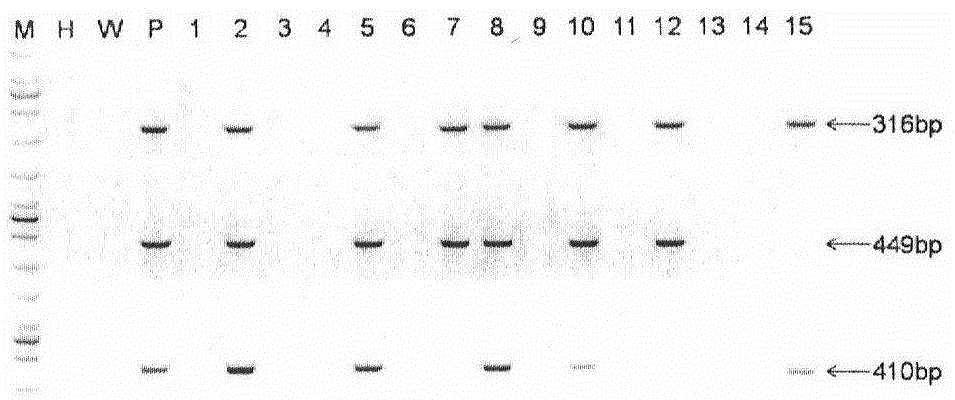
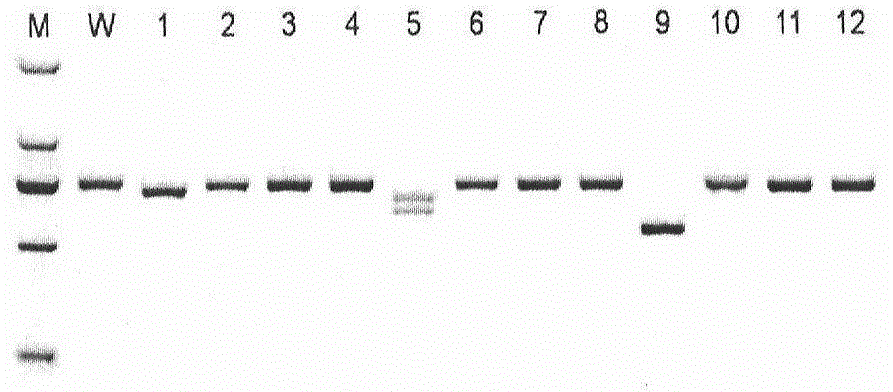
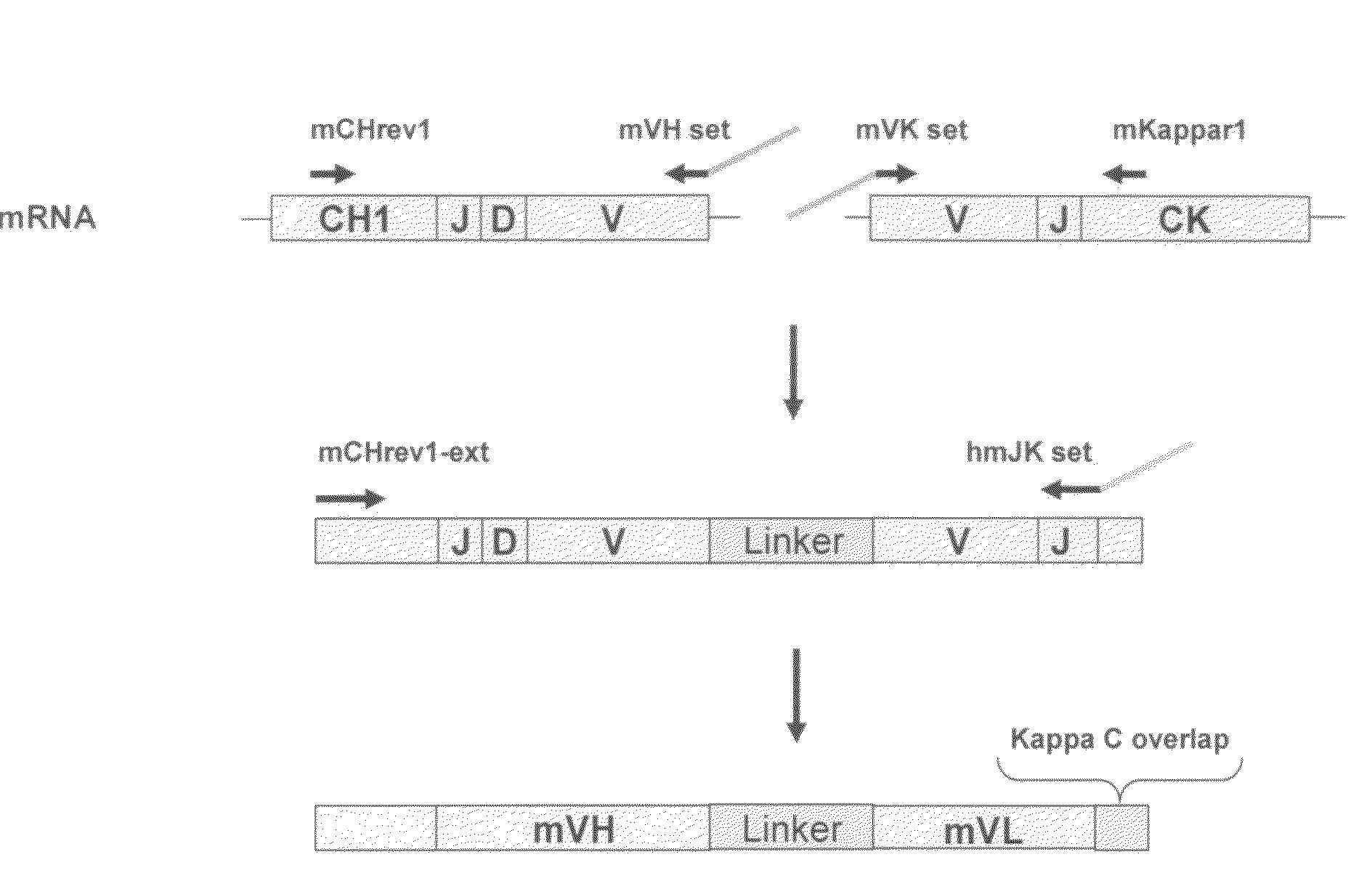
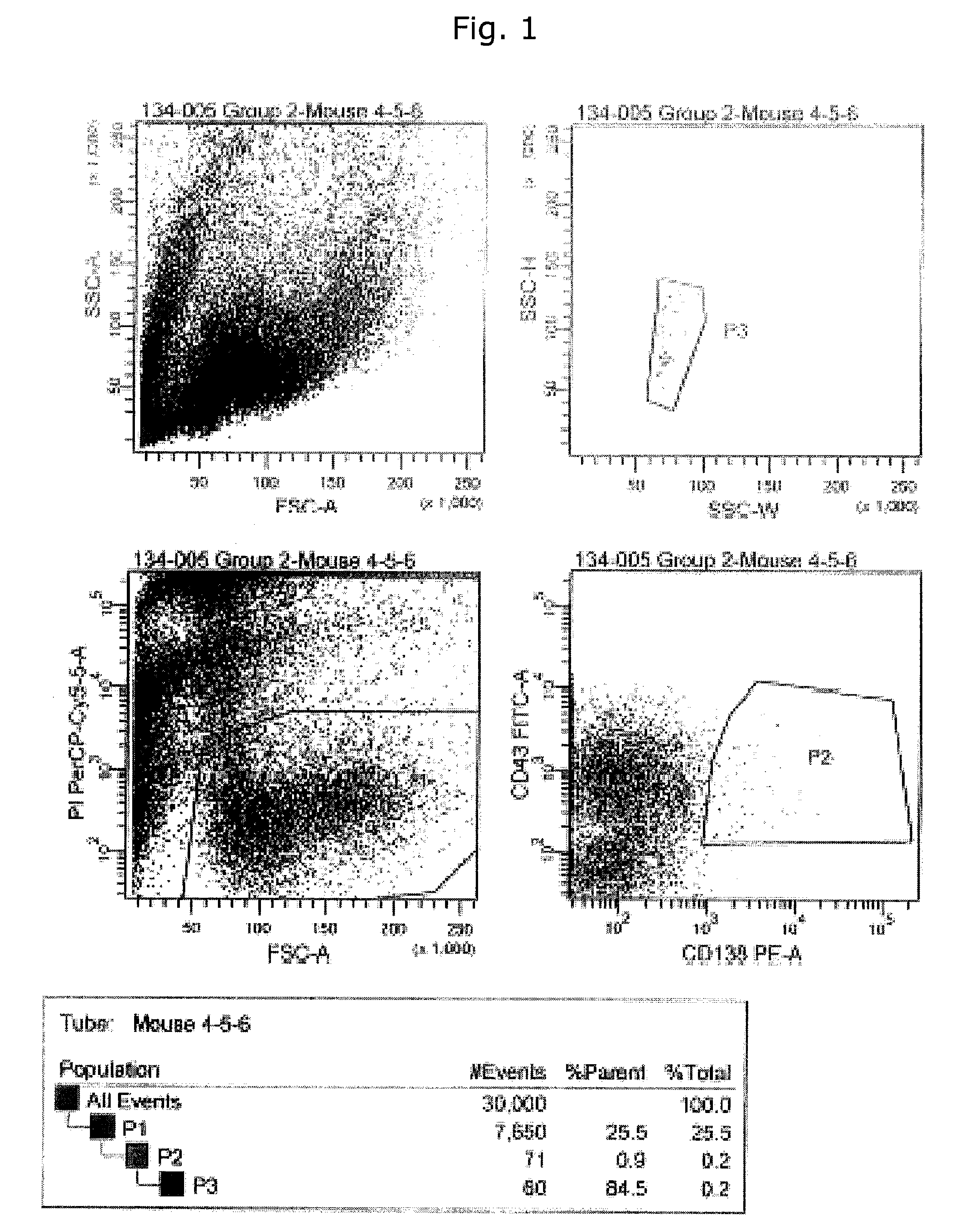
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4633 results about "Animal model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An animal model is a living, non-human animal used during the research and investigation of human disease, for the purpose of better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The animal chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles human physiology as needed. Many drugs, treatments and cures for human diseases have been developed with the use of animal models. Animal models representing specific taxonomic groups in the research and study of developmental processes are also referred to as model organisms. There are three main types of animal models: Homologous, Isomorphic and Predictive. Homologous animals have the same causes, symptoms and treatment options as would humans who have the same disease. Isomorphic animals share the same symptoms and treatments, only. Predictive models are similar to a particular human disease in only a couple of aspects. However, these are useful in isolating and making predictions about mechanisms of a set of disease features.
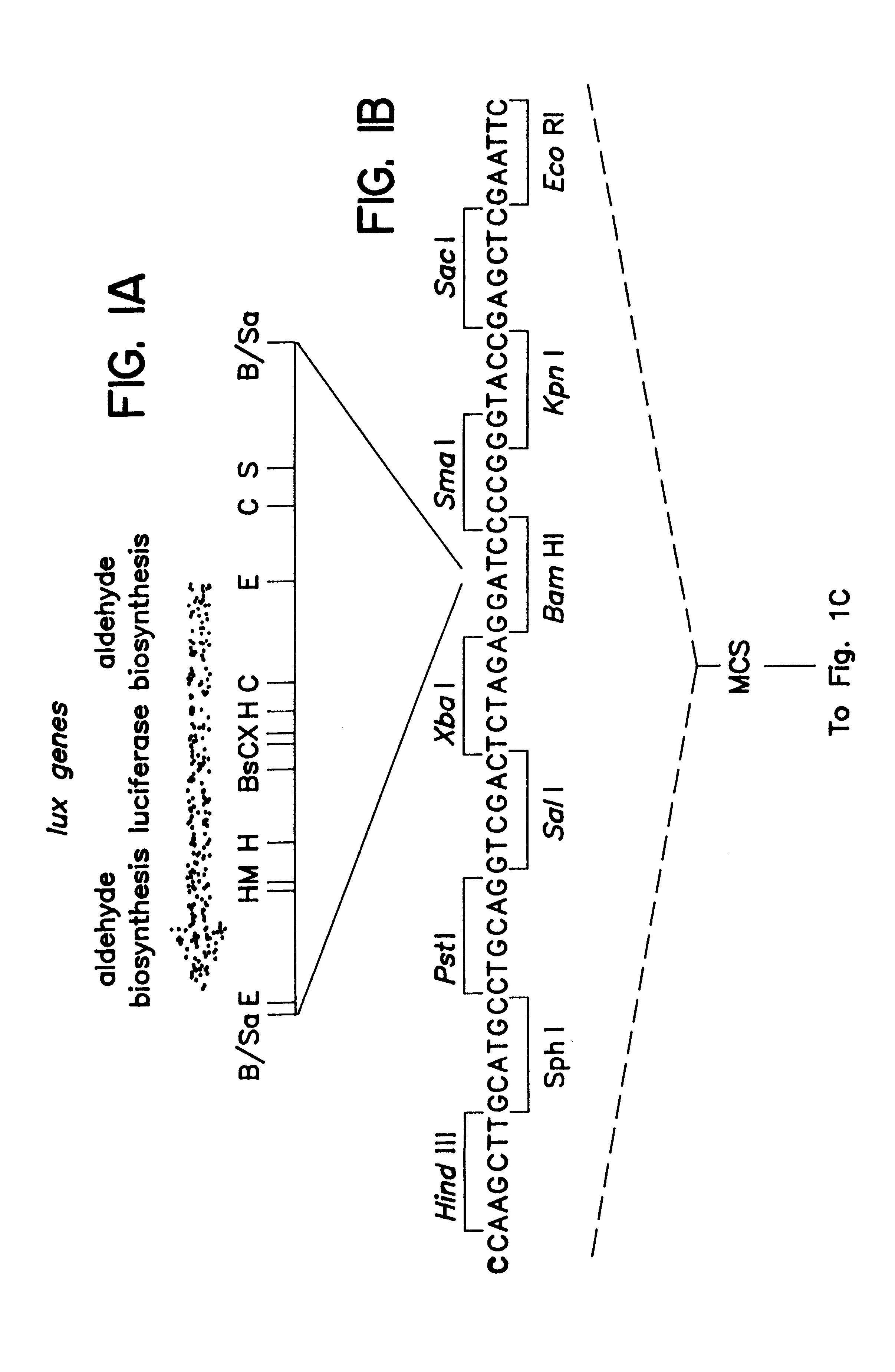
Non-invasive localization of a light-emitting conjugate in a mammal
InactiveUS6217847B1Accurate measurementEvenly distributedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBacteriaMammalNon invasive
Methods and compositions for detecting and localizing light originating from a mammal are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for tracking light emission to selected regions, as well as for tracking entities within the mammal. In addition, animal models for disease states are disclosed, as are methods for localizing and tracking the progression of disease or a pathogen within the animal, and for screening putative therapeutic compounds effective to inhibit the disease or pathogen.
Owner:LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV OF THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES THE
Rodent HER2 tumor model
The invention concerns HER<HIL><PDAT>2< / BOLD><PDAT>-transgenic non-human mammals, animal models for screening drug candidates for the treatment of diseases and disorders associated with the overexpression of HER<HIL><PDAT>2< / BOLD><PDAT>. In particular, the invention concerns animal models designed to test drug candidates for the treatment of HER<HIL><PDAT>2< / BOLD><PDAT>-overexpressing cancers, including breast cancer, that are not responding or poorly responding to current treatments.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SAN VALLEY SYST +1
Methods of isolating amyloid-inhibiting compounds and use of compounds isolated from Uncaria tomentosa and related plants
InactiveUS7285293B2Inhibition formationPromote mental alertnessBiocideNervous disorderAdditive ingredientFractionation
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Antisense compositions targeted to beta1-adrenoceptor-specific mRNA and methods of use
InactiveUS6489307B1Reduce inhibitionInhibit and reduce expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEccentric hypertrophyMammal
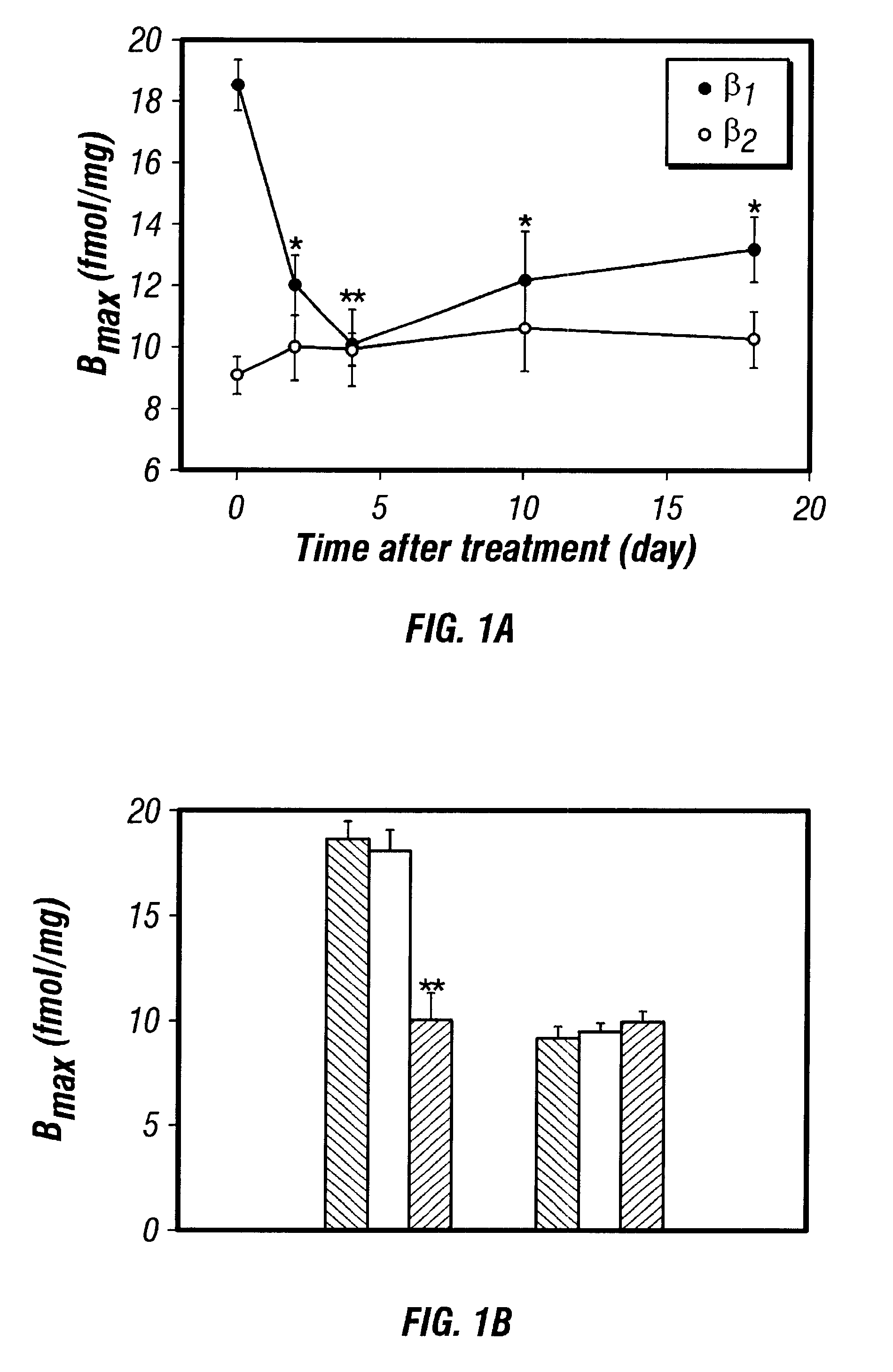
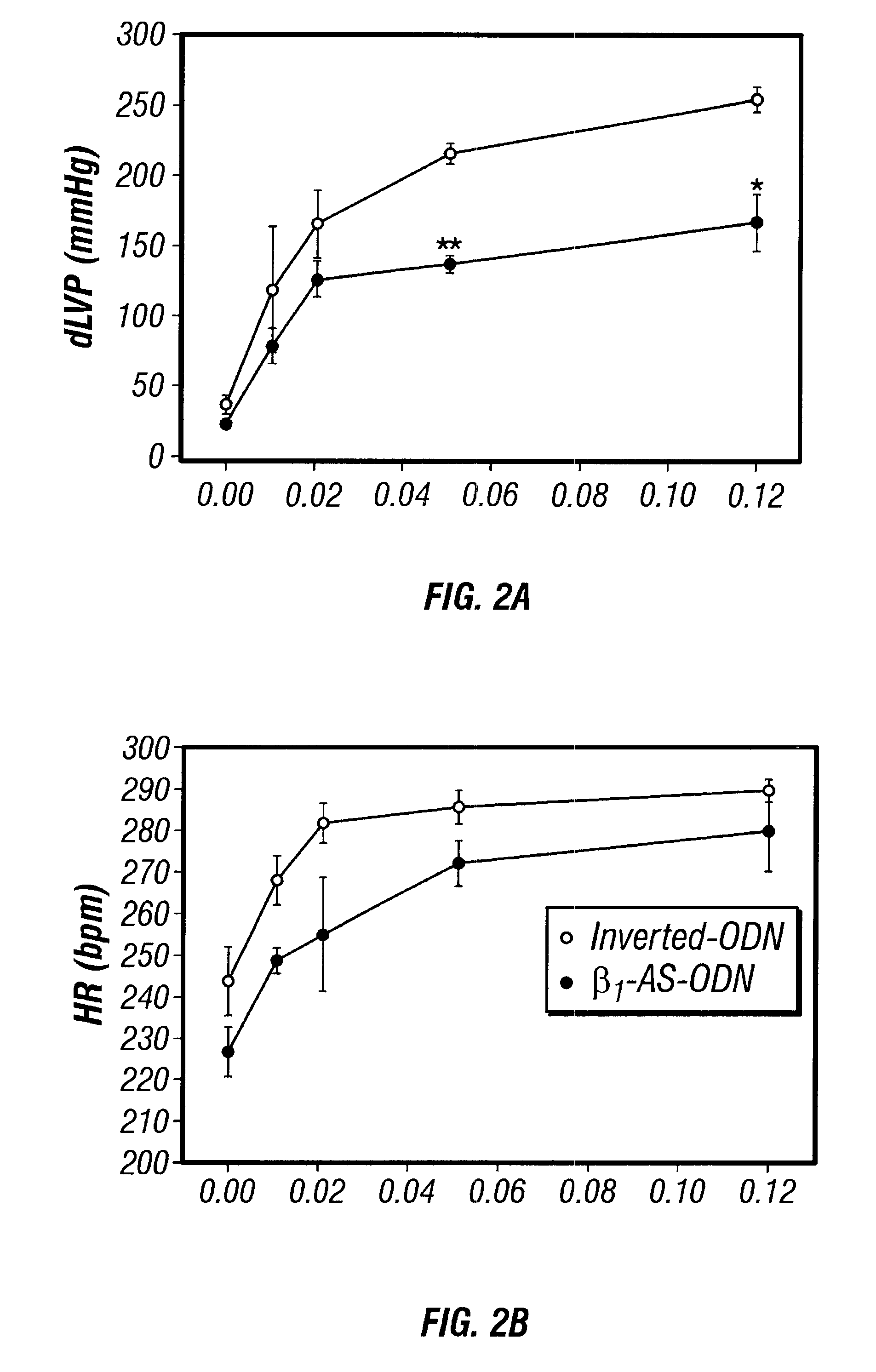
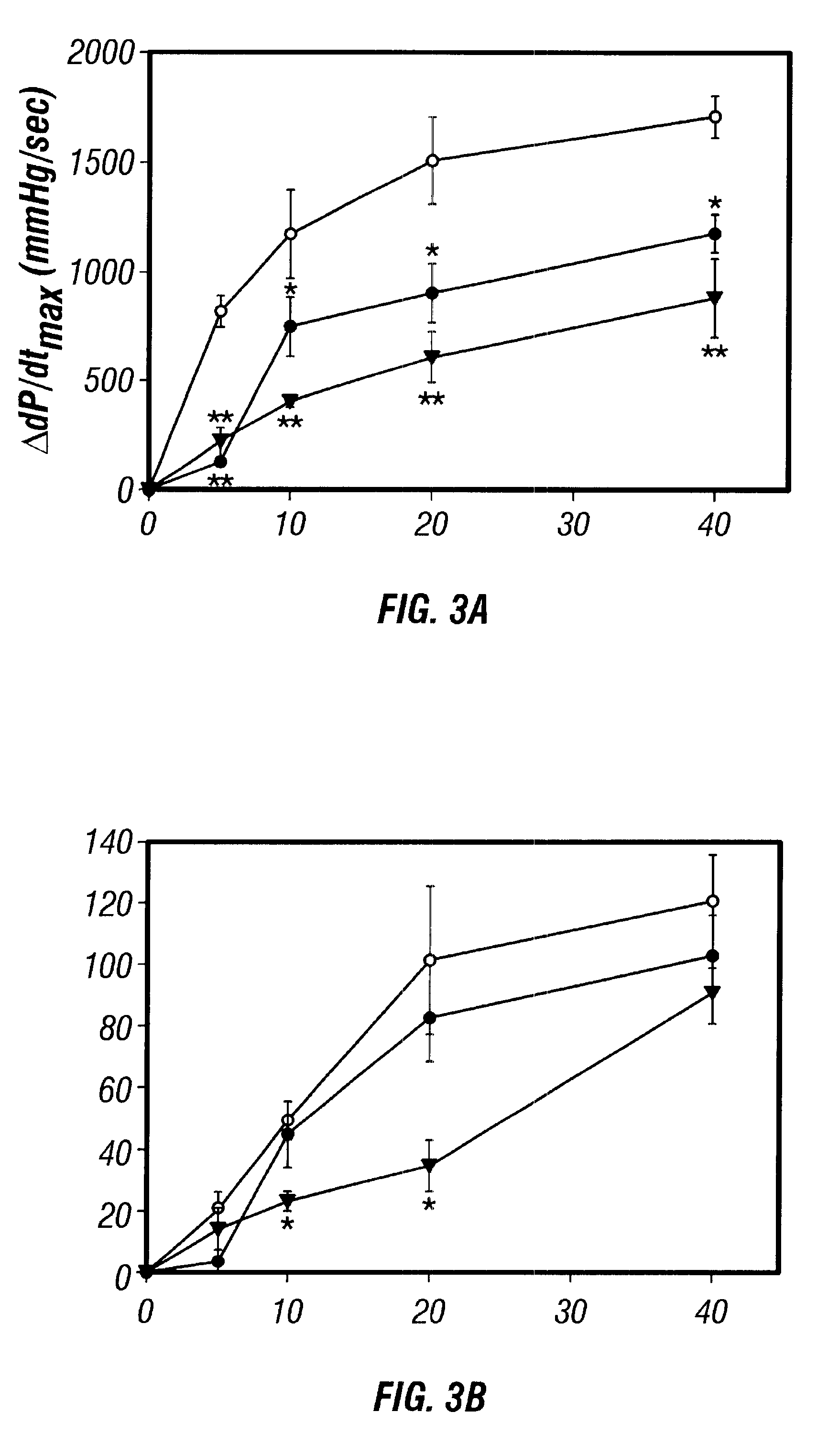
Disclosed are antisense oligonucleotide, polynucleotide, and peptide nucleic acid compounds that specifically bind to mammalian mRNA encoding a beta1-adrenoceptor polypeptide and that are useful in the control and / or treatment of cardiac dysfunction, hypertension, hypertrophy, myocardial ischemia, and other cardiovascular diseases in an affected mammal, and preferably, in a human subject. The antisense compounds disclosed herein, and pharmaceutical formulations thereof, provide sustained control of beta1-adrenoceptor expression over prolonged periods, and achieve therapeutic effects from as little as a single dose. Administration of these antisense compositions to approved animal models resulted in a decrease in blood pressure, but no significant change in heart rate. Use of such antisense compositions in the reduction of beta1-adrenoceptor polypeptides in a host cell expressing beta1-adrenoceptor-specific mRNA, and in the preparation of medicaments for treating human and animal diseases, and in particular, hypertension and other cardiac dysfunction is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Transgenic mouse model of alzheimer's disease and cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS6175057B1Lower Level RequirementsConvenient treatmentVectorsIn-vivo testing preparationsOrganismTgf beta1
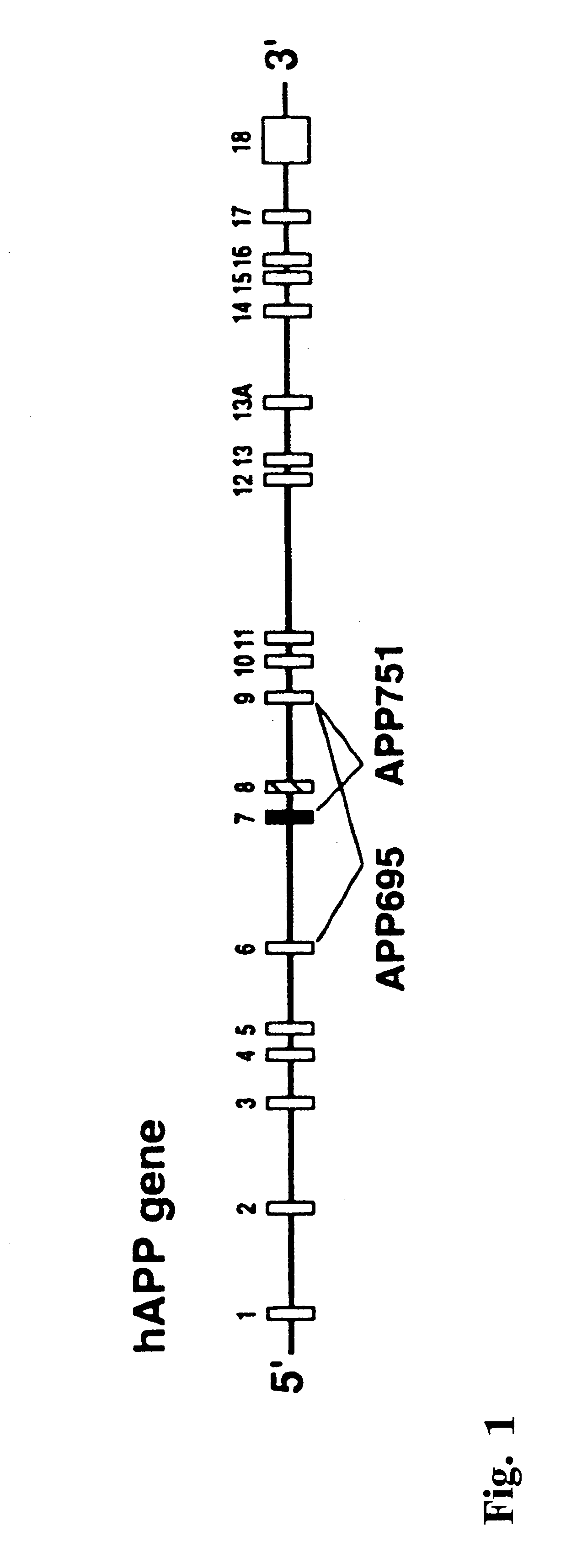
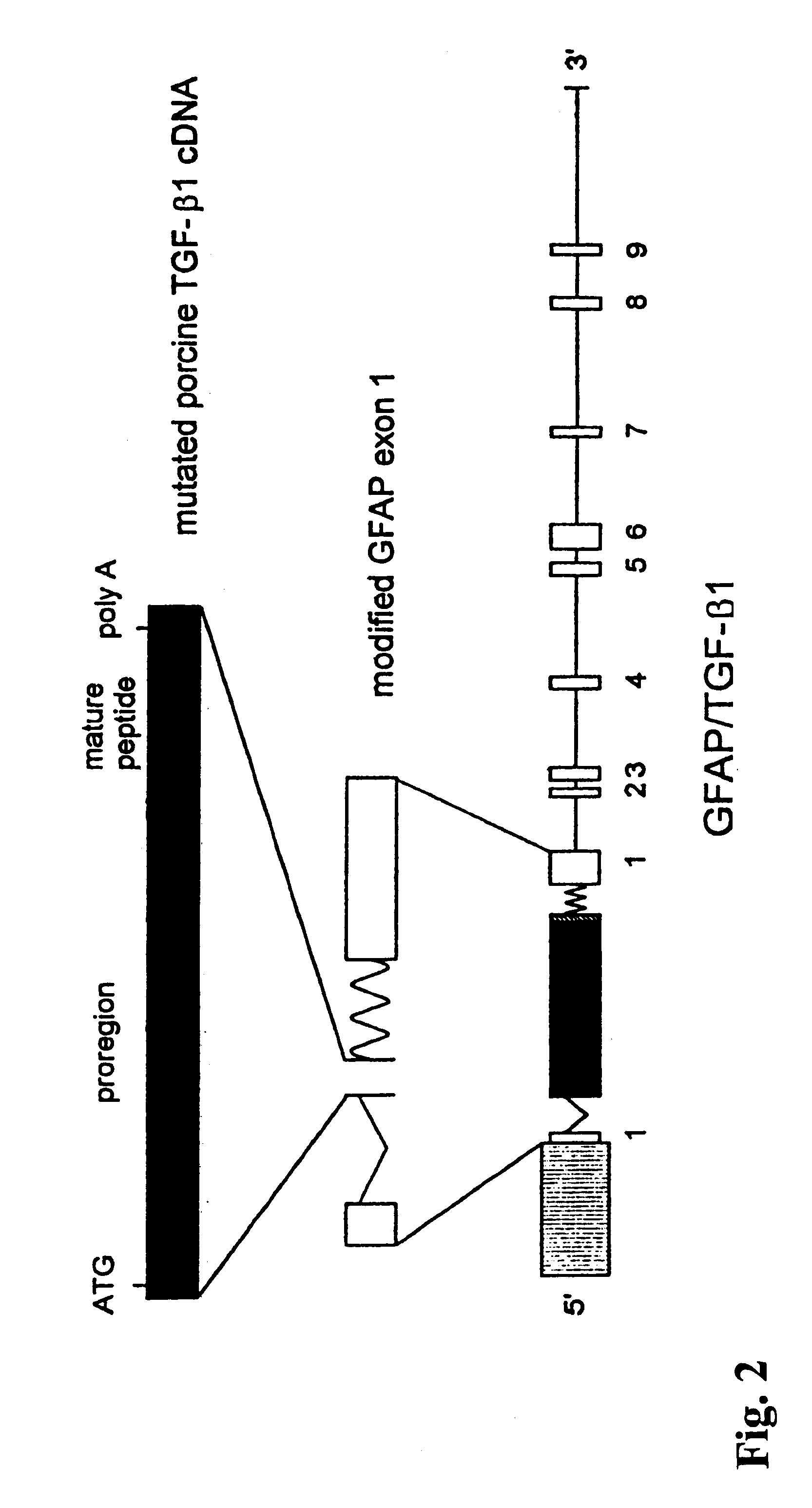
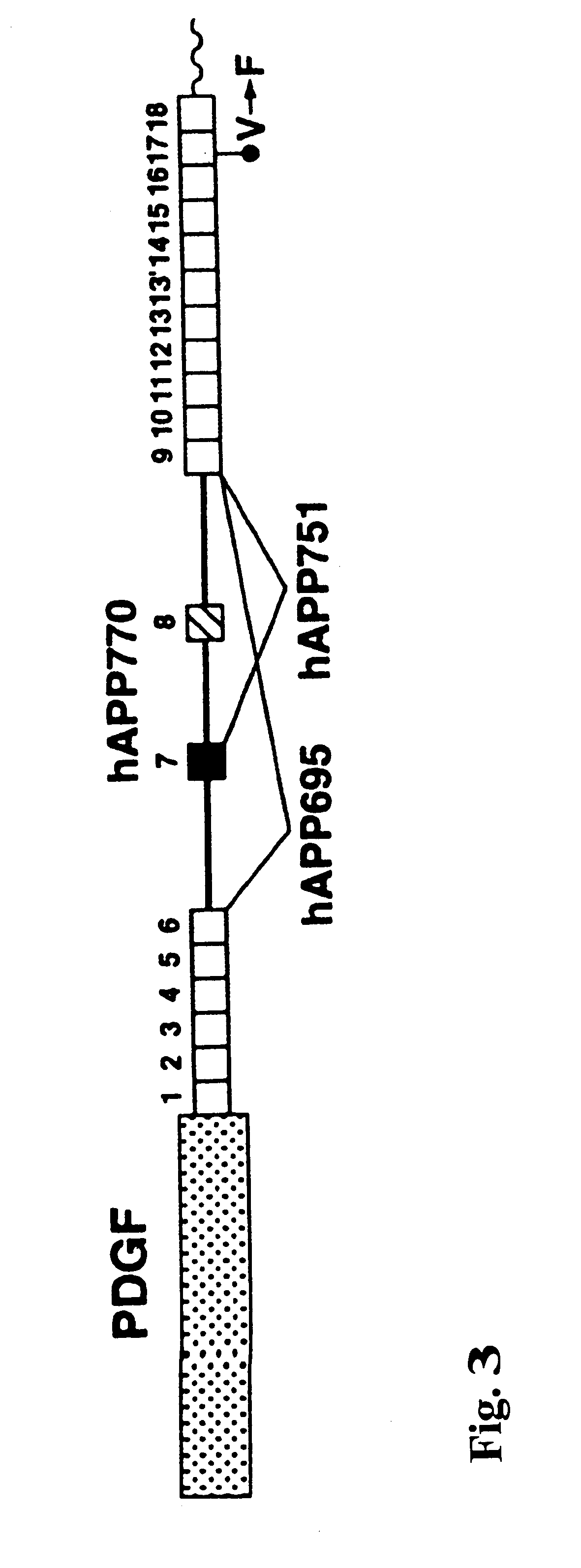
The present invention features non-human transgenic animal models for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and CAA, wherein the transgenic animal is characterized by 1) overexpression of bioactive transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) or 2) both overexpression of bioactive TGF-beta1 and expression of a human amyloid beta precursor protein (APP) gene product. The transgenic animals may be either homozygous or heterozygous for these alterations. Bigenic animals are further characterized by development of AD-associated and / or CAA-associated pathology within about two to three months of age.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Animal models and therapeutic molecules
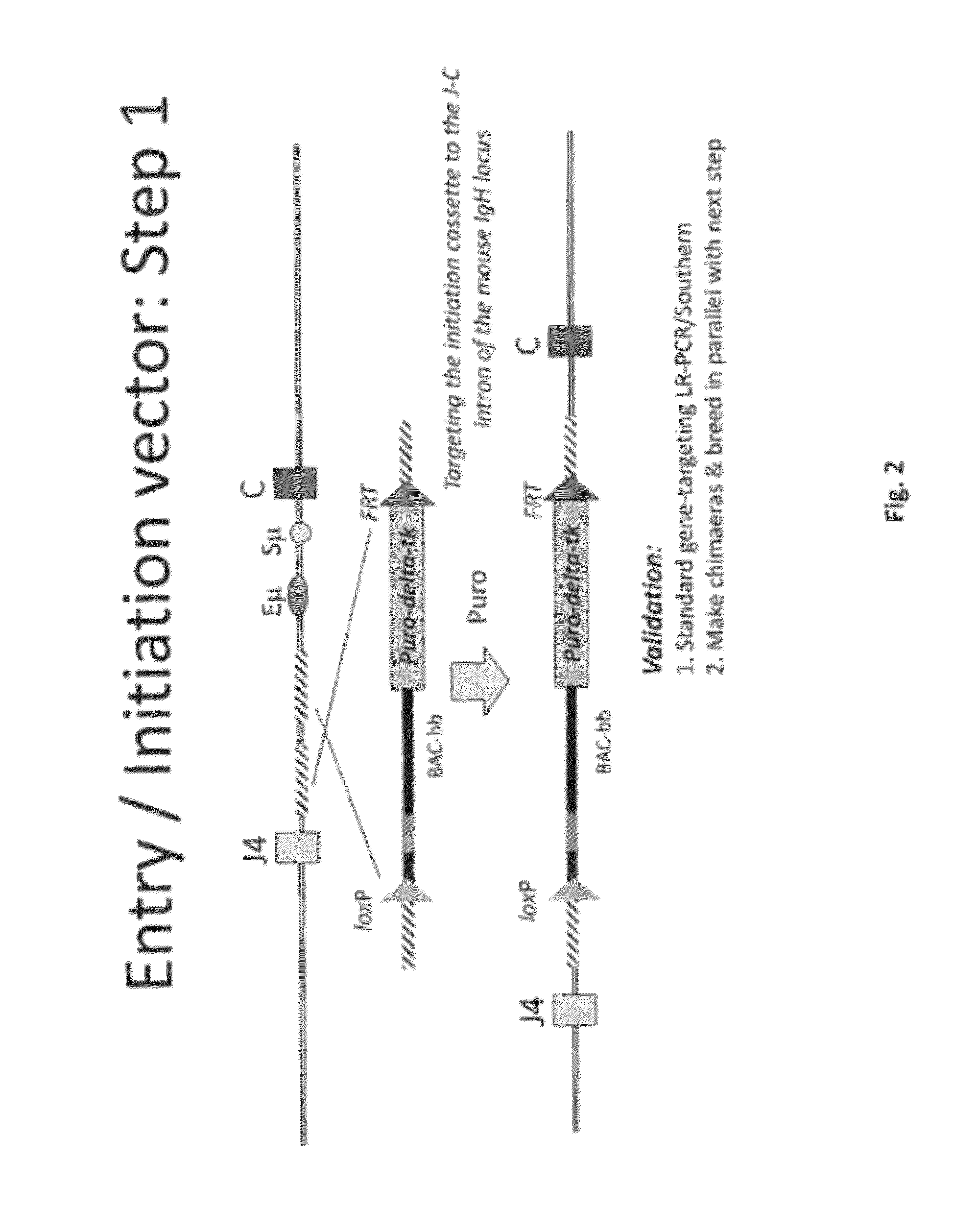
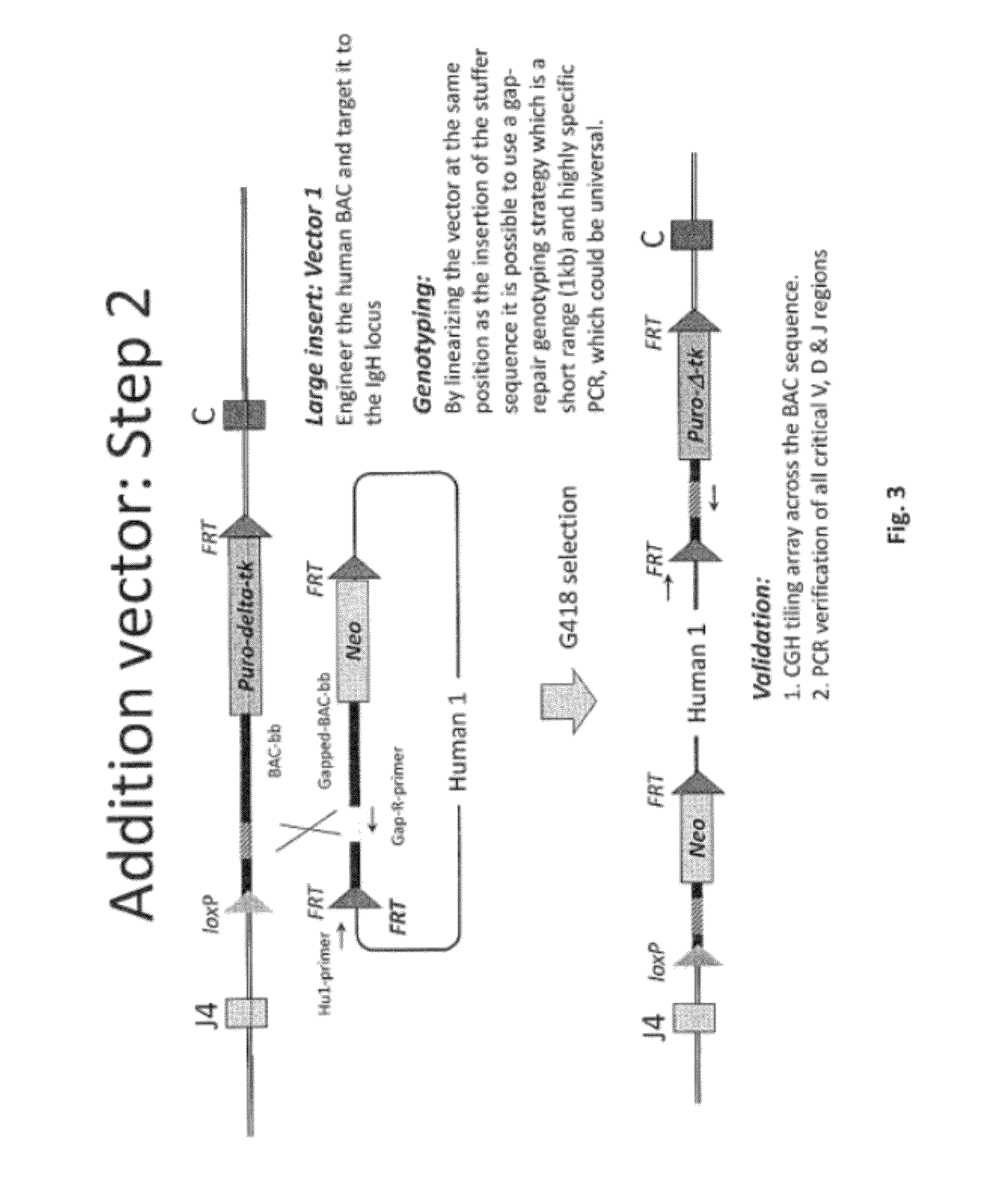
The invention discloses methods for the generation of chimaeric human—non-human antibodies and chimaeric antibody chains, antibodies and antibody chains so produced, and derivatives thereof including fully humanised antibodies; compositions comprising said antibodies, antibody chains and derivatives, as well as cells, non-human mammals and vectors, suitable for use in said methods.
Owner:KIMAB LTD
Animal Model of Prostate Cancer and Use Thereof
The present invention relates to an adult mammal which exhibits growth or replication of abnormal cells in a target tissue or organ by over-expressing Hedgehog protein in such target tissue or organ. The present invention also relates to a method of preparing an adult animal model of prostate cancer. The invention further relates to a method of evaluating an agent for treating prostate cancer.
Owner:CHUNG SHAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
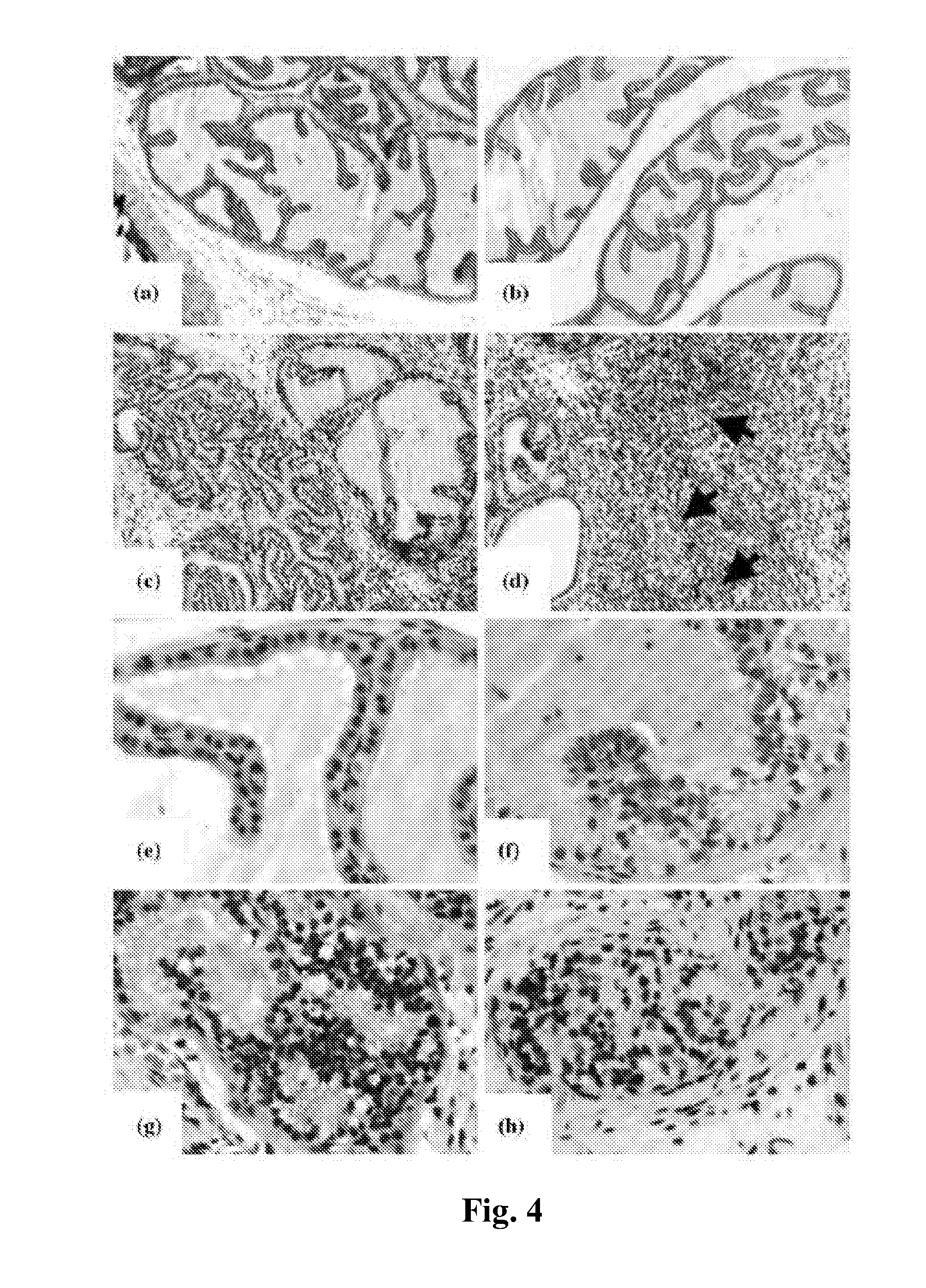
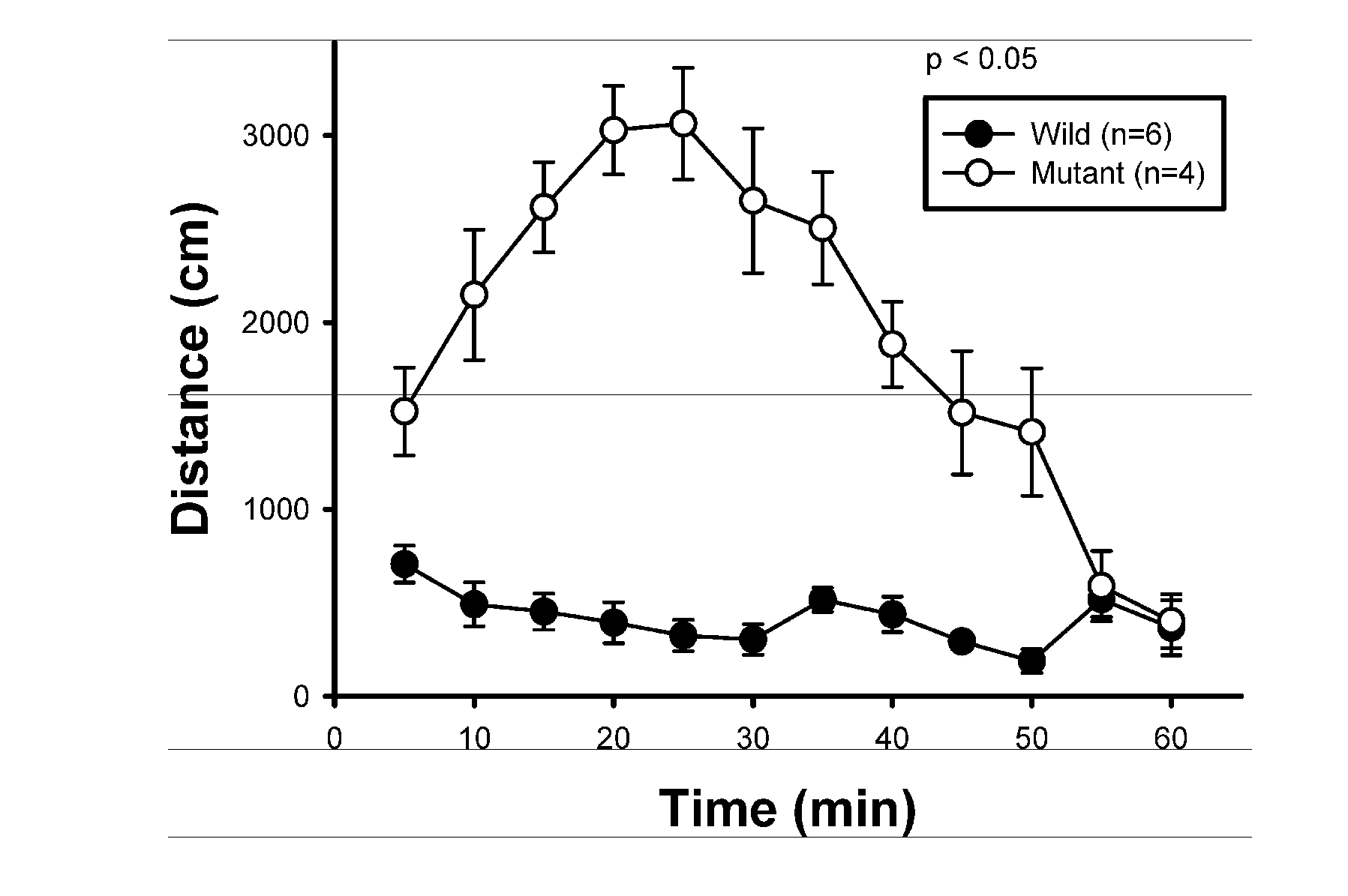
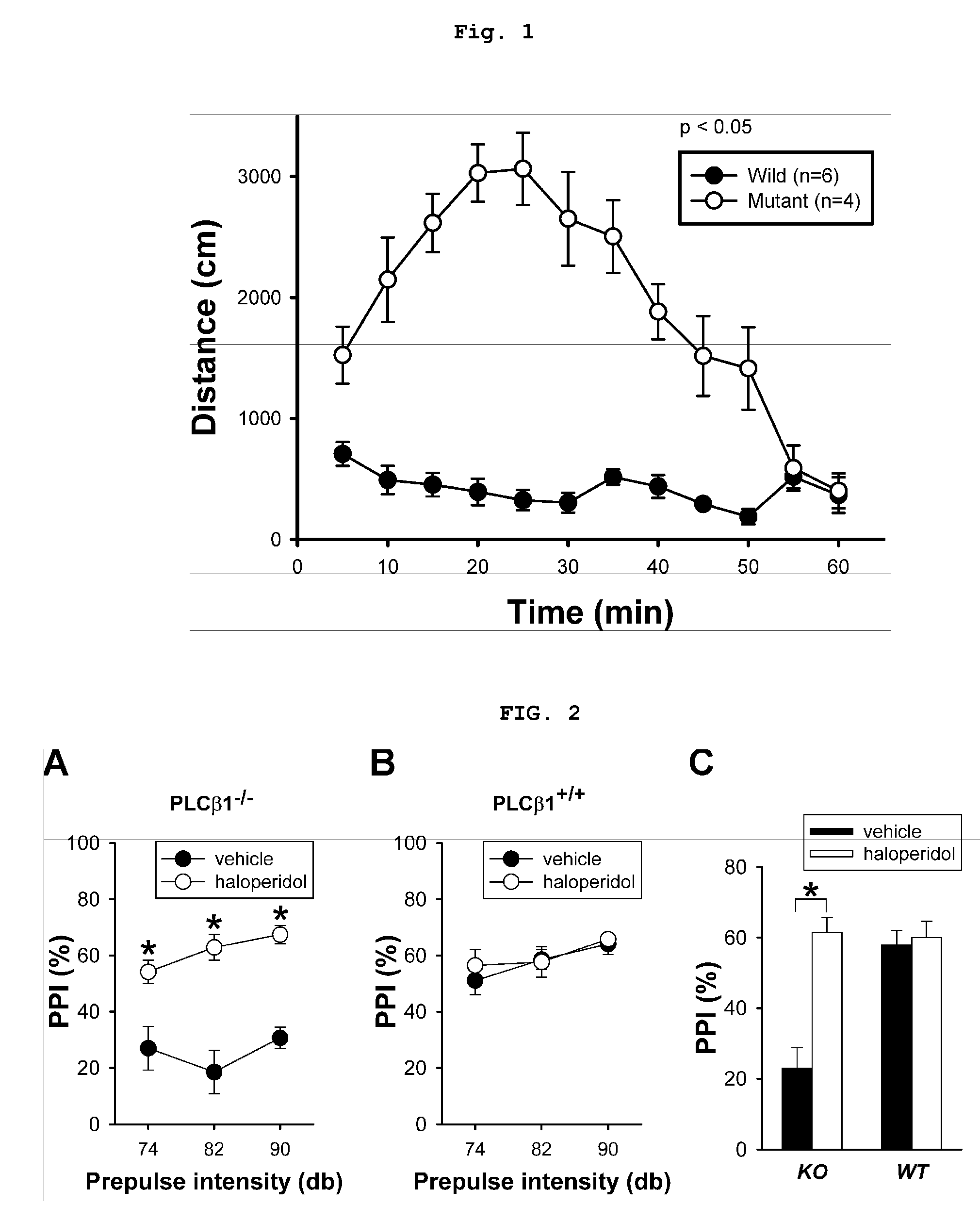
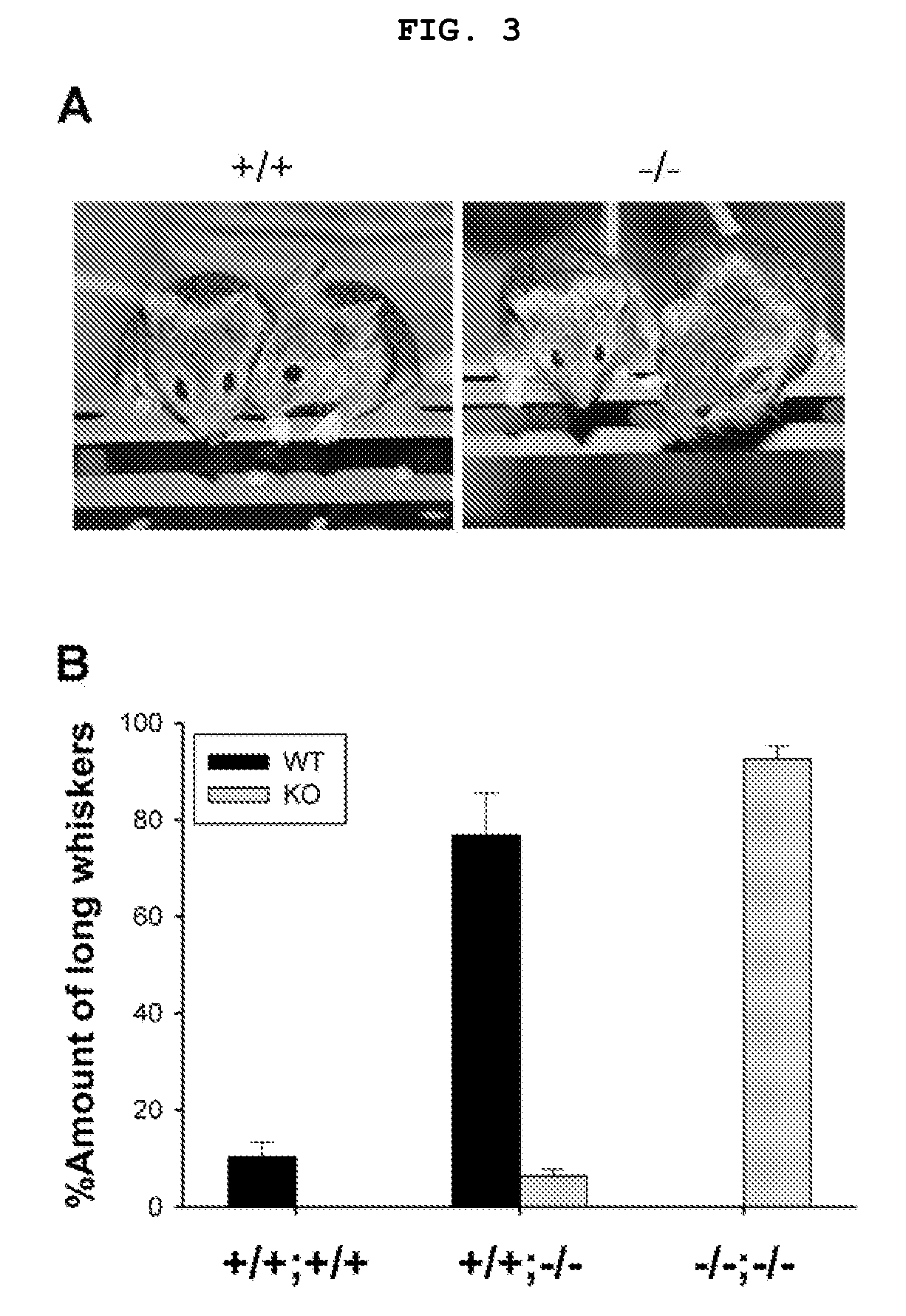
Phospholipase c beta1 (plcbeta1) knockout mice as a model system for testing schizophrenia drugs
The present invention relates to a method for screening therapeutic drugs of schizophrenia using an animal model of the disease. More specifically, this invention relates to a screening method based on the phospholipase C β1 (PLCβ1) knockout mouse as an animal model of schizophrenia with all the major symptoms of the human disease. This knockout mouse exhibits symptoms similar to human schizophrenia such as locomotor hyperactivity, impaired prepulse inhibition of the startle response, lack of barbering and nesting behaviors, socially subordinate status, impaired learning, and lack of type II theta rhythm which has been implicated in working memory. Thus, the knockout mouse of the present invention can be useful as an animal for screening therapeutic drugs against schizophrenia.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
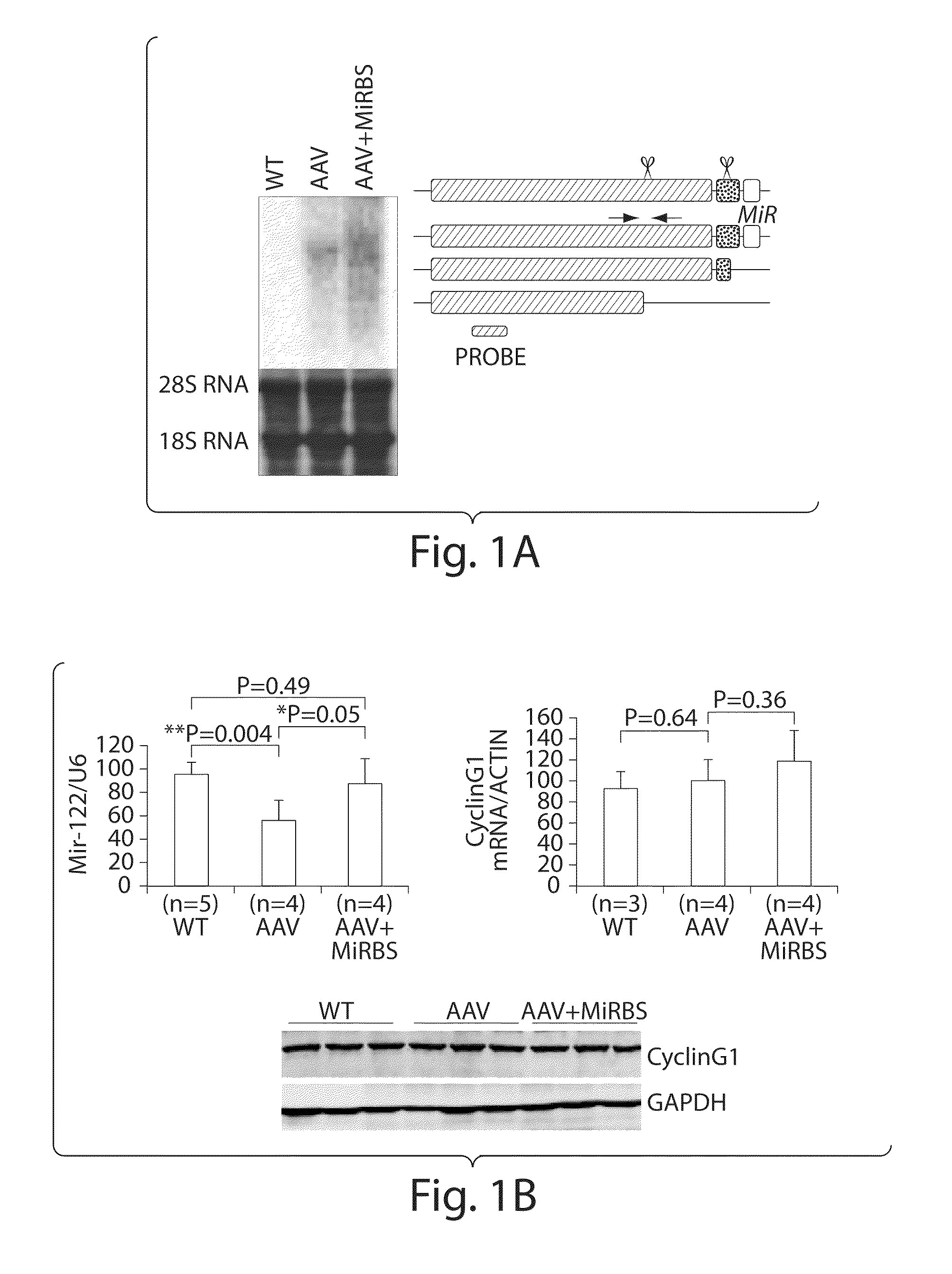
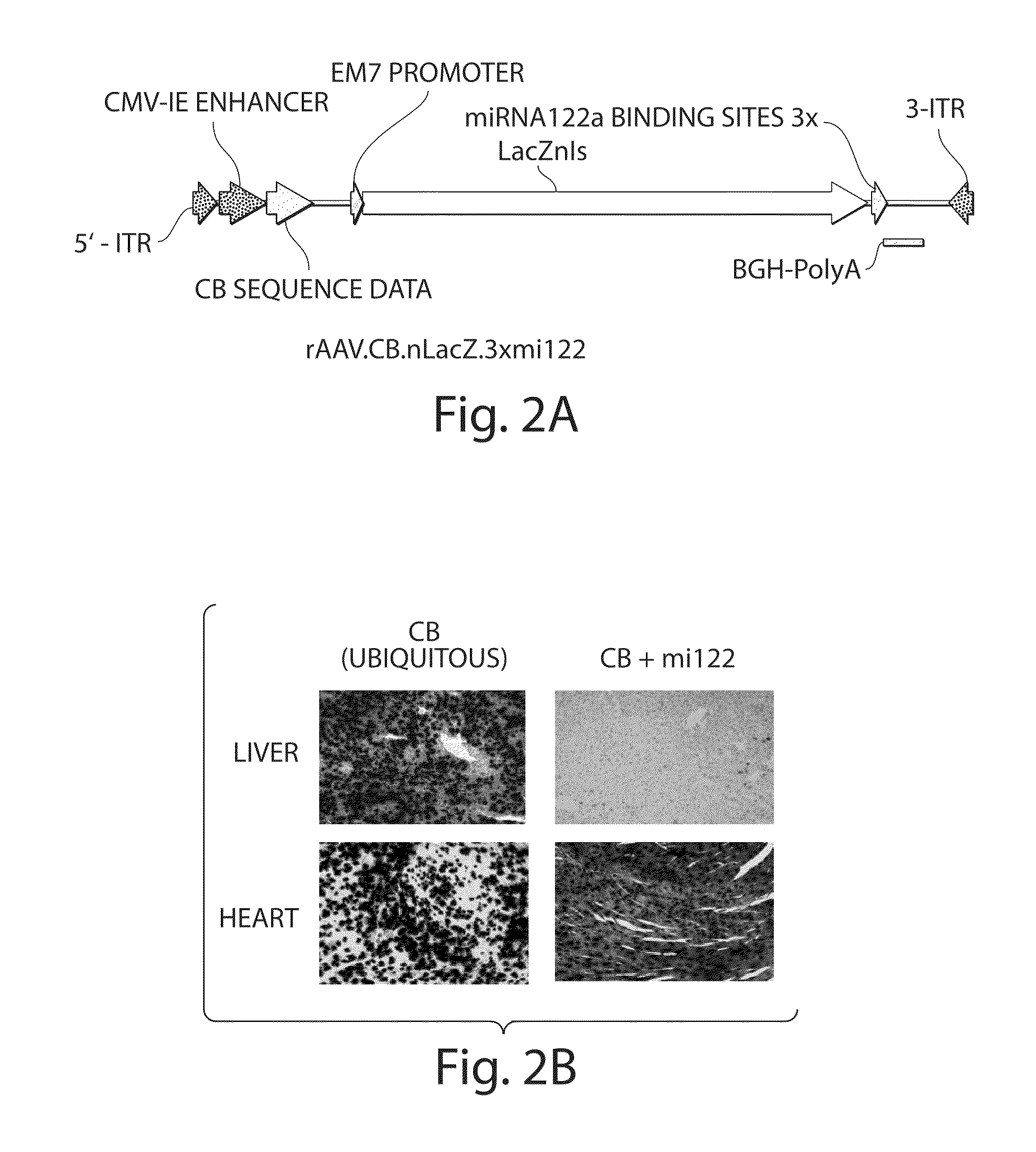
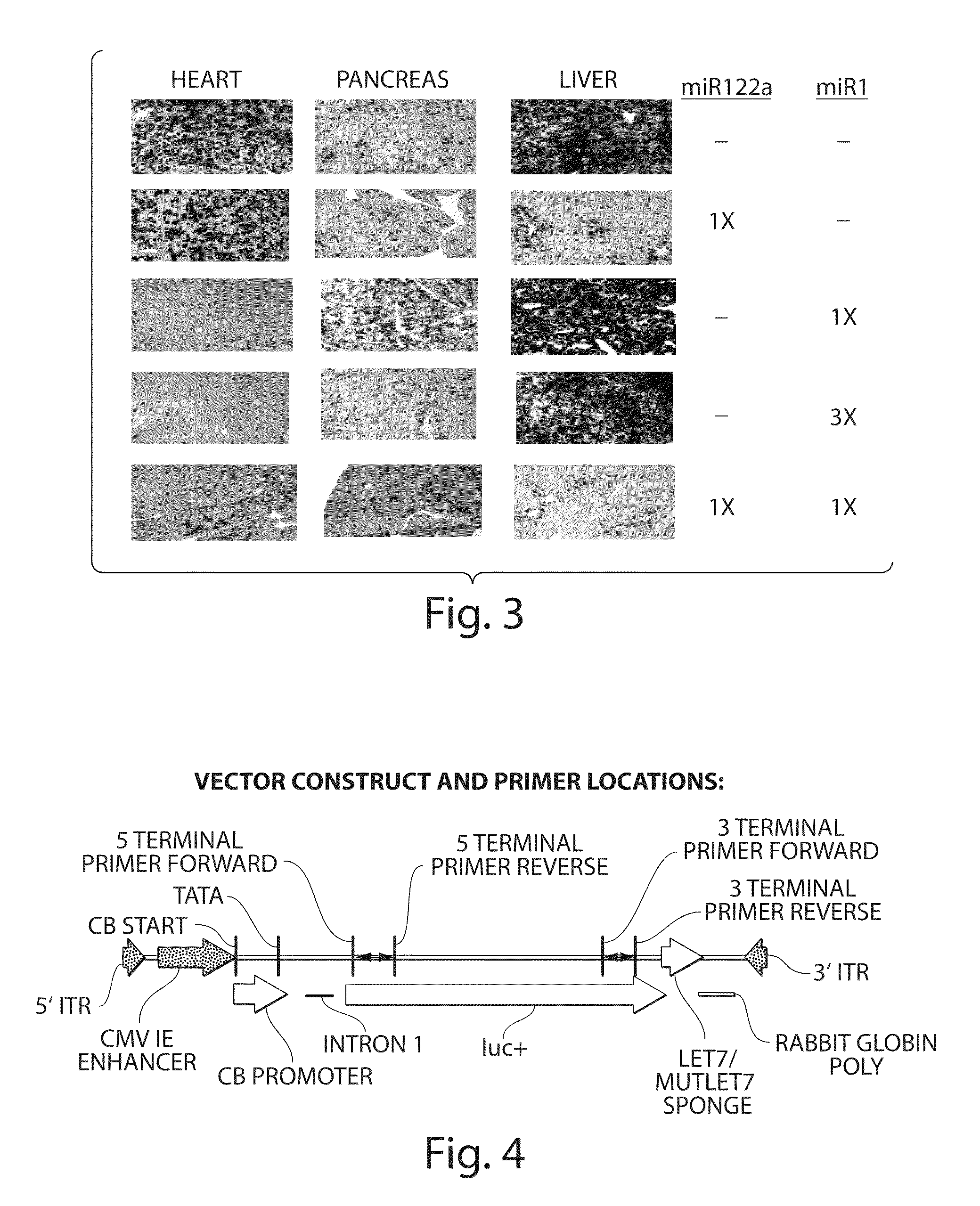
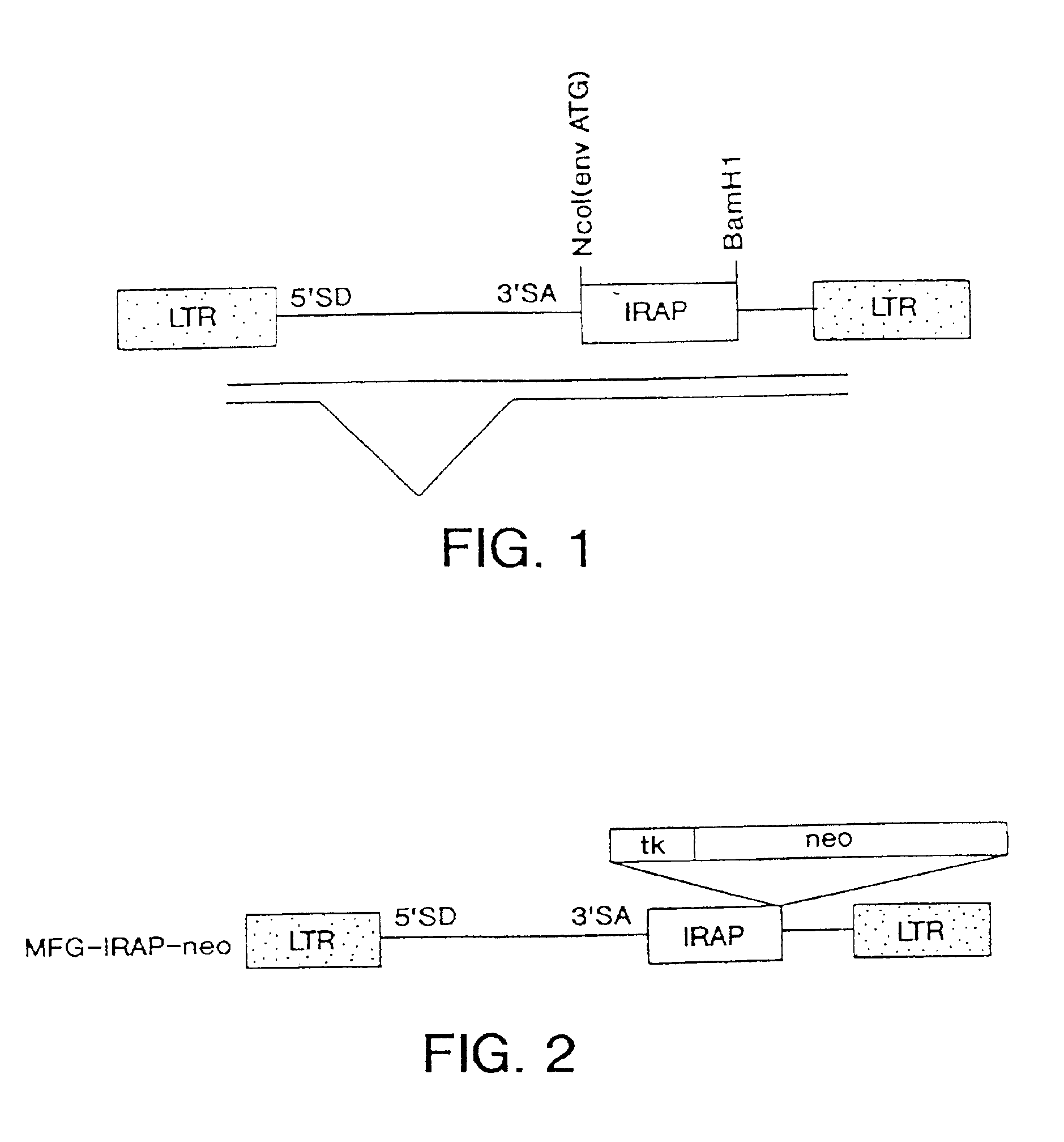
Isolation Of Novel AAV'S And Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20100186103A1Determine effectAvoid time-consume and costly processVectorsSpecial deliveryAdeno associate virusBinding site
The invention in some aspects relates to isolated nucleic acids, compositions, and kits useful for identifying adeno-associated viruses in cells. In some aspects, the invention provides kits and methods for producing somatic transgenic animal models using recombinant AAV (rAAV) to an animal having at least one transgene that expresses a small interfering nucleic acid or at least one binding site for a miRNA.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
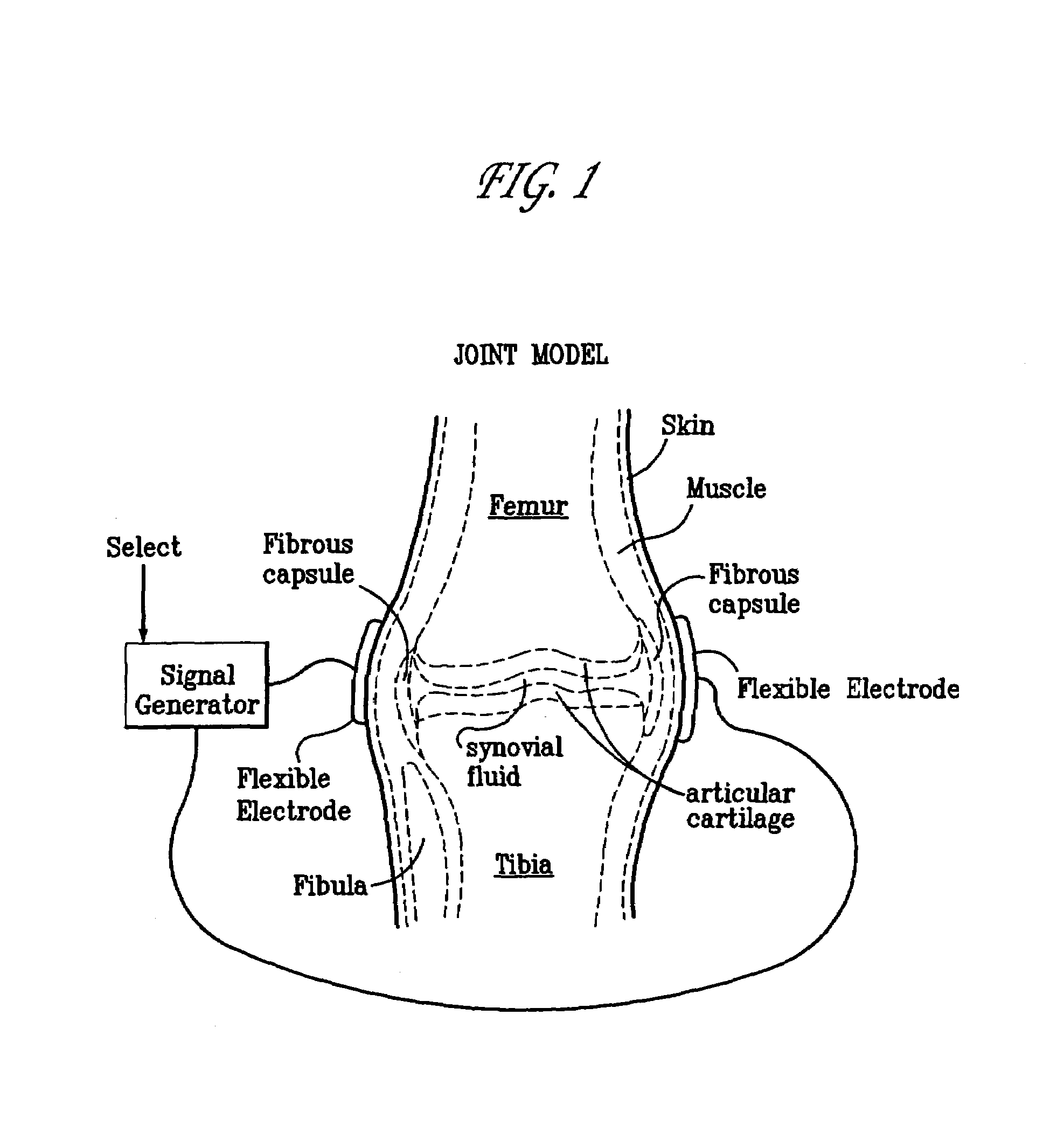
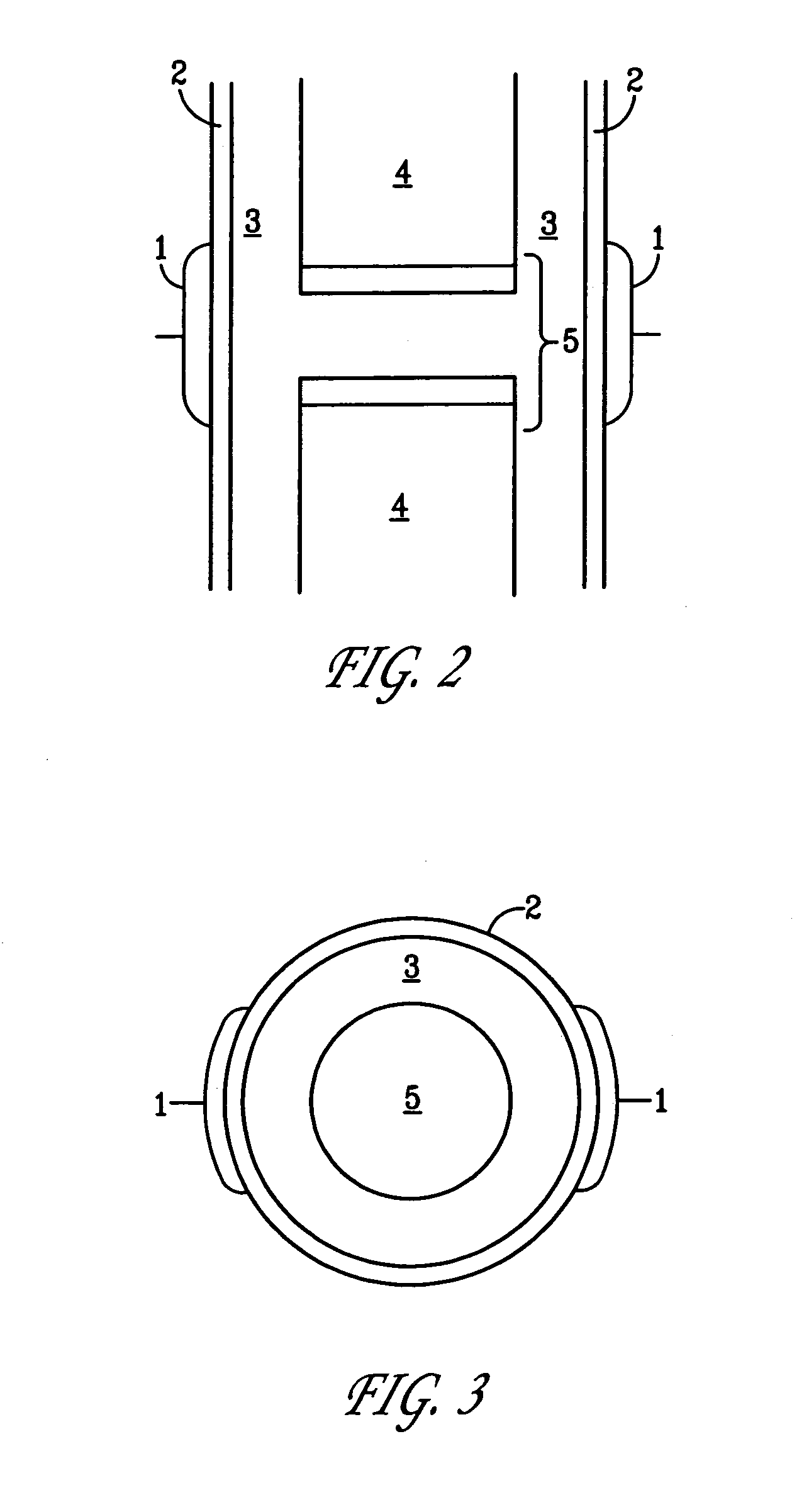
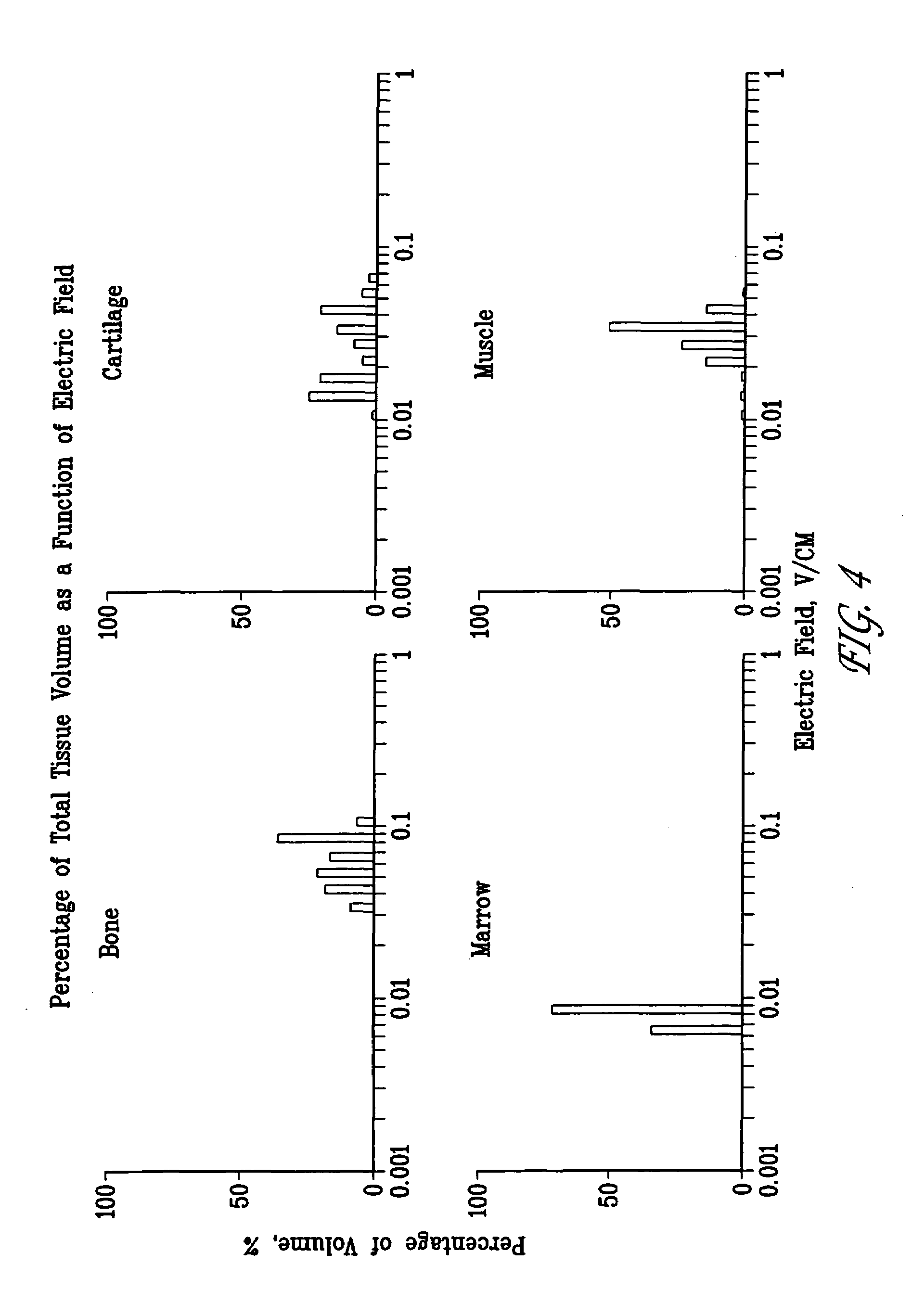
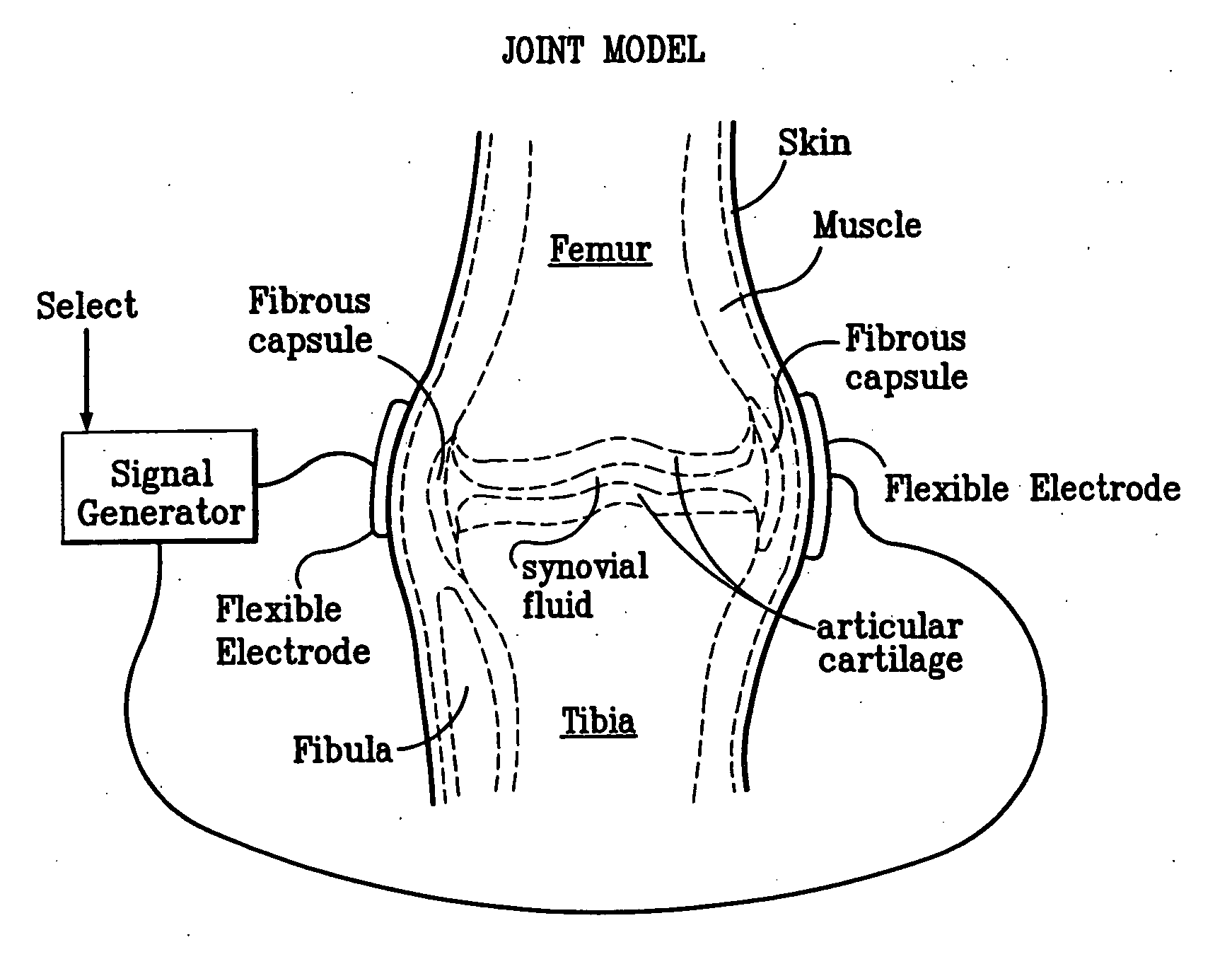
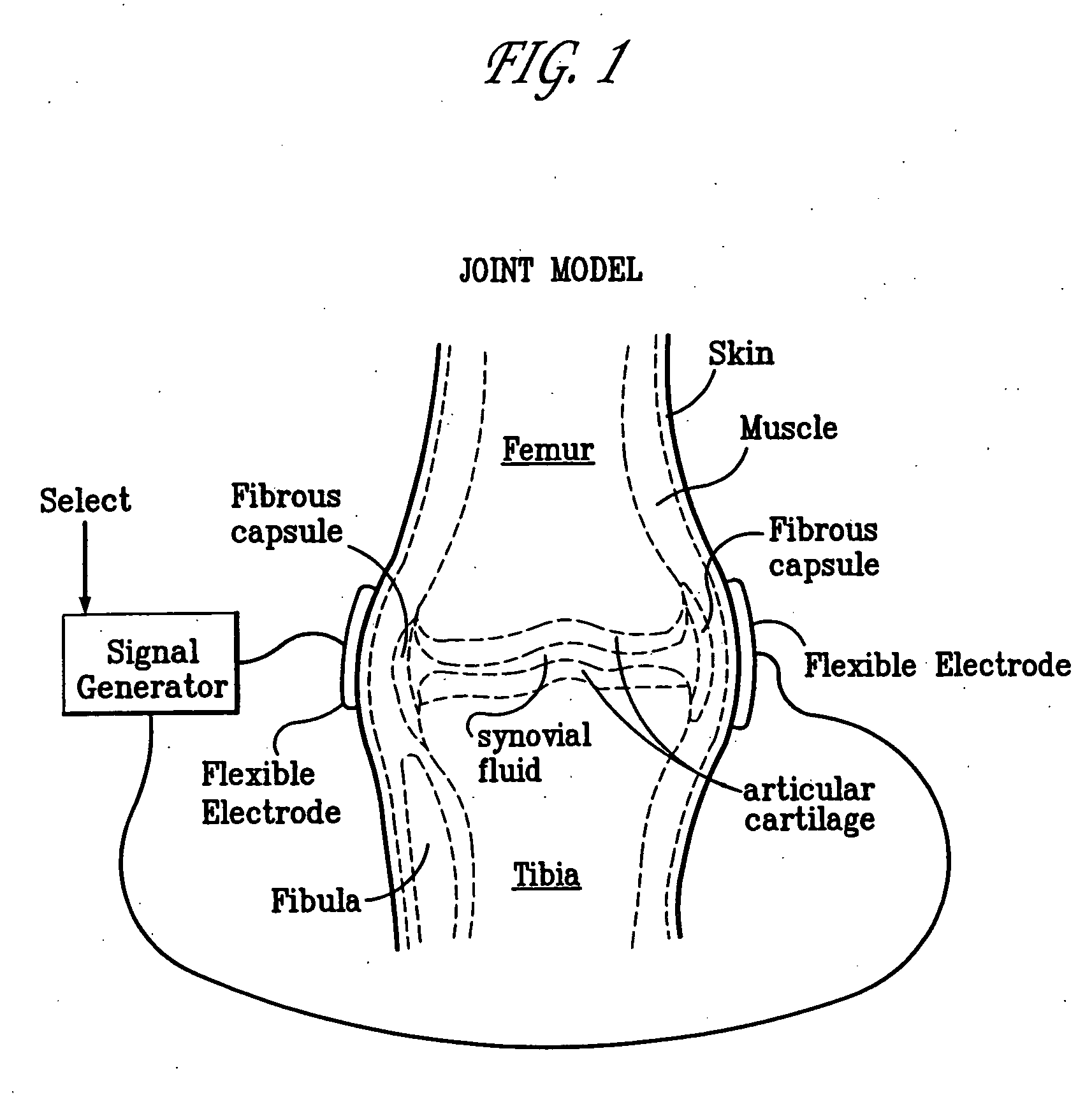
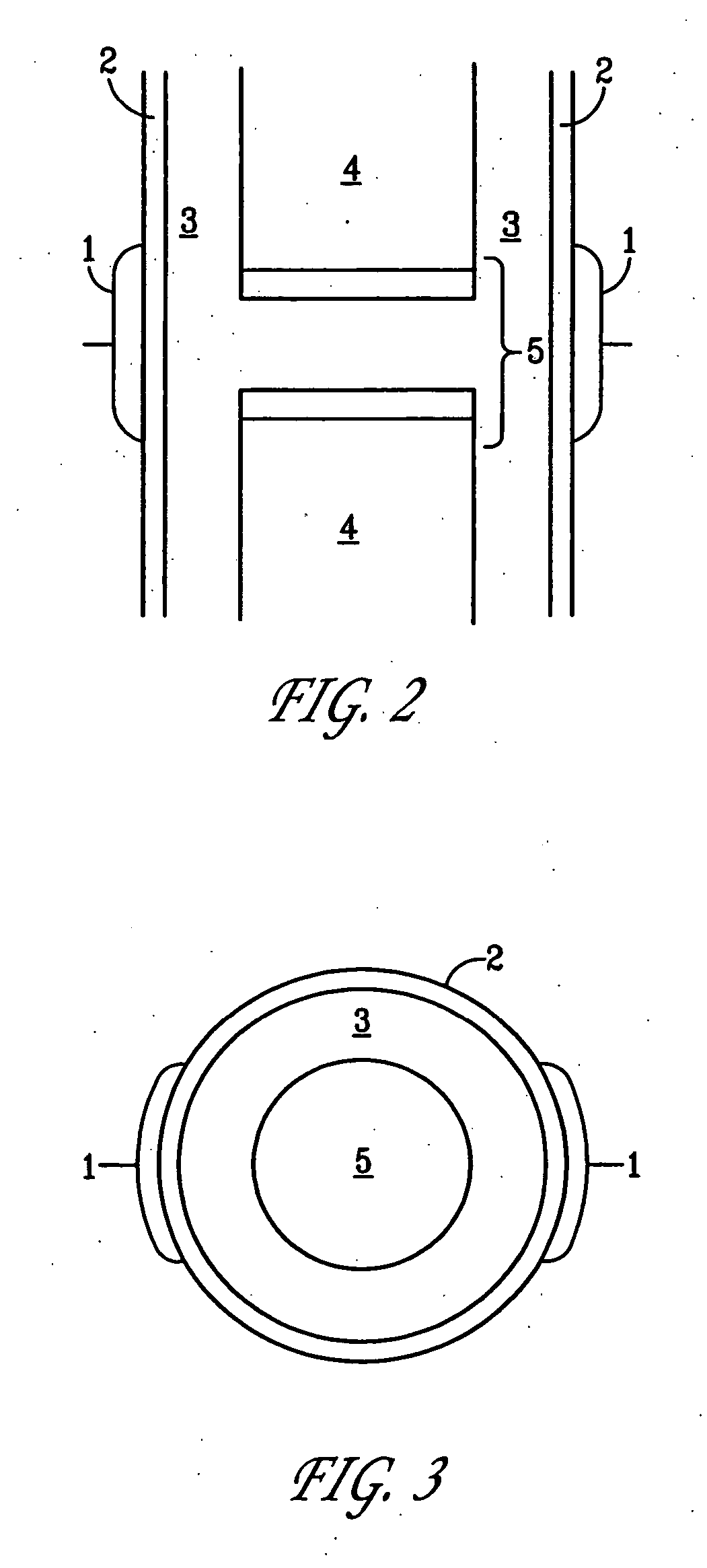
Method and device for treating osteoarthritis, cartilage disease, defects and injuries in the human knee
InactiveUS7022506B2Heart defibrillatorsMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsHuman useCells transplantation
A method of determining the voltage and current output required for the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to diseased articular cartilage in the treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage defects due to trauma or sports injury, or used as an adjunct with other therapies (cell transplantation, tissue-engineered scaffolds, growth factors, etc.) for treating cartilage defects in the human knee joint and a device for delivering such signals to a patient's knee. An analytical model of the human knee is developed whereby the total tissue volume in the human knee may be determined for comparison to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model using electric field and current density histograms. The voltage and current output used in the animal model is scaled based on the ratio of the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue of the human to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model and the resulting field is applied to the diseased tissue of the human using at least two electrodes applied to the knee or a coil or solenoid placed around the knee. The voltage of the signal applied to the electrodes, coil or solenoid is varied based on the size of the knee joint; larger knee joints require larger voltages to generate the effective electric field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
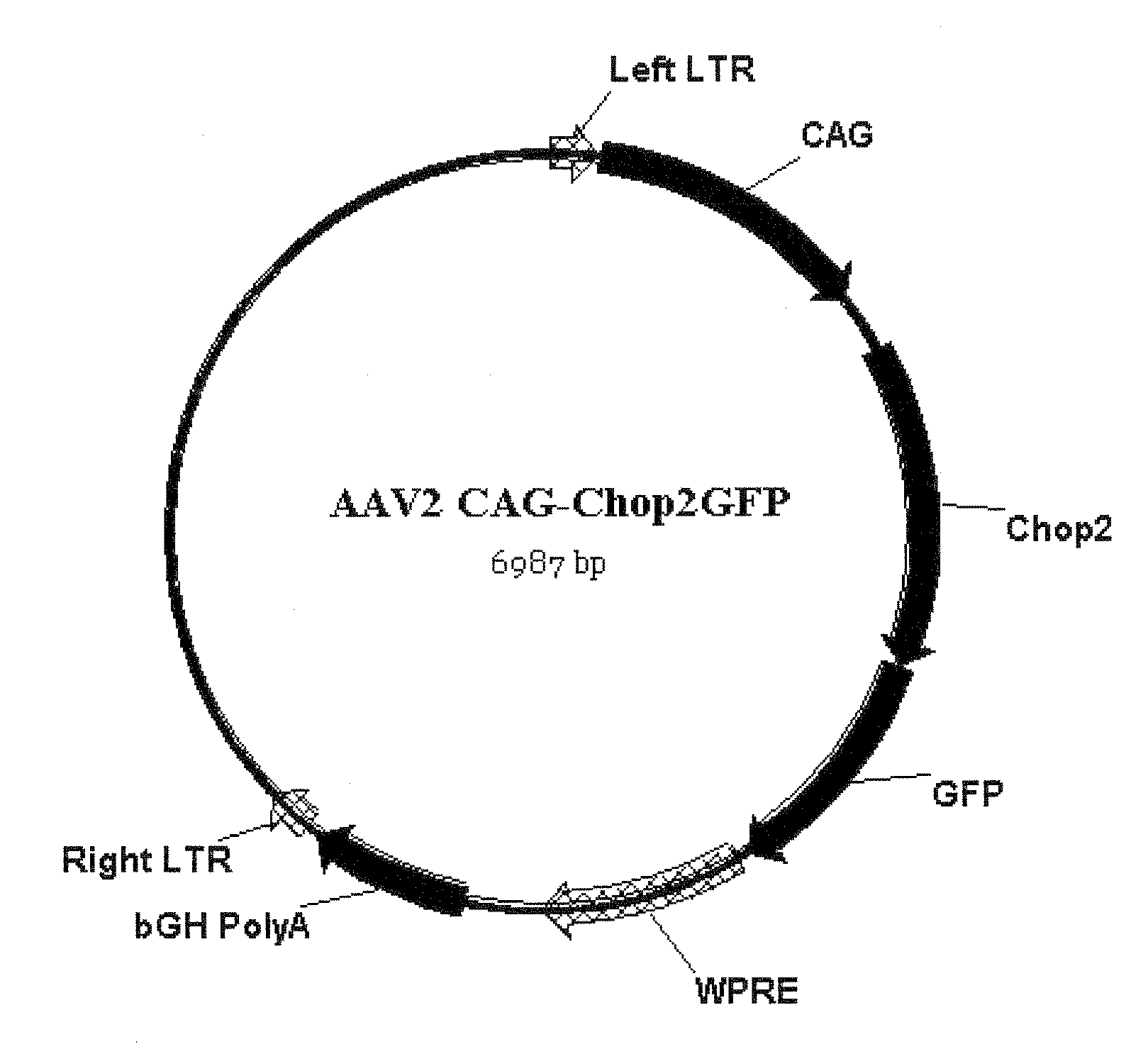
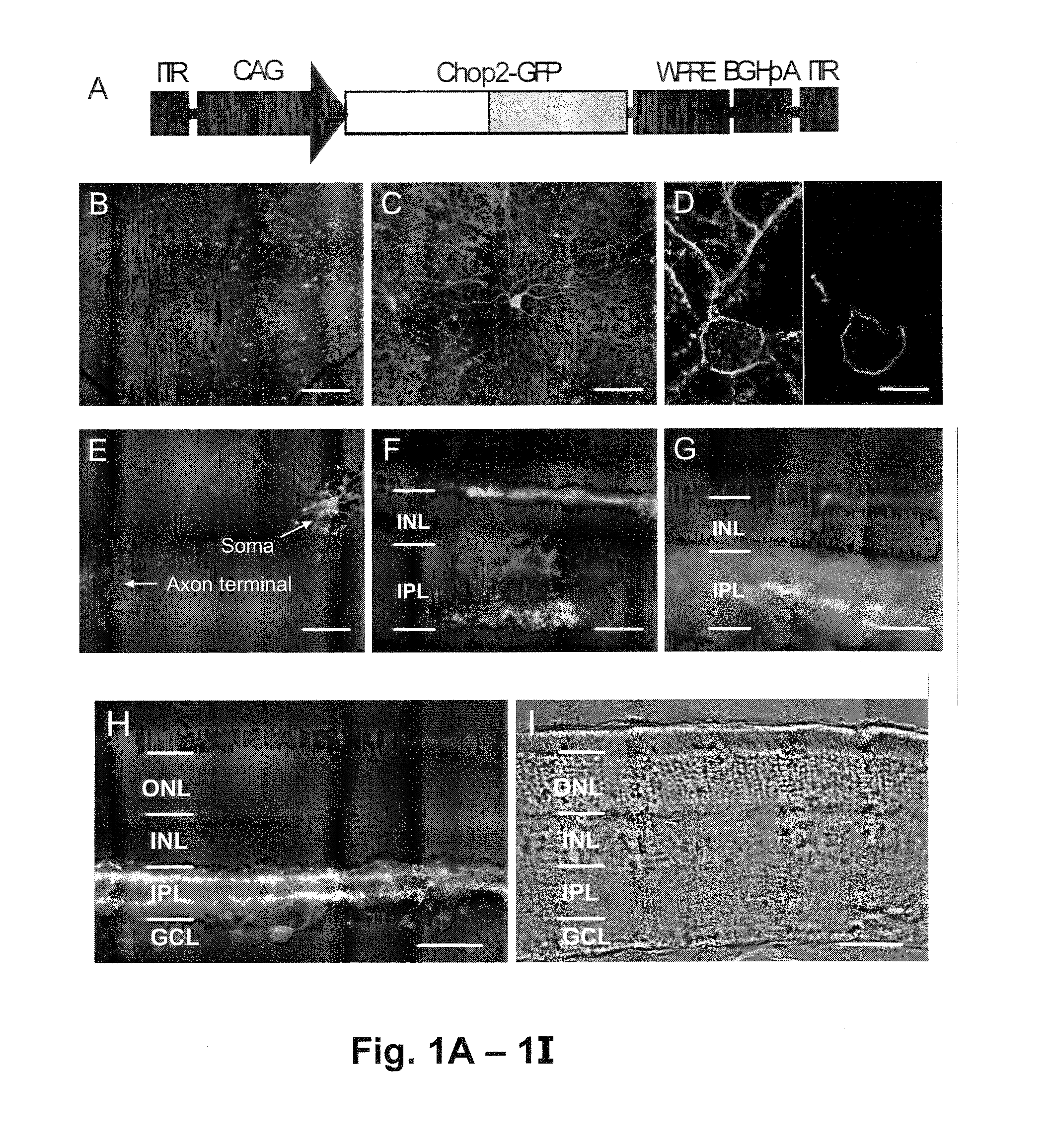
Restoration of visual responses by in vivo delivery of rhodopsin nucleic acids
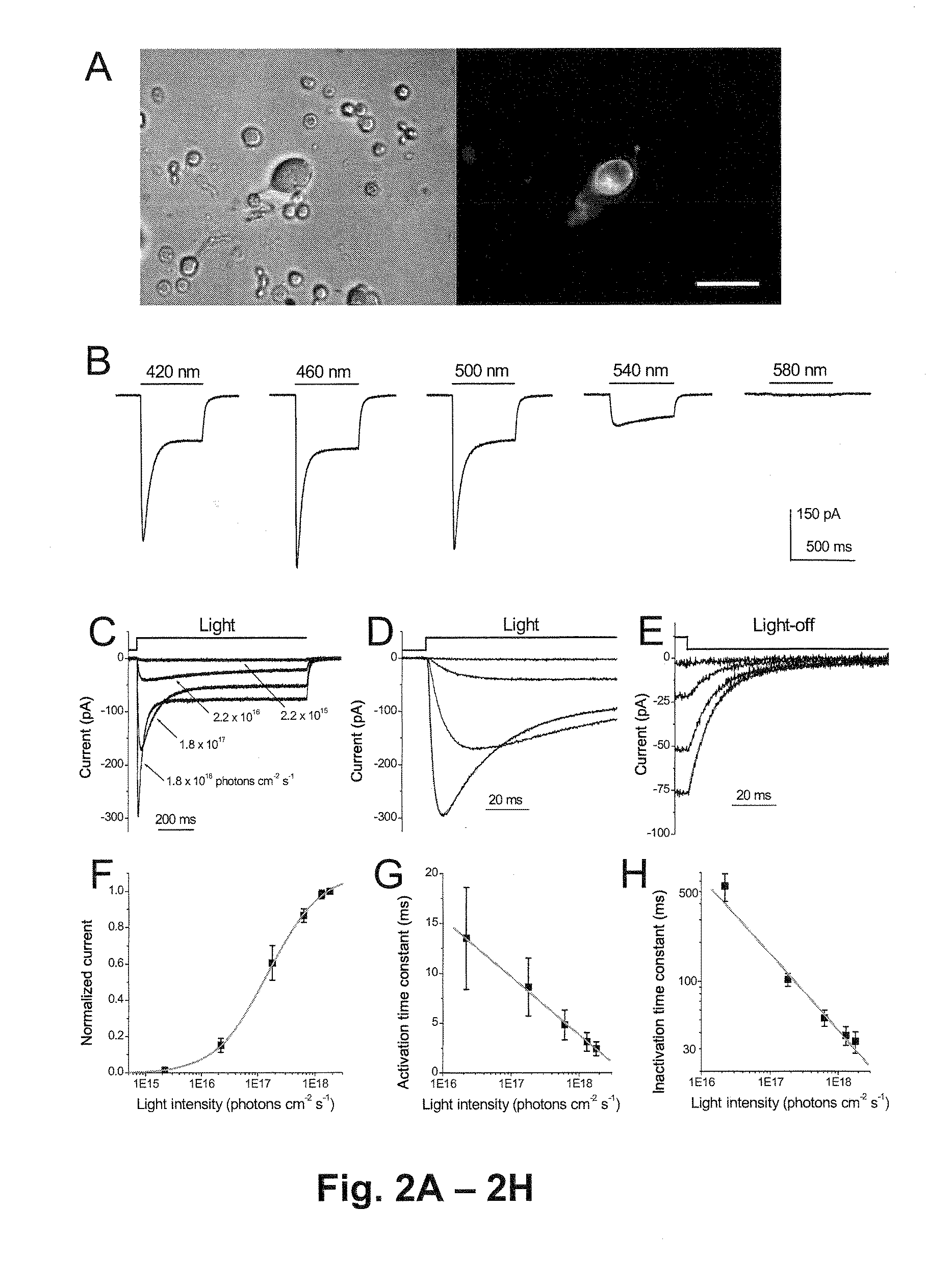
ActiveUS20100015095A1Restoring light sensitivityLoss can be compensatedOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOpen reading frameIn vivo
Nucleic acid vectors encoding light-gated cation-selective membrane channels, in particular channelrhodopsin-2 (Chop2), converted inner retinal neurons to photosensitive cells in photoreceptor-degenerated retina in an animal model. Such treatment restored visual perception and various aspects of vision. A method of restoring light sensitivity to a retina of a subject suffering from vision loss due to photoreceptor degeneration, as in retinitis pigmentosa or macular degeneration, is provided. The method comprises delivering to the subject by intravitreal or subretinal injection, the above nucleic acid vector which comprises an open reading frame encoding a rhodopsin, to which is operatively linked a promoter and transcriptional regulatory sequences, so that the nucleic acid is expressed in inner retinal neurons. These cells, normally light-insensitive, are converted to a light-sensitive state and transmit visual information to the brain, compensating for the loss, and leading to restoration of various visual capabilities.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
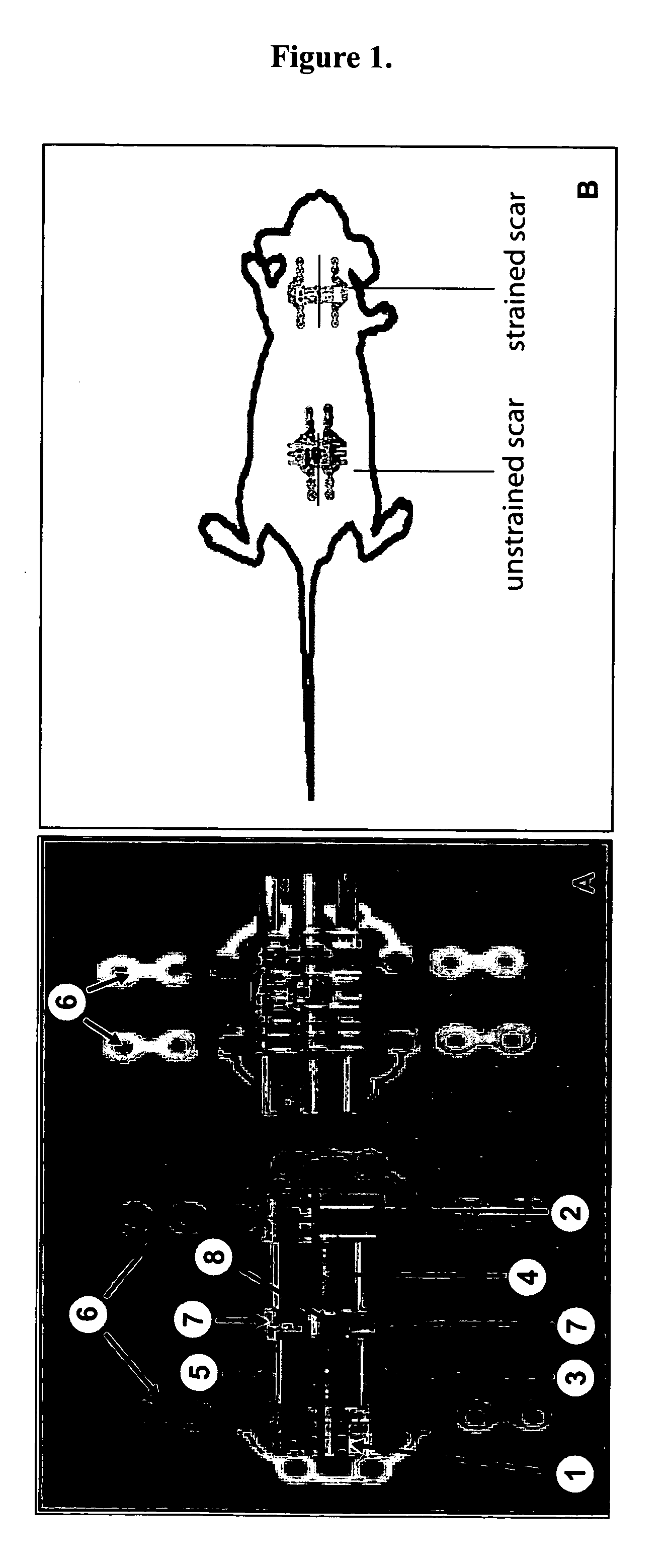
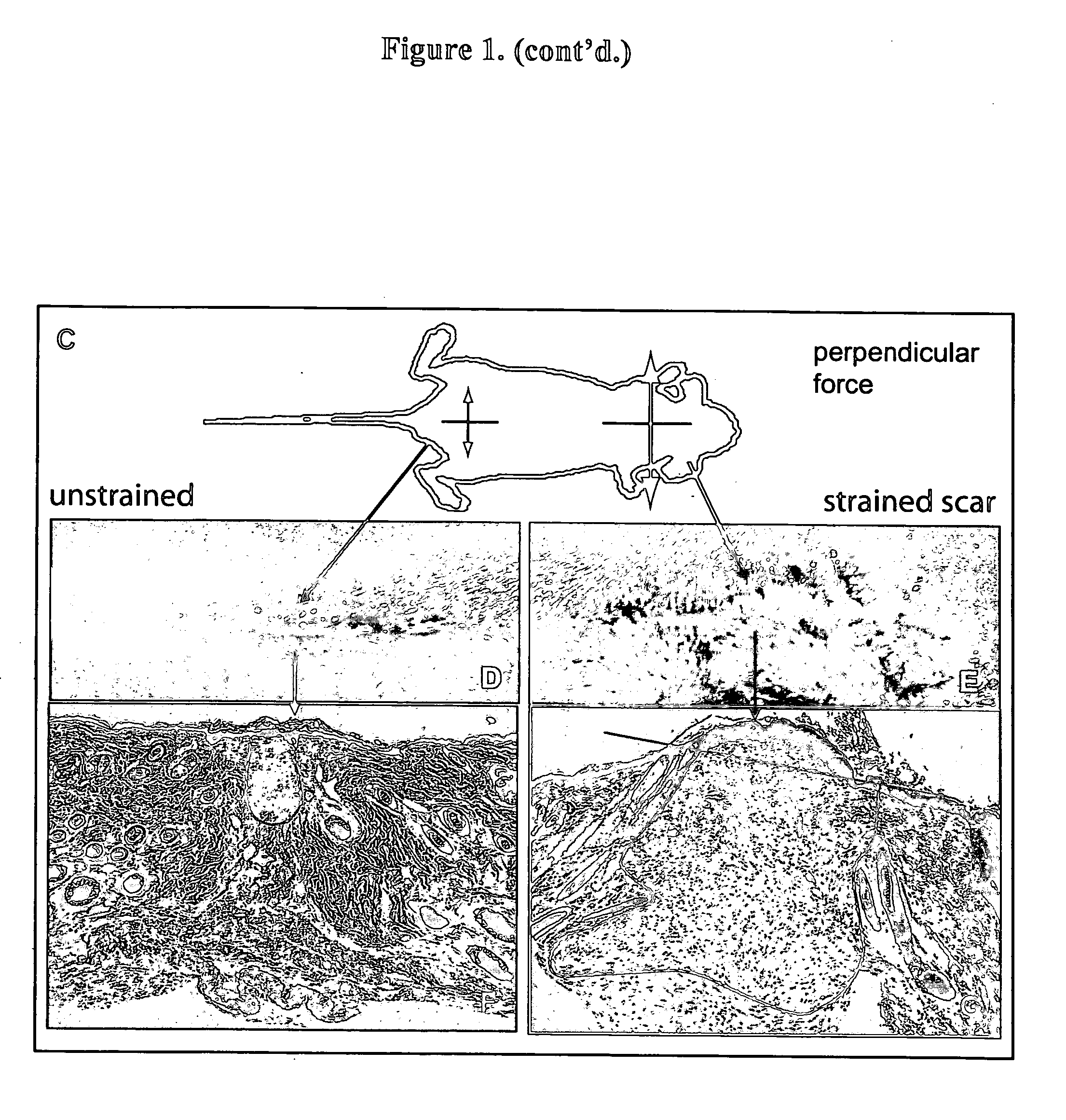
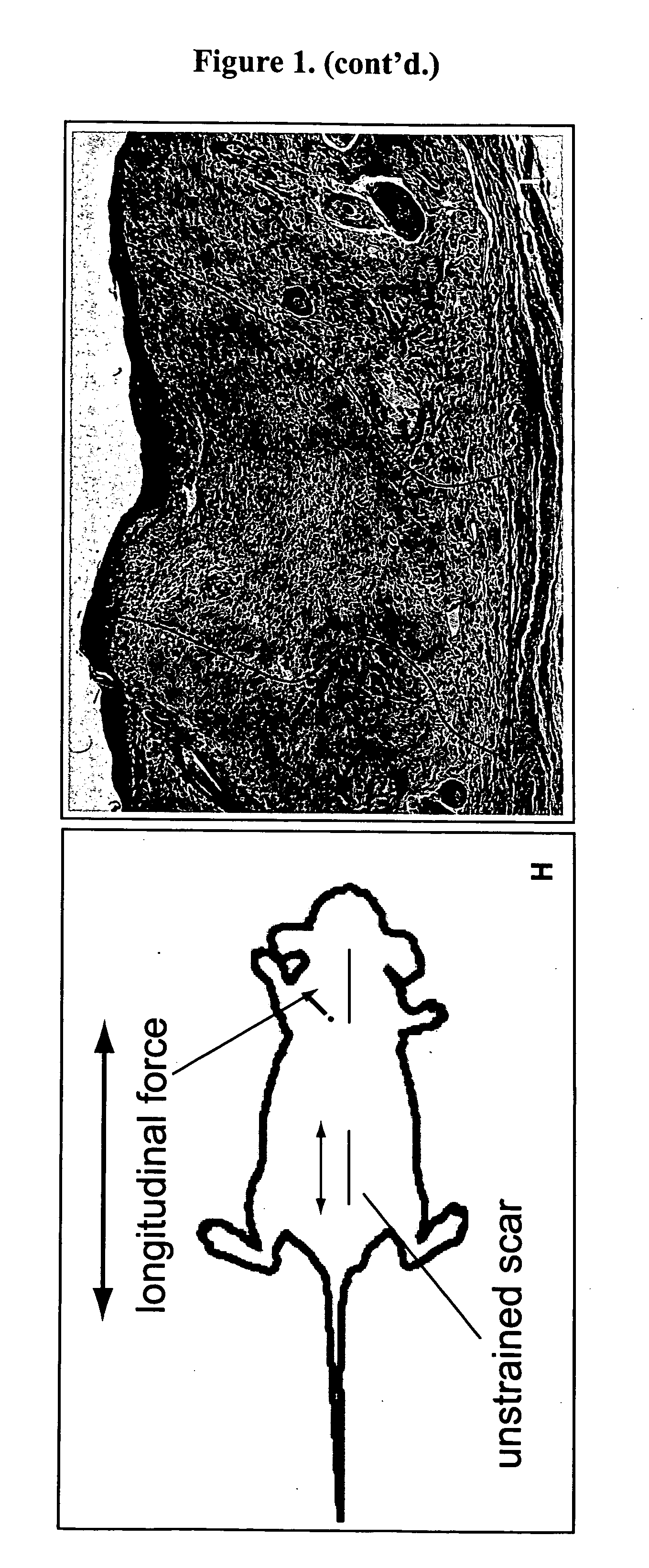
Method for producing hypertrophic scarring animal model for identification of agents for prevention and treatment of human hypertrophic scarring
InactiveUS20060037091A1Risk minimizationMinimal scarringPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseHuman animal
The present invention relates to a method of producing a non-human animal model of hypertrophic scarring. This involves producing an incision in a non-human animal and applying mechanical strain over the incision under conditions effective to produce hypertrophic scarring, thereby producing a non-human animal model of hypertrophic scarring. The present invention also relates to a method of determining the efficacy of an agent for prevention or treatment of a disease condition. This method involves providing a non-human animal having an incision over which mechanical strain is applied under conditions effective to produce hypertrophic scarring, administering an agent to the incision, and determining whether the agent is efficacious for prevention or treatment of a disease condition. Also provided is a non-human animal model of hypertrophic scarring. This involves a non-human animal having an incision over which mechanical strain has been applied under conditions effective to produce hypertrophic scarring.
Owner:GURTNER GEOFFREY C +1
Process and architecture of robotic system to mimic animal behavior in the natural environment
ActiveUS20050065651A1Programme-controlled manipulatorArtificial lifeBiomechanicsFinite-state machine
A robotic architecture for capturing the autonomous performance advantages the animal models enjoy in the natural environment is disclosed. A biomimesis process is employed to allow selective utilization of basic physical components and adaptation of a common control paradigm for each of different vehicle types. The biomimetic architecture involves five functional elements: a basic biomorphic plant for capturing the biomechanical advantages of the model organism; a neural circuit-based controller consisting of a finite state machine; myomorphic actuators producing linear graded force in response to trains of current pulses for mediating movements; labeled line code output by neuromorphic sensors; and a reactive behavioral sequencer executing command sequences defined within a behavioral library.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Transgenic animal model for modelling pathological anxiety, a method for identifying compounds for treatment of diseases or disorders caused by pathological anxiety and a method for using wfs1 protein as a target for identifying effective compounds against pathological anxiety
InactiveUS20100146645A1Low environmental changeImprove anxietyCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingTolerabilityClinical psychology
The invention discloses the transgenic animal model for pathological anxiety, the method to generate this model, the method to test drugs and drug candidates for the treatment of pathological anxiety and the method to use Wfs1 as target for screening of new anxiolytic drugs to treat pathological anxiety. This animal model is useful to test potential drug candidates for the treatment of diseases caused by pathological anxiety and to screen therapeutic compounds for the psychiatric disorders caused by reduces stress-tolerance and deficiency in adaptation to environmental challenges.
Owner:TARTU ULIKOOL THE UNIV OF TARTU
Isolation of novel AAV'S and uses thereof
ActiveUS9217155B2Avoid time-consume and costly processVectorsSpecial deliveryBinding siteAdeno associate virus
The invention in some aspects relates to isolated nucleic acids, compositions, and kits useful for identifying adeno-associated viruses in cells. In some aspects, the invention provides kits and methods for producing somatic transgenic animal models using recombinant AAV (rAAV) to an animal having at least one transgene that expresses a small interfering nucleic acid or at least one binding site for a miRNA.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
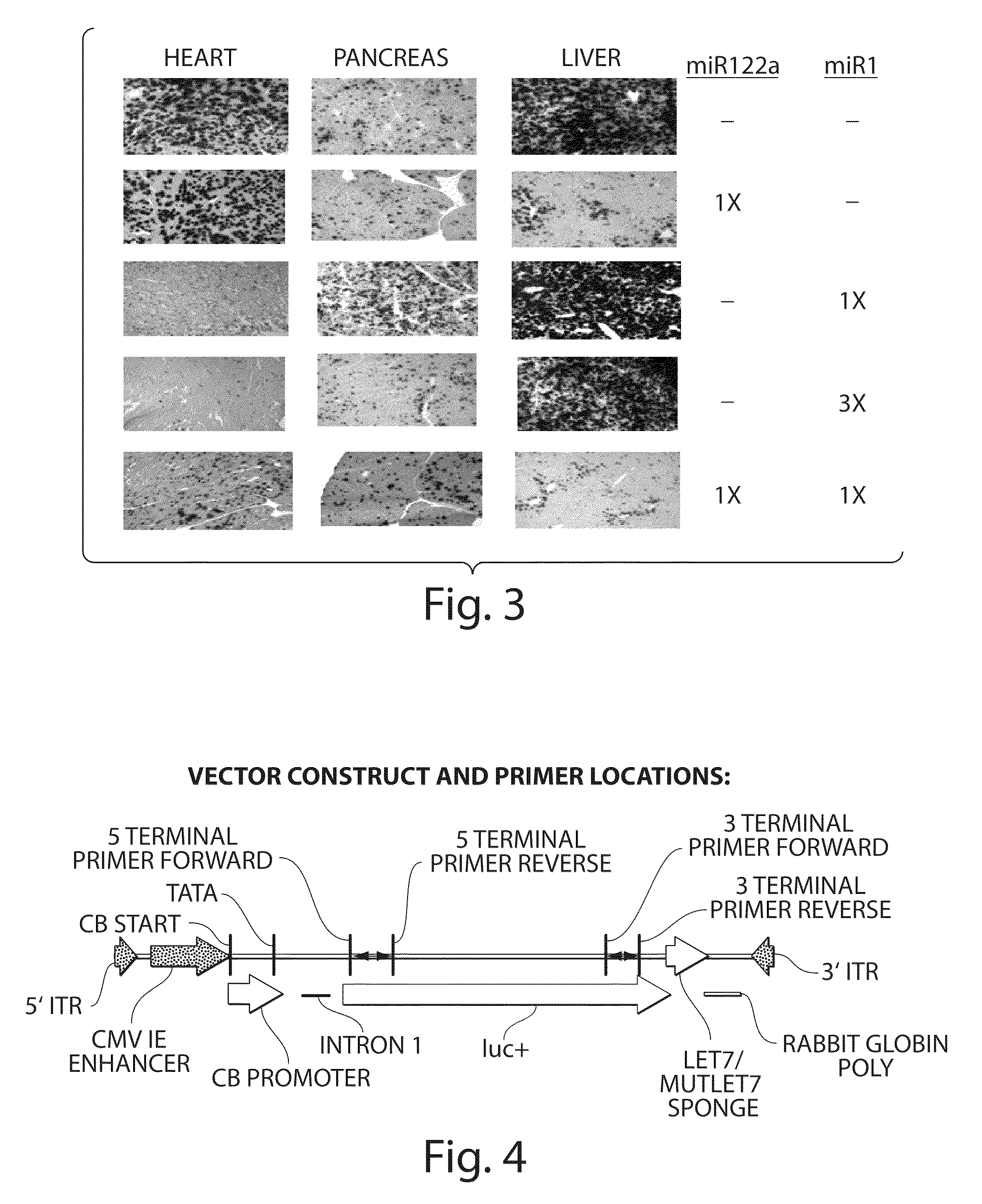
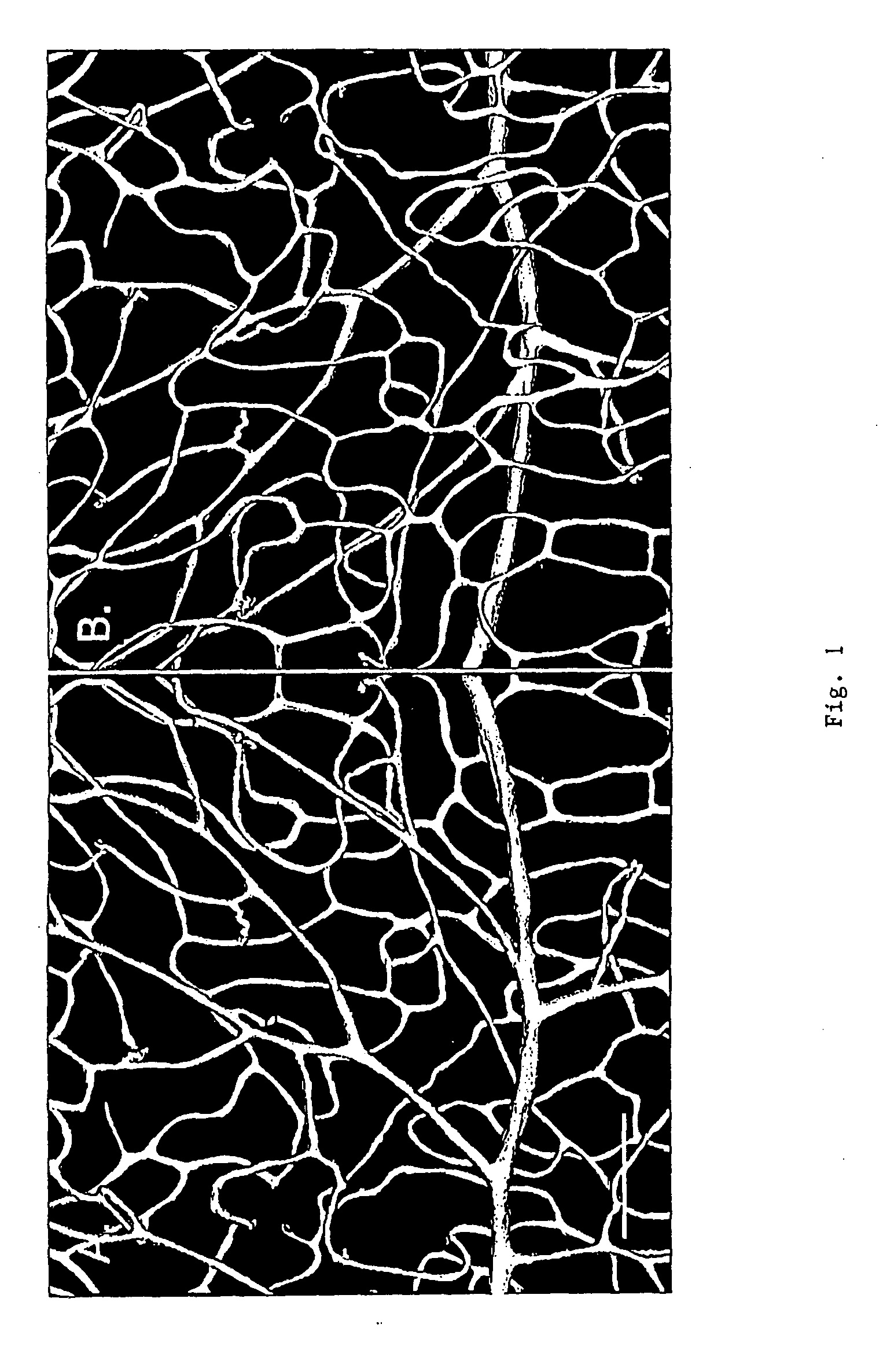
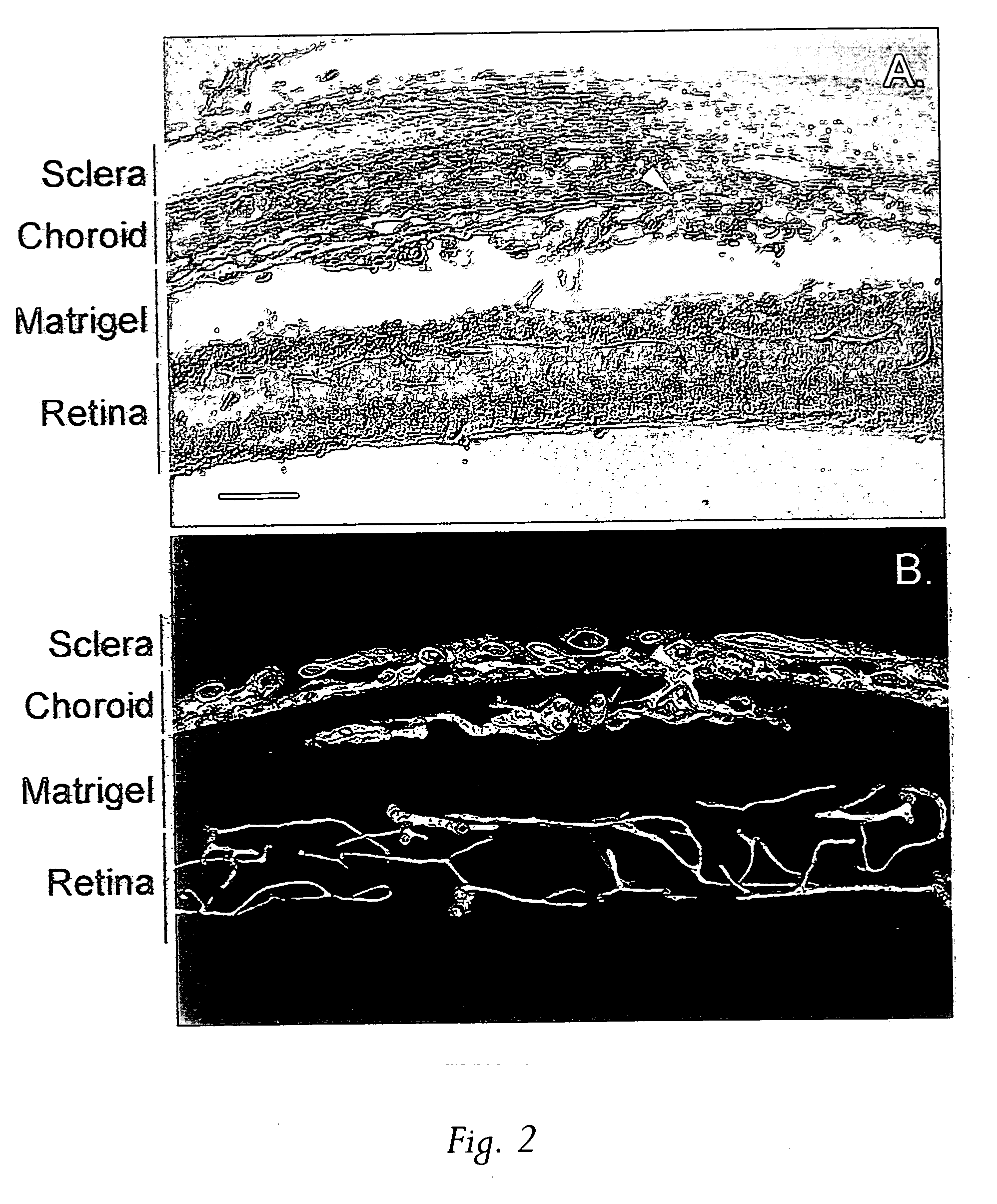
Method of inhibiting choroidal neovascularization
ActiveUS20050187241A1Reduce lossesQuick identificationBiocideSenses disorderAngiogenesis growth factorNeovascularization
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting unwanted angiogenesis, particularly those of ocular tissues. The treatment, inhibition, and / or prevention of choroidal neovasculature (CNV) is provided, along with an animal model for CNV and imaging techniques that permit the screening of potential agents as anti-angiogenesis and anti-CNV agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
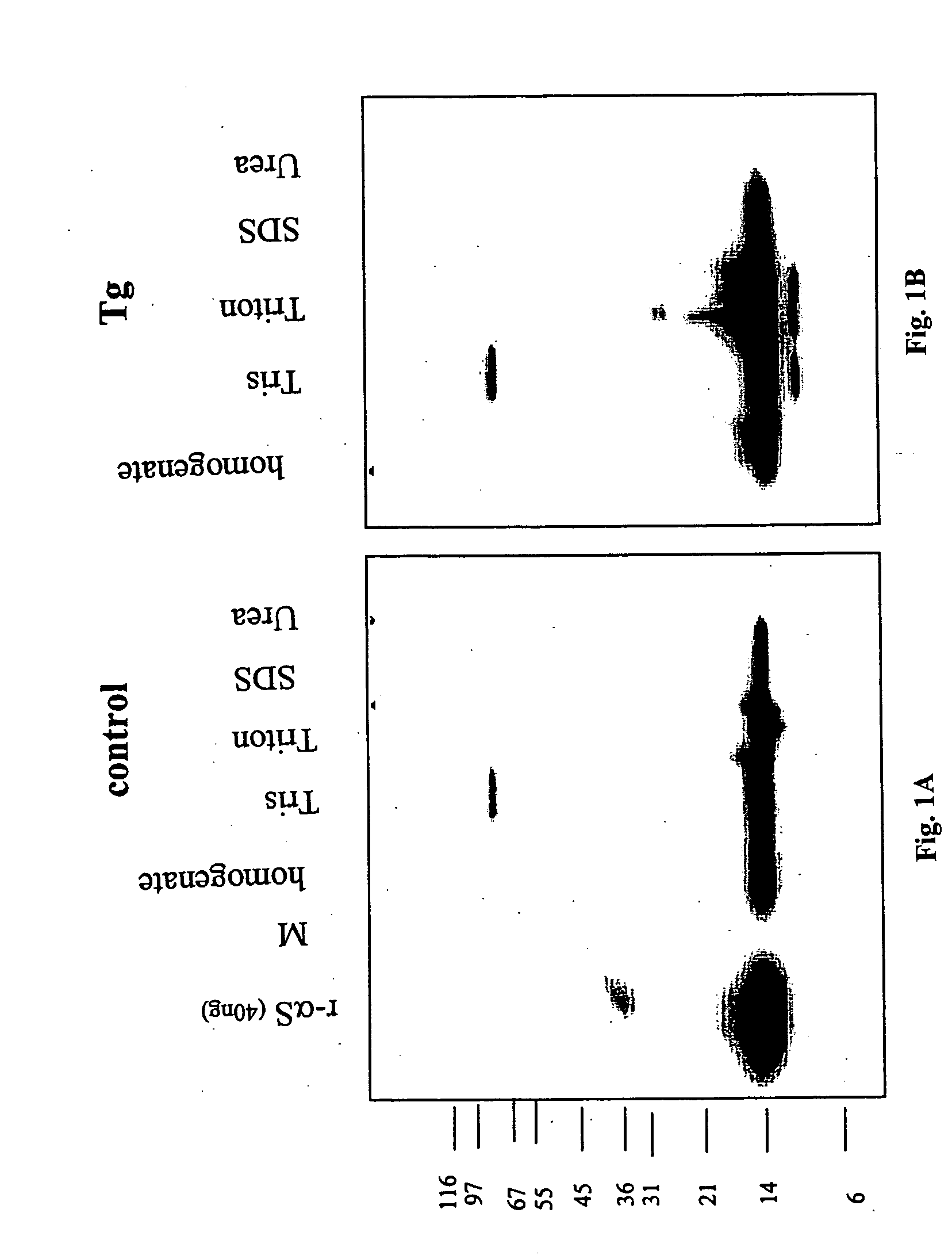
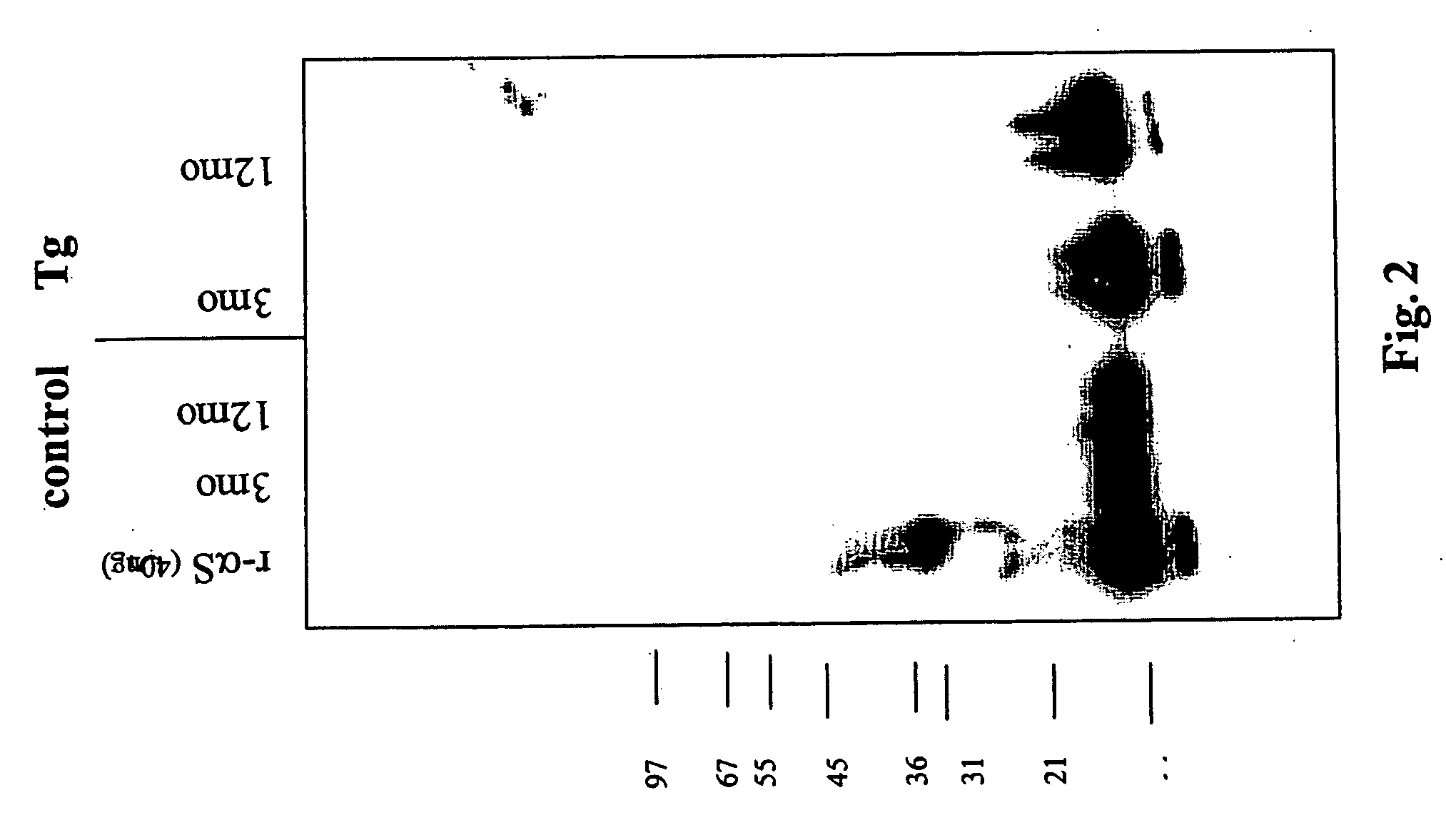
Truncated fragments of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disease
ActiveUS20050198694A1Useful pharmacological activityBiocideNervous disorderGel electrophoresisC-terminus
The application identifies novel fragments of alpha-synuclein in patients with Lewy Body Disease (LBD) and transgenic animal models thereof. These diseases are characterized by aggregations of alpha-synuclein. The fragments have a truncated C-terminus relative to fill-length alpha-synuclein. Some fragments are characterized by a molecular weight of about 12 kDa as determined by SDS gel electrophoresis in tricine buffer and a truncation of at least ten contiguous amino acids from the C-terminus of natural alpha-synuclein. The site of cleavage preferably occurs after residue 117 and before residue 126 of natural alpha-synuclein. The identification of these novel fragments of alpha-synuclein has a number of application in for example, drug discovery, diagnostics, therapeutics, and transgenic animals.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF FLINDERS UNIV +2
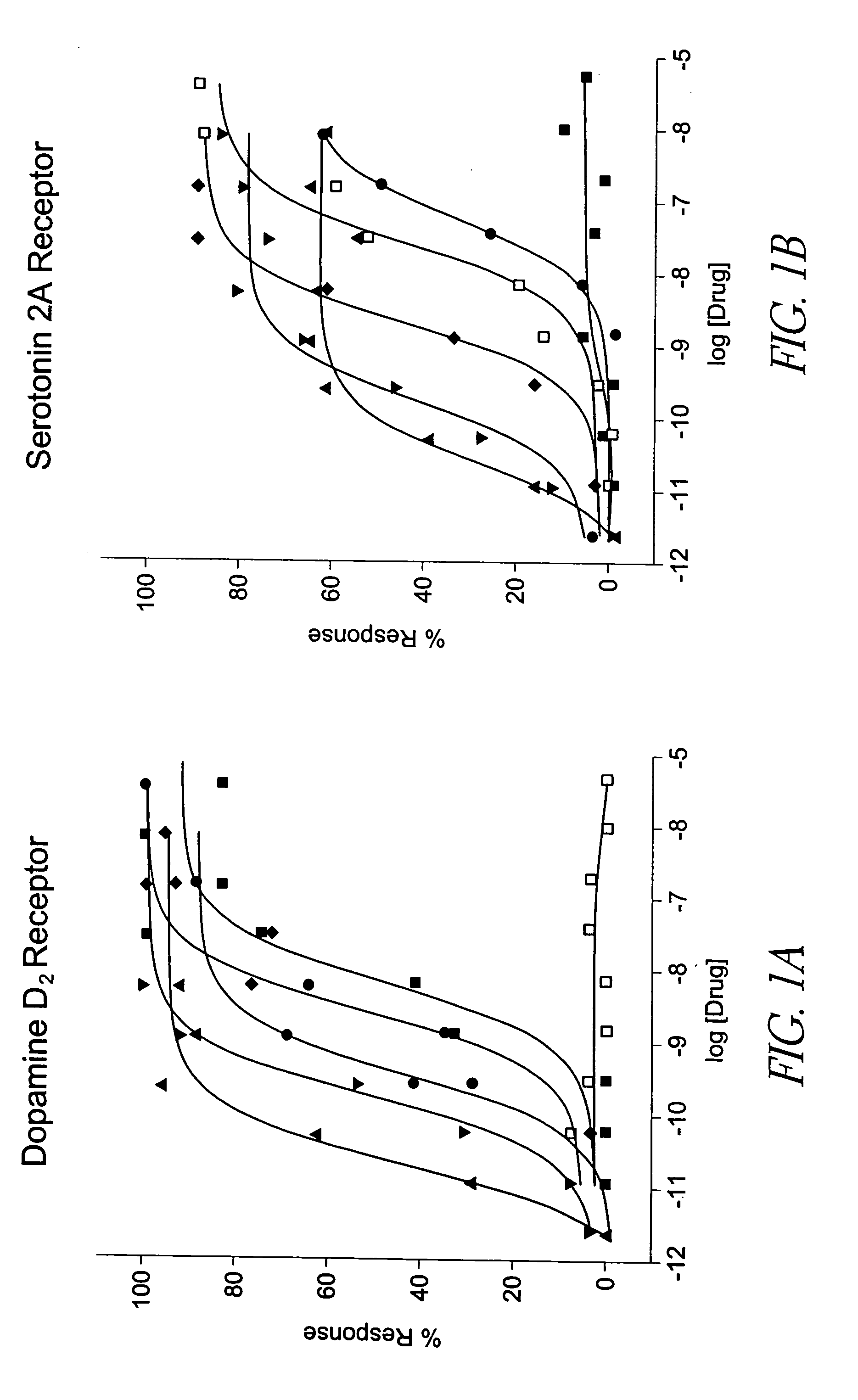
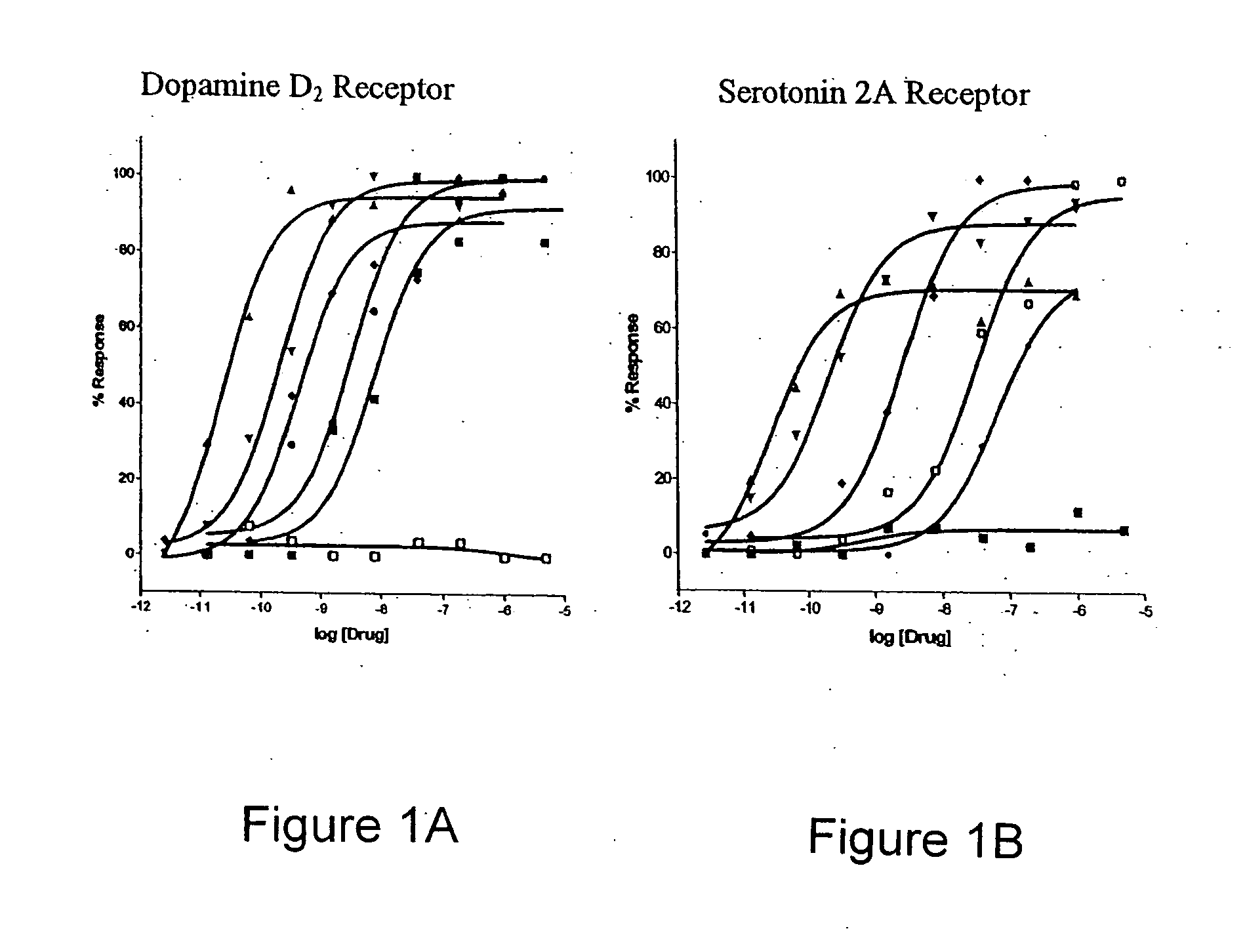
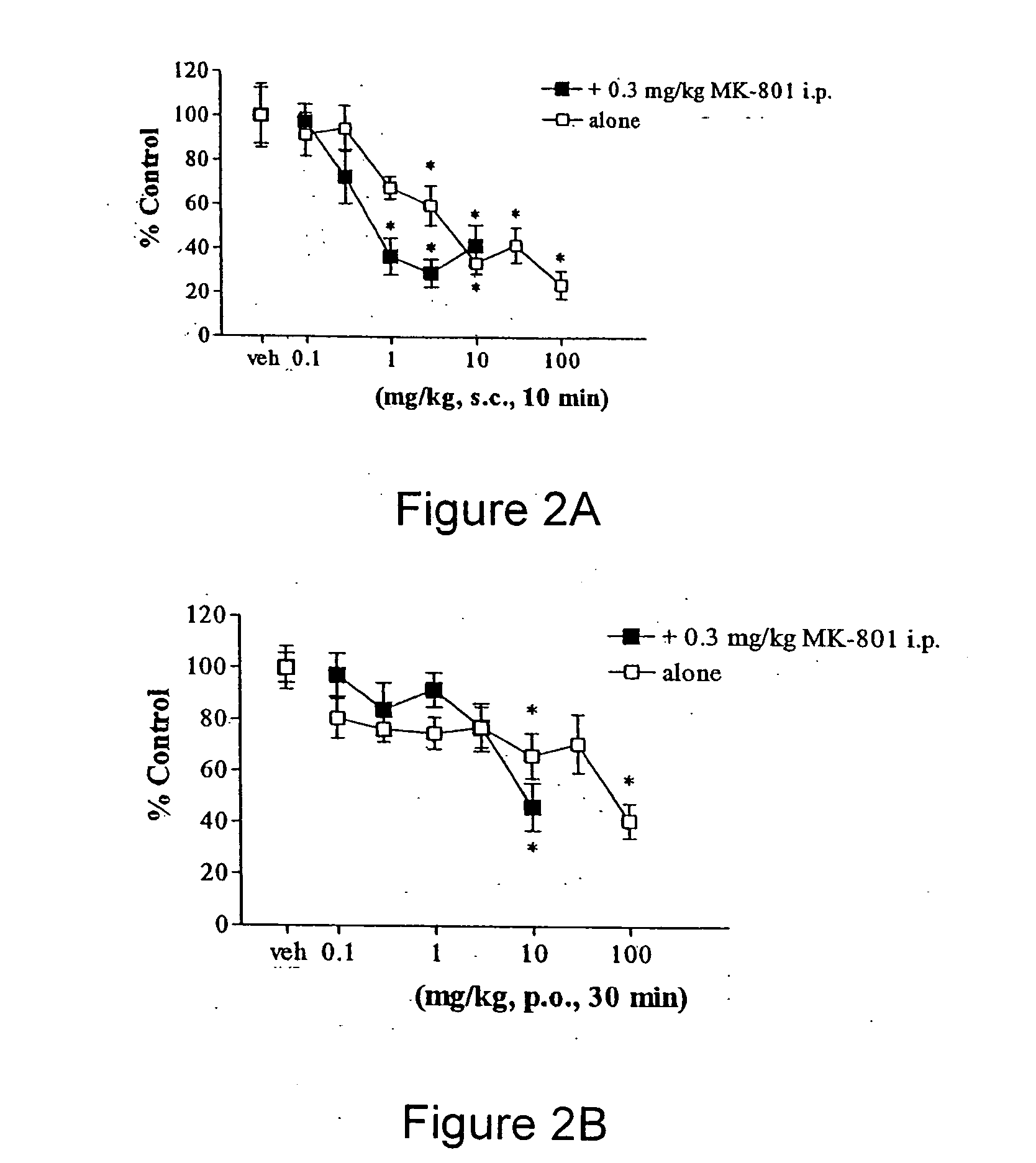
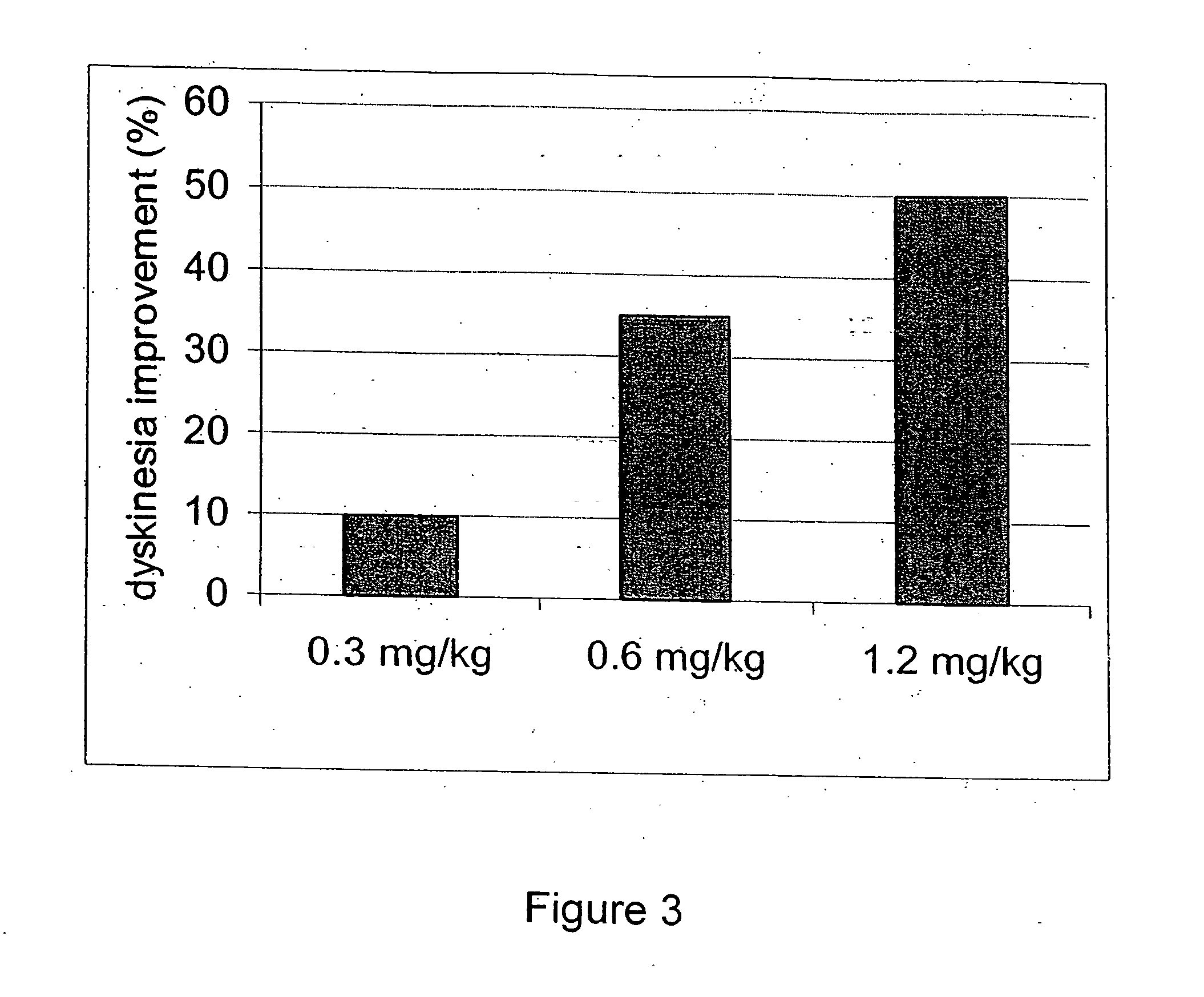
Selective serotonin 2A/2C receptor inverse agonists as therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases
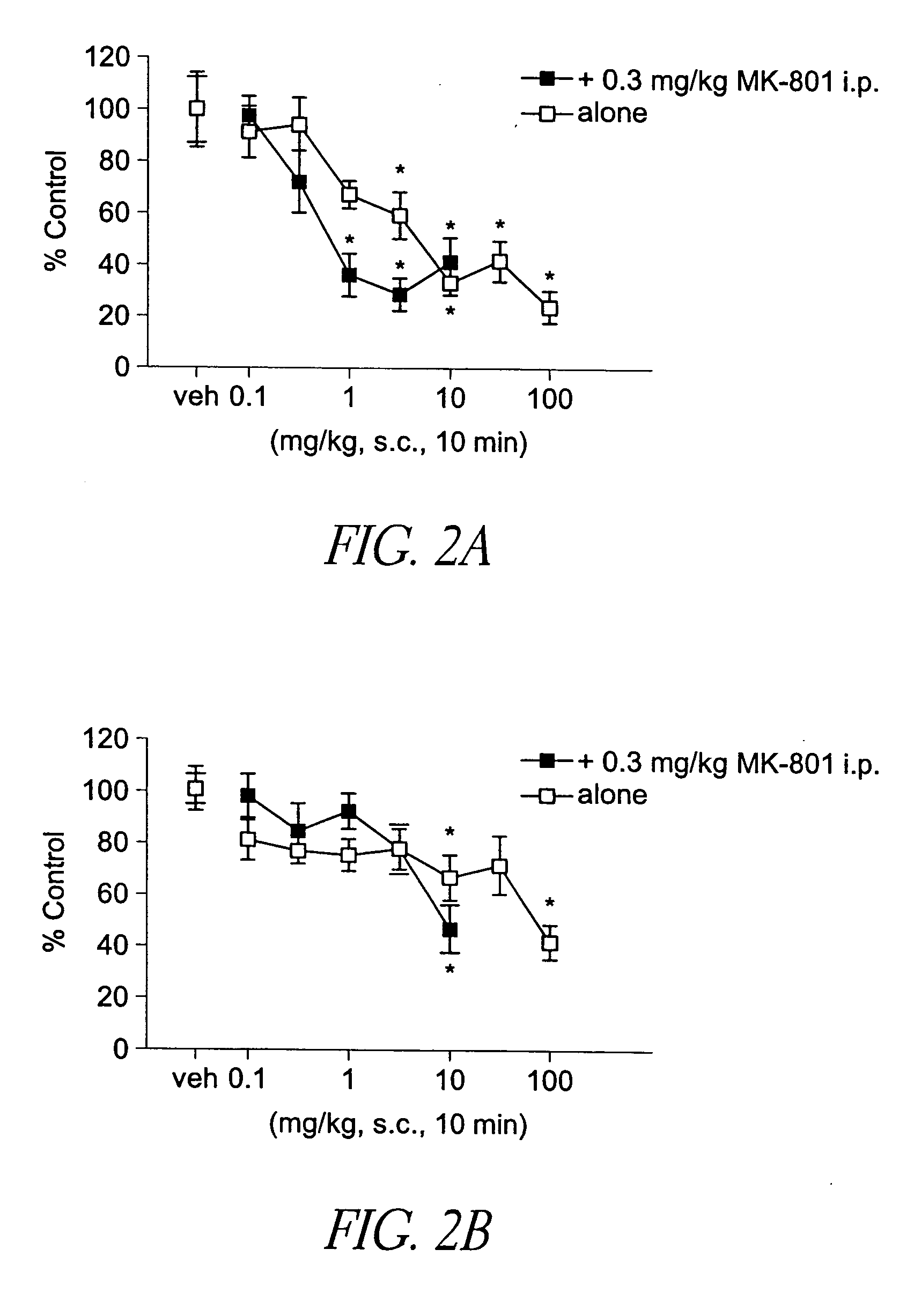
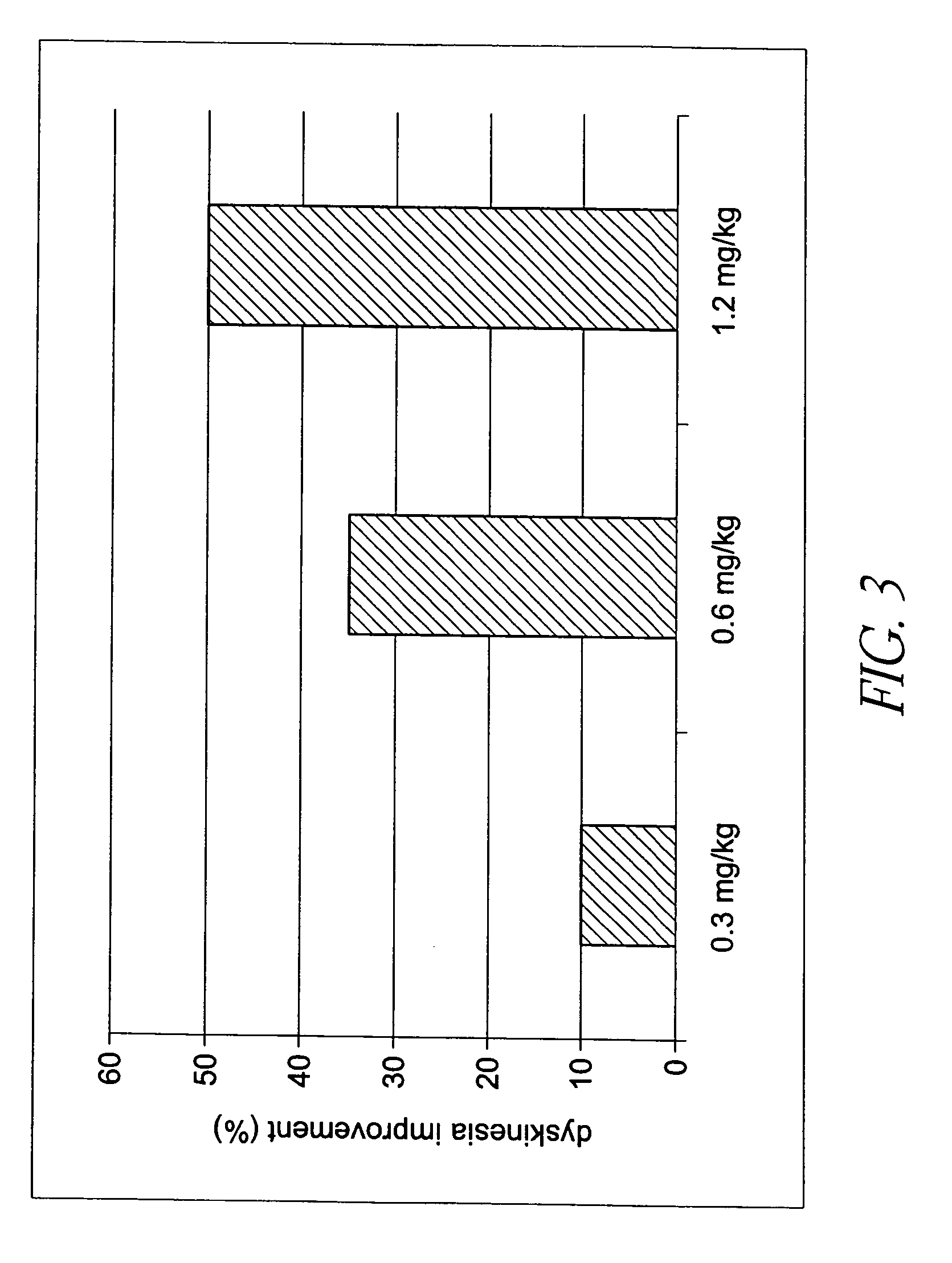
Behavioral pharmacological data with the compound of formula (I), a novel and selective 5HT2A / 2C receptor inverse agonist, demonstrate in vivo efficacy in models of psychosis and dyskinesias. This includes activity in reversing MK-801 induced locomotor behaviors, suggesting that this compound may be an efficacious anti-psychotic, and activity in an MPTP primate model of dyskinesias, suggesting efficacy as an anti-dyskinesia agent. These data support the hypothesis that 5HT2A / 2C receptor inverse agonism may confer antipsychotic and anti-dyskinetic efficacy in humans, and indicate a use of the compound of formula (I) and related agents as novel therapeutics for Parkinson's Disease, related human neurodegenerative diseases, and psychosis.
Owner:ACADIA PHARMA INC
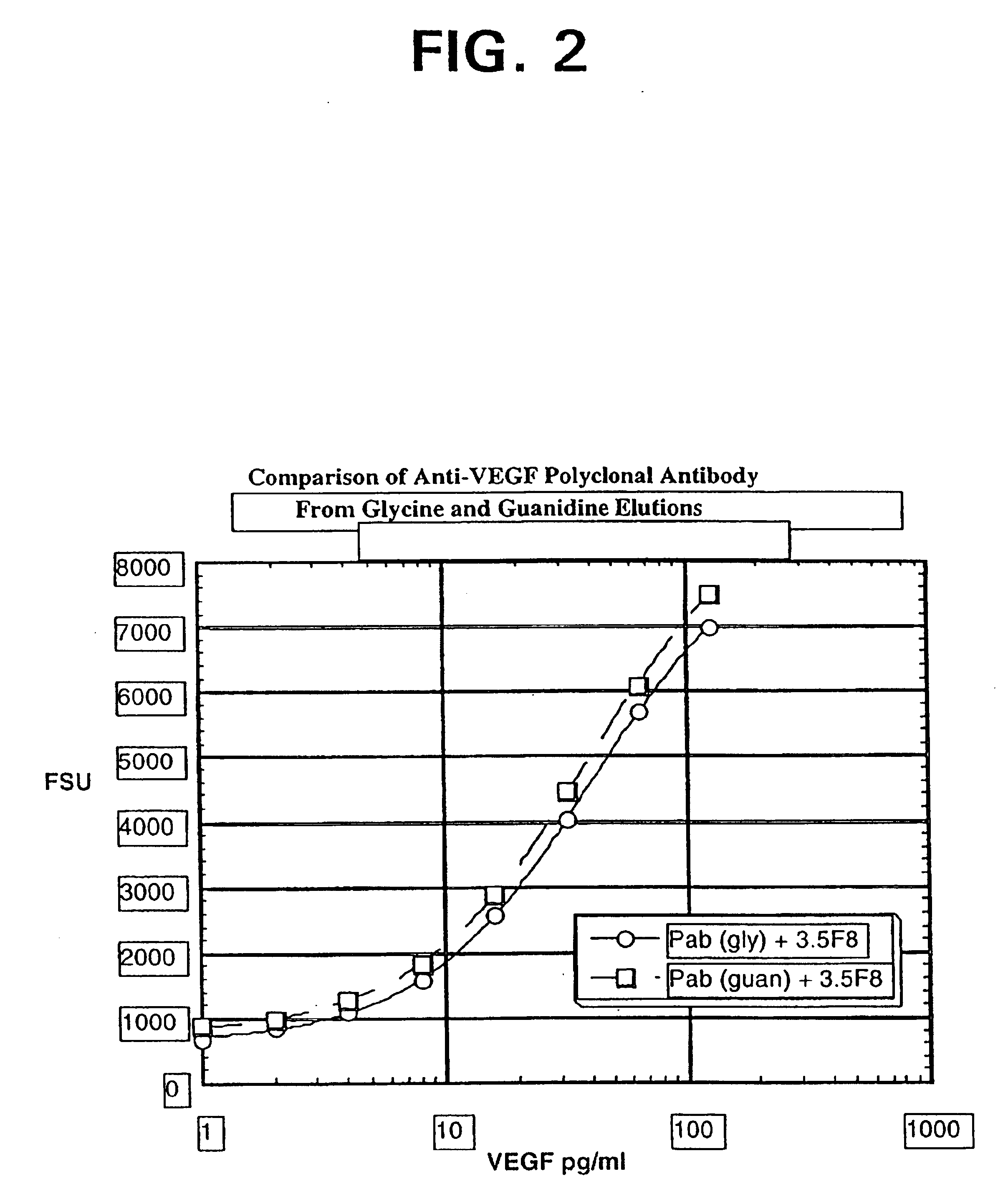
ELISA for VEGF
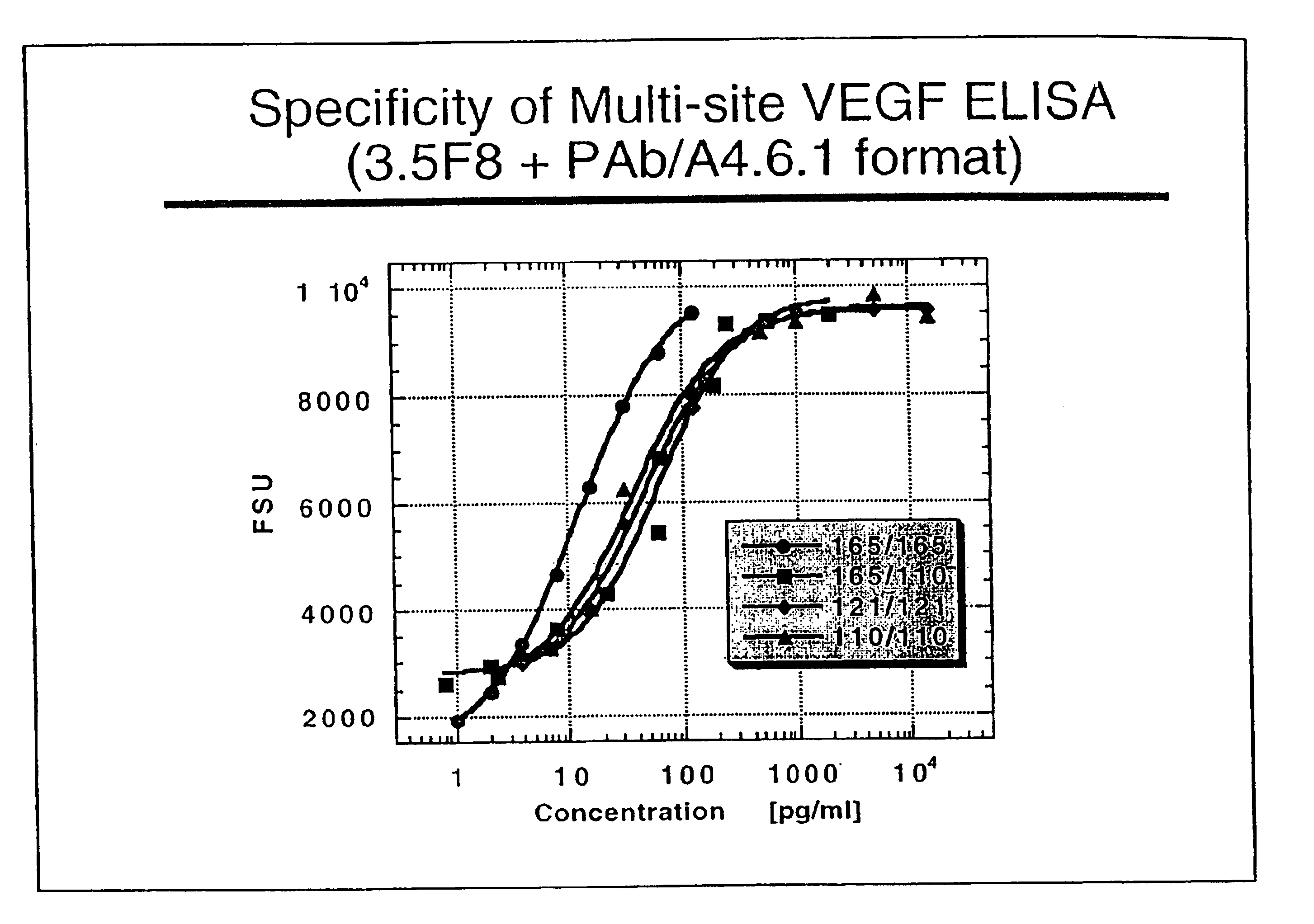
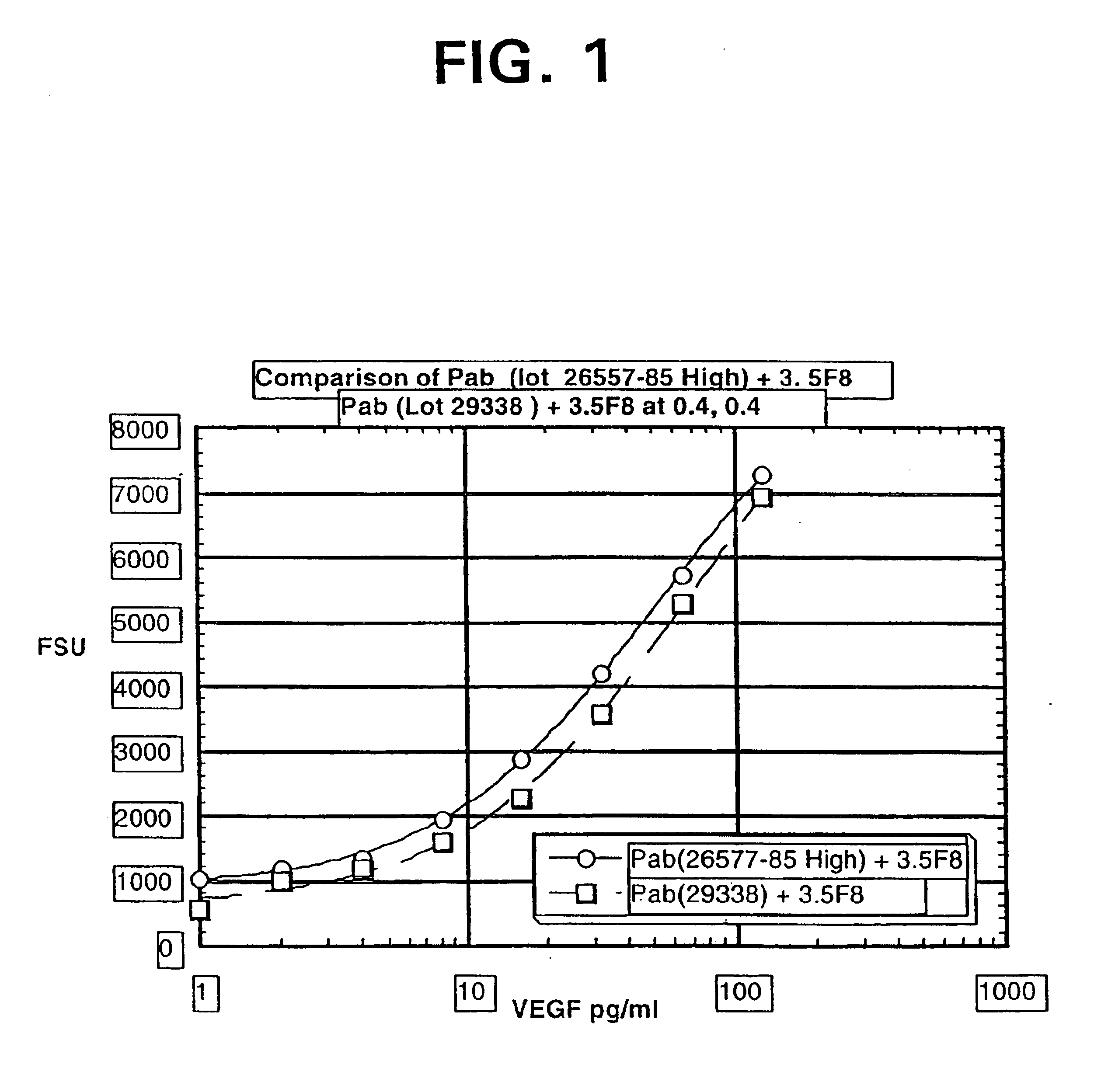
InactiveUS6855508B2Sensitivity of assay is lostLose sensitivityAnimal cellsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiabetes mellitusAntigen
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) activity in a patient's bloodstream or other biological sample can serve as a diagnostic and prognostic index for cancer, diabetes, heart conditions, and other pathologies. Antibody-sandwich ELISA method and kits for VEGF as an antigen were developed to detect VEGF levels in biological samples from animal models and human patients and are used as a diagnostic / prognostic index.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Selective serotonin 2A/2C receptor inverse agonists as therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS20060199842A1Inhibition of activationInhibition is effectiveBiocideNervous disorderMPTPNeuro-degenerative disease
Behavioral pharmacological data with the compound of formula (I), a novel and selective 5HT2A / 2C receptor inverse agonist, demonstrate in vivo efficacy in models of psychosis and dyskinesias. This includes activity in reversing MK-801 induced locomotor behaviors, suggesting that this compound may be an efficacious anti-psychotic, and activity in an MPTP primate model of dyskinesias, suggesting efficacy as an anti-dyskinesia agent. These data support the hypothesis that 5HT2A / 2C receptor inverse agonism may confer antipsychotic and anti-dyskinetic efficacy in humans, and indicate a use of the compound of formula (I) and related agents as novel therapeutics for Parkinson's Disease, related human neurodegenerative diseases, and psychosis.
Owner:ACADIA PHARMA INC
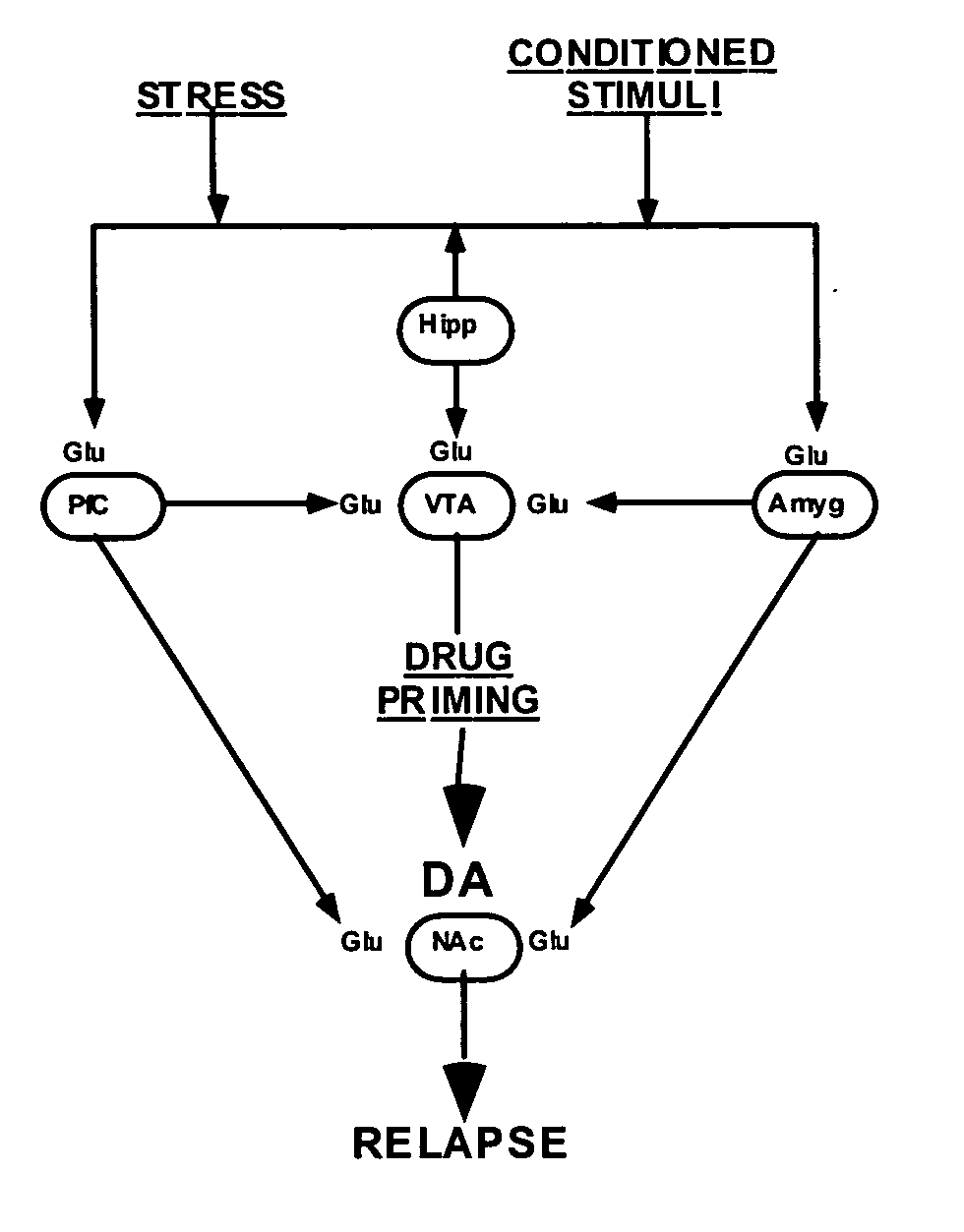
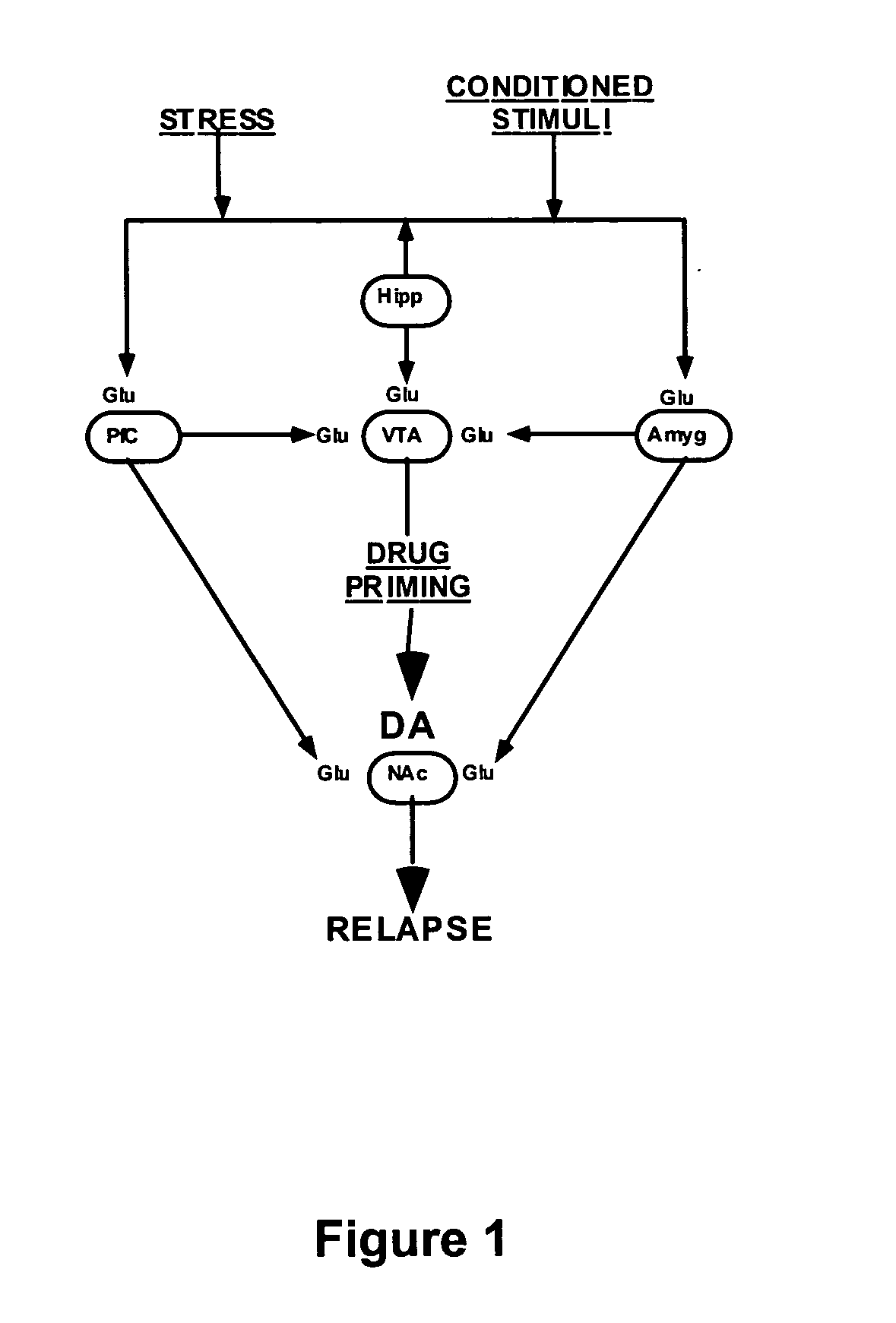
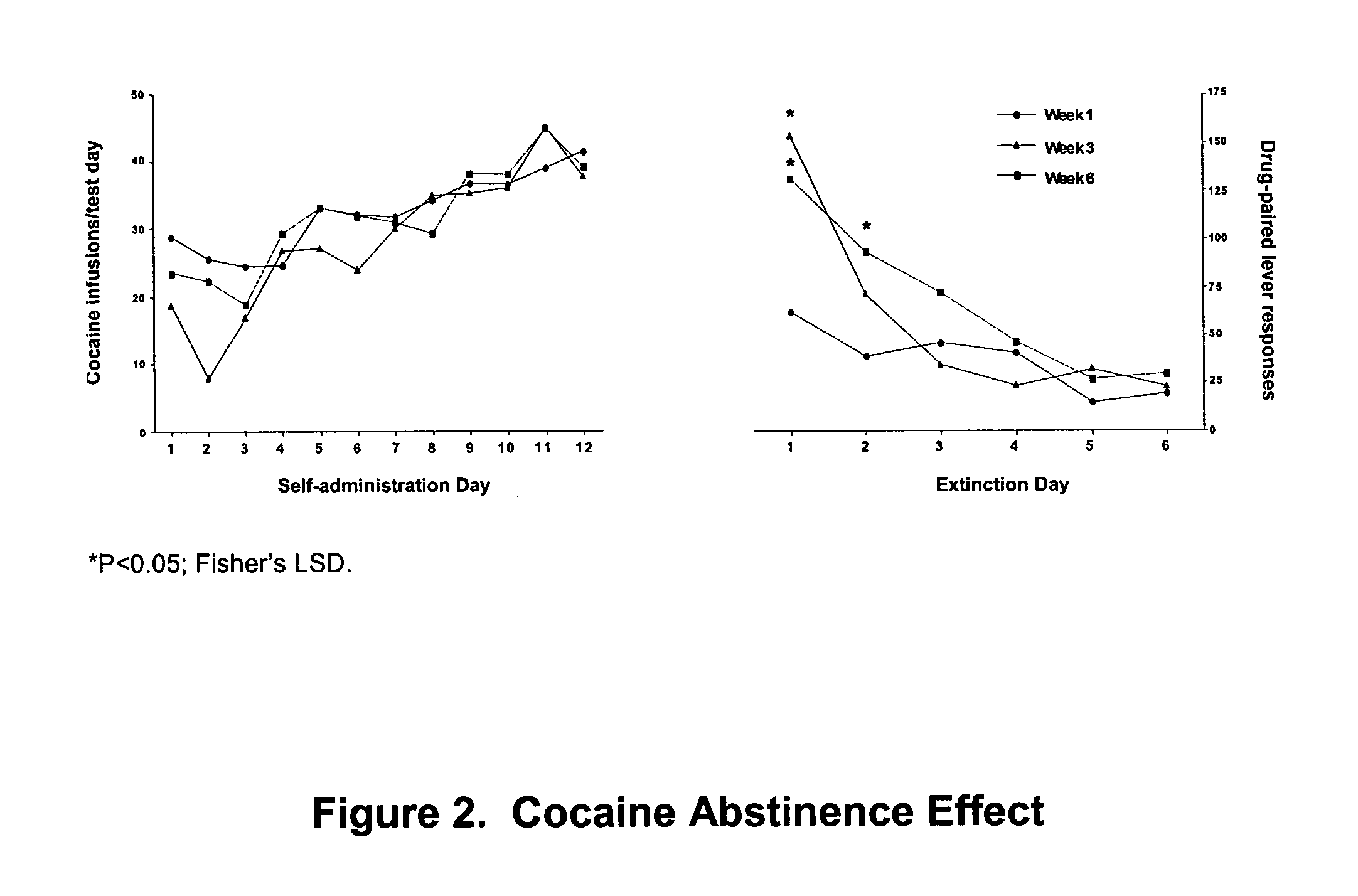
Methods for treating drug addiction
This invention describes gene targets for the development of therapeutics to treat drug addiction. Animal models of drug craving and relapse have been developed and used to find gene expression changes in key brain regions implicated in cocaine addiction. The genes whose expression levels are altered serve as pharmacological targets with the purpose of preventing or inhibiting cocaine craving and relapse in human cocaine addicts.
Owner:IRM
Gene transfer for studying and treating a connective tissue of a mammalian host
InactiveUS7037492B2Reducing at least one deleterious joint pathologyCompounds screening/testingBiocideConnective tissue fiberMammal
Methods for introducing at least one gene encoding a product into at least one target cell of a mammalian host for use in treating the mammalian host are disclosed. These methods include employing recombinant techniques to produce a vector molecule that contains the gene encoding for the product, and infecting the target cells of the mammalian host using the DNA vector molecule. A method to produce an animal model for the study of connective tissue pathology is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Method and device for treating osteoarthritis, cartilage disease, defects and injuries in the human knee
InactiveUS20060190043A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsHuman useArticular cartilage
A method of determining the voltage and current output required for the application of specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals to diseased articular cartilage in the treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage defects due to trauma or sports injury, or used as an adjunct with other therapies (cell transplantation, tissue-engineered scaffolds, growth factors, etc.) for treating cartilage defects in the human knee joint and a device for delivering such signals to a patient's knee. An analytical model of the human knee is developed whereby the total tissue volume in the human knee may be determined for comparison to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model using electric field and current density histograms. The voltage and current output used in the animal model is scaled based on the ratio of the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue of the human to the total tissue volume of the diseased tissue in the animal model and the resulting field is applied to the diseased tissue of the human using at least two electrodes applied to the knee or a coil or solenoid placed around the knee. The voltage of the signal applied to the electrodes, coil or solenoid is varied based on the size of the knee joint; larger knee joints require larger voltages to generate the effective electric field.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for establishing humanized rat drug evaluation animal model
InactiveCN104593418AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryLarge fragmentEngineered genetic
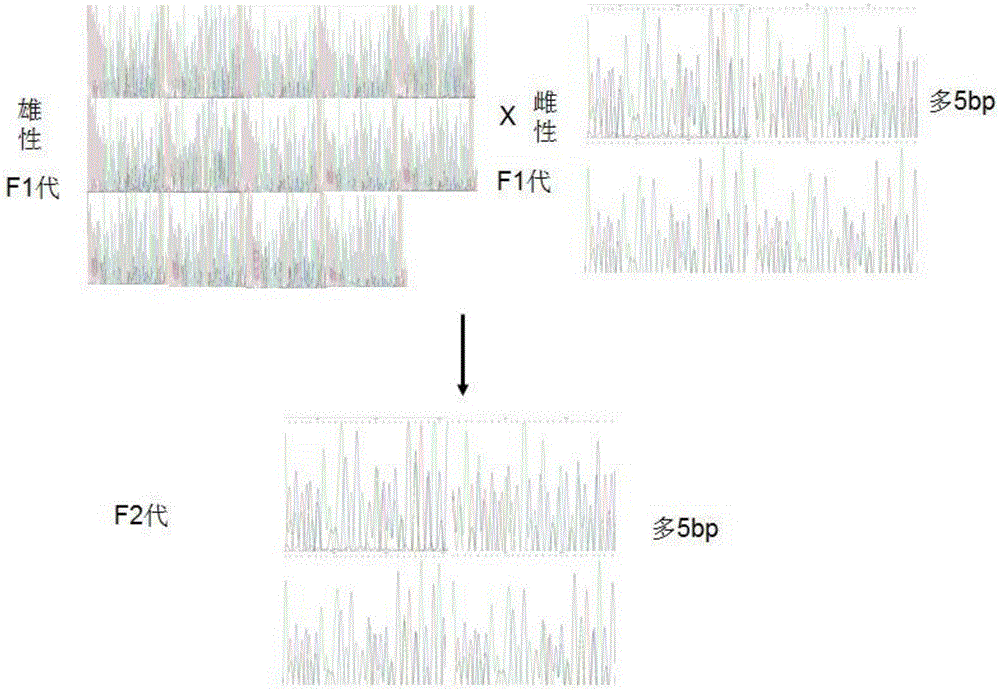
The invention provides a method for establishing a humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. According to the method, a multidrug resistance gene 1 (Abcb1)-knocked-out genetically engineered rat is obtained through a microinjection method by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology and 153kb bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) fragments containing a humanized Abcb1 promoter and cDNA is simultaneously inoculated into the rat genome through the microinjection method by virtue of a large fragment transgenic technology to obtain a transgenic rat capable of stably expressing human Abcb1 and the genetically engineered rat and the transgenic rat are hybridized to establish the humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. RT-PCR analysis shows that Abcb1 expression profiles of humanized Abcb1 rat are significantly different from those of the rat endogenous Abcb1. The method has the beneficial effects that the humanized rat capable of expressing human Abcb1 is obtained and the rat is used for expressing human Abcb1 genes and has closer expression profiles to those of human so that the model can be well used for the efficacy evaluation of newly developed drugs.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Recombinant anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody compositions
ActiveUS7887805B2Reduce exerciseReduction tendencyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationHuman cancerCancer cell
Owner:LES LAB SERVIER SA
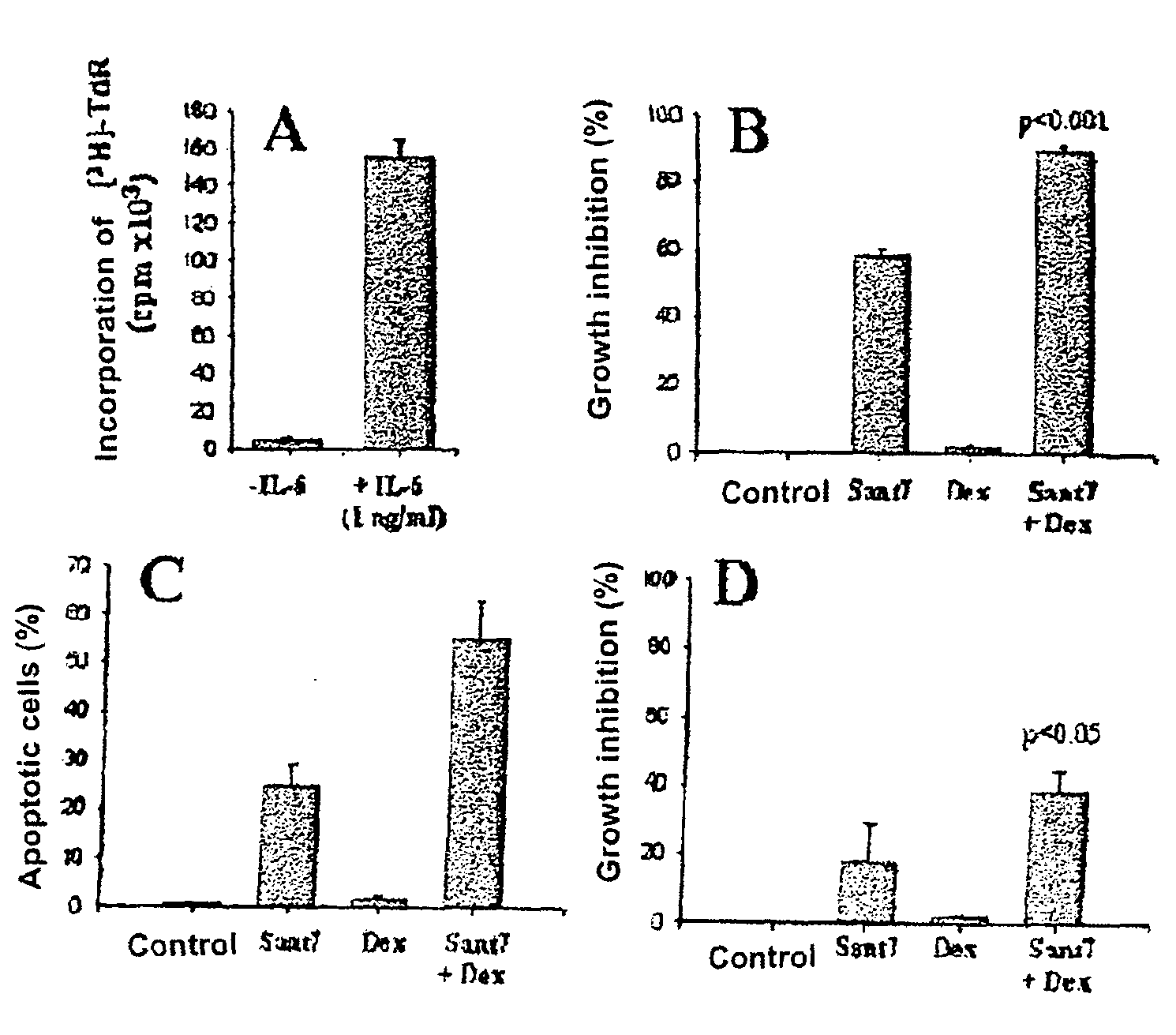
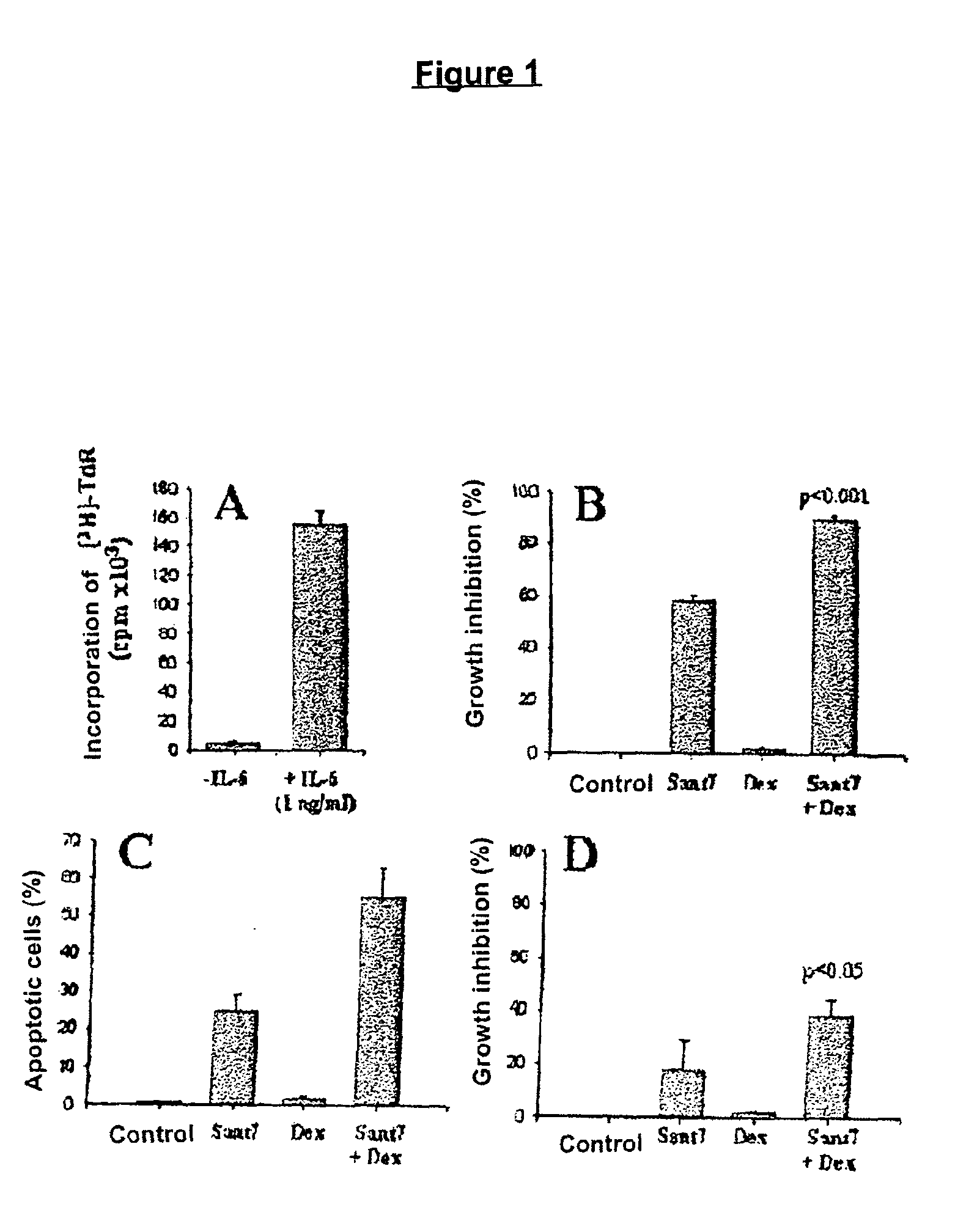
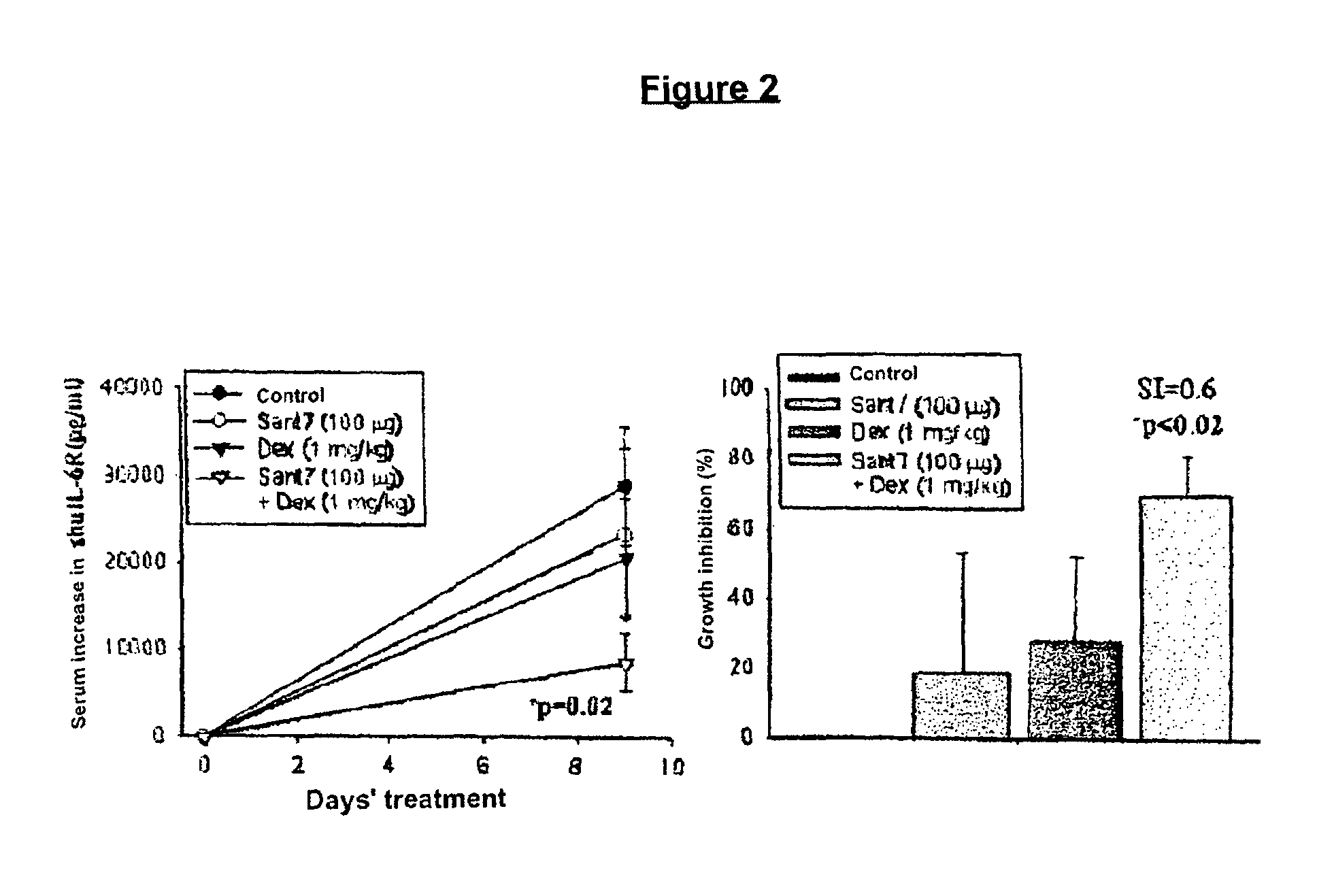
Combination of interleukin-6 antagonists and antiproliferative drugs
InactiveUS20090035281A1Good effectCounteracts paracrine actionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDexamethasoneInterleukin 6
The combination of an interleukin-6 (IL-6) antagonist and an antiproliferative drug is described. In its preferred embodiment, the present invention describes the combination of an IL-6 superantagonist, particularly a superantagonist totally incapable of binding gp130 and an antiproliferative drug belonging to the glucocorticoid class (SANT-7 and dexamethasone). The combination according to the present invention has shown surprising synergism in an animal model of multiple myeloma and the ability to overcome the resistance to the antiproliferative drug developed by myeloid cells. The combination according to the present invention is useful for the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of tumours, particularly IL-6-dependent tumours.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI MAGNA GRAECIA DI CATANZARO
Lung and lung cancer tissue culture method and method using lung and lung cancer tissue culture method to build lung cancer mouse animal model
ActiveCN106967672AGenetic stabilityGenetic uniformityCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsImmunofluorescent stainLung tissue
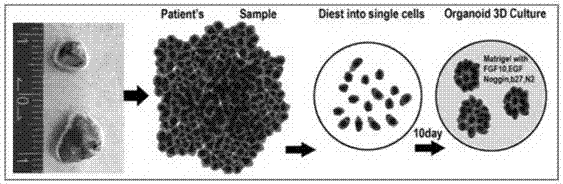
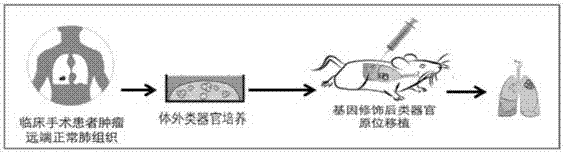
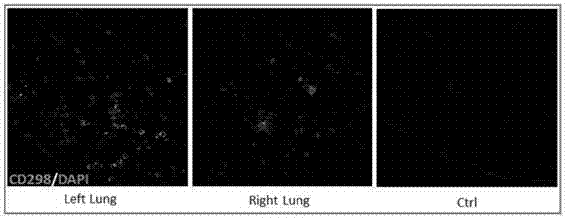
The invention discloses a method for culturing normal human lung tissue and a lung cancer tissue organoid in an in-vitro manner. The method includes: acquiring fresh human-derived lung tissue cells, and performing collagen digestion on the fresh human-derived lung tissue cells to obtain single cells; culturing human lung tissue and the lung cancer tissue organoid under in-vitro 3D culture conditions; performing H&E staining to determining the structure and form, and using q-PCR to detect related gene expression; using immunofluorescent staining to authenticate cell sources and detect related protein expression. The invention further discloses a method for building a mouse animal model based on the organoid. The method for culturing the normal human lung tissue and the lung cancer tissue organoid and the method for building the mouse animal model have the advantages that the methods are significant to the building of large-scale and good-consistency human-derived in-situ lung cancer animal models, and a good basis and related application prospect are provided for the fundamental researches of lung cancer.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Method for establishing obese rat animal model based on CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) gene knockout technology
InactiveCN103614415AImprove the level ofDeepen understanding of gene regulationVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryDiseaseLepr gene
The invention provides a method for establishing an obese rat animal model based on a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) gene knockout technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing an Lep / Lepr gene knockout rat model; (2) carrying out the authentication and related analysis on the obese rat animal model; (3) evaluating the energy metabolism and the body fat rate of the obese rat animal model. According to the method, a CRISPR / Cas system is used for respectively or simultaneously knocking out Lep and LepR genes so as to obtain the rat model modified by a corresponding target gene, so that the understanding of gene regulation in the obesity morbidity process can be deepened, and the high-level animal model can be provided for the translational medicine and the new medicine research and development.
Owner:SUZHOU TONGSHAN BIO TECH
Preparation method of zebrafish with hepcidin gene knocked out by use of CRISPR / Cas9 technology
The present invention mainly relates to formation of zebrafish with hepcidin gene knocked out, by the use of CRISPR / Cas9 technology, a unique PAM region is designed, so that the hepcidin gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, and other genes are not accidentally injured. The first case of hepcidin knockout transgenic animal model zebrafish has great significance, the hepcidin is a major factor in the regulation of iron, once the hepcidin is knocked out, an animal model can be successfully molded into an iron overload animal model, the human factor intervention can be excluded, the hepcidin has great significance to iron expression researches, meanwhile compared with the traditional gene knockout technology, the CRISPR / Cas9 technology has low toxicity, high accuracy, high efficiency, short success cycle and other characteristics, and the hepcidin gene can be faster knocked out.
Owner:徐又佳
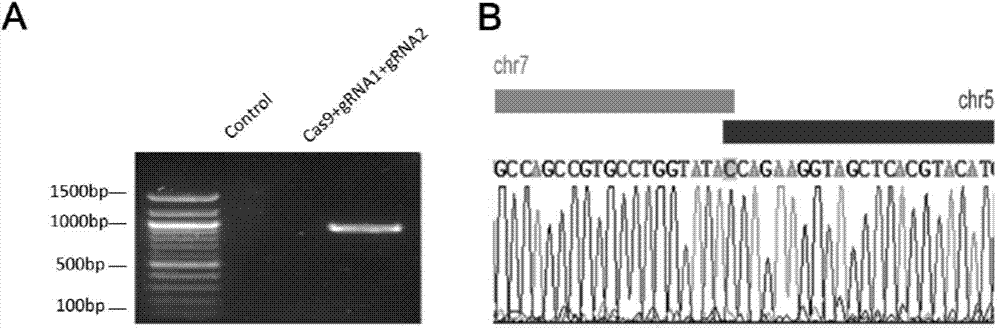
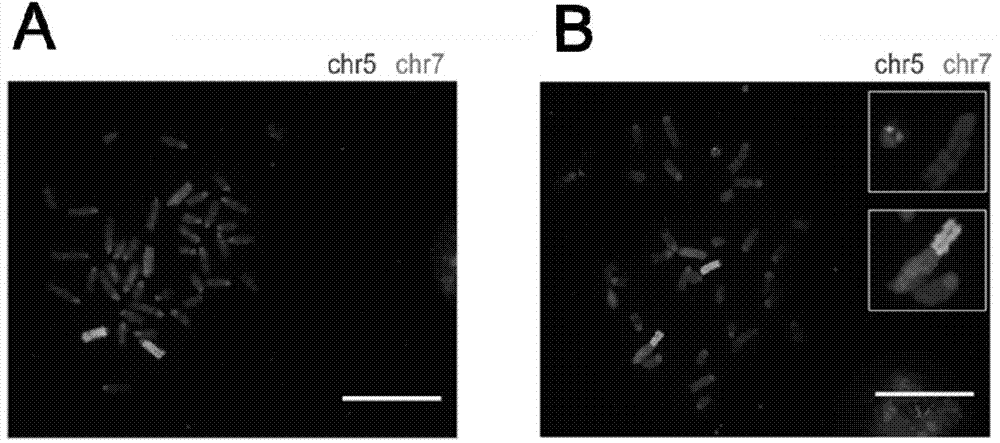
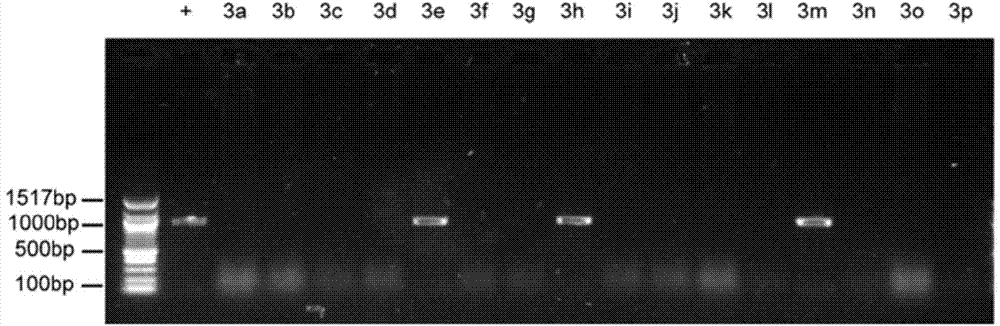
Method for constructing chromosome translocation stem cell and animal model by CRISPR-Cas9 technology
The invention relates to a method for preparing a chromosome translocation stem cell model and an animal model. The method mainly comprises the steps of inducing occurrence of specific site chromosome translocation in stem cells by means of CRISPR / Cas9 technology, preparing a cell model and further constructing an animal model carrying the specific site chromosome translocation by utilizing embryonic stem cell technology. The method particularly comprises the steps of simultaneously introducing Cas9 and gRNA aiming at two target chromosome sites into the stem cells to artificially inducing chromosome dislocation of specific sites, and screening to obtain the cell model carrying the chromosome translocation. The animal model carrying chromosome translation of the specific sites can be further prepared from the chromosome translocation animal embryonic stem cells carrying chromosome translation by utilizing a chimera technology. The method has relatively large application prospect in studies on chromosome translocation and functions of fusion genes, researches on chromosome interaction and medicine screening evaluation.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com