibitors of serine proteases, Urokinase (uPA), Factor Xa (FXa), and / or Factor VIIa (FVIIa), and have utility as anti cancer agents and / or as anticoagulants for the treatment or prevention of thromboembolic disorders in mammals.
Owner:AXYX PHARMA INC
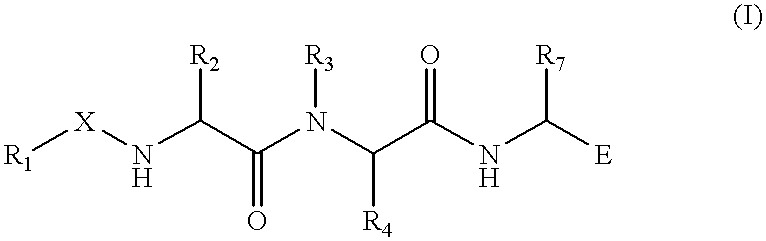
Treating or preventing the early stages of degeneration of articular cartilage or subchondral bone in mammals using carprofen and derivatives
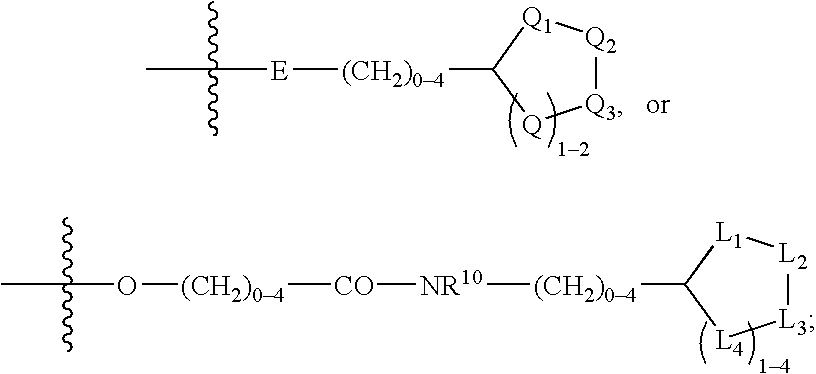
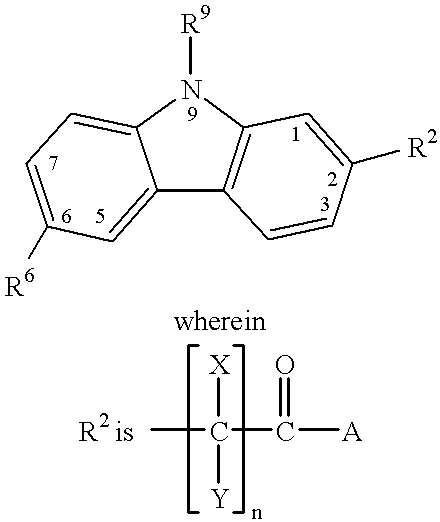
Treating or preventing the early stages of degeneration of articular cartilage or subchondral bone in the affected joint of a mammal is accomplished by administering a chondroprotective compound of Formula (I):where A is hydroxy, (C1-C4)alkoxy, amino, hydroxy-amino, mono-(C1-C2)alkylamino, di-(C1-C2)alkylamino; X and Y are independently H or (C1-C2)alkyl; and n is 1 or 2; R6 is halogen, (C1-C3)alkyl, trifluoromethyl, or nitro; R9 is H; (C1-C2)alkyl; phenyl or phenyl-(C1-C2)alkyl, where phenyl is optionally mono-substituted by fluoro or chloro; -C(=O)-R, where R is (C1-C2)alkyl or phenyl, optionally mono-substituted by fluoro or chloro; or -C(=O)-O-R', where R1 is (C1-C2)alkyl.This treatment ameliorates, diminishes, actively treats, reverses or prevents any injury, damage or loss of articular cartilage or subchondral bone subsequent to said early stage of said degeneration. Whether or not a mammal needs such treatment is determined by whether or not it exhibits a statistically significant deviation from normal standard values in synovial fluid or membrane from the affected joint, with respect to at least five of the following substances: increased interleukin-1 beta (IL-1beta); increased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha); increased ratio of IL-1beta to IL-1 receptor antagonist protein (IRAP); increased expression of p55 TNF receptors (p55 TNF-R); increased interleukin-6 (IL-6); increased leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF); decreased insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1); decreased transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta); decreased platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); decreased basic fibroblast growth factor (b-FGF); increased keratan sulfate; increased stromelysin; increased ratio of stromelysin to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases (TIMP); increased osteocalcin; increased alkaline phosphatase; increased cAMP responsive to hormone challenge; increased urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA); increased cartilage oligomeric matrix protein; and increased collagenase.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Non-covalent inhibitors of urokinase and blood vessel formation
InactiveUS6586405B2Promote cell adhesionImprove cell adhesionTripeptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesBiochemistryIn vivo
Owner:KEVIN S HELMBACHER GENERAL COUNSEL +1
Method and tool for predicting cancer and other diseases
ActiveUS20100098705A1Monitor progressMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorReceptor
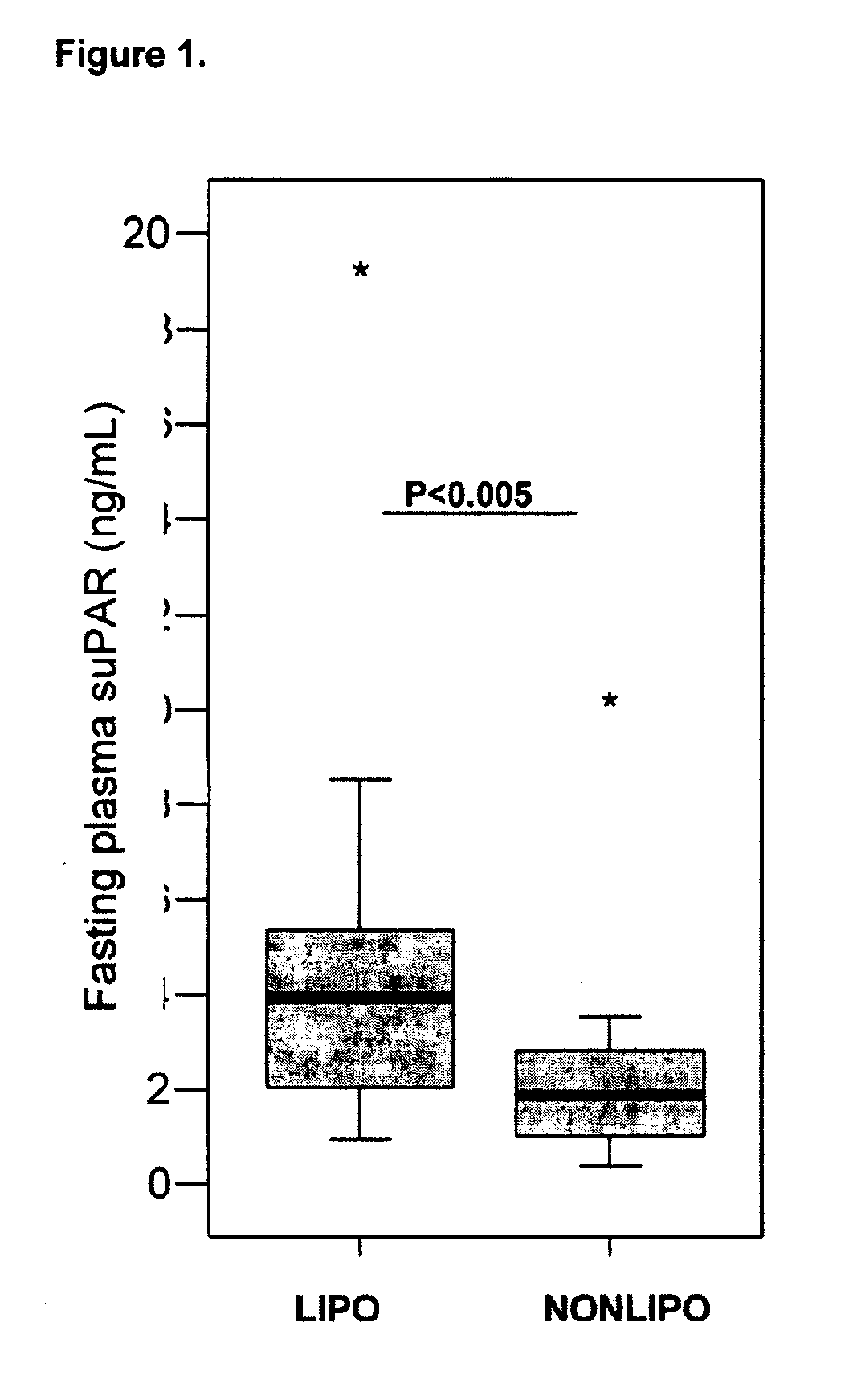
The invention concerns a marker for low-grade inflammation and metabolic syndrome (MS) and MS-related diseases and / or low-grade inflammation-related diseases such as cardiovasculardisease, ischemic heart disease and type 2 diabetes. More particularly it concerns the measurement of the concentration of soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) in human biological fluids (sputum, cystic fluid, ascites, serum, plasma, urine) as a tool of diagnosing and / or prognosticating low-grade inflammation and metabolic syndrome and the risk of development of the related diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, ischemic heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
Non-covalent inhibitors of urokinase and blood vessel formation
InactiveUS20020037857A1Promote cell adhesionImprove cell adhesionDipeptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorIn vivo
Novel compounds having activity as non-covalent inhibitors of urokinase and having activity in reducing or inhibiting blood vessel formation are provided. These compounds have Pi a group having an amidino or guanidino moiety or derivative thereof. These compounds are useful in vitro for monitoring plasminogen activator levels and in vivo in treatment of conditions which are ameliorated by inhibition of or decreased activity of urokinase and in treating pathologic conditions wherein blood vessel formation is related to a pathologic condition.
Owner:KEVIN S HELMBACHER GENERAL COUNSEL +1
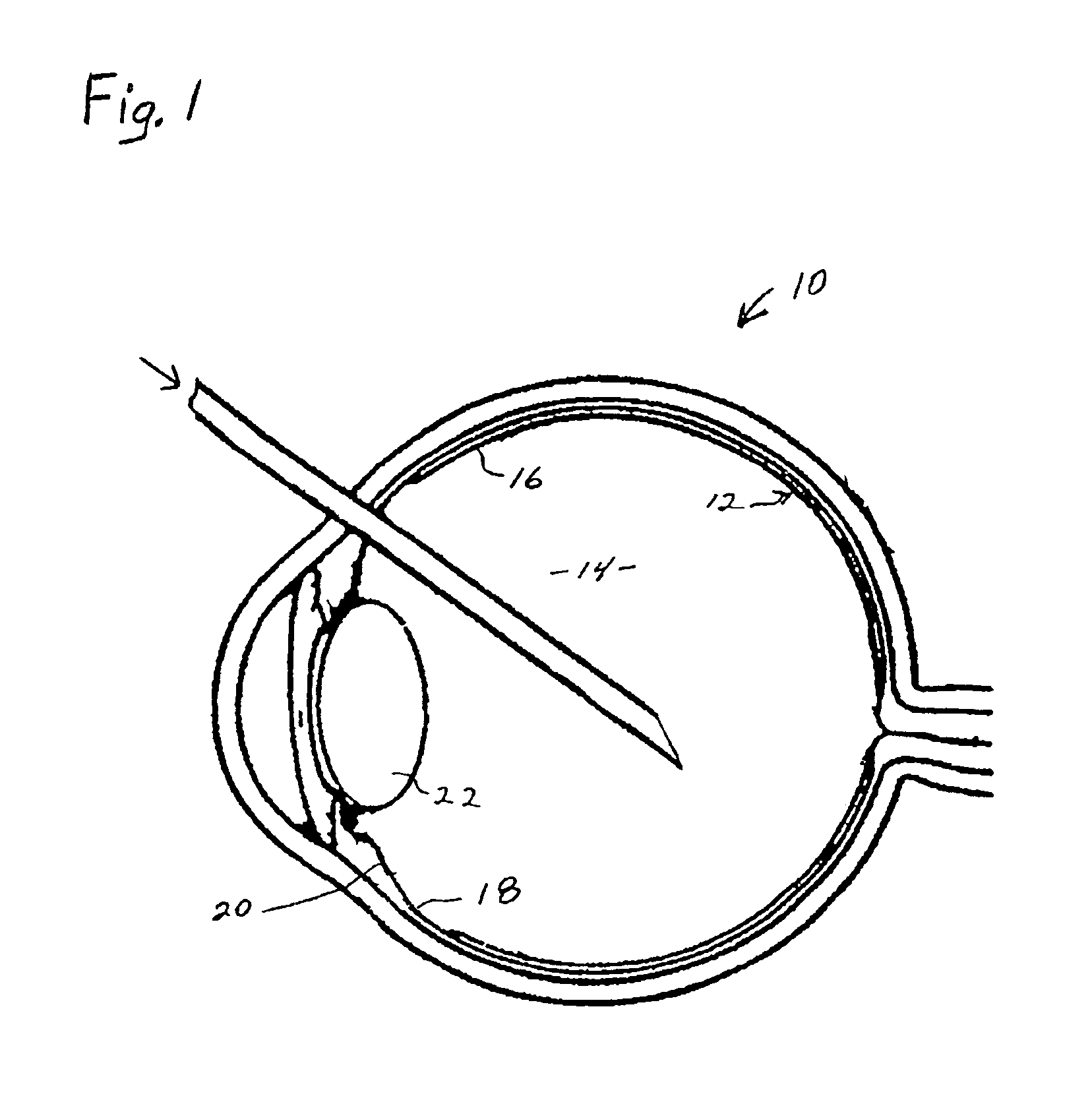
Process for generating plasmin in the vitreous of the eye and inducing separation of the posterior hyaloid from the retina
InactiveUS6899877B2Inhibiting retinal tearReducing and preventing effectSenses disorderEye implantsUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorVascular proliferation
A process for inhibiting vascular proliferation separately introduces components into the eye to generate plasmin in the eye in amounts to induce complete posterior vitreous detachment where the vitreoretinal interface is devoid of cortical vitreous remnants. The process administers a combination of lysine-plasminogen, at least one recombinant plasminogen activator selected from the group consisting of urokinase, streptokinase, tissue plasminogen activator, chondroitinase, pro-urokinase, retavase, metaloproteinase, and thermolysin and a gaseous adjuvant to form a cavity in the vitreous. The composition is introduced into the vitreous in an amount effective to induce crosslinking of the vitreous and to induce substantially complete posterior vitreous detachment from the retina without causing inflammation of the retina. The gaseous adjuvant material is introduced into the vitreous simultaneously with or after the lysine-plasminogen and recombinant plasminogen activator such as recombinant urokinase to compress the vitreous against the retina while the composition induces the complete posterior vitreous detachment.
Owner:MINU
Application of earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme in resistance to liver fibrosis
InactiveCN101628113AAnthropod material medical ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEarthworm fibrinolytic enzymeCollagenan
The invention relates to an application of an earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme in preparation of liver fibrosis resistant medicine or liver protection health-care food, which belongs to the technical field of biology. The effective dose of an oral liver fibrosis resistant earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme is 1,000-3,000 urokinase unit / person / day. Proved by experiments, earthworm collagenase can degrade collagen but cannot degrade (ox blood) fibrin, and the earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme can degrade the (ox blood) fibrin and can also degrade the collagen, thus the activity of the earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme is higher than the activity of the earthworm collagenase and the activity of a collagenase standard product (Sigma I type). Proved by a liver fibrosis resistant experiment by using a rat, the oral liver fibrosis resistant earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme has obvious effect and no obvious poisonous and side effect, but the oral liver fibrosis resistant earthworm collagenase does not have obvious effect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Inhibitors of urokinase and blood vessel formation
InactiveUS6432922B1Positive maintenanceInhibition effectSenses disorderAntipyreticPLG - PlasminogenArginine
Novel compounds having activity inhibitors of urokinase and in reducing or inhibiting blood vessel formation are provided. These compounds have an arginine or arginine mimic aldehyde or an arginine ketoamide group at P1. These compounds are useful in vitro for monitoring plasminogen activator levels and in vivo in treatment of conditions which are ameliorated by inhibition of or decreased activity of urokinase and in treating pathologic conditions wherein blood vessel formation is related to a pathologic condition.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA INC
Fusion protein of urokinase type plasminogen activator a chain and melittin and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101337992AAvoid stickingInhibit migrationFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsMelittinProtein C
The invention provides a fusion protein formed by the combination of urokinase-type plasminogen activator a chain and melittin, the preparation method thereof, and the application of the fusion protein in tumor treatment.
Owner:吉林圣元科技有限责任公司
Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor as a target for diagnosis of metastases
InactiveUS6077508AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsZymogenUrokinase Plasminogen Activator
The present invention relates to the use of molecules capable of specifically binding a urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) as diagnostic reagents for the detection of metastases in vivo. Such metastases can include, but are not limited to, micrometastases.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV +1
Purification of recommbined human urokinase zymogen
ActiveCN1680550AEasy to fillLarge amount of processingPeptide preparation methodsPeptidasesZymogenUrokinase Plasminogen Activator
The invention is about a method to purify the recombined human urokinase by the chromatography. The invention relates to recovery the gene engineering production from the mammal cell culture using the Streamline-SP, Sephacryl S-200, Sepharose Fast Flow and DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow method. The recombined human urokinase can meet the SFDA standard and the percent recovery is above 70%, the purity is above 99% by using the method.
Owner:TASLY BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Method for enriching urine protein directly
InactiveCN101863974AAvoid the collection stepLow costHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsURINARY TRYPSIN INHIBITORUrokinase Plasminogen Activator
The invention relates to a urine protein enriching method. In the method, urine protein in urine is absorbed directly by an adsorbent in a urinal or a pee hopper, and the adsorbent for adsorbing the urine protein is conveyed to a working point for follow-up treatment; and based on the isoelectric point properties of specific urine protein, the urine protein such as urinary trypsin inhibitor, human urinary kininogenase, urokinase and the like is adsorbed directly and effectively by using the specific adsorbent such as ion exchange resin, and thus, the step of collecting the urine is avoided. The method does not influence sanitation of toilets obviously, reduces the cost of urine transportation substantially and solves a series of environmental problems.
Owner:GUANGDONG TECHPOOL BIO-PHARMA CO LTD +1
Title inhibitors of urokinase
InactiveUS6576613B1Promote cell adhesionImprove cell adhesionSenses disorderDipeptide ingredientsZymogenPLG - Plasminogen
Novel inhibitors of urokinase are provided which have an arginine or arginine mimic aldehyde or an arginine ketoamide group at P1. These compounds are useful in vitro for monitoring plasminogen activator levels and in vivo in treatment of conditions which are ameliorated by inhibition of or decreased activity of urokinase.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA INC
Thrombolytic agents and methods of treatment for thrombosis
The foregoing invention relates to a new microbubble preparation and thrombolytic therapy which relies on microbubbles and ultrasound for its lytic activity. The pharmaceutical composition of the invention comprises a liquid solution of microbubbles with an internal atmosphere enhanced with the perfluorocarbon gas which cavitate in the presence of an ultrasound field following intravenous injection or infusion of said composition into said host. For thrombolysis the area of a thrombus is exposed to an ultrasound field in the presence of the microbubbles and significant lysis is experienced. The method and pharmaceutical composition of the invention exhibit thrombolytic properties similar to those of other thrombolytic agents such as urokinase and are less toxic and are clot specific in that they do not introduce a systemic lytic state to a said animal.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
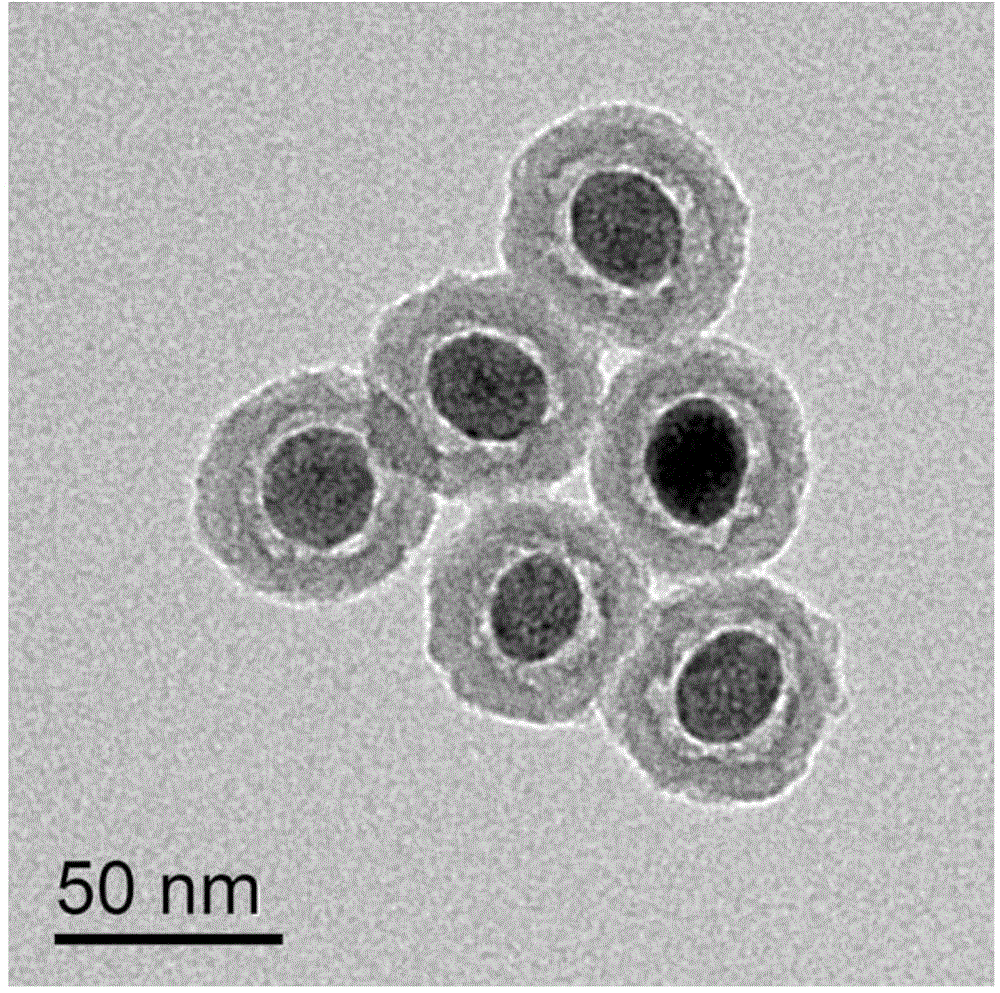
Tumor-targeted hollow core-shell structure nano diagnosis-treatment agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104784707AIncrease loadReduce reunionEnergy modified materialsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsTumor targetOrganic inorganic
The invention relates to a tumor-targeted hollow core-shell structure nano diagnosis-treatment agent and a preparation method thereof. The nano diagnosis-treatment agent comprises an upconversion nanoparticle inner core, an organic-inorganic hybrid silica shell layer and an intermediate cavity structure, can improve the load capacity of a photosensitizer and reduce the photosensitizer aggregation, and can specifically recognize cancer cells by connecting tumor-targeted molecules (such as urokinase ammonia terminal fragments) to the surface; under the irradiation of 980 nm laser, a visible light emission sensitizing photosensitizer of the nano diagnosis-treatment agent generates singlet oxygen, so that the photodynamic therapy of cancer cells can be performed; in addition, the nano diagnosis-treatment agent can be used for the upconversion luminescence and CT dual-mode imaging by utilizing the upconversion luminescence and strong X-ray absorption characteristics.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Expression, purification and crystallization of urokinase catalyst structure domain mutant
InactiveCN101024827ALow costImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySerine proteinasesPichia pastoris
The invneiton relates to expression, purification and crystallization of urokinase catalytic domain mutant, relating to the field of medicine, biotechnique, and structural biology. And the invention provides a techical method of expression, purification and crystallization of urokinase catalytic domain mutant in Pichia pastoris. And the cultured urokinase catalytic domain mutant has crystallographic space group R3, and unit cell parameters: a=b=120.48, c=42.45, alpha=beta=90.0deg, and gama=120.0 deg. And this protein has serine proteinase activity, appliable to high flux screening of urokinase inhibitor; and its high resolution crystal provides a research and development platform for design and development of urokinase inhibitor.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Separation purification method of urokinase
The invention relates to a separation purification method of urokinase. The separation purification method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) separating the urokinase; and (2) purifying the urokinase. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: (a) collecting urine of men, adjusting the pH value of the urine to 8.5 at the temperature of 10 DEG C or lower, standing for 2h, and removing precipitates, thus obtaining supernatant; (b) taking the supernatant, adjusting the pH to 5.0 to 5.5, acidifying to obtain acidified urine, and adsorbing the acidified urine by virtue of a diatomite column; (c) washing the diatomite column by cold water of 5 DEG C, eluting by utilizing 1% ammonia water and sodium chloride to obtain an elution solution; (d) salting out the elution solution by utilizing saturated ammonium sulfate and 4% ammonia water to obtain a urokinase crude product; and (e) adding a given amount of ammonia water into the precipitates, sufficiently dissociating the urokinase in the precipitates to obtain a urokinase solution.
Owner:JIANGSU YOULIKA BIOTECHNOLOYG CO LTD
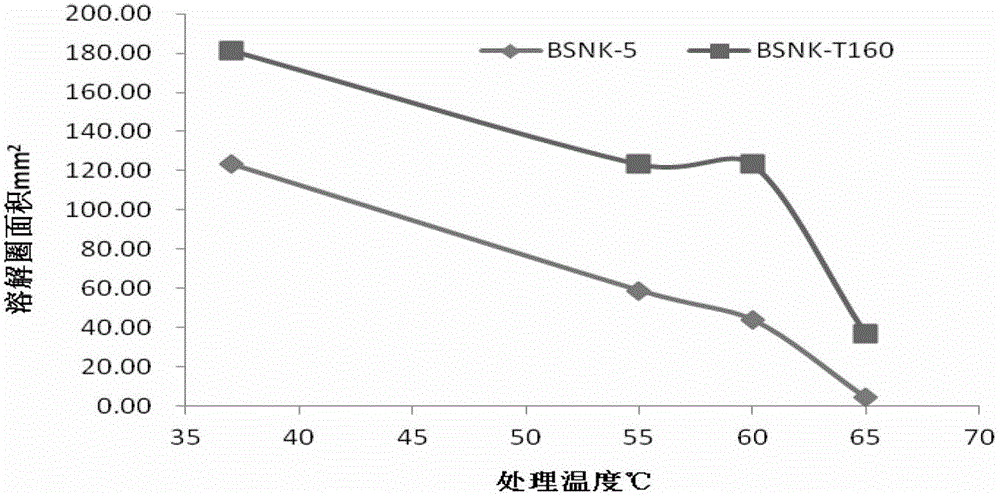
Strain for nattokinase with high activity and thermal stability and fermented product thereof
ActiveCN102943060AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesThermal stabilityHigh activity
A novel natto bacillus subtilis BSNK-T160 is obtained through irradiation mutagenesis. Compared with the wild fungus BSNK-5, the casein hydrolytic activity of the BSNK-T160 is improved by 46.9% and the thermal stability at a temperature of 65 DEG C is improved by eight times; the fibrin activity is improved by 29.62% and the thermal stability is improved by 82.31% compared with a urokinase. The strain BSNK-T160 can be used for producing the nattokinase with the high activity and thermal stability. The nattoes with superior quality can be produced through fermentation of soybeans for 24h by using the stain.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Specific purified high-molecular urokinase chromatography media as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101693748AEasy to makeMild reaction conditionsEnzymesCross-linkUrokinase Plasminogen Activator
A specific purified high-molecular urokinase chromatography media is characterized by having a structure as follows: HOOC-(CH2)4(NH)C-O-R-O-C(NH)NH(CH2)4-CO-X,X=NHC6H5C(NH)NH2, wherein R represents cross-linked agarose substrate. The specific purified high-molecular urokinase chromatography media has the advantages of being simple in preparation process and mild for reaction conditions, being applicable to high-efficiency separation of high-molecular urokinase media and low-molecular urokinase media, and being capable of implementing industrial production of high-purification and high-molecular urokinase.
Owner:江西浩然生物制药有限公司
Malarial animal model having a chimeric human liver
InactiveUS7273963B2Full recoveryUseful for developmentVectorsGenetic engineeringHuman animalHepatica
The present invention features a non-human animal model of malaria, e.g., Plasmodium, particularly Plasmodium falciparum. The model is based on a non-human, immunocompromised transgenic animal having a human-mouse chimeric liver, where the transgene provides for expression of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator in the liver. The invention also features methods for identifying candidate therapeutic agents, e.g., agents having anti-pathogenic activity against malaria.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE +1
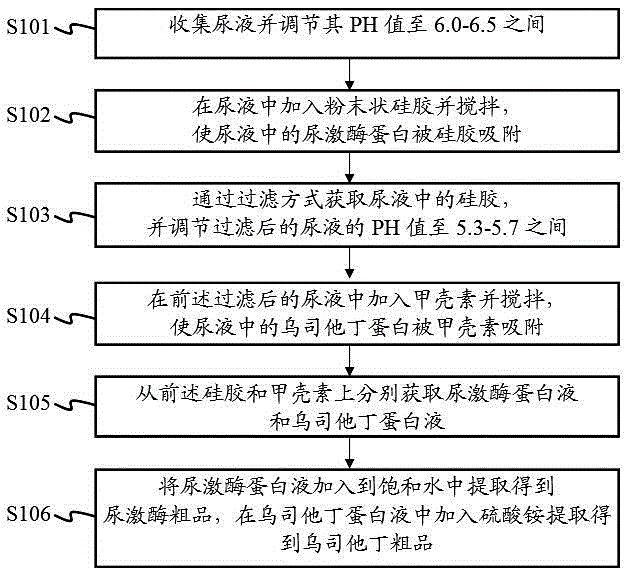
Method for extracting urokinase and ulinastatin from urine
InactiveCN105238771AHigh economic valueIncrease productionProtease inhibitorsAnimals/human peptidesMedicineSilica gel
The invention provides a method for extracting urokinase and ulinastatin from urine. The method comprises the following steps: collecting the urine, and adjusting the pH value of the urine; adding silica gel powder into the urine, and stirring so that urokinase protein in the urine is adsorbed by the silica gel; acquiring the silica gel through a filtering method, and adjusting the pH value of the filtered urine; adding chitin into the filtered urine so that ulinastatin protein in the urine is adsorbed by the chitin; acquiring urokinase protein fluid and ulinastatin protein fluid from the silica gel and the chitin, respectively; and adding the urokinase protein fluid into saturated water, and extracting to obtain urokinase, and adding ammonium sulfate into the ulinastatin protein fluid, and extracting to obtain ulinastatin. According to the method provided by the invention, the urokinase crude product and the ulinastatin crude product can be extracted from the urine, so that the economic value of the urine is greatly improved.
Owner:张昭
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor epitope, monoclonal antibodies derived therefrom and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080199476A1Downregulate the number of uPAR molecules on the cell membraneCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention relates to antibodies, and antigen-binding fragments thereof, specific for urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and uses thereof for the treatment or prevention of cancer. In particular, the antibodies of the invention are specific for a particular epitope on uPAR. These antibodies interfere with uPAR signaling. Such antibodies are used in diagnostic and therapeutic methods, particularly against cancer.
Owner:TACTIC PHARMA
Biomarkers useful in liver fibrosis diagnosis
InactiveUS20100136579A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMetalloproteinaseGastroenterology
Identification of urokinase-type plasminogen, matrix metalloproteinase 9, and β-2-microglobulin as novel biomarkers associated with liver fibrosis and uses thereof in diagnosing liver fibrosis.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
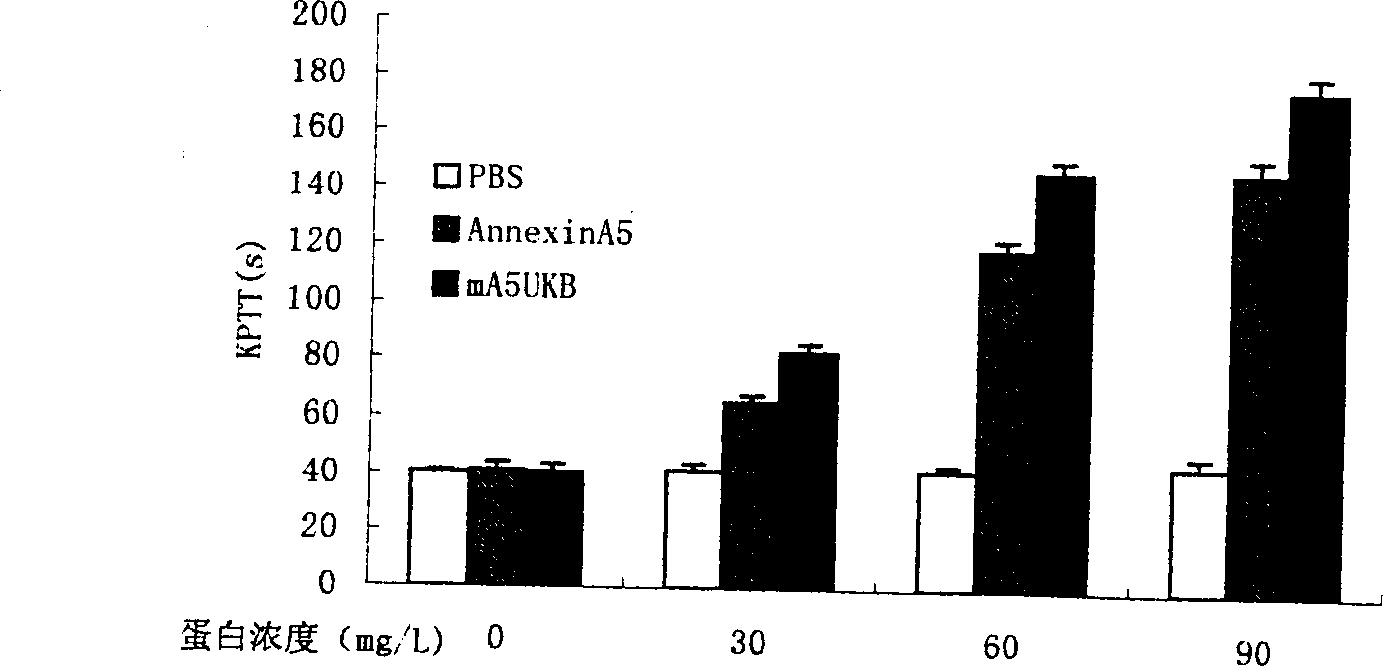
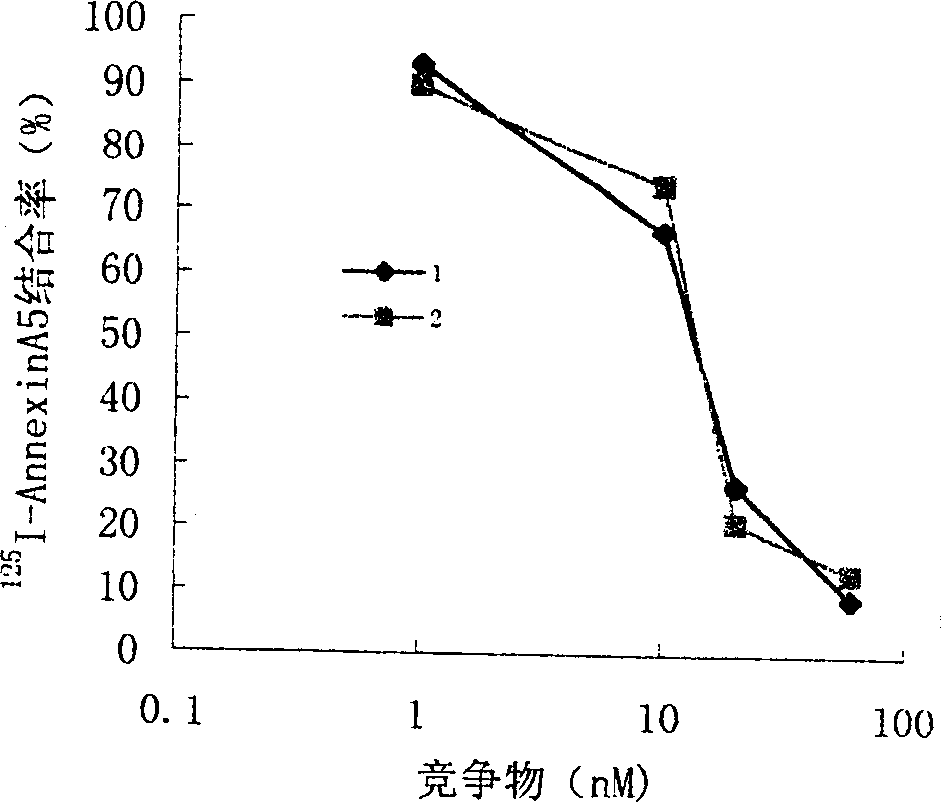
Anticoagulation and thrombolytic thrombus target fusion mA5UKB
InactiveCN1401662AHigh anticoagulant activityHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorThrombus
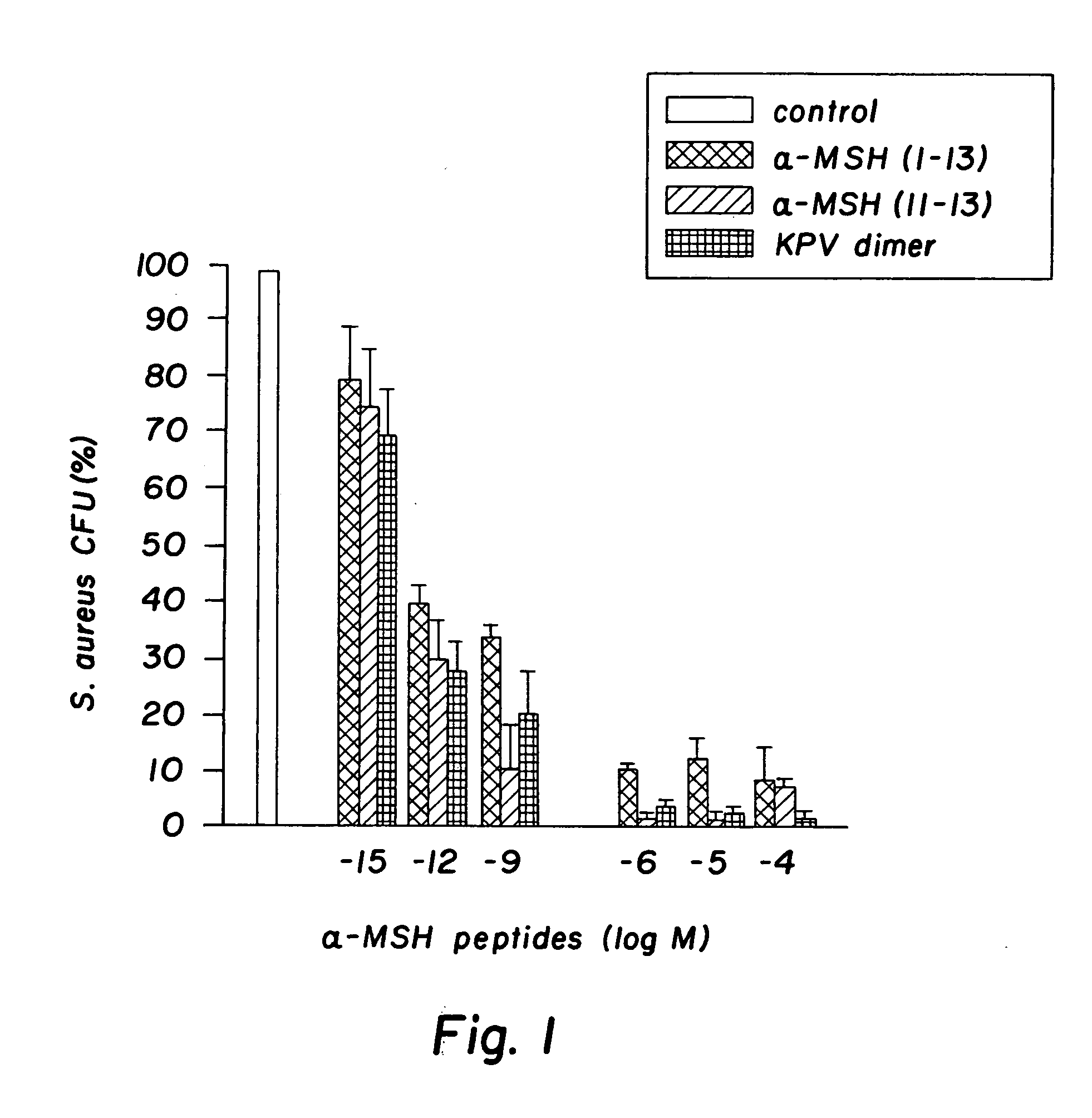
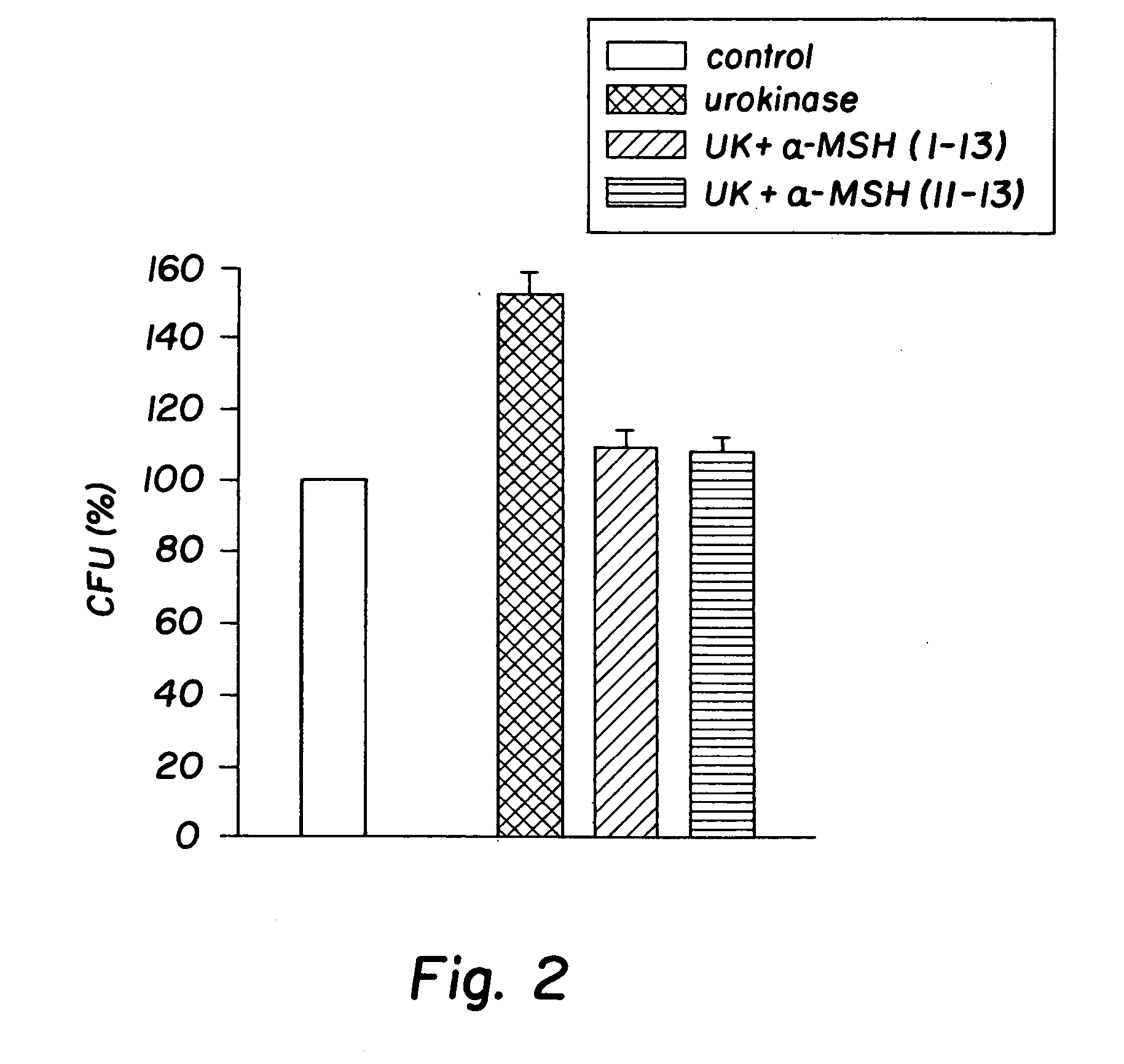
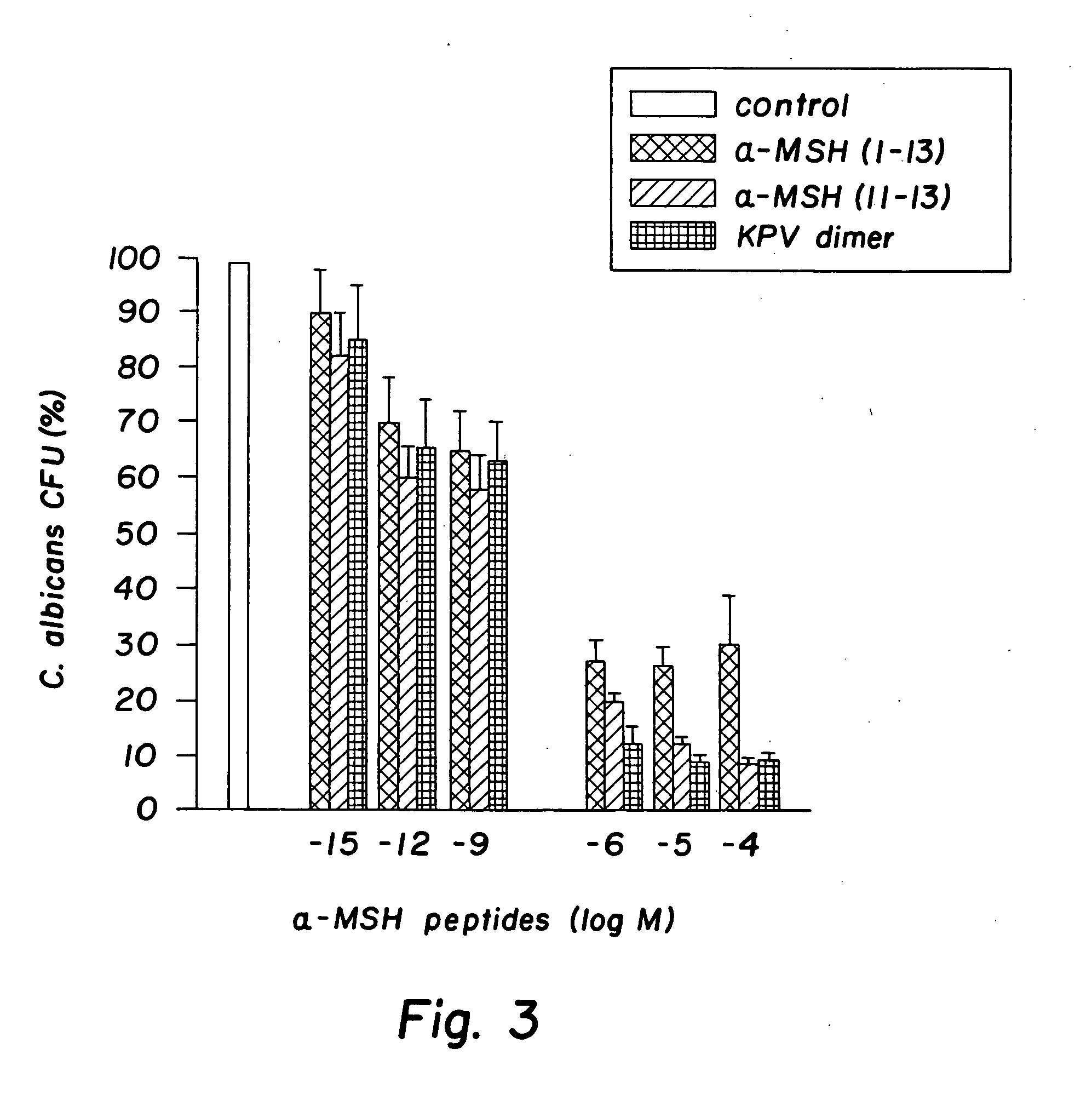
Antimicrobial amino acid sequences derived from alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone
InactiveUS20060111300A1Reduced viabilityAccelerate the accumulation processBiocideAntimycoticsDiseaseAmino acid
Owner:ZENGEN
Method for preparing urokinase and freeze-dried powder of urokinase
ActiveCN110894495ARealize separation and purificationHigh levels of urokinasePeptidasesPhysical chemistryIon exchange
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity macromolecular urokinase and freeze-dried powder of the urokinase and belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering. The methodspecifically comprises the steps: (1) preparing a urokinase crude product; (2) preparing a urokinase fine product; and (3) carrying out purifying, wherein in the step (3), the urokinase fine product obtained in the step (2) is dissolved, and then, the urokinase fine product solution is added into a cation exchange chromatography column for purification; and the purified urokinase is subjected to freeze-drying, thereby obtaining the freeze-dried powder of the urokinase. Fillers filled in the cation exchange chromatography column comprise one of Capto S impAct, SP sepharose HP and source 30S. According to the method for preparing the urokinase and the freeze-dried powder of the urokinase, high-resolution ion-exchange chromatography is selected, so that on the premise of guaranteeing purity,activity and yield, the production cost is reduced greatly, and large-scale production of high-purity high-molecular-weight urokinase becomes possible.
Owner:JIANGSU YOULIKA BIOTECHNOLOYG CO LTD
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
InactiveUS20030027981A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeUrokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptors
A polypeptide presenting an epitope cross-reactive with an epitope of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, and / or having uPA binding activity, is described.
Owner:DANO KELD +20
Method for preparing urokinase
ActiveCN105087531AImprove adsorption capacitySimple structurePeptidasesURINARY TRYPSIN INHIBITORSilica gel
The invention relates to a urinary protein enriching method which comprises the steps of directly adsorbing urinary proteins in urine in urinals or urinating buckets with filter cloth bags loaded with modified silica gel, and transporting the urinary protein adsorbed filter cloth bags to working points for subsequent treatment. According to the method, the isoelectric point property of specific urinary proteins is utilized, and urinary proteins such as urinary trypsin inhibitors, human urinary kininogenase, urokinase and the like are effectively absorbed directly by using the modified silica gel, macroporous resin, chitin, ionic resin and the like, so that a urine collecting step is avoided. The method is free of obvious influence on sanitary conditions of toilets, and the cost for urine transportation and a series of environmental problems resulting from urine transportation are greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG TECHPOOL BIO-PHARMA CO LTD
Vector of uPA expression regulated by Tet-on system and application thereof
InactiveCN101948860AEasy constructionVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorNucleotide
The invention discloses an effect vector of uPA expression regulated by a Tet-on system. The nucleotide sequence of the effect vector comprises a bacteria tetracycline drug-resistant operon sequence, an immediate early promoter sequence of macrophages, a mice pro-urokinase activator expression cassette sequence and a sequence behind the last exon of the mice pro-urokinase activator expression cassette, the four sequences are serially connected in turn. The invention establishes a transgenic mice model of uPA expression regulated by the Tet-on system or tetracycline derivative inducible expression system, and lays solid foundation for further establishing a transgenic animal model of tissue specificity regulatable expression uPA for uPA function research in specific tissues.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Use of Prourokinase and Variants Thereof in Facilitated Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction
ActiveUS20110229454A1High selectivityPrevent hemorrhagic complicationPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymesUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorCardiac muscle
In the field of biological medicines, a use of prourokinase (proUK) and variants thereof in facilitated percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with acute myocardial infarction is provided. The use includes: within 6 hrs after a patient is afflicted with accurate myocardial infarction (AMI), firstly, performing thrombolytic therapy with proUK or variants thereof, and then, performing a PCI operation, to dredge the infarction related artery (IRA) as soon as possible, and re-establish an effective forward blood flow, such that an ischemic myocardium is reperfused. According to the present invention, the facilitated PCI for treatment of AMI with the proUK or variants thereof has an effect superior to that of direct PCI.
Owner:BOSTON PI CARDIO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com